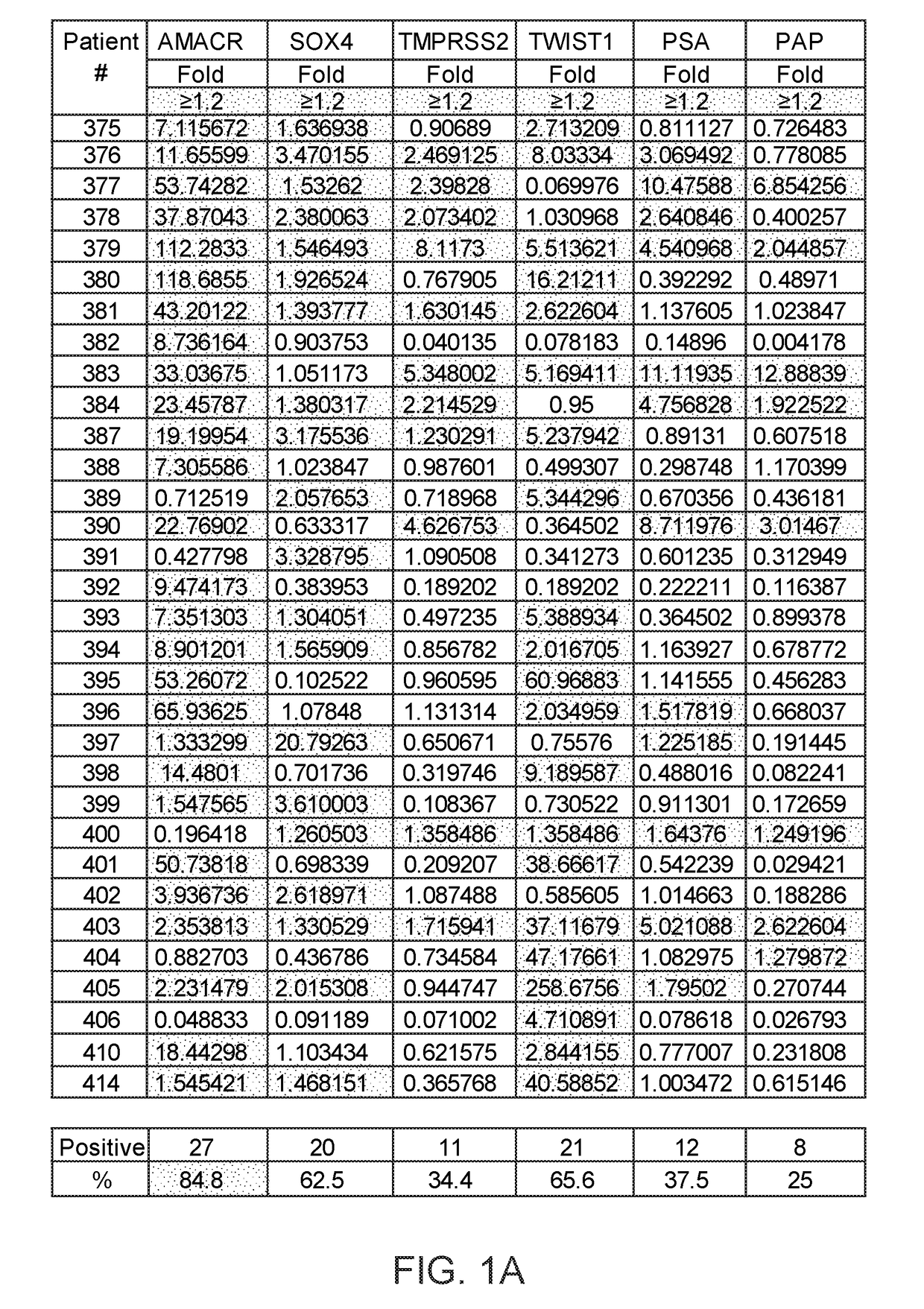
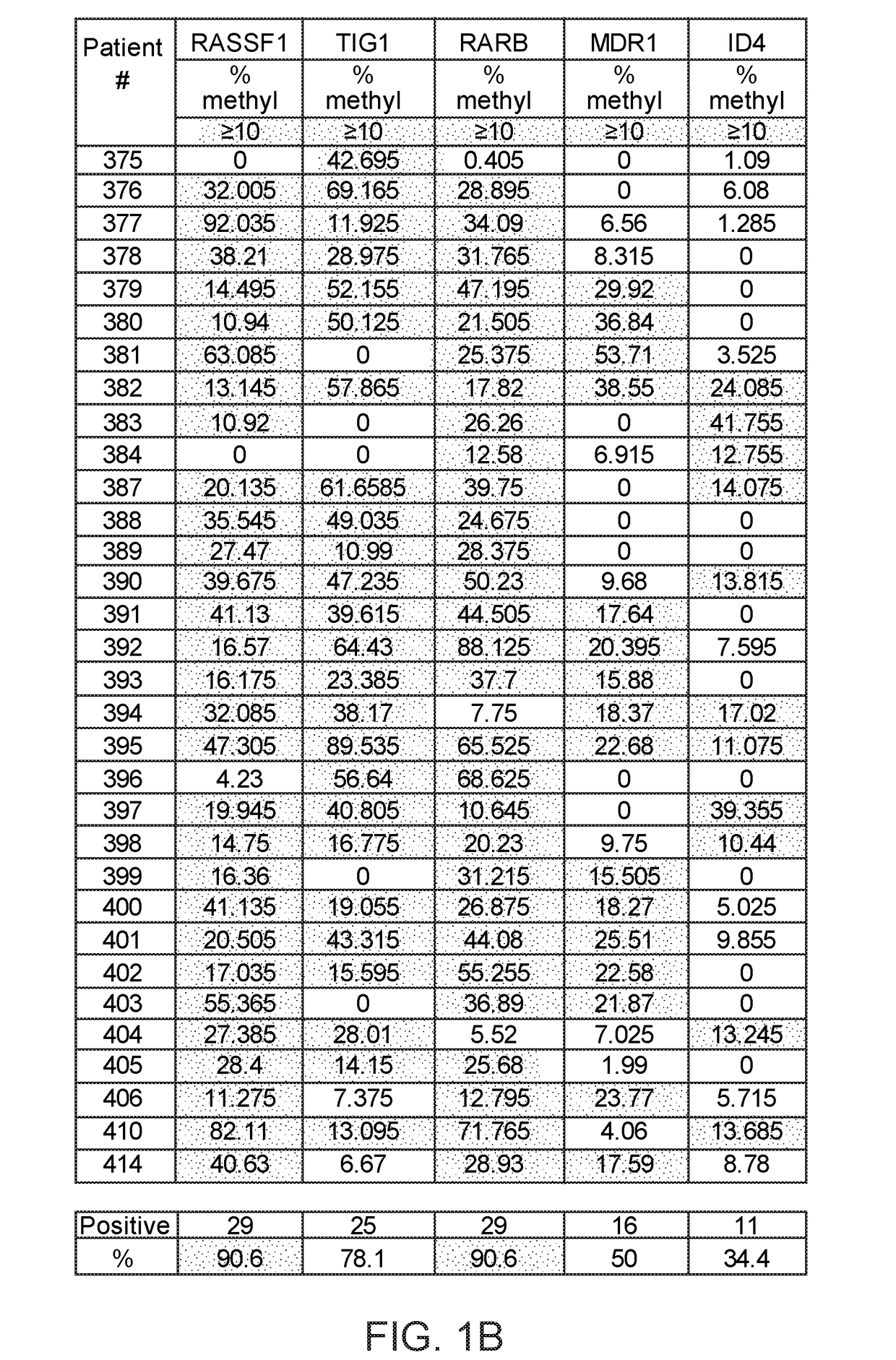
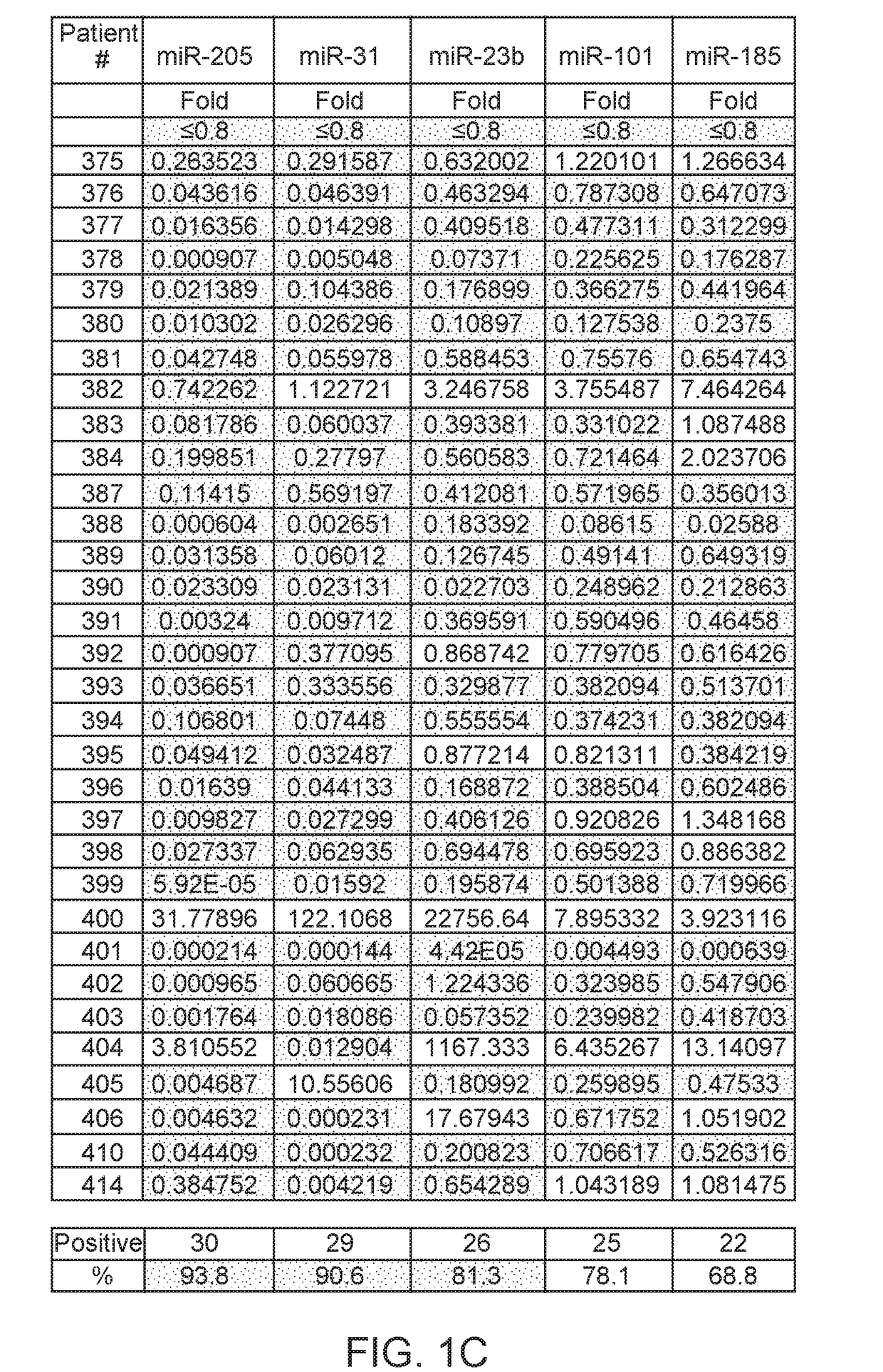
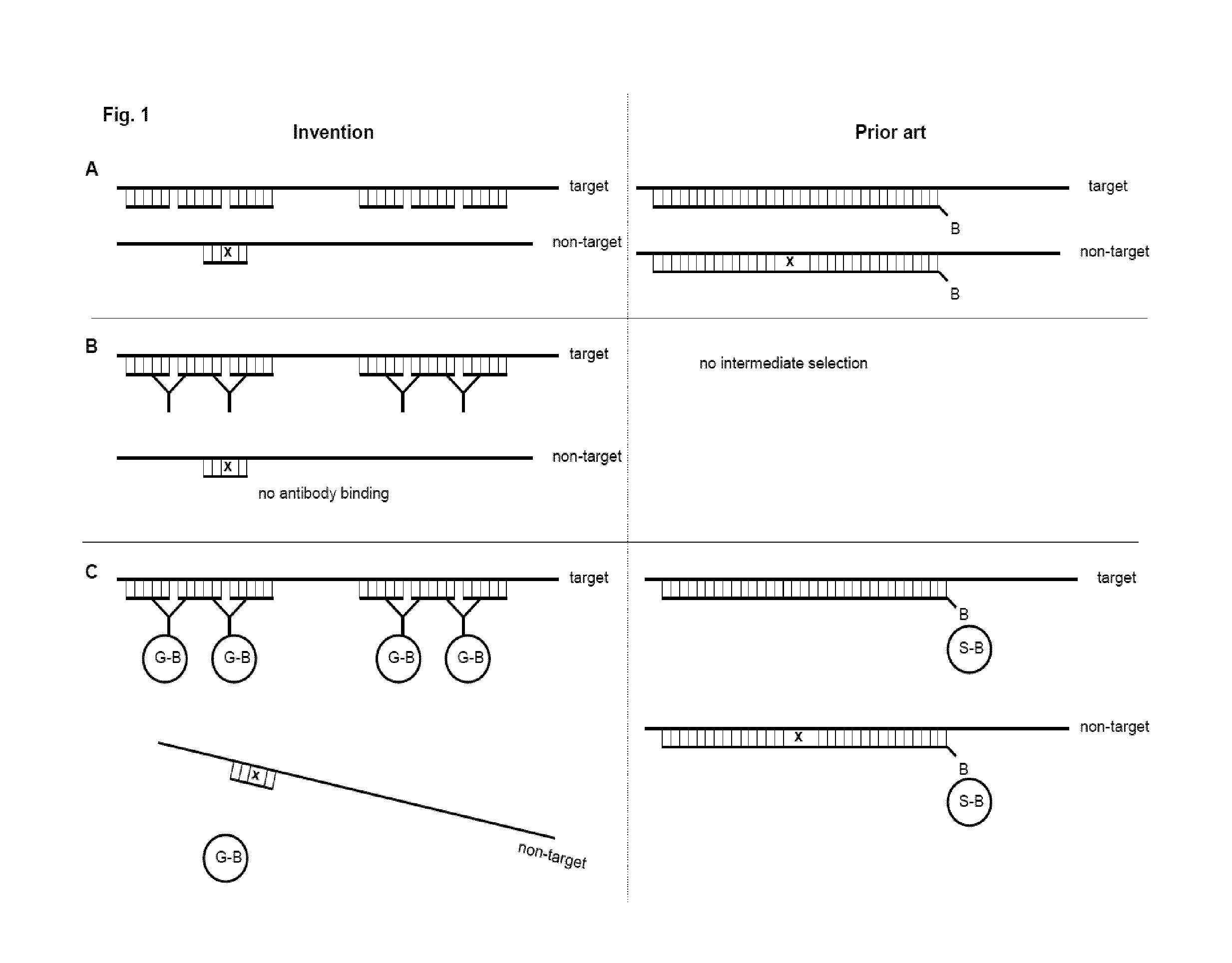
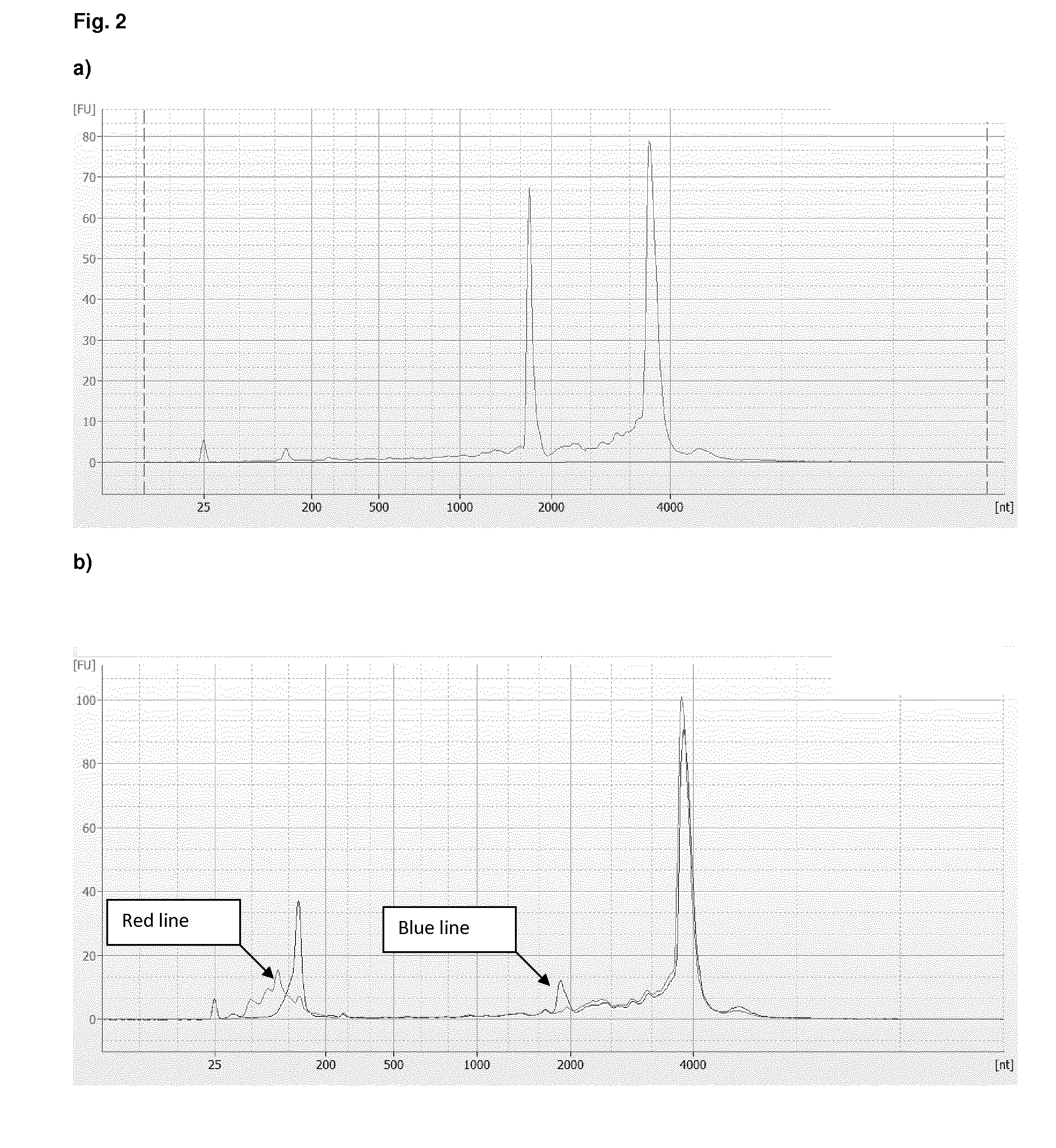
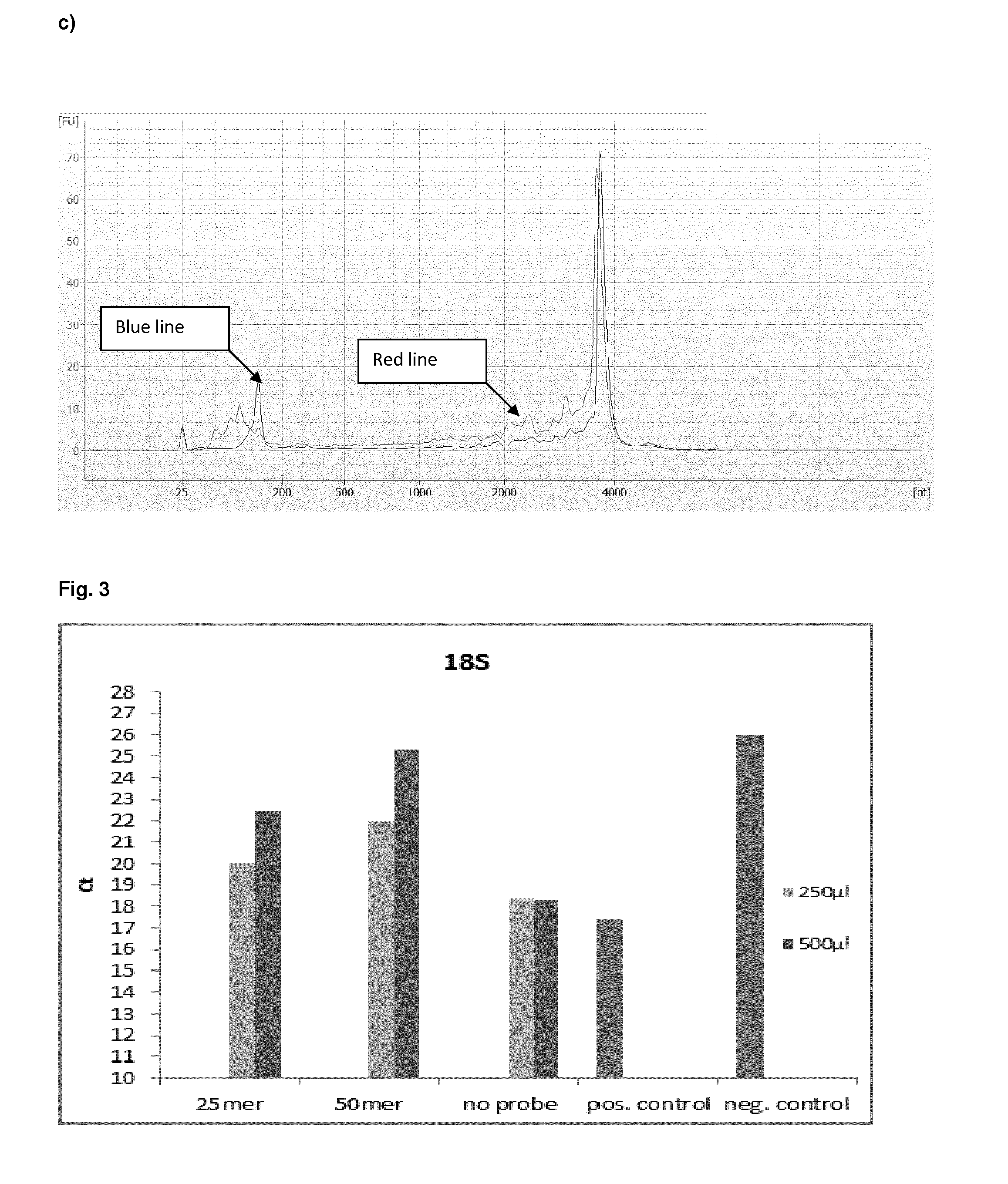
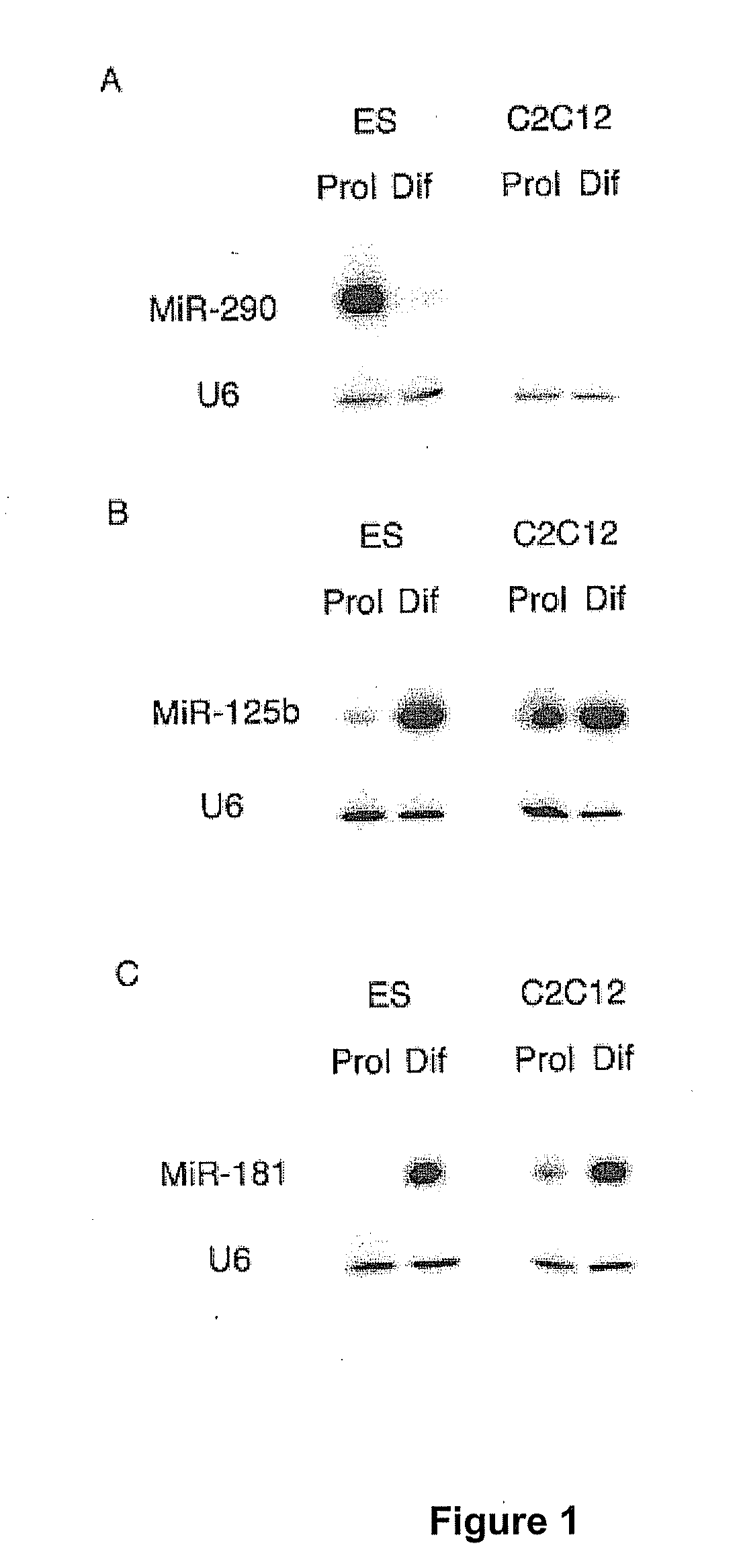
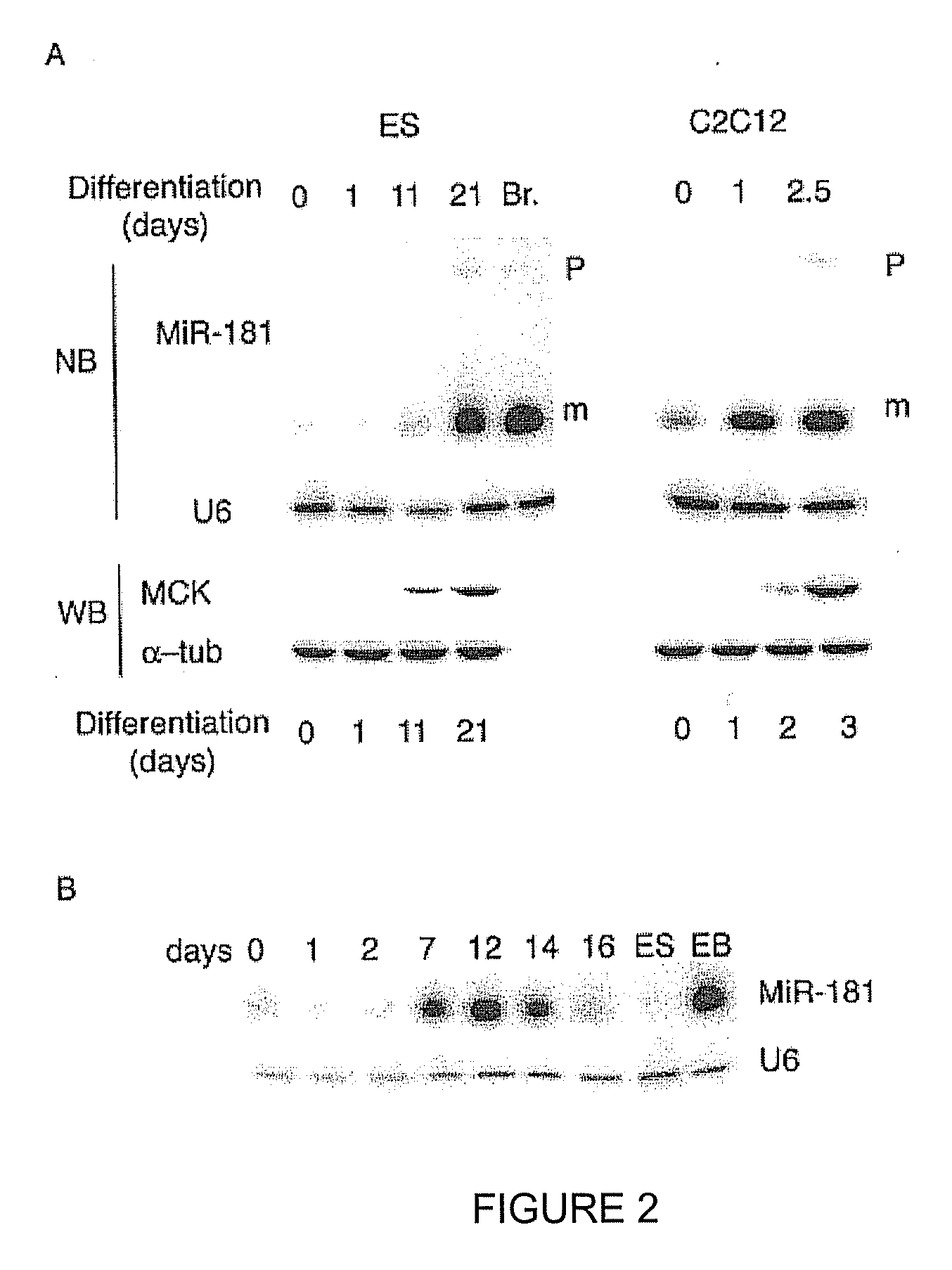
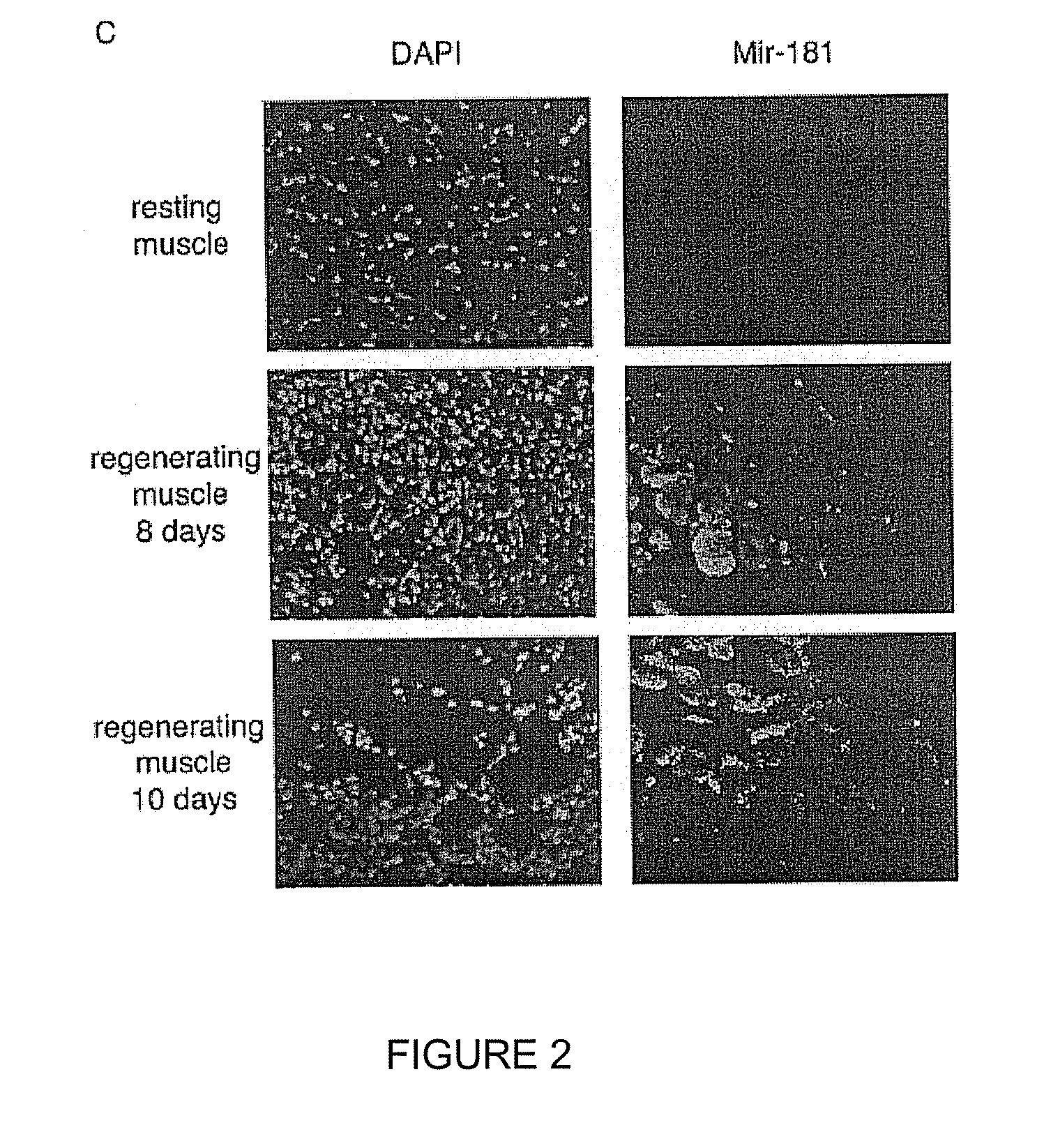
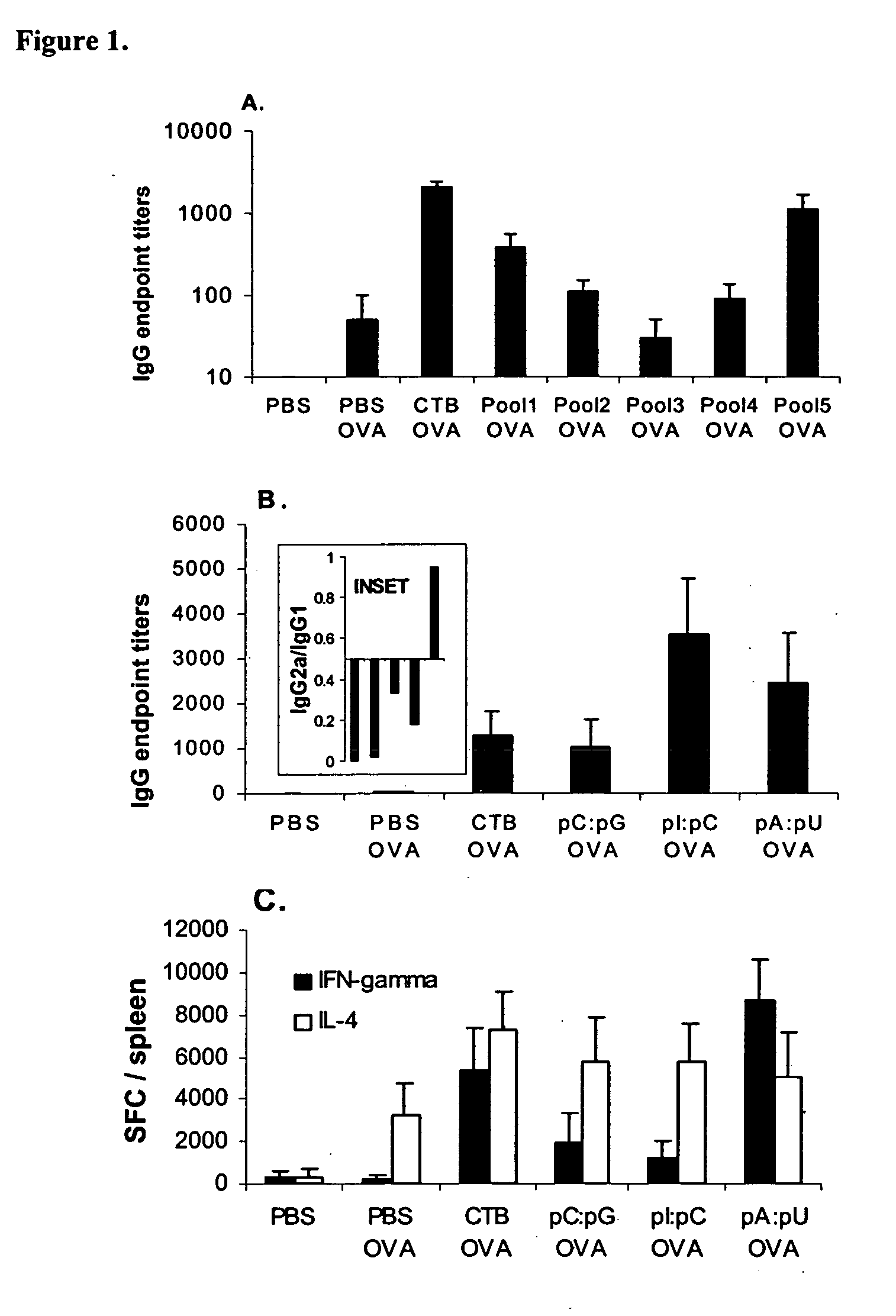
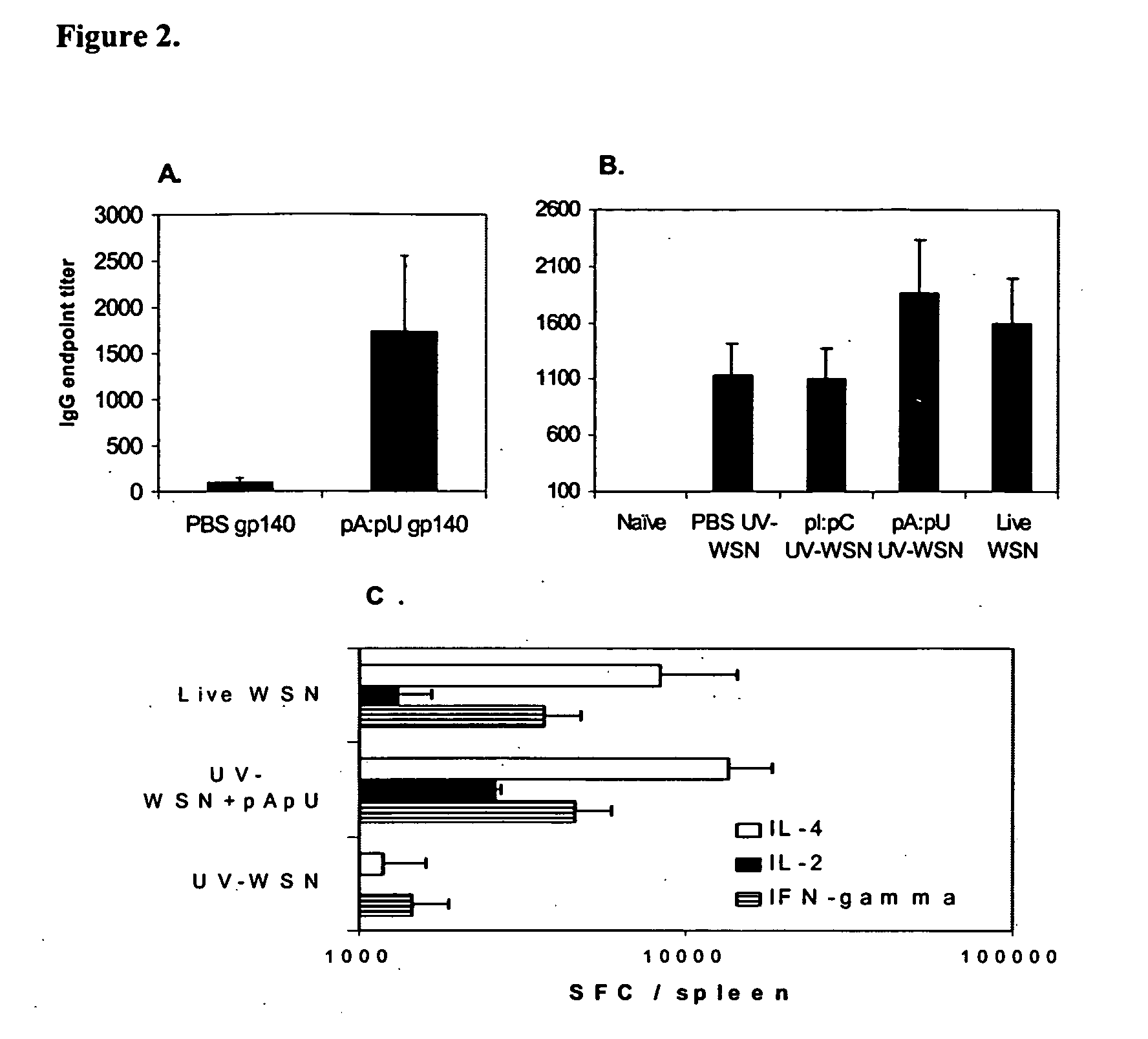
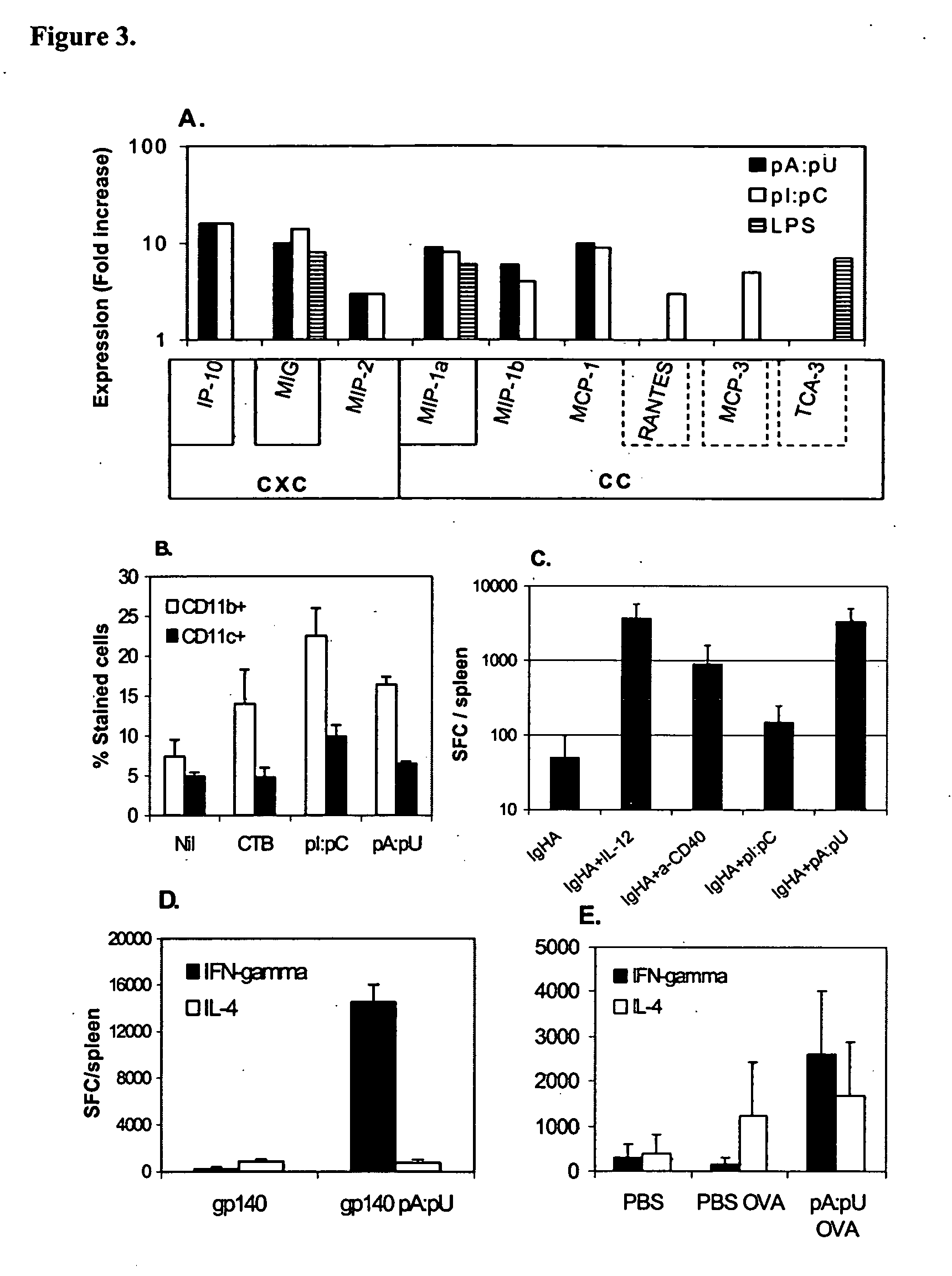
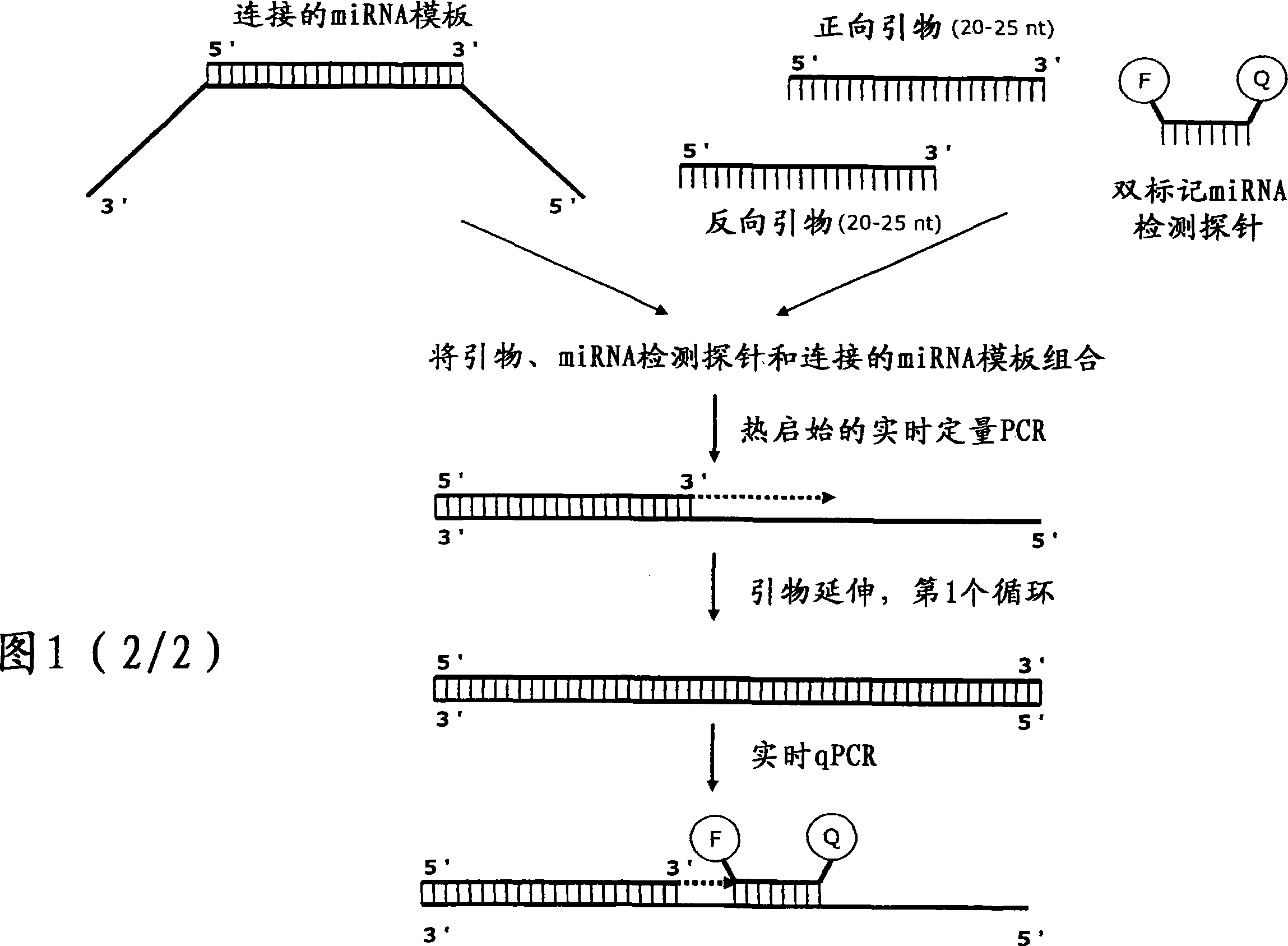
Patents
Literature
385 results about "Non-coding RNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR.
Novel methods for quantification of microRNAs and small interfering RNAs
ActiveUS20050272075A1Highly sensitive and specific hybridizationHighly sensitive and specific and ligationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroRNAAllele
The invention relates to ribonucleic acids, probes and methods for detection, quantification as well as monitoring the expression of mature microRNAs and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The invention furthermore relates to methods for monitoring the expression of other non-coding RNAs, mRNA splice variants, as well as detecting and quantifying RNA editing, allelic variants of single transcripts, mutations, deletions, or duplications of particular exons in transcripts, e.g., alterations associated with human disease such as cancer. The invention furthermore relates to methods for detection, quantification as well as monitoring the expression of deoxy nucleic acids.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of microRNA related diseases
InactiveUS20090298916A1Inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseasePrimate
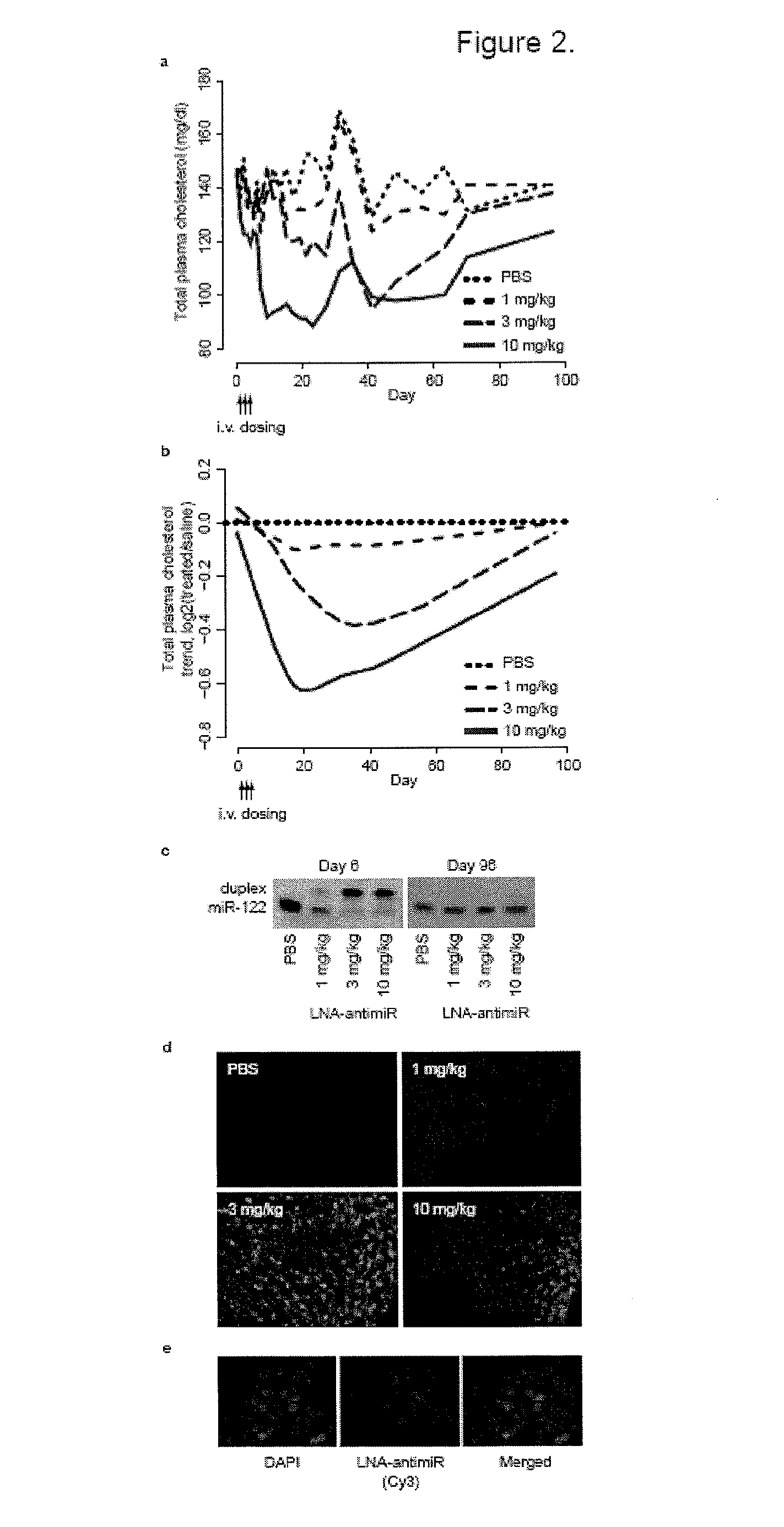
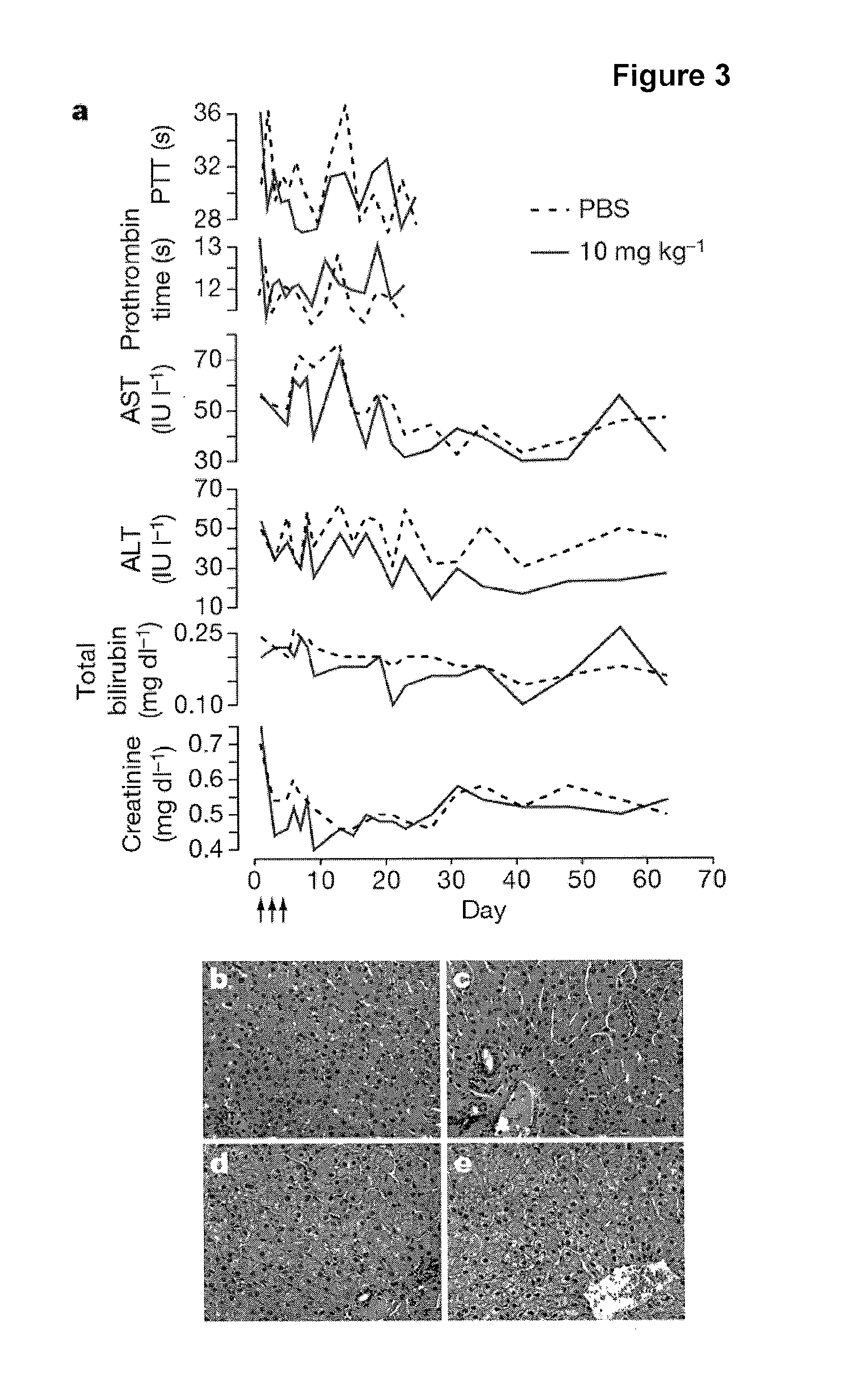
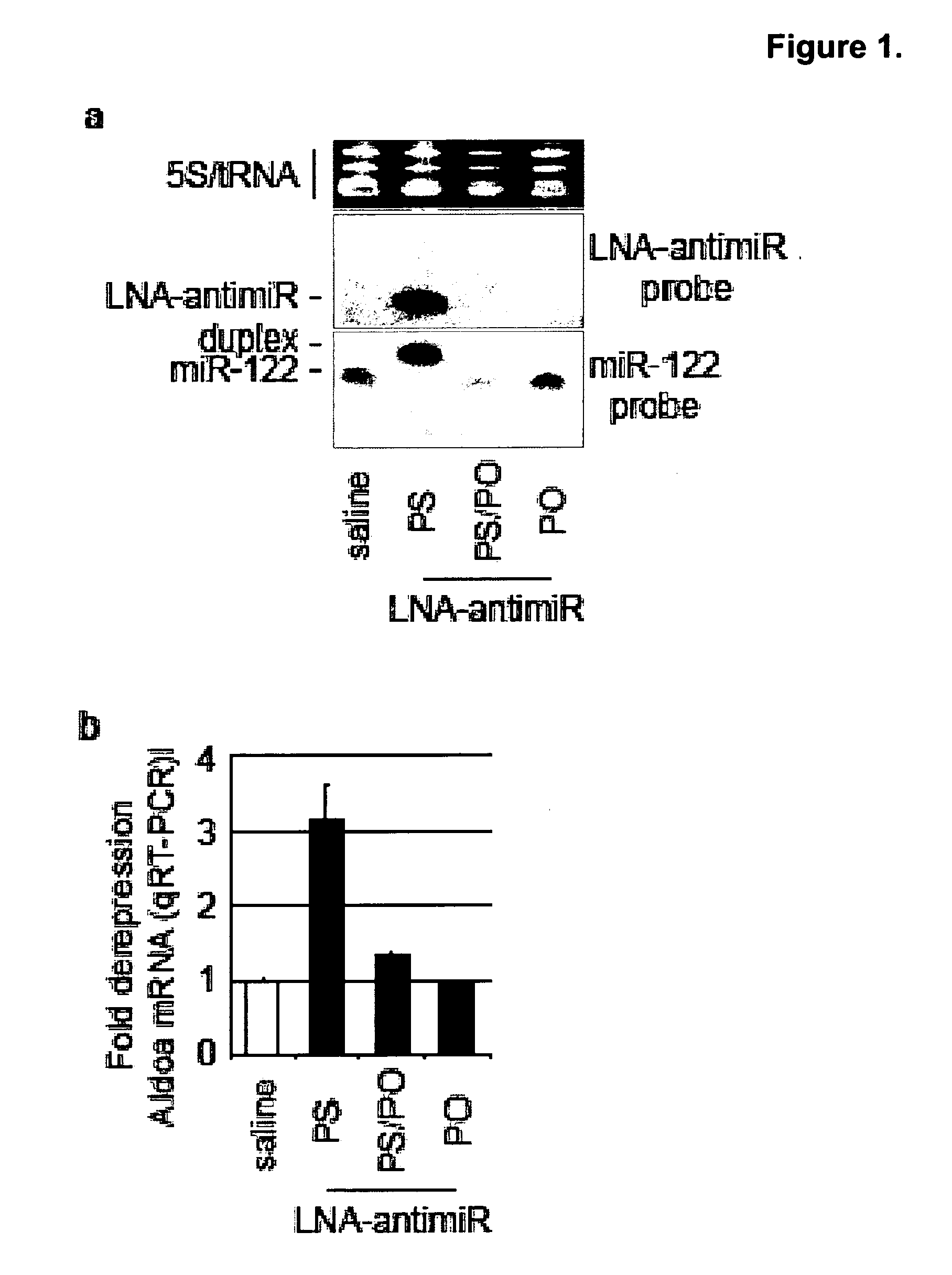
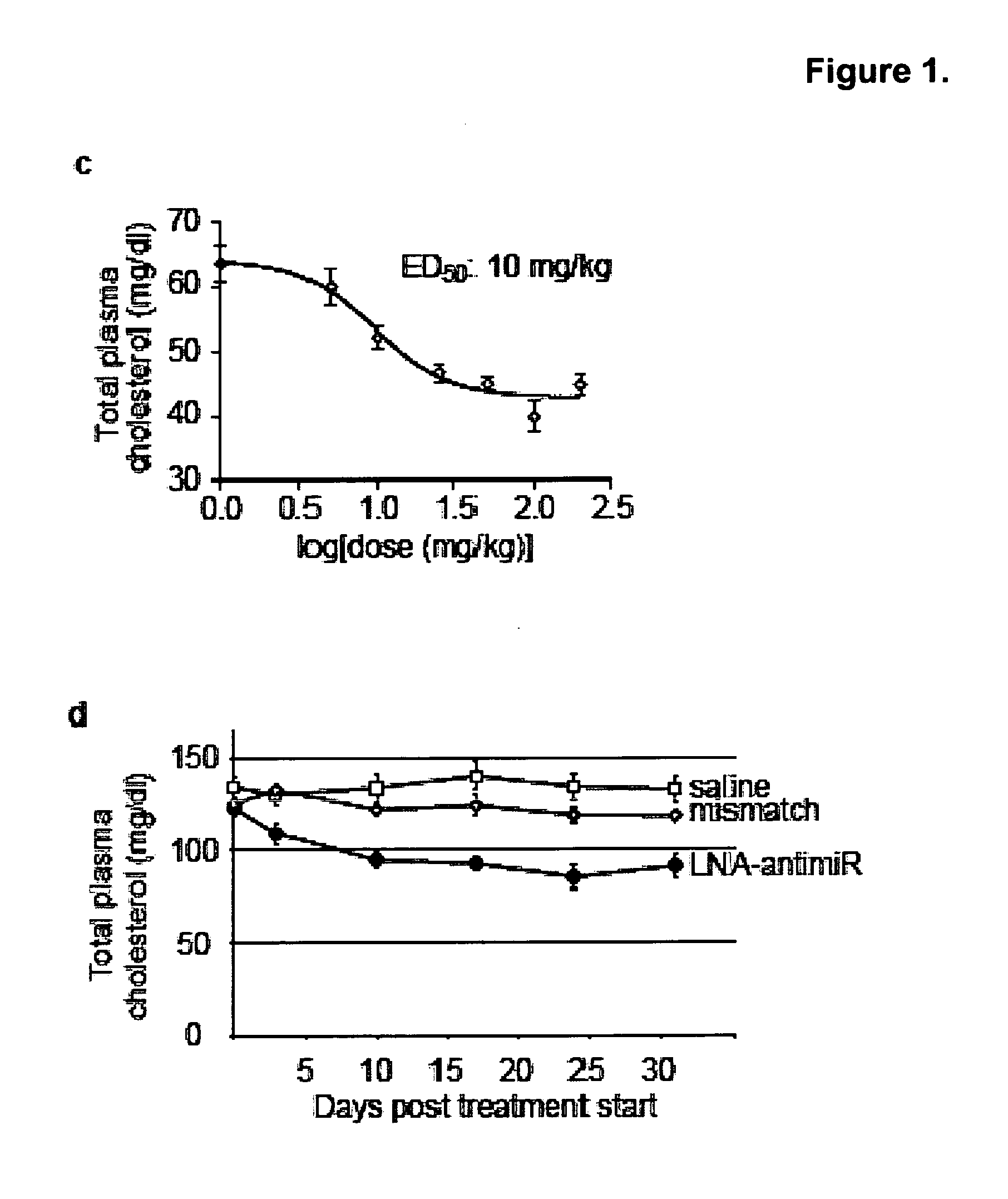
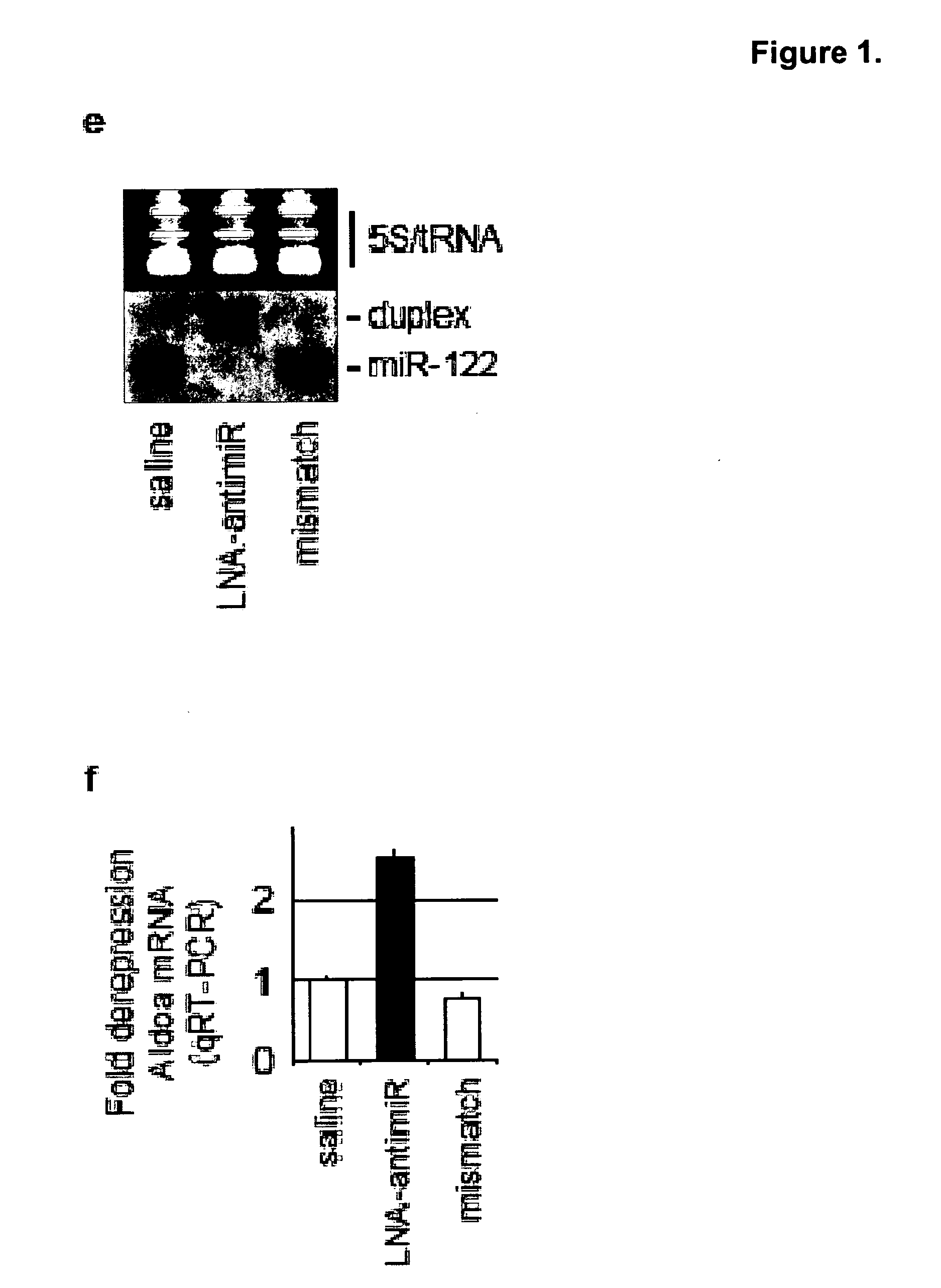
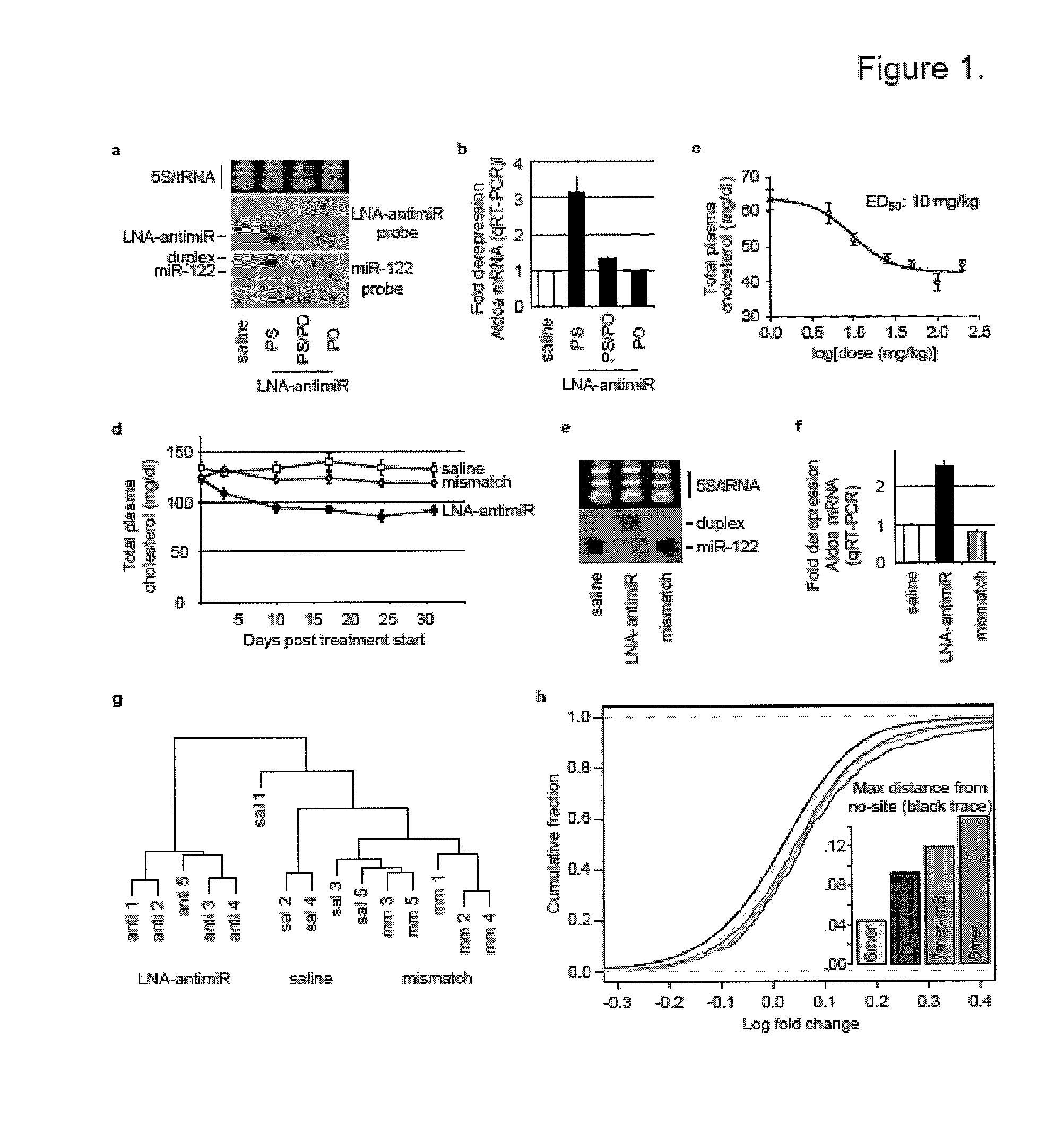
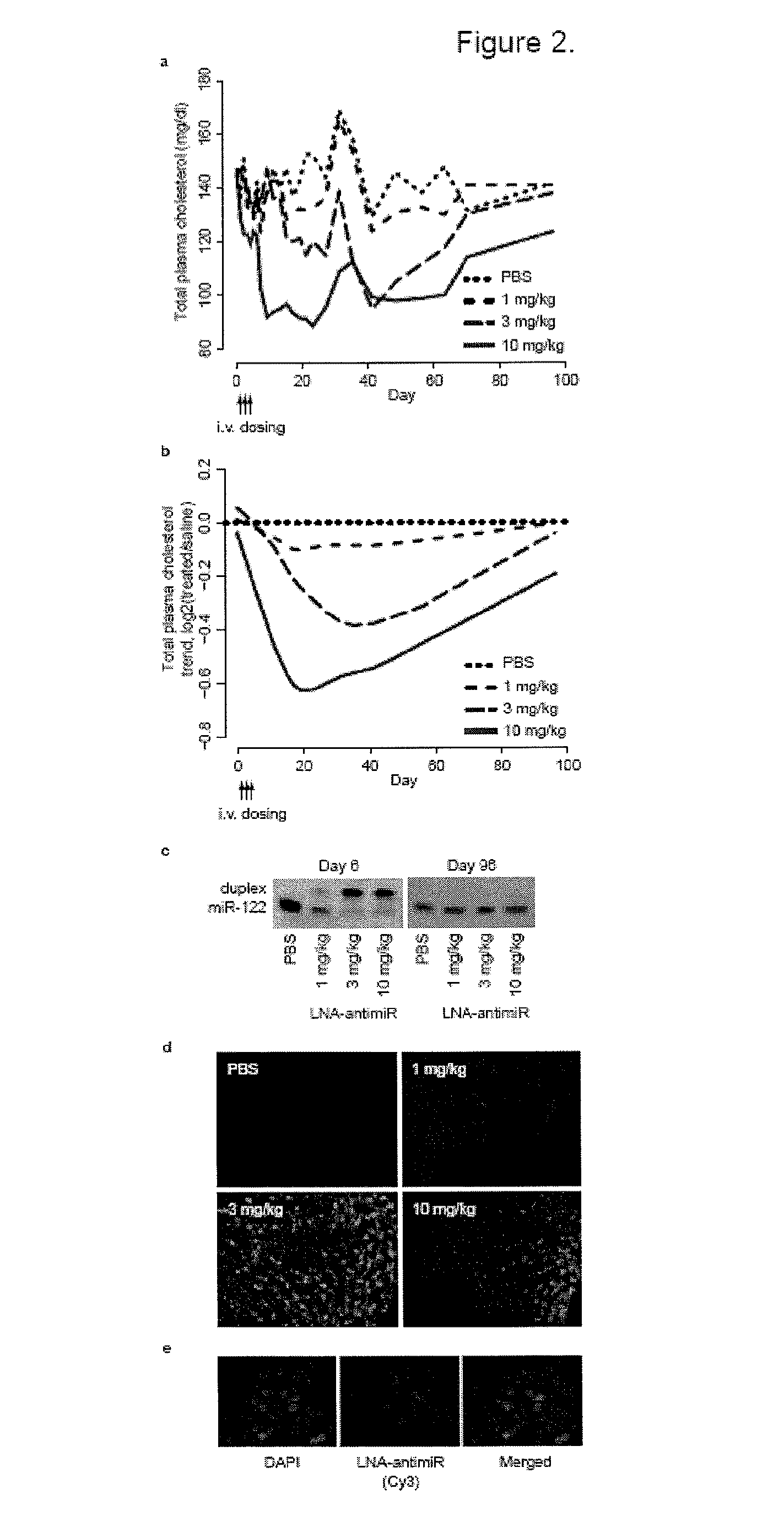
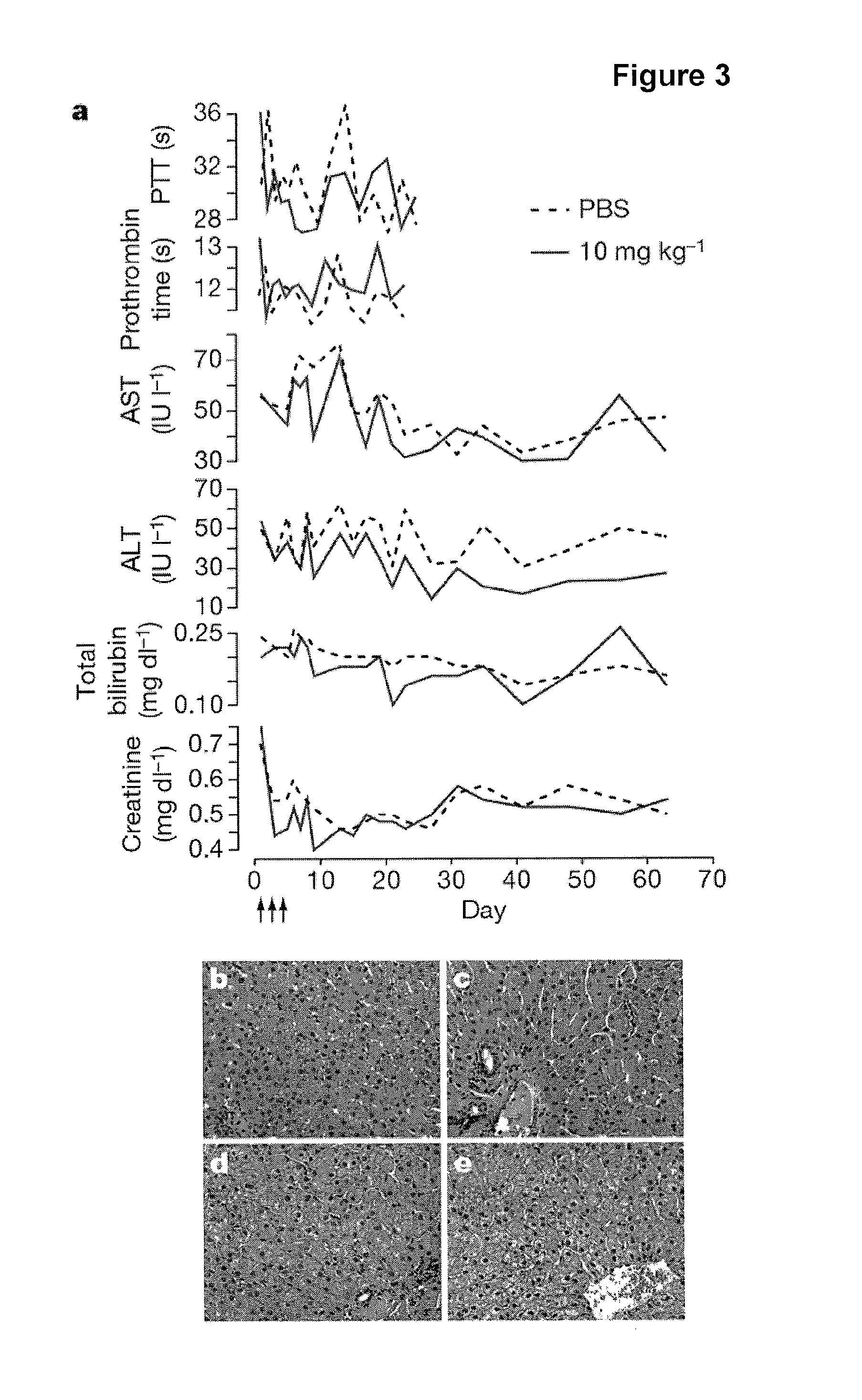
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases that are sensitive to drugs that downregulate the function of microRNA's, mRNA, non-coding RNA, or viral genomes. In particular, it has been discovered that a very long term effect of an anti microRNA oligonucleotide may be obtained when administered to a primate. Therefore, the present invention relate to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of primates, including humans wherein the compositions are administered with a long time interval.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Novel oligonucleotide compositions and probe sequences useful for detection and analysis of microRNAS and their target mRNAS
InactiveUS20070065840A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget mrnaAllele
The invention relates to ribonucleic acids and oligonucleotide probes useful for detection and analysis of microRNAs and their target mRNAs, as well as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The invention furthermore relates to oligonucleotide probes for detection and analysis of other non-coding RNAs, mRNAs, mRNA splice variants, allelic variants of single transcripts, mutations, deletions, or duplications of particular exons in transcripts, e.g. alterations associated with human disease, such as cancer.
Owner:EXIQON AS
Pharmaceutical Compositions for Treatment of MicroRNA Related Diseases
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases that are sensitive to drugs that downregulate the function of microRNA's, mRNA, non-coding RNA, or viral genomes. In particular, it has been discovered that a very long term effect of an anti microRNA oligonucleotide may be obtained when administered to a primate. Therefore, the present invention relate to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of primates, including humans wherein the compositions are administered with a long time interval.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Method for obtaining temperature-sensitive sterile line by performing site-specific mutagenesis on P/TMS12-1 through CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)/Cas9 system
ActiveCN104651392AAvoid possible risksAvoid damageVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgricultural scienceTransgenesis
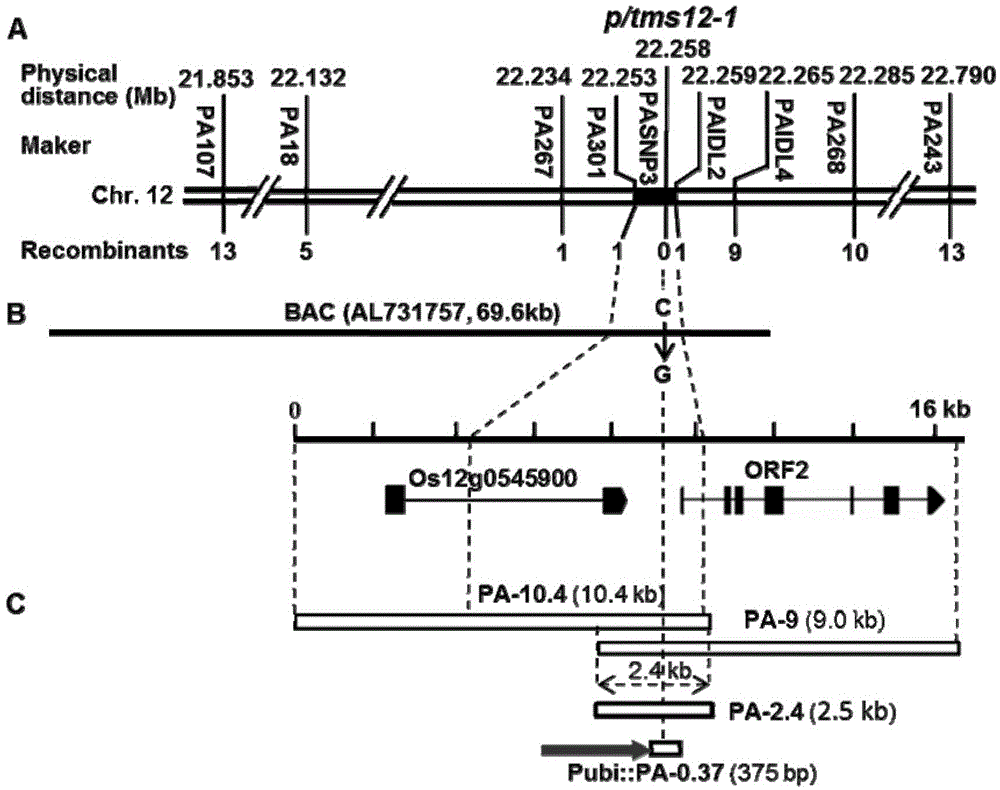
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a temperature-sensitive sterile line by performing site-specific mutagenesis on P / TMS12-1 through a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: cloning and controlling a Pei'ai 64S temperature-sensitive sterile major gene P / TMS12-1 fragment; designing a target sequence according to the P / TMS12-1 sequence; constructing a pU3-gRNA carrier of the target-containing sequence fragment; constructing a pCRISPR / Cas9 carrier; obtaining a positive transgenic seedling by utilizing the pCRISPR / Cas9 carrier containing the target sequence fragment; screening a mutant plant from the positive transgenic seeding; performing subculture planting on the mutant plant to obtain the temperature-sensitive sterile line without transgenic components. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the CRISPR / Cas9 system is utilized to completely inactivate P / TMS12-1 non-coding RNA, and the temperature-sensitive sterile line without transgenic components is artificially cultivated. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being strong in purposiveness, small in genome damages and capable of avoiding transgenic interference.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Use of short oligonucleotides for reagent redundancy experiments in RNA functional analysis
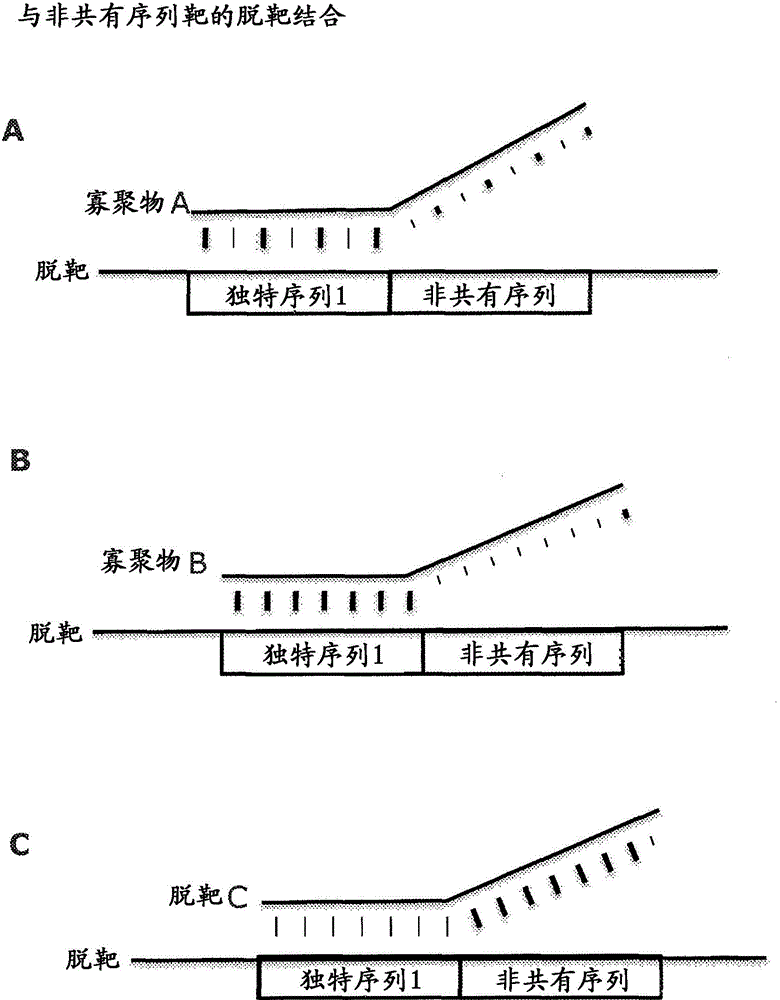
InactiveUS20100261175A1High affinityReduce the binding forceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisGeneticsNon-coding RNA
The present invention relates to functional analysis of miRNAs or other short non-coding RNAs involving the use of two or more sequence distinct miRNAs antagonising oligomeric compounds, which enables the reagent redundancy experiments to reduce the risk of reporting false positive effects of miRNA / ncRNA antagonists.
Owner:EXIQON AS
Use of endo-lysosomal system and secreted vesicles (exosome-like) in treatments and diagnostics based on small RNA and experimental study of small RNA
InactiveUS20110177054A1Increase reduce activityGood effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideRegulatory rnaLipid formation
The present invention relates to a method for determining the delivery rates and / or efficiency of a siRNA, miRNA or related molecule to target organs or cells, a kit and the use of proteins or lipids involved in the formation of the endolysosomal system for modulating the activity and / or the cell-to-cell transfer of RNA, small RNA, for example miRNA, siRNA and piRNA, mRNA or non-coding RNA.It finds many applications in particular in methods for identifying the target(s) of miRNA or siRNA therapeutics, in methods for determining the efficiency of a treatment with siRNA and / or miRNA therapeutics, in methods for determining the efficiency of a treatment with siRNA and / or miRNA therapeutics, and in methods for genotyping and / or characterizing the condition of a person, a tumor or a fetus.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Application of long-chain non-coding RNA as blood molecular marker for disease diagnosis
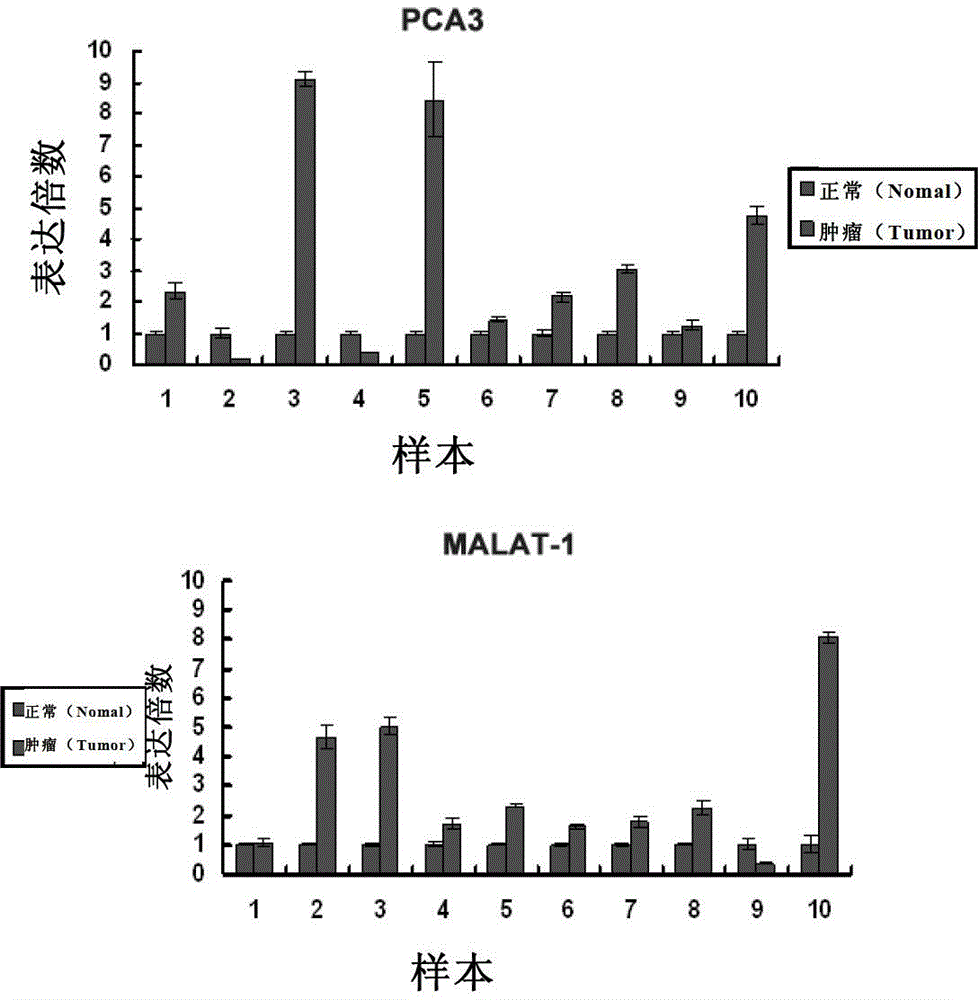
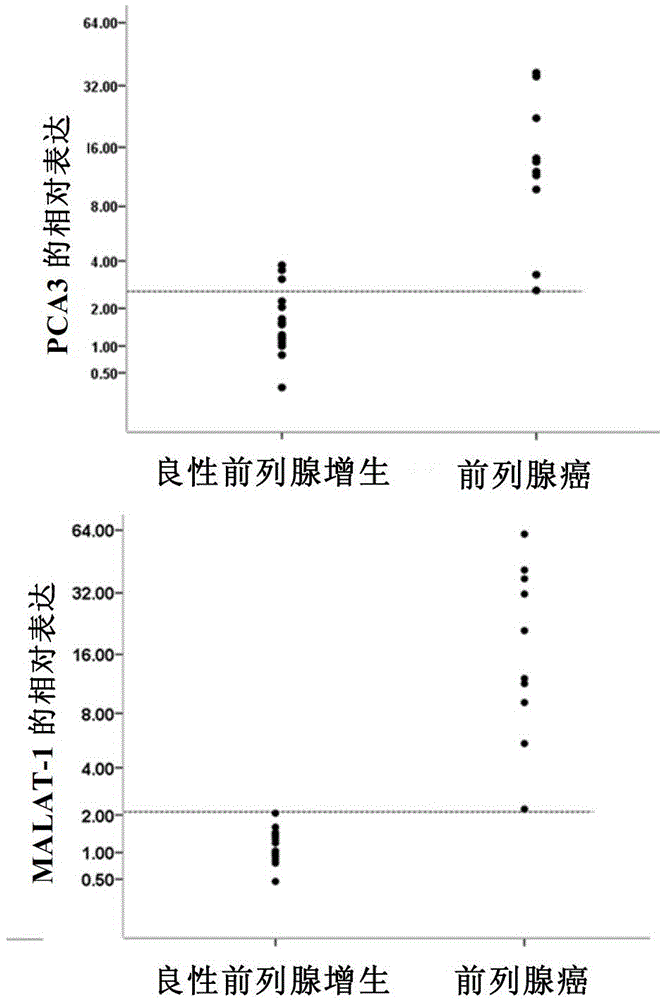
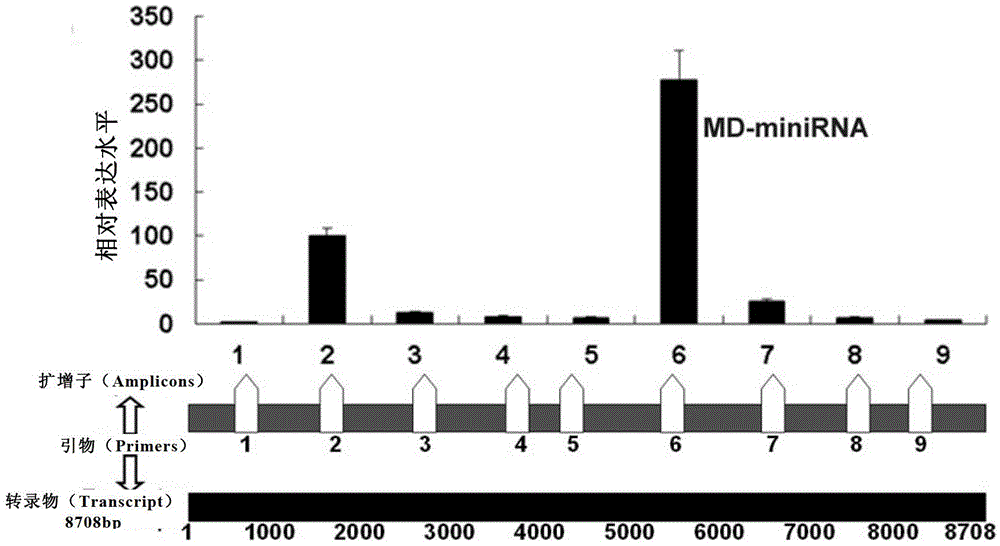
The invention relates to application of a long-chain non-coding RNA as a blood molecular marker for disease diagnosis. Specifically, the inventor successfully isolates and detects a long-chain non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in blood of human or non-human mammal; the long-chain non-coding RNA in blood of human or non-human mammal stably exists in form of fragments with different expressive abundance; a short-chain RNA (named as MD miniRNA)from lncRNA MALAT-1 in blood is from prostate cancer (PCa) cells, and releases into blood; PCa cells cultured in vitro can secrete MD-miniRNA and release into a nutrient solution; and high expression of MD-miniRNA can be detected in transplanted tumor mice plasma. In addition, expression of MD-miniRNA is in positive correlation with morbidity of PCa, and the MD-miniRNA realizes sensitivity higher than 40% and specificity higher than 80% in distinguishing prostate puncture positive and negative patients. Therefore, the MD-miniRNA is a novel cancer (especially prostate cancer) blood molecular diagnostic marker, and can significantly improve the accuracy of diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
Regulation of epigenetic control of gene expression
Methods are provided for the identification of compounds that selectively modulate epigenetic changes in gene expression. Compounds, compositions, kits or assays devices, and methods are provided for modulating the expression, endogenous levels or the function of small non-coding RNAs cognate to or transcribed by heterochromatic regions subject to epigenetic regulation (i.e., promoters, enhancers, centromeres, telomeres, origins of DNA replication, imprinted loci, or loci marked by dosage-compensation), and for modulating the formation or function of heterochromatin in cells, tissues or animals.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of microRNA related diseases
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases that are sensitive to drugs that downregulate the function of microRNA's, mRNA, non-coding RNA, or viral genomes. In particular, it has been discovered that a very long term effect of an anti microRNA oligonucleotide may be obtained when administered to a primate. Therefore, the present invention relate to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of primates, including humans wherein the compositions are administered with a long time interval.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Non-coding rnas and uses thereof
ActiveUS20160160295A1Improve expression levelMicrobiological testing/measurementCancers diagnosisNon-coding RNA
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Long chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) gene and application method thereof
ActiveCN103146693ADeep meaningFar-reaching promotionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExpression vectorRNA interference
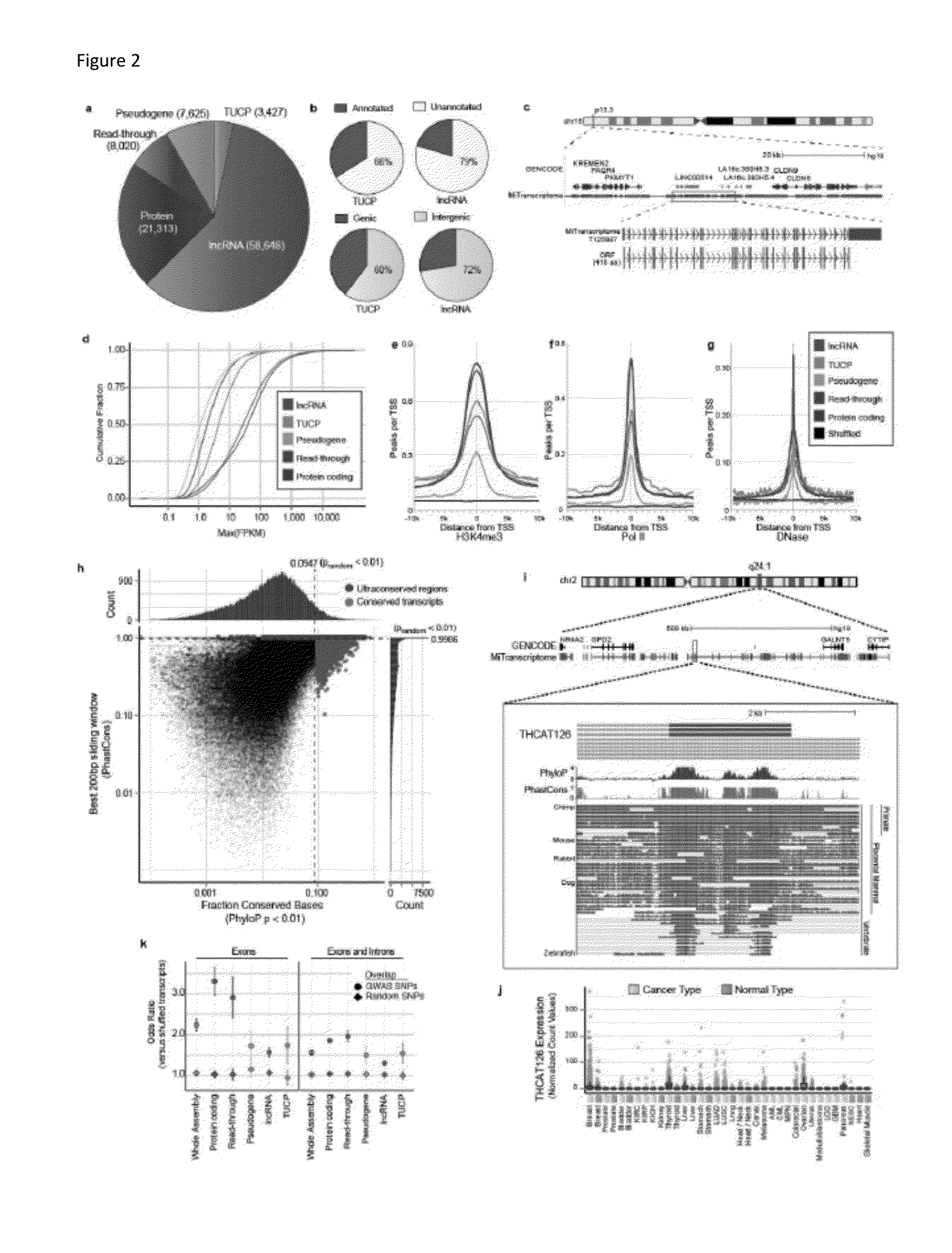
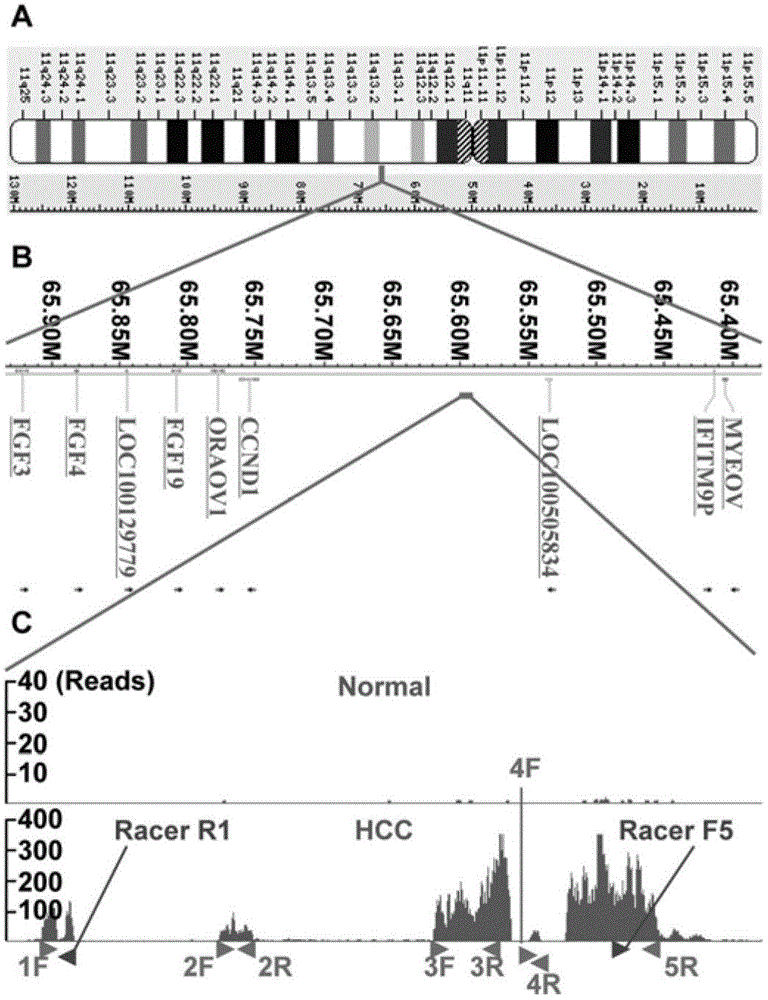
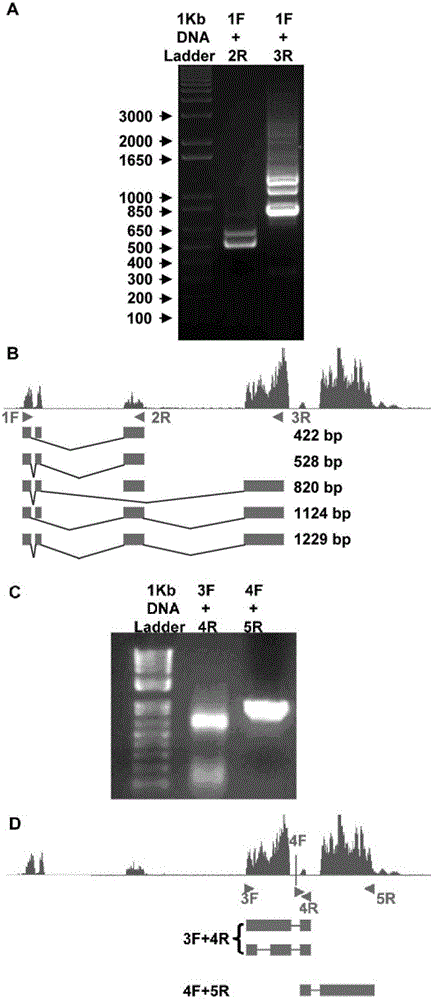
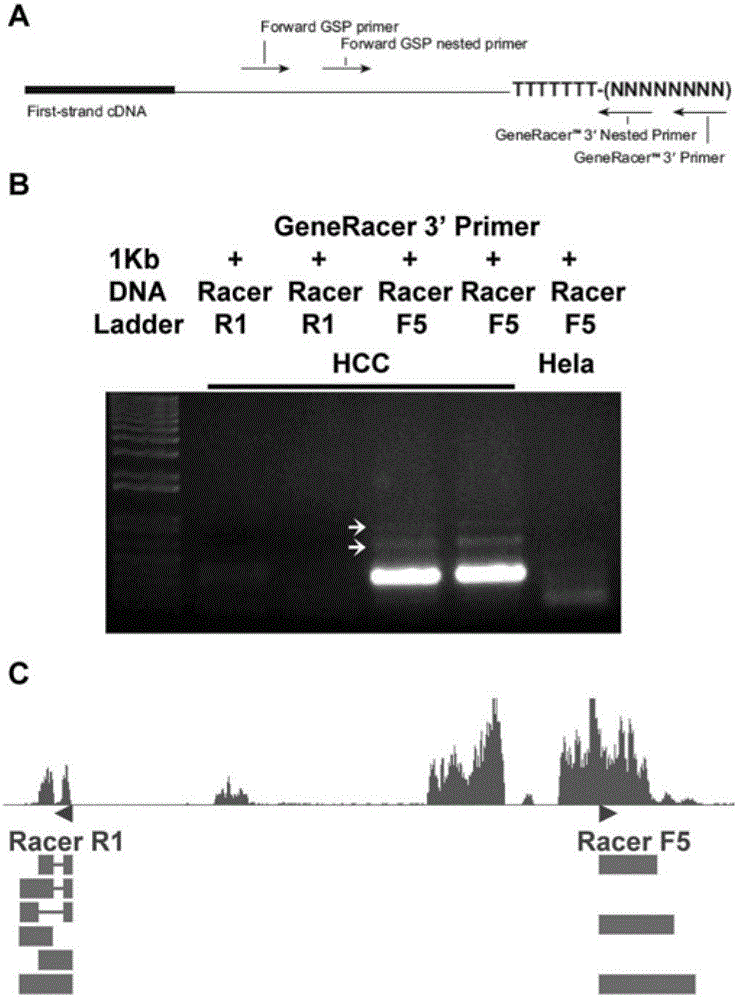
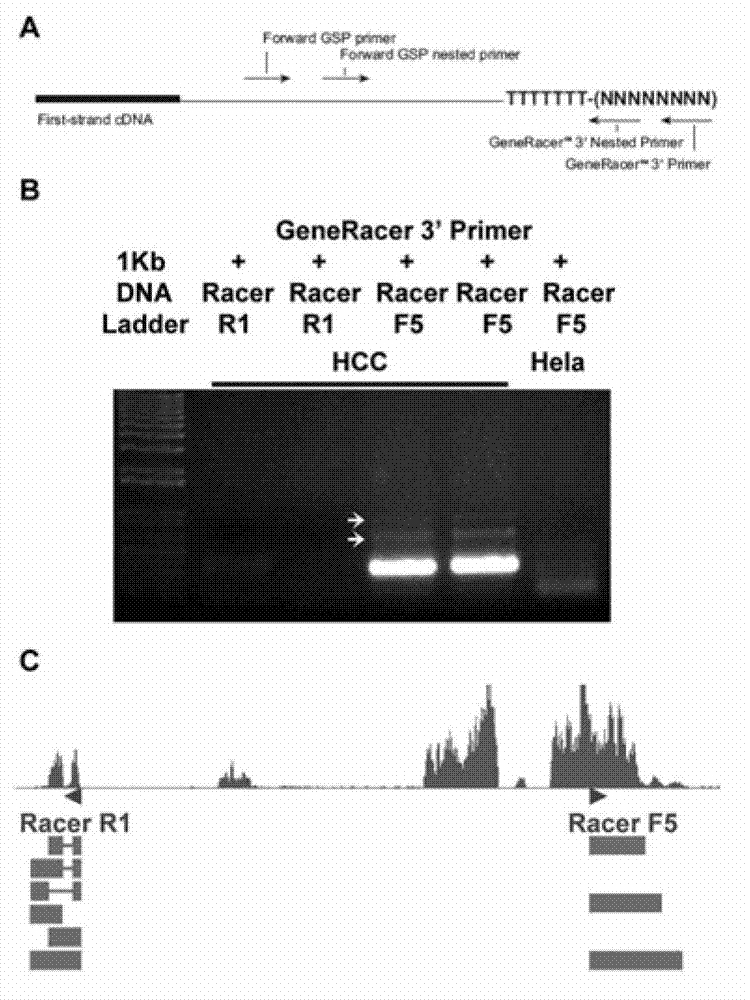
The invention relates to a newly cloned full-length sequence of a long chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) gene and an application method thereof. The gene can be detected in a separation sample by methods including a hybrid method or an amplification method; and the gene can be used as a tumor marker, in particular a marker of liver cancer. According to the gene sequence, a real-time quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer and an in situ hybridization probe are designed and synthesized; and by detecting the expression level of the long chain non-coding RNA in a liver cancer clinical case sample, expression of the long chain non-coding RNA in liver cancer is up-regulated remarkably, and prognosis of patients with liver caner with high expression of long chain non-coding RNA is poorer. According to the gene sequence, a RNA eukaryotic expression vector in a short hairpin structure for closing the expression of the long chain non-coding RNA by RNA interference is designed and synthesized; and the expression of the long chain non-coding RN in a liver cancer cell line A is inhibited successfully by using the vector.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of analysis allowing avoidance of surgery
ActiveUS20170275702A1Prevent removalAvoid surgeryMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisDNA methylationCervix
A multi-gene-based assay for analysis of the following: (a) oncogene expression; (b) DNA methylation of tumor suppressor genes; (c) non-coding RNA expression (microRNA profiling); and (d) long non-coding RNA expression in cancer samples is disclosed. The assay method and device for conducting the assay are applicable to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of various cancers such as lung, breast, colorectal, prostate, liver, bladder; kidney, cervix, pancreatic, gastric, brain, oral, endometrium, and ovary. The assay methods allow avoidance of surgery to remove cancerous tissue.
Owner:GENEVERIFY INC
Method and kit for preparing a target RNA depleted sample
InactiveUS20150275267A1Simple methodDepleting unwanted target RNAPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaNon-coding RNA
The present invention provides a method of preparing a target RNA depleted composition from an initial RNA containing composition, comprising a) contacting the initial RNA containing composition with one or more groups of probe molecules, wherein a group of probe molecules has the following characteristics: i) the group comprises two or more different probe molecules having a length of 100 nt or less; ii) the probe molecules comprised in said group are complementary to a target region of a target RNA; iii) when hybridized to said target region, the two or more different probe molecules are located adjacent to each other in the formed double-stranded hybrid; and generating a double-stranded hybrid between the target RNA and the probe molecules; b) capturing the double-stranded hybrid by using a binding agent which binds the double-stranded hybrid, thereby forming a hybrid / binding agent complex; c) separating the hybrid / binding agent complexes from the composition, thereby providing a target RNA depleted composition. By combining hybrid capturing with a unique probe design, an improved depletion method is provided which effectively and specifically removes unwanted target RNA such as ribosomal RNA (rRNA) from total RNA, while ensuring recovery of mRNA and noncoding RNA from various species, including human, mouse, and rat. By improving the ratio of useful data, decreasing bias, and preserving non-coding RNA species, the method provides high-quality RNA that is especially suited for next-generation sequencing (NGS) applications. By integrating said depletion method in common sequencing applications, in particular NGS applications such as transcriptome sequencing, improved methods for sequencing RNA molecules are provided.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
NOVEL OLIGONUCLEOTIDE COMPOSITIONS AND PROBE SEQUENCES USEFUL FOR DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF microRNAs AND THEIR TARGET mRNAs
InactiveUS20090053718A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processTarget mrnaAllele
The invention relates to ribonucleic acids and oligonucleotide probes useful for detection and analysis of microRNAs and their target mRNAs, as well as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The invention furthermore relates to oligonucleotide probes for detection and analysis of other non-coding RNAs, mRNAs, mRNA splice variants, allelic variants of single transcripts, mutations, deletions, or duplications of particular exons in transcripts, e.g. alterations associated with human disease, such as cancer.
Owner:EXIQON AS
Compositions and methods to initiate or enhance antibody and major-histocompatibility class I or class II-restricted t cell responses by using immunomodulatory, non-coding rna motifs
InactiveUS20050222060A1Effectively turningPotent and differential impact on the adaptive immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsRNA MotifsMajor histocompatibility
Owner:BOT ADRIAN L +4
Method for generating a rna-sequencing library
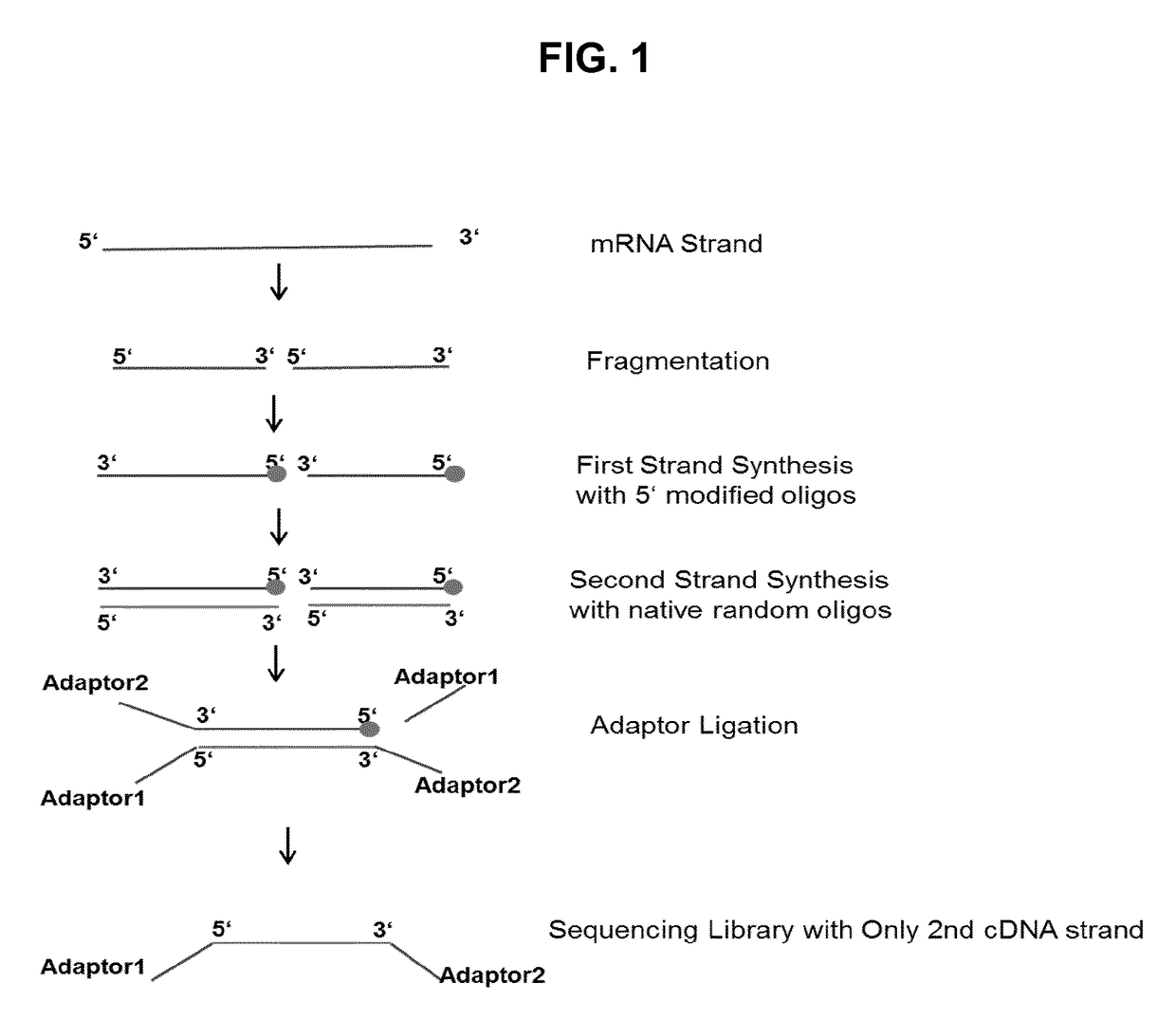
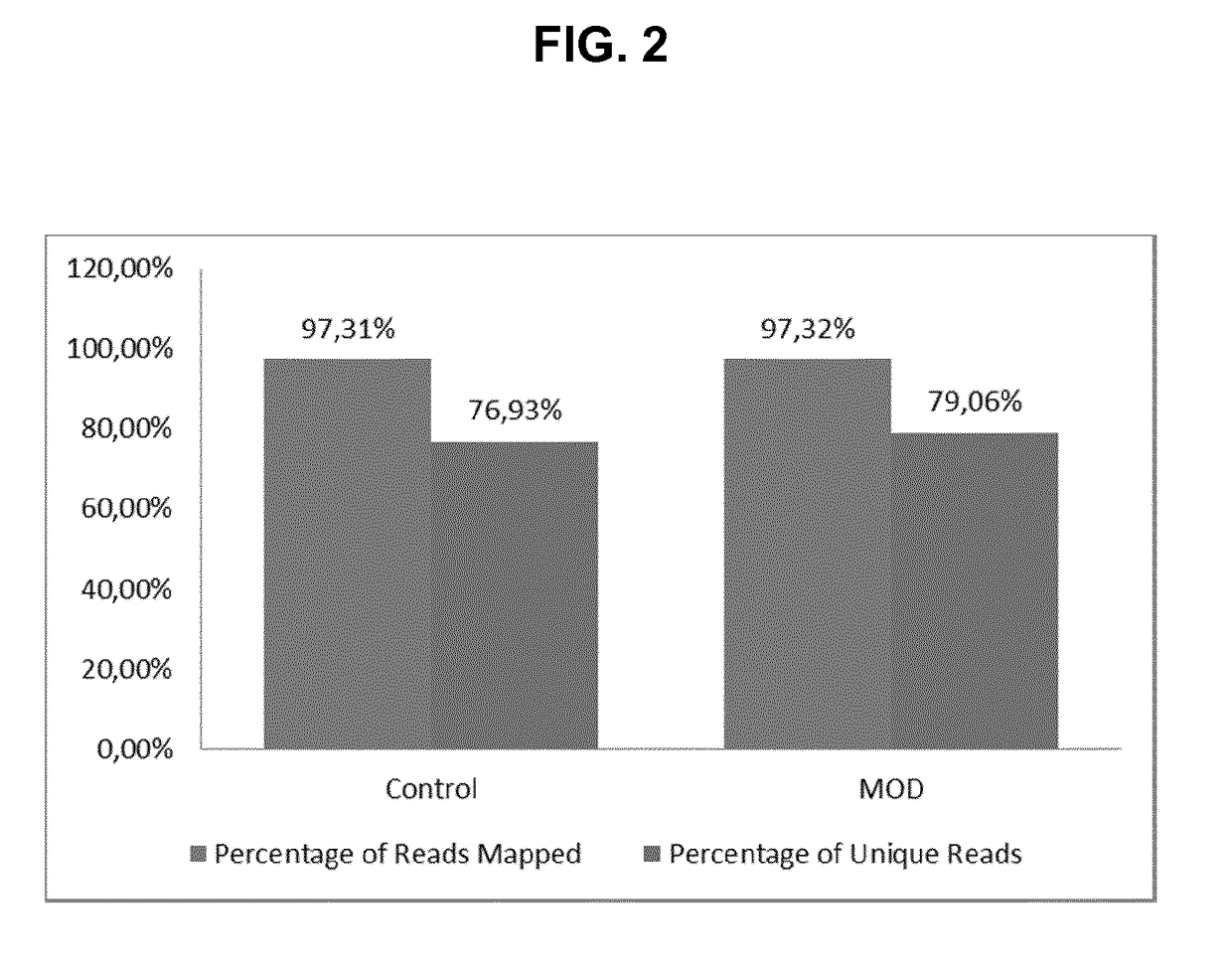
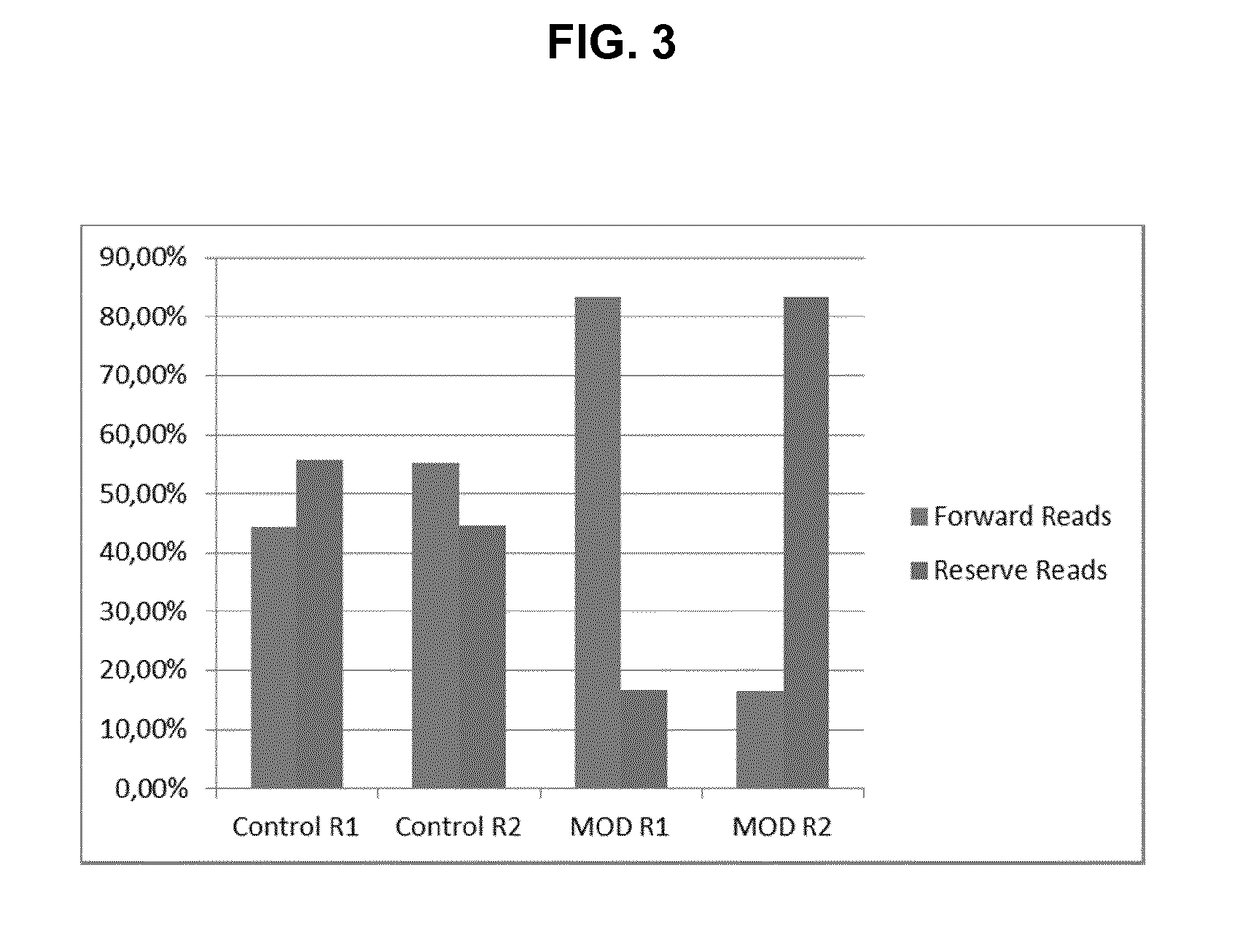
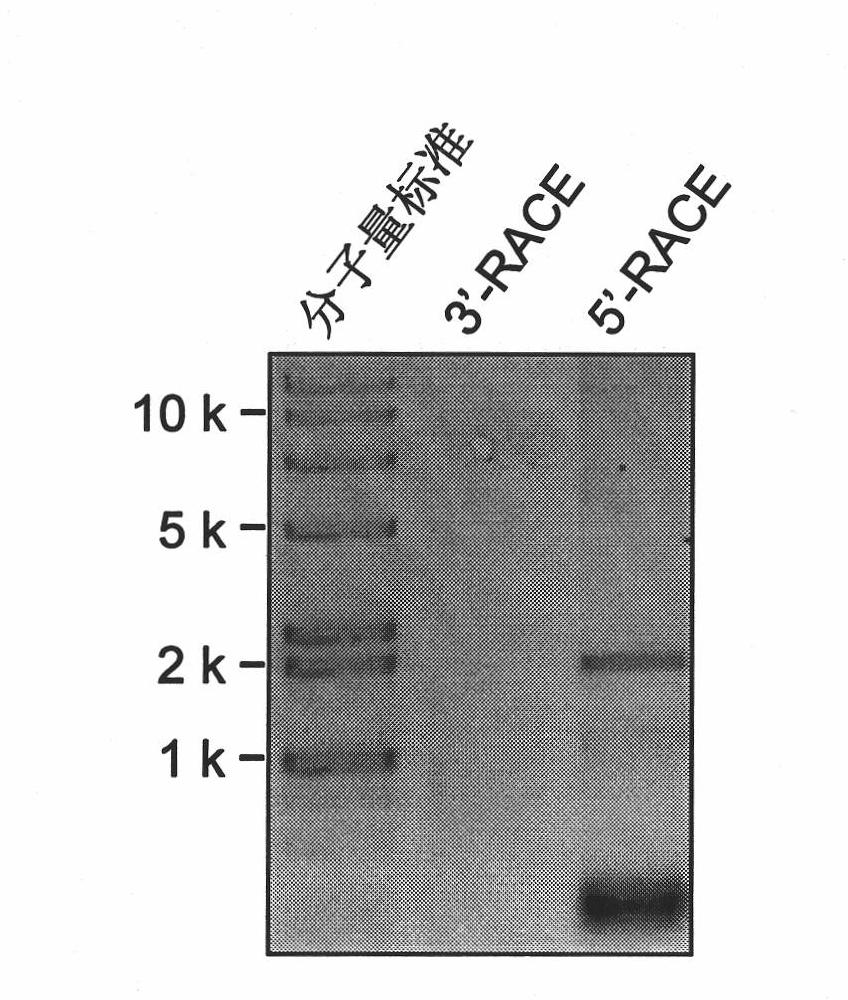
The invention refers to a novel method of preparing strand-specific RNA-sequencing libraries that can be used to identify DNA coding and non-coding strands that are transcribed mRNA Strand to RNA. Such strand-specific RNA-sequencing libraries are especially useful in discovering anti-sense RNA and non-coding RNA. Random primer oligonucleotides, covalently coupled to a moiety, which blocks ligation, are used for RT reaction or the subsequent generation of the second DNA strand so that only one strand of the generated double-stranded DNA is ligated to sequencing adapters at the 5′ nucleotide and sequenced by paired-end sequencing.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Long non-coding RNA and application thereof
InactiveCN102433326AInhibit expressionPrevent proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsNon-coding RNA
The invention provides a long non-coding RNA and an application thereof. The long non-coding RNA has a sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1. The invention also provides a purpose of the long non-coding RNA as a tumor marker, and probes and primers used for detecting the long non-coding RNA. The invention also provides an inhibitor of the long non-coding RNA. The inhibitor assists in inhibiting the expression of the long non-coding RNA and tumor cell proliferation. The invention further provides a medicine composition comprising the inhibitor.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Oligomers with improved off-target profile
ActiveCN104955950AOff-target binding is not easySugar derivativesActivity regulationLow affinityOligomer
Owner:GUANGDONG MAIJINJIA BIOTECH CO LTD
Application of long-chain non-coding RNA in preparation of non-small cell lung cancer treatment drugs
ActiveCN103316359APromote apoptosisInhibit apoptosisGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsApoptosisNon-coding RNA
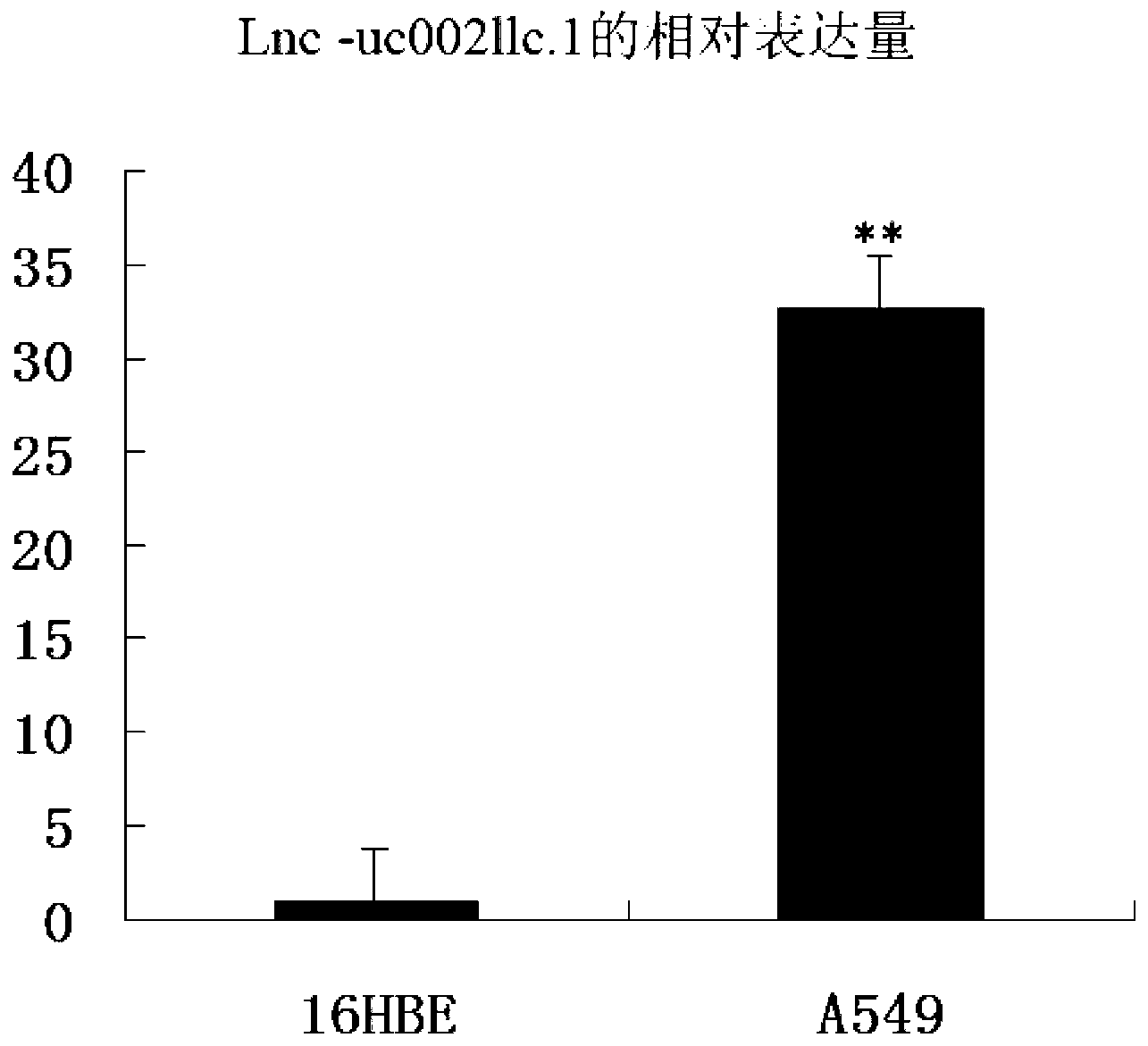
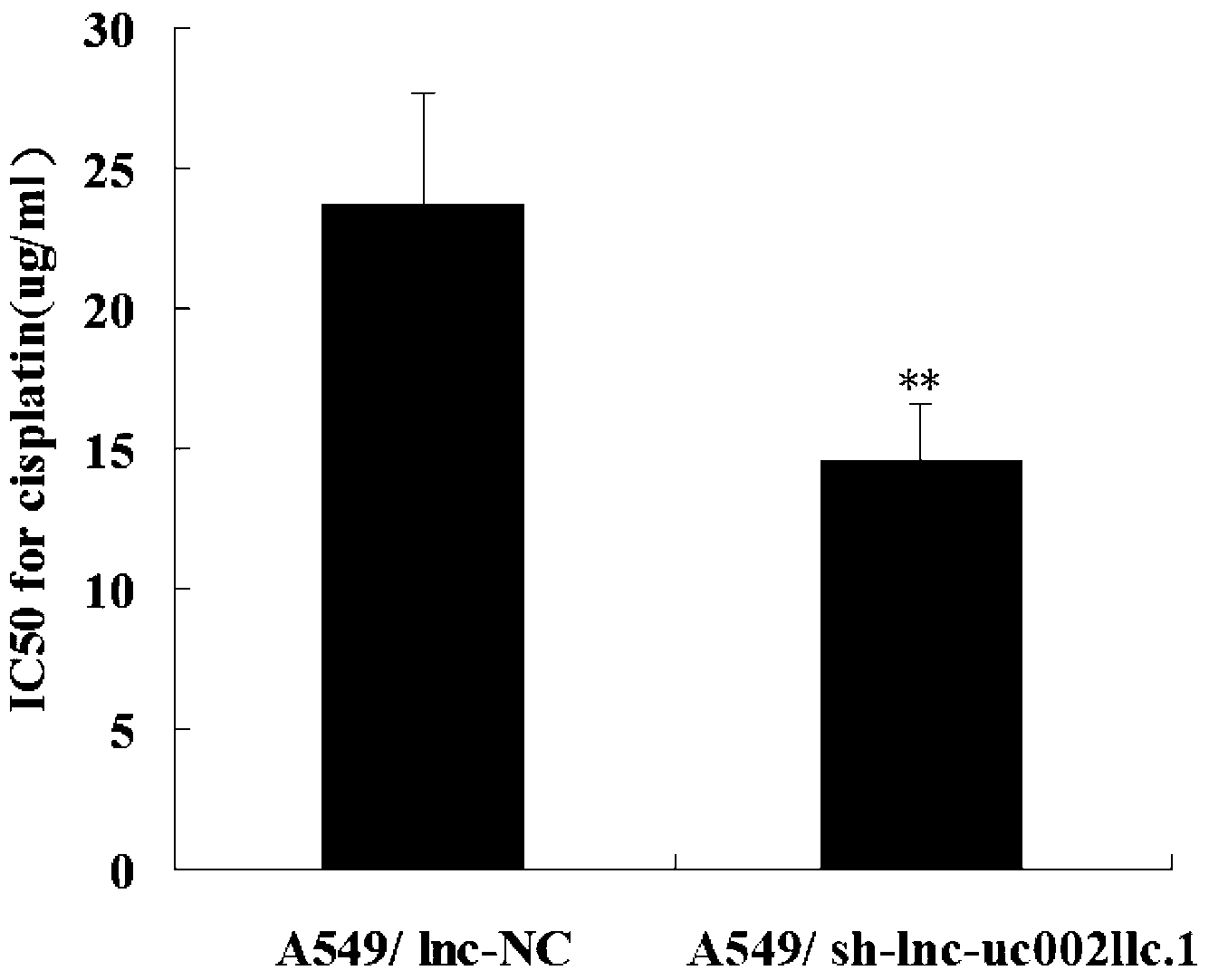
The invention belongs to the genetic engineering field, and especially relates to an application of long-chain non-coding RNA in the preparation of non-small cell lung cancer treatment drugs. The change of the lnc-uc002llc.1 expression has influences on the apoptosis, proliferation, the drug susceptibility and the like of non-small cell lung cancer cells, so the reduction of the lnc-uc002llc.1 expression can realize the apoptosis promotion, proliferation inhibition and chemotherapy drug susceptibility enhancement of the non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Method for constructing transcriptome library
InactiveCN104630206AAvoid wasting human and financial resourcesReduce adverse effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationTotal rnaNon-coding RNA
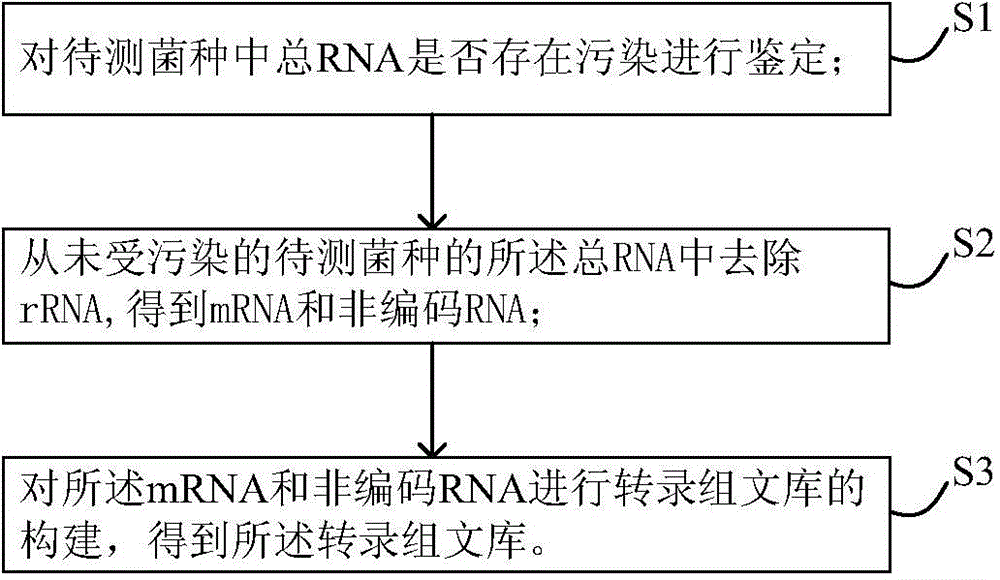
The invention discloses a method for constructing a transcriptome library. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1, verifying whether total RNA in a strain to be measured is polluted; S2, removing rRNA from the total RNA of the unpolluted strain to be measured to obtain mRNA and non-coding RNA; and S3, using the mRNA and the non-coding RNA to construct the transcriptome library to obtain the transcriptome library. In the method, a step of controlling the quality of the total RNA is added to ensure that the RNA sample is not polluted, and a subsequent transcriptome library construction step is carried out to avoid the waste of manpower and financial resources caused by the polluted RNA and perfect the problem of low comparison rate of subsequent sequencing data. Few samples are needed in the verification step, the operation is simple, a result is obtained quickly and accurately, and the verification step has high throughput capacity, so that the verification step can be widely used in the transcriptome library construction step to verify the total RNA to the strain to be measured.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
Application method of long-chain non-coding ribonucleic acid (RNA) gene in preparation of interference inhibitor
ActiveCN103160537ADeep meaningFar-reaching promotionAntineoplastic agentsVector-based foreign material introductionHepatoma cell lineRna expression
The invention relates to an application method of a newly cloned long-chain non-coding ribonucleic acid (RNA) gene, in particular to the application method of the long-chain non-coding RNA method in preparation of an interference inhibitor. The application method of the long-chain non-coding RNA method in preparation of the interference inhibitor comprises designing and combining a short hairpin structure RNA eukaryotic expression vector for closing expression of the long-chain non-coding RNA in an RNA interference mode according to a gene sequence of the long-chain non-coding RNA, and using the short hairpin structure RNA eukaryotic expression vector to successfully restrain the expression of the long-chain non-coding RNA in a liver cancer cell line.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Natural antisense and non-coding RNA transcripts as drug targets
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) knock down antisense transcripts, and regulate the expression of their sense partners. This regulation can either be discordant (antisense knockdown results in sense transcript elevation) or concordant (antisense knockdown results in concomitant sense transcript reduction).
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Prognosis marker for lung cancer and application thereof
InactiveCN109136370AImproved prognosisConvenience prognostic survival is very correlated by markerMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular levelCvd risk
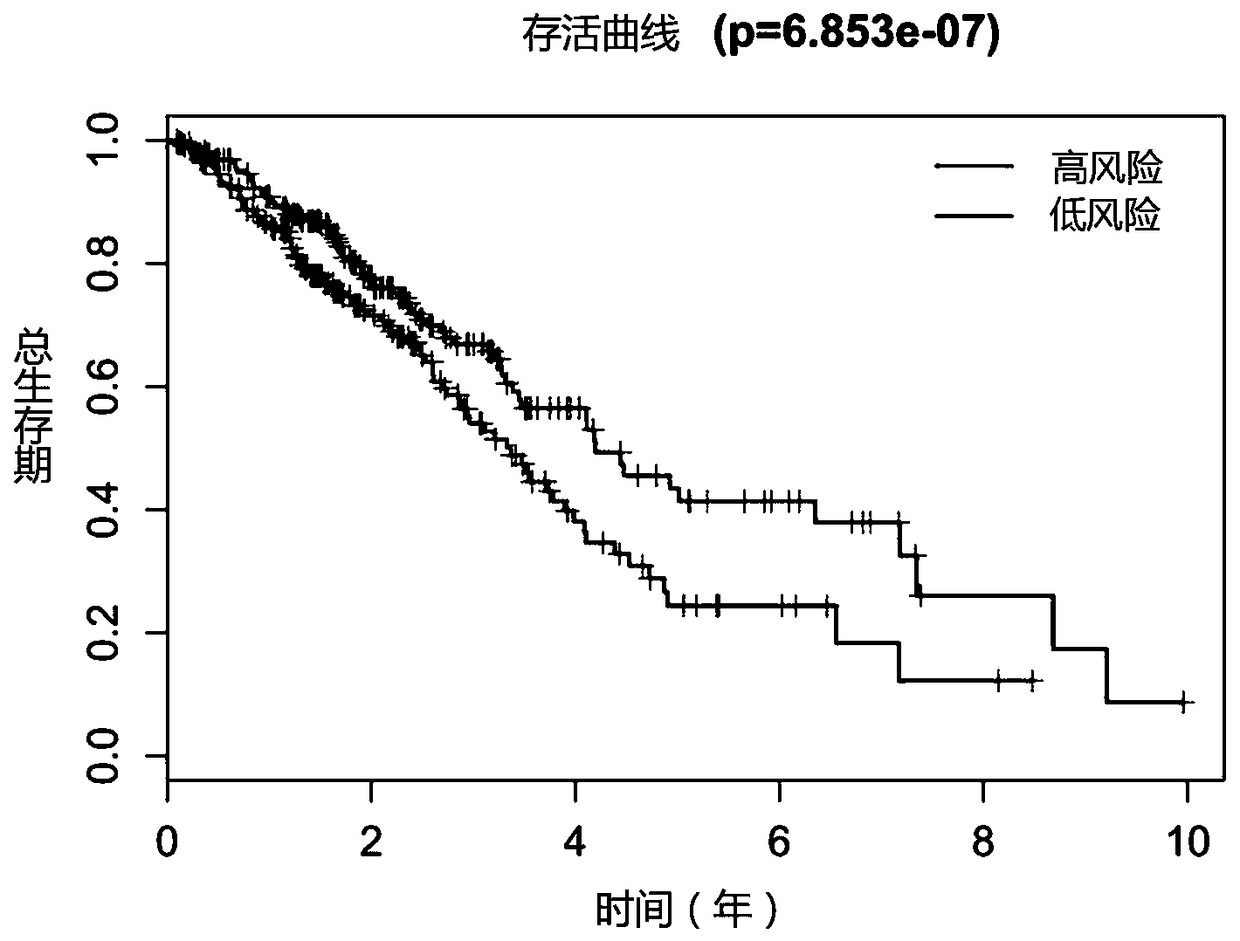
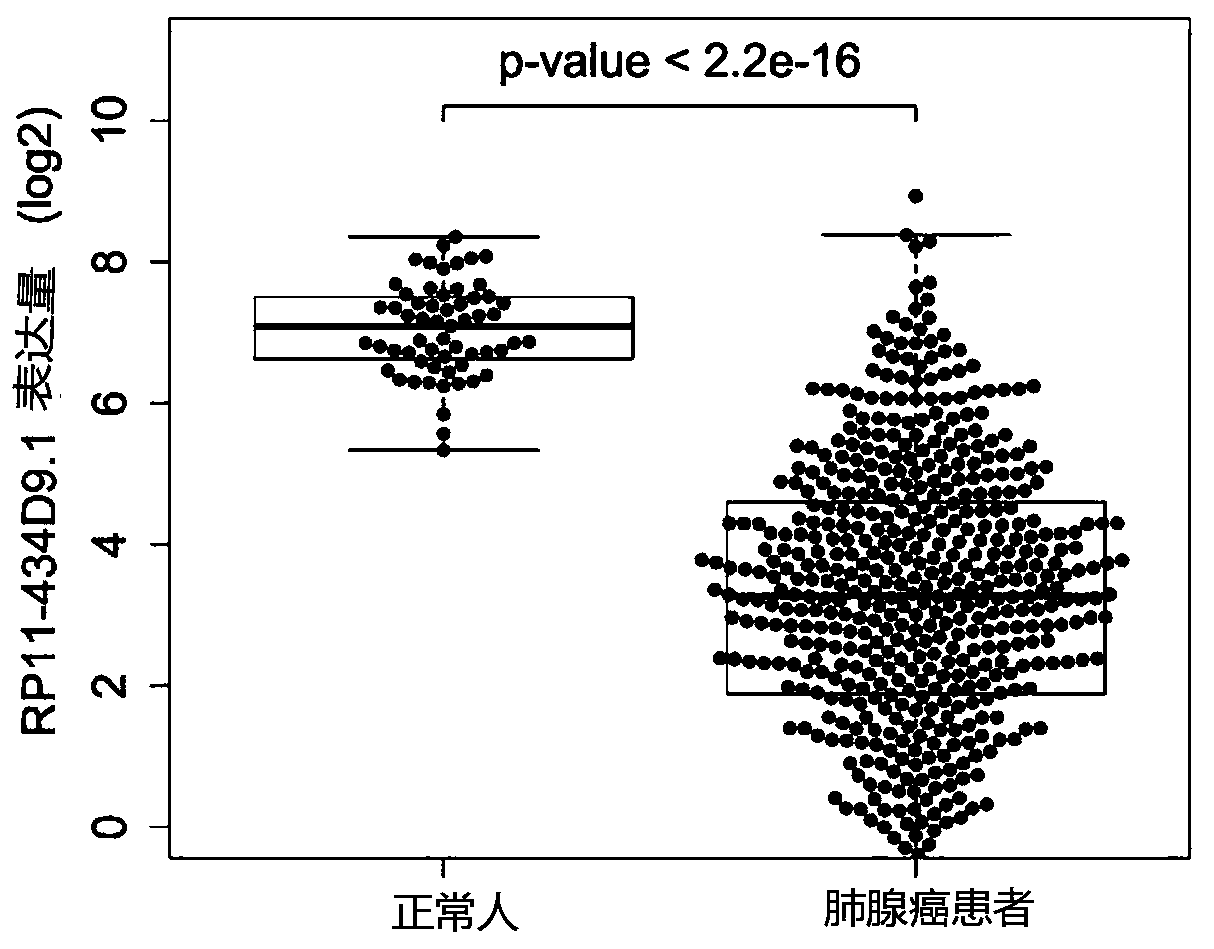
The invention discloses a prognosis marker for the lung cancer and application thereof. The long chain non-coding RNA gene RP11-434D9.1 of the marker is quite related to the prognosis period of patients with the lung cancer, through the marker and expression for detecting the marker, lung cancer prognosis is rapidly, accurately and conveniently predicted, the grading and layering of lung cancer risks are realized according to molecular levels, and patients with different grades of risks are separated obviously. Through co-expression analysis, 238 genes related to the long chain non-coding RP1-434D9.1 are found out, through an enrichment analysis on GO and KEGG pathways of the 238 genes, the molecular functions of the long-chain non-coding RP1-434D9.1 are found out, and important biologicalexperiment clues are provided for improving prognosis molecular diagnosis of the patients with the lung cancer and related medicine targets.
Owner:广州表观生物科技有限公司 +1
Prostate cancer-specific exosome, IncRNA and preparation methods and application thereof
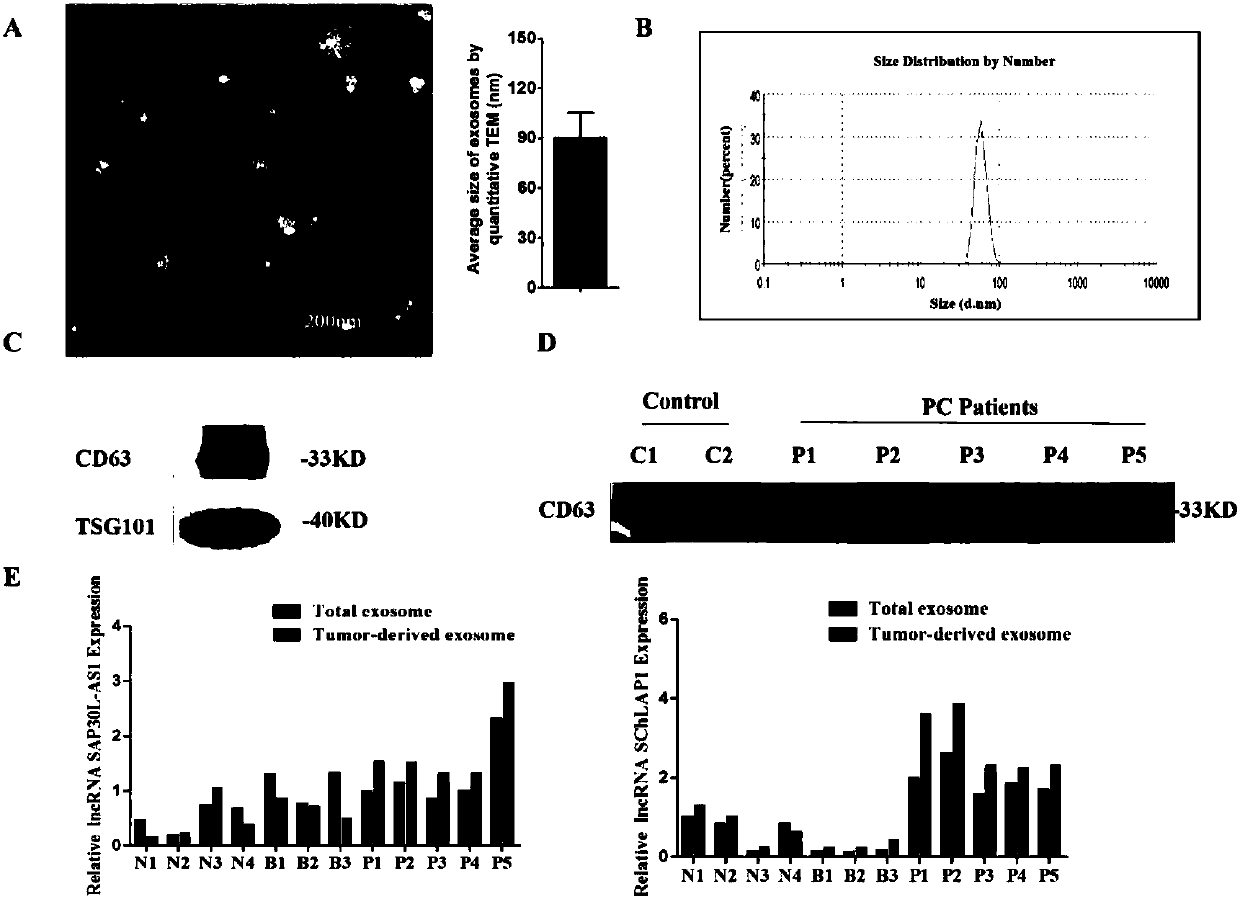
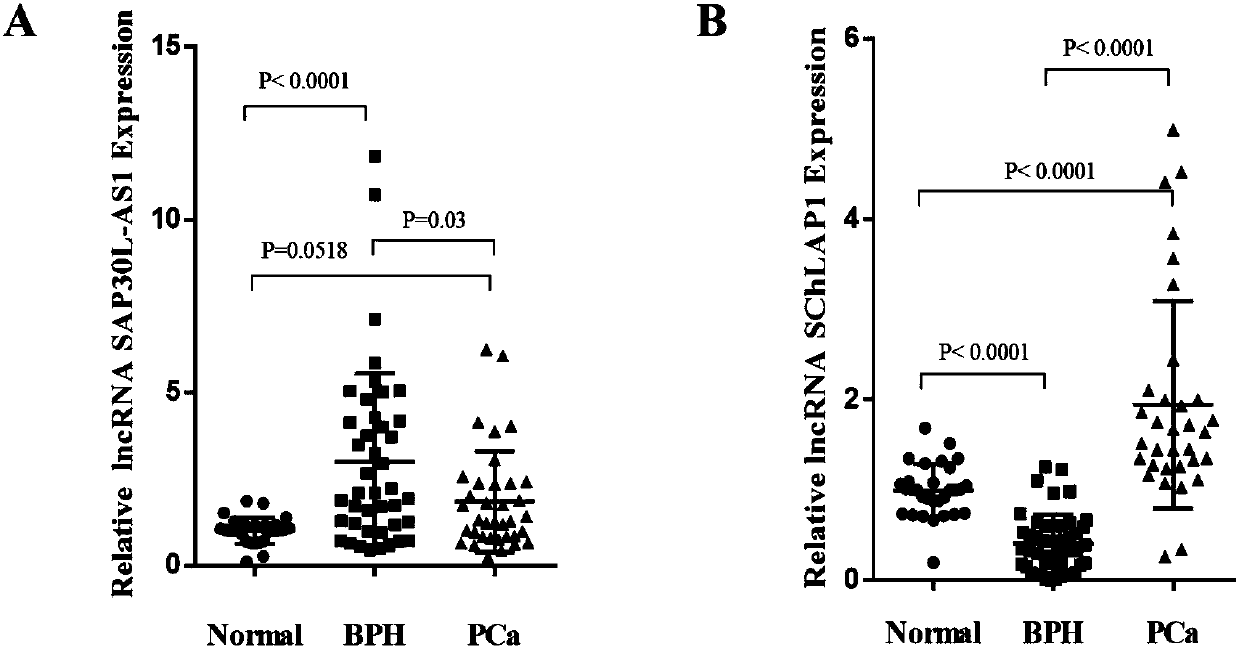
ActiveCN107828779AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTrue positive rateProstate cancer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a prostate cancer-specific exosome. The invention further discloses the prostate cancer-specific exosome and application thereof. The invention furtherdiscloses a preparation method of a long-chain non-coding RNA SAP30L-AS1 and SChLAP1 in the prostate cancer exosome. The invention further discloses application of a reagent for assaying expression quantities of the long-chain non-coding RNA SAP30L-AS1 and SChLAP1 in the prostate cancer exosome in the preparation of a prostate cancer diagnosis reagent. The invention further discloses a prostate cancer diagnosis kit. The prostate cancer-specific exosome in the plasma of a patient with prostate cancer can be successfully separated, and the long-chain non-coding RNA SAP30L-AS1 and SChLAP1 can bedetected. The diagnostic efficacy and sensitivity and specificity are all remarkably increased.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Induced malignant stem cells
The present invention addresses the problem of providing malignant stem cells that can be grown in vitro and are useful in cancer therapy research and drug discovery research for cancer therapy, a method for producing same, cancer cells induced from the cells, and use for the cells. Provided are induced malignant stem cells that can be grown in vitro, the induced malignant stem cells being characterized in (1) having at least one type of abnormality selected from among (a) abnormal methylation (hypermethylation or hypomethylation) of a cancer suppressor gene or cancer-related gene region in the endogenous genome DNA, (b) somatic mutation of a cancer suppressor gene in the endogenous genome DNA or somatic mutation of an endogenous cancer-related gene, (c) abnormal expression (increased expression or decreased / lost expression); of an endogenous cancer gene or endogenous cancer suppressor gene, (d) abnormal expression (increased expression or decreased / lost expression) of non-coding RNA such as endogenous cancer-related micro RNA, (e) abnormal expression (increased expression or decreased / lost expression) of an endogenous cancer-related protein, (f) endogenous cancer-related metabolism abnormality (hypermetabolism or hypometabolism), or (g) abnormal endogenous cancer-related carbohydrate; and (2) expressing the POU5F1 gene, NANOG gene, SOX2 gene, and ZFP42 gene.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT +1
Detection method and application of long-chain non-coded RNA for screening bladder cancer
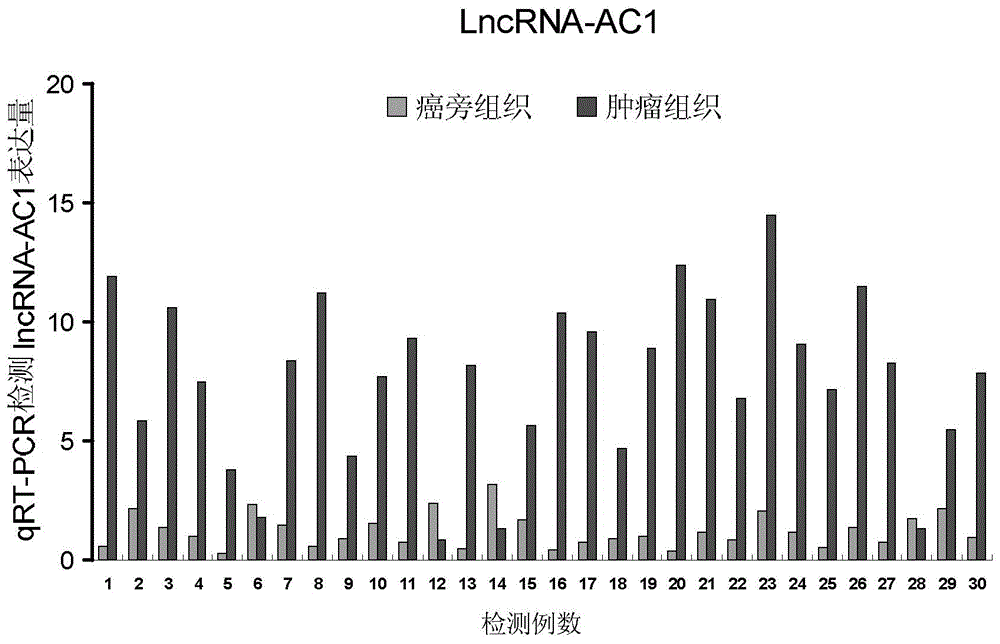
ActiveCN104357443AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHuman bladderBladder cancer screening
The invention relates to a detection method and application of a long-chain non-coded RNA for screening a bladder cancer. Specifically, an lncRNA which is remarkably and highly expressed in human bladder cancer tissues is screened through variation analysis by utilizing a long-chain non-coded expression profile chip technology, and named as lncRNA-AC1. In comparison with the expression in normal tissues, the lncRNA-AC1 is remarkably and highly expressed in the human bladder cancer tissues, and a large sample fluorescent quantitative PCR experiment further proves that the expression quantity of the lncRNA-AC1 in the human bladder cancer tissues is obviously higher than that in the normal tissues. Researches on pathogenesis of the bladder cancer can be further enriched by the new lncRAN-AC1, and a new tumor marker and a new therapeutic target are provided for early diagnosis and prognosis monitoring of the bladder cancer.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Non-coding RNA of Salmonella and identification and use thereof
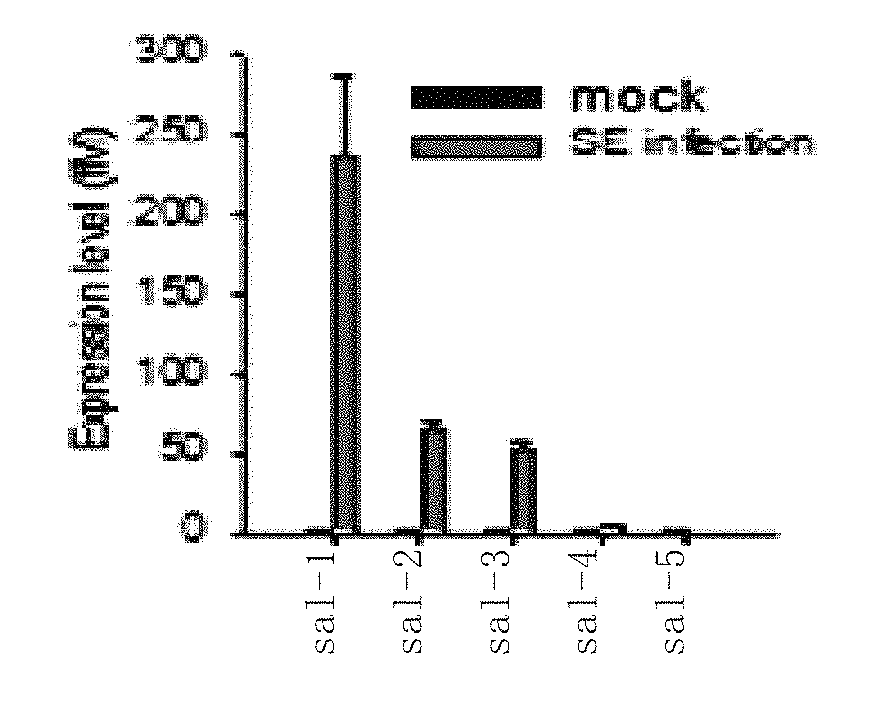
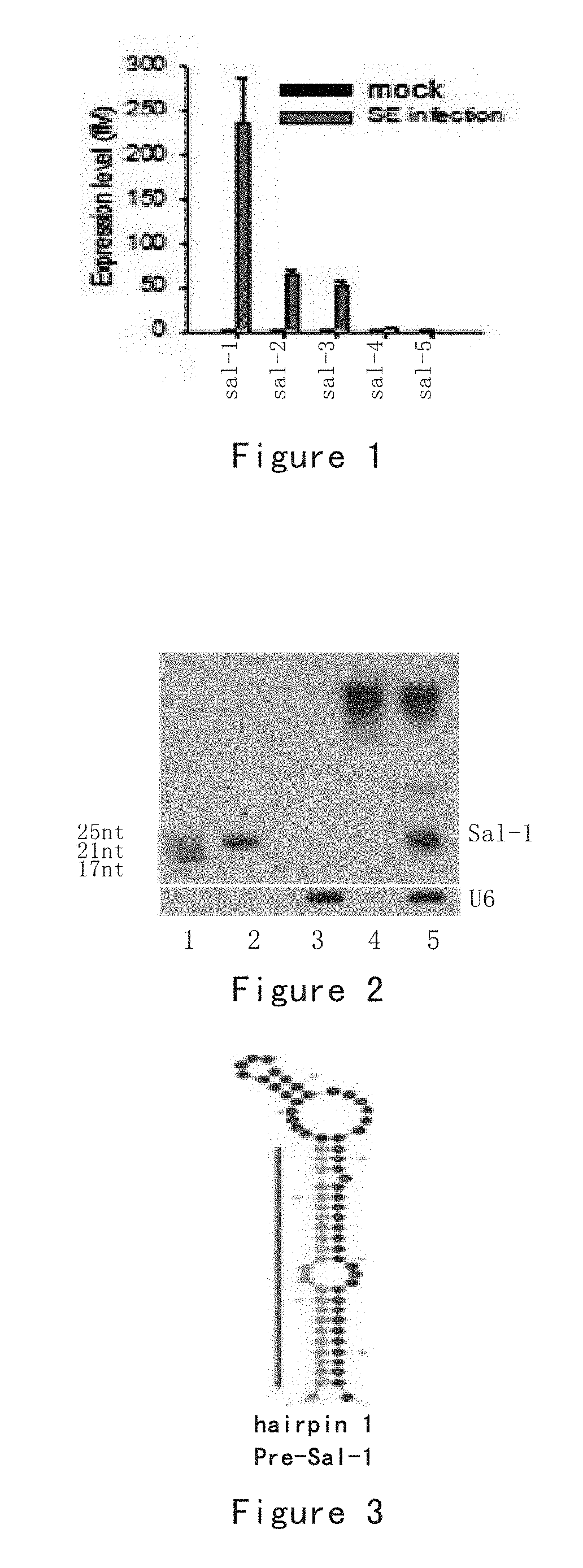
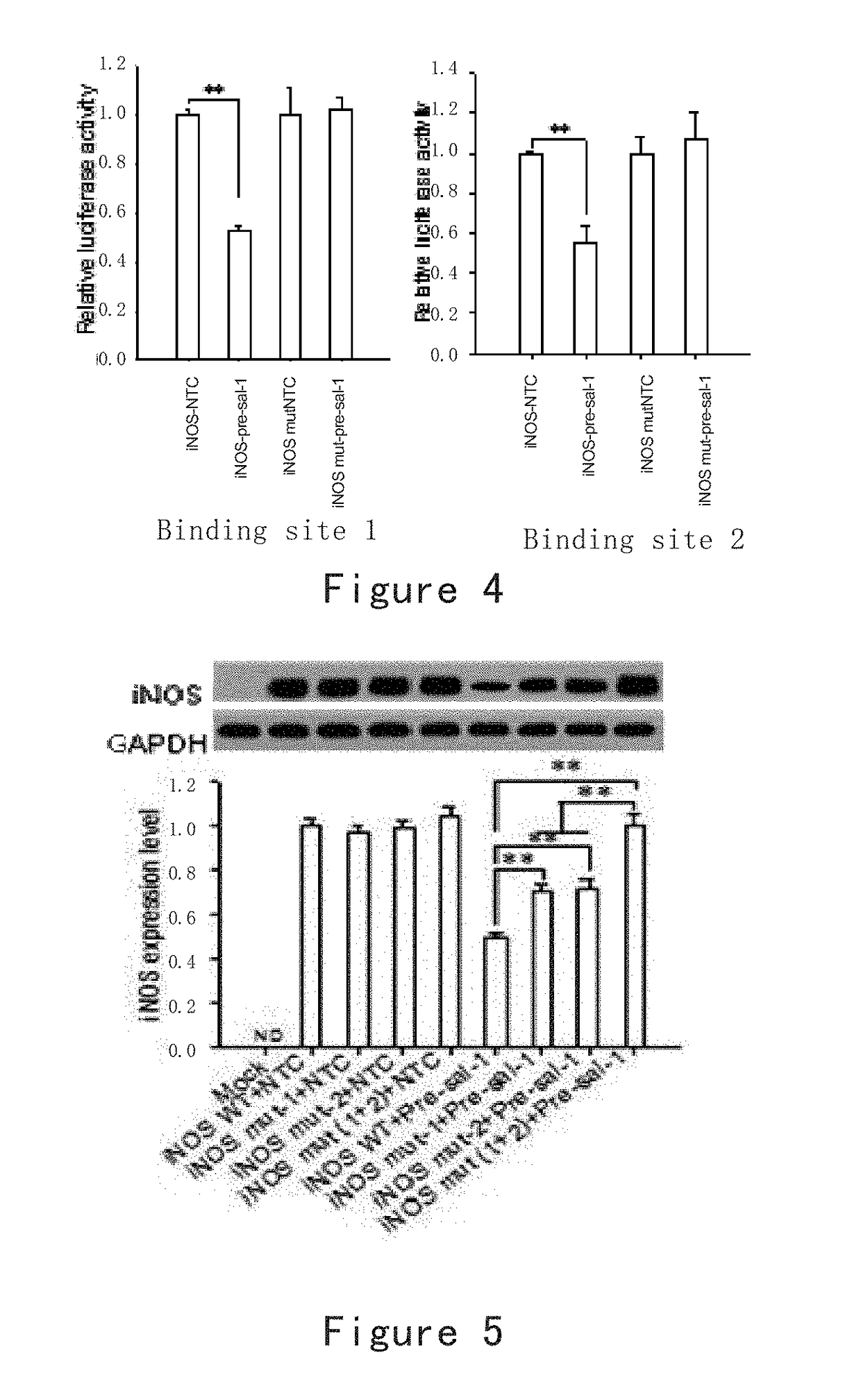
The present invention provides Salmonella non-coding RNA and the identification and application thereof. In particular, the present invention proves through experiments that a Salmonella bacterium delivers non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) encoded by the bacterium itself into a host cell, generates milRNAs similar to microRNAs by means of a microRNA splicing system in the cell, regulates the immune system with the milRNAs, and further protects the Salmonella bacterium from being cleared by the host. Adsorbing milRNAs using milRNA inhibitors can effectively inhibit the survival ability of the bacterium in the cell, leading to a reduced vitality of the bacterium. The present invention further provides relevant reagents and methods for effective detection of, treatment to and study on Salmonella bacteria or Salmonella infectious diseases.
Owner:JIANGSU MICROMEDMARK BIOTECH
Key genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs or combination thereof used for identifying or regulating cell pluripotency
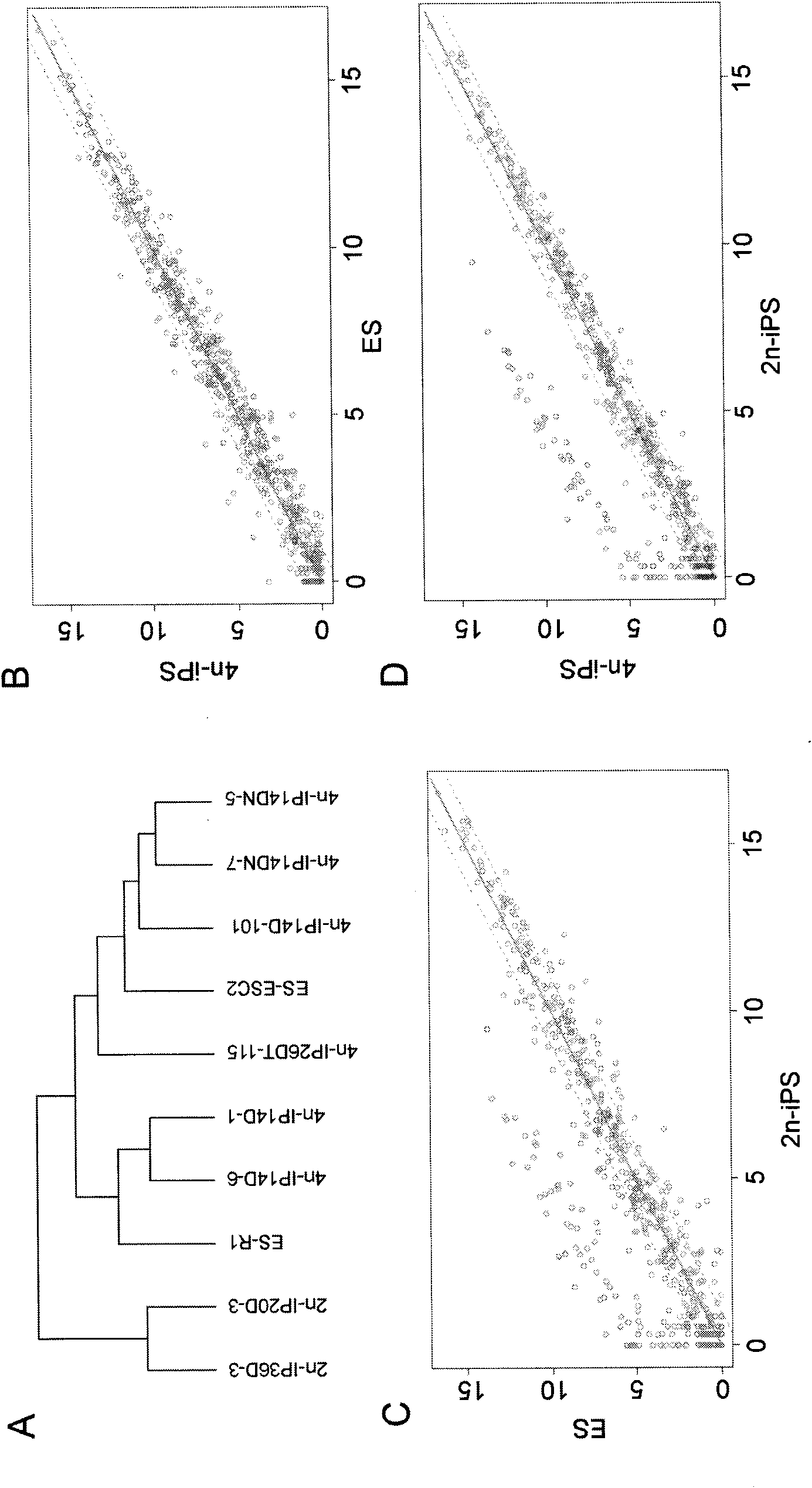
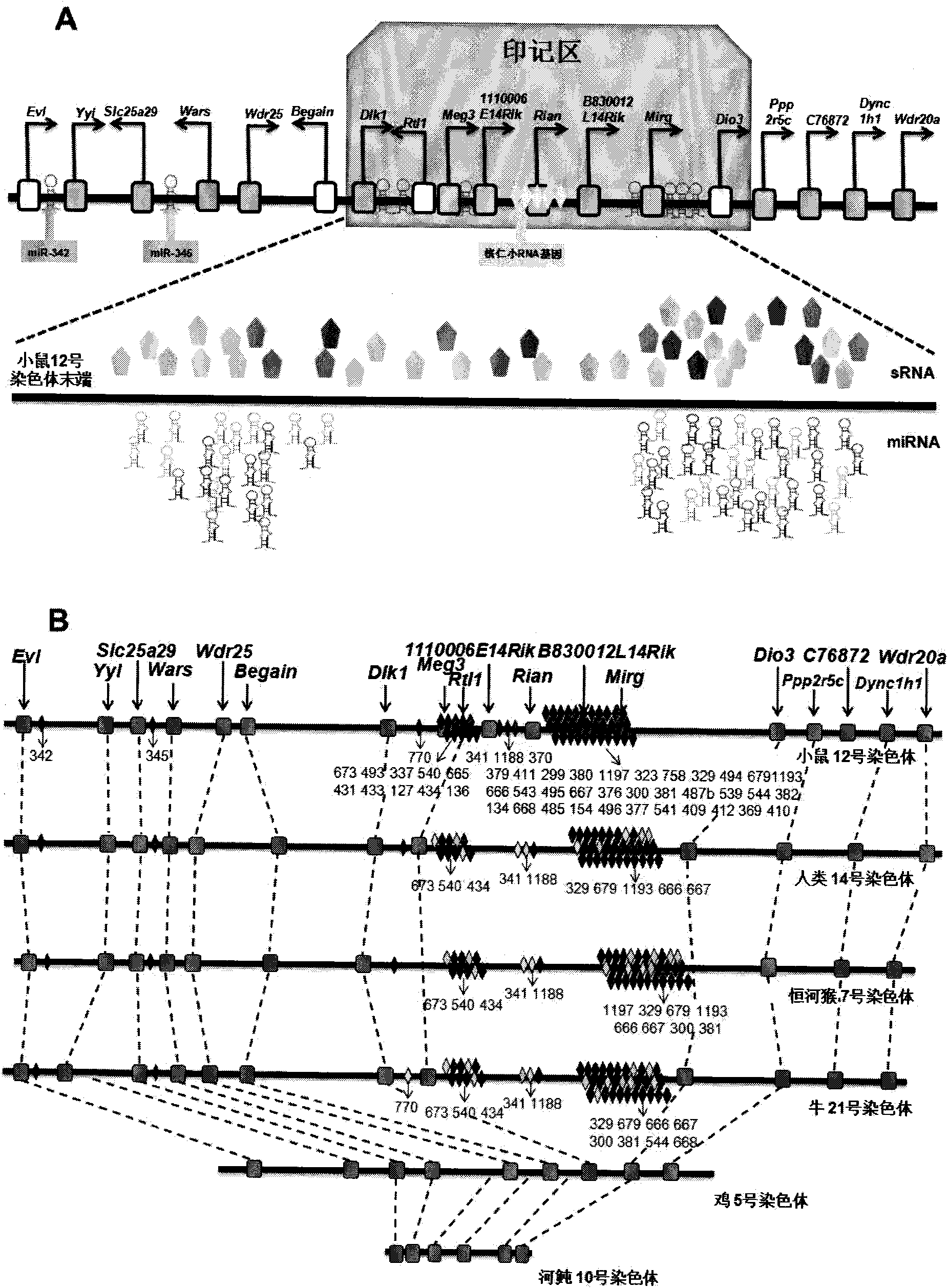
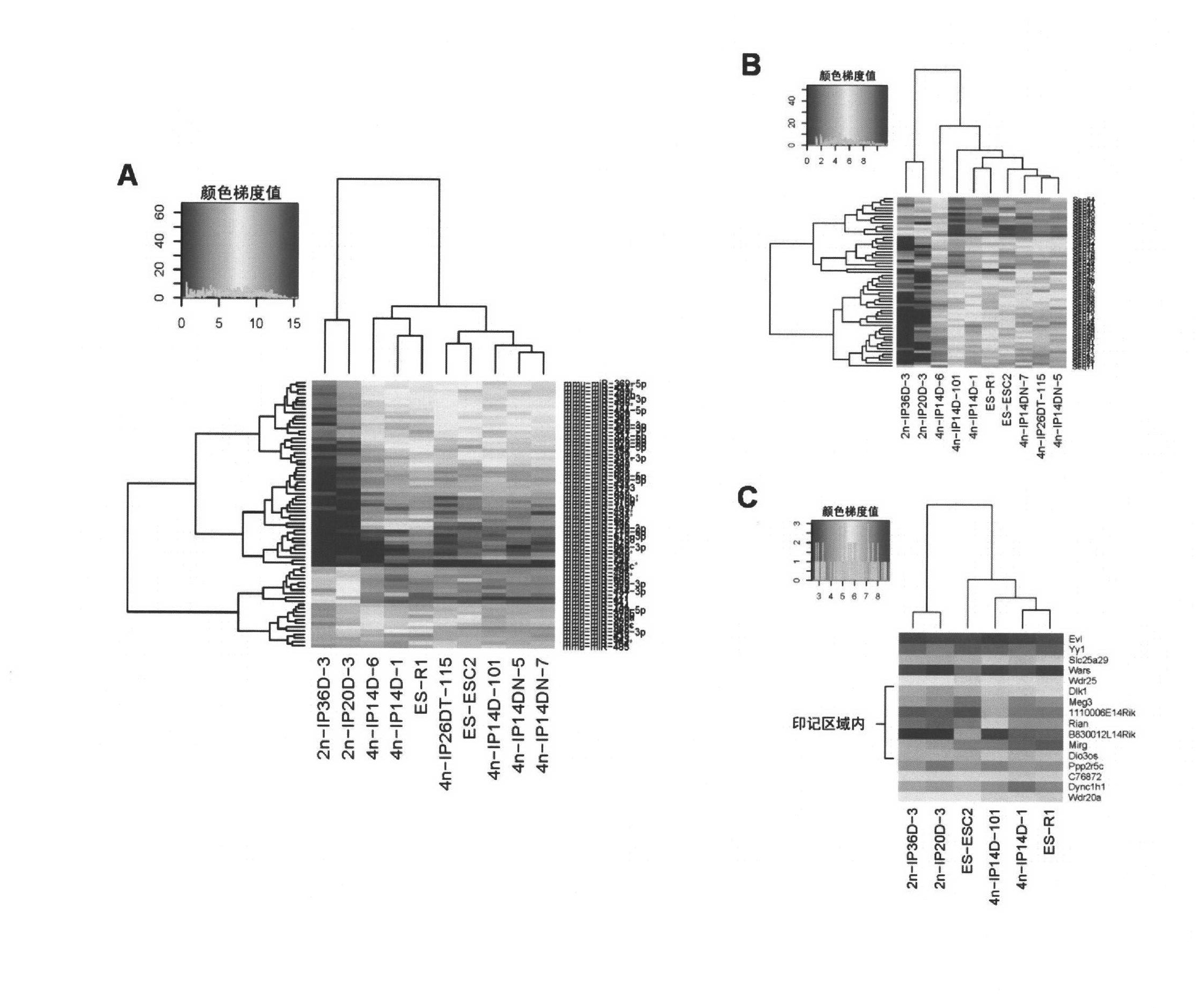
The invention relates to key genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, or a combination thereof used for identifying or regulating cell pluripotency. The invention is characterized in that the key genes, microRNAs, other non-coding RNAs or a combination is highly expressed in the stem cell with complete pluripotency and the expression is obviously repressed or silent in the stem cell without complete pluripotency. The genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs are the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs positioned in the chromosome imprinting region named as Dlk1-Dio3 on the long arm of mouse chromosome 12 and the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs in the genome collinearity regions of other mammals, which have 70%-100% of homology. The invention also relates to applications of the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, or the combination thereof used for identifying the pluripotency of the stem cell and regulating cell pluripotency, applications in stem cell typing, applications for regulating the cell pluripotency and the pluripotency state and level of the cell, applications in disease treatment, and applications in the drug target development of tumor treatment or the development of antitumor drugs.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
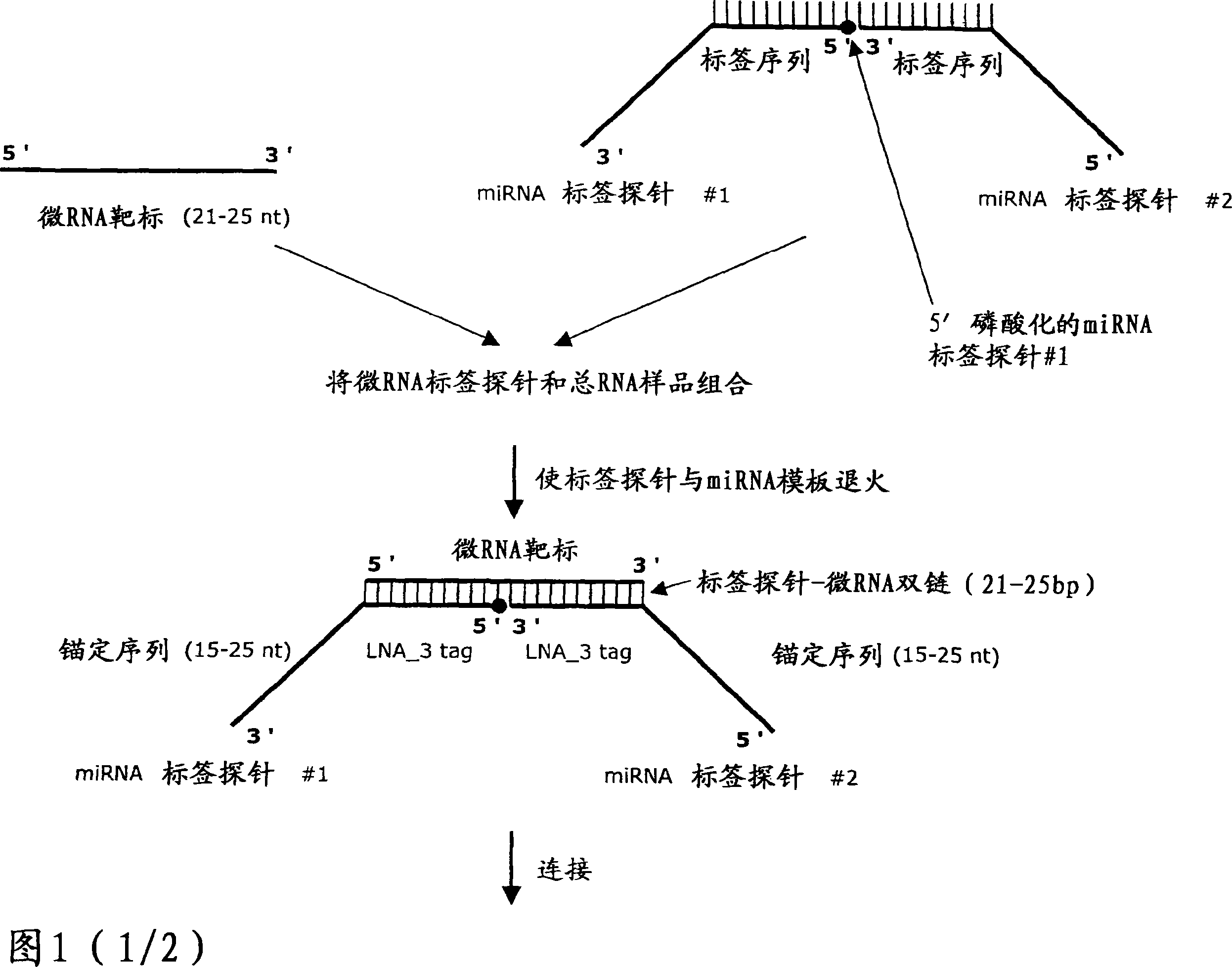
Methods for quantification of microRNA and small interfering RNA
The invention relates to ribonucleic acids, probes and methods for detection, quantification as well as monitoring the expression of mature microRNAs and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The invention furthermore relates to method s for monitoring the expression of other non-coding RNAs, mRNA splice variants, as well as detecting and quantifying RNA editing, allelic variants of single transcripts, mutations, deletions, or duplications of particular exons in transcripts, e.g., alterations associated with human disease such as cancer. The invention furthermore relates to methods for detection, quantification a s well as monitoring the expression of deoxy nucleic acids.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com