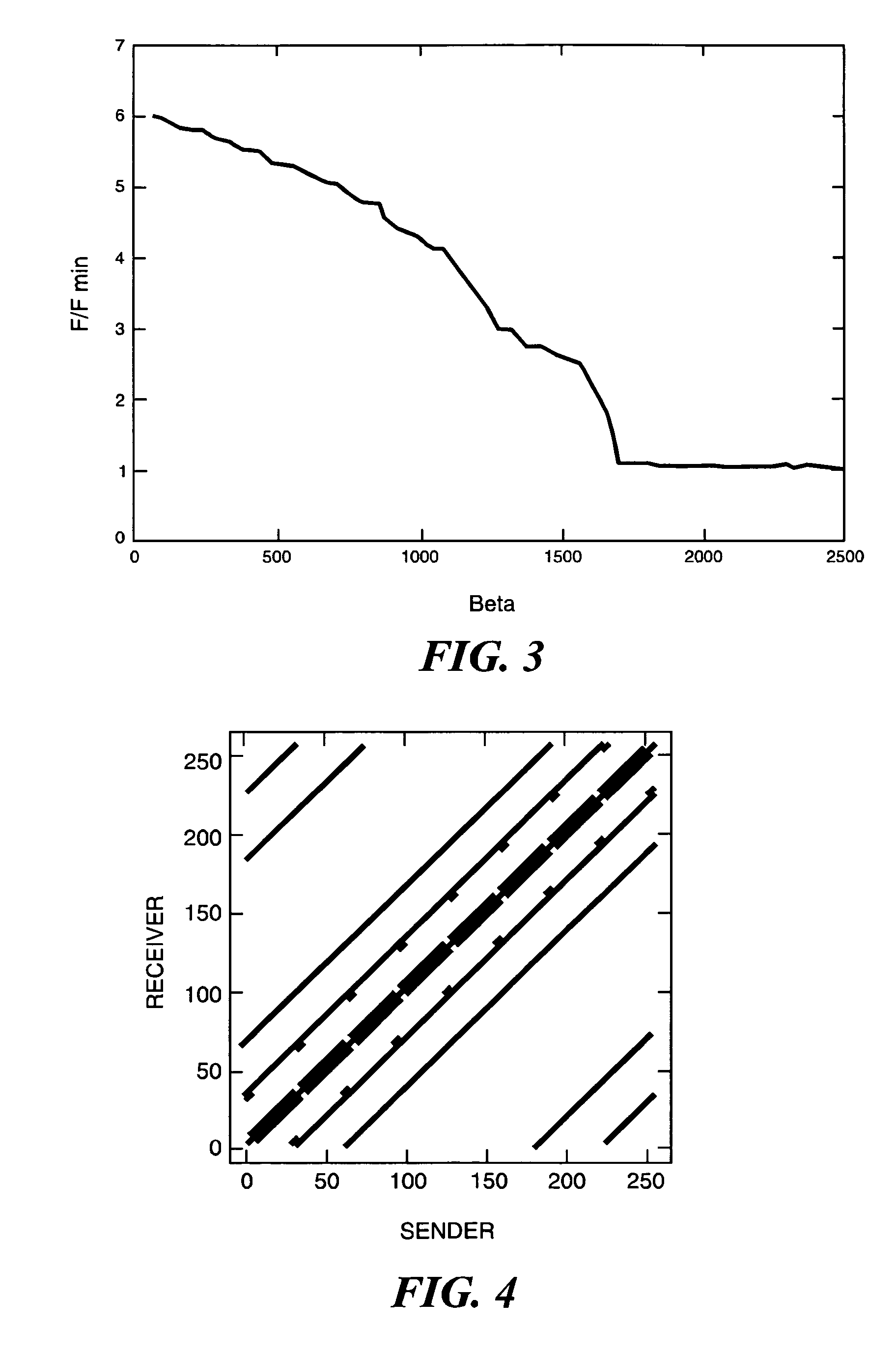
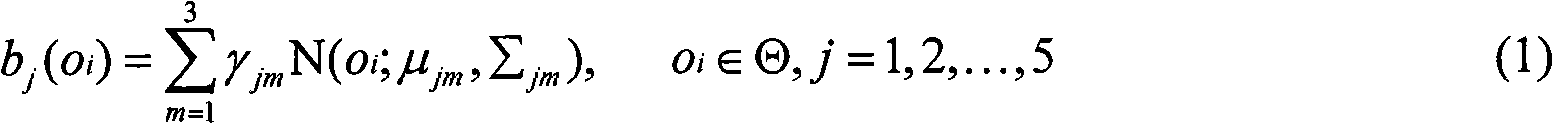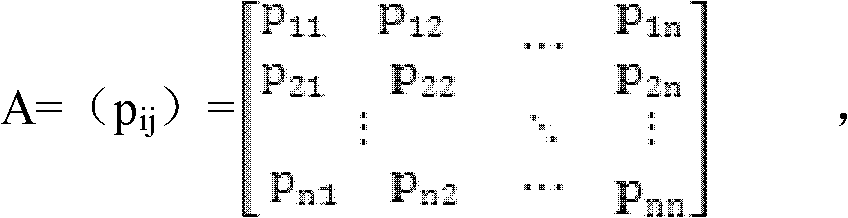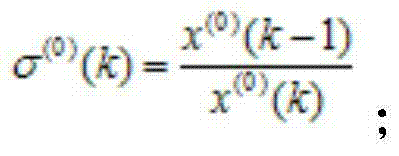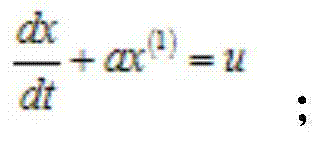Patents
Literature
818 results about "Markov chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
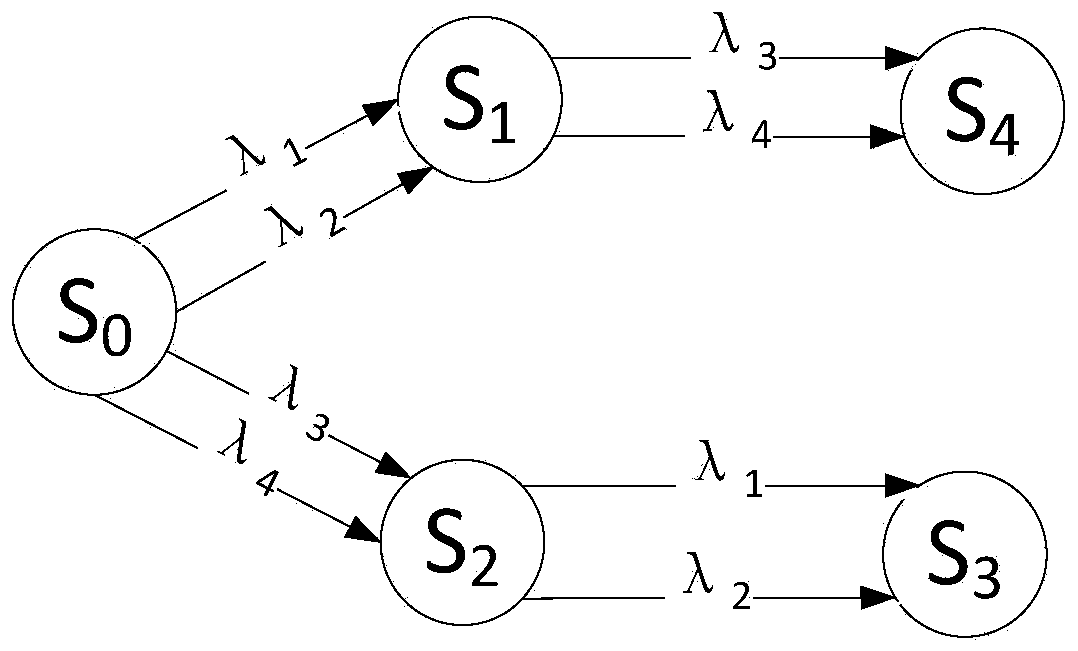
A Markov chain is a stochastic model describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event. In probability theory and related fields, a Markov process, named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov, is a stochastic process that satisfies the Markov property (sometimes characterized as "memorylessness"). Roughly speaking, a process satisfies the Markov property if one can make predictions for the future of the process based solely on its present state just as well as one could knowing the process's full history, hence independently from such history, that is, conditional on the present state of the system, its future and past states are independent.
Design of computer based risk and safety management system of complex production and multifunctional process facilities-application to fpso's
InactiveUS20120317058A1Strong robust attributeStrong robust attributesDigital computer detailsFuzzy logic based systemsProcess systemsNerve network
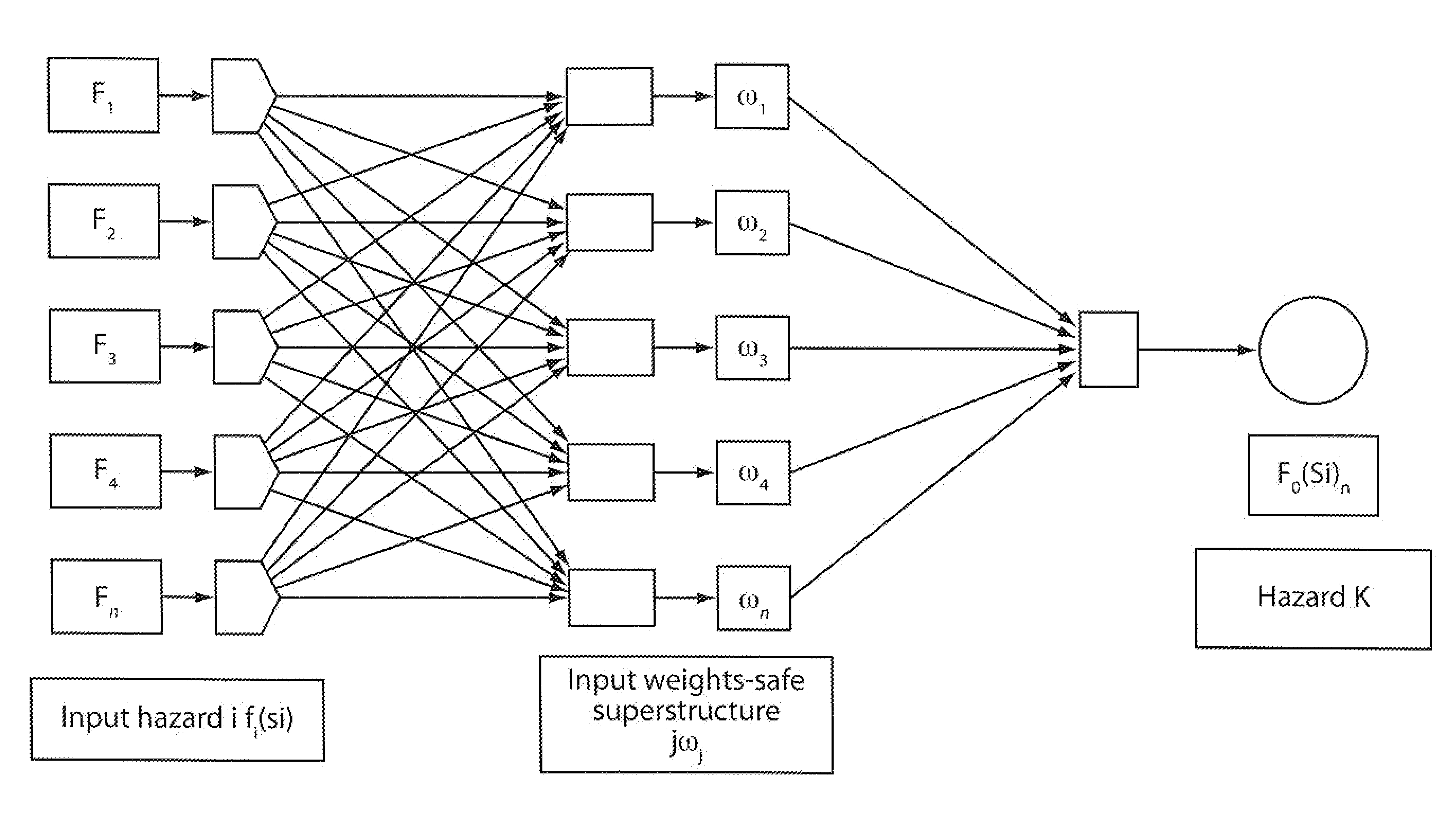
A method for predicting risk and designing safety management systems of complex production and process systems which has been applied to an FPSO System operating in deep waters. The methods for the design were derived from the inclusion of a weight index in a fuzzy class belief variable in the risk model to assign the relative numerical value or importance a safety device or system has contain a risk hazards within the barrier. The weights index distributes the relative importance of risk events in series or parallel in several interactive risk and safety device systems. The fault tree, the FMECA and the Bow Tie now contains weights in fizzy belief class for implementing safety management programs critical to the process systems. The techniques uses the results of neural networks derived from fuzzy belief systems of weight index to implement the safety design systems thereby limiting use of experienced procedures and benchmarks. The weight index incorporate Safety Factors sets SFri {0, 0.1, 0.2 . . . 1}, and Markov Chain Network to allow the possibility of evaluating the impact of different risks or reliability of multifunctional systems in transient state process. The application of this technique and results of simulation to typical FPSO / Riser systems has been discussed in this invention.
Owner:ABHULIMEN KINGSLEY E
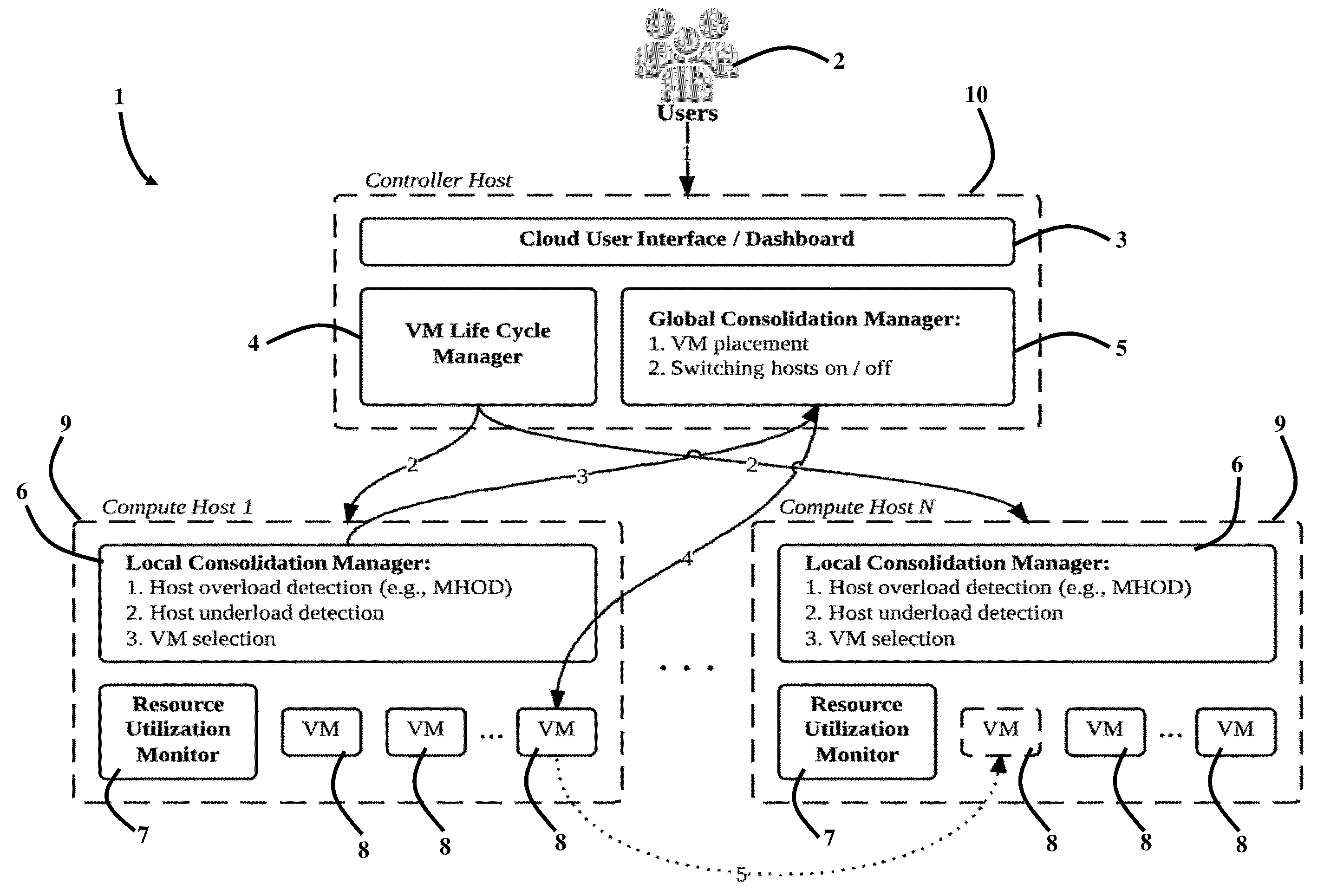
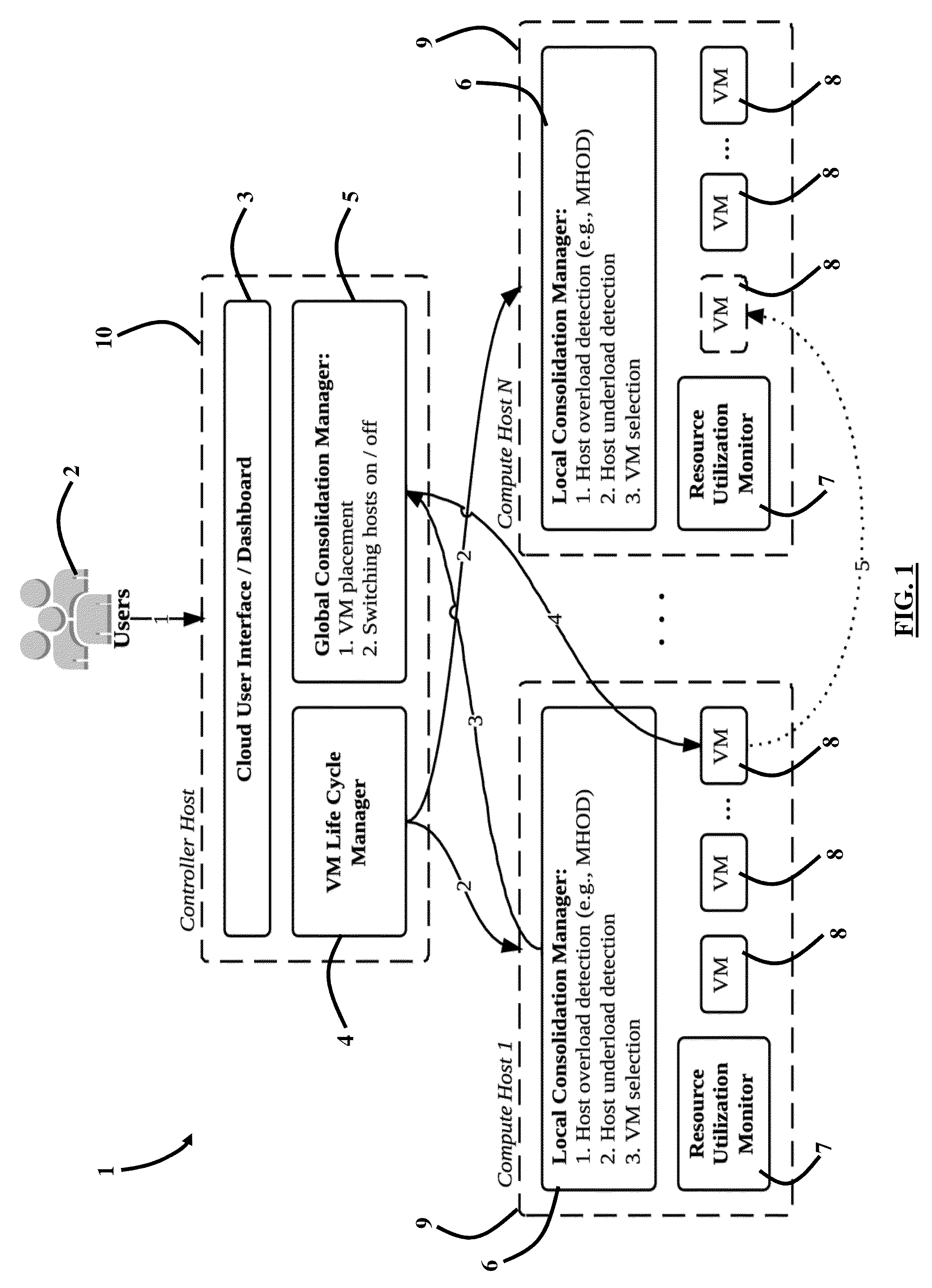
System, Method and Computer Program Product for Energy-Efficient and Service Level Agreement (SLA)-Based Management of Data Centers for Cloud Computing
ActiveUS20150039764A1Increase profitReduce energy consumptionDigital computer detailsProgram controlService-level agreementLevel of service
Improving the utilization of physical resources and reducing energy consumption in a cloud data center includes providing a plurality of virtual machines in the cloud data center; periodically reallocating resources of the plurality of virtual machines according to a current resource demand of the plurality of virtual machines in order to minimize a number of active physical servers required to handle a workload of the physical servers; maximizing a mean inter-migration time between virtual machine migrations under the quality of service requirement based on a Markov chain model; and using a multisize sliding window workload estimation process for a non-stationary workload to maximize the mean inter-migration time.
Owner:MANJRASOFT PTY LTD
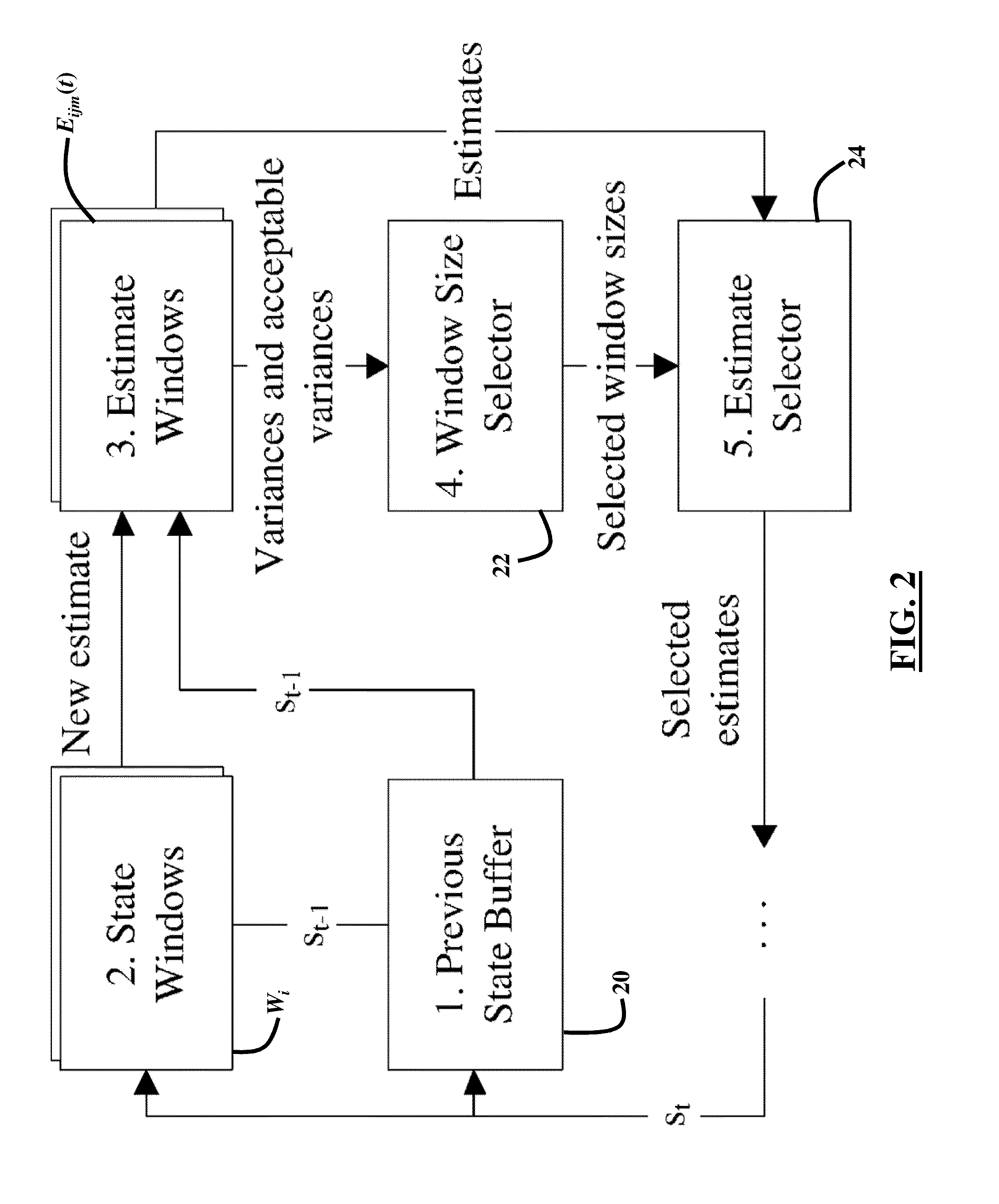
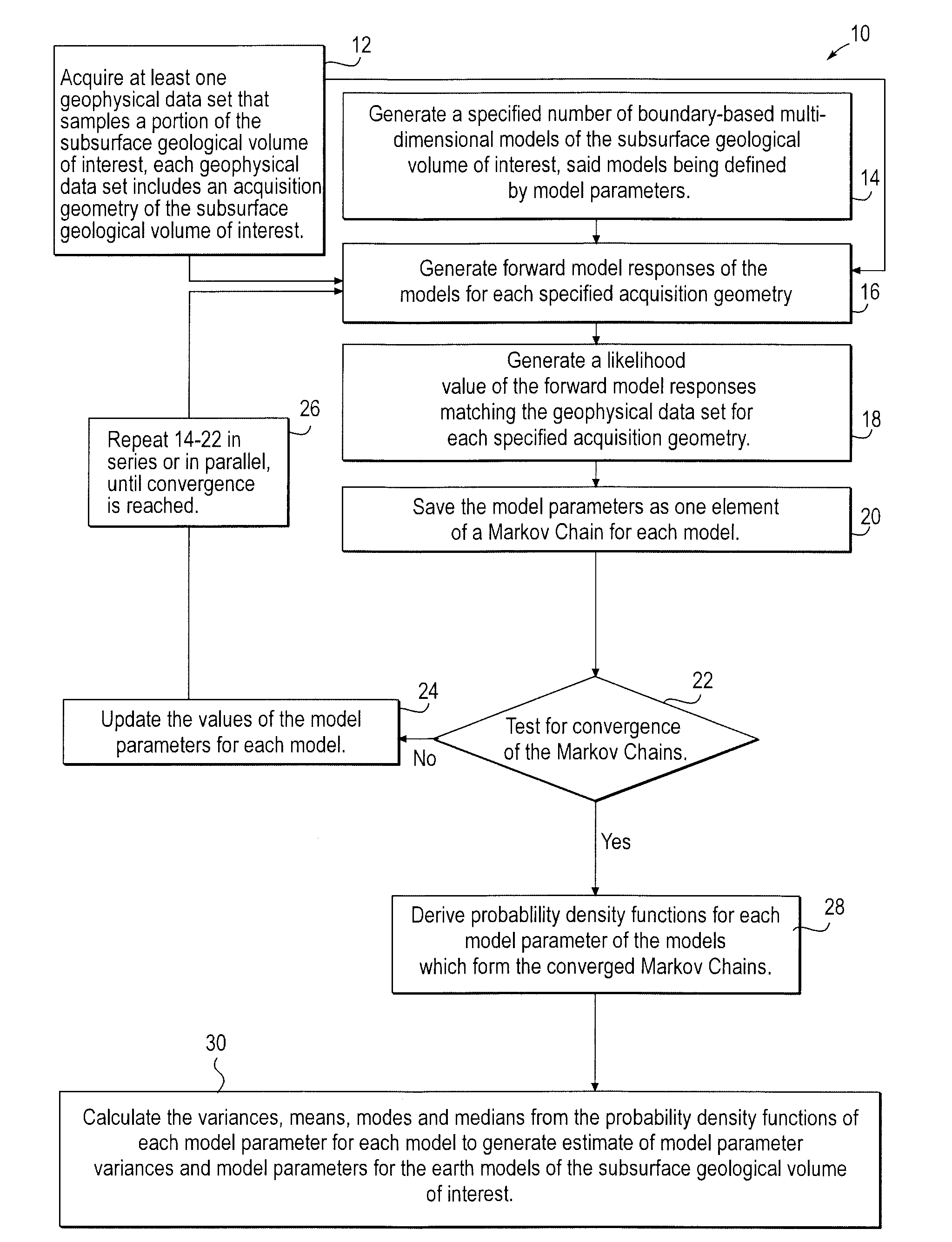
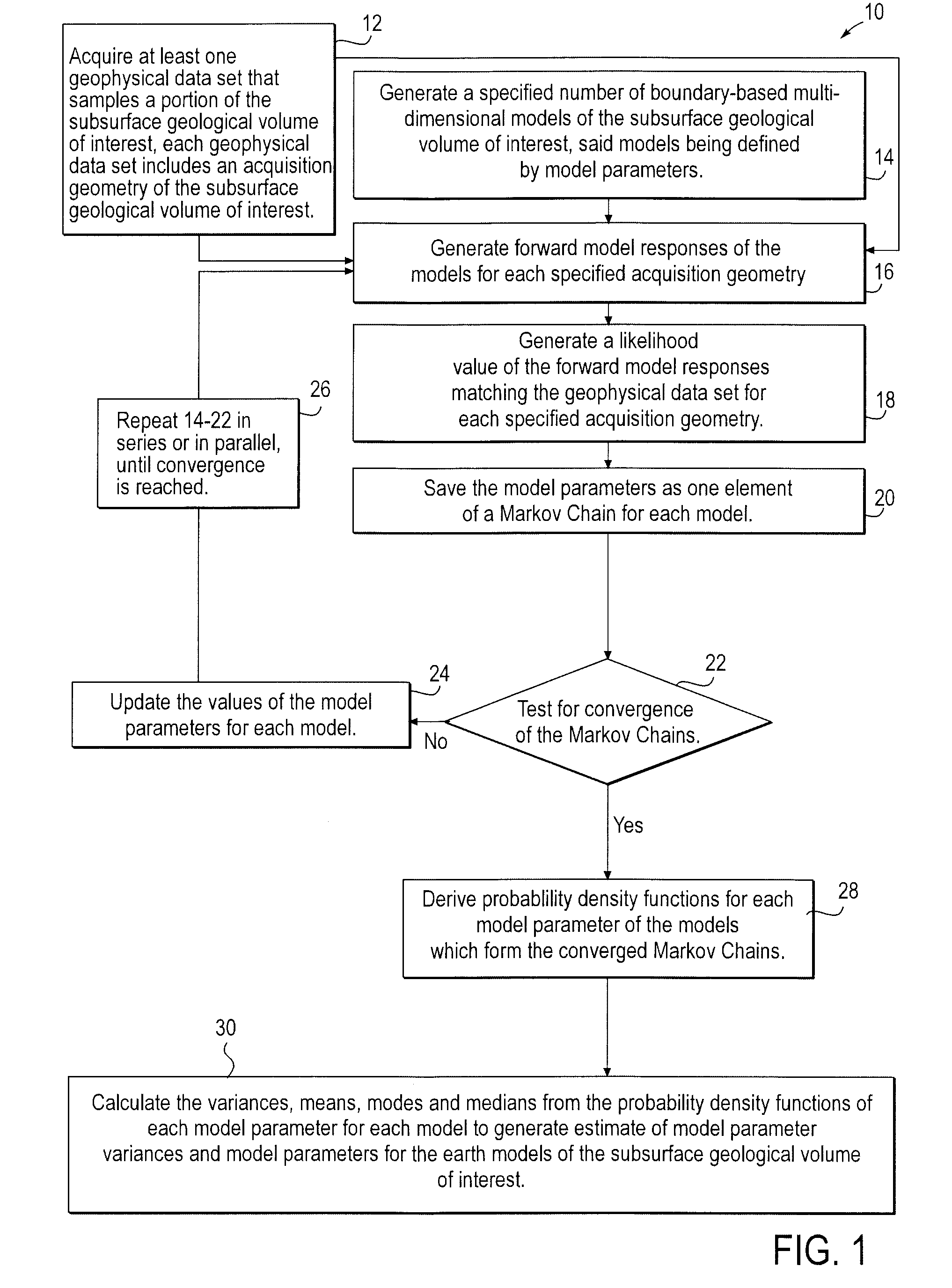
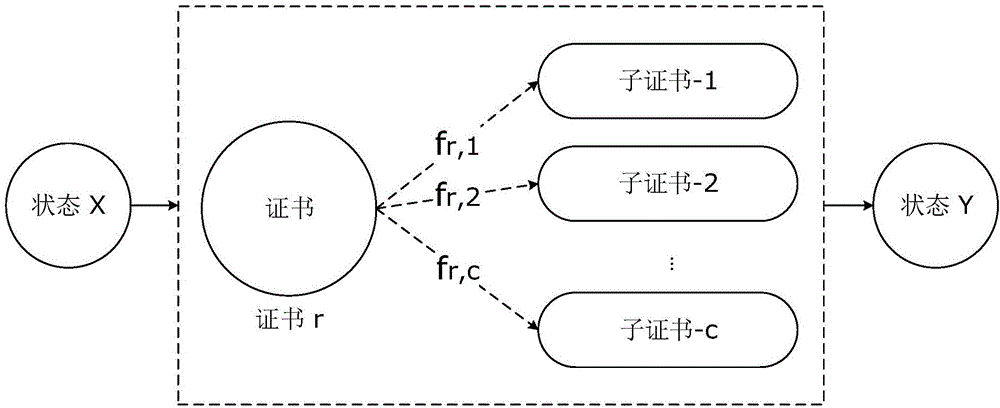
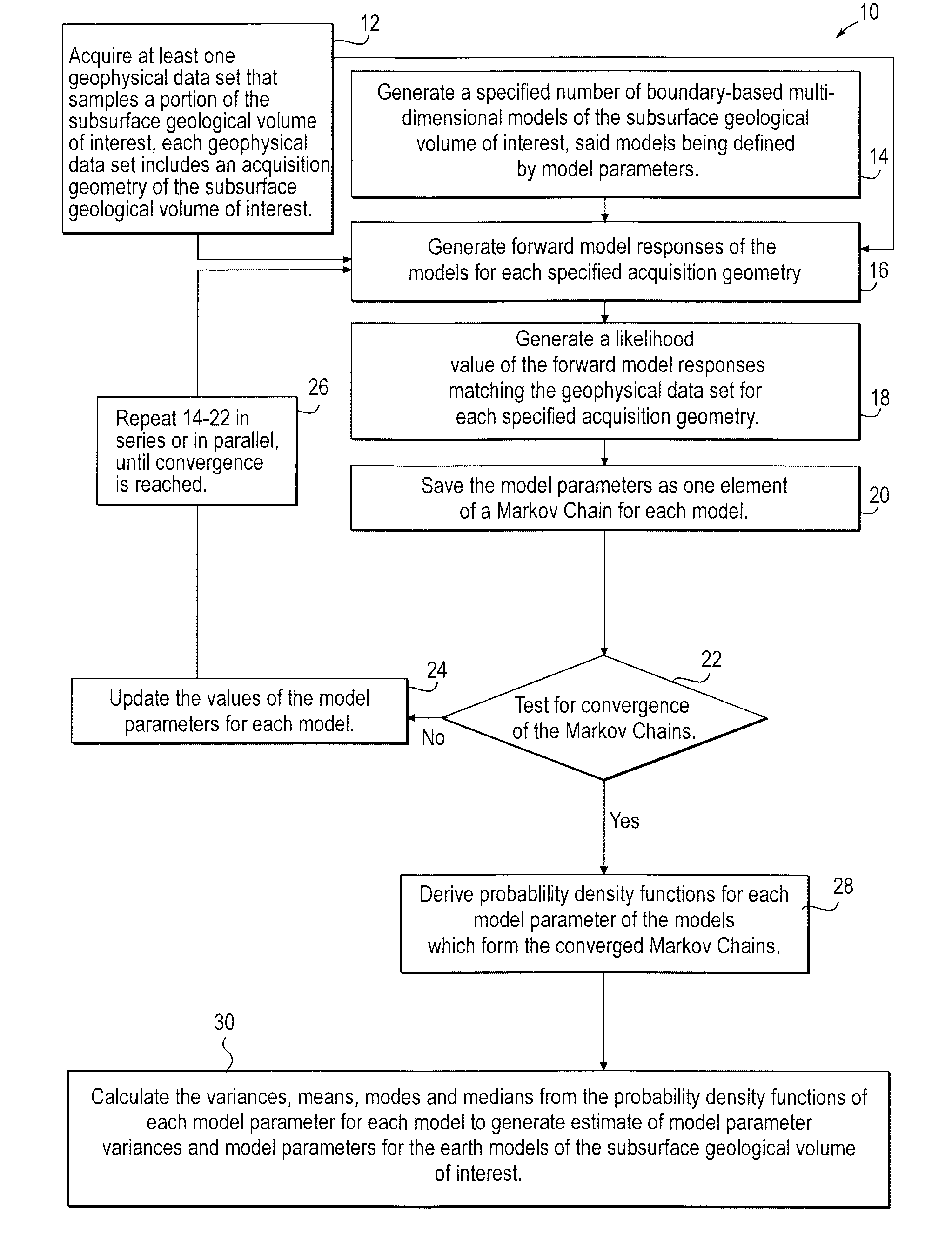
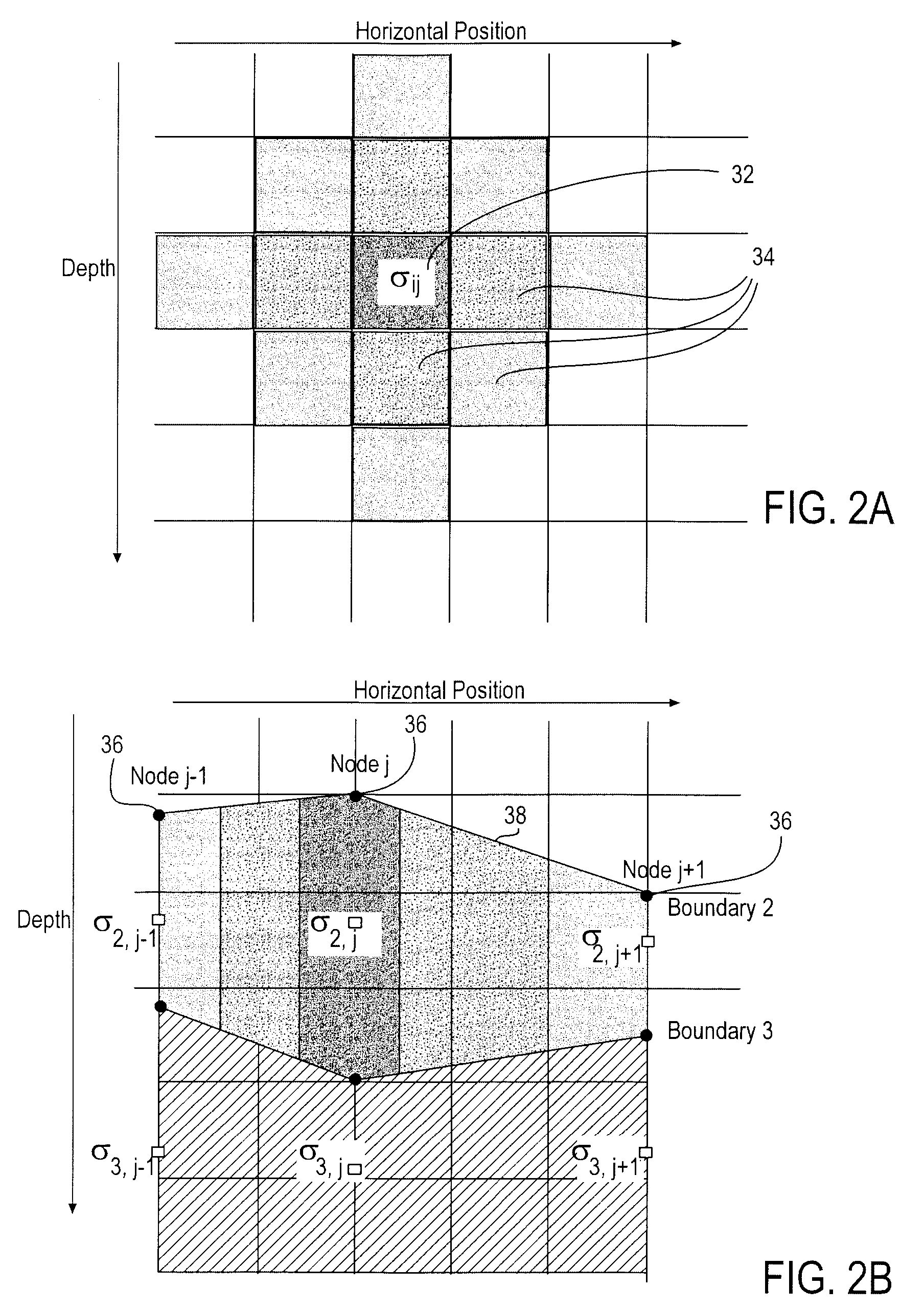
Stochastic inversion of geophysical data for estimating earth model parameters
A computer implemented stochastic inversion method for estimating model parameters of an earth model. In an embodiment, the method utilizes a sampling-based stochastic technique to determine the probability density functions (PDF) of the model parameters that define a boundary-based multi-dimensional model of the subsurface. In some embodiments a sampling technique known as Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is utilized. MCMC techniques fall into the class of “importance sampling” techniques, in which the posterior probability distribution is sampled in proportion to the model's ability to fit or match the specified acquisition geometry. In another embodiment, the inversion includes the joint inversion of multiple geophysical data sets. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a computer system configured to perform a method for estimating model parameters for accurate interpretation of the earth's subsurface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Optimizing layout of an application on a massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS20060101104A1Shorten the timeMinimize cost functionDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsMarkov chainSupercomputer
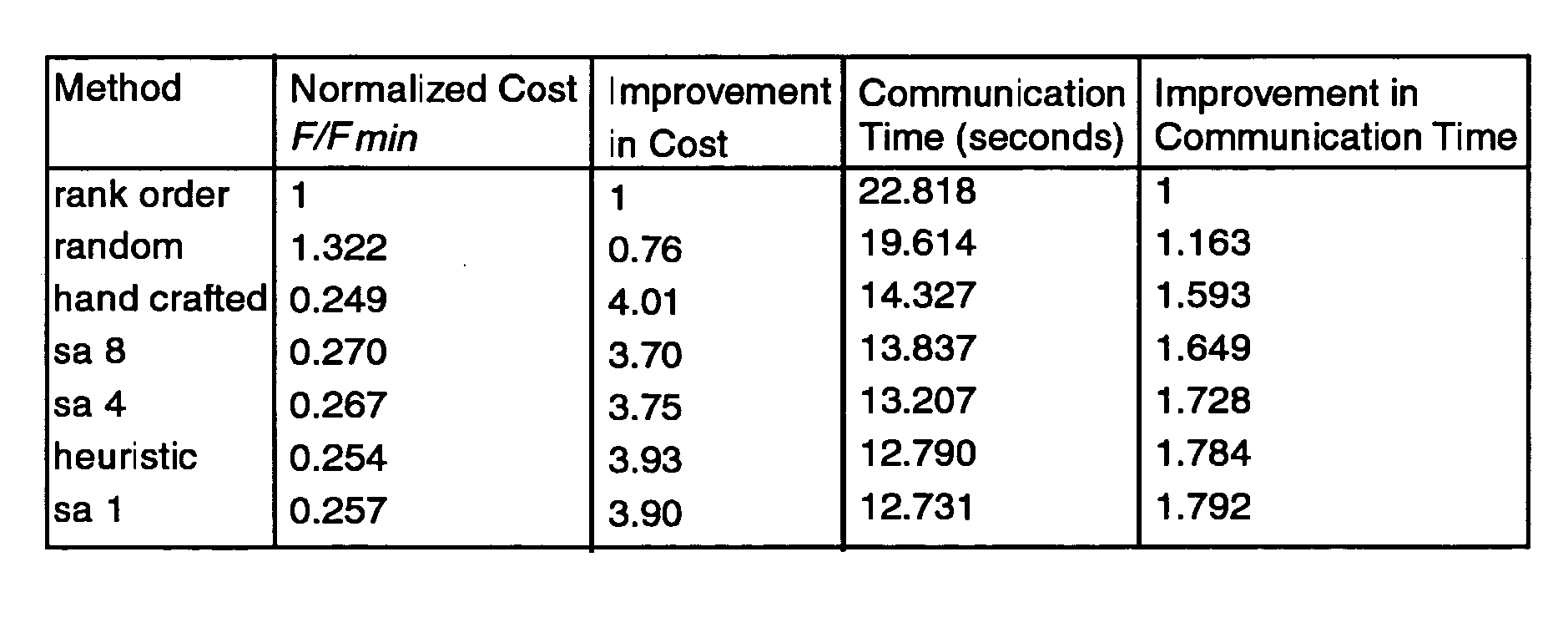
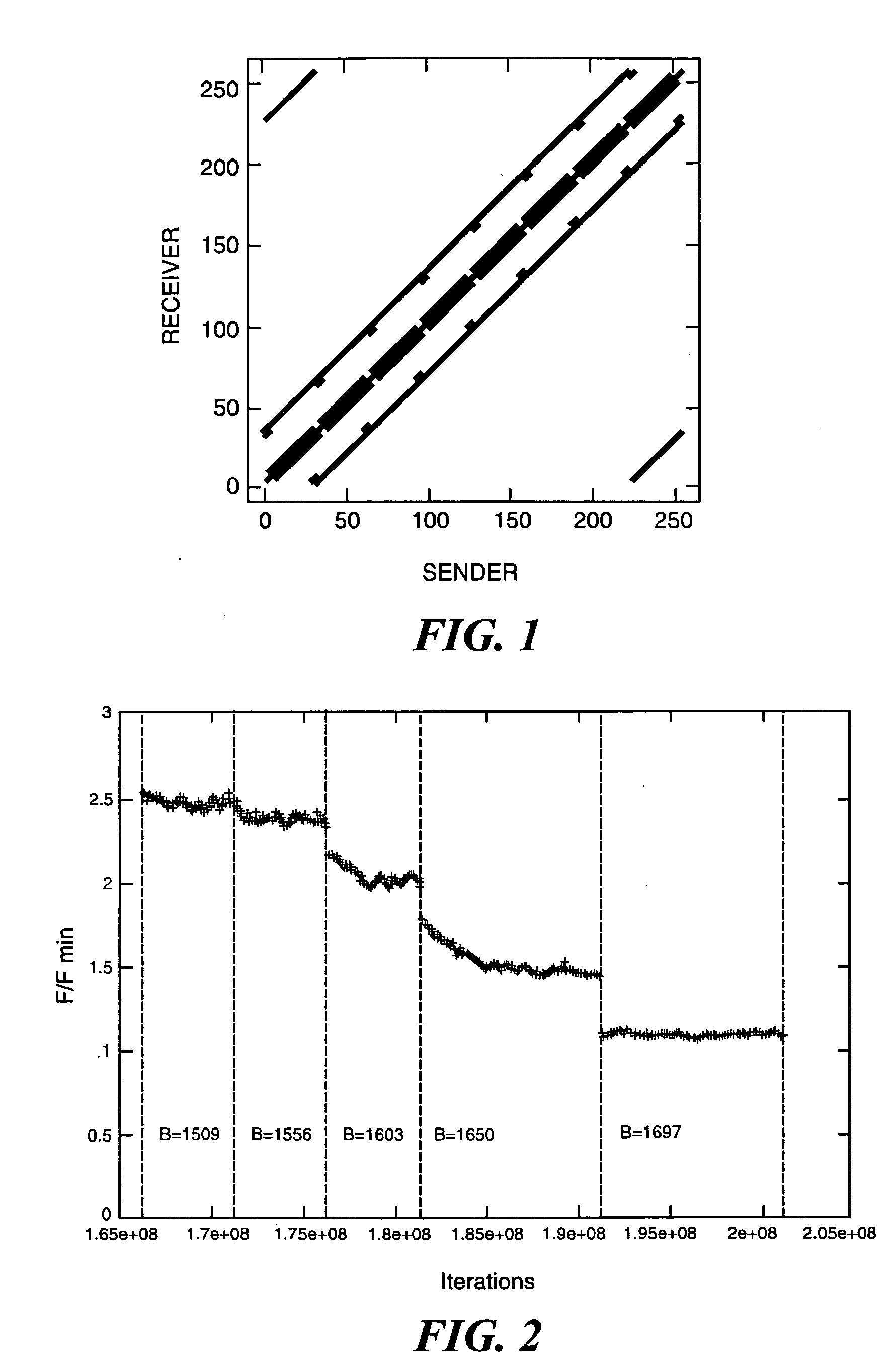
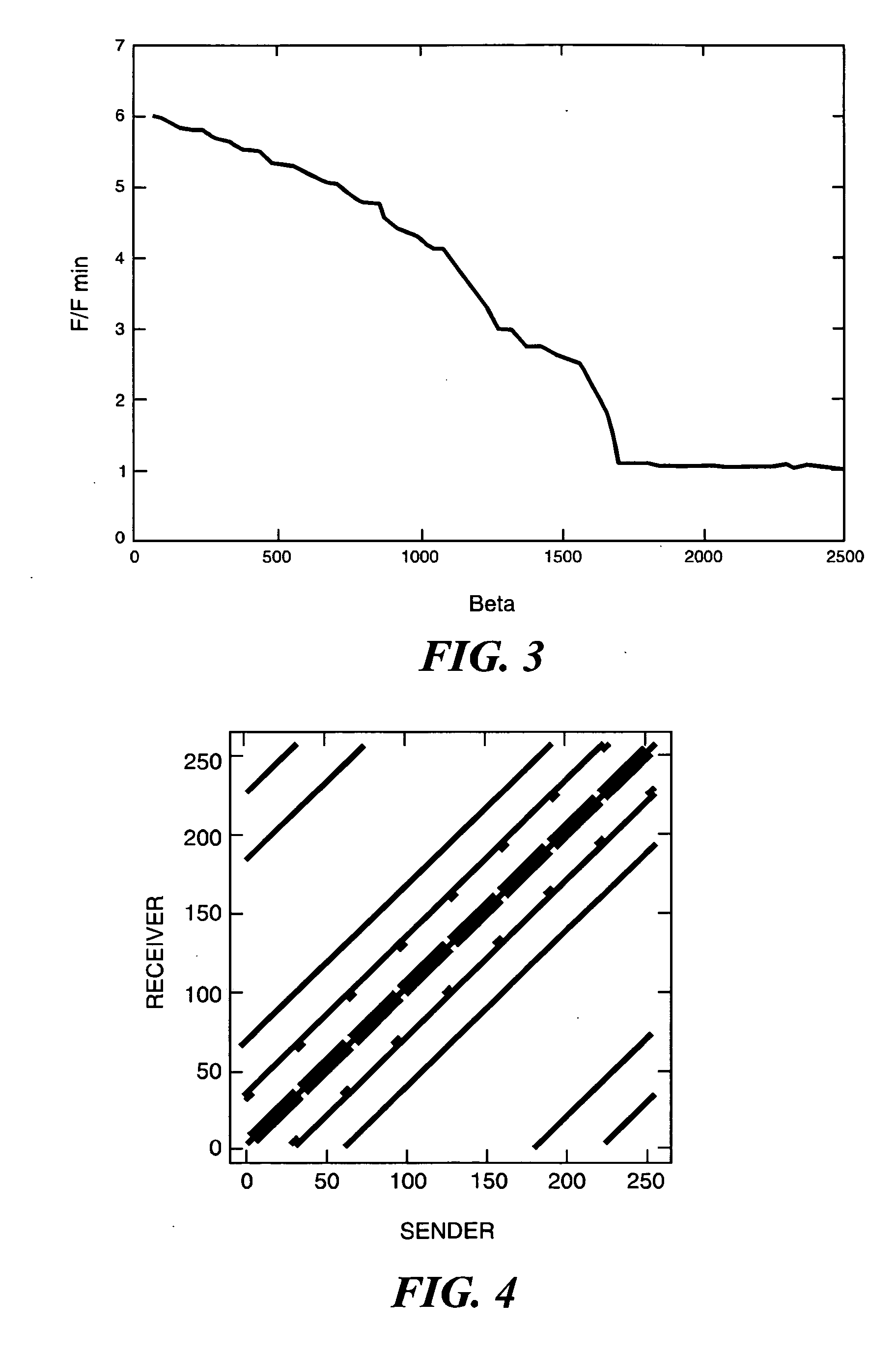
A general computer-implement method and apparatus to optimize problem layout on a massively parallel supercomputer is described. The method takes as input the communication matrix of an arbitrary problem in the form of an array whose entries C(i, j) are the amount to data communicated from domain i to domain j. Given C(i, j), first implement a heuristic map is implemented which attempts sequentially to map a domain and its communications neighbors either to the same supercomputer node or to near-neighbor nodes on the supercomputer torus while keeping the number of domains mapped to a supercomputer node constant (as much as possible). Next a Markov Chain of maps is generated from the initial map using Monte Carlo simulation with Free Energy (cost function) F=Σi,jC(i,j)H(i,j)—where H(i,j) is the smallest number of hops on the supercomputer torus between domain i and domain j. On the cases tested, found was that the method produces good mappings and has the potential to be used as a general layout optimization tool for parallel codes. At the moment, the serial code implemented to test the method is un-optimized so that computation time to find the optimum map can be several hours on a typical PC. For production implementation, good parallel code for our algorithm would be required which could itself be implemented on supercomputer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for automatic detection and tracking of multiple targets with multiple cameras and system therefor
ActiveUS20100166260A1The result is stable and accurateEfficient integrationCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsMarkov chainMulti camera
A method for automatically detecting and tracking multiple targets in a multi-camera surveillance zone and system thereof. In each camera view of the system only a simple object detection algorithm is needed. The detection results from multiple cameras are fused into a posterior distribution, named TDP, based on the Bayesian rule. This TDP distribution represents a likelihood of presence of some moving targets on the ground plane. To properly handle the tracking of multiple moving targets with time, a sample-based framework which combines Markov Chain Monte carlo (MCMC), Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC), and Mean-Shift Clustering, is provided. The detection and tracking accuracy is evaluated by both synthesized videos and real videos. The experimental results show that this method and system can accurately track a varying number of targets.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
System and method for localization over a wireless network
InactiveUS20060087425A1Reduce areaSufficient roomPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsOutdoor areaMarkov chain
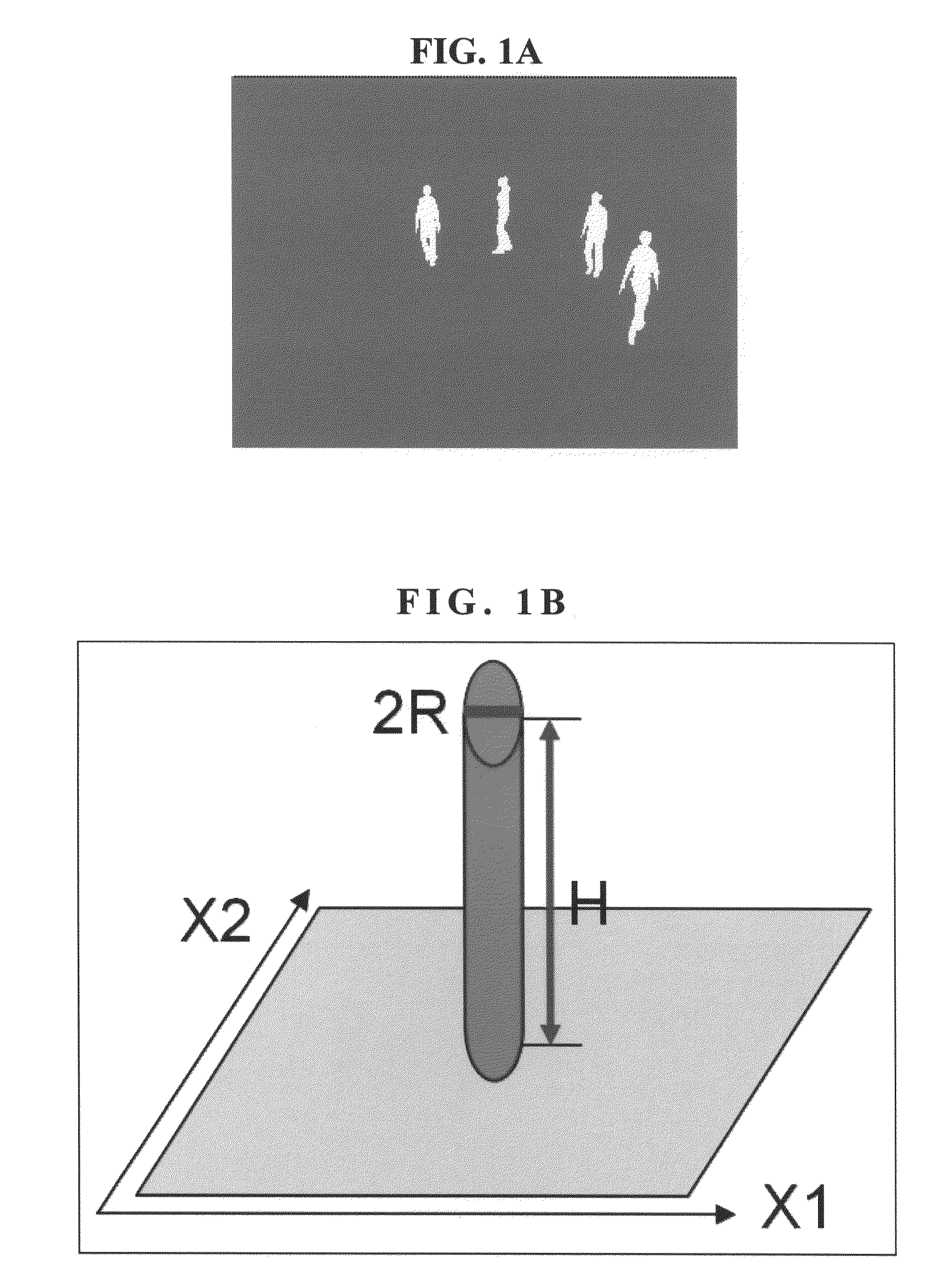
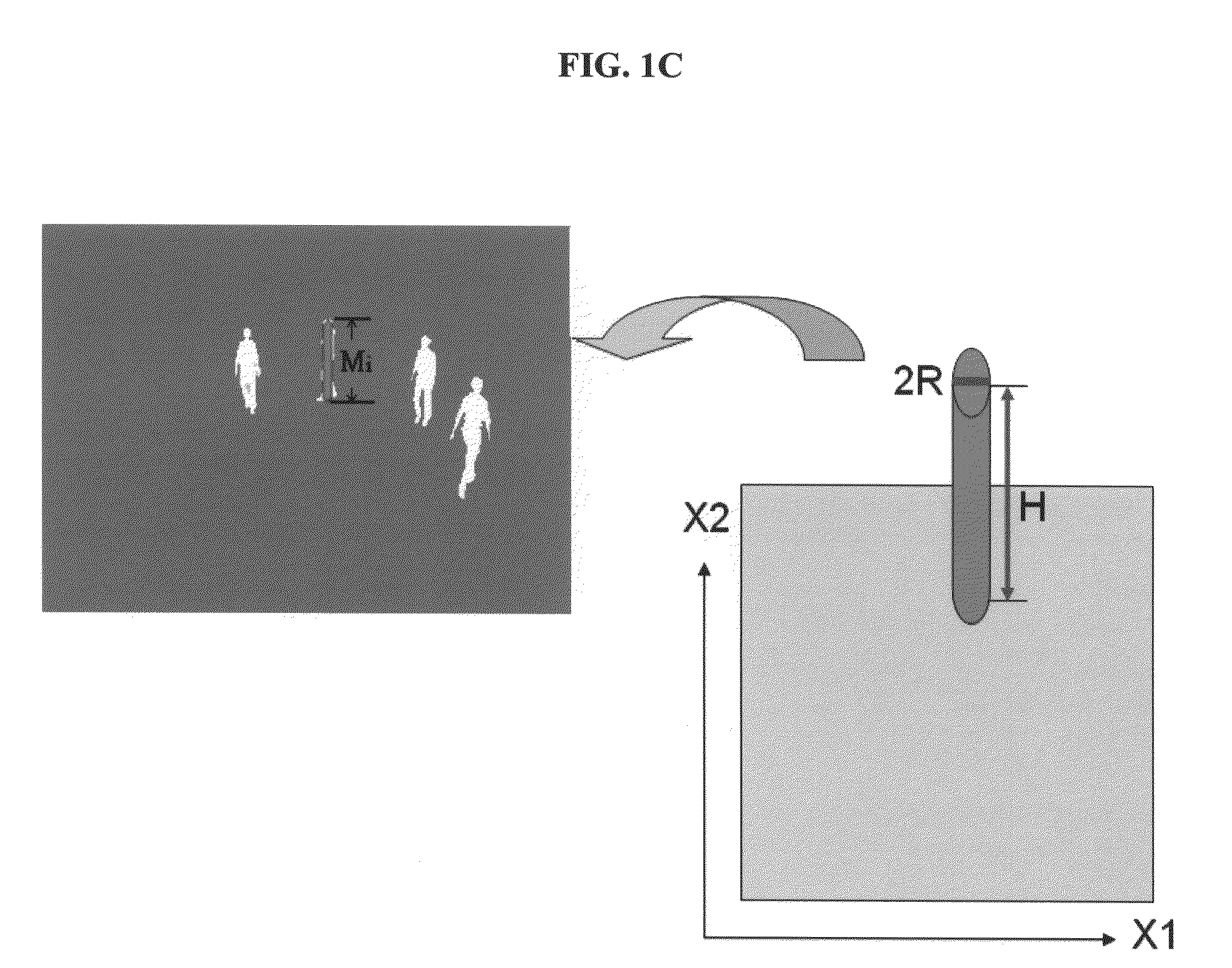
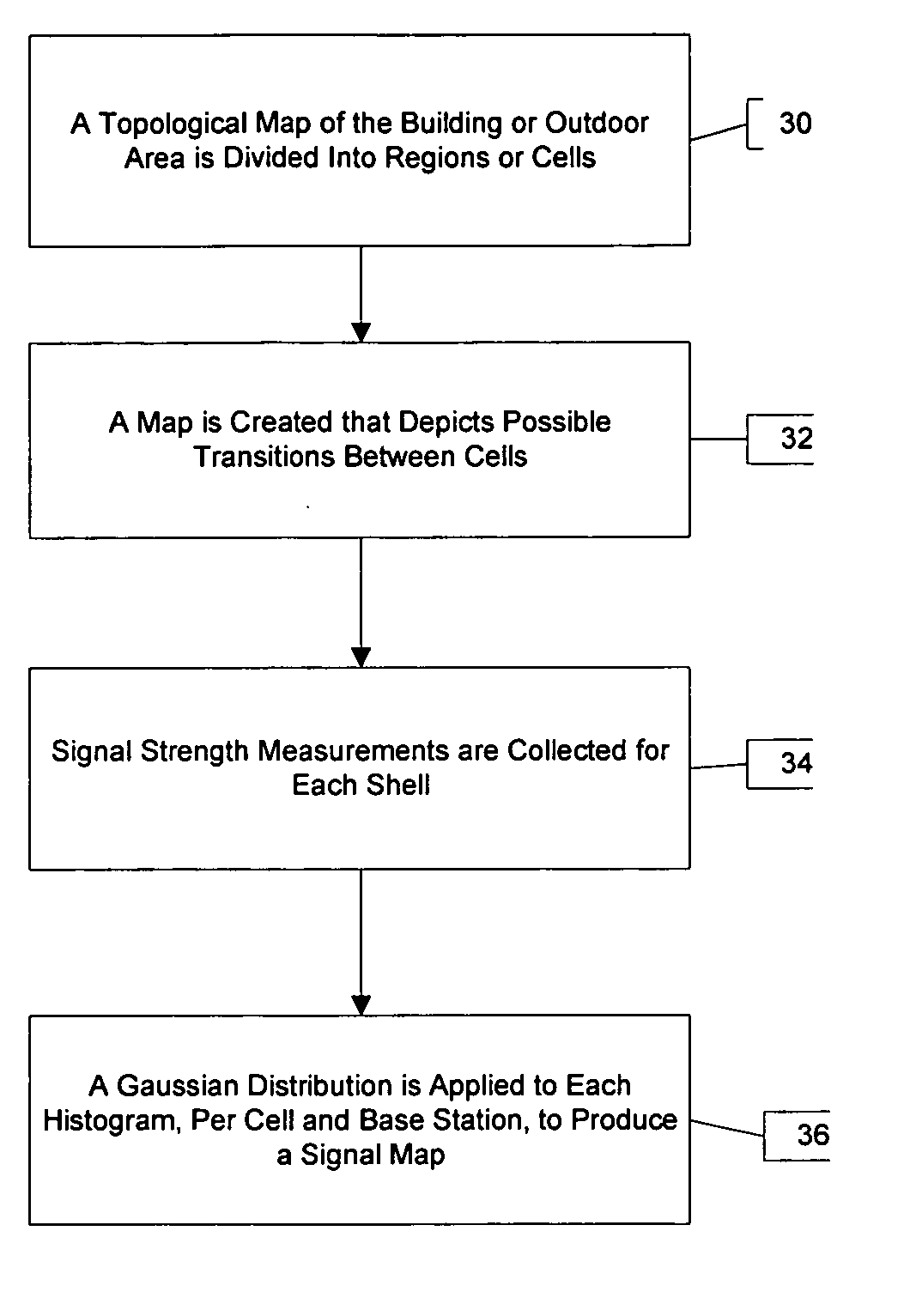
A system for locating a wireless device involves the use of the measured signal strength of various base stations in the building or outdoor area under analysis. A topological map of the building or outdoor area under analysis is created. The map is divided into cells, and signal intensities are collected in each cell. For each cell, the signal from a particular base station is fit to a statistical distribution, such as a Gaussian distribution, and the parameters of the statistical distribution are estimated. After a device obtains a set of signal strength measurements, a probabilistic technique is employed to estimate the probability of the existence of the measurements in each of the cells of the building or area under analysis. The estimated location is the cell with the highest probability. A mobile user is tracked with the use of a Markov chain and the system can be calibrated to account for equipment and environmental variations.
Owner:RICE UNIV
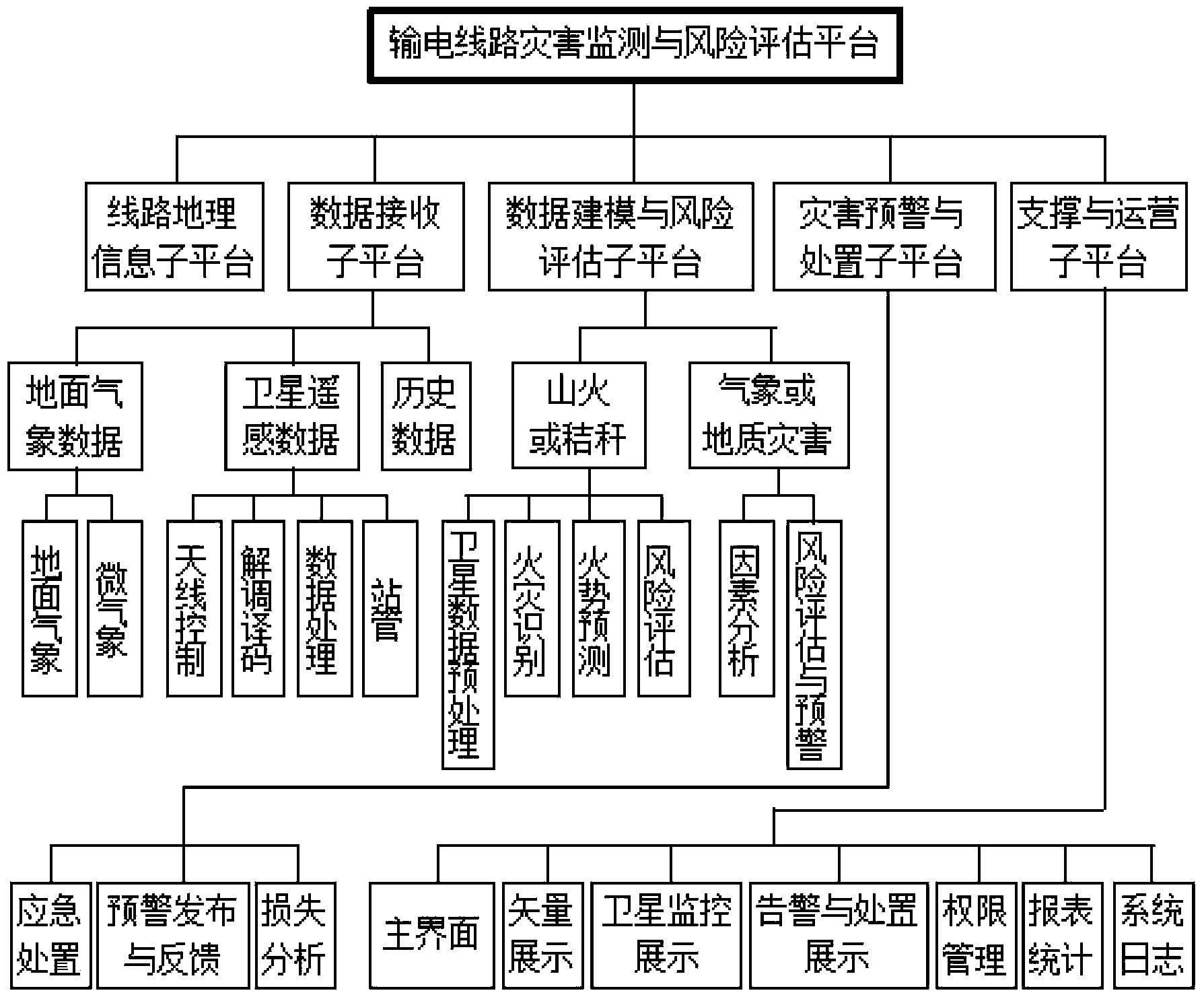
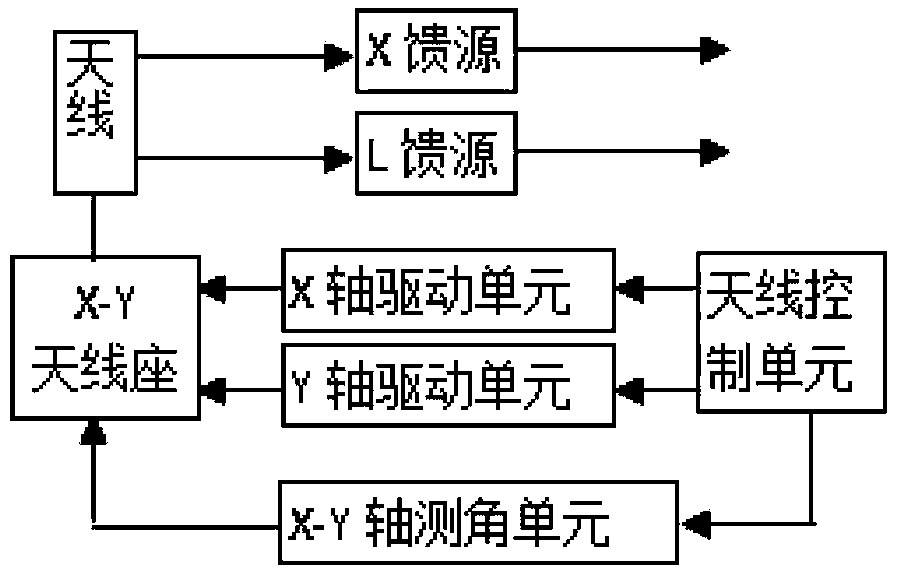
Power transmission line disaster monitoring and risk assessment platform based on satellite and weather information
ActiveCN103455708AImprove the immunityReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationMoving averageData modeling
The invention provides a power transmission line disaster monitoring and risk assessment platform based on satellite and weather information in order to effectively warn disasters. The platform comprises a power transmission line geographic information sub-platform, a satellite remote sensing data receiving sub-platform, a data modeling and risk assessment sub-platform, a disaster warning and treatment sub-platform, and a support and operation sub-platform. The data modeling and risk assessment sub-platform comprises a fire development trend prediction submodule; the submodule predicts time sequence of fire data by a time prediction method, auto-regressive integrated moving average, captures cross-fire hidden spatial correlation by a spatial prediction method through dynamic regression neural network, simulates stochastic disturbance by a Markov chain model, and acquires space-time integrated and disturbance-removing prediction results by means of statistical regression.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER
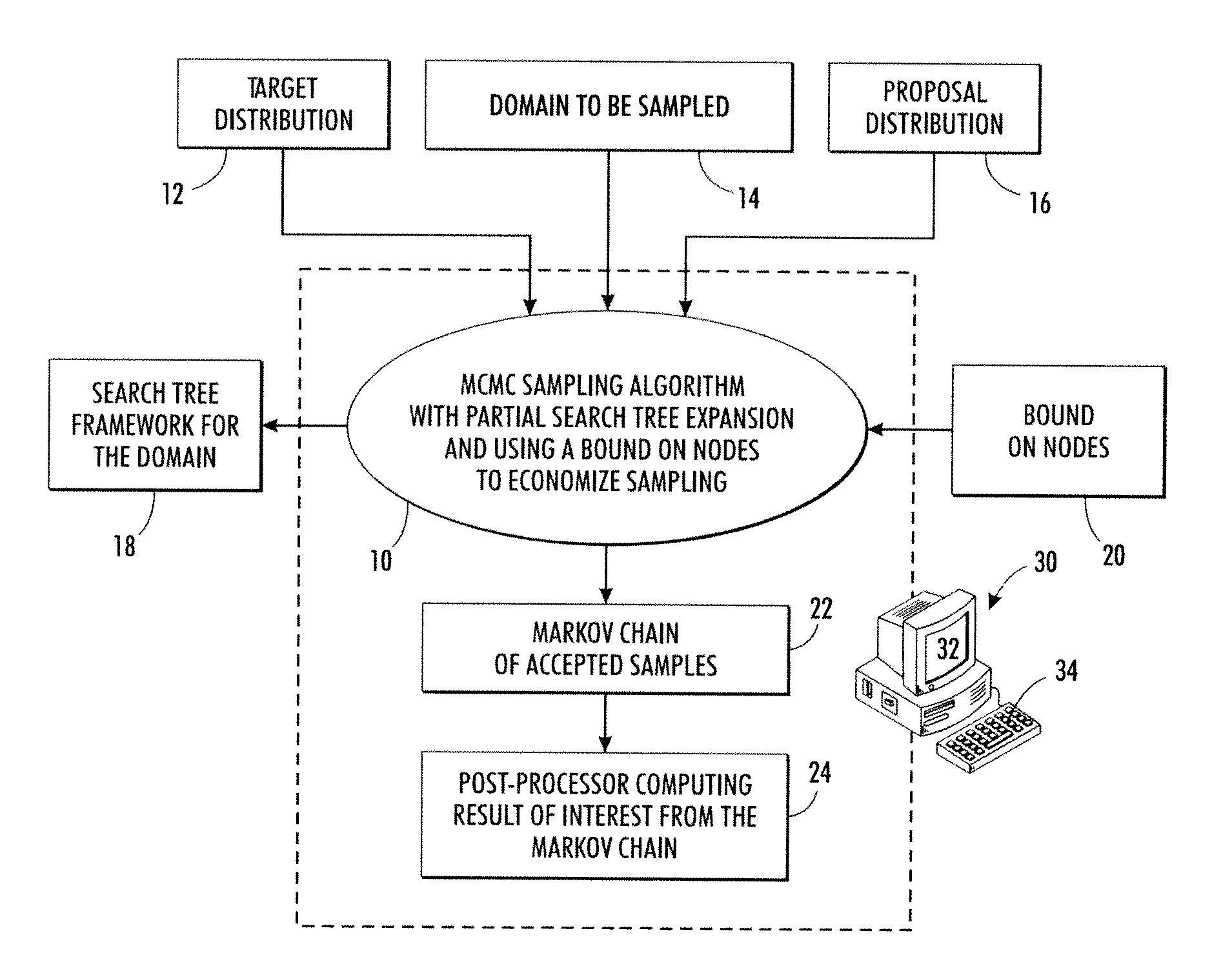
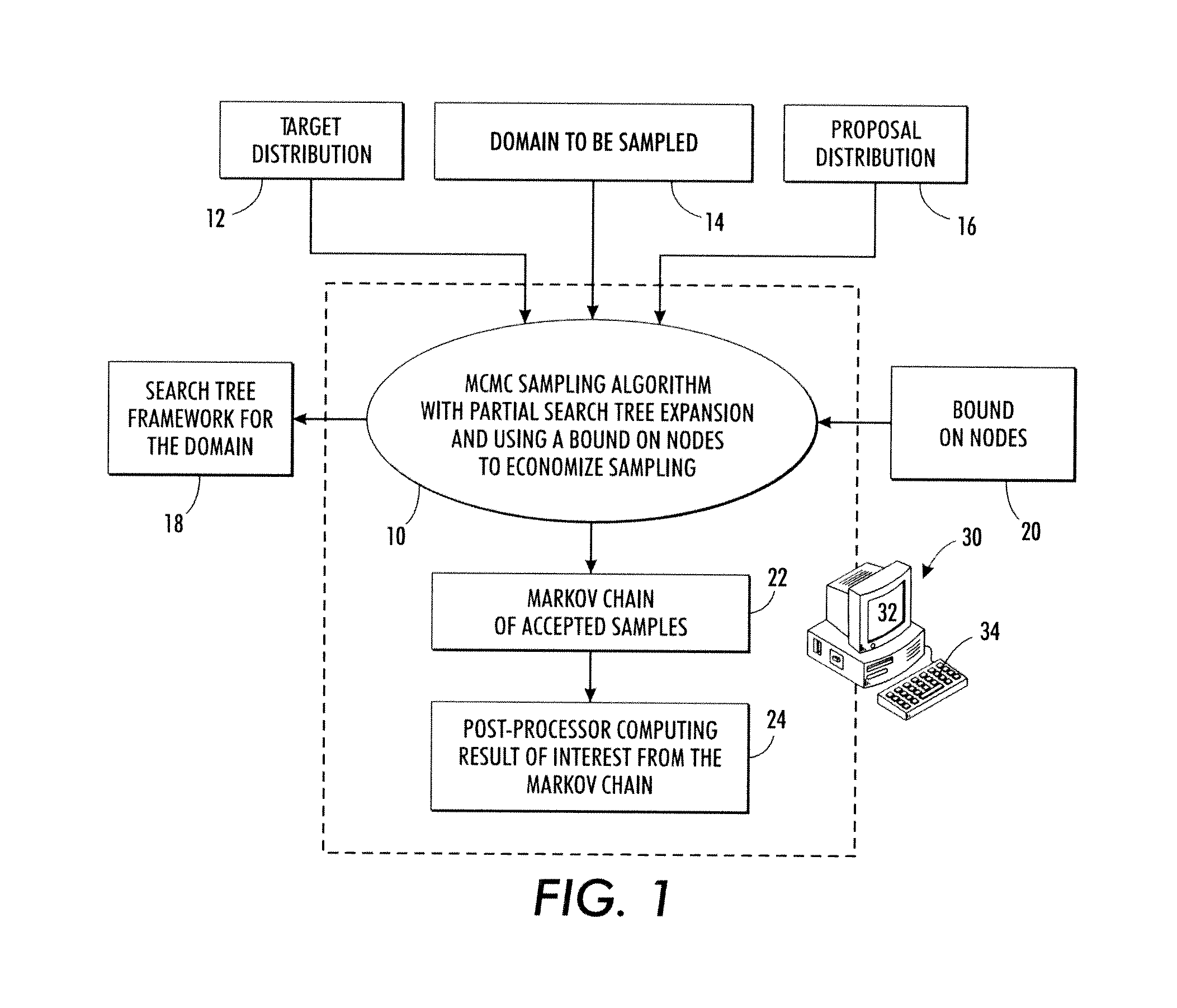
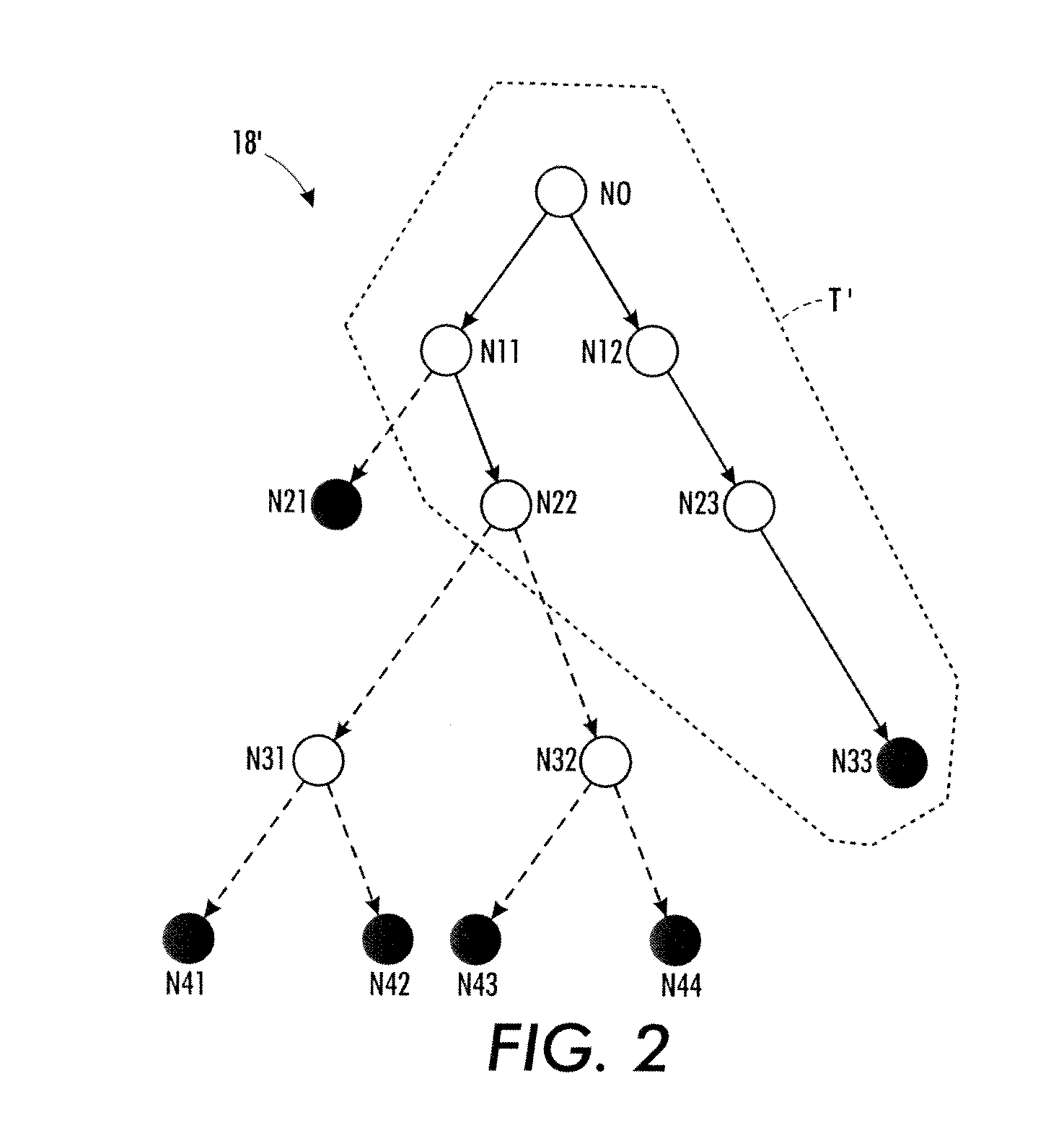
Probabilistic sampling using search trees constrained by heuristic bounds
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling of elements of a domain to be sampled is performed to generate a set of samples. The MCMC sampling is performed over a search tree of decision sequences representing the domain to be sampled and having terminal nodes corresponding to elements of the domain. In some embodiments the MCMC sampling is performed by Metropolis-Hastings (MH) sampling. The MCMC sampling is constrained using a bound on nodes of the search tree. The constraint may entail detecting a node whose bound value ensures that an acceptable element cannot be identified by continuing traversal of the tree past that node, and terminating the traversal in response. The constraint may entail selecting a node to serve as a starting node for a sampling attempt in accordance with a statistical promise distribution indicating likelihood that following a decision sequence rooted at the node will identify an acceptable element.
Owner:XEROX CORP
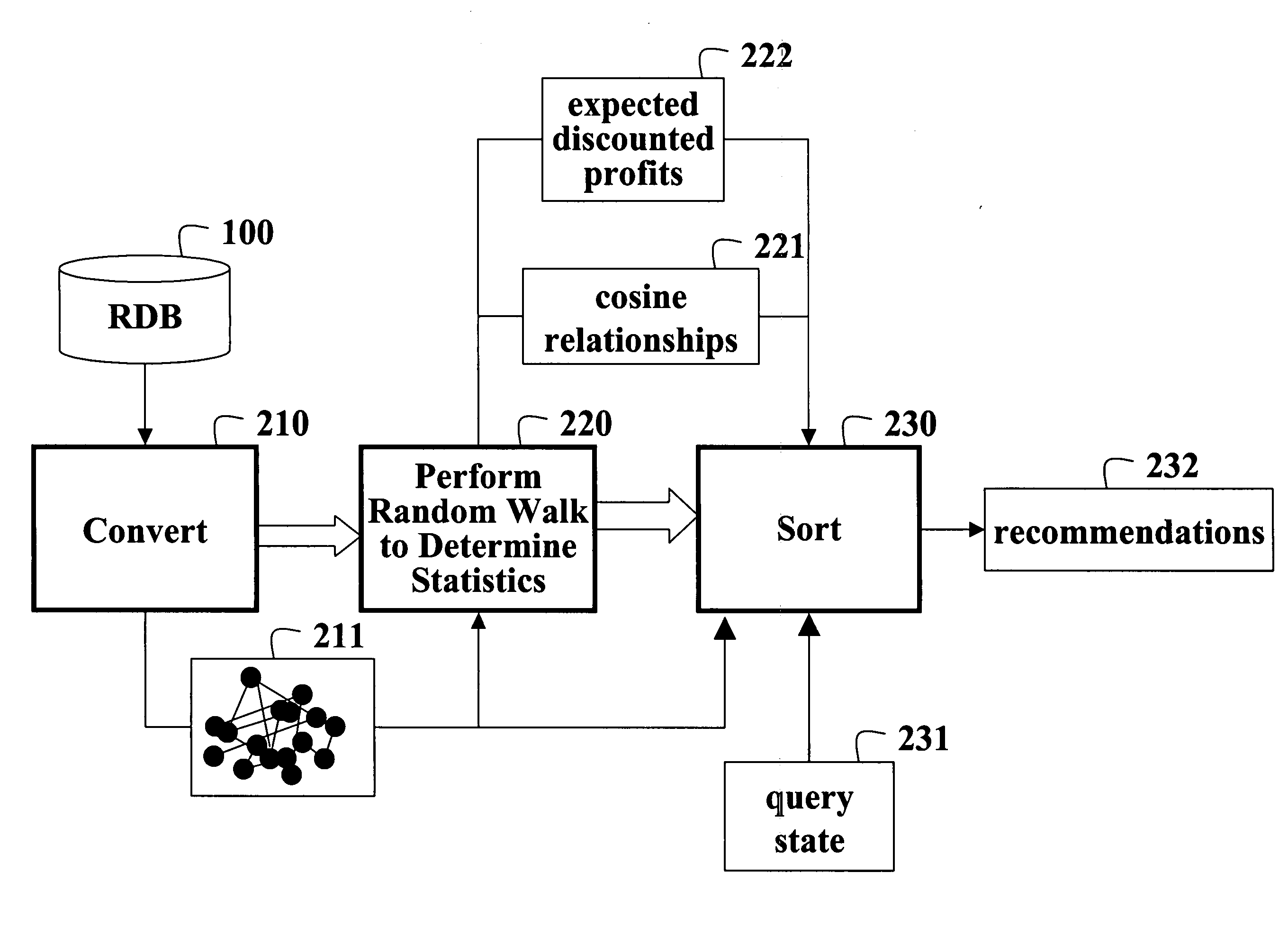
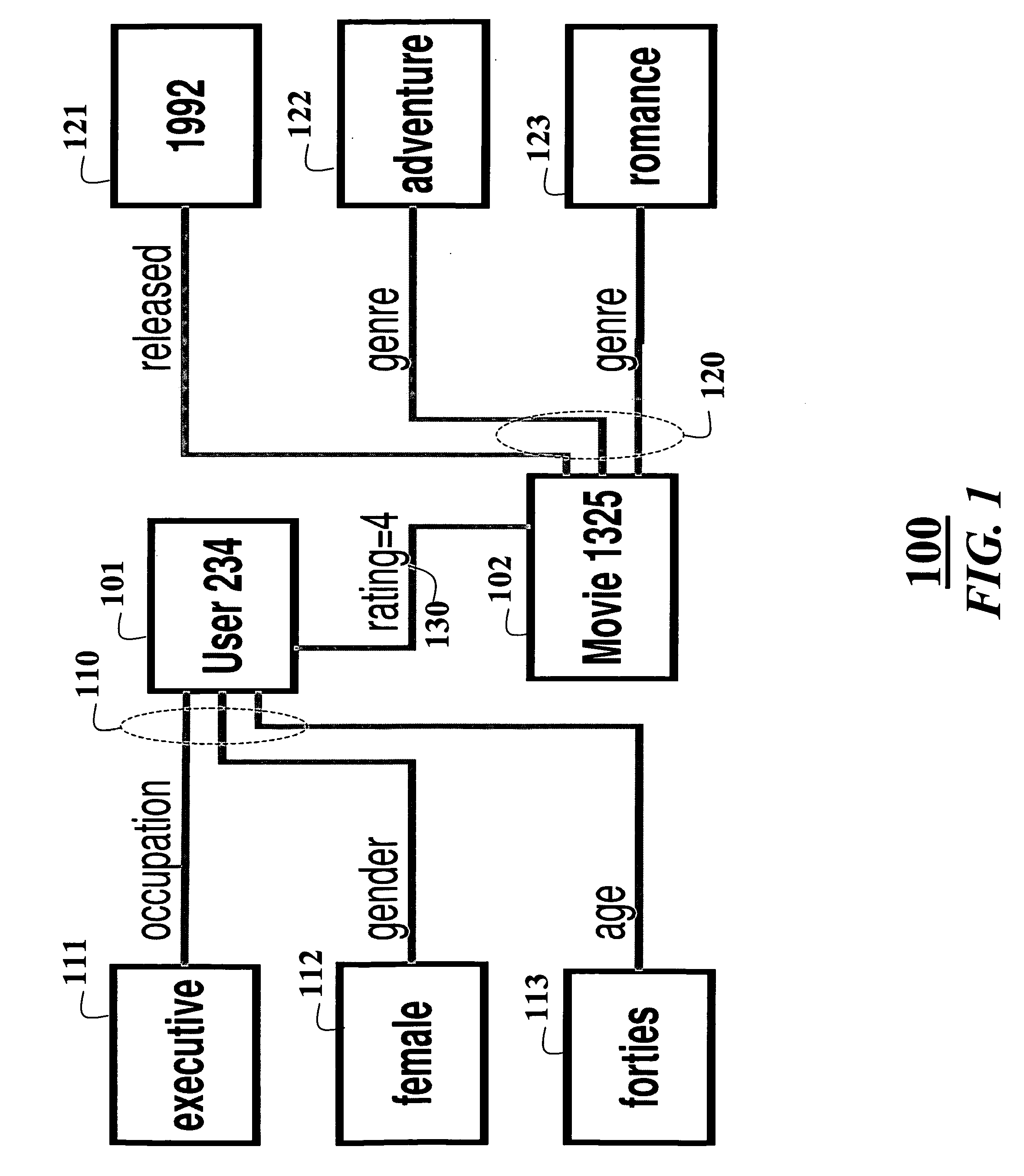
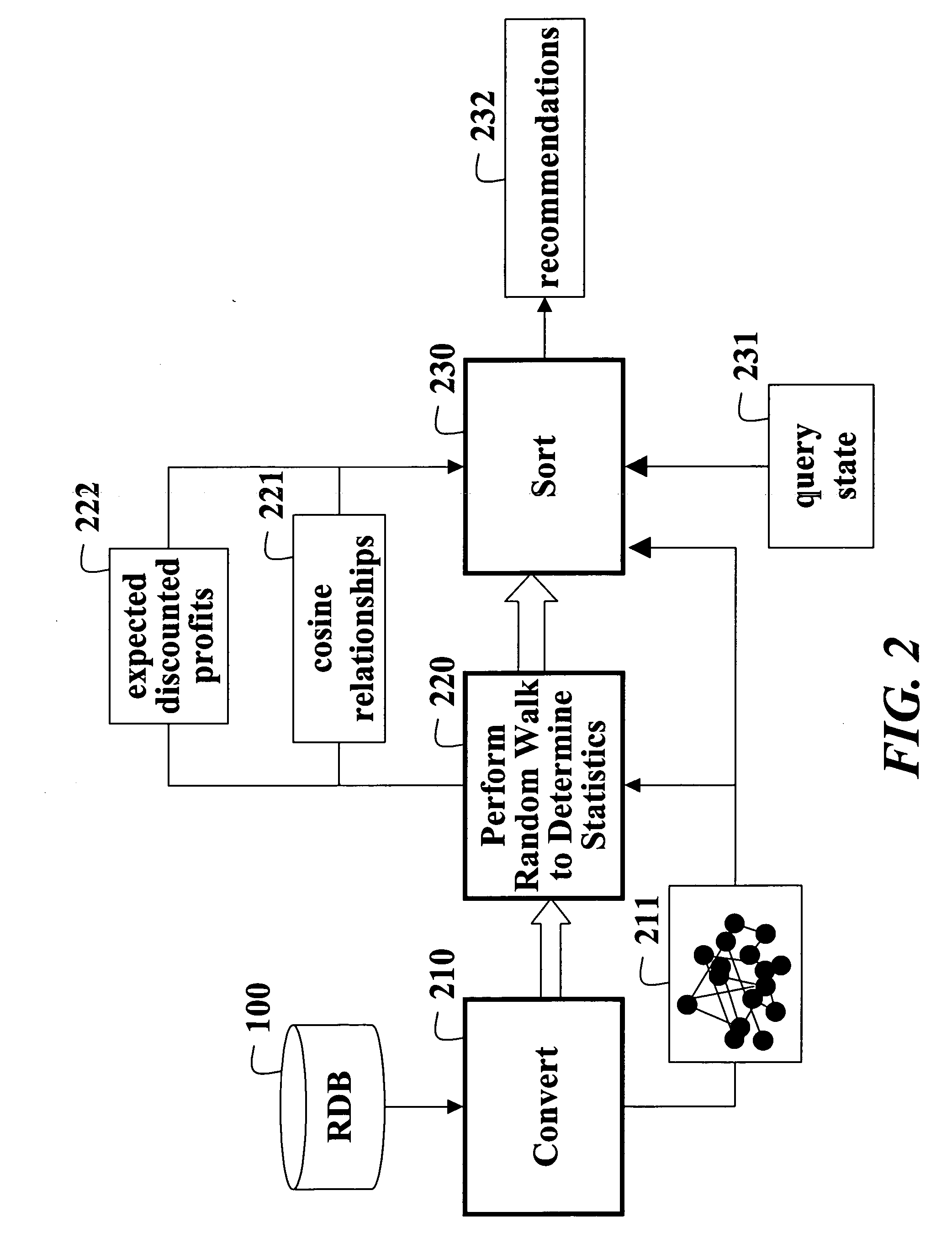
Collaborative filtering using random walks of Markov chains
InactiveUS20060190225A1Facilitate information retrievalImprove forecastDigital data information retrievalComputation using non-denominational number representationMarkov chainAlgorithm
A collaborative filtering method first converts a relational database to a graph of nodes connected by edges. The relational database includes consumer attributes, product attributes, and product ratings. Statistics of a Markov chain random walk on the graph are determined. Then, in response to a query state, states of the Markov chain are determined according to the statistics to make a recommendation.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
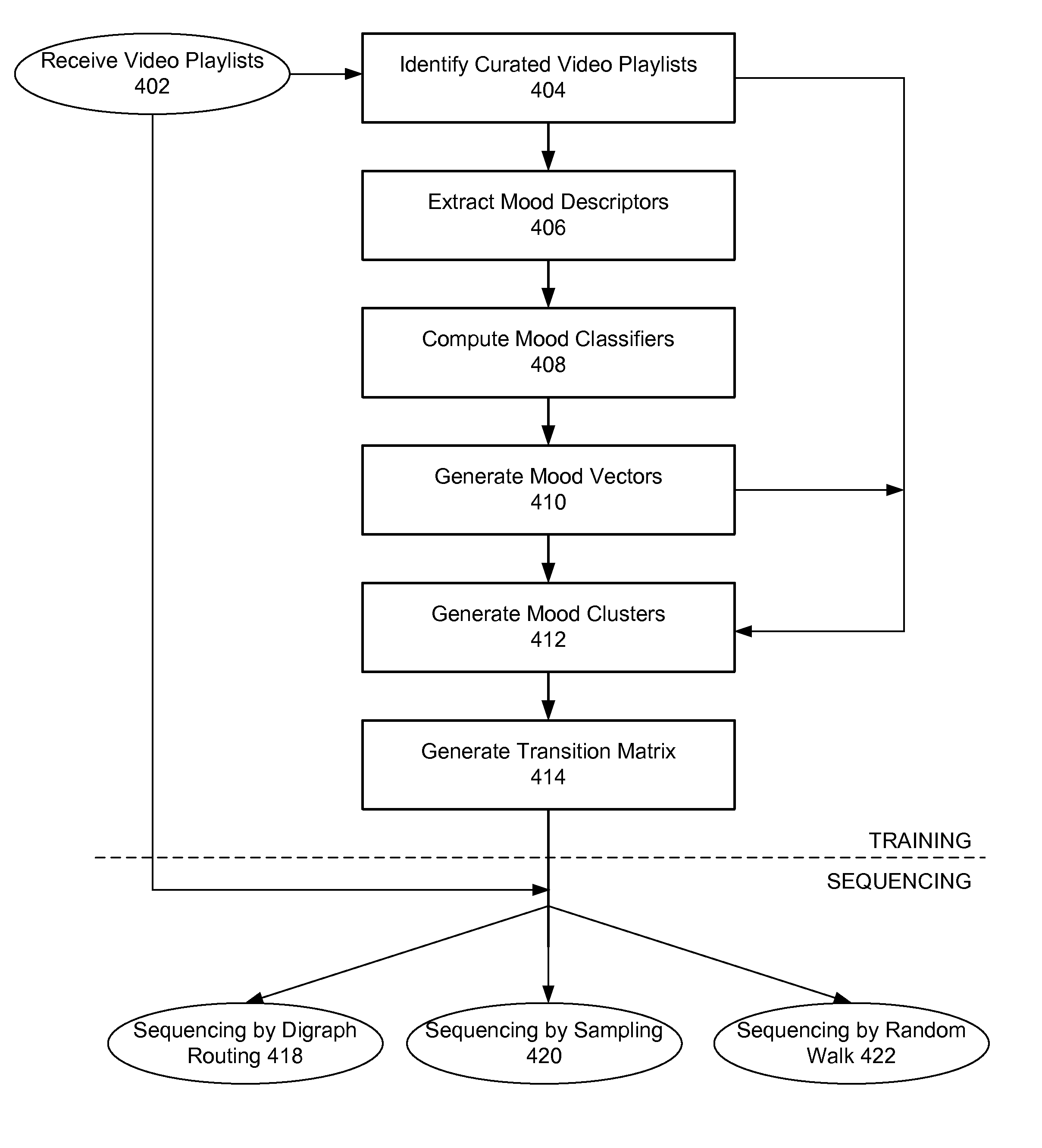
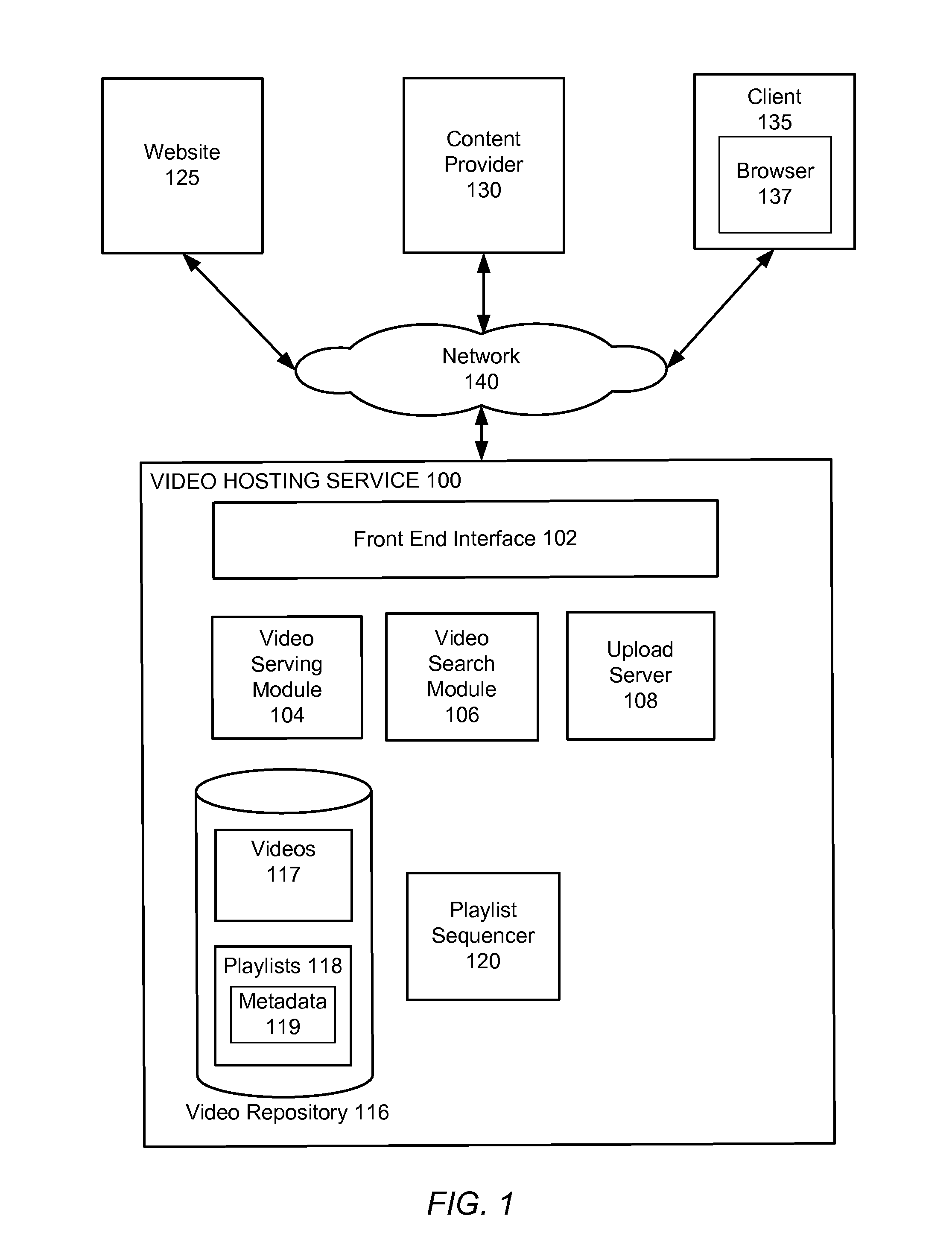
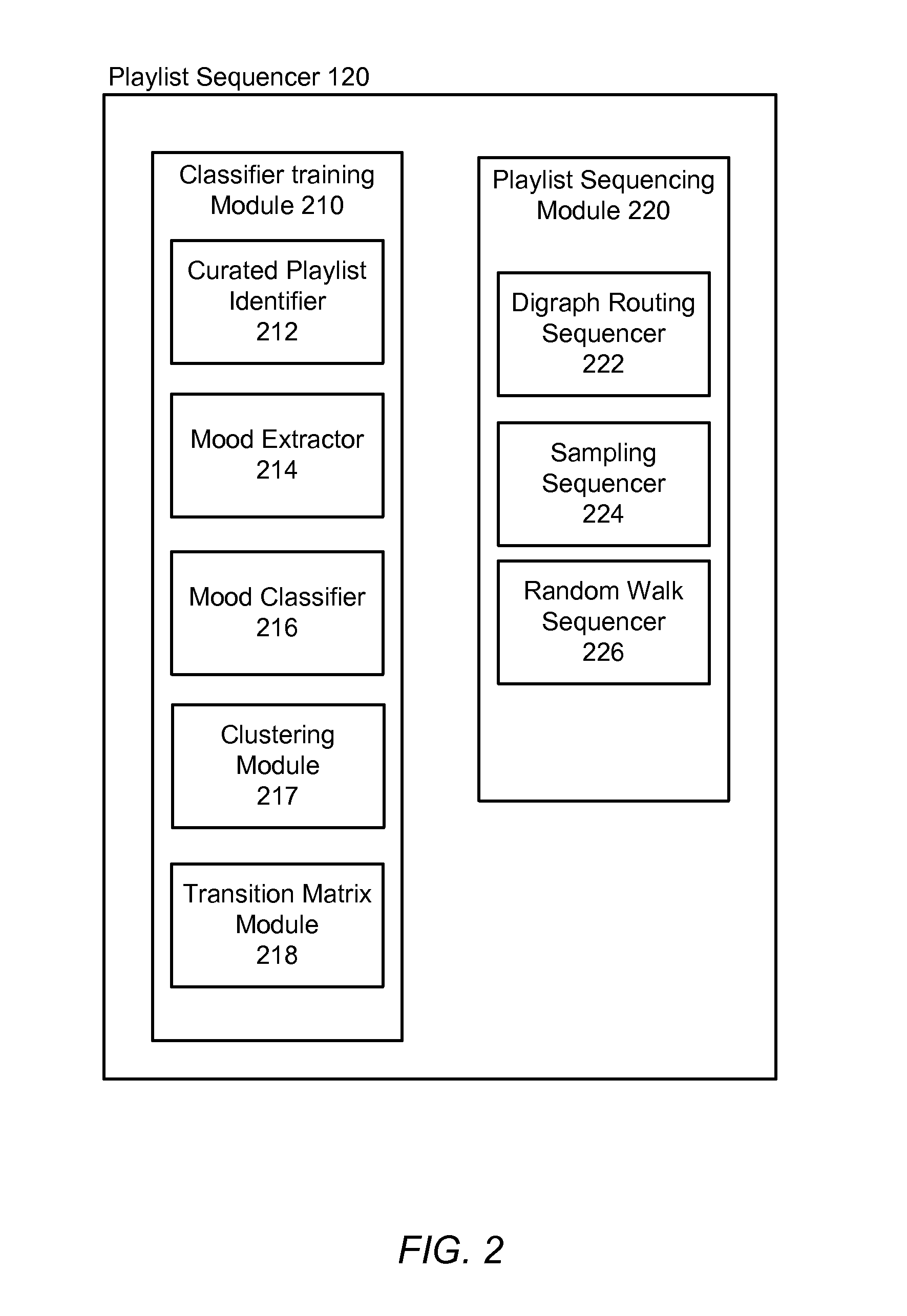
Automatic sequencing of video playlists based on mood classification of each video and video cluster transitions
ActiveUS9165255B1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsRecord information storageMarkov chainSemantic feature
A given set of videos are sequenced in an aesthetically pleasing manner using models learned from human curated playlists. Semantic features associated with each video in the curated playlists are identified and a first order Markov chain model is learned from curated playlists. In one method, a directed graph using the Markov model is induced, wherein sequencing is obtained by finding the shortest path through the directed graph. In another method a sampling based approach is implemented to produce paths on the digraph. Multiple samples are generated and the best scoring sample is returned as the output. In a third method, a relevance based random walk sampling algorithm is modified to produce a reordering of the playlist.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
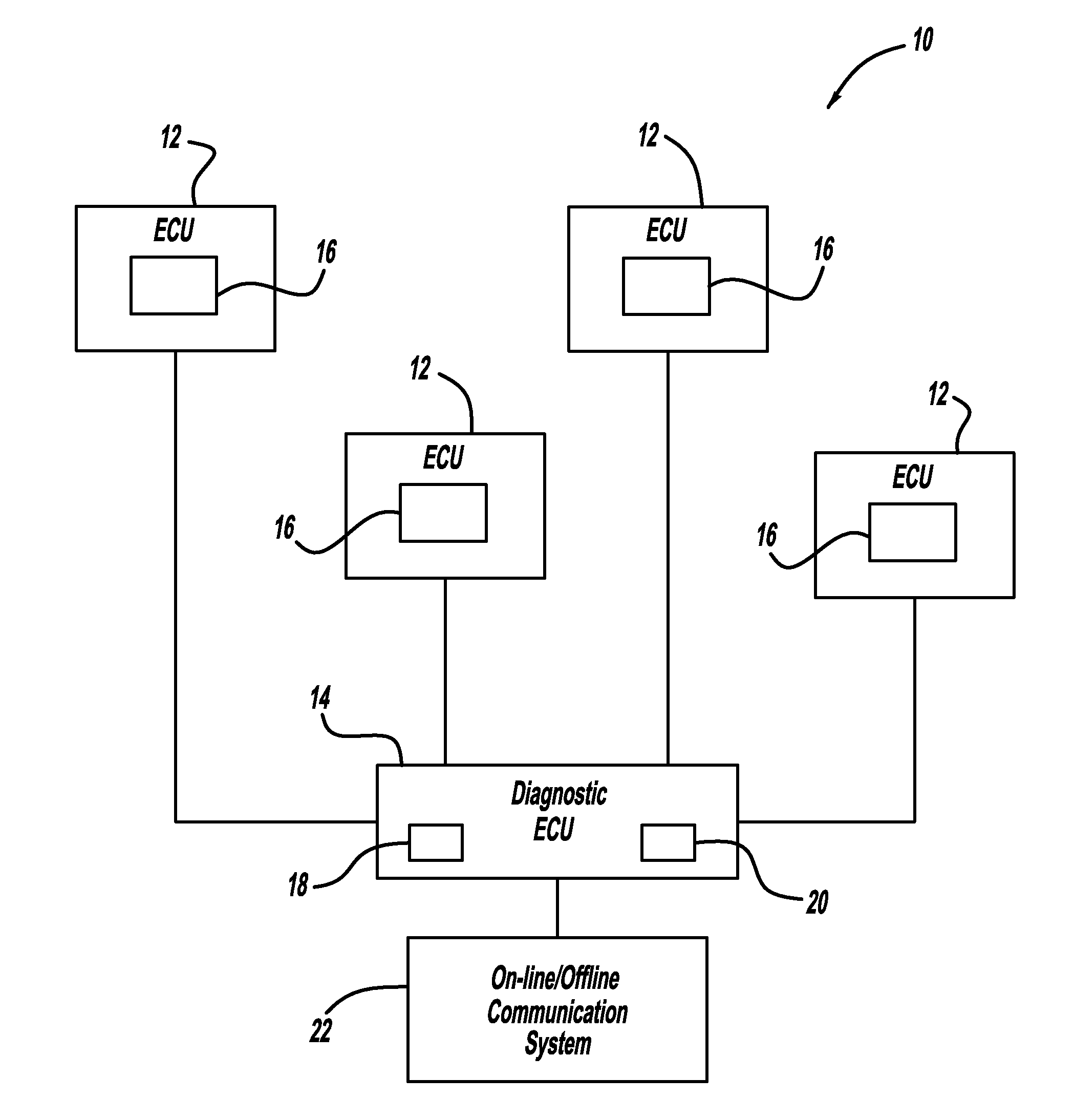
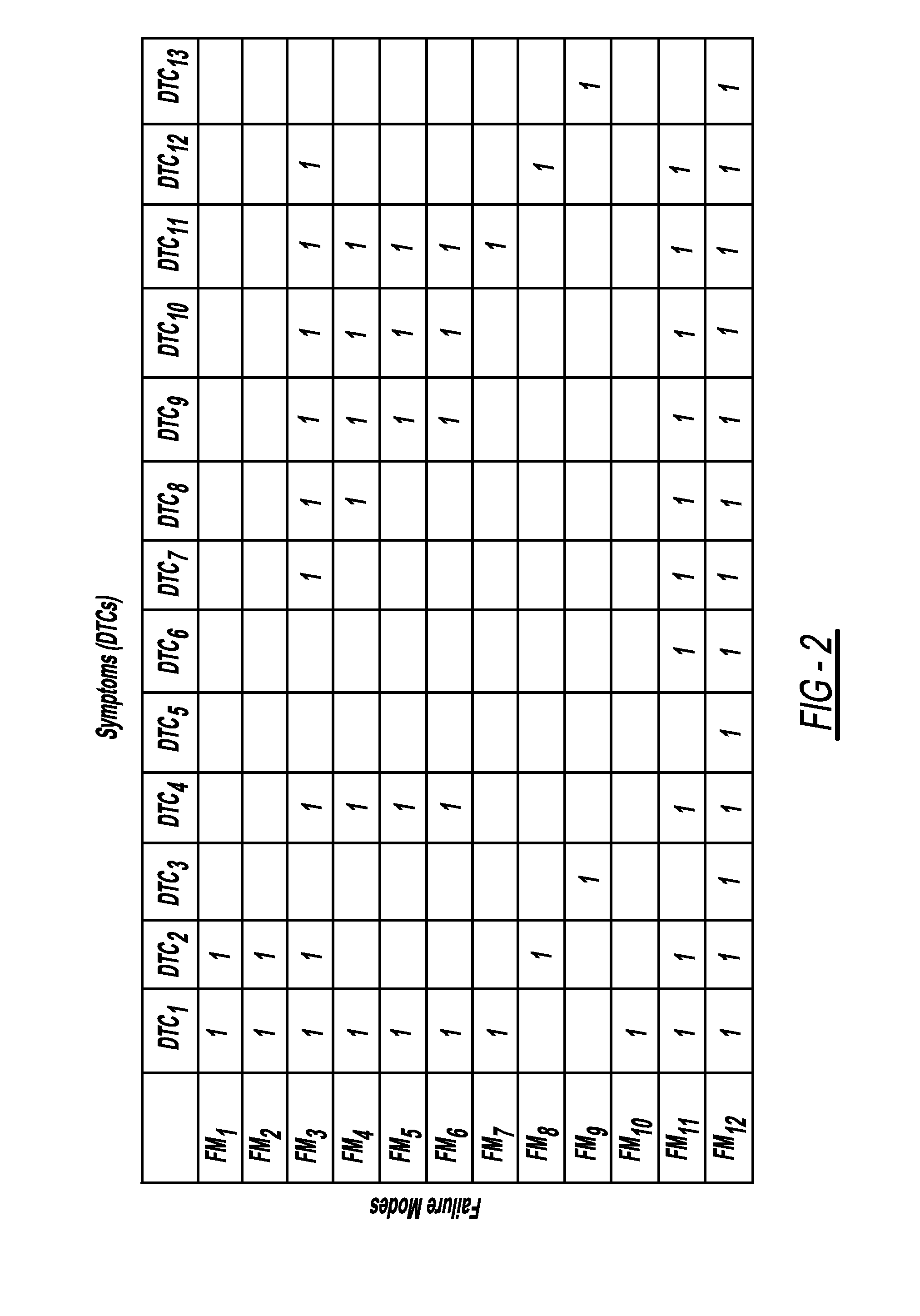
Fault diagnosis and prognosis using diagnostic trouble code markov chains
ActiveUS20110118932A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMarkov chainState parameter
A system and method for fault diagnosis includes receiving information defining a relationship between failure modes and diagnostic trouble codes and extracting diagnostic trouble code data, including set times, frequency data and diagnostic trouble code sequence information for a plurality of diagnostic trouble codes relating to a plurality of failure modes. The system and method further include constructing a Markov chain using the diagnostic trouble code data for each of the plurality of failure modes, training the Markov chain to learn a set of state parameters using the diagnostic trouble code data, and computing a likelihood of a diagnostic trouble code sequence for each of the plurality of failure modes using the trained Markov chains.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
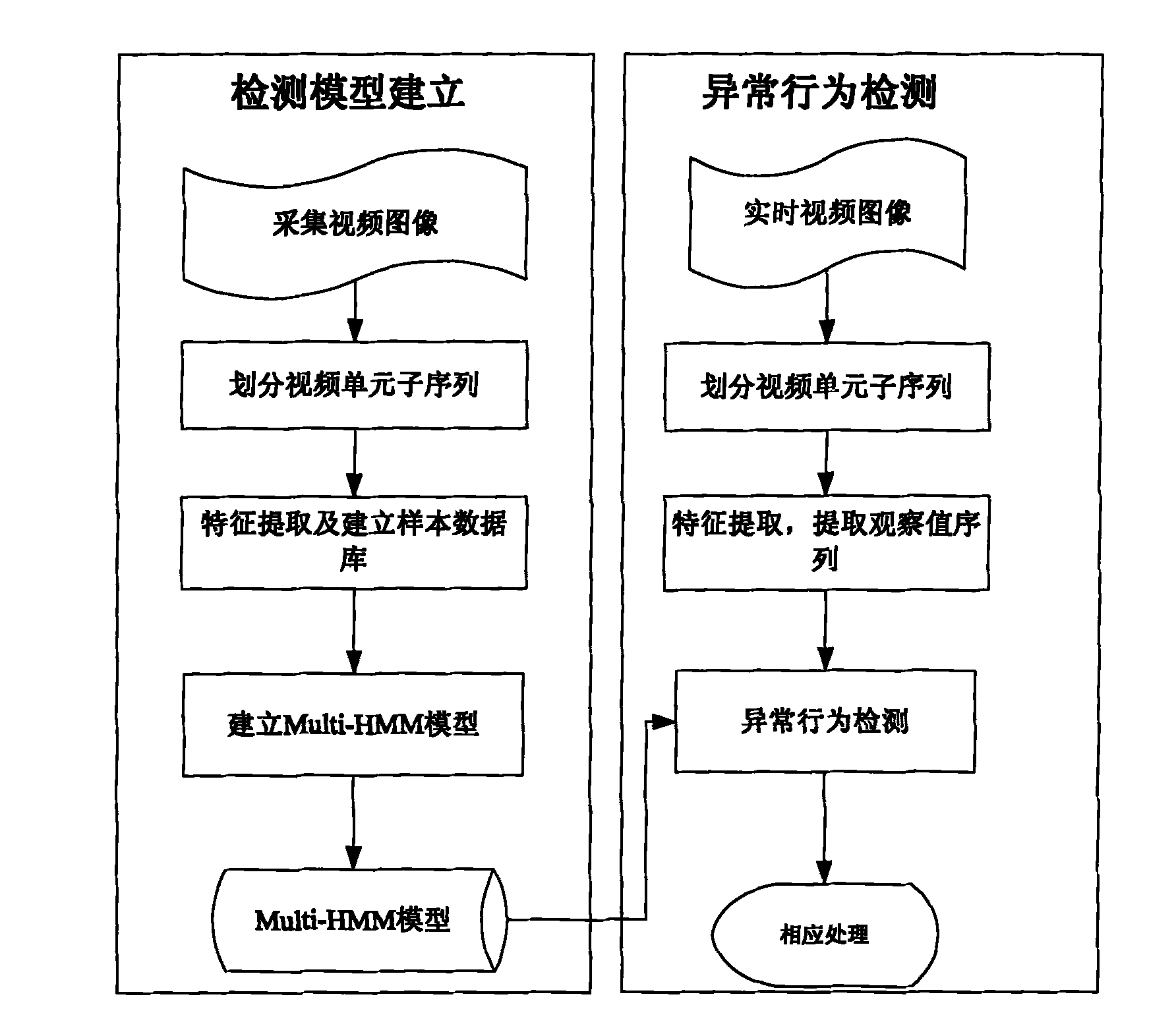
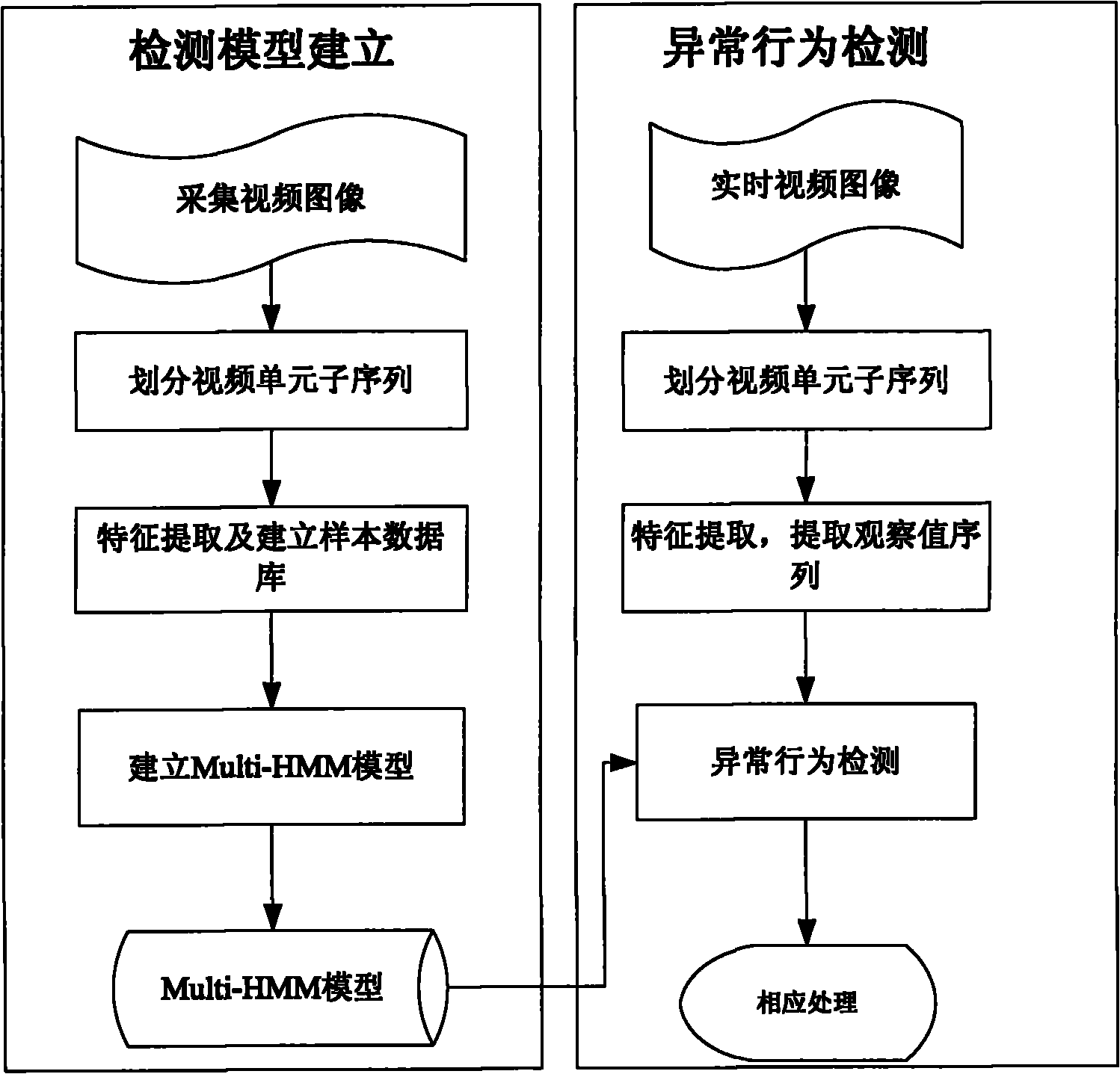
Detection method based on group environment abnormal behavior
InactiveCN101872418AImprove detection efficiencyImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsMarkov chainFeature extraction
The invention belongs to a detection method based on a group environment abnormal behavior in the technical field of computer motion image identification and monitoring, comprising the following steps of: dividing video unit subsequences in the establishment of a detection model, extracting characteristics, establishing a sample database and establishing an Multi-HMM model; extracting the sequence of each observed value from a video sequence of the current monitoring scene in abnormal behavior detection, confirming the optimal hidden Markov chains corresponding to the sequences of the observed values, and judging and warming abnormal behaviors. By accurately and rapidly extracting the dynamic changing characteristic of a video sequence on the frequency domain along with the change of time based on the whole angle and automatically detecting abnormal behaviors under group environments in real time according to the established model, the invention achieves the accuracy rate of about 90 percent, thereby having the characteristics of accurately and rapidly extracting the behavior characteristic of the current monitored scene, being widely used for detecting the abnormal behaviors happened under the group environments, having high detection efficiency, accuracy and reliability, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi Markov chain-based content recommendation method
InactiveCN101826114AHigh precisionImprove scalabilityMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationMarkov chain
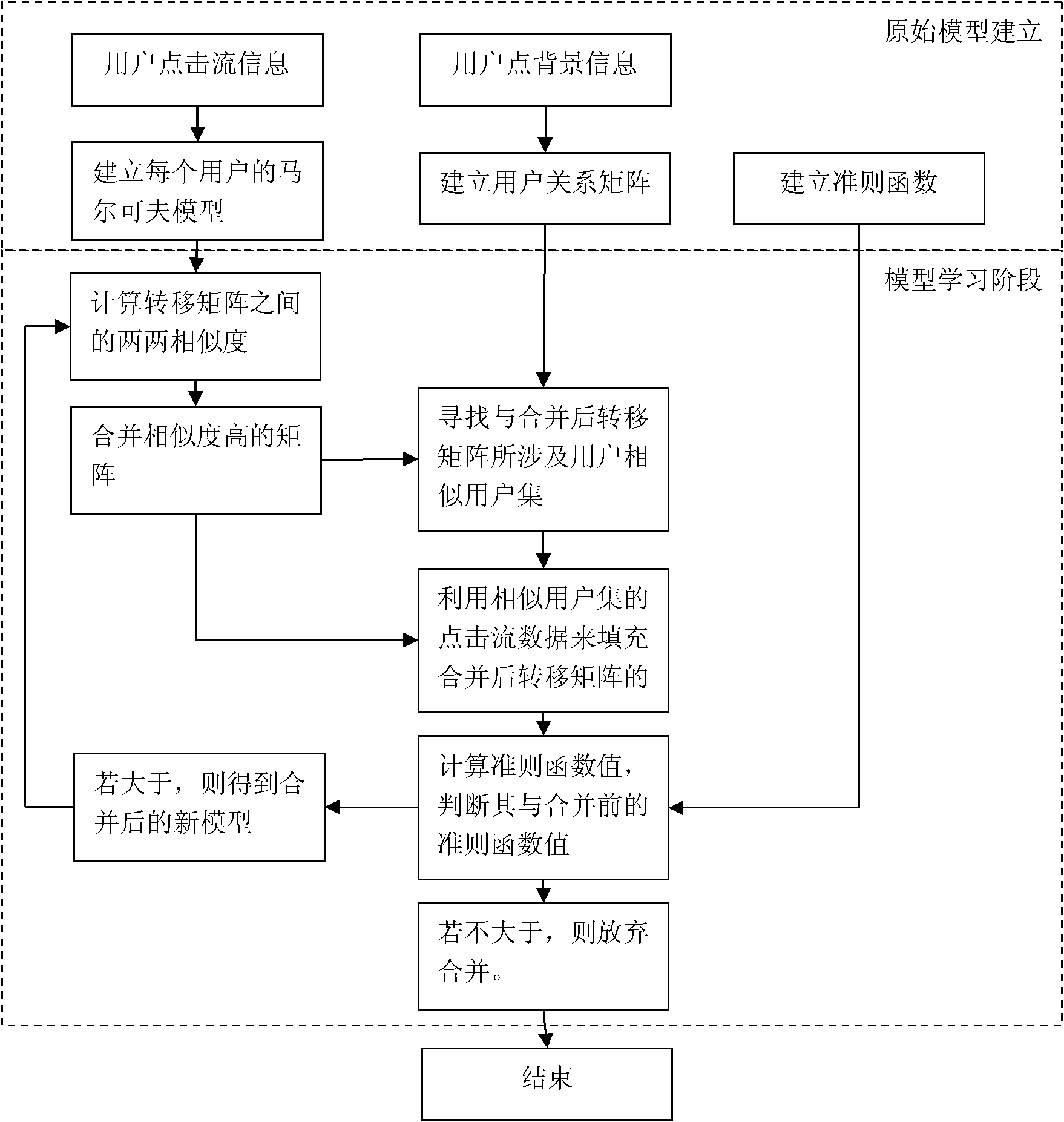
The invention discloses a multi Markov chain-based content recommendation method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing Markov models by using information of click stream of a user and establishing a user relationship matrix by using the background information of the user; combining the similar Markov models; and filling sparse items in the zero line of the combined Markov model according to the click stream of the similar user aggregates obtained by the user relationship matrix. The content recommendation method is individualized information recommendation technology on the network, and by the method, the interesting commodity and information are recommended to the user according to the characteristics of the interest, the behavior and the personal information. The interesting information and commodity are recommended to the user in a vast database, so that the browsing time is reduced, the problems of less user rating items and more sparse items in the collaborative recommendation are solved and the accuracy of the recommendation is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Equipment integration system reliability analysis method based on dynamic fault tree
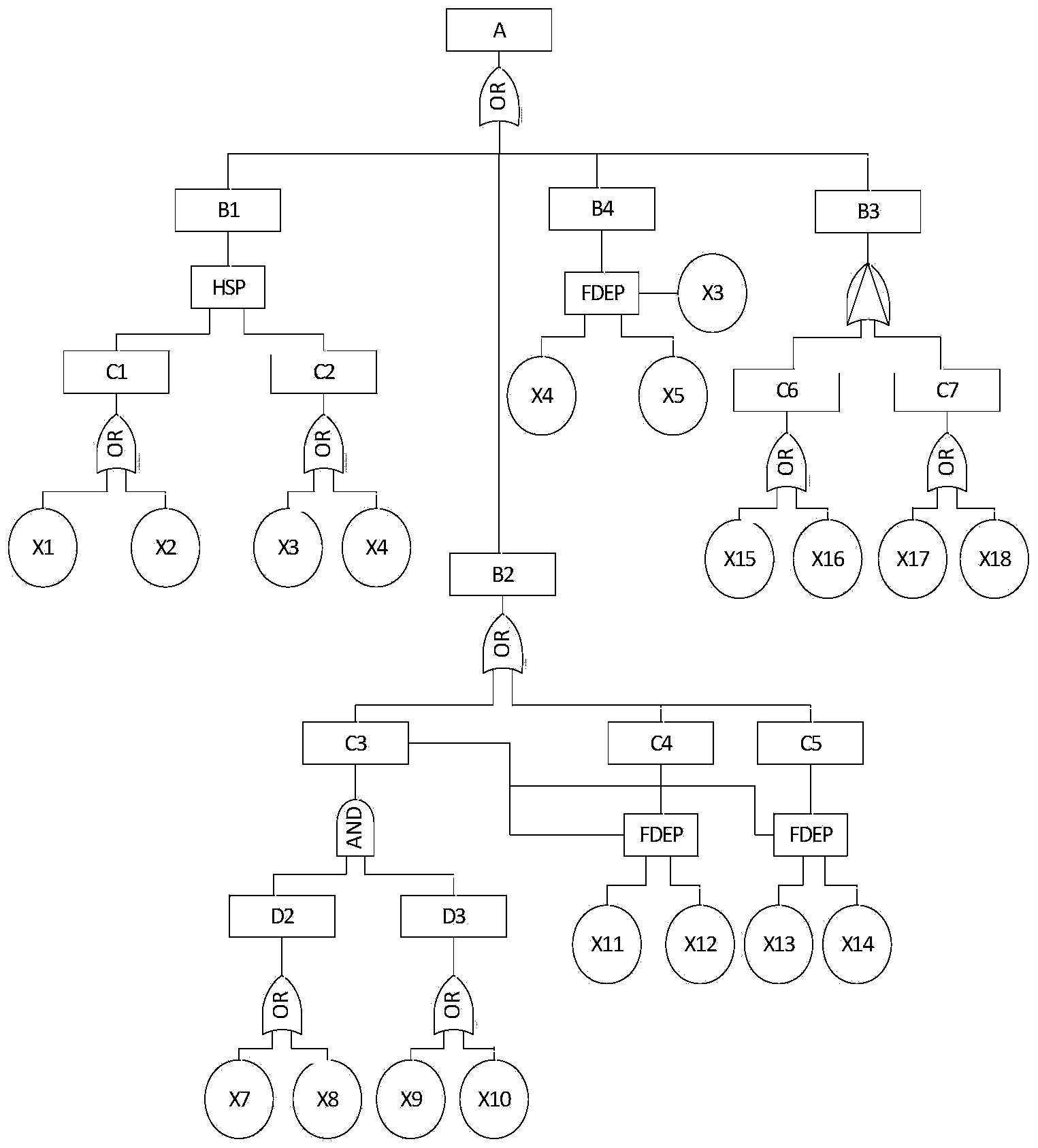
InactiveCN104392072AImprove efficiencyImprove analysis efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsMarkov chainStructure function
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Network application encrypted traffic recognition method and device based on protocol attributes
The invention relates to a network application encrypted traffic recognition method and device based on protocol attributes, and belongs to the technical field of computer network service security. The device comprises an offline training module and an online identification module. The offline training module is composed of a data set obtaining module, a message type fingerprint establishment module based on a second order Markov chain and a certificate length clustering module. A training set is obtained through a data set obtaining module. Application fingerprints are obtained and stored according to the training set by the message type fingerprint establishment module based on the second order Markov chain; clustering results and application certificate cluster distribution probability are obtained and stored according to the training set by the certificate length clustering module. The offline training module is composed of a network traffic capturing module and a recognition module. The recognition module matches the network traffic obtained by the capturing module with a stored application fingerprint library one by one; moreover, the certificate clustering results are taken into consideration, thus obtaining a recognition probability; the recognition result is an application corresponding to the highest probability. Compared with the prior art, the method and the device have the advantage of improving the recognition accuracy and efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Stochastic inversion of geophysical data for estimating earth model parameters
A computer implemented stochastic inversion method for estimating model parameters of an earth model. In an embodiment, the method utilizes a sampling-based stochastic technique to determine the probability density functions (PDF) of the model parameters that define a boundary-based multi-dimensional model of the subsurface. In some embodiments a sampling technique known as Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is utilized. MCMC techniques fall into the class of “importance sampling” techniques, in which the posterior probability distribution is sampled in proportion to the model's ability to fit or match the specified acquisition geometry. In another embodiment, the inversion includes the joint inversion of multiple geophysical data sets. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a computer system configured to perform a method for estimating model parameters for accurate interpretation of the earth's subsurface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Improved-gray-Markov-model-based power equipment fault prediction method
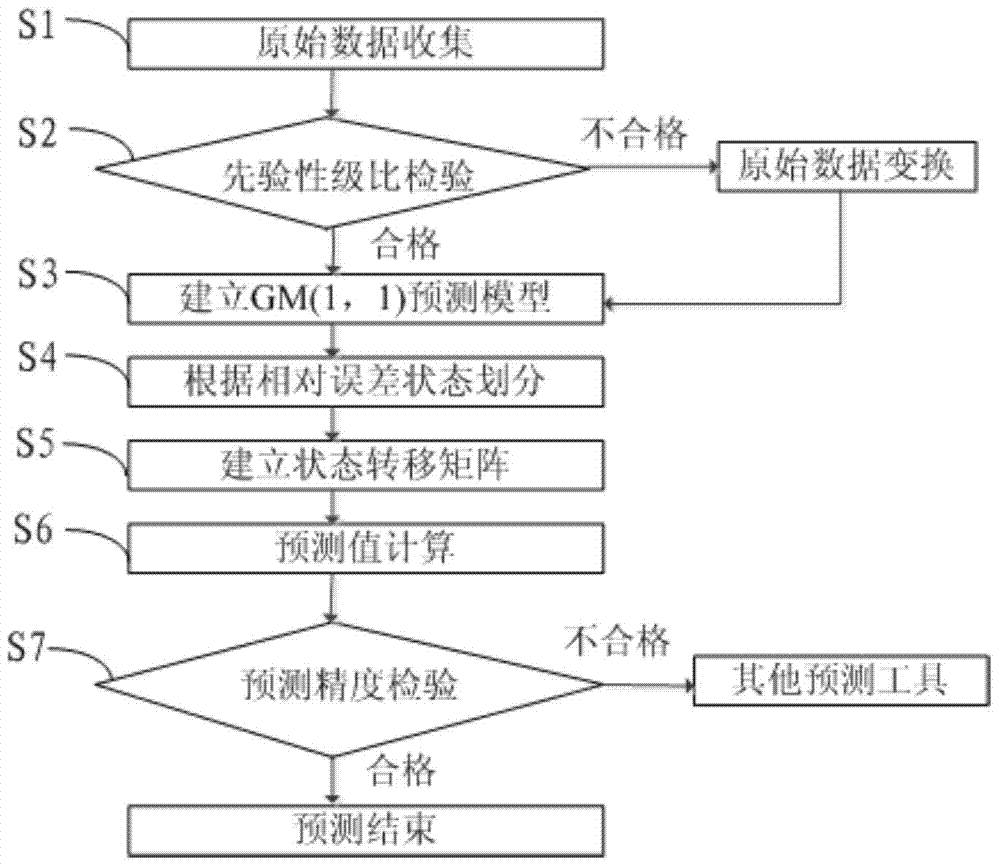
Provided in the invention is an improved-gray-Markov-model-based power equipment fault prediction method. The method comprises: original data collection is executed on power equipment; apriority step ratio checking on is executed according to fault interval data in the original data; under the circumstances that the apriority step ratio checking is done successfully, a GM (1,1) gray model is established directly; under the circumstances that the apriority step ratio checking is not done successfully, original data transformation is executed and then a GM (1,1) gray model is established; according to the markov chain property, an initial prediction value is determined based on the GM (1,1) gray model, state division is carried out, and then a state transition matrix is established, thereby obtaining a Markov prediction model; and an improved Markov prediction model is obtained based on the obtained Markov prediction model, and a calculation result of the gray model is corrected by using the improved Markov prediction model, thereby obtaining a final prediction value.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
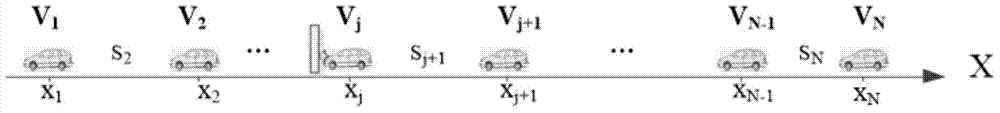
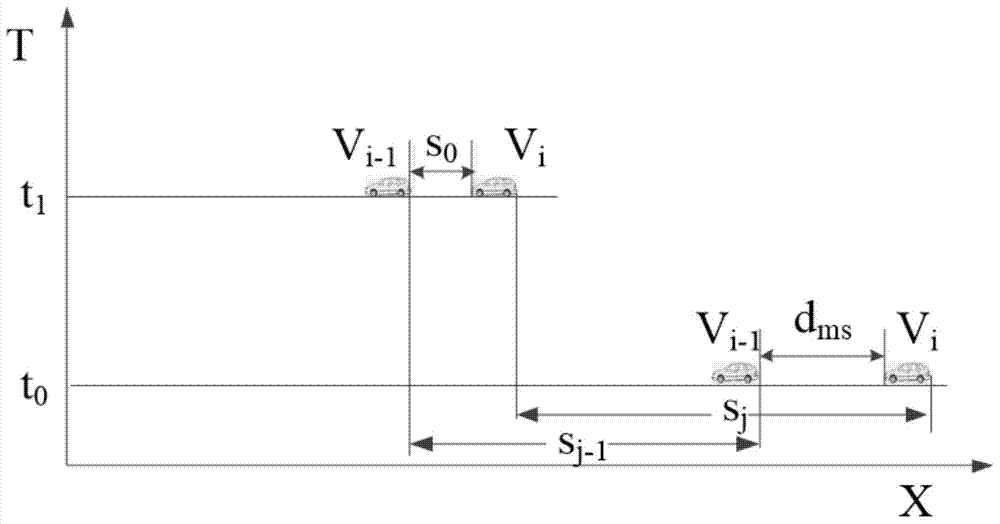
Collision prediction method based on vehicle distance probability distribution for internet of vehicles
InactiveCN103544850AImprove accuracyImprove scalabilityAnti-collision systemsExtensibilityPrediction algorithms
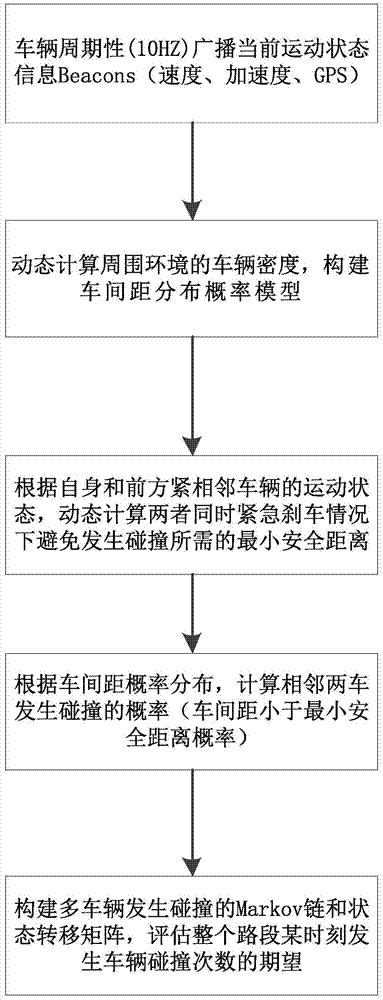
The invention discloses a vehicle collision prediction method based on vehicle distance probability distribution under a highway model. The method includes the steps of a vehicle periodically (under 10Hz) broadcasts current motion statuses Beacons (speed, acceleration and GPS); the density of vehicles in the surrounding environment is dynamically calculated to build a vehicle distance distribution probability model; a minimum safety distance required to avoid collision when two adjacent vehicles emergently brake is dynamically calculated according the motion status of one vehicle and the motion status of the adjacent vehicle ahead; the collision probability (the probability for the vehicle distance being smaller than the minimum safety distance) of the two adjacent vehicles is calculated according to vehicle distance probability distribution; a multi-vehicle collision Markov chain and a state transition matrix are established, and expectation for the number of vehicle collisions on the whole section at certain time is estimated. The method is high in innovation level and extensibility; the defects of poor GPS data precision and instability in the current vehicle-location-based collision prediction algorithm are well made up; the method plays an excellent role especially in GPS satellite signal blind areas and has promising application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY USTC
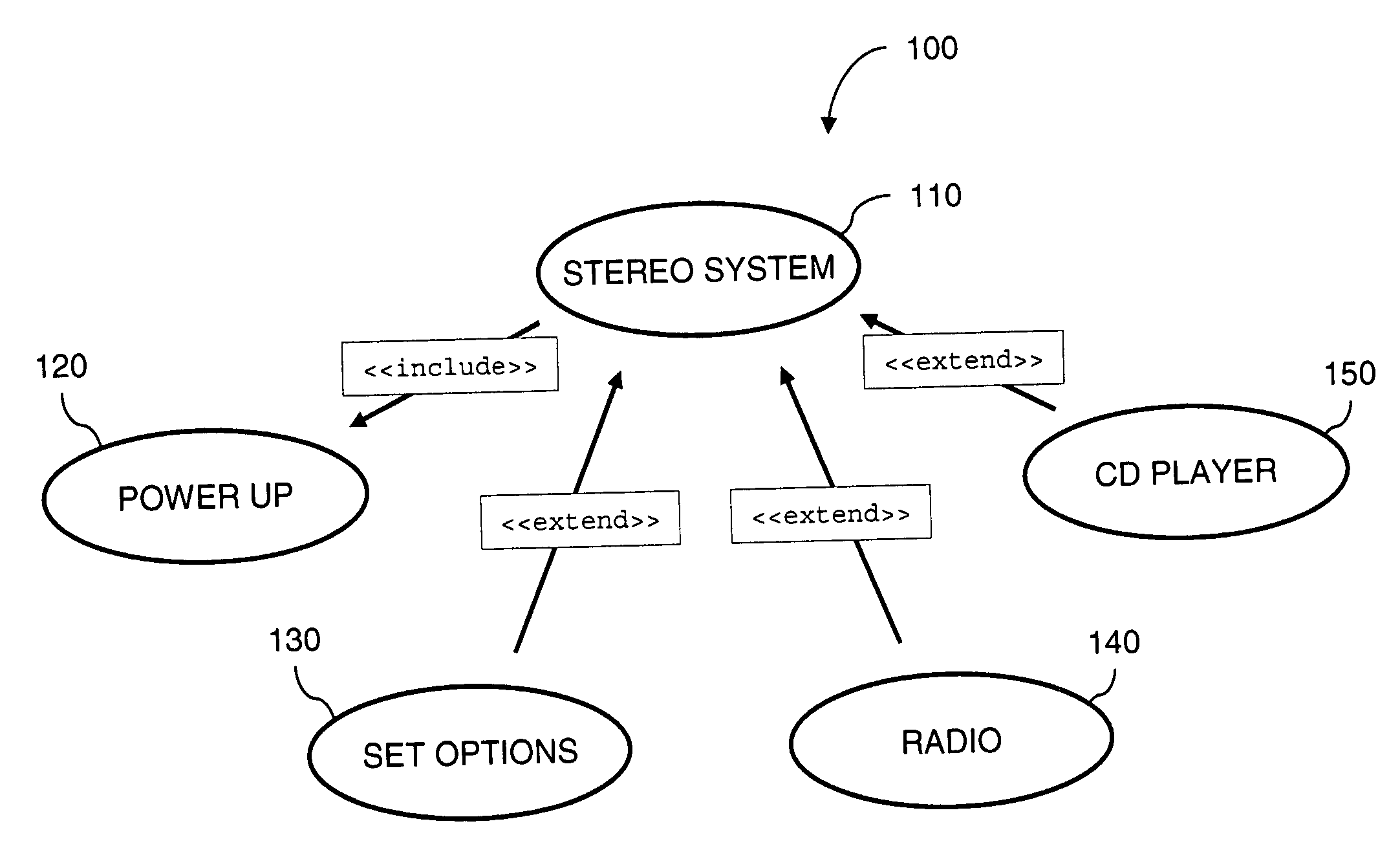
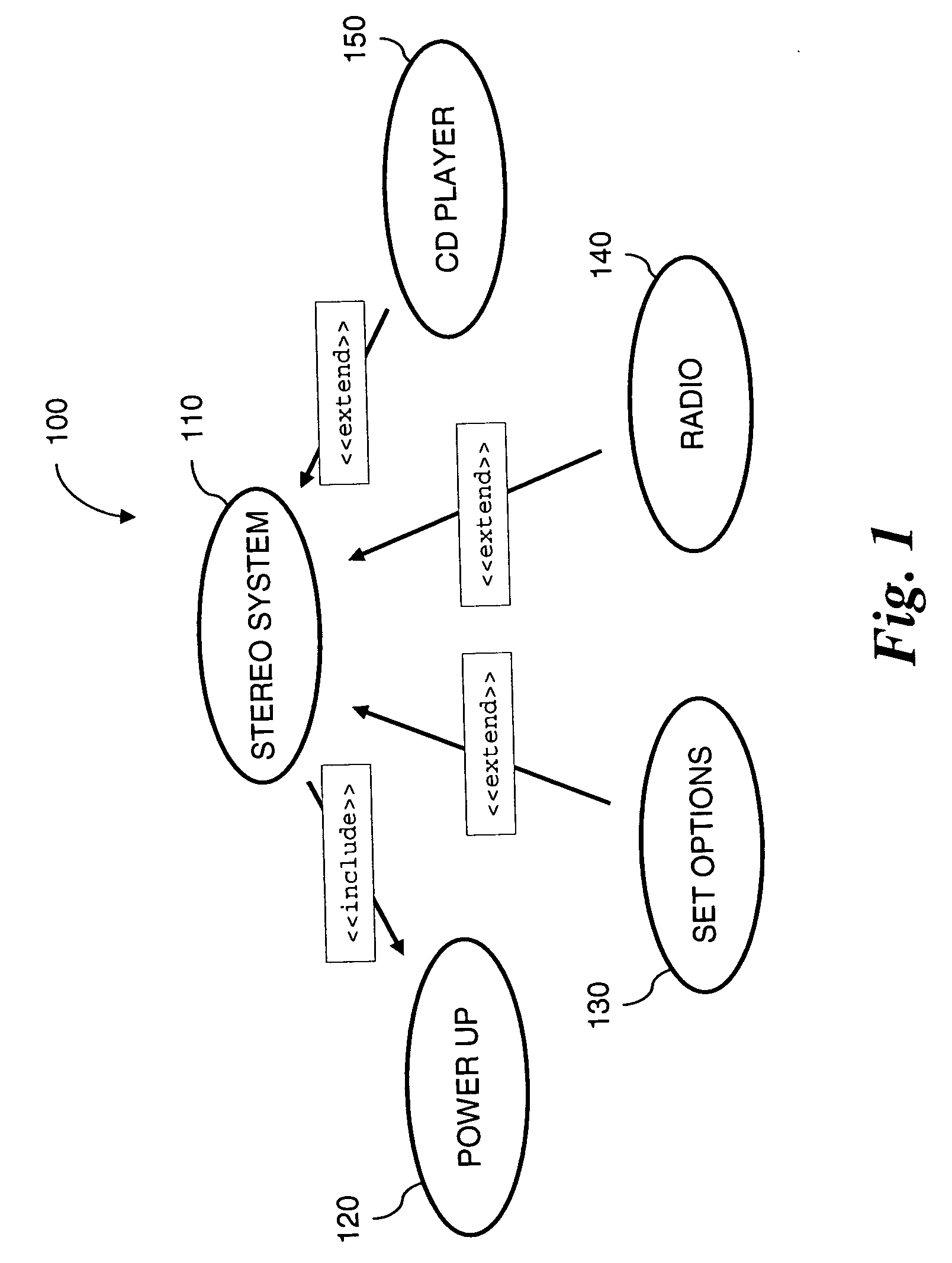
Generating performance tests from UML specifications using markov chains
InactiveUS20060253839A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware development processMarkov chain
An automated approach to generating test cases for performance testing may be used for test case planning, early in the software development process, when a UML use case model and its activity diagram refinement are specified. The planned performance tests are executed later in the software development process, after the system is developed. The use case model is annotated with operation arrival rates and departure rates. Deterministic state testing (DST) generation and execution are applied for performance test generation and execution. In addition, a technique is described to generate the most likely test scenarios, labeling each arch in the activity diagram with transition probabilities and applying a breadth first search algorithm to select the most likely paths to be tested for each state generated by the DST algorithm.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Markov chain and neural network based traffic congestion state combined prediction method
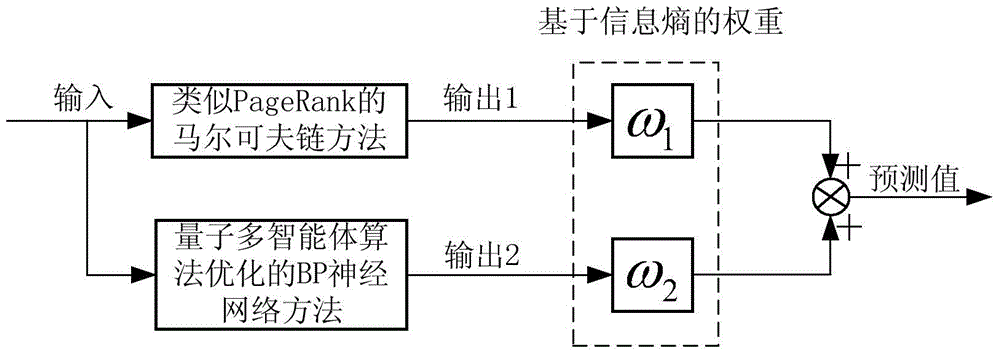
InactiveCN104616498AApplicable congestion state predictionImprove forecast accuracyDetection of traffic movementBiological neural network modelsMarkov chainNerve network
The invention relates to a Markov chain and neural network based traffic congestion state combined prediction method. The Markov chain and neural network based traffic congestion state combined prediction method comprises the following steps of 1 adopting a similar-PageRank Markov chain method to perform traffic congestion state prediction so as to obtain a first prediction result, 2 adopting a quantum multi-agent algorithm optimized back-propagating (BP) neural network method to perform traffic congestion state prediction so as to obtain a second prediction result, 3 obtaining the weight of the first prediction result and the weight of the second prediction result based on information entropy, 4 obtaining a final prediction result according to the first prediction result, the second prediction result and the corresponding weights. Compared with the prior art, the Markov chain and neural network based traffic congestion state combined prediction method has the advantages of being good in prediction real-timeliness, high in accuracy, good in extension and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Monitoring system behavior using empirical distributions and cumulative distribution norms
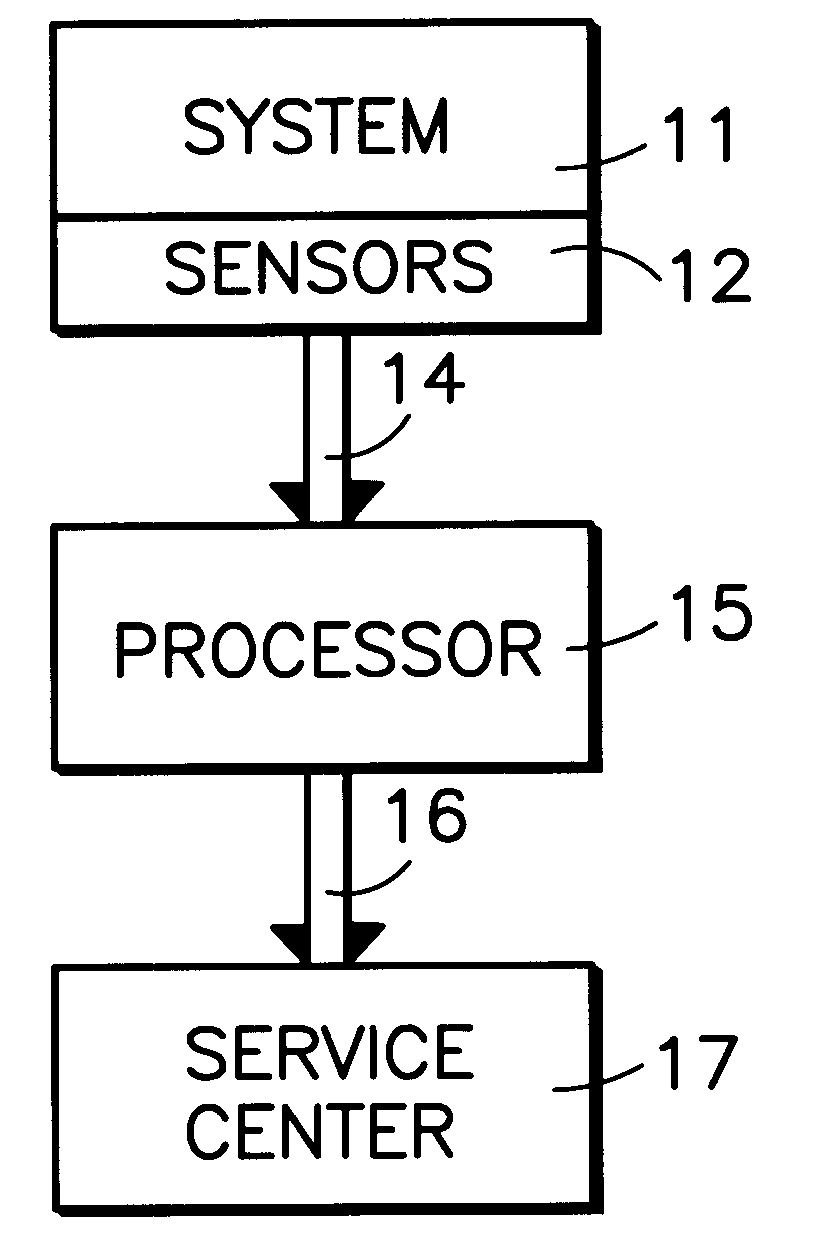
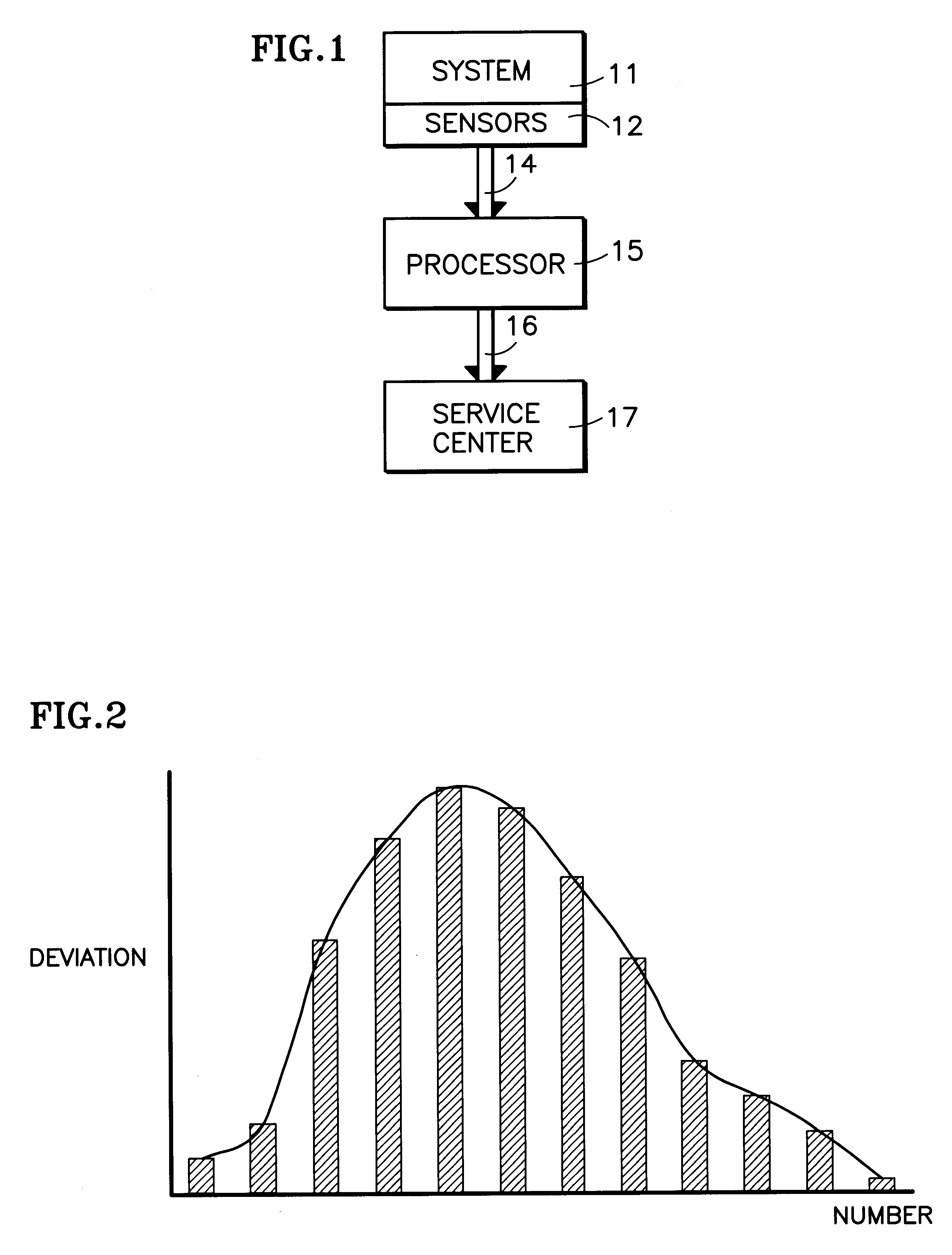
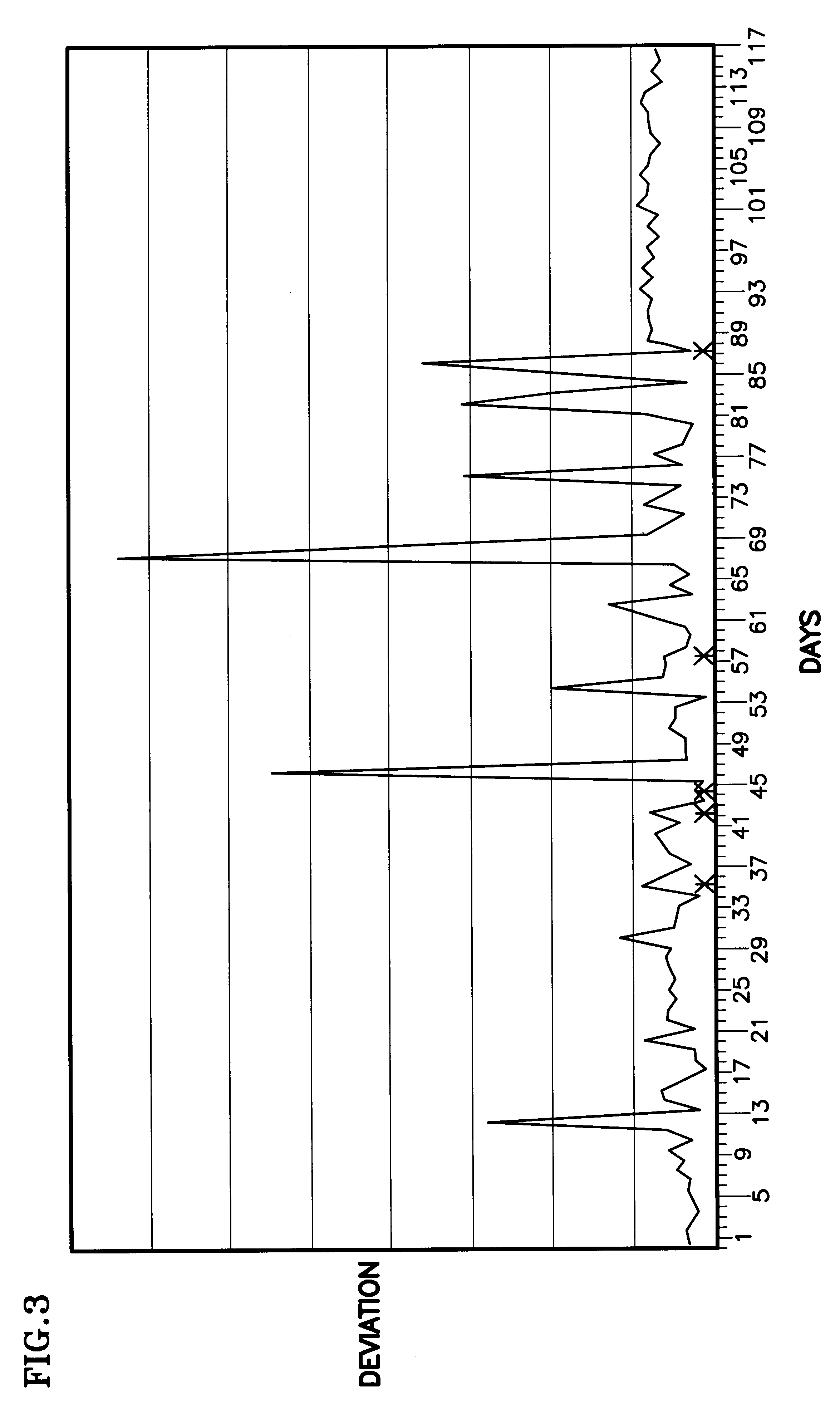
InactiveUS6477485B1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceElectric testing/monitoringMarkov chainElevator system
Sensors (12) attached to various parameters of a system (11), such as an elevator system or a chiller, provide values (14) of corresponding parameters which are utilized to build (15) an empirical distribution of the process, such as by means of bootstrapping methodology using a five-dimensional Markov chain model. In normal operation thereafter, the sensors are read periodically and in response to events, and an abnormality is determined by comparison of current information against the empirical distribution of the process. Deviations from normal behavior provide quantitative measure of system malfunction or abnormality; eliminating data from one or more sensors in each iteration of processing identifies one or more sensors associated with the abnormality. By utilizing cumulative distribution norm of deviation from normal behavior, the relative health of one system can be compared with the relative health of other, similar or dissimilar systems.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Electric network metering early-warning system and method based on load characteristic pre-estimation
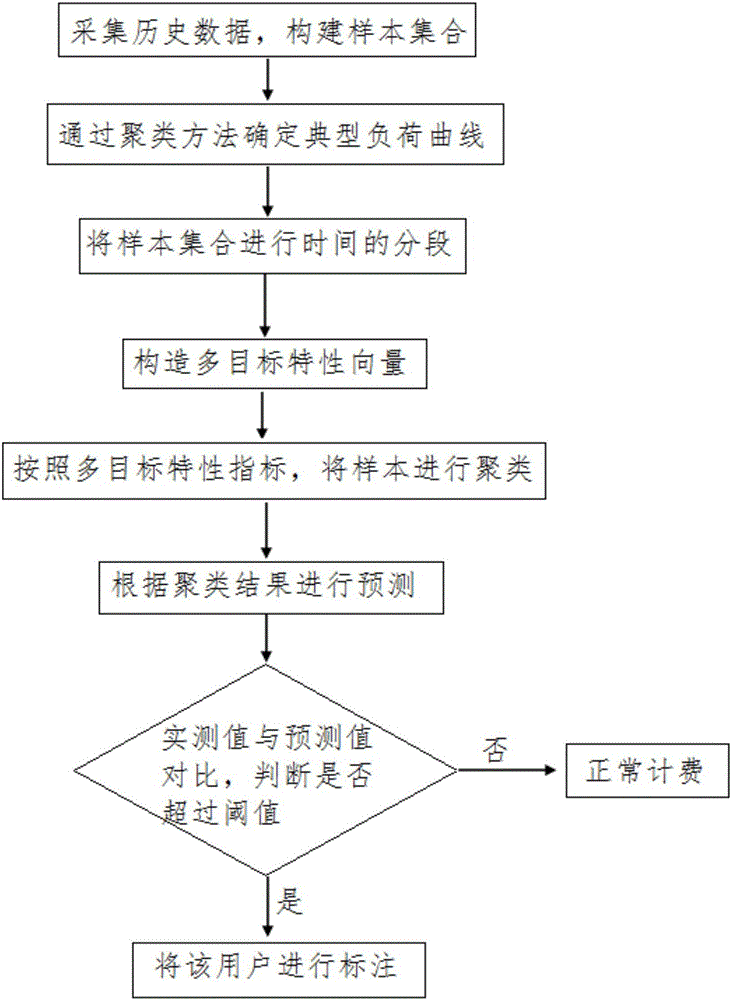
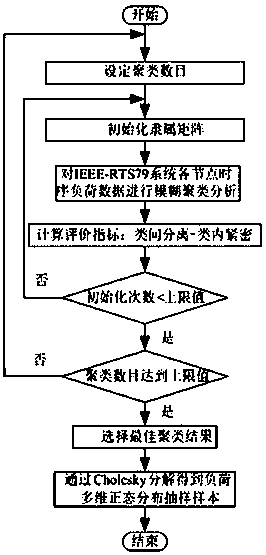
ActiveCN105825298AImprove orderReflect the characteristics of the time period of the dayForecastingFeature vectorMarkov chain
The invention discloses an electric network metering early-warning system and method based on load characteristic pre-estimation. Historical data of power load is collected, a load curve is drafted, a sample set is constructed, and a K-MEDOIDS algorithm is used to determine a typical load curve of a power user; sample data is segmented in a unified manner according to time interval, multiple targets are used as characteristic vectors, and a characteristic index is selected from a typical daily load curve; and a clustering result is combined with a Markov chain to establish a prediction chain, prediction is carried out, a prediction result is compared with actual measurement data detected by a metering device to determine whether invalid power utilization occurs and whether the metering device works normally, and it is determined that invalid power utilization occurs or the metering device is abnormal, invalid power utilization or the metering device is marked, and early warning is carried out.
Owner:梁海东
Optimizing layout of an application on a massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS8117288B2Minimize timeShorten the timeDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsMarkov chainSupercomputer
A general computer-implement method and apparatus to optimize problem layout on a massively parallel supercomputer is described. The method takes as input the communication matrix of an arbitrary problem in the form of an array whose entries C(i, j) are the amount to data communicated from domain i to domain j. Given C(i, j), first implement a heuristic map is implemented which attempts sequentially to map a domain and its communications neighbors either to the same supercomputer node or to near-neighbor nodes on the supercomputer torus while keeping the number of domains mapped to a supercomputer node constant (as much as possible). Next a Markov Chain of maps is generated from the initial map using Monte Carlo simulation with Free Energy (cost function) F=Σi,jC(i,j)H(i,j)− where H(i,j) is the smallest number of hops on the supercomputer torus between domain i and domain j. On the cases tested, found was that the method produces good mappings and has the potential to be used as a general layout optimization tool for parallel codes. At the moment, the serial code implemented to test the method is un-optimized so that computation time to find the optimum map can be several hours on a typical PC. For production implementation, good parallel code for our algorithm would be required which could itself be implemented on supercomputer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Vehicle operating condition multi-scale predicting method based on Markov chain
The invention discloses a vehicle operating condition multi-scale predicting method based on the Markov chain. The method establishes a Markov chain prediction model for the vehicle operating condition. The method comprises the steps of computing a state transferring matrix by maximum likelihood estimation according to the history information of vehicle operating condition; performing the vehicle operating condition predicting of different time scales according to the obtained state transferring matrix by utilizing the Markov chain and Monte Carlo analogy method; restoring the predicted outcomes of different time scales into data under a history operating condition sampling frequency through linear interpolation; dividing the predicted outcomes of different time scales into different confidence grades according to simulated sample quantity, and computing the linear weight coefficient under different confidence grades of the predicted outcome every time by adopting a linear weighting method; and merging all the predicted values of each scale of predicted outcome every time according to the weight coefficients and merging the different scales of predicted outcomes under the original data frequency to obtain the vehicle operating condition multi-scale predicting outcome. The vehicle operating condition multi-scale predicting method based on the Markov chain can meet the predicting precision requirements of the vehicle operating condition and the requirements of vehicle real-time control.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
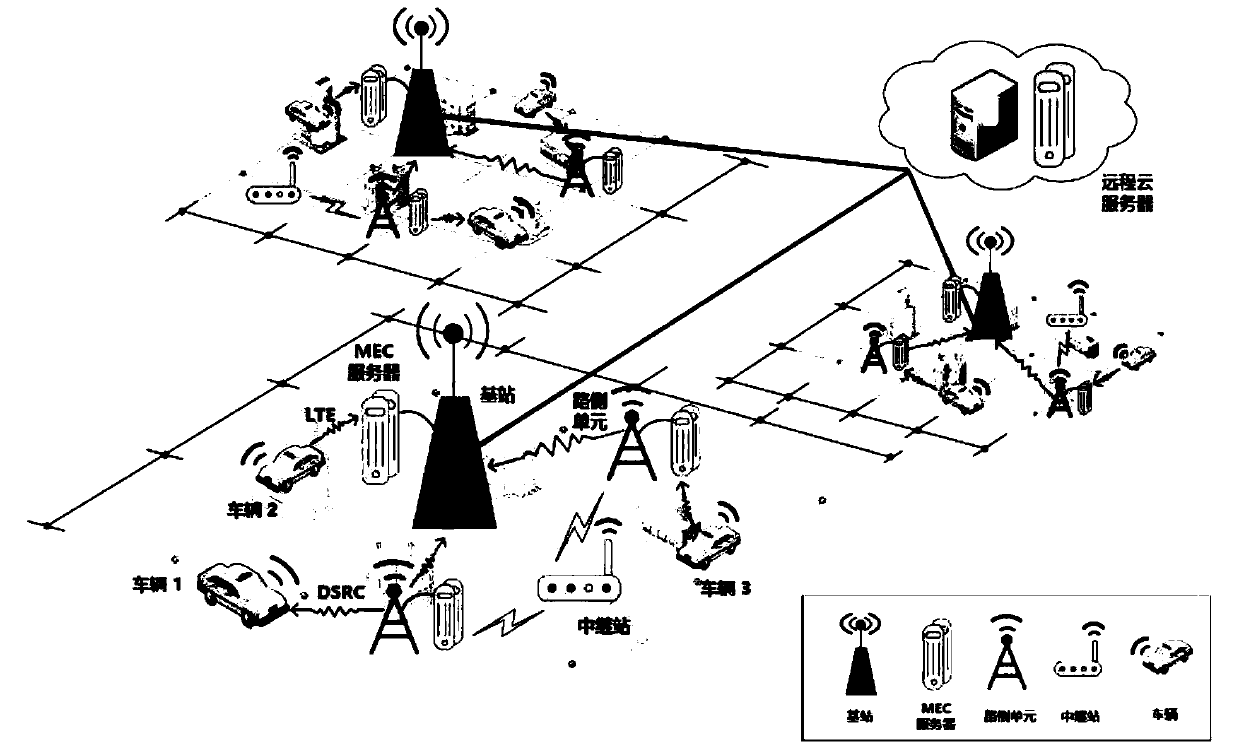
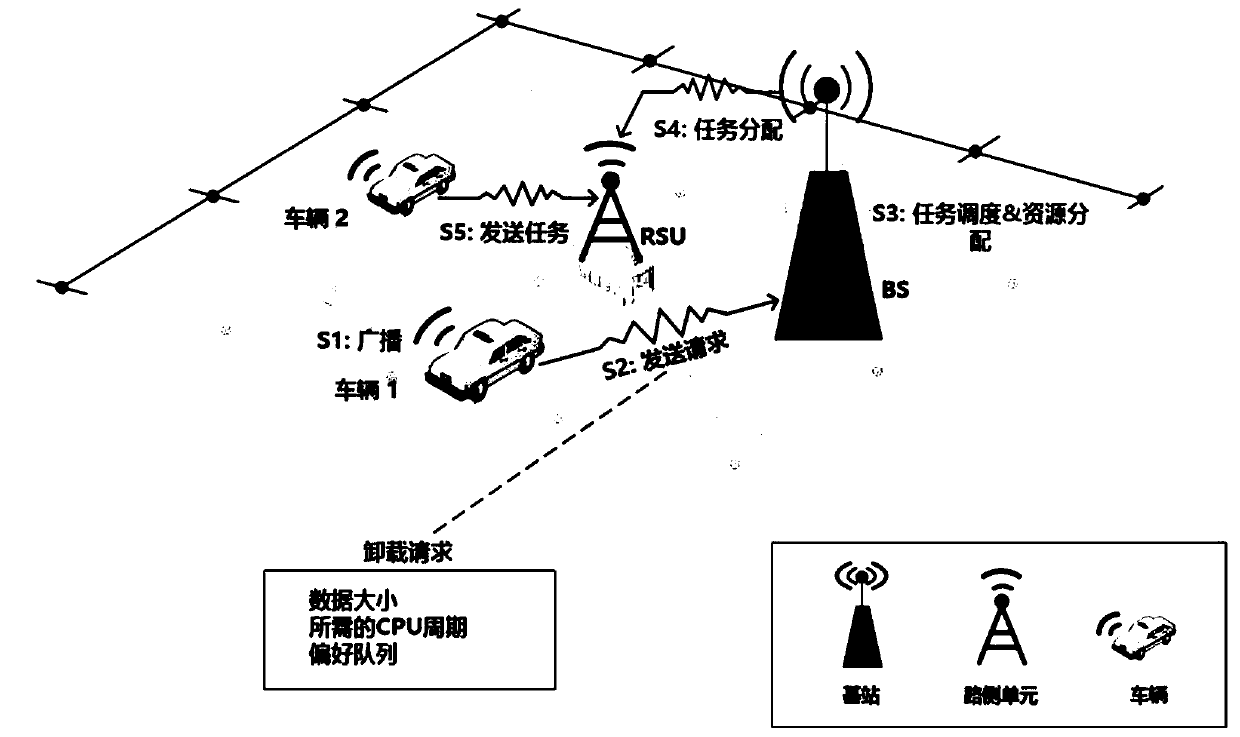
Intelligent computing unloading method under a vehicle-mounted network
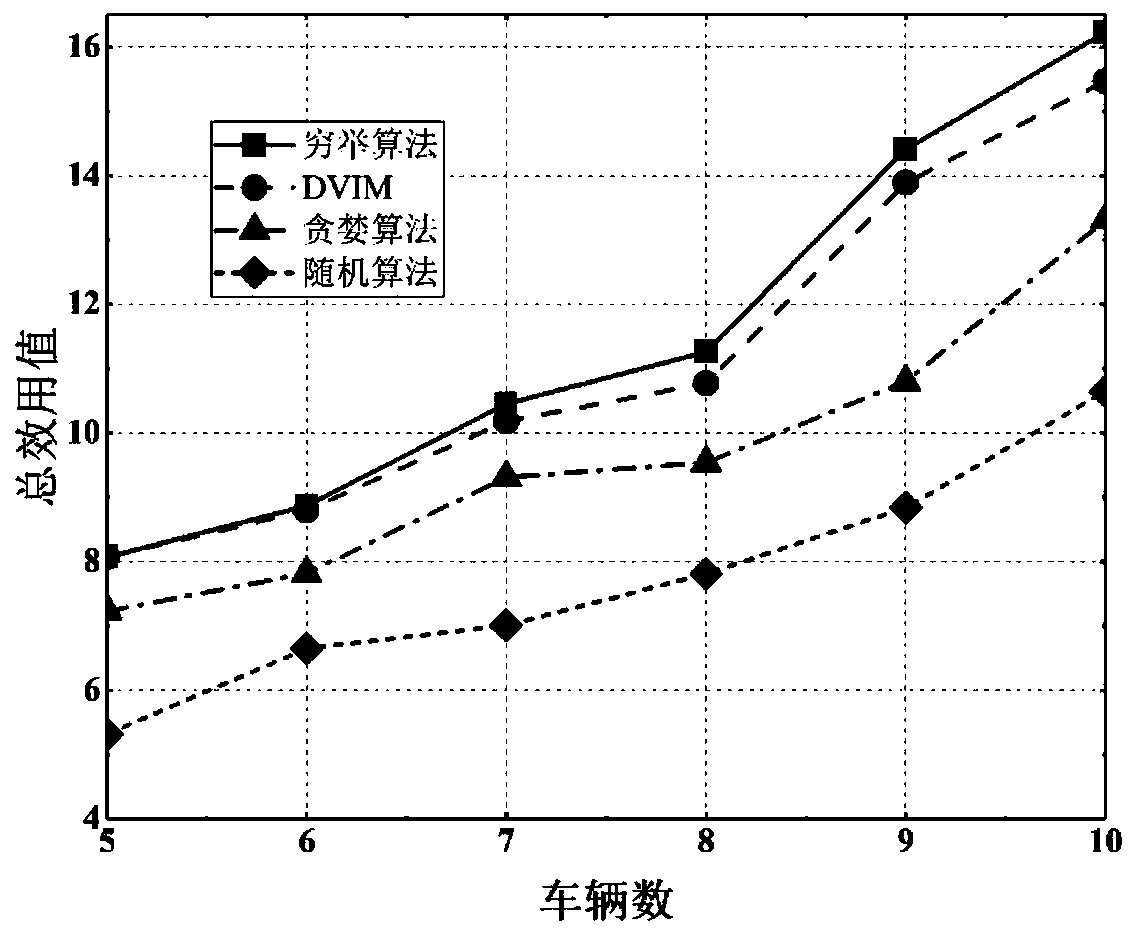
The invention discloses an intelligent computing unloading method under a vehicle-mounted network, which combines a deep reinforcement learning algorithm with vehicle edge computing, studies the optimization problem of task scheduling and resource allocation in the vehicle-mounted network, and gives a computing unloading method. On the basis of the limited Markov chain, the intelligent unloading model under the vehicle-mounted network is constructed, and the service experience quality of a user is considered while the profit of a network operator is maximized. According to the invention, the joint optimization problem of initial task scheduling and resource allocation is decomposed into two sub-optimization problems. For the first sub-problem, a utility function is designed to measure theservice experience quality grade of a user, and then a task scheduling algorithm based on a bilateral matching model is provided to solve the sub-problem. Based on an improved deep reinforcement learning algorithm, a reinforcement learning model under a vehicle-mounted network unloading system is constructed, and a resource allocation algorithm is provided to solve a second sub-problem. Experimental results prove the high efficiency of the algorithm provided by the invention.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Wind power grid-connection system operational reliability evaluation method considering uncertainty factors
ActiveCN107681691AGuaranteed uptimeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectric power systemAssessment methods
The invention relates to a reliability analysis method of an electric power system, specifically a wind power grid-connection system operational reliability evaluation method considering uncertainty factors, and solves the problems of incomplete consideration, long time consumption, slow convergence, resource occupation and incapability of realizing real-time prediction and evaluation of the existing method. A scheme comprises the processes as follows: I, uncertainty factor modeling: A, load comprehensive uncertainty; B, a conventional power generator comprehensive time varying operation model; C, comprehensive time varying operation modeling; D, wind power plant operational reliability modeling; and II, a Markov chain model: E, a Markov process and a Markov chain; F, a wind power Markov chain model; and G a wind power reliability evaluation index. The beneficial effects are achieved as follows: by performing quantitative analysis and comparison on the degree of influence of load fluctuation, element state and wind power output on the operational state and reliability level, the reliability level at the current moment can be evaluated, and the state probability at the future momentcan be quickly predicted, so that planning, overhaul, operation optimization and dispatching of the electric power system can be guided, thereby overcoming the shortcomings of the conventional evaluation method.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for establishing fault diagnosis technique based on contingent Bayesian networks
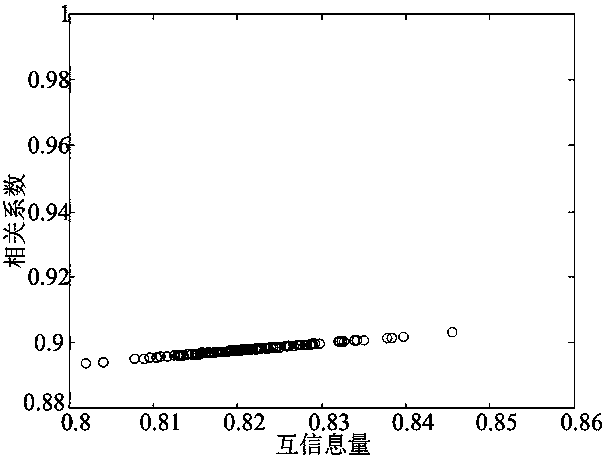
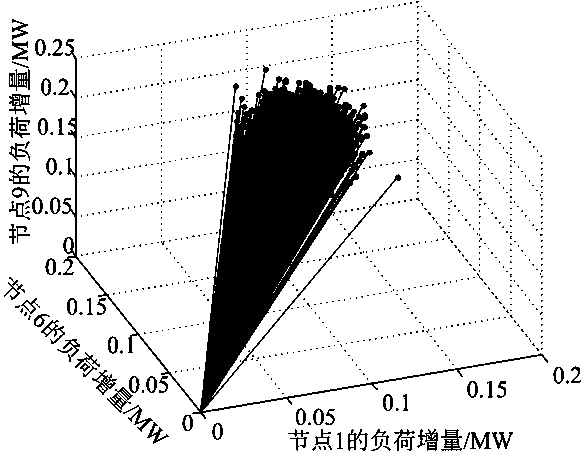
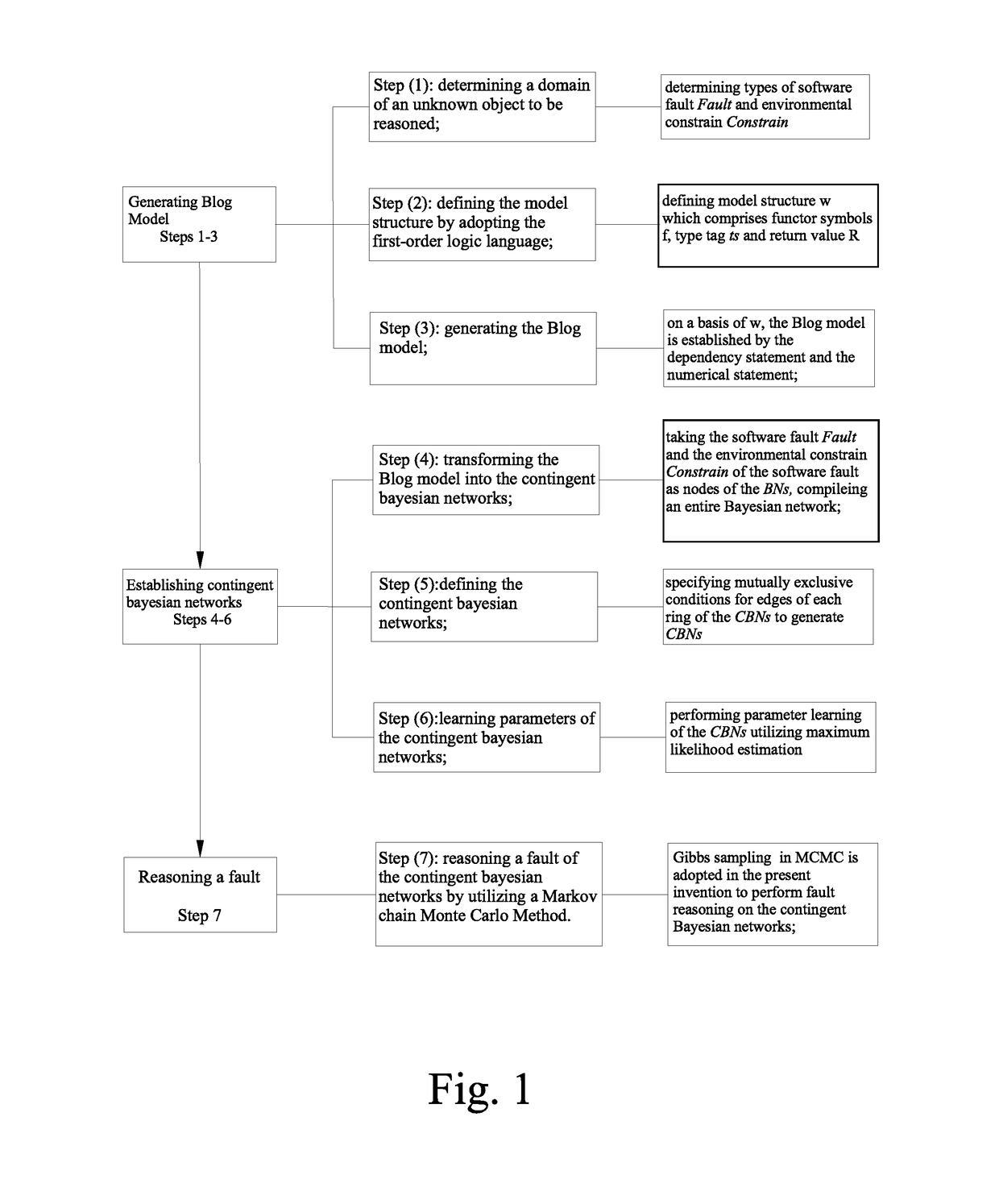
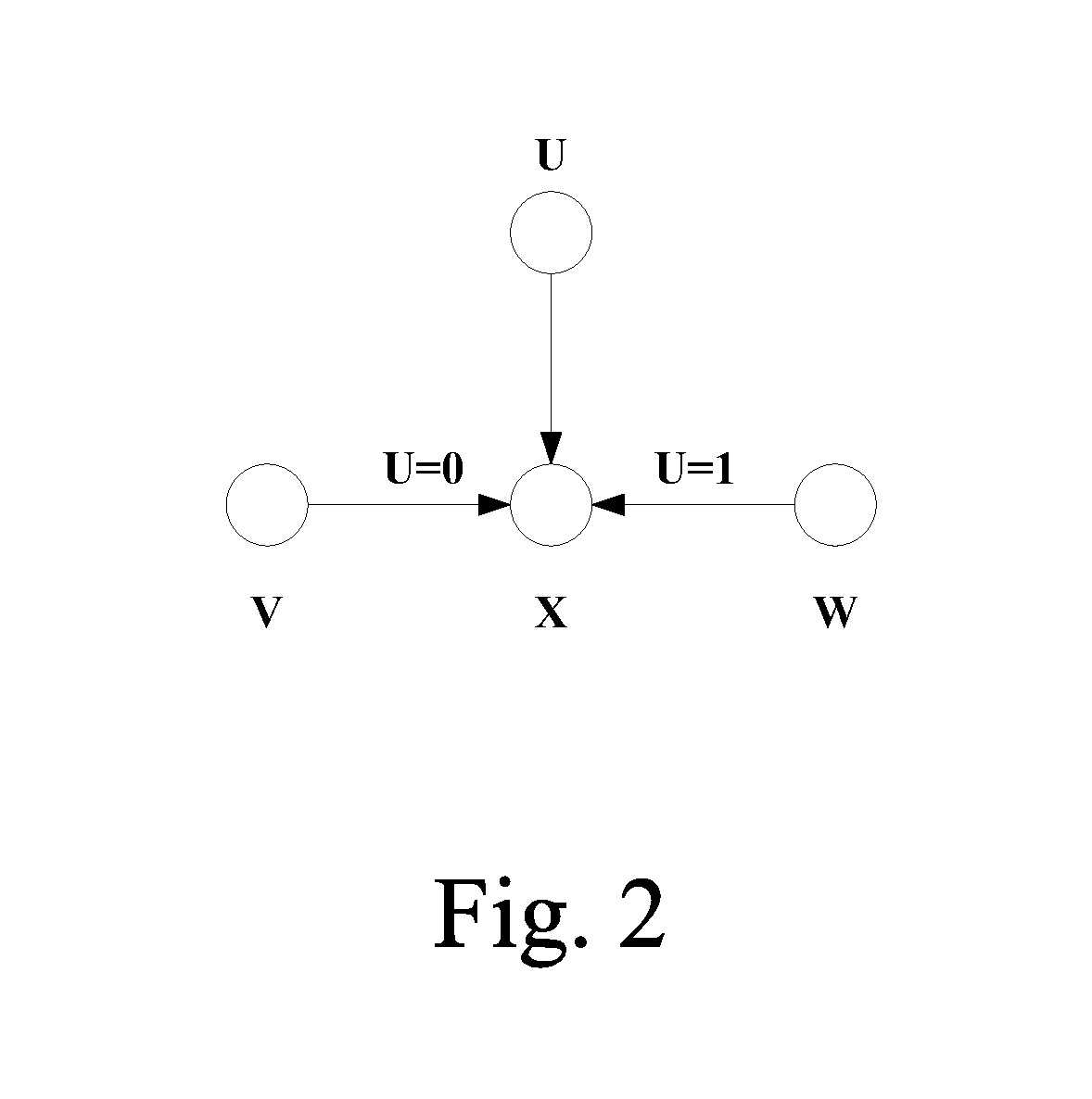
ActiveUS20190087294A1Good effectProbabilistic networksDetecting faulty hardware using expert systemsFirst-order logicMarkov chain
A method for establishing fault diagnosis technique based on contingent Bayesian networks, comprising steps of: step (1) determining a domain of an unknown object to be reasoned; step (2) defining a model structure by adopting a first-order logic language; step (3) generating a Blog model; step (4) transforming the Blog model into the contingent Bayesian networks; step (5) defining the contingent Bayesian networks; step (6) learning parameters of the contingent Bayesian networks; and step (7) reasoning a fault of the contingent Bayesian networks by utilizing a Markov chain Monte Carlo Method. By the steps mentioned above, establishing fault diagnosis technique based on contingent Bayesian networks is achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for self-adaptive load balancing based on future load prediction
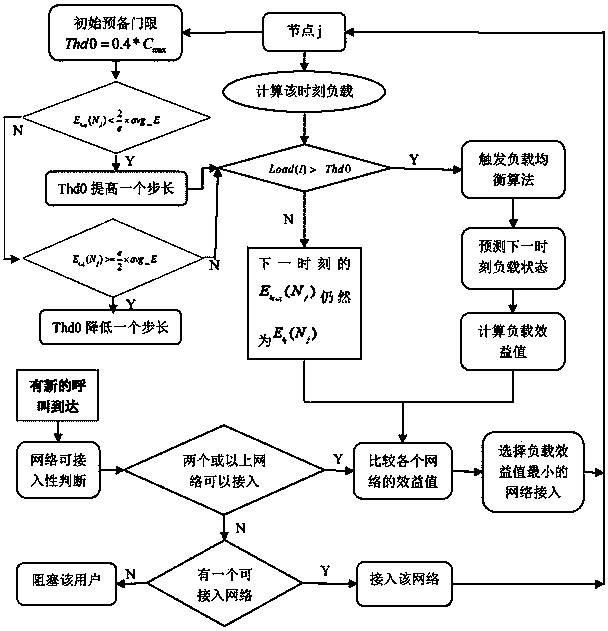
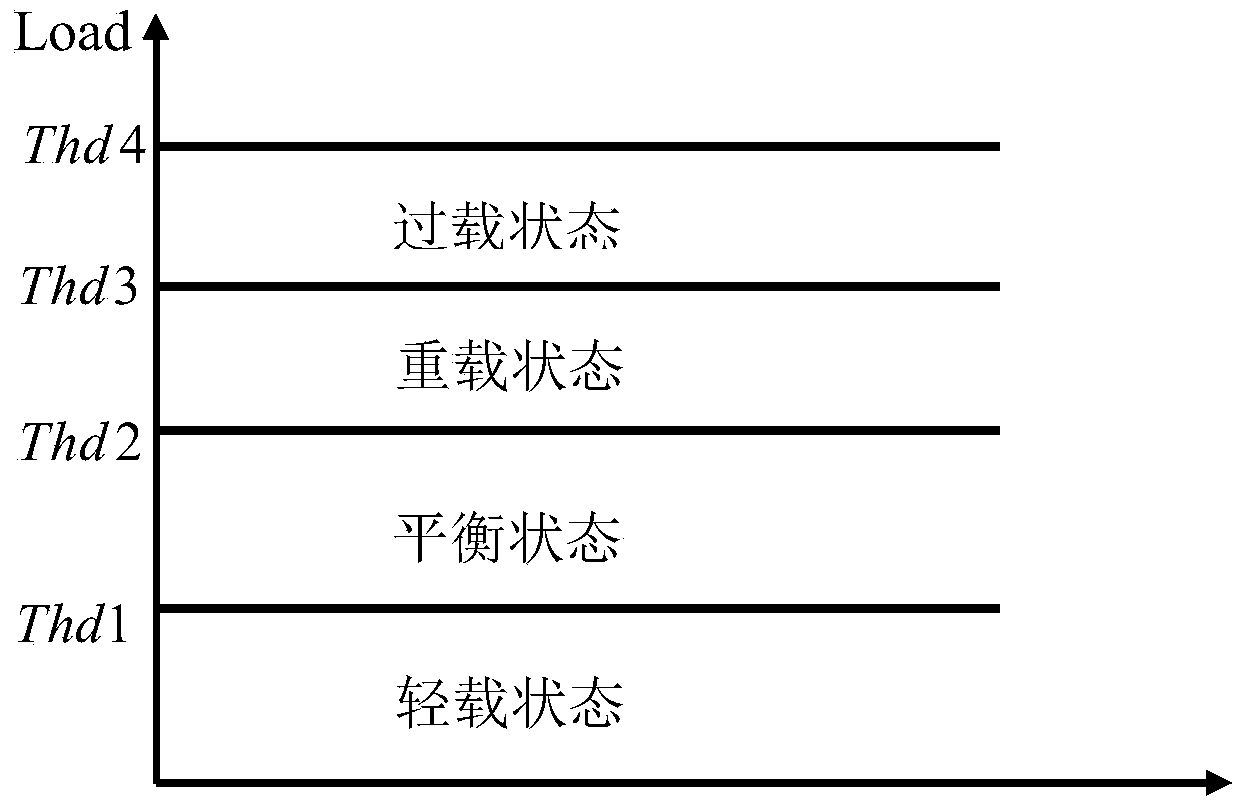
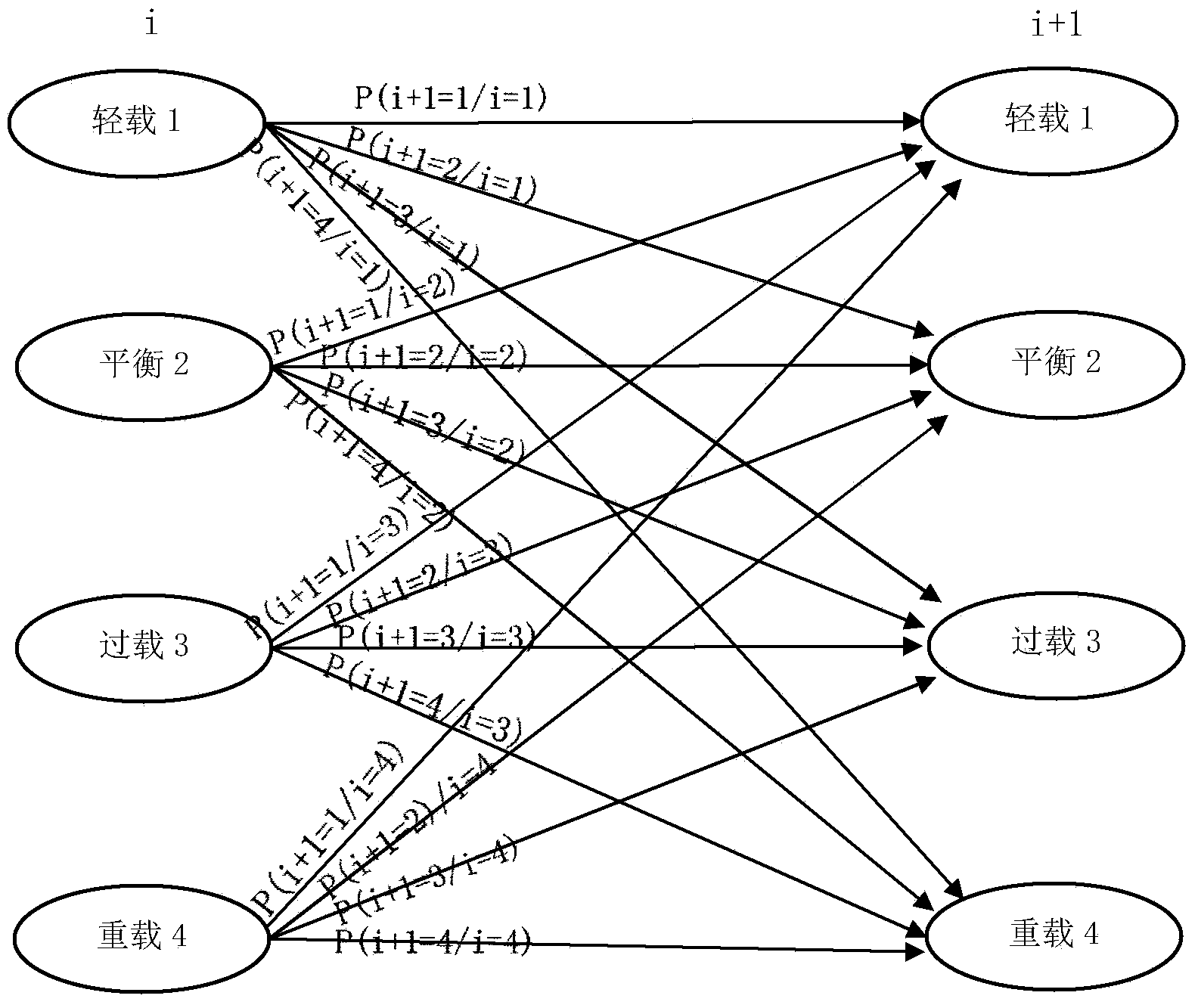
InactiveCN103889001ALoad balancingRaise or lower the thresholdNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionMarkov chainDynamic load balancing
The invention provides a method for self-adaptive load balancing based on future load prediction. According to the method, the Markov chain is used for predicting the load of a network at the next moment, so that the threshold of a trigger load balancing method is adjusted in a self-adaptive mode and modeling of an access control method is conducted. According to the method for self-adaptive load balancing, the probability of the light load or the heavy load in a future moment is calculated according to the previous load condition of the network through the transition probability defined through the method; a future load benefit value of the network is calculated through the calculated probability according to a load benefit function defined through the method. When a user requests access to be switched or an access request is newly sent in a network, the network with the small load benefit value is preferably selected to serve as a target network for access, so that the load of the whole heterogeneous network is balanced and the call drop rate and the access blocking rate of the switch are effectively reduced. Meanwhile, if it is predicated that the probability of the future light load is large, the threshold of the trigger load balancing method is dynamically improved, and the network is prevented from executing unnecessary load balancing operation.
Owner:南京恒云信息科技有限公司
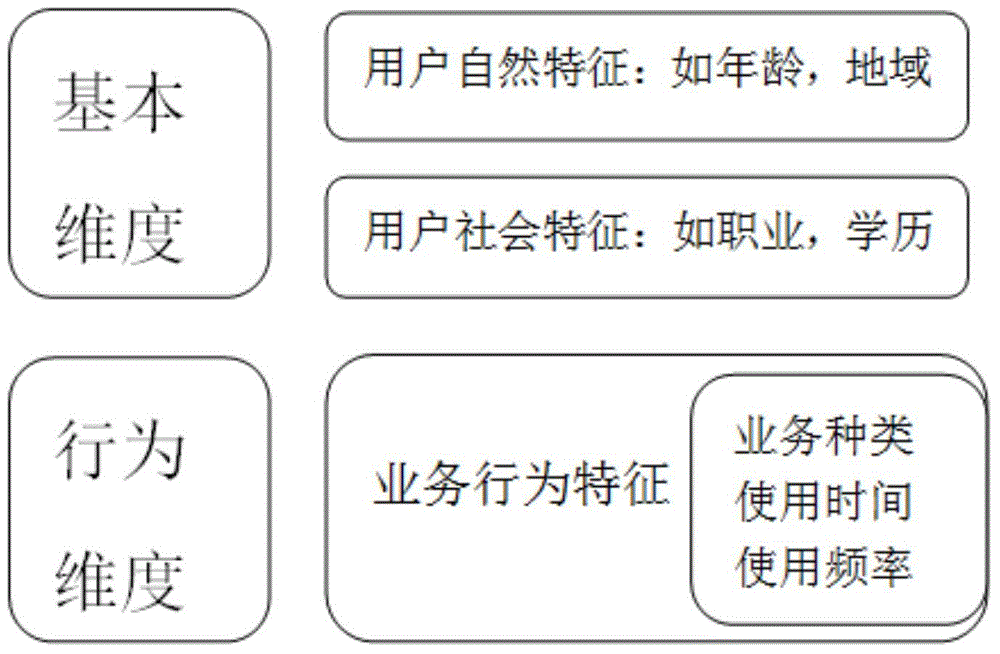
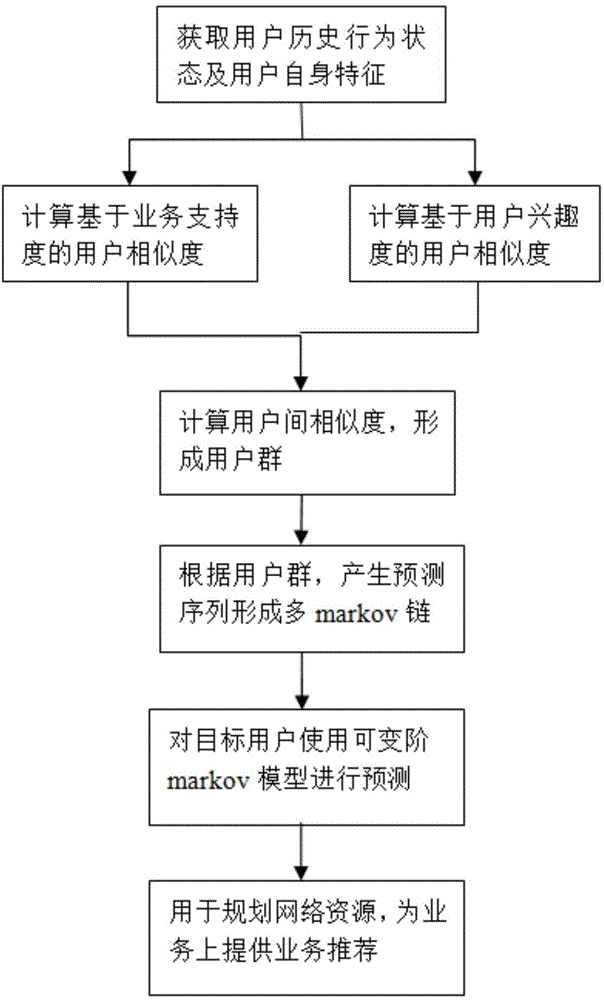
User similarity-based business behavior prediction method under ubiquitous network
The invention discloses a user similarity-based business behavior prediction method under a ubiquitous network. The objective of the invention is to realize effective mining and prediction of user behavior rules under a wireless ubiquitous environment. The method of the invention includes the followings steps that: an interest-based user behavior mining algorithm is researched, so that complete construction and cluster formation of user basic clusters can be realized; behavior rules of the user clusters are researched, and the behavior rules of the user clusters are combined so as to form behavior rules of user individuals; and a variable order Markov chain-based prediction model is researched, and complete mathematical descriptions of a whole theory model are constructed, and the solving of the model can be realized. With the user similarity-based business behavior prediction method under the ubiquitous network adopted, business states of user behaviors can be accurately predicted, and decision references can be provided for personalized customization of businesses, recommendation of optimal businesses and planning and construction of future networks, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
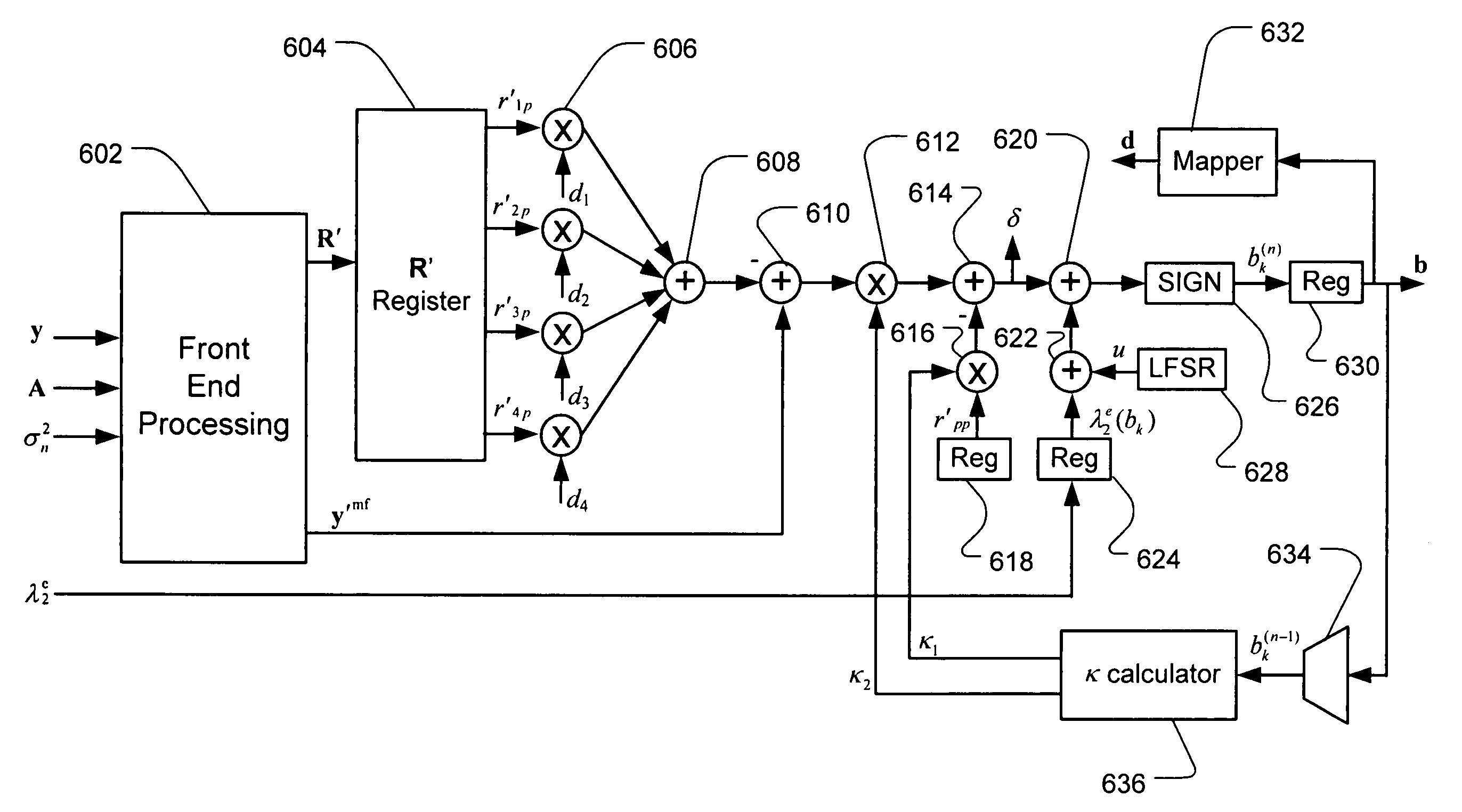
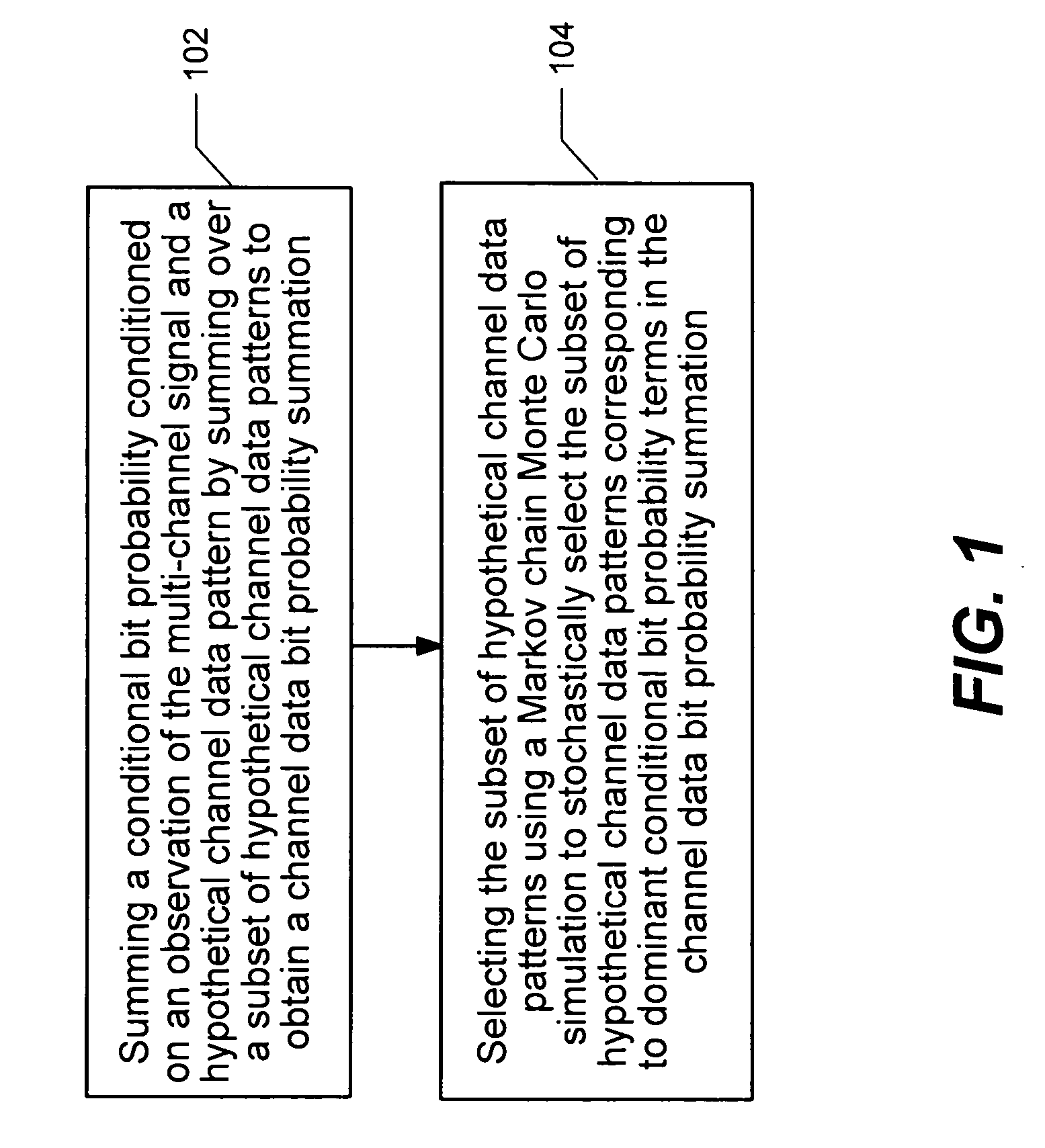
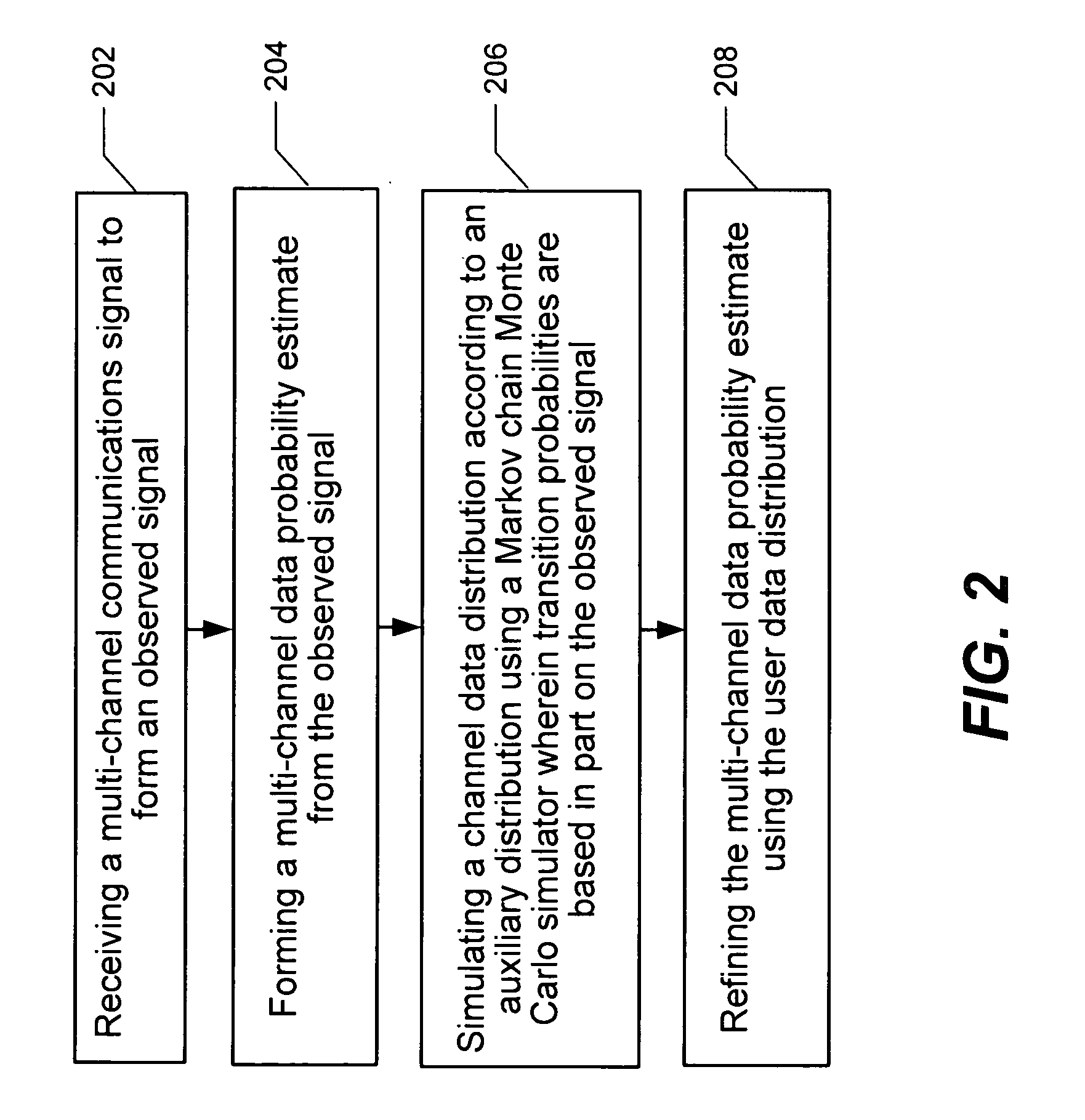
Multi-channel communication method and apparatus using plural Markov Chain Monte Carlo Simulations
InactiveUS20070076669A1Improve performanceImprove method performanceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel dataMarkov chain
A technique for estimating channel data probability in a multi-user or multiple-input multiple-output communication system is disclosed. The technique uses parallel Markov Chain Monte Carlo simulation to select a plurality of hypothetical channel data patterns. Channel data bit probabilities are obtained by summing conditional bit probabilities, where the conditional bit probabilities are conditioned on an observation of the multi-channel signal and the hypothetical channel data patterns.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com