System and method for security inspection using microwave imaging
a technology of security inspection and microwave imaging, applied in the direction of individually energised antenna arrays, instruments, using reradiation, etc., can solve the problems of inability to detect non-metallic objects, inability to reliably and invasively, and inability to physically inspect security personnel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] As used herein, the terms microwave radiation and microwave illumination each refer to the band of electromagnetic radiation having wavelengths between 0.3 mm and 30 cm, corresponding to frequencies of about 1 GHz to about 1,000 GHz. Thus, the terms microwave radiation and microwave illumination each include traditional microwave radiation, as well as what is commonly known as millimeter-wave radiation.
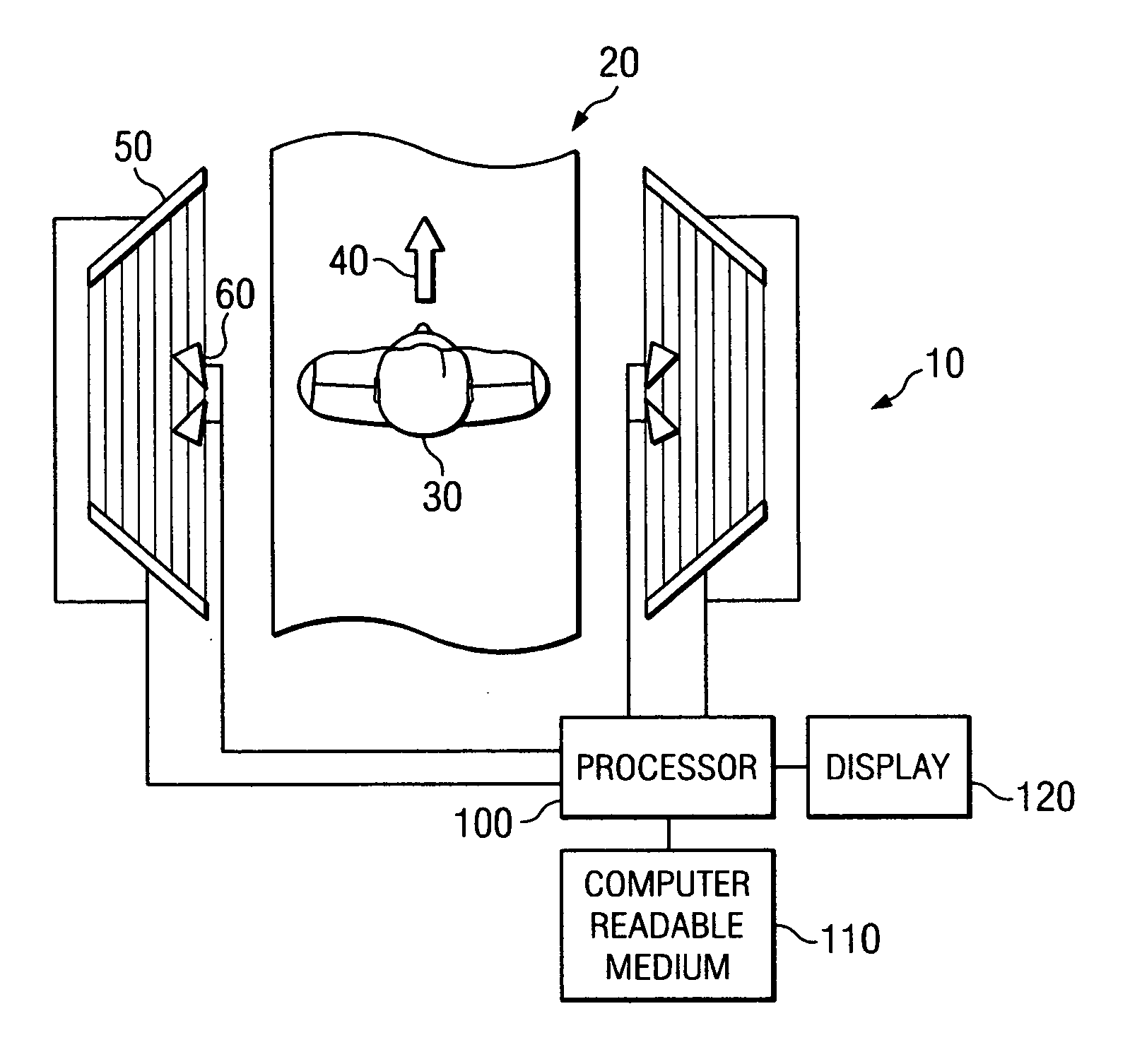
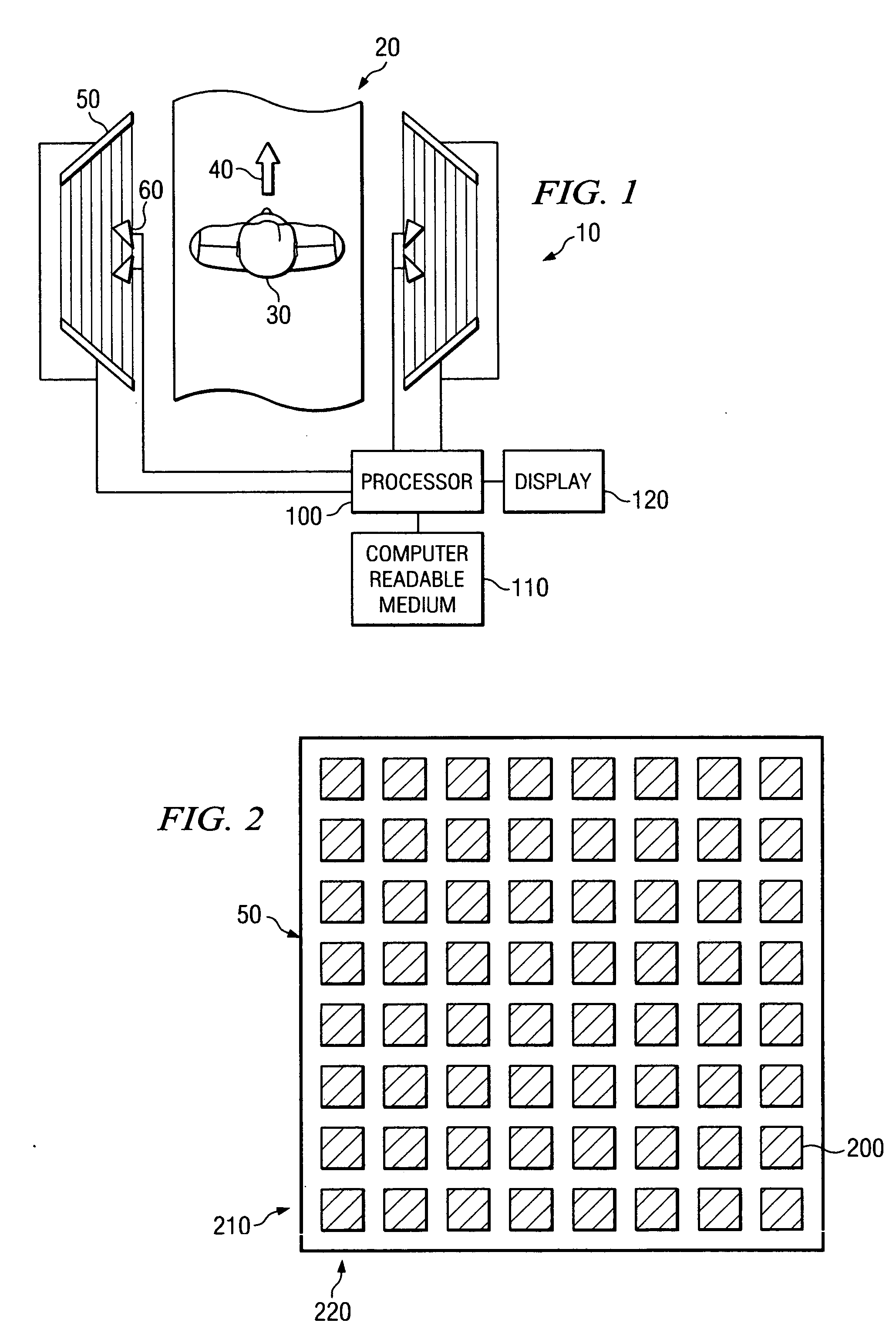
[0023]FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a simplified exemplary microwave security inspection system 10, in accordance with embodiments of the present invention. The microwave security inspection system 10 includes a portal 20 through which a human subject 30 is capable of walking. The portal 20 does not include any moving parts, and therefore, the human subject 30 is able to walk at a normal pace in a single direction 40 through the portal 20. By enabling the human subject 30 to walk through the portal 20, the throughput of the system 10 is maximized, while also minimizing the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com