Detection method and application of long-chain non-coded RNA for screening bladder cancer
A technology for bladder cancer and its application, which is applied in the field of tumor molecular biology, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory overall curative effect and poor specificity, and achieve good application prospects, high sensitivity and good specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Analysis of lncRNA chip expression in human bladder cancer and paracancerous tissues
[0048] 1. Materials and methods
[0049] 1. Materials
[0050] Tissue samples were obtained from 3 pairs of inpatient surgical resection samples of bladder cancer patients, each pair containing bladder cancer tissue and paired paracancerous tissue.
[0051] 2. Method
[0052] (1) Extraction of total RNA from tumor tissue and normal tissue: Total RNA from bladder cancer tissue and paracancerous tissue was extracted according to the instructions of Qiagen's RNA extraction kit (RNeasy Micro Kit, Cat. No. 74004).
[0053] (2) Cy5 fluorescent labeling of sample RNA (entrust Shanghai Kangcheng Bioengineering Co., Ltd. to carry out "ArrayStar Human LncRNA Microarray V3.0Service" for labeling service)
[0054] (3) Synthesis of first-strand cDNA by reverse transcription: start with Total RNA, Oligo(dT)Primer (Shanghai Kangcheng Bioengineering Co., Ltd.) company) to synthesize firs...
Embodiment 2
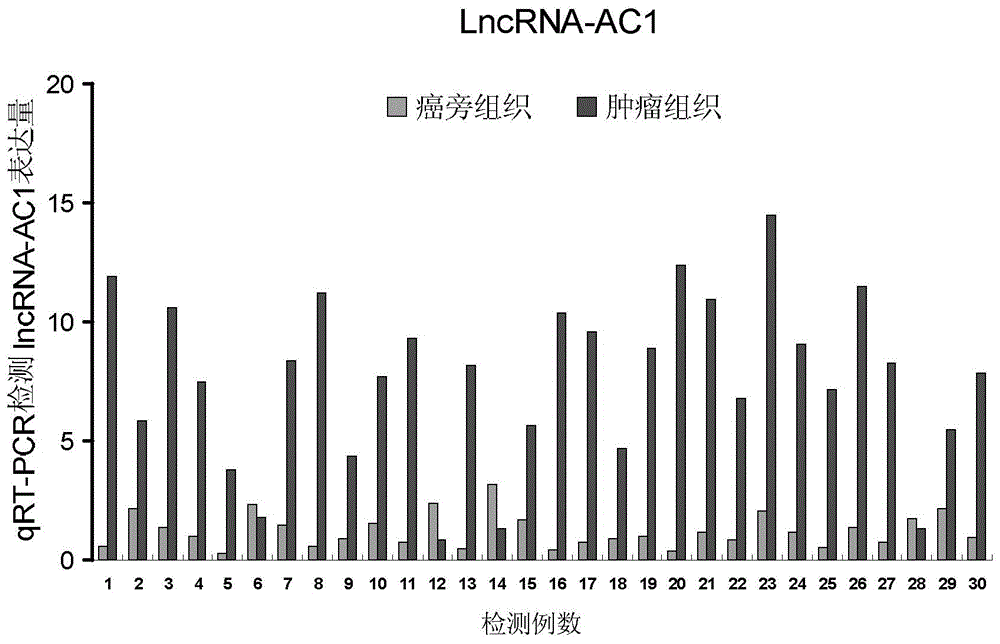
[0062] Example 2: qRT-PCR preliminary verification of differential expression of lncRNA-AC1 in bladder cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues
[0063] 1. Experimental materials
[0064] 30 pairs (different from the samples tested by the microarray) of human bladder cancer tissues (provided by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University) and paired paracancerous tissues were selected to verify the expression difference of lncRNA-AC1 by qRT-PCR.
[0065] 2. Experimental methods and results
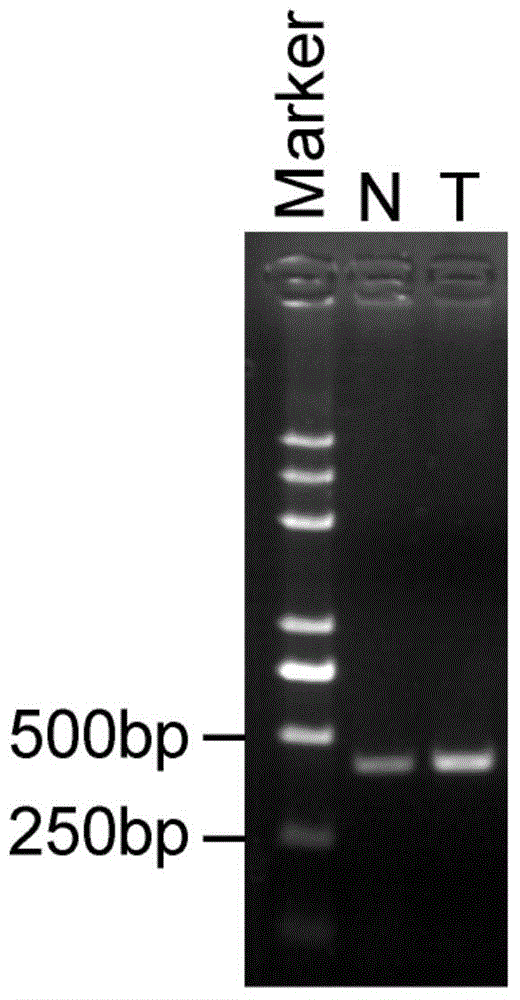
[0066] 1. Identification of primer specificity
[0067] (1) Design of specific primers: extract lncRNA-AC1-related transcript sequences from the Ensemble database, and use the primer design tool (Primer BLAST) of NCBI to design primers according to the sequence of the transcript;
[0068] The designed primer sequences are as follows:
[0069] Upstream primer: SEQ ID No.2
[0070] Downstream primer: SEQ ID No.3
[0071] (2) Extract total RNA from human bladder cancer t...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3: Screening of bladder cancer tissue by differential expression of lncRNA-AC1
[0113] 1. Experimental materials
[0114] 100 human bladder cancer tissues and 100 paracancerous tissues (provided by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University) were selected to detect the expression difference of lncRNA-AC1 by qRT-PCR.
[0115] 2. Experimental methods and results
[0116] 1. Identification of primer specificity
[0117] (1) Use the following specific primer sequences:
[0118] Upstream primer: SEQ ID No.2
[0119] Downstream primer: SEQ ID No.3
[0120] (2) Extract total RNA from human bladder cancer tissue and paracancerous tissues according to the reagents and steps required by SIGMA's TRIZOL reagent (product number T9424), and then quantify the extracted RNA with a 7300 real time PCR system nucleic acid quantifier (Applied Biosystems AB). RNA purity and concentration.
[0121] (3) Using StarScript II One-step RT-PCR Kit (Product No. A215...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com