Patents
Literature
633 results about "Distributed servers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
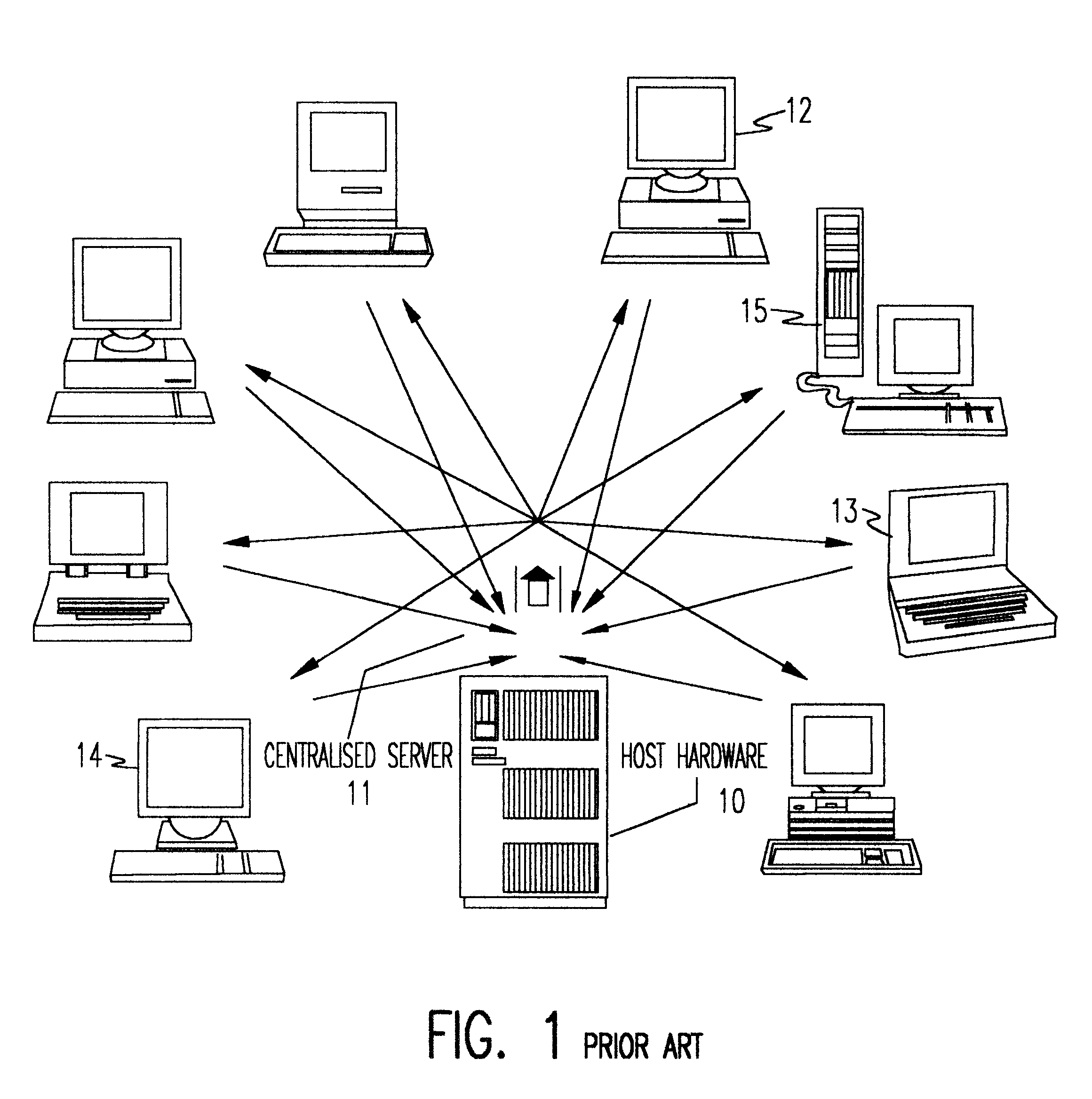
A distributed file system is a client/server -based application that allows clients to access and process data stored on the server as if it were on their own computer. When a user accesses a file on the server, the server sends the user a copy of the file, which is cached on the user's computer while the data is being processed...
Agent based instruction system and method
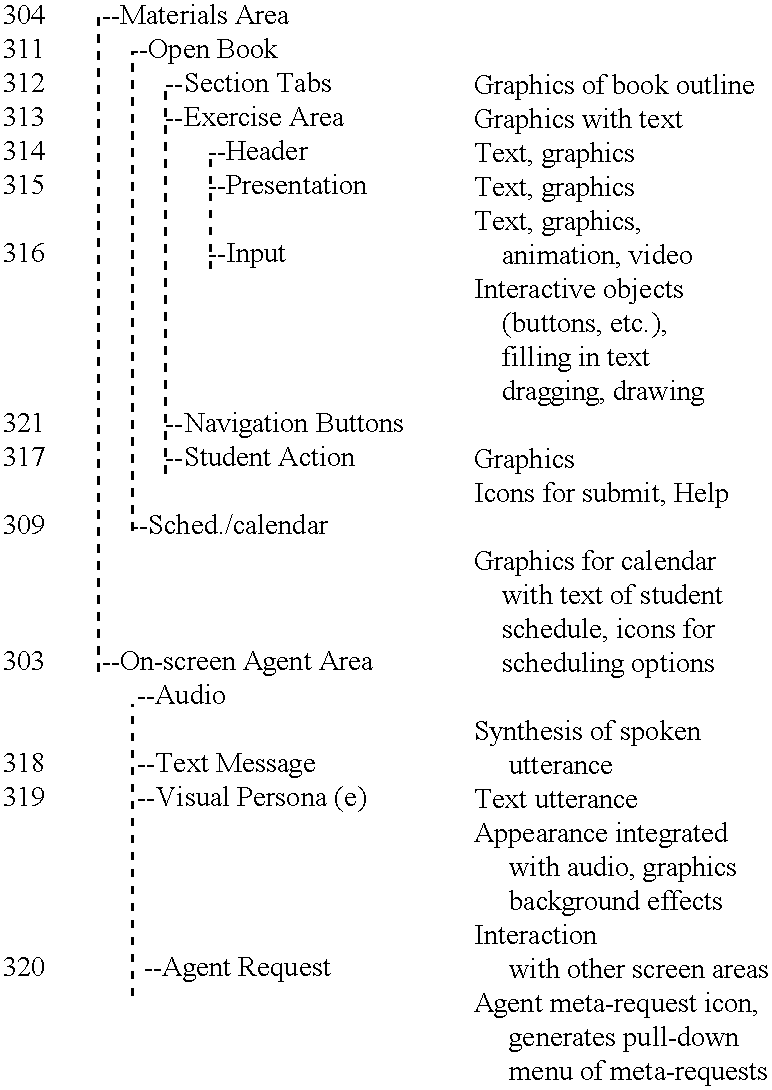
InactiveUS6201948B1Highly configurableEffectively guide and engageData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsPersonalizationInterface standard
This invention relates to a system and method for interactive, adaptive, and individualized computer-assisted instruction. This invention includes an agent for each student which adapts to its student and provides individualized guidance to the student and controls to the augmented computer-assisted instructional materials. The instructional materials of this invention are augmented to communicate the student's performance and the material's pedagogical characteristics to the agent and to receive control from the agent. Preferably, the content of the communication between the agent and the materials conforms to specified interface standards so that the agent acts independently of the content of the particular materials. Also preferably, the agent can project using various I / O modalities integrated, engaging, life-like display persona(e) appropriate to the preferences of its student and appear as a virtual tutor to the student. Finally, preferably this invention is implemented on computers interconnected by a network so that instruction can be delivered to geographically distributed students from geographically distributed servers. An important application of this invention is delivering interactive, adaptive, and individualized homework to students in their homes and other locations.
Owner:CONVERGYS CUSTOMER MANAGEMENT GROUP
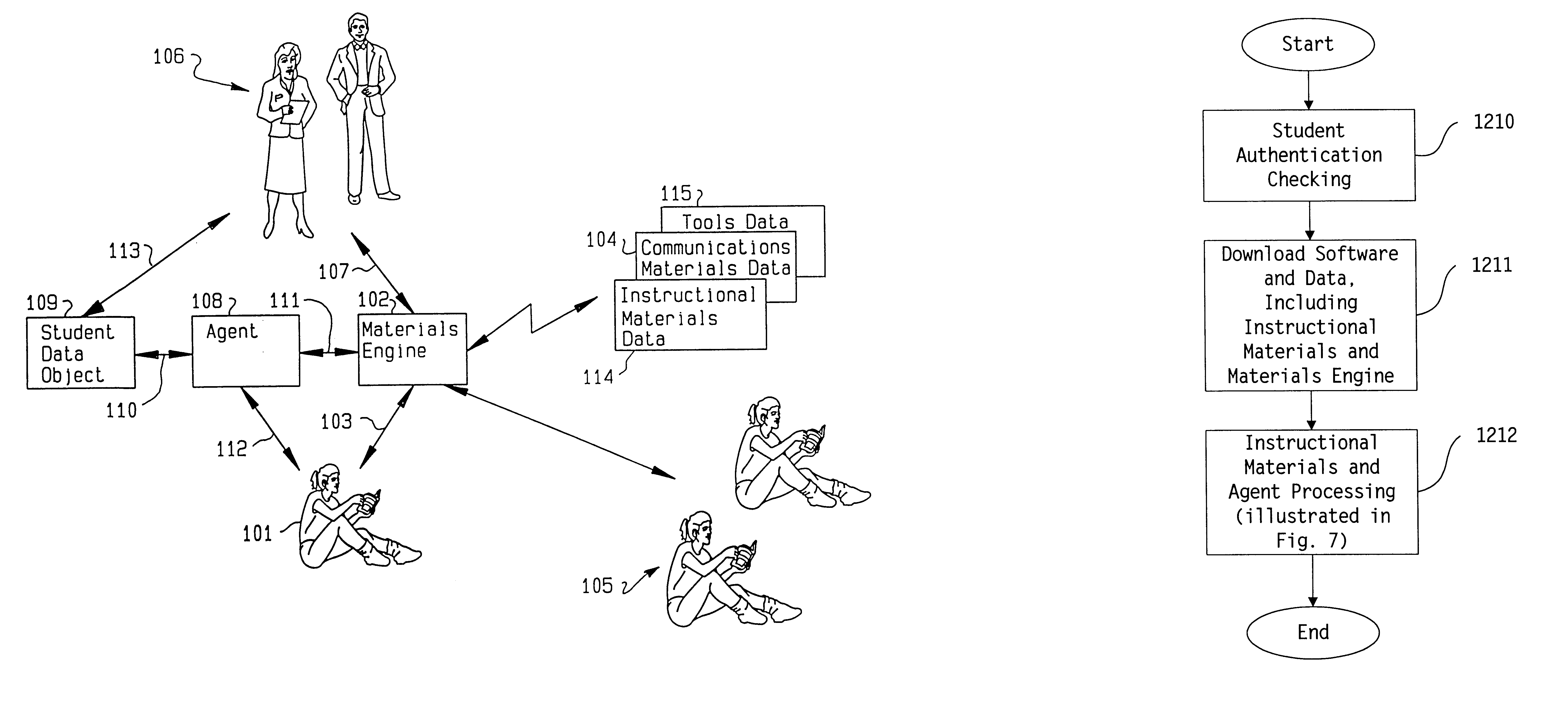
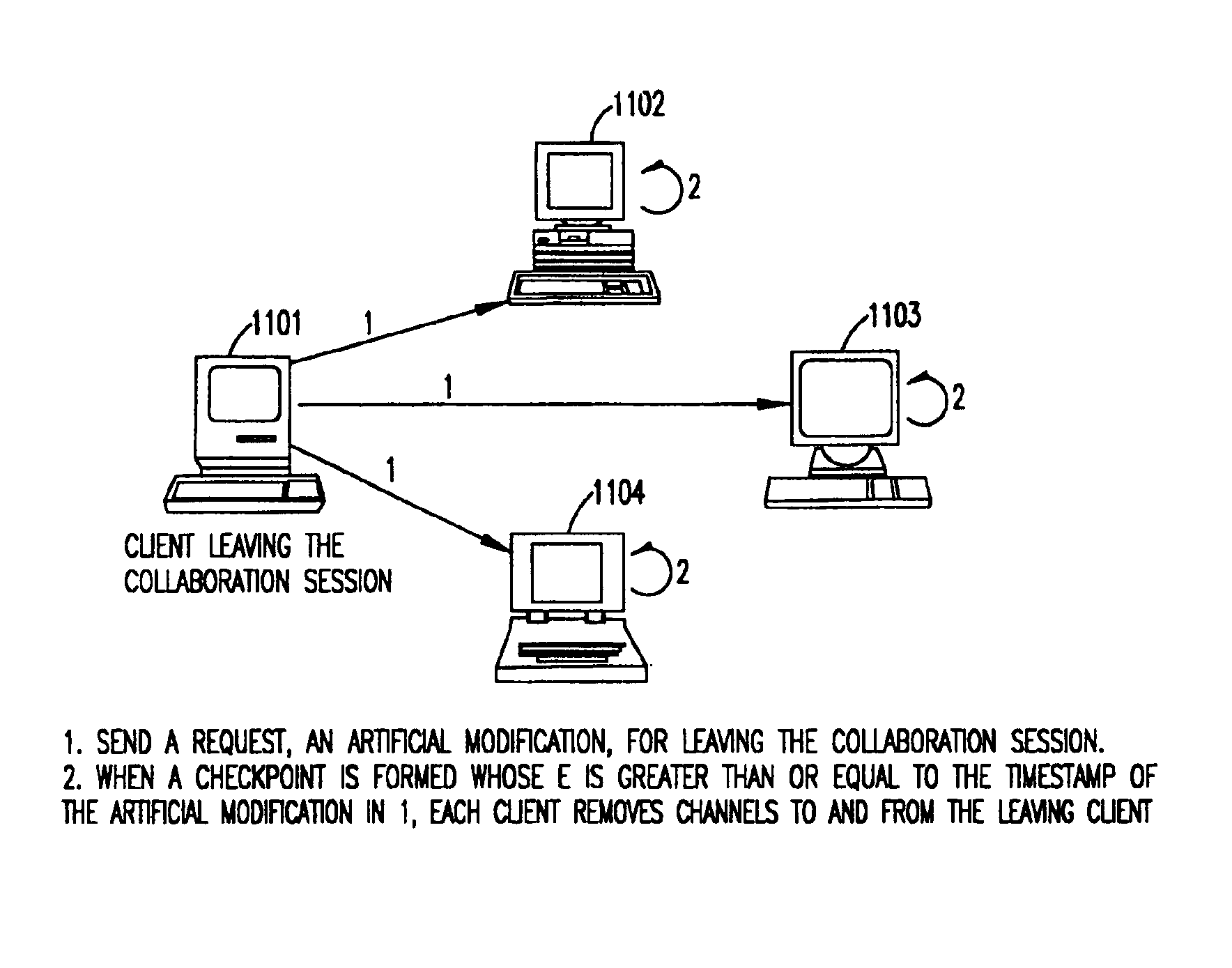
Synchronous collaboration based on peer-to-peer communication
InactiveUS6898642B2Eliminate useFully treatDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsTimestampWorkspace
A peer-to-peer protocol is based on the use of global timestamps and client priorities in serializing modifications to a shared workspace of real-time collaboration. The method caters to dynamic clients wherein a client can leave or join an ongoing collaboration session as long as there is always at least one client present / remaining in the collaboration session. The method can support multiple definitions of a modification, including partitioning-based definitions, wherein the method provides full support for locking of partitions, and a full treatment of inter-partition synchronization via a modification definition over multiple partitions. The method is capable of utilizing the many standard methods of creating a global, distributed, synchronized clock for the global timestamps utilized by it. The method is rollback-based for correcting tentative but incorrect serializations, and provides additional backup in terms of checkpoints for additional safety and for the support of lightweight, pervasive clients. The method includes many optimizations for efficiency, and includes a method of switching to and back from distributed server-based serialization for the periods when the network response is better suited to a distributed server than the peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
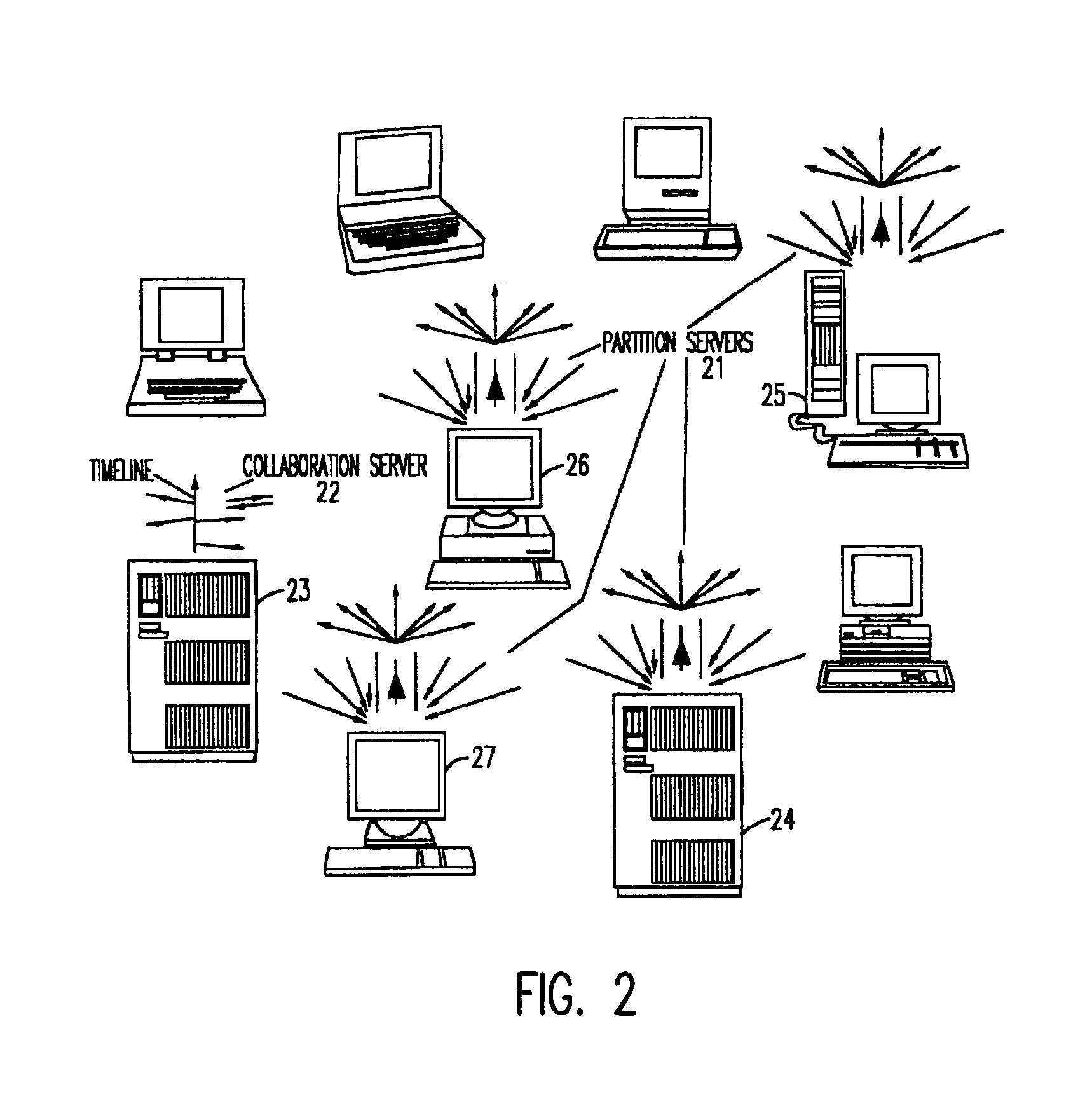
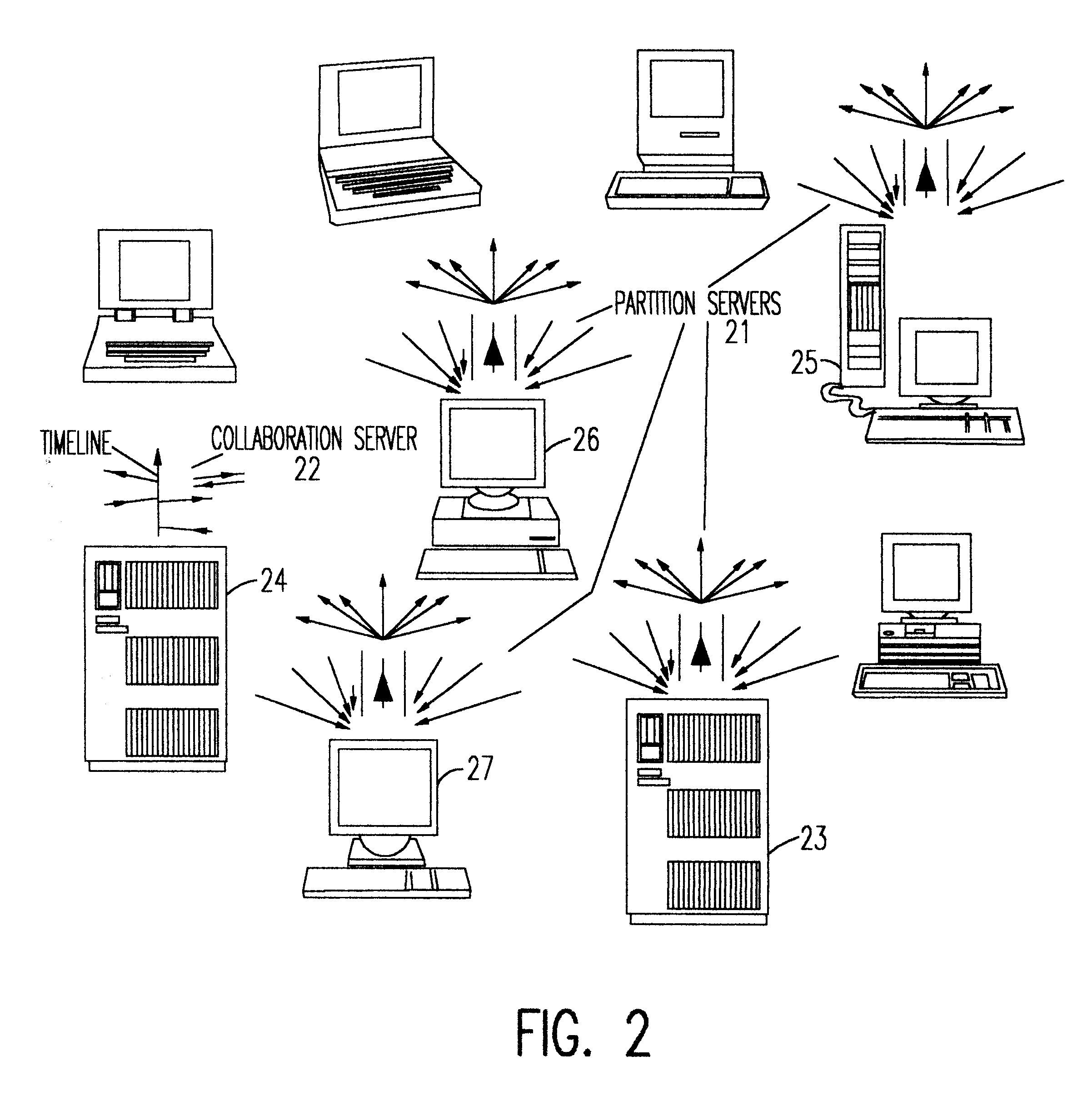
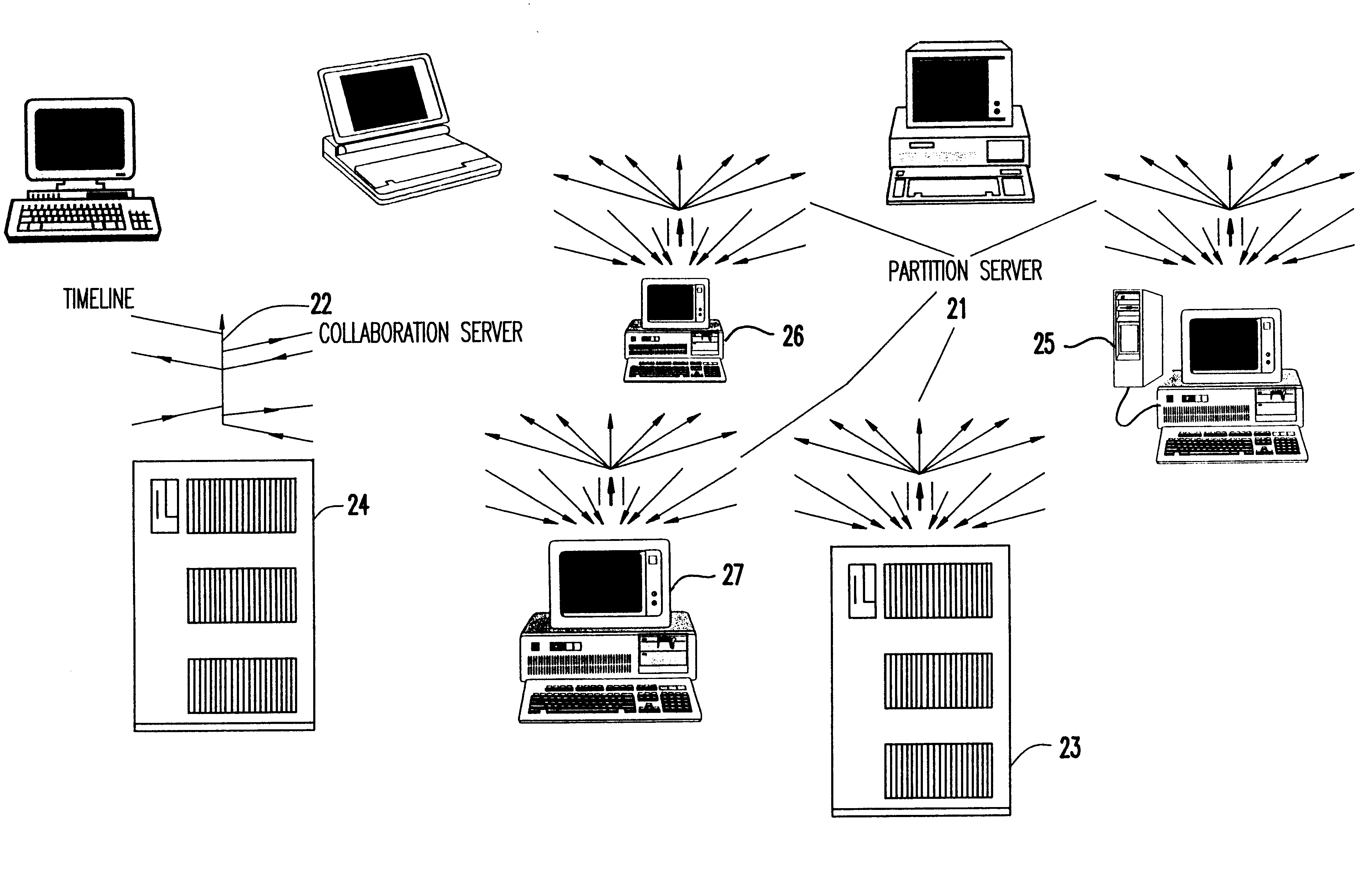
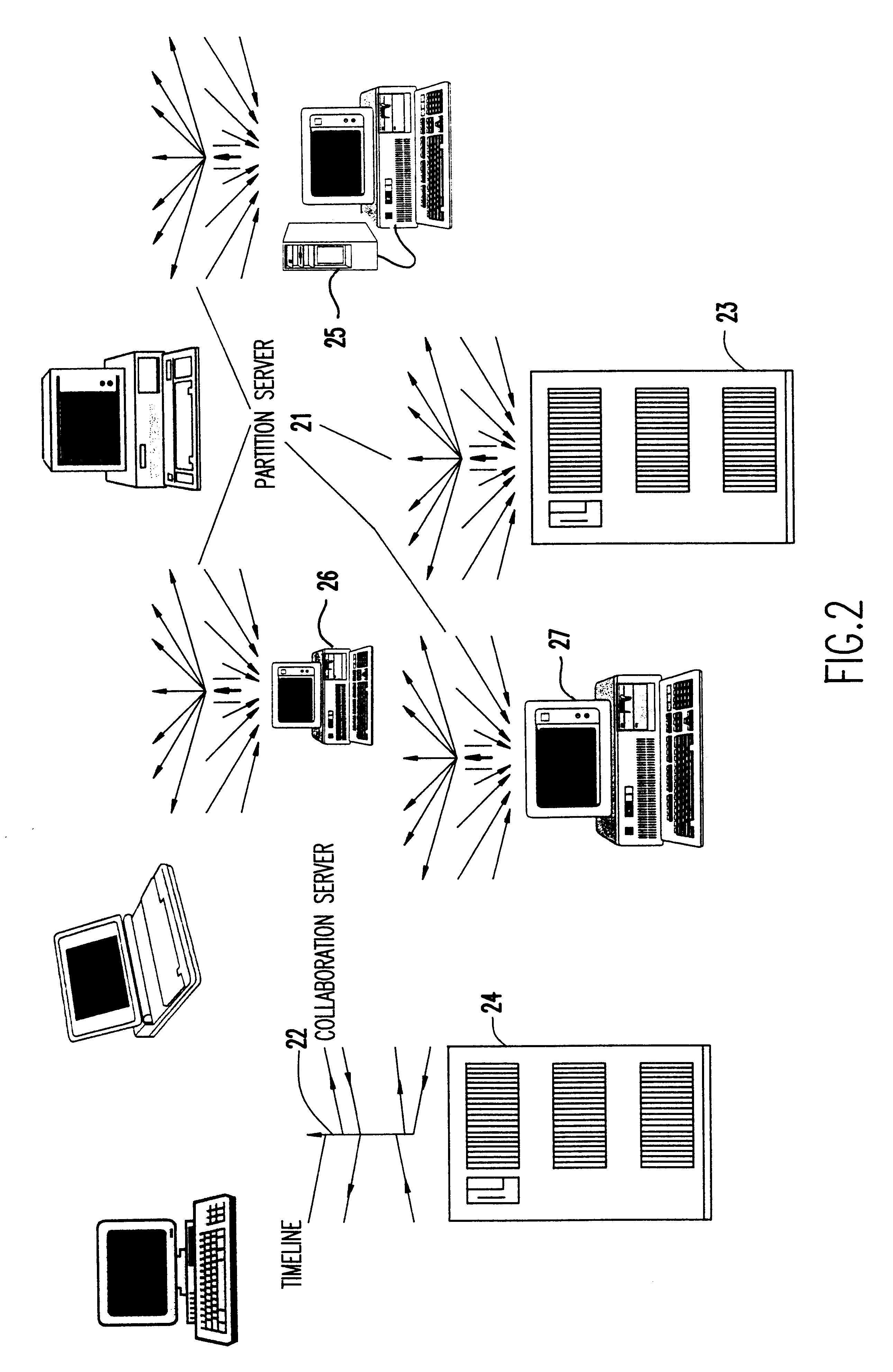
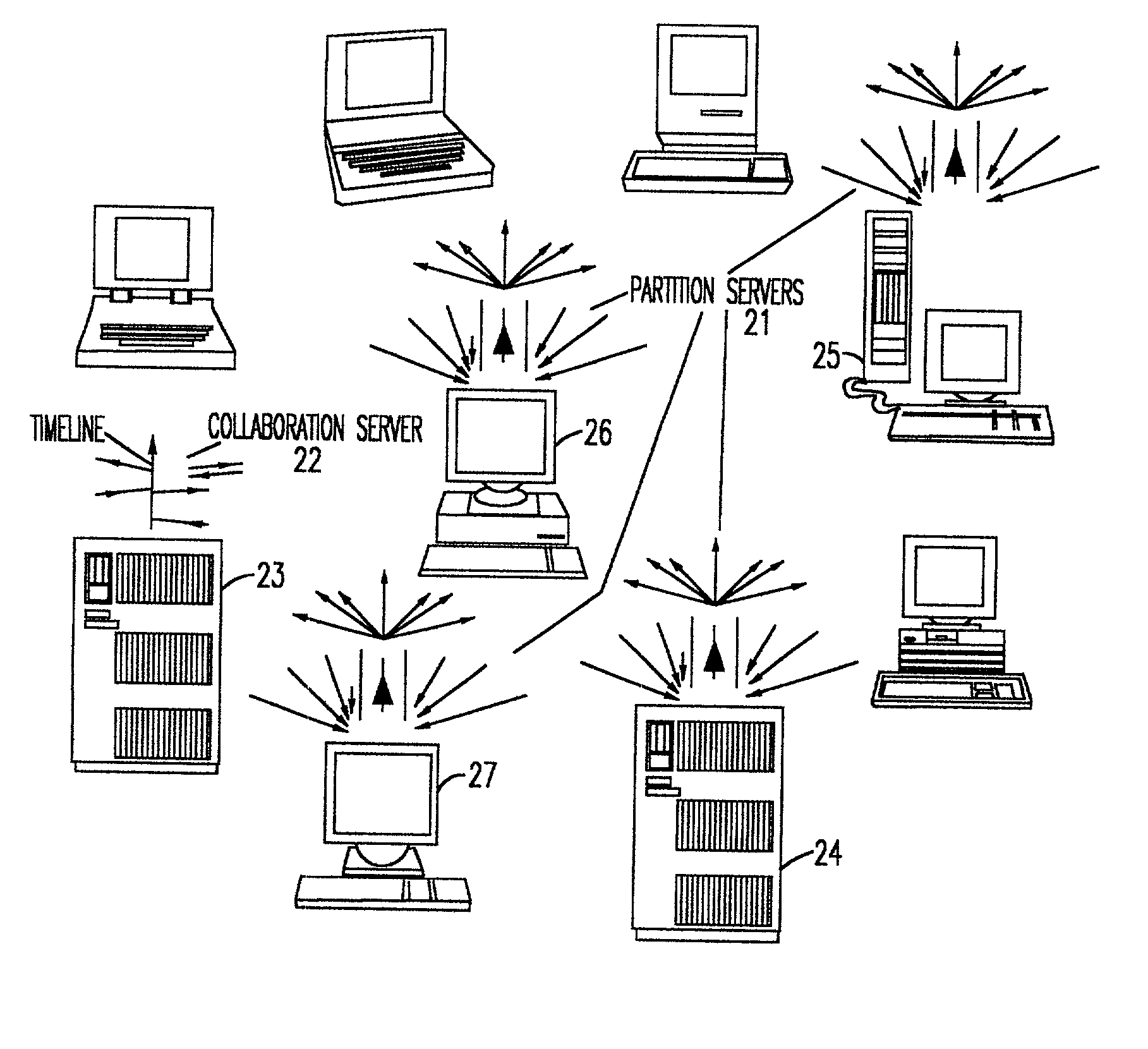
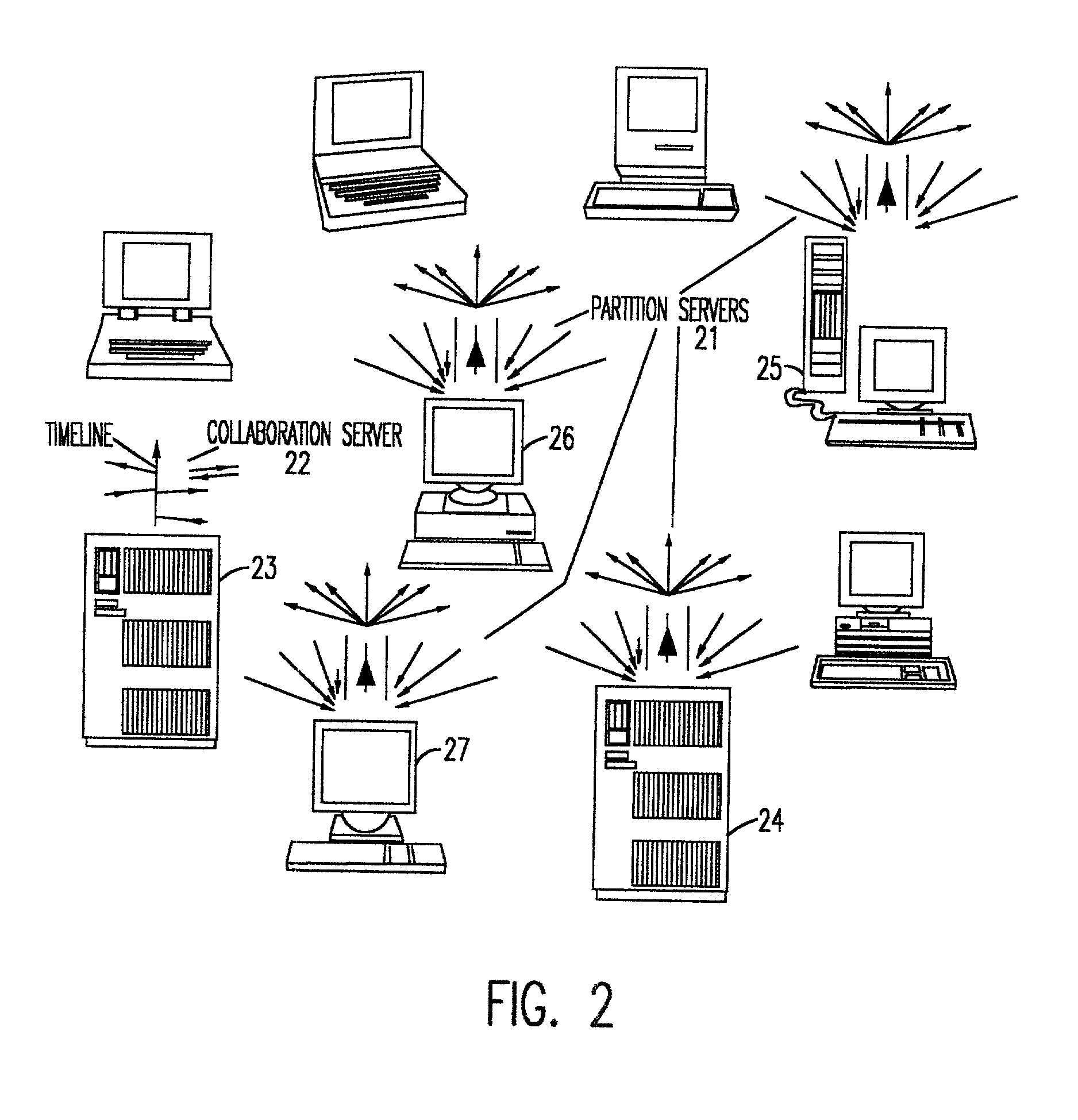
Dynamic clients, dynamic partitions, locking, and migration capability for distributed server for real-time collaboration
InactiveUS6336134B1Special service provision for substationMultiprogramming arrangementsData collaborationWorkspace
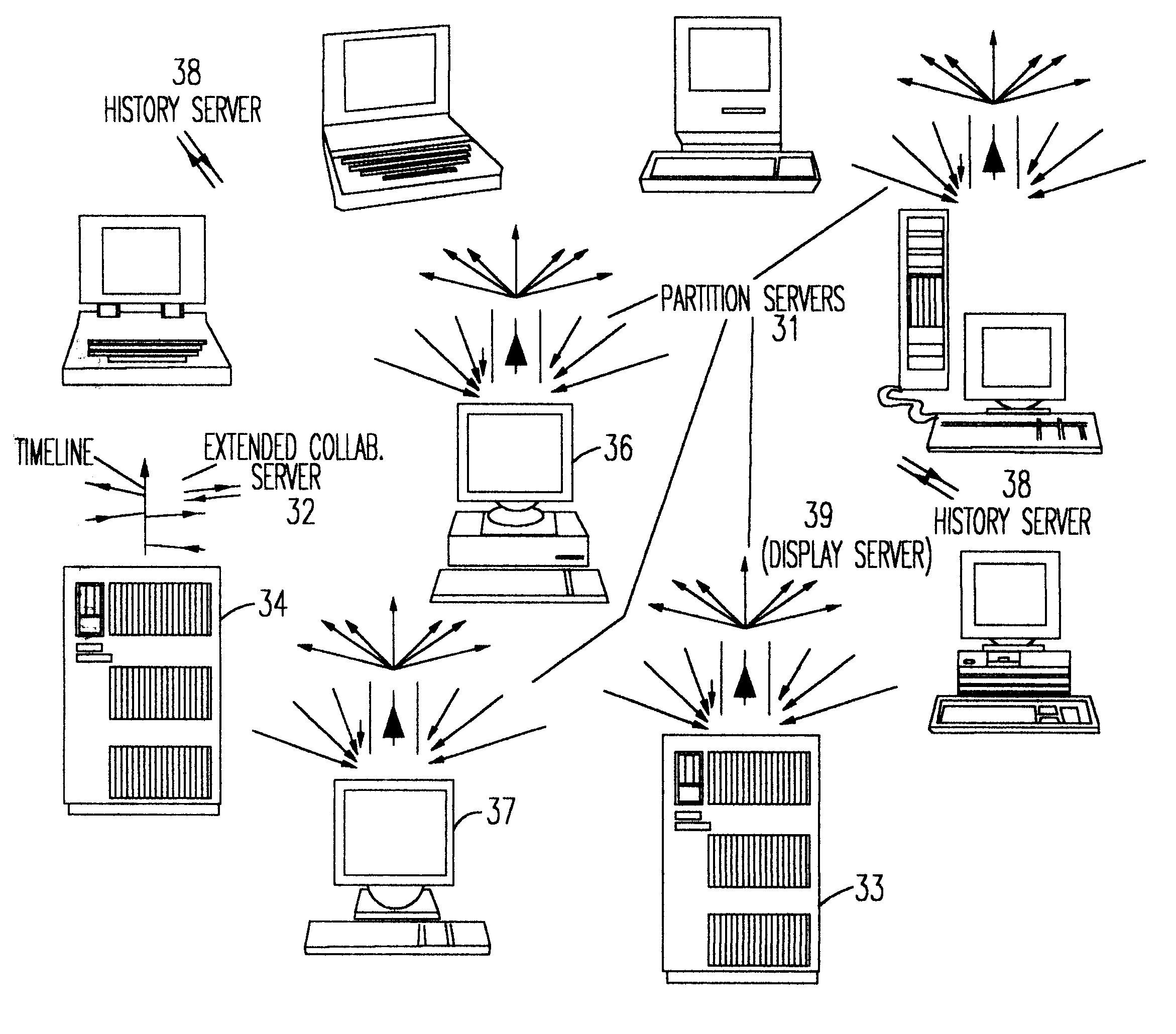
A method for building a locking, migration, dynamic clients, and dynamic partitions capable distributed server for a real-time collaboration session supports the synchronous creation and deletion of partitions by clients as well as the addition and withdrawal of clients during a current collaboration session. The method is based on history servers for providing a history of modifications so that a newly-added client can compute the current state of a shared workspace. The history servers cache and granularize intermediate modification sequences so that computation space and time are reduced. The method supports migrating partition server(s), history server(s), a creation / deletion server, and a collaboration server to different machines. Partition(s) can be dynamically locked and unlocked and, in an extension of this procedure, creation and deletion of partition(s) can be pre-announced and supported. Advanced dynamic-partitioning activities like splitting a partition, merging partitions, shifting data from partition to partition are carried out naturally by locking the concerned partitions during the process of execution.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
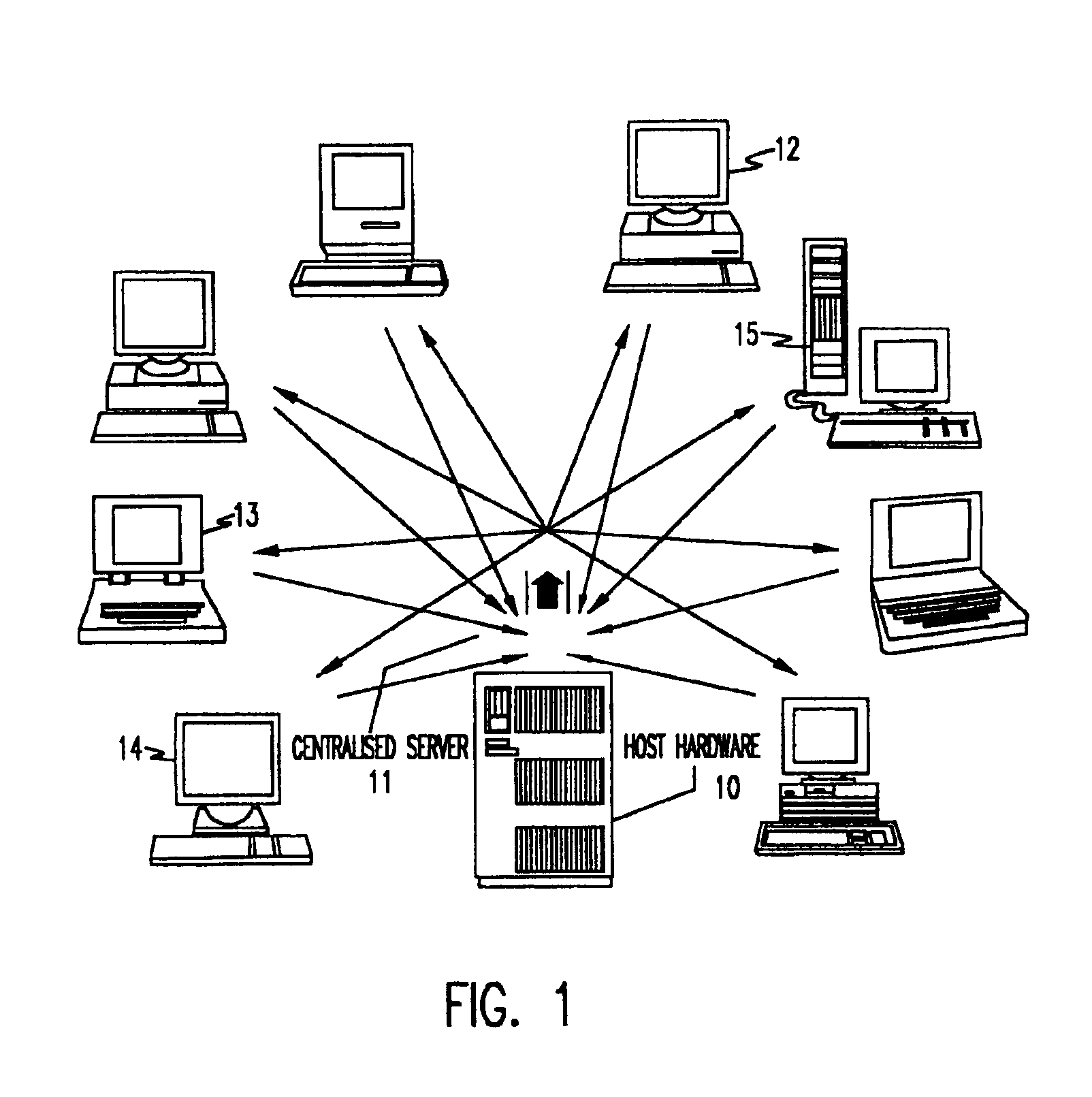
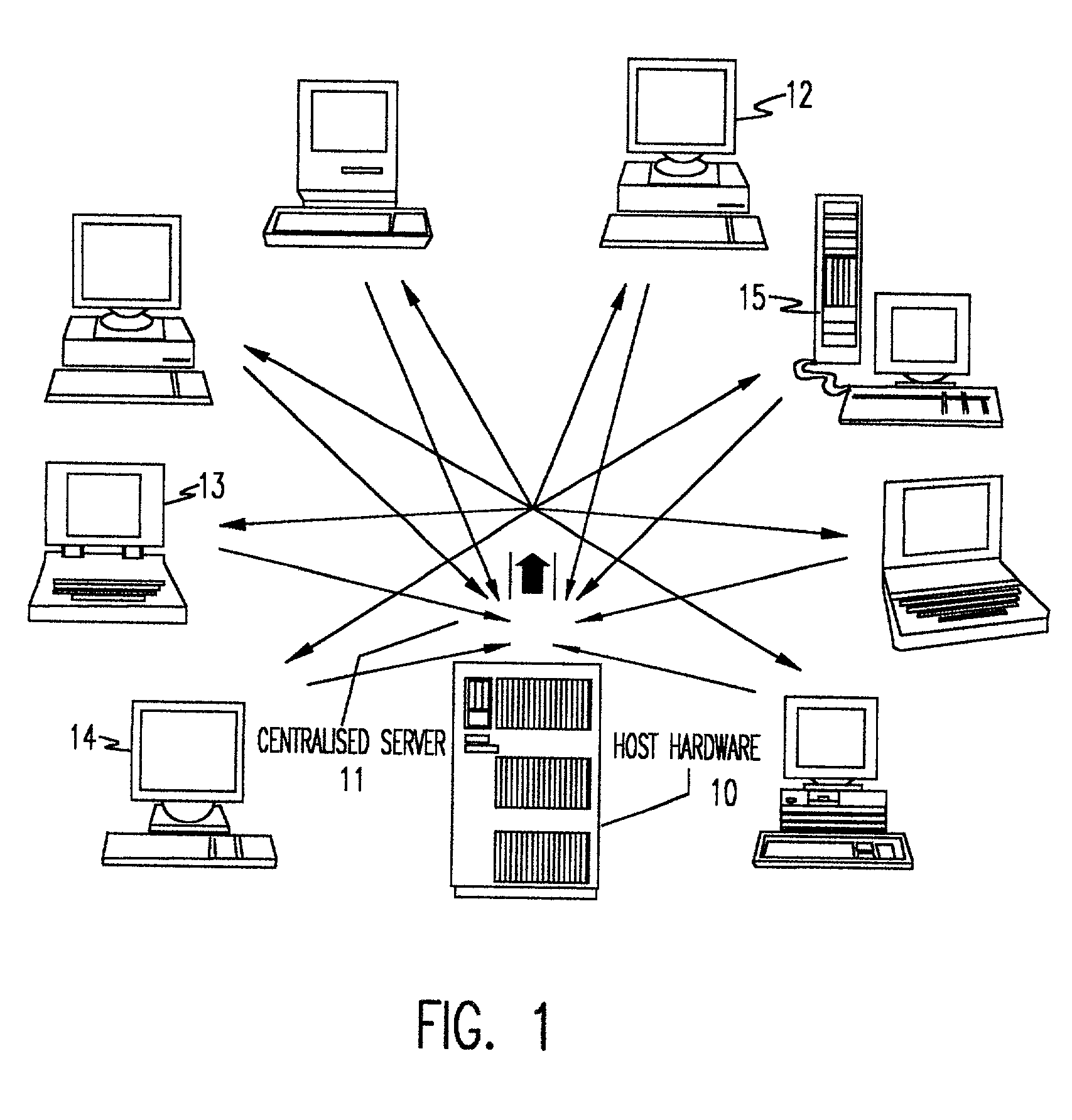
Distributed server for real-time collaboration
InactiveUS6334141B1Avoid focusSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsExtensibilityData collaboration
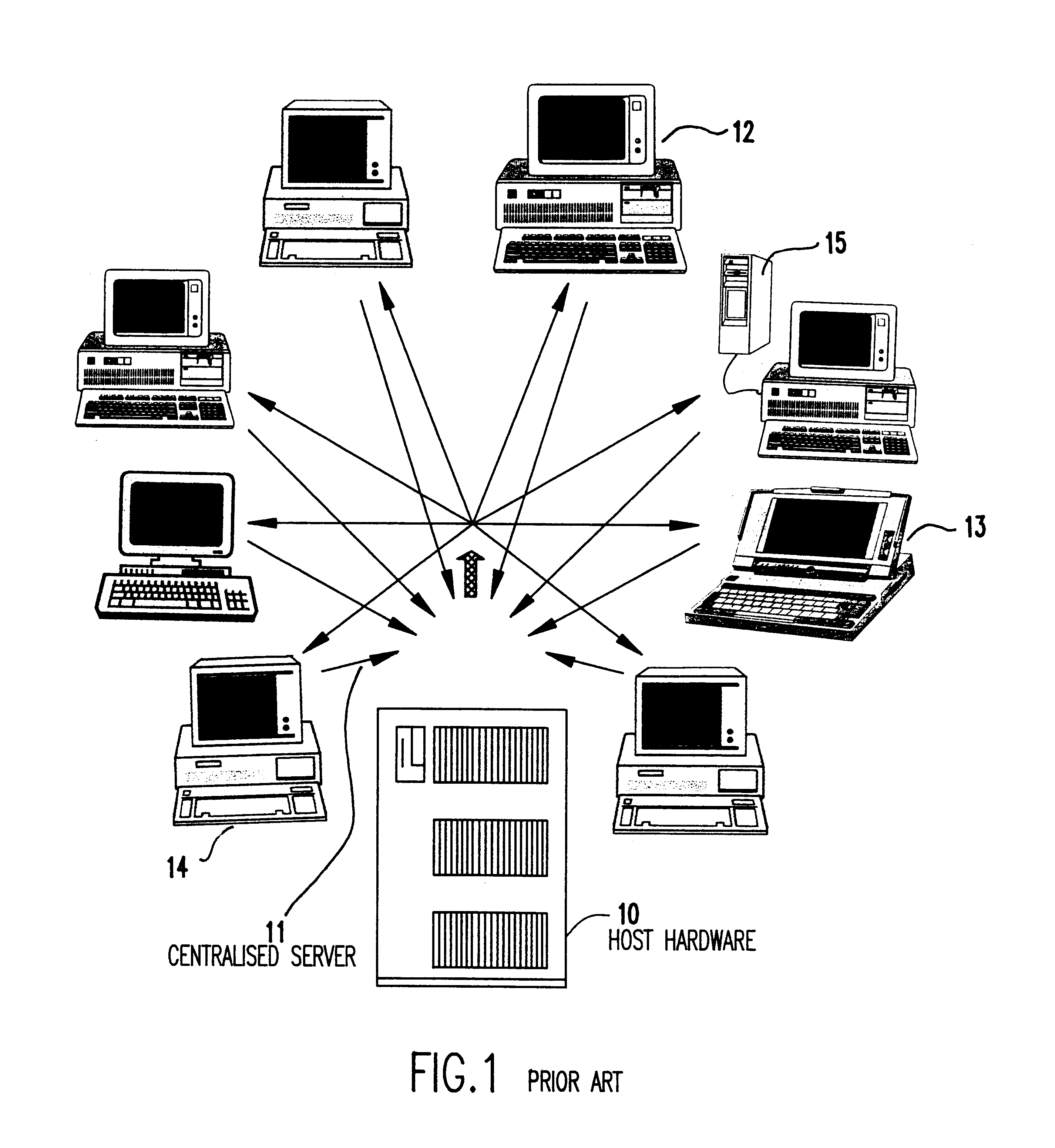
A distributed server for real-time collaboration is substituted for a centralized server to address the problem of the development of unacceptable communication and computation bottlenecks resulting from the use of a one-software-process-based centralized server running somewhere on the available network. The substitute distributed server improves scaleability of real-time collaboration by being based on multiple, independently-communicating, asynchronous, independent (i.e., no shared memory, data, variables, etc.) software processes. The processes can be distributed to multiple machines throughout the network and run simultaneously in order to avoid the centralized server's bottlenecks. To be used, a distributed server requires a disjoint, fully covering partitioning of a work space, wherein it can handle partition hierarchies and groups comprehensively. The distributed server solution is general because of the ability of distributed servers to work with different definitions of a modification. The distributed server solution is extensible because of its simple and comprehensive treatment of inter-partition synchronization.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
Method and system for providing access to electronic learning and social interaction within a single application
InactiveUS20050227216A1Improve the level ofData processing applicationsElectrical appliancesDistributed serversApplication software
A system for managing academic and social life for students includes a central server connected to a wide-area network and storing a repertoire of logic functions for use by students in managing academic activities; and a plurality of computerized appliances associated with individual students, the computerized appliances connectable to the wide-area network. The students may download logic from the central server, and execute the logic to configure and manage activities related to classes and studies in a college or university, and may interact with other students through the central server. In one aspect the system further includes one or more distributed servers connected to the wide-area-network the servers adapted for network-based academic learning and for communication with the central server over the network; and one or more content servers connected to the wide-area-network, the content servers adapted to provide Web-based content and services to students through the central server.
Owner:SOUNDSTARTS
Providing Location-Based Services in a Distributed Environment Without Direct Control Over the Point of Access
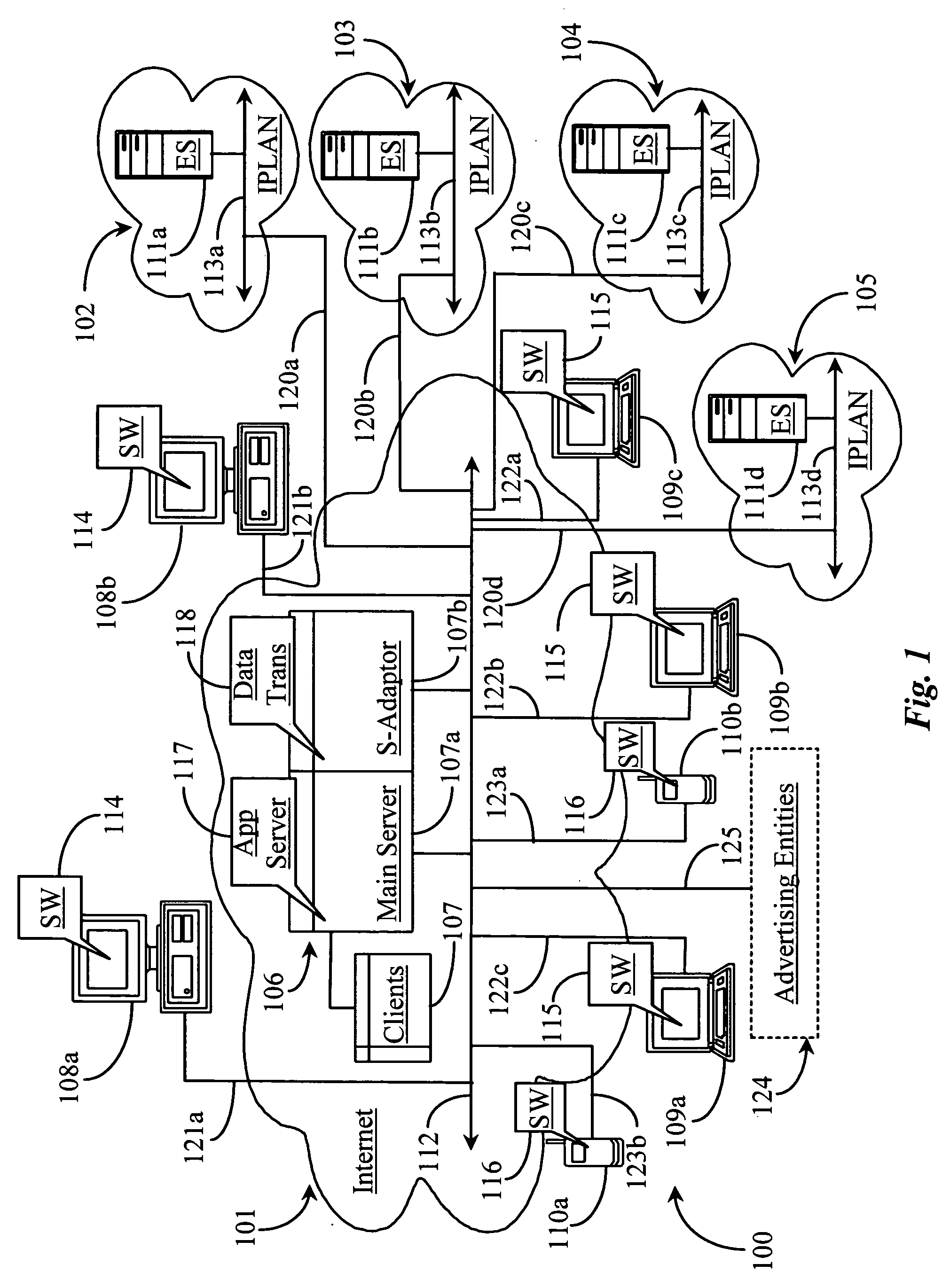
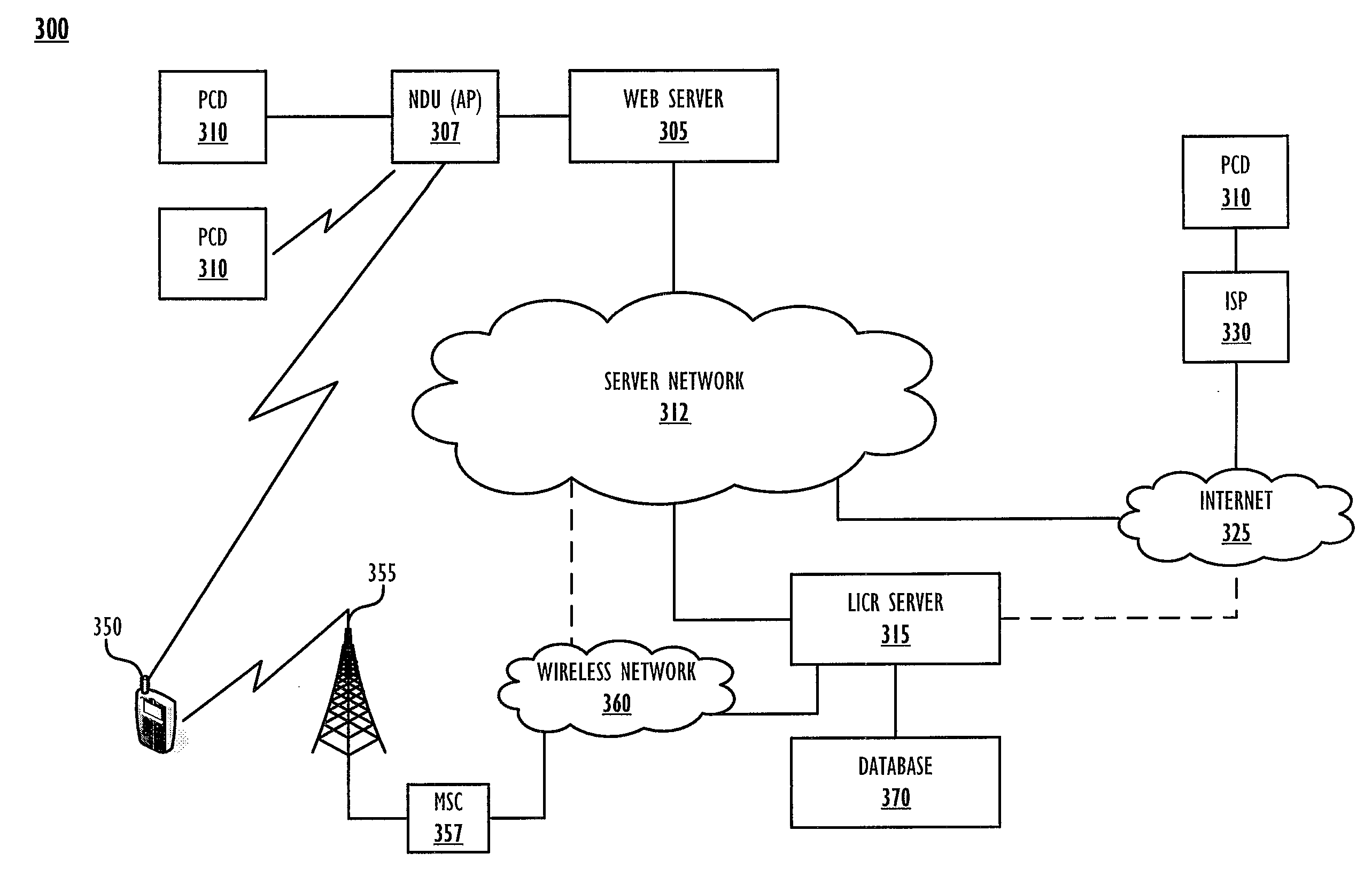
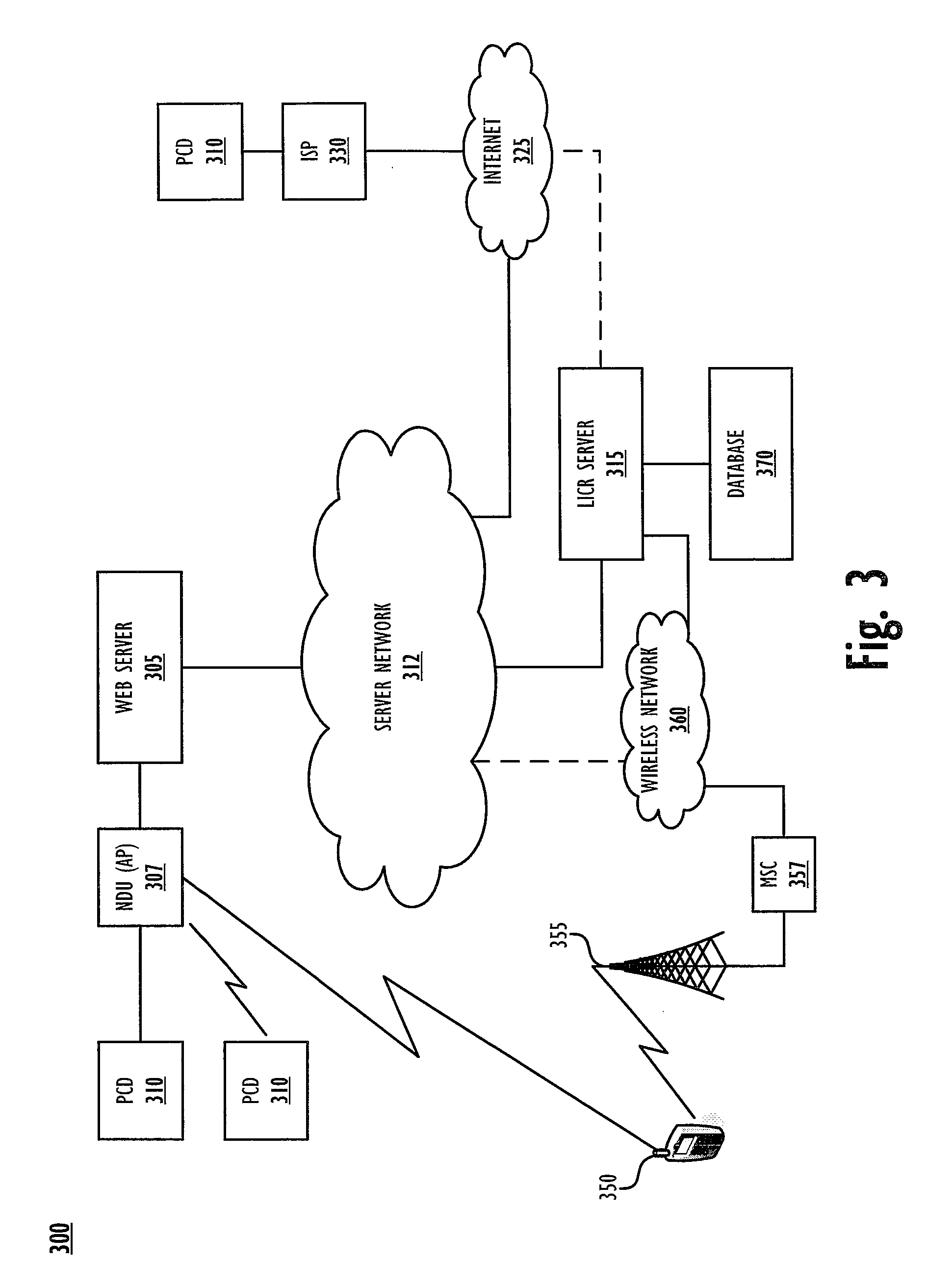
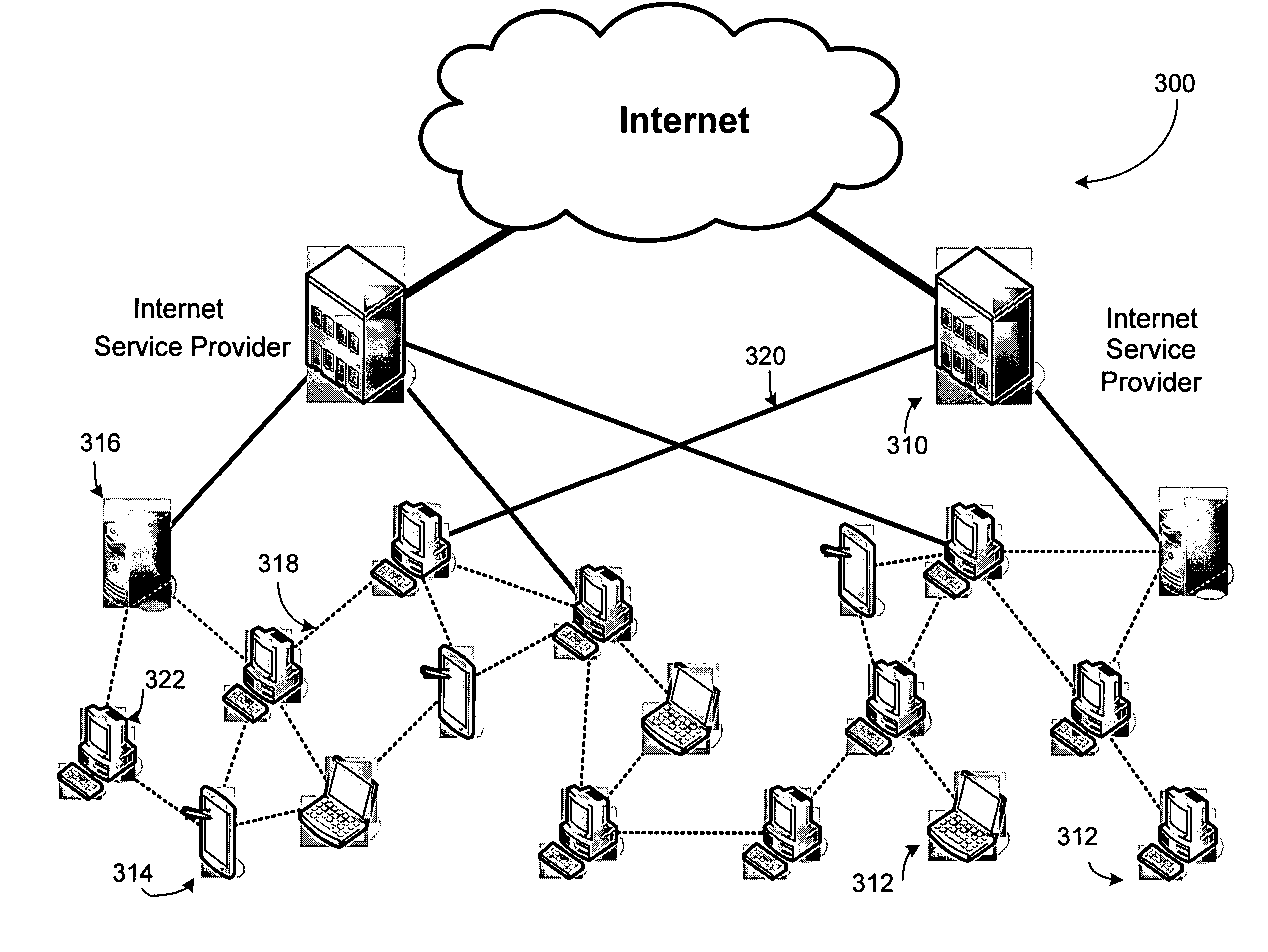
A method, system and computer program product for providing location-specific content to a personal computing device (PCD) connected to a distributed server network (such as the Internet) without requiring an access control gateway to provide such content. Location-specific (and user-specific) content / services are provided by a client-server architecture utilizing a location database and a location look-up utility of a location identifier and content retrieval (LICR) server. Specifically, a utility executing on the PCD provides PCD location parameters to the LICR server, which is equipped with a location look up engine / functionality and a location content retrieval engine / functionality (both within a LICR utility) that responds by providing location-specific and user-specific content to the PCD.
Owner:WAYPORT
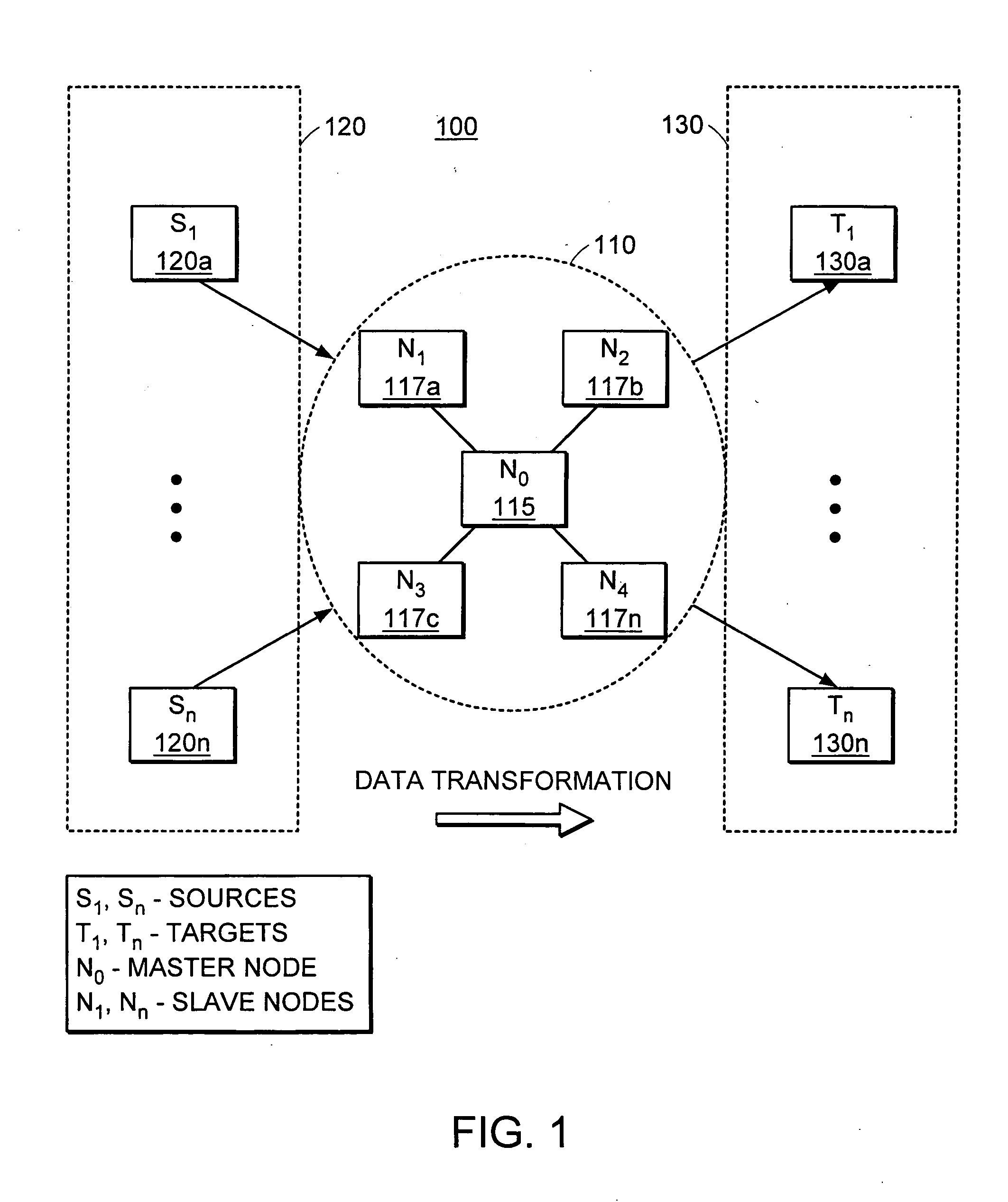
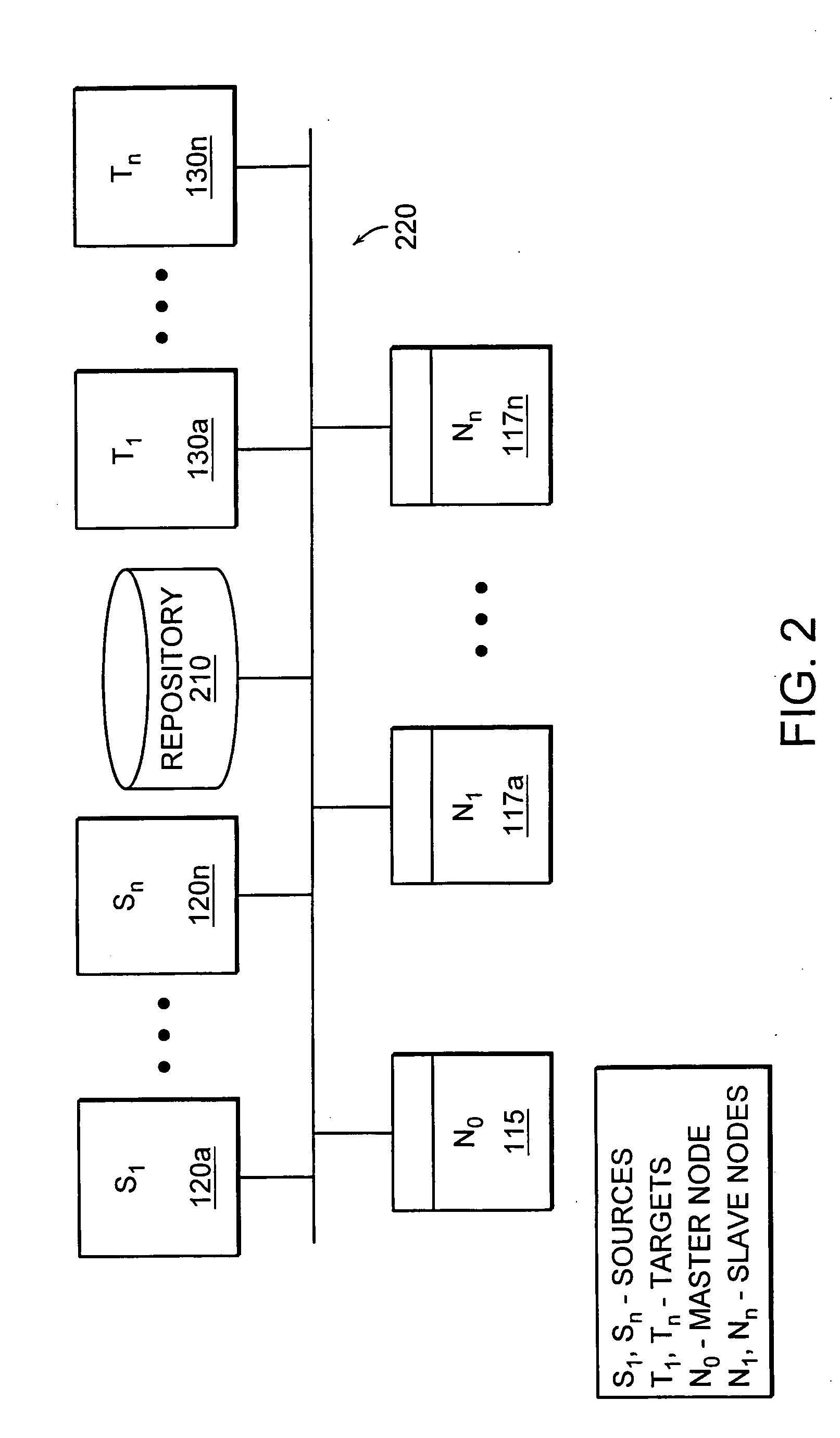
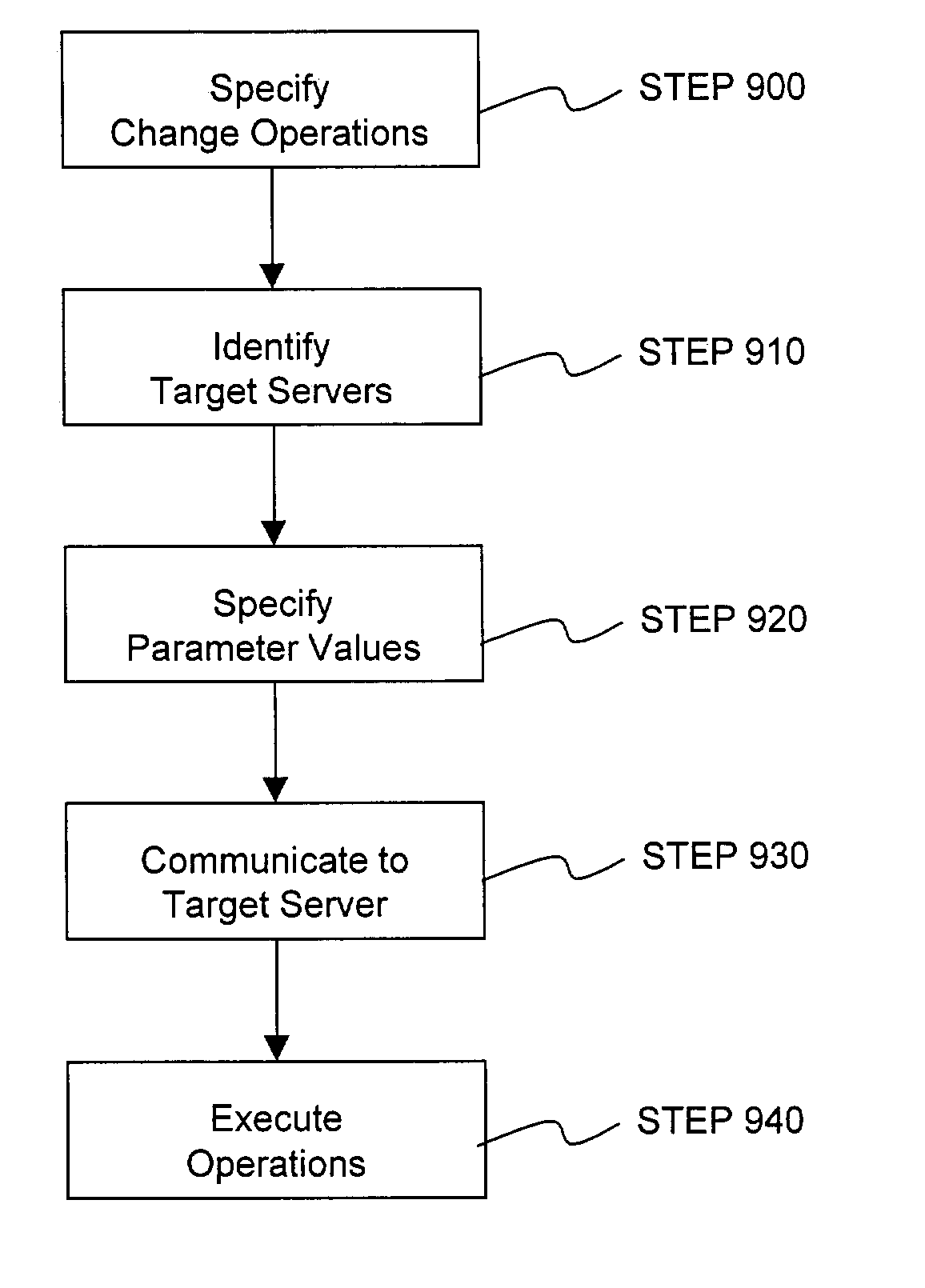
Method and system for executing and undoing distributed server change operations
ActiveUS20030233385A1Error detection/correctionInterprogram communicationDistributed serversComputer science
A method and system for executing and undoing distributed server change operations for a collection of server objects across multiple target servers in a transaction-safe manner is provided. In one embodiment, server change operations for a collection of server objects, such as files and configuration file entries, are specified in a transaction package. The target servers to which the specified change operation are directed are also identified in the transaction package. Parameter values for each of the identified target servers are specified through a parameter file in the transaction package. The transaction package is sent to the identified target servers, which execute the change operations on the target servers in a transaction-safe manner using these parameter values.
Owner:BLADELOGIC
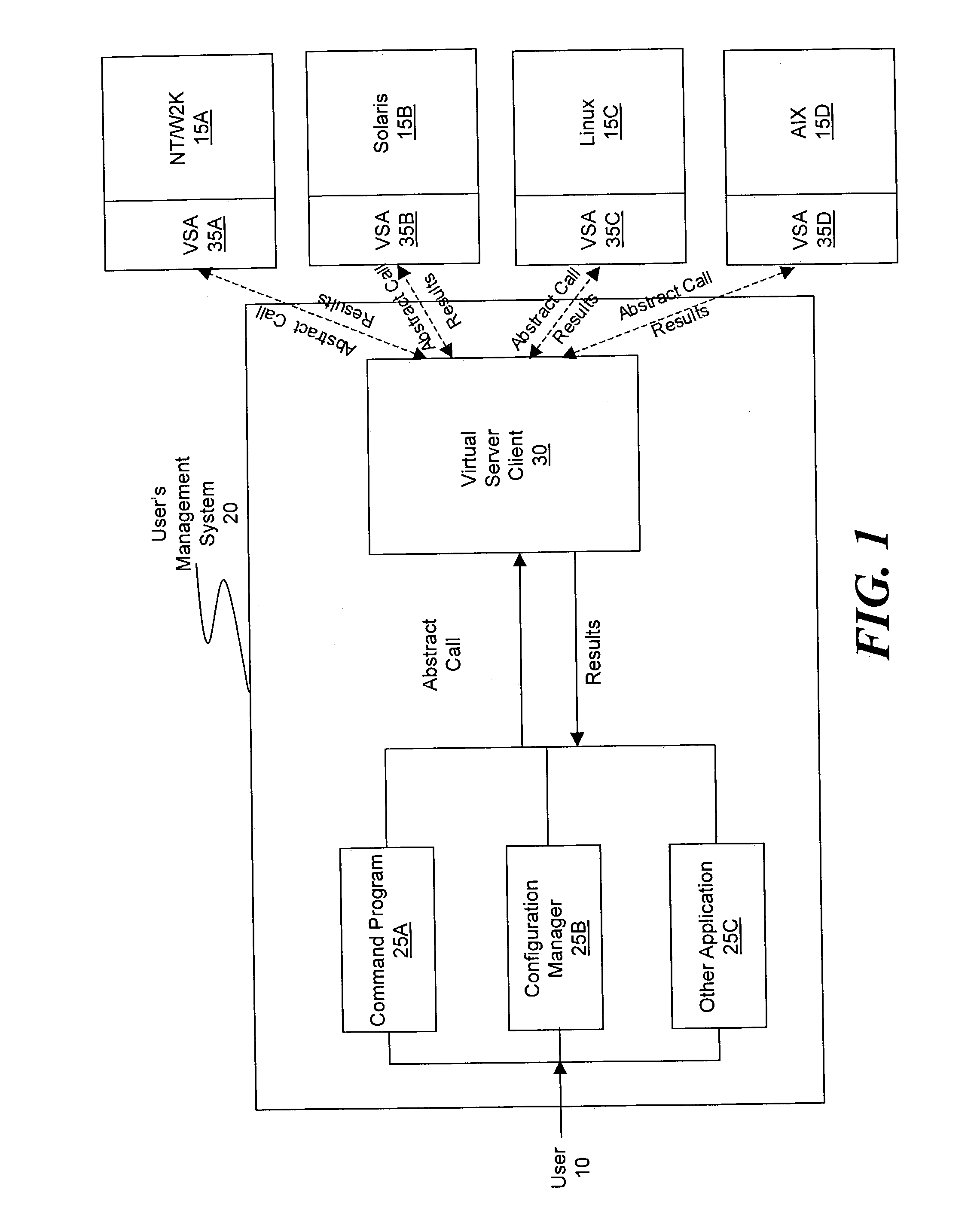
Method and system for simplifying distributed server management
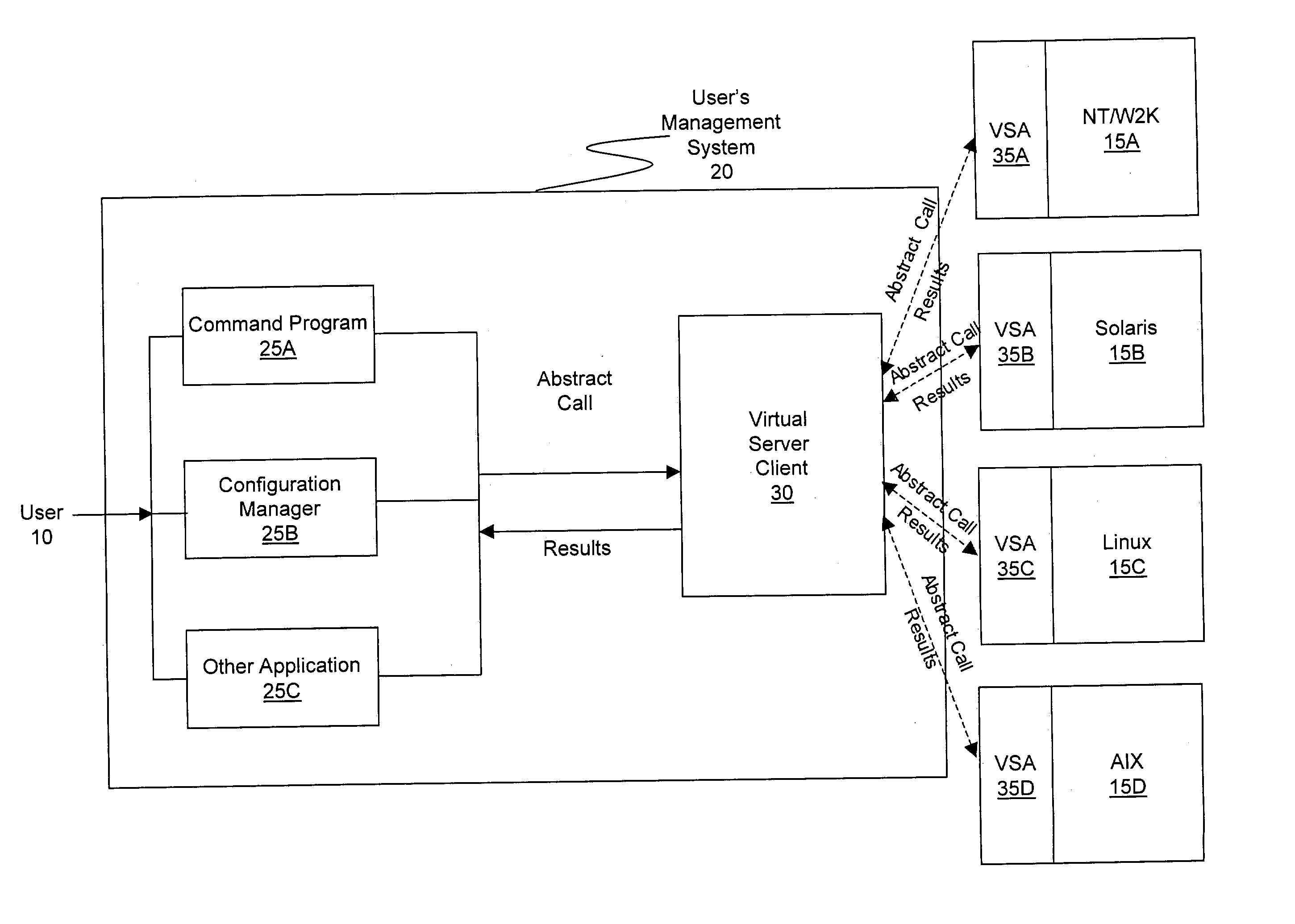
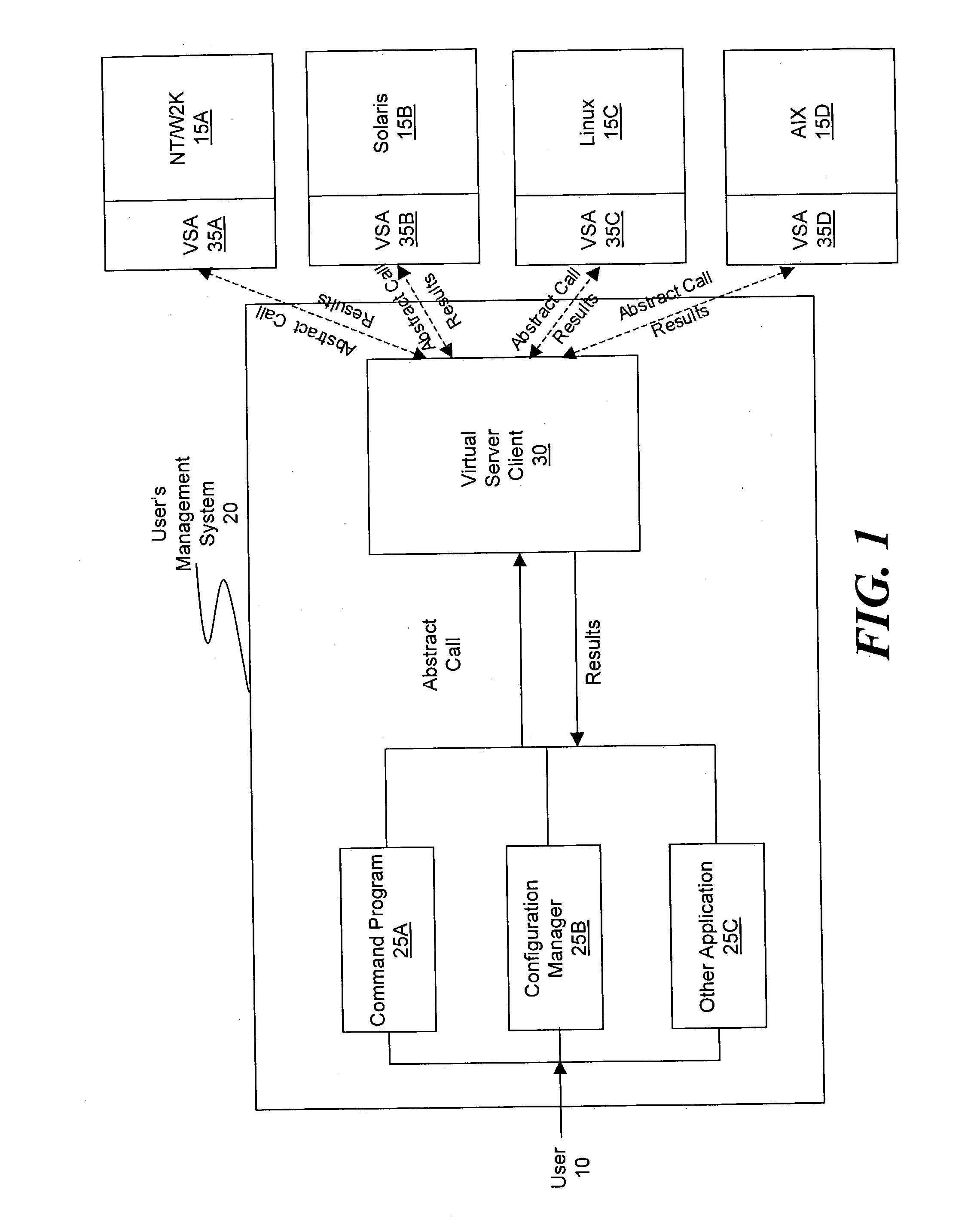
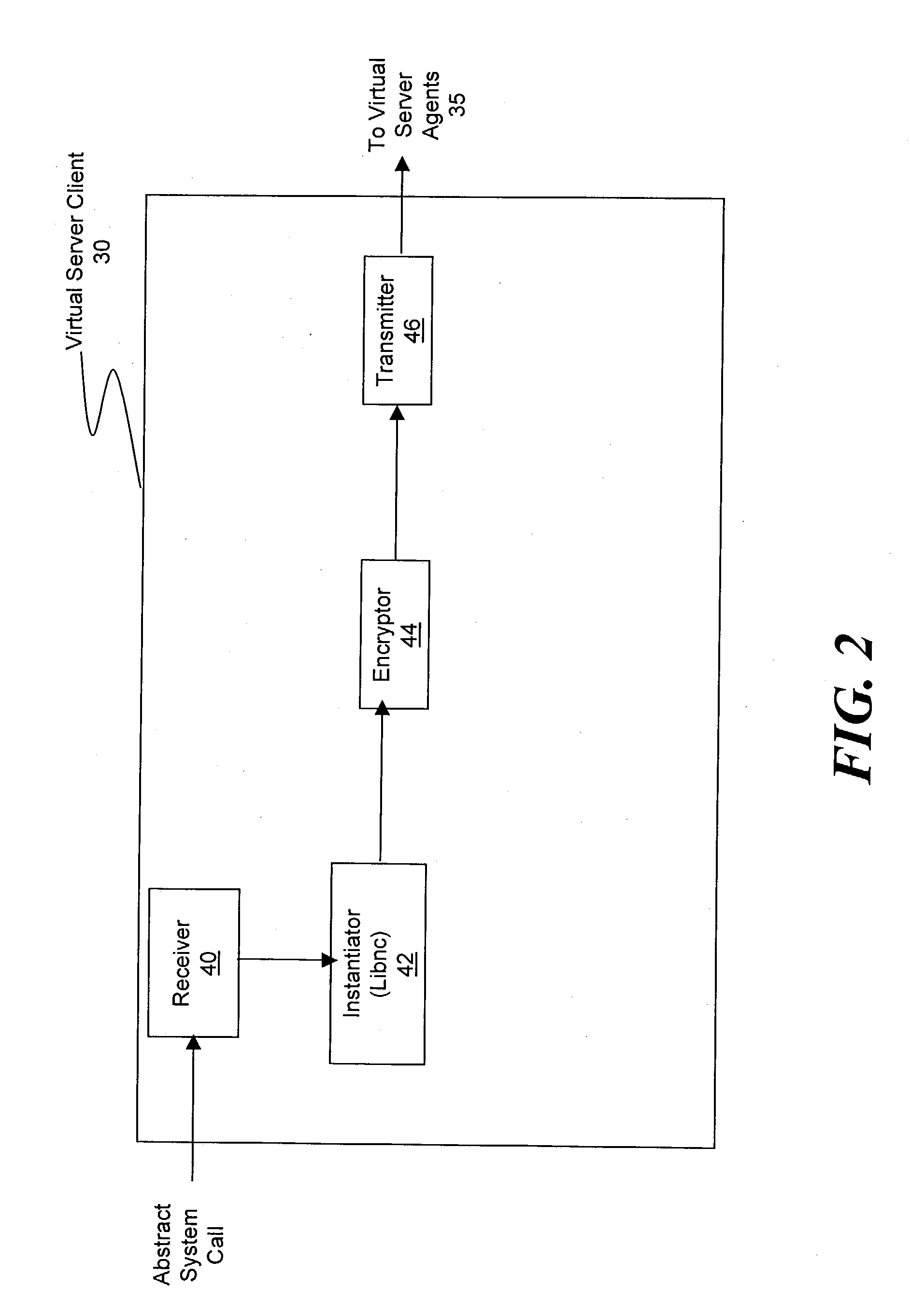
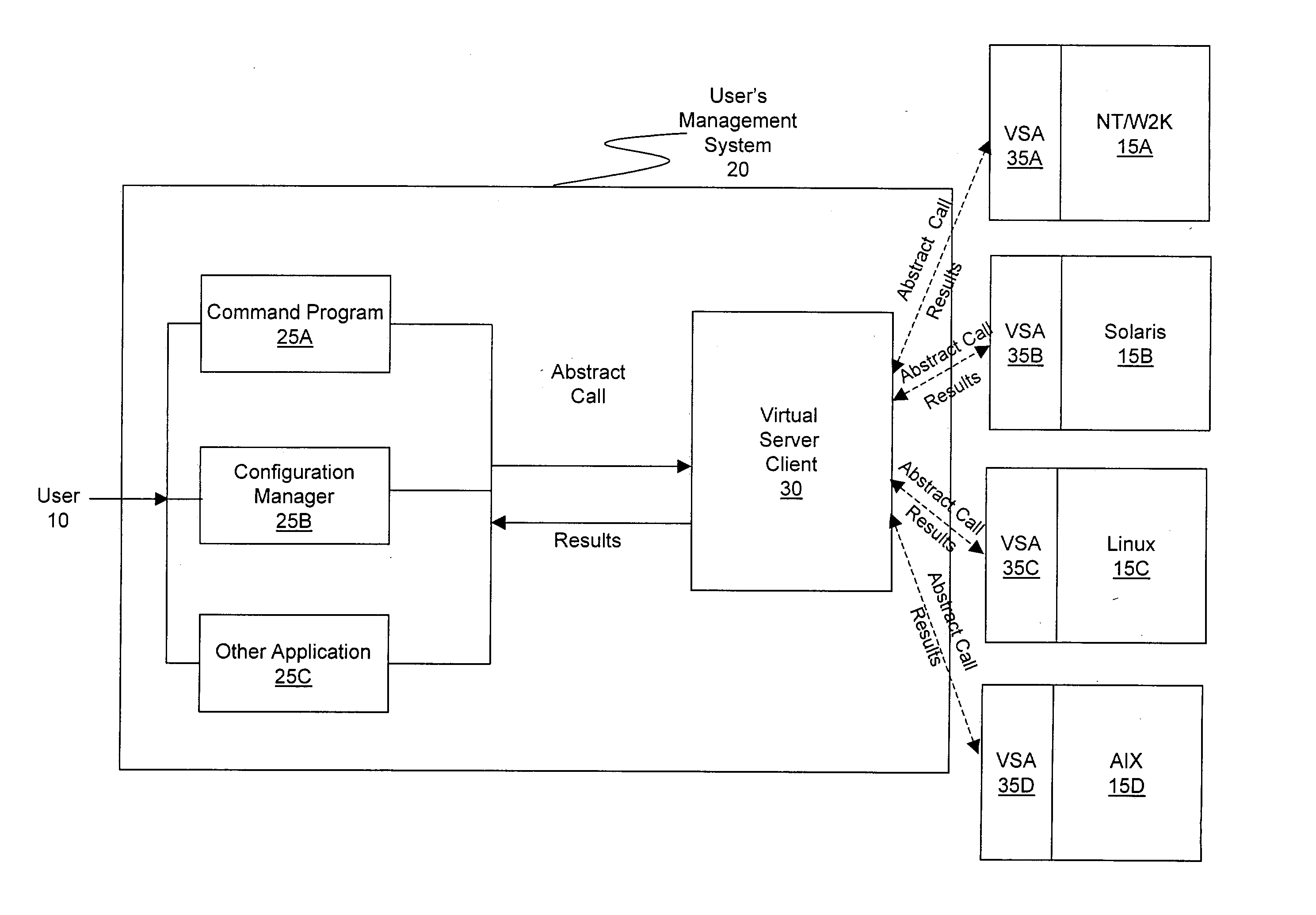
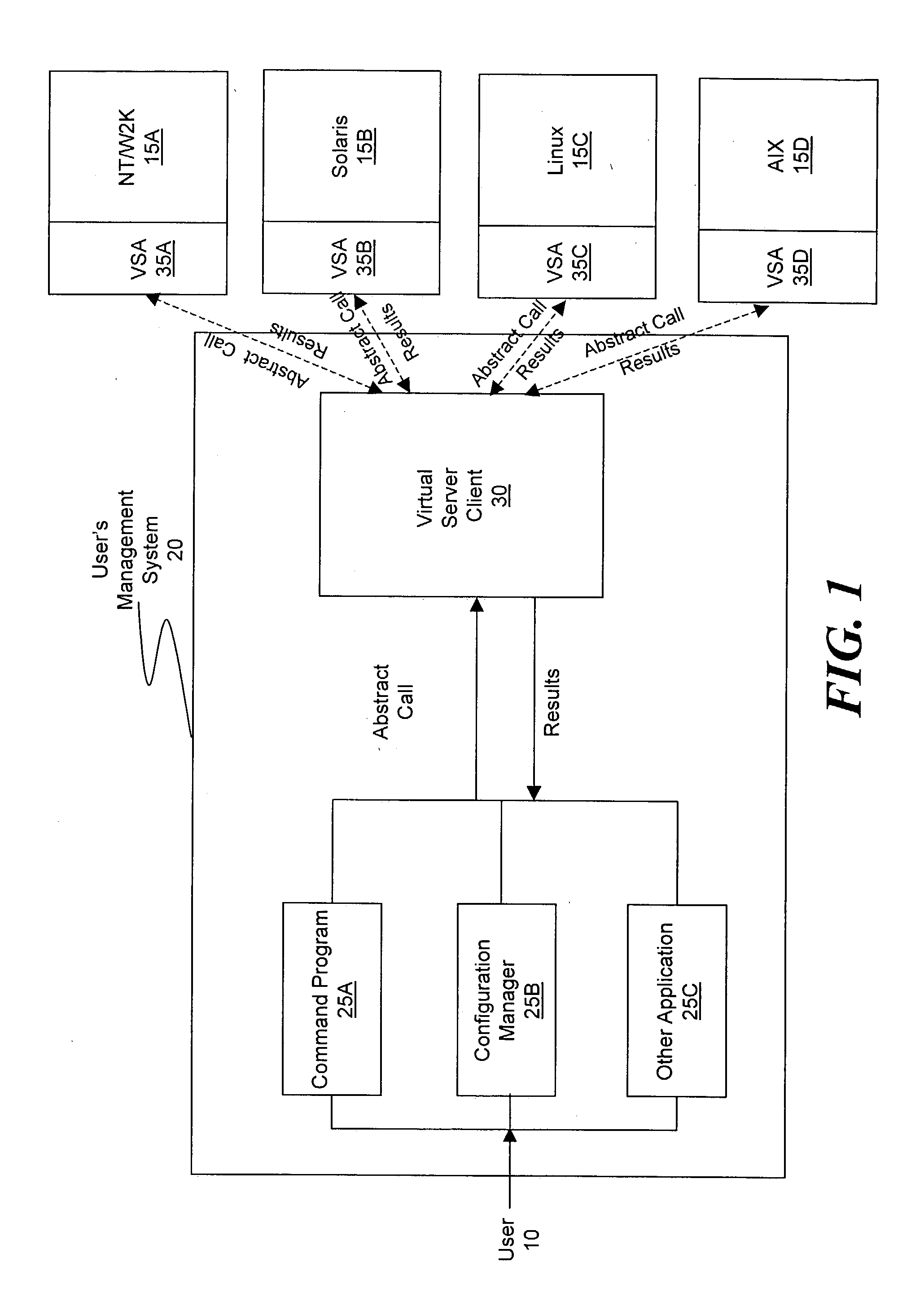
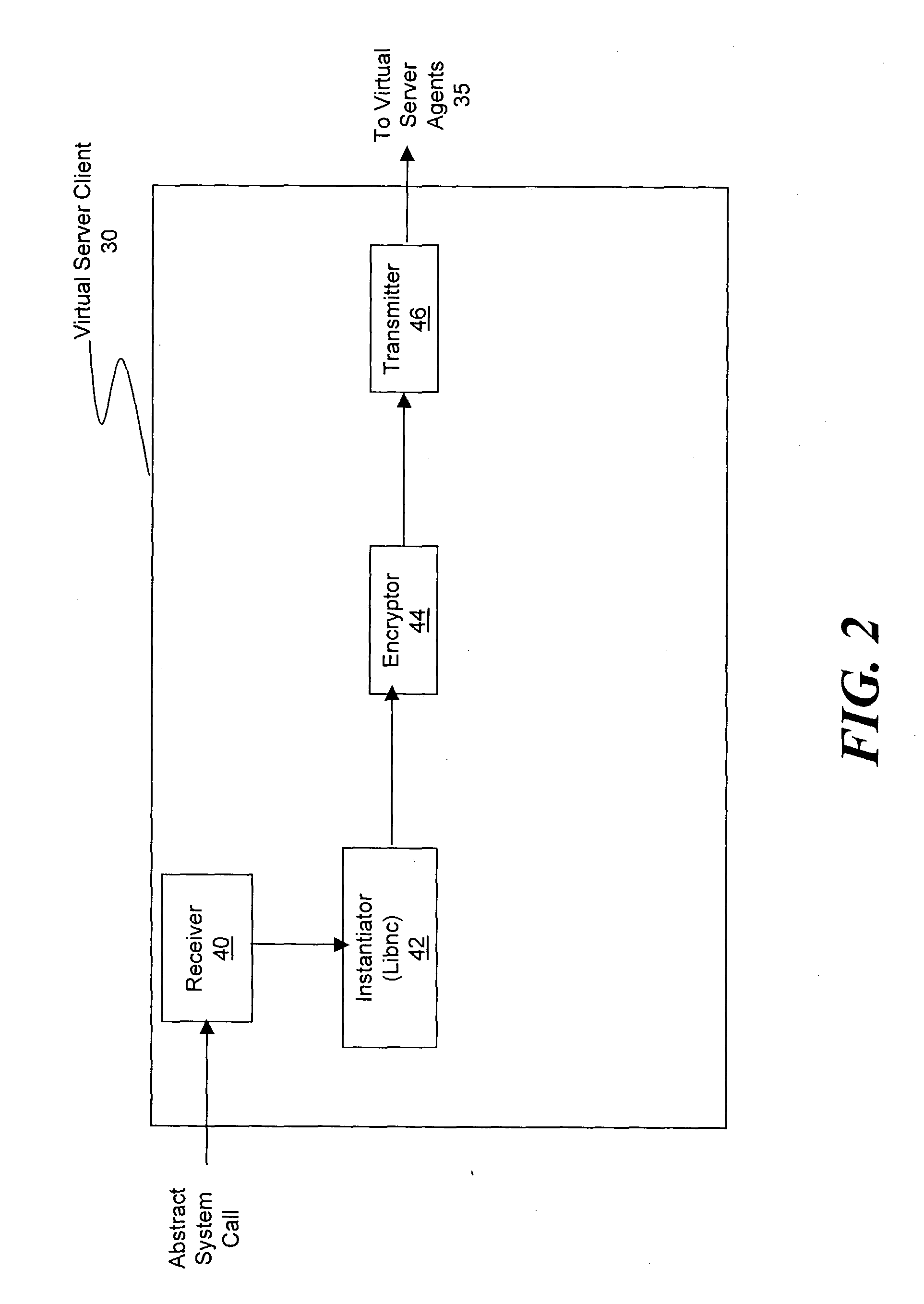
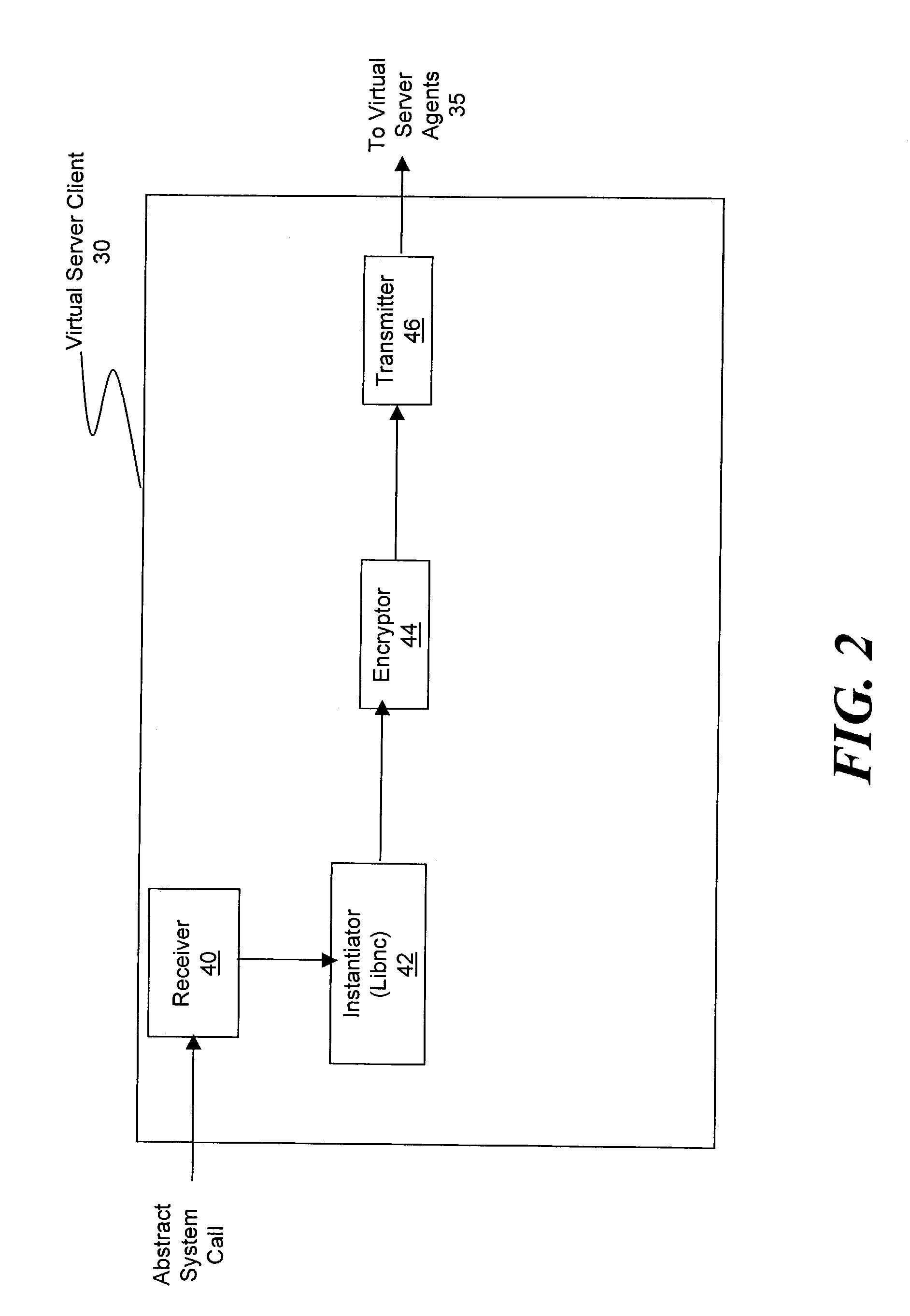
ActiveUS20030233571A1Error detection/correctionInterprogram communicationOperational systemSystem call
A method and system for managing a large number of servers and their server components distributed throughout a heterogeneous computing environment is provided. In one embodiment, an authenticated user, such as a IT system administrator, can securely and simultaneously control and configure multiple servers, supporting different operating systems, through a "virtual server." A virtual server is an abstract model representing a collection of actual target servers. To represent multiple physical servers as one virtual server, abstract system calls that extend execution of operating-system-specific system calls to multiple servers, regardless of their supported operating systems, are used. A virtual server is implemented by a virtual server client and a collection of virtual server agents associated with a collection of actual servers.
Owner:BLADELOGIC
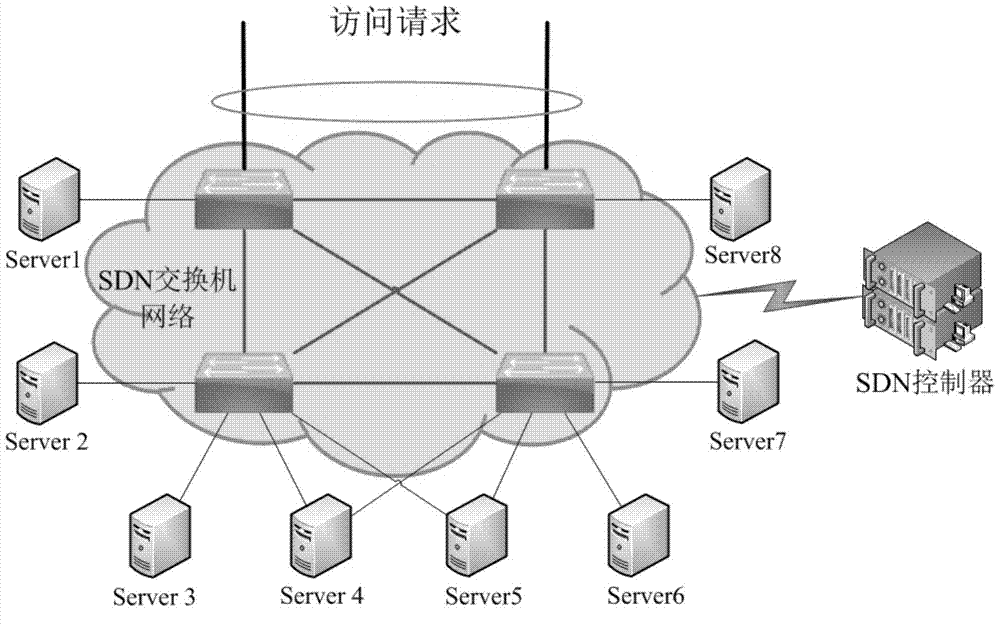
Distributed server load balancing method based on SDN
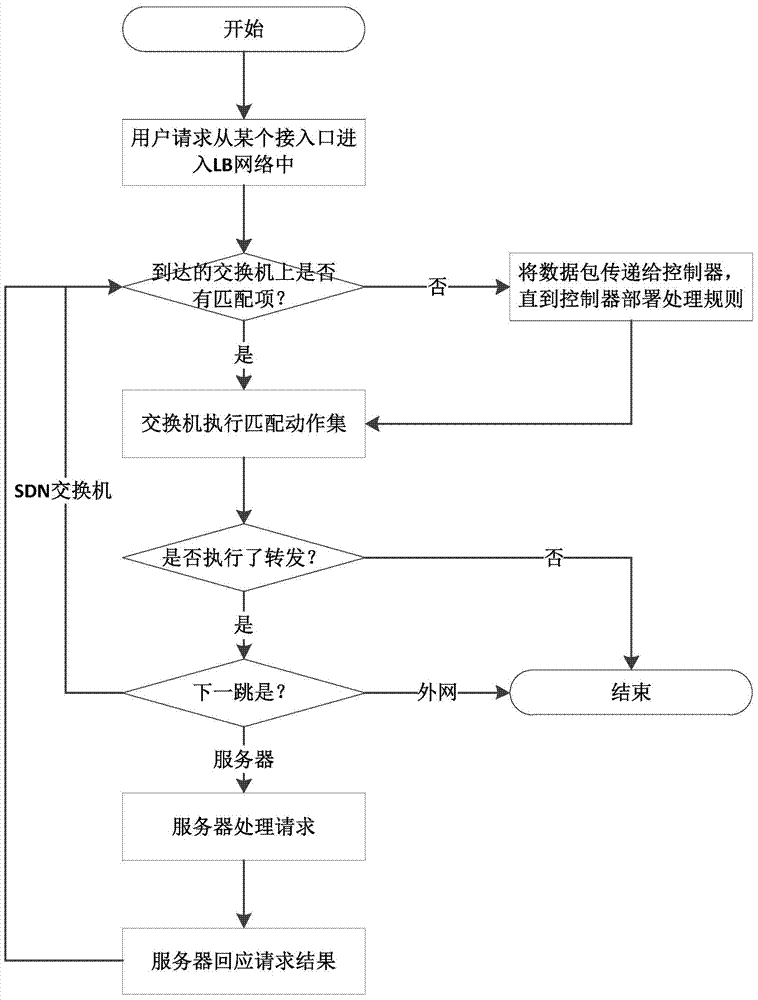
InactiveCN103795805AReal-time collectionDoes not affect normal workTransmissionFault toleranceDistributed servers
The invention discloses a distributed server load balancing method based on the SDN. Through the advantage of the SDN structure where a control face and a forwarding face are separated, a user access request arrives at a certain device on the SDN, then, an SDN controller dynamically dispatches the user access request to an appropriate server according to the network running state, and therefore server load balancing is achieved. By means of the distributed server load balancing method, comprehensive fault tolerance can be achieved from the access process and the forwarding process to the service process, the total load bearing capacity of a server cluster is brought into full play, and running expandability and running reliability of the whole system are improved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY USTC
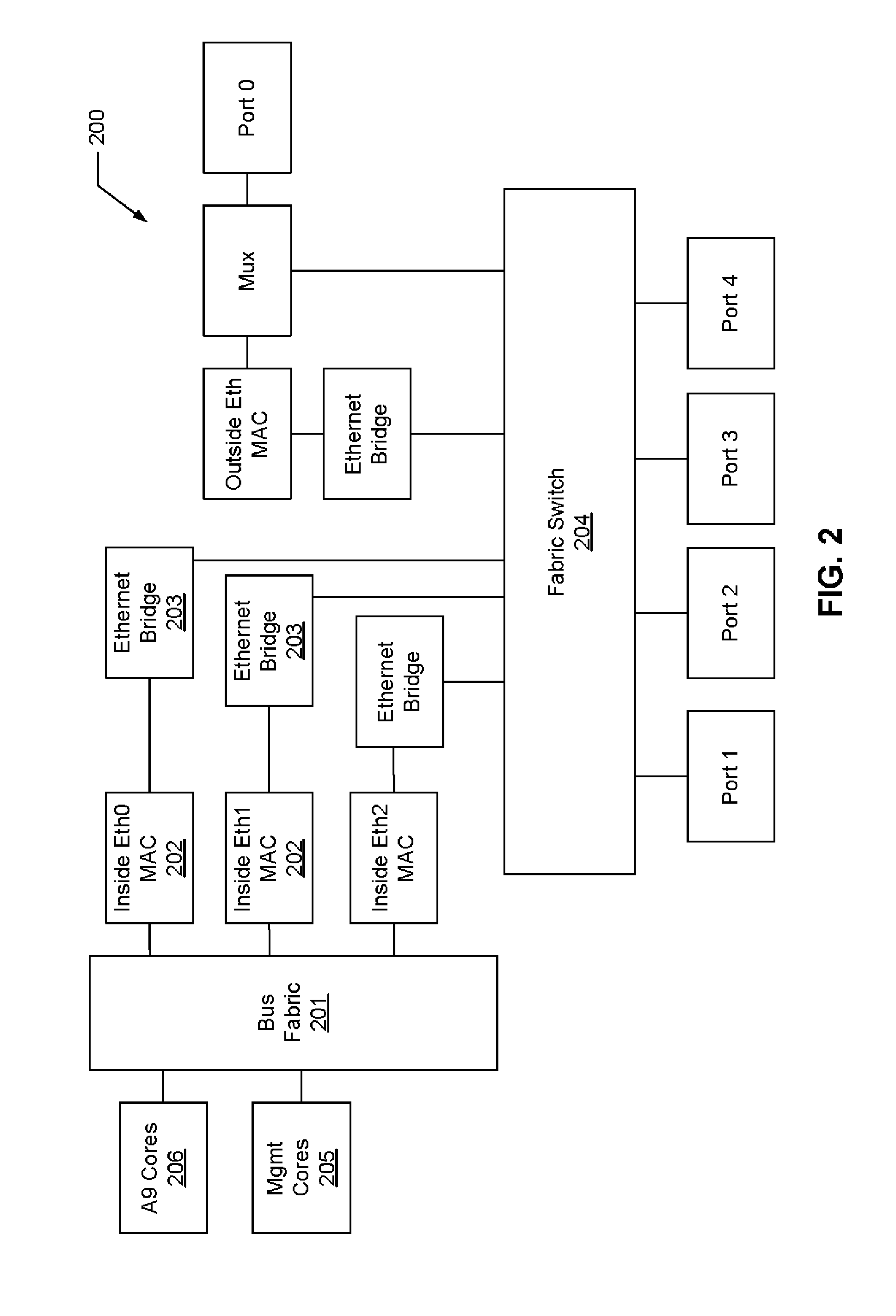
System and Method for Using a Multi-Protocol Fabric Module Across a Distributed Server Interconnect Fabric
ActiveUS20120207165A1Improve functionalityImprove optimizationDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationPersonalizationStructure of Management Information
A multi-protocol personality module enabling load / store from remote memory, remote DMA transactions, and remote interrupts, which permits enhanced performance, power utilization and functionality. In one form, the module is used as a node in a network fabric and adds a routing header to packets entering the fabric, maintains the routing header for efficient node-to-node transport, and strips the header when the packet leaves the fabric. In particular, a remote bus personality component is described. Several use cases of the Remote Bus Fabric Personality Module are disclosed: 1) memory sharing across a fabric connected set of servers; 2) the ability to access physically remote I / O devices across this fabric of connected servers; and 3) the sharing of such physically remote I / O devices, such as storage peripherals, by multiple fabric connected servers.
Owner:III HLDG 2
System and method for providing a scalable on demand hosting system
ActiveUS20050108712A1Fine grained controlDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsResource managementWorkload
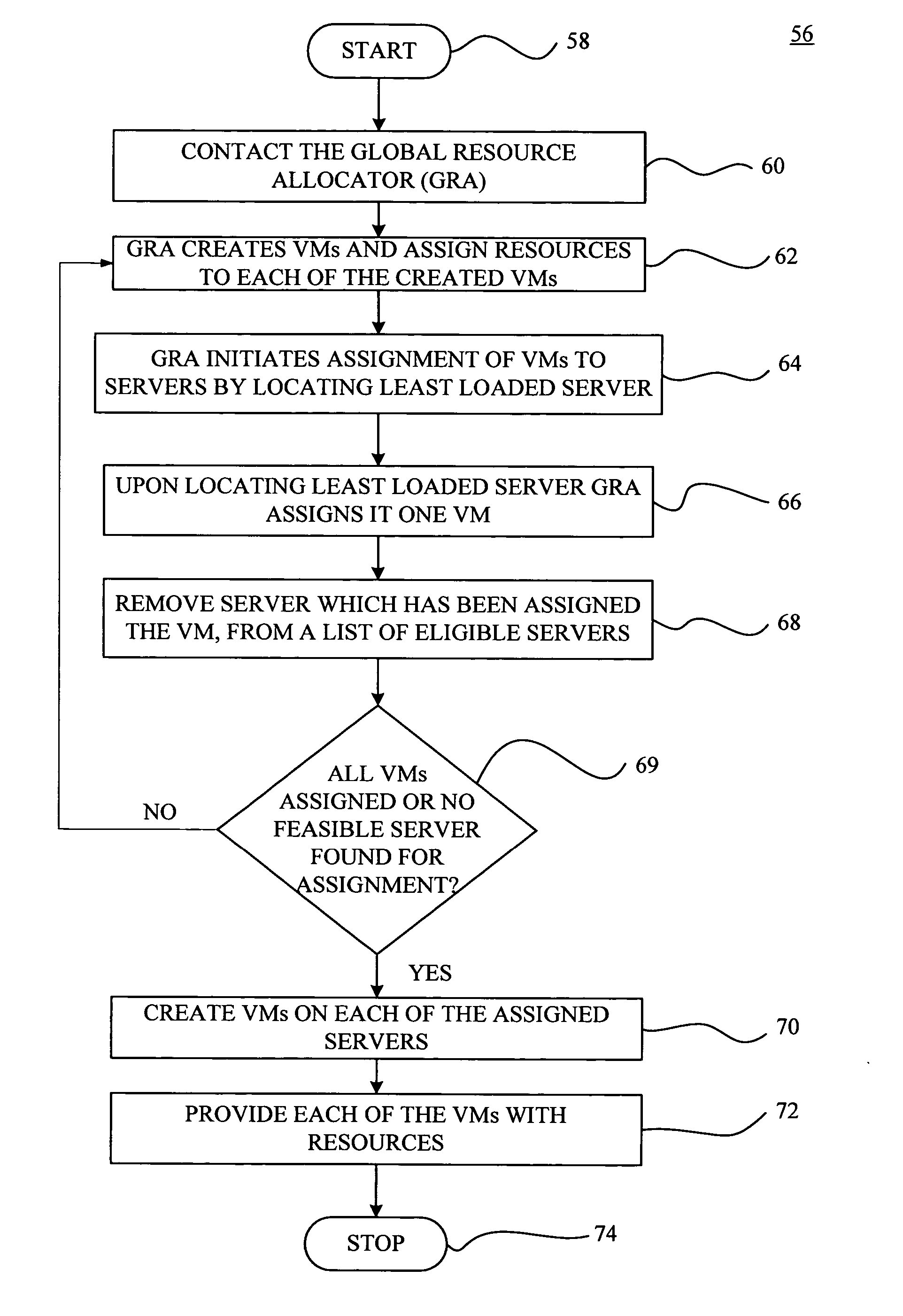
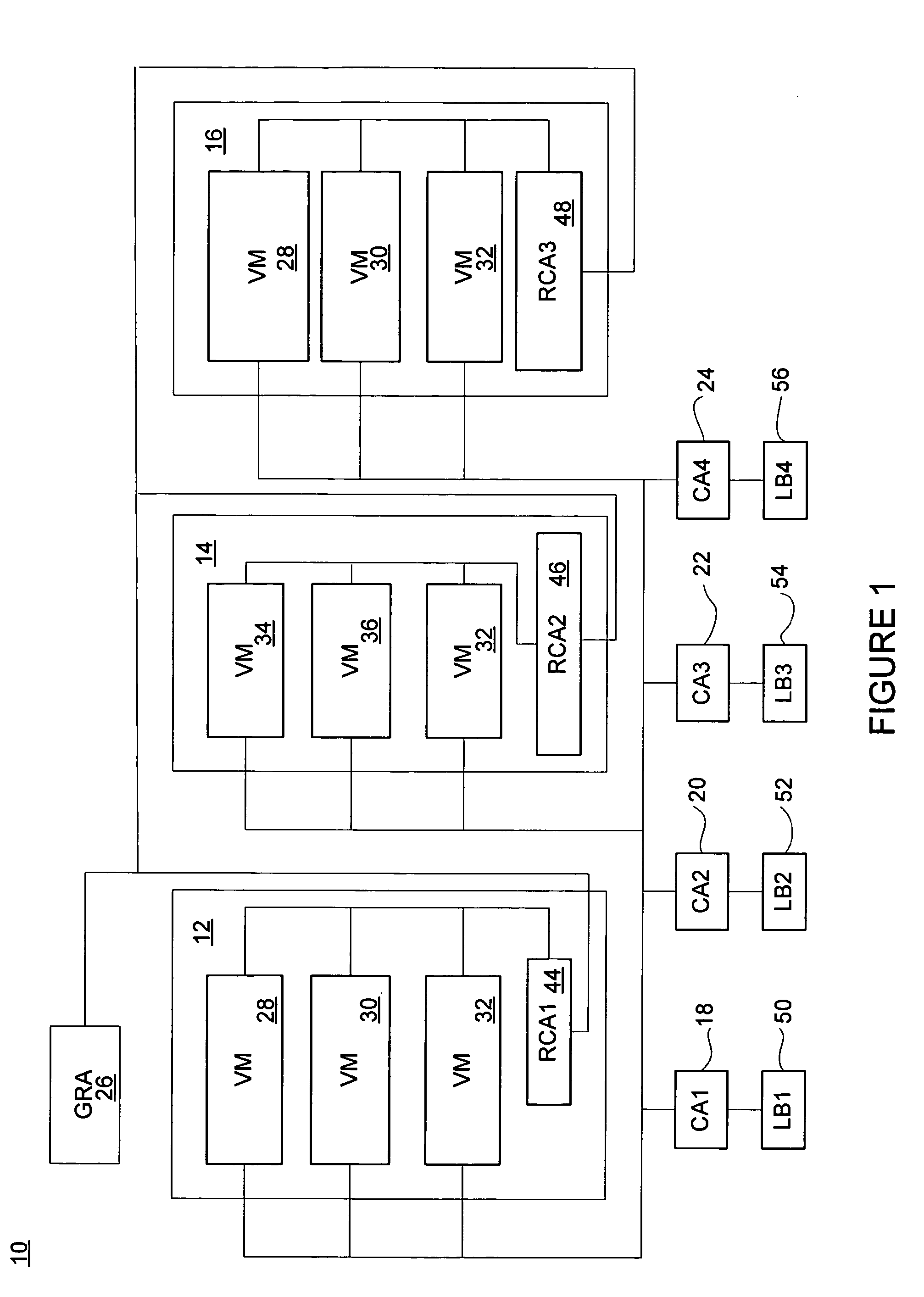
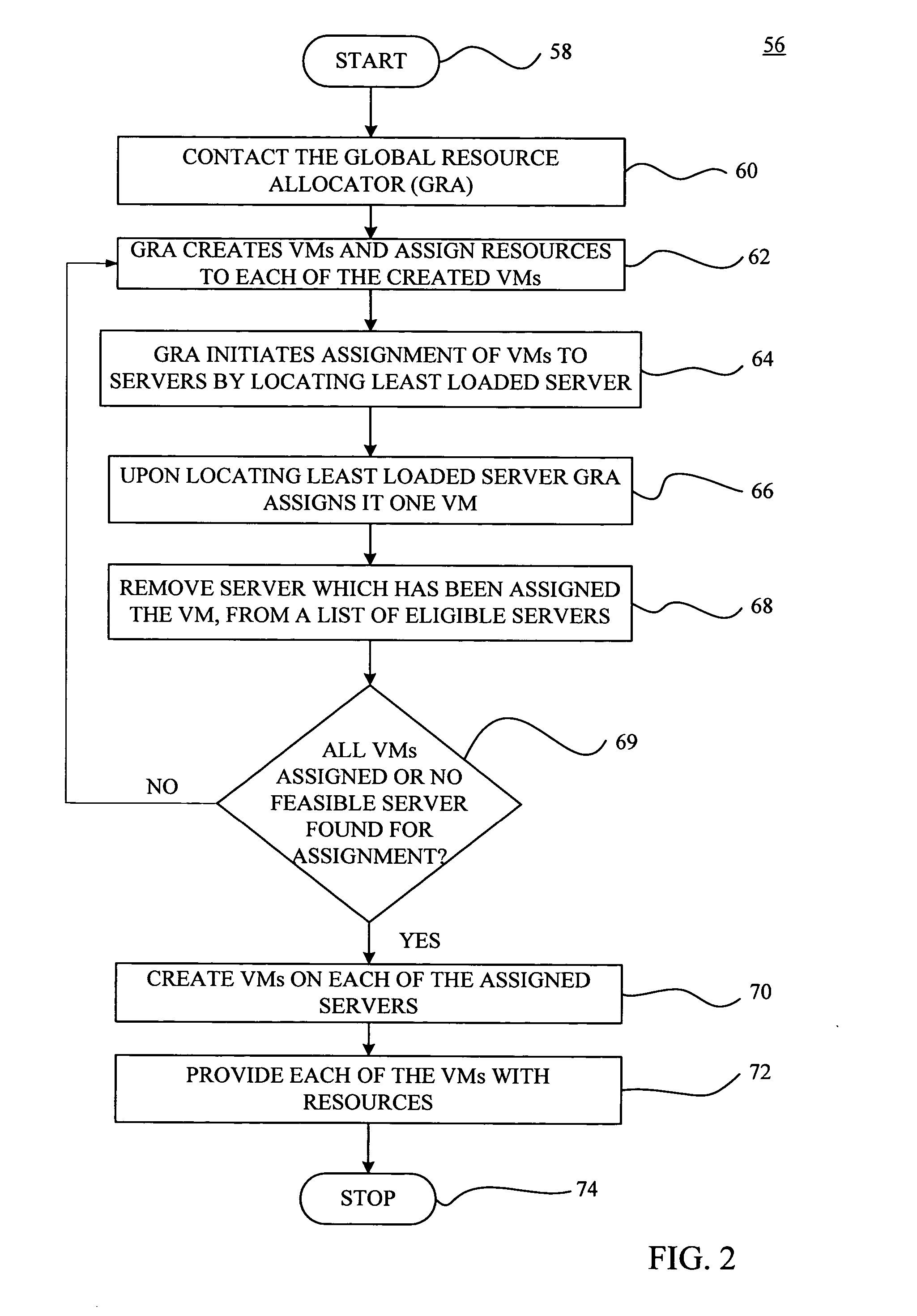
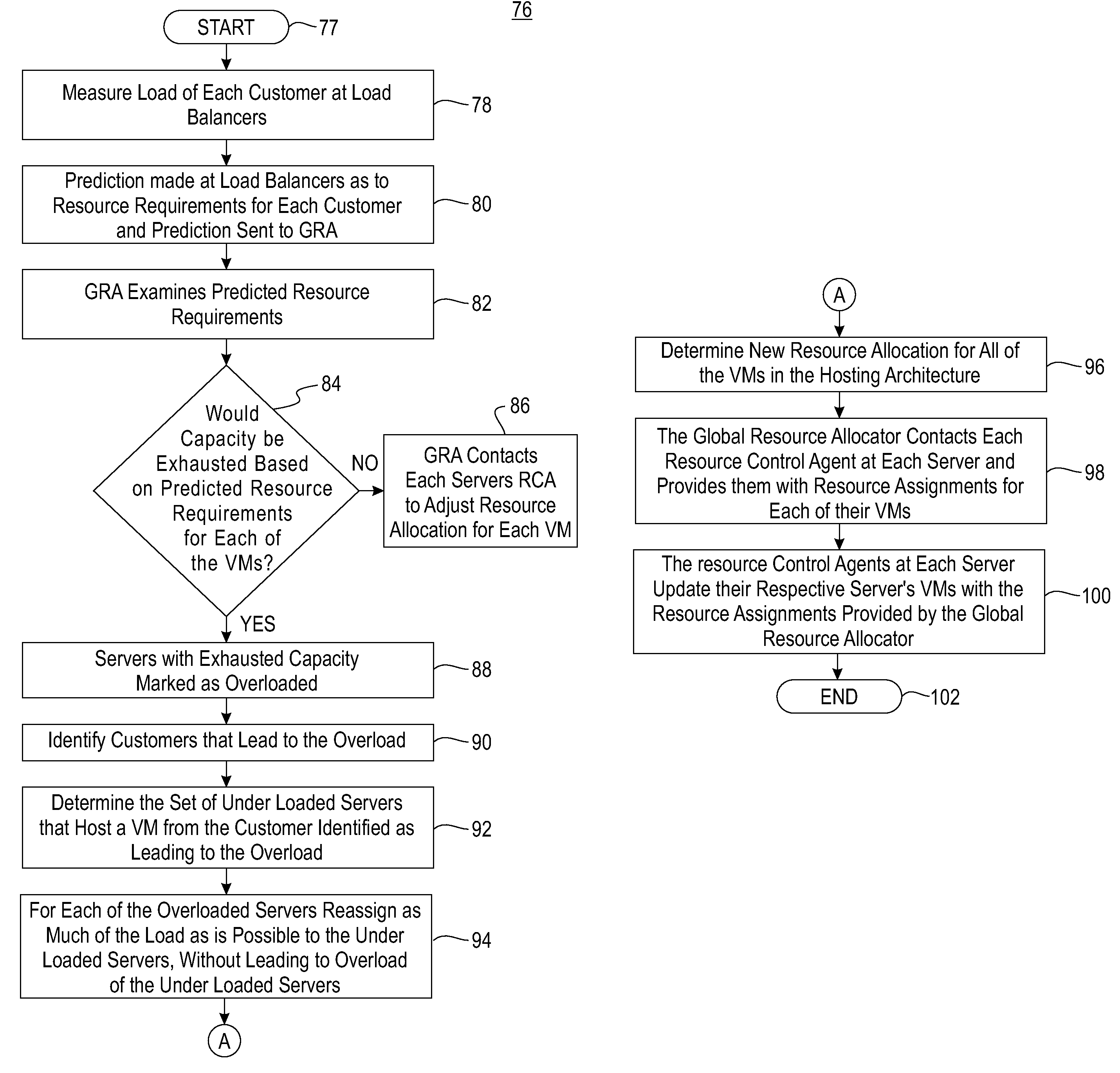
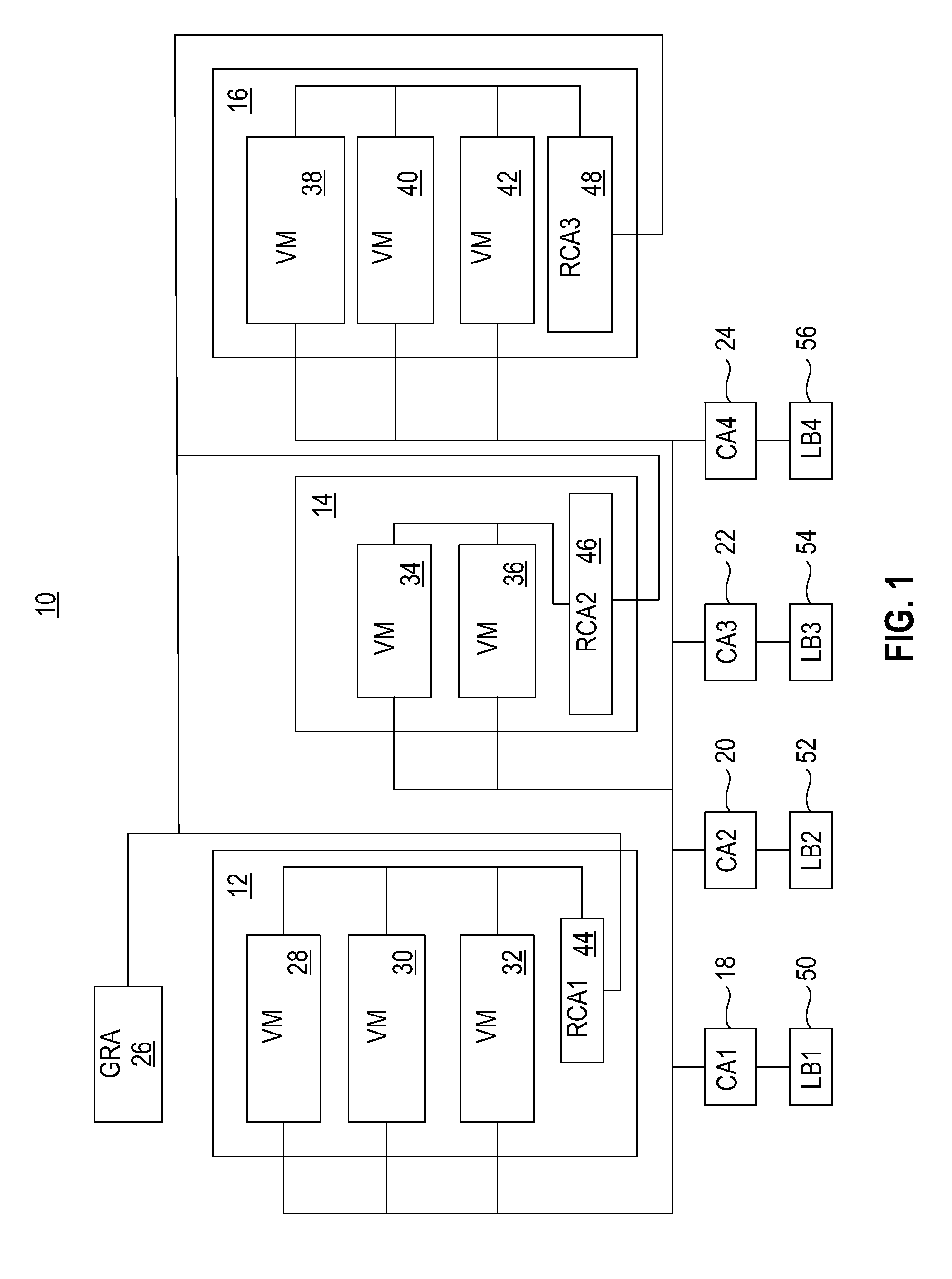
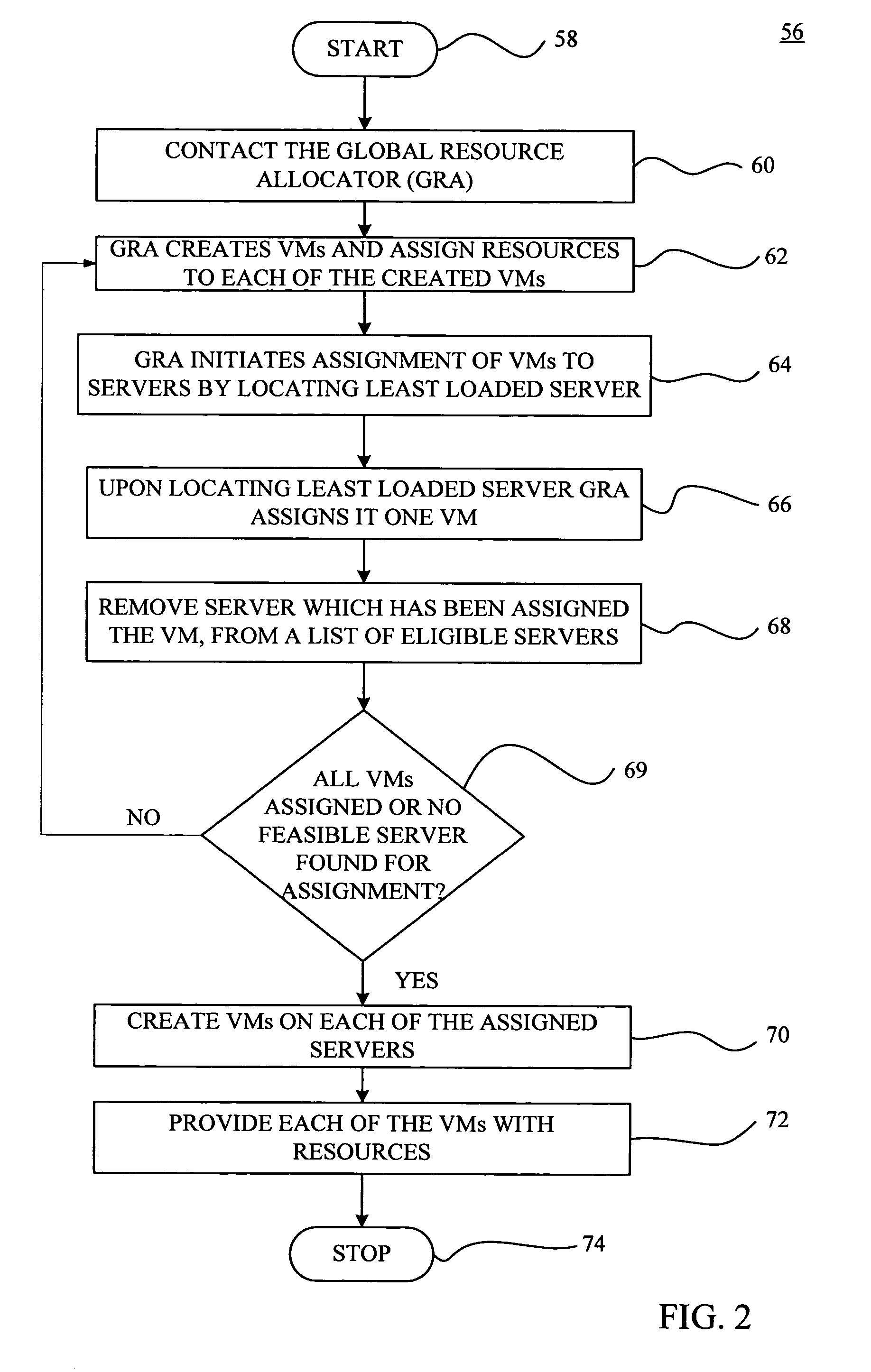
A VM based hosting architecture system in which finder grain control in optimizing multiple workloads across multiple servers is provided. The system includes a plurality of servers to be utilized by multiple workloads. In addition, the system includes a plurality of virtual machines (VMs) at each of the plurality of servers, wherein the plurality of VMs at each of the plurality of servers each serve a different one of the multiple workloads. Moreover, the system includes resource management logic to distribute server resources to each of the plurality of VMs according to predicted resource needs of each of the multiple workloads. Each of the multiple workloads are distributed across the plurality of servers, wherein fractions of each of the multiple workloads are handles by the plurality of VMs. The distribution of multiple workloads over multiple servers has the effect of achieving a finer grain control in optimizing workloads across the plurality of servers.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
System and method for providing a scalable on demand hosting system
ActiveUS7437730B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsResource managementDistributed servers
A VM based hosting architecture system in which finer grain control in optimizing multiple workloads across multiple servers is provided. The system includes a plurality of servers to be utilized by multiple workloads. In addition, the system includes a plurality of virtual machines (VMs) at each of the plurality of servers, wherein the plurality of VMs at each of the plurality of servers each serve a different one of the multiple workloads. Moreover, the system includes resource management logic to distribute server resources to each of the plurality of VMs according to predicted resource needs of each of the multiple workloads. Each of the multiple workloads are distributed across the plurality of servers, wherein fractions of each of the multiple workloads are handled by the plurality of VMs. The distribution of multiple workloads over multiple servers has the effect of achieving a finer grain control in optimizing workloads across the plurality of servers.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
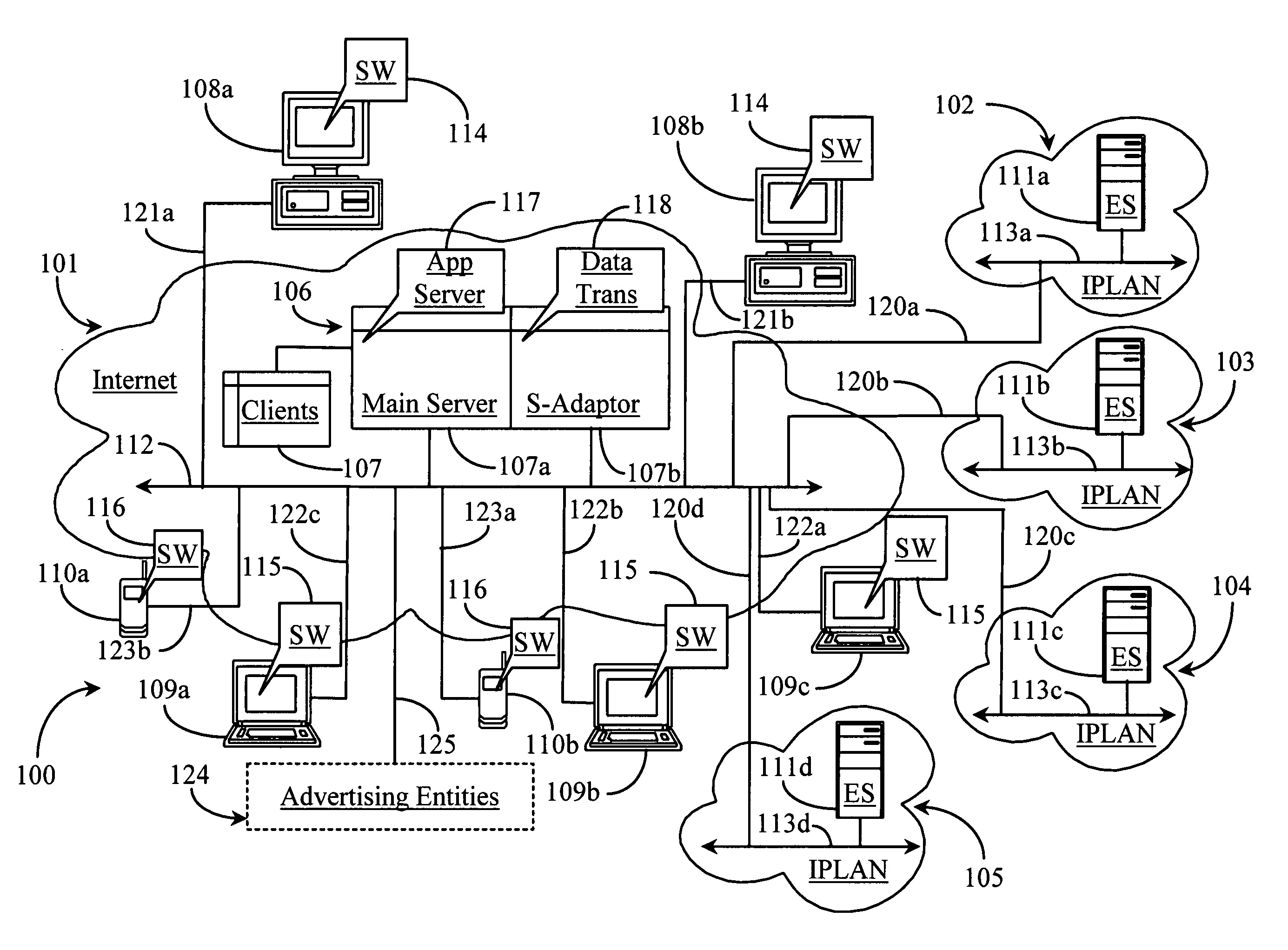
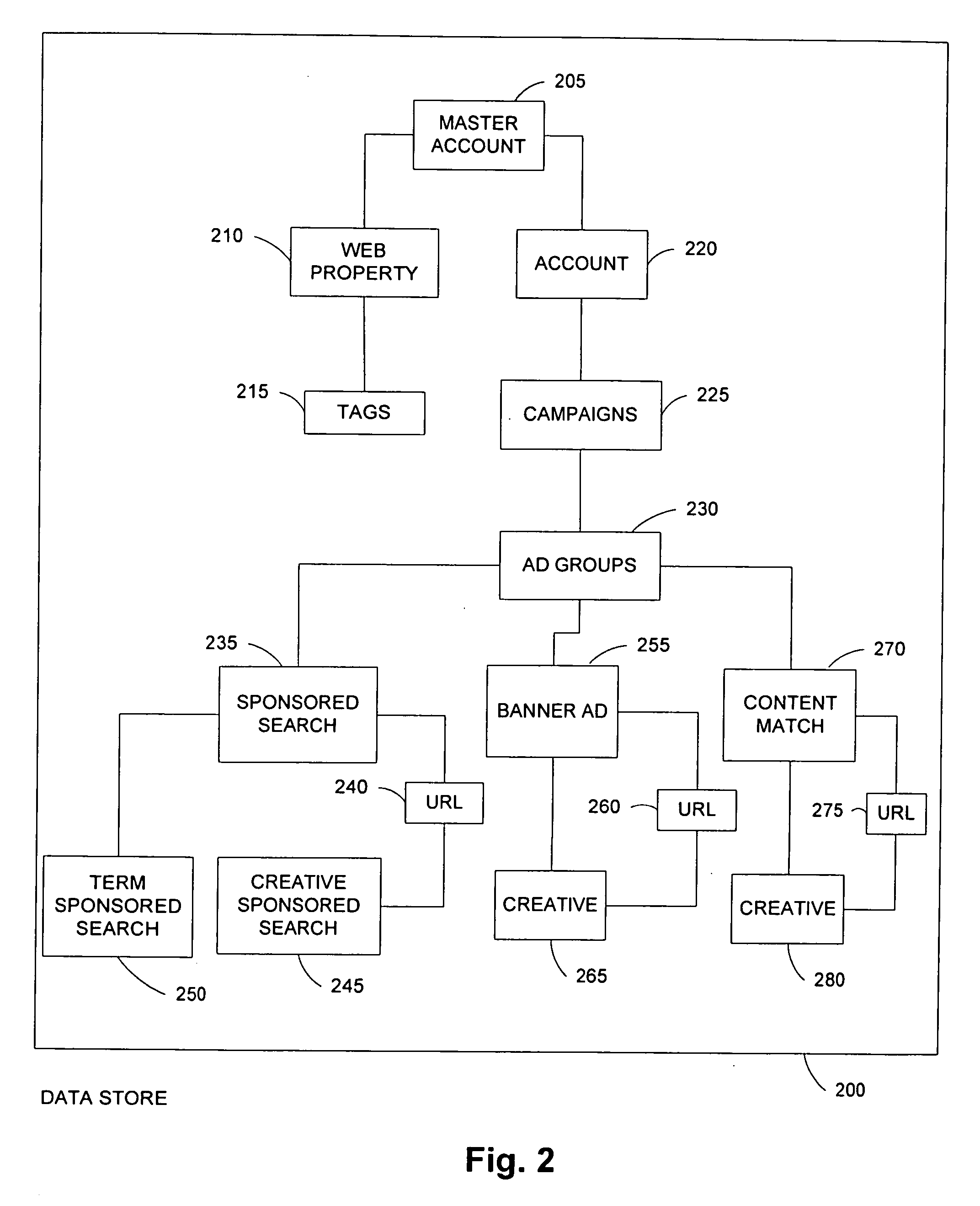
Architecture for distribution of advertising content and change propagation
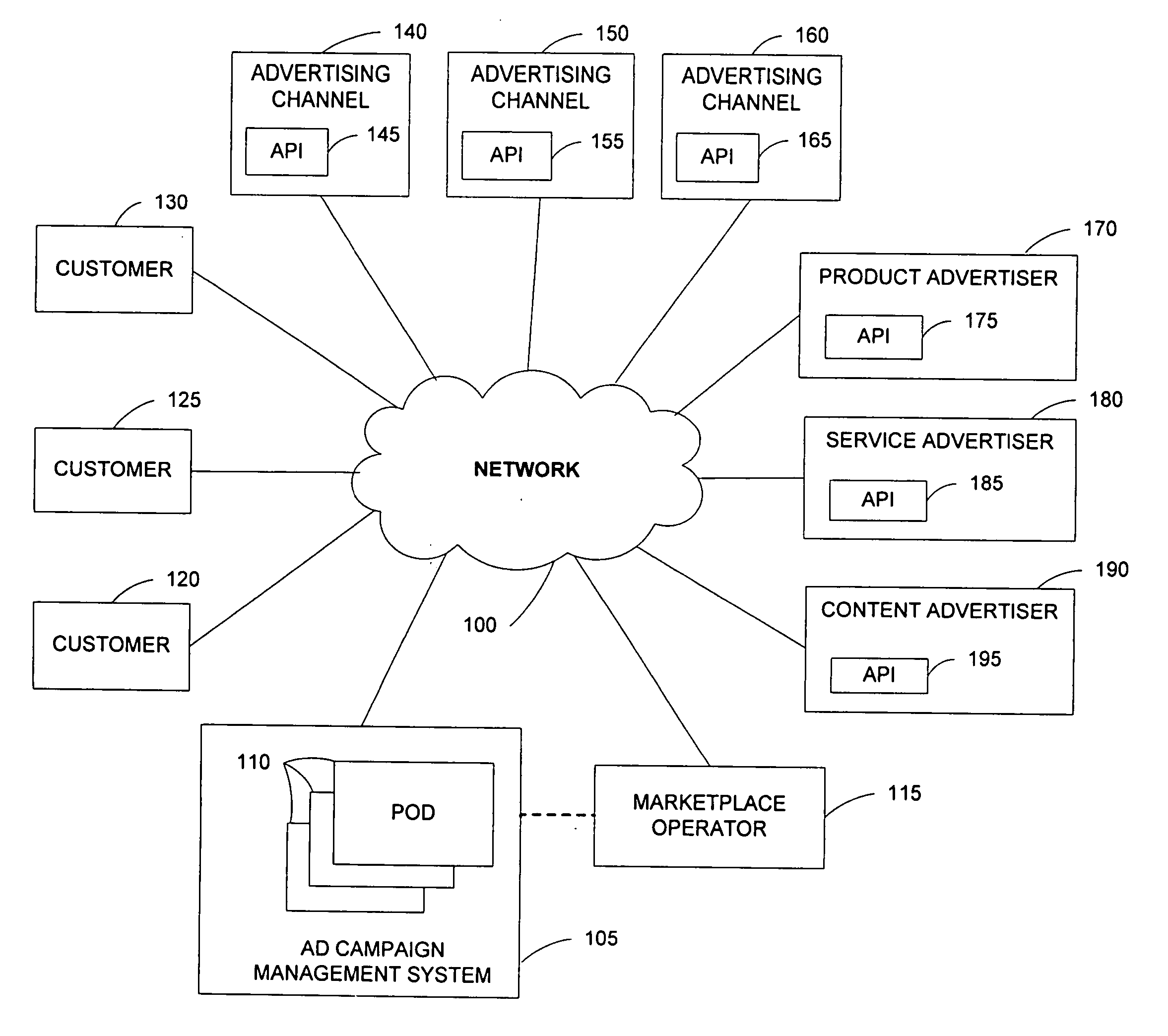
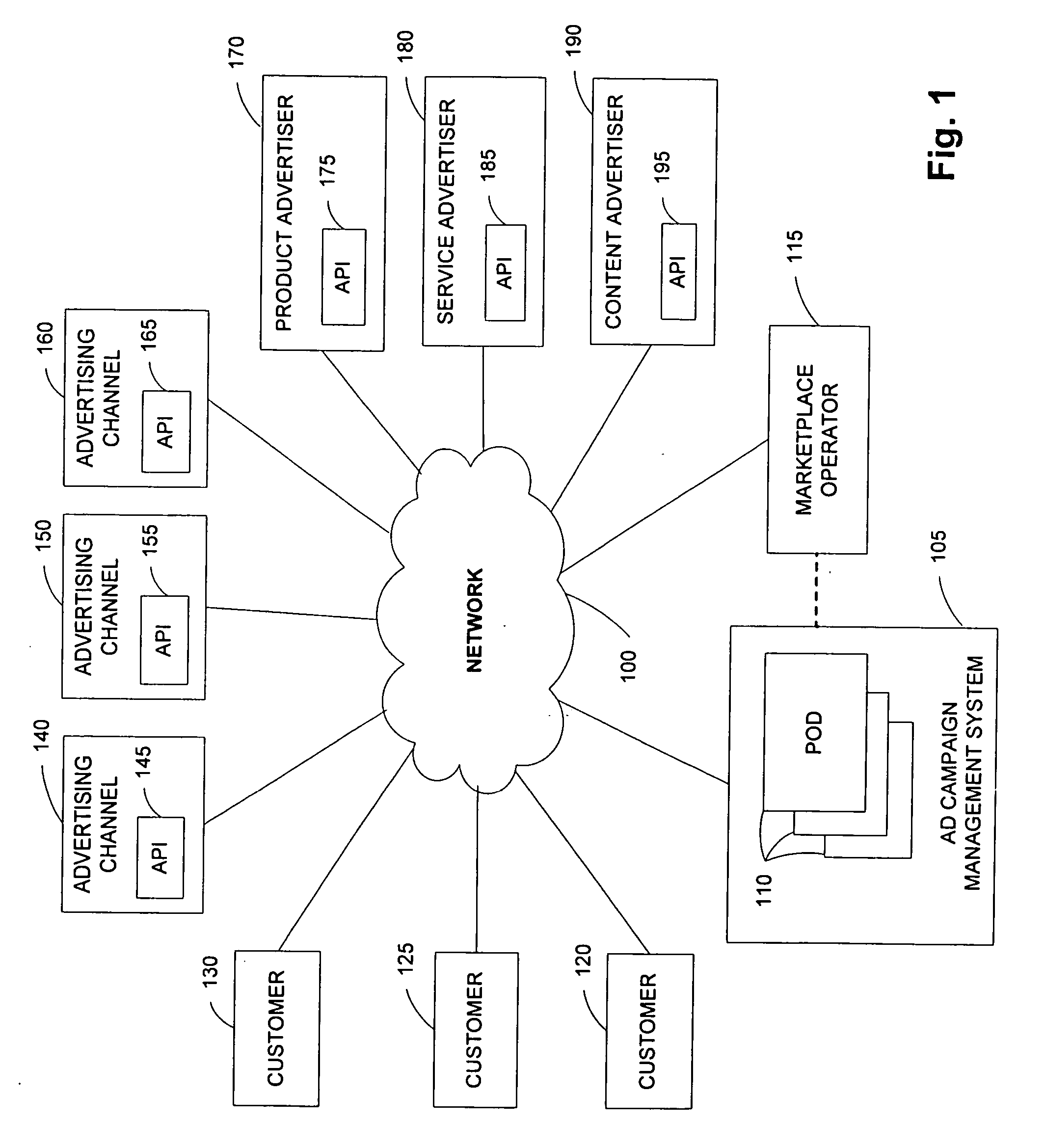
A system comprises an interface for enabling a user having a web property to input advertisement information including a web property advertisement, criteria indicating when presentation of the advertisement is desired by the user, a bid for the presentation of the advertisement when the criteria are met, and subsequent modifications to the advertisement information; geographically distributed servers, a plurality of the geographically distributed servers for storing the advertisement information, at least one of the geographically distributed servers for receiving a request for advertisement content from an advertising channel, at least one of the geographically distributed servers for determining whether the request meets the criteria, and at least one of the geographically distributed servers for forwarding the advertisement to the advertising channel in response to the request when the criteria have been met; and a distribution component for propagating the advertisement information to the geographically distributed servers according to an arrangement.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
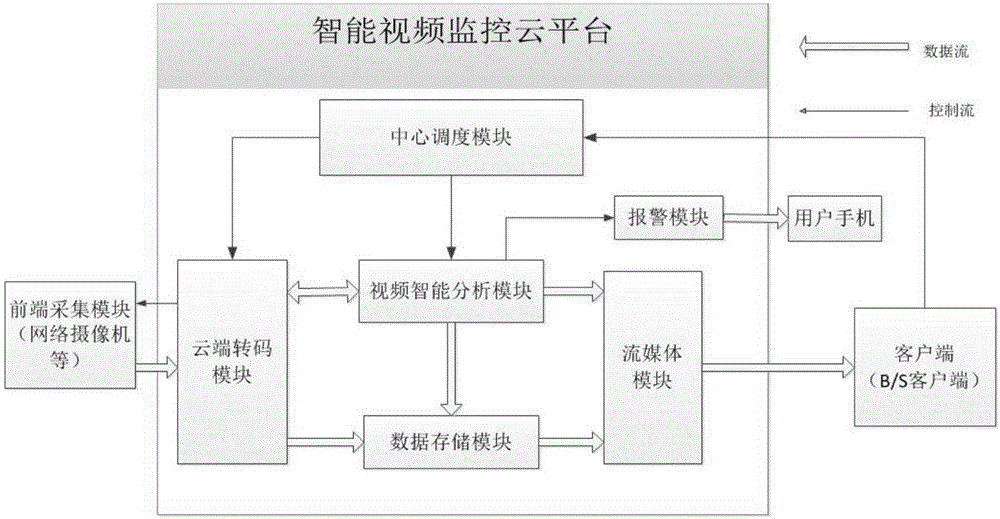
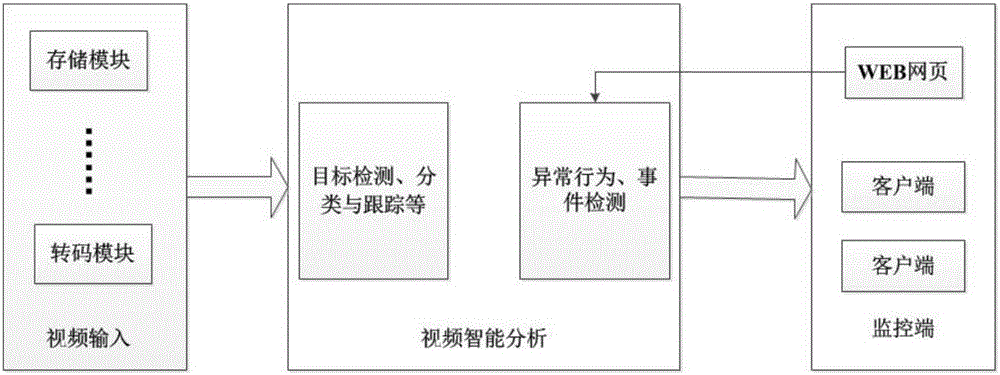
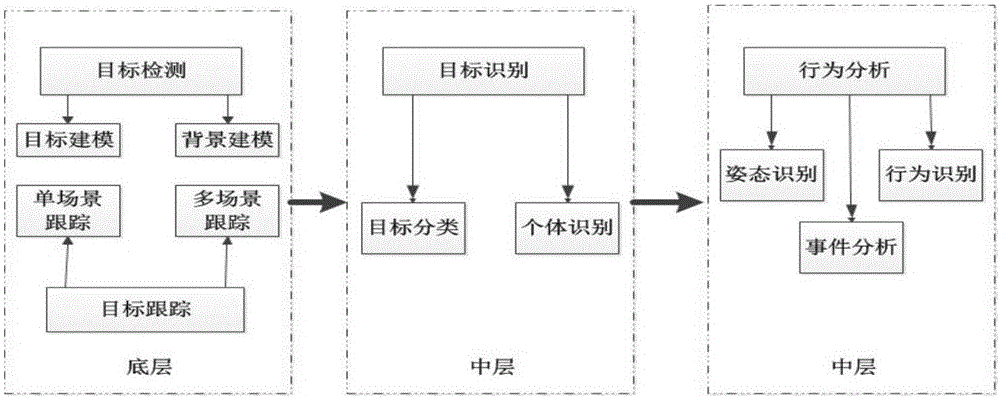
Smart video monitoring system based on cloud platform
InactiveCN106375721AImprove bindingQuality improvementClosed circuit television systemsTransmissionVideo monitoringTranscoding
The invention relates to a smart video monitoring system based on a cloud platform, and belongs to the technical field of remote smart monitoring. The system is characterized in that a video monitoring cloud platform is developed on a server cluster established on the basis of a Hadoop cloud computing platform, and video data acquired by front-end equipment are transmitted to a server in a stream way; through adoption of a massive distributed cloud computing technology, real-time tracking, processing, analysis and outputting of video streams are realized; and a service is provided externally, so that a terminal user can perform checking and calling conveniently. In the system, the characteristics of distributed high-concurrence access storage, high availability, rapid response, easiness in management and maintenance and the like are integrated. Video acquisition, video encoding and transcoding, video data storage, a streaming media distributed server and a client are all distributed on a physical host node in an access network. Compared with a conventional video monitoring system, the smart video monitoring system has the advantages that video real-time processing and transcoding efficiency and video data storage capacity are increased greatly; the requirement of people on the video monitoring system in a big data era is met; and a relatively large commercial value is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
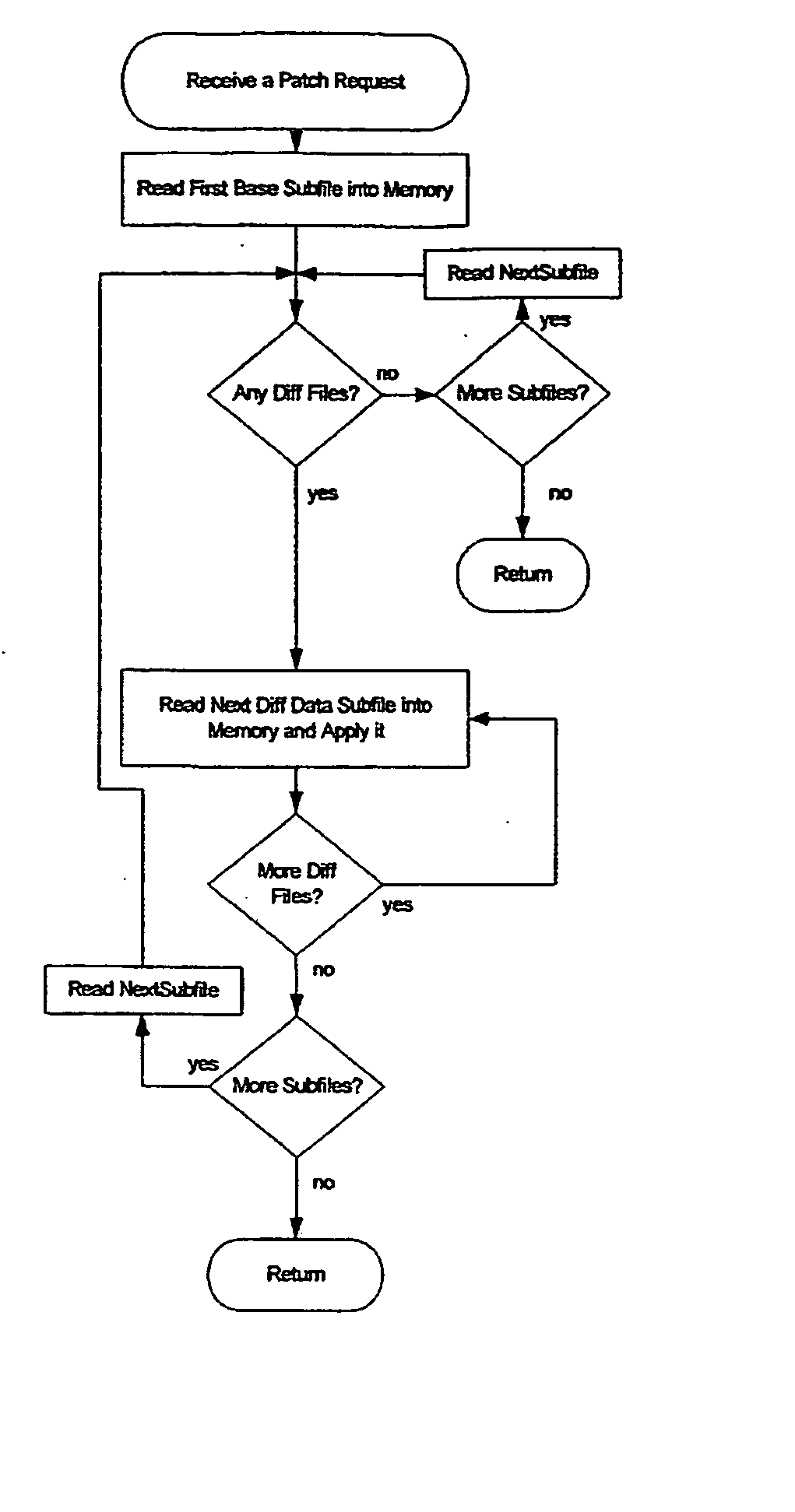
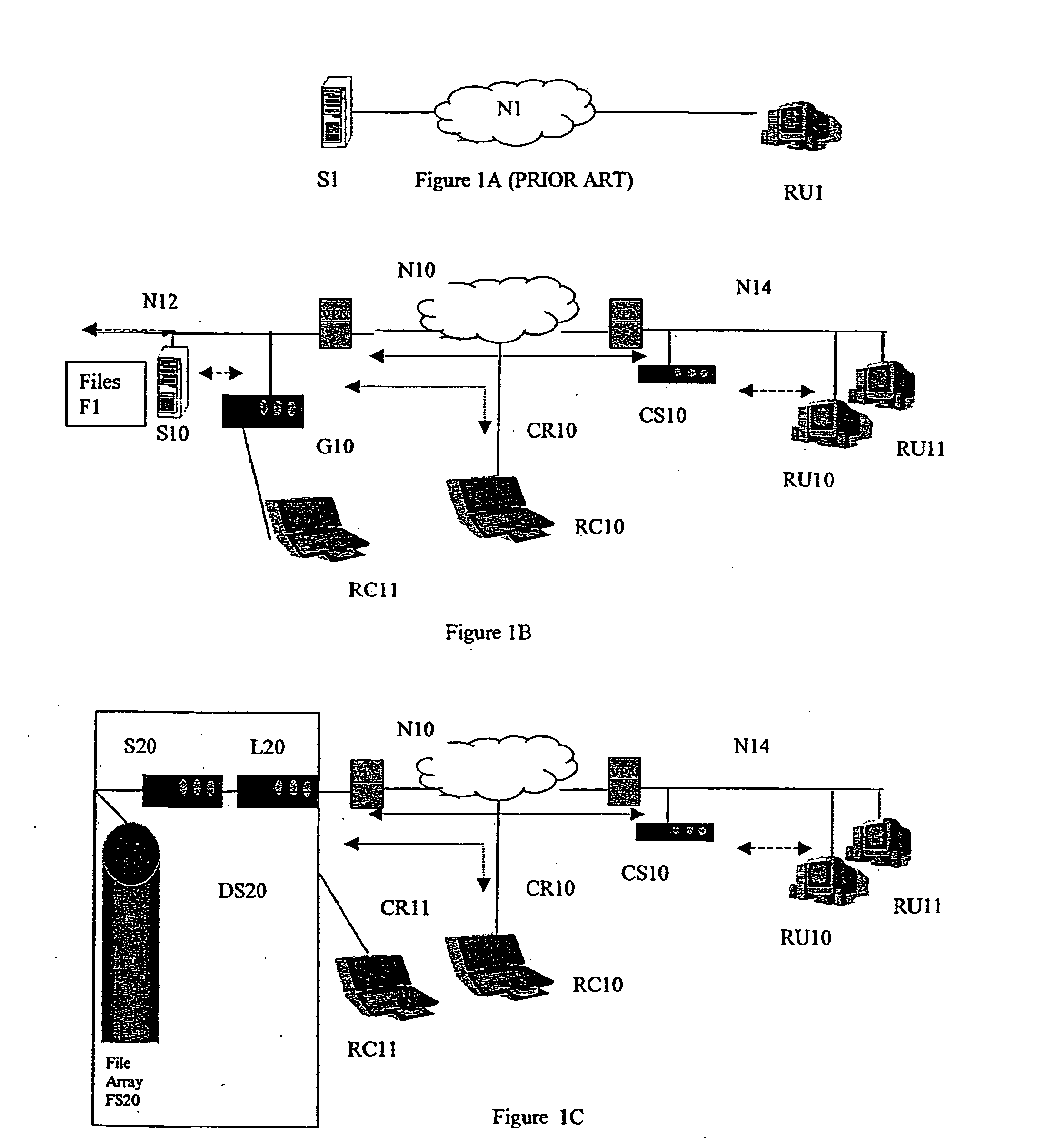
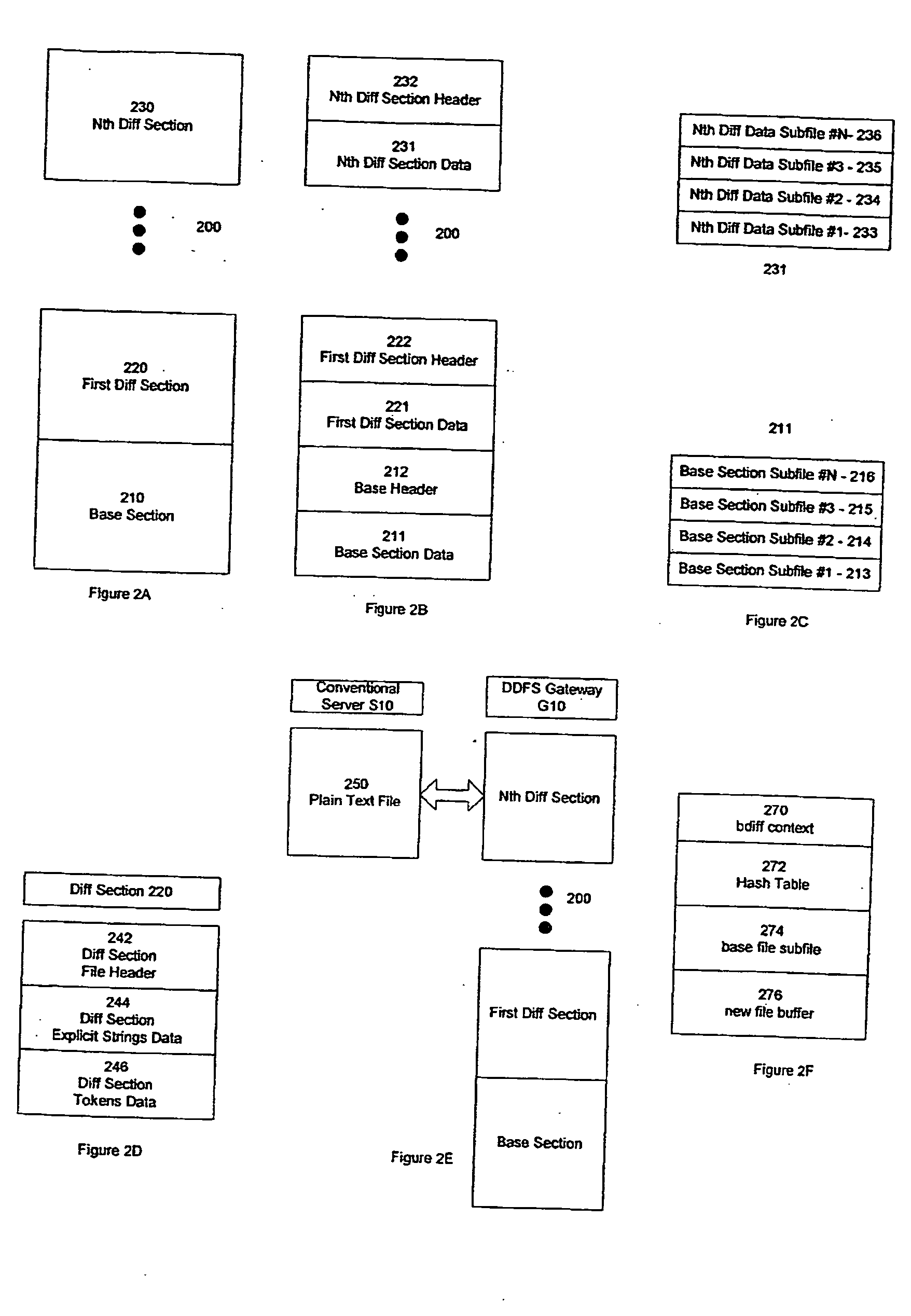
Method and system for differential distributed data file storage, management and access
A method and system providing a distributed filesystem and distributed filesystem protocol utilizing a version-controlled filesystem with two-way differential transfer across a network is disclosed. A remote client interacts with a distributed file server across a network. Files having more than one version are maintained as version-controlled files having a literal base and at least one delta section. The client maintains a local cache of files from the distributed server that are utilized. If a later version of a file is transferred across a network, the transfer may include only the required delta sections.
Owner:DISKSITES RES & DEV
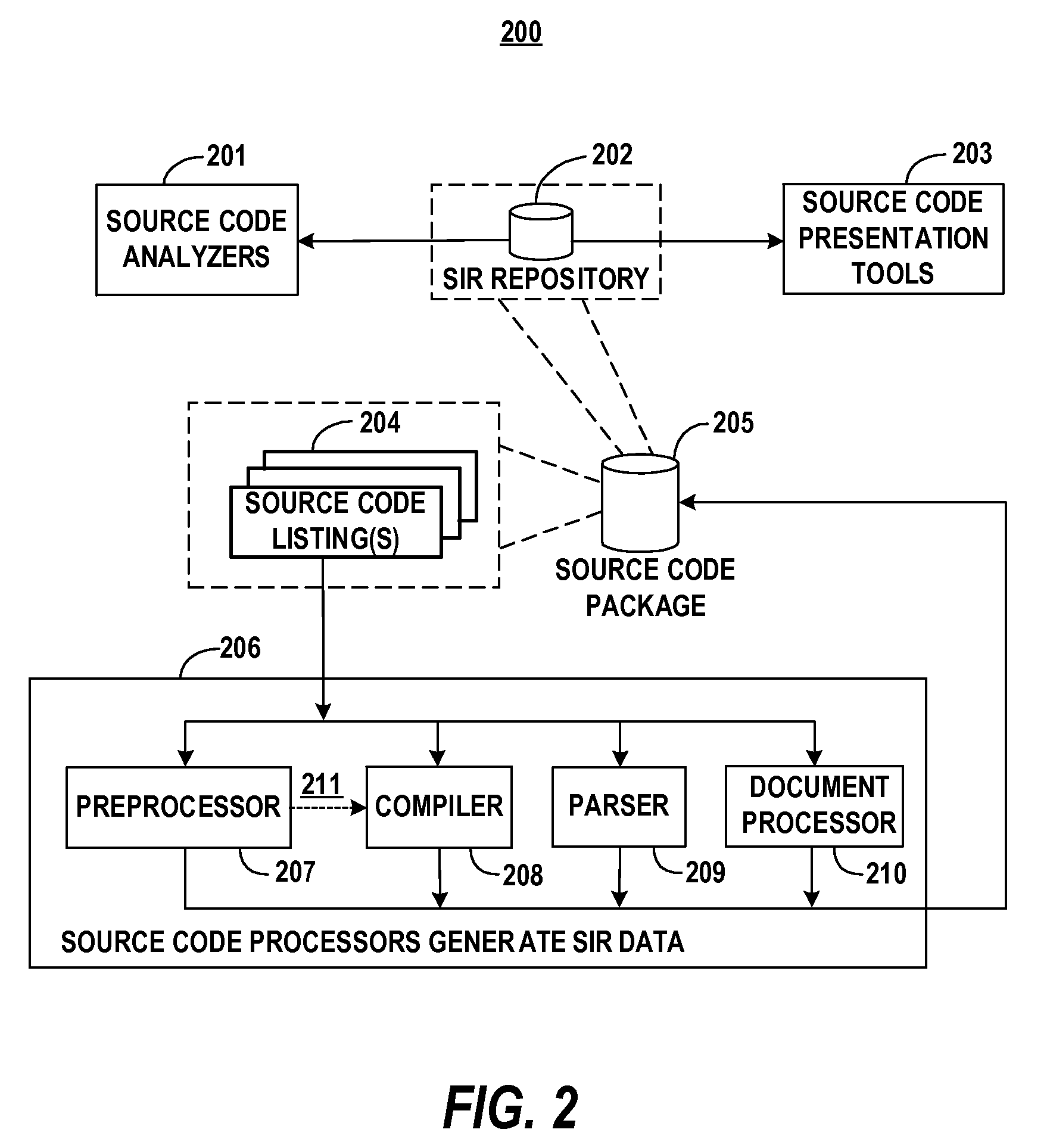
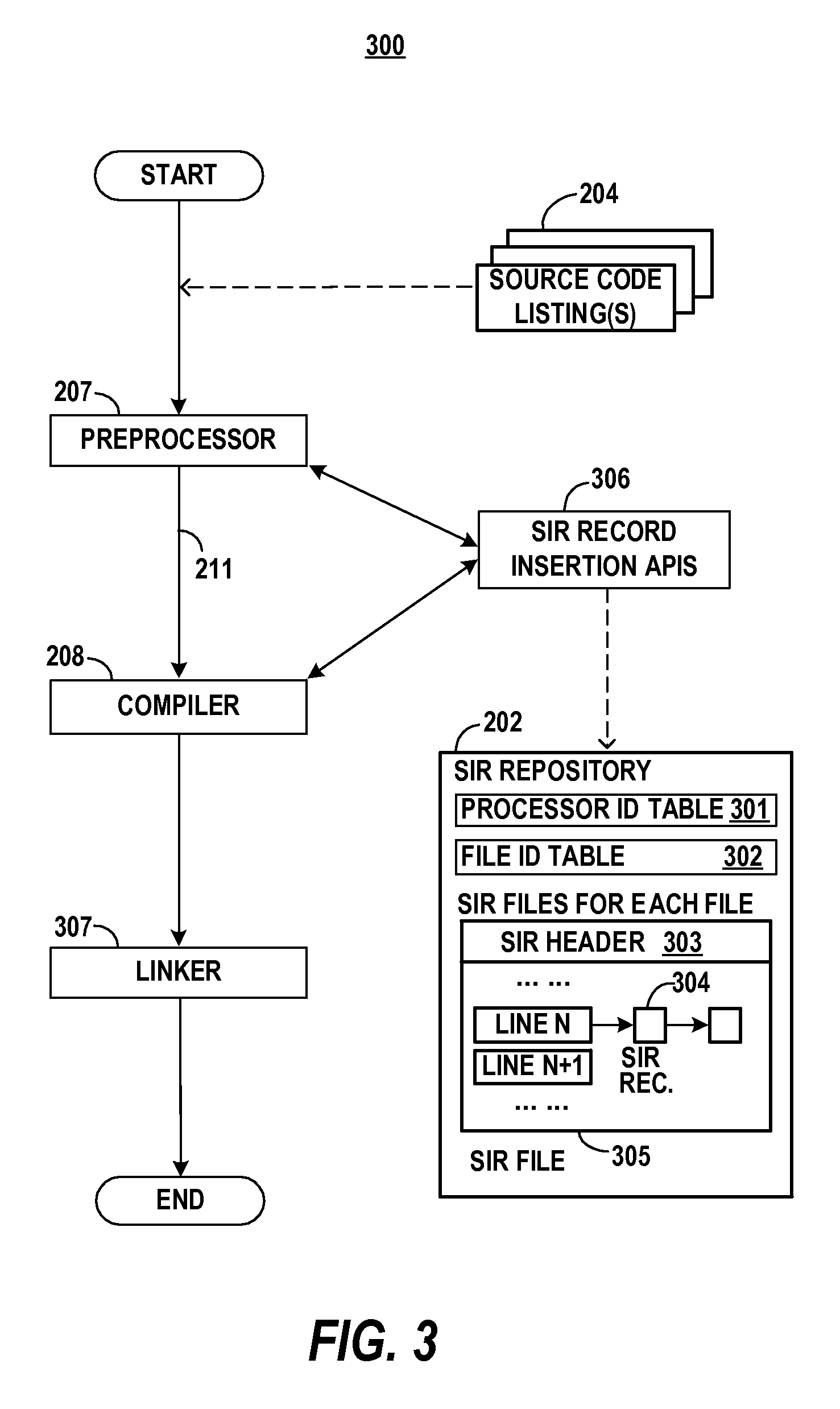
Method and System for presenting and analyzing software source code through intermediate representation
The present invention provides a method and system for producing intermediate representation of source code listings with possibly mixed syntaxes to assist software development applications in presenting and analyzing the source code listings through reading the intermediate representation. A source code processor calls Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to preserve source code information, which includes intermediate representation data sets and is preferably stored in a file-based repository. The source code processor is of a compiler, a preprocessor, a parser, or a comment document processor. The data sets capture lexical, syntax and semantic information of source code construct elements, and comprise of location, processor identification, construct category, and attribute data. A software development environment through a source code search engine is able to present source code construct elements, outlines, and symbol references from software packages over a plurality of distributed servers in a network such as the Internet.
Owner:ZHAO KAN
System and method for using a multi-protocol fabric module across a distributed server interconnect fabric
ActiveUS8599863B2Extend performance and power optimization and functionalityDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationPersonalizationStructure of Management Information
A multi-protocol personality module enabling load / store from remote memory, remote Direct memory Access (DMA) transactions, and remote interrupts, which permits enhanced performance, power utilization and functionality. In one form, the module is used as a node in a network fabric and adds a routing header to packets entering the fabric, maintains the routing header for efficient node-to-node transport, and strips the header when the packet leaves the fabric. In particular, a remote bus personality component is described. Several use cases of the Remote Bus Fabric Personality Module are disclosed: 1) memory sharing across a fabric connected set of servers; 2) the ability to access physically remote Input Output (I / O) devices across this fabric of connected servers; and 3) the sharing of such physically remote I / O devices, such as storage peripherals, by multiple fabric connected servers.
Owner:III HLDG 2
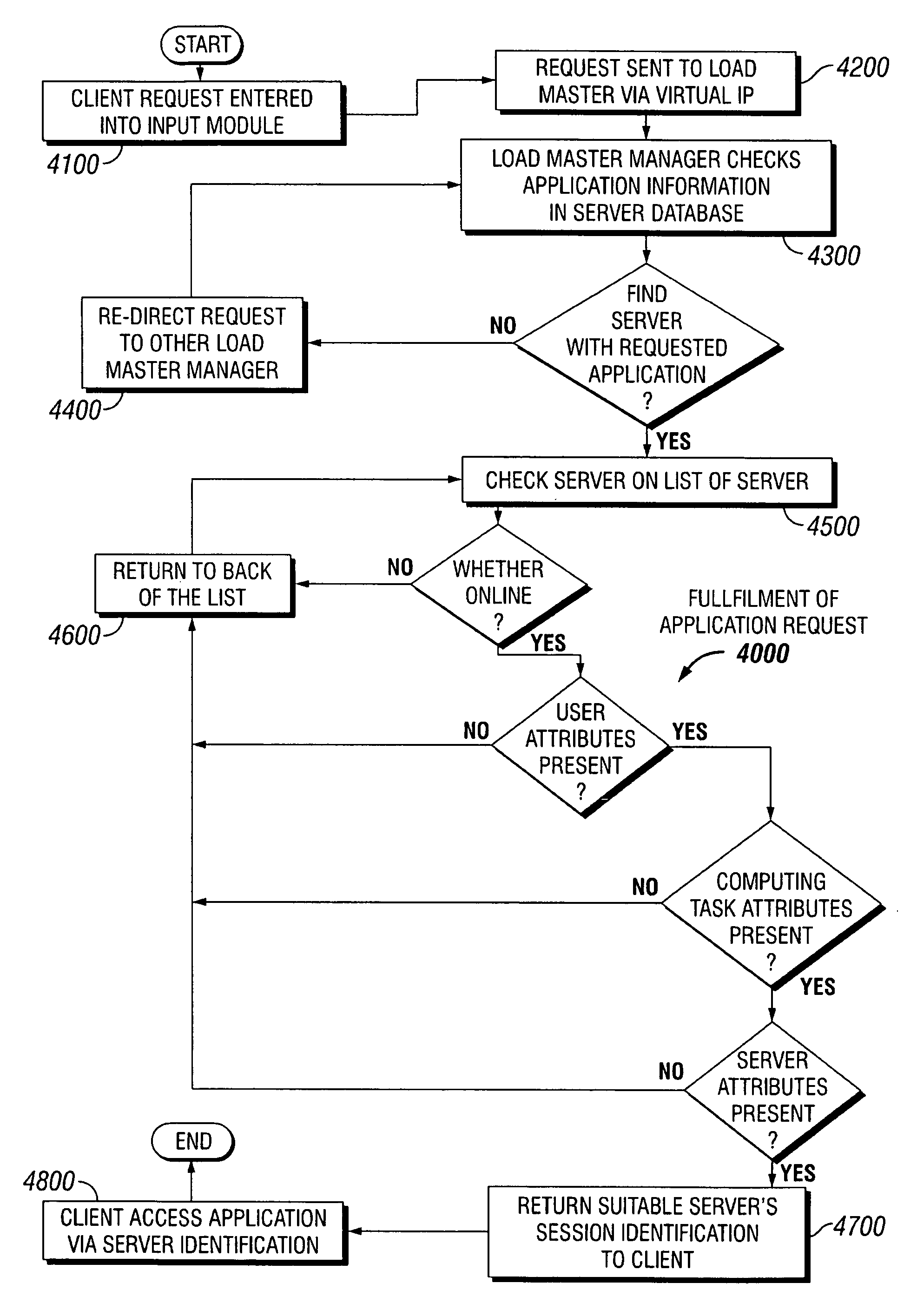
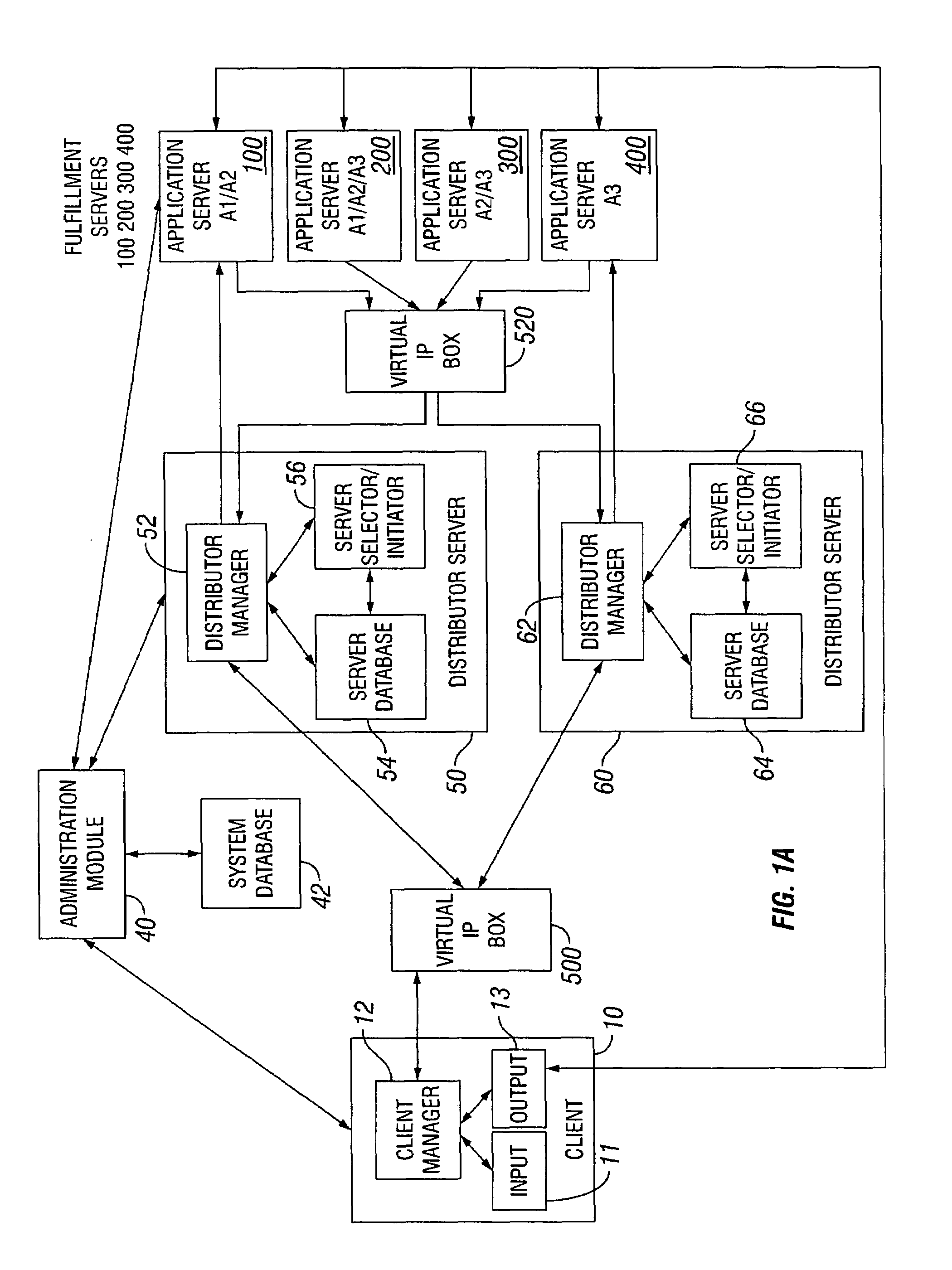
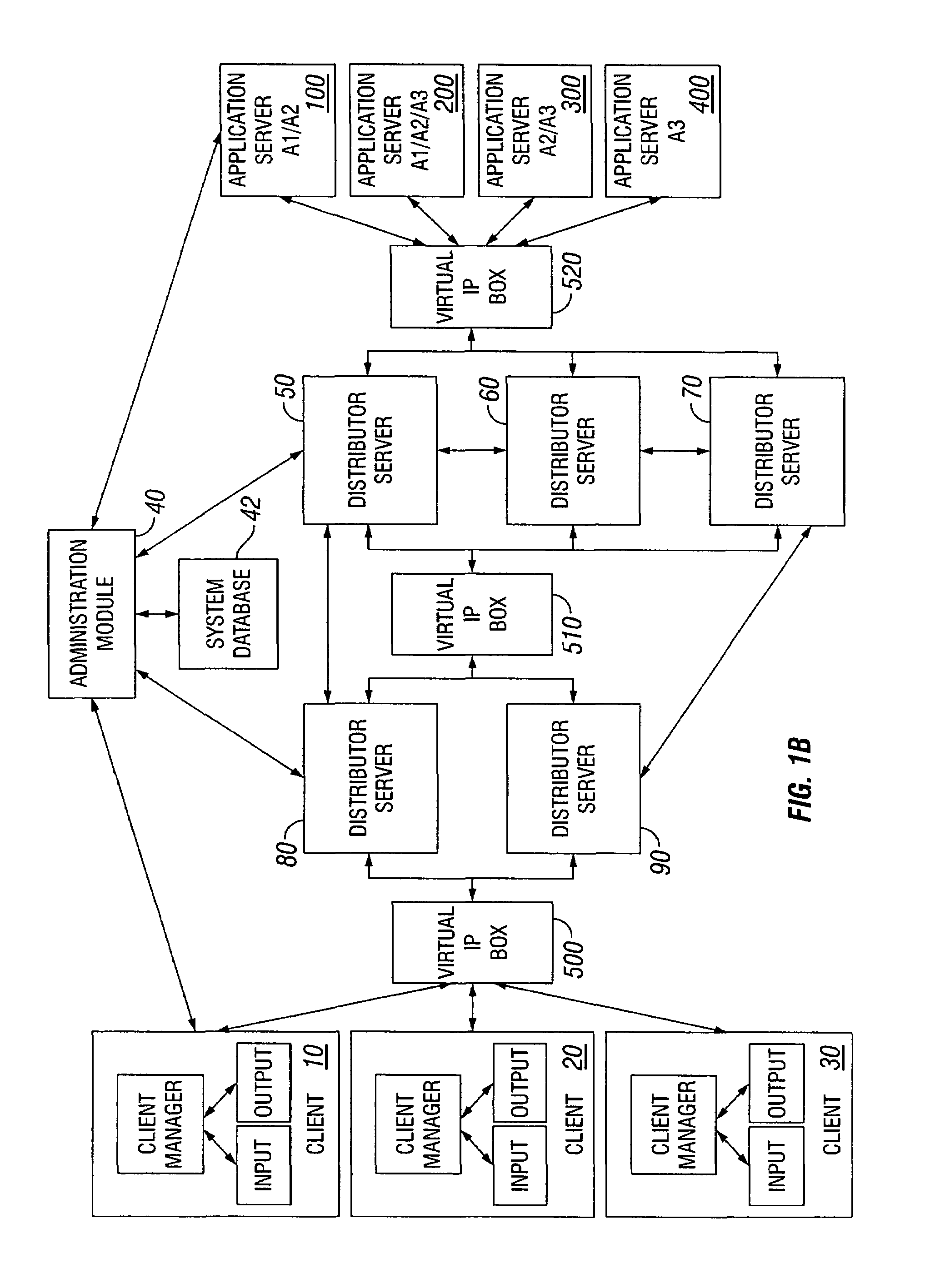
Dynamic allocation of computing tasks by second distributed server set
InactiveUS7111300B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsServer allocationDistributed servers
A method for dynamic allocation of computing tasks includes requesting a computing task by a client; receiving the computing task by a first distributor server set; redirecting the computing task to a second distributor server set, the second distributor server set including a first server; and allocating the computing task from the first server to a second server that executes the computing task, where the allocation is based on matching an attribute of the second server to an attribute of the computing task.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Synchronous collaboration based on peer-to-peer communication
InactiveUS20020152271A1Fully treatImprove interoperabilityDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsTimestampWorkspace
A peer-to-peer protocol is based on the use of global timestamps and client priorities in serializing modifications to a shared workspace of real-time collaboration. The method caters to dynamic clients wherein a client can leave or join an ongoing collaboration session as long as there is always at least one client present / remaining in the collaboration session. The method can support multiple definitions of a modification, including partitioning-based definitions, wherein the method provides full support for locking of partitions, and a full treatment of inter-partition synchronisation via a modification definition over multiple partitions. The method is capable of utilizing the many standard methods of creating a global, distributed, synchronized clock for the global timestamps utilized by it. The method is rollback-based for correcting tentative but incorrect serializations, and provides additional backup in terms of checkpoints for additional safety and for the support of lightweight, pervasive clients. The method includes many optimizations for efficiency, and includes a method of switching to and back from distributed server-based serialization for the periods when the network response is better suited to a distributed server than the peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:IBM CORP
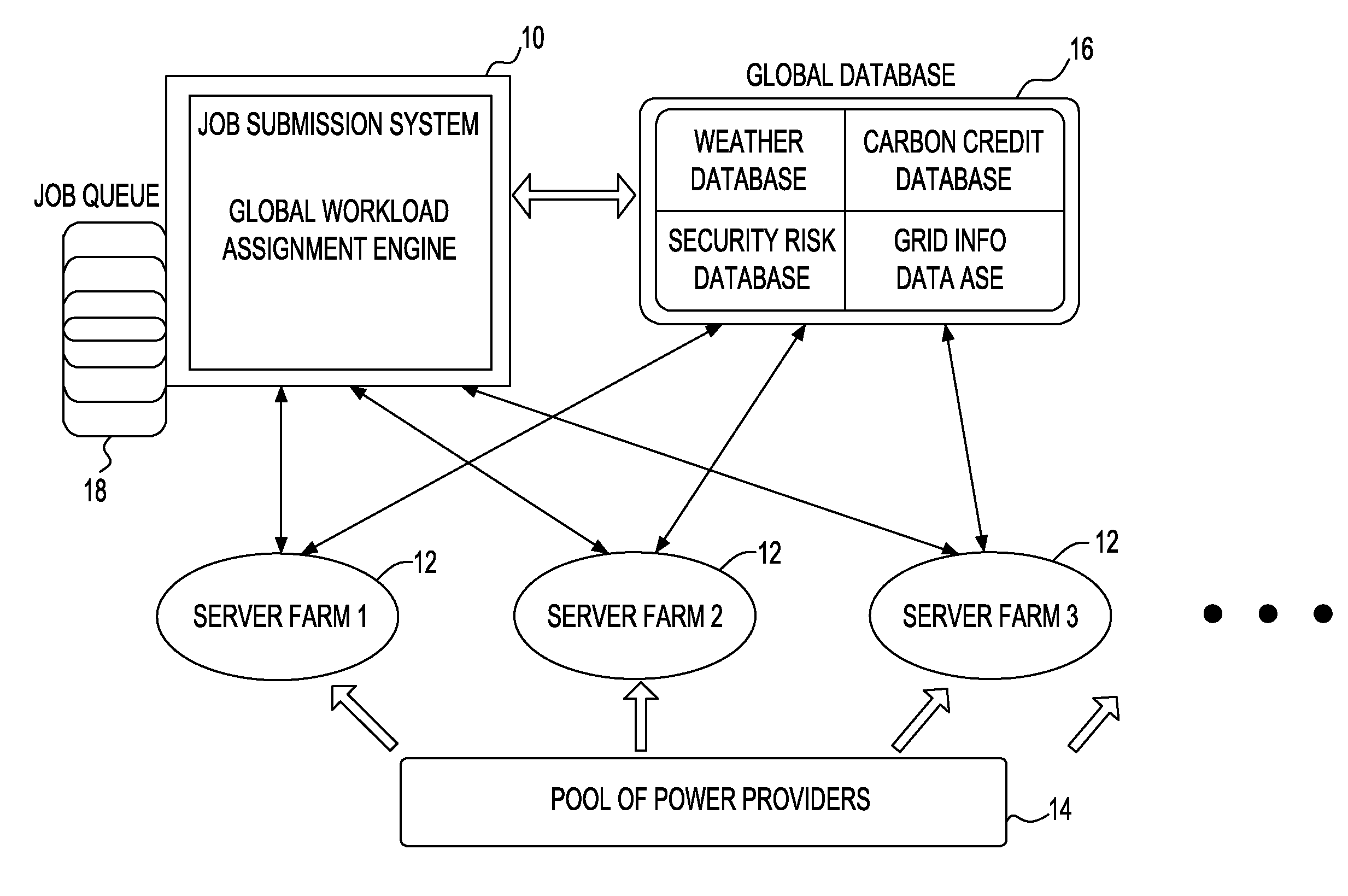
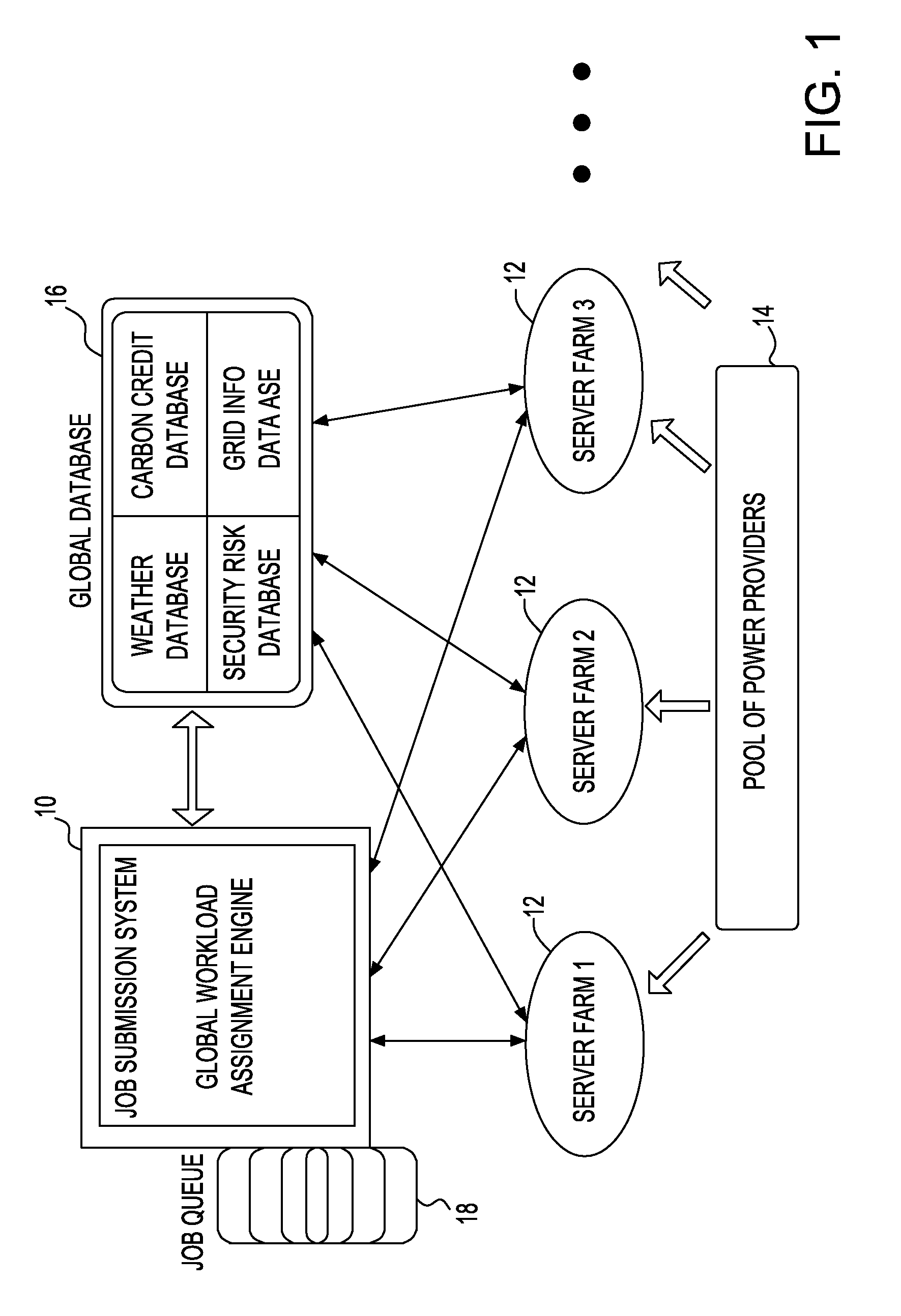
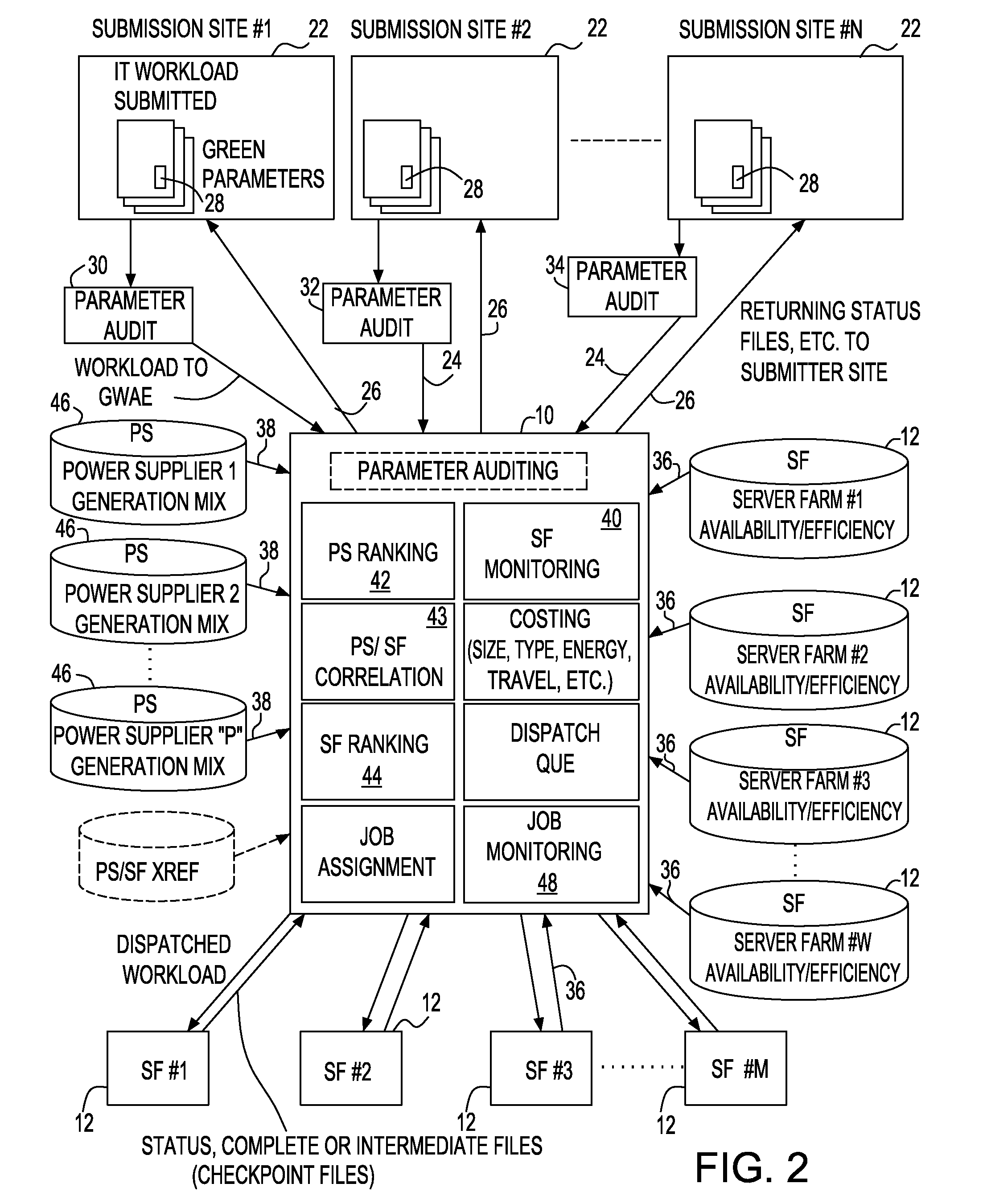
Environmental and computing cost reduction with improved reliability in workload assignment to distributed computing nodes
InactiveUS20100228861A1Increase powerEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationMultiple criteriaDependability
A system and method of allocating a job submission for a computational task to a set of distributed server farms each having at least one processing entity comprising; receiving a workload request from at least one processing entity for submission to at least one of the set of distributed server farms; using at least one or more conditions associated with the computational task for accepting or rejecting at least one of the server farms to which the job submission is to be allocated; determining a server farm that can optimize the one or more conditions; and dispatching the job submission to the server farm which optimizes the at least one of the one or more conditions associated with the computational task and used for selecting the at least one of the server farms.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and apparatus to manage data using a peer-to-peer network and the blockchain
ActiveUS20190158594A1Low costStrong incentiveKey distribution for secure communicationStructured data retrievalClient-sideDistributed servers
A method of answering a data request directed to a network of distributed servers includes receiving the data request from a client at a server. The method further includes extracting identifying information of requested data in the data request, using the server. The method further includes obtaining location information of the requested data indicating which of the distributed servers is storing the requested data, by comparing the identifying information to a distributed ledger. The method further includes sending the requested data from the server to the client.
Owner:SHADMON MOSHE +3
System and method for using a multi-protocol fabric module across a distributed server interconnect fabric
ActiveUS20150103826A1Extend performance and power optimization and functionalityData switching by path configurationPersonalizationStructure of Management Information
A multi-protocol personality module enabling load / store from remote memory, remote Direct Memory Access (DMA) transactions, and remote interrupts, which permits enhanced performance, power utilization and functionality. In one form, the module is used as a node in a network fabric and adds a routing header to packets entering the fabric, maintains the routing header for efficient node-to-node transport, and strips the header when the packet leaves the fabric. In particular, a remote bus personality component is described. Several use cases of the Remote Bus Fabric Personality Module are disclosed: 1) memory sharing across a fabric connected set of servers; 2) the ability to access physically remote Input Output (I / O) devices across this fabric of connected servers; and 3) the sharing of such physically remote I / O devices, such as storage peripherals, by multiple fabric connected servers.
Owner:III HLDG 2
Server module and a distributed server-based internet access scheme and method of operating the same
InactiveUS20030108018A1Special service provision for substationMultiprogramming arrangementsAccess networkNetwork connection
A wide area data carrier network is described comprising: one or more access networks; a plurality of server units housed in a server module and installed on said wide area data carrier network so that each server module is accessible from the one or more access networks, the server module being adapted so that it may be located at any position in the wide area network; and an operations centre for management of the server module, the server module being connected to the operations centre for the exchange of management messages through a network connection. The server module comprises at least one server card insertable in the server module, the server card having a central processing unit and at least one rewritable, non-volatile disc memory device mounted on the card. Preferably a local management system is provided in each server module capable of receiving a command from the operations centre and for executing the command to modify a service performance of at least one server unit.
Owner:REALSCALE TECH
Method and system for managing data using parallel processing in a clustered network
InactiveUS20050071842A1Quick installationQuick to useMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsNetwork onEngineering
An ETL / EAI data warehouse management system and method for processing data by dynamically distributing the computational load across a cluster network of distributed servers using a master node and multiple servant nodes, where each of the servant nodes owns all of its resources independently of the other nodes.
Owner:TOTALETL
Data storage method and a server applied to distributed server cluster
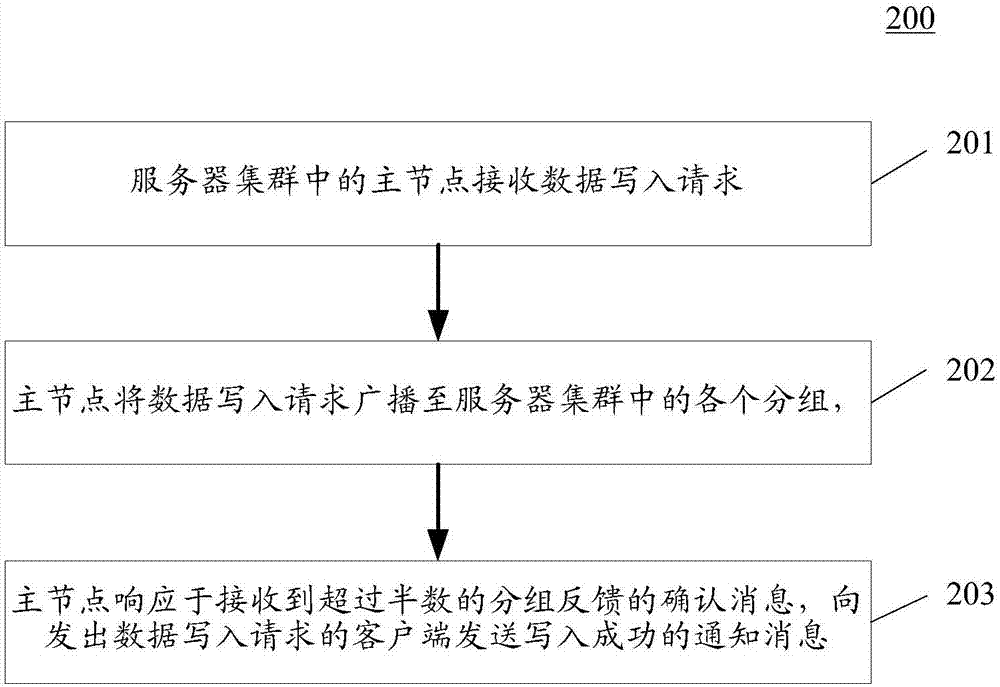
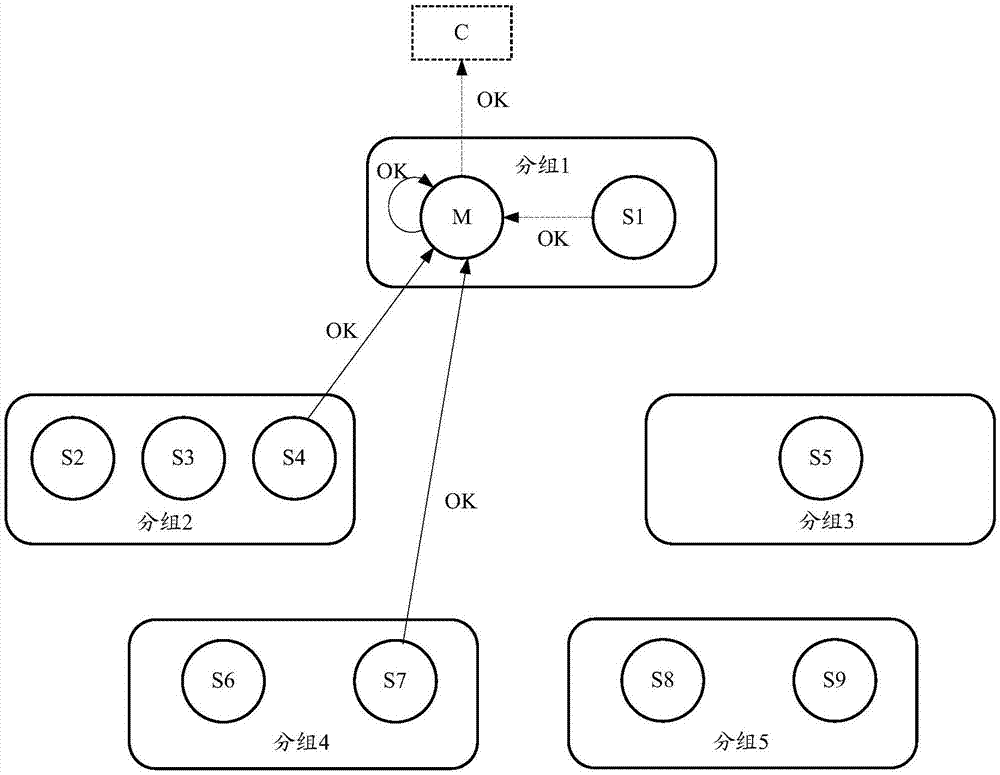
ActiveCN107295080AEnsure consistencyReduce the number of nodesTransmissionTerm memoryDistributed servers
The invention discloses a data storage method and a server applied to a distributed server cluster that includes multiple nodes. One embodiment of the method includes: receiving by the main node in the server cluster a data write-in request, wherein the data write-in request contains the data to be written in; broadcasting by the main node the data write-in request to each packet in the server cluster, wherein the each packet contains at least one node; responding by the main node to the confirmation information fed back by more than a half of the packets; sending to the user terminal initiating the data write-in request the notification information that the data are successfully written-in, wherein if the packets do not include the main node, the packet successfully writes the data to be written in the memory in response to at least one node in the packet and feeds back confirmation information to the main node. The embodiments of the invention can improve service availability while ensuring data consistency of the distributed data server cluster.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
System and method for a distributed server for peer-to-peer networks
InactiveUS20060126611A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationSelf formingDistributed servers
A logical distributed server is generated for managing (Internet Protocol (IP) address allocation for an ad-hoc, self-forming peer-to-peer (P2P) network. The logical distributed server is generated according to messaging scheme where nodes on the P2P network allocate addresses for themselves and for clients connected to them. Each node implements a server that listens on the incoming client connections. Each node maintains data structures that represent the current state of an address database. Routing requests are fielded by the nodes from the clients and the messaging scheme is used to inform other nodes of its action so a consistent address space is maintained between all the nodes on the P2P network.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
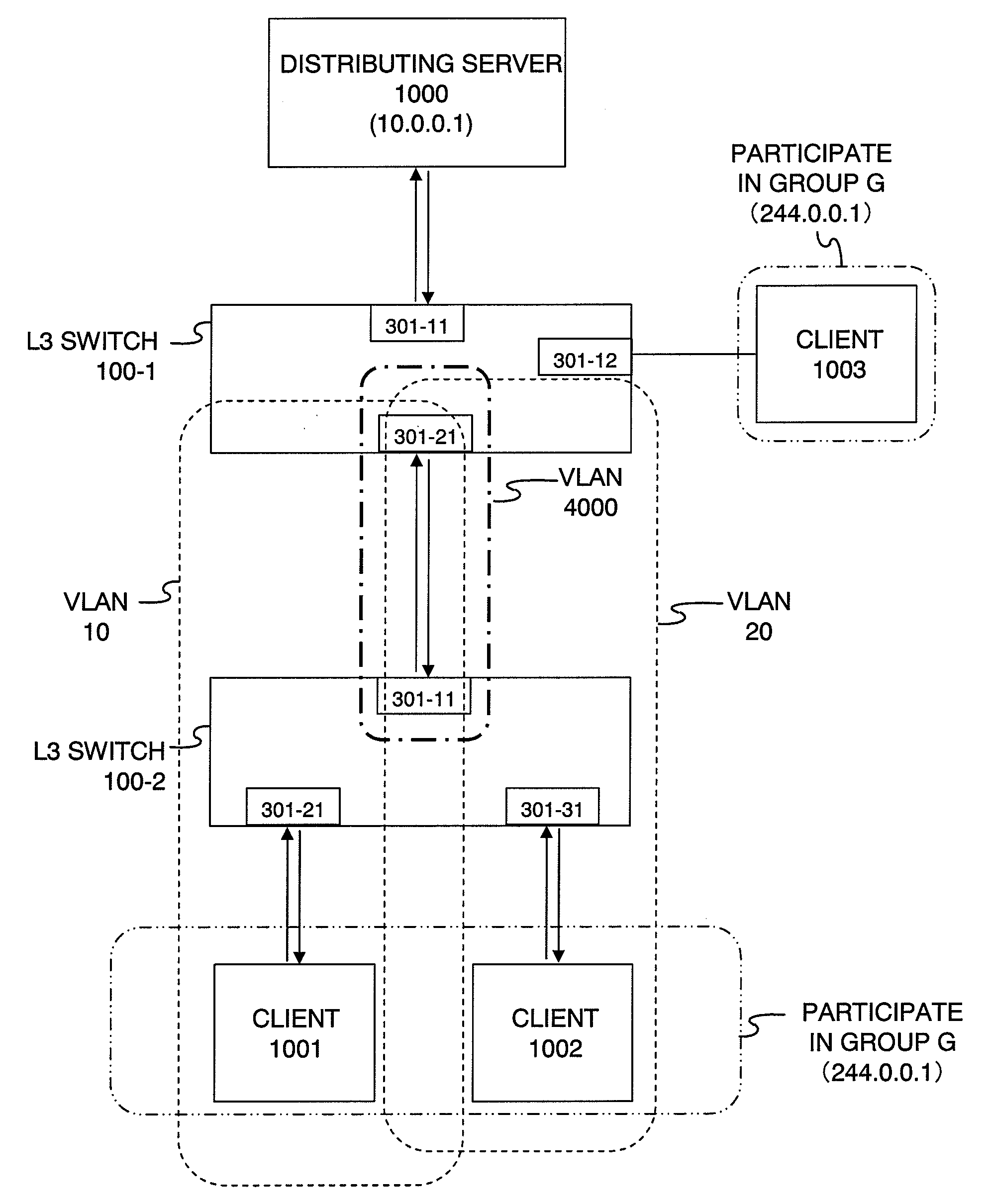
Frame Transfer System
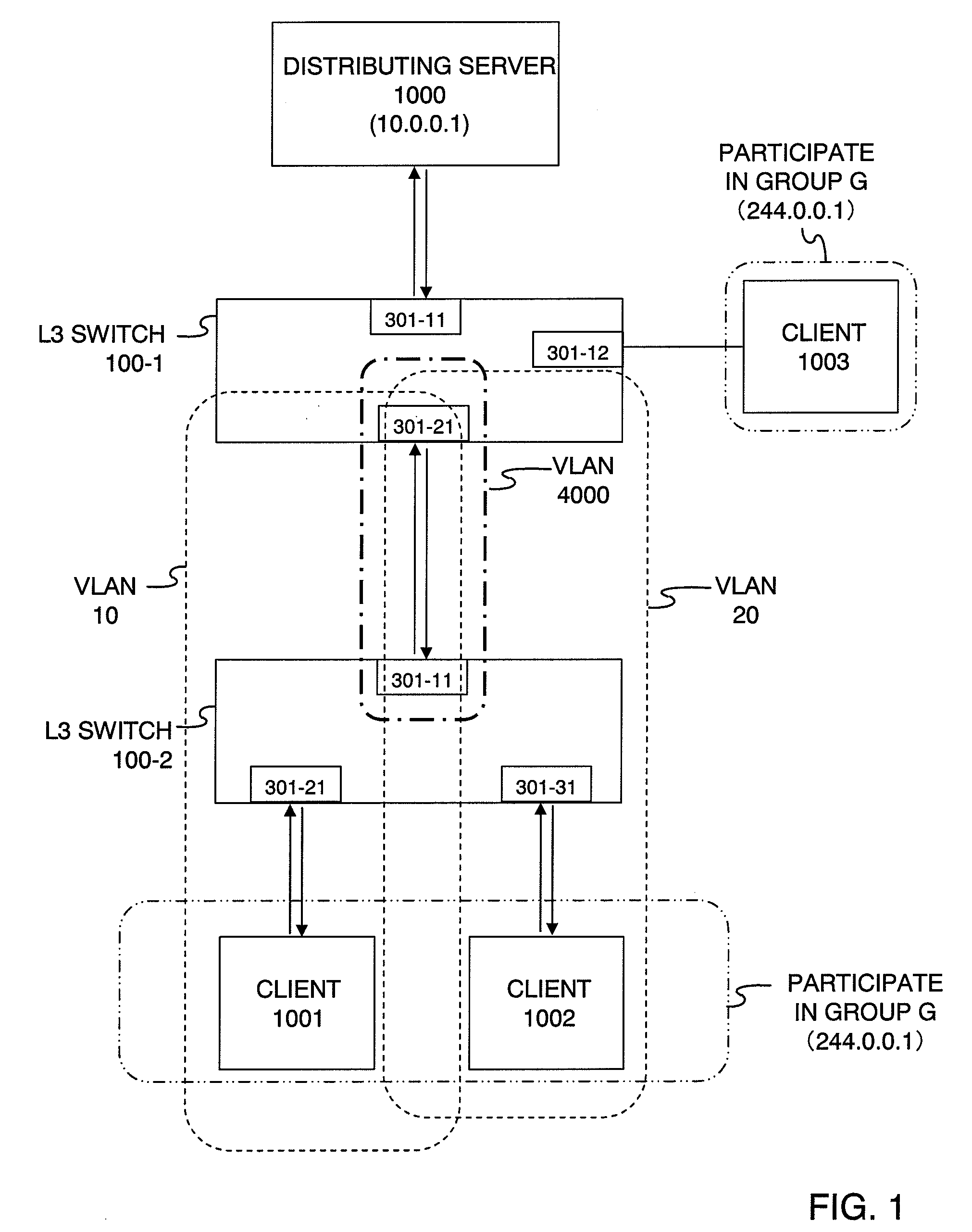
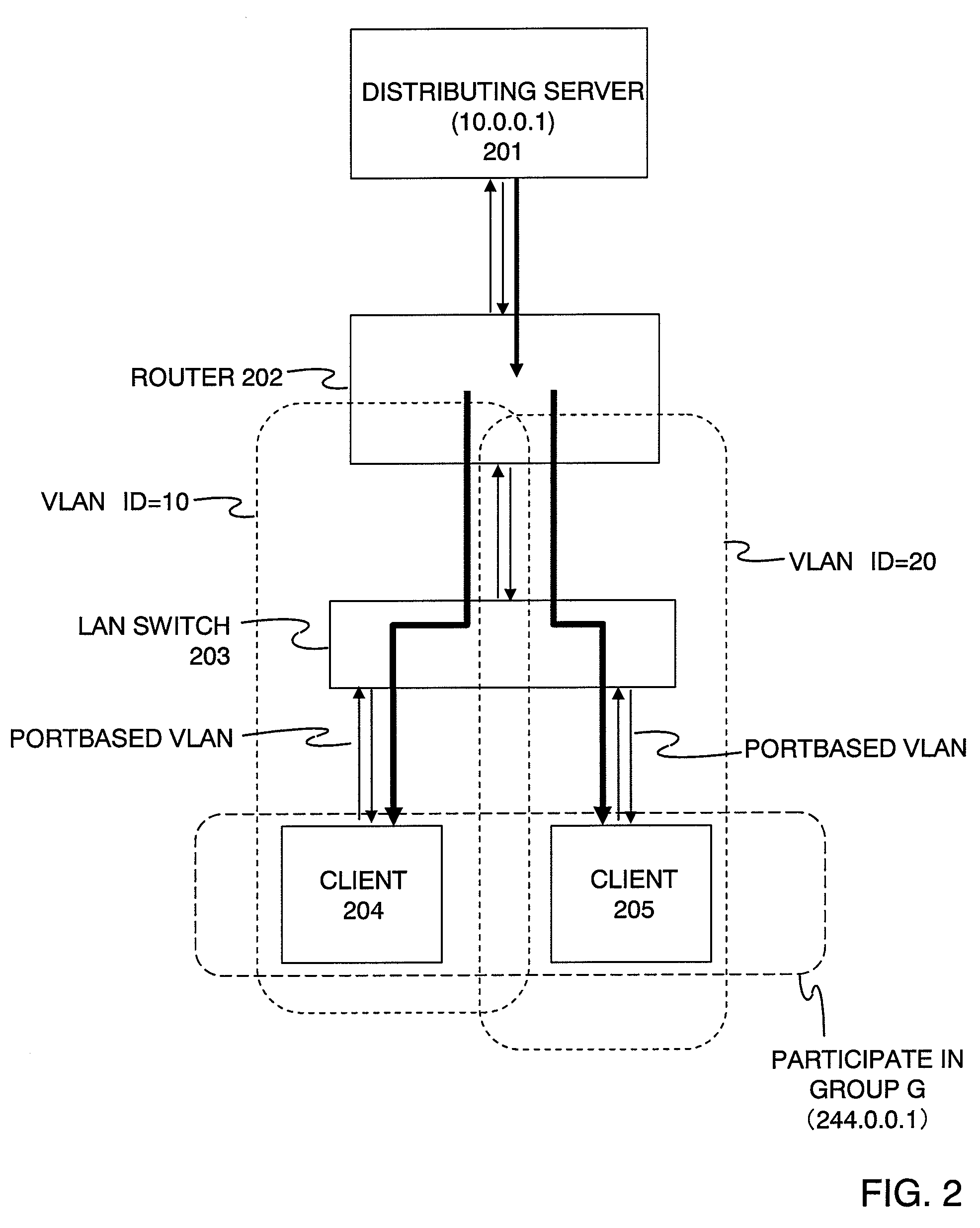
InactiveUS20080075078A1Enhance line use efficiencyInhibitionNetworks interconnectionMultiplexingComputer network
When are multiplexed to a line for connecting a router and a LAN switch, another VLAN is set between the router and the LAN switch. The router receives affiliation requests containing the identifiers of desired groups from a client terminal belonging to VLAN and a client terminal belonging to VLAN. The router outputs a multicast frame of the group received from a distributing server is output through the logical interface corresponding to VLAN to the LAN switch. The LAN switch copies and transmits the received multicast frame to the client terminals.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for optimizing network service
There is presently no single accepted scheme to support Quality of Service guarantees for IP based applications, although RSVP is the prevailing standard for network resource reservation. Thus, providing end-to-end Quality of Service guarantees for content delivery across the Internet presents a challenge for Service Providers. Typically load balancing algorithms are used for picking the best server, with respect to server capacity for satisfying a request, but they can not guarantee Quality of Service for the whole duration of the network transaction. The invention proposes a method of distributing server load in an IP network, comprising building an association between a subscriber edge device and a server controller using a packet switched network Quality of Service mechanism. A fair share of server bandwidth is offered out to the subscriber edge device, and a resource request from the client is directed, via the subscriber edge device and through a server controller, to a server having an amount of server bandwidth required by the client. The required fair share of server bandwidth is then reserved for meeting the client's resource request. The invention also proposes a subscriber edge device, a data center device, and a communications network comprising each. The subscriber edge device comprises, a resource requester for sending a request to the server controller associated with the source location of the requested resource, a resource reserver that reserves an amount of bandwidth using a Quality of Service mechanism and releases any unneeded bandwidth, and a resource returner that returns the requested resource to the client. The data center device comprises, a resource allocator that allocates fair shares of server bandwidth to the network, and a server controller that offers fair shares of server bandwidth using a Quality of Service mechanism.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
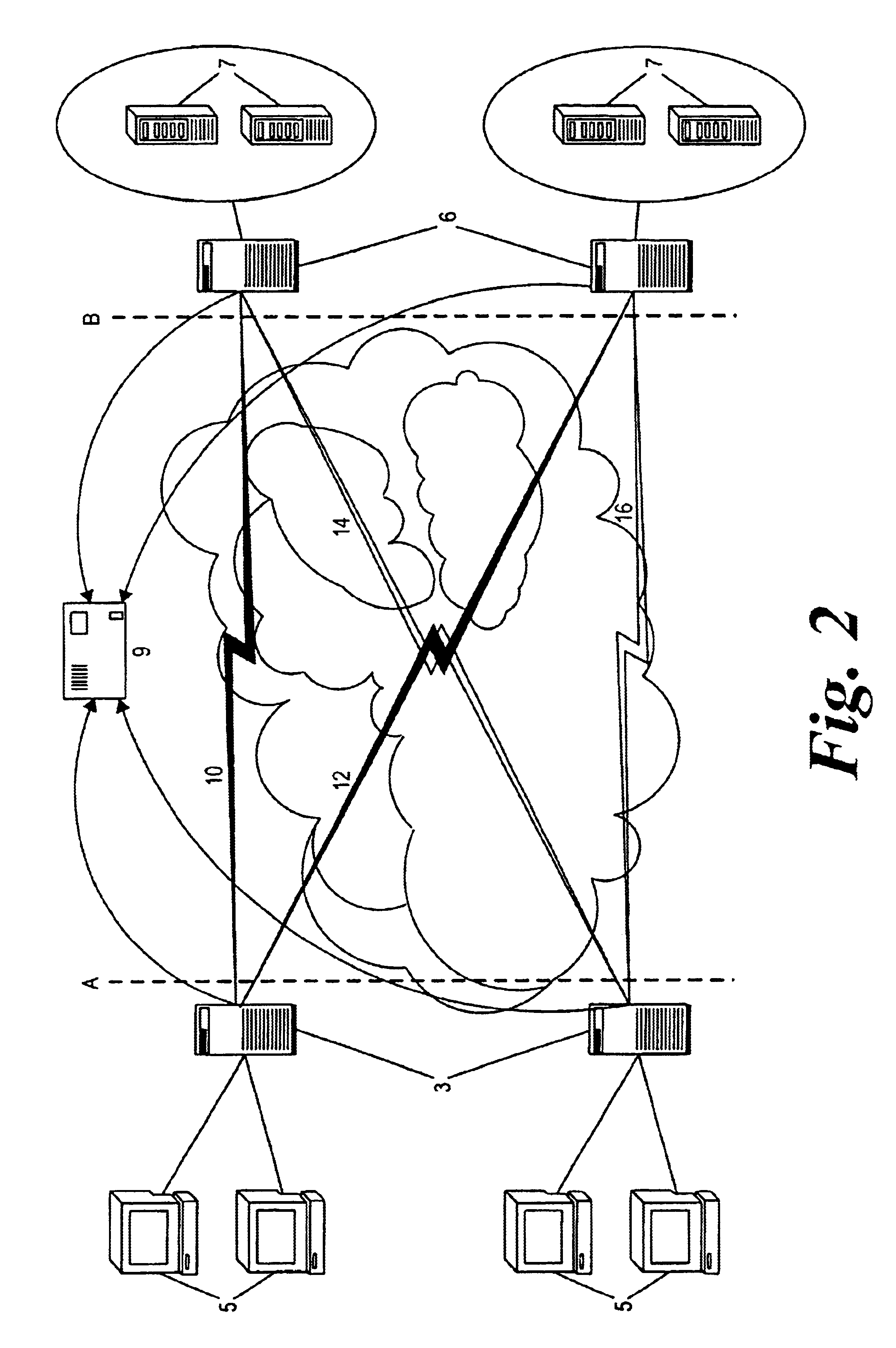
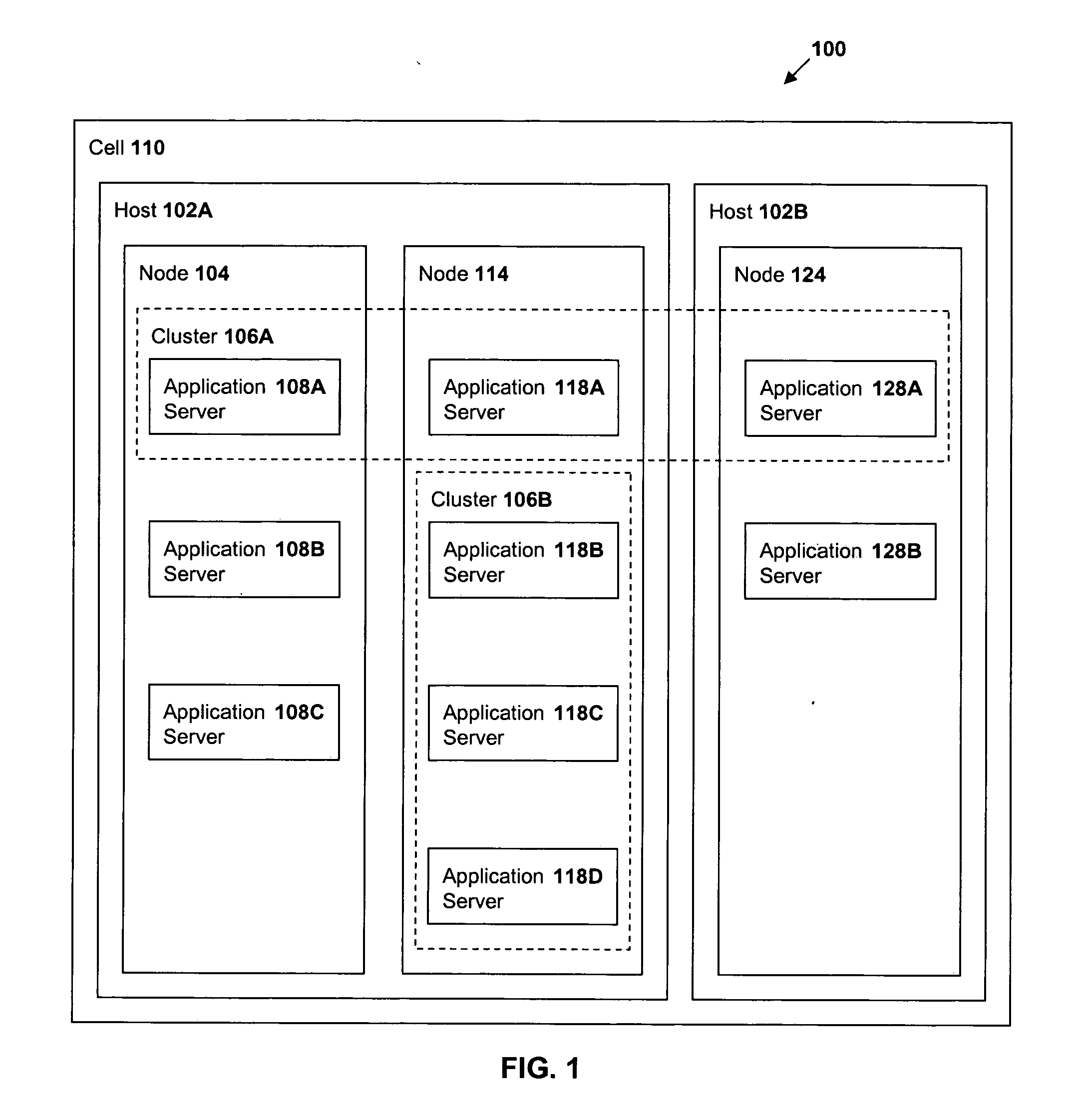
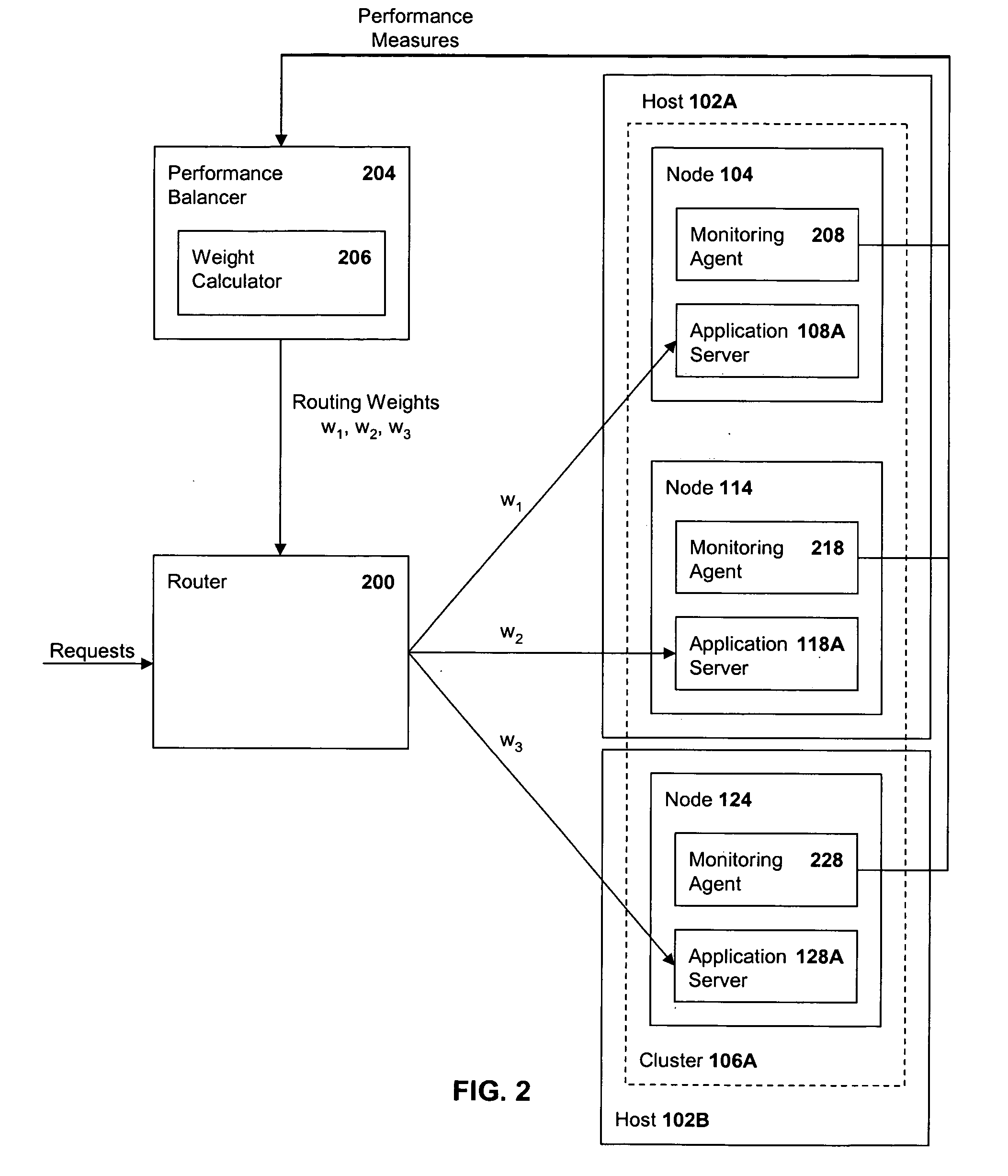
Method and system for performance balancing in a distributed computer system
InactiveUS20060236324A1Digital data processing detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsApplication serverComputerized system
A method of dynamic performance balancing in a distributed computer system including collecting average service time statistics for application requests distributed from multiple application servers and collecting application server CPU utilization statistics from multiple hosts where each host is associated with at least one of the application servers. In addition, the method includes periodically calculating scaled routing weights from the average service time and CPU utilization statistics and distributing server requests to the application servers in accordance with the scaled routing weights. Also disclosed is a distributed computer system configured to accomplish dynamic performance balancing as described above, and an article of manufacture for use in programming a distributed computer system containing instructions to accomplish dynamic performance balancing of server requests as described above.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com