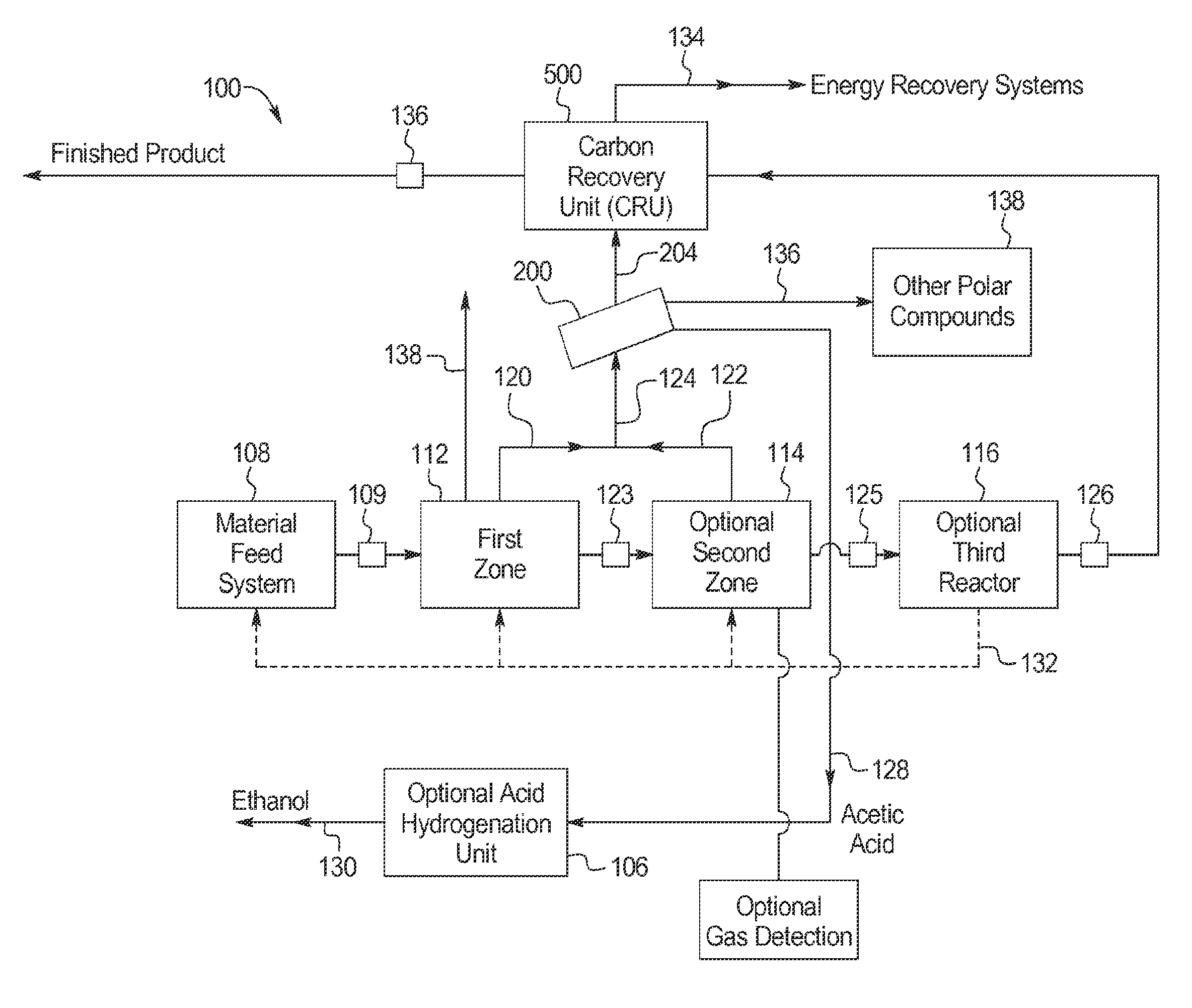
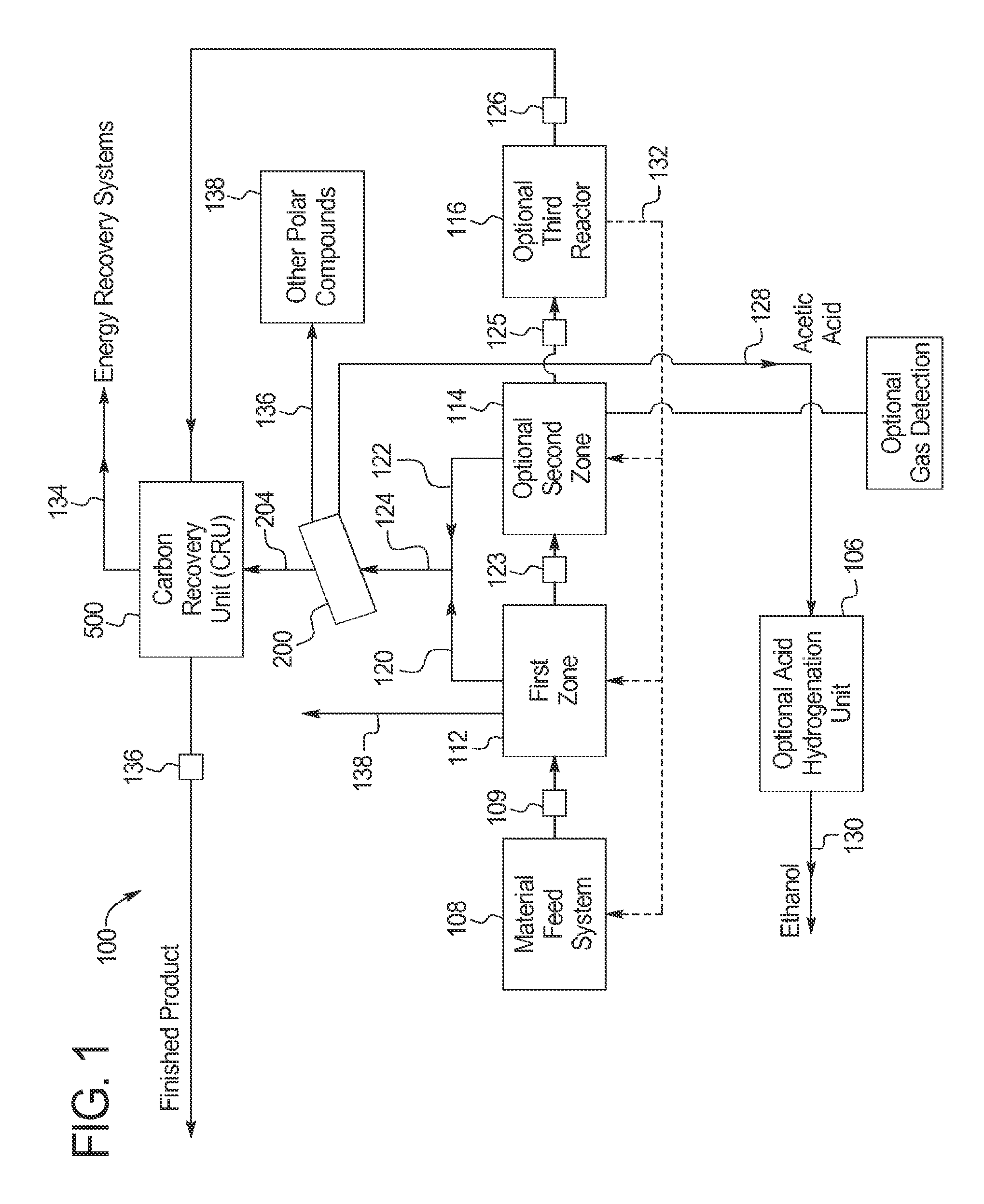
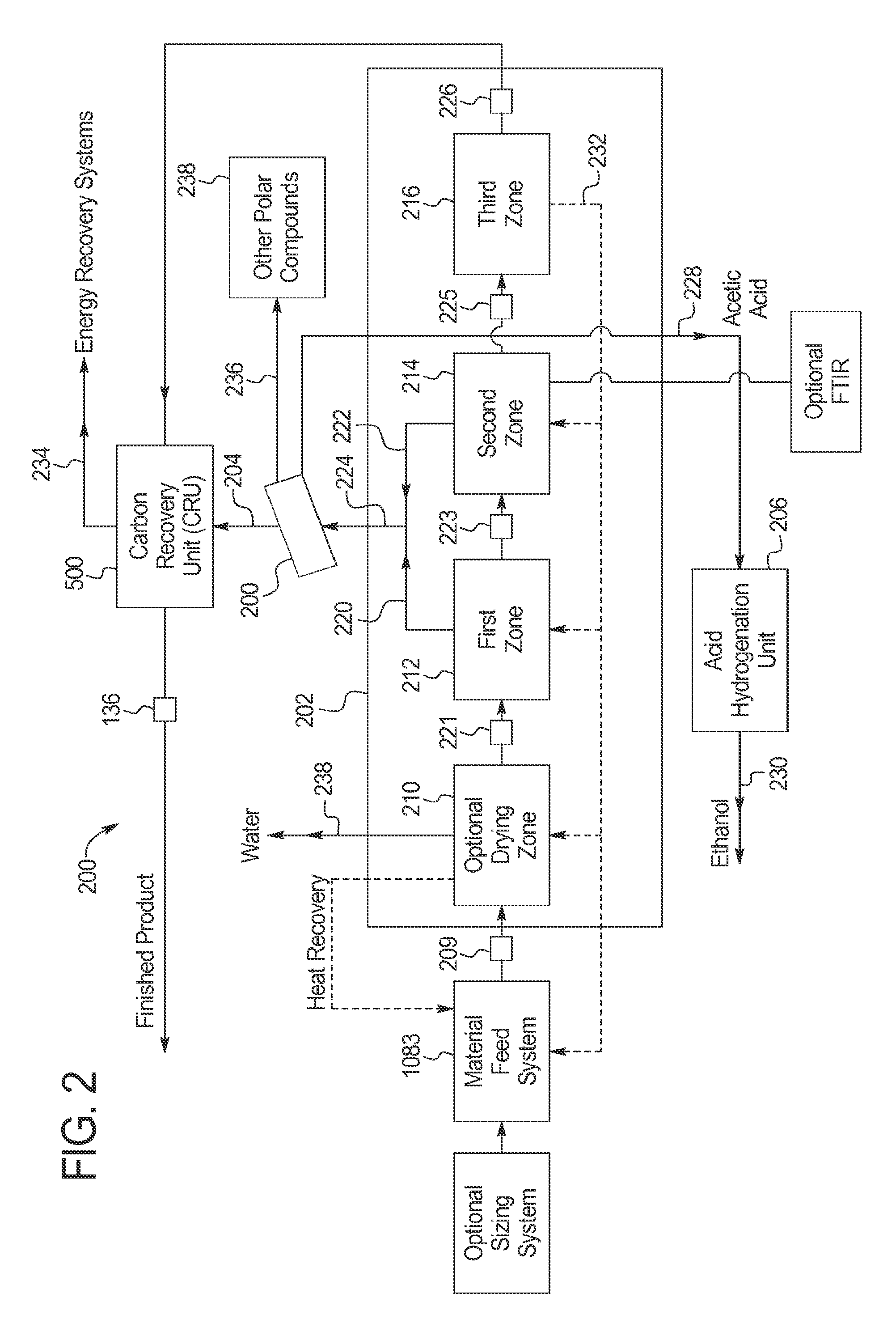
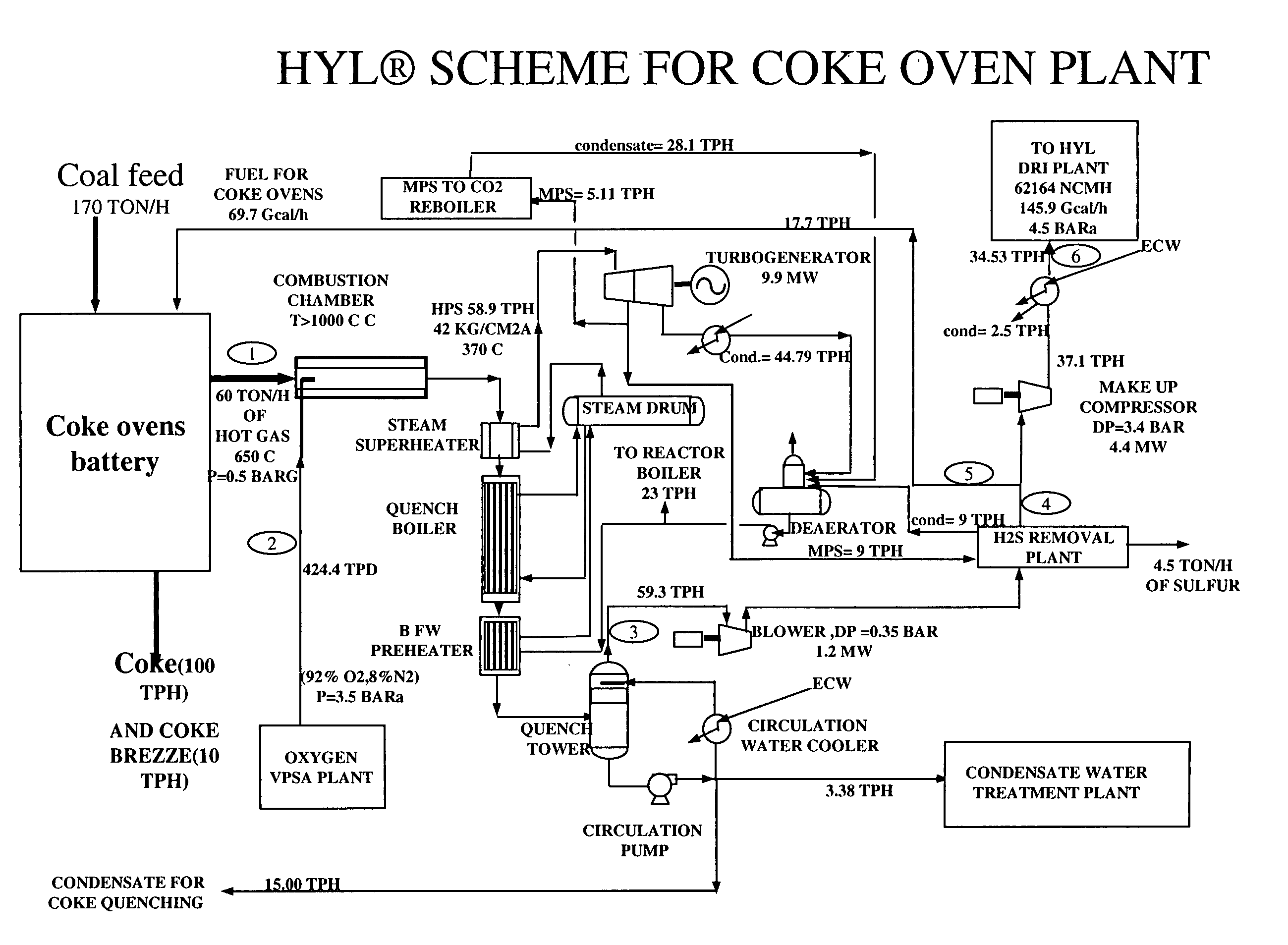
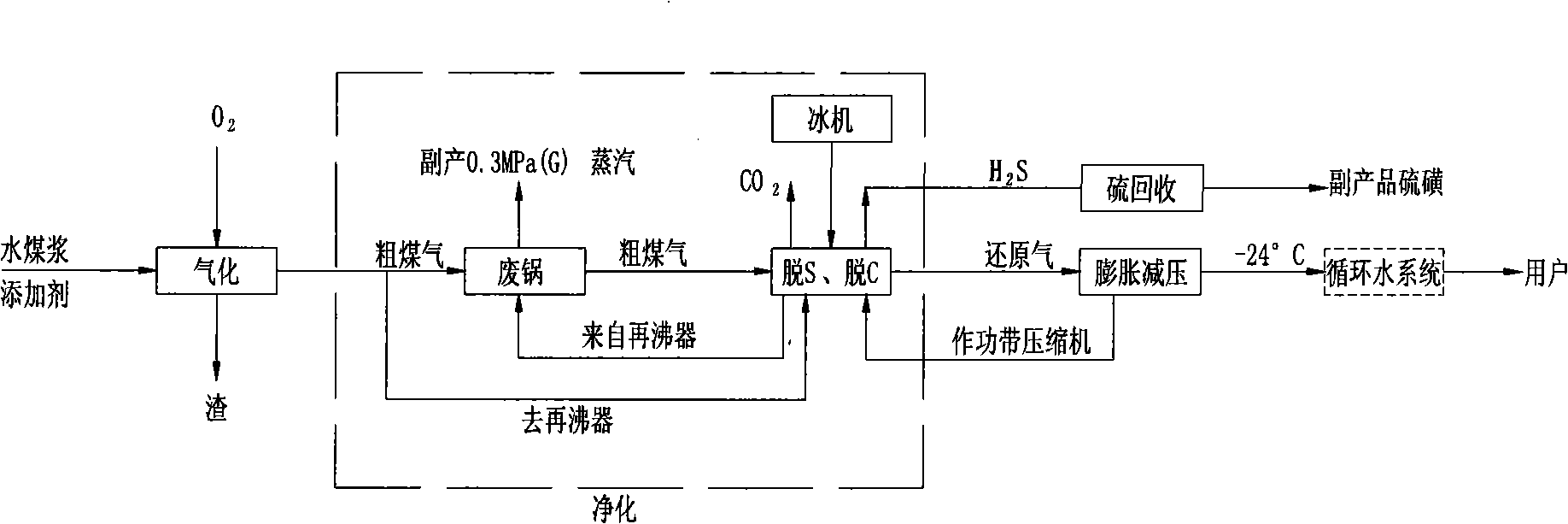
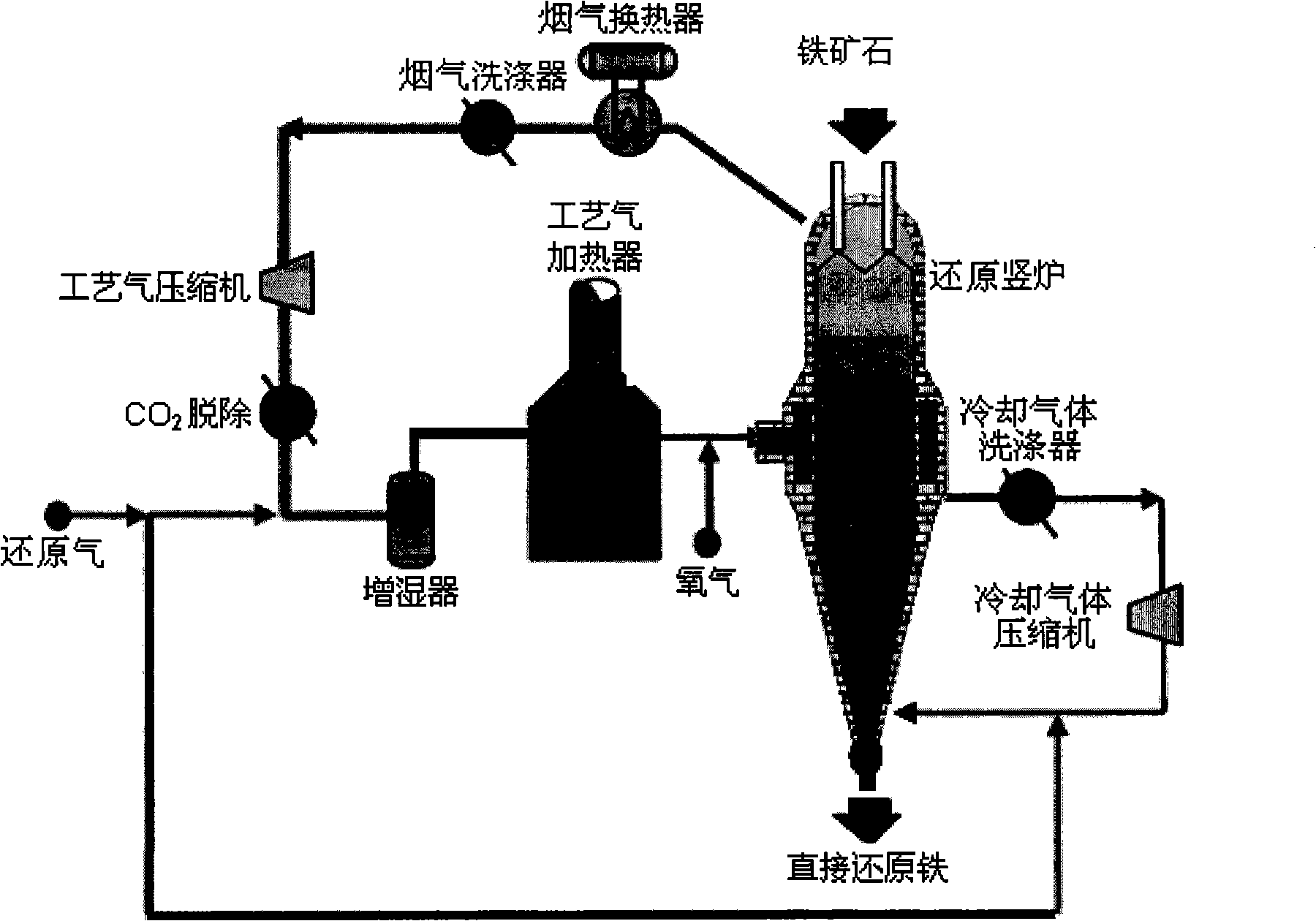
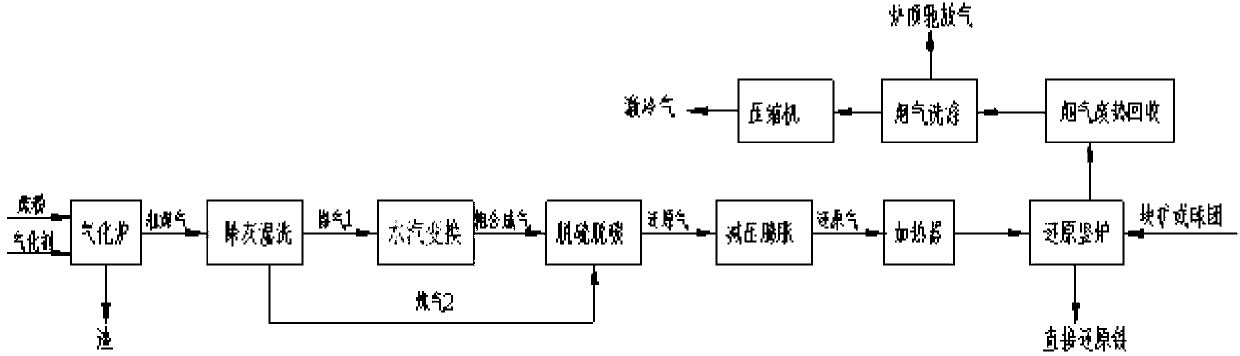
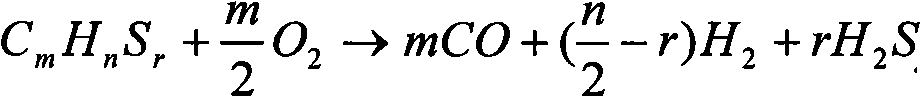Patents
Literature
2003results about "Gas emission reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
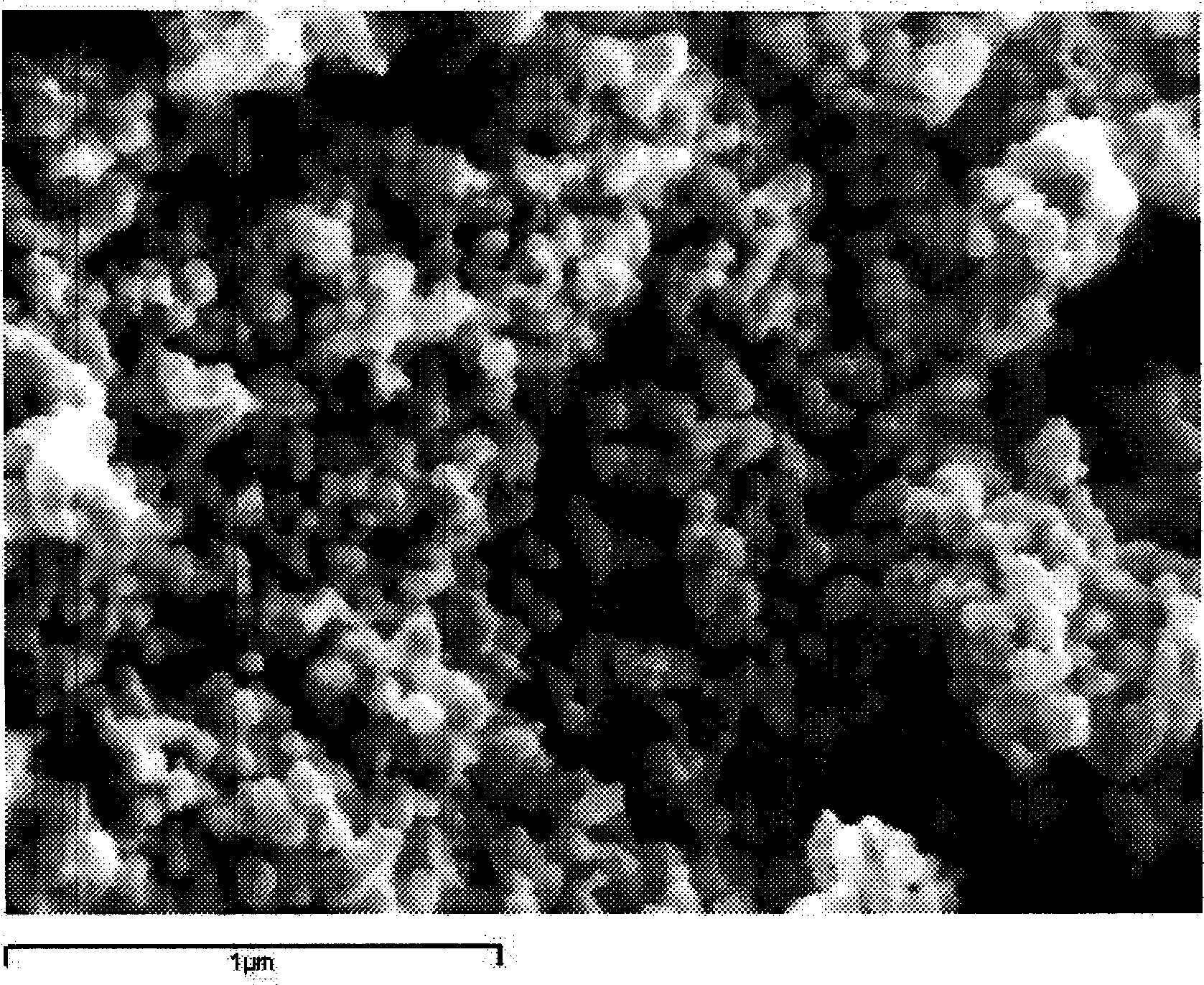
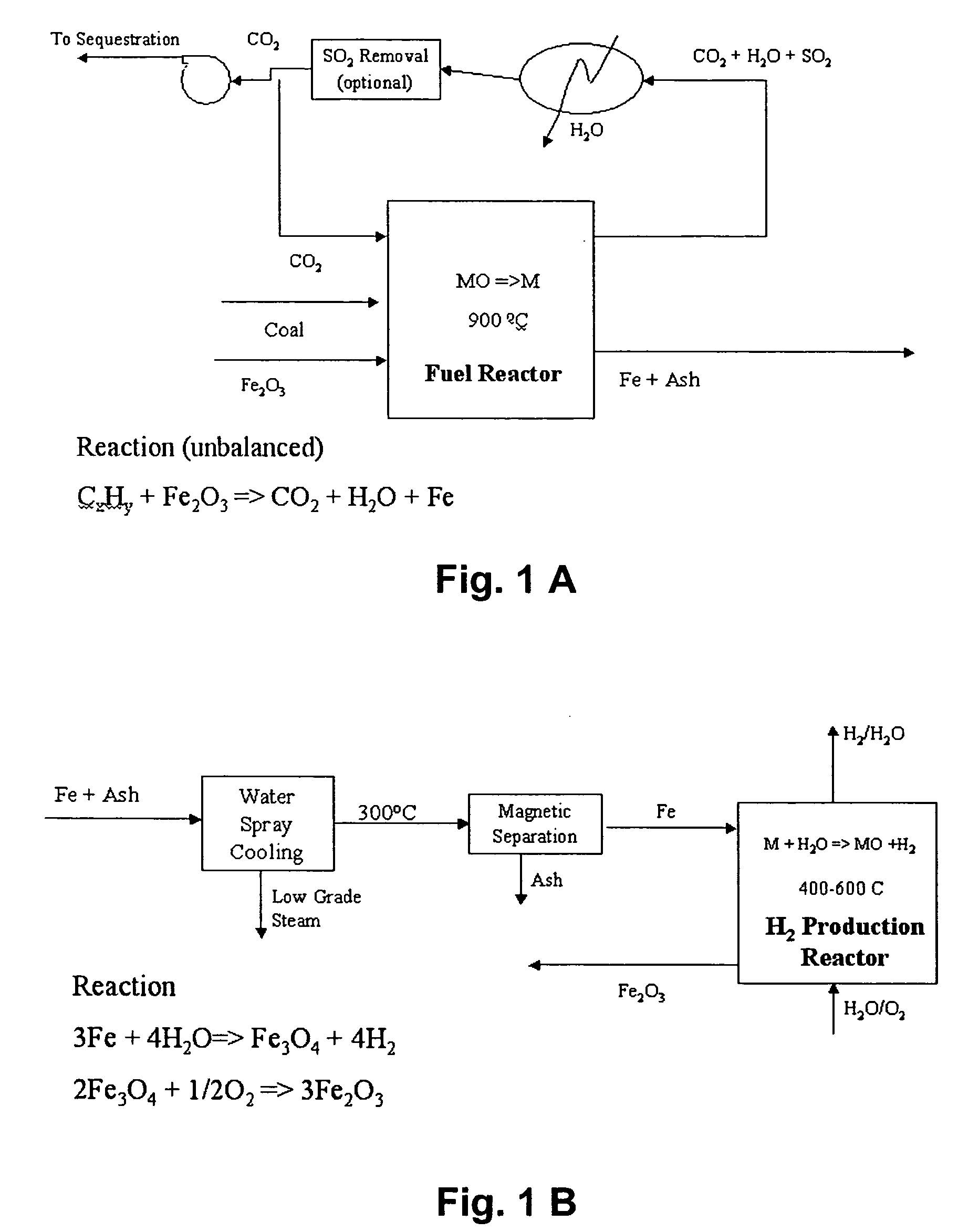
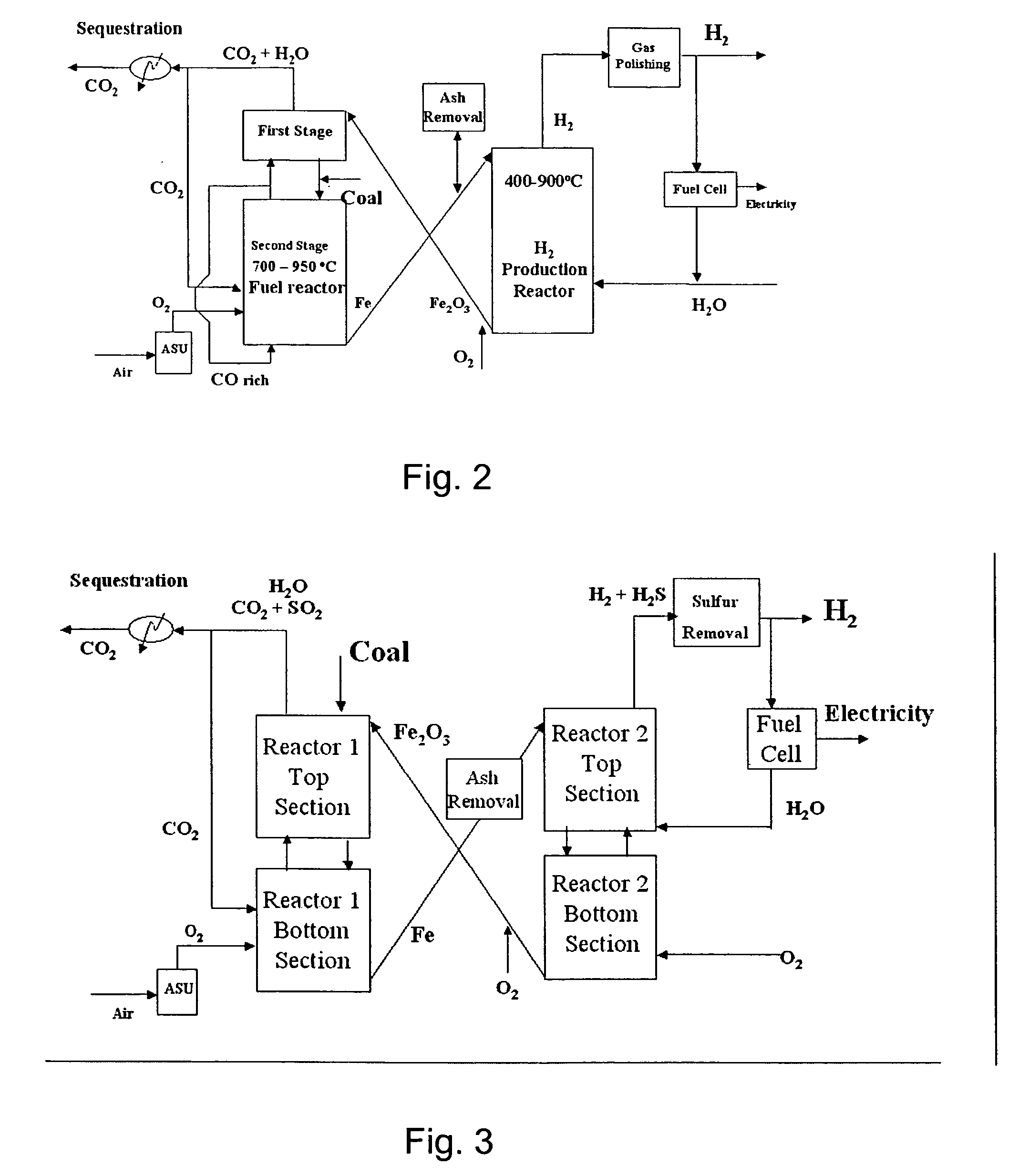
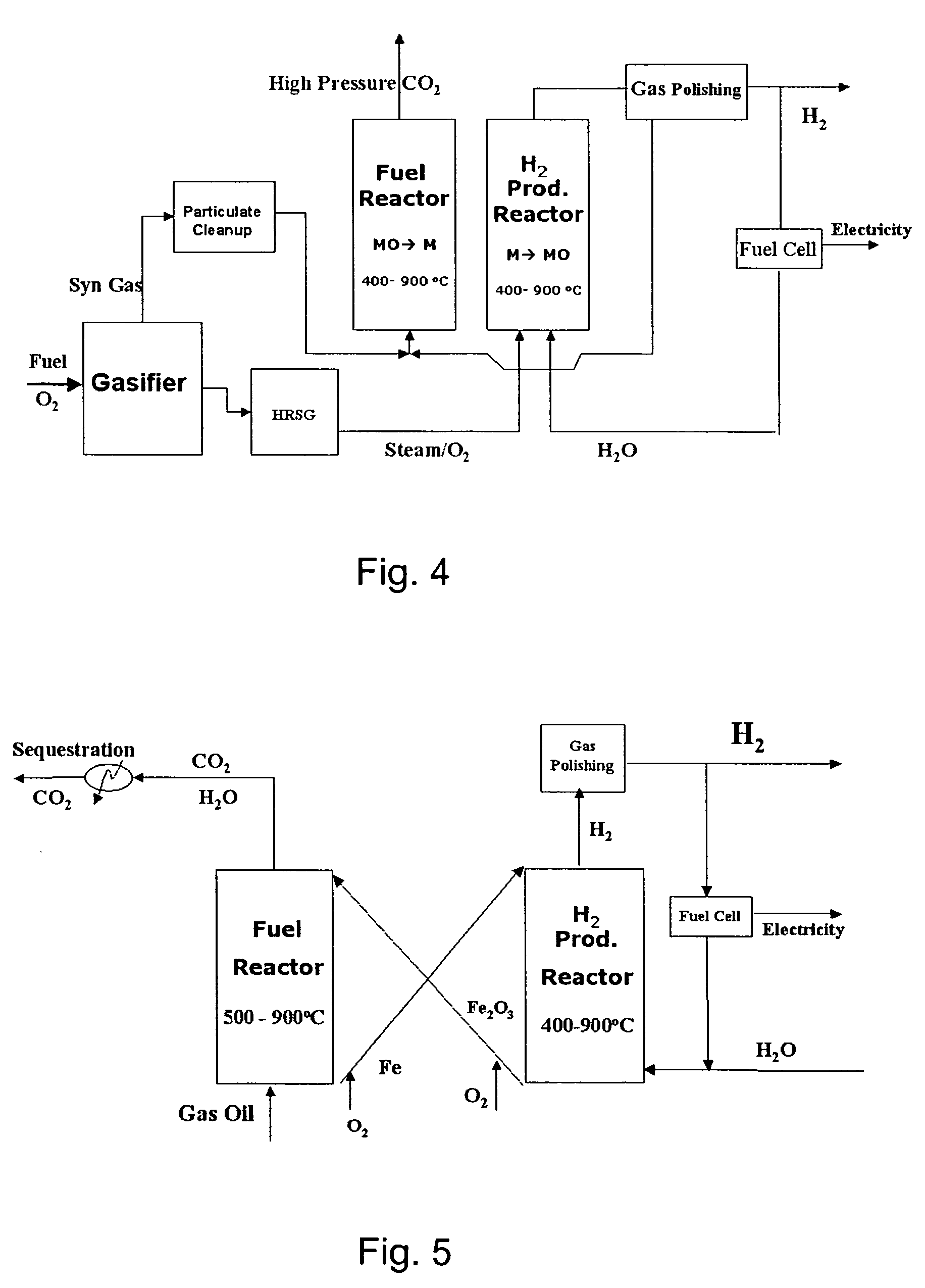
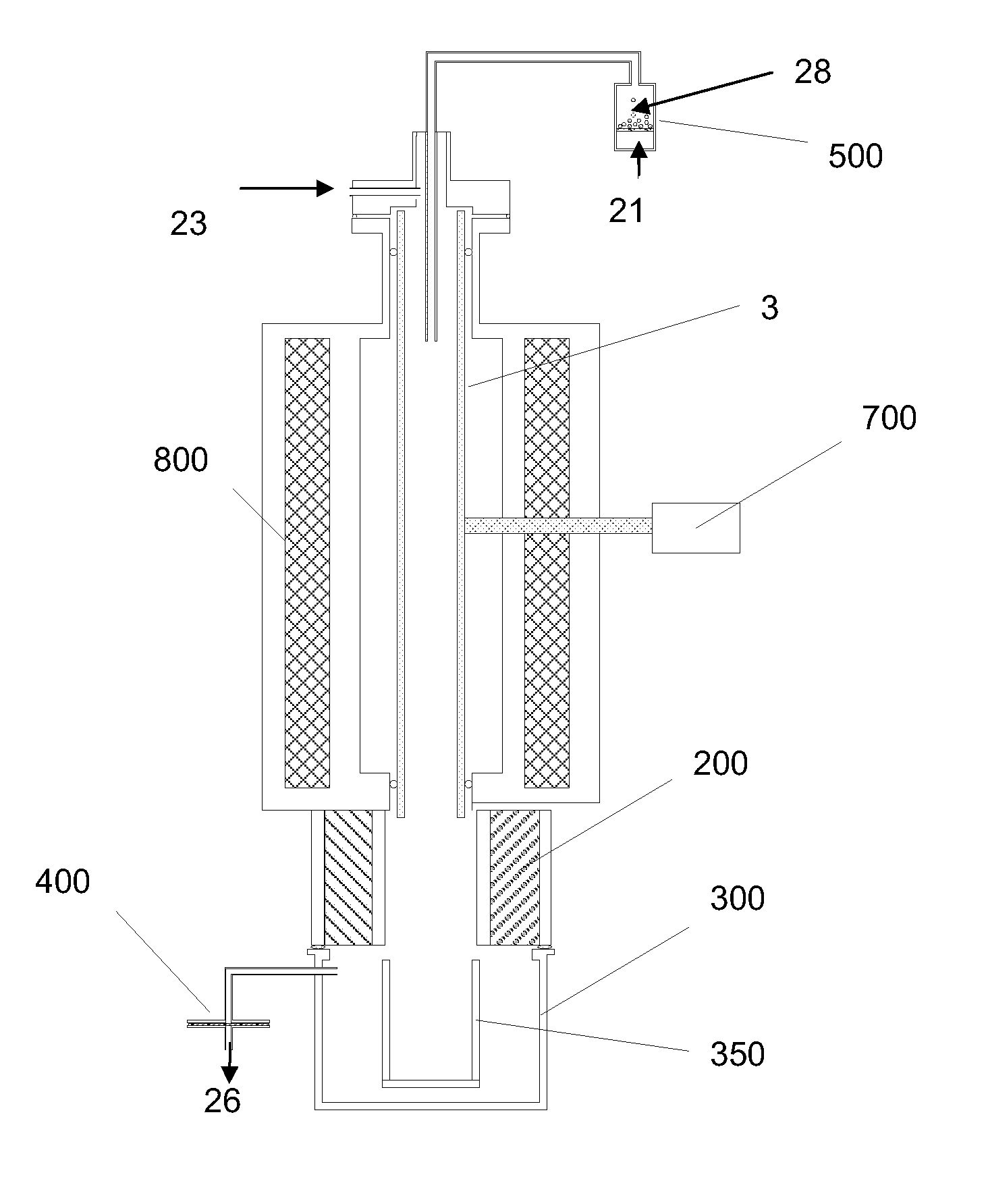
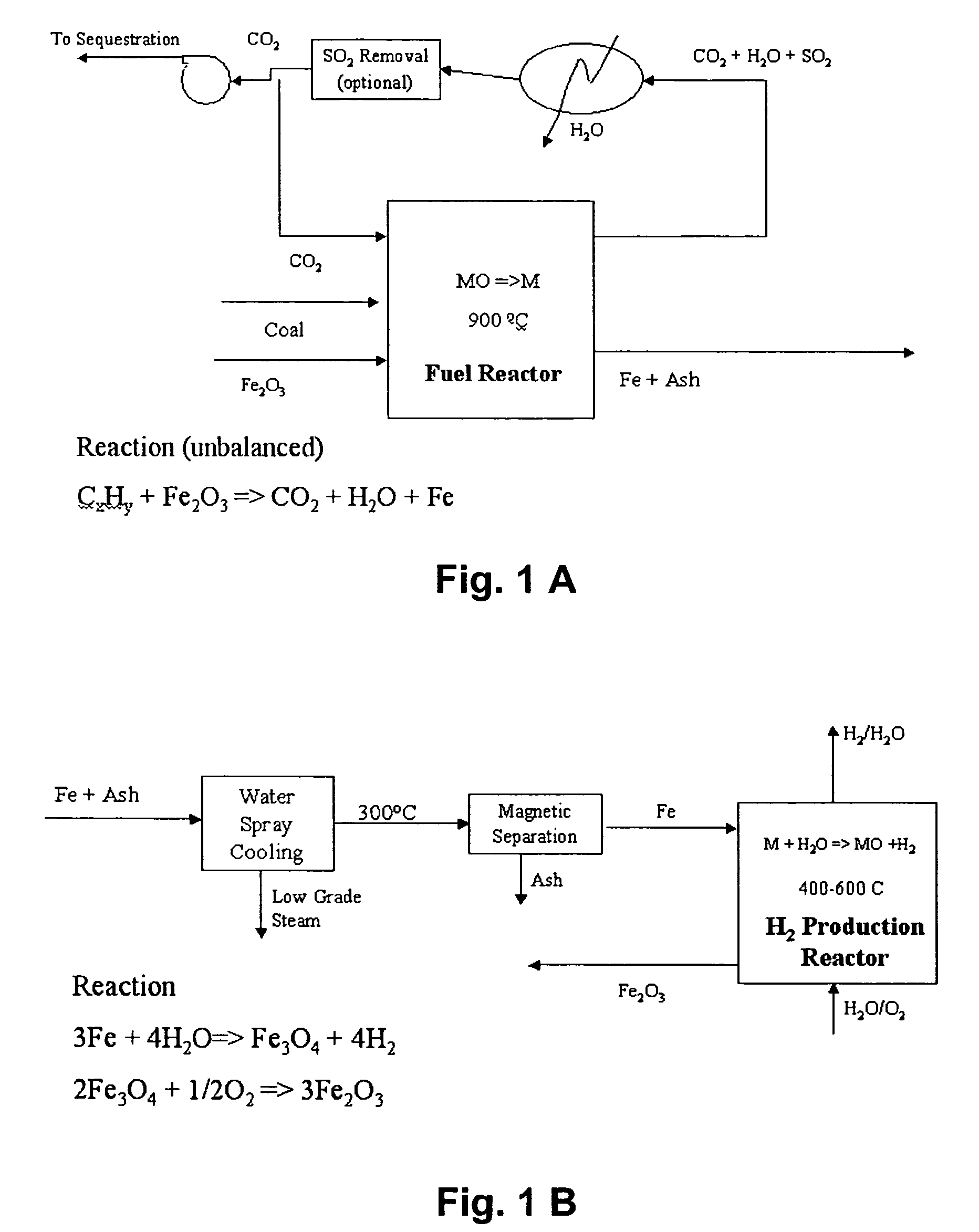
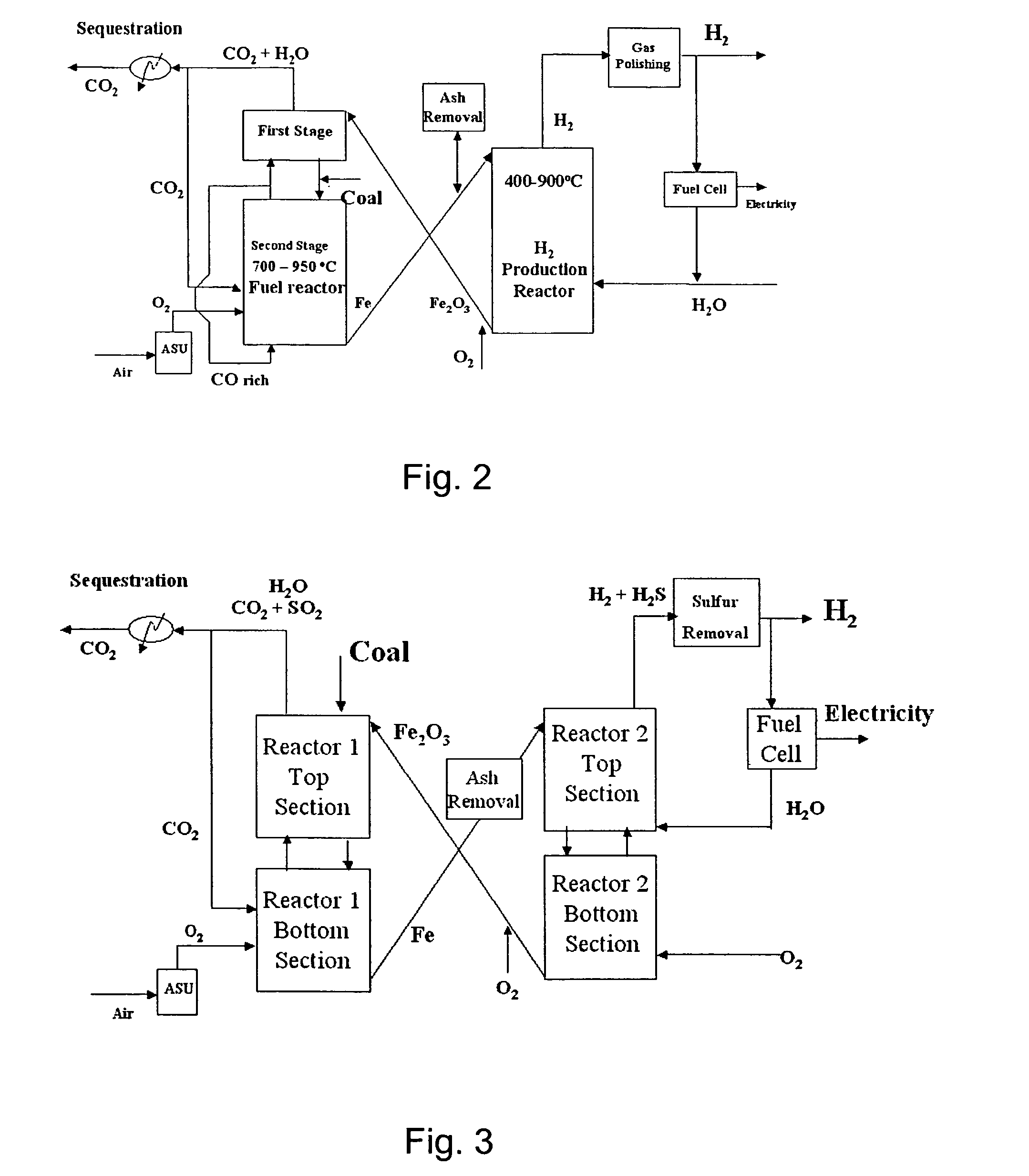
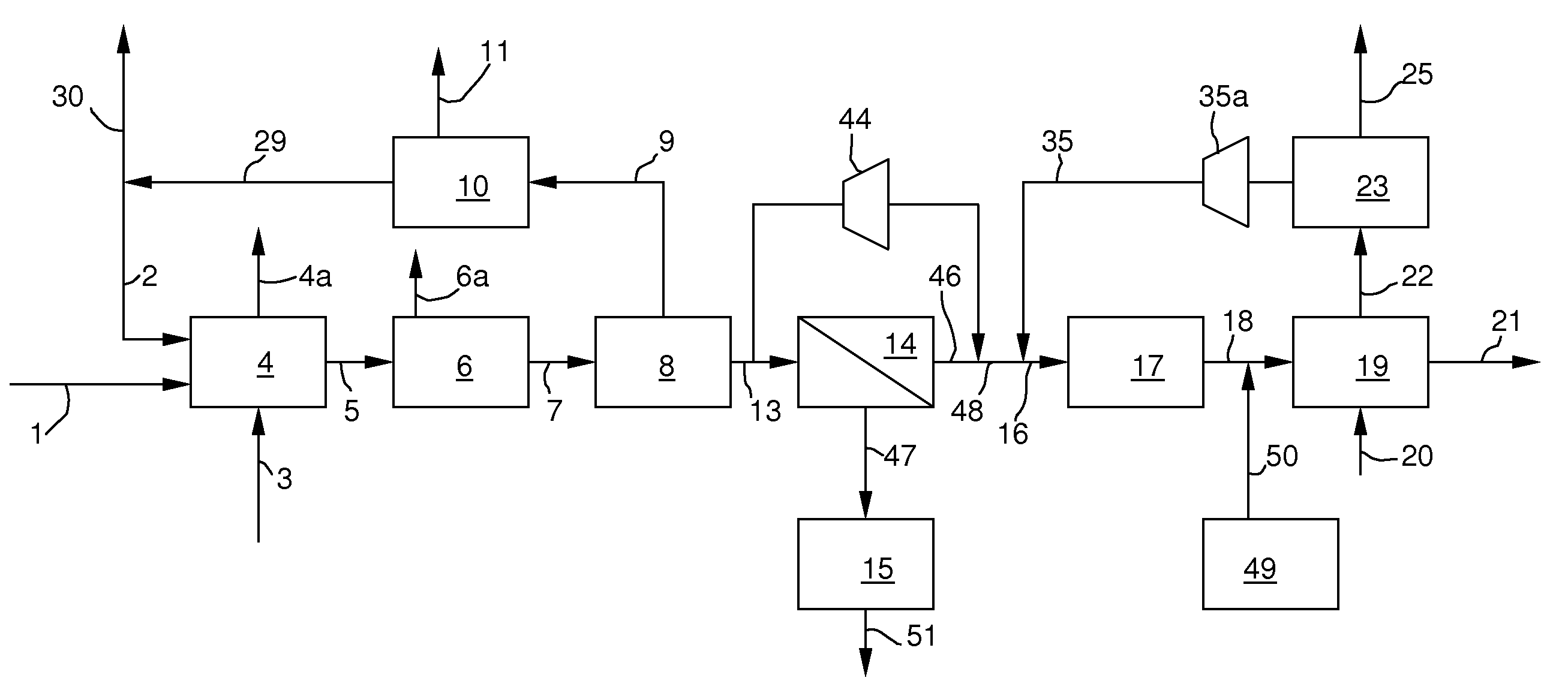
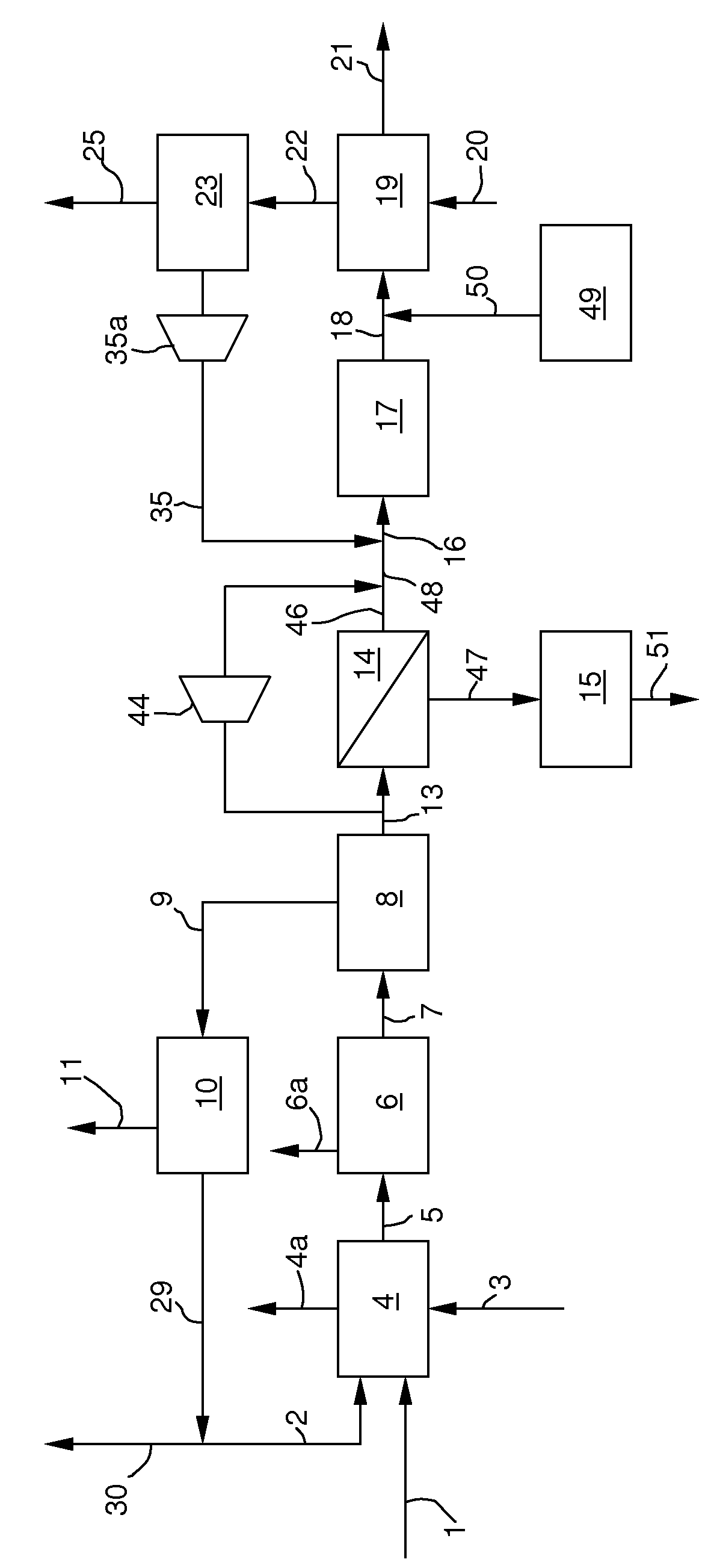
Combustion looping using composite oxygen carriers
ActiveUS20050175533A1Increase surface areaImprove energy conversion efficiencyHydrogen productionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationHydrogenCombustion
A method for producing hydrogen gas is provided and comprises reducing a metal oxide in a reduction reaction between a carbon-based fuel and a metal oxide to provide a reduced metal or metal oxide having a lower oxidation state, and oxidizing the reduced metal or metal oxide to produce hydrogen and a metal oxide having a higher oxidation state. The metal or metal oxide is provided in the form of a porous composite of a ceramic material containing the metal or metal oxide. The porous composite may comprise either a monolith, pellets, or particles.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Rapid solar-thermal conversion of biomass to syngas
ActiveUS20080086946A1Improve reaction kineticsWide rangeElectrical coke oven heatingSolar heating energySyngasReactor design
Methods for carrying out high temperature reactions such as biomass pyrolysis or gasification using solar energy. The biomass particles are rapidly heated in a solar thermal entrainment reactor. The residence time of the particles in the reactor can be 5 seconds or less. The biomass particles may be directly or indirectly heated depending on the reactor design. Metal oxide particles can be fed into the reactor concurrently with the biomass particles, allowing carbothermic reduction of the metal oxide particles by biomass pyrolysis products. The reduced metal oxide particles can be reacted with steam to produce hydrogen in a subsequent process step.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
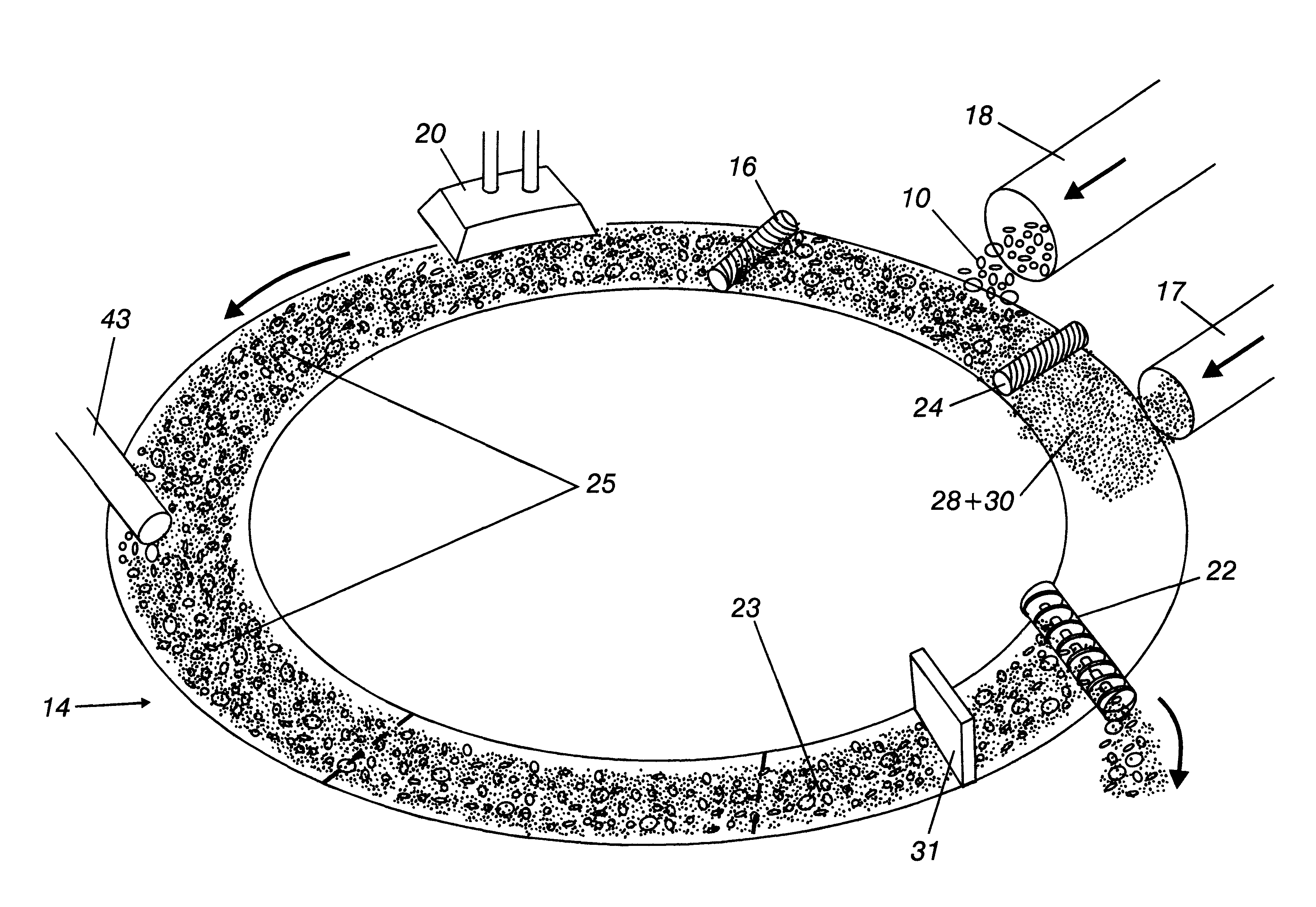
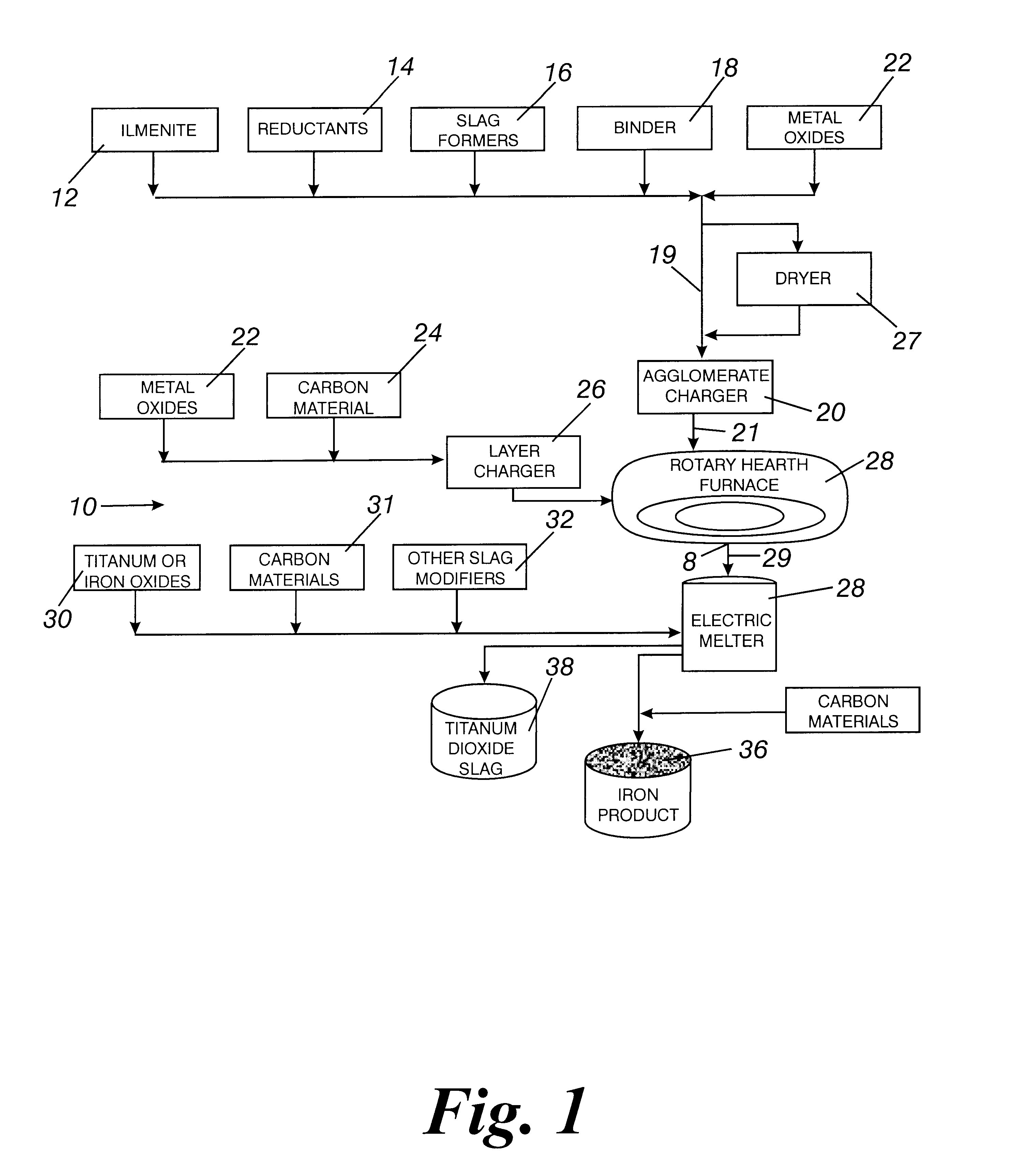
Method of producing a reduced metal, and traveling hearth furnace for producing same
InactiveUS6126718ALow gangue and ash contentSmall amountProcess efficiency improvementGas emission reductionHearthMetal
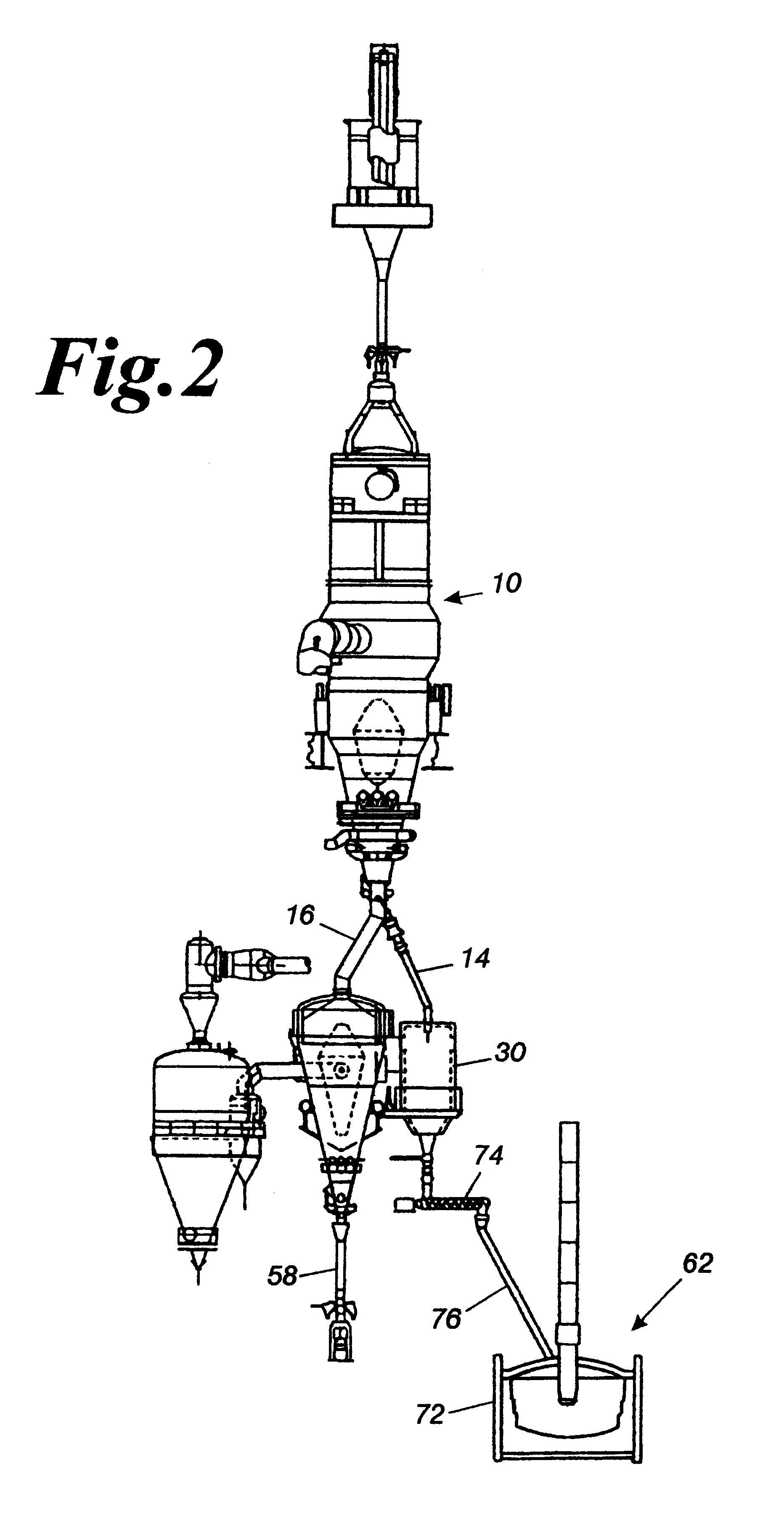
Producing reduced metal by charging and stacking a raw material containing a metal-containing material and a solid reducing material on a horizontally moving hearth of a traveling hearth furnace, by disposing a solid reducing material layer on the hearth, forming concave portions at the solid reducing material surface, stacking the raw material on the surface of the solid reducing material layer, reducing raw material by at least once heating and melting the material on the hearth to separate metal and gangue and ash ingredients, and discharging metal from the hearth.
Owner:KAWASAKI STEEL CORP
Method and apparatus for making metallic iron
InactiveUS6036744AHigh purityReadily and efficiently madeBlast furnace componentsRotary drum furnacesMolten slagCoal
A method of making metallic iron in which a compact, containing iron oxide such as iron ore or the like and a carbonaceous reductant such as coal or the like, is used as material, and the iron oxide is reduced through the application of heat, thereby making metallic iron. In the course of this reduction, a shell composed of metallic iron is generated and grown on the surface of the compact, and slag aggregates inside the shell. This reduction continues until substantially no iron oxide is present within the metallic iron shell. Subsequently, heating is further performed to melt the metallic iron and slag. Molten metallic iron and molten slag are separated one from the other, thereby obtaining metallic iron with a relatively high metallization ratio. Through the employment of an apparatus for making metallic iron of the present invention, the above-described method is efficiently carried out, and metallic iron having a high iron purity can be made continuously as well as productively not only from iron oxide having a high iron content but also from iron oxide having a relatively low iron content.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
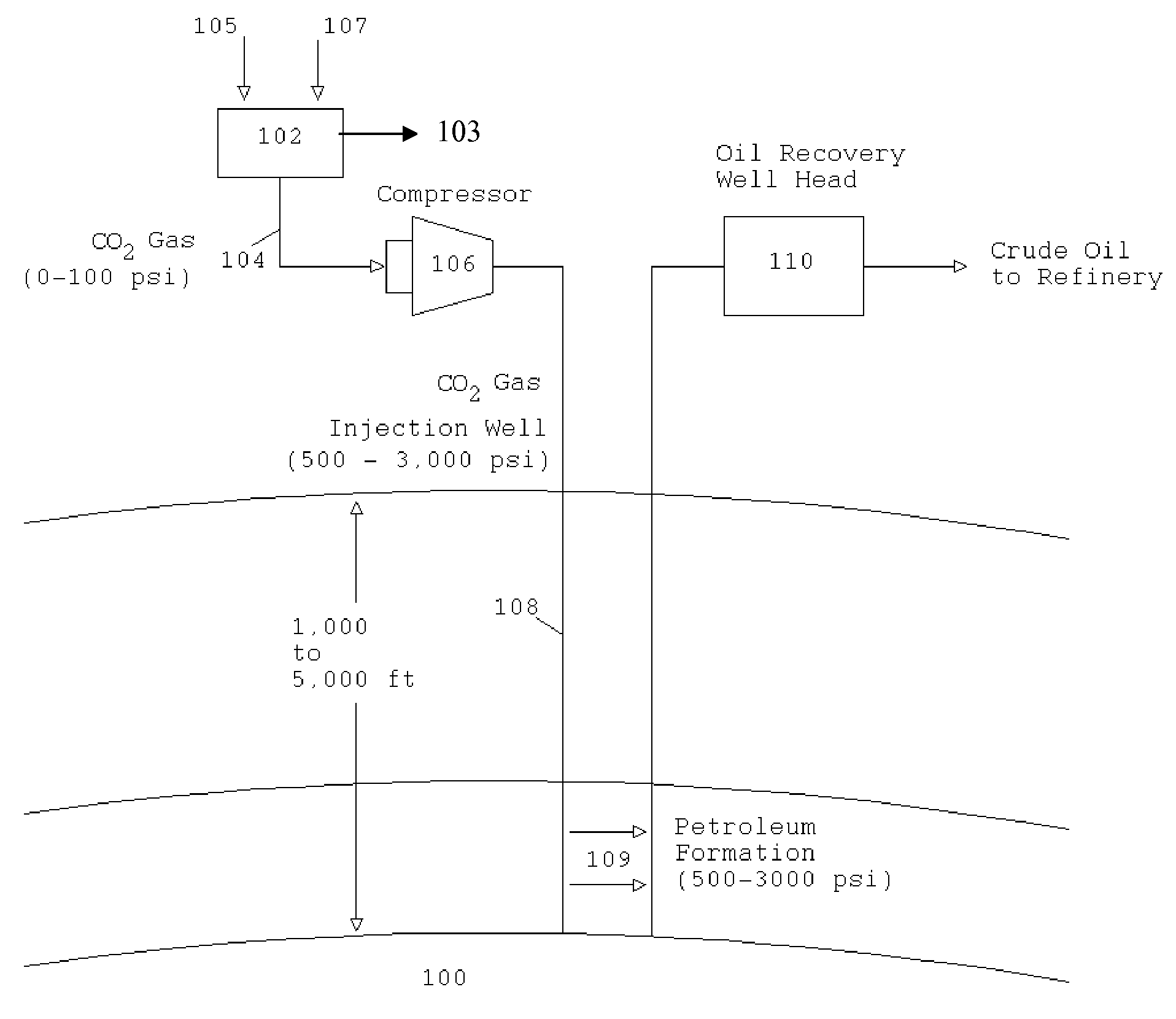
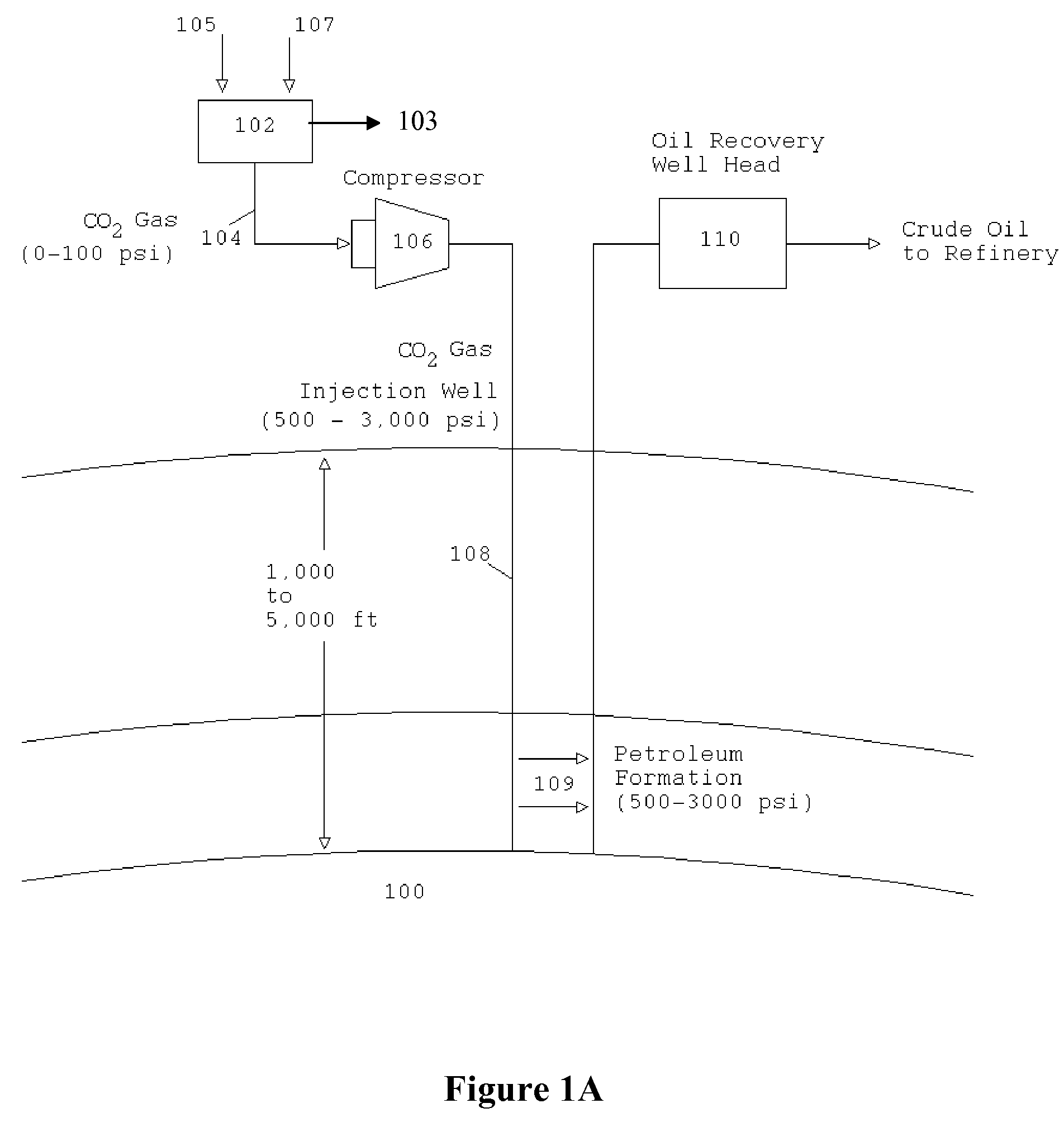
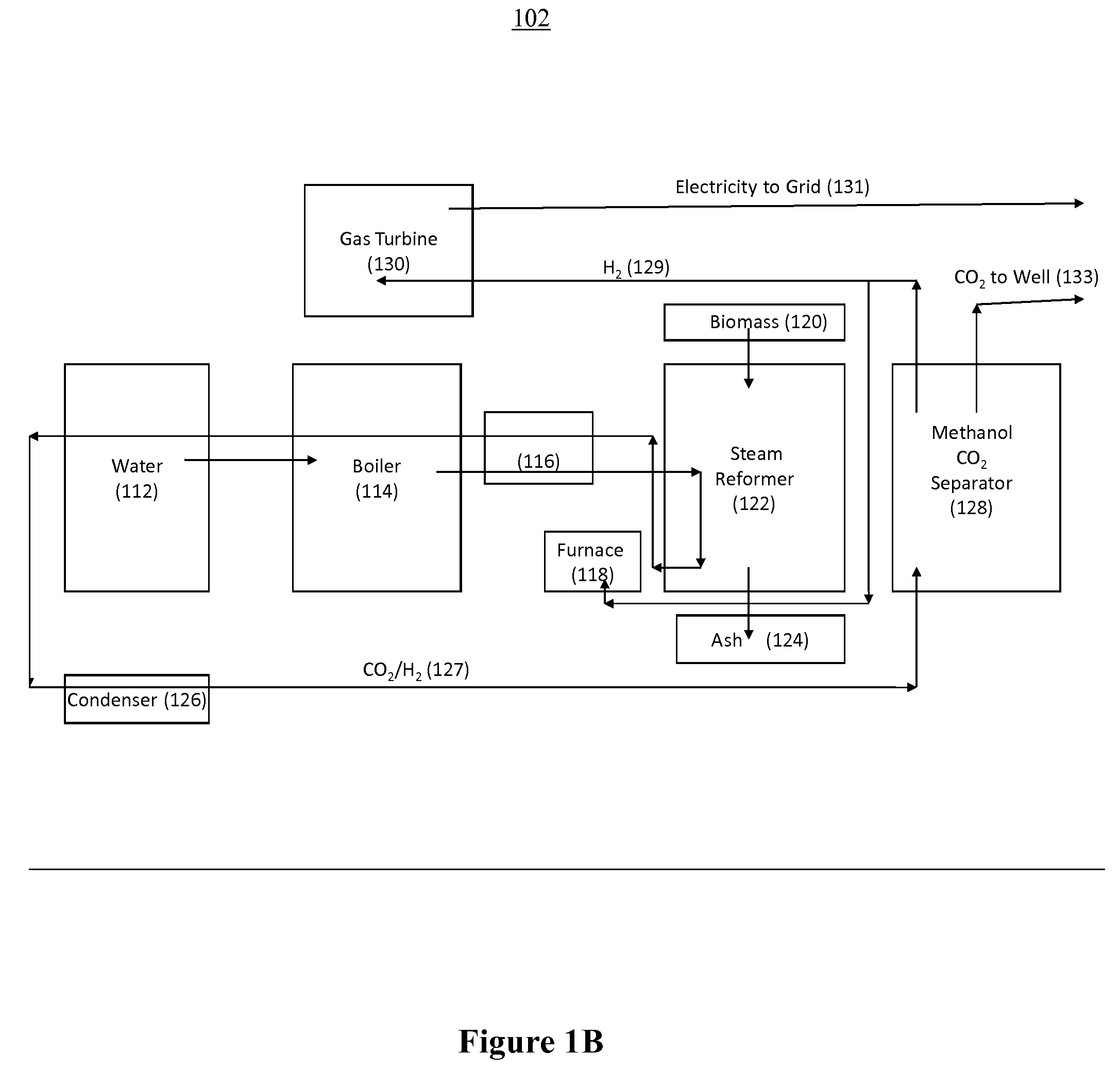
Portable apparatus for extracting low carbon petroleum and for generating low carbon electricity
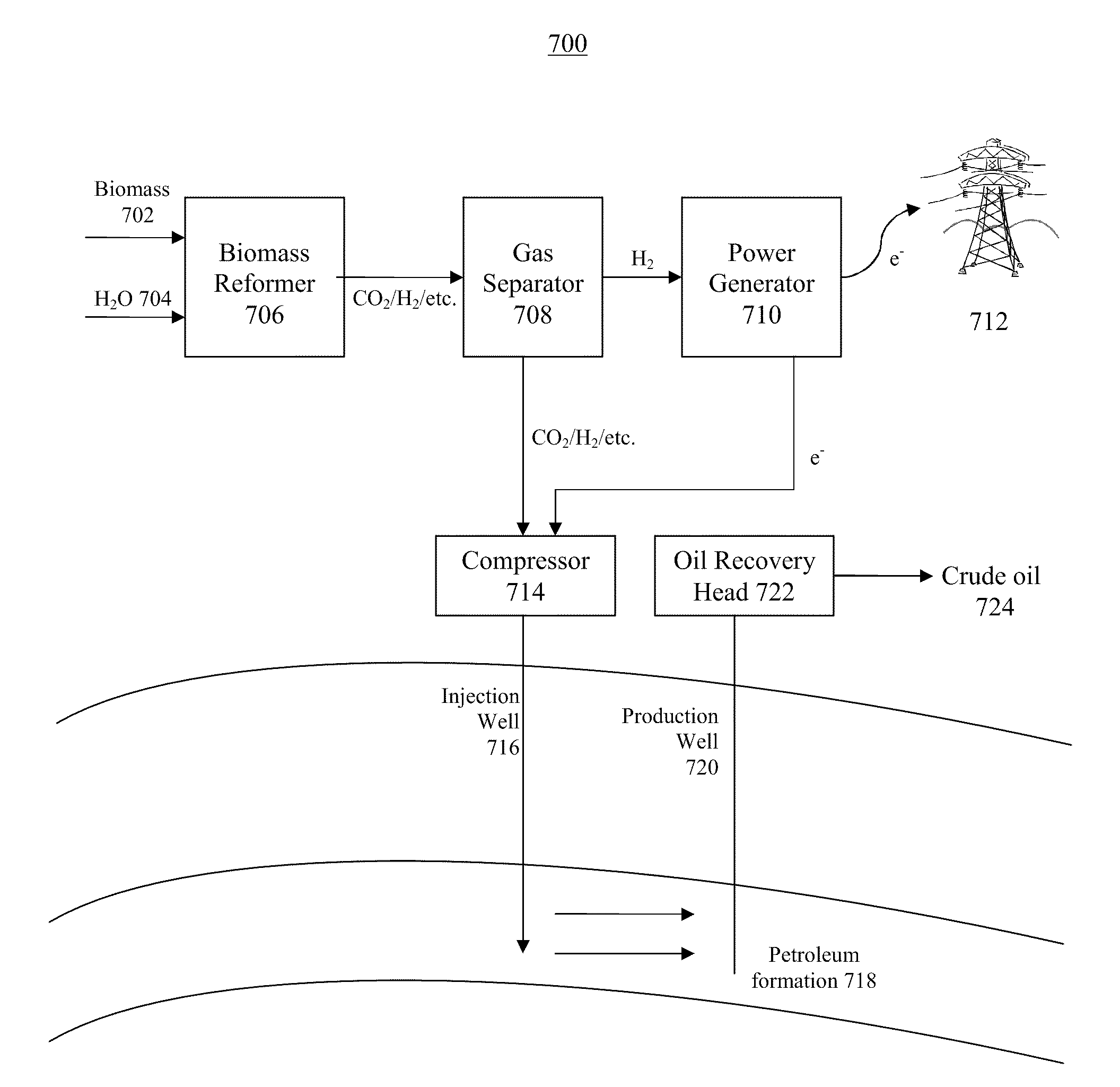
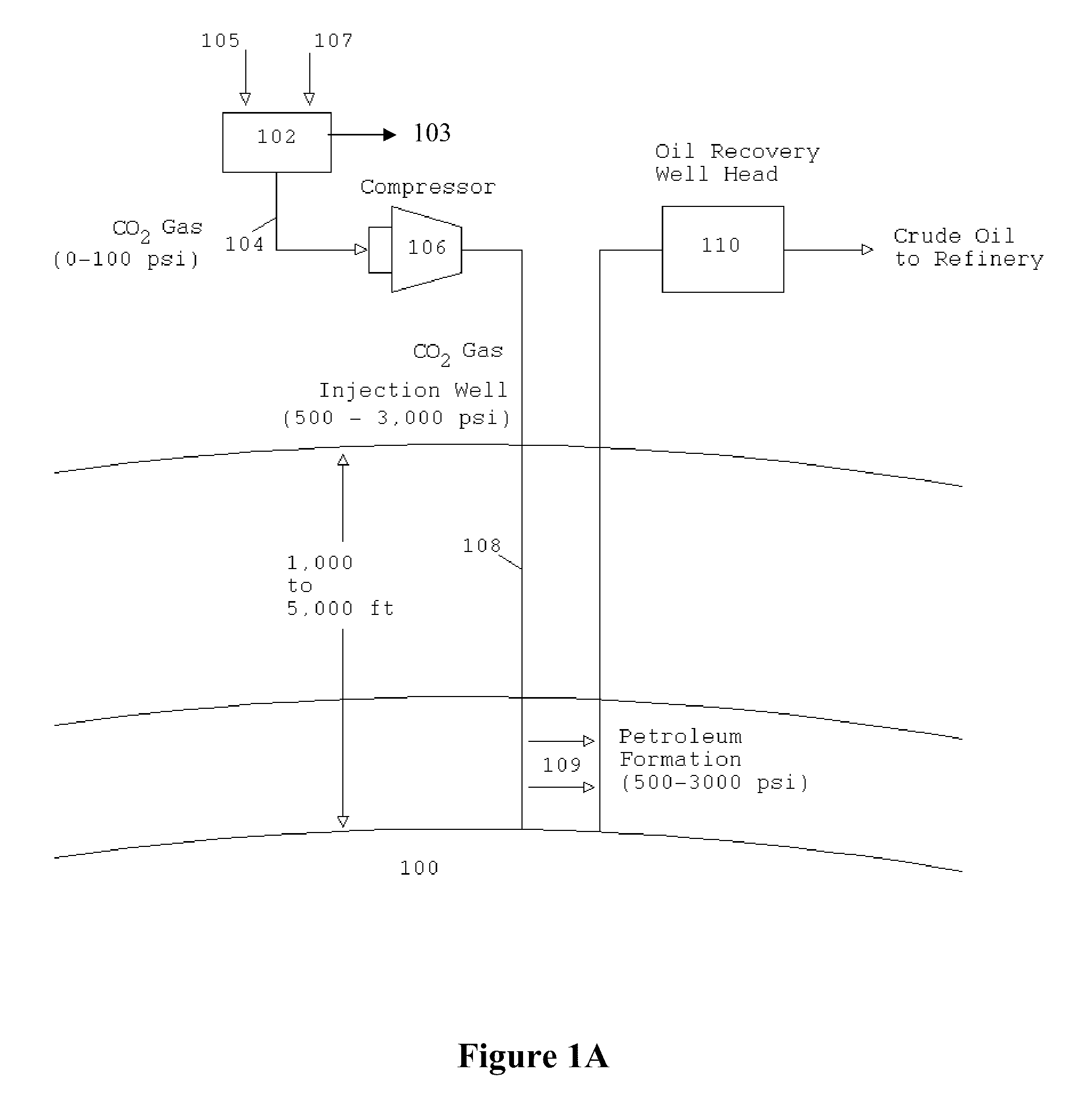
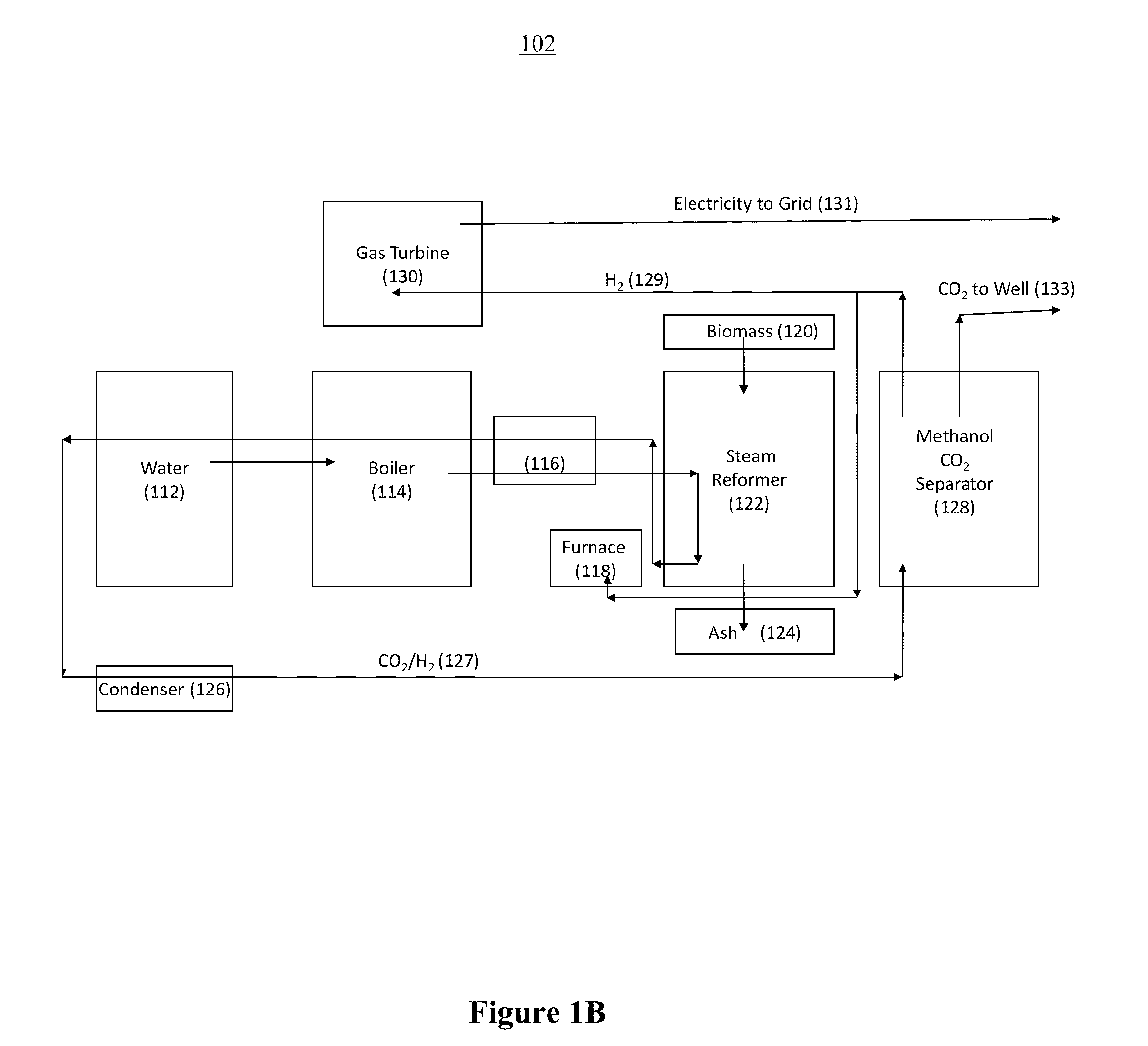
The Portable Renewable Energy System for Enhanced Oil Recovery (“PRESEOR”) is a truck mobile system that reforms biomass into CO2 and hydrogen, following which the gases are separated, with the CO2 sequestered underground for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) and the hydrogen used to generate several megawatts of carbon-free electricity. In contrast to large central power plants that are generally not well-located to support EOR, the small PRESEOR can go directly to the oilfields where it is needed, and do so in a timely manner. The PRESEOR sequesters more biomass-derived carbon than is released by the burning of the oil it yields, thereby producing not only carbon-free electricity but carbon-free oil. Using PRESEOR, over 80 billion barrels of U.S. oil would be made recoverable, without the need to drill new wells in pristine areas.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
Combustion looping using composite oxygen carriers
ActiveUS7767191B2Increase surface areaImprove energy conversion efficiencyHydrogen productionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationHydrogenCombustion
A method for producing hydrogen gas is provided and comprises reducing a metal oxide in a reduction reaction between a carbon-based fuel and a metal oxide to provide a reduced metal or metal oxide having a lower oxidation state, and oxidizing the reduced metal or metal oxide to produce hydrogen and a metal oxide having a higher oxidation state. The metal or metal oxide is provided in the form of a porous composite of a ceramic material containing the metal or metal oxide. The porous composite may comprise either a monolith, pellets, or particles.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Method of making iron and steel
InactiveUS6149709AEasy to getLess impurity contentProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceHigh energyRefractory
Molten iron is prepared by (1) providing iron oxide and a carbonaceous reducing agent, (2) preparing a shaped product from the carbonaceous reducing agent and the iron oxide, (3) preparing solid reduced iron from the shaped product, wherein the solid reduced iron has a metallization of at least 60%, a specific gravity of at least 1.7, and a carbon content of at least 50% of the theoretical amount required for reducing the iron oxide remaining in the solid reduced iron, and, (4) before substantial cooling occurs, heating the solid reduced iron in an arc heating-type melting furnace at a high temperature. The molten iron can be prepared efficiently from iron ores of relatively low iron content without causing erosion of refractories, at high energy and high reduction efficiencies, and by a simple operation in a simple facility.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
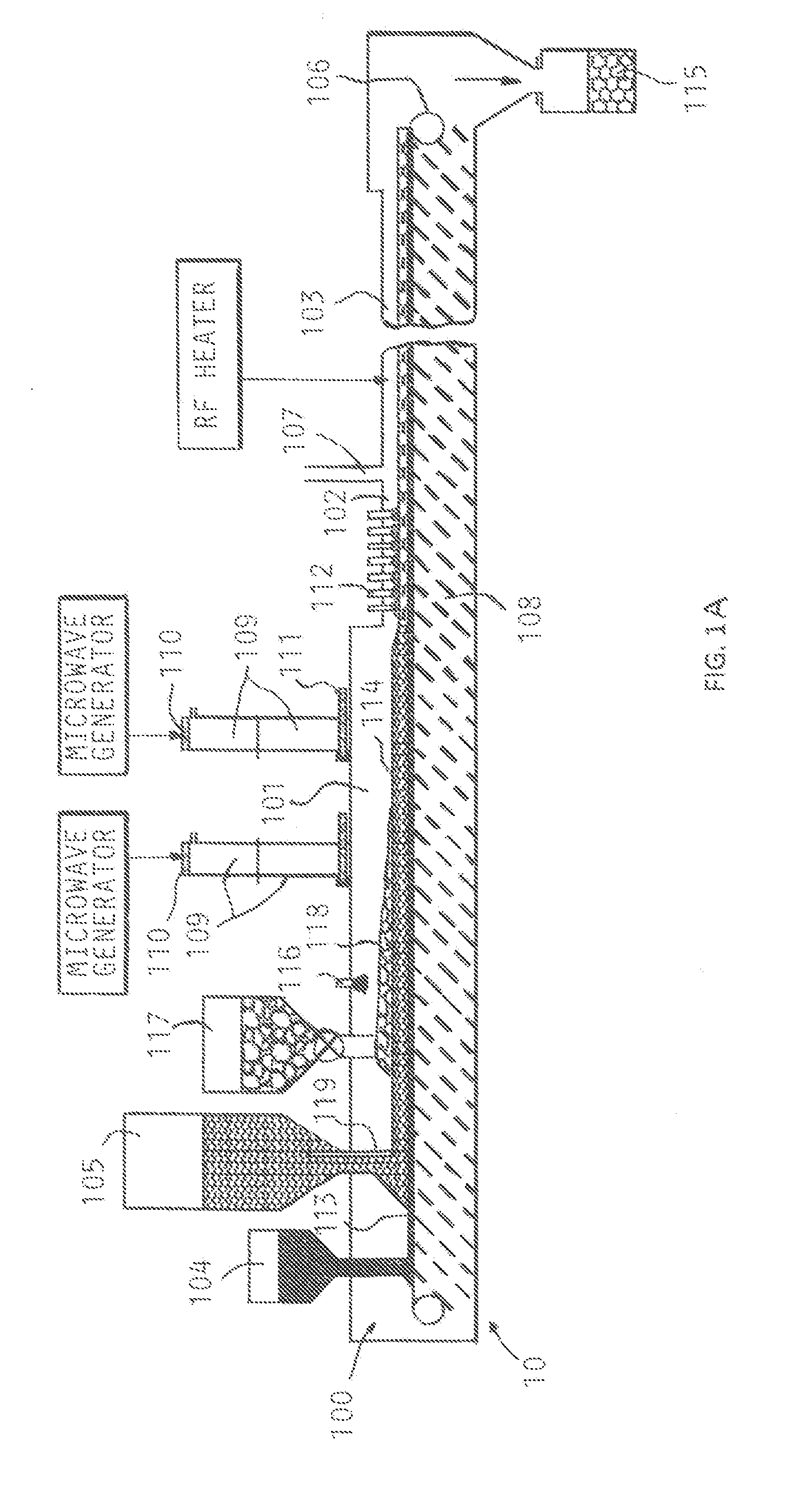
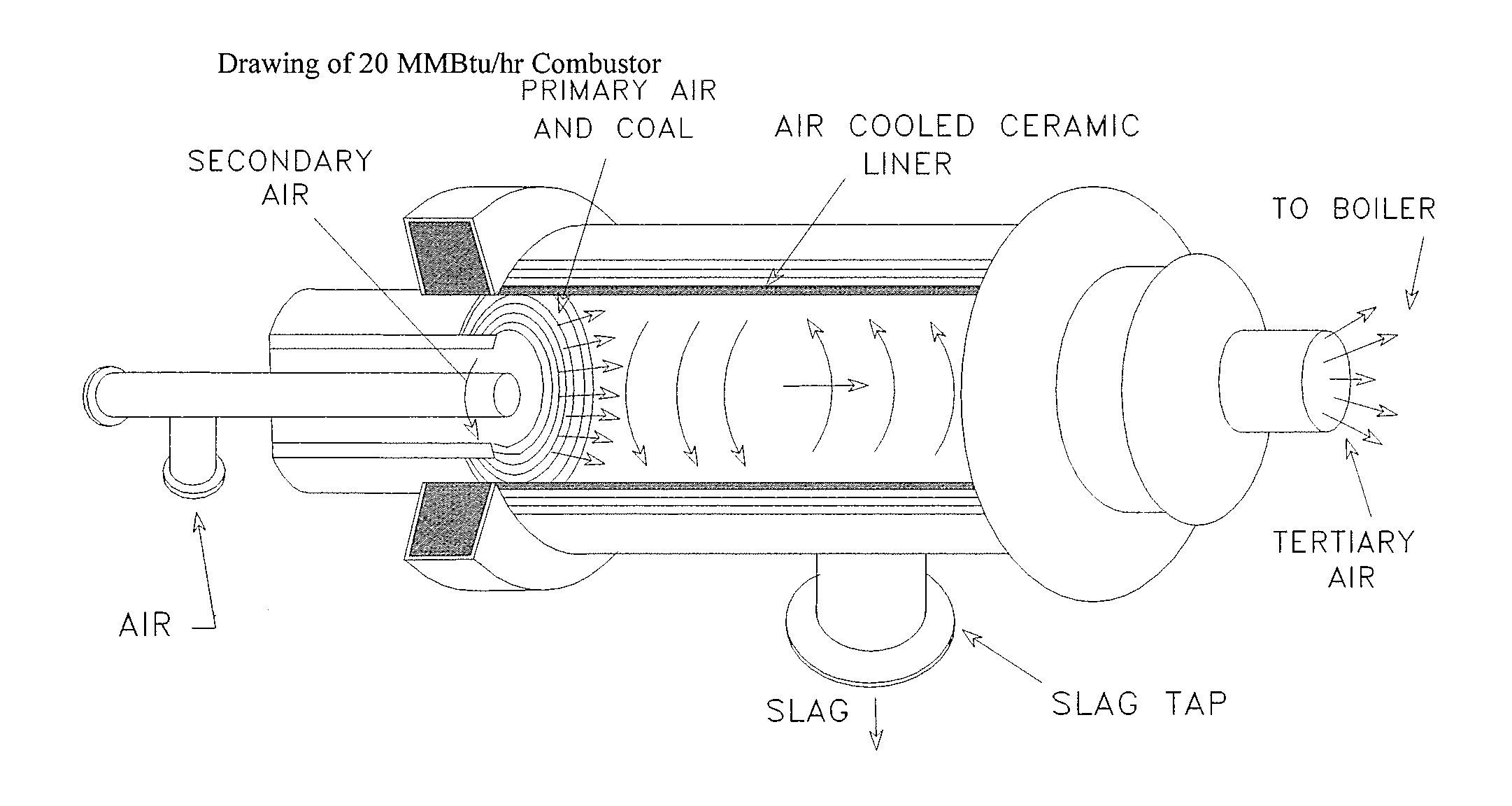
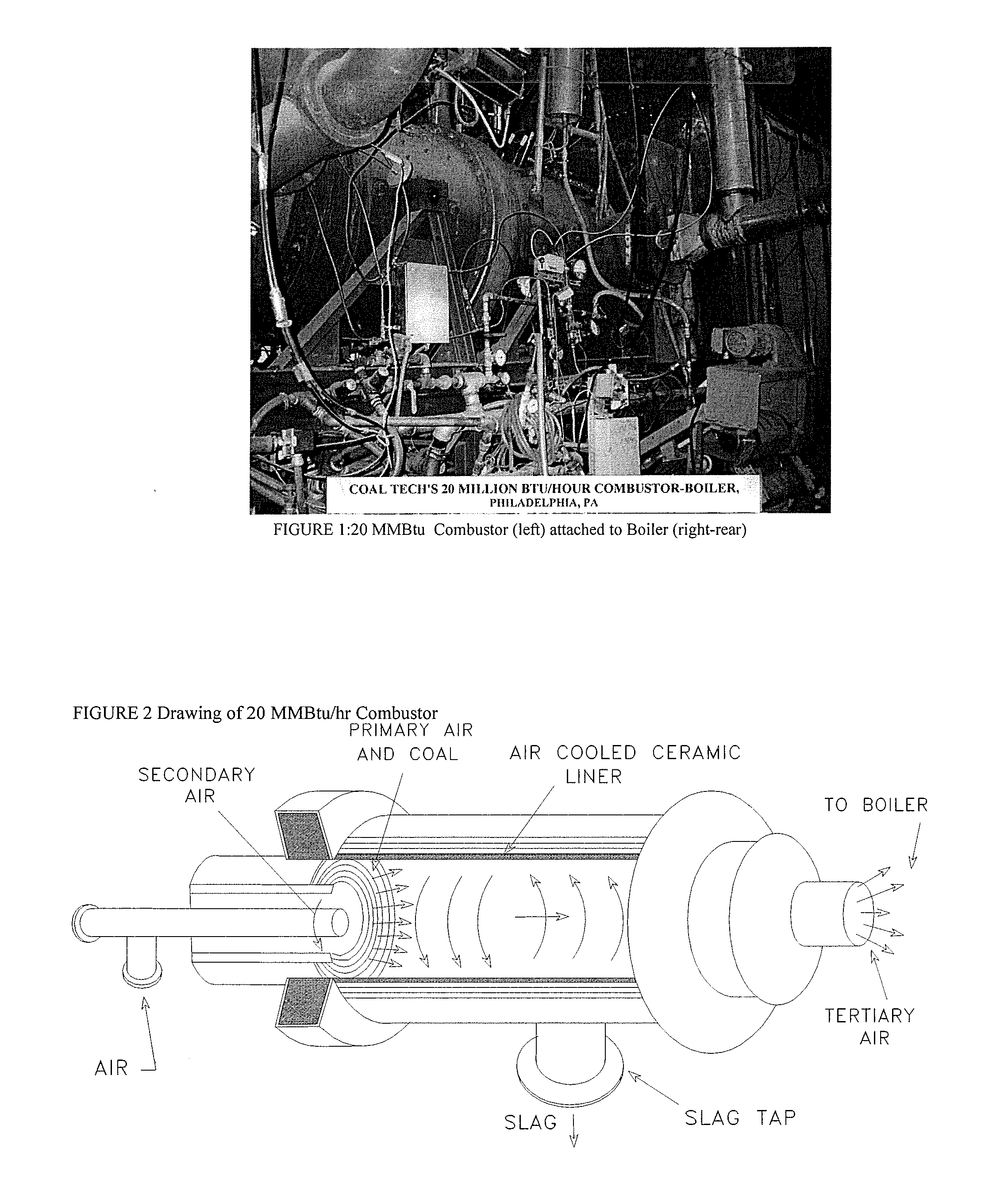
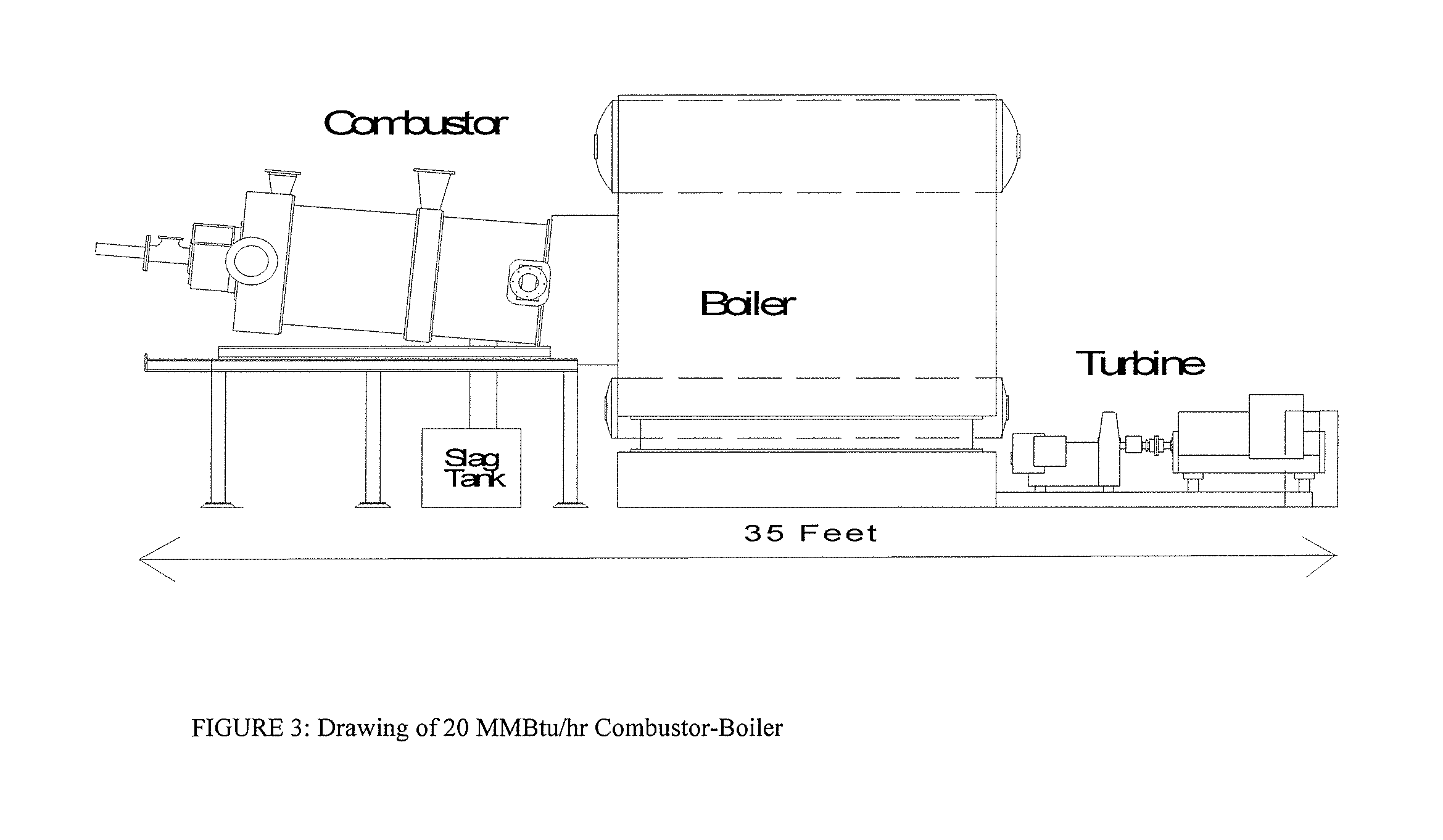
Slagging coal combustor for cementitious slag production, metal oxide reduction, shale gas and oil recovery, enviromental remediation, emission control and CO2 sequestration
InactiveUS8337613B2Reduce transportationMinimize disfiguringNitrogen compoundsSulfur compoundsCombustorEnvironmental remediation
Systems, methods and processes teach by specific examples how the cost of sequestering carbon dioxide (CO2) can be totally offset and turned into profits during coal powered electricity generation from revenue and co-benefits. The process is provided whereby fly ash-carbon mixtures, or de-volatilized coal char, or anthracite coal culm is co-fired in an air-cooled, slagging combustor with limestone or similar slag fluxing materials converts the ash into cementitious slag with properties similar to ground granulated blast furnace slag.
Owner:ZAUDERER BERT
Multi-purpose, multi-oxy-fuel, power burner/injector/oxygen lance device
InactiveUS20030075843A1Reduce the numberSmall sizeTuyeresCharge manipulationSteelmakingLiquid medium
A multi-purpose, multi-oxy-fuel High Temperature Power Burner / Injector / Oxygen Lance, Mechanical System Apparatus Device, for steelmaking from recycled scrap and / or virgin ferrous charge, which can be employed in multi-oxy-fuel (natural gas; pulverized carbonaceous matter; heavy oil), especially by Oxygen Combusted mixture of Natural Gas / Pulverized Carbonaceous Matter in High Temperature Power Burner Mode, for efficient and rapid melting of solid ferrous charge (cold or preheated) in a special steelmaking Metallurgical Furnace or Open Hearth Furnace, Tandem Furnace, BOF, EAF, as its augmenting or only source of thermal energy; more than one Device in Oxygen-Natural Gas / Pulverized Carbonaceous Matter Power Burner Mode, can be employed as the only source of thermal energy in a modified, originally Electric Arc Furnace, as total replacement of Graphite Electrodes and Electric Arc System, the replacement being noticeably more primary energy efficient than the thermal energy provided by Graphite Electrode / Arc System; it also can be employed in an Solid Particles Injector Mode, for injecting of adequately granulated carbonaceous materials or lime into the molten steel for its carburizing or for foamy slag control; further it can be employed in a natural gas shrouded, pulsating oxygen stream, for vertically to the charge oriented soft blow supersonic Oxygen Injection Lance Mode, for decarburization of the molten metal contained in the hearth of the metallurgical furnace and foamy slag control; in one of the embodiments-generally arcuate-pivotally mounted, liquid media cooled composite body, is pivoted into and out of a furnace vessel through a small opening in the shell wall for auto-regulated constant optimal positioning of the Composite Body Tip against solid or molten charge, in each and all multi-purpose modes; furthermore, when inserted into the furnace vessel, the arcuate composite body can be rotated about its longitudinal axis for directing the oxy-fuel high temperature flame towards unmolten charge in the furnace; in an other-generally linear-embodiment, the liquid cooled composite body is attached to the mast type carrier allowing vertical movement of the composite body which enters the furnace vessel through a small opening in the furnace roof; the bimetallic, liquid cooled special tip assembly of both-arcuate and linear embodiments-of the composite body includes easy replaceable, independent, multi-opening nozzles, mounted in a protective, retracted position inside of the liquid cooled special tip assembly.
Owner:EMPCO (CANADA) LTD
Process for production of elemental iron
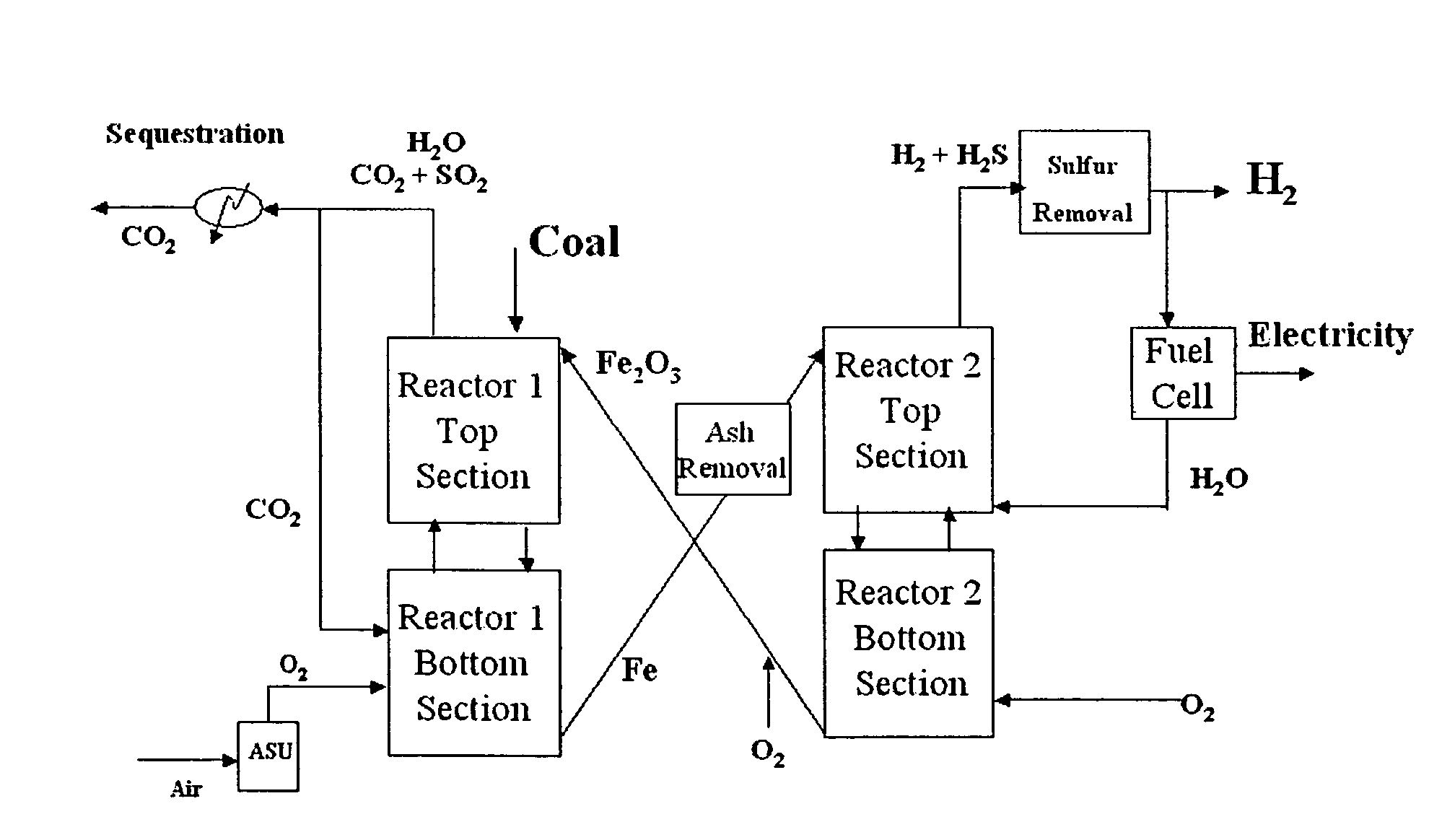
InactiveUS7931731B2Easy to processIsotope separationHydrogen/synthetic gas productionPartial oxidationFerric
A process to prepare elemental iron by contacting an iron ore feed with a reducing gas at a pressure of between 1 and 10 bar to obtain iron and an off-gas includes preparing the reducing gas by performing the following steps: (a) partially oxidizing a mixture comprising a solid or liquid carbonaceous fuel and oxygen at a pressure of between 10 and 80 bar, thereby obtaining a gas comprising H2 and CO; (b) removing CO2 and H2S from the gas obtained in step (a) to obtain an intermediate gas comprising H2 and CO; (c) supplying the intermediate gas obtained in step (b) to a H2-selective membrane to obtain a H2-rich permeate gas and a CO-rich retentate; and (d) heating H2-rich permeate to obtain a heated H2-rich permeate as the reducing gas.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
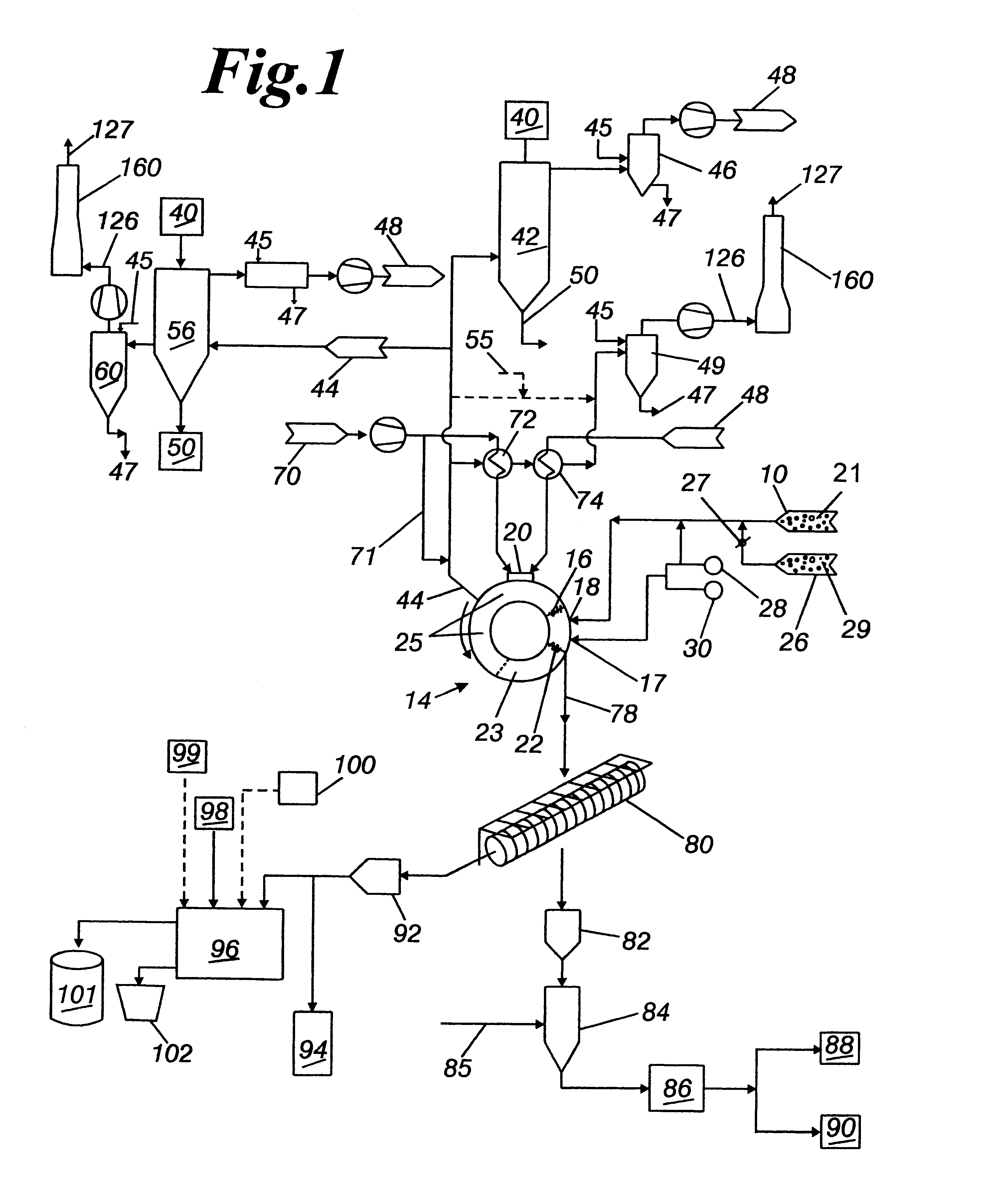
Method of direct iron-making / steel-making via gas or coal-based direct reduction and apparatus
The invention is a method and apparatus for iron-making / steel-making using a modified rotary hearth furnace, that is a finisher-hearth-melter (FHM) furnace. In the method the refractory surface of the hearth is coated with carbonaceous hearth conditioners and refractory compounds, where onto said hearth is charged with pre-reduced metallized iron. The pre-reduced metallized iron is leveled, then heated until molten, and then reacted with the carbon and reducing gas burner gases until any residual iron oxide is converted to iron having a low sulfur content. Nascent slag separates from the molted iron forming carburized iron nuggets. The nuggets are cooled, and then the iron nuggets and the hearth conditioners, including the refractory compounds, are discharged onto a screen, which separate the iron nuggets from the hearth conditioner. The hearth conditioner is recycled, and the iron nuggets are either prepared for sale or for additional treatment, such as alloying, in a final melter, where the final melter is preferably an electric furnace. Exhaust gases from the FHM furnace are recovered for calcining coal into fuel gases and coke.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
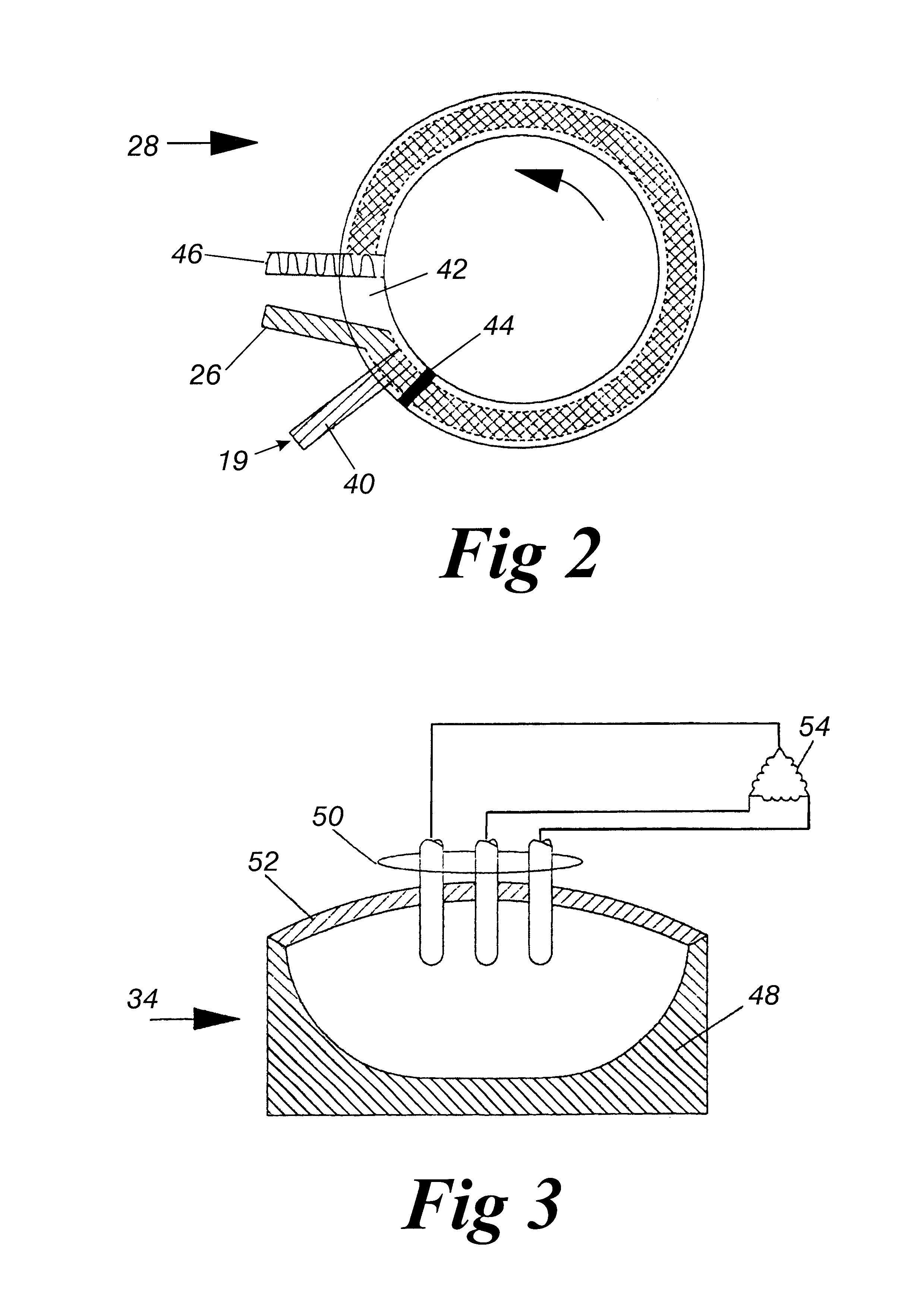
Iron production method of operation in a rotary hearth furnace and improved furnace apparatus
The present invention is an apparatus and method for the direct reduction of iron oxide utilizing a rotary hearth furnace to form a high purity carbon-containing iron metal button. The hearth layer may be a refractory or a vitreous hearth layer of iron oxide, carbon, and silica compounds. Additionally, coating materials may be introduced onto the refractory or vitreous hearth layer before iron oxide ore and carbon materials are added, with the coating materials preventing attack of the molten iron on the hearth layer. The coating materials may include compounds of carbon, iron oxide, silicon oxide, magnesium oxide, and / or aluminum oxide. The coating materials may be placed as a solid or a slurry on the hearth layer and heated, which provides a protective layer onto which the iron oxide ores and carbon materials are placed. The iron oxide is reduced and forms molten globules of high purity iron and residual carbon, which remain separate from the hearth layer. An improved apparatus includes a cooling plate that is placed in close proximity with the refractory or vitreous hearth layer, cooling the molten globules to form iron metal buttons that are removed from the hearth layer. The improvements due to the present apparatus and method of operation provide high purity iron and carbon solid buttons, which are separate from slag particulates, and discharged without significant loss of iron product to the interior surfaces of the furnace.
Owner:MIDREX INT B V ROTTERDAM
High-carbon biogenic reagents and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120285080A1High carbon contentImprove energy efficiencyCoke quenchingCoke oven safety devicesHigh carbonReagent
This invention provides processes and systems for converting biomass into high-carbon biogenic reagents that are suitable for a variety of commercial applications. High carbon biogenic reagents are also provided.
Owner:CARBON TECH HLDG LLC
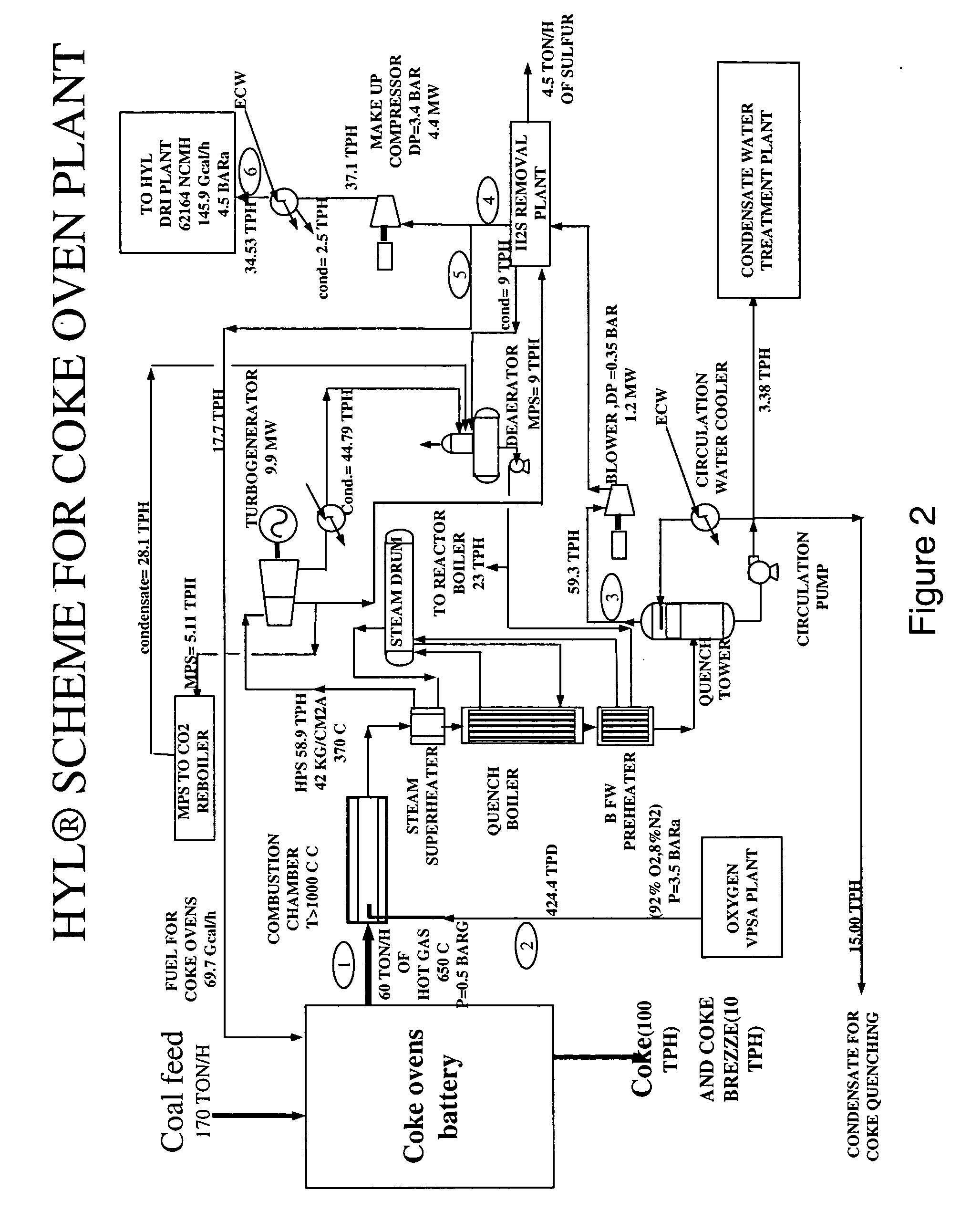
Method and apparatus for producing clean reducing gases from coke oven gas
InactiveUS20060027043A1Avoiding complex and expensiveOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideHydrogen separationProcess engineeringCoke oven
A process and system for producing reducing gases are disclosed, wherein volatile components derived from coal are transformed into reducing gases suitable for utilization as synthesis gas, as a reducing agent for the direct reduction of iron ores and / or as a clean fuel.
Owner:HYLSA SA DE CV
Method and system for energy-optimized and CO2 emission-optimized iron production
InactiveUS8419825B2Emission reductionIncrease profitBlast furnace detailsExhaust gas handlingProcess engineeringProduct gas
A process for energy- and emission-optimized iron production and an installation for carrying out the process. A first partial amount of a generator gas produced in a melter gasifier is used as a first reducing gas in a first reduction zone. A second partial amount is fed to at least one further reduction zone as a second reducing gas. In addition, after CO2 scrubbing, a partial amount of top gas removed from the first reduction zone is admixed with the generator gas after the latter leaves the melter gasifier, for cooling the generator gas.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH AUSTRIA GMBH
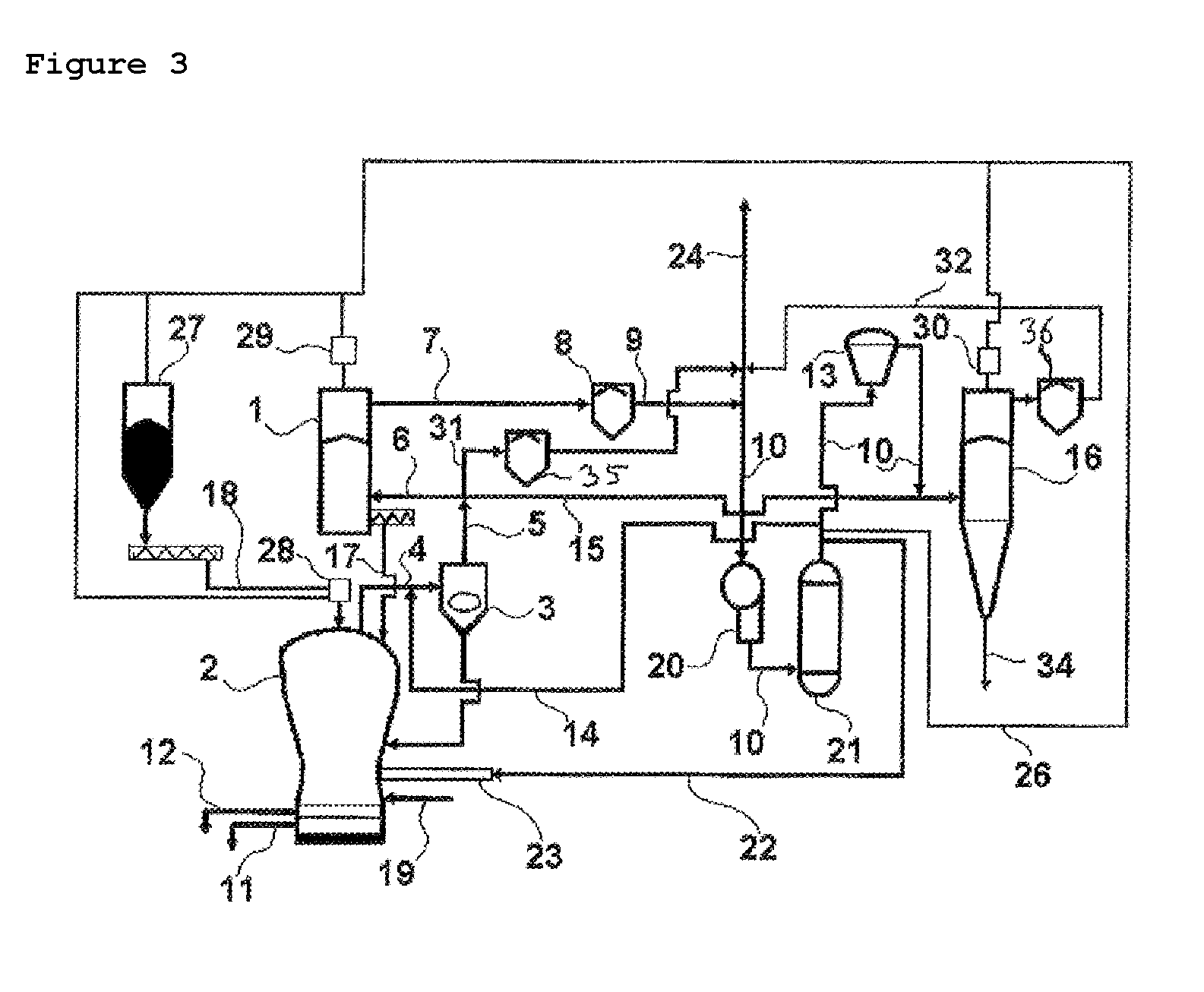
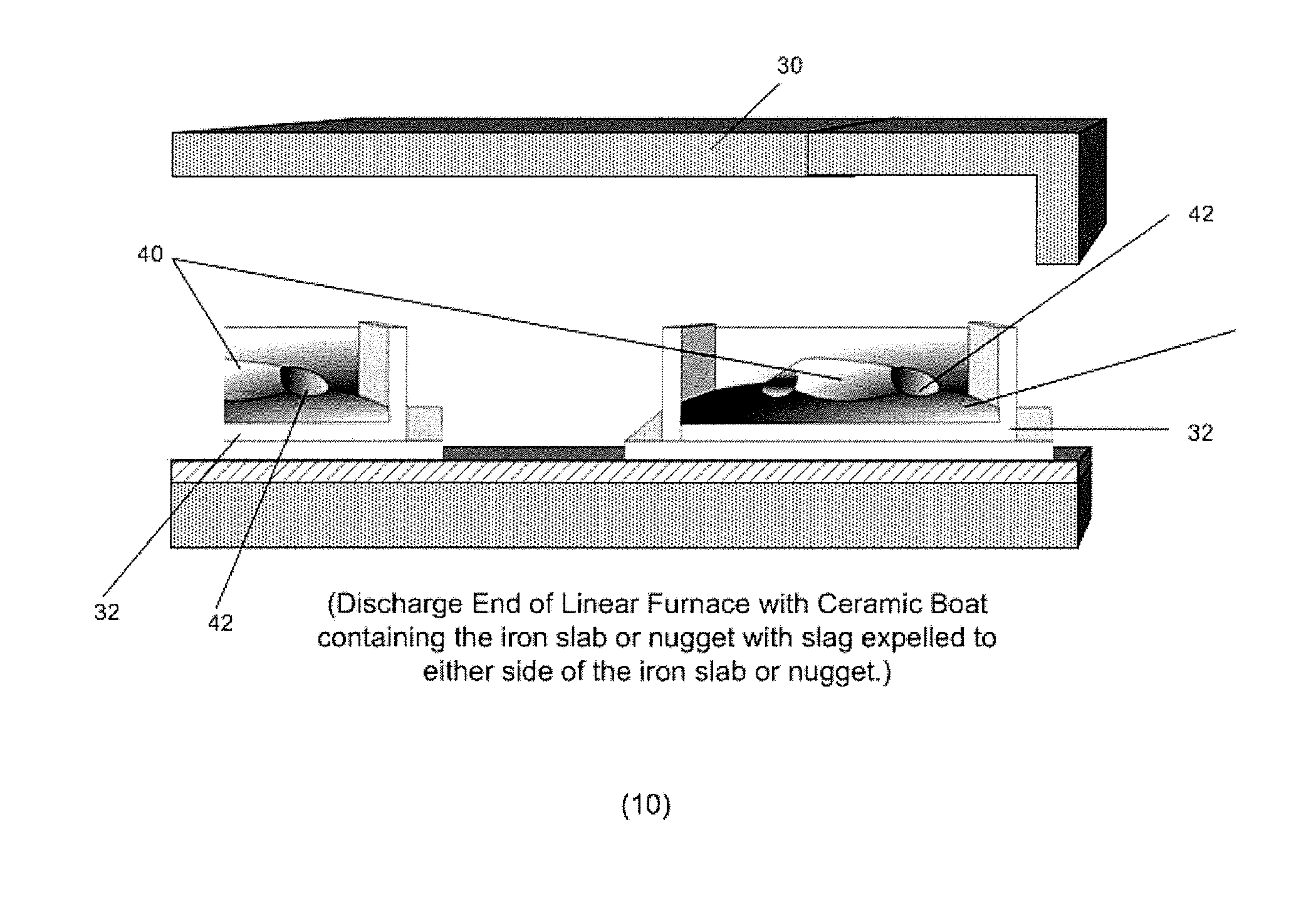
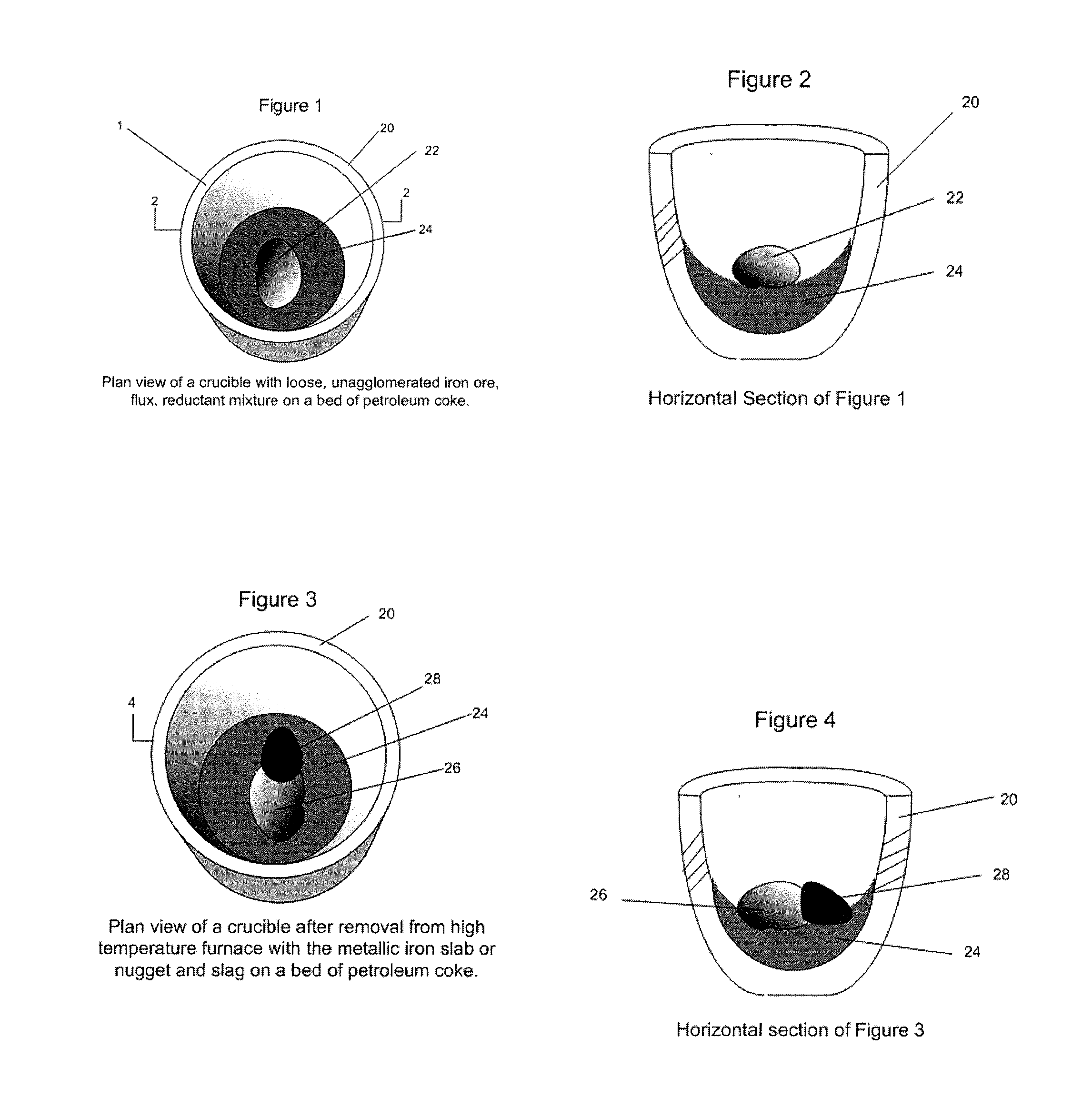
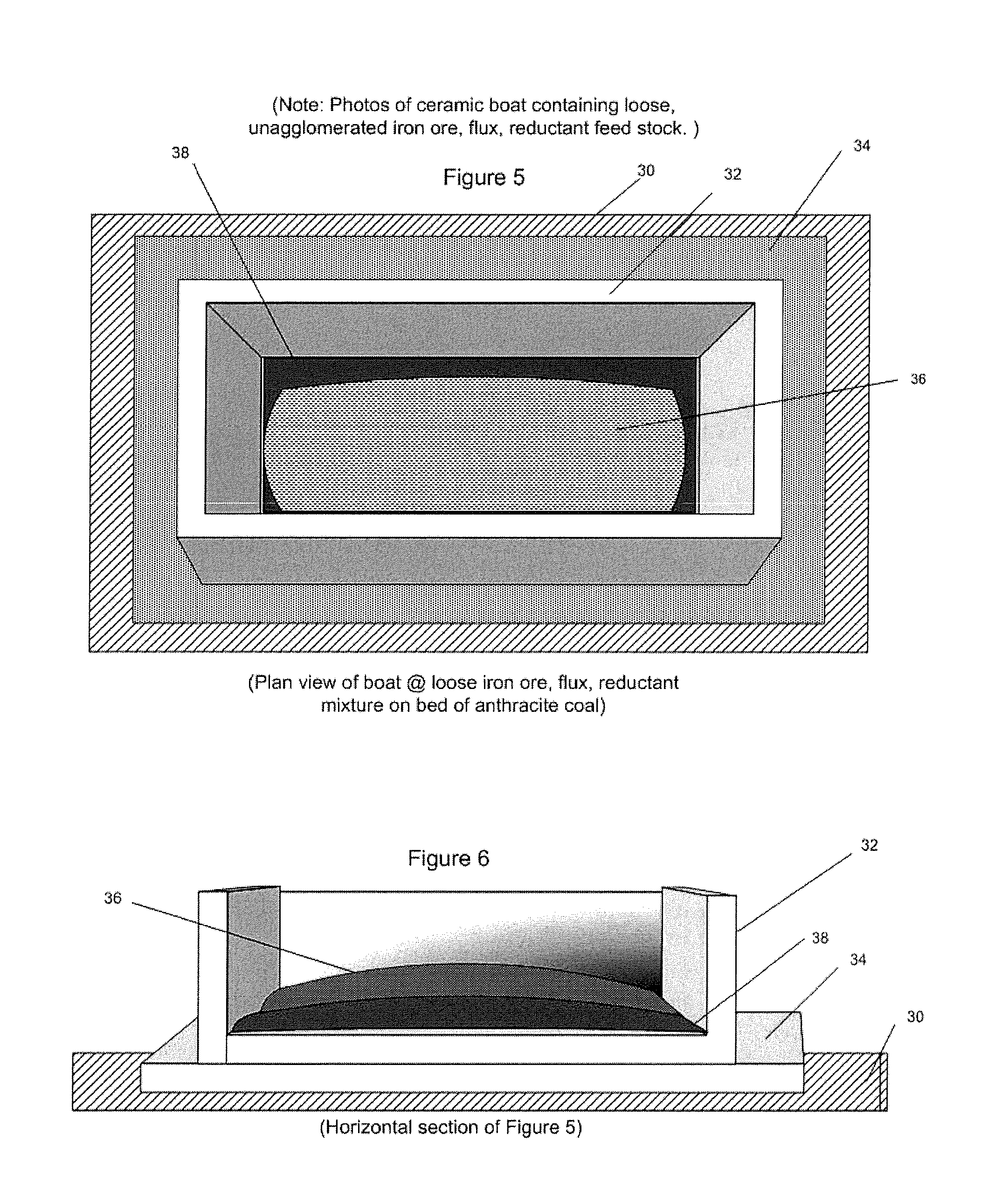
Direct Production of Iron Slabs and Nuggets From Ore Without Pelletizing or Briquetting
ActiveUS20130081516A1Lower cost of capitalReduce operating costsExhaust gas handlingGas emission reductionParticulatesIronstone
Metallic iron is produced from a composition formed from a mixture of iron ore particles and particles of a reductant made of a biomass material, a coal or coke in a particulate form together with a flux and is processed in a loose, un-agglomerated non-pelletized, non-briquetted form in a reducing furnace to produce metallic iron directly from the ore. An excess of biomass or coal or coke reductant can be used to provide CO and H that can be recovered as a synthetic gas and converted to electrical or other energy. Metallic iron nuggets or slabs can be produced from manganiferous ores or concentrates. Manganese can be caused to enter the nugget or slab or the slag by adjusting the furnace temperature. Titaniferous ores or concentrates can be used to produce metallic iron slabs or nuggets and a titanium-rich slag.
Owner:SIMMONS JOHN J
Portable renewable energy system for enhanced oil recovery (preseor) using biomass having net negative co2 emissions and for generating electricity having zero co2 emissions
InactiveUS20100038082A1Increase blockingPromote recoveryBiofuelsWaste based fuelPetroleumElectric power
The Portable Renewable Energy System for Enhanced Oil Recovery (“PRESEOR”) is a truck mobile system that reforms biomass into CO2 and hydrogen, following which the gases are separated, with the CO2 sequestered underground for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) and the hydrogen used to generate several megawatts of carbon-free electricity. In contrast to large central power plants that are generally not well-located to support EOR, the small PRESEOR can go directly to the oilfields where it is needed, and do so in a timely manner. The PRESEOR sequesters more biomass-derived carbon than is released by the burning of the oil it yields, thereby producing not only carbon-free electricity but carbon-free oil. Using PRESEOR, over 80 billion barrels of U.S. oil would be made recoverable, without the need to drill new wells in pristine areas.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
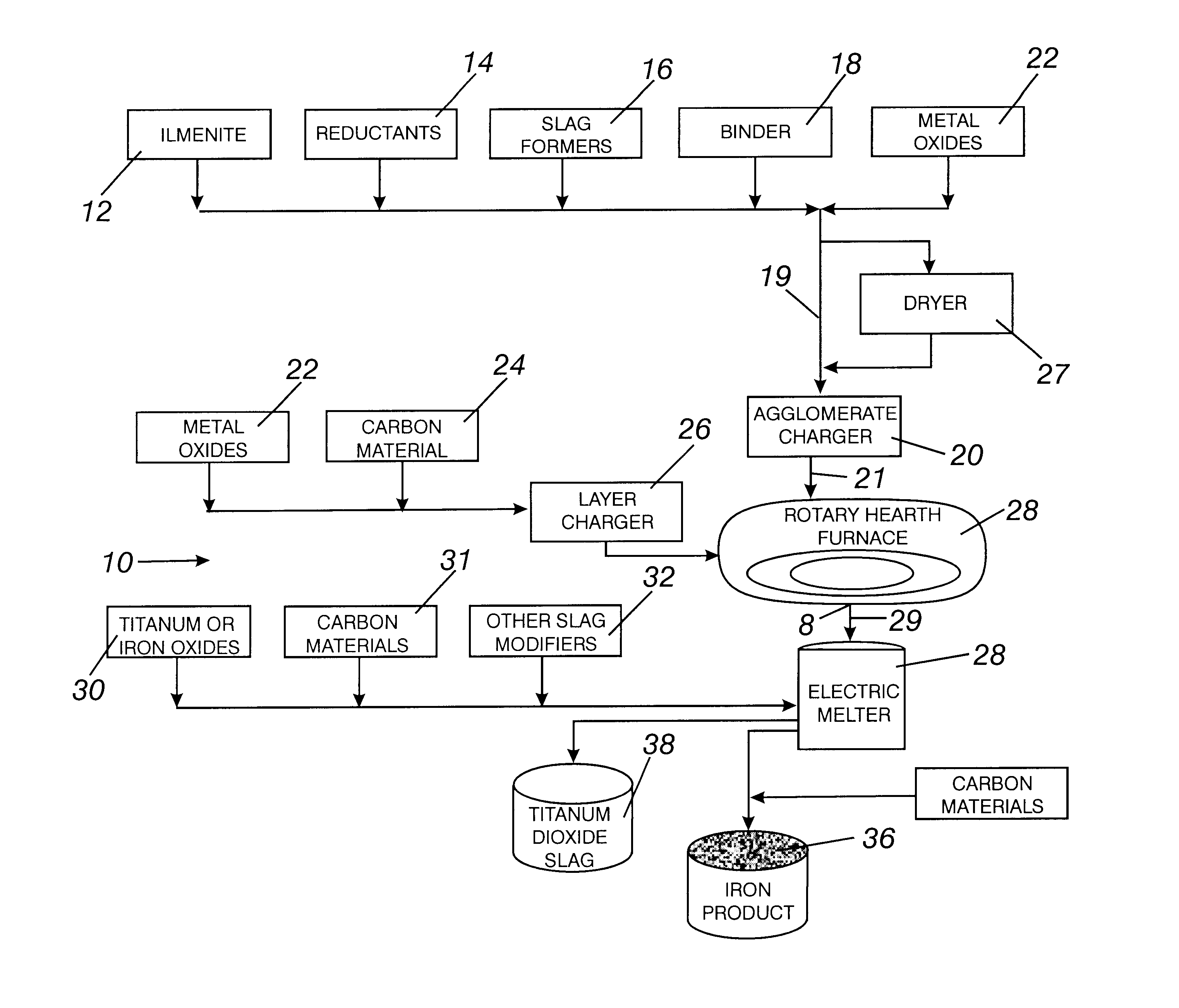
Method for producing beneficiated titanium oxides
The invention is a method and apparatus for producing beneficiated titanium oxides using a modified rotary hearth furnace, that is a finisher-hearth-melter (FHM) furnace. In the method the refractory surface of the hearth is coated with carbonaceous hearth conditioners and refractory compounds, where onto said hearth is charged with pre-reduced agglomerates. The pre-reduced agglomerates is leveled, then heated until molten, and then reacted with the carbon and reducing gas burner gases until any residual iron oxide is converted to iron having a low sulfur content. Fluid slag and molted iron forms melted agglomerates. The fluid slag is rich in titanium. The melted agglomerates are cooled, and then the melted agglomerates and the hearth conditioners, including the refractory compounds, are discharged onto a screen, which separate the melted agglomerates from the hearth conditioner. The hearth conditioner is recycled, and the melted agglomerates are prepared for sale or for additional treatment in a final melter, where the final melter is preferably an electric furnace. Exhaust gases from the FHM furnace are recovered for calcining coal into fuel gases and coke.
Owner:MIDREX TECH INC
Direct reduced iron discharge system and method
InactiveUS6214086B1No loss in metallizationWide range of sizesMolten spray coatingNuclear energy generationEngineeringDirect reduced iron
A method and apparatus for simultaneously supplying varying proportions of hot and cold direct reduced iron(DRI) material from a source of hot DRI for melting, storage, briquetting, or transport. The system uses gravity to transport hot DRI material from a reduction furnace to a furnace discharge section, which transports desired amounts to a cooling receptacle and to a hot DRI vessel. The cooling section of the apparatus is connected to the furnace discharge section through a dynamic seal leg. The hot section is also connected to the furnace discharge section through separate a dynamic sealing leg and can feed a surge vessel, a briquetter, a storage vessel or a melting furnace. The method of operation is also disclosed.
Owner:IDREX INT BV ROTTERDAM ZURICH BRANCH
Method of producing iron nuggets
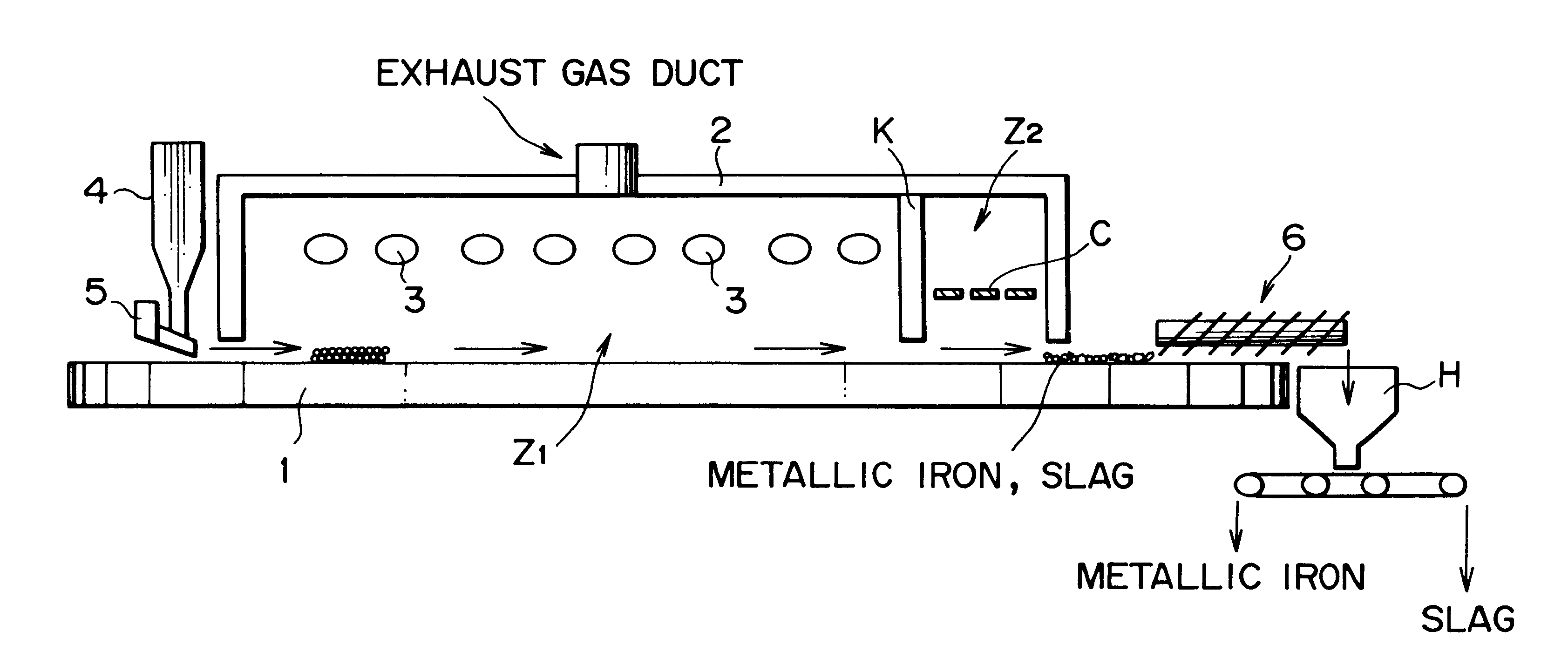
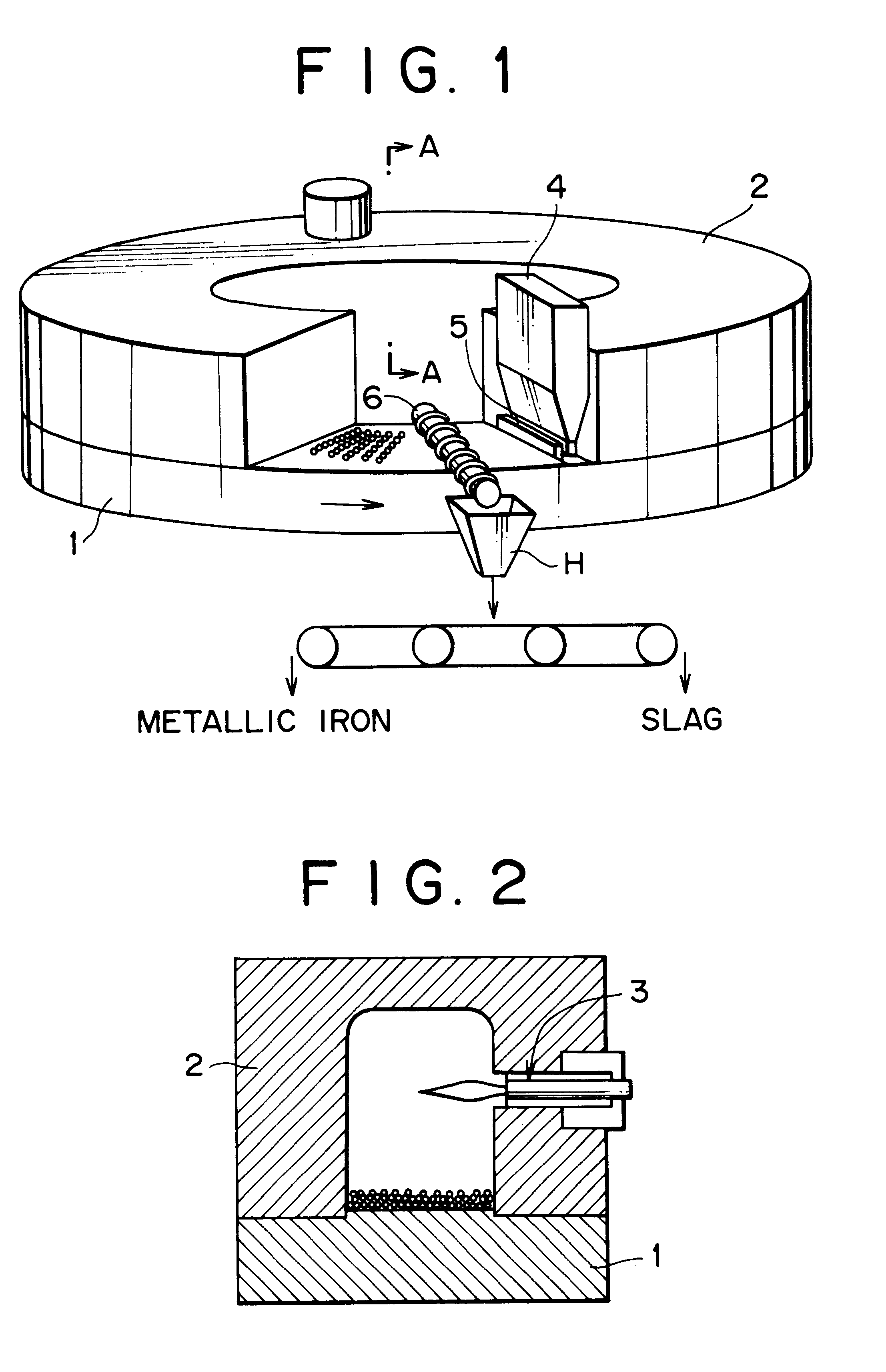
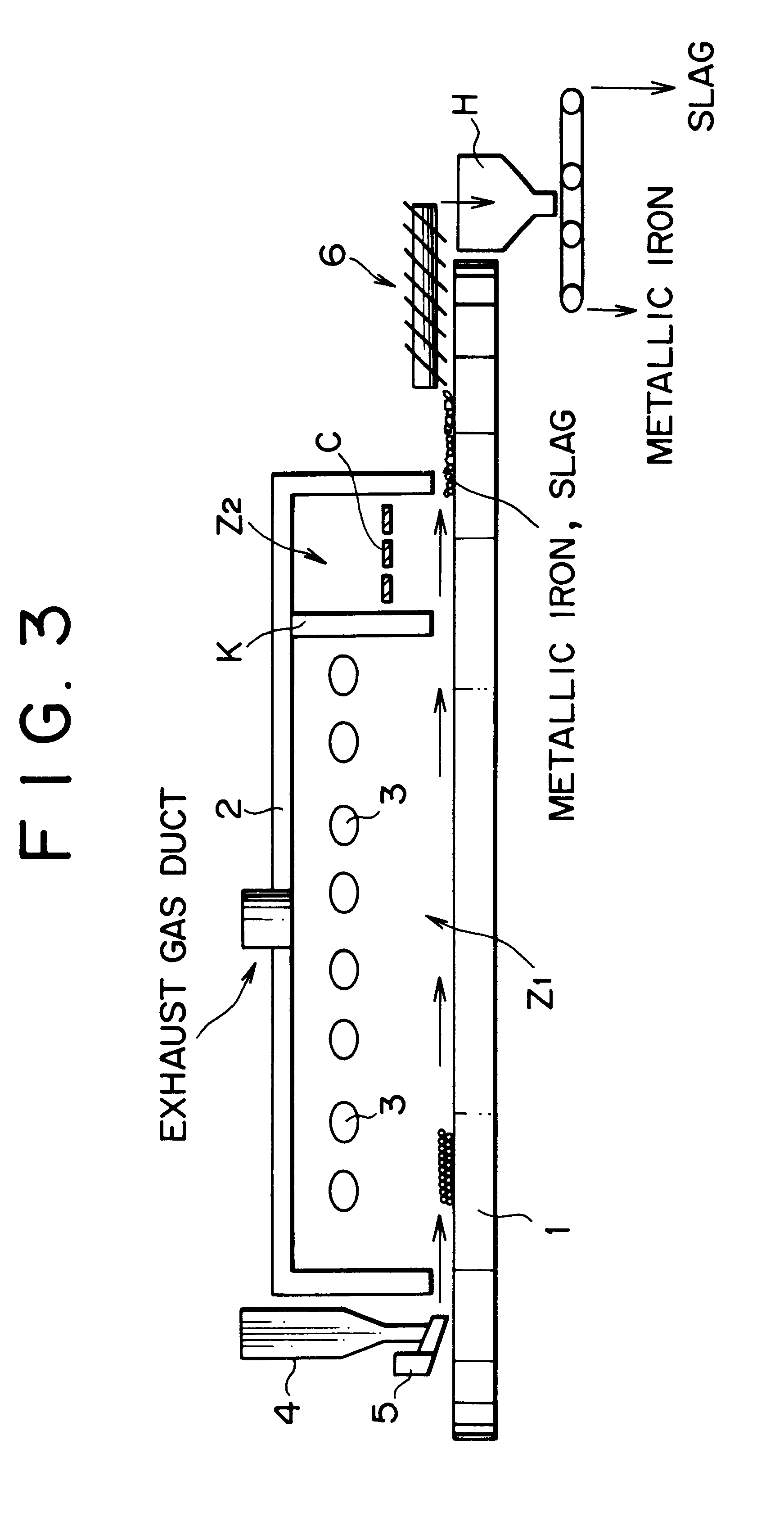
InactiveUS6592649B2Avoid smallImprove productivityProcess efficiency improvementGas emission reductionProduction rateSlag
The present invention provides a method of producing metallic iron nuggets with a high yield and good productivity, and more particularly a method which can produce metallic iron nuggets which have a high Fe purity and are excellent in transporting and handling due to a large grain diameter with a high yield and good productivity, when they are produced by reducing and melting raw material containing iron oxide such as iron ore and carbonaceous reducing agent such as coke. The method of producing metallic iron nuggets comprises steps of: heating raw material containing carbonaceous reducing agent and iron oxide-containing material in a reducing / melting furnace, reducing iron oxide in the raw material, and then heating and melting the metallic iron produced by the reduction and simultaneously making it coalesce while separating the metallic iron nuggets from slag components characterized in that the fixed carbon content ratio as the carbonaceous reducing agent is at least 73% and the volatile matter content in the raw material is not more than 3.9% are used, and the mixing content of carbonaceous reducing agent is restrained to be not more than 45% in relation to the iron oxide components, which is contained in the iron oxide-containing material of the raw material.
Owner:IDREX INT BV ROTTERDAM ZURICH BRANCH
High pressure dry coal slurry extrusion pump
A system for providing highly pressurized raw fuel to a pressure reactor. The system includes an inlet for receiving the raw fuel and a roller system communicating with the inlet. The roller system includes a plurality of independent rollers arranged in two converging planes. The rollers of the roller system successively compress the raw fuel as the raw fuel passes through the roller system between the rollers, such that the fuel is highly pressurized when it reaches an output end of the roller system. An outlet is located adjacent the output end of the roller system to dispense the pressurized raw fuel to the pressure reactor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO +1
Heat exchanger
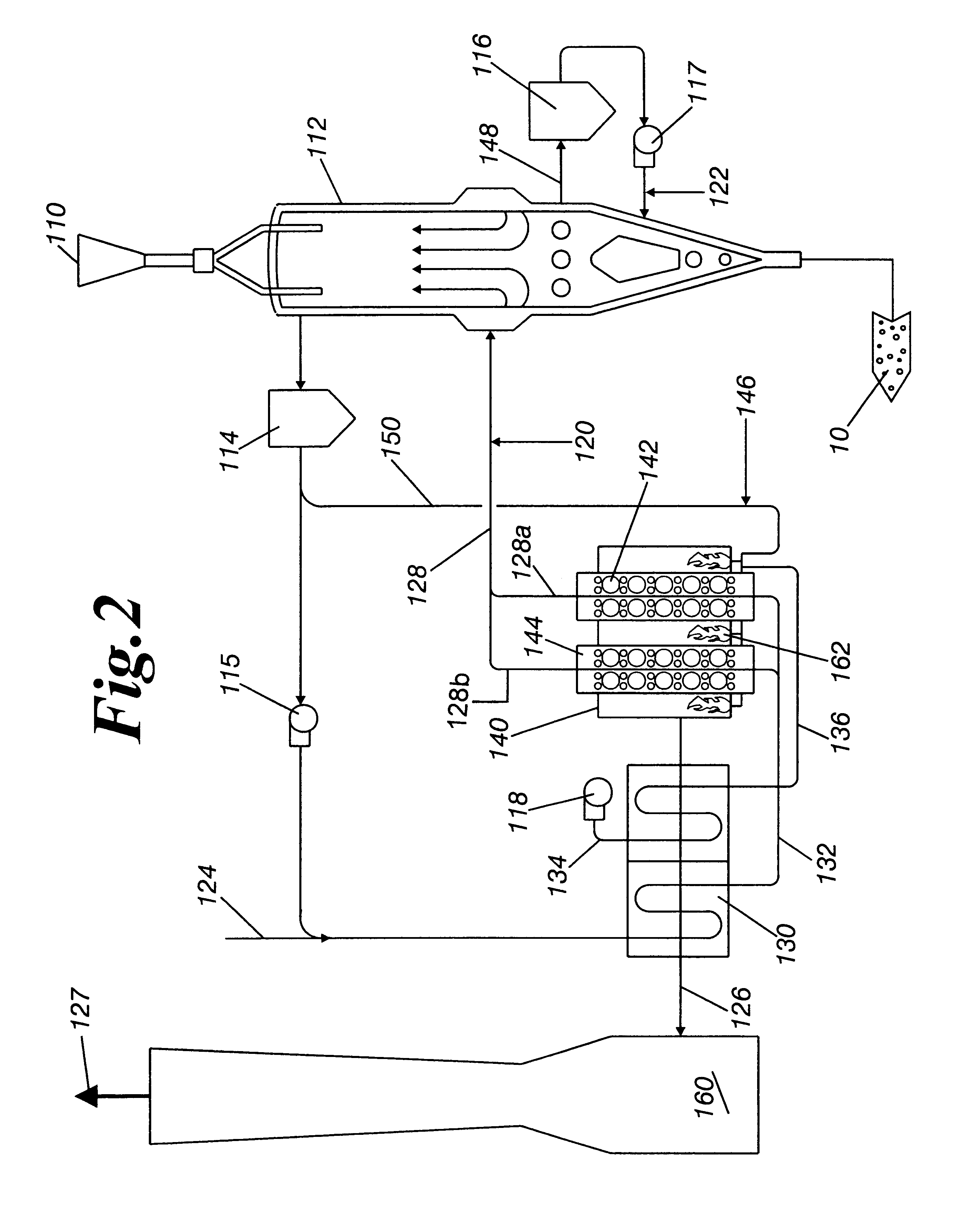
ActiveUS7901617B2Lower overall pressure dropImprove heat transfer performanceBlast furnace detailsManufacturing convertersEngineeringCooling fluid
A heat exchanger 10 includes a conduit 12 for conveying cooling fluid relative to a body to be cooled. A heat transfer arrangement 62 is arranged in communication with an interior of the conduit 12, the heat transfer arrangement 62 and the conduit 12 together defining an assembly that is mountable adjacent the body to be cooled, convective heat exchange occurring, in use, due to movement of the cooling fluid relative to the body and the heat transfer arrangement 62 of the assembly and radiant heat exchange occurring between the body and at least part of the heat transfer arrangement 62 of the assembly.
Owner:ENPOT HLDG LTD
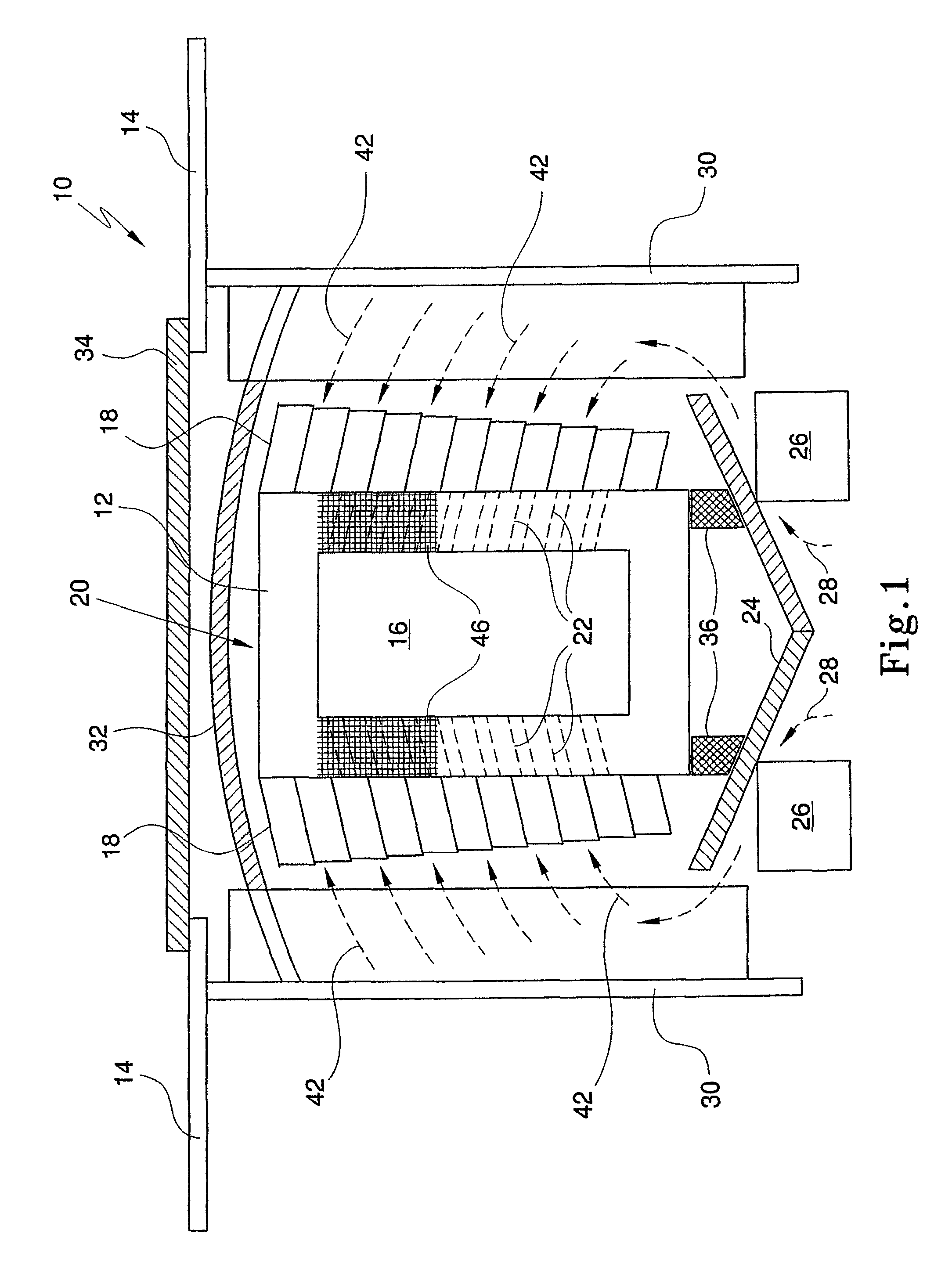
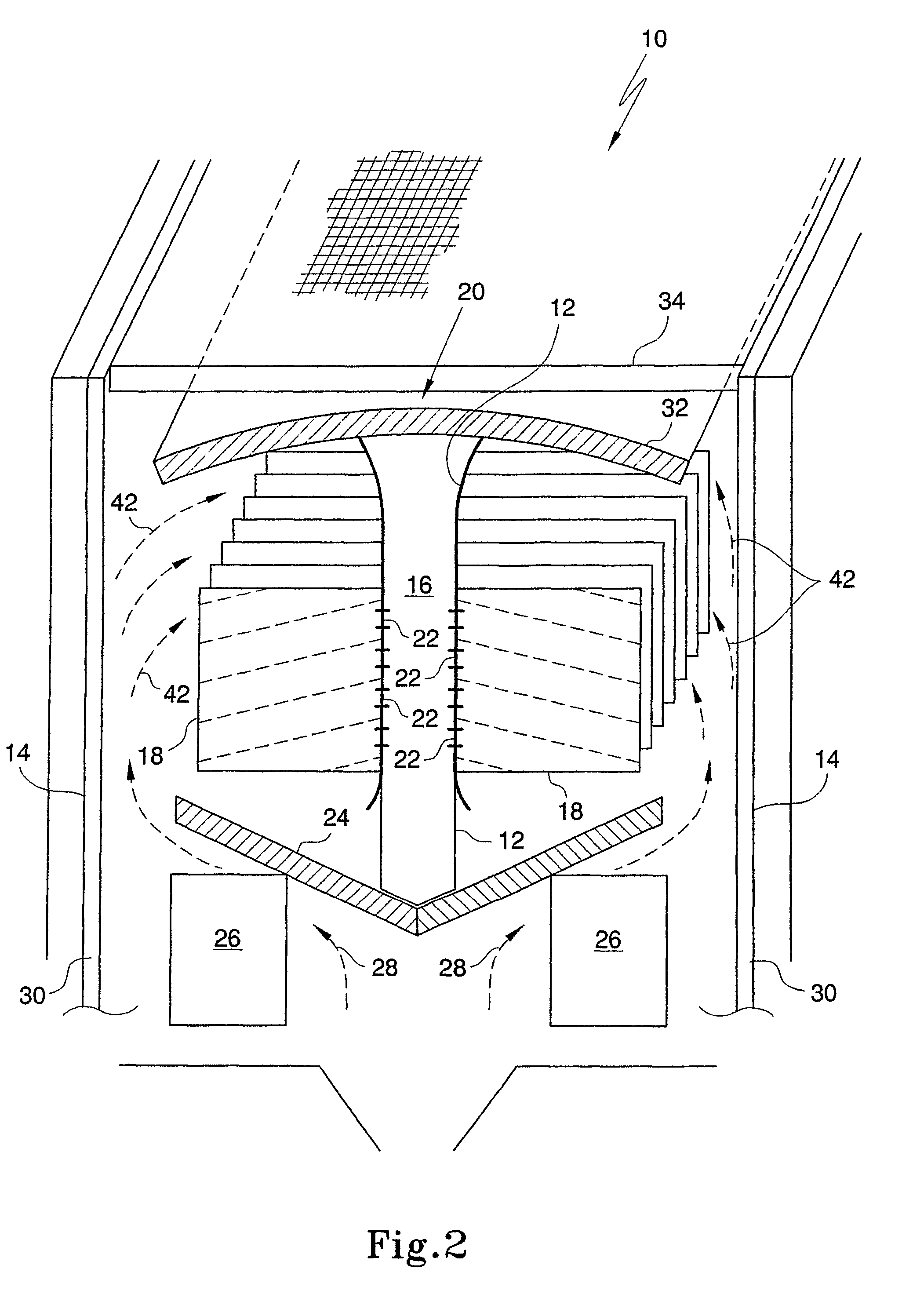
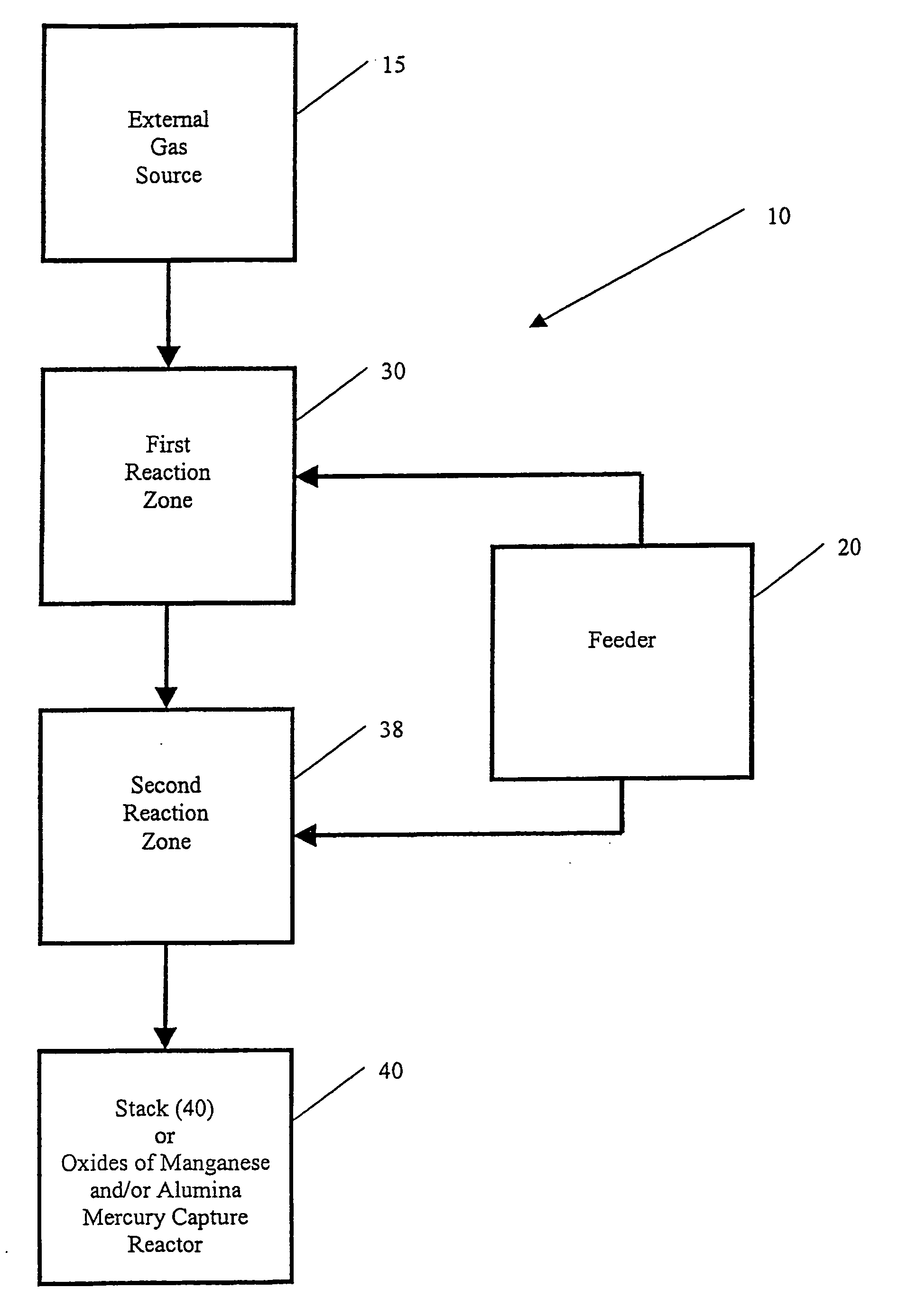
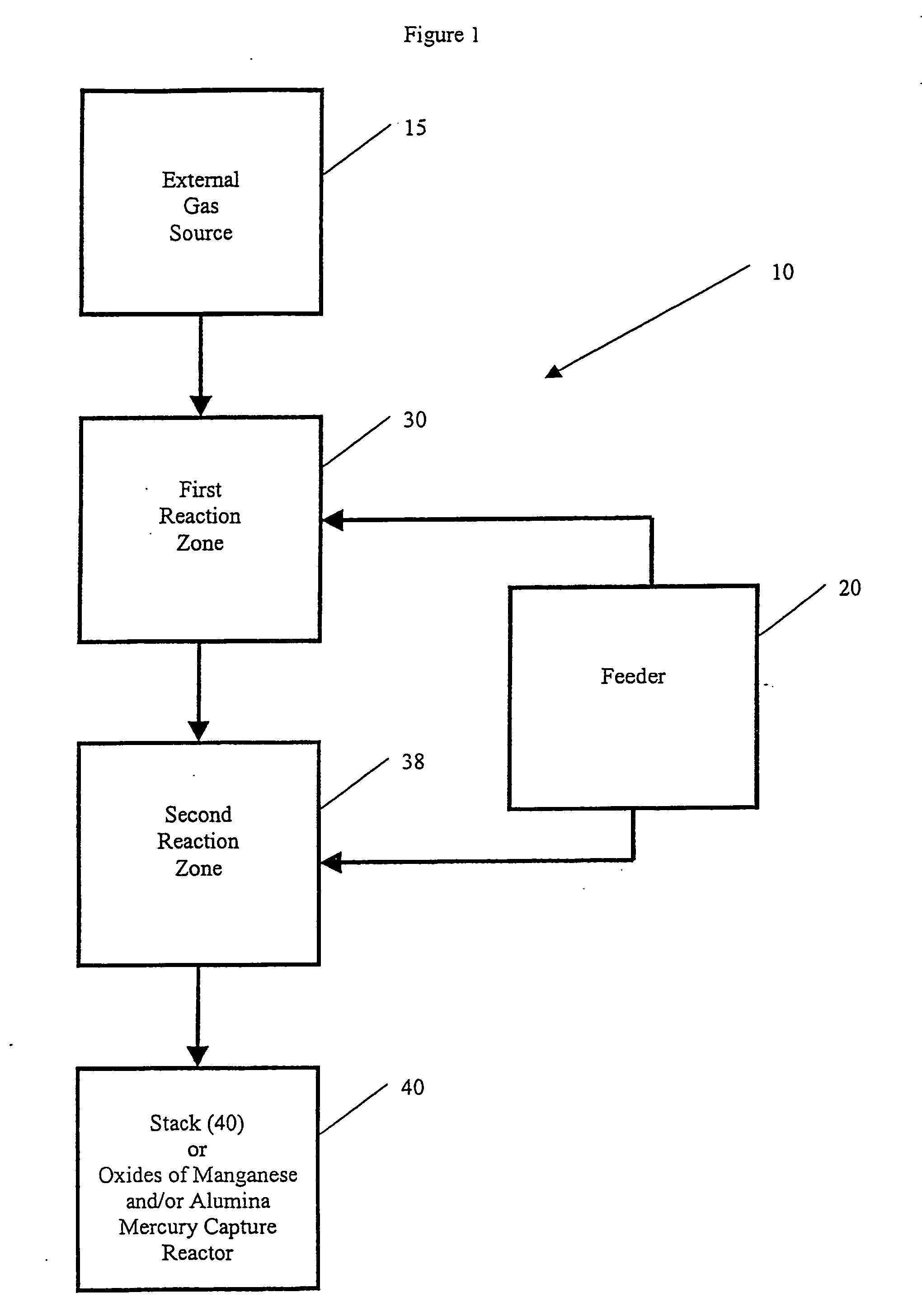
Electronic controls for pollutant removal
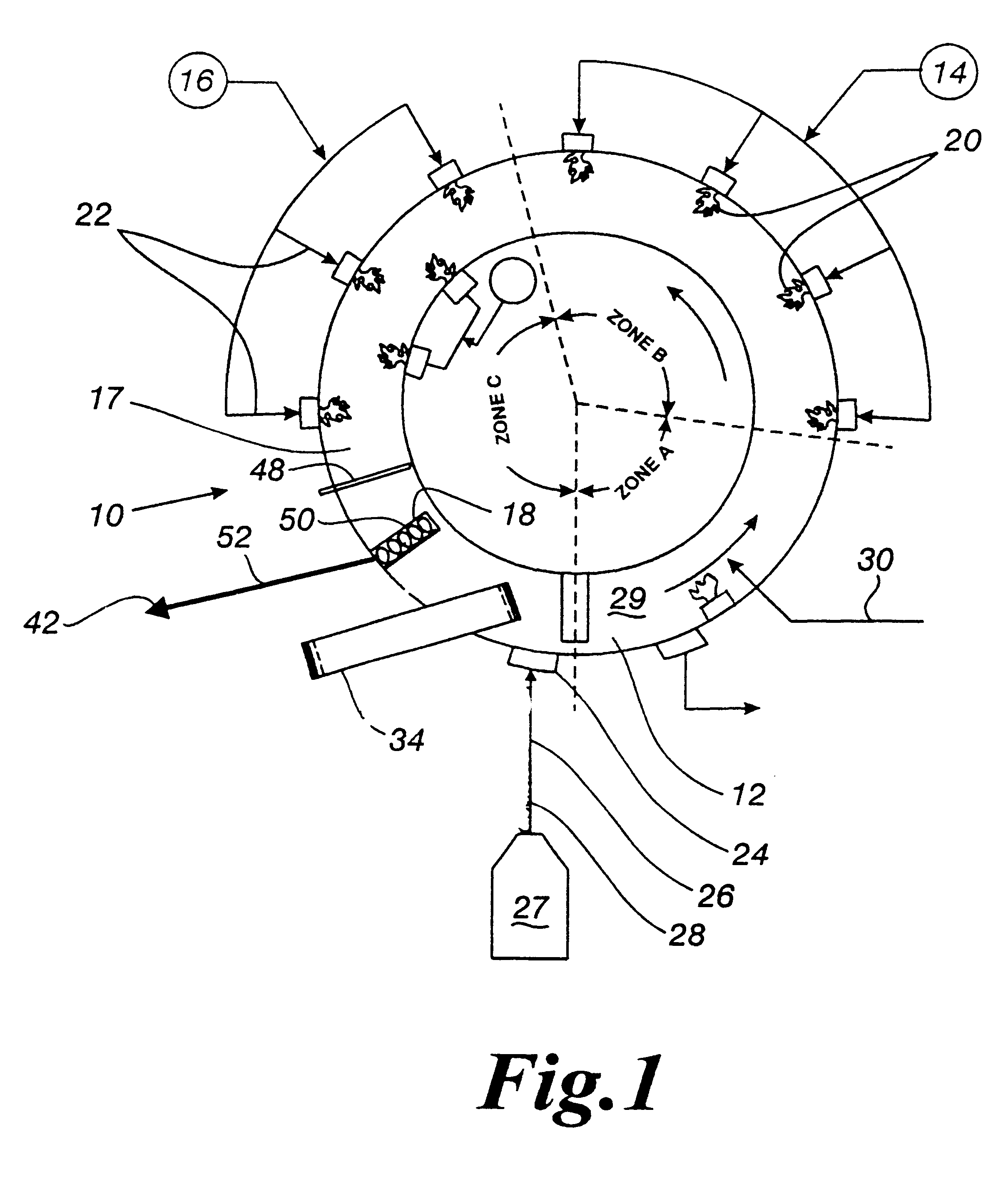
An electronic control system for regulating operational parameters in a pollution removal system. The pollution removal system may contain at least one reaction zone connected to a source of gas and a sorbent feeder containing a supply of sorbent. The system may include a pollutant concentration sensor that measures the concentration of at least one target pollutant in a gas exiting a reaction zone, a differential pressure sensor that measures the differential pressure across a reaction zone, a sorbent feed rate controller that regulates sorbent feed rate to the reaction zone, and a controller in communication with these elements. The controller may use the measured values to adjust sorbent feeder rate to ensure that the target pollutant concentration in a gas exiting the reaction zone is within an acceptable range and that differential pressure across the reaction zone is no greater than a predetermined level.
Owner:ENVIROSCRUB TECH CORP
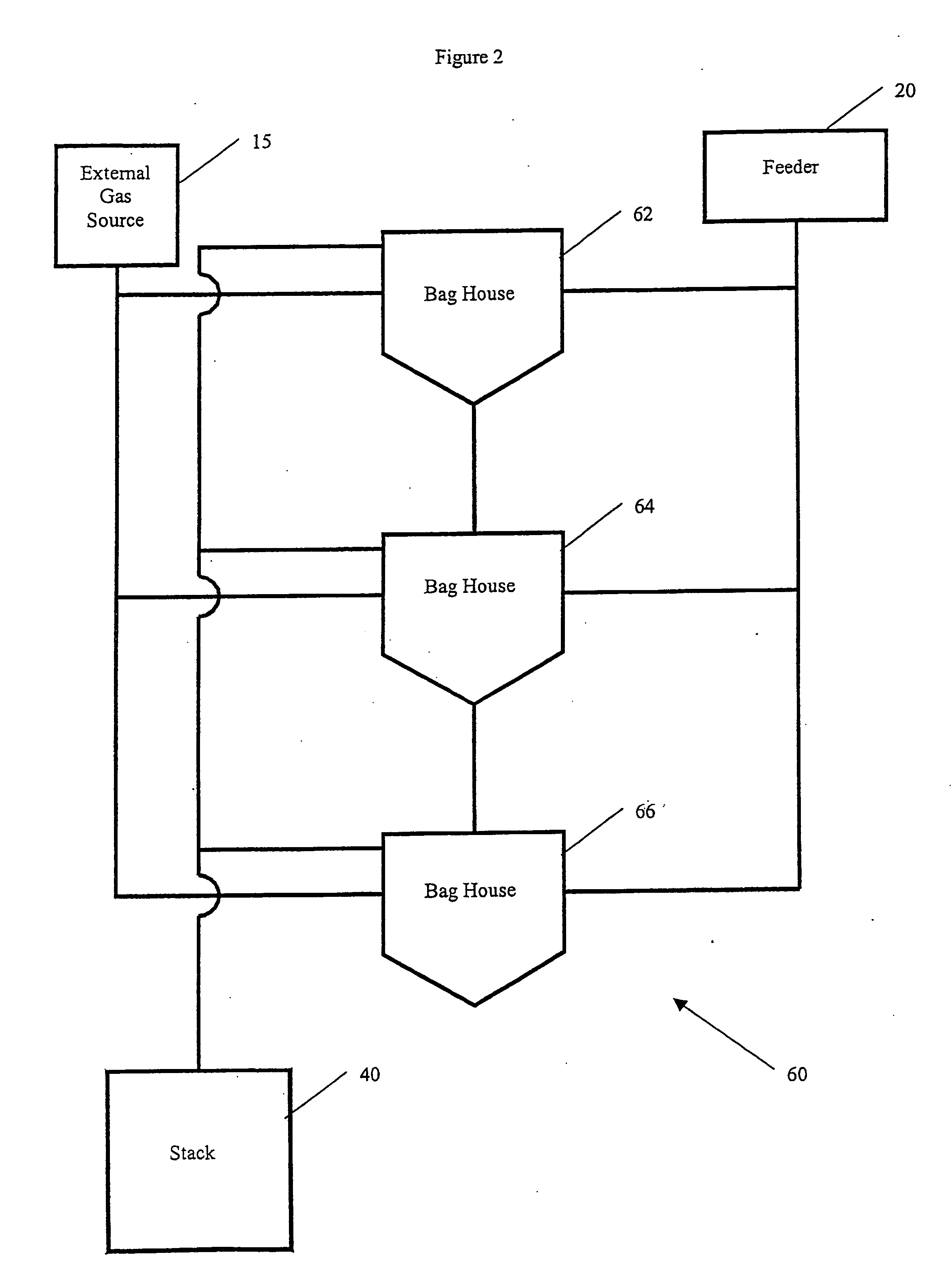
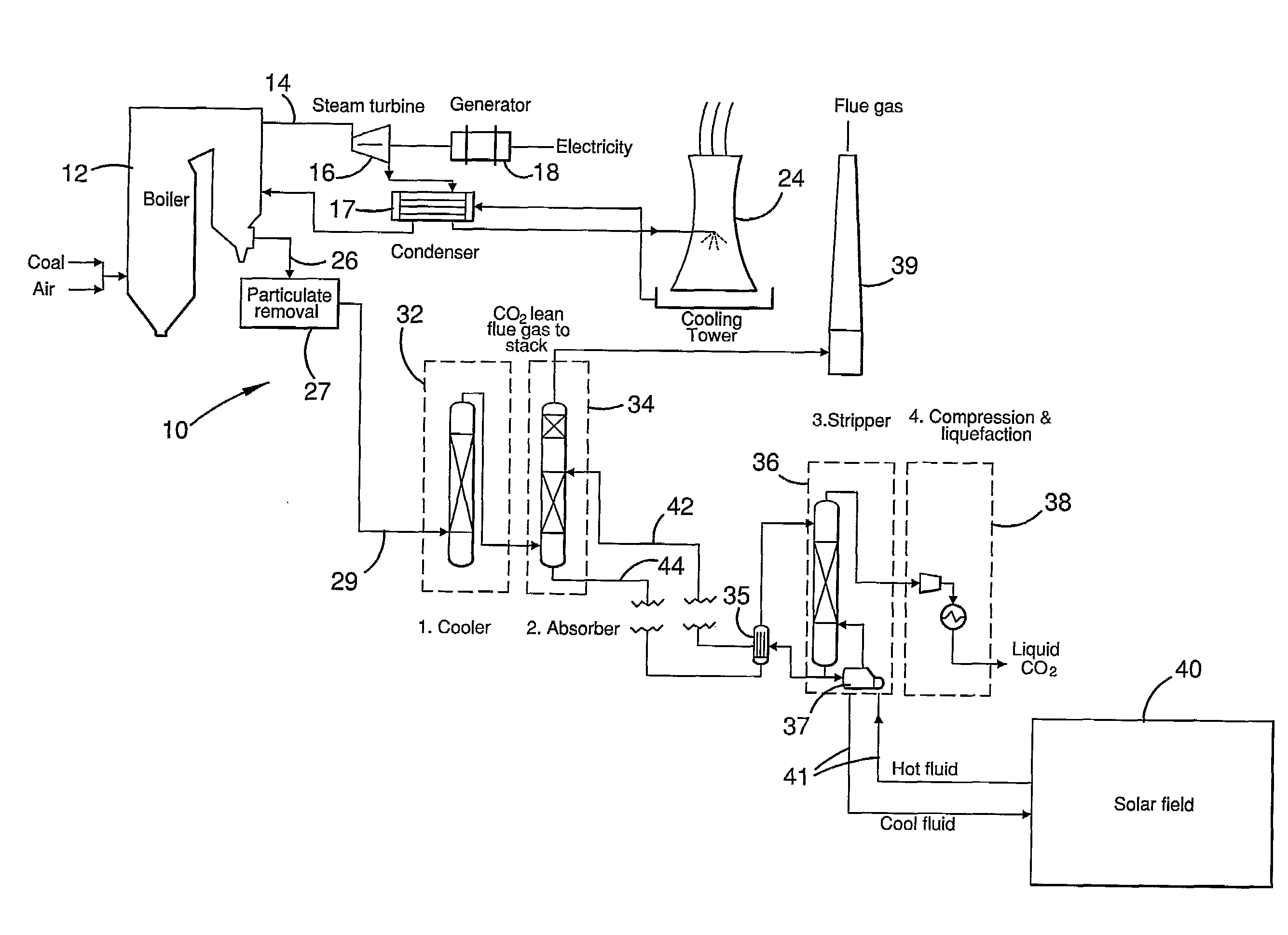
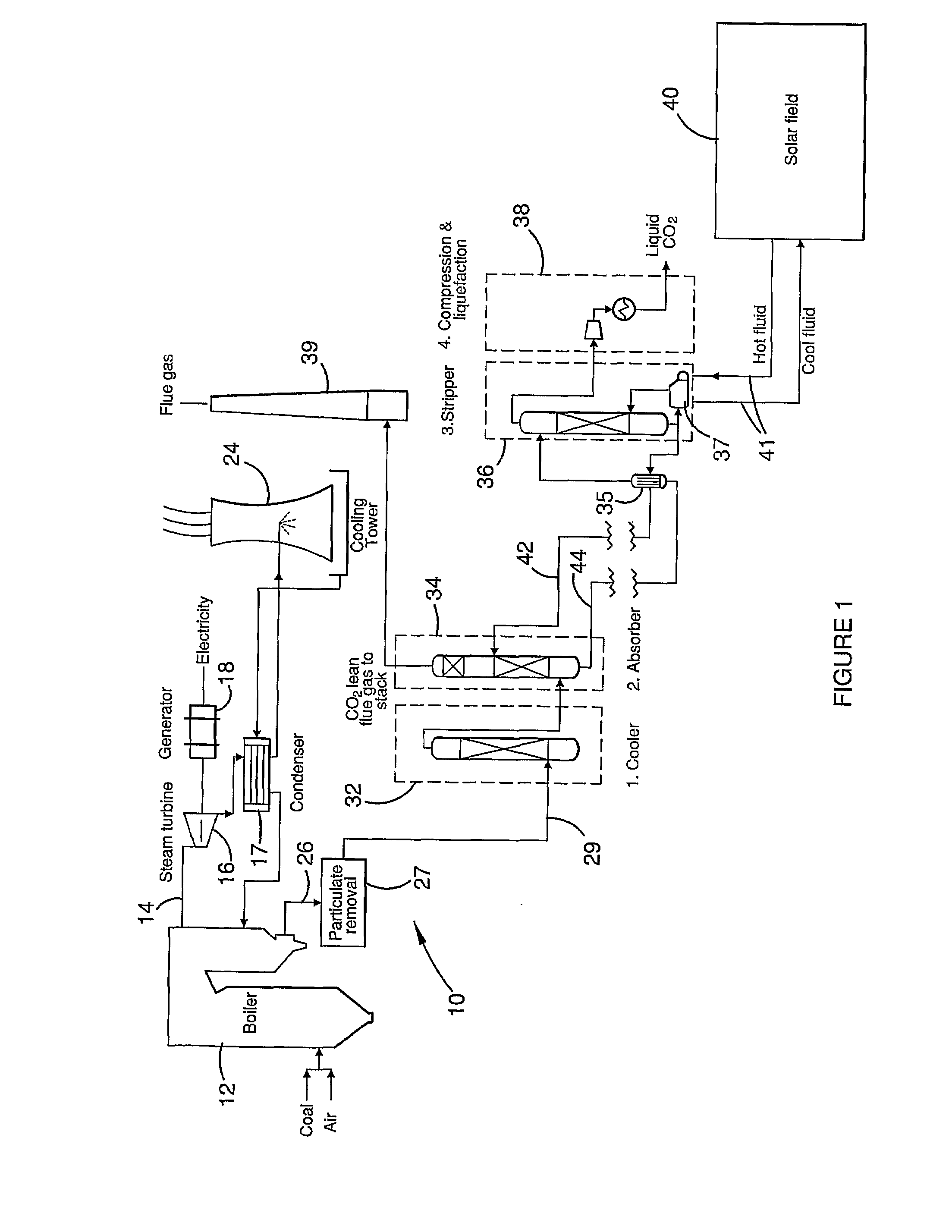
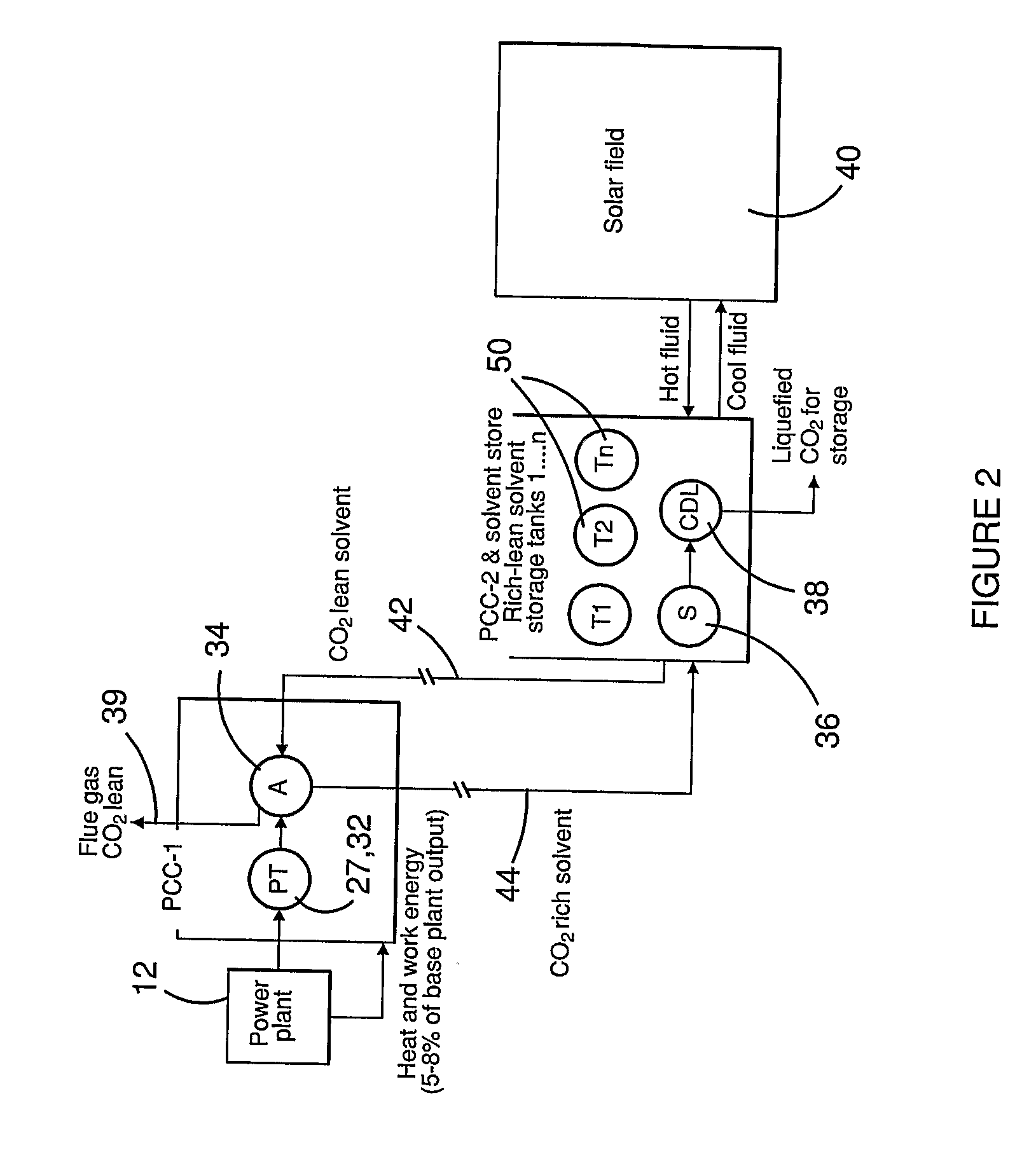
Co2 capture using solar thermal energy
InactiveUS20100005966A1Efficiently employedImprove efficiencySolar heating energyLiquid degasificationThermal energyWorking fluid
At an absorber station, CO2 is absorbed from a gas stream into a suitable solvent whereby to convert the solvent into a CO2-enriched medium, which is conveyed to a desorber station, typically nearer to a solar energy field than to the absorber station. Working fluid, heated in the solar energy field by insolation, is employed to effect desorption of CO2 from the CO2-enriched medium, whereby to produce separate CO2 and regenerated solvent streams. The regenerated solvent stream is recycled to the absorber station. The CO2-enriched medium and / or the regenerated solvent stream may be selectively accumulated so as to respectively optimise the timing and rate of absorption and desorption of CO2 and / or to provide a storage of solar energy.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Coal reducing gas direct reduction metallurgical process in gas-based shaft kiln and system
ActiveCN101358258ASimple structureReduce processing costsExhaust gas handlingShaft furnaceGas heaterProduct gas
The invention discloses a coal-derived reducing gas base shaft furnace direct reduction metallurgical method and a system thereof. Reducing gases with CO and H2 serving as the main components are prepared from coal through a coal-derived reducing gas system, and are treated by the reducing reaction with iron ore through a direct reduction metallurgical system. The reducing gases are mainly used as the reducing agents of the reducing flow, the cooling agents of the cooling flow and the fuel of the direct reducing metallurgical system. The reducing flow is composed of a reducing shaft furnace, a furnace top gas heat exchanger, a furnace top gas shock chilling / scrubbing system, a process gas recycle compressor, a compressor secondary cooler, a CO2 absorber, a process gas humidifier, a process gas heater, etc. The conical part of the lower part of the shaft furnace is the cooling zone of the shaft furnace direct reduction metallurgical furnace. The cooling gases are sprayed in from the conical region of the lower part of the shaft furnace direct reduction metallurgical furnace, and flow upwards across the metallurgical furnace. The hot cooling gases flow away the cooling region and then are cooled, compressed and recycled. The system is simple in structure and low in process cost.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Method and system for pulverized coal gasification for gas generation and direct reduction metallurgy of gas-based shaft furnace
ActiveCN102994678AGet rid of dependenceOvercome limitationsShaft furnaceGas emission reductionWater vaporShaft furnace
The invention provides a method for pulverized coal gasification for gas generation and direct reduction metallurgy of a gas-based shaft furnace. According to the method, feed coal is ground and then enters a gasification furnace in a form of pulverized coal; the pulverized coal reacts with a gasification agent oxygen and water vapor to generate crude gas rich in CO and H2; the high-temperature raw gas generated by the gasification furnace is subjected to cooling and wet cleaning for dust removal to obtain crude synthesis gas mainly containing CO and H2; the crude synthesis gas is adjusted into a reducing agent for a gas-based shaft furnace through water vapor conversion and purification; and the reducing agent enters the shaft furnace and reacts with lump ores or pellets to generate reducing iron. Through the invention, the coal gasification is combined with a gas-based direct reduction shaft furnace technology, thus the limitation on total natural gas of a gas-based direct reducing method is overcome, and large-scale production is realized; and the method has the advantages of low energy consumption, little pollution and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Method for directly restoring and recovering copper iron from smelting copper slag
ActiveCN102952952AMeet the requirements of energy saving and emission reductionEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementGas emission reductionMolten stateOxygen
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for directly restoring and recovering copper iron from smelting copper slag. The method comprises the following steps of: transferring high-temperature molten state copper slag to a high-temperature reducing furnace by a tundish, jetting oxygen to previously desulfurize, adding slagging constituent to keep temperature, jetting natural gas to carry out smelting reduction, slowly cooling to 1096 DEG C at the speed of 1.5-2 DEG C / min, and keeping the temperature for 1h to obtain 7.3at% Cu-Fe copper alloy melt and gamma pig iron, or slowly cooling to 850 DEG C at the speed of 1.5-2 DEG C / min, and keeping the temperature for 1h to obtain 2.7at% Cu-Fe copper alloy melt and gamma pig iron. According to the method provided by the invention, the total recovery use of valuable components, i.e. copper, iron and the like, can be realized, and the alloy melt obtained by the reduction smelting is slowly cooled and separated to obtain copper-rich alloy and low-sulfur gamma pig iron, so that separation of copper and iron is realized and the additional values of products can be improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Preparation method of high specific surface area tantalum powder and/or niobium powder
A tantalum powder and / or a niobium powder with high specific surface area are prepared through reaction between the oxides one of tantalum and / or niobium, alkali metal and halide of at least of Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba and Ce. Its advantages are simple preparing process, and high specific surface area, purity and flowability, and thus it is especially suitable for making the anode of capacitor.
Owner:NINGXIA ORIENT TANTALUM IND
Method and Apparatus For Coproduction of Pig Iron and High Quality Syngas
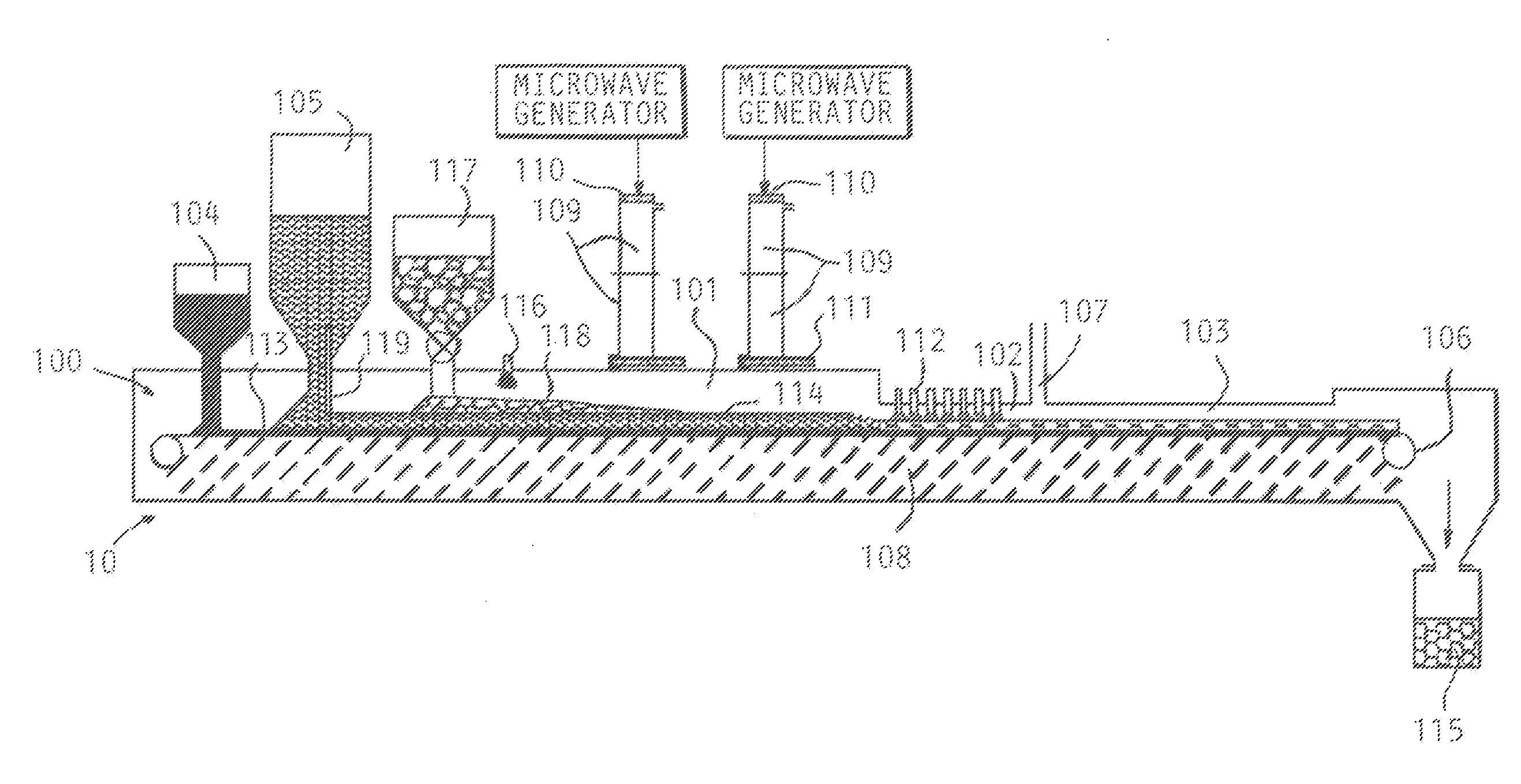
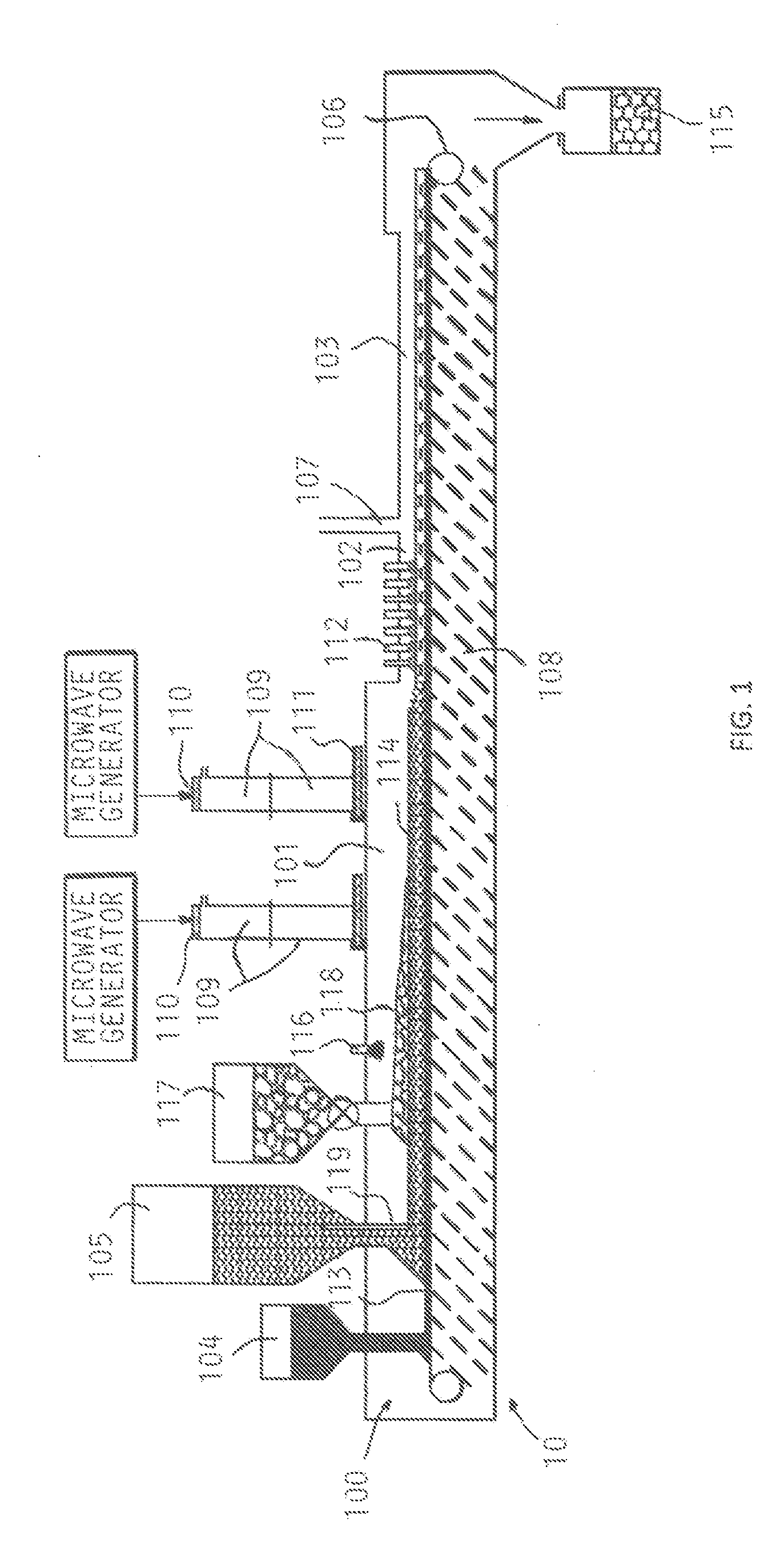
ActiveUS20120031232A1Improve microwave absorption performanceHeating up fastBlast furnace detailsCharge manipulationSludgeLiquid fuel
Combined microwave heating and plasma / electric arc heating is utilized in several processes and apparatus which involve co-production of pig iron and high quality syngas, biomass to liquid fuel production, coal to liquid fuel production, co-gasification of biomass and coal, municipal solid waste treatment, waste-to-energy (agriculture waste, ASR and PEF), EAF dust and BOF sludge treatment to recover zinc and iron, hazardous bottom ash vitrification, and bromine, chlorine and sulfur removal / recycling.
Owner:HUANG XIAODI +1
Slagging coal combustor for cementitious slag production, metal oxide reduction, shale gas and oil recovery, enviromental remediation, emission control and co2 sequestration
InactiveUS20110173139A1Reduce transportationMinimize disfiguringNitrogen compoundsSulfur compoundsMaterials scienceChar
Systems, methods and processes teach by specific examples how the cost of sequestering carbon dioxide (CO2) can be totally offset and turned into profits during coal powered electricity generation from revenue and co-benefits. The process is provided whereby fly ash-carbon mixtures, or de-volatilized coal char, or anthracite coal culm is co-fired in an air-cooled, slagging combustor with limestone or similar slag fluxing materials converts the ash into cementitious slag with properties similar to ground granulated blast furnace slag.
Owner:ZAUDERER BERT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com