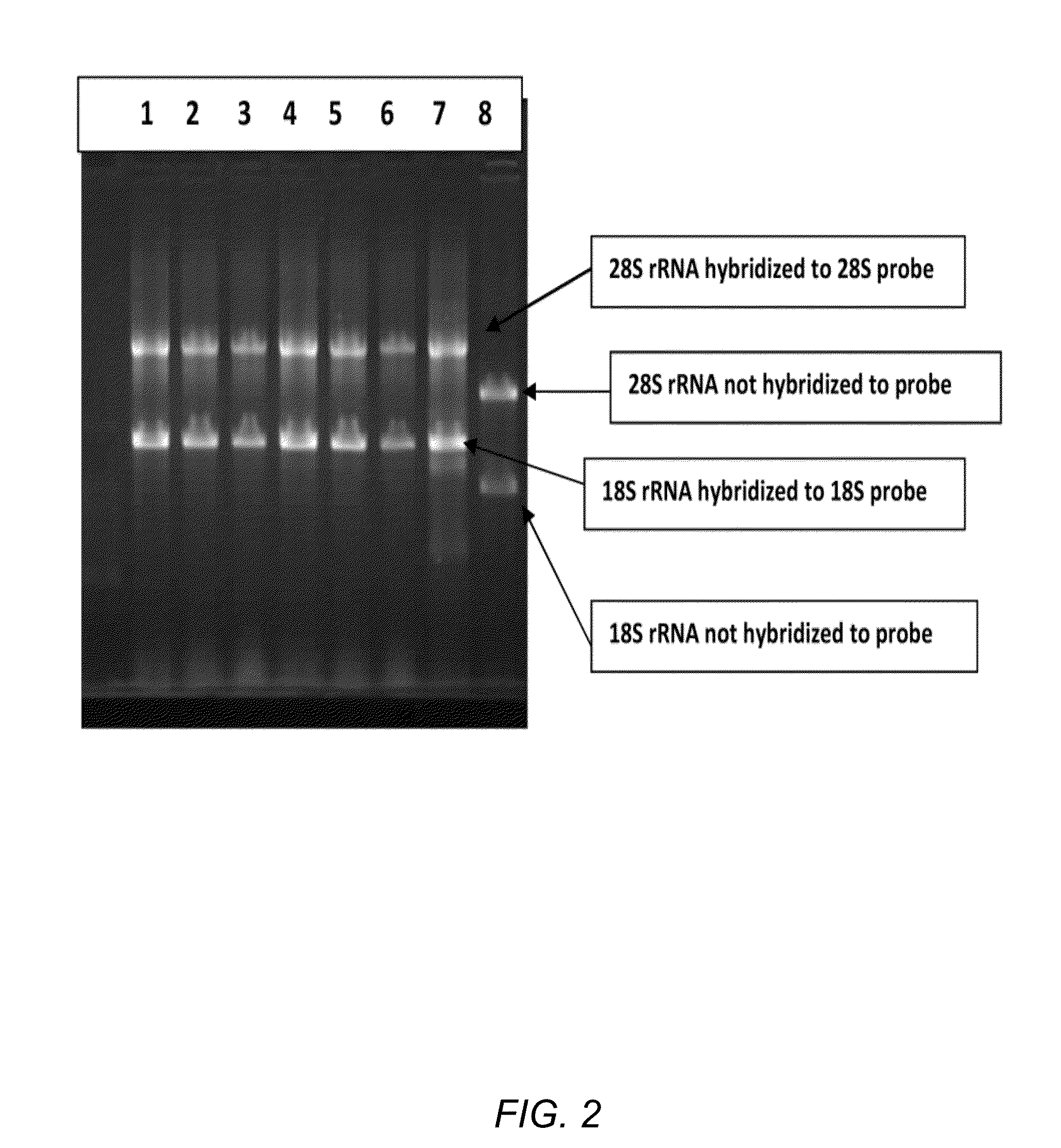
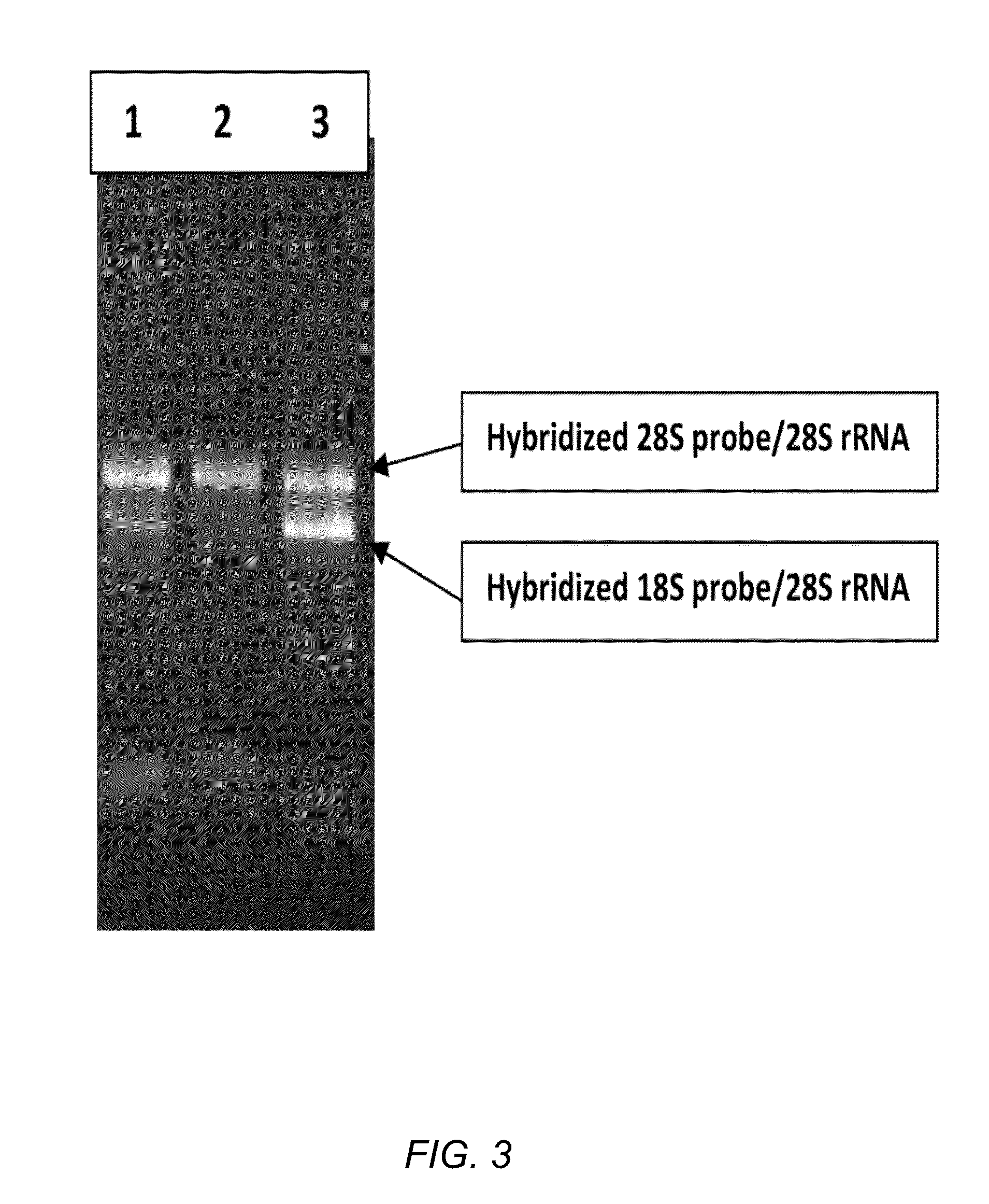
Patents
Literature
93 results about "Ribosomal RNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
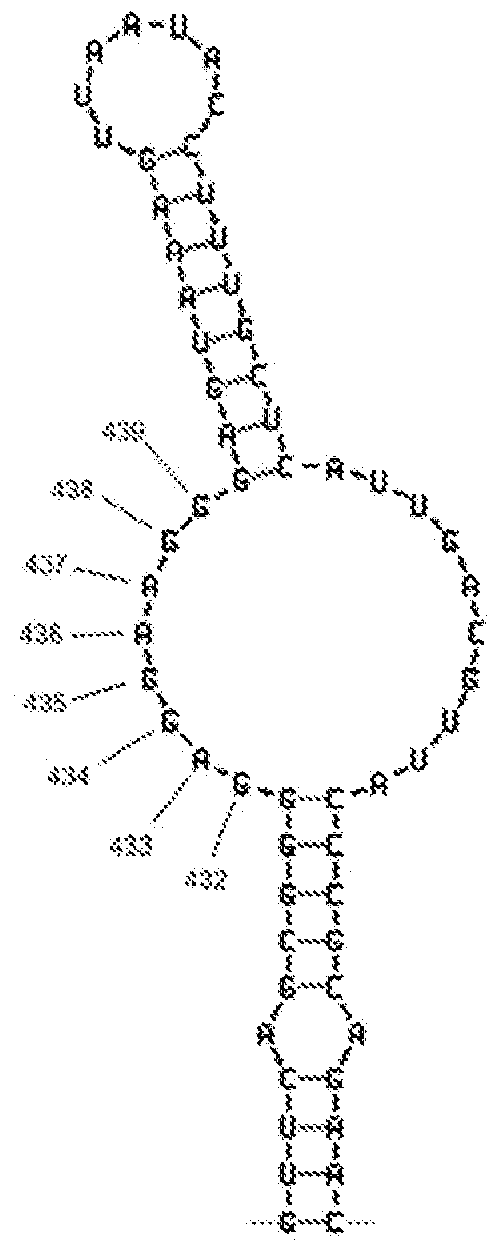
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is the RNA component of the ribosome, which is essential for protein synthesis in all living organisms. rRNA is the predominant RNA in most cells, composing around 80% of cellular RNA. Ribosomes are approximately 60% rRNA and 40% protein by weight. A ribosome contains two subunits, the large ribosomal subunit (LSU) and small ribosomal subunit (SSU).
Novel strain of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use
InactiveUS20100143316A1Inhibits pathogenic growthPromote biodegradationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyAmylase
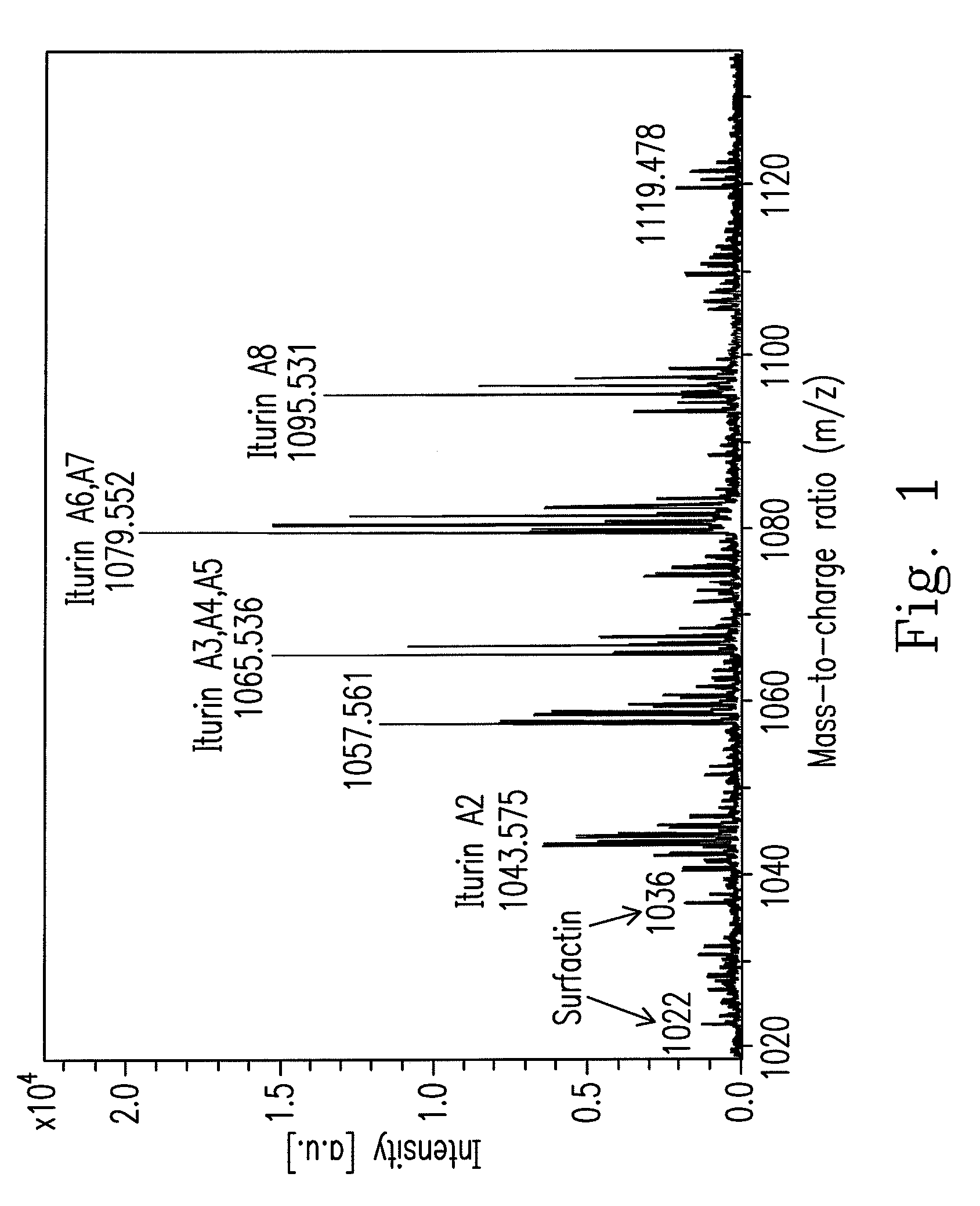
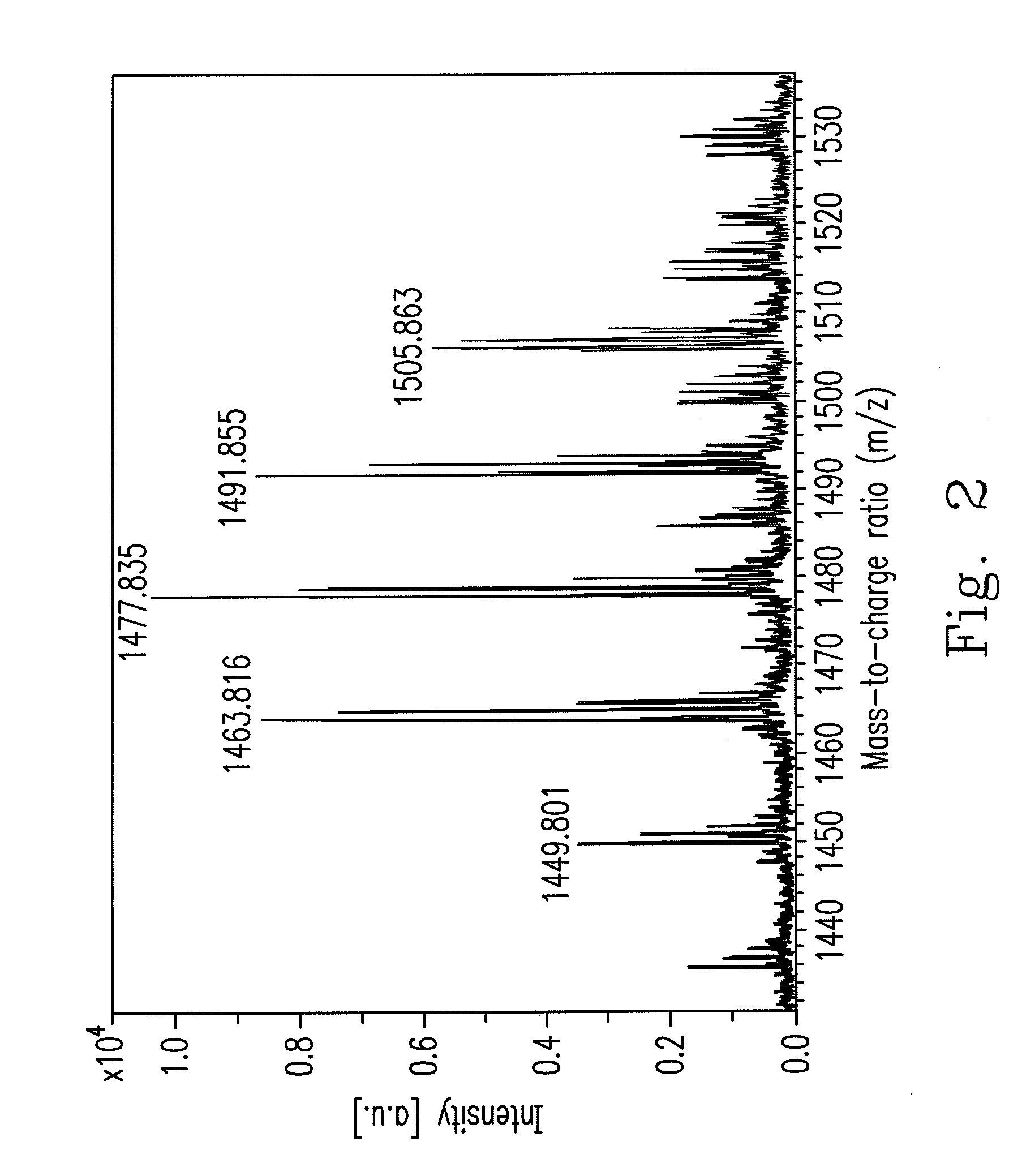
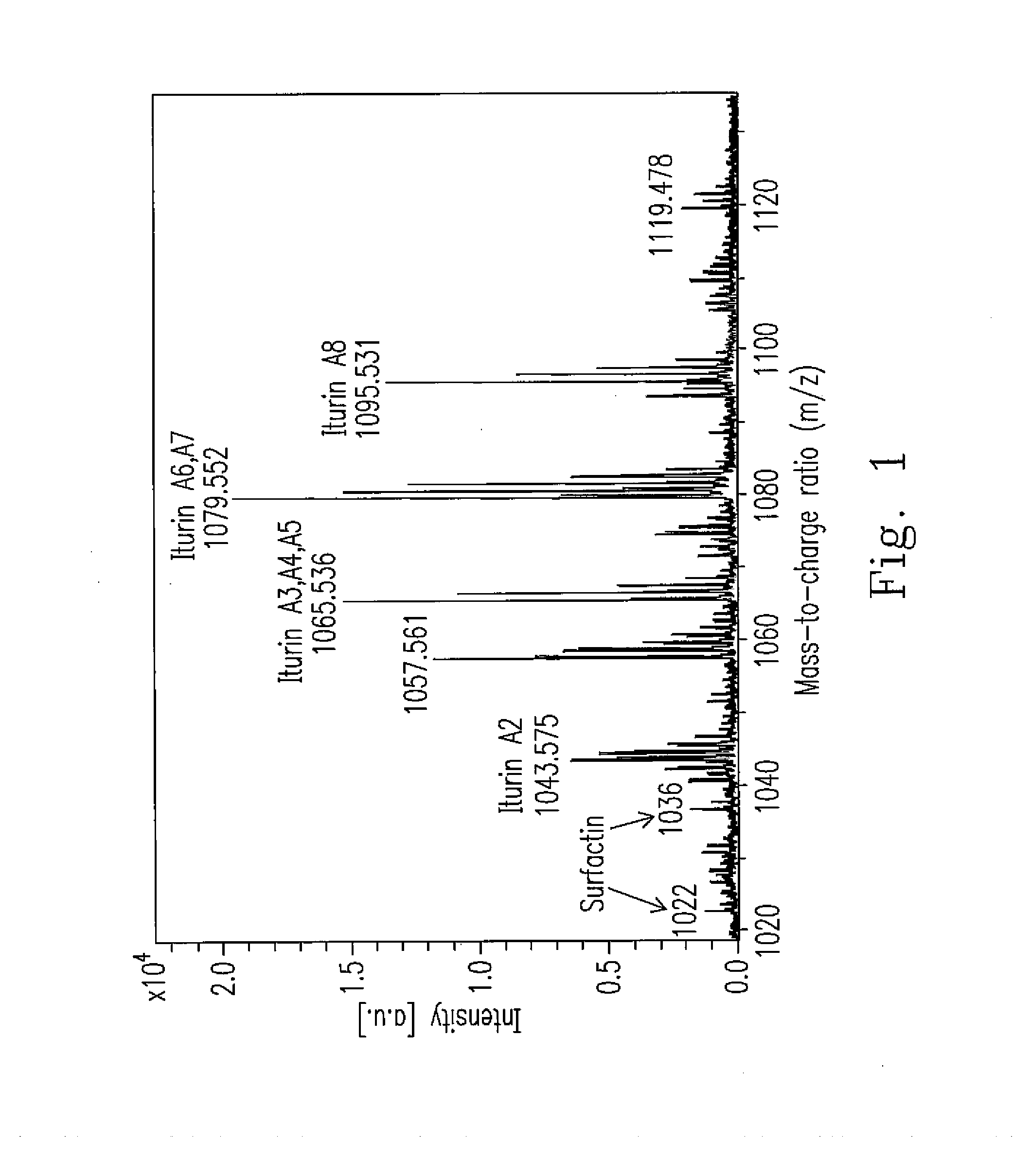
An isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 having an Accession No. of DSM 21836 is provided. This novel strain has unique 16S ribosomal RNA sequenced as SEQ ID NO:1 and produces amylase, protease, cellulase and lipase, fibrinolytic enzyme to show their biodegradation capacities. Further, B. amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 produces the antibiotic substances, such as iturin, fengycin and surfactin, and has antimicrobial capacity for inhibiting the fungal or bacterial growth. In conclusion, the novel strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 and its products can be applied in agriculture, wastewater treatment, food industry and chemical industry.
Owner:AGRI CHEM & TOXIC SUBSTANCES RES INST COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
Microbial identification based on the overall composition of characteristic oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20050142584A1Create accuracyCreate speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBiological body
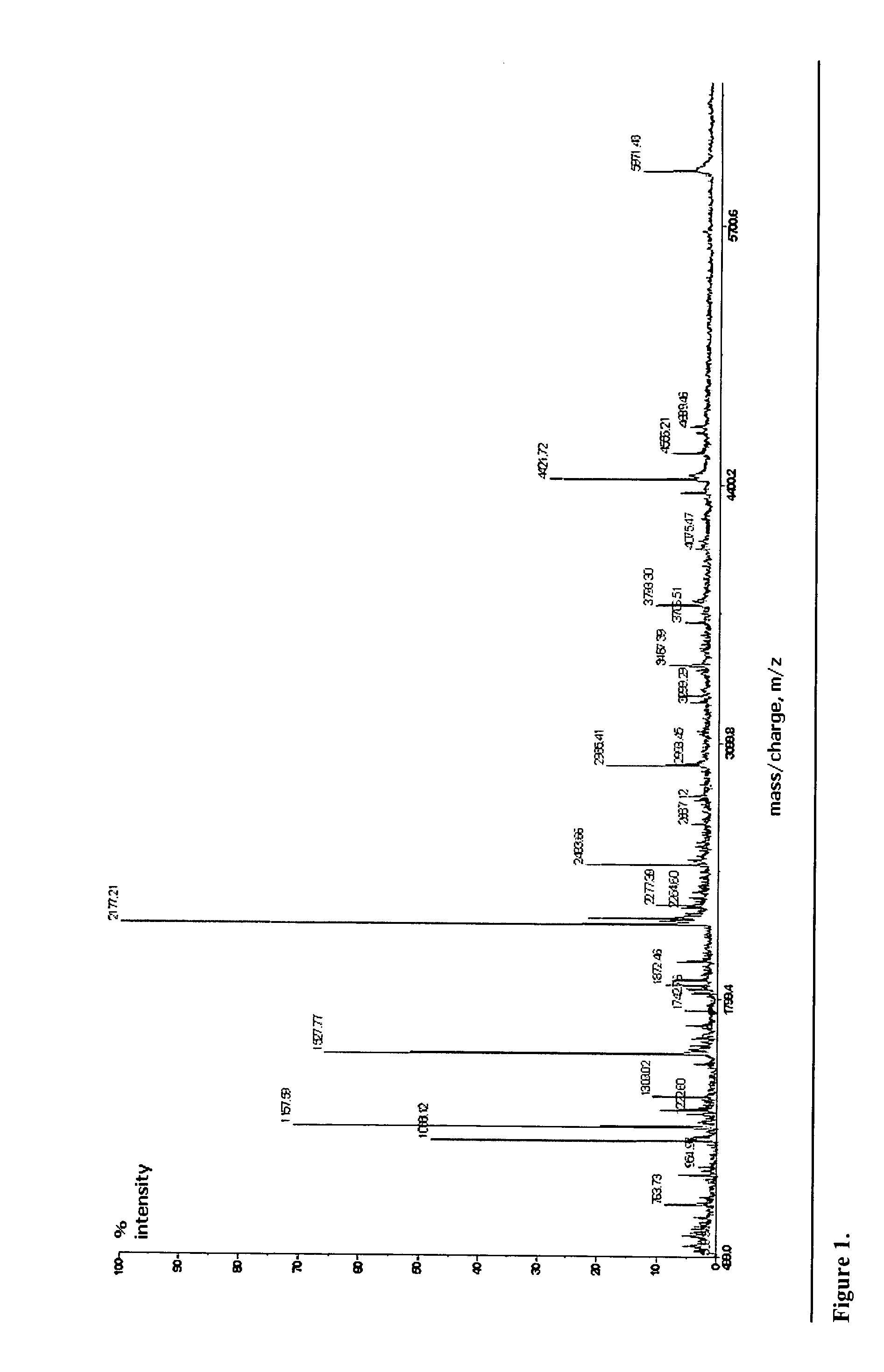
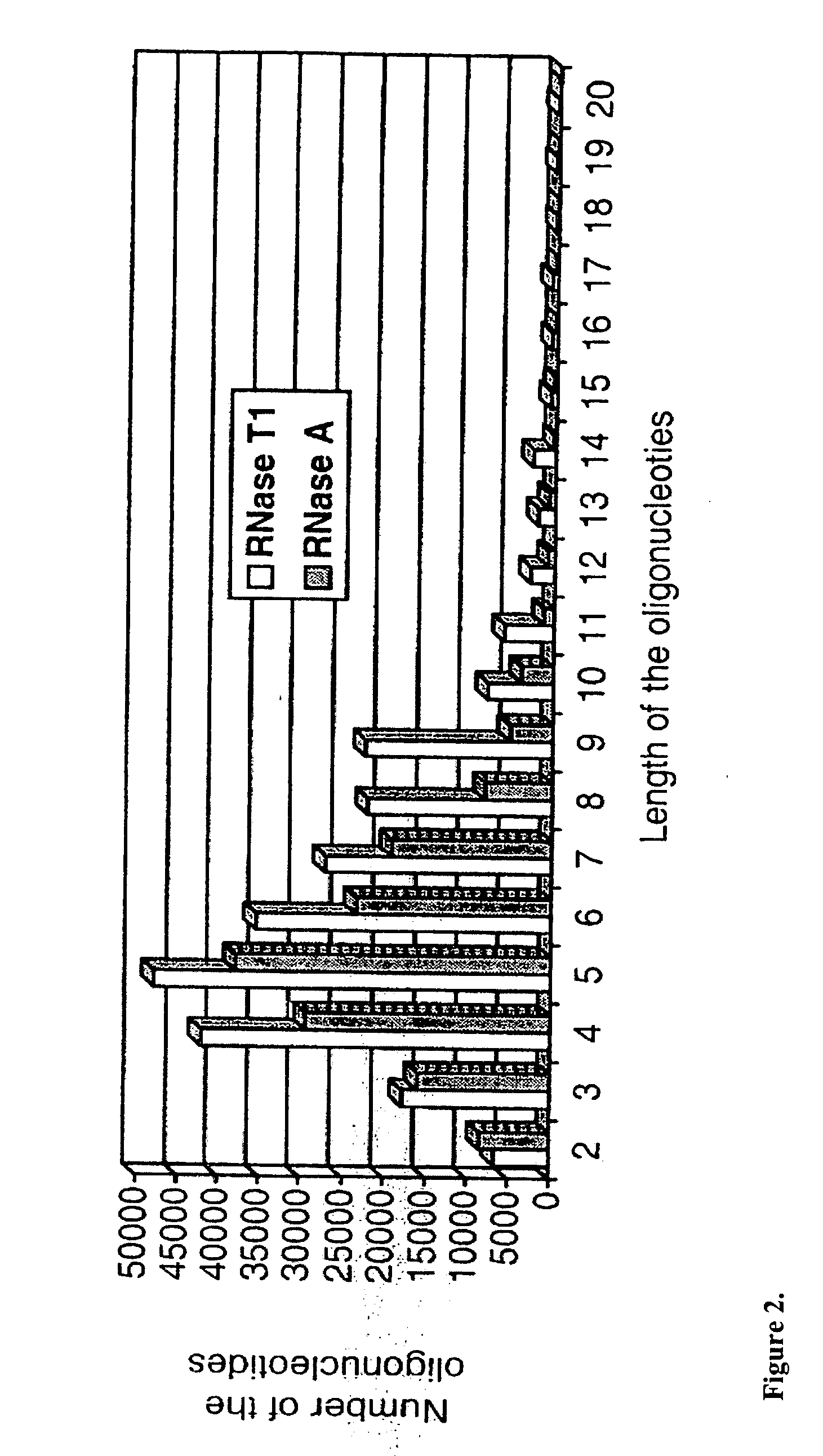
Identification of microorganisms based on the sequences of their 5S, 23S and particularly 16S ribosomal RNAs is growing in utility as the database of known ribosomal RNA sequences expands. Experimental identification is usually based on matching the experimentally-determined sequence of an organisms rRNA to a previously-determined sequence in the databank, or hybridization of the organisms rRNA or encoding rDNA to an oligonucleotide probe specific for an organism anticipated to be present in the sample. Here we propose the identification of microorganisms based on the overall composition (not sequence or hybridization propensity) of characteristic molecules derived from their rRNA or rDNA sequences by enzymatic cleavage or localized amplification. Ribonuclease T1 fragments of rRNA composition determination by mass spectrometry are especially favored. The characteristic molecules used can be chosen to be “compositional signatures” whose presence / absence is known to be associated with particular groups of organisms.
Owner:JACKSON GEORGE W
Compositions and methods for negative selection of non-desired nucleic acid sequences
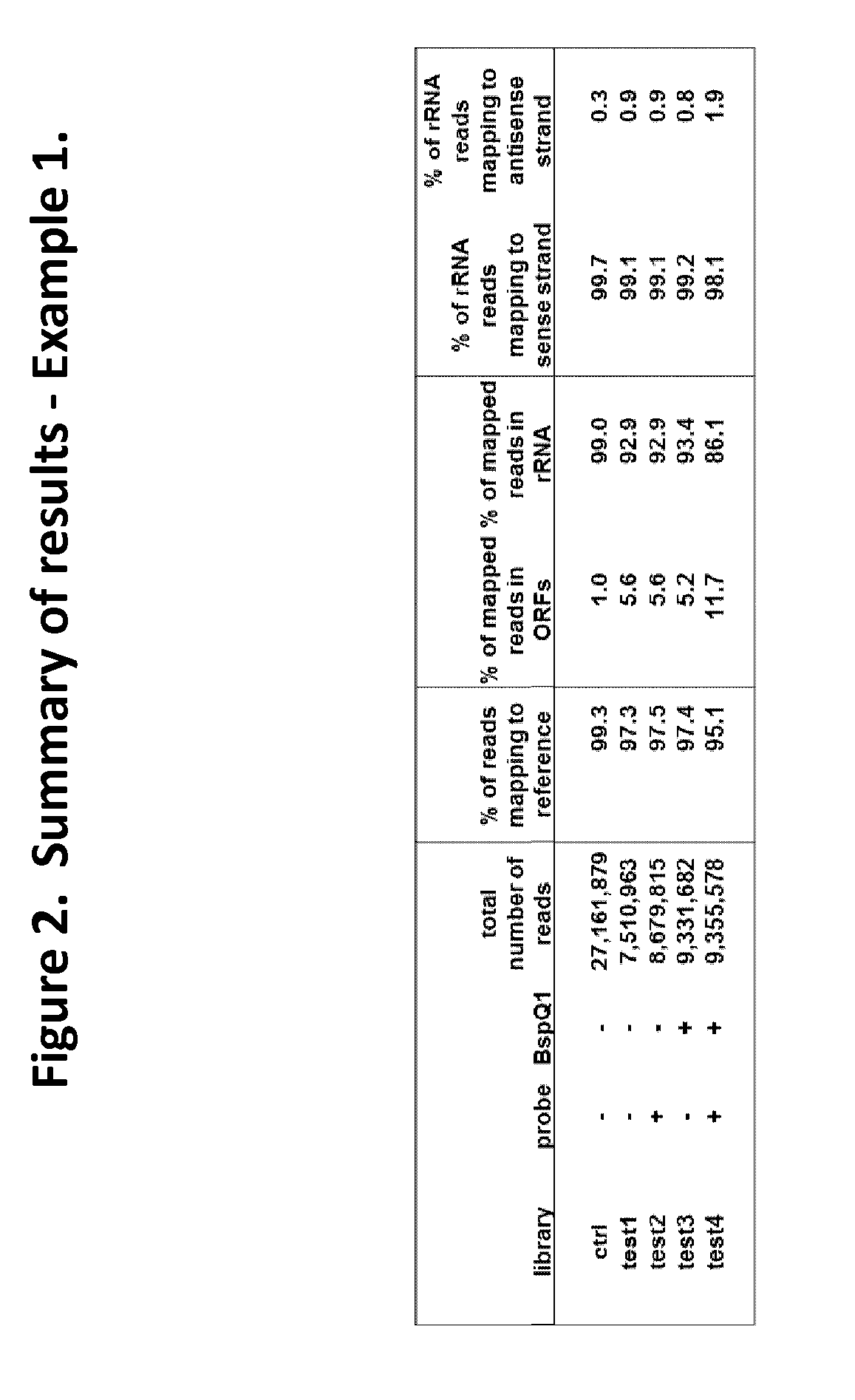
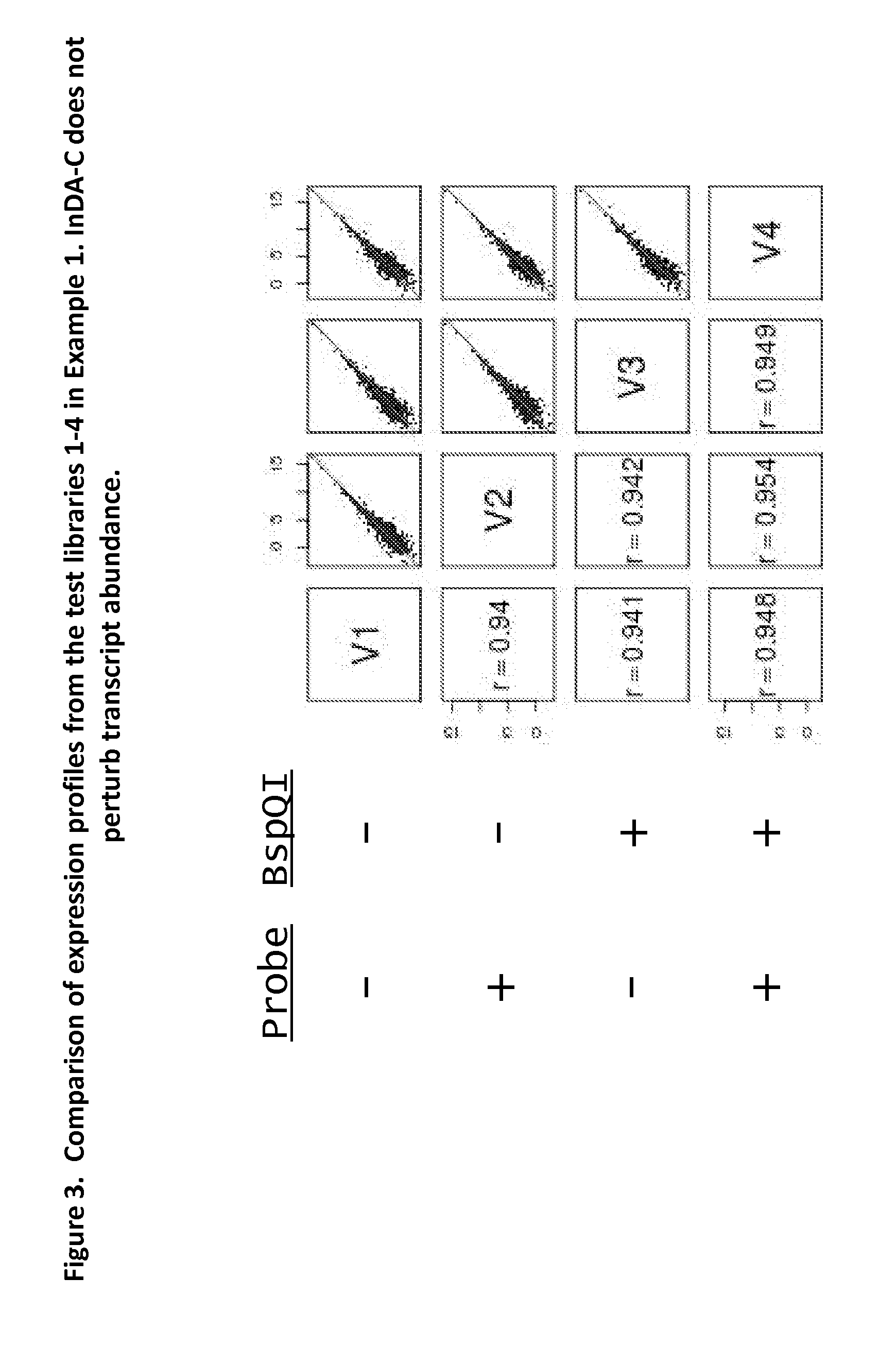
ActiveUS20150299767A1Decrease abundance ratioReduce the ratioNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaRibosomal RNA
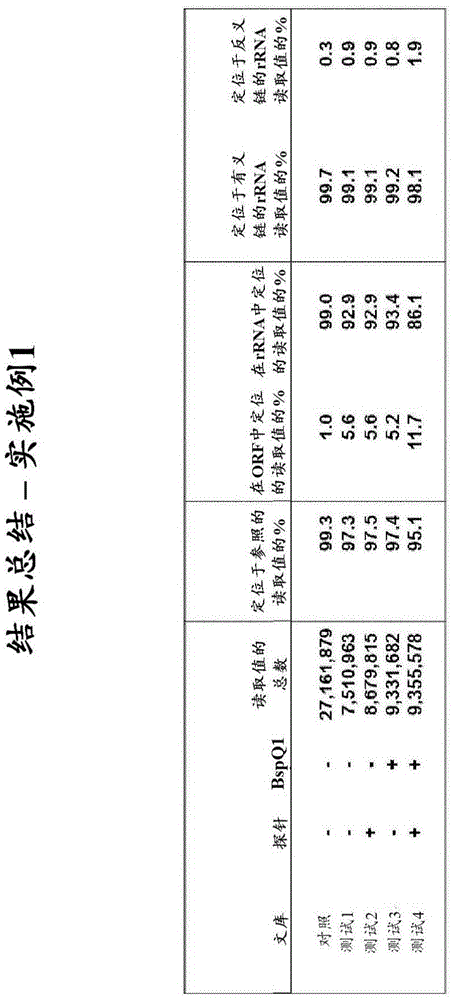
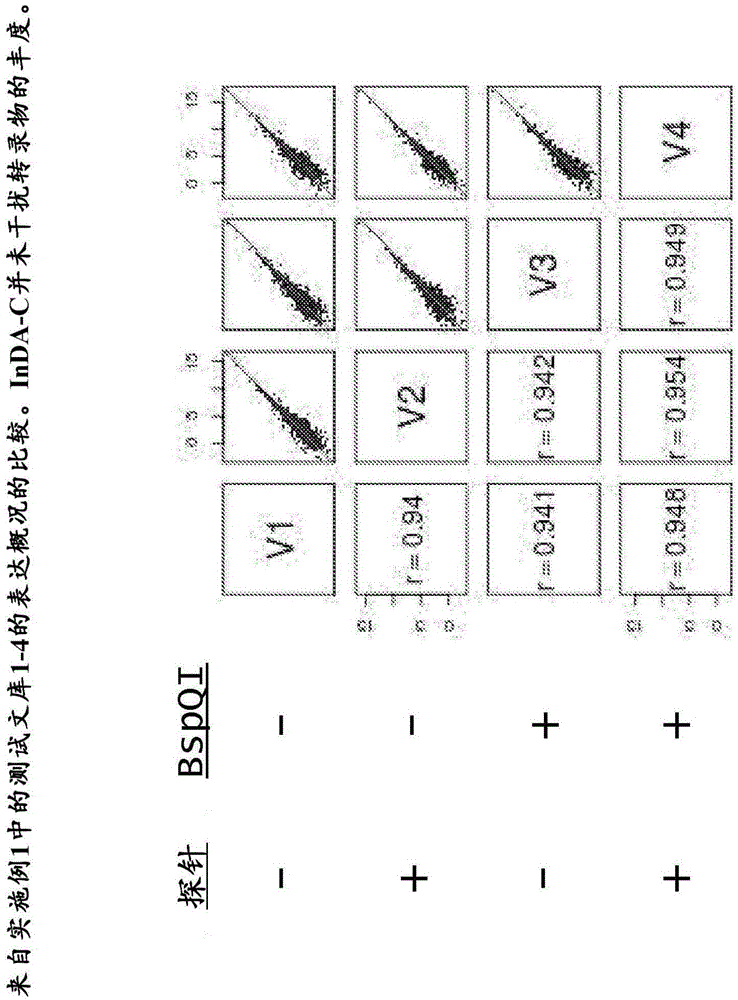
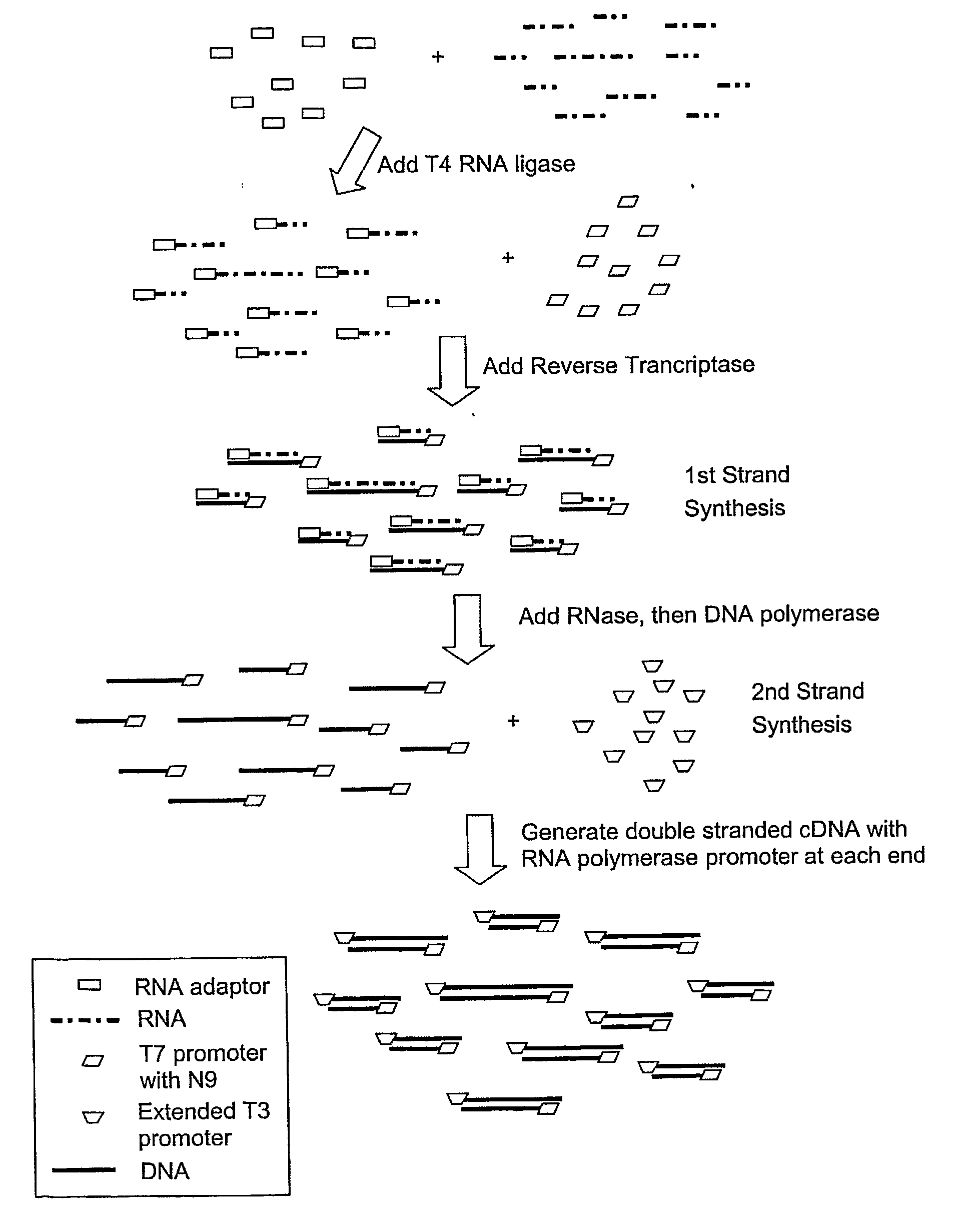
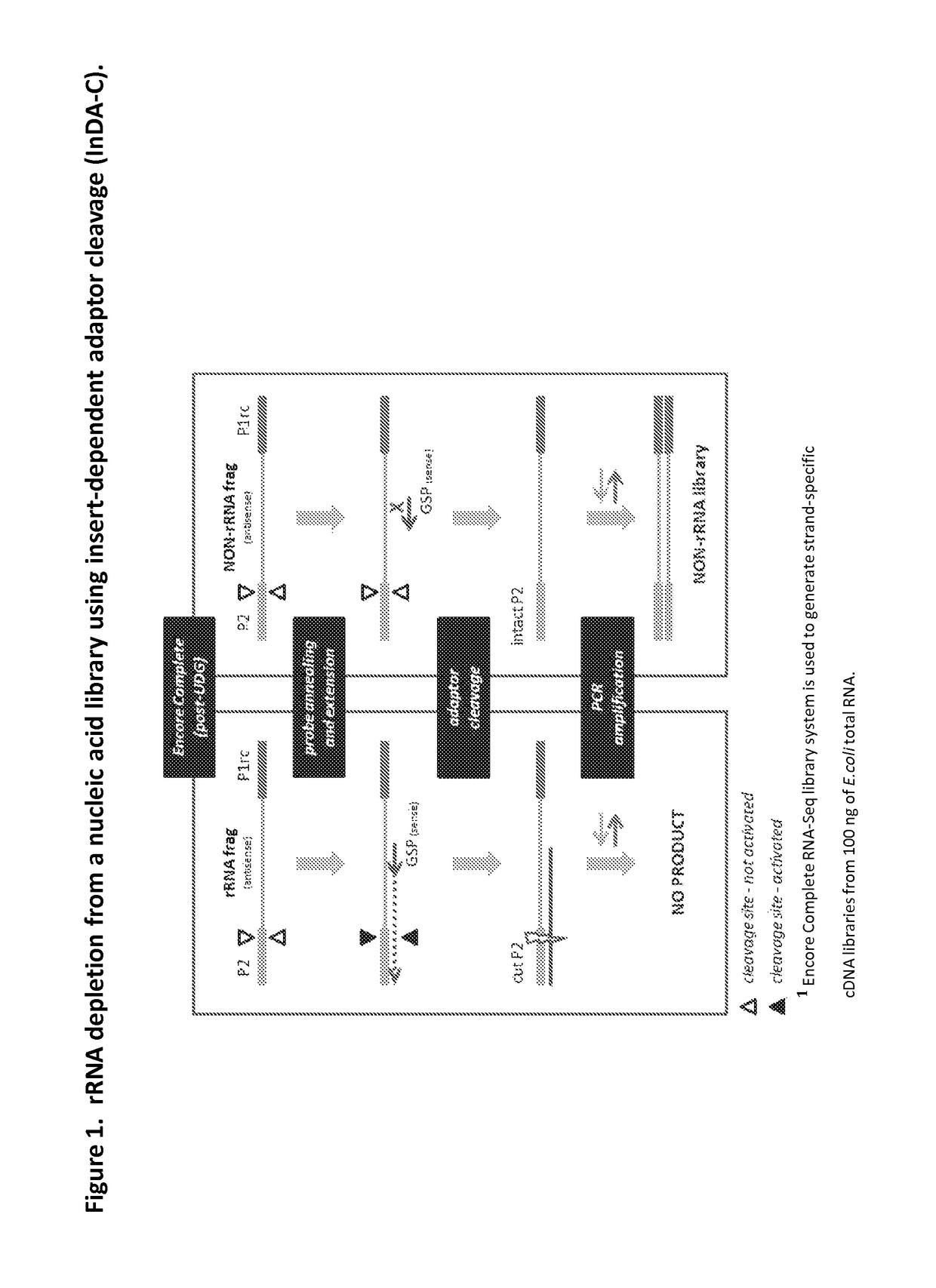
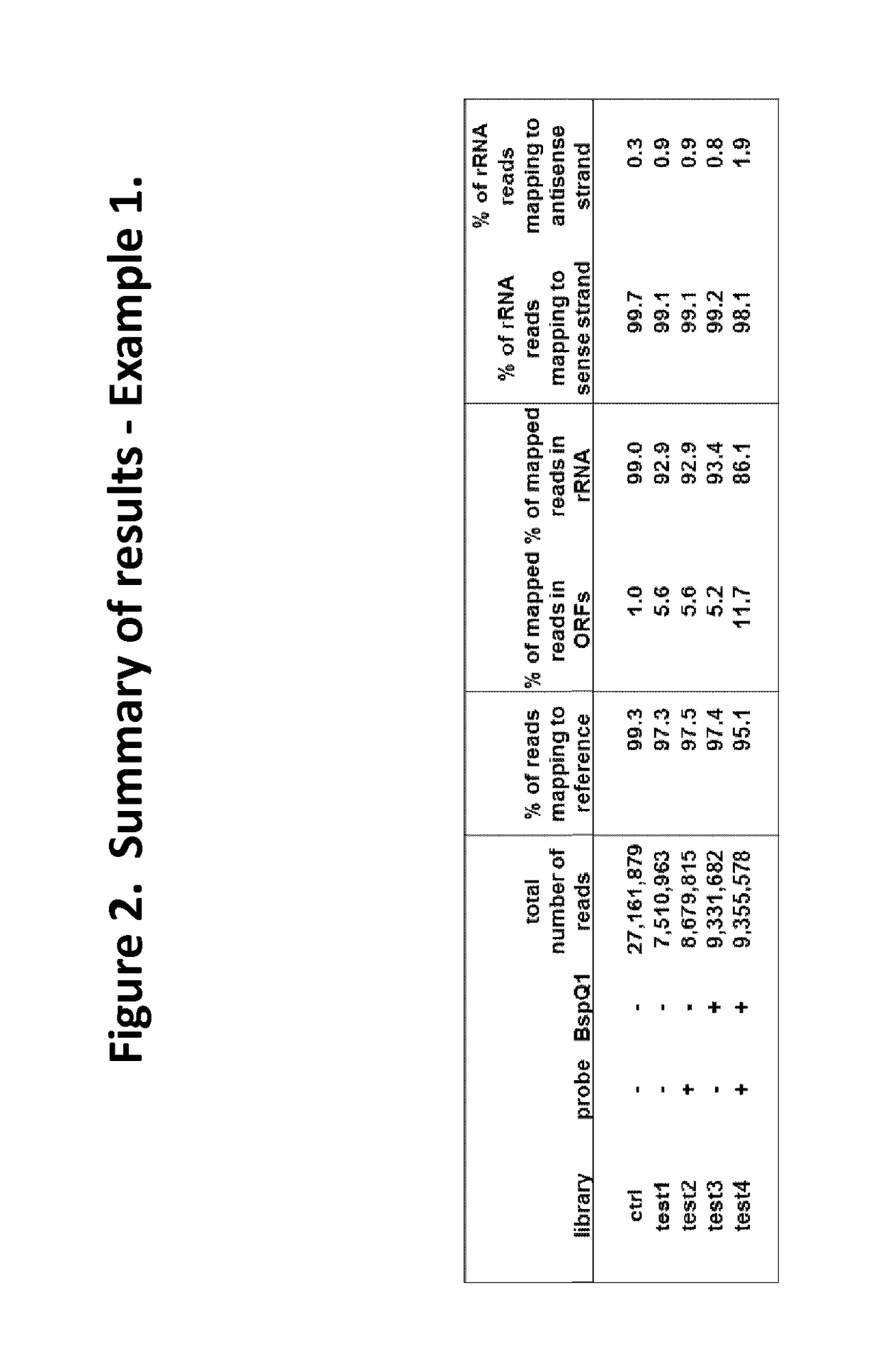
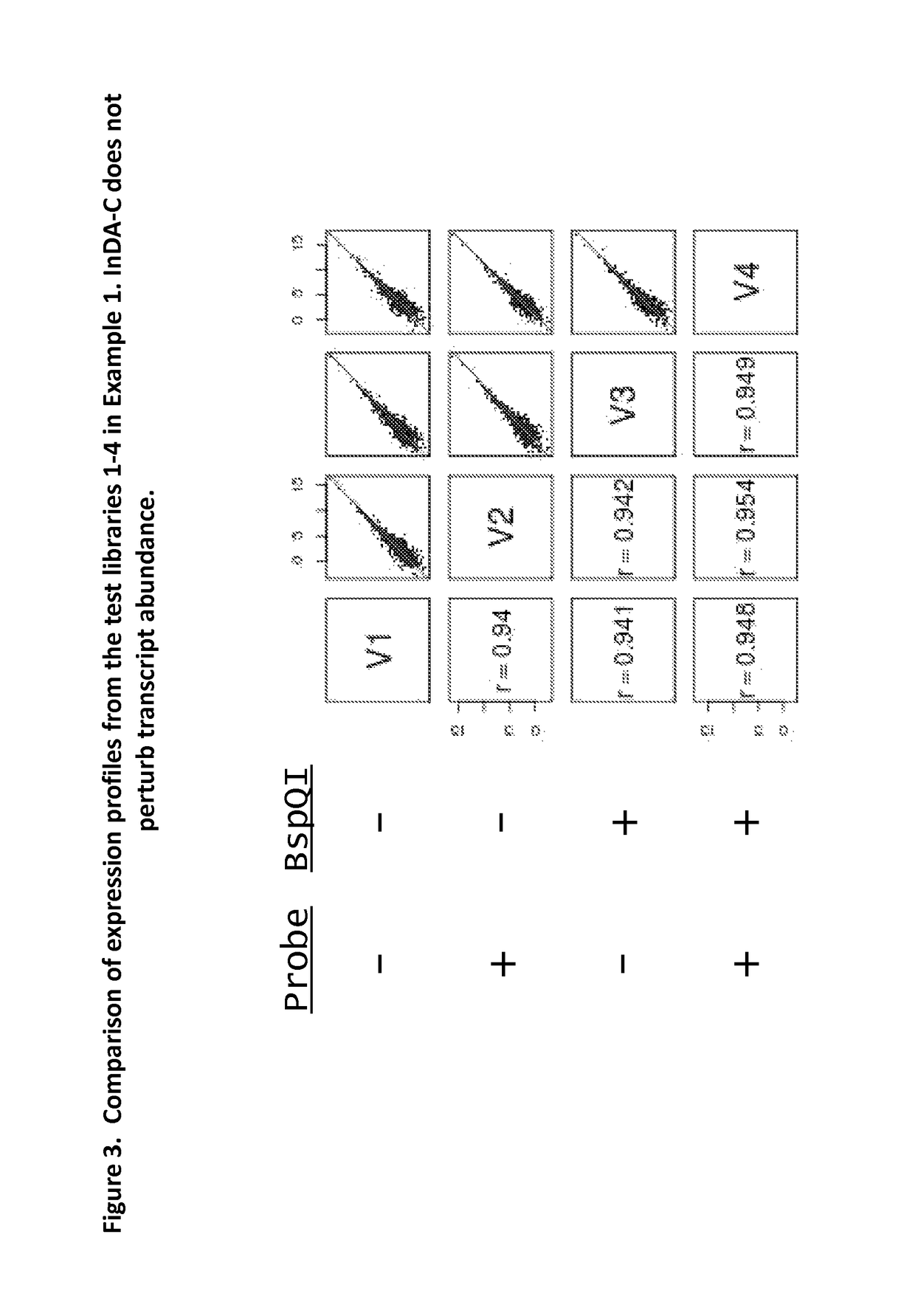
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for the generation of next generation sequencing (NGS) libraries in which non-desired nucleic acid sequences have been depleted or substantially reduced. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein are useful, for example, for the production of libraries from total RNA with reduced ribosomal RNA and for the reduction of common mRNA species in expression profiling from mixed samples where the mRNAs of interest are present at low levels. The methods of the invention can be employed for the elimination of non-desired nucleic acid sequences in a sequence-specific manner, and consequently, for the enrichment of nucleic acid sequences of interest in a nucleic acid library.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Apparatus, methods and compositions for biotechnical separations
InactiveUS20020010145A1Low costImprove performanceGenetic material ingredientsTyresFractional PrecipitationPlasmid dna
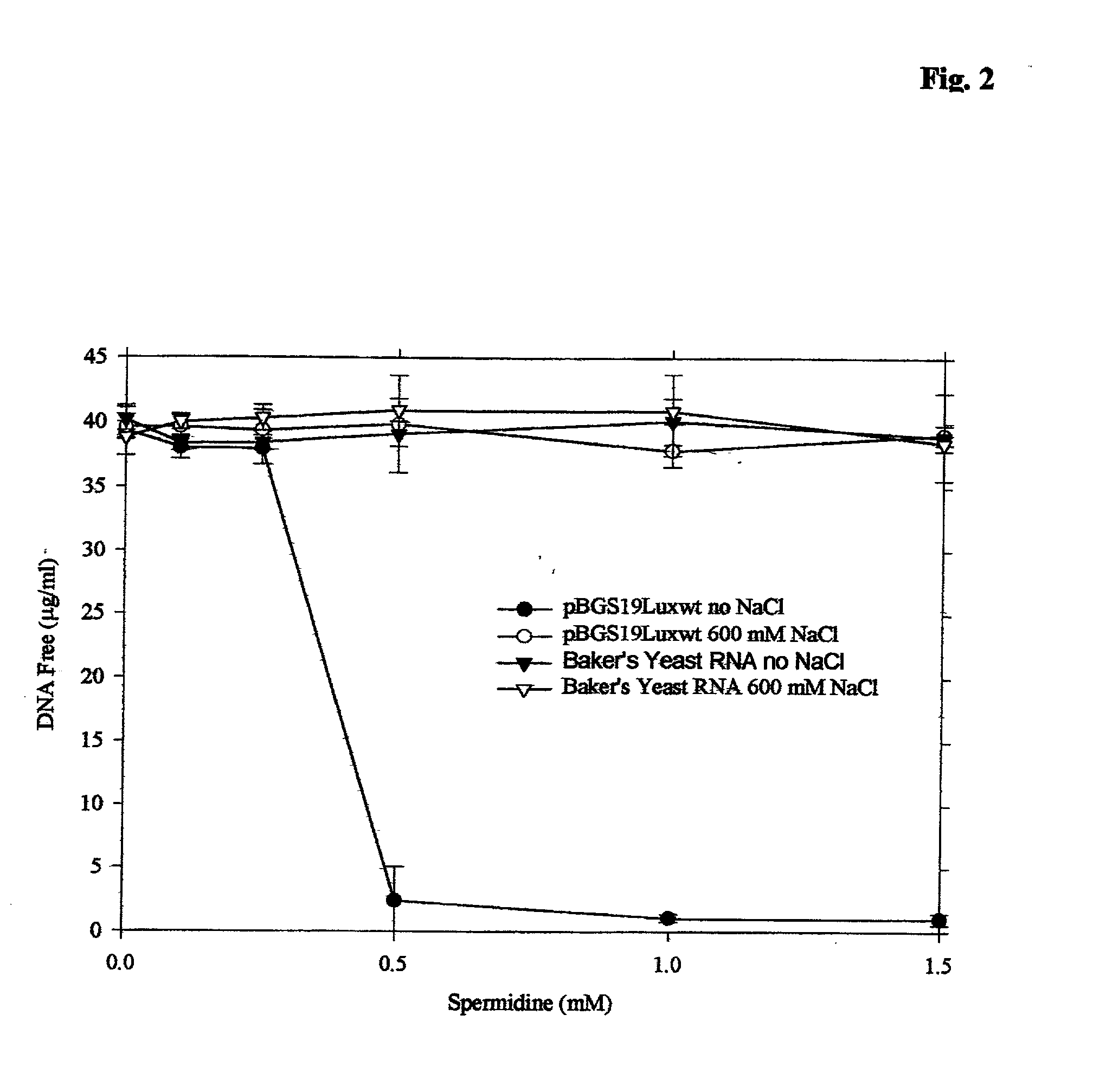
embodiments of the invention include purification of DNA, preferably plasmid DNA, by use of selective precipitation, preferably by addition of compaction agents Also included is a scaleable method for the liquid-phase separation of DNA from RNA. RNA may also be recovered by fractional precipitation according to the invention. RNA, commonly the major contaminant in DNA preparations, can be left in solution while valuable purified plasmid DNA is directly precipitated. Endotoxin can also be kept to very low levels. The invention includes mini-preps, preferably of plasmid and chromosomal DNA to obtain sequenceable and restriction digestible DNA in high yields in multiple simultaneous procedures. As a method of assay, a labeled probe is precipitated by hybridizing it to a target, (erg. chromosomal DNA, oligonucleotides, Ribosomal RNA, tRNA), and thereafter precipitating the probe / target complex with compaction agents and leaving in solution any unhybridized probe.
Owner:WILLSON RICHARD C III +1
Novel strain of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use
InactiveUS20150147303A1Inhibits pathogenic growthPromote biodegradationBiocideFruit and vegetables preservationBacteroidesBacilli
An isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 having an Accession No. of DSM 21836 is provided. This novel strain has unique 16S ribosomal RNA sequenced as SEQ ID NO:1 and produces amylase, protease, cellulase and lipase, fibrinolytic enzyme to show their biodegradation capacities. Further, B. amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 produces the antibiotic substances, such as iturin, fengycin and surfactin, and has antimicrobial capacity for inhibiting the fungal or bacterial growth. In conclusion, the novel strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 and its products can be applied in agriculture, wastewater treatment, food industry and chemical industry.
Owner:HSIEH FENG CHIA
Probes and methods for detection of pathogens and antibiotic resistance
ActiveUS20080199863A1Increase assayRapid detection of antimicrobialSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic resistanceNucleic acid sequencing
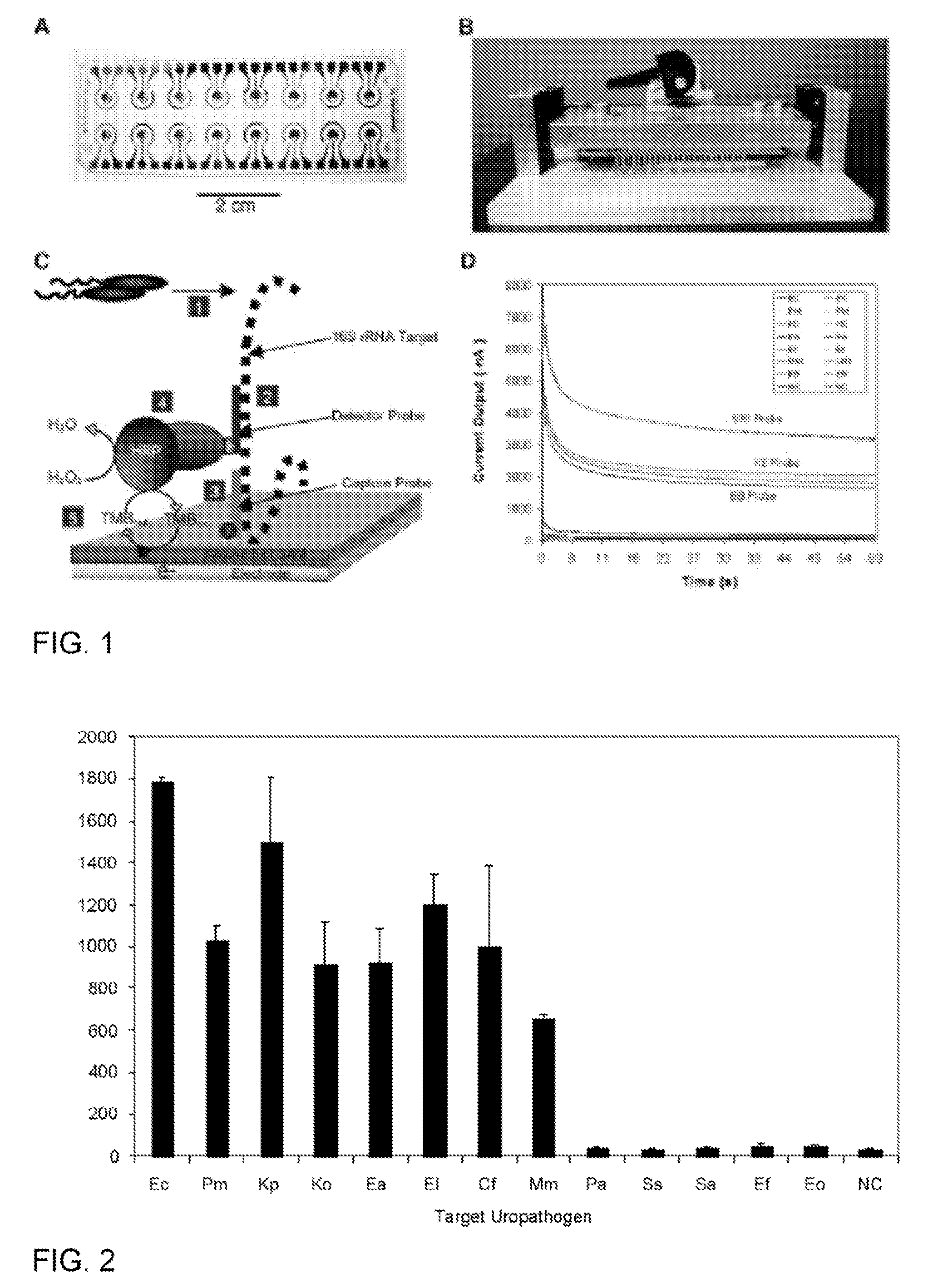
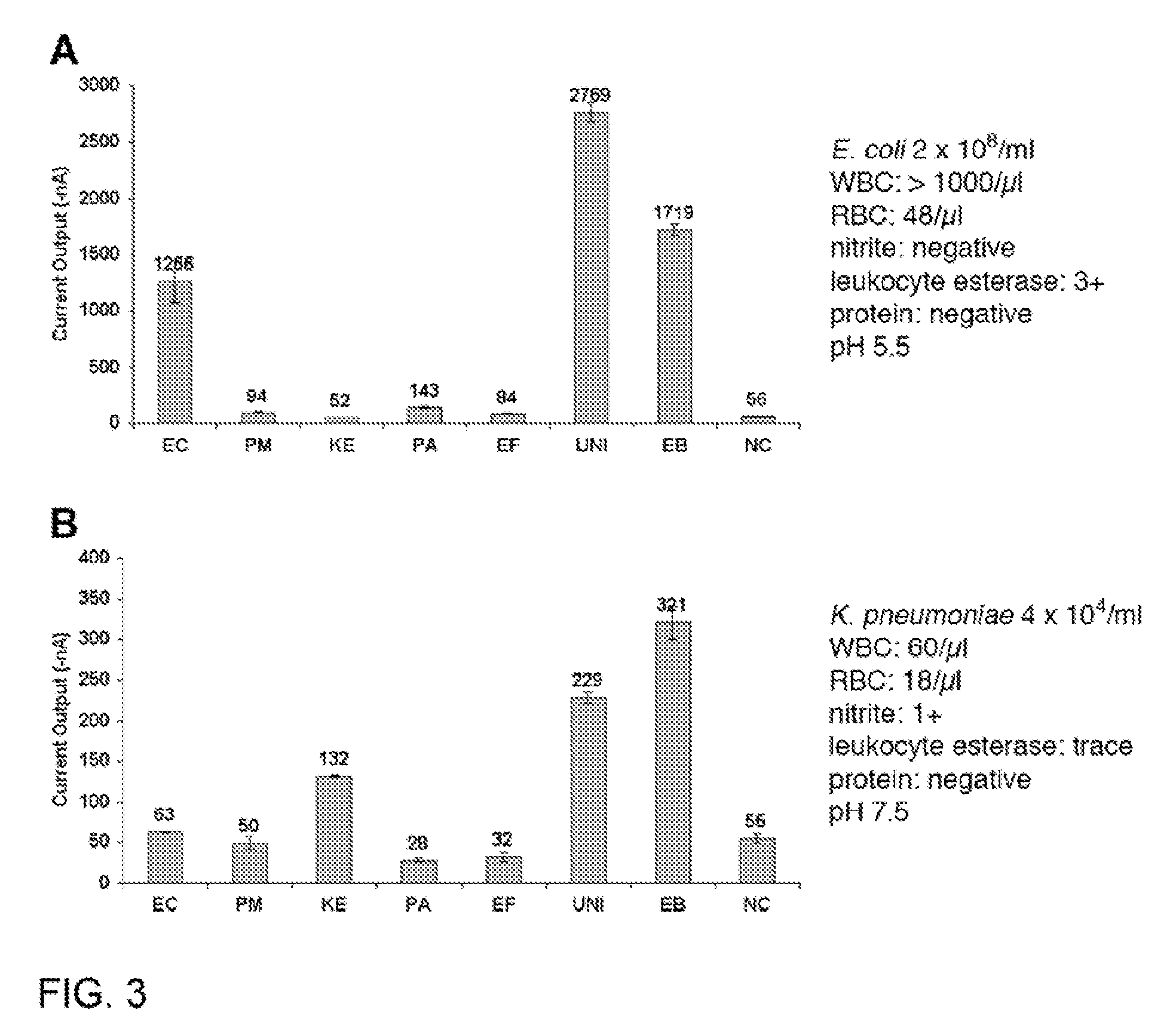
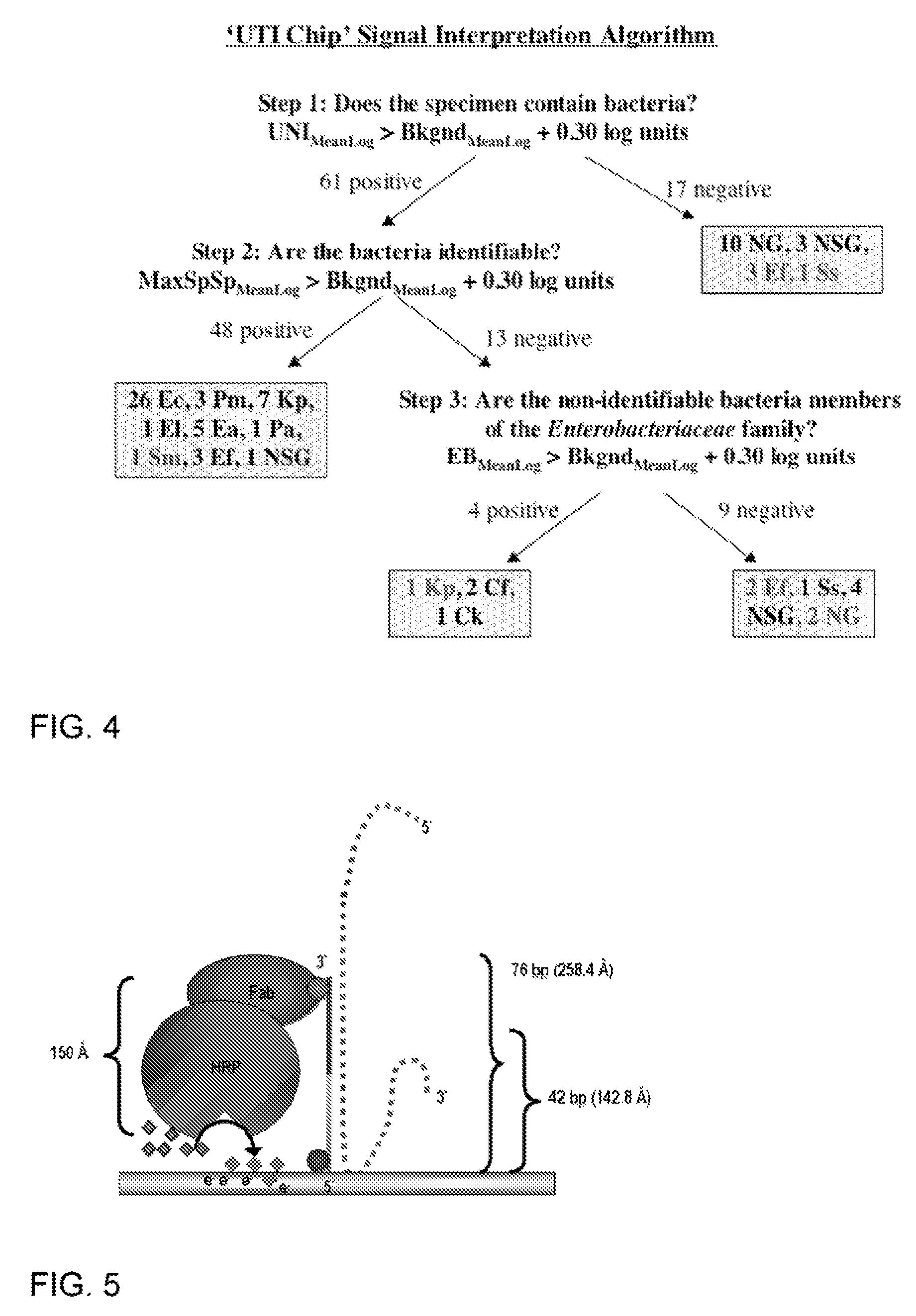
Described are probes and methods for detecting pathogens and antibiotic resistance of a specimen. The method comprises contacting the specimen with a growth medium; and lysing the specimen to release nucleic acid molecules from the specimen. The lysate of the specimen is contacted with a capture probe immobilized on a substrate, wherein the capture probe comprises an oligonucleotide that specifically hybridizes with a first target nucleic acid sequence region of ribosomal RNA. The lysate is in contact with a detector probe that comprises a detectably labeled oligonucleotide that specifically hybridizes with a second target nucleic acid sequence region of ribosomal RNA. The presence or absence of labeled oligonucleotide complexed with the substrate is determined. Detection of labeled oligonucleotide complexed with the substrate is indicative of the presence of pathogen. Performing the method in the presence and absence of an antibiotic permits detection of antibiotic resistance.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Compositions and methods for whole transcriptome analysis
InactiveUS20110189679A1Reduction and substantial eliminationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRibosomal RNABioinformatics
The present invention provides methods and compositions, including kits, for the generation of cDNA from mRNA with reduced ribosomal RNA representation.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
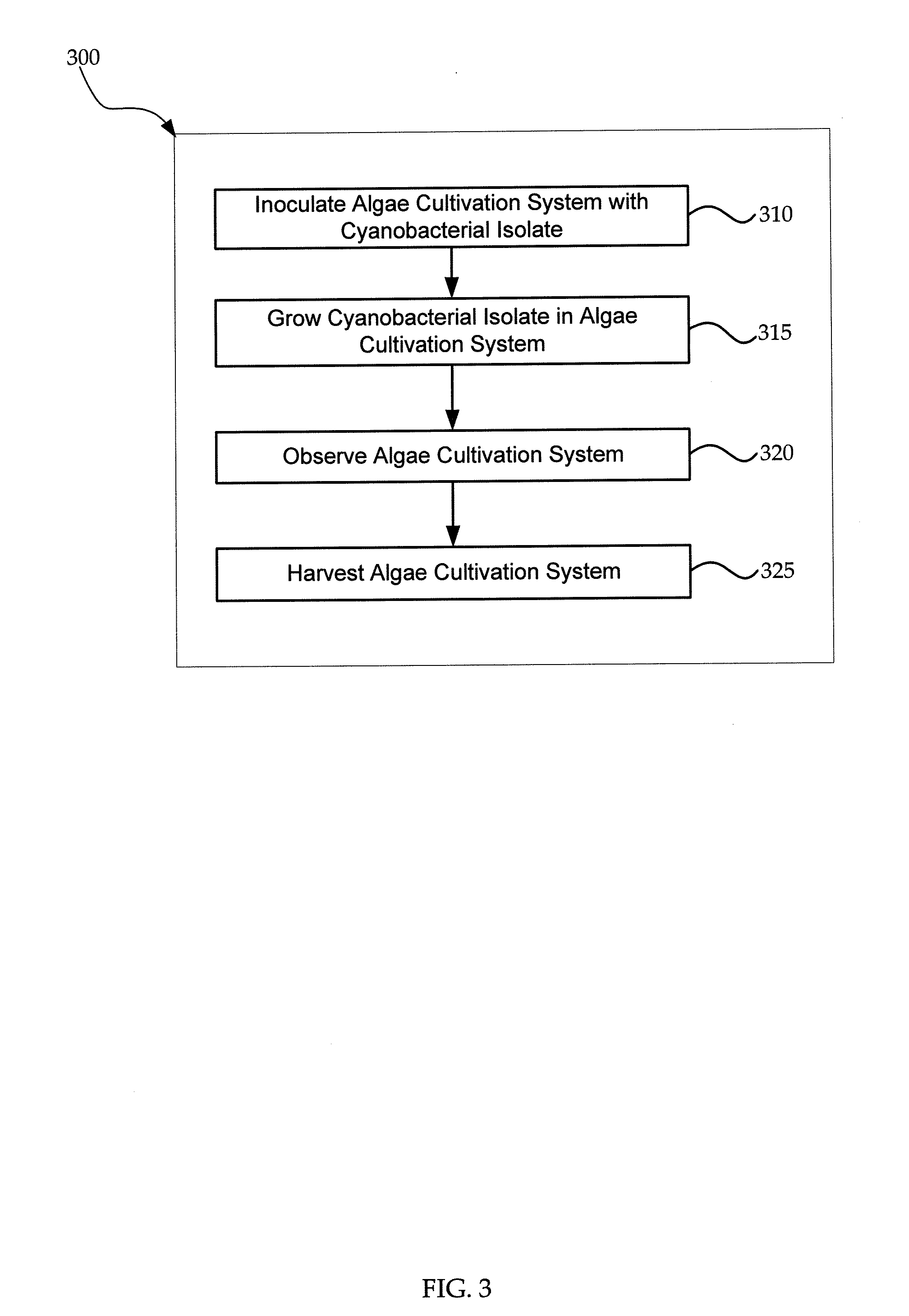
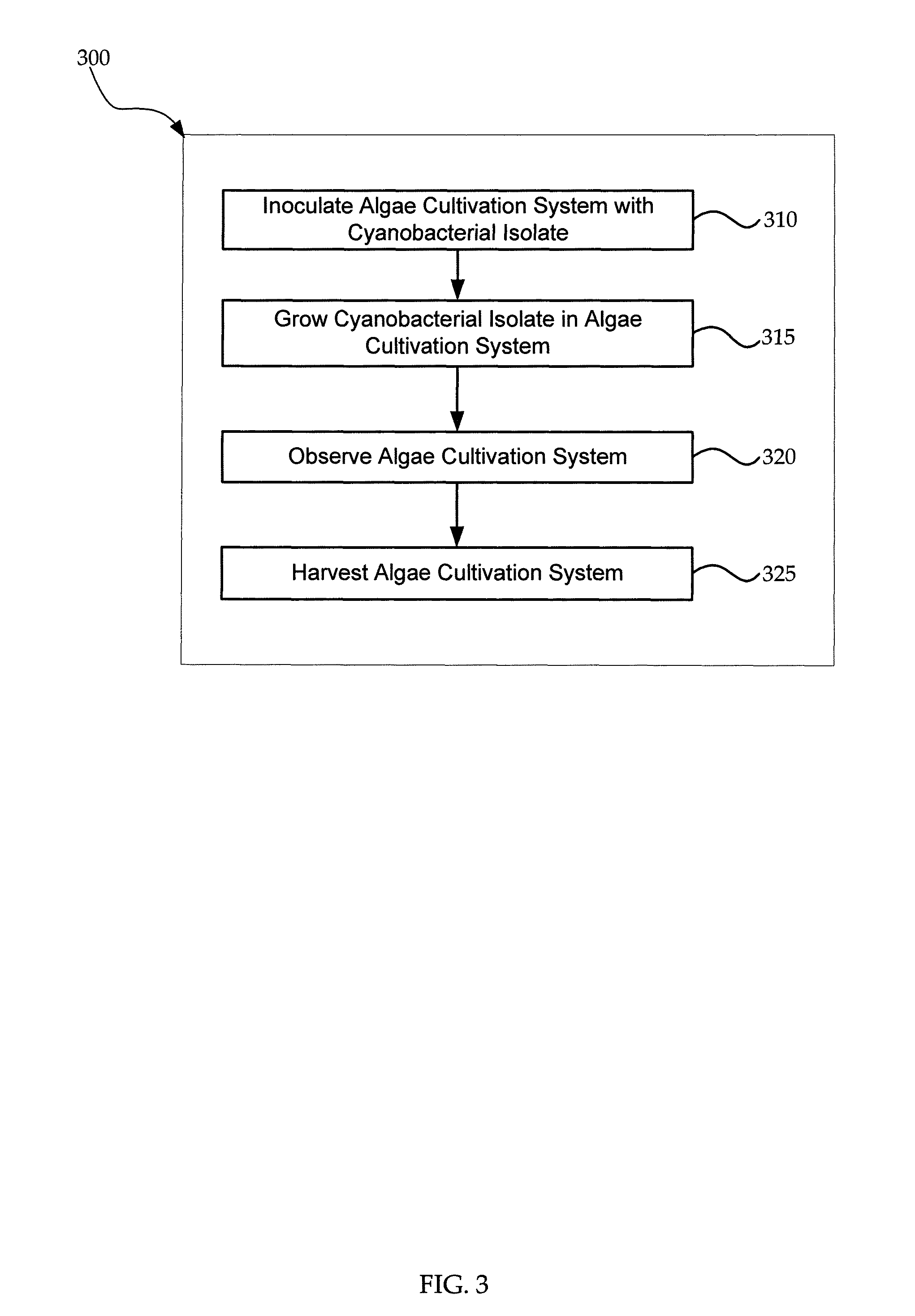
Cyanobacterial Isolates Having Auto-Flocculation and Settling Properties
Provided herein are exemplary methods for production of biomass with a cyanobacterial isolate having auto-flocculation properties. One exemplary method includes isolating a cyanobacterial strain having a 16S ribosomal RNA sequence corresponding to SEQ. ID. NO. 1 herein, inoculating an algae cultivation system with the cyanobacterial strain, growing the cyanobacterial strain, and harvesting the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain. According to a further method, the harvesting of the biomass comprises ceasing agitation of the algae cultivation system, and pooling a slurry of the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain. In a further method, the harvesting of the biomass may comprise ceasing agitation within the algae cultivation system and / or allowing the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain to settle to near or at a bottom of the algae cultivation system. Also provided herein are exemplary cyanobacterial strains having flocculation properties for production of a biomass.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
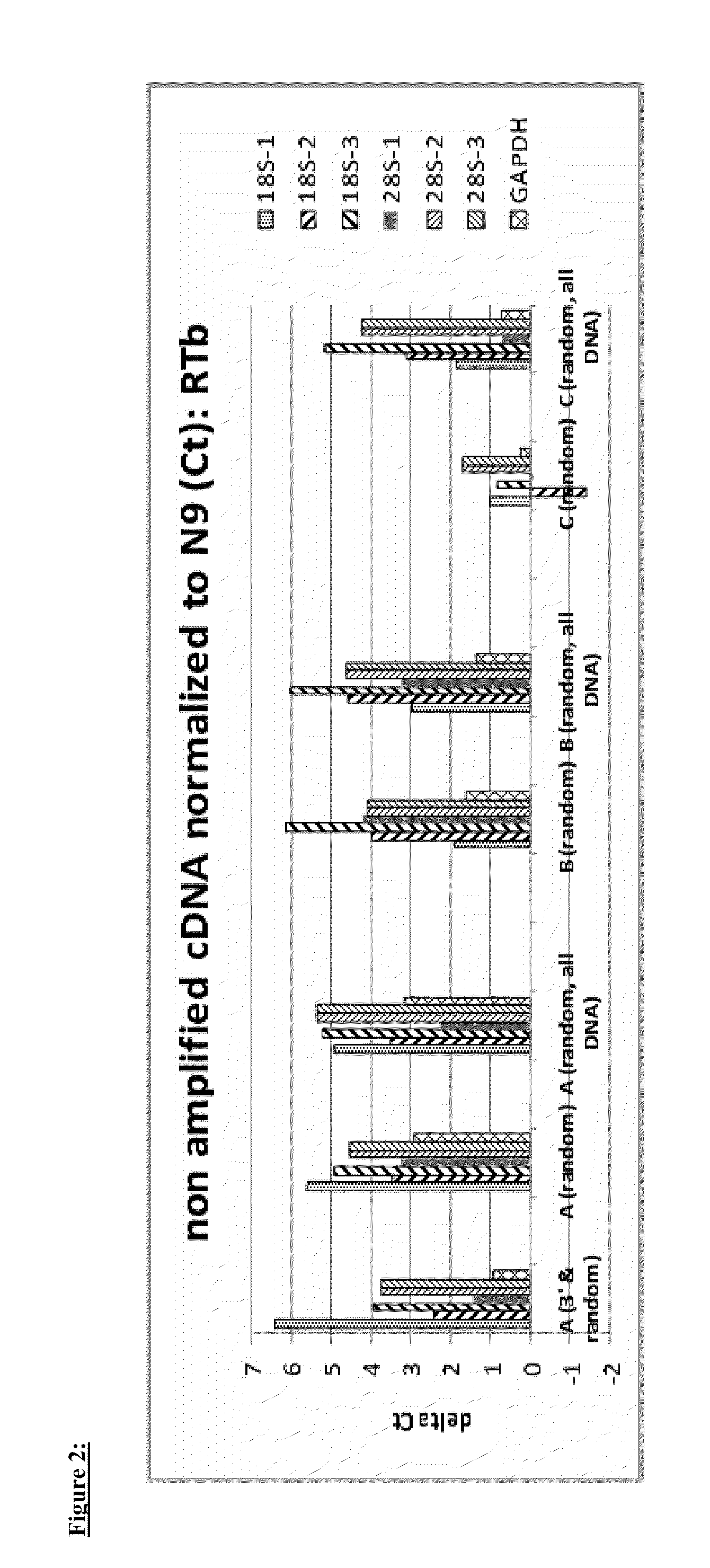
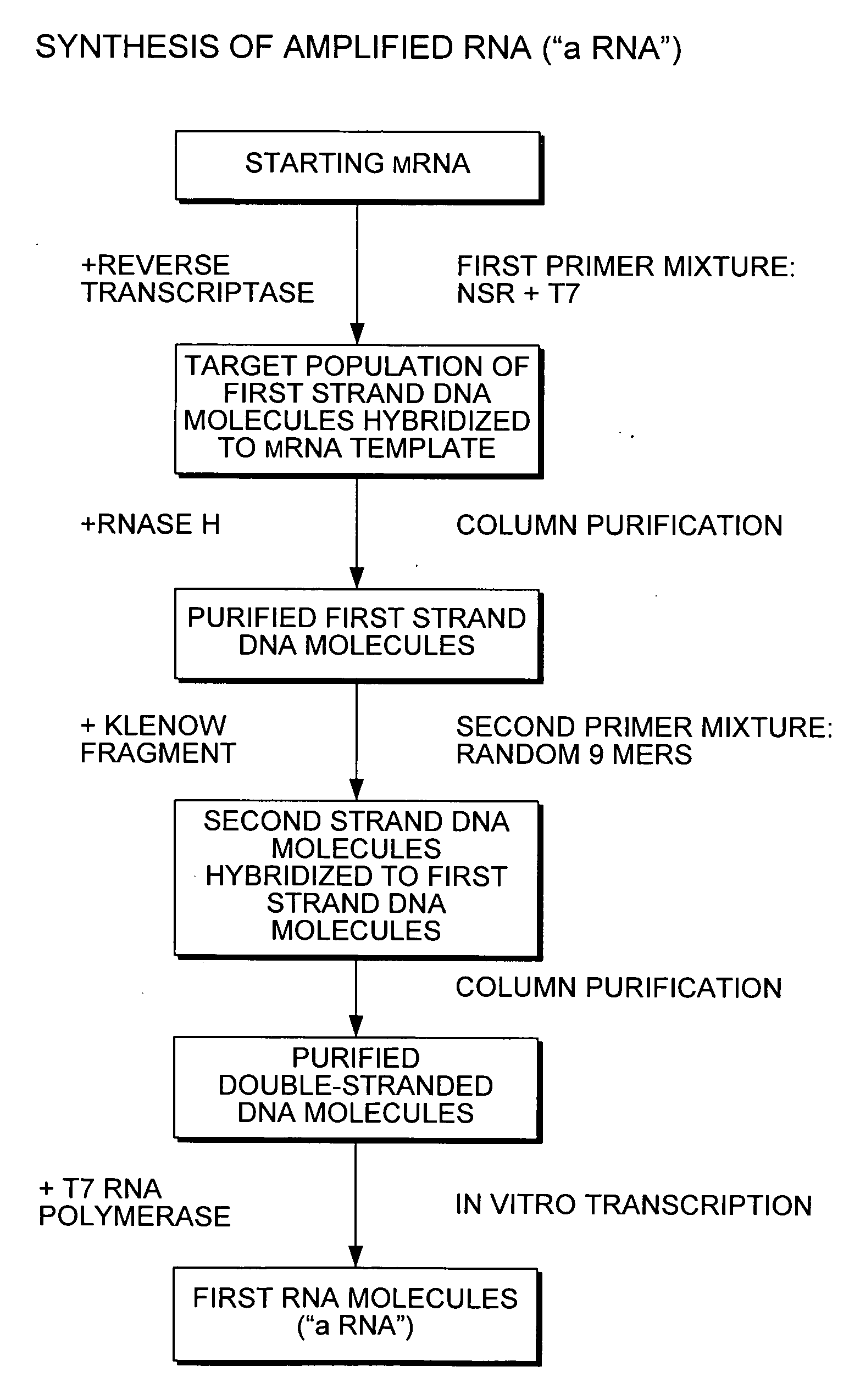
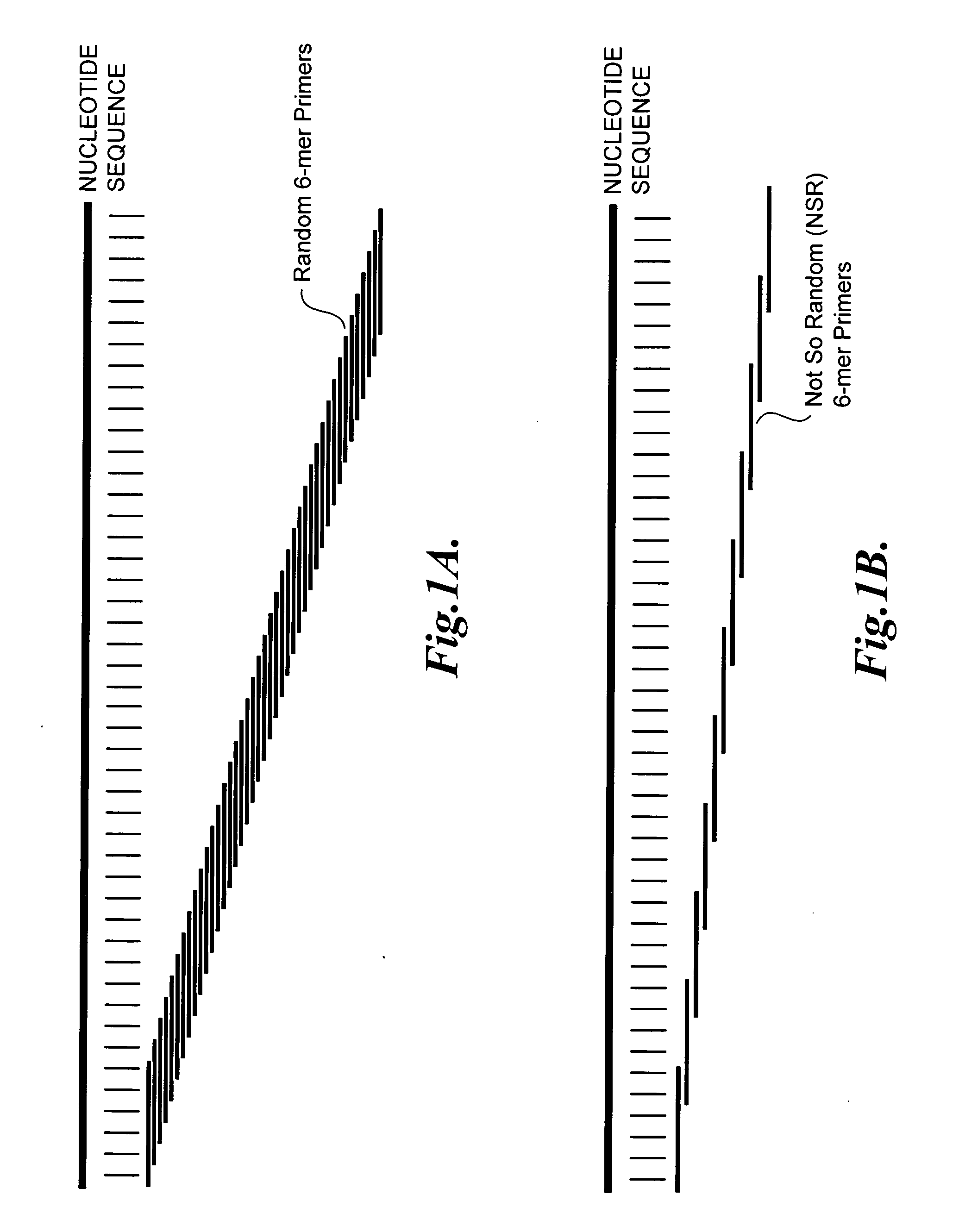
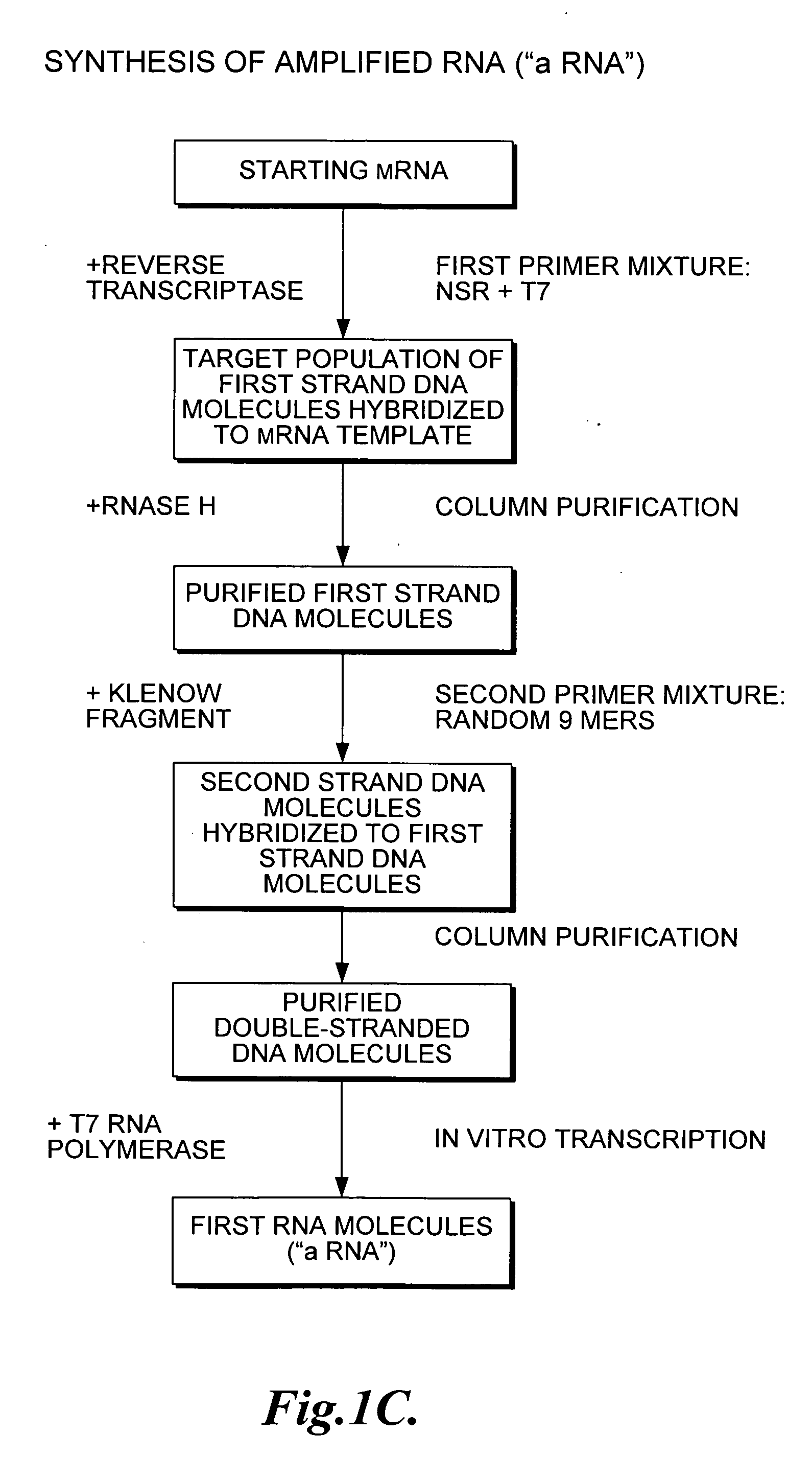
Nucleic acid amplification using non-random primers
InactiveUS20080187969A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingRibosomal RNA
The present invention provides methods for selectively amplifying a target population of nucleic acid molecules (e.g., all mRNA molecules expressed in a cell type except for the most highly expressed mRNA species). The present invention also provides populations of oligonucleotides including the nucleic acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOS:1-933. These oligonucleotides can be used, for example, to prime the synthesis of cDNA molecules complementary to mRNA molecules isolated from mammalian blood without priming the synthesis of cDNA molecules complementary to globin mRNA, or ribosomal RNA molecules.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method and kit for preparing a target RNA depleted sample
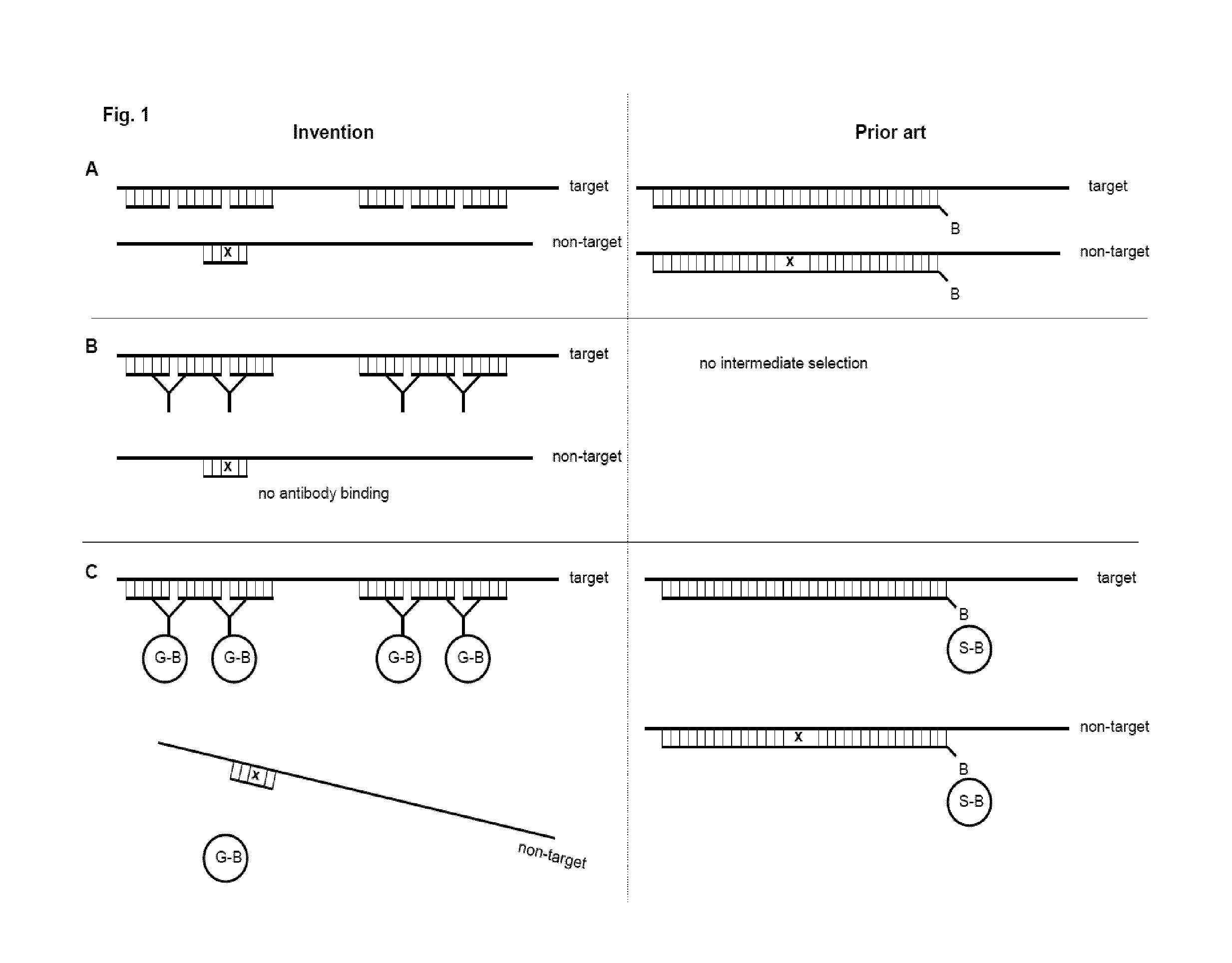
InactiveUS20150275267A1Simple methodDepleting unwanted target RNAPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaNon-coding RNA
The present invention provides a method of preparing a target RNA depleted composition from an initial RNA containing composition, comprising a) contacting the initial RNA containing composition with one or more groups of probe molecules, wherein a group of probe molecules has the following characteristics: i) the group comprises two or more different probe molecules having a length of 100 nt or less; ii) the probe molecules comprised in said group are complementary to a target region of a target RNA; iii) when hybridized to said target region, the two or more different probe molecules are located adjacent to each other in the formed double-stranded hybrid; and generating a double-stranded hybrid between the target RNA and the probe molecules; b) capturing the double-stranded hybrid by using a binding agent which binds the double-stranded hybrid, thereby forming a hybrid / binding agent complex; c) separating the hybrid / binding agent complexes from the composition, thereby providing a target RNA depleted composition. By combining hybrid capturing with a unique probe design, an improved depletion method is provided which effectively and specifically removes unwanted target RNA such as ribosomal RNA (rRNA) from total RNA, while ensuring recovery of mRNA and noncoding RNA from various species, including human, mouse, and rat. By improving the ratio of useful data, decreasing bias, and preserving non-coding RNA species, the method provides high-quality RNA that is especially suited for next-generation sequencing (NGS) applications. By integrating said depletion method in common sequencing applications, in particular NGS applications such as transcriptome sequencing, improved methods for sequencing RNA molecules are provided.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
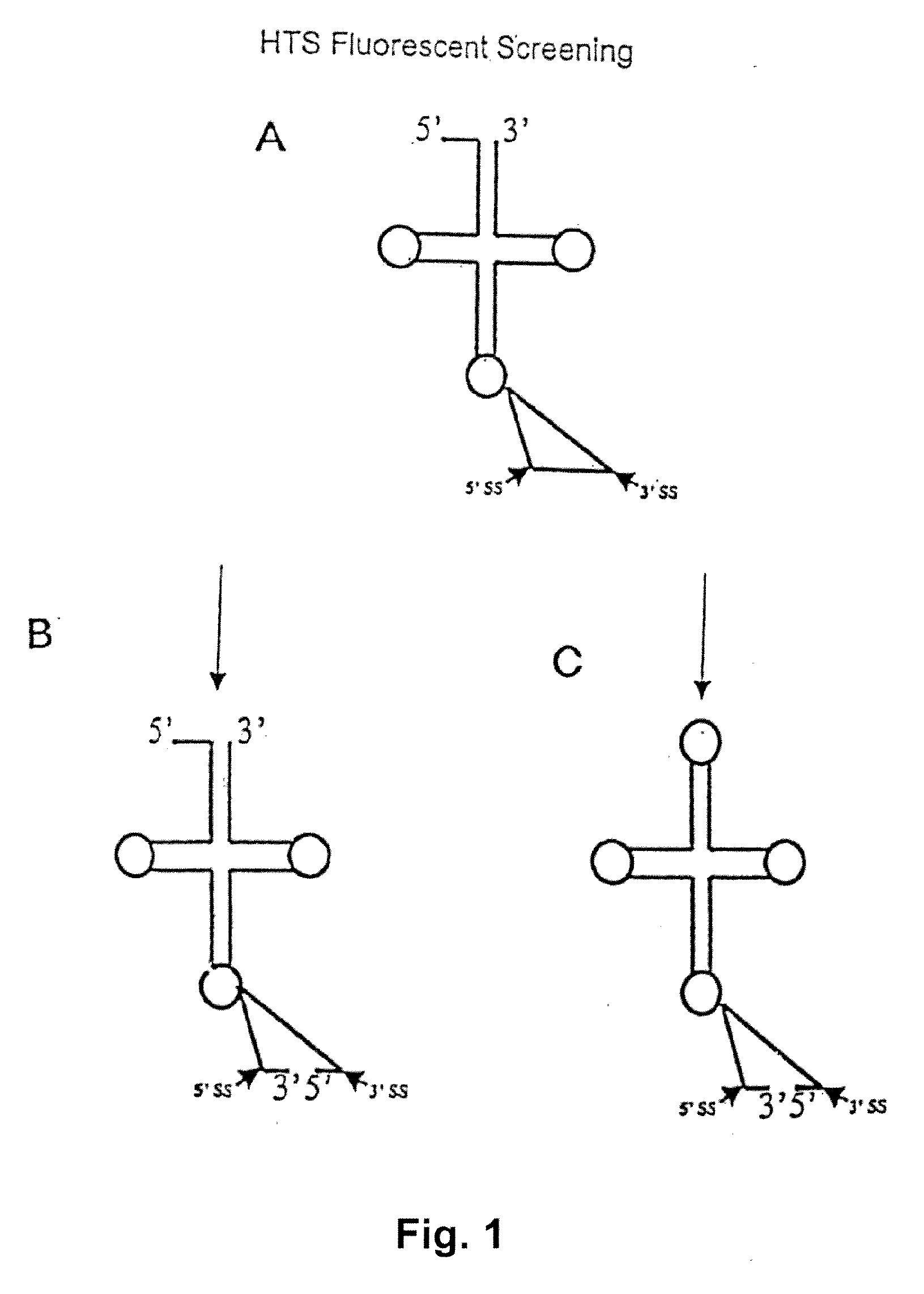
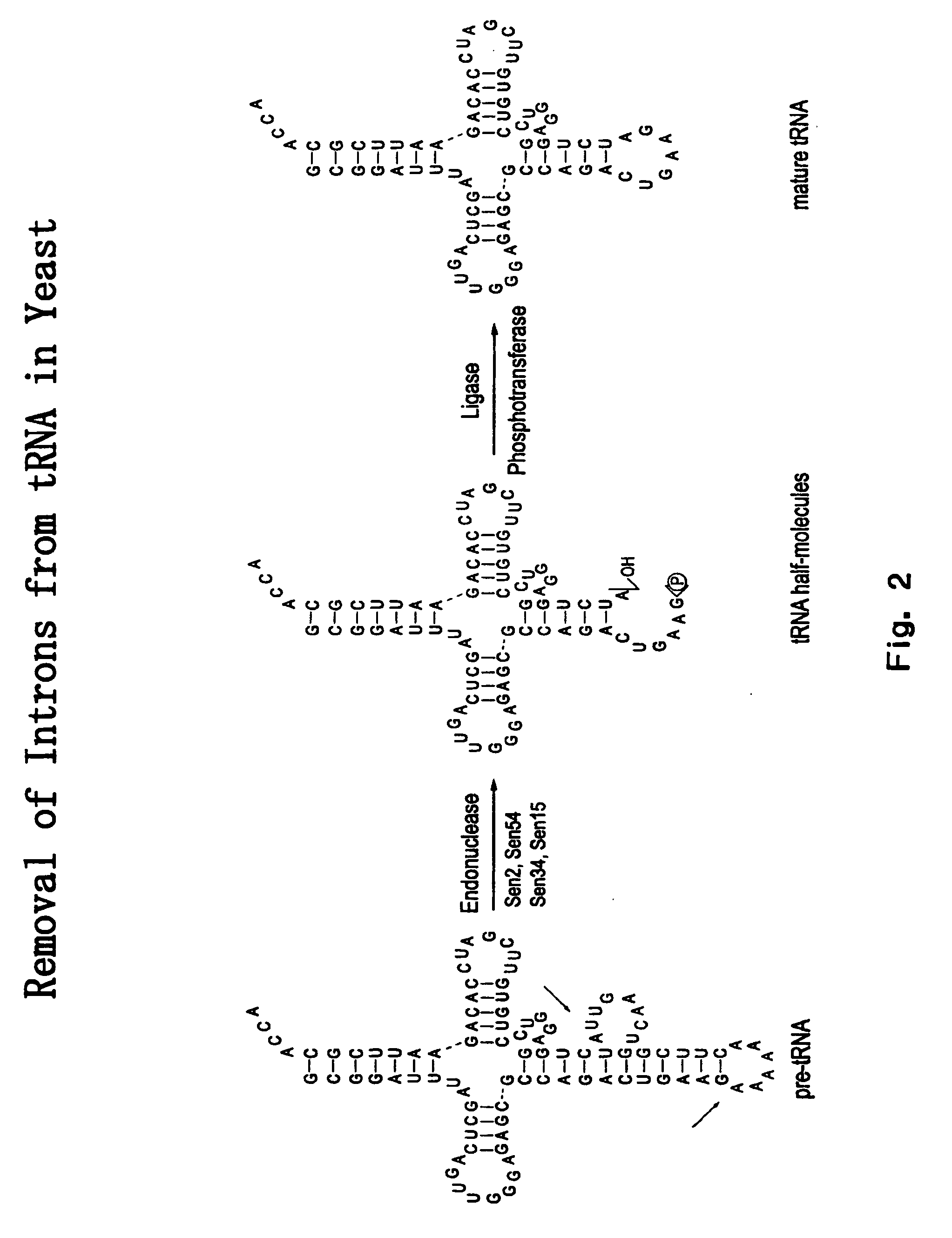
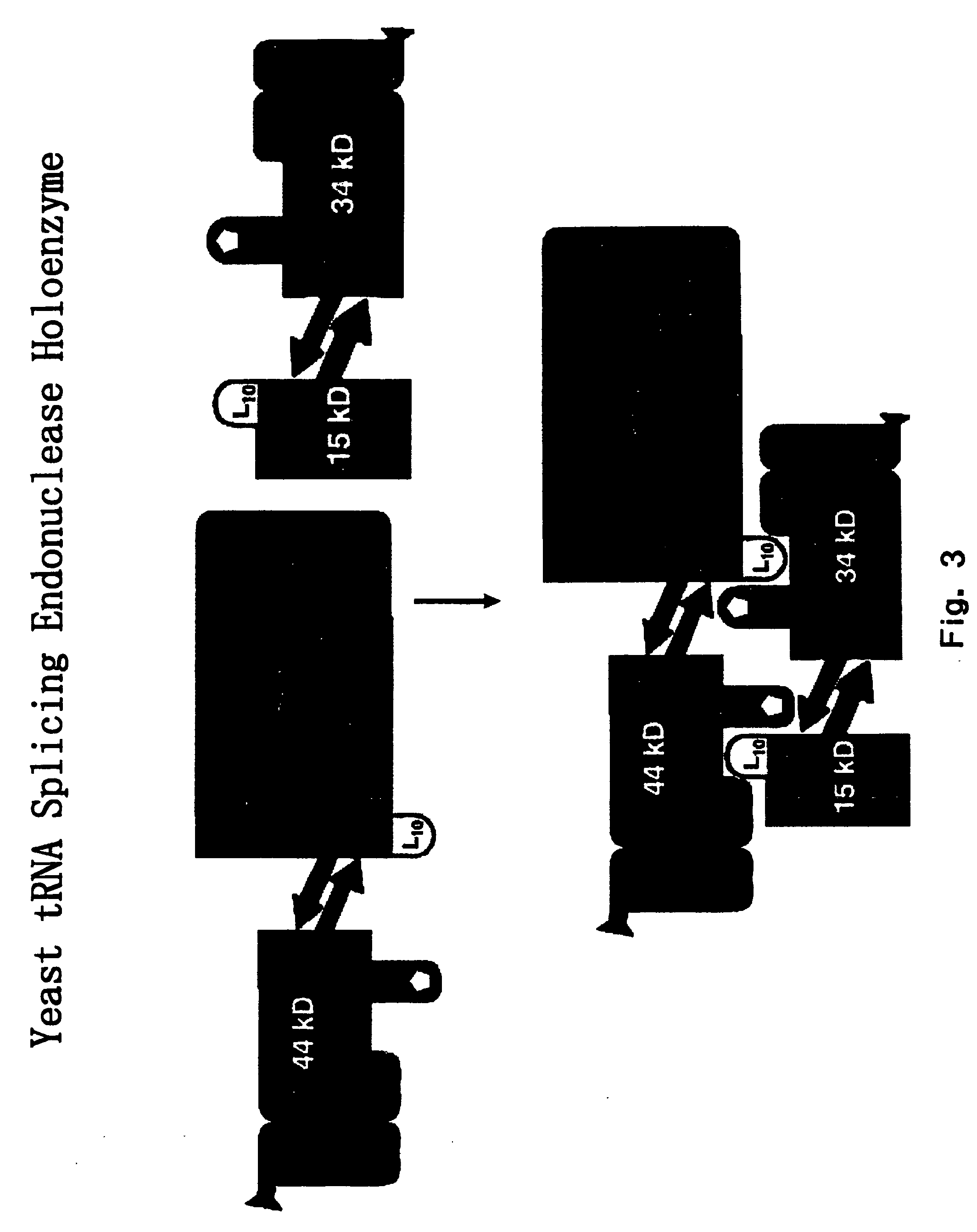
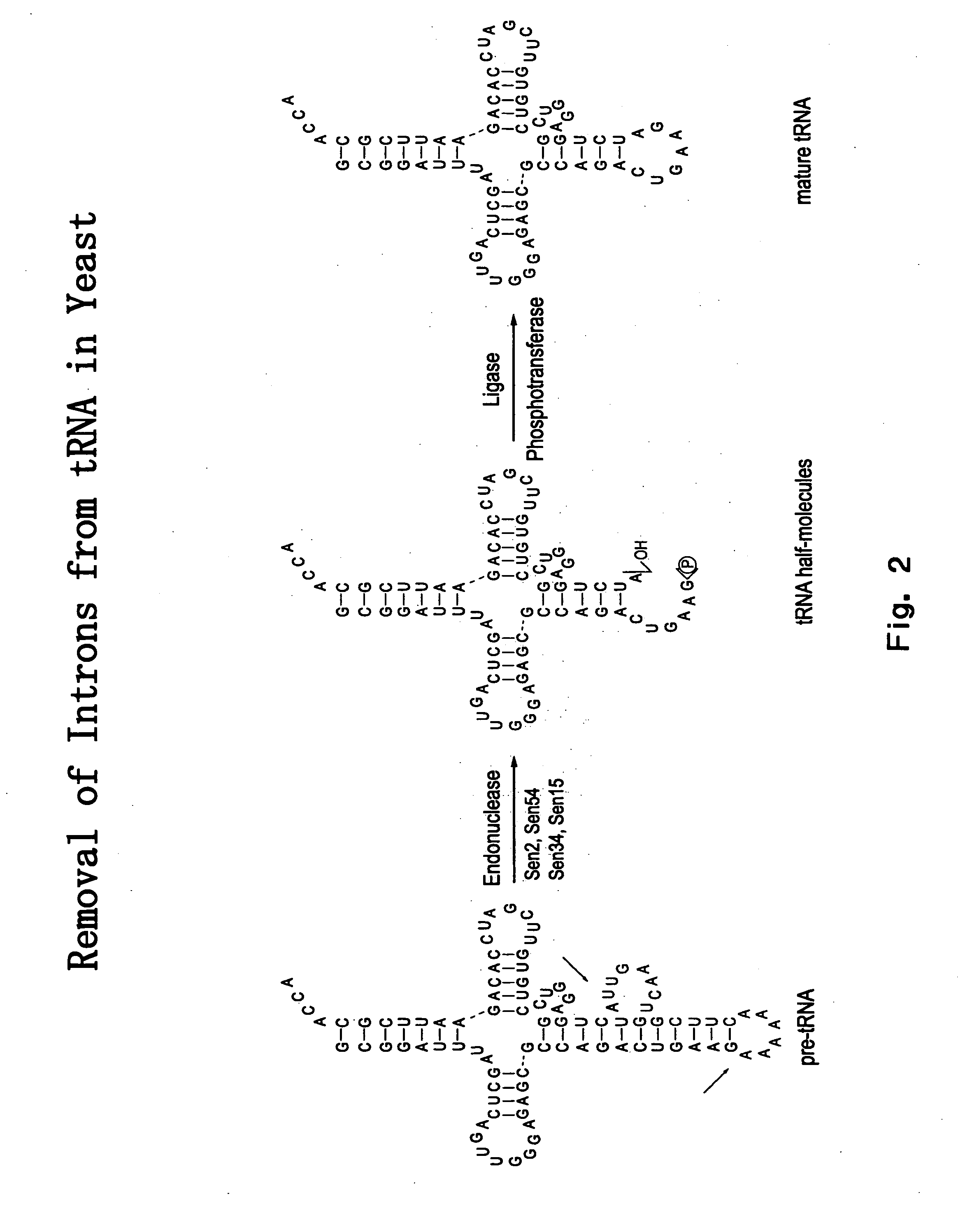
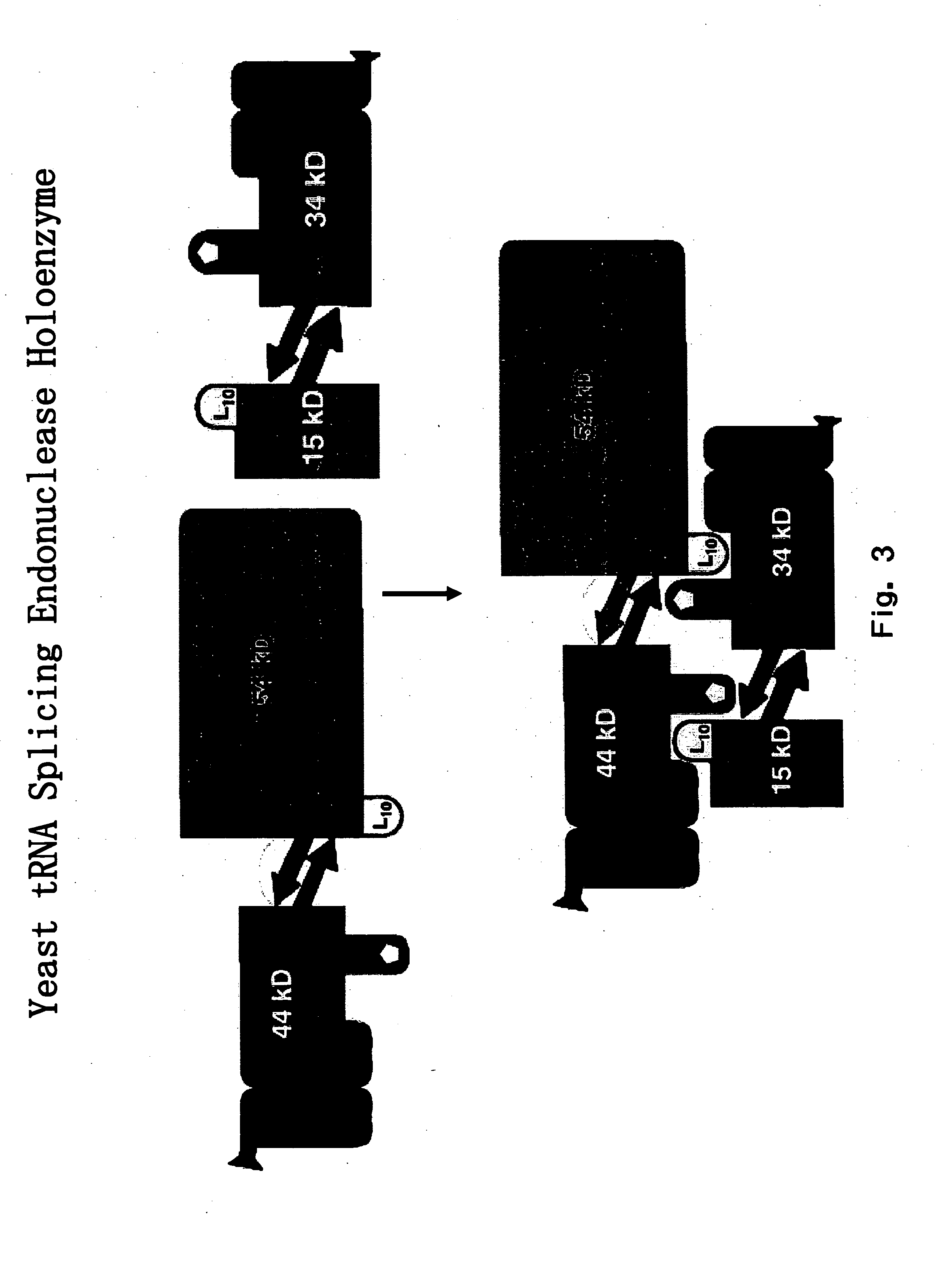
RNA processing protein complexes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100136710A1Improve accuracyFidelity of of reducedSugar derivativesHydrolasesDiseaseProtein-protein complex
The invention provides human protein complexes with endonuclease activity. In particular, the invention provides human protein complexes with tRNA splicing endonuclease activity and / or 3′ end pre-mRNA endonuclease activity. The invention also provides a splice variant of human Sen2, namely human Sen2deltaEx8, and human protein complexes comprising human Sen2deltaEx8. The human Sen2deltaEx8 complexes have pre-tRNA cleavage activity and / or 3′ end pre-mRNA endonuclease activity. The invention also provides human protein complexes with pre-ribosomal RNA cleavage activity. The invention also provides antibodies that immunospecifically bind to a complex described herein or a component thereof, and methods of diagnosing, preventing, treating, managing or ameliorating a disorder utilizing such antibodies. The present invention also provides methods utilizing the complexes described herein, inter alia, in screening, diagnosis, and therapy. The invention further provides methods of preparing and purifying the complexes. The present invention further provides methods of identifying a compound that modulates the expression of a component of a complex described herein, the formation of a complex described herein or the activity of a complex described herein, and methods of preventing, treating, managing or ameliorating a disorder, such as a proliferative disorder, or a symptom thereof utilizing a compound identified in accordance with the methods.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
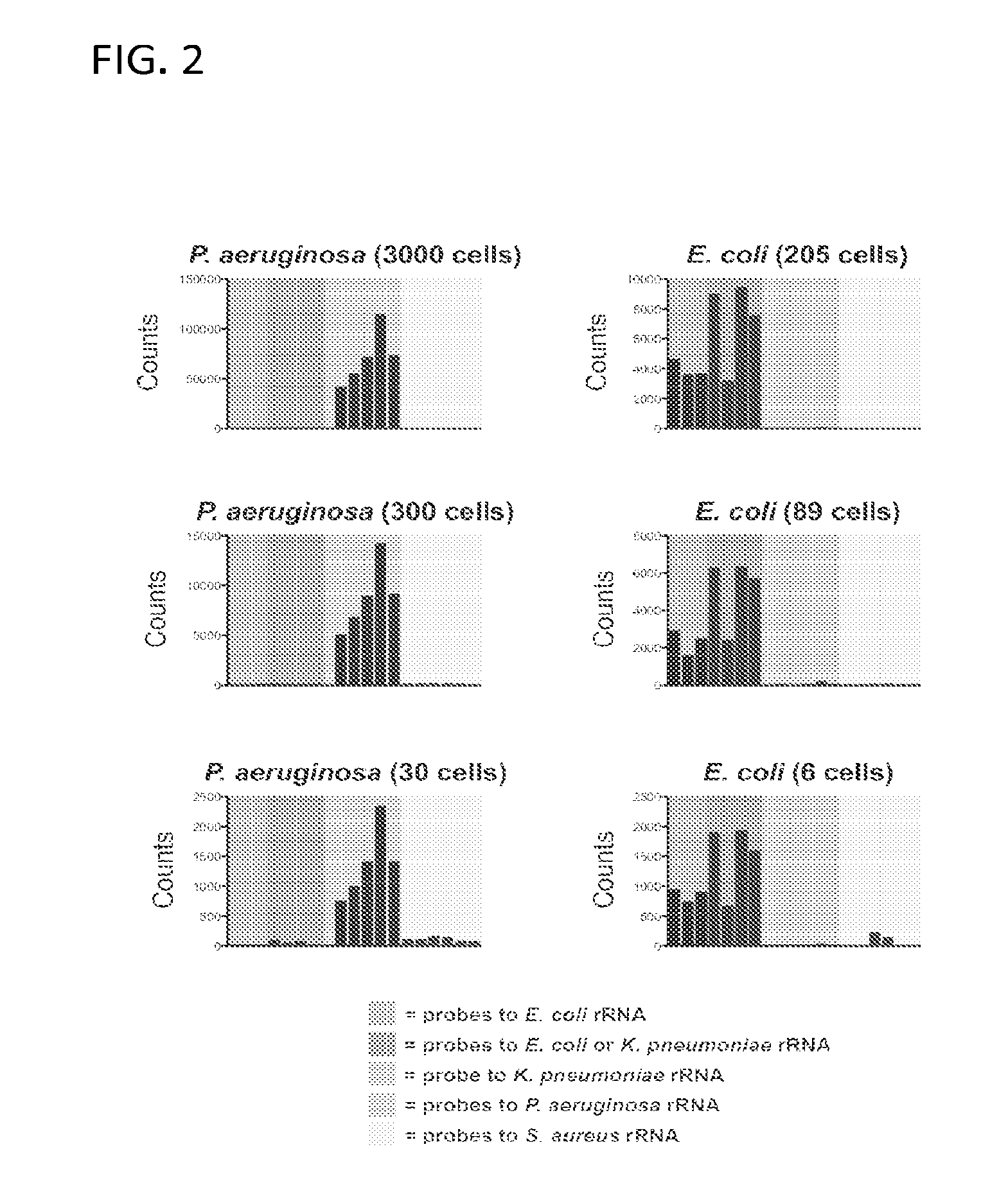
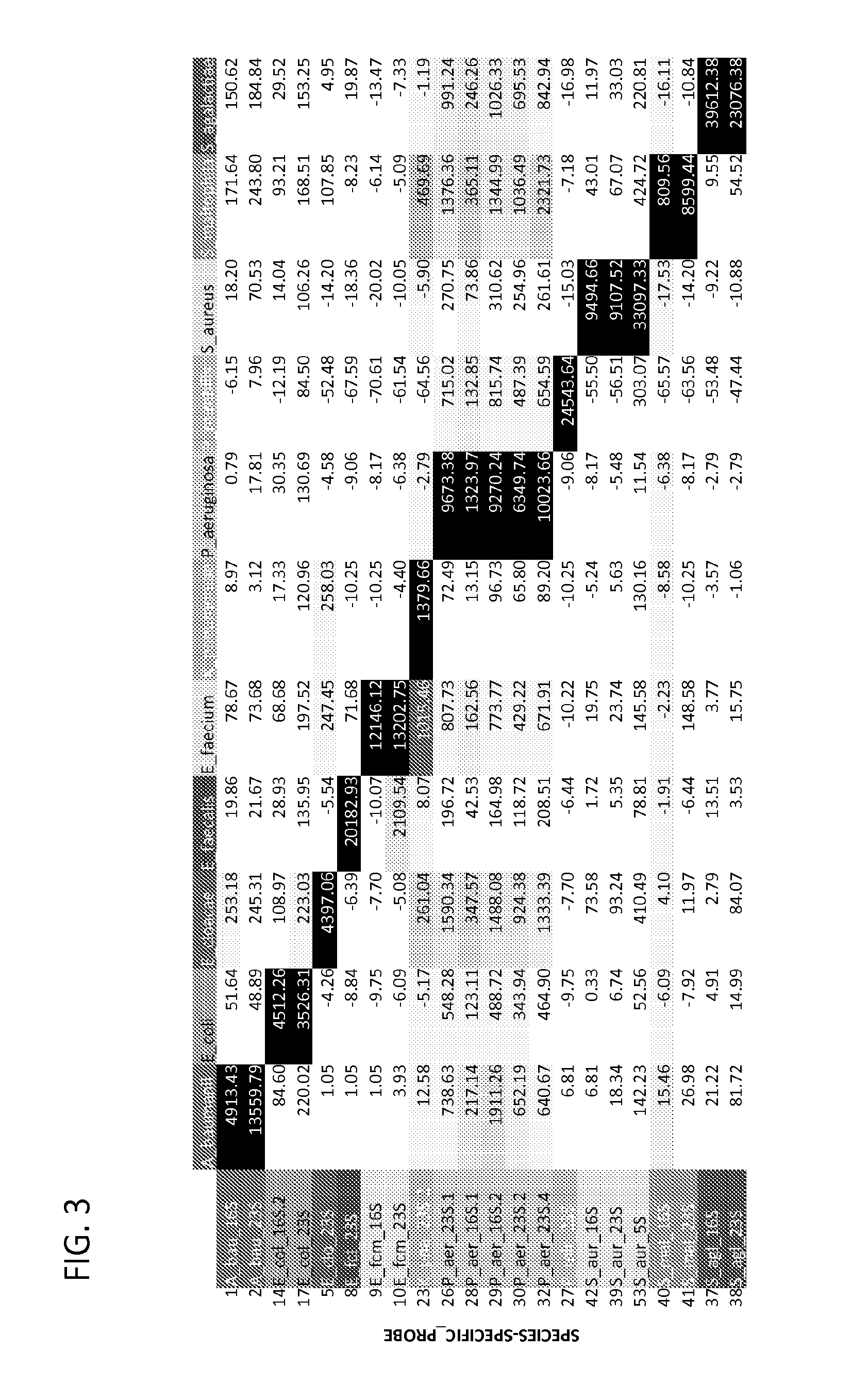
Ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid Hybridization for Organism Identification
The present disclosure relates to method of distinguishing between two or more species of one or more organisms in a sample, by contacting a biological sample comprising ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) with a set of antisense probes, wherein the set of probes contains at least one detectable probe that is specific for a target rRNA sequence of each species to be tested, and wherein the individual probes specific for each species comprises less than about 85% sequence identity; and, detecting hybridization between one or more of the probes and the rRNA, thereby distinguishing between two or more species in a sample.
Owner:NANOSTRING TECH INC +2
Ricin inhibitors and methods for use thereof
Ricin A-chain is an N-glycosidase that attacks ribosomal RNA at a highly conserved adenine residue. Crystallographic studies show that not only adenine and formycin, but also pterin-based rings can bind in the ricin active site. For a better understanding of the recognition mode between ricin, and adenine-like rings, the interaction energies and geometries were calculated for a number of complexes. Shiga toxin, a compound essentially identical to the protein originally isolated from Shigella dysenteriae, has an active protein chain that is a homologue of the ricin active chain, and catalyzes the same depurination reaction. The present invention is drawn to identifying inhibitors of ricin and Shiga toxin, using methods molecular mechanics and ab initio methods and using the identified inhibitors as antidotes to ricin or Shiga toxin, or to facilitate immunotoxin treatment by controlling non-specific cytotoxicity.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
RNA processing protein complexes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050053985A1High expressionInhibit and reduce expressionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePrecursor mRNA
The invention provides human protein complexes with endonuclease activity. In particular, the invention provides human protein complexes with tRNA splicing endonuclease activity and / or 3' end pre-mRNA endonuclease activity. The invention also provides a splice variant of human Sen2, namely human Sen2deltaEx8, and human protein complexes comprising human Sen2deltaEx8. The human Sen2deltaEx8 complexes have pre-tRNA cleavage activity and / or 3' end pre-mRNA endonuclease activity. The invention also provides human protein complexes with pre-ribosomal RNA cleavage activity. The invention also provides antibodies that immunospecifically bind to a complex described herein or a component thereof, and methods of diagnosing, preventing, treating, managing or ameliorating a disorder utilizing such antibodies. The present invention also provides methods utilizing the complexes described herein, inter alia, in screening, diagnosis, and therapy. The invention further provides methods of preparing and purifying the complexes. The present invention further provides methods of identifying a compound that modulates the expression of a component of a complex described herein, the formation of a complex described herein or the activity of a complex described herein, and methods of preventing, treating, managing or ameliorating a disorder, such as a proliferative disorder, or a symptom thereof utilizing a compound identified in accordance with the methods.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Cyanobacterial isolates having auto-flocculation and settling properties
Provided herein are exemplary methods for production of biomass with a cyanobacterial isolate having auto-flocculation properties. One exemplary method includes isolating a cyanobacterial strain having a 16S ribosomal RNA sequence corresponding to SEQ. ID. NO. 1 herein, inoculating an algae cultivation system with the cyanobacterial strain, growing the cyanobacterial strain, and harvesting the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain. According to a further method, the harvesting of the biomass comprises ceasing agitation of the algae cultivation system, and pooling a slurry of the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain. In a further method, the harvesting of the biomass may comprise ceasing agitation within the algae cultivation system and / or allowing the biomass produced by the cyanobacterial strain to settle to near or at a bottom of the algae cultivation system. Also provided herein are exemplary cyanobacterial strains having flocculation properties for production of a biomass.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
Compositions and methods for negative selection of non-desired nucleic acid sequences
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Microbial markers and uses therefor
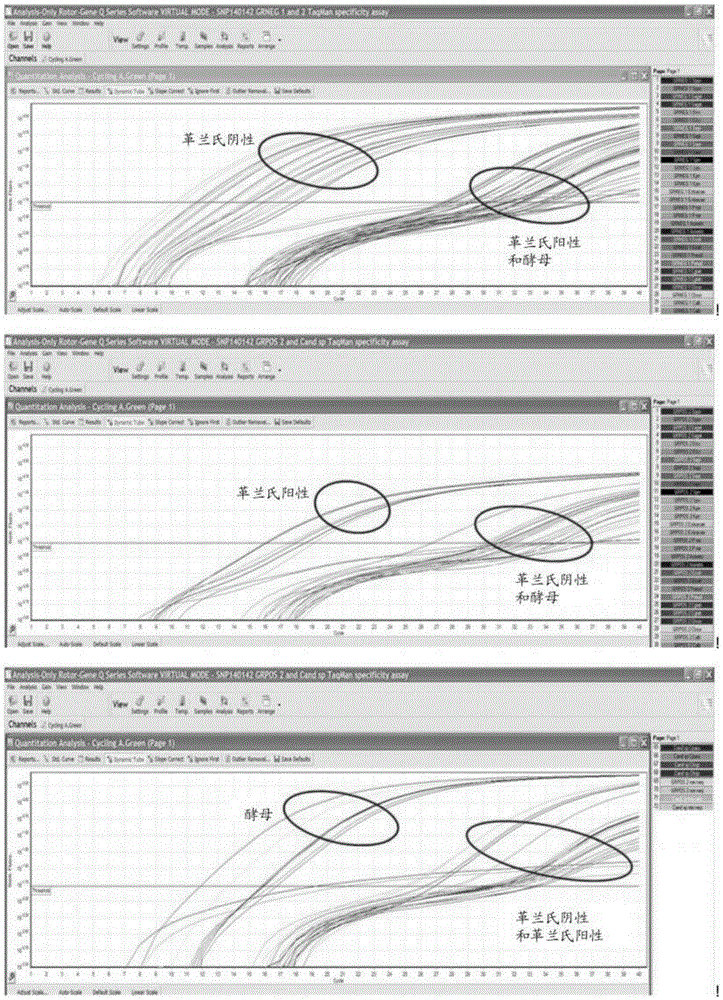
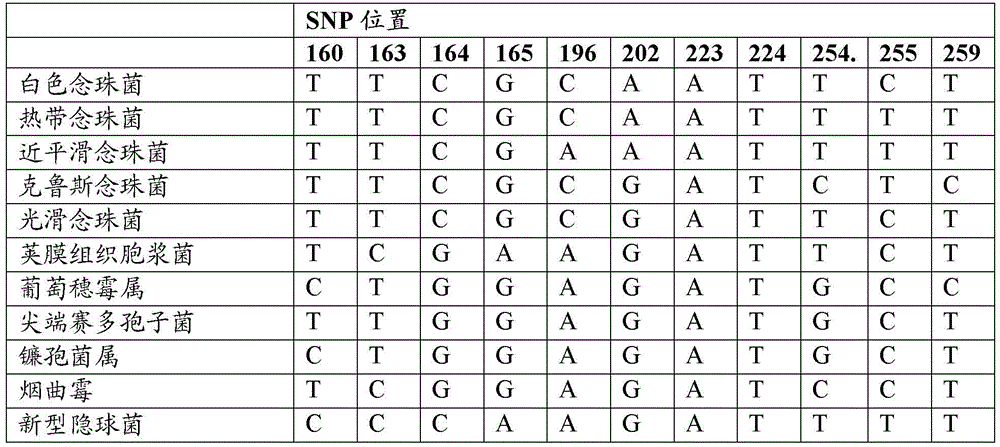
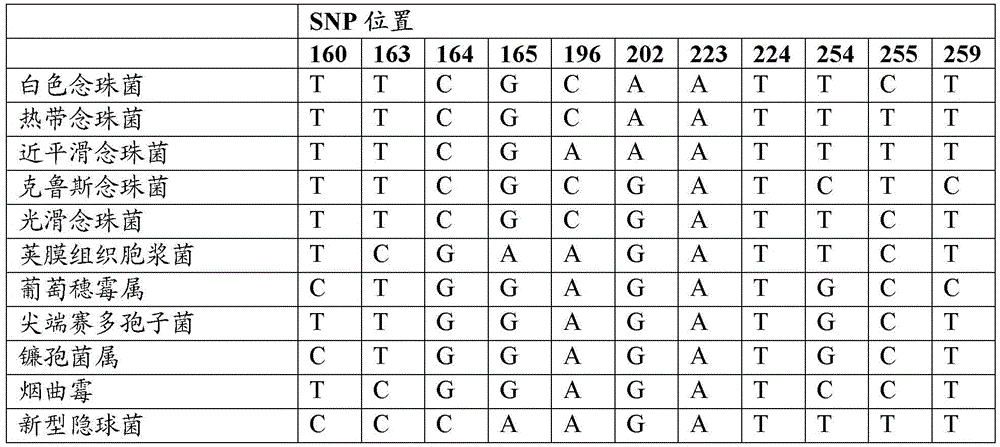
Disclosed are methods for identifying and / or classifying microbes using one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 16S ribosomal RNA (16S rRNA) of prokaryotes and / or one or more SNPs in 5.8S ribosomal RNA (5.8S rRNA) of eukaryotes. Also disclosed are probes, primers and kits that are useful in those methods. Methods for the diagnosis of sepsis based upon these SNPs are also disclosed.
Owner:IMMUNEXPRESS
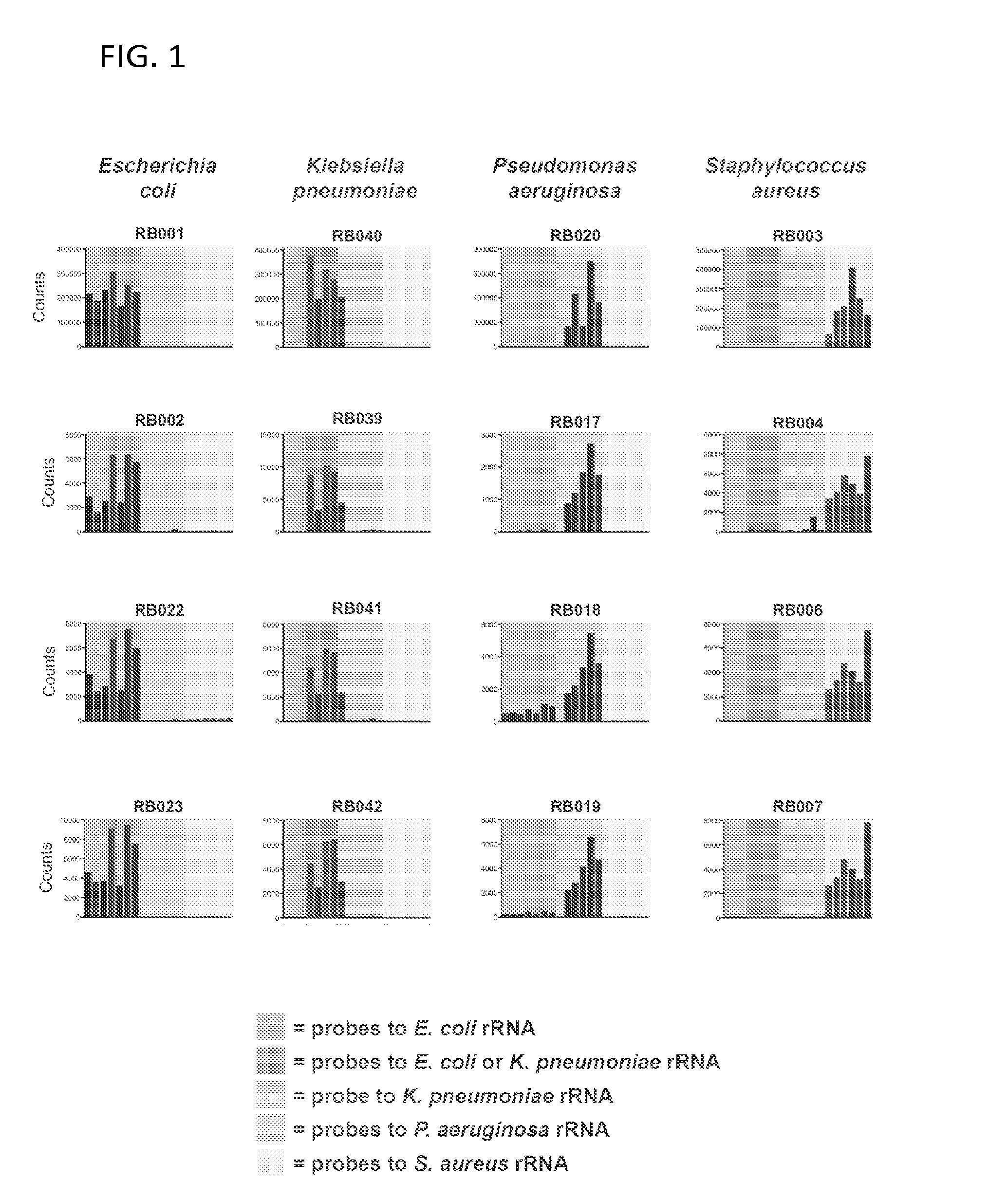
Probes and methods for detection of Escherichia coli and antibiotic resistance
ActiveUS7763426B2Rapid and species-specific detectionRapid detection of antimicrobialSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliAntibiotic resistance
Described are probes and methods for detecting pathogens and antibiotic resistance of a specimen. The method comprises contacting the specimen with a growth medium; and lysing the specimen to release nucleic acid molecules from the specimen. The lysate of the specimen is contacted with a capture probe immobilized on a substrate, wherein the capture probe comprises an oligonucleotide that specifically hybridizes with a first target nucleic acid sequence region of ribosomal RNA. The lysate is in contact with a detector probe that comprises a detectably labeled oligonucleotide that specifically hybridizes with a second target nucleic acid sequence region of ribosomal RNA. The presence or absence of labeled oligonucleotide complexed with the substrate is determined. Detection of labeled oligonucleotide complexed with the substrate is indicative of the presence of pathogen. Performing the method in the presence and absence of an antibiotic permits detection of antibiotic resistance.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Extraction of nucleic acid
InactiveUS20050053941A1Avoid harsh conditionsIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionGenomic DNAPlasmid dna
Methods of obtaining a sample of target nucleic acid from cells containing the target nucleic acid and genomic DNA or RNA are disclosed. In contrast to prior art protocols, this method does not require the cells containing the target nucleic acid to be lysed and instead is based on the observation when cells are suspended in an aqueous medium and the target nucleic acid are released into the medium through the cell walls. The invention therefore helps to avoid the use of cell lysis, heating, extremes of pH, water immiscible solvents, and electrical fields used in prior art nucleic acid extraction methods. The present invention is particularly applicable to the separation of non-genomic nucleic acid, such as cellular vector DNA or RNA, self-replicating satellite nucleic acids or plasmid DNA, from genomic nucleic acids, such as host cell chromosomes and ribosomal RNA.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
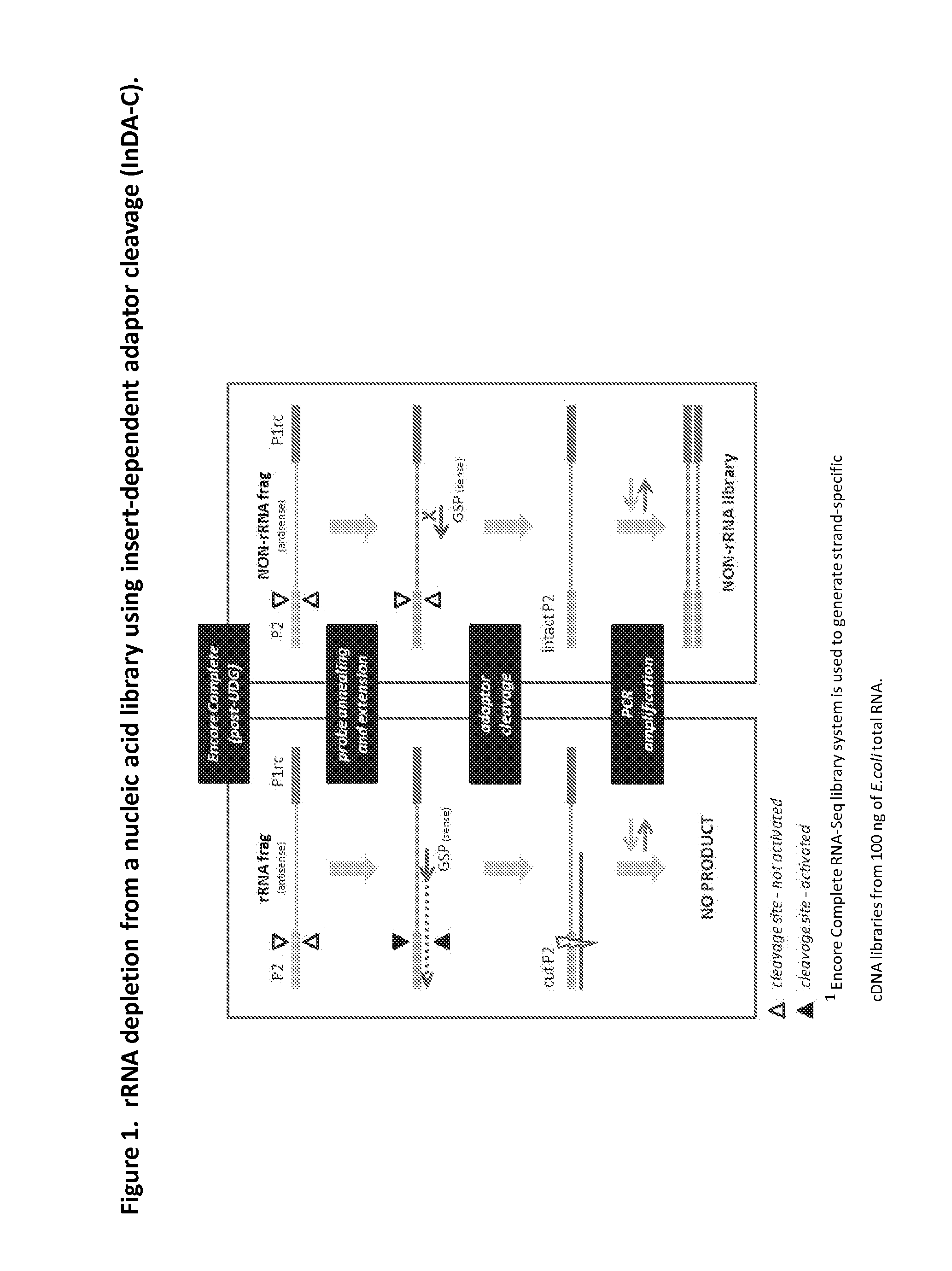
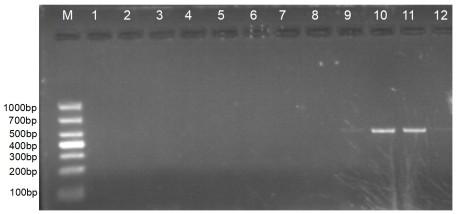
Method for constructing Ribo-seq sequencing libraries
ActiveCN108624651AControllable enzymatic hydrolysis processEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationEnzyme digestionRibosomal RNA
The invention discloses a method for constructing Ribo-seq sequencing libraries. The method includes separating Ribosome-nascent chain complexes (RNC); carrying out enzyme digestion on the RNC; directly constructing the libraries without rRNA [ribosomal RNA (ribonucleic acid)] removal; selecting RPF (ribosome protected fragments) bands and carrying out sequencing on RPF. The method has the advantages that rRNA does not need to be removed, accordingly, expensive rRNA removal reagent kits can be omitted, optional species can be coped, and the method is wide in application range; RPF reads proportions of the method are higher than RPF reads proportions of the traditional methods, the flux requirements can be lowered, and accordingly the sequencing cost can be lowered.
Owner:CHI BIOTECH CO LTD
Ribosomal RNA sequence of pathogenic bacterium Septoria sp of oak abnormally withered disease and application thereof
ActiveCN109652580AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesDiseaseSpecific detection
The invention discloses a ribosomal RNA sequence of a pathogenic bacterium Septoria sp of an oak abnormally withered disease and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal RNA geneof the pathogenic bacterium Septoria sp of the oak abnormally withered disease is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the sequence can be utilized to detect the pathogenic bacterium Septoria sp of the oak abnormally withered disease and can also be applied to research on the classification of fungal species. In addition, the invention also provides a primer for detecting the pathogenic bacteria Septoria spof the oak abnormally withered disease. The primer has good specificity, a specific detection method and a specific detection kit are established based on the primer, the required detection time is short, the detection is rapid and efficient, and the primer has a good application prospect in detection of the pathogenic bacteria Septoria sp of the oak abnormally withered disease.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
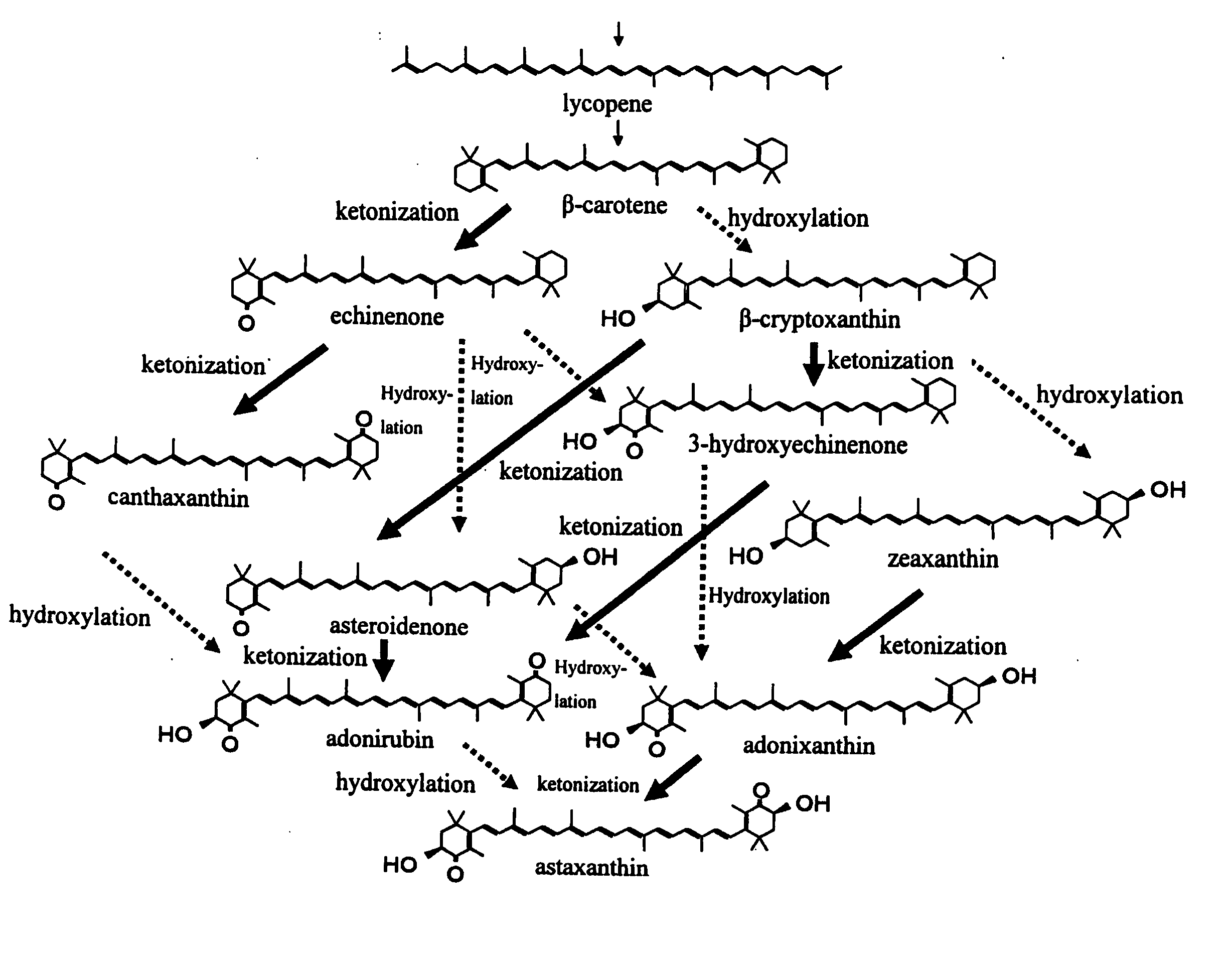
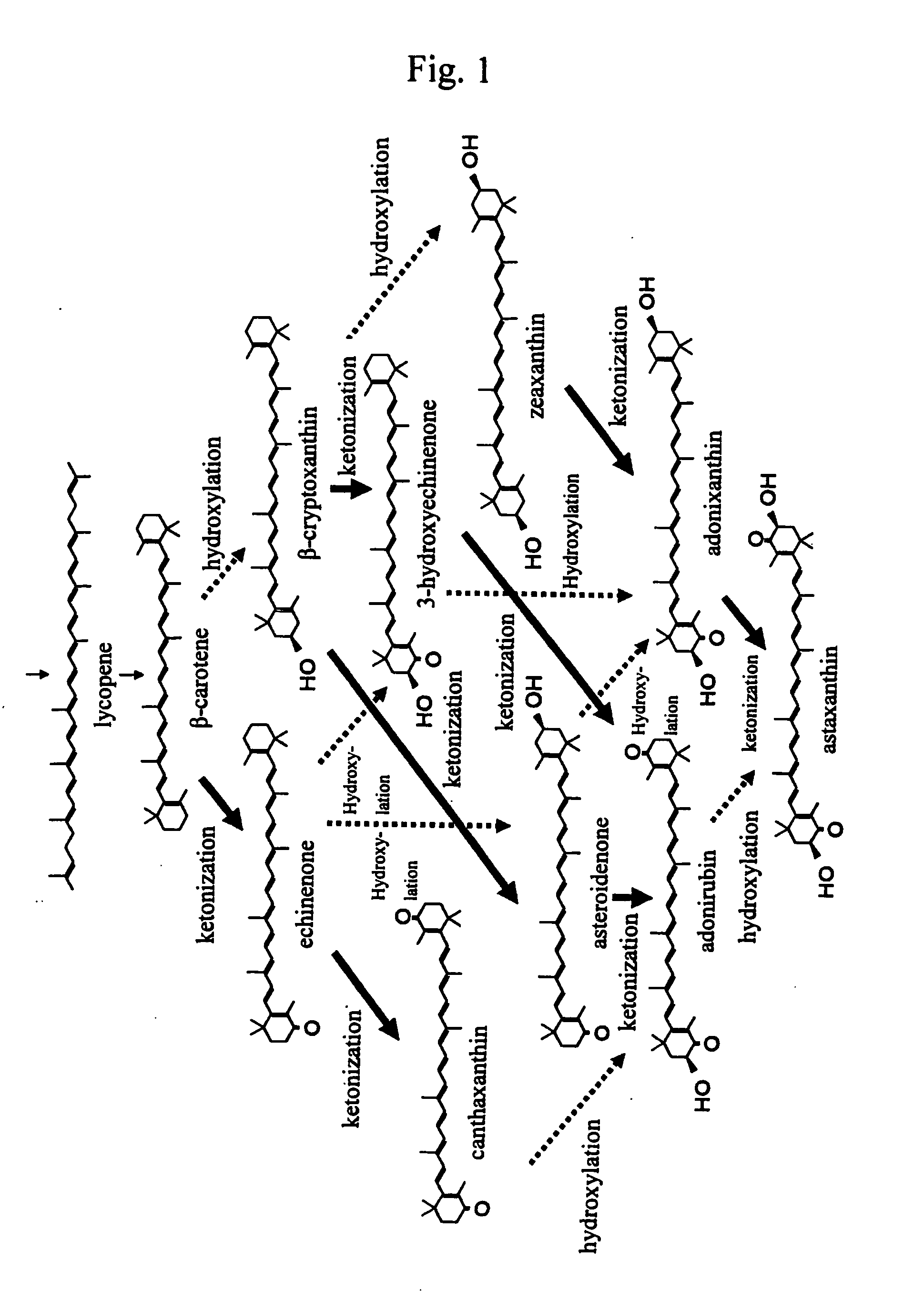
Process for producing carotenoid compound
The present invention relates to a process for producing zeaxanthin, β-carotene, or lycopene, comprising inducing mutation in a carotenoid-producing microorganism in which the base sequence of DNA corresponding to 16S ribosomal RNA is substantially homologous to the base sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 1; screening for a mutant strain having a high product proportion of zeaxanthin, β-carotene, or lycopene to the whole production amount of carotenoids to provide a microorganism producing zeaxanthin, β-carotene, or lycopene; culturing the mutant microorganism; and harvesting zeaxanthin, β-carotene, lycopene or a carotenoid mixture containing the same from the resultant culture.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
Method and kit capable of removing ribosomal RNA with high efficiency for construction of transcriptome sequencing library
ActiveCN107893260AImprove data qualityImprove effectivenessLibrary creationDNA preparationRibosomal RNAA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for construction of a transcriptome sequencing library. The method comprises the following steps: providing a DNA molecule containing to-be-removed rRNA; carrying outdesigning on account of a DNA sequence of the to-be-removed rRNA so as to obtain a Crispr RNA pool; and allowing a DNA sample to contact with the Crispr RNA pool and Crispr protein so as to obtain a sample compiled by a Crispr system and obtain the transcriptome sequencing library and a kit used for construction of the transcriptome sequencing library. The method and the kit provided by the invention can remove a large number of redundant RNA like rRNA with high efficiency, enrich other molecules in the sample, improve the data quality and the effective data ratio of initial transcriptome sequencing, and reduce the cost of sequencing.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RIBOBIO
Methods and compositions for improving removal of ribosomal RNA from biological samples
The invention generally relates to compositions for maximizing capture of affinity-labeled molecules on solid supports. The disclosed methods and compositions were developed to maximize depletion of ribosomal RNA from total RNA samples, which is useful to improve the quality of RNA preparations used for applications such as massively parallel sequencing. The RNA depletion method is based on using long affinity-labeled RNA molecules that are complementary to all or part of the target ribosomal RNAs, as subtractive hybridization probes.
Owner:BICO SCI CORP
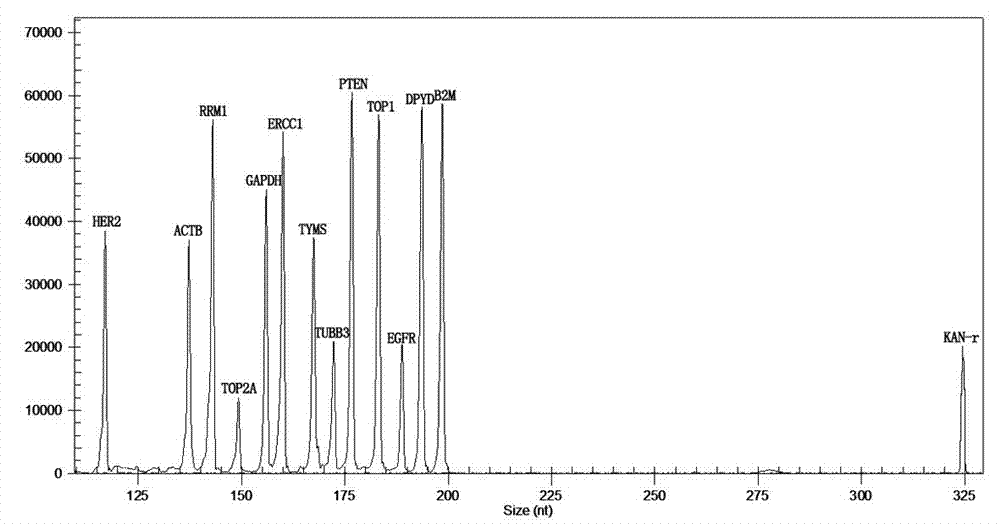
Multiple-gene detecting kit related to antitumor drugs
ActiveCN103882138AEasy to analyzeReliable analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDPYDReference genes
The invention relates to a multiple-gene detecting kit related to antitumor drugs. The multiple-gene detecting kit comprises a mixture of RT (reverse transcription) primers and a mixture of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification primers, wherein each RT primer and each PCR amplification primer based on genetic groups, reference genes and a reaction internal label are respectively contained in each of the mixture of the RT primers and the mixture of the PCR amplification primers; the multiple-gene detecting kit is characterized in that the genetic groups comprise PTEN, EGFR, DPYD, HER2, RRM1, ERCC1, TUBB3, TOP1, TYMS and TOP2A; the reference genes comprise ACTB, GAPDH and B2M; the reaction internal label is KAN-rRNA (ribosomal RNA). The multiple-gene detecting kit related to antitumor drugs disclosed by the invention can be used for systemically detecting the expression level of a plurality of genes closely related to the antitumor drugs by one step, is simple and convenient to use, good in accuracy and high in detecting efficiency, and can be used for guiding chemotherapy drugs and selecting chemotherapy regimens very well.
Owner:南昌市赛尔医药科技有限公司
Intestinal flora for diagnosing sarcopenia and application of intestinal flora
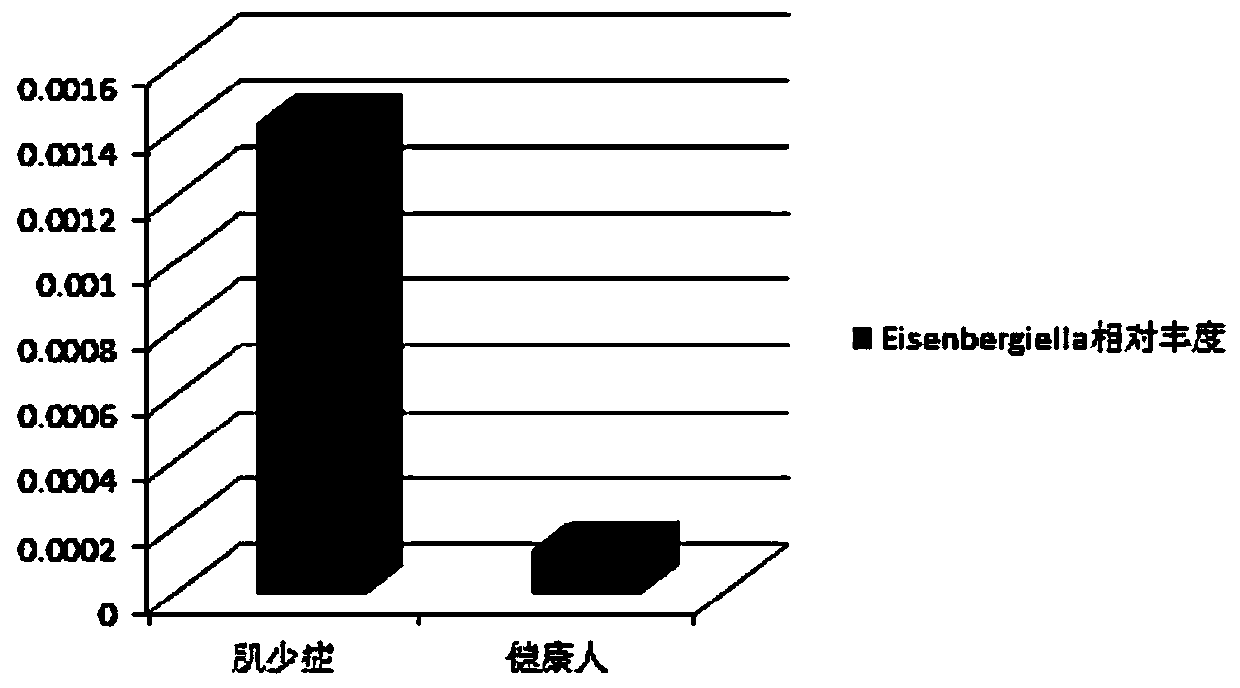
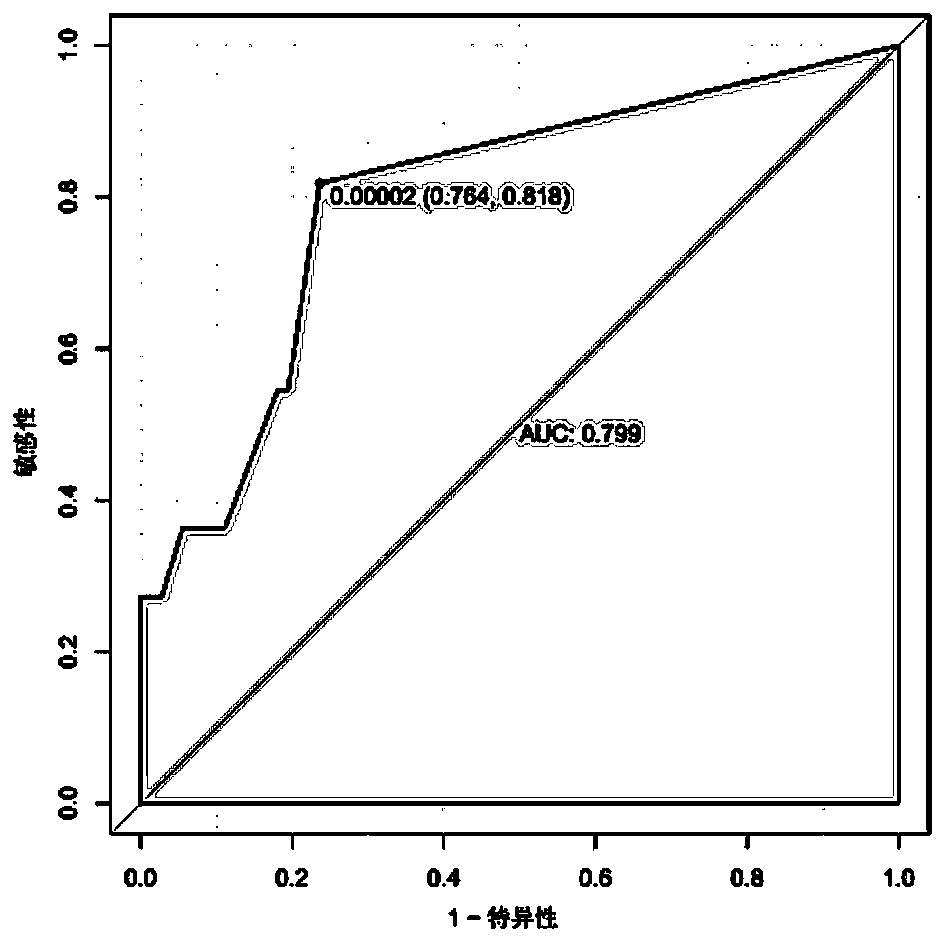
The invention discloses an intestinal flora for diagnosing sarcopenia and application of the intestinal flora. The intestinal flora is Eisenbergiella. Through 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid sequencing, the situation that Eisenbergiella is remarkably increased in sarcopenia is found for a first time, the situation that high specificity and sensitivity can be achieved when sarcopenia and healthy people are distinguished by using Eisenbergiella as a detection variable is further found, so that on the basis, Eisenbergiella can be applied to noninvasive diagnosis on sarcopenia.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
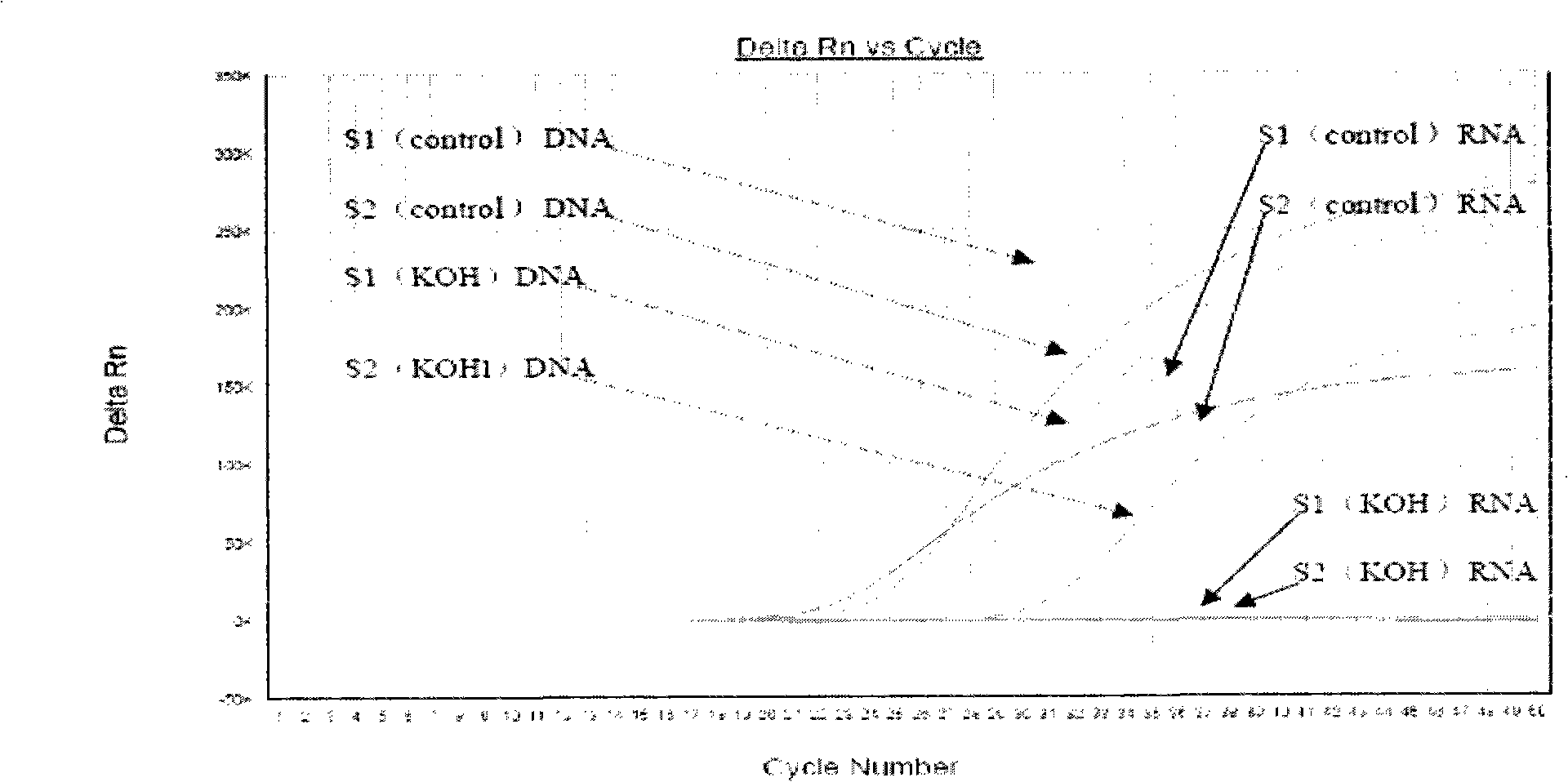
Nucleic acid amplification detection method and detection kit for distinguishing DNA from corresponding RNA
InactiveCN101948908AEasy to understand the status of growth and reproductionOvercoming detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceReverse transcriptaseNucleic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical detection, in particular relates to a nucleic acid amplification detection method for distinguishing DNA from correspondingly transcribed RNA and provides a corresponding detection kit. The kit comprises pyrolysis solution, nucleic acid extracting solution, lysozyme solution, reverse transcription buffer solution, a reverse transcriptase system, tuberculosis DNA PCR reaction solution, tuberculosis RNA PCR reaction solution and the like, wherein selected primers aim at a section of ITS sequence or IS6110 sequence and a section of 16S rRNA sequence on ribosomal RNA respectively; and a probe is Tagman MGB probe preferably and labeled by different fluorescein. The kit comprises a glycosidase (UNG) component, can judge the relative 16S rRNA content of each bacterium and is used for judging the growth condition of mycobacterium tuberculosis in a sample so as to monitor infection state. The kit is simple, convenient and fast, can specifically detect the RNA and DNA and provides more comprehensive information for clinical use.
Owner:SHANGHAI KEHUA BIO ENG
SUBTRACTIVE SEPARATION AND AMPLIFICATION OF NON-RIBOSOMAL TRANSCRIBED RNA (nrRNA)
InactiveUS20090137415A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRibosomal RNABioinformatics
The invention provides a method of separating non-ribosomal transcribed RNA (nrRNA) fragments from ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and rRNA fragments. The method comprises (i) providing a sample comprising rRNA, rRNA fragments, and nrRNA fragments, and (ii) providing a plurality of probes. The probes hybridize to RNA targeting sequences of at least 50% of the contiguous regions of the rRNA and to rRNA fragments comprising the rRNA targeting sequences. The method further comprises (iii) adding the plurality of probes to the sample, (iv) hybridizing the probes to the rRNA and rRNA fragments to form rRNA-probe complexes and rRNA fragment-probe complexes, and (v) separating the rRNA-probe complexes and rRNA fragment-probe complexes. The invention also provides a method of amplifying an nrRNA fragment, a method of analyzing nrRNA expression, a method of determining the level of nrRNA in a sample, and a kit and system useful in any of the foregoing methods.
Owner:EUCLID DIAGNOSTICS
Composition, method and kit for detecting bacteria by means of sequencing
InactiveUS20130157265A1Reduce in quantityImprove performanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobiology
The present invention describes a method for detecting the presence and type of a microorganism present in a sample by means of stabilization and sequencing techniques and subsequent analysis of microsequences in genes encoding the ribosomal RNA most conserved, and on specific areas of the 16-S region with taxonomic value.
Owner:MINGORANCE CRUZ JESUS +2
Compositions and methods for negative selection of non-desired nucleic acid sequences
ActiveUS9957549B2Reduce the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTotal rnaNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for the generation of next generation sequencing (NGS) libraries in which non-desired nucleic acid sequences have been depleted or substantially reduced. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein are useful, for example, for the production of libraries from total RNA with reduced ribosomal RNA and for the reduction of common mRNA species in expression profiling from mixed samples where the mRNAs of interest are present at low levels. The methods of the invention can be employed for the elimination of non-desired nucleic acid sequences in a sequence-specific manner, and consequently, for the enrichment of nucleic acid sequences of interest in a nucleic acid library.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com