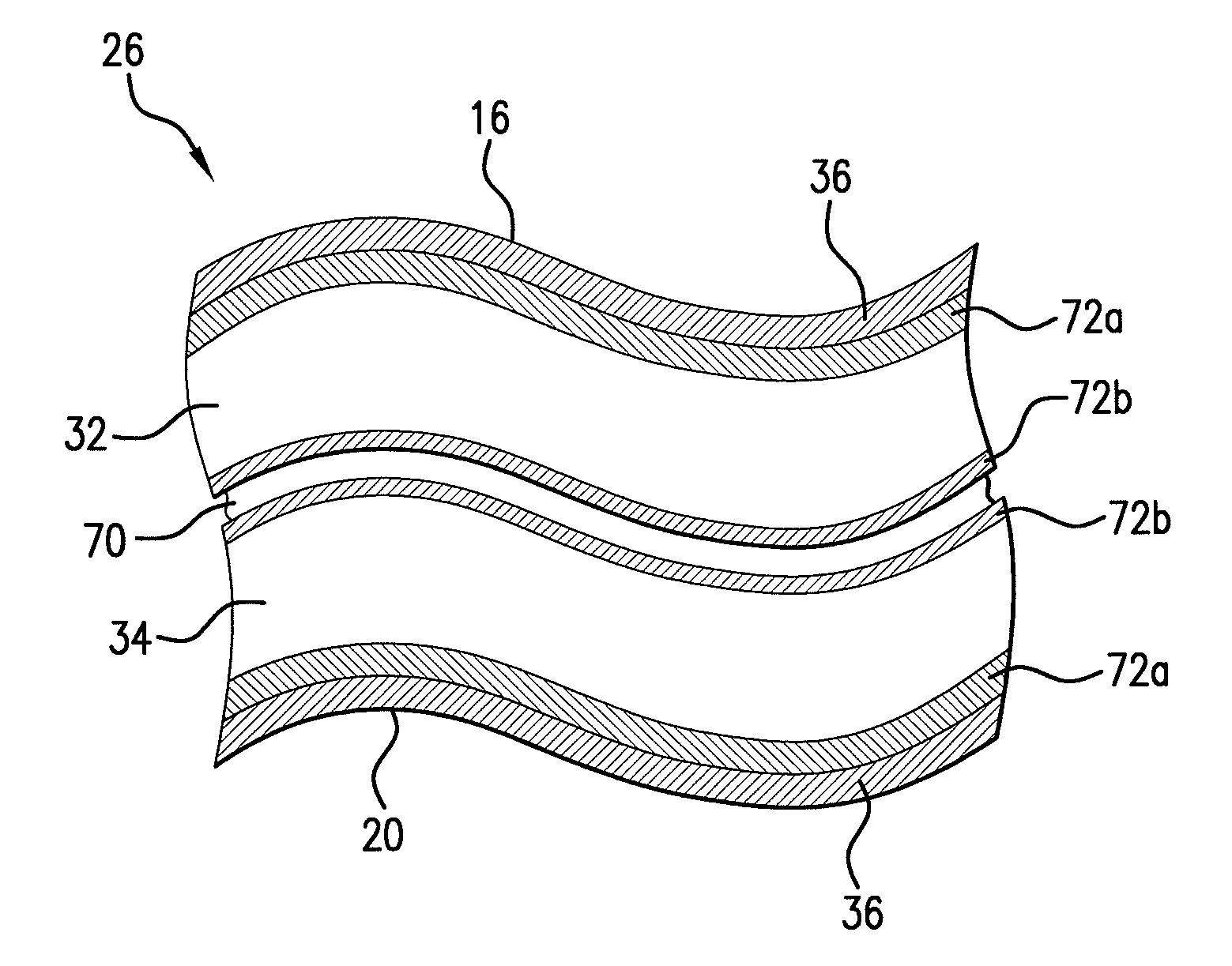
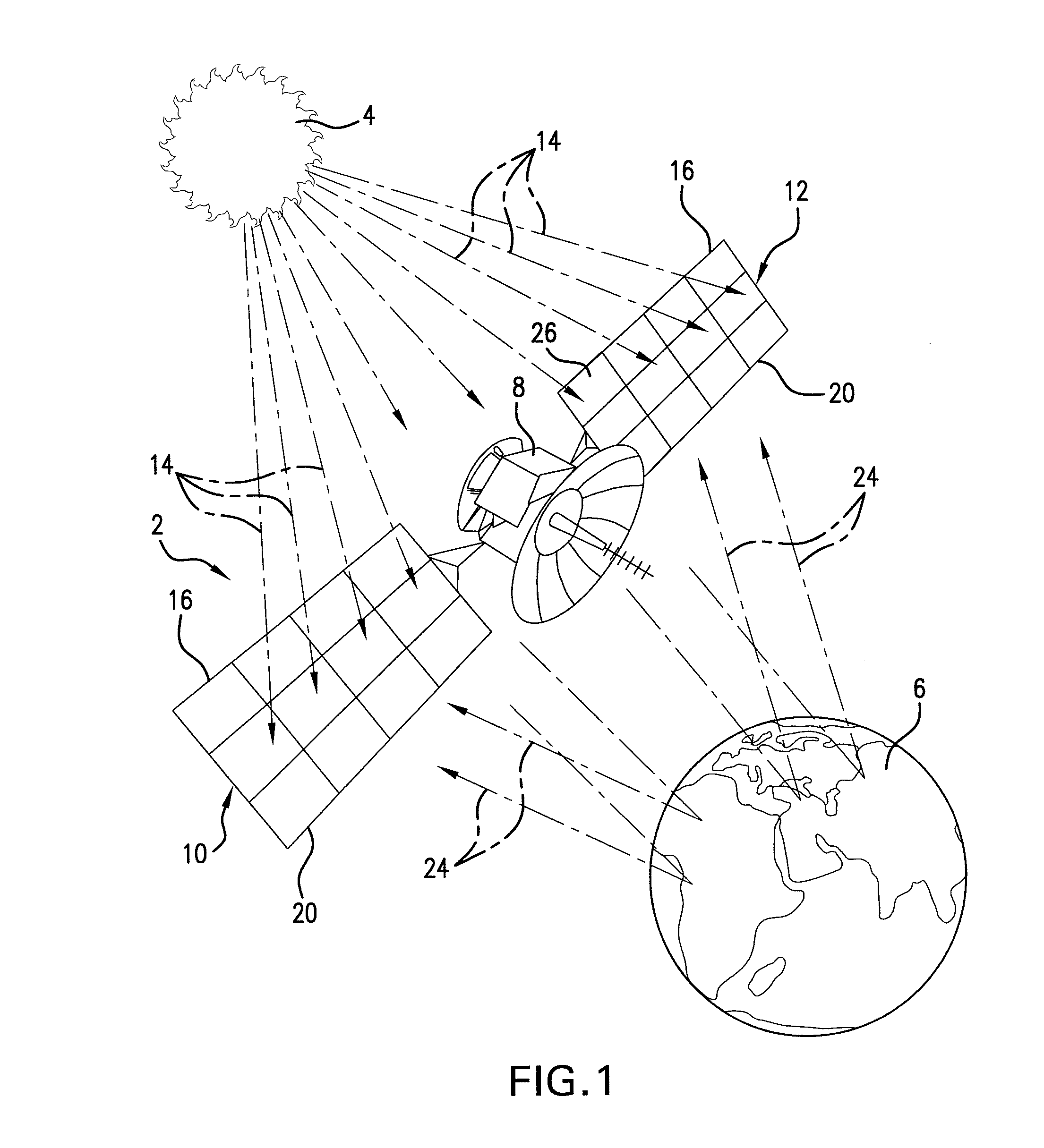
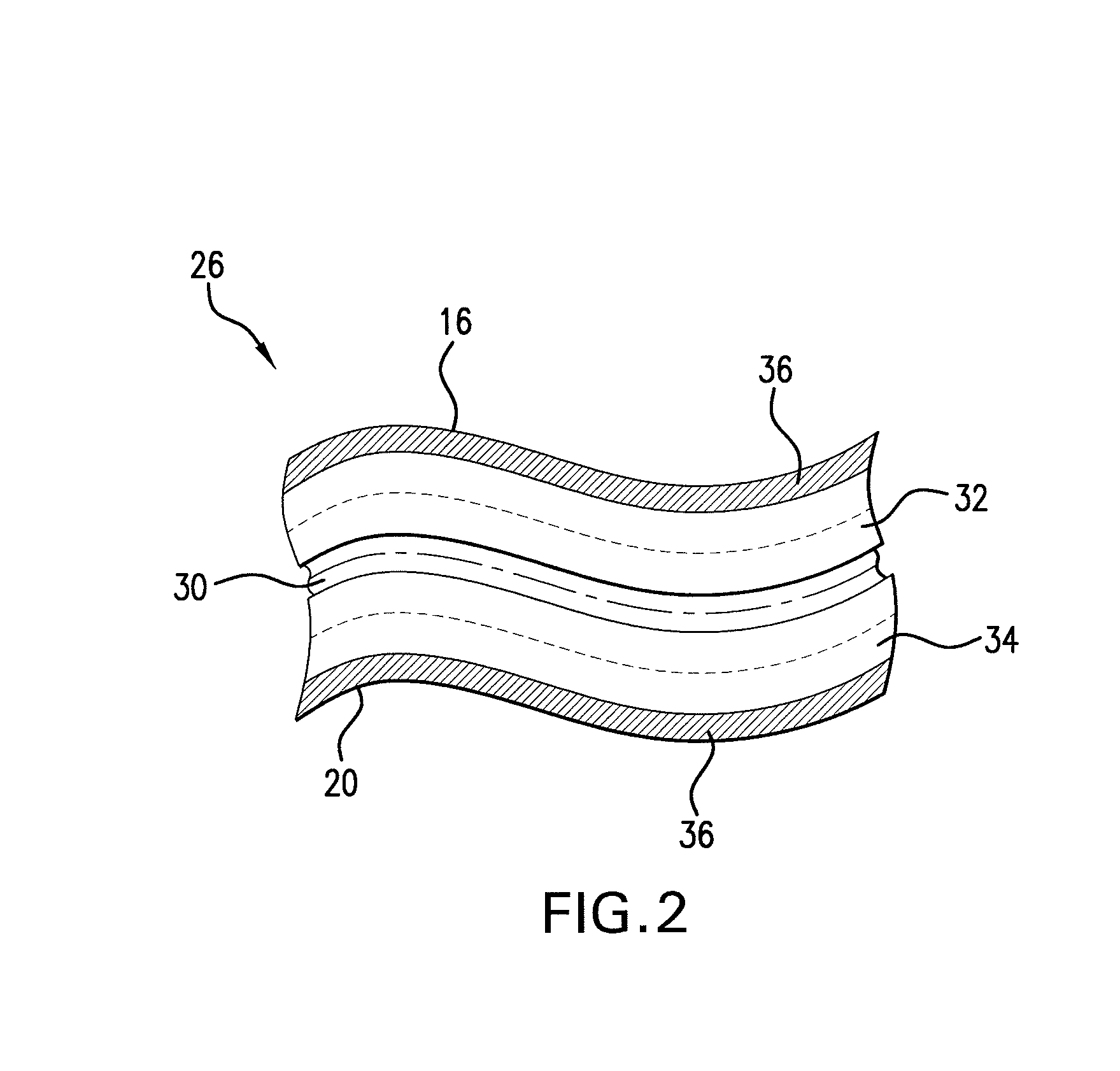
Patents
Literature
3064results about "Cosmonautic parts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
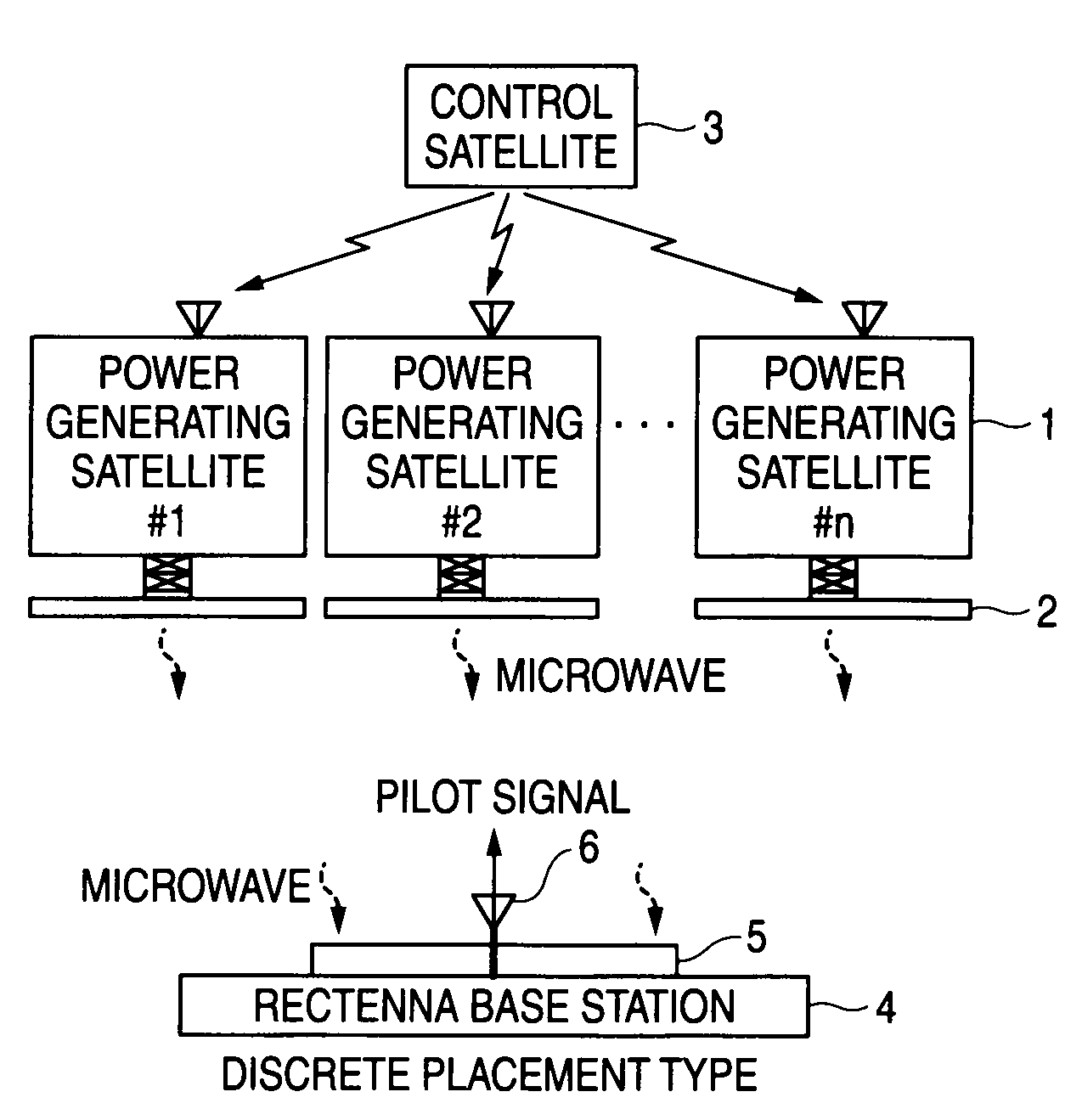
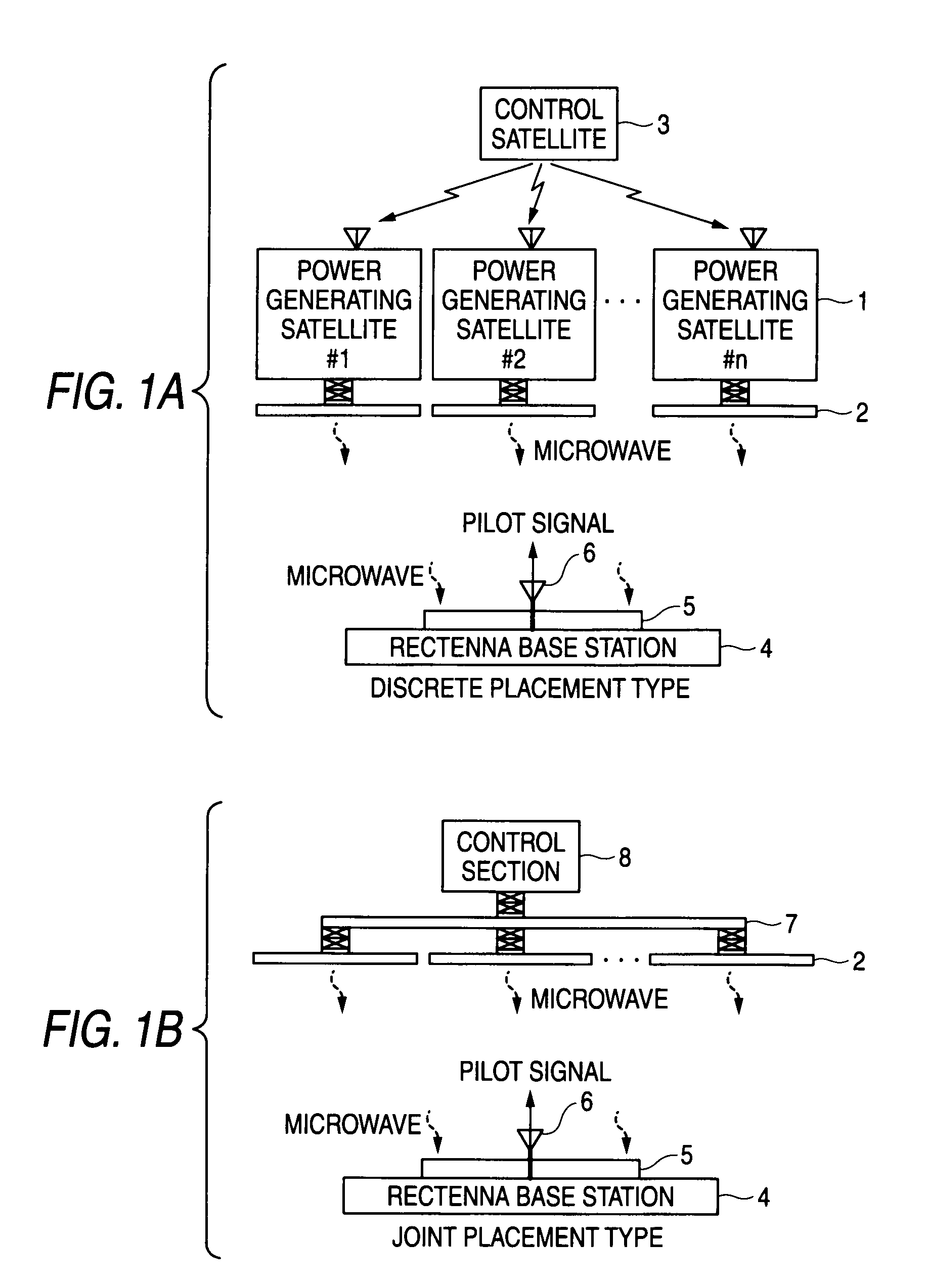
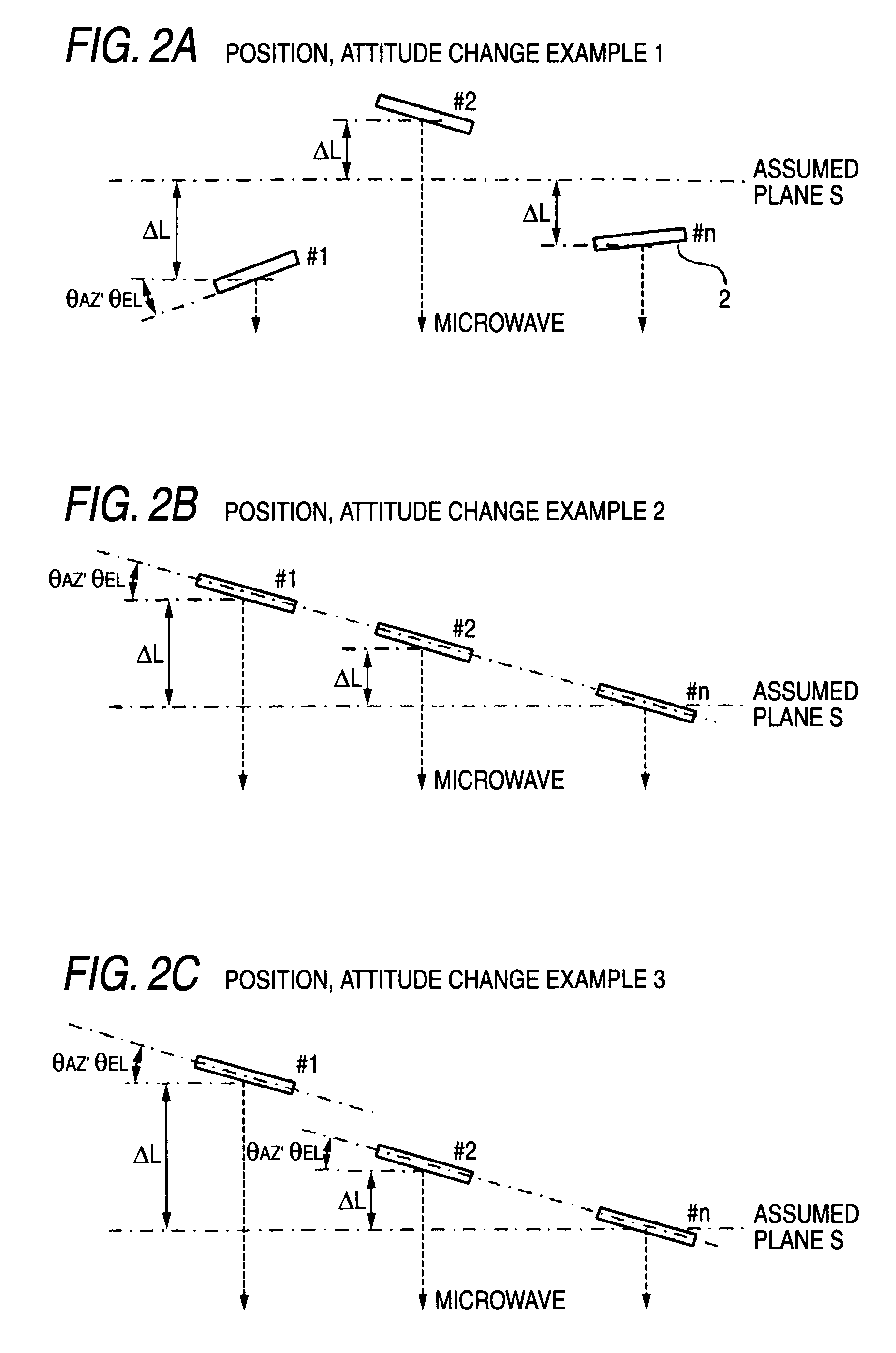
Wireless power transfer system, power transmitter, and rectenna base station
ActiveUS20090315412A1Efficient preparationImprove scaleSpatial transmit diversityCosmonautic vehiclesElectric power transmissionMicrowave
A wireless power transfer system includes: a plurality of power transmitters, each of which transmits a microwave; and a rectenna base station which receives the microwave to generate power. The rectenna base station includes: a rectenna; and control section which specifies an identification code for identifying each power transmitter and generates a command signal to change a phase of the power transmitter specified by identification code so as to increase a power value received at the rectenna. Each of the power transmitters comprises: a plurality of transmission antenna elements, each of which transmits the microwave to the rectenna base station; and a phase controller which makes phase change of the microwave based on the command signal from the phase monitor and control section of the rectenna base station if the identification code matches a stored identification code.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
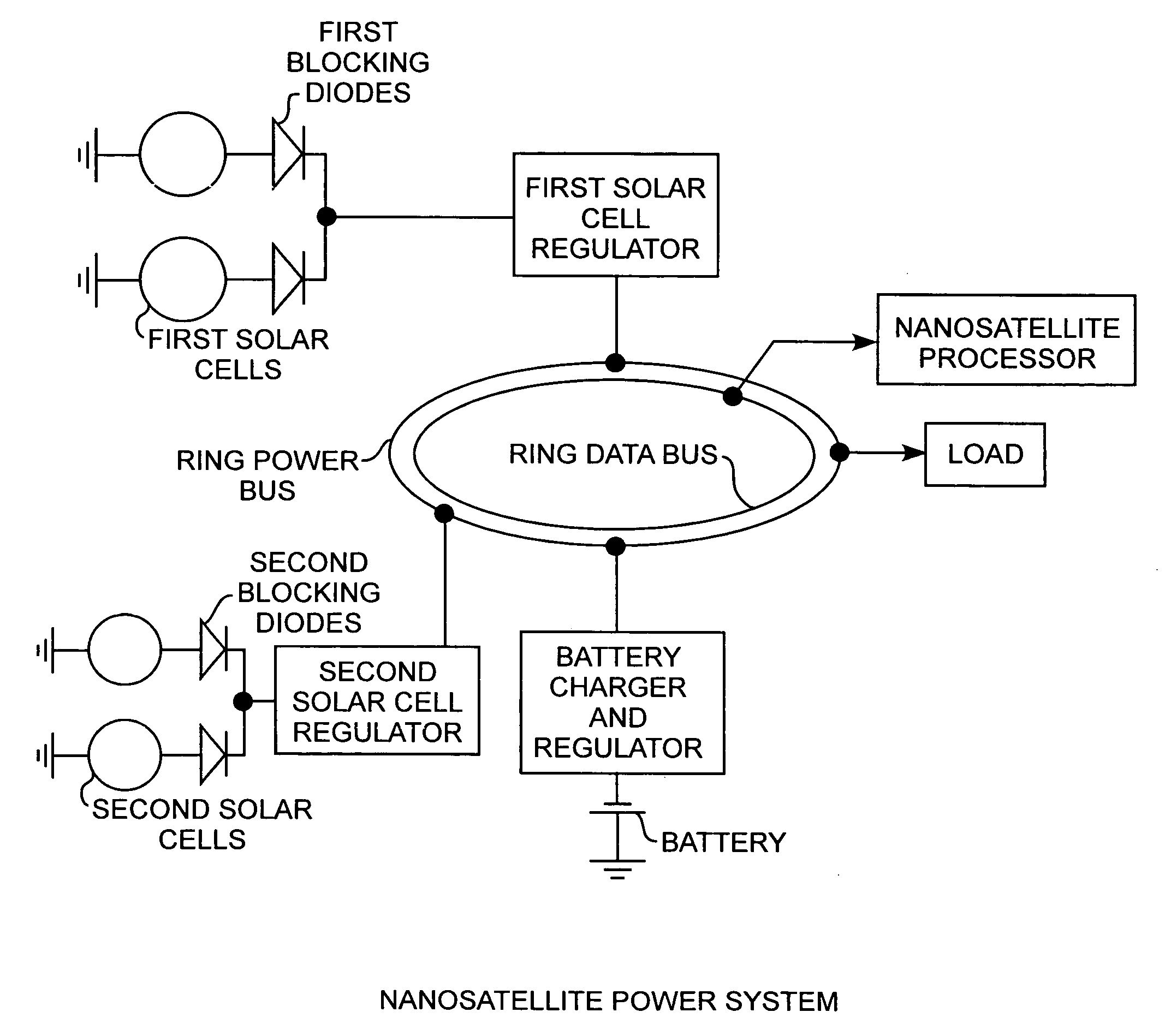
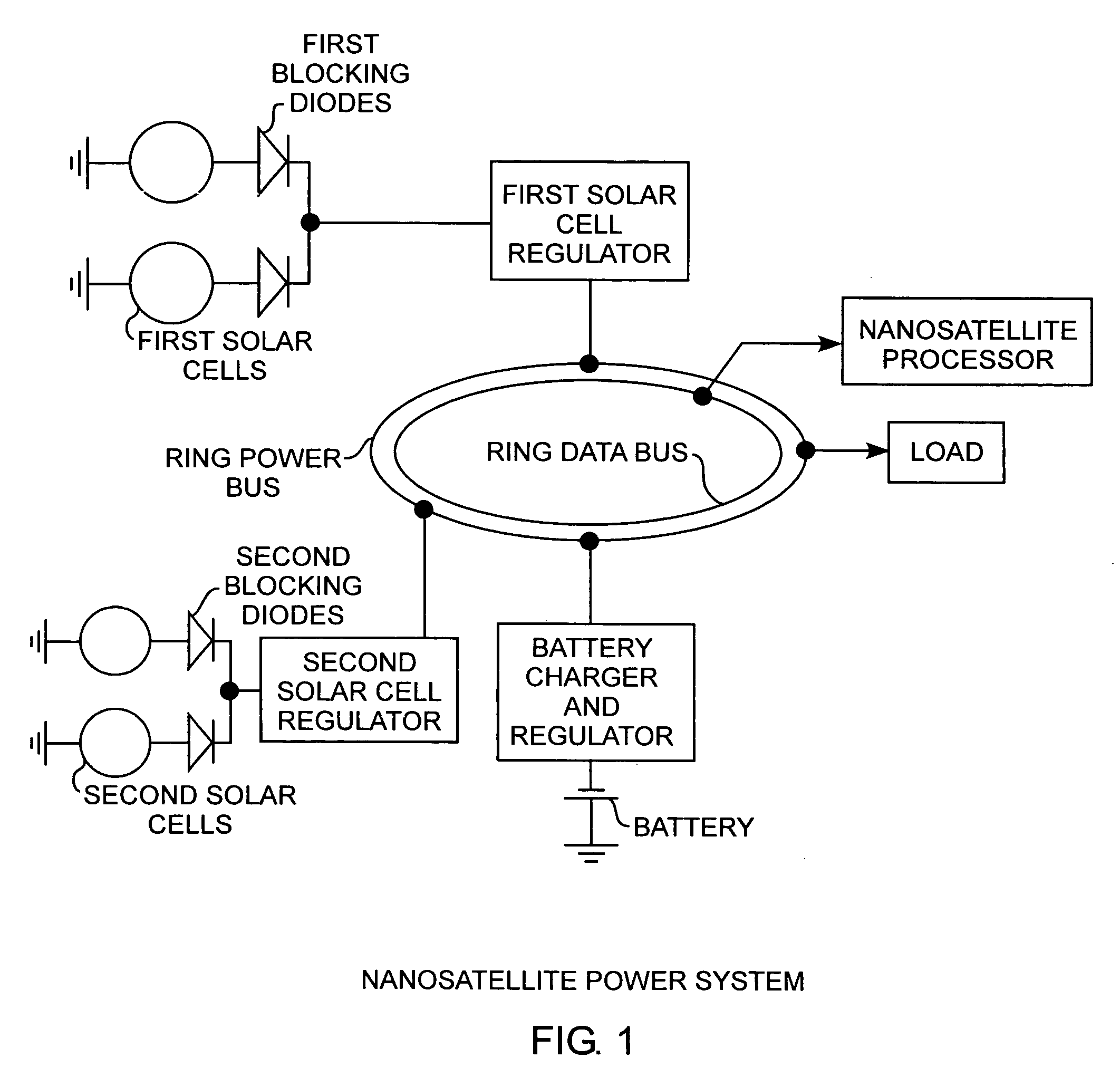
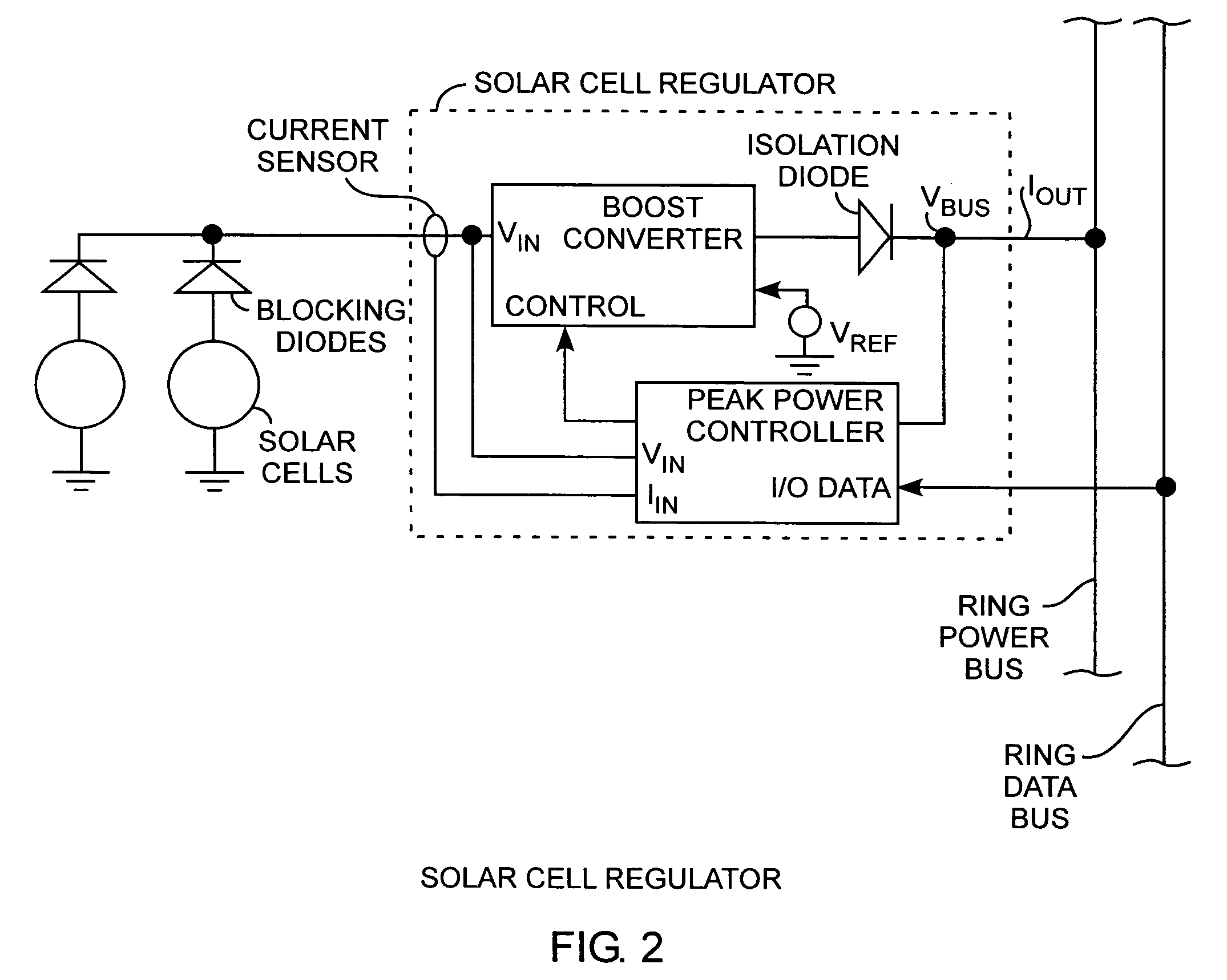
Nanosatellite solar cell regulator
A solar cell regulator in a nanosatellite includes a pulse width modulated DC-DC boost converter and a peak power tracking controller for converting solar cell power to bus power for charging of system batteries and powering loads while the controller controls the pulse width modulation operation of the converter for sensing solar cell currents and voltages along a power characteristic curve of the solar cell for peak power tracking, for determining any power data point, including a peak power point, an open circuit voltage point, and a short circuit current point along the power characteristic curve of the solar cell, and for communicating the power data to a satellite processor for monitoring the performance of the solar cell during operational use of the satellite.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Apparatus and method of production of thin film photovoltaic modules
InactiveUS7271333B2Reduce weightSimple and cheap to manufactureCosmonautic vehiclesPV power plantsEngineeringMethods of production
Owner:ASCENT SOLAR TECH
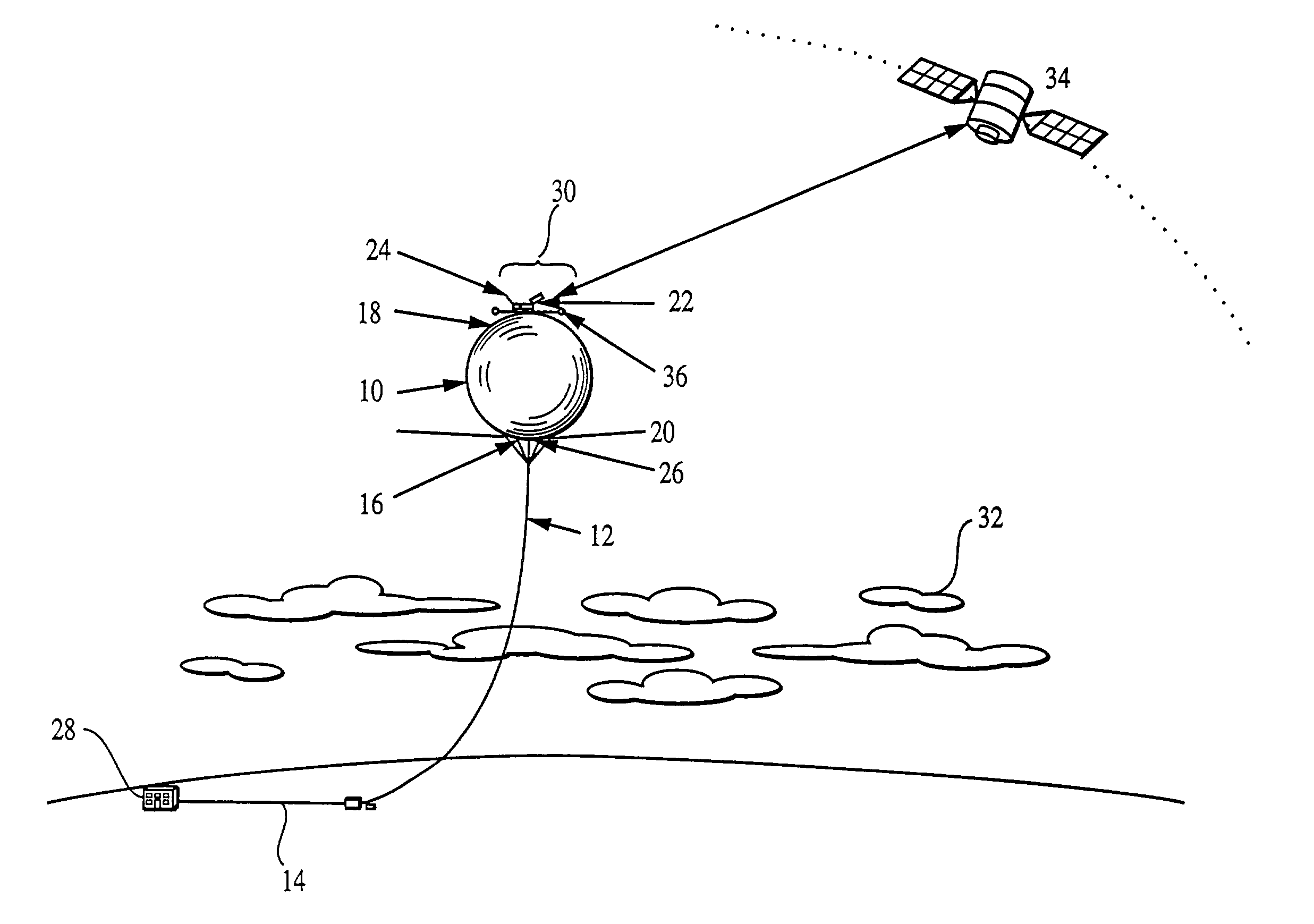
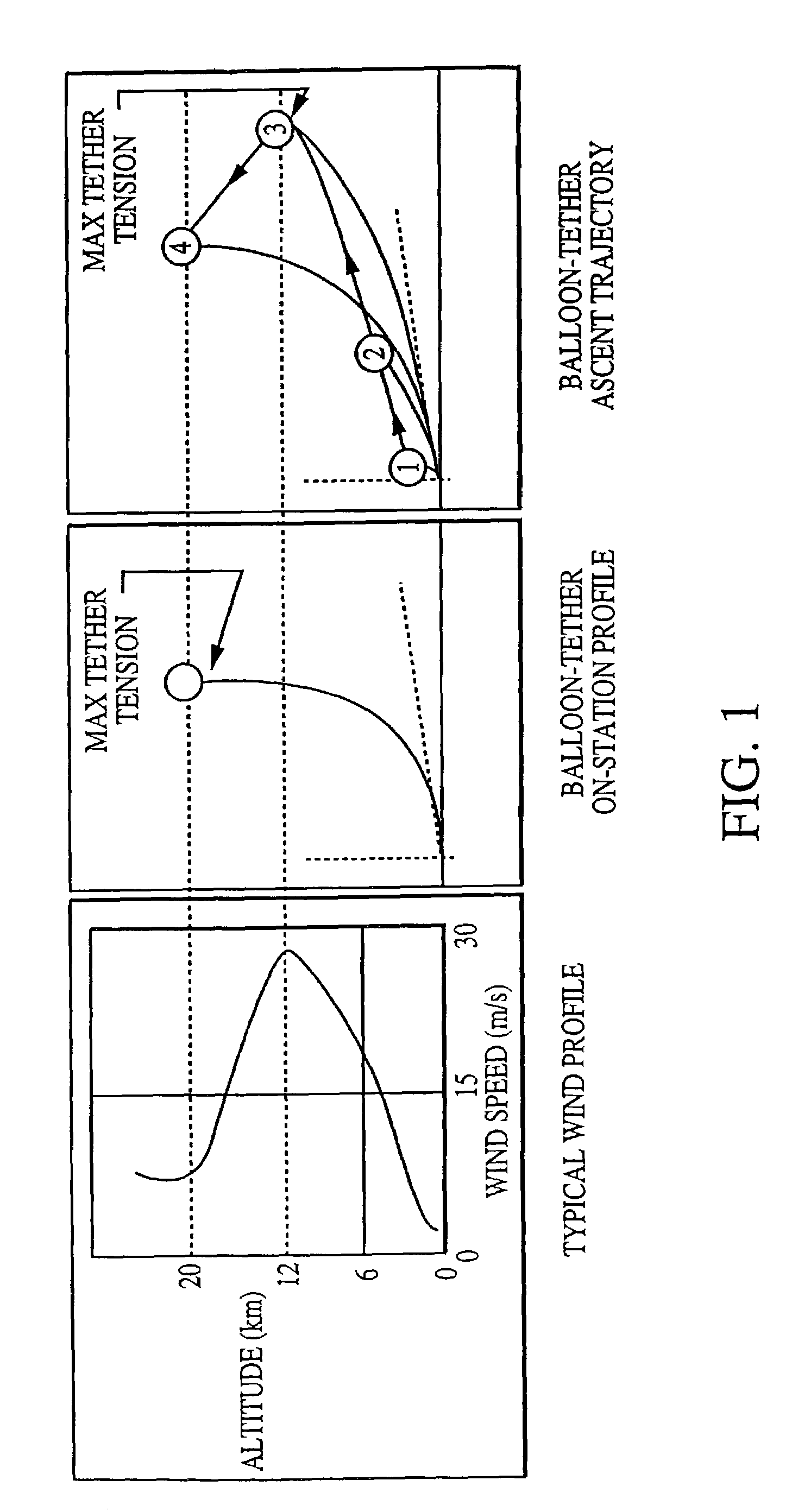
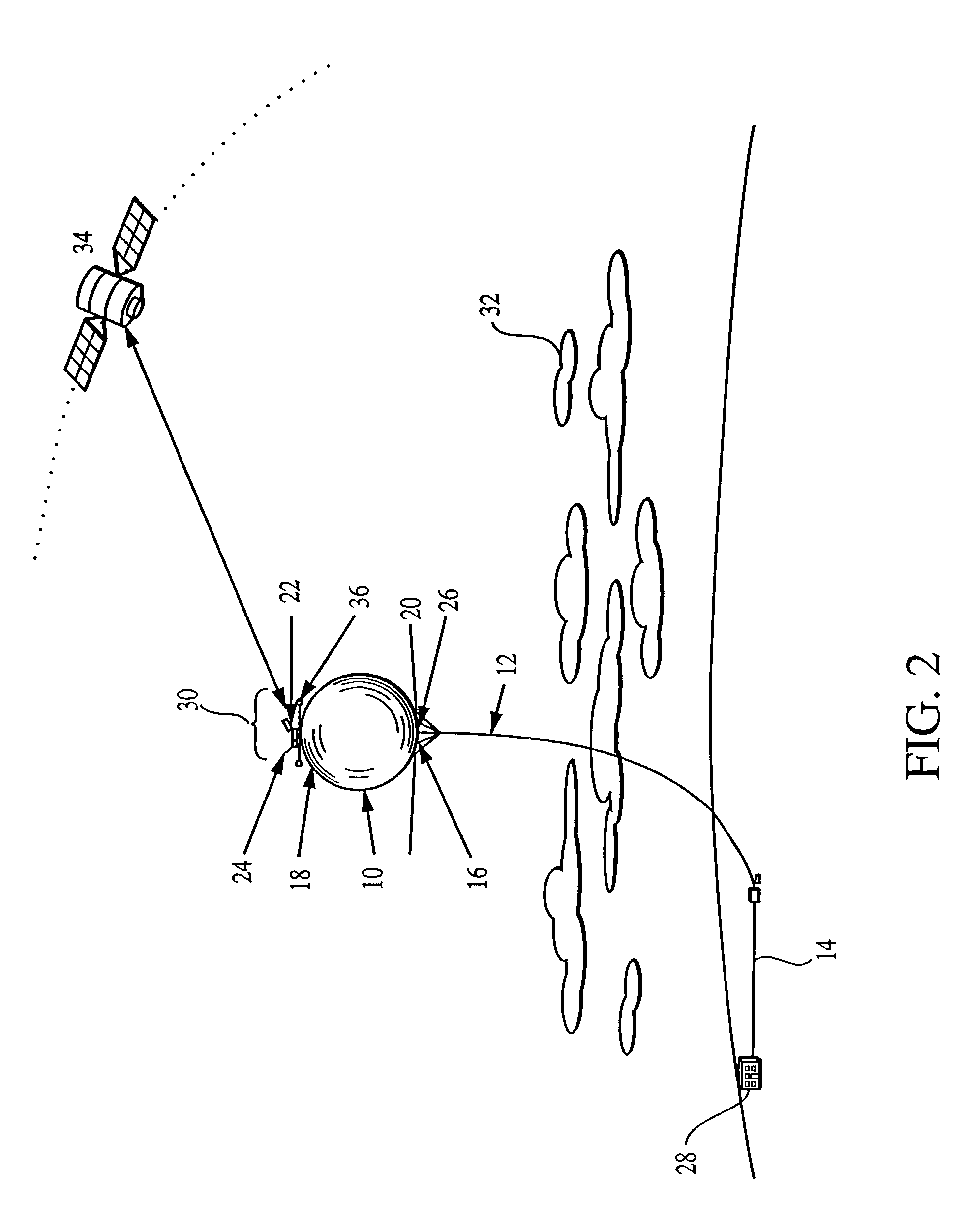
Optical communication system using a high altitude tethered balloon
InactiveUS7046934B2Reduce atmospheric disturbancesIncrease data transfer rateCosmonautic ground equipmentsCosmonautic partsFiberTransceiver
An optical communication system using a high altitude tethered balloon 10 that operates above most clouds and atmospheric turbulence. An optical communication system includes a balloon 10 with an optical communication payload 30, a fiber optic cable attached to the tether 12, an automated winch system 14, and a ground station 28. The balloon 10 is designed for sustained flight at, and recovery from, high altitude using the automated winch system 14. An acquisition, tracking and pointing (ATP) system 22 enables a balloon-based optical transceiver 24 to maintain line-of-sight optical communications with an overhead satellite 34. The optical link between the satellite 34 and the balloon 10 is an open channel. Data is transmitted to the ground station 28 from the balloon 10 through the secure fiber optic closed channel attached to the tether 12.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
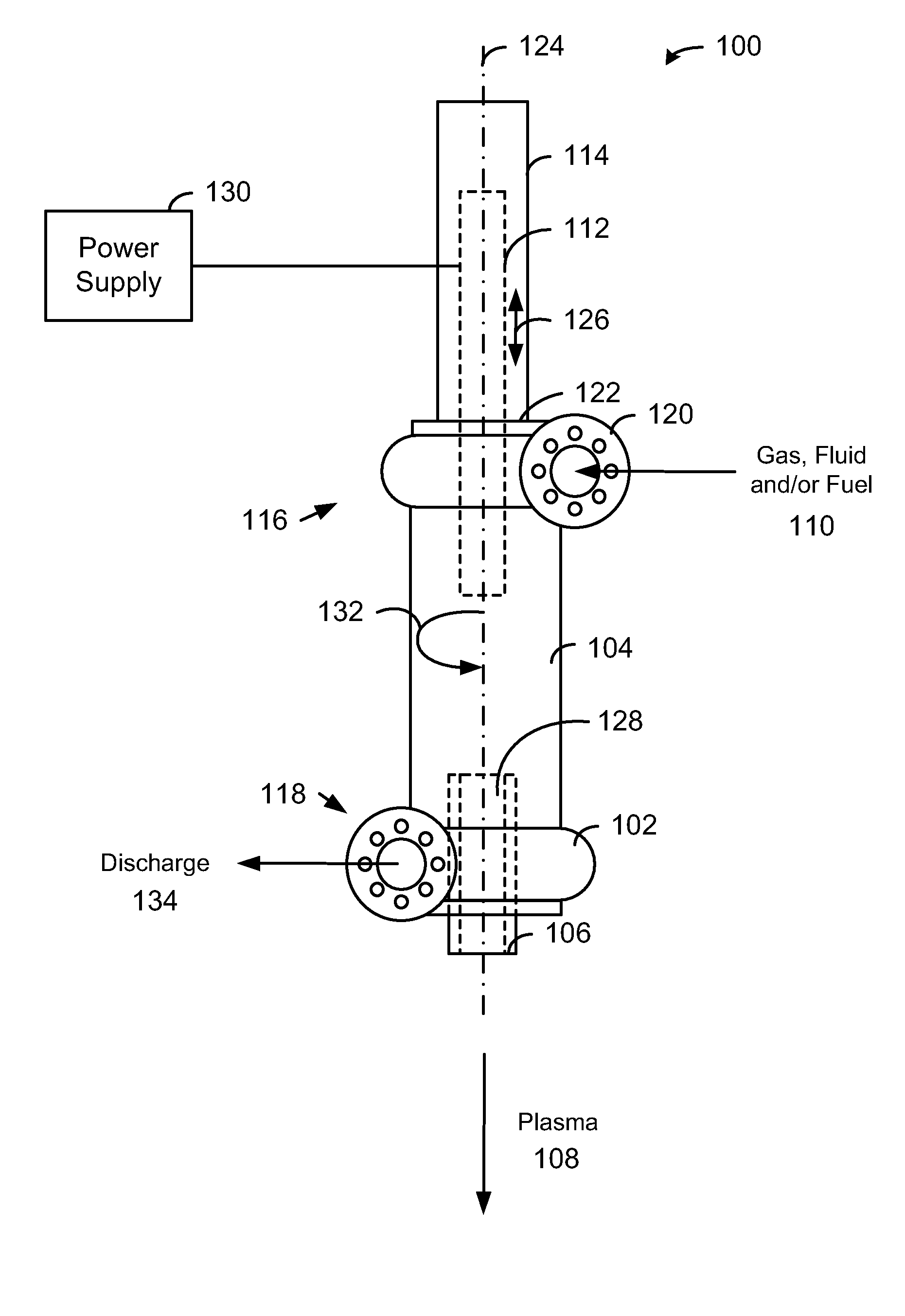
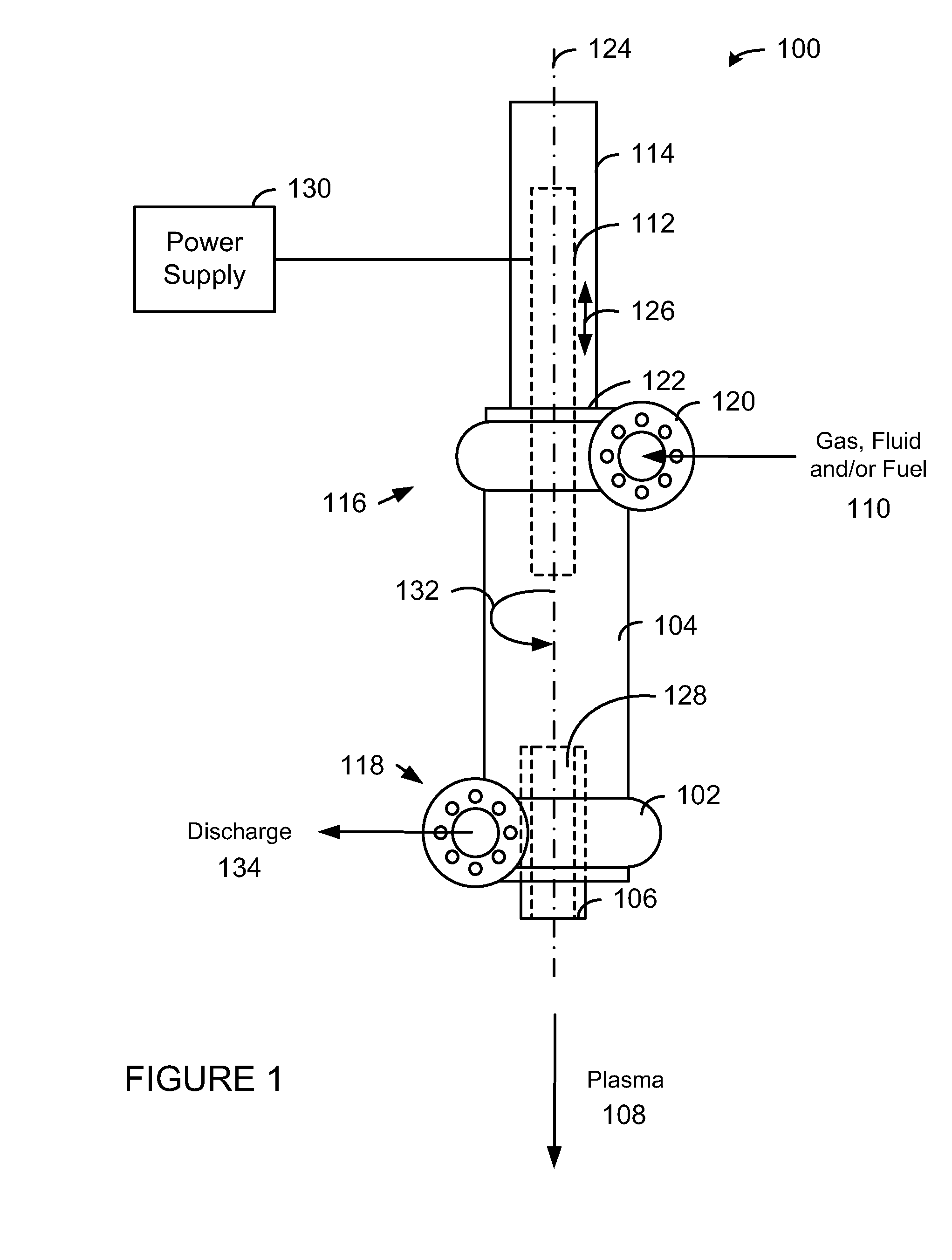
System, method and apparatus for lean combustion with plasma from an electrical arc
The present invention provides a plasma arc torch that can be used for lean combustion. The plasma arc torch includes a cylindrical vessel, an electrode housing connected to the first end of the cylindrical vessel such that a first electrode is (a) aligned with a longitudinal axis of the cylindrical vessel, (b) extends into the cylindrical vessel, and (c) can be moved along the longitudinal axis, a linear actuator connected to the first electrode to adjust a position of the first electrode, a hollow electrode nozzle connected to the second end of the cylindrical vessel such that the center line of the hollow electrode nozzle is aligned with the longitudinal axis of the cylindrical vessel, and wherein the tangential inlet and the tangential outlet create a vortex within the cylindrical vessel, and the first electrode and the hollow electrode nozzle creates a plasma that discharges through the hollow electrode nozzle.
Owner:FORET PLASMA LABS
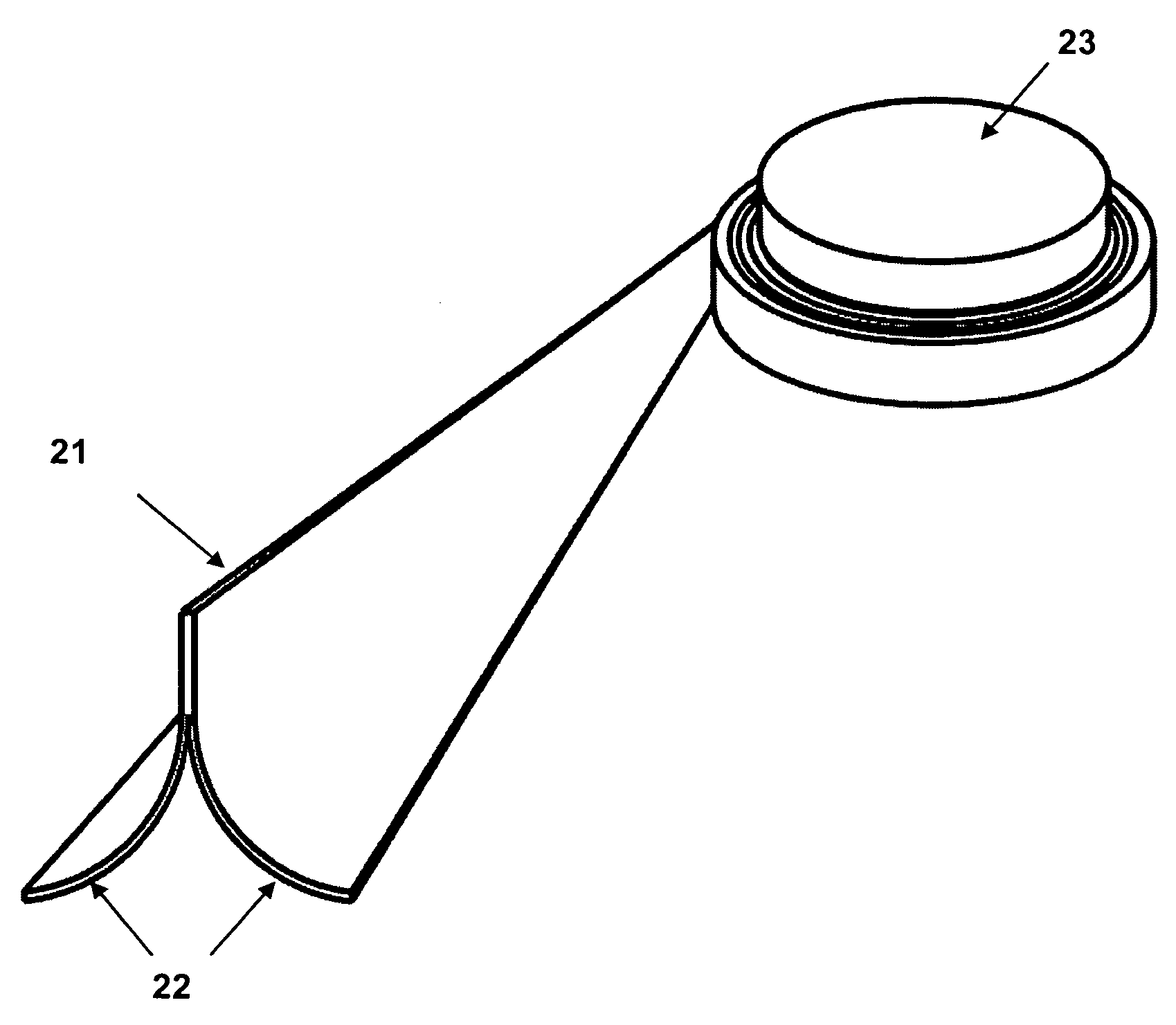
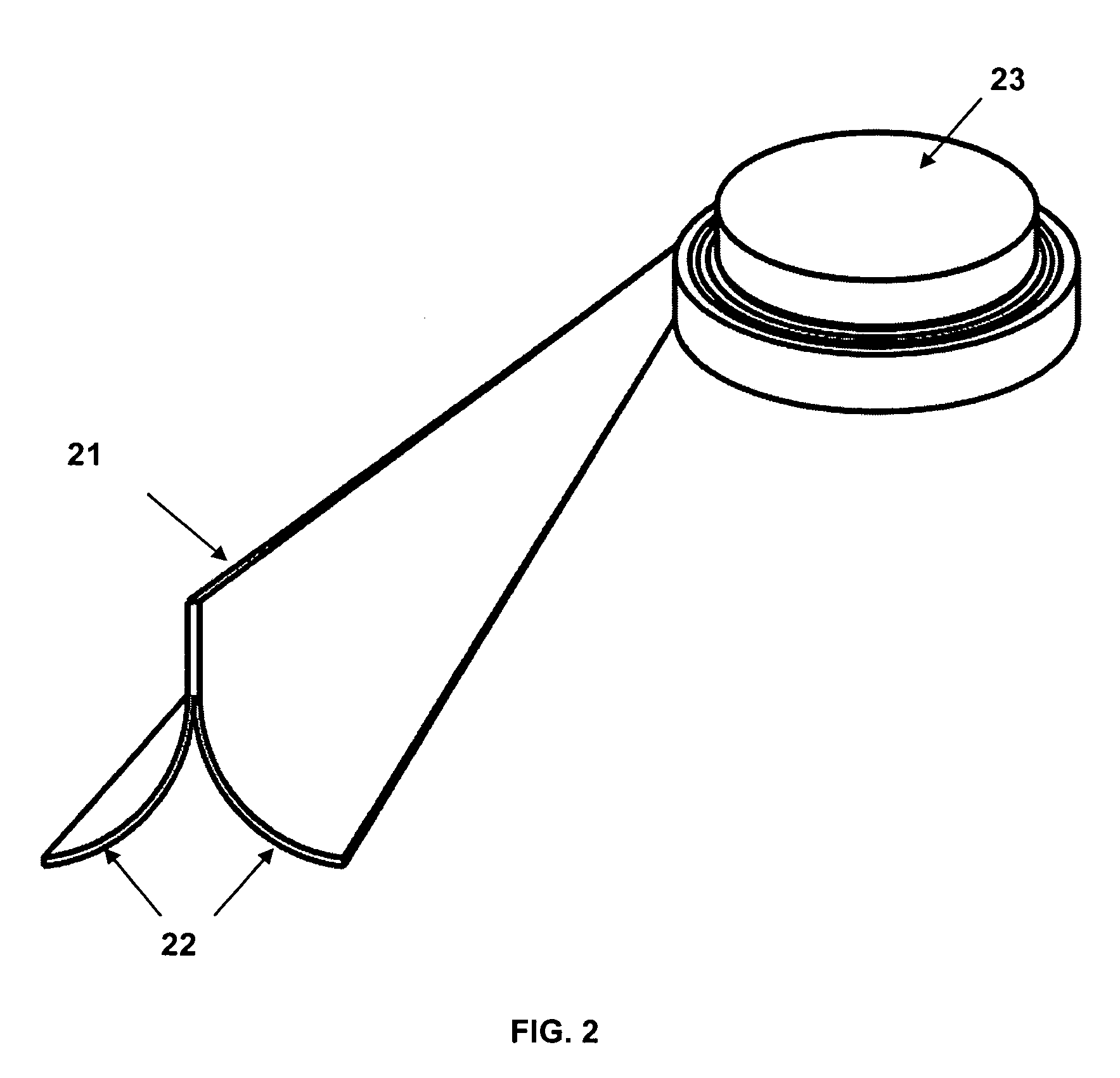
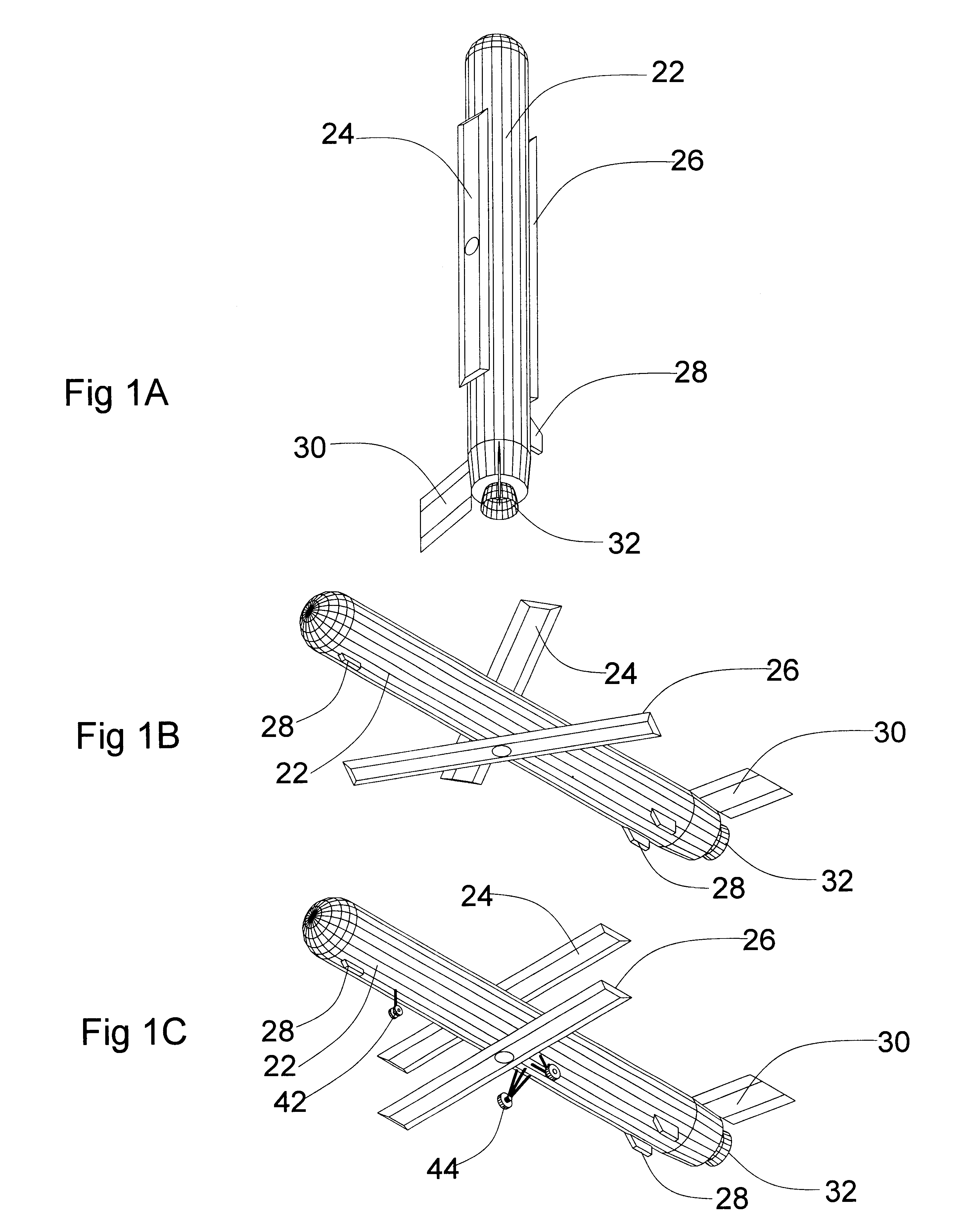
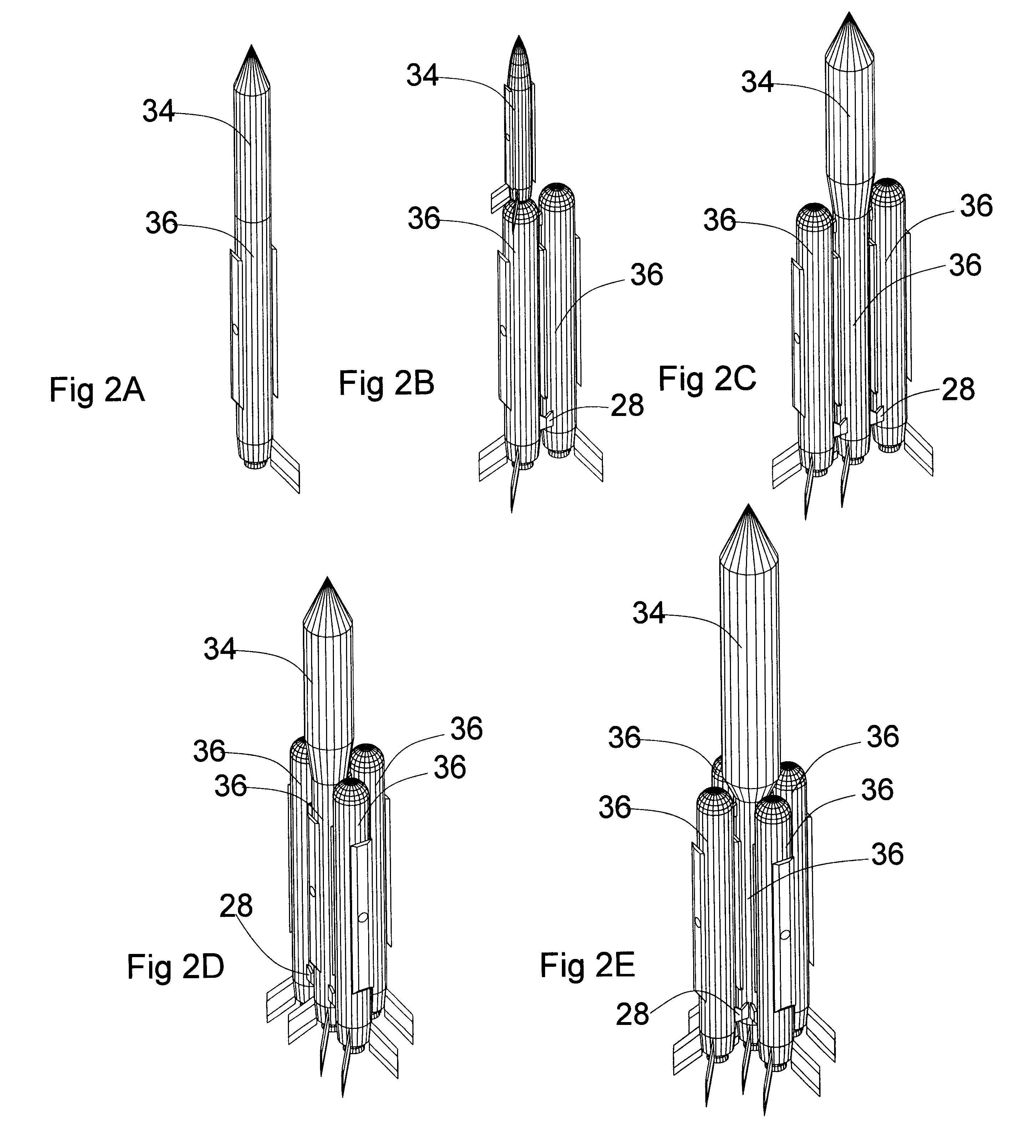
Foldable member
InactiveUS6374565B1Weight increaseDimensional instabilityBuilding roofsCosmonautic vehiclesMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
Method and Associated Apparatus for Capturing, Servicing and De-Orbiting Earth Satellites Using Robotics
ActiveUS20070125910A1Facilitate servicingReduce amountLaunch systemsArtificial satellitesPopulationSpacecraft
This invention is a method and supporting apparatus for autonomously capturing, servicing and de-orbiting a free-flying spacecraft, such as a satellite, using robotics. The capture of the spacecraft includes the steps of optically seeking and ranging the satellite using LIDAR; and matching tumble rates, rendezvousing and berthing with the satellite. Servicing of the spacecraft may be done using supervised autonomy, which is allowing a robot to execute a sequence of instructions without intervention from a remote human-occupied location. These instructions may be packaged at the remote station in a script and uplinked to the robot for execution upon remote command giving authority to proceed. Alternately, the instructions may be generated by Artificial Intelligence (AI) logic onboard the robot. In either case, the remote operator maintains the ability to abort an instruction or script at any time, as well as the ability to intervene using manual override to teleoperate the robot. In one embodiment, a vehicle used for carrying out the method of this invention comprises an ejection module, which includes the robot, and a de-orbit module. Once servicing is completed by the robot, the ejection module separates from the de-orbit module, leaving the de-orbit module attached to the satellite for de-orbiting the same at a future time. Upon separation, the ejection module can either de-orbit itself or rendezvous with another satellite for servicing. The ability to de-orbit a spacecraft further allows the opportunity to direct the landing of the spent satellite in a safe location away from population centers, such as the ocean.
Owner:NASA
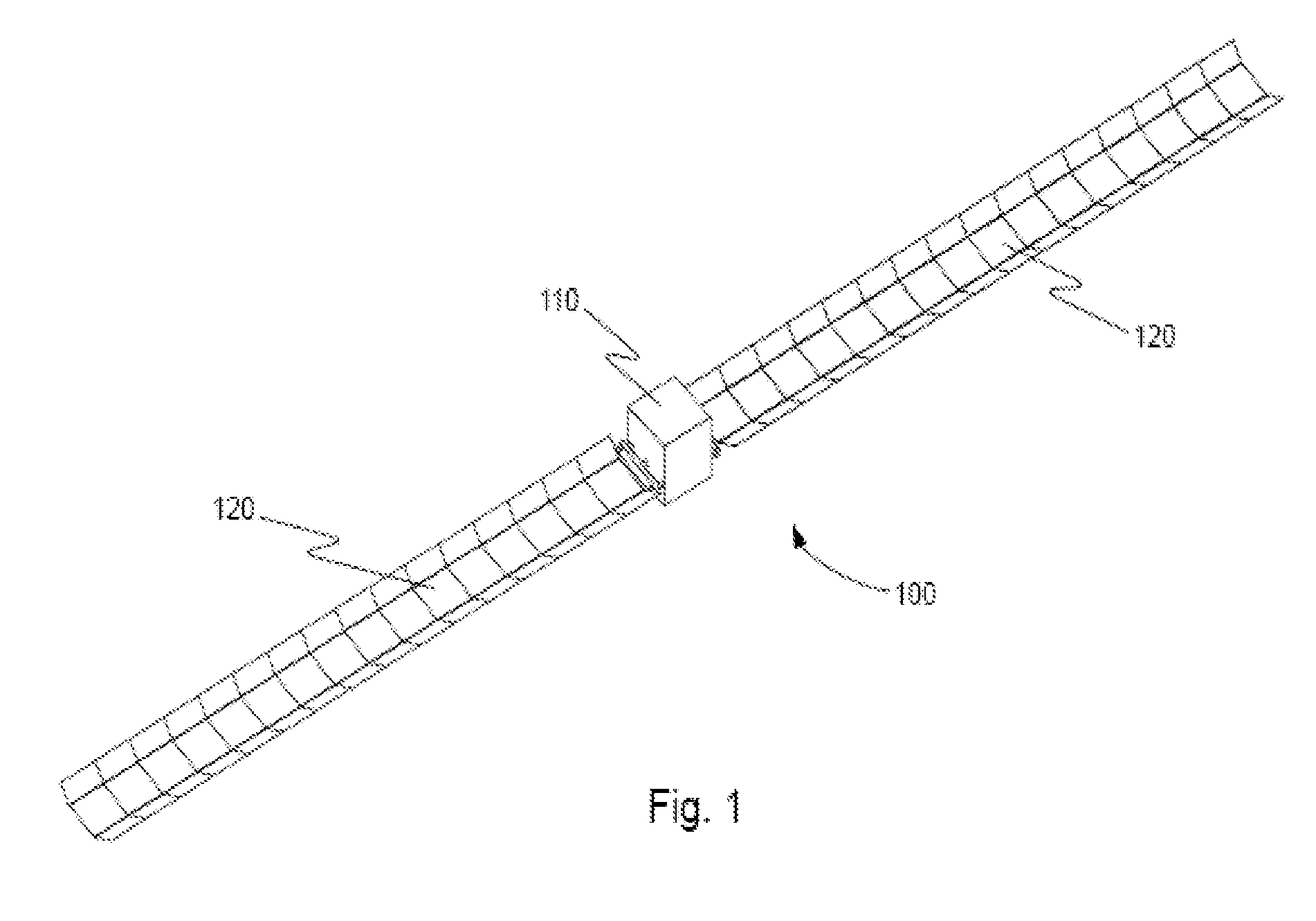
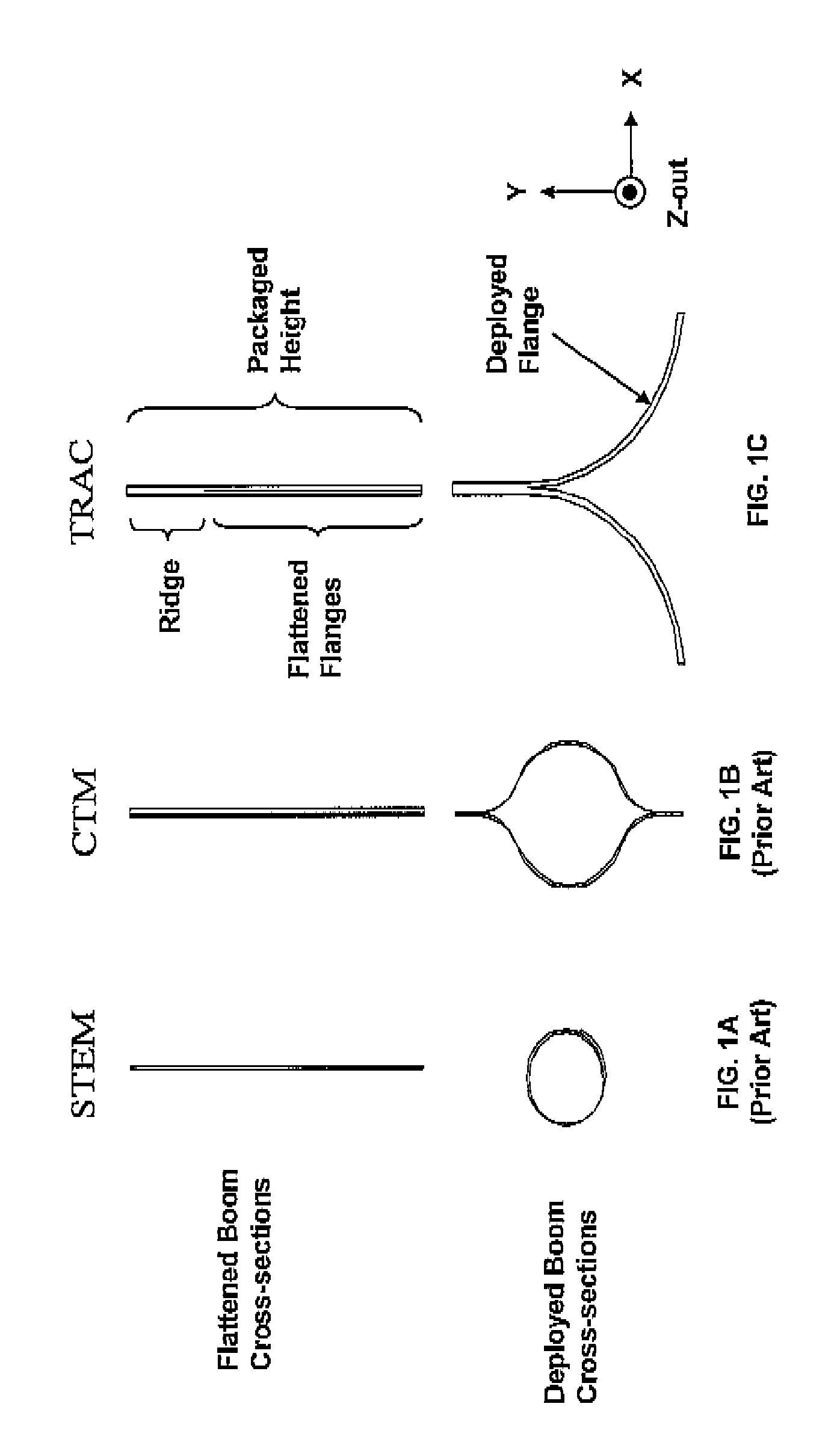
Large-Scale Deployable Solar Array
InactiveUS20070262204A1Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsEngineeringDeployable structure
A deployable structure is disclosed. The deployable structure may include one or more slit-tube longerons; and one or more flat sheets coupled with the one or more slit-tube longerons. The one or more slit-tube longerons and the one or more flat sheets may be stowed by rolling the one or more slit-tube longerons and the one or more flat sheets together into a roll. In one embodiment, at least a portion of the one or more slit-tube longerons may be exposed when stowed. In another embodiment, the one or more slit-tube longerons may be manufactured from a shape memory material. These slit-tube longerons unroll into to a straight configuration when exposed to heat.
Owner:COMPOSITE TECH DEV
Modular platform architecture for satellites
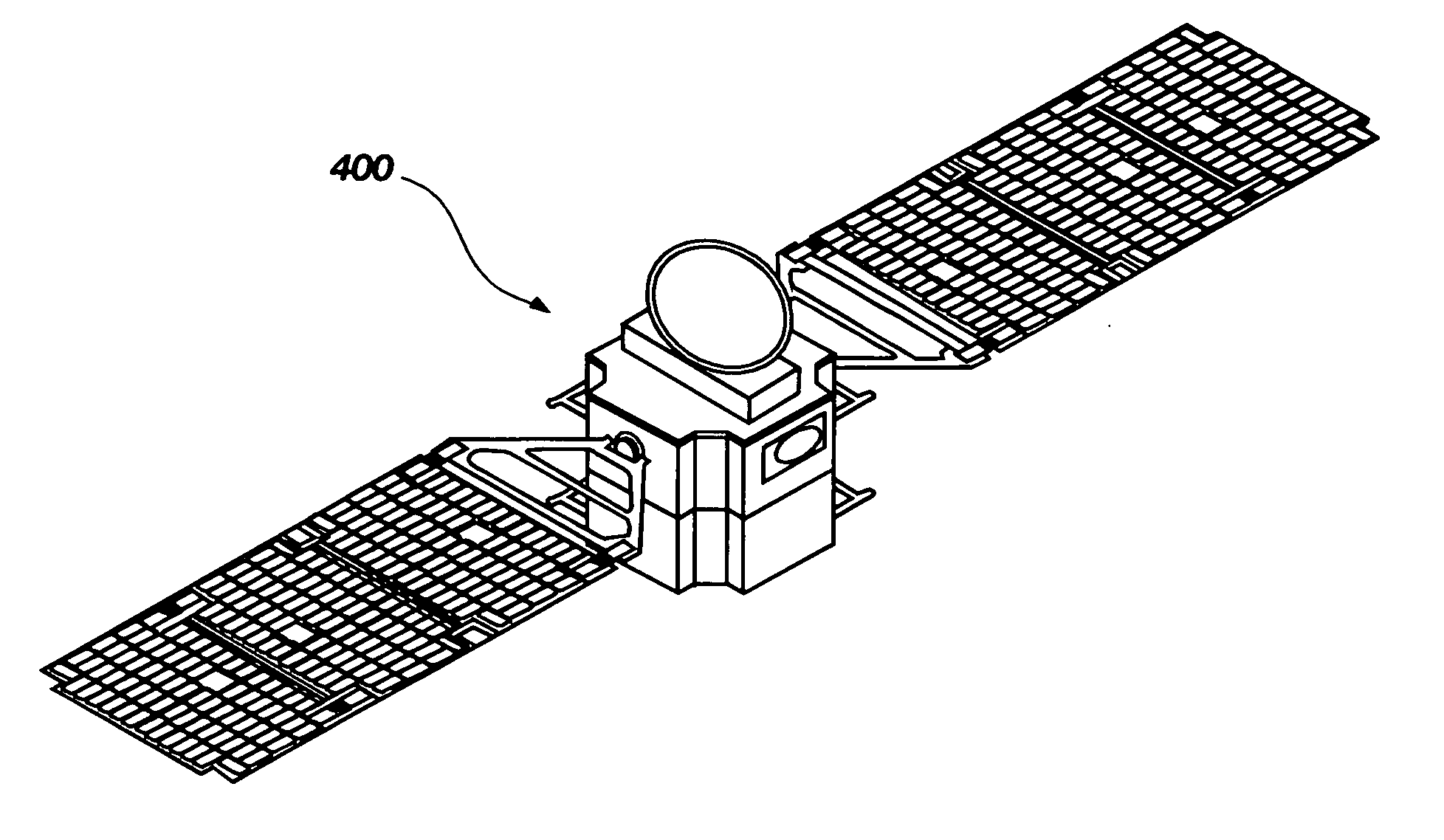
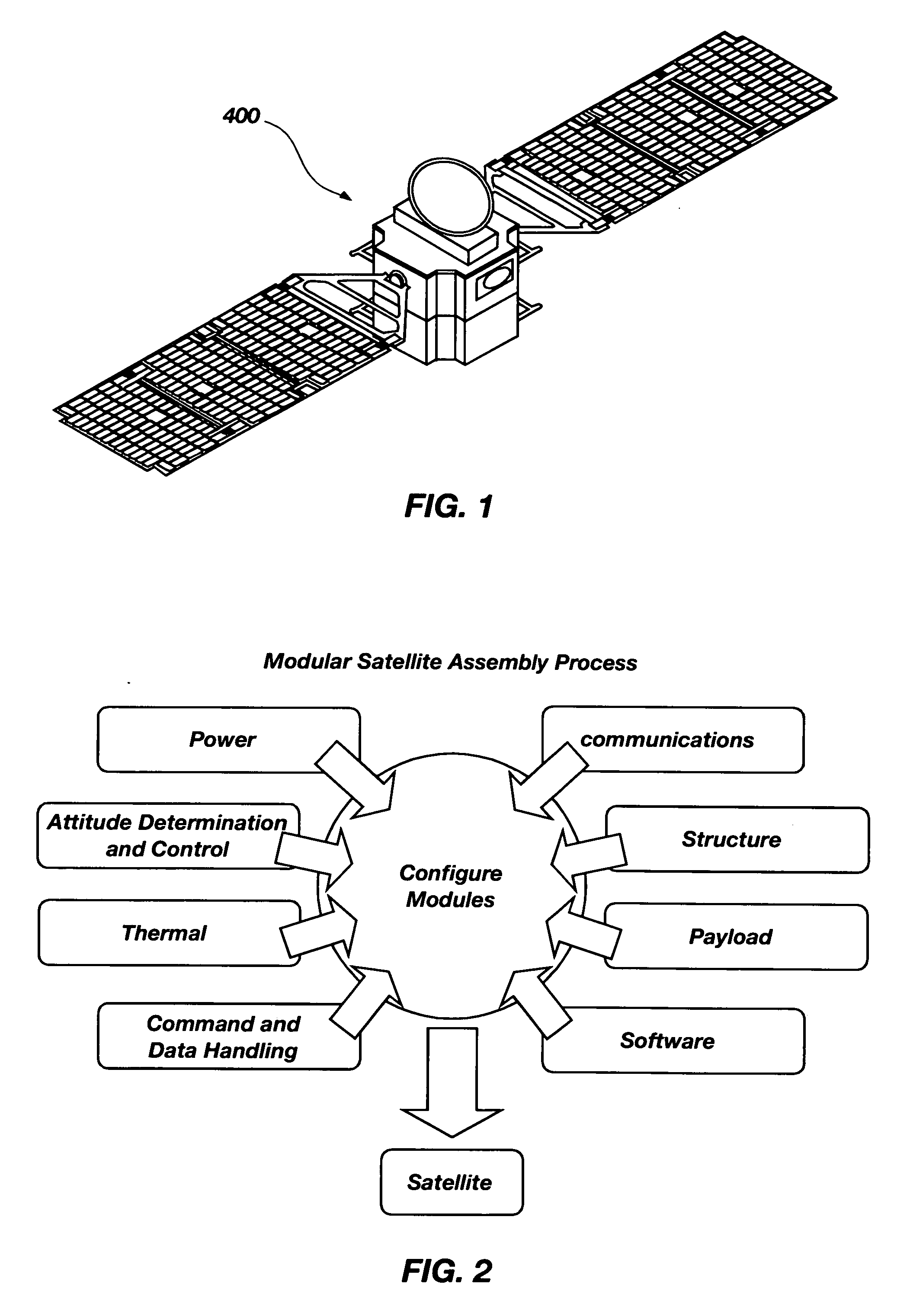
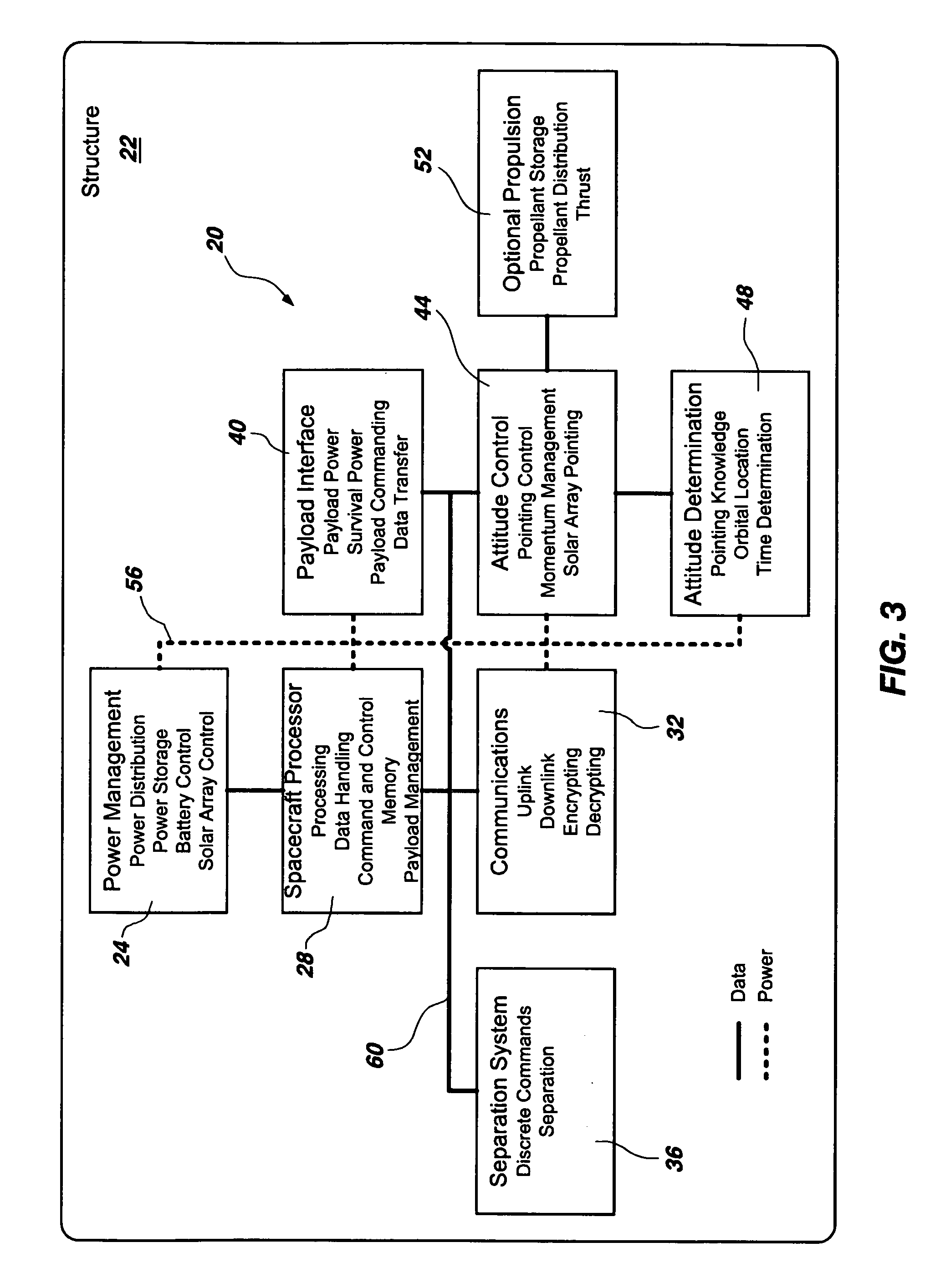
InactiveUS20070029446A1Improve performanceCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesModularityEngineering
A method for implementing a modular platform for the construction of satellites and other spacecraft based on modular platform architecture, the method comprising: (a) identifying a plurality of functional elements and their associated functional routines that may be operable within at least one satellite; (b) associating the functional routines with one another in a strategic manner; (c) dividing the functional routines to define a plurality of subsystems; and (d) deriving a plurality of modules from the plurality of subsystems, each of the modules being configured to operably interface with at least one other module to construct a working satellite capable of carrying out a pre-determined number of the functional routines.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
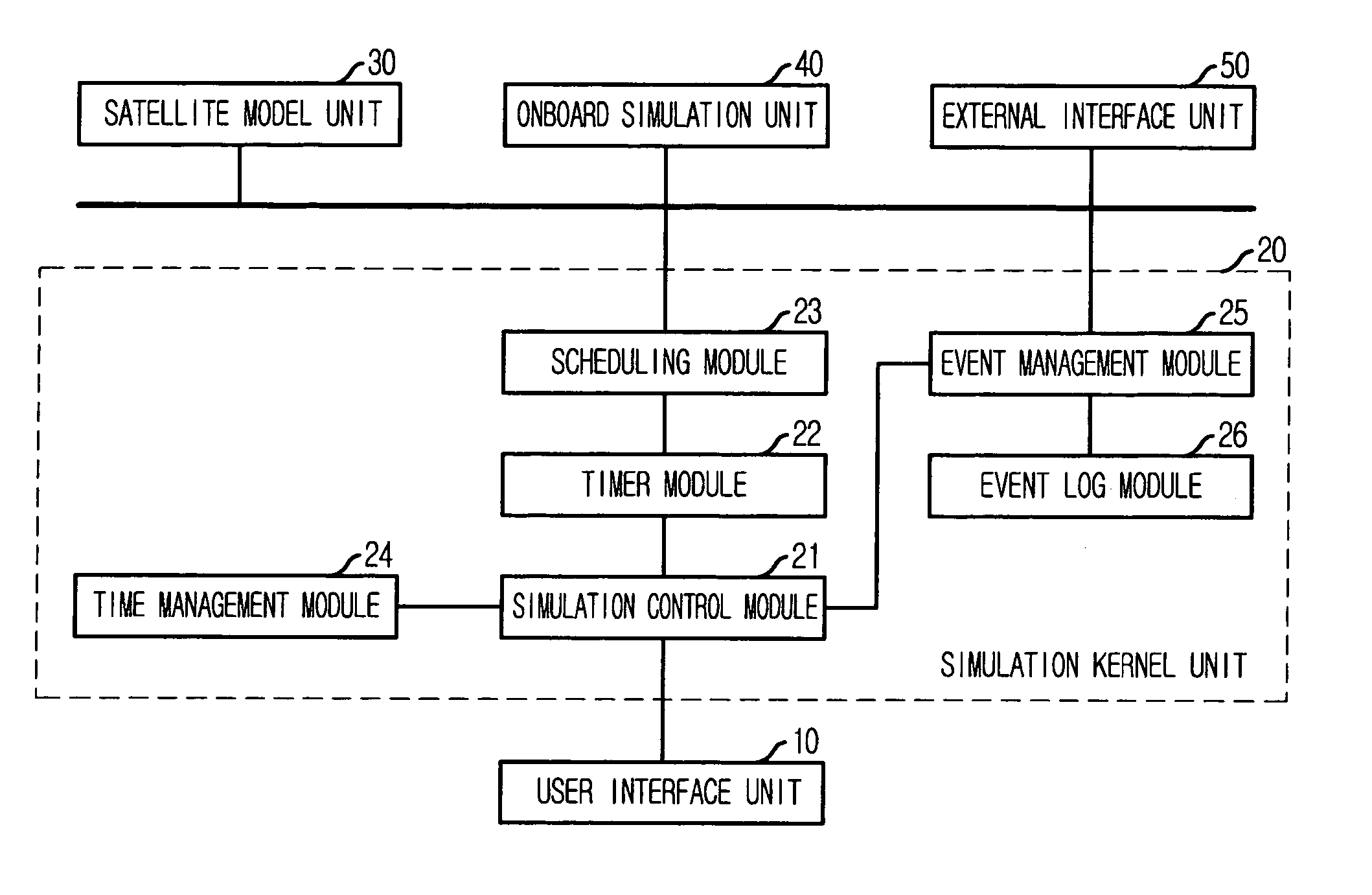
Satellite simulation system using component-based satellite modeling
InactiveUS20070129922A1Cosmonautic partsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusControl systemExecution control
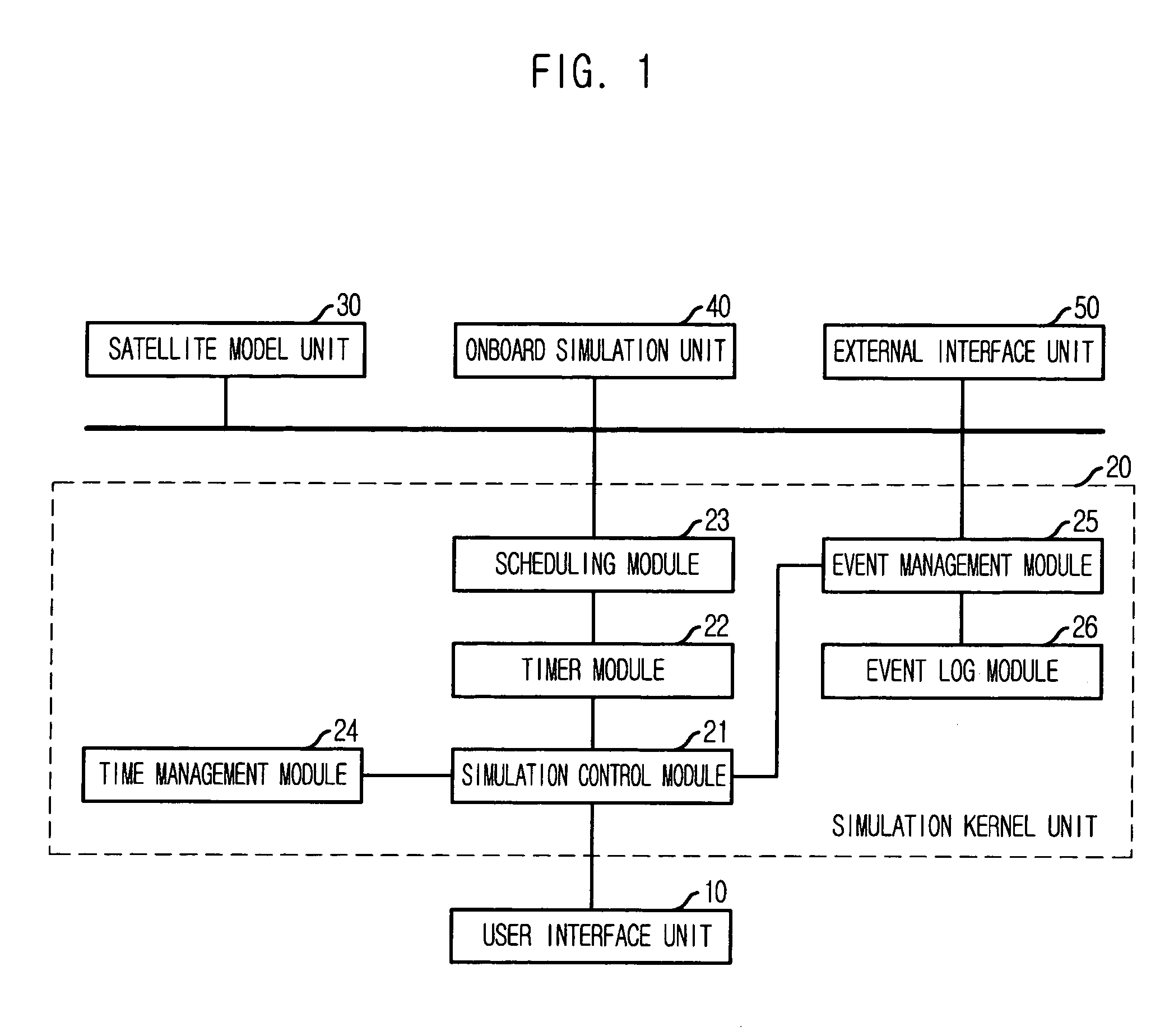
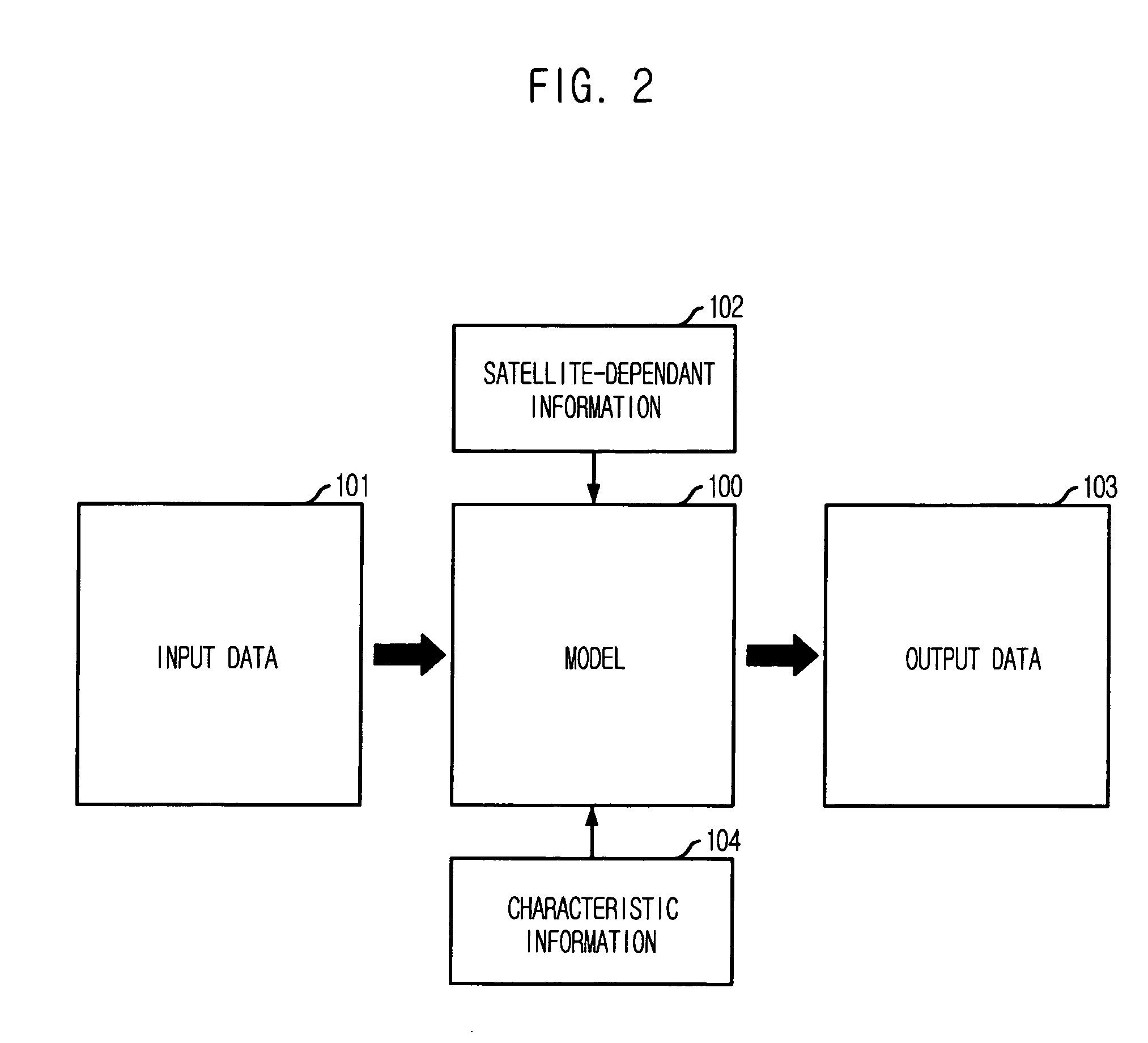
Provided is a satellite simulation system based on component-based satellite modeling. The system includes: a user interface unit for receiving simulation control commands and data and parameter required for simulation from a user; a satellite model unit for individually storing information dependant on the satellite, characteristics of the simulation object model and parameter information based on the characteristics, and performing simulation upon receipt of simulation control commands; and a simulation kernel unit for creating a schedule control command for simulation control of the satellite model unit, the onboard simulation unit and the external interface unit by the control command receiving / transmitting from / to the control command / telemetry to satellite control system, performing control and collecting and managing simulation results.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Rocket-powered entertainment vehicle
InactiveUS20100096491A1Aircraft navigation controlRocket type power plantsRocketAutomotive engineering
A rocket-powered vehicle used for entertainment, namely races, exhibitions, competitions, and revenue-generating events.
Owner:ROCKET RACING
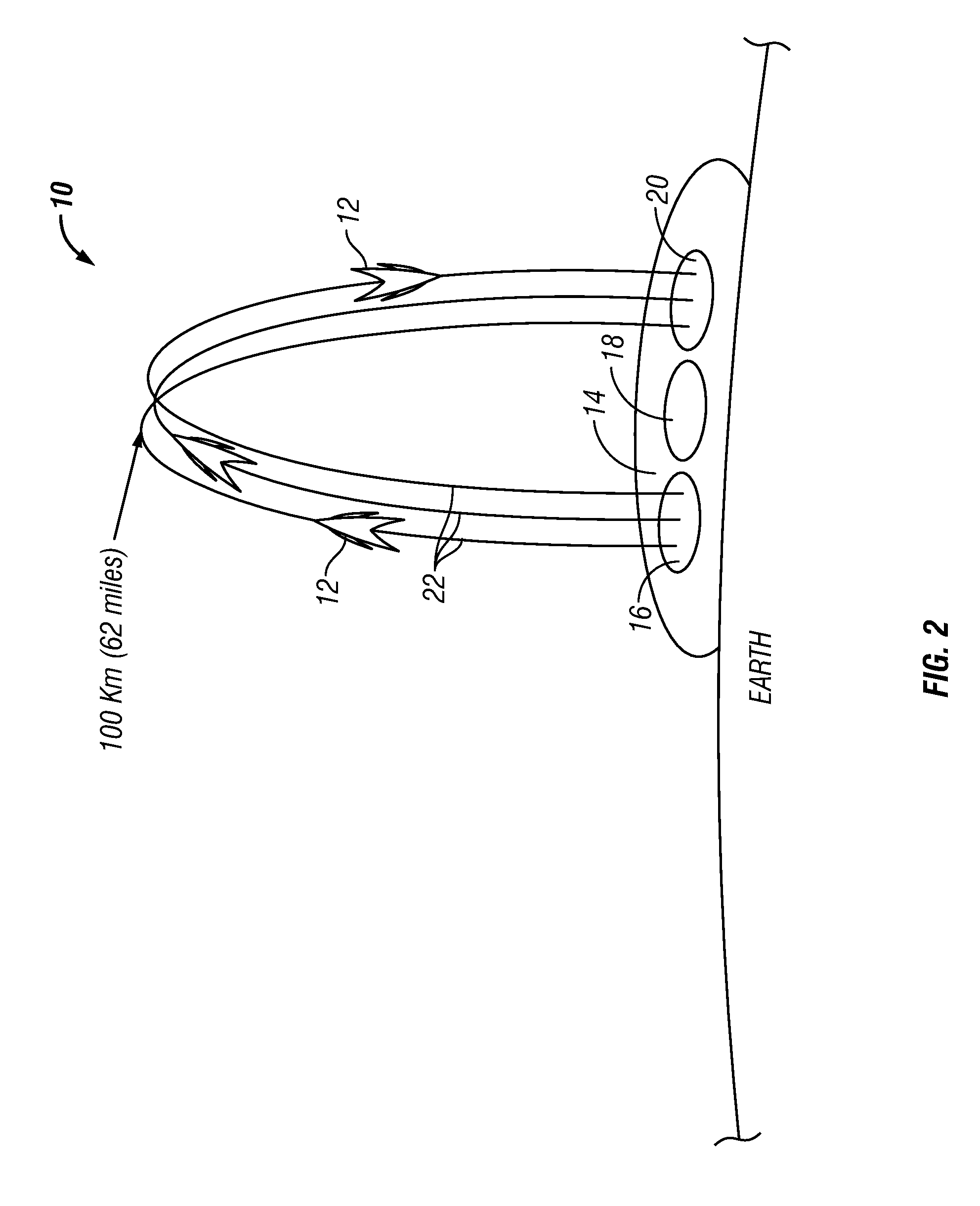
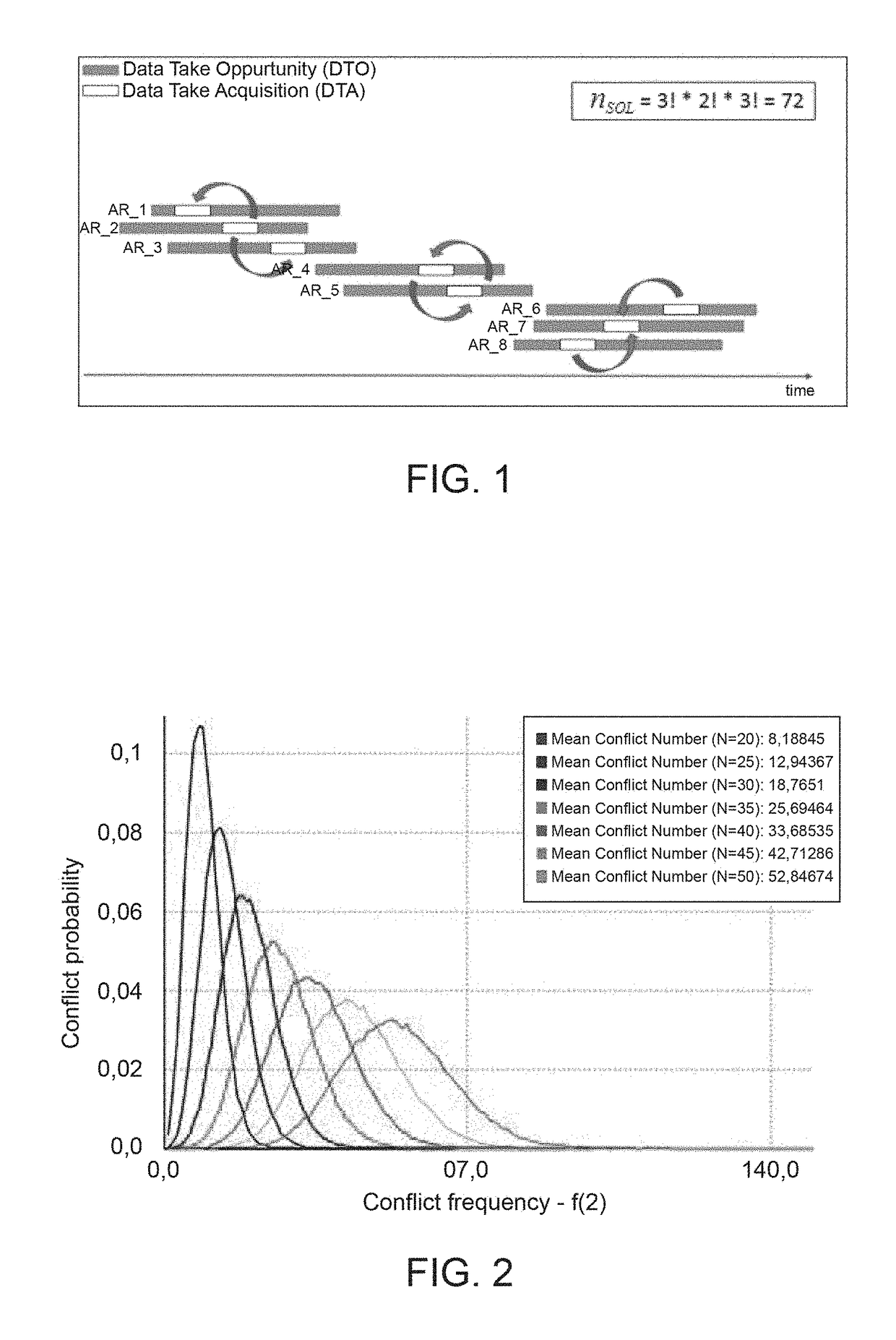
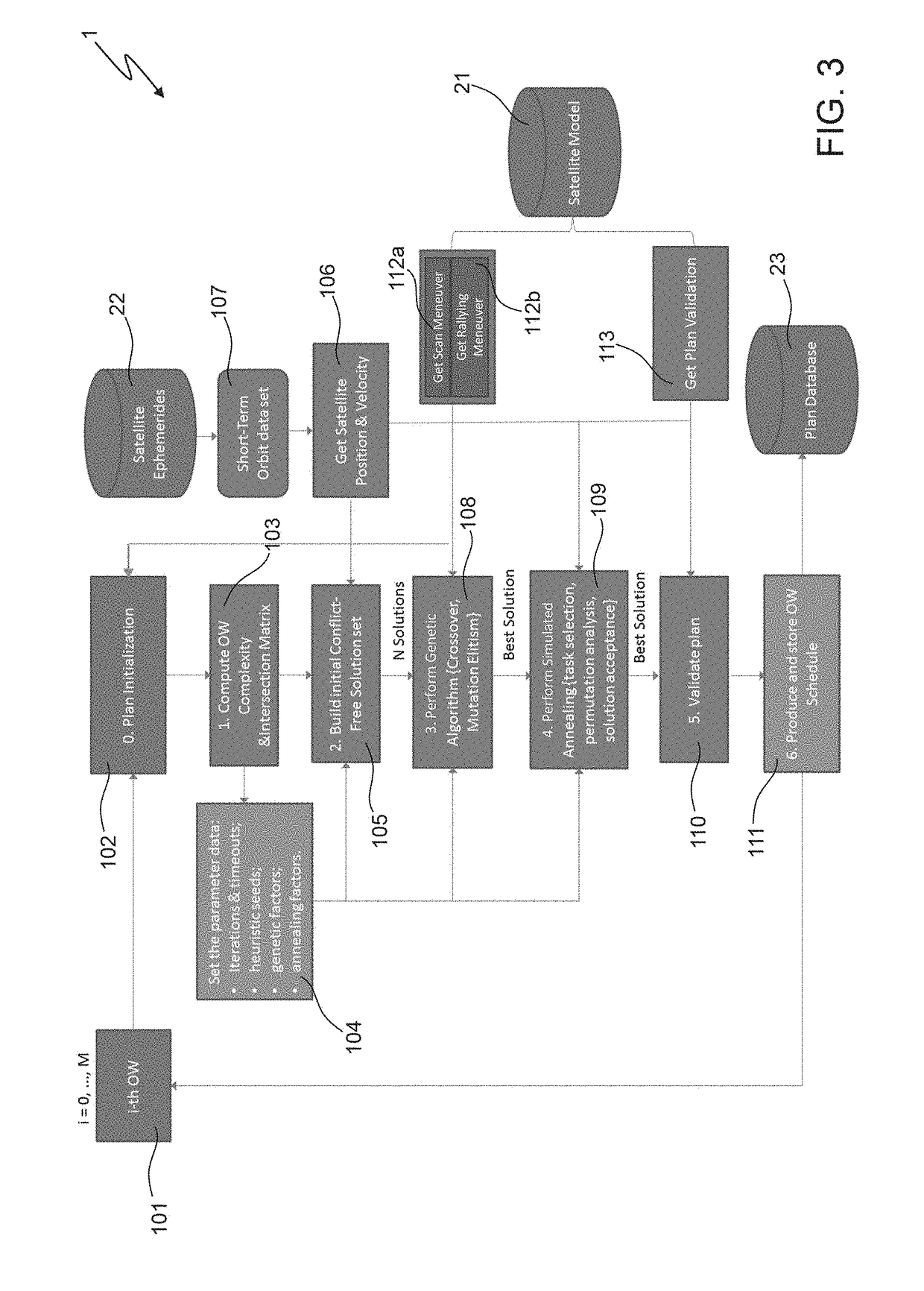
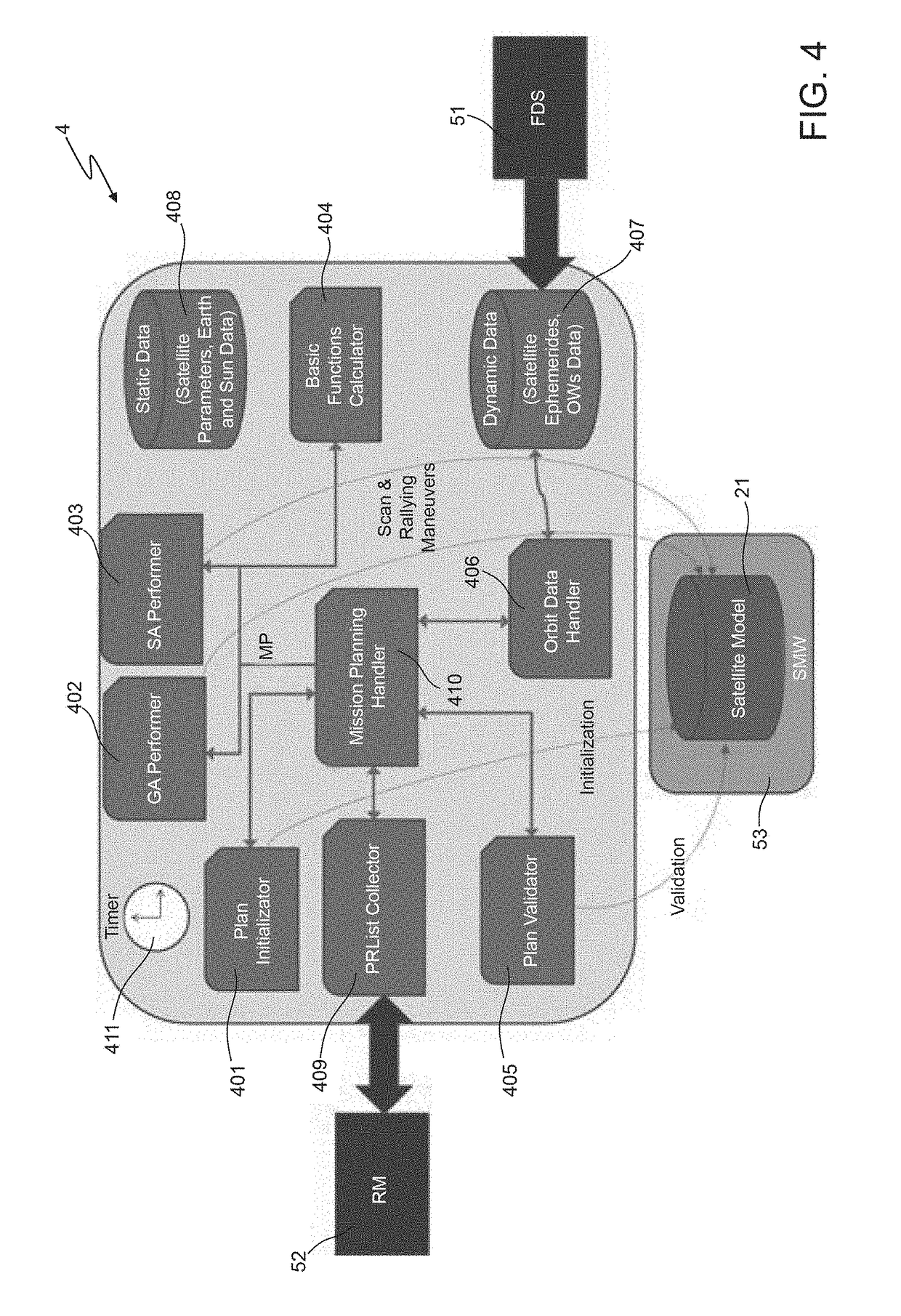
Innovative satellite scheduling method based on genetic algorithms and simulated annealing and related mission planner
ActiveUS20180341894A1Maximal diversityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsSimulation basedGenetic algorithm
A method includes: a) producing initial scheduling plans based on requests related to tasks to be performed within a time period by a remote sensing satellite; wherein each initial scheduling plan schedules respective tasks, which do not conflict with each other in time and in using satellite resources; and each task is scheduled in at least one of the initial scheduling plans; b) applying a genetic-algorithm-based processing to the initial scheduling plans to produce a genetic-algorithm-based scheduling plan which is for mission objectives, and complies with constraints related to the satellite resources, to the tasks, and to the time period; and c) applying a simulated-annealing-based processing to the genetic-algorithm-based scheduling plan to produce a simulated-annealing-based scheduling plan that fits the mission objectives, complies with the constraints, and in which a larger number of tasks is scheduled than in the genetic-algorithm-based scheduling plan.
Owner:TELESPAZIO SPA
Zero-G emulating testbed for spacecraft control system
InactiveUS20050230557A1Reduces system uncertaintyReduce frictionCosmonautic condition simulationsCosmonautic ground equipmentsControl systemSpace vehicle control
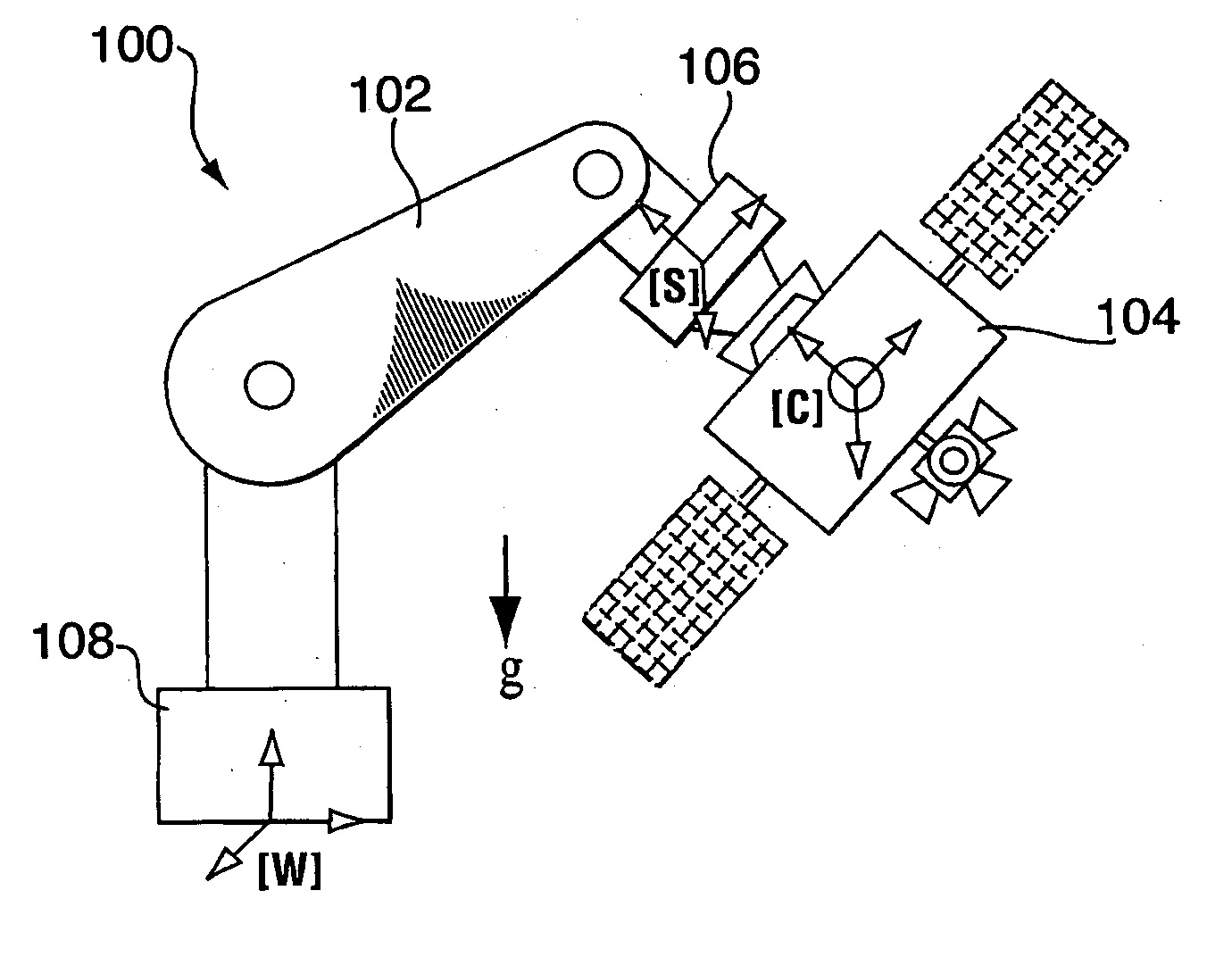
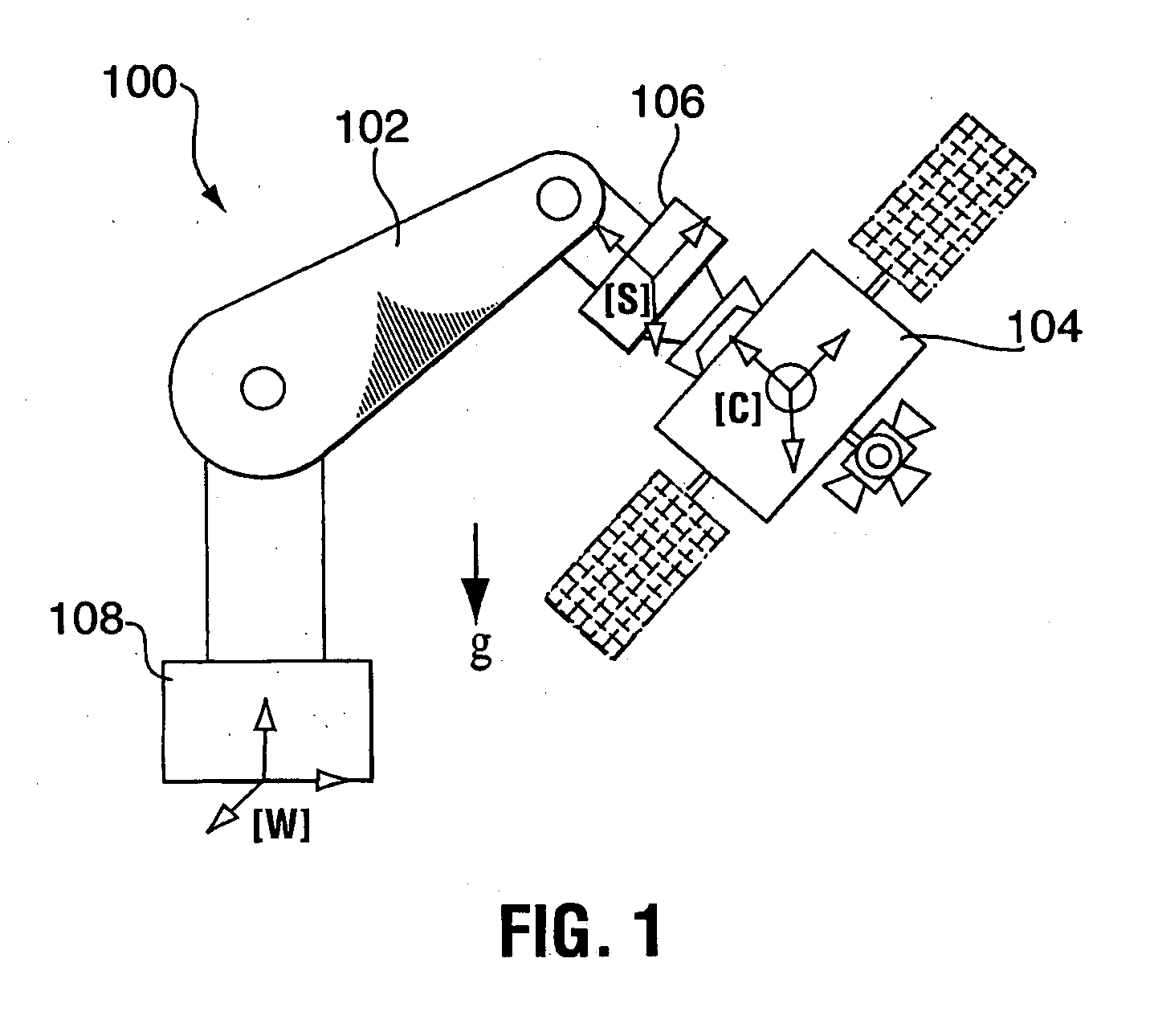
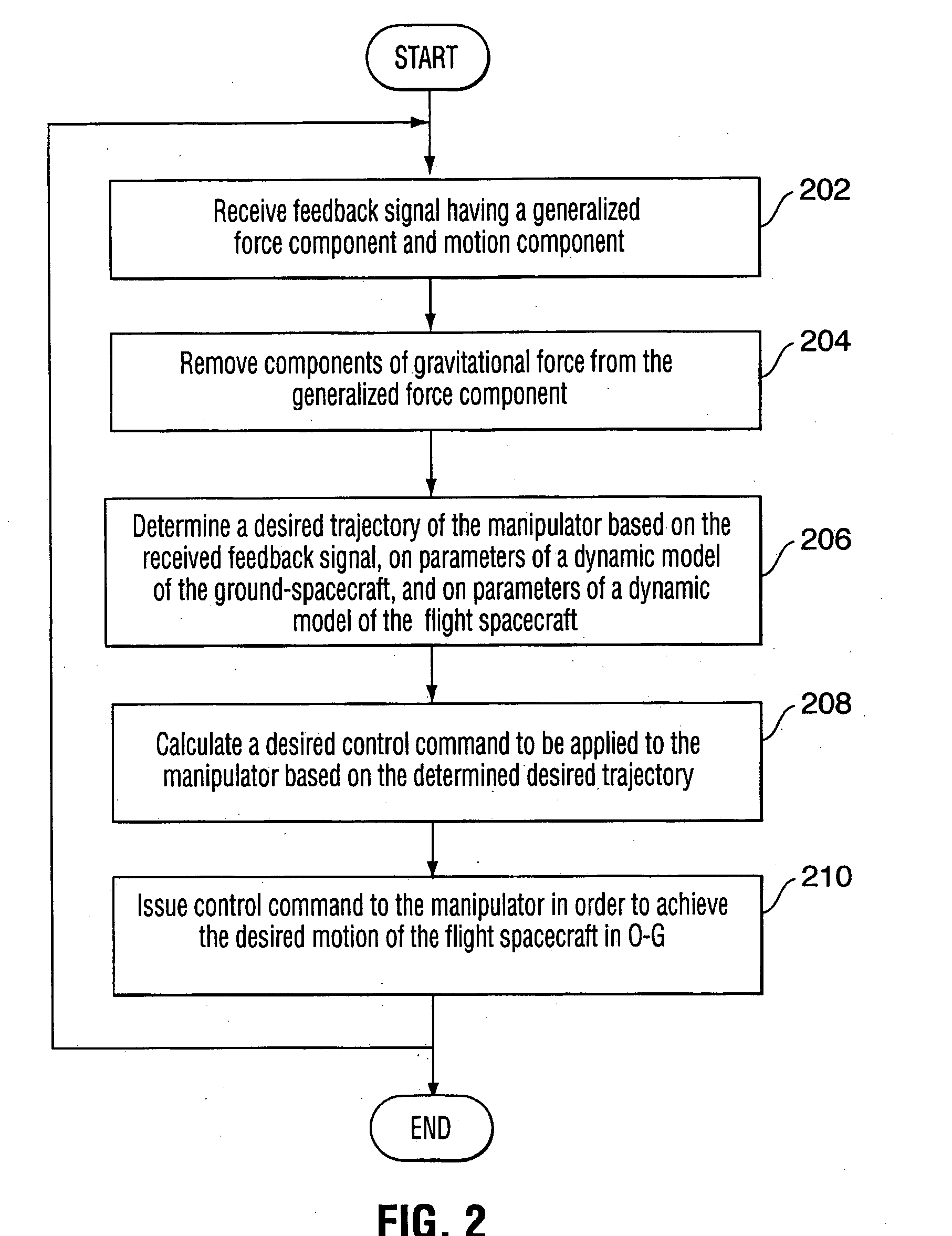
The present invention provides an emulation system having a control system that allows the testing of a satellite control system with all of its hardware in place, i.e. fully integrated. The emulation methodology is applicable to the case of either a rigid spacecraft or a flexible spacecraft, provided that the spacecraft's sensors and actuators are stowed to the rigid part of spacecraft in the case of a flexible spacecraft. Practically, the latter condition is not restrictive, as the actuators and sensors are usually placed rigidly in the satellite bus, while the satellite solar panels constitute the flexible elements. The control system is used to tune the mass properties and dynamic behaviour of a rigid ground-spacecraft in a 1-G environment to those of a flight-spacecraft in 0-G. A six-axis force / moment sensor is placed at an interface of the ground-spacecraft and a manipulator. Signals received from the force / moment sensor, and in some cases signals relating to the position and velocity of manipulator joints, are received into the control system.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
Inflatable flying body for the rescue descent of a person
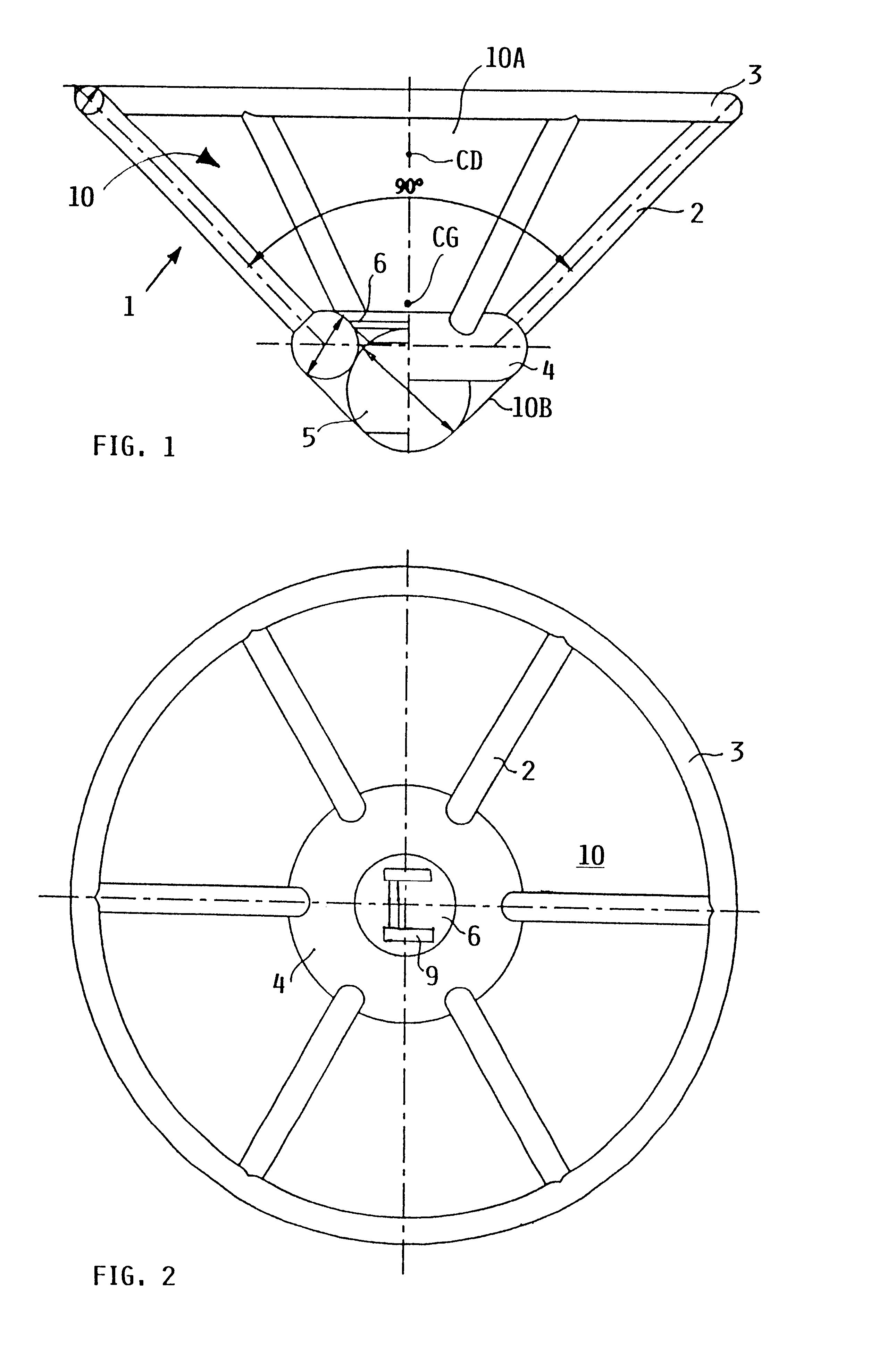
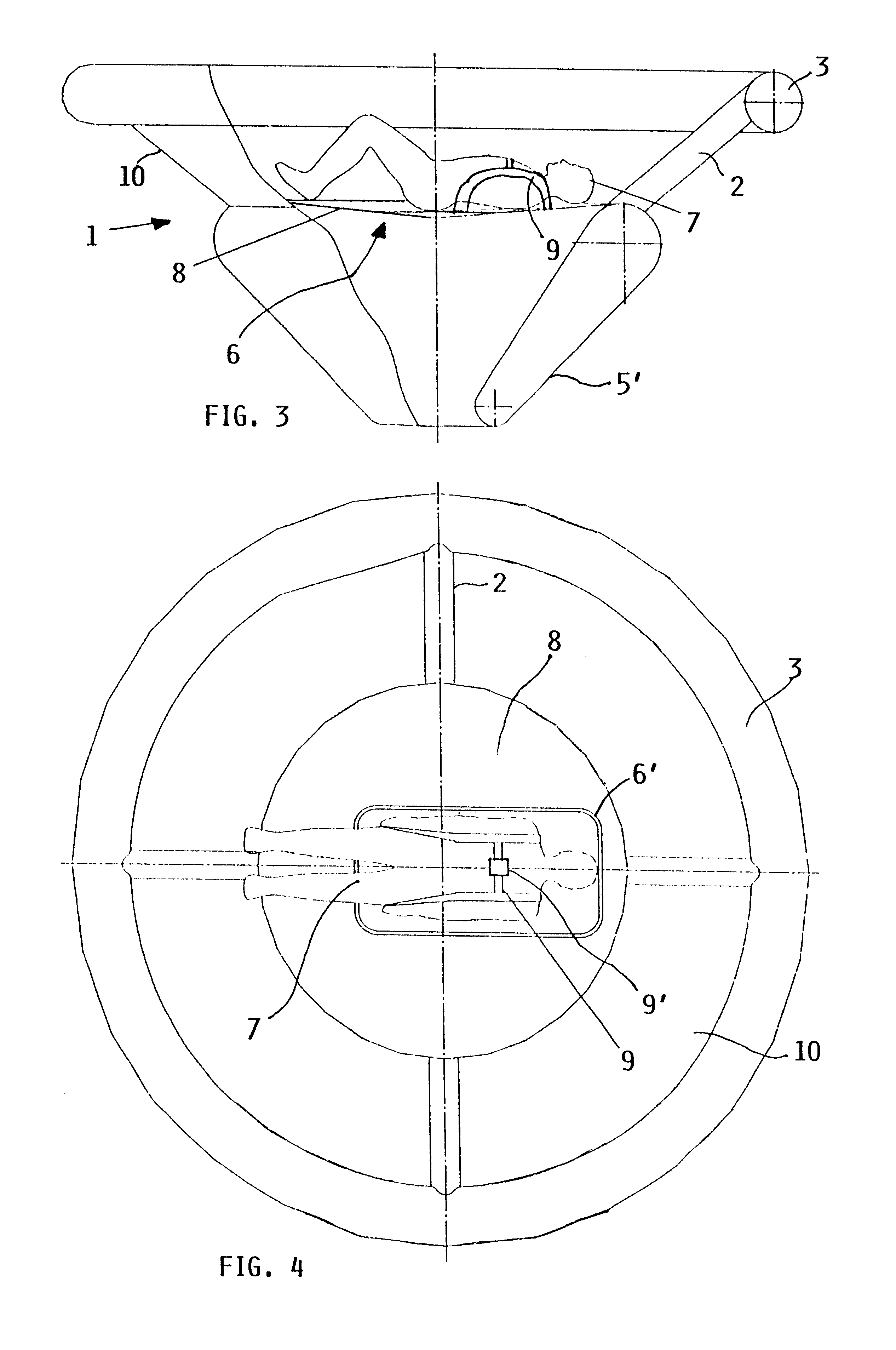
InactiveUS6607166B1Slow its descentDistribute over timeAircraft ejection meansCosmonautic partsConical formsNose
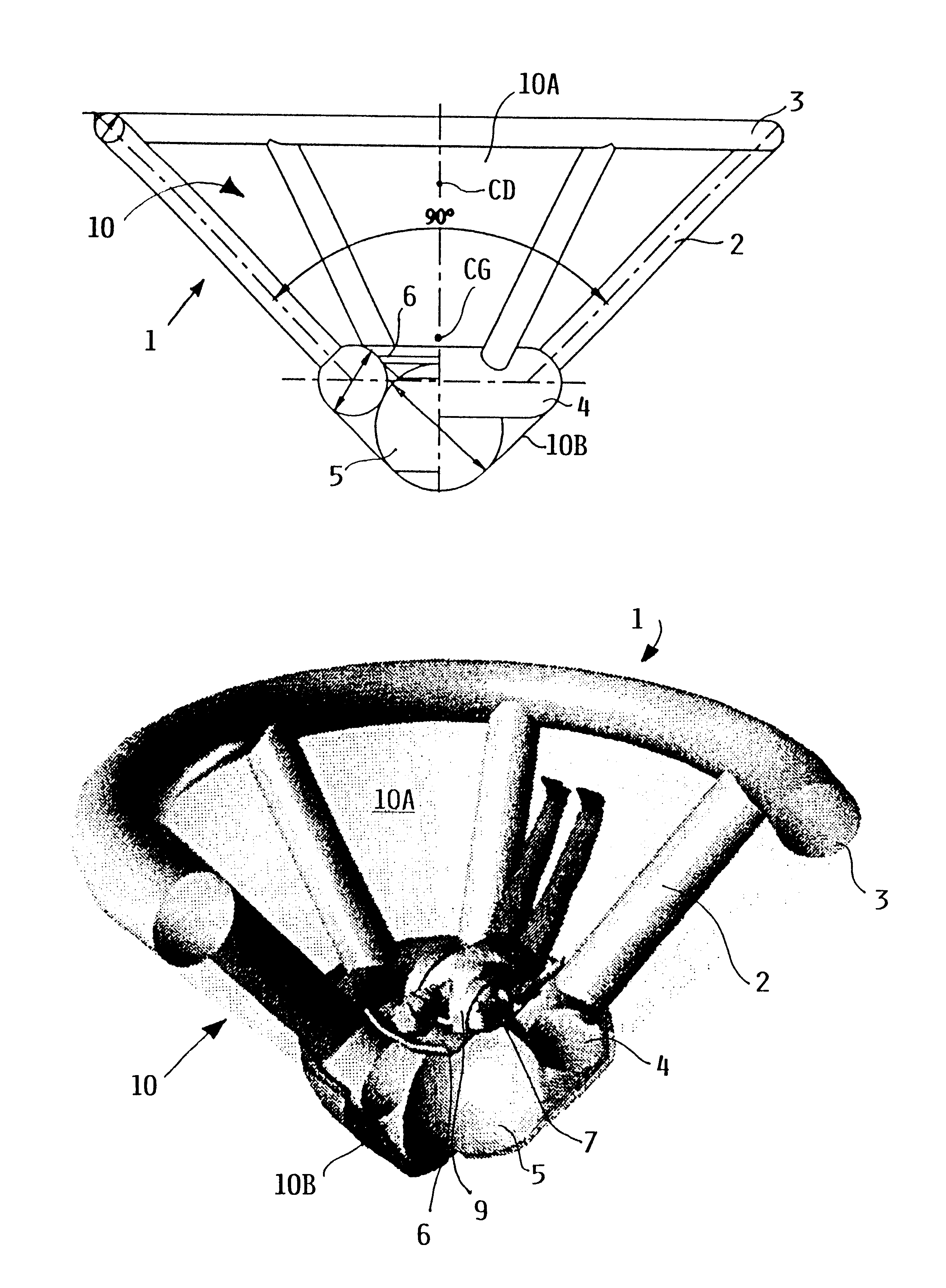
A person can safely descend from a burning high-rise building or the like using an inflatable flying body that has a hollow conical form in an inflated deployed condition, but is deflated and folded into a backpack form in a stowed condition. The flying body includes an upper stabilizing ring, a lower nose structure with a pneumatic damping body, spoke struts extending conically therebetween, a cover skin covering the abovementioned inflatable components to form the conical outer surface and provide aerodynamic braking drag, and gas generators to inflate the inflatable components. A person straps on the apparatus in the stowed backpack form and pulls a handle to actuate the gas generators for inflating the apparatus, whereby the expanding apparatus ejects the person from the building and then orients itself in a nose-down attitude during the descent. The pneumatic damping body damps and dissipates the landing impact energy.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
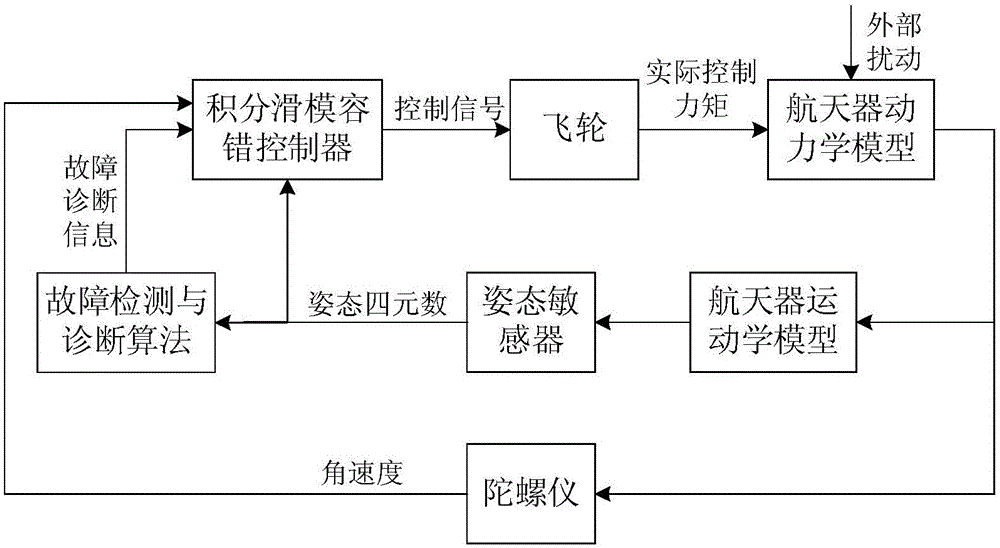
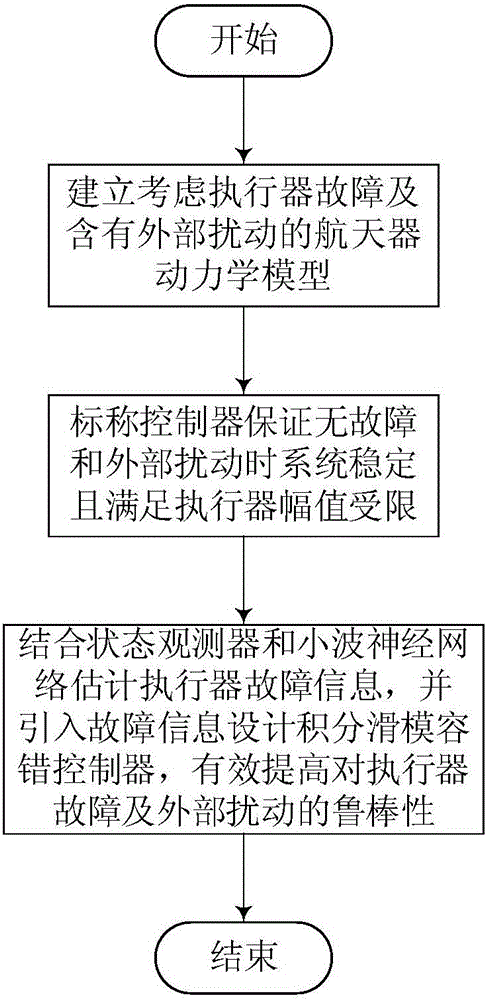
Spacecraft attitude integral sliding mode fault tolerance control method taking consideration of performer fault
ActiveCN105843240AEasy to satisfy control torque limited constraintsSatisfy the control torque limited constraintCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsActive faultDynamic models
The invention relates to a spacecraft attitude integral sliding mode fault tolerance control method taking consideration of a performer fault and provides a robustness attitude active fault tolerance control method based on an integral sliding mode surface for problems of the performer fault, external disturbance and control moment amplitude limits in a spacecraft attitude control process. The method comprises steps that firstly, a spacecraft attitude dynamics model taking consideration of the performer fault and containing external disturbance is established; secondly, on the condition that a performer is not in fault, a designed nominal controller can guarantee system stability, and input saturation amplitude limits can be easily satisfied through adjusting controller parameters; lastly, the fault information is introduced to design an integral sliding mode controller, robustness of external disturbance and the performer fault can be effectively improved, system stability is analyzed on the basis of an Lyapunov method. The method is advantaged in that stability of the attitude control system is guaranteed when a spacecraft operating on orbit generates the performer fault, and relatively strong fault tolerance capability and external disturbance robustness are realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Methods, apparatus and systems for enhanced synthetic vision and multi-sensor data fusion to improve operational capabilities of unmanned aerial vehicles
ActiveUS7747364B2Improve the display effectStation can be limitedVehicle testingCosmonautic vehiclesSynthetic vision systemSensor fusion
The invention provides, in some aspects, improved methods, apparatus and systems for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) operation that utilize multiple data links between a UAV and a control station in order to transmit control and actionable intelligence data. Such methods, apparatus and systems can be used, for example, to monitor a selected environment (e.g., an oil field or other terrain / environment of interest). In a related aspect, such data links comprise satellite communication channels.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
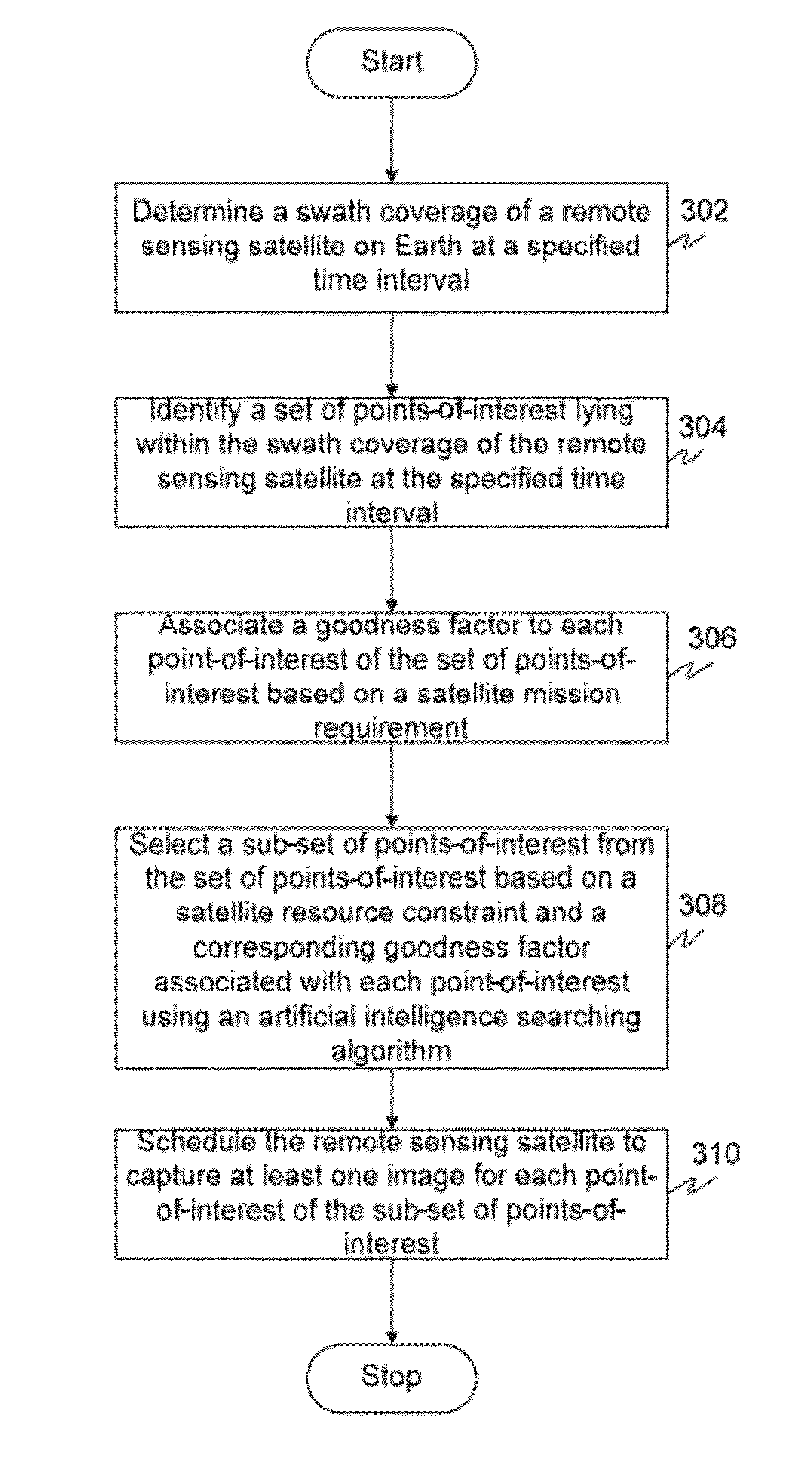
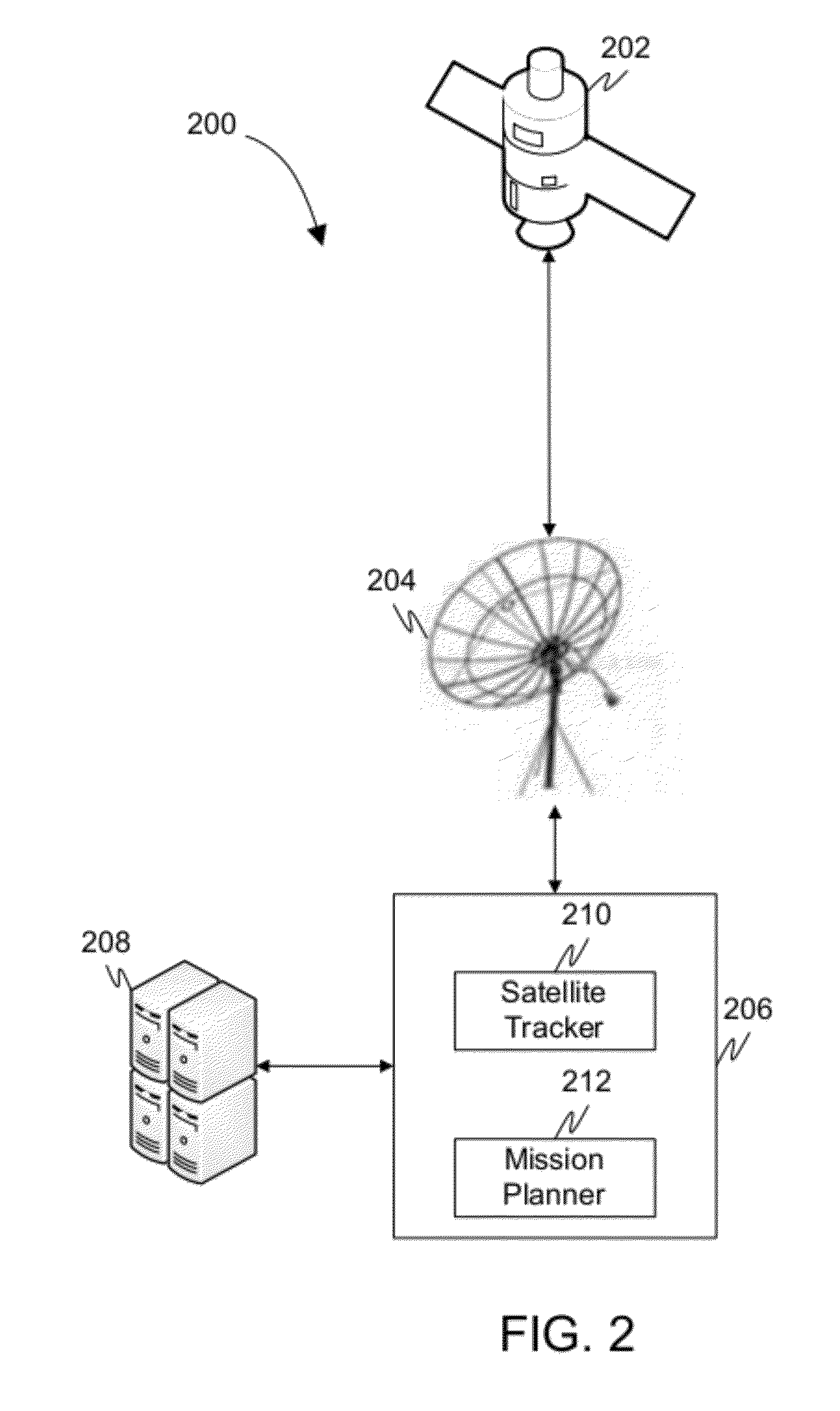
Method and system for automatically planning and scheduling a remote sensing satellite mission
InactiveUS20120029812A1Cosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationGround stationResource constraints
The present invention provides method and system for automatically planning and scheduling a remote sensing satellite mission. A swath coverage of a remote sensing satellite at a specified time interval is determined from a ground station. Thereafter, a set of points-of-interest lying within the swath coverage of the remote sensing satellite at the specified time interval is identified. The method further includes associating a goodness factor to each point-of-interest of the set of points-of-interest based on a satellite mission requirement. An artificial intelligence searching algorithm is utilized to select a sub-set of points-of-interest from the set of points-of-interest based on a satellite resource constraint and a corresponding goodness factor associated with each point-of-interest. Finally, the method schedules the remote sensing satellite to capture at least one image for each point-of-interest of the sub-set of points-of-interest.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ CITY FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for the manufacture of electronic devices on substrates and devices related thereto
Methods for manufacturing electronic devices and devices produced by those methods are disclosed. One such method includes releasably bonding a first surface of a device substrate to a face of a first carrier substrate using a first bonding agent to produce a first composite substrate, where the face of the first carrier substrate includes a pattern of trenches. The method also includes processing the device substrate to manufacture an electronic device on a second surface of the device substrate. The method further includes releasing the device substrate from the first carrier substrate by a releasing agent.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
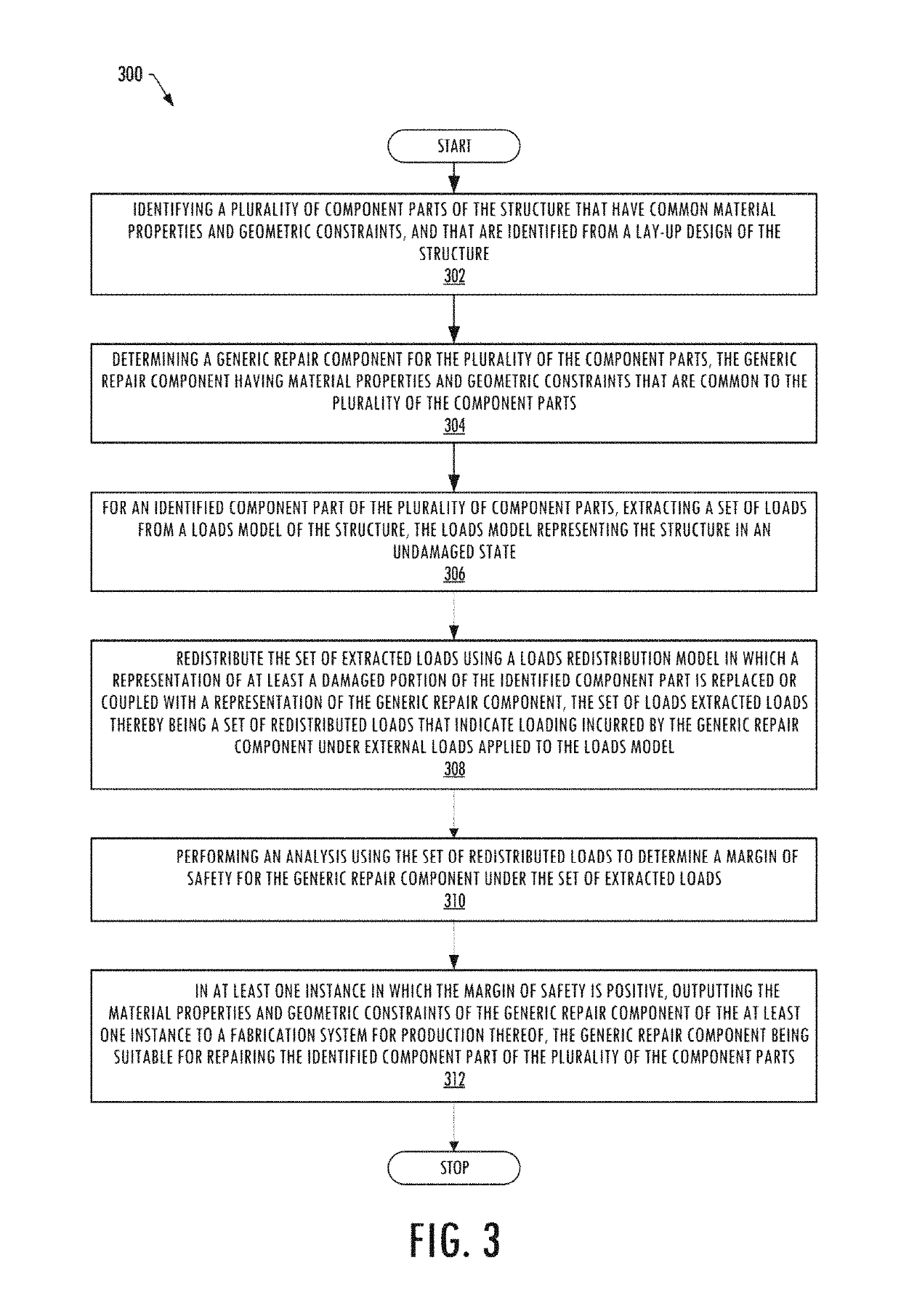
System for analysis of a repair for a structure
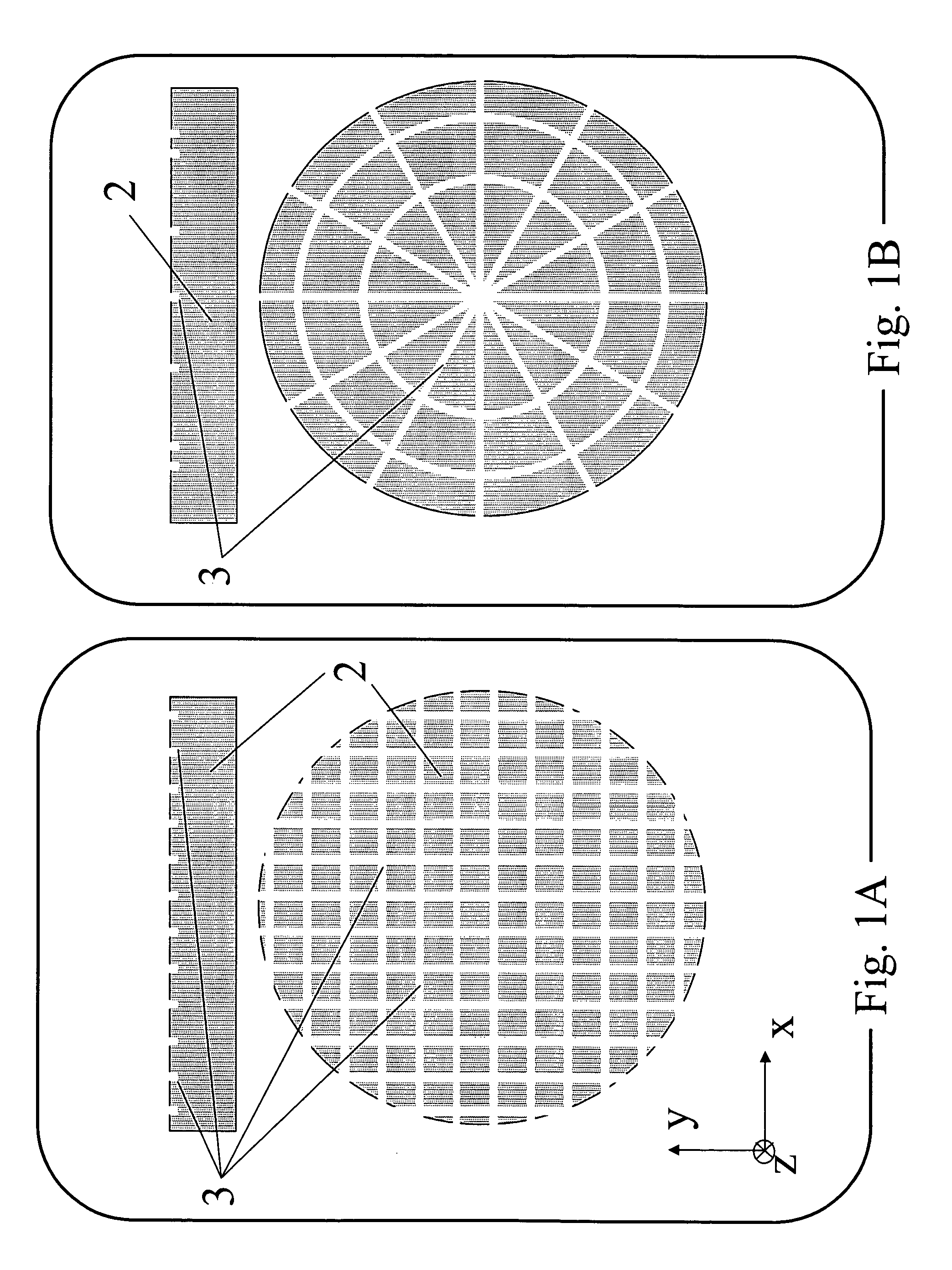
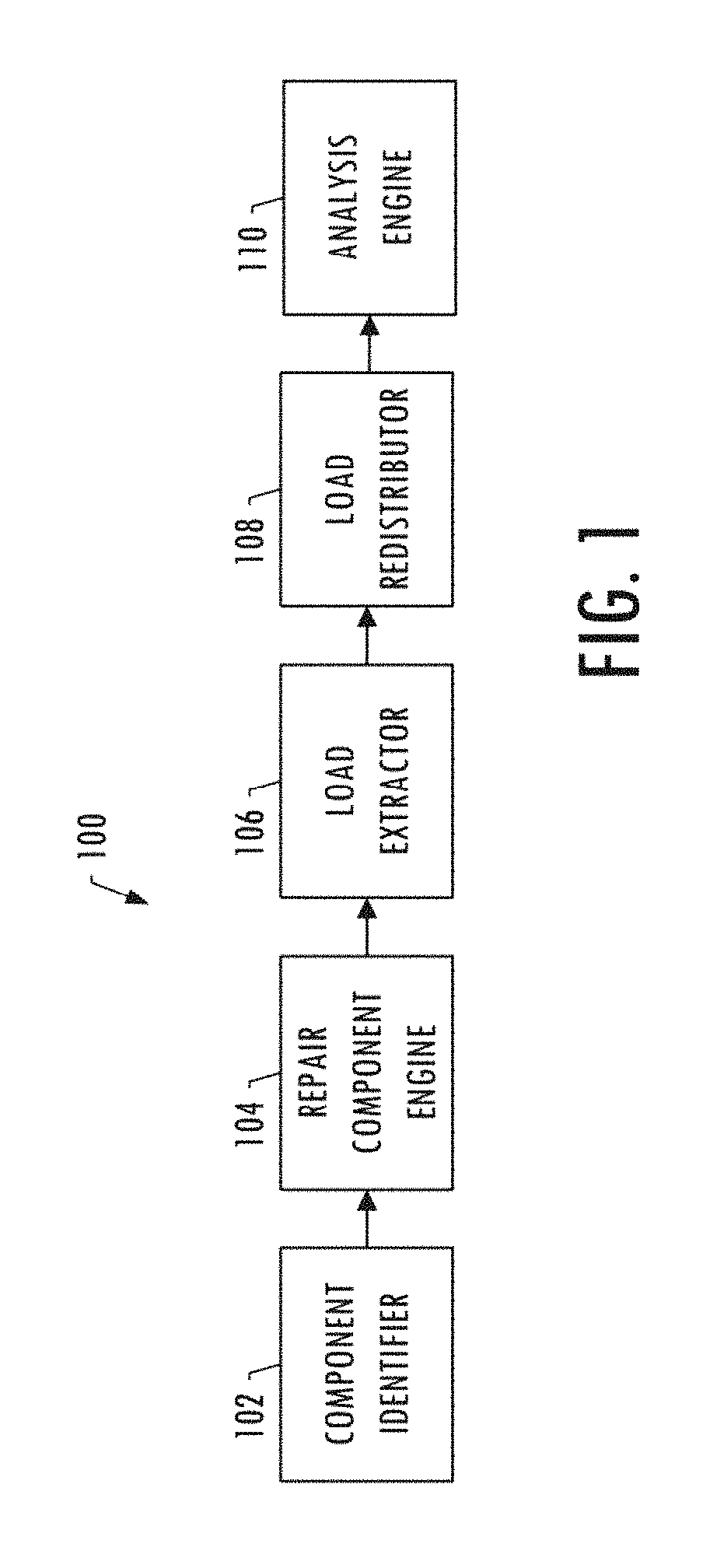
ActiveUS10275564B2Simple methodEffective timeGeometric CADCosmonautic vehiclesLoad modelLoad redistribution
An apparatus is provided for analysis of a repair for a structure by identifying component parts of the structure that have common material properties and geometric constraints, and based thereon determining a generic repair component for the component parts that also have the common material properties and the geometric constraints. A set of loads are extracted from a loads model of the undamaged structure and redistributed in a loads redistribution model at a damaged or defective portion of the component part. The set of redistributed loads indicate loading incurred by the generic repair component under an external load. The apparatus then uses the redistributed loads to perform an analysis to determine a margin of safety of the generic repair component and, in instances in which the margin of safety is positive, outputs the material properties and geometric constraints of the generic repair component to a fabrication system for production thereof.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
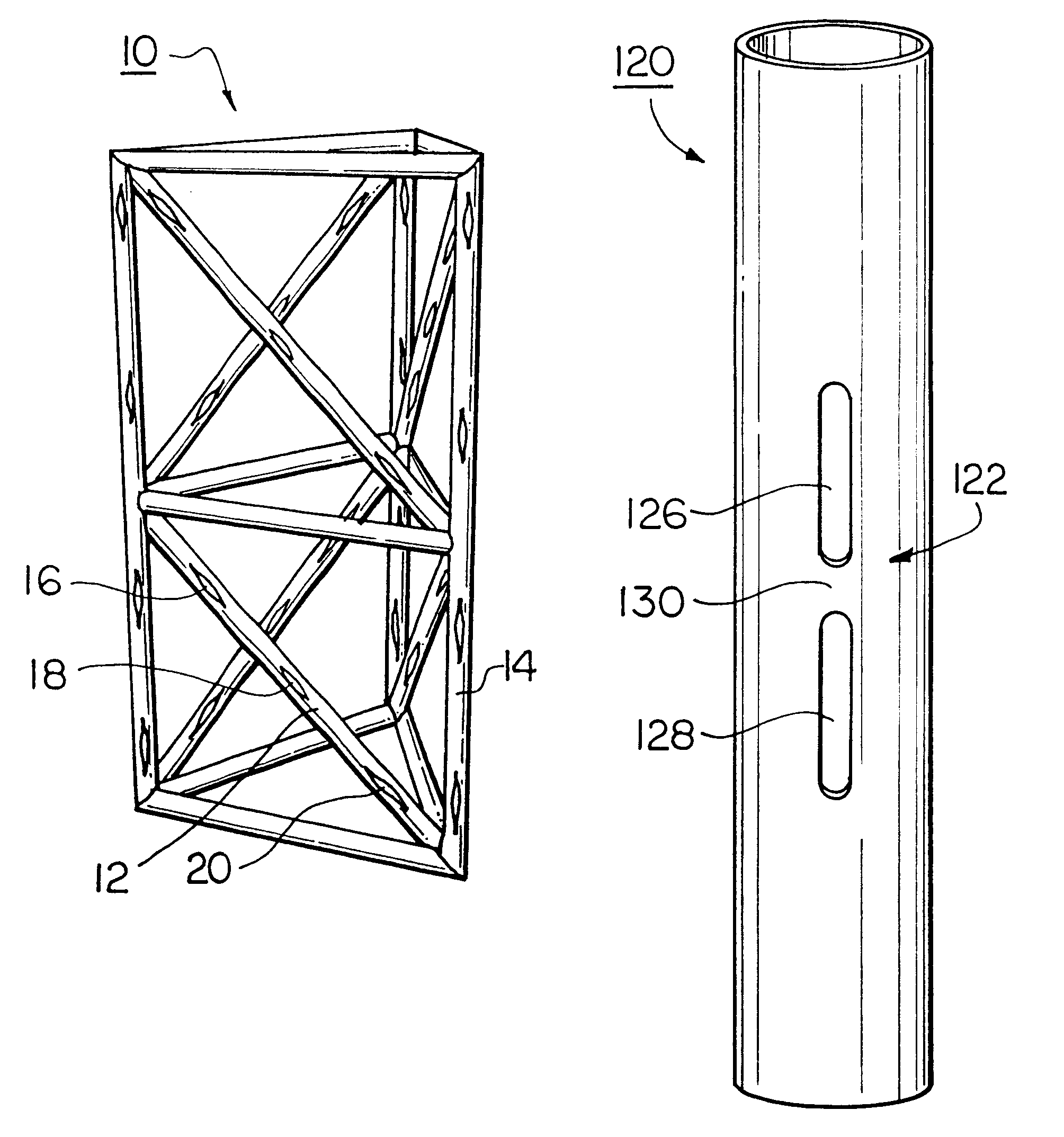
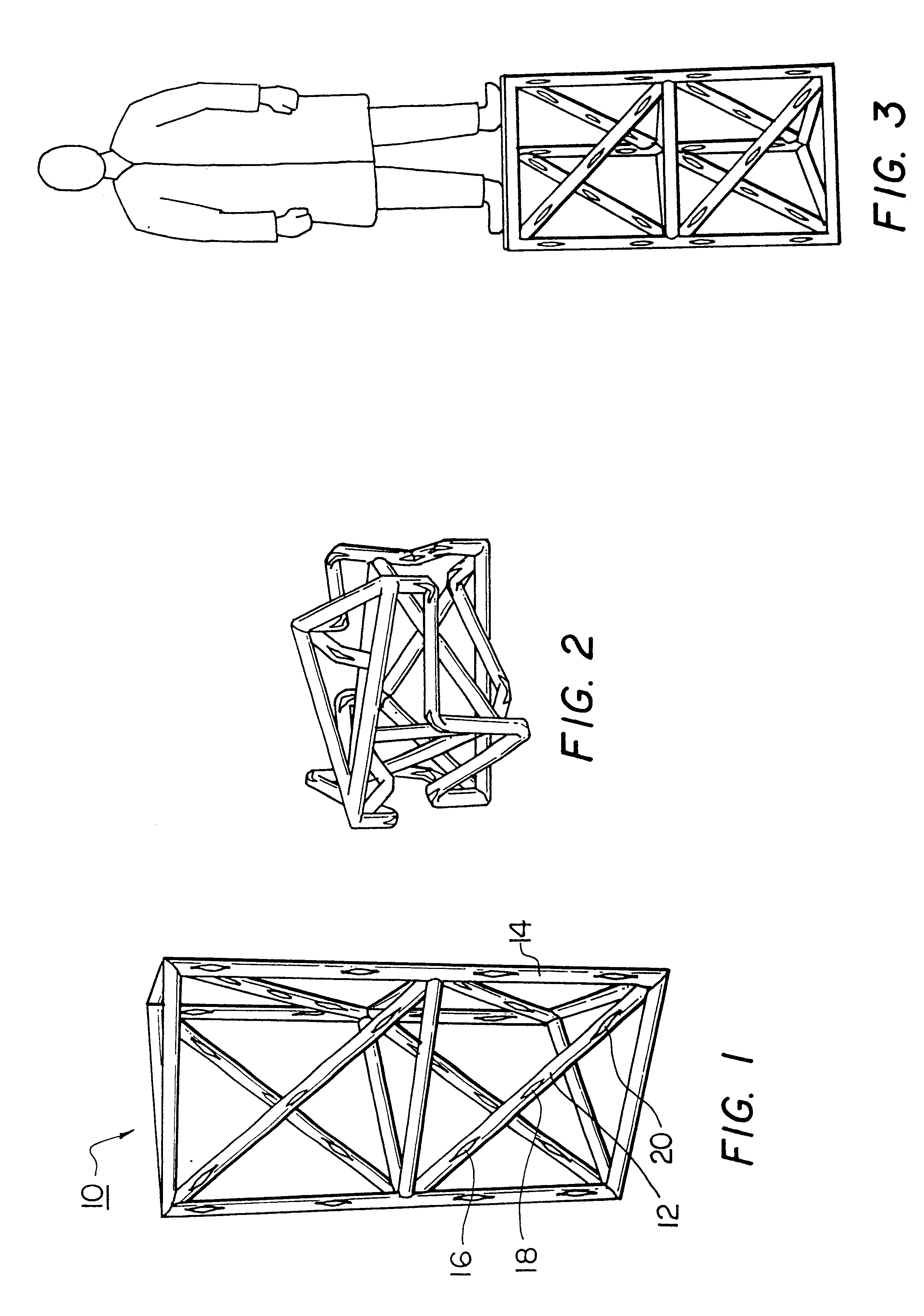
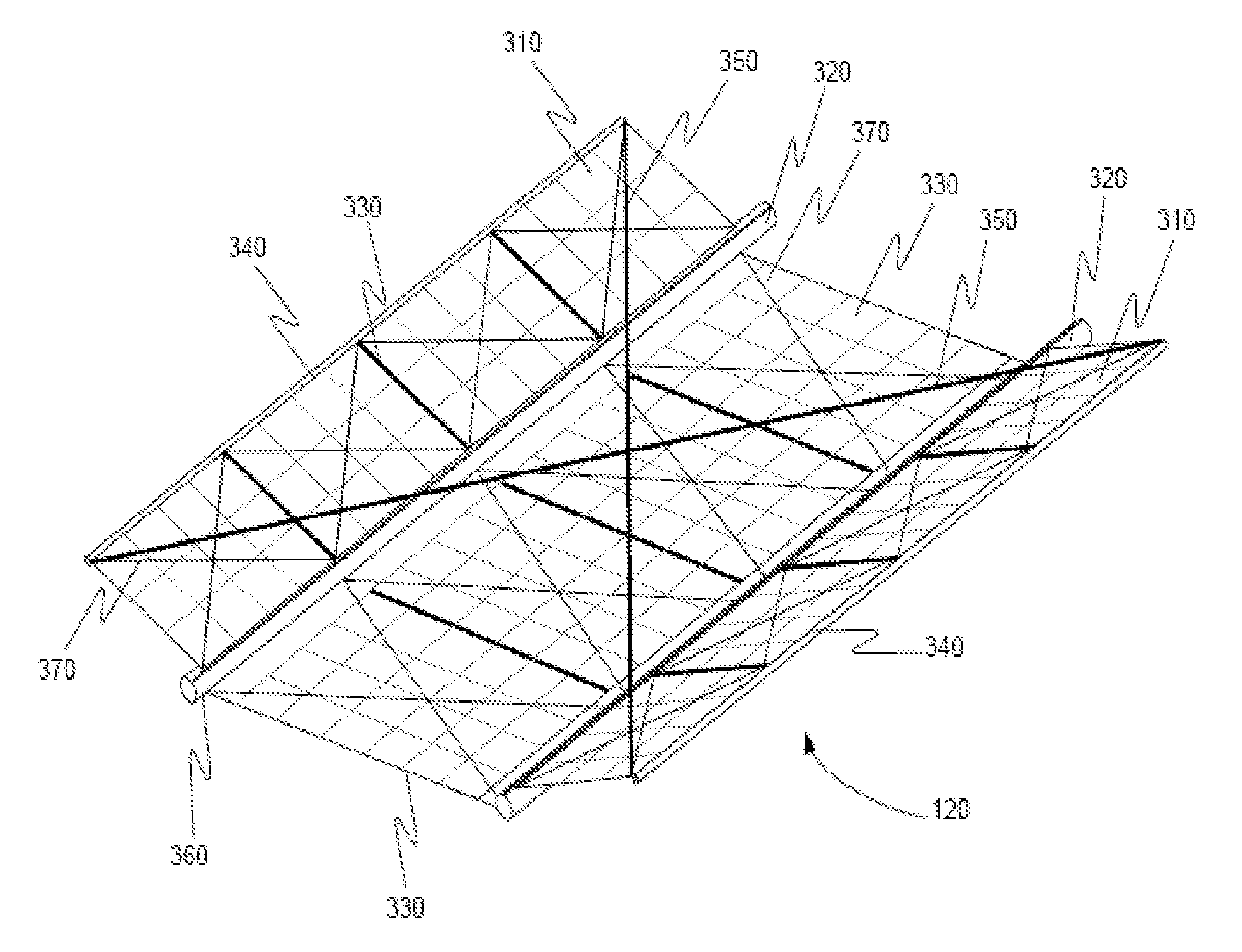
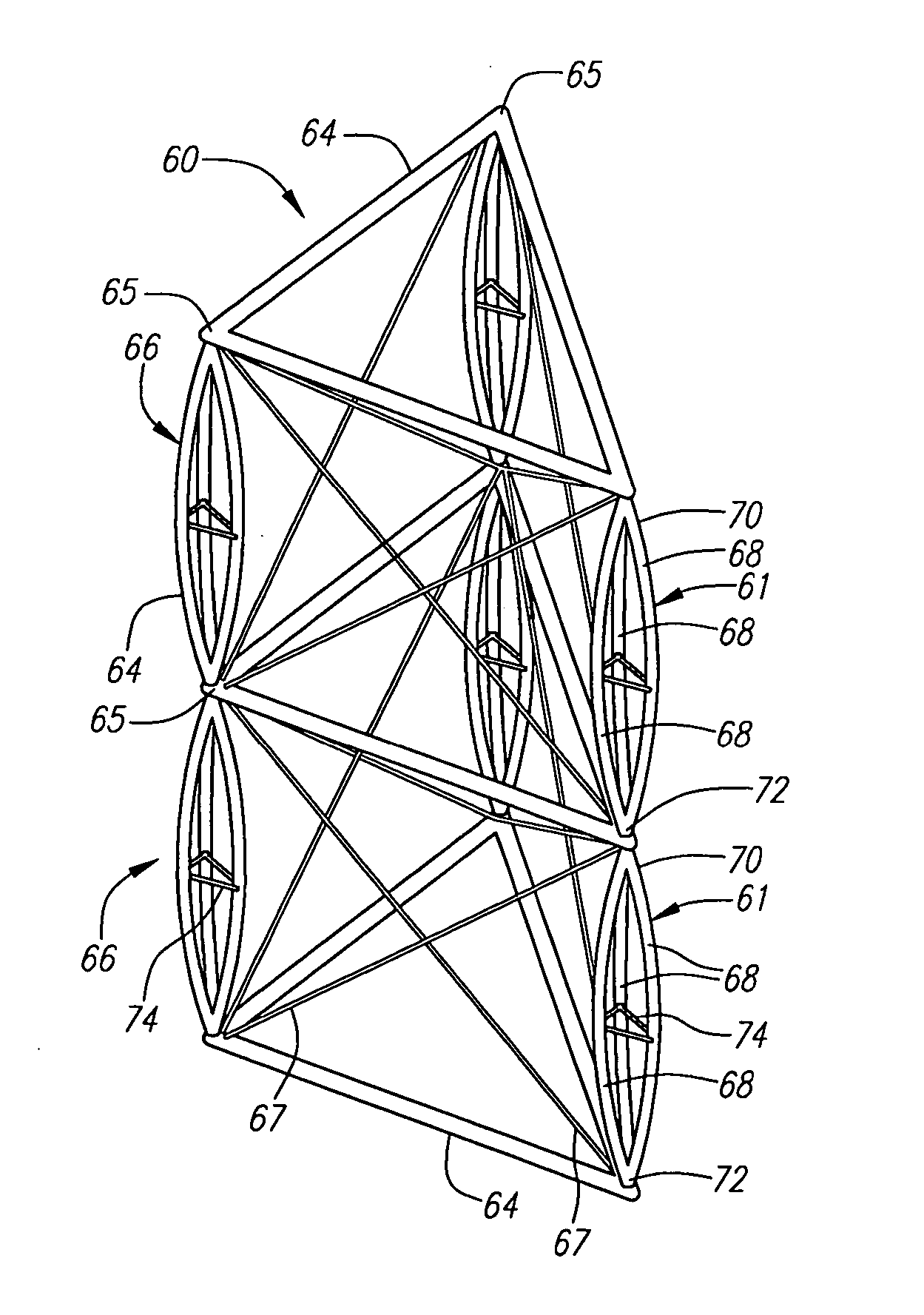
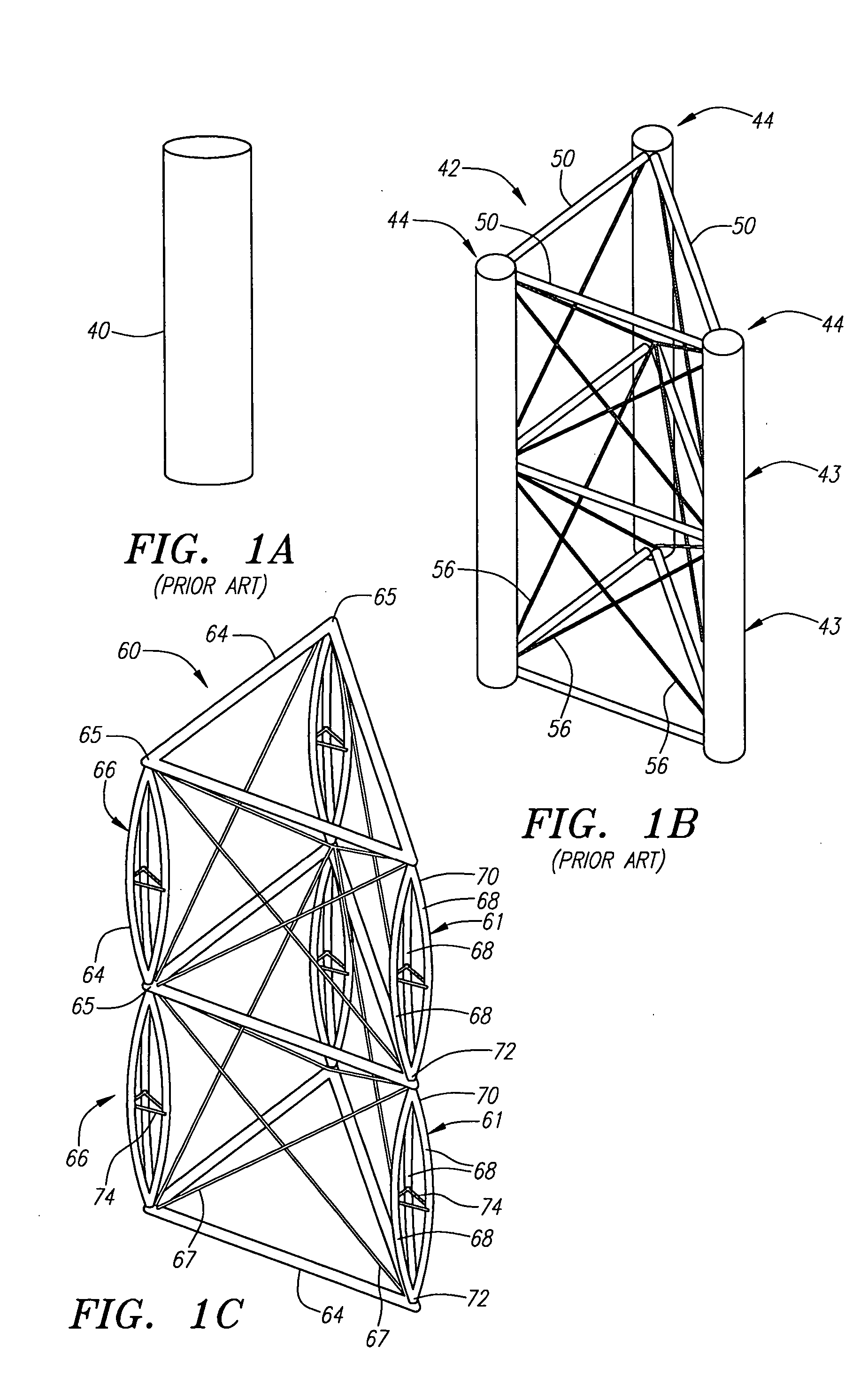
Deployable truss having second order augmentation
ActiveUS20050126106A1Decreases free buckling lengthIncrease its moment of inertiaCollapsable antennas meansCosmonautic vehiclesEngineeringMoment of inertia
A deployable truss is formed from a plurality of column members connected at their ends where at least some of the column members are formed from column assemblies, each including a plurality of strut members that are at least connected to each other at a first and second end of the column assembly. For added rigidity, strut members of a column assembly may be connected to each other between the first and second ends using, for example, a rigidizable resin, a fixed spacer, or a deployable spacer. Connecting strut members between the ends of the column assembly provides mutual bracing to the strut members and decreases the free buckling length of the individual strut members. Spacers are preferably configured to radially space the strut members away from the longitudinal centerline of the column assembly to increase its moment of inertia, and hence its buckling strength.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
System and method for safely flying unmanned aerial vehicles in civilian airspace
InactiveUS8838289B2Safely share airspace with other usersMinimize changesCosmonautic vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficSynthetic vision systemUnmanned air vehicle
A system and method for safely flying an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV), or remotely piloted vehicle (RPV) in civilian airspace uses a remotely located pilot to control the aircraft using a synthetic vision system during at least selected phases of the flight such as during take-offs and landings.
Owner:MARGOLIN JED
Network architecture and protocol for spacecraft systems
InactiveUS20060015299A1Optimize potentialImprove vehicle reliabilityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsNetwork architectureDistributed computing
A network architecture and protocol provides “plug and play” spacecraft capabilities. A distributed-control architecture is used, wherein each component operates semi-autonomously, and interacts with other components on a task / resource level. Each component announces its requirement for system resources as a request to the network, and components that can provide some or all of the requested resources respond to the request. An arbitration device centralizes and coordinates requests for critical and / or singular resources, such as requests for a specific orientation of the spacecraft. To facilitate such distributed control, requests are made in advance of the requirement for the resource, and include a time interval during which the resource is required. A configuration and test system is provided to process the mission requirements and provide a set of components that can be configured to satisfy the requirements.
Owner:AEROASTRO
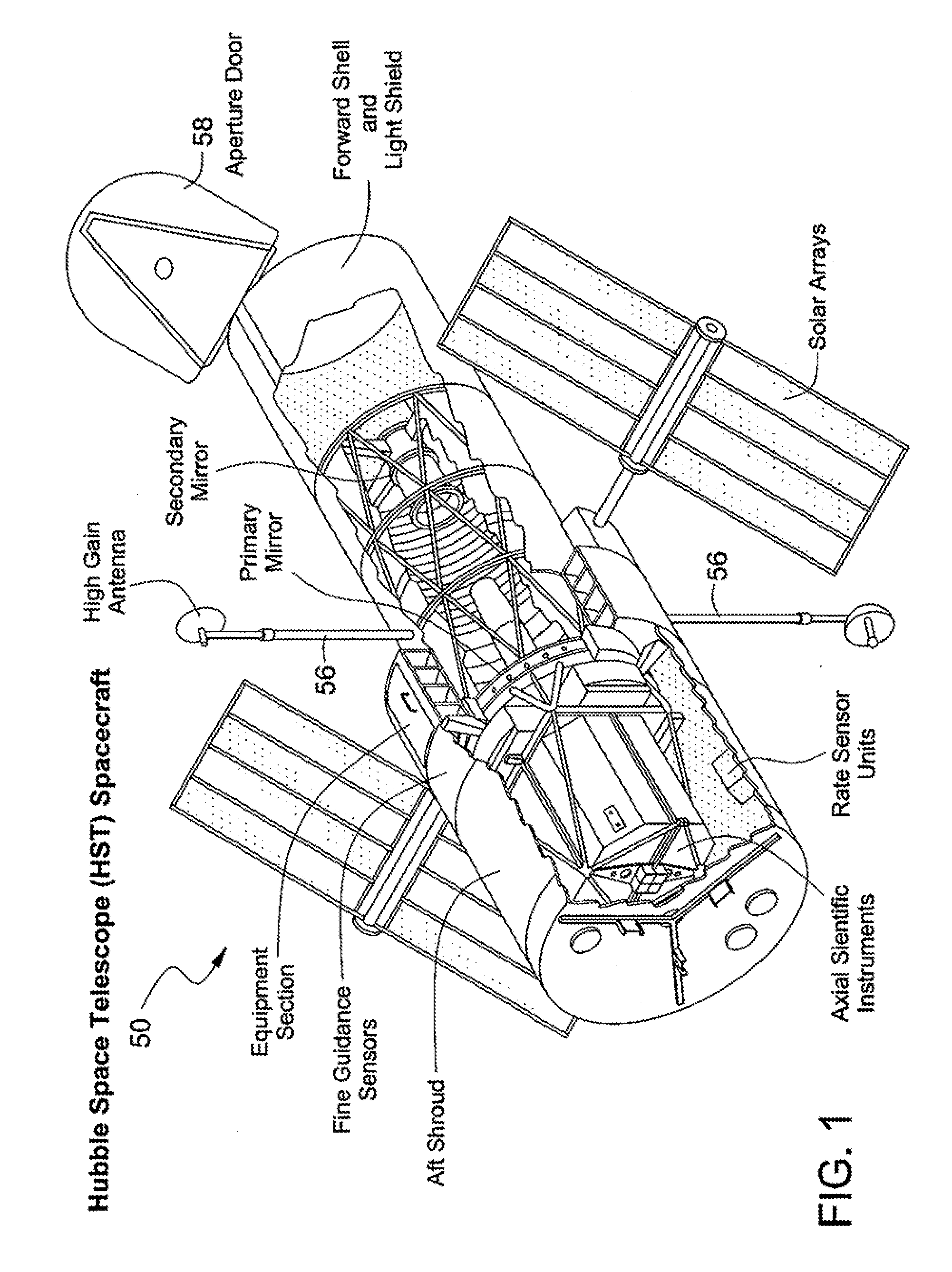
Main load-carrying structure of spacecraft
ActiveCN101381003AMeet the stiffnessFulfil requirementsCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsEngineeringLoad carrying
The invention discloses a novel aircraft main bearing structure, comprising a pushing cabin structure, a star-shaped truss structure (6) and an electronic cabin main framework structure; the upper part of the propelling cabin structure is connected with the electronic cabin main framework and the lower part thereof is taken as a whole star precision detection benchmark surface and an installation surface used for the propelling cabin instruments; the star-shaped truss structure (6) is a load installation frame supported by a supporting rod and arranged in the electronic cabin main framework structure and used for installing effective loads; the lower end of the supporting rod is fixedly connected with the upper part of the propelling cabin structure; as the main bearing structure adopts an external framework side plate structure and an internal start-shaped truss structure to form a mixed main structure with dual bearing paths (internal bearing path and external bearing path) so as to transmit the whole star load, the force transmission path is short and continuous, the structure is compact, the center of mass is low, and the main bearing structure meets the requirement of the whole satellite of high rigidity and small inertia.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Dual Sided Photovoltaic Package
InactiveUS20090223554A1Easy to generate electricityFlexible structureCosmonautic vehiclesPV power plantsMultijunction photovoltaic cellElectric energy
A double-sided photovoltaic package with an incident photovoltaic cell and a reflective photovoltaic cell. Both photovoltaic cells have a corresponding absorbing surface for absorbing solar radiation. The incident photovoltaic cell and the reflective photovoltaic cell are arranged so that when the absorbing surface of the incident photovoltaic cell is located to receive incident non-reflected solar radiation the absorbing surface of the reflective photovoltaic cell is located to receive reflected solar radiation. The structure of the incident photovoltaic cell is adapted to convert non-reflected light to electrical energy and the structure of the reflective photovoltaic cell is adapted to convert reflected light to electrical energy. Additionally, in the preferred embodiment, the incident photovoltaic cell and the reflective photovoltaic cell both comprise inverted metamorphic multijunction photovoltaic cells. Furthermore, a plurality of double-sided photovoltaic packages according to the present invention may be interconnected in a string formation and mounted on a transparent panel to form an array.
Owner:EMCORE SOLAR POWER
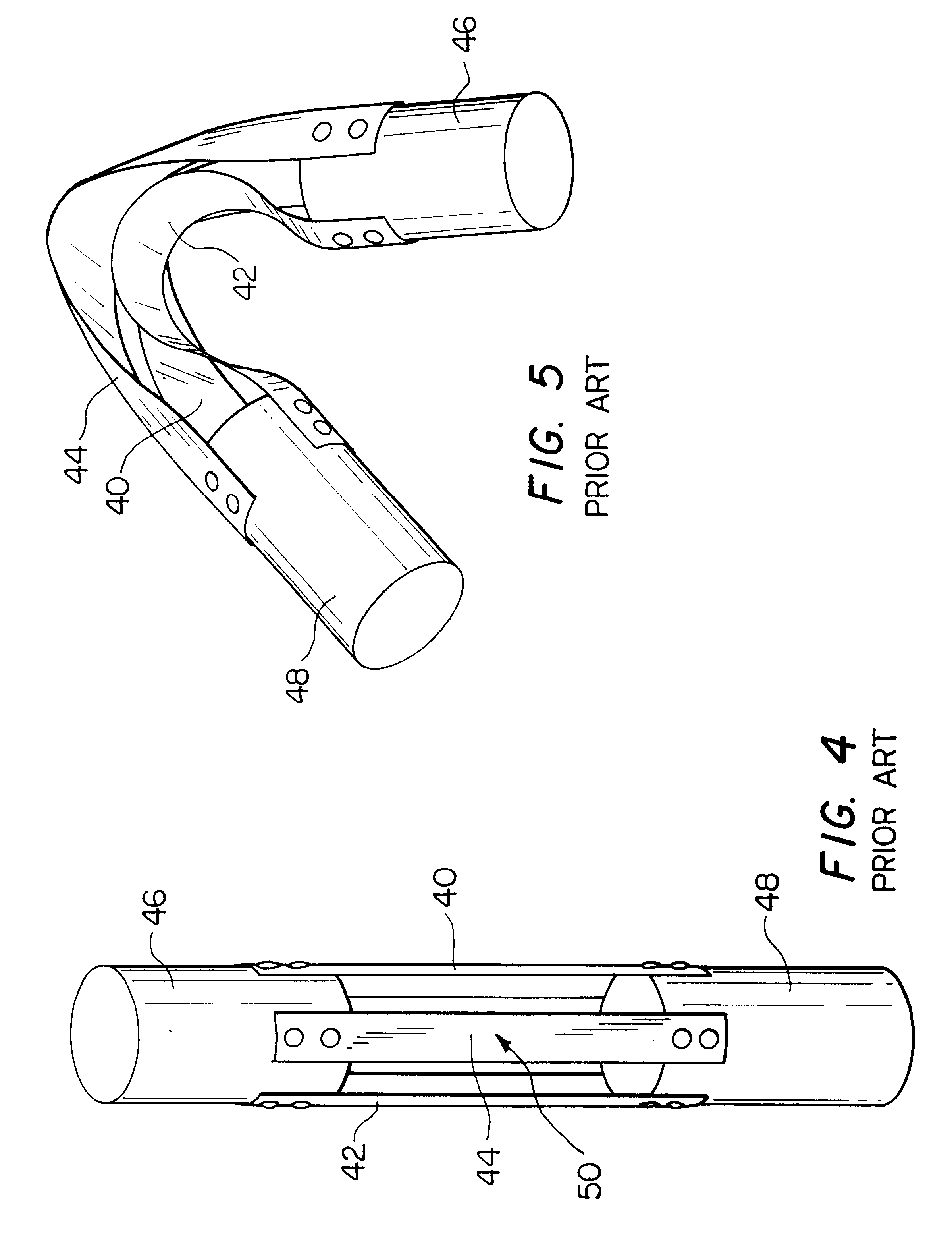
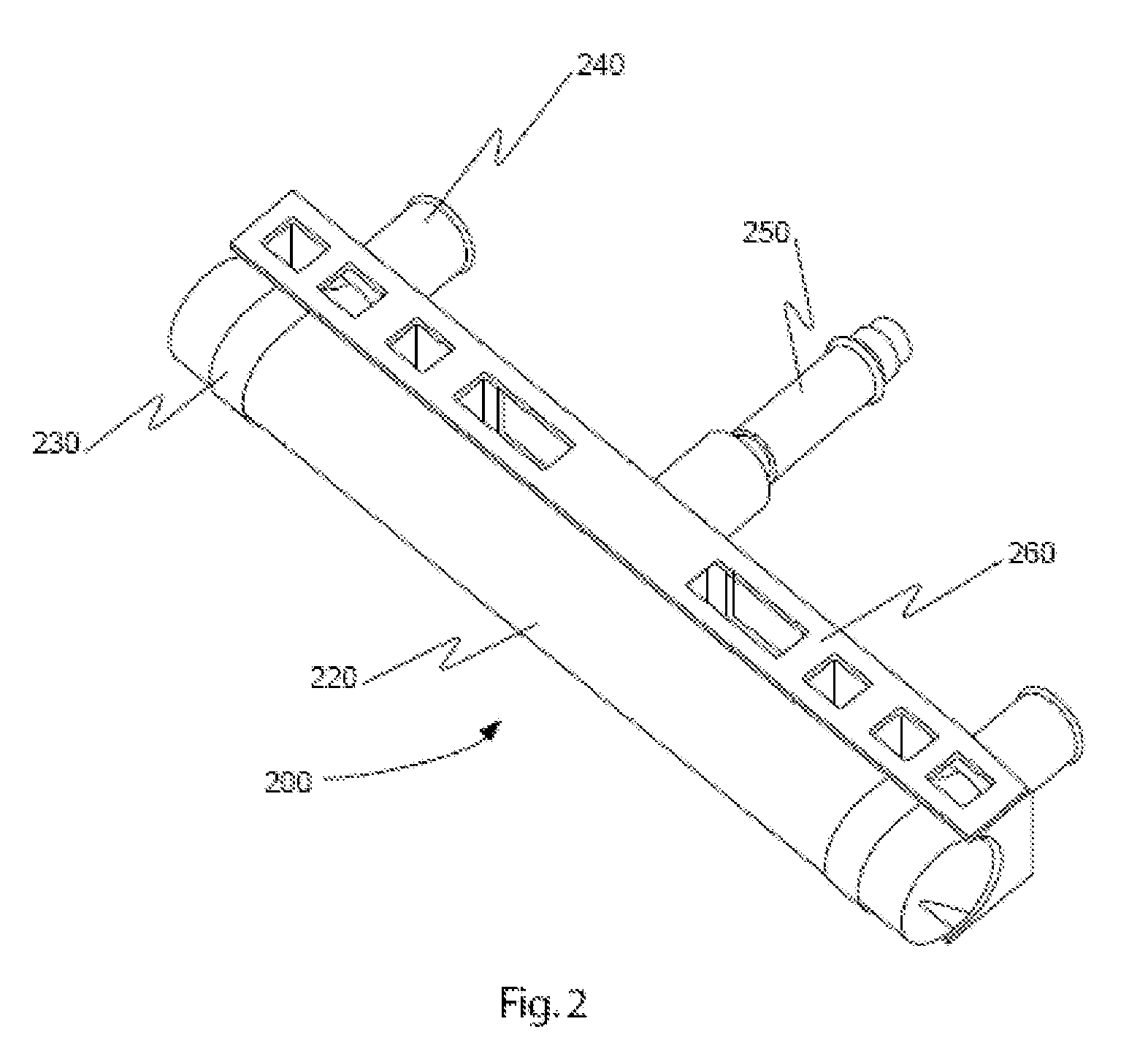
Triangular rollable and collapsible boom
ActiveUS7895795B1Reduced torsional stiffnessIncreased bending stiffnessCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsFiberCarbon fibers
An elastic space-deployable boom of carbon fiber reinforced plastic or other resilient material having an open substantially triangular cross-section when deployed and stowed with a flattened cross-section about a circular hub.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPSESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Spacecraft and aerospace plane having scissors wings
InactiveUS6745979B1Form differentAvoid connectionLaunch systemsCosmonautic partsJet aeroplaneAviation
A spacecraft such as a fly back booster or a reusable launch vehicle, or an aerospace plane has a fuselage and a set of scissors wings consisting of two main wings. Both of the main wings are rotatably mounted on the fuselage and can be yawed at opposite directions. If the spacecraft is launched vertically, both of its main wings can be yawed to be generally parallel with its fuselage so that it can connect with other vehicle or vehicles to form different launch configurations. When the spacecraft or aerospace plane is flying in the air, landing, or taking off horizontally, it can yaw both of its main wings in opposite directions to maximize its lift-to-drag ratio by optimizing the yaw angle of the main wings according to flying conditions. It can also produce desired aerodynamic characteristics such as forming a high drag configuration by adjusting the yaw angle of its main wings. The scissors wings can be used on a spacecraft that is launched vertically on the ground, or a spacecraft that is carried to the air and launched in the mid-air, or a spacecraft that takes off horizontally like an aircraft or glider. The scissors wings can also be used on an aerospace plane.
Owner:CHEN ZHUO
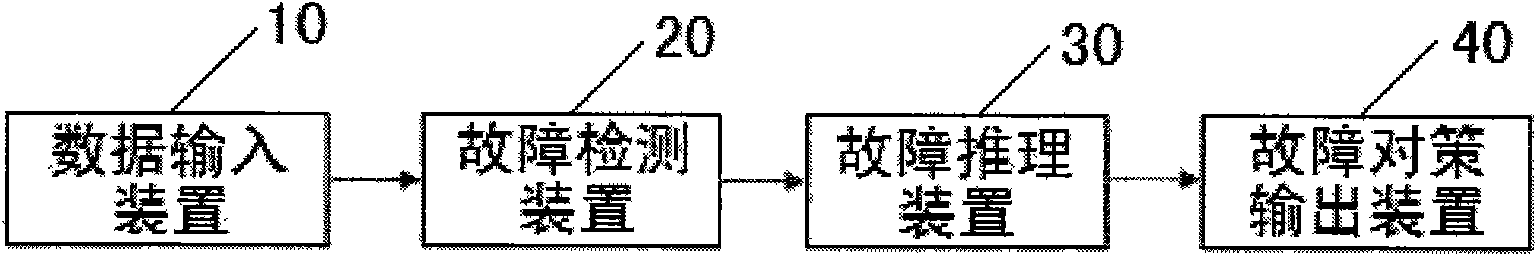
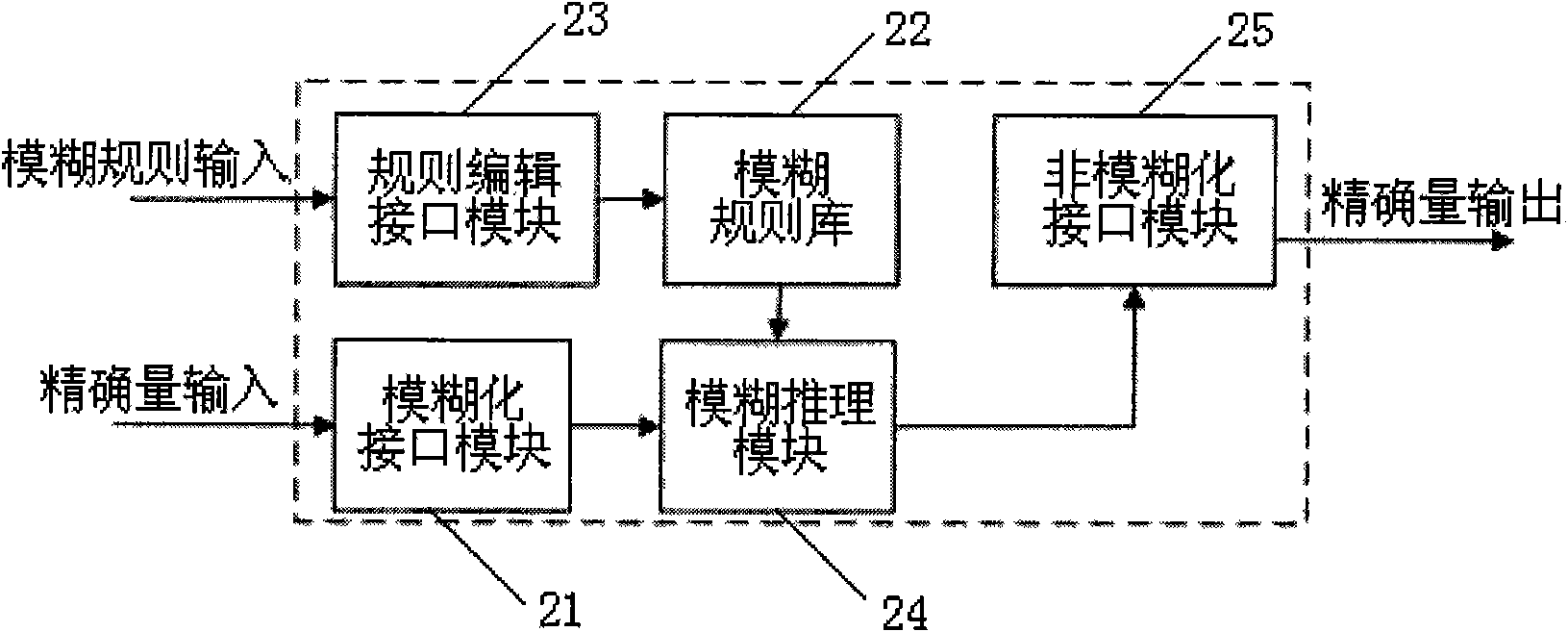
Method for automatic fault diagnosis of satellite and diagnostic system thereof
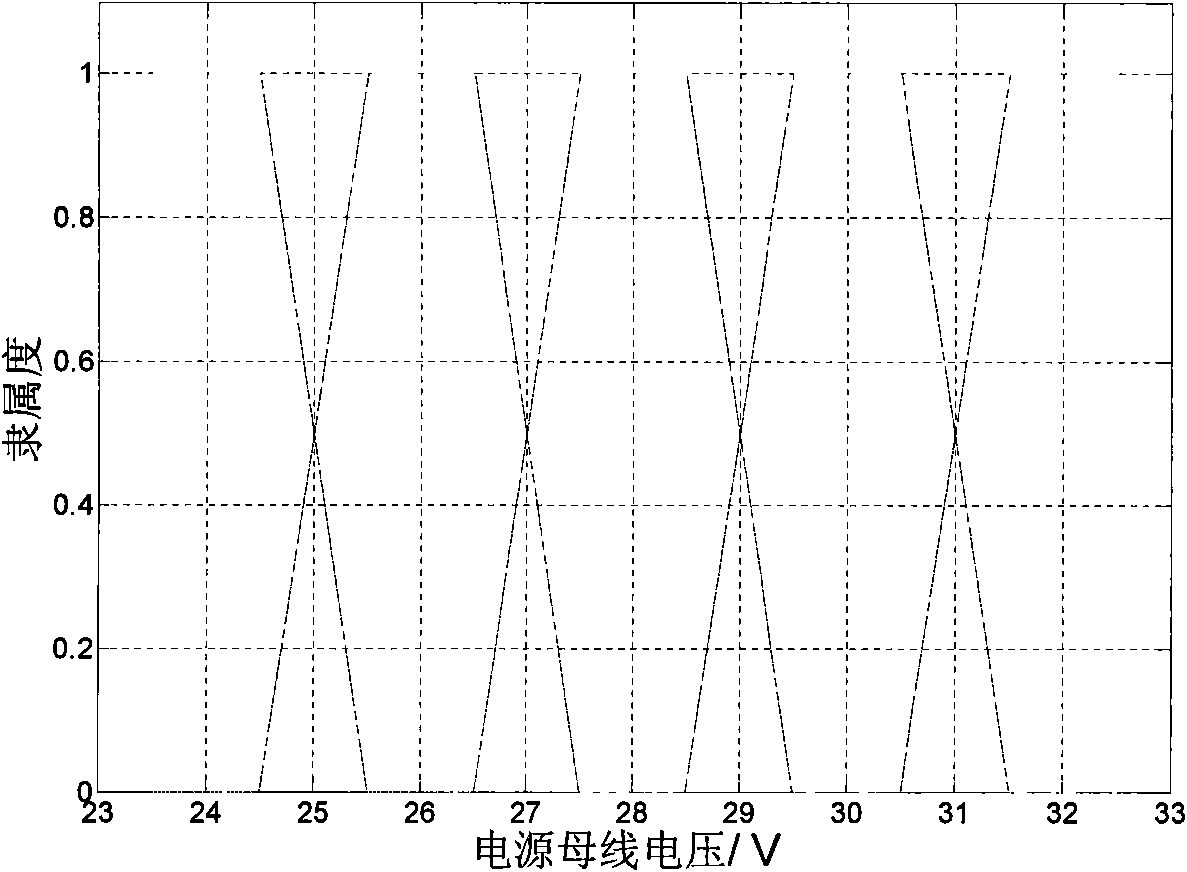
InactiveCN101590918AReduce false alarm rateReduce false negative rateCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsDependabilityFalse alarm
The invention relates to a method for automatic fault diagnosis of a satellite and a diagnostic system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: dividing the satellite fault into a component level fault, a subsystem level fault and a system level fault; adopting a fault detection method based on a fuzzy set to fuzzify a precise sensor sampling value; defining different alarm weight values for fuzzy subset based on the membership grade belonging to each fuzzy subset; and determining whether to alarm or not by calculating the relation between the summation of the alarm weight values in a time window and an alarm threshold value. The method can effectively overcome the defects of a common fault detection method and effectively reduce the false alarm rate and the rate of missing report; and when certain fault is caused by a plurality of sub-faults, the method performs heuristic search according to the reliability of a system corresponding to each sub-fault and searches a sub-fault node corresponding to a system with low reliability preferentially. Besides, in order to adapt to the synergistic diagnosis between distributed satellites in the future, a synergistic interface is designed to provide diagnosis services for other satellites, thus the aim of the invention is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
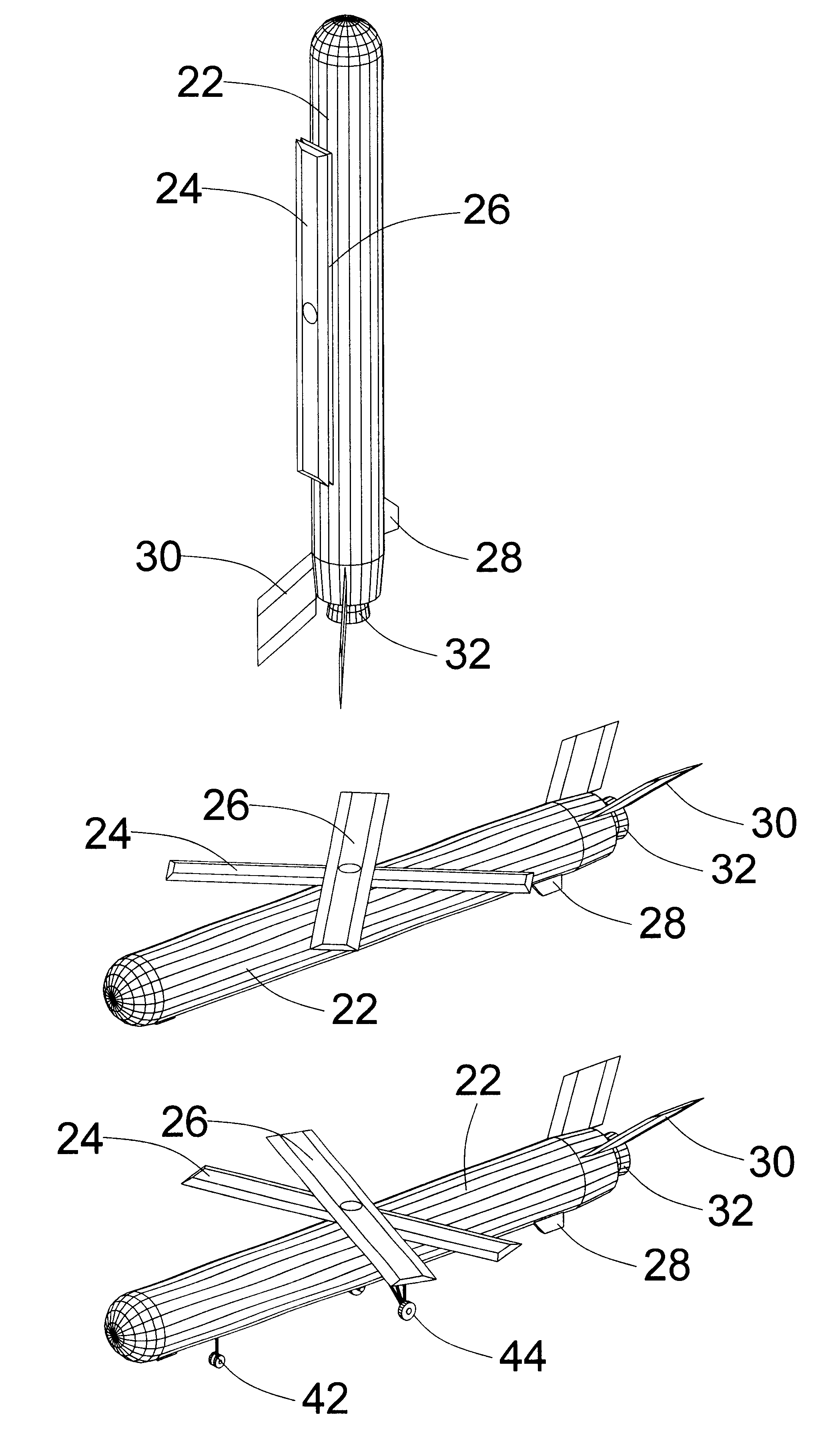
Inflatable wing flight vehicle
InactiveUS20090108135A1Improved lift characteristicThin atmosphereCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsNatural satelliteLow speed
The invention is an aircraft having an inflatable wing connected to a base unit, with the inflatable wing inflated with a lifting gas such as helium. The inflatable wing has a series of cell structures, and may be configured with ballonets to selectively introduce and expel outside air within the inflatable wing to vary the buoyancy and / or airfoil properties of the inflatable wing. The aircraft is particularly useful at low speeds and in thin atmospheres (such as at high Earth altitudes and on Mars), and can be used for interplanetary missions to explore planetary bodies, such as moons and planets, having atmospheres.
Owner:SHAW DONALD ORVAL
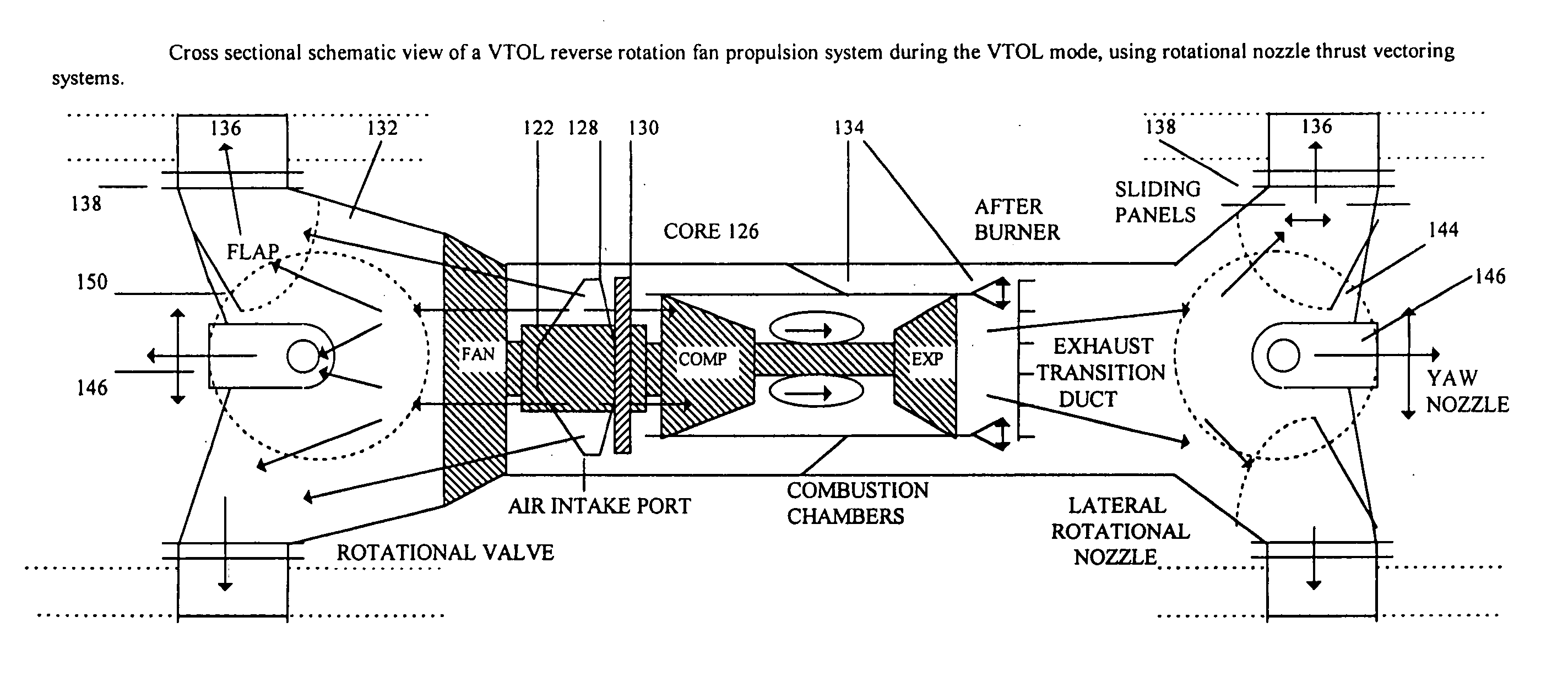
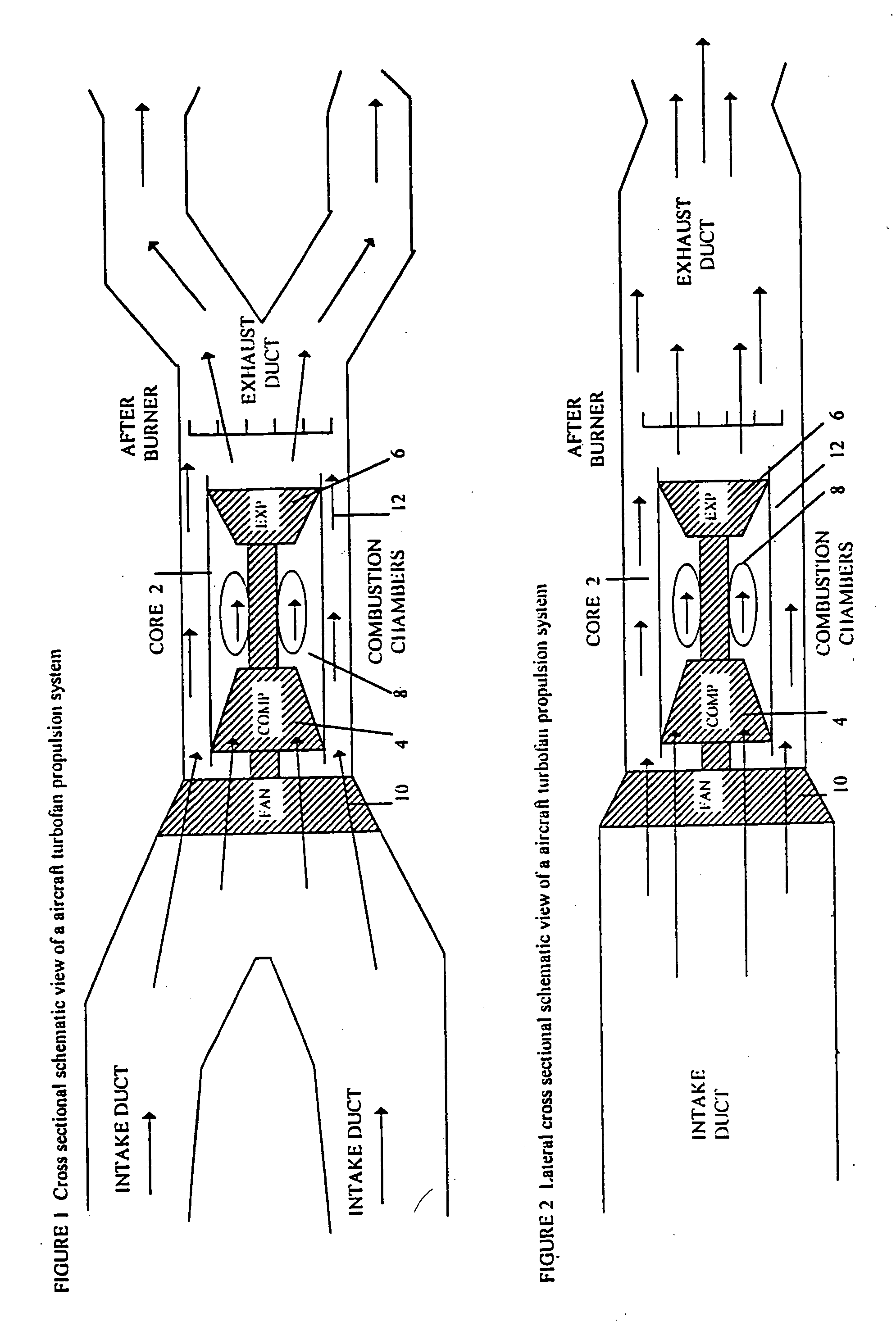
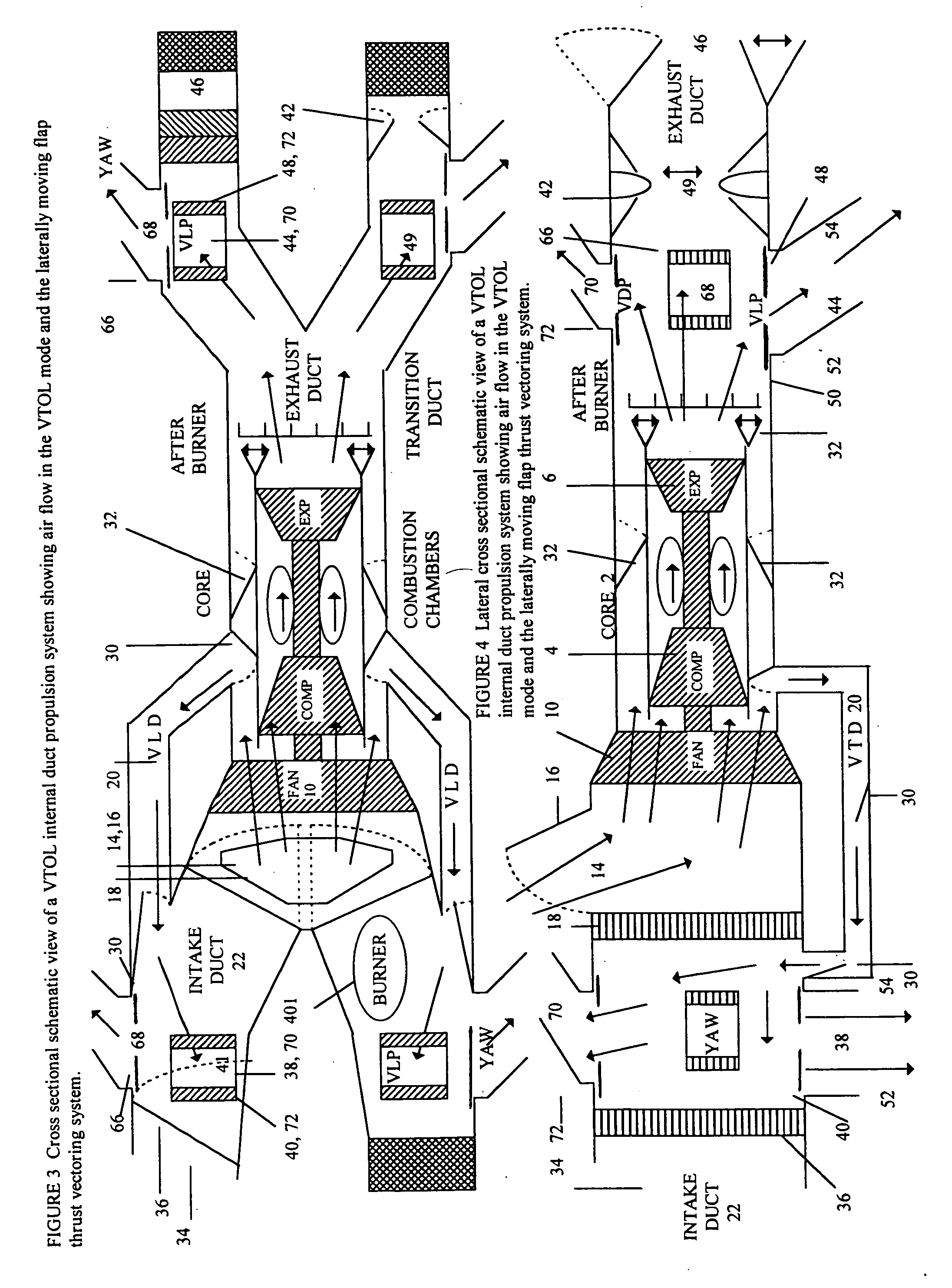
Thrust vectoring
InactiveUS20070018034A1Reduces forward thrustPromote productionAircraft navigation controlCosmonautic vehiclesAttitude controlFlight vehicle
Thrust vectoring enhances aircraft and spacecraft maneuverability. The propulsion systems of aircraft, using gas turbine engines, and spacecraft, using solid or liquid rockets, generate compressed gases that are directed through a nozzle to generate forward thrust. This patent describes opening ports to release gases from aircraft and spacecraft in a direction other than the direction of forward propulsion. By altering the direction of gas flows leaving the craft pitch, roll, yaw and attitude control is obtained. To control gas flow from ports a variable throat thrust vectoring nozzle is described. Independent operation of ports, rotational nozzles, laterally moving flaps and rotational vanes assists the thrust vectoring of gases leaving aircraft or spacecraft ports. The ability to direct gases enhances maneuverability during vertical takeoff and landing, forward flight and space flight.
Owner:DICKAU JOHN EUGENE
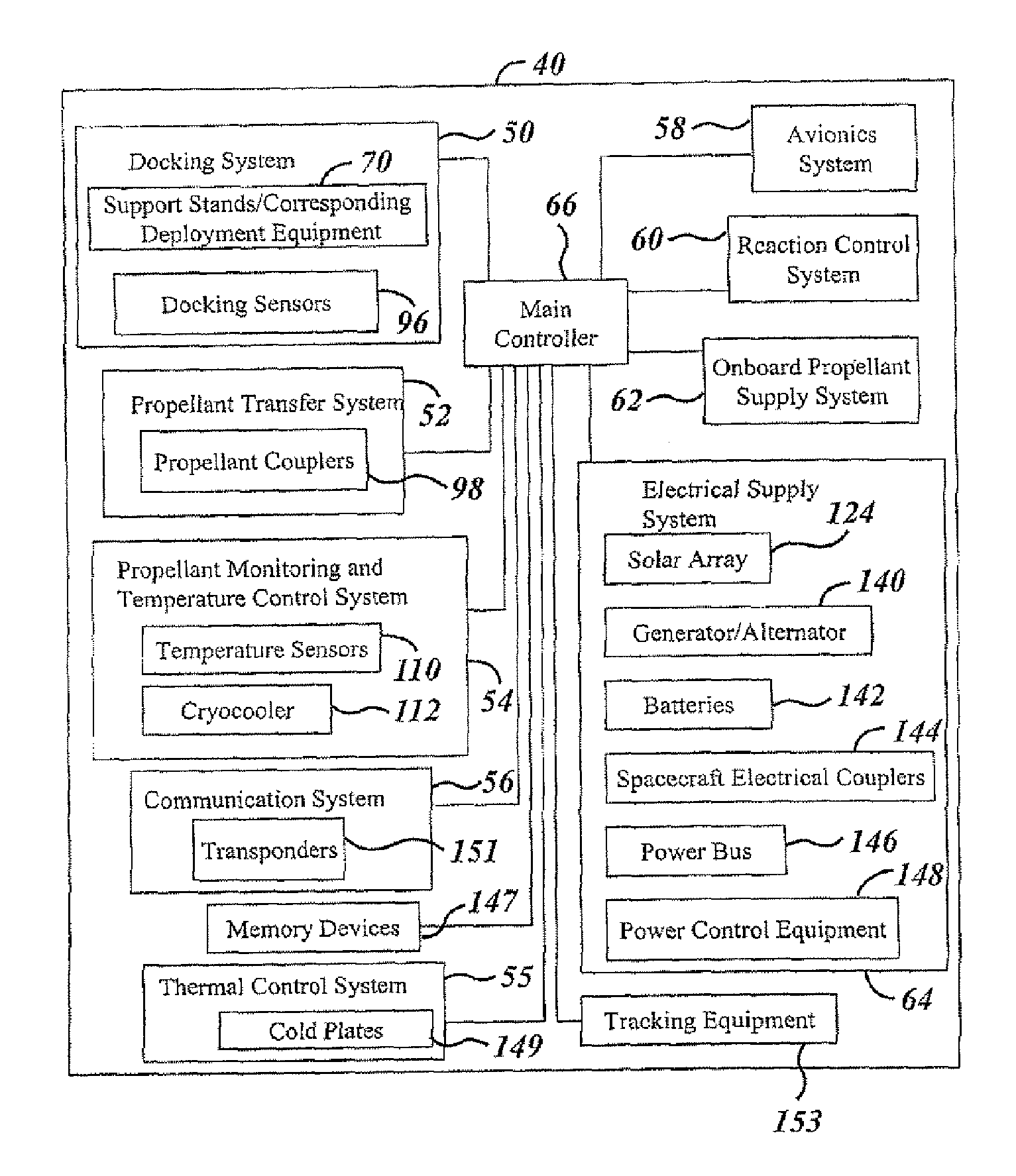
Space depot for spacecraft resupply
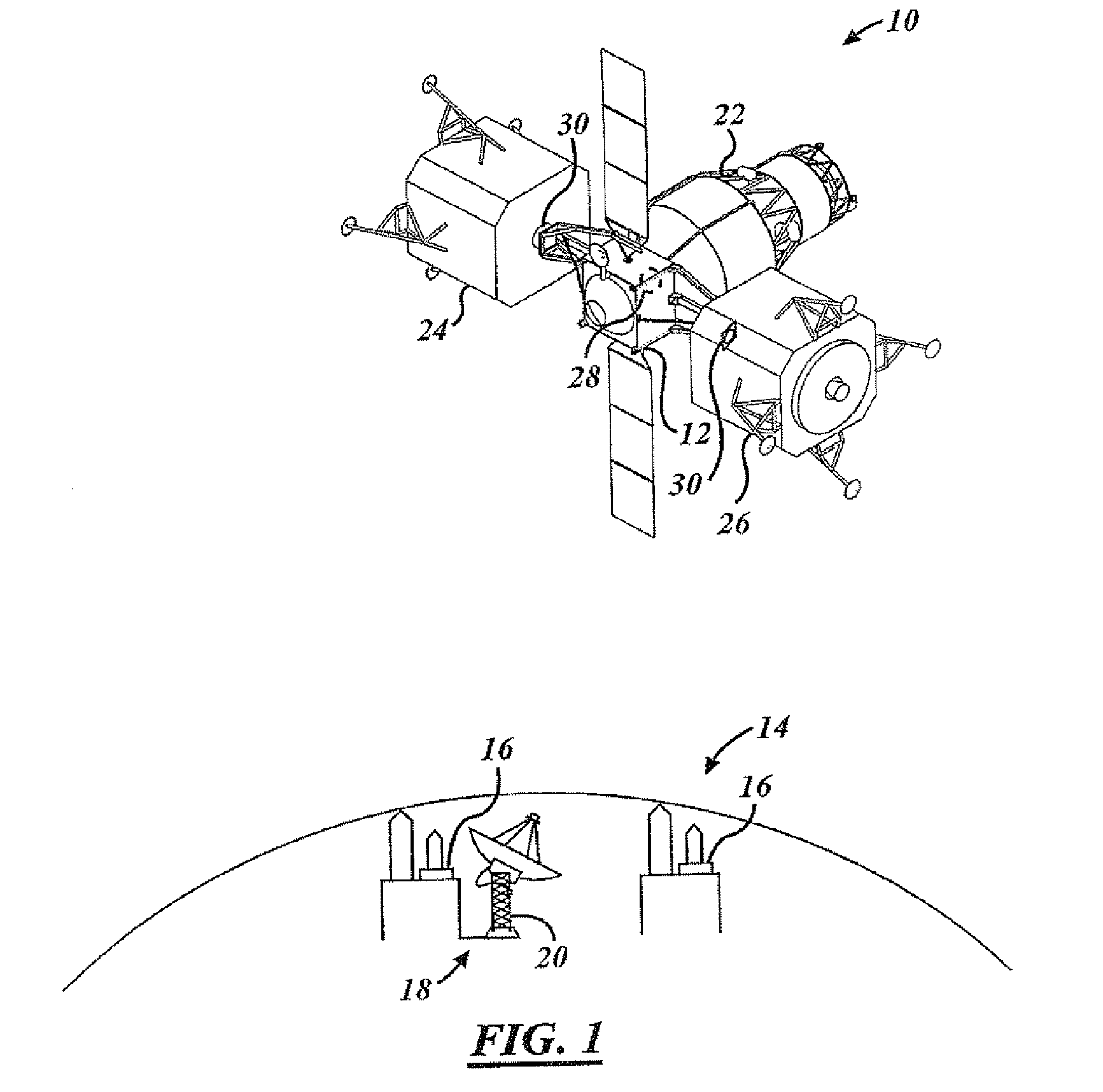
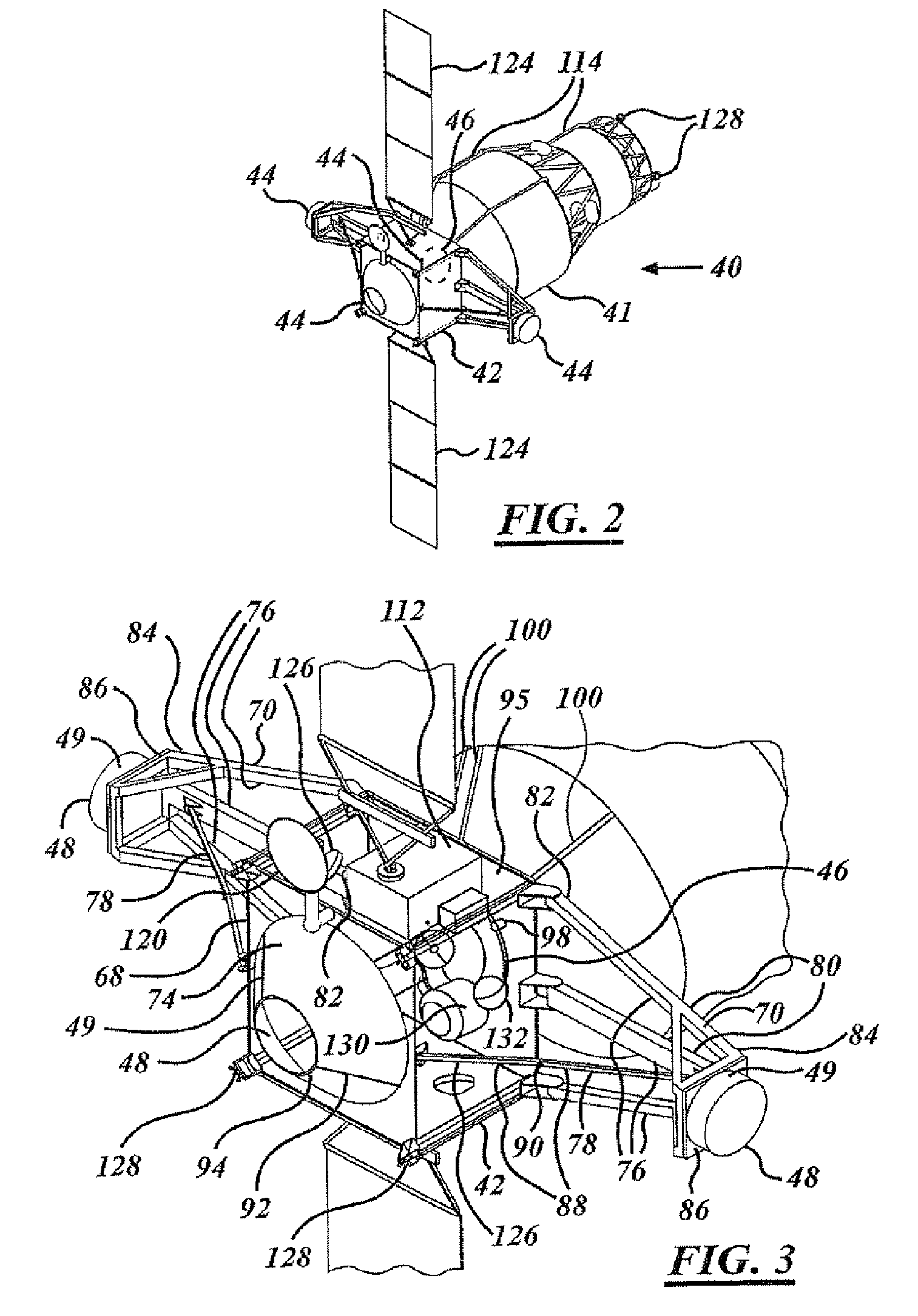
InactiveUS20070051854A1Efficient and inexpensive techniqueLow costCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic component separationPropellant depotSpace vehicle control
A propellant depot (40, 150) includes a utility box (42, 42′) that has space flight equipment. A propellant cartridge adaptor (95) is coupled to the utility box (42, 42′) and to an exchangeable propellant cartridge system (41). The propellant depot (40, 150) also includes a docking adaptor (44) for coupling to an approaching spacecraft (24). A controller (66) controls the transfer of propellant from within the exchangeable propellant cartridge system (41) to the spacecraft (24). A method of providing propellant to a spacecraft in space includes launching an orbital propellant depot (40, 150) into space. The spacecraft is docked to the orbital propellant depot (40, 150) in space. Propellant is transferred to the spacecraft. The spacecraft is separated from the orbital propellant depot (40, 150).
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com