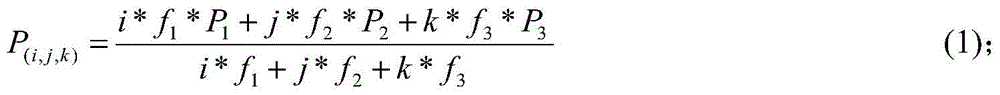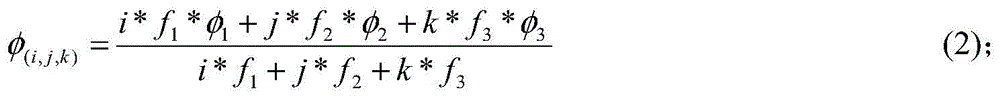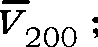Patents
Literature
96 results about "Orbital period" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The orbital period is the time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object, and applies in astronomy usually to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars.
Method for formation configuration of distributed satellites with synthetic aperture radars
InactiveCN101520511AApplicable interference processingStable baselineRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOrbital periodSynthetic aperture sonar
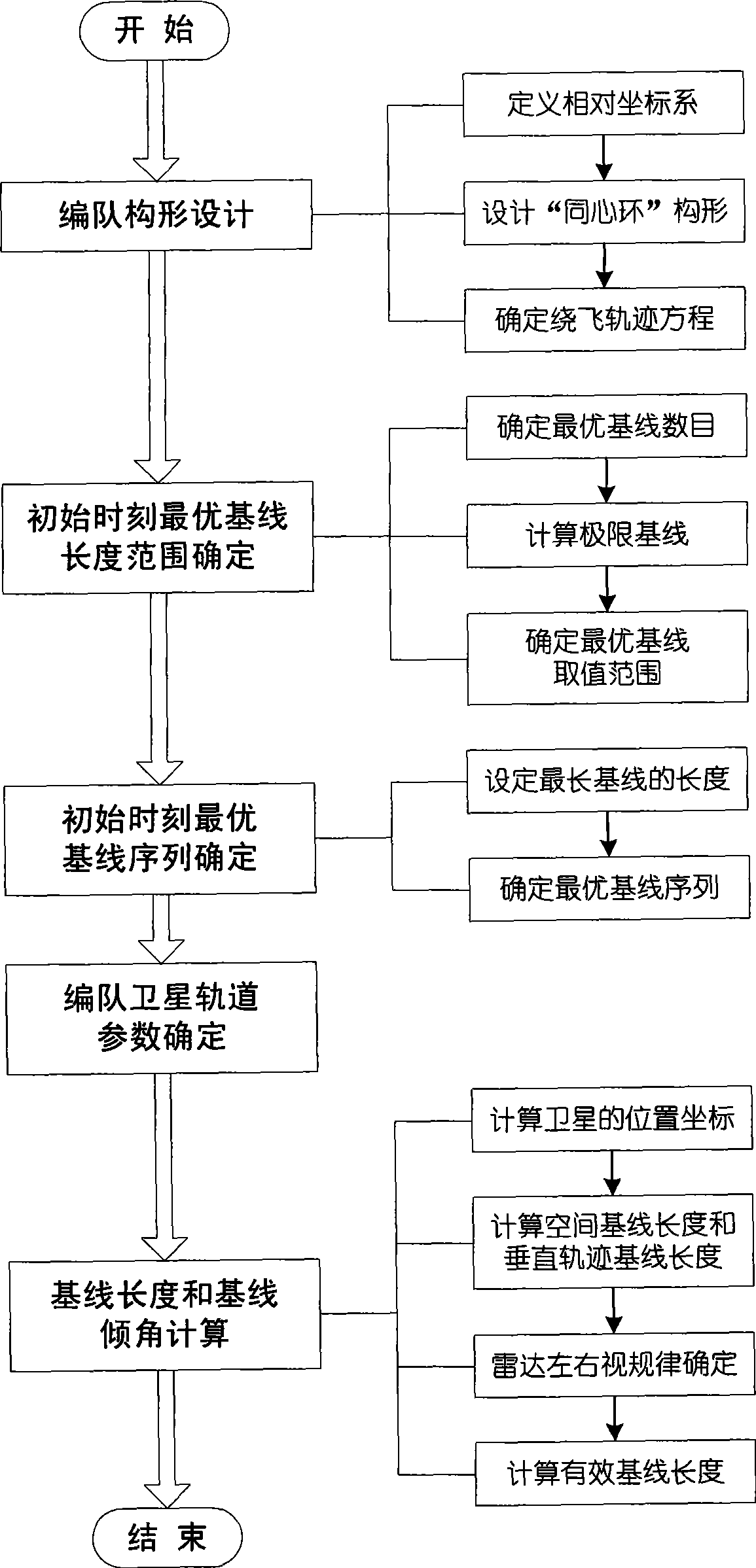
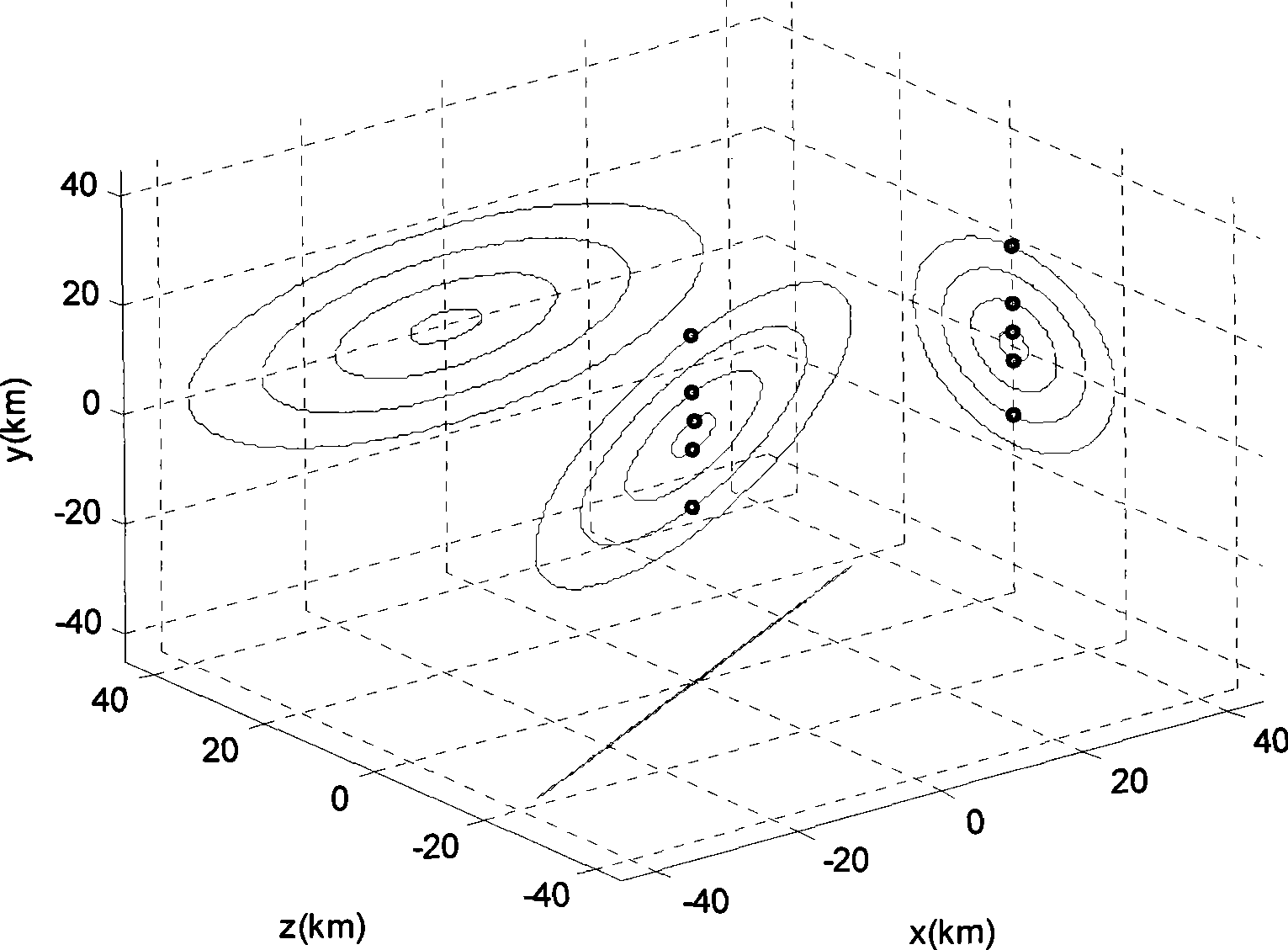
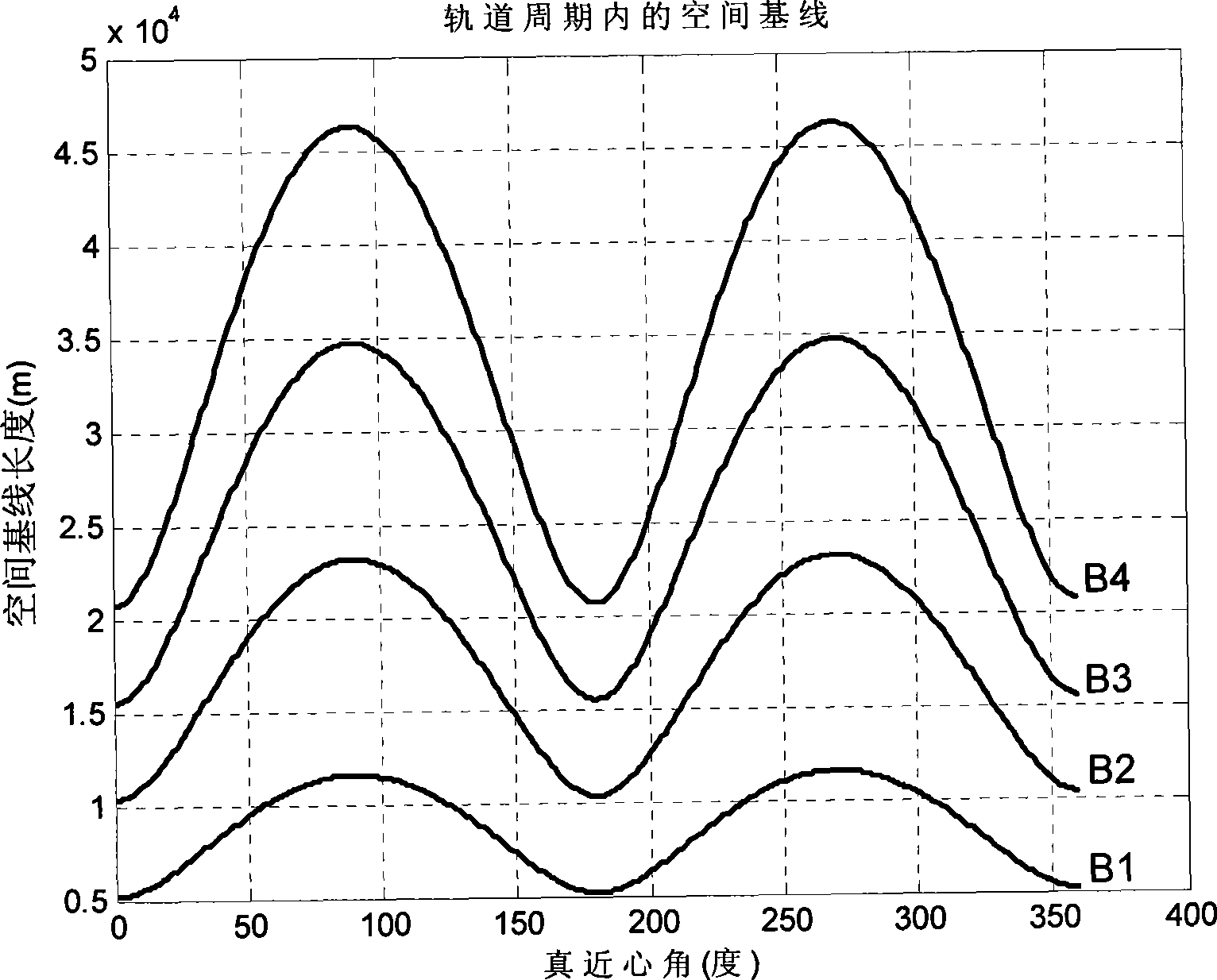
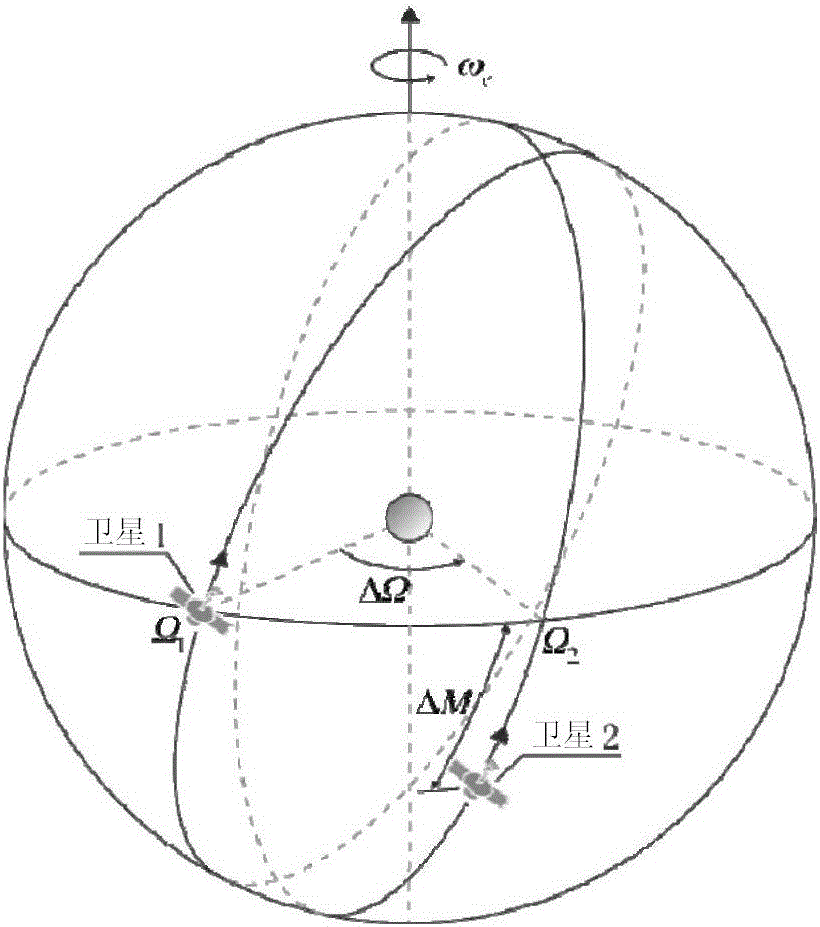
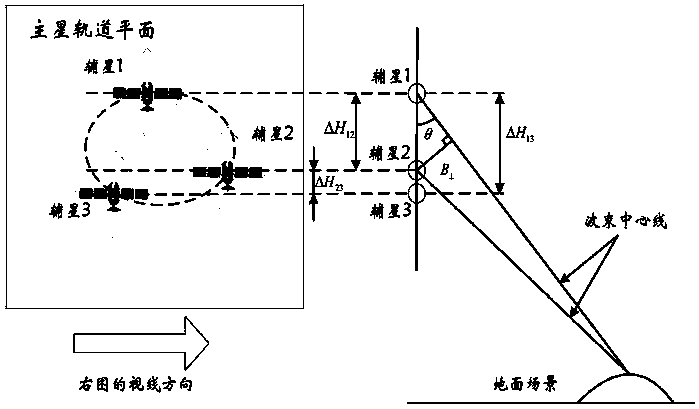
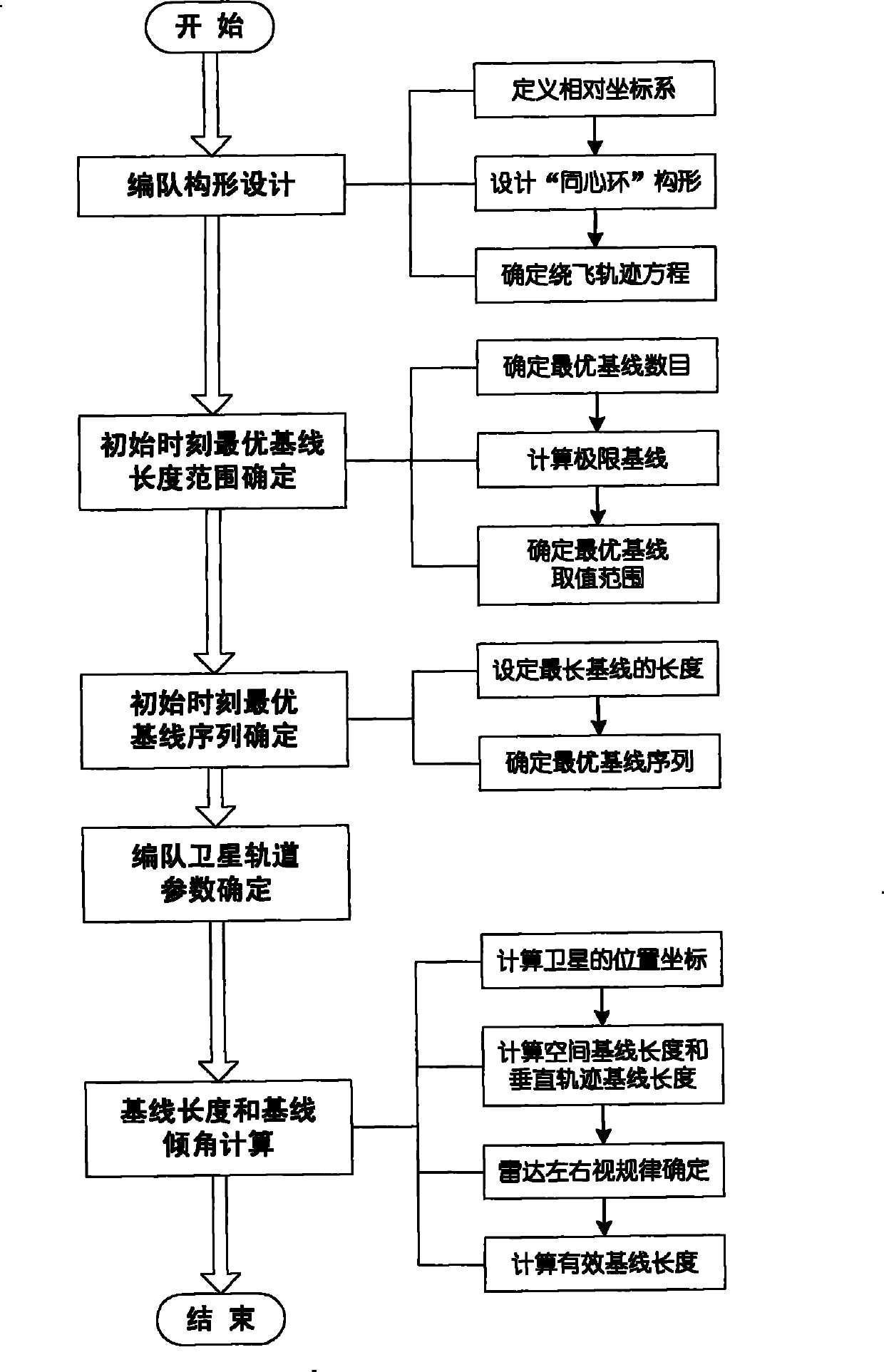
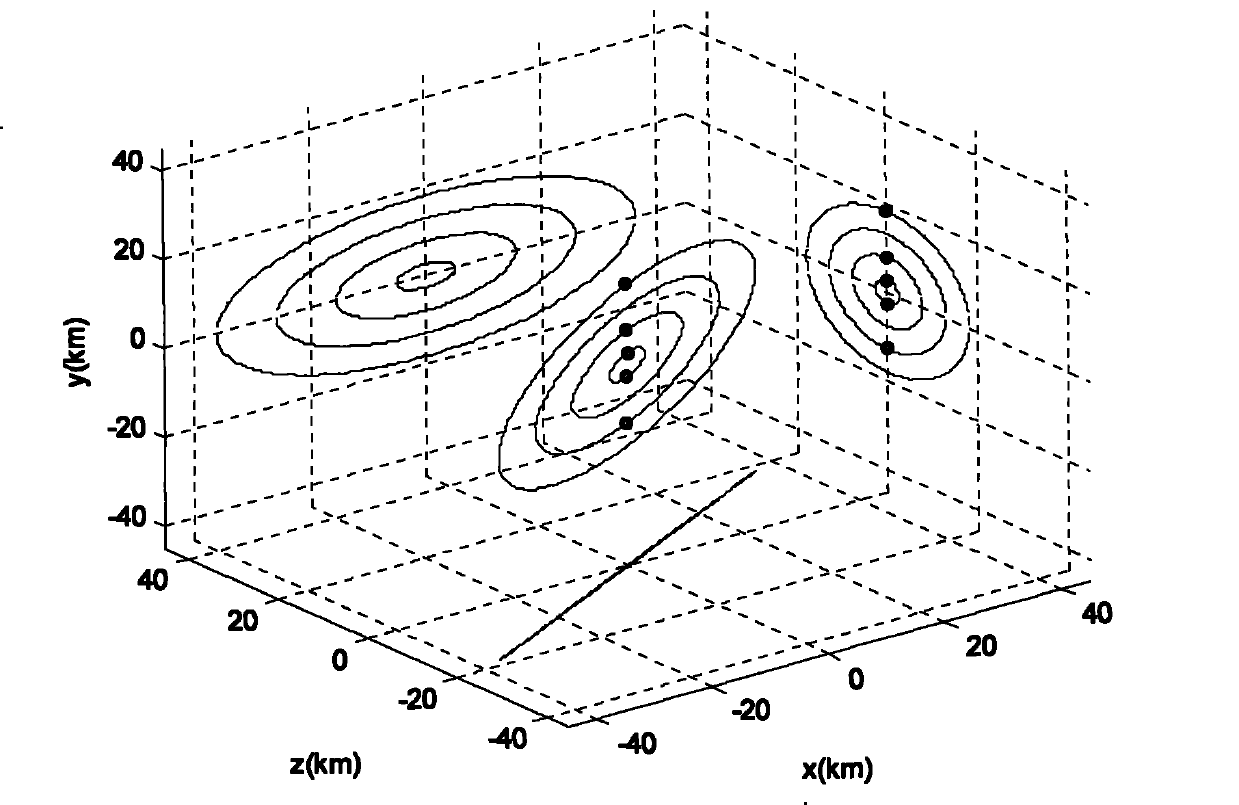
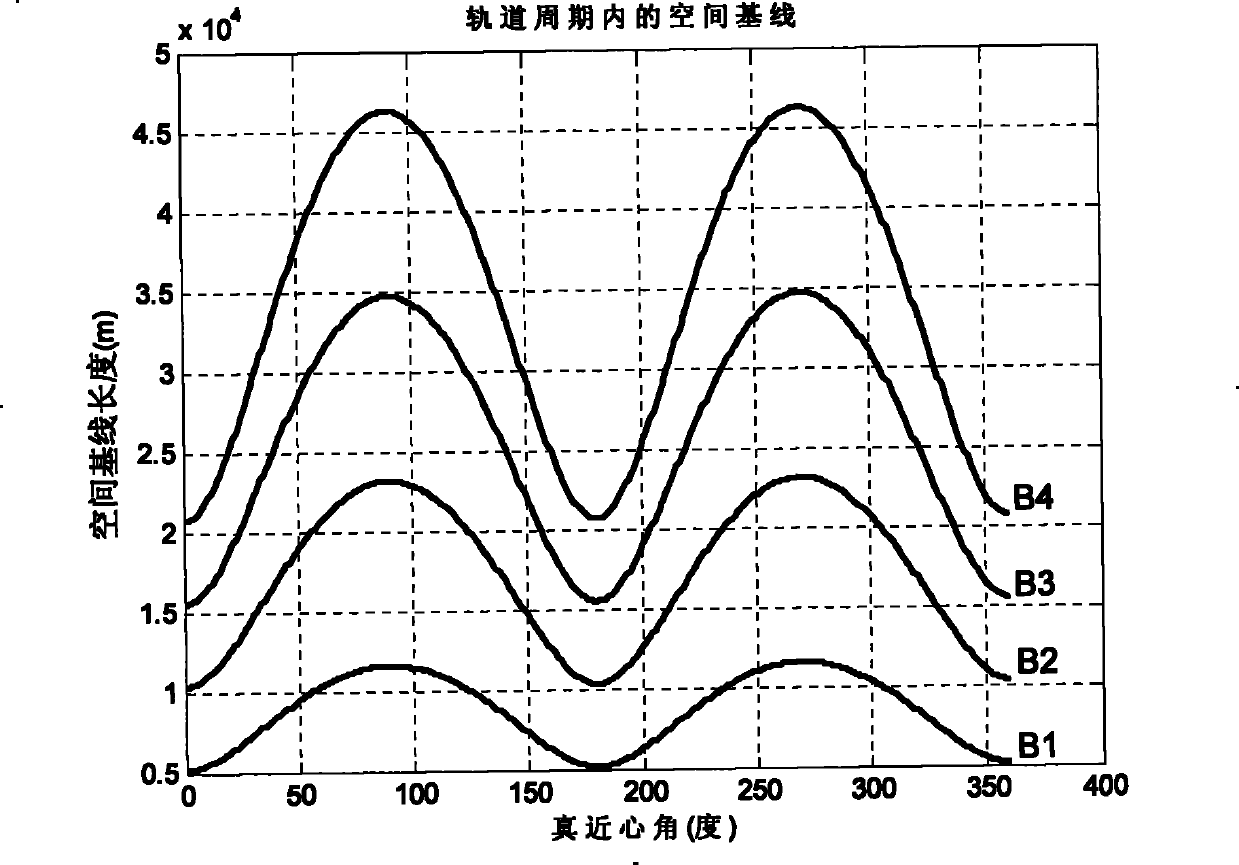
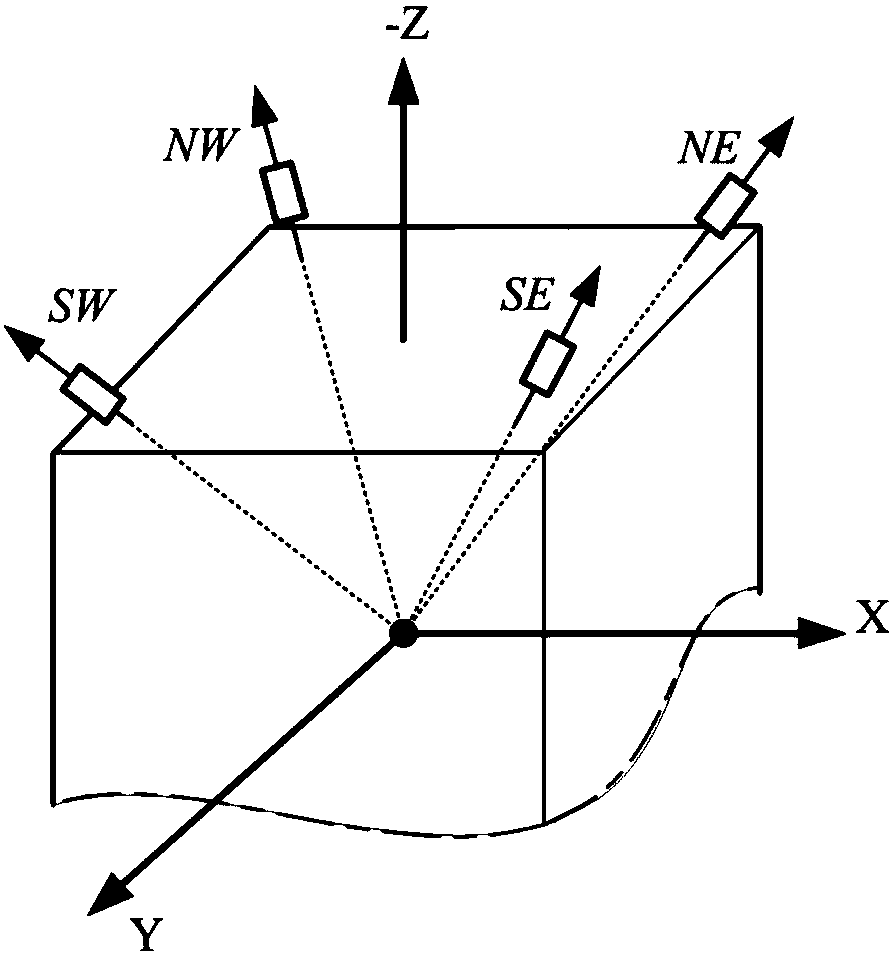
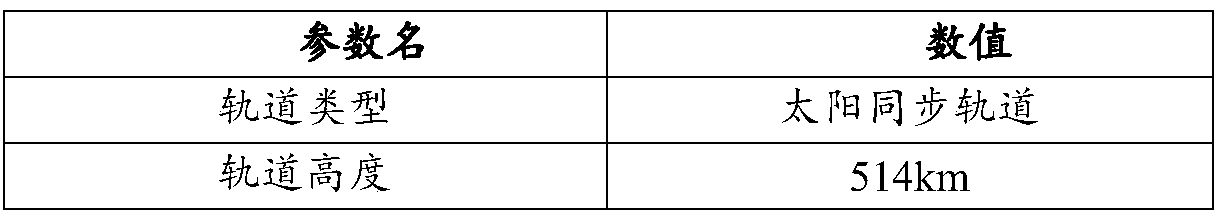
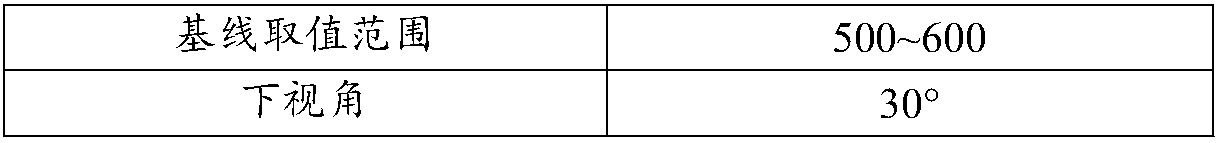
The invention relates to a design method for the formation configuration of distributed satellites with synthetic aperture radars (SAR). The method comprises the following five operation steps: step 1: designing the formation configuration of the distributed satellites and conforming fly-by path equations; step 2: confirming an optimal base line length range of the distributed satellites in start time; step 3: confirming an optimal base line sequence of the distributed satellites in start time; step 4: confirming track parameters of the formed satellites forming a concentric circle configuration; and step 5: calculating effective base lines and vertical path base lines in a track period. The invention provides the concentric circle formation configuration, uses the optimal base line combined constraint conditions of multi-base line interference SARs as design input parameters and designs a control law of radar antenna visual angles to realize that a distributed satellite SAR system can satisfy the design requirements of the optimal base line combined constraint conditions in any time in a track operation period and a basis is provided for the distributed satellite SAR system to obtain high-precision DEM products by a multi-base line interference SAR treatment method.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Global communication constellation designing method for realizing on-demand coverage of key areas
ActiveCN106209205AReduce the numberReduce complexityRadio transmissionHigh elevationEarth's rotation
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite communication, and particularly relates to a global communication constellation designing method for realizing on-demand coverage of key areas. In particular, a constellation comprises a plurality of orbital planes which are uniformly distributed along an equator; only one satellite exists on each orbital plane; an orbital period of each satellite is one integer of a rotation period of the earth; and sub-satellite point tracks of all satellites in the constellation coincide. The constellation can provide a high-elevation communication coverage service for the key areas as required according to a task demand by adjusting design parameters of the constellation such as a regression period, an orbit inclination, an eccentricity ratio, an argument of perigee, an ascending node geographic longitude of a first satellite and a mean anomaly. Area coverage can be realized through the constellation designed by the method; a sub-satellite point track repeating and high-elevation communication service can be provided specific to specific areas of a southern / northern hemisphere by adjusting constellation designing parameters; the number of satellites required by a coverage demand is reduced; the complexity of space and ground systems is lowered; and the systems are more economical.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
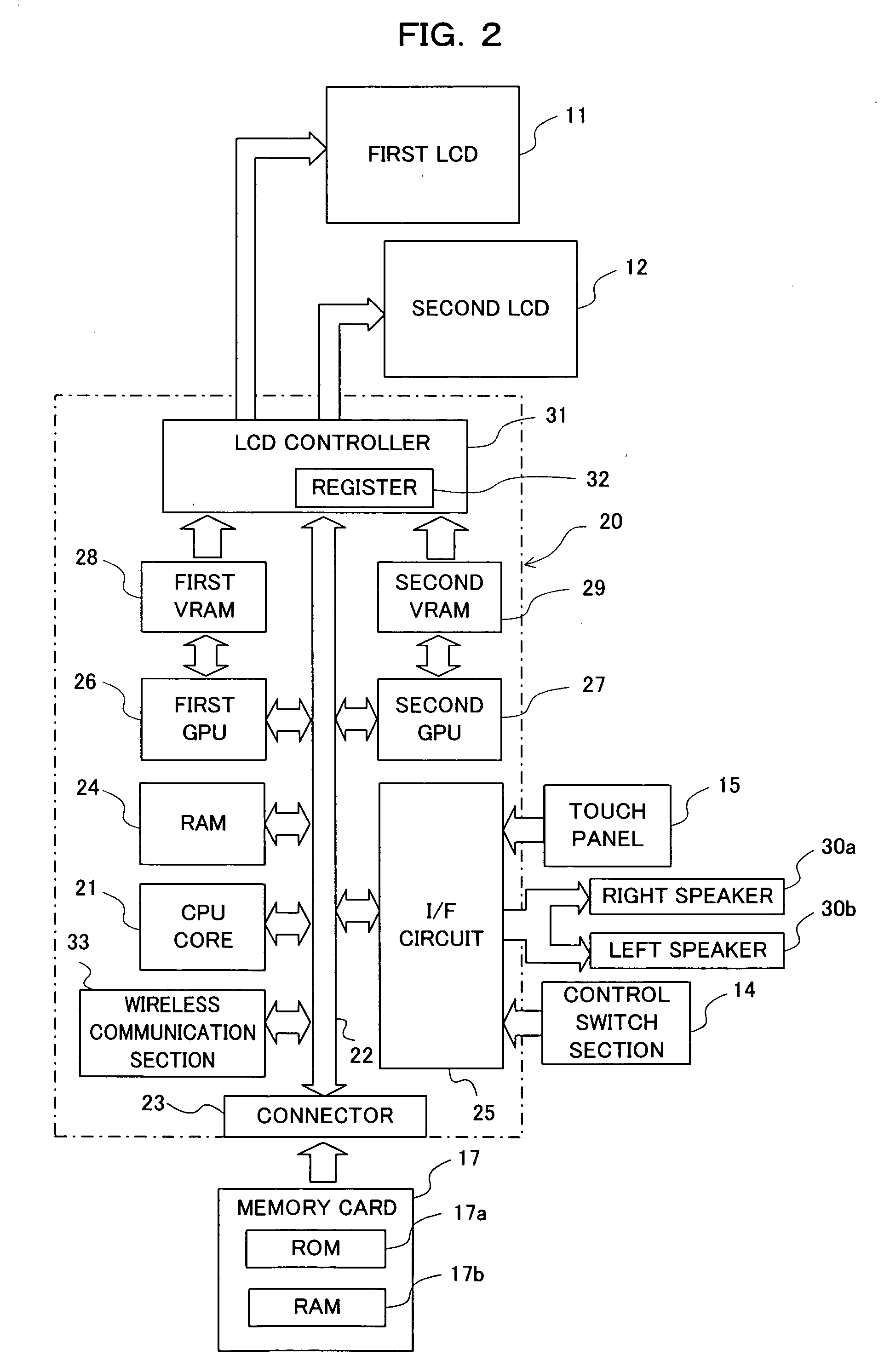
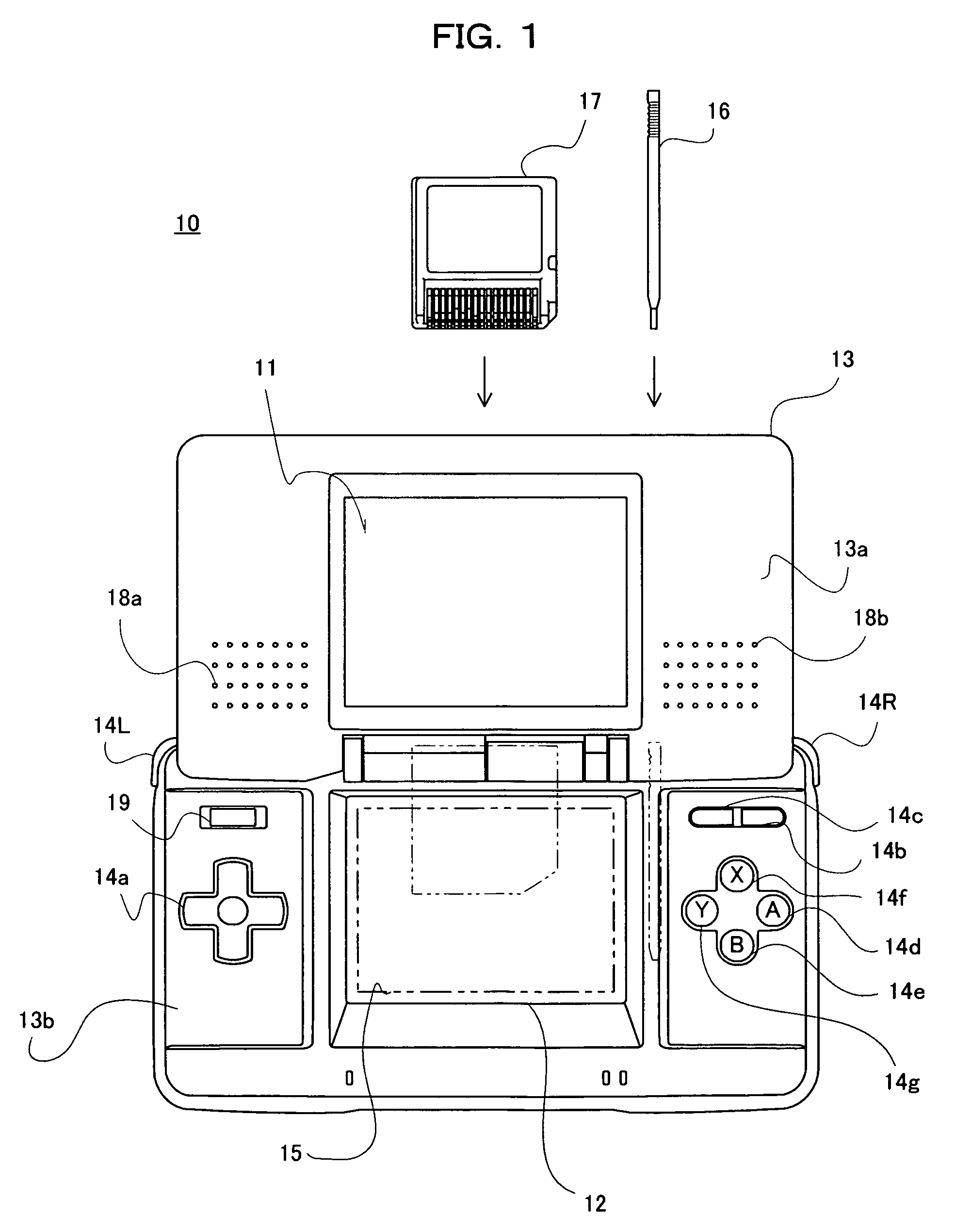
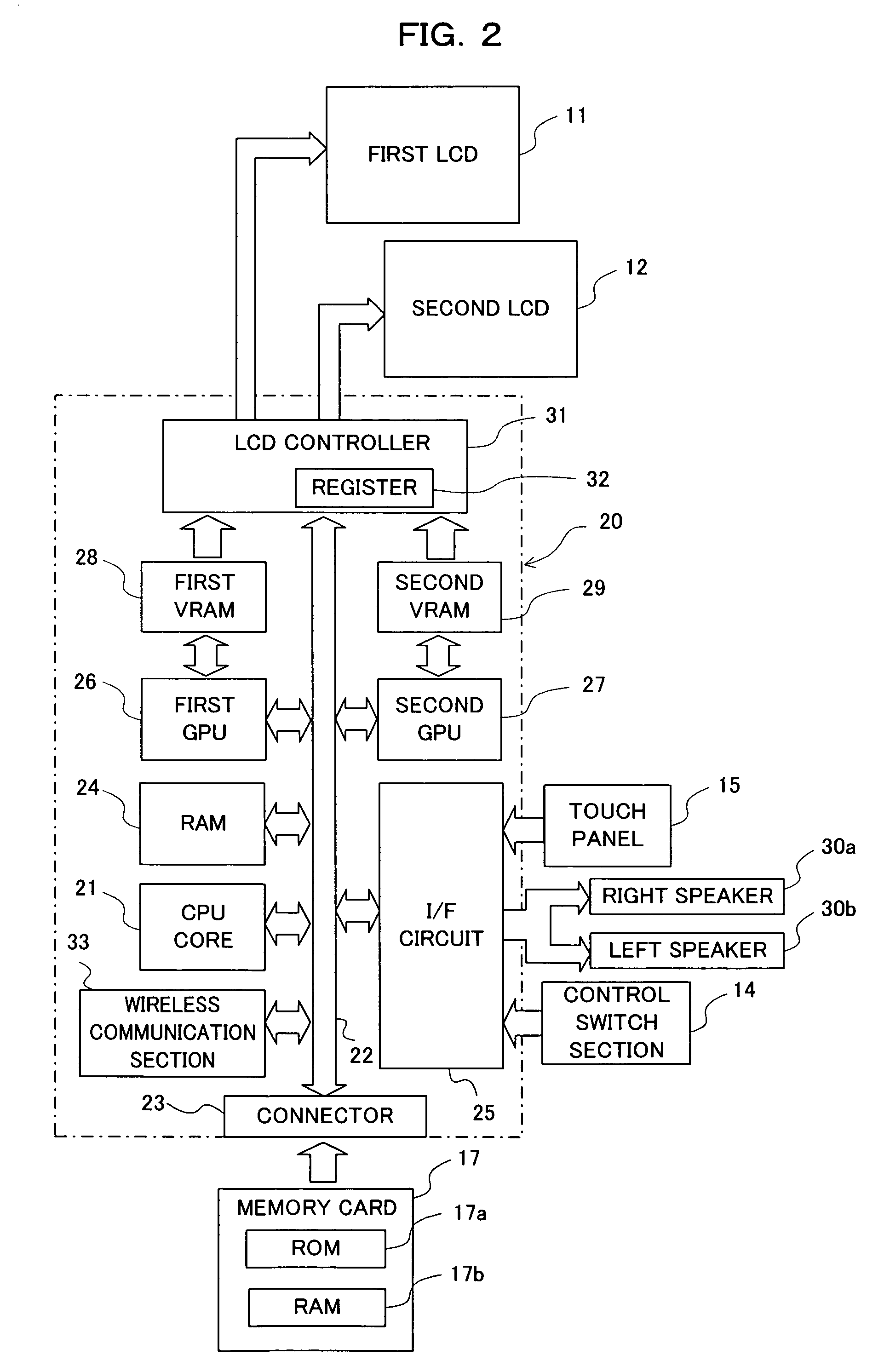
Video game program and video game device
ActiveUS20070076015A1Sure easyHigh playabilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnimationOrbital periodLiquid-crystal display
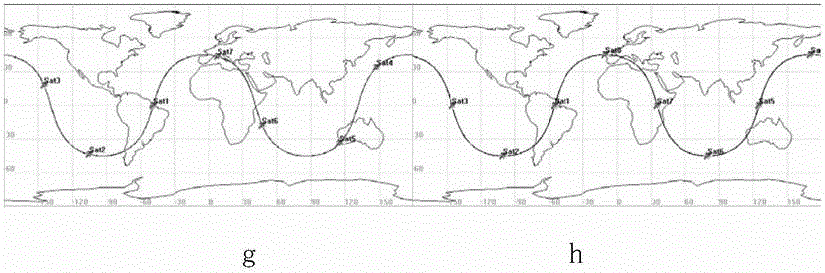
Displayed on a first LCD 11 are a “fire” planet 40a, a “wood” planet 40b; an “earth” planet 40c, a “wind” planet 40d and a “water” planet 40e,each traveling along an orbit by a unique orbital period. While an attribute symbol is traveling through an active zone that is associated with the attribute symbol, the status of the attribute represented by the attribute symbol is active. An attribute being active affects the space attribute, which is the attribute of a particular space in the game world. The space attribute affects the ability parameters of characters of the same attribute. Thus, it is possible to enrich the strategic aspect of a video game using characters' attributes.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
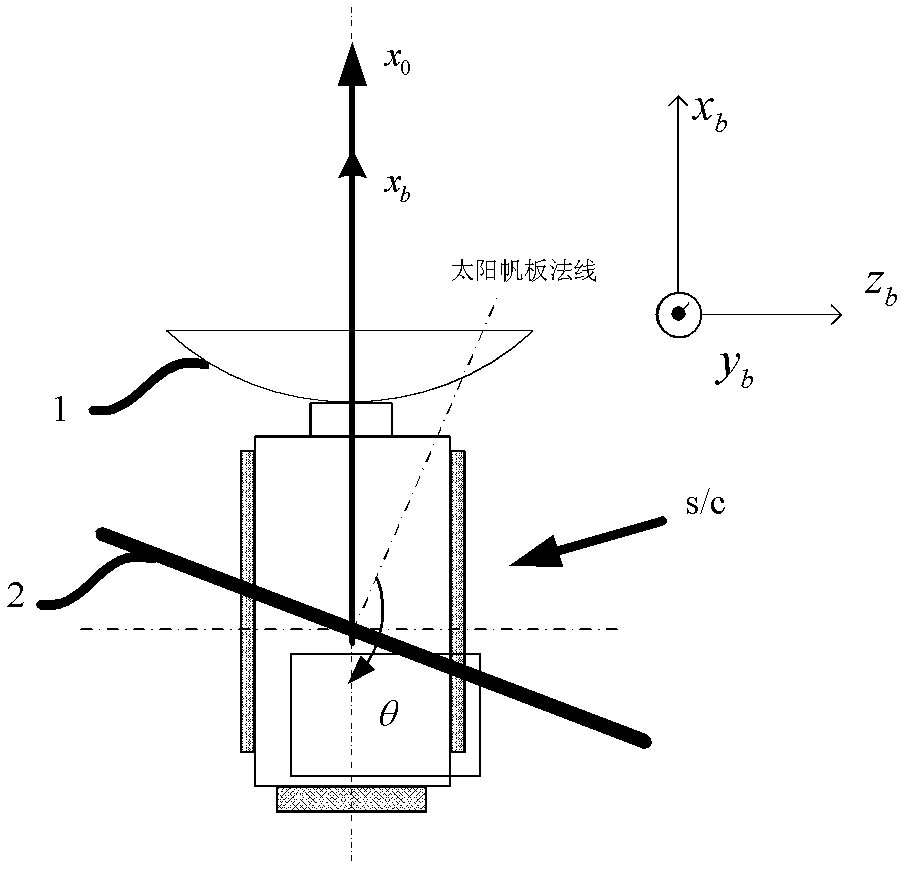
Halo orbit detector structure of sun-earth system and attitude directing thereof
ActiveCN102431659AOvercomes the need for more moving partsLong-term orientationSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital periodEngineering
The invention discloses a halo orbit detector structure of a sun-earth system and an attitude directing thereof, belonging to the design field of spacecrafts. A digital antenna is fixedly arranged on the +xb surface of a detector body; a shaft of the digital antenna is along the xb shaft direction; solar arrays are fixedly arranged on the + / -yb surface of the detector, the axial line is vertical to the + / -yb surface of the detector body, and the included angle between the normal and the -xb shaft is theta which is the installation angle of the solar array and is calculated by average halo orbit information. The xb shaft of the detector body is directional to the ground during the running time of the detector. The normal of the solar array directs to the sun, after the theta is selected, the solar incident angle of the solar array changes within a certain range and is 90 degrees on average in the orbit cycle. The halo orbit detector structure has the advantages that the long-term direction of the digital antenna to the ground is realized by means of one fixed digital antenna and one pair of fixed solar arrays, the solar arrays are directional to the sun for a long term through the digital antenna with low digital code rate, moving parts of the detector are few, the controllability and reliability of the detector are greatly improved, and the control difficulty is reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for fixing narrow lane ambiguity of Beidou ground based augmentation system base station
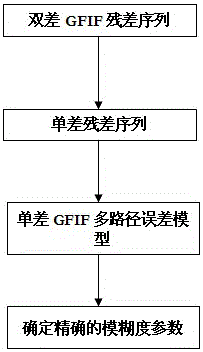
The invention discloses a method for fixing narrow lane ambiguity of the Beidou ground based augmentation system base station. According to the method, Beidou tri-frequency observed quantity is employed; fixing ambiguity of ultra-wide lane and wide lane in succession; establishing a narrow lane ambiguity multi-path error model; according to the repeatability of navigational satellite orbital period, performing multi-path error model correction to the narrow lane ambiguity sequence of the day to quickly fixing the narrow lane ambiguity, and to quickly obtain high-precision positioning results at centimeter-level.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Accompanying initialization control method based on relative motion characteristic quantities among space vehicles
InactiveCN102991728AGuaranteed control effectAvoid billingSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital periodRelative motion
The invention discloses a method for accompanying initialization control according to relative motion characteristic quantities behind near-circular orbit space vehicles. The method comprises an orbit period calculating module, a relative motion characteristic quantity calculating module, an orbit control strategy module and a thruster startup / shutdown control module. The control method is stored in a data processing unit of a tracking space vehicle and controls the tracking space vehicle to change from an approaching state to a long-term and stable accompanying state in the rear region of a target space vehicle by the aid of a relative tracking device, an inertial navigation system (INS) / global positioning system (GPS) combined navigation device and a thruster which are installed on the tracking space vehicle. The control method has the advantages of being concise in data processing process, small in calculation amount and good in control effect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Main and auxiliary satellite distributed SAR detection integrated imaging satellite system
InactiveCN109164448AImprove relevanceHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputOrbital period
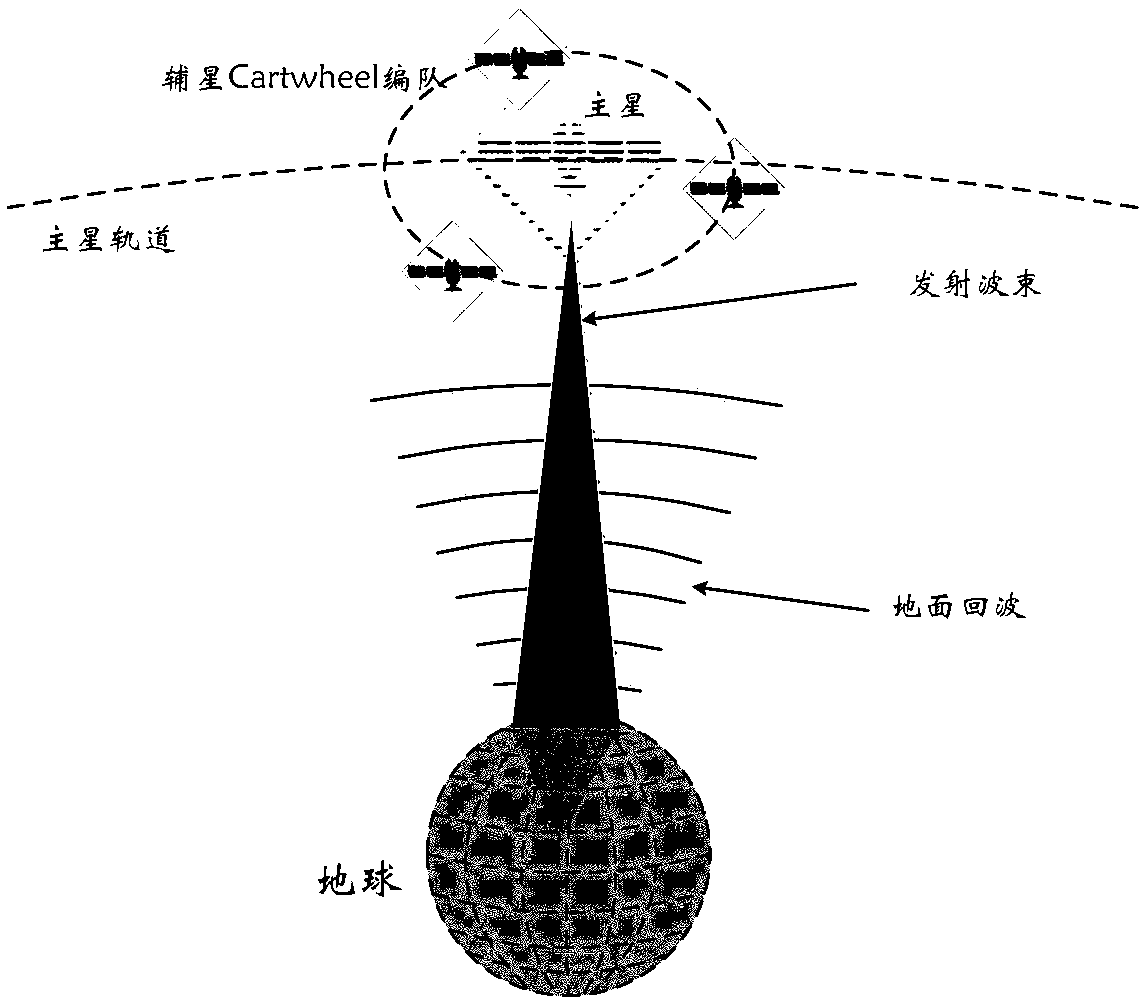
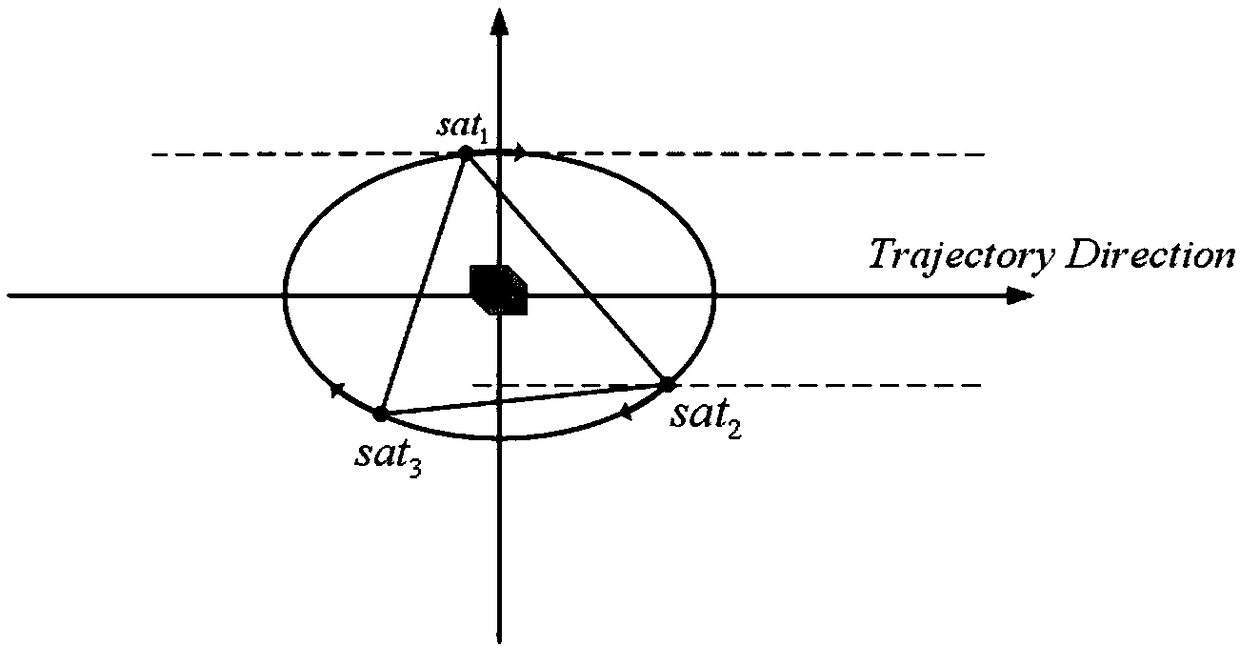
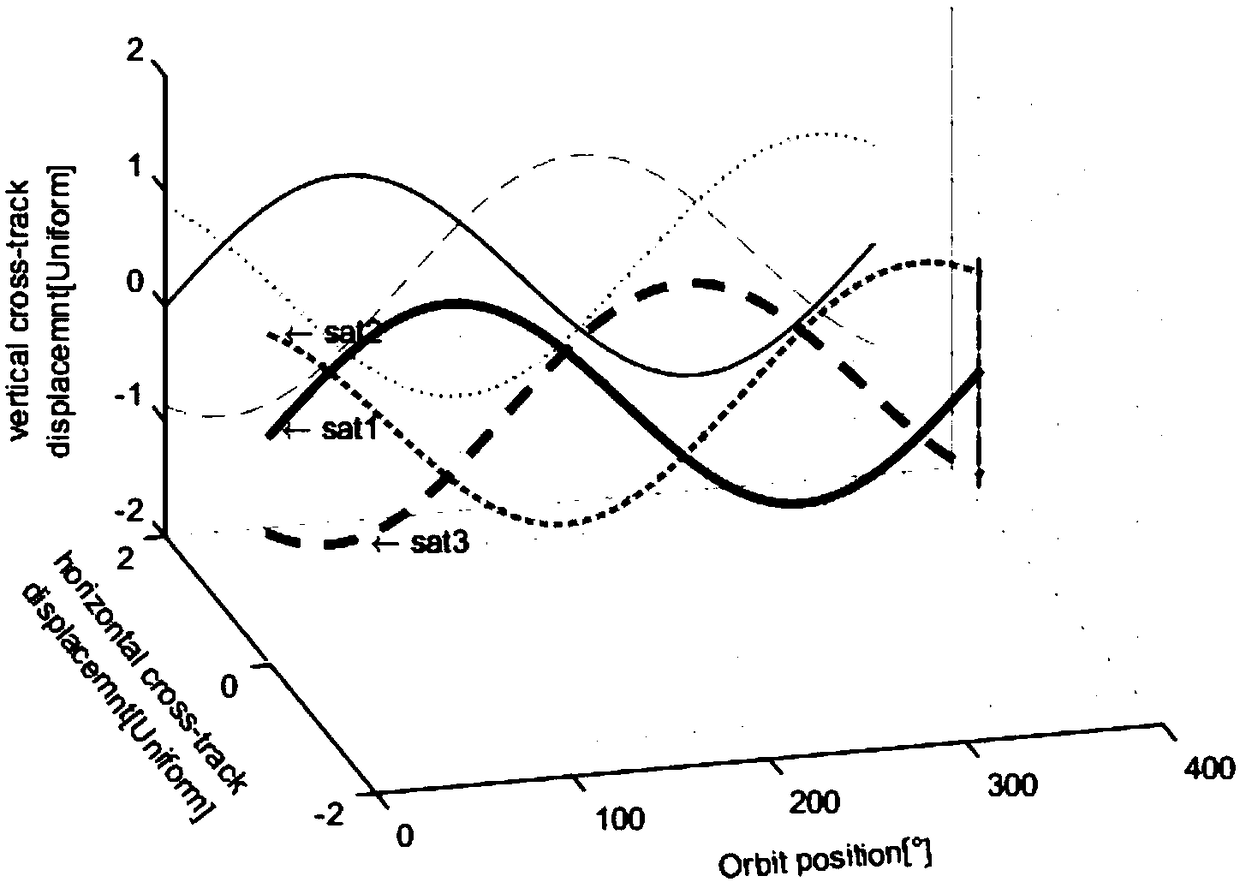
The invention discloses a main and auxiliary satellite distributed SAR detection integrated imaging satellite system. The invention can be used to realize high-resolution SAR imaging, high-precision interferometric SAR height measurement and three-dimensional tomographic SAR imaging. The main and auxiliary satellite distributed SAR detection integrated imaging satellite system utilizes a one-output multi-input or multi-output multi-input work system, and provides 1+N observation data at the same time to strengthen the correlation of the data, so that the imaging data is acquired more efficientand effective; meanwhile, by locating the main satellites at the center, and making the auxiliary satellites fly along with a configured co-orbital plane of the Carwheel wheel trajectory, short baselines that satisfy the optimal vertical effective baseline requirements and are formed between the main and auxiliary satellites and long baselines that are formed between the auxiliary satellites andcan guide the short baselines to perform relevant interference processing exist at any time throughout the entire orbital period, which improves the system efficiency and the interferometric height measurement precision; and the wheel trajectory of the auxiliary satellites changes in the orbit by the orbit changing technique. Therefore, the main and auxiliary satellite distributed SAR detection integrated imaging satellite system has more compact configuration, and forms a spatial virtual large aperture, which is advantageous for using the sparse aperture algorithm for imaging of higher resolution.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Distributed SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) configuration with primary component in center and secondary components in cartwheel formation
InactiveCN109031297AOptimal Interferometric Signal ProcessingMeet the needs of surveying and drawingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOrbital periodSecondary component
The invention discloses a distributed SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) configuration with a primary component in the center and secondary components in cartwheel formation. With the distributed SAR configuration, stable vertical effective baselines can be formed, a long vertical effective baseline and a short vertical effective baseline exist at any moment in one orbital period, the interferometricprecision can be effectively improved and the energy consumption is low. The distributed SAR configuration comprises one primary component and multiple secondary components, wherein the primary component and the secondary components are located on the same orbital plane; the secondary components are uniformly distributed on a cartwheel elliptical orbit with the primary component as the center andfly around the primary component along the cartwheel elliptical orbit; under the configuration, the long vertical effective baseline formed by two secondary components and the optimal short vertical effective baseline formed by the primary component and one secondary component exist at any moment of the running period of the whole orbit, thus the optimal interference signal treatment can be performed by using the long and short baselines, a high-precision DEM (Dynamic Effect Model) of a surveying area is efficiently obtained in high quality, the relative height accuracy can reach 0.5 m and canmeet the surveying and drawing requirement of the proportional scale of 1:5000.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Satellite entry-exit independent telemetry processing control method
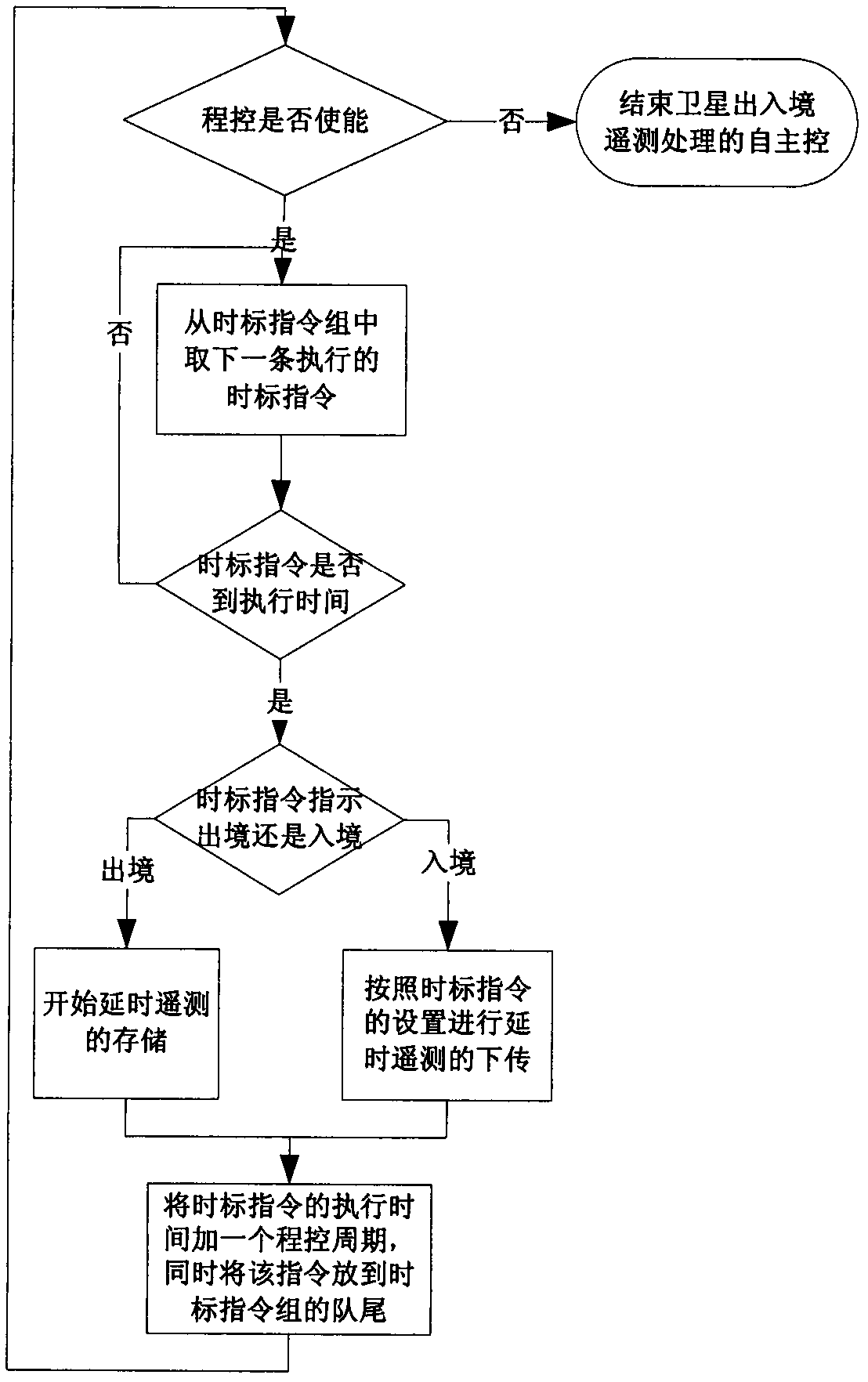
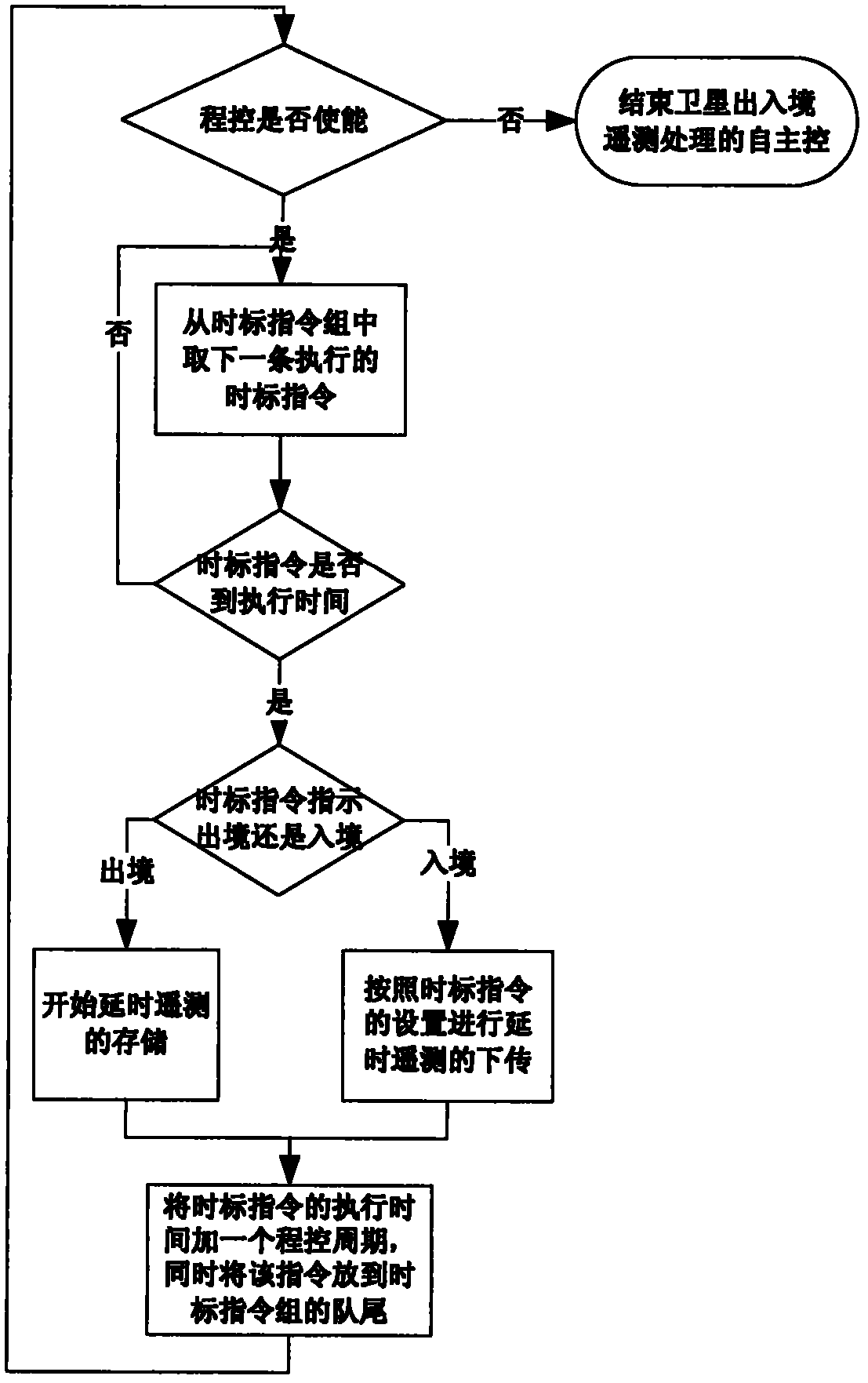
InactiveCN102436394AAutomated entry and exit managementAutomated Telemetry ManagementMultiprogramming arrangementsOrbital periodTime mark
A satellite entry-exit independent telemetry processing control method sets a time mark instruction group for each satellite mission. Each time mark instruction group is composed of time mark instructions with time marks, and the execution time of the time mark instructions is the time indicated by corresponding time marks. A program control cycle is set according to a satellite orbit cycle, timemark instruction groups required by one program control cycle are injected on the ground in one time, a satellite retrieves corresponding time mark instruction groups according to the current executing mission, then corresponding instructions in the time mark instruction groups are executed according to the current satellite time, and all the time mark instructions are executed sequentially according to the time marks. After one instruction is completed, the instruction is automatically arranged at the rears of the time mark instruction groups, and one program control cycle is added on an original execution time so as to serve as the next execution time. If overtime occurs in the time mark instruction execution process, the instruction is executed at once or given up. The method can achieve satellite entry-exit independent telemetry management.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Synchronous orbit electric propulsion position maintenance and angular momentum unloading joint control method
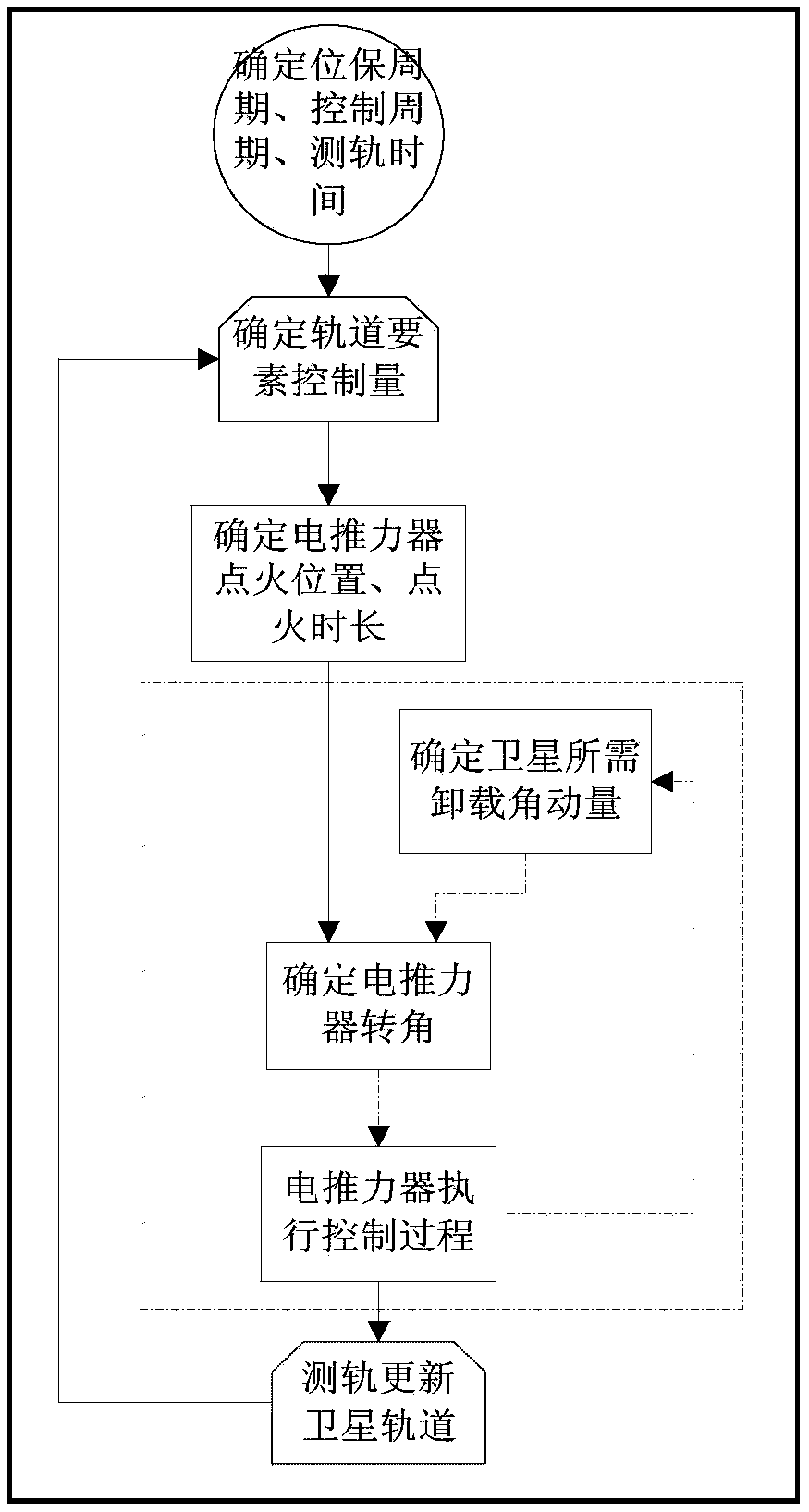
ActiveCN105373133AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce consumptionAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsOrbital periodElectricity
The invention relates to a synchronous orbit electric propulsion position maintenance and angular momentum unloading joint control method comprising the steps that a position maintenance cycle Ts, a control cycle Tc and orbit measurement time Tm are determined; the control cycle Tc is total time including completion of one time of the ignition process of all thrusters respectively; the orbit measurement time Tm is obtained in a way that time required by orbit measurement is rounded up to an integer of integer orbit cycles; one position maintenance cycle Ts includes one orbit measurement process Tm and multiple control cycles Tc: orbit element control variables, including inclination angle control variable vectors (deltaix, deltaiy), eccentricity control variable vectors (deltaex, deltaey) and a flat longitude drift rate control variable deltaD, of each control cycle are calculated before starting of each position maintenance cycle Ts; the electric thruster ignition parameters of each control cycle are determined, and the ignition parameters include ignition duration and an ignition position; and an electric thruster rotating angle is determined according to the electric thruster ignition parameters and angular momentum unloading quantity before starting of each control cycle Tc.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
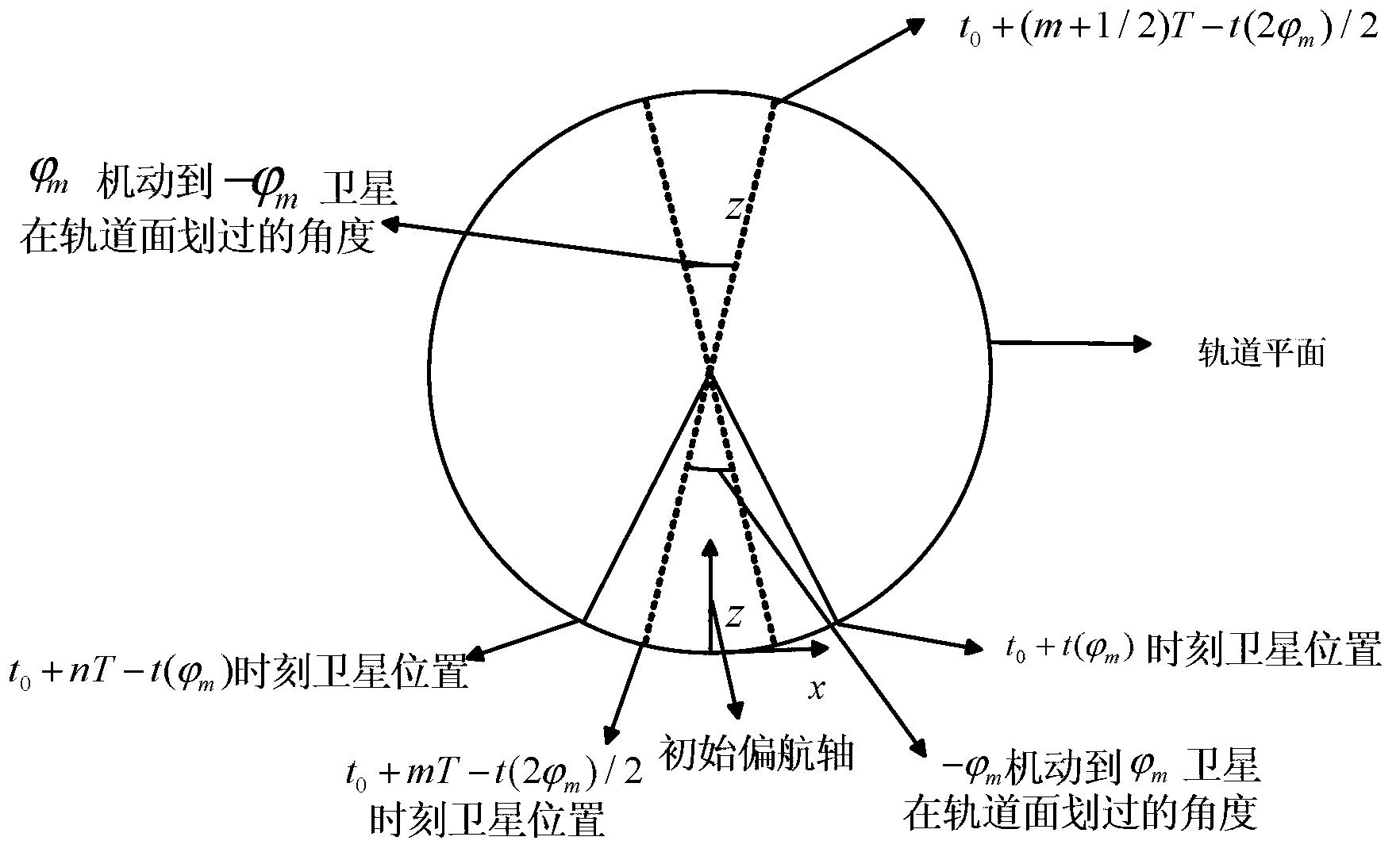
Method of using satellite rolling-axis rapid attitude manoeuvre to unload angular momentum of rolling axis and yawing axis
The invention provides a method of using satellite rolling-axis rapid attitude manoeuvre to unload the angular momentum of a rolling axis and a yawing axis, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft attitude control. The method resolves the problems that at present, an unloading device needs to be additionally installed on a satellite to unload the angular momentum absorbed by momentum exchange actuating mechanisms of the satellite, and therefore manufacturing cost of the satellite is increased, and the size and the weight of the satellite are increased. A body system and an inertial coordinate system of the satellite are defined, and an initial unloading moment is confirmed; and unloading is conducted by means of confirmation of the gravity gradient force moment borne by the satellite, accumulated angular momentum vectors of the gravity gradient force moment inside each orbital period, the angular momentum, needing to be unloaded, of all the momentum exchange actuating mechanisms on the rolling axis, the angular momentum, needing to be unloaded, of all the momentum exchange actuating mechanisms on the yawing axis, the number of turns of unloaded orbits of the satellite, the maneuvering angle in a satellite unloading process, and time used by the satellite rolling-axis maneuvering angle. The method can be widely applied to accumulated angular momentum unloading requirements of the actuating mechanisms.
Owner:哈尔滨工大卫星技术有限公司
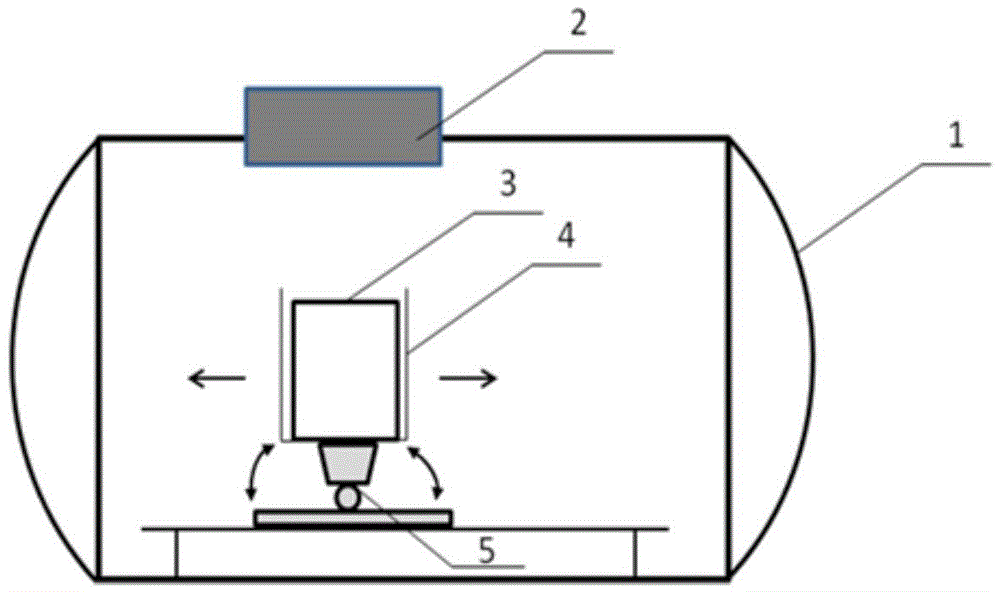
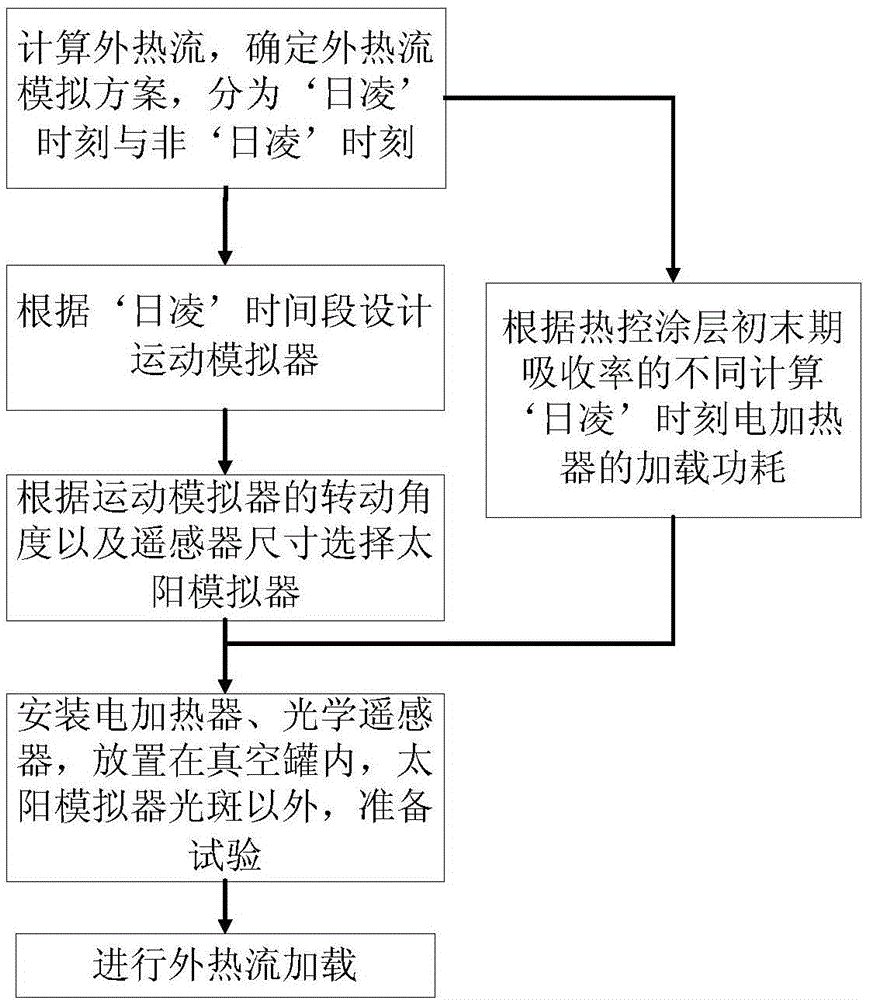
High-orbit optical remote sensor vacuum hot test external heat flow simulation method
ActiveCN104803012ADoes not affect surface stateAchieve absorptionCosmonautic condition simulationsOrbital periodSolar absorptance
A high-orbit optical remote sensor vacuum hot test external heat flow simulation method comprises the steps of firstly determining solar radiation heat flow according to on-orbit solar absorptance of an optical remote sensor (3), secondarily arranging the optical remote sensor (3) in a vacuum environment simulation chamber (1), then determining a 'sun outage' time period by judging whether the solar radiation heat flow Q1 (t) absorbed by an optical system within a orbit period is 0 or not, determining the time period of the Q1 (t) unequal to 0 as the 'sun outage' time period, adopting a solar simulator (2) and electric heater combined simulation scheme to perform outer heat flow simulation, determining that the time period of the Q1 (t) equal to 0 is a 'non-sun outage' time period, and adopting an independent electric heater simulation scheme to perform outer heat flow simulation. The problem that an existing non-contact space optical remote sensor outer heat flow simulation method does not have a solar spectral energy spectrum characteristic and directionality is solved, energy distribution of solar spectrum of the remote sensor on orbit can be accurately simulated, simulation accuracy is high, and project realization is promoted.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
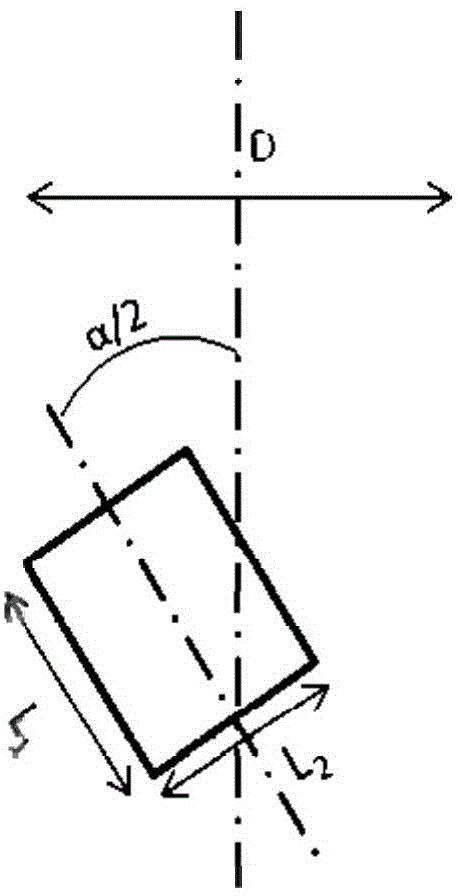
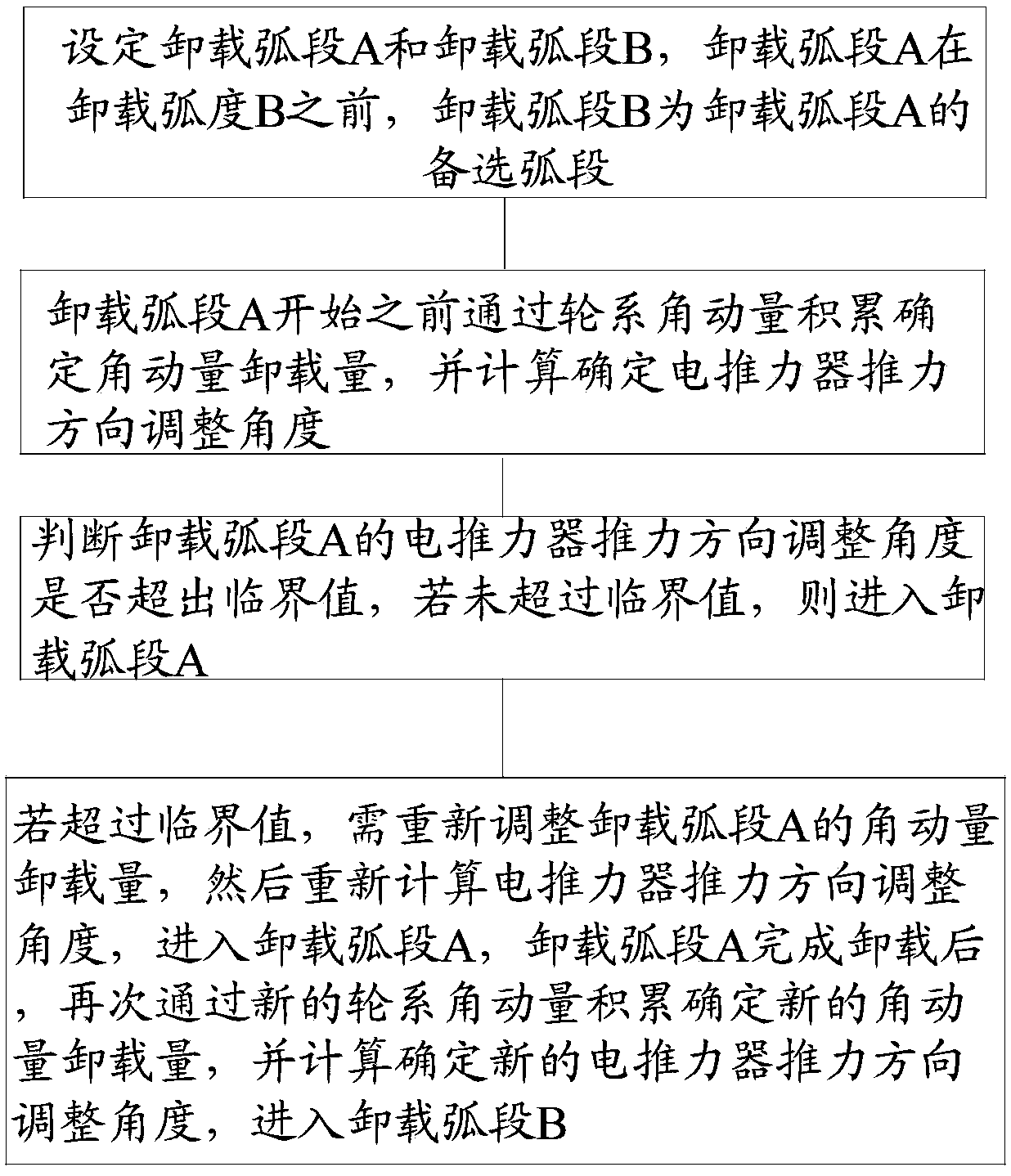
Angular momentum unloading method and system for orbit-changing process of all-electric propulsion satellite
ActiveCN108516106AAvoid losing controlRealize joint controlCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusNatural satelliteElectricity
The invention discloses an angular momentum unloading method for an orbit-changing process of an all-electric propulsion satellite. The method comprises the following steps: setting an unloading arc segment A and an unloading arc segment B before each orbit period starts; determining adjusting angles in thrust directions of electric thrusters by calculations; determining whether adjusting angles in the thrust directions of the electric thrusters of the unloading arc segment A exceed the critical value or not, and entering the unlading arc segment A if not; if so, adjusting angular momentum unloading amount of the unloading arc segment A again, then calculating adjusting angles in the thrust directions of the electric thrusters again, entering the unloading arc segment A, determining a newangular momentum unloading amount through new accumulation of wheel-angular momentum after the unloading arc segment A finishes unloading, calculating adjusting angles in thrust directions of new electric thrusters and entering the unloading arc segment B. The angular momentum unloading problem is resolved when the electric thrusters perform an orbit maneuvering control task during the orbit-changing process. Therefore, combined control over orbit maneuvering and angular momentum unloading is achieved by the all-electric propulsion satellite.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
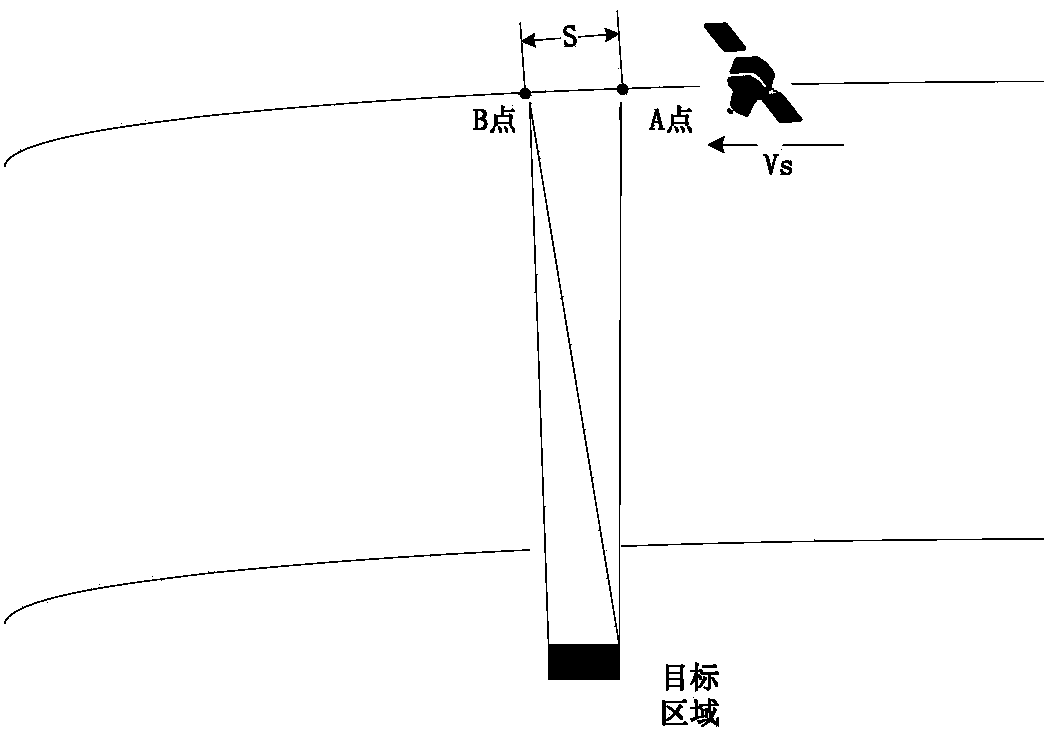
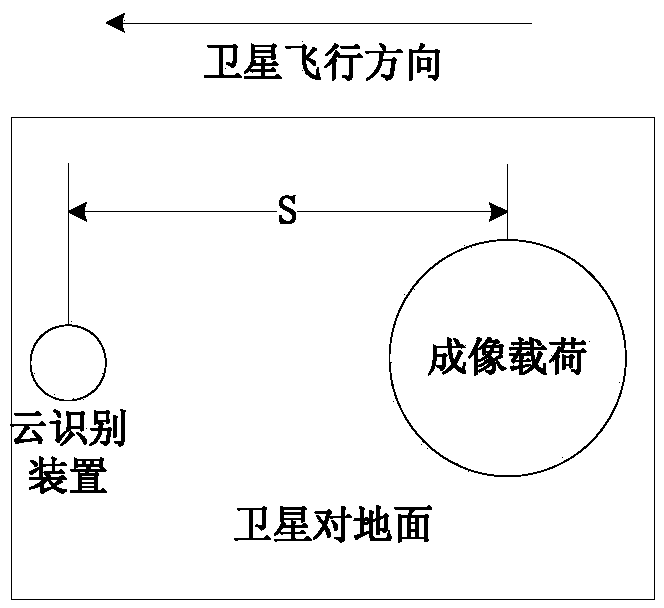
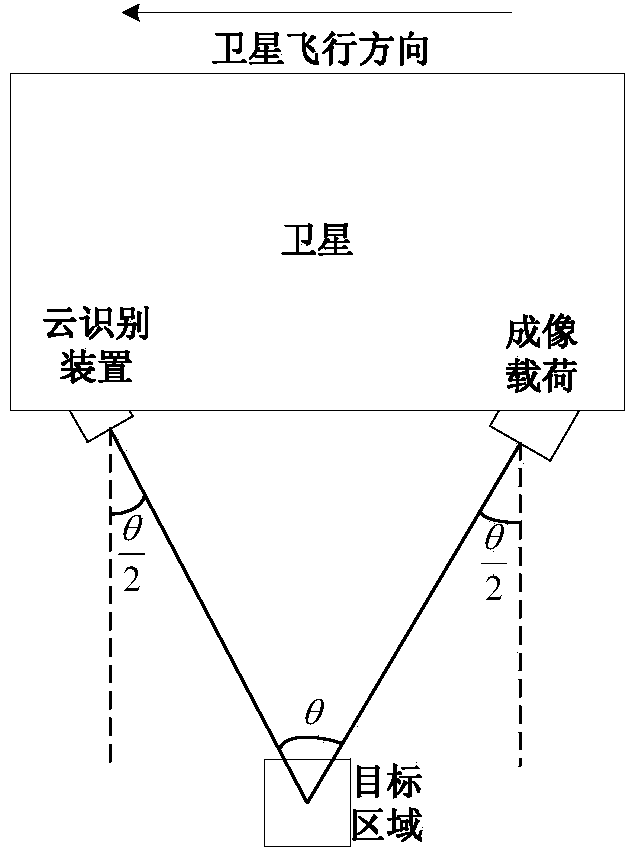
Satellite cloud-avoiding observation method
ActiveCN103954269ASaving data transmissionSave data transmission and other resourcesPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryElectromagnetic wave reradiationOrbital periodFlight direction
The invention discloses a satellite cloud-avoiding observation method which comprises the following steps: (1) respectively mounting a cloud identification device and an imaging load on the ground of a satellite along the satellite flight direction, wherein the cloud identification device is in the front, and the imaging load is in the rear; (2) determining the observation starting and ending positions of the imaging load in an orbit period in the imaging process aiming at a target area according to the attitude maneuver capability of the satellite; (3) enabling the view field of the cloud identification device and the view field of the imaging load to point to the target area through attitude maneuver between the satellite observation starting and ending positions, imaging the target area through the cloud identification device, calculating a cloud coverage rate, and transmitting an imaging load imaging starting construction or imaging stopping instruction according to a relationship between a calculation result and a preset threshold value; (4) repeating the step (3) in each orbit period, and thus finishing imaging of the target area. According to the method, due to additional arrangement of the cloud identification device and reasonable layout of the imaging load, cloud gap finding and satellite cloud-avoiding imaging are realized.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
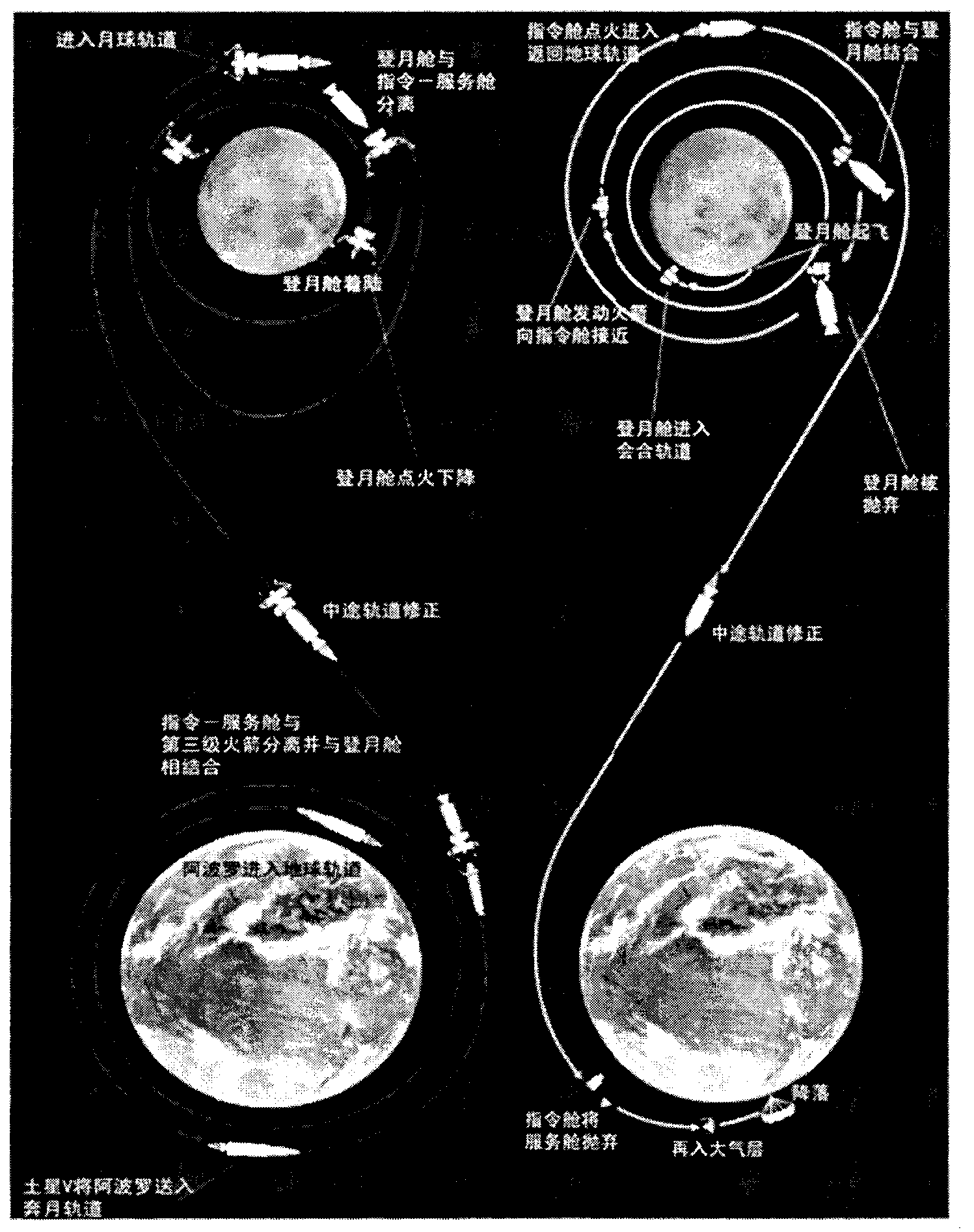
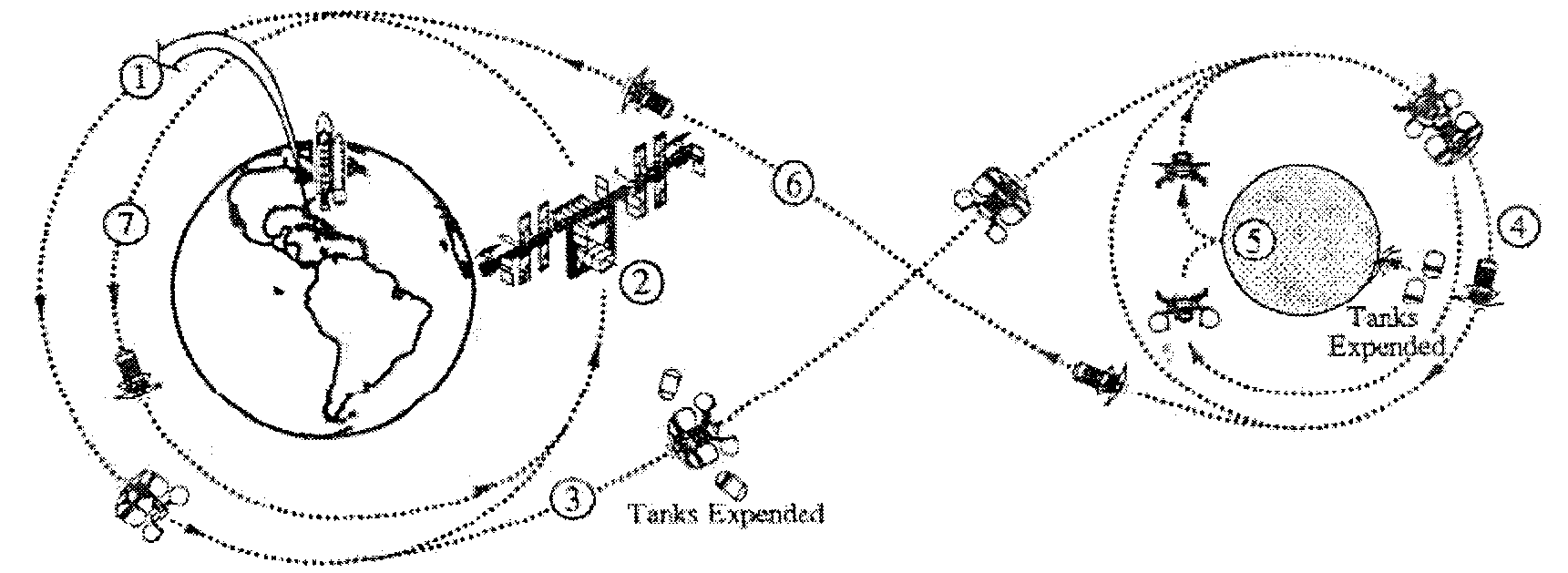
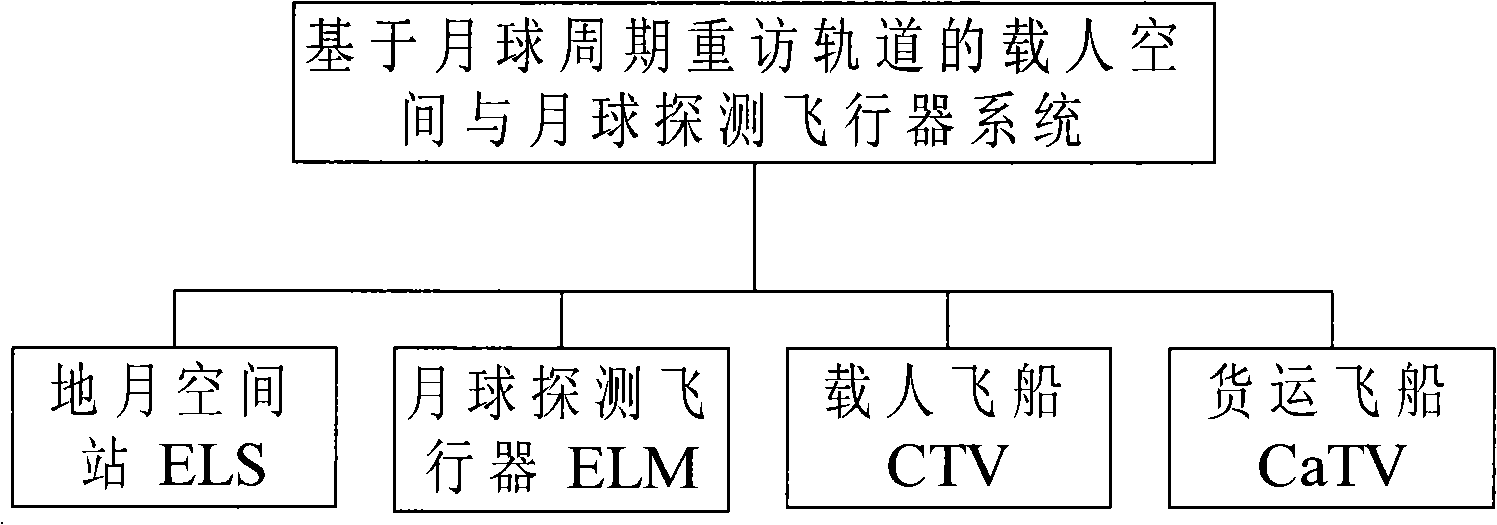
Manned space and lunar exploration spacecraft system based on lunar cycle revisiting orbit and exploration method
InactiveCN102730200AImprove exploration abilityFull of mission goalsArtificial satellitesOrbital periodControl system
The invention discloses a manned space and lunar exploration spacecraft system scheme based on a lunar cycle revisiting orbit and an exploration method. A spacecraft system comprises four spacecrafts which are an earth lunar spaceport (ELS), a lunar exploration module (LEM), a crew transfer vehicle (CTV) and a cargo transfer vehicle (CaTV). With the cooperation of an astronaut system, a carrier rocket system and an exploration and control system, earth lunar space and lunar manned exploration are realized. A relatively entire exploration process of manned space and lunar exploration mission cycle is that the ELS is launched to an earth lunar cycle revisiting orbit by a carrier rocket to become an earth lunar spaceport which surrounds the earth, periodically revisits the moon, and chronically and stably moves on a large oval orbit of which the cycle is half of the lunar orbit cycle; then the lunar exploration module, the crew transfer vehicle and the cargo transfer vehicle are orderly launched to a cycle revisiting orbit by the carrier rocket for rendezvous and docking with the earth lunar spaceport; then the lunar exploration module is separated from the earth lunar spaceport to execute lunar manned field exploration; and finally the lunar exploration module returns to the earth lunar spaceport after finishing the lunar mission, and the crew transfer vehicle is separated from the earth lunar spaceport and then returns to the earth.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
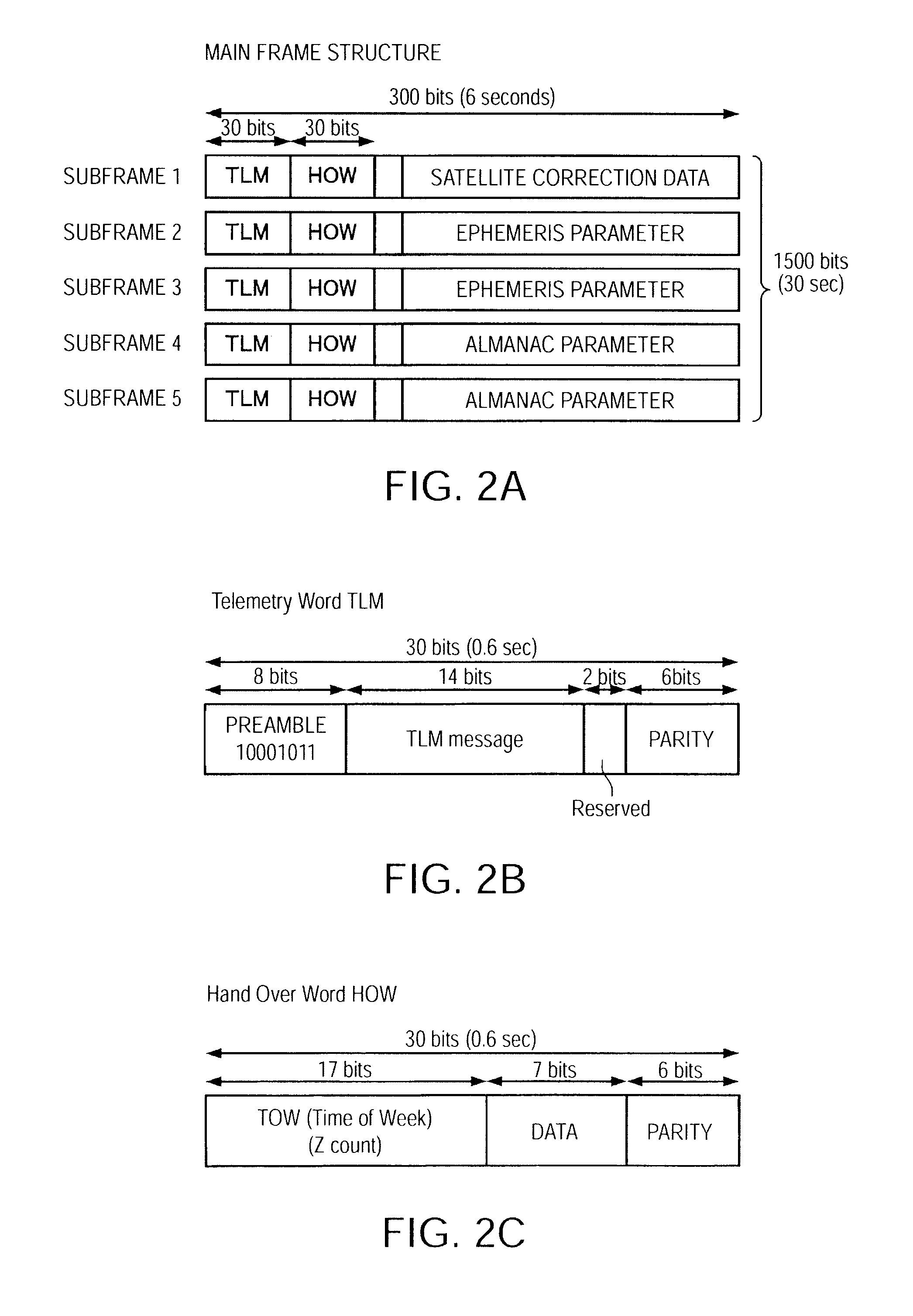
Satellite Signal Reception Device, Timekeeping Device, and Satellite Signal Reception Method
ActiveUS20100091614A1Reduce current consumptionReduce power consumptionMechanical clocksTime-pieces with integrated devicesOrbital periodSatellite
A satellite signal reception device according to an aspect of the invention comprises a reception operation unit that executes a reception operation process to receive a satellite signal transmitted from a positioning information satellite and generates positioning information from the satellite signal. The satellite signal has precise and coarse information orbit periods containing precise and coarse orbit information respectively for the positioning information satellite. The reception operation unit executes the reception operation process in the precise orbit information period, uses the coarse orbit information period as a suspended reception period, and pauses at least a part of the reception operation process in the suspended reception period.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Communication system, communication receiving device and communication terminal in the system
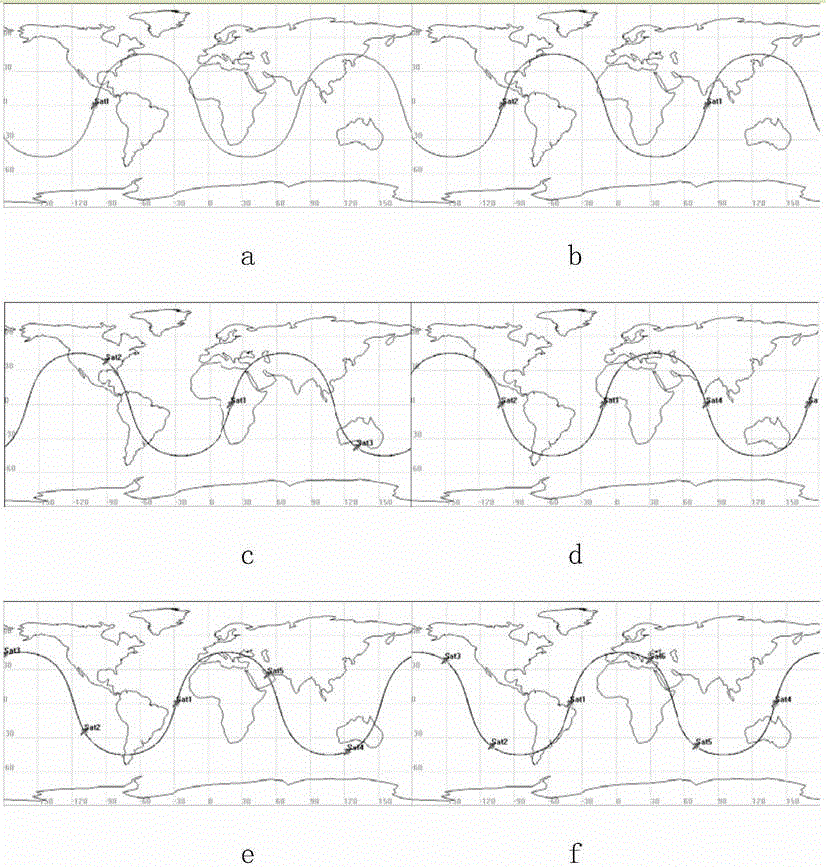
InactiveUS20050178918A1Easy to optimizeImproves the orbital elementsArtificial satellitesRadio transmissionOrbital periodCommunications system
A communication system having a plurality of artificial satellites each having a communication unit traveling on elliptical orbits with an orbital period of 24 hours. Arguments of perigee are set to values with a predetermined allowance in a setting process of the plurality of artificial satellites.
Owner:MAEDA TOSHIHIDE +7
Method for formation configuration of distributed satellites with synthetic aperture radars
InactiveCN101520511BApplicable interference processingStable baselineRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOrbital periodStart time
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
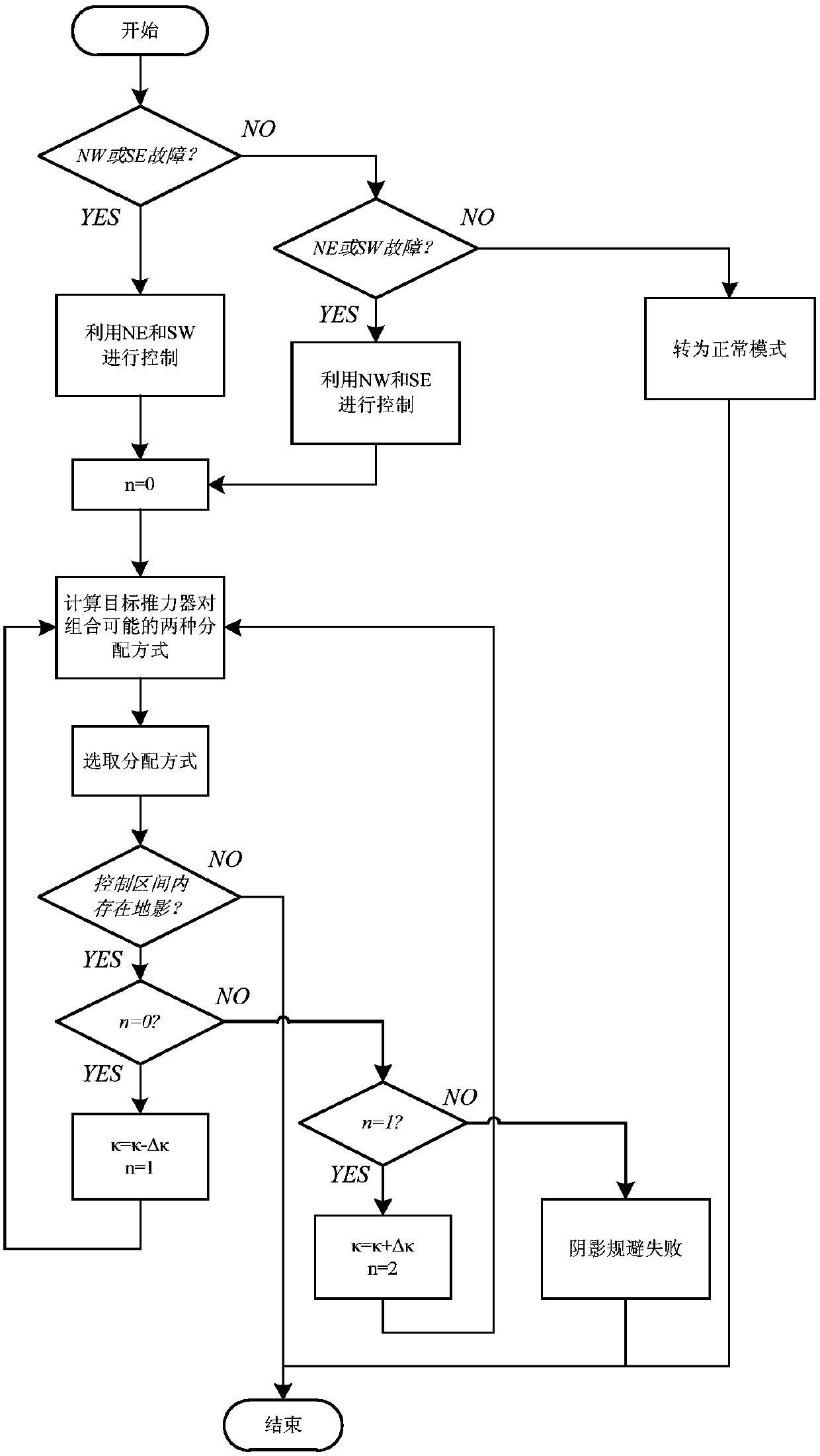
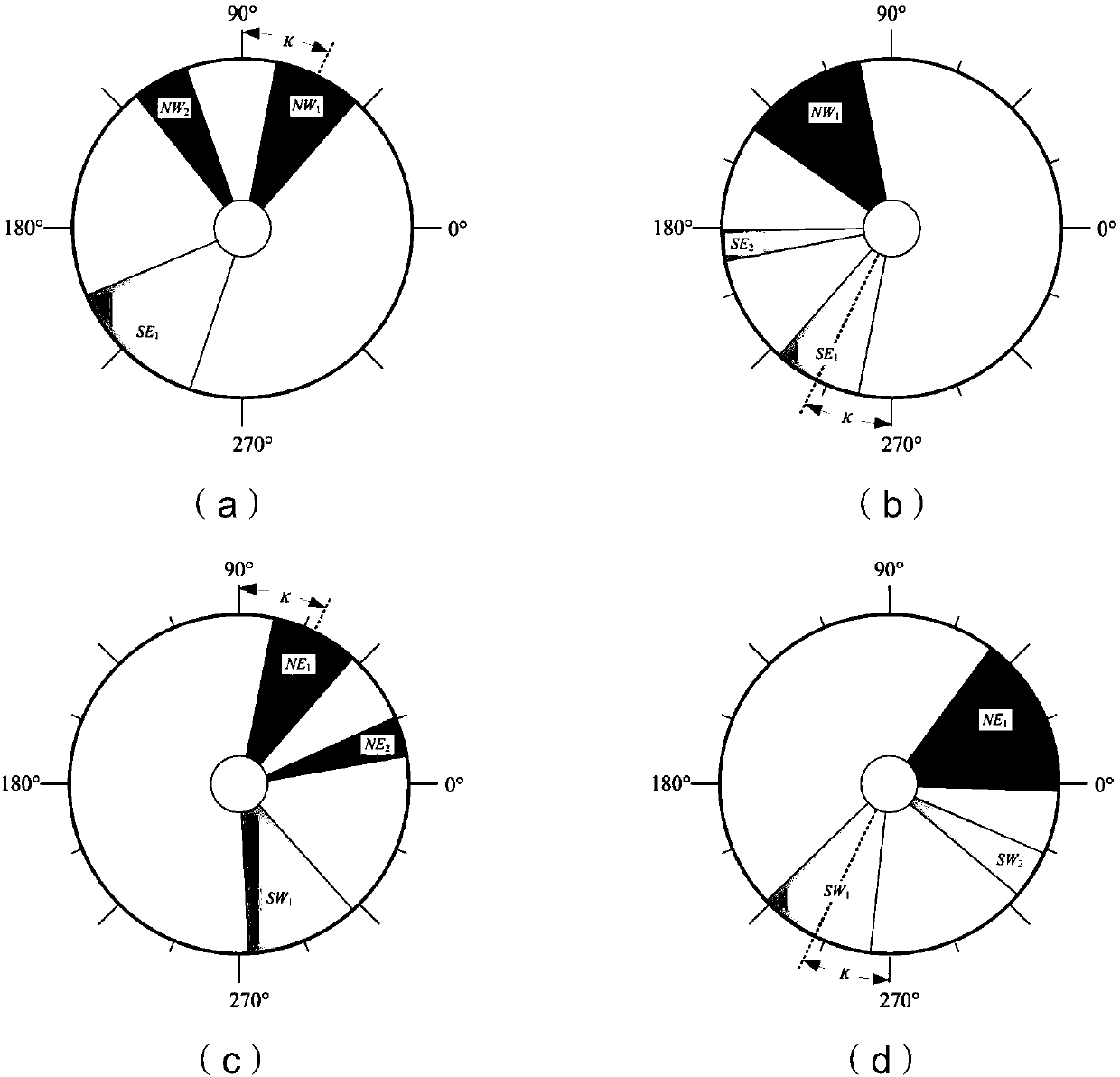
Method for optimum thrust distribution of position keeping of conical layout electric propulsion satellite in fault mode
ActiveCN107891997AReduce consumptionExtend your lifeCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusElectricityOrbital period
The invention provides a method for optimum thrust distribution of position keeping of a conical layout electric propulsion satellite in a fault mode. According to the method, an analytical method isadopted for conducting position keeping control distribution of electric thrusters in a conical layout fault mode; firstly, a pair of thrusters which have no faults and are used for position keeping control are selected according to a thruster with faults; secondly, two different distribution modes of the thruster pair are obtained and selected; finally, the startup time of the electric thrustersis changed to avoid a shadow zone. According to the method, the completely analytical mode is adopted, and the distribution purpose of the electric propulsion position keeping thrusters in the fault mode is achieved, so that the fuel consumption is optimized, the startup frequency of the thrusters within an orbital period is reduced at the same time, and therefore the effective thruster distribution method is provided for electric propulsion position keeping of the geostationary orbit satellite in the fault mode.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
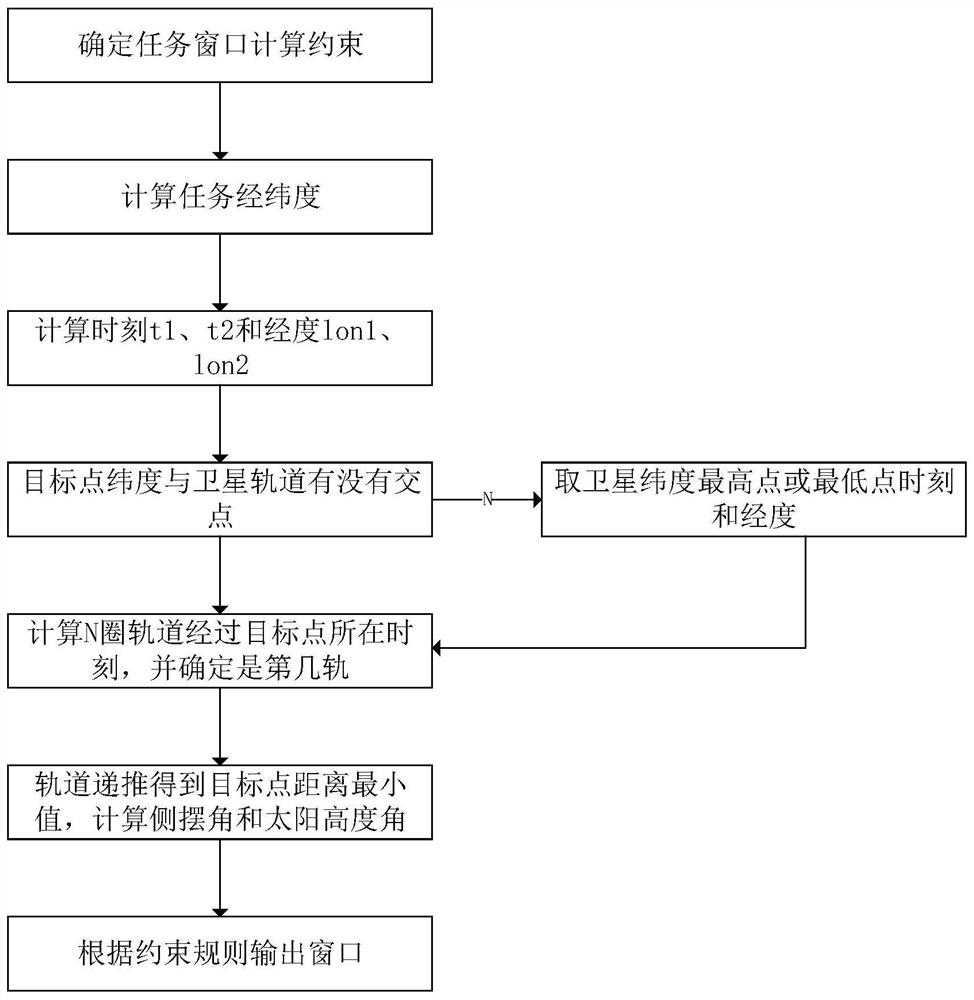
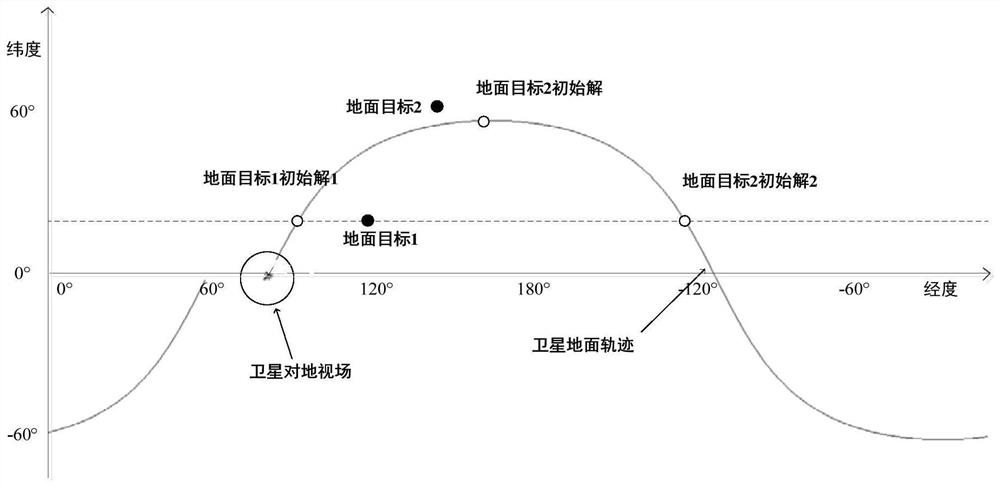
On-satellite rapid calculation method and system suitable for multiple time windows of ground detection tasks
PendingCN111949922AAccurate calculationRun fastGeological measurementsComplex mathematical operationsOrbital periodLongitude
The invention provides an on-satellite rapid calculation method and system suitable for multiple time windows of a ground detection task. The method comprises the steps that S1, determining task window calculation constraints ; S2, calculating coordinates of longitude and latitude of tasks under a J2000 system; S3, calculating a time parameter and a longitude parameter of the latitude where a first orbit passes through a target point after the set time of each satellite; S4, calculating the time when 2N satellites pass through the latitude where the target point is located within the set timeN circles of orbit periods, finding out a time point when the longitude difference between each orbit and the ground target point is small, and obtaining the orbit number information corresponding tothe vertex; S5, performing orbit recursion to obtain a minimum value point of the distance between each satellite and each target point, and calculating a side swing angle and a solar altitude angle.S6, outputting a window calculation result according to the constraint condition and the screening rule; and S7, obtaining on-satellite rapid calculation result information suitable for multiple timewindows of the ground detection task. The invention can be well applied to various satellites.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
In-orbit fuel consumption balancing method of formation satellite system
ActiveCN106681138AStrong engineering achievabilityIncrease the level of autonomyAdaptive controlOrbital periodHandoff control
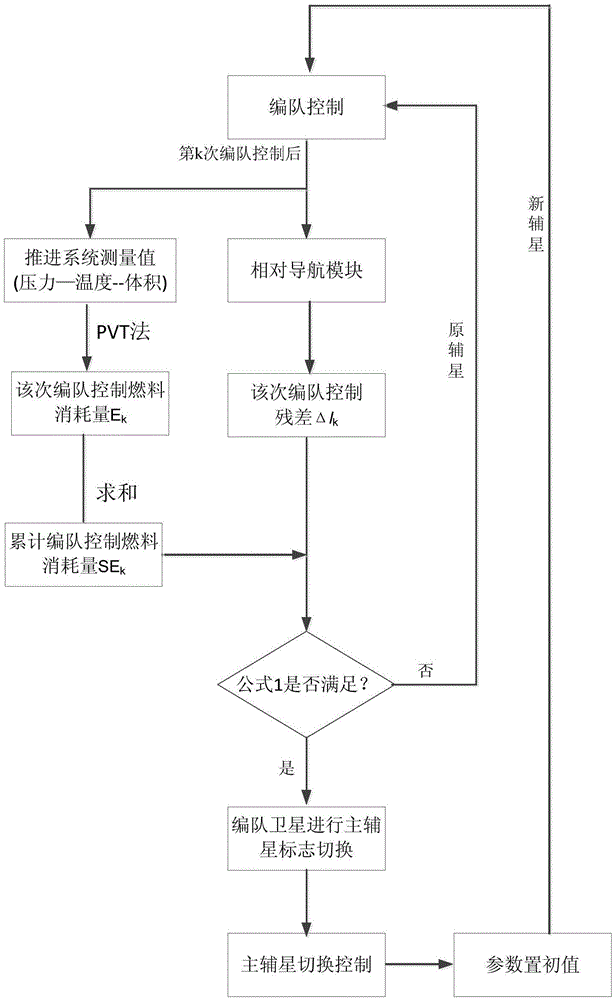
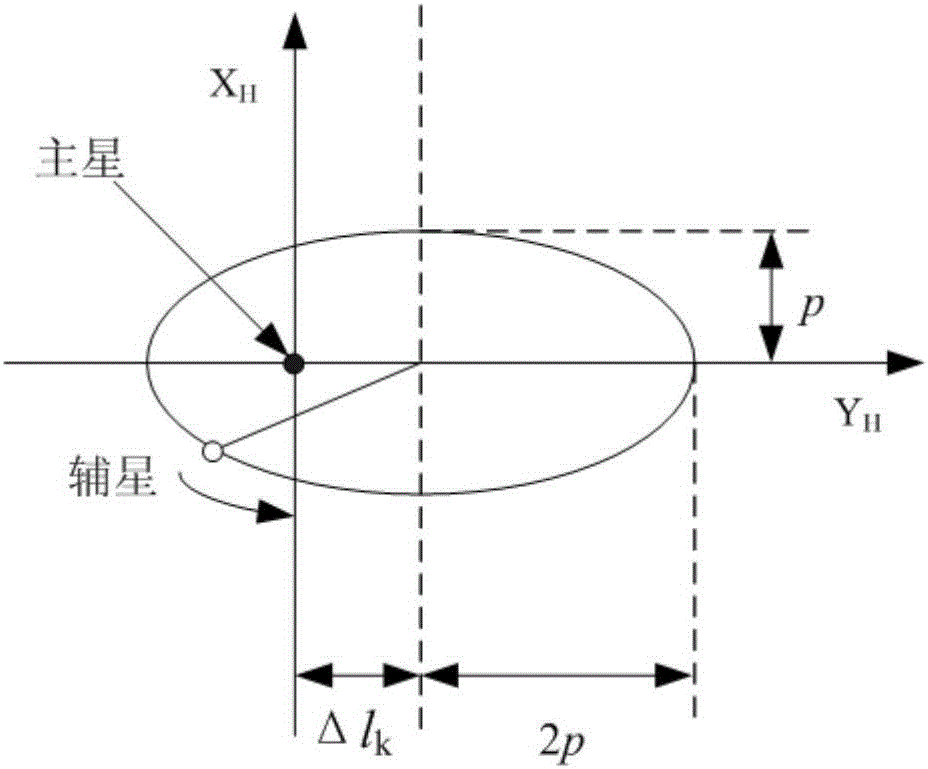
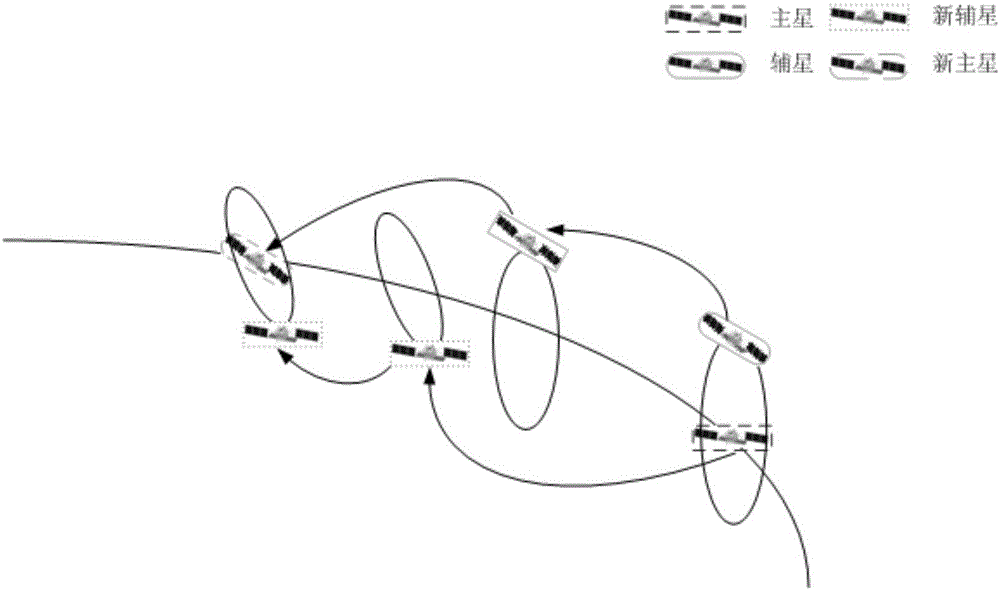
The invention relates to an in-orbit fuel consumption balancing method of a formation satellite system. The method comprises the following steps that 1) after kth formation control, the fuel consumption Ek of the formation control is calculated; 2) after the kth formation control, a formation control parameter [delta]lk of two satellite orbit periods is determined; 3) the sum SEk of cumulative fuel consumption of formation control and a residual error [delta]lk of present formation control are substituted into a formula SEk>=k1&&[delta]lk>=k2 for determination; and 4) if the formula is valid, marks of main and auxiliary satellites are switched autonomous on the satellites, main and auxiliary satellite switching control is carried out via a ground annotation instruction or on satellites autonomously so that a new main satellite operates in a reference orbit, parameters are set as initial values, a new auxiliary satellite executes a formation control task, and the steps 1) to 3) are repeated; or if the formula is invalid, the original auxiliary satellite continues to carry out formation control. The method is high in engineering realization performance, can be used to save fuels, requirements of formation satellite tasks are taken into consideration, and the autonomous level of the satellites can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Four-satellite Helix formation configuration capable of providing stable long and short baselines
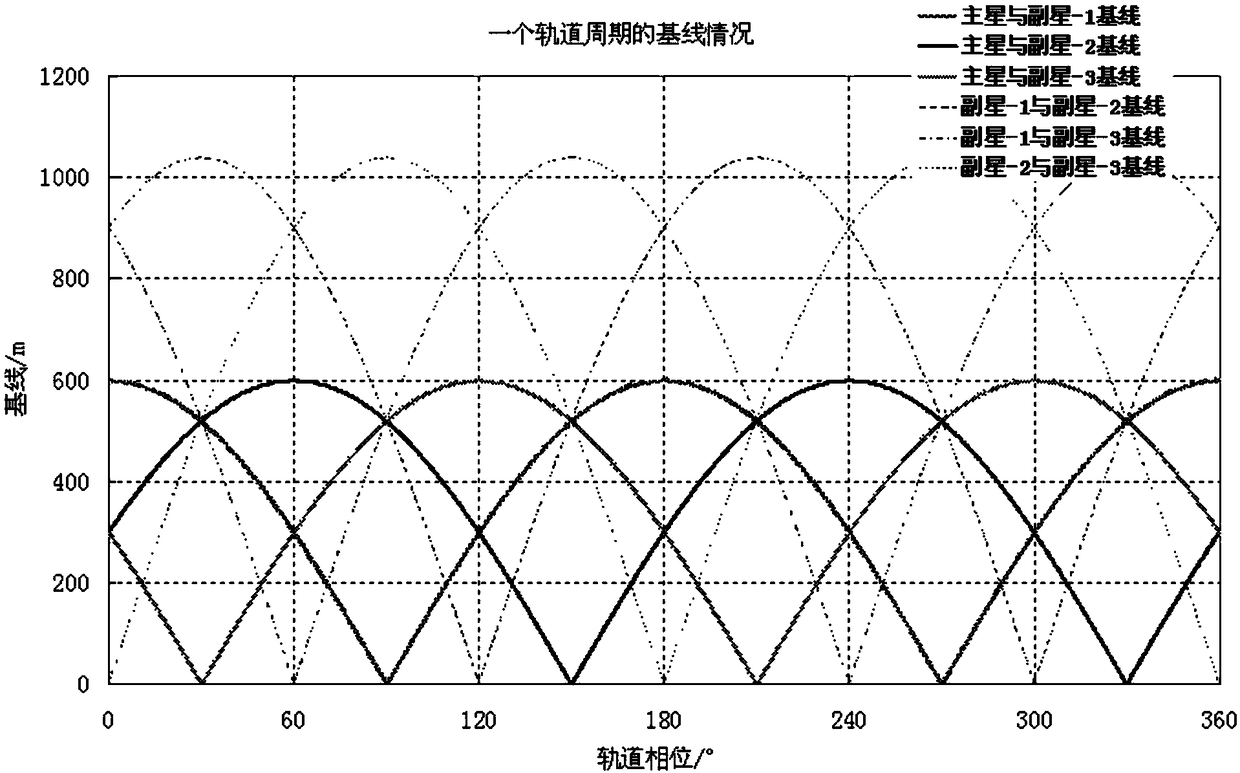
ActiveCN109085586ASatisfy the value range indexMeet the requirements of high-precision interferometric altimetryRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOrbital periodEngineering
The invention discloses a four-satellite Helix formation configuration capable of providing stable long and short baselines. By using the method provided by the invention, stable vertical effective long baselines and vertical effective short baselines can be provided in one track cycle, so that the high precision interference measurement can be realized using baselines combining the long baselinesand the short baselines. The configuration of the invention comprises 1 main satellite and three auxiliary satellites. A main satellite orbit and each auxiliary satellite orbit are respectively double helix tracks that satisfy the Helix configuration. According to the four-satellite Helix formation configuration capable of providing stable long and short baselines, at any moment in the formationflight process, the main satellite can form an optimal vertical effective baseline with one auxiliary satellite, so that a range indicator of optimal baseline values can be satisfied. An effective long baseline formed between two auxiliary satellites is present at any moment, and therefore, a stable set of effective long baselines and short baselines are always present at any moment in the whole track period, so that the high precision interference measurement can be realized using baselines combining the long baselines and the short baselines.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Orbit control method by utilizing interference accumulation angular momentum self balance
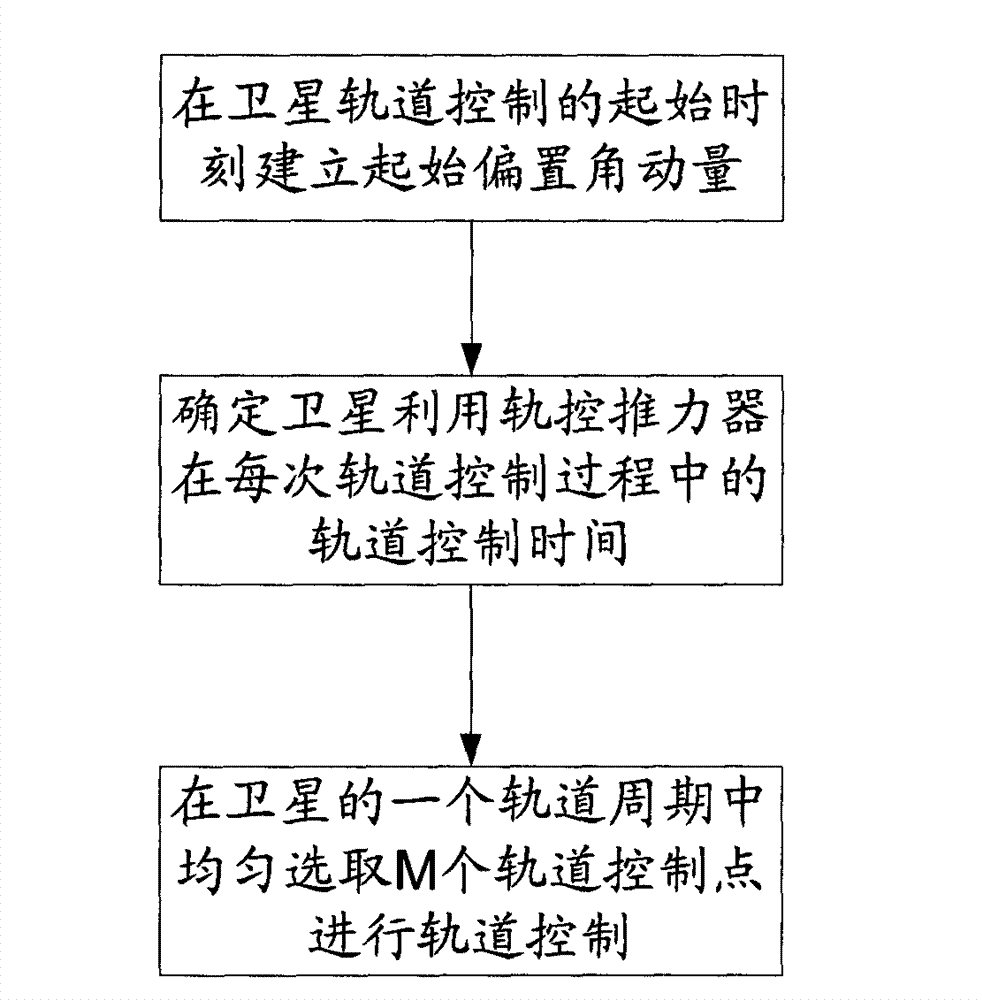
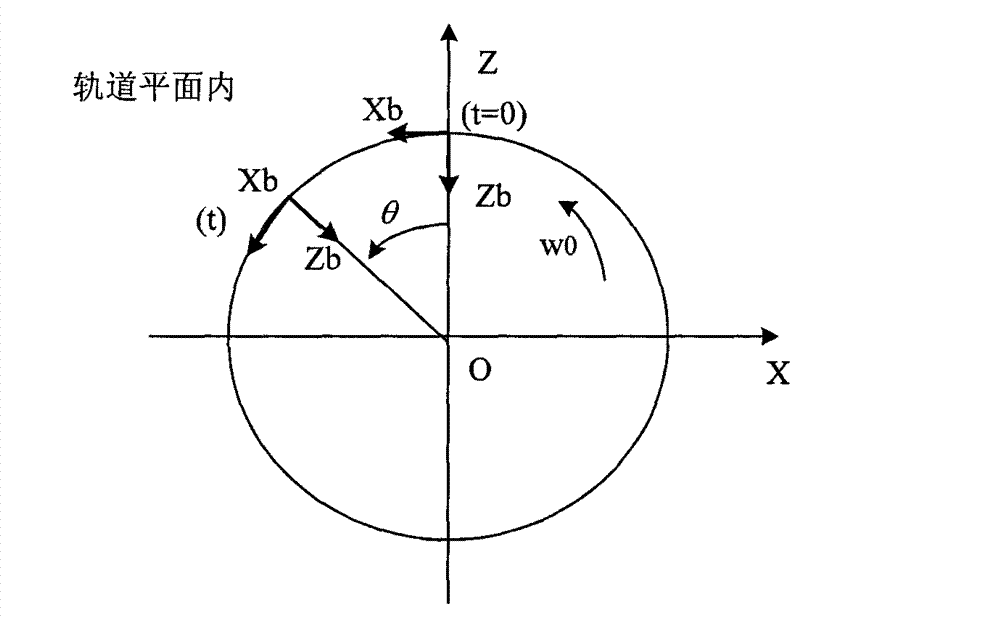
ActiveCN103076809AAchieving Disturbance Angular Momentum Self-balancingEasy to adjustPosition/course control in three dimensionsOrbital periodMomentum
The invention discloses an orbit control method by utilizing the interference accumulation angular momentum self balance. The method comprises the following steps that the starting offset angular momentum is built at the starting moment of the satellite orbit control; the orbit control time Tp of the satellite by utilizing an orbit control thruster in each orbit control process is determined; and in one orbit period of the satellite, M orbit control points are uniformly selected for carrying out orbit control. After the orbit control method is adopted, the goal that the interference accumulation angular momentum generated by utilizing the orbit control thruster in the orbit semi-major axis regulating process is used for controlling the satellite orbit is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
High-orbit zero-momentum satellite sailboard rotation fault judgment method based on angular momentum estimation
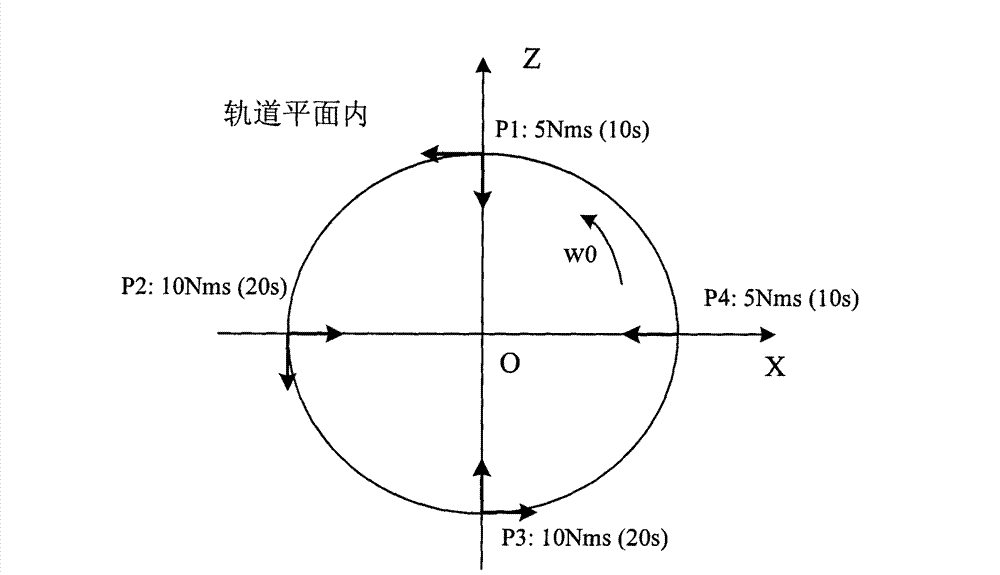
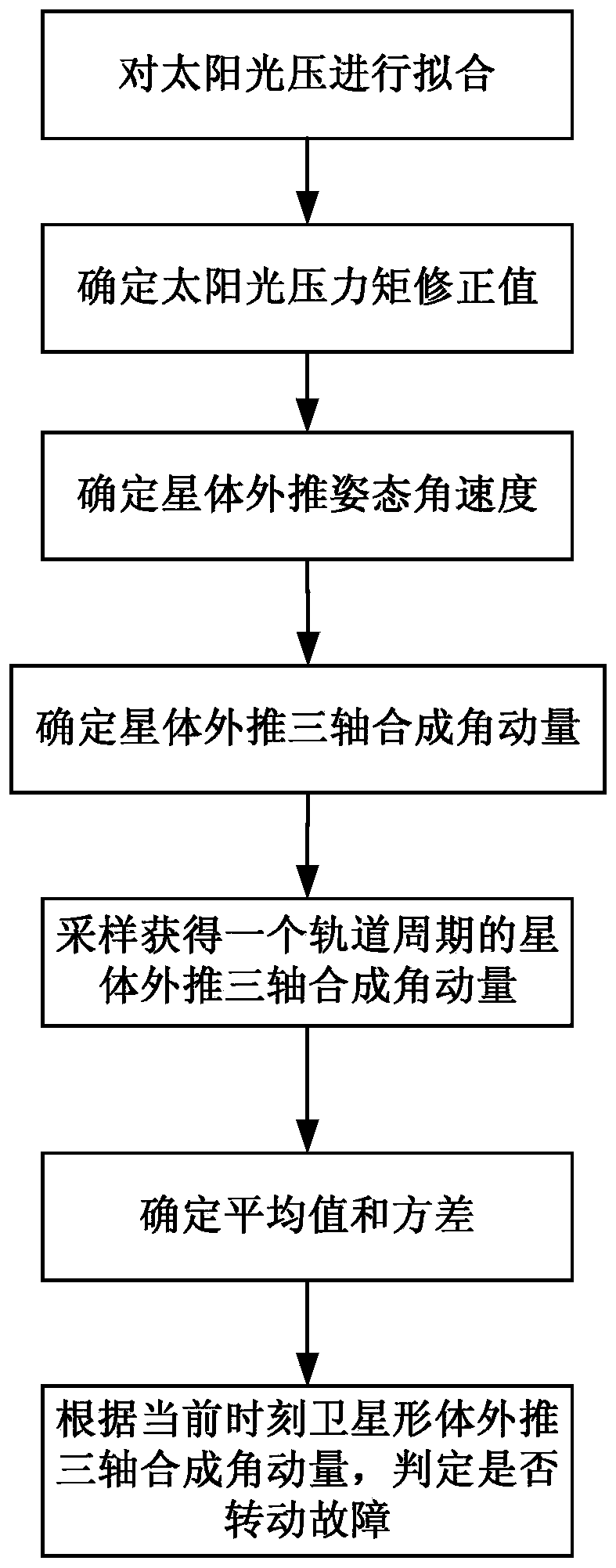
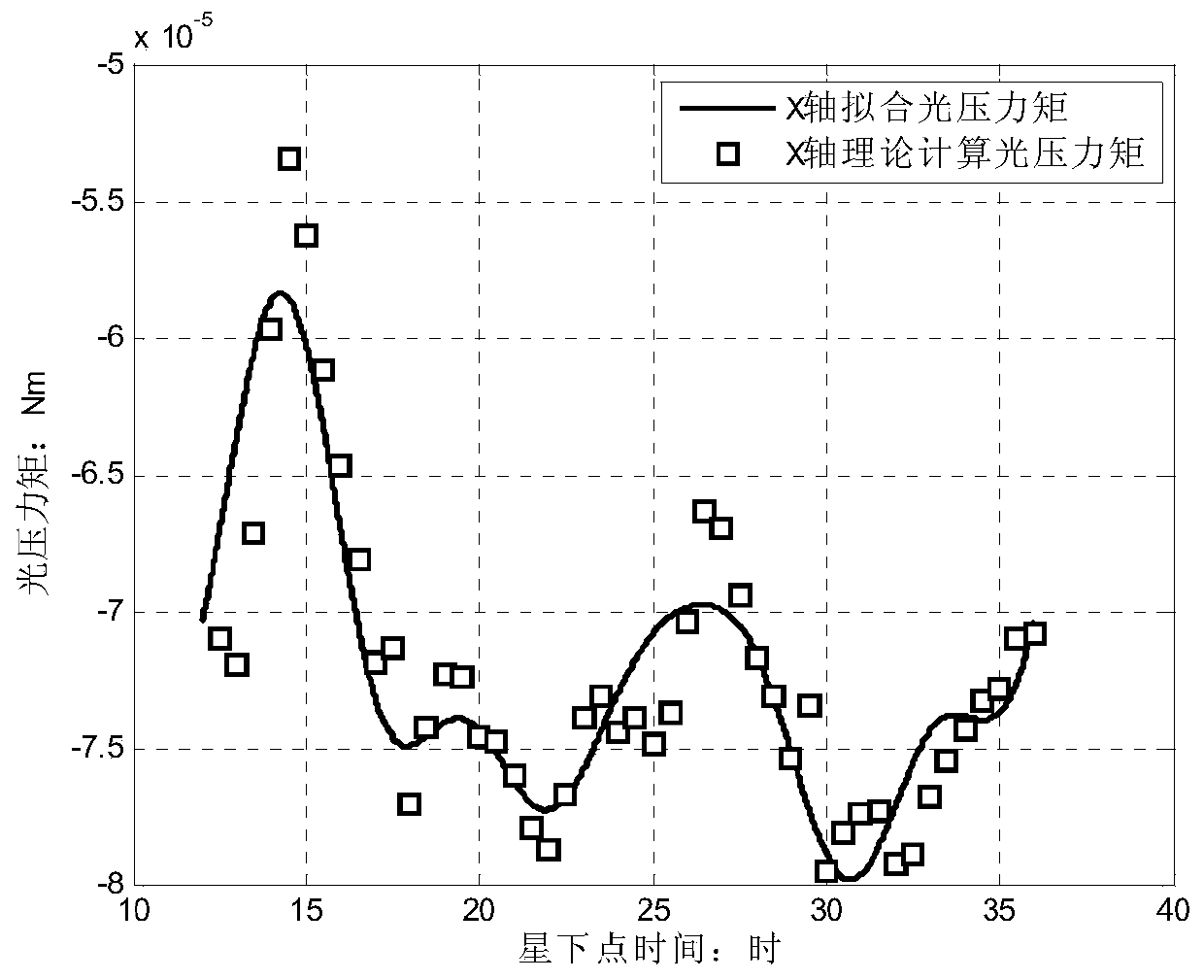
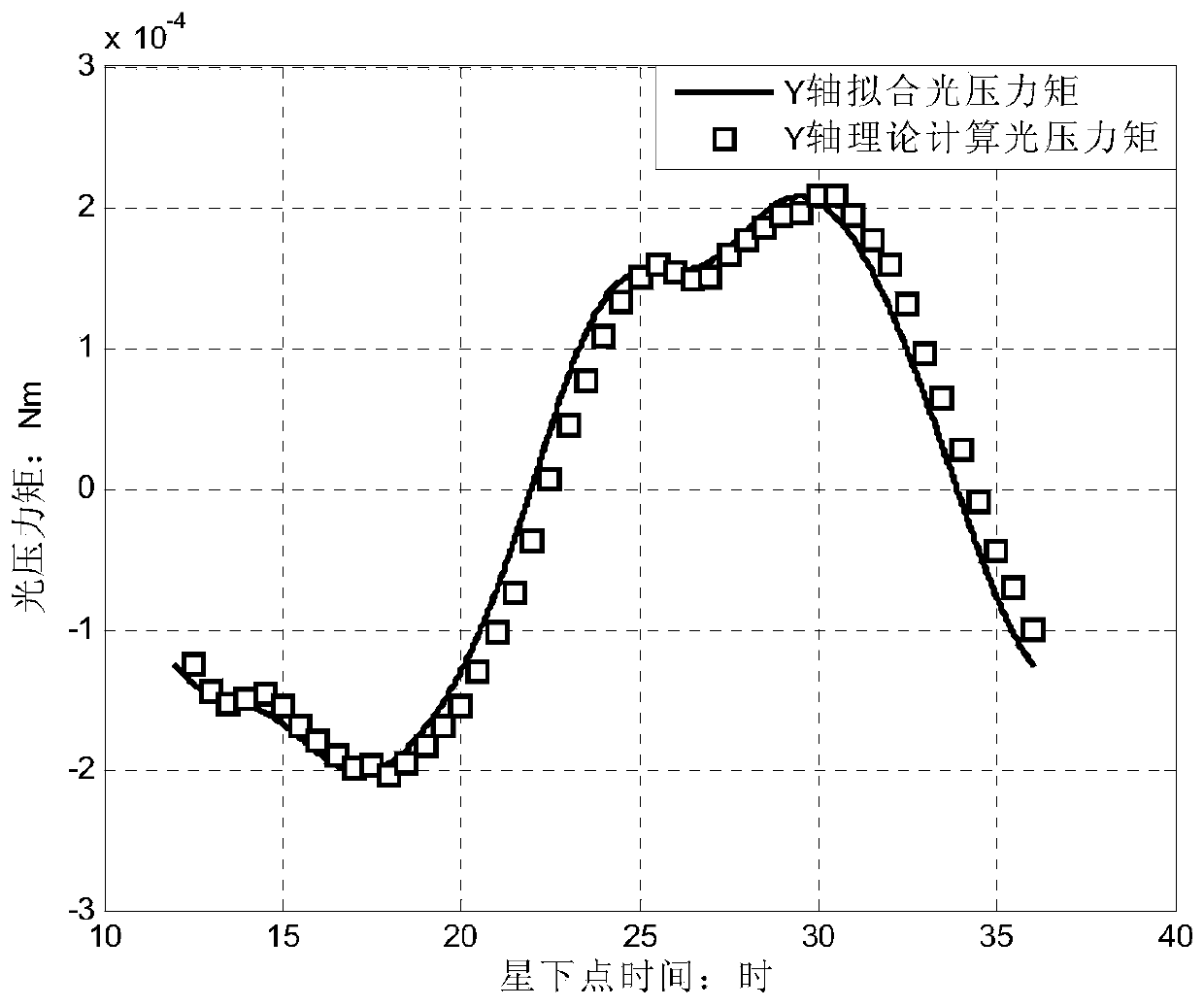
ActiveCN110048674AThe judgment method is simple and reliableReduce economic costsPhotovoltaic monitoringCosmonautic vehiclesNatural satelliteOrbital period
The invention discloses a high-orbit zero-momentum satellite sailboard rotation fault judgment method based on angular momentum estimation. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining a sunlight pressure fitting curve on a satellite solar panel; 2) determining a sunlight pressure moment correction value at the current moment according to the fitted curve and the estimated values of thesunlight pressure moments before the n orbit periods; 3) determining the extrapolated attitude angular velocity of the satellite body according to the corrected value of the sunlight pressure moment at the current moment; 4) according to the extrapolated attitude angular velocity of the satellite body, determining extrapolated triaxial synthetic angular momentum of the satellite body; 5) taking Ras a sampling period, and sampling to obtain an average value and a variance of the extrapolated triaxial synthetic angular momentum of the satellite body in the orbit period before the current moment; and 6) judging whether the satellite sailboard has a rotation fault or not at the current moment according to the average value and the variance. According to the method, whether the satellite sailboard has the rotation fault or not can be autonomously diagnosed on a faulty satellite without additionally adding a sun sensor.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Orbit maneuvering method for ground exploration of on-orbit satellite
InactiveCN107323689ARealize Coverage ObservationRealize prospectingCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital periodLongitude
The invention provides an orbit maneuvering method for ground exploration of an on-orbit satellite. The covering capability of a satellite load wave beam in the direction of a ground target is calculated through a satellite earth-fixed system ephemeris; the encountering time difference of the ground target and a satellite load ground projection is calculated according to the orbit maneuvering time and by comparing the longitude of the ground target and the longitude of the satellite passing the latitude circle same as that of the ground target; and the orbit period of the satellite for meeting the exploration requirement is calculated through the encountering time difference and the number of operation circles, and accordingly the adjustment amount required by the satellite orbit maneuvering semi-major axis is obtained, the minimum control amount in the satellite-control window period and the corresponding grounding target covering time are screened out, and the control amount is the orbit maneuvering control amount which can furthest save fuel under the restrained condition. Exploring of the ground target by orbit maneuvering in the specific time period is achieved in the short time in the mode of furthest saving the fuel.
Owner:中国人民解放军63789部队
Video game program and video game device for generating an attribute status image
ActiveUS8089484B2High playabilityEnrich the strategic aspect of a video gameCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnimationOrbital periodSimulation
Displayed on a first LCD 11 are a “fire” planet 40a, a “wood” planet 40b; an “earth” planet 40c, a “wind” planet 40d and a “water” planet 40e, each traveling along an orbit by a unique orbital period. While an attribute symbol is traveling through an active zone that is associated with the attribute symbol, the status of the attribute represented by the attribute symbol is active. An attribute being active affects the space attribute, which is the attribute of a particular space in the game world. The space attribute affects the ability parameters of characters of the same attribute. Thus, it is possible to enrich the strategic aspect of a video game using characters' attributes.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
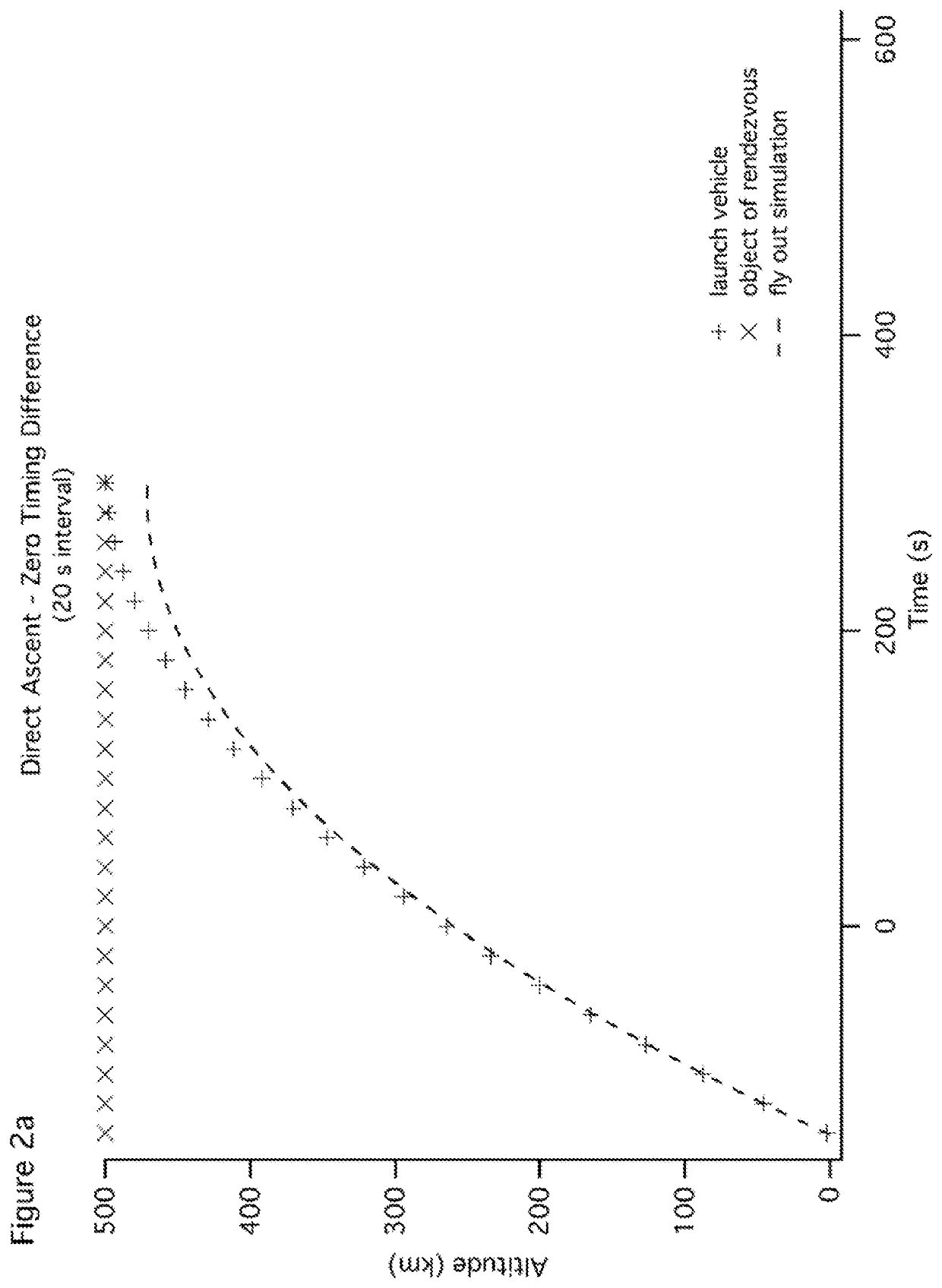
Orbital mechanics of impulsive launch
ActiveUS20190352021A1Reduce time differenceLaunch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusOrbital mechanicsOrbital period
Methods of launching a vehicle using impulsive force are disclosed. In one instance, a vehicle is launched easterly with impulsive force in a plane corresponding to the vehicle's elliptical orbital path. In another instance, a method of closing a timing difference is disclosed. The vehicle undergoes a series of forces after impulsive launch. The first force establishes an orbit having a period significantly different from the orbital period of a satellite or desired vehicle location, closing the difference in an integer number of orbits. The second force establishes the vehicle in circular orbit with the satellite or desired vehicle location. In another instance, the vehicle launched impulsively from a first celestial body travels a first path, and the vehicle experiences a second force along a hyperbolic path about the second celestial body and enters circular orbit about the second celestial body.
Owner:QUICKLAUNCH
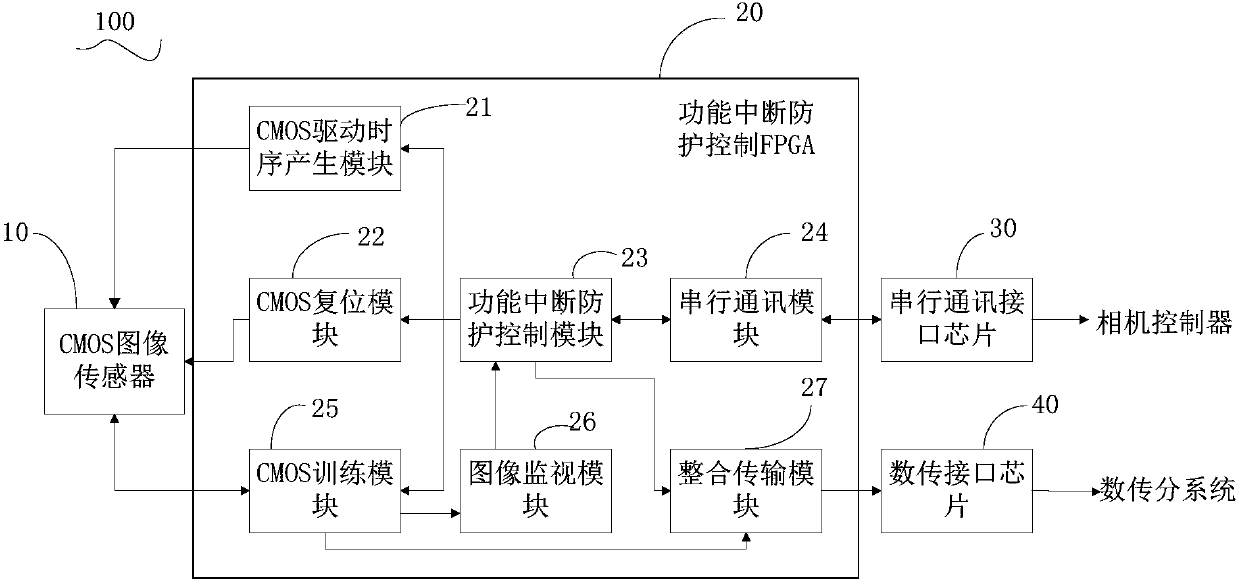
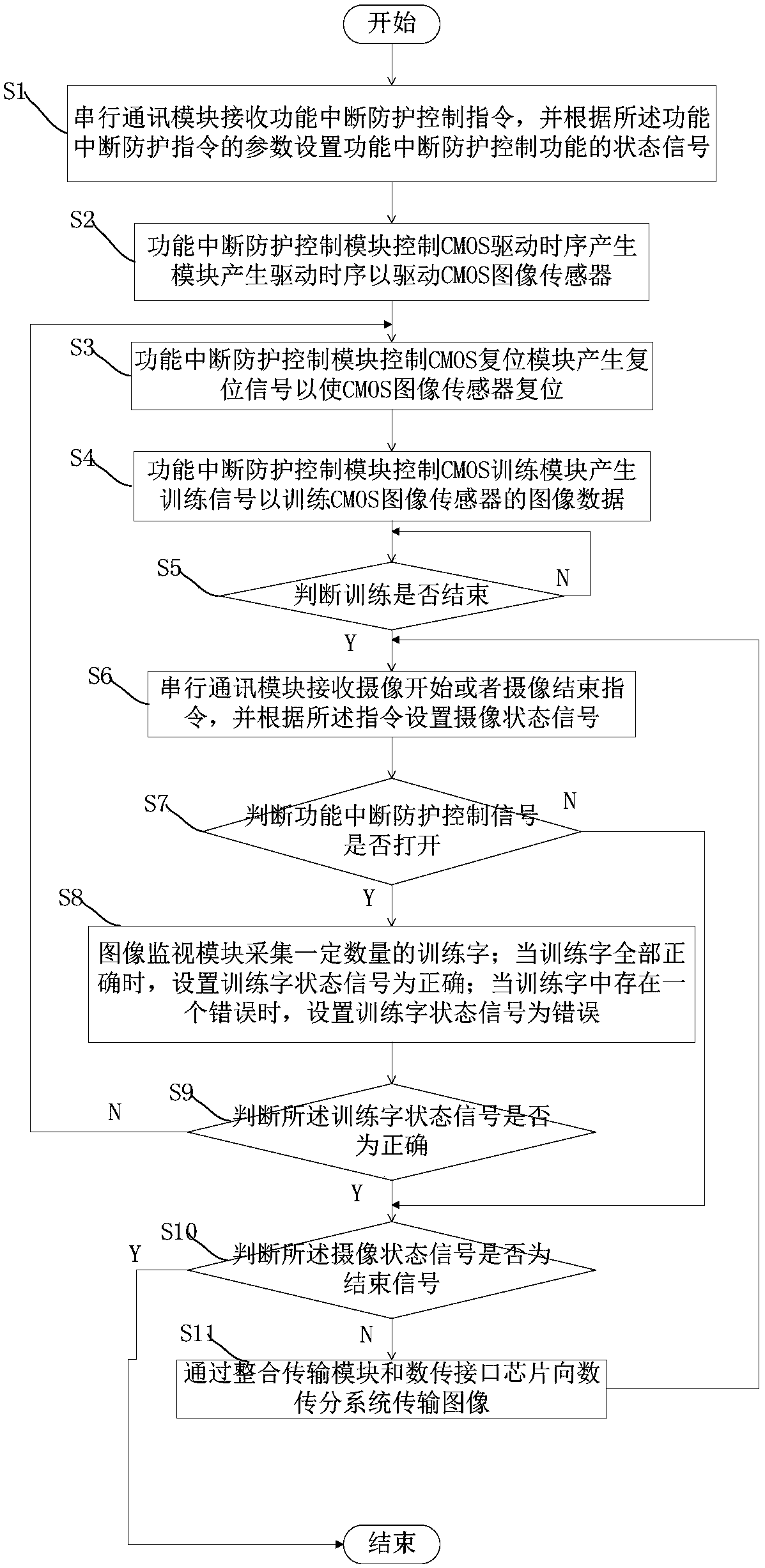
Single event functional interrupt protection system and method for CMOS image sensor
ActiveCN108055489AImprove efficiencyImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOrbital periodCMOS
The embodiment of the invention discloses a single event functional interrupt protection system and corresponding method for a CMOS image sensor. The protection system comprises the CMOS image sensor,a functional interrupt protection control FPGA, a serial communication interface chip and a data transmission interface chip, wherein the CMOS image sensor is used for converting an optical signal into a digital image signal; the functional interrupt protection control FPGA is used for receiving and processing the digital image signal generated by the CMOS image sensor and providing a preset signal for the CMOS image sensor; the serial communication interface chip is used for transmitting a related state signal to the functional interrupt protection control FPGA; and the data transmission interface chip is used for transmitting the digital image signal processed by the functional interrupt protection control FPGA to a data transmission subsystem. The single event functional interrupt protection system and corresponding method for the CMOS image sensor, which are disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, solve the problem of image anomaly in the orbital period space camera shootingprocess, which is caused by a case that the single event functional interrupt occurs to an existing CMOS image sensor.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
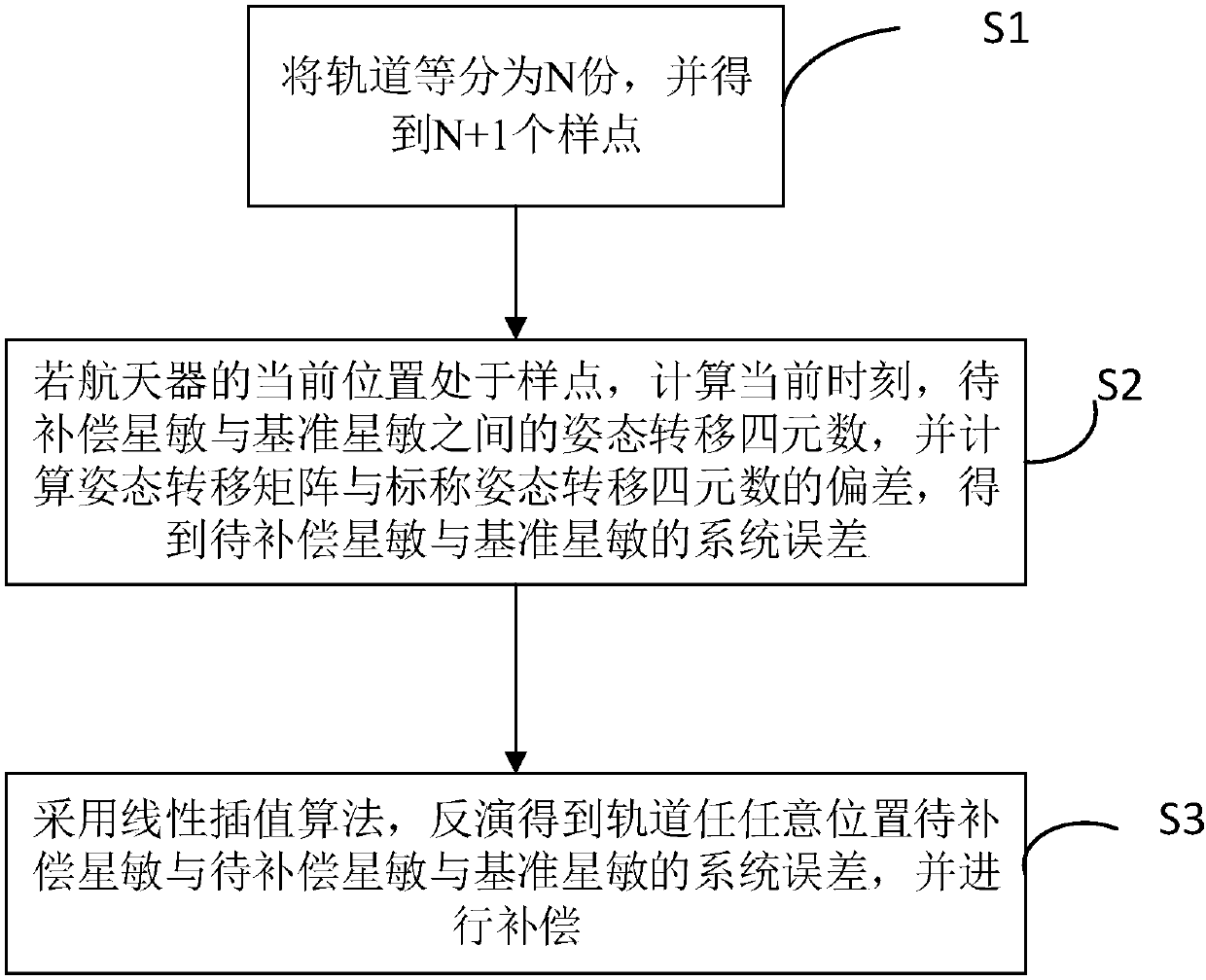
Method for online identification and compensation of orbital period system error between star sensors
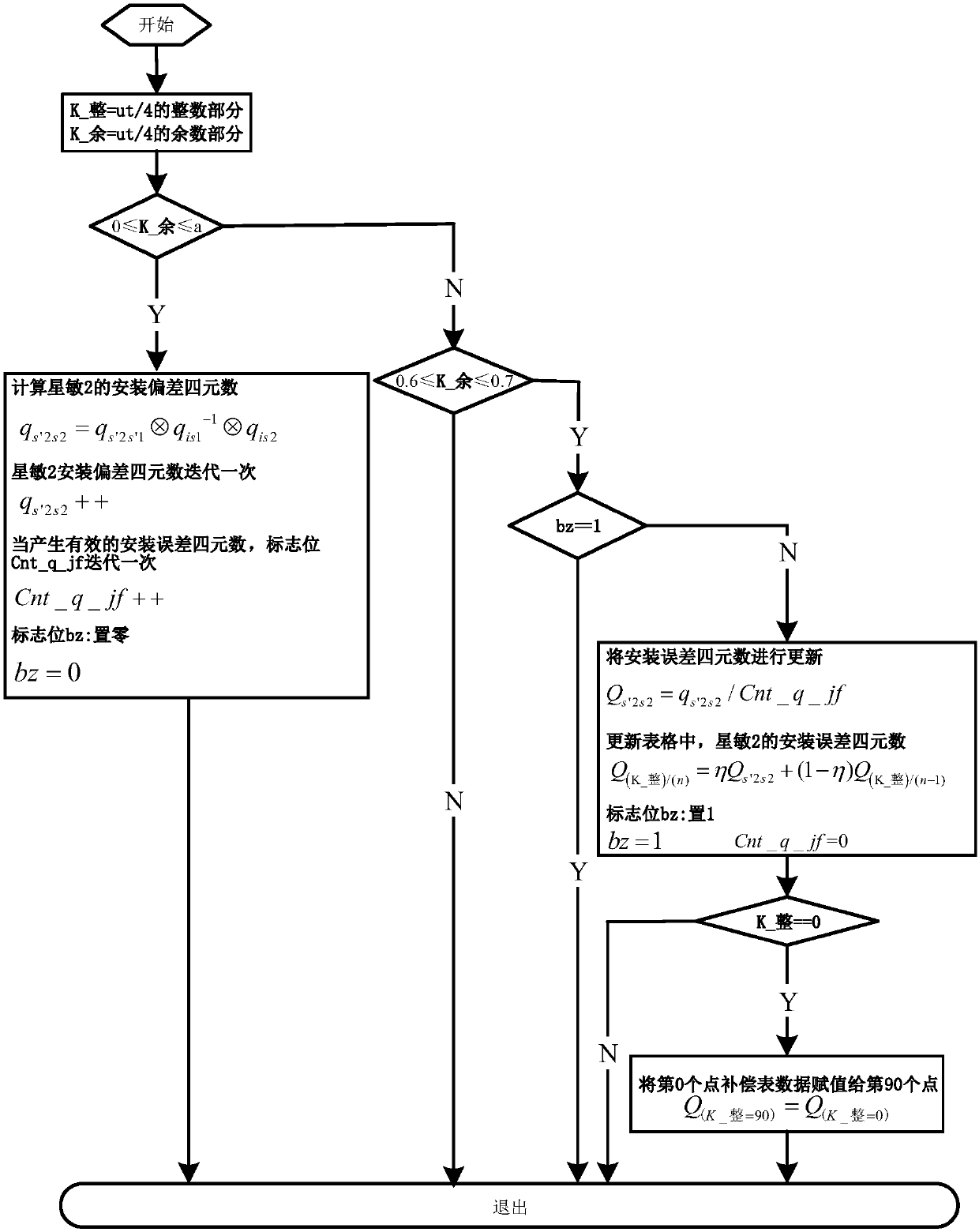
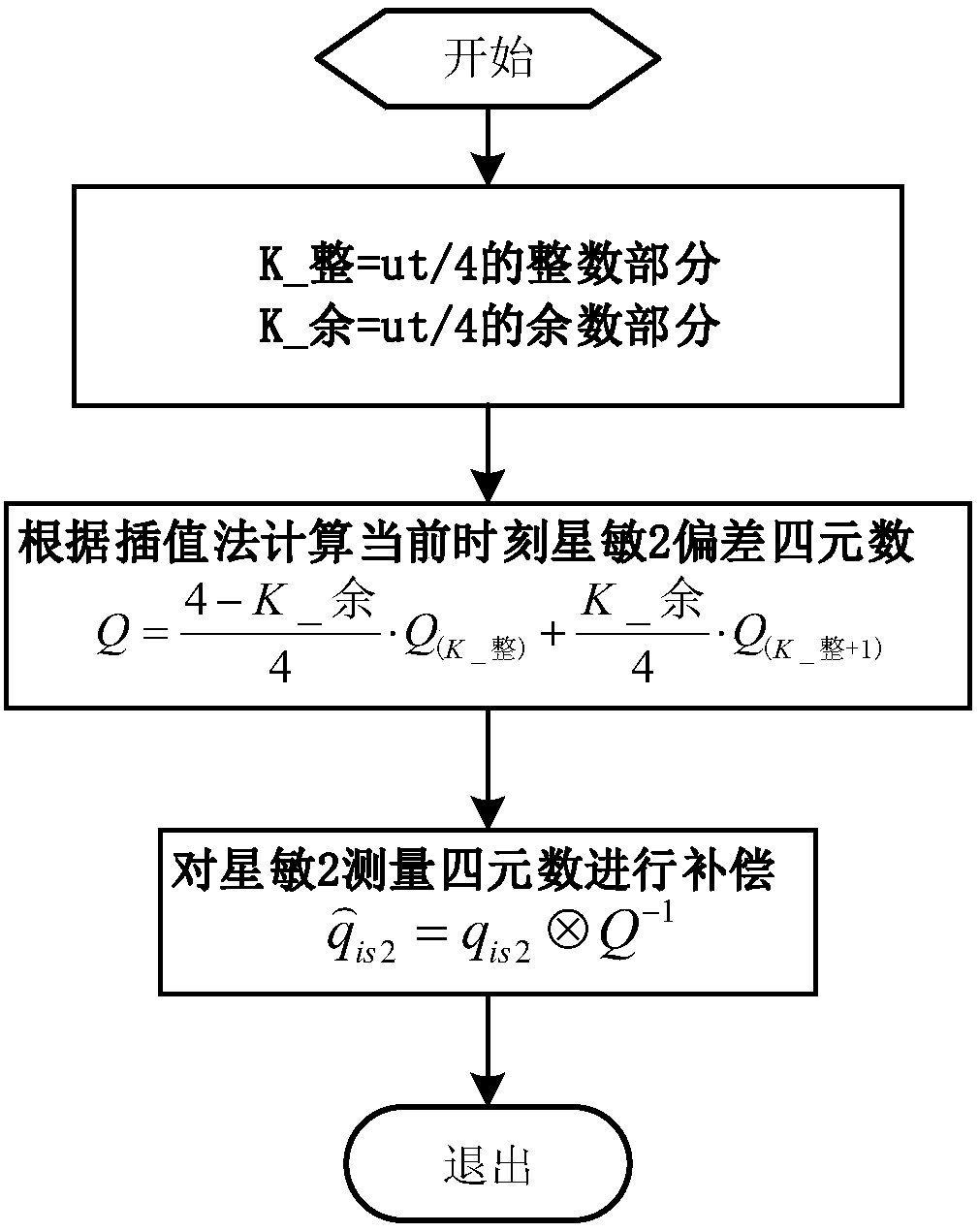
ActiveCN107747946AResolving Baseline MismatchesRealize online identificationNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationOrbital periodQuaternion
The present invention discloses a method for online identification and compensation of orbital period system error between star sensors. The method comprises: S1, equally dividing an orbit into N parts to obtain N+1 sample points; S2, if the current spacecraft is positioned at the sampling point, calculating the attitude transfer quaternion between a star sensor to be compensated and a reference star sensor at the current moment, and calculating the deviation between the attitude transfer matrix and a nominal attitude transfer quaternion to obtain the system error of the star sensor to be compensated and the reference star sensor; and S3, based on the N+1 sample points, inverting by using a linear interpolation algorithm to obtain the system error of the star sensor to be compensated and the reference star sensor at any position of the orbit, and compensating.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Method for quickly analyzing service life of space target track based on single-group TLE
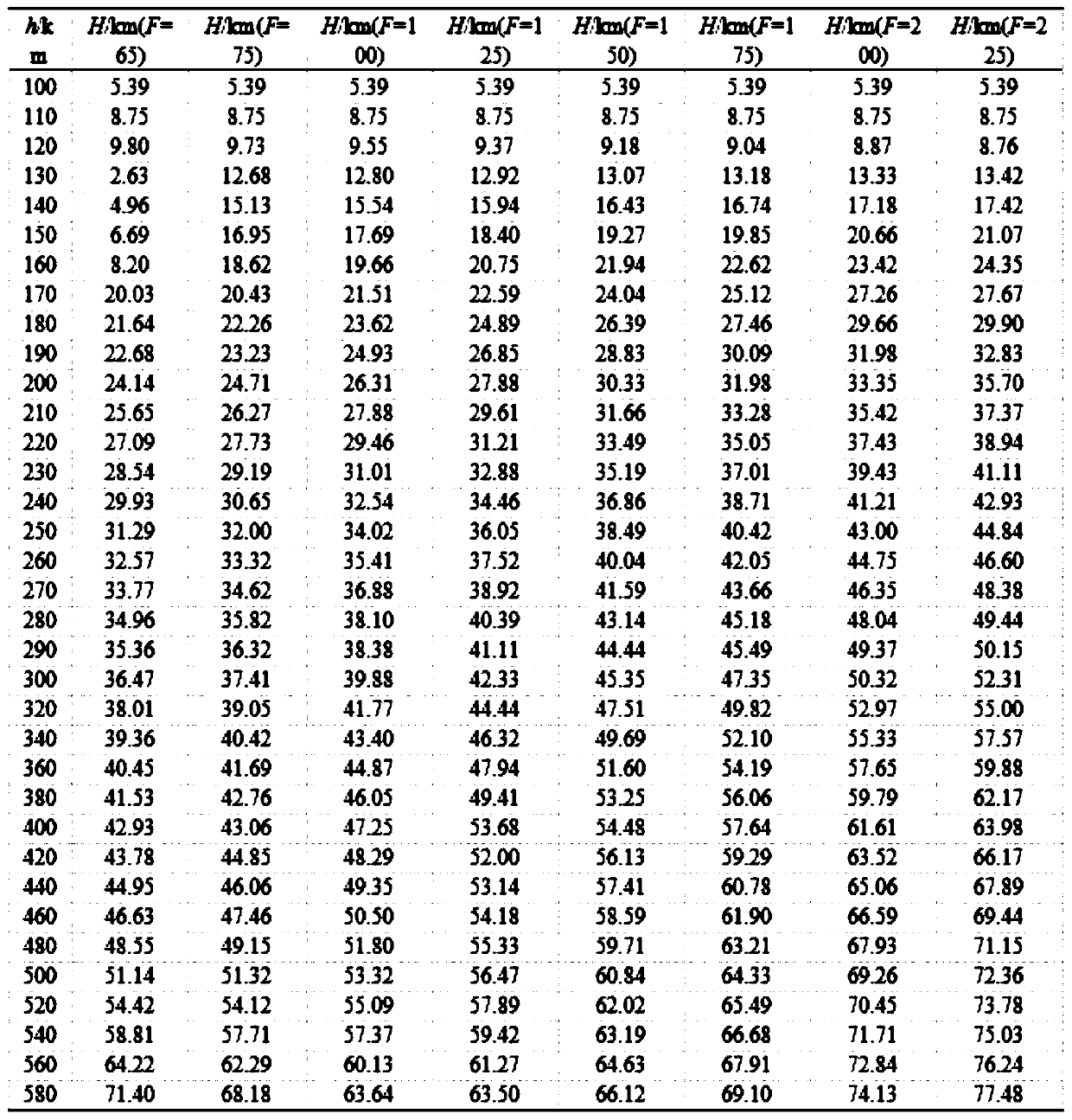
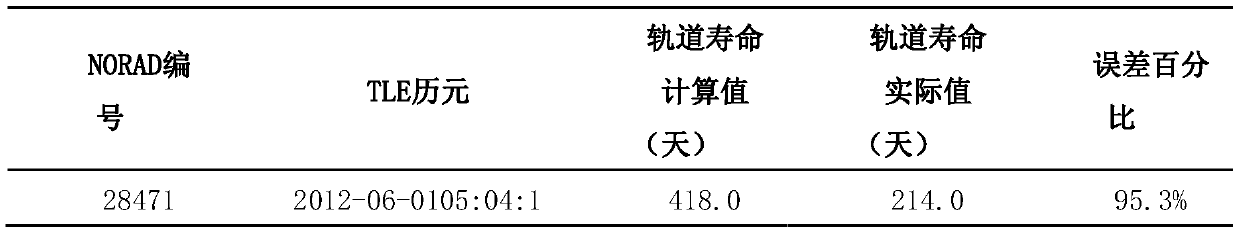
ActiveCN110427727AImprove life calculation accuracySolve the errorSpecial data processing applicationsUltrasound attenuationOrbital period
The invention discloses a method for quickly analyzing the service life of a space target track based on a single-group TLE. The method specifically comprises the following steps: S1, calculating theorbit period first-order attenuation deltaT of a space target based on a single group of TLE, S2, calculating the atmospheric density reference height H, and S3, calculating the orbit service life L.The invention relates to the technical field of aerospace measurement and control. The invention discloses a method for quickly analyzing the service life of a space target track based on single-groupTLE. The track service life calculation precision is greatly improved; practical application requirements are met, the problems that the calculation error is too large when an SGP4 model is used during track life calculation, the difficulty of solving the ballistic coefficient through a single group of TLE is large, and the efficiency of a numerical integration method is low are effectively solved; the track service life calculation precision is basically less than 20%, and the analysis method is used for direct calculation, so that the calculation efficiency has obvious advantages compared with a numerical integration method, and the actual application requirements of large-batch space target track service life calculation are completely met.
Owner:中国人民解放军32035部队
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com