Patents
Literature
227 results about "Elemental iron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elemental iron is the total amount of iron in the supplement available for absorption by your body. Each type of iron has a different percent of elemental iron. For instance: Carbonyl has 100% elemental iron. Ferrous fumarate has approximately 33% elemental iron. Ferrous sulfate has 20% elemental iron.
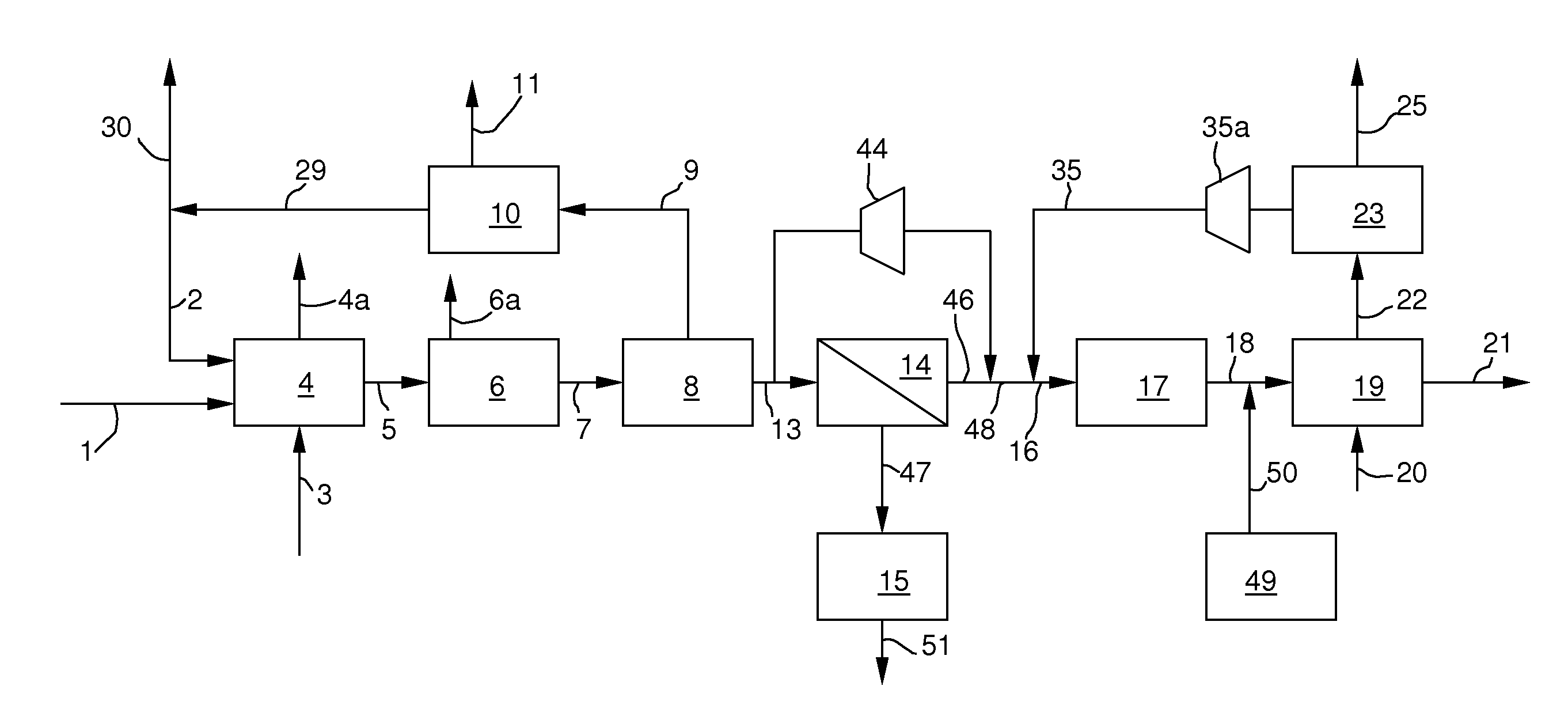
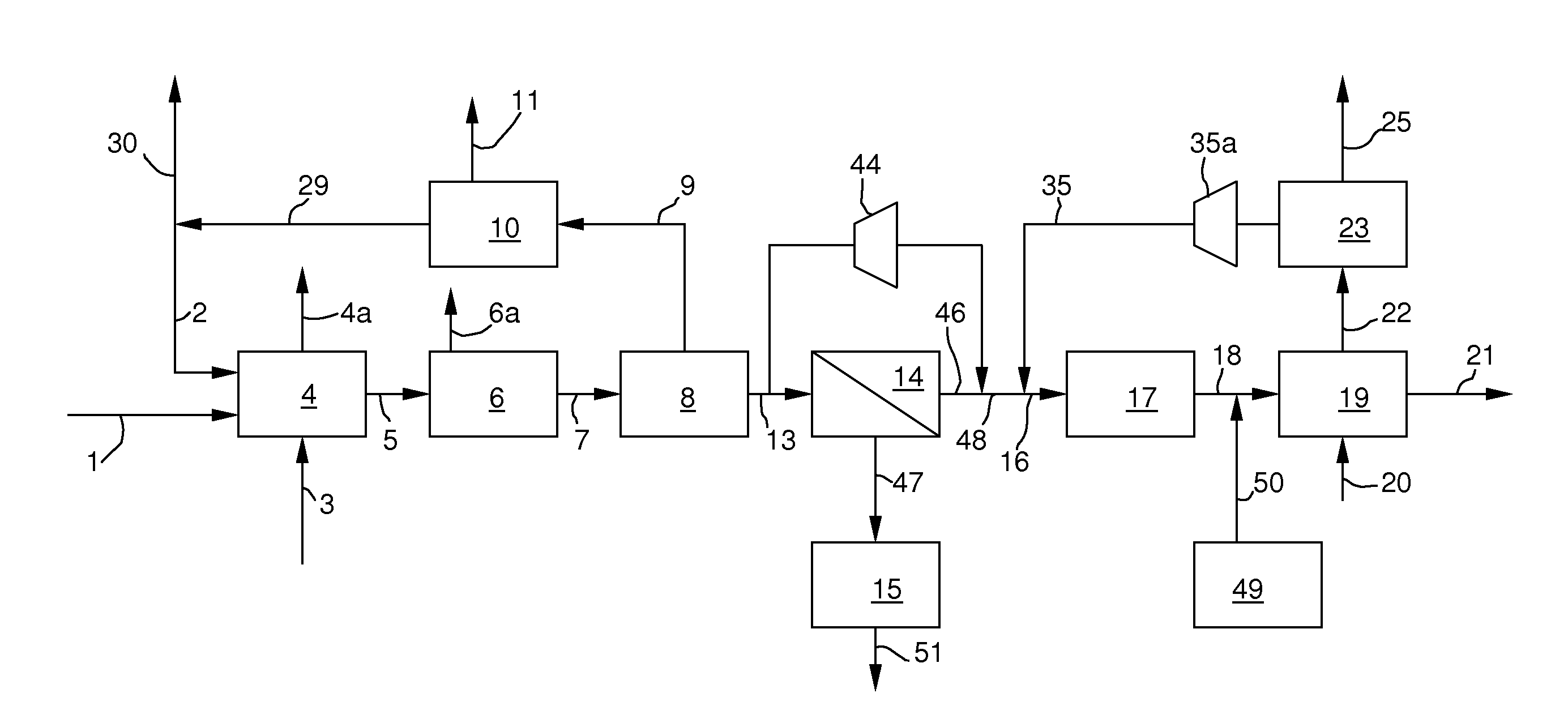
Process for production of elemental iron
InactiveUS7931731B2Easy to processIsotope separationHydrogen/synthetic gas productionPartial oxidationFerric
A process to prepare elemental iron by contacting an iron ore feed with a reducing gas at a pressure of between 1 and 10 bar to obtain iron and an off-gas includes preparing the reducing gas by performing the following steps: (a) partially oxidizing a mixture comprising a solid or liquid carbonaceous fuel and oxygen at a pressure of between 10 and 80 bar, thereby obtaining a gas comprising H2 and CO; (b) removing CO2 and H2S from the gas obtained in step (a) to obtain an intermediate gas comprising H2 and CO; (c) supplying the intermediate gas obtained in step (b) to a H2-selective membrane to obtain a H2-rich permeate gas and a CO-rich retentate; and (d) heating H2-rich permeate to obtain a heated H2-rich permeate as the reducing gas.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Methods and compositions for administration of iron
ActiveUS20070161600A1Safe and efficientBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNeutral phIron carbohydrate complex
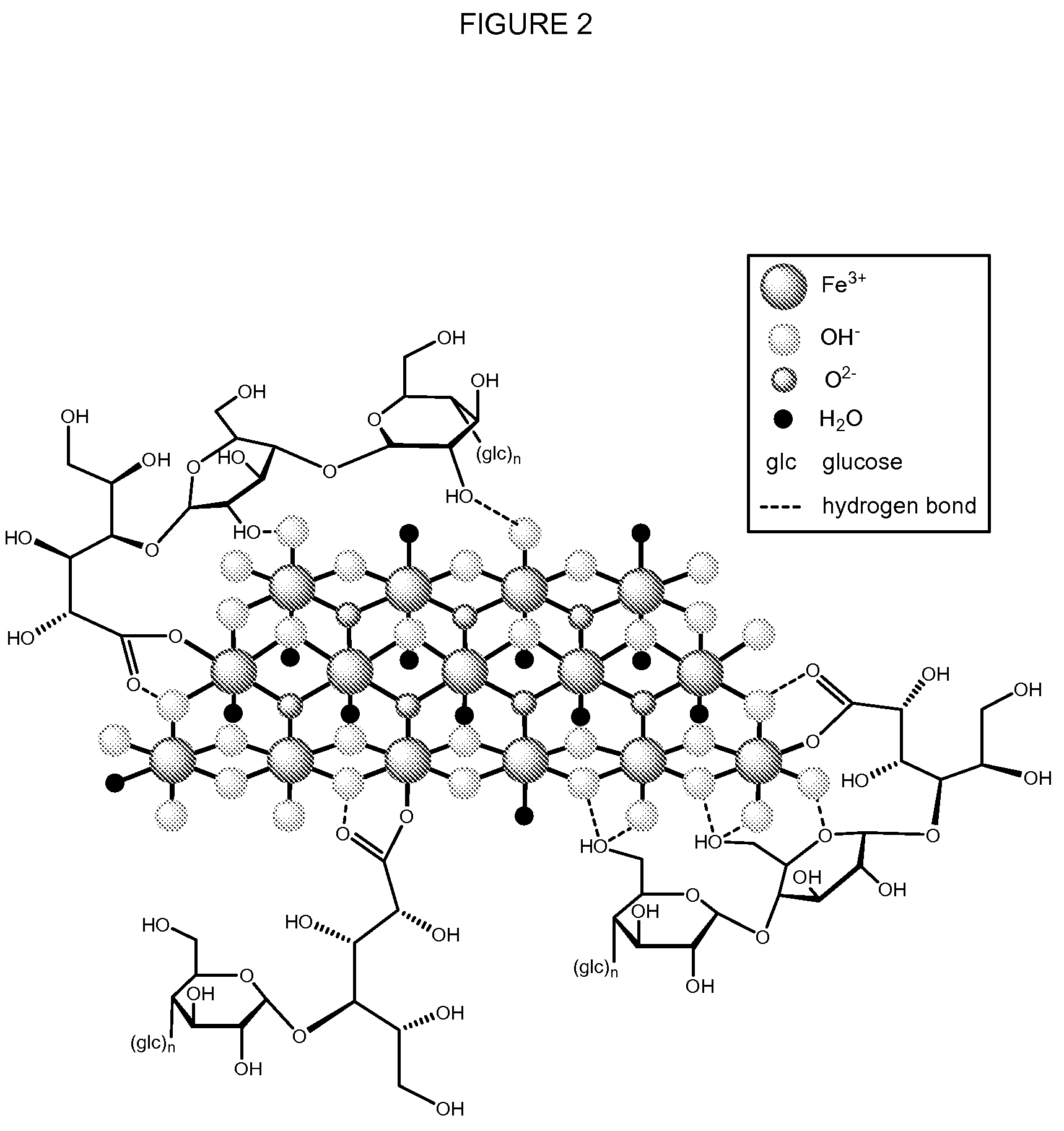
The present invention generally relates to treatment of iron-related conditions with iron carbohydrate complexes. One aspect of the invention is a method of treatment of iron-related conditions with a single unit dosage of at least about 0.6 grams of elemental iron via an iron carbohydrate complex. The method generally employs iron carbohydrate complexes with nearly neutral pH, physiological osmolarity, and stable and non-immunogenic carbohydrate components so as to rapidly administer high single unit doses of iron intravenously to patients in need thereof.
Owner:AMERICAN REGENT INC
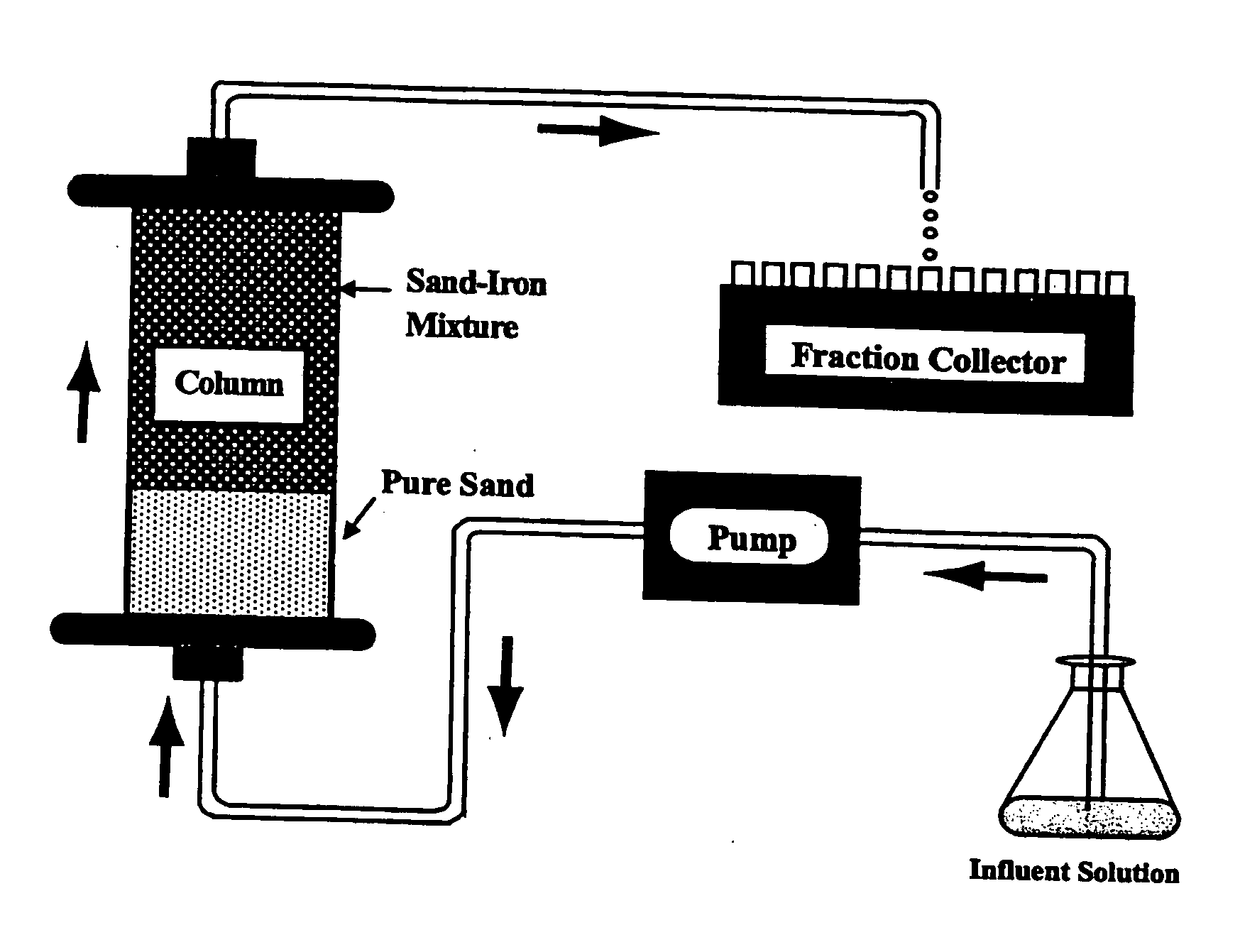
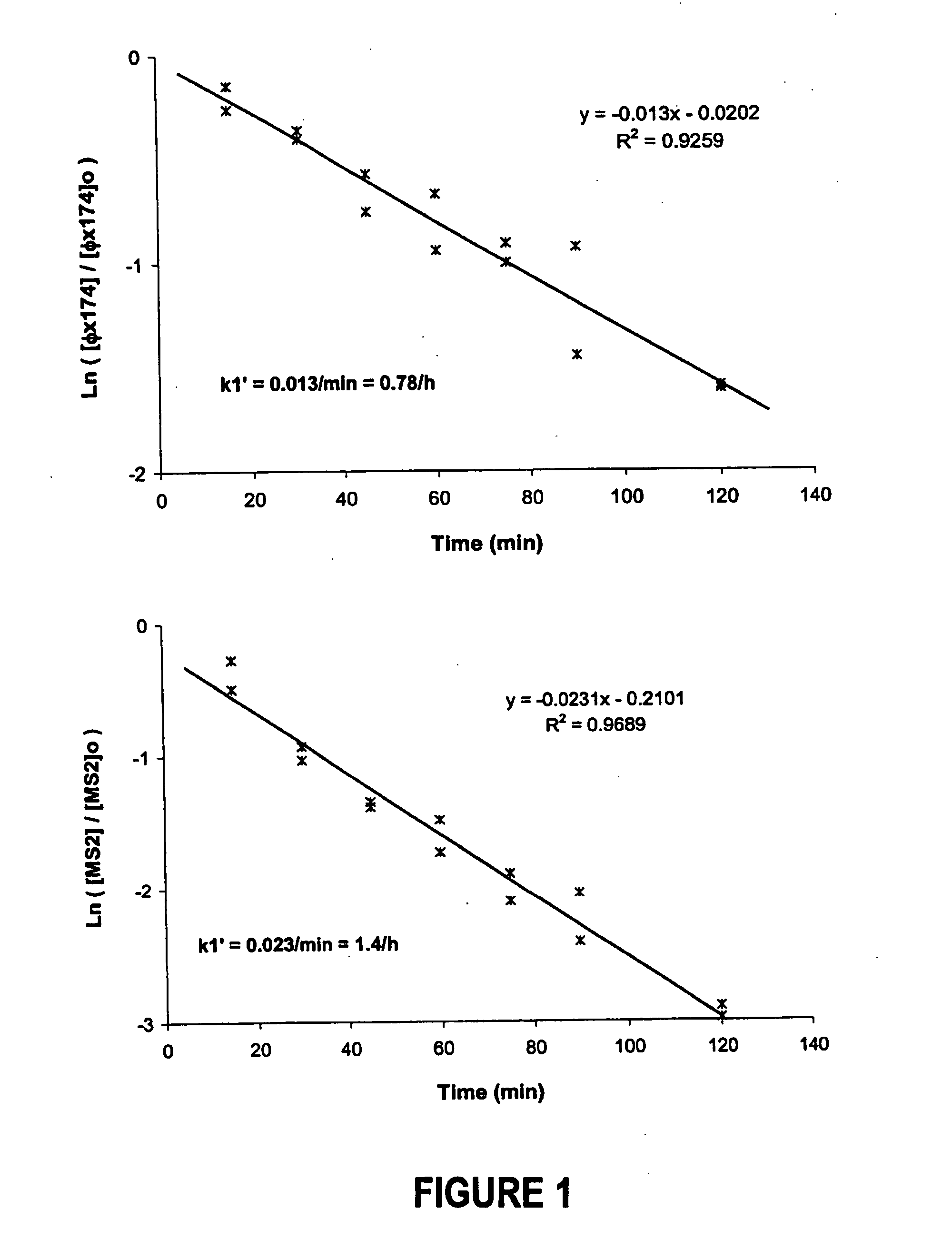
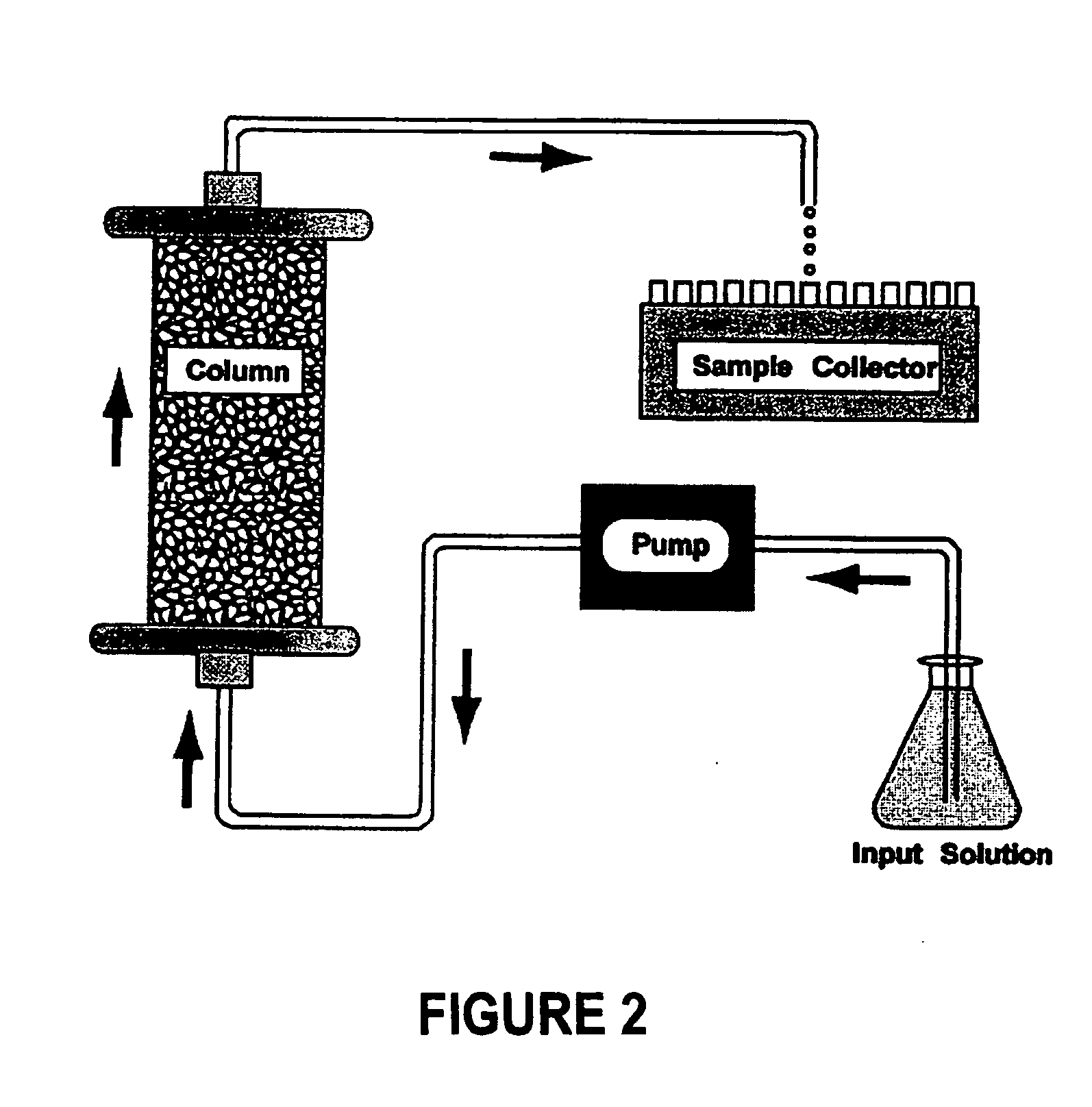
Removal of microorganisms and disinfection byproduct precursors using elemental iron or aluminum
InactiveUS20060249465A1Other chemical processesTreatment involving filtrationMicroorganismDisinfection by-product
A process for removing microorganisms and / or precursors of disinfection by-products from a medium sought to be treated comprising treating the medium with one or more elements capable of forming an oxide, a hydroxide, and / or an oxyhydroxide through corrosion is disclosed. A system for effecting the removal or inactivation of microorganisms and / or disinfection by-product precursors is also contemplated.
Owner:UD TECH CORP
Methods and compositions for administration of iron
The present invention generally relates to treatment of iron-related conditions with iron carbohydrate complexes. One aspect of the invention is a method of treatment of iron-related conditions with a single unit dosage of at least about 0.6 grams of elemental iron via an iron carbohydrate complex. The method generally employs iron carbohydrate complexes with nearly neutral pH, physiological osmolarity, and stable and non-immunogenic carbohydrate components so as to rapidly administer high single unit doses of iron intravenously to patients in need thereof.
Owner:AMERICAN REGENT INC
Chemically bonded phosphate ceramics of trivalent oxides of iron and manganese
A new method for combining elemental iron and other metals to form an inexpensive ceramic to stabilize arsenic, alkaline red mud wastes, swarfs, and other iron or metal-based additives, to create products and waste forms which can be poured or dye cast.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF +1
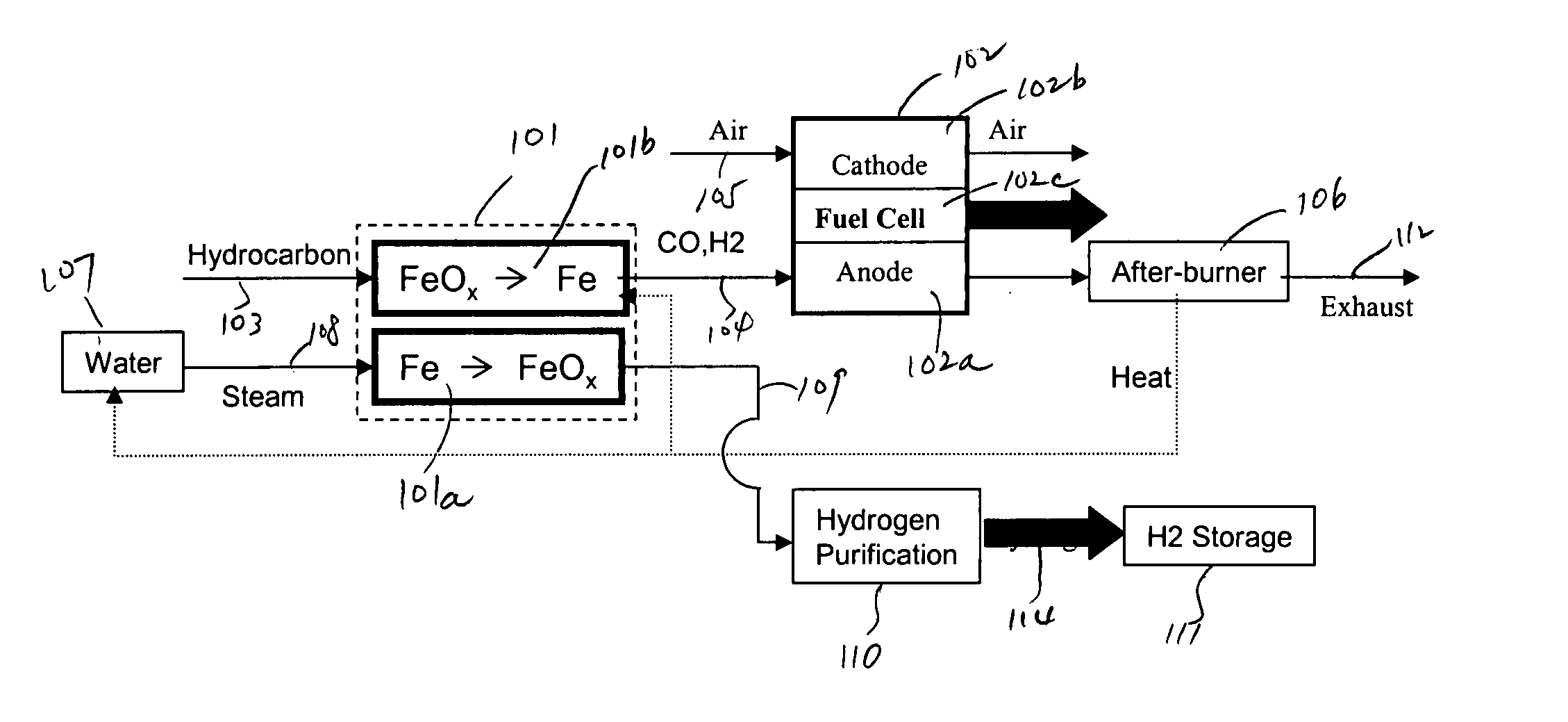
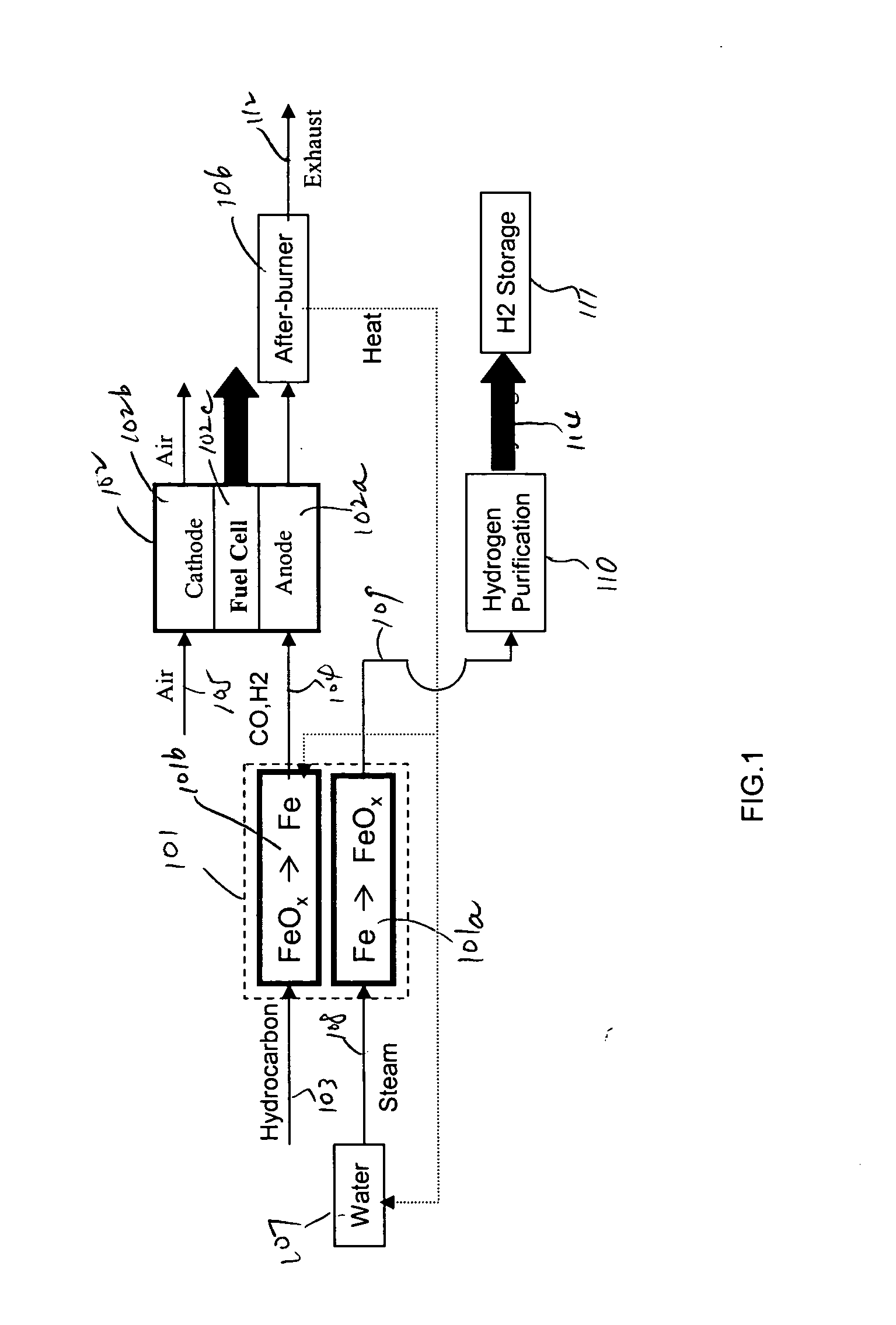
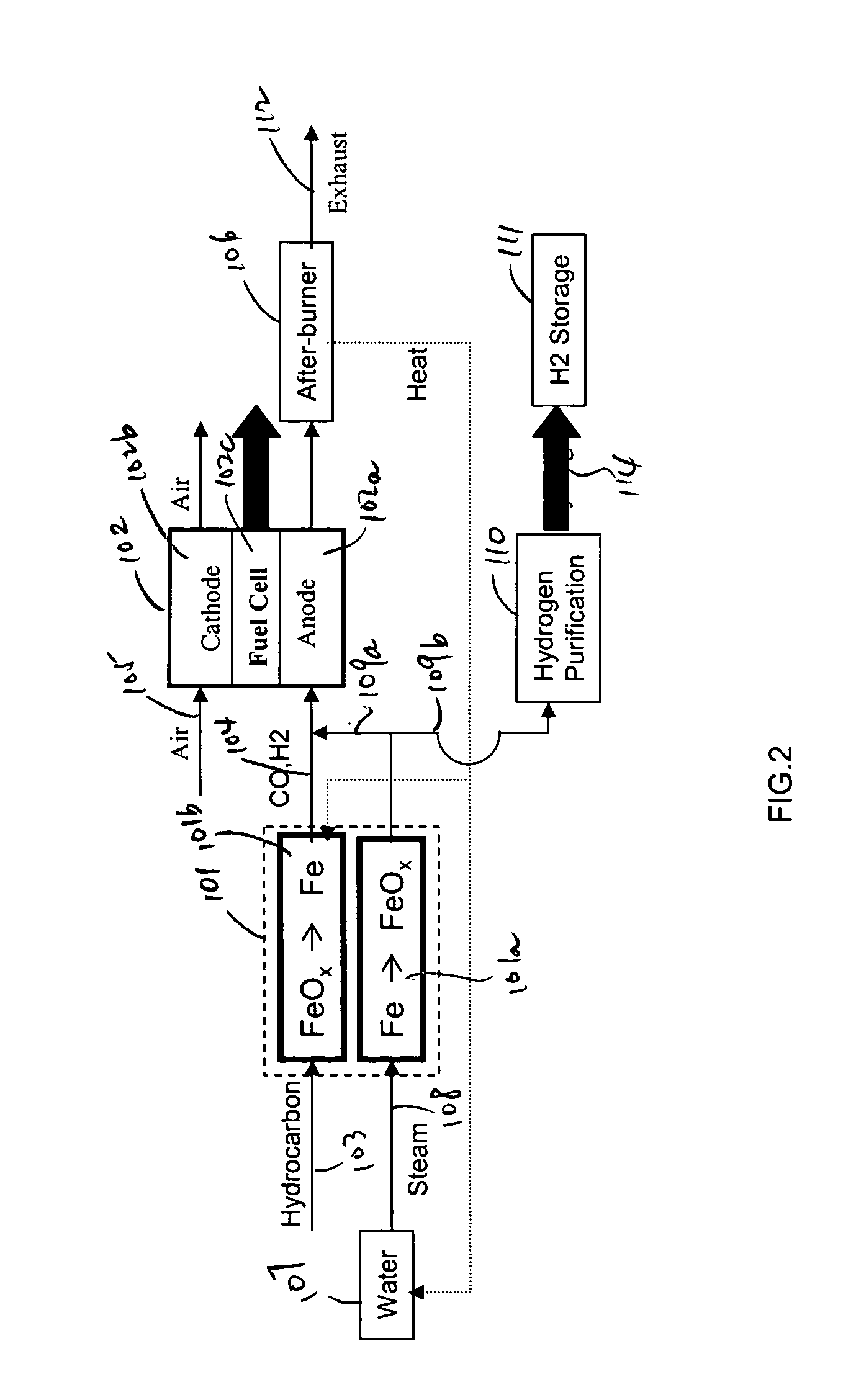
Method for hydrogen and electricity production using steam-iron process and solid oxide fuel cells
InactiveUS20050037245A1Good flexibilityImprove efficiencyHydrogenFuel cell auxillariesElectrochemistryElectric power
A method and a system for the co-production of electricity and hydrogen fuel are provided. The system may include a fuel conditioning unit, two or more iron / iron oxide beds and a high temperature electrochemical generator. In one embodiment, a reduction bed contains iron oxides. A hydrocarbon fuel, such as natural gas, is conditioned to carbon dioxide and hydrogen by the reduction bed. The conditioned fuel is then converted electrochemically to generate electricity in a fuel cell. Operating simultaneously is an oxidation bed that oxidizes elemental iron to iron oxides and produces hydrogen. The oxidation bed may previously have served as the reduction bed. The hydrogen thus produced is sufficiently pure to be used in a refueling application. The heat necessary for the endothermic reduction may be provided by the high temperature electrochemical generator. The two beds may operate concurrently or sequentially, and alternate their roles when their reactants are partially exhausted.
Owner:EVOGY
Biodegradable iron-containing compositions, methods of preparing and applications therefor
The invention relates to biodegradable iron alloy-containing compositions for use in preparing medical devices. In addition, biodegradable crystalline and amorphous compositions of the invention exhibit properties that make them suitable for use as medical devices for implantation into a body of a patient. The compositions include elemental iron and one or more elements selected from manganese, magnesium, zirconium, zinc and calcium. The compositions can be prepared using a high energy milling technique. The resulting compositions and the devices formed therefrom are useful in various surgical procedures, such as but not limited to orthopedic, craniofacial and cardiovascular.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
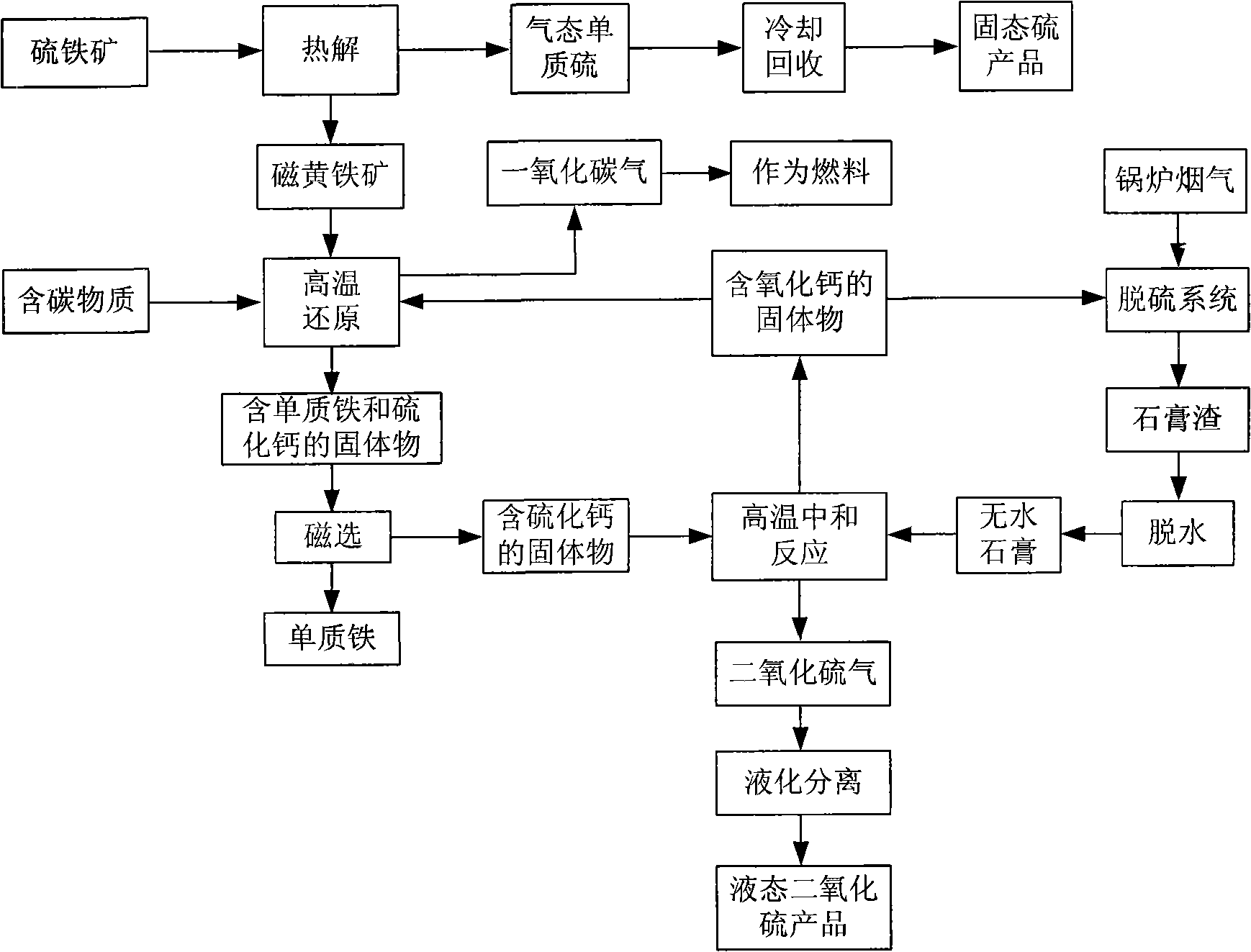
Method for utilizing comprehensive resource of sulfur-containing solid waste
InactiveCN101570341ATo promote metabolismSave resourcesDispersed particle separationSulfur compoundsSulfur containingPollution
The invention discloses a method for utilizing comprehensive resource of sulfur-containing solid waste, which comprises the following steps: (1) pyrolyzing sulfurous iron ore to obtain pyrrhotite and an elemental sulfur product; (2) mixing the pyrrhotite, a carbon-containing substance and a calcium-containing substance to carry out reduction reaction under a high temperature to obtain a solid mixture of elemental iron and calcium sulfide; (3) magnetically separating the solid mixture, and separating and recovering the solid mixture to obtain the elemental iron; (4) mixing and heating the solid containing the calcium sulfide and dehydrated gypsum to obtain tail gas containing SO2 and solid containing calcium oxide; and (5) separating the tail gas containing the SO2 through liquefying to obtain a liquid SO2 product, and using the solid containing the calcium oxide as the calcium-containing substance to participate in the reaction of the step (2) and as flue gas desulfurizing agent for cyclically utilization. The method solves the problems of occupied floor due to the stacking of desulfurization gypsum and coal washing sulfurous iron ore, environment pollution and potential safety hazard, makes full use of calcium, sulfur and iron resources rich in the wastes, and can realize recycling economy and clean production.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chemically bonded phosphate ceramics of trivalent oxides of iron and manganese
InactiveUS20020123422A1Reduce oxideReduce decreaseSludge treatmentSolid waste managementPhosphateRed mud
A new method for combining elemental iron and other metals to form an inexpensive ceramic to stabilize arsenic, alkaline red mud wastes, swarfs, and other iron or metal-based additives, to create products and waste forms which can be poured or dye cast.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF +1
Magnetic carbon-based iron oxide compound material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103280577AHigh degree of crystallizationStrong loadCell electrodesWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMagnetic carbonIron oxide
The invention discloses a magnetic carbon-based iron oxide compound material and a preparation method of the magnetic carbon-based iron oxide compound material. Particularly, the invention discloses a prepraation method of the magnetic carbon-based iron oxide compound material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (a) providing a mixture comprising a carbon-based precursor, elemental iron and a solvent; and (b) carrying out heating reaction on the mixture in the step (a), thus obtaining the carbon-based iron oxide compound material. The method has the advantages that materials are common and are easily available, and the process is simple, safe and effective and the like. The obtained compound material has stable magnetism, and is wide in application.
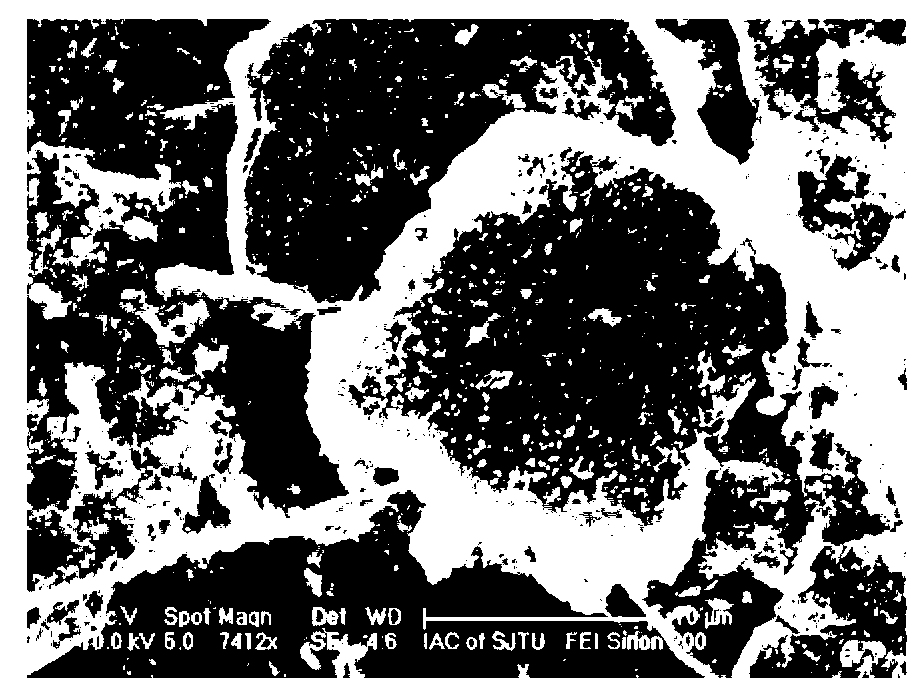
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Biological mineral compound fertilizer and production method thereof
InactiveCN101475417APromote absorptionImprove qualityOrganic fertilisersUrea compound fertilisersAdditive ingredientPotassium
The invention relates to a biomineral compound fertilizer, which comprises the following effective ingredients: 15 to 20 weight percent of organic substances, 5.8 to 10.3 weight percent of potassium oxide, 2 to 2.95 weight percent of microelements such as iron and copper, 1.5 to 2 weight percent of medium elements such as calcium, magnesium and sulfur, 1 to 5 weight percent of urea, 3 to 5 weightpercent of phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacteria, and the balance being water and impurities, wherein the pH value of the fertilizer is between 6.5 and 7. The biomineral compound fertilizer contains the effective ingredients required by various crops, and has most nutritive compositions required for crop growth. The phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacteria in the biomineral compound fertilizer can also decompose insoluble phosphorus and potassium elements in soil, and are favorable for crop absorption. Moreover, the biomineral compound fertilizer promotes material exchange and beneficial cycle of a cropland biosphere 'soil-plant-animal-microorganism'.
Owner:SHANXI LUTU BIOTECH CO LTD
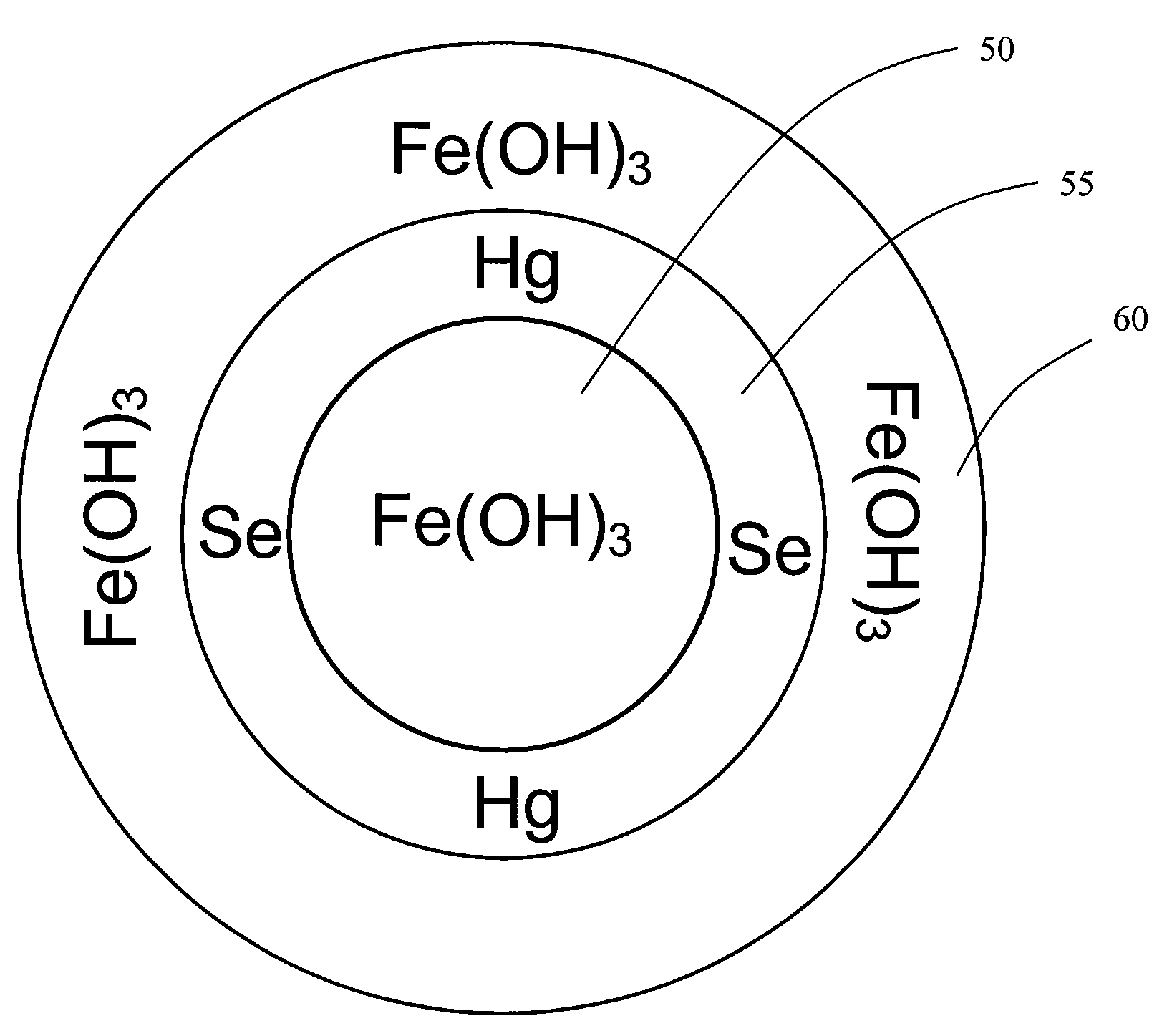
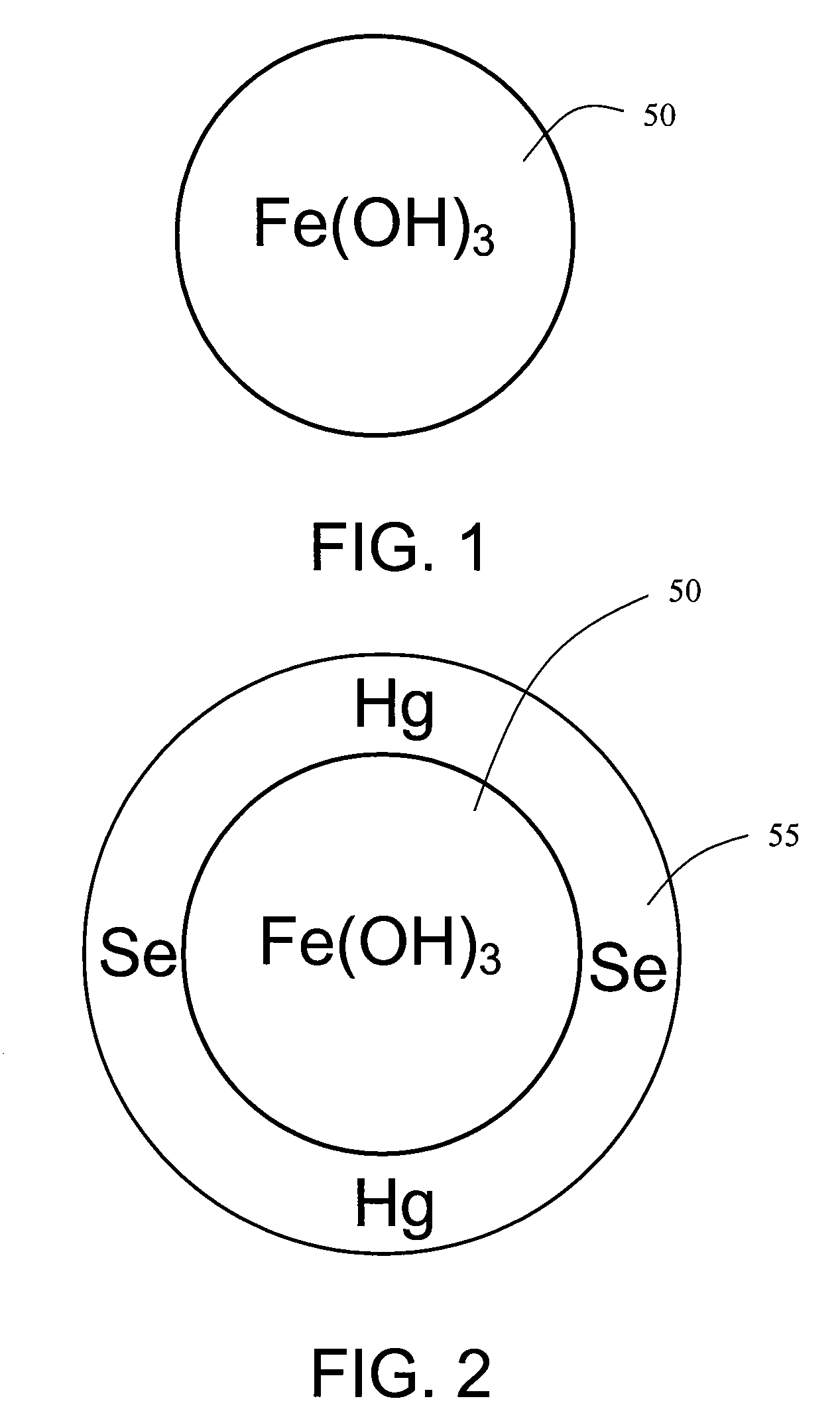
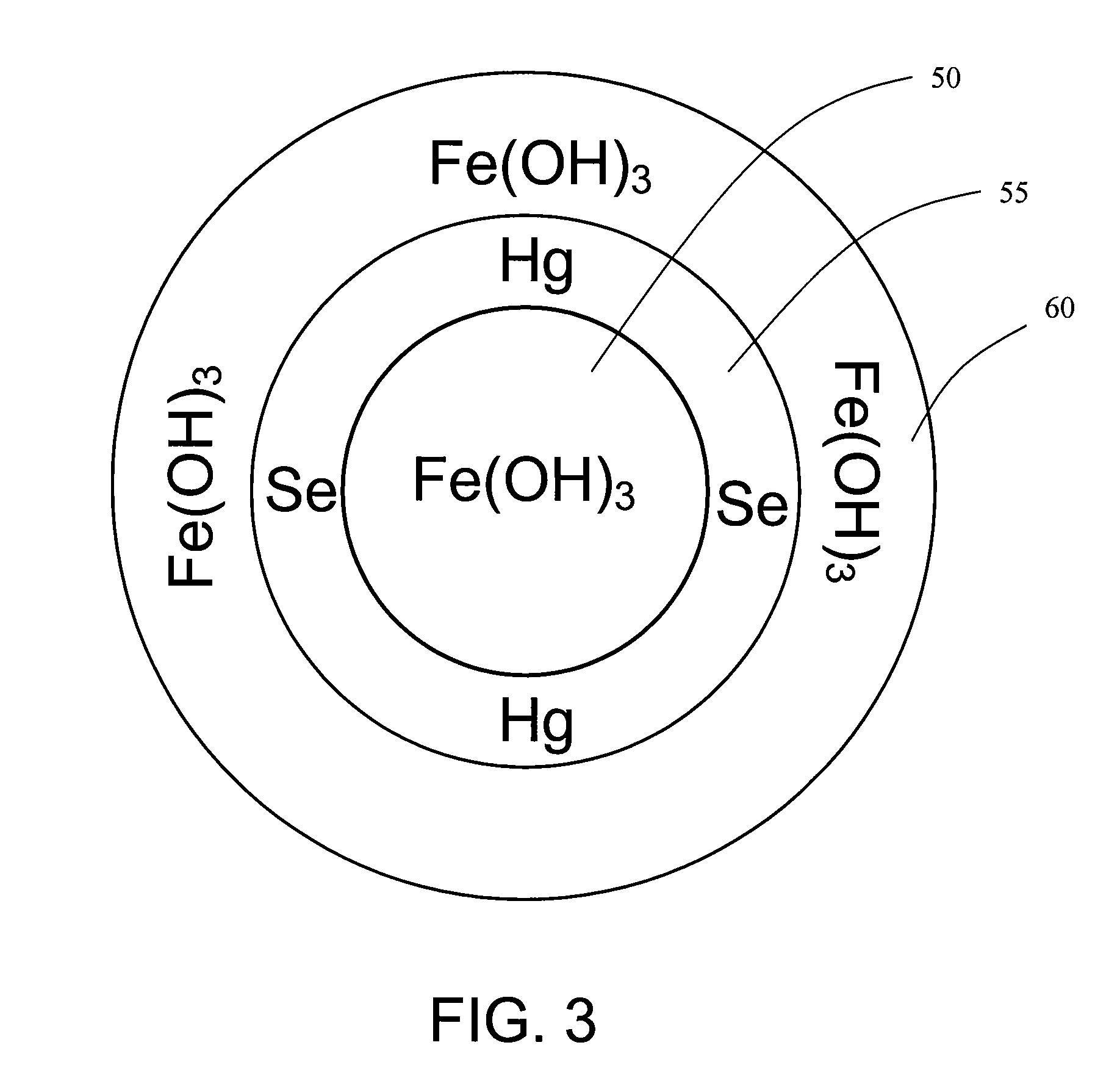
Methods and systems for enhancing mercury, selenium and heavy metal removal from flue gas
A method for treating flue gas may include adding iron to a slurry in a ratio between approximately 20-to-1 and 5000-to-1 by weight of iron to a weight of mercury, selenium or other heavy metal to be removed from the flue gas, and contacting the slurry with the flue gas in a flue gas desulfurization system. A system for treating flue gas may include a scrubber, a slurry tank, and a water source. Water and limestone may be combined in the slurry tank to form a limestone slurry. At least a portion of the limestone slurry may be used to treat flue gas in the scrubber. Iron may be added to at least a portion of the limestone slurry used to treat flue gas in the scrubber. The iron used in either the method or system may be a ferrous or ferric salt, or elemental iron.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Process for Production of Elemental Iron
InactiveUS20100050812A1Easy to processIsotope separationHydrogen/synthetic gas productionOxygenFerric
A process to prepare elemental iron by contacting an iron ore feed with a reducing gas at a pressure of between 1 and 10 bar to obtain iron and an off-gas includes preparing the reducing gas by performing the following steps: (a) partially oxidizing a mixture comprising a solid or liquid carbonaceous fuel and oxygen at a pressure of between 10 and 80 bar, thereby obtaining a gas comprising H2 and CO; (b) removing CO2 and H2S from the gas obtained in step (a) to obtain an intermediate gas comprising H2 and CO; (c) supplying the intermediate gas obtained in step (b) to a H2-selective membrane to obtain a H2-rich permeate gas and a CO-rich retentate; and (d) heating H2-rich permeate to obtain a heated H2-rich permeate as the reducing gas.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
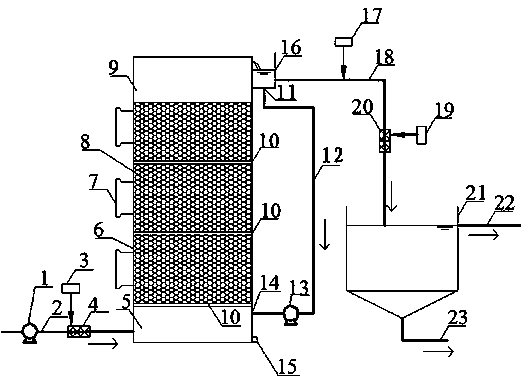
Multistage ferric-carbon microelectrolysis coupled Fenton oxidation bed reactor
ActiveCN103880225ASolve ammonia nitrogenSolve total nitrogenMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandHazardous substance
The invention discloses a multistage ferric-carbon microelectrolysis coupled Fenton oxidation bed reactor. The multistage ferric-carbon microelectrolysis coupled Fenton oxidation bed reactor is characterized by comprising a lifting water pump, a water inlet pipeline, a hydrogen peroxide dosing device, a water inlet pipeline mixer, a water distribution chamber, a multistage ferric-carbon microelectrolysis coupled Fenton oxidation bed reactor body, a material taking and replacing port, an elemental iron and granular activated carbon mixture layer, an outlet water clarification zone, a sieve plate water distribution system, a sludge discharging opening, a reactor draining ditch, a water outlet pipe and a precipitation tank, wherein the precipitation tank comprises a precipitation tank body, a water outlet pipeline and a sludge discharging pipeline. According to the multistage ferric-carbon microelectrolysis coupled Fenton oxidation bed reactor disclosed by the invention, the problems of the traditional coking wastewater treatment processes that COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand), ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and chromaticity in outlet water do not reach the standards and the like due to the fact that the effect of removal of refractory and complicated organic pollutants is not ideal are solved, and the treatment on refractory polycyclic and heterocyclic organic substances and toxic and harmful substances in wastewater is extremely effective.
Owner:HUAQI ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION SCI & TECH
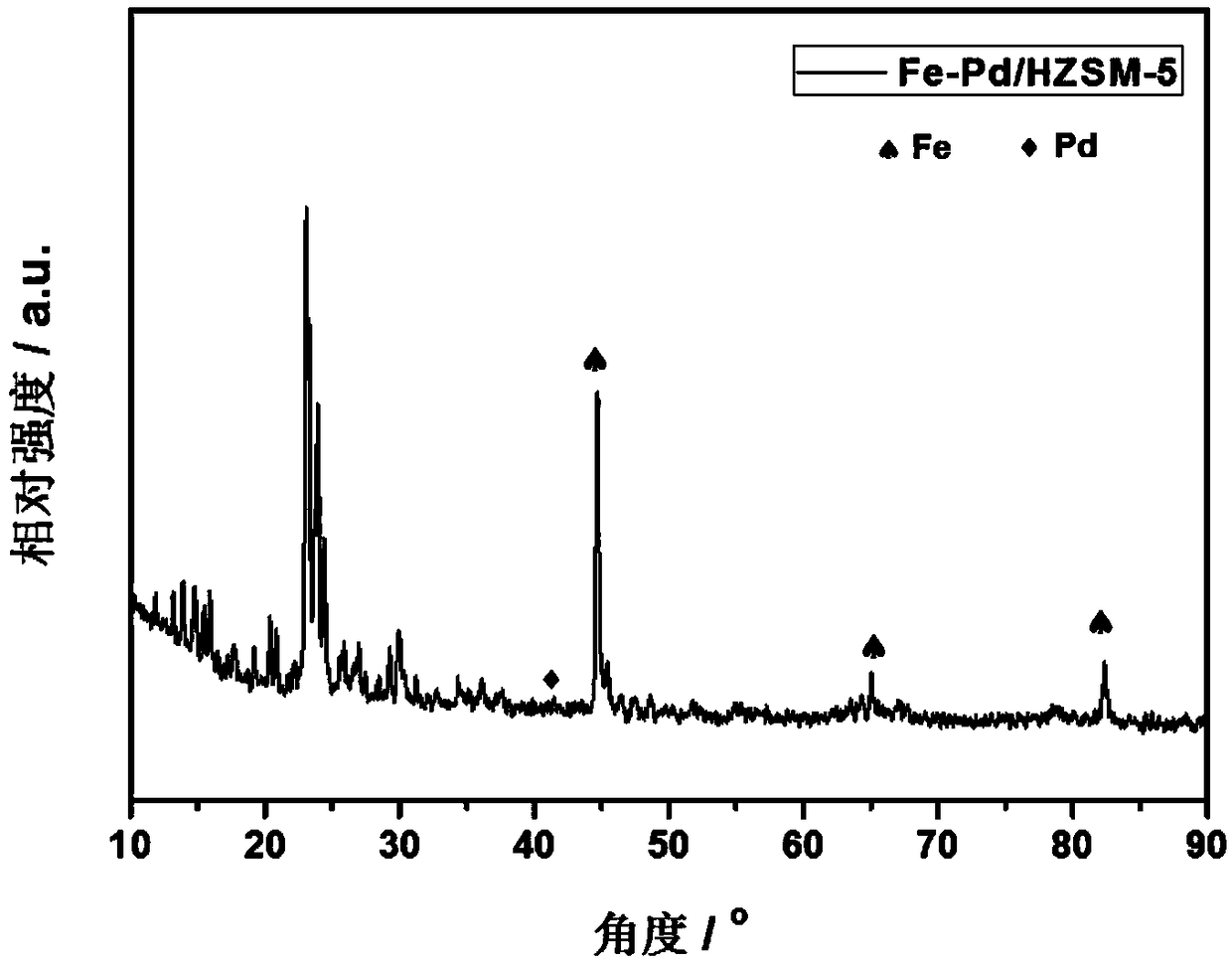
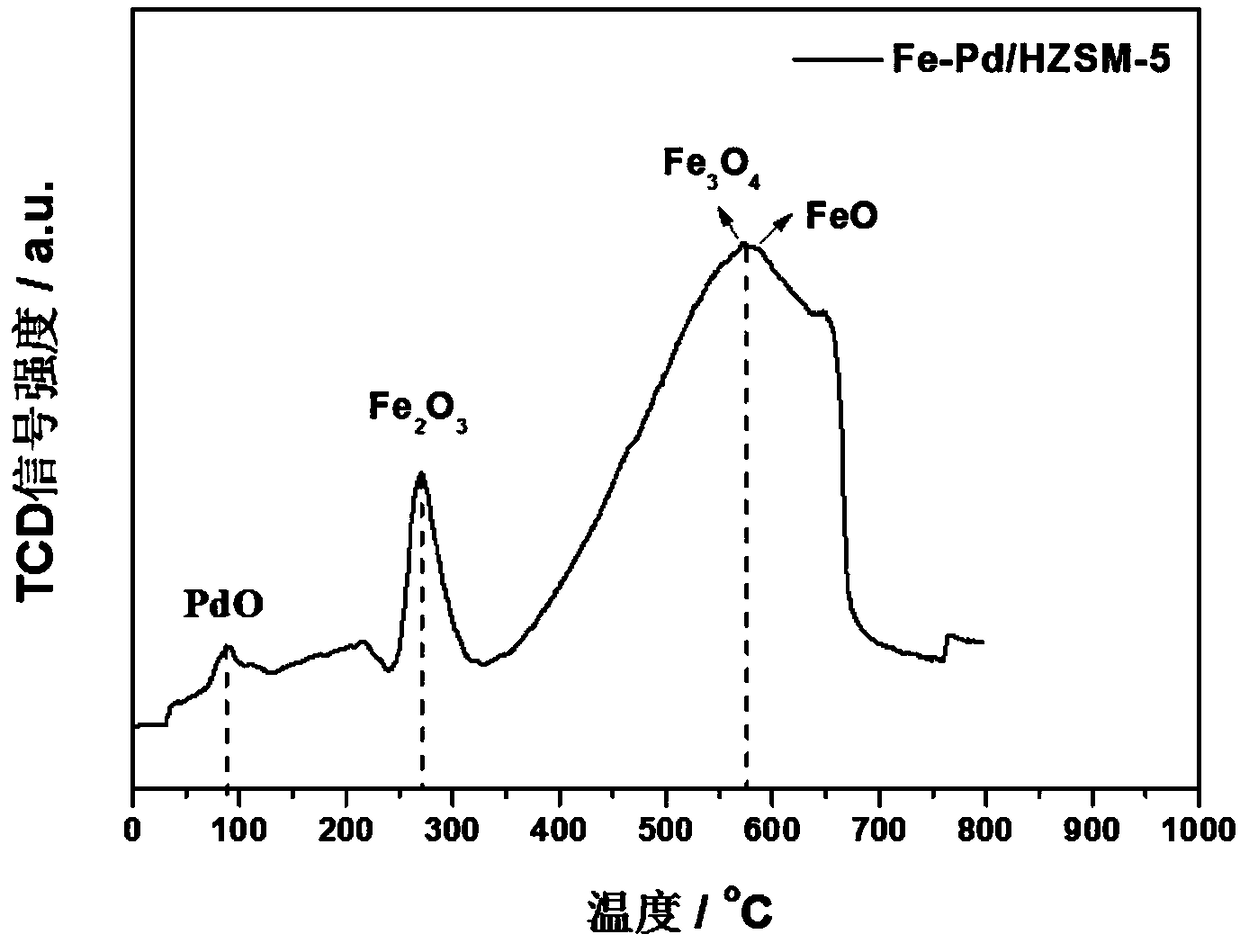
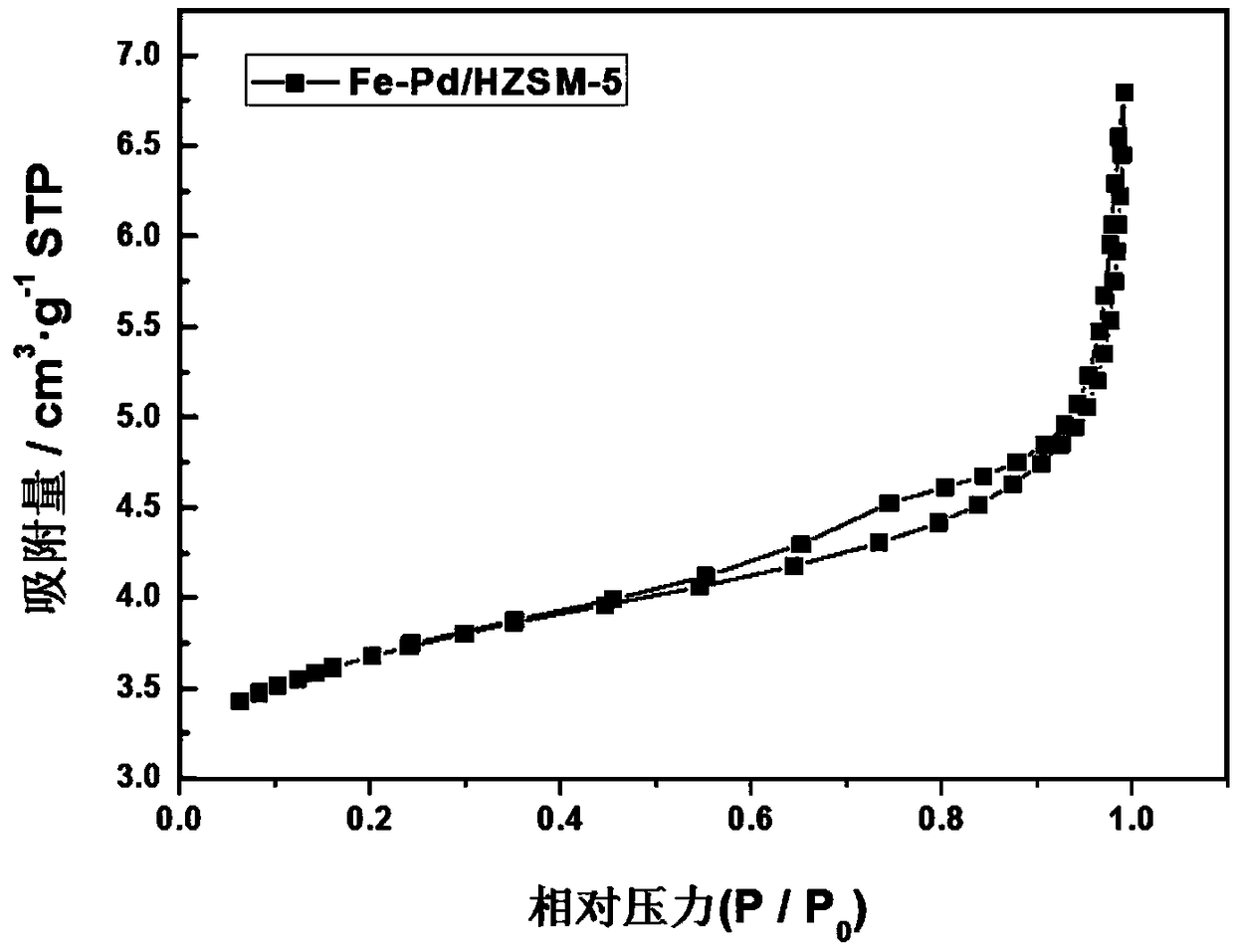
HZSM-5 supported Fe-Pd bimetallic catalyst for lignin hydrogenation and depolymerization and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109289903AHigh activityGood dispersionMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionDepolymerizationCalcination
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalysts, and discloses a HZSM-5 supported Fe-Pd bimetallic catalyst for lignin hydrogenation and depolymerization and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the invention uses an iron source and a palladium source as raw materials, the materials are dispersed on the surface of a HZSM-5 molecular sieve by an impregnation method, andthe catalyst is prepared by high-temperature calcination and hydrogen reduction. The method of the invention simultaneously loads Fe and Pd onto a carrier to realize the reduction of elemental iron,the Fe promotes the high dispersion of Pd, and improves the catalytic efficiency and the catalytic selectivity; a molecular sieve HZSM-5 is used as the carrier to improve the dispersibility and activecatalytic sites of the active metal, and the catalytic activity can be improved, the obtained HZSM-5 supported Fe-Pd bimetallic catalyst for lignin hydrogenation and depolymerization is applied to catalytic hydrogenation and depolymerization of lignin, the conversion rate of lignin hydrogenolysis is 98.1wt%, the yield of bio-oil is 78.5 wt%, and the yield of a monophenol compound is as high as 27.9wt%.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Novel efficient grapheme loaded nano-iron material for adsorbing phosphorus in water
InactiveCN103011328AEfficient removalThe hazards of eutrophicationOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionEutrophicationPhosphate
The invention relates to a novel efficient grapheme loaded nano-iron material for adsorbing phosphorus in water. The grapheme loaded nano-iron material is composed of nano-iron and grapheme, wherein the nano-iron accounts for 10-70 percent of the total weight of the material. The macrostructure of the material is powder-shaped, and as for the microstructure, the grapheme adopts a sheet-shaped structure, the nano-iron is uniformly dispersed on the surface of the grapheme, when the nano-iron accounts for 30 percent or less than 30 percent of the total weight of the material, the nano-iron adopts a dot-shaped structure, and when the nano-iron accounts for more than 30 percent of the total weight of the material, the nano-iron adopts a chain structure; the particle diameter of nano-iron is 50-70 nm; the nano-iron is loaded on grapheme, firstly, elemental iron reacts with hydrogen ions to generate ferrous iron, and then ferrous iron, phosphate radical and water molecules are reacted to quickly generate hydrated ferrous phosphate or hydrated iron phosphate; and under the condition that the initial concentration of phosphate radical in water is less than 4 mg / L, the grapheme loaded nano-iron can remove over 99 percent of phosphate radical, so that the effluent concentration of phosphate radical is under 0.02 mg / L, as a result, when the concentration of phosphate radical in inflow water quality of lakes is less than 0.02 mg / L, eutrophication cannot occur.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods and compositions for administration of iron
The present invention generally relates to treatment of iron-related conditions with iron carbohydrate complexes. One aspect of the invention is a method of treatment of iron-related conditions with a single unit dosage of at least about 0.6 grams of elemental iron via an iron carbohydrate complex. The method generally employs iron carbohydrate complexes with nearly neutral pH, physiological osmolarity, and stable and non-immunogenic carbohydrate components so as to rapidly administer high single unit doses of iron intravenously to patients in need thereof.
Owner:AMERICAN REGENT INC
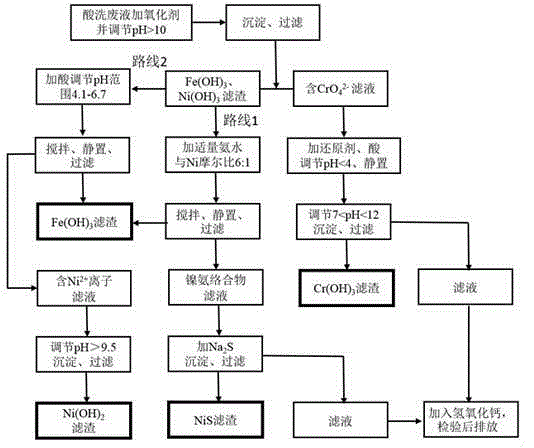
Recovery processing method of stainless steel acid pickling waste liquid containing iron, chromium and nickel
InactiveCN104787928AEasy to separateSolve the problem of low purityIron oxides/hydroxidesMultistage water/sewage treatmentFractional PrecipitationSS - Stainless steel
The invention discloses a recovery processing method of stainless steel acid pickling waste liquid containing iron, chromium and nickel. The recovery processing method comprises the following steps: (1) oxidizing chrome (III) ions in an alkaline condition, and separating the oxidized chrome (III) ions from iron and nickel; (2) reducing chrome in an acidic condition to trivalent chrome, and precipitating the trivalent chrome in the form of hydroxide; (3) separating nickel and iron elements through the ammonia leaching or fractional precipitation method, separating the iron elements in the form of Fe (OH)3, and obtaining the final product of the nickel element in the form of NiS or Ni(OH)2. According to the invention, the technological universality is high, the stainless steel acid pickling waste liquid with different concentrations can be separated, the characteristics of low cost, easiness in control of technological conditions, simple equipment and high recycling rate of valuable metal elements are realized, the problem about the sewage pollution of a stainless steel production enterprise can be effectively solved, the recycled metal elements can be reutilized, the economic benefit of the enterprise can be increased, and the dual significances of environmental protection and resource utilization are realized.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
A method to realize synchronous denitrification and dephosphorization of sewage
InactiveCN102295353AWide variety of sourcesLow priceTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeElectron donor
A method for realizing synchronous denitrification and phosphorus removal of sewage, the steps are as follows: (1) use anaerobic activated sludge as the source of bacteria, and screen out the target bacteria that can use elemental iron for autotrophic denitrification; (2) use After pretreatment, the biochemically treatable sewage enters the aerobic nitrification tank for oxidation treatment of organic matter, organic nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen; (3) introduces the above-mentioned treated sewage into the denitrification tank where the mixed solution is anoxic, and adds Elemental iron and denitrifying bacteria that can use elemental iron; in the initial stage of operation, the denitrification tank runs intermittently, and after the denitrification operation is stable, it runs continuously; 4) Set up a sedimentation tank after the denitrification tank to remove iron phosphate precipitates and Suspended solids complete sewage treatment. The invention introduces elemental iron as an electron donor and nitrate as an electron acceptor, organically combines biological nitrogen removal and chemical phosphorus removal, and simultaneously realizes nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
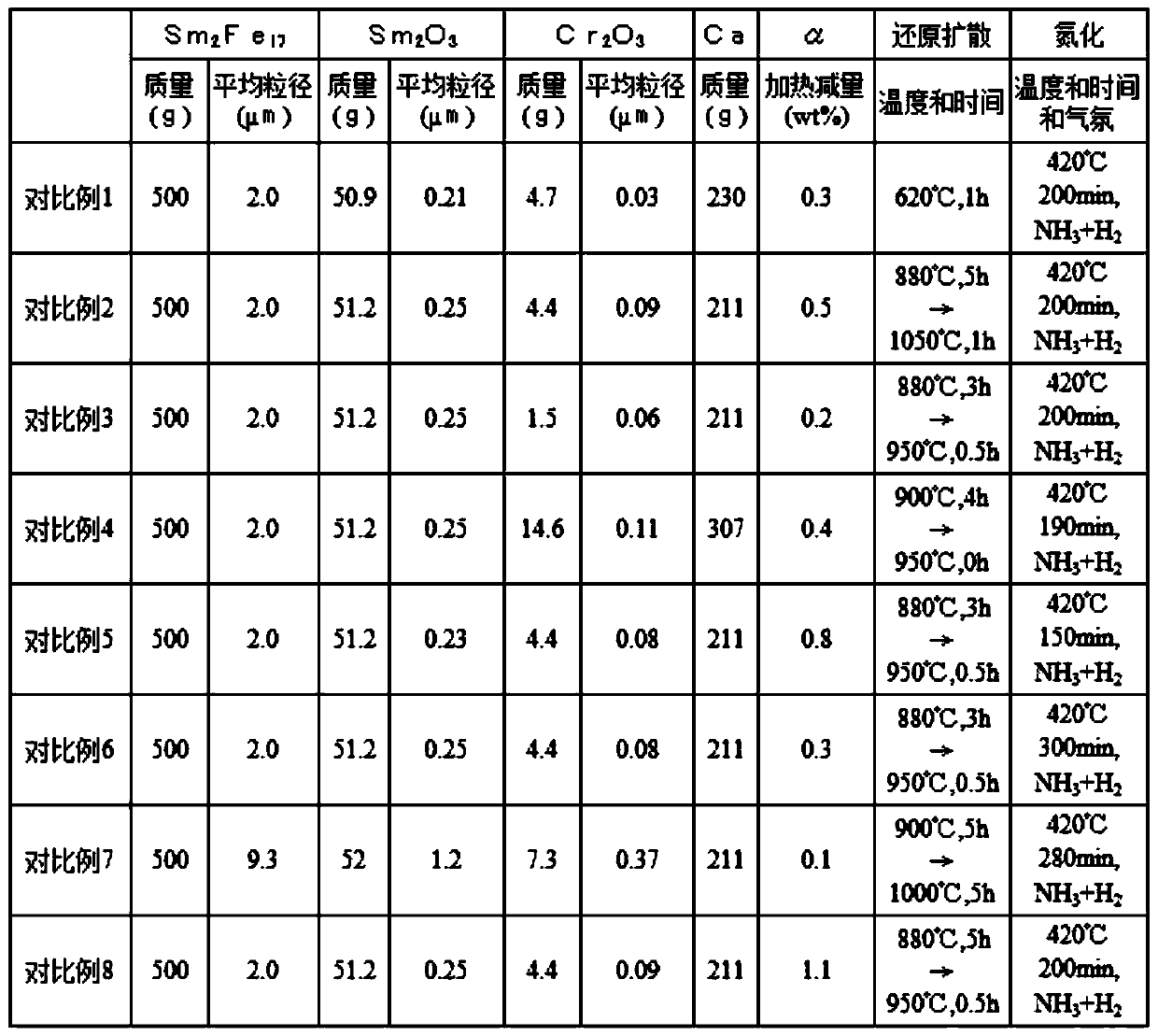
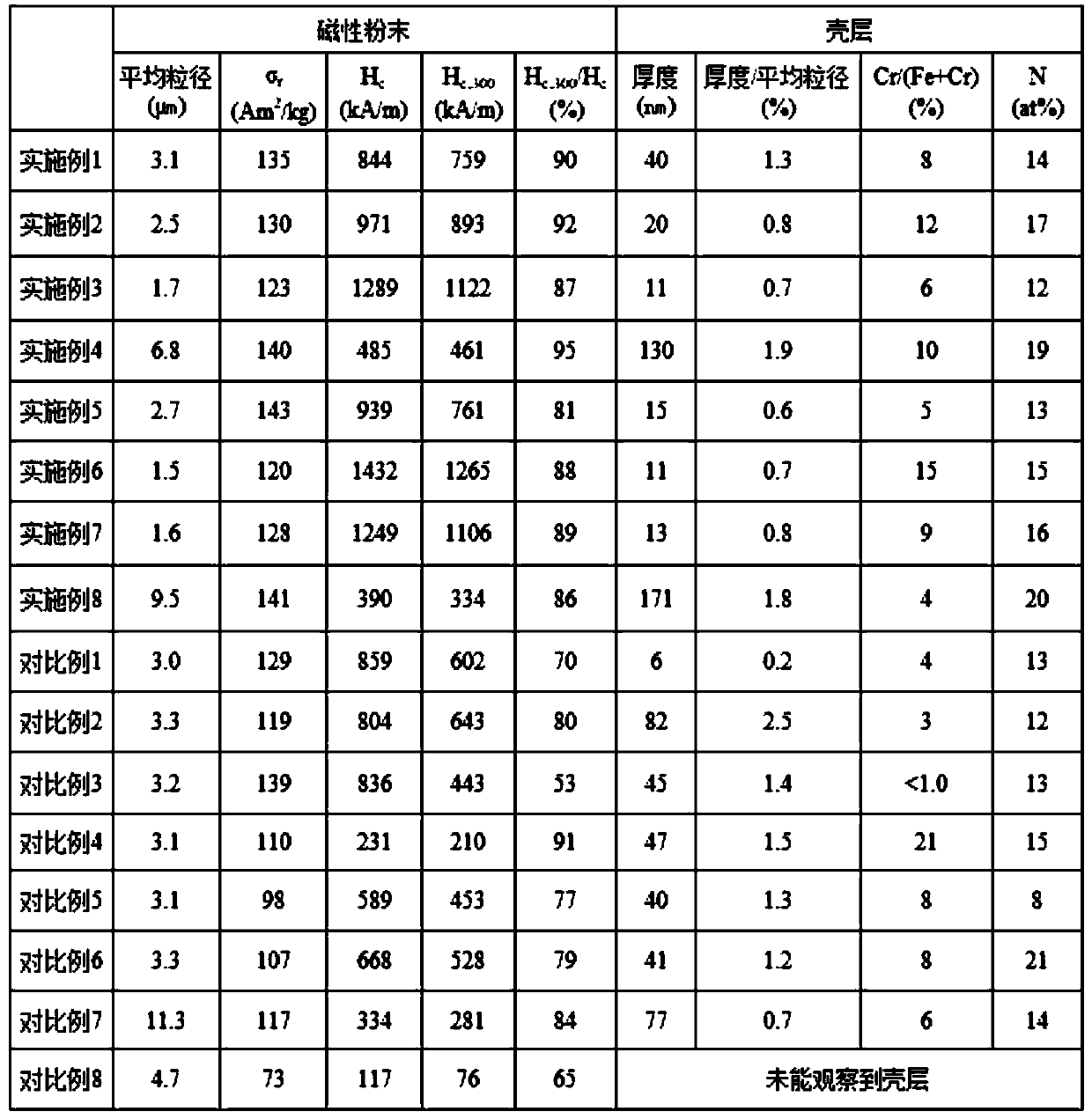
Rare earth-iron-nitrogen system magnetic powder and method for producing same
ActiveCN109982791AImprove heat resistanceSuppresses deterioration of coercive forceTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusRare-earth elementCrystal structure
The present invention relates to: a rare earth-iron-nitrogen system magnetic powder which has excellent heat resistance and magnetic characteristics, especially excellent coercivity and magnetization;and a method for producing this rare earth-iron-nitrogen system magnetic powder. This rare earth-iron-nitrogen system magnetic powder contains a rare earth element R, iron Fe and nitrogen N as main constituents, while having a crystal structure of Th2Zn17 type, Th2Ni17 type or TbCu7 type and an average particle diameter of from 1 mum to 10 mum (inclusive), and is characterized in that a shell layer having a thickness of 10 nm or more but less than 200 nm, which is less than 2% of the average particle diameter of the powder, is formed on the particle surfaces of the powder, said shell layer having the same crystal structure, with from 1% by atom to 20% by atom (inclusive) of Fe being substituted by Cr, and with N being contained in an amount of from 10% by atom to 20% by atom (inclusive).
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV +1
Incorporation of metal nanoparticles into wood substrate and methods
Metal nano articles were incorporated into wood. Ionic liquids were used to expand the wood cell wall structure for nanoparticle incorporation into the cell wall structure. Nanoparticles of elemental gold or silver were found to be effective surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) imaging contrast or sensing agents. Nanoparticles of elemental iron were found to be efficient microwave absorbers and caused localized heating for disrupting the integrity of the lignocellulosic matrix. Controls suggest that the localized beating around the iron nanoparticles reduces losses of cellulose in the form of water volatiles and CO2. The ionic liquid is needed during the incorporation process at room temperature. The use of small amounts of ionic liquid combined with the absence of an ionic liquid purification step and a lower energy and water use are expected to reduce costs in an up-scaled pretreatment process.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Chemical core cutting wire for underwater wet method electric arc cutting
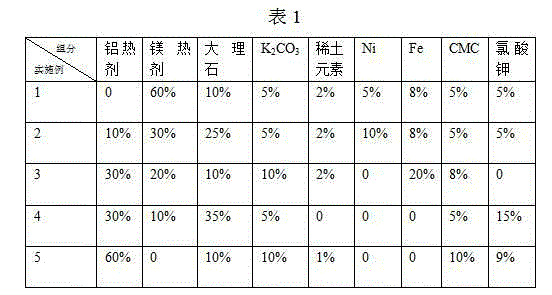
ActiveCN104858565ACut wire light weightEasy to carryWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaRare-earth elementIron powder
The invention discloses a chemical core cutting wire for underwater wet method electric arc cutting. The chemical core cutting wire is composed of external metal skin and a powdery chemical core. The external metal skin is a pure aluminum belt. The inner chemical core comprises, by mass, 40%-60% of aluminum thermit and magnesium thermit, 10%-35% of marble,5%-10% of potassium carbonate, 1%-2% of a rare earth element, 0-20% of iron powder, 0-10% of nickel powder, 0-15% of potassium chlorate and 5%-10% of hydroxymethyl cellulose. According to the chemical core cutting wire, under the action of electric arc heat and the heating function of exothermic components added to the chemical core, extra oxygen supply and gas protection are not needed, an underwater metal structure can be cut, and the chemical core cutting wire has the advantages of being easy to manufacture, low in cost and high in cutting speed.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Micronutrient supplement dispensing package
Provided herein is a prenatal and postpartum multivitamin and mineral supplement package provided in the form of a plurality of solid oral dosage units individually contained in blister packs wherein a portion of the dosage forms are iron-containing while at least half of the dosage units are essentially iron-free and wherein the total amount of iron in the package as sold to purchasers is less than about 1300 mg of elemental iron.
Owner:DUCHESNAY INC
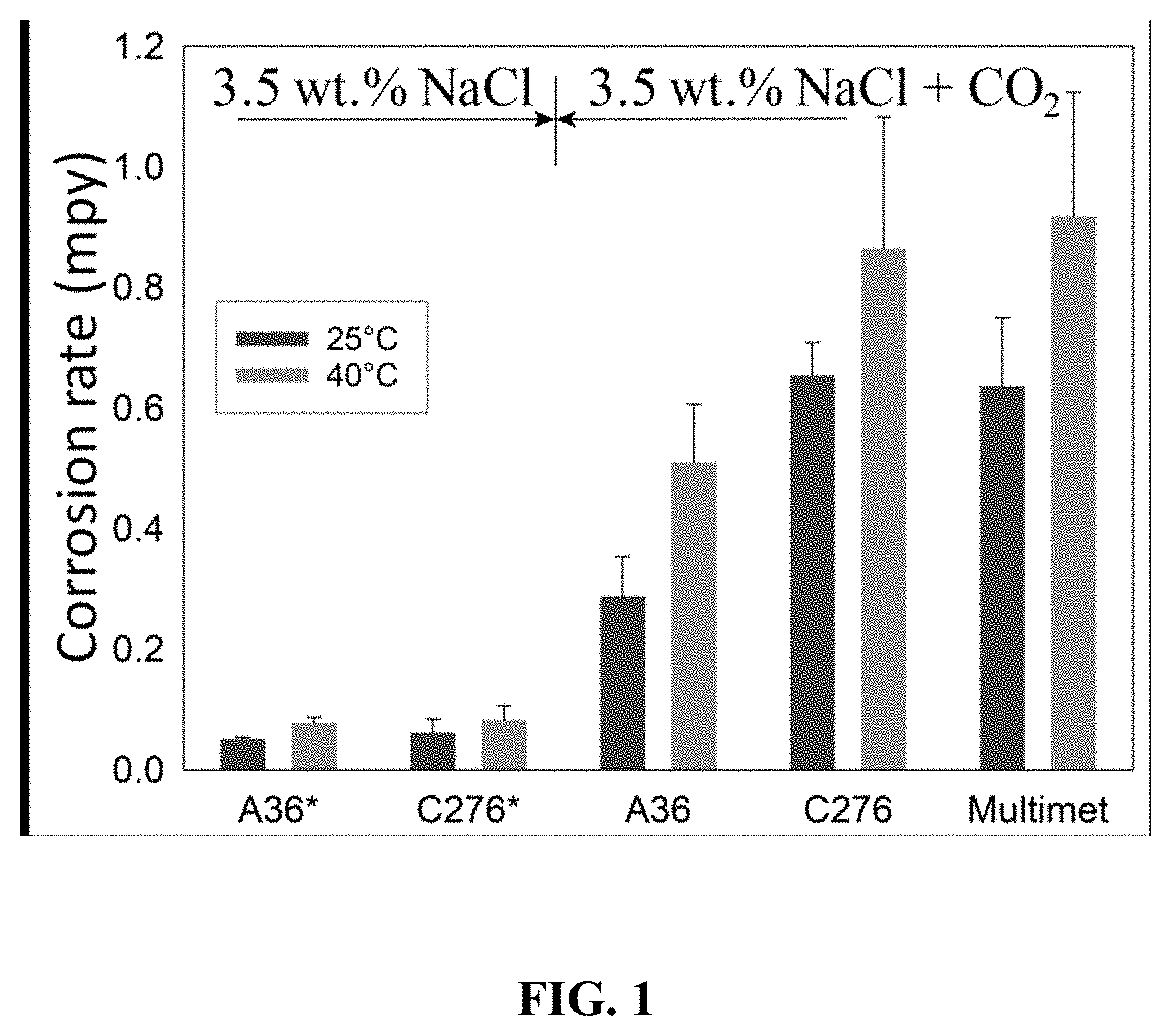
High-Performance Corrosion-Resistant High-Entropy Alloys
This disclosure provides alloy compositions comprising the main constituent elements iron, nickel, cobalt, molybdenum, and chromium. In one embodiment, the alloy comprises 10.0 to 30.0 wt % iron; 30.0 to 60.0 wt % nickel; 10.0 to 25.0 wt % cobalt; 1.0 to 15.0 wt % molybdenum; 15.0 to 25.0 wt % chromium by weight; where the sum of iron and nickel is at least 50 wt %; and, where the balance comprises minor elements, the total amount of minor elements being about 5% or less by weight. The alloy compositions have use as coatings to protect metals and alloys from corrosion in extreme environments where corrosion is a major concern such as with exposure to sea water or sea water with CO2.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Lithium ferromanganese phosphate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109650367AImprove economyAvoid washingSecondary cellsPositive electrodesHydrogen phosphatePhosphate
The invention relates to a preparation method of lithium ferromanganese phosphate. The method comprises the steps of: (1) mixing elemental iron, manganese dioxide and a phosphoric acid aqueous solution to obtain a mixture A, and subjecting the mixture A to ball milling to obtain ferromanganese hydrogen phosphate; and (2) mixing the ferromanganese hydrogen phosphate, lithium carbonate and glucose,and performing sand milling to a product particle size D50 of 0.2microm-1microm, and conducting drying and calcination to obtain lithium ferromanganese phosphate. The method has the characteristics ofsimple equipment and process, good atomic economy, small environmental pressure and low manufacturing cost, is easy for industrial production, and by controlling the particle size of the final product, the specific discharge capacity of lithium ferromanganese phosphate serving as a battery cathode material is increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUANGHUA SCI TECH +1
Method for preparing iron-based amorphous and nanocrystalline coating
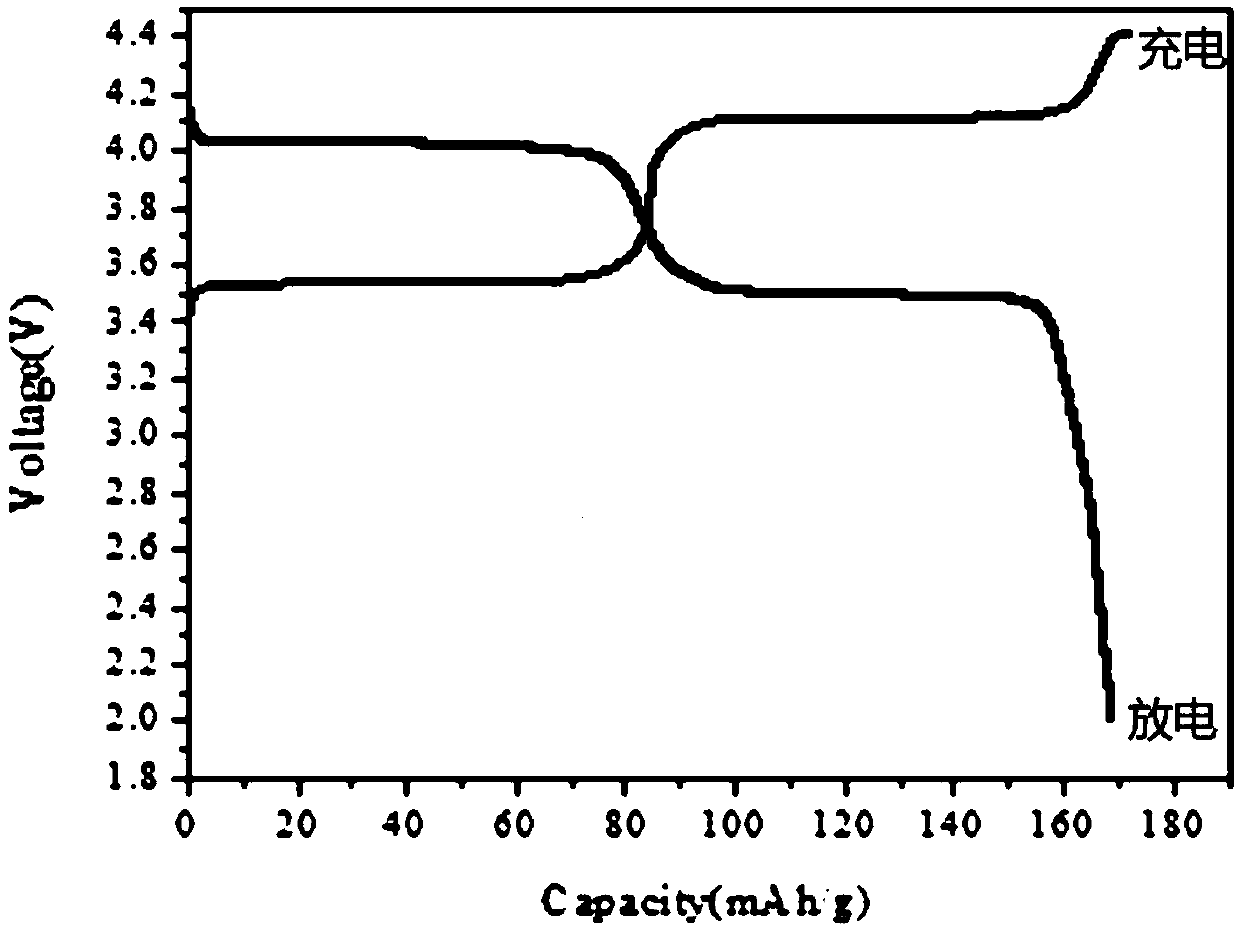
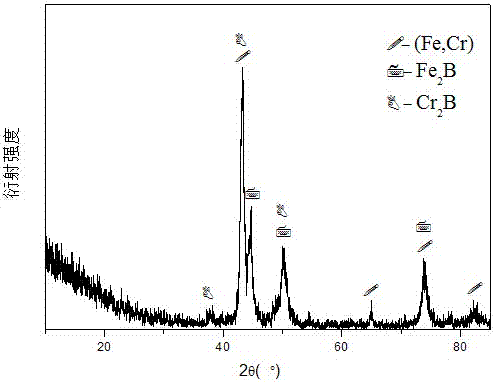
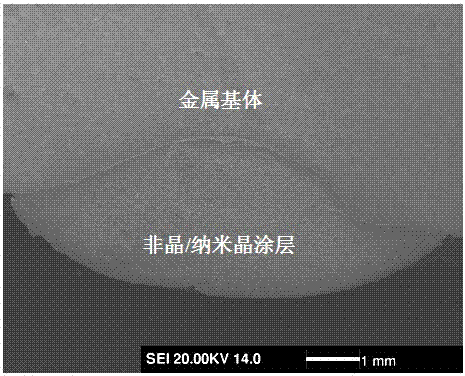
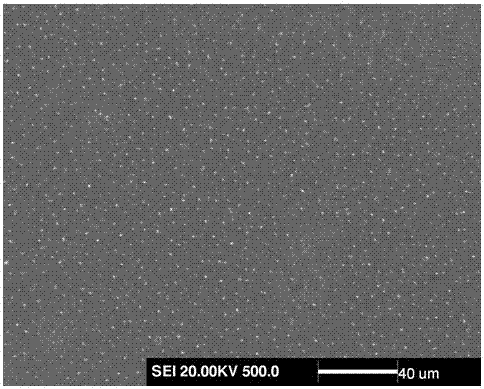
ActiveCN106929845AImprove bindingEasy to operateTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusSurface engineeringNiobium
The invention provides a method for preparing an iron-based amorphous and nanocrystalline coating and belongs to the technical field of metal surface engineering. The method comprises the steps that elemental iron powder, chromium powder, boron powder, silicon powder and niobium powder are used as raw materials; the powder and hard alloy balls are put into a ball-milling tank to be subjected to ball milling and fully mixed; then an organic bonding agent is added; a mixture is pressed into a rod shape through a cylindrical mold to obtain a composite rod; the composite rod is naturally dried at the normal temperature and dried through a drying oven; and the composite rod is subjected to cladding through arc heat generated by an argon arc welding machine tungsten electrode, put on the surface of a metal substrate in a low-temperature tank and solidified to obtain the iron-based amorphous and nanocrystalline coating. The iron-based amorphous and nanocrystalline coating is well combined with the metal substrate, and nanocrystalline particles are uniformly distributed; the technological process is simple, easy to operate and low in equipment price; and compared with amorphous and nanocrystalline coatings prepared through laser cladding, the method for preparing the amorphous and nanocrystalline coating through argon arc cladding of the composite rod has the characteristics of being easy to operate, high in powder utilization rate, capable of reducing the production cost and the like.
Owner:无锡海韵新材料科技有限公司
Process for Creating An Oxygen Scavenging Particle
InactiveUS20070200091A1Liquid surface applicatorsLiquid degasificationAluminium chlorideSodium bisulfate
A method is disclosed for manufacturing one or more oxygen scavenging particles, wherein the particle(s) comprises an oxidizable metal particle, such as elemental iron; an acidifying electrolyte such as sodium or potassium bisulfate and optionally a water hydrolysable Lewis acid, such as aluminum chloride. The method comprises the step of coating the oxidizable particle with a first compound and then reacting the first compound with a second compound to form a third compound, wherein the third compound promotes the reaction of the oxidizable particle with oxygen.
Owner:MULTISORB TECH INC
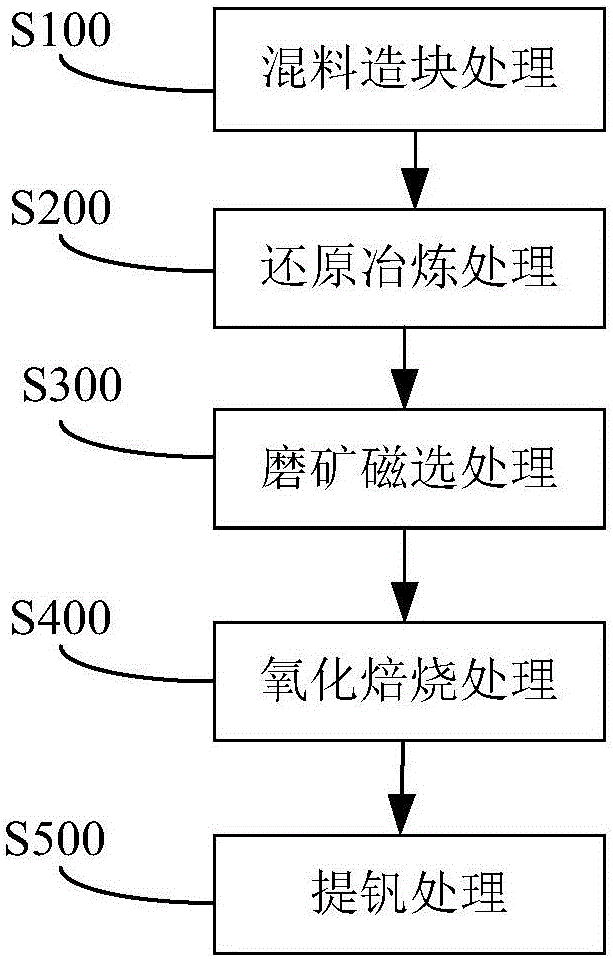
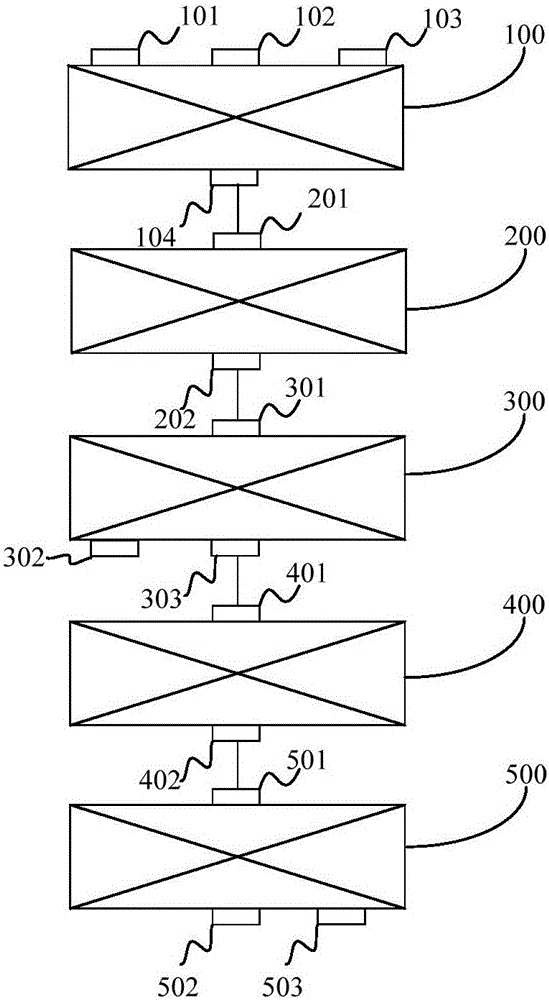
Comprehensive treatment method for vanadium slag and application thereof
PendingCN106086431AIncrease metallization rateHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementSlagMixed materials
The invention discloses a comprehensive treatment method for vanadium slag and application thereof. The comprehensive treatment method for the vanadium slag includes the steps that the vanadium slag, sodium salt and a reducing agent are subjected to mixing and briquetting treatment, so that mixed material briquettes are obtained; the mixed material briquettes are subjected to reducing smelting treatment, so that metalized briquettes are obtained; the metalized briquettes are subjected to grinding magnetic separation treatment, so that reduced iron and vanadium-rich slag are obtained; the vanadium-rich slag is subjected to oxidizing roasting treatment, so that vanadium slag clinker is obtained; and the vanadium slag clinker is subjected to vanadium extraction treatment, so that vanadium pentoxide is obtained. According to the comprehensive treatment method, the vanadium slag, the reducing agent and the sodium salt are mixed, then the iron in the vanadium slag is recovered through reducing smelting, vanadium is enriched after the iron is recovered from the vanadium slag, and the vanadium-rich slag is obtained; and the vanadium-rich slag is subjected to oxidizing roasting to obtain water-soluble sodium vanadate, and the vanadium pentoxide is extracted from the vanadium slag. The comprehensive treatment method for the vanadium slag realizes step-by-step extraction of valuable elements of the iron and the vanadium in the vanadium slag, and the recovery rate of the iron and the vanadium is high.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
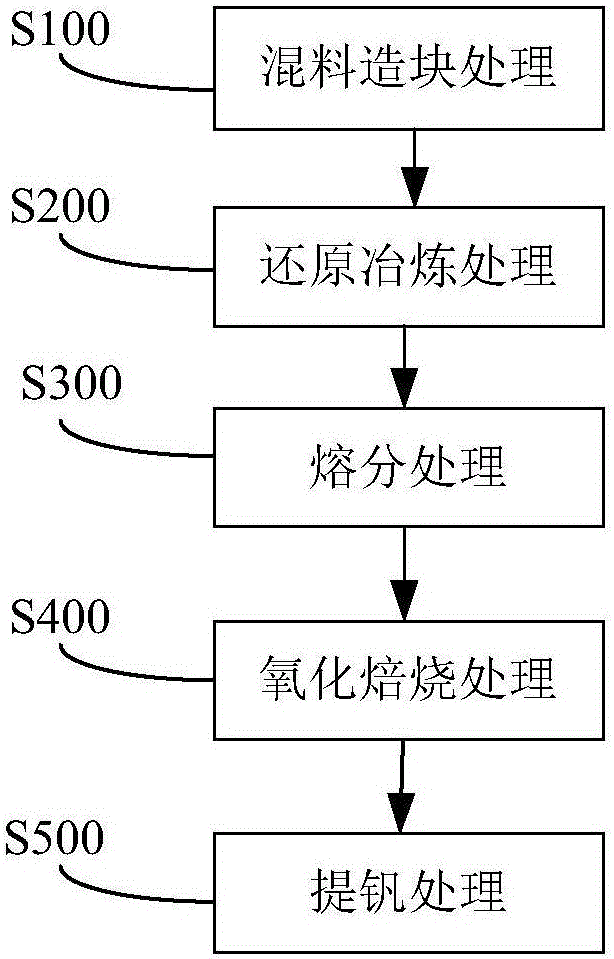
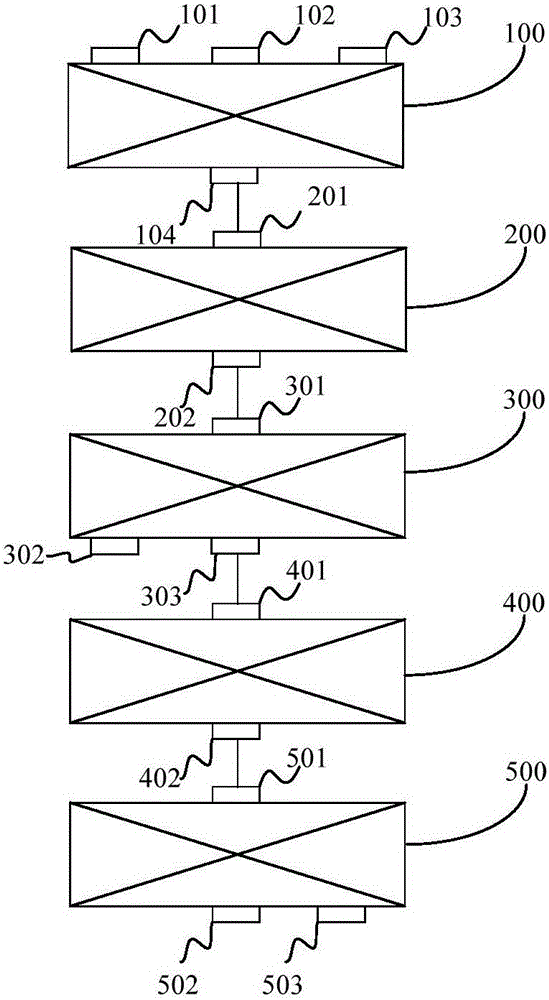
Vanadium slag comprehensive treatment method and application thereof
PendingCN105925813AIncrease metallization rateHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementSlagSodium salt
The invention discloses a vanadium slag comprehensive treatment method and application thereof. The vanadium slag comprehensive treatment method comprises the steps that vanadium slag, sodium salt and a reducing agent are subjected to mixing and agglomeration treatment to obtain mixed material agglomerates; the mixed material agglomerates are subjected to reducing and smelting treatment to obtain metallized agglomerates; the metallized agglomerates are subjected to melting and separation treatment to obtain reduced iron and vanadium-enriched slag; the vanadium-enriched slag is subjected to oxidizing roasting treatment to obtain vanadium slag clinker; and the vanadium slag clinker is subjected to vanadium extraction treatment to obtain vanadium pentoxide. According to the method, the vanadium-enriched slag, the reducing agent and the sodium salt are mixed and subjected to reducing smelting to recover iron in the vanadium slag; vanadium in the vanadium slag of which iron is recovered is enriched, and the vanadium-enriched slag is obtained; the vanadium-enriched slag is subjected to oxidizing roasting to obtain water-soluble sodium vanadate; and then the vanadium pentoxide in the vanadium-enriched slag is extracted. Through the method, sequential extraction of valuable elemental iron and vanadium in the vanadium slag is realized, and the recovery rate of iron and vanadium is high.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Method for recovering nonferrous metals, rare and noble metals and iron powder from steelmaking flue dust
InactiveCN106282582AEfficient separationImprove thermal efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingResource utilization
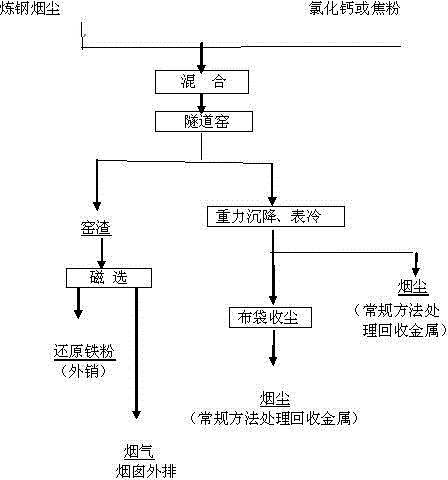
The invention provides a method for recovering nonferrous metals, rare and noble metals and iron powder from steelmaking flue dust. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the steelmaking flue dust with a chlorination agent and a reducing agent, adding the obtained mixture to a tunnel furnace, and carrying out a two-stage reaction, wherein a primary stage reaction is a medium temperature chlorination reaction and allows nonferrous metals and precious metals to volatilize and enter flue gas, the flue gas is used as a nonferrous metal and precious metal extraction raw material after dusts are collected, and a secondary stage reaction is a high temperature reduction reaction and reduces iron into elemental iron which is discharged with kiln slag; and carrying out cooling, crushing and ball milling on the kiln slag to form a slag slurry with the granularity being smaller than 60 meshes, and carrying out magnetic separation to obtain the elemental iron powder and waste slag, wherein the iron content of the iron powder is greater than 86%, the iron powder can be used as commercial reduced iron powder, and the waste slag is sold to cement mills. The method allowing the chlorination and reduction metallurgy processes to be carried out in the tunnel furnace in a segmental manner has the advantages of process simplification, simplicity in operation, high thermal efficiency, low production cost and high comprehensive utilization rate, and is a new way for reasonable recovery of valuable metals in the steelmaking flue dust and high-efficiency resource utilization.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com