Patents
Literature
711 results about "Server allocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
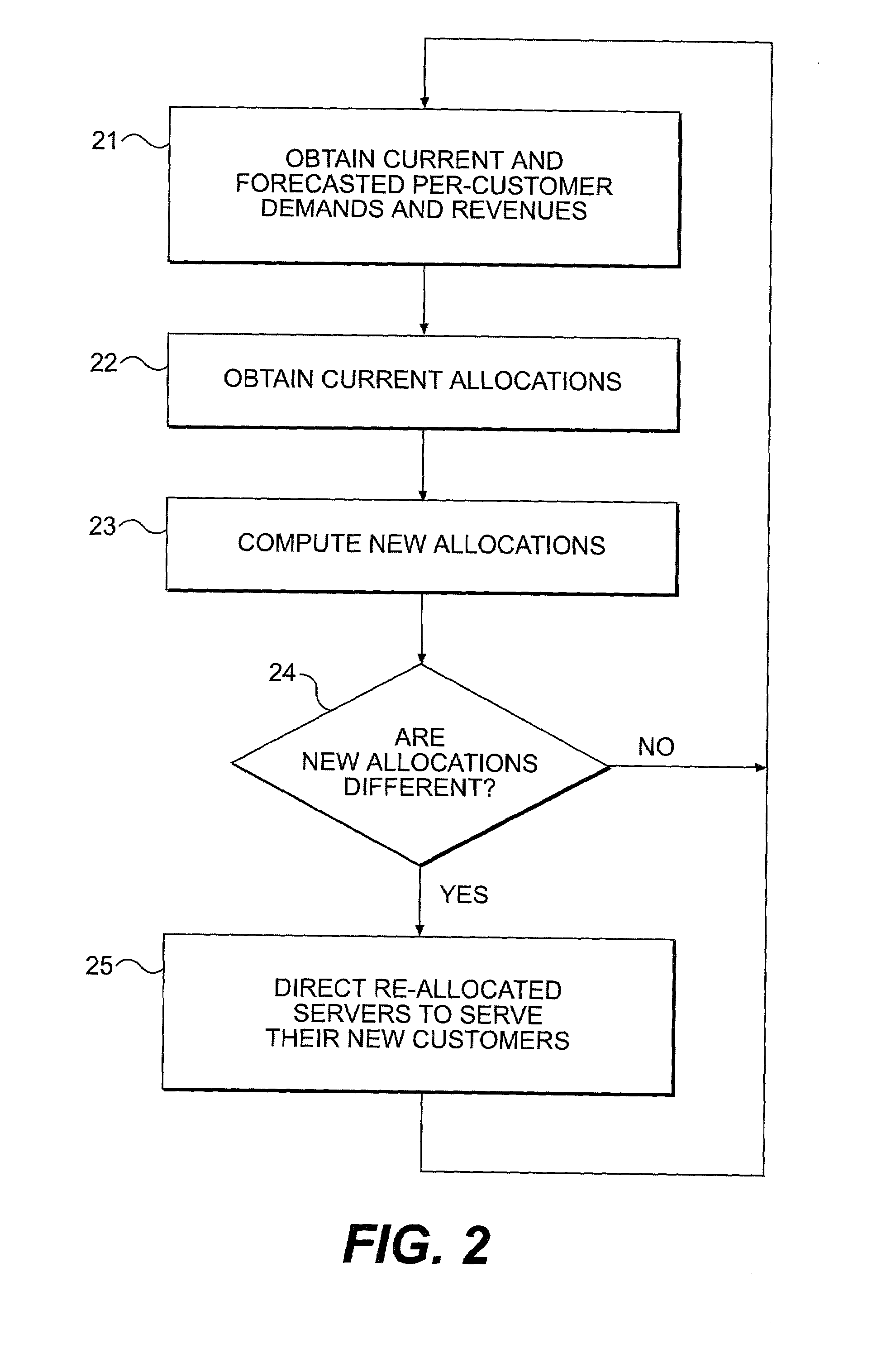
Load balancing method in a communication network
InactiveUS7062556B1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemServer allocation
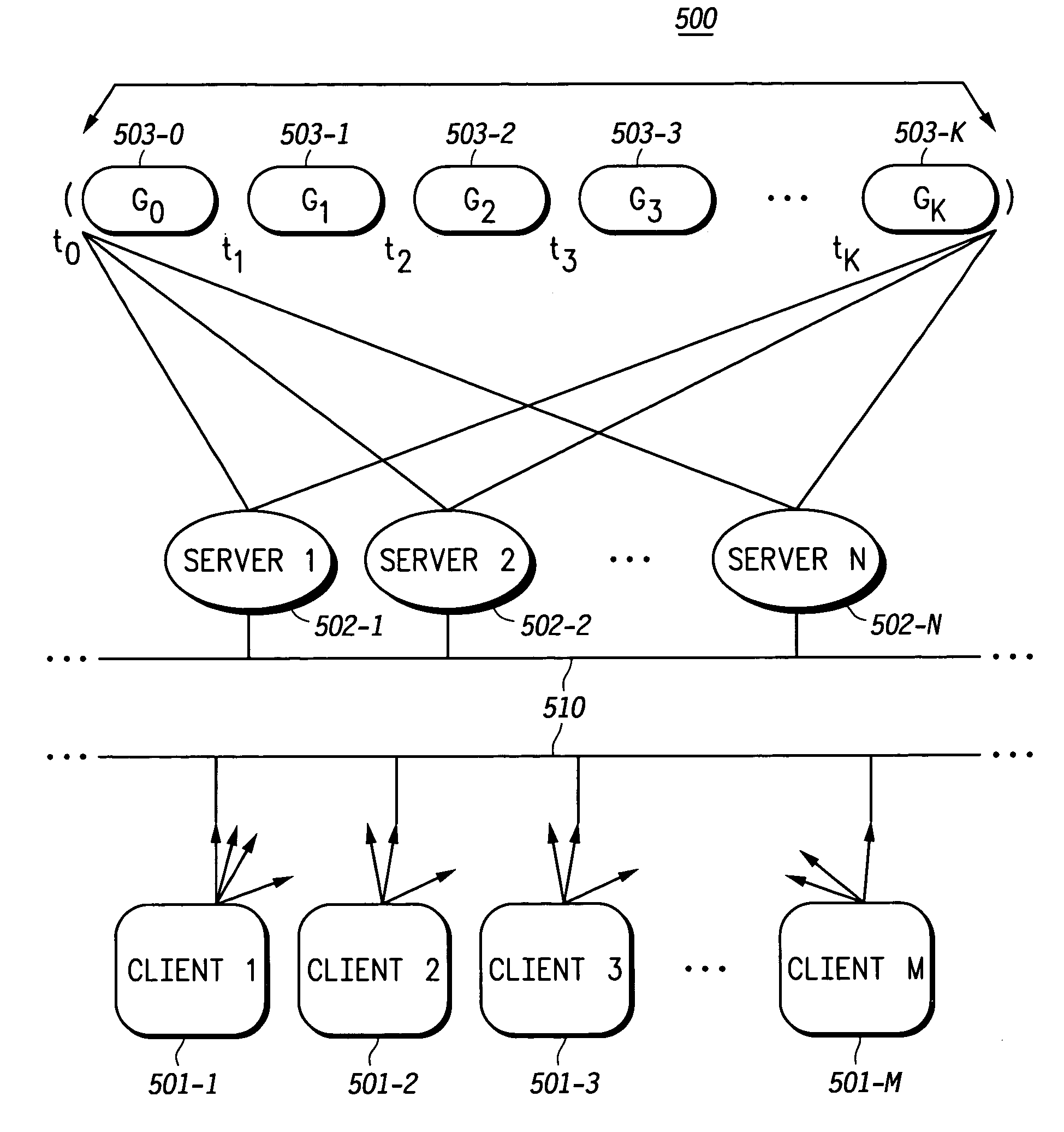
A communication system network (500) having a plurality of servers (502-1 through N), each having a load level based on serving a number of clients (501-1 through M), a method includes grouping plurality of servers (502-1 through N) into a plurality of server groups G0 through Gk (503-0 through k) respectively having load levels progressively from a least amount of load level to a most amount of load level, calculating a plurality of time periods T1 through Tk corresponding to the server groups G1 through Gk, assigning load to a server selected from the servers in the server group G0 from an initial time until expiration of the time period T1, after expiration of each of the time periods T1 through Tk measured from the initial time, load assignment takes place by assigning load to a server selected from the servers in the server groups from G0 and and at least one other server group, in server groups G1 through Gk, corresponding to an expiring time period.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
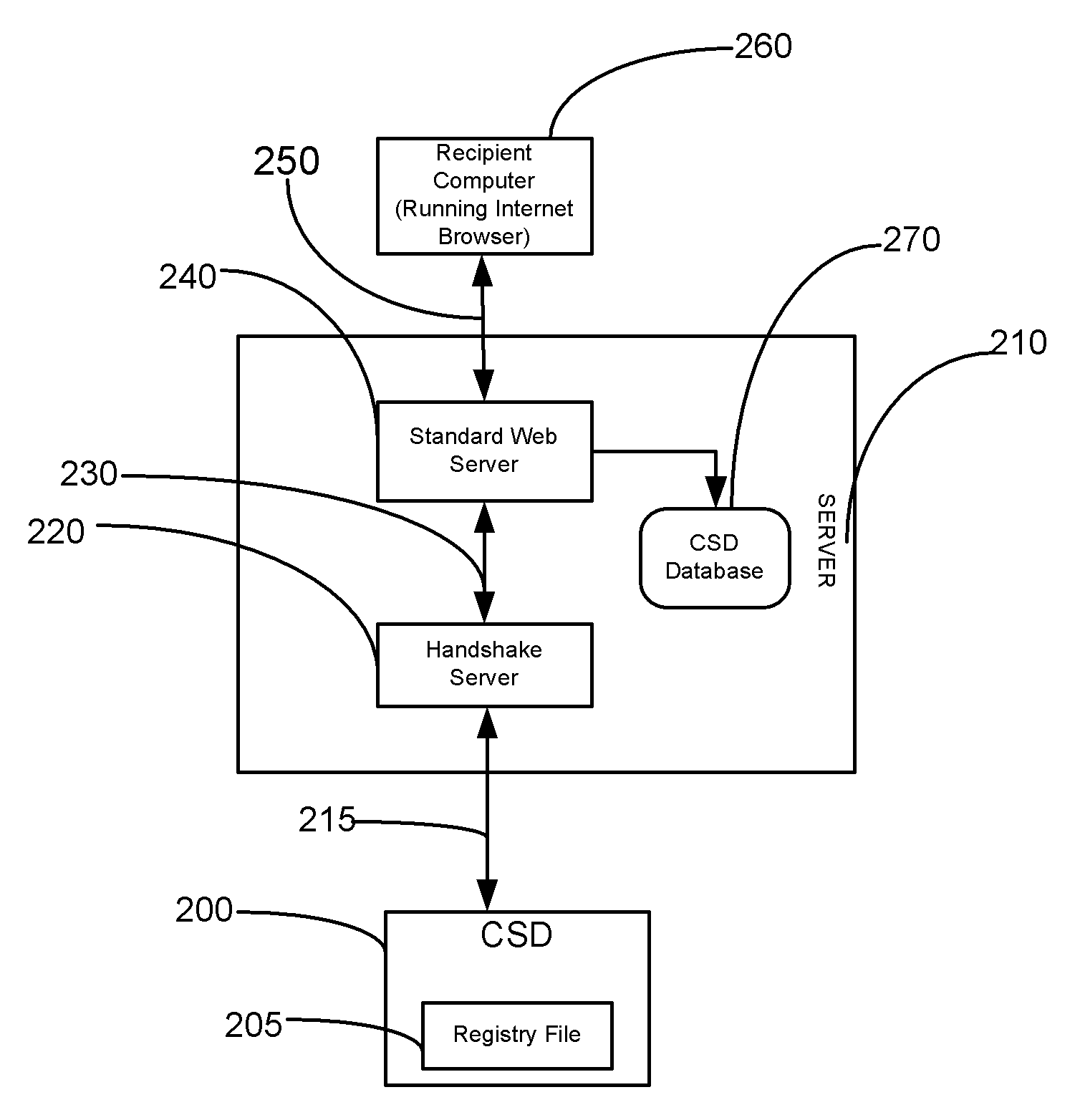
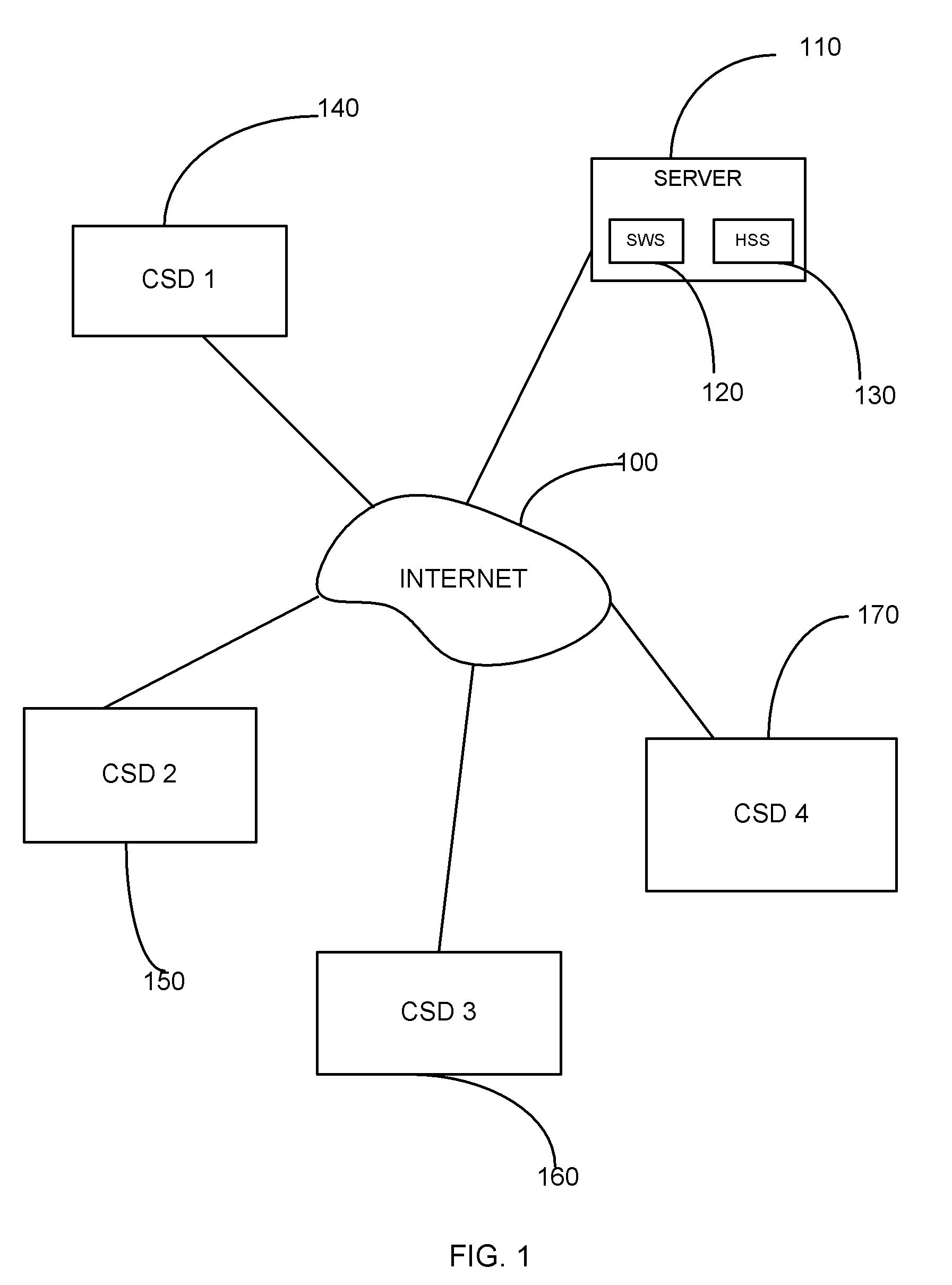
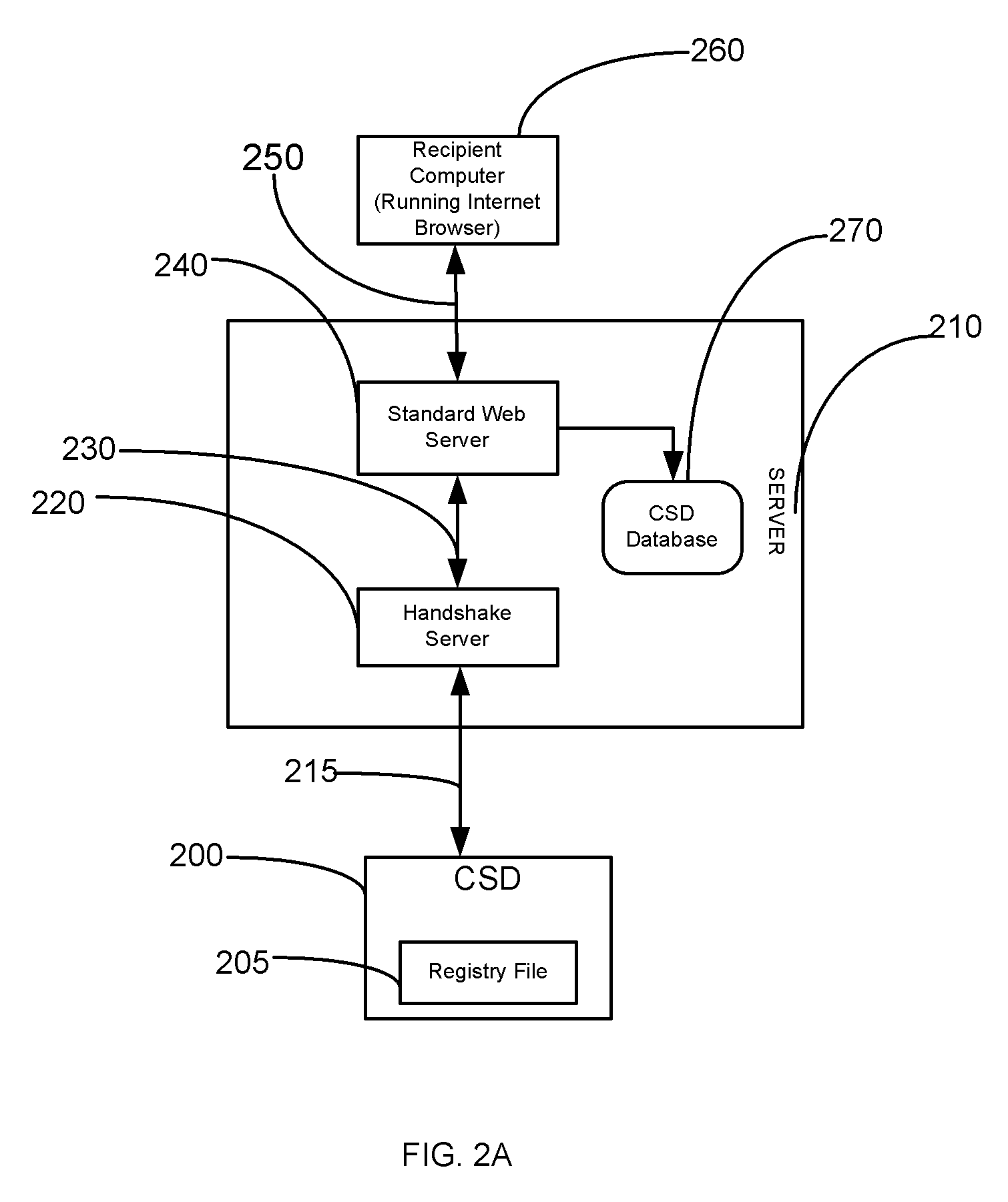
Method for enabling internet access to information hosted on csd
InactiveUS20090013063A1Uniform loadingDistributed loadDigital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsWeb serverSoftware
The disclosure describes a method for enabling internet access to information hosted on a computer or a storage device (CSD), even without having a web server software on the CSD. The CSD is registered with a server and assigned an ID by the server. Information about all CSDs is stored in a database on the server. A unique resource locator (URL) is created for each file intended to be shared. The URLs of all hosted files are stored in a file called the registry file residing on the CSD. An intending recipient may enter the URL of the desired file in a web browser. The URL is sent from the web browser to the server. The server forwards the URL to the CSD The file is retrieved from the CSD and sent to the server. The server forwards the file to the recipient computer, where the web browser displays it.
Owner:SANGHI MRS NIRALI
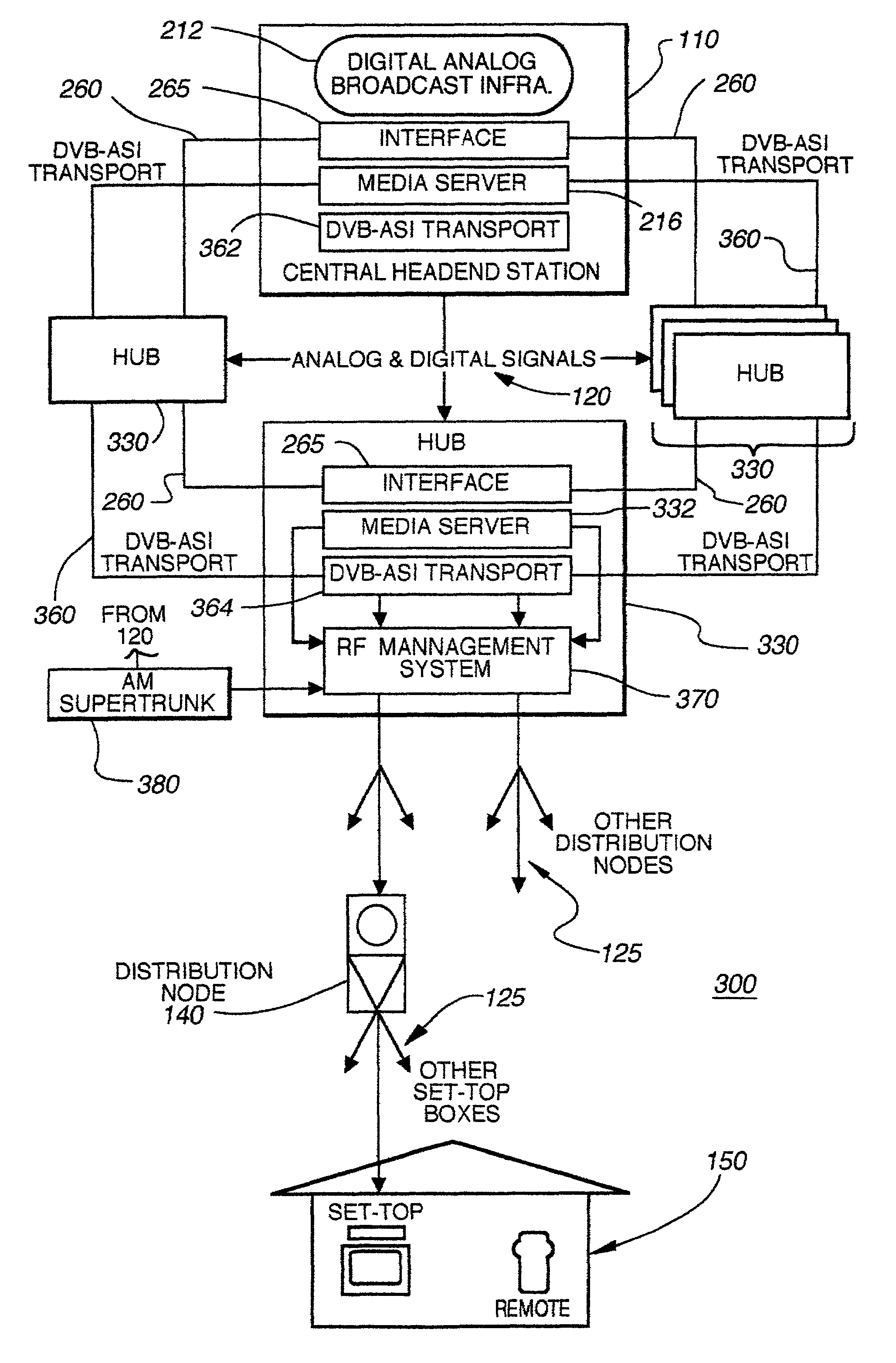
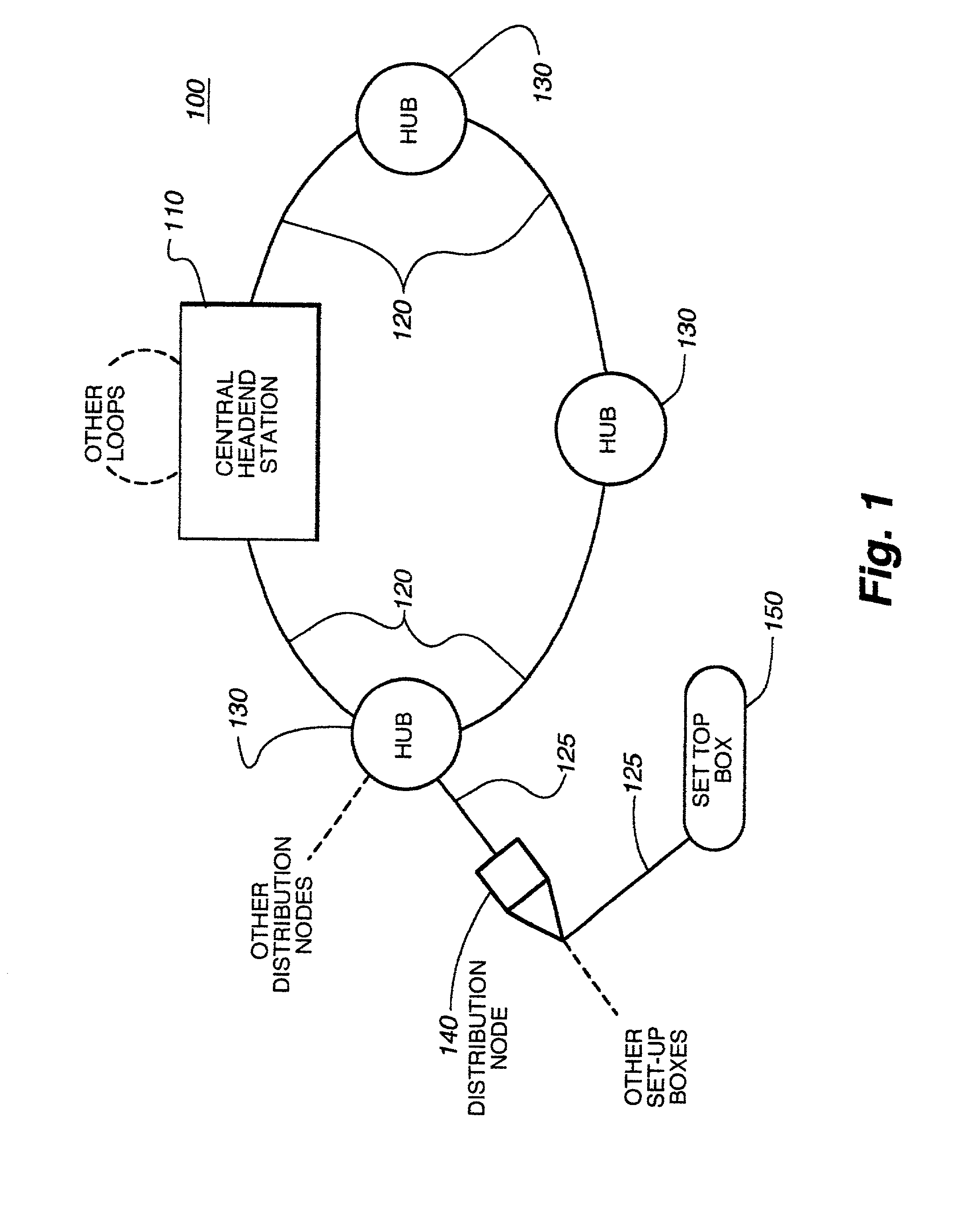
Hybrid central/distributed VOD system with tiered content structure
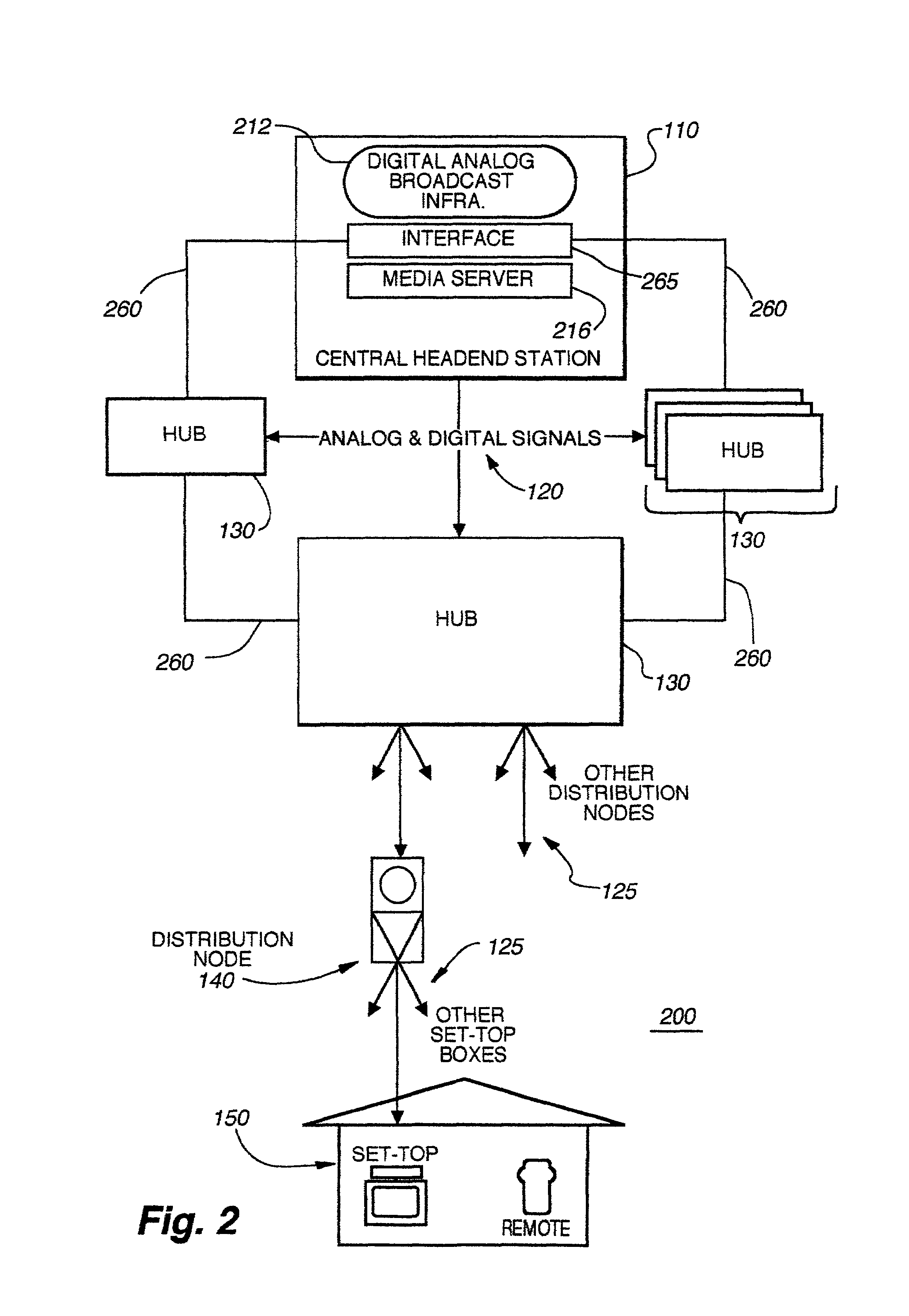
ActiveUS7690020B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsContent distributionFiber
The present invention provides a hybrid central / distributed and tiered video on demand (VOD) service network with tiered content structure. In particular, the present invention uses media servers located in both the headend station and the hub stations. Set-top boxes generally would be supplied VOD services from the high-demand content media servers located in the hub station nearest to the user. The central media server located in the headend would be used as an installed backup to the hub media servers; as the primary source for lower demand VOD services and as the source of the real time, centrally encoded programs with PVR (personal video recorder) capabilities.By distributing the servers to the hub stations, the size of the fiber transport network associated with delivering VOD services from the central headend media server is reduced. The invention provides that each user has access to several server ports located on at least two servers. Multiple paths and channels are available for content distribution to each user, assuring high system reliability and enhanced asset availability. Substantial cost benefits are derived from the reduced need for a large content distribution network and the reduced storage capacity requirements for hub servers.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
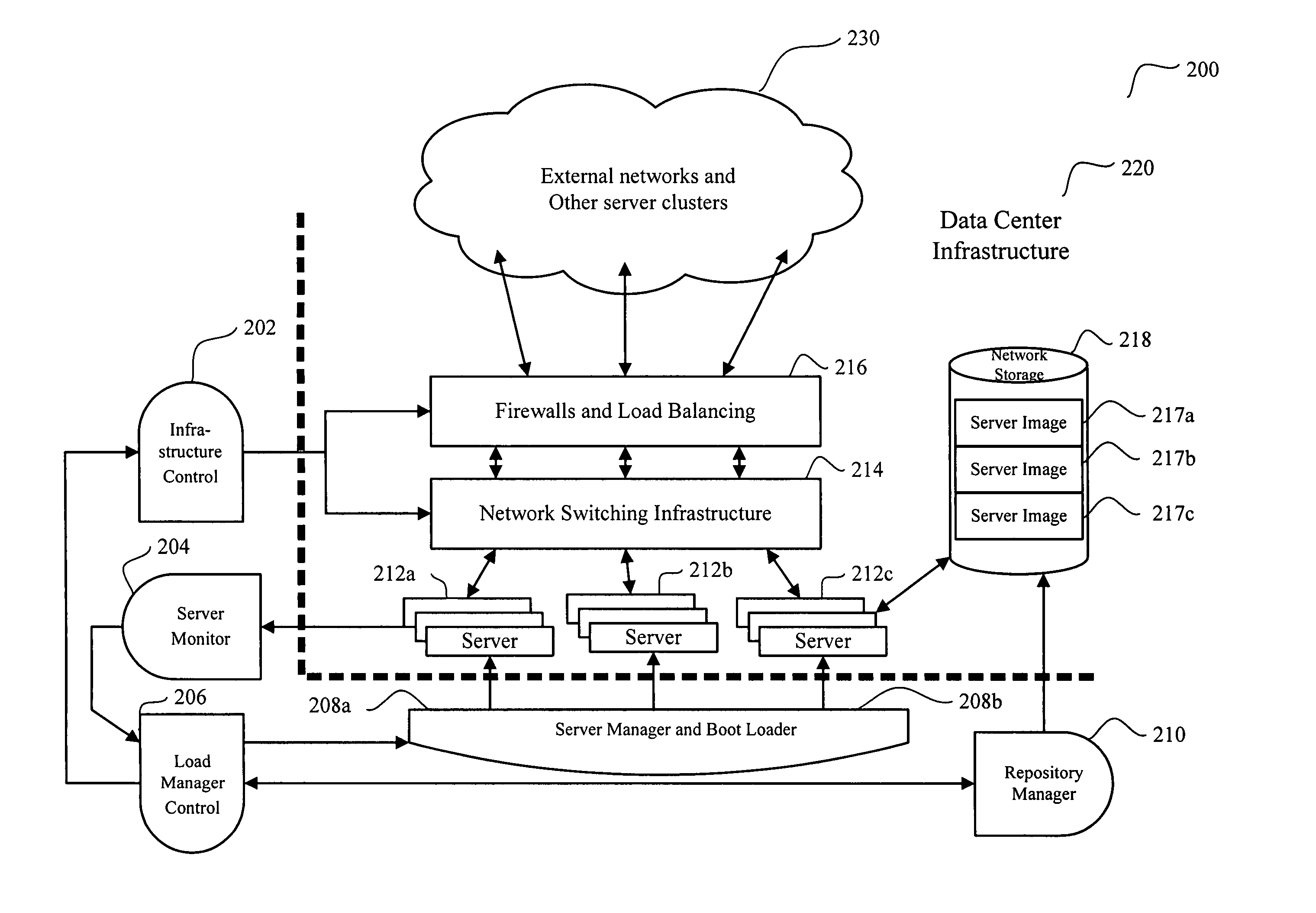
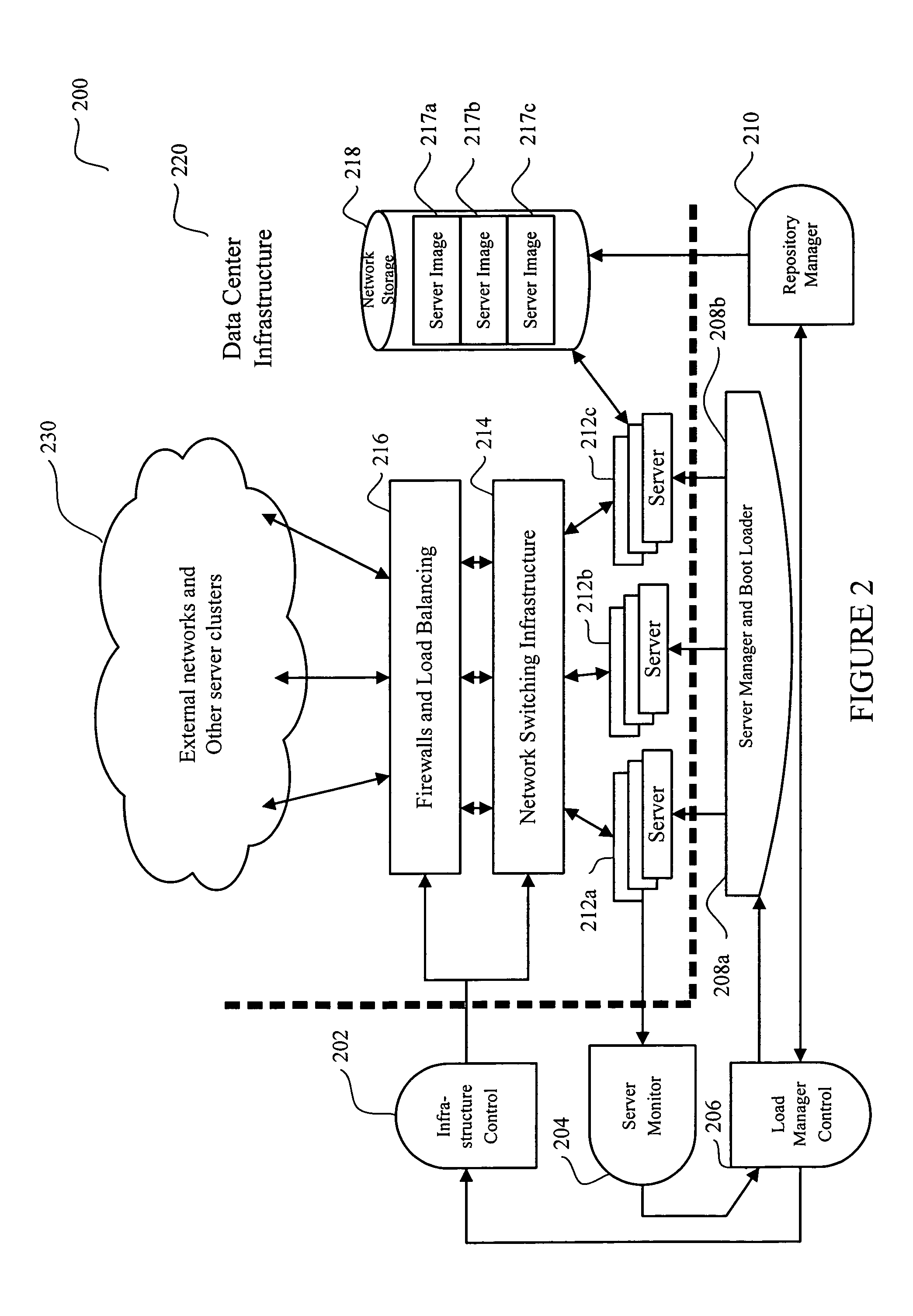
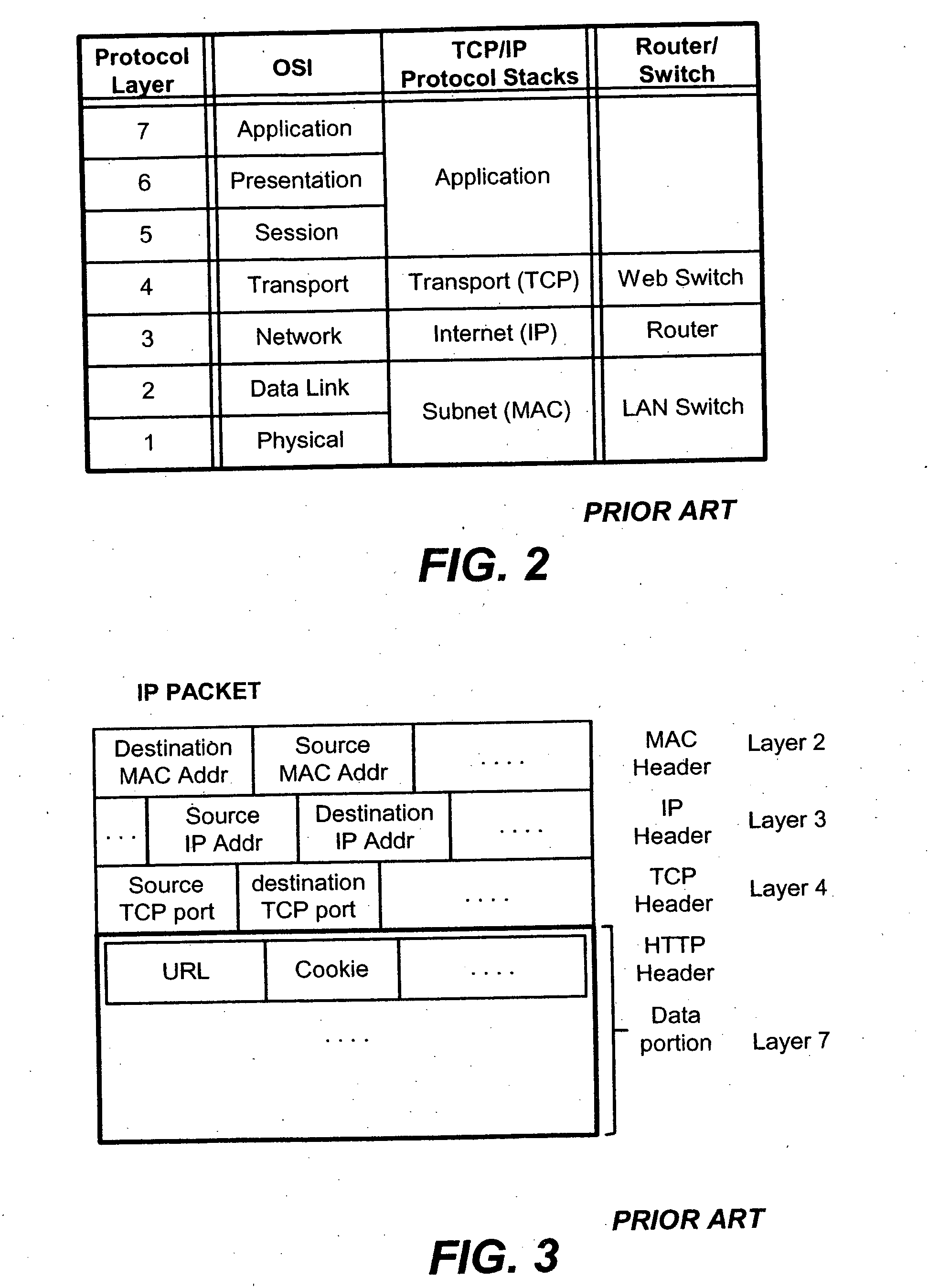
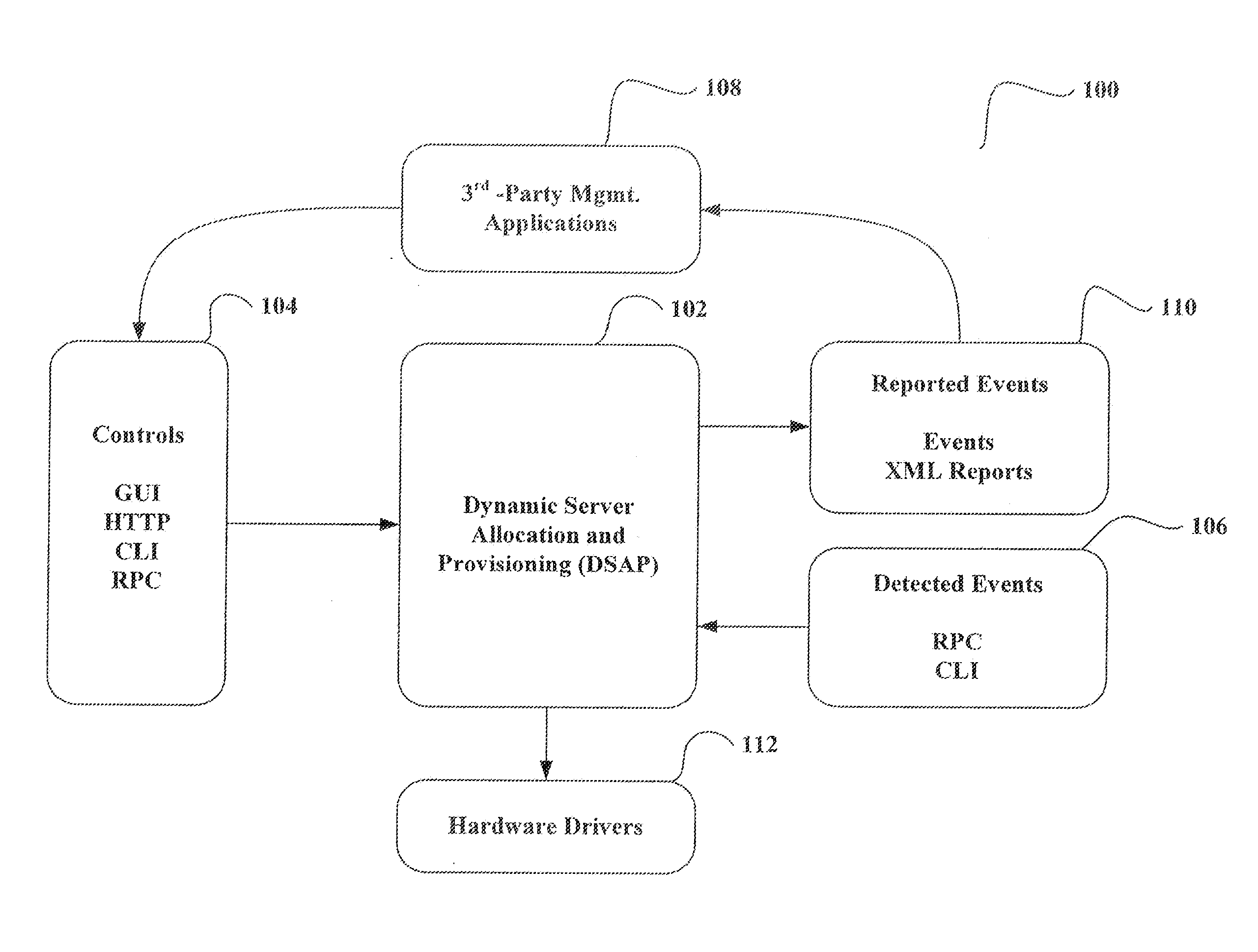
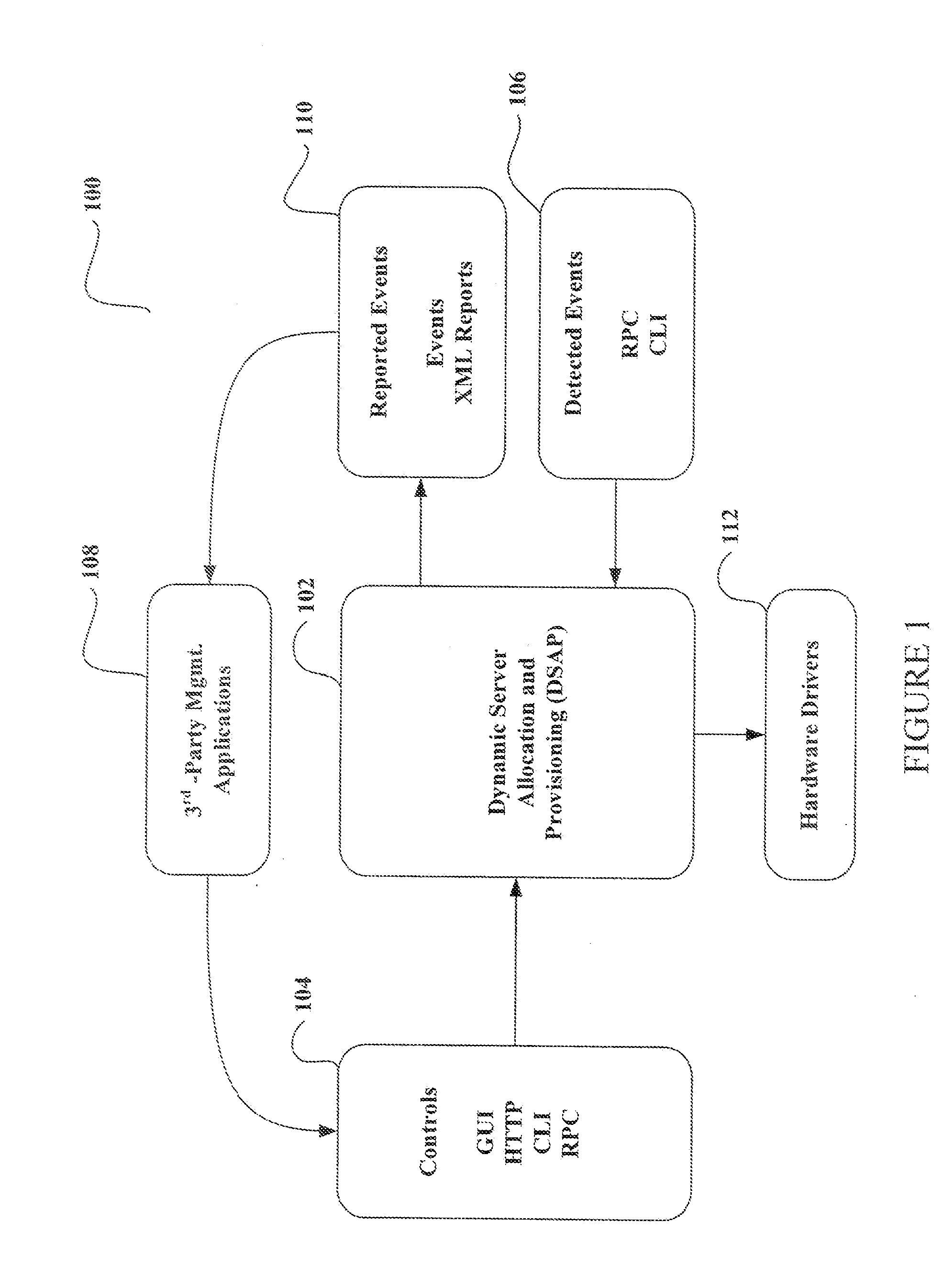
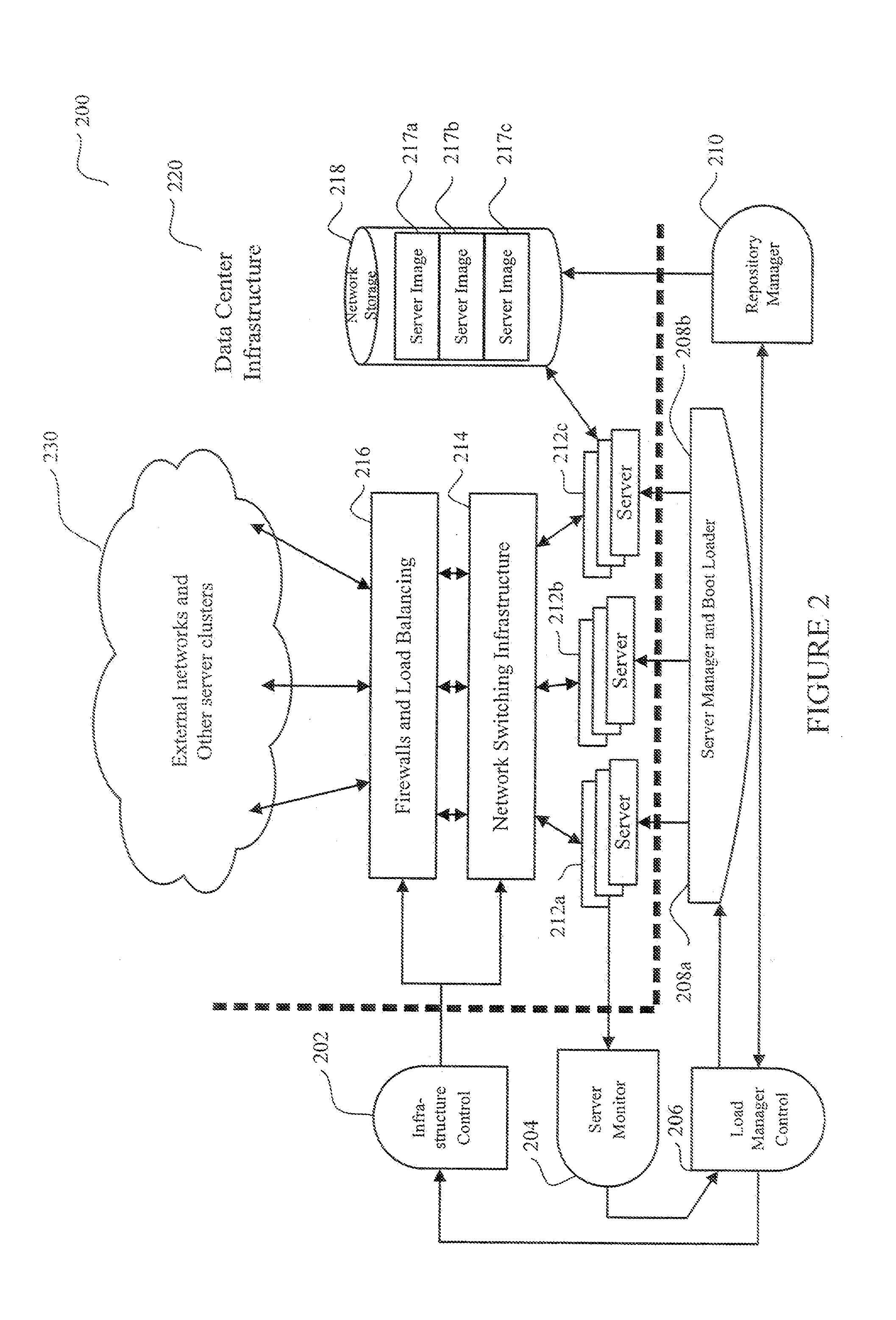
System and method for dynamic server allocation and provisioning
ActiveUS7213065B2Lower cost of capitalQuality improvementResource allocationDigital computer detailsManagement toolVirtual LAN
A management tool that streamlines the server allocation and provisioning processes within a data center is provided. The system, method, and computer program product divide the server provisioning and allocation into two separate tasks. Provisioning a server is accomplished by generating a fully configured, bootable system image, complete with network address assignments, virtual LAN (VLAN) configuration, load balancing configuration, and the like. System images are stored in a storage repository and are accessible to more than one server. Allocation is accomplished using a switching mechanism which matches each server with an appropriate system image based upon current configuration or requirements of the data center. Thus, real-time provisioning and allocation of servers in the form of automated responses to changing conditions within the data center is possible. The ability to instantly re-provision servers, safely and securely switch under-utilized server capacity to more productive tasks, and improve server utilization is also provided.
Owner:RACEMI
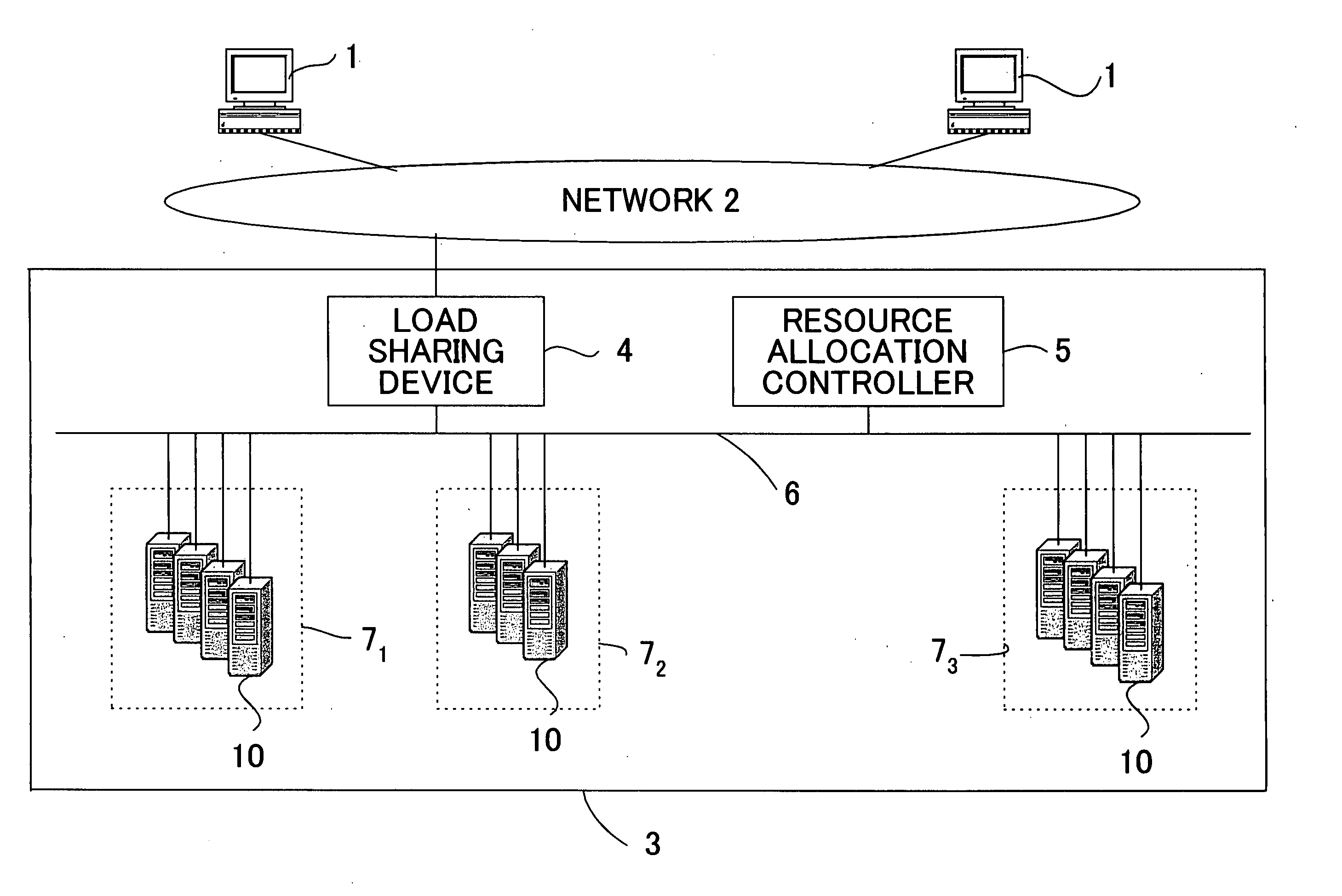
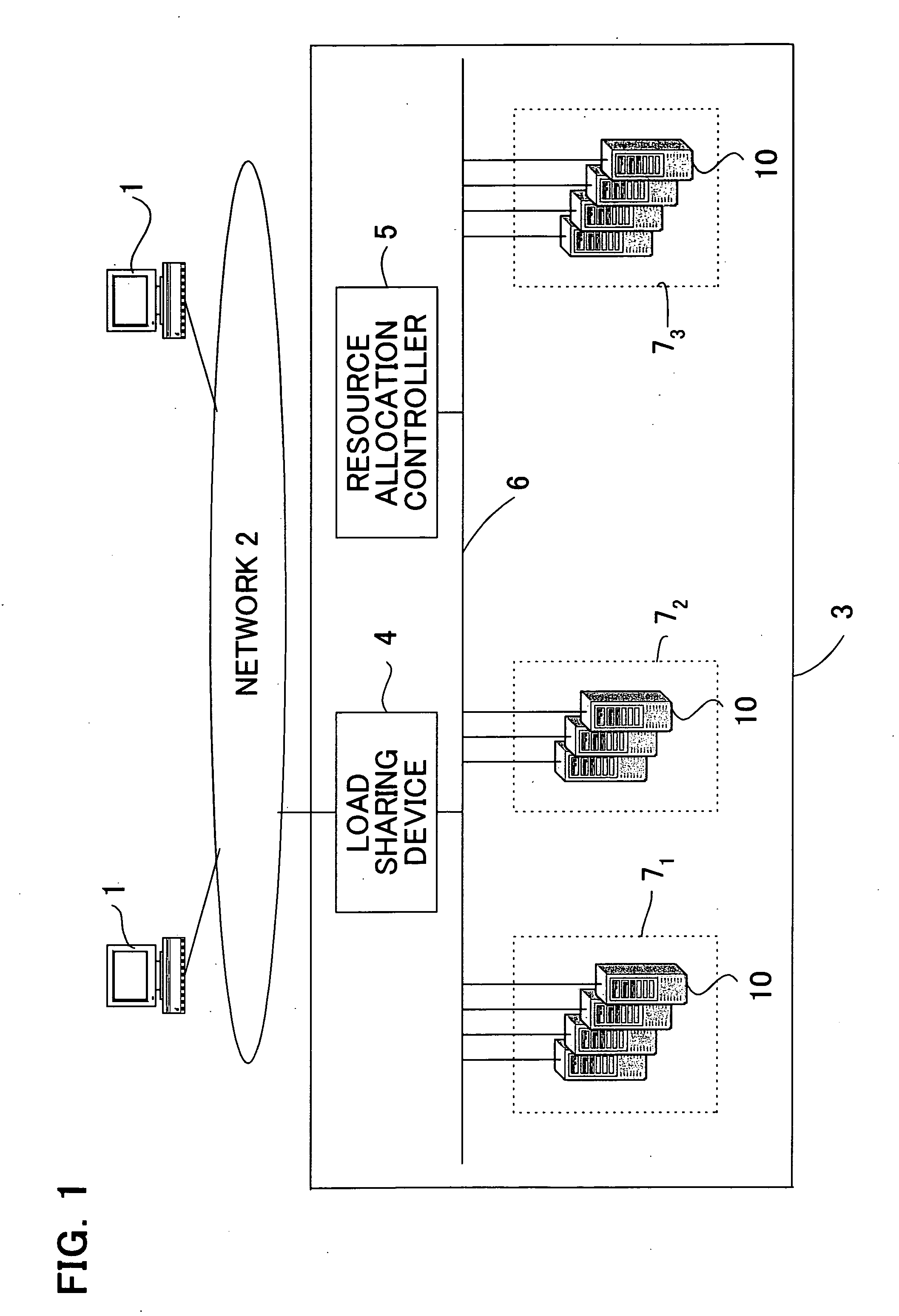
Server allocation control method
A method to automatically allocate servers to network services in a data center in real time and without need for operators for a load sharing device is provided. In the method, fluctuations in quantity of requests arriving at the network services can be monitored, the value of the quantity of requests for a subsequent fixed time interval can be predicted and, in accordance with the magnitude of the predicted value of the quantity of requests, the quantity of servers allocated to the network services can be controlled. Here, where traffic of the quantity indicated by the predicted value of the quantity of requests arrives at the network services, the number of servers allocated to the network services can be set in such a way that the average response time to the user terminals is equivalent to a response time threshold value or less set in advance by the operations manager.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
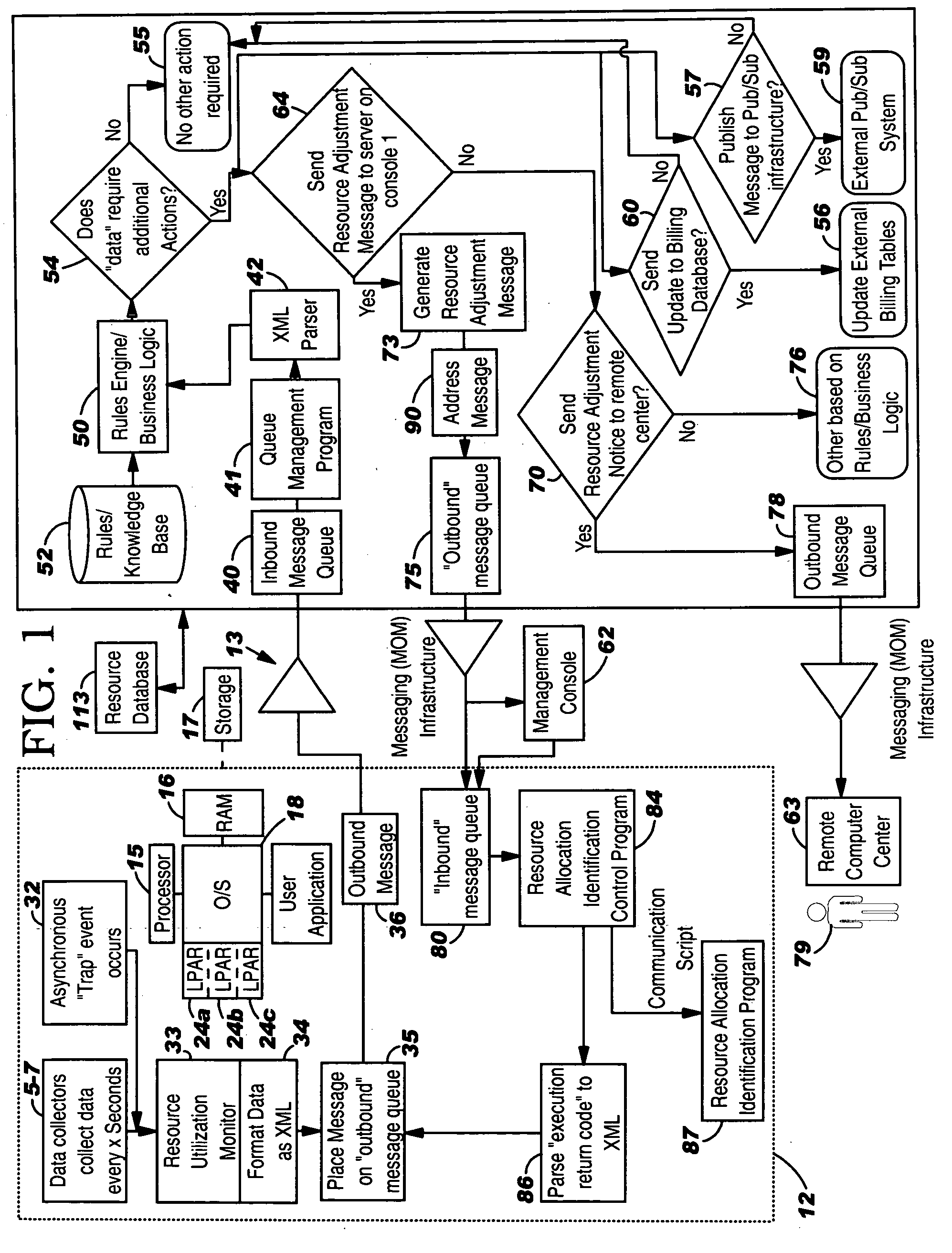
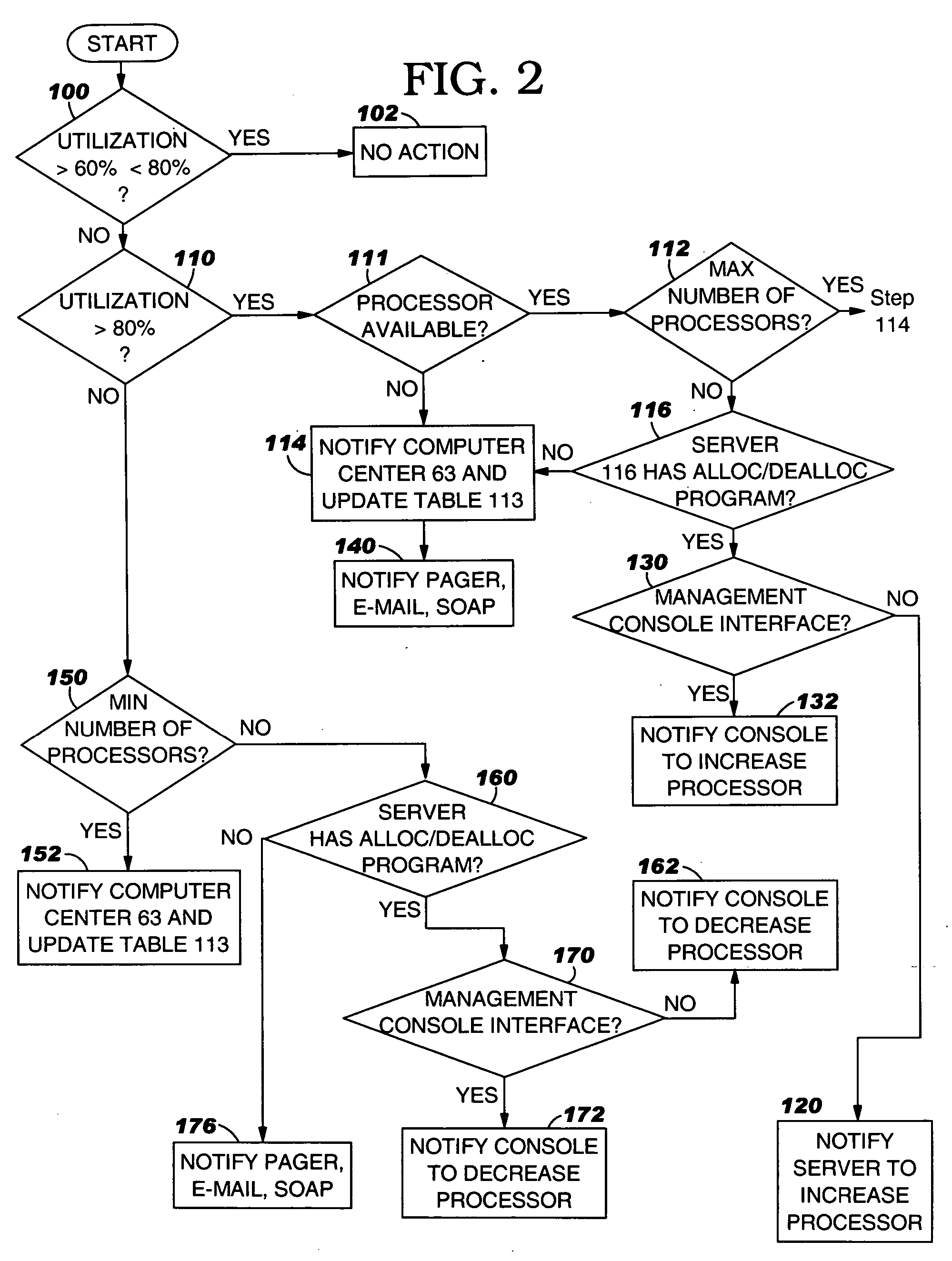
System, method and program to automatically adjust allocation of computer resources
InactiveUS20060136761A1Volume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsComputer resourcesProgram instruction
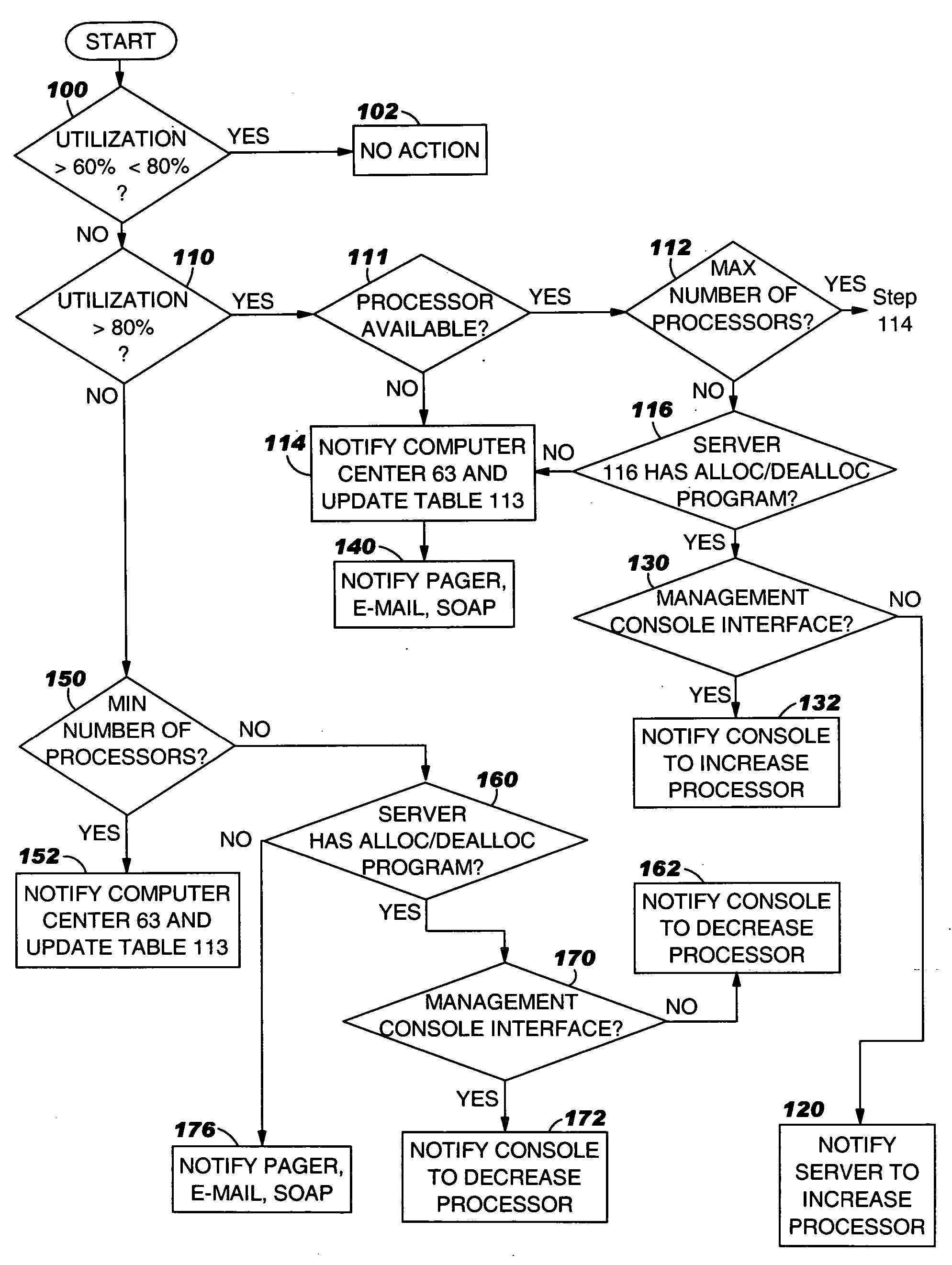
System and computer program product for automatically adjusting allocation of processing power in a server. The server includes means for monitoring utilization of the processing power in the server and reporting the utilization of the processing power to the system, or means for monitoring availability of the processing power in the server and reporting the availability of the processing power to the system. The system comprises means or program instructions, responsive to a report that the processor utilization is above a first predetermined upper threshold or the processor availability is below a first predetermined lower threshold, for determining if the server can accommodate allocation of additional processing power, and if so, generating a request to allocate additional processing power to the server. The system also comprises other means or program instructions, responsive to a report that the processor utilization is below a second predetermined lower threshold or the processor availability is above a second predetermined upper threshold, for determining if the server can accommodate a de allocation of processing power, and if so, generating a request to de allocate some of the currently allocated processing power from the server. The system and program product also automatically adjust allocation of memory in the server.
Owner:IBM CORP
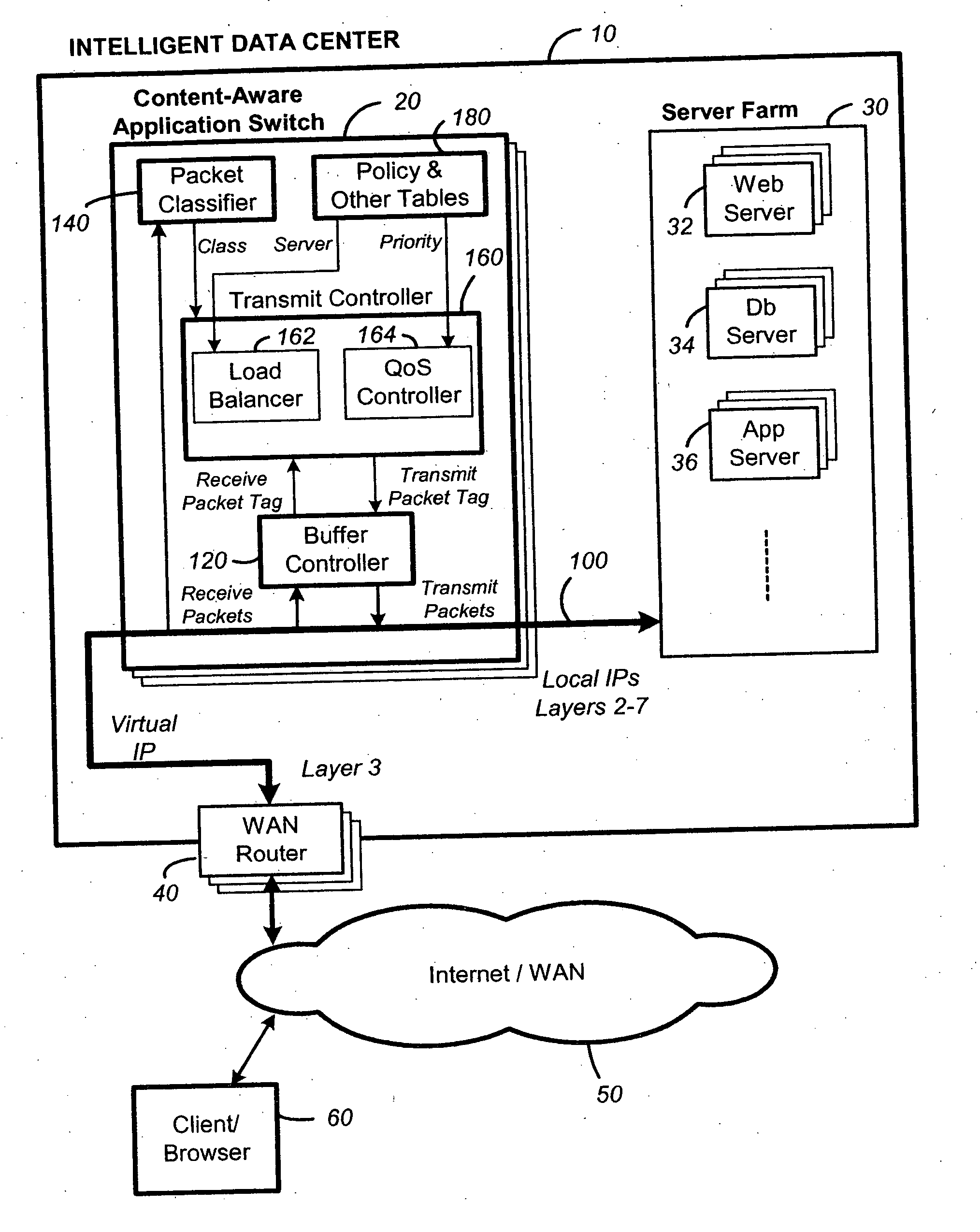
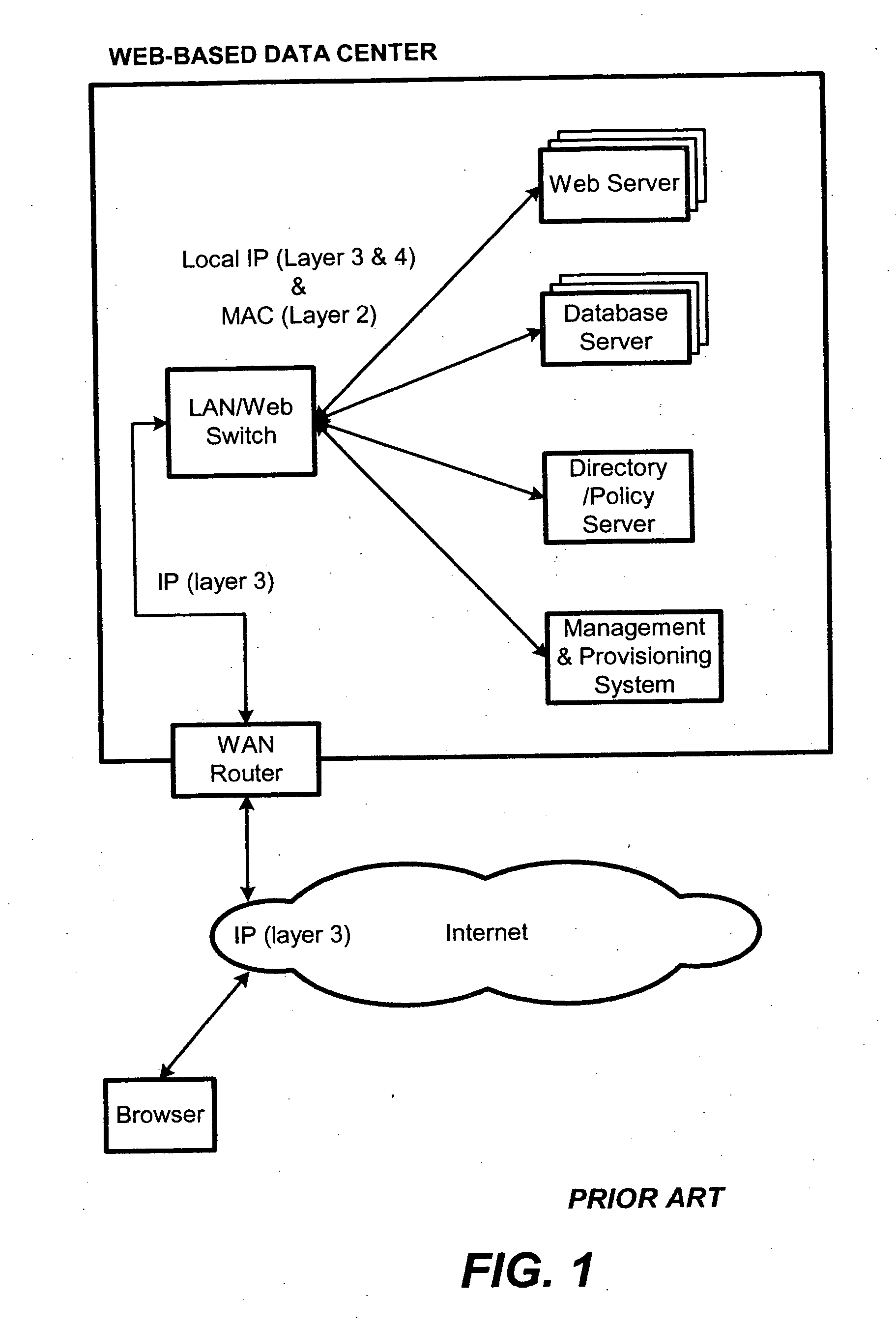
Packet switch and method thereof dependent on application content
InactiveUS20060031374A1Easy to controlControl moreMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData packQuality of service
A content-aware application switch and methods thereof intelligently switch client packets to one server among a group of servers in a server farm. The switch uses Layer 7 or application content parsed from a packet to help select the server and to schedule the transmitting of the packet to the server. This enables refined load-balancing and Quality-of-Service control tailored to the application being switched. In another aspect of the invention, a slow-start server selection method assigned an initially boosted server load metric to a server newly added to the group of servers under load balancing. This alleviates the problem of the new server being swamped initially due to a very low load metric compared to that of others. In yet another aspect of the invention, a switching method dependent on Layer 7 content avoids delayed binding in a new TCP session. Layer 7 content is not available during the initial handshaking phase of a new TCP session. The method uses the Layer 7 content from a previous session as an estimate to help select the server and uses a default priority to scheduling the transmitting of the handshaking packets. Updated Layer 7 content available after the handshaking phase is then used to reset the priority for the transmit schedule and becomes available for use in load balancing of the next TCP session.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for dynamic server allocation and provisioning
InactiveUS20070250608A1Lower cost of capitalQuality improvementResource allocationDigital computer detailsLoad SheddingManagement tool
A management tool that streamlines the server allocation and provisioning processes within a data center is provided. The system, method, and computer program product divide the server provisioning and allocation into two separate tasks. Provisioning a server is accomplished by generating a fully configured, bootable system image, complete with network address assignments, virtual LAN (VLAN) configuration, load balancing configuration, and the like. System images are stored in a storage repository and are accessible to more than one server. Allocation is accomplished using a switching mechanism which matches each server with an appropriate system image based upon current configuration or requirements of the data center. Thus, real-time provisioning and allocation of servers in the form of automated responses to changing conditions within the data center is possible. The ability to instantly re-provision servers, safely and securely switch under-utilized server capacity to more productive tasks, and improve server utilization is also provided.
Owner:RACEMI
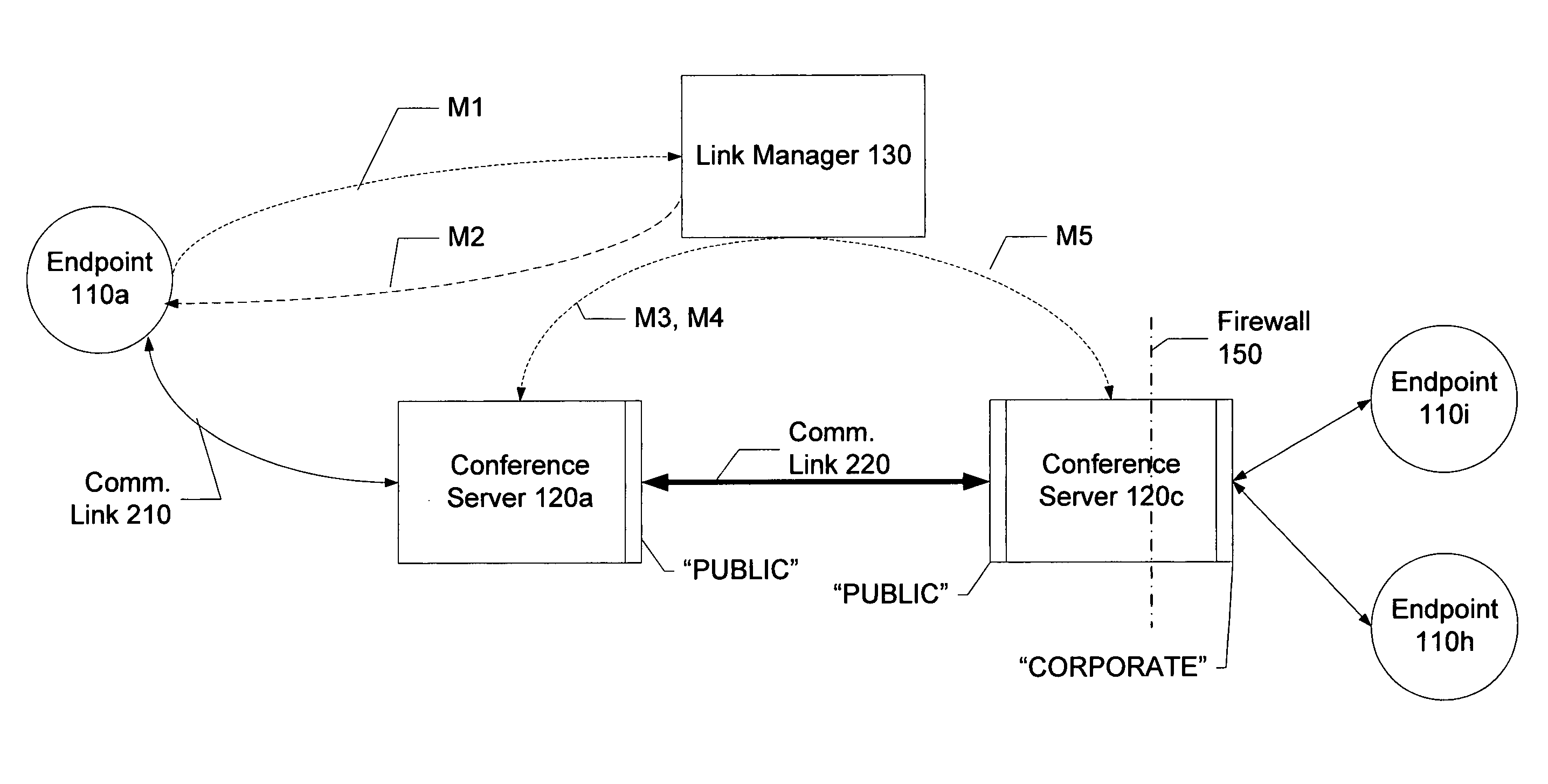
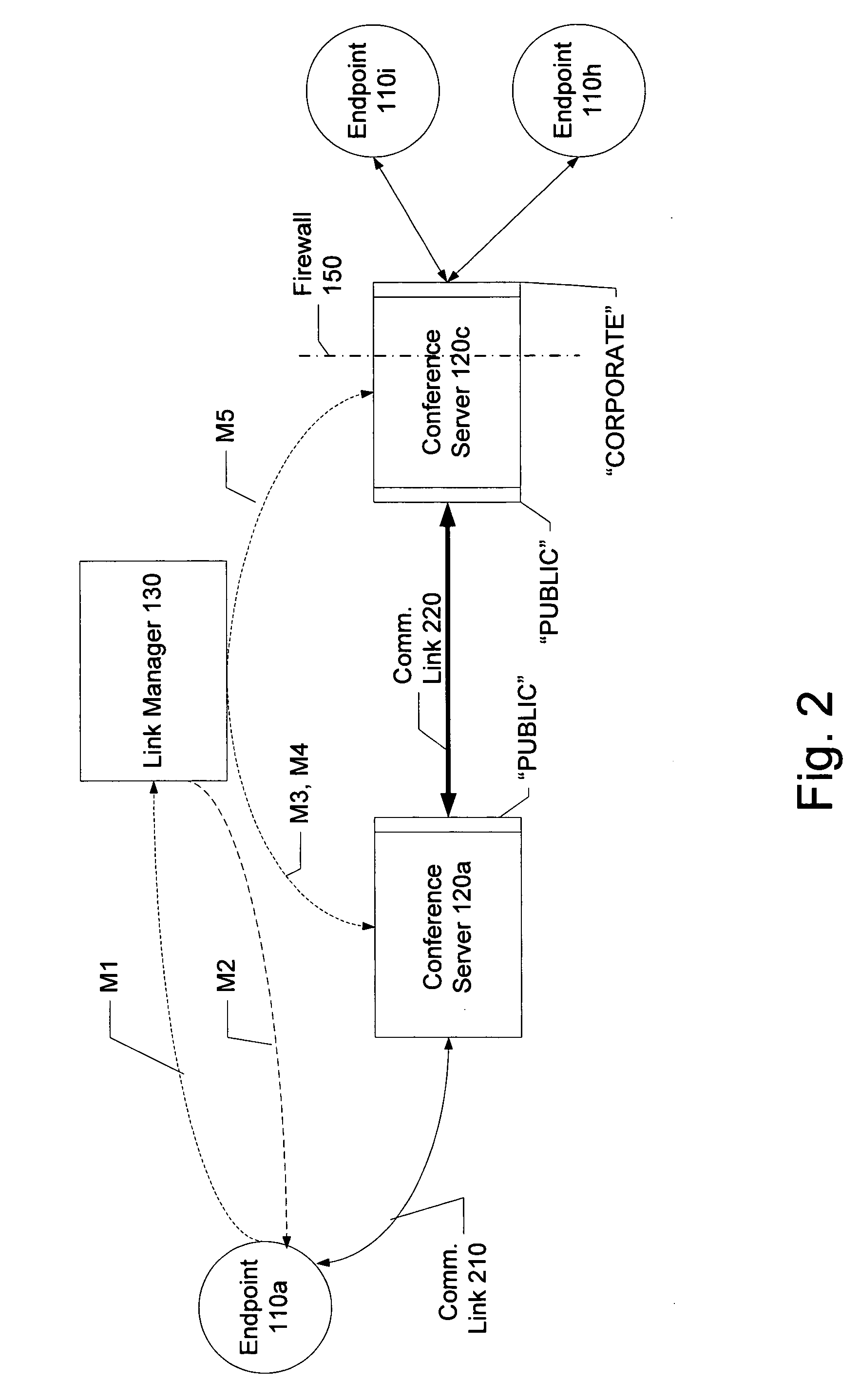
Distributed multipoint conferencing with automatic endpoint address detection and dynamic endpoint-server allocation
ActiveUS20050108328A1Save network bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationIp addressServer allocation
An embodiment of the invention is a multipoint conferencing system having the ability to dynamically assign an endpoint to a “closest” one of multiple conference servers is disclosed. In one embodiment, when an endpoint first connects to the conferencing system, its Endpoint ID (e.g., IP address, E164 address) is determined. Based on the Endpoint ID, the conferencing system selects the most appropriate ones of the conference servers to act as the endpoint's “local” conference server. That is, the endpoint will transmit and receive conference data from other endpoints via the selected conference server. If no other endpoints across the network happen to be viewing a particular endpoint's video stream, the stream is not provided to the network, thus conserving network bandwidth. An embodiment further creates appropriate linking between conference servers automatically, manages conference server topology and determines link type (e.g., Unicast vs. Multicast linking) automatically.
Owner:AVAYA INC +2
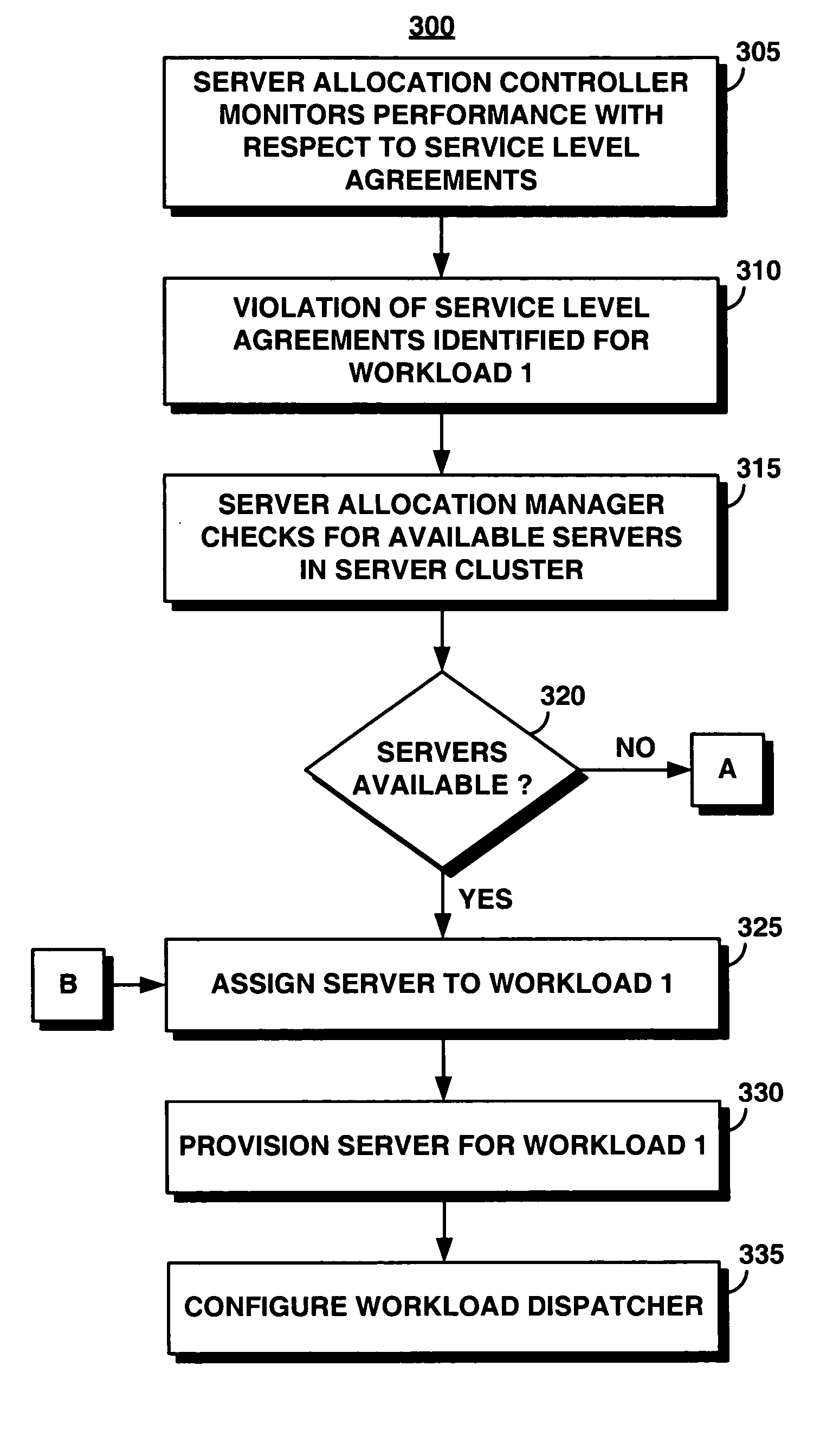
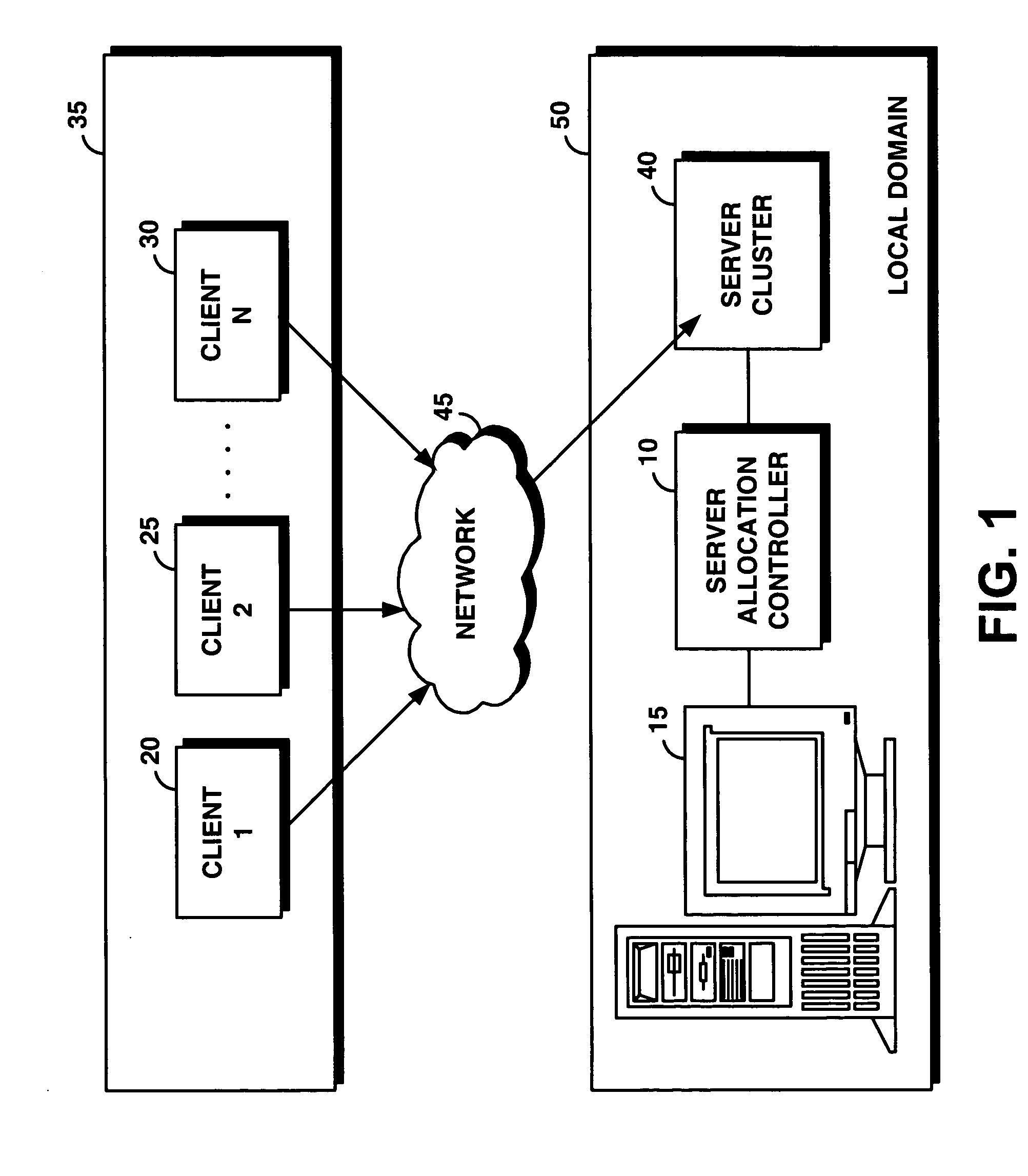
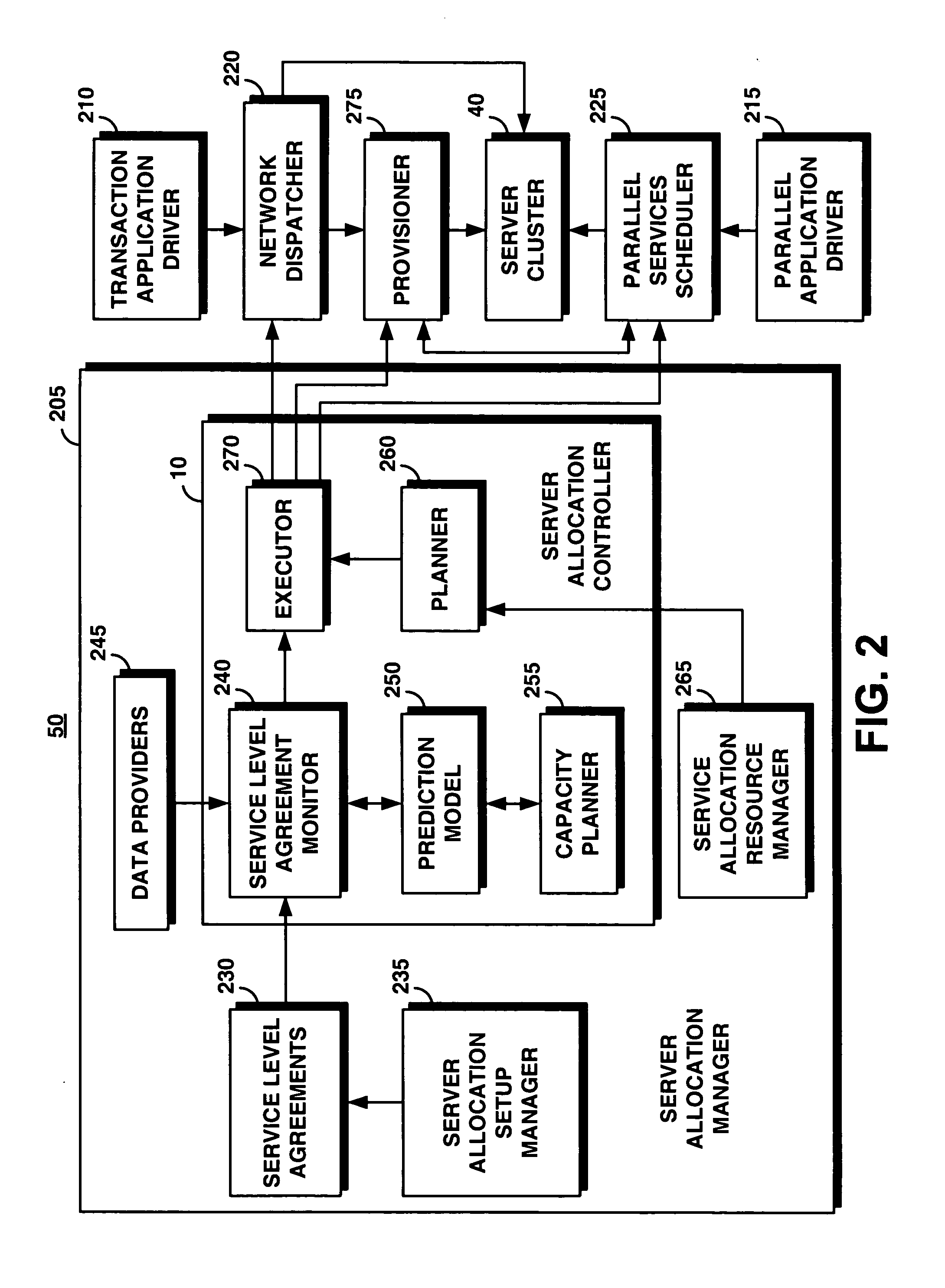
System and method for supporting transaction and parallel services in a clustered system based on a service level agreement
InactiveUS20050188075A1Facilitates dynamic allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionService-level agreementData processing system
A server allocation controller provides an improved distributed data processing system for facilitating dynamic allocation of computing resources. The server allocation controller supports transaction and parallel services across multiple data centers enabling dynamic allocation of computing resources based on the current workload and service level agreements. The server allocation controller provides a method for dynamic re-partitioning of the workload to handle workload surges. Computing resources are dynamically assigned among transaction and parallel application classes, based on the current and predicted workload. Based on a service level agreement, the server allocation controller monitors and predicts the load on the system. If the current or predicted load cannot be handled with the current system configuration the server allocation controller determines additional resources needed to handle the current or predicted workload. The server cluster is reconfigured to meet the service level agreement.
Owner:IBM CORP
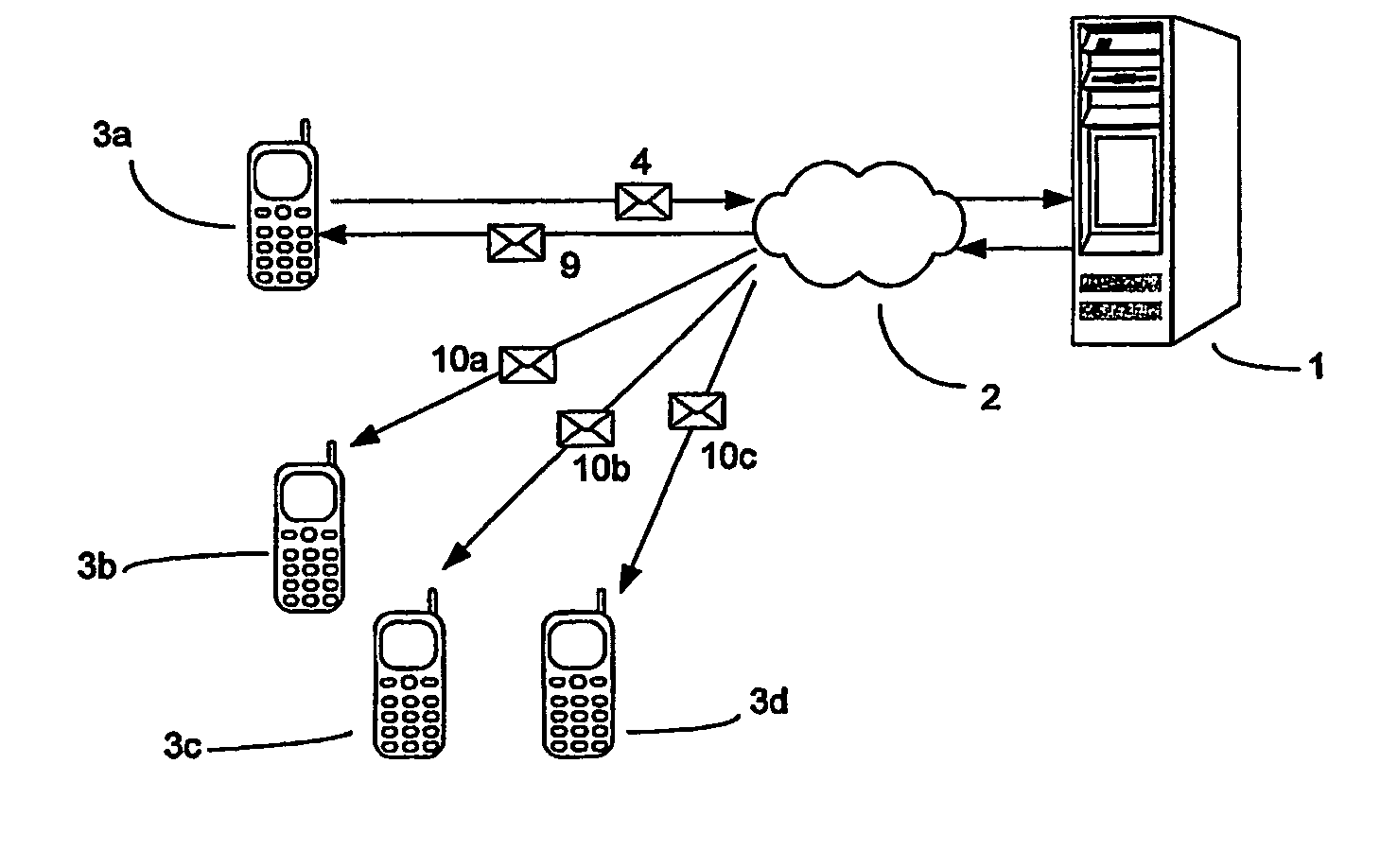
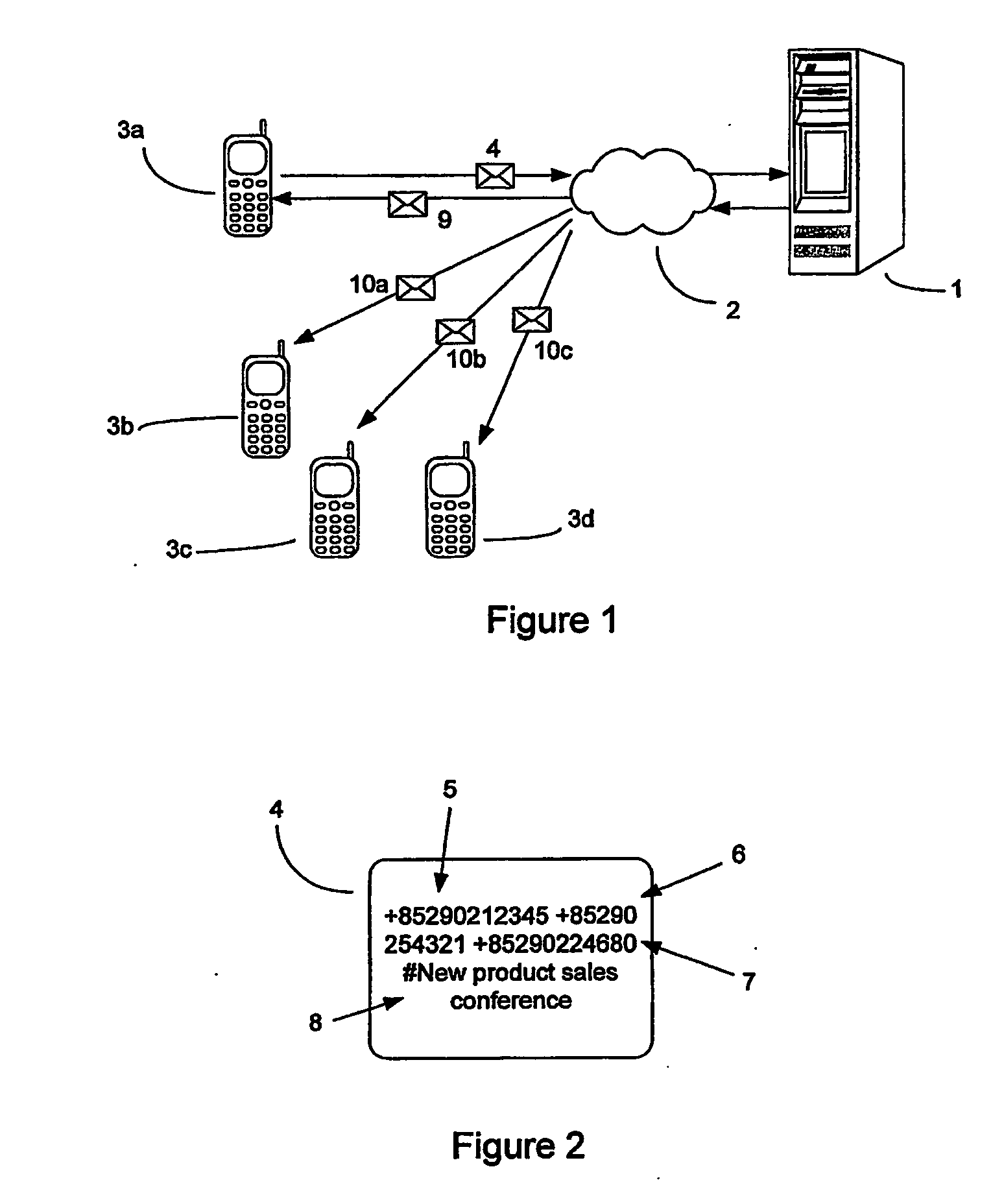
Conference call facility
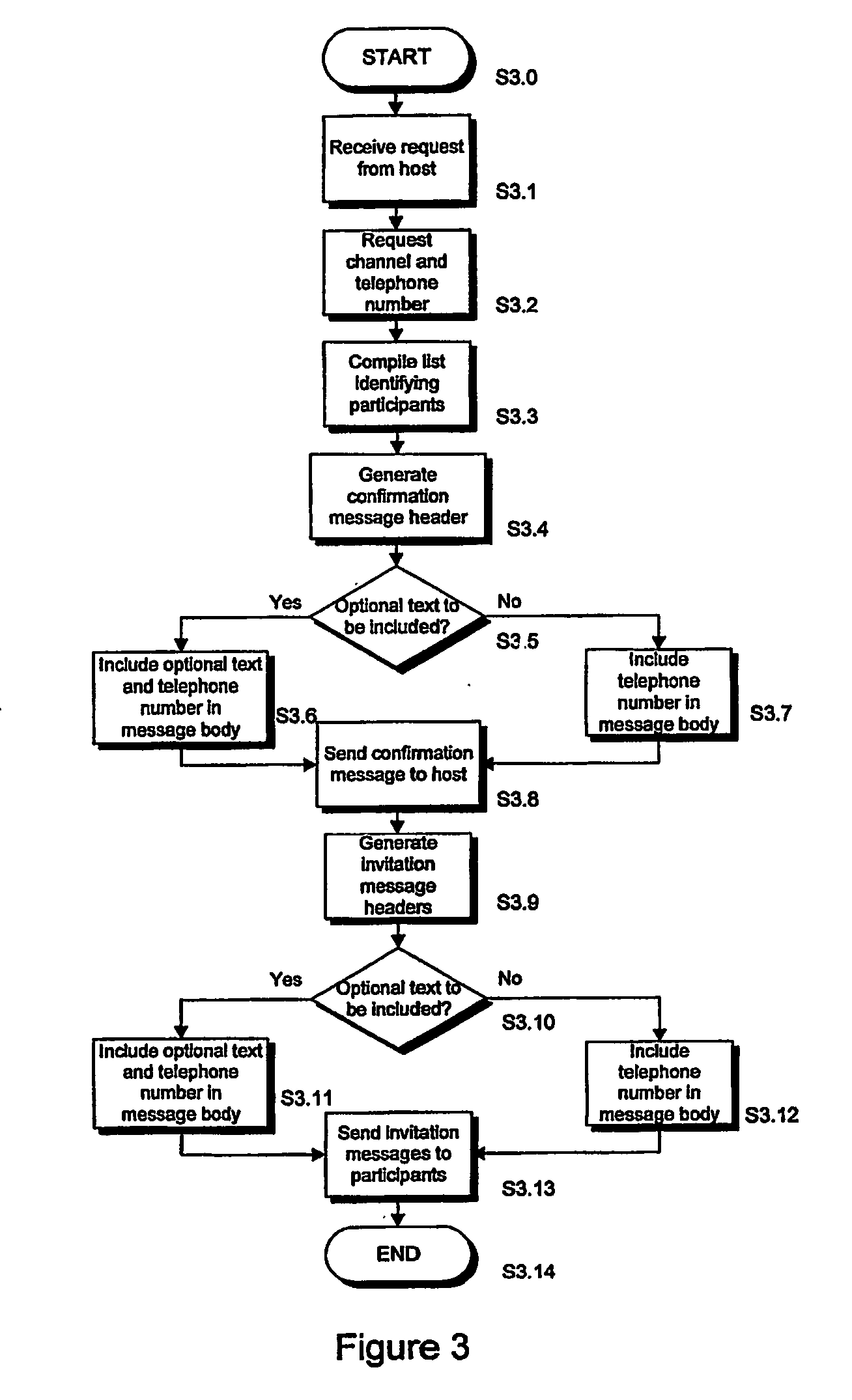
InactiveUS20060250987A1Cost and convenience benefitEasy accessSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsServer allocationTeleconference
A conference call is established in response to receiving a request 4 from a first communication terminal 3a. The request 4 preferably is an SMS or MMS and comprises one or more identifiers 5, 6, 7, e.g. telephone numbers, relating to a plurality of other communication terminals 3b-3d. A conference call server I allocates a conference call channel and an associated identifier, such as a telephone number. Messages 10a-10c alerting the conference participants are then sent to the other communication terminals 3a-3c, each message including the identifier associated with the conference call channel. Access to the conference call may be restricted to authorised users by compating identifiers, such as CLIs, of incoming callers to the identifiers provided in the request 4 and allowing access only if there is a correspondence or match. In the event that an incoming caller has withheld their CLI, or it is otherwise nondeterminable, access is refused and a message may be sent reminding conference participants who have yet to join the conference call not to withhold this information. Alternatively, the server calls the participants at the appropriate time.
Owner:WHITE CHRISTOPHER +1
System and method for creating pathfiles for use to predict patterns of web surfaces
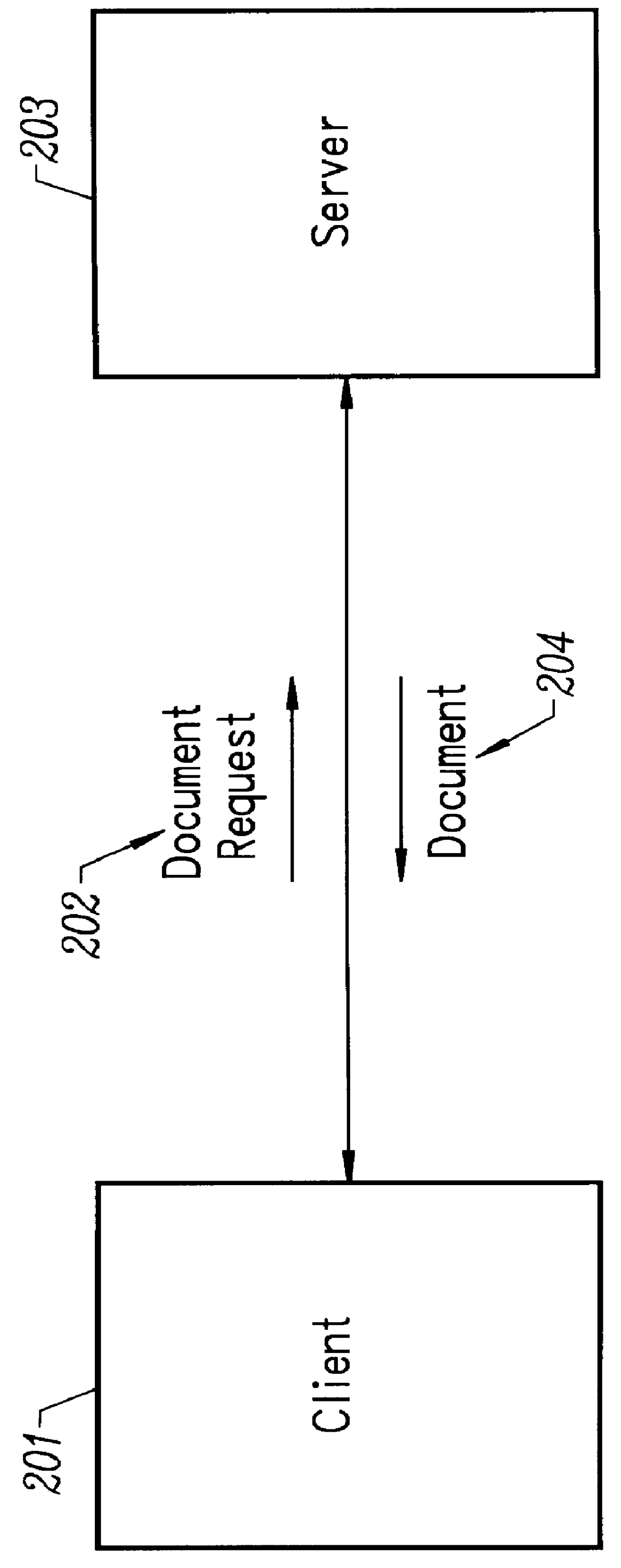
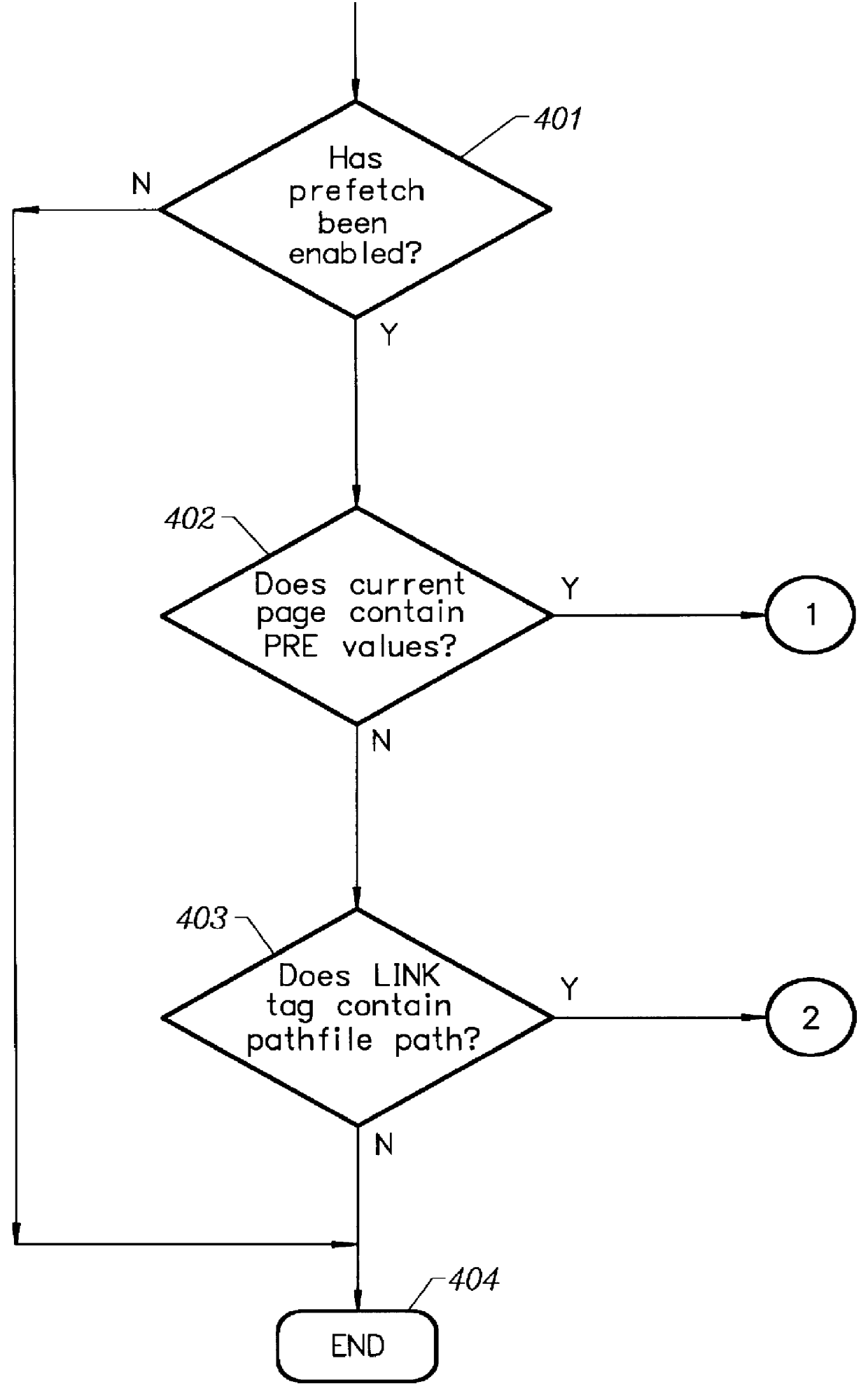
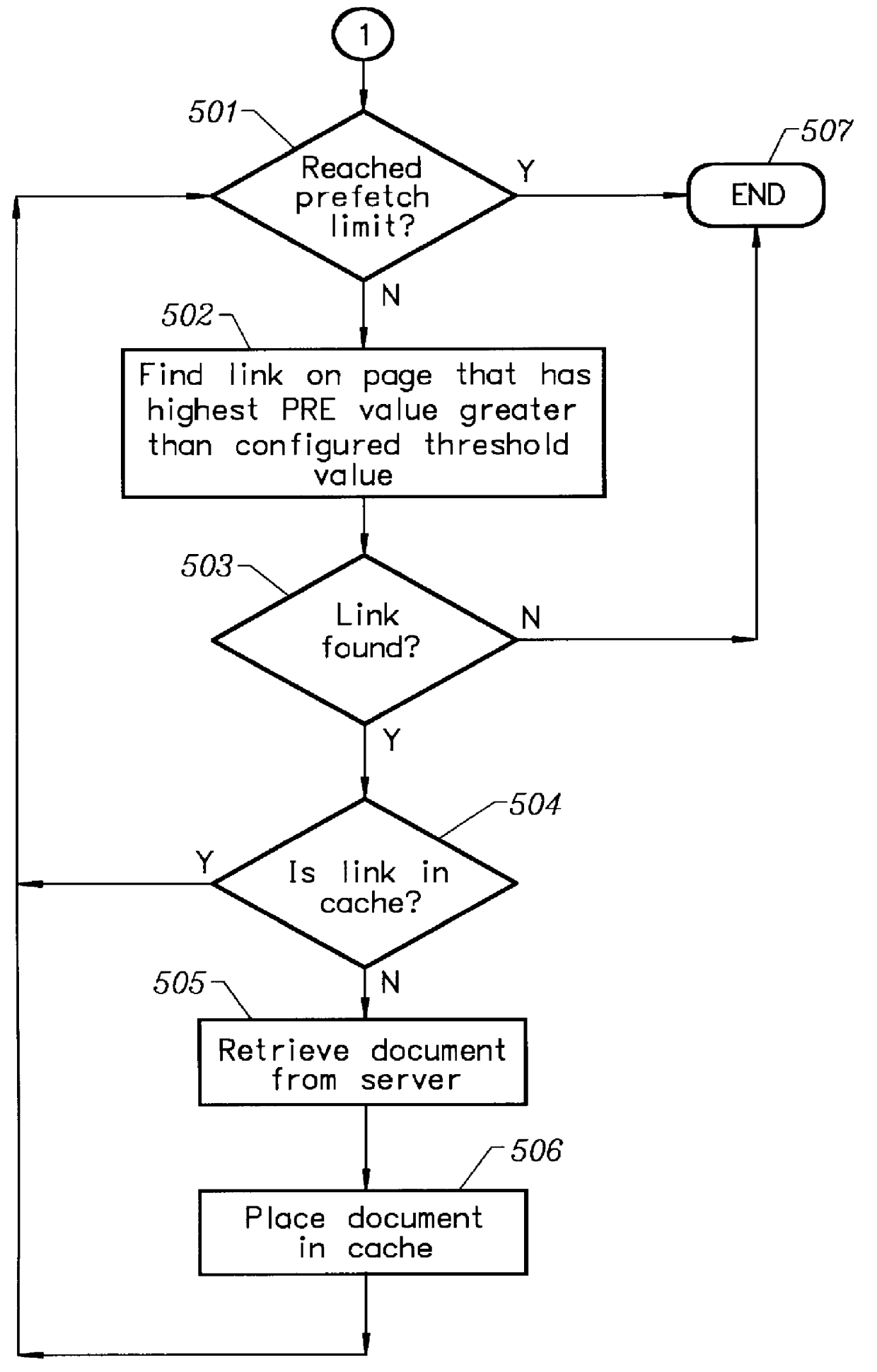
InactiveUS6055572AEfficiently uses its free bandwidthReduce demandDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsControl systemServer allocation
A prefetching and control system for a computer network environment. The user configures the client's prefetch parameters which are: enabling / disabling prefetching, prefetch threshold value, and the maximum number of documents to prefetch. A prefetch value or weight is contained in the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) page or prefetch file, called a pathfile, for each link. The HTML page contains the prefetch values for each of its links, while pathfile contains the weights for every link on the HTML page associated with the Universal Resource Locator (URL). The client compares the prefetch or weight values of each link with its threshold value to decide if the link should be prefetched and placed in the local cache as long as the maximum number of documents to prefetch is not exceeded. Pathfiles reside on the server and are created by the server or web administrator / author. The server automatically creates the pathfiles from its log files which are filtered to retain all of the valid document requests and average paths are derived from the filtered results. Weights are assigned to each path in the URL by the server and inserted into the pathfile along with the associated paths. If no log files exist on the server, then the web administrator / author may manually enter in the weights for each path.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
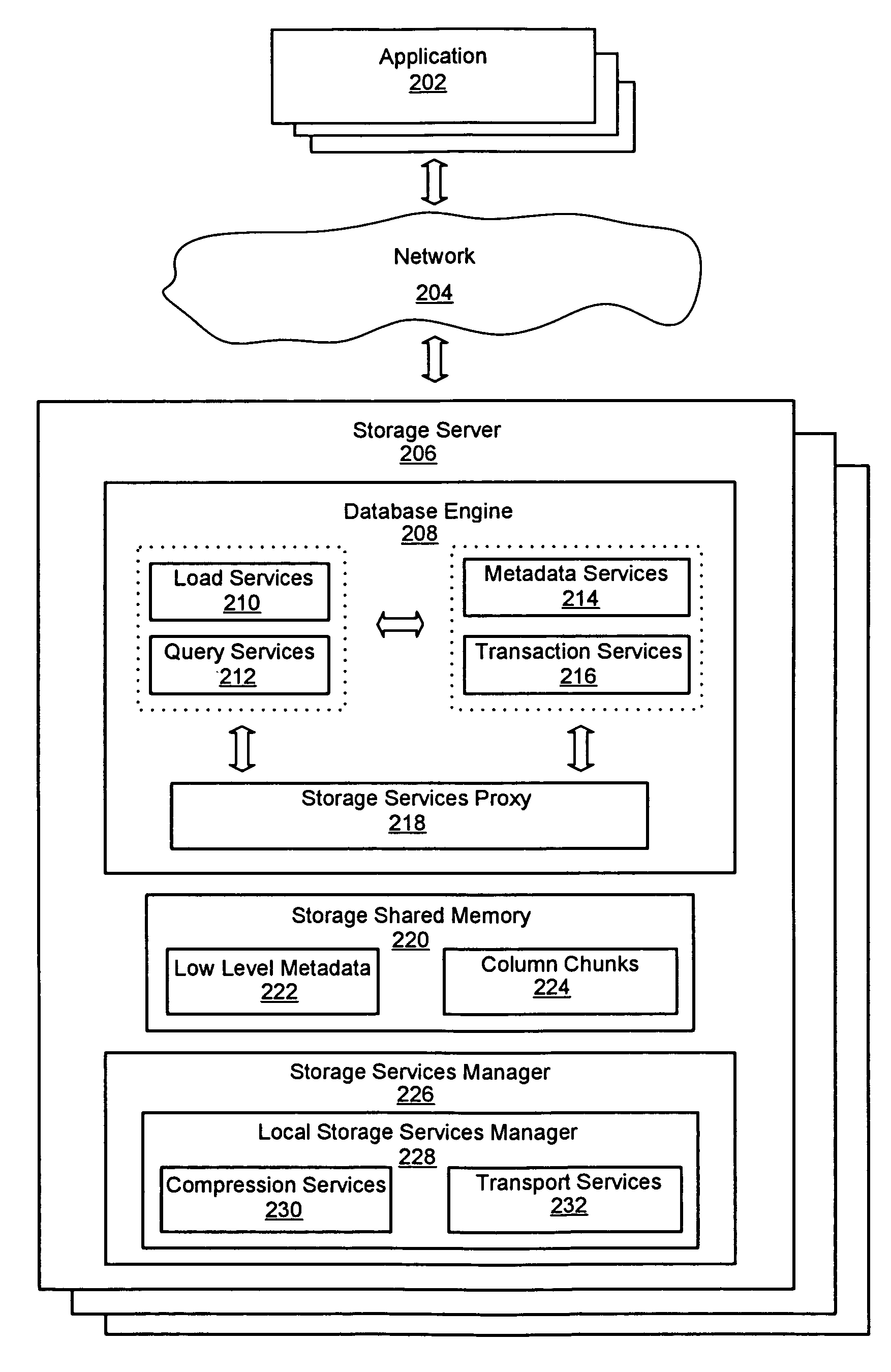
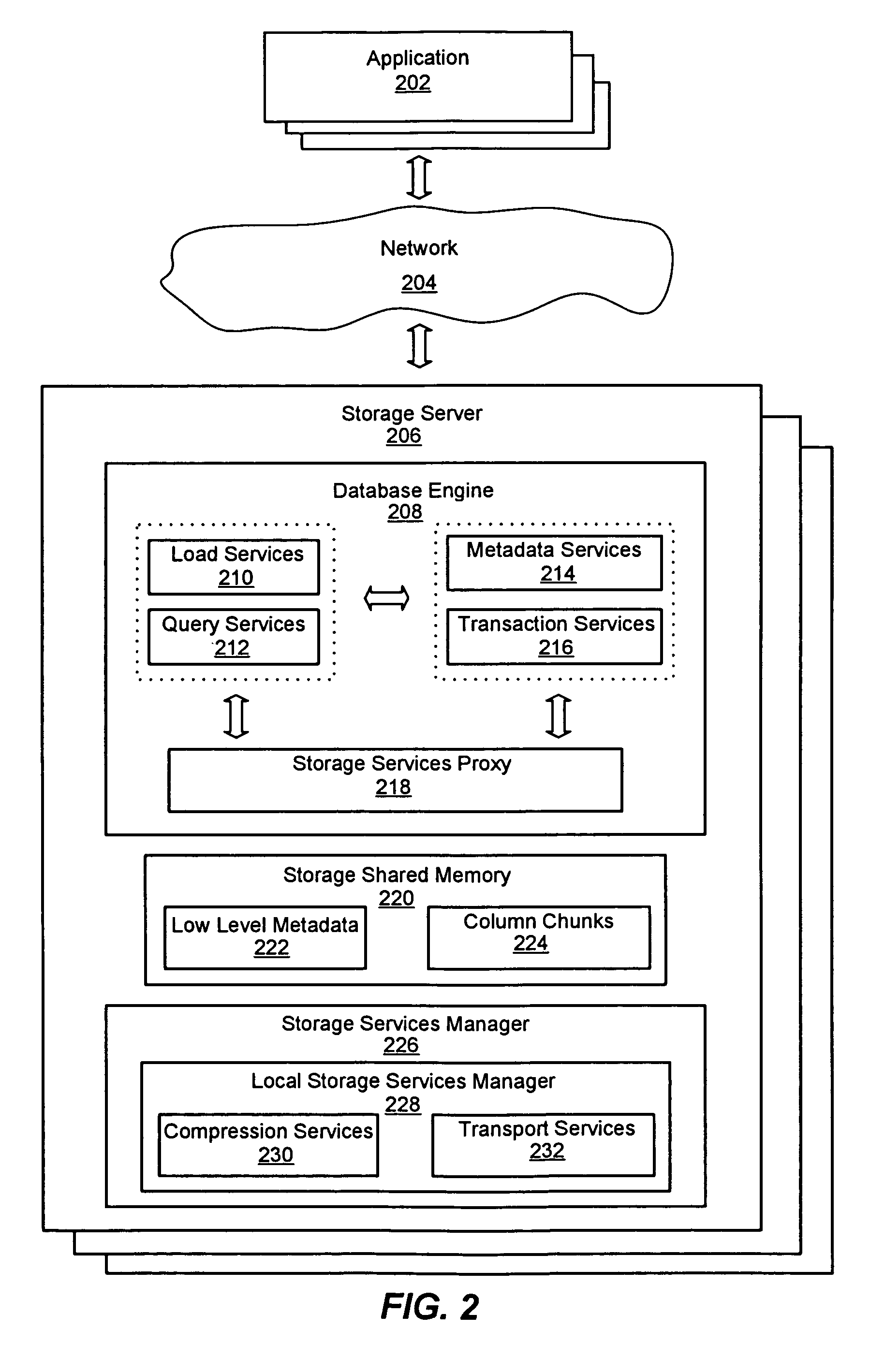
System for a distributed column chunk data store
ActiveUS7447839B2Storage requirements is greatly reducedReduce transfer timeError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationServer allocationDatabase engine
An improved system and method for a distributed column chunk data store is provided. A distributed column chunk data store may be provided by multiple storage servers operably coupled to a network. A storage server may include a database engine for partitioning a data table into the column chunks for distributing across multiple storage servers, a storage shared memory for storing the column chunks during processing of semantic operations performed on the column chunks, and a storage services manager for striping column chunks of a partitioned data table across multiple storage servers. Any data table may be flexibly partitioned into column chunks using one or more columns as a key with various partitioning methods. There may also be a storage policy for specifying how to partition a data table for distributing column chunks across multiple servers and for specifying a level of redundancy for recovery from failure of storage servers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
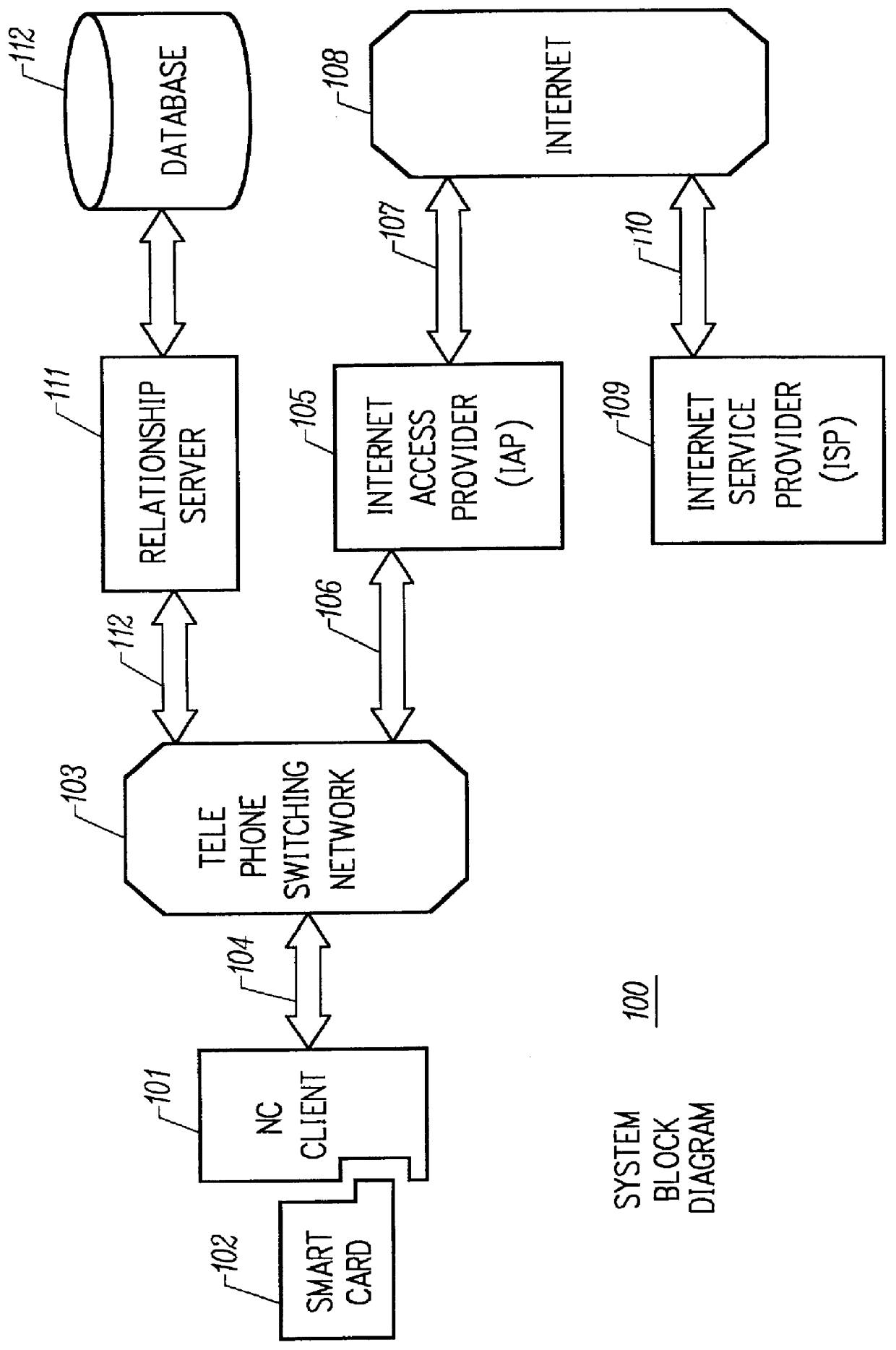
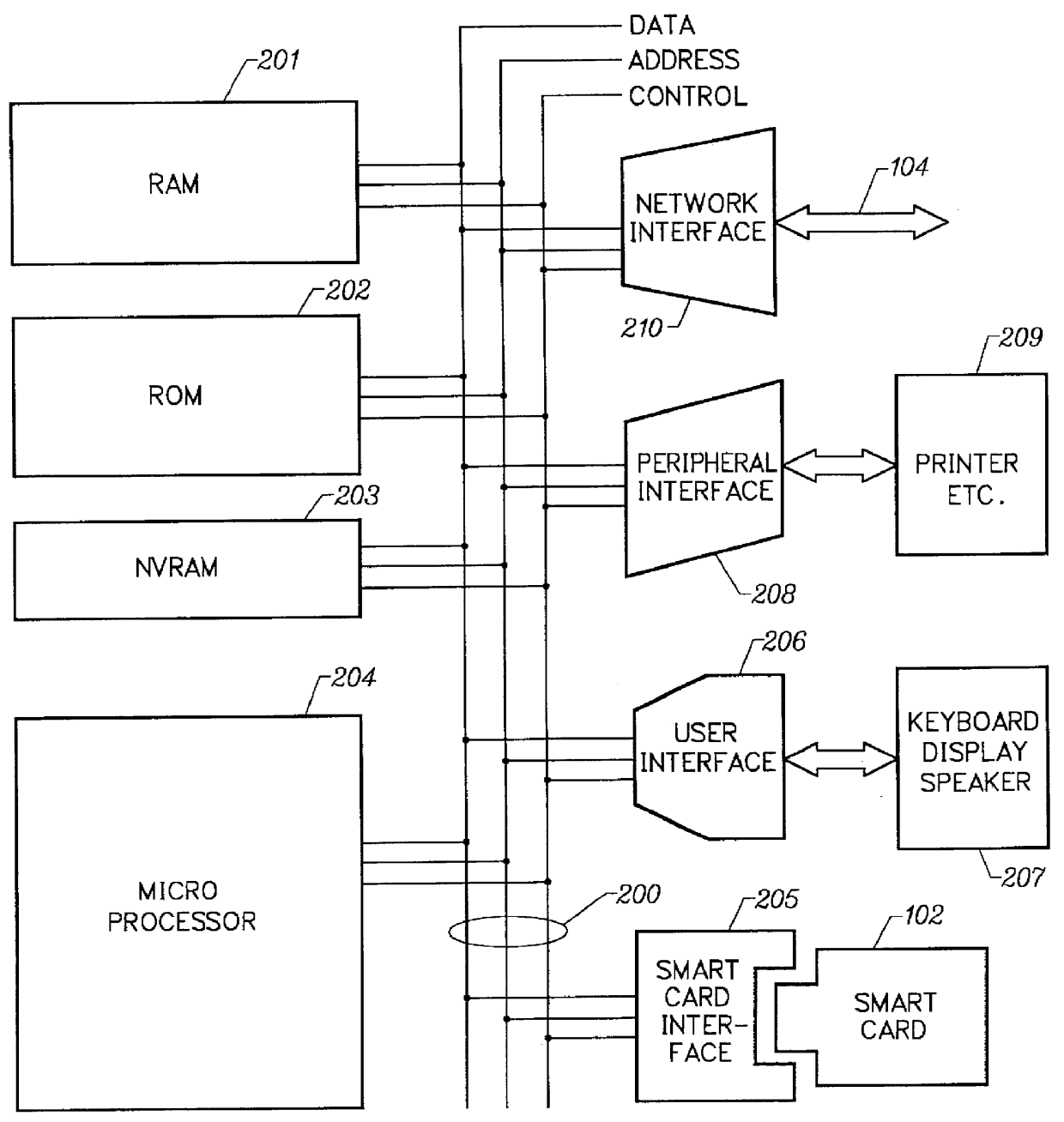
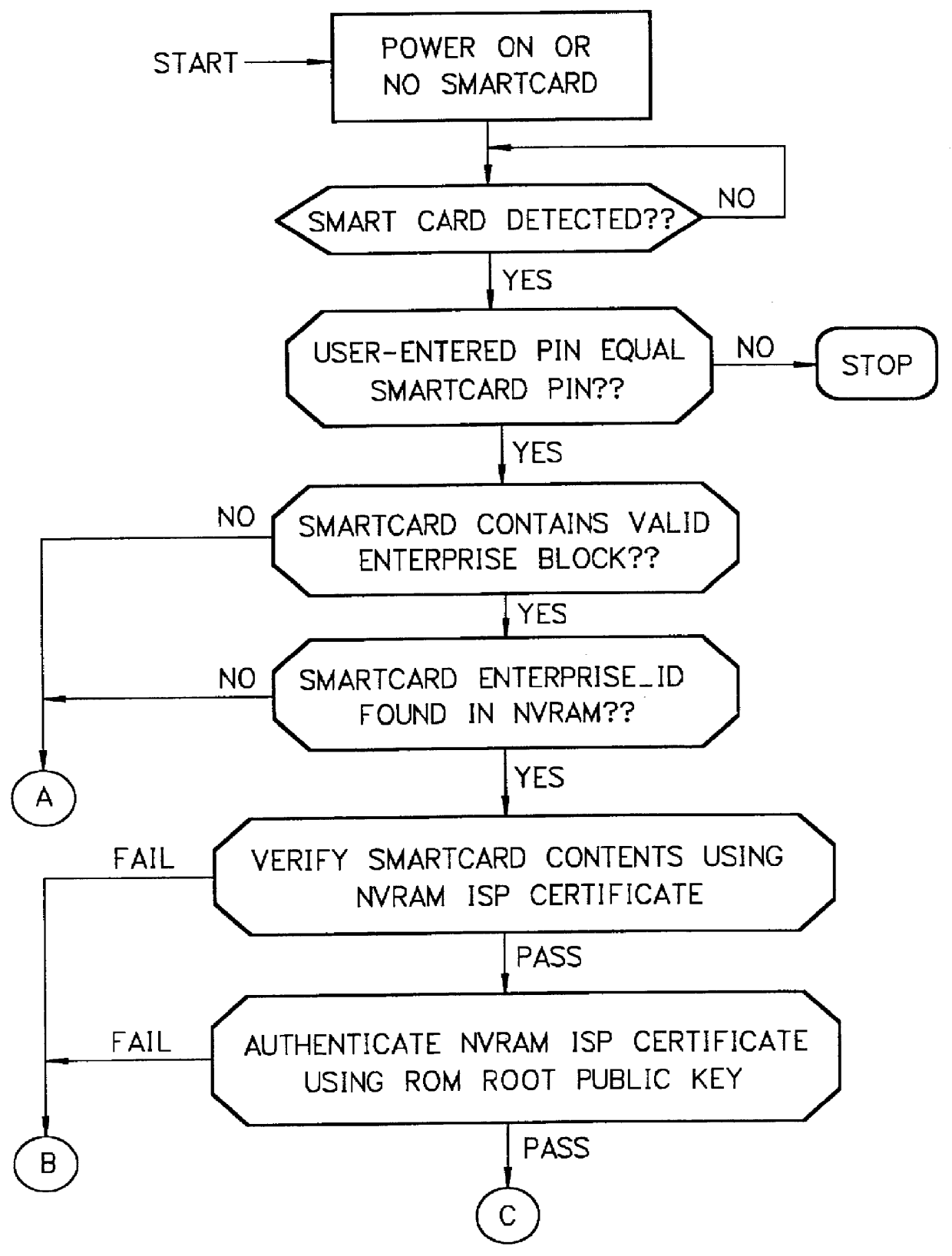
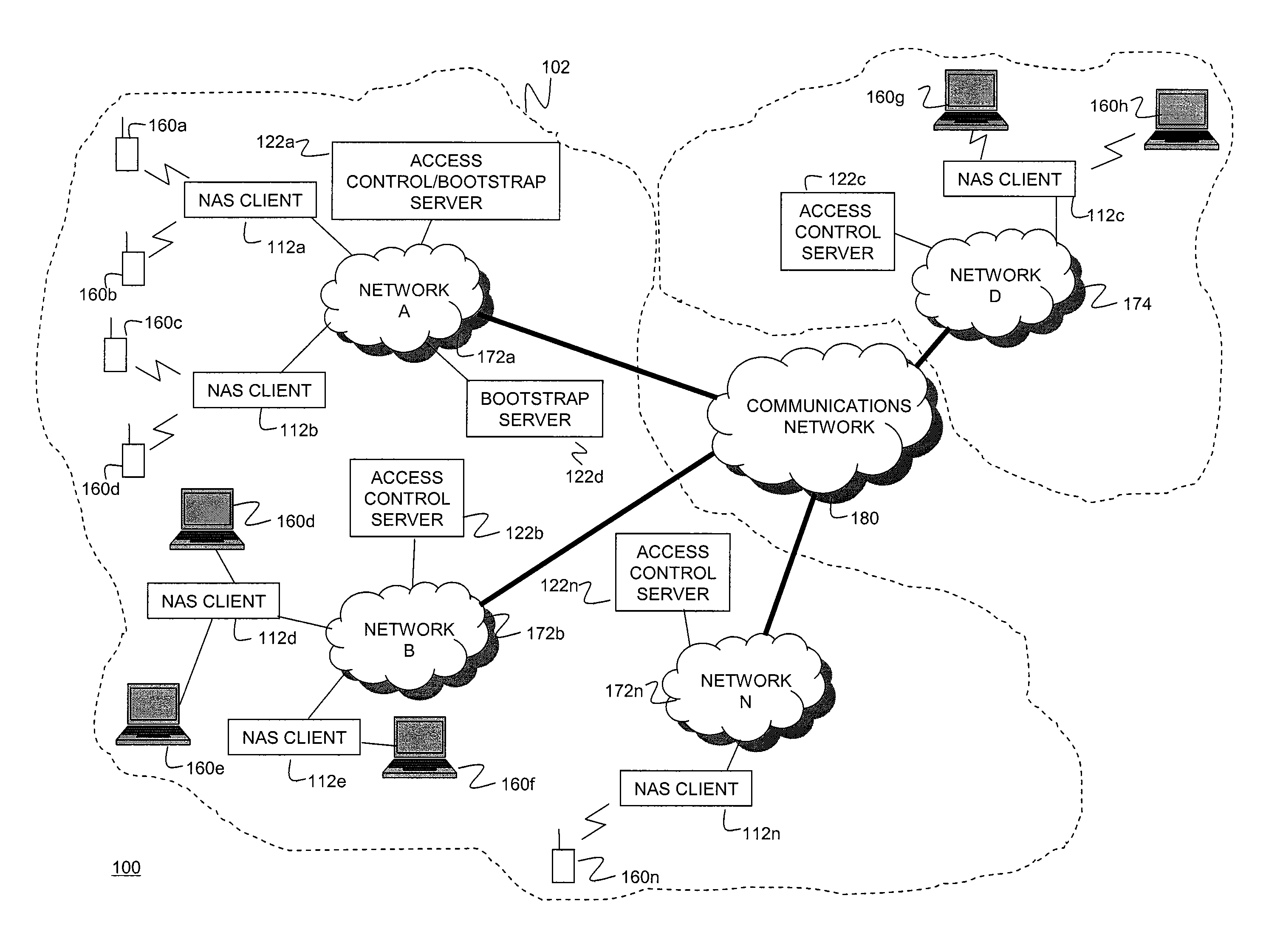
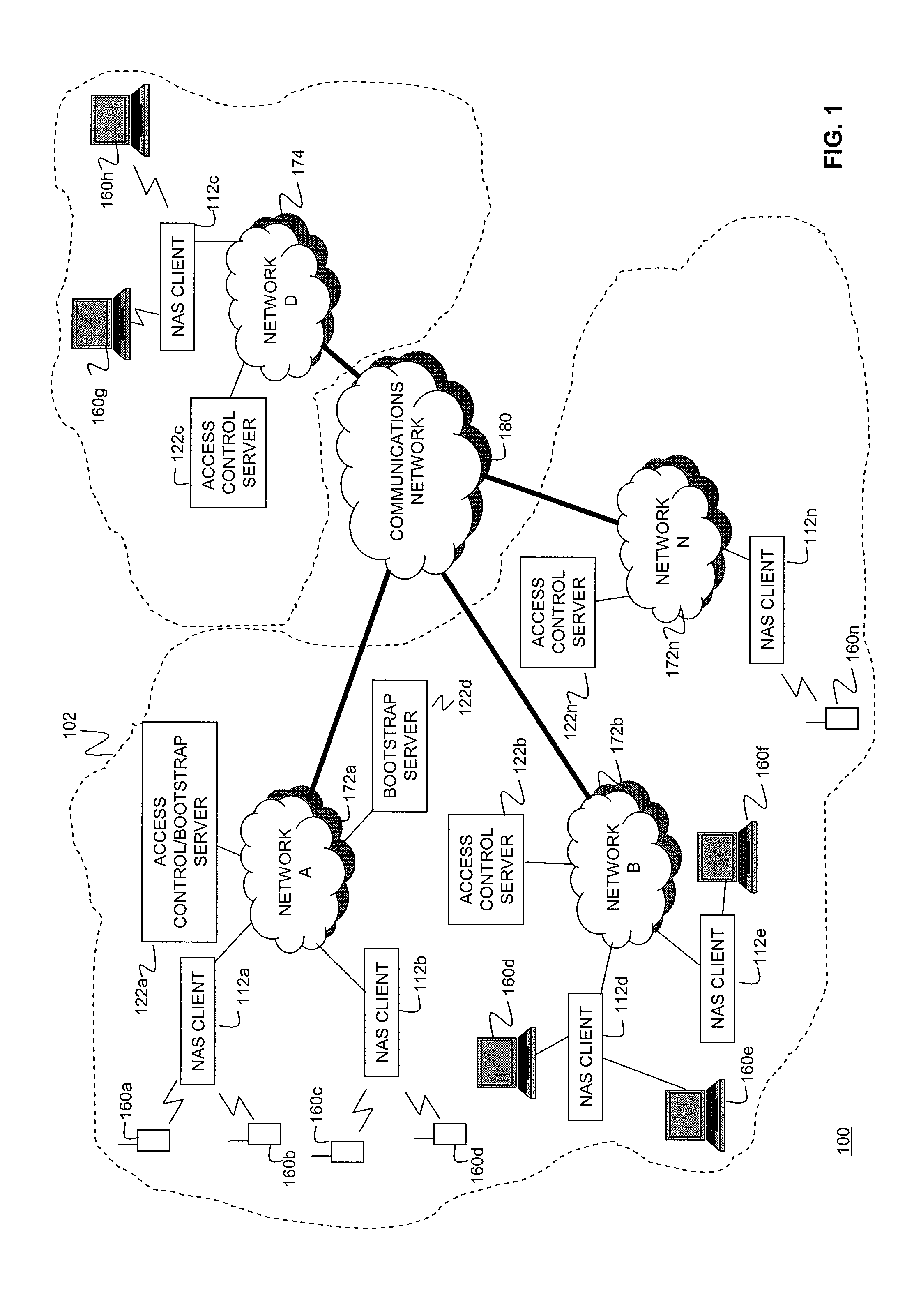
Mechanism for users with internet service provider smart cards to roam among geographically disparate authorized network computer client devices without mediation of a central authority
InactiveUS6108789ADigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureServer allocation
User specific internet service provider (ISP) account information is stored on the user's smart card, but the ISP specific connection information is stored within a network computer client device (NC). When the NC is first powered on and used, it calls the relationship server to receive connection information corresponding to the ISP that is either specified on the first user's smart card or is otherwise chosen by the first user. This connection information is preferably stored in non-volatile memory within the NC, so that even if the NC is powered down, it maintains the ability to connect to the ISP designated by its previous user. Each ISP is designated by a unique enterprise identification number assigned by the relationship server. When a subsequent user inserts his smart card into an NC, the NC compares the enterprise identification number on the smart card to the enterprise identification number within the NC. If the enterprise identification numbers match, the NC connects to the IAP already stored in the NC without dialing the relationship server. Only if the enterprise identification numbers do not match must the NC then dial the relationship server to download connection information for the ISP designated by the smart card enterprise identification number. In the preferred embodiment, the ISP contents of the smart card are digitally signed by the ISP. If the enterprise identification numbers match, then the ISP contents of the smart card are cryptographically authenticated using the public key within the authorized usage certificate for the ISP. If the cryptographic authentication fails, then the NC reprograms the smart card.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM MANAGEMENT LLC
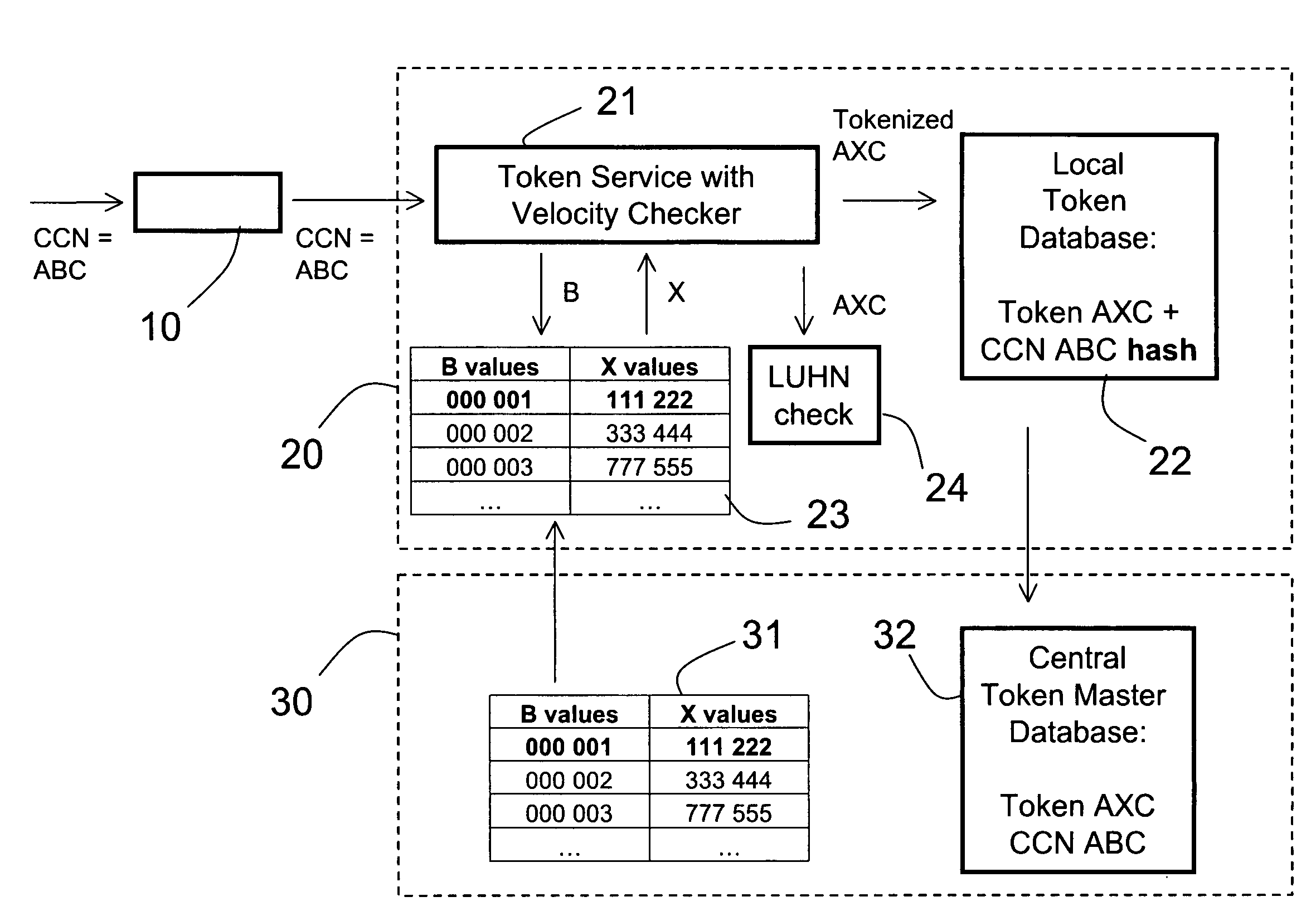
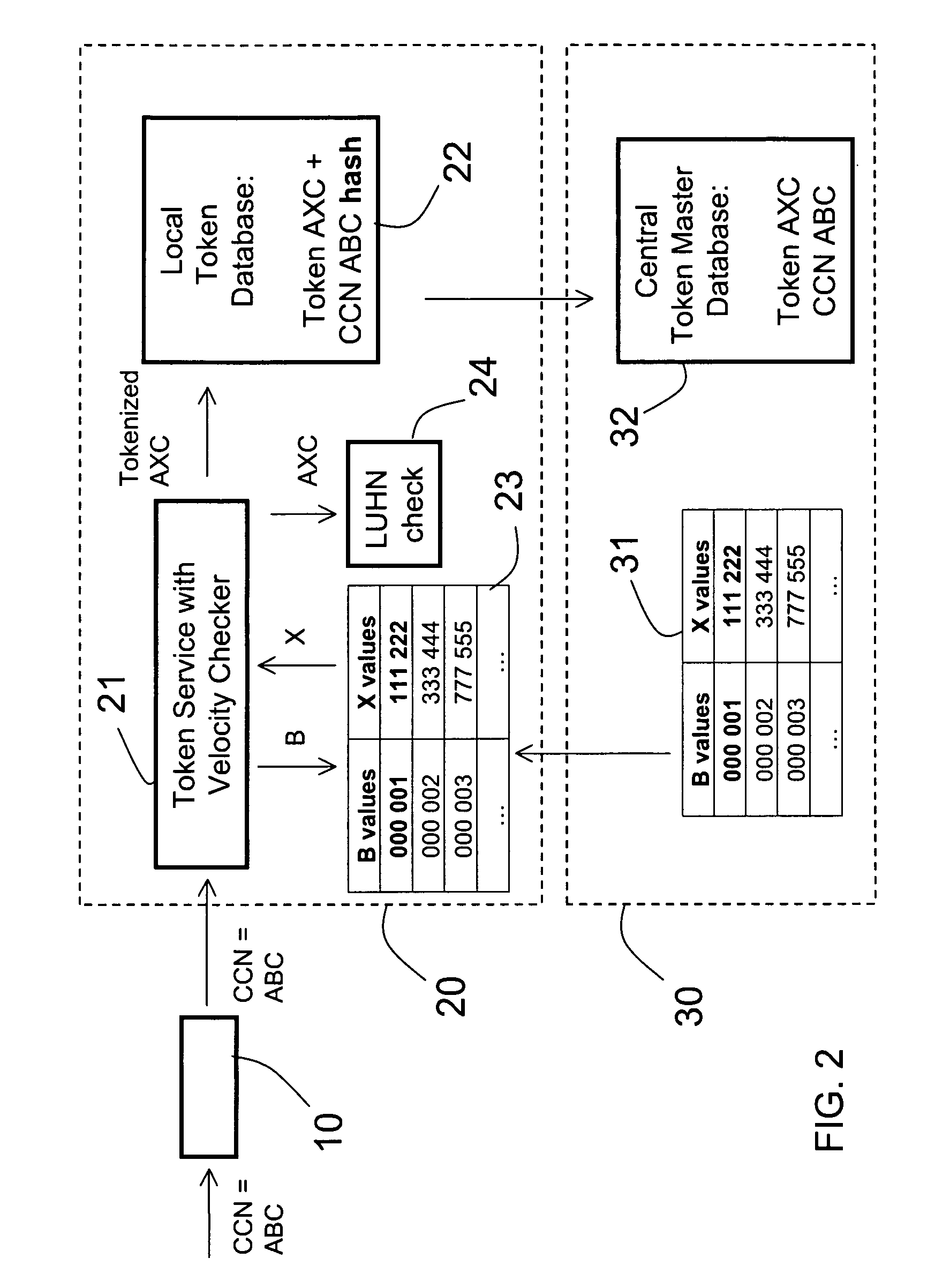
Method and apparatus for tokenization of sensitive sets of characters
ActiveUS20090249082A1Simple methodSafe handlingAcutation objectsUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer networkServer allocation
A method and system for secure handling of sensitive sets of characters in a distributed hierarchical system are disclosed, comprising at least one local server on a lower hierarchic level and at least one central server at a higher hierarchic level. The method comprises the steps: receiving a sensitive set of characters in said local server; replacing a part of said sensitive set of characters with a token to form a tokenized set of characters, said token belonging to a subset of possible tokens assigned to the local server by the central server; transferring at least one of said sensitive set of characters and said tokenized set of characters to the central server; and canceling said sensitive set of characters from said local server within a limited time from said transferring, while maintaining said tokenized set of characters in a local database connected to said local server.
Owner:PROTEGRITY CORP
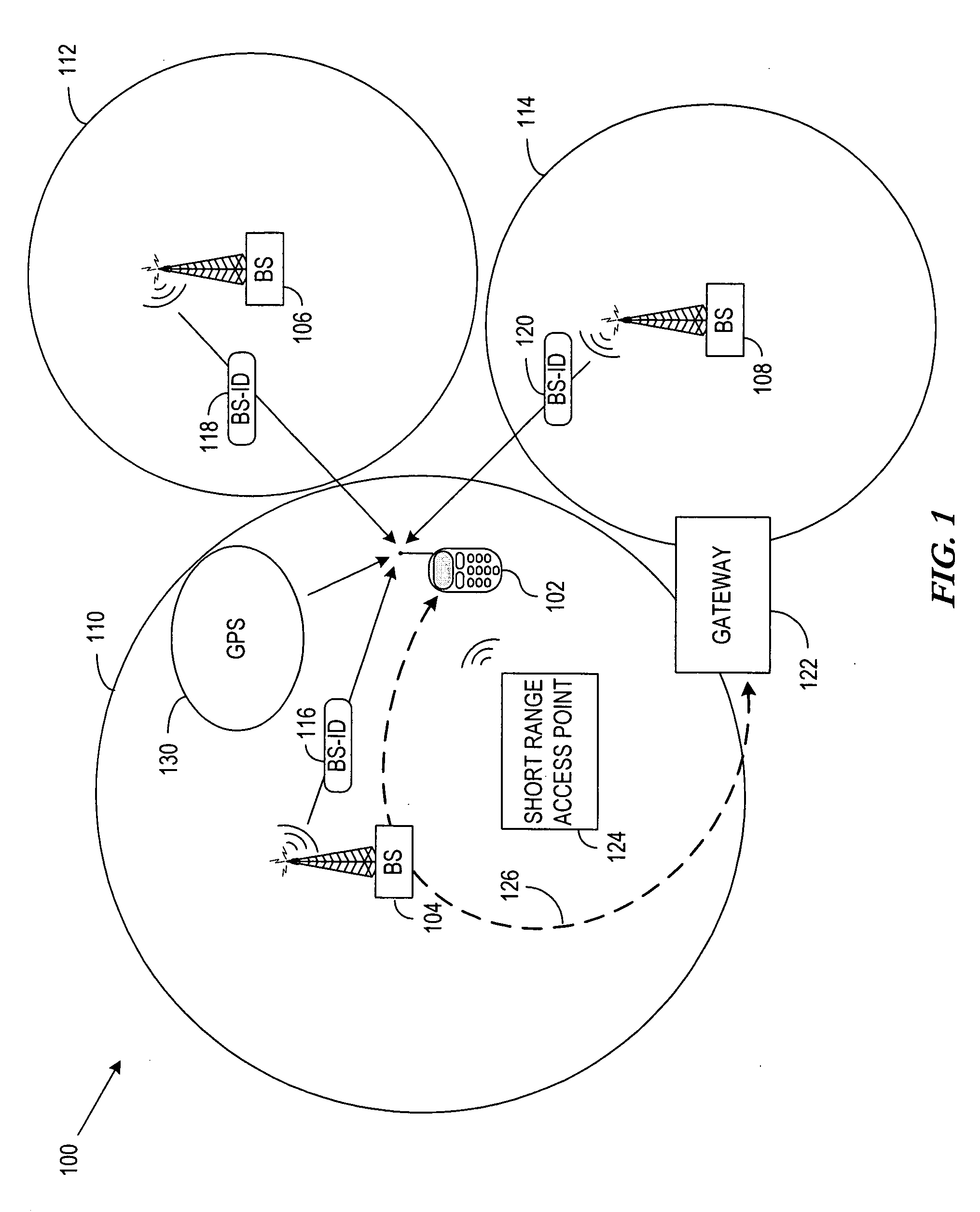
System and method for controlling idle mode location in a broadband wireless access communication system
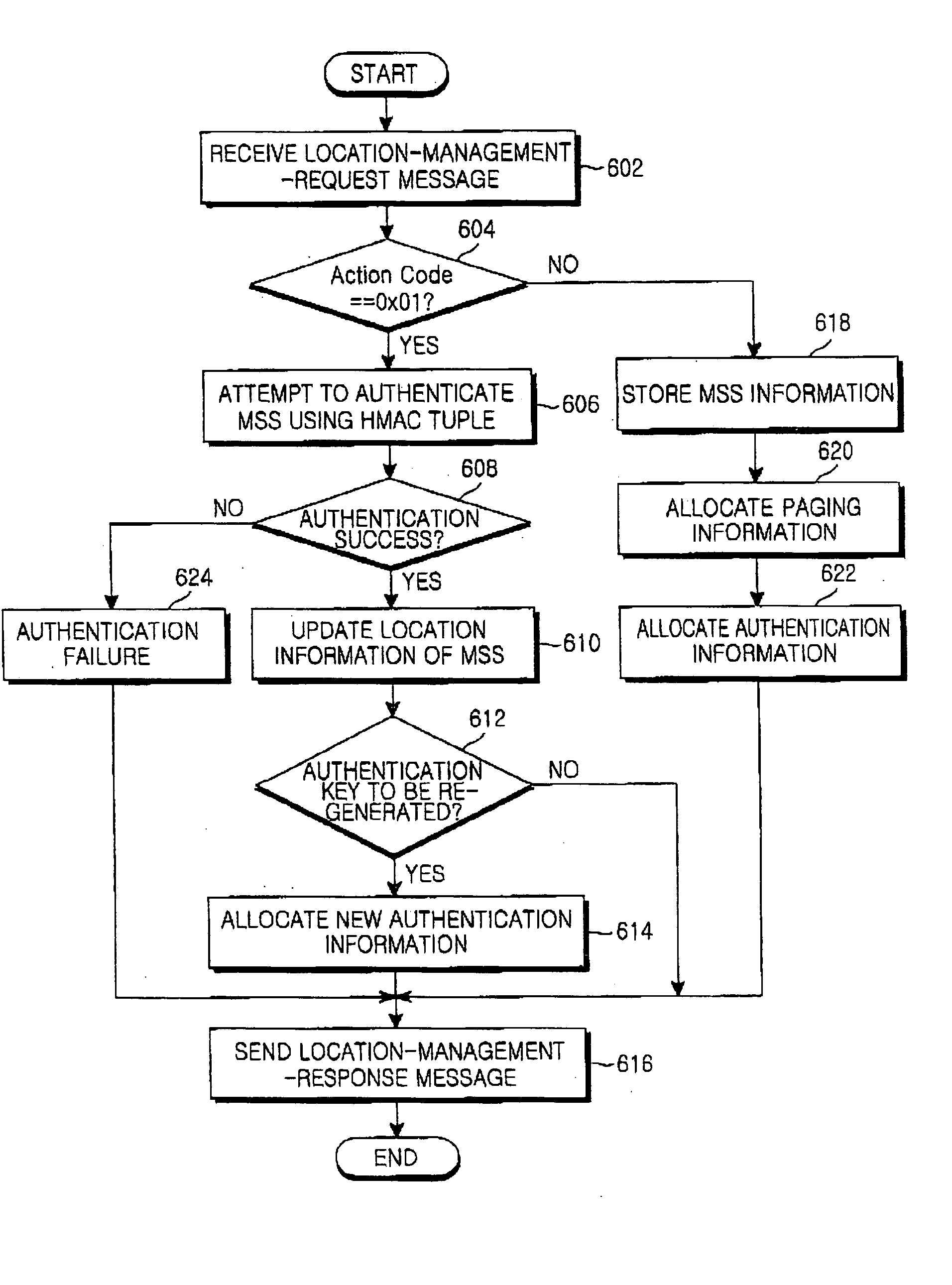
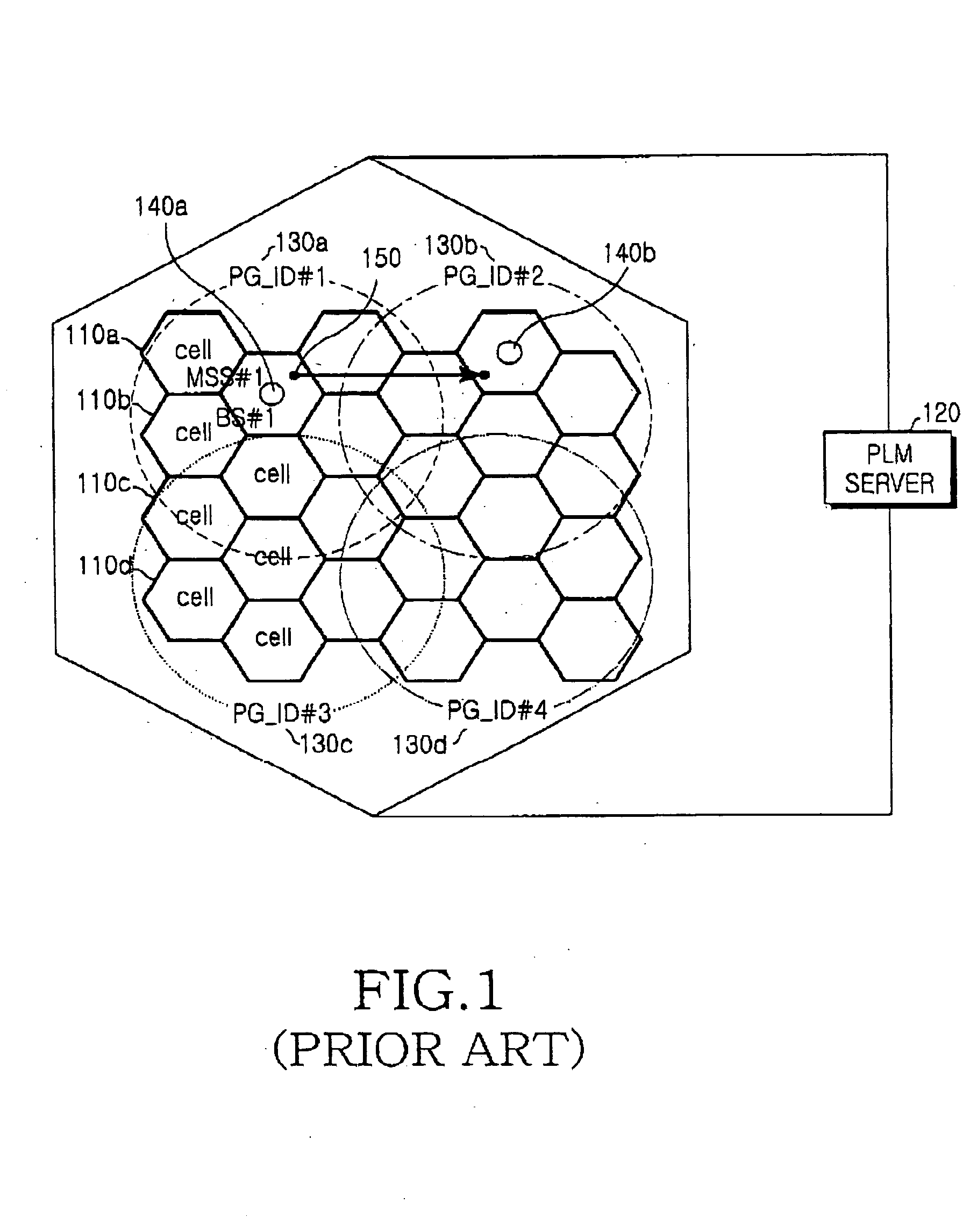
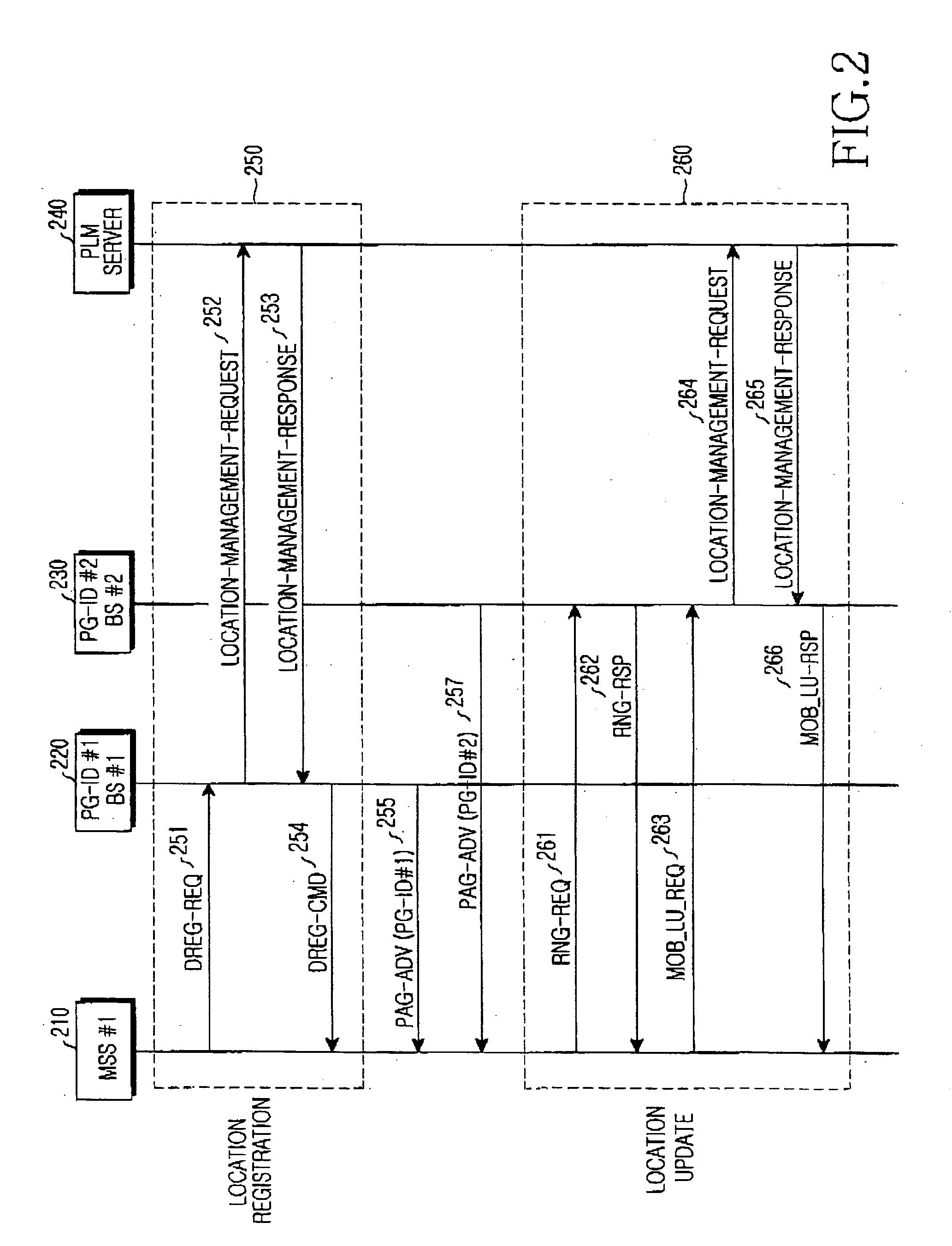
InactiveUS20050250474A1Effective controlMinimize power consumptionPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemServer allocation
A method is provided for performing an authentication procedure according to location registration and update for a mobile subscriber station (MSS) in a broadband wireless access (BWA) communication system. The system includes the MSS operating in idle mode to minimize power consumption, paging groups each being formed by a plurality of adjacent cells in which a plurality of MSSs are paged, base stations (BSs) for paging the plurality of MSSs within each paging group, and a server for controlling location registration and authentication for the plurality of MSSs. The server determines whether to approve a request for transition to the idle mode received from the MSS through a BS. If the server approves the request for the transition to the idle mode, it allocates authentication information to the MSS through the BS and registers location of the MSS. When it is determined that the MSS has moved to a different paging group, the MSS sends a location update request including a resulting value computed using the authentication information allocated from the server. The server authenticates the MSS according to the authentication information included in the location update request and registers the changed location of the MSS authenticated successfully.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
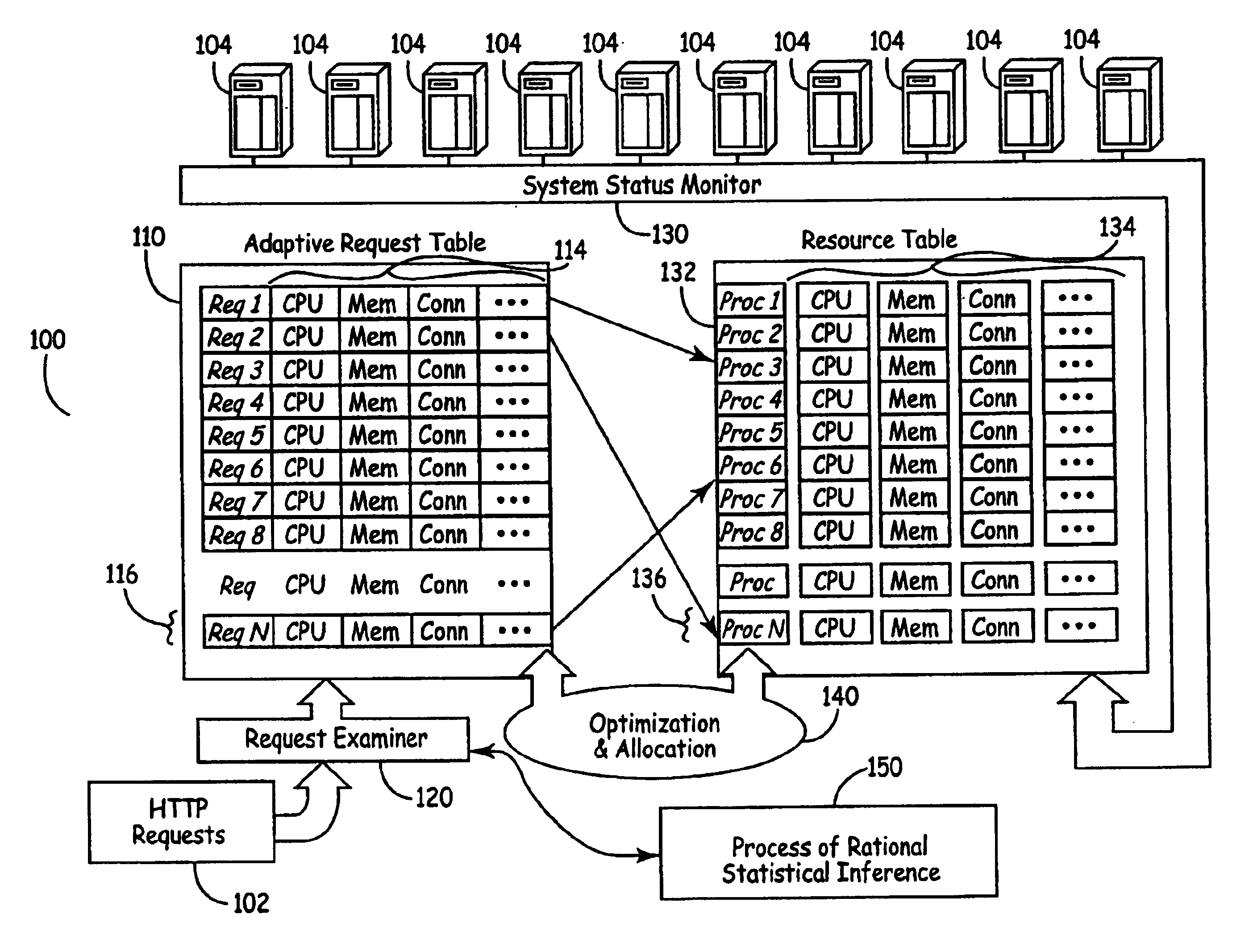
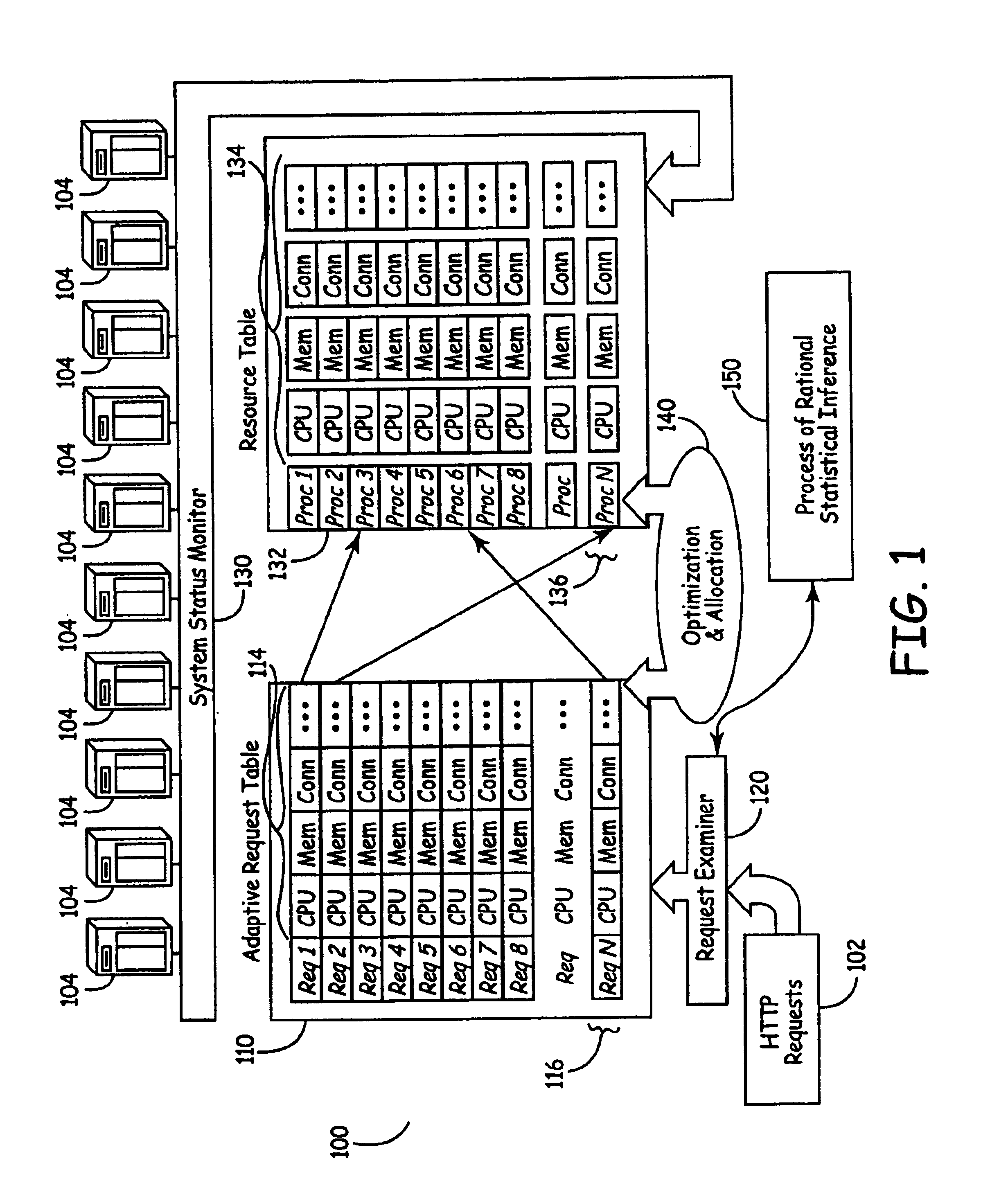
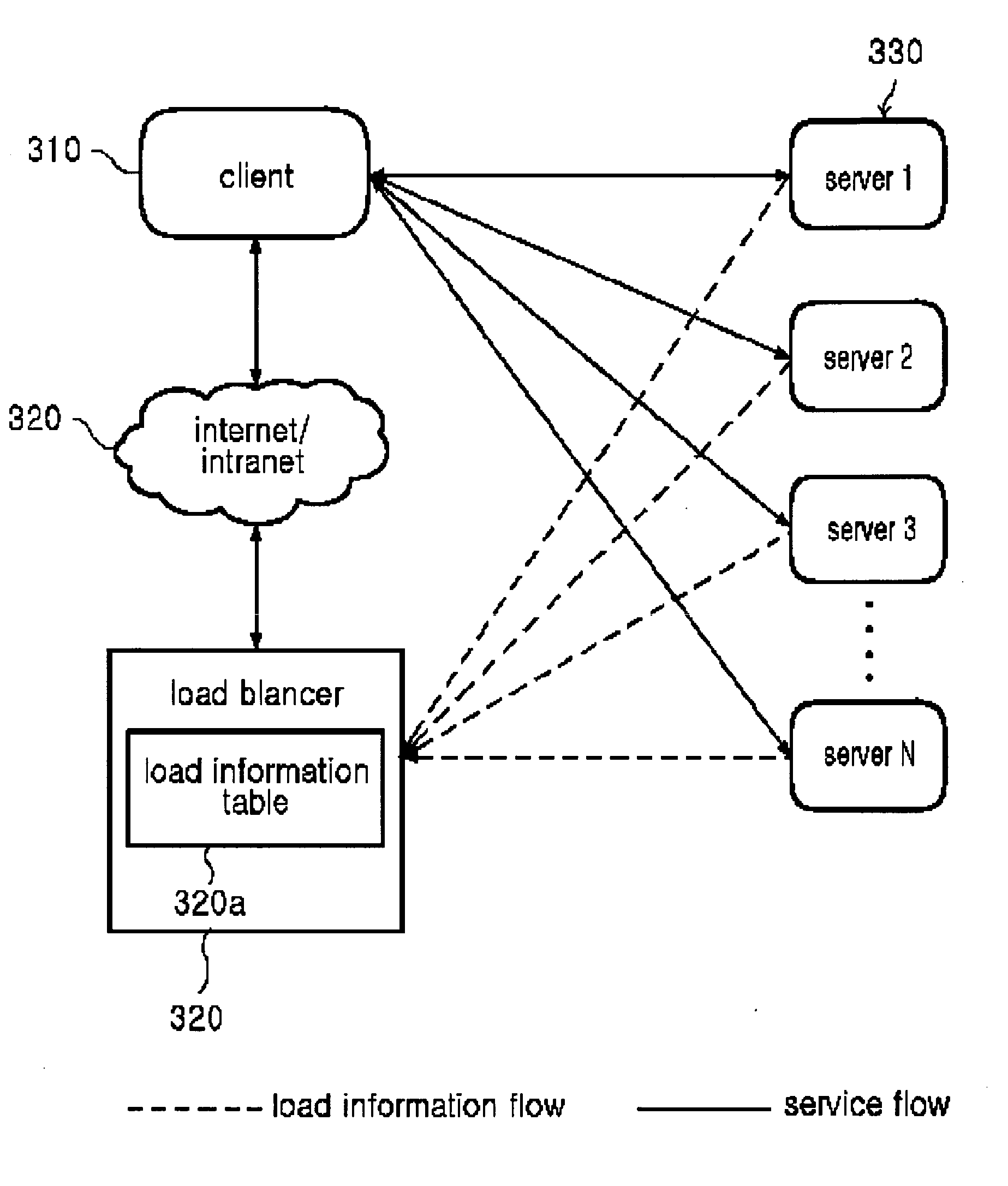
System for balance distribution of requests across multiple servers using dynamic metrics
InactiveUS6938256B2Improve performanceMaximizing numberResource allocationHardware monitoringDynamic metricsRelational database
A system for distributing incoming client requests across multiple servers in a networked client-server computer environment processes all requests as a set that occur within a given time interval and collects information on both the attributes of the requests and the resource capability of the servers to dynamically allocate the requests in a set to the appropriate servers upon the completion of the time interval. Preferably, the system includes a request table to collect at least two requests incoming within a predetermined time interval. A request examiner routine analyzes each collected request with respect to at least one attribute. A system status monitor collects resource capability information of each server in a resource table. An optimization and allocation process distributes collected requests in the request table across the multiple servers upon completion of said time interval based on an optimization of potential pairings of the requests in the request table with the servers in the resource table. The optimization and allocation process preferably analyzes metrics maintained in the request table and resource table as part of a relational database to allocate requests to servers based on a minimization of the metric distance between pairings of requests and servers. Preferably, the request table is part of a dynamic, relational database and a process of statistical inference for ascertaining expected demand patterns involving said the attributes adds predictive information about client requests as part of the request examiner routine.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
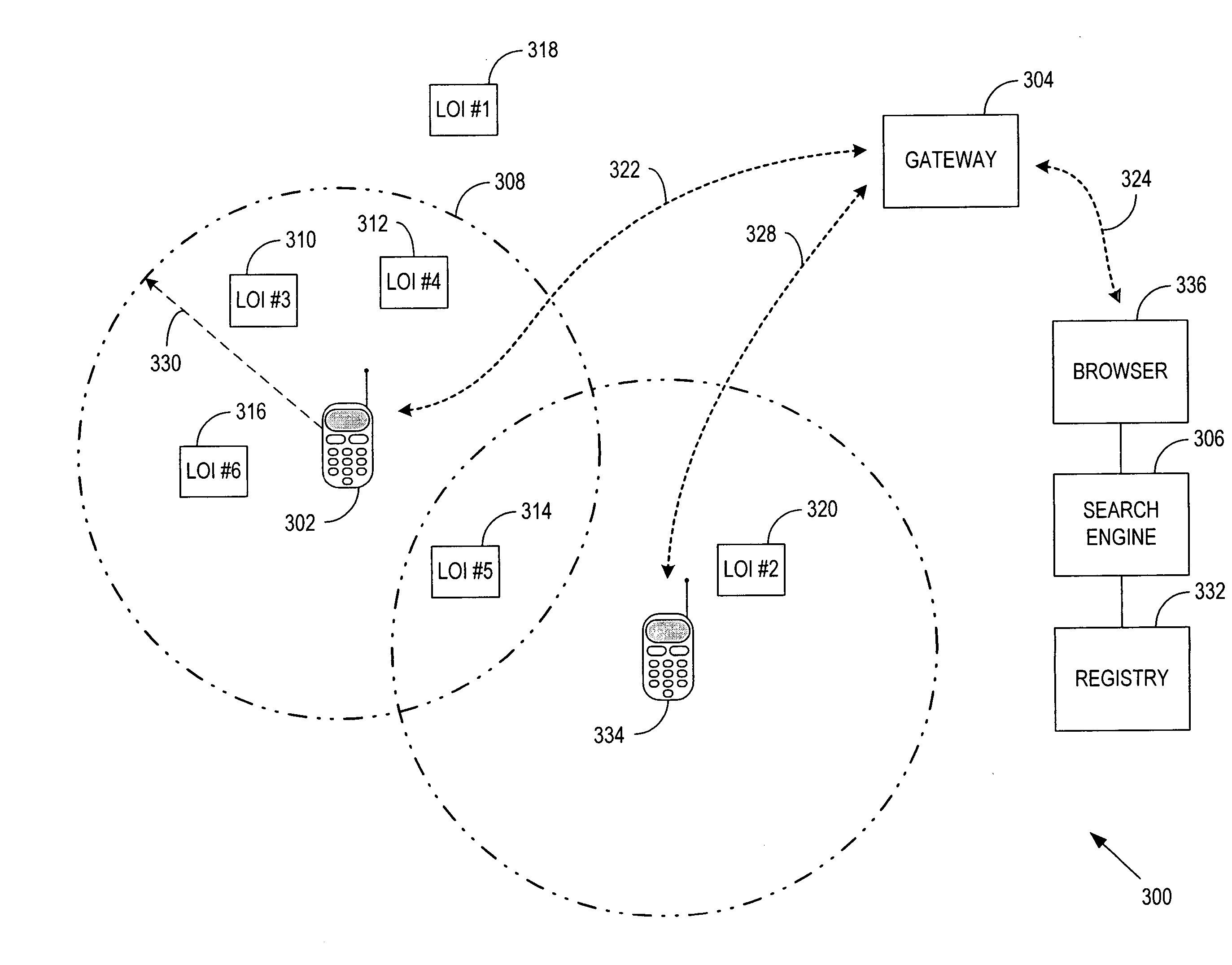
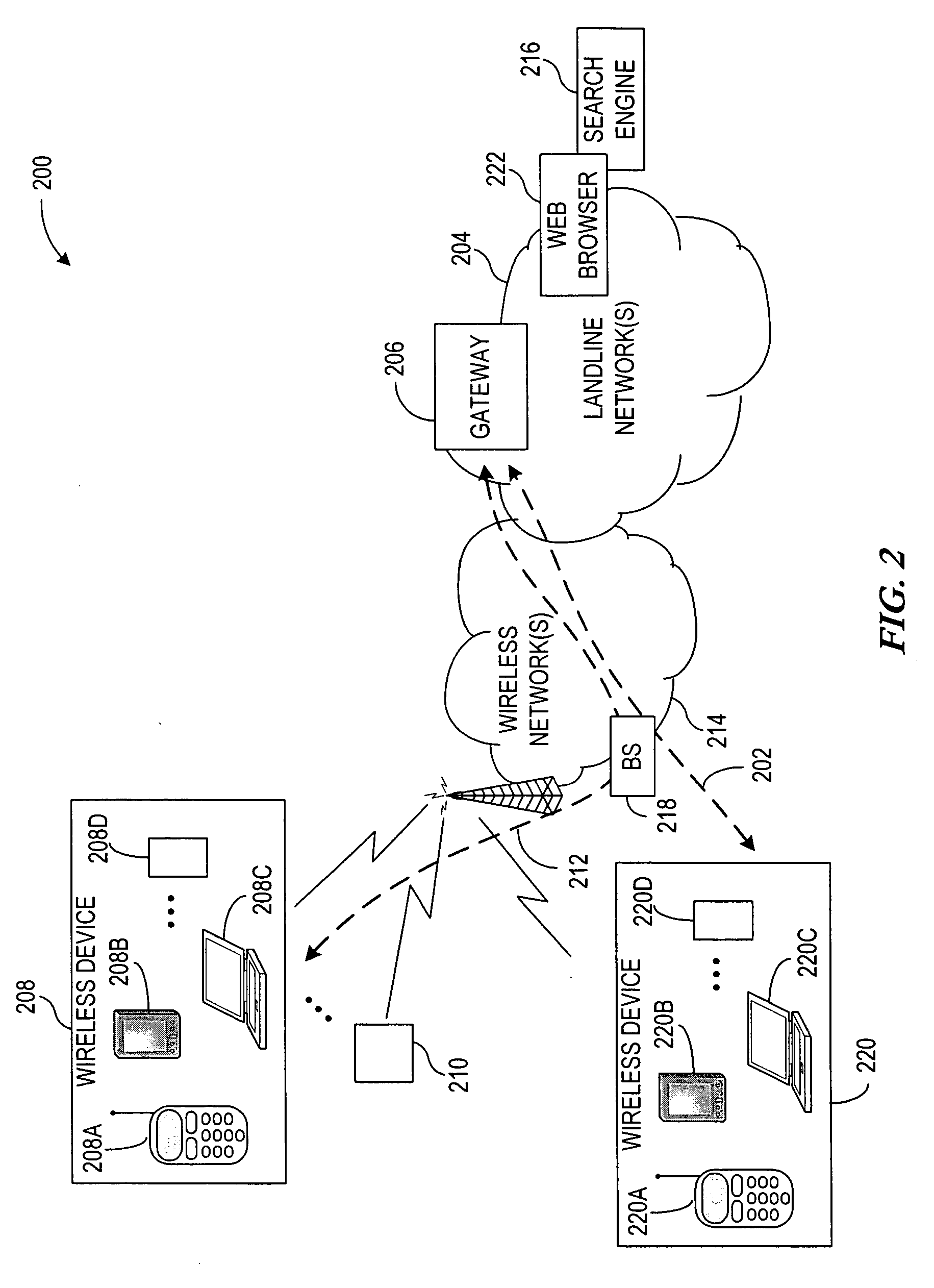
Method and apparatus for implementing a mobile web server based system
ActiveUS20060200541A1Easy to optimizeSpecial service for subscribersMultiprogramming arrangementsServer allocationUniform resource locator
A method and apparatus for facilitating access to mobile Web servers by any requesting entity from within a network. The mobile Web servers are allocated Uniform Resource Locators (URL), which are discoverable by the requesting entities through conventional use of search engines, service discovery mechanisms, registries, etc. A direct communication link exists between the mobile Web servers and the gateway to allow specific information to be obtained from the mobile Web servers and subsequently advertised by the gateway in the form of an indexed list. The indexed list allows the requesting entities to browse the mobile Web servers sponsored by the gateway for any location specific content / data that may be of interest to the requesting entities. The mobile Web servers facilitate the ability for the requesting entities to influence the content / data that is offered by the mobile Web servers.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Load Balancing Method and Apparatus, and Software Streaming System Using the Same
InactiveUS20090125625A1Efficient loadingThe right amountMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionServer allocationClient-side
Disclosed herein is a load balancing method and apparatus which can efficiently distribute load to a plurality of servers providing a software streaming service where a bandwidth-on-demand is different depending on sending times, and a software streaming system using the same. Sessions established between the servers and clients are classified into first sessions which send data for initial execution and second sessions which send data desired by users after the initial execution is completed, and the resulting session information of each of the servers is collected. A total load amount of each of the servers is calculated under the condition that different load weights are applied to the first and second sessions. A server with a minimum one of the total load amounts is selected from among the servers by comparing the total load amounts of the servers with one another, and the selected server is allocated to a new client requesting the software streaming service.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
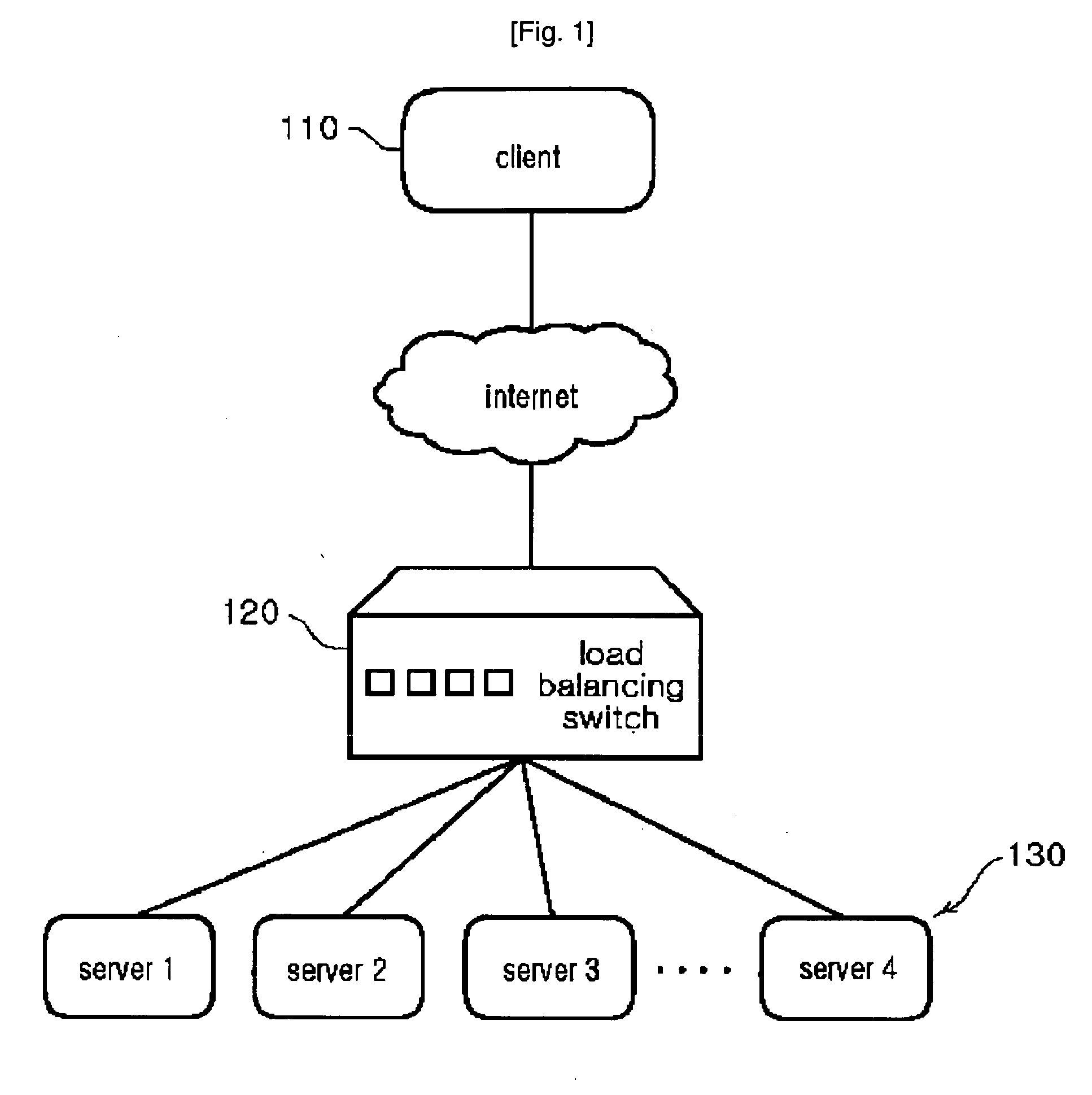
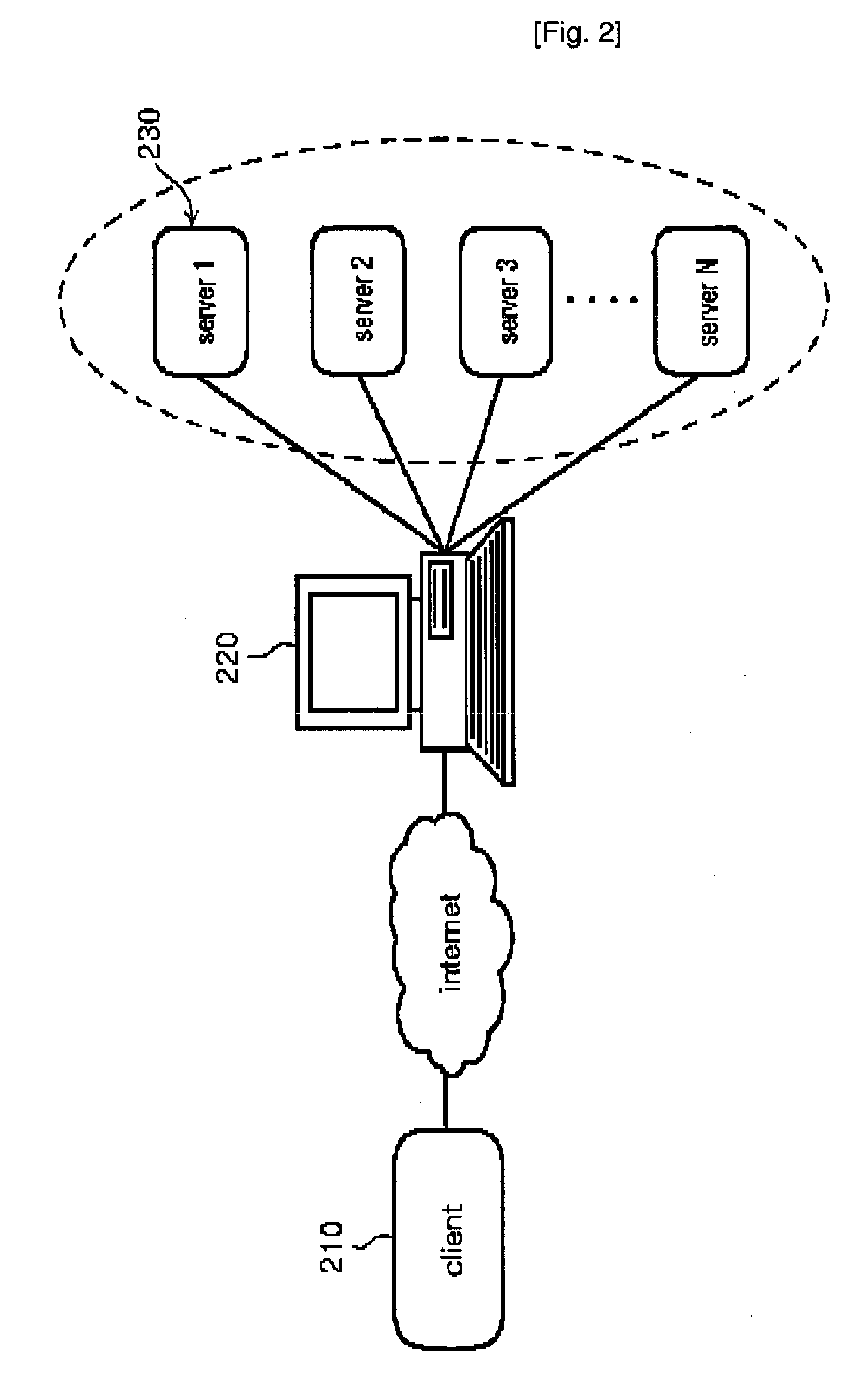
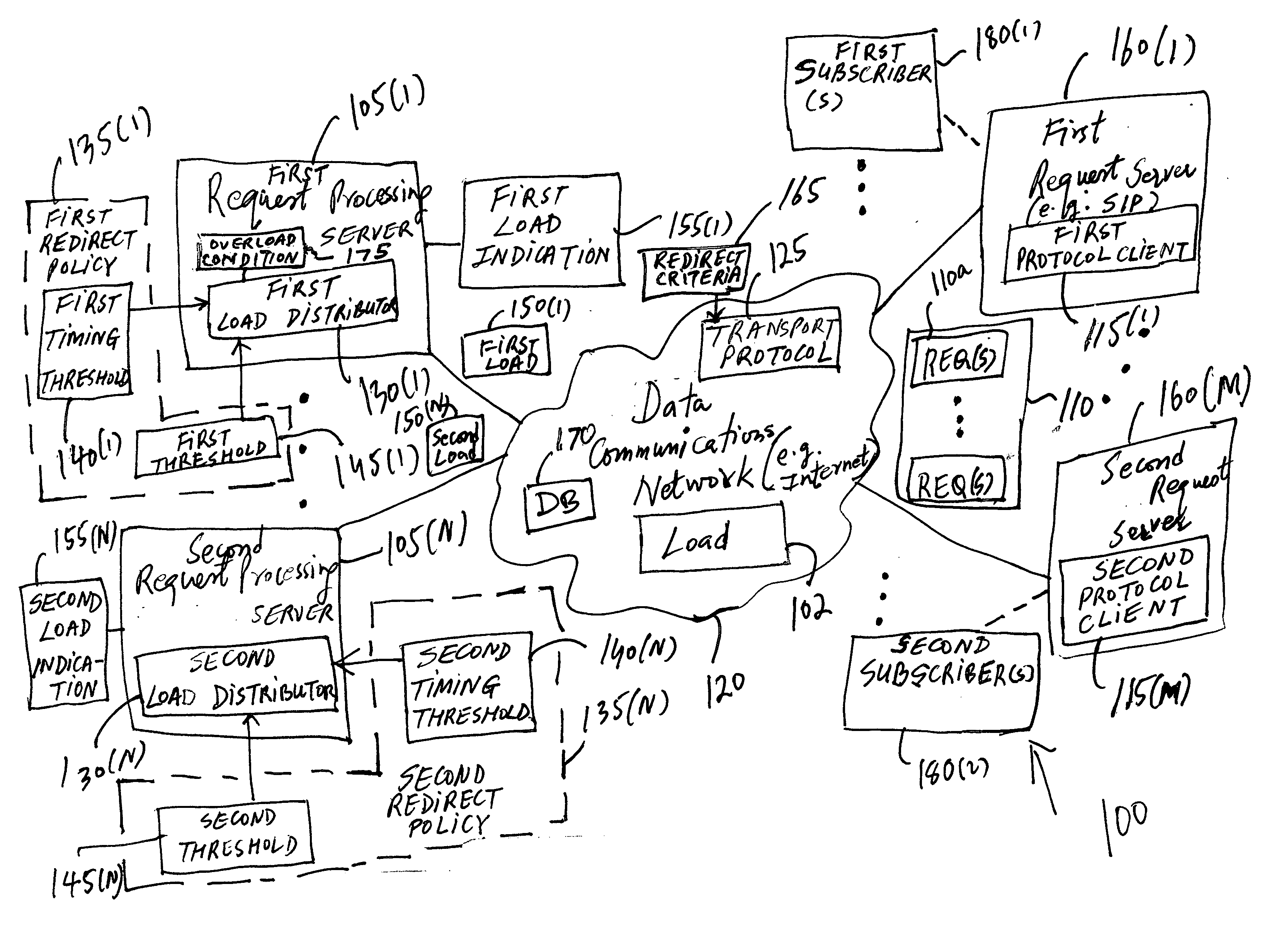
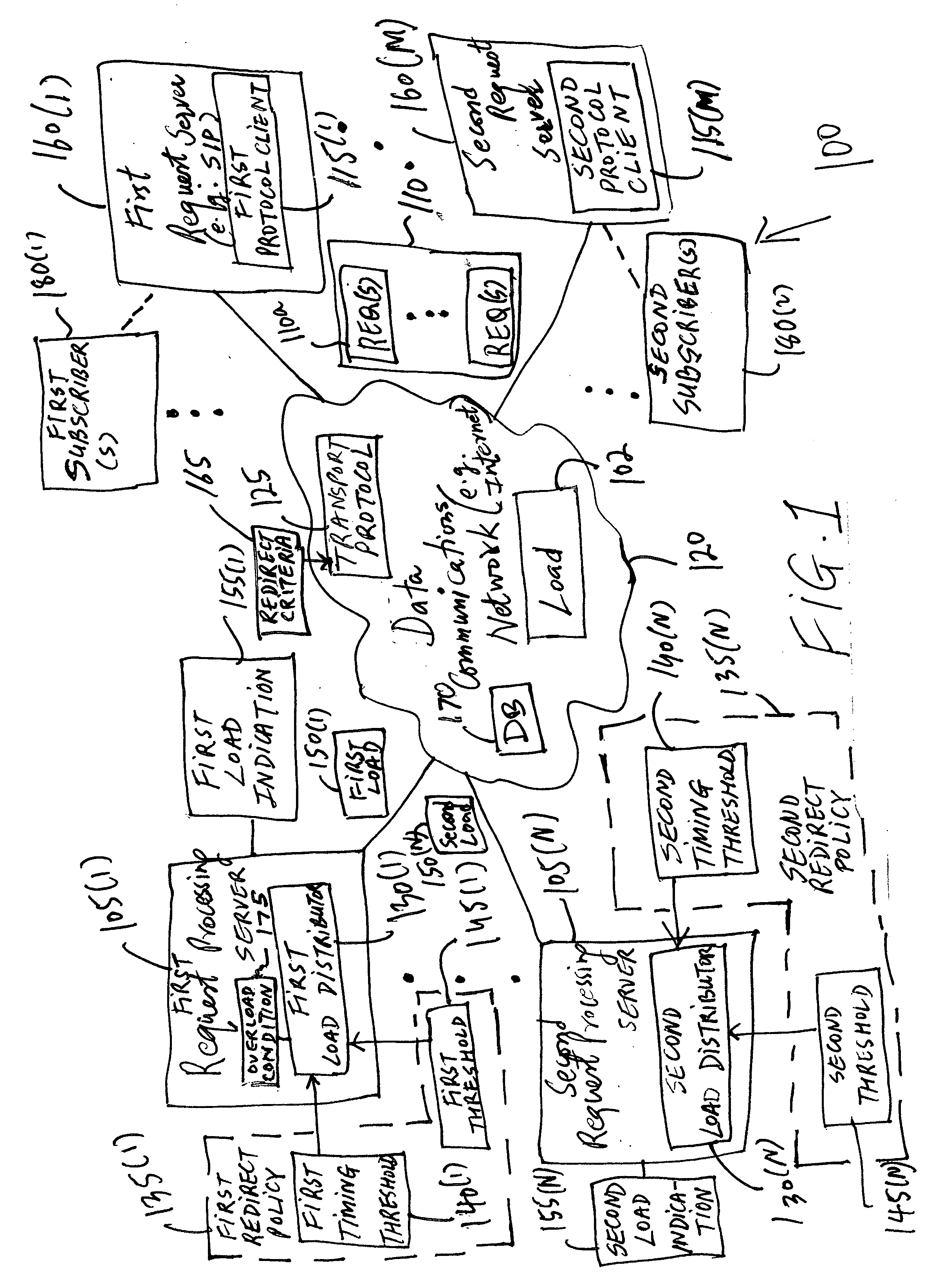
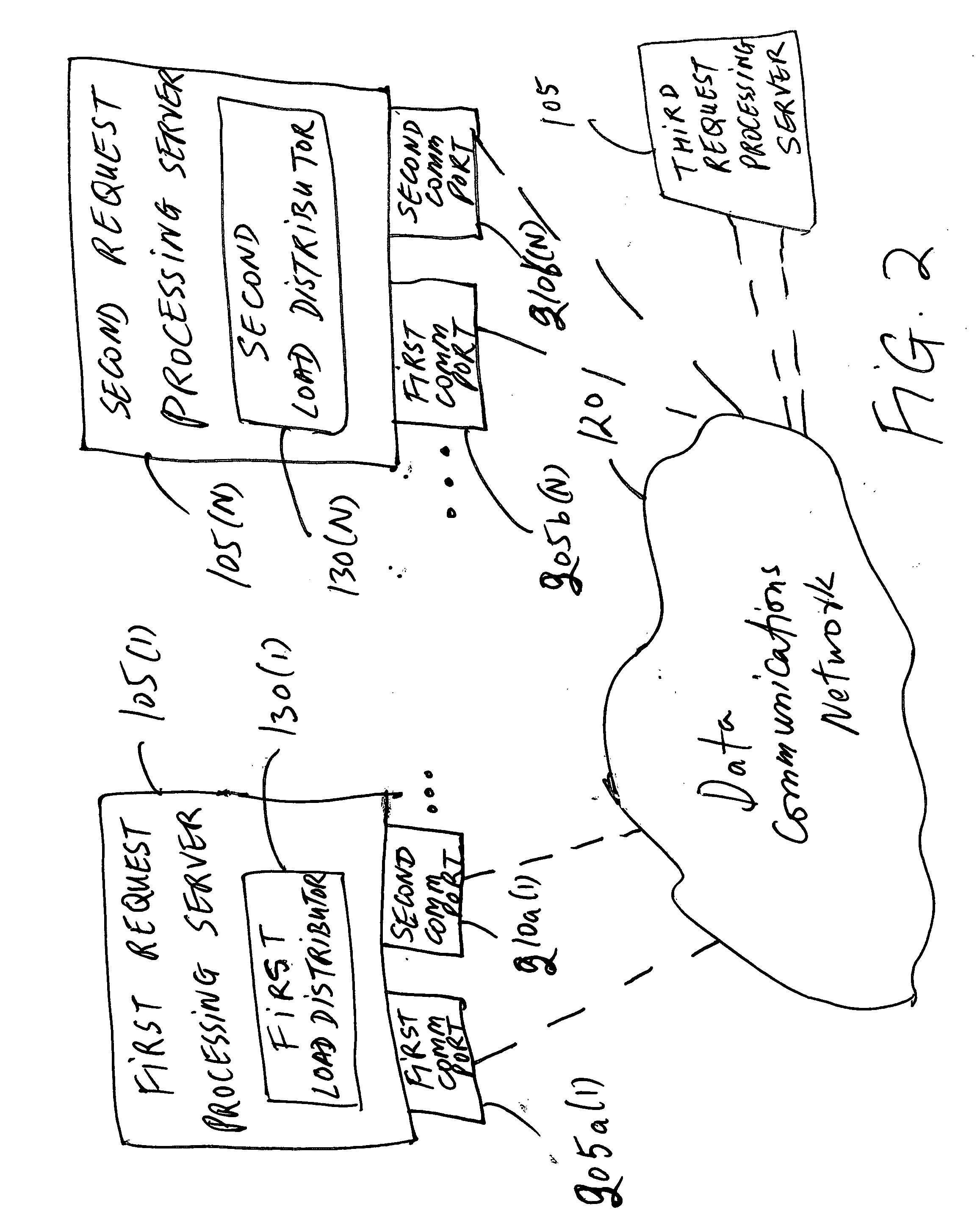
Distributing load of requests from clients over multiple servers
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for balancing load of a plurality of requests from at least one of first and second clients between a first and a second server. The method comprises comparing the load of the plurality of requests to a threshold of processing requests at the first server to determine whether the first server can process the plurality of requests. The method further comprises selectively redirecting a set of requests from the plurality of requests to the second server based on a policy associated with the first server, if the first server can not process the plurality of requests based on the threshold.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
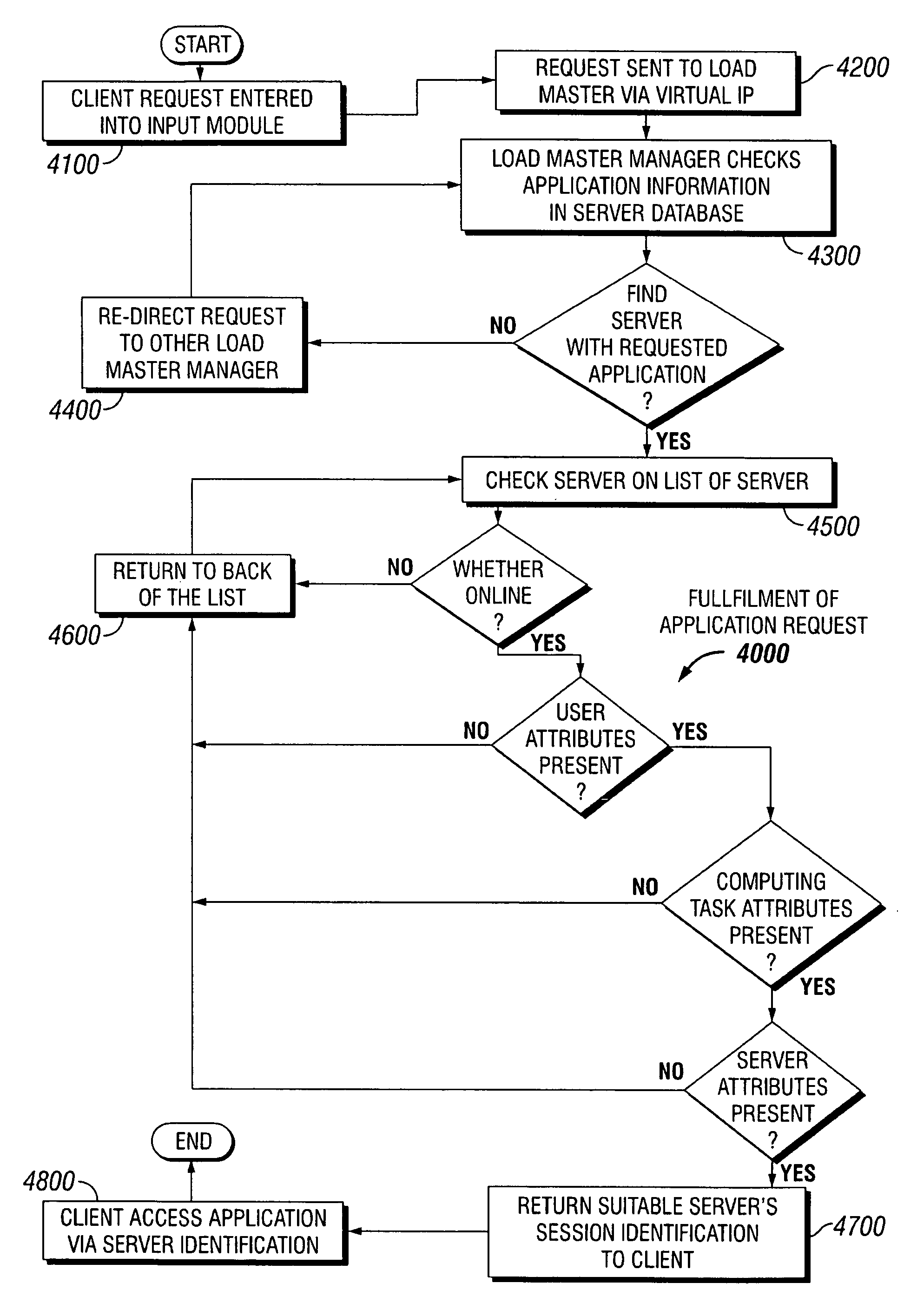
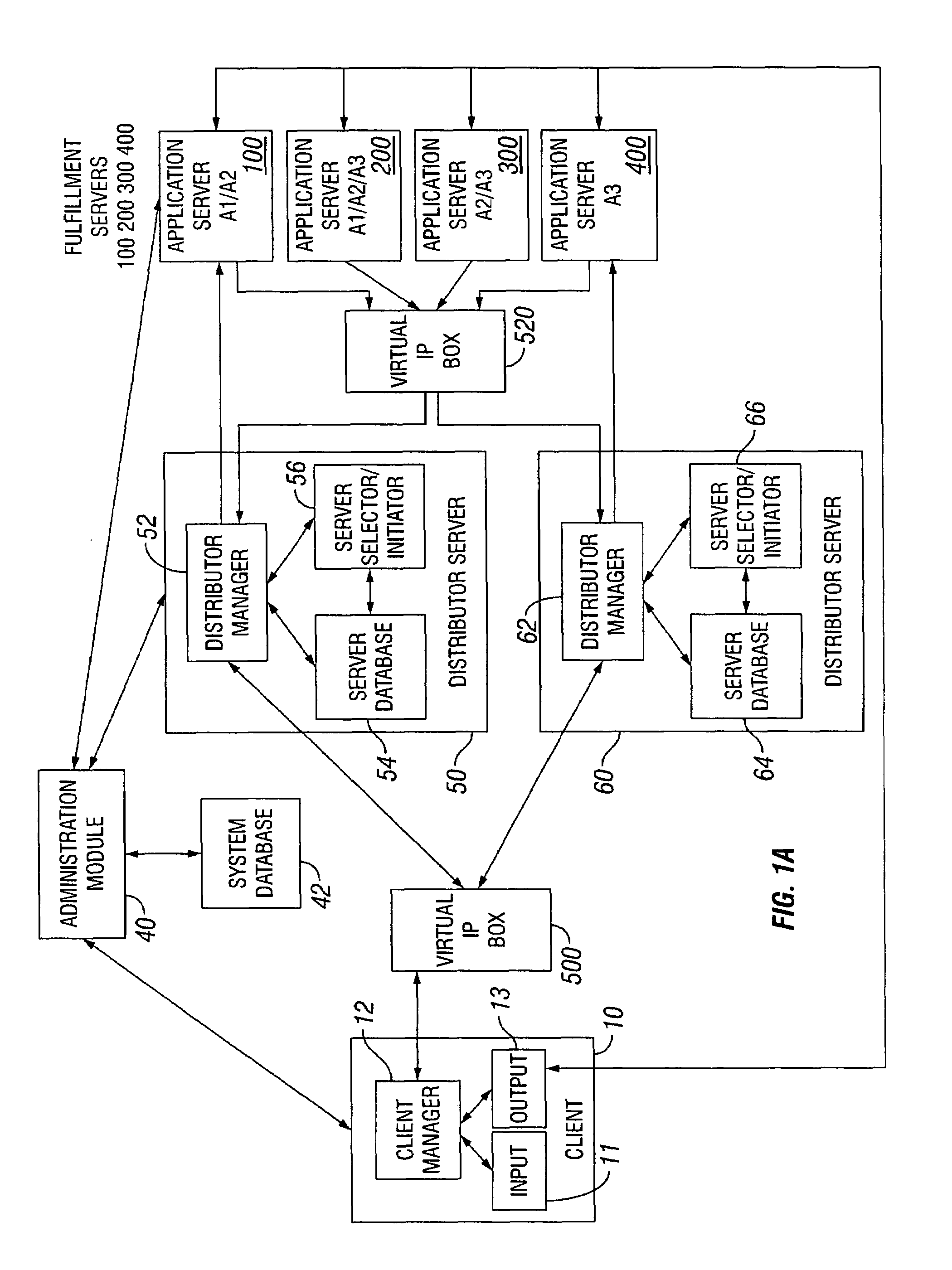
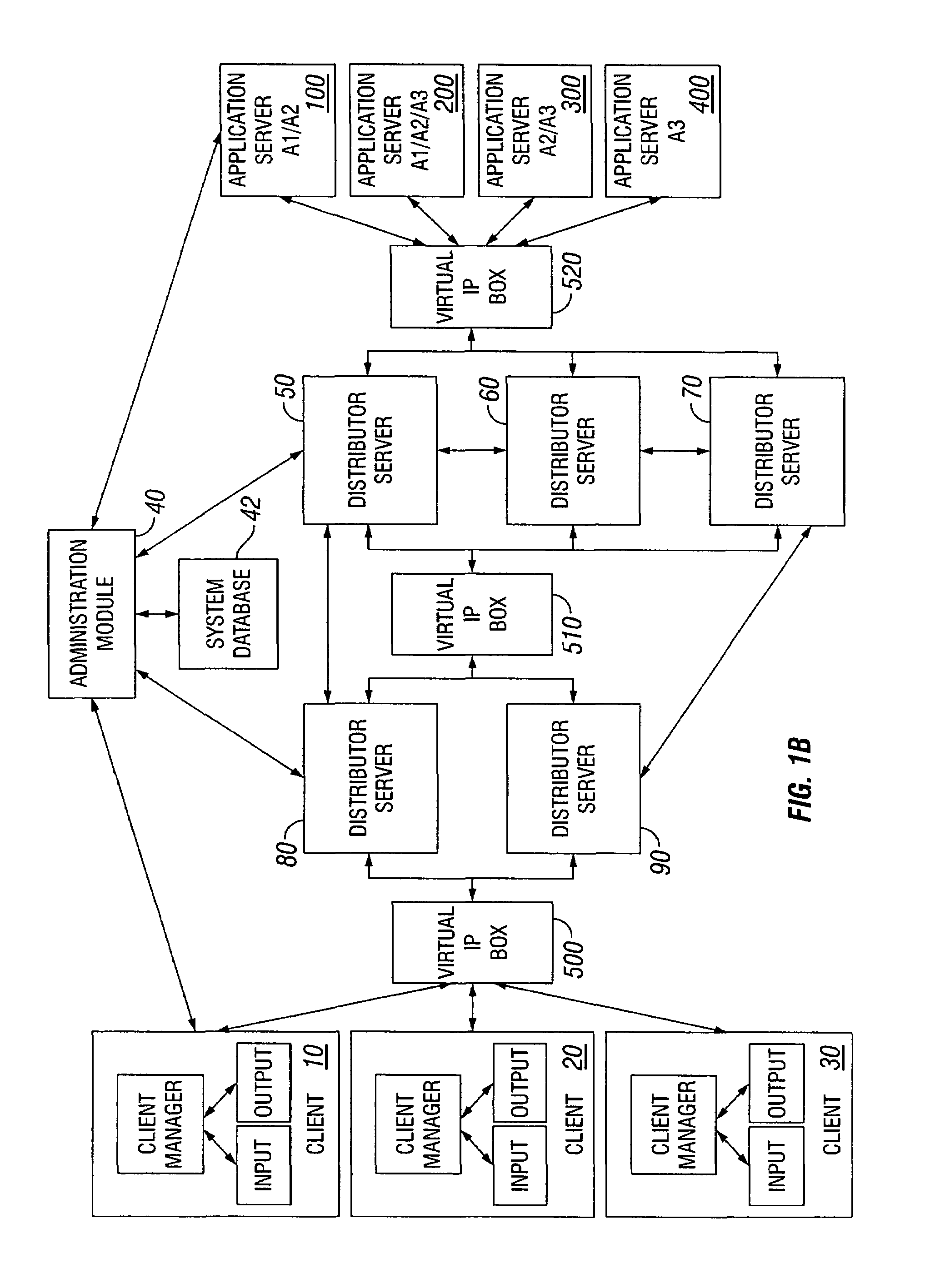
Dynamic allocation of computing tasks by second distributed server set
InactiveUS7111300B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsServer allocationDistributed servers
A method for dynamic allocation of computing tasks includes requesting a computing task by a client; receiving the computing task by a first distributor server set; redirecting the computing task to a second distributor server set, the second distributor server set including a first server; and allocating the computing task from the first server to a second server that executes the computing task, where the allocation is based on matching an attribute of the second server to an attribute of the computing task.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
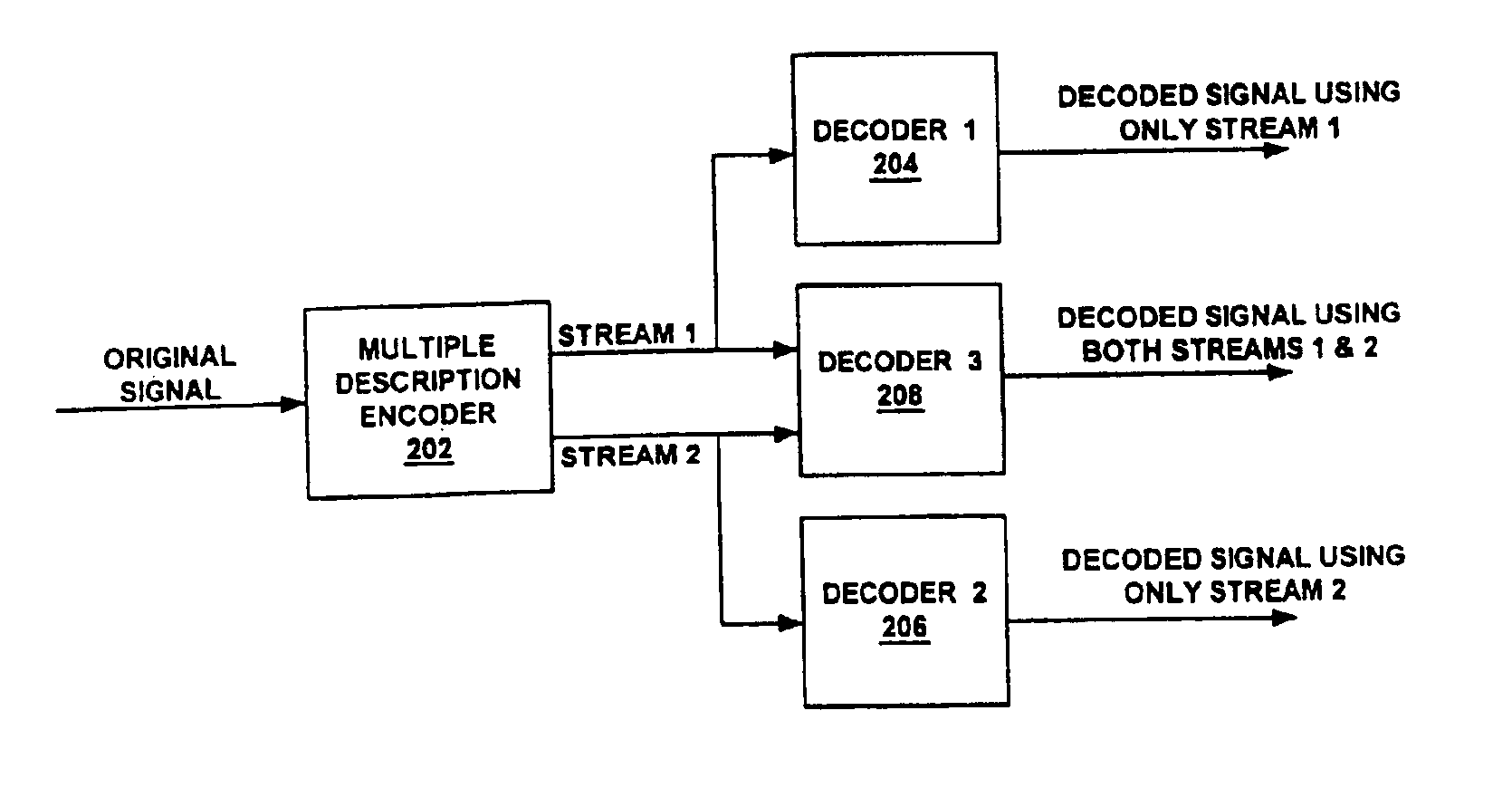
Method for assigning a streaming media session to a server in fixed and mobile streaming media systems
InactiveUS6941378B2Increased reliability and efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPresent methodData stream
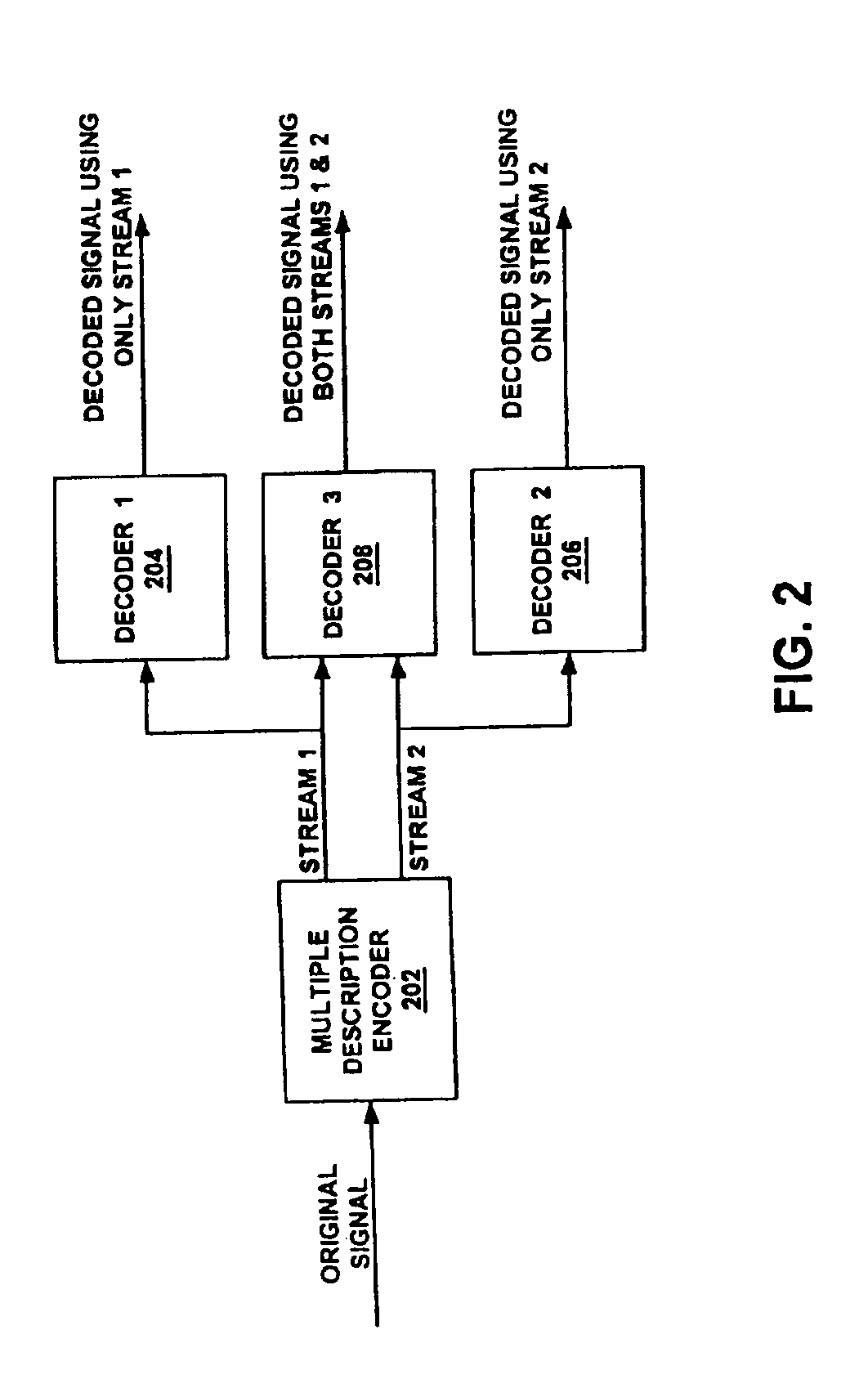
A method for assigning servers to provide multiple description bitstreams to a mobile client (in a mobile client environment) or to a fixed client (in a fixed client environment). In one embodiment, the present invention, upon receiving a request from a mobile client to have media data streamed thereto, analyzes a plurality of servers to determine a first candidate server for providing a first multiple description bitstream to the base station along a first path. The present method also determines a second candidate server for providing a second multiple description bitstream to the base station along a second path. The present method then sends a request to the first candidate server to provide the first multiple description bitstream to a mobile client through a base station along the first path, and also sends a request to the second candidate server to provide the second multiple description bitstream to the mobile client through the same base station along a second path. In another embodiment, there are two separate paths from two separate servers to two separate base stations and then from each base station there is a separate path to the mobile client. In still another embodiment, there are two paths from a single server to two separate base stations and then from each base station there is a separate path to the mobile client. In one fixed client embodiment, the present invention is able to assign a plurality of servers to provide a plurality of MD bitstreams to the fixed client.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
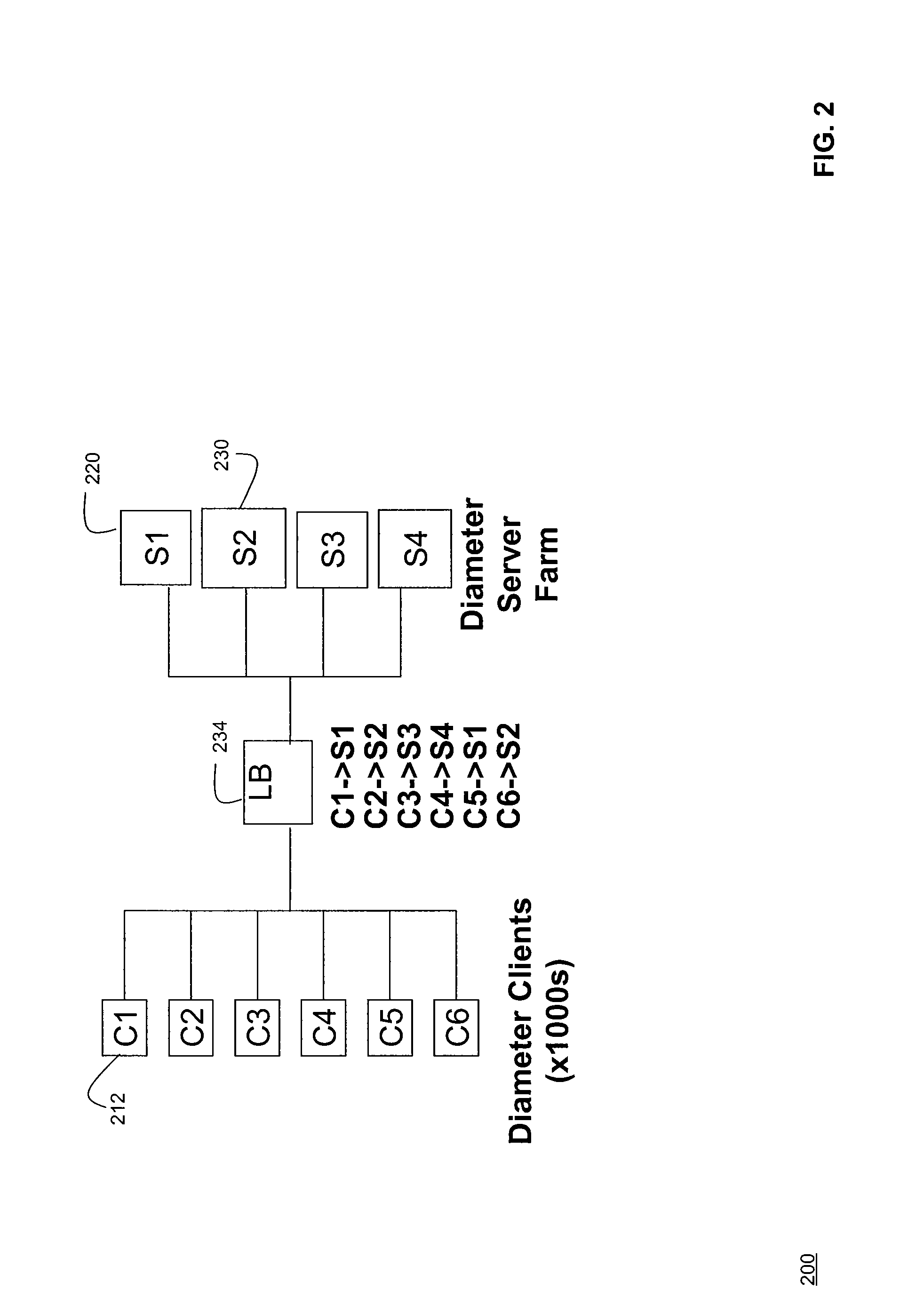
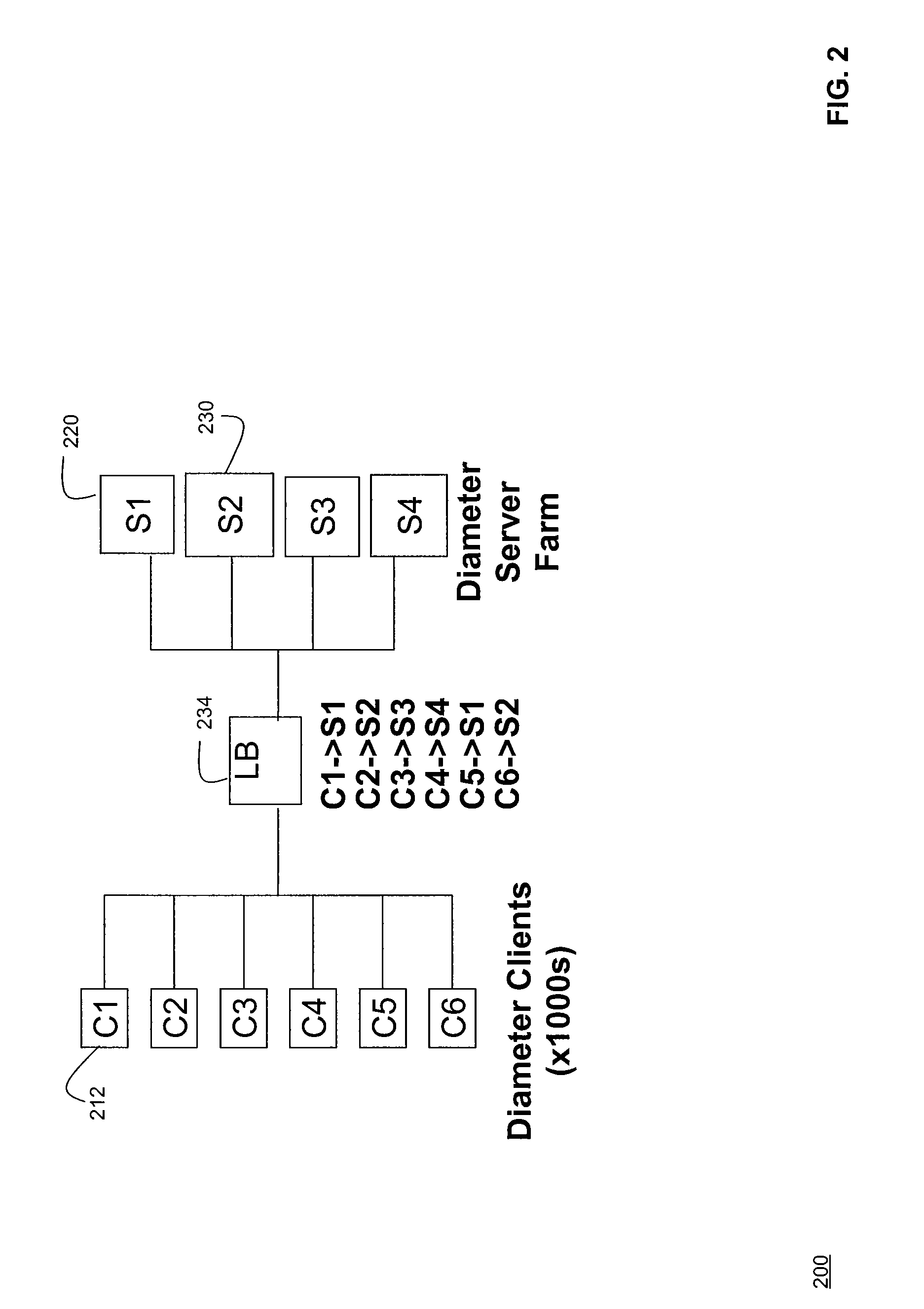
Systems and Methods for Server Load Balancing Using Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting Protocols
InactiveUS20090083861A1Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsServer allocationClient-side
Systems and methods for dynamically load-balancing clients across available servers without the need for a load balancer in front of a network are provided. Exemplary methods assign servers to clients in wireless and wireline networks based on server load. Methods and systems for using the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) protocols to load-balance network servers are provided. The load-balancing systems and methods further include using the Diameter AAA protocol routing attribute value pairs (AVPs) to implement bootstrap functionality and load balancing. Methods and systems using the Diameter protocol to manage client assignments are disclosed. Methods and systems for dynamically load-balancing clients across available servers using an AAA protocol are further described. Methods and systems to redirect clients to available servers with the least load are disclosed.
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
Systems and methods for server load balancing using authentication, authorization, and accounting protocols
InactiveUS8201219B2Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsServer allocationClient-side
Systems and methods for dynamically load-balancing clients across available servers without the need for a load balancer in front of a network are provided. Exemplary methods assign servers to clients in wireless and wireline networks based on server load. Methods and systems for using the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) protocols to load-balance network servers are provided. The load-balancing systems and methods further include using the Diameter AAA protocol routing attribute value pairs (AVPs) to implement bootstrap functionality and load balancing. Methods and systems using the Diameter protocol to manage client assignments are disclosed. Methods and systems for dynamically load-balancing clients across available servers using an AAA protocol are further described. Methods and systems to redirect clients to available servers with the least load are disclosed.
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
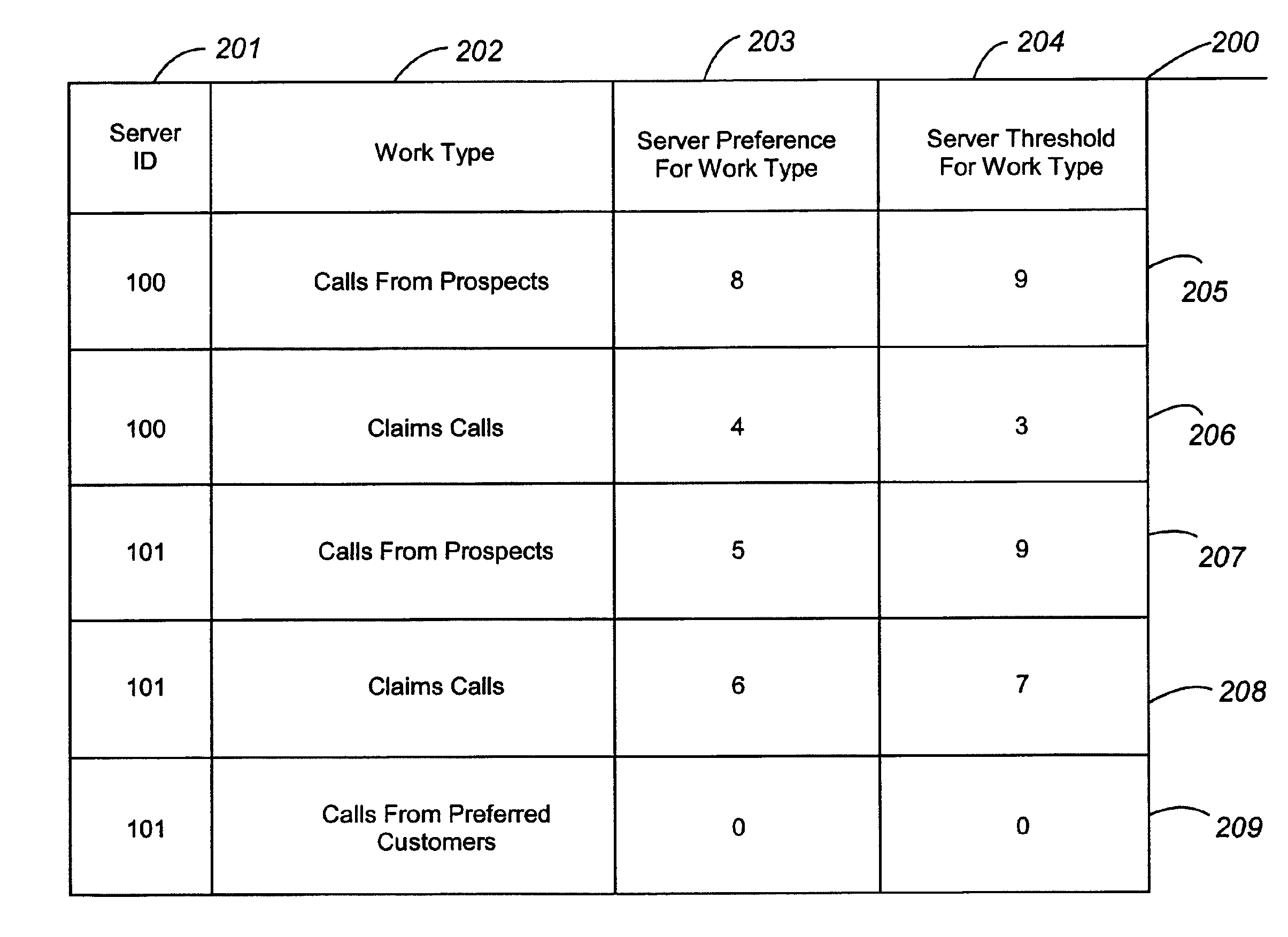
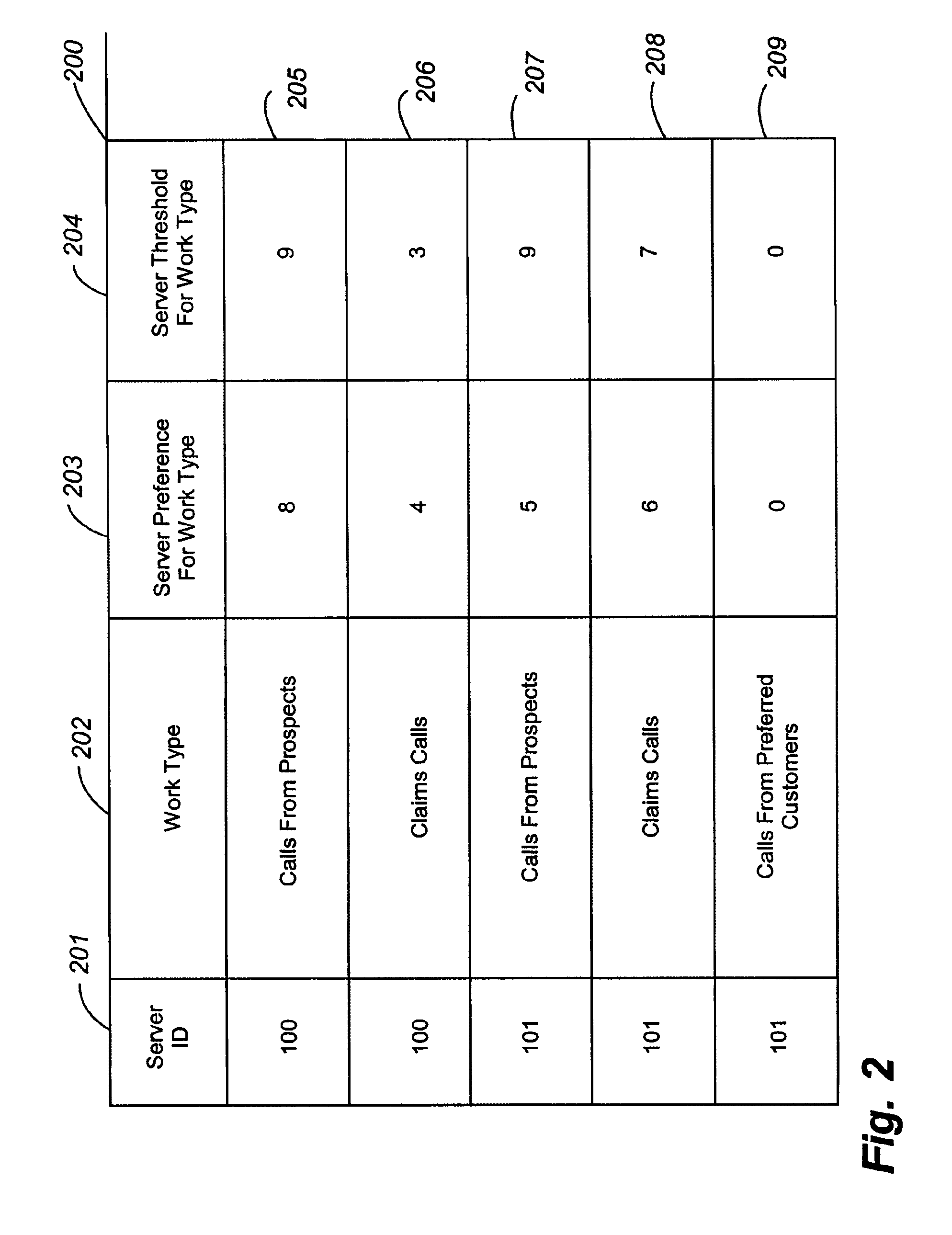
Dynamically allocating server resources to competing classes of work based upon achievement of service goals
A facility for adjusting a number of servers assigned to server pools for performing certain work types on the basis of unmet service needs in a work processing facility. Servers may include service agents, both human and robotic. A server assignor and corresponding server assignment method may each be employed in a work distributor or an automatic call distributor (“ACD”) to conditionally adjust server availability in server pools. The server assignor compares a composite preference value for a work type against each server's threshold value for the work type. When the server assignor determines that the composite preference value is greater than or equal to a server's threshold value, then the server assignor indicates that the server may be included in the server pool for that work type. Each server has preference values and threshold values for different kinds of work. The magnitude of a preference value represents an affinity for the work type. The server's threshold value represents a reluctance to perform work having that work type. The server does not normally receive work for which the preference value is less than the threshold value, unless the server assignor determines that the composite preference value exceeds the server's threshold value for that work type. The server assignor and corresponding server assignment method may compute the composite preference value from a number of user-selectable inputs and utilize a number of user-selectable functions.
Owner:AVAYA TECH CORP
Server power management with automatically-expiring server power allocations
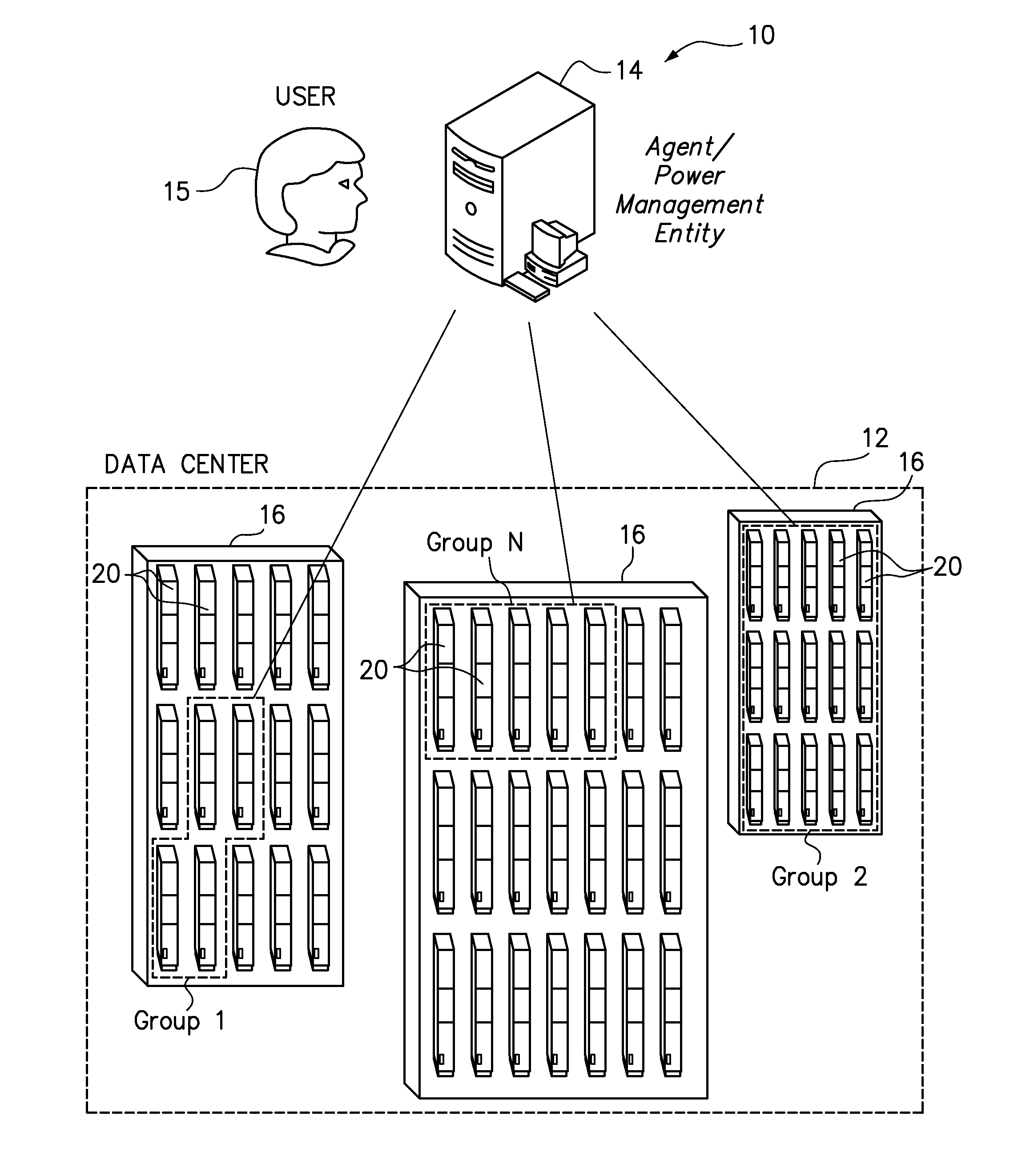
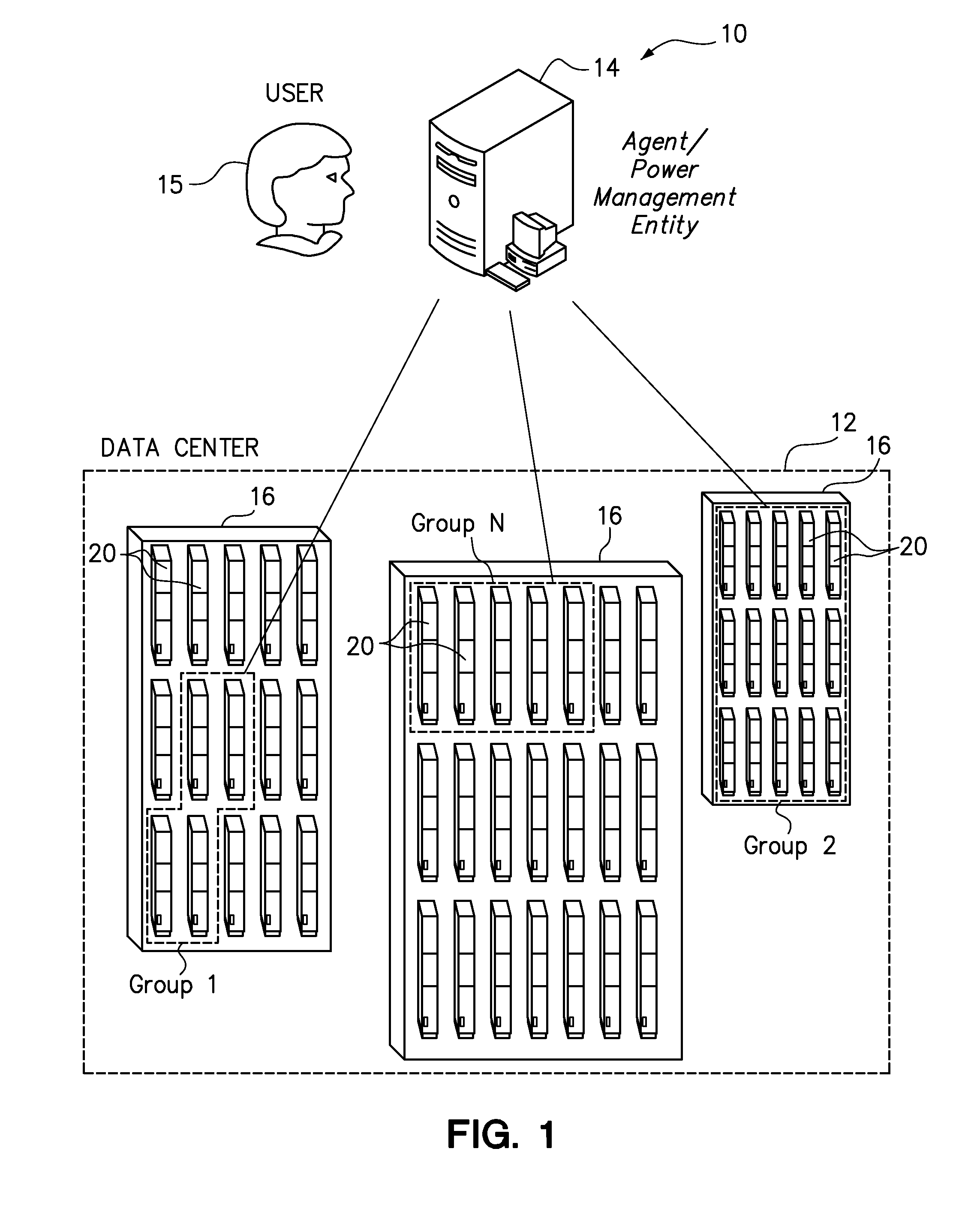
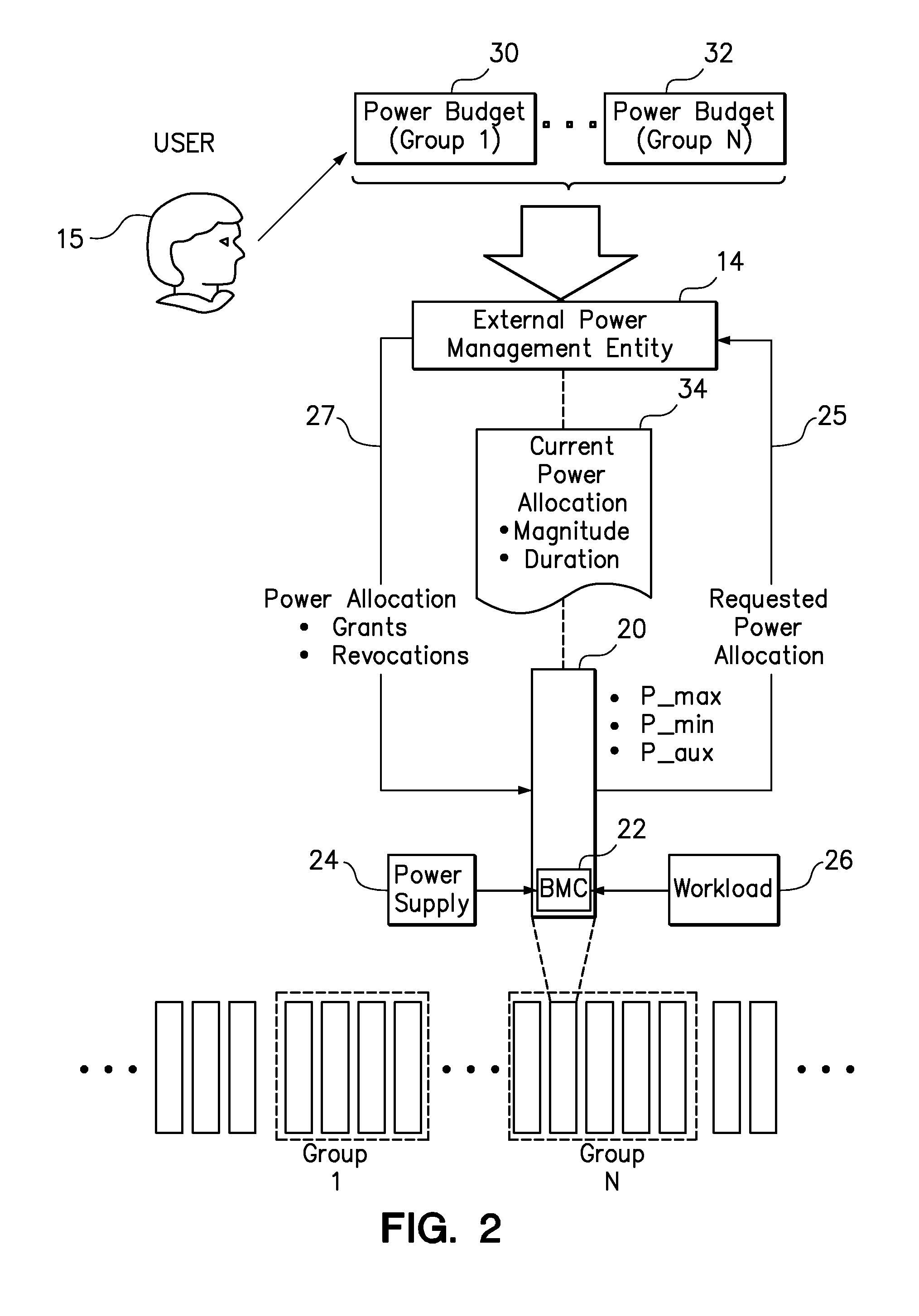
One embodiment provides a power management method for servers in a data center. A group of servers is selected, and the total power allocated to a group of servers is limited to within a group power budget. A separate server power allocation is individually requested for each of a plurality of the servers. Within the constraints of the group power budget, the requested server power allocations are selectively granted for a specified magnitude and duration. The granted server power allocations are also selectively renewed, either automatically or upon request of the servers. Each server that has not received a renewed server power allocation from a group power management entity upon the expiration of the specified duration automatically reduces its own power consumption, such as by the server powering itself off.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Dynamic resource allocation using known future benefits
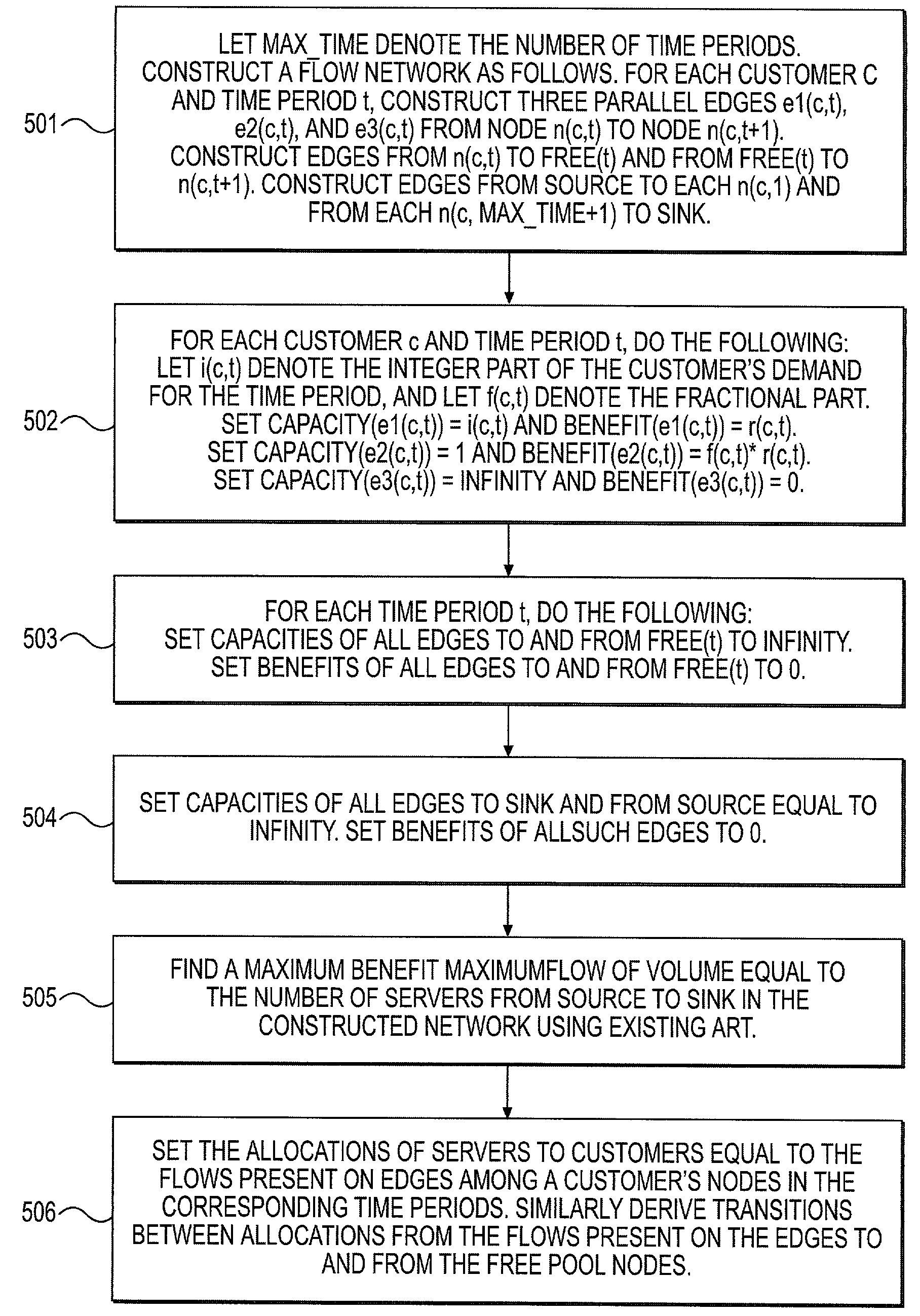
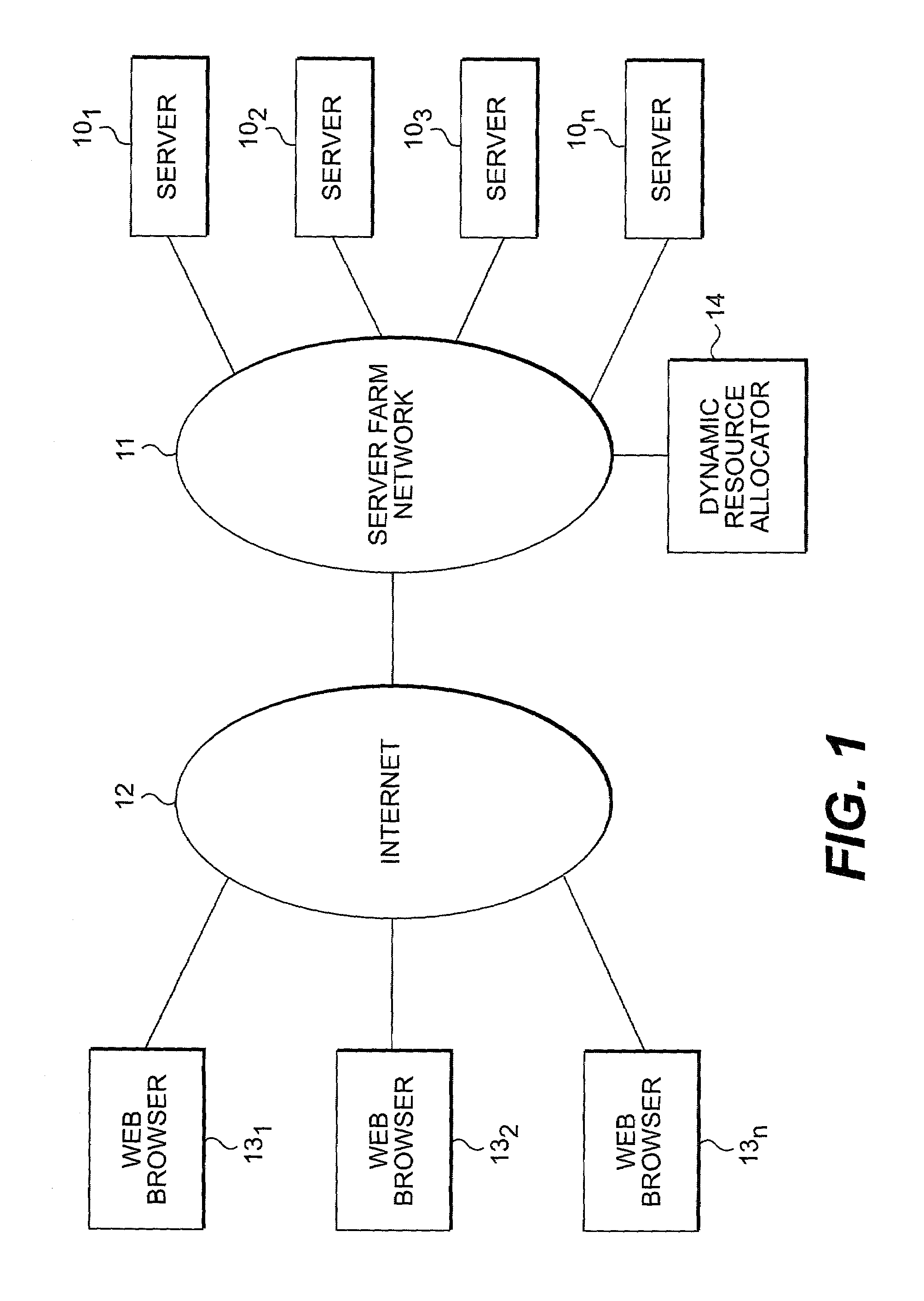
InactiveUS7085837B2Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsDynamic resourceWeb service
A benefit task system implements a policy for allocating resources to yield some benefit. The method implemented may be applied to a variety of problems, and the benefit may be either tangible (e.g., profit) or intangible (e.g., customer satisfaction). In one example, the method is applied to server allocation in a Web site server “farm” given full information regarding future loads to maximize profits for the Web hosting service provider. In another example, the method is applied to the allocation of telephone help in a way to improve customer satisfaction. In yet another example, the method is applied to distributed computing problem where the resources to be allocated are general purpose computers connected in a network and used to solve computationally intensive problems. Solution of the Web server “farm” problem is based on information regarding future loads to achieve close to the greatest possible revenue based on the assumption that revenue is proportional to the utilization of servers and differentiated by customer class. The method of server allocation uses an approach which reduces the Web server farm problem to a minimum-cost network flow problem, which can be solved in polynomial time. Similar solutions are applicable to other resource allocation problems.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
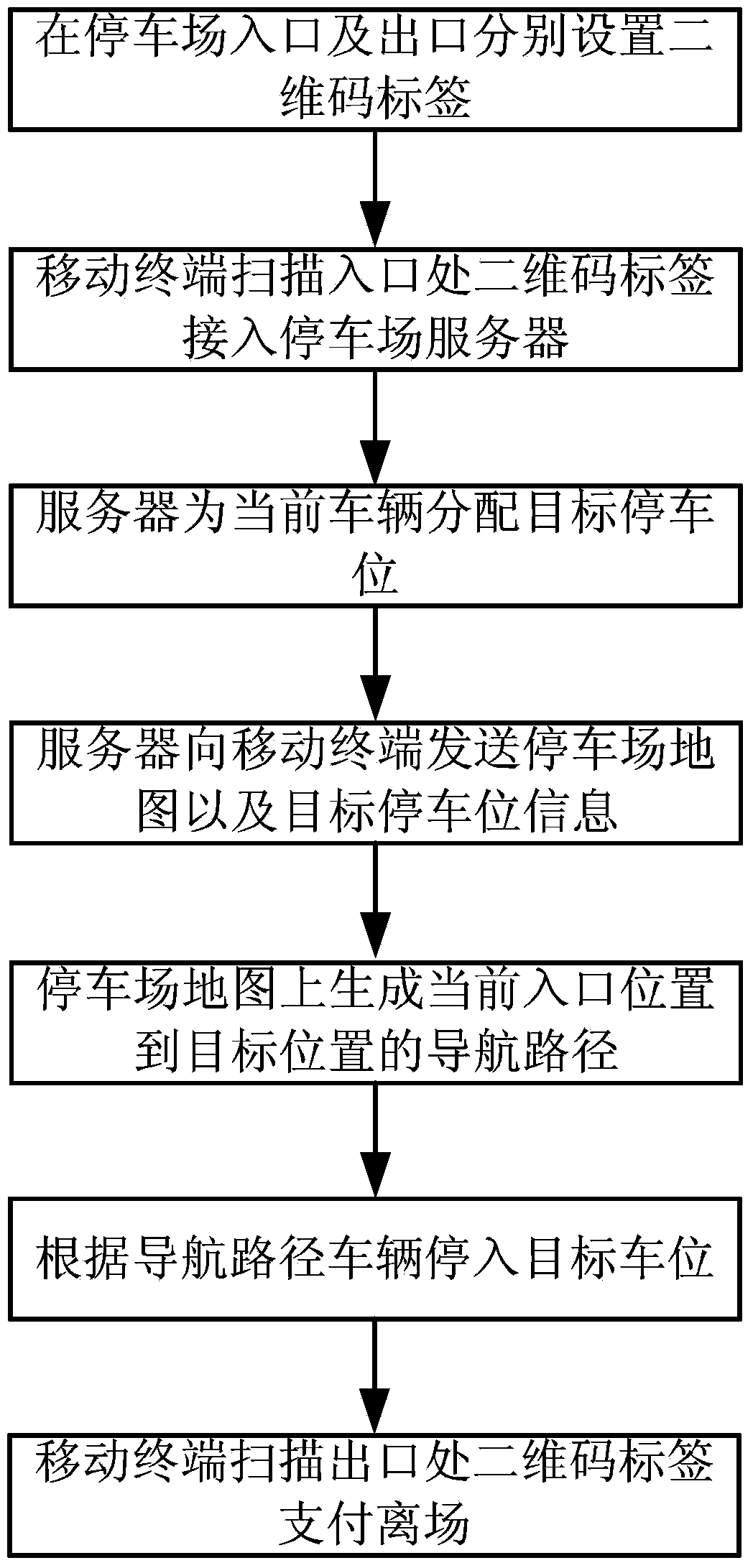
Unattended parking lot management method
ActiveCN103714716AReduce operating costsImprove operational efficiencyIndication of parksing free spacesParking areaOperational costs
The invention provides an unattended parking lot management method. The method includes the following steps that firstly, two-dimension code labels are arranged at the entrance and the exit of a parking lot respectively; secondly, the two-dimension code label at the entrance is scanned by a mobile terminal and the mobile terminal has access to a server of the parking lot; thirdly, the server distributes target parking spaces; fourthly, the server sends a parking lot map and target parking space information; fifthly, a navigation path from the current entrance position to a target position is generated on the parking lot map; sixthly, a car is parked into one target parking space according to the navigation path; seventhly, the two-dimension code label at the exit is scanned and the car leaves the parking lot after a car owner pays for parking. By the adoption of the technical scheme, car owners can be guided to unoccupied parking spaces when entering the parking lot to park cars and can be helped to quickly find the parking spaces where the cars are parked when looking for the cars to leave the parking lot, so that the time consumed in parking the cars and looking for the cars is shortened for the car owners, and the operating efficiency of the parking lot is improved as well; meanwhile, by the adoption of the mobile payment mode, workers are not needed, and the operating cost of the parking cost is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
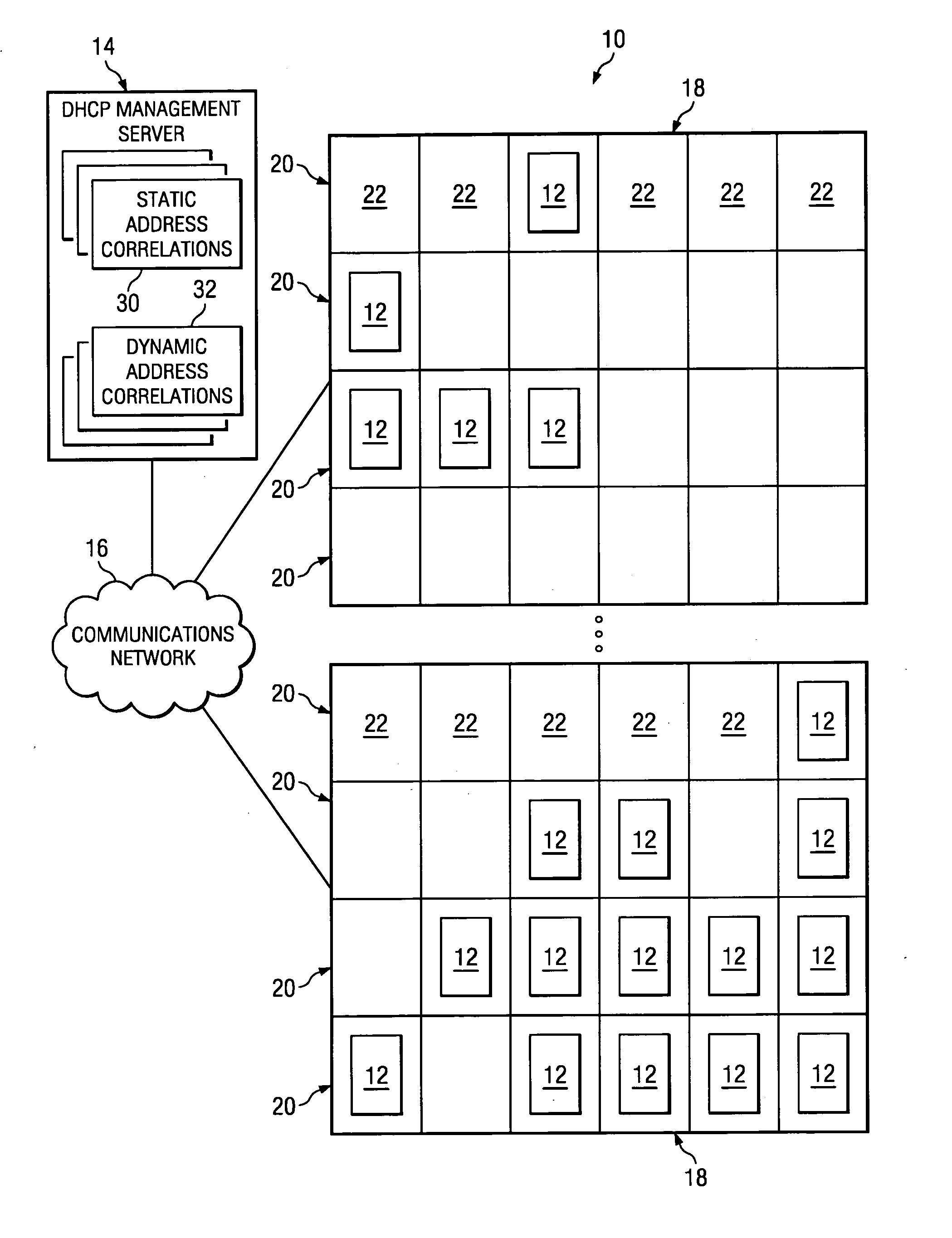
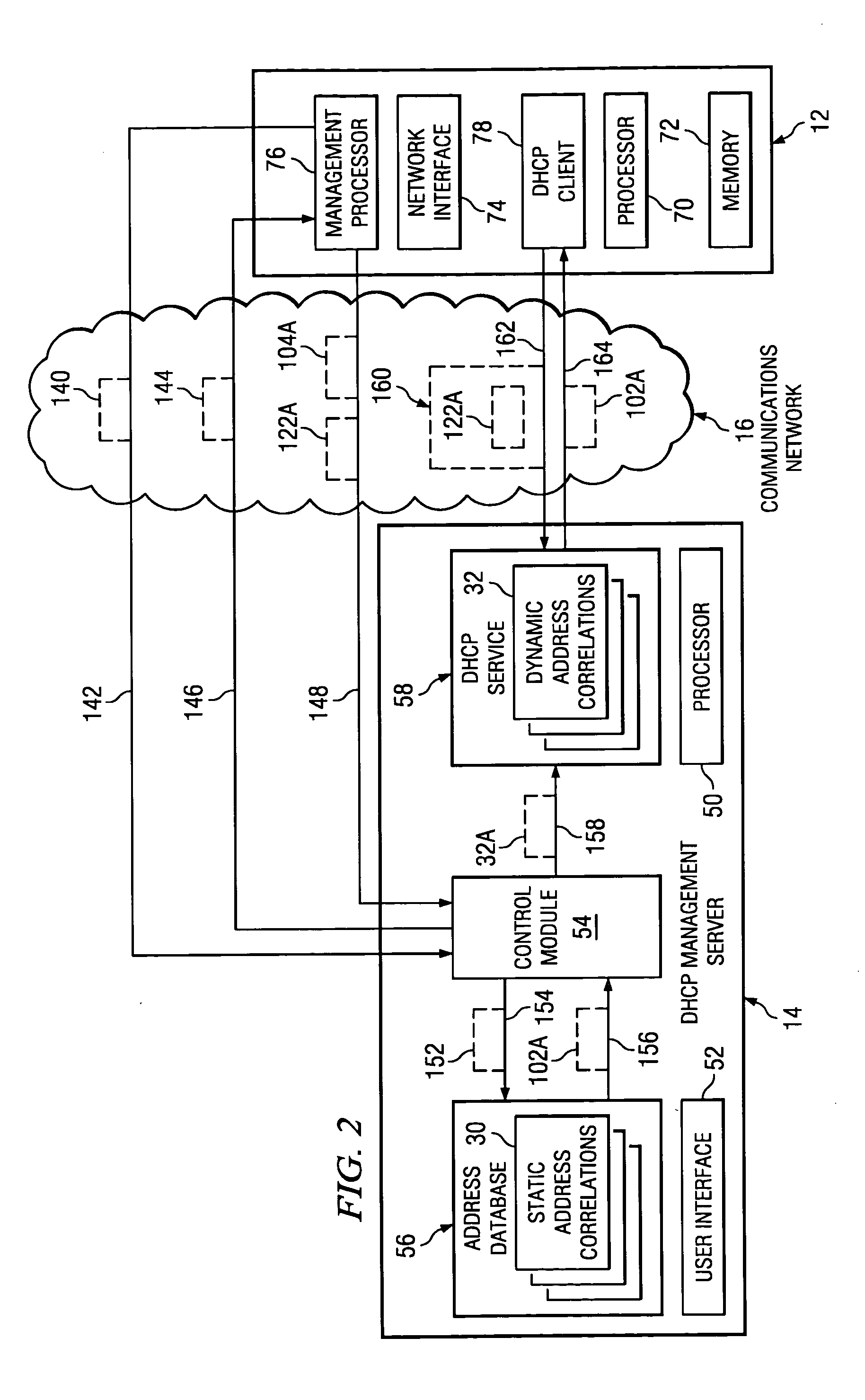
System and method for DHCP-based assignment of IP addresses to servers based on geographic identifiers
InactiveUS20050262218A1Easy to operateMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionIp addressServer allocation
A method of assigning IP addresses to a plurality of managed servers coupled is provided. A set of address correlations is stored, at least temporarily, at a management server coupled to the managed servers. Each address correlation comprises a correlation between one of a plurality of geographic identifiers and one of a plurality of IP addresses. Each geographic identifier identifies a possible physical location of a managed server. A geographic identifier at least partially identifying the physical location of the managed server is received at the management server from a particular managed server. The IP address corresponding to the received geographic identifier is determined from the set of address correlations and assigned to the particular managed server.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
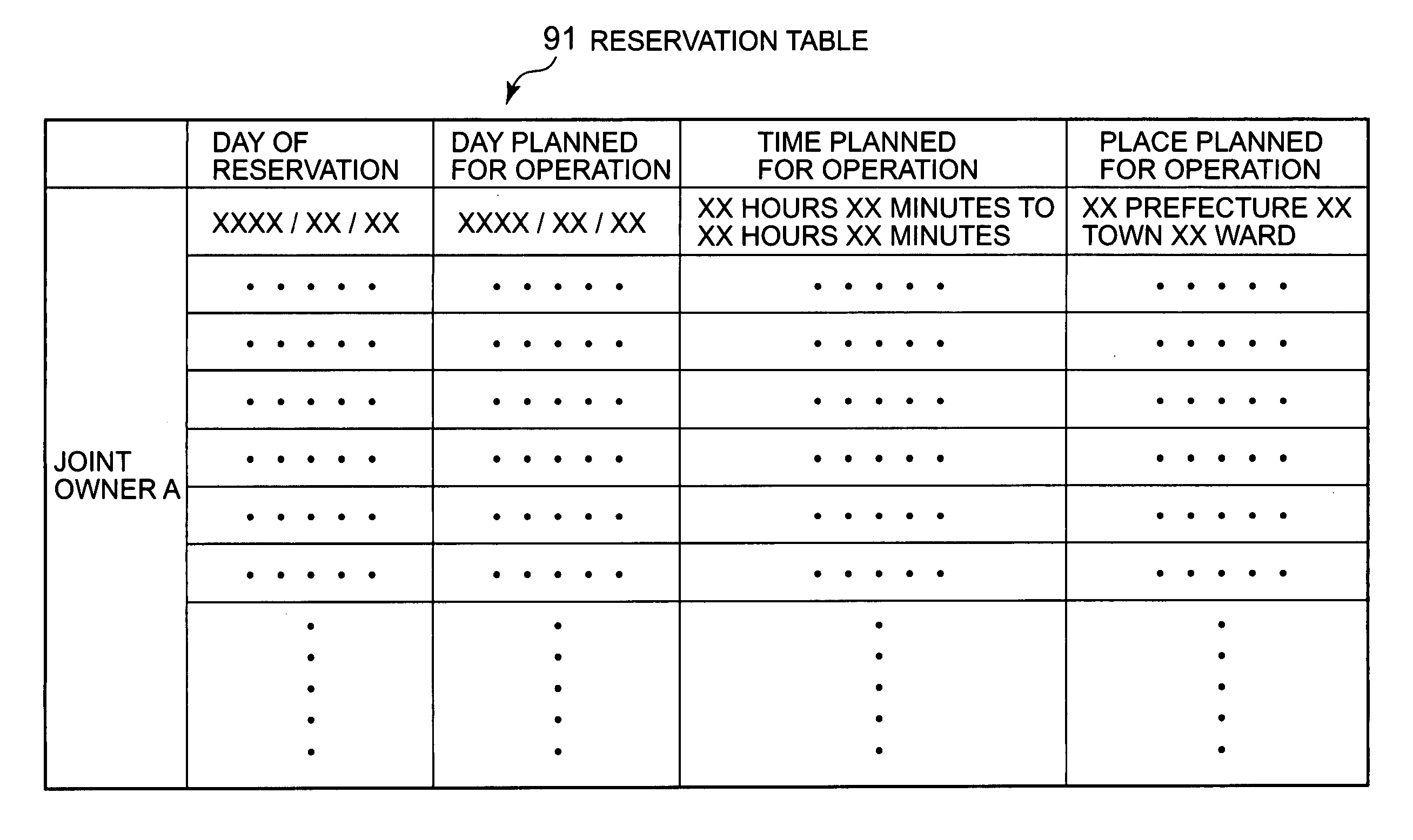
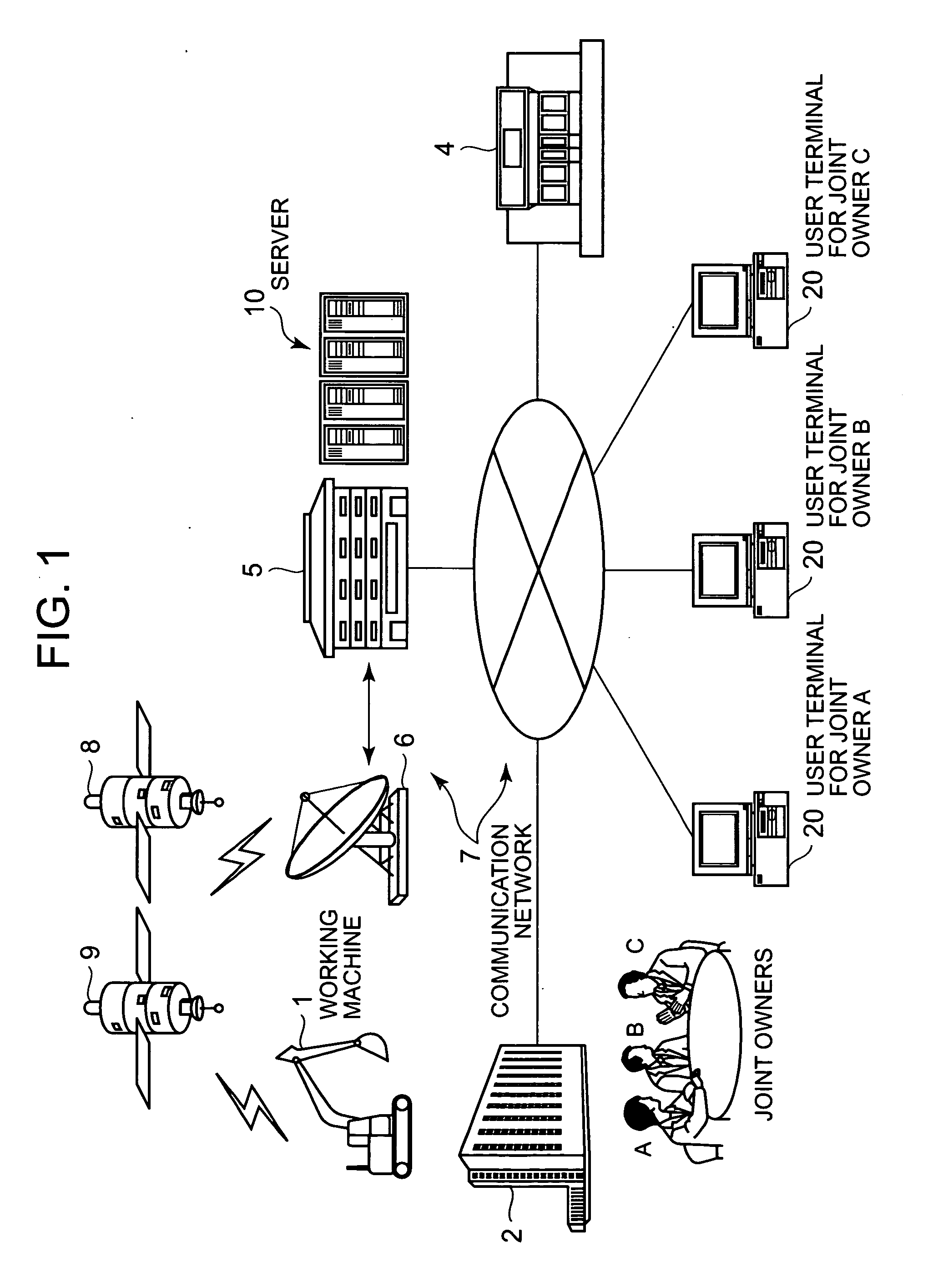
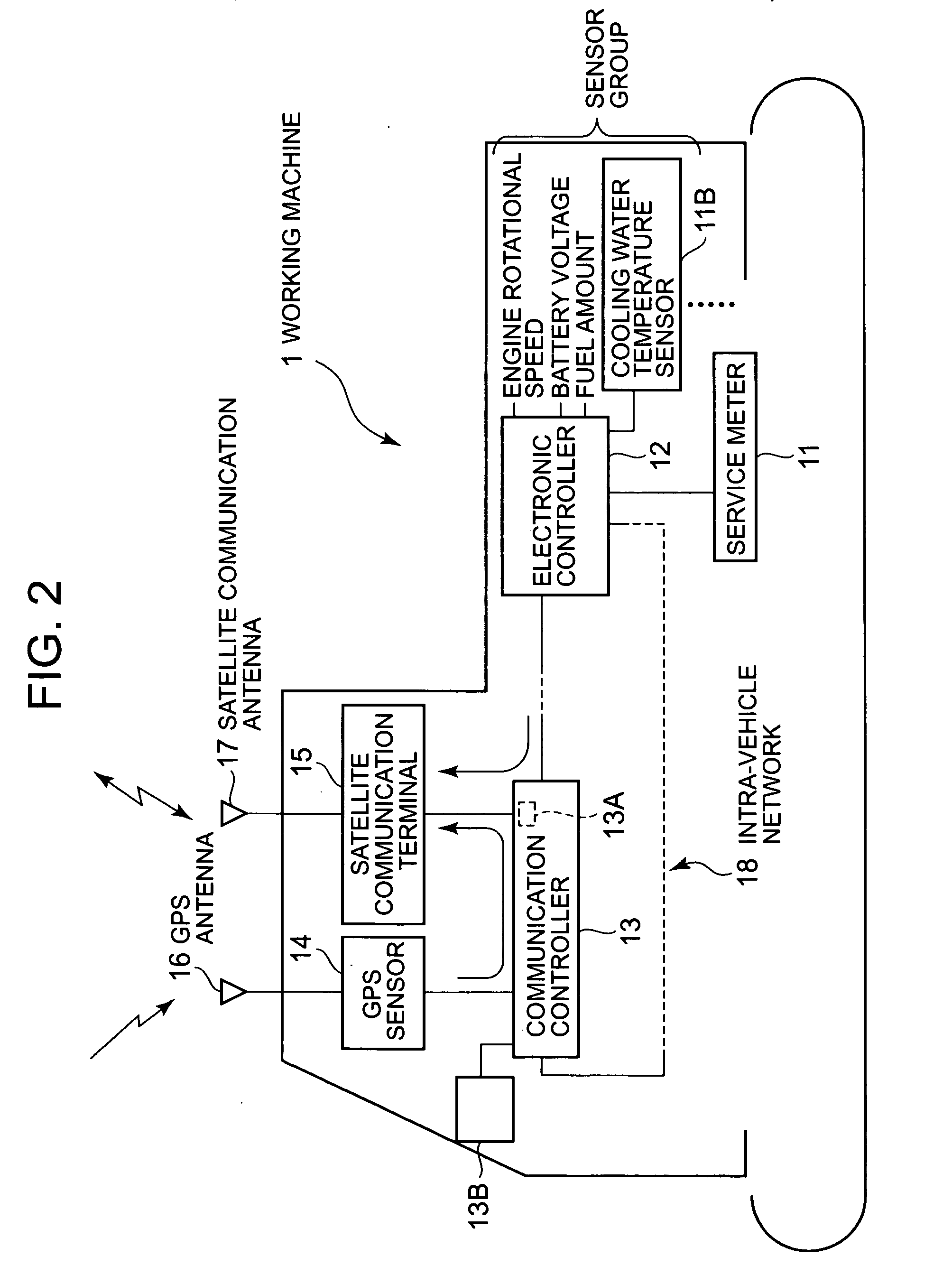
Working machine management system
InactiveUS20070094055A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesRoad vehicles traffic controlServer allocationWorld Wide Web
A server (10) enables users (A-B) sharing the same working machine (1) to mutually monitor a usage state by each user. The server (10) receives a user ID, the working time, the engine cooling water temperature, and the current position that are detected in the working machine (1) through a satellite communication network, and calculates the usage time, the usage location, the load amount, and a usage proportion for each user. The server (10) sends a warning to the user terminals 20 when the usage time or location is not as planned, or the load amount is excessive. The server (10) periodically reports the usage times and locations, the load amounts, and the usage proportions for the users (A-B) to the user terminals (20). The server (10) allocates maintenance costs of the working machine (1) automatically between the users (A-B) according to the usage proportions of the users (A-B).
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com