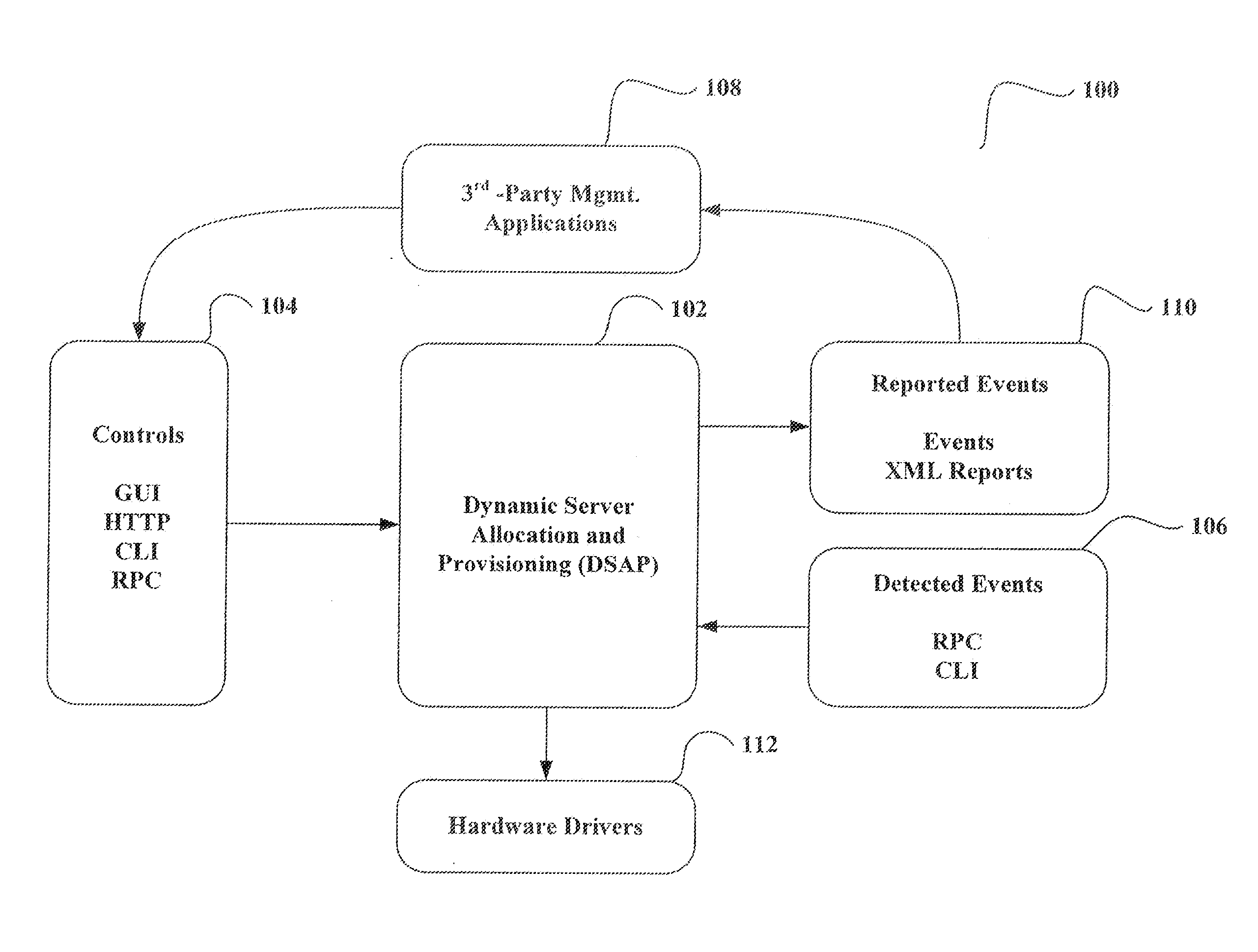
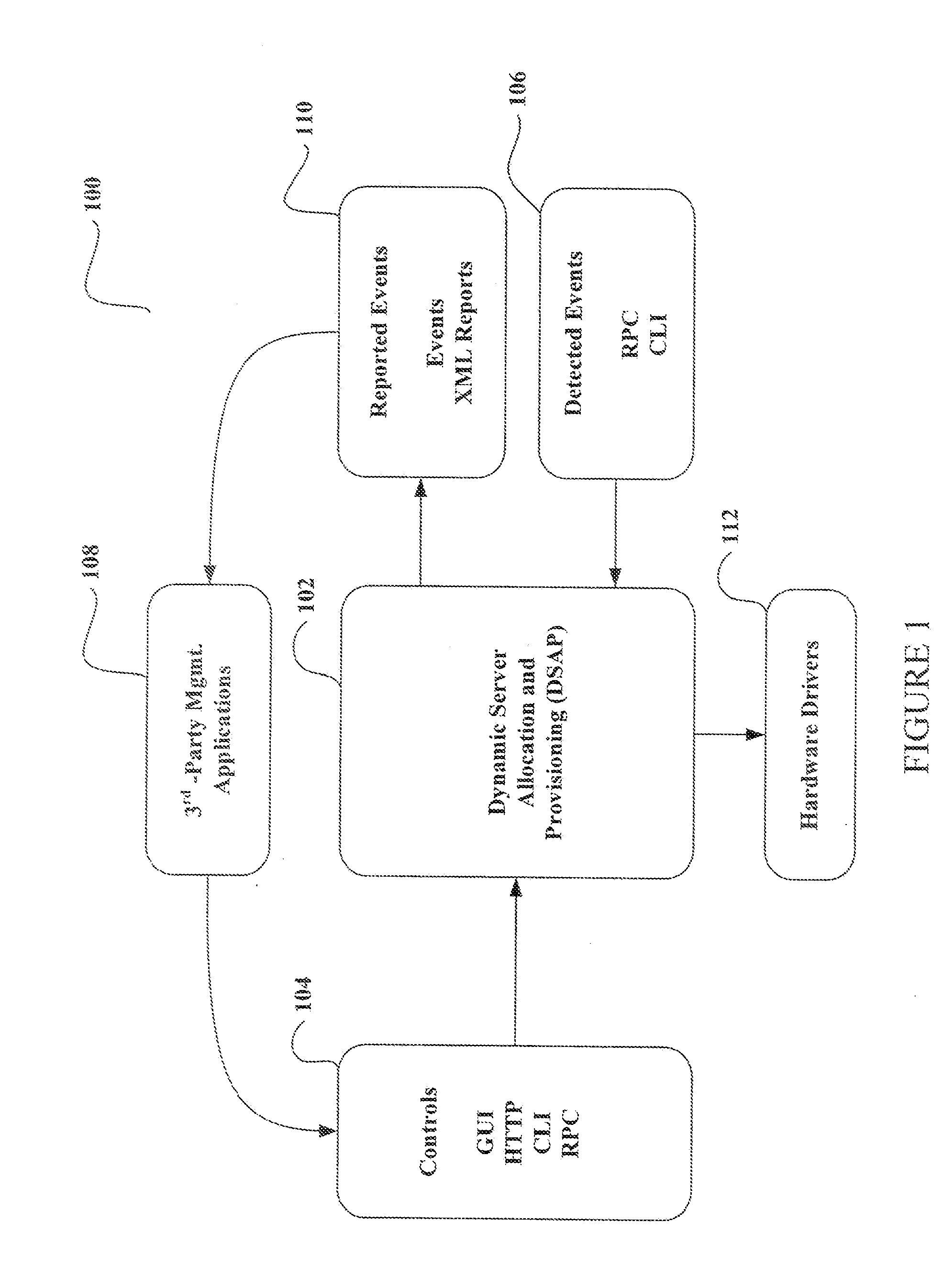
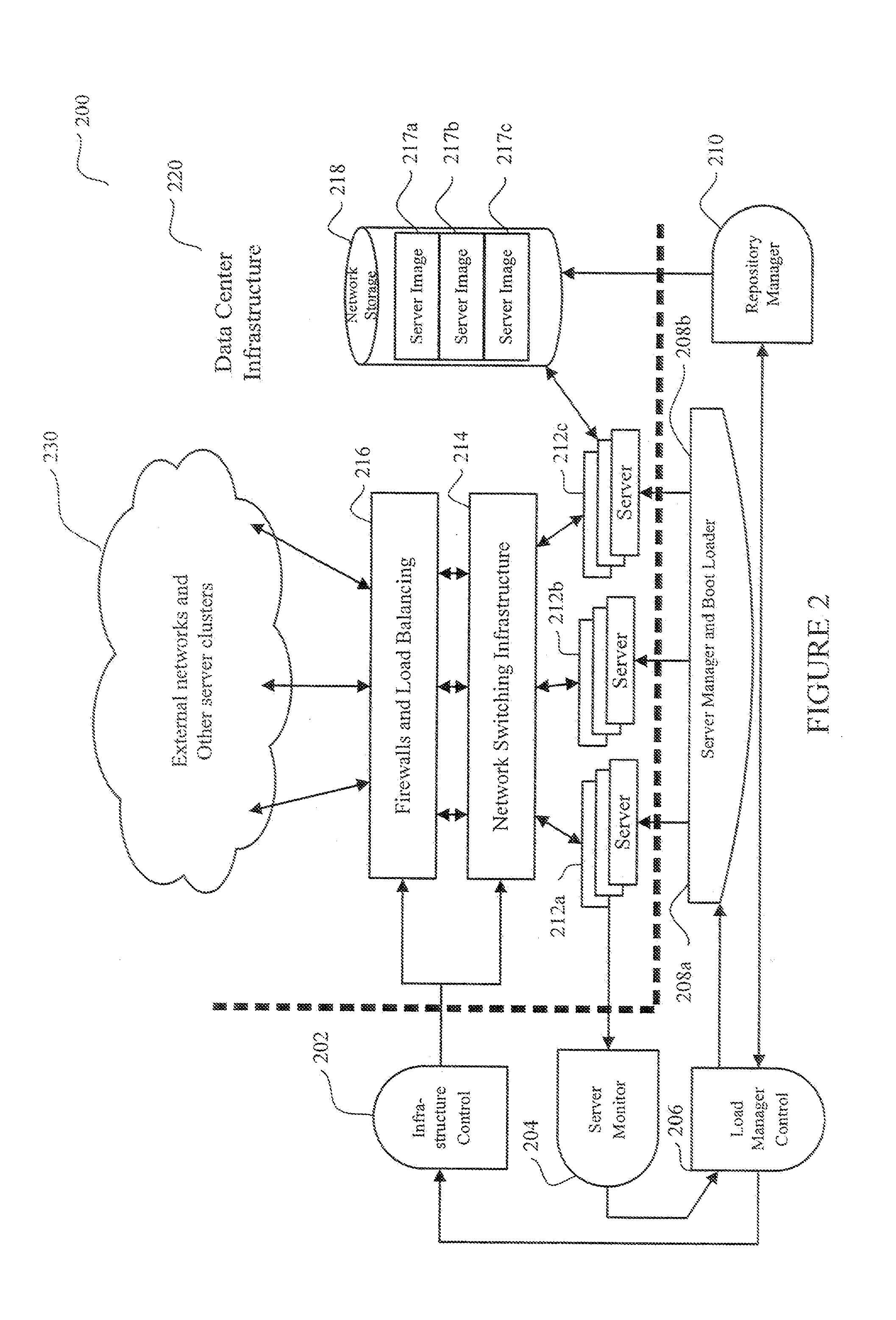
System and method for dynamic server allocation and provisioning
a server allocation and dynamic technology, applied in the field of computer resource management systems and methods, can solve the problems of irreversible changes to the server's disk drive, time-consuming, manual operation, etc., and achieve the effects of fewer servers, reduced capital costs, and massive improvements in server utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example implementations
[0135] VII. Example Implementations
[0136] Generally, as will be appreciated by one skilled in the relevant art(s) after reading the description herein, the present invention (i.e., DSAP system 102 and / or any components(s) or function(s) thereof) may be implemented using hardware, software or a combination thereof and may be implemented in one or more computer systems or other processing systems. In fact, in one embodiment, the invention is directed toward one or more computer systems capable of carrying out the functionality described herein. An example of a computer system 500 is shown in FIG. 5. Computer system 500 includes one or more processors, such as processor 504. The processor 504 is connected to a communication infrastructure 506 (e.g., a communications bus, cross-over bar, or network). Various software embodiments are described in terms of this exemplary computer system. After reading this description, it will become apparent to a person skilled in the relevant art(s) how...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com