Patents
Literature
19231 results about "Dependability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
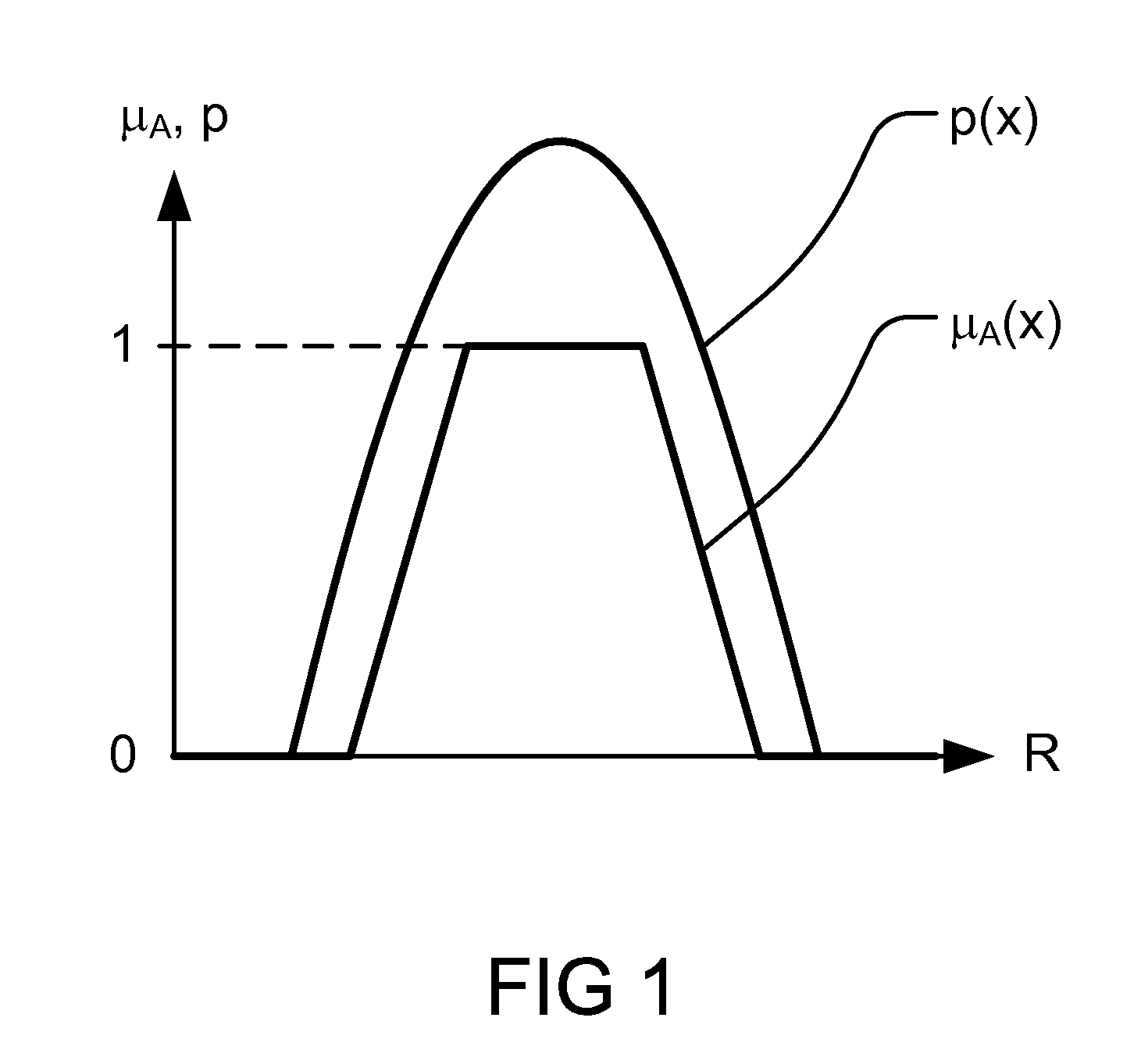
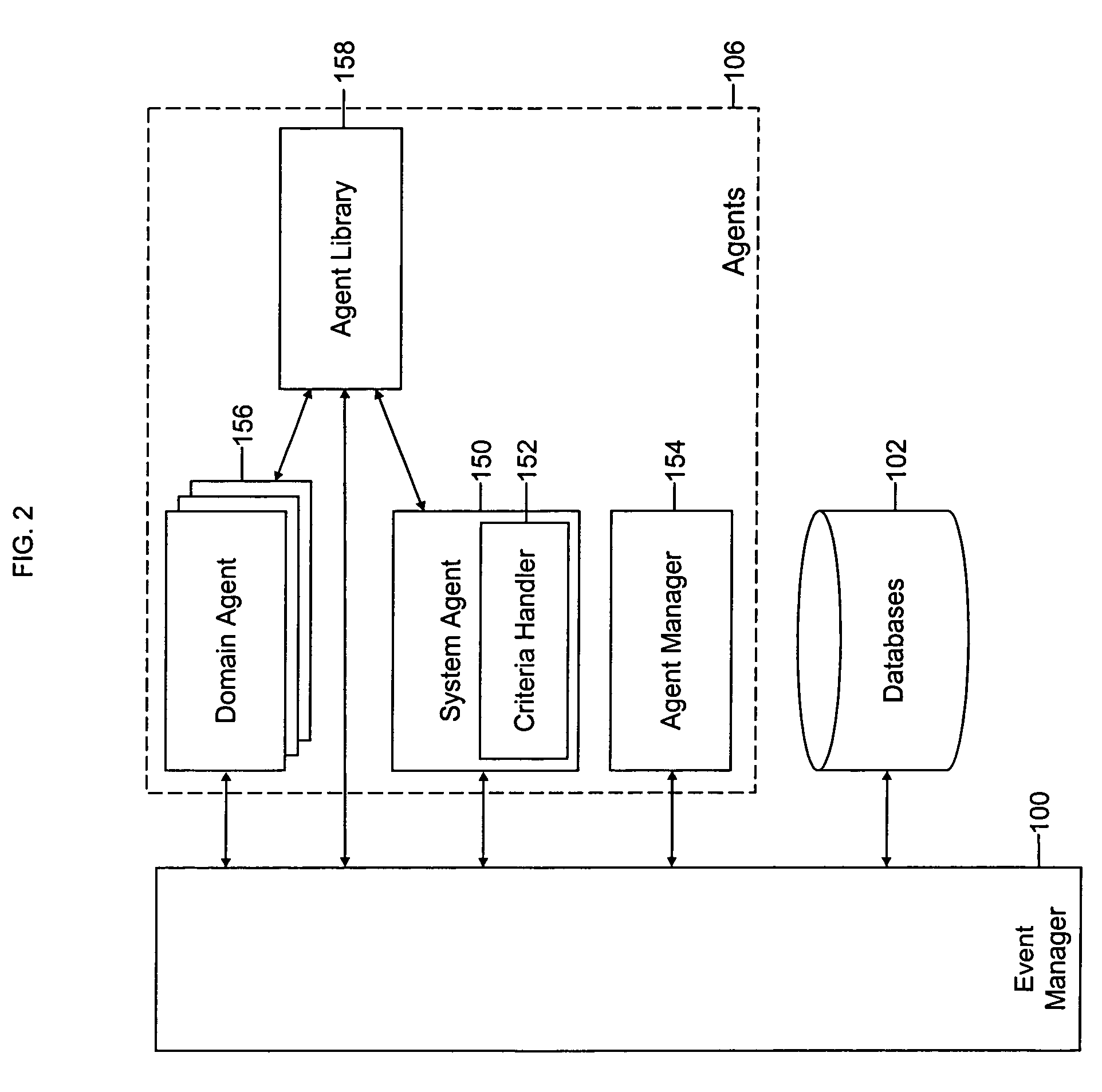
In systems engineering, dependability is a measure of a system's availability, reliability, and its maintainability, and maintenance support performance, and, in some cases, other characteristics such as durability, safety and security. In software engineering, dependability is the ability to provide services that can defensibly be trusted within a time-period. This may also encompass mechanisms designed to increase and maintain the dependability of a system or software.
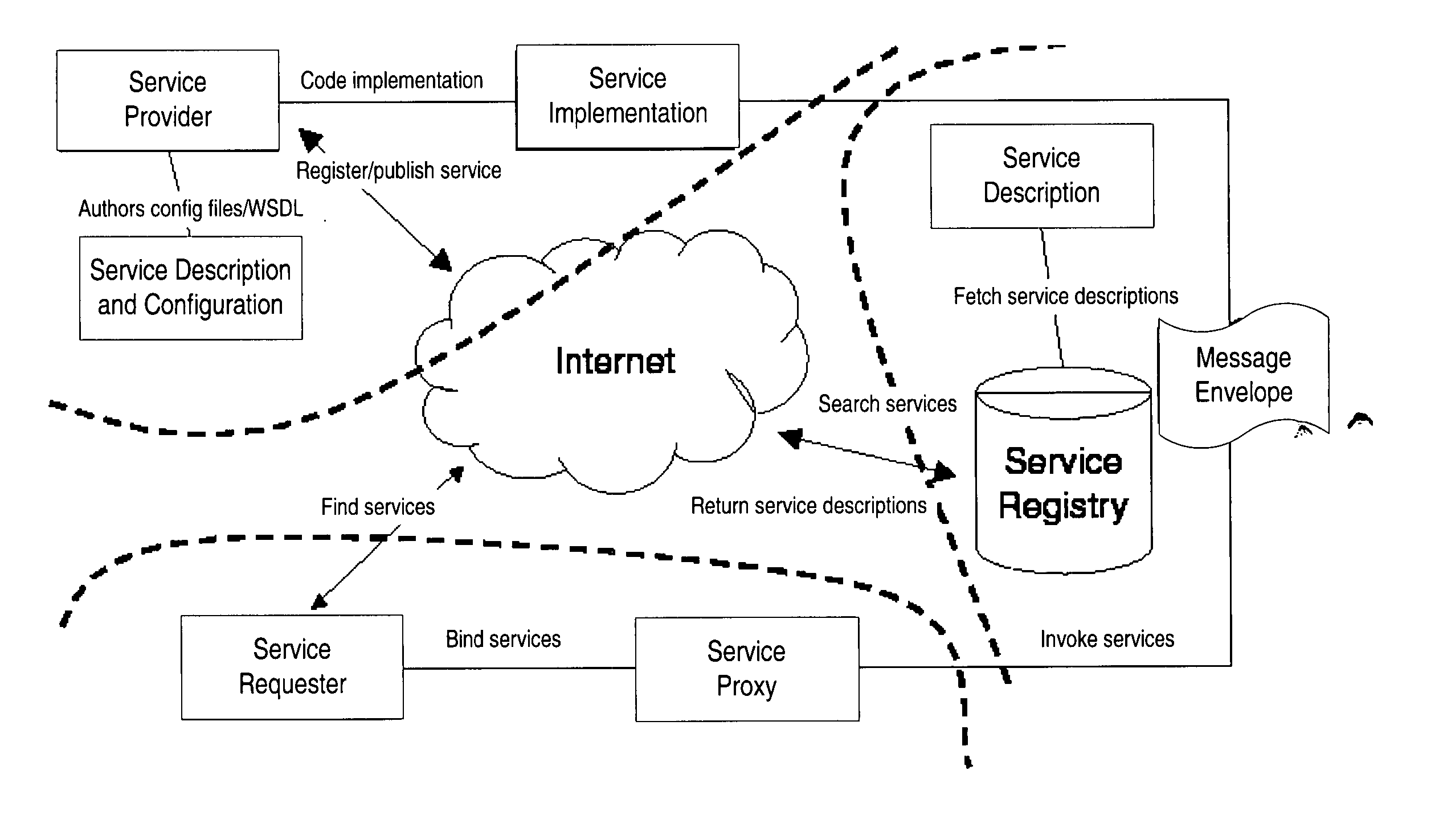
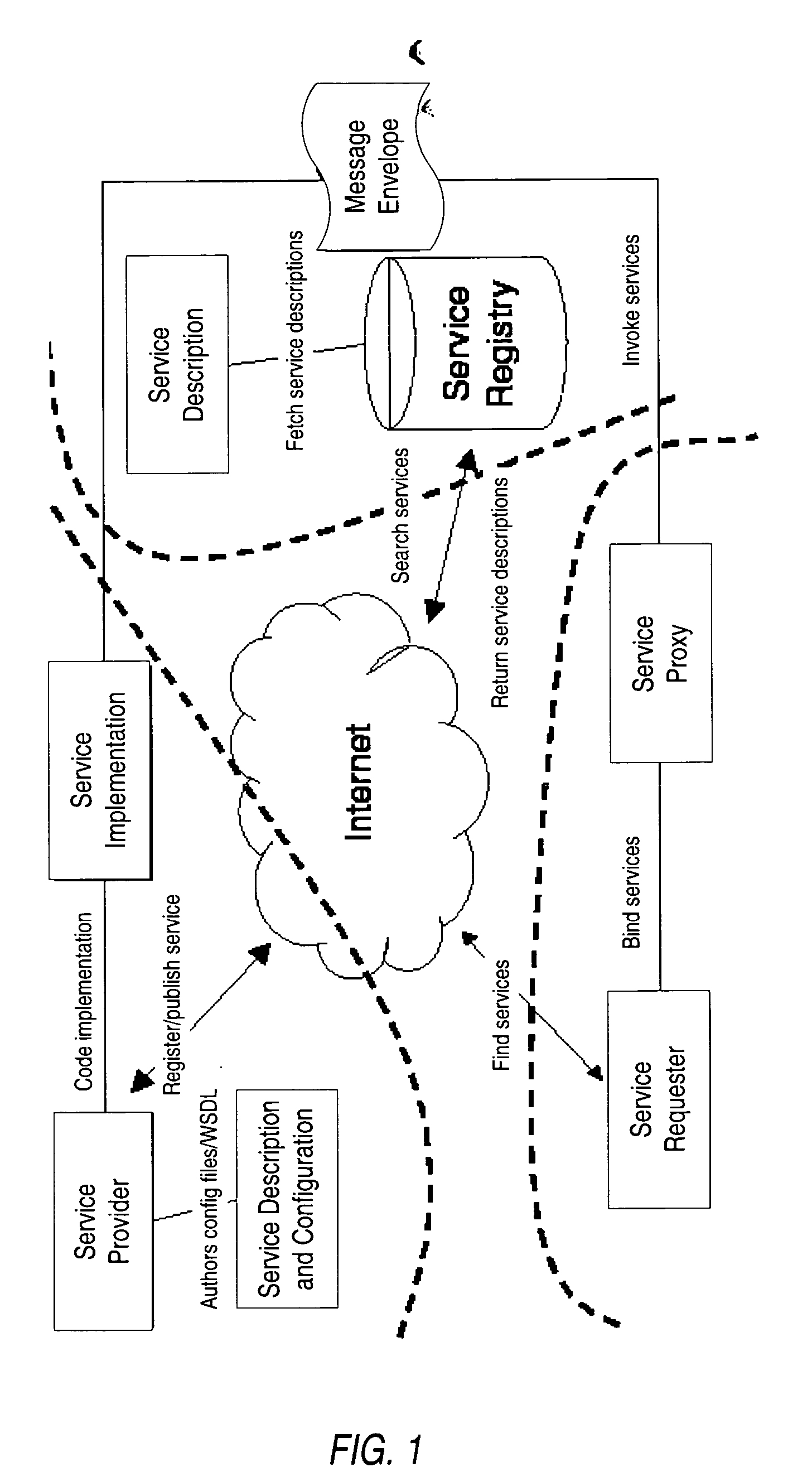
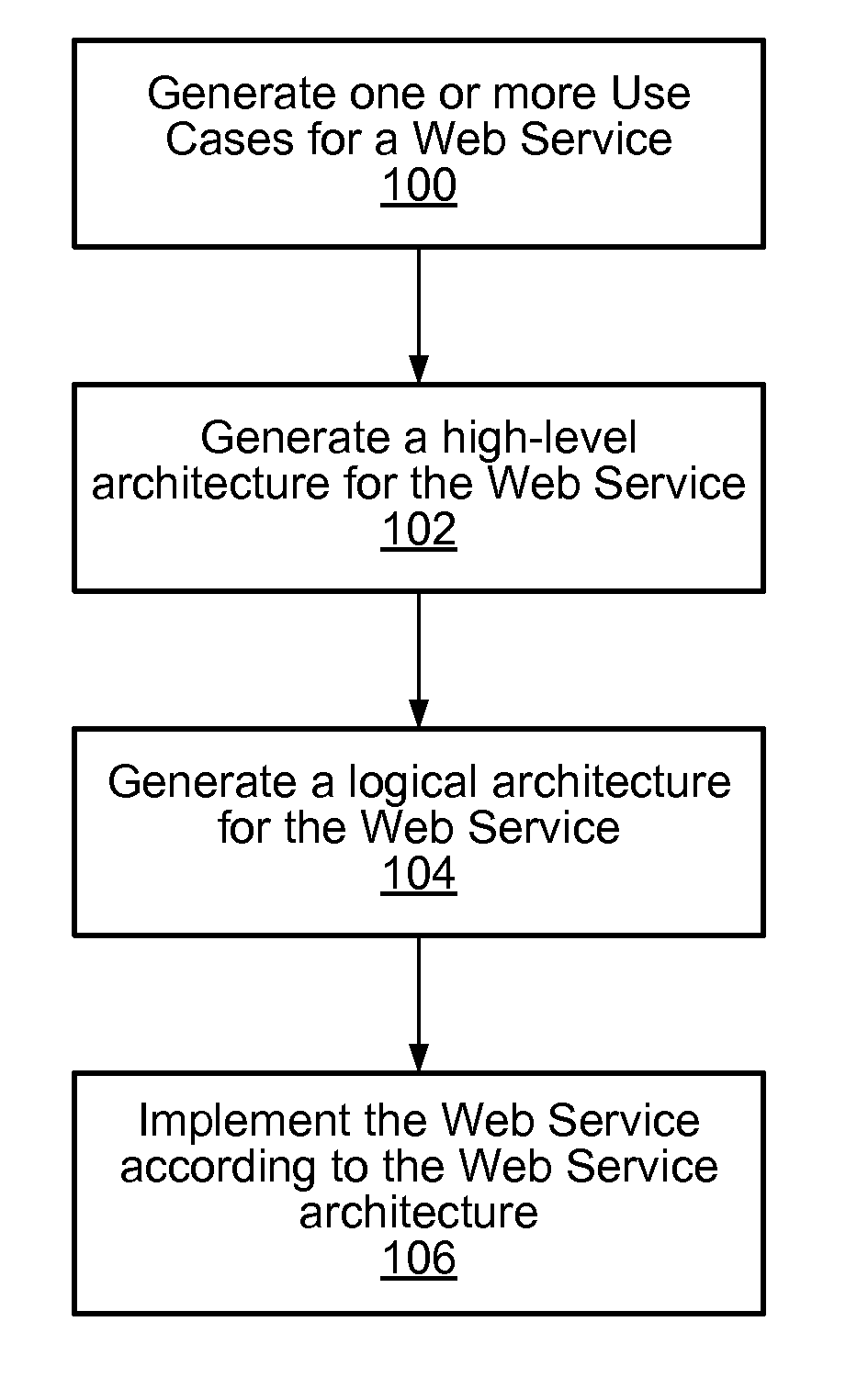
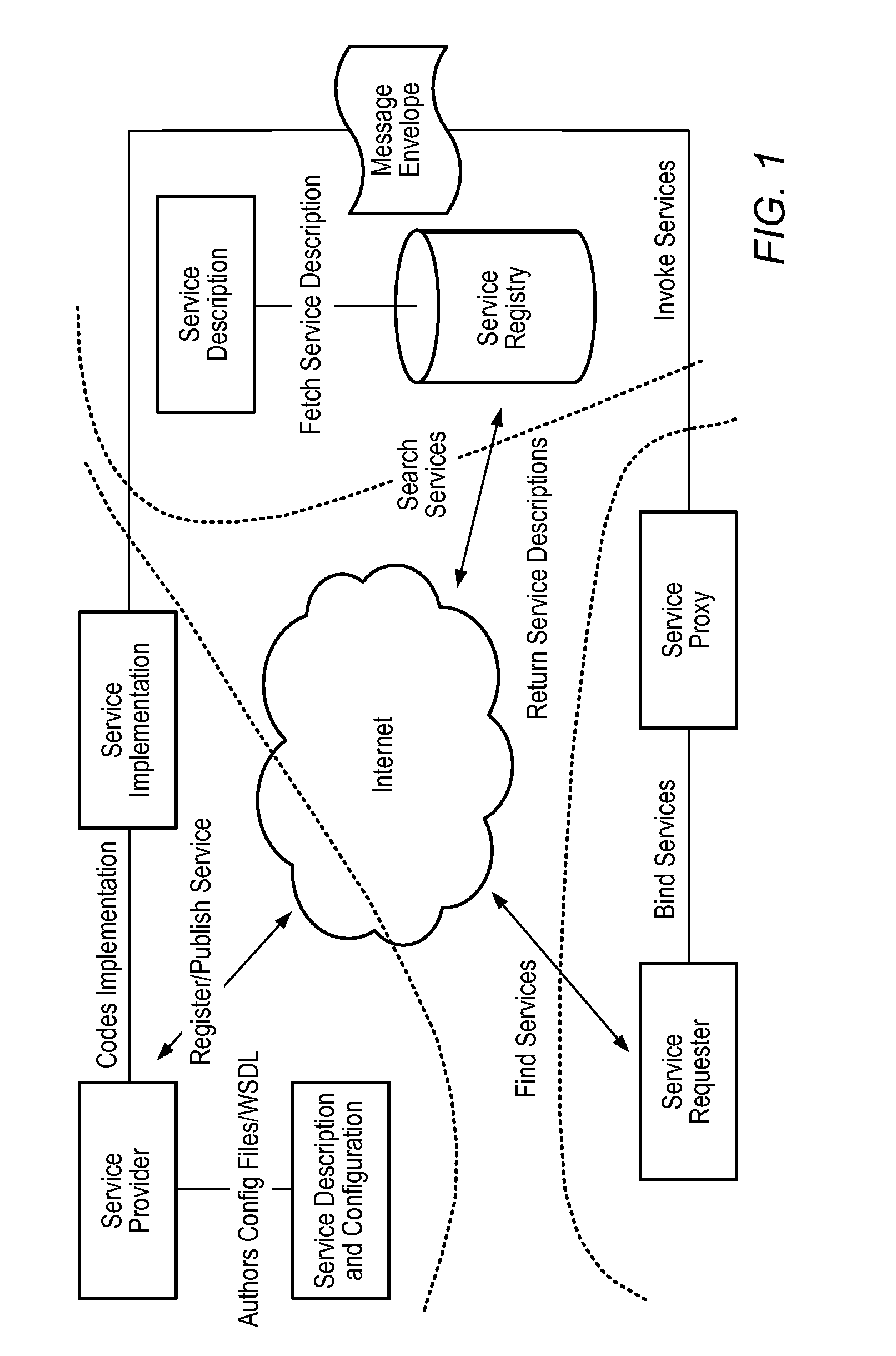
Structured methodology and design patterns for web services
ActiveUS20050044197A1Multiple digital computer combinationsDigital dataQuality of serviceBusiness-to-business
System and method for designing and implementing Web Services according to a structured methodology and design patterns. Embodiments may incorporate a structured methodology, best practices and design patterns that address reliability, availability and scalability of Web Services architecture. Embodiments may provide mechanisms for integrating heterogeneous technology components into Web Services. Embodiments may provide a vendor-independent Web Services architecture framework and reusable Web Services design patterns, which may be used in creating end-to-end solutions based on past experience and best practices. Embodiments may include design patterns and best practices for delivering Web Services solutions with Quality of Services. One embodiment may provide a Business-to-Business Integration (B2Bi) integration framework for Web Services. Embodiments may provide a Web Security framework and design patterns for designing end-to-end Web Services security.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
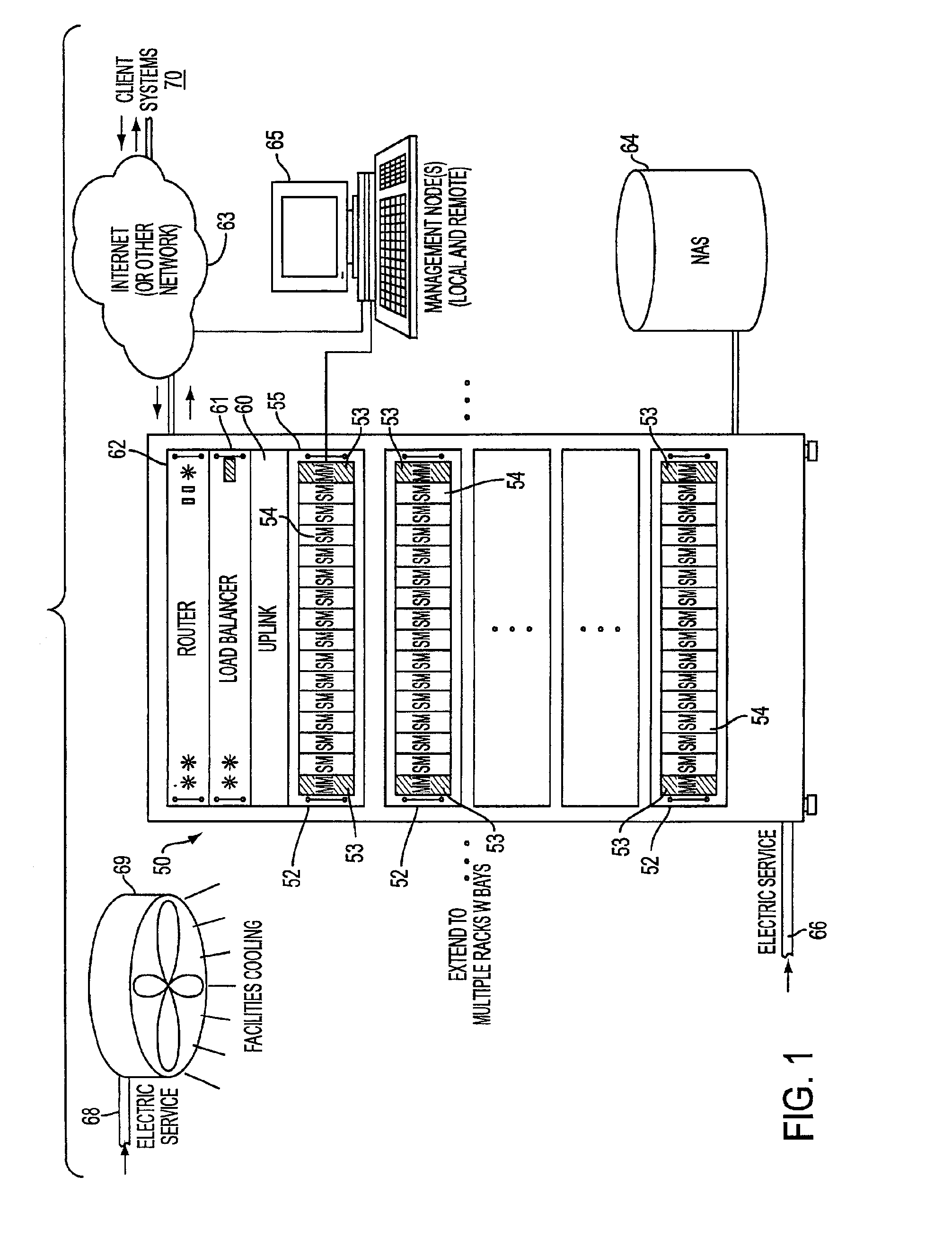
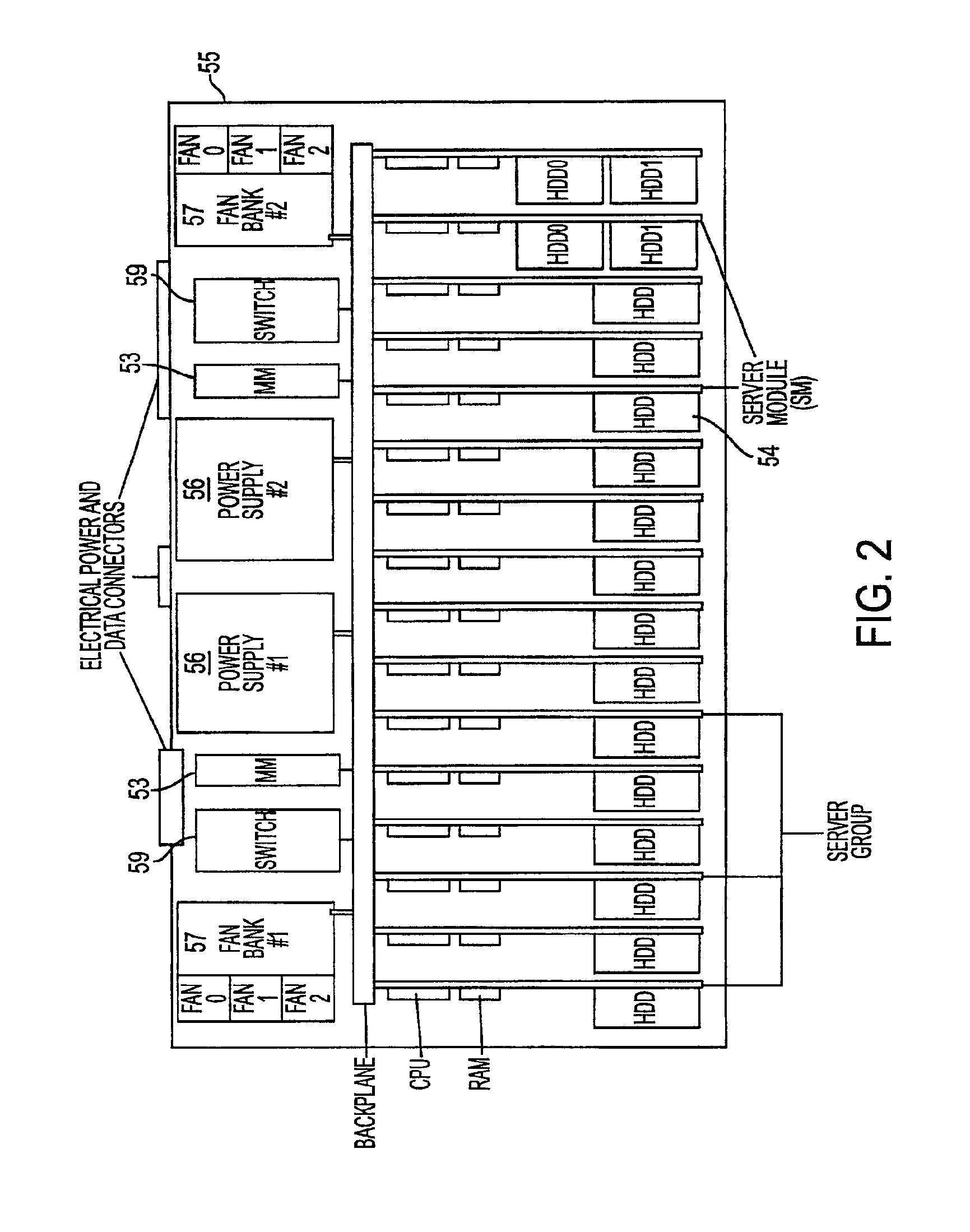
System, method, and architecture for dynamic server power management and dynamic workload management for multi-server environment
InactiveUS6859882B2Save energyConserving methodEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementNetwork architectureWorkload management
Network architecture, computer system and / or server, circuit, device, apparatus, method, and computer program and control mechanism for managing power consumption and workload in computer system and data and information servers. Further provides power and energy consumption and workload management and control systems and architectures for high-density and modular multi-server computer systems that maintain performance while conserving energy and method for power management and workload management. Dynamic server power management and optional dynamic workload management for multi-server environments is provided by aspects of the invention. Modular network devices and integrated server system, including modular servers, management units, switches and switching fabrics, modular power supplies and modular fans and a special backplane architecture are provided as well as dynamically reconfigurable multi-purpose modules and servers. Backplane architecture, structure, and method that has no active components and separate power supply lines and protection to provide high reliability in server environment.
Owner:HURON IP
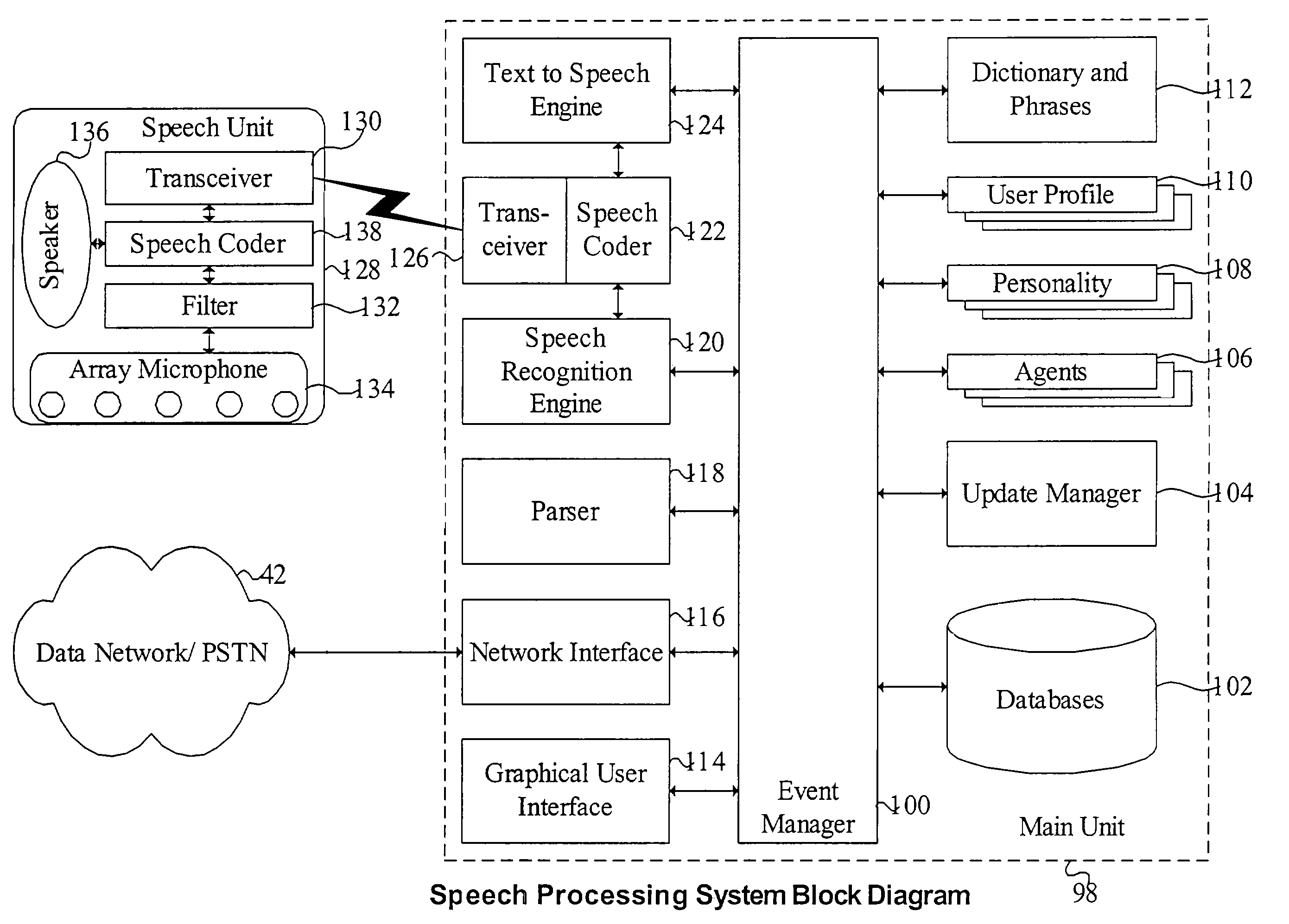
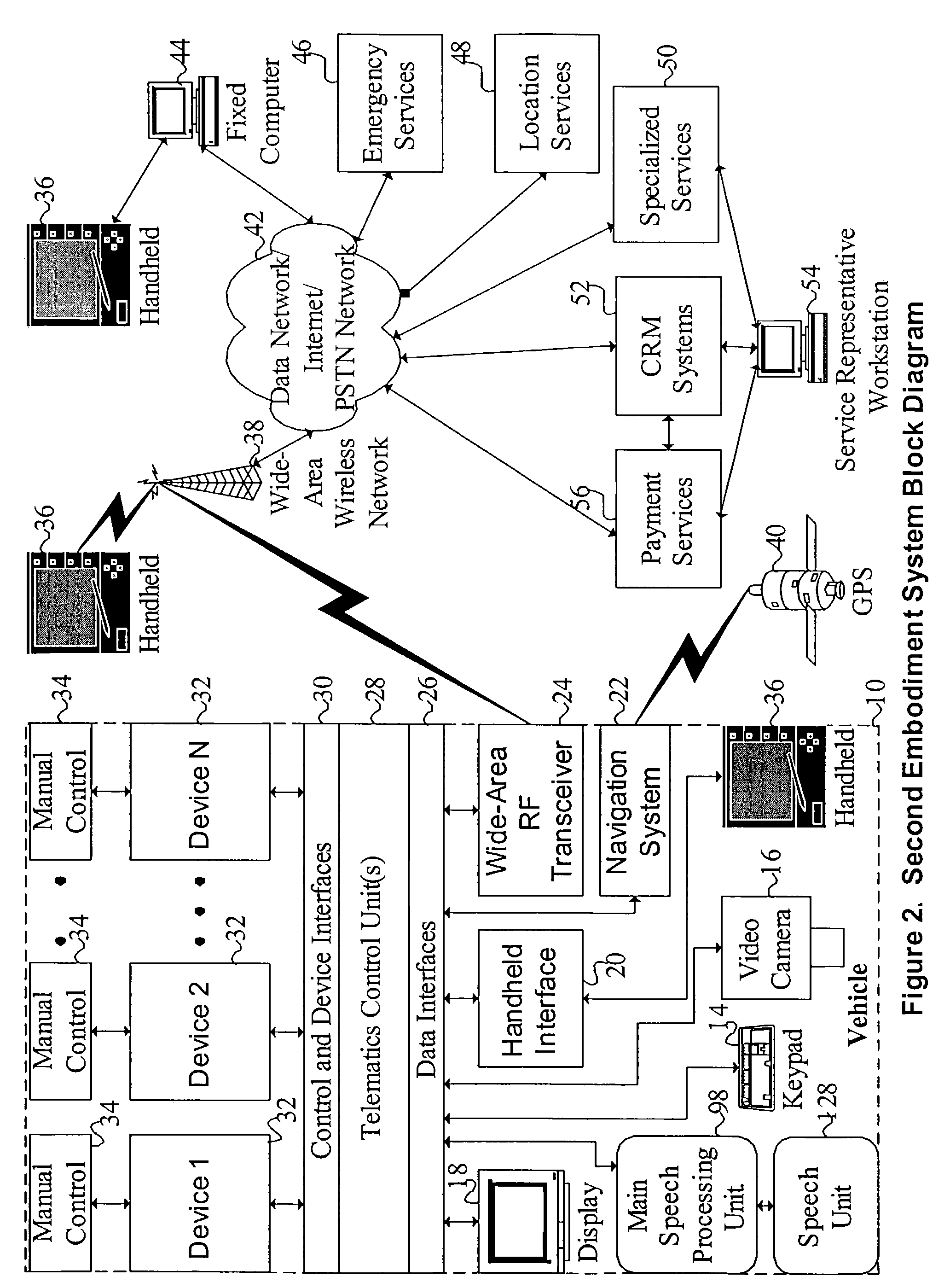
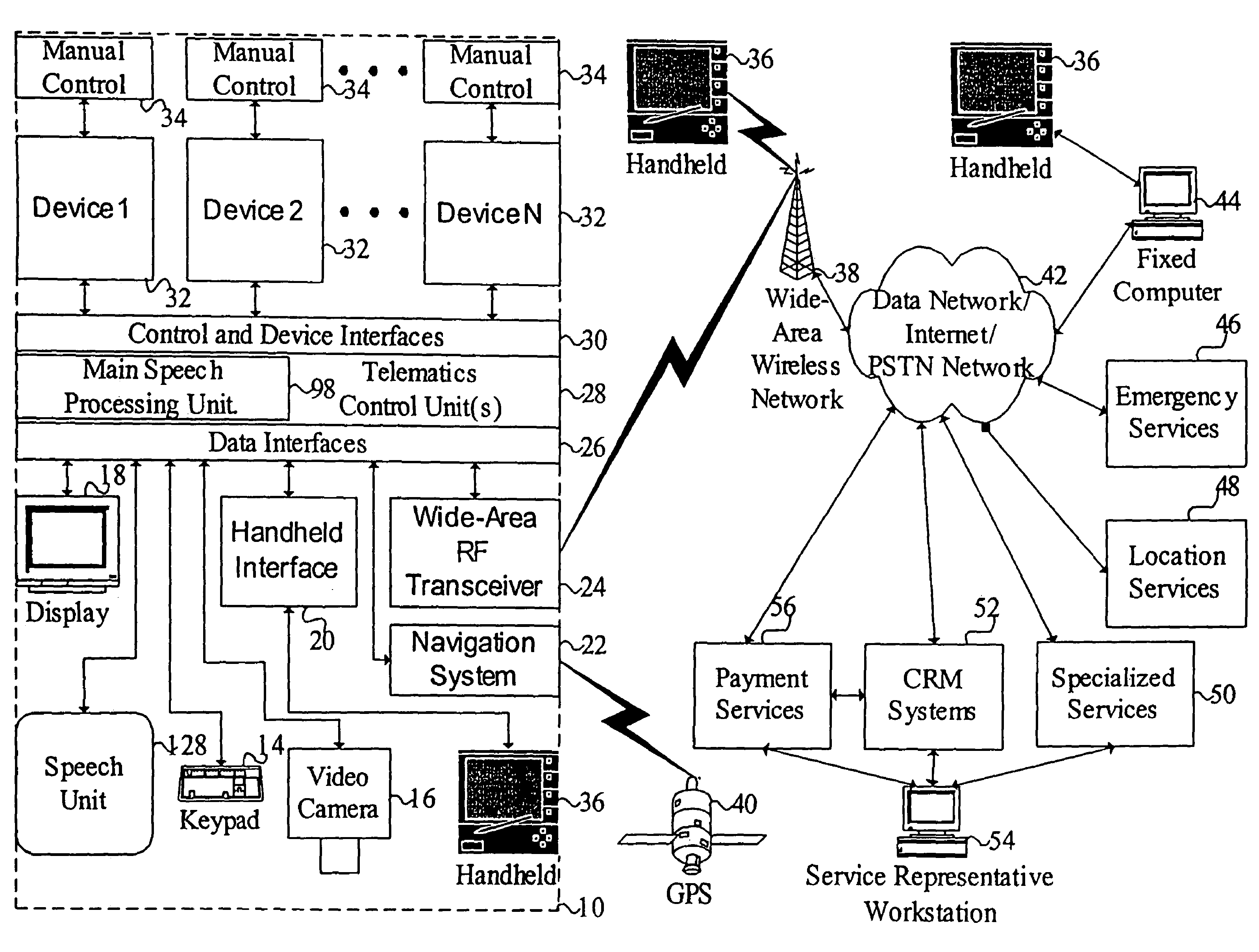
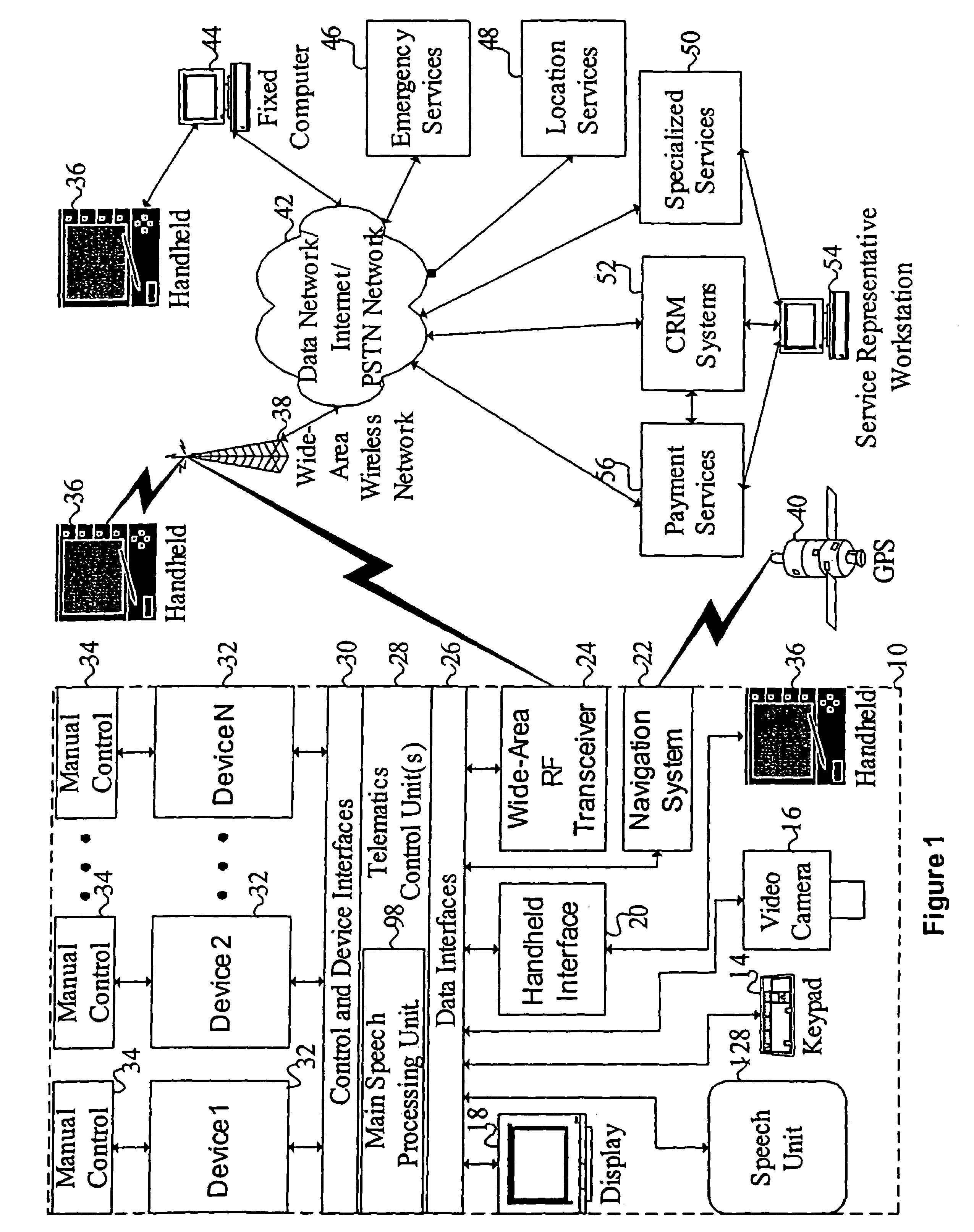
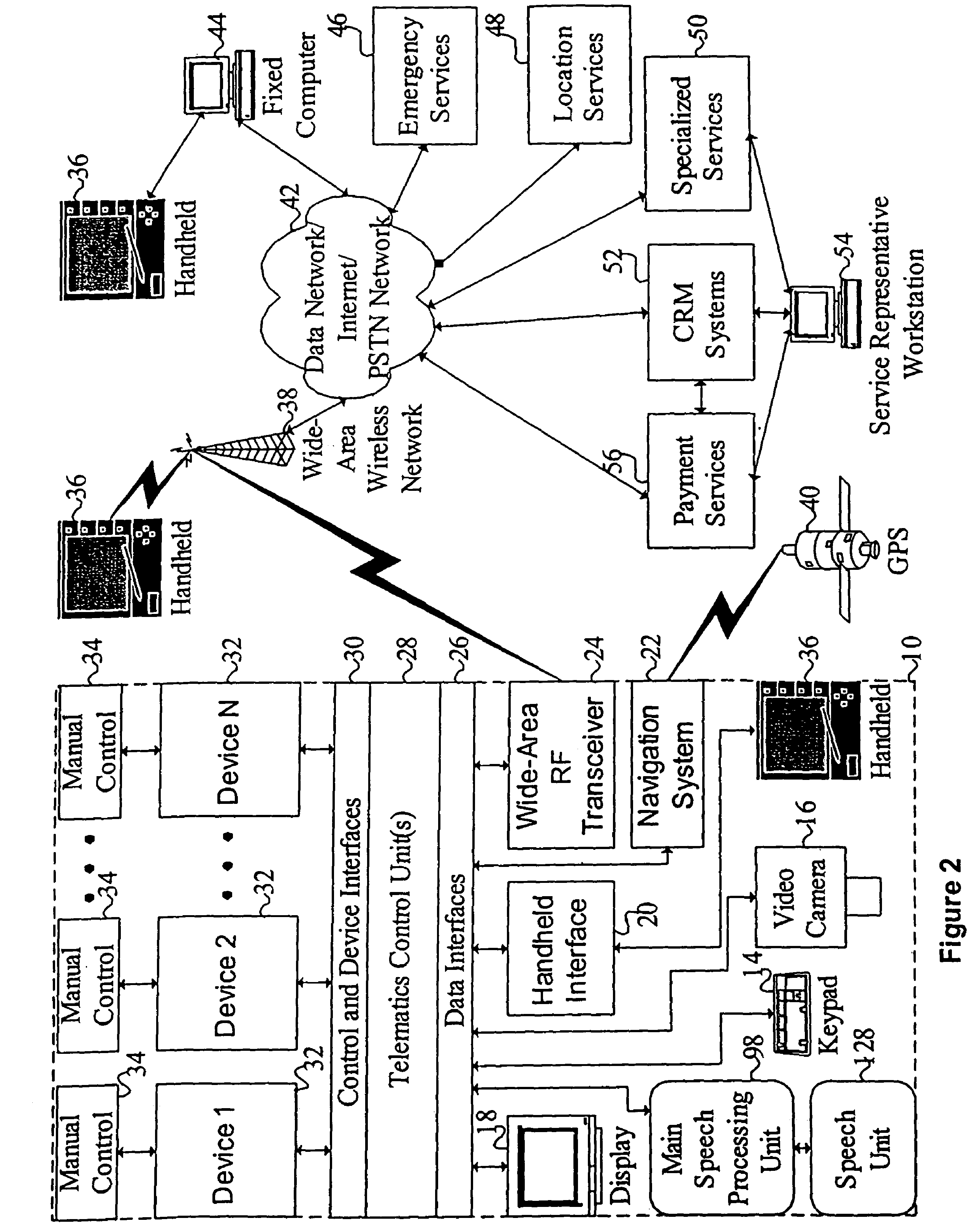
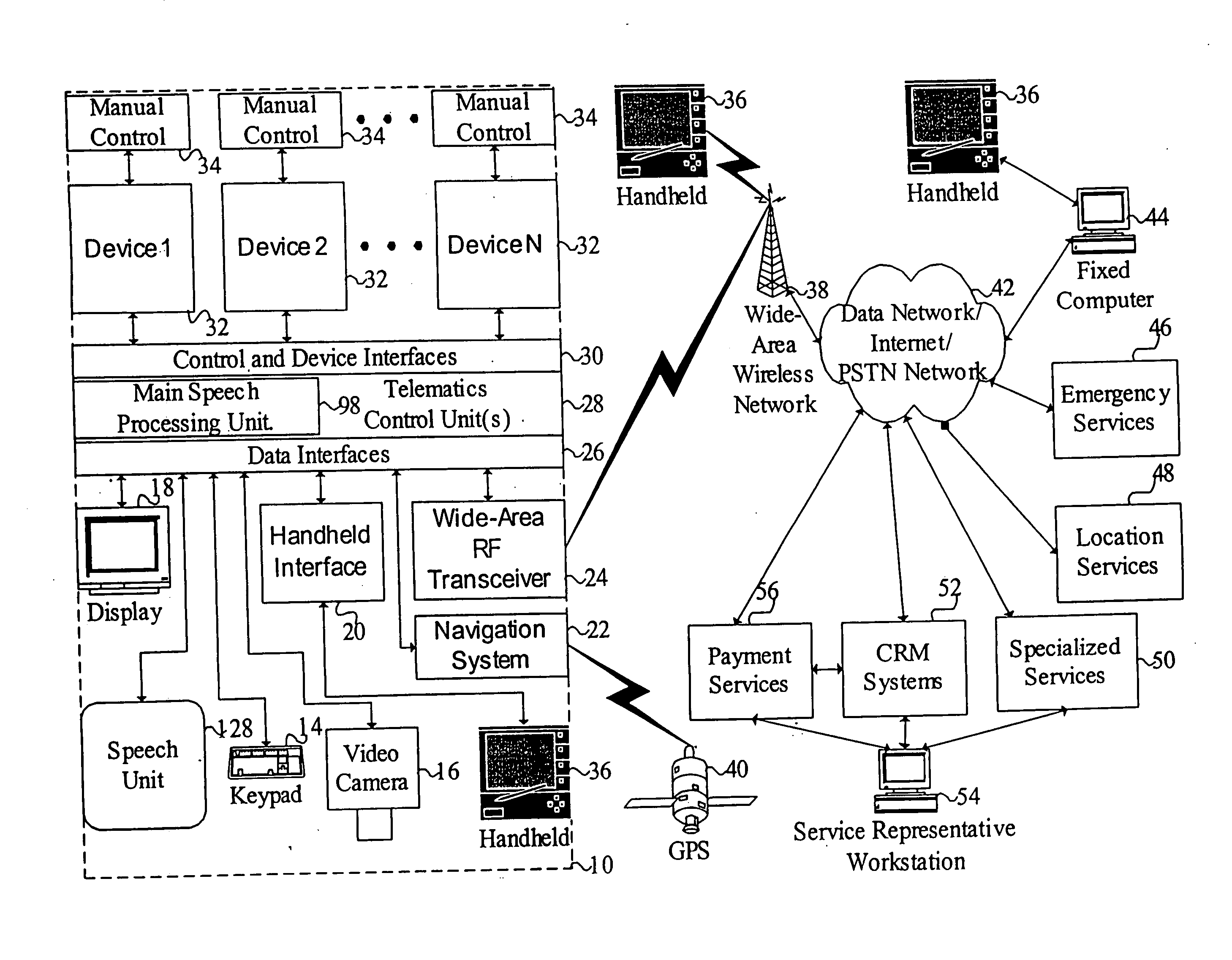
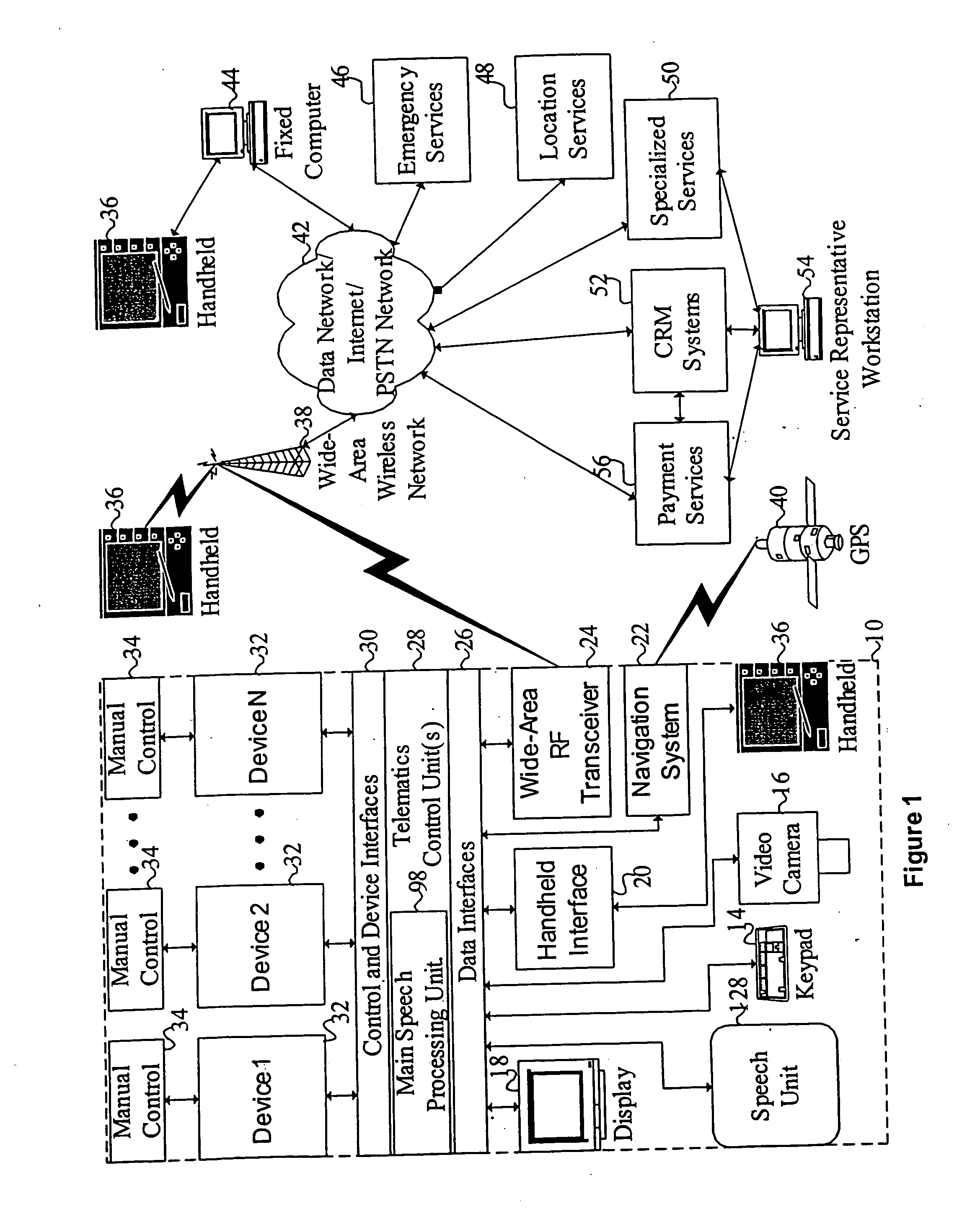
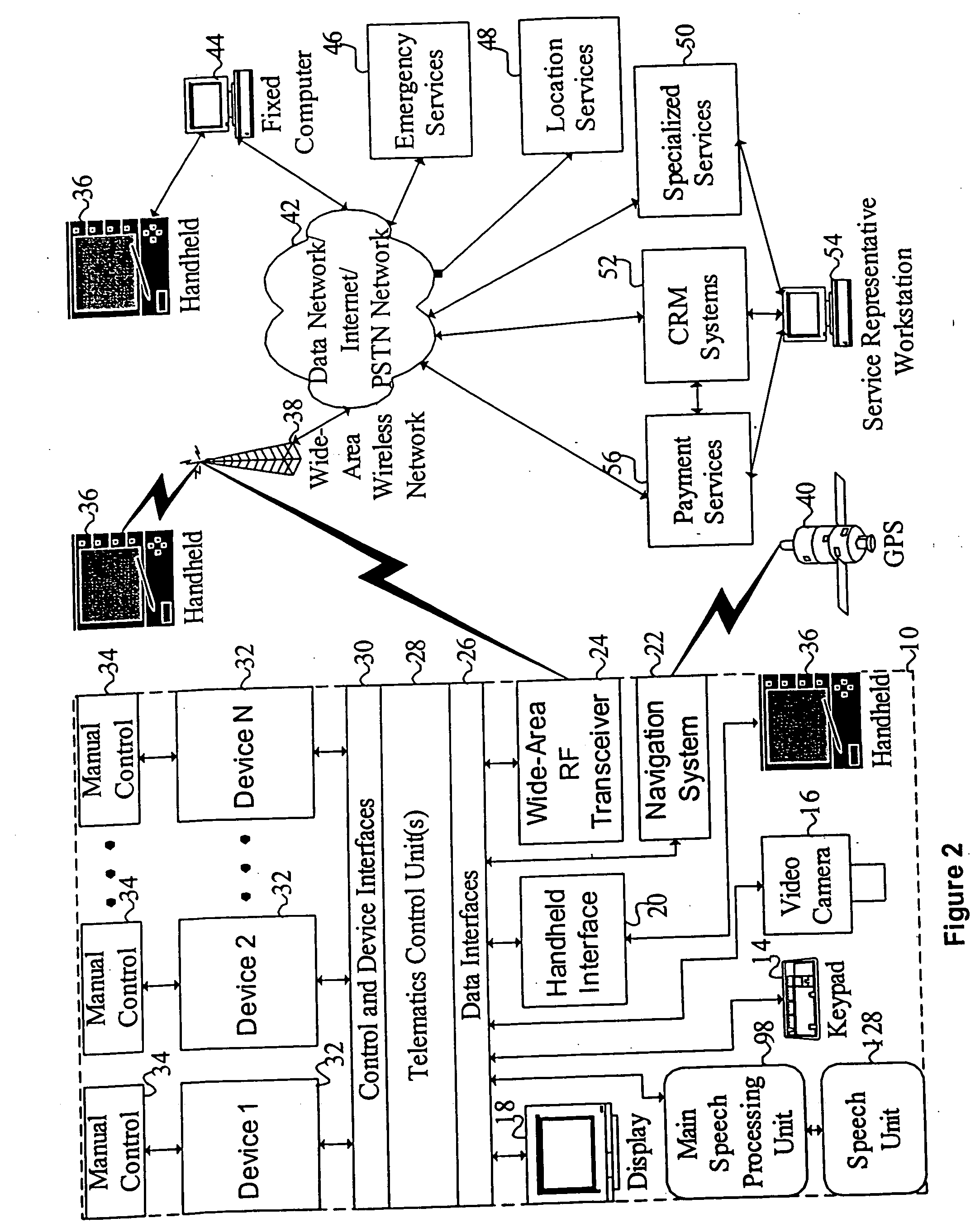
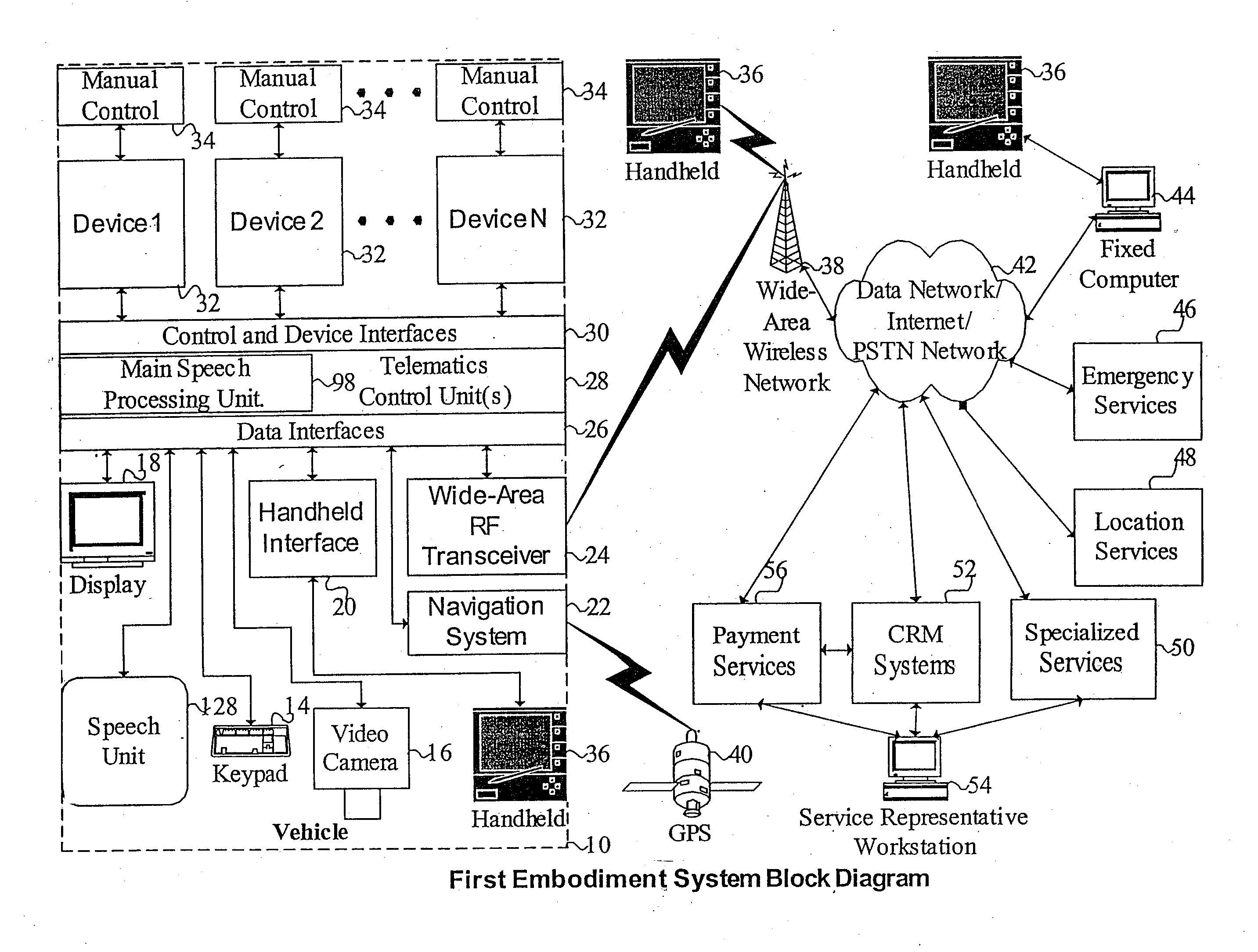
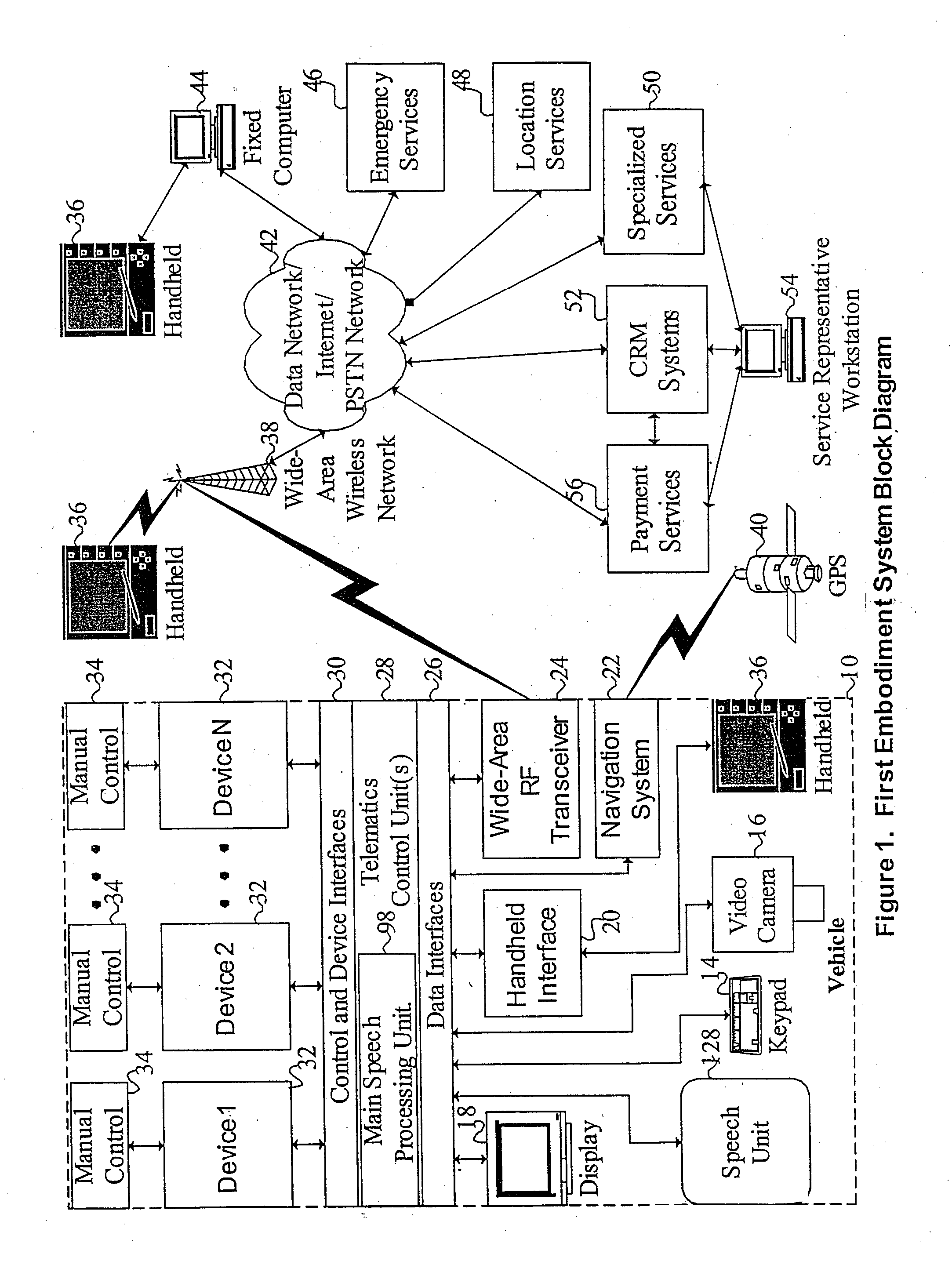
Mobile systems and methods for responding to natural language speech utterance
ActiveUS7693720B2Promotes feeling of naturalOvercome deficienciesDigital data information retrievalSpeech recognitionRemote systemTelematics
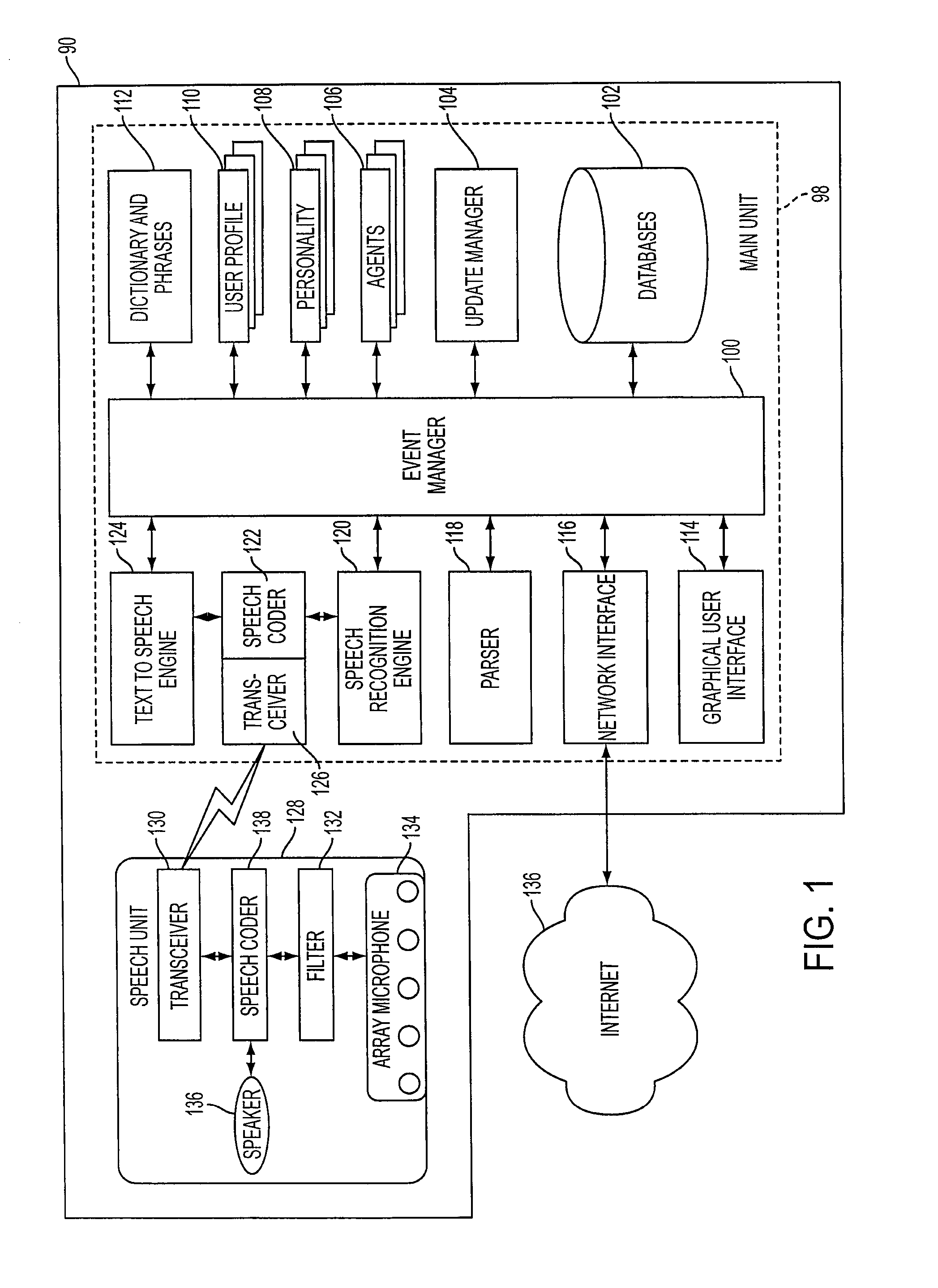
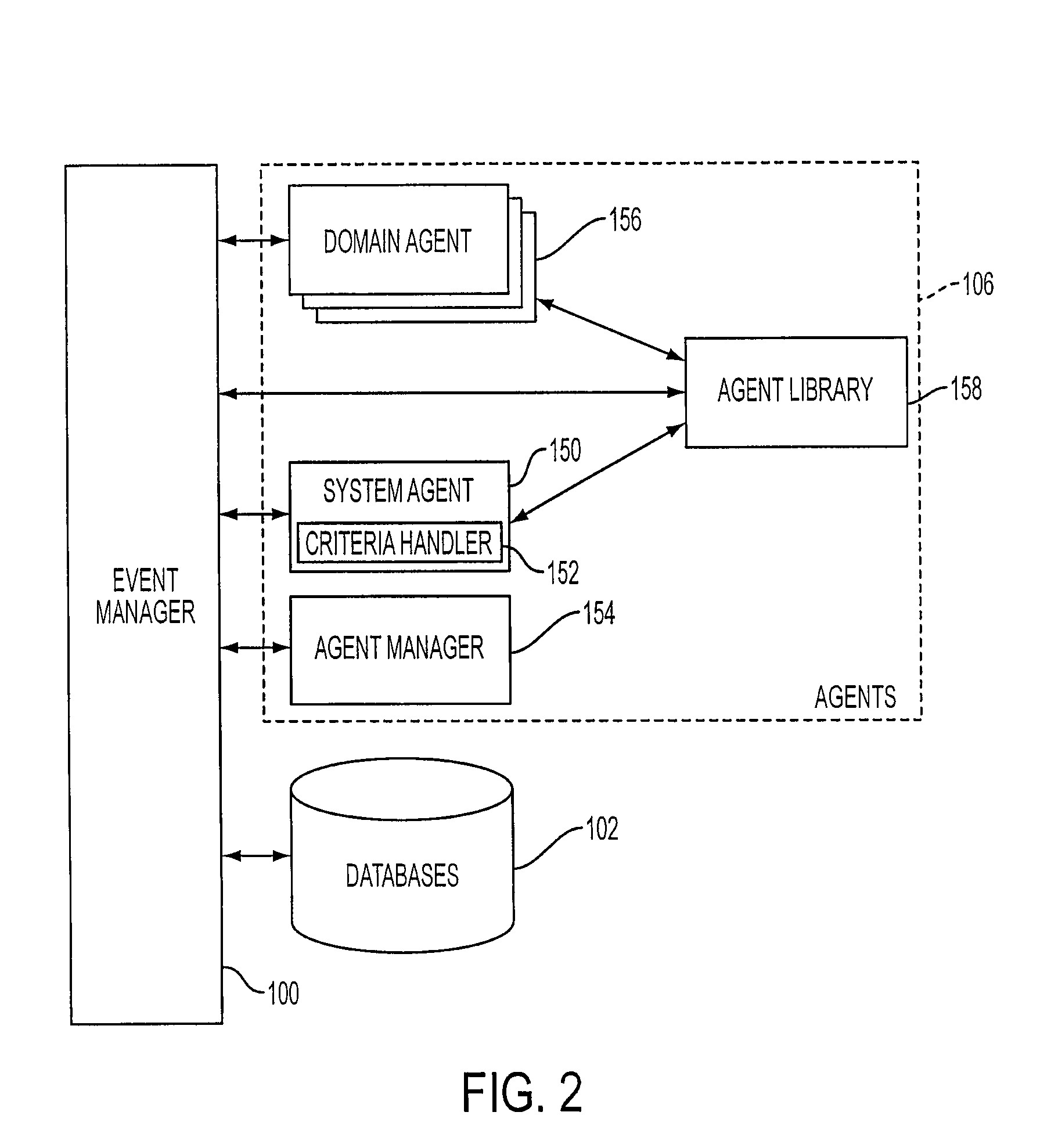
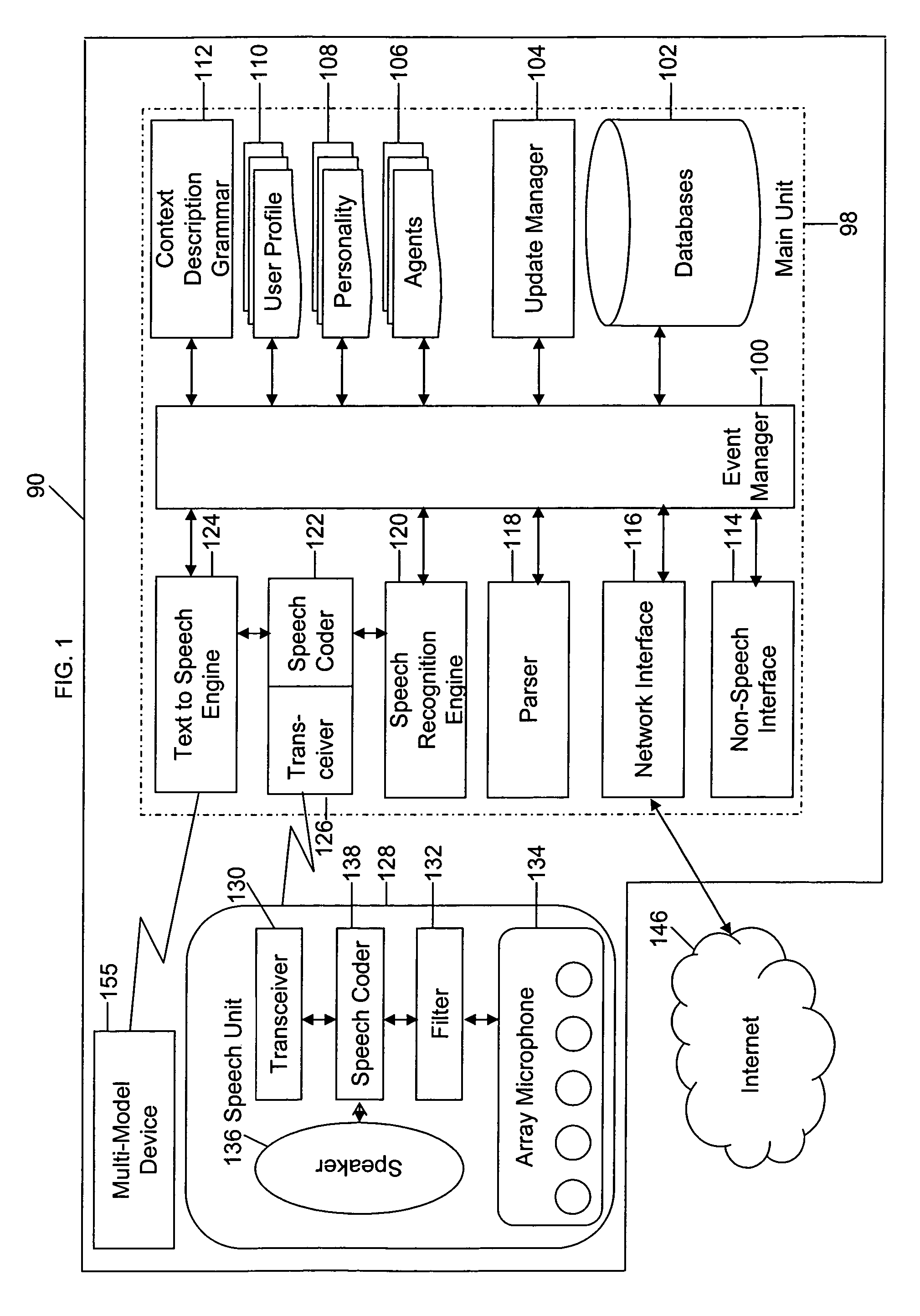
Mobile systems and methods that overcomes the deficiencies of prior art speech-based interfaces for telematics applications through the use of a complete speech-based information query, retrieval, presentation and local or remote command environment. This environment makes significant use of context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for one or more users making queries or commands in multiple domains. Through this integrated approach, a complete speech-based natural language query and response environment can be created. The invention creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command. The invention may organize domain specific behavior and information into agents, that are distributable or updateable over a wide area network. The invention can be used in dynamic environments such as those of mobile vehicles to control and communicate with both vehicle systems and remote systems and devices.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
Mobile systems and methods of supporting natural language human-machine interactions
ActiveUS7949529B2Promotes feeling of naturalConvenient timeWeb data indexingDevices with voice recognitionTelematicsWide area network
A mobile system is provided that includes speech-based and non-speech-based interfaces for telematics applications. The mobile system identifies and uses context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for users that submit requests and / or commands in multiple domains. The invention creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command. The invention may organize domain specific behavior and information into agents, that are distributable or updateable over a wide area network.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
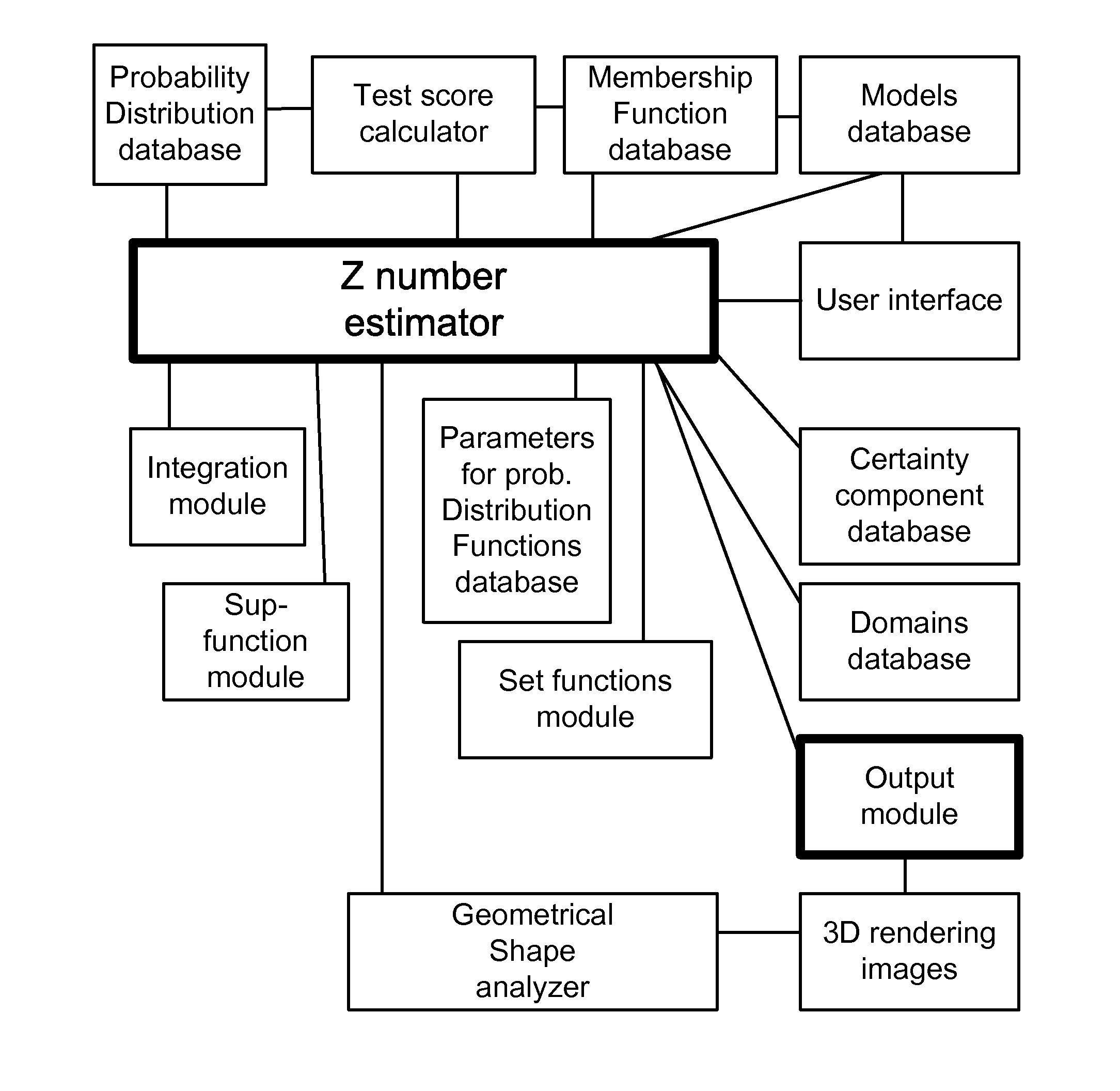
Application of Z-Webs and Z-factors to Analytics, Search Engine, Learning, Recognition, Natural Language, and Other Utilities
Here, we introduce Z-webs, including Z-factors and Z-nodes, for the understanding of relationships between objects, subjects, abstract ideas, concepts, or the like, including face, car, images, people, emotions, mood, text, natural language, voice, music, video, locations, formulas, facts, historical data, landmarks, personalities, ownership, family, friends, love, happiness, social behavior, voting behavior, and the like, to be used for many applications in our life, including on the search engine, analytics, Big Data processing, natural language processing, economy forecasting, face recognition, dealing with reliability and certainty, medical diagnosis, pattern recognition, object recognition, biometrics, security analysis, risk analysis, fraud detection, satellite image analysis, machine generated data analysis, machine learning, training samples, extracting data or patterns (from the video, images, and the like), editing video or images, and the like. Z-factors include reliability factor, confidence factor, expertise factor, bias factor, and the like, which is associated with each Z-node in the Z-web.
Owner:Z ADVANCED COMPUTING
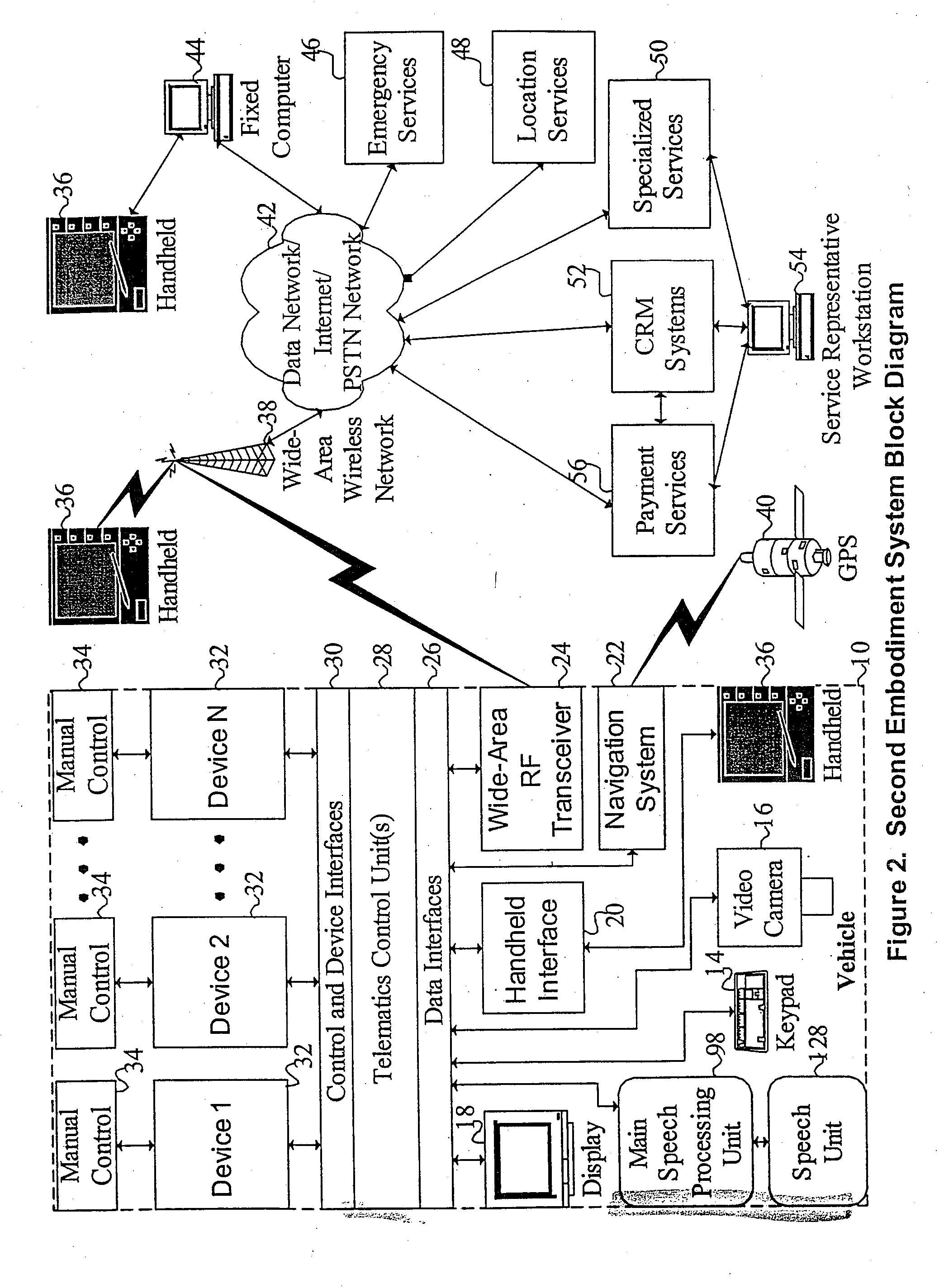
Mobile systems and methods of supporting natural language human-machine interactions
ActiveUS20070050191A1Improve maximizationHigh bandwidthWeb data indexingDevices with voice recognitionNatural languageDependability
A mobile system is provided that includes speech-based and non-speech-based interfaces for telematics applications. The mobile system identifies and uses context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for users that submit requests and / or commands in multiple domains. The invention creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command. The invention may organize domain specific behavior and information into agents, that are distributable or updateable over a wide area network.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
System and method
PendingUS20100317420A1Discounts/incentivesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingDependabilityUser interface
A system and method providing for communication and reolution of utility functions between participants, wherein the utility function is evaluated based on local information at the recipient to determine a cost value thereof. A user interface having express representation of both information elements, and associated reliability of the information. An automated system for optimally conveying information based on relevance and reliability.
Owner:HOFFBERG FAMILY TRUST 2
Mobile systems and methods for responding to natural language speech utterance
ActiveUS20100145700A1Promotes feeling of naturalOvercome deficienciesVehicle testingInstruments for road network navigationInformation processingRemote system
Owner:DIALECT LLC
Systems and methods for responding to natural language speech utterance
ActiveUS7398209B2Promotes feeling of naturalOvercome deficienciesData processing applicationsNatural language data processingPrior informationDependability
Systems and methods for receiving natural language queries and / or commands and execute the queries and / or commands. The systems and methods overcomes the deficiencies of prior art speech query and response systems through the application of a complete speech-based information query, retrieval, presentation and command environment. This environment makes significant use of context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for one or more users making queries or commands in multiple domains. Through this integrated approach, a complete speech-based natural language query and response environment can be created. The systems and methods creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
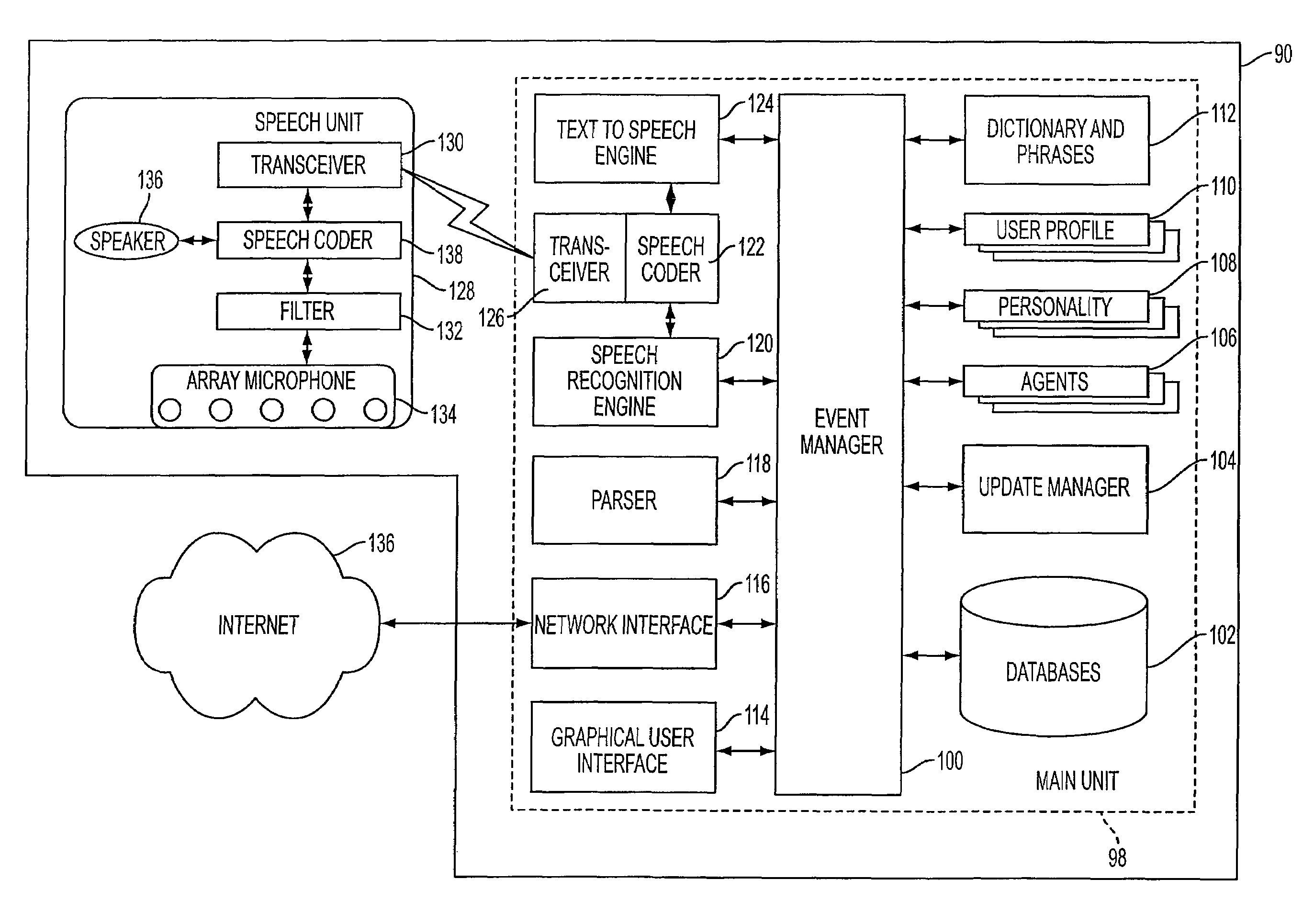
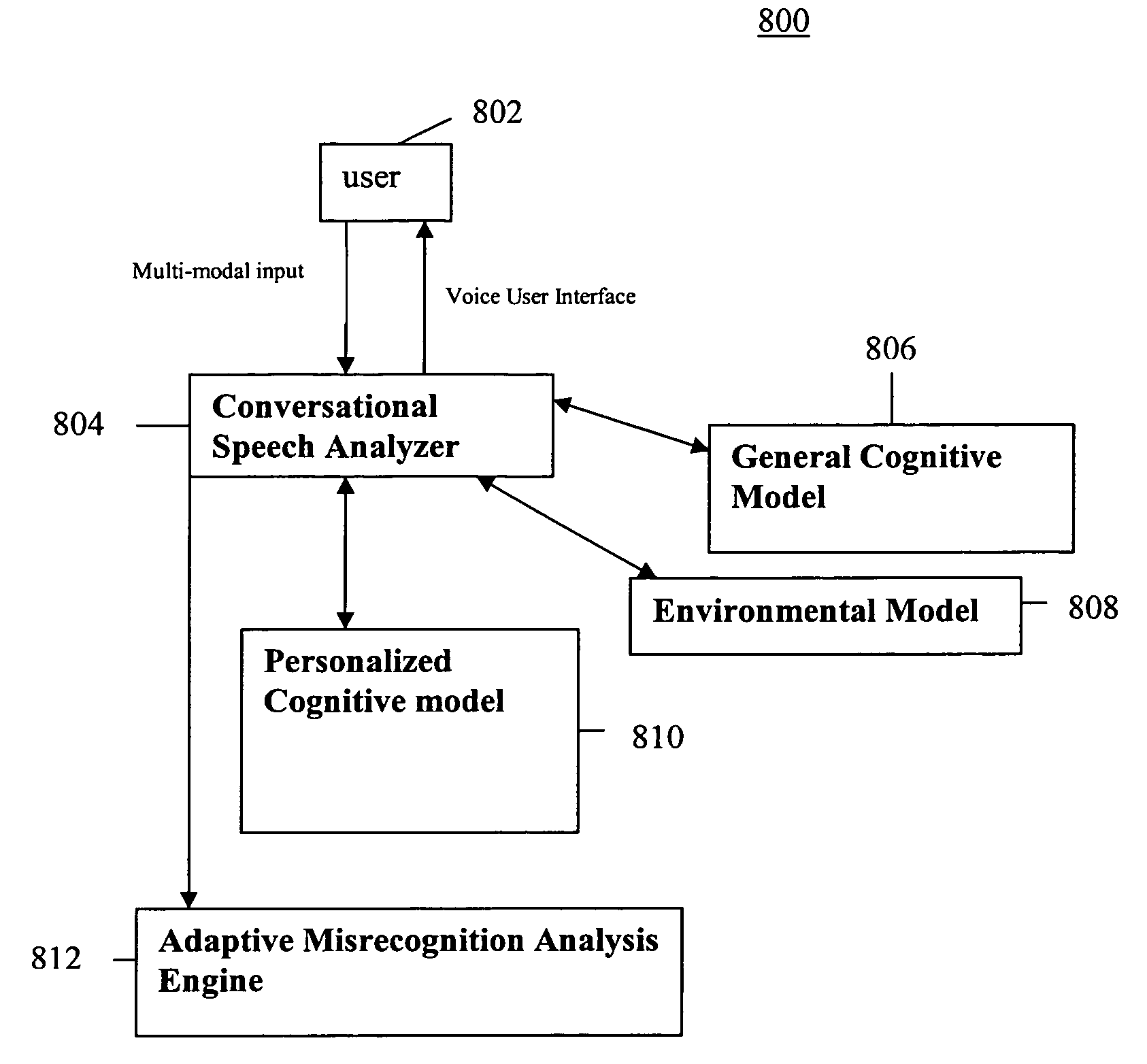
System and method of supporting adaptive misrecognition in conversational speech
ActiveUS7620549B2Promotes feeling of naturalSignificant to useNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionPersonalizationHuman–machine interface
A system and method are provided for receiving speech and / or non-speech communications of natural language questions and / or commands and executing the questions and / or commands. The invention provides a conversational human-machine interface that includes a conversational speech analyzer, a general cognitive model, an environmental model, and a personalized cognitive model to determine context, domain knowledge, and invoke prior information to interpret a spoken utterance or a received non-spoken message. The system and method creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context of the speech or non-speech communication and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
Medical emergency alert system and method
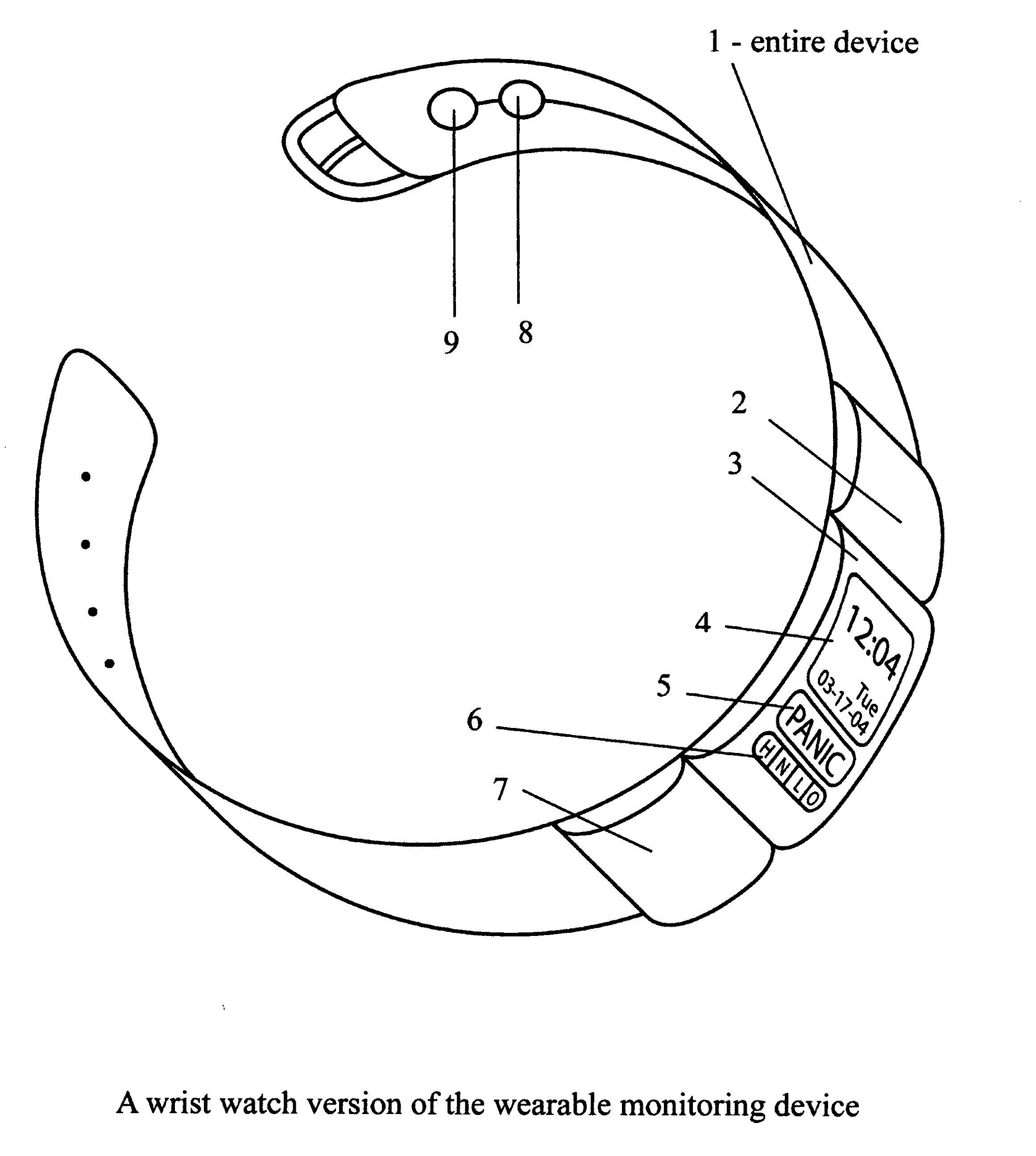
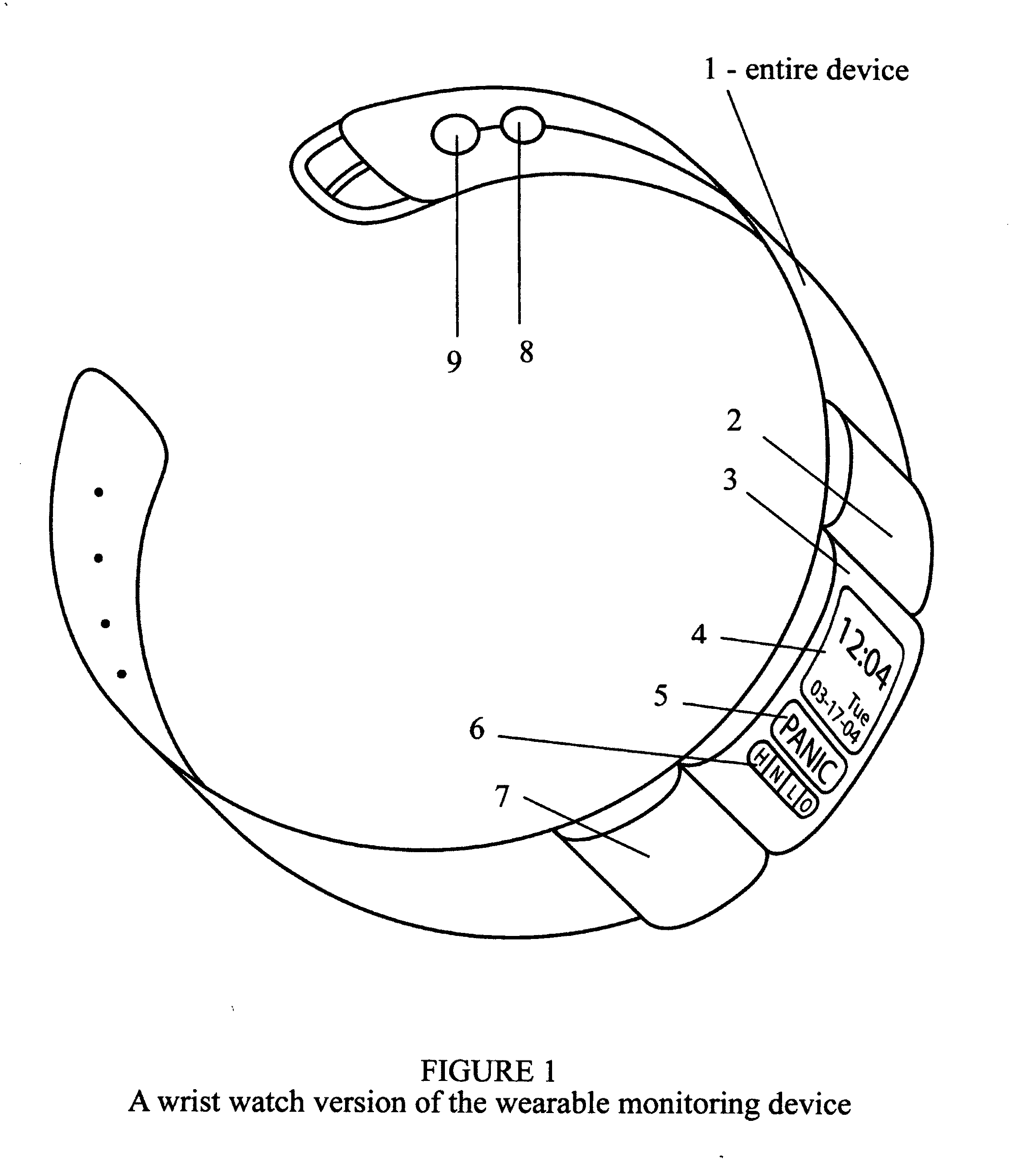
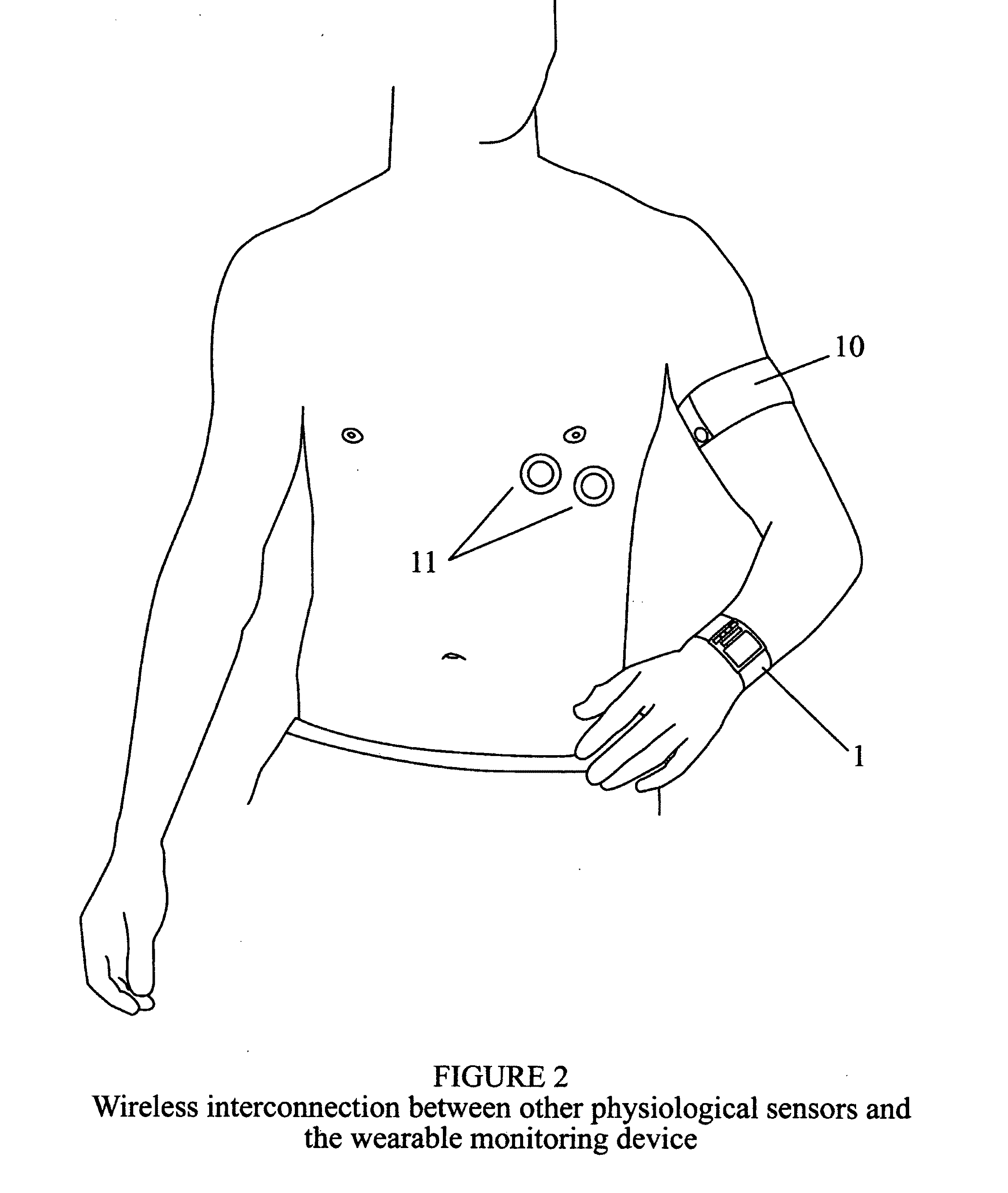
A medical emergency reporting system and methodology that utilize a wearable monitoring device to continuously monitor key physiological parameters of a person, and when measurements exceed programmed threshold levels, it will automatically issue a medical emergency alert along with location information to a remote monitoring center via a wireless network and the Internet for immediate local response. This system will also provide manual emergency alert activation, continuous updates with key physiological measurements to the emergency response personnel along with the medical history of the subject as well as redundancy in emergency alert reporting and malfunction diagnosis to assure ultimate accuracy, immediacy and reliability for the person that requires medical assistance.
Owner:HWANG FRLIN DUN JEN +1
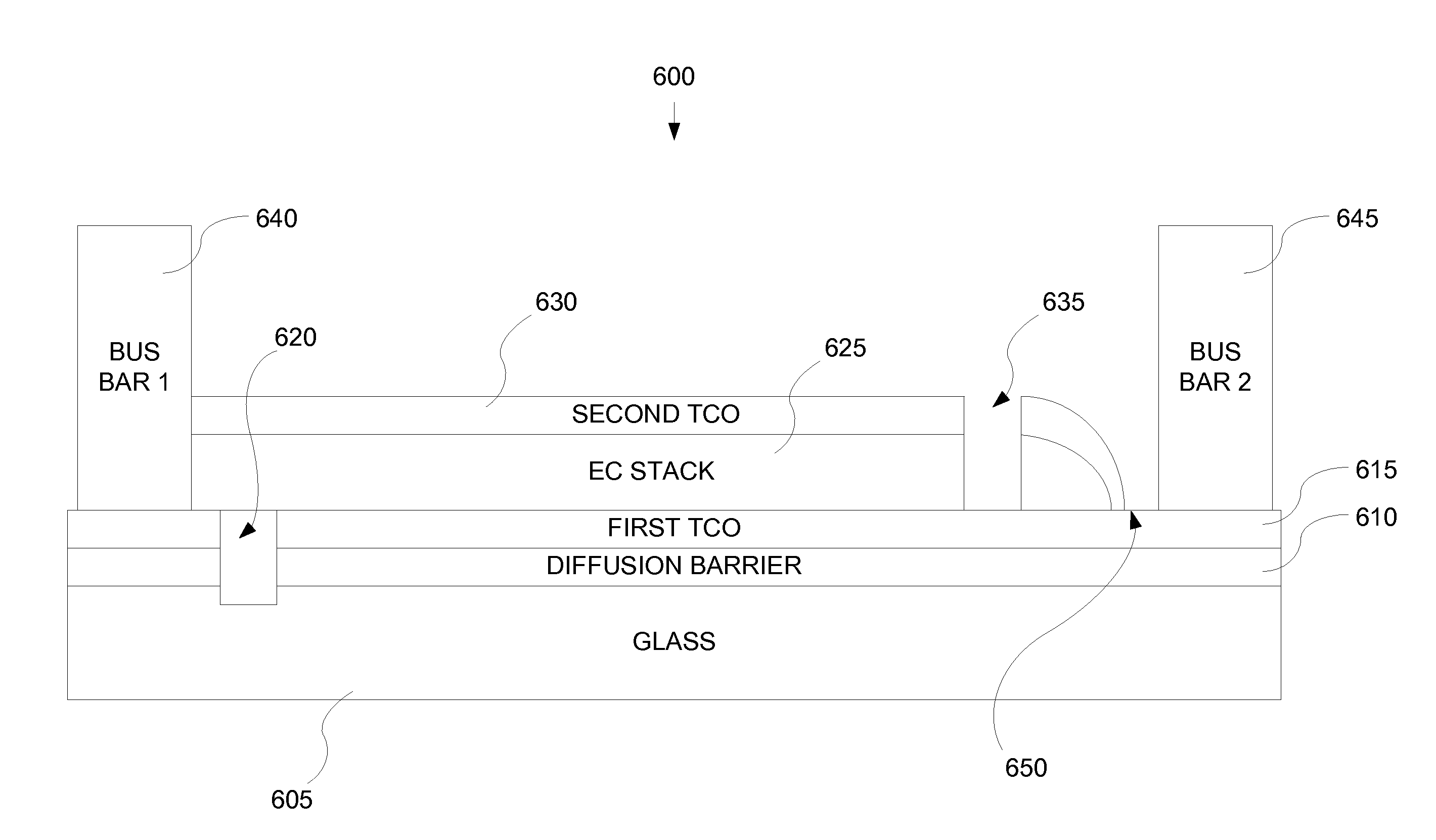
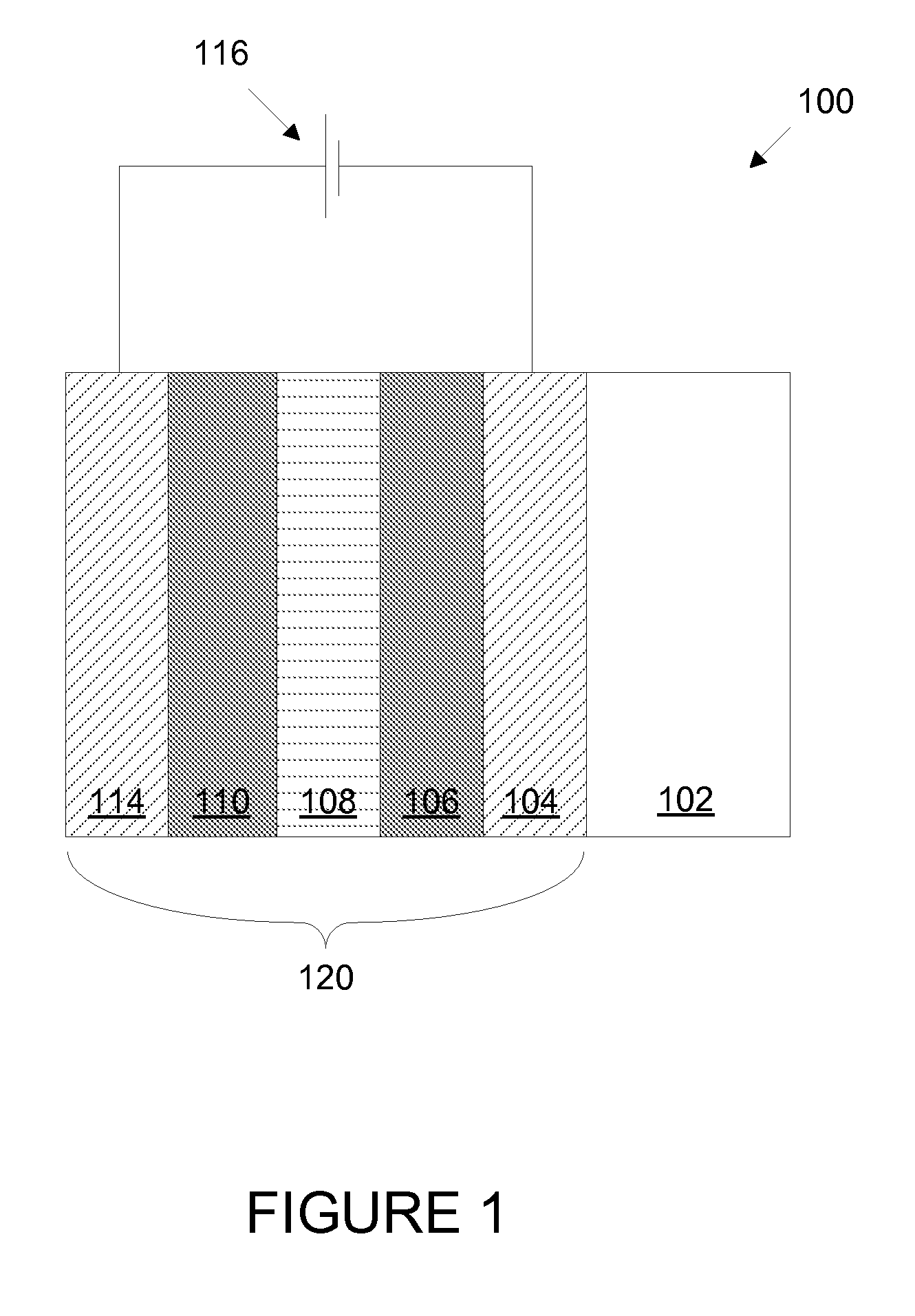
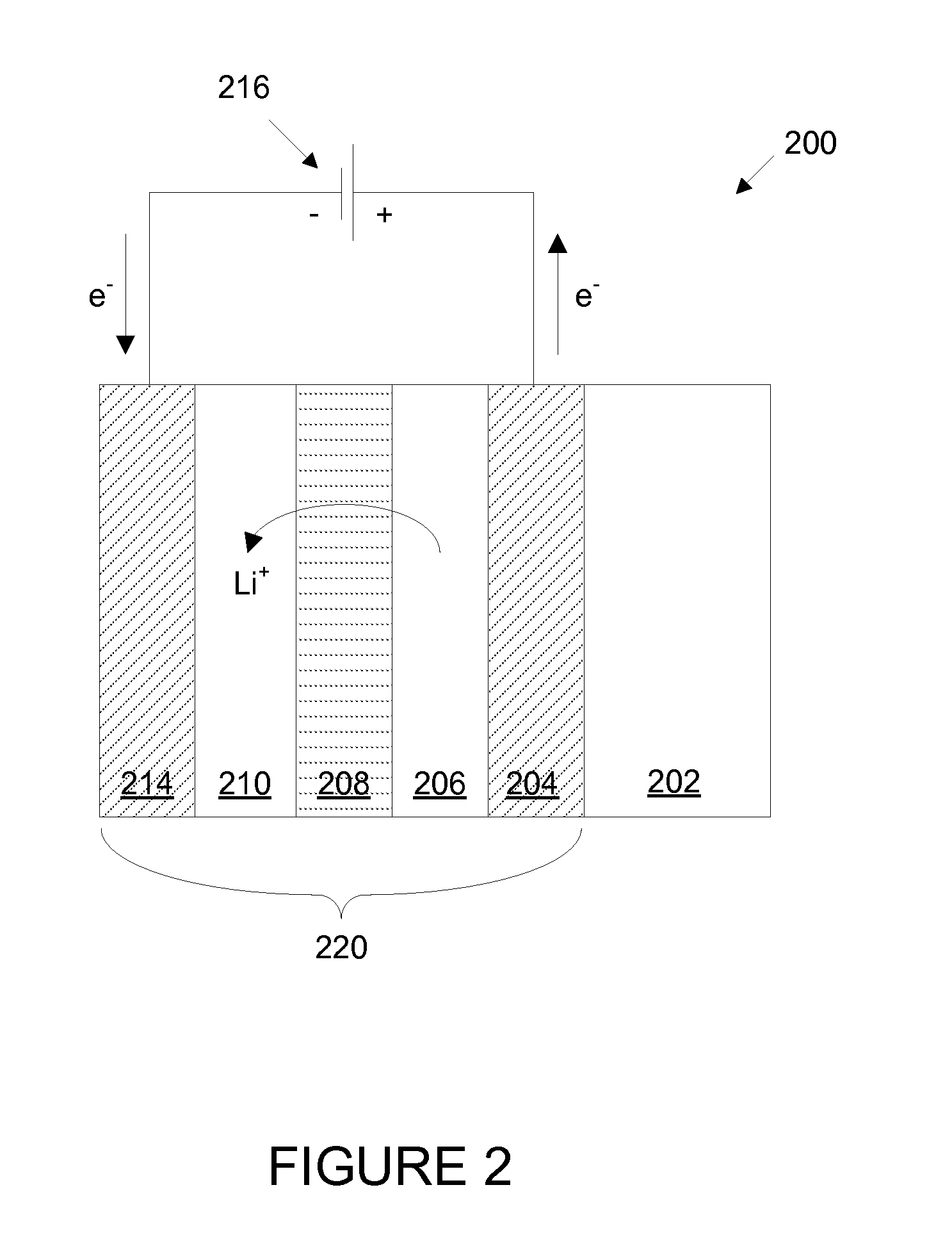
Electrochromic devices
ActiveUS20100245973A1Improve equipment reliabilityImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingElectricityLithium
Prior electrochromic devices frequently suffer from poor reliability and poor performance. Some of the difficulties result from inappropriate design and construction of the devices. In order to improve device reliability two layers of an electrochromic device, the counter electrode layer and the electrochromic layer, can each be fabricated to include defined amounts of lithium. Further, the electrochromic device may be subjected to a multistep thermochemical conditioning operation to improve performance. Additionally, careful choice of the materials and morphology of some components of the electrochromic device provides improvements in performance and reliability. In some devices, all layers of the device are entirely solid and inorganic.
Owner:VIEW INC
Methods for improving performance and reliability of biosensors
InactiveUS6885883B2Microbiological testing/measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringCurve fittingMonitoring system
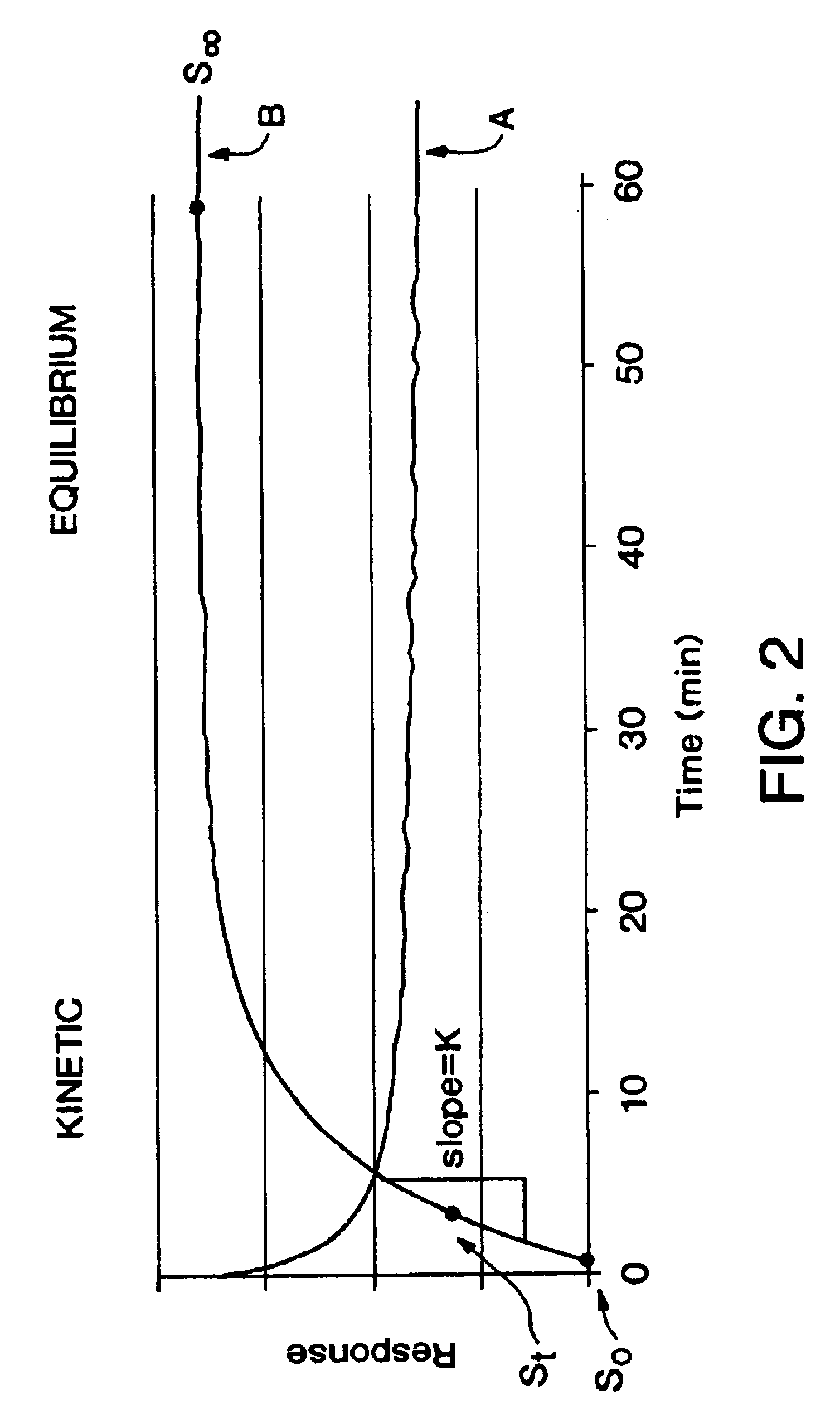
The present invention relates to a predictive-kinetic method for use with data processing of a sensor-generated signal, as well as, microprocessors and monitoring systems employing such a predictive-kinetic method. Data from a transient region of a signal is used with suitable models and curve-fitting methods to predict the signal that would be measured for the system at the completion of the reaction. The values resulting from data processing of sensor response using the methods of the present invention are less sensitive to measurement variables.
Owner:ANIMAS TECH +1
Variable gain active noise canceling system with improved residual noise sensing
InactiveUS6118878AReduce the possibilityCancellation system retains its effectiveness across its bandwidthNoise generationSound producing devicesInstabilityEngineering
An active noise cancellation system includes a series of features for more effective cancellation, greater reliability, and improved stability. A particular feature adapted for headset systems includes locating a residual microphone radially offset from the center of a sound generator to detect a signal more similar to that incident upon the eardrum of the user. In addition, an open back headset design includes perforations on the side of the headset instead of the back, so that the perforations are less susceptible to inadvertent blockage. The system also includes a mechanism for detecting changes in the acoustic characteristics of the environment that may be caused, for example, by pressure exerted upon the earpieces, and that may destabilize the cancellation system. The system automatically responds to such changes, for example, by reducing the gain or the frequency response of the system to preserve stability. The system further includes other methods for detecting imminent instability and compensating, such as detecting the onset of signals within enhancement frequencies characteristic of the onset of instability, and adjusting the gain or frequency response of the system or suppressing the enhanced signals. The system further includes a mechanism for conserving battery life by turning the system off when sound levels are low, or adjusting the power supply to the system to correspond to the current power requirements of the system.
Owner:NOISE CANCELLATION TECH
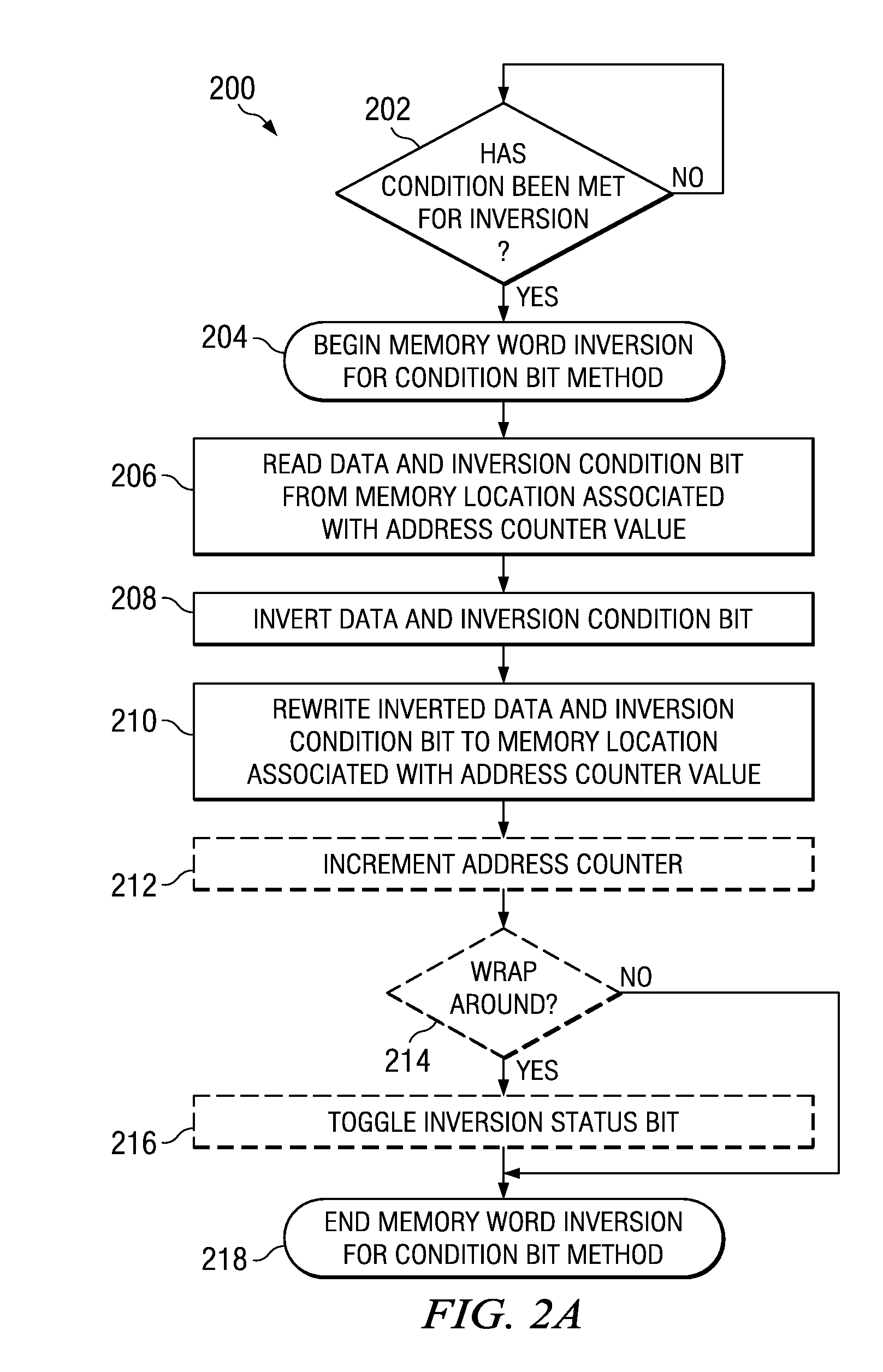
Technique for memory imprint reliability improvement
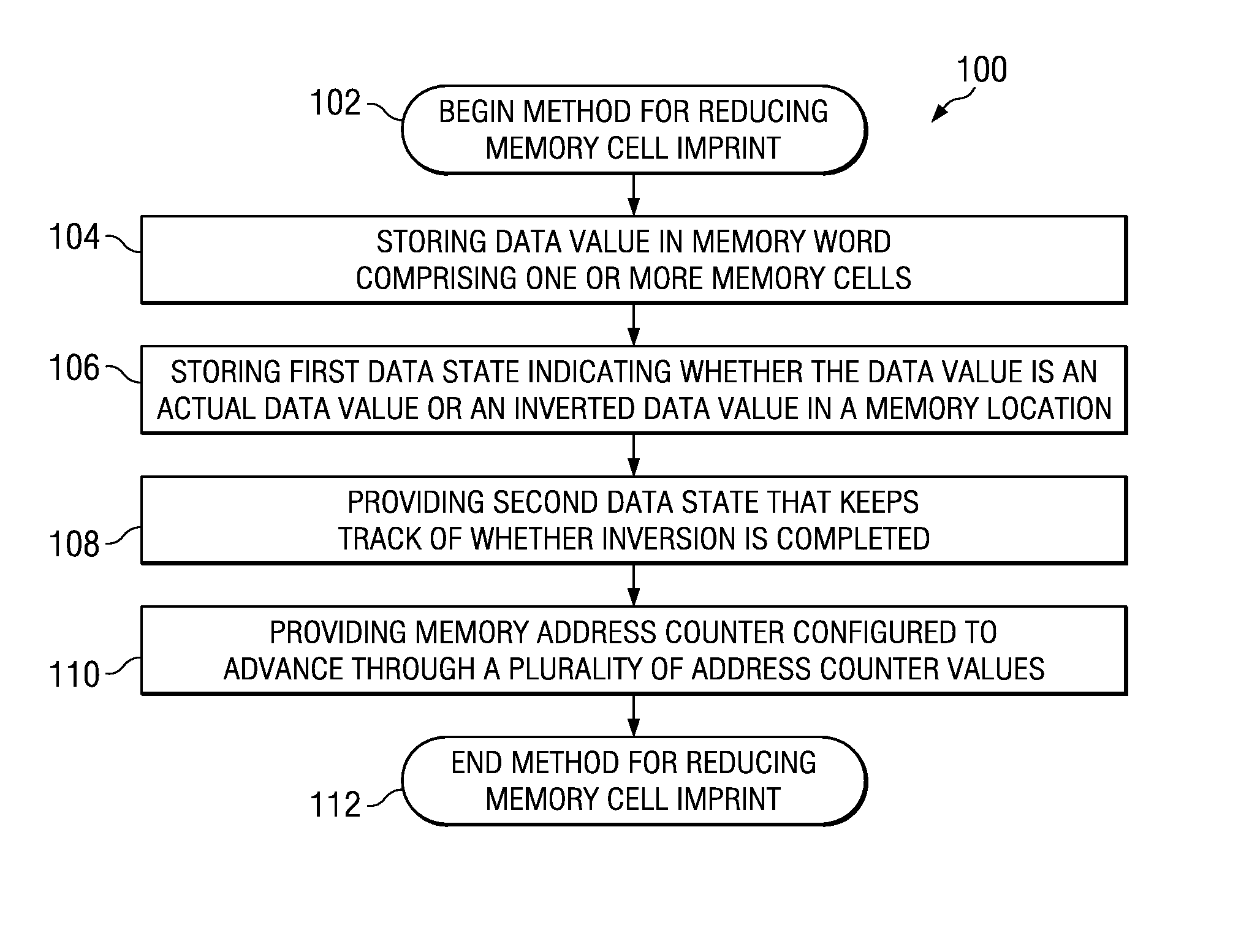
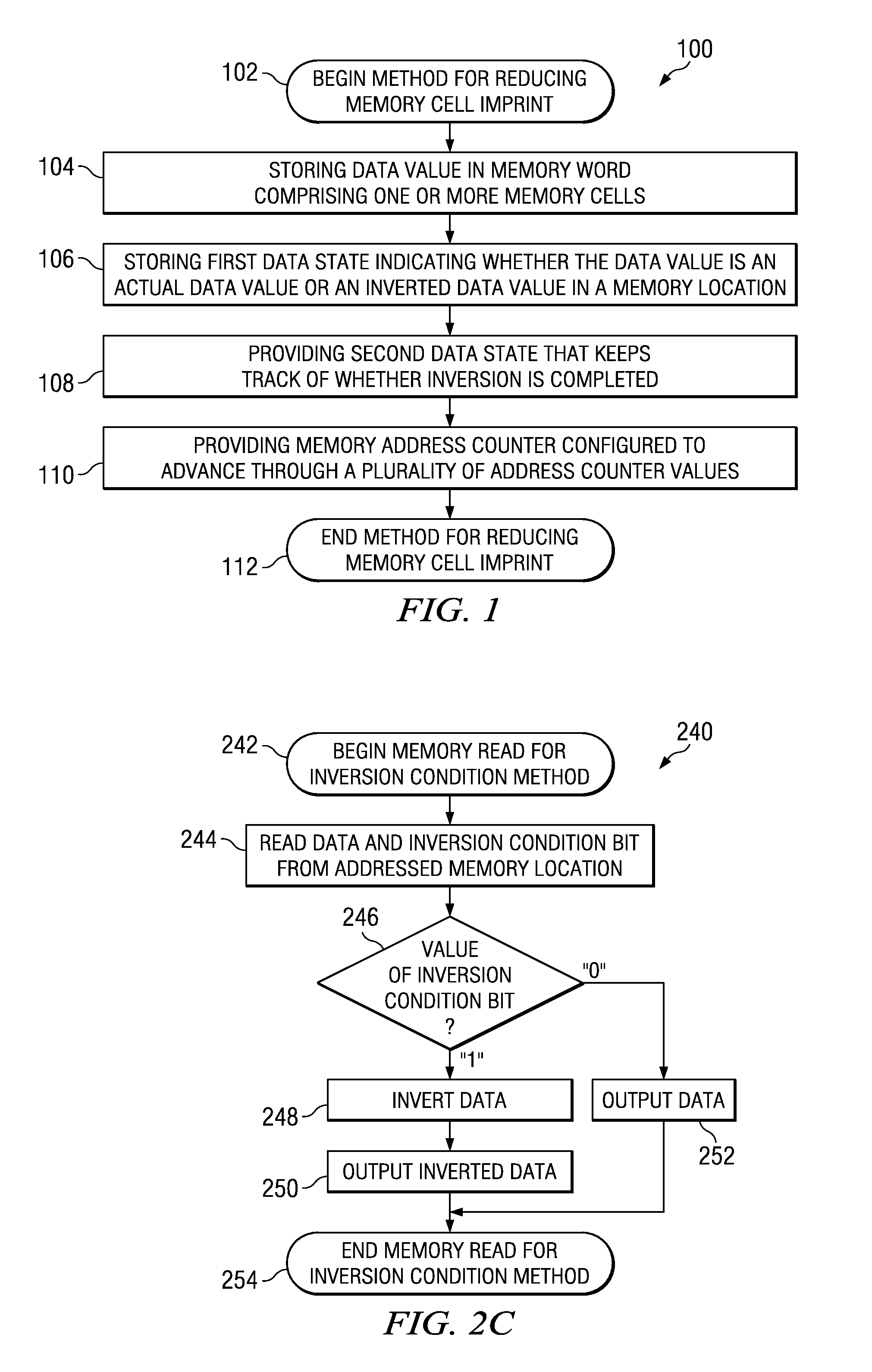
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of reducing imprint of a memory cell. The method comprises adding an inversion condition bit operably associated with one or more memory cells storing a memory word. The inversion condition bit indicates whether the memory word represents an actual payload or an inversion of the actual payload. The inversion condition bit and memory word are selectively toggled by a control circuitry. Inversion is performed by reading the inversion condition bit and memory word and rewriting the memory word back to the one or more memory cells in an inverted or non-inverted state, depending on an inversion condition bit. The inversion condition bit is then written to the inversion status bit value. The memory address is incremented, and the inversion status data state is toggled once the address counter addresses the entire memory array. Other methods and circuits are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
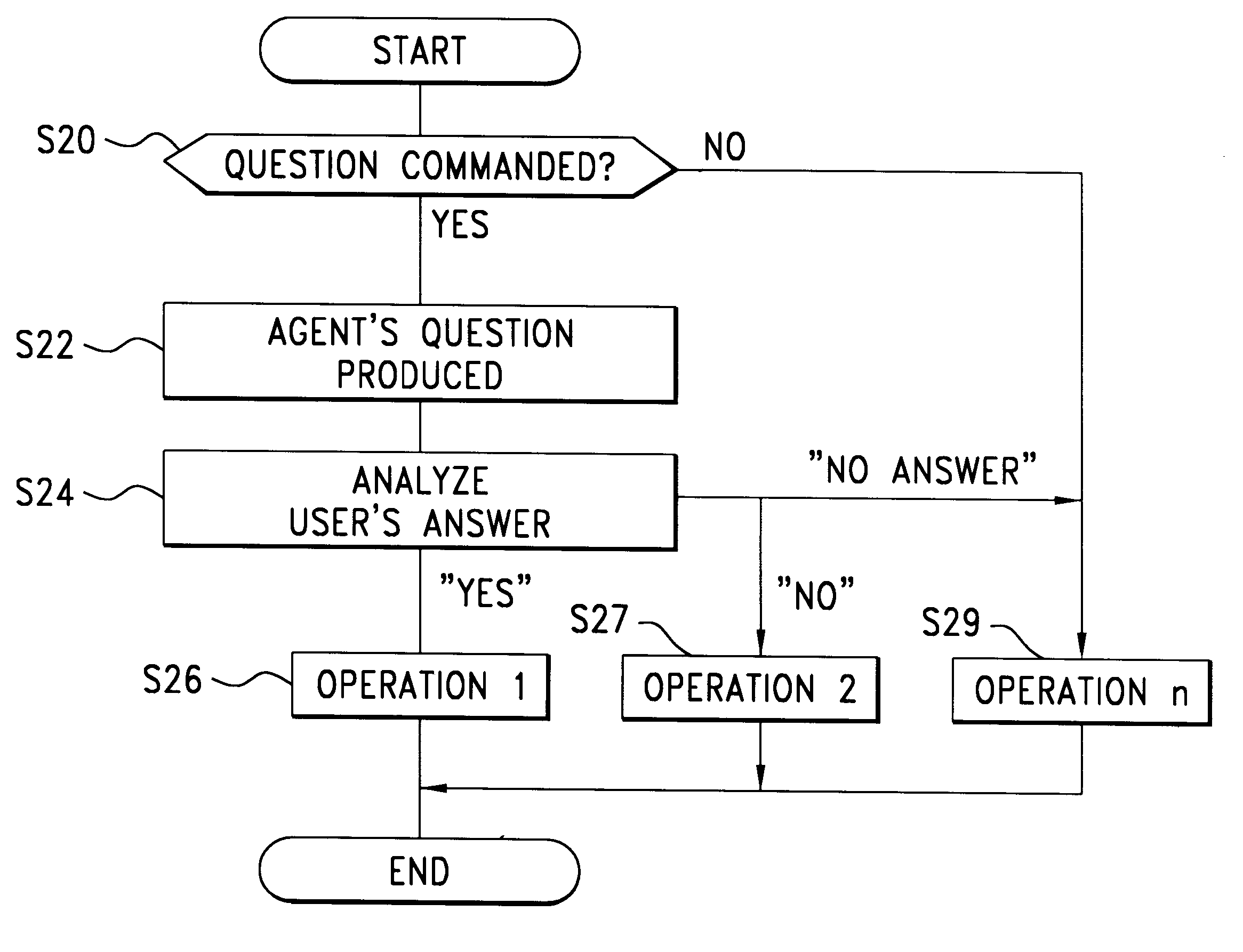
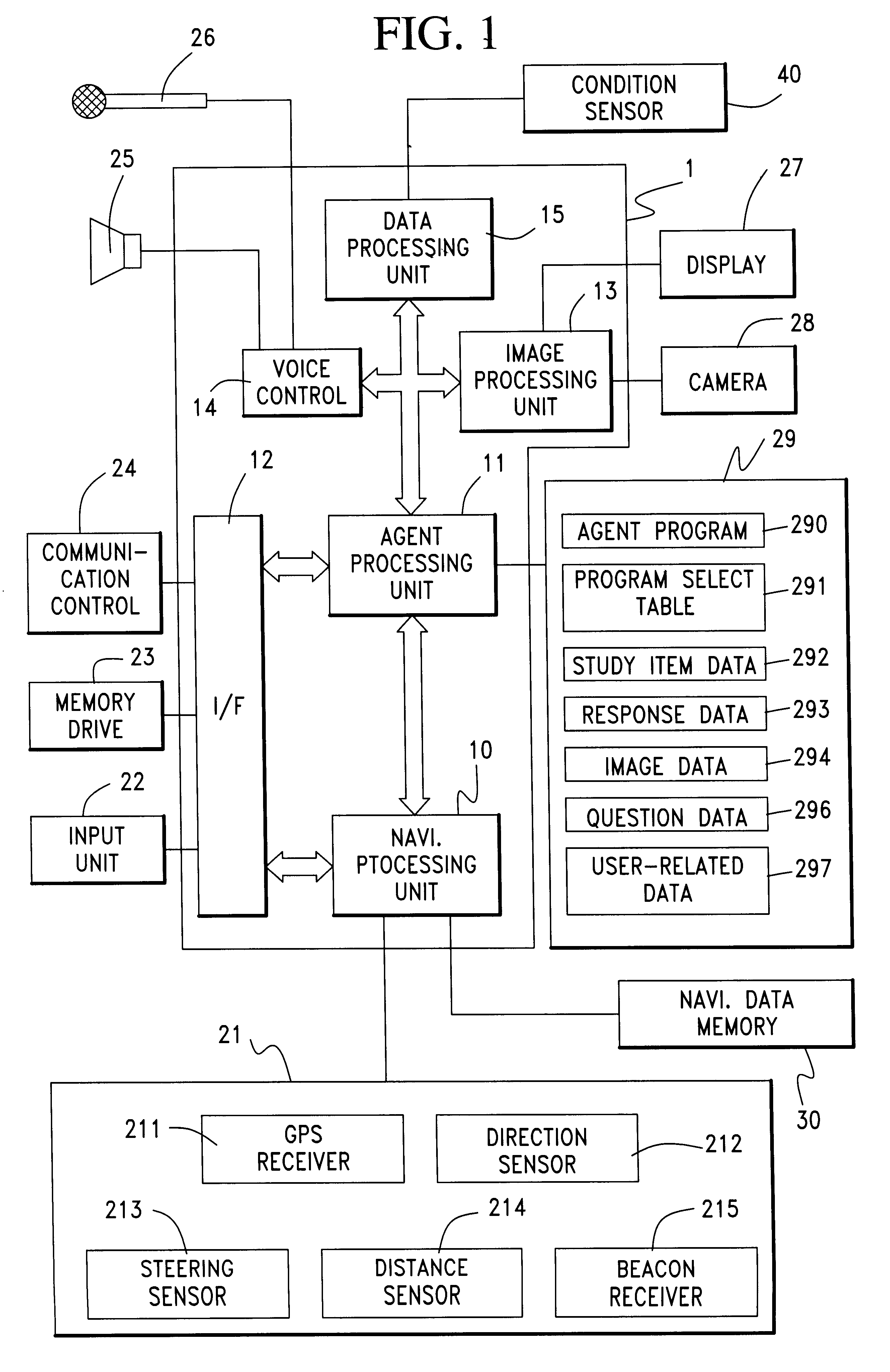
Interactive vehicle control system
InactiveUS6351698B1Facilitate communicationImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsDriver/operatorDisplay device
An interactive navigation system includes a navigation processing unit, a current position sensor, a speaker, a microphone and a display. When it is preliminary inferred, based on receipt of a detection signal from the sensor, that a vehicle has probably been diverted from a drive route determined by the navigation processing unit, a machine voice question is produced through the speaker for confirmation of the inferred probability of diversion. A driver or user in the vehicle answers the question, which is input through the microphone and analyzed to be affirmative or negative, from which a final decision is made as to the vehicle diversion. In a preferred embodiment the question is spoken by a personified agent who appears on the display. The agent's activities are controlled by an agent processing unit. Communication between the agent and the user improves reliability and accuracy of inference of any vehicle condition which could not be determined perfectly by a sensor only.
Owner:EQUOS RES
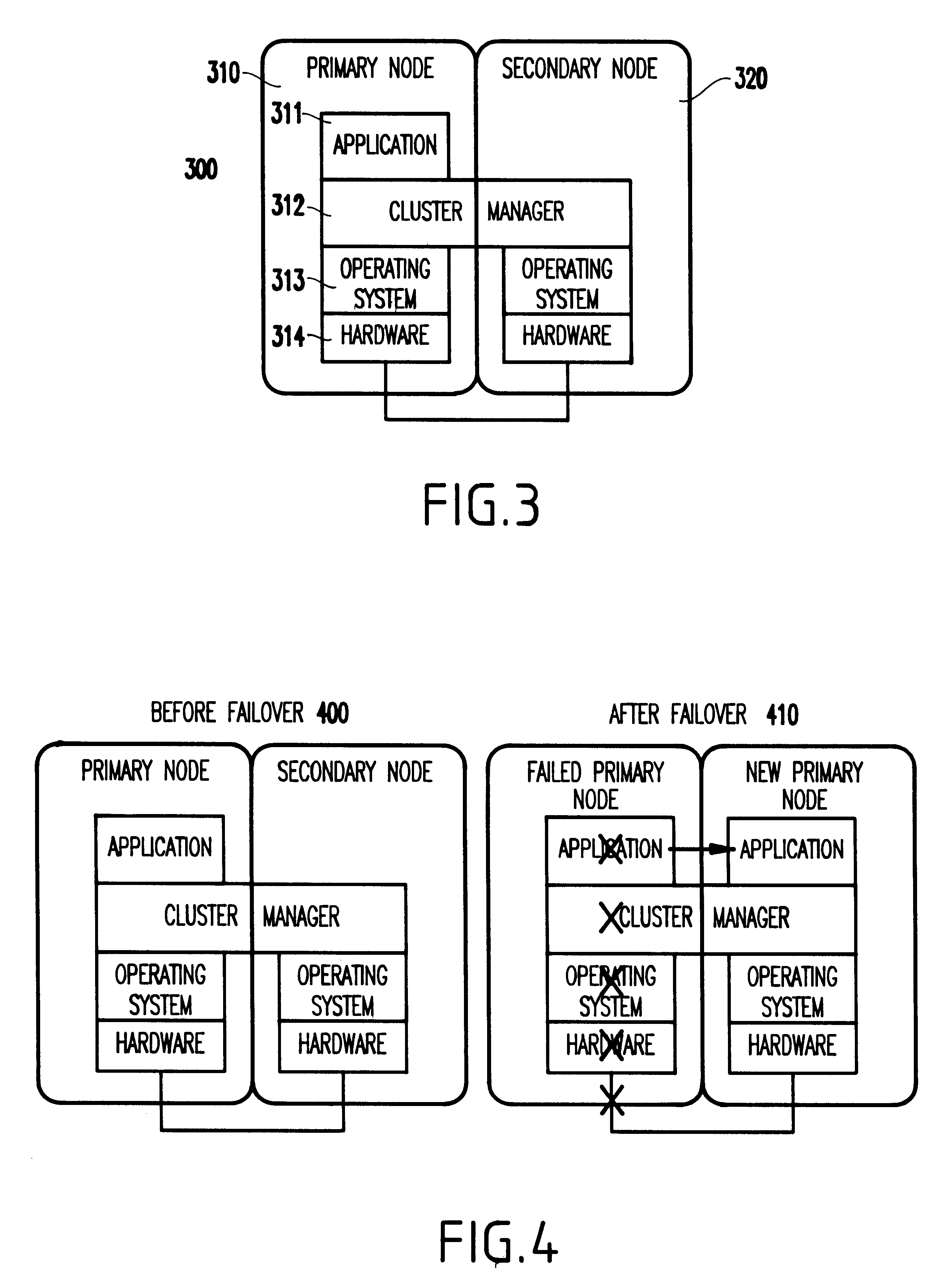
Method and system for high reliability cluster management
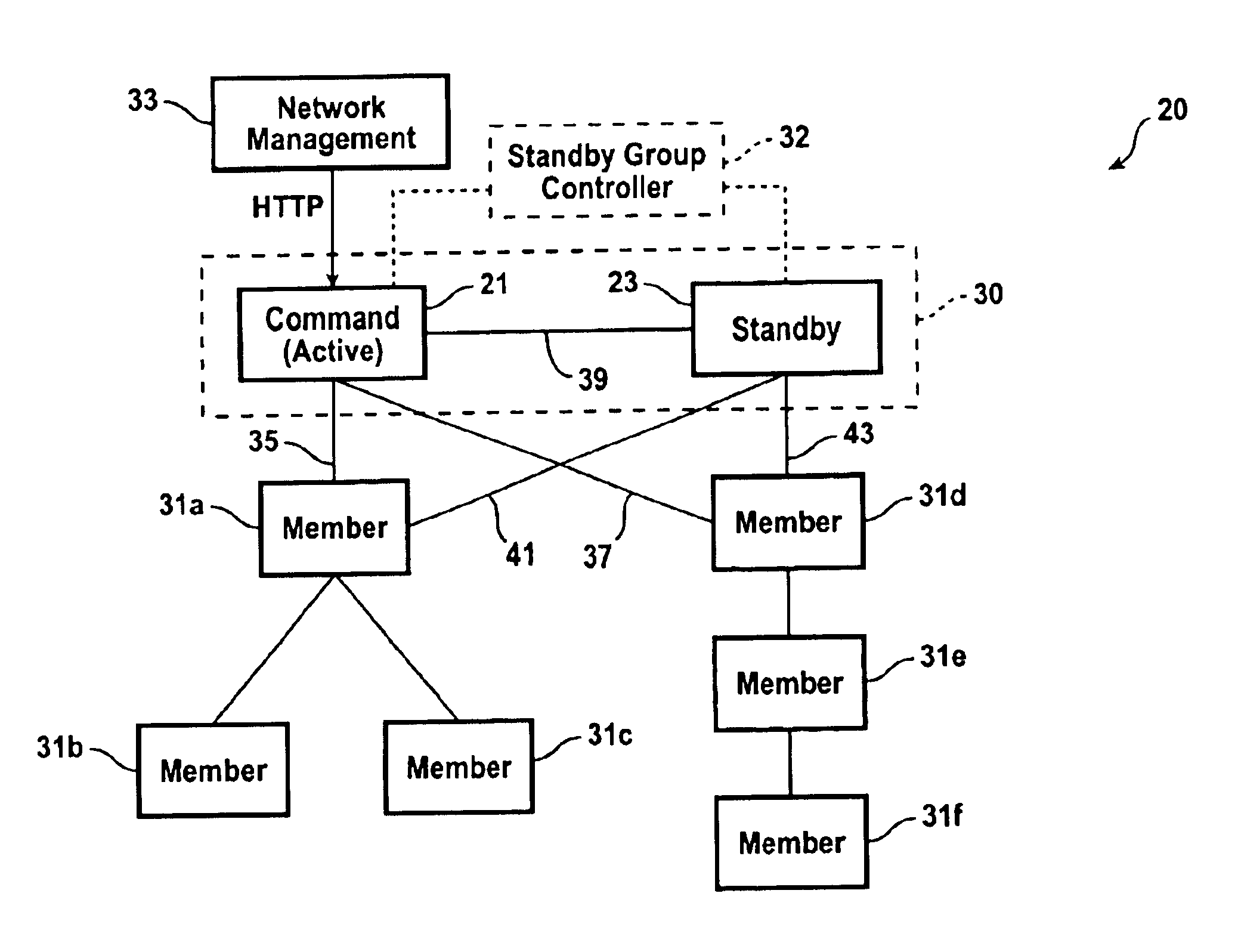
InactiveUS6856591B1Improve reliabilityError preventionTransmission systemsDependabilityDistributed computing
A method provides high reliability to management of a cluster of network devices. The cluster including a command network device and at least one member network device. The command network device has a commander IP address and a commander MAC address. The method includes: defining a standby group by assigning a virtual IP address and a virtual MAC address; selecting a first network device; which is the command network device, for the standby group; selecting at least one second network device, which has an IP address, for the standby group; defining a standby priority for each network device in the standby group; and binding the standby group to the cluster, by replacing the commander IP address with the virtual IP address and replacing the commander MAC address with the virtual MAC address. Upon the binding, the network device with a highest priority becomes an active commander, and the network device with a second highest priority becomes a standby commander. The the network device with a third highest priority, if any, becomes a passive commander. The cluster is controlled through the active commander using the virtual IP address. The active commander periodically forwards the cluster configuration information to the passive commander. The control of the cluster is switched from the active commander to the standby commander upon a failure of the active commander, the standby commander becoming a current active commander.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Evaluating public records of supply transactions for financial investment decisions
ActiveUS20110173093A1Promote generationEasy to shareFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsThird partyDecision taking
Owner:PANJIVA
Methods and apparatus for deduplication in storage system
InactiveUS7870105B2Digital data processing detailsError detection/correctionComputer terminalData deduplication
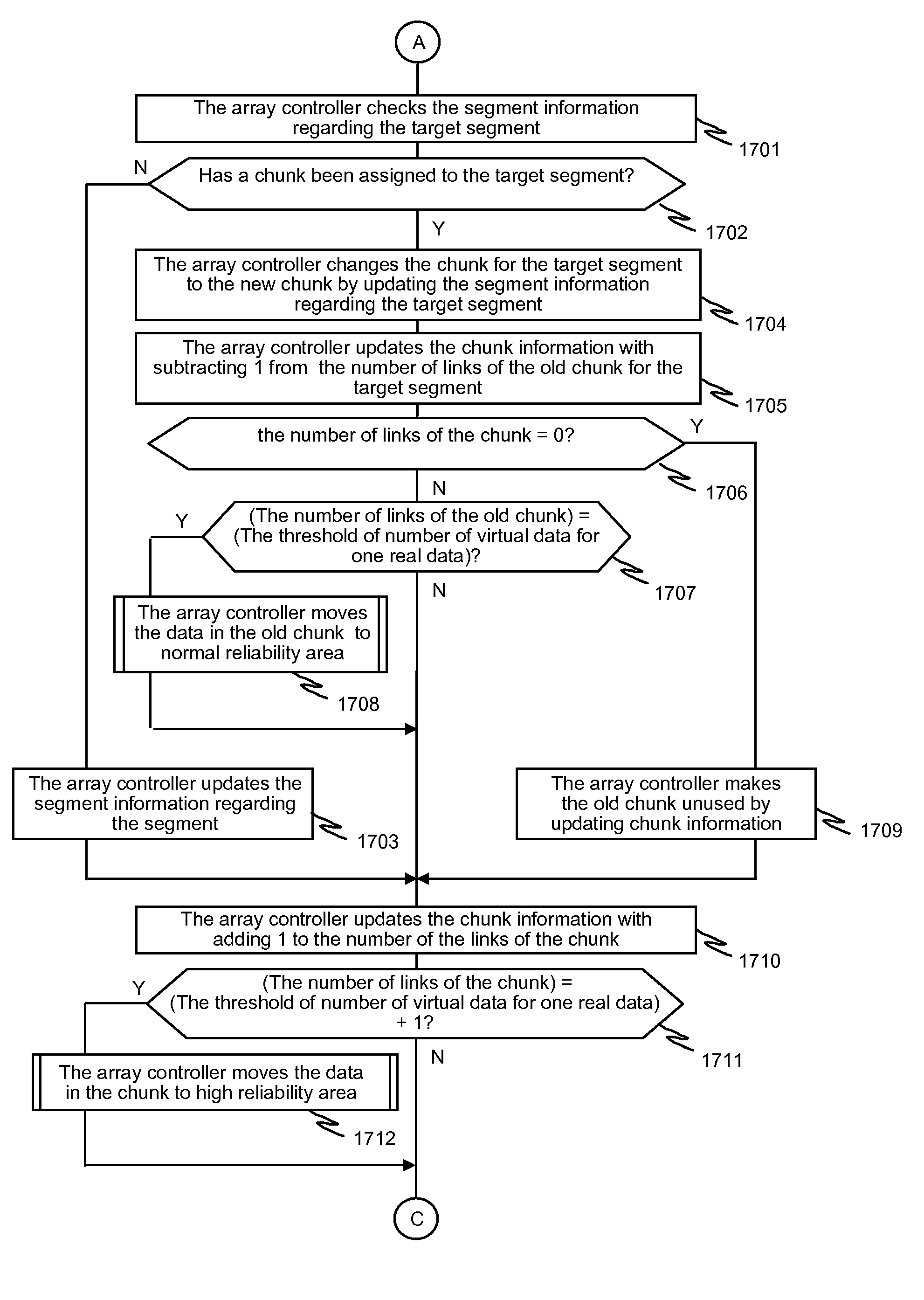
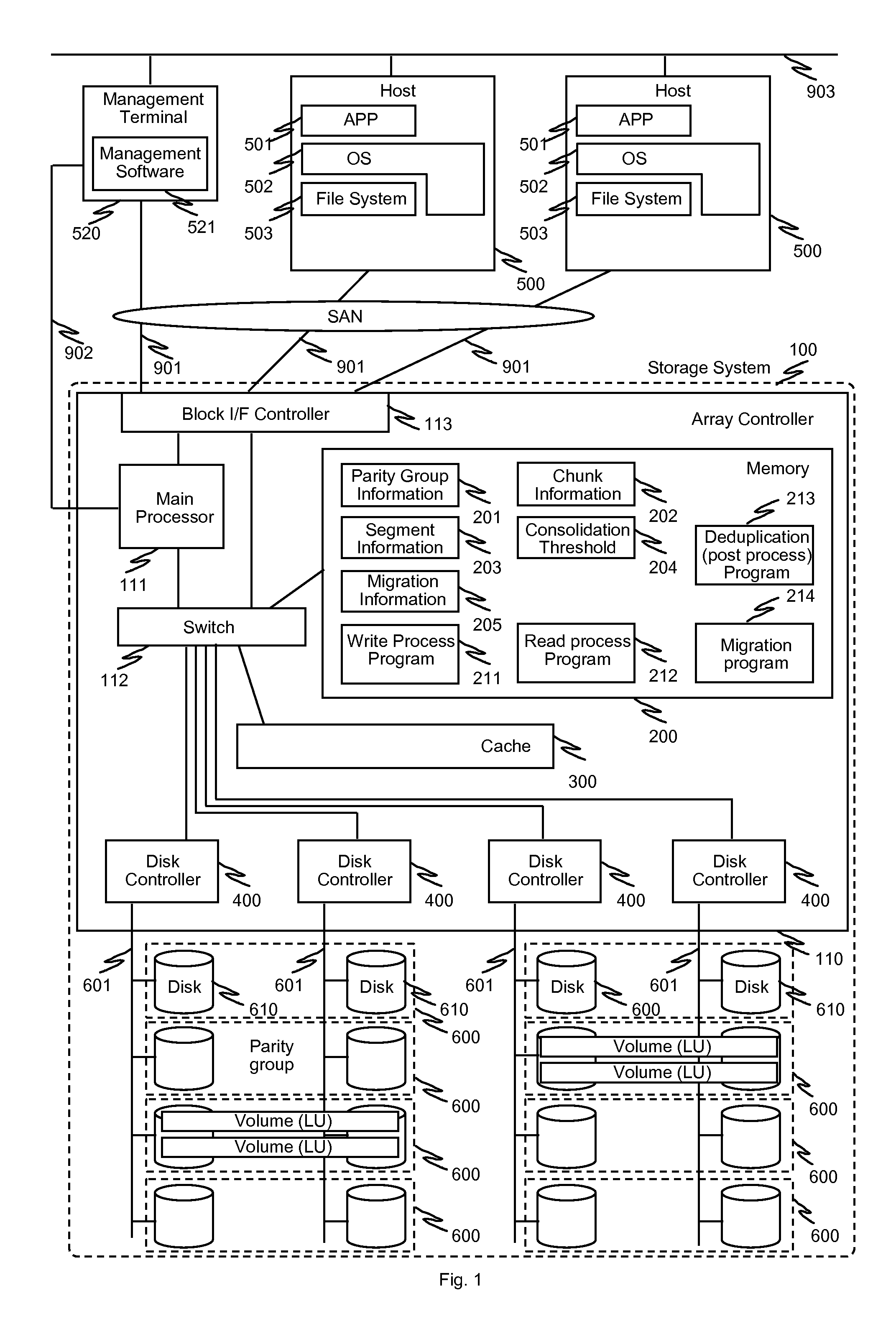
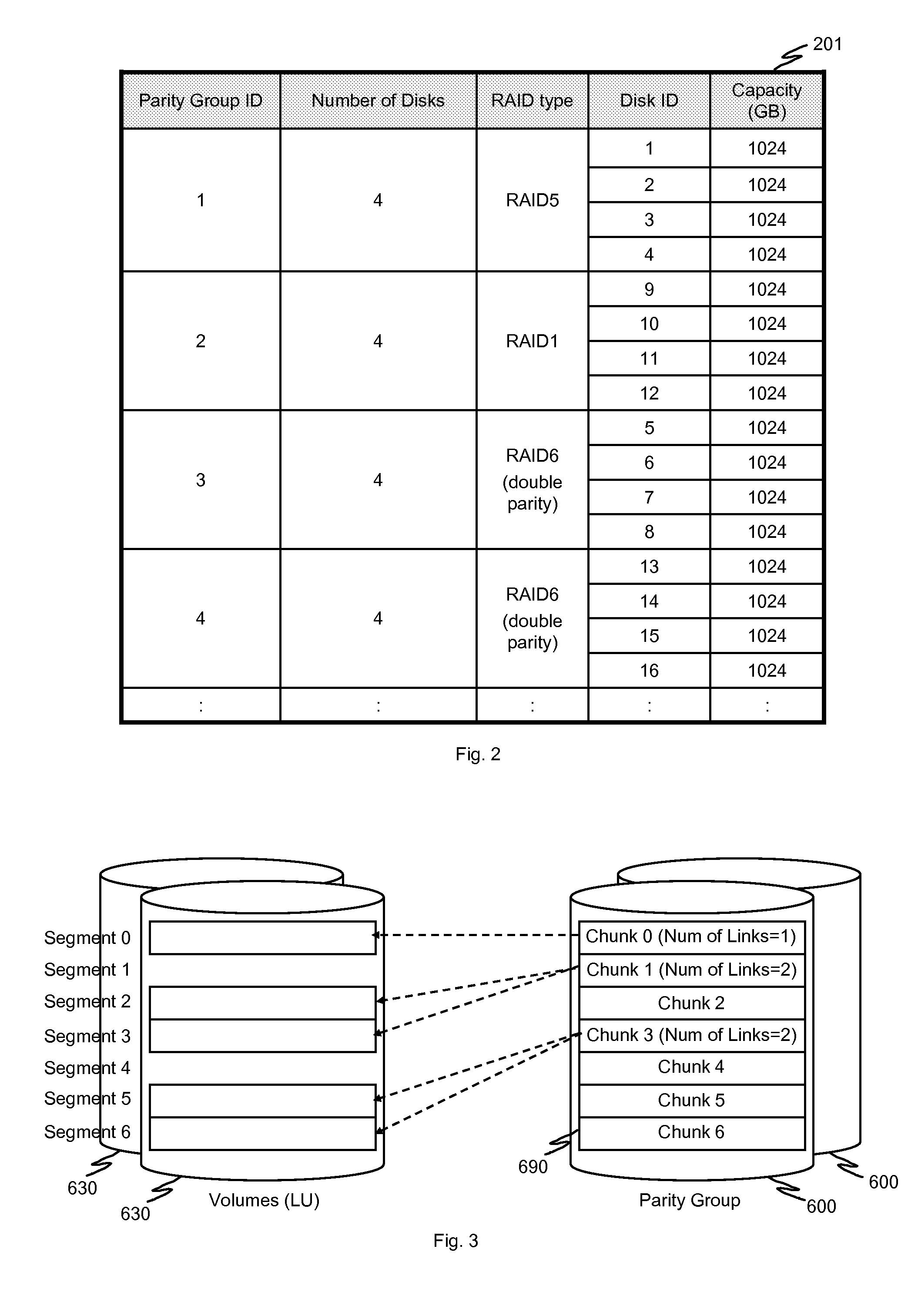
In one implementation, a storage system comprises host computers, a management terminal and a storage system having block interface to communicate with the host computers / clients. The storage system also incorporates a deduplication capability using chunks (divided storage area). The storage system maintains a threshold (upper limit) with respect to the degree of deduplication (i.e. number of virtual data for one real data) specified by users or the management software. The storage system counts the number of links for each chunk and does not perform deduplication when the number of reduced data for a chunk exceeds the threshold, even if duplication is detected. In another implementation, the storage system additionally incorporates a data migration capability and migrates physical data to high reliability area such as area protected with double parity (i.e. RAID6) when the deduplication level for a chunk exceeds the threshold.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Pervasive, domain and situational-aware, adaptive, automated, and coordinated analysis and control of enterprise-wide computers, networks, and applications for mitigation of business and operational risks and enhancement of cyber security
ActiveUS20130104236A1Reduce analysisLower control priorityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionApplication softwareBusiness process
Real time security, integrity, and reliability postures of operational (OT), information (IT), and security (ST) systems, as well as slower changing security and operational blueprint, policies, processes, and rules governing the enterprise security and business risk management process, dynamically evolve and adapt to domain, context, and situational awareness, as well as the controls implemented across the operational and information systems that are controlled. Embodiments of the invention are systematized and pervasively applied across interconnected, interdependent, and diverse operational, information, and security systems to mitigate system-wide business risk, to improve efficiency and effectiveness of business processes and to enhance security control which conventional perimeter, network, or host based control and protection schemes cannot successfully perform.
Owner:ALBEADO
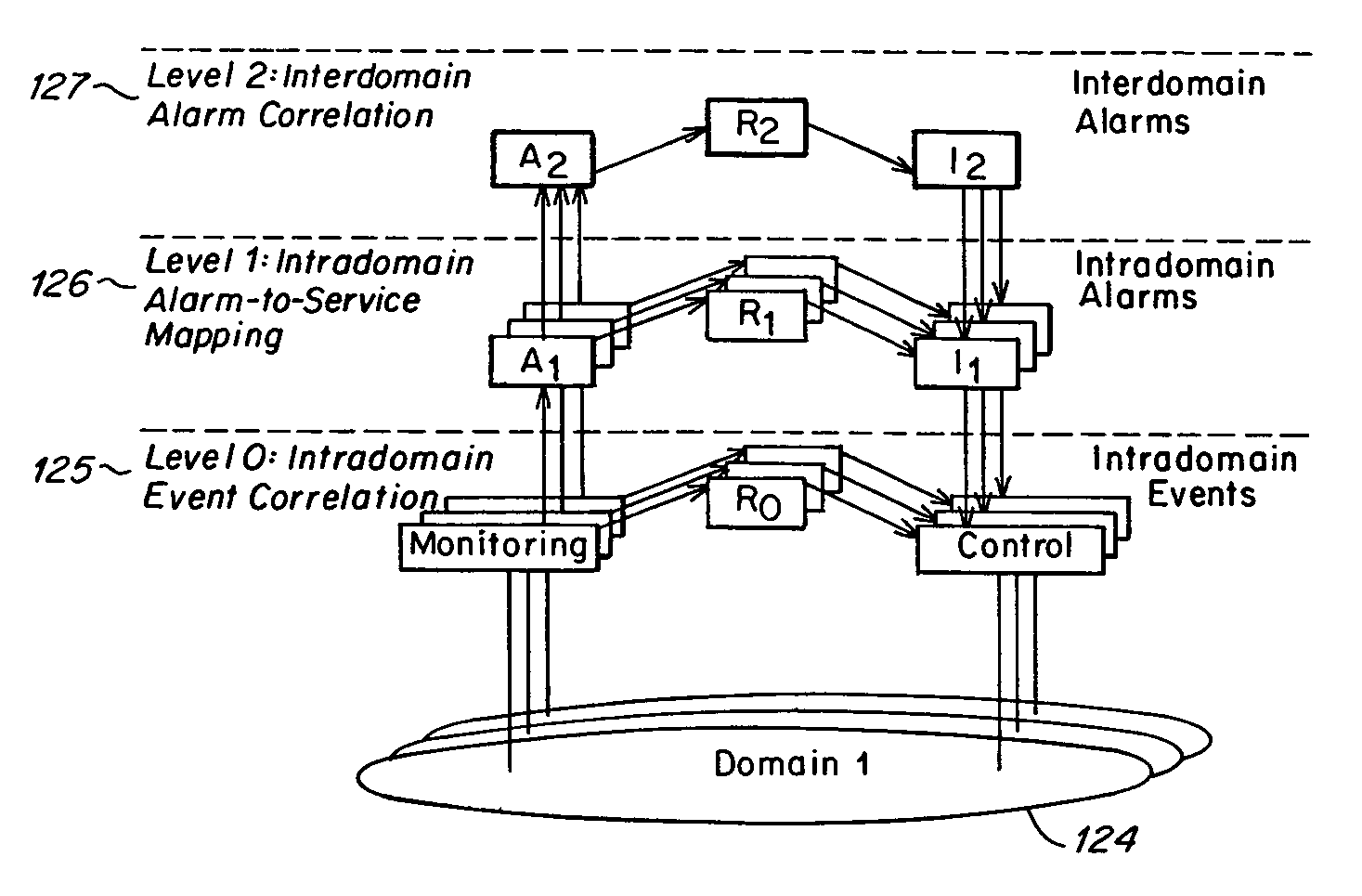
Method and apparatus for component to service mapping in service level management (SLM)
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
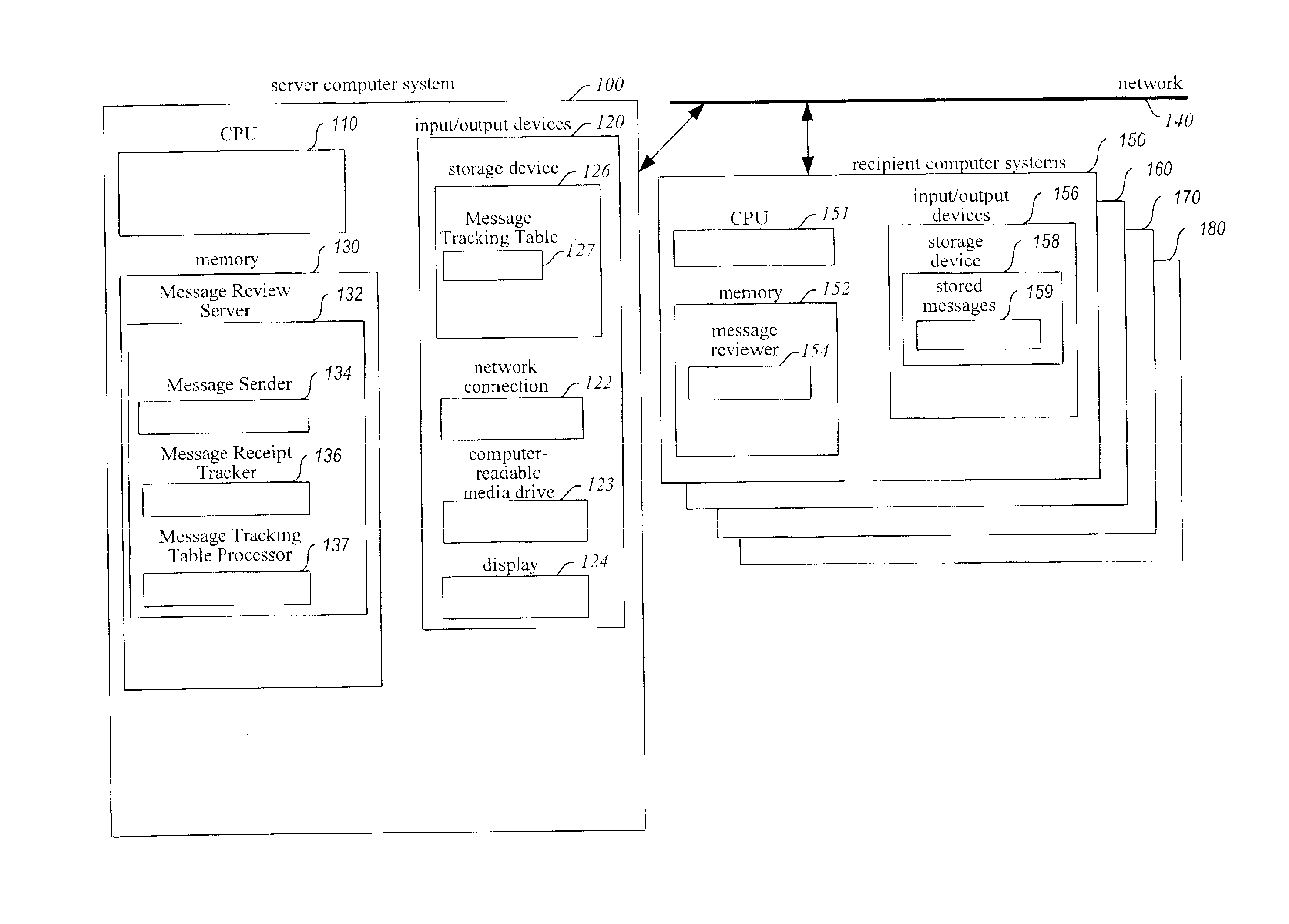
Method and system for enhancing reliability of communication with electronic messages
InactiveUS6854007B1Improve reliabilitySpecific activityMultiple digital computer combinationsPersonalizationComputer hardware
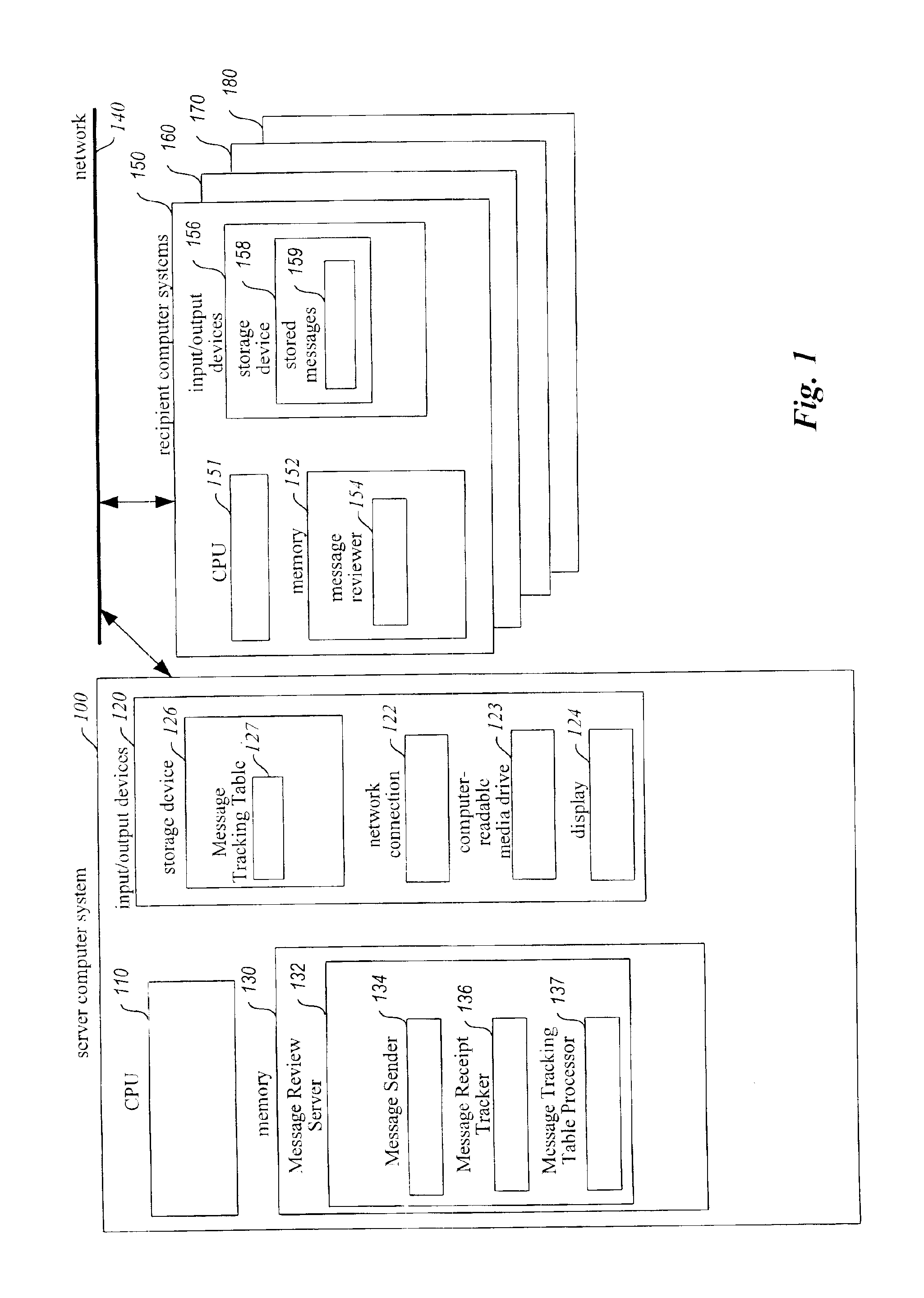
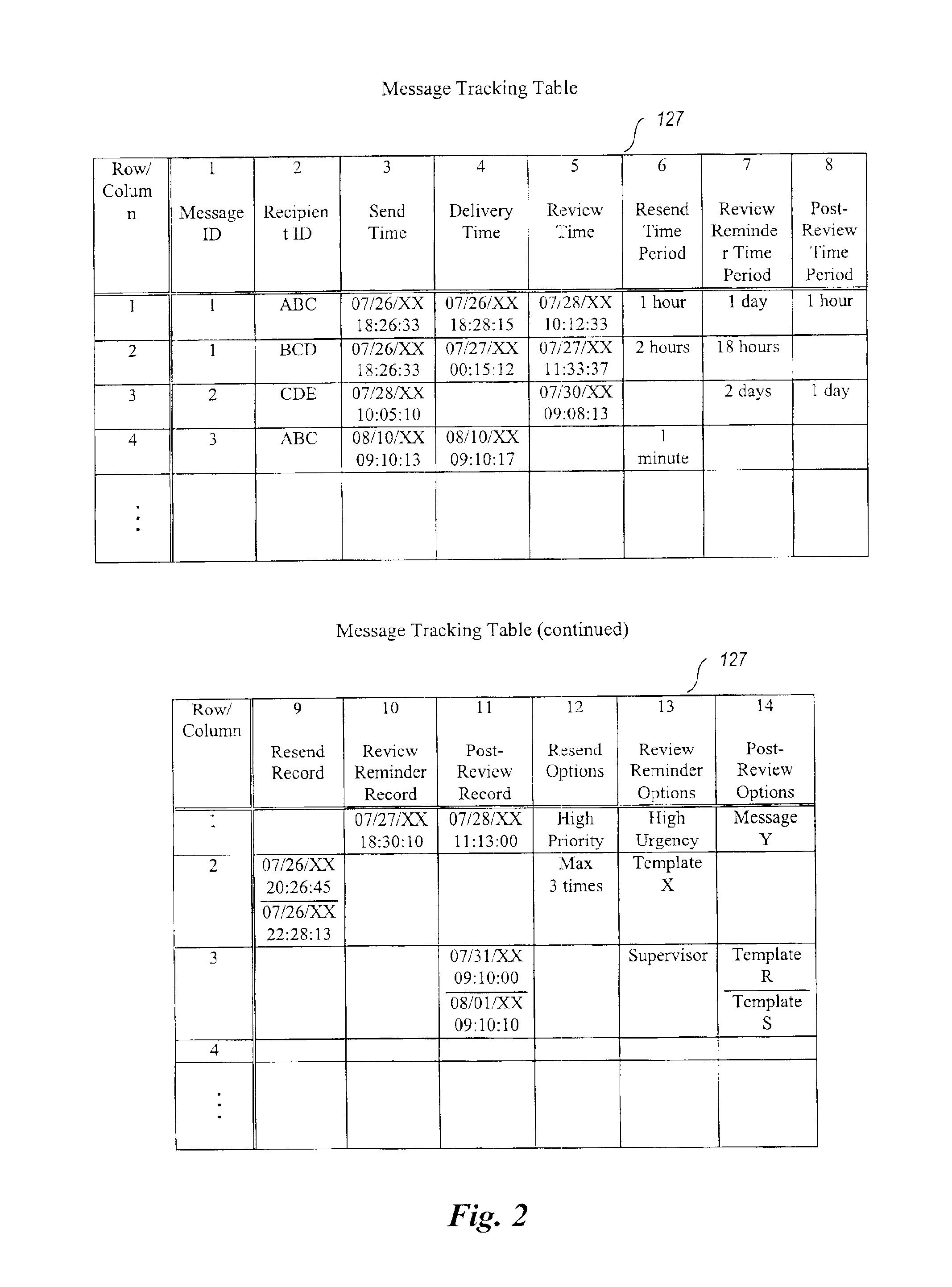
A system for enhancing the reliability of communicating with electronic messages. The system sends an electronic message to designated recipients, and then automatically helps ensure that each message has been successfully delivered within a specified period of time and that each message has been reviewed within a specified period of time. In addition, the system automatically performs specified activities after review of a message takes place. The sender of an electronic message initiates reliability-enhanced messaging by specifying message delivery information and message review information. The sender can specify that if delivery or review notifications are not received within specified periods of time, the message will be resent to the recipient or a reminder message will be sent to the recipient or to another user. The message information can include various frequency and duration options, such as resending a message only once or resending it every 2 hours for a week. Message information can also specify to resend the message with a higher transmission priority or review urgency so that its delivery and review is more likely, or could specify to use a different recipient system for the recipient (e.g., to a second email address if a first address fails, or to a pager if a cellular phone is not available). Each recipient of a message can have individualized message delivery information. The system tracks whether each message has been delivered to each recipient, and uses the message delivery information to resend the messages whose delivery and review was not confirmed.
Owner:MEI CALIFORNIA
System for performing context-sensitive decisions about ideal communication modalities considering information about channel reliability
InactiveUS7103806B1Easy to determineGood choiceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorError detection/correctionTelecommunicationsDependability
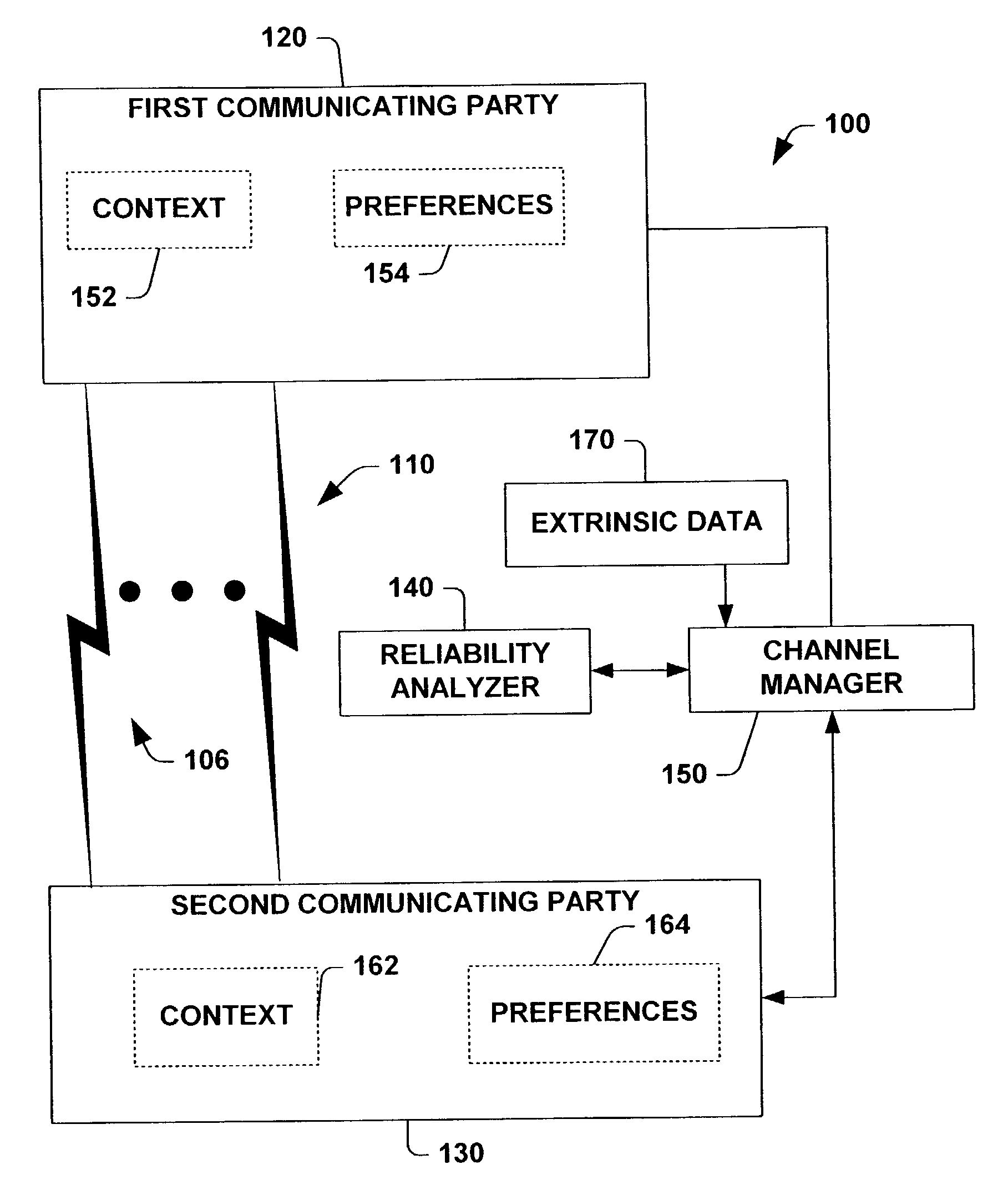
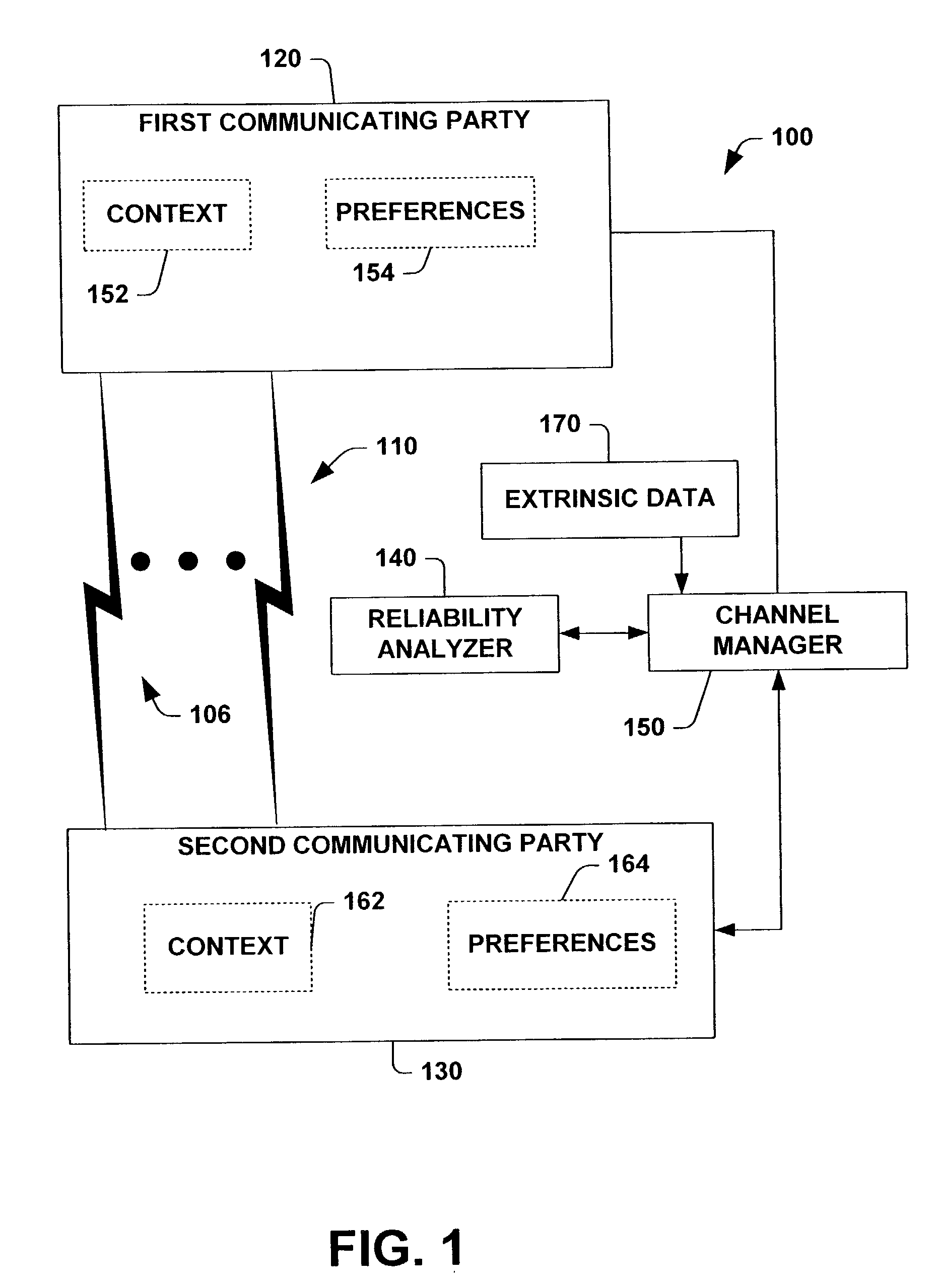
A system and method for identifying ideal channels for communications based on an analysis of communication channel reliability, communicating party preferences, and communicating party contexts is provided. The system attempts to optimize the utility of a communication based on inferred or directly accessed channel reliability data, communicating party preferences and communicating party contexts. Such optimization can be achieved using reliabilities, preferences and policies concerning handling the attempted contact based on a deterministic specification or through inferring reliability, context, content and task under uncertainty by employing decision-theoretic inferences. The methods may consider channels currently available as well as channels available at later times. Thus, the service can include automated rescheduling of communications based on a consideration of forecasts of reliability and availability. The approach may include the use of forecasts about the time required for a communication and the likelihood that a connection will be dropped or will lose fidelity over this period of time. The methods may also include a consideration of metadata within a standard schema that is transmitted along with a communication attempt, the metadata representing information about attributes like the potential communication channels, the identity of the contactor, the task at hand, and the context of the communicating parties. The invocation of the communication service may be performed in a variety of ways, including single button invocations, and via a communication service that is more deeply integrated with other applications and functionalities.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
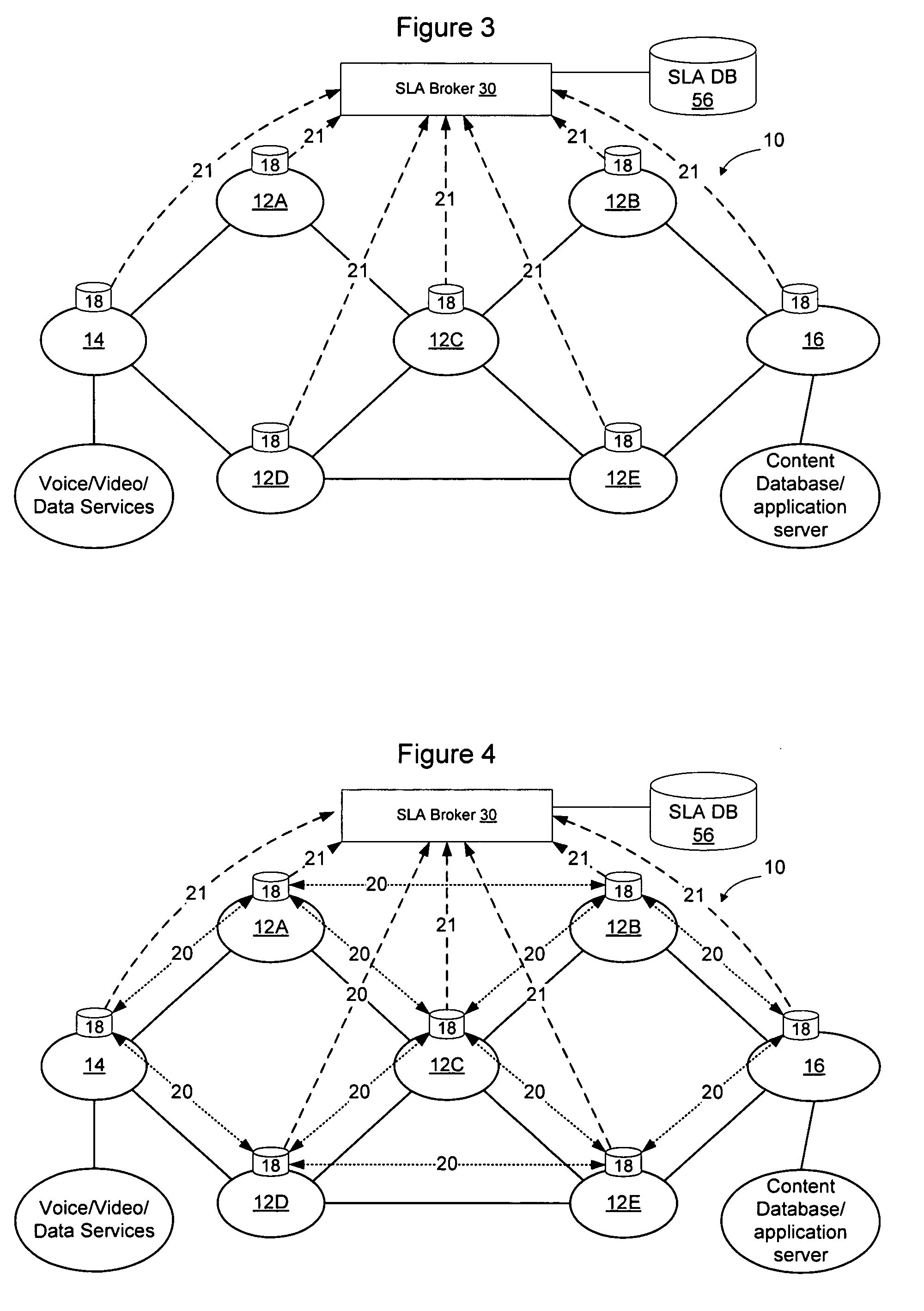
Method and apparatus for discovering, negotiating, and provisioning end-to-end SLAs between multiple service provider domains
Domains (multiple collaborating service providers) create service offerings between pairs of edge nodes that interconnect with other domains in the network. The service offerings may specify the available bandwidth, quality of service, reliability, available security, price, subscriber and service contextual specific and other SLA information. When a new service is to be created, the service definition is used along with information about the available service offerings to determine a set of networks to implement the service. Information associated with the service offerings may be flooded to all other networks. Alternatively, the service offering information may be provided to a trusted third party (SLA broker) which may provide SLA services on the network to select sets of domains to implement inter-domain services, and may also proxy to set up the service for the SLA requesting party. A hybrid approach may also be used wherein some SLA information is flooded and other information is retained in secret and provided only to the SLA broker.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Design of computer based risk and safety management system of complex production and multifunctional process facilities-application to fpso's
InactiveUS20120317058A1Strong robust attributeStrong robust attributesDigital computer detailsFuzzy logic based systemsProcess systemsNerve network
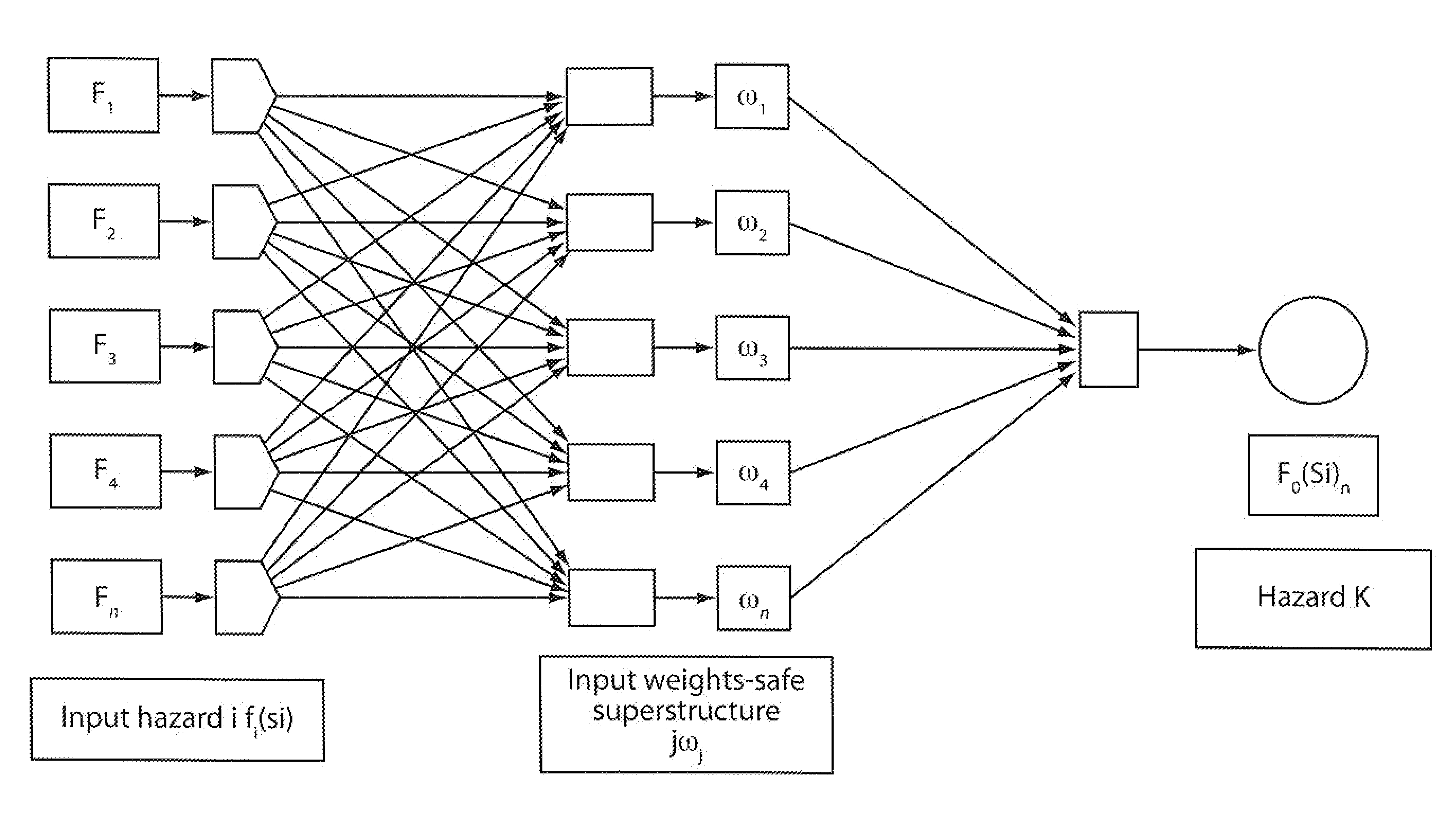
A method for predicting risk and designing safety management systems of complex production and process systems which has been applied to an FPSO System operating in deep waters. The methods for the design were derived from the inclusion of a weight index in a fuzzy class belief variable in the risk model to assign the relative numerical value or importance a safety device or system has contain a risk hazards within the barrier. The weights index distributes the relative importance of risk events in series or parallel in several interactive risk and safety device systems. The fault tree, the FMECA and the Bow Tie now contains weights in fizzy belief class for implementing safety management programs critical to the process systems. The techniques uses the results of neural networks derived from fuzzy belief systems of weight index to implement the safety design systems thereby limiting use of experienced procedures and benchmarks. The weight index incorporate Safety Factors sets SFri {0, 0.1, 0.2 . . . 1}, and Markov Chain Network to allow the possibility of evaluating the impact of different risks or reliability of multifunctional systems in transient state process. The application of this technique and results of simulation to typical FPSO / Riser systems has been discussed in this invention.
Owner:ABHULIMEN KINGSLEY E
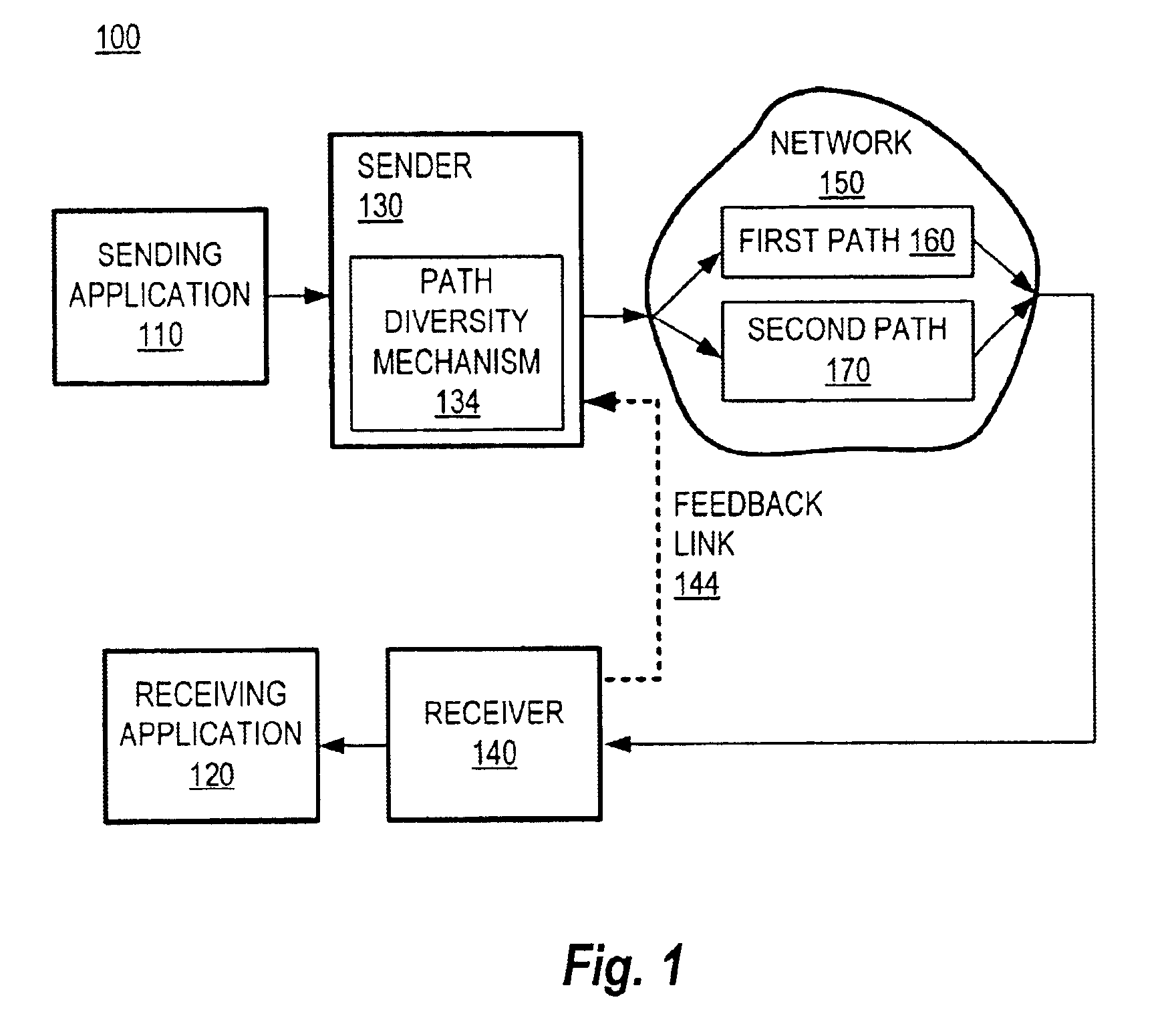
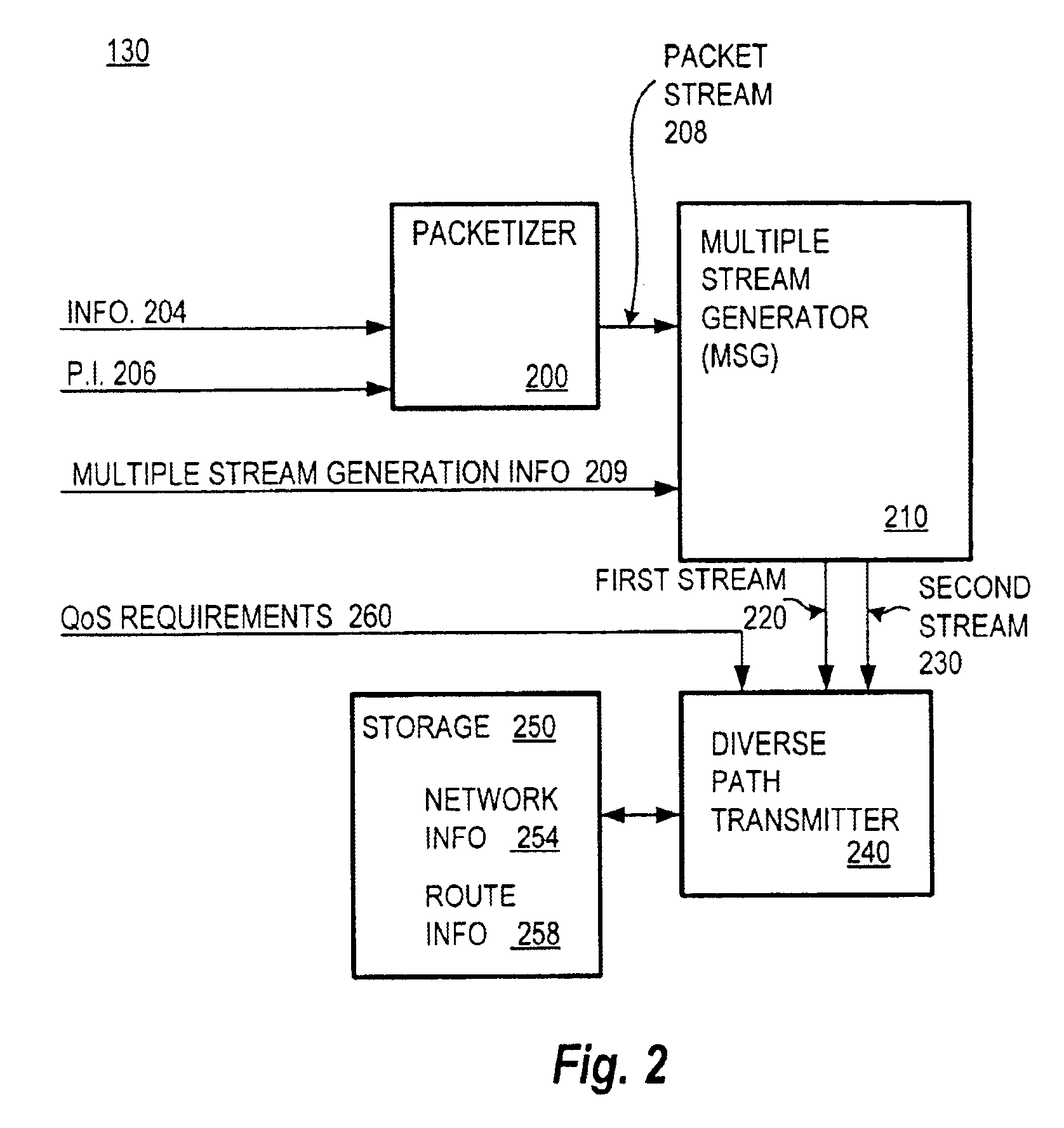
Method and system for packet communication employing path diversity
InactiveUS6868083B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationPacket loss
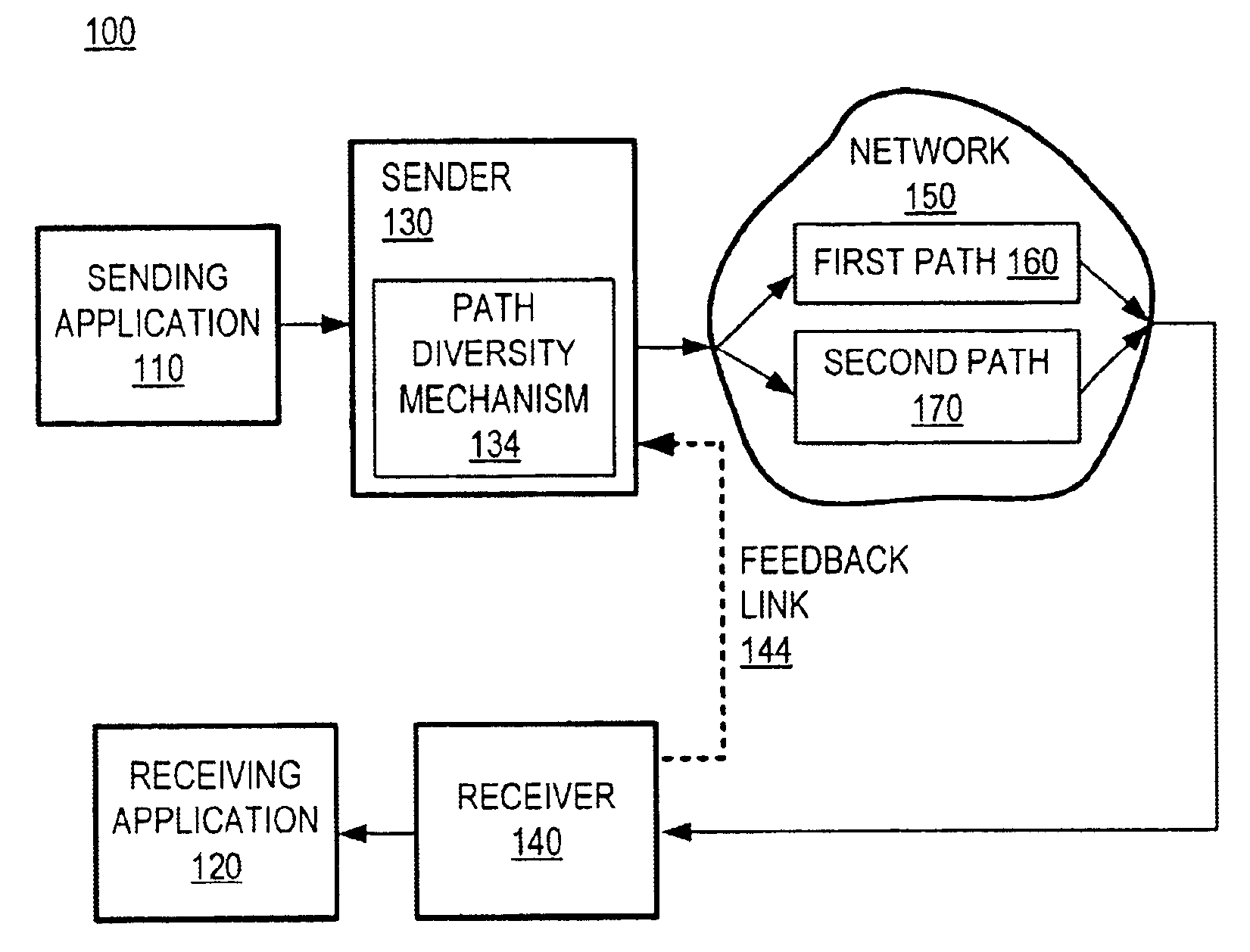
Communication over lossy packet networks such as the Internet is hampered by limited bandwidth and packet loss. The present invention provides a path diversity transmission system for improving the quality of communication over a lossy packet network. The path diversity transmission system explicitly sends different subsets of packets over different paths, thereby enabling the end-to-end application to effectively see an average path behavior. Generally, seeing this average path behavior provides better performance than seeing the behavior of any individual random path. For example, the probability that all of the multiple paths are simultaneously congested is much less than the probability that a single path is congested. The resulting path diversity can provide a number of benefits, including enabling real-time multimedia communication and simplifying system design (e.g., error correction system design). Two exemplary architectures for achieving path diversity are described herein. The first architecture is based on source routing, and the second architecture is based on a relay infrastructure. The second architecture routes traffic through semi-intelligent nodes at strategic locations in the Internet, thereby providing a service of improved reliability while leveraging the infrastructure of the Internet.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
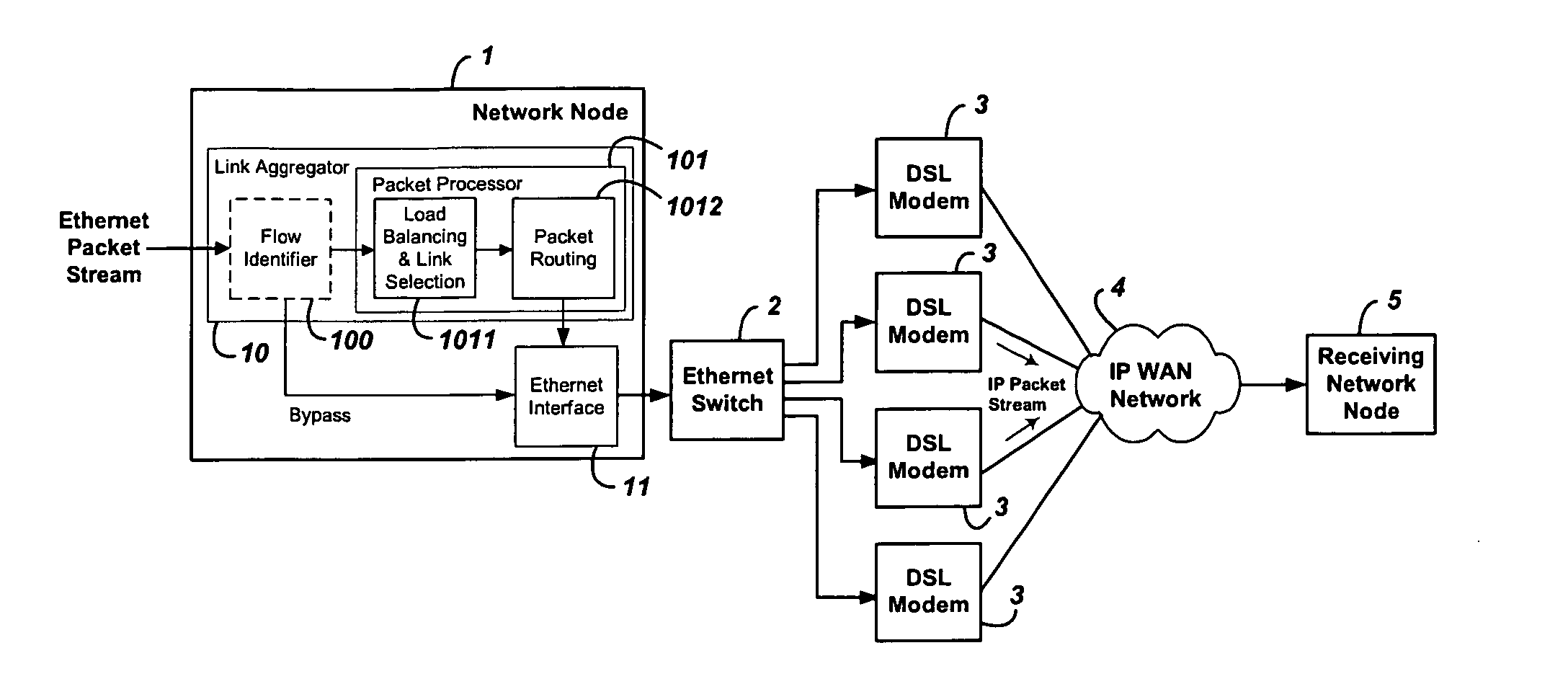
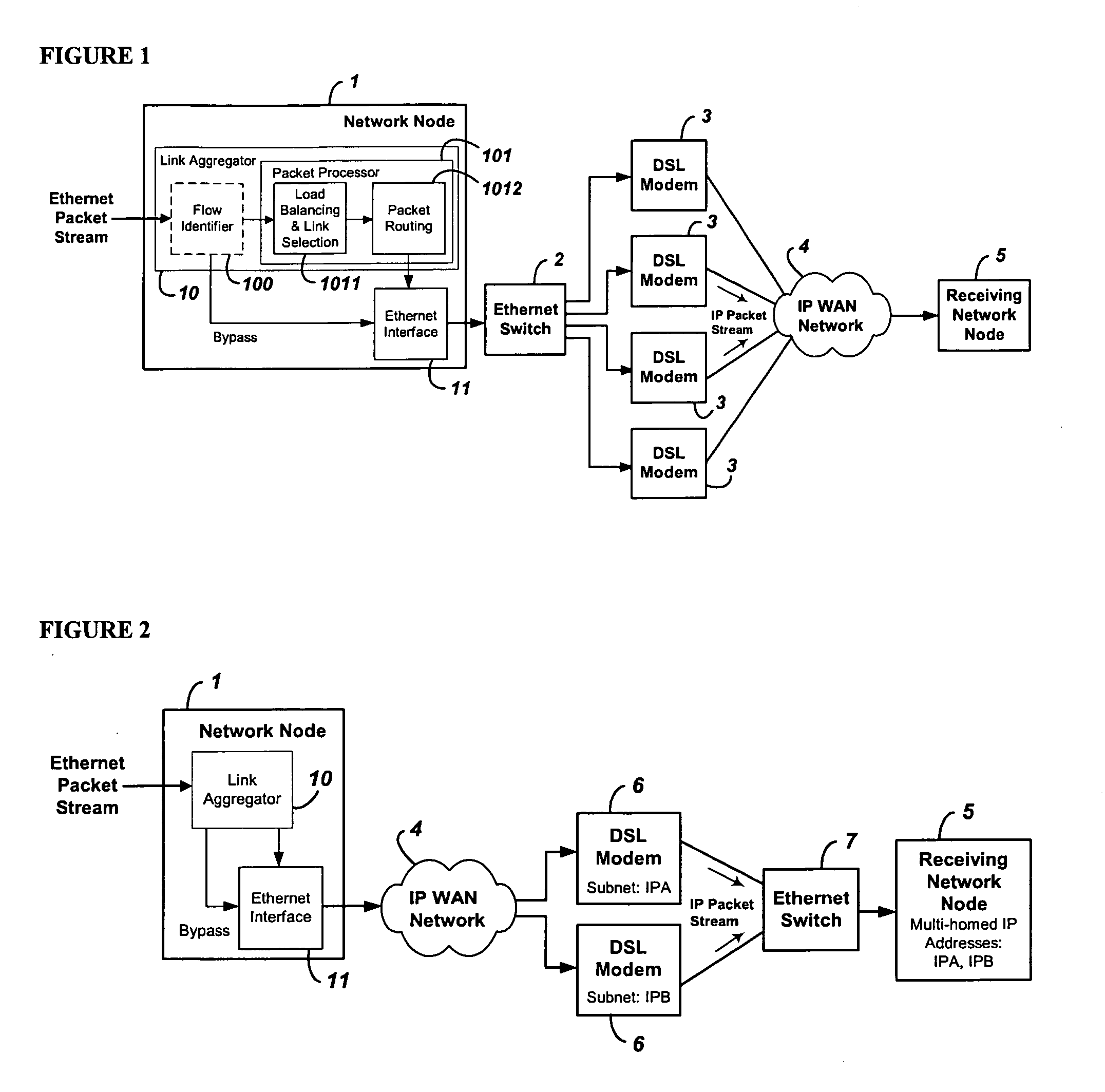
System and method for the virtual aggregation of network links
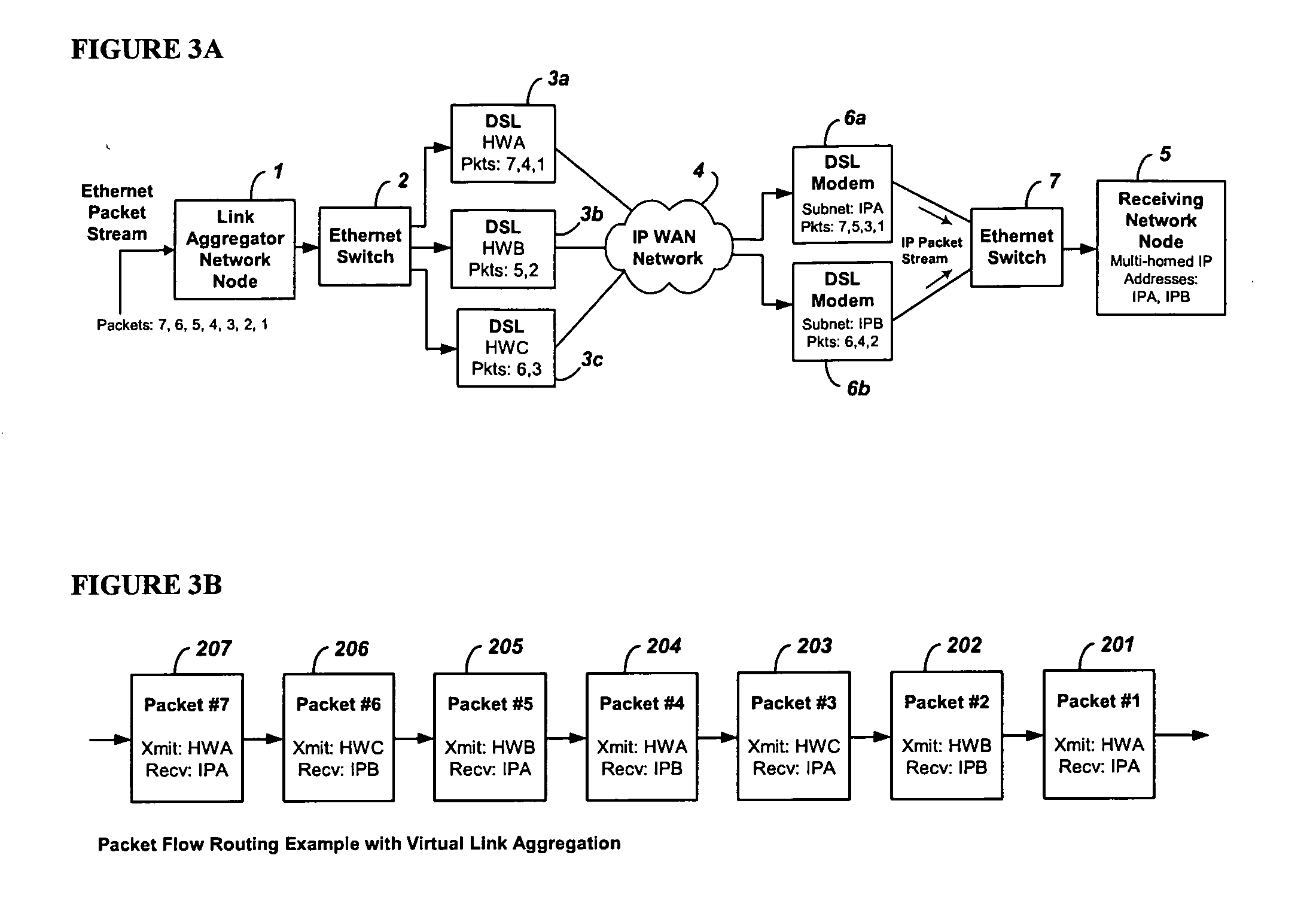
InactiveUS20060098573A1Improve throughputImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient ICTError preventionNetwork linkRewriting
A system and method for virtual link aggregation for combining network links of various types and speeds to increase throughput and reliability for packetized transport. In contrast with physical port trunking, the system does not require direct control over ports or network interfaces. Instead, the system rewrites packet addresses and works through existing networking equipment, without requiring any new or special protocols, processing, or equipment within the network. The system works through low-level rerouting by rewriting hardware addresses and / or high-level routing by rewriting logical addresses. Thus packets are redirected through multiple routes to a common destination via alternate gateways and links. Different algorithms may be employed to balance the load on each link and determine an optimal route for each packet. Embodiments may also employ packet flow or stream identification and thereby only provide link aggregation for a specified set of packet flows.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
Method of reducing fraud in on-line transactions
ActiveUS20180039975A1Reduce inconvenienceShorten the timeBuying/selling/leasing transactionsLocation information based serviceInternet usersGeolocation
The invention provides a method for verifying the identity of an internet user, or for detecting the misuse of an identity, during an on-line transaction. The method involves comparing the geographic location of the transaction to the geographic location of the user's cell phone or other mobile device, and taking a geographically close location relationship between the two as a positive indication of identity. Various additional factors are taken into account so as to reduce the incidence of false negatives, and to improve the reliability of positive identifications.
Owner:SPRIV LLC
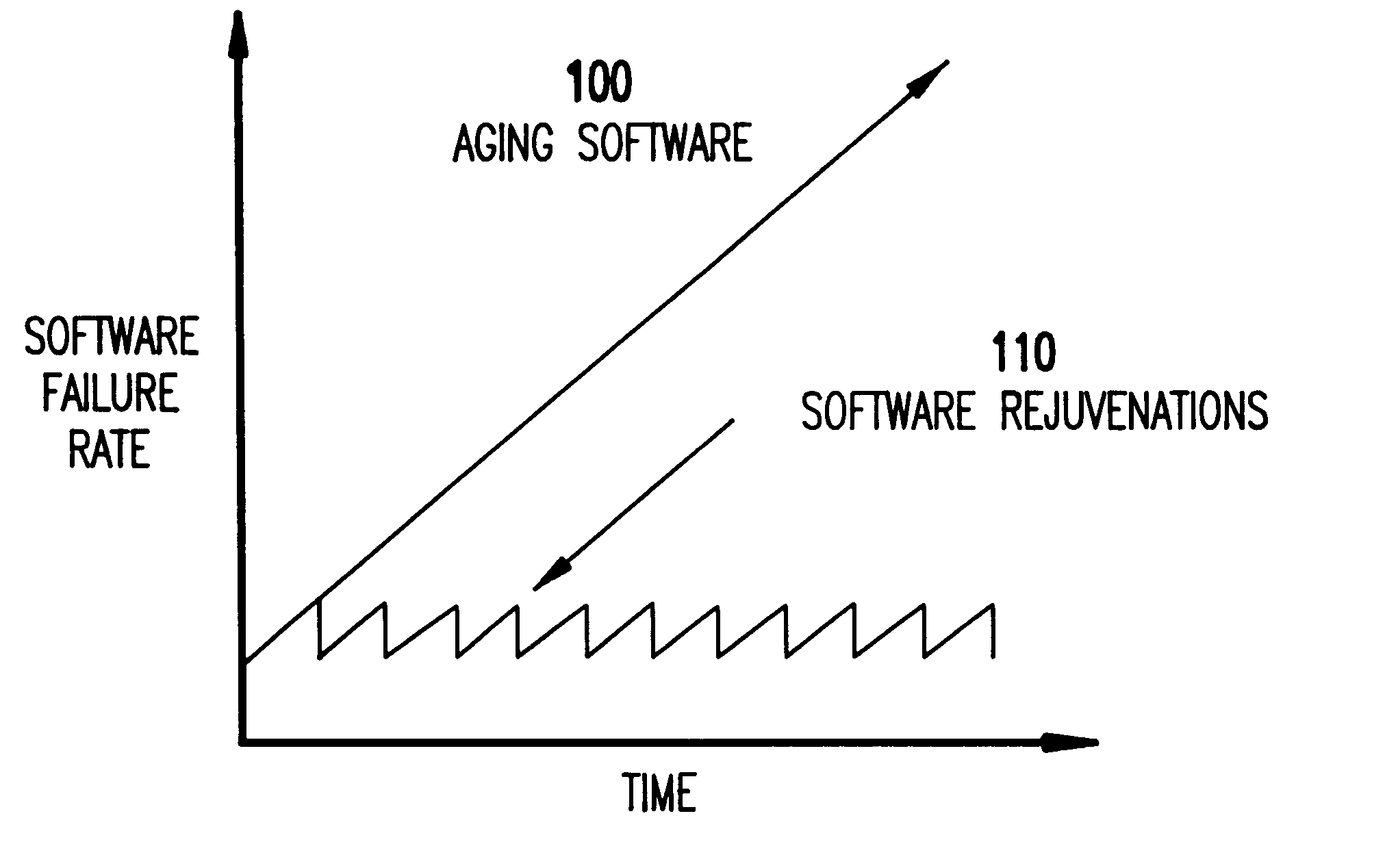
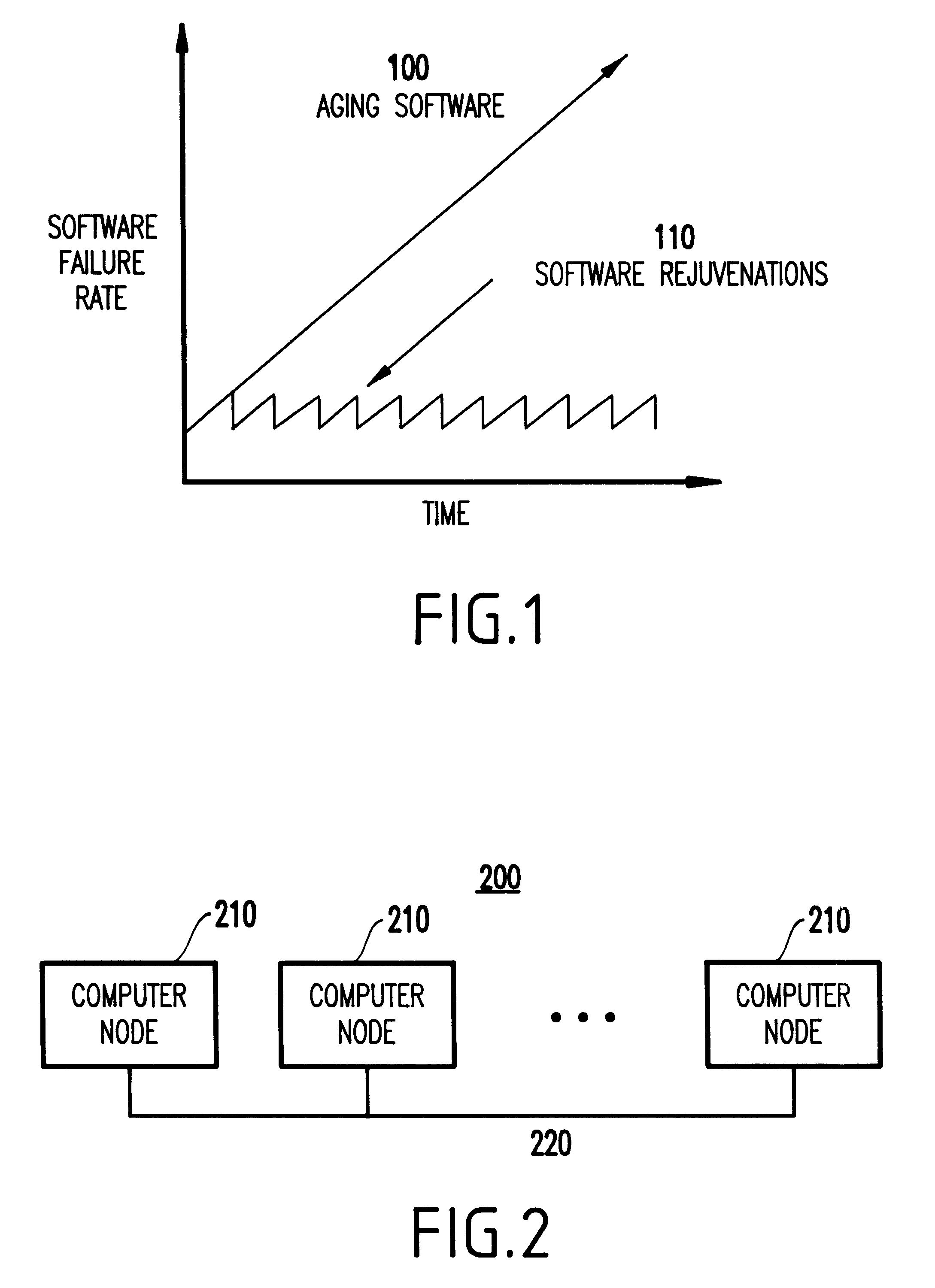
Method and system for transparent symptom-based selective software rejuvenation
InactiveUS6629266B1Hardware monitoringRedundant operation error correctionParallel computingDependability
A method (and system) for increased software dependability, includes learning how to predict an outage of a software system running on a computer, and, based on the learning, predicting an imminent outage, and avoiding the outage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Structured methodology and design patterns for web services
ActiveUS7831693B2Multiple digital computer combinationsDigital dataQuality of serviceBusiness-to-business
System and method for designing and implementing Web Services according to a structured methodology and design patterns. Embodiments may incorporate a structured methodology, best practices and design patterns that address reliability, availability and scalability of Web Services architecture. Embodiments may provide mechanisms for integrating heterogeneous technology components into Web Services. Embodiments may provide a vendor-independent Web Services architecture framework and reusable Web Services design patterns, which may be used in creating end-to-end solutions based on past experience and best practices. Embodiments may include design patterns and best practices for delivering Web Services solutions with Quality of Services. One embodiment may provide a Business-to-Business Integration (B2Bi) integration framework for Web Services. Embodiments may provide a Web Security framework and design patterns for designing end-to-end Web Services security.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com