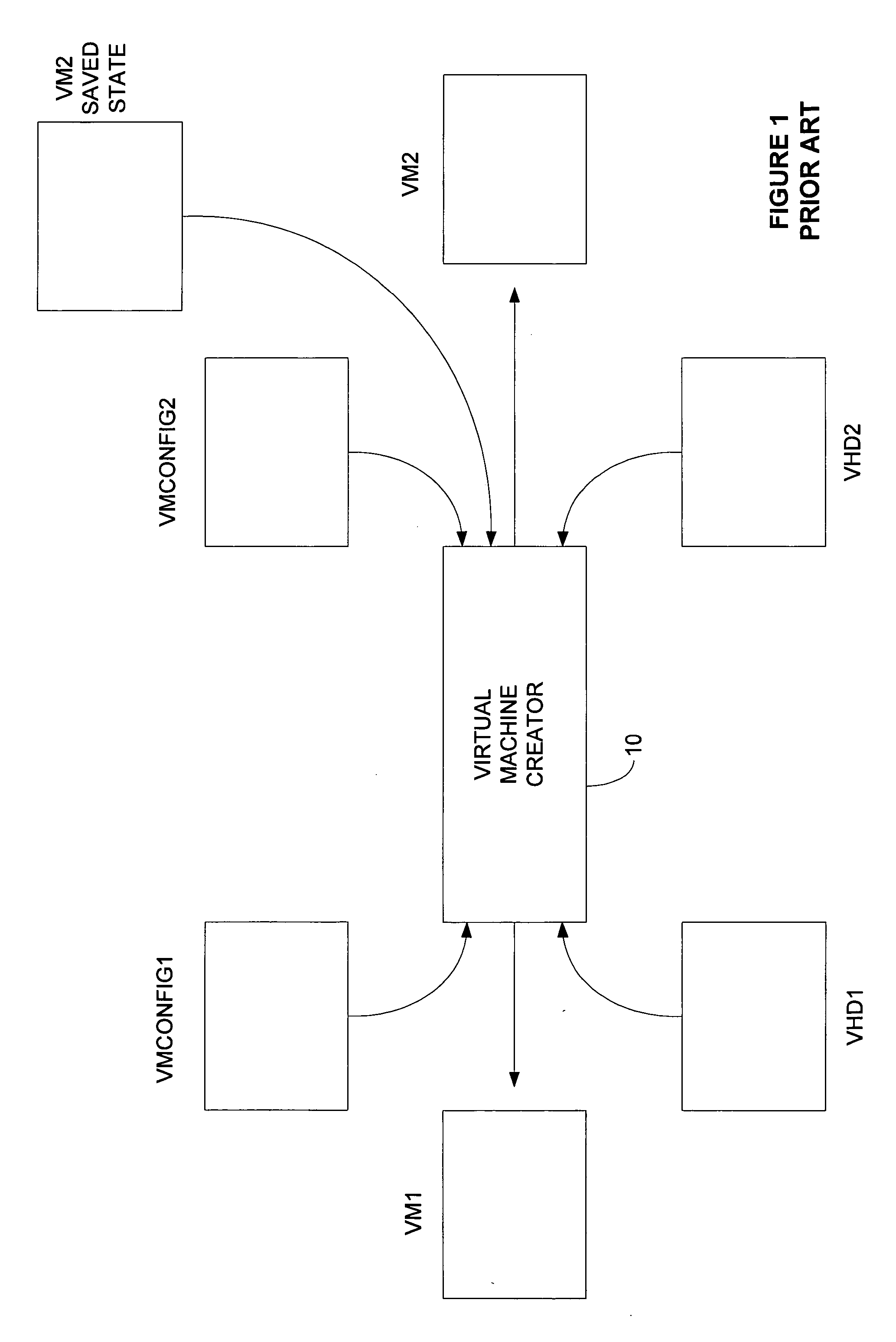
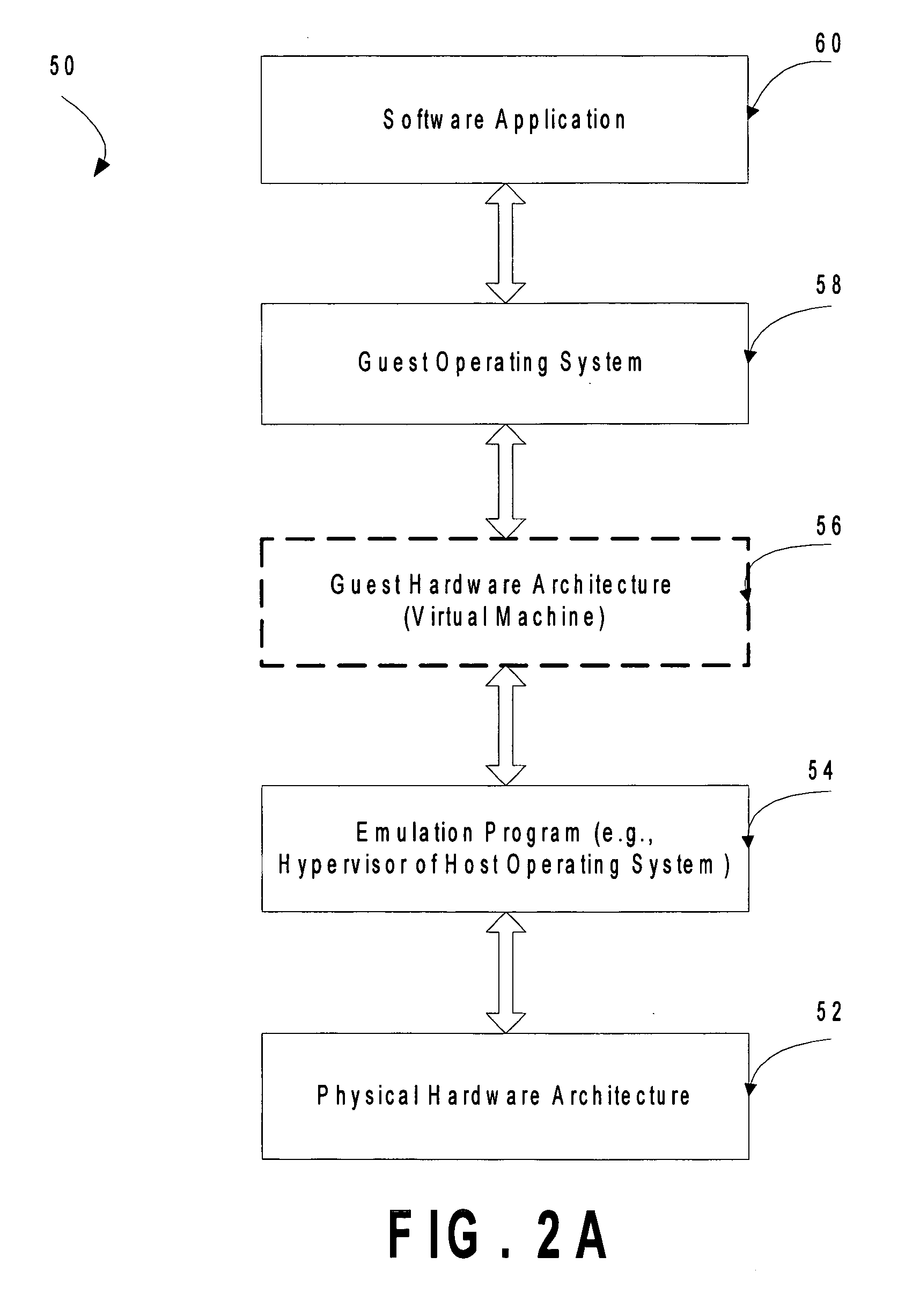
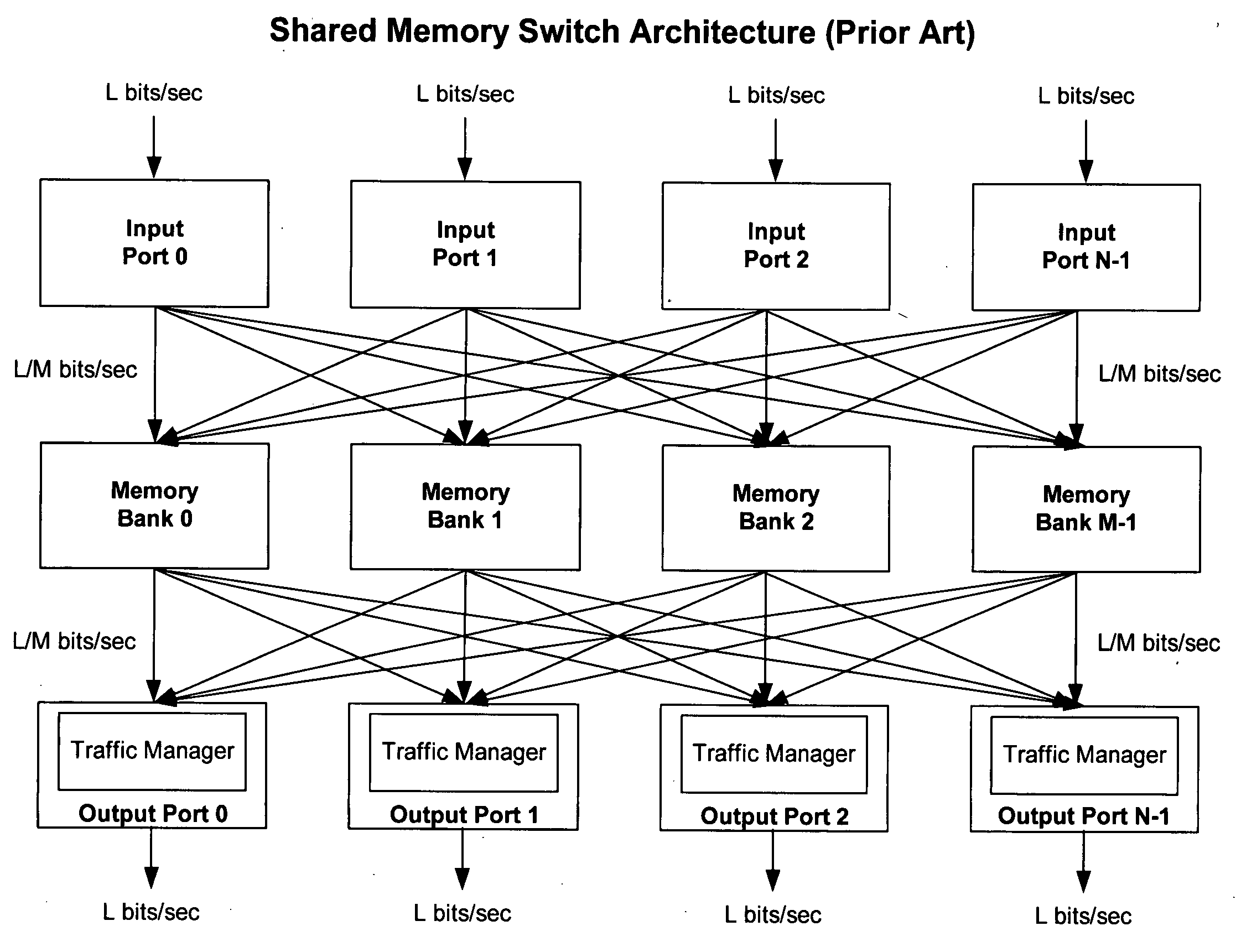
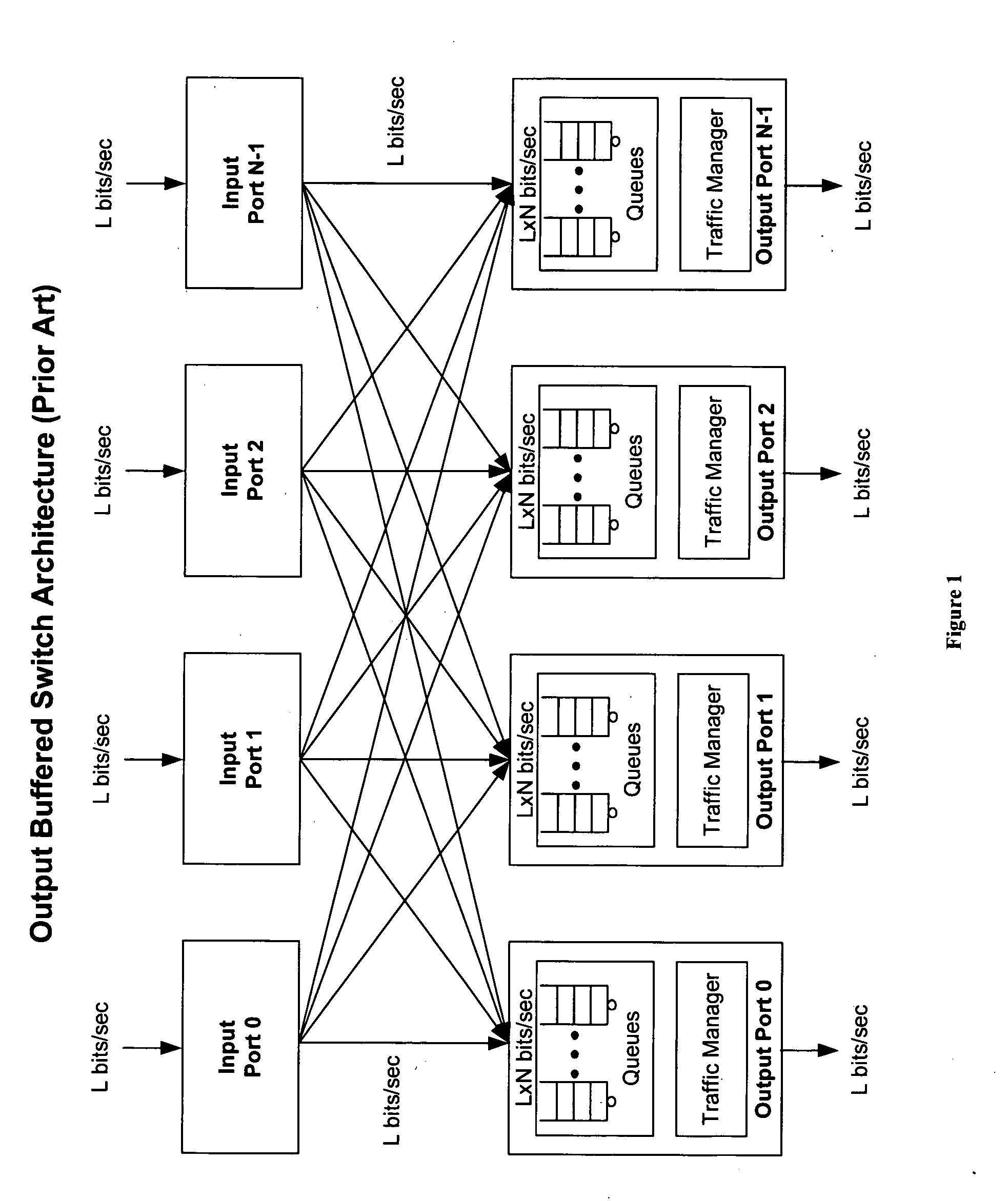
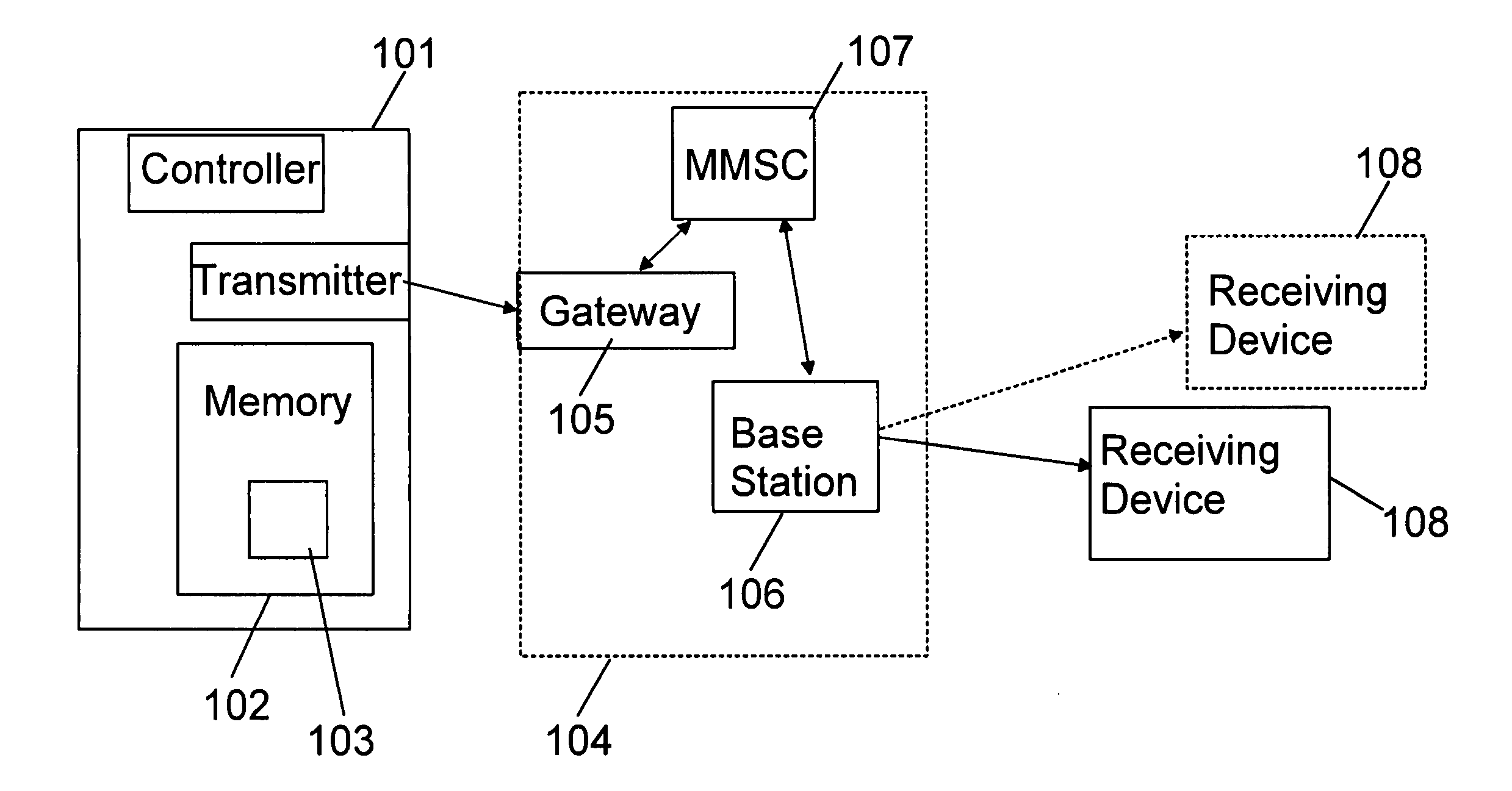
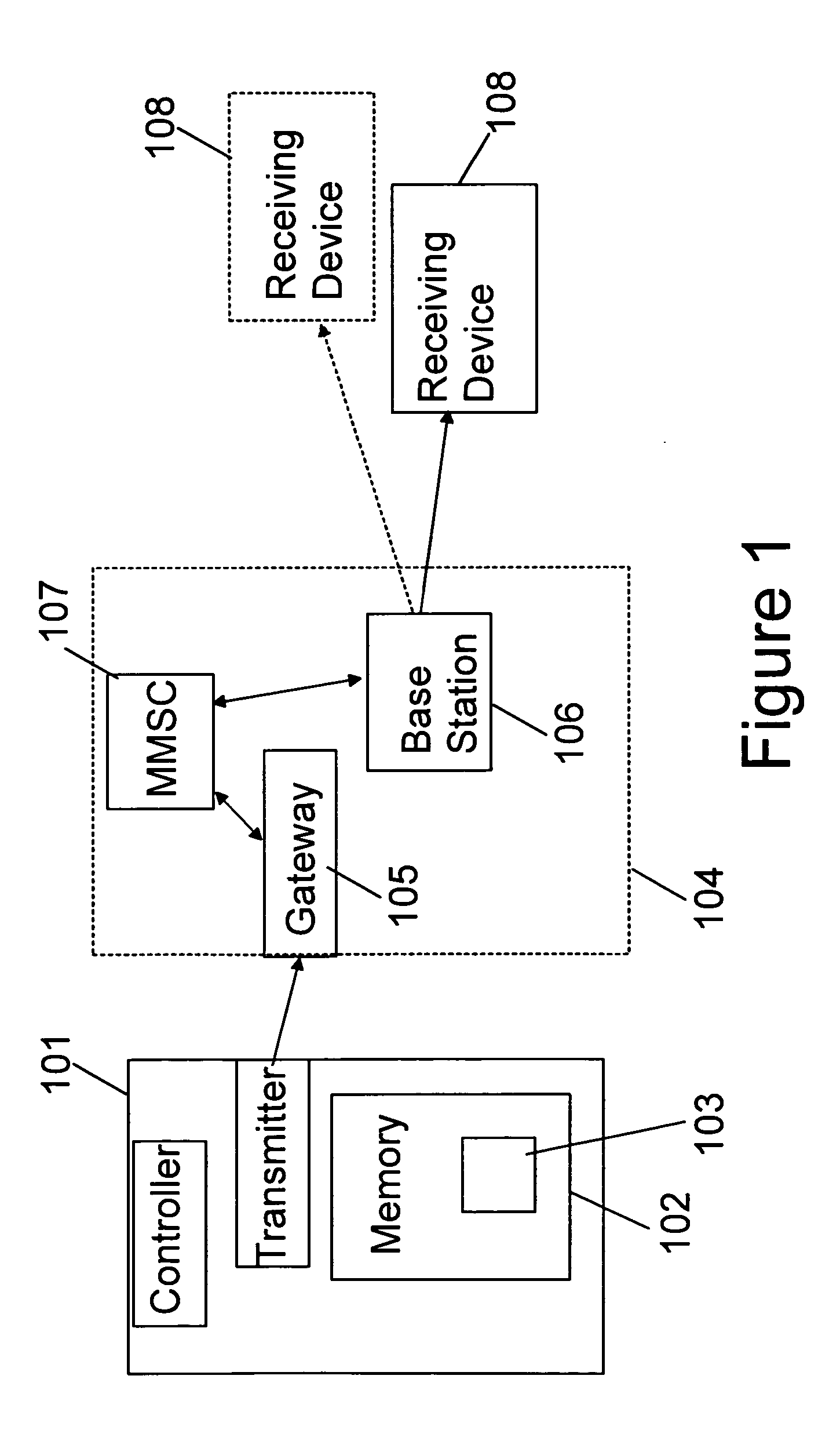
Patents
Literature
4852 results about "Extensibility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Extensibility is a software engineering and systems design principle that provides for future growth. Extensibility is a measure of the ability to extend a system and the level of effort required to implement the extension. Extensions can be through the addition of new functionality or through modification of existing functionality. The principle provides for enhancements without impairing existing system functions.
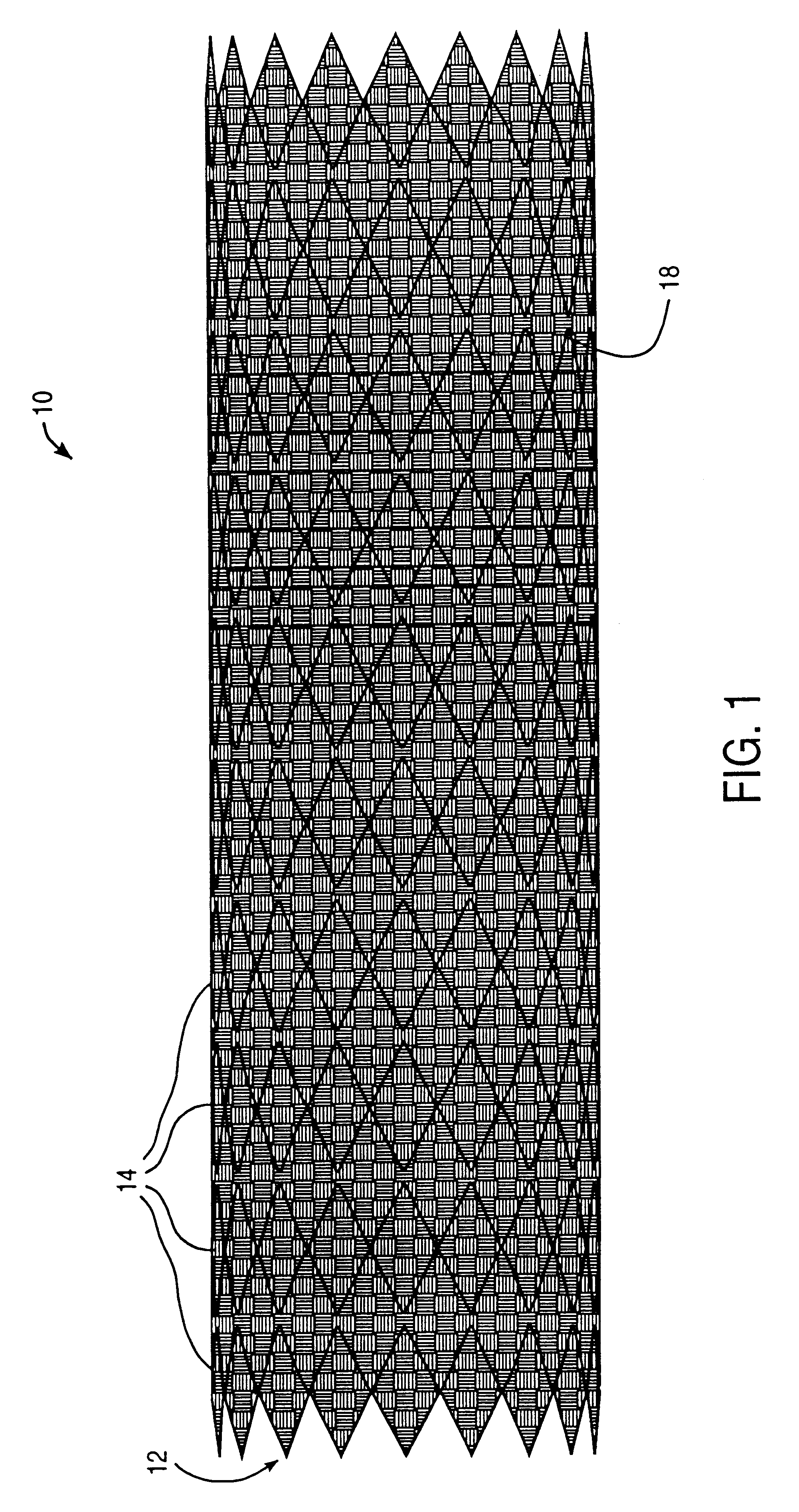
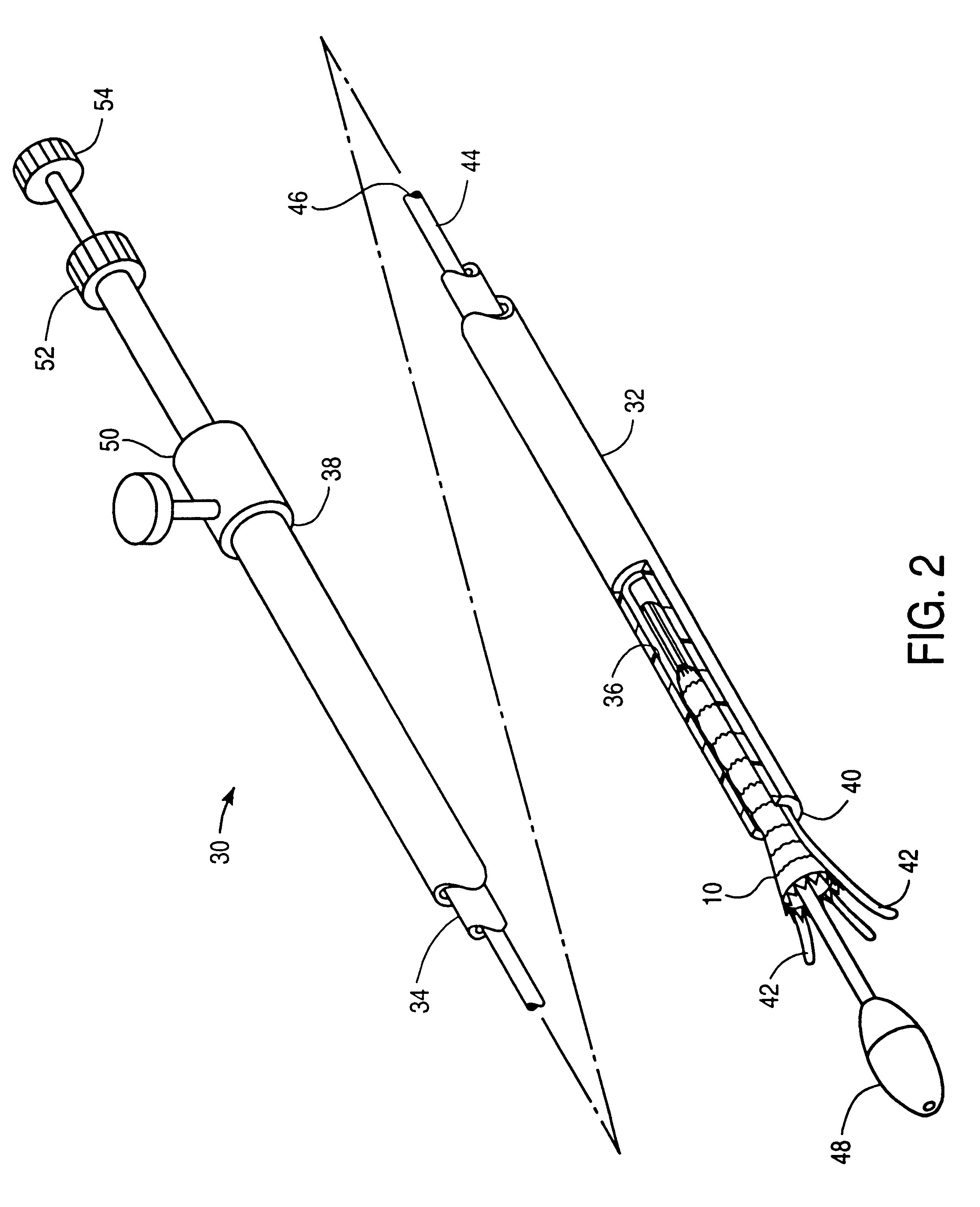
Porous implant with effective extensibility and methods of forming an implant
The implant includes an outer layer of ePTFE which exhibits extensibility normally not associated with ePTFE. The ePTFE is reduced in length by deforming the fibrils between the nodes while maintaining the nodes in a substantially flat configuration. Various implant configurations that can include the outer layer described are also disclosed.
Owner:EVERA MEDICAL
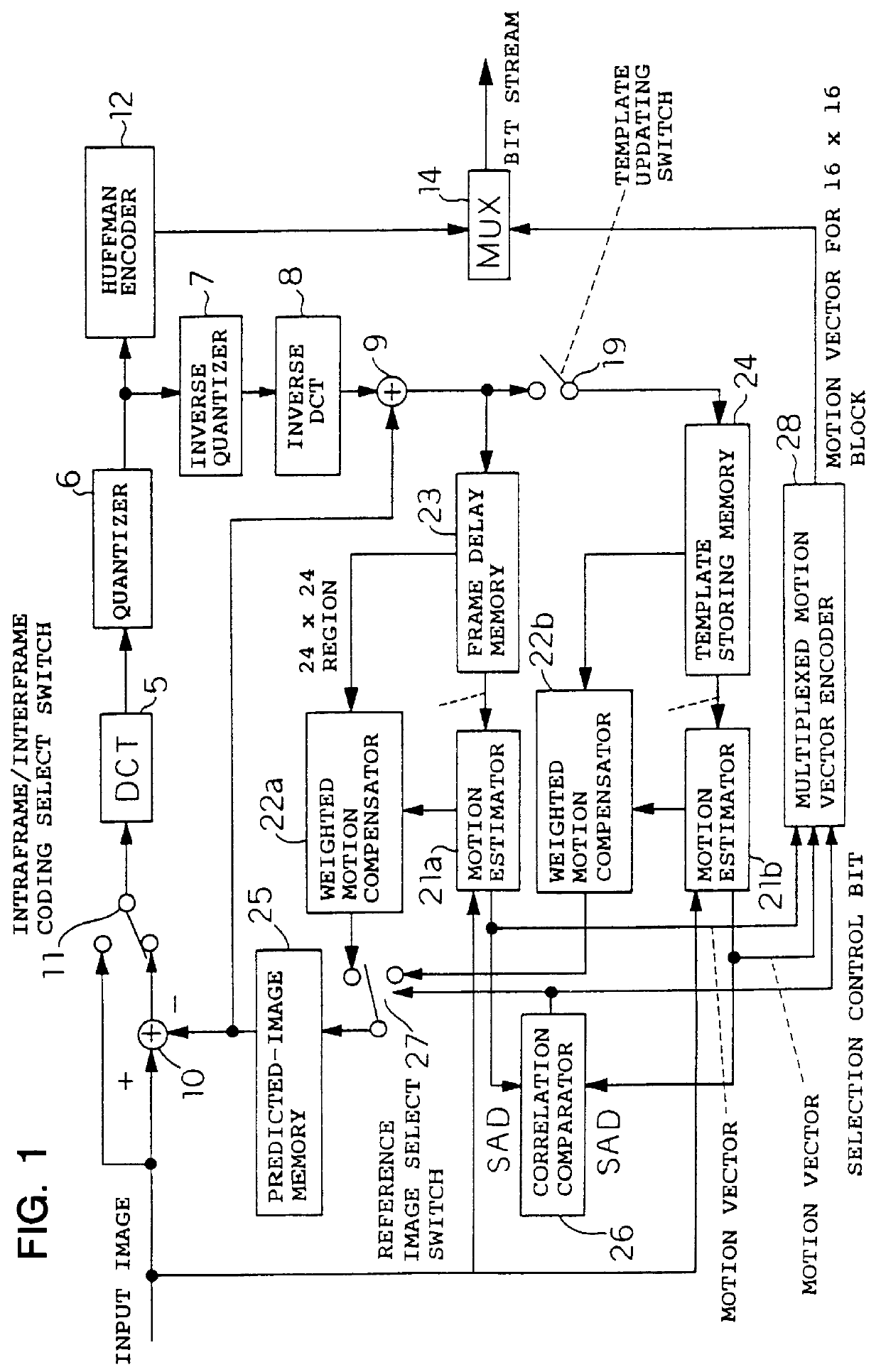
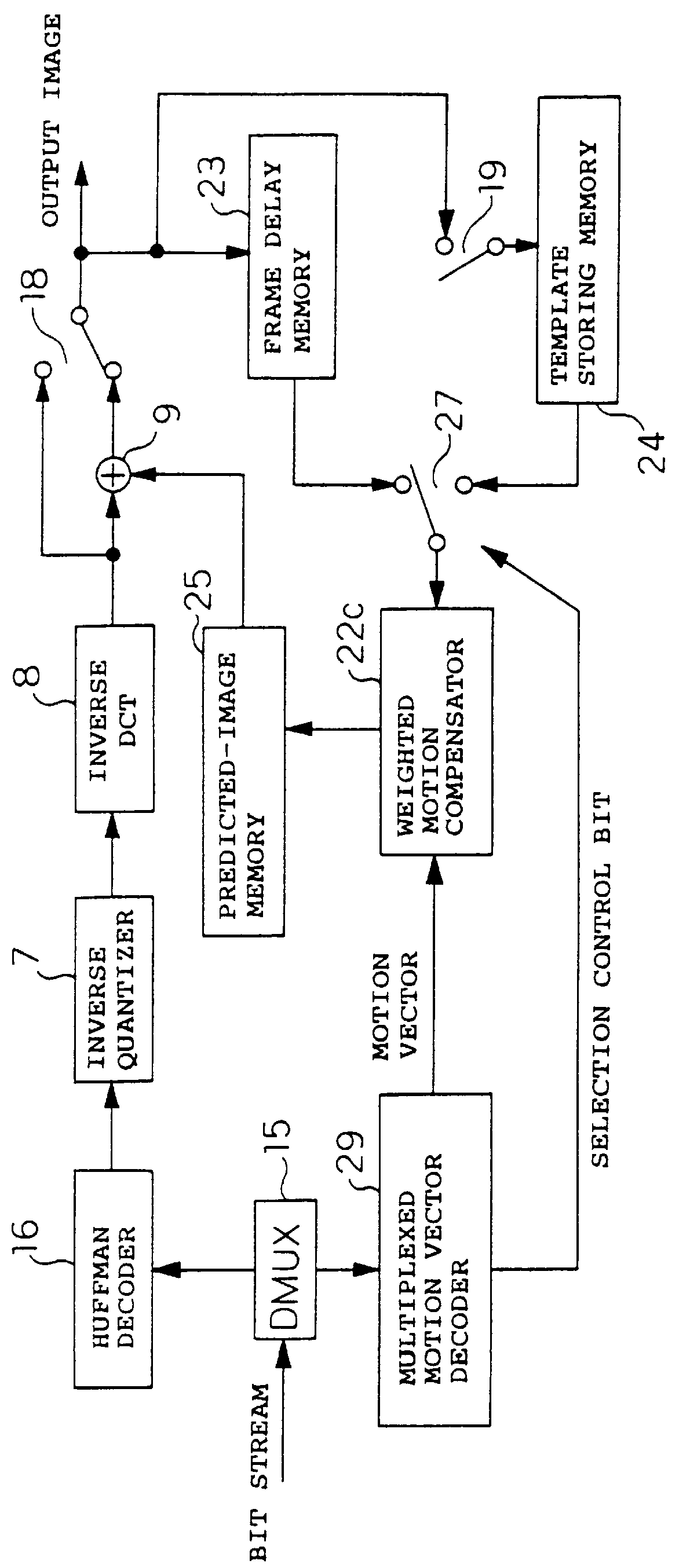
Image coding and decoding apparatus and methods thereof
InactiveUS6081551APicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionExtensibilityMotion vector
To achieve an image encoding apparatus that has extensibility by not limiting an image to be referenced, and that can reduce processing time satisfactorily if the processing of an ordinary frame is skipped, the apparatus of the present invention comprises: motion detecting means for detecting a motion vector for each block of a prescribed size from a reference image and an input image; weighted motion-compensation means for, based on the detected motion vector, extracting from the reference image an area of a prescribed size which is wider than the prescribed block size and which contains an area corresponding to each block of the input image, and for creating a predicted image for the input image by applying a predetermined weight to each of pixels in the wider area and by using the weighted pixels of the wider area; a predicted-image memory for storing the predicted image; encoding means for taking a residual between the stored predicted image and the input image, and for encoding the residual; and decoding means for decoding the encoded image data and thereby obtaining a reference image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
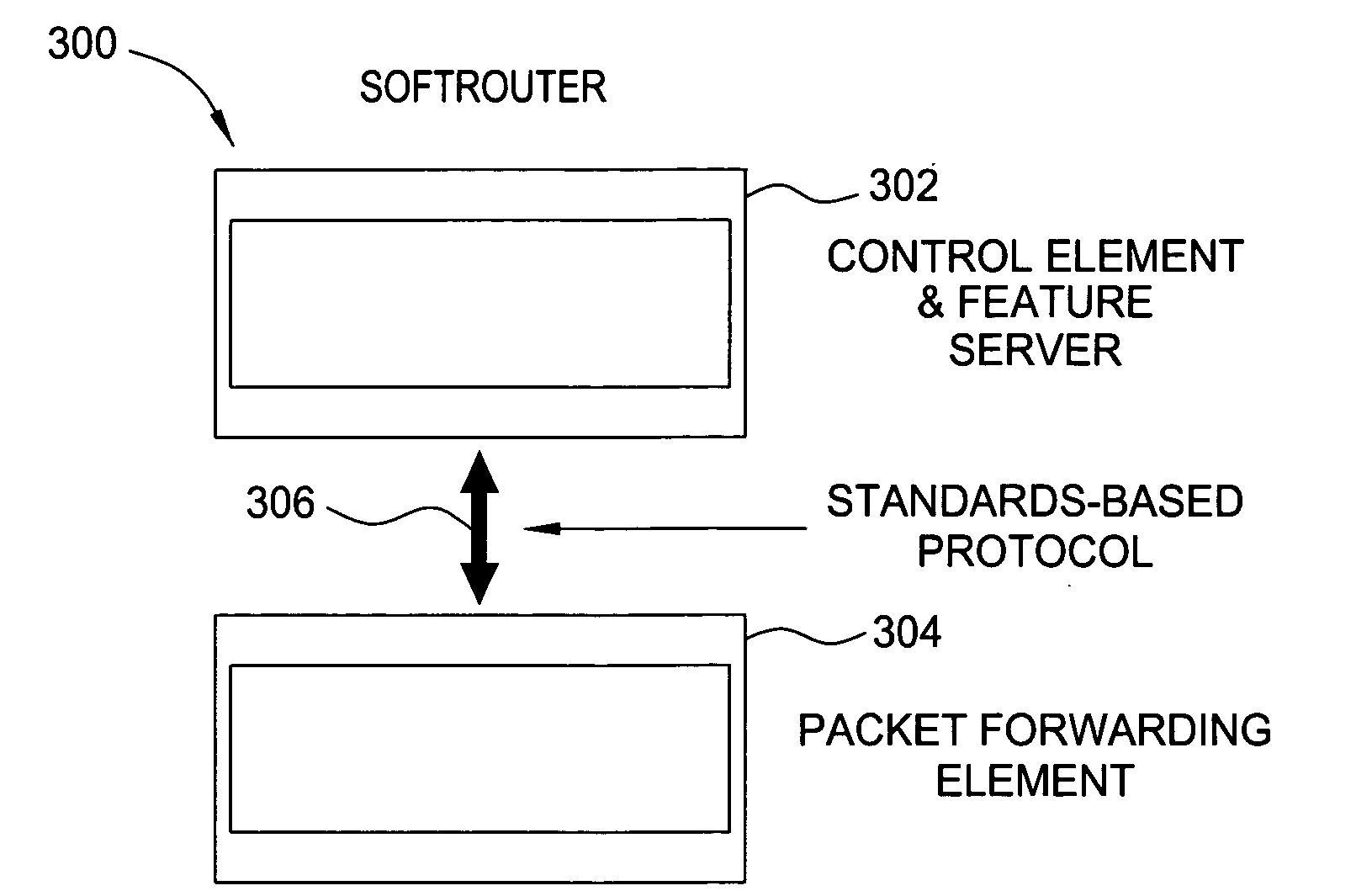
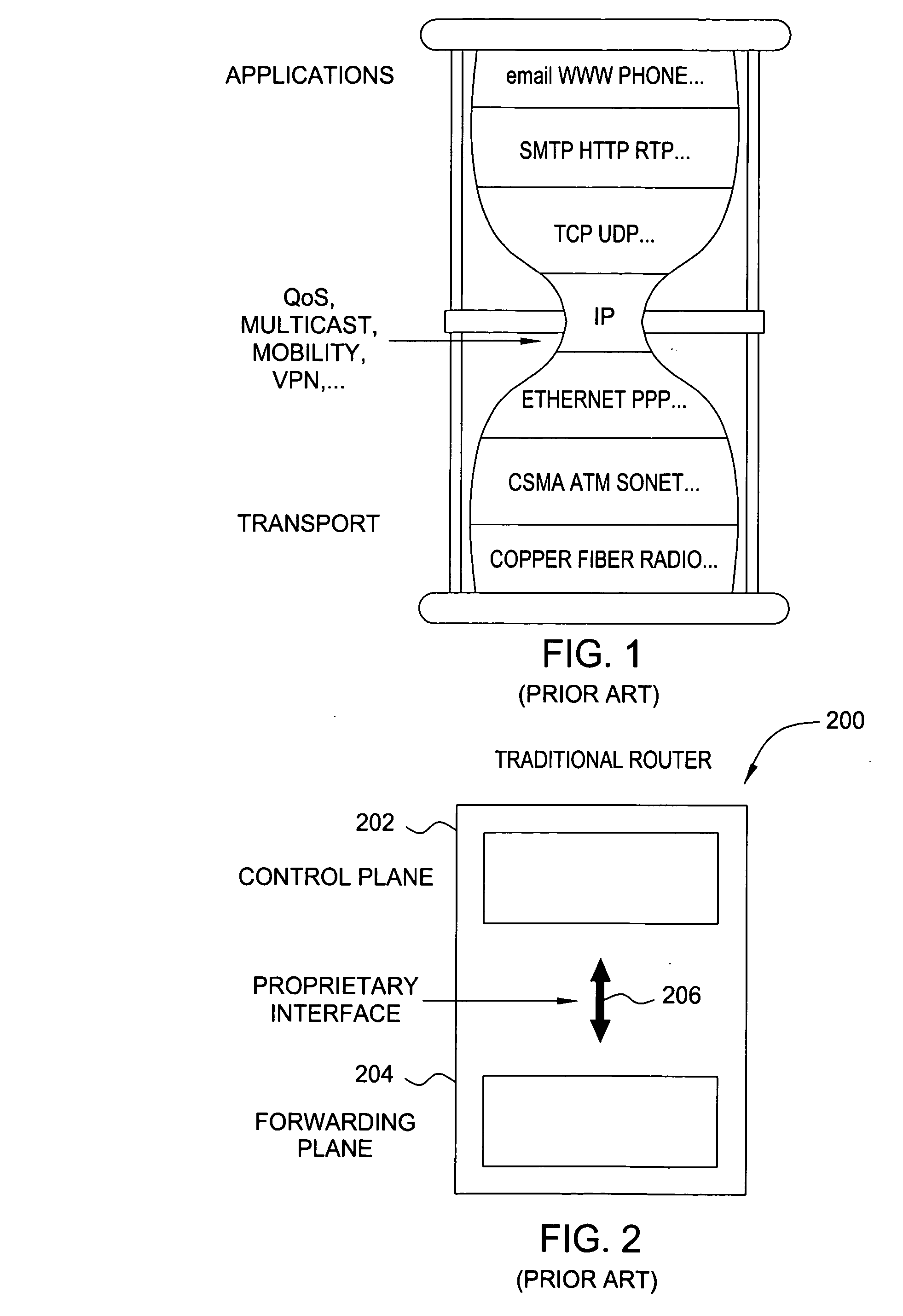
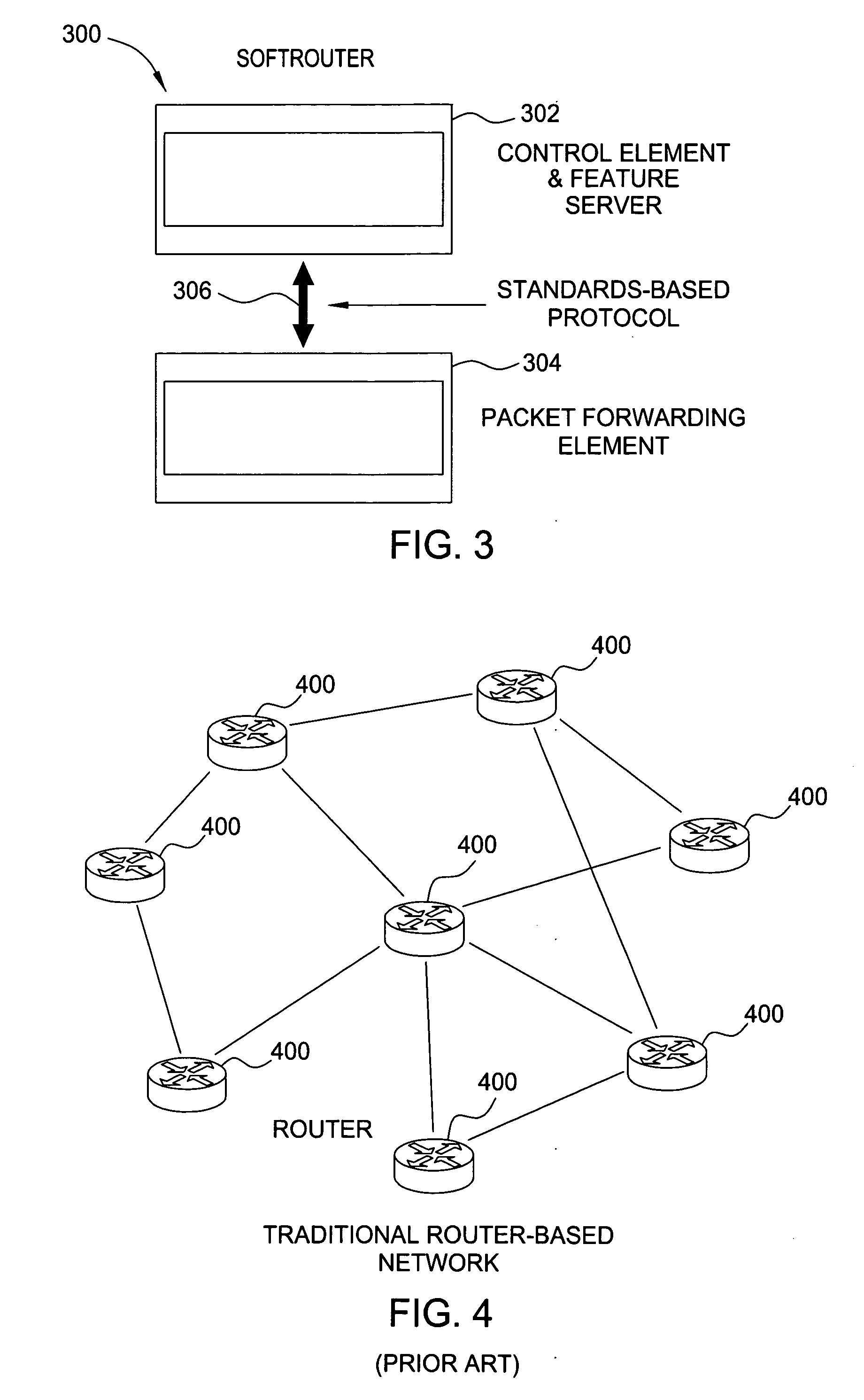
Softrouter separate control network
ActiveUS20060092976A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityExtensibility
An embodiment of the exemplary SoftRouter architecture includes two physically separate networks, a control plane network and a data plane network. The data plane network is one physical network for the data traffic, while the control plane network is another physical network for the control traffic. The topology of the data plane network is made up of interconnected forwarding elements (FEs). The topology of the control plane network is made up interconnected control elements (CEs). This physical independence of the control plane network from the data plane network provides for a secure mechanism to communicate among the CEs in the control plane network. In addition, this physical independence provides improved reliability and improved scalability, when compared to the traditional router architecture, where control plane message are in-band with the data plane.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
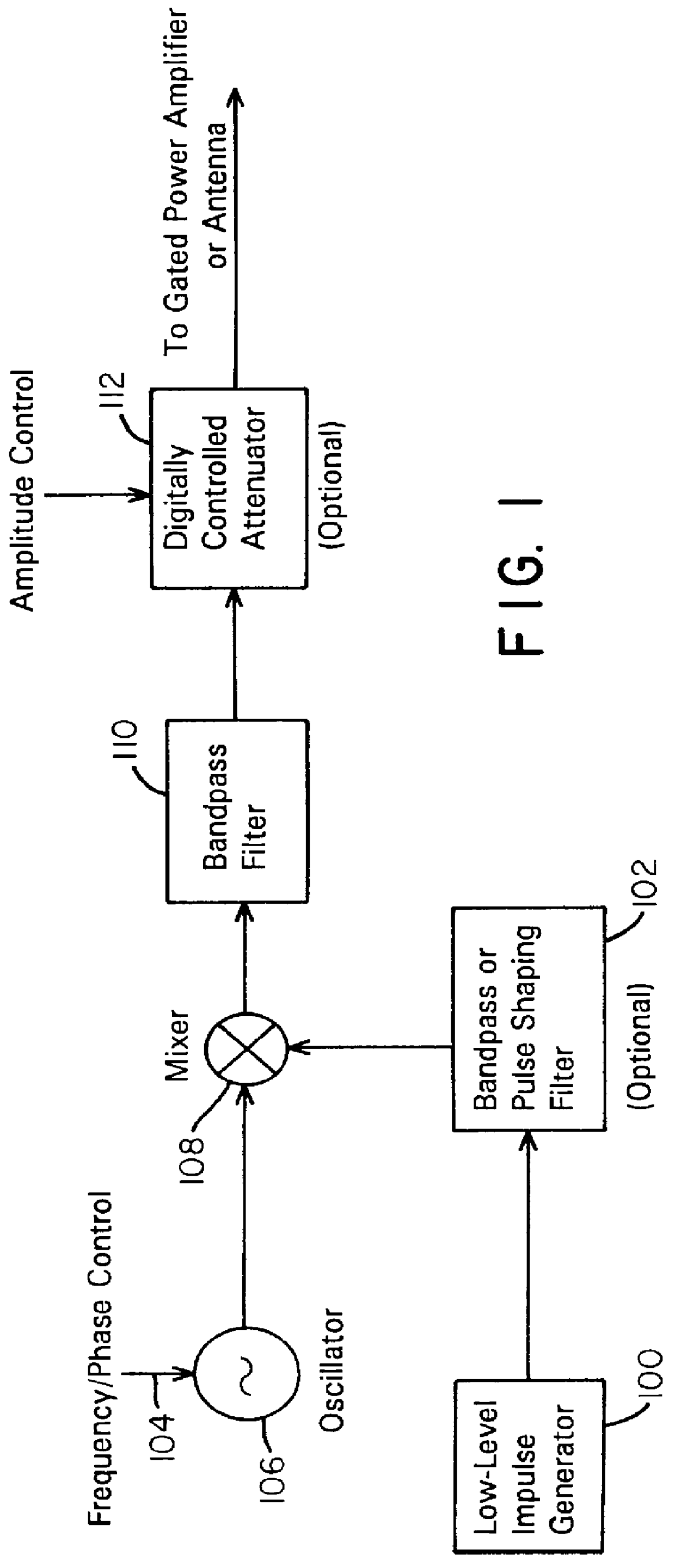
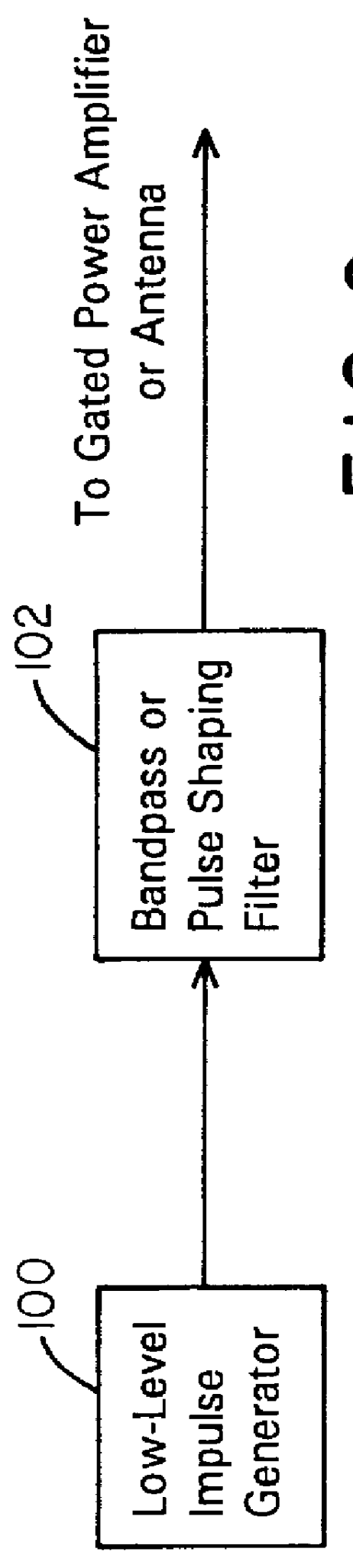
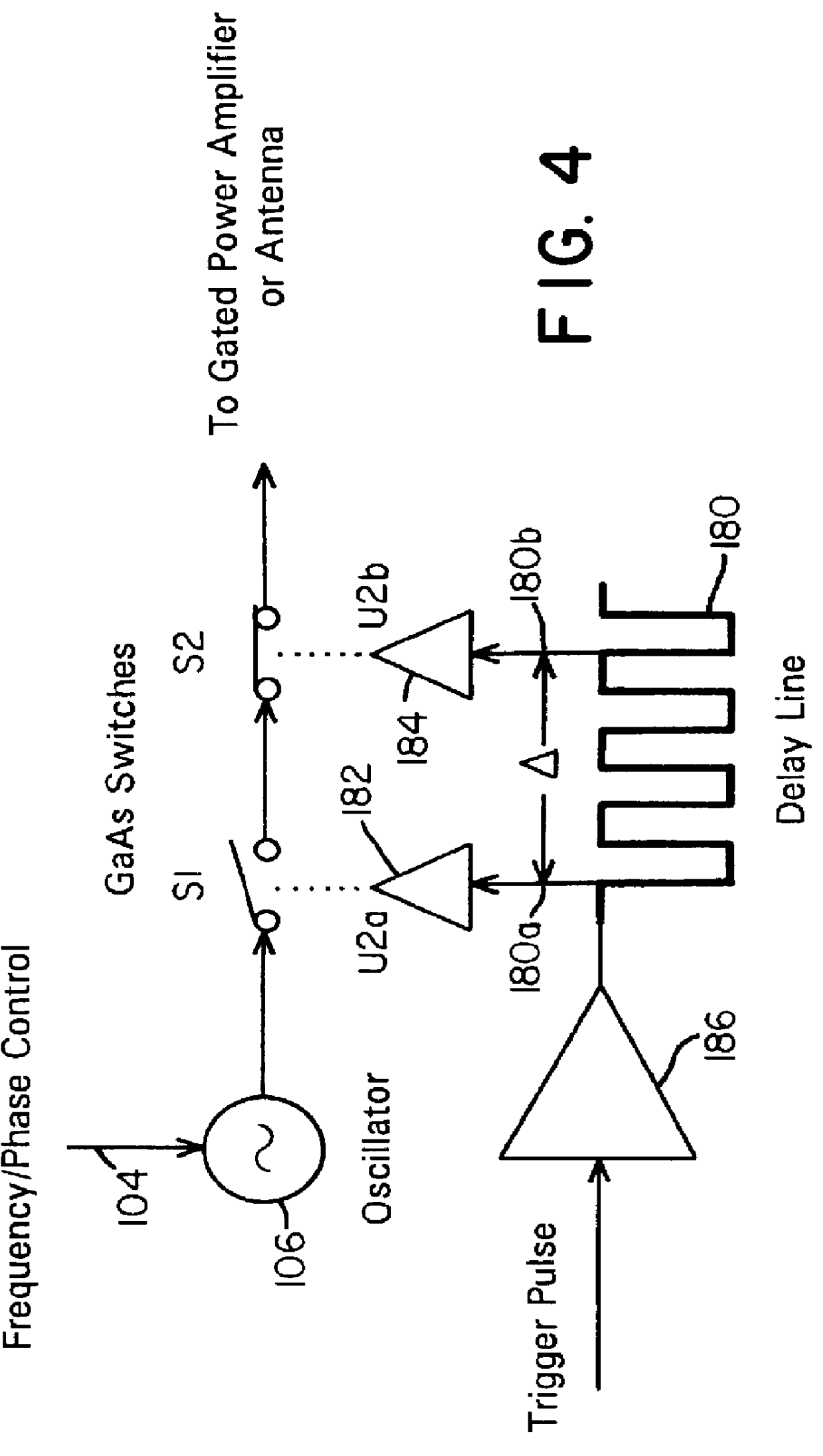
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
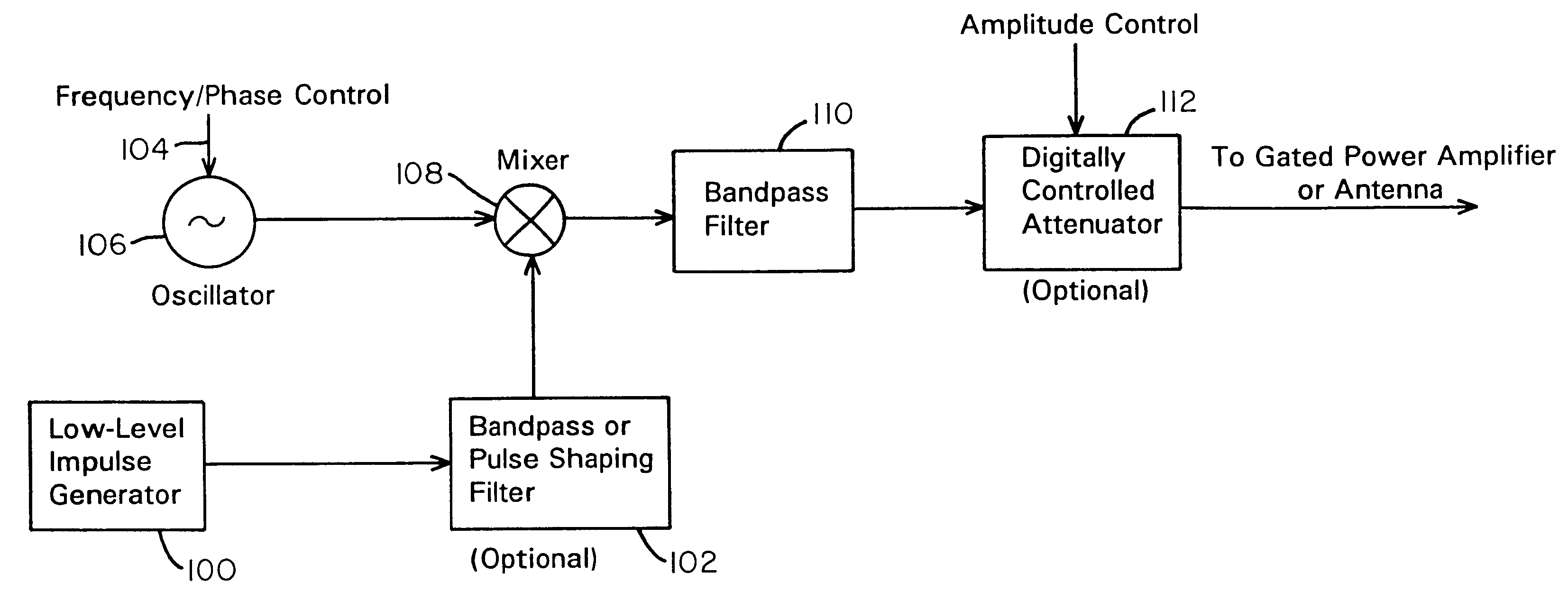
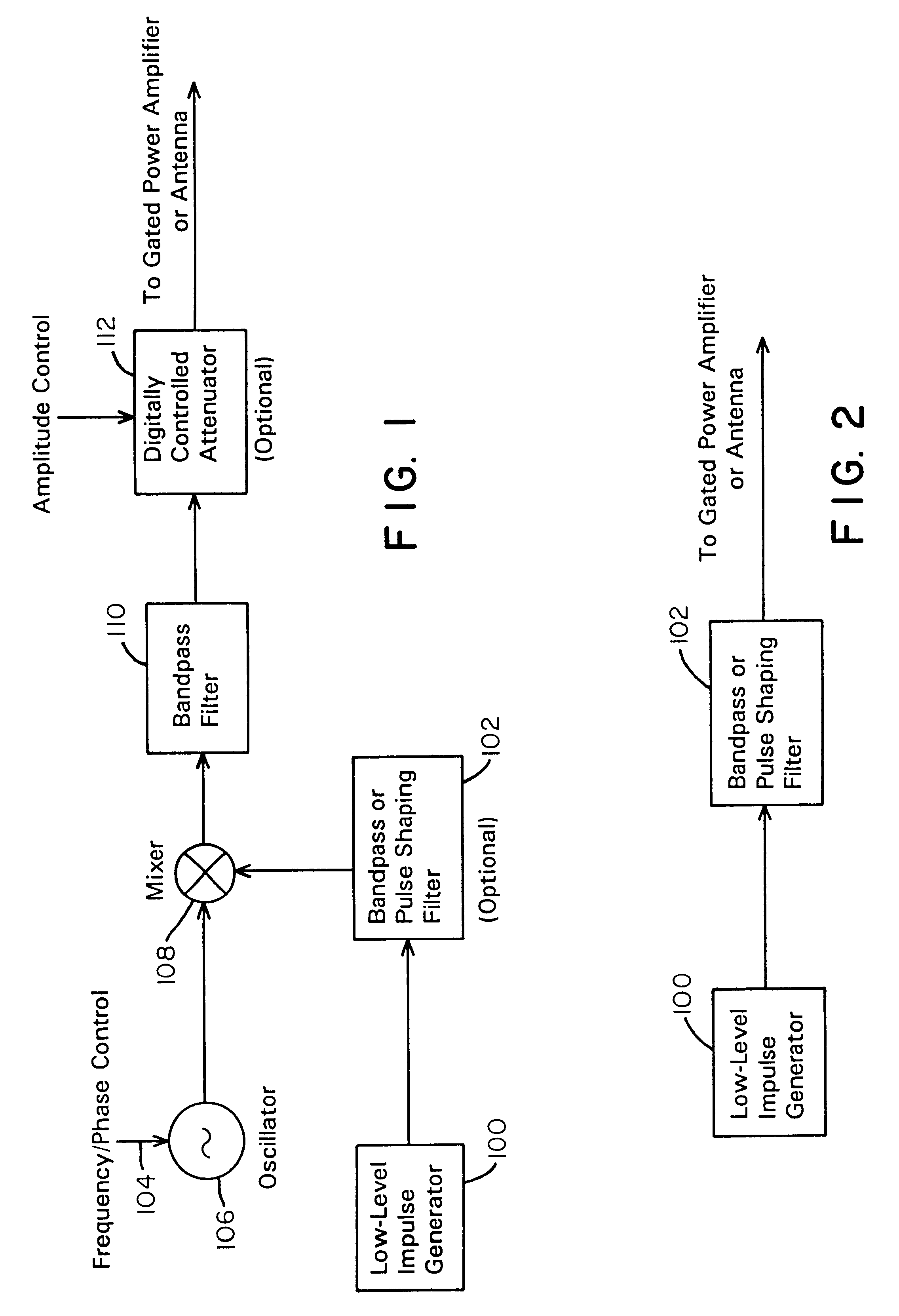
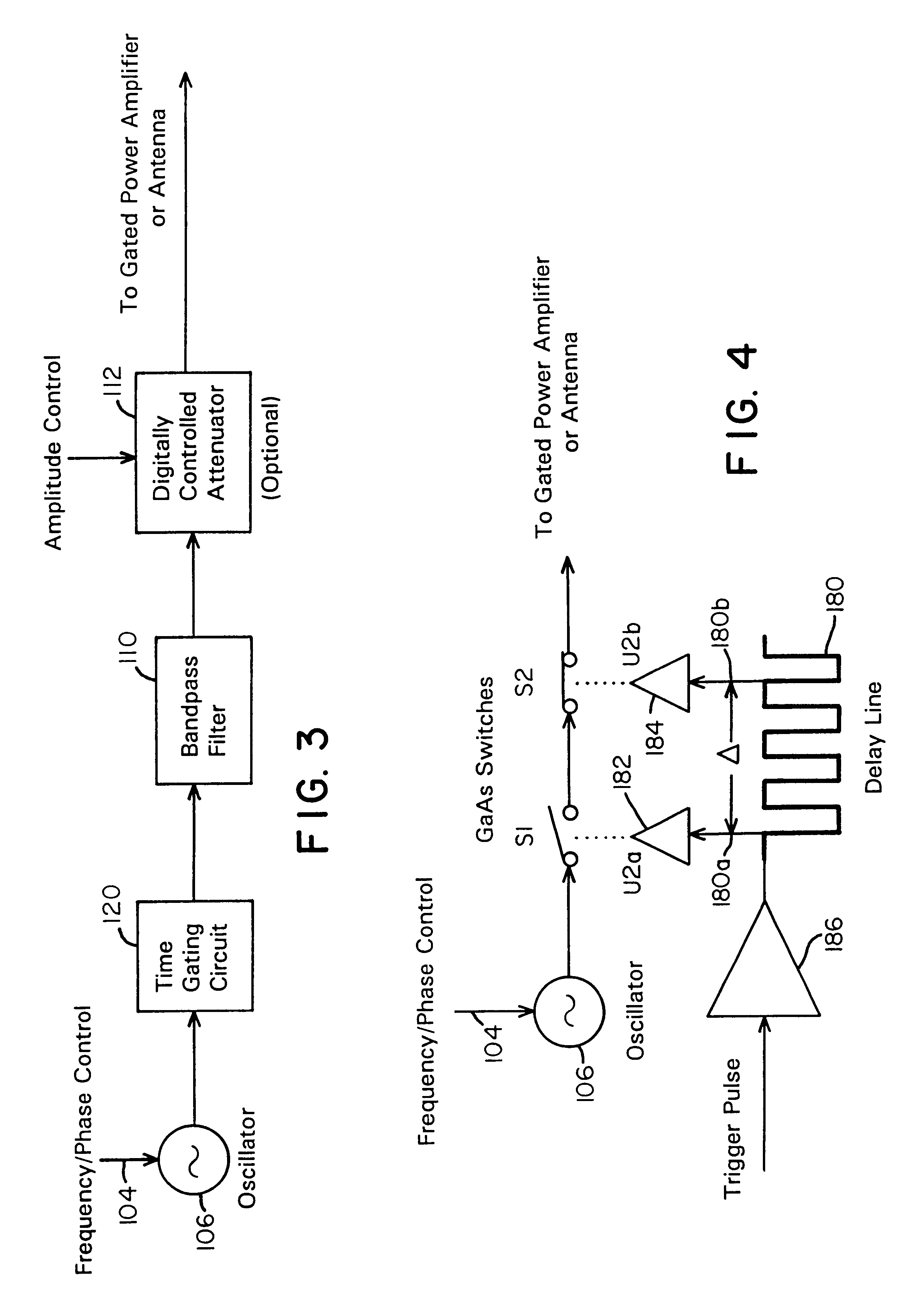
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
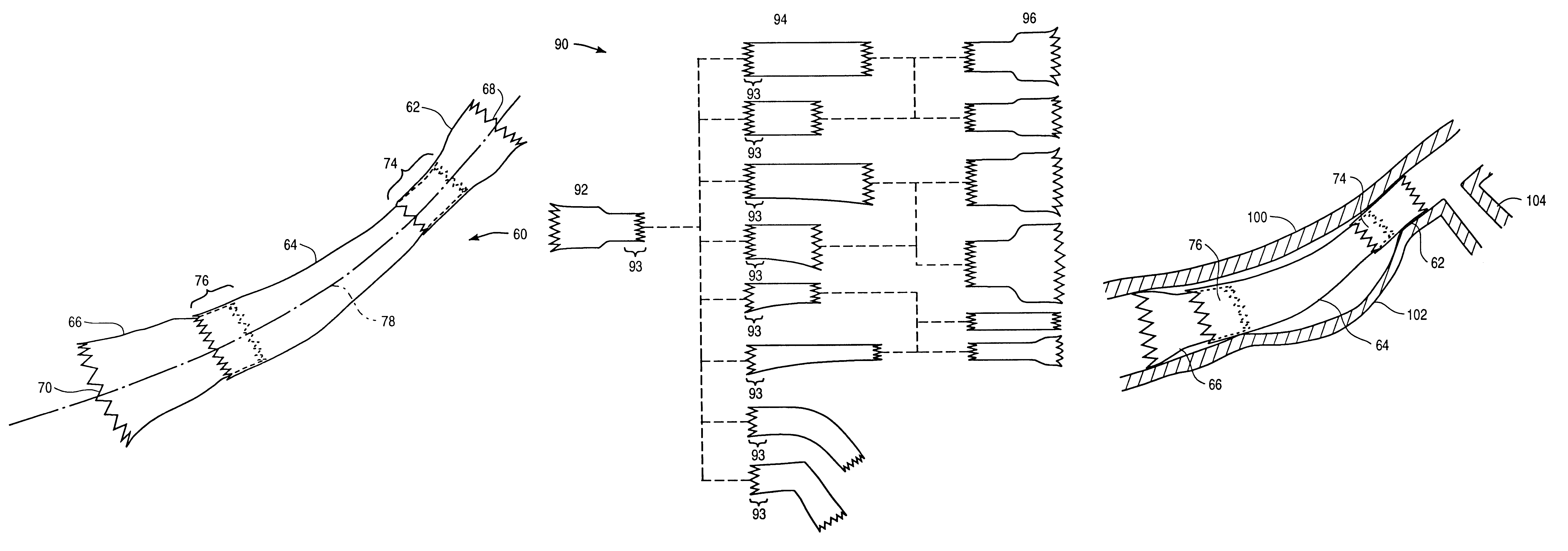
Modular intraluminal prosteheses construction and methods
InactiveUS6193745B1Unnecessary expansive forcePrevent radial movementStentsBlood vesselsDiseaseExtensibility
The present invention provides modular intraluminal tubular prostheses, particularly stents and stent-grafts, for the treatment of disease conditions, particularly aneurysms. Modular sections of the prostheses, or "prosthetic modules," may be selectively combined to form a composite prosthesis having characteristics which are tailored to the specific requirements of the patient. Each prosthetic module preferably includes one or more standard interface ends for engaging another module, the module / module interface typically comprising ends which overlap and / or lock within a predetermined axial range. Advantageously, the axial length, cross-section, perimeter, resilient expansive force, axial flexibility, liner permeability, liner extensibility, radial conformability, liner / tubal wall sealing and anchoring, and other prosthetic characteristics may be varied along the axis of the composite prosthesis, and also along the axis of each prosthetic module. The modules are preferably individually introduced into a lumen system of a patient body so that the composite prosthesis is assembled in situ. Ideally, selection of appropriate prosthetic modules and the flexibility of the interface overlap range provides a custom fit intraluminal prosthesis which provides a therapy tailored to the individual patient's needs.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
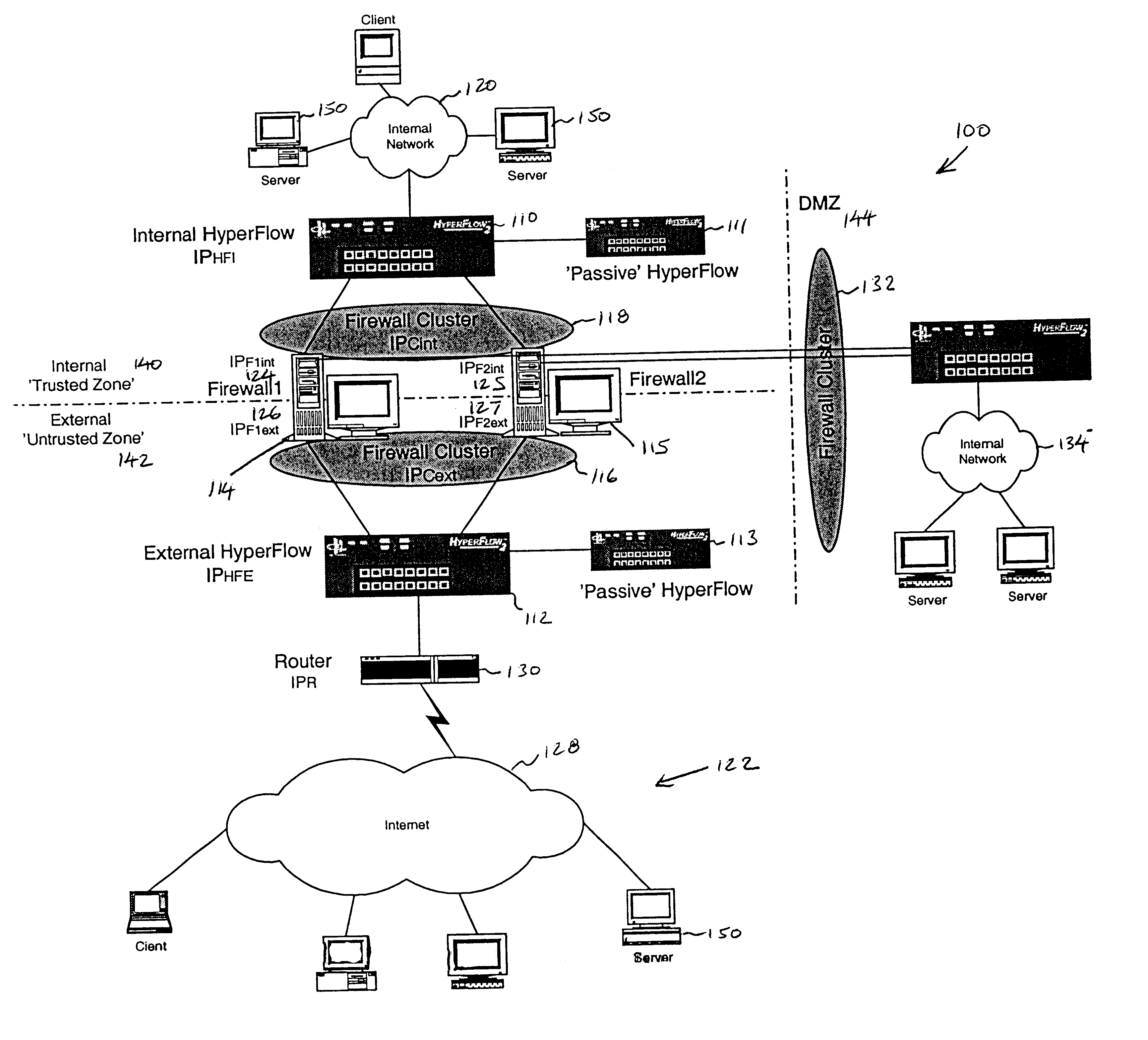
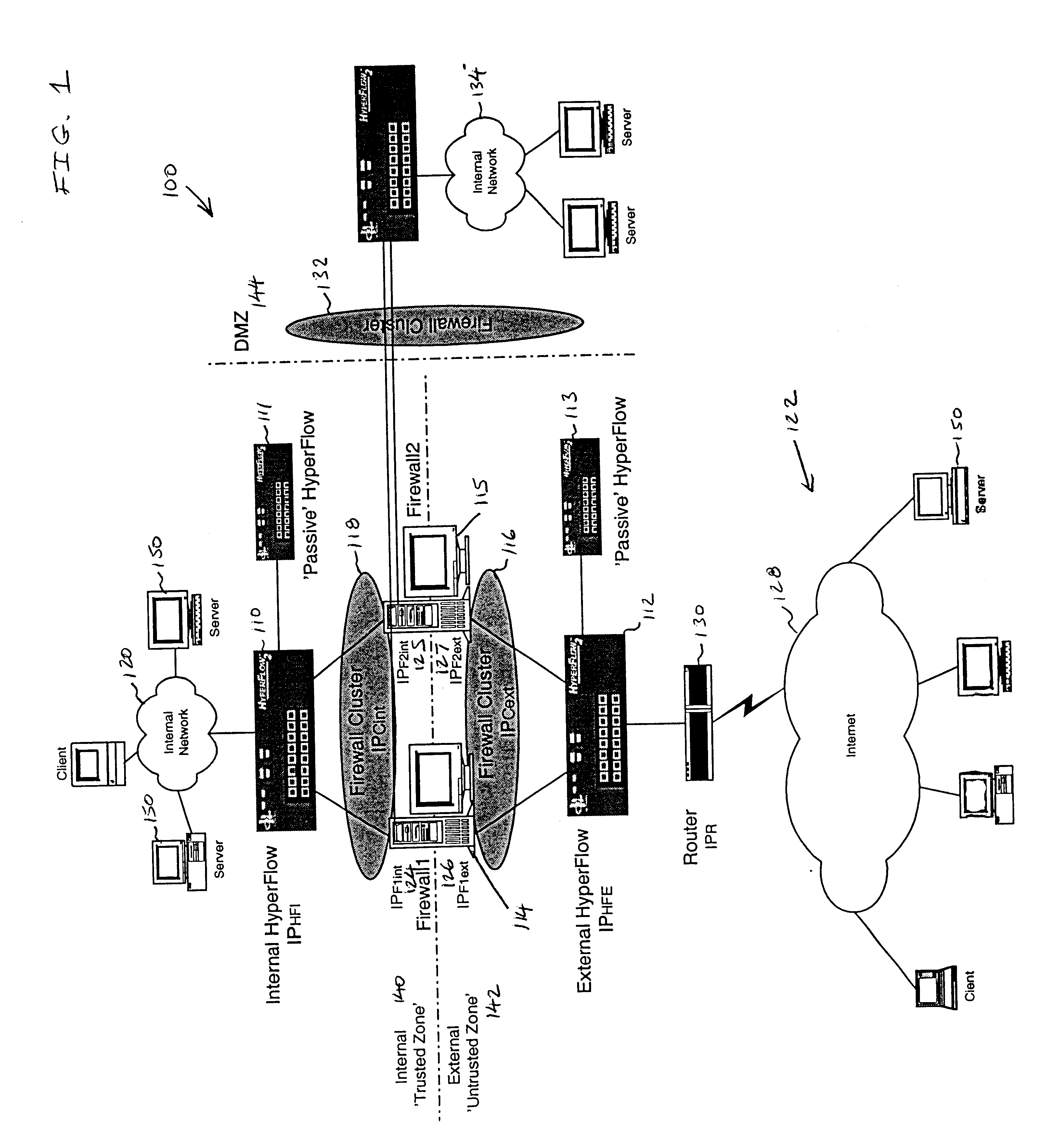
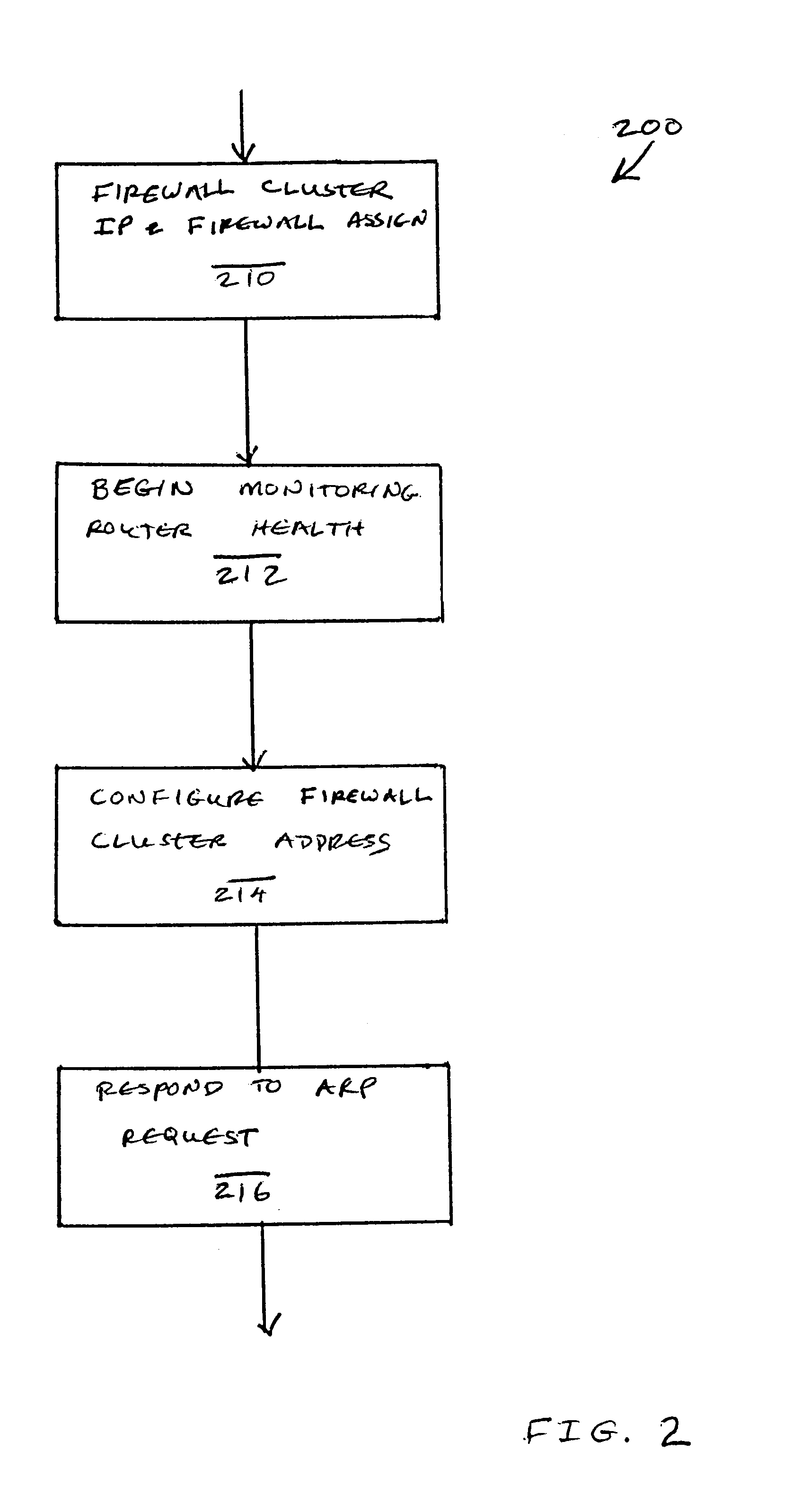
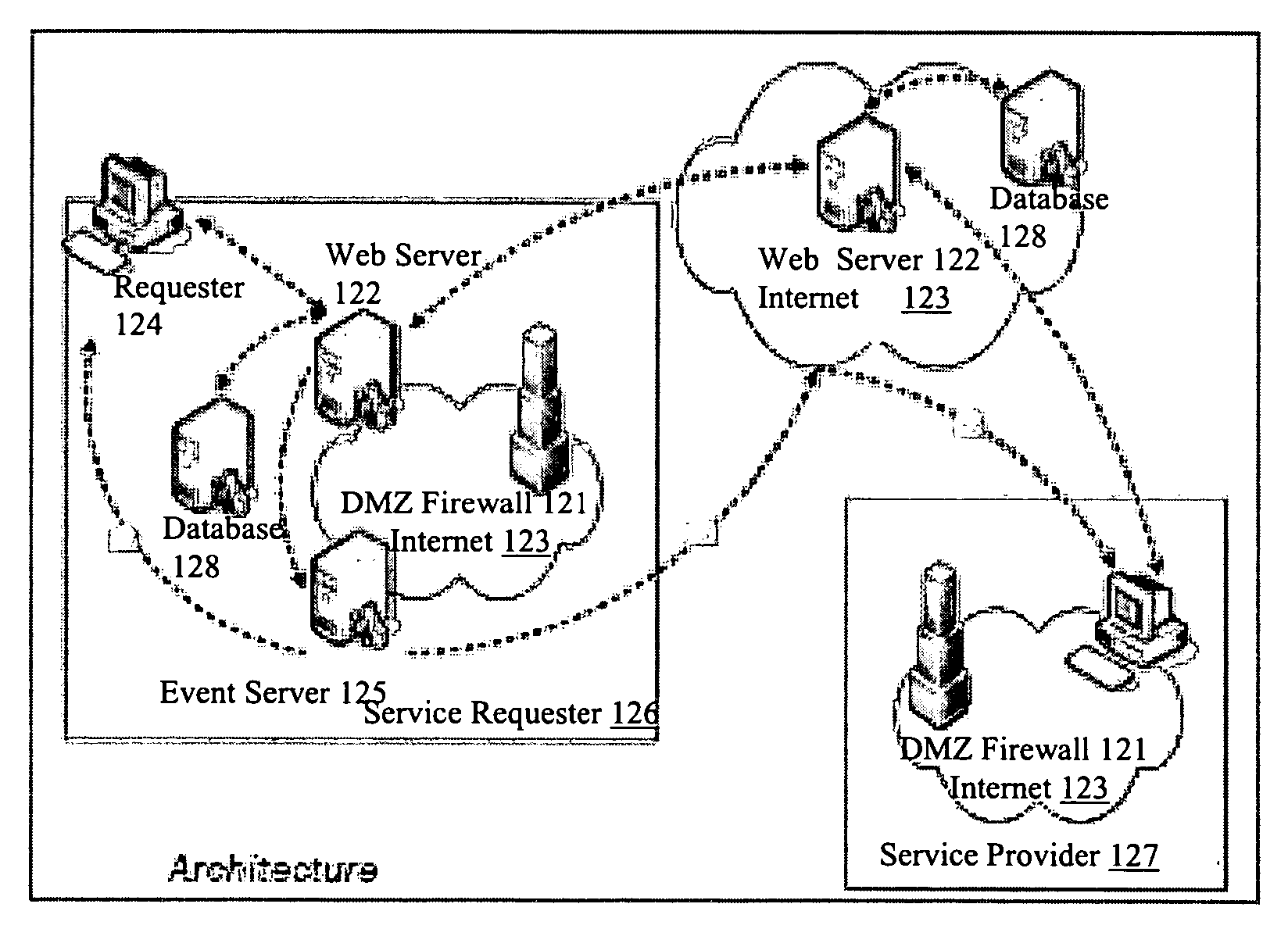
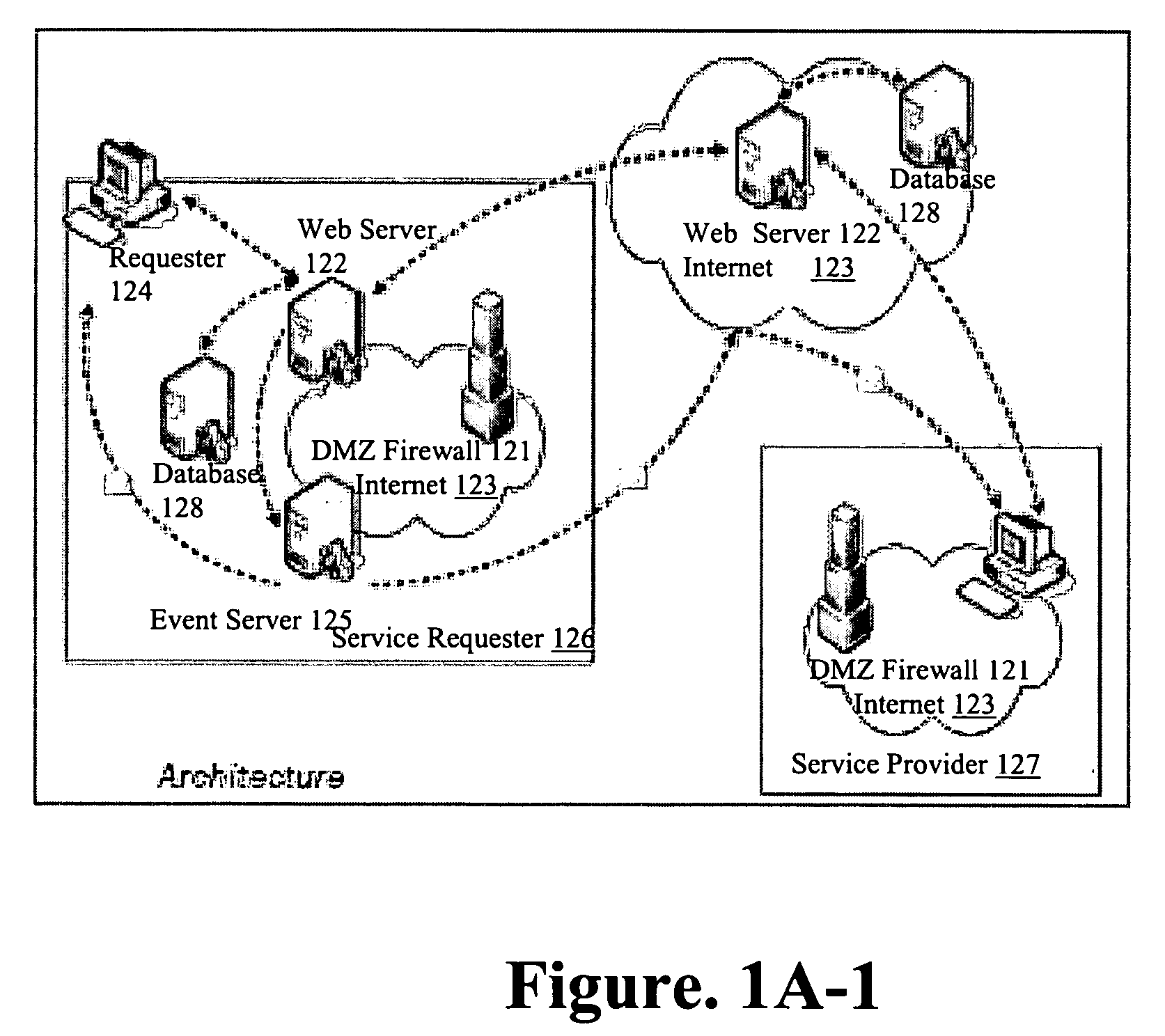
Firewall clustering for multiple network servers
InactiveUS6880089B1Increase capacityReduce calculationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlTraffic capacityExtensibility
A firewall clustering system connects two or more firewalls between an internal network and an external network. The plurality of two or more firewalls are combined to supply high-availability and scaling of processing capacity. Firewalls maintain client-server state information. Flow controllers are connected to the firewalls and placed on both the internal “trusted” side and the external “untrusted” side of the firewalls. Flow controllers are placed on both sides of the firewalls to ensure that traffic for a given client-server session flows through the same firewall in both inbound and outbound directions. The firewalls perform filtering operations and / or network address translation (NAT) services. In both cases, the flow controllers supply high availability, scalability, and traffic distribution for the firewalls in the firewall cluster.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
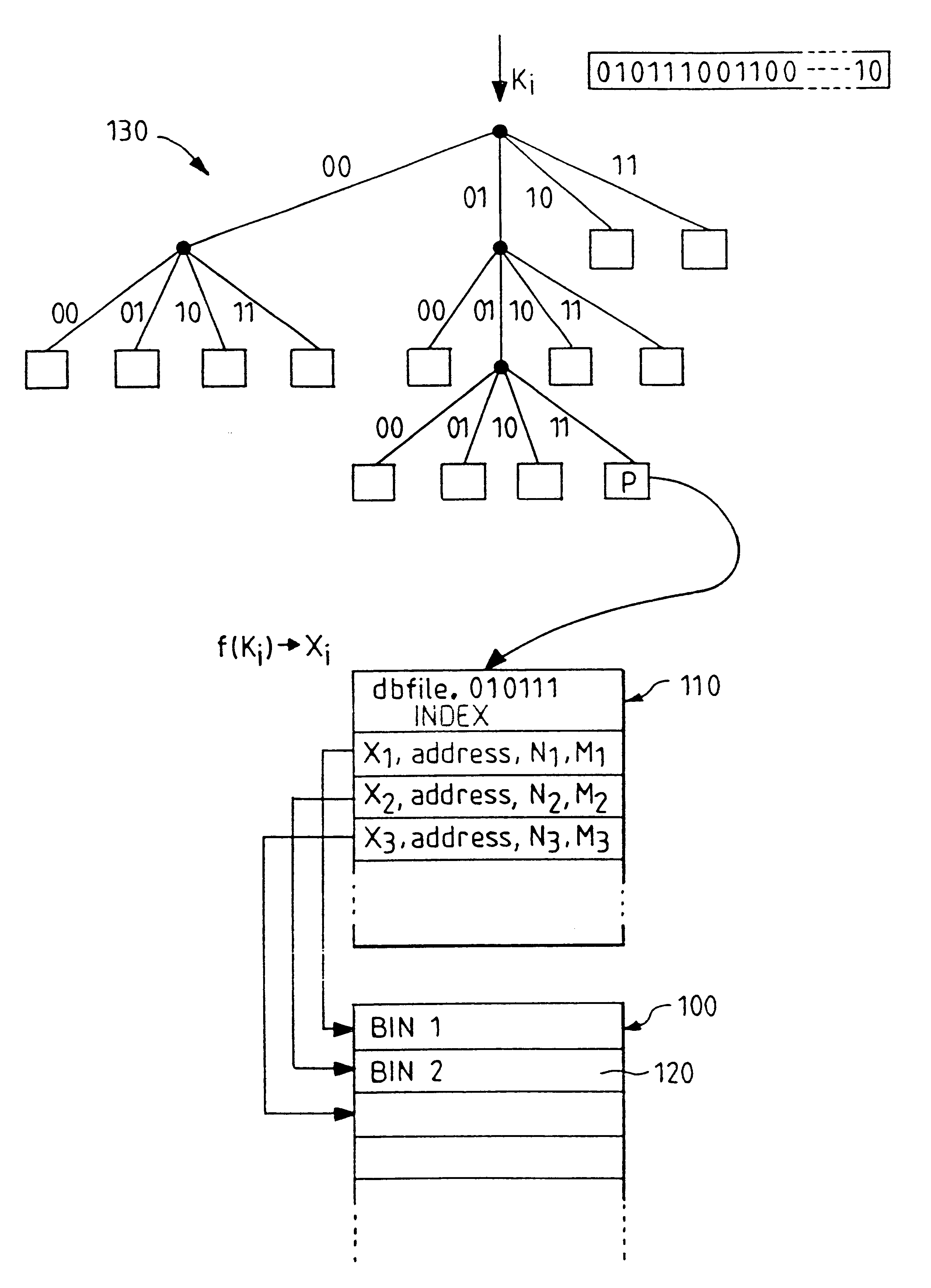
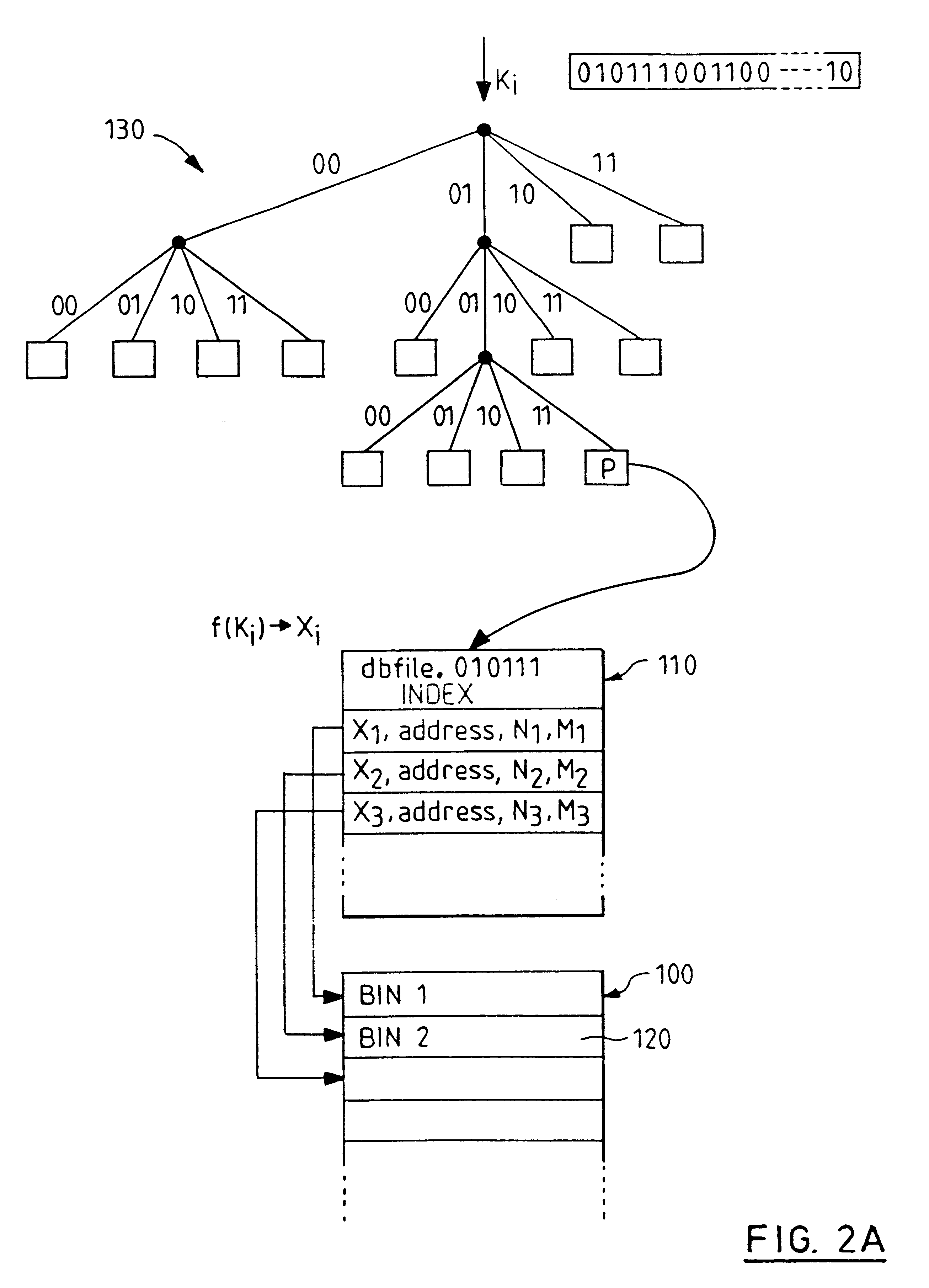
Indexed file system and a method and a mechanism for accessing data records from such a system
InactiveUS6292795B1Efficient access to dataWastefulData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExtensibilityCollision detection
A computer filing system includes a data access and allocation mechanism including a directory and a plurality of indexed data files or hash tables. The directory is preferably a radix tree including directory entries which contain pointers to respective ones of the hash tables. Using a plurality of hash tables avoids the whole database ever having to be re-hashed all at once. If a hash table exceeds a preset maximum size as data is added, it is replaced by two hash tables and the directory is updated to include two separate directory entries each containing a pointer to one of the new hash tables. The directory is locally extensible such that new levels are added to the directory only where necessary to distinguish between the hash tables. Local extensibility prevents unnecessary expansion of the size of the directory while also allowing the size of the hash tables to be controlled. This allows optimisation of the data access mechanism such that an optimal combination of directory-look-up and hashing processes is used. Additionally, if the number of keys mapped to an indexed data file is less than a threshold number (corresponding to the number of entries which can be held in a reasonable index), the index for the data file is built with a one-to-one relationship between keys and index entries such that each index entry identifies a data block holding data for only one key. This avoids the overhead of the collision detection of hashing when it ceases to be useful.
Owner:IBM CORP
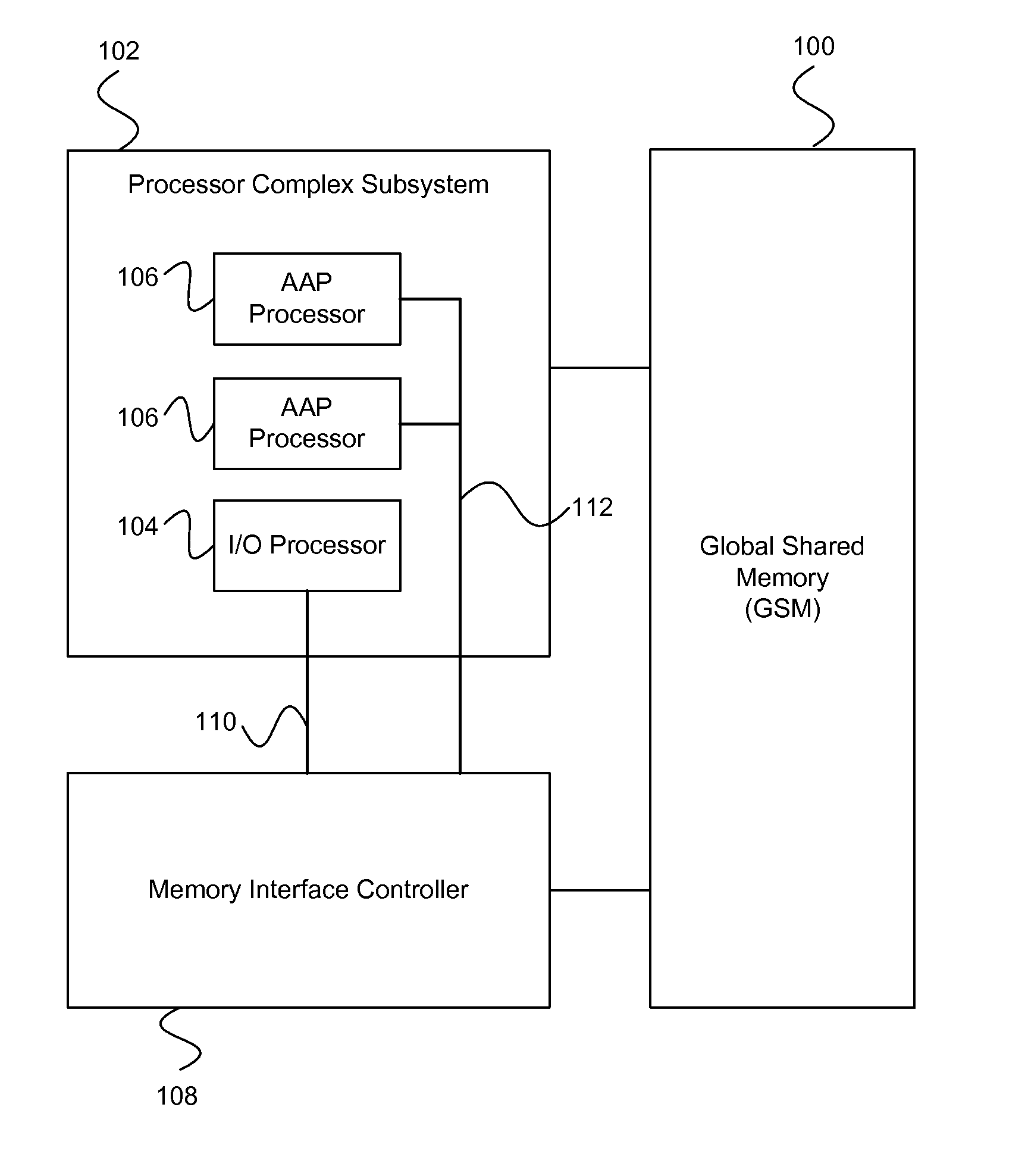
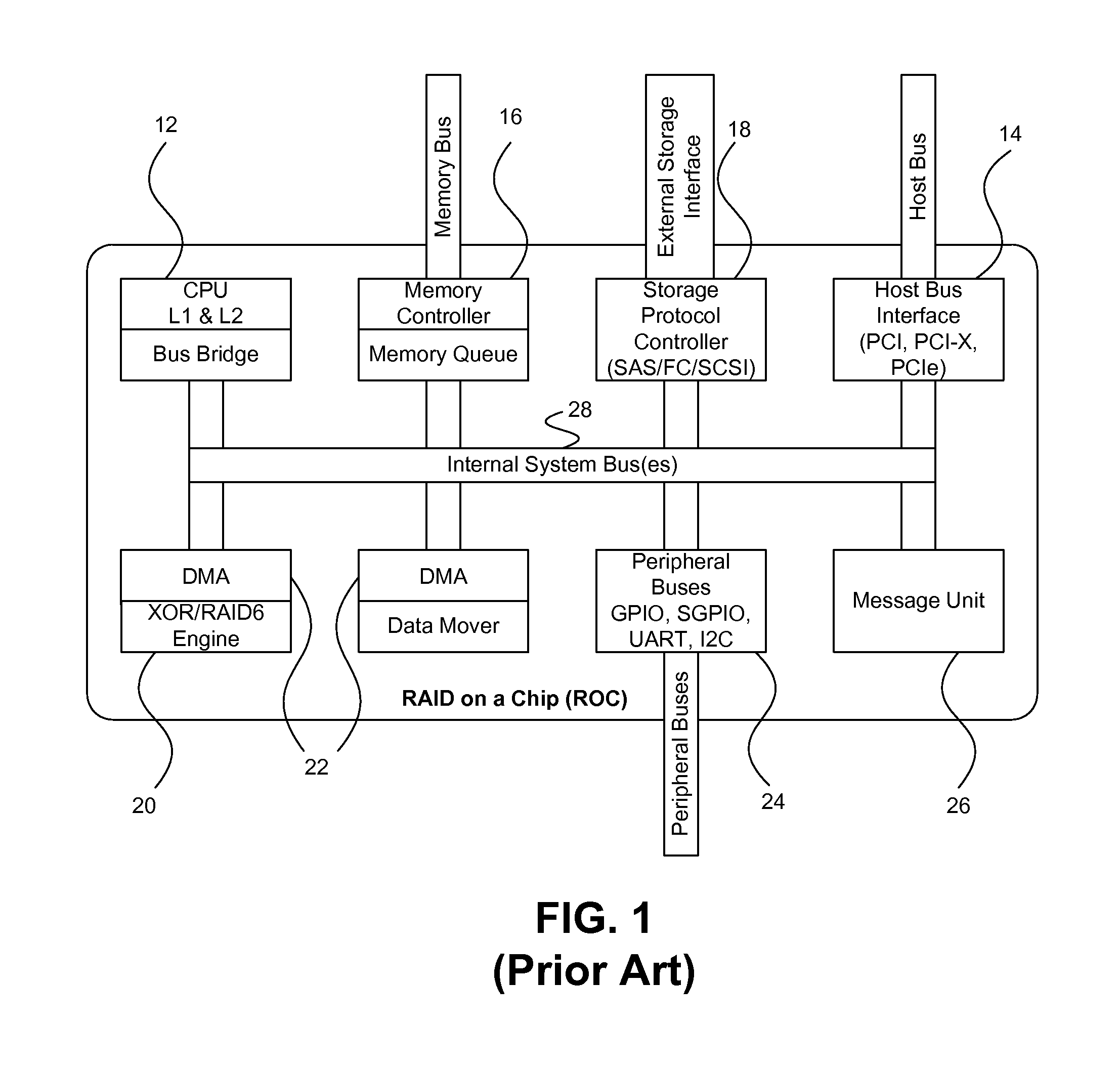
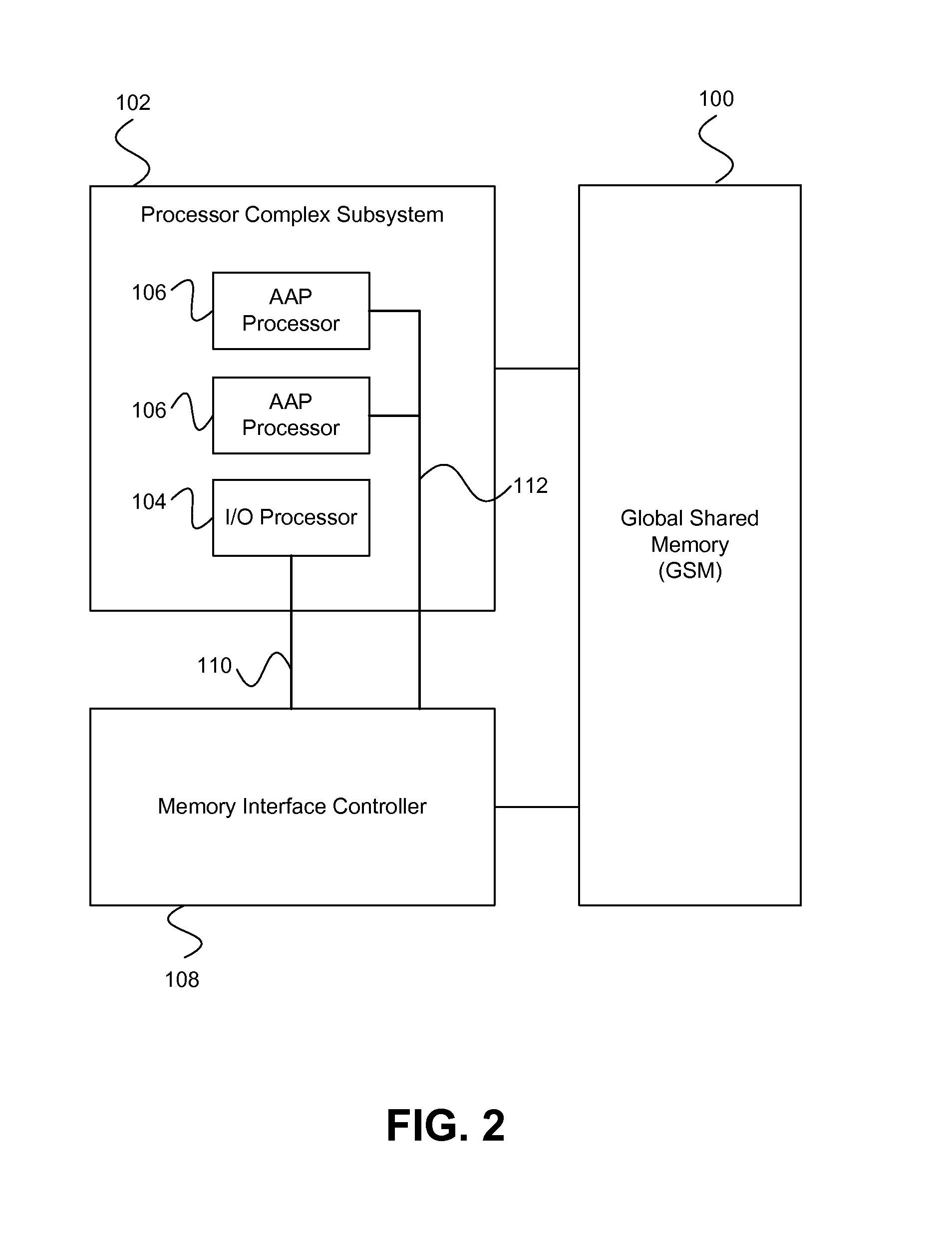
On-chip shared memory based device architecture
ActiveUS7743191B1Reduce disadvantagesLow costRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsRecord information storageExtensibilityRAID
A method and architecture are provided for SOC (System on a Chip) devices for RAID processing, which is commonly referred as RAID-on-a-Chip (ROC). The architecture utilizes a shared memory structure as interconnect mechanism among hardware components, CPUs and software entities. The shared memory structure provides a common scratchpad buffer space for holding data that is processed by the various entities, provides interconnection for process / engine communications, and provides a queue for message passing using a common communication method that is agnostic to whether the engines are implemented in hardware or software. A plurality of hardware engines are supported as masters of the shared memory. The architectures provide superior throughput performance, flexibility in software / hardware co-design, scalability of both functionality and performance, and support a very simple abstracted parallel programming model for parallel processing.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Stitched stent grafts and methods for their fabrication
InactiveUS6123722AUnnecessary expansive forcePrevent radial movementStentsBlood vesselsExtensibilityStent grafting
The present invention provides modular intraluminal tubular prostheses, particularly stents and stent-grafts, for the treatment of disease conditions, particularly aneurysms. Modular sections of the prostheses, or "prosthetic modules," may be selectively combined to form a composite prosthesis having characteristics which are tailored to the specific requirements of the patient. Each prosthetic module preferably includes one or more standard interface ends for engaging another module, the module / module interface typically comprising ends which overlap and / or lock within a predetermined axial range. Advantageously, the axial length, cross-section, perimeter, resilient expansive force, axial flexibility, liner permeability, liner extensibility, radial conformability, liner / tubal wall sealing and anchoring, and other prosthetic characteristics may be varied along the axis of the composite prosthesis, and also along the axis of each prosthetic module. The modules are preferably individually introduced into a lumen system of a patient body so that the composite prosthesis is assembled in situ. Ideally, selection of appropriate prosthetic modules and the flexibility of the interface overlap range provides a custom fit intraluminal prosthesis which provides a therapy tailored to the individual patient's needs.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
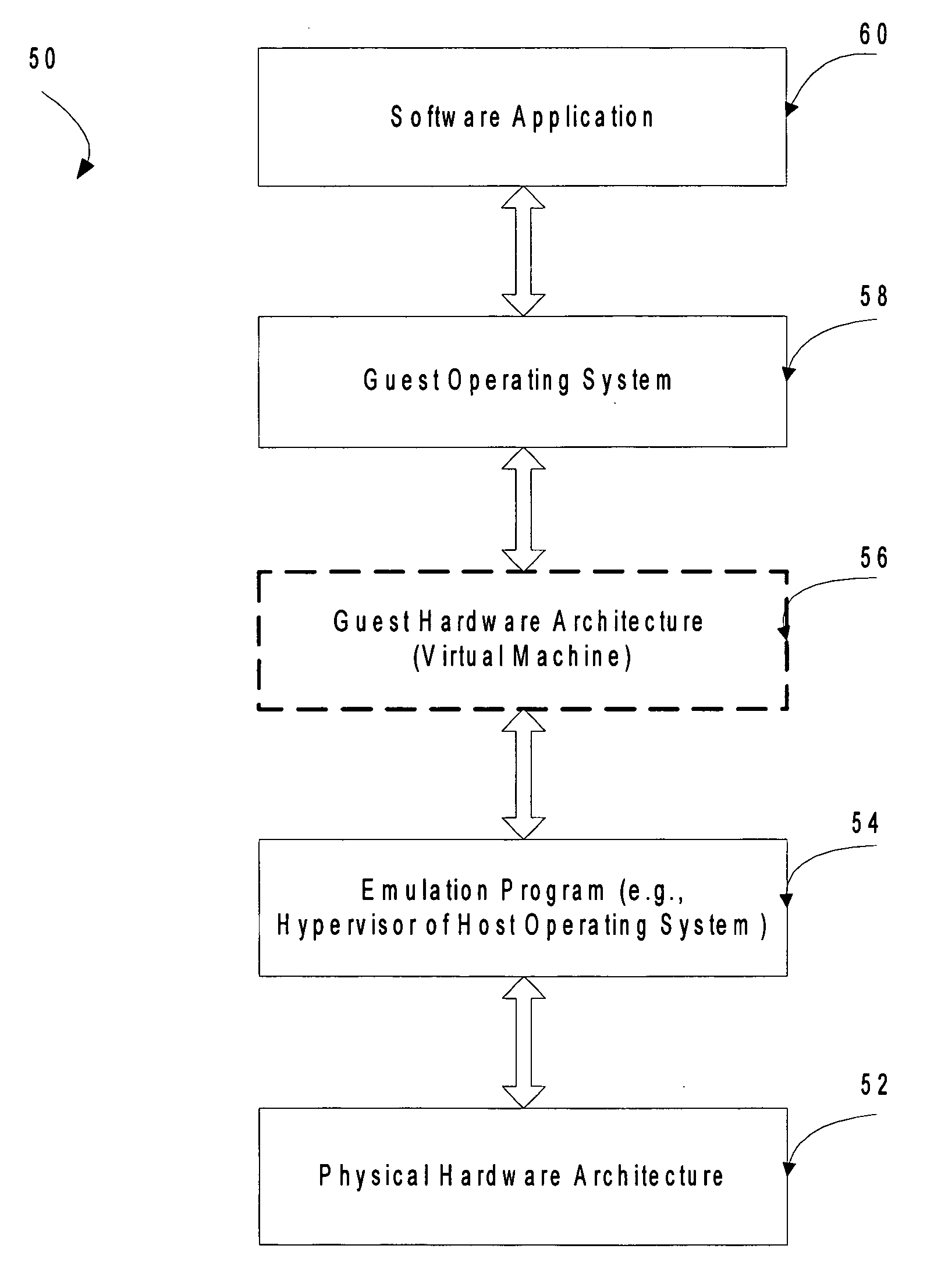
Mechanism to store information describing a virtual machine in a virtual disk image
ActiveUS20060218544A1Reduce in quantityTightly coupledSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsExtensibilityOperational system
A mechanism is provided for making information about the virtual disk image file and / or its associated virtual image configuration file more readily available to a user. The virtual disk image file format is expanded to include fields in which information about the data in the file can be stored. Extensible information on file content, compatible HW configurations, compatible host OSes, timeout status, DRM status, patch state, and network topology, tag data for indexing, configuration files, saved state files, operation history data, and the like is stored in a location within a virtual disk image file that can be read without executing the virtual machine. This information can then be used to search the contents of the virtual disk image, to enforce usage policies, to provide extensibility for vendors, and the like.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of and system for physically distributed, logically shared, and data slice-synchronized shared memory switching
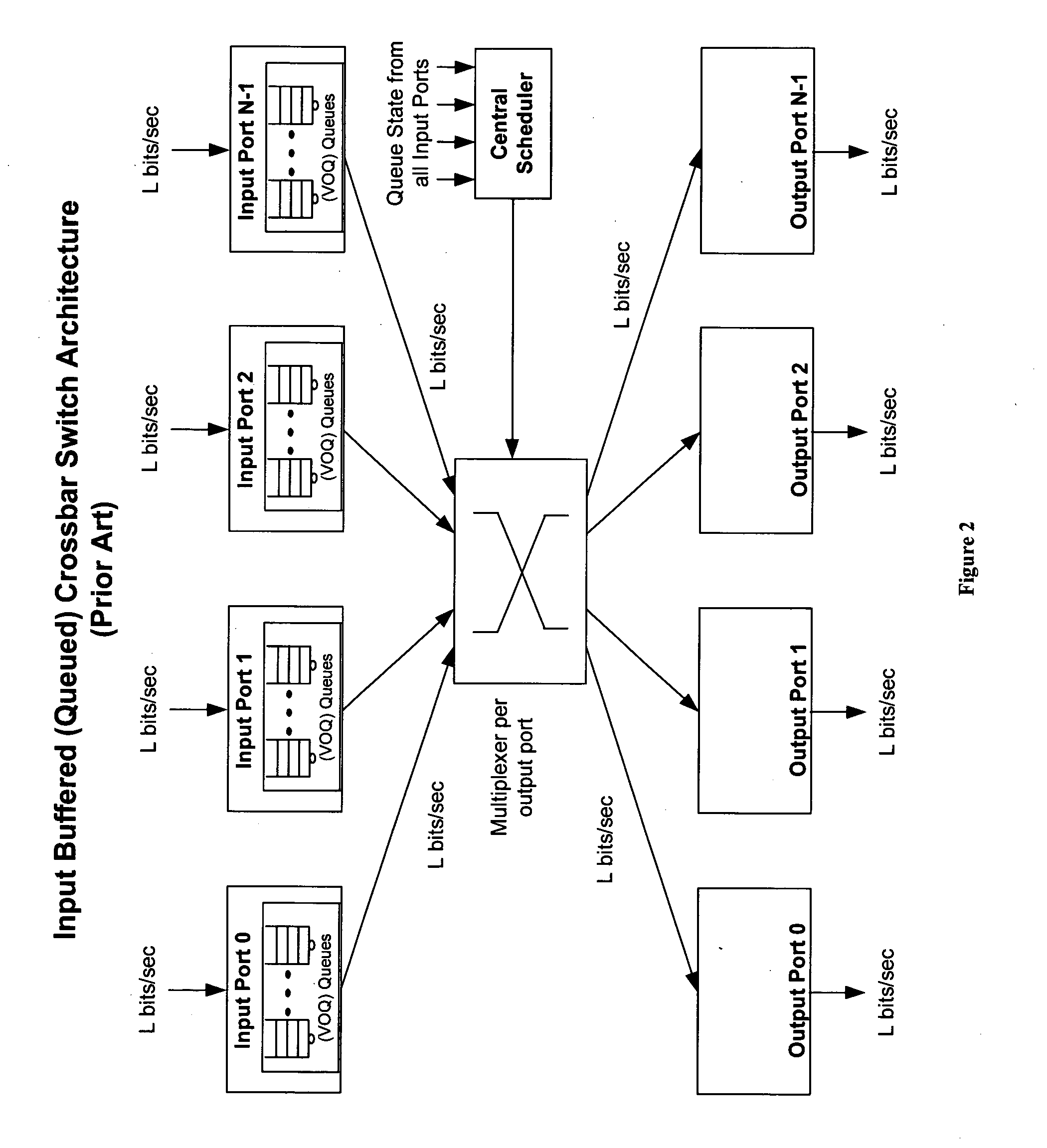
An improved data networking technique and apparatus using a novel physically distributed but logically shared and data-sliced synchronized shared memory switching datapath architecture integrated with a novel distributed data control path architecture to provide ideal output-buffered switching of data in networking systems, such as routers and switches, to support the increasing port densities and line rates with maximized network utilization and with per flow bit-rate latency and jitter guarantees, all while maintaining optimal throughput and quality of services under all data traffic scenarios, and with features of scalability in terms of number of data queues, ports and line rates, particularly for requirements ranging from network edge routers to the core of the network, thereby to eliminate both the need for the complication of centralized control for gathering system-wide information and for processing the same for egress traffic management functions and the need for a centralized scheduler, and eliminating also the need for buffering other than in the actual shared memory itself,—all with complete non-blocking data switching between ingress and egress ports, under all circumstances and scenarios.
Owner:QOS LOGIX
Ultra wideband data transmission system and method
InactiveUS6690741B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationBandpass filteringExtensibility
A data-modulated ultra wideband transmitter that modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
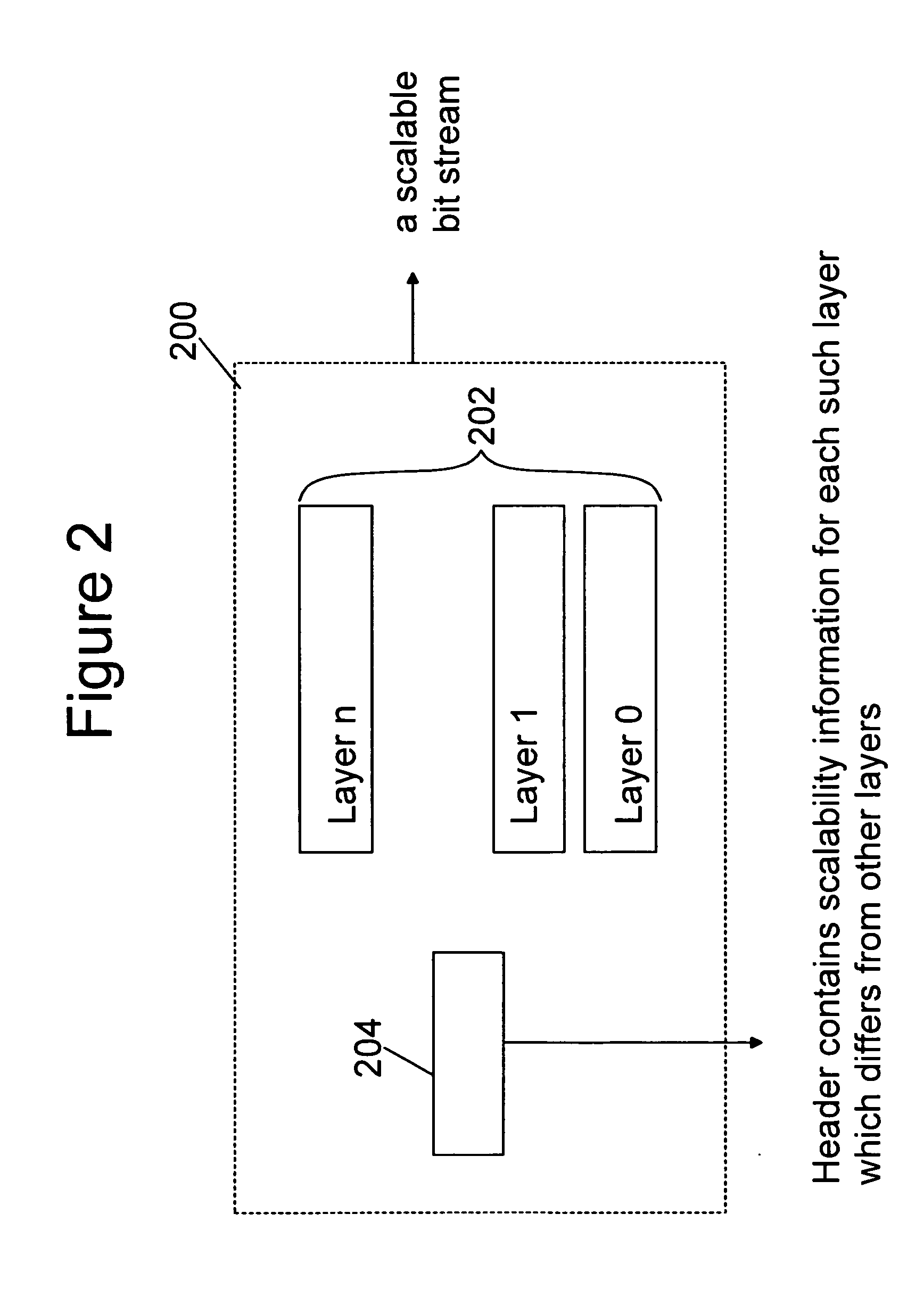
Coding, storage and signalling of scalability information
ActiveUS20060256851A1Reduce computational complexityAvoid inclusionsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionExtensibilityComputer architecture
A method and device for encoding, decoding, storage and transmission of a scalable data stream to include layers having different coding properties including: producing one or more layers of the scalable data stream, wherein the coding properties include at least one of the following: Fine granularity scalability information; Region-of-interest scalability information; Sub-sample scalable layer information; Decoding dependency information; and Initial parameter sets, and signaling the layers with the characterized coding property such that they are readable by a decoder without the need to decode the entire layers. A corresponding method of encoding, decoding, storage, and transmission of a scalable bit stream is also disclosed, wherein at least two scalability layers are present and each layer has a set of at least one property, such as those above identified.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
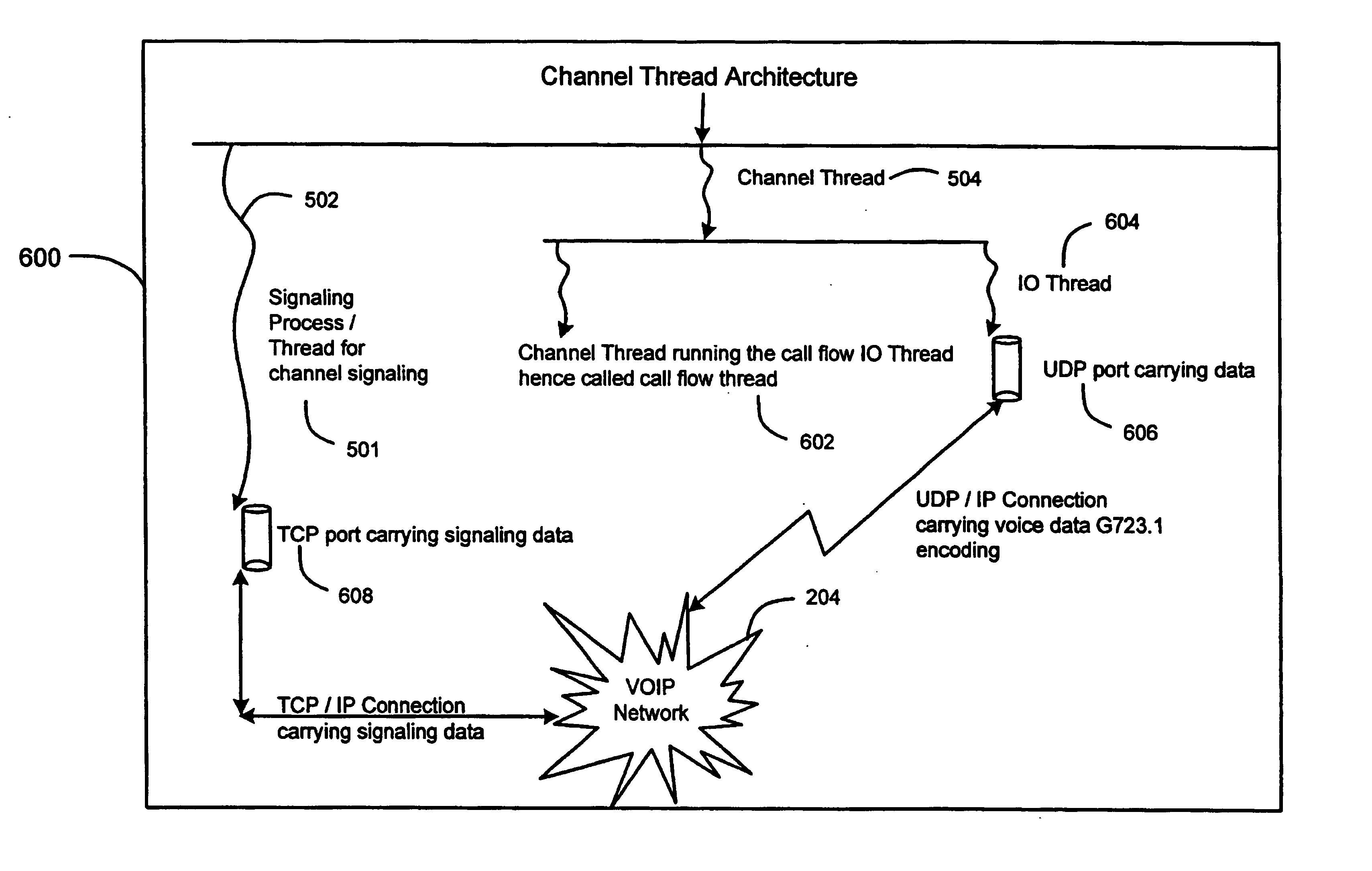
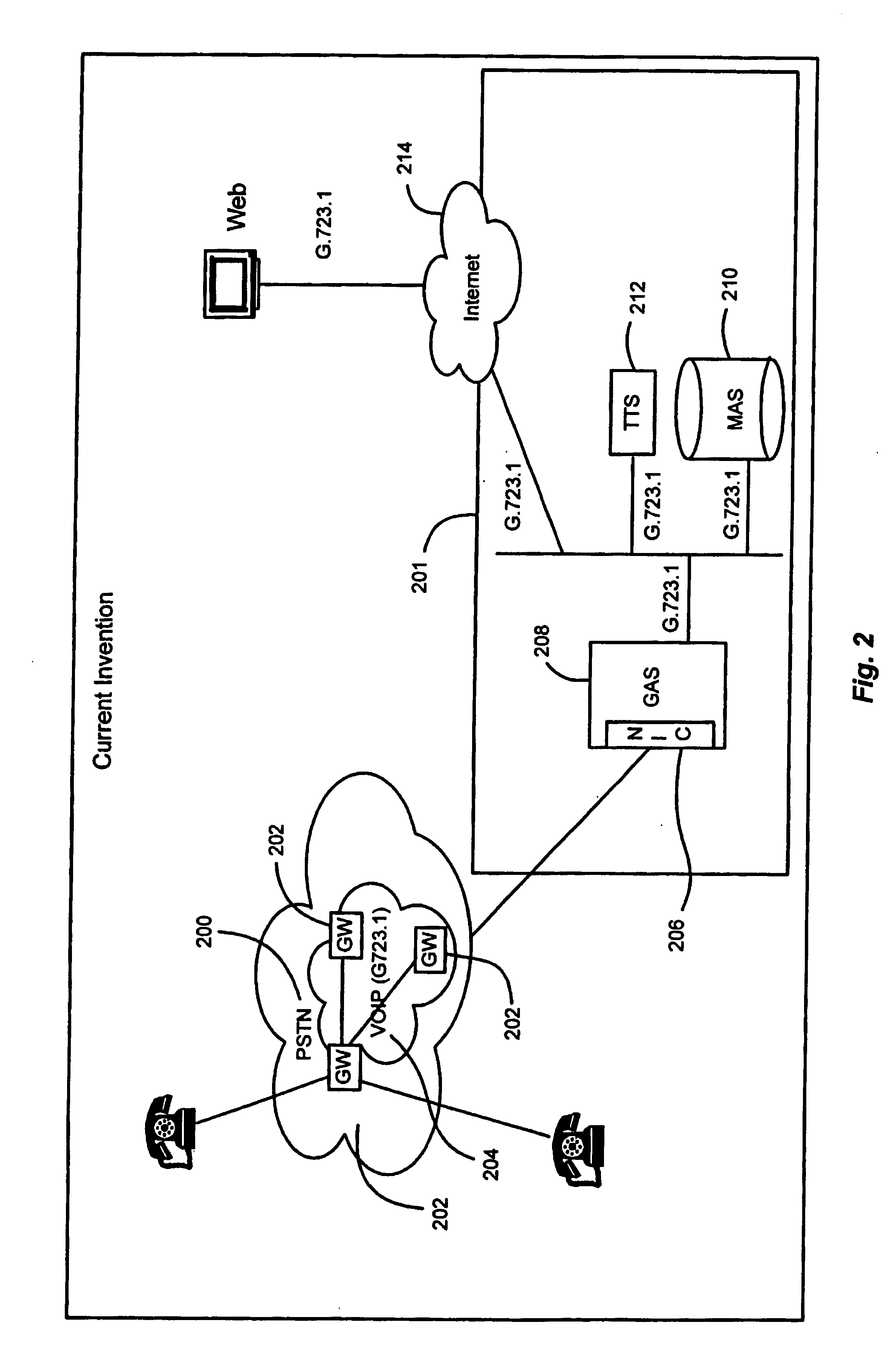
Voice integrated VOIP system
InactiveUS7095733B1Minimize delayImprove storage efficiencyInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexExtensibilityTranscoding
An integrated VoIP unified message processing system includes a voice platform that processes data in native VoIP format. There is no use of hardware telephone interface cards (TICs) or software transcoding to transform data to PCM or other formats. Cost reductions are achieved by the elimination of expensive dedicated hardware and scalability is achieved by obviating the need for software transcoding.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
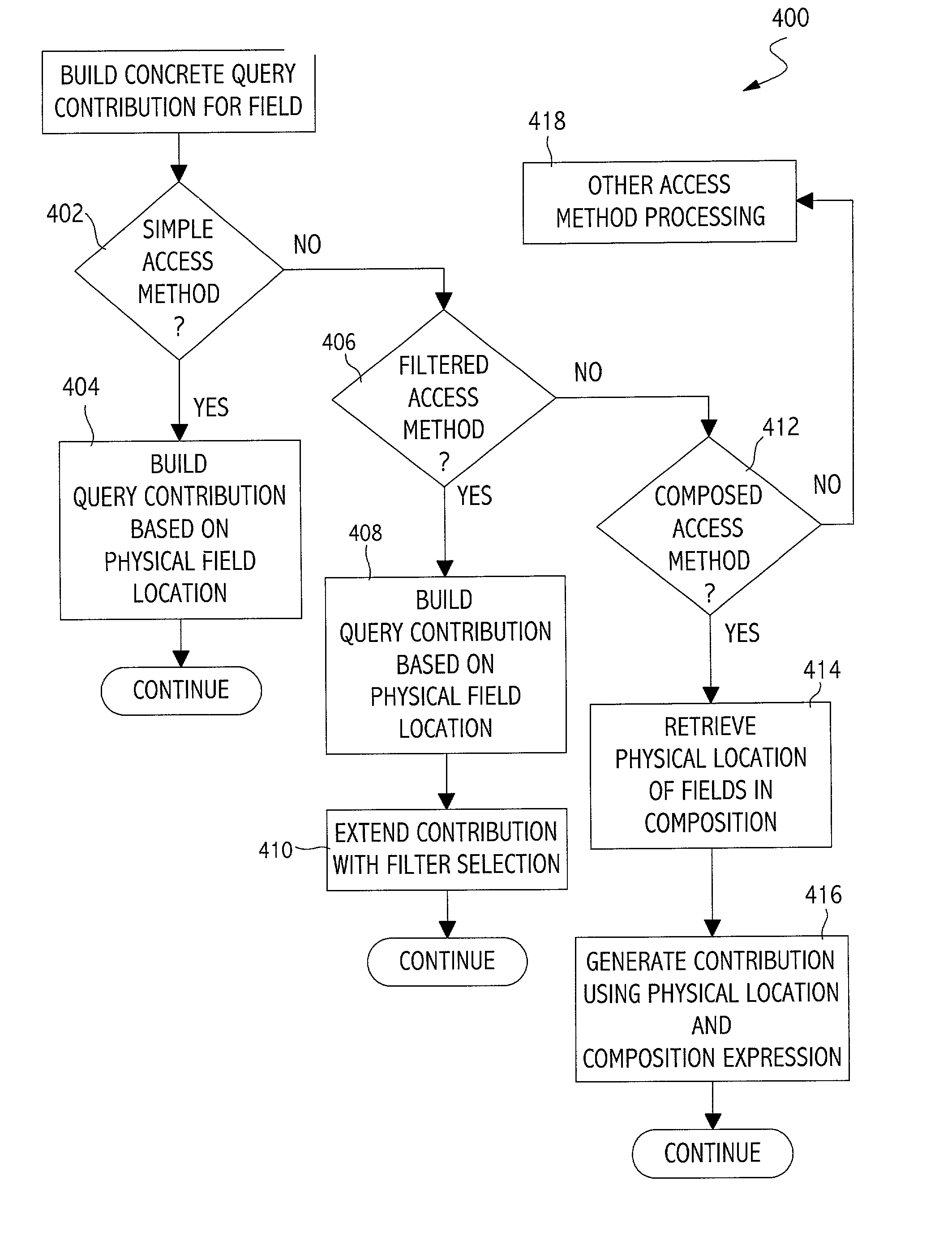
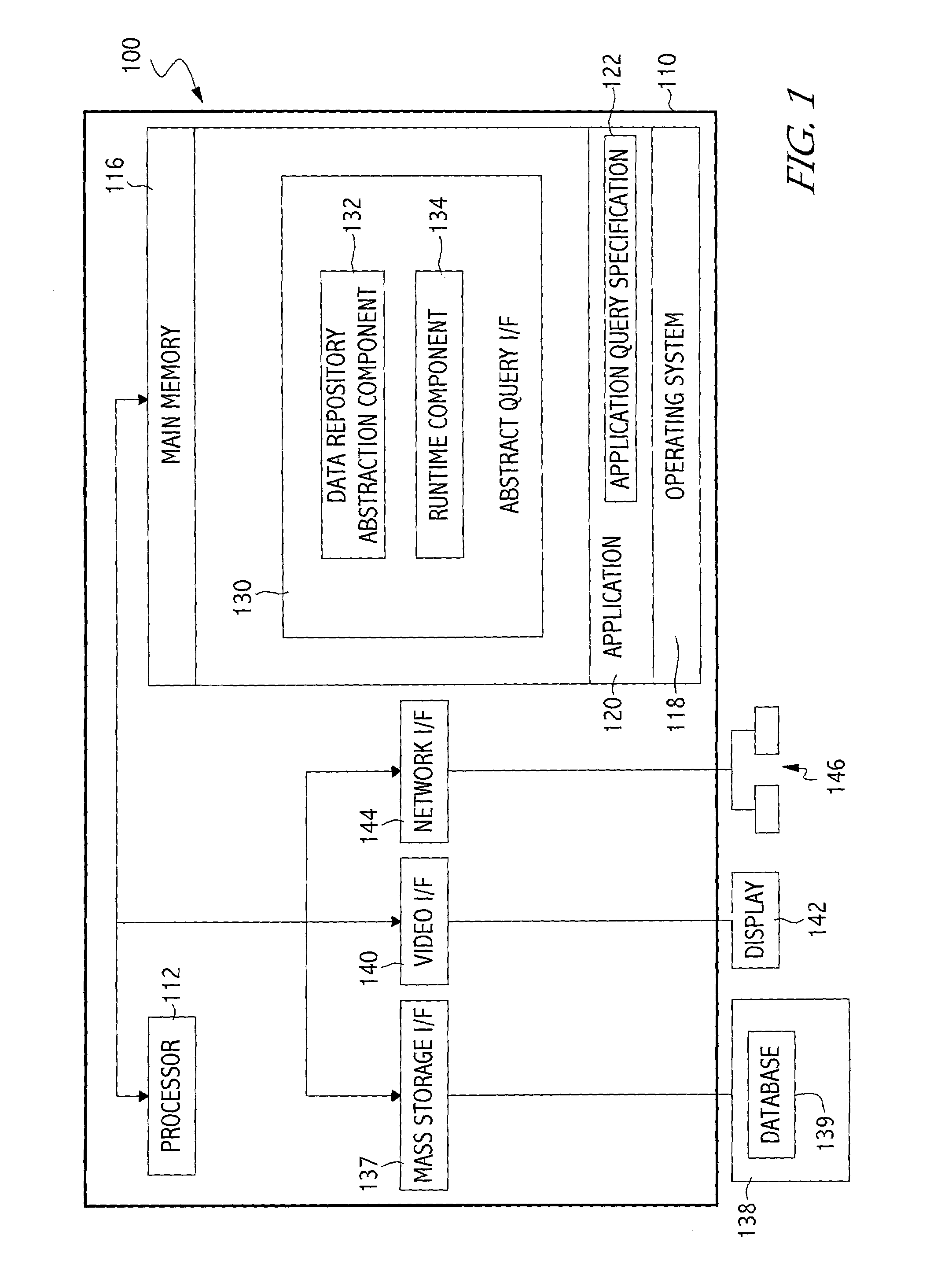
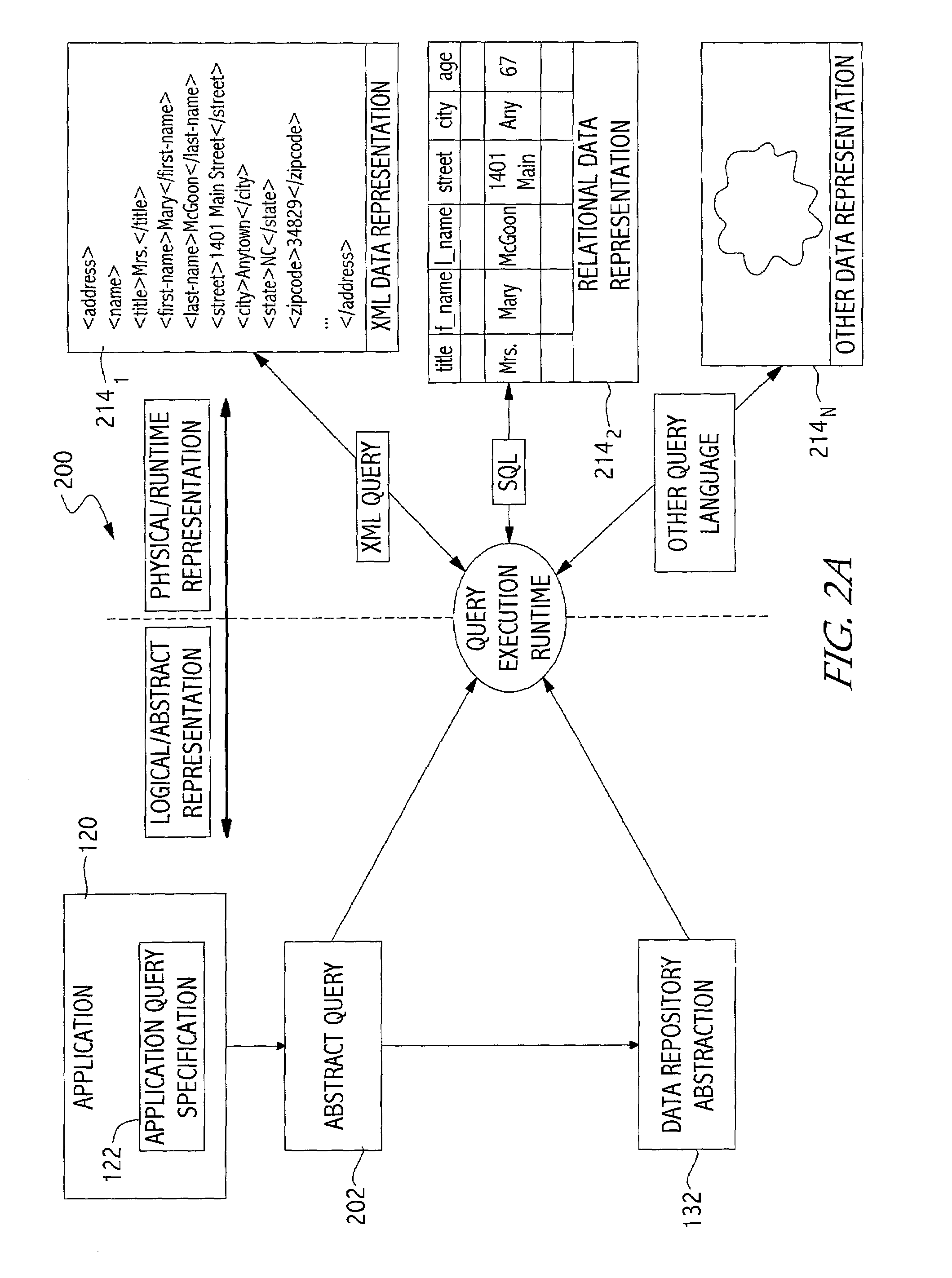
Application portability and extensibility through database schema and query abstraction
InactiveUS6996558B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExtensibilityAbstraction layer
The present invention generally is directed to a system, method and article of manufacture for accessing data independent of the particular manner in which the data is physically represented. In one embodiment, a data repository abstraction layer provides a logical view of the underlying data repository that is independent of the particular manner of data representation. A query abstraction layer is also provided and is based on the data repository abstraction layer. A runtime component performs translation of an abstract query into a form that can be used against a particular physical data representation.
Owner:WORKDAY INC
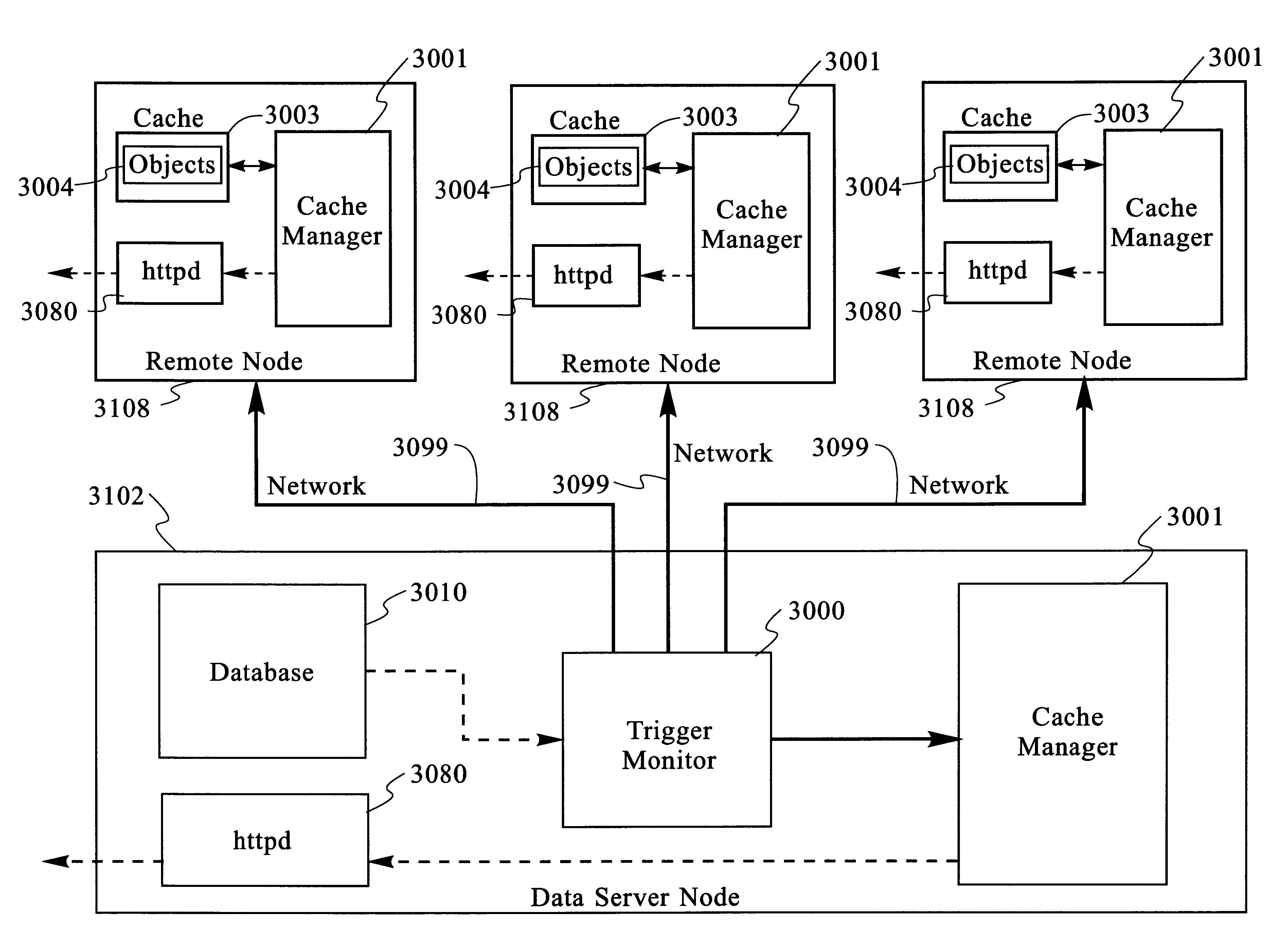
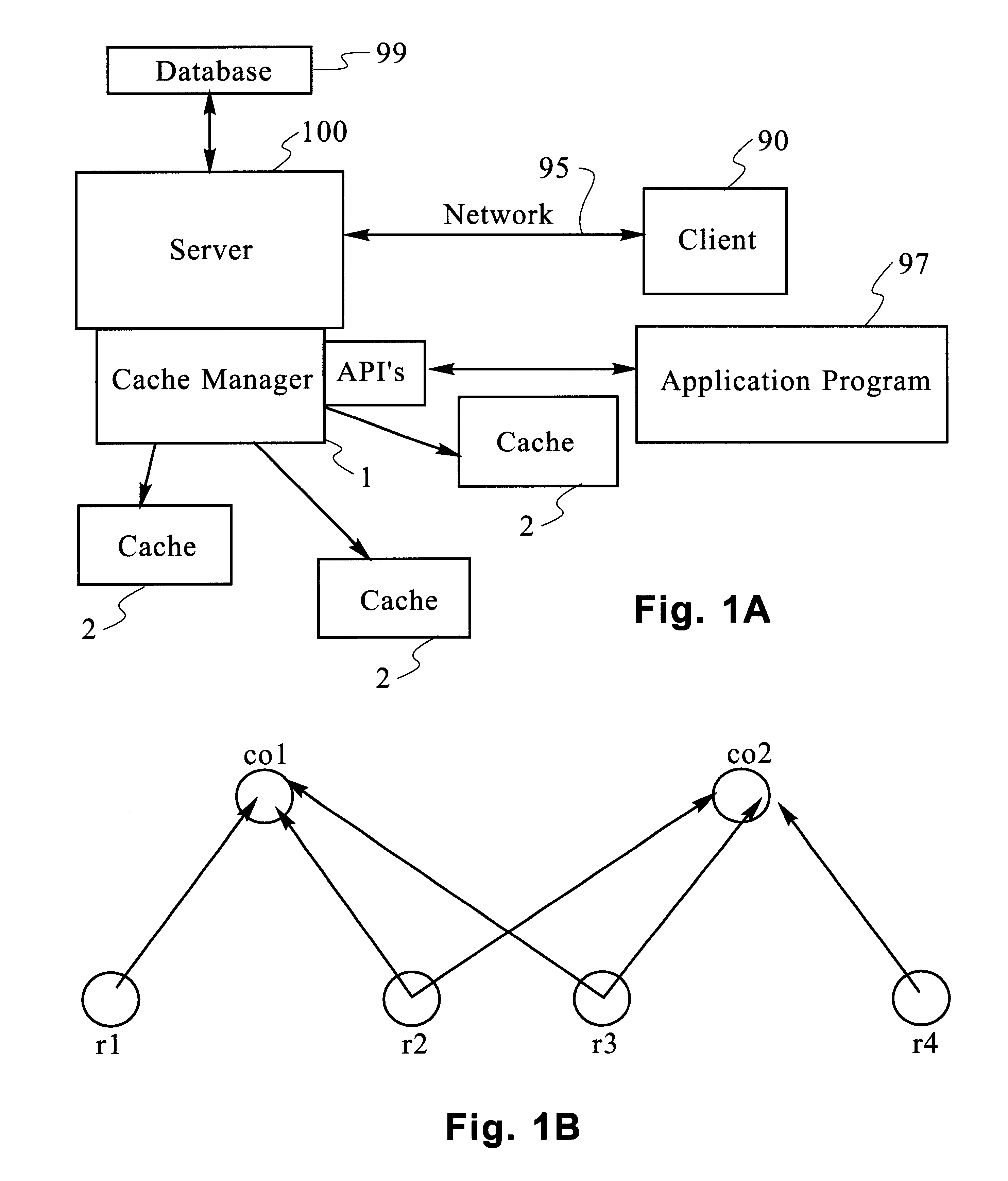
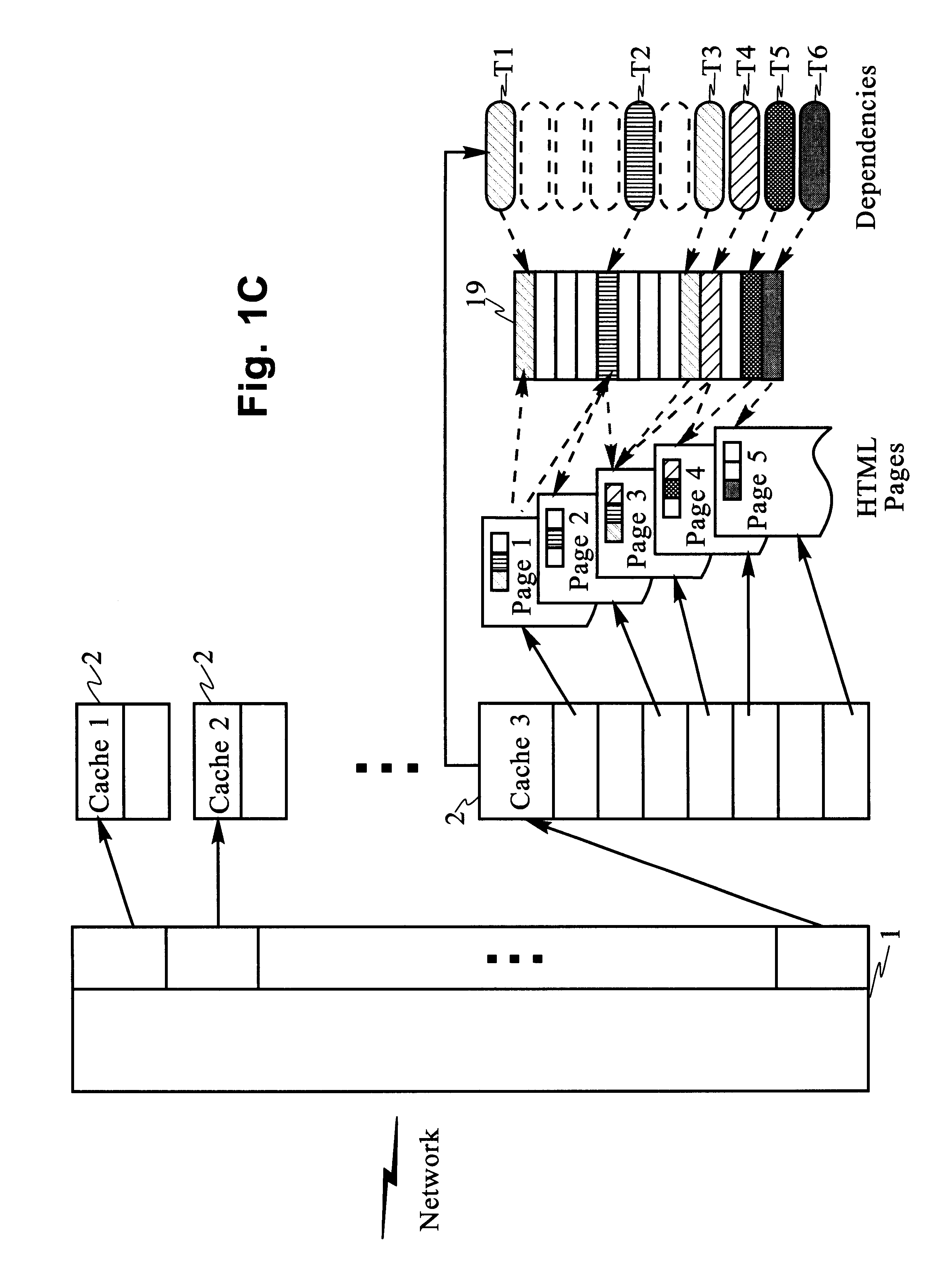
Scaleable method for maintaining and making consistent updates to caches
InactiveUS6256712B1High degreeData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData synchronizationExtensibility
A determination can be made of how changes to underlying data affect the value of objects. Examples of applications are: caching dynamic Web pages; client-server applications whereby a server sending objects (which are changing all the time) to multiple clients can track which versions are sent to which clients and how obsolete the versions are; and any situation where it is necessary to maintain and uniquely identify several versions of objects, update obsolete objects, quantitatively assess how different two versions of the same object are, and / or maintain consistency among a set of objects. A directed graph called an object dependence graph, may be used to represent the data dependencies between objects. Another aspect is constructing and maintaining objects to associate changes in remote data with cached objects. If data in a remote data source changes, database change notifications are used to "trigger" a dynamic rebuild of associated objects. Thus, obsolete objects can be dynamically replaced with fresh objects. The objects can be complex objects, such as dynamic Web pages or compound-complex objects, and the data can be underlying data in a database. The update can include either: storing a new version of the object in the cache; or deleting an object from the cache. Caches on multiple servers can also be synchronized with the data in a single common database. Updated information, whether new pages or delete orders, can be broadcast to a set of server nodes, permitting many systems to simultaneously benefit from the advantages of prefetching and providing a high degree of scaleability.
Owner:IBM CORP
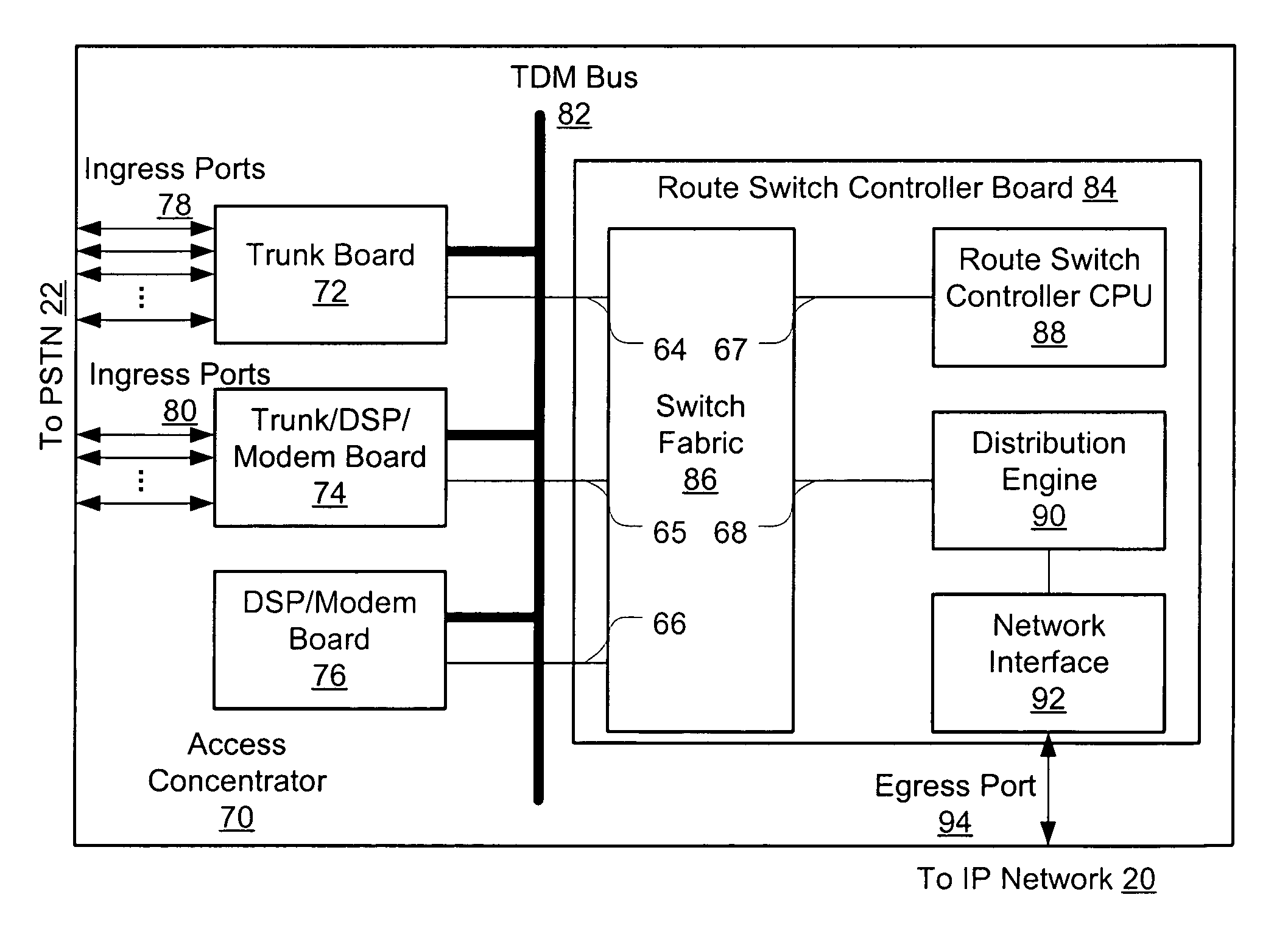
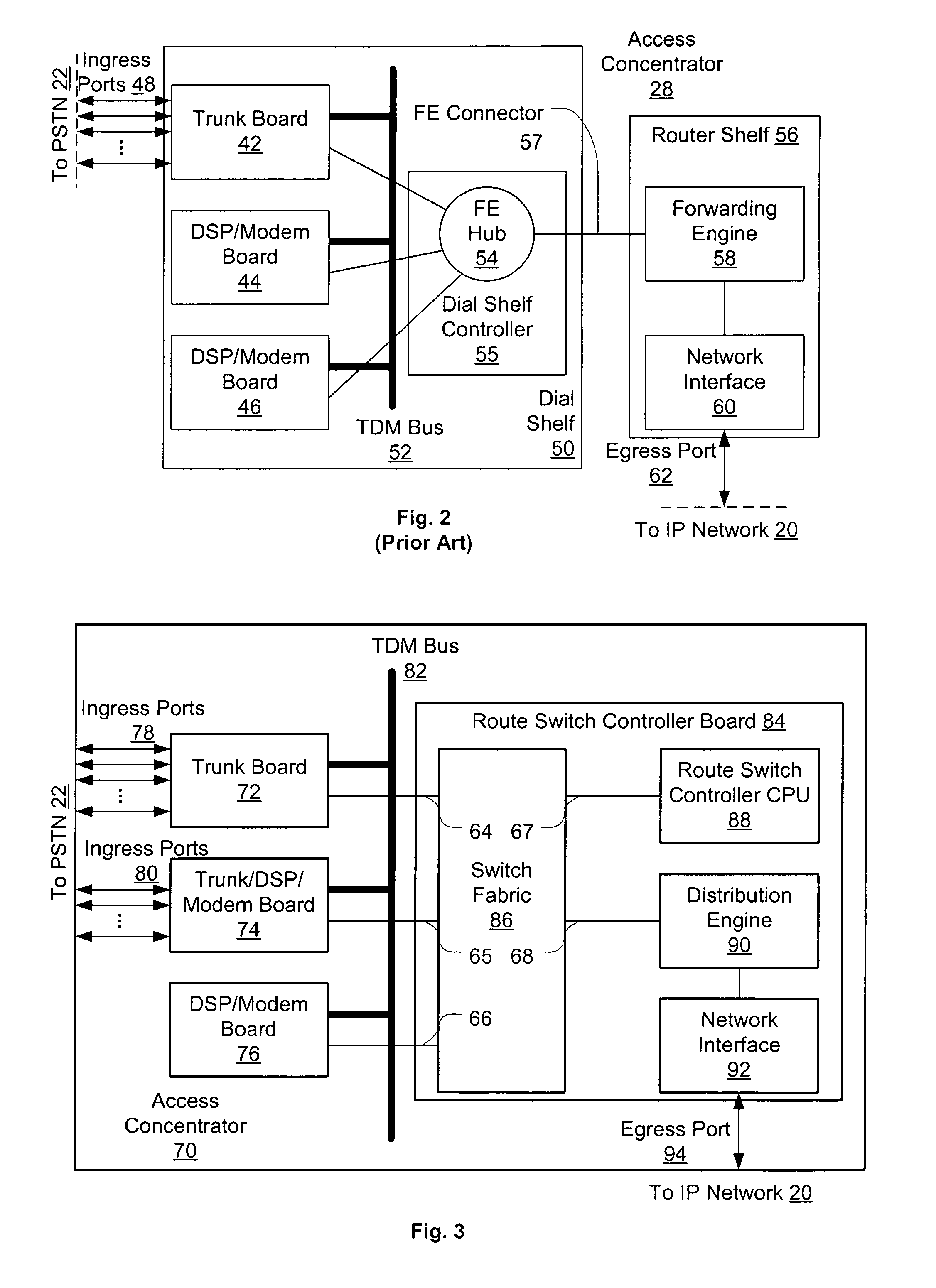
Distributed packet processing architecture for network access servers
InactiveUS6954463B1Increase the number ofRaise countData switching by path configurationNetwork access serverComputer hardware
An access server architecture, and methods for use of the architecture, are disclosed. The architecture and methods are designed to increase the scalability of and balance processor load for a network access server. In this architecture, packet forwarding and packet processing are distributed amongst the cards serving the low-speed access lines, such that each line card is responsible for performing forwarding and packet processing for packets associated with the low-speed ports that line card serves. As the number of line cards expands, forwarding resources are expanded in at least rough proportion. The NAS route switch controller, and the high-speed ports, are largely relieved of packet processing tasks because the egress port uses a distribution engine that performs a cursory examination on one or more header fields on packets received—comprehending only enough information to allow each packet to be distributed to the appropriate line card for full processing.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
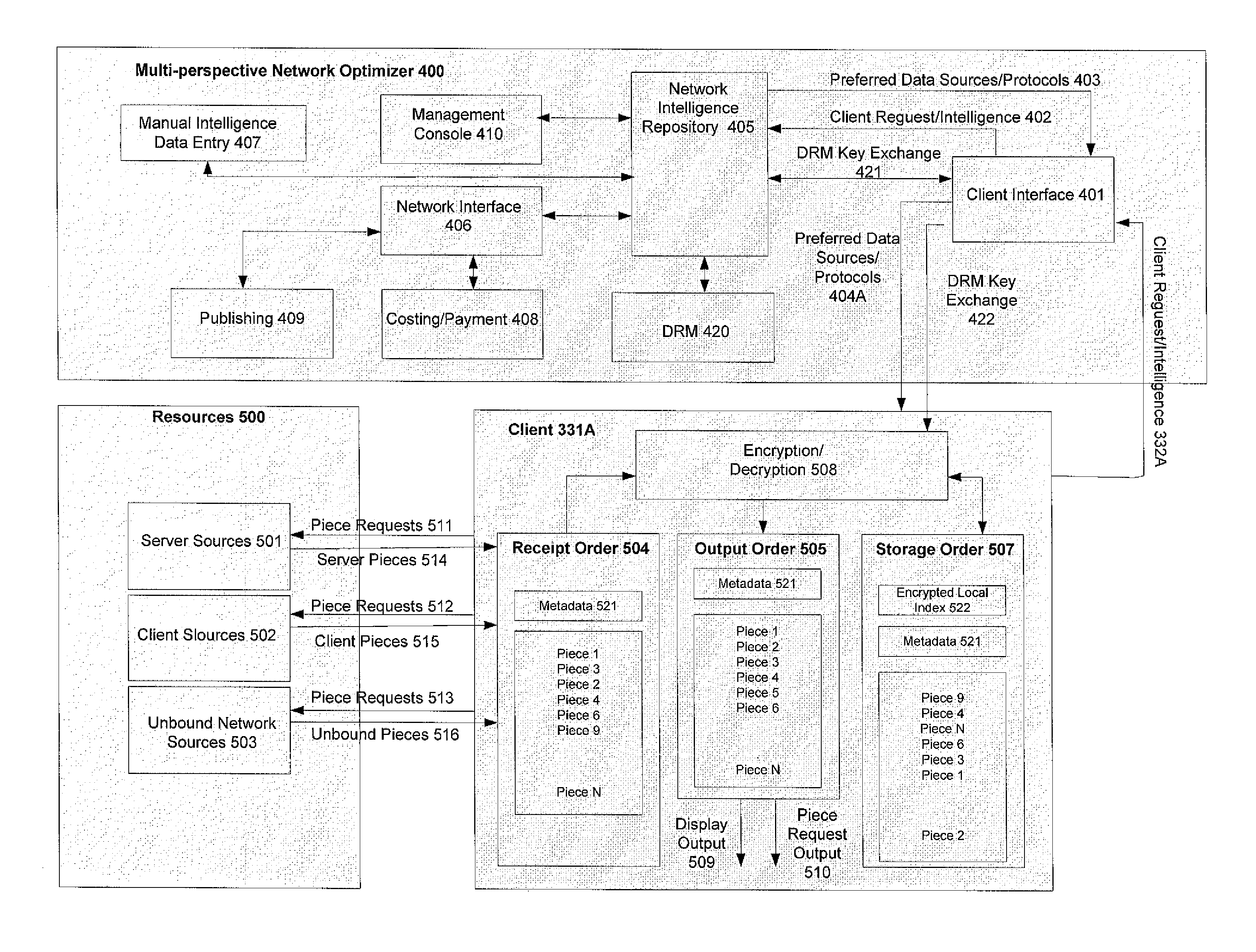
Systems and methods for multi-perspective optimization of data transfers in heterogeneous networks such as the internet
InactiveUS20070245010A1Performance maximizationMaximize scalabilityDigital computer detailsTransmissionExtensibilityNetwork intelligence
Systems and methods are described for optimizing network data transfers using multiple classes of network resources and network intelligence gathered and integrated by a multi-perspective network optimizer so as to maximize the performance, scalability and commercial controllability and minimize the cost of network data transfers in heterogeneous networks such as the internet.
Owner:ITIVA DIGITAL MEDIA
Classified ads software program
InactiveUS20020120506A1Easy to useInexpensive, dependableMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteExtensibility
A method and system for electronic classified advertising, including in a sophisticated edition, a seven-step installation wizard, portability to web servers, scalability, an intuitive and easy to use layout, customization features, fee-based options and features, ad display options and features, selected expiration of ads with optional notification, user set-up personal search agent which will automatically notify the user with new ads matching the database search criteria specified by the user, private messaging, a search engine for seven types of searches including browsing, keyword searches, retrieval of a specific ad by its database ID number, retrieval of all of a specific user's ads, retrieval of one specific ad for modification, and full database power searches, user registration, additional user posting and searching options, E-mail, Antispamming, detailed administrative controls, and security. Also available are banner ad modules, affiliate web sites, and internationalization features.
Owner:HAGEN PHILIP A
Method and apparatus to provide centralized call admission control and load balancing for a voice-over-IP network
InactiveUS6904017B1Improve service qualityBandwidth sharingInterconnection arrangementsError preventionExtensibilityBalancing network
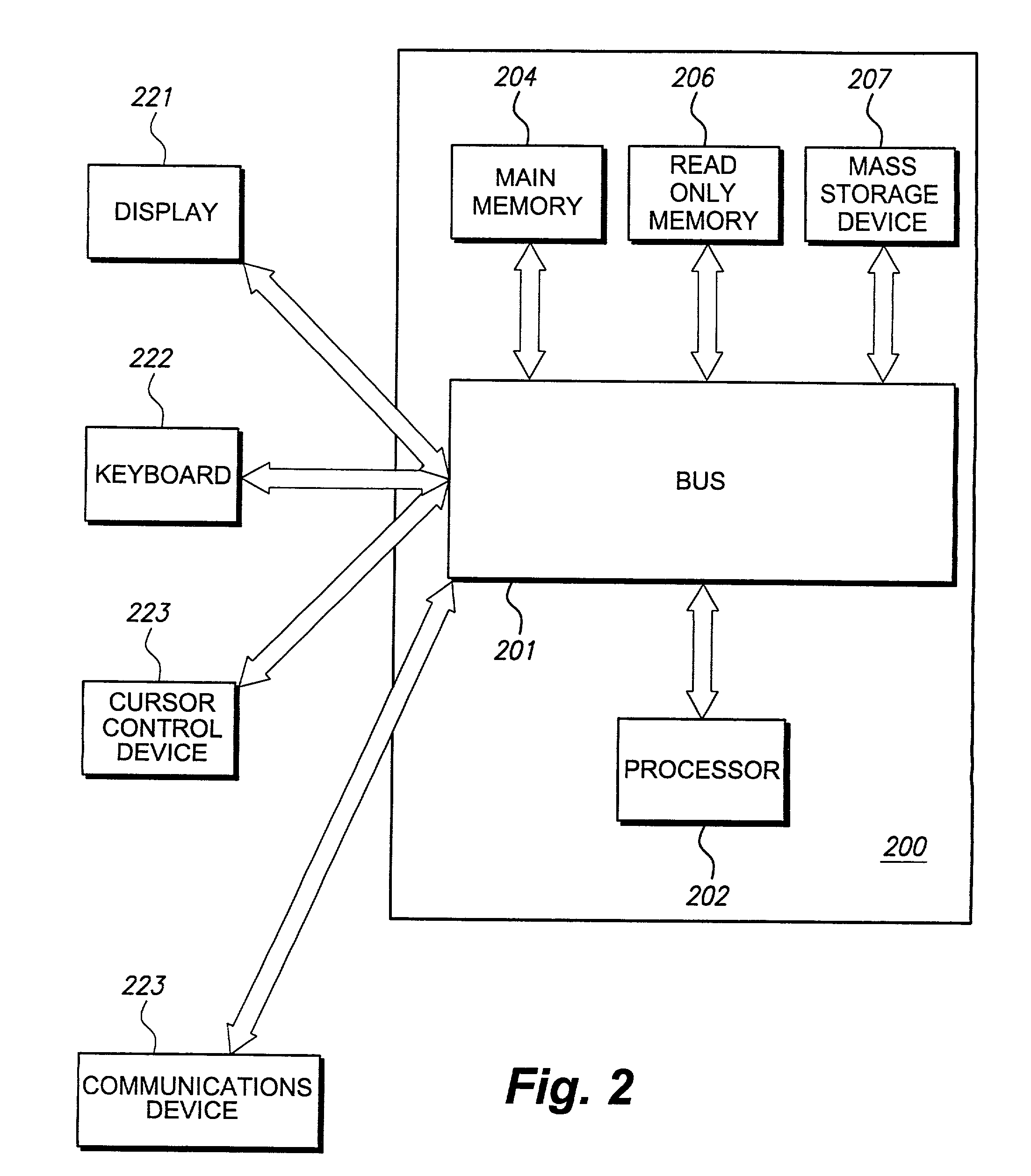
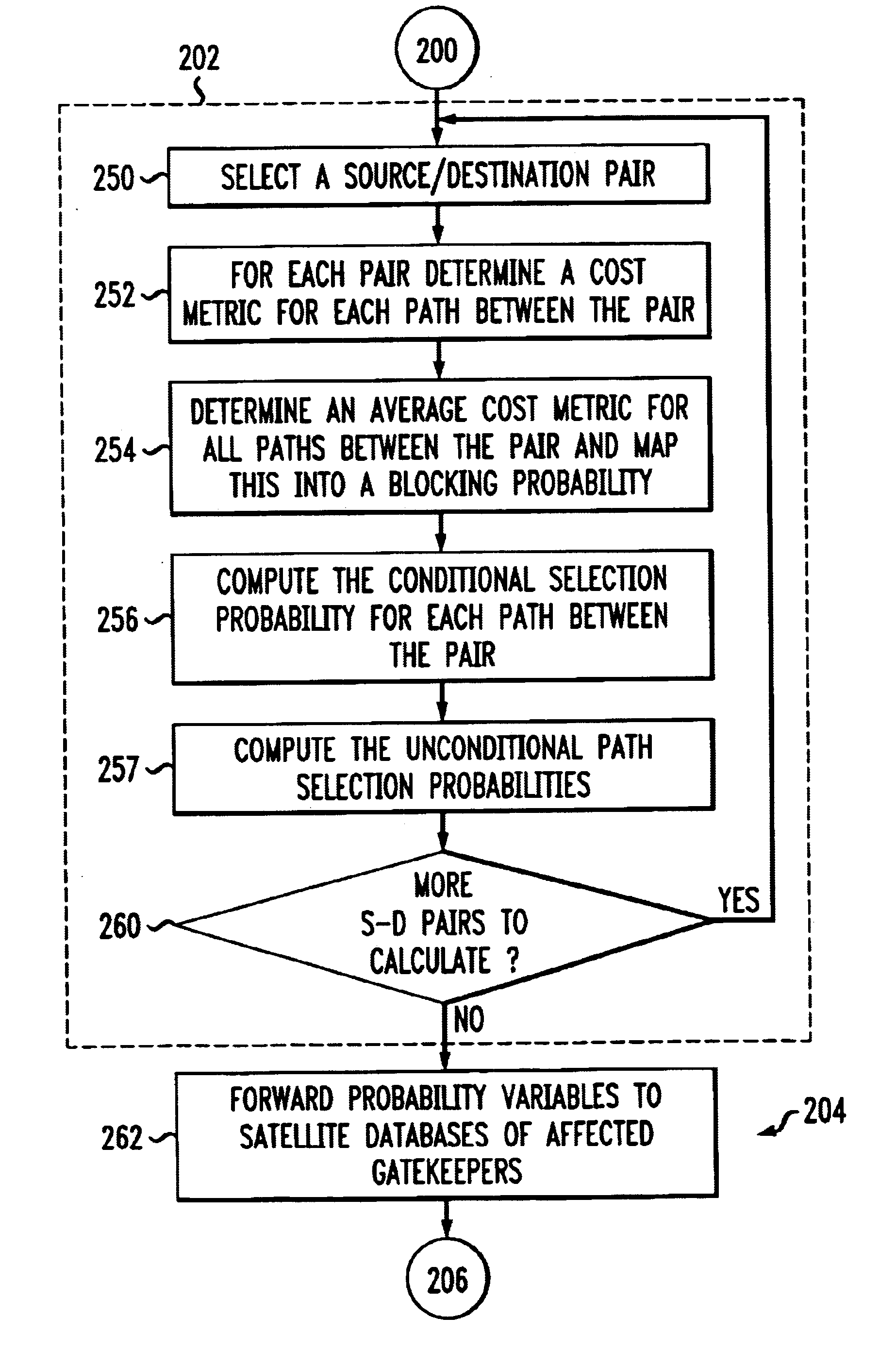
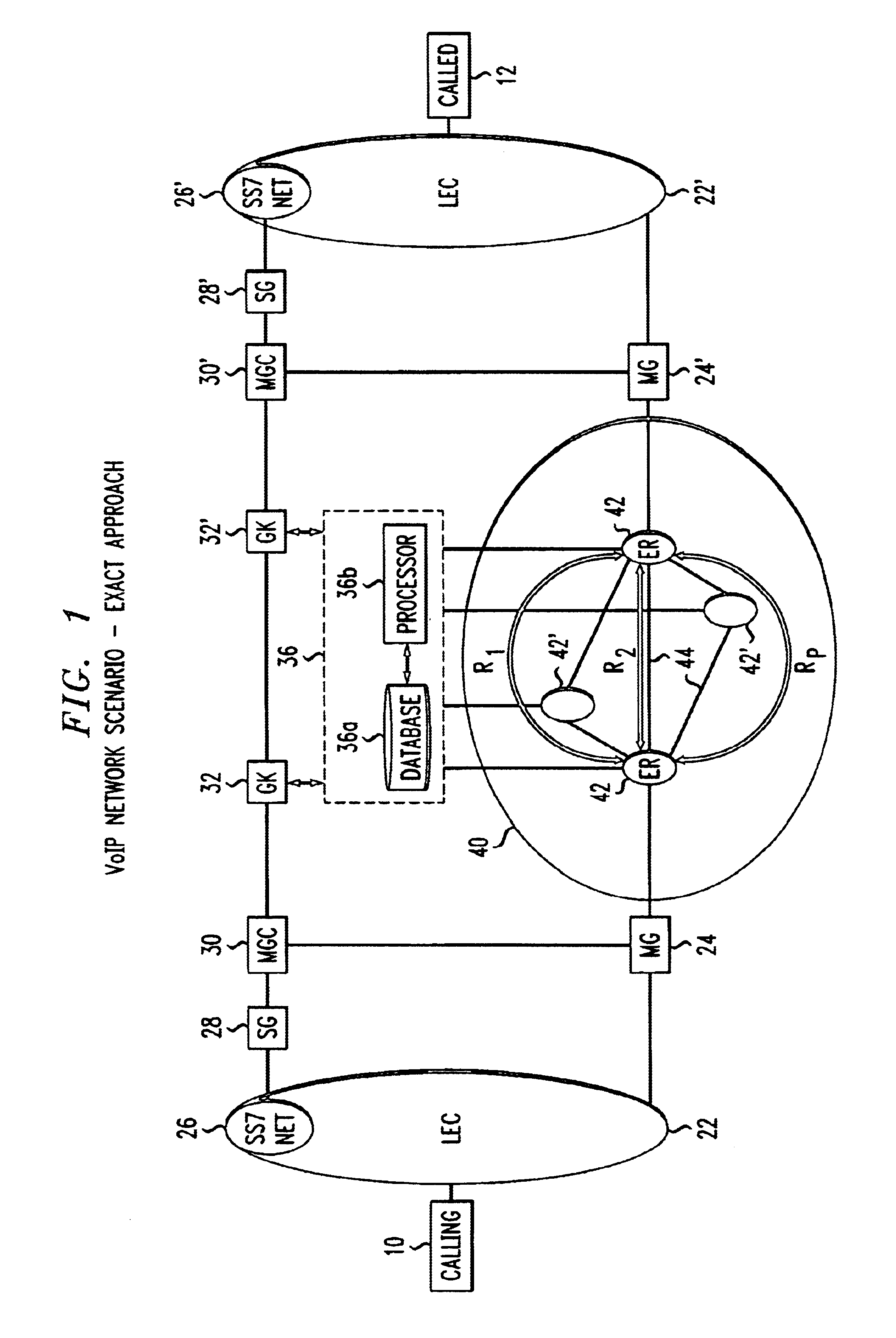
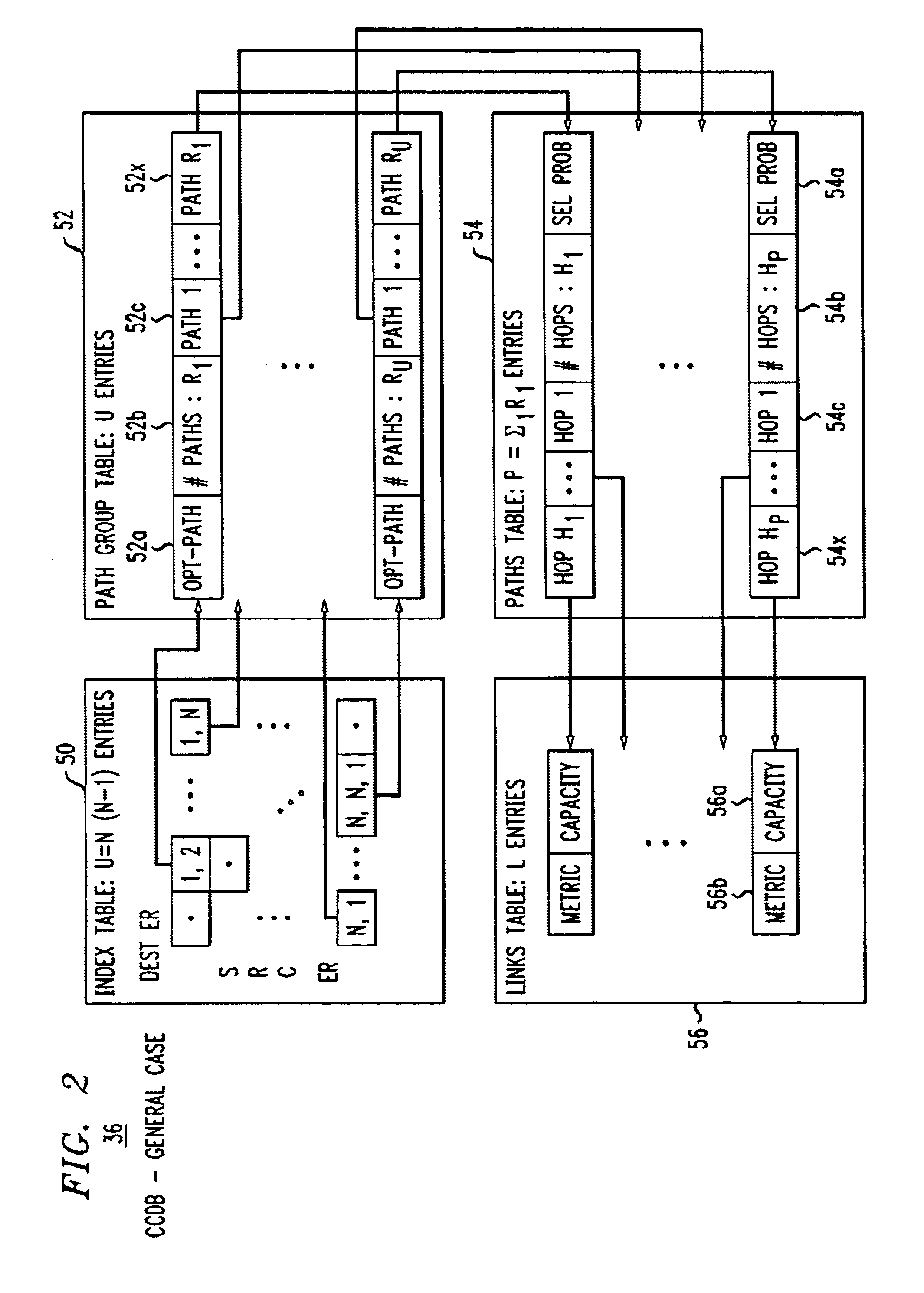
An admission control and load balancing system controls admission of packet streams or calls to a network and balances the packet traffic across the network, improving quality of service. The system includes a central database which stores information including cost data associated with individual paths and links across the network. A processor, in communication with the database, coordinates the admission control and load balancing decisions, and updates of the database cost data to reflect the dynamic network conditions, based on input from appropriate data sources. In one embodiment, referred to as the exact algorithm, the database is consulted by the admission control points or gatekeepers prior to admitting each arriving packet stream, and the database contents are updated call-by-call to reflect the allocation of resources to each admitted stream. In another embodiment, referred to as the inexact algorithm, control decision as well as database updates occur on a periodic rather than on a call-by-call basis to promote better scalability. In this embodiment, the processor periodically calculates admission decisions based on cost data in the central database. These admission decisions are then periodically forwarded to a satellite database associated with each gatekeeper, for storage and use in admission decisions until the next update epoch.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Transactions Across Blockchain Networks
In asynchronous public network, synchronous leaderless Byzantine consensus protocol operating with guaranteed safety and time-bound termination of individual protocol rounds is enabled with nodes having clustered architecture and highly available data transactions, and implemented with algorithm that defuses the effect of stop-faulty processes and bypasses the partitioned network links. Utilizing the time-bound consensus, a protocol and architecture for cross-chain transactions accomplish safe interoperability across blockchain networks. Multiple cross-chain transacting networks interconnected in a federation overcome the limitations of blockchain networks with monolithic ledgers in regard to transaction latency, scalability of throughput, volume of managed data, and openness for further interoperability.
Owner:KLIANEV IVAN
Distributed server for real-time collaboration
InactiveUS6334141B1Avoid focusSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsExtensibilityData collaboration
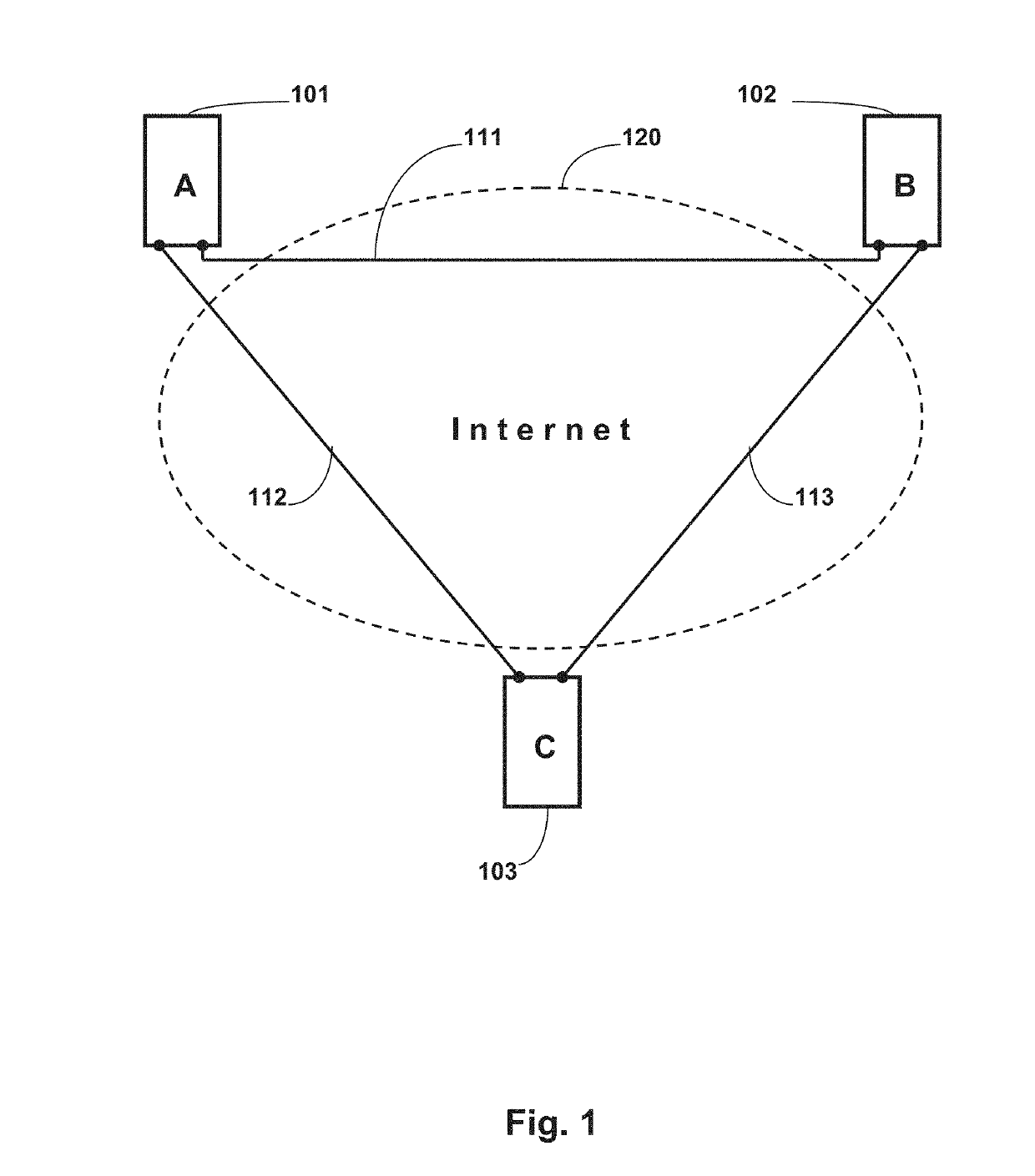
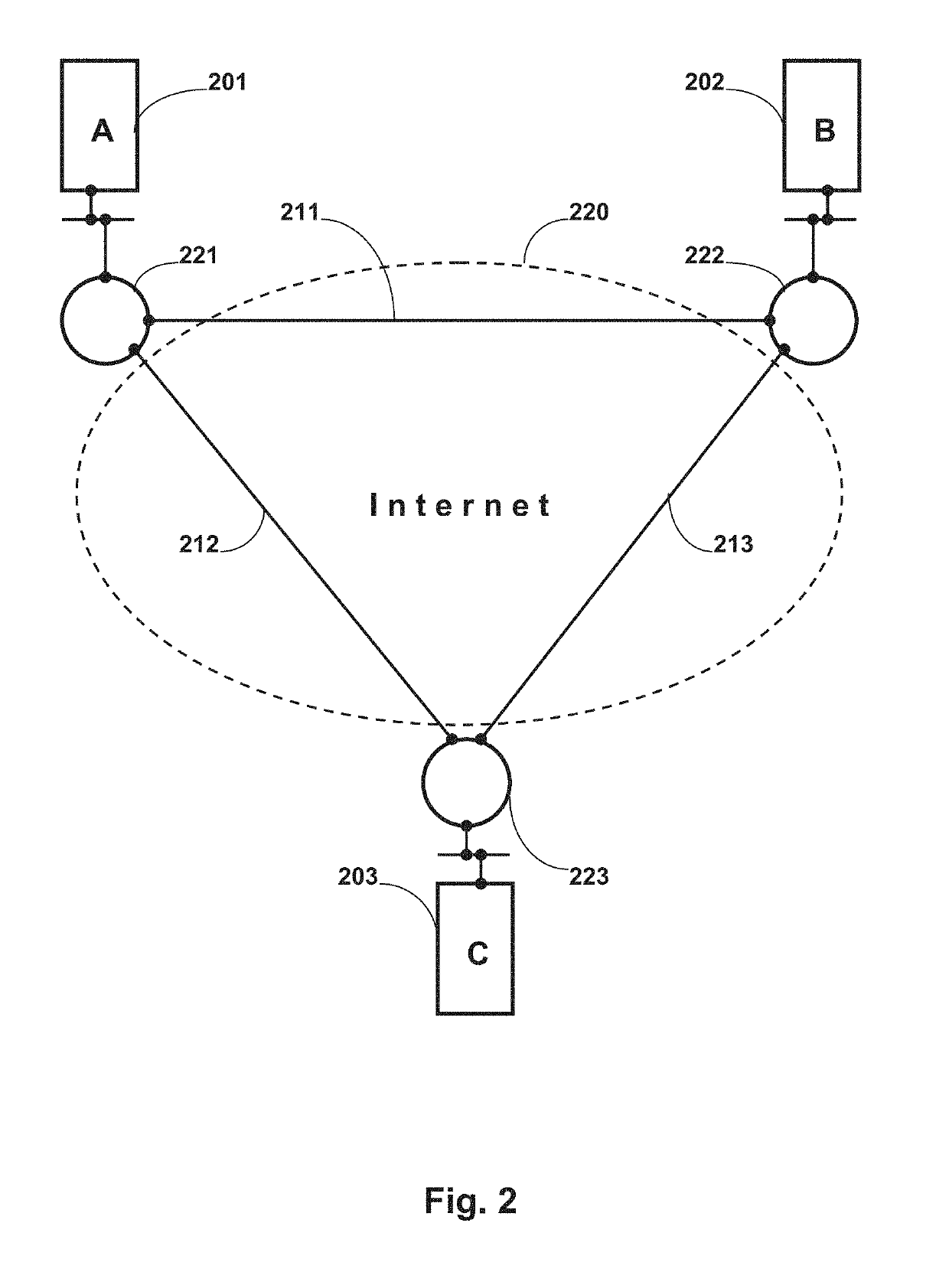
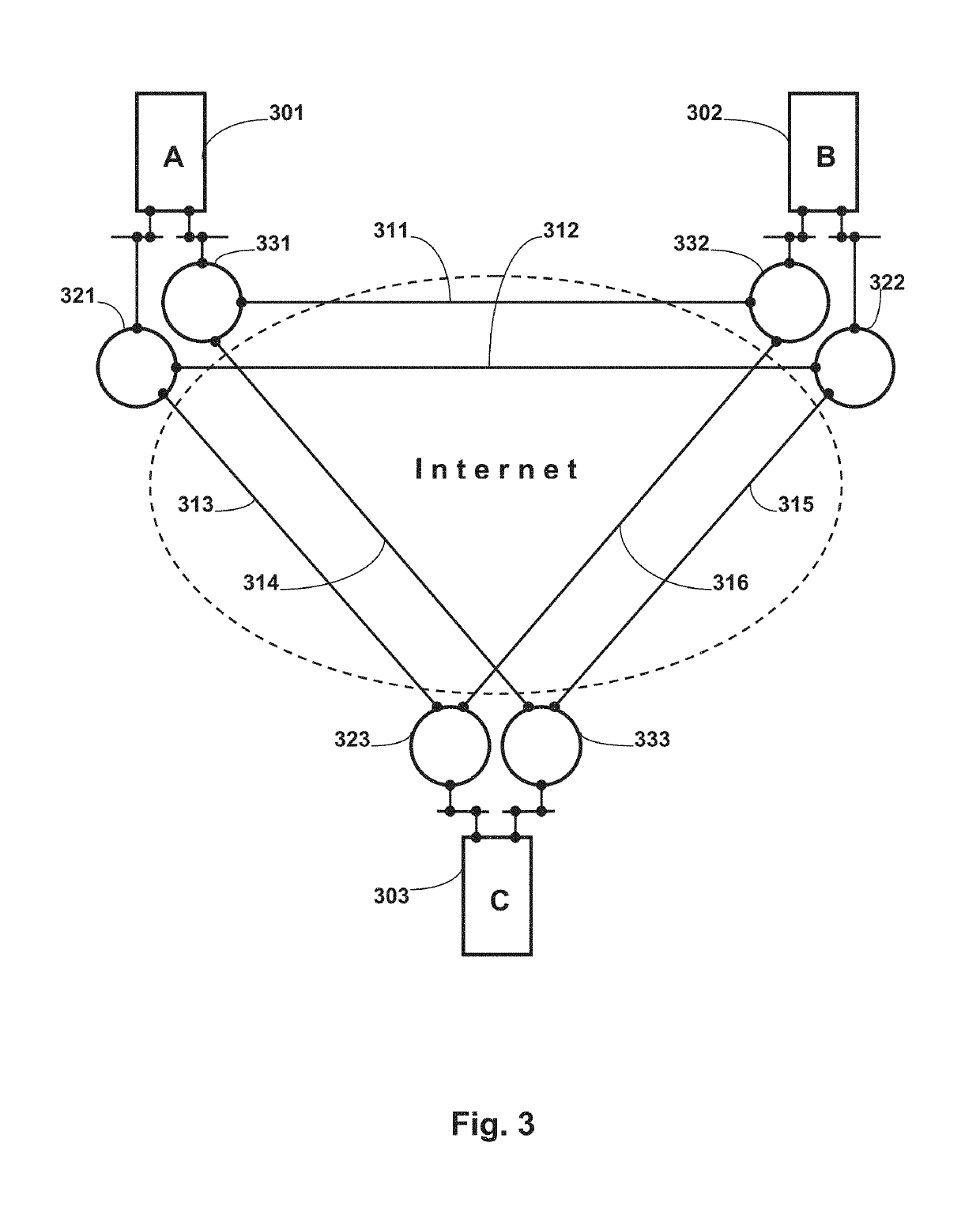
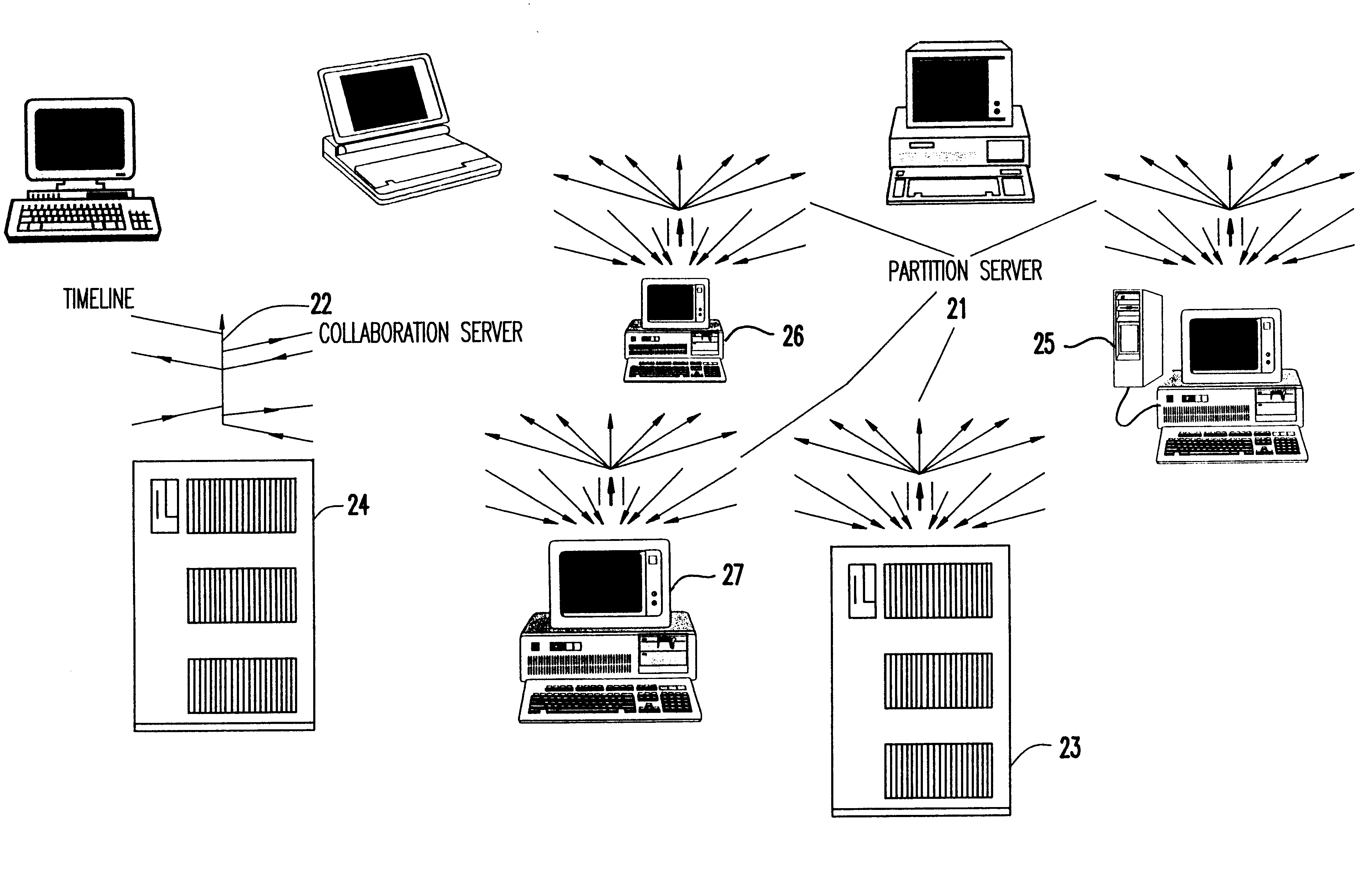
A distributed server for real-time collaboration is substituted for a centralized server to address the problem of the development of unacceptable communication and computation bottlenecks resulting from the use of a one-software-process-based centralized server running somewhere on the available network. The substitute distributed server improves scaleability of real-time collaboration by being based on multiple, independently-communicating, asynchronous, independent (i.e., no shared memory, data, variables, etc.) software processes. The processes can be distributed to multiple machines throughout the network and run simultaneously in order to avoid the centralized server's bottlenecks. To be used, a distributed server requires a disjoint, fully covering partitioning of a work space, wherein it can handle partition hierarchies and groups comprehensively. The distributed server solution is general because of the ability of distributed servers to work with different definitions of a modification. The distributed server solution is extensible because of its simple and comprehensive treatment of inter-partition synchronization.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
Programmable radio transceiver
ActiveUS20060030277A1Prevent leakageLow noise amplifierSolid-state devicesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesExtensibilityTransceiver
A fully integrated, programmable mixed-signal transceiver comprising a radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) which is frequency and protocol agnostic with digital inputs and outputs, the transceiver being programmable and configurable for multiple radio frequency bands and standards and being capable of connecting to many networks and service providers. The RFIC does not use spiral inductors and instead includes transmission line inductors allowing for improved scalability. Components of the transceiver are programmable to allow the transceiver to switch between different frequency bands of operating. Frequency switching can be accomplished though the content of digital registers coupled to the components.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
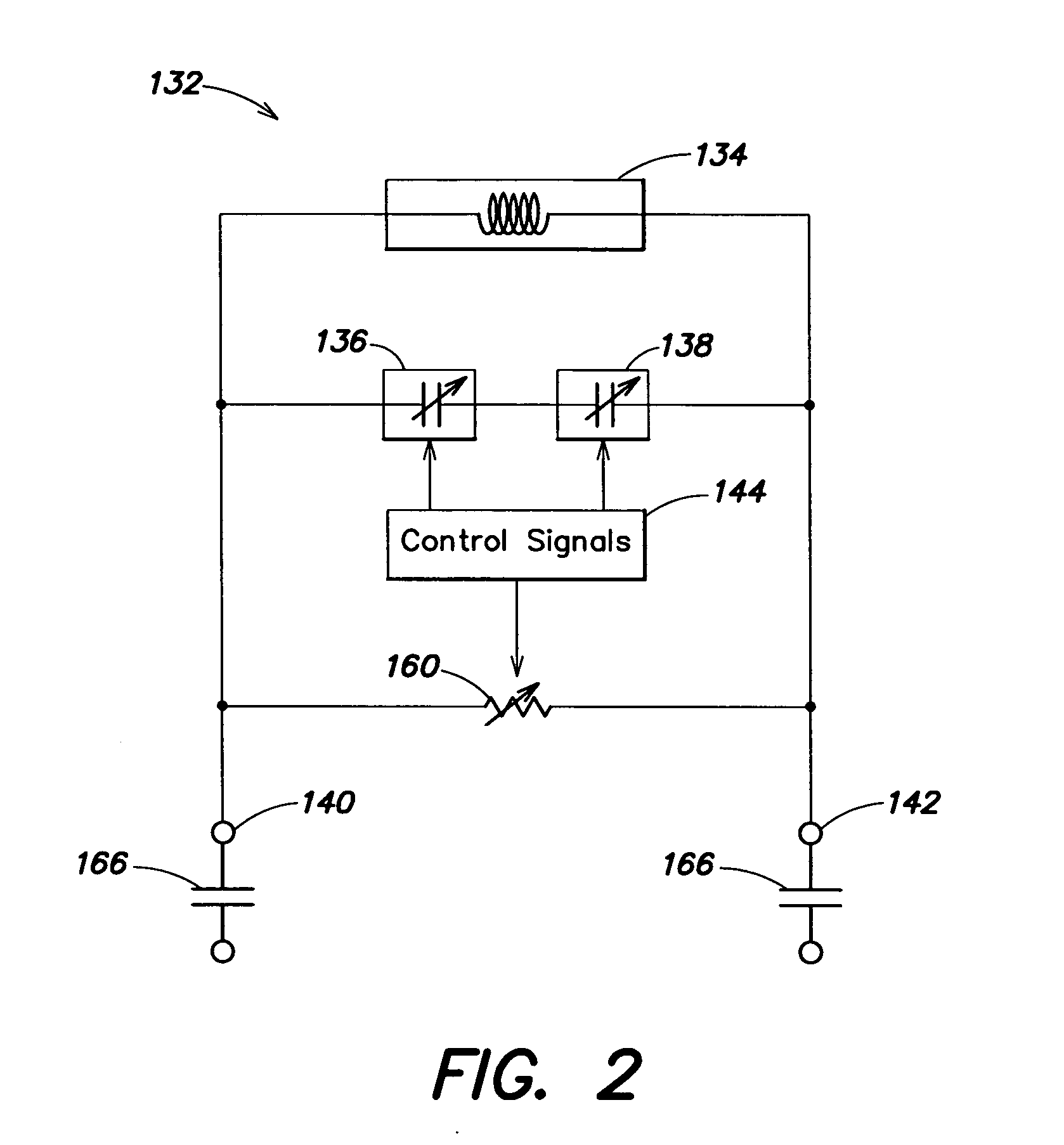
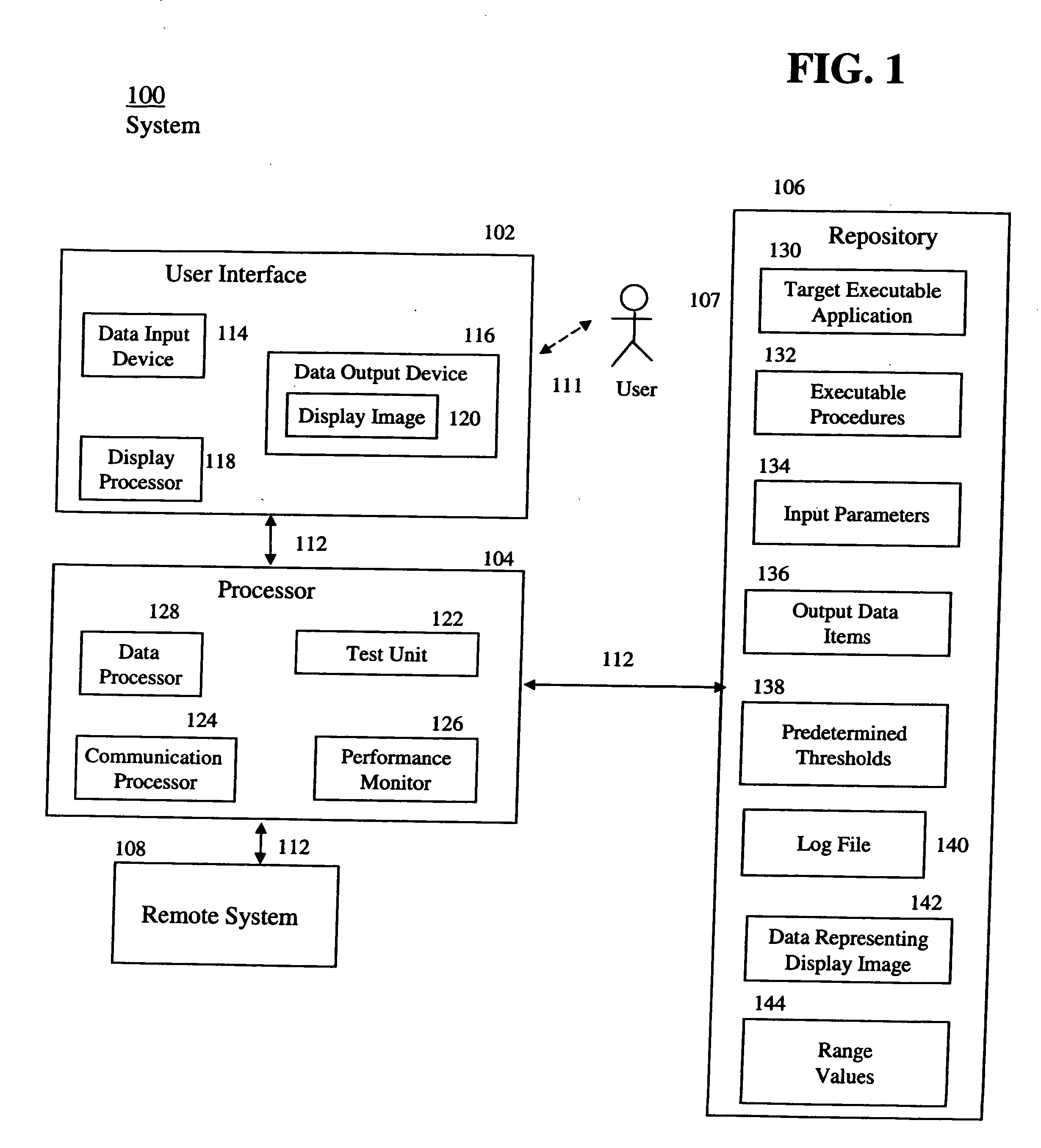
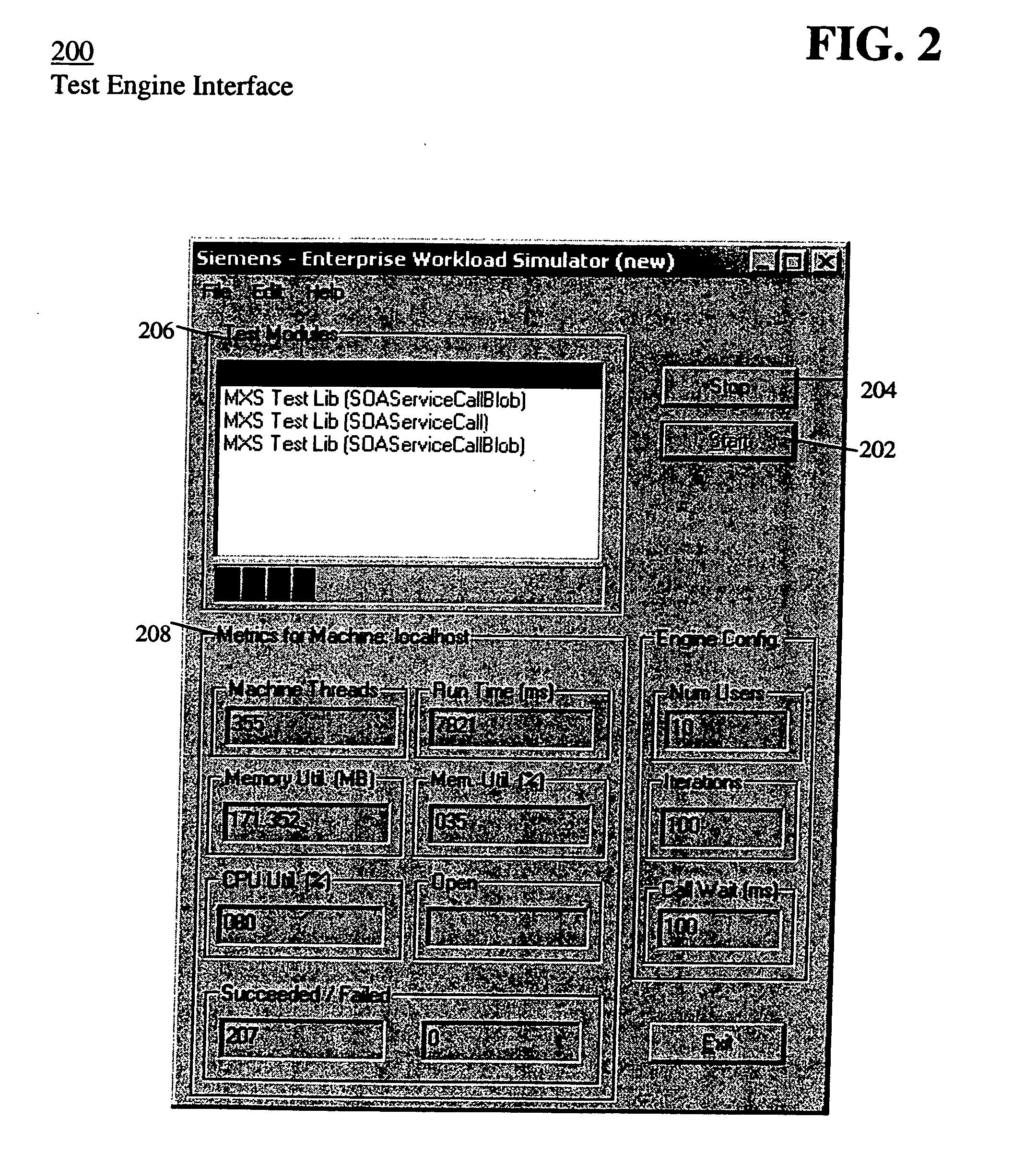
Software test and performance monitoring system
InactiveUS20060129992A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsExtensibilityRegression testing
A quality assurance benchmark system tests a target executable application under load stress conditions over an extended period of time. The system has user-controlled parameters to benchmark performance, scalability, and regression testing before deploying the application to customers. The system includes a display processor and a test unit. The display processor generates data representing a display image enabling a user to select: input parameters to be provided to the target executable application, and output data items to be received from the target executable application and associated expected range values of the data items. The test unit provides multiple concurrently operating executable procedures for interfacing with the target executable application to provide the input parameters to the target executable application, and to determine whether data items received from the target executable application are within corresponding associated expected range values of the data items.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Unified event monitoring system
InactiveUS20060178898A1Eliminates the duplicative, time-consuming, paper and fax-intensive processesOffice automationCommerceExtensibilityNetwork management
The present invention provides a system that integrates requests and responses thereto for Operation and Business Support Systems (OSS / BSS) that comprise many discrete and non-inclusive systems with disparate interfaces. The integration of these systems poses a complex problem. Moreover, costs of licenses, maintenance fees, and training for day-to-day use are prohibitively expensive. The present invention is an open and inclusive system that interfaces easily with existing OSS / BSS systems to provide visibility into all network elements and events. It is an advanced, multi-vendor management system designed to increase efficiency and productivity and reduce network administration costs by providing an integrated system for monitoring, troubleshooting, and managing the network. The present invention has as an objective to unite different systems under one common platform. The present invention collects and manipulates information centrally, within a single system, enabling critical data to be shared seamlessly between applications. This provides for Data Consolidation, Data Extendibility, and Reduced Cost. In addition, this solution is robust, as it is expandable and considerate of new systems and technologies as they emerge.
Owner:INTRACOMM
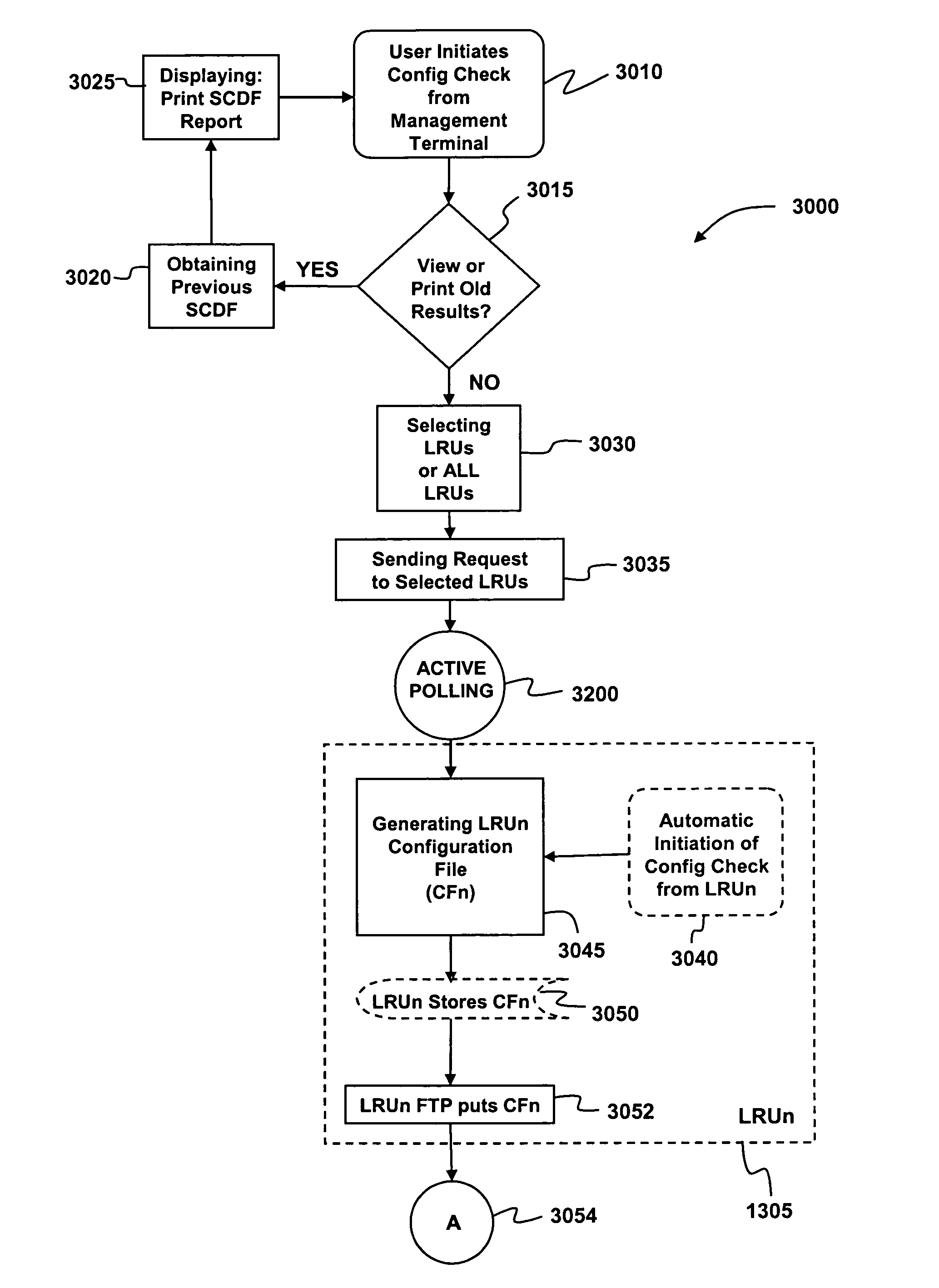
Method and system for configuration and download in a restricted architecture network
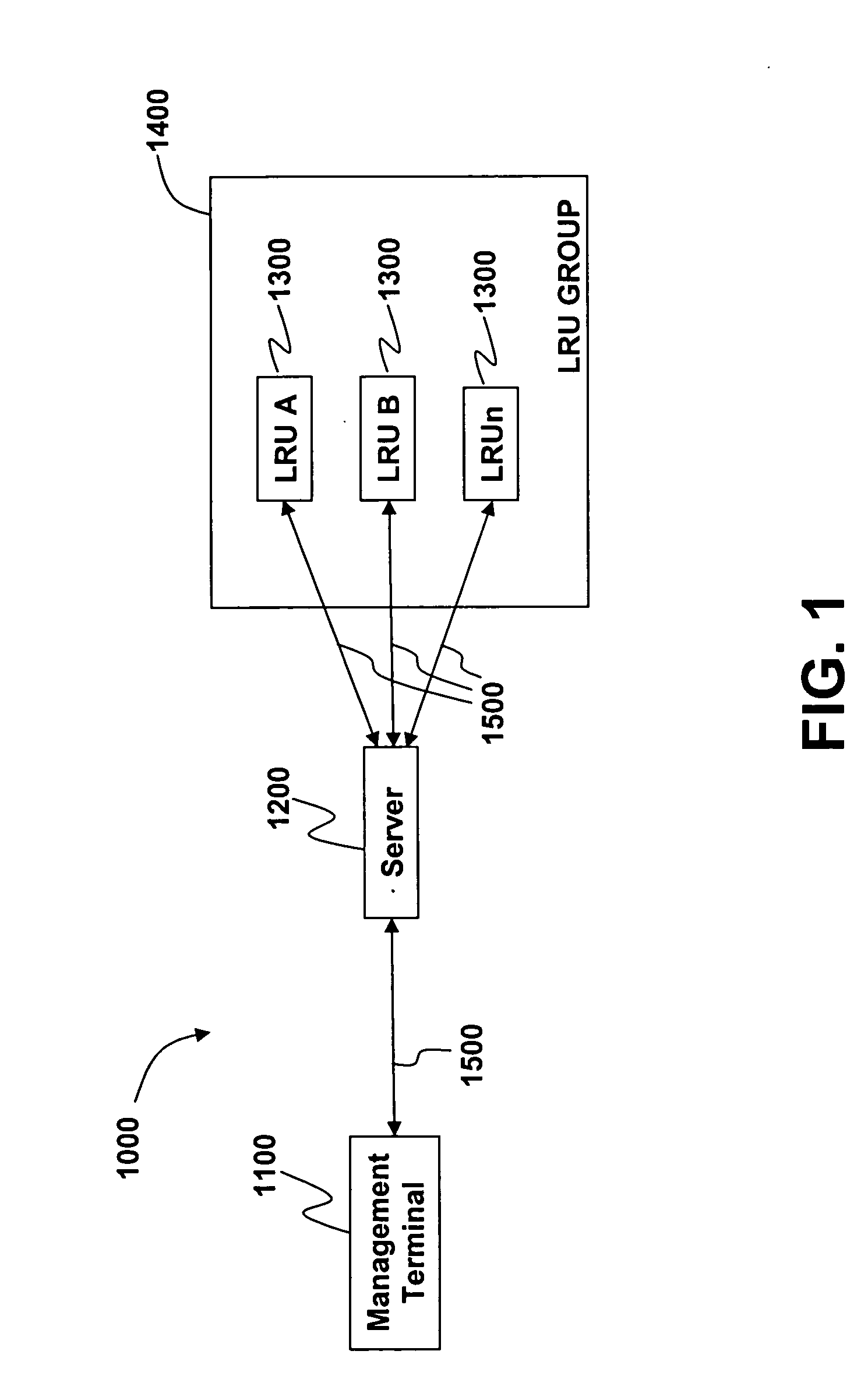
ActiveUS20060010438A1Avoids complication and difficultySimplify writingDigital computer detailsData resettingExtensibilityData file
A method and system are provided for updating software configurations of line-replaceable unit (LRU) computers in a restricted architecture network such as an in-flight entertainment system (IFES). Operating in an efficient and parallel manner, each of the LRUs independently creates an individual configuration file that identifies current software components. Each of the LRUs transmits its respective configuration file to a configuration server either automatically upon startup or manually upon request. The configuration server updates a system configuration data file with the current configuration files received from the individual LRUs. In a downloading method, a download server sends a list of desired software components to the LRUs. Each of the LRUs independently and simultaneously transfer (download) the needed software from the download server. The LRU independently requests the download server to download the needed software components. To improve scalability and reliability, the file transfers utilize standard protocols, such as FTP.
Owner:THALES AVIONICS INC
Cycle segmented prefix circuits
InactiveUS6609189B1Improve performanceAvoid performanceComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral purpose stored program computerExtensibilityScalar processor
The poor scalability of existing superscalar processors has been of great concern to the computer engineering community. In particular, the critical-path delays of many components in existing implementations grow quadratically with the issue width and the window size. This patent presents a novel way to reimplement these components and reduce their critical-path delay growth. It then describes an entire processor microarchitecture, called the Ultrascalar processor, that has better critical-path delay growth than existing superscalars. Most of our scalable designs are based on a single circuit, a cyclic segmented parallel prefix (cspp). We observe that processor components typically operate on a wrap-around sequence of instructions, computing some associative property of that sequence. For example, to assign an ALU to the oldest requesting instruction, each instruction in the instruction sequence must be told whether any preceding instructions are requesting an ALU. Similarly, to read an argument register, an instruction must somehow communicate with the most recent preceding instruction that wrote that register. A cspp circuit can implement such functions by computing for each instruction within a wrap-around instruction sequence the accumulative result of applying some associative operator to all the preceding instructions. A cspp circuit has a critical path gate delay logarithmic in the length of the instruction sequence. Depending on its associative operation and its layout, a cspp circuit can have a critical path wire delay sublinear in the length of the instruction sequence.
Owner:YALE UNIV
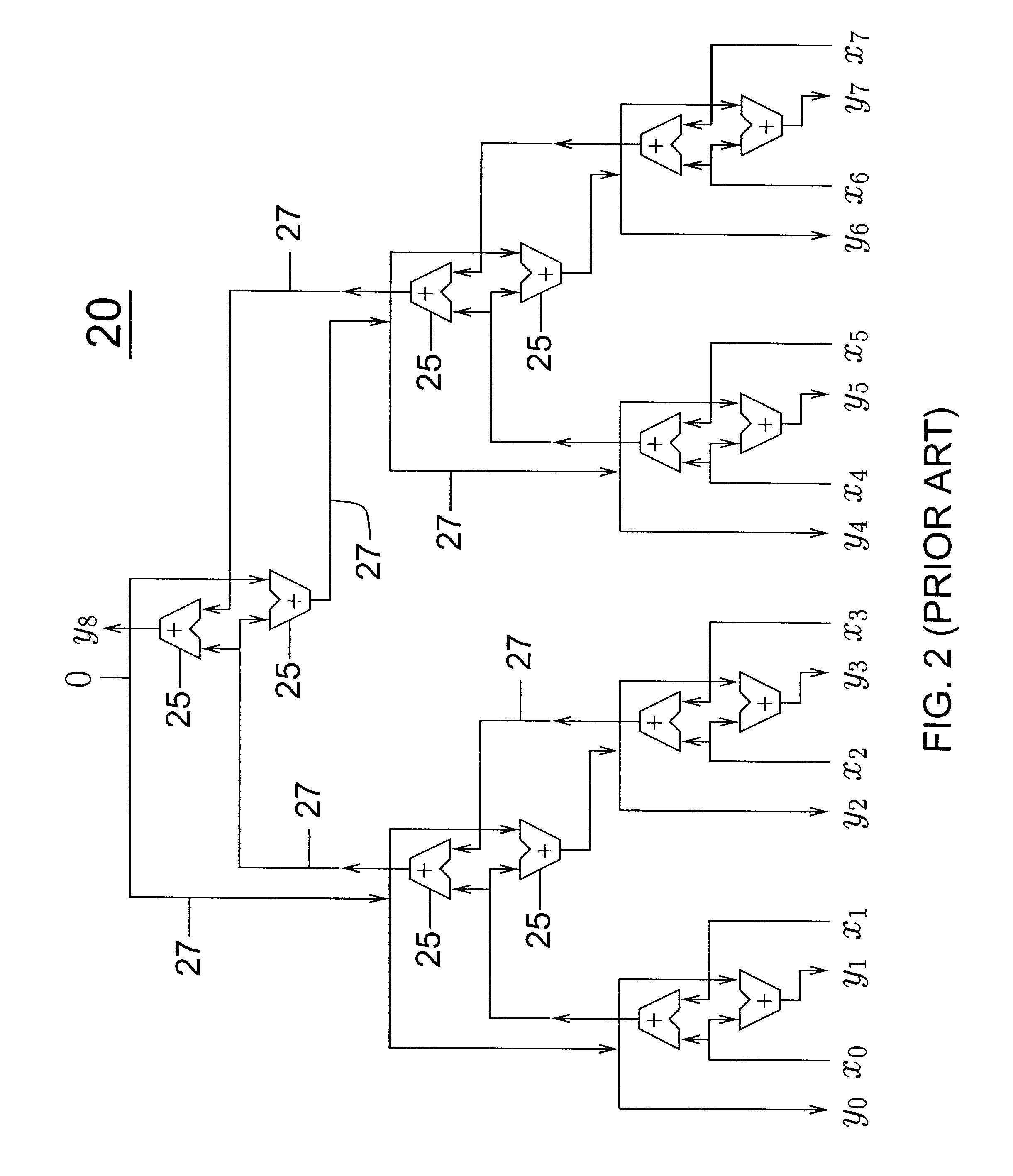
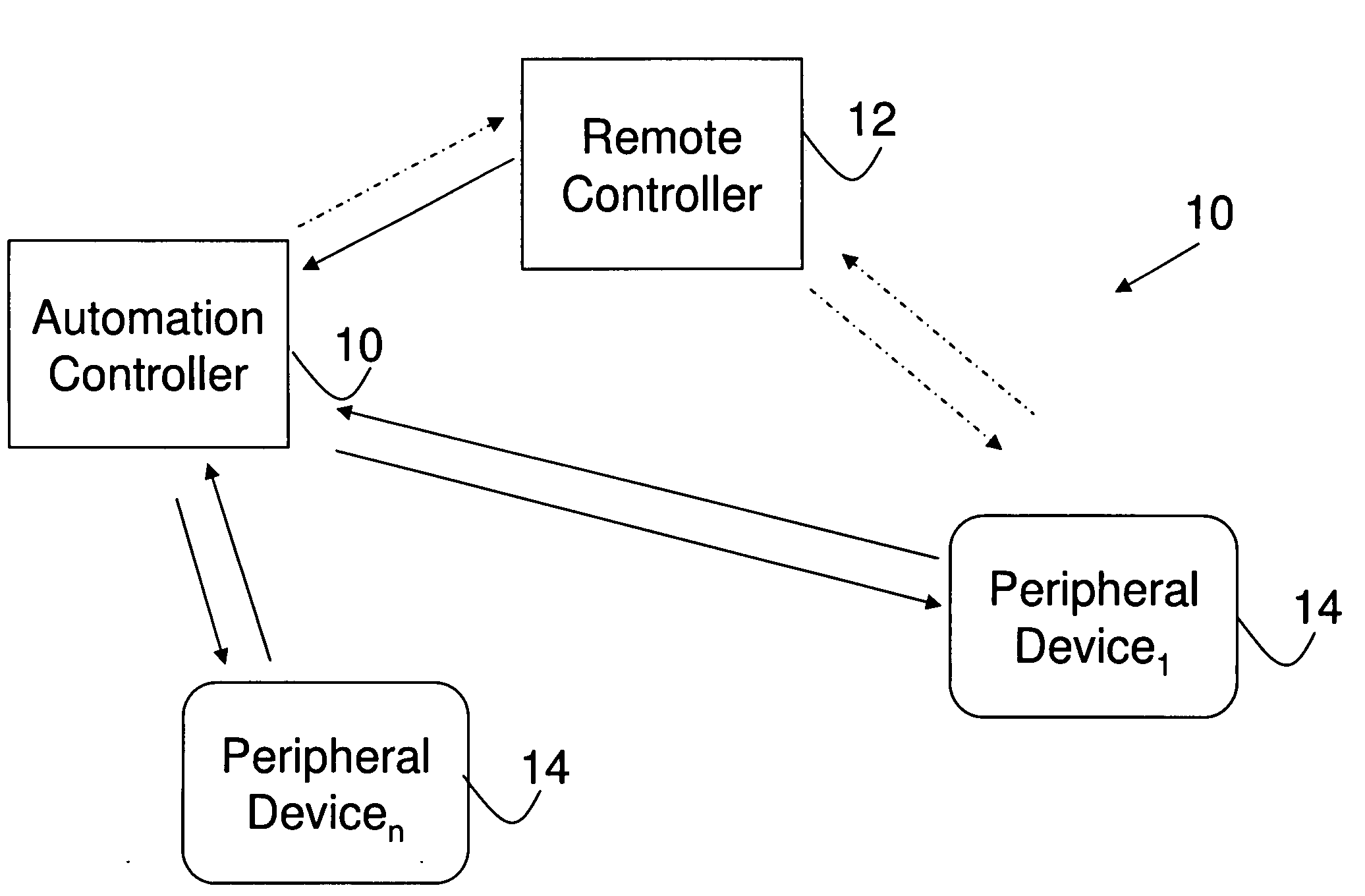
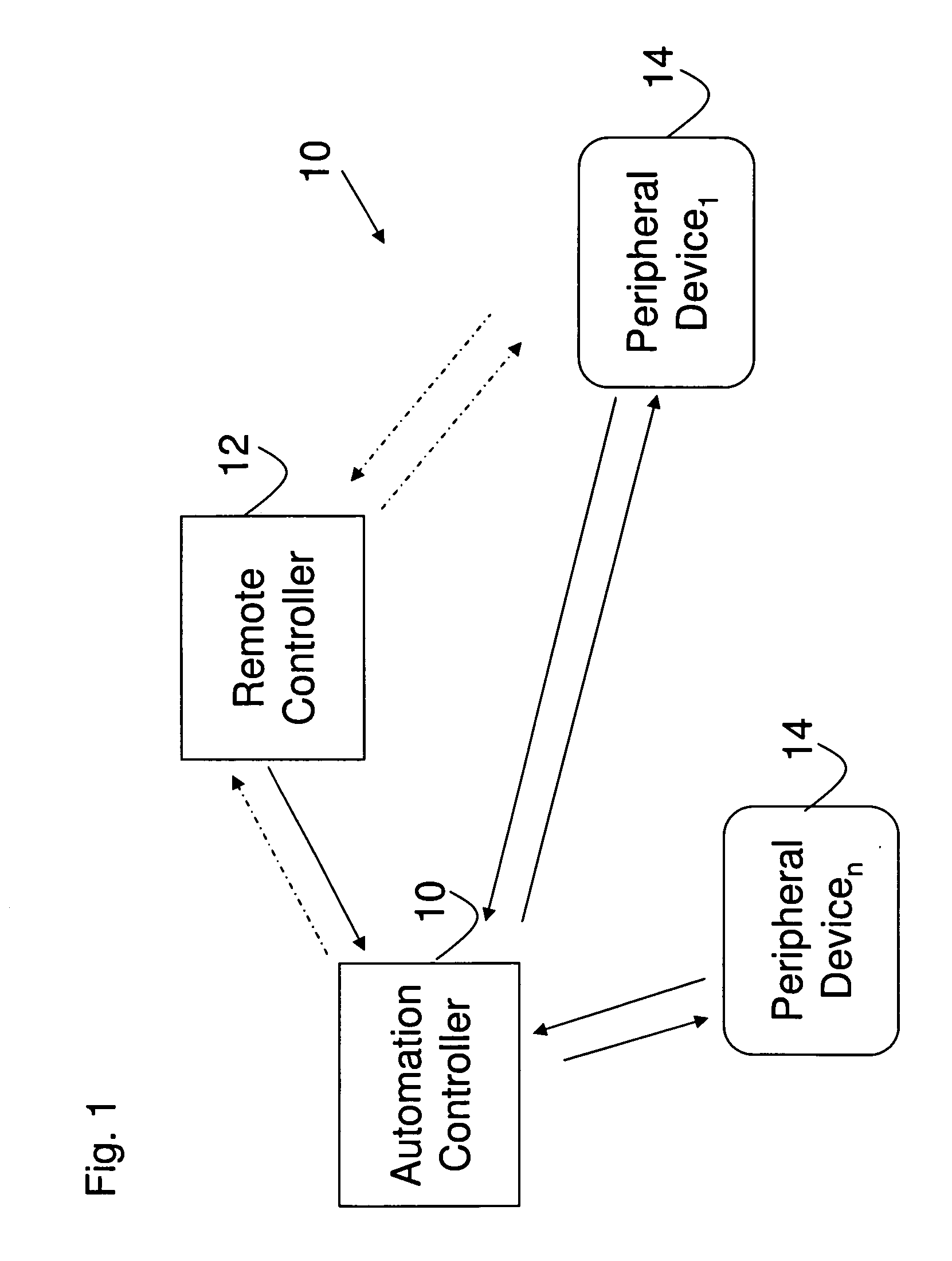
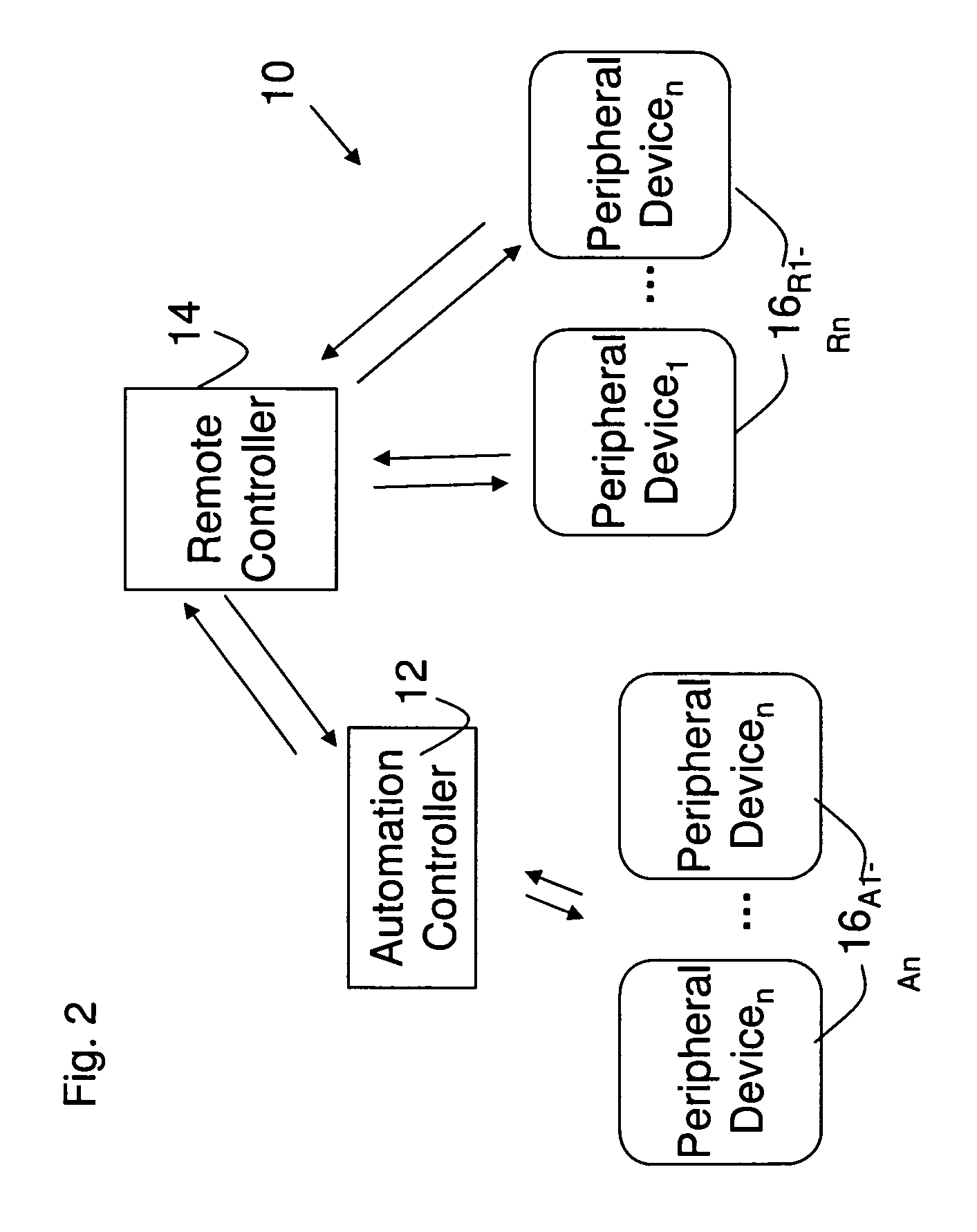
Upgradeable Automation Devices, Systems, Architectures, and Methods
ActiveUS20080183316A1Minimize consumptionReduce energy costsProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsExtensibilityCost effectiveness
A multi-level automation control architecture, methods, and systems are disclosed, which provide enhanced scalability, functionality, and cost effectiveness for energy, access, and control. The systems include various combinations of automation controllers, remote controllers and peripheral devices that are used to provide monitoring and control functionality over the various systems in a structure, such as HVAC, water, lighting, etc. In various embodiments, the automation controller and various peripheral devices are implemented to provide an integrated energy management system for the structure. The system allows the user to manage energy based on the day, time, the presence of people, and the availability of natural lighting and heating, as well as prioritize and participate in demand-response program. The system can be implemented using a remote controller and expanded through the addition of automation controllers, remote controllers, and peripheral devices to enable the system to be tailored to specific user requirements.
Owner:AUTANI LLC
Secure session keys context
InactiveUS20070060127A1Faster and efficient handoffUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsAccess networkExtensibility
Handoffs must be fast for wireless mobile nodes without sacrificing the security between a mobile node and wireless access points in an access network. A secure session keys context approach is shown having all the good features, like mobility and security optimization, of the currently existing proposals of key-request, pre-authentication, and pre-distribution but also providing improved scalability for the access network and for the mobile node. The new approach is compared to the existing proposals including memory requirements and especially how to reduce memory usage using a “just-in-time” transfer of security information between access points and a mobile node during a handover.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
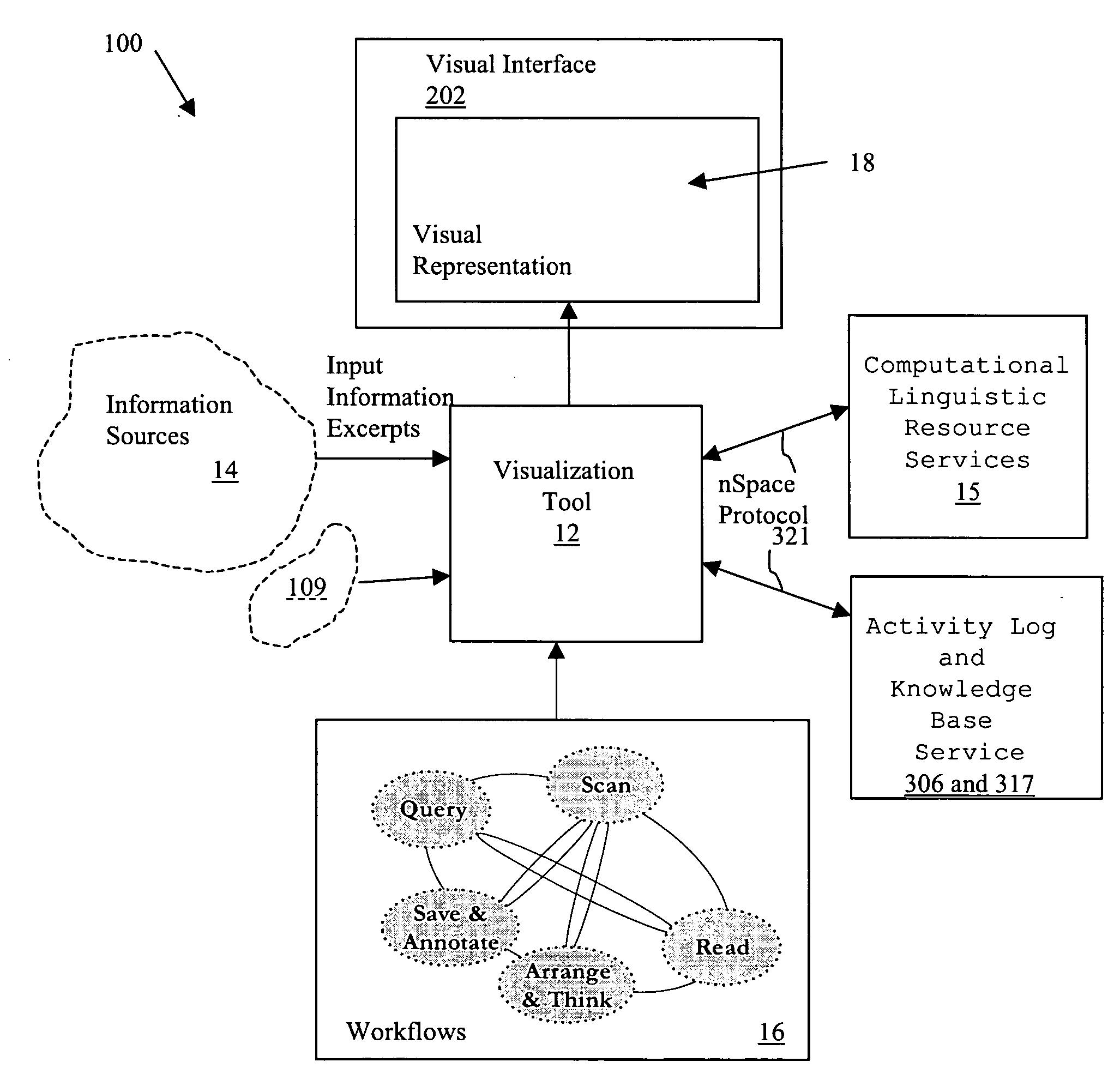
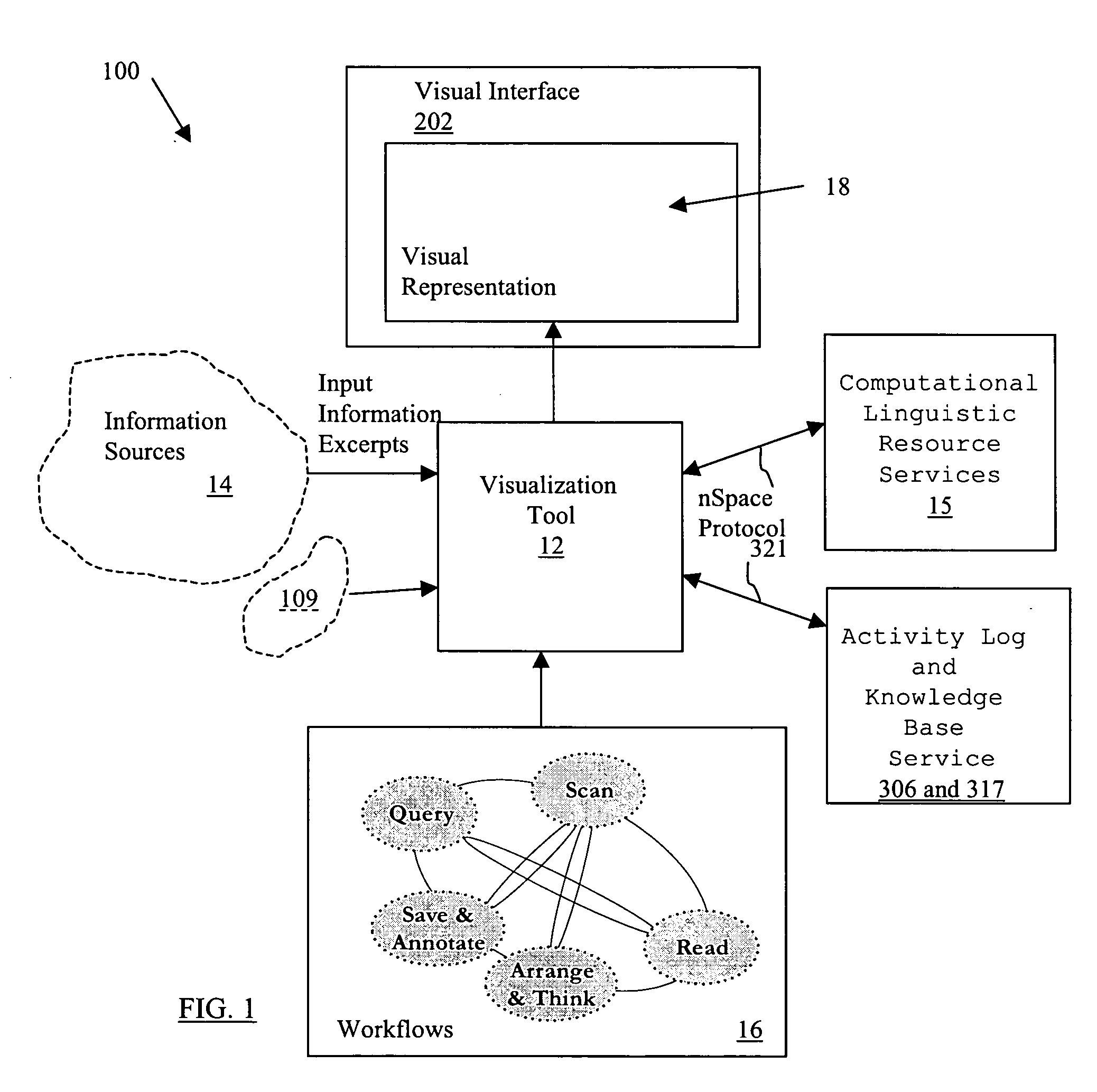
System and method for interactive visual representation of information content and relationships using layout and gestures
ActiveUS20060117067A1Many taskHuge taskDigital data processing detailsMultimedia data retrievalExtensibilityHuman interaction
This application relates to information analysis and more particularly to a system and method for interactive visual representation of information content and relationships using layouts and gestures. A visualization tool is provided which facilitates both ad-hoc and more formal analytical tasks as a flexible and expressive thinking environment. The tool provides a space focused on ‘Human Interaction with Information’ and enabling evidence marshalling. Capabilities of the tool include put-this-there cognition, automatic analysis templates, and gestures for the fluid expression of thought and scalability mechanisms to support large analysis tasks.
Owner:UNCHARTED SOFTWARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com