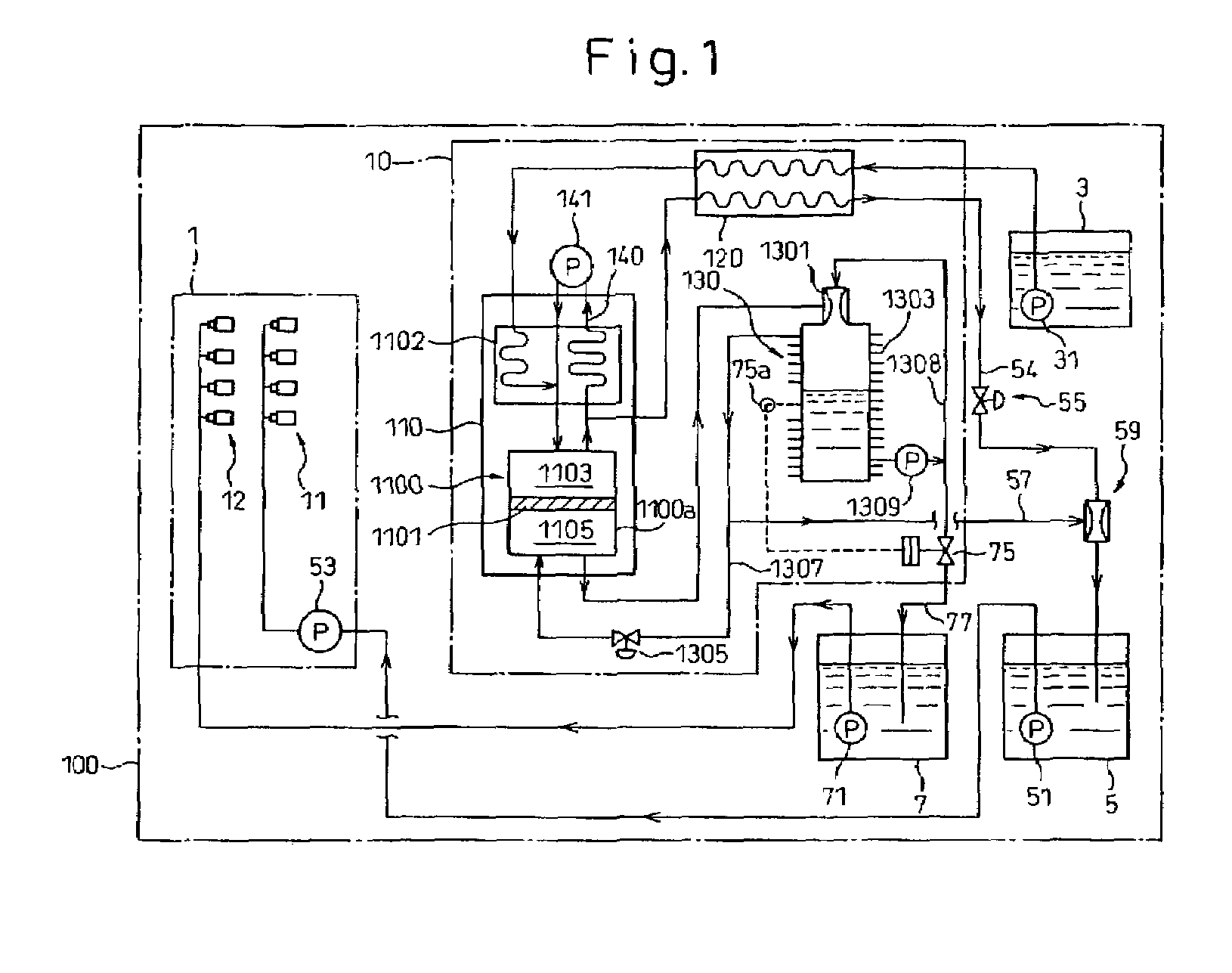
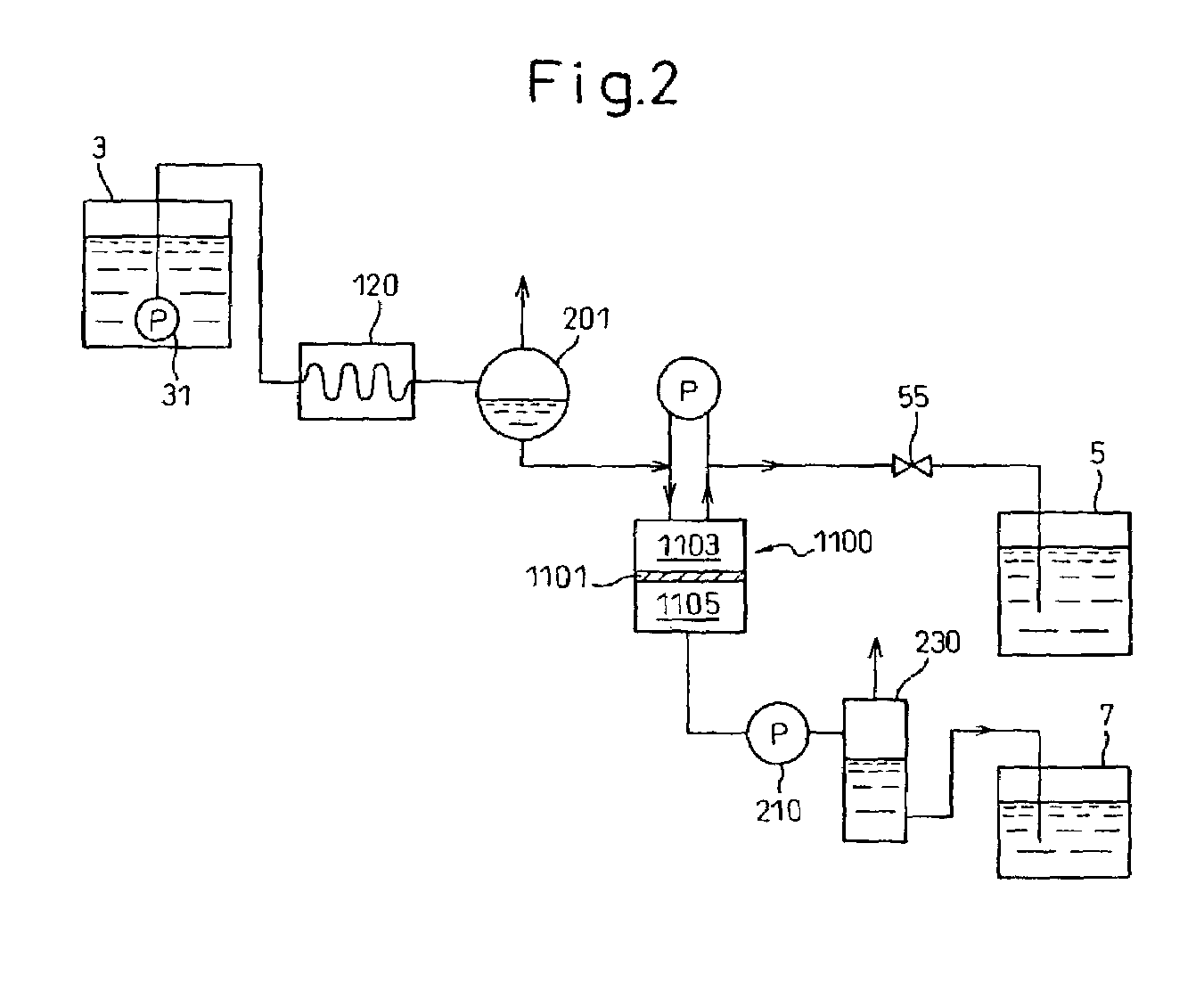
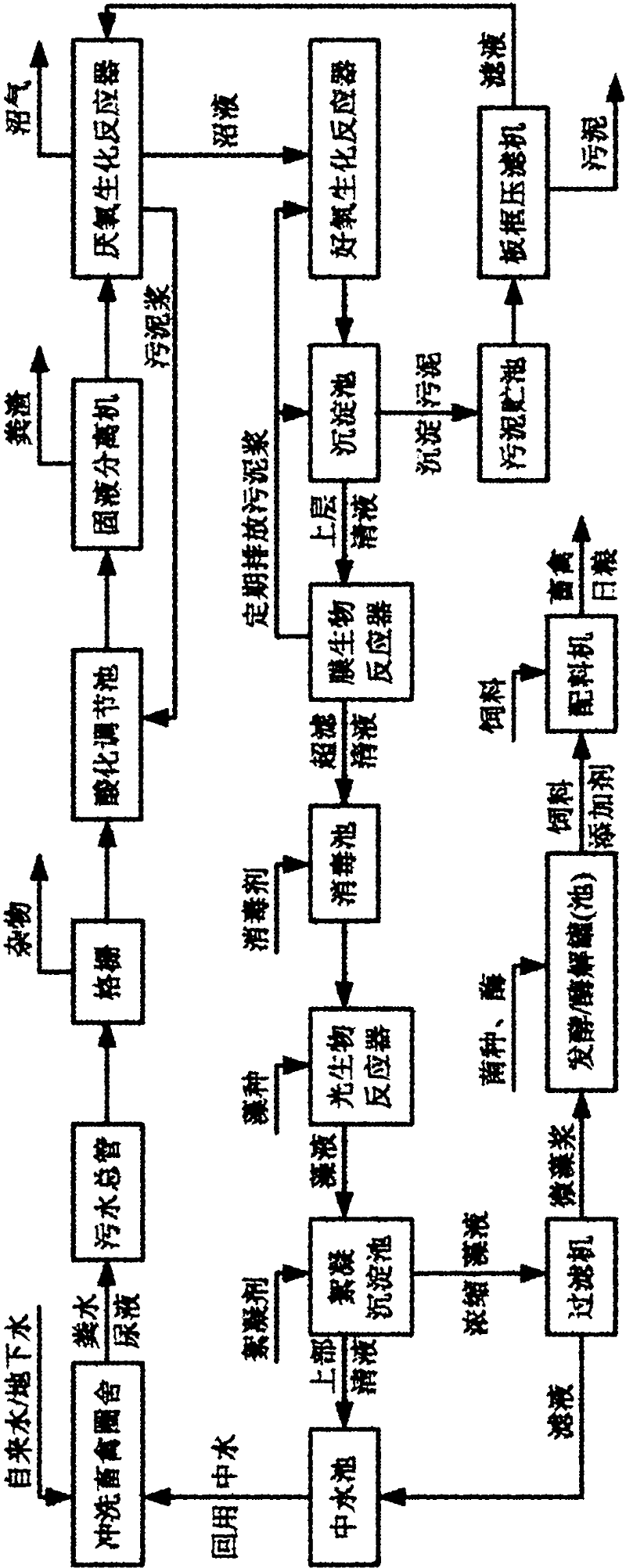
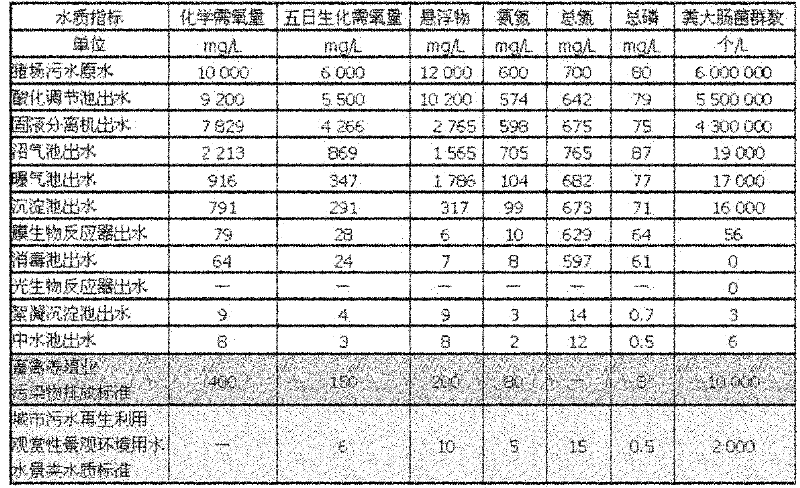
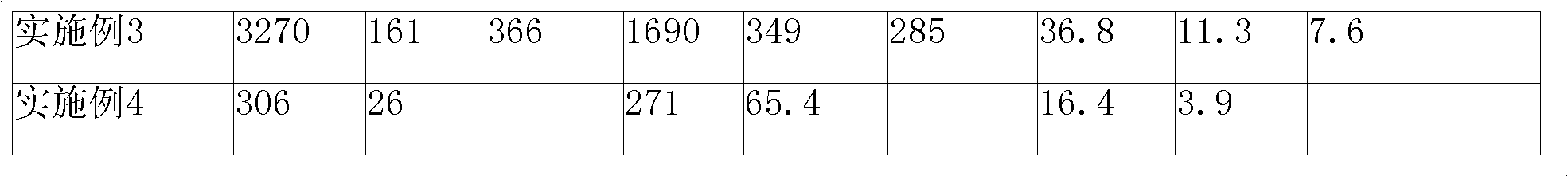Patents
Literature
13428results about "Treatment with aerobic and anaerobic processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalysis and micro-electrolysis combined technology for high-concentration refractory organic wastewater
InactiveCN101665311AReduce processing loadEasy to handleTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationElectrolysis
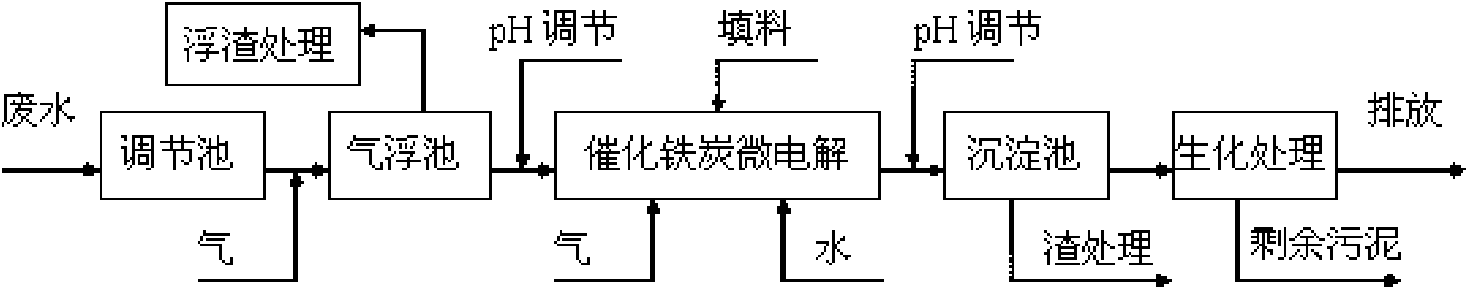
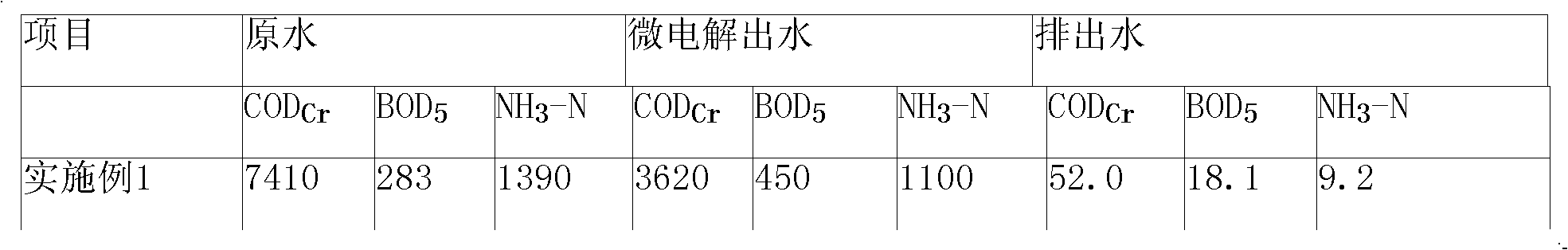
The invention relates to a catalysis and micro-electrolysis combined technology for high-concentration refractory organic wastewater; the organic wastewater is collected to an adjusting tank and enters an air floatation tank for air floatation treatment to remove part of the organic matters after the adjustment of water volume and water quality; the scruff is collected or recovered; the wastewatergoes through Ph adjustment and then enters a catalytic iron-carbon and micro-electrolysis unit to improve the biochemical quality; the effluent goes through Ph adjustment and then enters a sedimentation tank; the effluent of the sedimentation tank adopts anoxic-aerobic biochemistry treatment to remove the organic matters and ammonia nitrogen and then is emitted after reaching the standard; and the filler of the catalytic iron-carbon and micro-electrolysis unit comprises iron, carbon and a catalyst, wherein the mass ratio of the iron, carbon and catalyst is 1: (0.3-1.5): (0.01-0.5). The invention can effectively improve the micro-electrolysis electrochemical reaction efficiency and the degrading capability to the organic matters, and reduce the wastewater treatment cost with convenient technological operation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
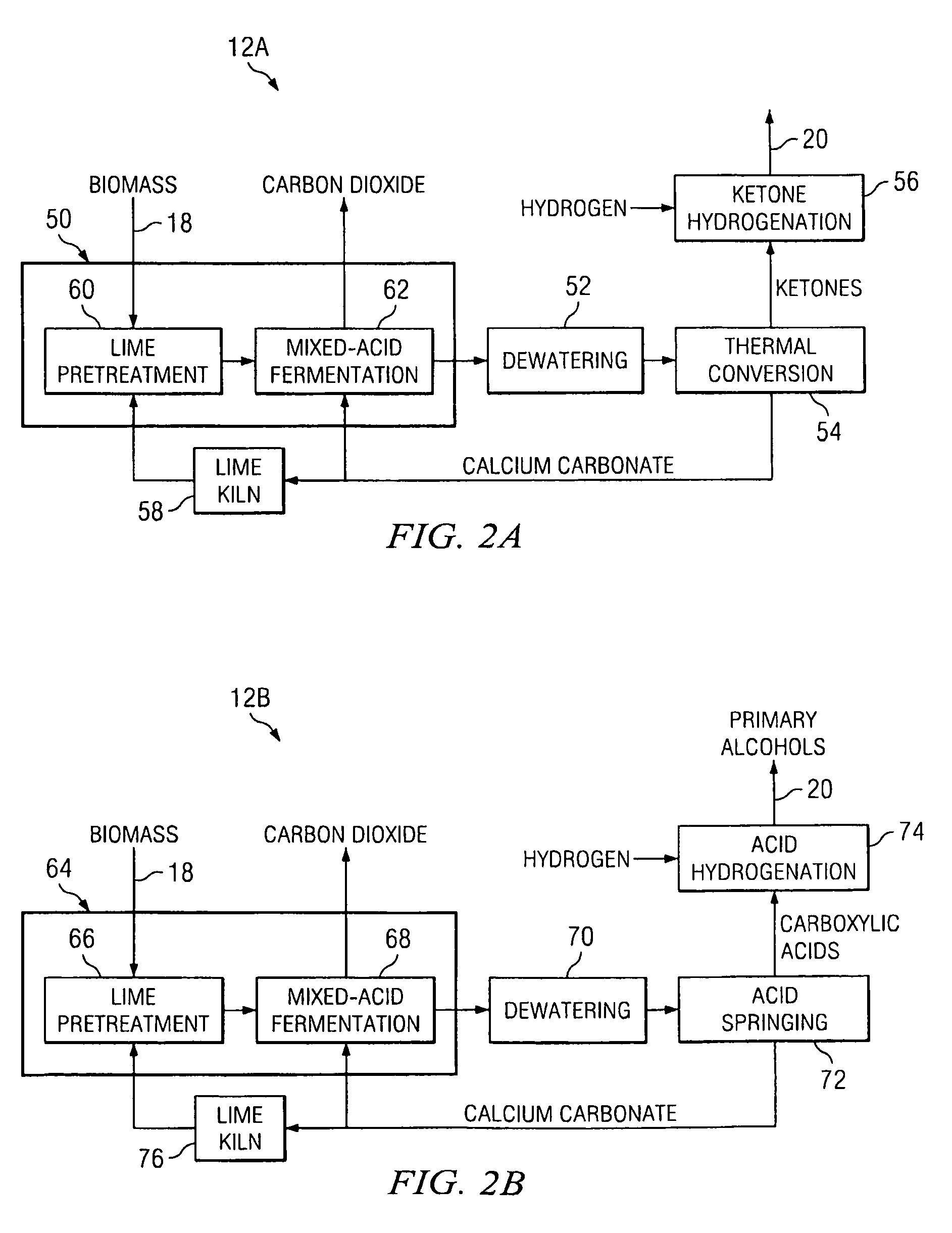
Slurry dewatering and conversion of biosolids to a renewable fuel
ActiveUS20060096163A1Readily removed mechanicallyLow oxygenBio-organic fraction processingBiofuelsEmission standardSlurry
In the processes for treating municipal sewage and storm water containing biosolids to discharge standards, biosolids, even after dewatering, contain typically about 80% water bound in the dead cells of the biosolids, which gives biosolids a negative heating value. It can be incinerated only at the expense of purchased fuel. Biosolids are heated to a temperature at which their cell structure is destroyed and, preferably, at which carbon dioxide is split off to lower the oxygen content of the biosolids. The resulting char is not hydrophilic, and it can be efficiently dewatered and / or dried and is a viable renewable fuel. This renewable fuel can be supplemented by also charging conventional biomass (yard and crop waste, etc.) in the same or in parallel facilities. Similarly, non-renewable hydrophilic fuels can be so processed in conjunction with the processing of biosolids to further augment the energy supply.
Owner:SGC ADVISORS
Wastewater treatment system and method
ActiveUS20070209999A1Treatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationActivated carbonWater treatment system
The invention is directed to a method and apparatus for treating wastewater. The wastewater treatment system includes a bioreactor including activated carbon and a first biological population. The wastewater treatment system may also include a membrane bioreactor and / or a wet oxidation unit.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Integrated closed loop system for industrial water purification
InactiveUS7001519B2Improve purification efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic matterIndustrial water
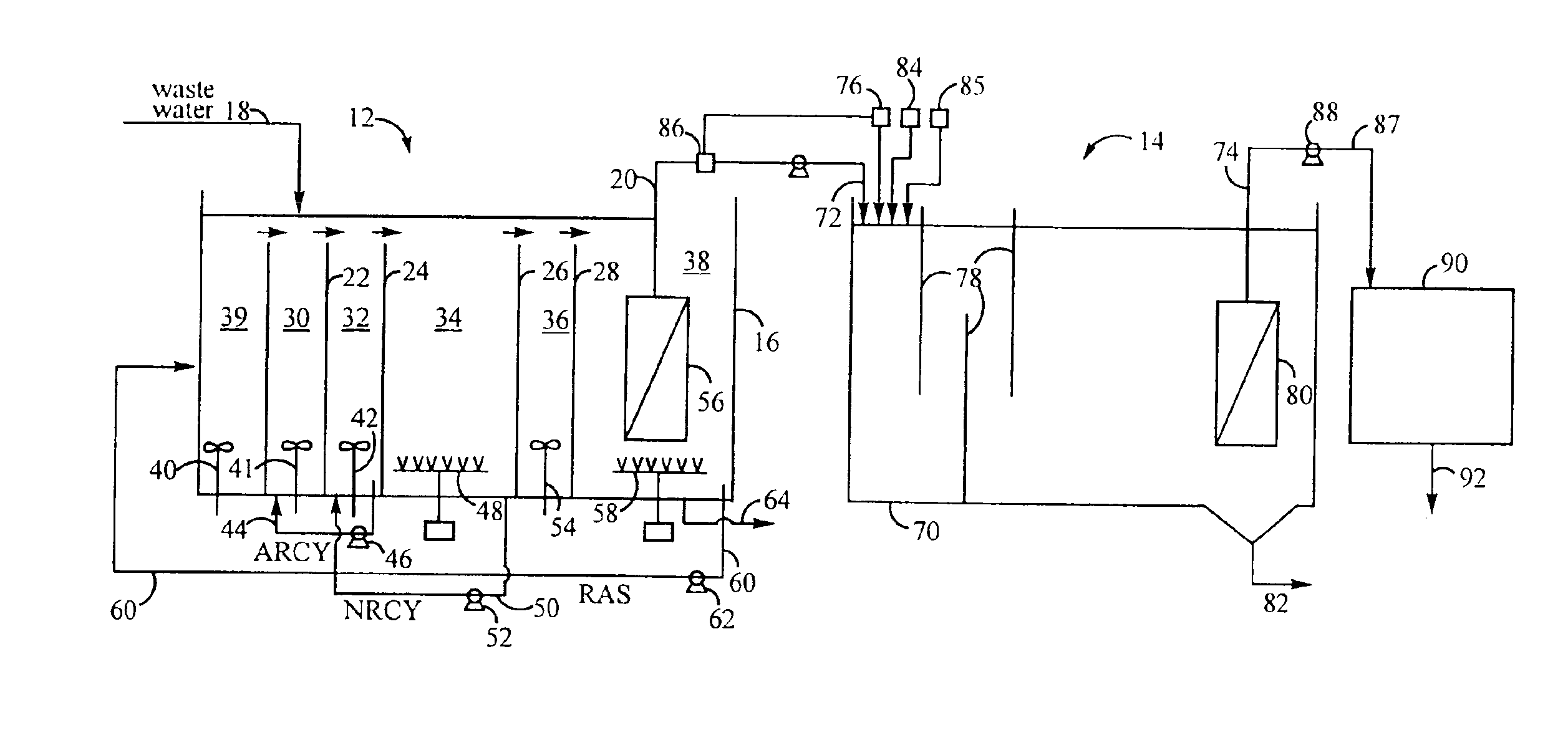
The present invention relates to an integrated closed loop system for aquaculture in at least one culturing tank and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic material, nitrogen and phosphorous, comprising: an integrated, partially or wholly closed loop system for waste water treatment, where the water contains nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances, comprising at least one production unit of such nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorous from the said water at continuous flow, comprising: a) at least one suspended carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under anoxic conditions to cause anaerobic denitrification, with one or several compartments, preceding b) at least one suspended-carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under oxic conditions to cause aerobic nitrification, c) the denitrification taking place after the production unit, and d) the nitrification taking place prior to the production unit in a by-pass mode as part of the continuous flow.
Owner:GREENFISH
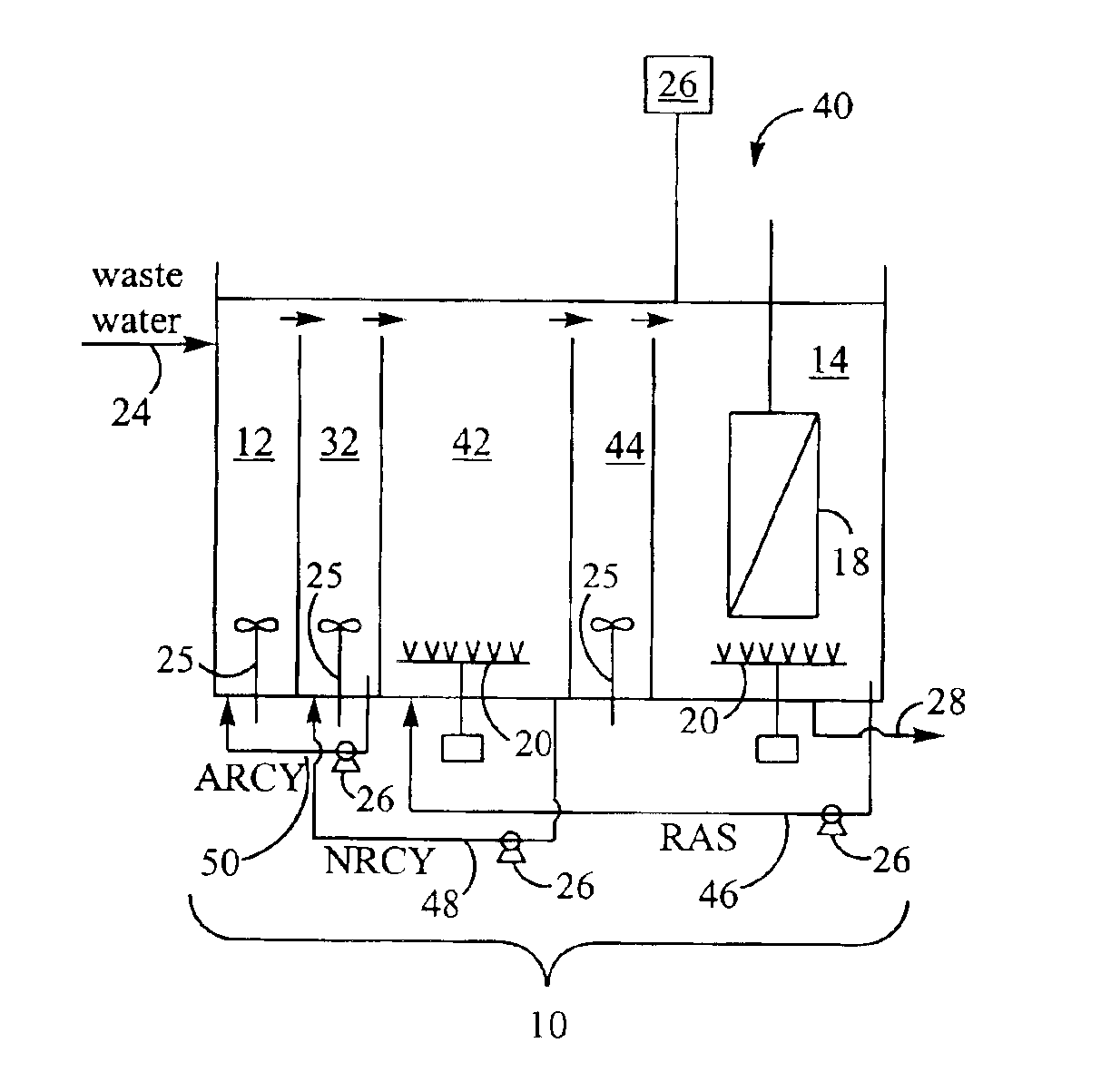
Method for treating wastewater in a membrane bioreactor to produce a low phosphorus effluent
ActiveUS20050045557A1Minimizing space requirementMinimizing attendant costTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesActivated sludgeMembrane bioreactor
Removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater yielding a low phosphorous (e.g., less than 0.25 mg / L) output includes providing a serial multistage bioreactor containing activated sludge having in hydraulic series an anaerobic zone and a downstream aerobic zone, with each zone having an upstream inlet and a downstream outlet. The wastewater is provided to the anaerobic zone inlet. A quantity of chemical sufficient to precipitate soluble and particulate phosphorous is added to the downstream aerobic zone in an amount sufficient to yield a low phosphorous output. Treated water is separated from the activated sludge and precipitated phosphorous and a return activated sludge separated from the treated water is recycled to the anaerobic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Subsurface upflow wetland system for nutrient and pathogen removal in wastewater treatment systems
ActiveUS8252182B1Low maintenance burdenHigh benefit cost ratioWater cleaningContaminated soil reclamationFecesTotal suspended solids
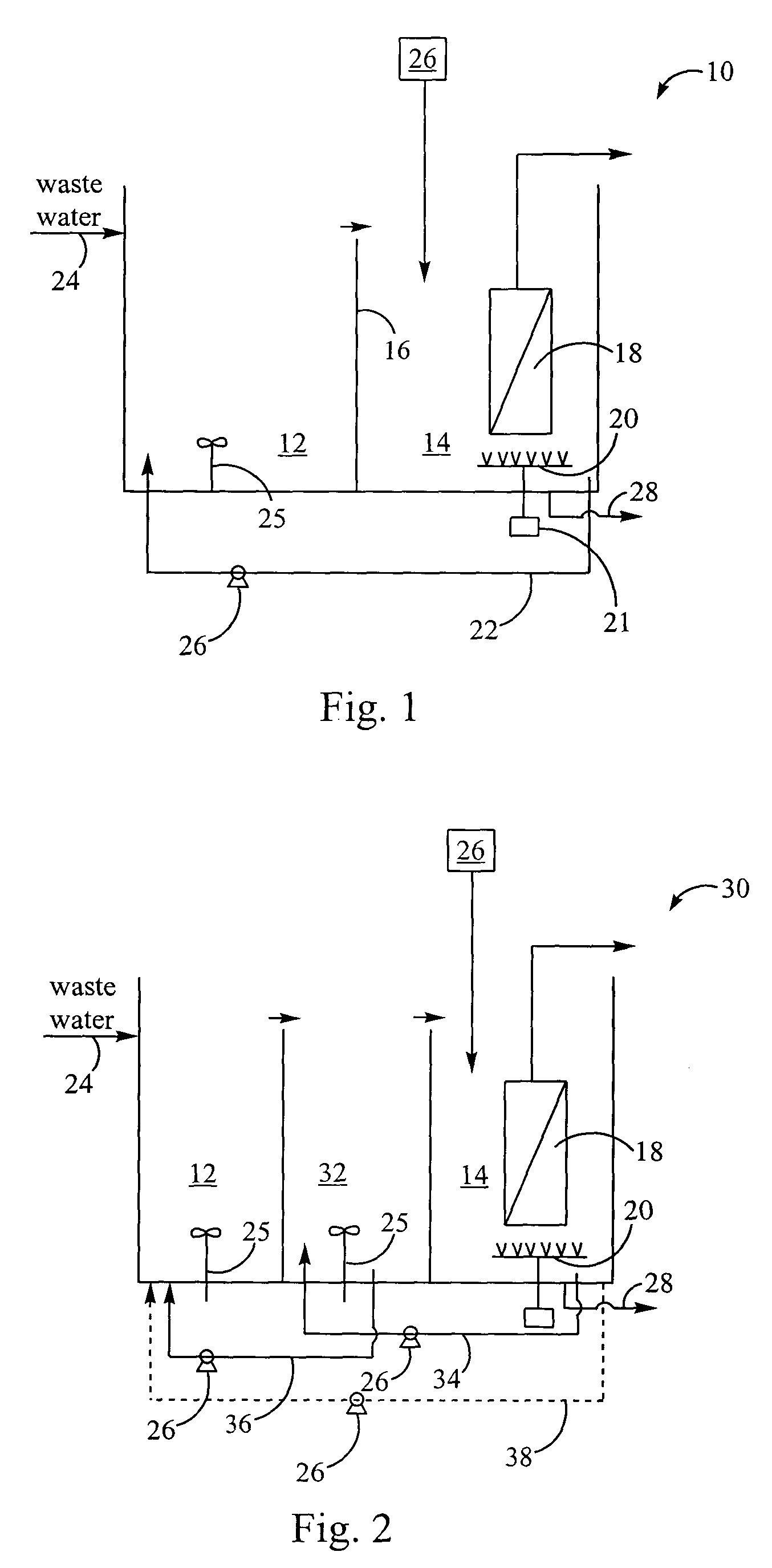
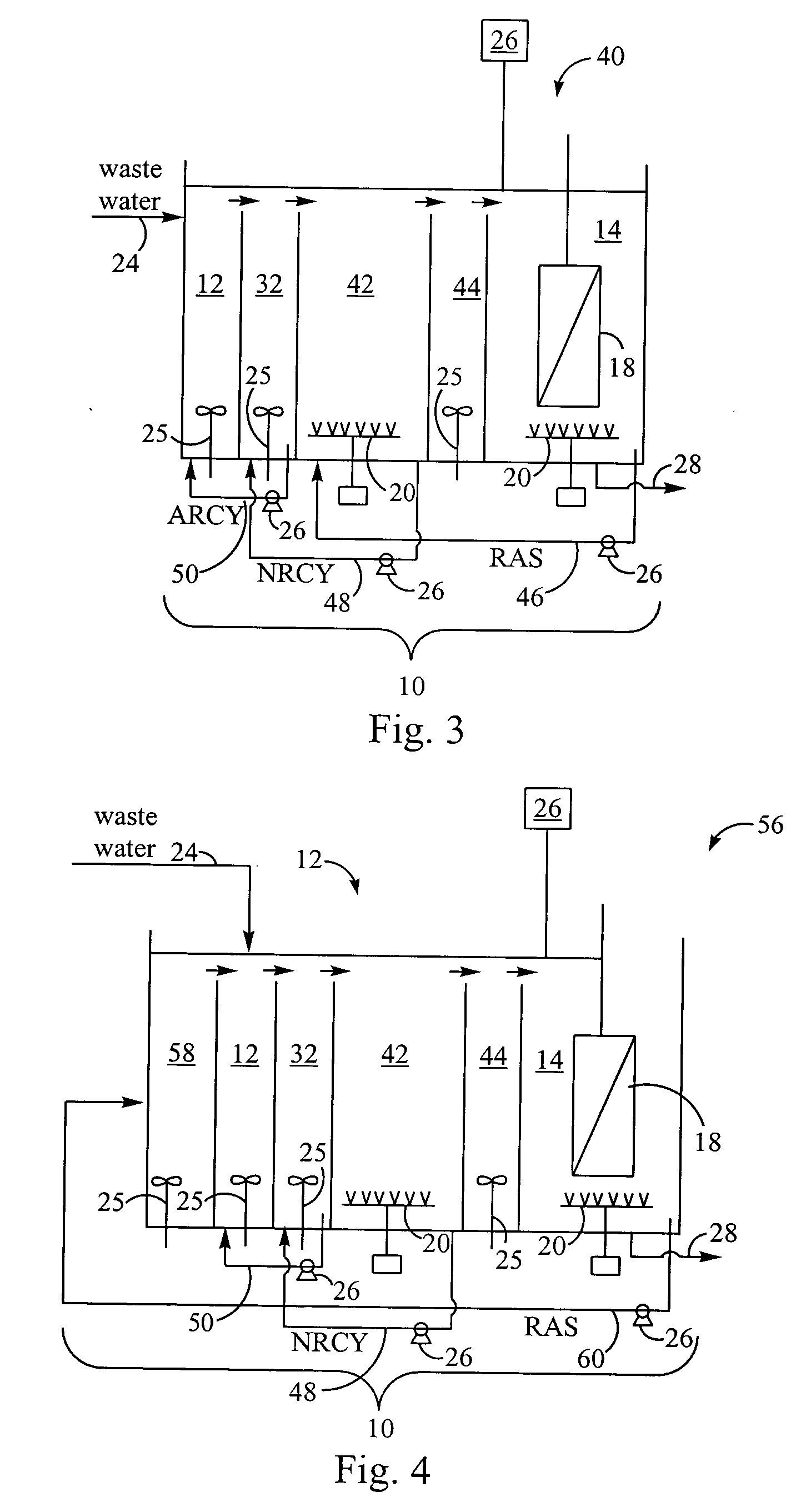
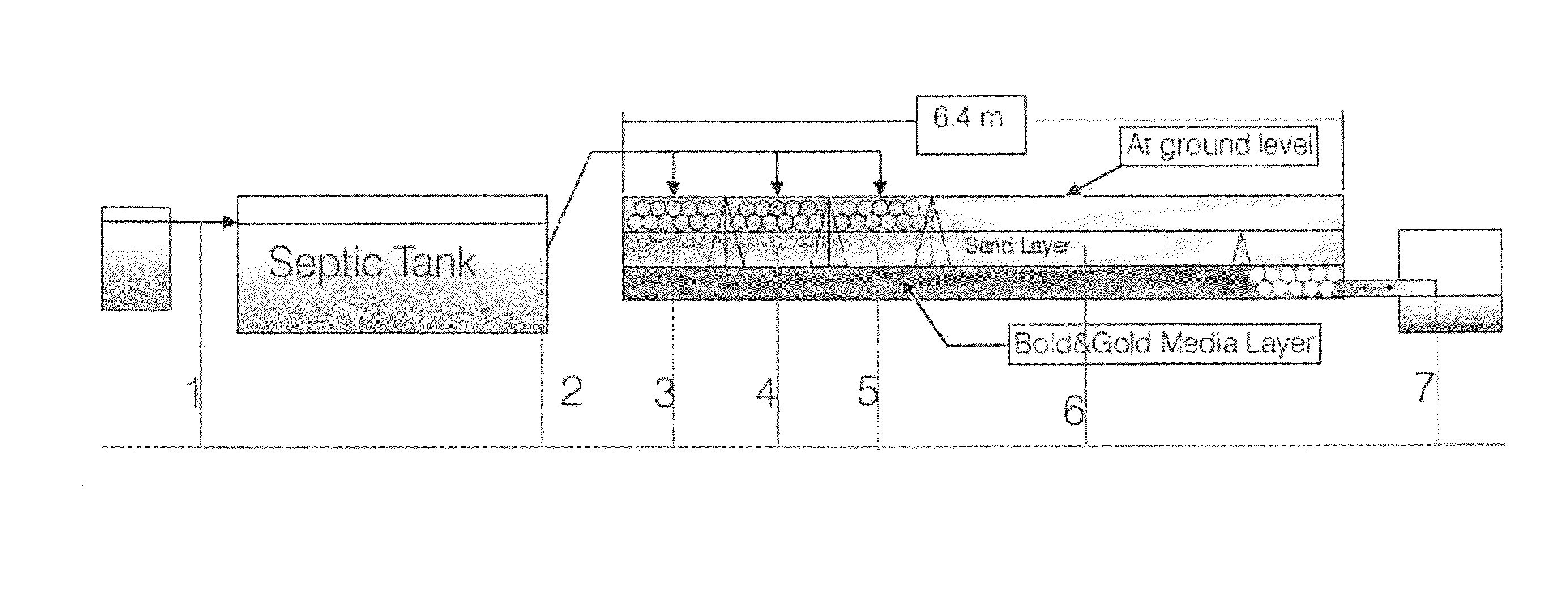
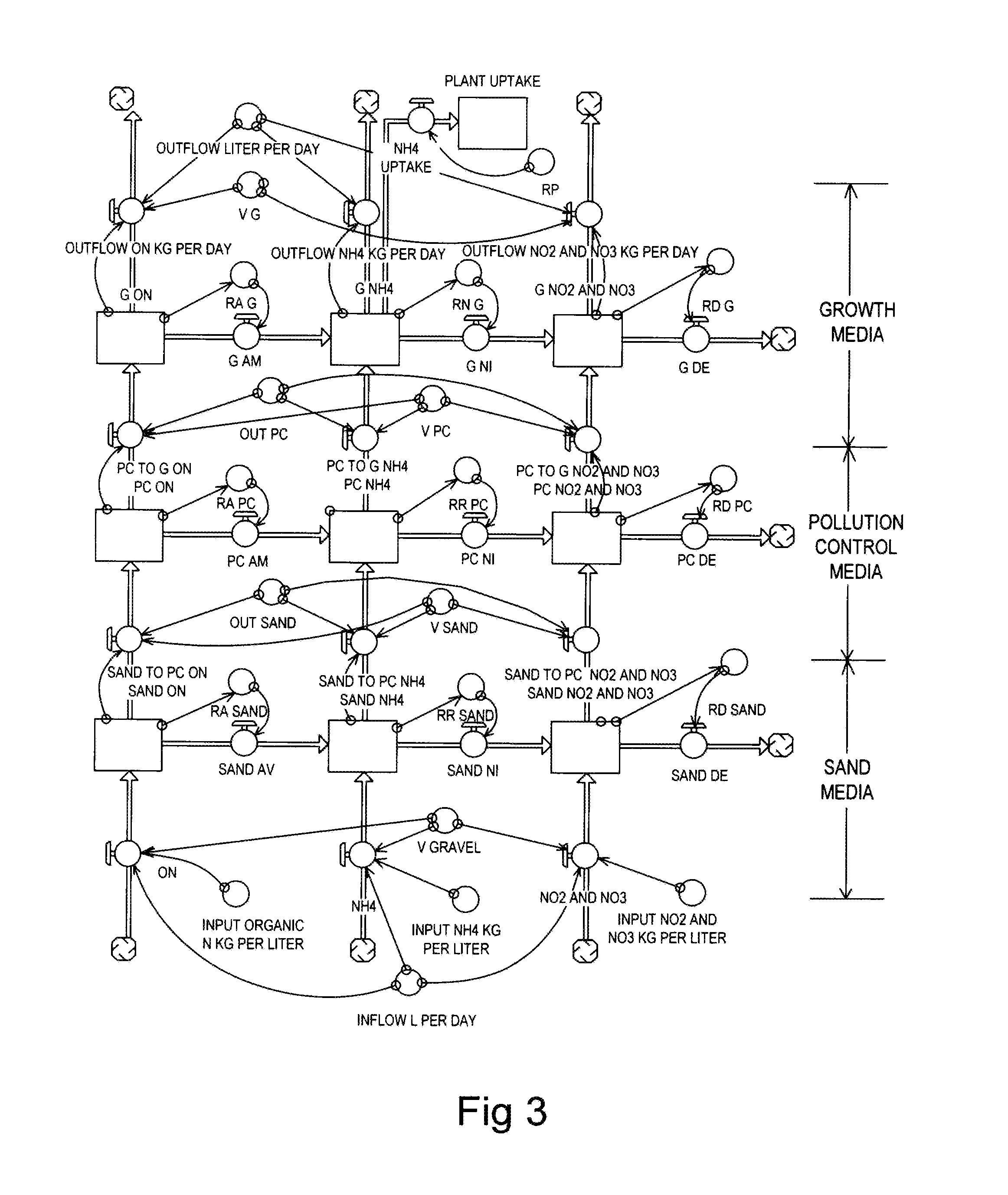
Methods and systems for a subsurface upflow wetland for wastewater treatment that includes a series of parallel treatment cells, each cell including from bottom to top, a layer of gravel, a layer of sand over the gravel to remove pathogens from a septic effluent, a pollution control medium above the sand layer to remove nutrients, total suspended solid, and biochemical oxygen demand and a growth media mixture layered on top of the pollution control media to grow plants, and a gravity distribution system to distribute effluent to the series of parallel treatment cells. The pollution control medium includes at least one recycled material and at least one naturally occurring material. In an embodiment it includes recycled tire crumb, sand and limestone or recycled tire crumb, compost, sand and limestone.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Process to enhance phosphorus removal for activated sludge wastewater treatment systems
InactiveUS20070000836A1Water/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater treatment parameter controlActivated sludgePhosphate
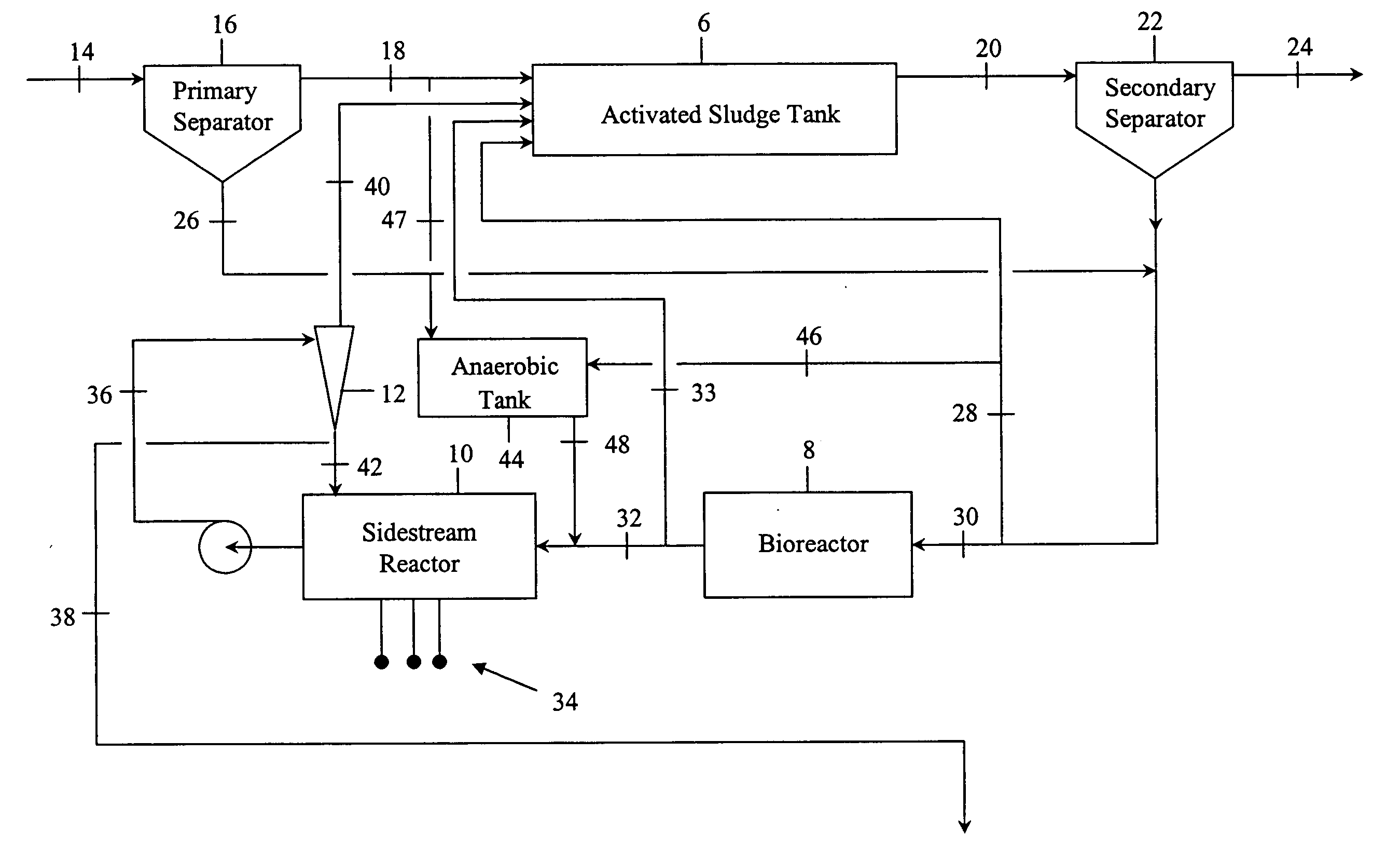
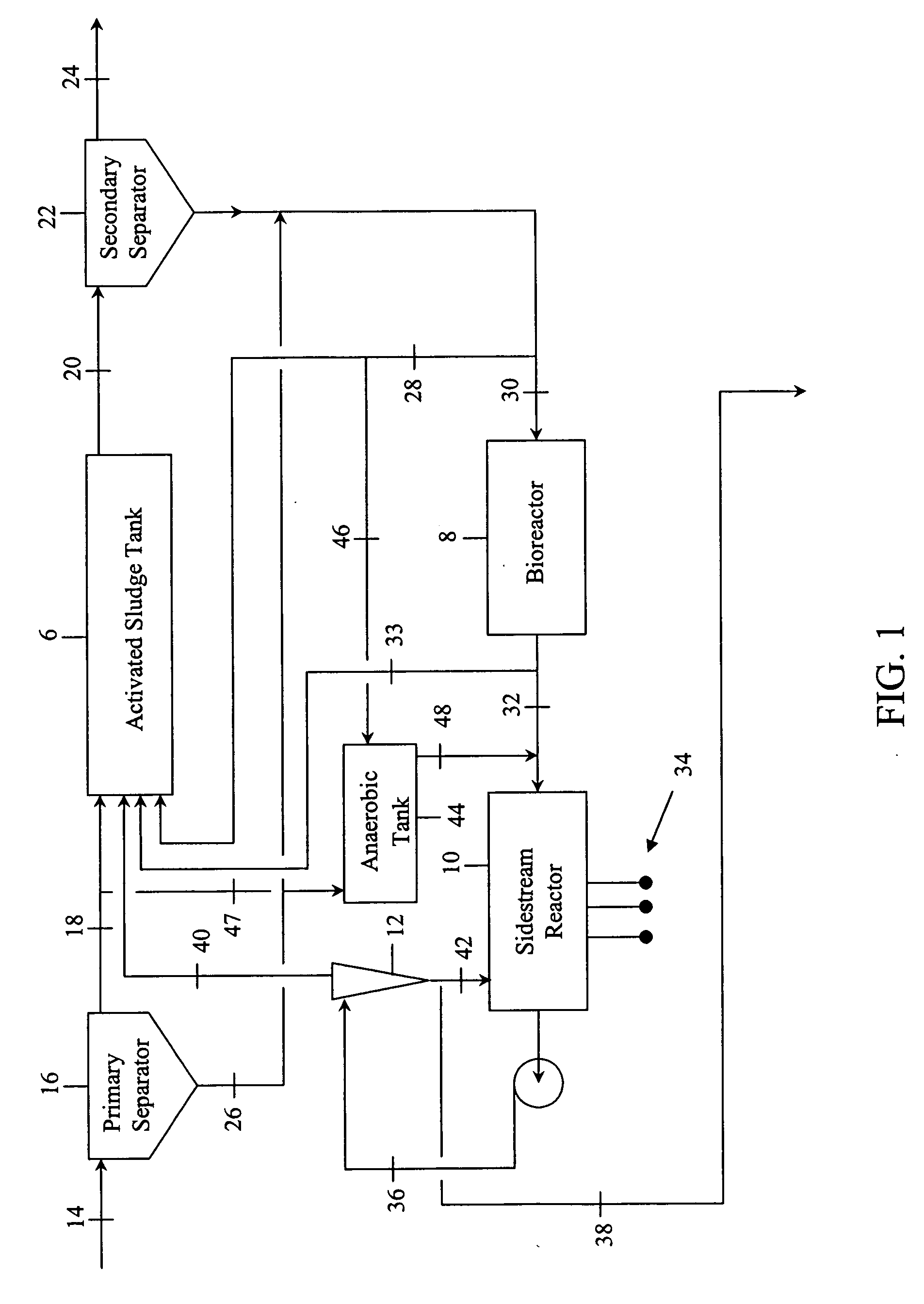
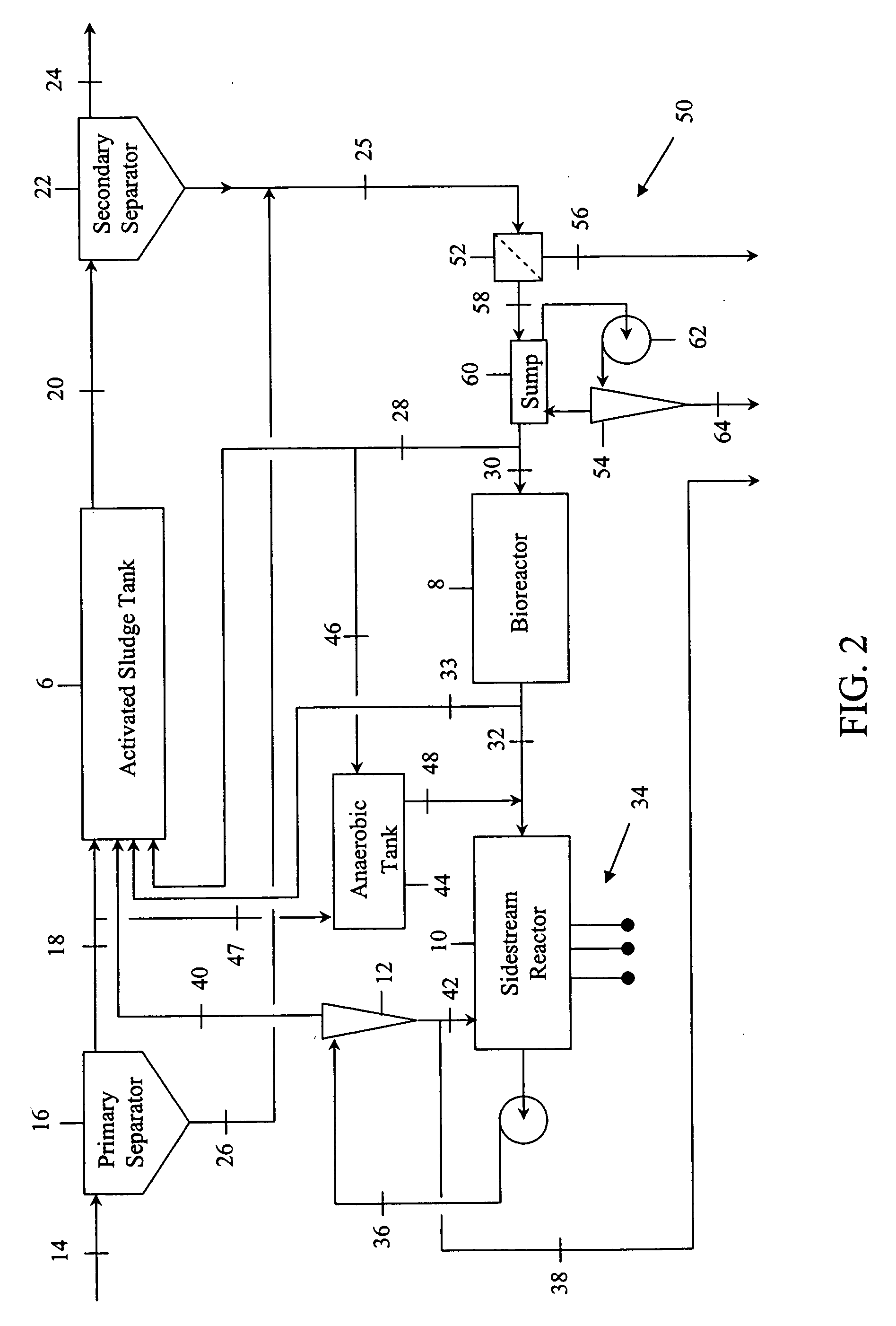
Contaminated wastewaters comprising biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), nitrogen and phosphorus are treated by an activated sludge process. The process utilizes an activated sludge tank, a solid-liquid separator, and a bioreactor to significantly reduce, or eliminate, waste activated sludge (WAS) within a sludge stream. A sidestream reactor is employed downstream from the bioreactor to remove soluble phosphates left in the sludge stream by the low WAS process. Within the sidestream reactor, a source of multivalent metal ions is added to a slightly alkaline sludge stream to precipitate the phosphates. The solid phosphates have a specific gravity higher than that of the organic matter in the sludge stream and may be separated from the sludge stream based upon differential settling velocity.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen
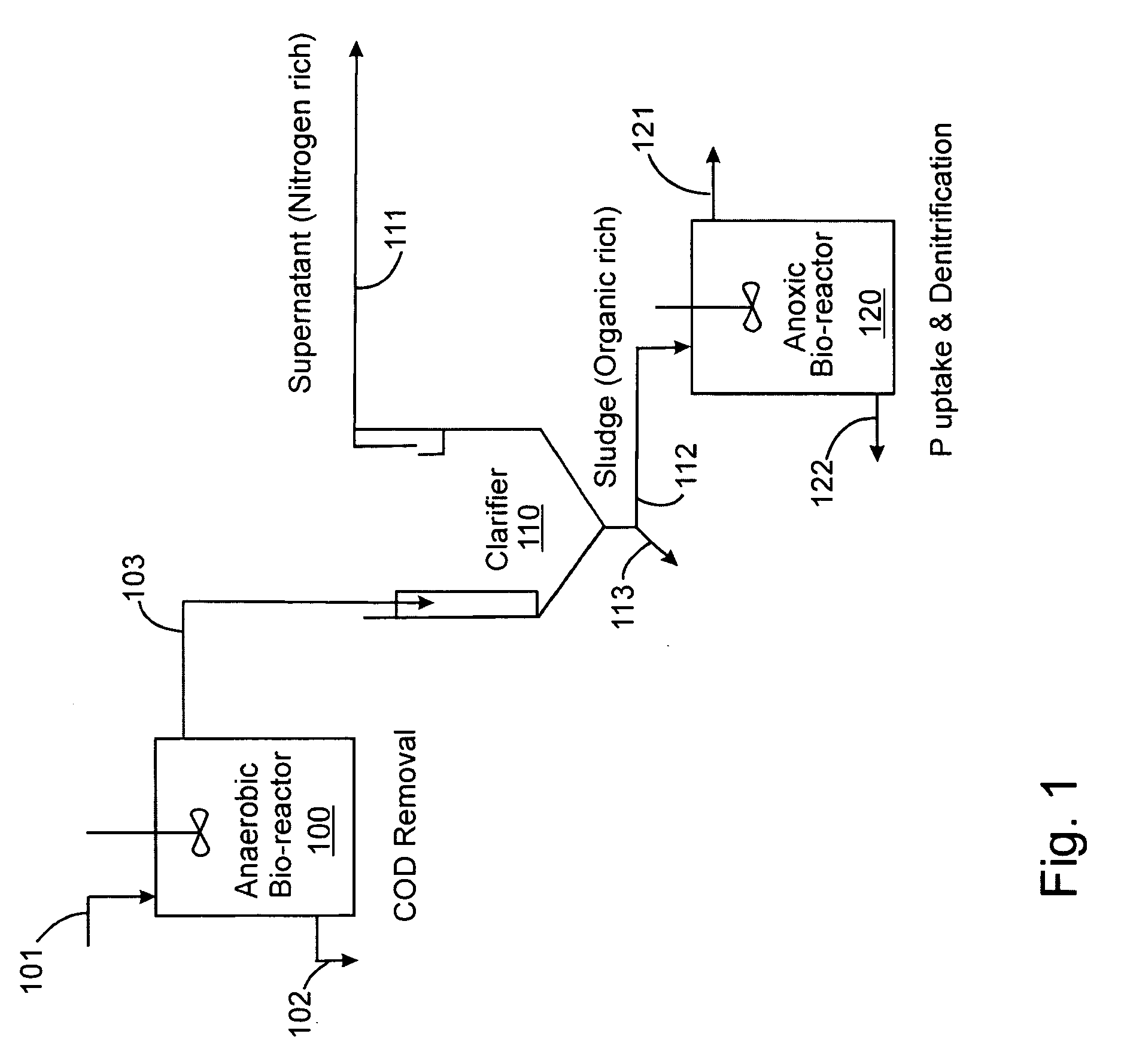
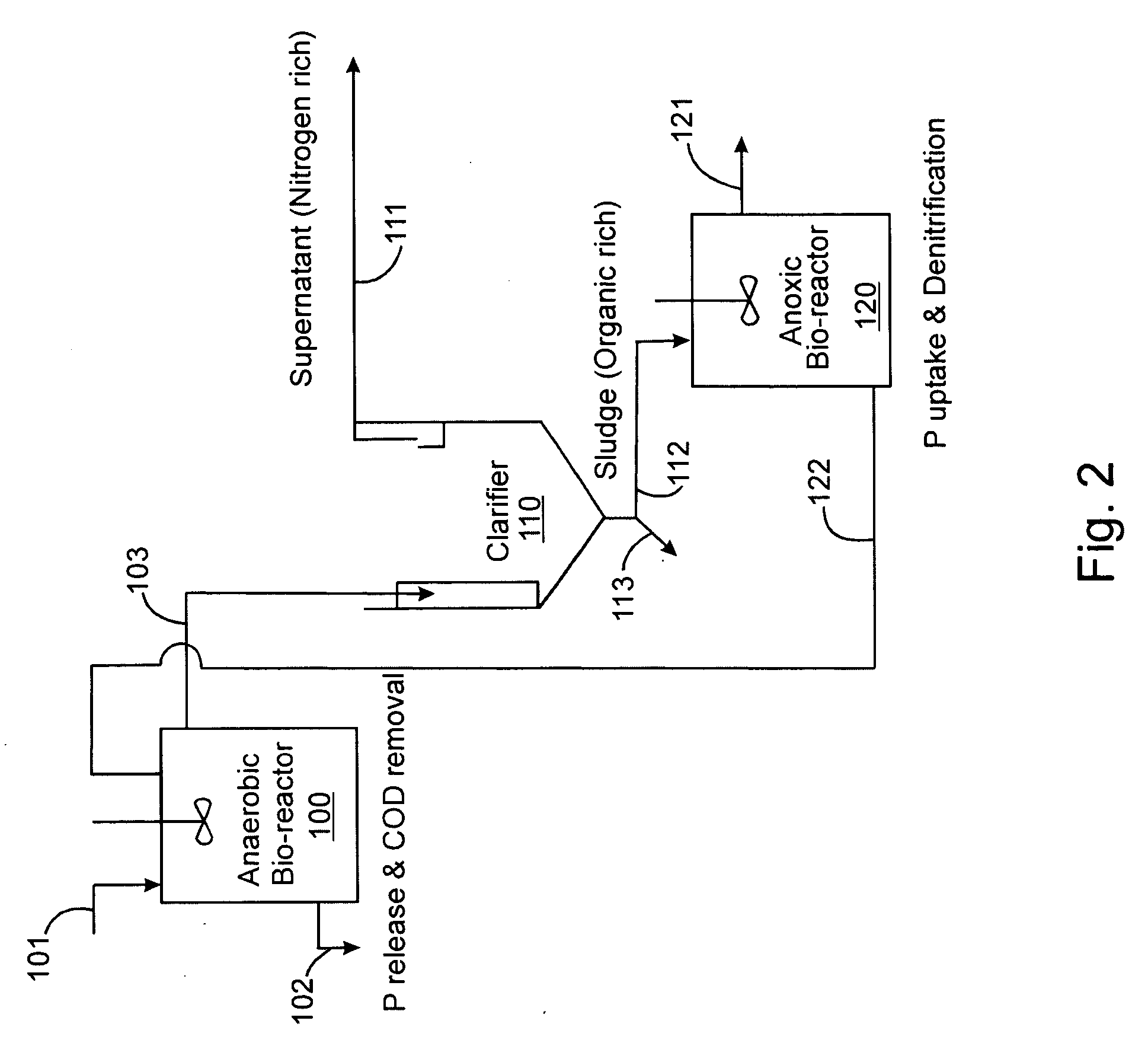
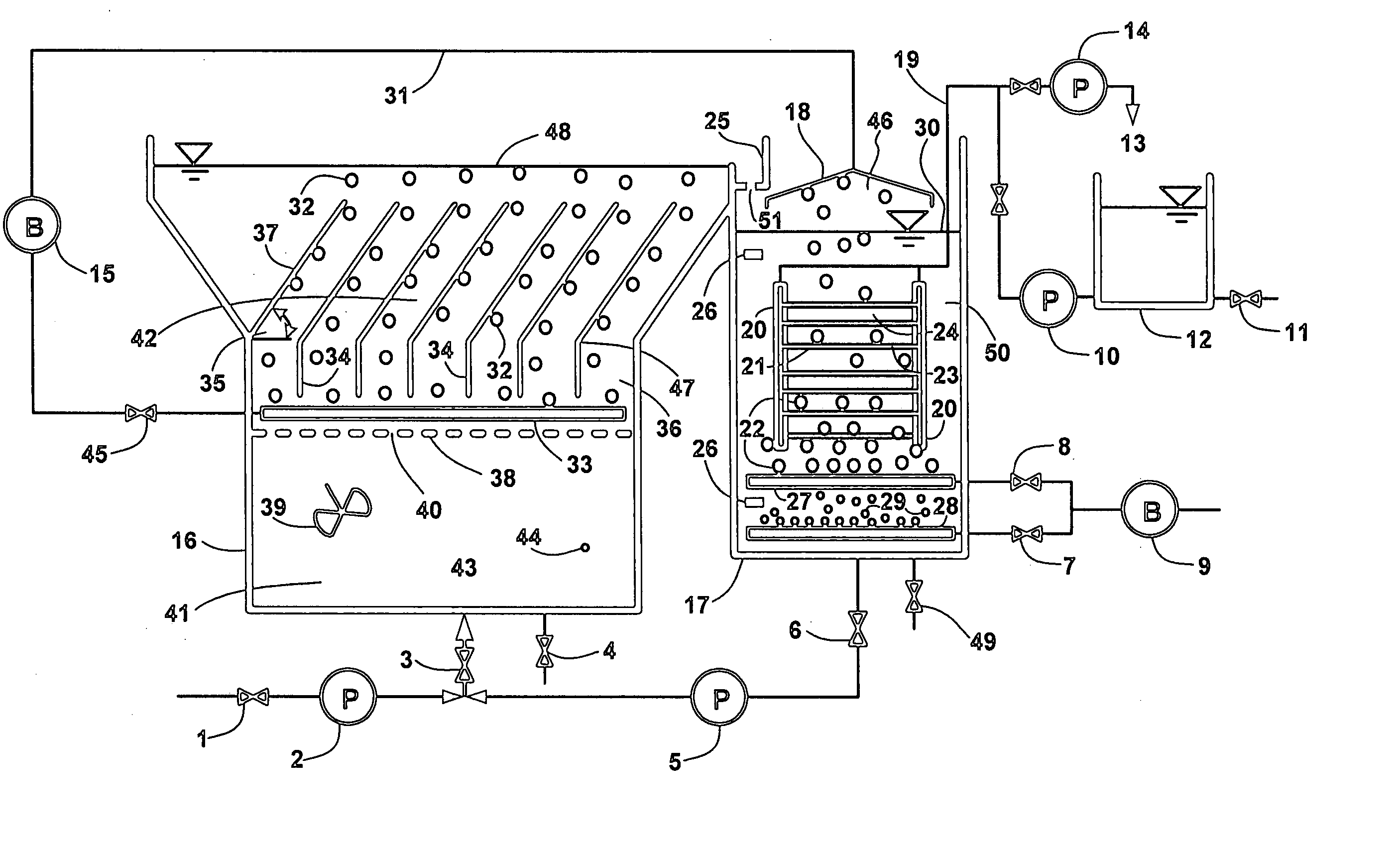
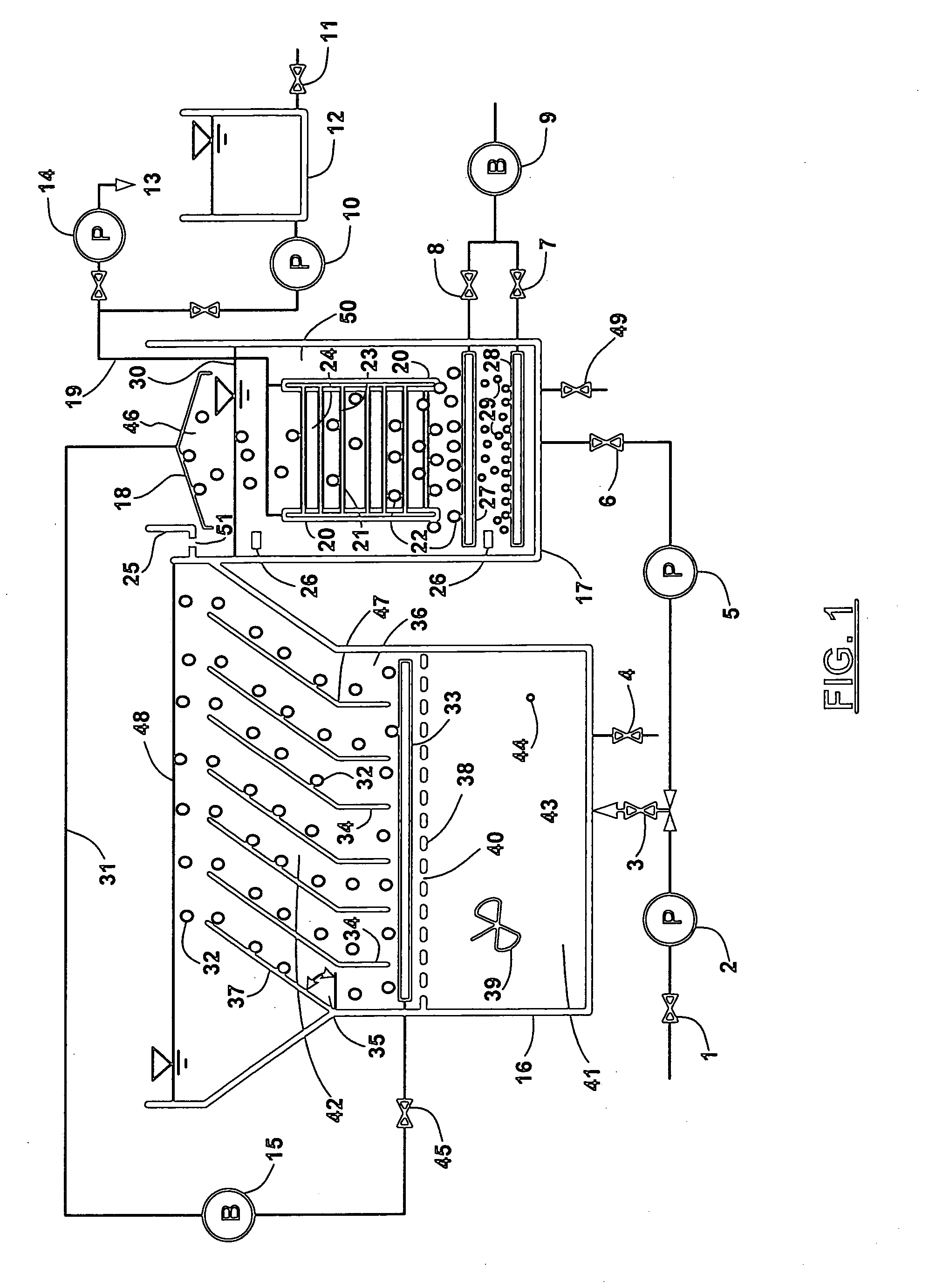
InactiveUS20060249449A1Great extent of P releaseHigh P uptakeTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesOxygenClarifier
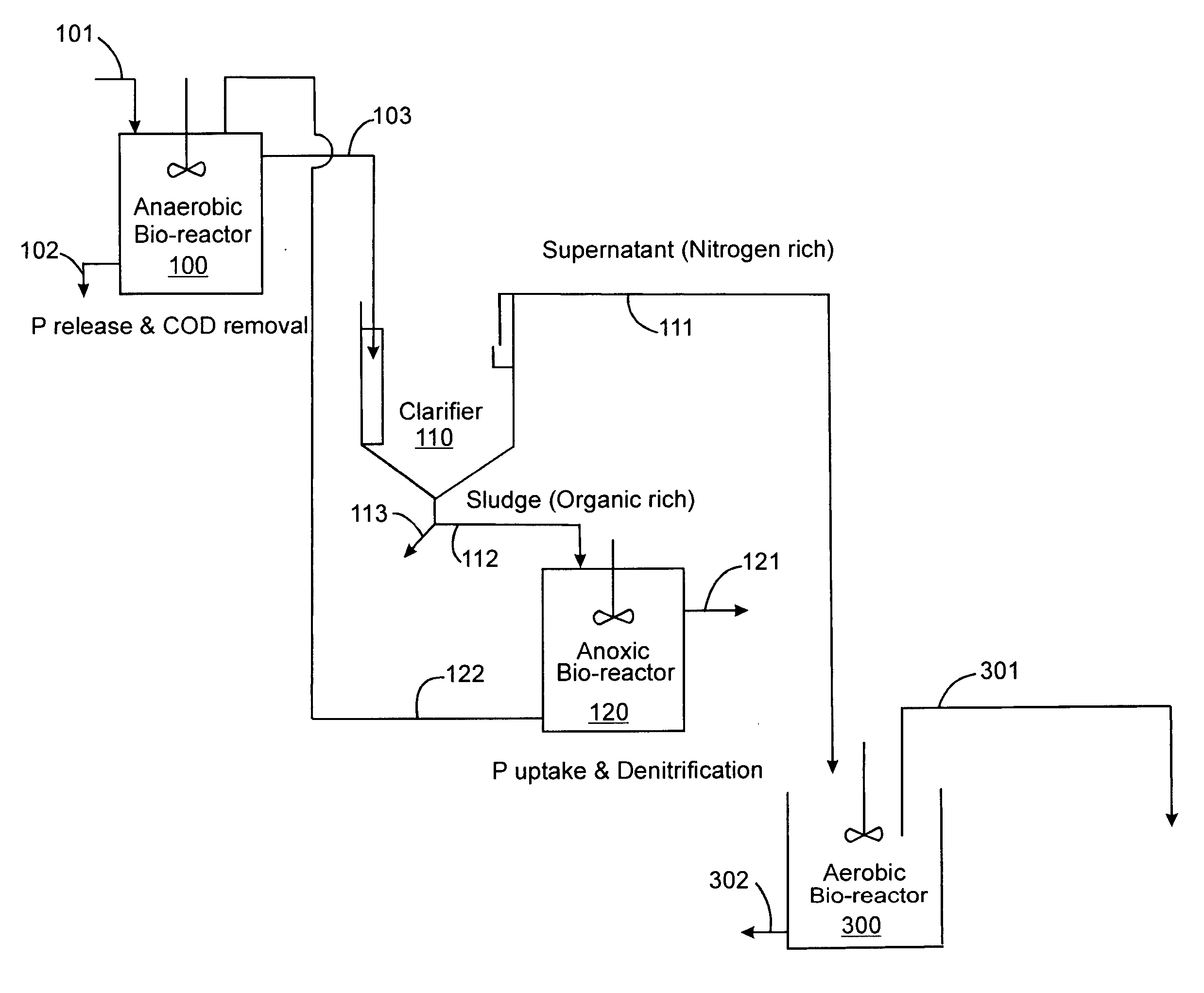
A method and process for the treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen. The wastewater is first anaerobically treated to produce an anaerobic effluent from which insoluble organic carbon is separated to form a sludge rich in organic carbon that is used as a substrate during anoxic treatment of the wastewater by de-nitrifying phosphorous accumulating organisms (DPAO's) and ordinary de-nitrifying organisms. The separation of insoluble organic carbon is normally conducted using a clarifier located intermediate the anaerobic and anoxic bio-reactors. In one embodiment, the ammonia rich clarifier supernatant is directed to an aerobic reactor for nitrification and the nitrate produced is recycled to the anoxic bio-reactor. The final effluent may be membrane filtered to retain nitrifying biomass within the aerobic bio-reactor. The invention reduces overall hydraulic residence time and sludge volume, which results in a smaller, less expensive wastewater treatment system.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Zero excess sludge membrane bioreactor
InactiveUS20050194310A1High yieldAcceptable levelTreatment using aerobic processesDialysis systemsChemical oxygen demandTotal nitrogen
An inclined plate coupled membrane bioreactor for treating feed water having excessive level of nutrients in particular chemical oxygen demand and total nitrogen and suspended solids has an aerobic bioreactor for nitrification and aerobic biodegradation in which membranes are submerged for permeate extraction, and an anoxic bioreactor for denitrification within which the inclined plates are outfitted to confine as much anoxic sludge as possible. An air oxygenating and an air scouring are continuously provided to the aerobic bioreactor to maintain a desired aerobic environment and to mitigate membrane fouling while an intermittent air blowing is provided to the anoxic bioreactor to blow out gaseous content generated through denitrification and to rectify the uniformed flow along the inclined plates. The aerobic sludge is recycled to the lower compartment of anoxic bioreactor and the supernatant of anoxic bioreactor is collected as weir effluent and delivered to the downstream aerobic bioreactor. Permeate is intermittently extracted from the membranes by a suction pump. There is no excess sludge withdrawn from the inclined plate coupled membrane bioreactor throughout the experiment.
Owner:YAMAMOTO KAZUO +1
Method and system for nitrifying and denitrifying wastewater
ActiveUS7147778B1Reducing and minimizing dissolved oxygen concentrationReduces and minimizes dissolved oxygen concentrationTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesActivated sludgeOxygen
A wastewater treatment system is provided that includes first and second reactors, each operative to nitrify or denitrify wastewater contained therein. Downstream from the first and second reactors is a membrane reactor that operates under aerobic conditions and includes one or more submersed membranes for separating solids. Extending between the membrane reactor and each of the first and second reactors is a return activated sludge line with appropriate controls for permitting return activated sludge to be directed to one of the reactors at a time. To nitrify and denitrify wastewater, a wastewater influent stream is alternatively directed to the anoxic reactors which are alternatively operated under aerobic and anoxic conditions so as to nitrify or denitrify the wastewater contained therein. To reduce or minimize the dissolved oxygen return from the membrane reactor to the first and second reactors, the flow of return activated sludge is controlled such that generally return activated sludge is returned to the reactor operating under aerobic conditions.
Owner:KRUGER I INC
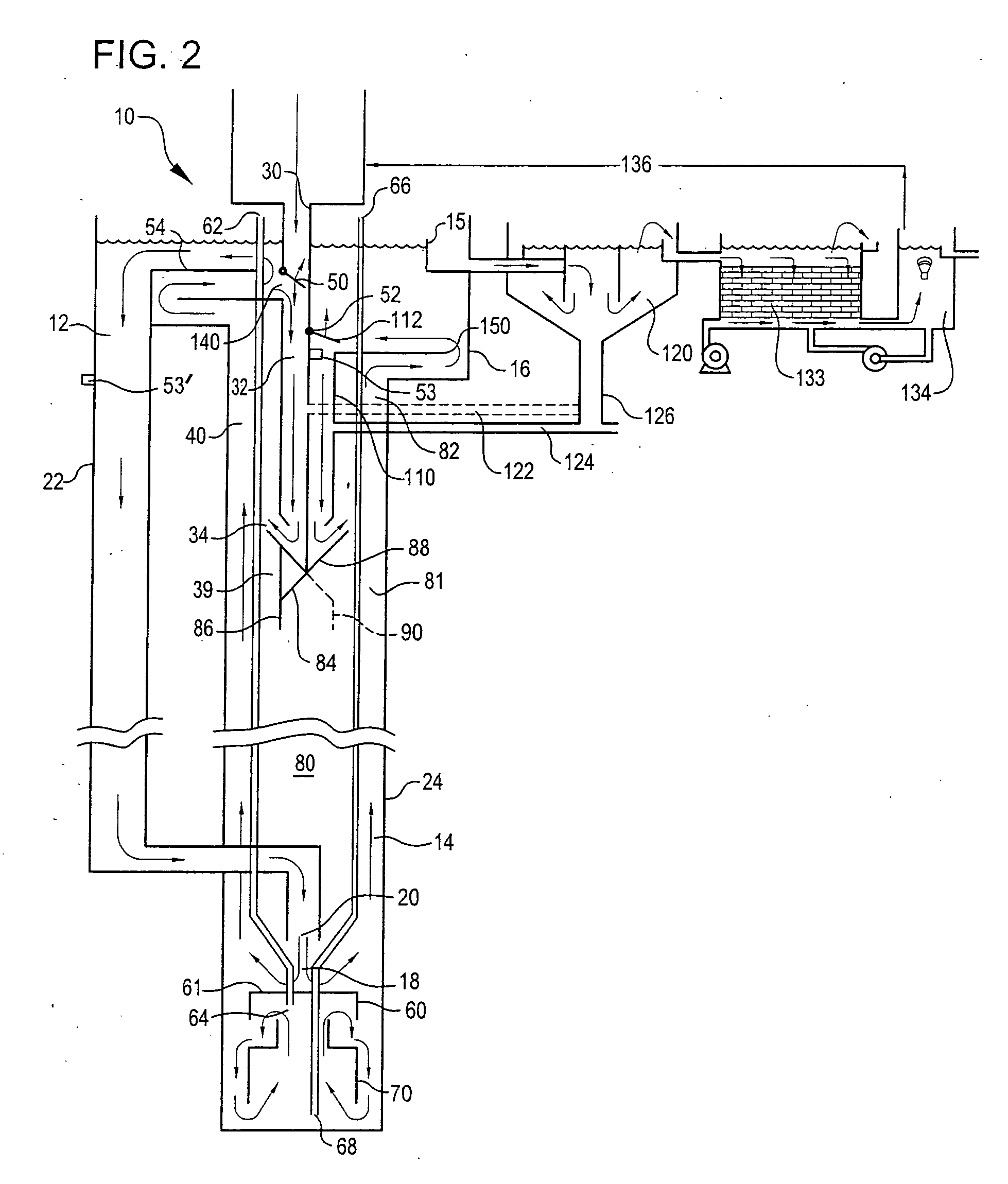
Anaerobic digester system and method
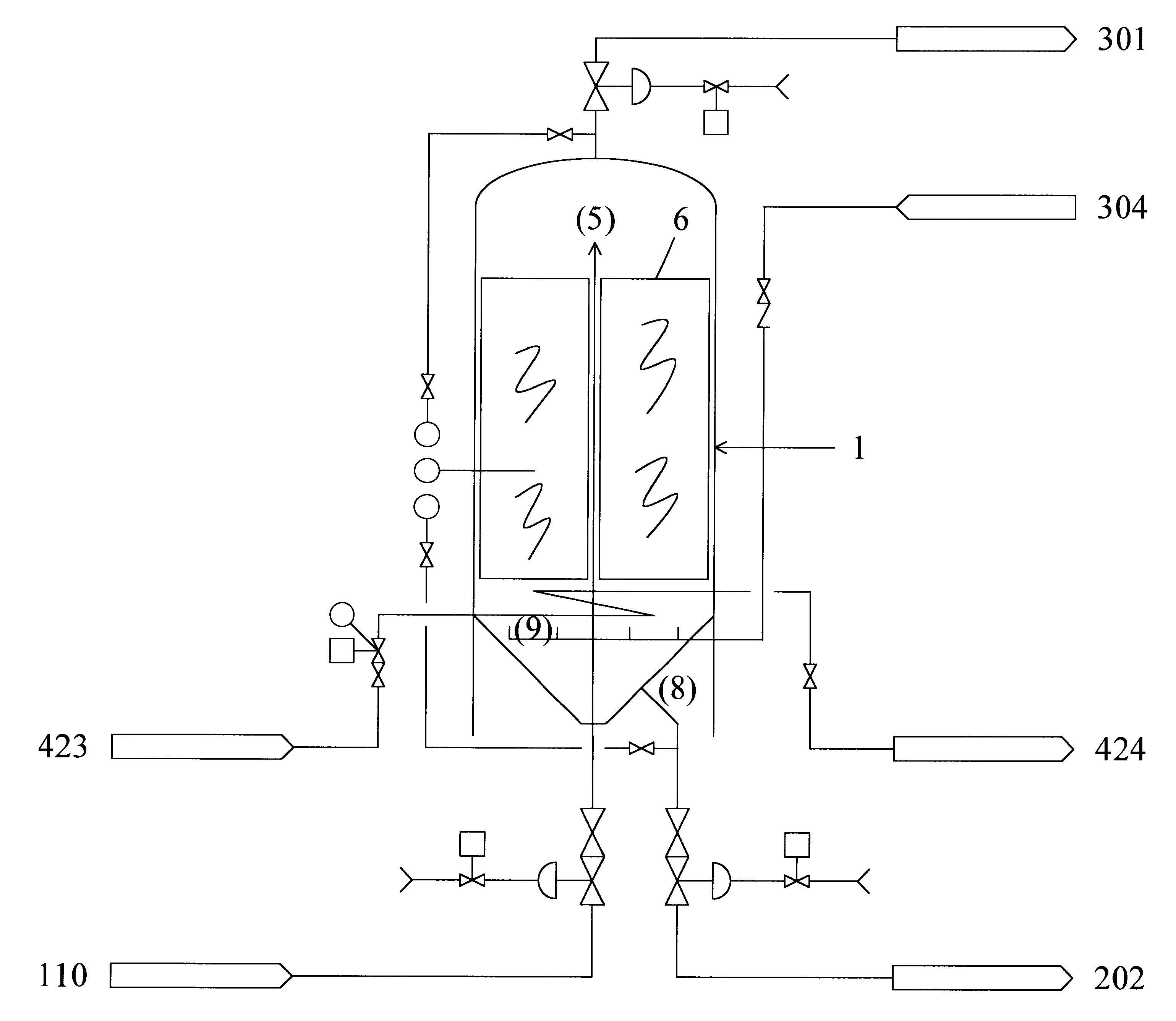
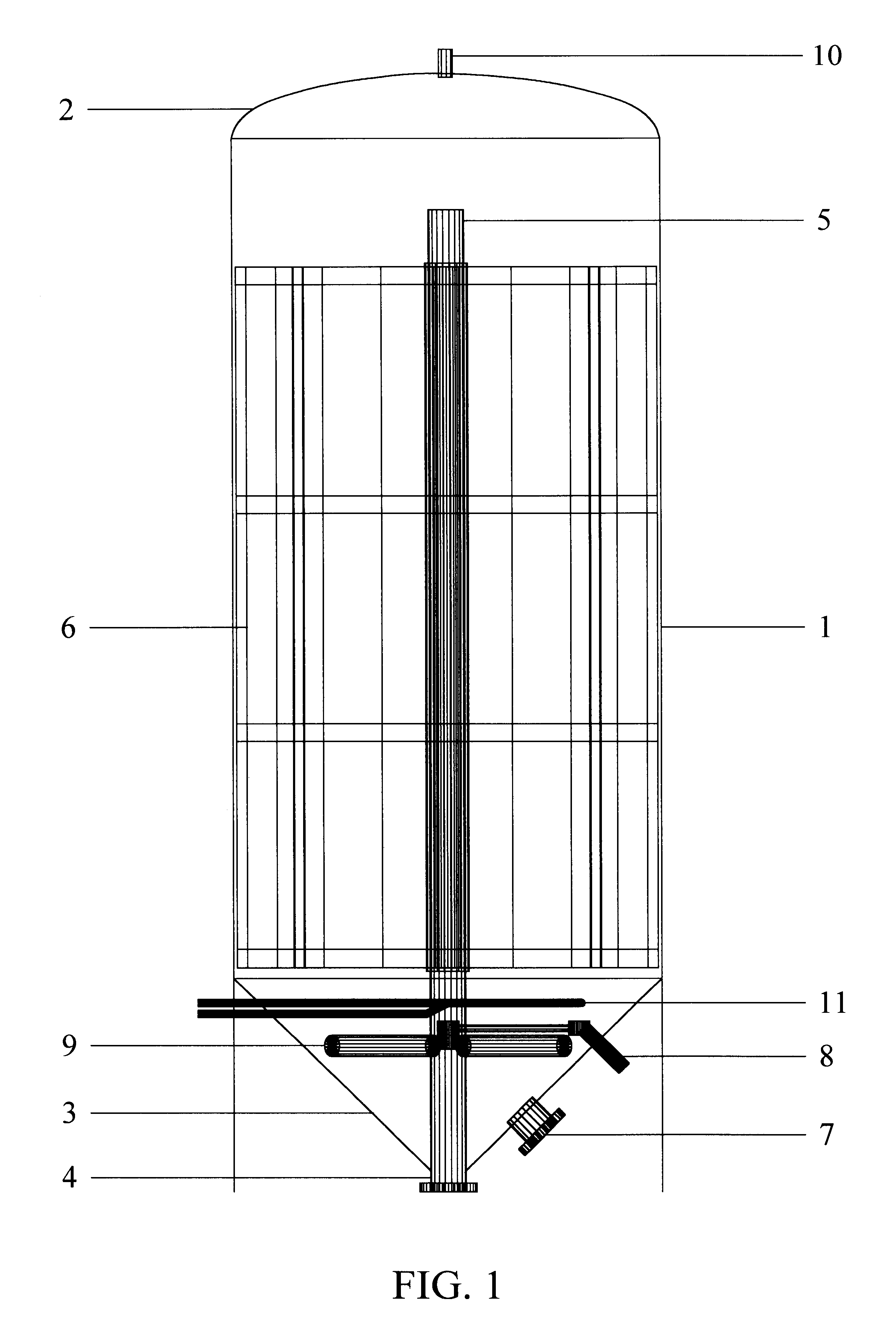
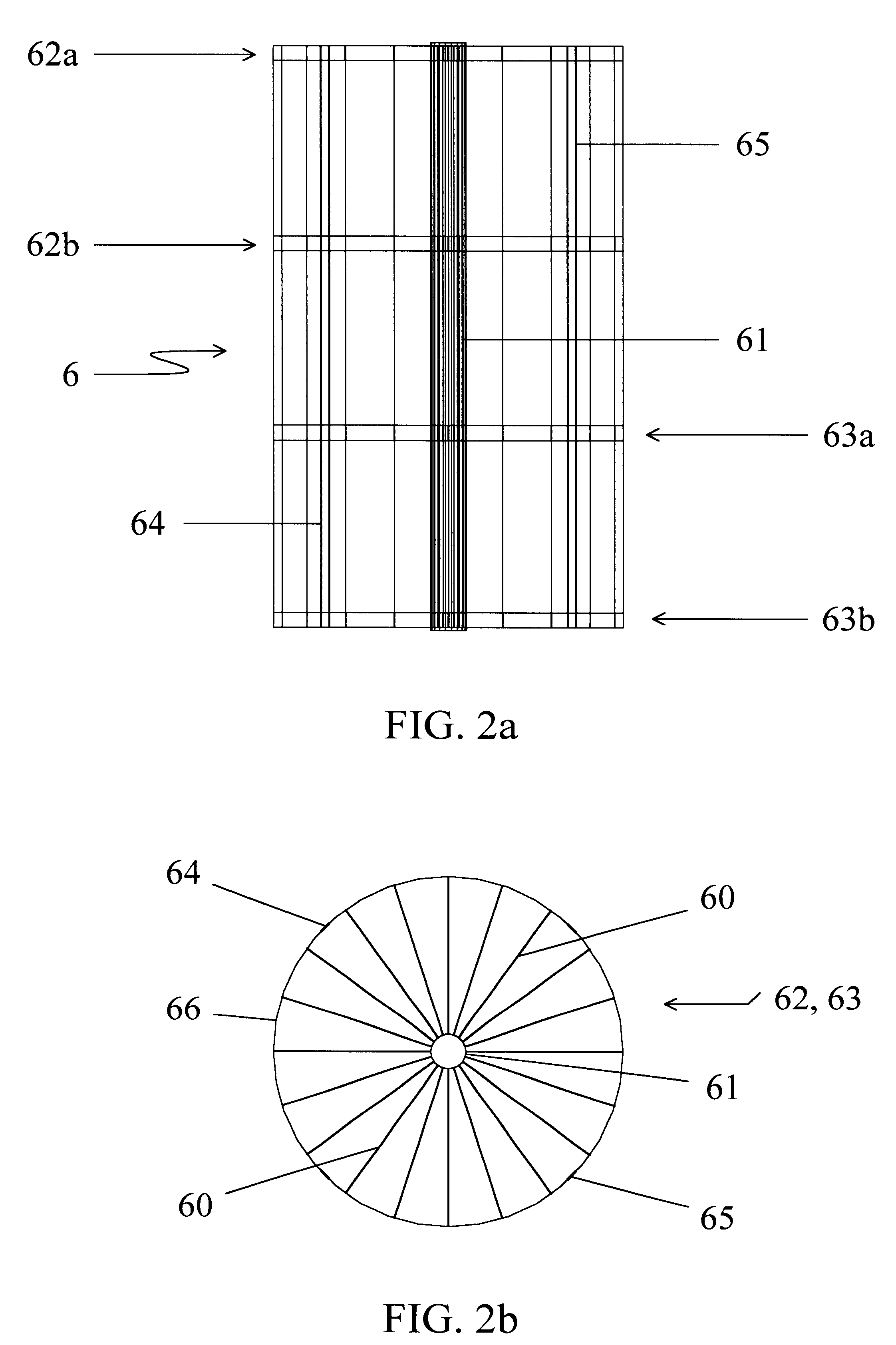
InactiveUS6254775B1High densityIncrease alkalinityGas production bioreactorsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSlurryMethane gas
An anaerobic digester system has a vertically upright vessel, a matrix arranged in the vessel supporting a microorganism biomass thereon, an input for supplying an input slurry of liquid and suspended solids at an upper portion of the vessel above the matrix, a gas output at the top of the vessel for withdrawing gas generated by anaerobic digestion of solids, and an effluent output at the bottom of the vessel for withdrawing liquid and remaining solids. The vessel has a preferred liquid height to diameter ratio of 2 to 1, and is constructed of inert fiberglass-reinforced plastic coated with a translucent blue gel pigment layer for filtering light at wavelengths that promote biomass cultivation. The matrix is formed as an array of panels mounted to a spindle with wheels fixed at spaced intervals along its vertical height, and the panel are made of a polyethylene grass matting providing a high surface area to volume ratio of at least 20 to 1. Gas from the top of the vessel is recycled to the bottom to generate bubbles for mixing the feedstock. The related method of anaerobic digestion includes comminuting input wastes with a slurry grinder into a pumpable slurry 8-10 % by weight solids, and providing as the biomass hydrolytic bacteria, and fermentative bacteria including acetogenic and methanogenic bacteria to produce a methane gas product. Other products include an organic soil additive, bacterial solids plant food, and a filtrate used as plant tonic.
Owner:RENERGY
Method and apparatus for treating wastewater using membrane filters
InactiveUS6863818B2Good removal effectEfficient workTreatment using aerobic processesBiological treatment regulationActivated sludgeBioreactor
An apparatus using activated sludge for the removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater includes a bioreactor for containing a mixture of wastewater under treatment and activated sludge. The bioreactor is divided into a plurality of serially connected treatment zones and includes a wastewater inlet, a downstream aerobic zone and an upstream aerobic zone between the wastewater inlet and the downstream aerobic zone, the upstream and downstream aerobic zones being separated by an anoxic zone. A method for removal of nutrients from a wastewater includes providing a wastewater to an inlet of a serial, multi-zone, activated sludge bioreactor containing an activated sludge. The bioreactor has a downstream aerobic zone from which water is removed and an upstream aerobic zone between the wastewater inlet and the downstream aerobic zone, the upstream and downstream aerobic zones being separated by an anoxic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Membrane coupled activated sludge method and apparatus operating anoxic/anaerobic process alternately for removal of nitrogen and phosphorous
ActiveUS20070108125A1Quality improvementSimple processTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsActivated sludgeNitrogen
Disclosed are a membrane coupled activated sludge method and apparatus operating anoxic / anaerobic processes alternately for removal of nitrogen and phosporus, wherein nitrogen and phosphorous together with organics in the sewage, wastewater, filthy water etc. can be simultaneously removed with an economic and efficient manner, an operation thereof is easy and efficient, a capacity thereof is high and the method is economic due to the reduced operating costs with performing measurement and control of a recycle rate, a recycle time of alternate operation of the anoxic and anaerobic process, an amount of sludge, an amount of aeration and an operation of a blower for an intermittent membrane cleaning.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Integrated closed loop system for industrial water purification
InactiveUS20050061737A1Small surface areaIncreasing biofilm thicknessTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic matterIndustrial water
The present invention relates to an integrated closed loop system for aquaculture in at least one culturing tank and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic material, nitrogen and phosphorous, comprising: an integrated, partially or wholly closed loop system for waste water treatment, where the water contains nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances, comprising at least one production unit of such nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorous from the said water at continuous flow, comprising: a) at least one suspended carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under anoxic conditions to cause anaerobic denitrification, with one or several compartments, preceding b) at least one suspended-carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under oxic conditions to cause aerobic nitrification, c) the denitrification taking place after the production unit, and d) the nitrification taking place prior to the production unit in a by-pass mode as part of the continuous flow.
Owner:GREENFISH
Dynamically responsive aerobic to anoxic inter-zone flow control system for single vessel multi-zone bioreactor wastewater treatment plants
InactiveUS20040035770A1Improve adaptabilityStable and fastLiquid separation auxillary apparatusWater treatment parameter controlProgram instructionProgrammable logic controller
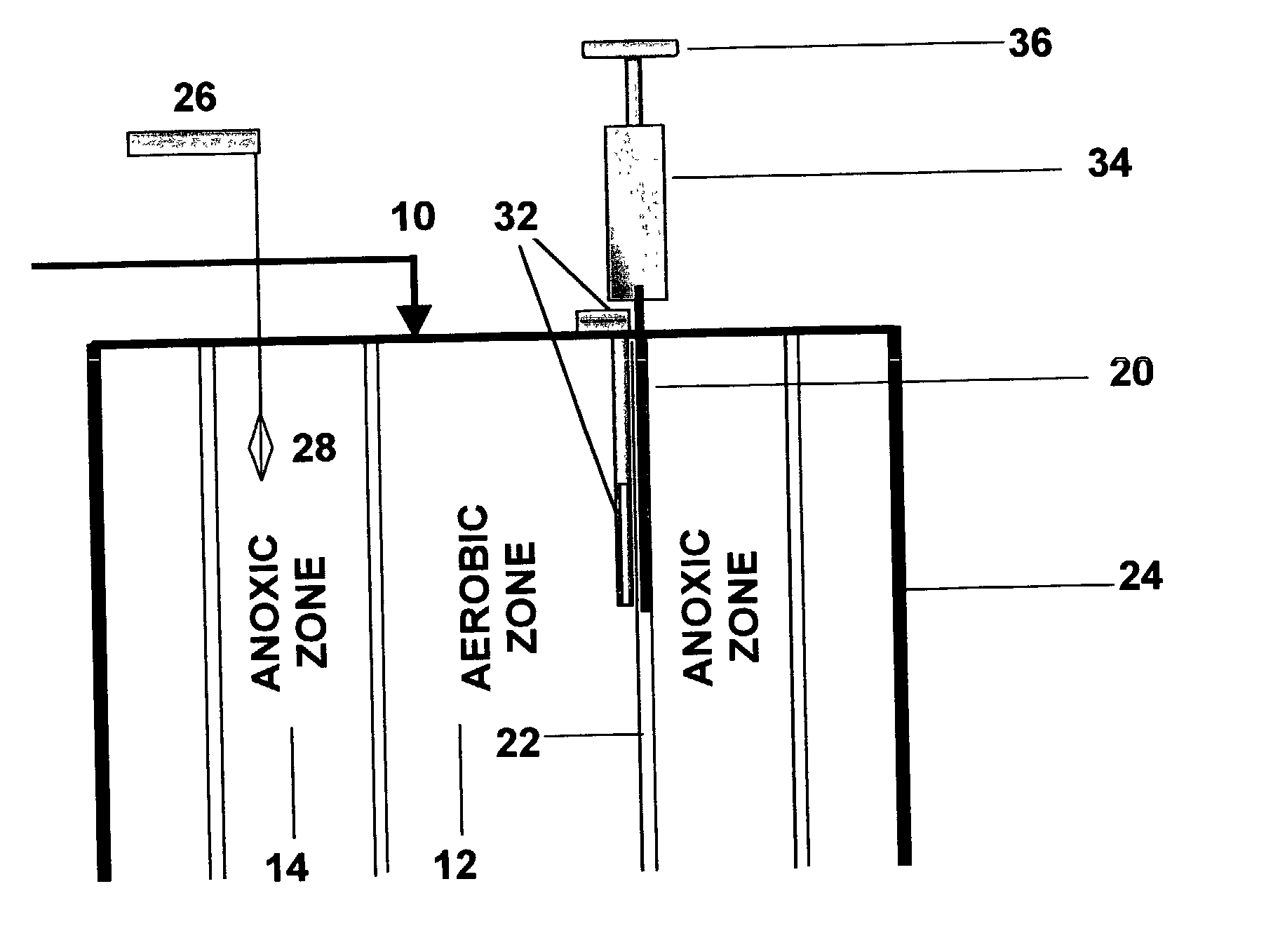
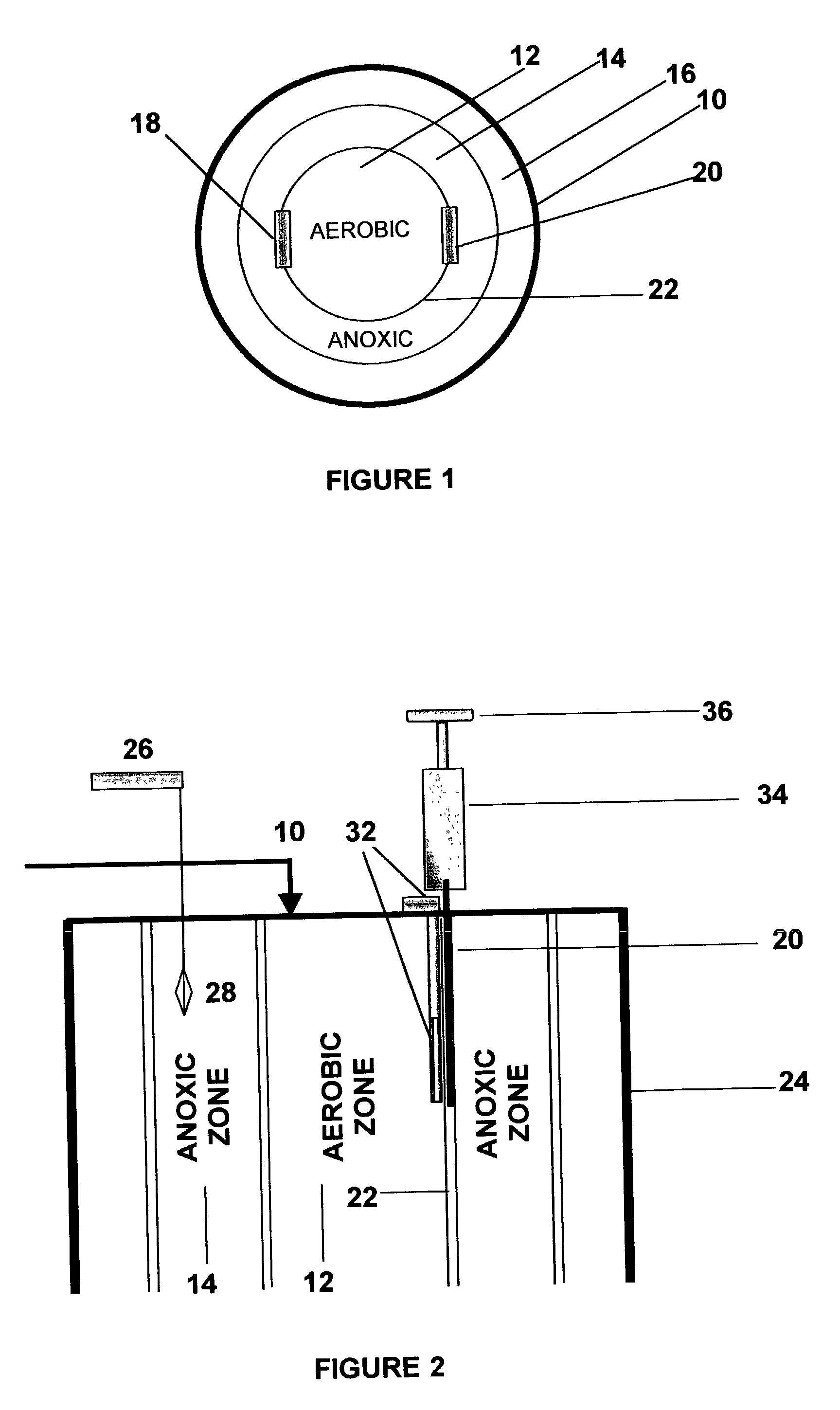
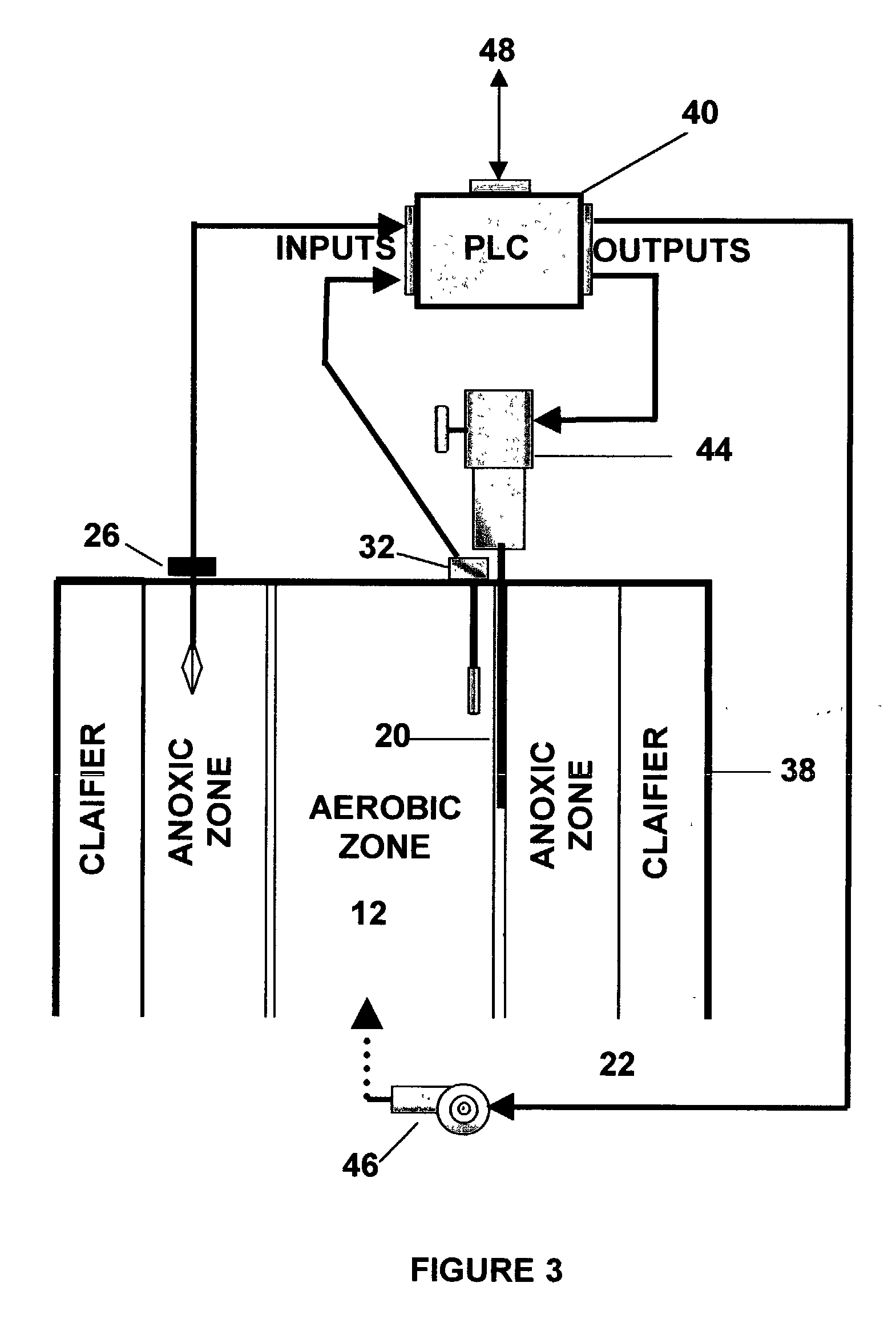
An inter-zone aerobic to anoxic zone flow rate control system for single vessel multi-zone bioreactor plants for wastewater treatment is described herein. The system of the invention provides control of the relative treatment times of the mixed liquor in the horizontally disposed and adjacent aerobic and anoxic treatment zones of the bioreactor by providing one or more flow rate adjusting gates located between the aerobic and anoxic zones of the bioreactor. The opening of the gates is adjustable in accordance with sensed conditions in the treatment zones. An automated embodiment of the invention includes a programmable logic controller that provides control scripts for adjusting the opening of one or more flow control gates according to inputs from sensors and per programmed instructions. An automated and supervised embodiment of the invention includes a computer interfaced with a programmable automating controller. The computer provides status reports, commands to the programmable automating controller, storage and analysis of data, as well as a means of communicating to remote monitoring centers and networks.
Owner:ATARA ENVIRONMENTAL
Onboard fuel separation apparatus for an automobile
InactiveUS6972093B2Increase volumeBoost octaneInternal combustion piston enginesUsing liquid separation agentVolatilesEngineering
An onboard fuel separation apparatus separates a material fuel (gasoline) into a high-octane fuel having a higher octane value than the material fuel and a low-octane fuel having a lower octane value than the material fuel using a separation membrane which selectively allows high-octane value components (such as aromatic components) permeate through the membrane. The apparatus increases the ratio of the amount of the high-octane value components permeating through the membrane to the amount of the high-octane value components contained in the material fuel by, (A) Controlling the temperature of the material fuel supplied to the membrane (B) Increasing partial pressure of the low-octane value components on the high-octane fuel side of the membrane and removing volatiles from the permeate, and (C) Bypassing volatiles in the material feed around the membrane.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO +1
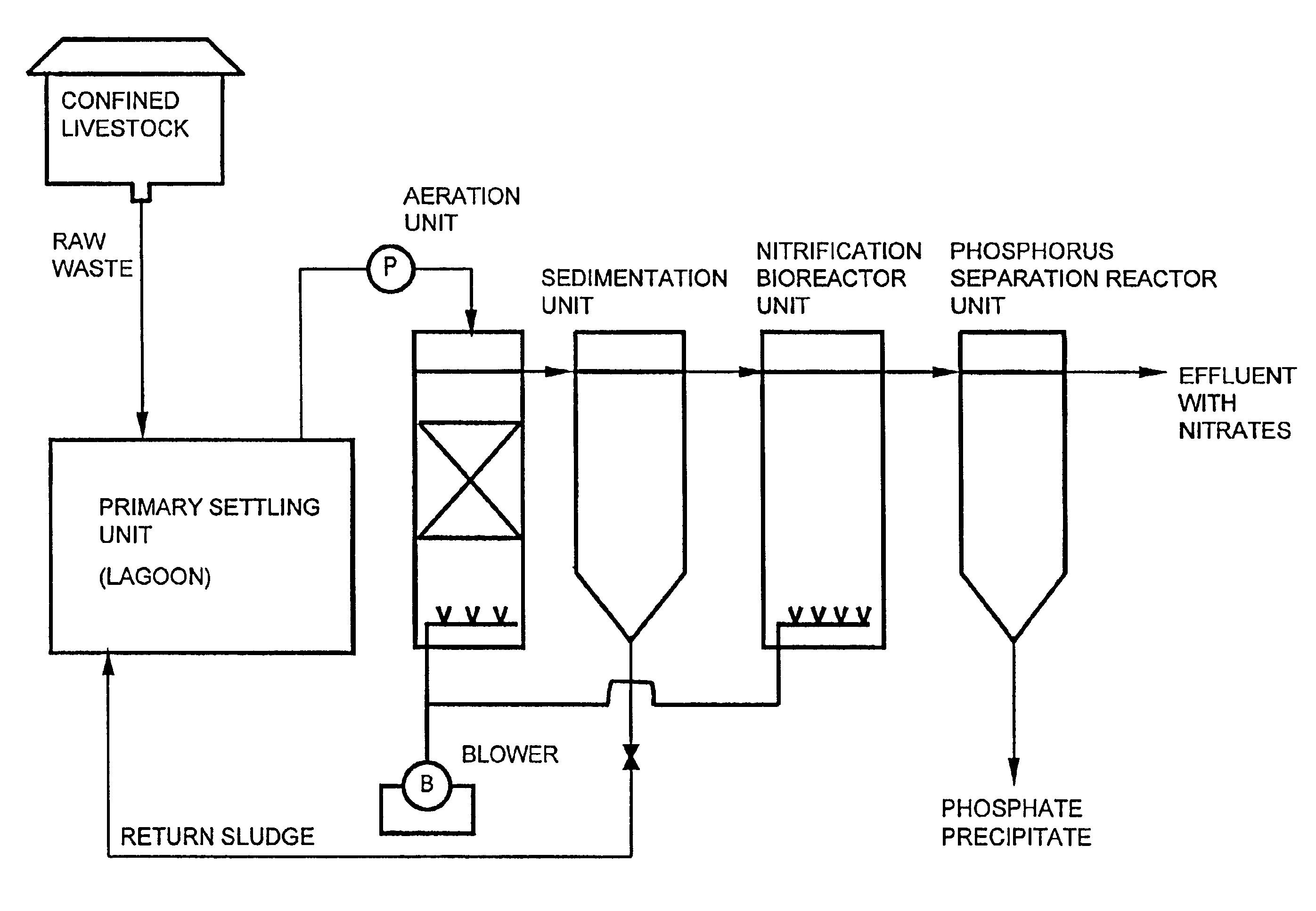
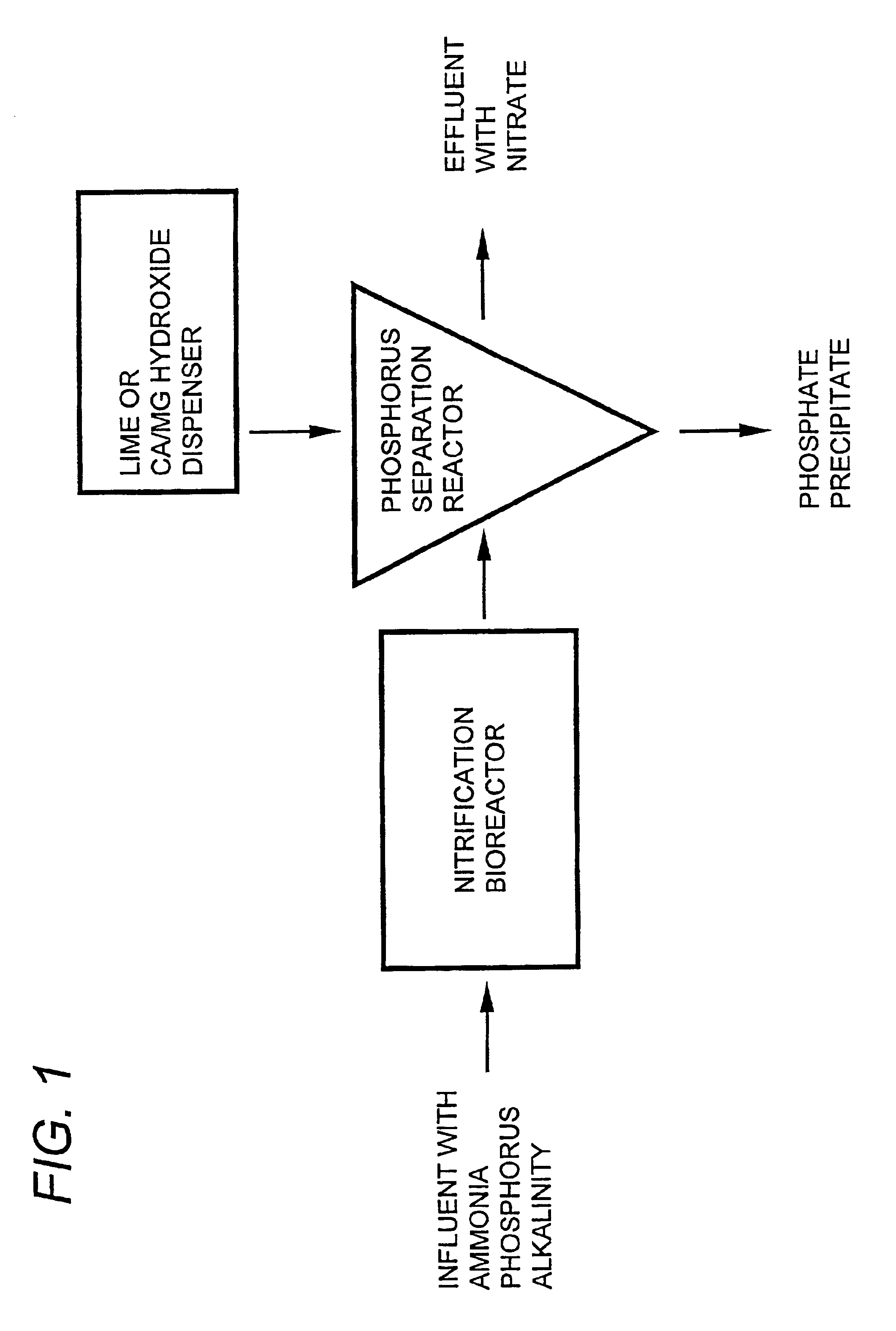
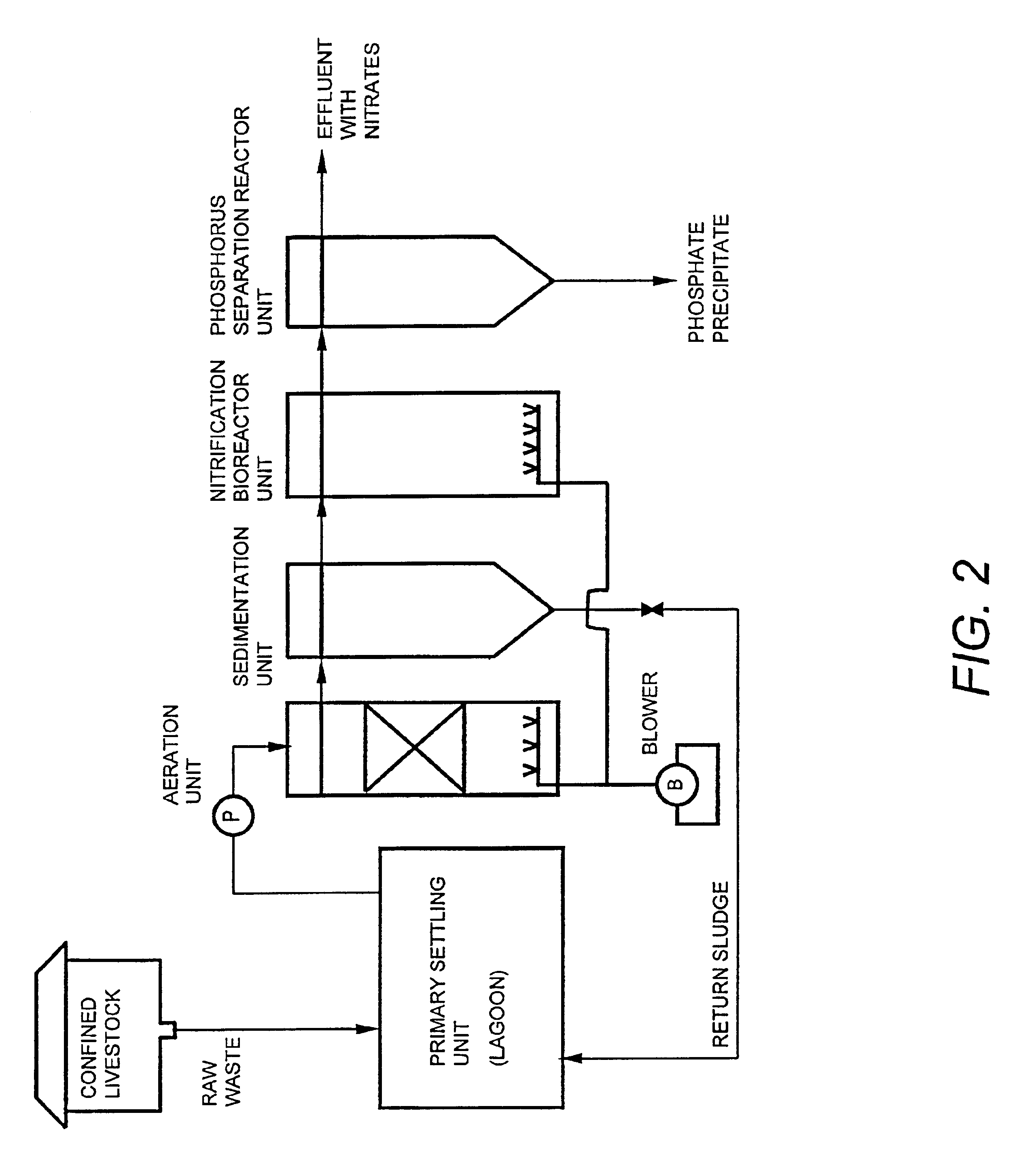
Method for producing feed additive from livestock and poultry breeding wastewater and purifying breeding wastewater to reclaimed water
InactiveCN102161550AReduce water consumptionAchieving zero emissionsWaste water treatment from animal husbandryAnimal feeding stuffUltrafiltrationSlurry
The invention relates to the fields of environmental technology and the breeding and processing of microalgae, in particular to a method for producing feed additive from livestock and poultry breeding wastewater and purifying breeding wastewater to reclaimed water. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that: wastewater enters an acidification adjusting tank through a grille, and the acidified wastewater enters an anaerobic biochemical reactor for treatment and then enters an aerobic biochemical reactor; after the aerobic biochemical treatment, the obtained biogas slurry enters a settling tank for settling, the supernatant enters a membrane bioreactor for further aerobic treatment and is filtered by an ultrafiltration membrane, the generated ultrafiltration clear liquid is sterilized and neutralized and then enters a photobioreactor, algae are added into the photobioreactor to perform microalgae cultivation, and the algae liquid is discharged from the photobioreactor and then enters a flocculation and settling tank; and after flocculation and settling, the supernatant is used for water recycling, the concentrated algae liquid at the bottom enters a filter, and the separated microalgae slurry enters a fermentation / enzymolysis pot (tank) to perform fermentation / enzymolysis to be used as the feed additive. The invention has the advantages of high economic adaptability, zero discharge and the like.
Owner:蔡志武 +1
Wastewater treatment system
InactiveUS6893567B1Expand the populationShorten treatment timeTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsEnteropathogenic bacteriaTreatment system
Wastewater treatment systems and processes for: removal of solids, pathogens, nitrogen, and phosphorus from municipal and agricultural wastewater include nitrification of wastewater and increasing the pH of the nitrified wastewater by adding a metallic-containing salt and hydroxide to precipitate phosphorus to form a useable effluent having a specified nitrogen:phosphorus ratio that is useful as a fertilizer or spray for remediation of contaminated soils. The presence of infectious microorganism such as enteropathogenic bacteria and picarnoviruses will be reduced in the useable effluent. The precipitated phosphorus is recovered and used to form useable phosphorus products.
Owner:AGRI UNTED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC +1
Method for treating wastewater in a membrane bioreactor to produce a low phosphorus effluent
InactiveUS6946073B2Reduce outputPromoting robust nutrient uptakeTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesActivated sludgeMembrane bioreactor
Removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater yielding a low phosphorous (e.g., less than 0.25 mg / L) output includes providing a serial multistage bioreactor containing activated sludge having in hydraulic series an anaerobic zone and a downstream aerobic zone, with each zone having an upstream inlet and a downstream outlet. The wastewater is provided to the anaerobic zone inlet. A quantity of chemical sufficient to precipitate soluble and particulate phosphorous is added to the downstream aerobic zone in an amount sufficient to yield a low phosphorous output. Treated water is separated from the activated sludge and precipitated phosphorous and a return activated sludge separated from the treated water is recycled to the anaerobic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Membrane bioreactor, process and aerator
InactiveUS6863817B2Increase pressureEasy to moveTreatment using aerobic processesUsing liquid separation agentSiphonGravity flow
A reactor has an aerobic tank, an anoxic tank and a sealed membrane tank with conduits for circulating mixed liquor between them. Permeation starts when the mixed liquor reaches a high level and stops when the mixed liquor reaches a low level. A sensor, for detecting the mixed liquor level, may stop and start permeation. Pressure builds in the membrane tank when membrane air is on. Transmembrane pressure is also provided by gravity flow or siphon. Membrane air generates an air lift which drives the mixed liquor circulation. The total amount of air provided by an air source is divided and varied in time between the membrane aerator and the process aerator. The process aerator acts as a screening inlet to the conduit to the membrane tank. Chemical maintenance cleaning is provided by gravity flow.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNESHIP
High performance, energy efficient system and method for wastewater treatment with resource recovery and reduced residual solids generation
ActiveUS20080223783A1Treatment with anaerobic baffled reactorsWater treatment parameter controlRetention timeCell mass
A wastewater treatment system is provided including an aerobic membrane bioreactor and an anaerobic digester system connected to receive wasted solids continuously from the aerobic membrane bioreactor and also connected to return effluent from the anaerobic digester system continuously to the aerobic membrane bioreactor. Further, a process is provided for treating wastewater including the step of wasting a volume fraction of organic cell mass from an aerobic membrane bioreactor to an anaerobic digester system and maintaining a solids retention time (SRT) in the bioreactor that is (1) greater than a time needed to achieve growth of organisms suitable for converting carbonaceous biochemical oxygen demand (CBOD) into cell mass and (2) less than a time at which substantial decay of the organisms occurs. The system and process may further include optional pretreatment and / or phosphorus and / or nitrogen removal downstream of the membrane bioreactor system.
Owner:HSBC BANK
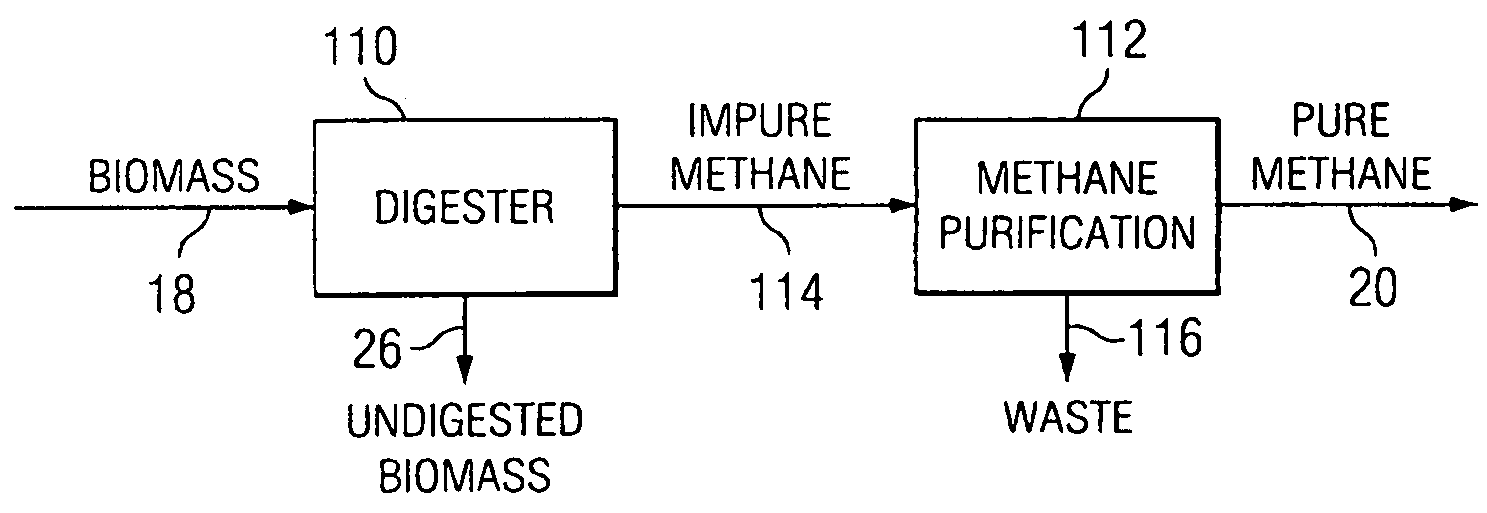
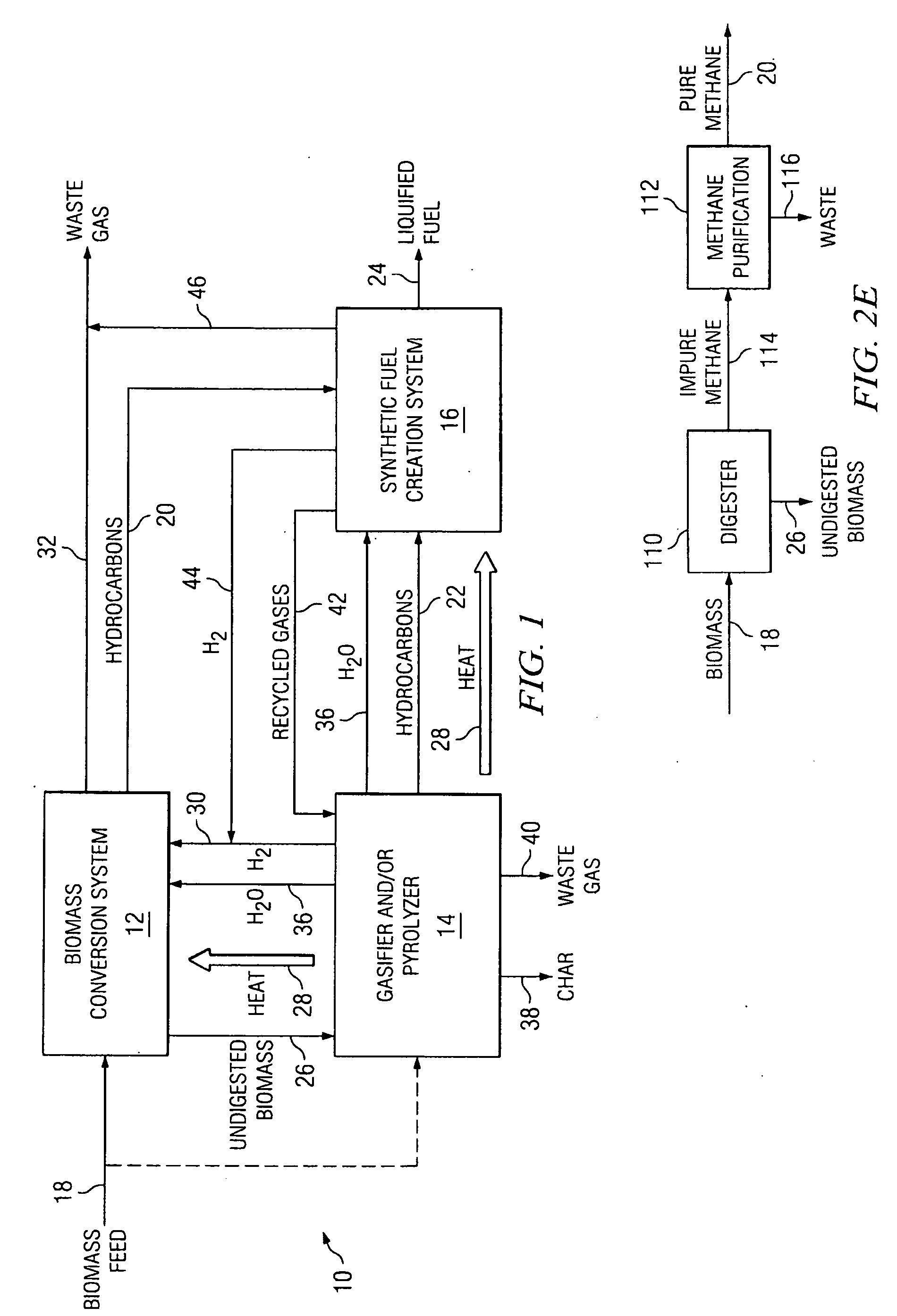
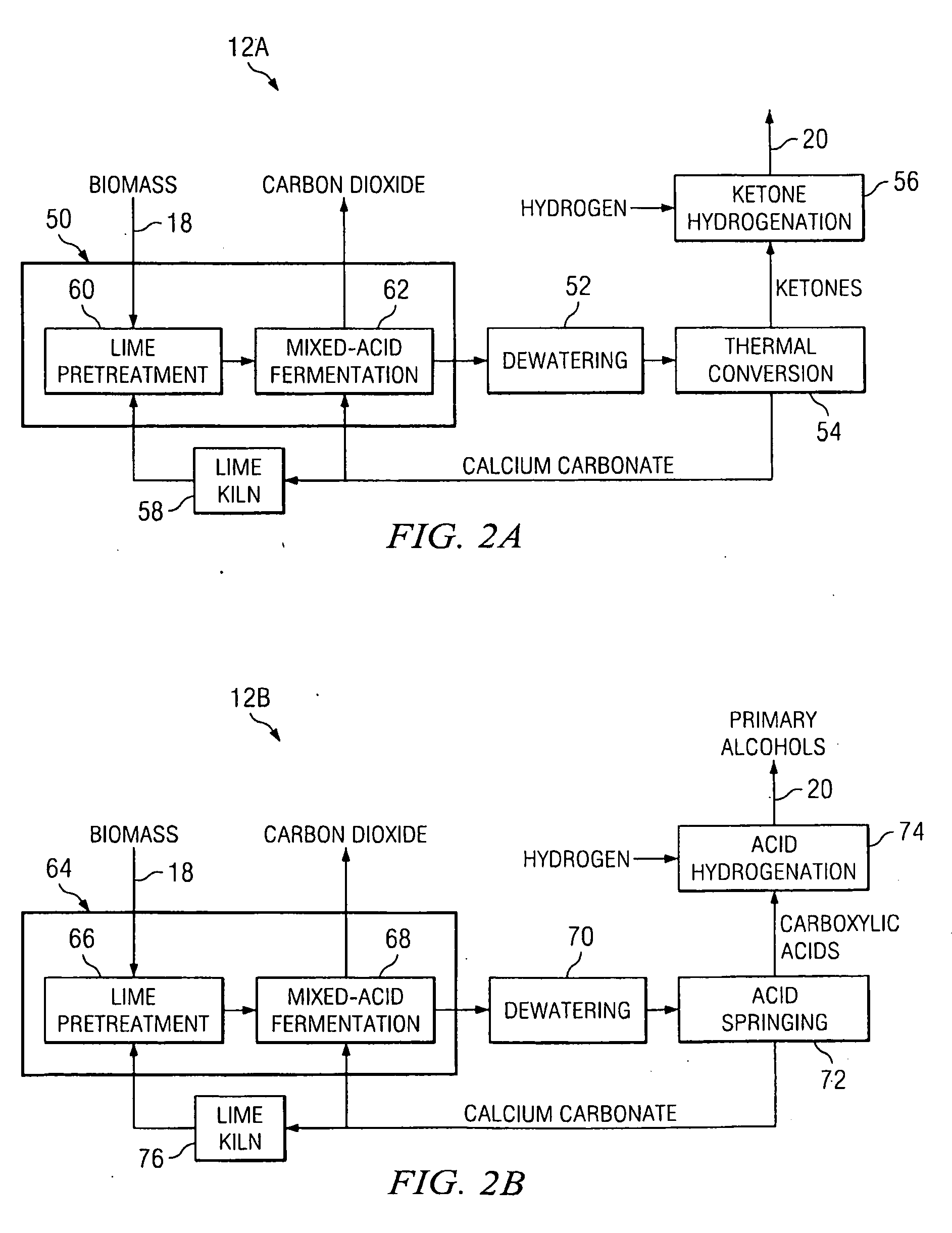
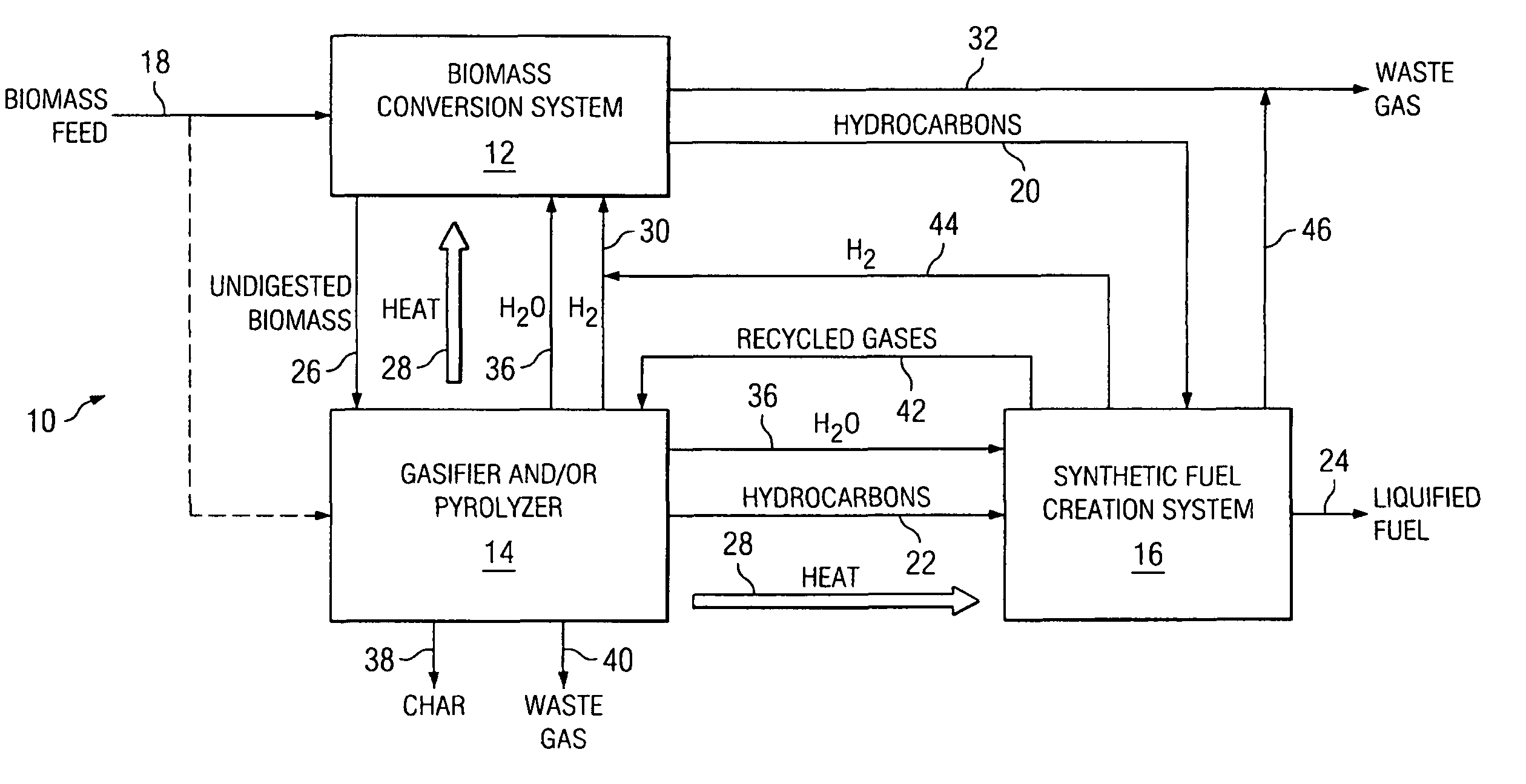
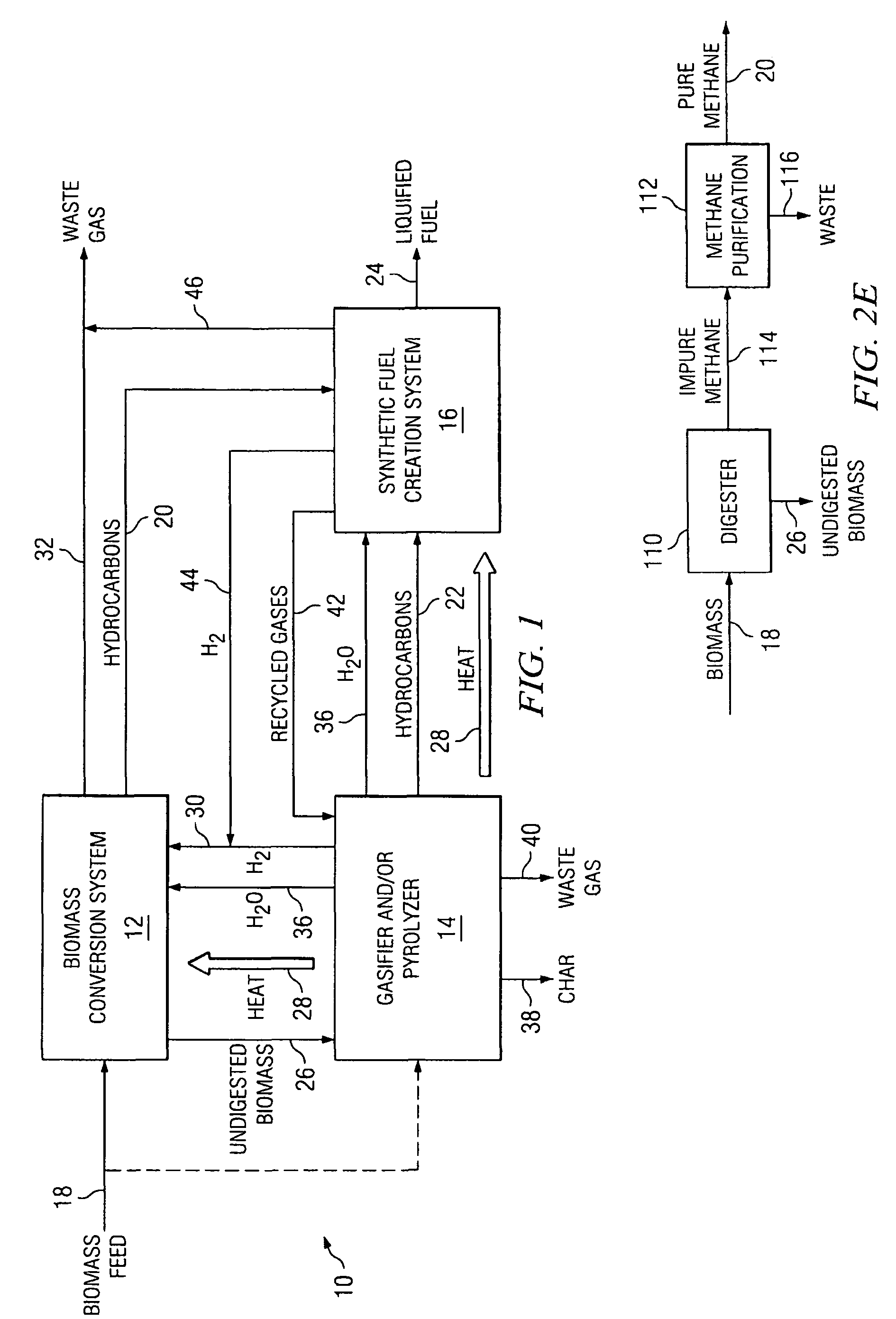
Integrated Biofuel Production System
InactiveUS20090239279A1Increase energy densityImprove conversion efficiencyWaste based fuelSedimentation separationThermal energyResidual biomass
According to an embodiment, a biomass conversion subsystem produces methane and / or alcohol and residual biomass. A pyrolysis or a gasification subsystem is used to produce thermal energy and / or process gasses. The thermal energy may be stored thermal energy in the form of a pyrolysis oil. A fuel conversion subsystem produces liquid hydrocarbon fuels from the methane and / or alcohol using thermal energy and / or process gasses produced by the gasification or pyrolysis subsystem. Because the biomass production system integrates the residual products from biomass conversion and the residual thermal energy from pyrolysis or gasification, the overall efficiency of the integrated biomass production system is greatly enhanced.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
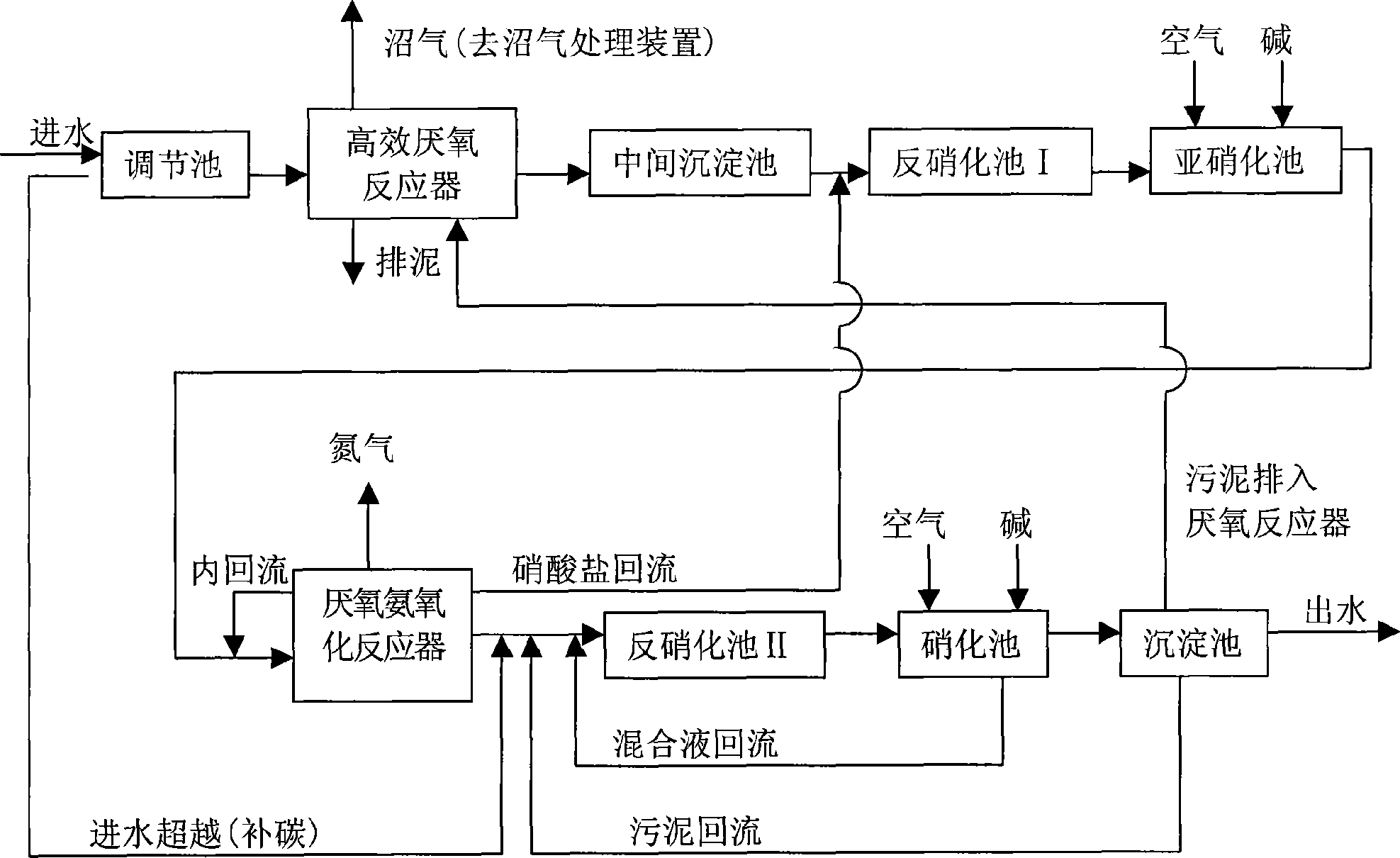
Deepness denitrogenation method for treating organic wastewater in high concentration
ActiveCN101050026AGuaranteed emission standardsThe process route is compactWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHigh concentrationTotal nitrogen
This invention discloses a method for deep denitrification treatment of high-concentration organic wastewater. The apparatus comprises an anaerobic decarbonization zone, an aerobic nitrosation / anaerobic ammoxidation denitrification zone, and a traditional nitrification / denitrification zone. In the anaerobic decarbonization zone, an anaerobic bioreactor is utilized to perform anaerobic biotreatment on the organic pollutants in raw water to remove the majority of organic matters. In the aerobic nitrosation / anaerobic ammoxidation denitrification zone, ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen are removed in the form of nitrogen gas. In the traditional nitrification / denitrification zone, nitrate in the water discharged from the aerobic nitrosation / anaerobic ammoxidation denitrification zone is subjected to denitrification and removed in the form of nitrogen gas. Excess organic matters are subjected to aerobic bioreaction and removed. The method can ensure COD; total nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen contents in the treated water are qualified for discharge. The method has such advantages as high decarbonization and denitrification efficiency, low energy consumption, and high running stability.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL RES INST OF ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION
Combined activated sludge-biofilm sequencing batch reactor and process
InactiveUS20040206699A1Similar oxygen transfer efficiencyRemoval can be promoted and increasedTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
A new biofilm-activated sludge Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) treatment process for sewage or wastewater has successfully been developed as the third generation SBR (SBR3). This new SBR3 process utilizes a multi-stage and multi-sludge SBR configuration receiving either continuous or intermittent inflow of wastewater. Each stage has individually controlled continuous or alternating anaerobic / anoxic / aerobic operation, with or without mixing and recycling from the other stage(s). The configuration and operation is dependent upon the treatment objectives and effluent discharge requirements. In the preferred embodiment, carriers are used to facilitate control of operating conditions.
Owner:KINGSFORD ENVIRONMENTAL H K
Apparatus and method for purification of agricultural animal waste
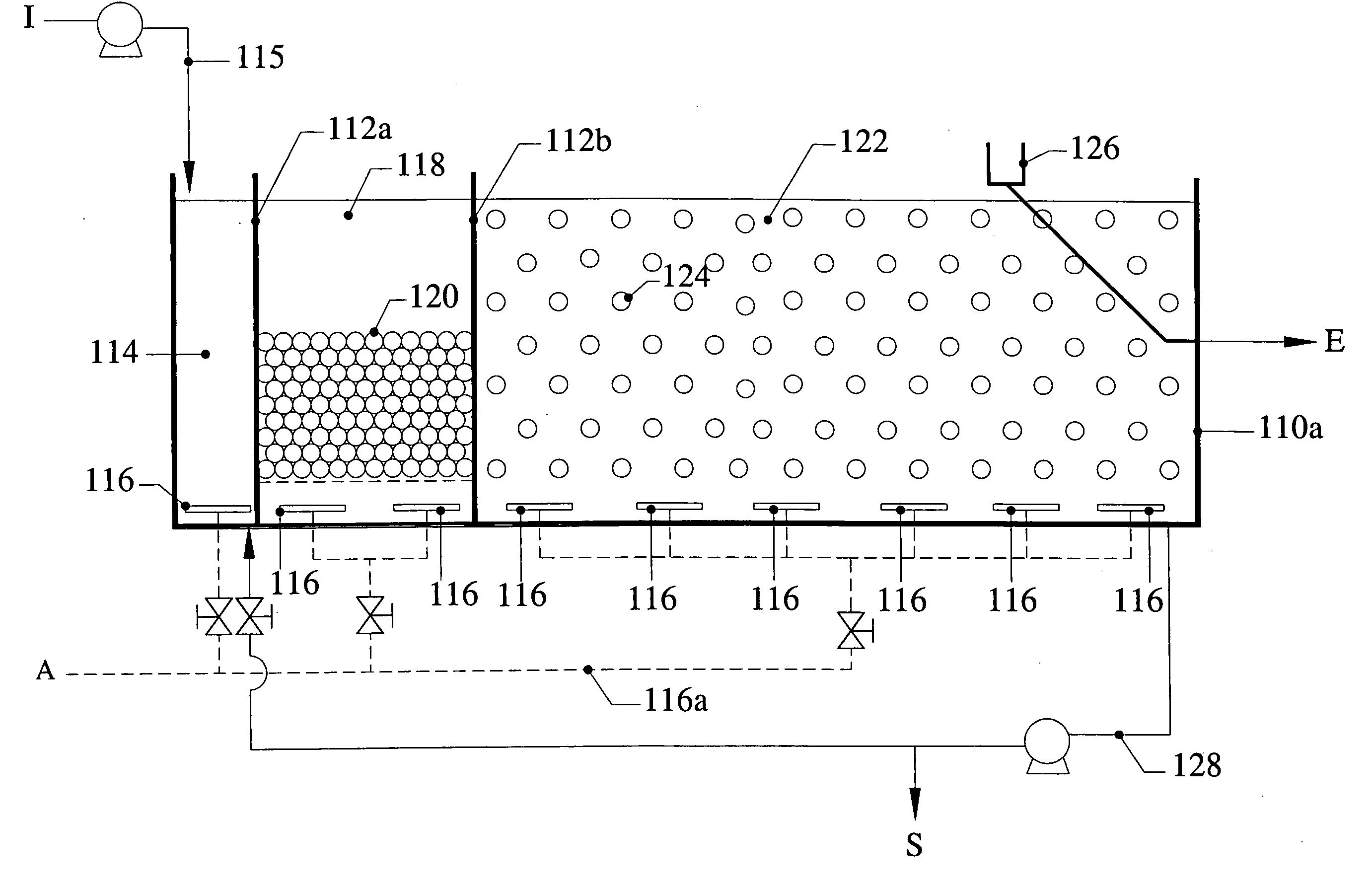
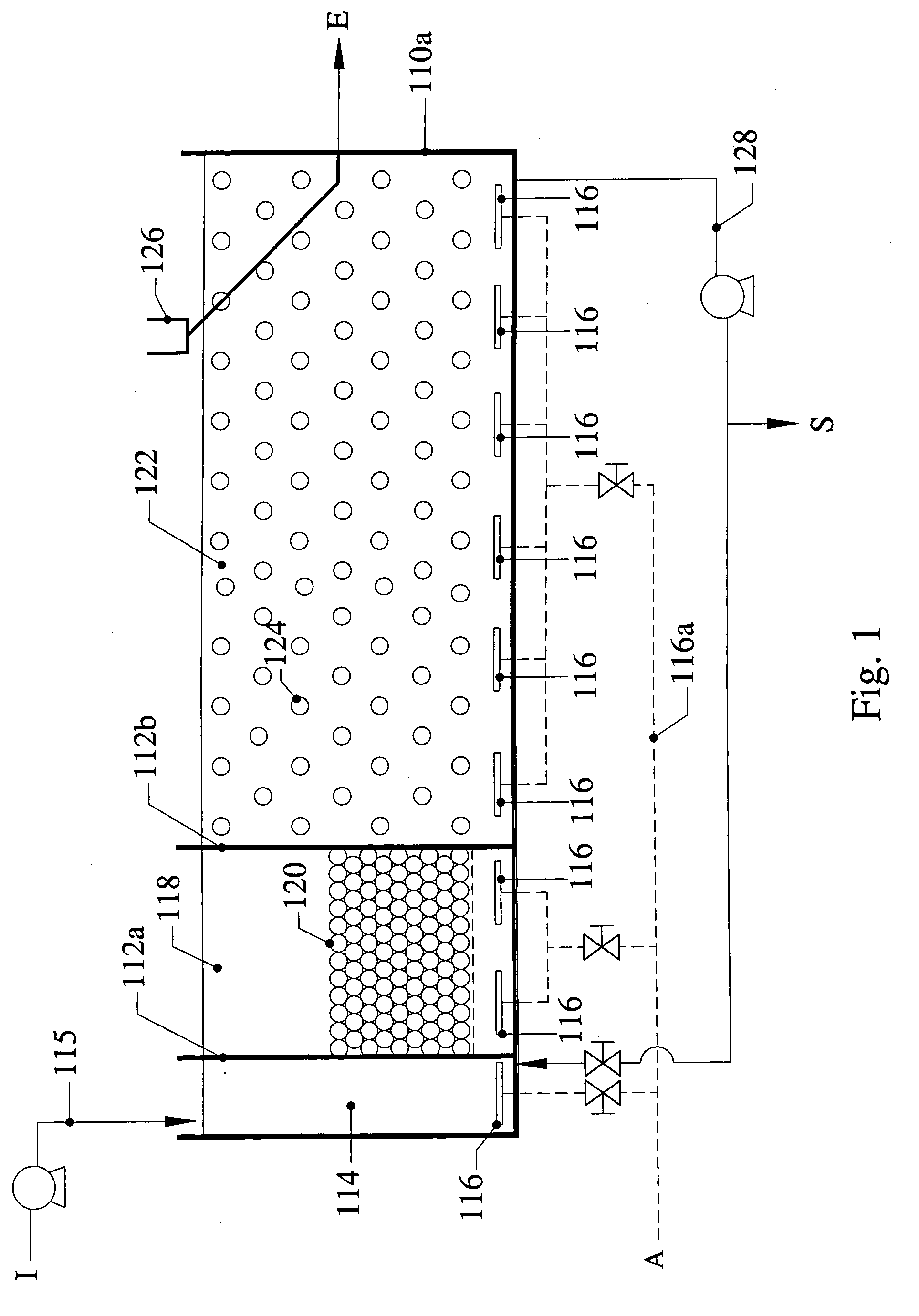
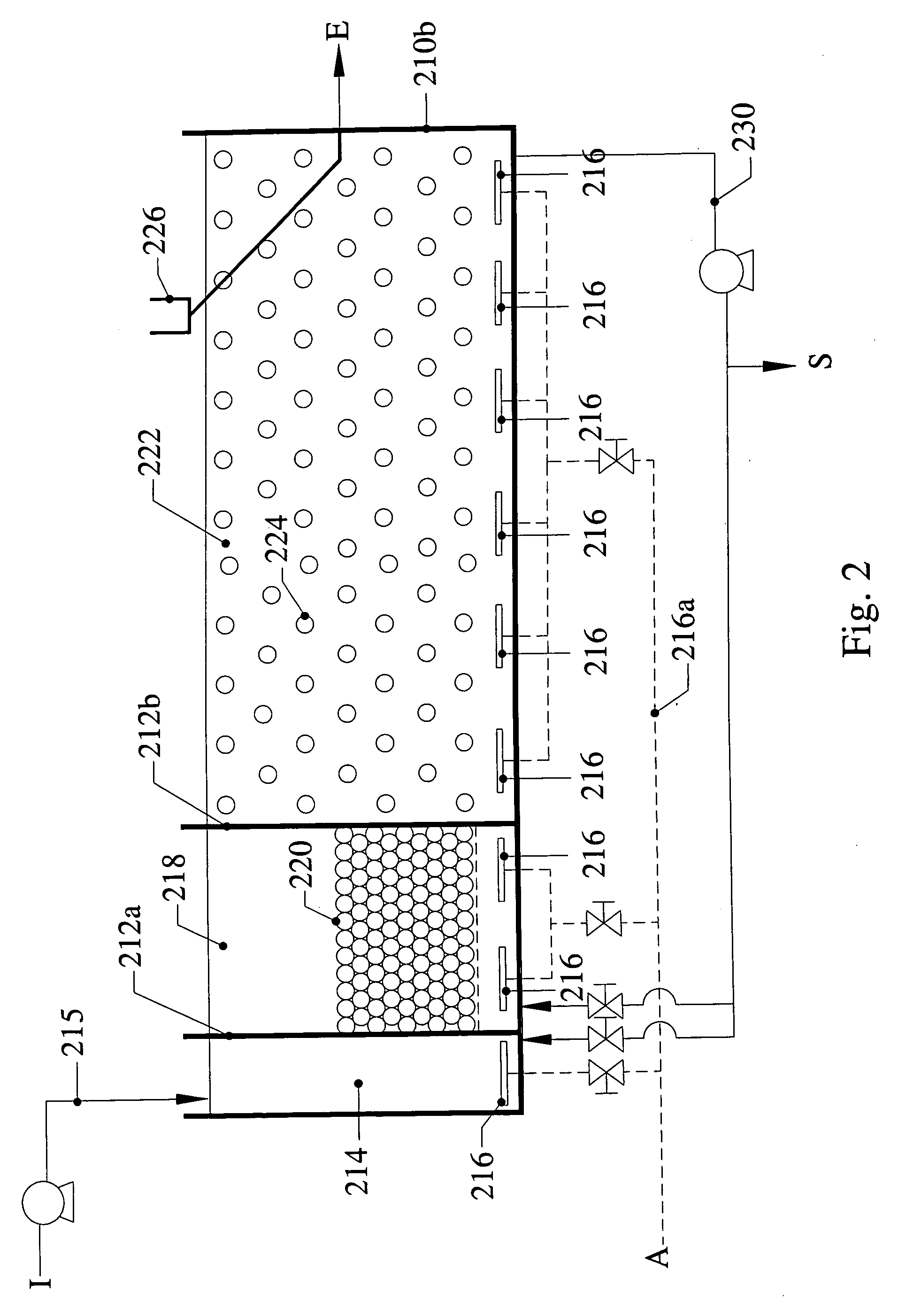
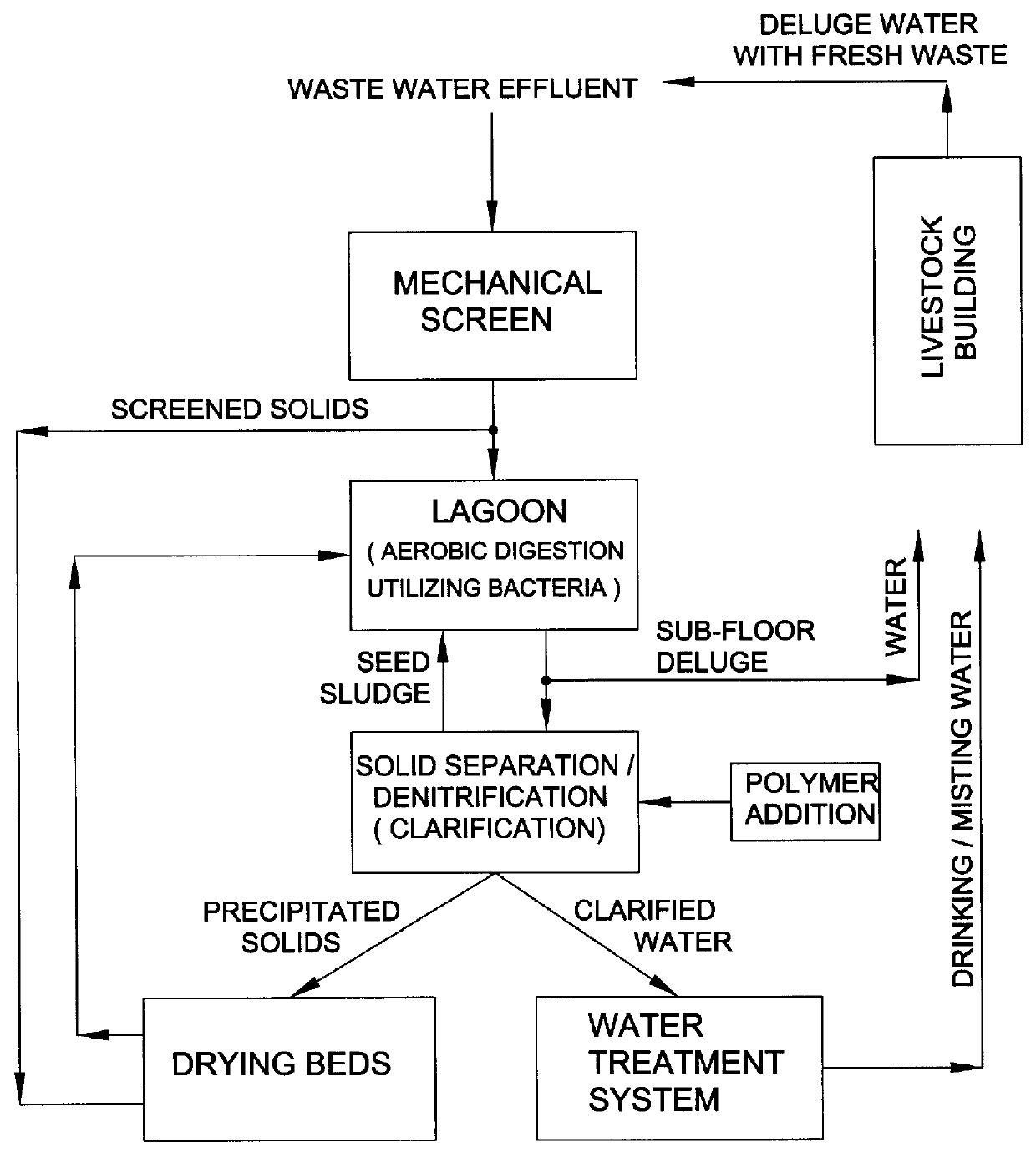
InactiveUS6039874AEffective treatment of wastewaterReducing fertilizer nutrientTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesAbove groundFiltration
An apparatus and method for treating and reusing the wastewater discharged from agricultural animal farms. The apparatus and method of the present invention is designed to be a zero discharge system in which no wastewater will be discharged or spray irrigated. The wastewater effluent is first passed through a mechanical screen were bulk solids are separated and partially de-watered. The screened effluent is then directed to a primary plastic-lined earthen lagoon where it undergoes aerobic digestion utilizing specially selected bacteria. After treatment in the primary lagoon, the wastewater effluent is used to wash the floors of the hog houses or undergoes a purification phase including solids separation / denitrification, filtration and sterilization. The solids separation / denitrification phase (clarification) preferably takes place in an anoxic environment in preferably above-ground tanks where suspended solids removal will occur as well as denitrification for nitrate reduction. The clarification process may be facilitated through use of polymer addition. The majority of solids will be sent to a plurality of drying beds for de-watering and subsequent removal.
Owner:AGRIMOND USA CORP
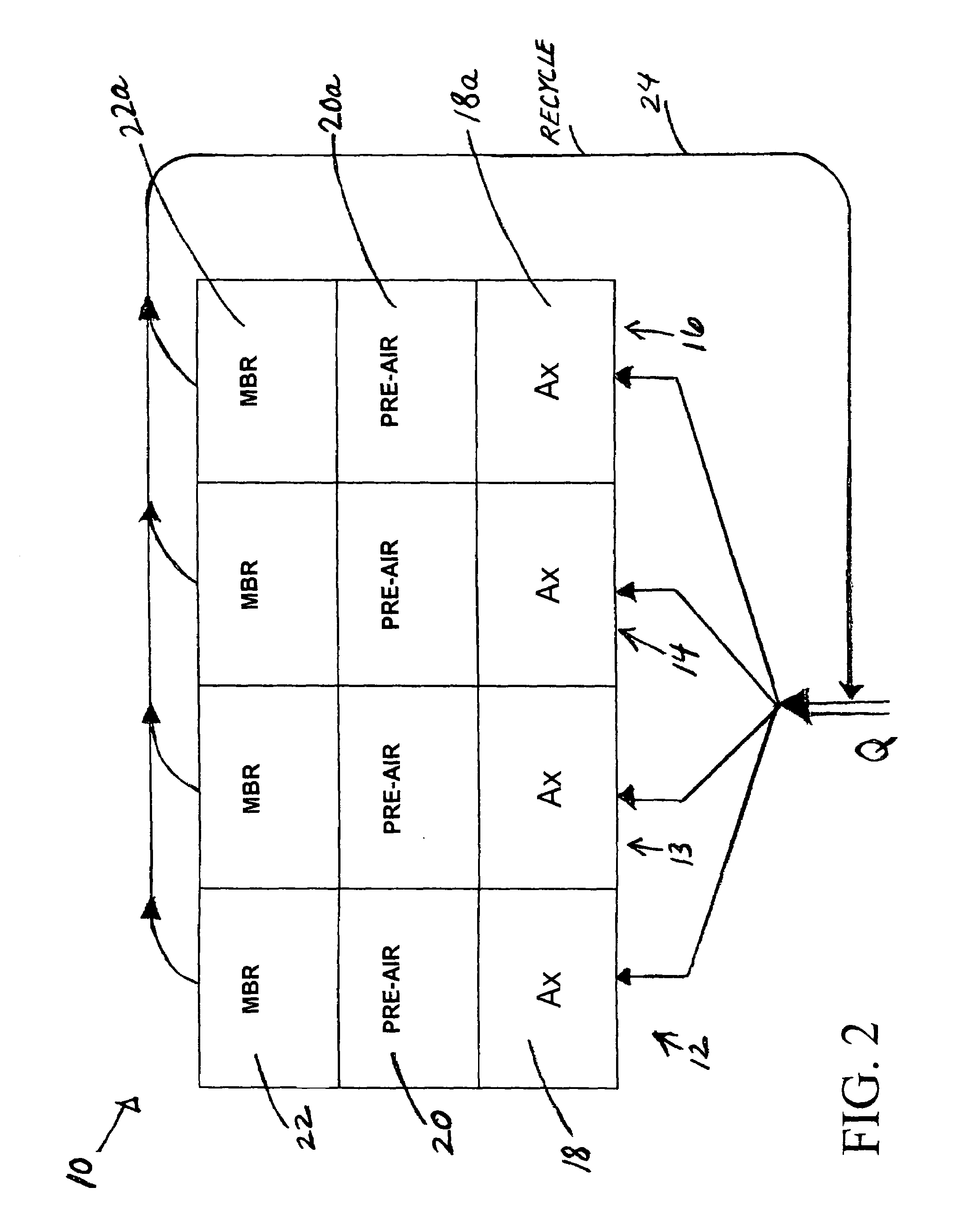
Wastewater treatment system with membrane separators and provision for storm flow conditions
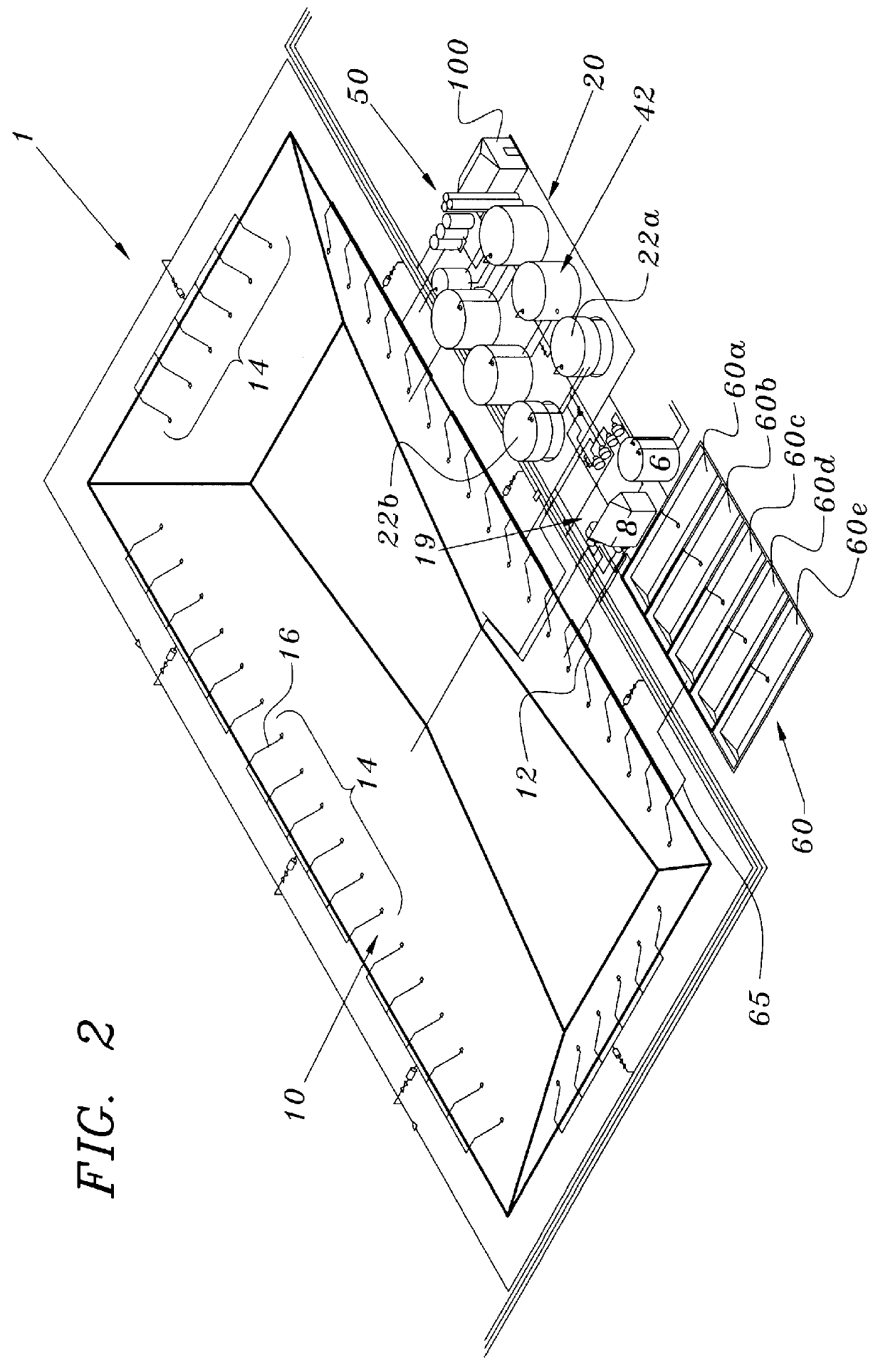
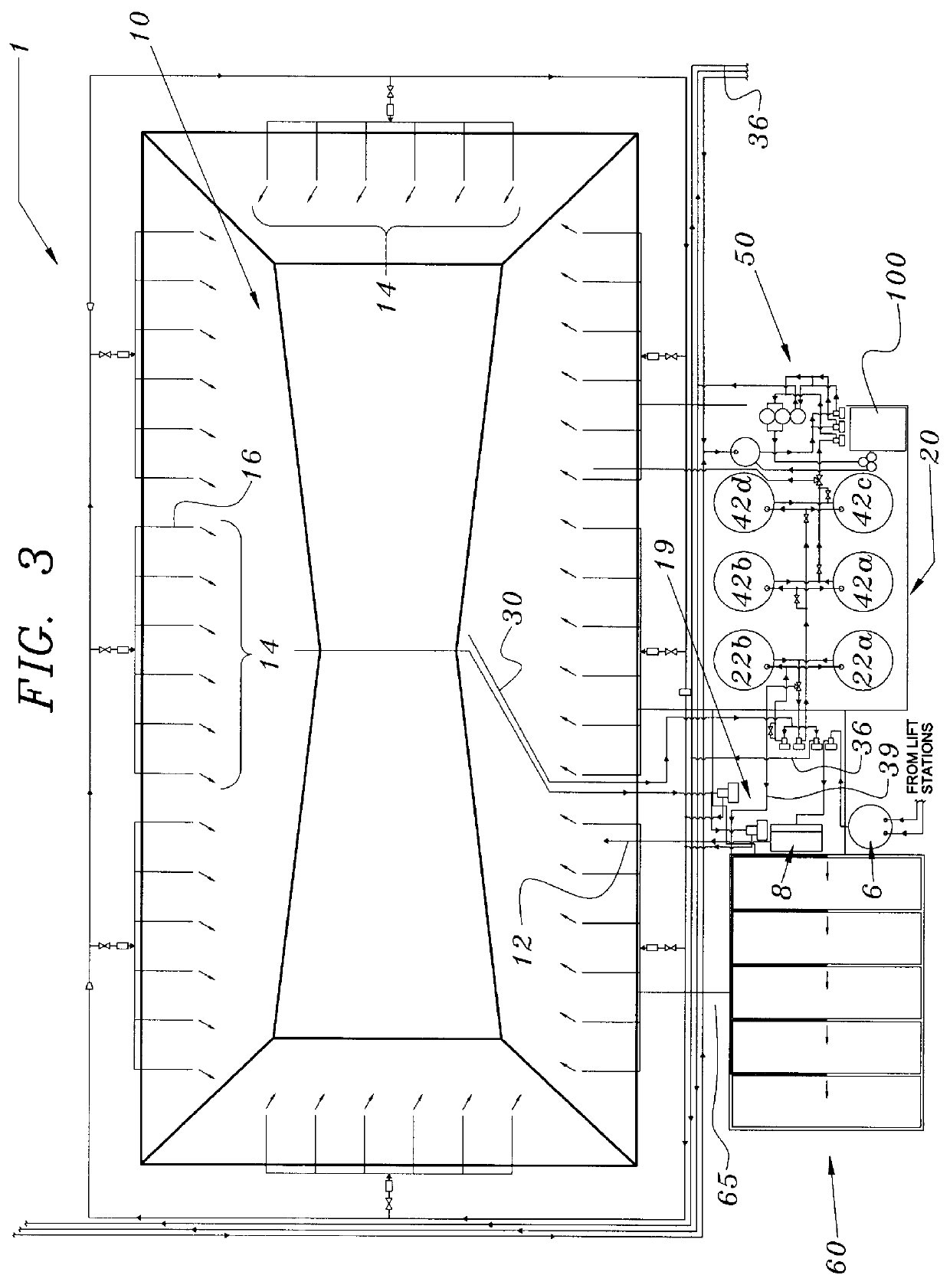
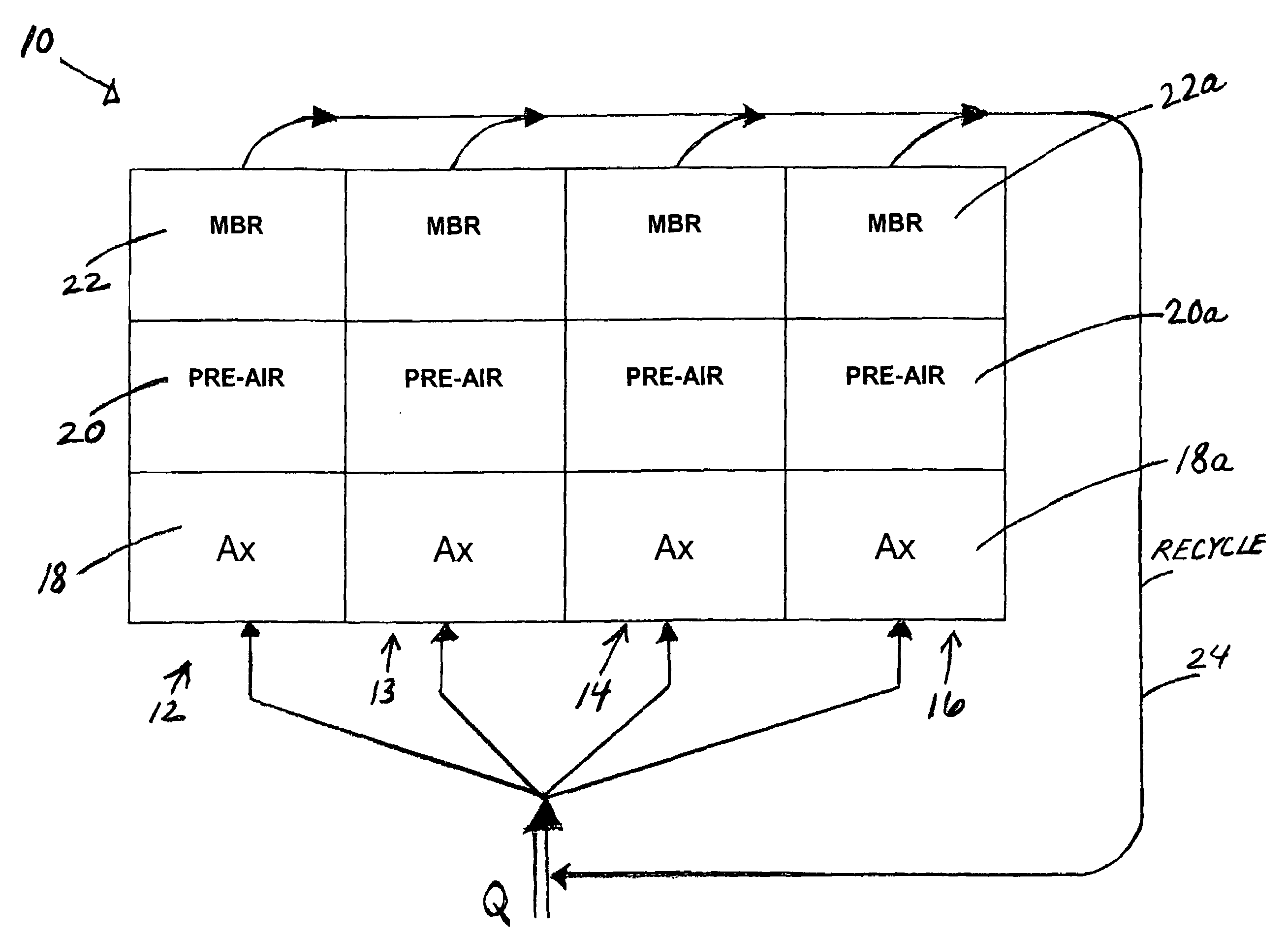
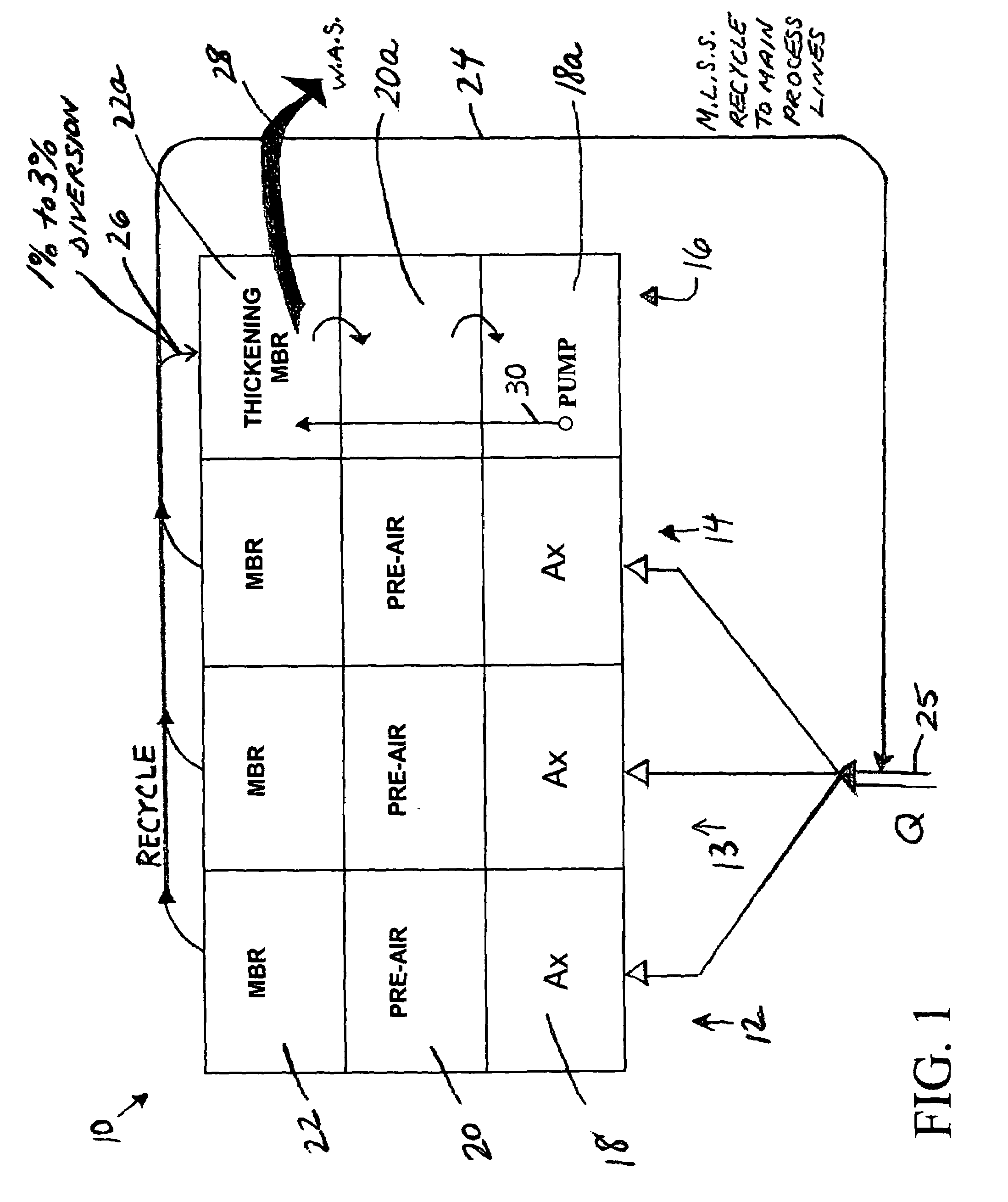
ActiveUS7147777B1Increase biomassTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesStreamflowTreatment system
In a wastewater treatment system and process utilizing membrane bioreactors (MBRs), multiple, parallel series of tanks or stages each include, an MBR stage. Under conditions of normal flow volume into the system, influent passes through several parallel series of stages or process lines, which might be, for example, an anoxic stage, an aeration stage and an MBR stage. From the MBR stages a portion of M.L.S.S. is cycled through one or more thickening MBRs of similar process lines, for further thickening and further processing and digesting of the sludge, while a majority portion of the M.L.S.S. is recycled back into the main process lines. During peak flow conditions, such as storm conditions in a combined storm water / wastewater system, all of the series of stages with their thickening MBRs are operated in parallel to accept the peak flow, which is more than twice normal flow. M.L.S.S. is recycled from all MBR stages to the upstream end of each of all the parallel process lines, mixing with influent wastewater, and the last one or several process lines no longer act to digest the sludge. Another advantage is that with the thickened sludge in the last process line of basins, which ordinally act to digest the sludge, there is always sufficient biomass in the system to handle peak flow, the biomass being available if needed for a sudden heavy flow or an event that might bring a toxic condition into the main basins.
Owner:OVIVO INC
Zero-discharge treatment method of salt-containing organic wastewater
InactiveCN105439395AEasy to handleEfficient reuseTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationEvaporationOrganic matter
The invention provides a zero-discharge treatment method of salt-containing organic wastewater. The method comprises the following steps that biochemical treatment and filtering treatment are performed on wastewater; then, membrane concentration is performed; pure-water-producing high-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water and optional low-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water are obtained; the high-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water is used for high-grade oxidation treatment; high-grade oxidation produced water is used for regulation treatment to obtain high-grade oxidation outlet water; the obtained high-grade oxidation outlet water is subjected to evaporation treatment; or the obtained high-grade oxidation outlet water and the low-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water are mixed under the condition that the low-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water exists in the step, and then, the evaporation treatment is carried out; external discharge concentration liquid of an evaporator and / or high-salt-content high-organic-matter-content wastewater discharged during the tank brushing of the evaporator are conveyed back into a high-grade oxidation treatment unit; after the liquid is mixed with the high-organic-matter-content membrane concentration concentrated water, the high-grade oxidation treatment is carried out. The wastewater treatment method is stable and reliable; the long-period and stable operation of an evaporation system can be ensured; the zero discharge of the industrial wastewater is realized.
Owner:DATANG INT CHEM TECH RESINST
Integrated biofuel production system
InactiveUS8153850B2Improve efficiencyIncrease energy densityGas production bioreactorsWaste based fuelThermal energySystem integration
According to an embodiment, a biomass conversion subsystem produces methane and / or alcohol and residual biomass. A pyrolysis or a gasification subsystem is used to produce thermal energy and / or process gasses. The thermal energy may be stored thermal energy in the form of a pyrolysis oil. A fuel conversion subsystem produces liquid hydrocarbon fuels from the methane and / or alcohol using thermal energy and / or process gasses produced by the gasification or pyrolysis subsystem. Because the biomass production system integrates the residual products from biomass conversion and the residual thermal energy from pyrolysis or gasification, the overall efficiency of the integrated biomass production system is greatly enhanced.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Methods and apparatus for biological treatment of waste waters
InactiveUS20050115880A1Liquid degasificationTreatment using aerobic processesIndustrial effluentPasteurization
In a vertical shaft bioreactor, improved devices and methods are provided for enhanced secondary and / or tertiary treatment of wastewater, including residential, municipal and industrial wastewater. The devices and methods of the invention are useful for enhanced secondary wastewater treatment, including BOD and TSS removal. Tertiary treatment can alternately or additionally be achieved in the bioreactor with nitrification of ammonia, with nitrification and denitrification, and with nitrification, denitrification, and chemical phosphorus removal. A vertical shaft bioreactor is also provided which achieves thermophilic aerobic digestion and pasteurization of sewage sludges, optionally to produce class A biosolids.
Owner:VOST ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
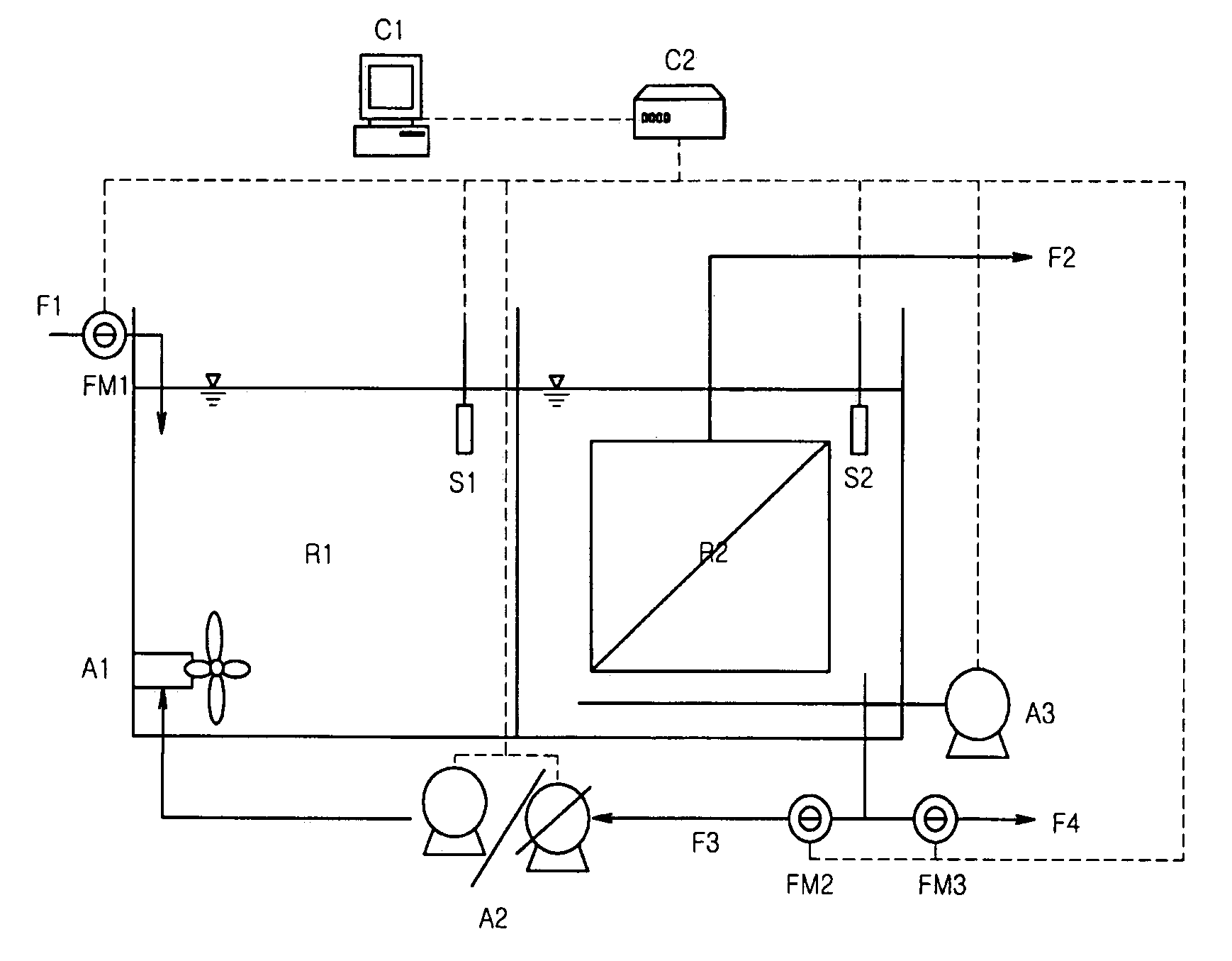
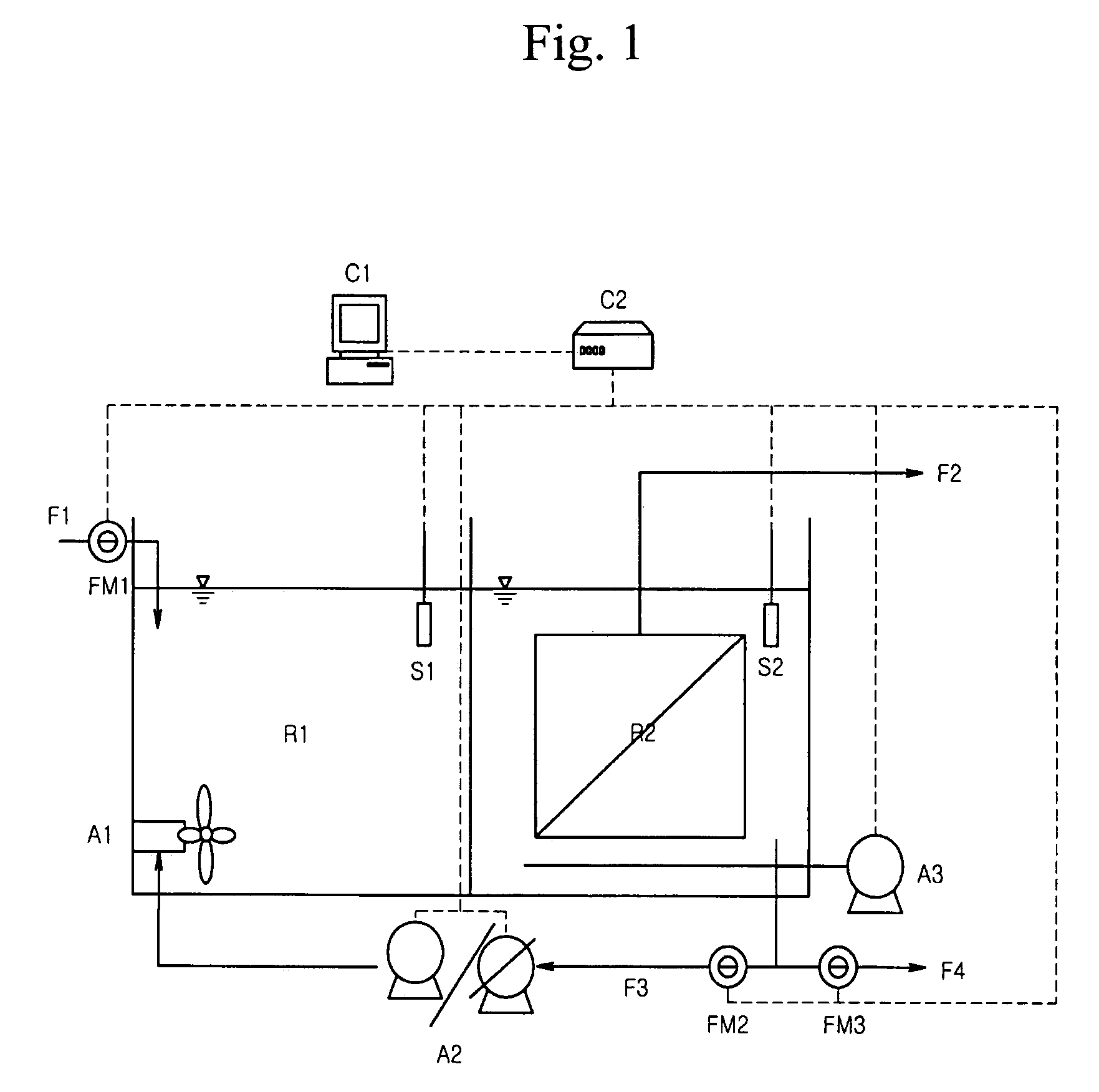
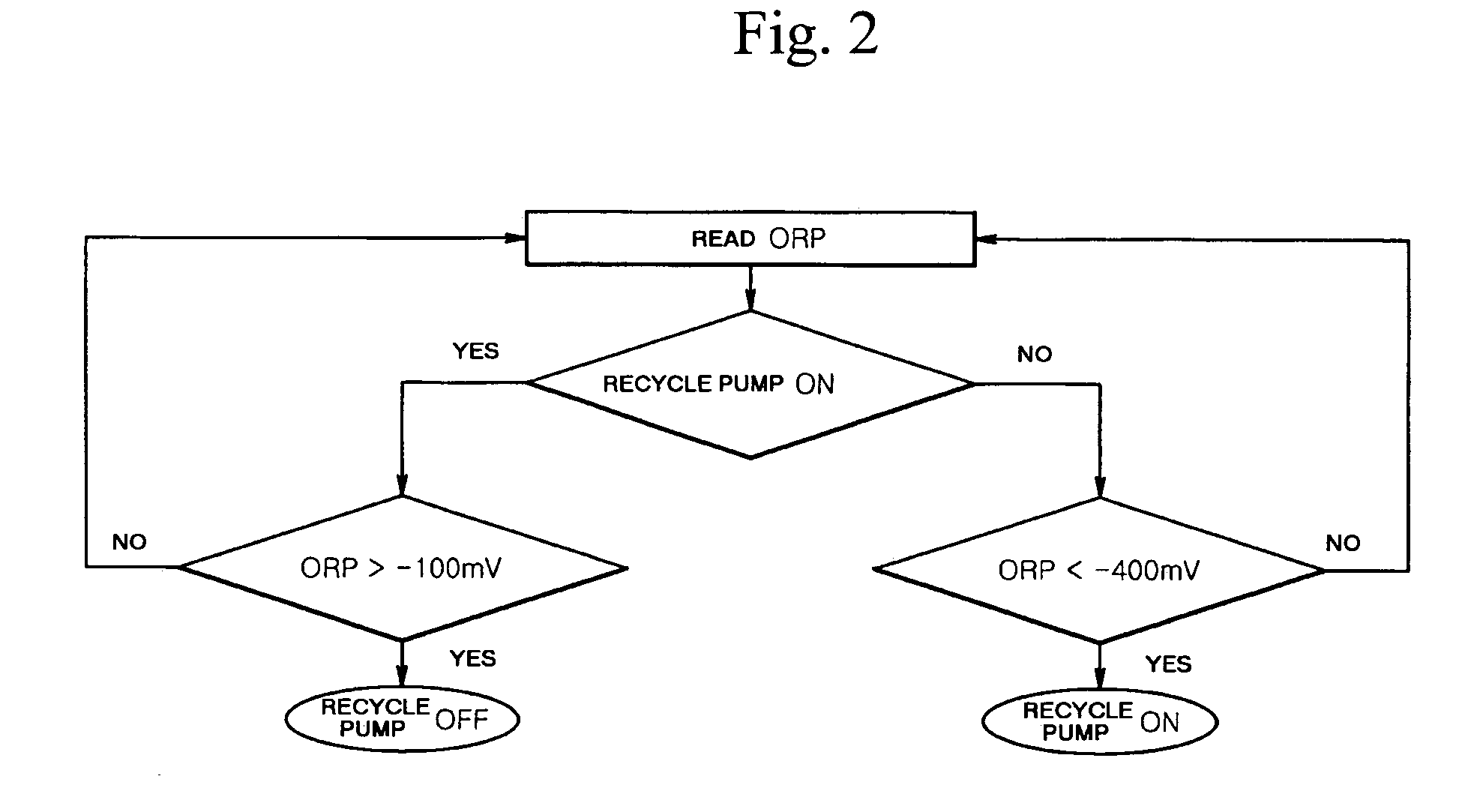
Membrane coupled activated sludge method and apparatus operating anoxic/anaerobic process alternately for removal of nitrogen and phosphorous
ActiveUS7314563B2Quality improvementSimple processTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsActivated sludgeNitrogen
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Popular searches
Water/sewage treatment by neutralisation Water/sewage treatment by flotation Energy based wastewater treatment Liquid hydrocarbon mixture production Ethylene production Water/sewage treatment by substance addition Bio-feedstock Runoff/storm water treatment Incinerator apparatus Combined combustion mitigation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com