Patents
Literature
268 results about "Microwave imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microwave imaging is a science which has been evolved from older detecting/locating techniques (e.g., radar) in order to evaluate hidden or embedded objects in a structure (or media) using electromagnetic (EM) waves in microwave regime (i.e., ~300 MHz-300 GHz). Engineering and application oriented microwave imaging for non-destructive testing is called microwave testing, see below.
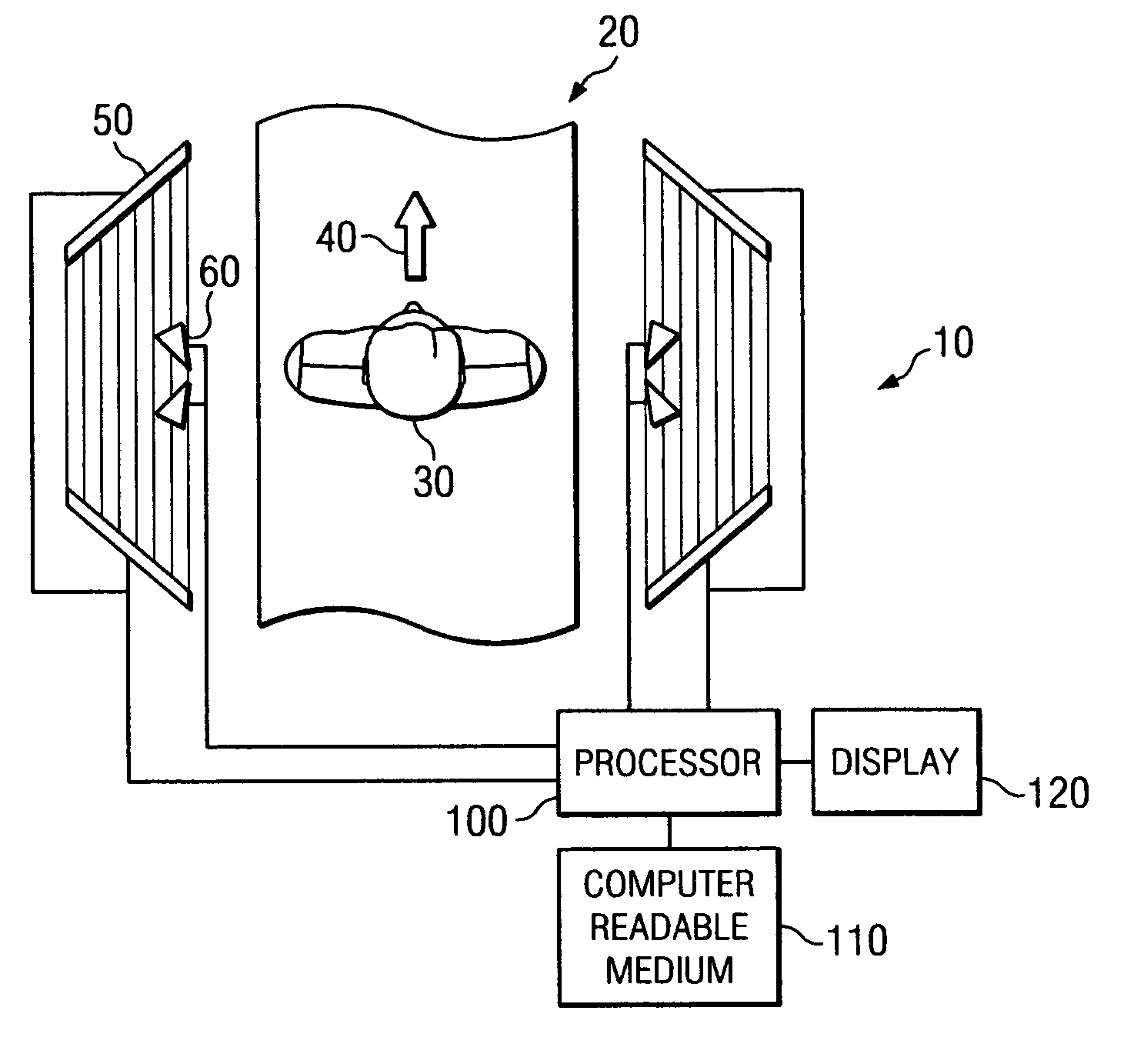
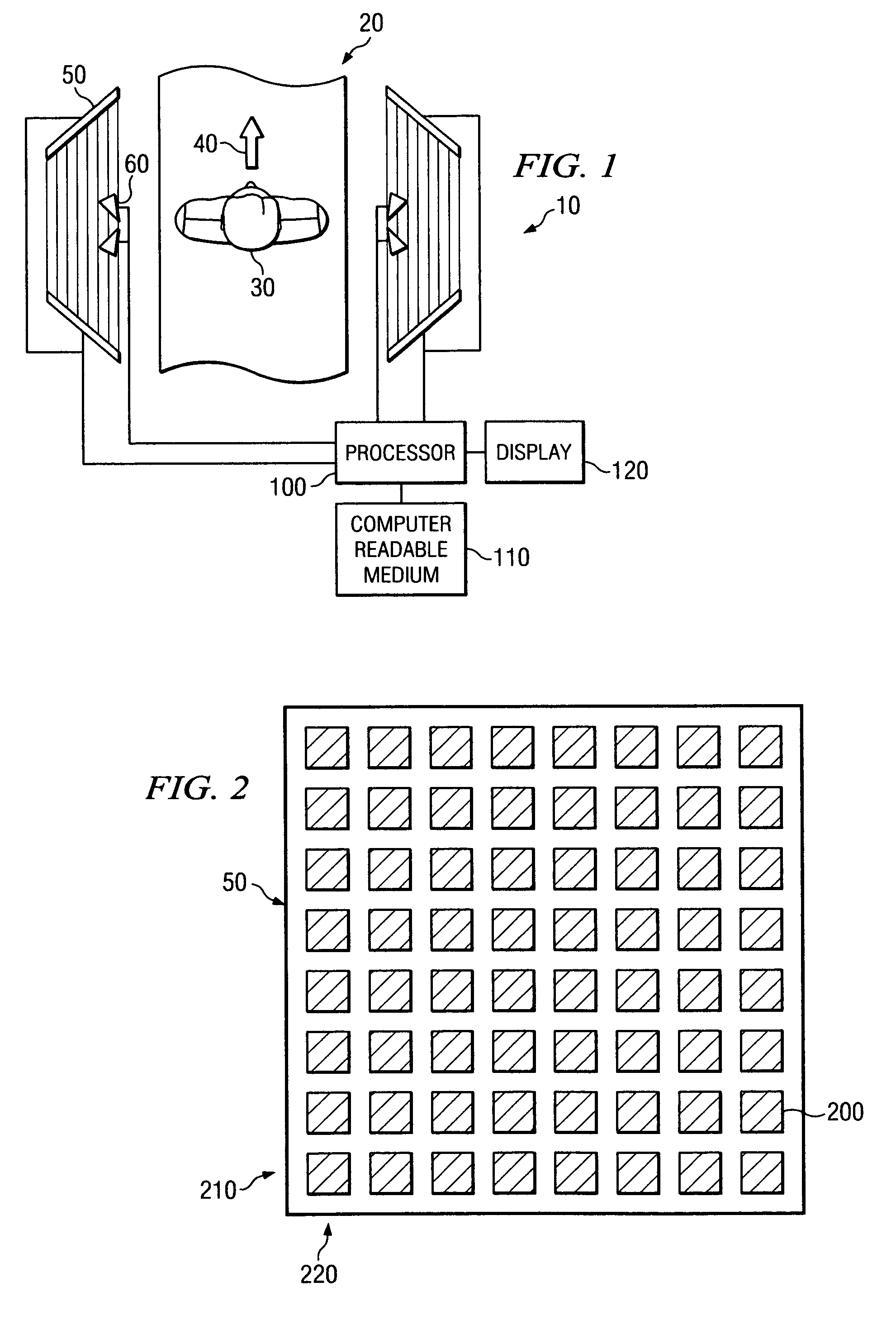
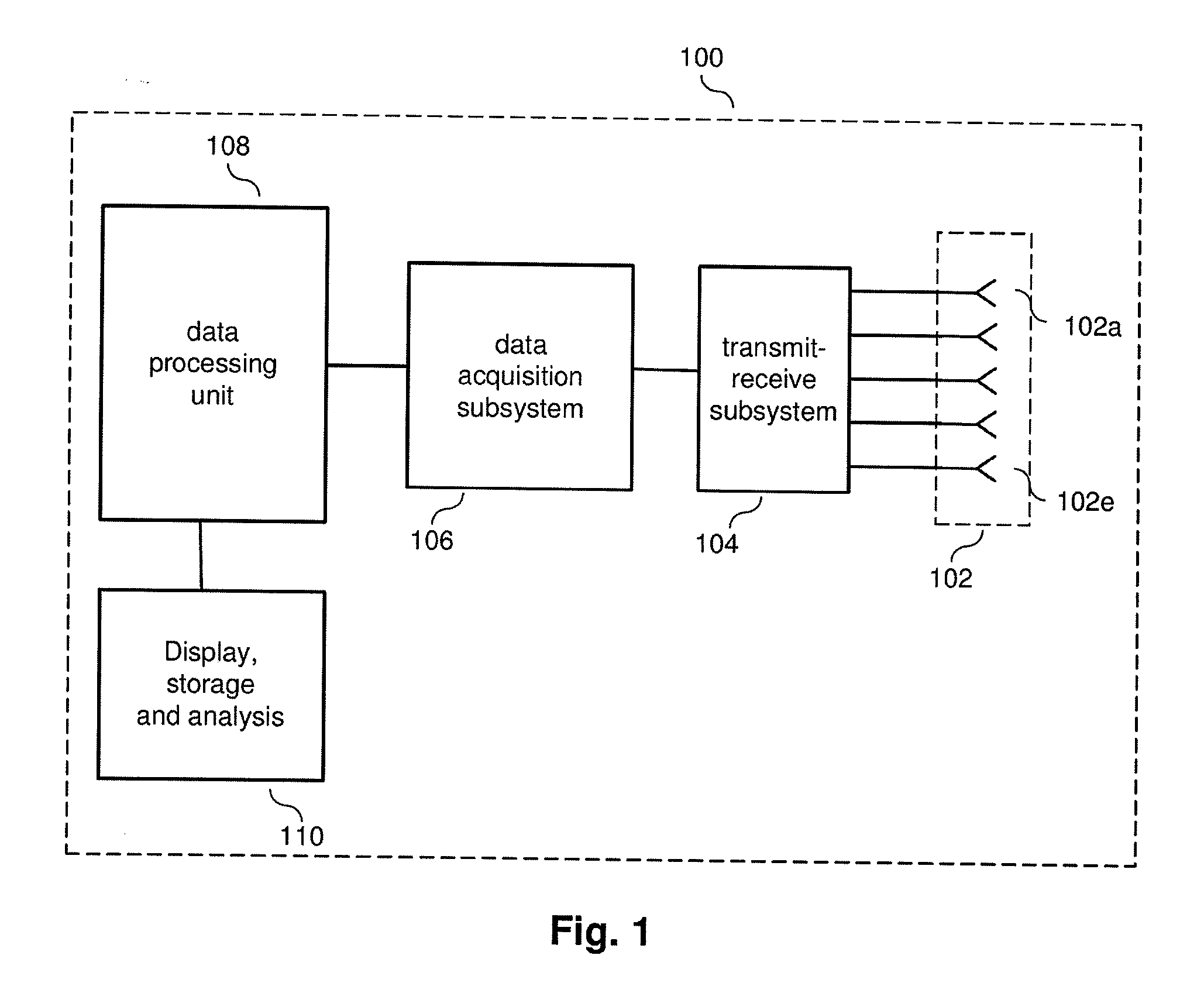
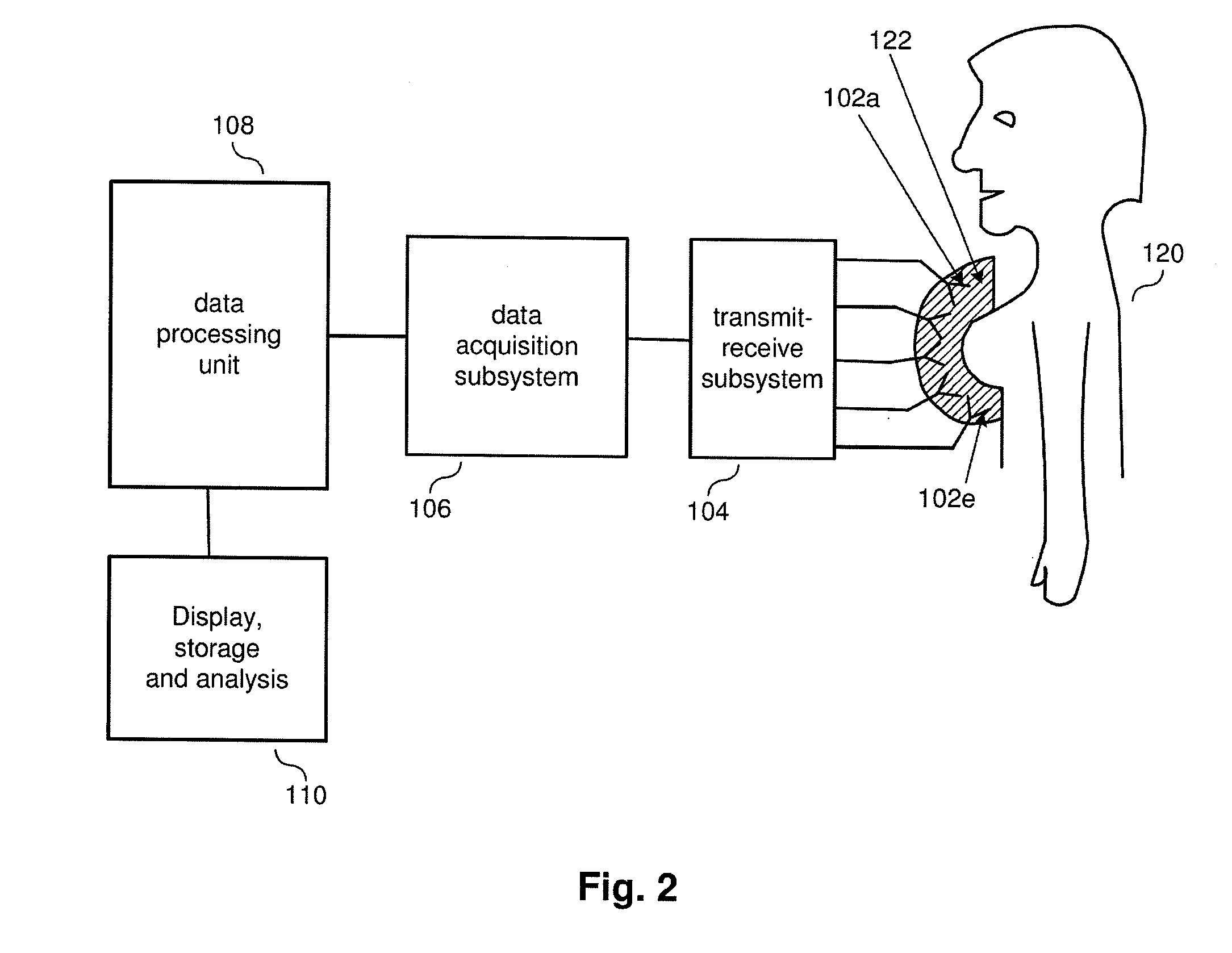
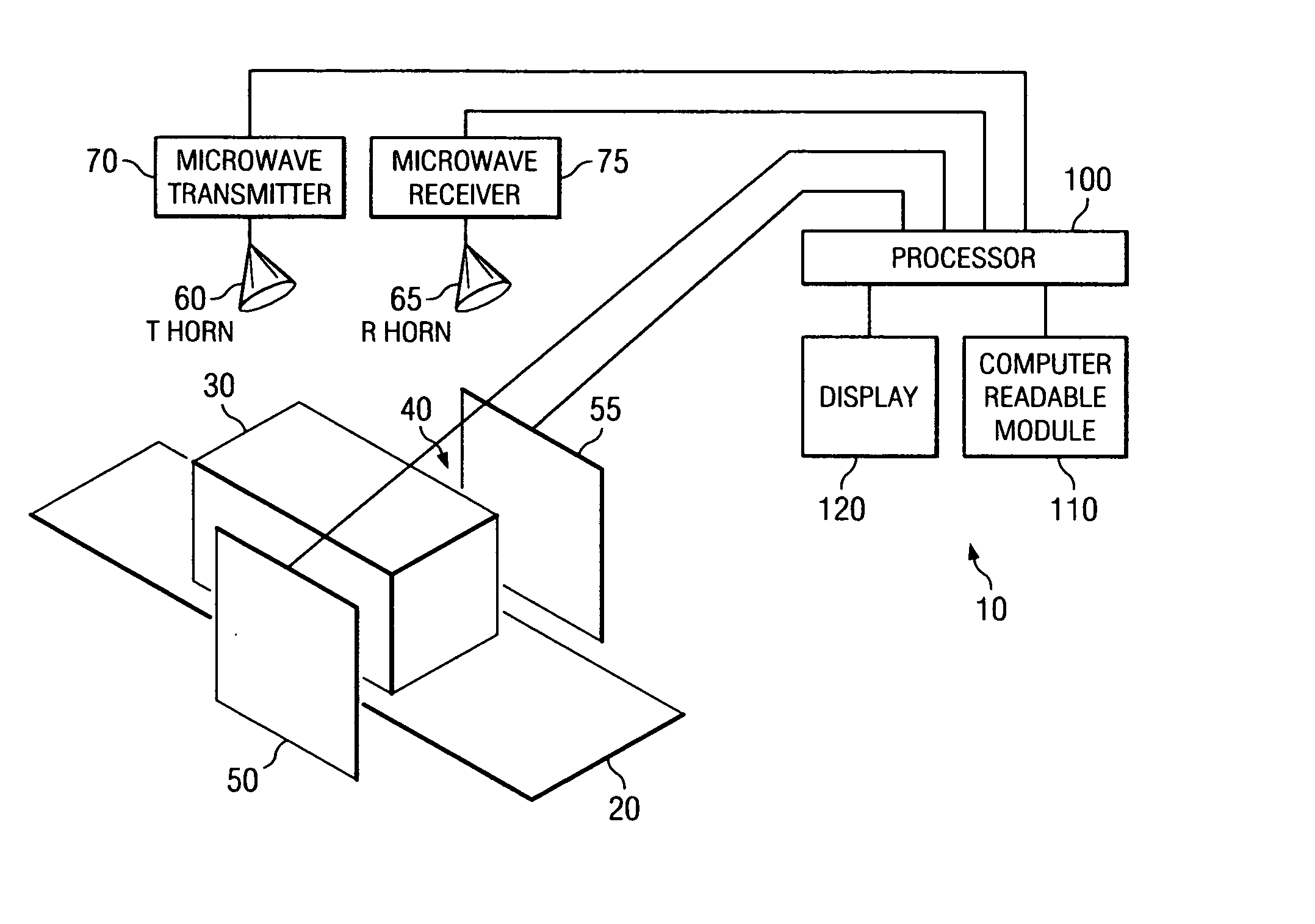
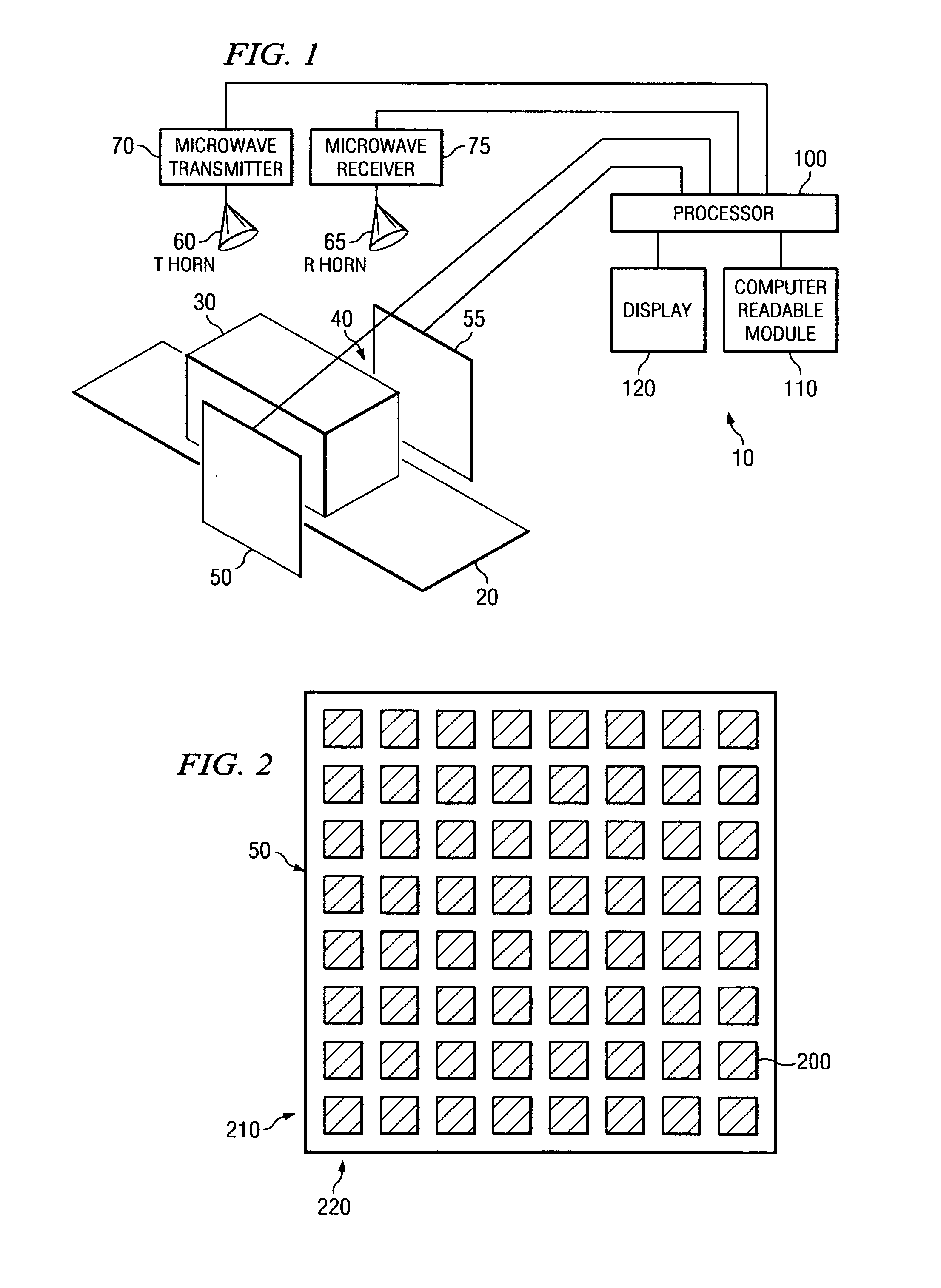
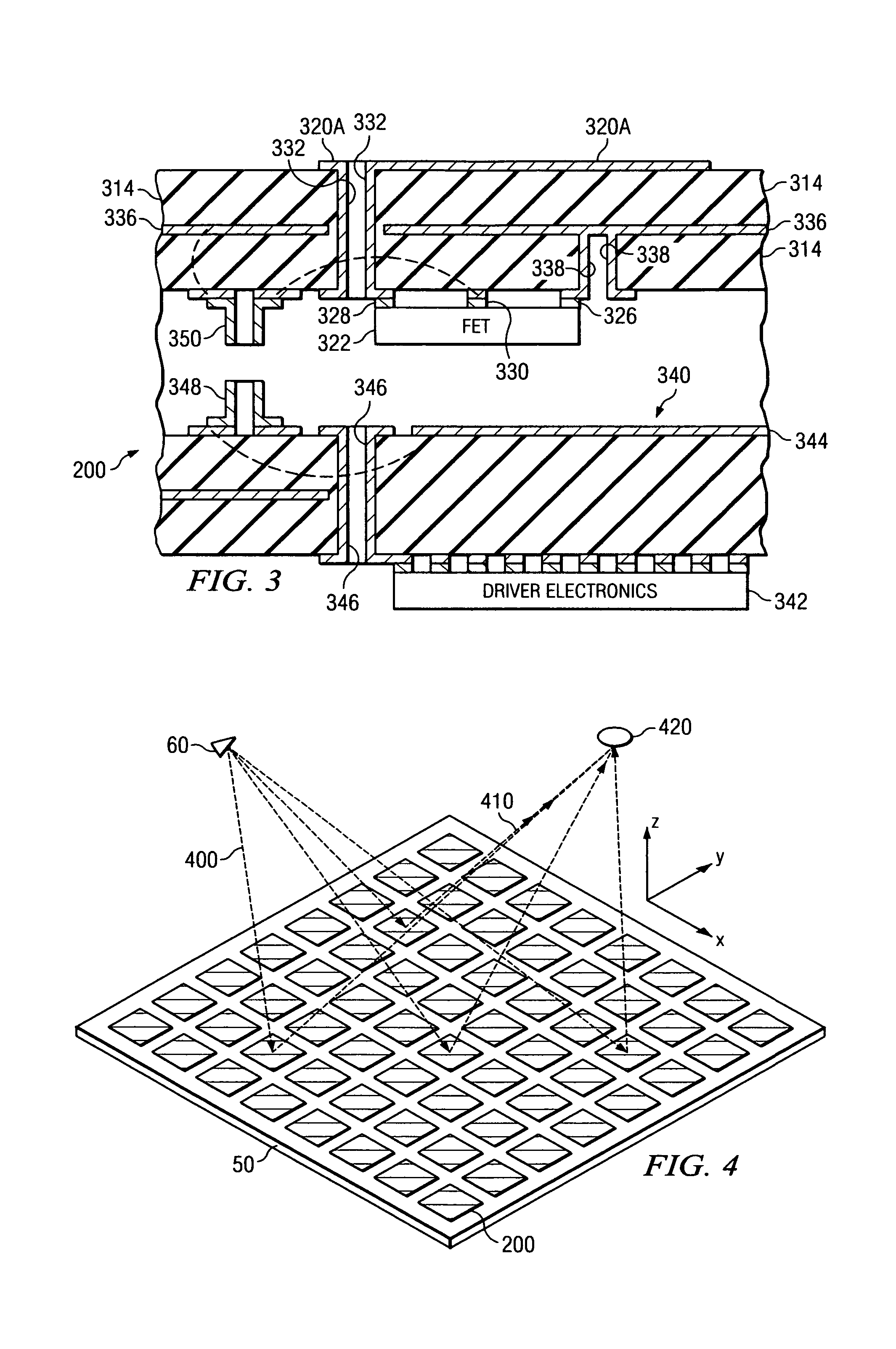
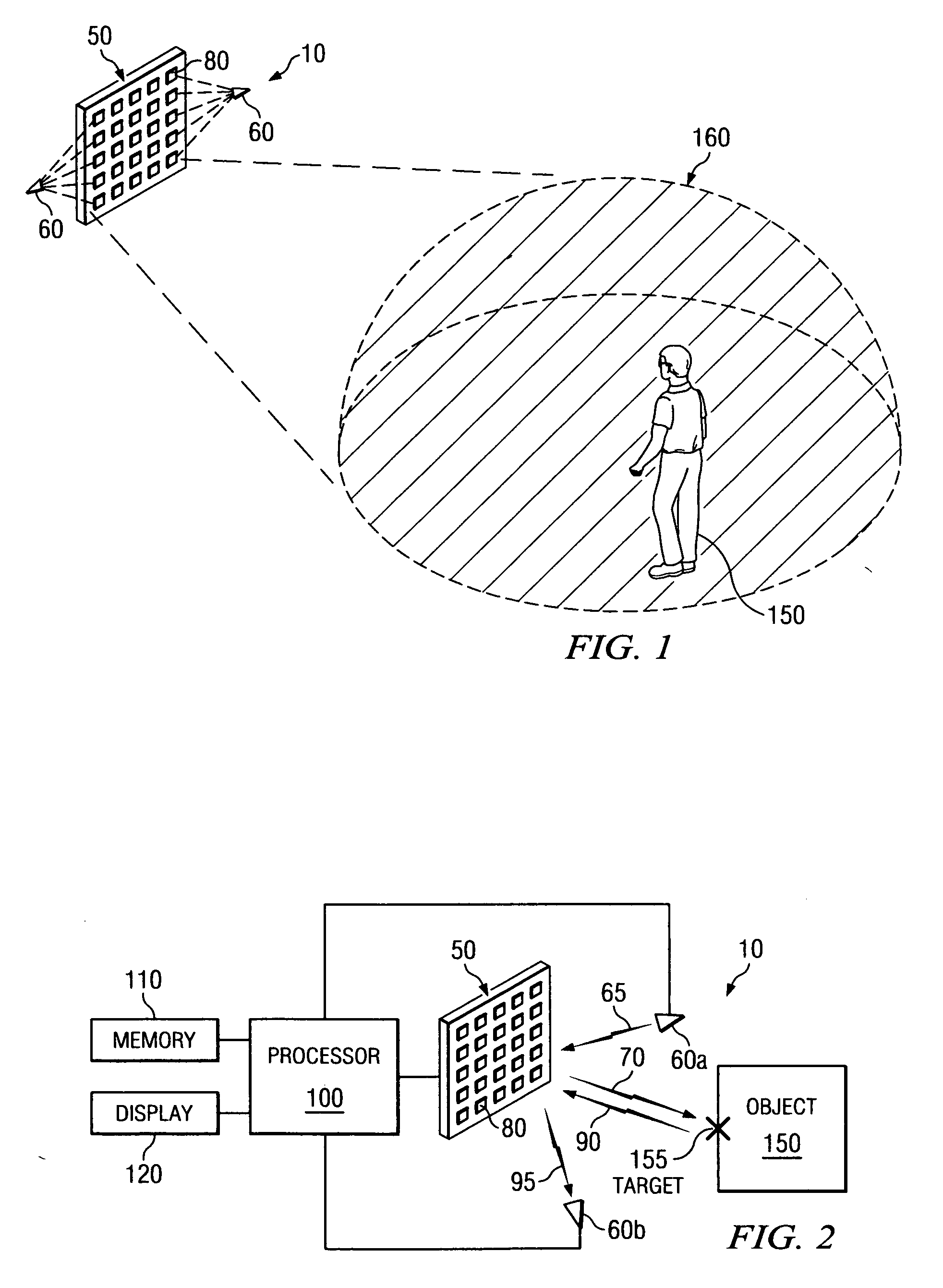
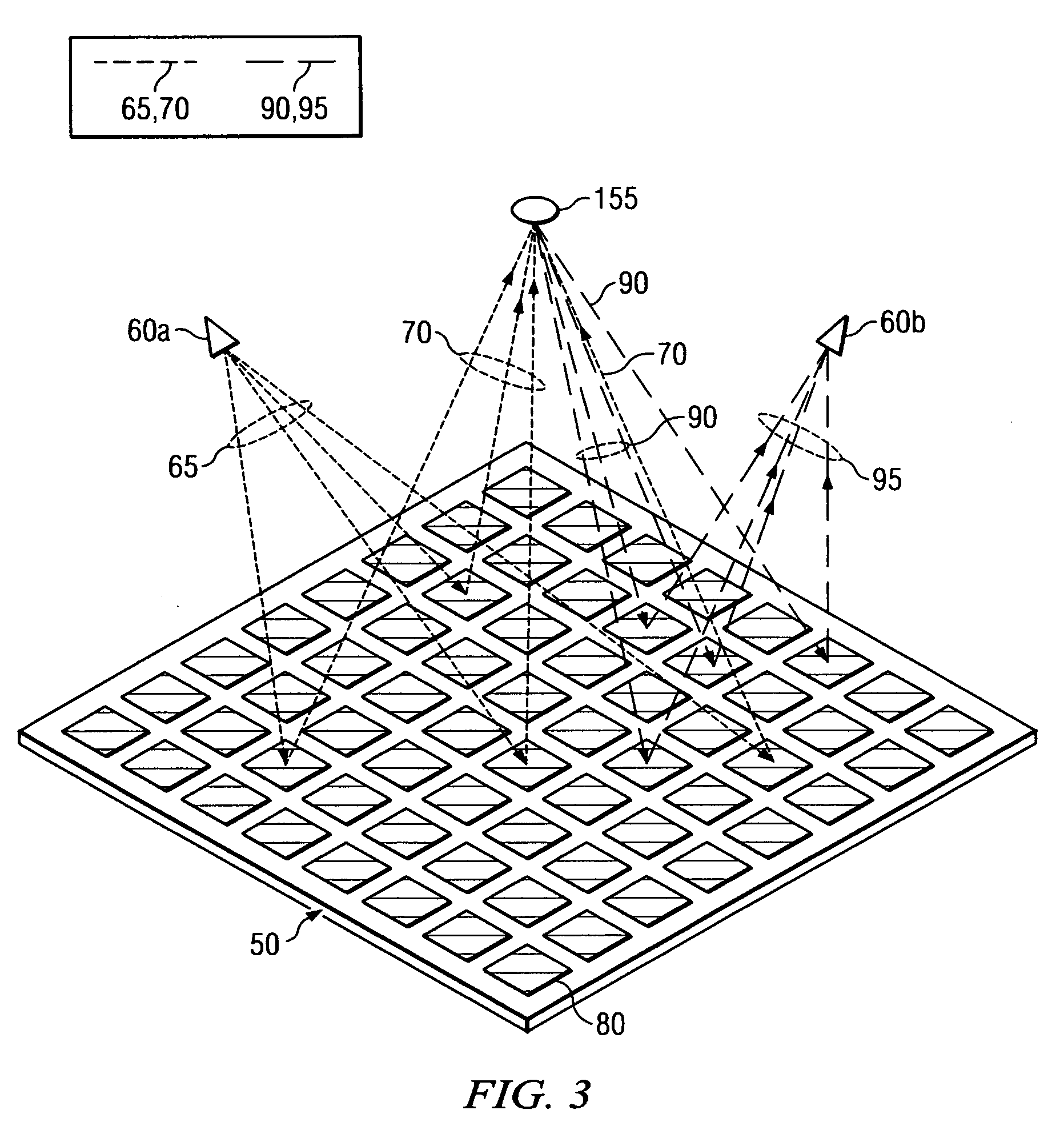
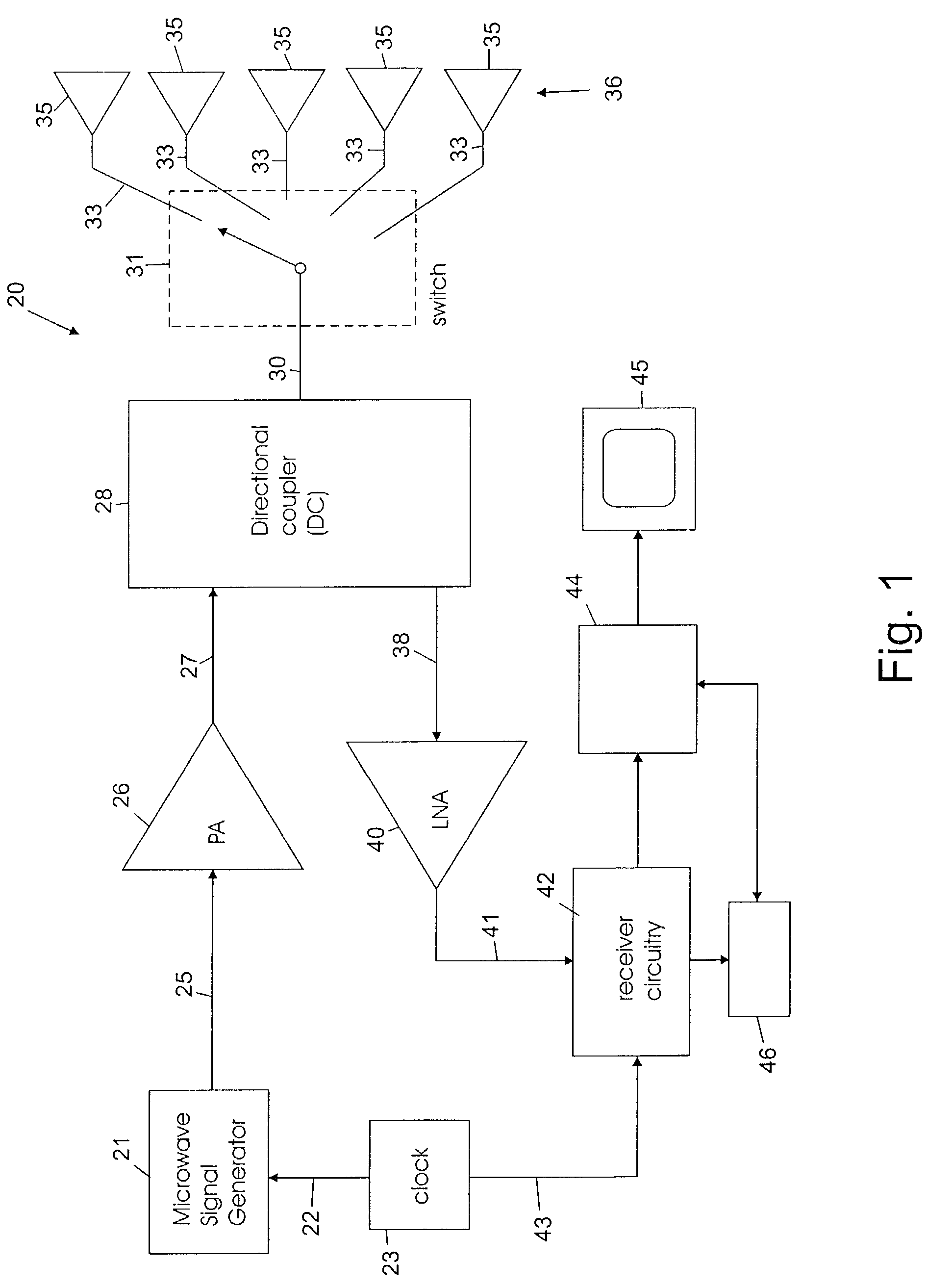
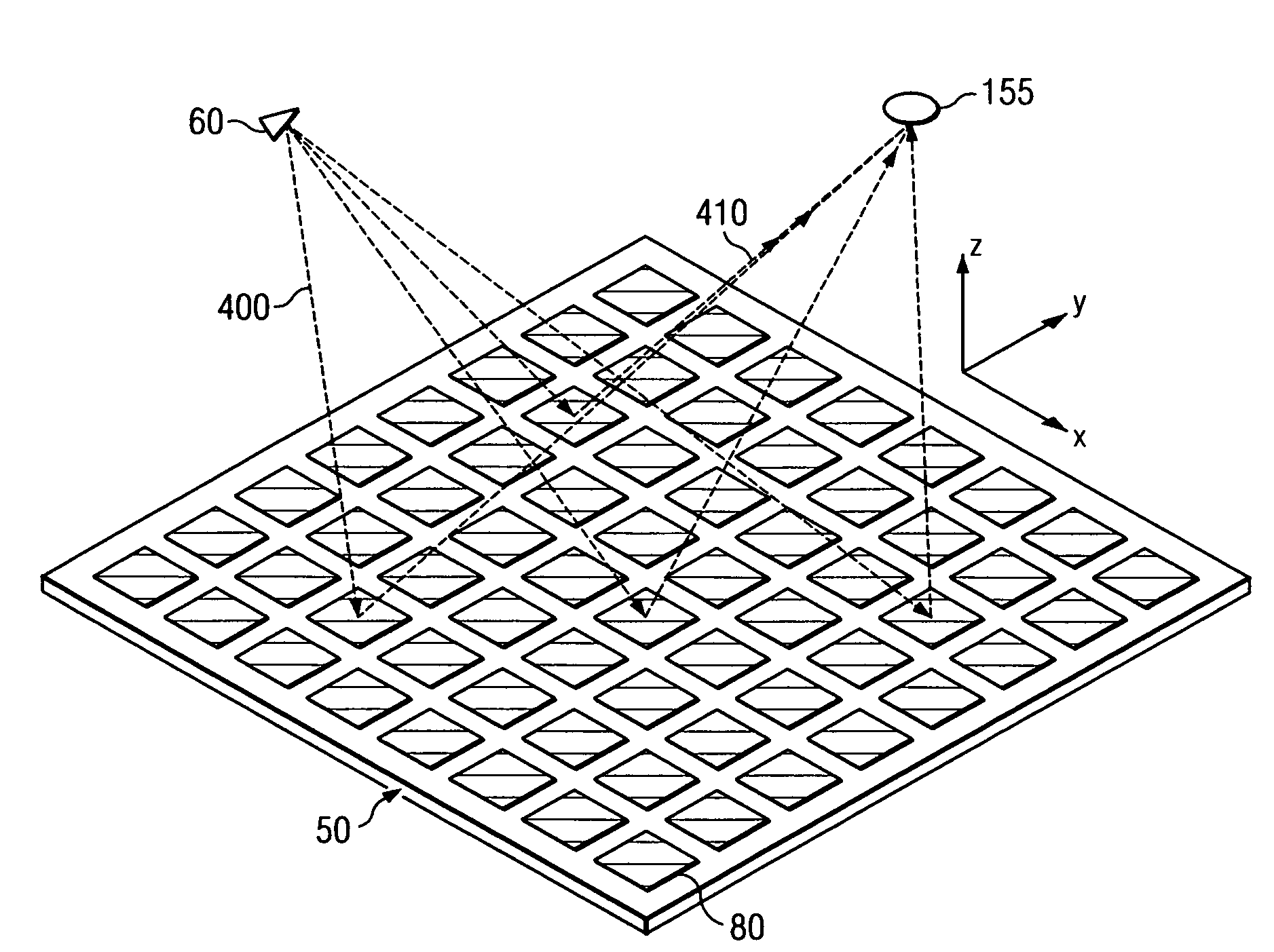
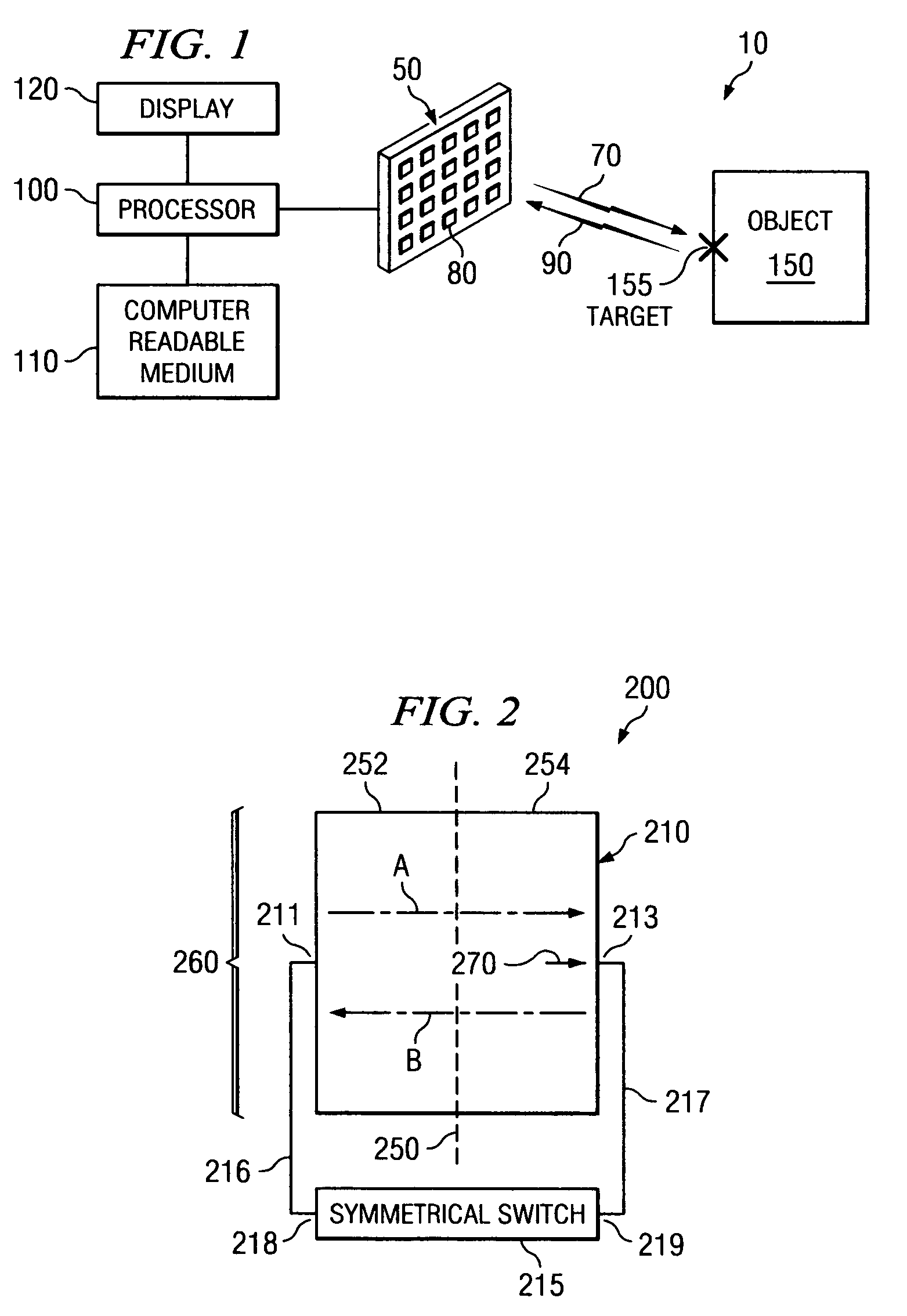
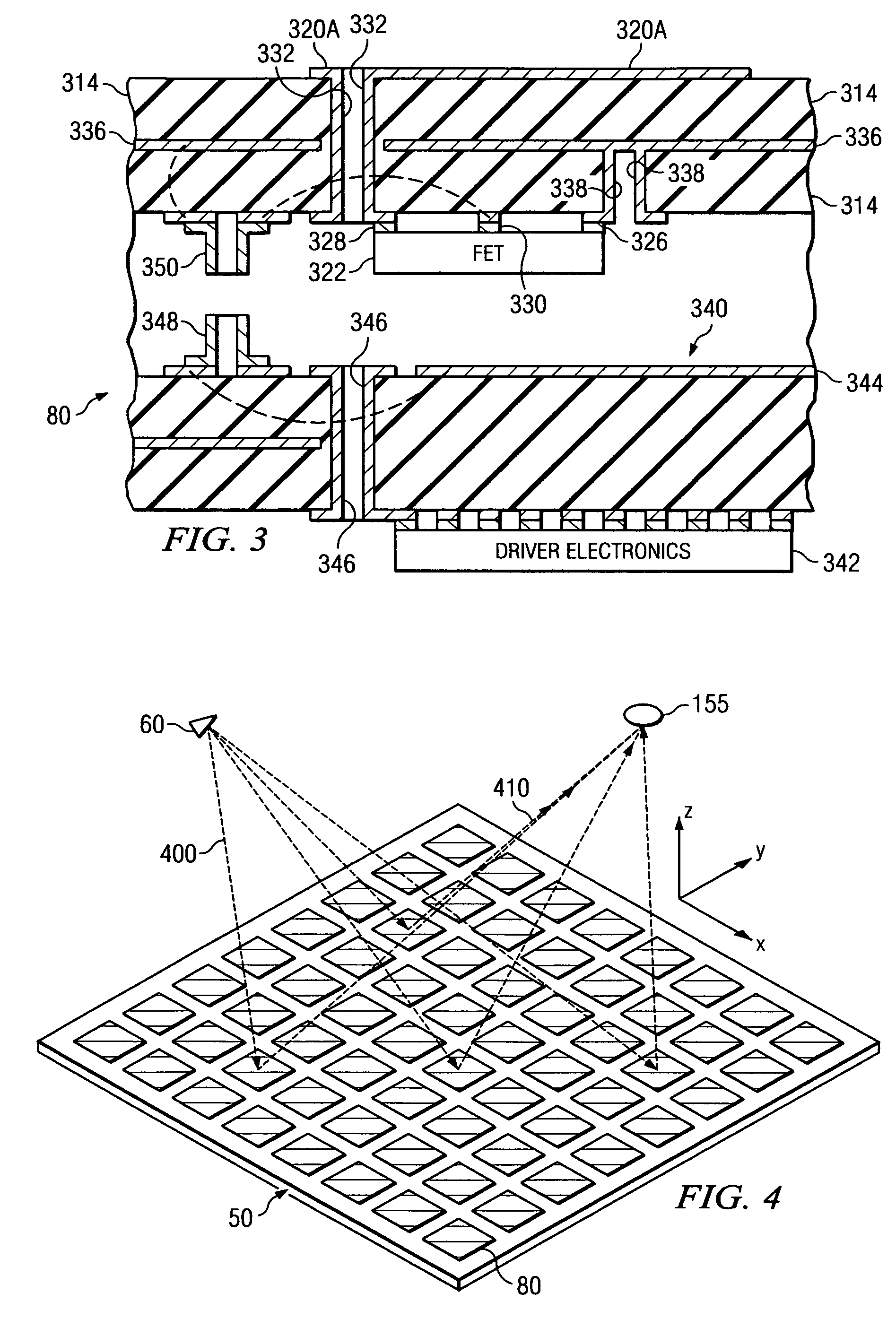
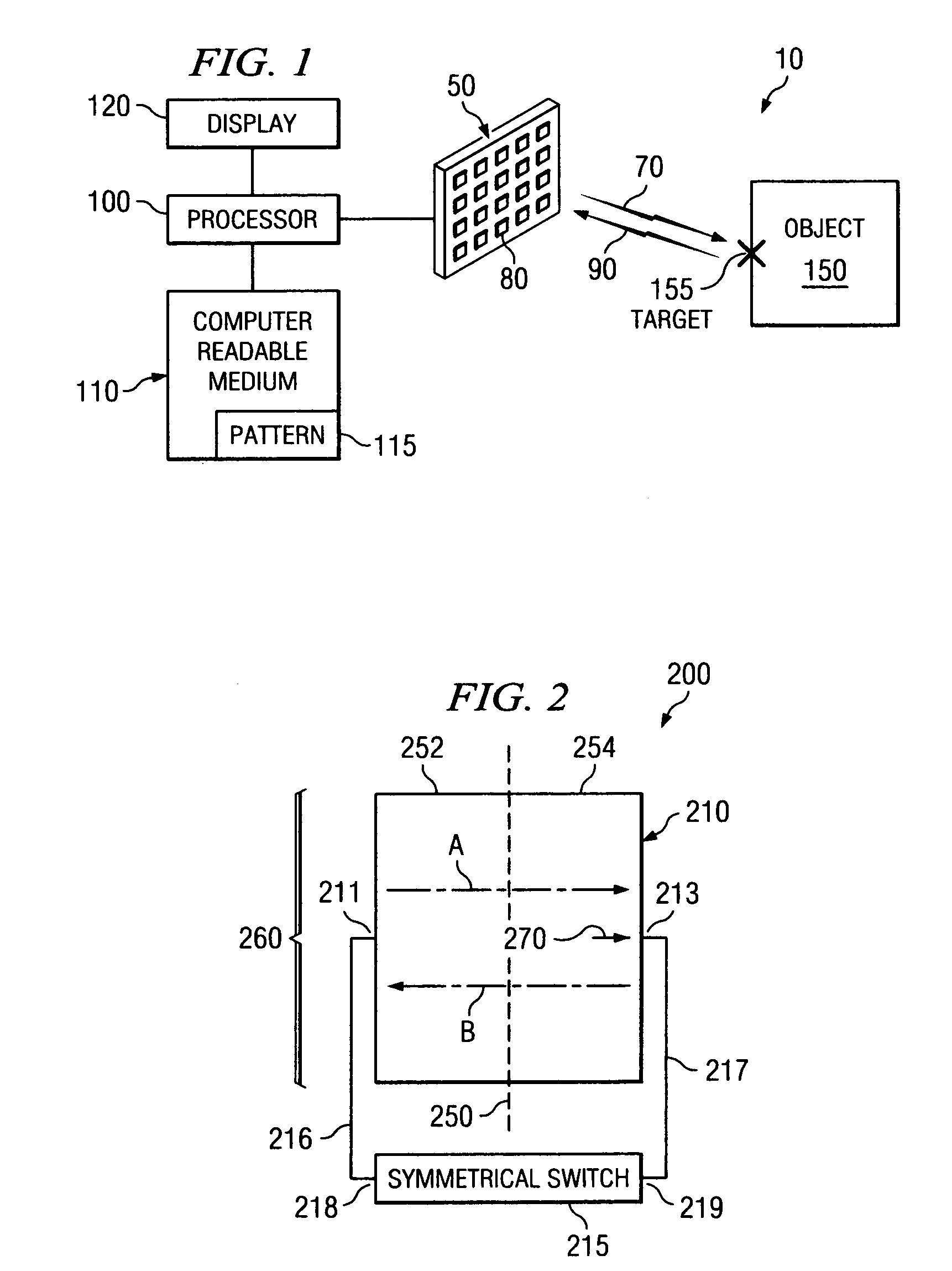
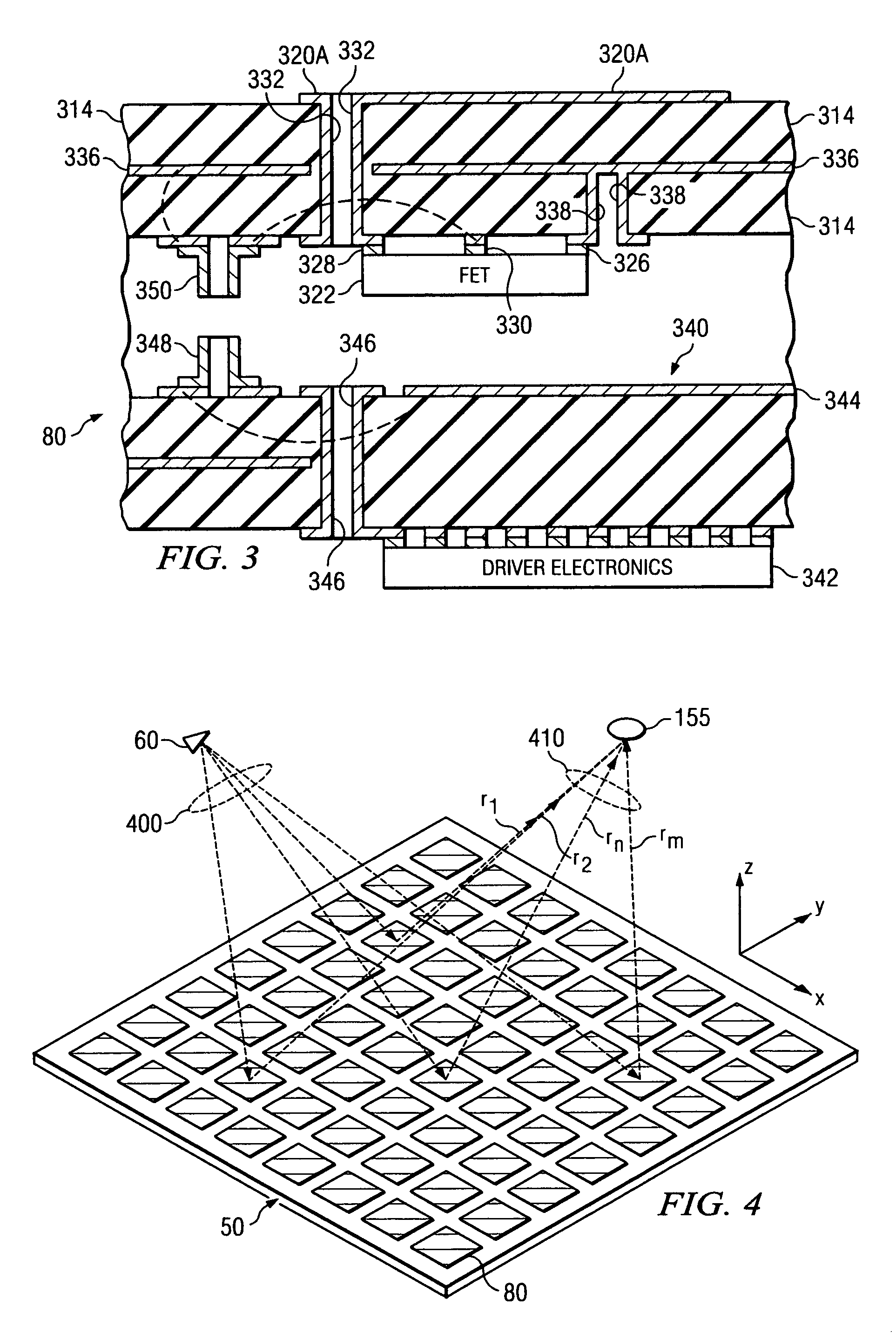
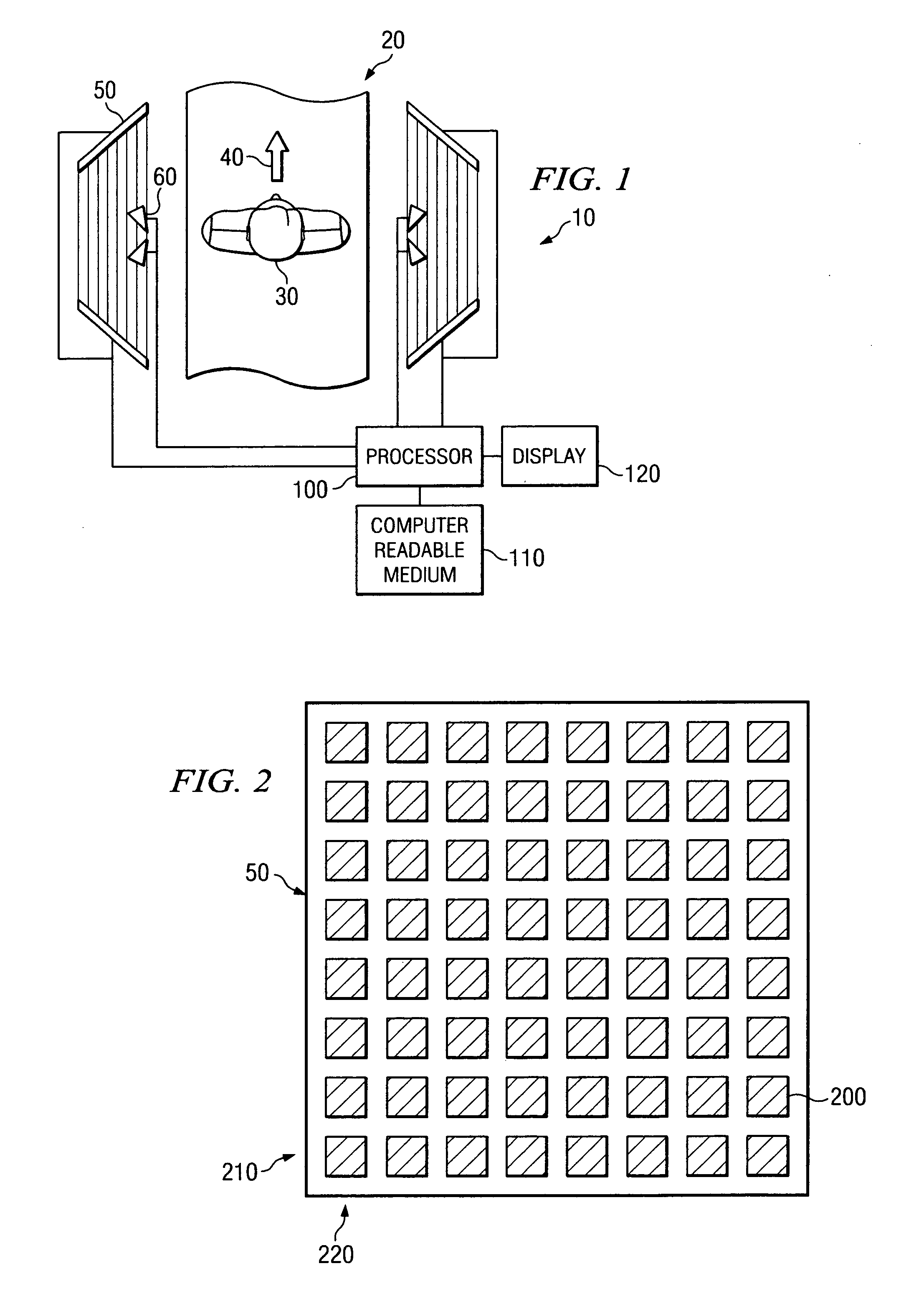
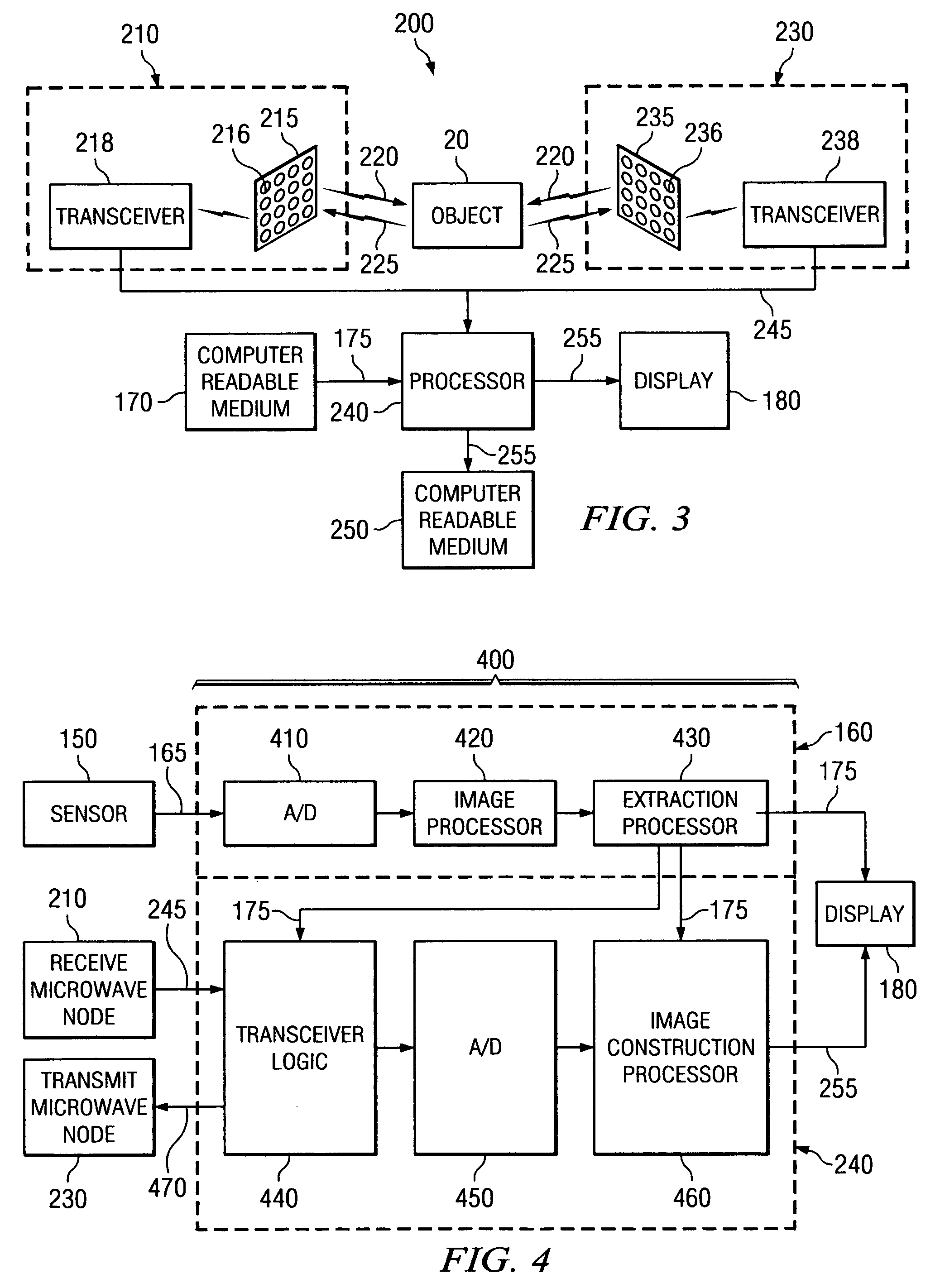
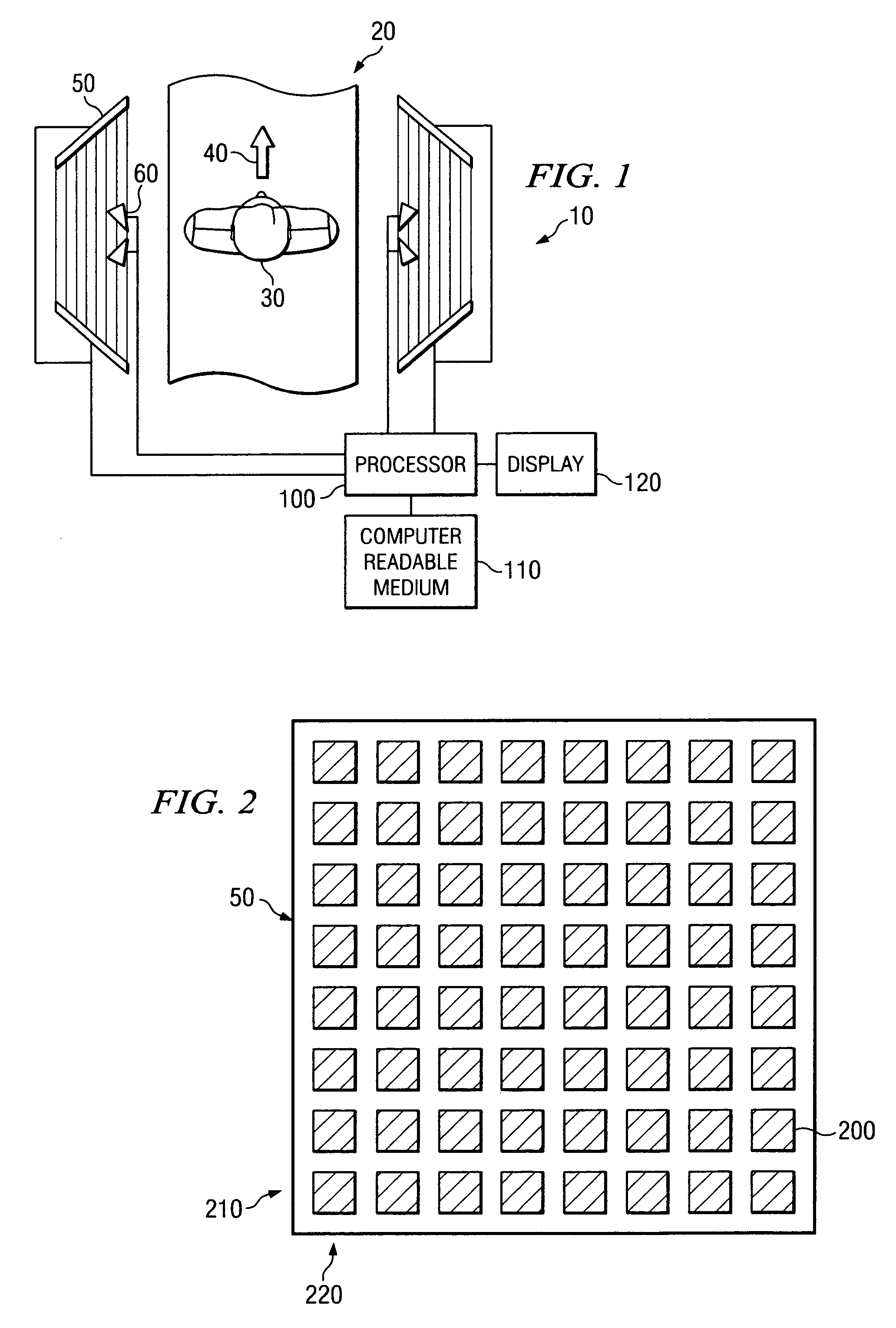
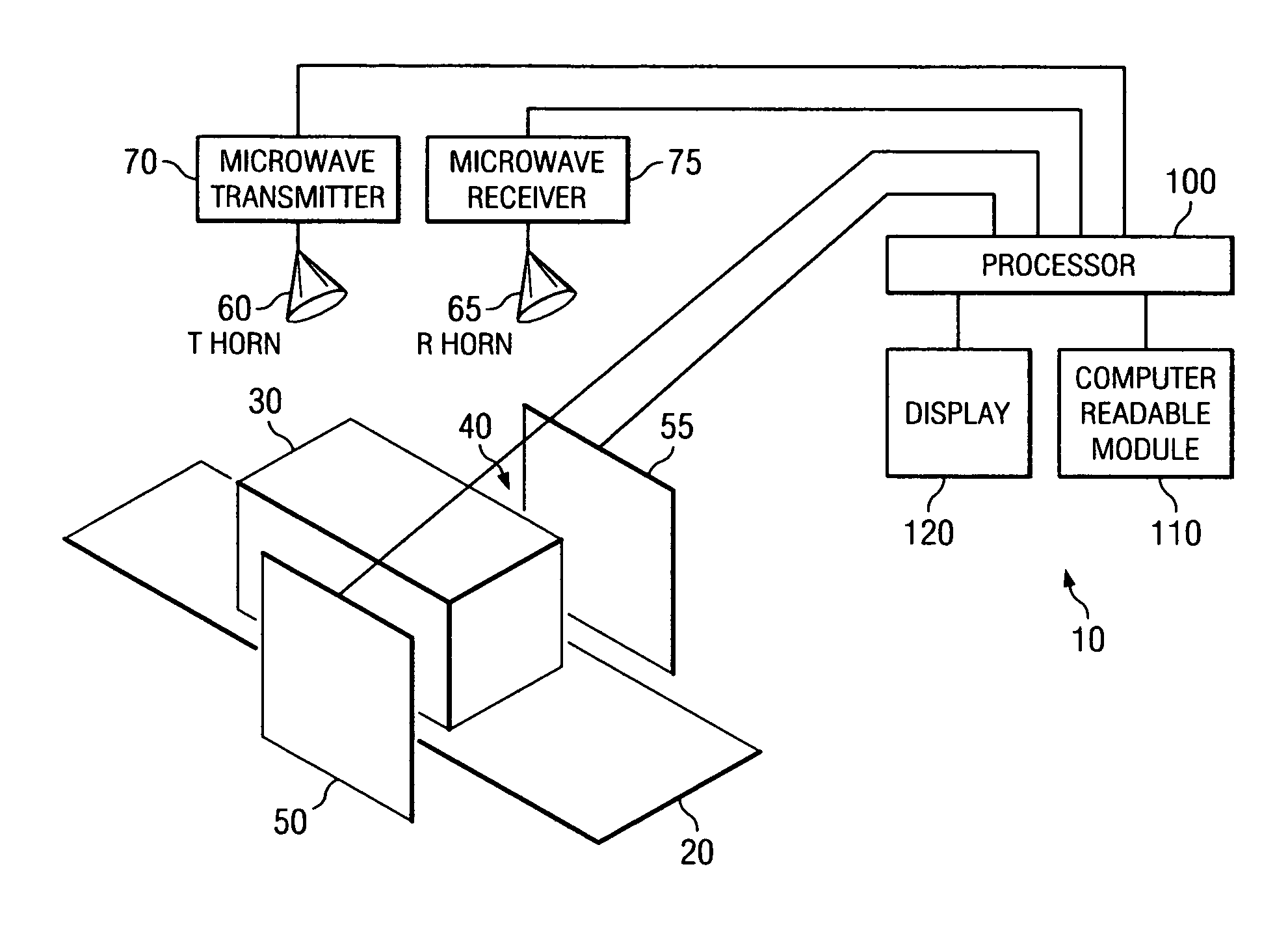
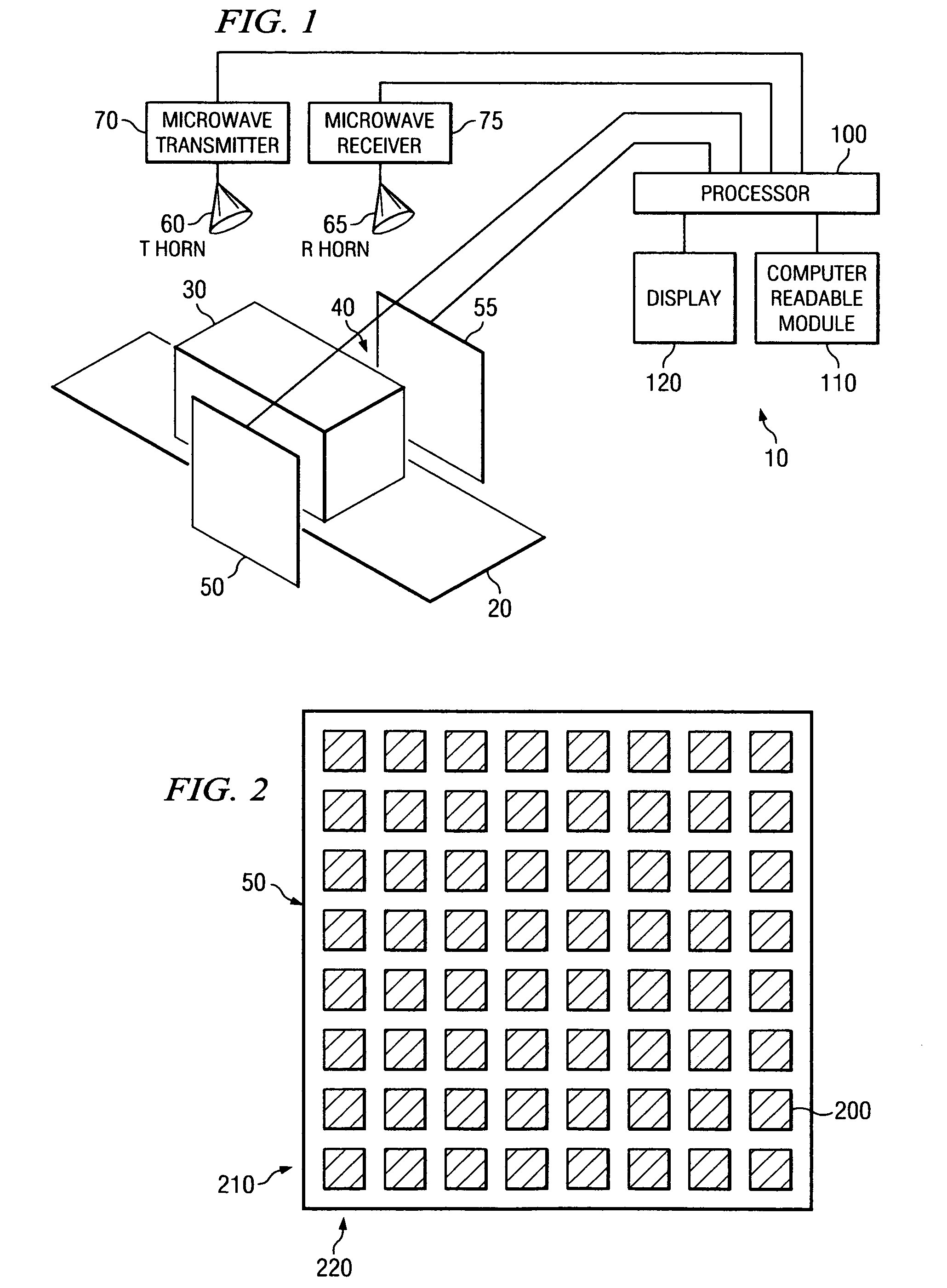
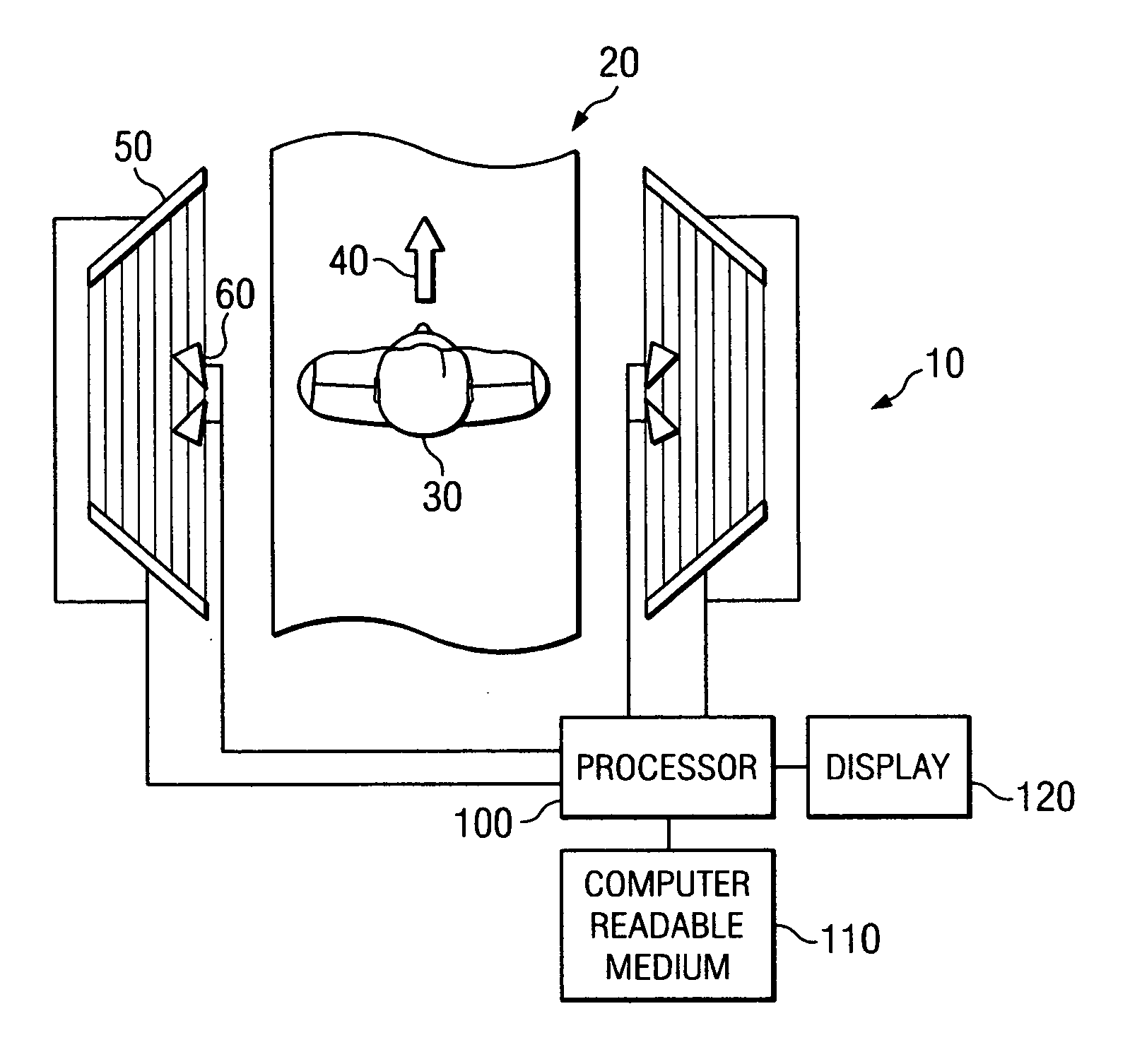
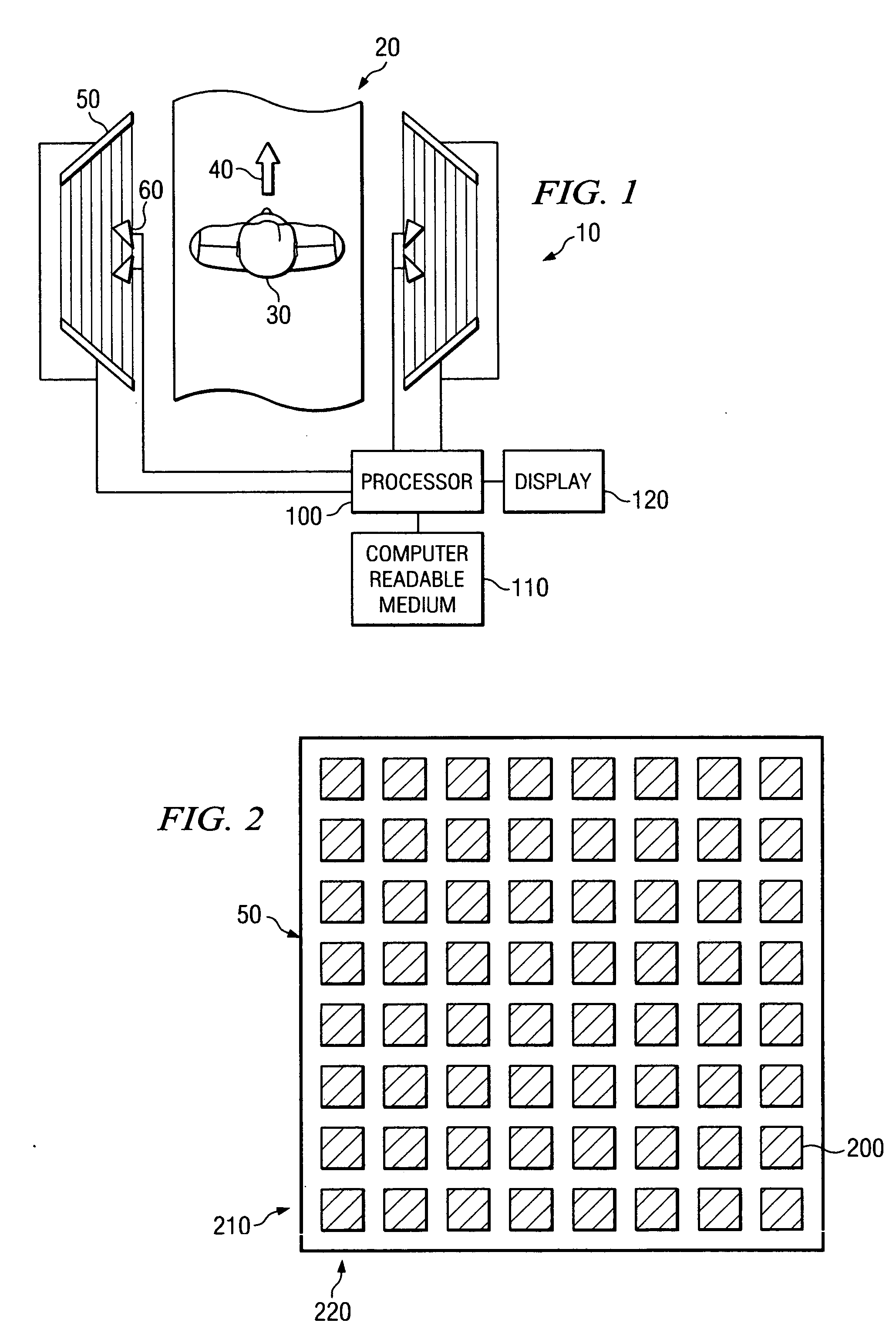
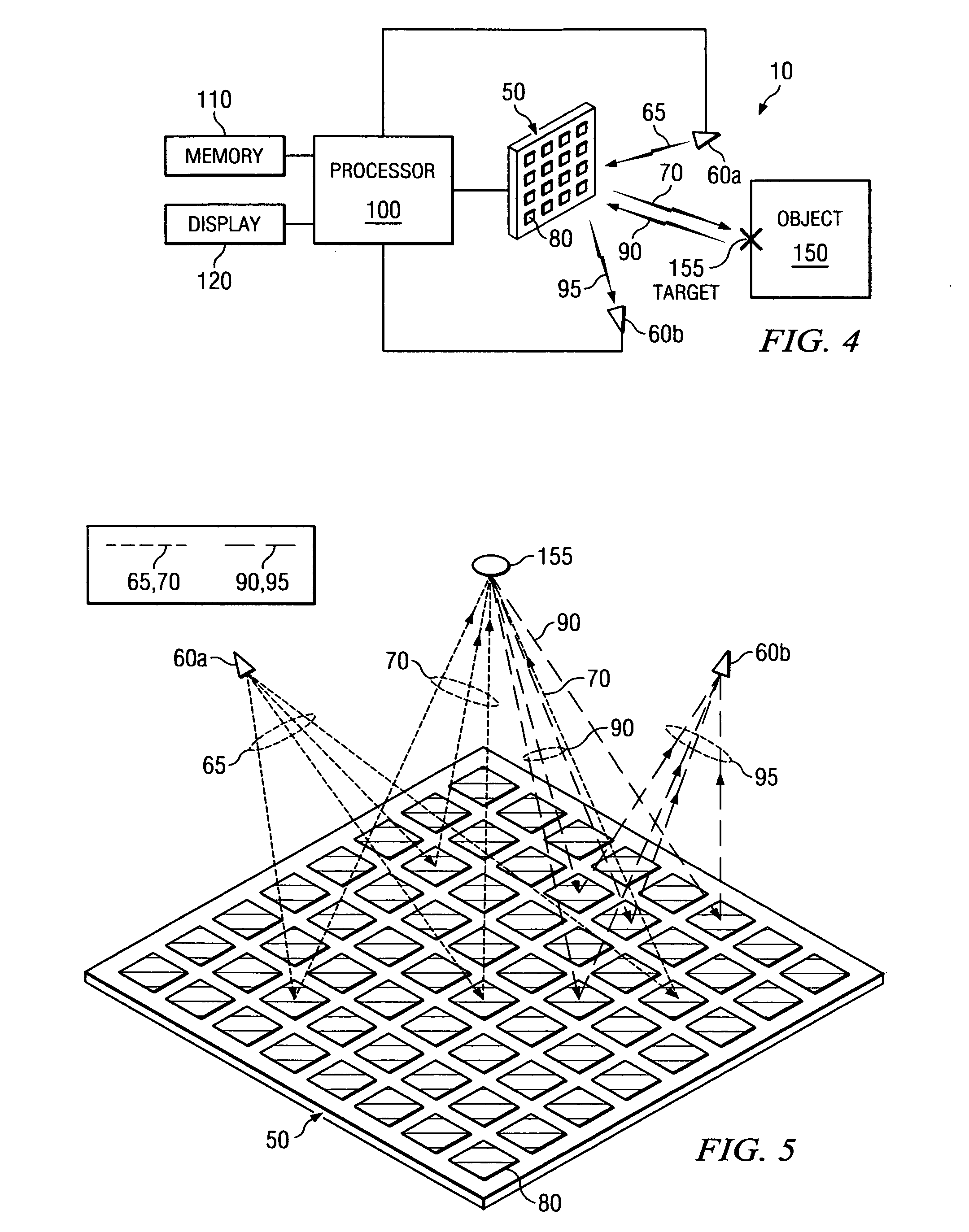
System and method for security inspection using microwave imaging
ActiveUS6965340B1Simple and cost-effectiveGeological detection using milimetre wavesAntenna supports/mountingsLight beamAntenna element
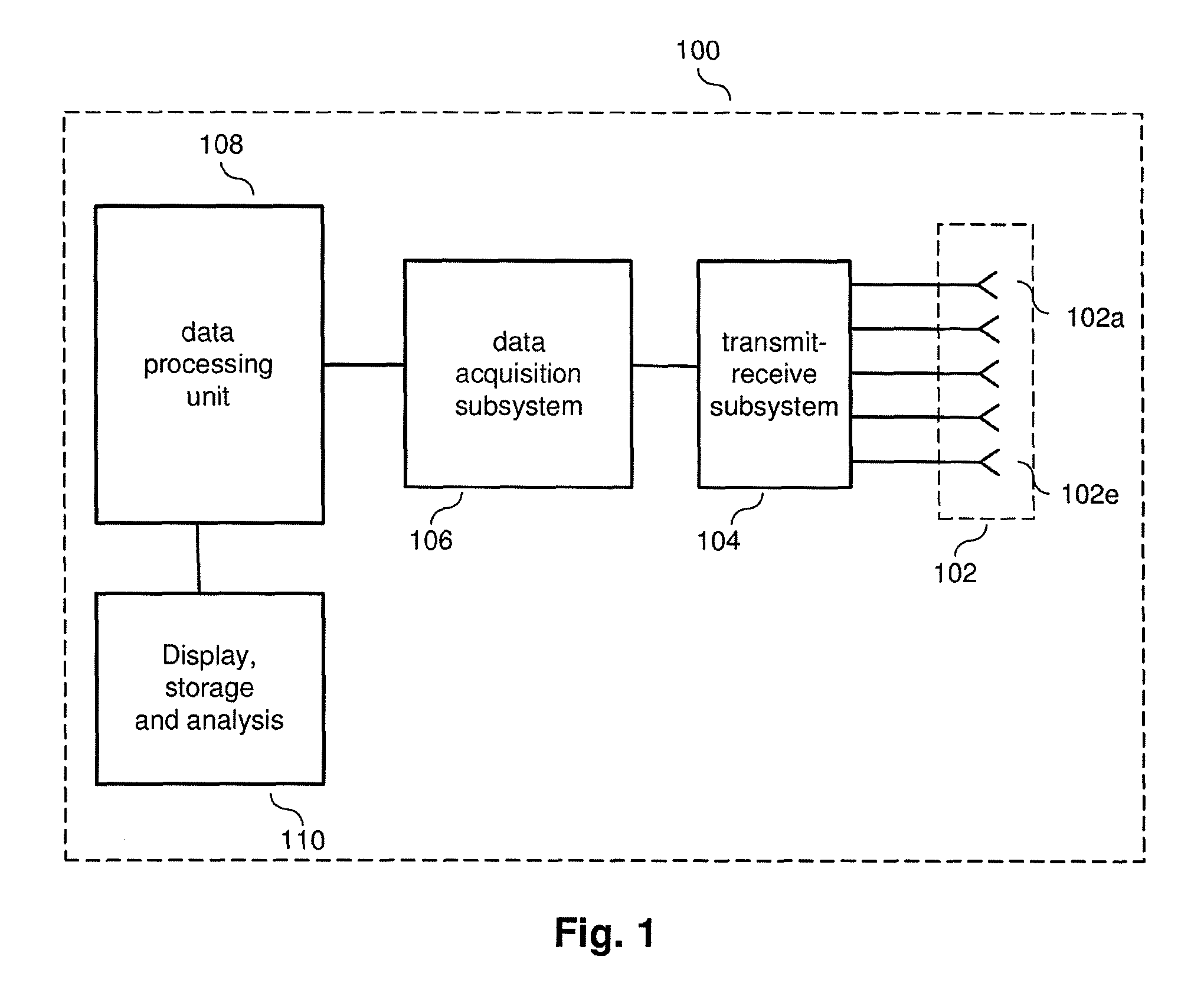
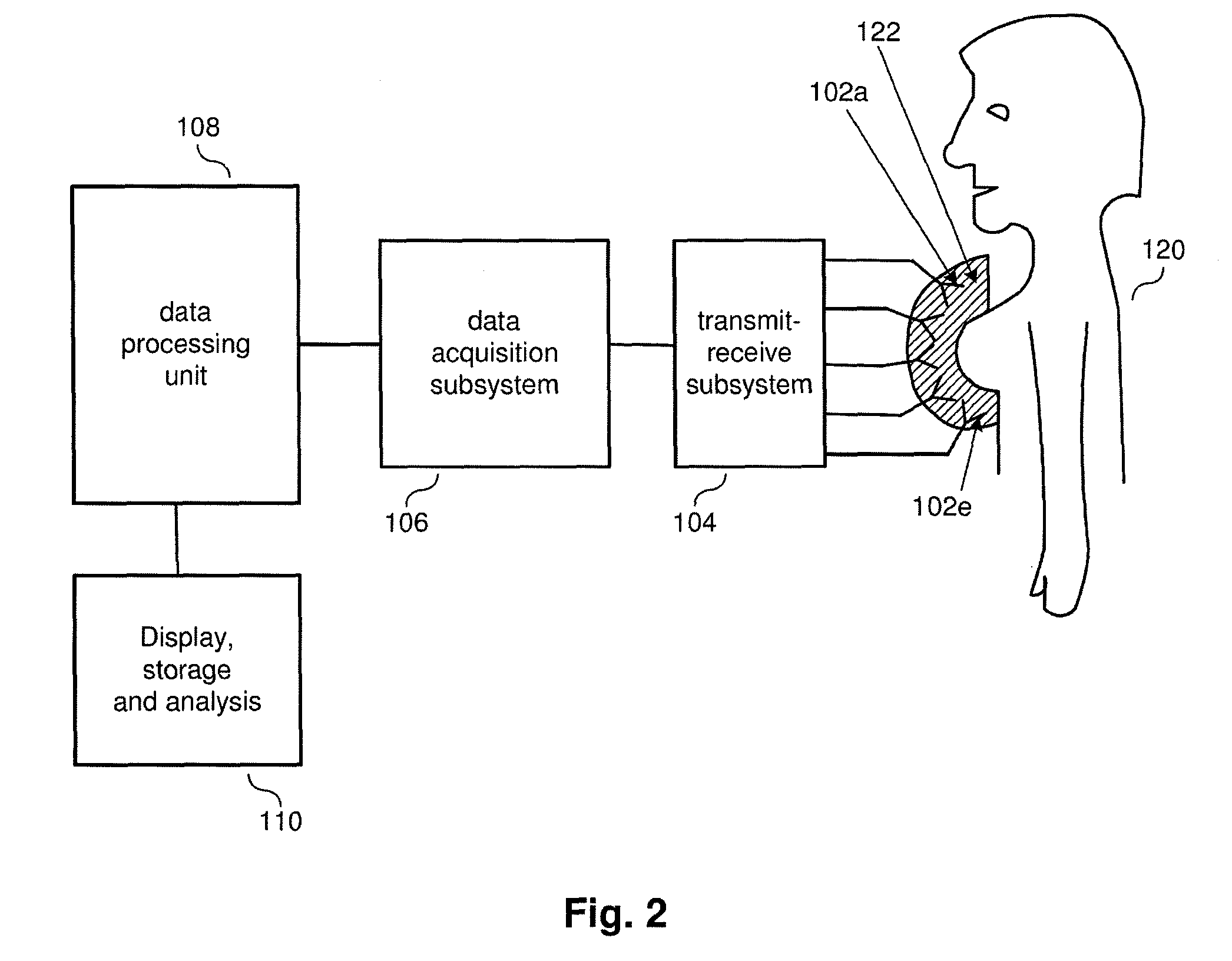
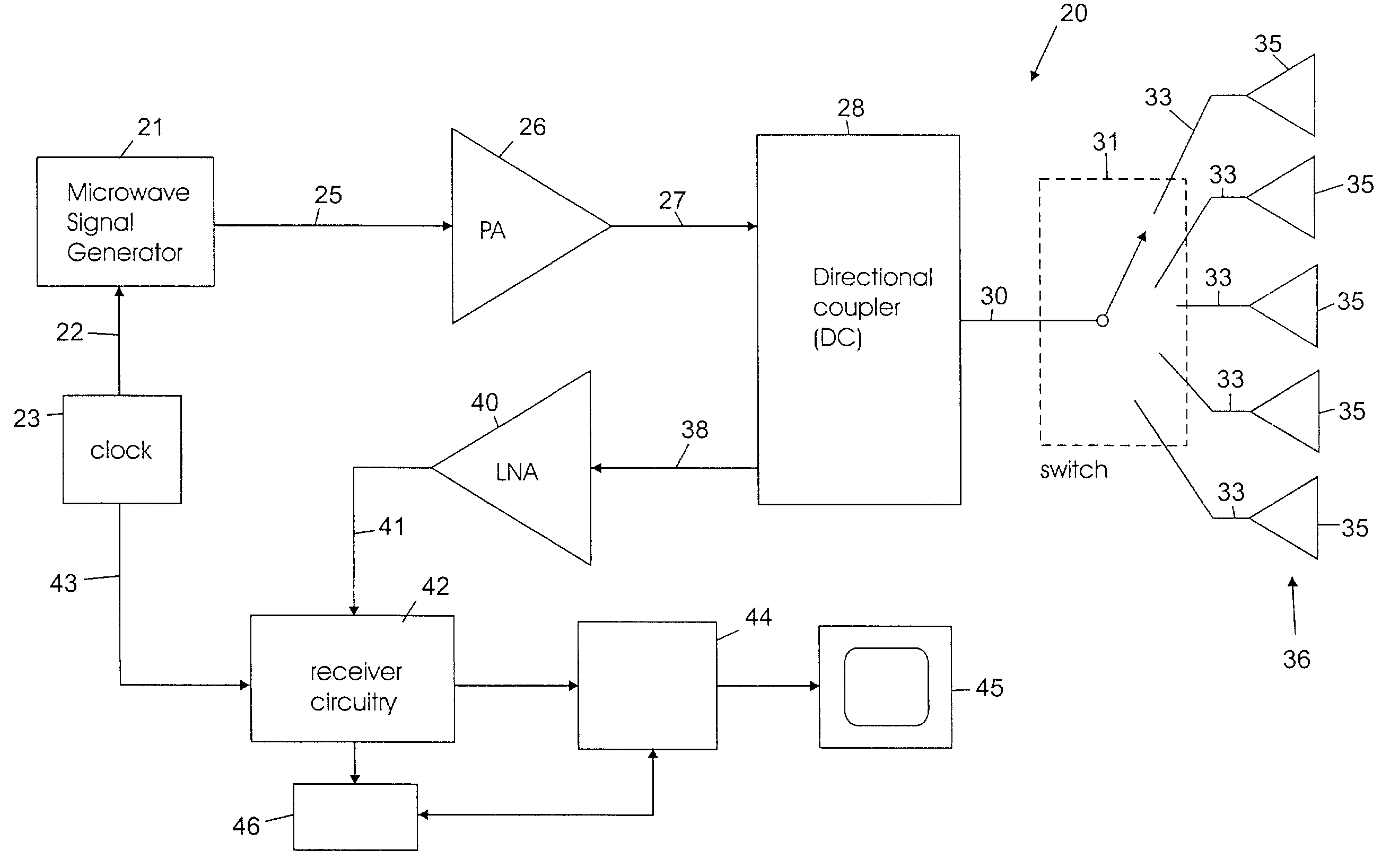
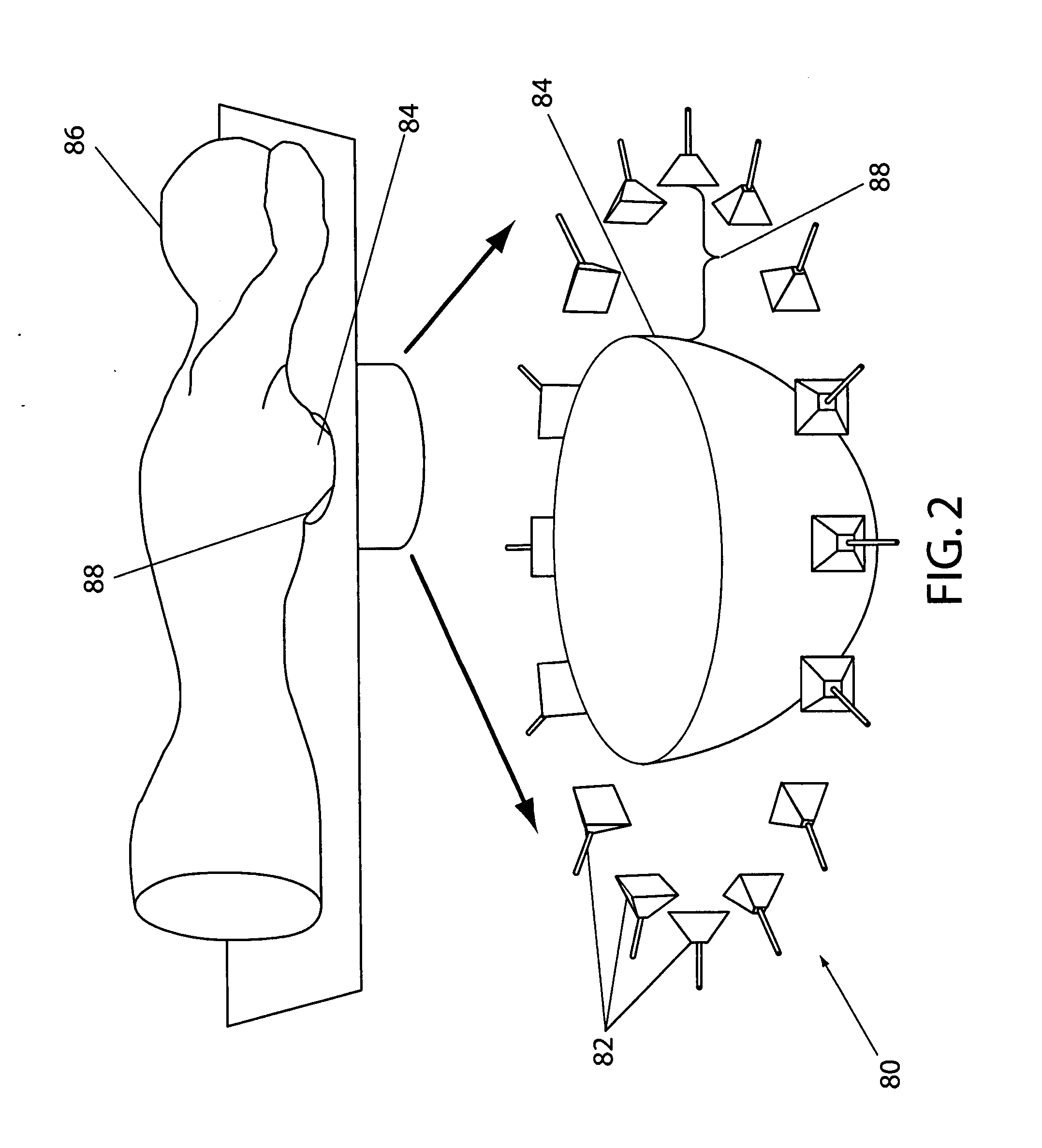
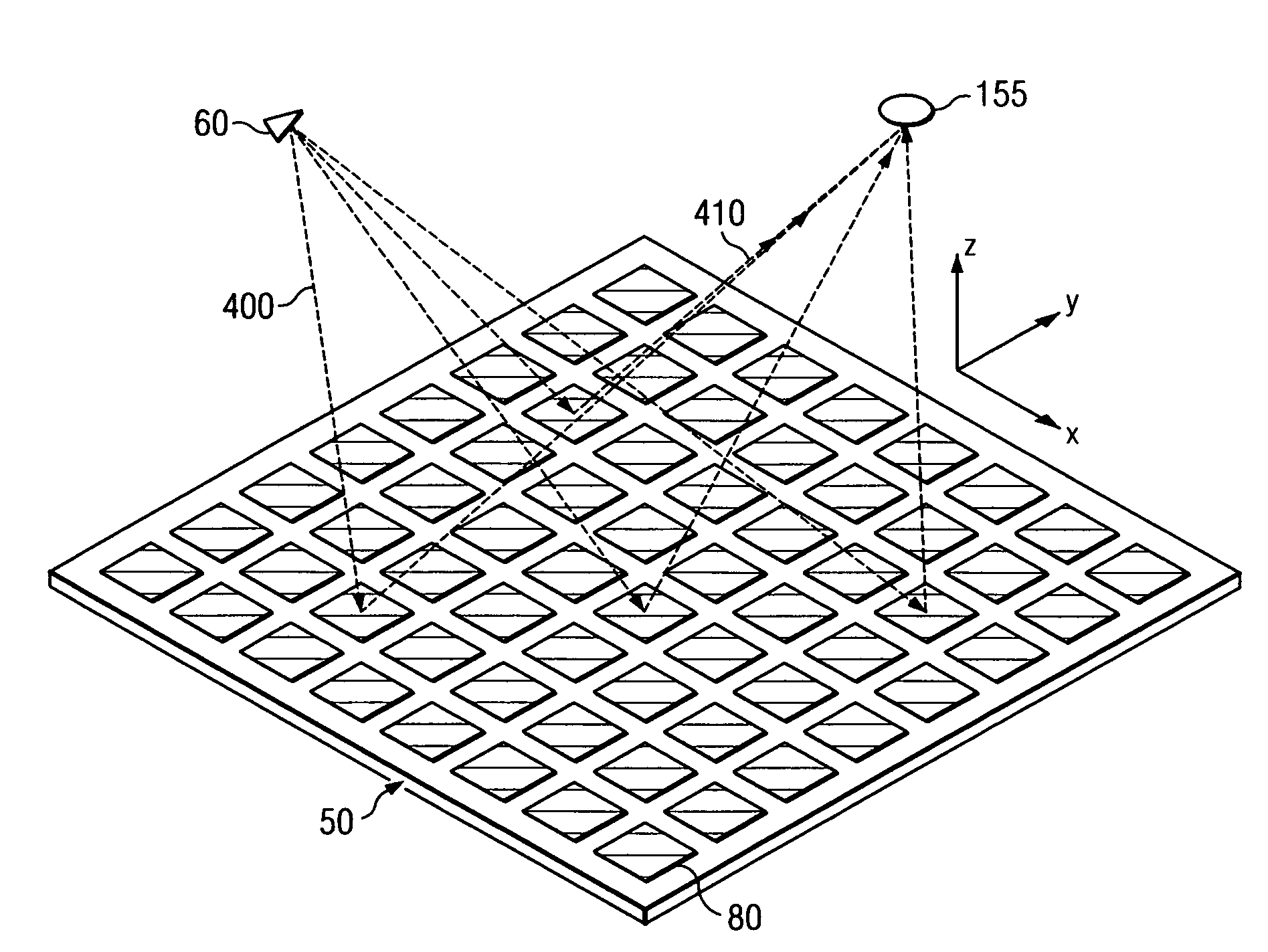
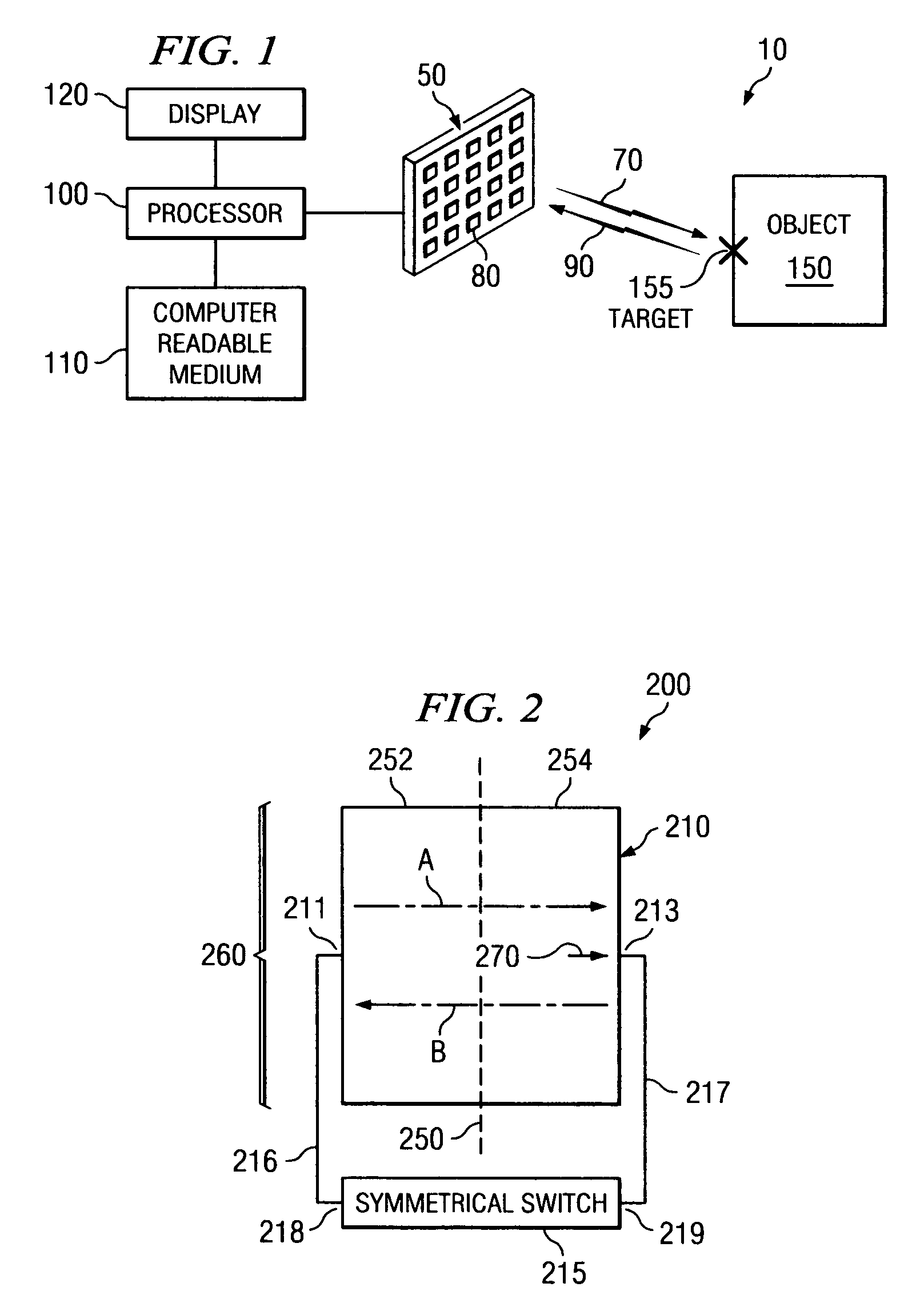
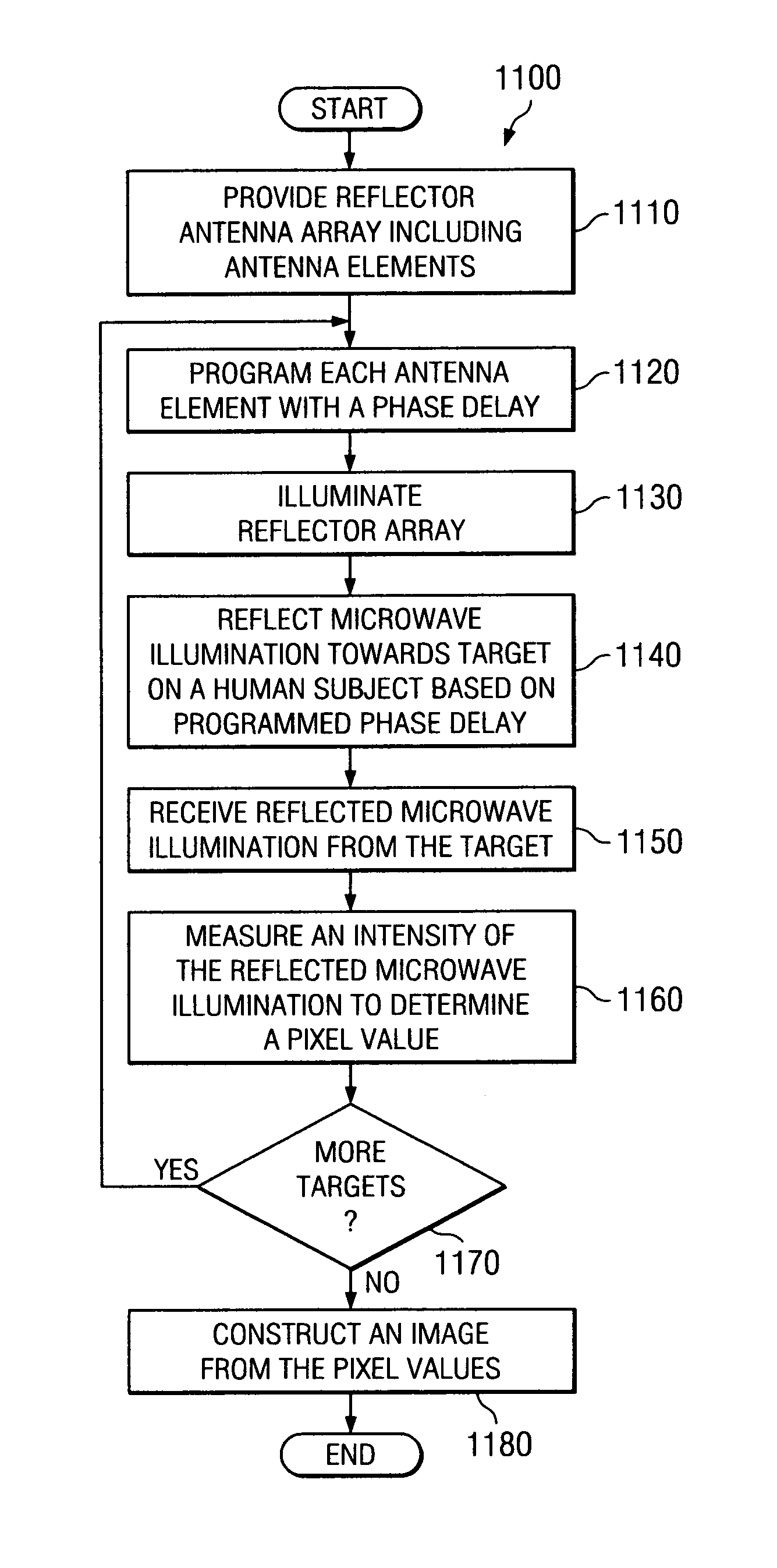
A security inspection system uses microwave radiation to image targets on a human subject or other item. The system includes an array of antenna elements that are programmable with a respective phase delay to direct a beam of microwave illumination toward a target on the human subject or item. The antenna elements are further capable of receiving reflected microwave illumination reflected from the target. A processor is operable to measure an intensity of the reflected microwave illumination to determine a value of a pixel within an image of the human subject or item. Multiple beams can be directed towards the human subject or item to obtain corresponding pixel values for use by the processor in constructing the image.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Apparatus and method for doppler-assisted MIMO radar microwave imaging
ActiveUS20110237939A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisObject motionMicrowave imaging
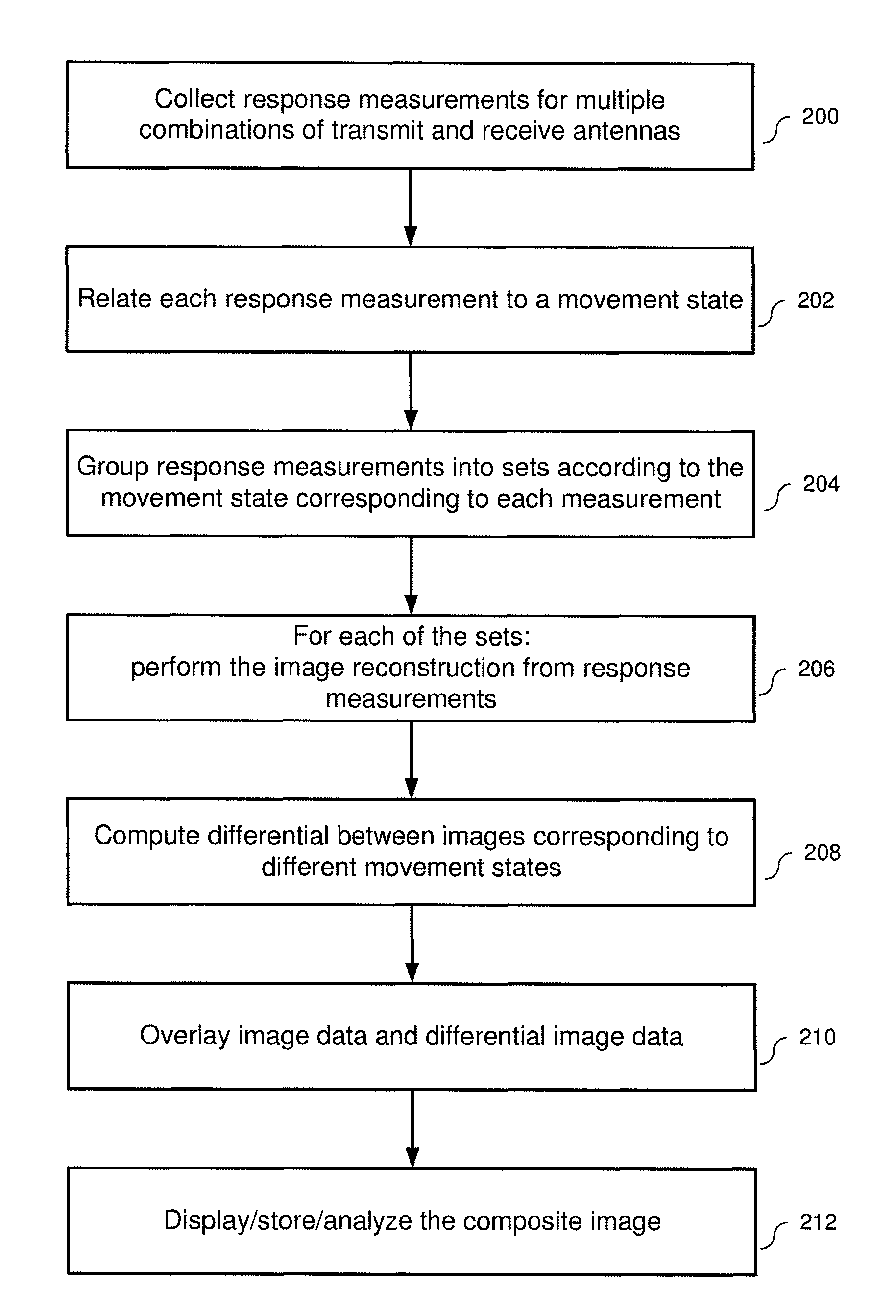
A method and apparatus for enhanced microwave imaging of an object collects microwave responses for multiple combinations of transmit antennas, receive antennas, and object movement states. The responses are grouped into sets of responses corresponding to at least two object movement states. An image is reconstructed from the set of responses for each movement state, and a differential image representative of object movement is generated from the reconstructed image for each of the at least two object movement states. The differential image is overlaid on a reconstructed image to obtain an enhanced composite image of the object.
Owner:VAYYAR IMAGING LTD
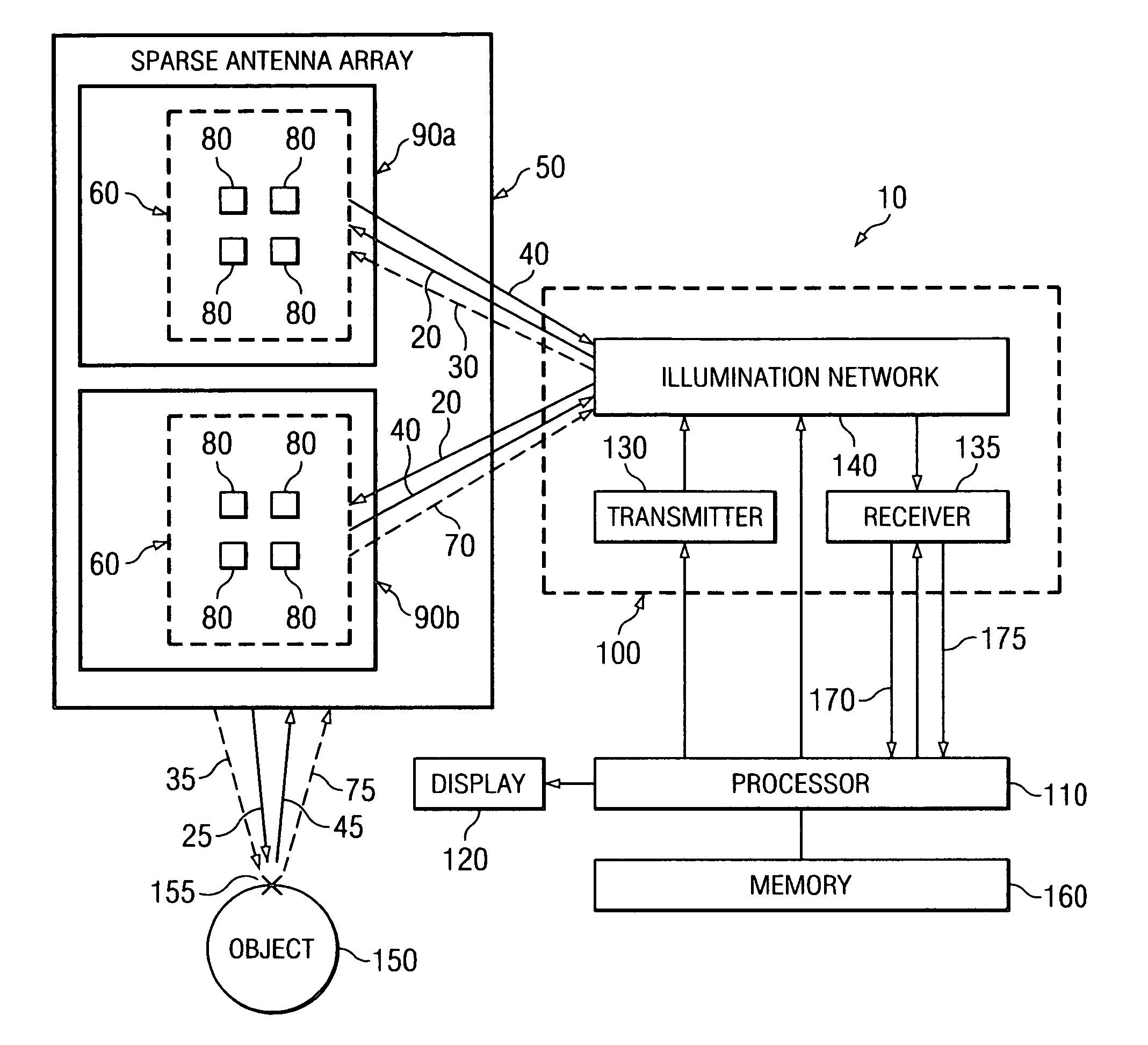
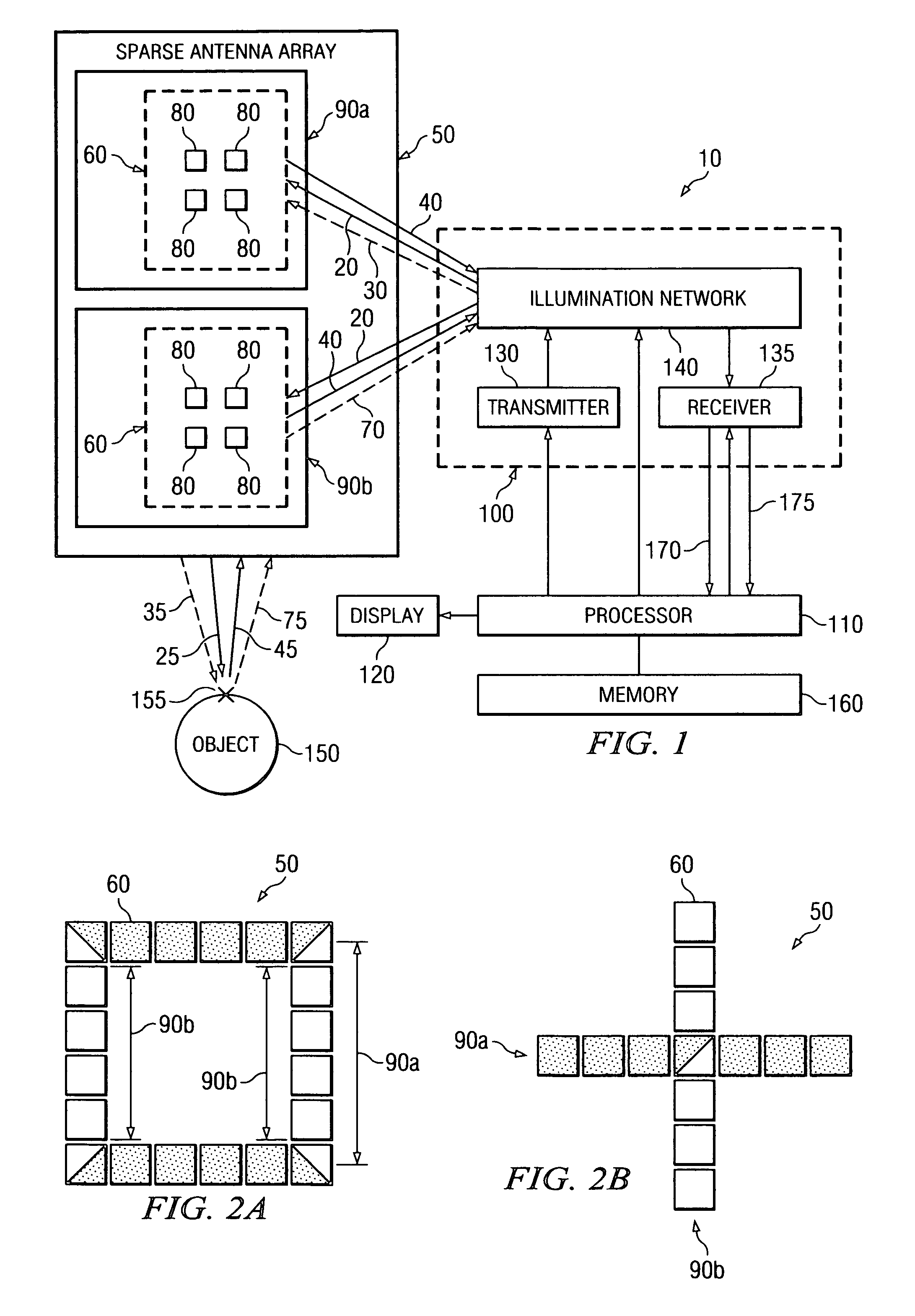
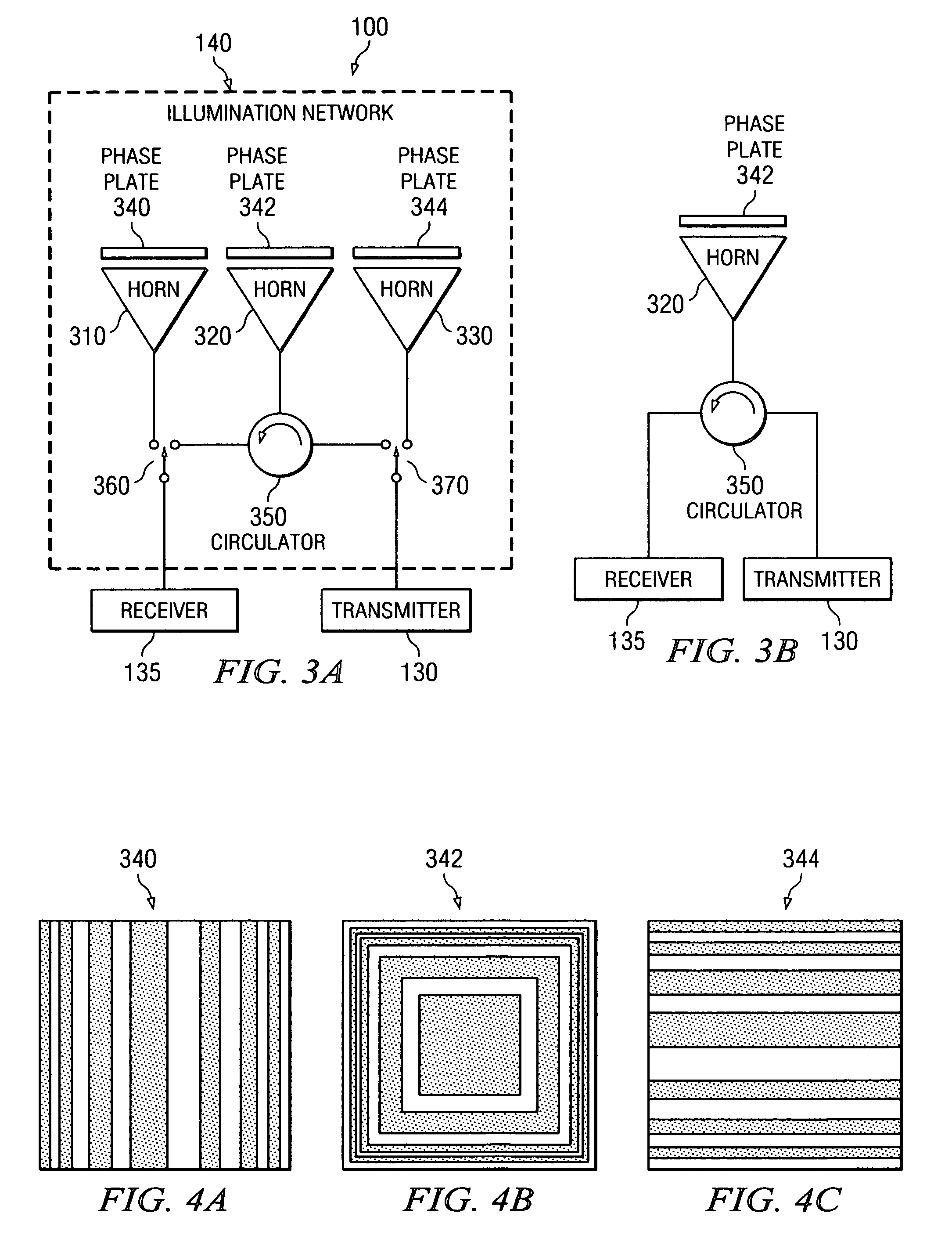
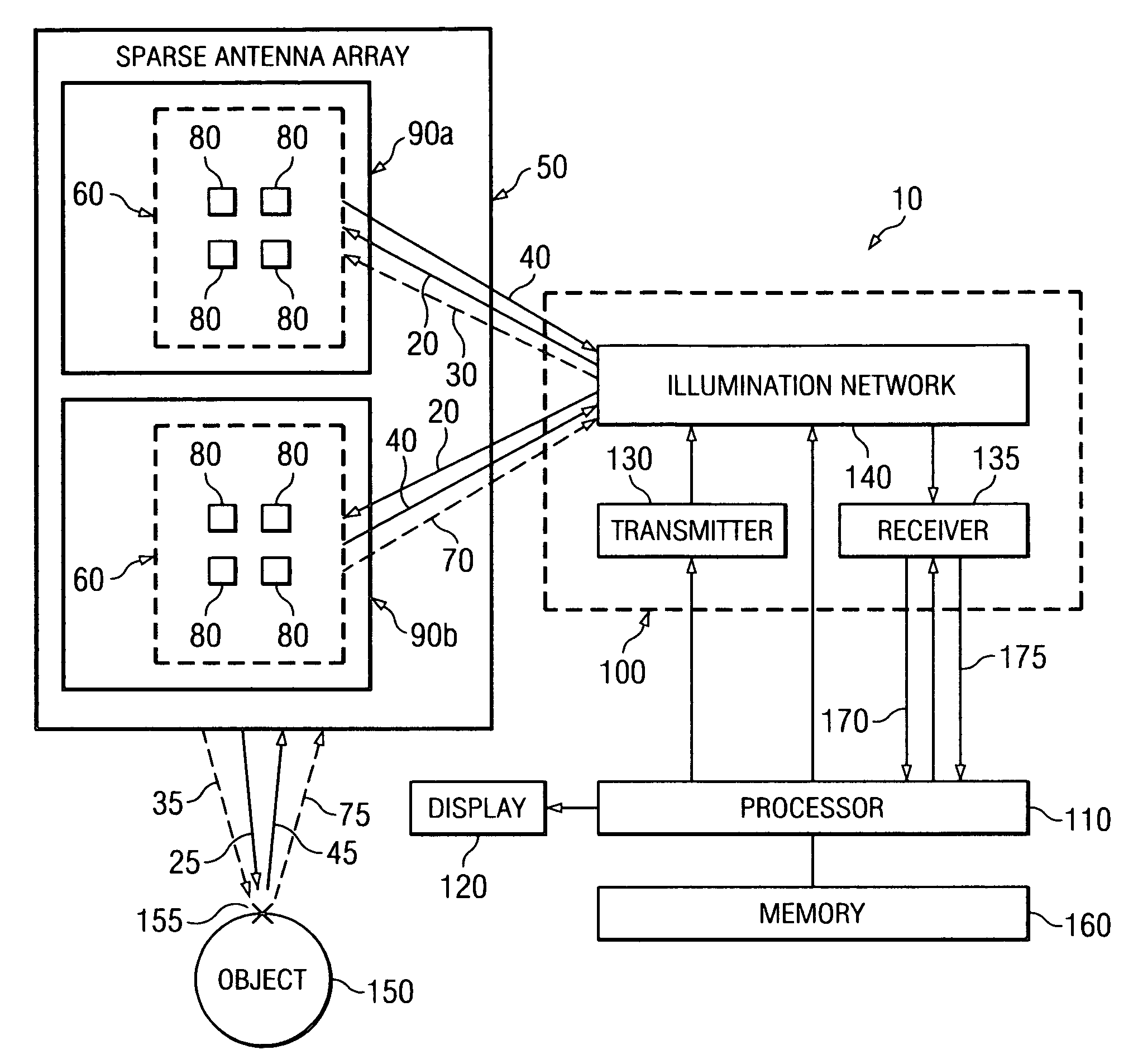
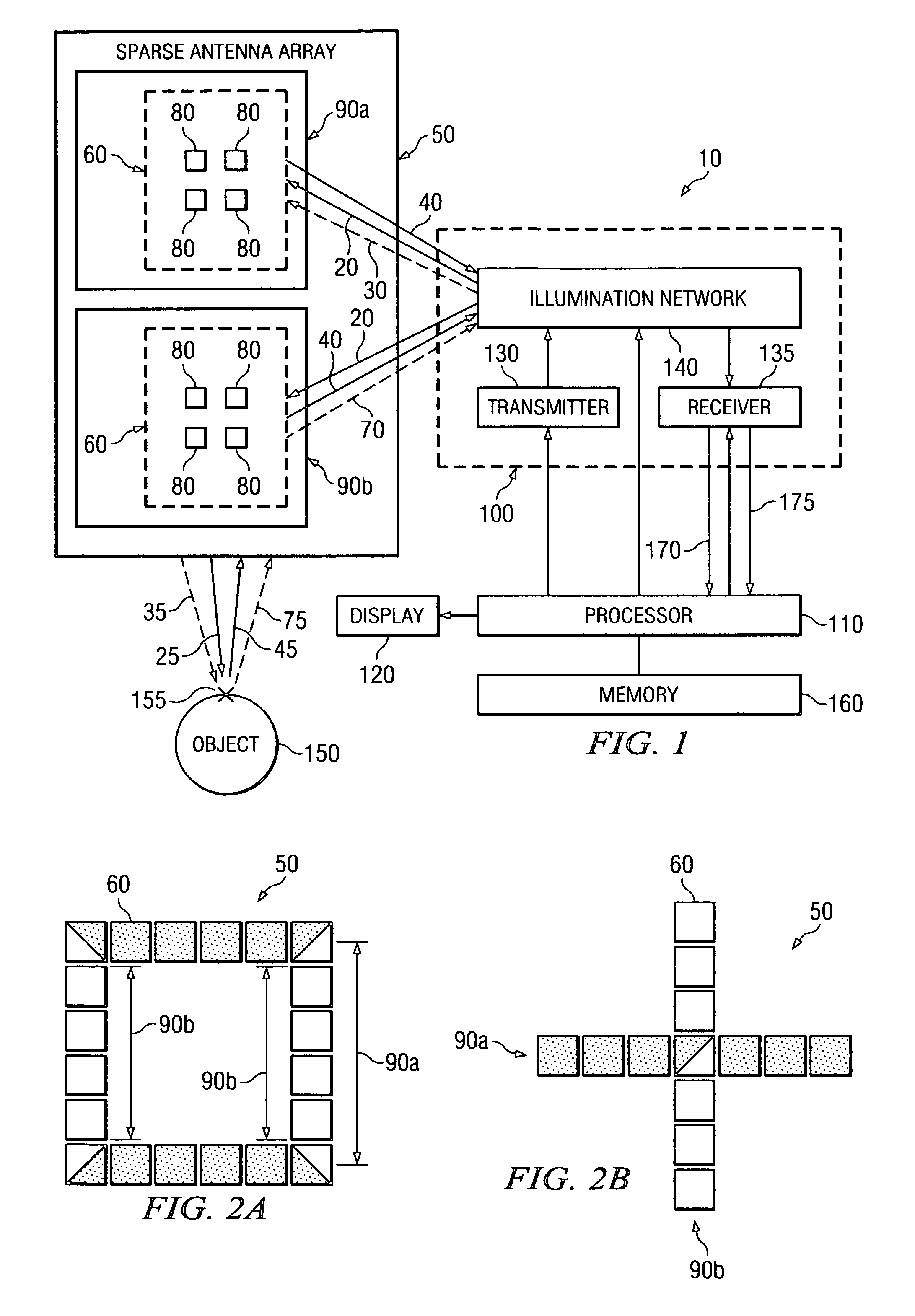
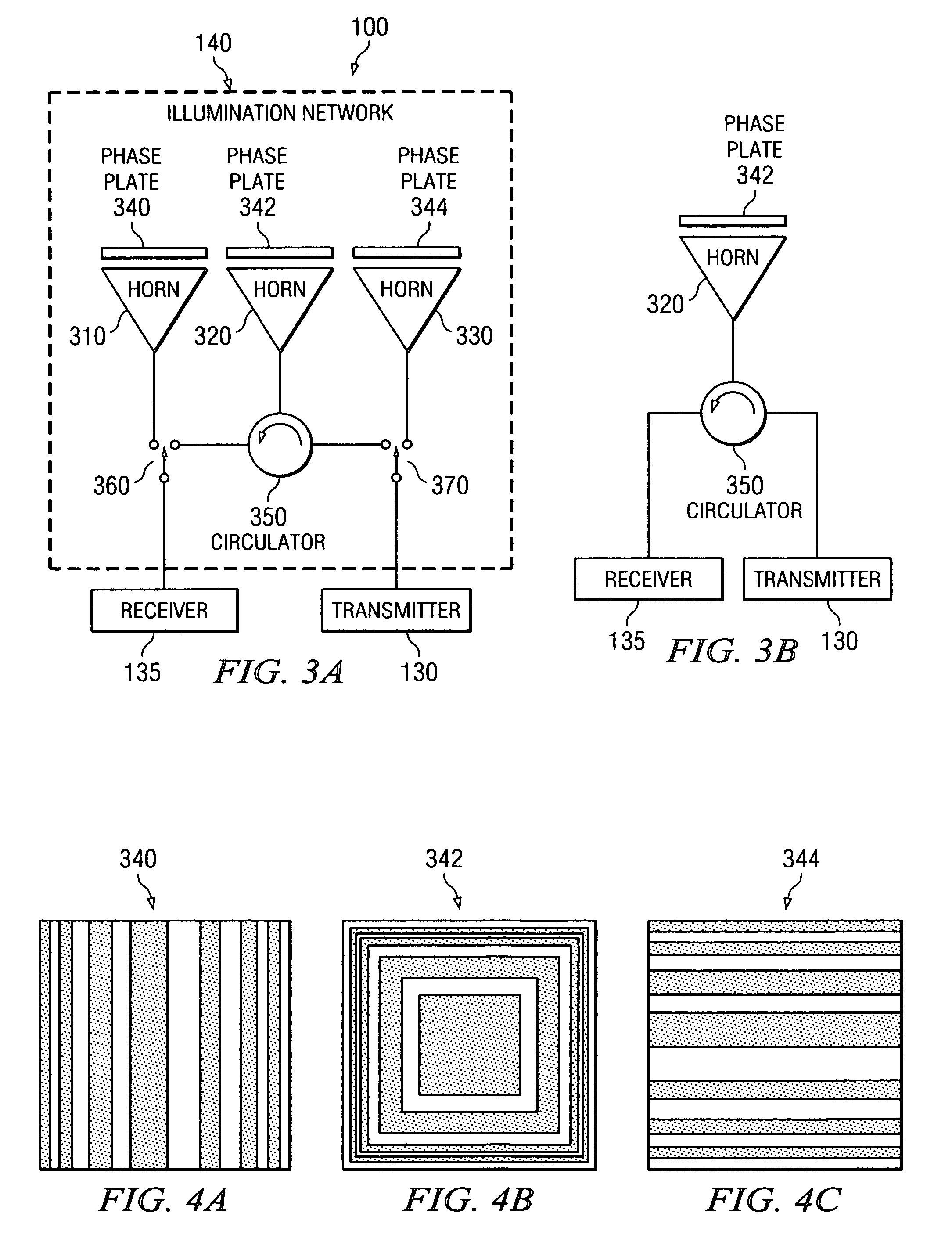
System and method for microwave imaging with suppressed sidelobes using a sparse antenna array
ActiveUS20070013575A1Suppresses sidelobesGeological detection using milimetre wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSide lobeLighting system
A microwave imaging system suppresses sidelobes in a microwave image captured using a sparse antenna array using an illumination system that operates in two different illumination modes. The antenna array including subarrays of antenna elements arranged in a sparse geometry to form complementary subarray patterns. The illumination system operates in a first mode to transmit microwave illumination to both of the complementary subarray patterns of the antenna array and receive reflected microwave illumination from both of the complementary subarray patterns of the antenna array to produce a first receive signal. The illumination system further operates in a second mode to transmit microwave illumination to a first one of the complementary subarray patterns of the antenna array and receive reflected microwave illumination from a second one of the complementary subarray patterns of the antenna array to produce a second receive signal. Sidelobes are suppressed using a linear combination of the first and second receive signals.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for microwave imaging with suppressed sidelobes using a sparse antenna array
ActiveUS7280068B2Geological detection using milimetre wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSide lobeLighting system
A microwave imaging system suppresses sidelobes in a microwave image captured using a sparse antenna array using an illumination system that operates in two different illumination modes. The antenna array including subarrays of antenna elements arranged in a sparse geometry to form complementary subarray patterns. The illumination system operates in a first mode to transmit microwave illumination to both of the complementary subarray patterns of the antenna array and receive reflected microwave illumination from both of the complementary subarray patterns of the antenna array to produce a first receive signal. The illumination system further operates in a second mode to transmit microwave illumination to a first one of the complementary subarray patterns of the antenna array and receive reflected microwave illumination from a second one of the complementary subarray patterns of the antenna array to produce a second receive signal. Sidelobes are suppressed using a linear combination of the first and second receive signals.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for inspecting transportable items using microwave imaging
InactiveUS20060214835A1Geological detection using milimetre wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansAntenna elementMicrowave imaging
An inspection system uses microwave radiation to capture a microwave image of a transportable item. The system includes a transmit scanning panel including a transmit array of transmit antenna elements, each being programmable with a respective phase delay to direct a transmit beam of microwave radiation toward a target of the transportable item for transmission of the microwave radiation through the target. The system further includes a receive scanning panel including a receive array of receive antenna elements, each being programmable with a respective phase delay to receive a receive beam of microwave radiation from the target. A processor measures the amplitude and phase of the microwave radiation in the receive beam to determine a relative value of a pixel within the microwave image of the transportable item based on a reference value of the pixel.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
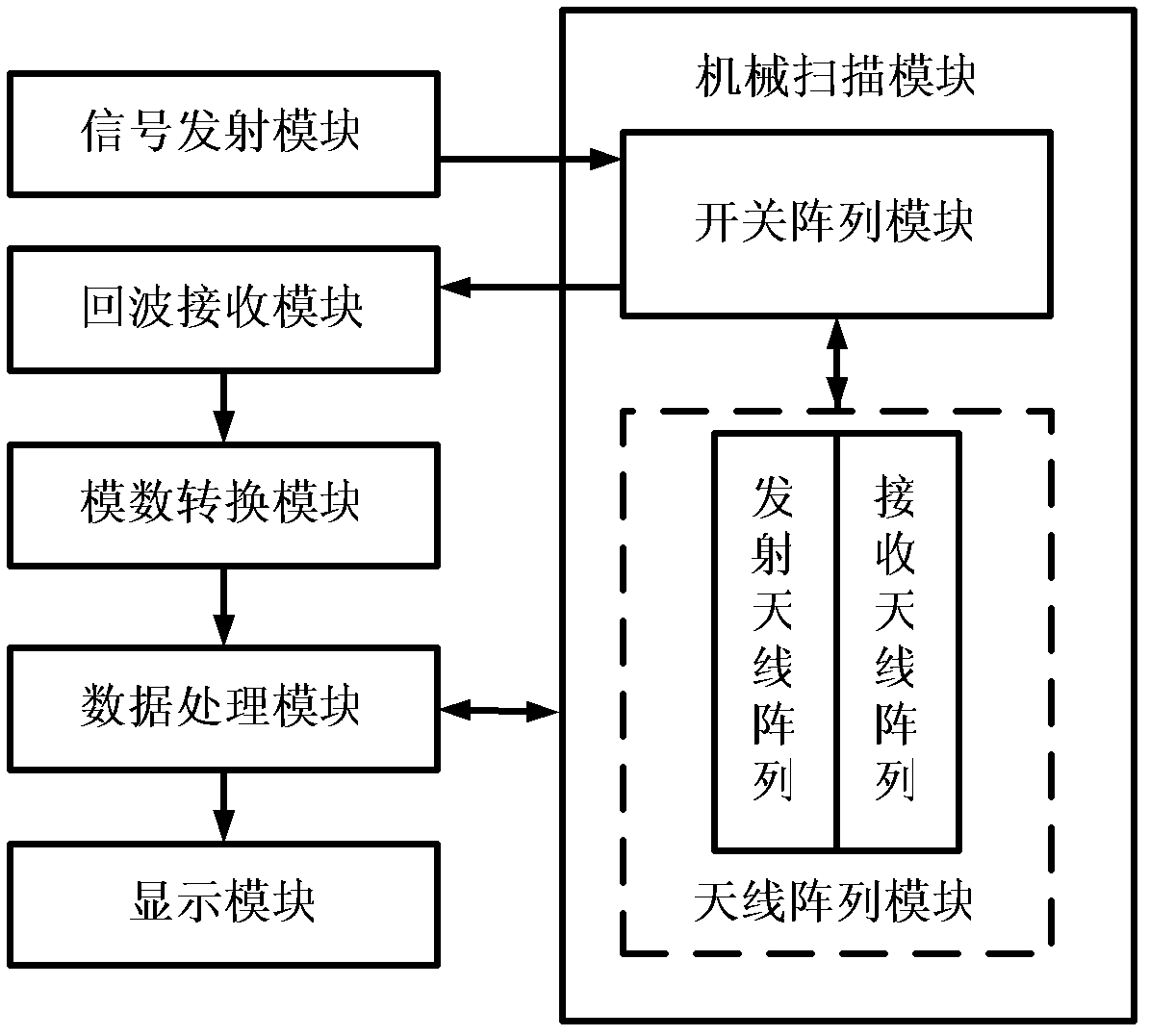
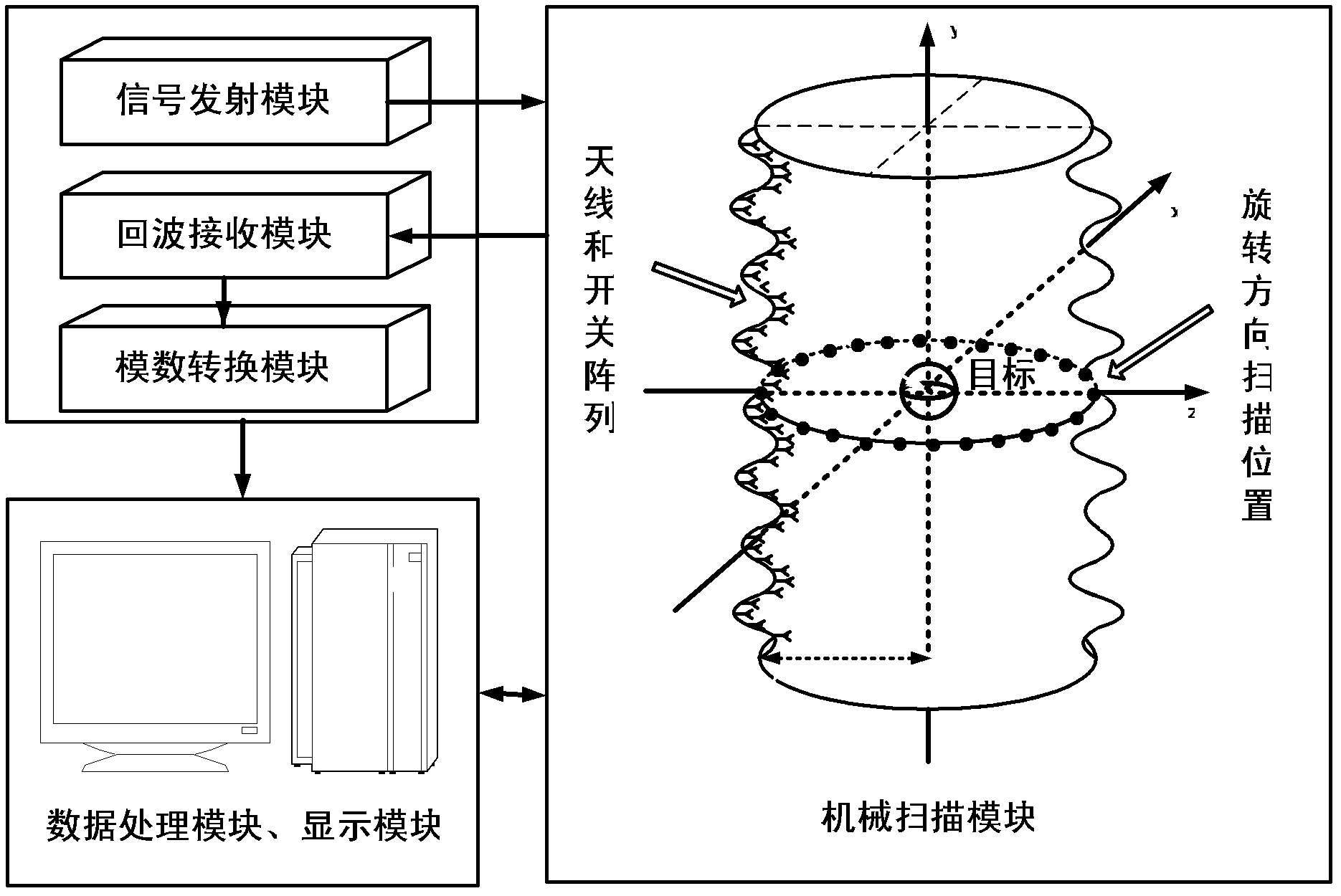
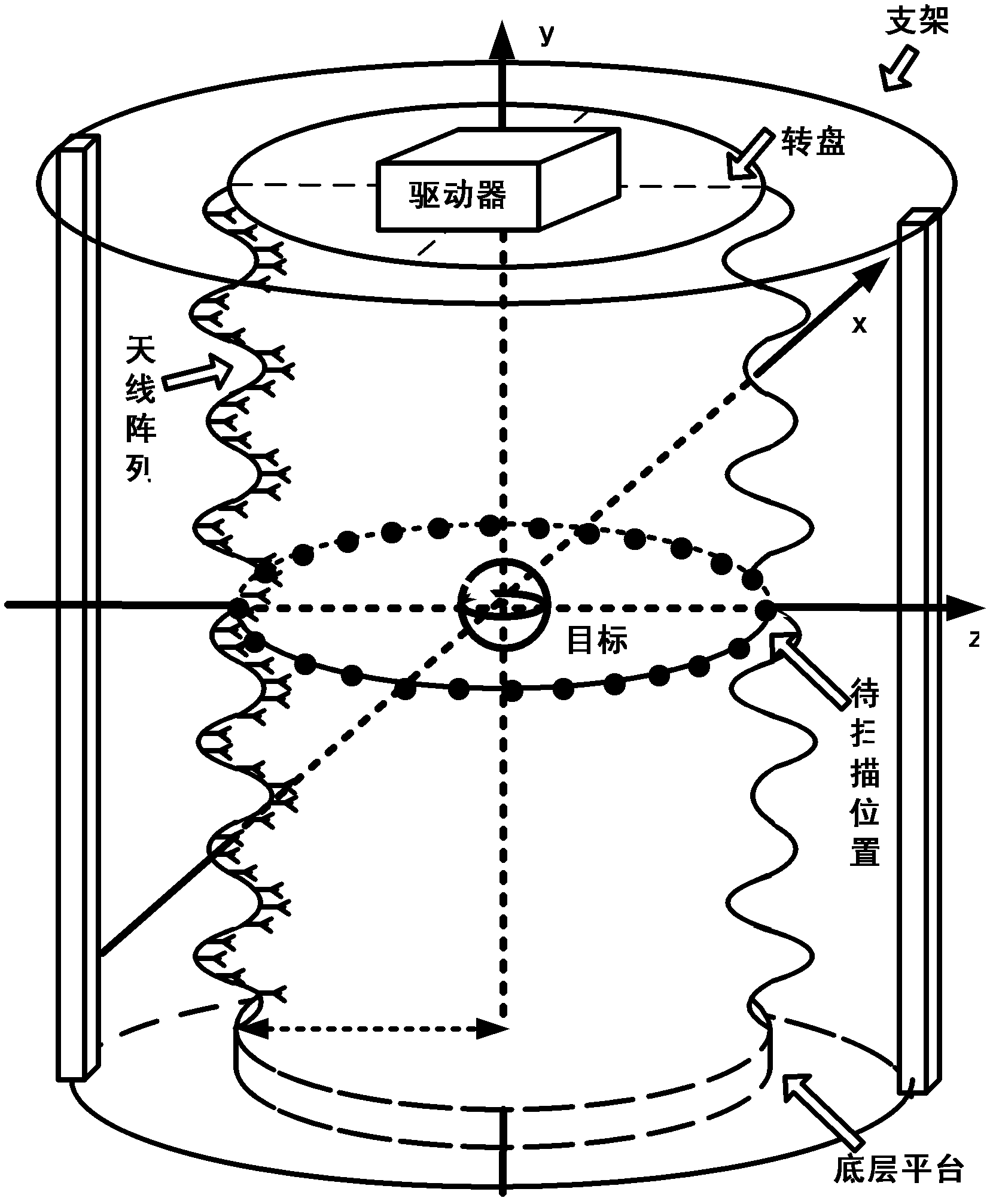
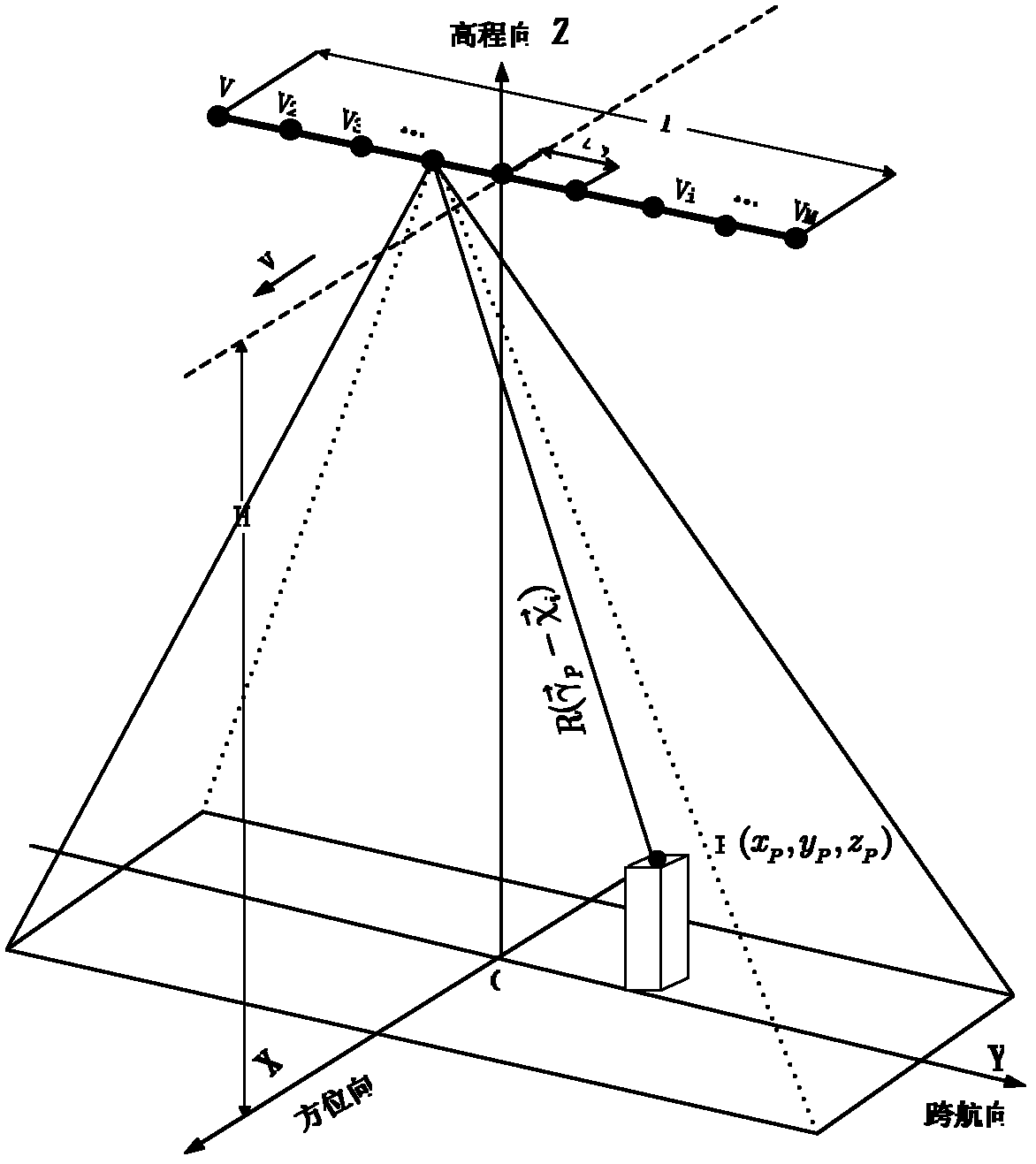
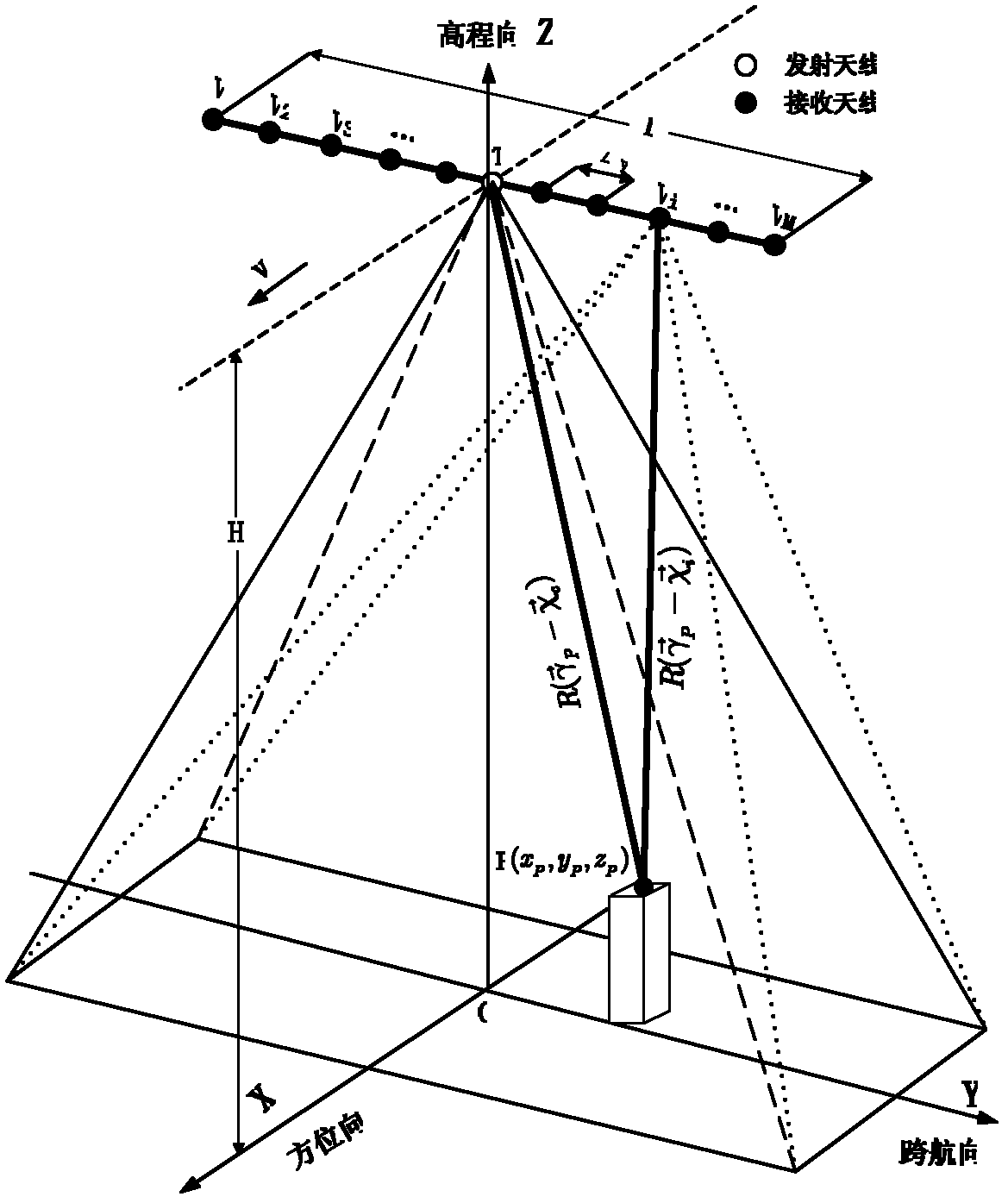
Microwave three-dimensional imaging method based on rotary antenna array
ActiveCN103018738AIncrease flexibilityImprove acquisition efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionArray elementDigital signal
The invention discloses a microwave three-dimensional imaging method based on a rotary antenna array, and relates to a microwave imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps of: generating an electromagnetic signal by a signal transmitting module; driving an antenna array module which is distributed in a straight line form or a curved line form to rate by a mechanical scanning module, meanwhile, controlling the antenna array module by a switch array module to transmit an electromagnetic signal at the same time, and receiving a signal which is reflected back from an observation target by a back wave receiving module; converting a reflecting signal into a digital signal by an analogue-digital conversion module; and using the digital signal as back wave data acquired by an array element position of the corresponding antenna array; imaging the back wave data by a data processing module to acquire a three-dimensional complex image of the observation target; and displaying the three-dimensional complex image of the observation target by a display module. The imaging method disclosed by the invention is used for application fields of human body surface microwave image acquisition and safe detection, three-dimensional data acquisition of a human body and action based on actual circumstances, nondestructive testing, radar target imaging diagnosis and the like.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
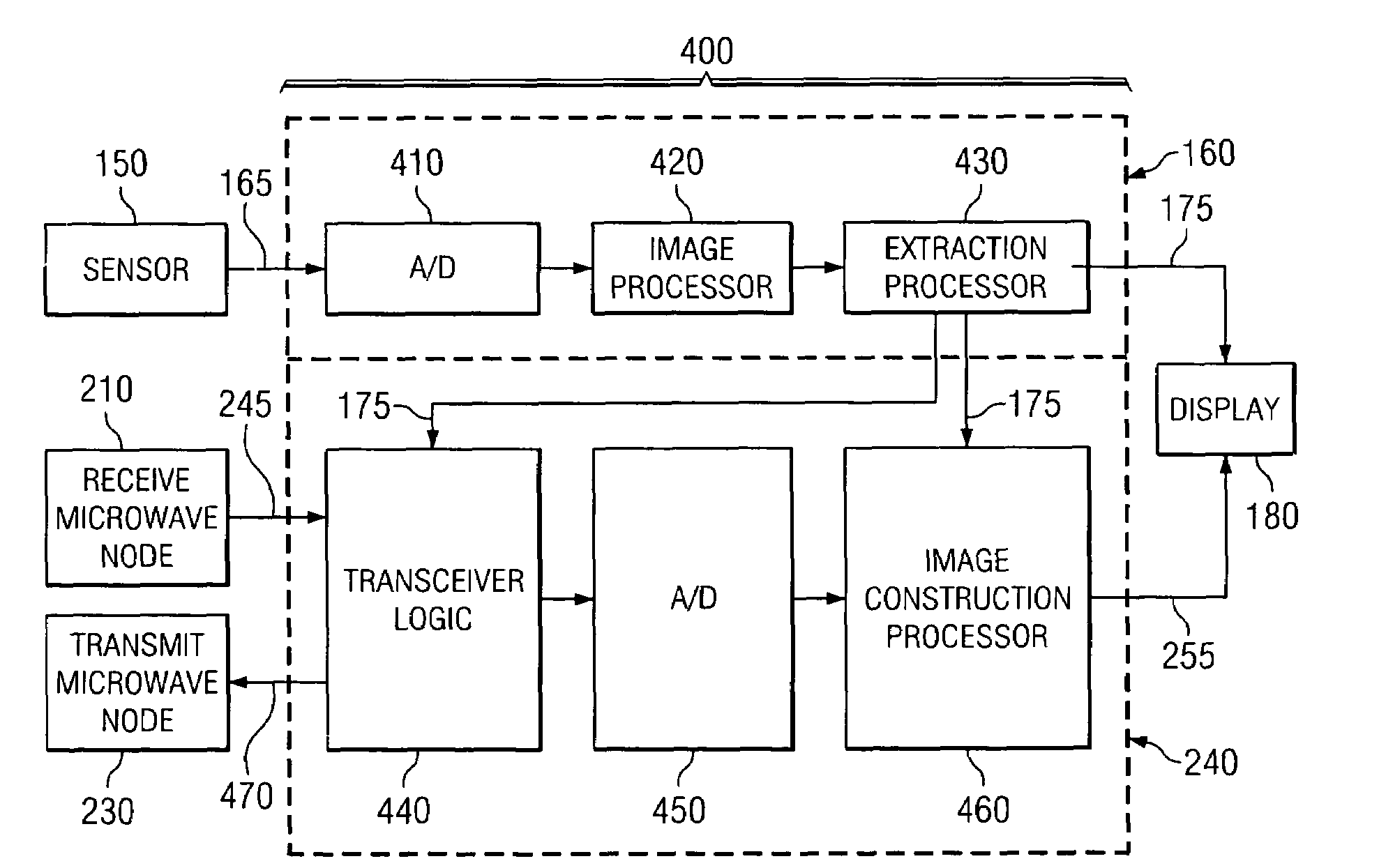
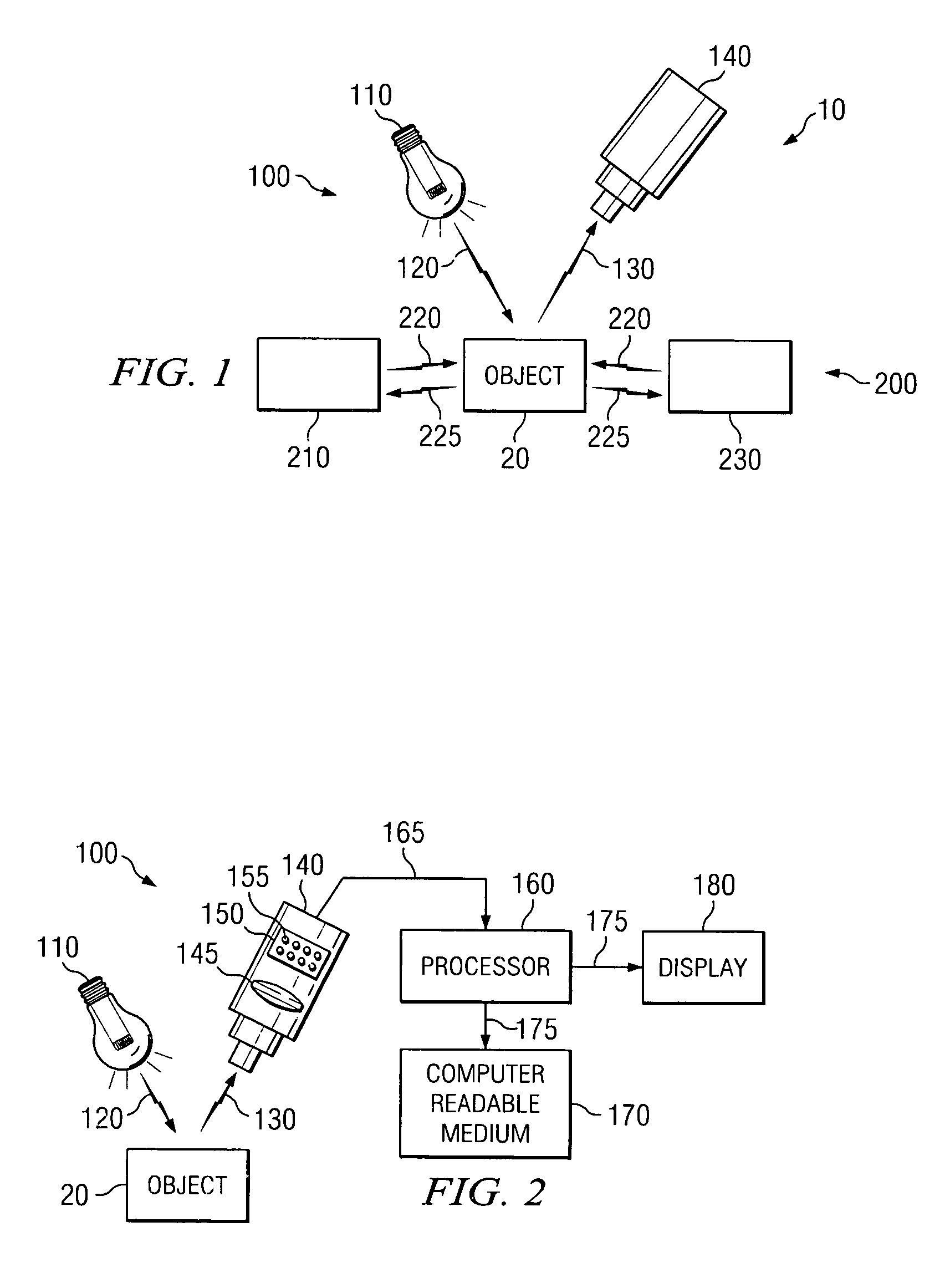
Optically-augmented microwave imaging system and method
ActiveUS6972714B1Fast and simple algorithmReduce computational complexityMaterial analysis using microwave meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationComputer scienceMicrowave imaging
An imaging system includes an optical (visible-light or near IR) imaging system and a microwave imaging system. The optical imaging system captures an optical image of the object, produces optical image data representing the optical image and extracts optical image information from the optical image data. The microwave imaging system produces microwave image data representing a microwave image of the object in response to the optical image information.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
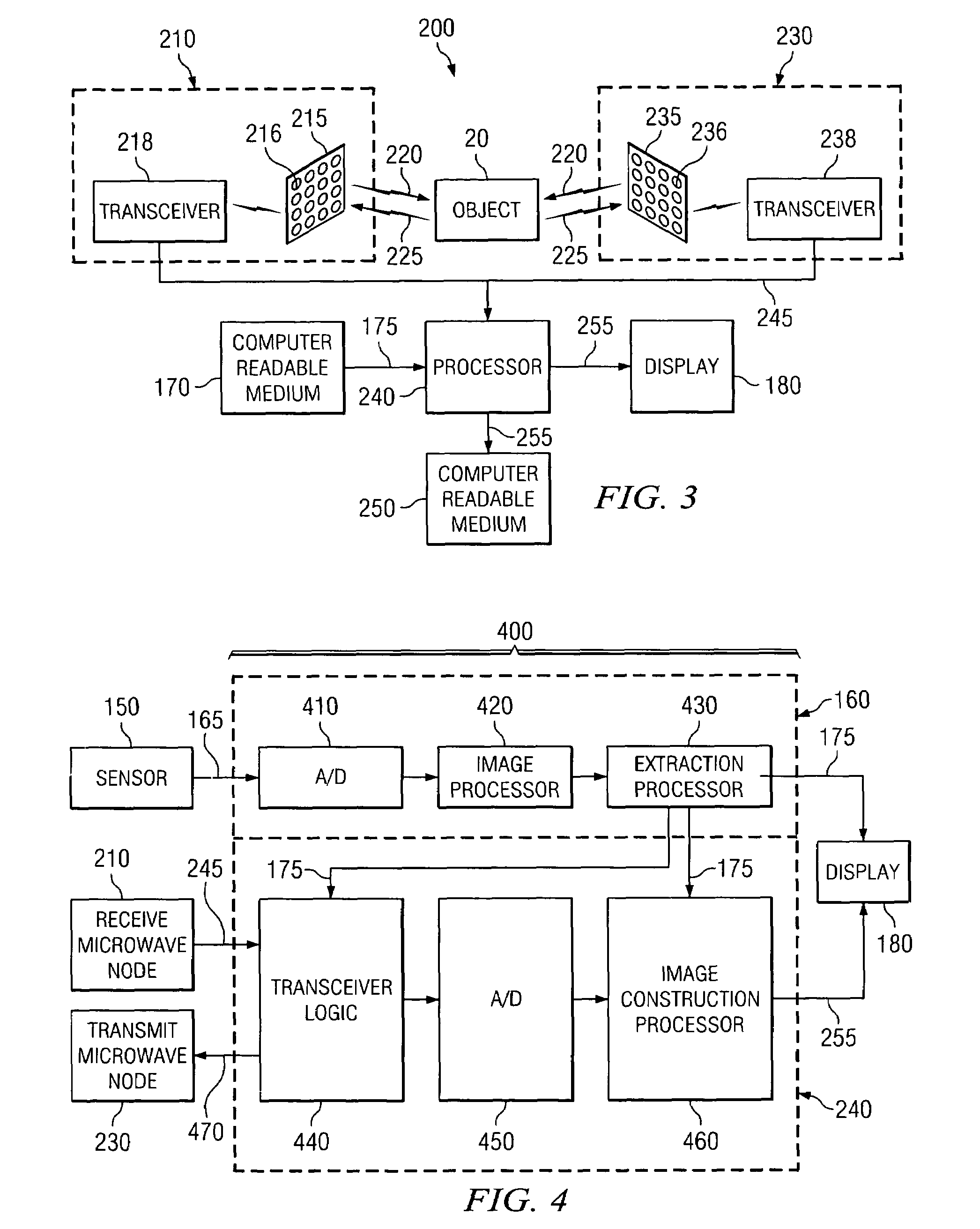
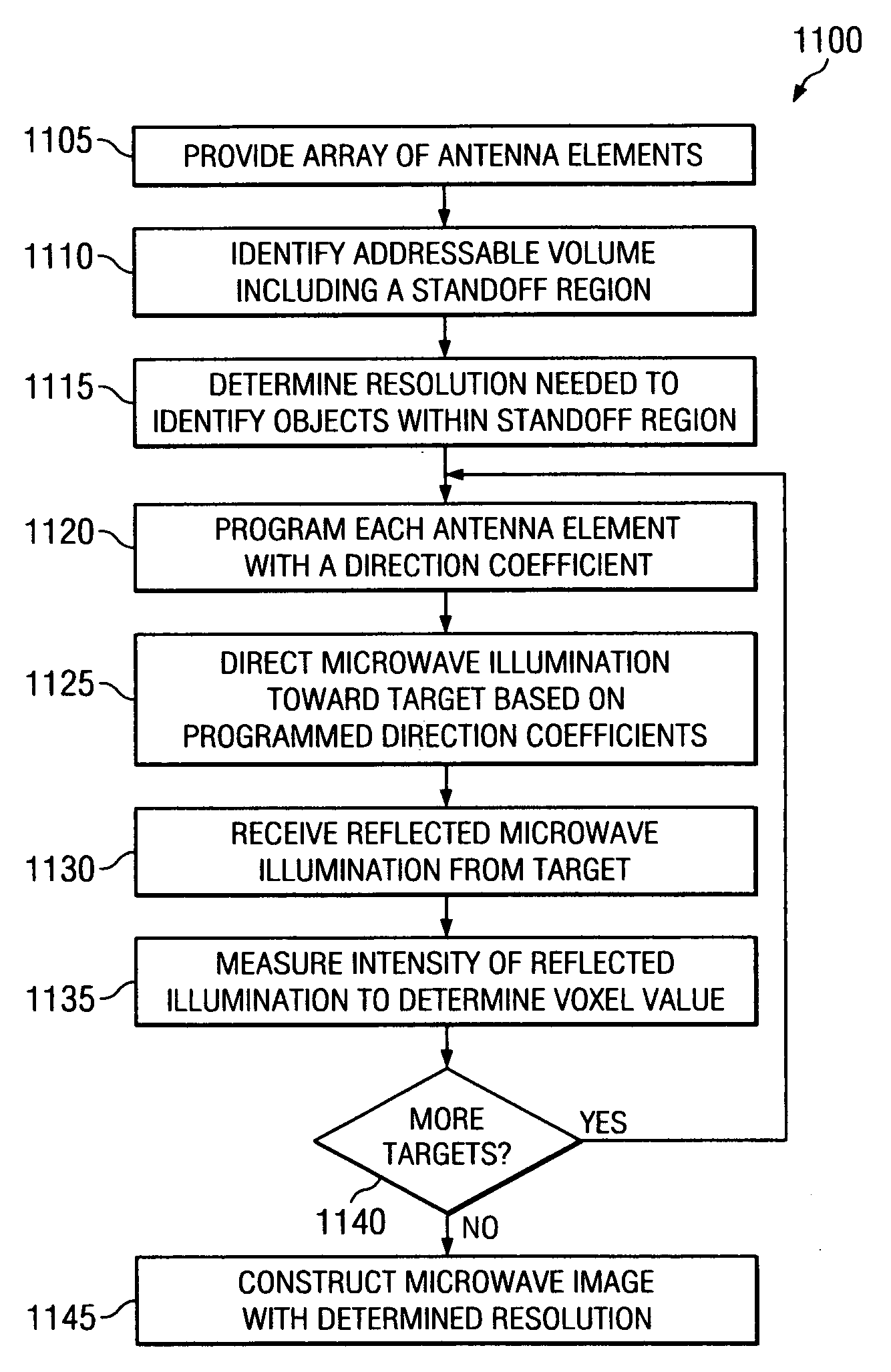
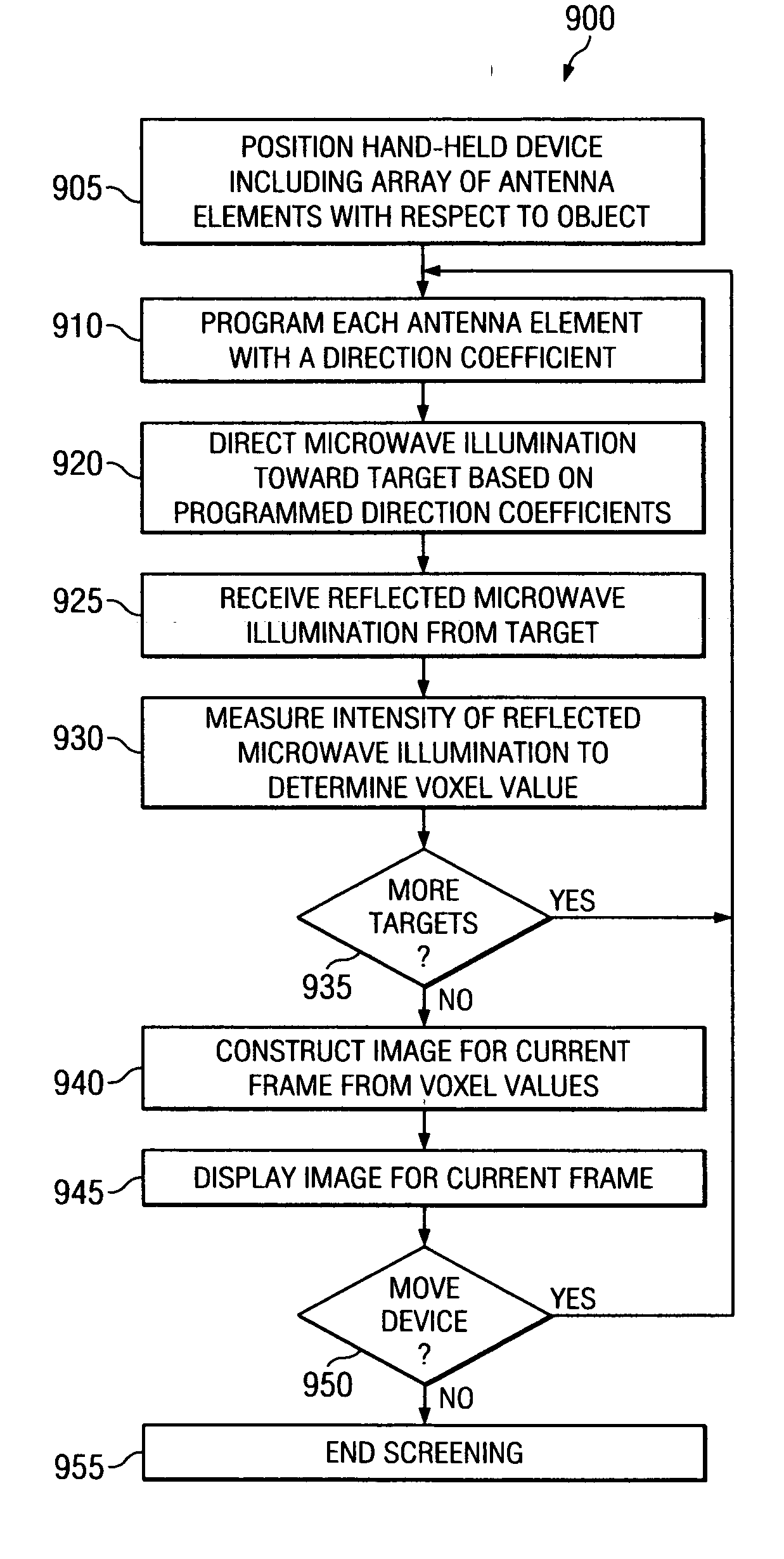
System and method for standoff microwave imaging
InactiveUS20070139248A1Minimized in sizeReduce in quantityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionVoxelImage resolution
A microwave imaging system for performing standoff microwave imaging includes an antenna array with a plurality of antenna elements, each capable of being programmed with a respective direction coefficient to direct microwave illumination toward a target within a volume that includes a standoff region, and each capable of being programmed with a respective additional direction coefficient to receive reflected microwave illumination reflected from the target. A processor measures an intensity of the reflected microwave illumination to determine a value of a voxel within a microwave image of the volume. The processor constructs the microwave image with a resolution sufficient to identify objects within the standoff region.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Apparatus and method for doppler-assisted MIMO radar microwave imaging
ActiveUS8494615B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisExercise stateMicrowave imaging
A method and apparatus for enhanced microwave imaging of an object collects microwave responses for multiple combinations of transmit antennas, receive antennas, and object movement states. The responses are grouped into sets of responses corresponding to at least two object movement states. An image is reconstructed from the set of responses for each movement state, and a differential image representative of object movement is generated from the reconstructed image for each of the at least two object movement states. The differential image is overlaid on a reconstructed image to obtain an enhanced composite image of the object.
Owner:VAYYAR IMAGING LTD
Space-time microwave imaging for cancer detection
ActiveUS7570063B2Reduce in quantityAvoid the needResistance/reactance/impedenceDiagnostic recording/measuringTime gatingEngineering
Microwave imaging via space-time beamforming is carried out by transmitting microwave signals from multiple antenna locations into an individual to be examined and receiving the backscattered microwave signals at multiple antenna locations to provide received signals from the antennas. The received signals are processed in a computer to remove the skin interface reflection component of the signal at each antenna to provide corrected signal data. The corrected signal data is provided to a beamformer process that time shifts the received signals to align the returns from a scatterer at a candidate location, and then passes the time aligned signals through a bank of filters, the outputs of which are summed, time-gated and the power therein calculated to produce the beamformer output signal at a candidate location. The beamformer is then scanned to a plurality of different locations in the individual by changing the time shifts, filter weights and time-gating of the beamformer process. The output power may be displayed as a function of scan location, with regions of large output power corresponding to significant microwave scatterers such as malignant lesions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
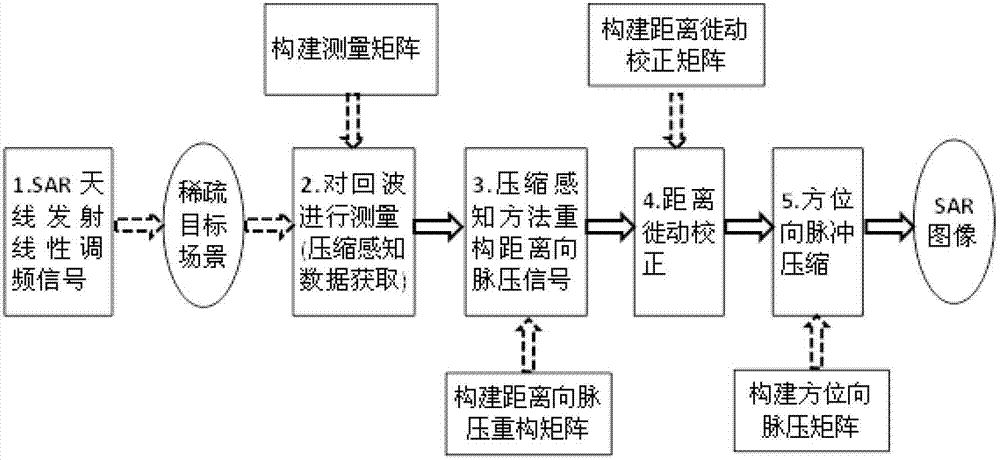
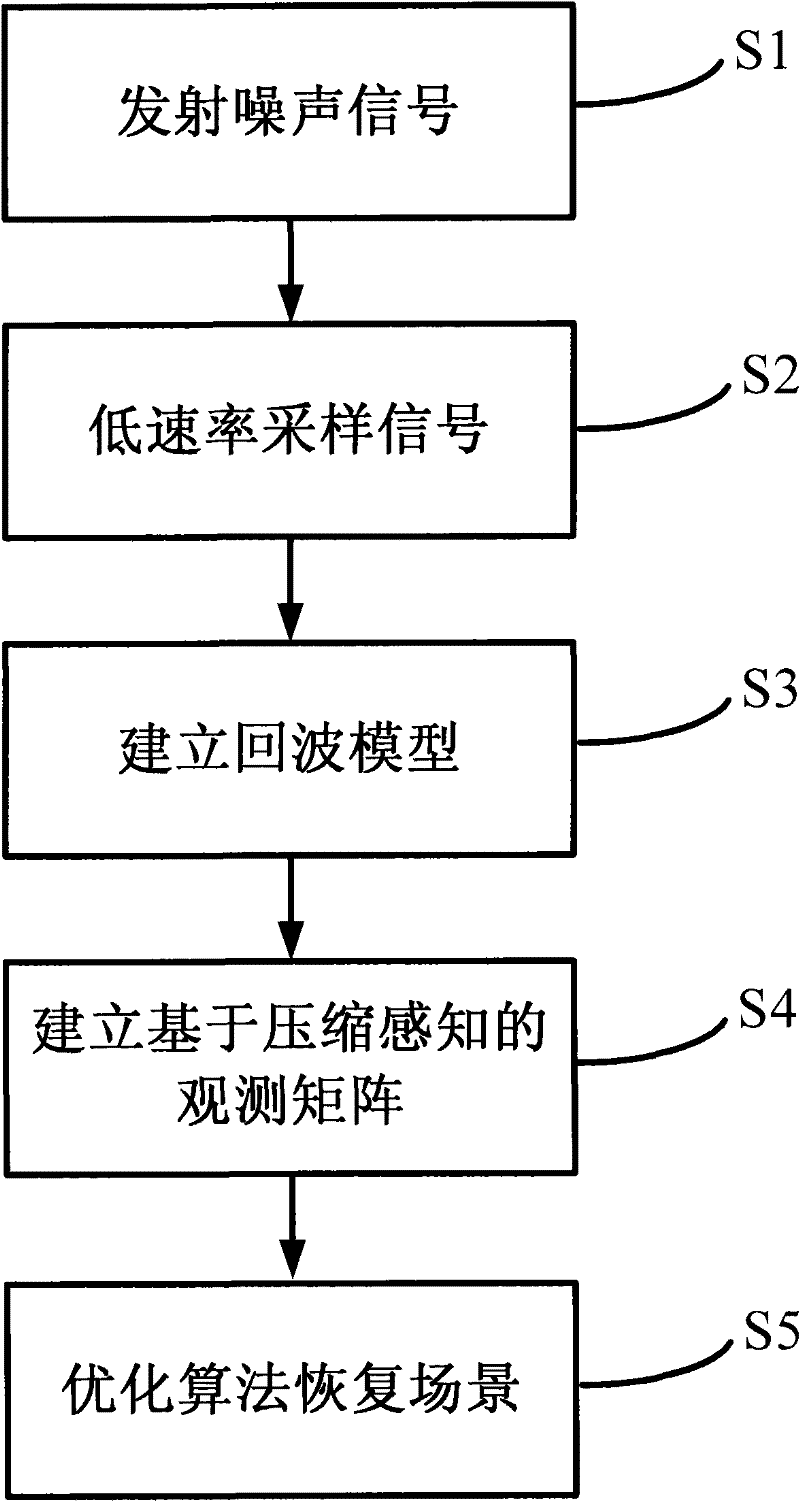
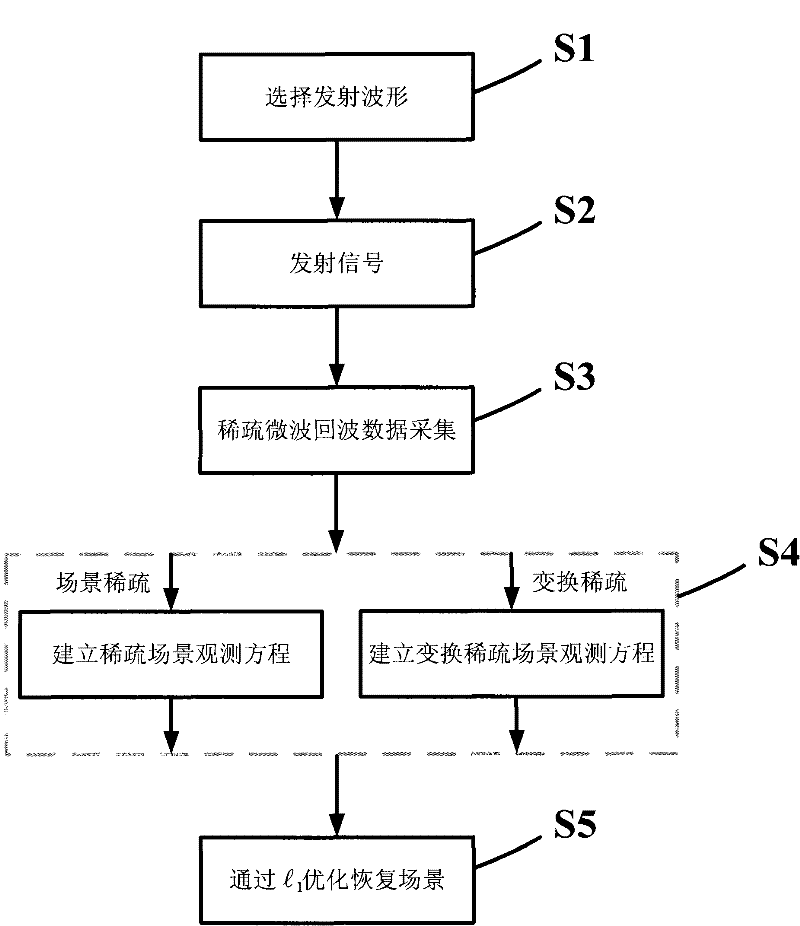
Compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging method based on fractional order fourier transformation
InactiveCN102879782AReduce the amount of measurement dataRelieve the pressure of signal storage and transmissionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarDimension measurement
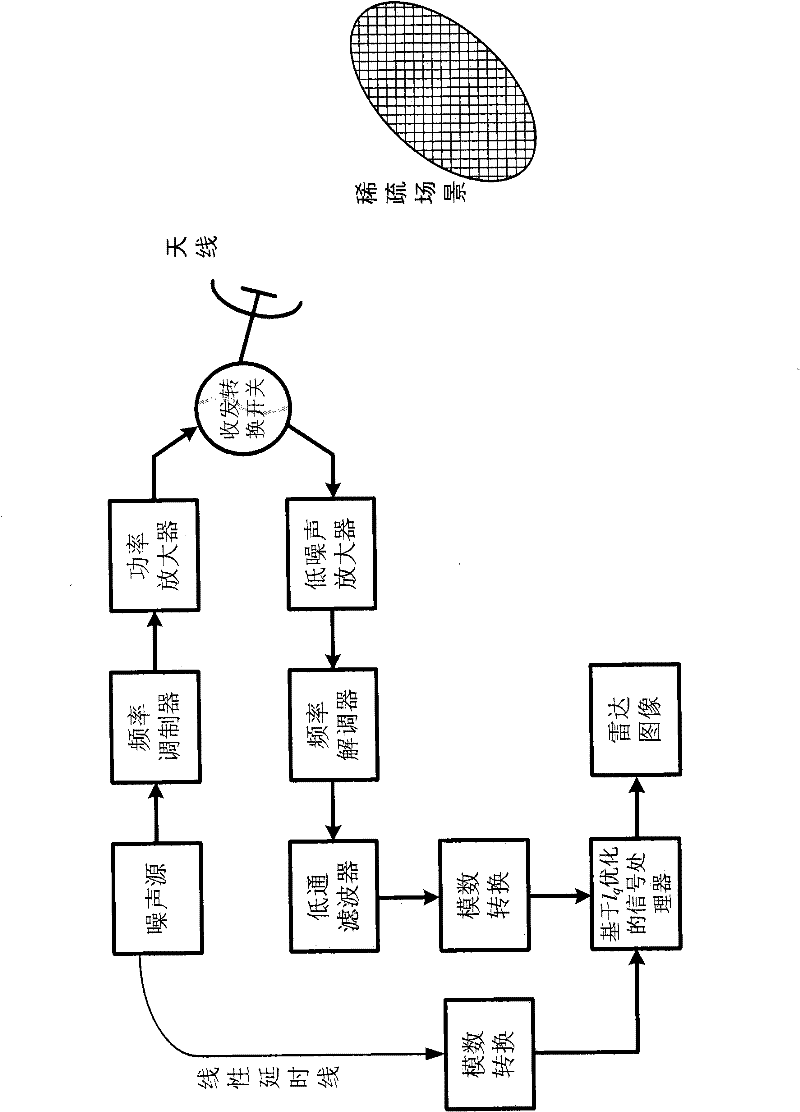
The invention provides a compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging method based on fractional order fourier transformation, and belongs to the technical field of microwave imaging. For a sparse target scene, a system emits a linear frequency modulation pulse signal; by adopting a method for projecting an echo signal to a low-dimension measurement matrix, measurement data which are much smaller than those required by a Nyquist sampling principle are acquired; due to the echo signal, after a reconstruction matrix is constructed by a simplified fractional order fourier transformation domain sparse mode and a data acquisition mode, a calculated distance pulse pressure result is optimized by a compressed sensing signal reconstruction method and is subjected to distance migration correction and direction pulse pressure to obtain a target scene imaging result. By the imaging method, the measurement data amount of a target scene with a sparse characteristic can be greatly reduced; and pressure on data storage and data transmission can be effectively relieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Device for detecting non-metallic objects located on a human subject
InactiveUS20070102629A1Simple designGood suitGeological detection using milimetre wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansJet aeroplaneHuman body
The field of the invention is that of devices for detecting objects concealed on human subjects. These devices are more particularly dedicated to the surveillance and protection of airport areas and transport airplanes. Currently, the devices rely either on X-ray detection or on microwave imaging. In the former case, the system can prove hazardous to human beings, and in the other case, the device raises ethical problems. The invention proposes a device whose operation relies on the reflective properties of the microwave signals polarized by the suspect objects that we are seeking to detect. This device can be portable or installed on security gates. This technique is simple to design, inexpensive, does not require any great computing power and is very well suited to the objects to be detected. The complete measurement is extremely quick and requires no sophisticated measuring instrument.
Owner:THALES SA
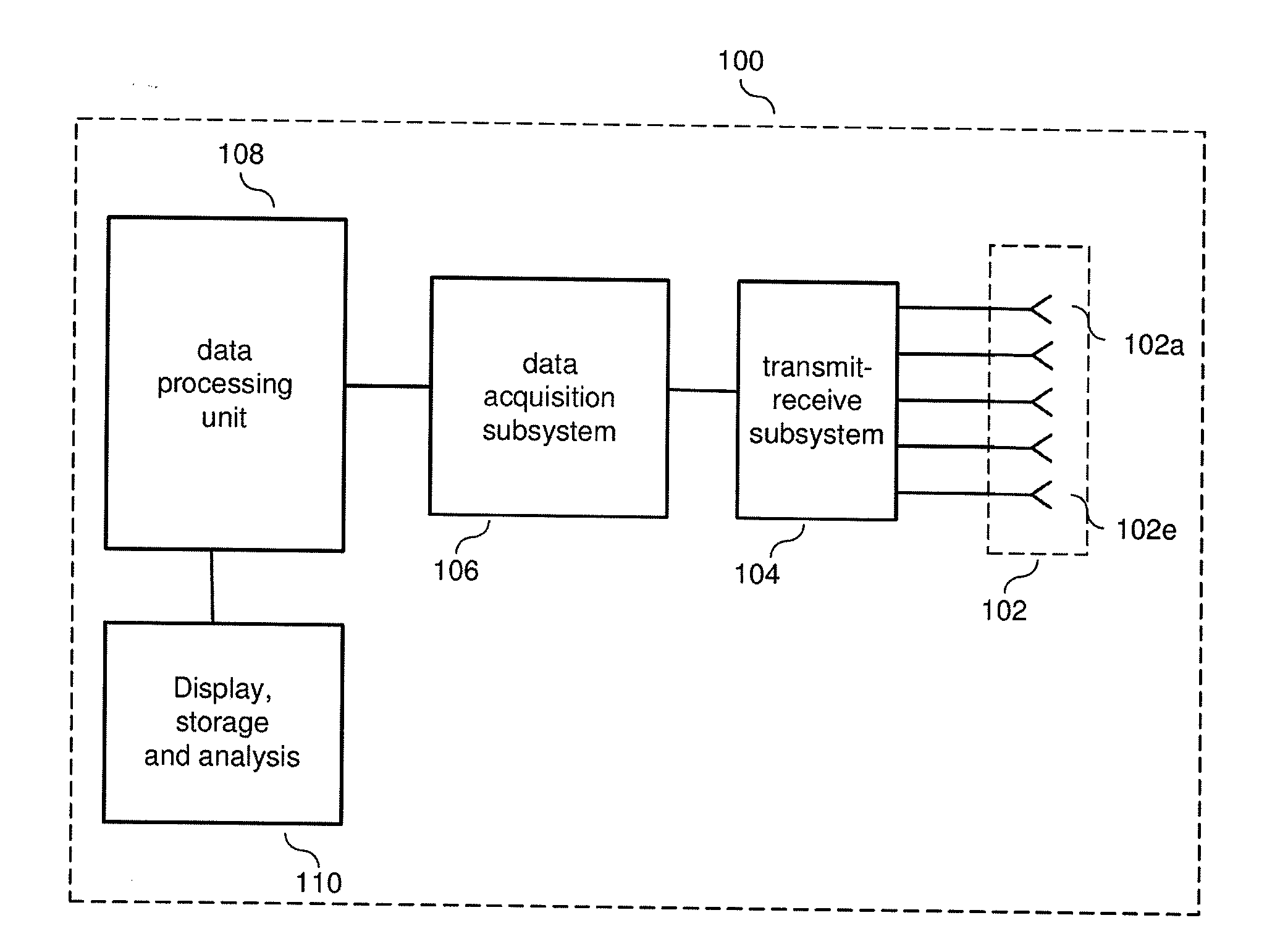
Time domain inverse scattering techniques for use in microwave imaging
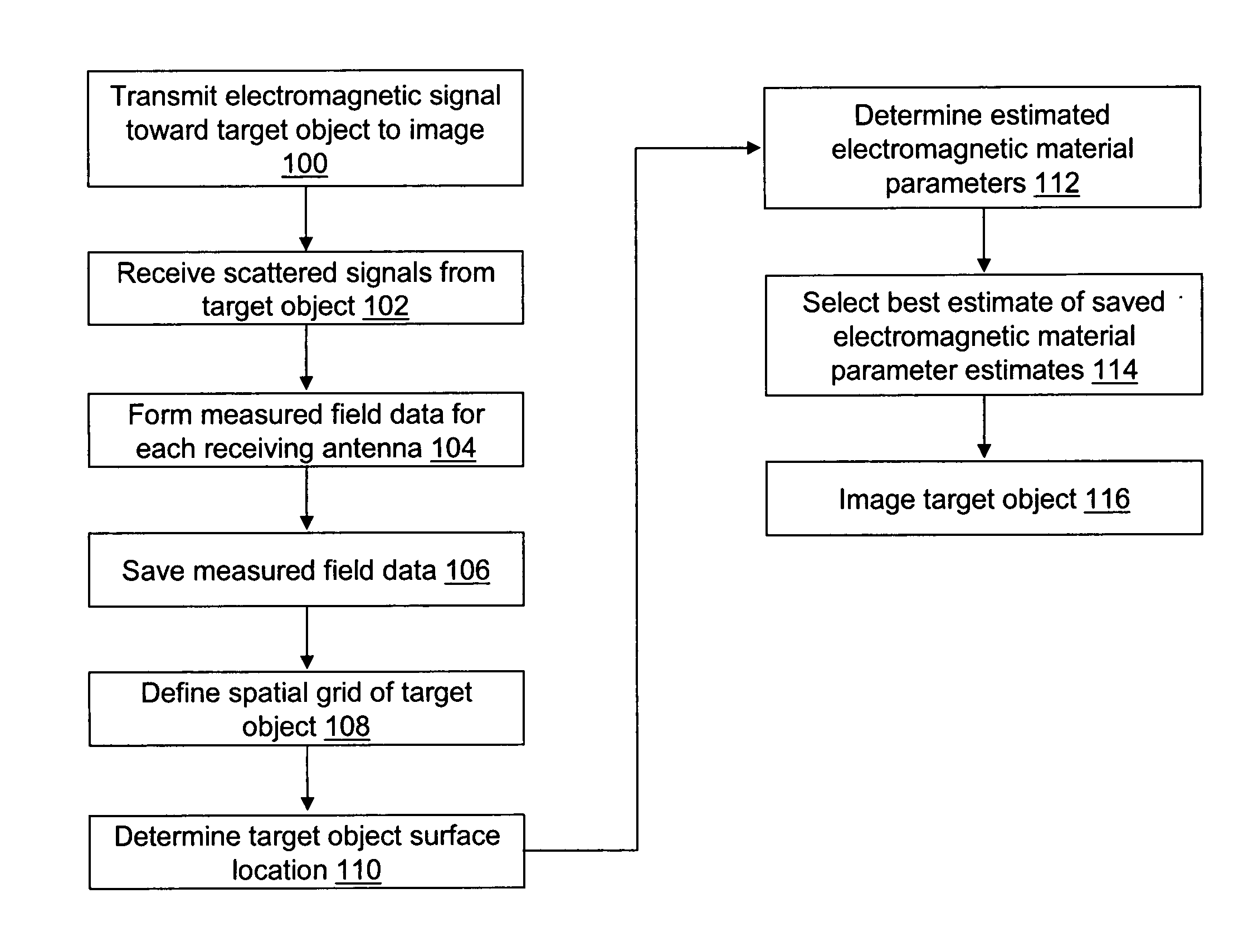
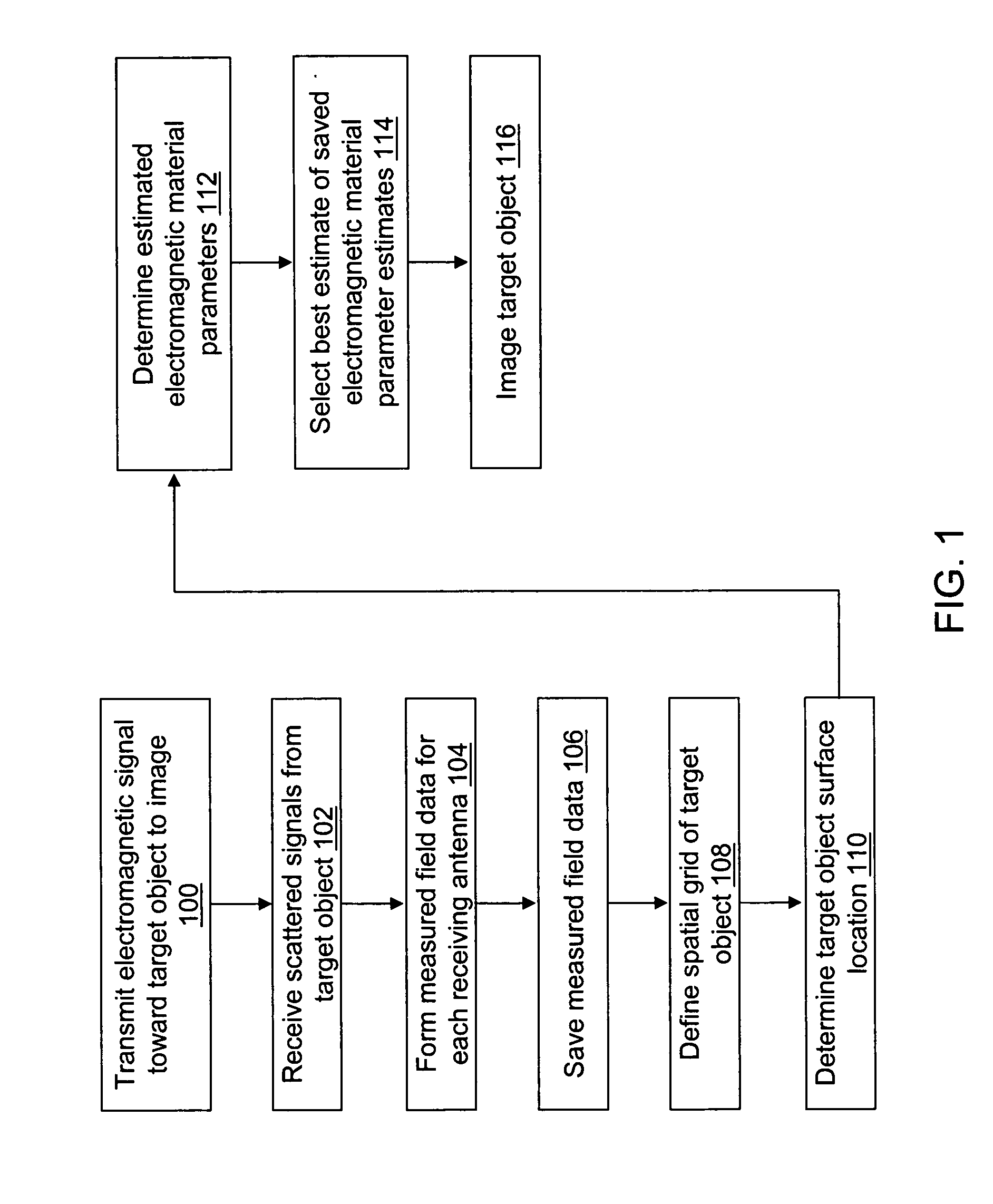
ActiveUS20060241409A1Accurate tumor localizationMinimize cost functionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityTime domain
A system and a method are provided for estimating the average dielectric properties of a plurality of regions in space. The application of this technique is illustrated for determining the average properties of breast tissue. The knowledge of average properties is important when UWB microwave radar signal processing algorithms are used for tumor detection and localization. The method is an extension of a time-domain inverse scattering algorithm based on the finite-difference time-domain method. A hybrid conjugate gradient optimization is used to minimize a cost function defined between a measured and a calculated total electromagnetic field at a series of antennas. The output of the method is an average set of electromagnetic material parameters that describe specific regions of interest in either a non-dispersive heterogeneous medium or a dispersive heterogeneous medium.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
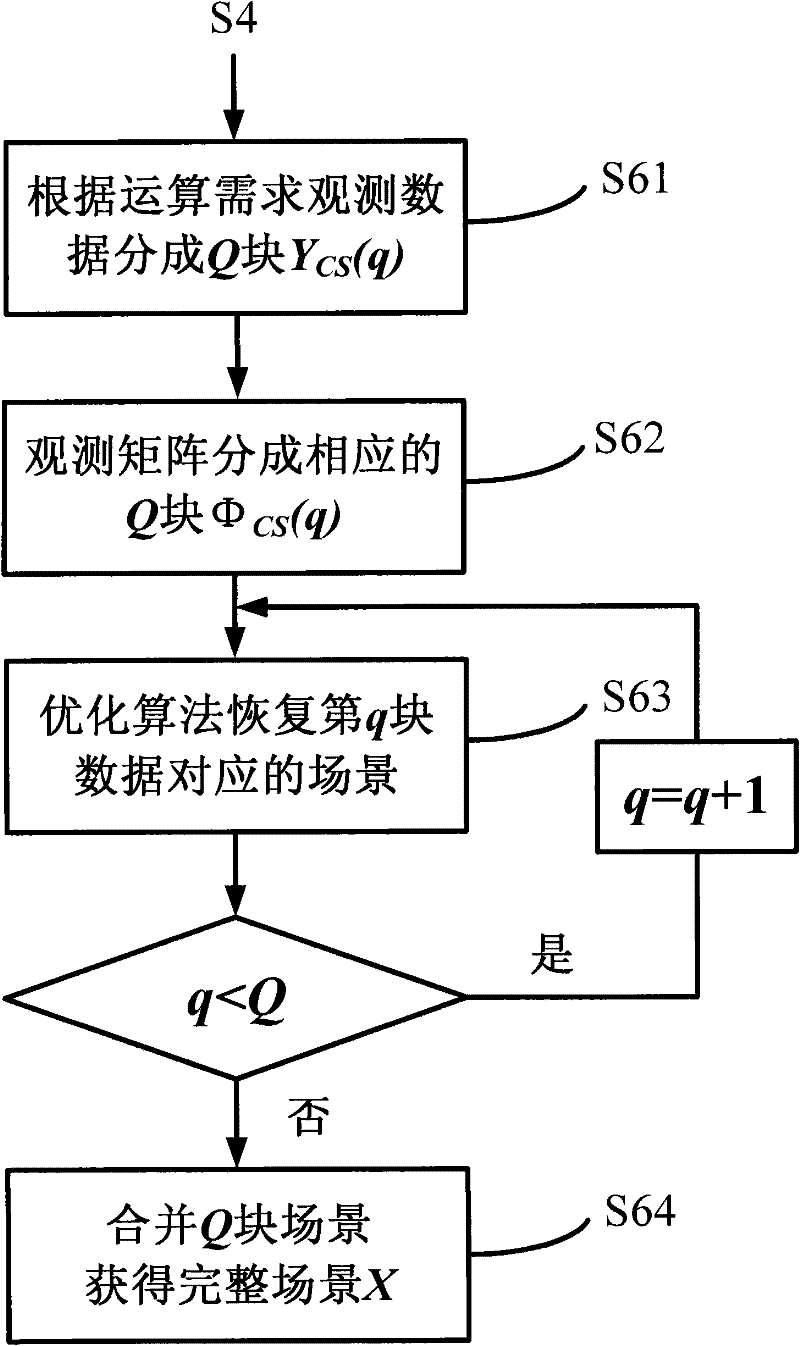
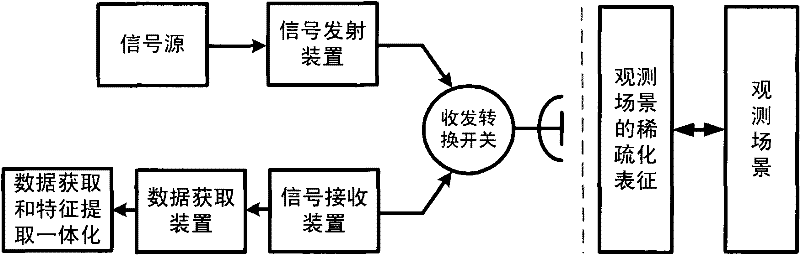
Signal processing method for random noise radar applicable to sparse microwave imaging
ActiveCN102207547AHigh resolutionRecover backscatter coefficientRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionRadar systems
The invention discloses a signal processing method for a random noise radar applicable to sparse microwave imaging, and relates to microwave imaging technologies. For a target scene with sparse characteristics, a transmit signal of a system is band-limited Gaussian random white noise; and observation data with observed quantity less than that required by a nyquist sampling theorem is obtained by a low-speed uniform sampling method during reception. After an observation matrix is set up in combination of a transmit signal form and a data acquisition manner, a backscattering coefficient of a scene target is obtained by optimizing and resolving the compressed sensing of a sparse signal processing theory, and high-resolution target detection and imaging are achieved. In order to improve calculating efficiency, a block signal processing method of the random noise radar applicable to the sparse microwave imaging is adopted; and during block processing, a corresponding block observation matrix is set up in combination with a block form of the data. Compared with the conventional radar system, the invention has the advantages that: a little observation data is needed to achieve the same resolution; and higher resolution can be achieved when the same observation data quantity is adopted.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
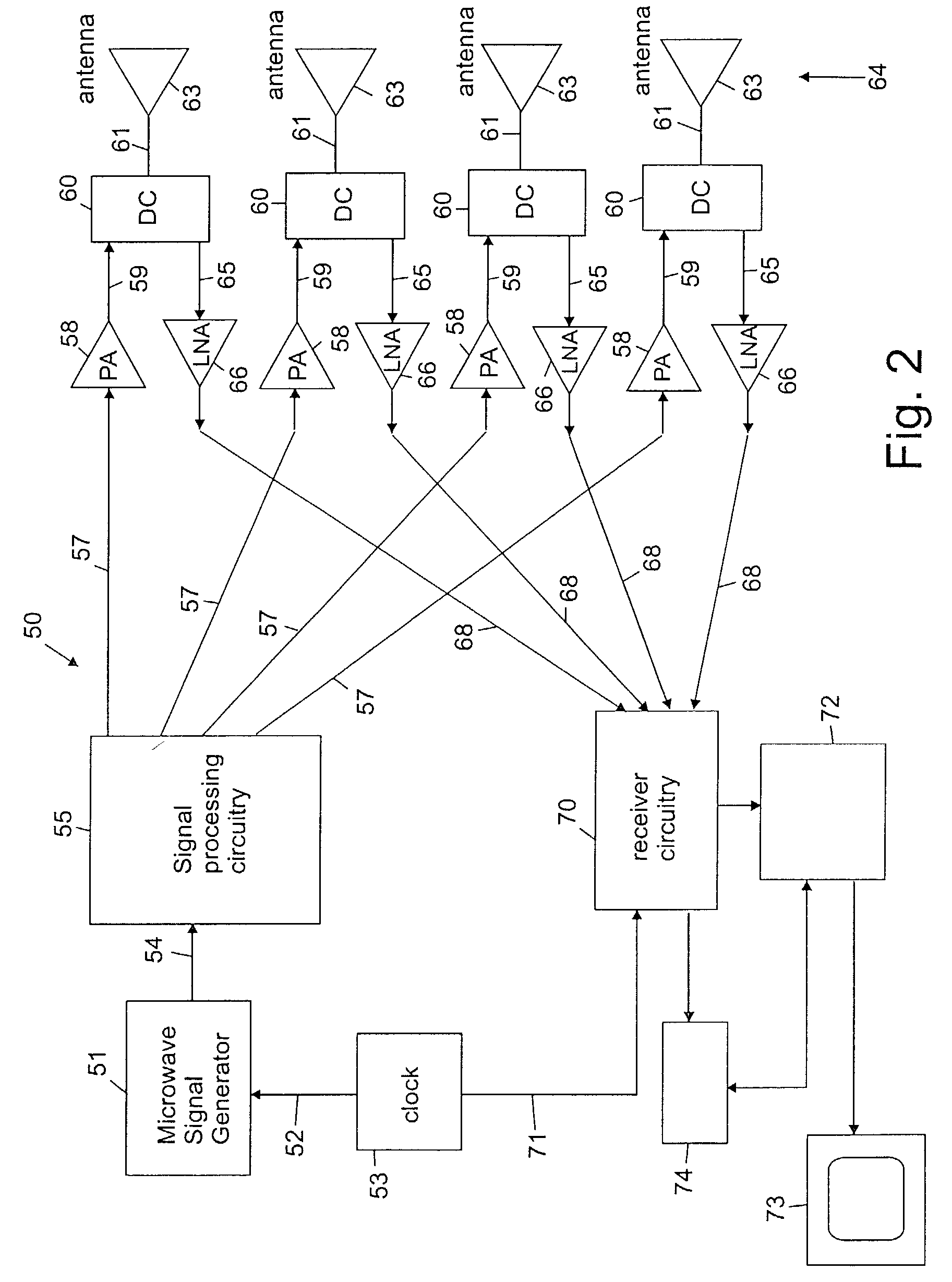
System and method for efficient, high-resolution microwave imaging using complementary transmit and receive beam patterns
ActiveUS7283085B2Individually energised antenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionBeam pattern
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional microwave imaging method for circular track of earth synchronization orbit
InactiveCN101430379ASolve the problem that it is difficult to obtain high-resolution 3D information of ground objectsSolve small problems with long revisit cyclesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainSynthetic aperture sonar
The invention discloses a circular synthetic aperture radar (CSAR) 3D microwave imaging method for an earth synchronous orbit. In the method, parameters of the earth synchronous orbit are designed to cause a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite platform to make a flight with an annular track around a target zone and above the target zone, and an antenna beam is caused to irradiate the target zone all the time by a circular synthetic aperture radar mode, and a ground object target is subject to continuous large-area fixed point observation to acquire high-resolution 3D imaging information of the ground object target. A CSAR system of the earth synchronous orbit provided by the system can acquire high-resolution 3D images of the ground object, solves the problem that the existing space-borne SARs are hard to acquire the high-resolution 3D information of the ground object; and is applicable to areas with complex and steep terrains as elevation information does not interfere with phase ambiguity in the SAR. The CSAR system of the earth synchronous orbit can realize the fixed point continuous observation of large-area zones, and solve the problems that the existing space-borne SARs have small observation zones and long revisit period.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
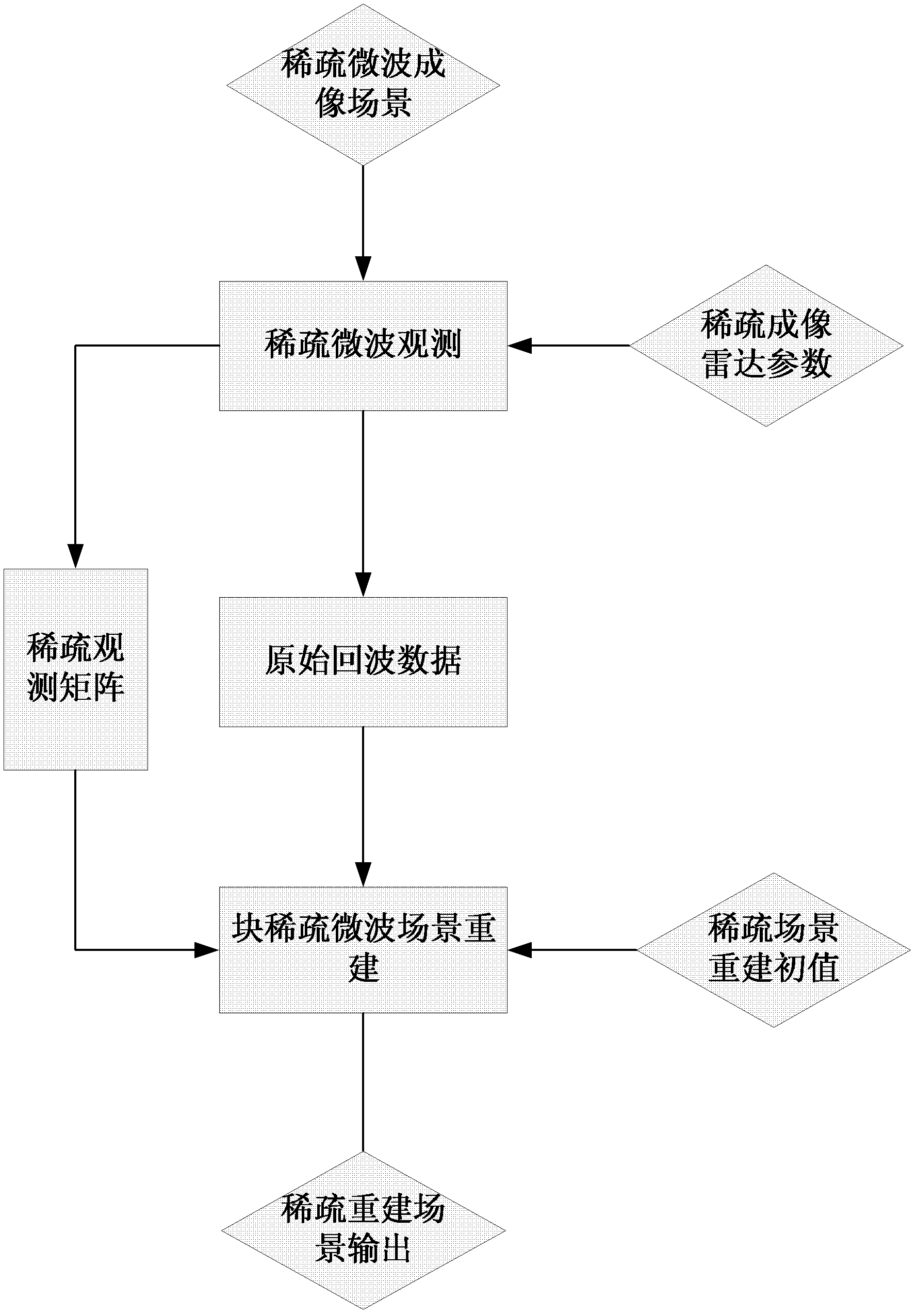
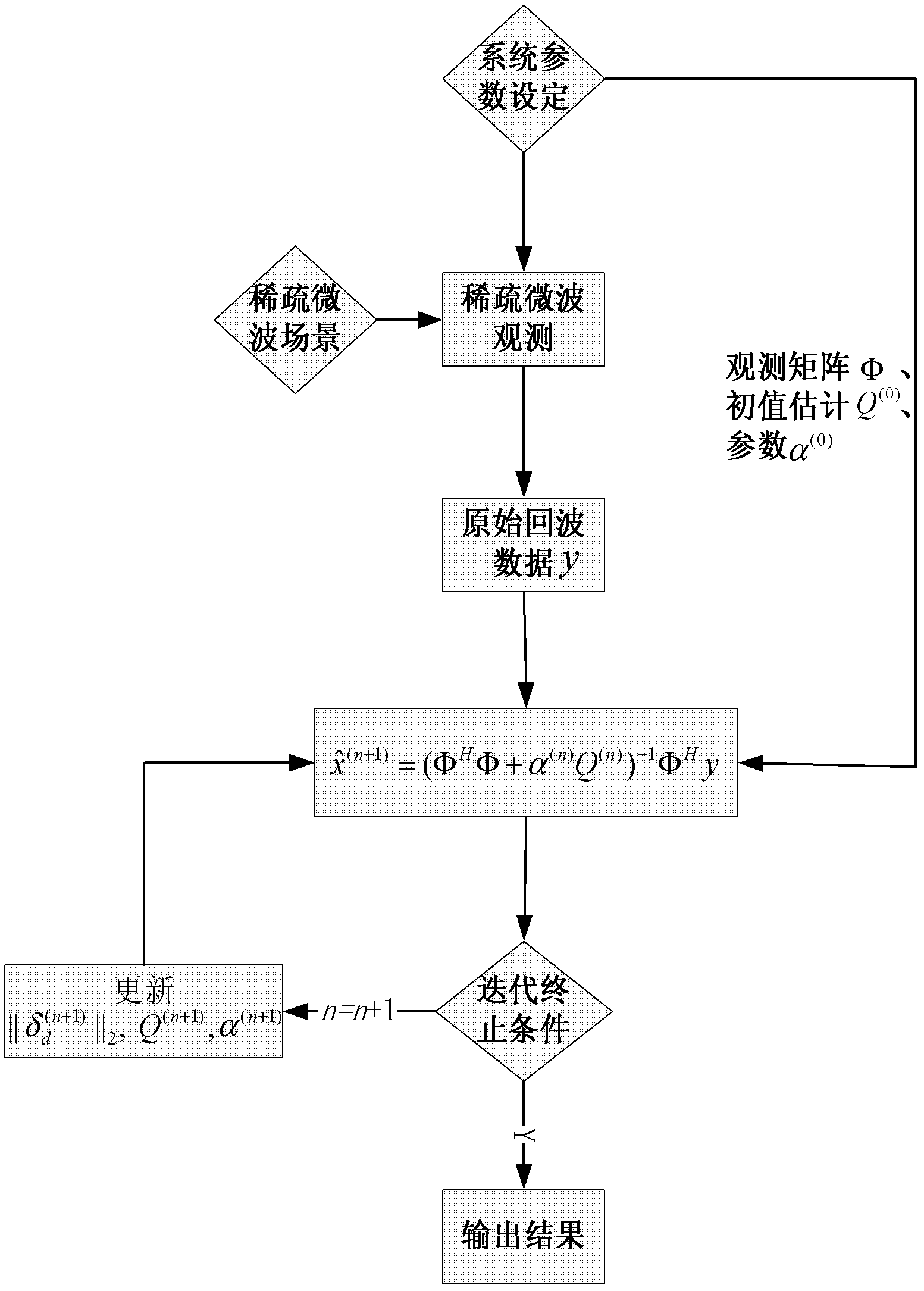
Model constructing method of sparse microwave imaging processing
InactiveCN102254054ASpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsLinear regression
The invention discloses a model constructing method of sparse microwave imaging processing. The model constructing method comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing a linear regression model of microwave imaging by using a linear operator characteristic of microwave imaging according to a radar system parameter and a geometrical relationship of a radar and a scene; secondly, establishing a linear regression model of sparse microwave imaging though construction of a sparse observation model and a sparse transformation matrix; and finally, establishing a reconstruction model of sparse microwave imaging by applying a sparse signal reconstruction theory in sparse signal processing. The model constructing method of the sparse microwave imaging processing provided by the invention provides a theoretical basis for the sparse microwave imaging.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microwave imaging method based on scenario block sparsity
ActiveCN103149561ASparse observationSparse sparse observationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar resolutionImage resolution
The invention discloses a microwave imaging method based on scenario block sparsity, and relates to a radar imaging technology. The method includes the steps of carrying out sparse observation over a block sparsity scenario in a compression sampling mode by utilizing a fact that the geometry size of a target in an actual imaging scenario is greater than the spatial resolution of high resolution microwave imaging radar and the imaging scenario usually covers multiple radar resolution units, and carrying out an efficient image reconstruction based on the block sparsity of the scenario. The method is different from an imaging method based on matched filtering; a sparse microwave imaging radar is based on sparse signal processing, recovers observed scarsity or transforms a domain sparsity scenario by that the method solves an optimization problem. Under the same sampling condition, the reconstruction of the sparse imaging scenario is more accurate than that of a conventional sparse microwave imaging, and sparser observation over the sparse scenario also can be achieved under the same reconfiguration performance conditions, so that the data rate of sampling is further reduced.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
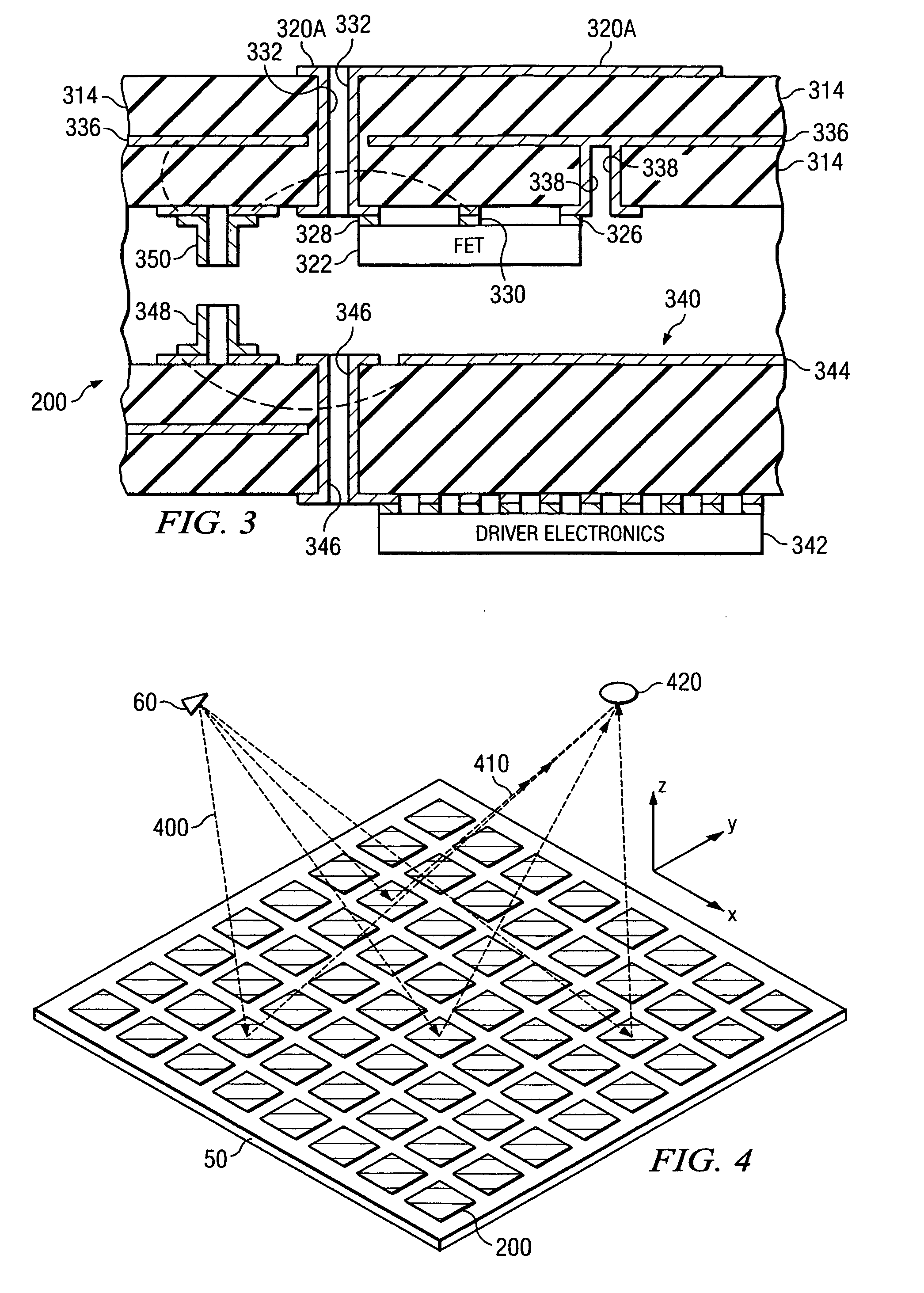
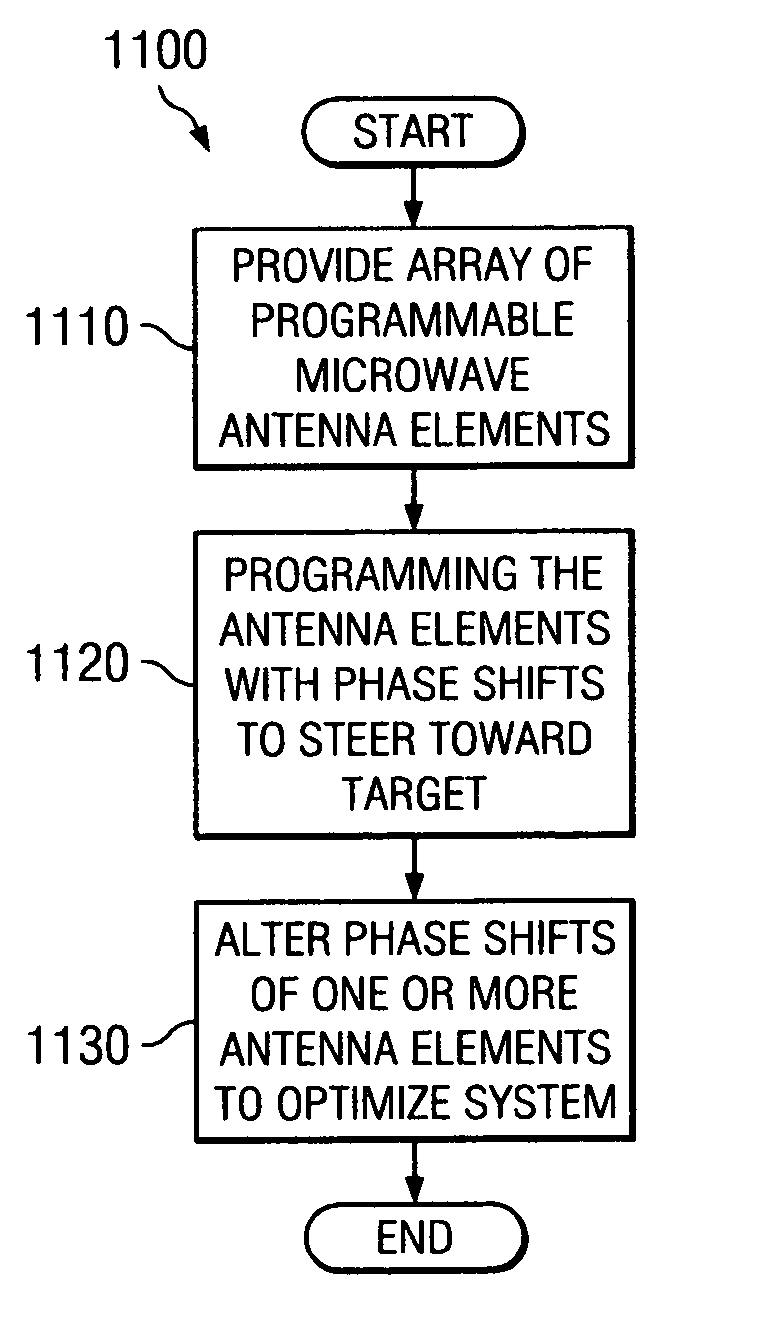
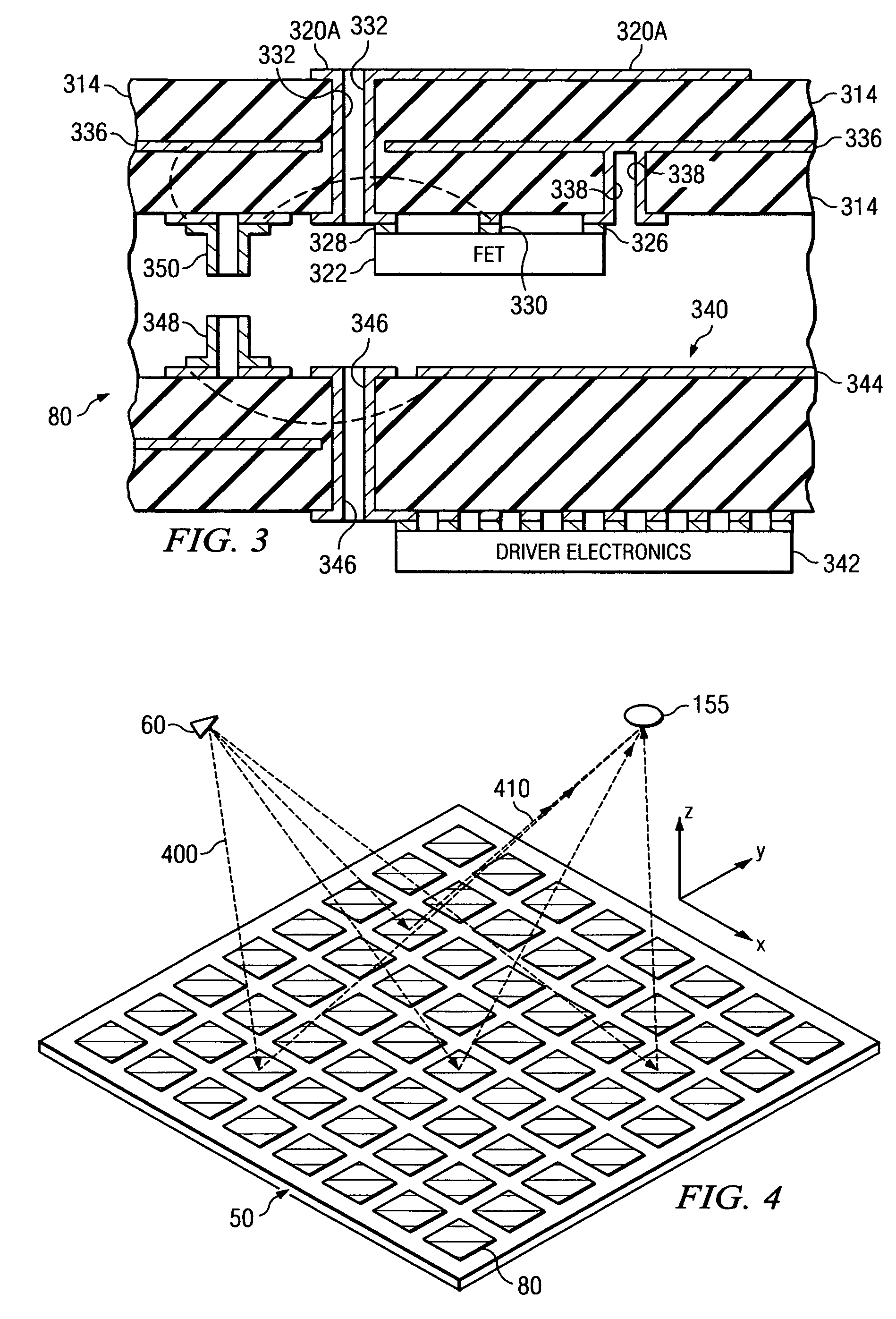
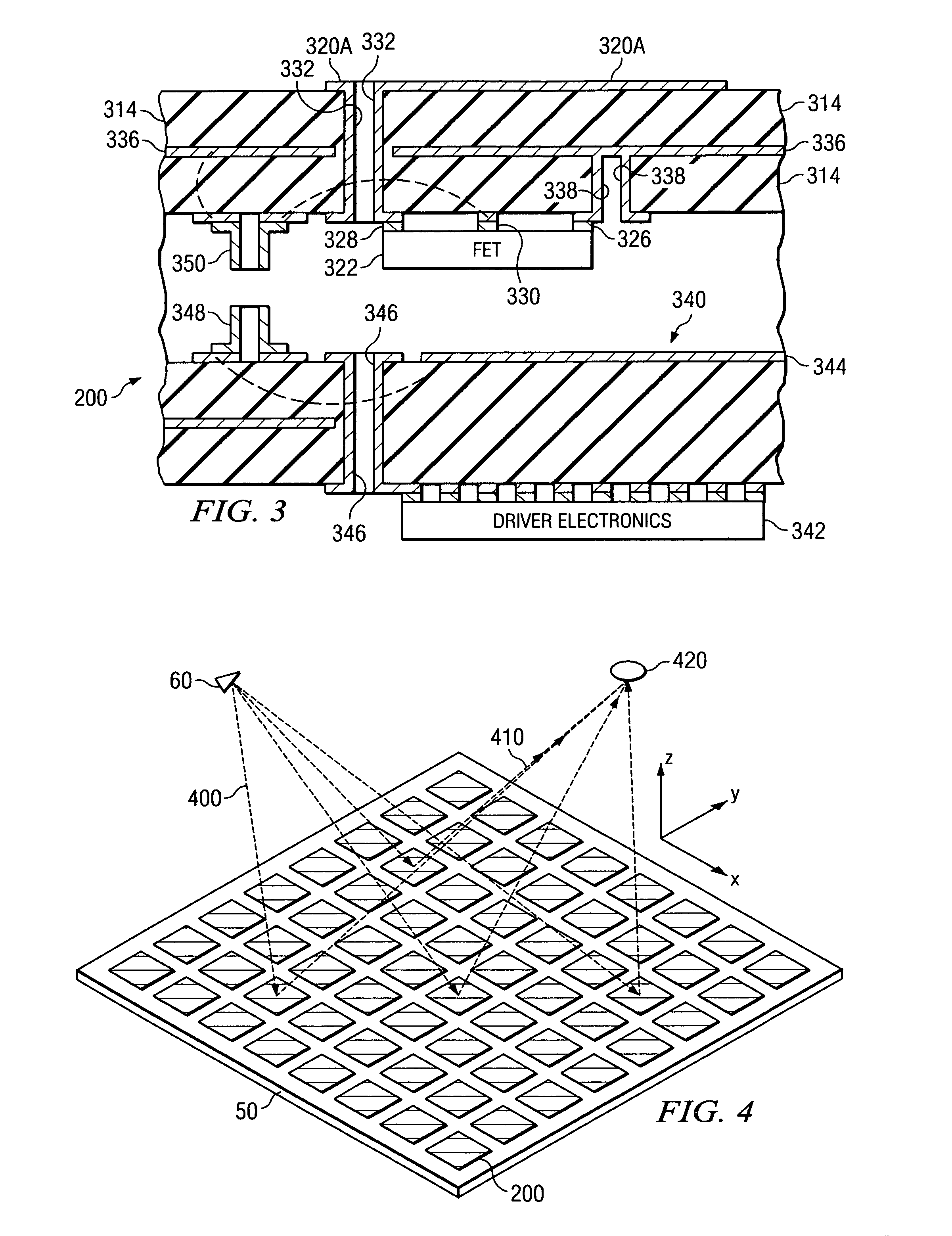
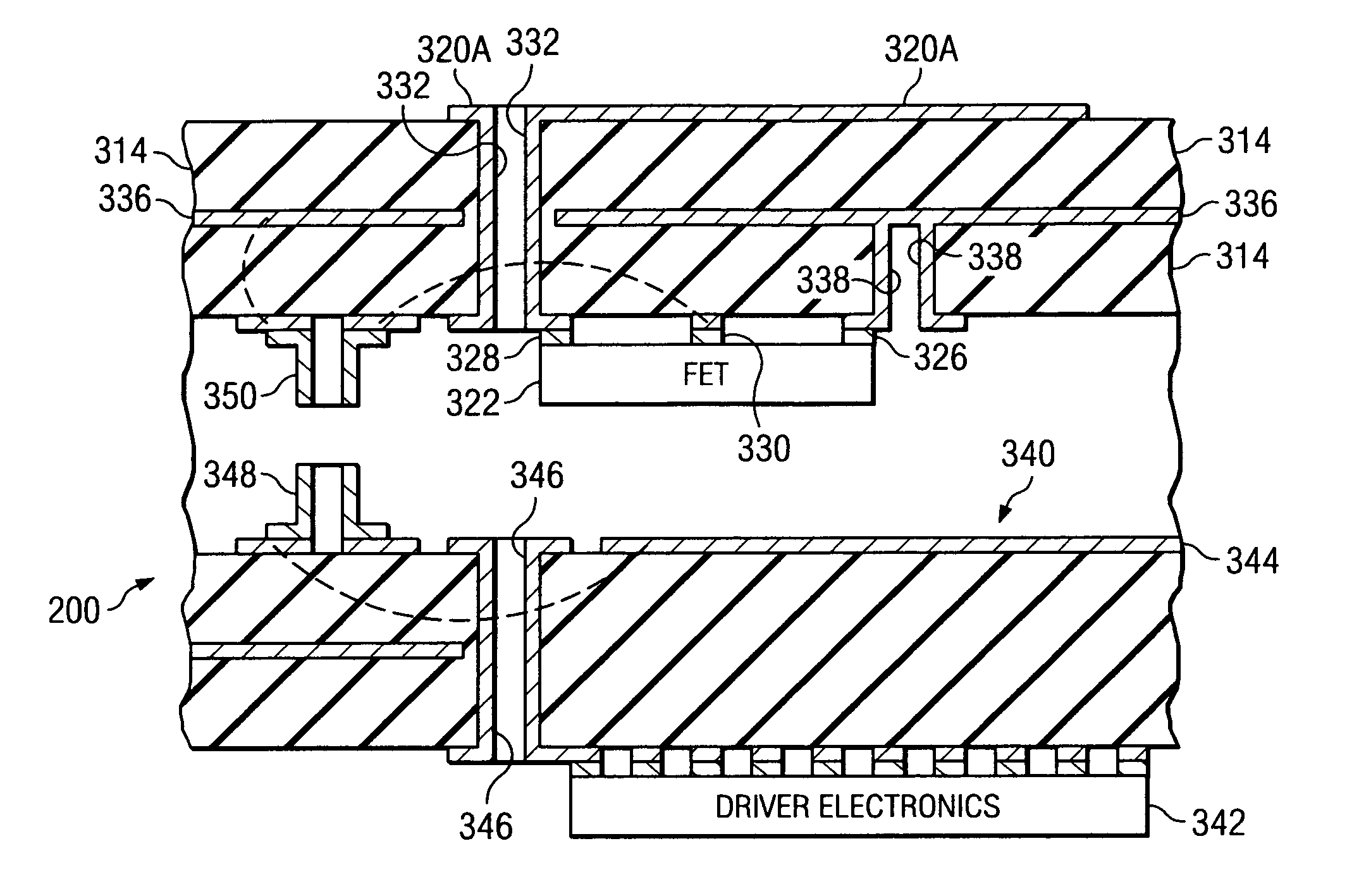
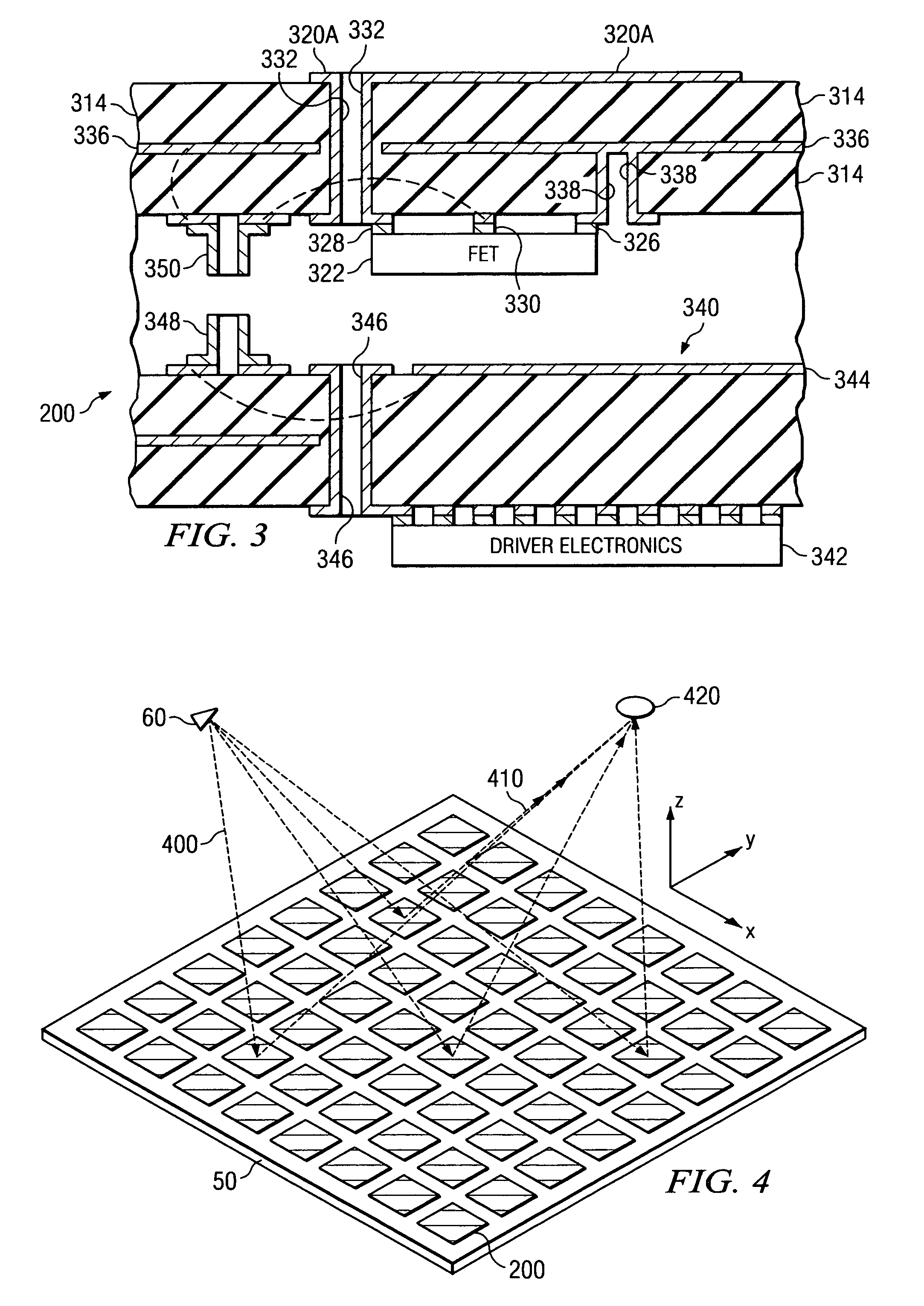
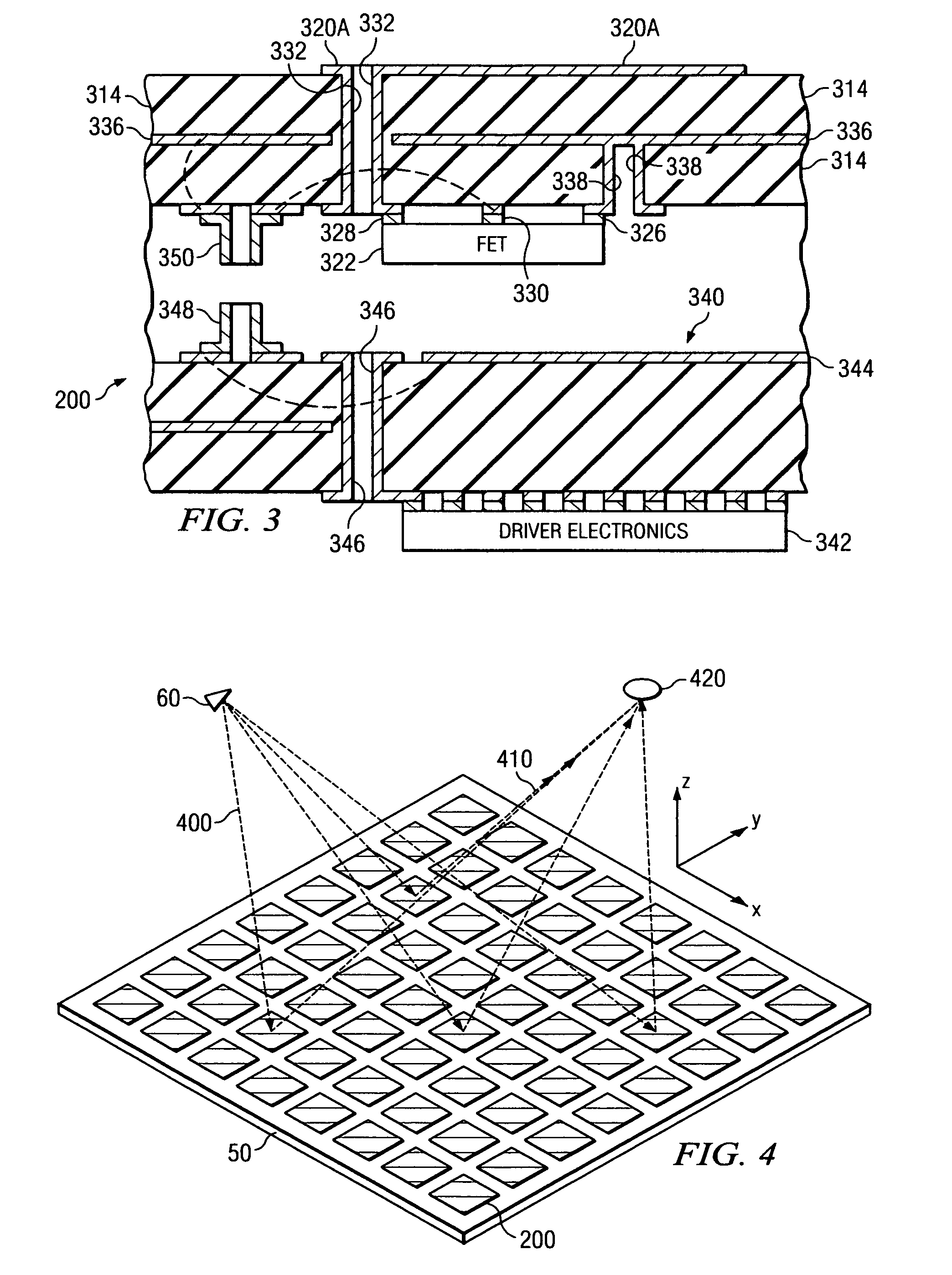
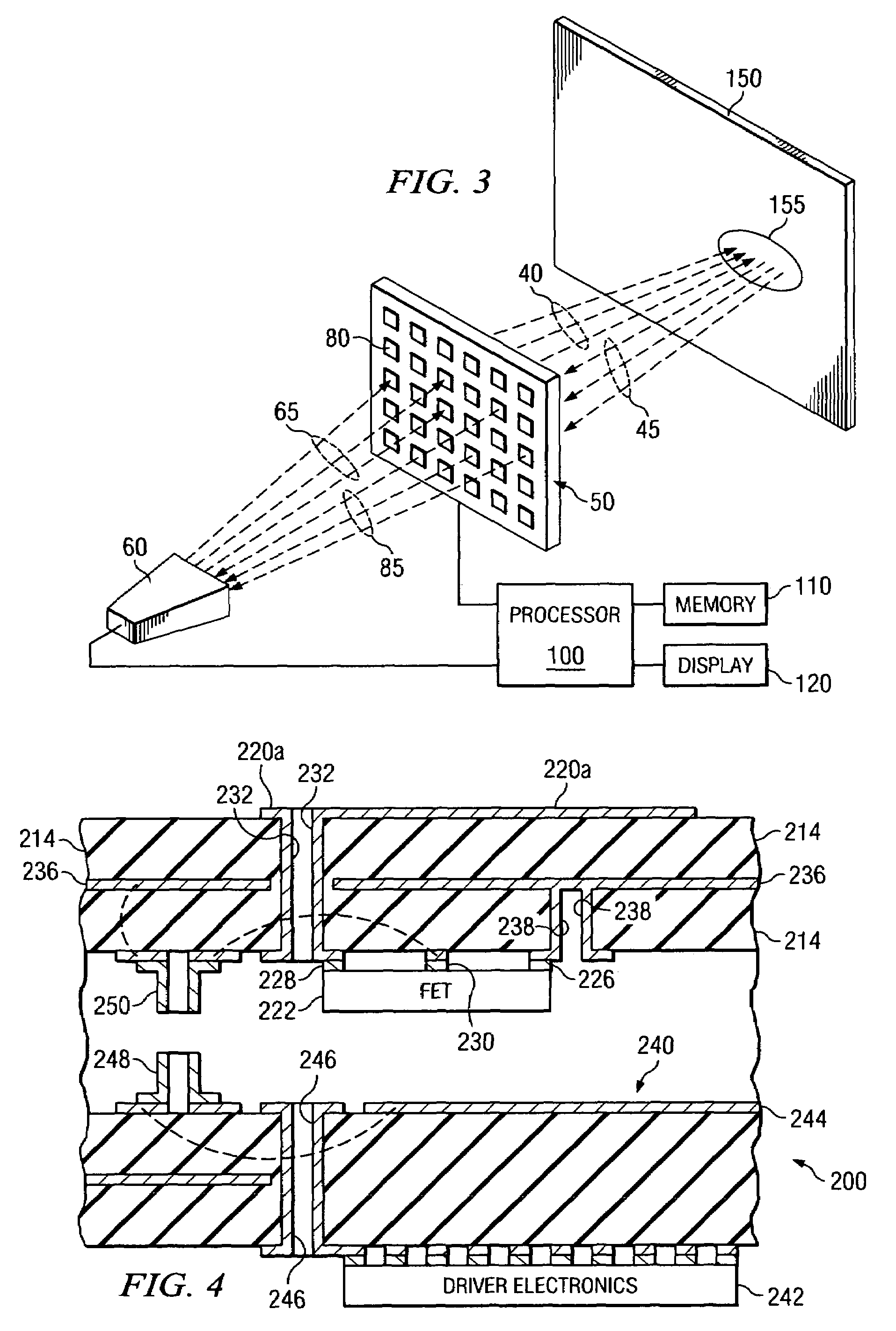
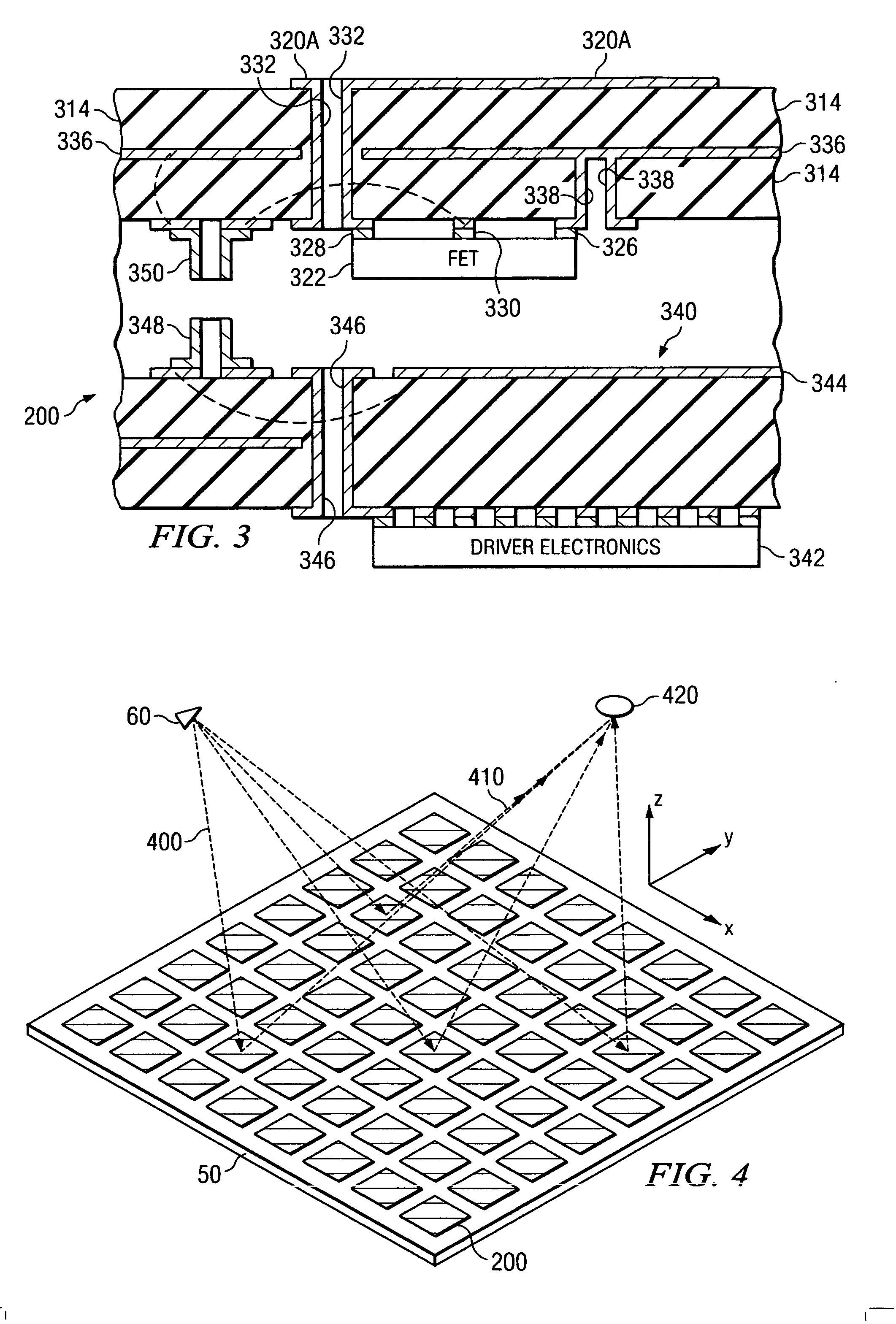
System and method for pattern design in microwave programmable arrays
ActiveUS20060214836A1Small storage spaceEasy to handleRadiating elements structural formsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase shiftedAntenna element
An antenna array for use within a microwave imaging system to capture a microwave image of a target is selectively programmed to optimize one or more parameters of the microwave imaging system. The array includes a plurality of antenna elements, each capable of being programmable with a respective phase shift to direct a beam of microwave radiation toward the target such that the microwave radiation from each of the plurality of antenna elements arrives at the target substantially in-phase. To optimize a parameter of the microwave imaging system, the phase shifts of selective ones of the antenna elements are altered, while still maintaining the substantially in-phase microwave radiation at the target.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for efficient, high-resolution microwave imaging using complementary transmit and receive beam patterns
ActiveUS20060214832A1Individually energised antenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBeam patternAntenna element
A scanning panel for use in a microwave imaging system captures a microwave image of a target using two complementary arrays of antenna elements. Each of the antenna elements in a first array is capable of being programmed with a respective phase delay to direct a transmit beam of microwave illumination toward the target in a transmit beam pattern, and each of the antenna elements in a second array is capable of receiving reflected microwave illumination reflected from the target in a receive beam in a receive beam pattern complementary to the transmit beam pattern. The microwave image of the target is formed at an intersection between the transmit beam and the receive beam.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
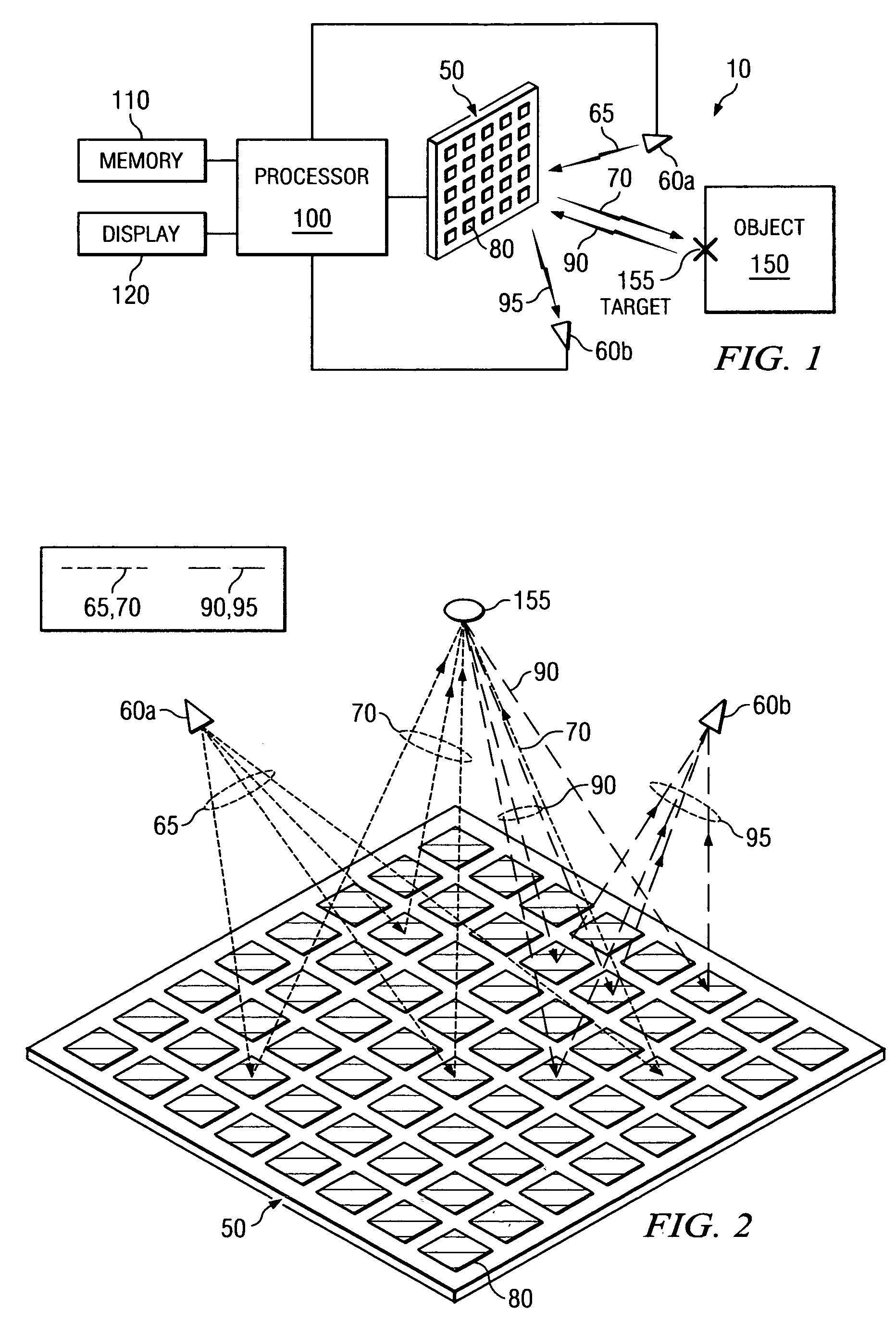
System and method for microwave imaging using programmable transmission array
ActiveUS20060109174A1Antenna arraysGeological detection using milimetre wavesLight beamTransmission coefficient
A microwave imaging system uses microwave radiation provided by a microwave source to image targets. The system includes an array of antenna elements that are capable of being programmed with a respective transmission coefficient to direct the microwave illumination from the microwave source toward a position on the target. The antenna elements are further capable of being programmed with a respective additional transmission coefficient to receive reflected microwave illumination reflected from the position on the target and direct the reflected microwave illumination towards a microwave receiver. A processor is operable to measure an intensity of the reflected microwave illumination to determine a value of a pixel within an image of the target. Multiple beams can be directed towards the target to obtain corresponding pixel values for use by the processor in constructing the image.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Optically-augmented microwave imaging system and method
ActiveUS20050270220A1Fast and simple algorithmComputational complexity is reducedMaterial analysis using microwave meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationComputer scienceMicrowave imaging
An imaging system includes an optical (visible-light or near IR) imaging system and a microwave imaging system. The optical imaging system captures an optical image of the object, produces optical image data representing the optical image and extracts optical image information from the optical image data. The microwave imaging system produces microwave image data representing a microwave image of the object in response to the optical image information.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for microwave imaging using programmable transmission array
ActiveUS7298318B2Antenna arraysGeological detection using milimetre wavesLight beamTransmission coefficient
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for inspecting transportable items using microwave imaging
InactiveUS7183963B2Geological detection using milimetre wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansLight beamAntenna element
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
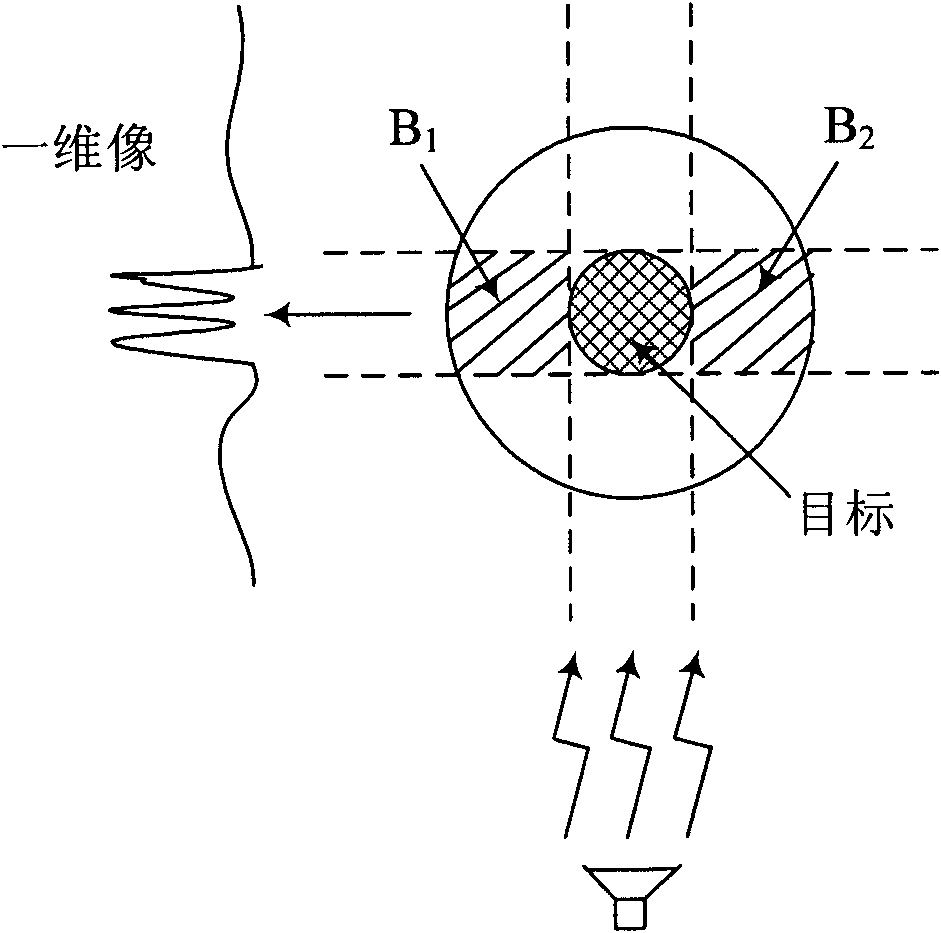
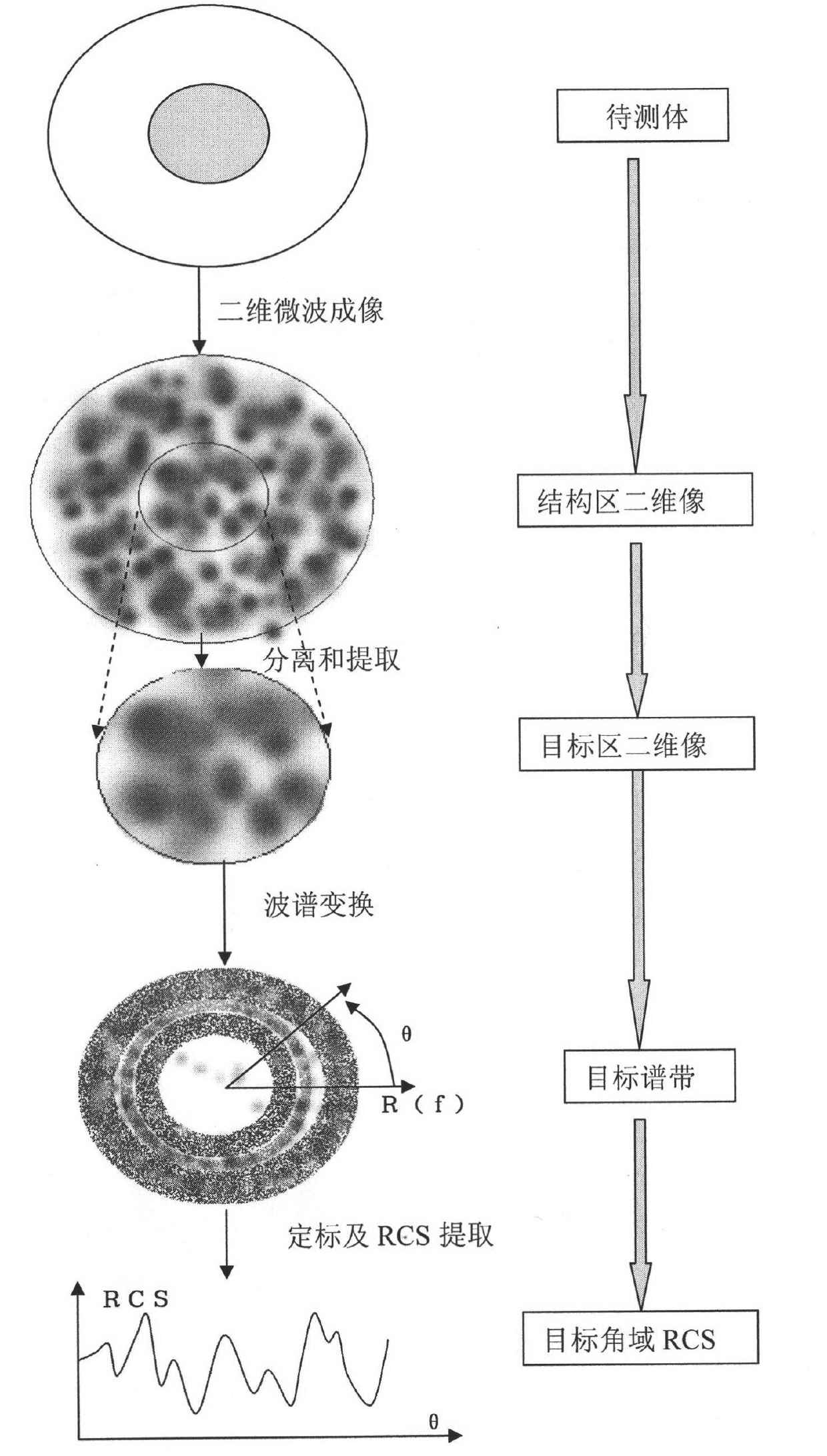
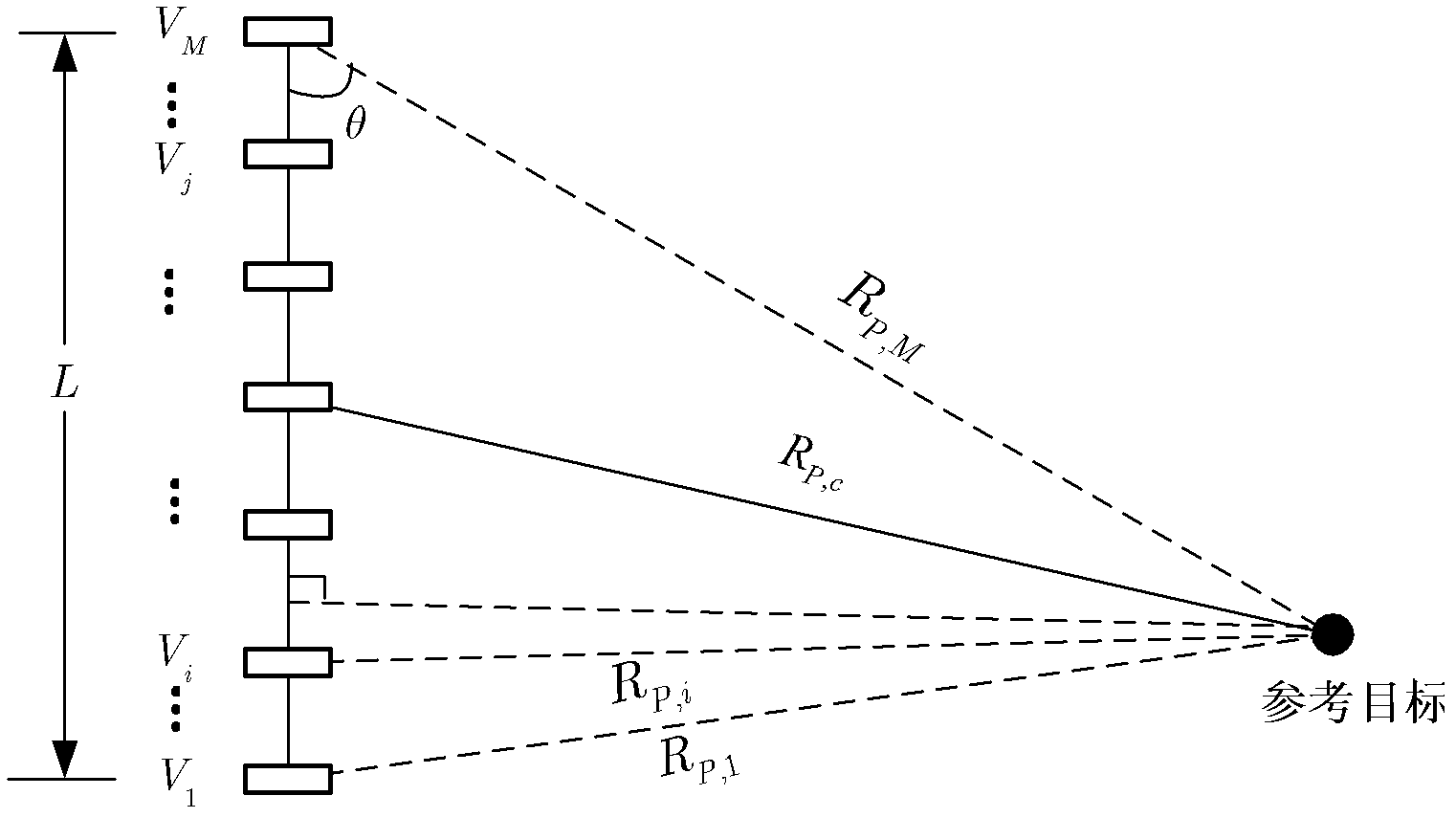
Method for testing RCS (radar cross section) of low-scattering conformal antenna based on two-dimensional microwave imaging
InactiveCN102253376AGood effectPromotion value of large projectsWave based measurement systemsSpectral domainFourier transform on finite groups
The invention relates to a method for testing an RCS (radar cross section) of a low-scattering conformal antenna based on two-dimensional microwave imaging, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out an RCS test on a metal envelope and a low-scattering conformal antenna in an installed state so as to obtain a two-dimensional microwave image; carrying out two-dimensional Fourier transform on the obtained new two-dimensional microwave image so as to obtain the data of a target spectral domain; carrying out an RCS test on a metal ball (the RCS of the metal ball is known) so as to obtain a two-dimensional microwave image, then carrying out two-dimensional Fourier transform on the obtained two-dimensional microwave image so as to obtain the data G0 (f, theta) of a scattered field of the metal ball, wherein the data of the scattered field varies with frequency and angle; and finally, obtaining the RCS of the conformal antenna, wherein the RCS of the conformal antenna meets the following formula: RCS= G1 (f, theta) (of the conformal antenna) - G0 (f, theta) (of the metal ball) + RCS (of the metal ball). The method provided by the invention is a method for testing an RCS (radar cross section) of a low-scattering conformal antenna in an installed state based on the two-dimensional microwave imaging technology, and after practicing, the obtained effect is good, therefore, the method provided by the invention has great engineering popularization value.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Sparse microwave imaging method
ActiveCN102221696AReduce complexityReduce data volumeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a sparse microwave imaging method, relating to the information acquisition and processing technology. By utilizing sparsity of microwave imaging observation, through introducing sparse signal processing theory into microwave imaging technology, after signal processing and information extraction, the geometrical and physical characteristics of an observation object such as space position, scattering characteristic and motion characteristic and the like are obtained, wherein the sparse signal processing theory is through searching sparse representation field of the observation object, obtaining sparse microwave signal of the observation object in space, time, frequency spectrum or polarizing field sparse sampling. According to the sparse microwave imaging method in the invention, the bottleneck problems existed in the prior art such as difficult system realization, complex imaging processing method, redundant information and difficult feature extraction and the like based on Nyquist sampling theorem and classic digital signal processing theory are solved, thus microwave imaging system structure and imaging complexity is reduced.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
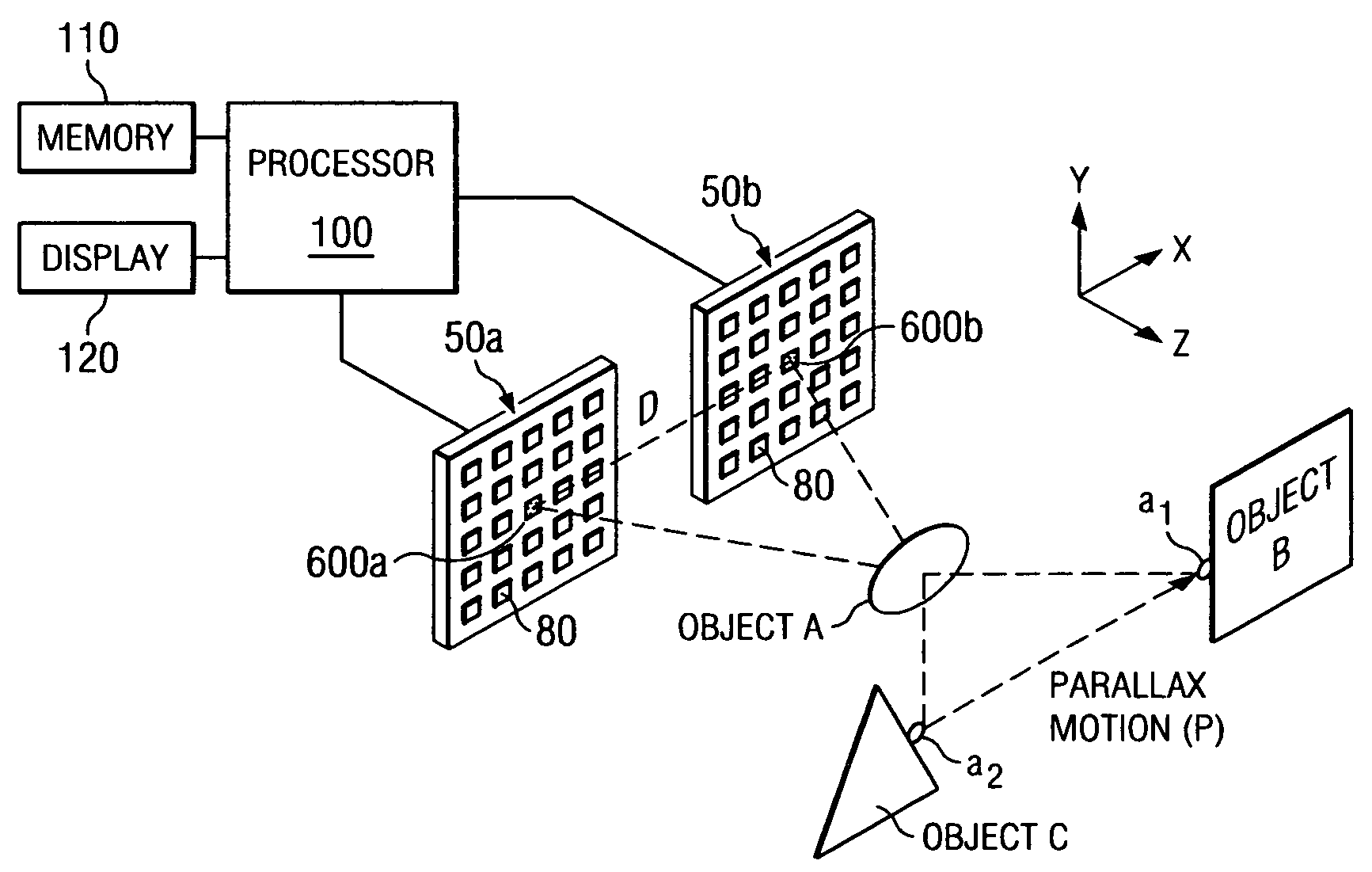
System and method for stereoscopic anomaly detection using microwave imaging
InactiveUS20080079625A1Detection using electromagnetic wavesAntennasAnomaly detectionAntenna element
A microwave imaging system for constructing a stereoscopic microwave image of an object includes an antenna array with a plurality of programmable antenna elements and a processor. Each of the antenna elements is capable of being programmed with a respective first direction coefficient to capture a first microwave image of the object from a first focal point on the array. In addition, each of the antenna elements is capable of being programmed with a respective second direction coefficient to capture a second microwave image of the object from a second focal point on the array. The processor constructs the stereoscopic microwave image from the first and second microwave images.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Three-dimensional microwave imaging method for correcting multi-channel amplitude-phase error
InactiveCN103018739AMethod steps are clear and conciseEasy to implementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFourier transform on finite groupsPeak value
The invention discloses a three-dimensional microwave imaging method for correcting a multi-channel amplitude-phase error, and relates to the technology of microwave three-dimensional imaging. The three-dimensional microwave imaging method for correcting the multi-channel amplitude-phase error comprises the following steps of: obtaining a two-dimensional image for each two-dimensional receiving channel datum in original three-dimensional microwave echo data by using a two-dimensional imaging algorithm; taking a scaler target as a reference target in all the two-dimensional images, taking the maximum amplitude value of each channel reference target as a reference, and performing amplitude correction on all the channel data; obtaining an actual distance and a ideal distance between the reference target and each receiving antenna, and taking the actual distance and the ideal distance as a filter H1(f) for correcting multi-channel distance offset; transforming a signal to a distance-direction frequency domain via Fourier transformation, performing multiplication with the filter, and then transforming the signal after the multiplication back to the distance-direction time domain via Fourier inverse transformation; getting an unwrapping phase at the peak value of the reference target in each two-dimensional image, and performing subtraction with the ideal phase progress value calculated by the ideal distance to obtain a factor H2(i) for correcting the multi-channel phase error; performing the multiplication on the H2(i) and the data after the two-dimensional imaging to compensate the influence of the phase error; and obtaining a three-dimensional image which is focused well in a target area by using a back-projection algorithm along the row-crossing direction Y.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for security inspection using microwave imaging
ActiveUS20060109160A1Geological detection using milimetre wavesAntenna supports/mountingsLight beamAntenna element
A microwave imaging system uses microwave radiation provided by a microwave source to image targets. The system includes an array of antenna elements that are capable of being programmed with a respective direction coefficient to direct the microwave illumination from the microwave source toward a position on the target. The antenna elements are further capable of being programmed to receive reflected microwave illumination reflected from the position on the target. A processor is operable to measure an intensity of the reflected microwave illumination to determine a value of a pixel within an image of the target. Multiple beams can be directed towards the target to obtain corresponding pixel values for use by the processor in constructing the image.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
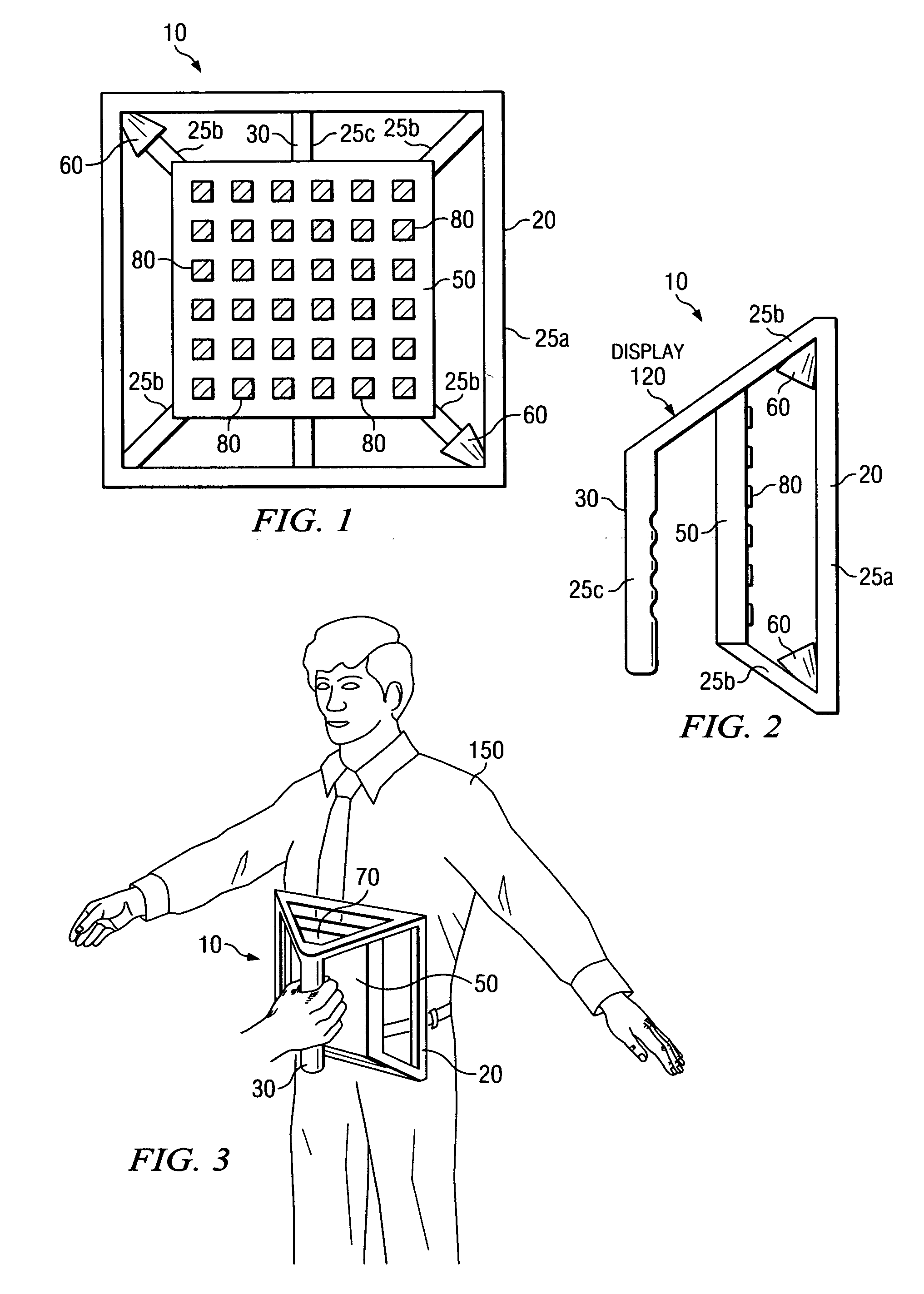
Handheld microwave imaging device
A handheld microwave imaging device provides screening of objects, such as persons and other items. The imaging device includes an antenna array of antenna elements, each capable of being programmed with a respective direction coefficient to direct microwave illumination toward a target associated with the object, and each capable of being programmed with a respective additional direction coefficient to receive reflected microwave illumination reflected from the target. The imaging device further includes a processor operable to measure an intensity of the reflected microwave illumination to determine a value of a voxel within a microwave image of the object. The antenna array is compliantly mounted in a first portion of a support structure, while a second portion of the support structure defines a handle for enabling a user to control movement of the device.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com