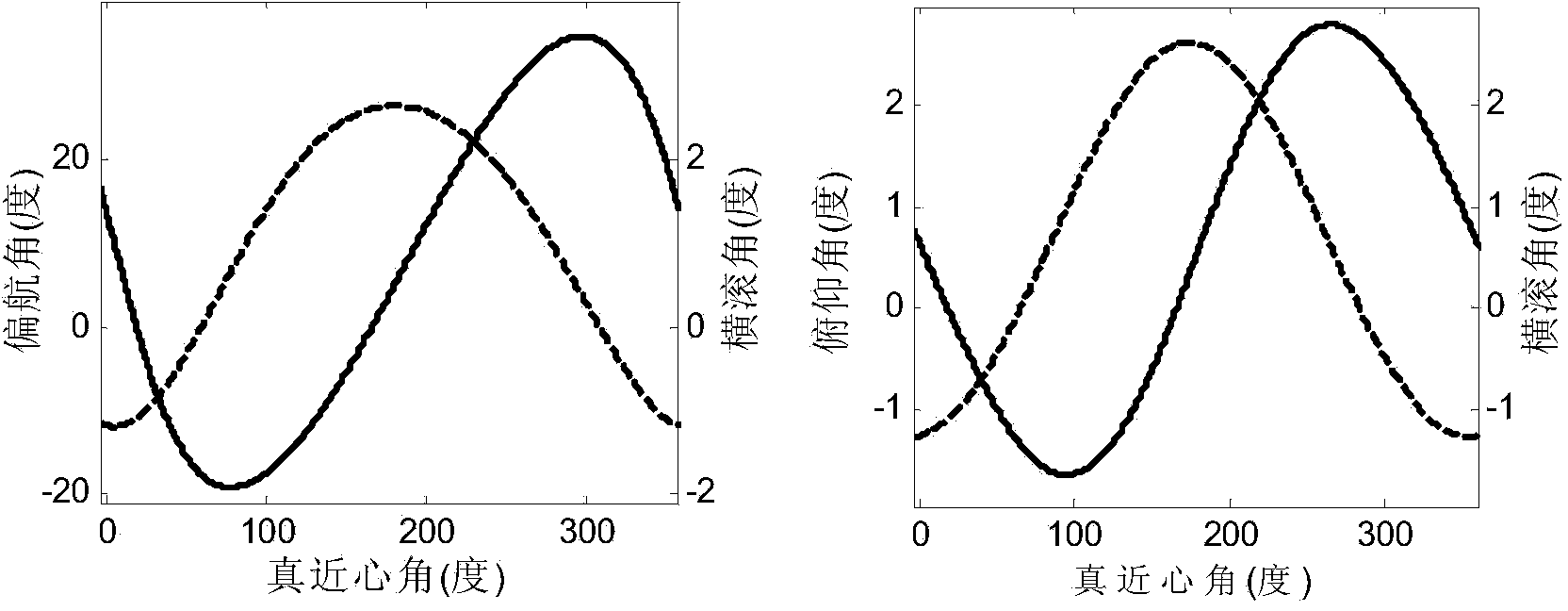
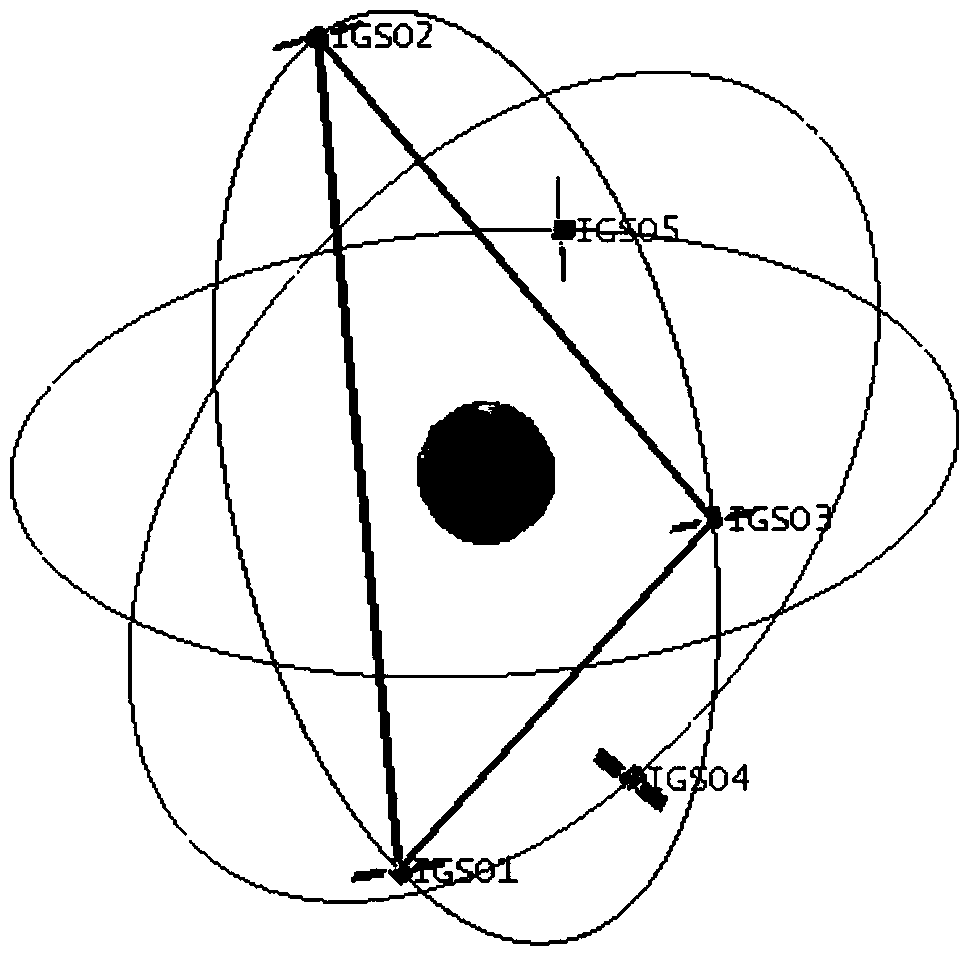
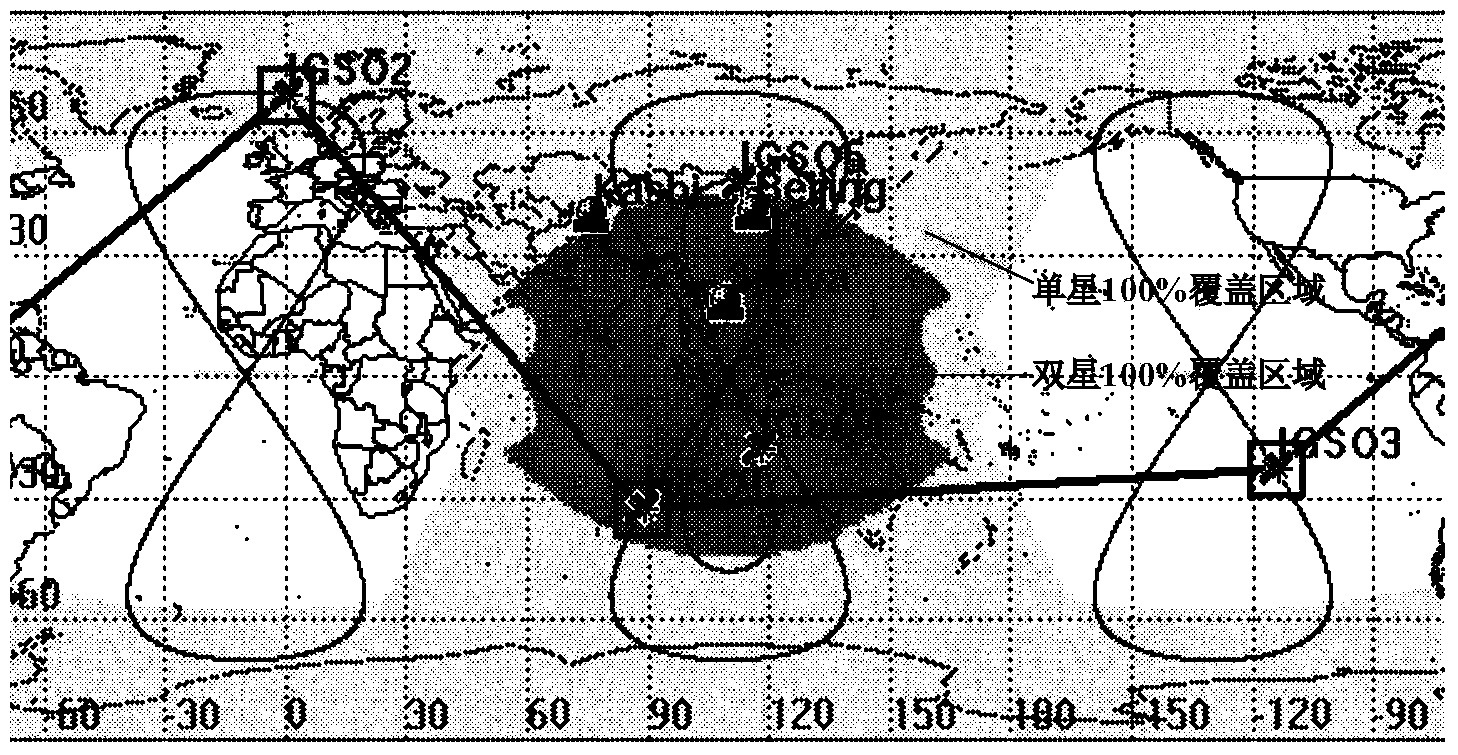
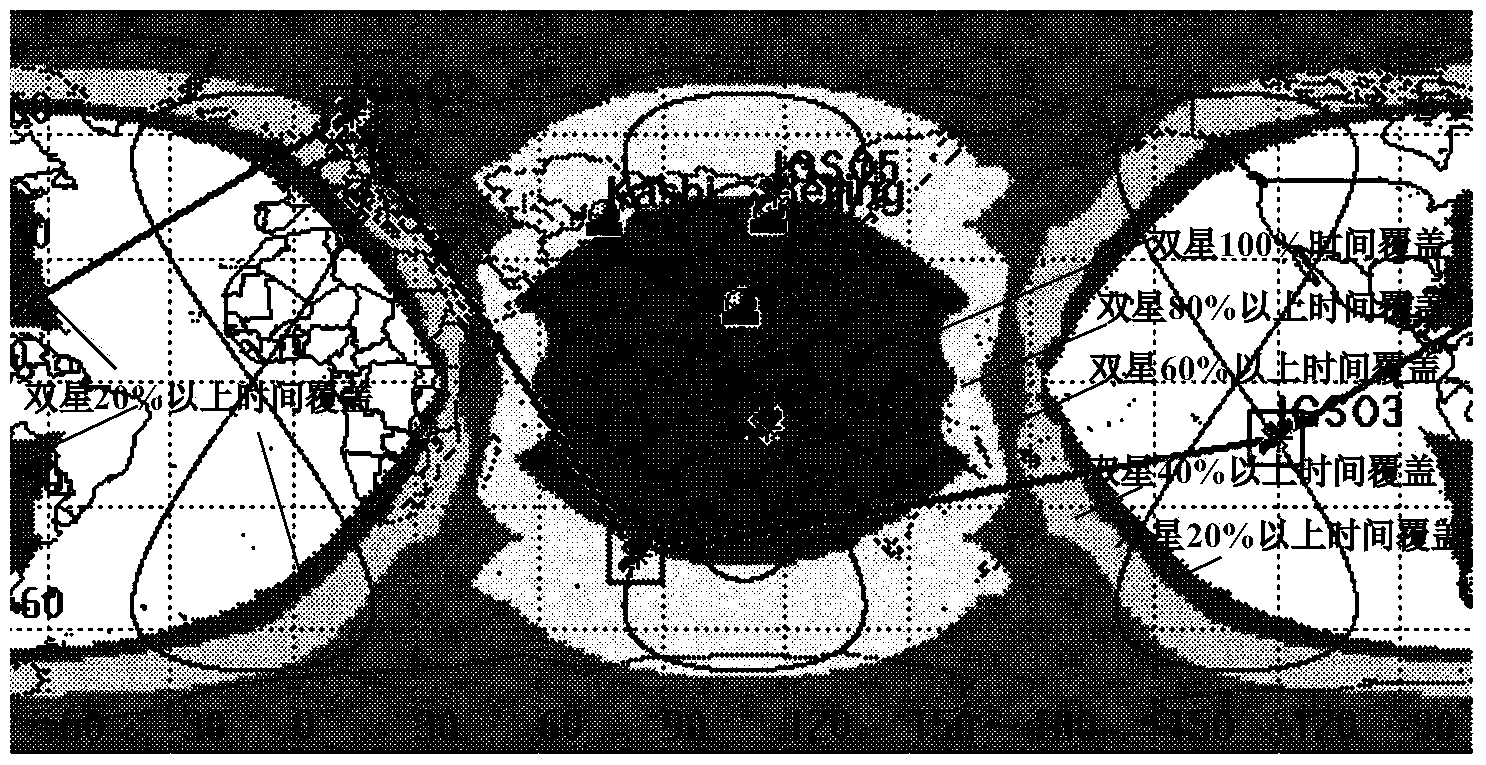
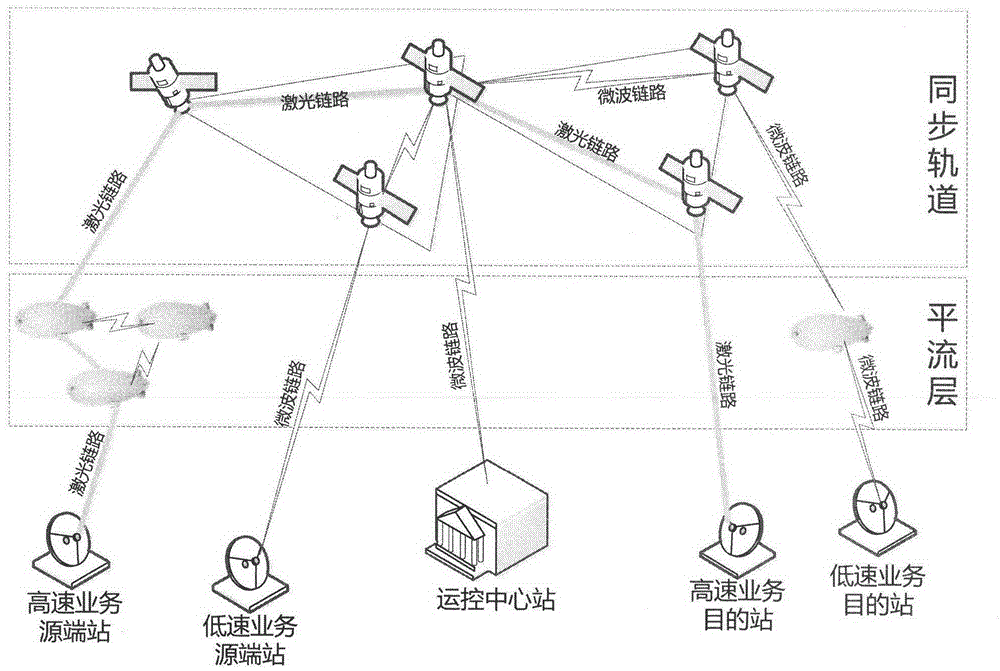
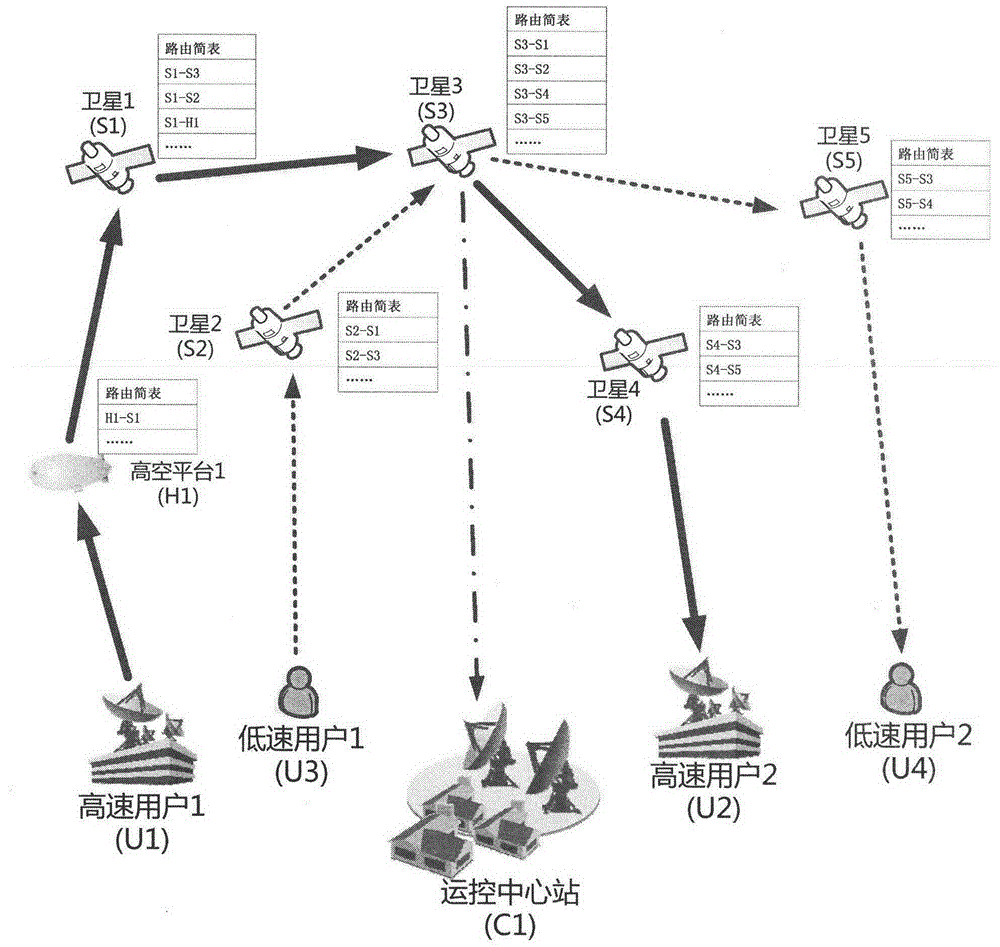
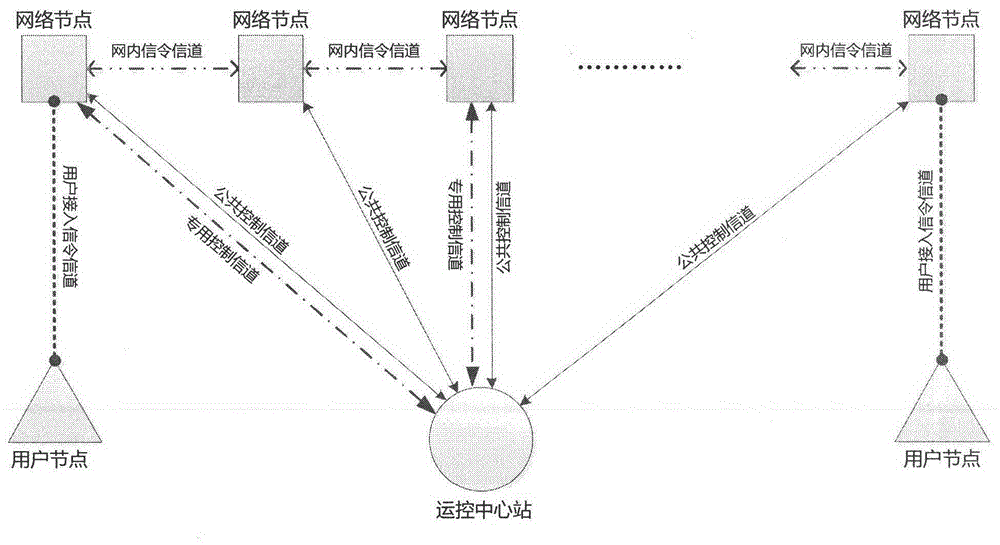
Patents
Literature
192 results about "Synchronous orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
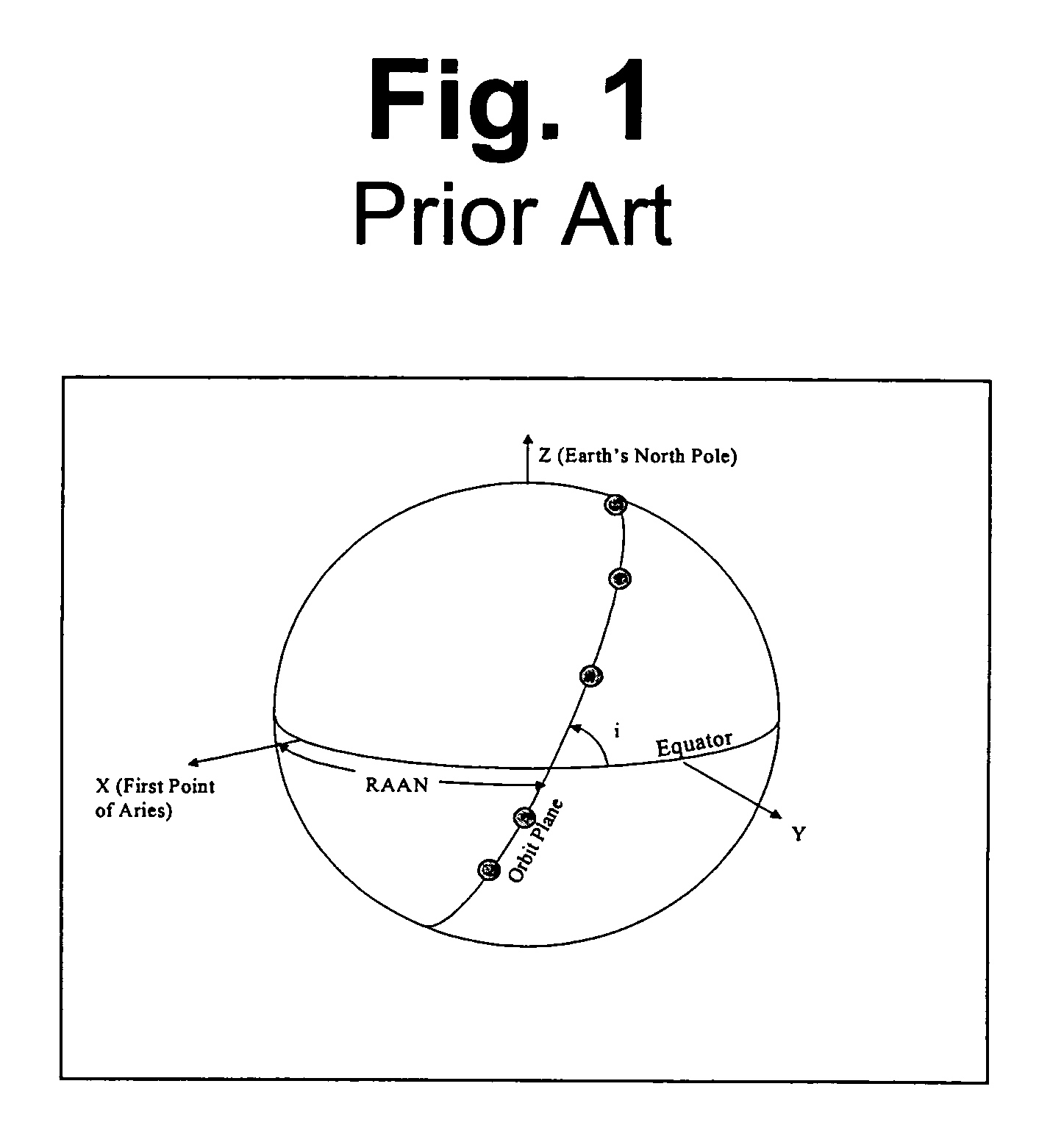
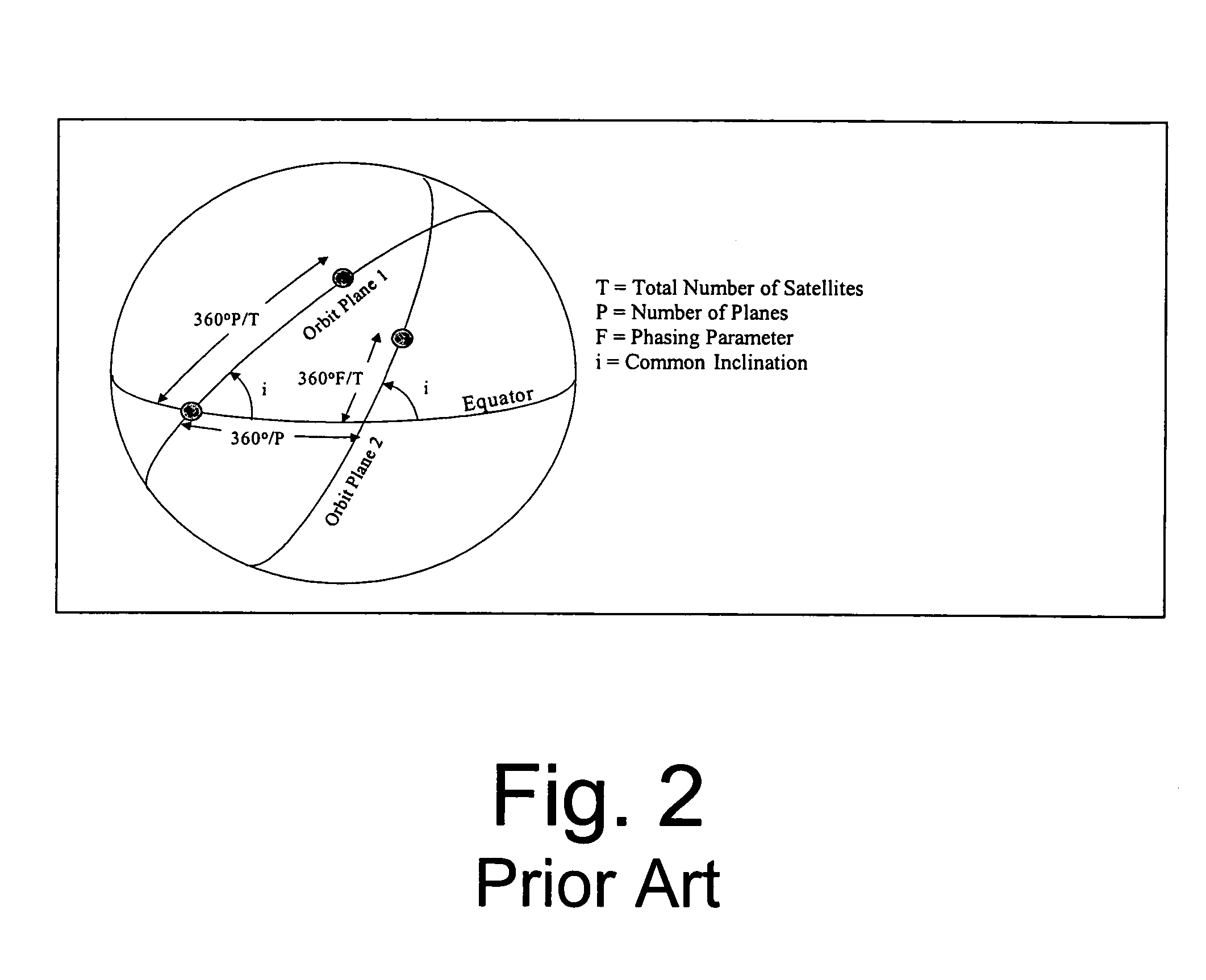
A synchronous orbit is an orbit in which an orbiting body (usually a satellite) has a period equal to the average rotational period of the body being orbited (usually a planet), and in the same direction of rotation as that body.
Practical orbit raising system and method for geosynchronous satellites
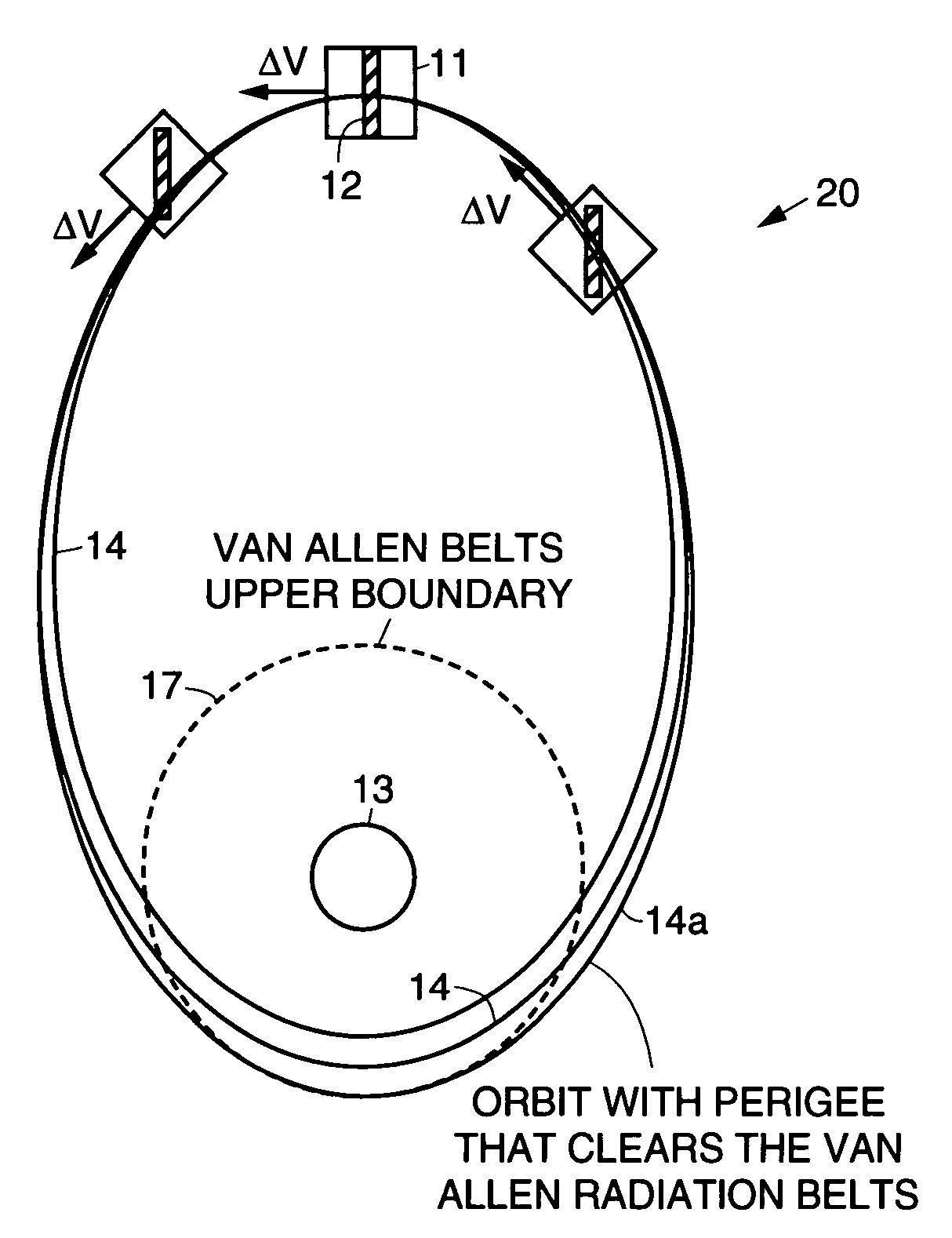
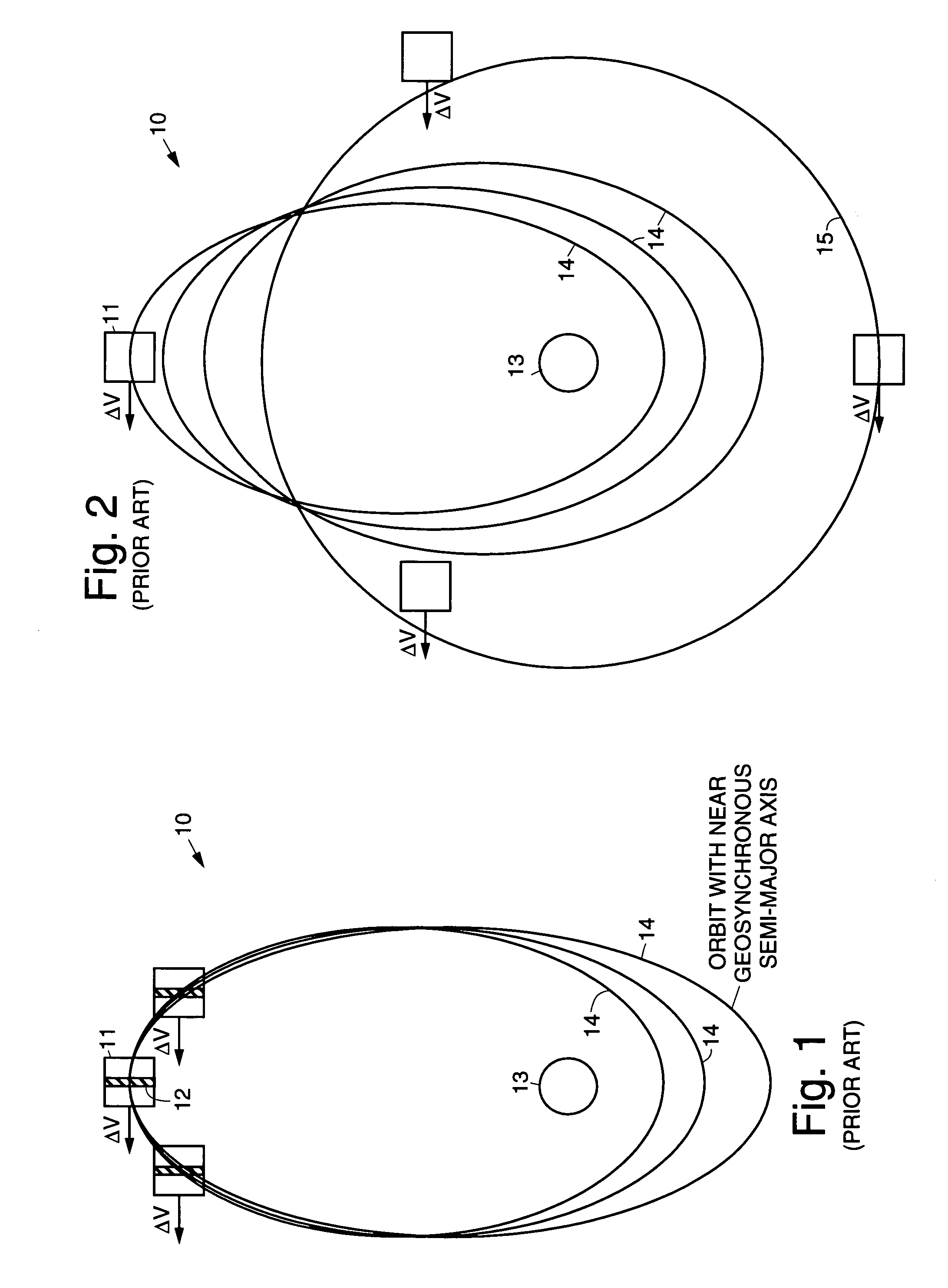
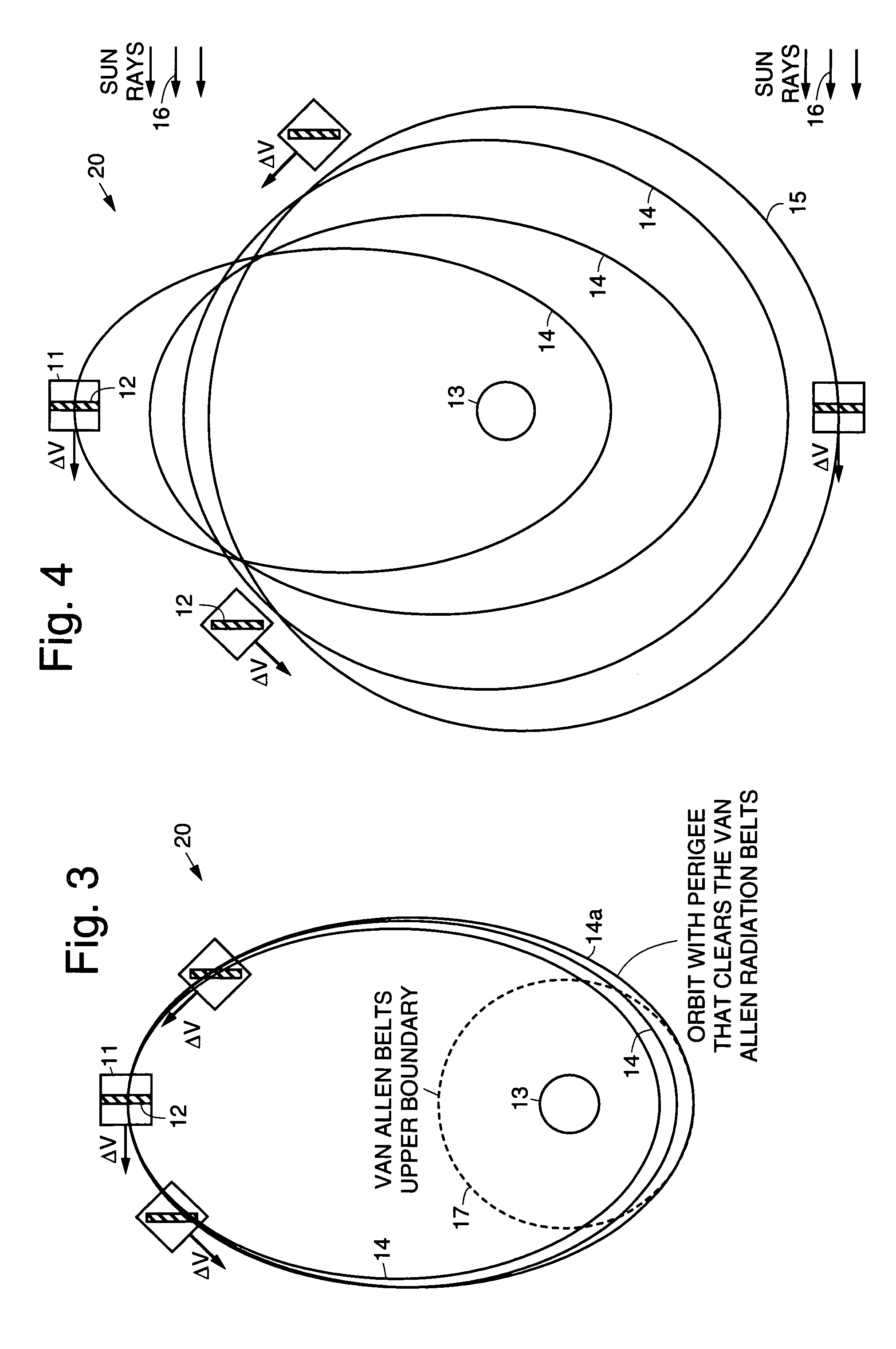
InactiveUS7113851B1Maximizing payload massMaximizing mission lifeLaunch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusElectricitySynchronous orbit
A practical orbit raising method and system wherein a satellite quickly escapes the Van Allen radiation belts and payload mass and mission life are maximized. A satellite is launched that contains high thrust chemical propulsion thrusters, high specific impulse electric propulsion thrusters and a solar array. The satellite quickly escapes the Van Allen radiation belts by firing the high thrust chemical propulsion thrusters at apogees of intermediate orbits, starting from the transfer orbit initiated by a launch vehicle, to successively raise the perigees until the perigee clears the Van Allen radiation belts. The payload mass and mission life are maximized by firing high specific impulse electric propulsion thrusters to raise the satellite to near synchronous orbit, while steering the thrust vector and solar array to maintain the sun's illumination on the solar array. The chemical and / or electric propulsion thrusters are then fired to achieve geosynchronous orbit.
Owner:SPACE SYST LORAL INC
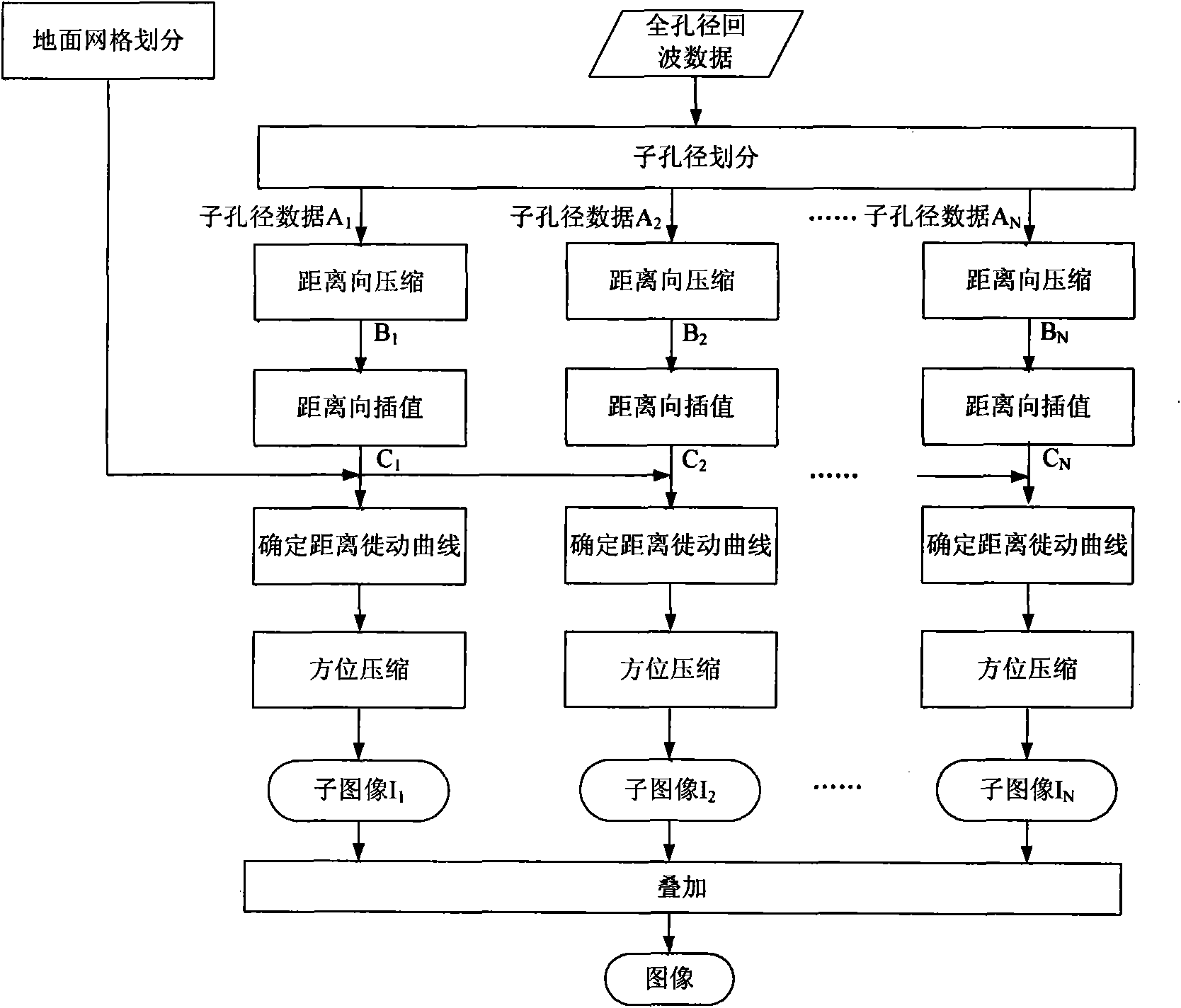
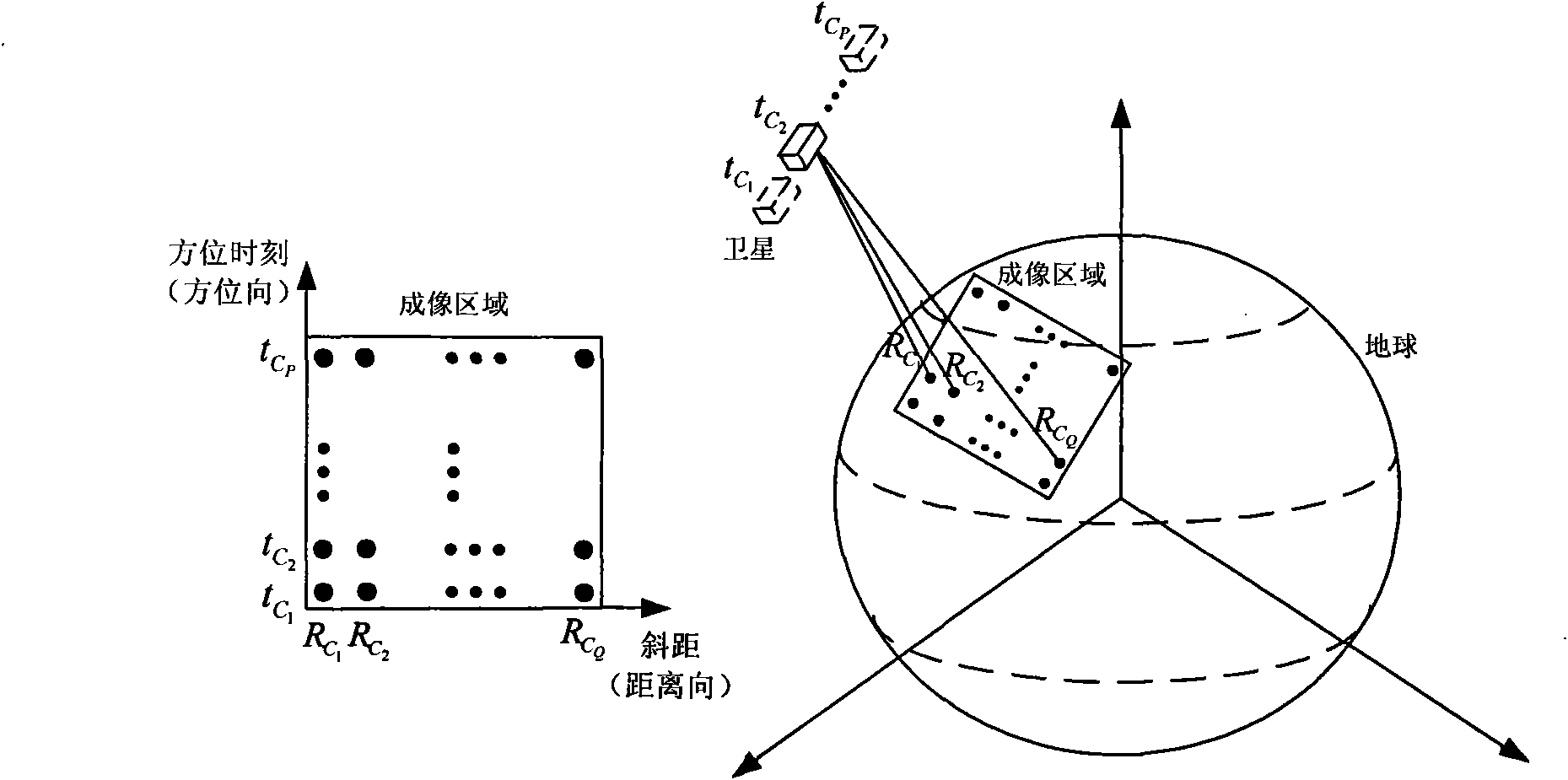
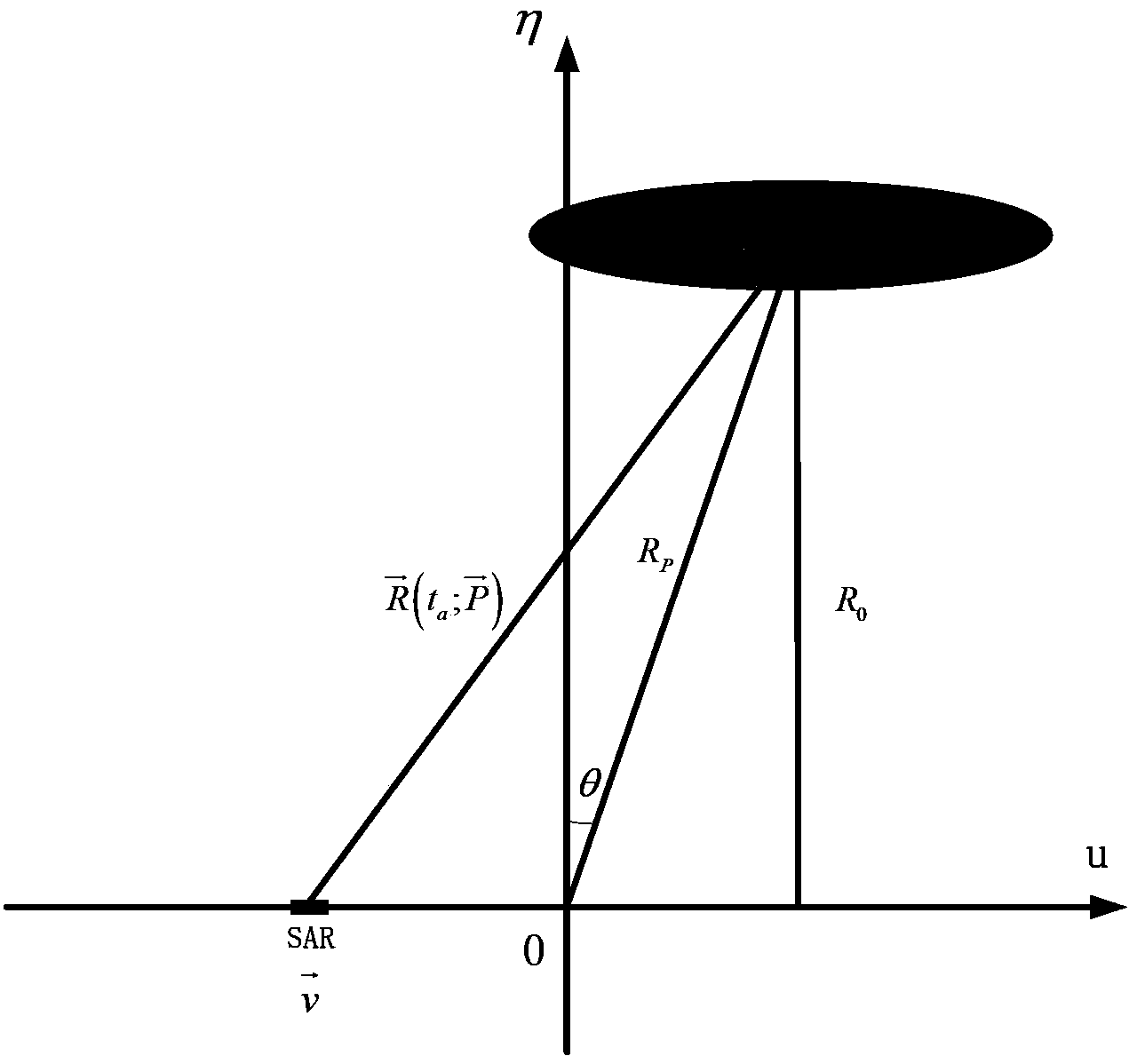
High-resolution imaging method for earth synchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar satellite
InactiveCN101915920AExcellent azimuth resolutionRealize multi-point target imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWide areaGrounding grid
The invention discloses a high-resolution imaging method for an earth synchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar satellite. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, dividing a sub-aperture; 2, performing range compression on the sub-aperture data; 3, performing range interpolation on the sub-aperture data; 4, dividing a ground grid; 5, determining a range migration curve; 6, performing azimuth compression processing; and 7, superposing sub-aperture images to obtain the final image. By the imaging method provided by the invention, high-resolution imaging can be realized by processing the full-aperture echo data of the earth synchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar satellite, multi-point target imaging can be realized, namely azimuth compression can be performed on different range migration curves of different range and azimuth targets, and imaging in a wide-area scene range can be realized and the method has the characteristic of free imaging area, namely imaging can be performed on scenes at different positions as required.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Ground station system and method for avoiding collinear interference with geostationary satellite
ActiveCN106027138ARealize coexistence at the same frequencyImprove usabilityRadio transmissionTelecommunications linkSynchronous orbit
The invention belongs to the field of satellite communication technologies and particularly relates to a ground station system and a method for avoiding collinear interference with a geostationary satellite. The system comprises a ground station located at one position of the earth and a non-geostationary satellite constellation connected to the ground station, wherein the ground station traces one satellite in the non-geostationary satellite constellation through controlling antenna beam and establishes a communication link with the satellite; when a connecting line between the ground station and one non-geostationary satellite points at the geostationary satellite, the ground station adjusts the beam direction and selects another non-geostationary satellite in the different direction in view to communicate, so that the collinear interference with the geostationary satellite is avoided. According to the ground station system and the method, the restriction that shutdown of the non-geostationary satellite is needed or the transmitting power of the non-geostationary satellite is greatly reduced when the collinear interference occurs is avoided, and the satellite communication of the ground station keeps continuous, so that the availability and the message capacity of the non-geostationary satellite constellation are improved and the same frequency coexistence of the non-geostationary satellite and the geostationary satellite is realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
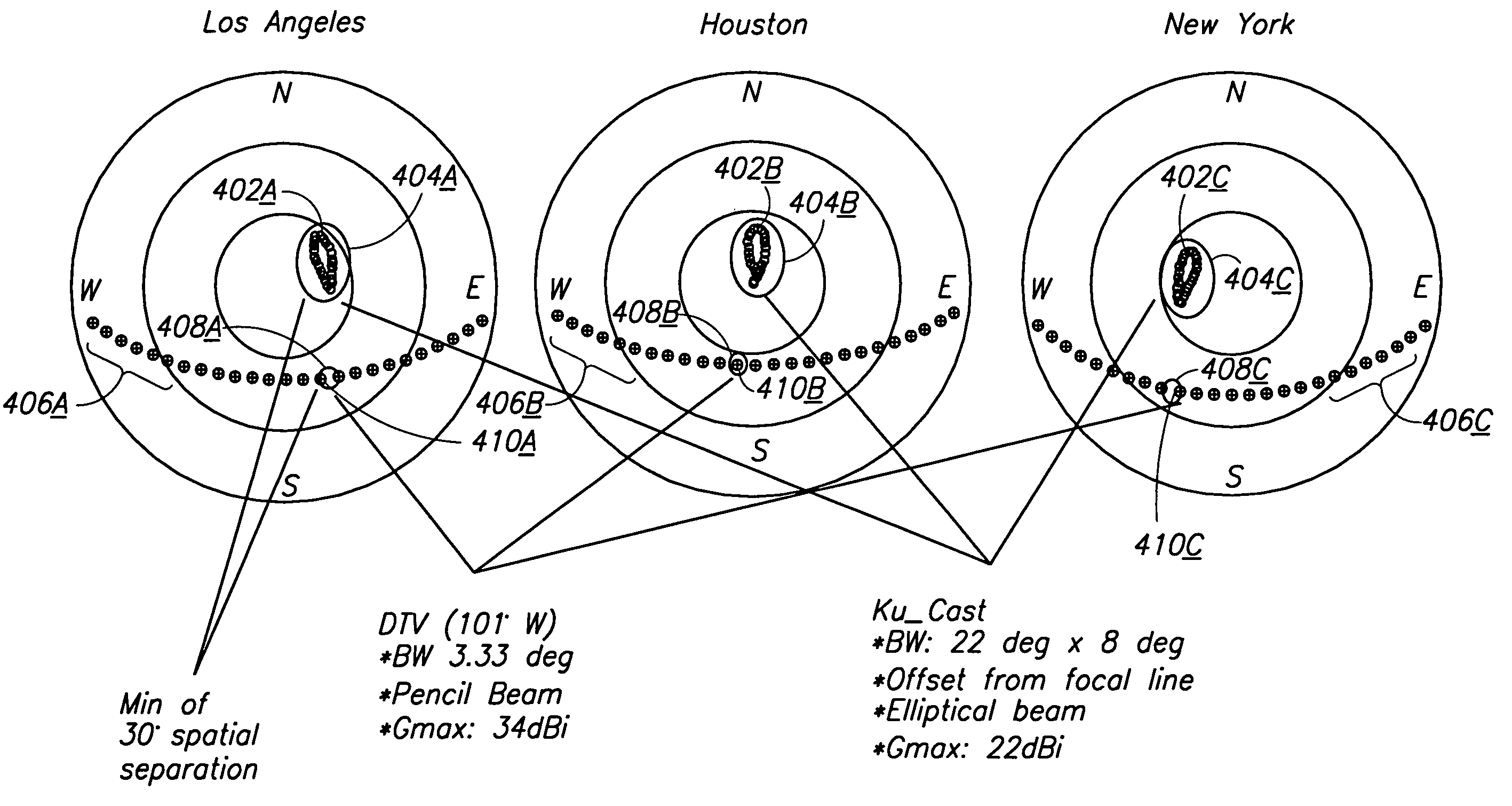
System and method for continuous broadcast service from non-geostationary orbits
InactiveUS20080307466A1GHz frequency transmissionRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsSynchronous orbit
A method, apparatus for providing at least near continuous broadcast services to one or more terrestrial receiver stations is disclosed. The system comprises a plurality of satellites, each satellite in an inclined, elliptical geosynchronous orbit, each satellite providing a portion of the at least near continuous broadcast service to the terrestrial receiver. In one embodiment, the system also comprises a receiver station having an legacy antenna modified so as to include a sensitivity pattern substantially matched to the track of the apparent position of the satellites actively broadcasting information to the receiver stations. The present invention is also embodied in a method for receiving at least near continuous broadcast service from at least one of a plurality of satellites at a time, each satellite in an inclined, elliptical, geosynchronous orbit.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
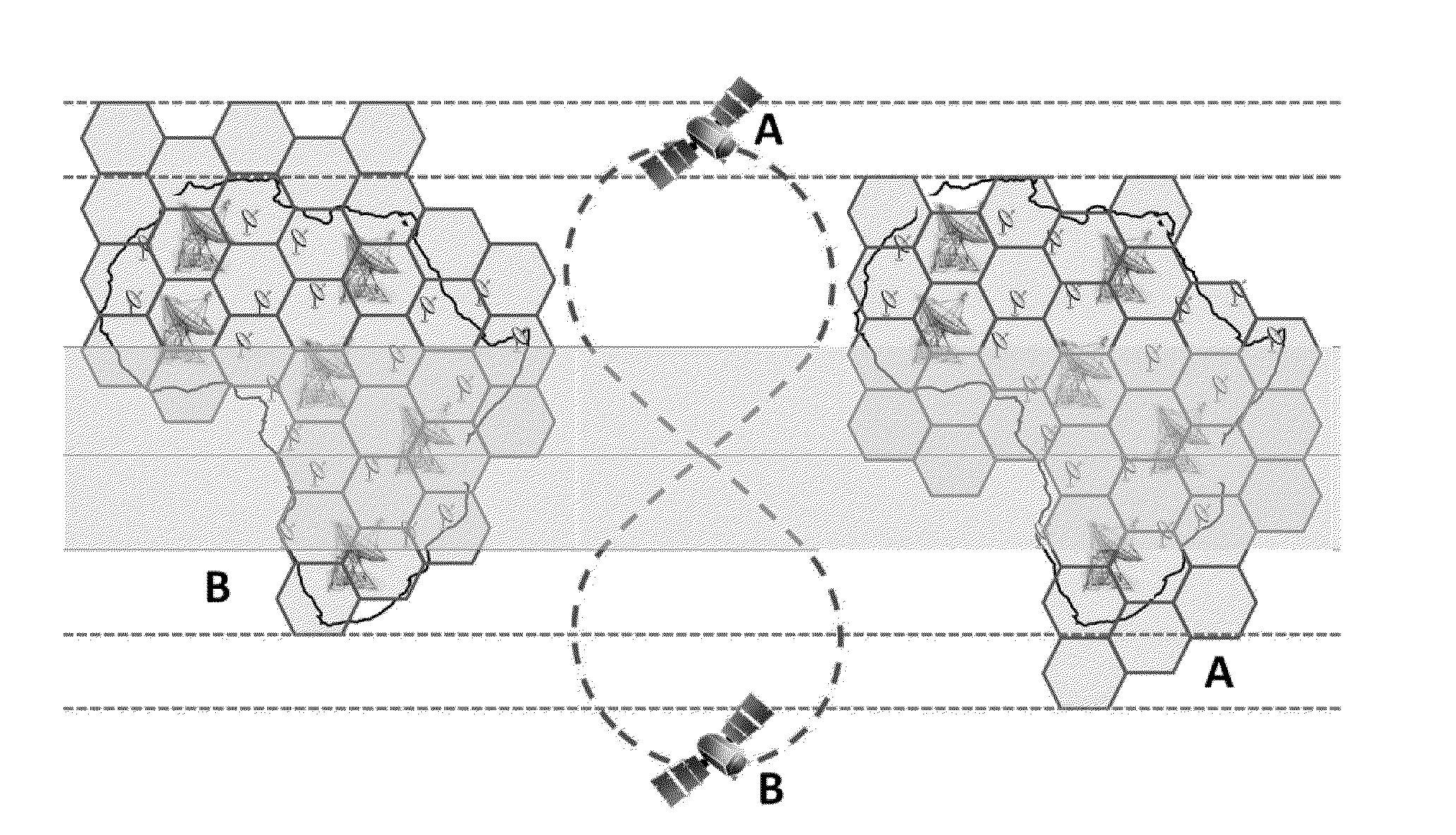
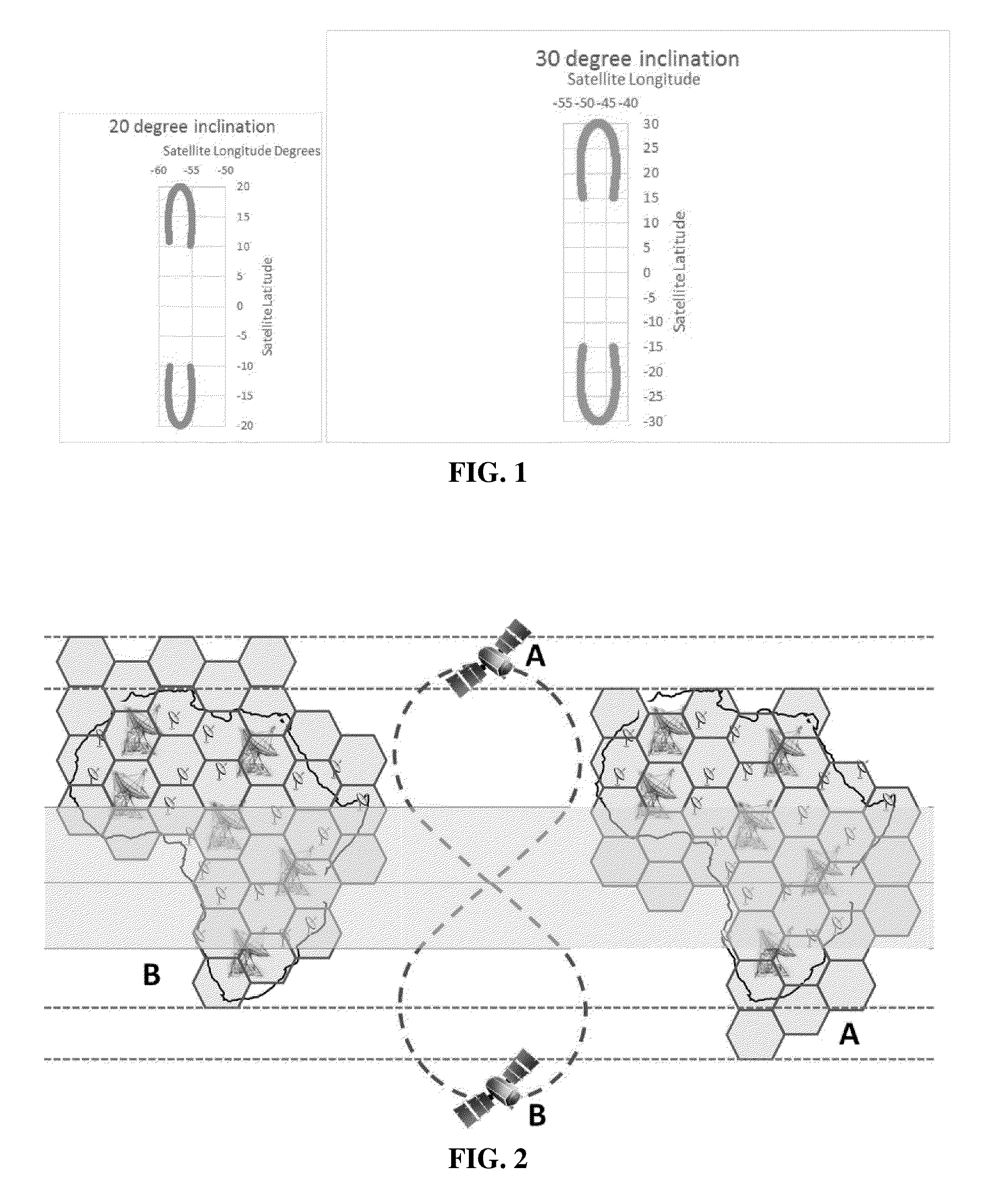
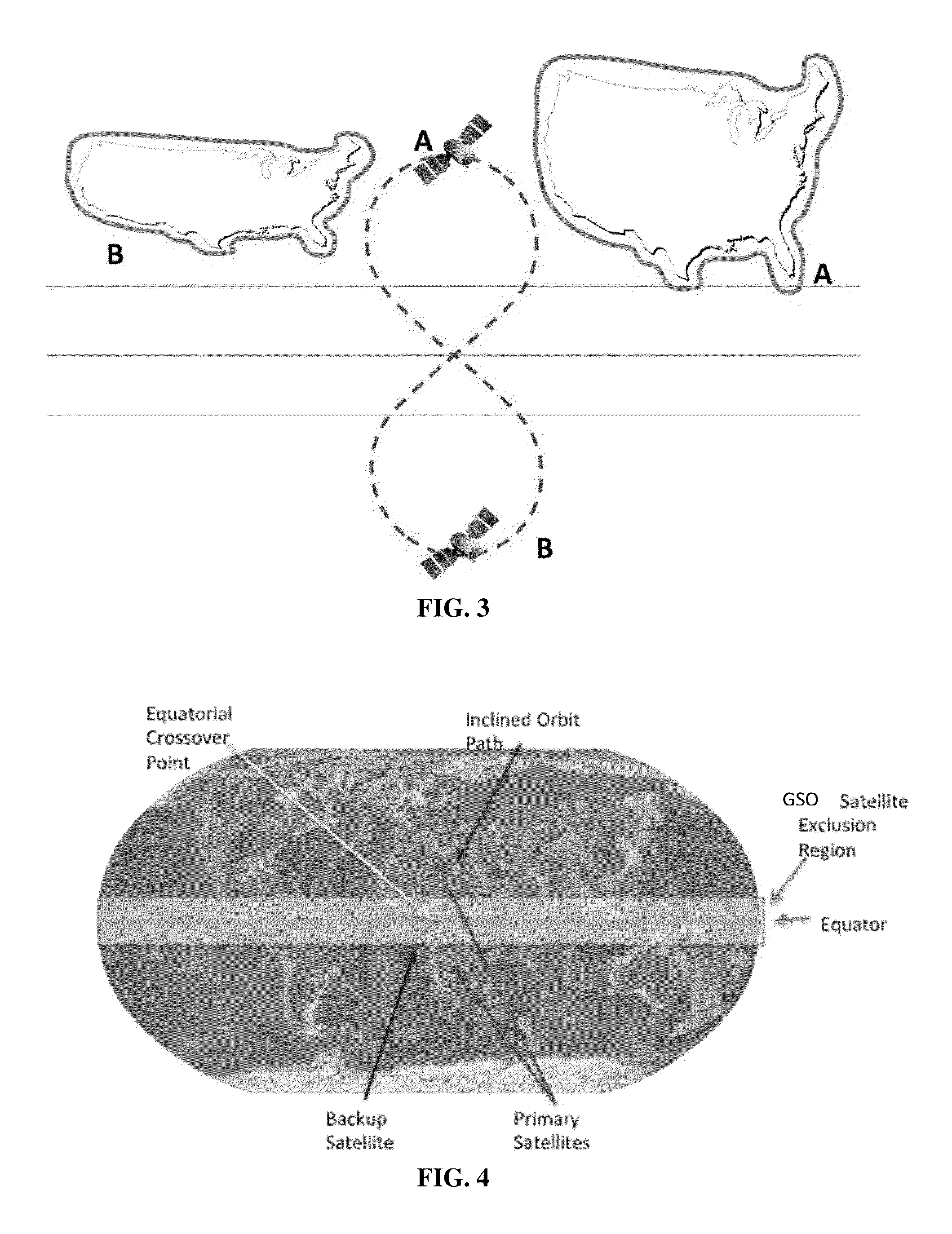
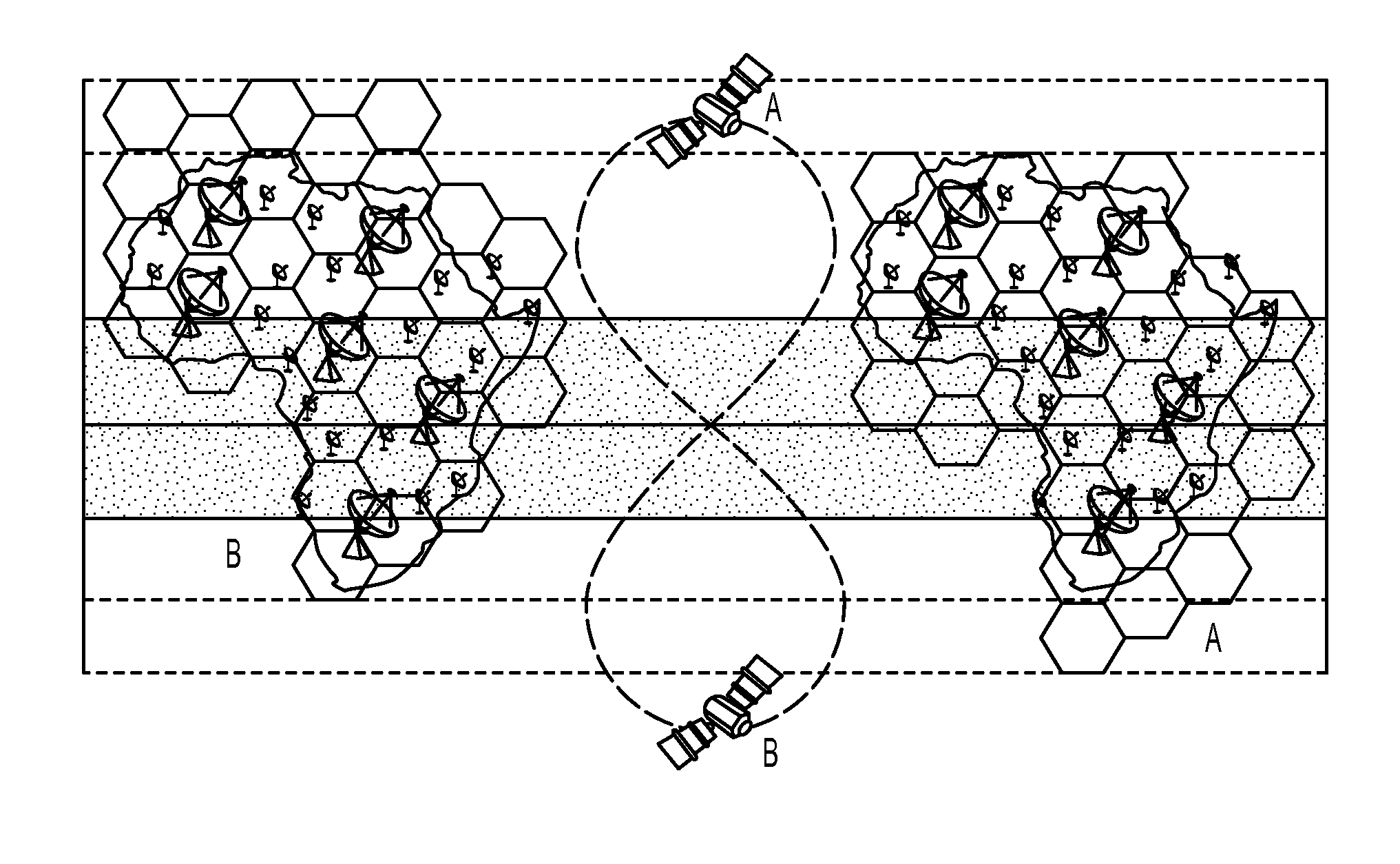
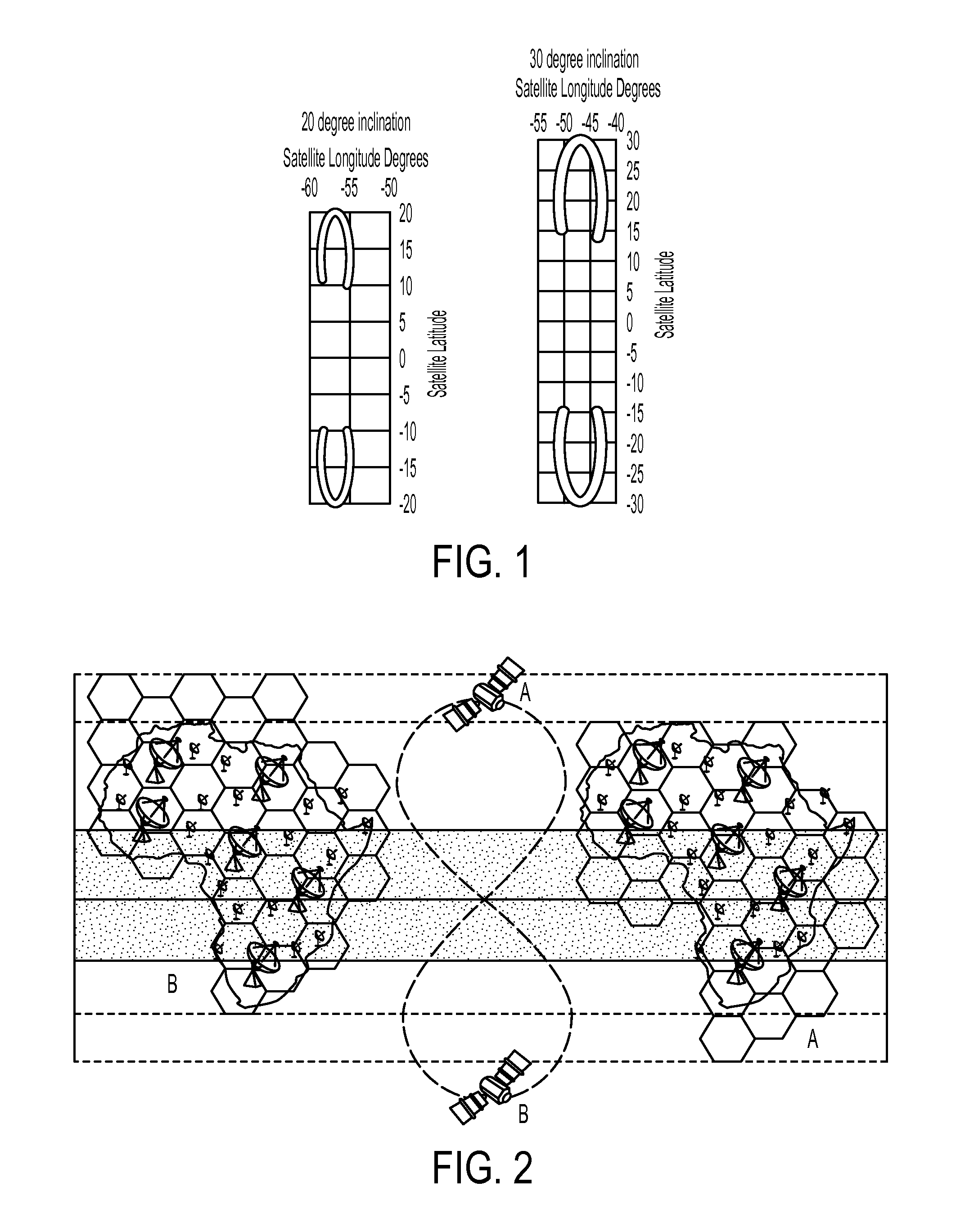
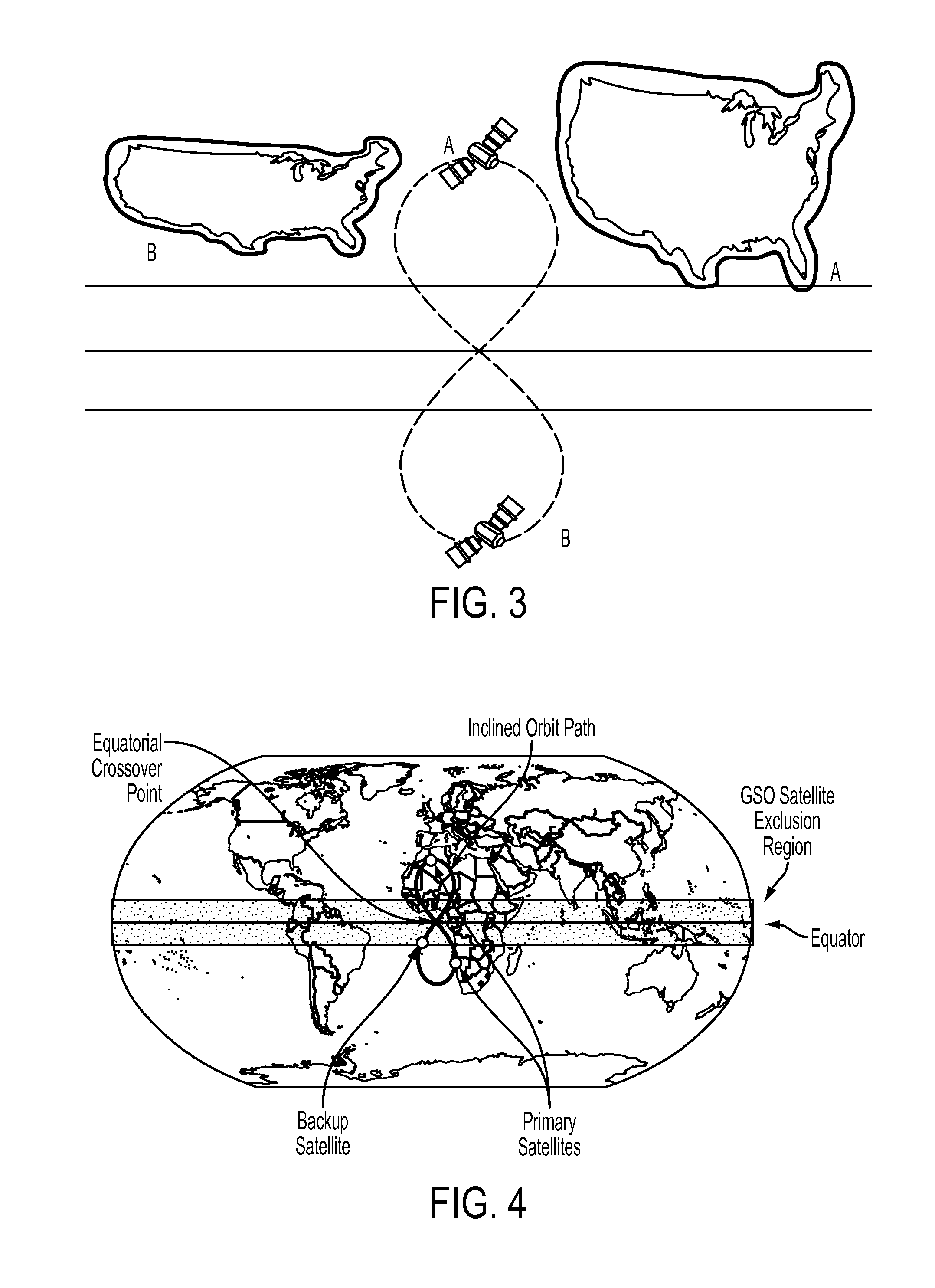
Inclined orbit satellite systems
InactiveUS20150158602A1Efficiently providedCosmonautic partsActive radio relay systemsContinuous/uninterruptedNatural satellite
The present disclosure is directed to an inclined geosynchronous orbit satellite system that can efficiently provide continuous communication to multiple geographic regions across the world using satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbital paths having an equatorial crossing and enabling the reuse of frequencies assigned within GSO orbital locations. The inclined orbit satellite system can include multiple inclined orbit satellites that are capable of co-existing with geostationary satellites to provide continuous uninterrupted service.
Owner:TAWSAT
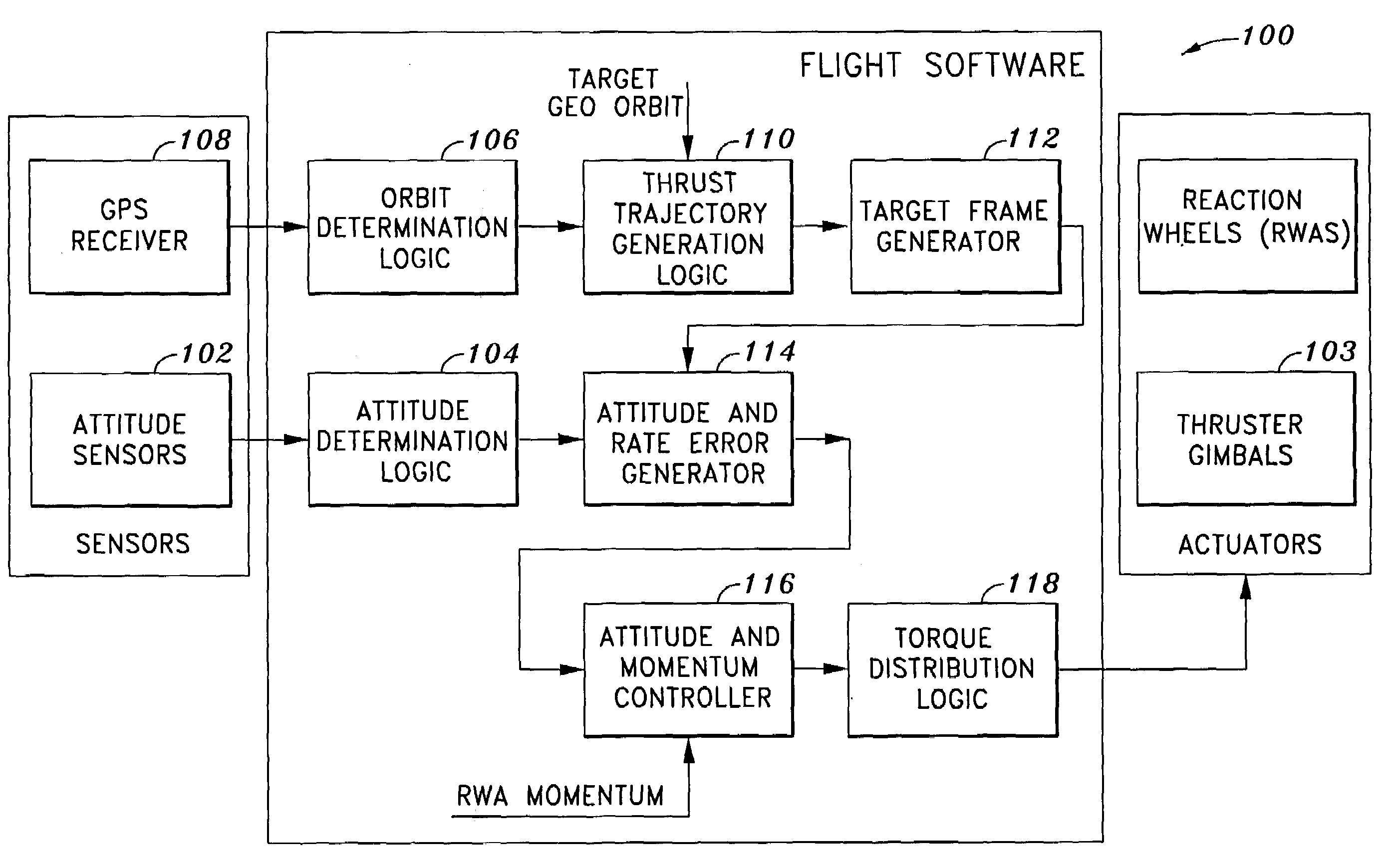
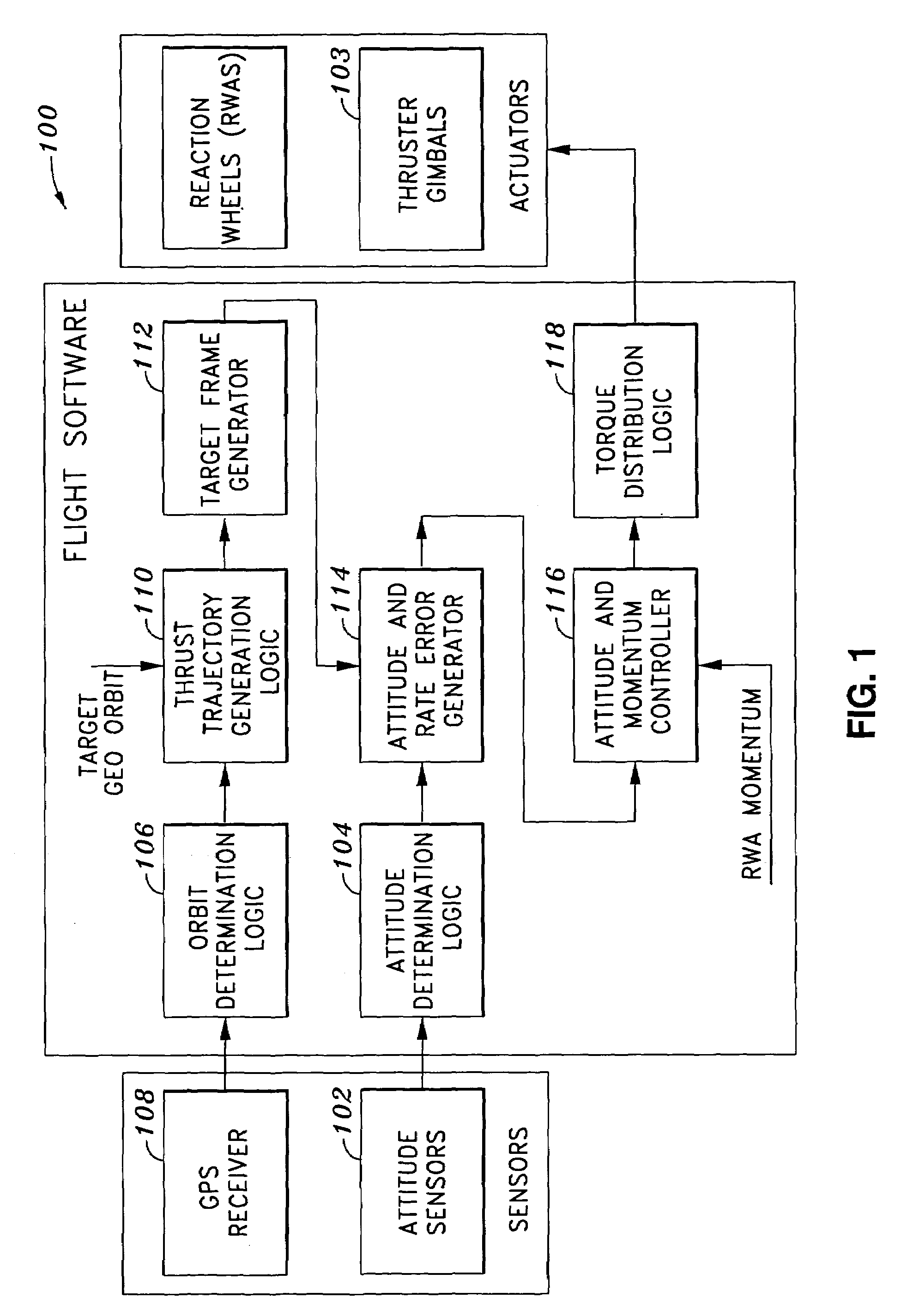
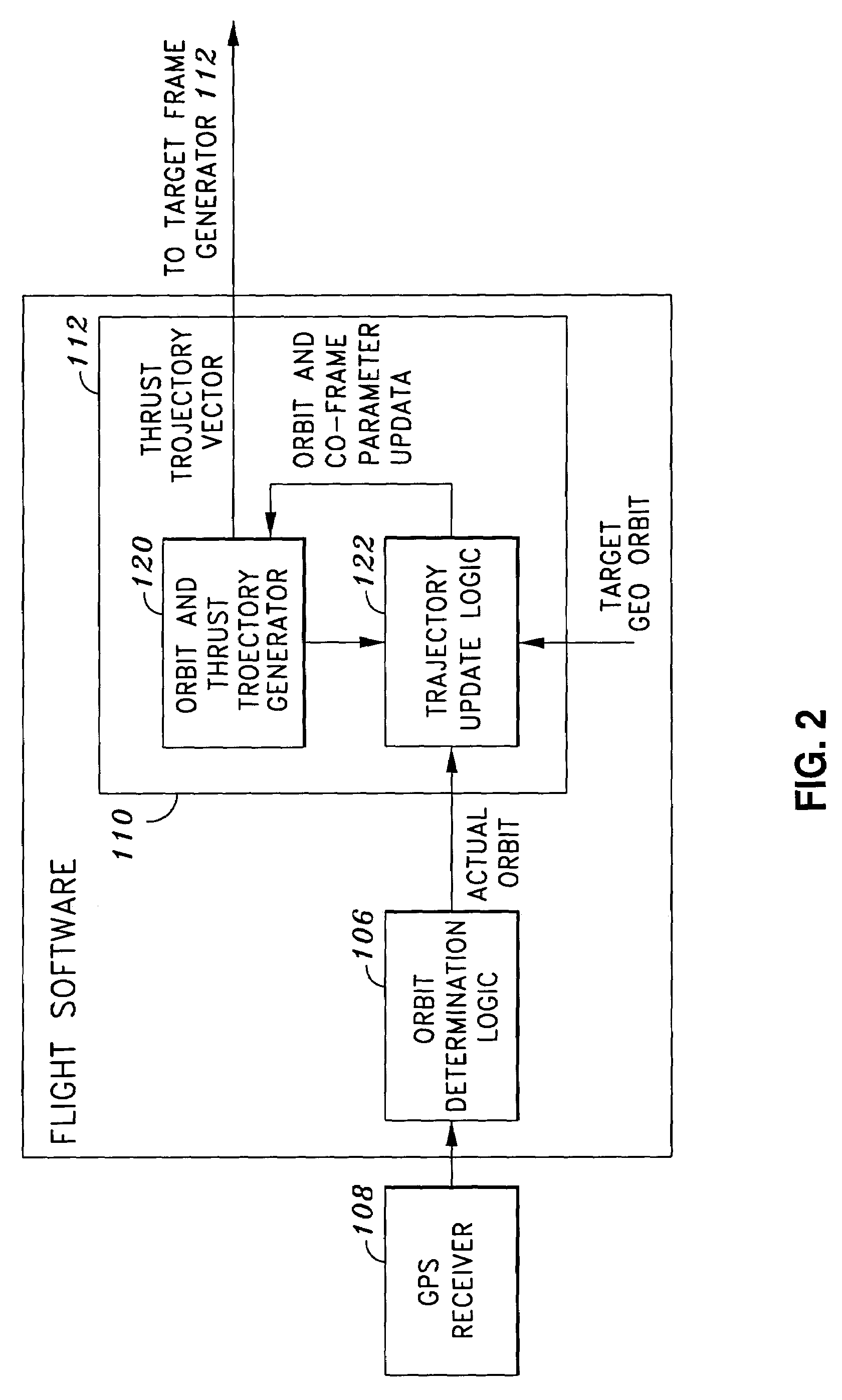
System and method of substantially autonomous geosynchronous time-optimal orbit transfer
InactiveUS7246775B1Reduce coverageImprove fuel efficiencyLaunch systemsVehicle position/course/altitude controlSynchronous orbitState parameter
Method of and system for on-board substantially autonomous control for transferring a spacecraft from an initial orbit to a final geosynchronous orbit, by a trajectory that minimizes remaining transfer time and orbit transfer fuel. The spacecraft determines its orbit using a GPS-based system to determine the spacecraft orbital elements. Based on the measured orbit error, corrected co-state parameters are calculated and used to generate an updated thrust trajectory. The corrections are calculated using an innovative numerical procedure, carried out repetitively at a fixed interval until the target geosynchronous orbit is achieved.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional microwave imaging method for circular track of earth synchronization orbit
InactiveCN101430379ASolve the problem that it is difficult to obtain high-resolution 3D information of ground objectsSolve small problems with long revisit cyclesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainSynthetic aperture sonar
The invention discloses a circular synthetic aperture radar (CSAR) 3D microwave imaging method for an earth synchronous orbit. In the method, parameters of the earth synchronous orbit are designed to cause a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite platform to make a flight with an annular track around a target zone and above the target zone, and an antenna beam is caused to irradiate the target zone all the time by a circular synthetic aperture radar mode, and a ground object target is subject to continuous large-area fixed point observation to acquire high-resolution 3D imaging information of the ground object target. A CSAR system of the earth synchronous orbit provided by the system can acquire high-resolution 3D images of the ground object, solves the problem that the existing space-borne SARs are hard to acquire the high-resolution 3D information of the ground object; and is applicable to areas with complex and steep terrains as elevation information does not interfere with phase ambiguity in the SAR. The CSAR system of the earth synchronous orbit can realize the fixed point continuous observation of large-area zones, and solve the problems that the existing space-borne SARs have small observation zones and long revisit period.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
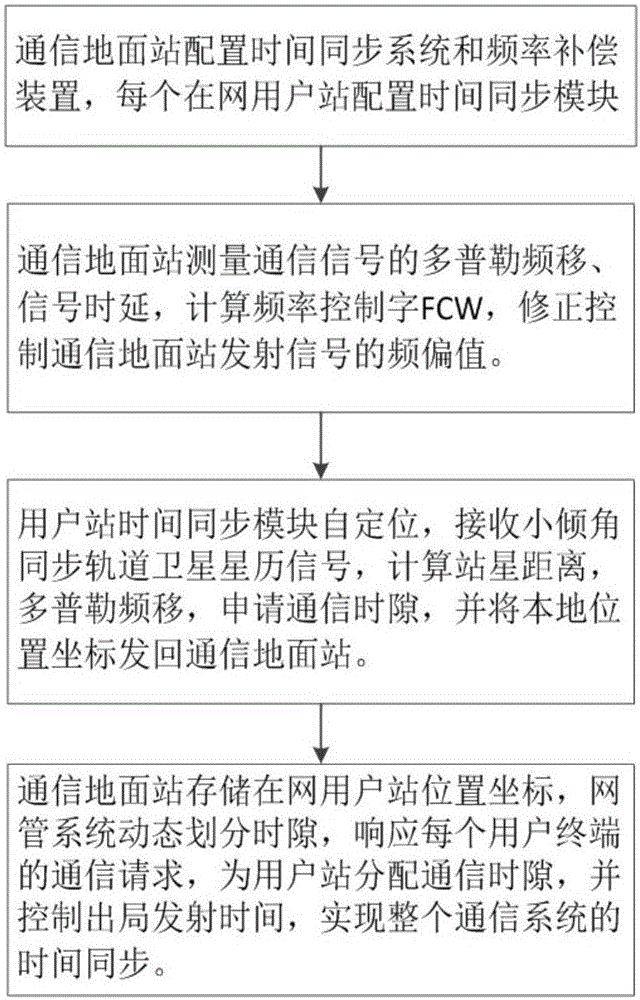
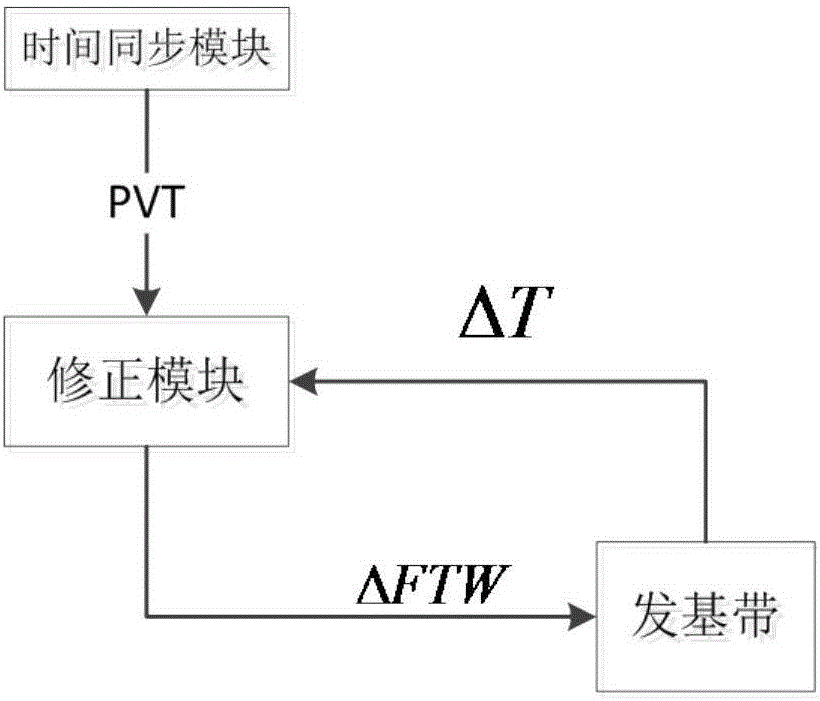
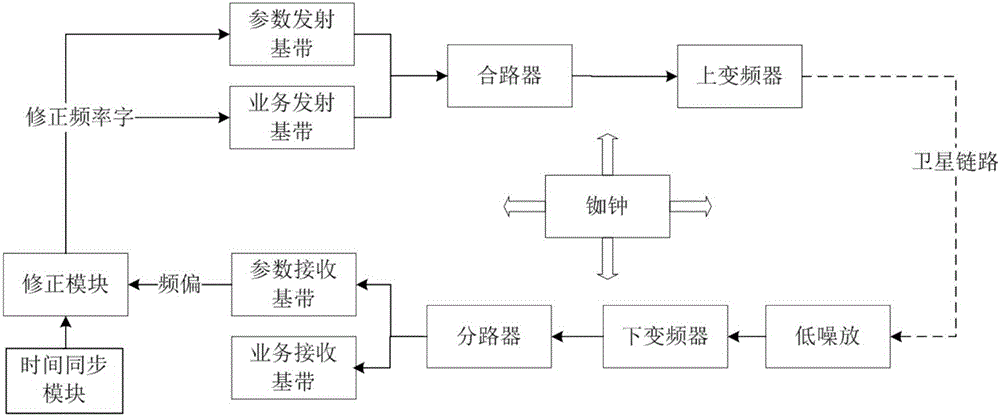
Time synchronization method, communication ground station and user terminal
ActiveCN105871495ARealize network-wide time synchronizationHigh speedTime-division multiplexClock driftSystem capacity
The invention discloses a time synchronization method and a time synchronization device based on small inclination synchronous orbit satellite communication system. The time synchronization device provided by the invention comprises a communication ground station and a user terminal, used for performing Doppler frequency compensation on received and transmitted signals, time synchronization on the whole network and pre-deviation on frequency of the transmitted signal. According to the method and device, the variation of a path and the Doppler frequency deviation of signals between the user terminal and the SIGSO satellite can be compensated based on the terminal; the communication ground station measures and compensates the path delay, Doppler frequency deviation and satellite transponder clock drifting between the communication ground station and the satellite; via time synchronization and pre-deviation on transmitting frequency, the communication ground station and the transmitter of the user terminal ensure that the time when the signal arrives the communication ground station or the terminal is just the begin of a communication time slot distributed by the system, which can greatly improve the capture speed of the communication signal, and thus the system capacity of the communication system is improved, and the unit communication cost is reduced.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for continuous broadcast service from non-geostationary orbits
InactiveUS7369809B1Broadcast transmission systemsRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsSynchronous orbit
A method, apparatus for providing at least near continuous broadcast services to one or more terrestrial receiver stations is disclosed. The system comprises a plurality of satellites, each satellite in an inclined, elliptical geosynchronous orbit, each satellite providing a portion of the at least near continuous broadcast service to the terrestrial receiver. In one embodiment, the system also comprises a receiver station having an legacy antenna modified so as to include a sensitivity pattern substantially matched to the track of the apparent position of the satellites actively broadcasting information to the receiver stations. The present invention is also embodied in a method for receiving at least near continuous broadcast service from at least one of a plurality of satellites at a time, each satellite in an inclined, elliptical, geosynchronous orbit.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GROUP
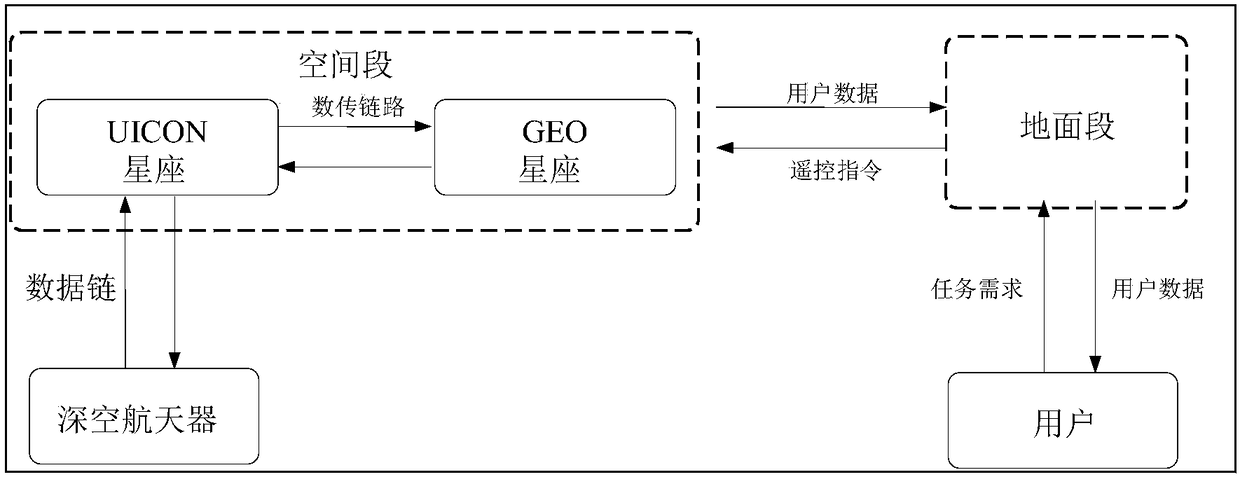
Space-based deep space relay communication satellite networking system
ActiveCN108494472AAvoid too small a problemReduce manufacturing costRadio transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersData accessGround station
The invention discloses a space-based deep space relay communication satellite networking system. The system comprises a spacecraft and a ground station, wherein the spacecraft comprises a UNICON heliocentric constellation and a geosynchronous orbit constellation; the heliocentric constellation comprises six UNICON communication satellites which are arranged on a heliocentric orbit through constellation layout, and the geosynchronous orbit constellation comprises three GEO satellites which are located on a geosynchronous orbit; a user deep space detector transmits data to the UNICON heliocentric constellation and then sends the data to the ground station through the geosynchronous orbit constellation; two laser communication telescopes are arranged at the top of each UNICON communication satellite, each laser communication telescope can rotate by 180 degrees along the longitudinal axis, so that 360-degree scanning is realized, and laser communication can be carried out between every two communication satellites. The satellite system can provide high-speed uplink and downlink data access services for deep space exploration tasks of different data rates and different orbits.
Owner:北京中科深链空间科技有限公司
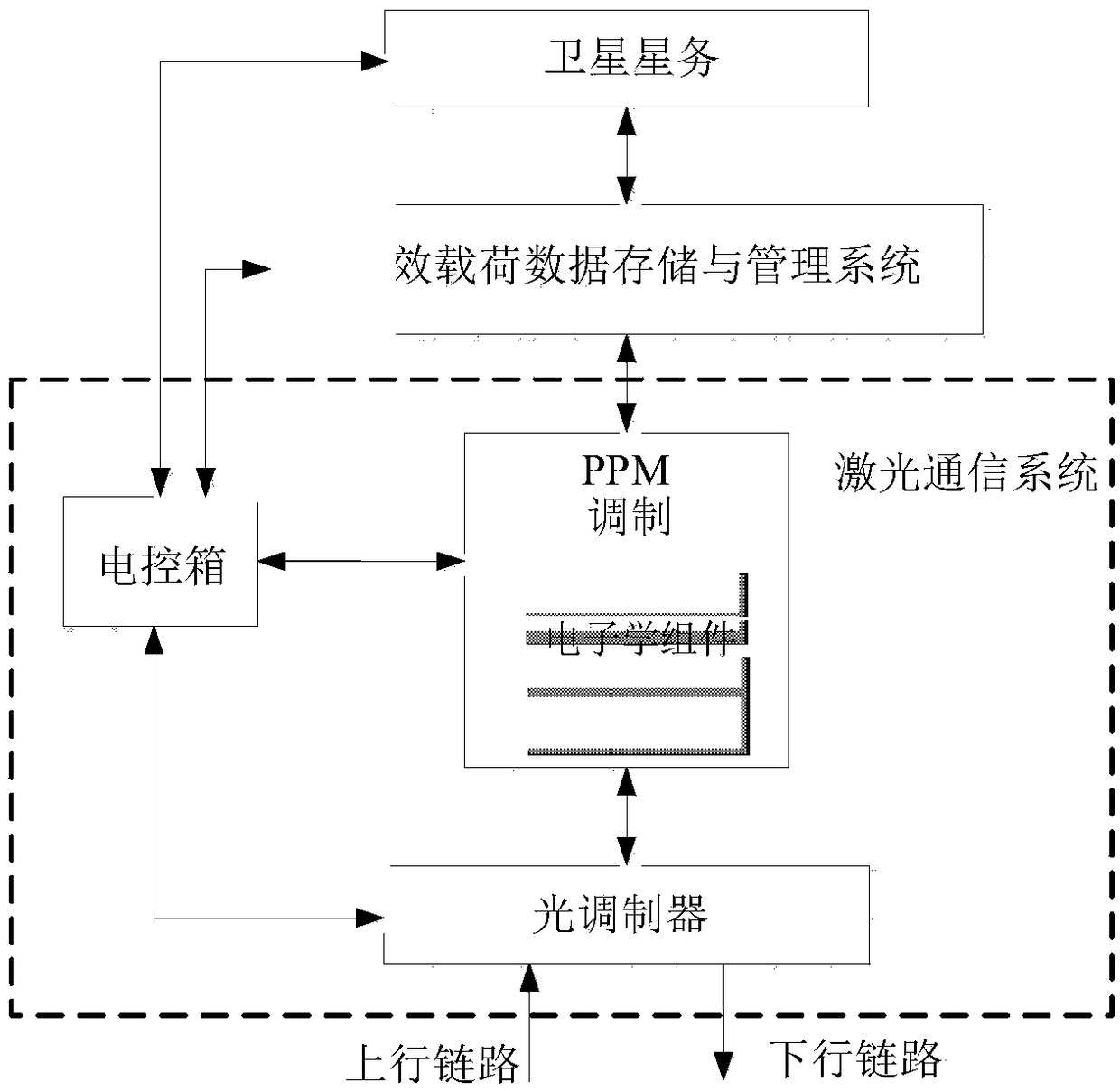
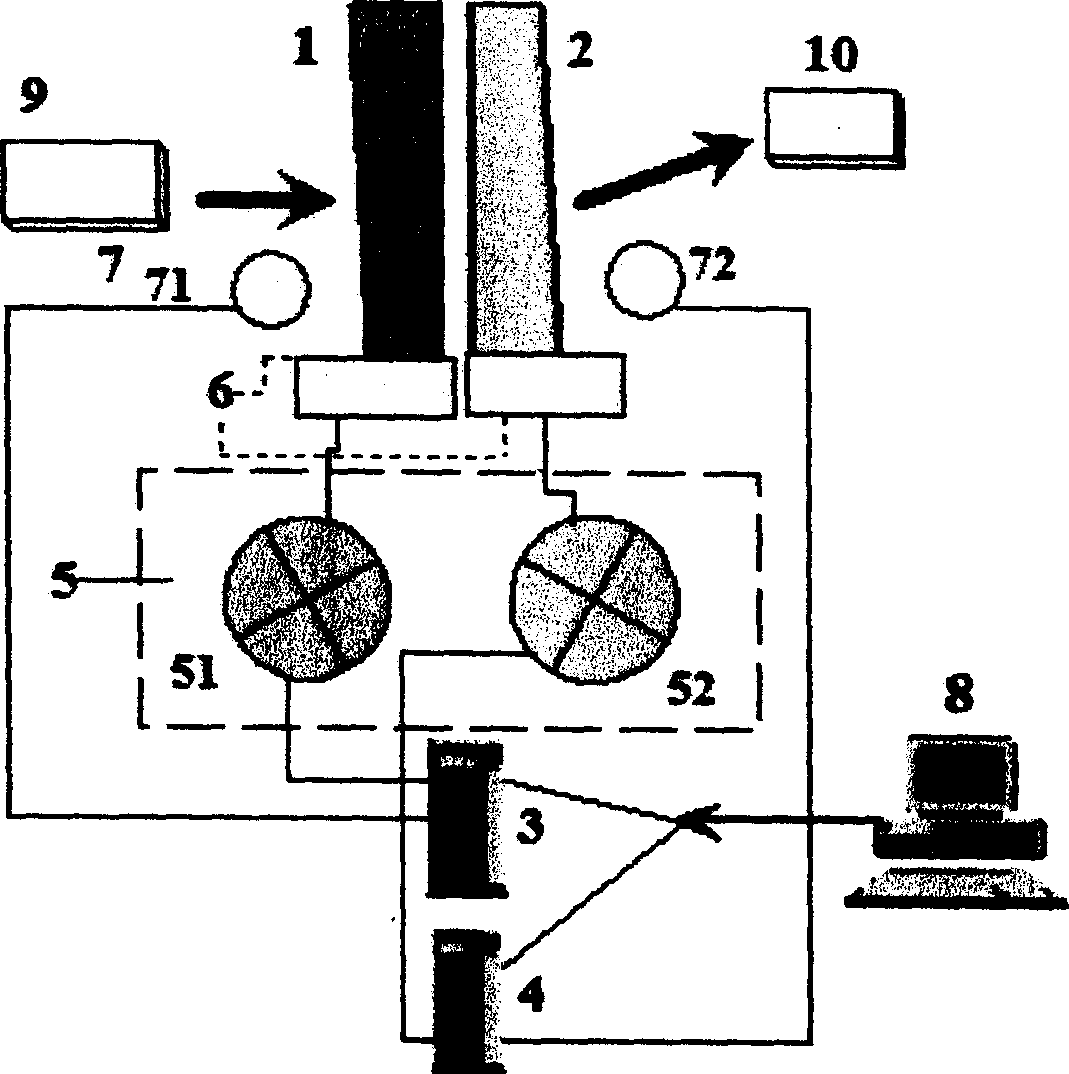
Optical device for simulating satellite trail
InactiveCN1463087ASimple control structurePracticalActive radio relay systemsTransmission monitoringComputer control systemSynchronous orbit
The device is utilized for measuring the parameters in the procedure of trailing satellites between the synchronous orbit and the low orbit. The device is composed of the three parts: the optical assembly, the electromechanical system and the computer control system. The usage of the device includes testing the trailing parameters, validating performances and evaluation of the satellite laser communication system from earth based laboratory. Meanwhile, the device provides an experimental analysis of feasibility of new technical executive plan for developing satellite laser communication system. The invention features simple structure, high practicability and accuracy. The device can generate 2D motion track and small floor space etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
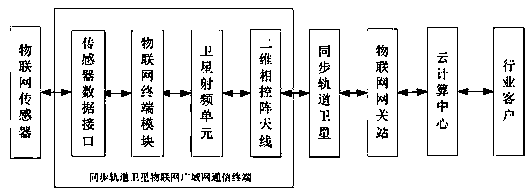
Wide-area low-power-consumption Internet-of-things communication system and transmission method thereof
ActiveCN110474971AExtended working hoursAchieve closureActive radio relay systemsHigh level techniquesWide areaSatellite radio
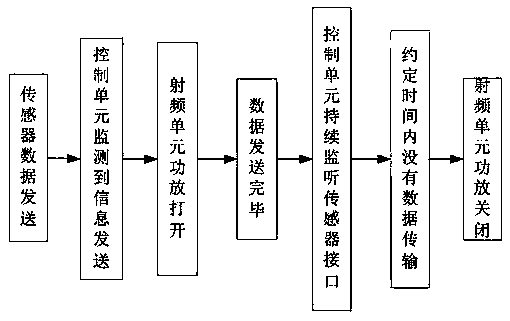
The invention discloses a wide-area low-power-consumption Internet-of-things communication system, and belongs to the technical field of Internet-of-things. The wide-area low-power-consumption Internet-of-things communication system comprises a plurality of Internet-of-things terminals. Data are received and preprocessed through the Internet-of-things terminal module. The signals are transmitted to the satellite radio frequency unit to realize frequency conversion; the synchronous orbit communication satellite receives the signal through the emission behavior of the two-dimensional phased array antenna, receives the information and forwards the information to the satellite Interent-of-things gateway station, the satellite Internet-of-things gateway station receives the information and transmits the information to the cloud computing center, and the cloud computing center processes the information and uploads the information to the client Internet-of-things application platform; the beneficial effects of the invention are that the system enables various types of IOT terminals to form a wide-area IOT network through employing the synchronous orbit satellite and the gateway station, and achieves the wide-area IOT communication; the low-power-consumption design is adopted, the terminal satellite radio frequency unit is automatically awakened and closed by monitoring data, and the working time of the terminal is prolonged.
Owner:天宸星通(深圳)科技有限公司
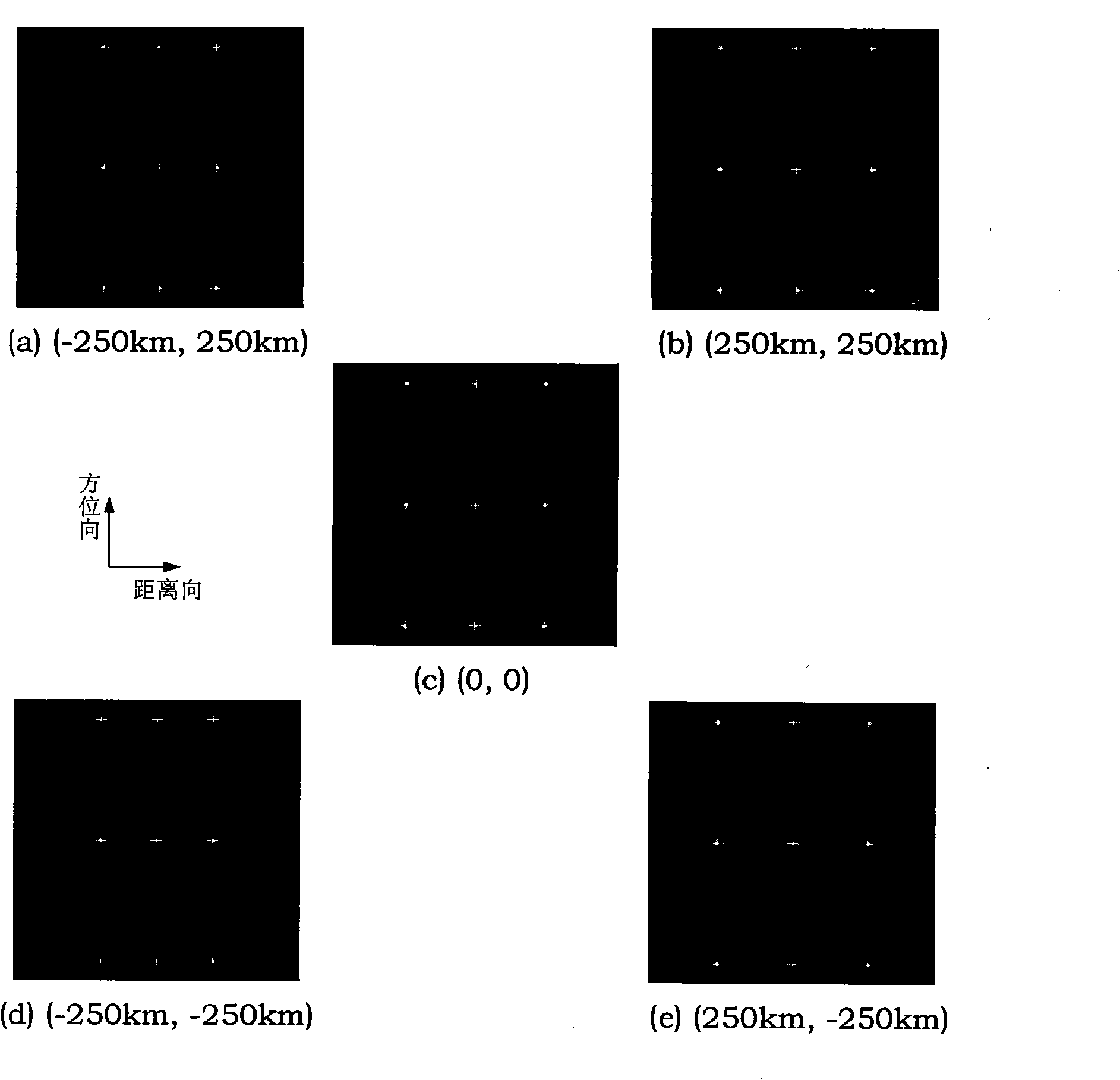
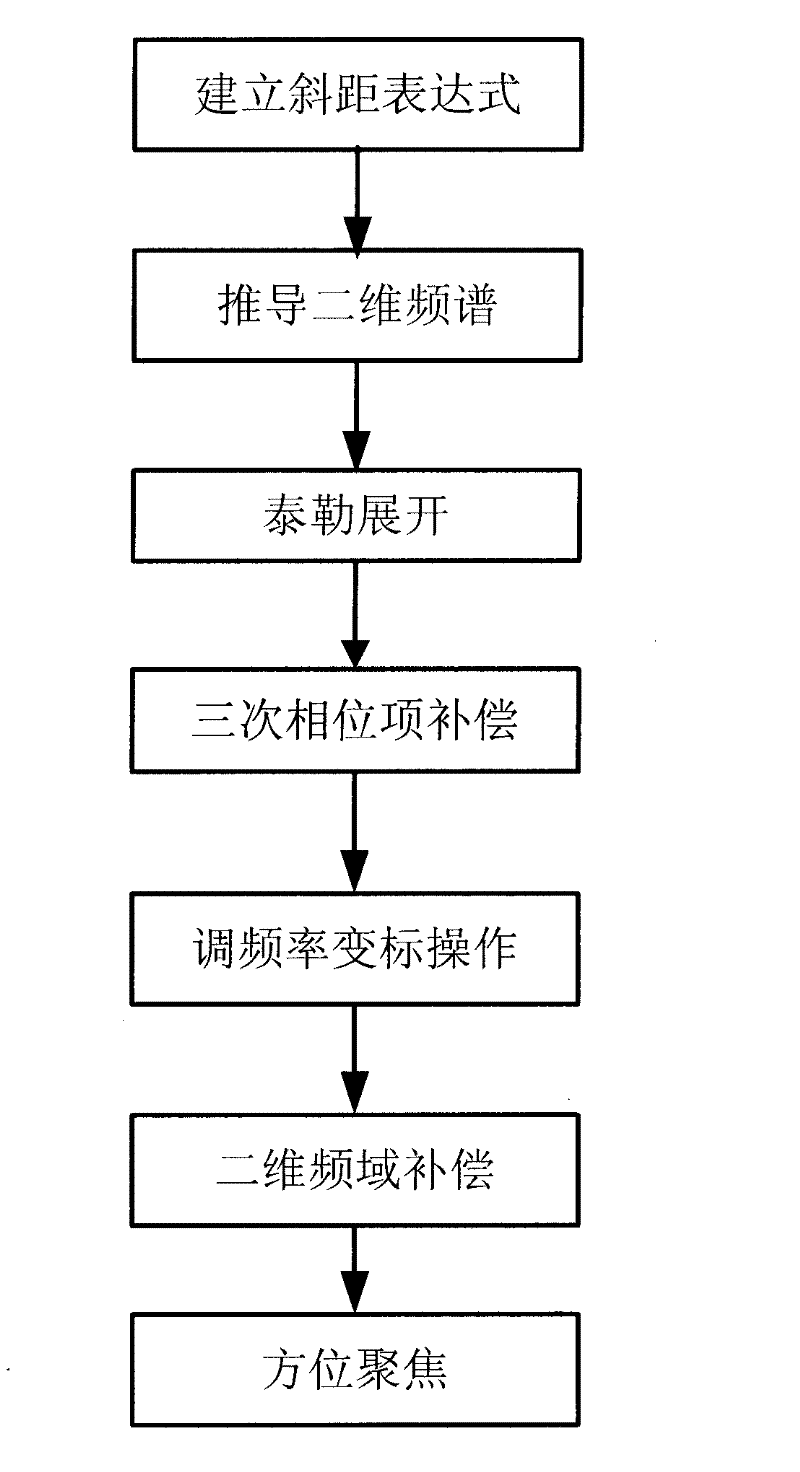
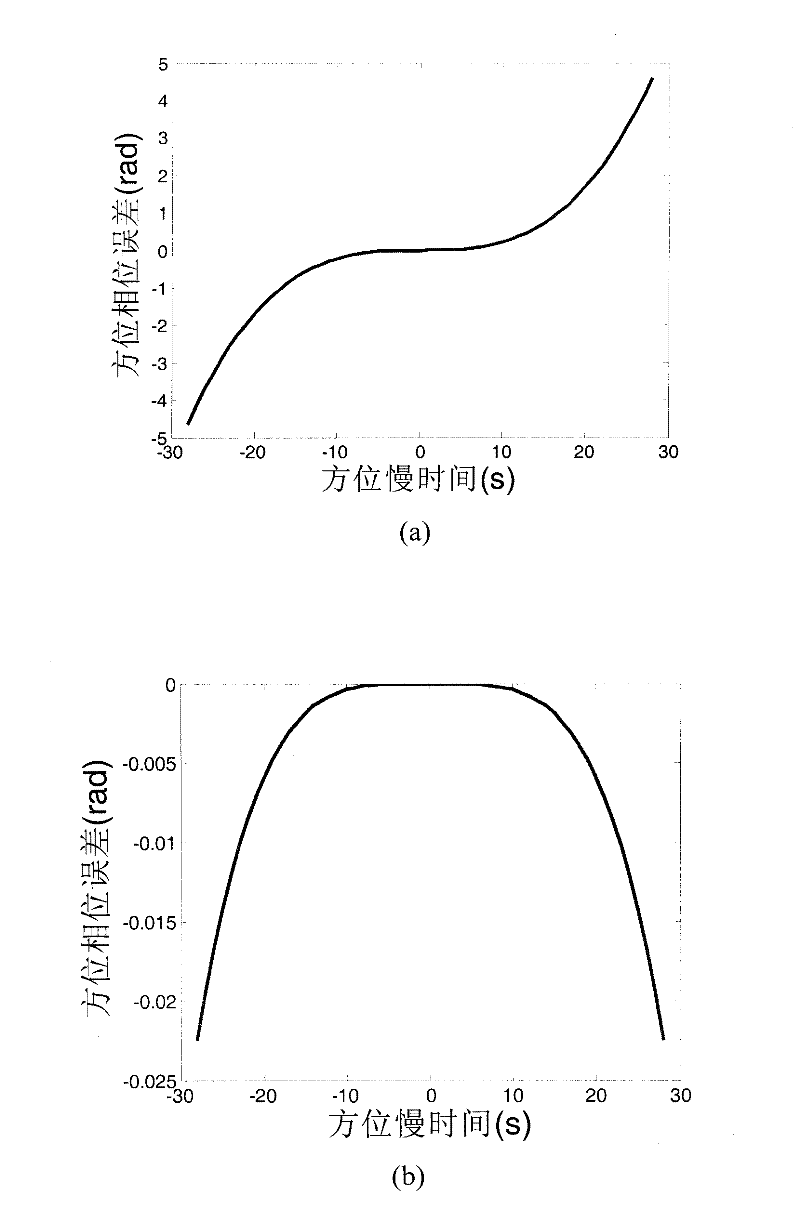
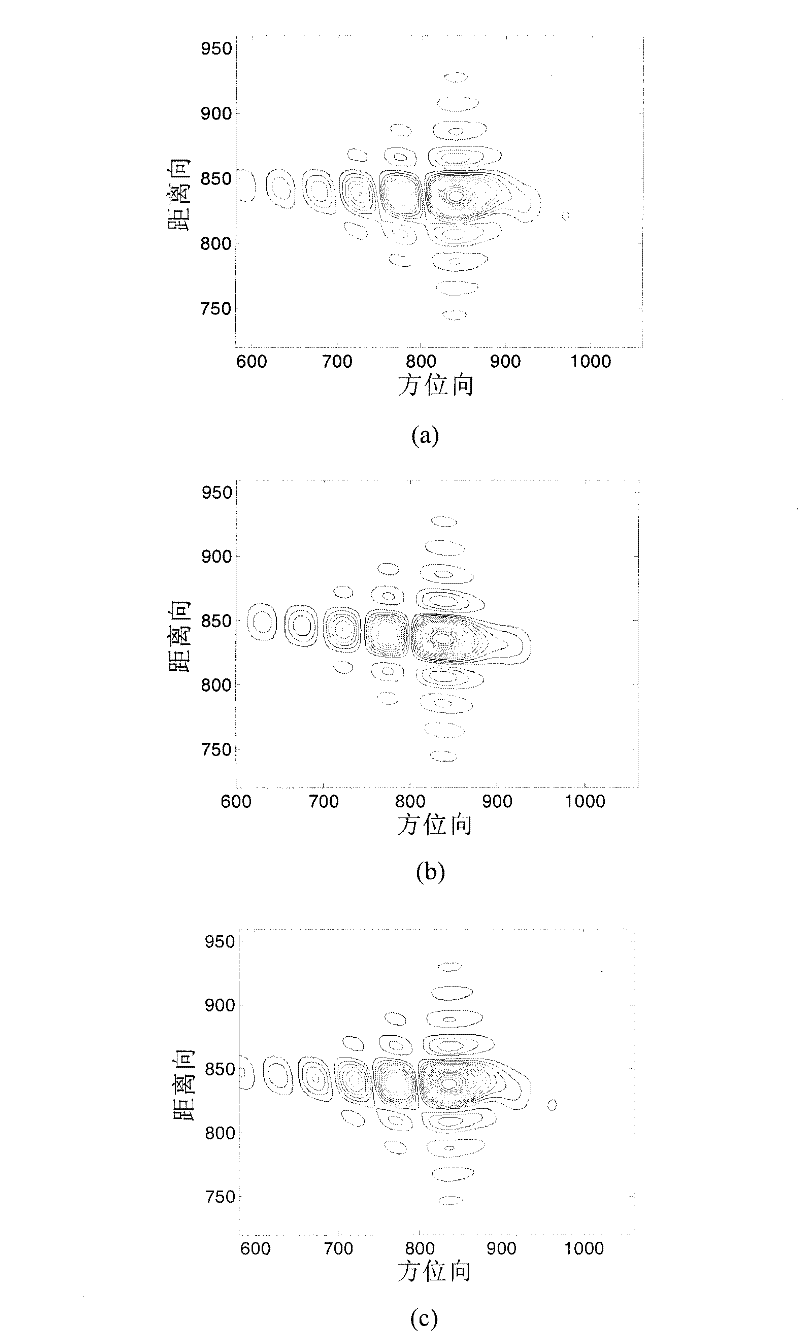
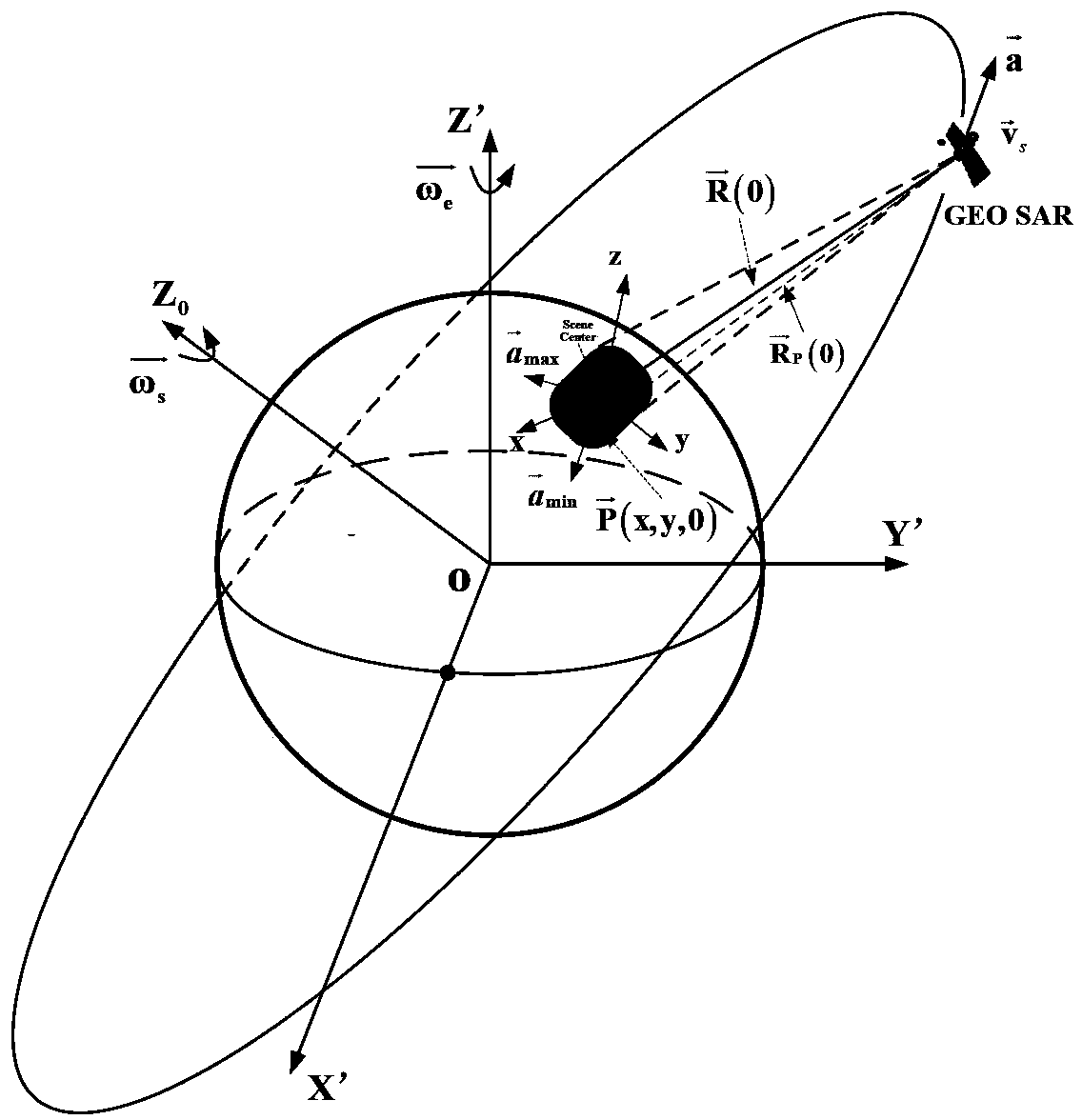
Geo-synchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) frequency modulation changeable standard imaging method under curve track model
InactiveCN102230964AReduce phase errorImproving Imaging AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a geo-synchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) frequency modulation changeable standard (CS) imaging method under a curve track model. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing an oblique-distance and high-order expression under the GEO SAR curve track model; deducing a two-dimensional spectrum expression of an echo signal; performing triple Taylor expansion of a distance frequency on the two-dimensional spectrum expression; compensating a triple phase item of the distance frequency in a two-dimensional frequency domain; calculating a distance migration curve in a distance-Doppler domain and multiplying the distance migration curve by a constructed CS phase function; deducing a distance compensation function to finish distance focusing and distance migration correction; and performing direction compression and direction residual phase correction to finish direction focusing. By the method, the spatial-variant properties of the distance migration can be compensated, a wider imaging plotting bandwidth can be obtained and full-aperture high-resolution imaging can be realized. All types of operation in the method are finished throughfast Fourier transform and phase dot product; furthermore, the efficiency is higher and the method is suitable for engineering implementation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Solar dominated satellite constellations capable of having repeating common ground tracks
InactiveUS7255308B1High revisit rateMinimal battery requirementCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesEarth's rotationSynchronous orbit
A new method of constellation design based on combining repeating ground tracks with common ground tracks and / or sun-synchronous orbits is used for performing high-precision change detection imagery for longer periods of time while minimizing battery usage. By precisely prescribing the orbital parameters, sharpened change detection images may be taken without the need to process out blurring by any special image re-working software. The relationship between the orbital parameters of the satellites is precisely tuned to the earth's rotation rate for the altitude of the satellites. The unique set of earth orbits minimizes satellite battery requirement while optimizing the ability to perform coherent change detection (CCD).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
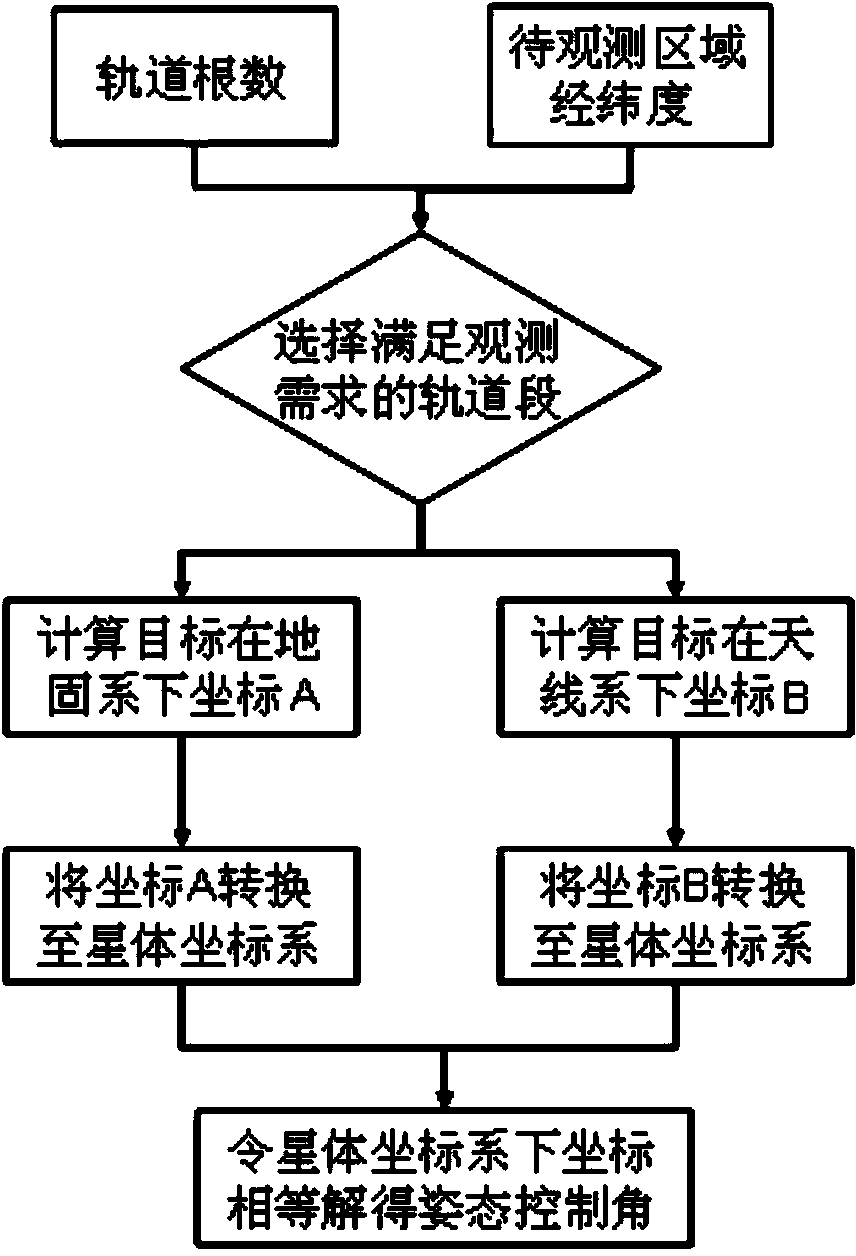
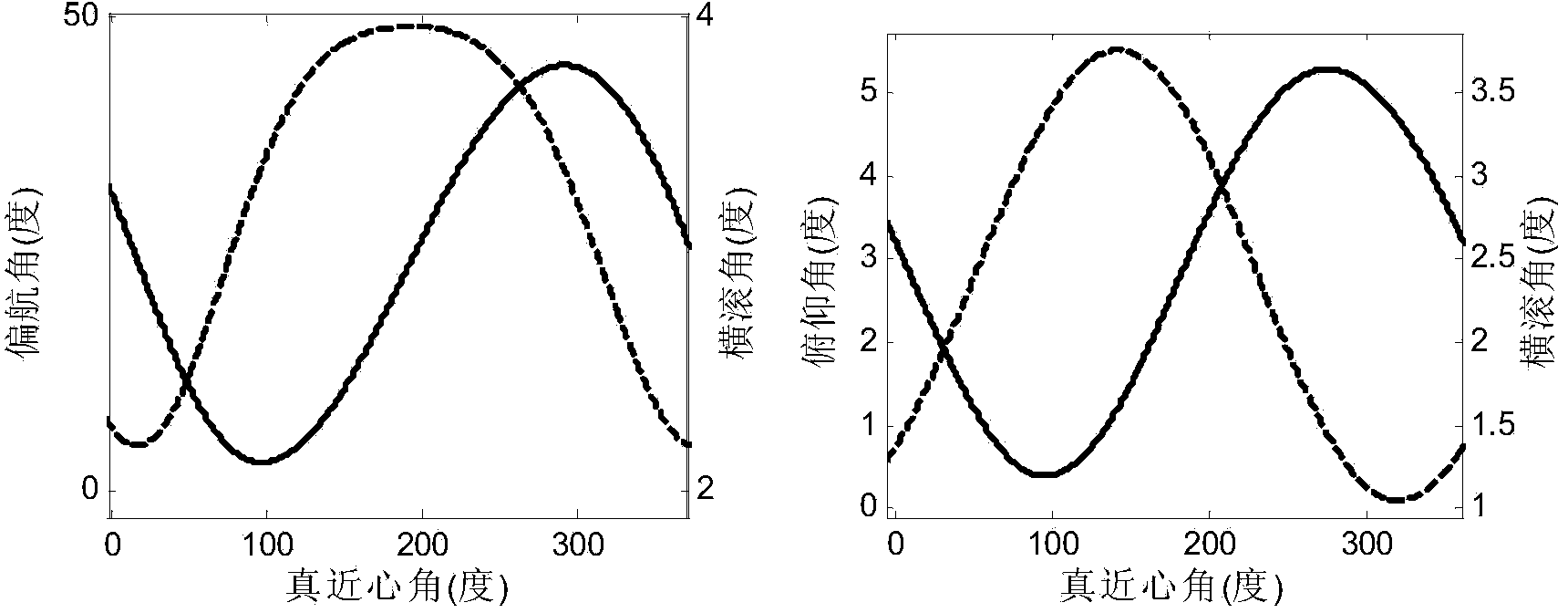
Method for geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar to realize continuous observation of coverage area
ActiveCN103809178AEasy to compare and analyzeA Simple and Practical Method for Solving Beam Steering VariablesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynchronous orbitAttitude control
The invention discloses a method for a geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar to continuously observe a coverage area. The method comprises the steps of firstly, determining an orbit segment, meeting observation application requirements, of a satellite according to the longitude and latitude of an area to be observed, calculating the distance between the satellite to a target area in the selected orbit segment, when the beam of an antenna points to the target area, taking the coordinates of the target under an antenna coordinate system as coordinates A and the coordinates of the target under a geocentric fixed coordinate system as coordinates B, transferring the coordinates A and the coordinates B into the same coordinate system so that the expressions of the coordinates A and the coordinates B contain a control variable for realizing beam pointing, and then obtaining the desired controlled quantity by equating the coordinates A with the coordinates B under the same coordinate system. The satellite pitching-rolling combined implementation model of the method is not limited by the scanning capacity of the antenna and sall in attitude control angle, and therefore, continuous observation, by the geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar, to a ground fixed target area, can be realized.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Mixed orbit IGSO (inclined geosynchronous satellite orbit) constellation capable of covering target area and global scale
ActiveCN103532611AMulti-star coverage is goodGood diversity effectDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSynchronous orbitEnvironmental geology
The invention discloses a mixed orbit IGSO (inclined geosynchronous satellite orbit) constellation capable of covering a target area and the global scale. The constellation comprises at least five IGSO satellites which are positioned on an earth synchronous orbit and are divided into two groups, wherein each group of IGSO satellites contains at least three IGSO satellites; the two groups of IGSO satellites share one IGSO satellite; the at least three IGSO satellites in the first group share one orbit surface, the right ascensions of ascending nodes are same, each mean anomaly is 120 degrees, the three IGSO satellites have the same orbit inclination angle, and the three IGSO satellites are connected by fixed inter-satellite links in a communication way; the at least three IGSO satellites in the second group have the same sub-satellite point across-equator longitude, each mean anomaly is 120 degrees, wherein the at least two IGSO satellites not shared by the first group have the same orbit inclination angle and the same ground track, inter-satellite links are not established among the three IGSO satellites in the second group, and the three IGSO satellites are always observed by a position-limited and signal-closing station by adjusting the orbit inclination angle. According to the mixed orbit IGSO constellation, the target area can be covered in a multiple way only in the way that the position-limited and signal-closing station lands, and meanwhile, the global scale is also covered by the mixed orbit IGSO constellation.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
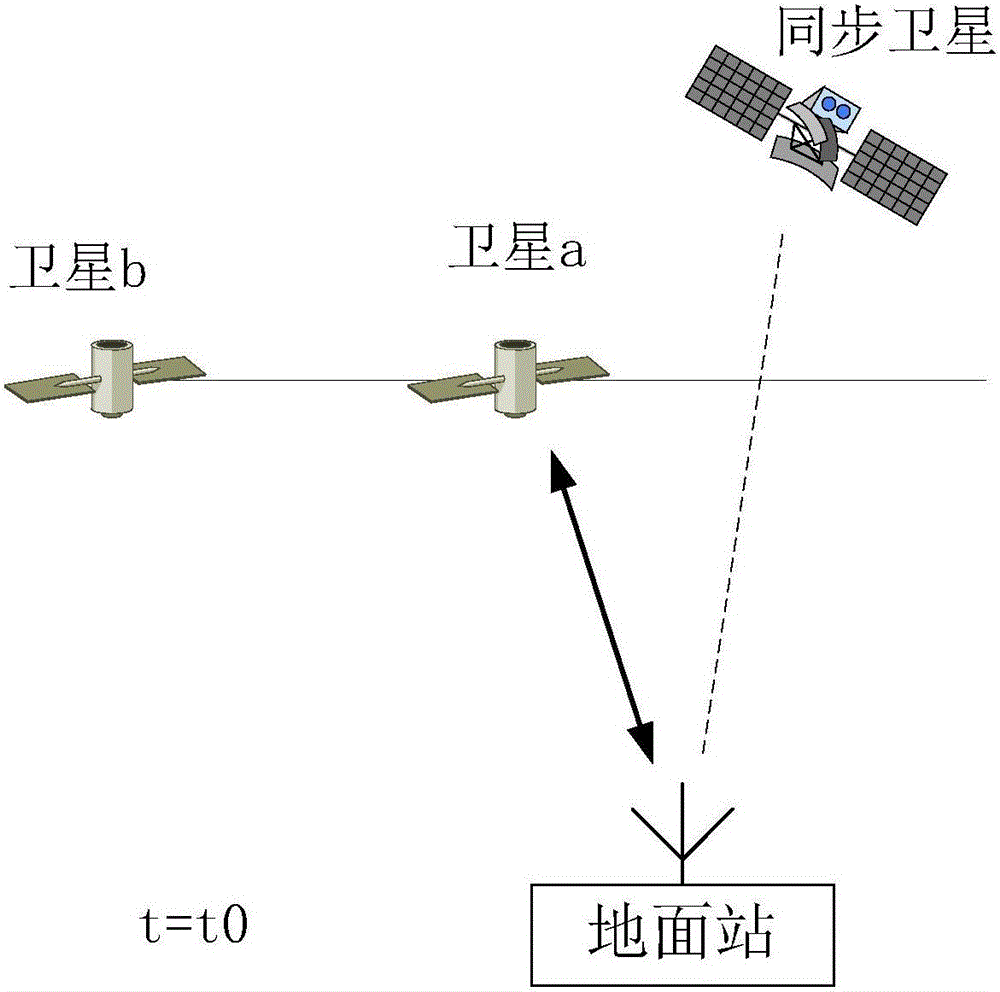
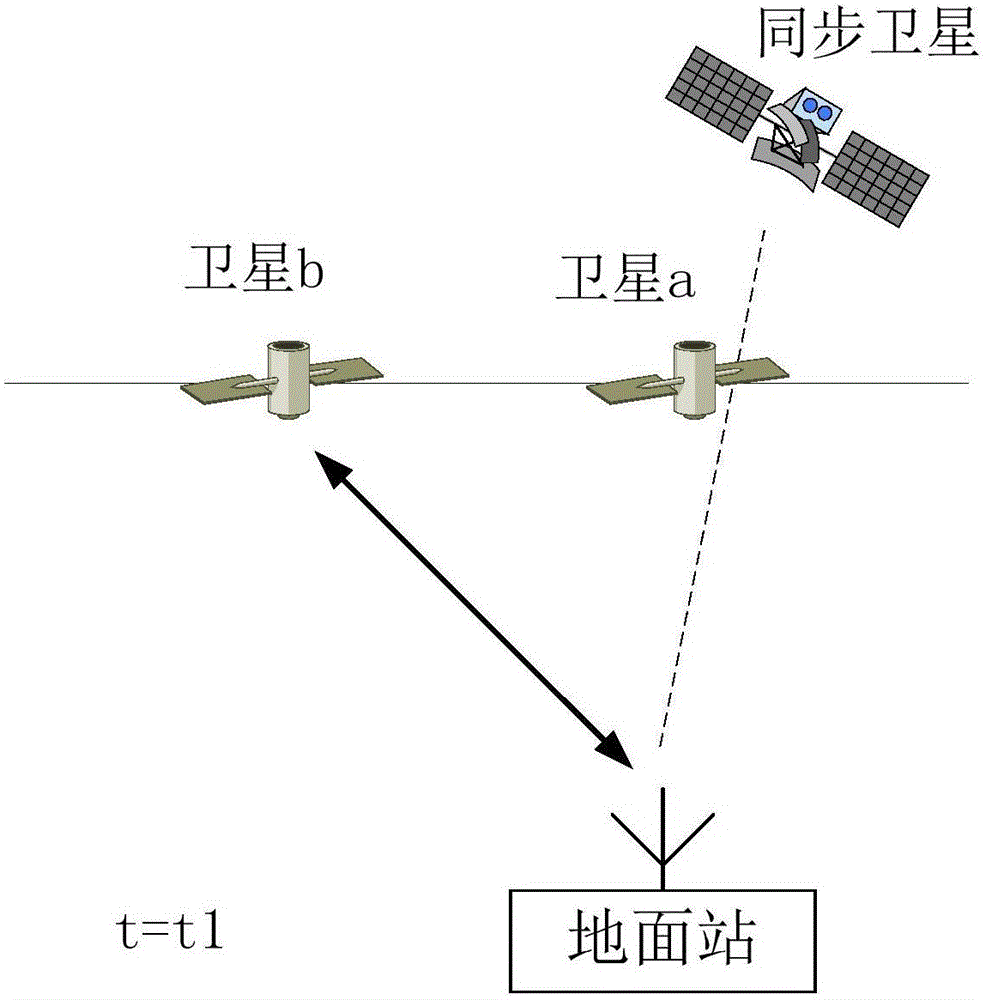
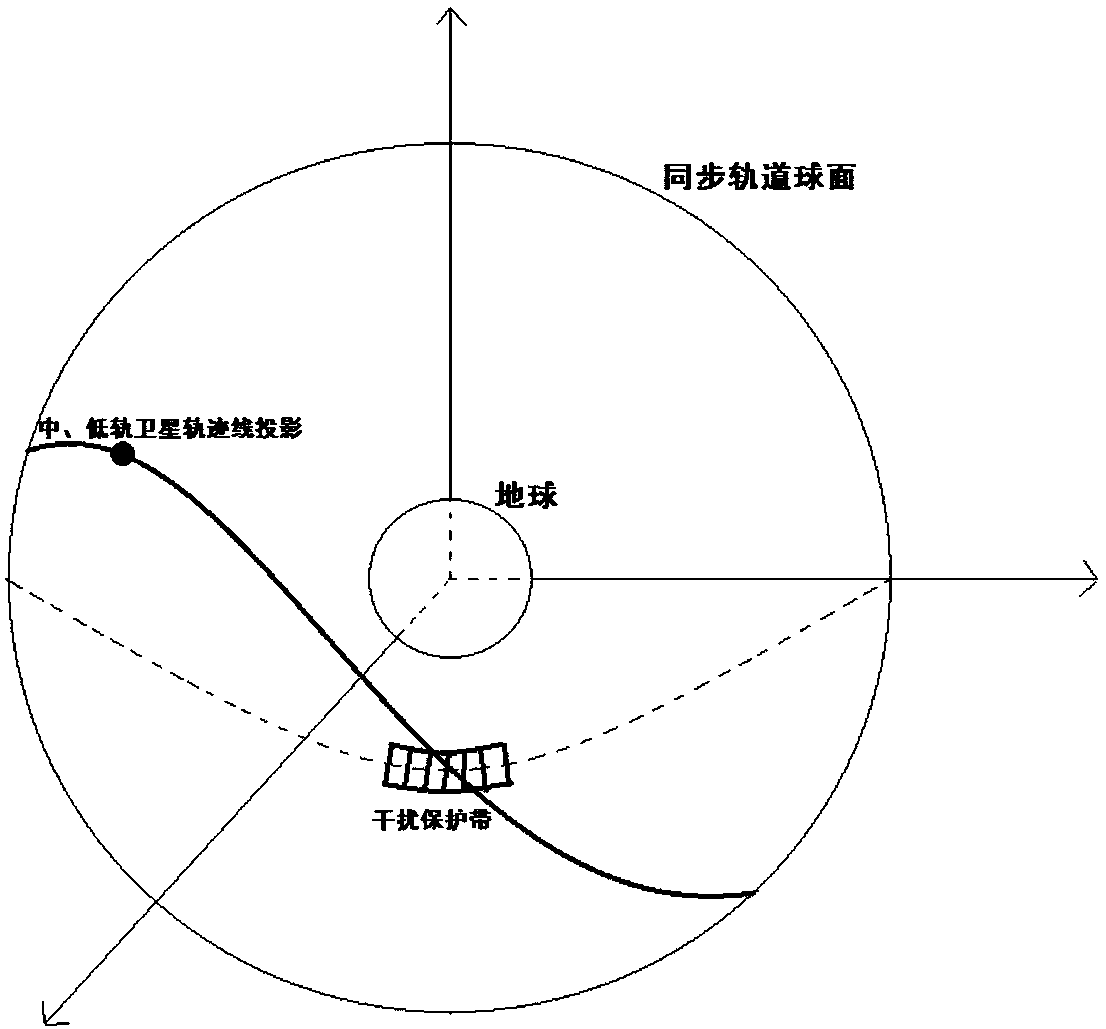
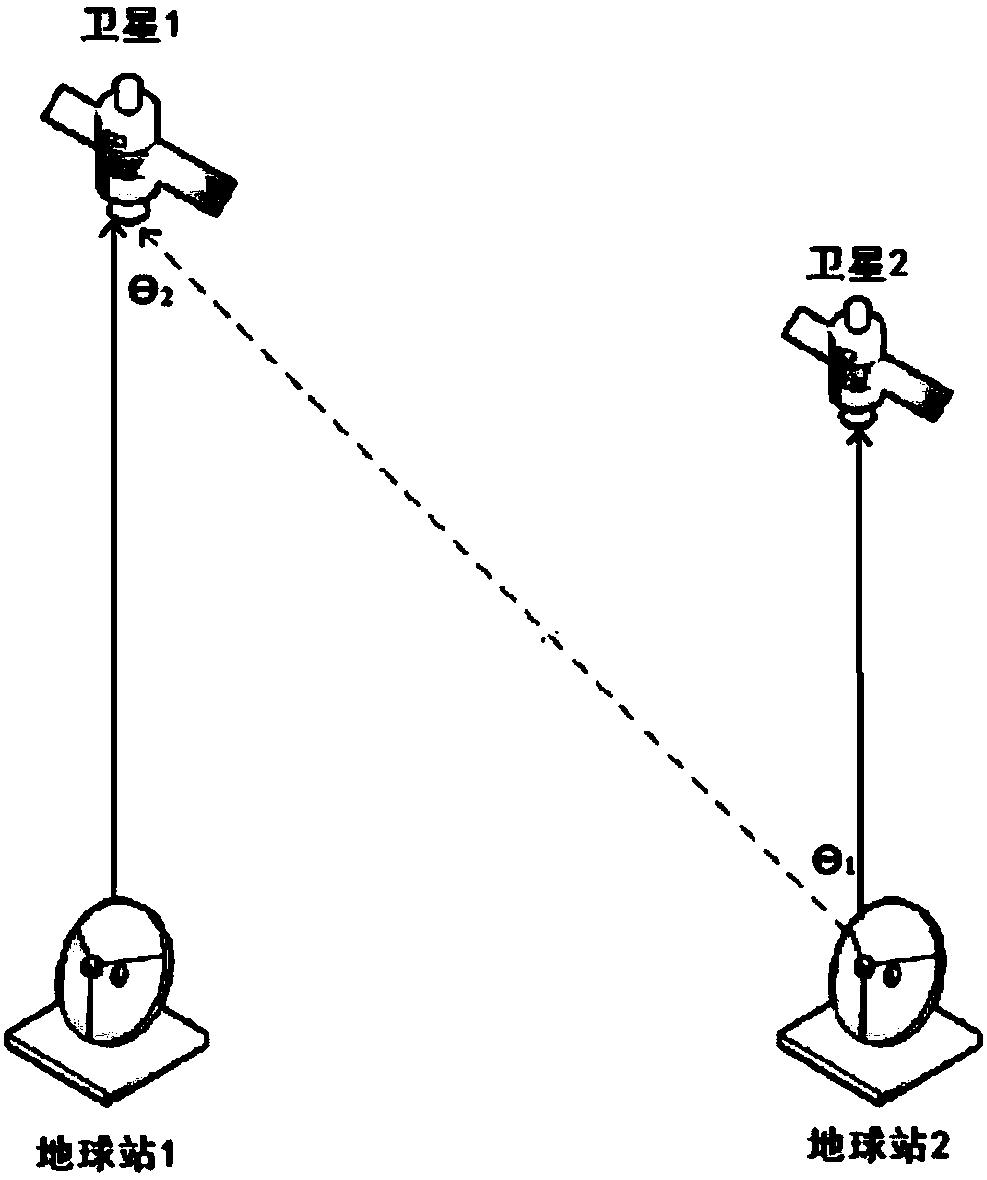
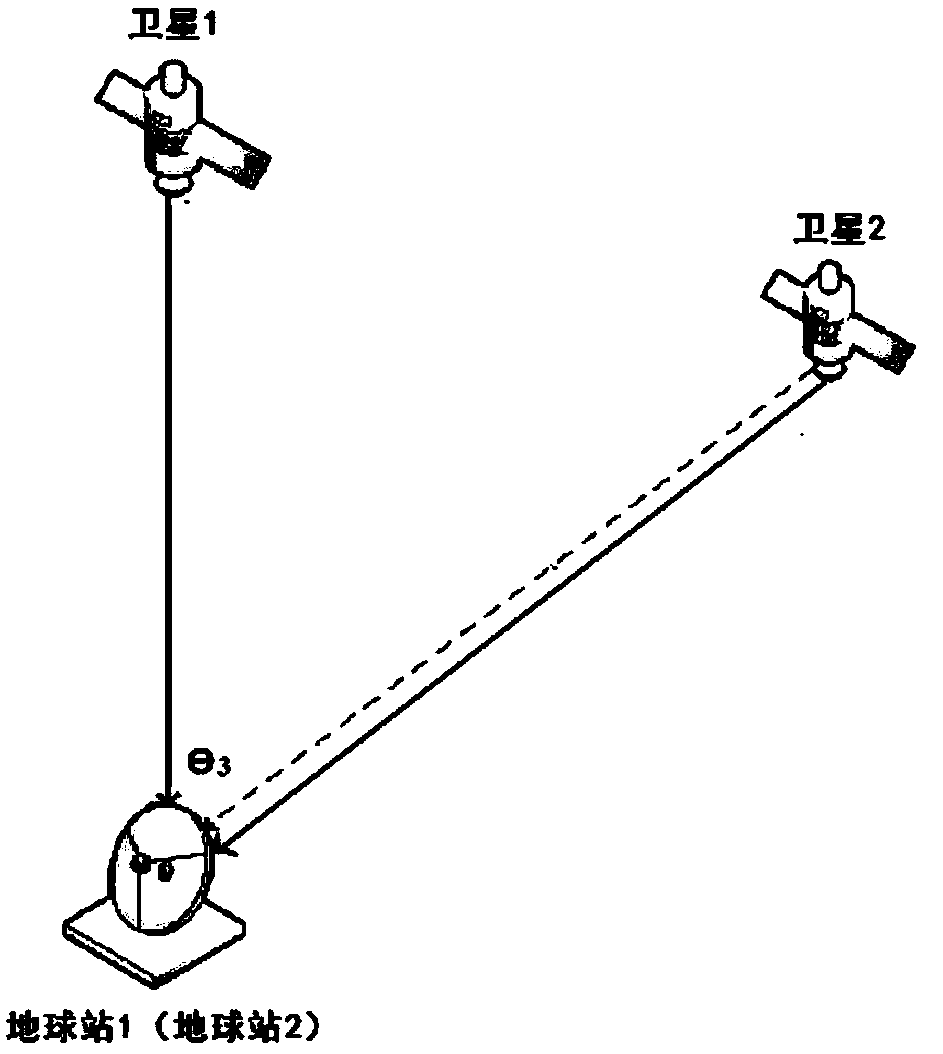
Method for performing interference analysis and avoidance on synchronous orbit satellite communication system
ActiveCN107809298AReduce the amount of online dataReduce the impact of communication qualityNetwork topologiesActive radio relay systemsCommunications systemSynchronous orbit
The invention relates to a method for performing interference analysis and avoidance on a synchronous orbit satellite communication system, characterized by including the following steps: 1) designinga recursive orbit for medium-earth and low-earth orbit satellites in a non-synchronous orbit satellite communication system to ensure that tracks of sub-satellite points of each satellite are periodically overlapped and cross over the equator at a plurality of fixed longitude points; 2) determining a range of the synchronous orbit satellite communication system that needs to perform interferenceanalysis according to relevant protection standards of the International Telecommunication Union; 3) performing interference analysis on the synchronous orbit satellite communication system, and setting corresponding interference protection belt zones for synchronous orbit satellites; and 4) enabling an earth station of the non-synchronous orbit satellite communication system to determine whetherthe medium-earth and low-earth orbit satellites need to take avoidance measures according to predicted system parameters and the running states of each medium-earth and low-earth orbit. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely applied in the field of interference analysis and avoidance of the synchronous orbit satellite communication system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar velocity spatial variability compensating method
InactiveCN103364782AImplement focus processingSolved - speed space variation compensation problemRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar velocity spatial variability compensating method. According to the method, the velocity spatial variability is compensated through self-adaptive phase compensation processing, so that a core problem, i.e. a velocity spatial variability compensation problem, of geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) large-scale scene imaging is solved, the GEO SAR large-scale scene imaging focusing processing of arbitrary position is realized, and a good effect is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
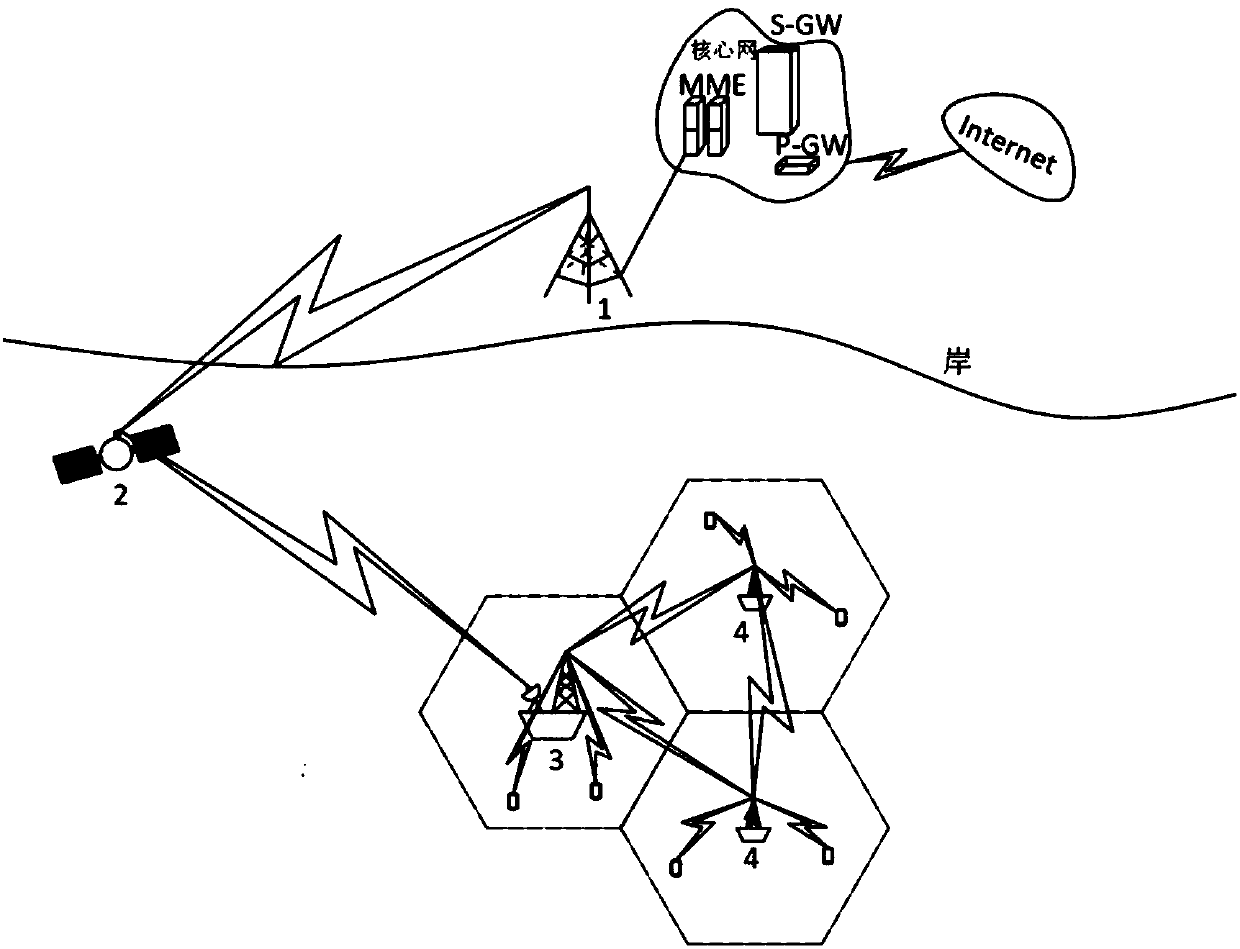
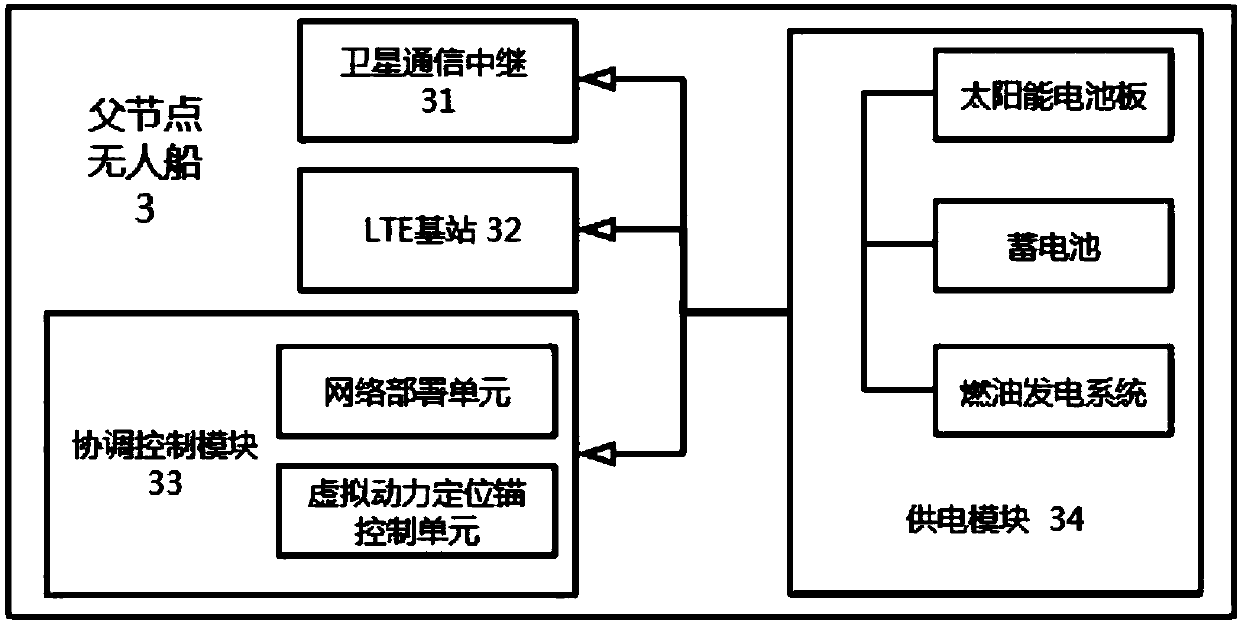
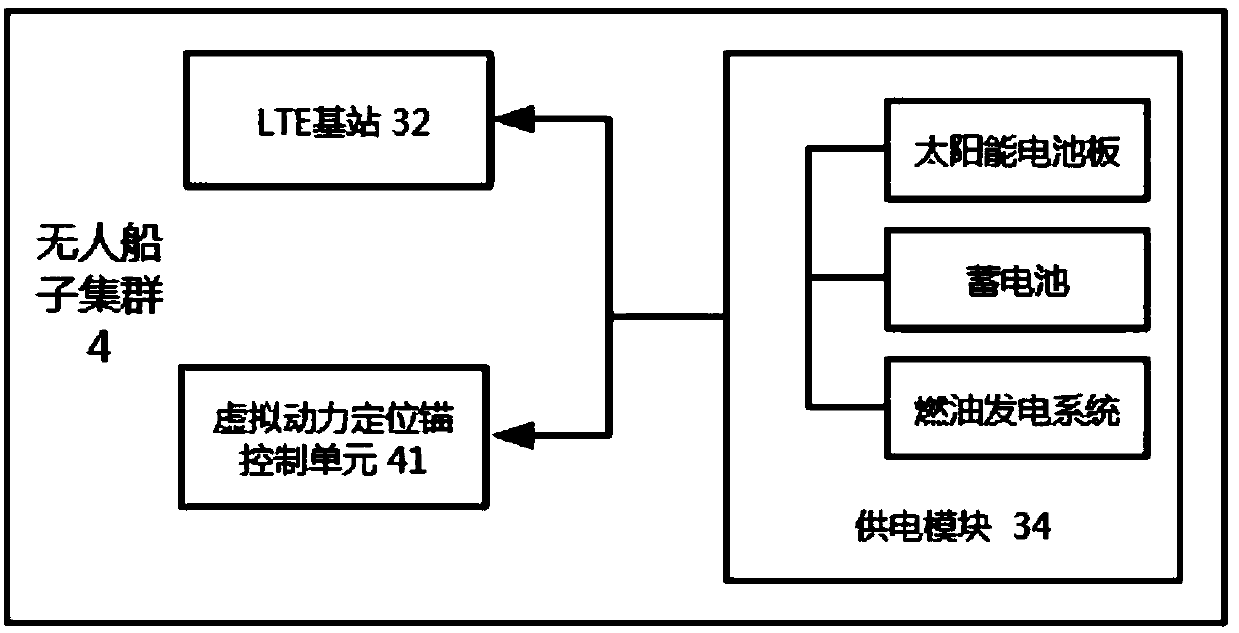
LTE maritime emergency communication system based on unmanned ship base station network
PendingCN107707292AFast and Flexible DeploymentChange the deployment methodWaterborne vesselsUnmanned surface vesselsSynchronous orbitCommunications system
The invention discloses an LTE maritime emergency communication system based on an unmanned ship base station network. The system comprises the unmanned ship base station network, a short LTE base station and a synchronous orbit communication satellite. The unmanned ship base station network comprises a parent node unmanned ship and an unmanned ship subset. The parent node unmanned ship is the relay station between the communication satellite and the unmanned ship subset and furthermore performs real-time monitoring and controlling on the chain state and stationary point position of the unmanned ship subset. According to the emergency communication system, a centralized deposition manner is utilized. Namely the parent node unmanned ship performs global configuration on the whole unmanned ship base station network, thereby constructing a sea environment oriented rescuing emergency communication system, and settling a problem of depositing the maritime emergency communication system by means of a satellite communication resource and an ad hoc network which is loaded by the unmanned ships.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
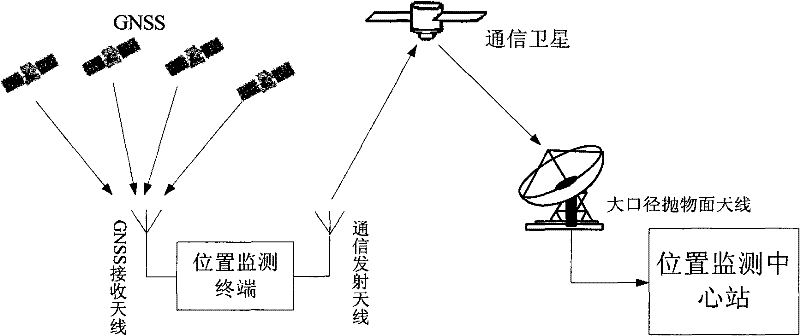
System with wide geographical coverage for monitoring positions in real time
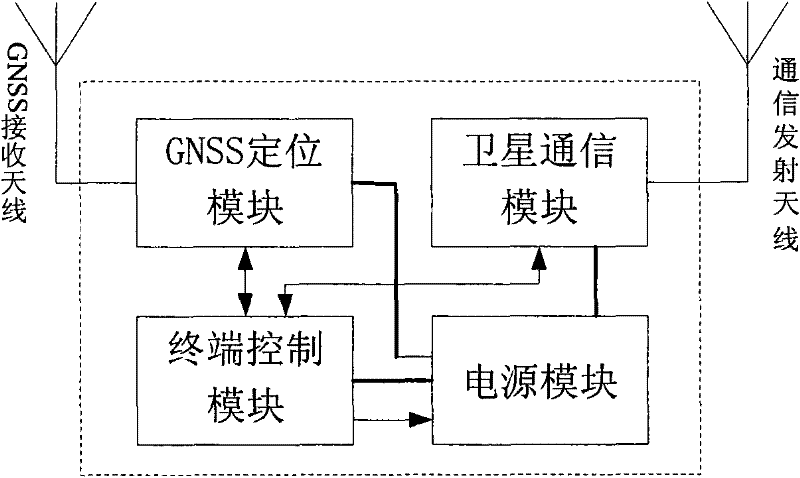
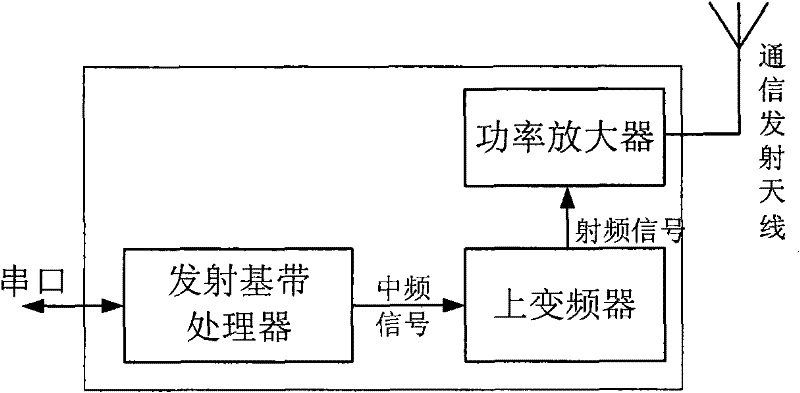
InactiveCN102244535ARealization of location monitoringReceive in real timeRadio transmissionSatellite radio beaconingCode division multiple accessCommunications receiver
The invention relates to a system with wide geographical coverage for monitoring positions in real time, comprising position monitoring terminals, a communication satellite and a position monitoring central station, wherein the position monitoring terminals comprise a GNSS (global navigation satellite system) positioning module, a satellite communication module, a control module and a power supply module respectively; the communication satellite is a synchronous orbit communication satellite; the position monitoring central station comprises a heavy caliber parabolic antenna, a satellite communication receiver and a data processing computer; and the position monitoring terminals are used for passing positioning information acquired by the positioning modules back to the monitoring central station by a satellite link, so that the central station can monitor the positions of the position monitoring terminals in real time. In the monitoring system, bandwidth resources of one satellite transponder are utilized, and an FDMA (frequency division multiple access) way, a CDMA (code division multiple access) way and a TDMA (time division multiple access) way are adopted to monitor the positions of the multiple position monitoring terminals in real time. The system is applied to regions with satellite signal coverage only without ground communication network coverage particularly. The system has the characteristics of instantaneity, multiple users and wide geographical coverage.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inclined orbit satellite systems
InactiveUS20150158603A1Efficiently provideEfficiently providedCosmonautic partsActive radio relay systemsContinuous/uninterruptedGeographic regions
The present disclosure is directed to an inclined geosynchronous orbit satellite system that can efficiently provide continuous communication to multiple geographic regions across the world using satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbital paths having an equatorial crossing and enabling the reuse of frequencies assigned within GSO orbital locations. The inclined orbit satellite system can include multiple inclined orbit satellites that are capable of co-existing with geostationary satellites to provide continuous uninterrupted service.
Owner:TAWSAT
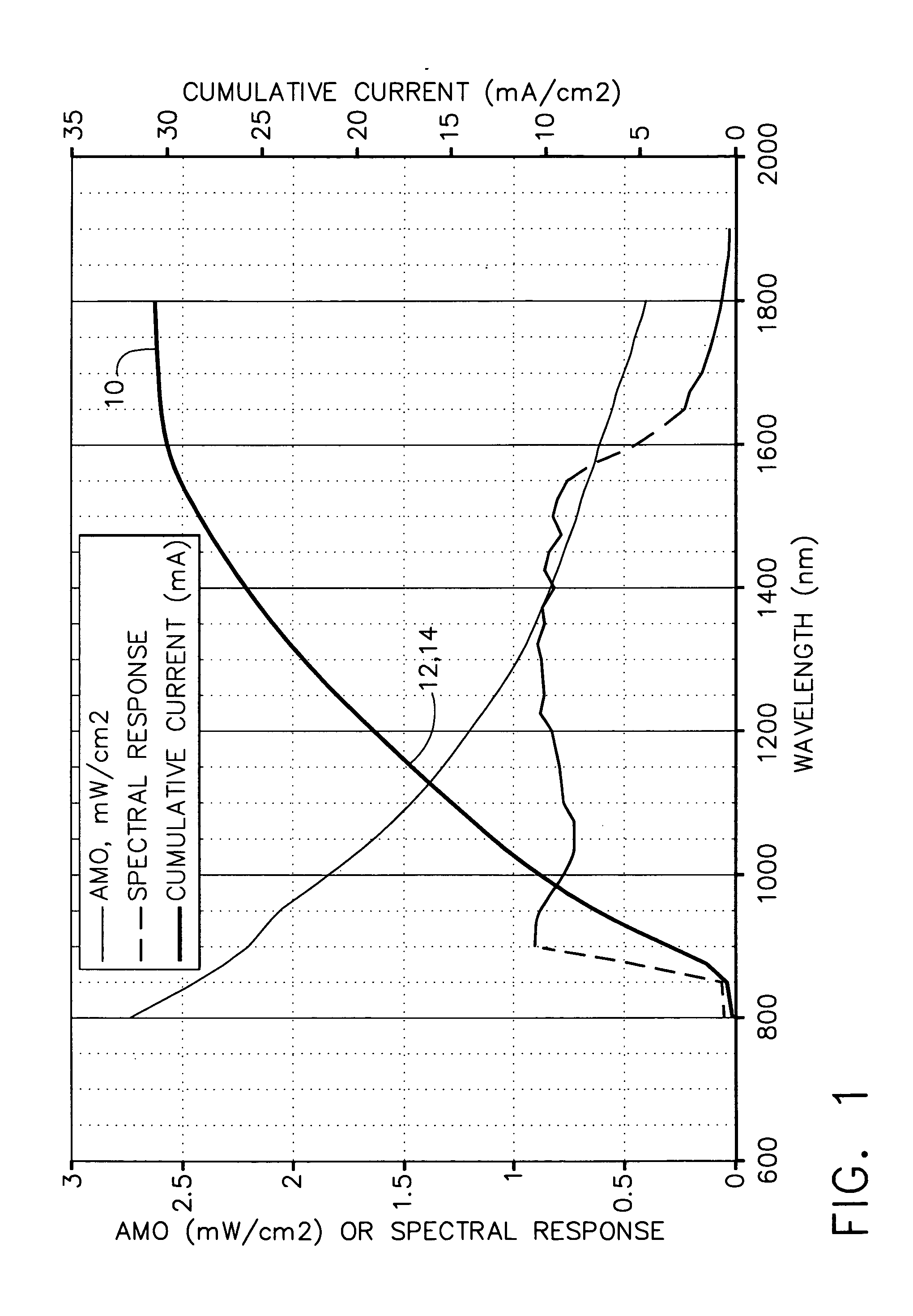
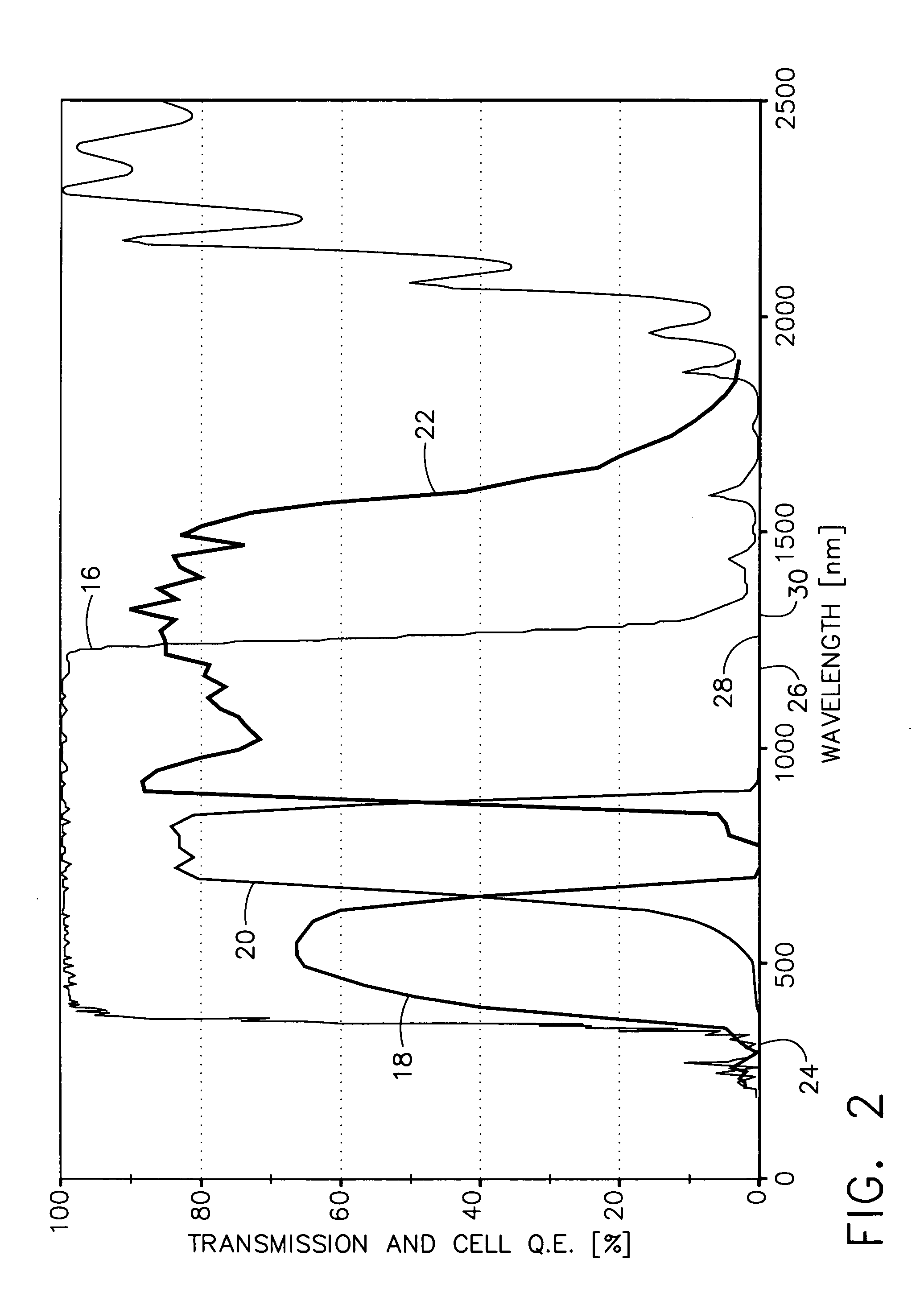
Solar power collection with near infrared wideband reflector coating
InactiveUS20050103374A1Lower operating temperatureImprove conversion efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationSolar angleLow earth orbit
A near infrared (NIR) wideband reflector coating designed to start reflecting solar energy wavelengths from at least 1.2 microns in a typical geosynchronous earth orbit or medium earth orbit satellite and from at least 1.3 microns in a typical low earth orbit satellite. Also, the (NIR) wideband reflector coating reflects solar energy wavelengths below 0.35 microns in all three applications. This invention works on triple junction (TJ) solar cells. The performance of at least 1.2-microns is on solar panels with near-normal incident solar angle, typical of Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) and Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites. The performance of at least 1.3-microns is on solar panels with wide range of incident solar angles, a design requirement for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Satellite temperature control method allowing rapid responding and multi-orbit adaption
InactiveCN105035365AReduce working conditionsSave research and development costsCosmonautic environmental control arrangementThermal insulationLacquer
The invention provides a satellite temperature control method allowing rapid responding and multi-orbit adaption, wherein by adopting a heat pipe network, reinforcing contact thermal conduction, and spraying a high-emissivity thermal control coating inside a satellite to reinforce in-cabin thermal conduction and radiation heat exchange, a temperature field is distributed uniformly in a cabin; a whole satellite temperature level is adjusted by a compensative electric heater; a nightside of a side plate of the satellite is taken as a major heat dissipation face, the outer surface of the nightside is sprayed with a white paint, and all the other outer surfaces of the satellite body, except for the major heat dissipation face, are covered by multiple layers of thermal insulation assemblies; and components outside the satellite are sprayed with a white paint thermal control coating. A propelling cabin has independent design, wherein the entire outside of the cabin is covered by the multiple layers of the thermal insulation assemblies, a baseplate inside the cabin is covered by the multiple layers of the thermal insulation assemblies, and the propelling cabin is finally integrated with a platform cabin. By integral design of machinery, heat and electricity, the satellite temperature control method allowing the rapid responding and the multi-orbit adaption provided by the invention realizes thermal control requirements of the whole satellite under conditions of a sun-synchronous orbit and an inclined track by the temperature control method.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
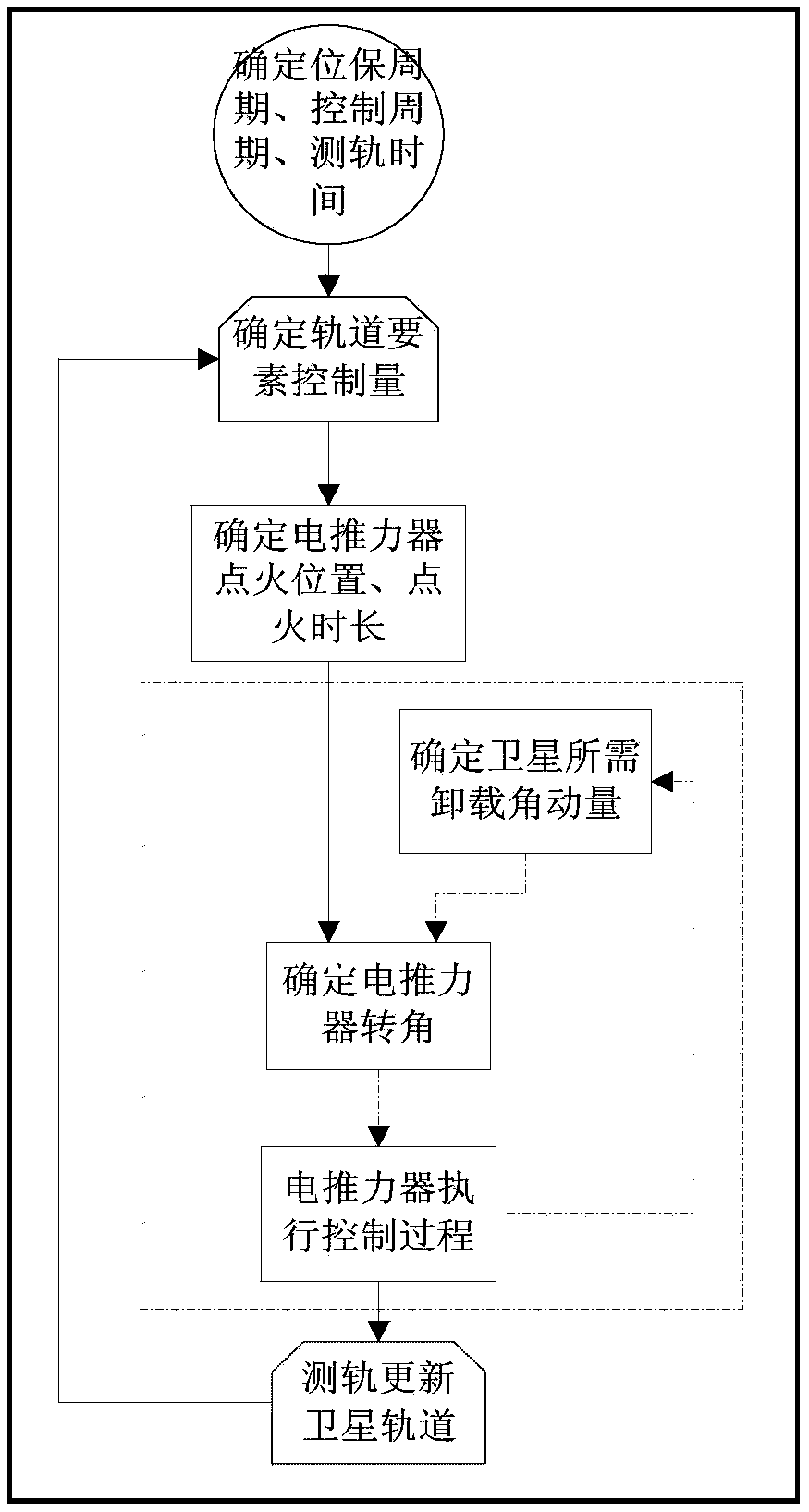
Synchronous orbit electric propulsion position maintenance and angular momentum unloading joint control method
ActiveCN105373133AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce consumptionAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsOrbital periodElectricity
The invention relates to a synchronous orbit electric propulsion position maintenance and angular momentum unloading joint control method comprising the steps that a position maintenance cycle Ts, a control cycle Tc and orbit measurement time Tm are determined; the control cycle Tc is total time including completion of one time of the ignition process of all thrusters respectively; the orbit measurement time Tm is obtained in a way that time required by orbit measurement is rounded up to an integer of integer orbit cycles; one position maintenance cycle Ts includes one orbit measurement process Tm and multiple control cycles Tc: orbit element control variables, including inclination angle control variable vectors (deltaix, deltaiy), eccentricity control variable vectors (deltaex, deltaey) and a flat longitude drift rate control variable deltaD, of each control cycle are calculated before starting of each position maintenance cycle Ts; the electric thruster ignition parameters of each control cycle are determined, and the ignition parameters include ignition duration and an ignition position; and an electric thruster rotating angle is determined according to the electric thruster ignition parameters and angular momentum unloading quantity before starting of each control cycle Tc.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Independent synchronous rail transit
The invention relates to independent synchronous rail transit, which is a new public transit mode and transit concept. Independent small cars and unidirectional small rails are used. The cars are synchronously, electrically and automatically controlled to run according to a uniform clock rhythm and run on the whole journey in a way of no stop (no crossroad wait and no stop at midway). The independent synchronous rail transit is mainly used for urban transit and long-distance transportation. The rails can be laid under the ground, on the ground or in the air. The carrying capacity of one rail can reach 30 thousand persons per hour, and the problem of urban traffic jams can be solved.
Owner:张宁 +1
Microwave-assisted spatial information network backbone networking transmission method
The invention relates to backbone network networking transmission technology in the spatial communication field, and discloses a microwave-assisted spatial information network backbone networking transmission method. The method comprises steps: (1) spatial information network backbone nodes comprise a large-capacity communication satellite located in a synchronous orbit and a high-altitude communication platform in the stratosphere, and each backbone node has microwave and laser transmission means; (2) a backbone node accessed to the network newly uses the microwave means to send an access network application in a public control channel, access network approval is completed by an operational control central station, and node routing information is updated in a special control channel; and (3) a user initiates an access application, a backbone node in charge of access judges service requirements, transmission of low-speed service is completed in the microwave means, and as for high-speed service, the microwave means first assists to build a laser link, and signal transmission is then completed in the laser link. The broadcasting ability of the microwave and the high-speed ability of the laser are combined, and a flexible and high-speed transmission ability is provided for the satellite backbone network.
Owner:军事科学院系统工程研究院网络信息研究所
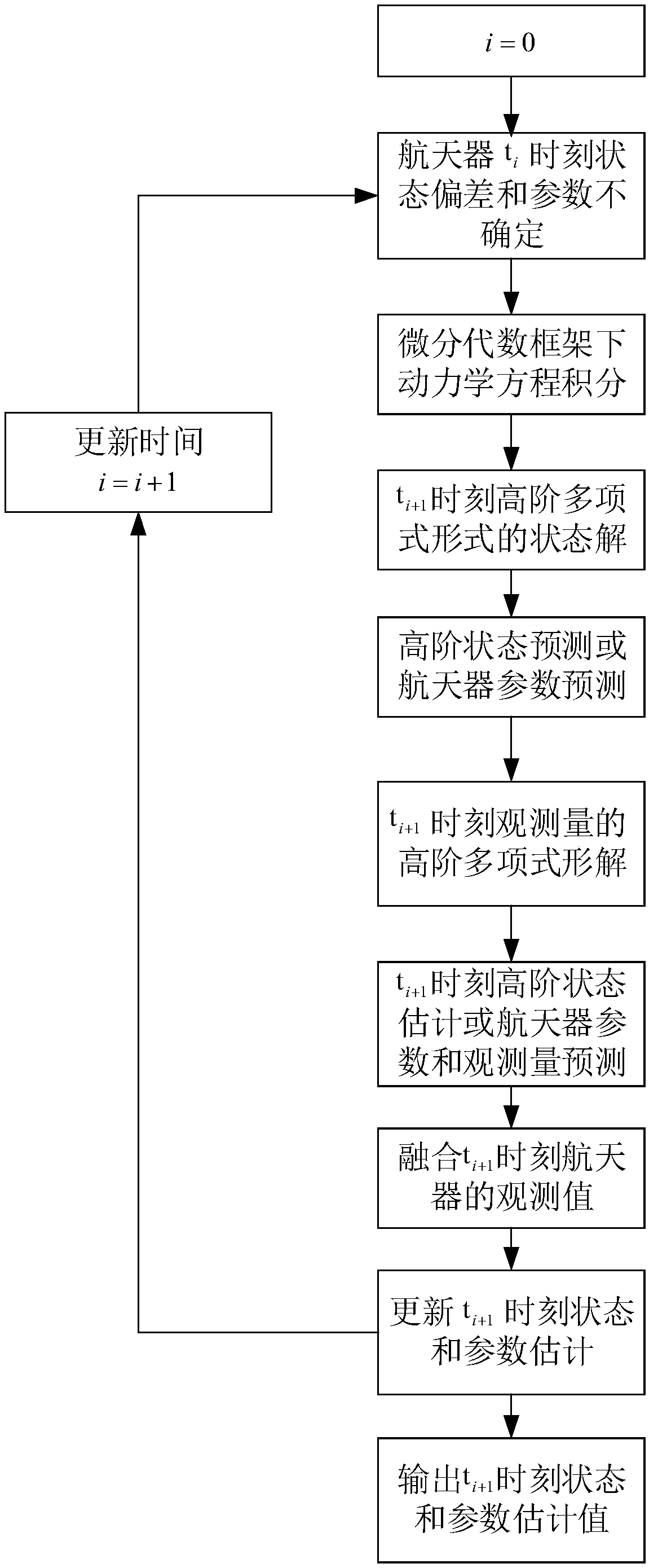
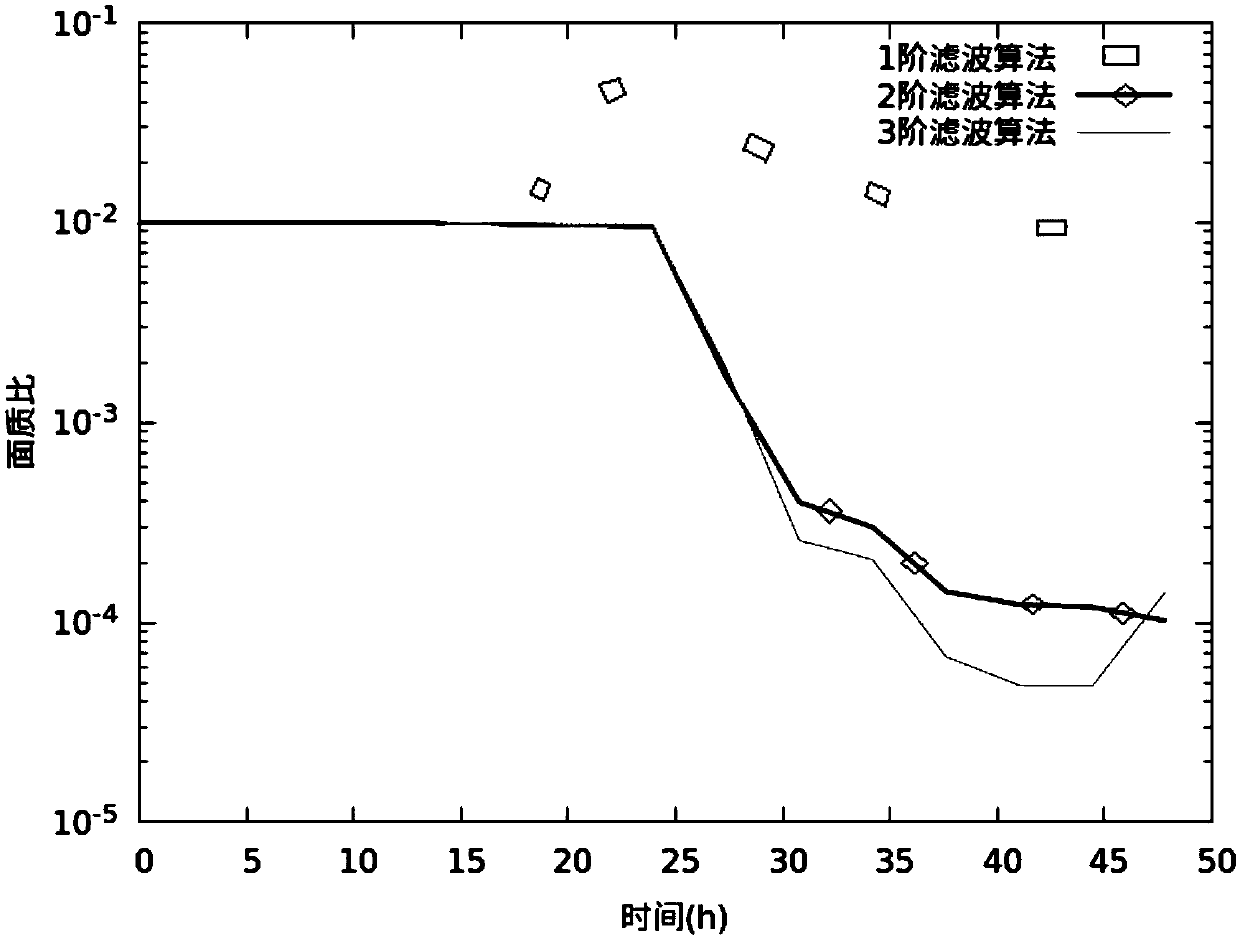
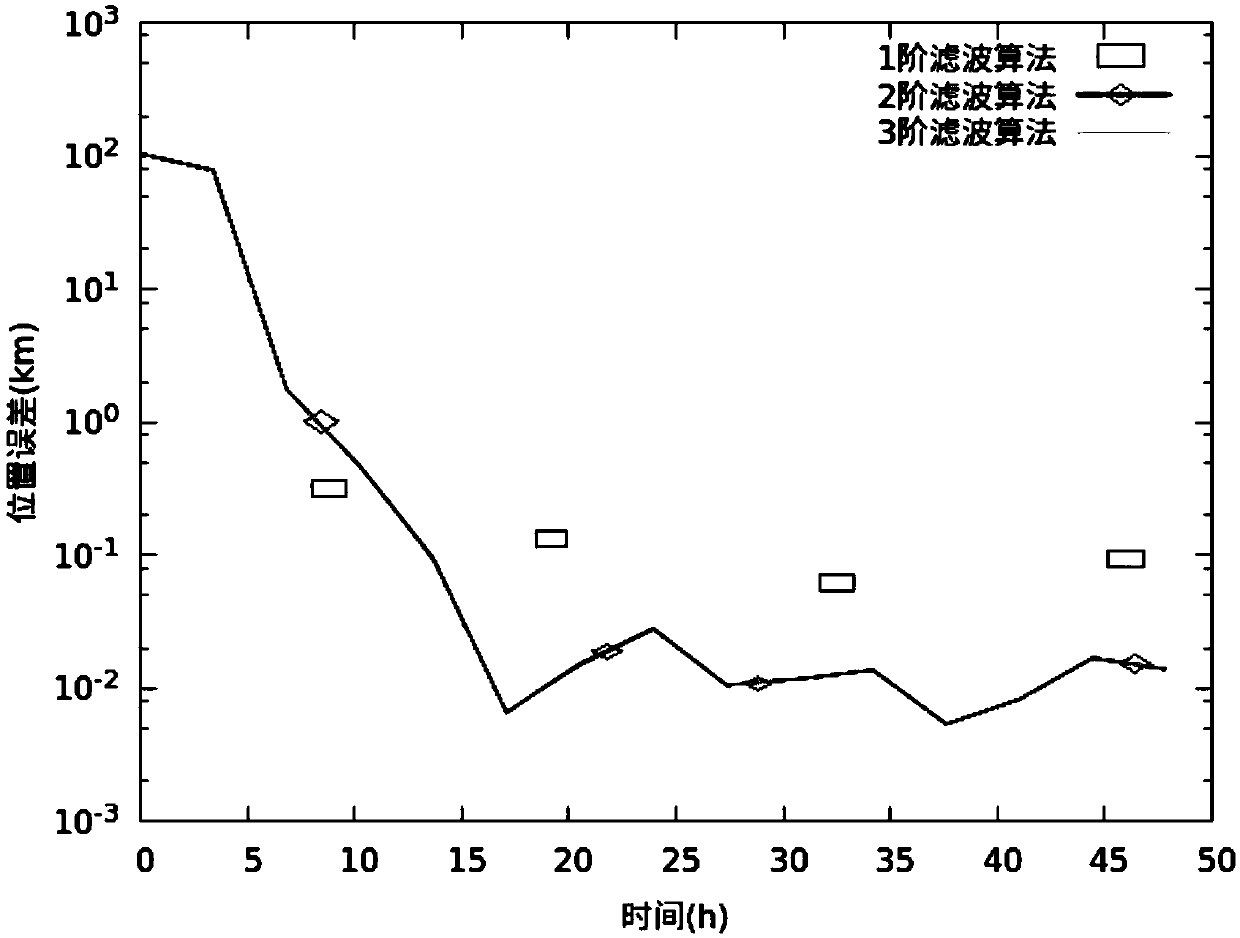
Geosynchronous orbit determination and parameter determination method based on differential algebra
ActiveCN109032176AAvoid singularitiesImprove estimation accuracyPosition/course control in three dimensionsSynchronous orbitGeosynchronous satellite
The invention discloses a geosynchronous orbit determination and parameter determination method based on differential algebra. A kinetic model described based on geosynchronous satellite orbit elements is selected and used, use of a relatively greater integration step in a numerical integration process is avoided and appearance of singular points is avoided for the kinetic model, moreover, a perturbative force item is added in the kinetic model, polynomial form integration is executed, thus, obit statuses and spacecraft parameters are obtained, high-order prediction is executed for the obtained parameters, and meanwhile, high-order prediction of observed quantity is executed; by means of nonlinear information of the kinetic model and an observation model, estimation accuracy is improved; in combination with actual observed values of a spacecraft, high-order prediction values of the obit status and the spacecraft parameters are updated and high-order estimated values as initial values are obtained; and by repeating the implementation process above, geosynchronous orbit determination and parameter determination can be completed. The method provided by the invention not only can improve accuracy of obit estimation and realize high-precision estimation of the parameters, but also can greatly reduce calculation cost.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for avoiding uplink interference of asynchronous orbit satellite to synchronous orbit satellite
ActiveCN110708110AGuaranteed service qualitySimplify Interference SituationsPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceSynchronous orbit
The invention provides a method for avoiding uplink interference of an asynchronous orbit satellite to a synchronous orbit satellite based on beam broadening in combination with user migration, the interference condition is simplified, and the beam operation of the satellite is divided into three types, namely closing, size adjustment and no change; the non-synchronous orbit satellite is closed ina strong interference area, so that the interference problem of the area can be well avoided; the beam size of the non-synchronous orbit satellite is adjusted in a weak interference area, the problemof a coverage blind area caused by beam closing of the non-synchronous orbit satellite can be solved, and the method is simple and easy to implement; and migrating the users possibly causing uplink interference to the adjacent asynchronous orbit satellites based on the user migration of the beam coverage service area. According to the method, the problem of uplink interference of the asynchronousorbit satellite system to the synchronous orbit satellite system is well solved, the service quality of a user is ensured, and the method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:北京中科晶上科技股份有限公司
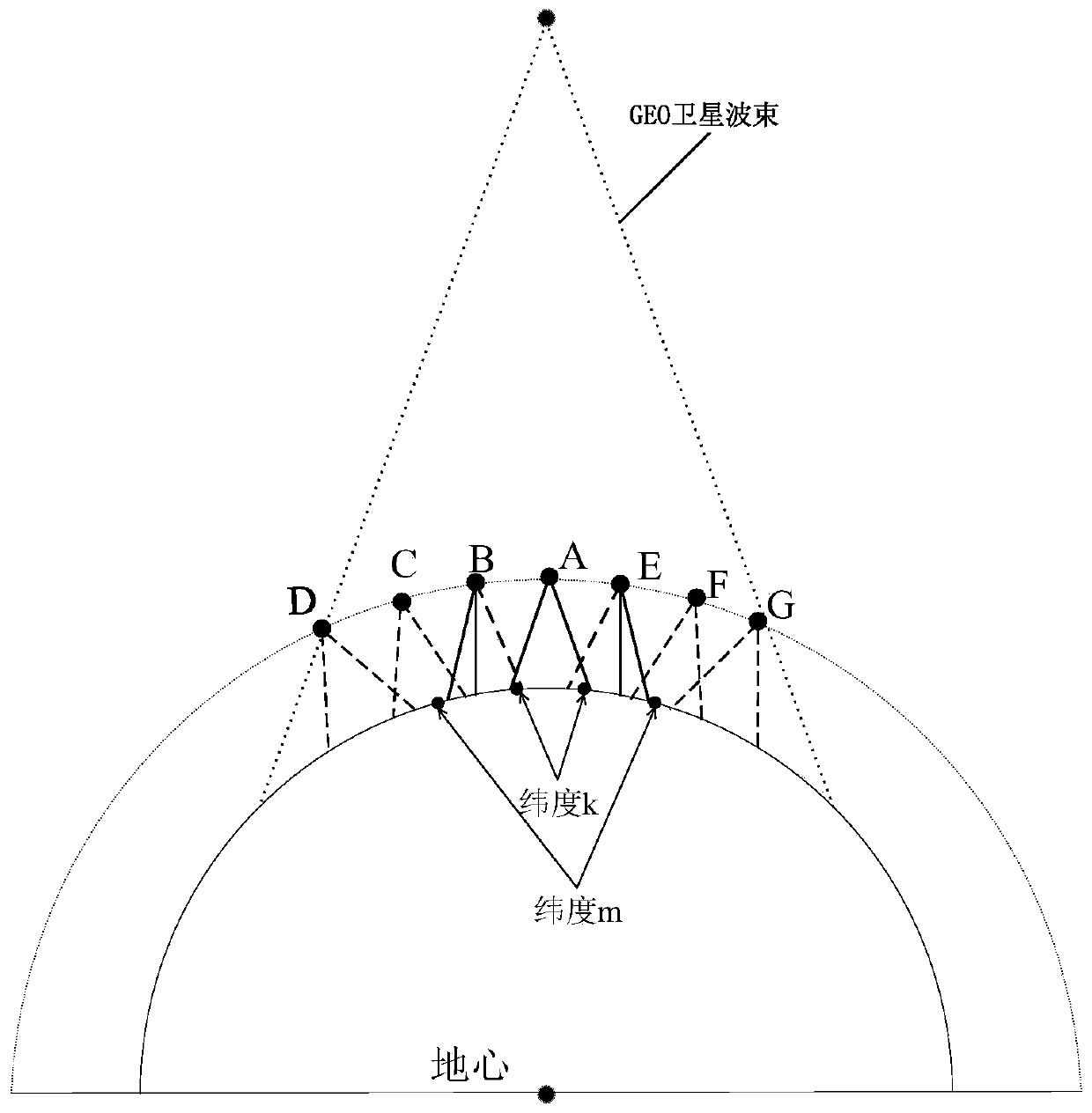
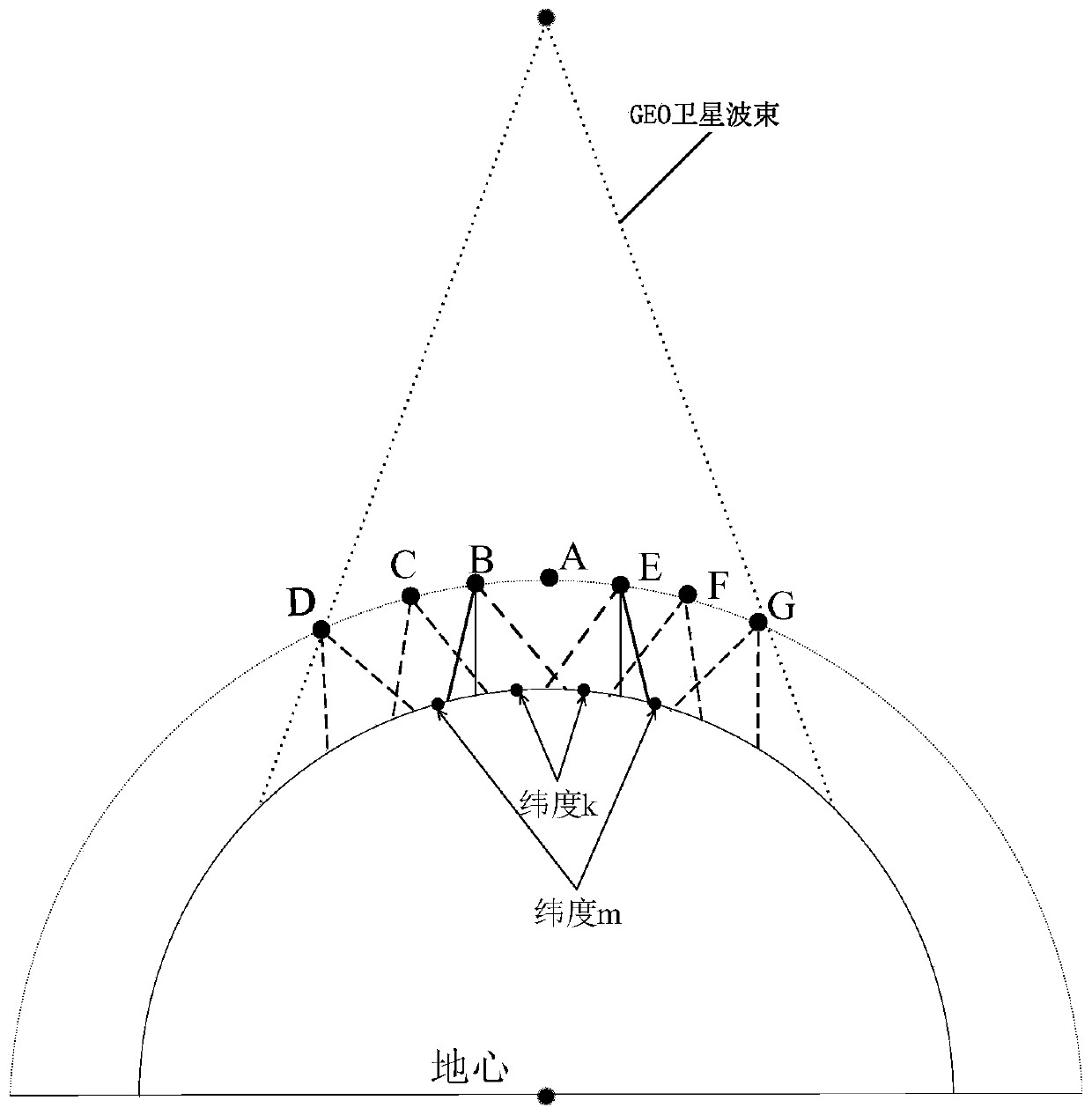
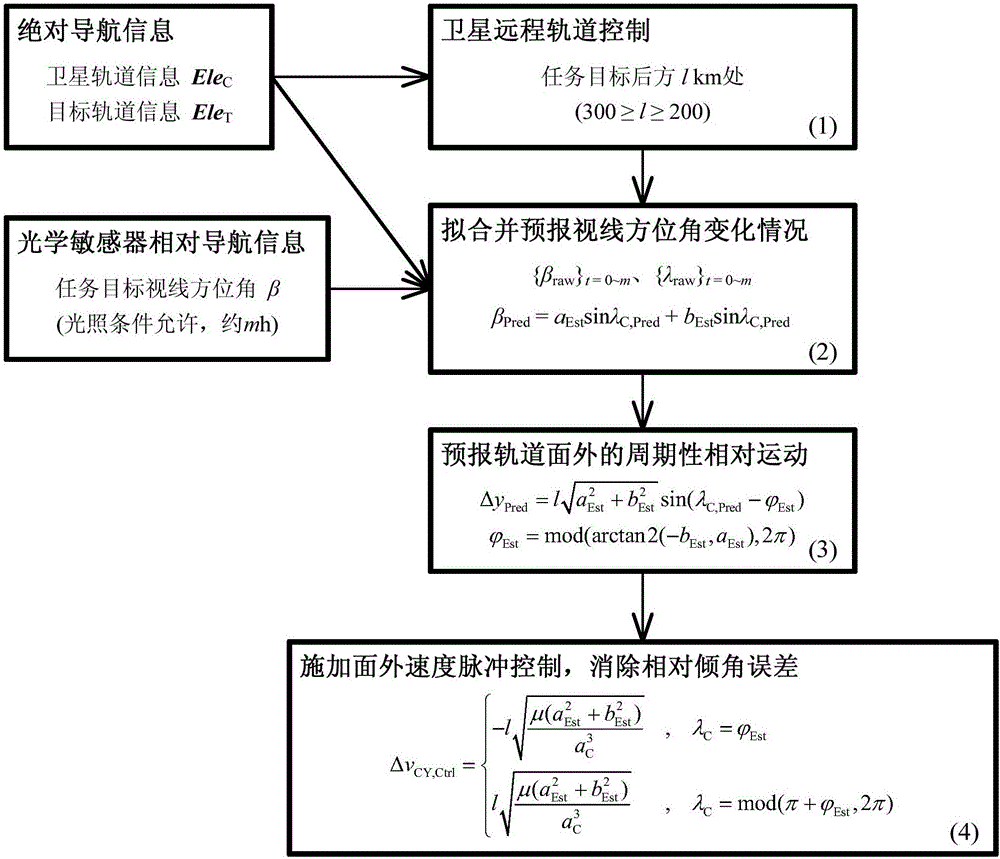
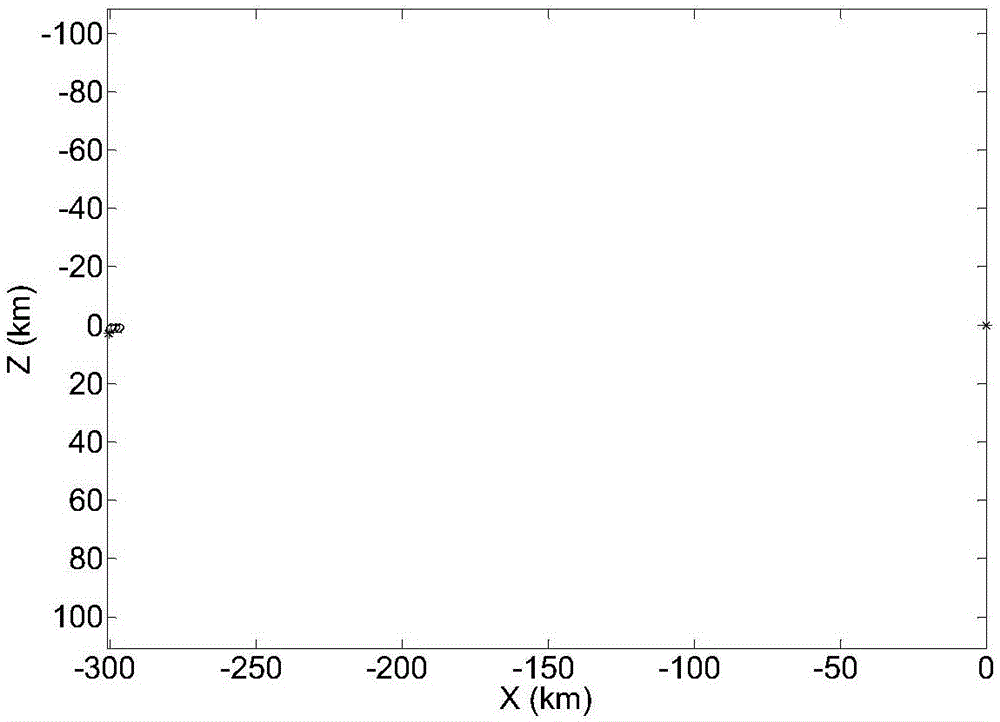
Synchronous orbit satellite relative dip angle remote correcting method based on line-of-sight measurement
ActiveCN106564622ACircumventing Observability ShortcomingsArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusRelative orbitRelative motion
The invention discloses a synchronous orbit satellite relative dip angle remote correcting method based on line-of-sight measurement. The method comprises the following steps: at first, carrying out remote orbit control on a synchronous orbit satellite through absolute navigation information provided by a ground measurement and control system, and directing the synchronous orbit satellite to a remote mooring point in the rear of a task object; then, through relative navigation information of an optical sensor and the absolute navigation information provided by the ground measurement and control system, and in combination with typical motion features of the relative orbit of a spacecraft, adopting the Least Squares method to fit and forecast variation of a line-of-sight azimuth angle; further, forecasting the periodic relative motion outside an orbital plane between the satellite and task object in combination with the nominal distance at the mooring point; and finally, carrying out velocity pulse control outside of the orbital plane on the operating satellite at the mooring point to eliminate relative position error outside of the orbital plane caused by the relative dip angle to avoid the situation that the task object is lost because the task object is beyond the field of view of the optical sensor, so that the satellite can rapidly and accurately approach the task object.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
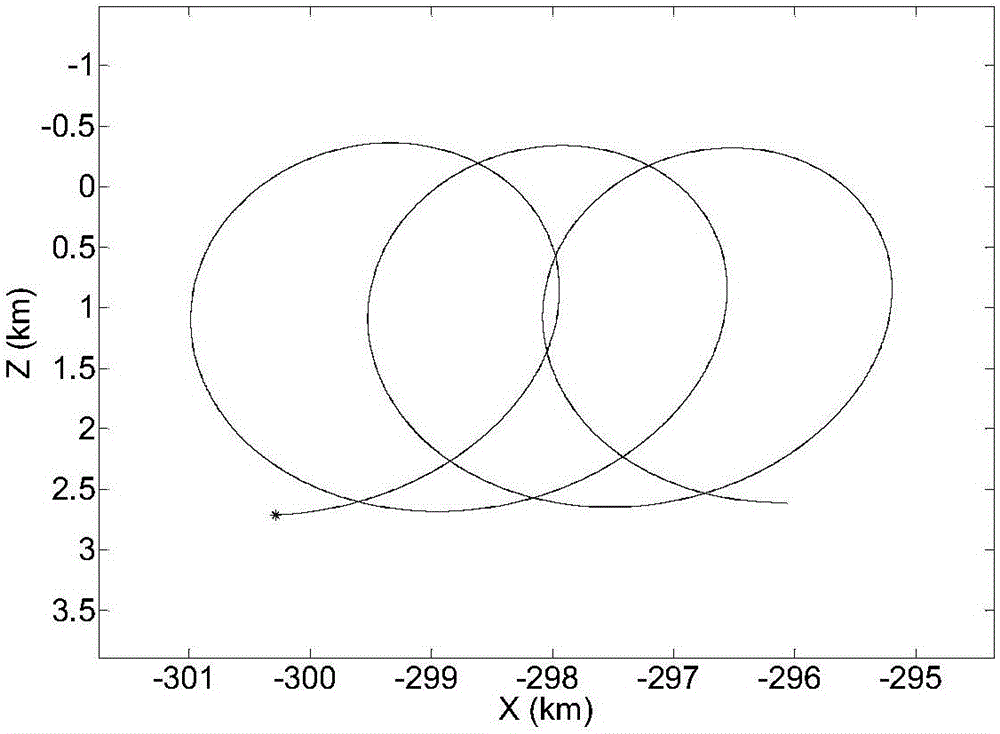
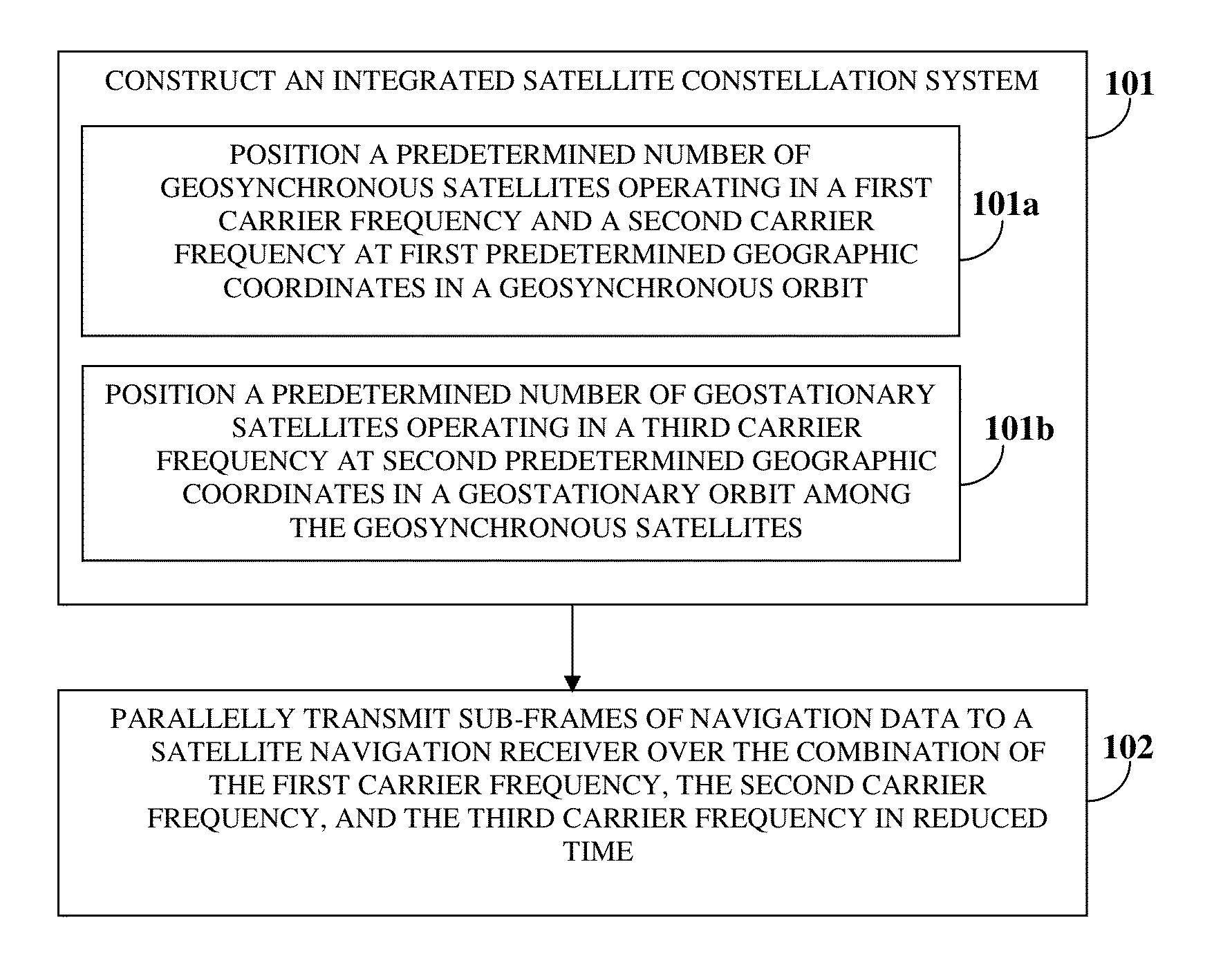
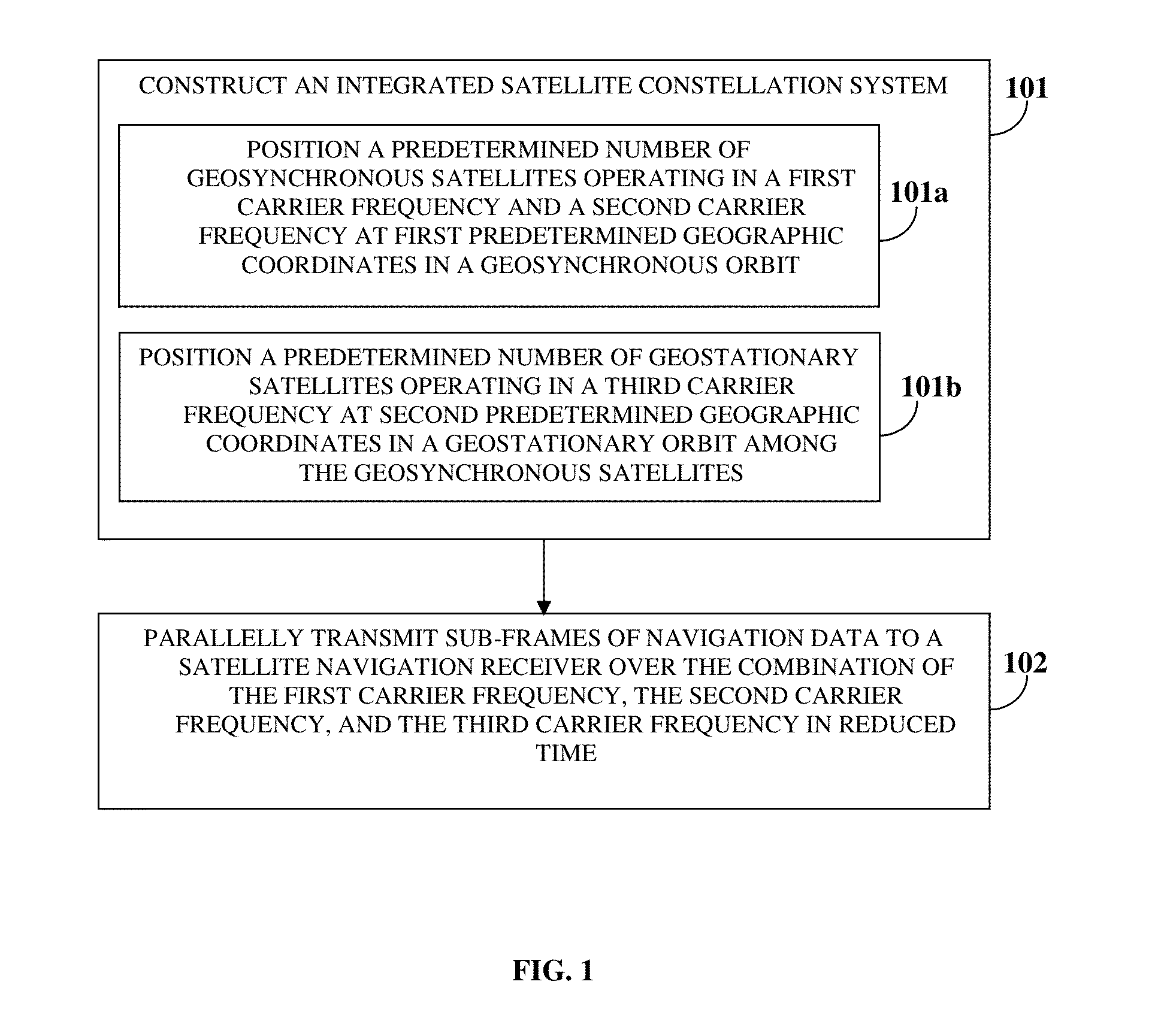
Time To First Fix Optimization In A Satellite Navigation Receiver
ActiveUS20150077288A1Shorten the timeHigh data rateSatellite radio beaconingSynchronous orbitGeosynchronous satellite
A method and a system for reducing time to first fix (TTFF) in a satellite navigation receiver (SNR) includes constructing an integrated satellite constellation system (ISCS) for transmitting navigation signals over a combination of a first carrier frequency, a second carrier frequency, and a third carrier frequency. The ISCS includes a predetermined number of geosynchronous satellites positioned at first predetermined geographic coordinates in a geosynchronous orbit and a predetermined number of geostationary satellites positioned at second predetermined geographic coordinates in a geostationary orbit. The ISCS transmits navigation data to the SNR over the combination of the first carrier frequency, the second carrier frequency, and the third carrier frequency in reduced time, thereby reducing the TTFF in the SNR. The method and the system also reduce TTFF in a hot start mode and a snap start mode of the SNR by utilizing the third carrier frequency as a data channel.
Owner:ACCORD SOFTWARE & SYST PVT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com