Patents
Literature
880 results about "Bacterial growth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial growth is the asexual reproduction, or cell division, of a bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing no event occurs, the resulting daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. Hence, bacterial growth occurs. Both daughter cells from the division do not necessarily survive. However, if the number surviving exceeds unity on average, the bacterial population undergoes exponential growth. The measurement of an exponential bacterial growth curve in batch culture was traditionally a part of the training of all microbiologists; the basic means requires bacterial enumeration (cell counting) by direct and individual (microscopic, flow cytometry), direct and bulk (biomass), indirect and individual (colony counting), or indirect and bulk (most probable number, turbidity, nutrient uptake) methods. Models reconcile theory with the measurements.
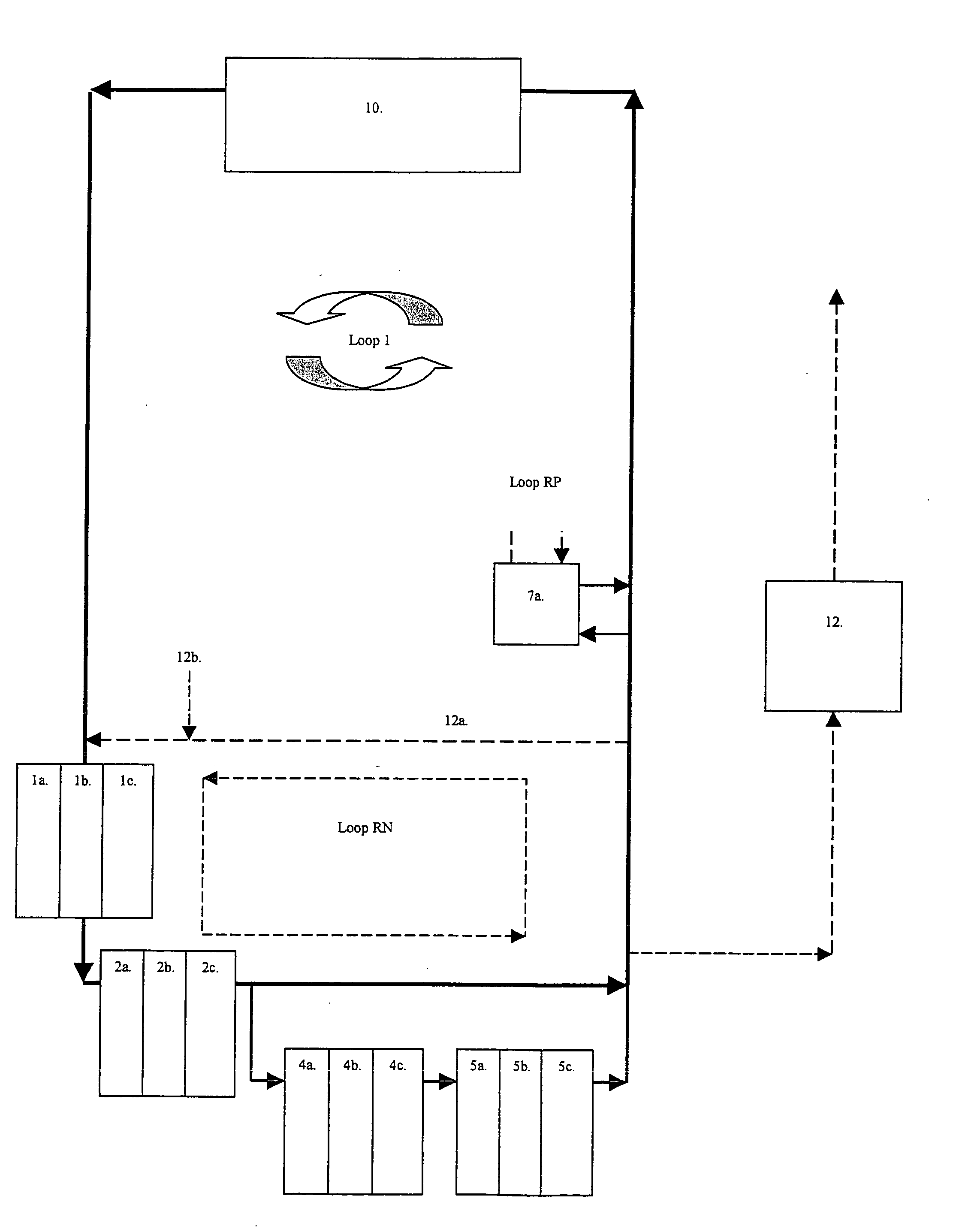
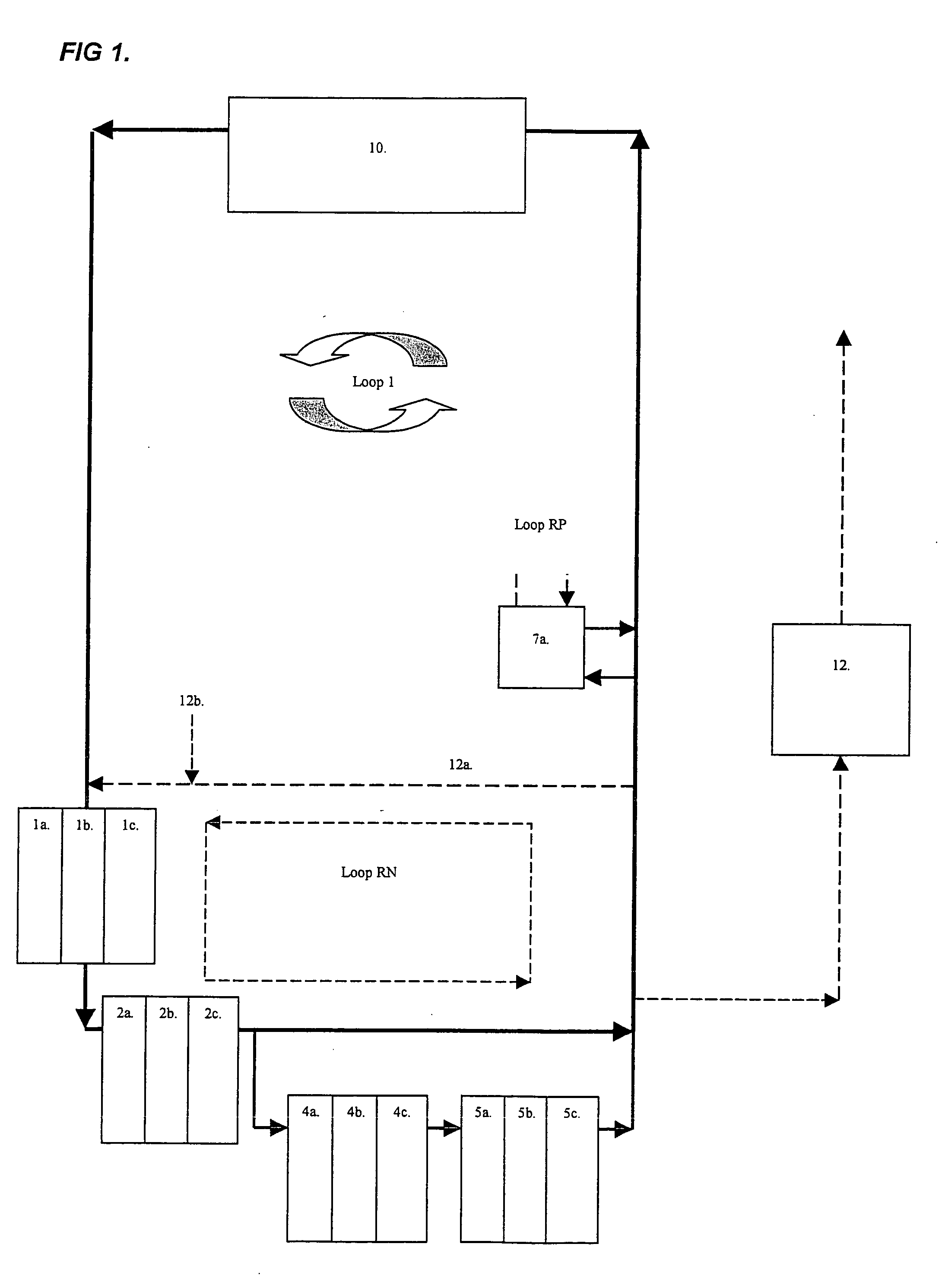
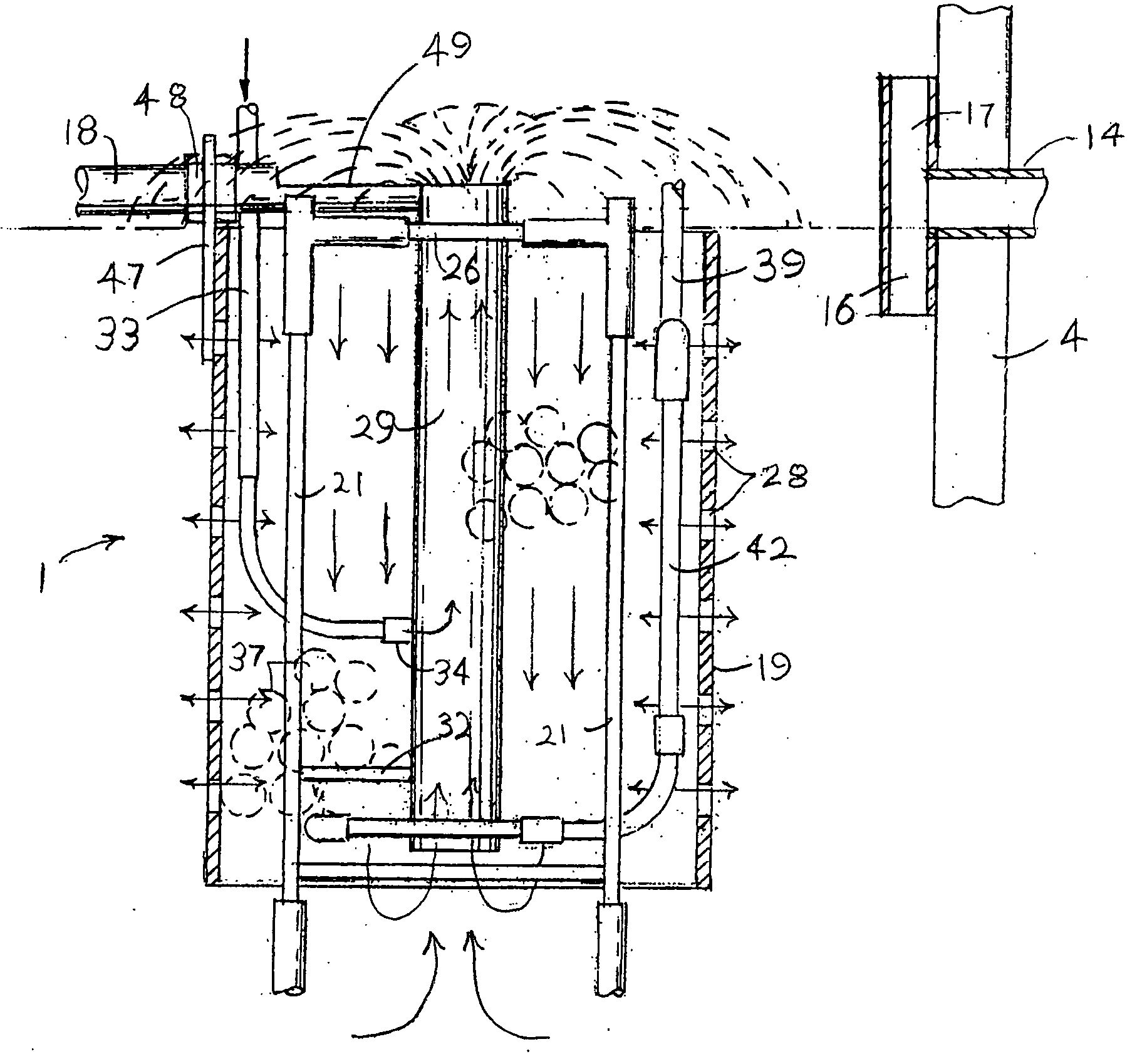
Integrated closed loop system for industrial water purification
InactiveUS7001519B2Improve purification efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic matterIndustrial water
The present invention relates to an integrated closed loop system for aquaculture in at least one culturing tank and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic material, nitrogen and phosphorous, comprising: an integrated, partially or wholly closed loop system for waste water treatment, where the water contains nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances, comprising at least one production unit of such nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorous from the said water at continuous flow, comprising: a) at least one suspended carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under anoxic conditions to cause anaerobic denitrification, with one or several compartments, preceding b) at least one suspended-carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under oxic conditions to cause aerobic nitrification, c) the denitrification taking place after the production unit, and d) the nitrification taking place prior to the production unit in a by-pass mode as part of the continuous flow.
Owner:GREENFISH
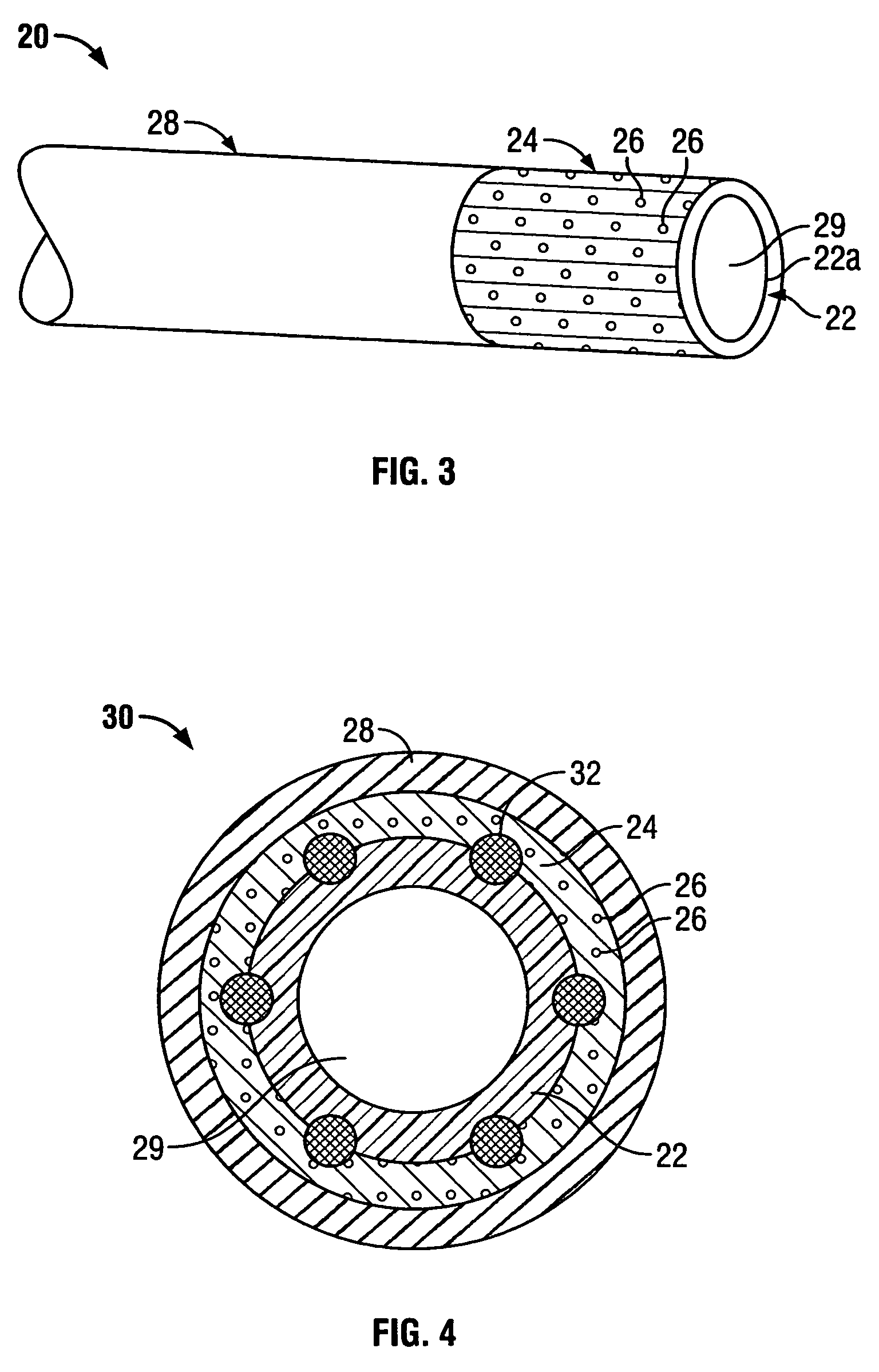
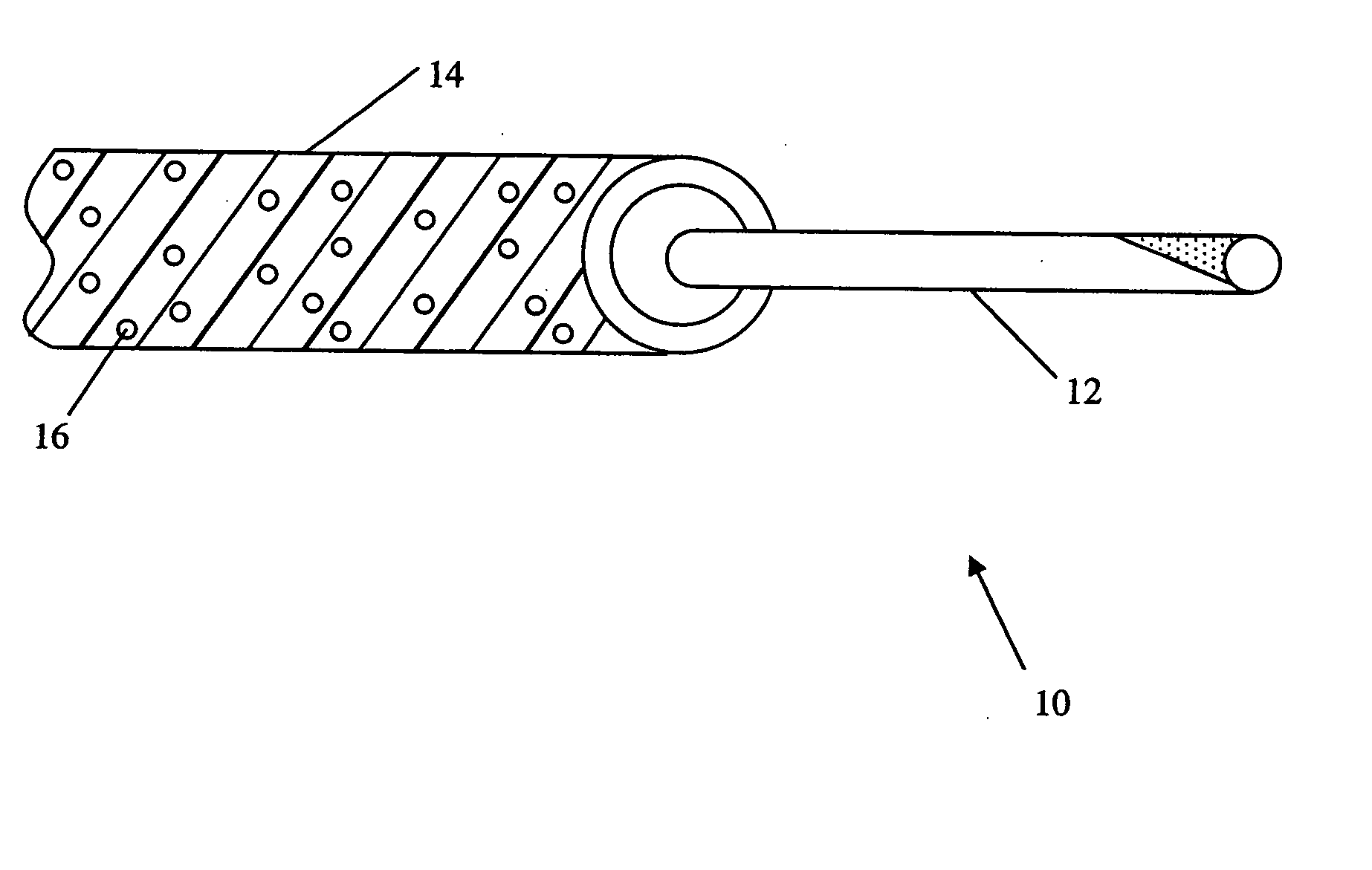
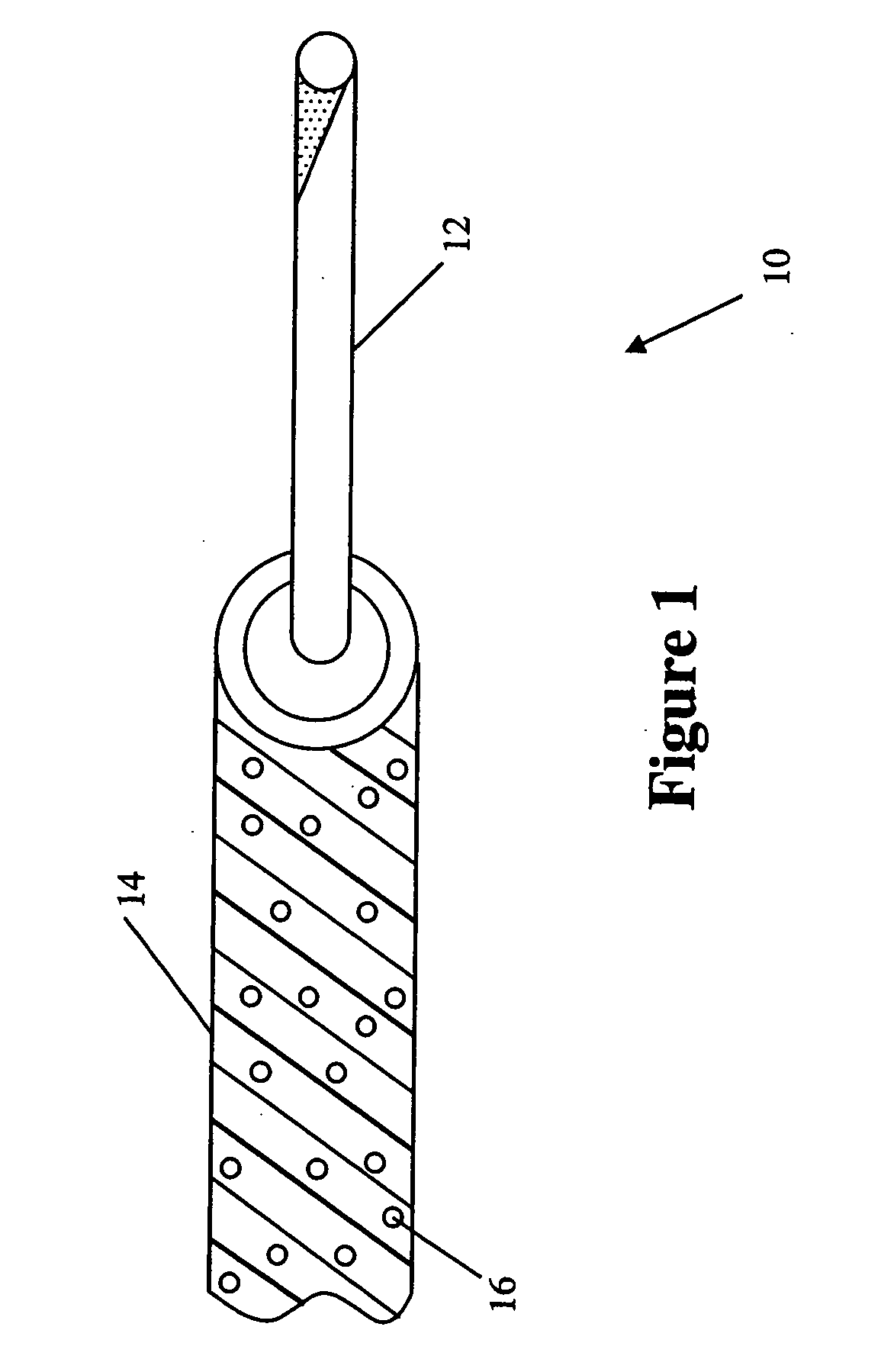
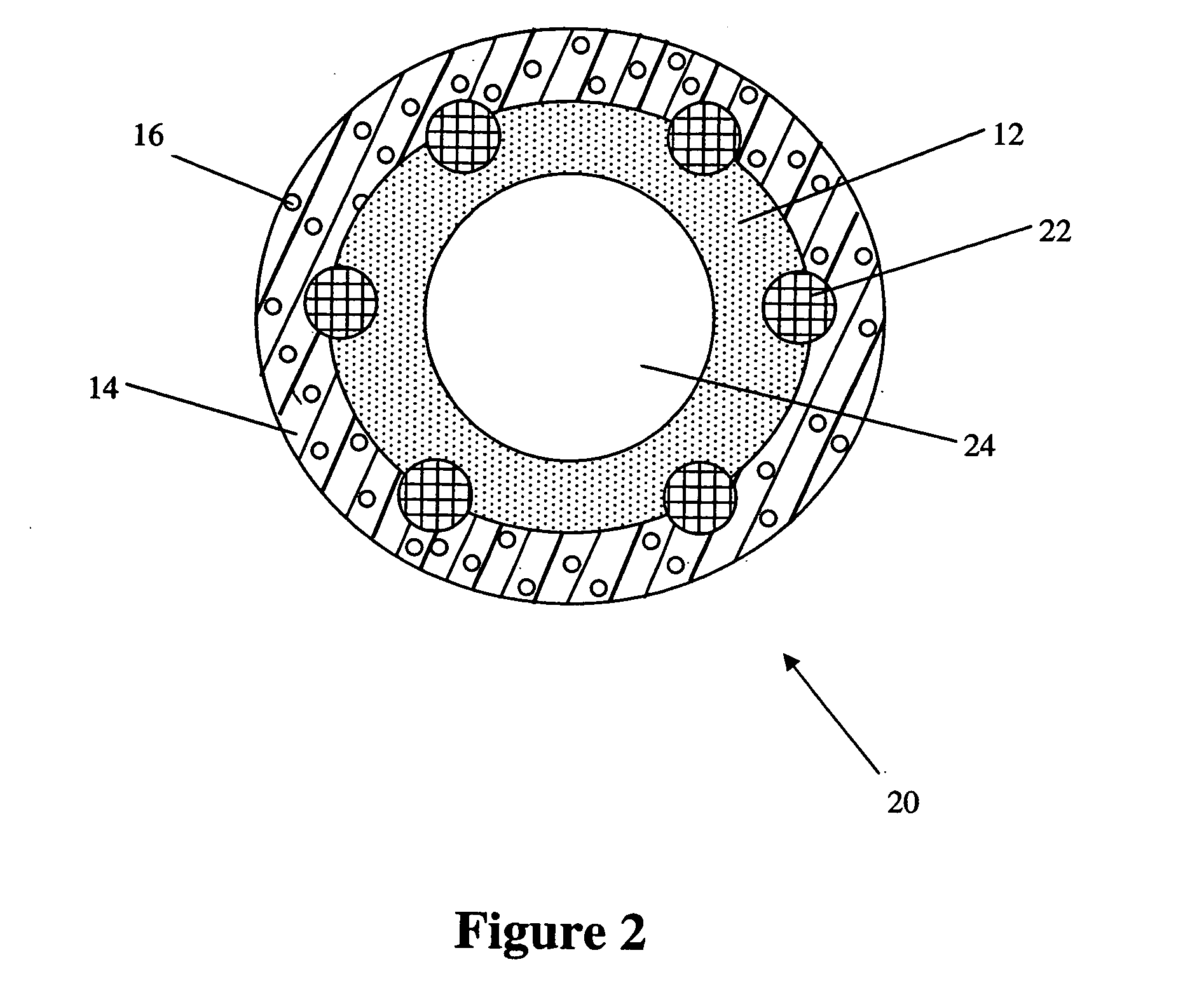
Composite vascular graft including bioactive agent coating and biodegradable sheath
A composite vascular graft incorporates bioactive agents to deliver therapeutic materials and / or inhibit or reduce bacterial growth during and following the introduction of the graft to the implantation site in a vascular system. A composite vascular graft includes a porous tubular graft member. One or more biodegradable, bioactive agent coating layers are disposed over the graft member, the coating layer including at least one bioactive agent. A biodegradable sheath is disposed over the coating layer. The sheath has a rigidity greater than the flexible tubular graft member and is biodegradable to expose the coating layer so as to re-establish the flexibility of the tubular graft member.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
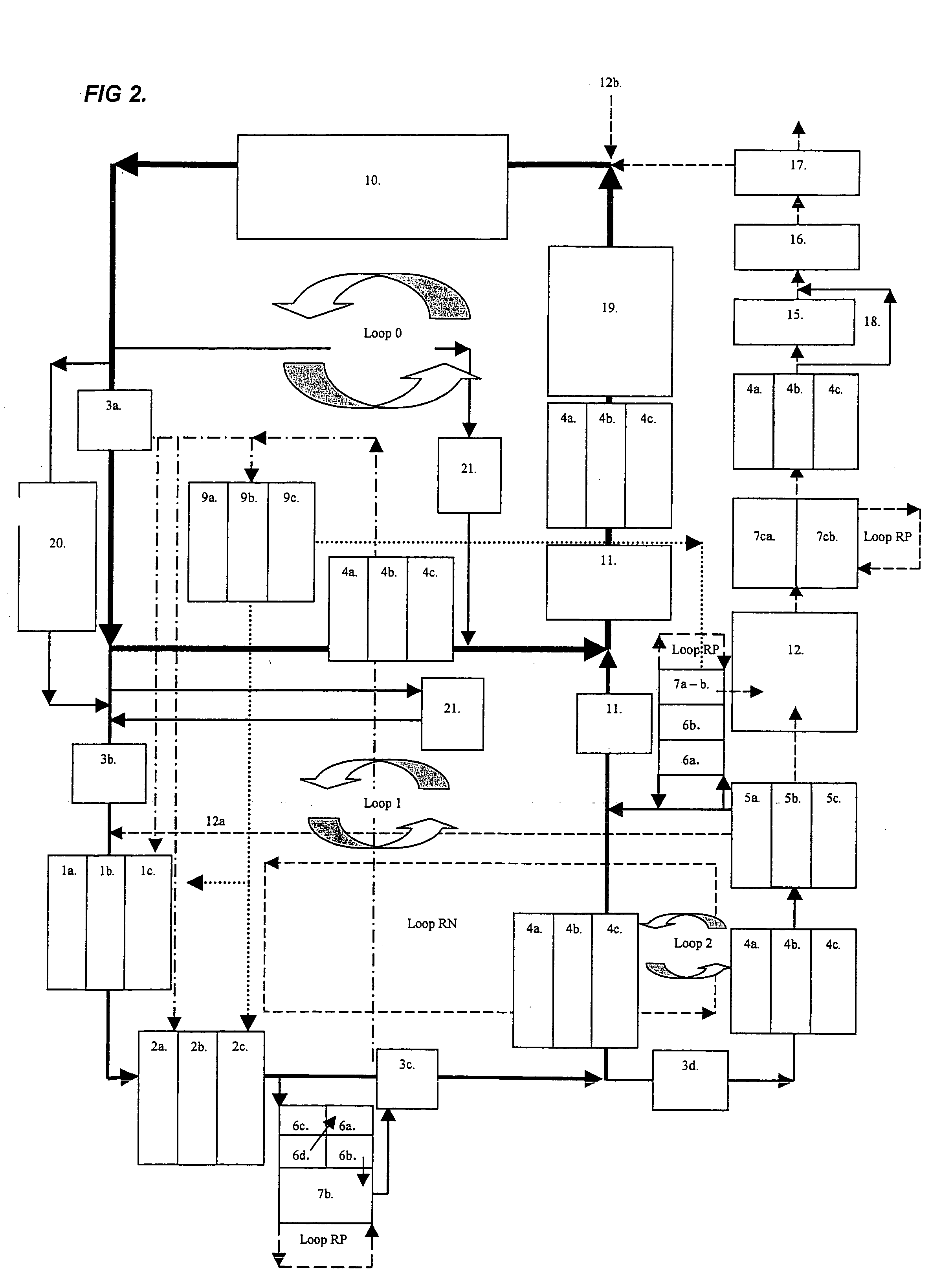
Integrated closed loop system for industrial water purification
InactiveUS20050061737A1Small surface areaIncreasing biofilm thicknessTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic matterIndustrial water
The present invention relates to an integrated closed loop system for aquaculture in at least one culturing tank and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic material, nitrogen and phosphorous, comprising: an integrated, partially or wholly closed loop system for waste water treatment, where the water contains nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances, comprising at least one production unit of such nitrogen containing compounds and / or substances and using continuous bioreactor technology for the biological treatment and removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorous from the said water at continuous flow, comprising: a) at least one suspended carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under anoxic conditions to cause anaerobic denitrification, with one or several compartments, preceding b) at least one suspended-carrier bioreactor for bacterial growth under oxic conditions to cause aerobic nitrification, c) the denitrification taking place after the production unit, and d) the nitrification taking place prior to the production unit in a by-pass mode as part of the continuous flow.
Owner:GREENFISH
Biocompatible hemostatic, antiblocking, healing-promoting and surgical wound-closing modified starch material
InactiveCN101485897AMaterials that promote healingPromote repairOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesTissue fluidBandage
The invention relates to a modified starch material for biocompatible hemostasis, biocompatible anti-adhesion, tissue healing promotion, absorbable surgery sealing and tissue adhesion. The invention applies biocompatible modified starch to animal tissues, wherein the modified starch material has the molecular weight of more than 15,000 daltons, and the particle diameter of between 1 and 1,000 mu m. The modified starch hemostatic material has stypticity, reduces hemorrhage, blood oozing and tissue fluid oozing of wounds, maintains relative moistening or drying of wound surfaces or the wounds, inhibits bacterium growth and inflammation reaction, and contributes to locally diminish inflammation of the wounds and relieve pain of patients. Moreover, the modified starch material can wash local parts after operation is over and remove redundant modified starch which does not participate in hemostasis, and can easily remove haemostatic under the condition of debridement treatment after self-help and first-aid treatment of war wounds; and hemostatic materials with a small amount of modified starch can be absorbed by the body, so that the pain of tearing of gauzes and bandages on people is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSAL LIKANG TECH CO LTD
Novel strain of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use
InactiveUS20100143316A1Inhibits pathogenic growthPromote biodegradationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyAmylase
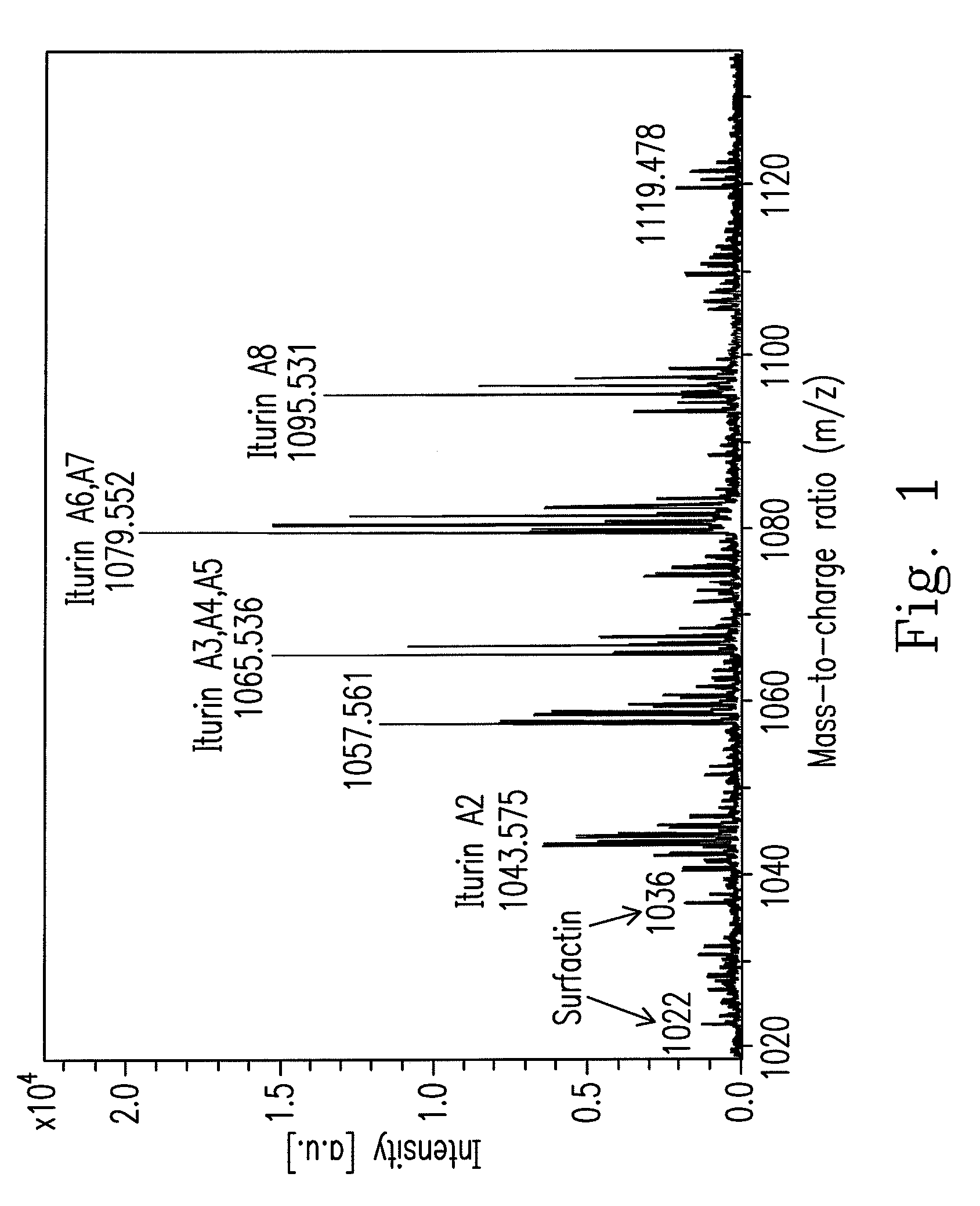
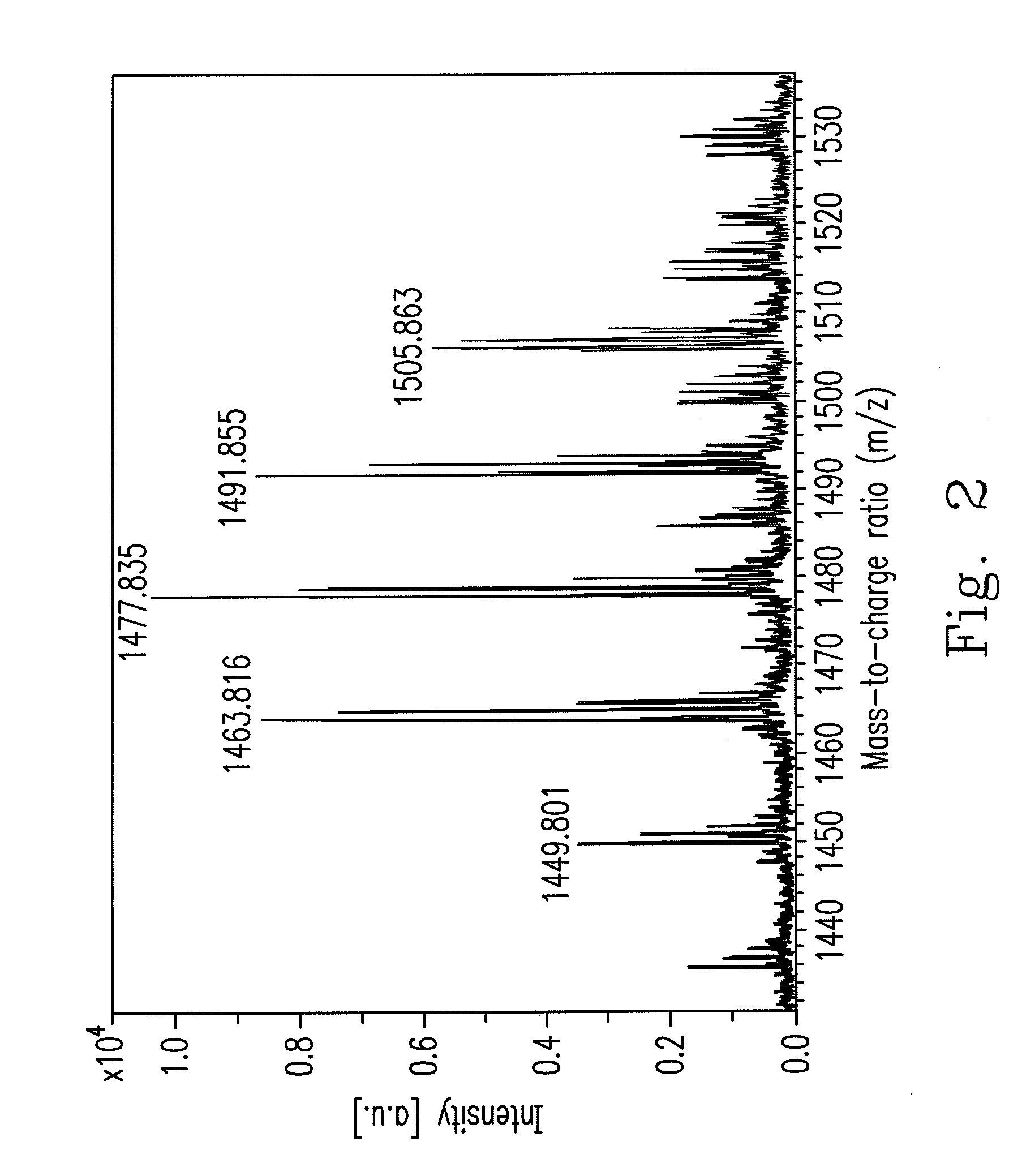
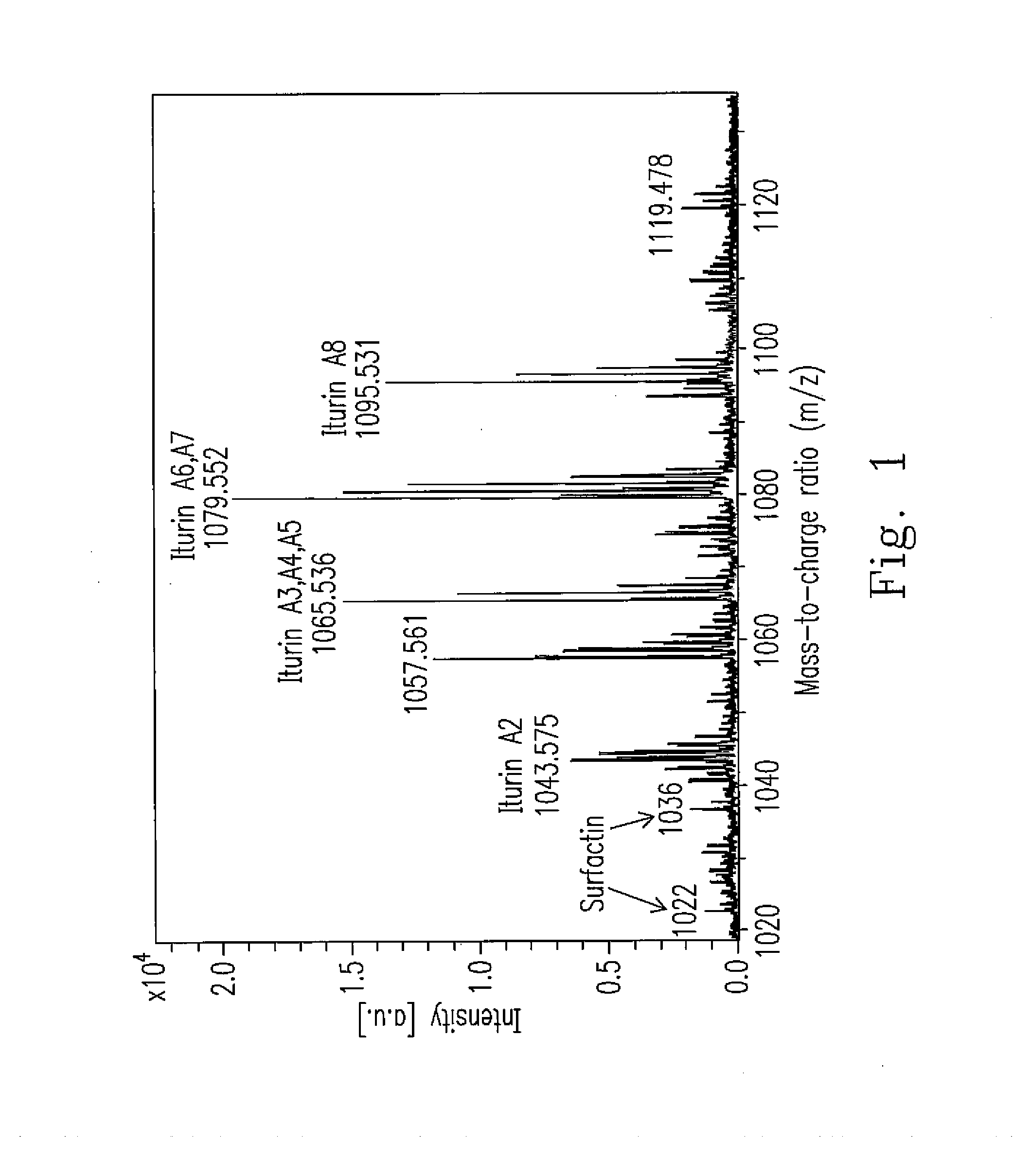
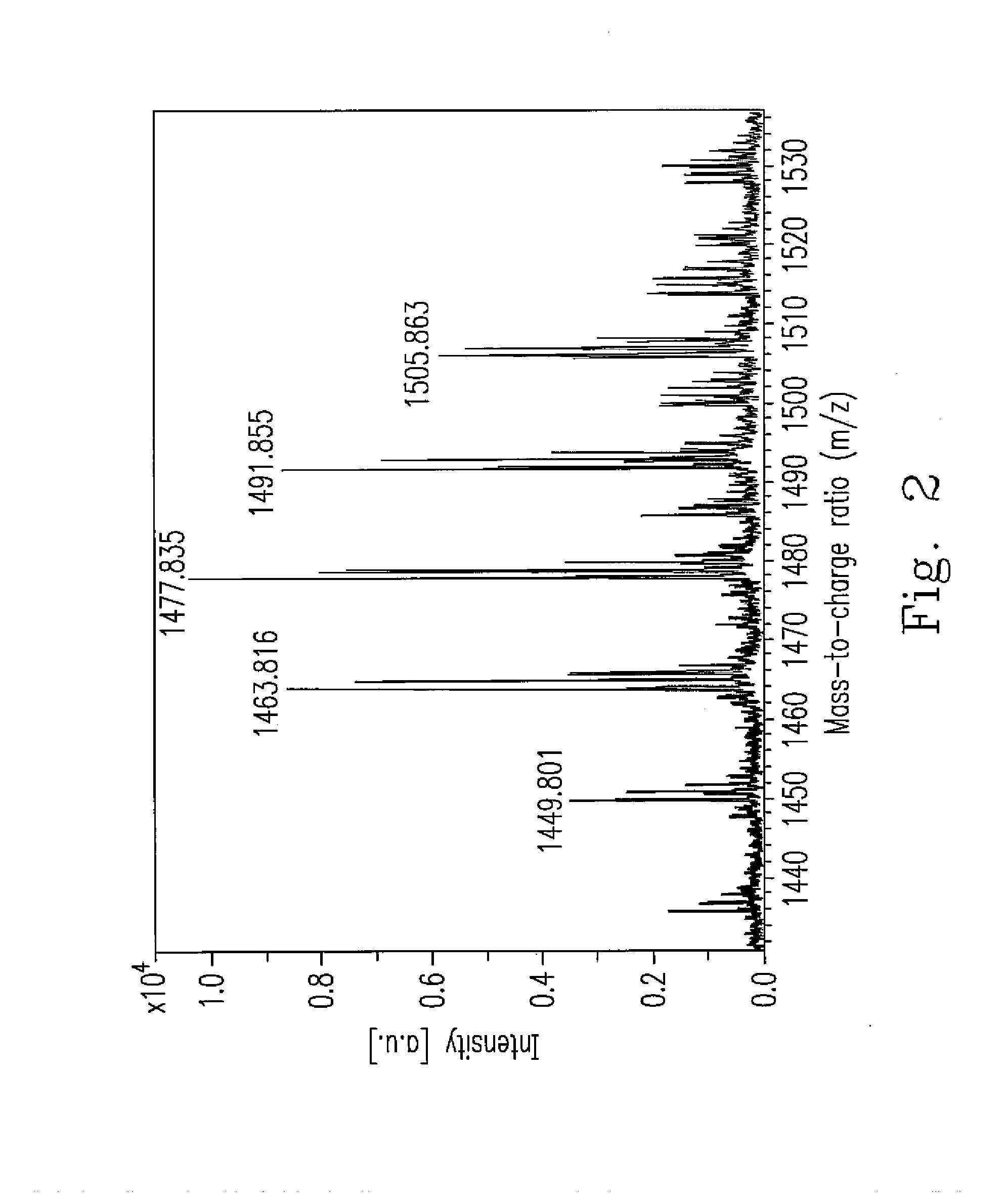
An isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 having an Accession No. of DSM 21836 is provided. This novel strain has unique 16S ribosomal RNA sequenced as SEQ ID NO:1 and produces amylase, protease, cellulase and lipase, fibrinolytic enzyme to show their biodegradation capacities. Further, B. amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 produces the antibiotic substances, such as iturin, fengycin and surfactin, and has antimicrobial capacity for inhibiting the fungal or bacterial growth. In conclusion, the novel strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 and its products can be applied in agriculture, wastewater treatment, food industry and chemical industry.
Owner:AGRI CHEM & TOXIC SUBSTANCES RES INST COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
Mesh Pouches for Implantable Medical Devices
ActiveUS20080132922A1Reduces and prevents implantReduces and prevents and surgery-related complicationElectrotherapyDiagnosticsFiberSide effect
Biodegradable polymer-coated surgical meshes formed into pouches are described for use with cardiac rhythm management devices (CRMs) and other implantable medical devices. Such meshes are formed into a receptacle, e.g., a pouch or other covering, capable of encasing, surrounding and / or holding the cardiac rhythm management device or other implantable medical device for the purpose of securing it in position, inhibiting or reducing bacterial growth, providing pain relief and / or inhibiting scarring or fibrosis on or around the CRM or other implantable medical device. Preferred embodiments include surgical mesh pouches coated with one or more biodegradable polymers that can act as a stiffening agent by coating the filaments or fibers of the mesh to temporarily immobilize the contact points of those filaments or fibers and / or by increasing the stiffness of the mesh by at least 1.1 times its original stiffness. The pouches of the invention can also provide relief from various post-operative complications associated with their implantation, insertion or surgical use, and, optionally, include one or more drugs in the polymer matrix of the coating to provide prophylactic effects and / or alleviate side effects or complications associated with the surgery or implantation of the CRM or other implantable medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Carbonated fortified milk-based beverage and method for suppressing bacterial growth in the beverage
InactiveUS6866877B2Increase attractivenessFast absorptionMilk preparationVitamin food ingredientsAdditive ingredientPasteurization
Dairy or non-diary based fortified carbonated beverage solutions that supply essential nutrients in the human diet. The solution contains per 354 ml, calcium, magnesium and potassium ions in the form of salts and optionally vitamins A, D, C, lutein, zeaxanthin and folic acid in specified amounts to provide dietary supplementation. Sweeteners, stabilizers, flavors and carbonation can also be added to enhance flavor, taste, mouth-feel, ingredient solubilization and product appearance. A method of making the beverages is also described. A method of using carbonation to reduce bacterial counts and reduce degradation of essential nutrients in milk-based beverages with or without pasteurization is also disclosed.
Owner:MAC FARMS
Carbonated fortified milk-based beverage and method for suppressing bacterial growth in the beverage
InactiveUS20030113408A1Great tasteIncrease bodyMilk preparationVitamin food ingredientsAdditive ingredientPasteurization
Dairy or non-diary based fortified carbonated beverage solutions that supply essential nutrients in the human diet. The solution contains per 354 ml, calcium, magnesium and potassium ions in the form of salts and optionally vitamins A, D, C, lutein, zeaxanthin and folic acid in specified amounts to provide dietary supplementation. Sweeteners, stabilizers, flavors and carbonation can also be added to enhance flavor, taste, mouth-feel, ingredient solubilization and product appearance. A method of making the beverages is also described. A method of using carbonation to reduce bacterial counts and reduce degradation of essential nutrients in milk-based beverages with or without pasteurization is also disclosed.
Owner:MAC FARMS
Protonated/acidified nucleic acids and methods of use
The novel discovery that protonated nucleic acids inhibit bacterial growth is reported and methods for the preparation and therapeutic use of nuclease resistant and acid resistant protonated / acidified nucleic acids for administration to animals including man, to treat or prevent a bacterial infection are described.
Owner:LAKEWOOD AMEDEX
Method for reusing ammonia nitrogen containing effluent as circular cooling water
The method of reusing ammonia nitrogen containing effluent as circular cooling water is characterized by the addition of alkali, bicarbonate, carbonate, hydrophosphate, dihydric phosphate or phosphate to increase the scaling factor of water and the cooperation with scale-inhibiting corrosion inhibitor and bactericide to control corrosion, scaling and bacterial growth in the reused effluent. The method of the present invention is suitable for reusing ammonia nitrogen containing effluent as circular cooling water.
Owner:RES INST OF BEIJING YANSHAN PETROCHEM
Food preservation systems
ActiveUS20060172048A1Large capacityIncreased physical sizeContainer/bottle contructionFruits/vegetable preservation using acidsFood safetyFood preservation
The present invention provides a food preservation system that includes a multi-phase bacterial inhibition food pad. The food pad includes absorbent media and / or material to absorb fluids emanating from the packaged food. The absorbent media / material includes one or more bacterial inhibitors that may possess bacteriostatic and / or bactericidal properties. In addition, the food pad may also include an atmosphere modification system capable of modifying an atmosphere in a food package. Optionally, one or more reaction promoters and / or one or more mechanisms to protect the food preservation system may also be included in the food pad. Overall, the food preservation system inhibits bacterial growth, thereby enhancing food preservation and / or food safety.
Owner:NOVIPAX INC
Antimicrobial composition and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20100086576A1Improve efficacyLow toxicityBiocideDead animal preservationBacteroidesBiofilm
An aqueous composition adapted to kill bacteria in both planktonic and biofilm states is lethal toward a wide spectrum of gram positive and gram negative bacteria as well as other microbes. The composition, which is slightly to moderately acidic, includes a significant amount of one or more surfactants and large amounts of osmotically active solutes. The composition can be applied directly to a site of bacterial growth. Even when the bacteria is in biofilm form, the surfactant component(s) begin to kill the bacteria before the macro-molecular matrix is removed or dislodged from the site.
Owner:NEXT SCI IP HLDG PTY LTD
Method for determining deleterious bacterial growth in packaged food utilizing hydrophilic polymers
InactiveUS6149952AMaximize likelihoodMaximize possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementConfectioneryHydrophilic polymersHydrophobic polymer
The present invention relates to a method for determining the presence or absence of contaminating bacteria in a packaged food sample comprising storing food in a package having as a lining a hydrophilic polymeric composition, said composition preferably being permeable to water and at least one gas dissolved in water or water vapor and being selected from the group consisting of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen and ammonia gas and containing an indicator for detecting the presence or abscence of said gas; said indicator being polymerized or dispersed throughout said polymeric composition or coated onto a hydrophobic polymeric composition.
Owner:INDICATOR SYST INT
Sanitary, vented and disposable dispensing assembly for post mix beverage dispenser
InactiveUS7111759B1Prevent and retard bacteria growthUniform consistencySpraying apparatusLiquid flow controllersPreservative freeDiluent
A sanitary, disposable dispensing assembly especially useful in producing a substantially contaminant-free reconstituted mixture of diluent and pure, preservative-free concentrate includes an inner member linearly slidable between open and closed positions in an outer member provided with a concentrate inlet. The dispensing assembly features a vent arrangement for enabling a complete draining of the mixture and preventing bacterial growth. A rib arrangement improves mixing of the combined diluent and concentrate, and prevents dispersion of the mixture when dispensed. The dispensing assembly is utilized in mechanical pump type and non-mechanical pump type applications on a post mix food and beverage dispenser.
Owner:KARMA INC
Method of attaching drug compounds to non-reactive polymer surfaces
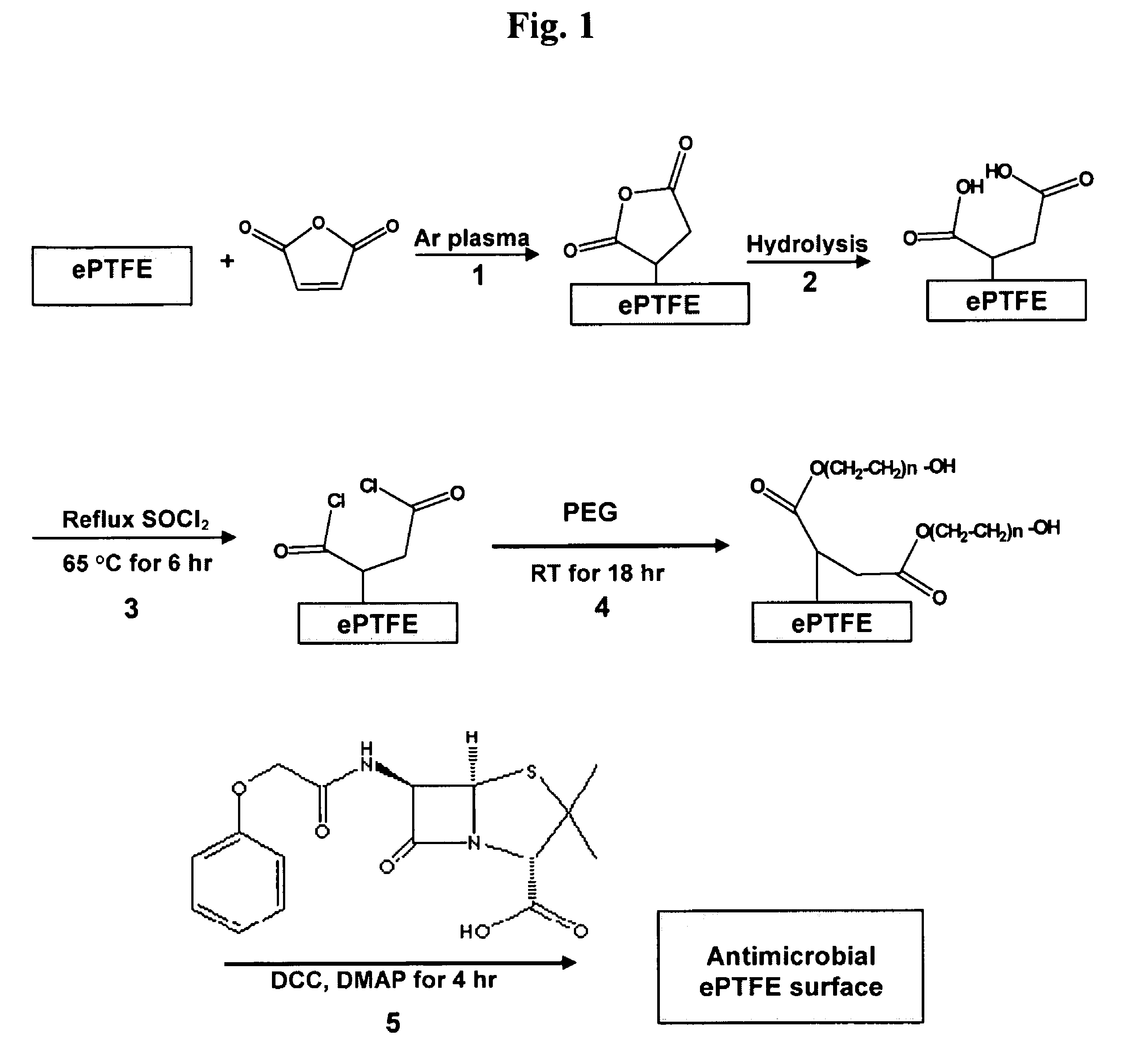
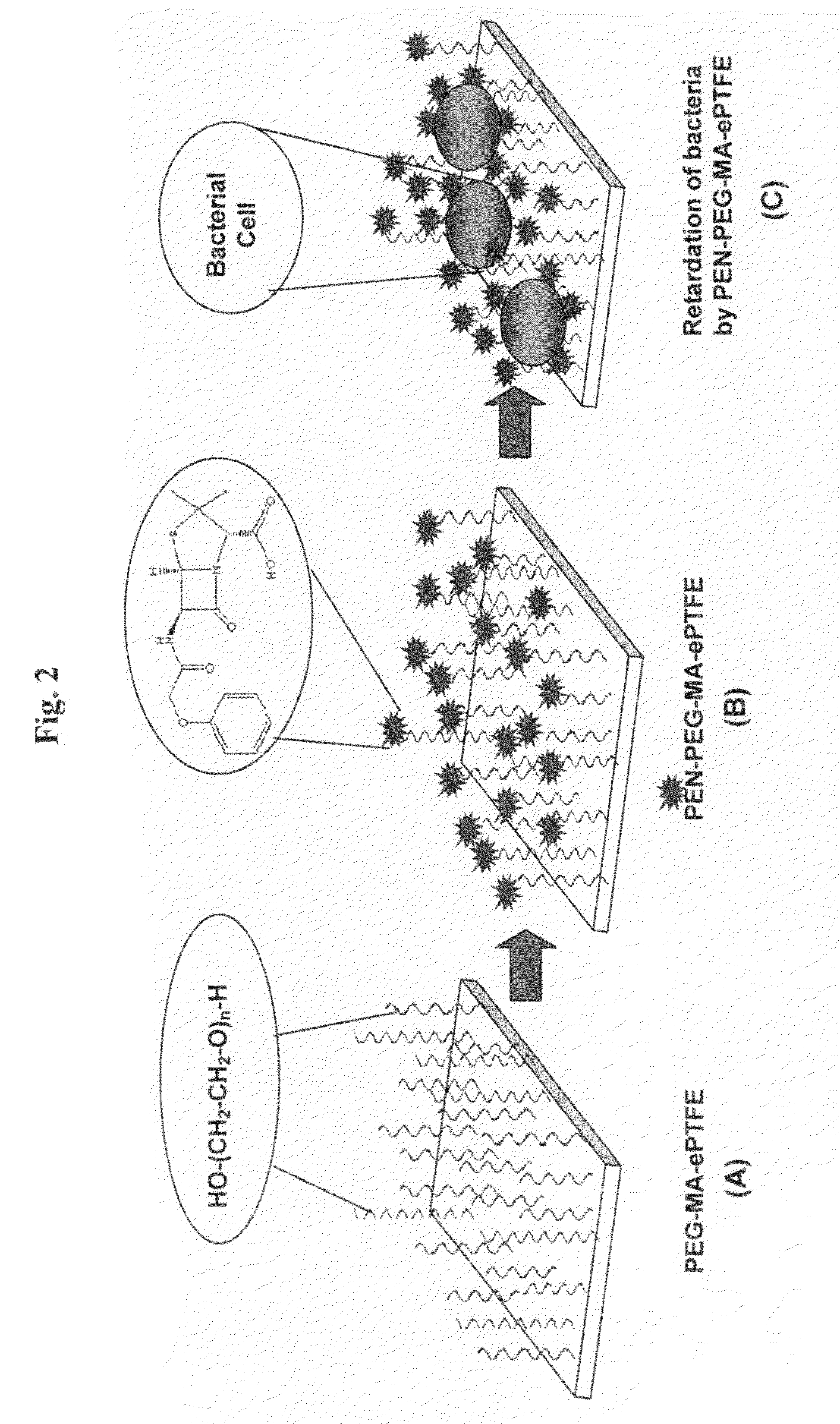
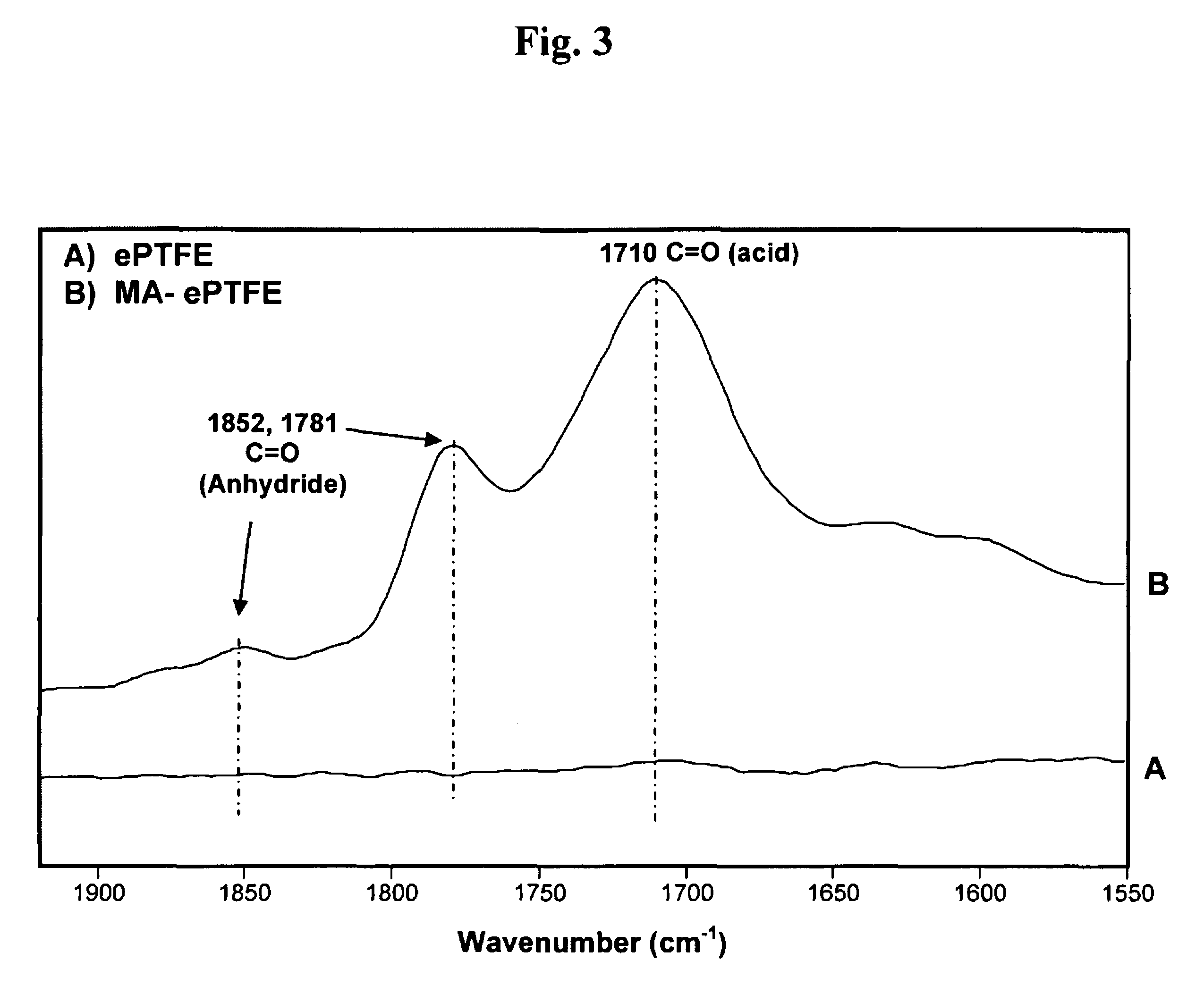
Polymers are disclosed that are chemically modified to retard bacterial growth. Such modified polymers (e.g. ePTFE and polypropylene) are produced by first creating acid groups on the polymer surface through reactions with an anhydride. The acid groups are then linked to polyethylene glycol (PEG) through esterification or other reactions such as amidation. Preferably, at least two different molecular weight PEG species are employed. The antimicrobial surface is completed by linking antibiotics (e.g. β-lactam antibiotics) to the PEG extensions. One preferred embodiment of such a modified polymer is produced using ePTFE, maleic anhydride (MA), and penicillin (PEN) to yield PEN-PEG-MA-ePTFE, which inhibits gram-positive bacteria. The PEG spacer is critical for PEN function in this context, since PEN-ePTFE is ineffective against bacterial growth. Another preferred embodiment incorporates ampicillin (AMP) and a heterobifunctional PEG, HOOC—(CH2—CH2—O)n—NH2, to yield AMP-PEG-MA-ePTFE. This latter example inhibits both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
Owner:SOUTHERN MISSISSIPPI THE UNIV OF
Bacteria resistant coating for surgical instrument
InactiveUS20060259020A1Prevent bacterial growthReduce infectionBiocideSurgeryCoated surfaceSurgical site
A surgical instrument for use in a surgical site includes a first surface that is positionable within or near the surgical site and has an anti-bacterial coating disposed on the surface. The anti-microbial coating includes anti-microbial particles disposed in a polymer matrix wherein the anti-microbial particles are in sufficient concentration and are positioned to provide an anti-microbial effect at the surgical site. Bacterial growth is also inhibited on the coated surface of the instrument.
Owner:MINNESOTA SCI
Platelet Storage Container
InactiveUS20140158604A1Minimize bacterial contaminationReduce riskOther blood circulation devicesSynthetic resin layered productsRoom temperaturePlatelet storage
Compositions, methods, devices and media are provided for platelet storage container that prevents bacterial growth in the stored platelets. The invention relates to blood bank needs in safely storing platelets collected from donors for more than 5 days at room temperature. The container is built with natural adsorbent media that have the characteristics in capturing and killing bacteria and viruses. The stored platelets are isolated from the natural adsorbent material during storage to preserve their medical quality and safety.
Owner:CHAMMAS JACQUES
Novel strain of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use
InactiveUS20150147303A1Inhibits pathogenic growthPromote biodegradationBiocideFruit and vegetables preservationBacteroidesBacilli
An isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 having an Accession No. of DSM 21836 is provided. This novel strain has unique 16S ribosomal RNA sequenced as SEQ ID NO:1 and produces amylase, protease, cellulase and lipase, fibrinolytic enzyme to show their biodegradation capacities. Further, B. amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 produces the antibiotic substances, such as iturin, fengycin and surfactin, and has antimicrobial capacity for inhibiting the fungal or bacterial growth. In conclusion, the novel strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 and its products can be applied in agriculture, wastewater treatment, food industry and chemical industry.
Owner:HSIEH FENG CHIA
Toy cleaning device
InactiveCN107931175ASpeed up evaporationAvoid re-breedingDrying gas arrangementsCleaning using toolsBristleEvaporation
The invention discloses a toy cleaning device. The toy cleaning device comprises a working box and supporting legs fixed to the bottom of the working box. The top of the working box communicates witha water outlet pipe, and first rotating shafts are symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the working box. The structure is simple; a to-be-cleaned toy is placed on a conveying belt, the conveyingbelt brings the toy into the working box, and the toy is cleaned through bristles; because of frictional force between the conveying belt and a friction wheel, the friction wheel is driven to rotateand drives L-shaped rods through a rotating cylinder to rotate so as to turn over the toy, and thus all the faces of the toy are cleaned; meanwhile, first magnets on the friction wheel rotate with thefriction wheel and attract with second magnets mutually, reciprocating moving of racks is achieved through the effect of second springs, the racks are engaged with sector-shaped gears to drive spraying heads to swing, thus, the toy is washed from various angles, and the cleaning effect is improved; and through a fan, evaporation of residual moisture of the toy can be accelerated, and the situation that bacteria breed again is avoided.
Owner:郭姗姗
Mesh pouches for implantable medical devices
Biodegradable polymer-coated surgical meshes formed into pouches are described for use with cardiac rhythm management devices (CRMs) and other implantable medical devices. Such meshes are formed into a receptacle, e.g., a pouch or other covering, capable of encasing, surrounding and / or holding the cardiac rhythm management device or other implantable medical device for the purpose of securing it in position, inhibiting or reducing bacterial growth, providing pain relief and / or inhibiting scarring or fibrosis on or around the CRM or other implantable medical device. Preferred embodiments include surgical mesh pouches coated with one or more biodegradable polymers that can act as a stiffening agent by coating the filaments or fibers of the mesh to temporarily immobilize the contact points of those filaments or fibers and / or by increasing the stiffness of the mesh by at least 1.1 times its original stiffness. The pouches of the invention can also provide relief from various post-operative complications associated with their implantation, insertion or surgical use, and, optionally, include one or more drugs in the polymer matrix of the coating to provide prophylactic effects and / or alleviate side effects or complications associated with the surgery or implantation of the CRM or other implantable medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Technology for carrying out fungus growing on loose tea
InactiveCN104286238AReduce the hassle of drinkingHigh viable countPre-extraction tea treatmentGreen teaFermentation
The invention discloses a technology for carrying out fungus growing on loose tea. The technology comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a fermenting agent, namely, separating out eurotium cristatum from fuzhuan tea, and preparing to obtain the solid pure strain fermenting agent; (2) treating raw dark green tea raw material, namely, removing the impurities in the raw dark green tea, steaming, carrying out pile fermentation and then feeding tea juice; (3) carrying out steaming inoculation and fungus growing, namely, steaming the raw dark green tea with the tea juice, then immediately feeding the solid pure strain fermenting agent and inoculating; after that, putting the inoculated raw dark green tea into a fungus growing culture room, and carrying out fungus growing culture; and (4) drying and packaging, namely, drying after fungus growing, and directly packaging the dried loose tea. After the technology is adopted, the fungus growing time is shortened, the bacterial pollution rate can be reduced in the fungus growing process of the loose tea, the problems that the existing loose tea is hard in fungus growing and easy in bacterial growth can be solved, the fungus growing rate of the loose tea reaches up to 100%, and the tea is widespread in golden flowers on the surface and the granules are plump.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Water treatment plant for combined biomass and biogas production
InactiveUS20120024780A1Easily harvested/collectedIncrease flexibilityBio-organic fraction processingWaste based fuelNitrifying bacteriaBiogas production
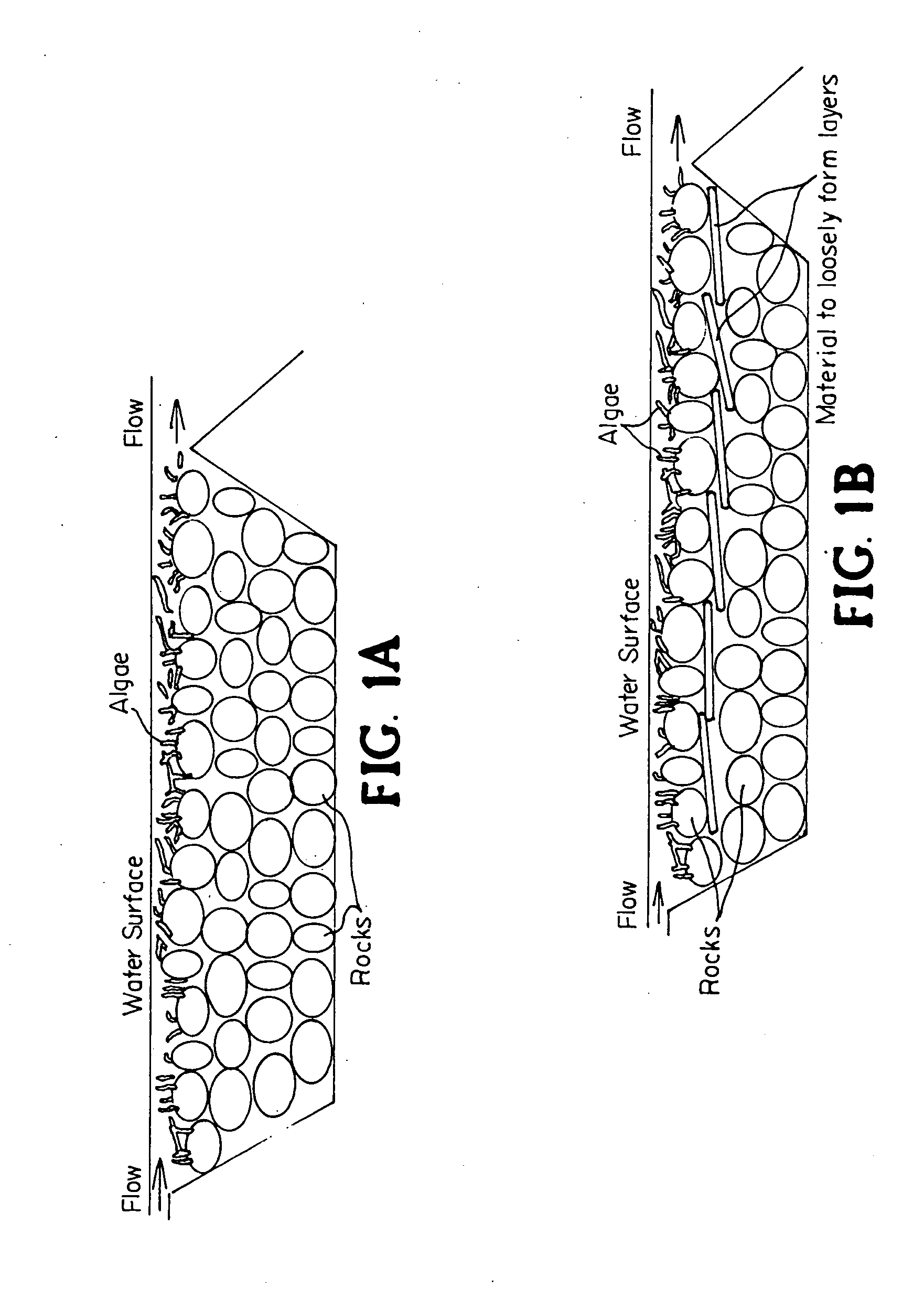
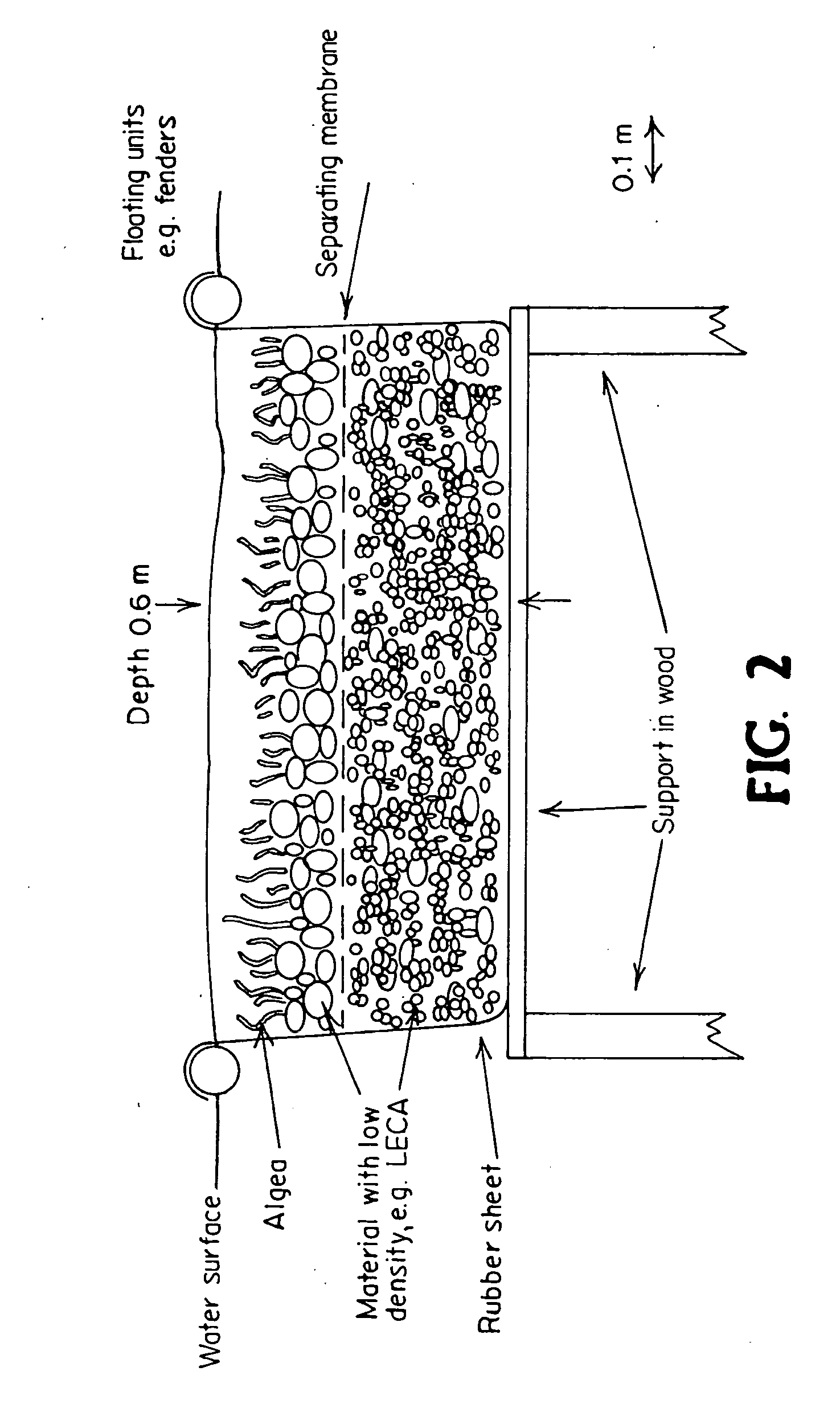
A waste water treatment system is provided that includes a basin for holding water; nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria; macroalgae; and a biobed having a at least one layer and being constructed of materials selected to provide sufficient level of pH for enabling bacterial growth. In the biobed de-nitrification and nitrification bacterial processes are separated. Oxygen produced by algae is used by the nitrifying bacteria. Water is provided continuously to the biobed at an inlet and exits the system downstream after having gone through the biobed. The system may be used with waste water in water treatment plants, domestic waste water (sewage), waste water from diverse industries, drain water from waste deposits, runoff water from roads, water waste treatment and recycling plants, agricultural and farm land and surrounding land of populated areas. The algae and bacteria are combined for symbiotic remediation of water that may be flexibly controlled to adapt to a broad range of applications.
Owner:CLEAR WATER ENERGY NORDIC
Treatment process of circulating cooling water with leaked ammonia nitrogen
InactiveCN102476871APromote growthEasy to controlMultistage water/sewage treatmentHypochloriteTungstate
The invention relates to a treatment method of circulating water with leaked ammonia nitrogen, which comprises the following steps: a) controlling the pH value of the circulating water to 7.5-9.0; b) adding a scale and corrosion inhibitor which comprises the following components: A) at least one salt selected from water-soluble borate, water-soluble molybdate, water-soluble tungstate, water-soluble gluconate, and water-soluble silicate, B) at least one scale inhibiting dispersant which is at least one phosphorus-free polymer with a carboxylic group, C) a zinc salt, and optional D) a copper corrosion inhibitor; c) adding at least one non-chlorine bactericide which is a bromine-containing bactericide or a chlorine-containing bactericide that does not generate hypochloric acid or hypochlorite in water. The invention controls the problems of corrosion, scaling, and bacterial growth in the circulating water system with leaked ammonia nitrogen by methods of adjusting the pH value of the circulating water, and combining with the phosphorus-free scale and corrosion inhibitor and the non-chlorine bactericide.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Health food capable of improving intestinal flora and preparation method of health food
ActiveCN104544086AIncrease typeOptimize quantityNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsGut floraNutrients substances
The invention discloses a health food capable of improving intestinal floras and a preparation method of the health food. The intestinal floras are adjusted on a plurality of aspects of increasing the probiotics variety and quantity, adding probiotic nutrient substances, inhibiting the harmful bacterial growth and increasing the human immunity, so that the gastrointestinal functions are improved. With probiotic powder such as lactobacillus plantarum as a main raw material, an edible mushroom extract is scientifically compounded, and dietary fibers are modified, so that the human immunity can be significantly improved; a saussurea involucrate culture extract has the efficacies of resisting inflammation, relieving pain, and resisting oxidation, radiation and fatigue; the variety of the intestinal beneficial bacteria floras is increased; the field planting capacity of endogenous and exogenous probiotics in human intestinal tracts is significantly enhanced and the field planting time of endogenous and exogenous probiotics in human intestinal tracts is significantly prolonged; the growth and the reproduction of intestinal harmful bacteria, especially gram negative bacteria, are effectively inhibited; the components of the intestinal beneficial bacteria floras are fully adjusted; and the health food which is high in probiotic property, and is capable of significantly improving the human immunity and improving the intestinal floras is prepared.
Owner:河南小杉健康科技服务有限公司
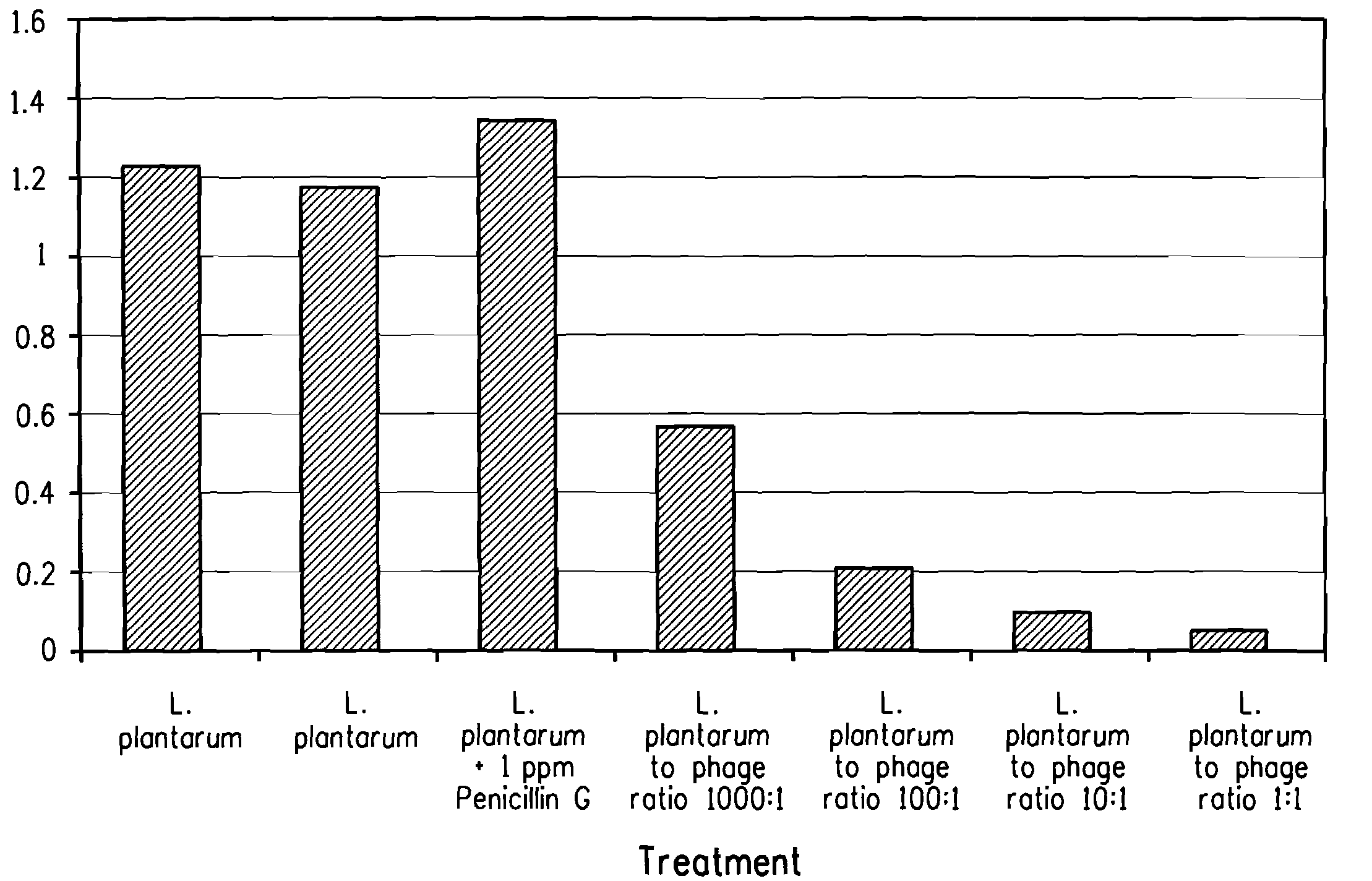
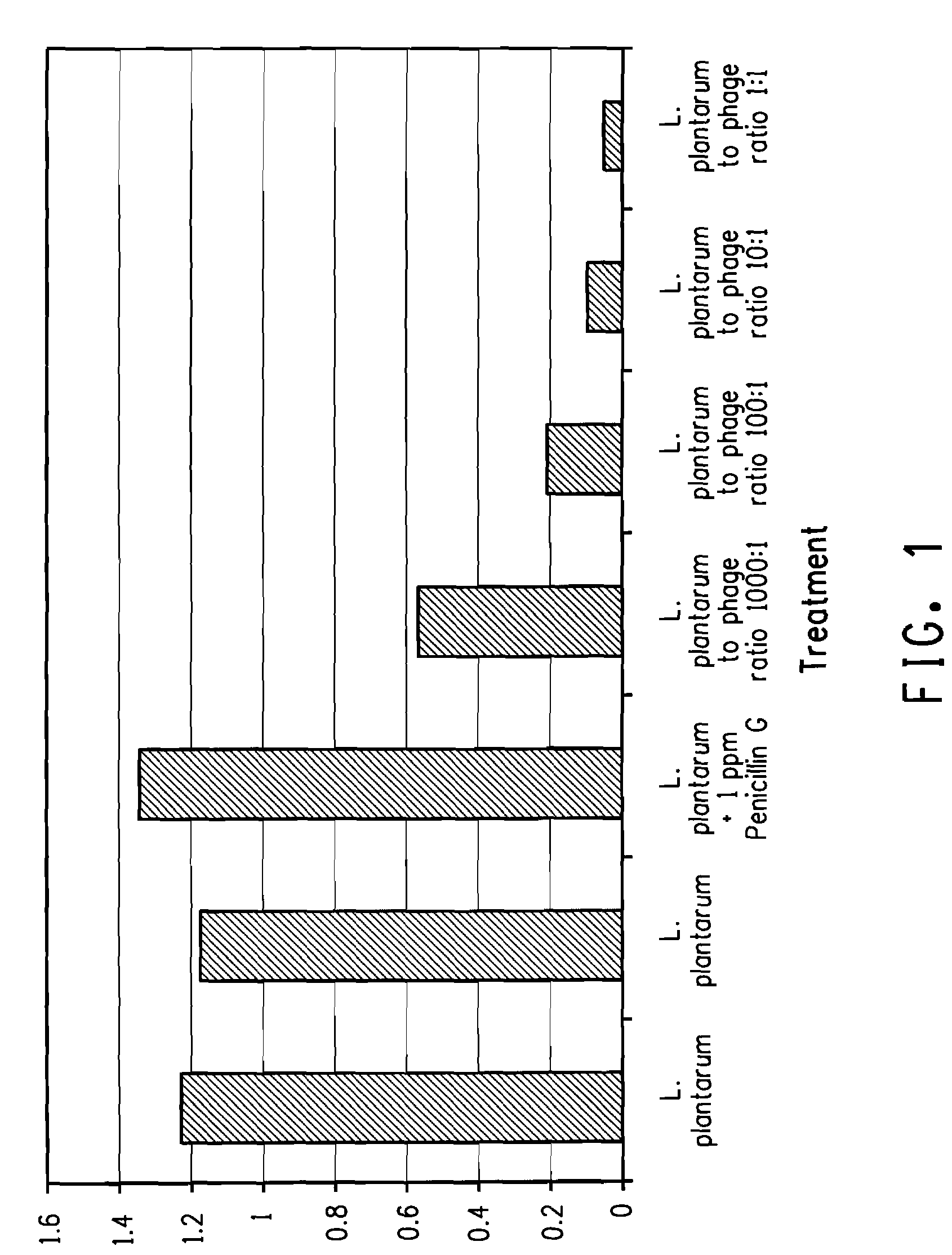
Utilization of bacteriophage to control bacterial contamination in fermentation processes
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
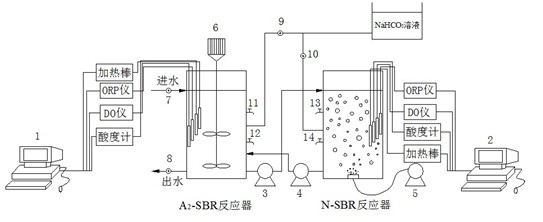
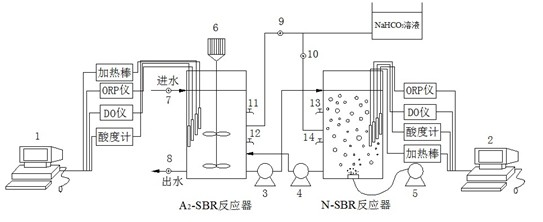
A2N-SBR (Anaerobic-anoxic/nitrification-sequencing batch reactor) process with shortcut nitrification-denitrification denitrifying and dephosphorizing function
InactiveCN102381818AReduce aerationLess sludgeTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemistryBacterial growth
The invention relates to an A2N-SBR (anaerobic-anoxic / nitrification-sequencing batch reactor) process with a shortcut nitrification-denitrification denitrifying and dephosphorizing function. Compared with an A2N-SBR process with a complete nitrification-denitrification denitrifying and dephosphorizing function, the A2N-SBR process provided by the invention saves aeration amount and organic carbonsource amount, greatly reduces residual sludge amount and saves operation cost. The A2N-SBR process provided by the invention comprises a main reaction tank and auxiliary equipment, wherein the main reaction tank comprises an A2-SBR and an N-SBR; and the auxiliary equipment comprises stirring equipment, aeration equipment, a dissolved oxygen detection device, a reflux pump, pH adjusting equipment, a pH detection device, heating equipment and a temperature detection device. The A2N-SBR process provided by the invention has the advantages that: two independent SBRs are adopted; nitrite bacteriaand denitrifying phosphate-accumulating bacteria grow separately in the two reactors through controlling proper conditions, so that denitrification is carried out when NH4<+>-N oxidation goes to NO2<-> stage, thus operation energy consumption is greatly saved, bacteria are not mutually influenced in the operation process, and the bacterial activity is higher in the whole bacterial growth process;and the process is simple, the arrangement is compact and the automation degree is high.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Method and composition for treating oral bacteria and inflammation
ActiveUS20050196359A1Growth inhibitionReduce inflammationCosmetic preparationsBiocideMaxillary gingivaBacterial growth
A composition and method for treating periodontal infections and gingivitis includes an extract of Centipeda cunninghami, coenzyme Q10, aloe vera and folic acid. The composition also contains additional plant extracts and nutrients that are effective in cell reproduction, wound healing and provide antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. The composition is applied to the teeth and gums to inhibit bacterial growth and reduce inflammation of the gums.
Owner:BIO BOTANICA
Composite vascular graft having bioactive agent
A composite vascular graft incorporates bioactive agents to deliver therapeutic materials and / or inhibit or reduce bacterial growth during and following the introduction of the graft to the implantation site in a vascular system. A composite vascular graft includes a porous tubular graft member. A flexible ePTFE sheath is disposed over the tubular graft member. The sheath includes the bioactive agents incorporated therein.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Wastewater treatment system and method
InactiveUS20060180546A1Improve efficiencyIncrease oxygen transferTreatment using aerobic processesLiquid displacementAtmospheric pressureSystems approaches
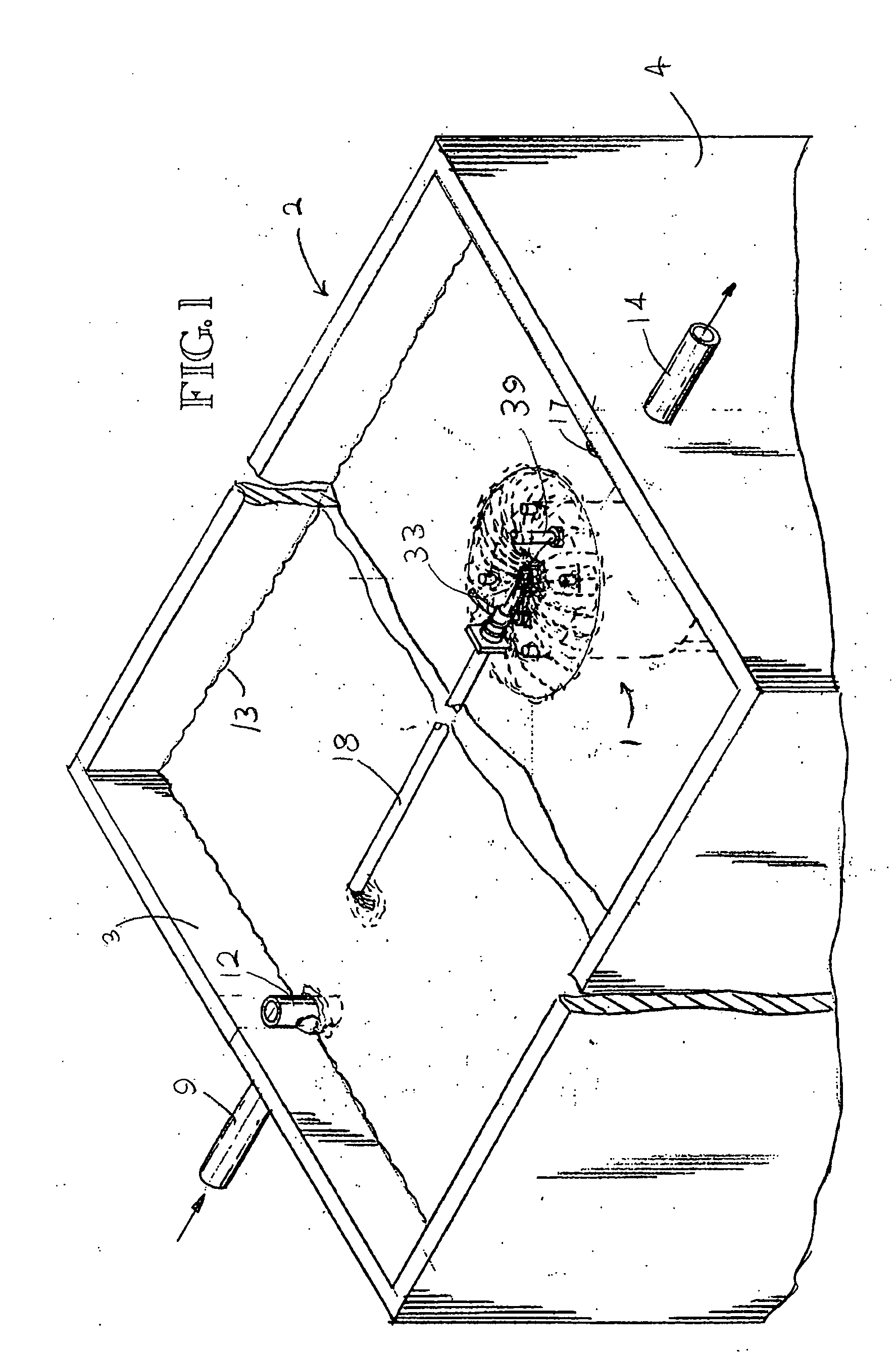
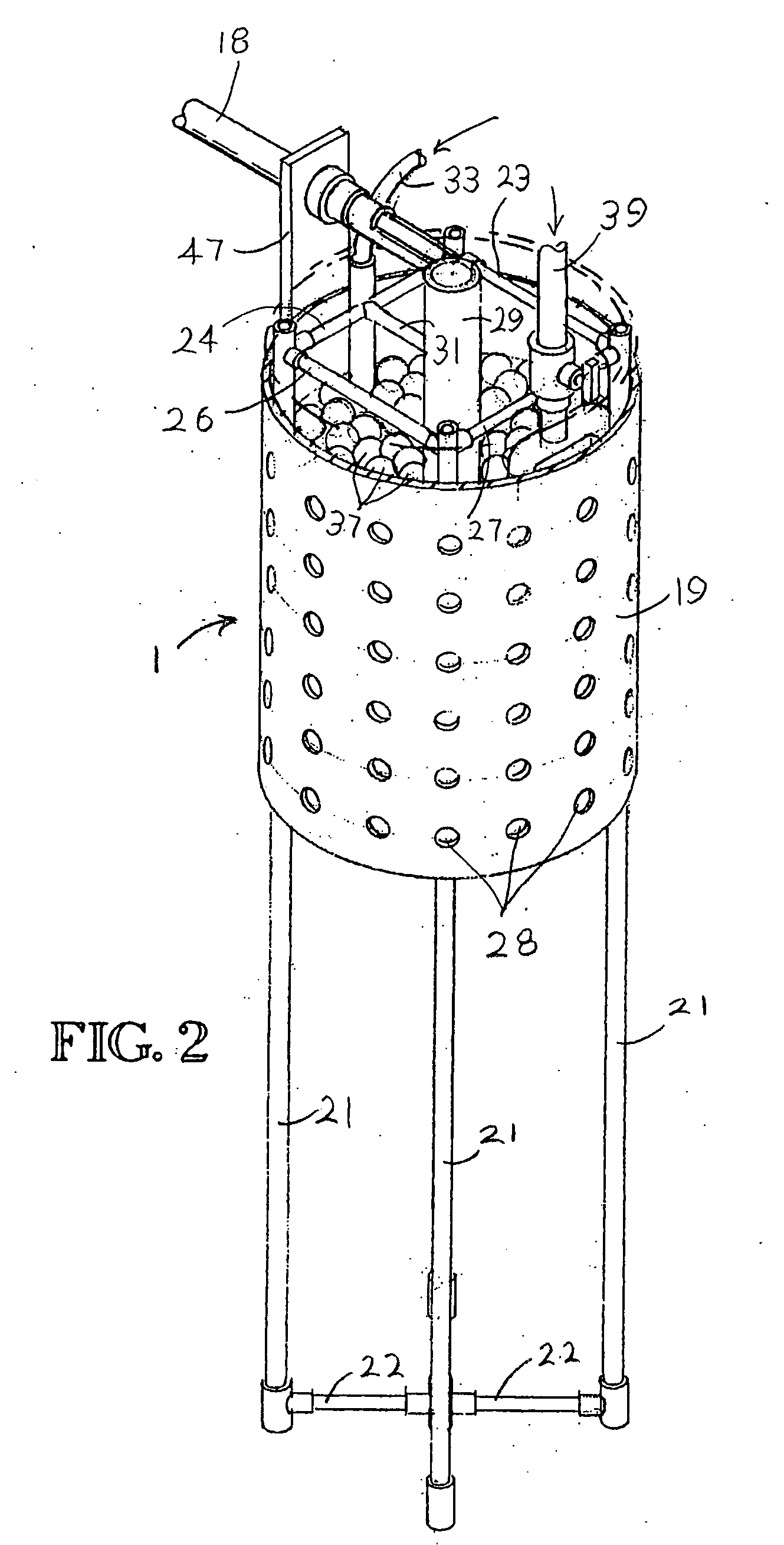
A system, method and apparatus for treating wastewater containing biodegradable material wherein a submerged stand alone perforated cylinder reactor pod containing aerobic bacterial growth media and a draft tube with air pressure induced pumping action creates a spray or splash pattern so as to recirculated aerated liquor through the media and also to the area surrounding the cylinder pod. Free interchange of mixed and unmixed liquor is provided via the perforations in the cylindrical pod wall. Provision is also made for back flushing the media and returning mixed liquor to an area remote from the reactor pod.
Owner:STUTH SR WILLIAM L
Preparation method of petroleum degrading bacteria solid inoculant and method for restoring petroleum-polluted soil by using prepared solid inoculant
ActiveCN104450597AImprove solubilitySolve the difficulty of dissolutionContaminated soil reclamationMicrobiology processesNutrientPetroleum
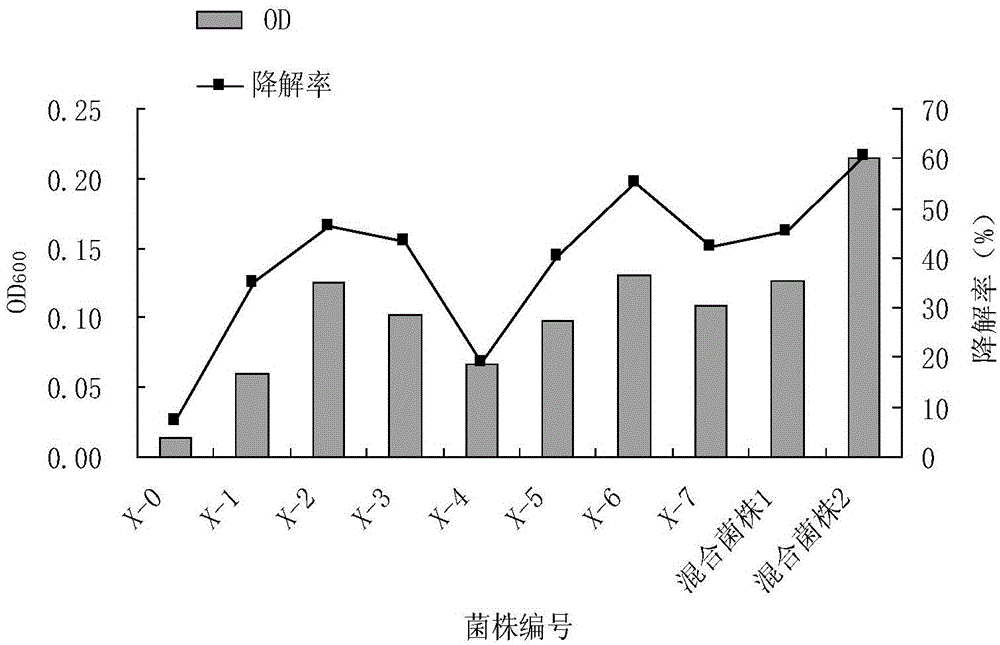
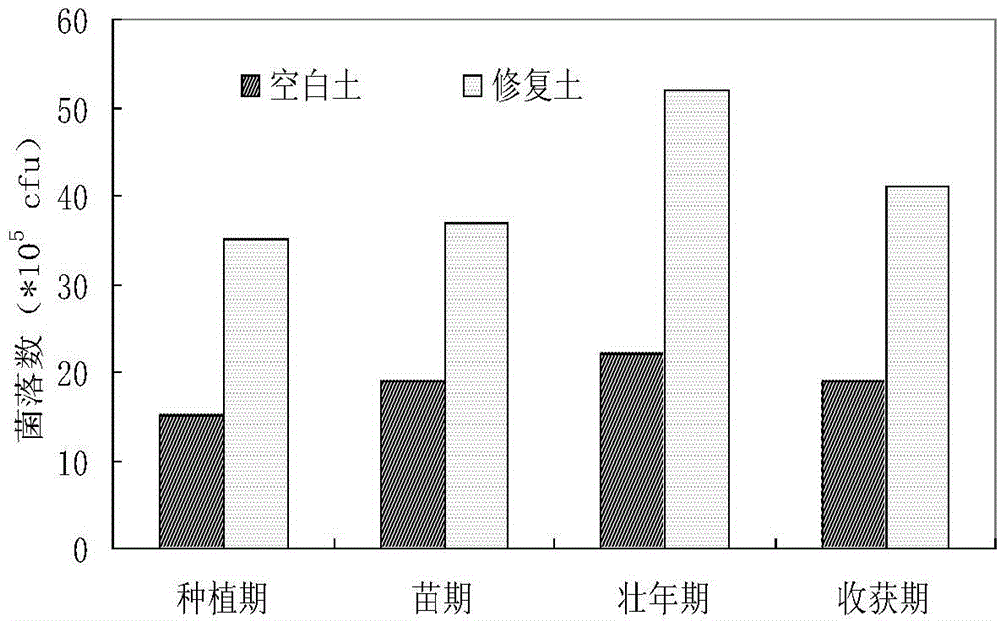
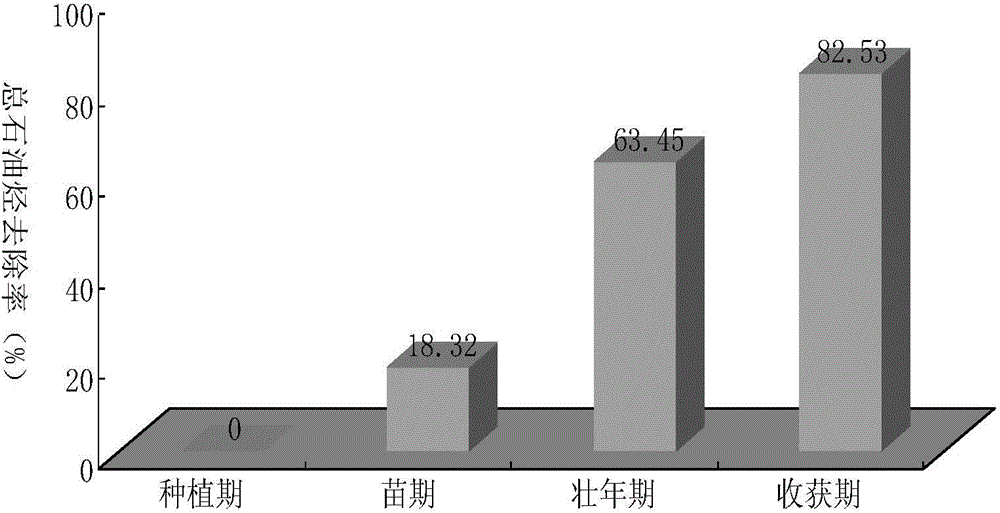
The invention relates to a preparation method of a petroleum degrading bacteria solid inoculant. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A, screening and domestication of the petroleum degrading bacteria; B, preparation of a seed culture solution; C, fermentation of the solid inoculant; and D, drying, pulverization, measurement and packaging of composted products. The petroleum degrading bacteria solid inoculant has the beneficial effect of improving the petroleum dissolution effect by taking a nonionic surfactantpolysorbate-80 (tween 80) as a solubilizer. The preparation method has the advantages that solid fermentation raw materials are easy to get and the process is relatively simple; and the solid inoculant contains a large amount of carbon and nutrient elements so as to provide more proper matrix for the growth of the bacteria, has strong affinity for the microorganisms, has immobilization efficiency, is capable of improving the competitiveness and degrading efficiency of the added microorganisms and indigenous microorganisms, and is convenient to transport and operate agriculturally and suitable for the large-scale in-situ biological remediation of the petroleum-polluted soil.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com