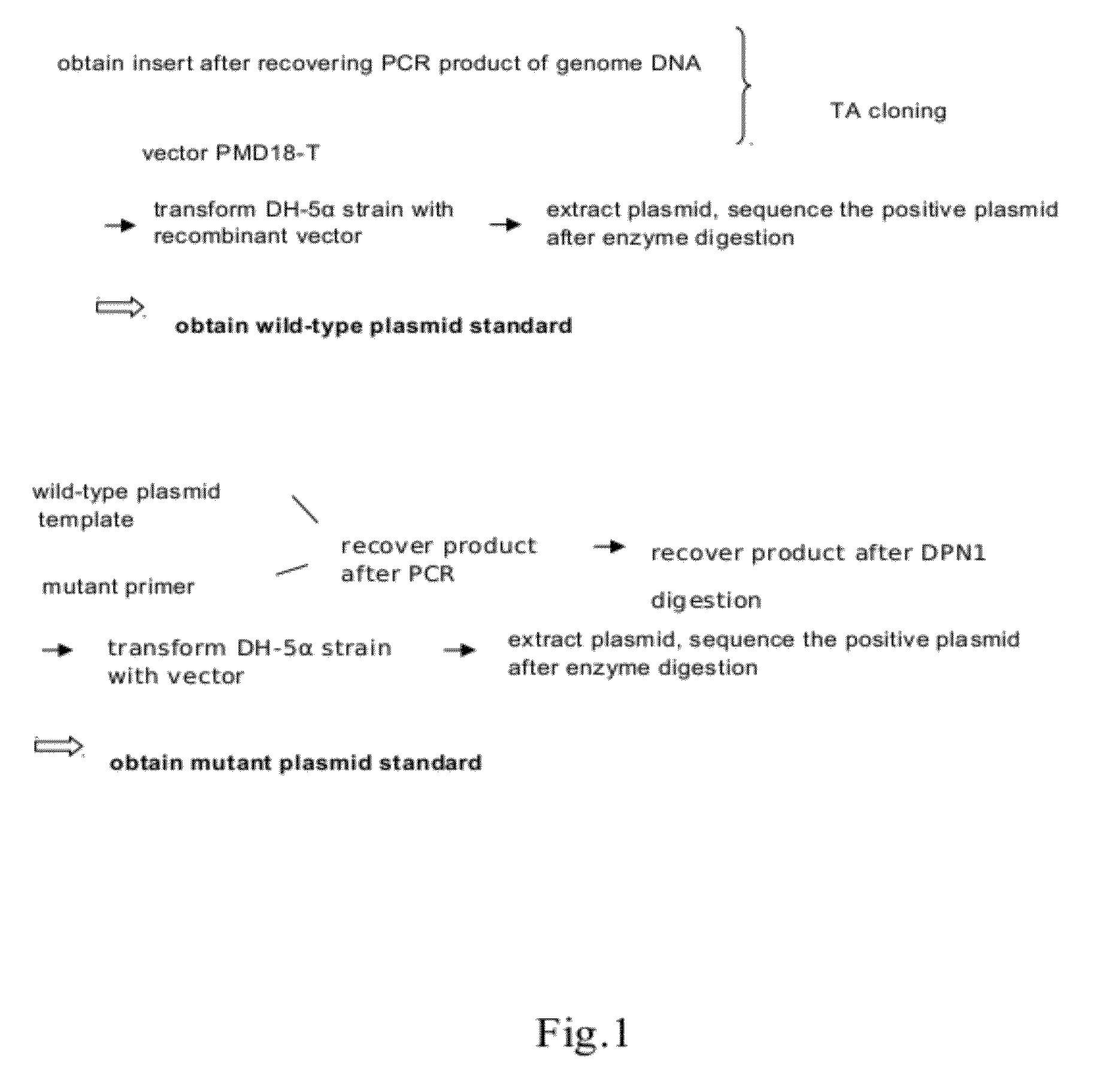
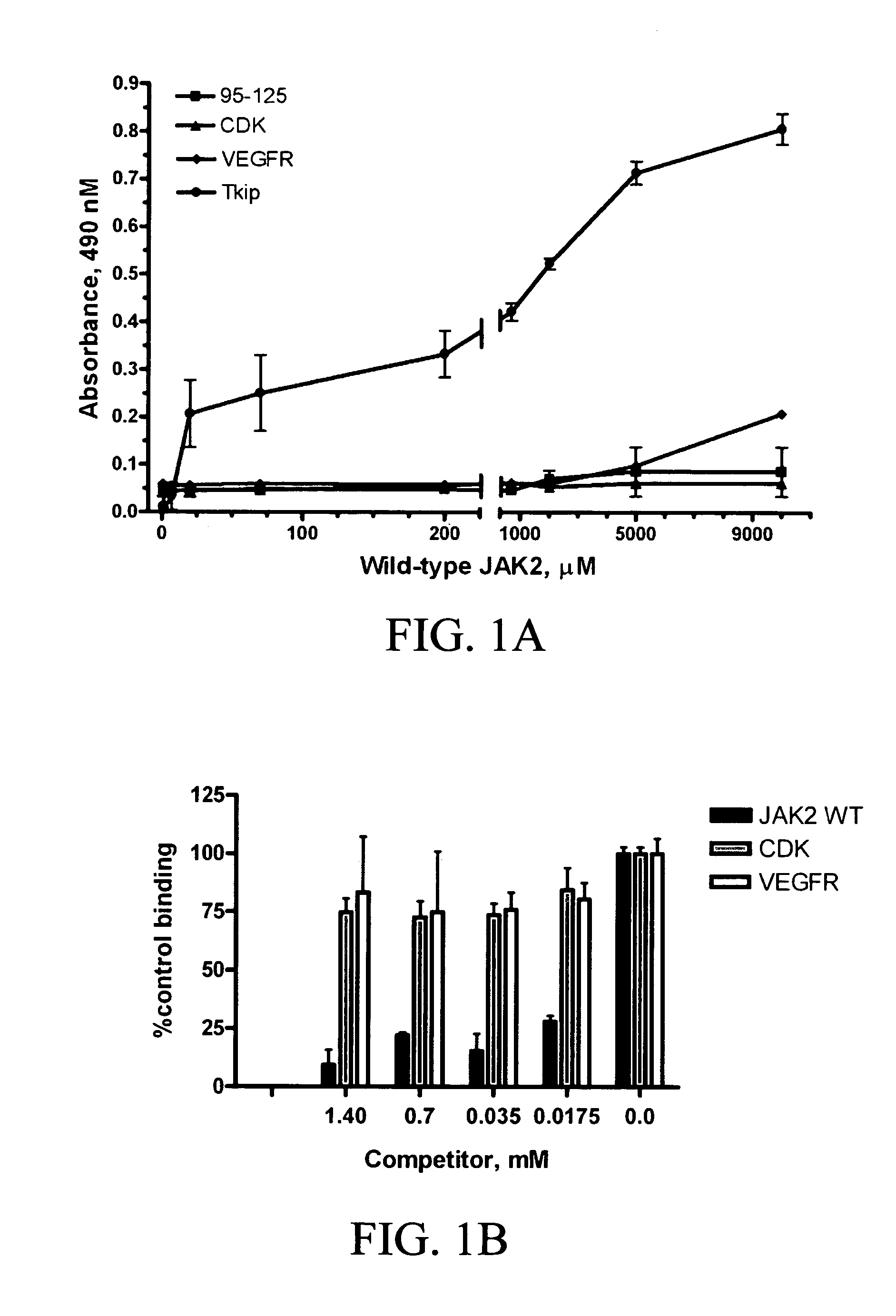
Patents
Literature
50 results about "Egfr tyrosine kinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
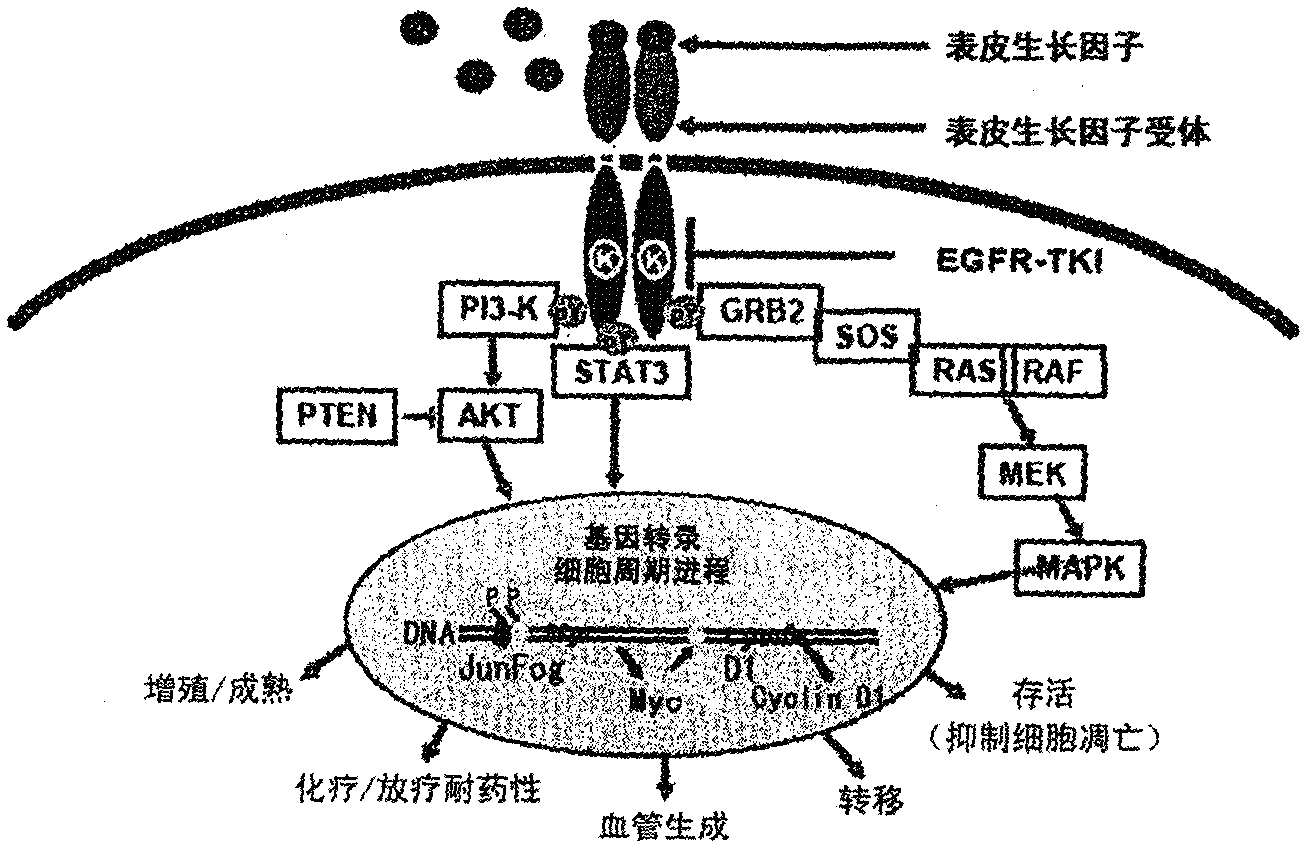
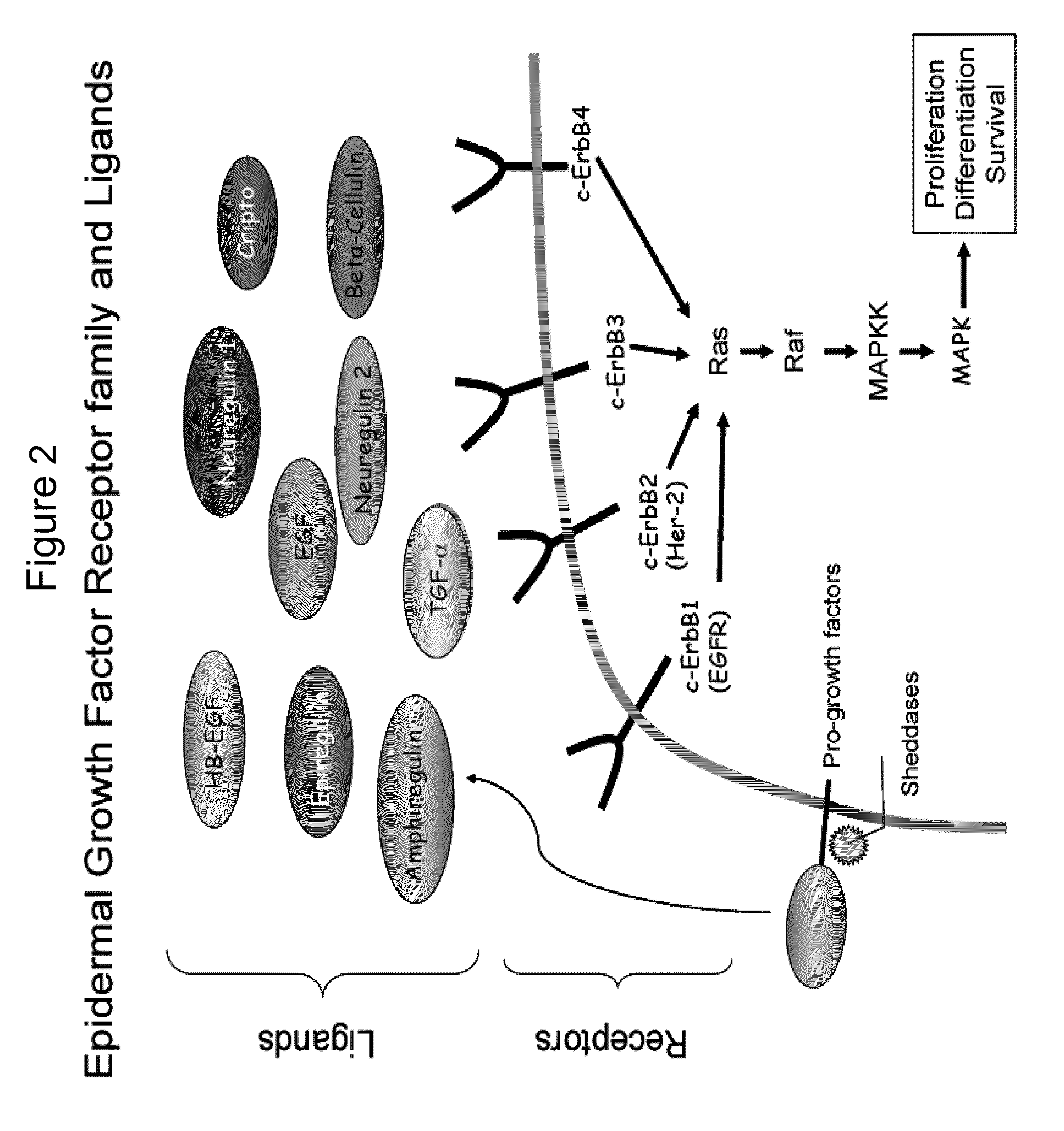
EGFR is the receptor for members of the EGF family and is a transmembrane glycoprotein that has tyrosine kinase activity. Binding of epidermal growth factor to EGFR induces receptor dimerization and tyrosine autophosphorylation and leads to cell proliferation, differentiation, motility and cell survival.
2,4-disubstituted phenyl-1,5-diamine derivatives and use thereof, and pharmaceutical composition and medicinal composition prepared from 2,4-disubstituted phenyl-1,5-diamine derivative
The present invention provides a class of 2,4-disubstituted phenylene-1,5-diamine derivatives, having an inhibiting effect on EGFR tyrosine kinases, and pharmaceutically acceptable salt, stereoisomer, solvate, or prodrug of said derivatives. See the description for the definitions of each group in the formula. In addition, the present invention also discloses pharmaceutical compositions, pharmaceutically acceptable compositions, and applications thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAIYAN PHARMA TECH +1
5-Chloropyrimidine compound and application of 5-Chloropyrimidine compound serving as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor
ActiveCN103159742AHigh inhibitory strengthSmall toxicityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryEGFR Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsHuman epidermal growth factor receptor
The invention discloses an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and the structural formula of the inhibitor is shown as in the formula (I). The invention further discloses an application of any compound shown as in the formula (I) and pharmacy-acceptable salt of the compound. The invention further provides a medicine compound for curing, and the medicine compound comprises the compound shown as in the formula (I) and an EGFR modifier.
Owner:BEIJING HANMI PHARMA CO LTD
Arylaminopyrimidine compound and use thereof and pharmaceutical composition and medicinal composition prepared from arylaminopyrimidine compound
Provided are an arylamino pyramidine compound having an inhibiting effect on EGFR tyrosine kinases, and pharmaceutically acceptable salt, stereoisomer, solvent compound, or prodrug of said arylamino pyramidine compound; also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and pharmaceutically acceptable compositions containing the arylamino pyramidine compound, and applications thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAIYAN PHARMA TECH +1
2,4-disubstituted phenylene-1,5-diamine derivatives and applications thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions and pharmaceutically acceptable compositions prepared therefrom
ActiveUS20170008889A1Strong inhibitory activityReduced inhibitory activityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryTyrosinePharmaceutical medicine
The present invention provides a class of 2,4-substituted phenylene-1,5-diamine derivatives, having an inhibiting effect on EGFR tyrosine kinases, and pharmaceutically acceptable salt, stereoisomer, solvate or prodrug of said derivatives. See the description for the definition of each group in the formula. In addition, the present invention also discloses pharmaceutical compositions, pharmaceutically acceptable compositions and applications thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAIYAN PHARMA TECH +1
Zinc binding group-containing irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
ActiveCN103965119AGood antitumor activityDelay drug resistanceOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryEGFR Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
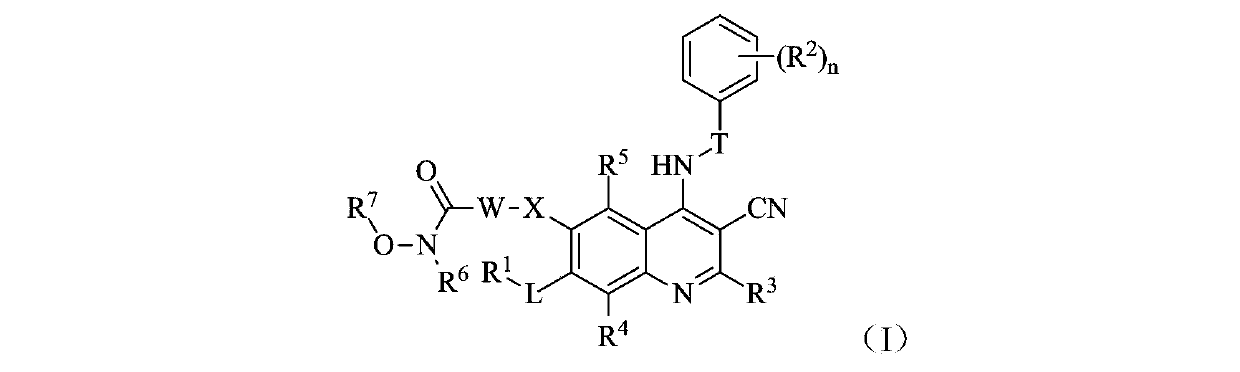
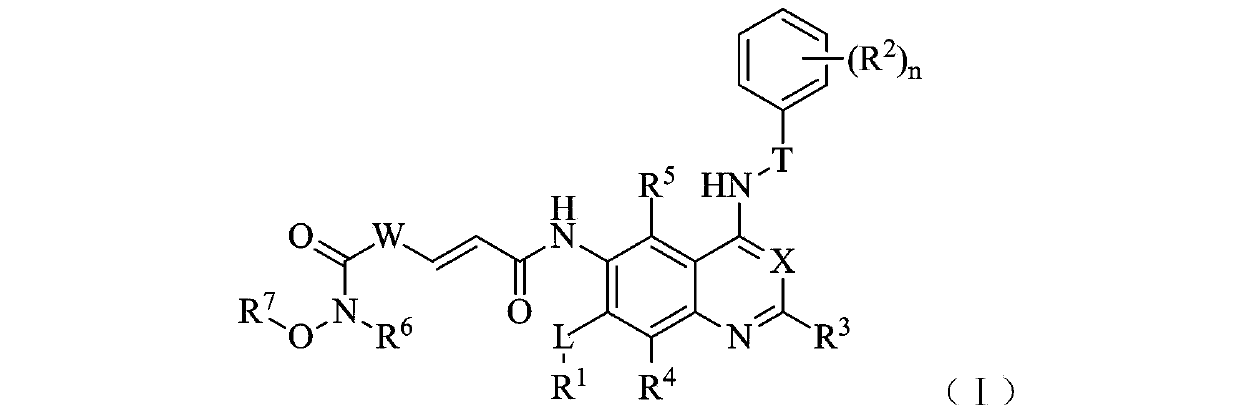
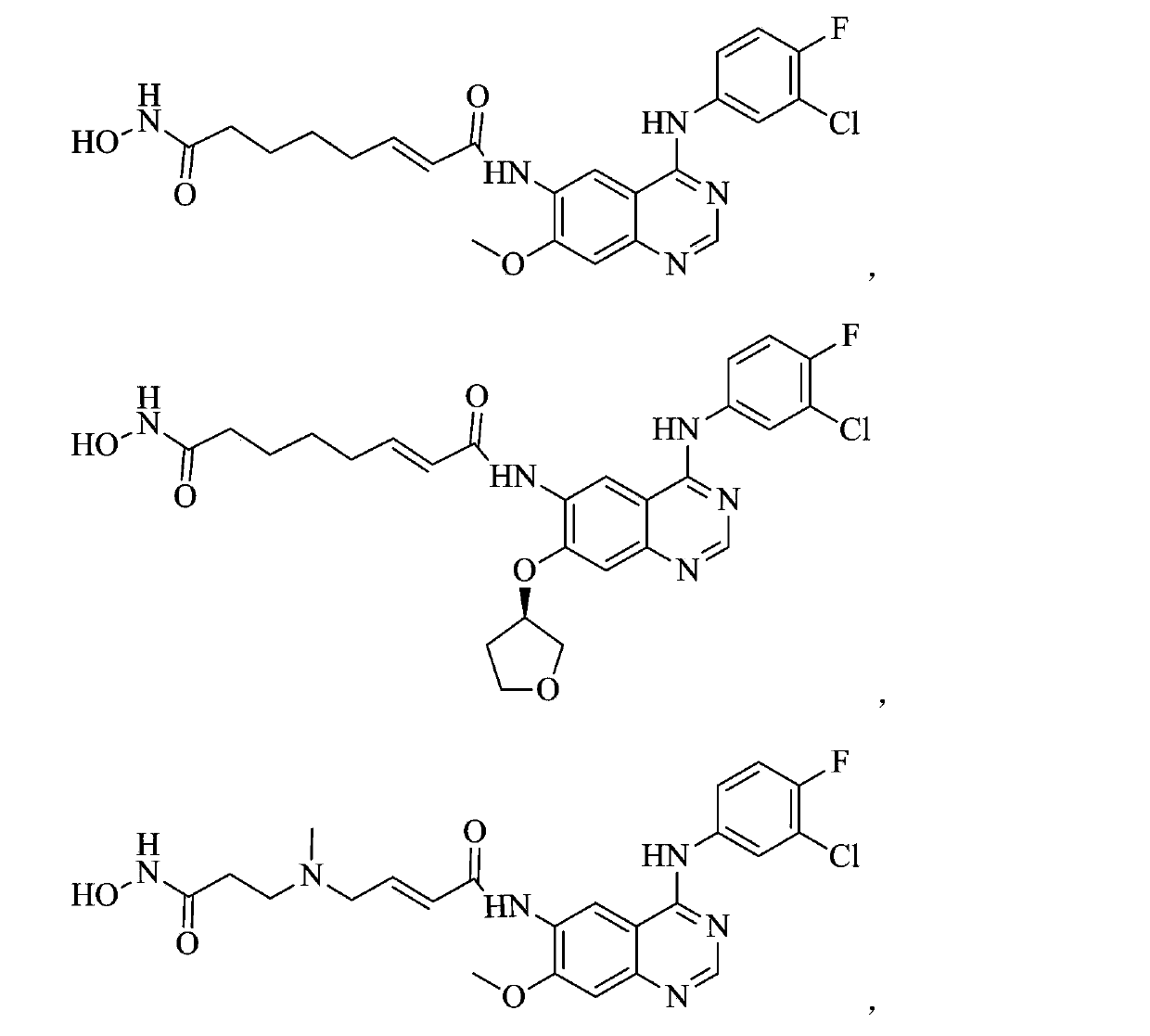
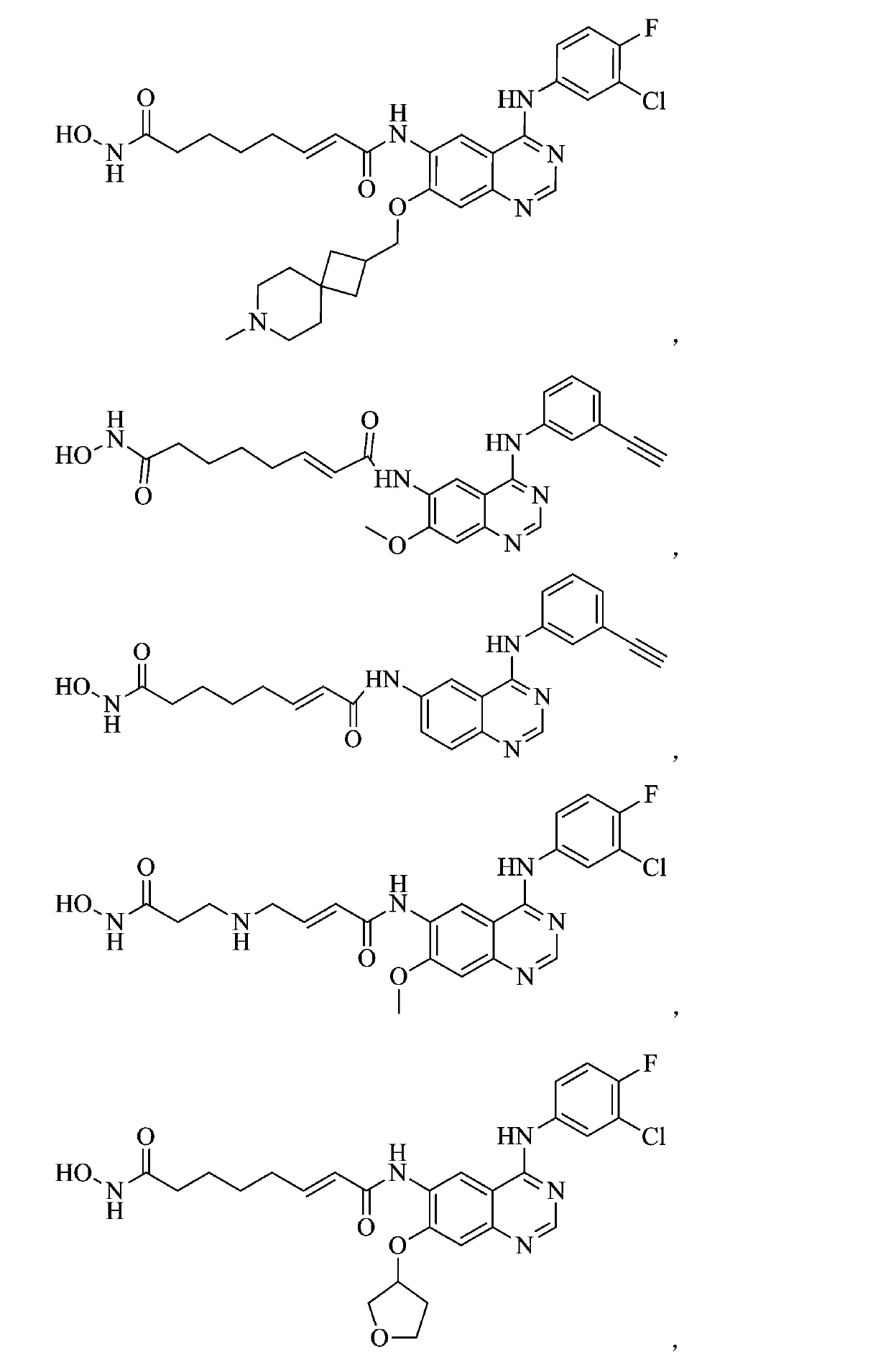
Belonging to the technical field of medicine, the invention in particular relates to a zinc binding group-containing irreversible EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) tyrosine kinase inhibitor shown as general formula (I), its deuterated compounds, pharmaceutically acceptable salts or stereoisomers, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, W, X, L, T, and n are defined as the specification. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the compounds, pharmaceutical preparations containing the compounds, and application of the compounds in preparation of drugs treating and / or preventing tumors. (formula I).
Owner:BEIJING AOHE DRUG RES INST
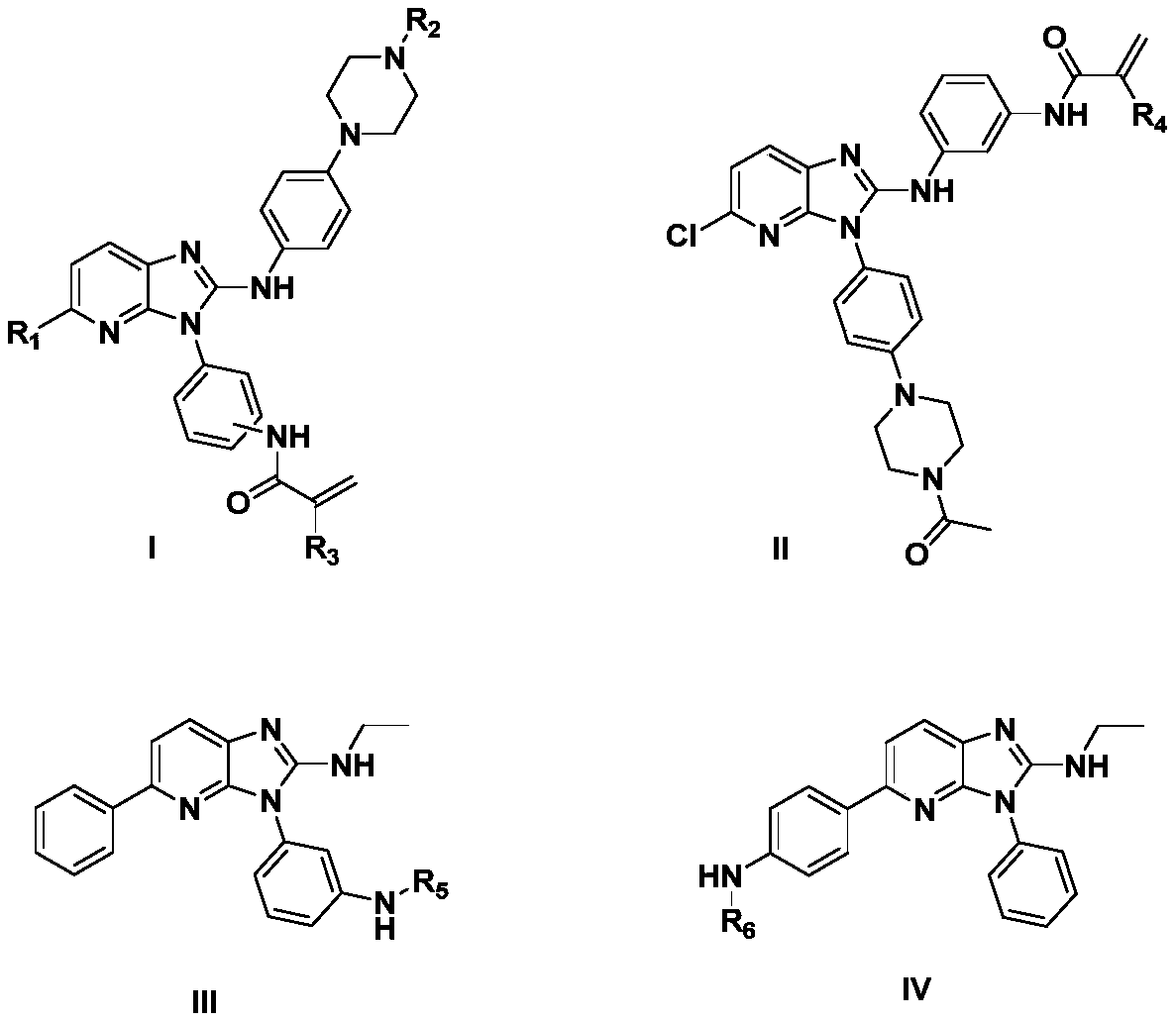
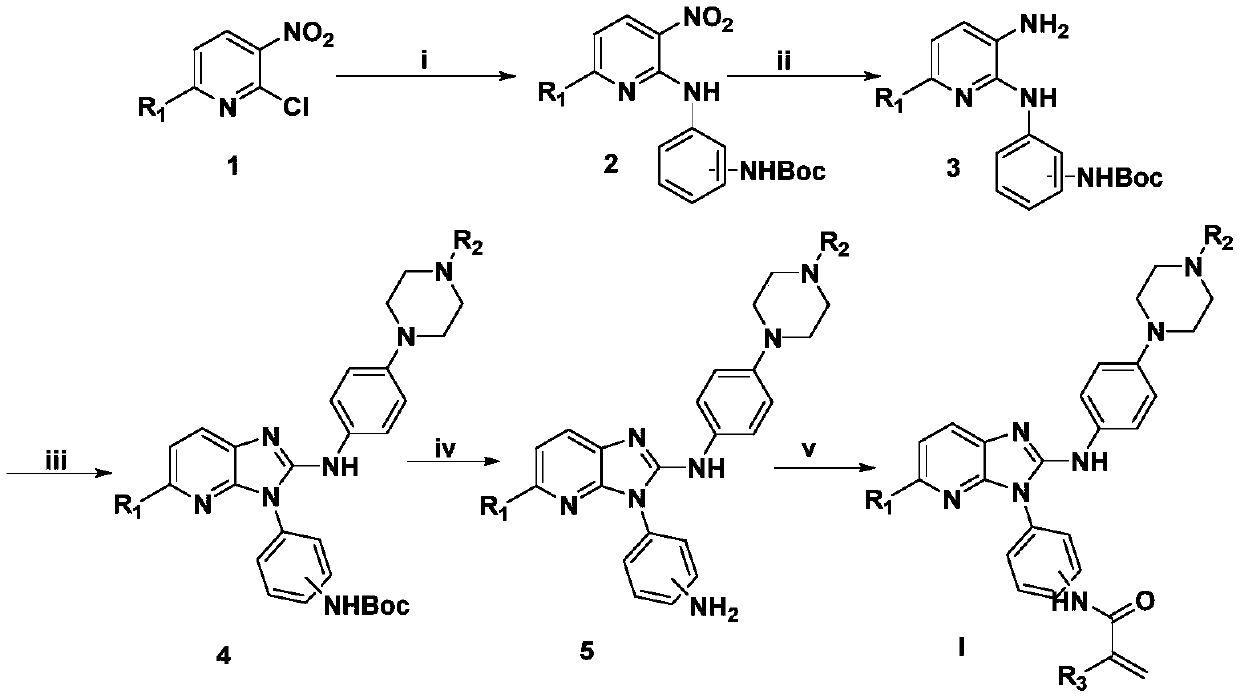
2-aminoimidazopyridine derivative as well as preparation and application
ActiveCN107383004AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood antitumor activityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsCarcinoma cell lineWild type
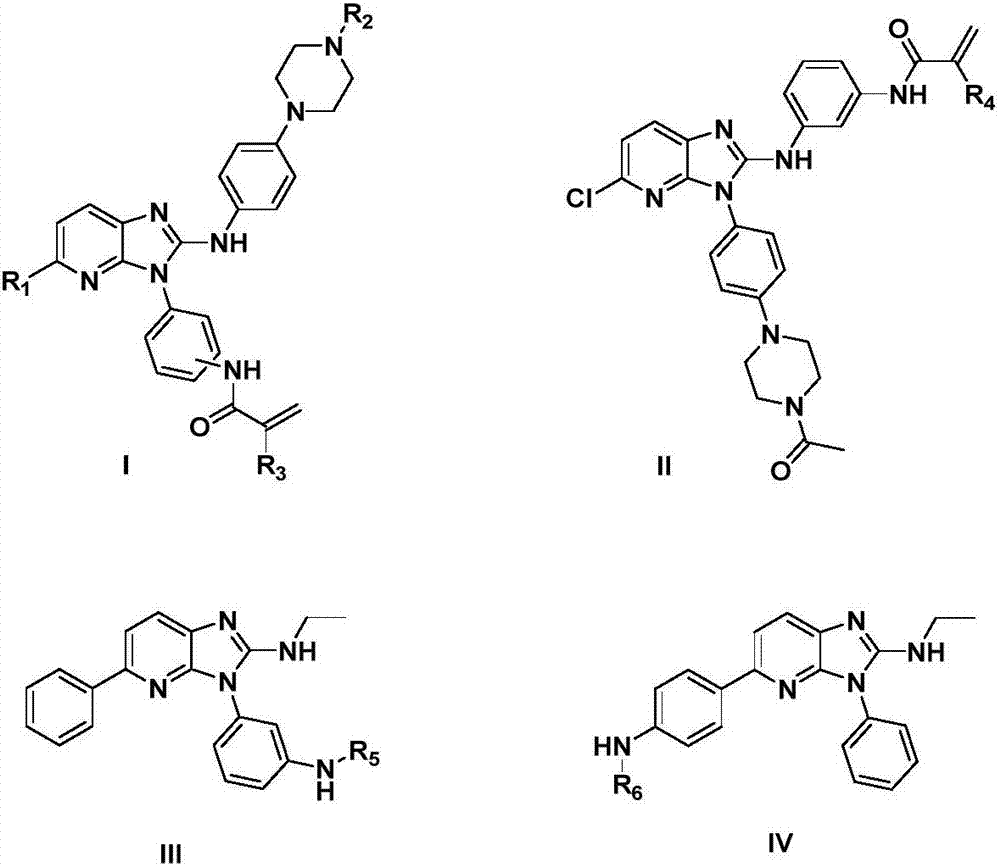
The invention provides a 2-aminoimidazopyridine derivative shown as a formula I, a formula II, a formula III or a formula IV and further provides a preparation method and application of the 2-aminoimidazopyridine derivative. An experiment shows that the 2-aminoimidazopyridine derivative has a remarkable proliferation inhibition effect on tumor cells (including an over-expressed wild type EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) human epidermal carcinoma cell line A431 and a Gefitinib drug-resisting human lung adenocarcinoma cell line H1975) related to the activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase in the aspect of a cell level, especially has a relatively good inhibition effect on the drug-resisting cell line H1975, has relatively weak inhibition activity on a low-expression EGFR human colon cancer cell line SW620 and can be applied to preparation of corresponding anti-tumor cell medicines. A general formula is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
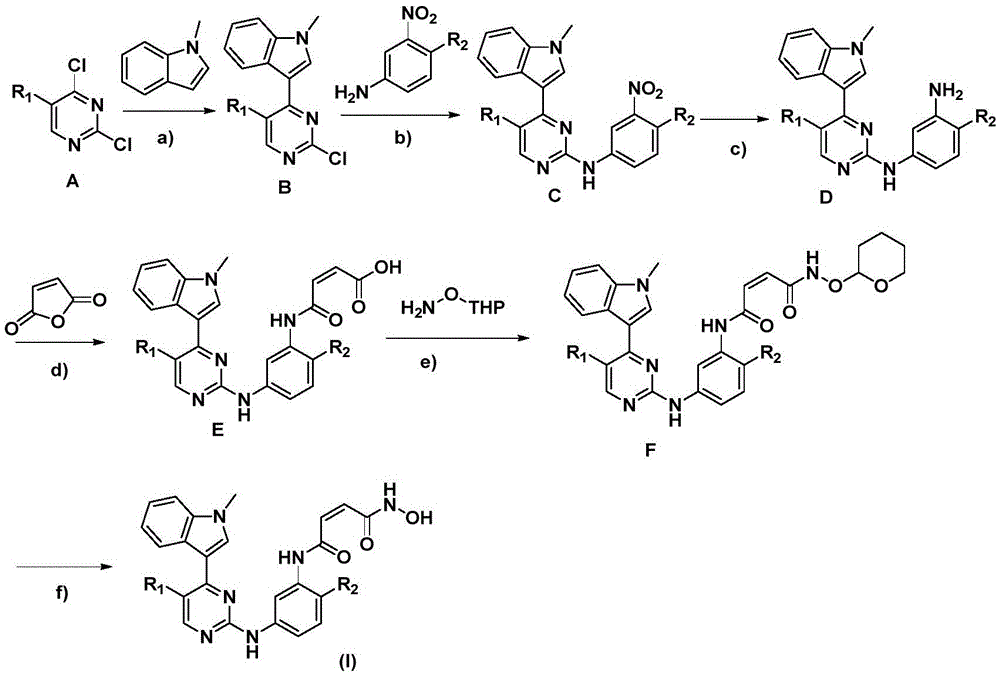
2-arylamine pyrimidine derivatives containing hydroxamic acid fragments and preparation and application
InactiveCN105646454AStrong growth inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsCarcinoma cell lineHydroxamic acid
The invention provides 2-arylamine pyrimidine derivatives containing hydroxamic acid fragments shown in the formulas I and II. 2-arylamine pyrimidine containing carboxyl fragments is mainly used as a parent nucleus and is subjected to single-step condensation and related modification with hydroxylamine protected by THP to obtain a target compound. An experiment proves that the derivatives has the remarkable anti-proliferative effect on tumor cells (an overexpression EGFR human epidermal carcinoma cell line A431 and a human pulmonary carcinoma cell line H1975 resisting Gefitinib) related to EGFR tyrosine kinase activity on the cellular level, and tumor cells (a human cervical carcinoma cell line Hela, a human hepatoma cell line HepG2, a human promyelocytic acute leukemia cell line HL60, a human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell line KB, a human colon cancer cell line SW620) related to the HDAC histone acetylase activity, and the corresponding medicine for resisting cancer cells can be prepared. The general structural formula is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
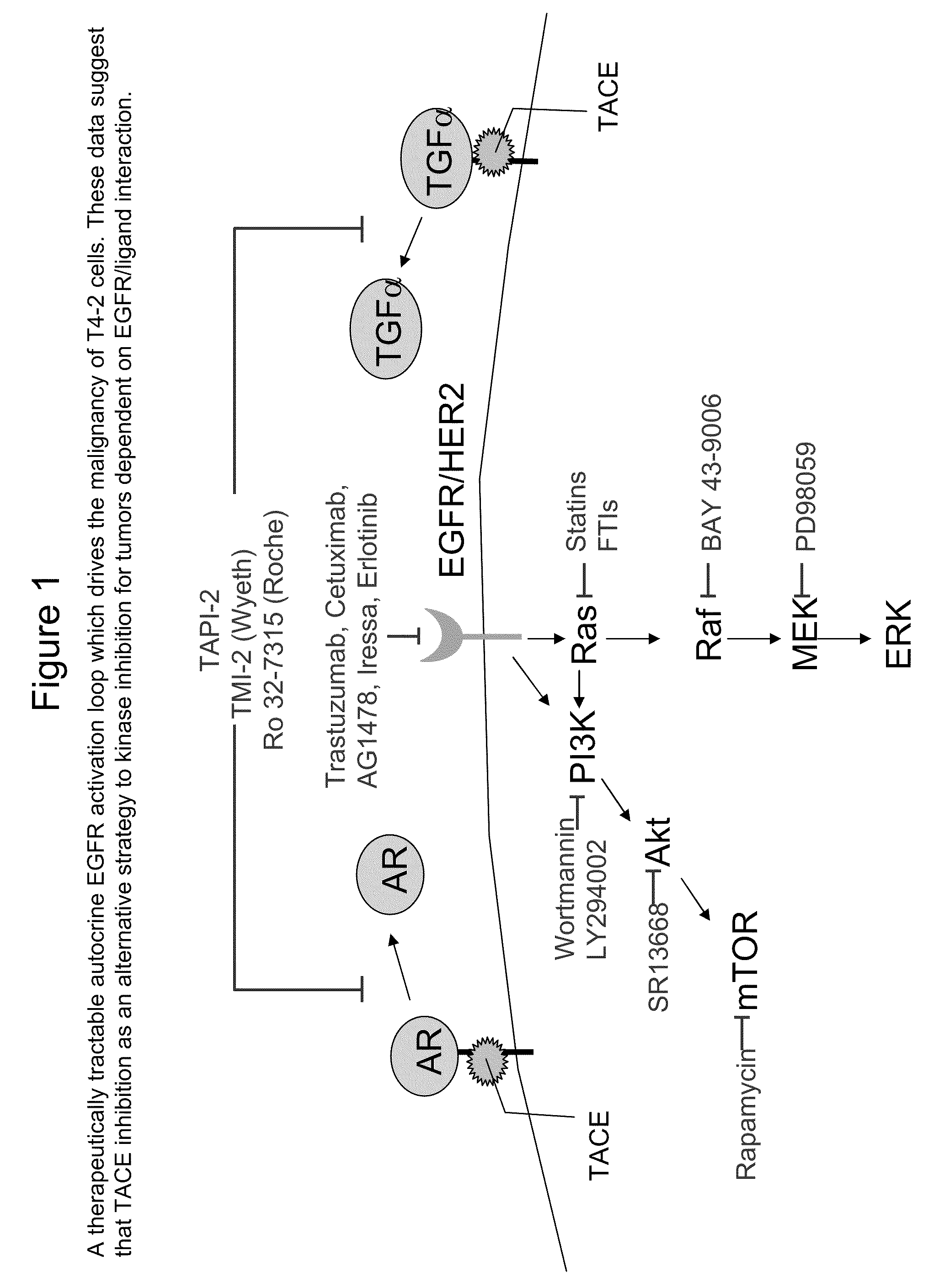
TARGETING TNF-alpha CONVERTING ENZYME(TACE)- DEPENDENT GROWTH FACTOR SHEDDING IN CANCER THERAPY
InactiveUS20090274626A1BiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsTace inhibitorEGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
The invention provides methods for modulating tumor cell proliferation by contacting cells (e.g. tumor cells) with a TACE inhibitor and a compound that inhibits EGFR tyrosine kinase, whereby the TACE inhibitor enhances the sensitivity of the cell to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Additionally, methods for treating cancer and methods for identifying TACE inhibitors is also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
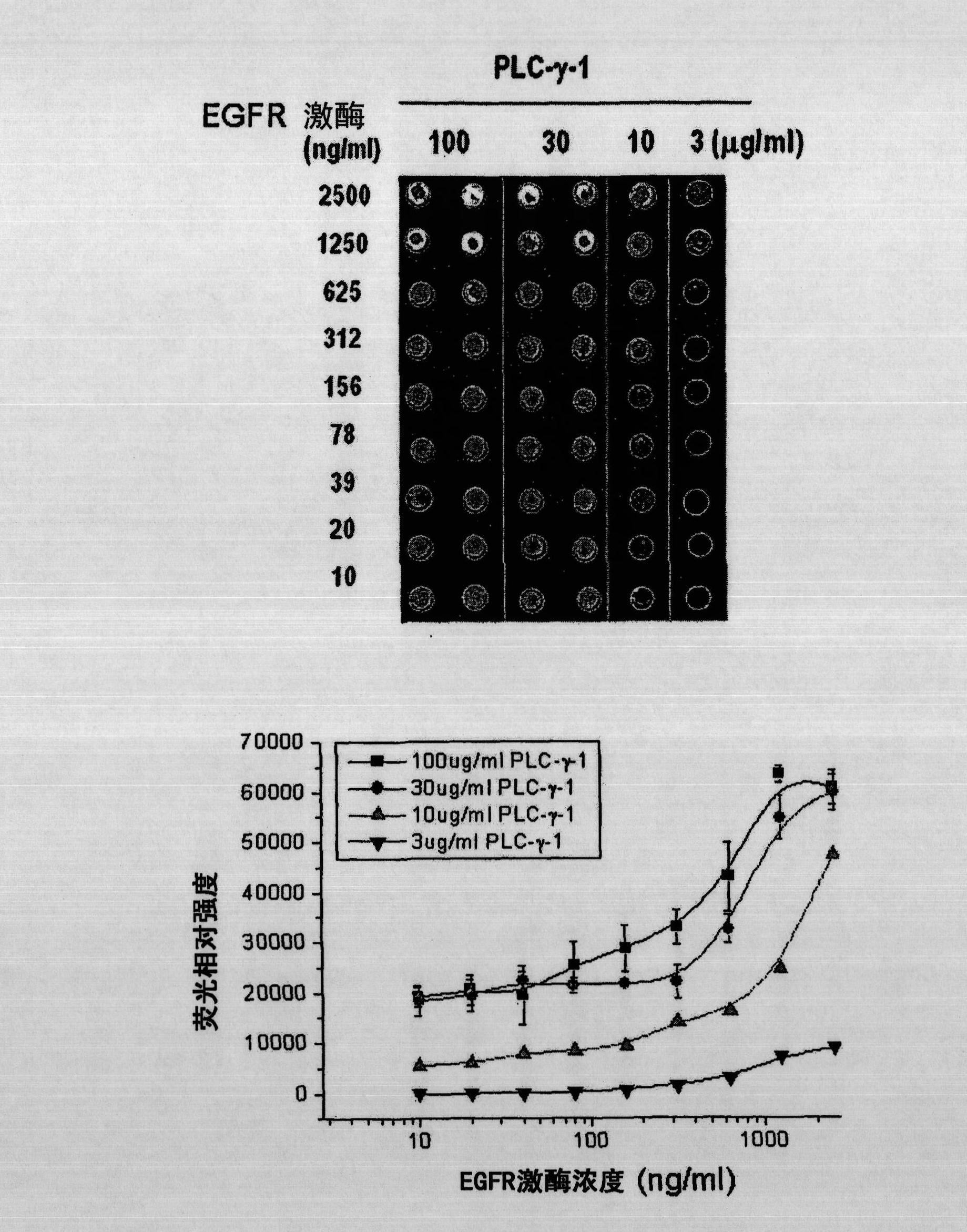
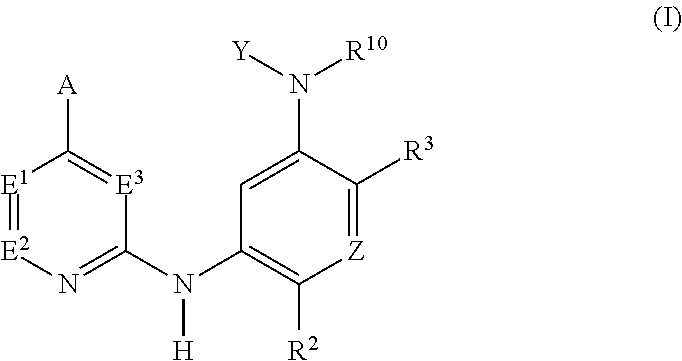
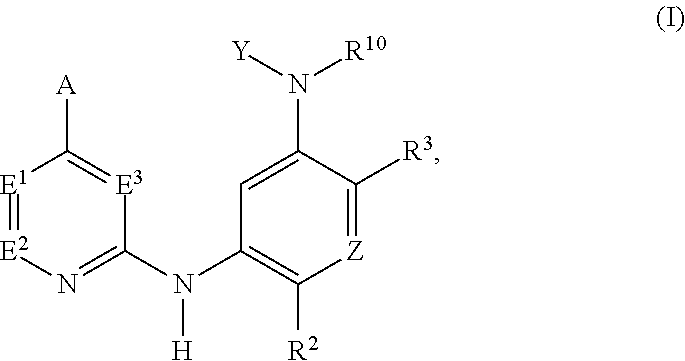
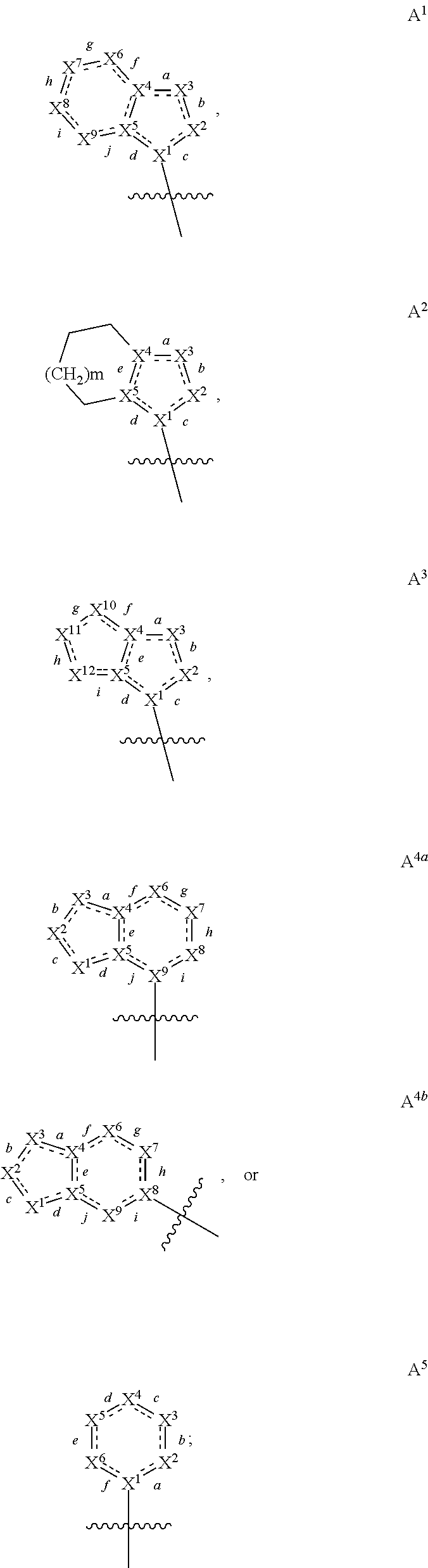
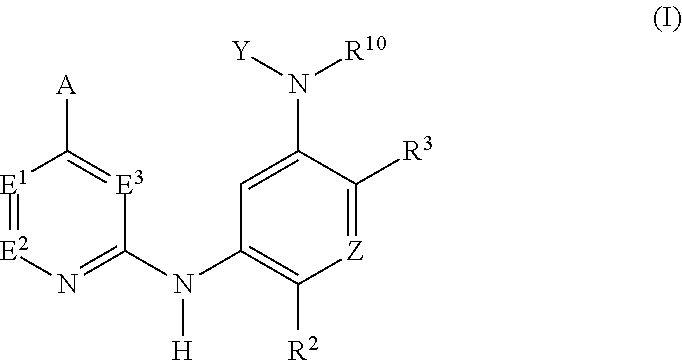
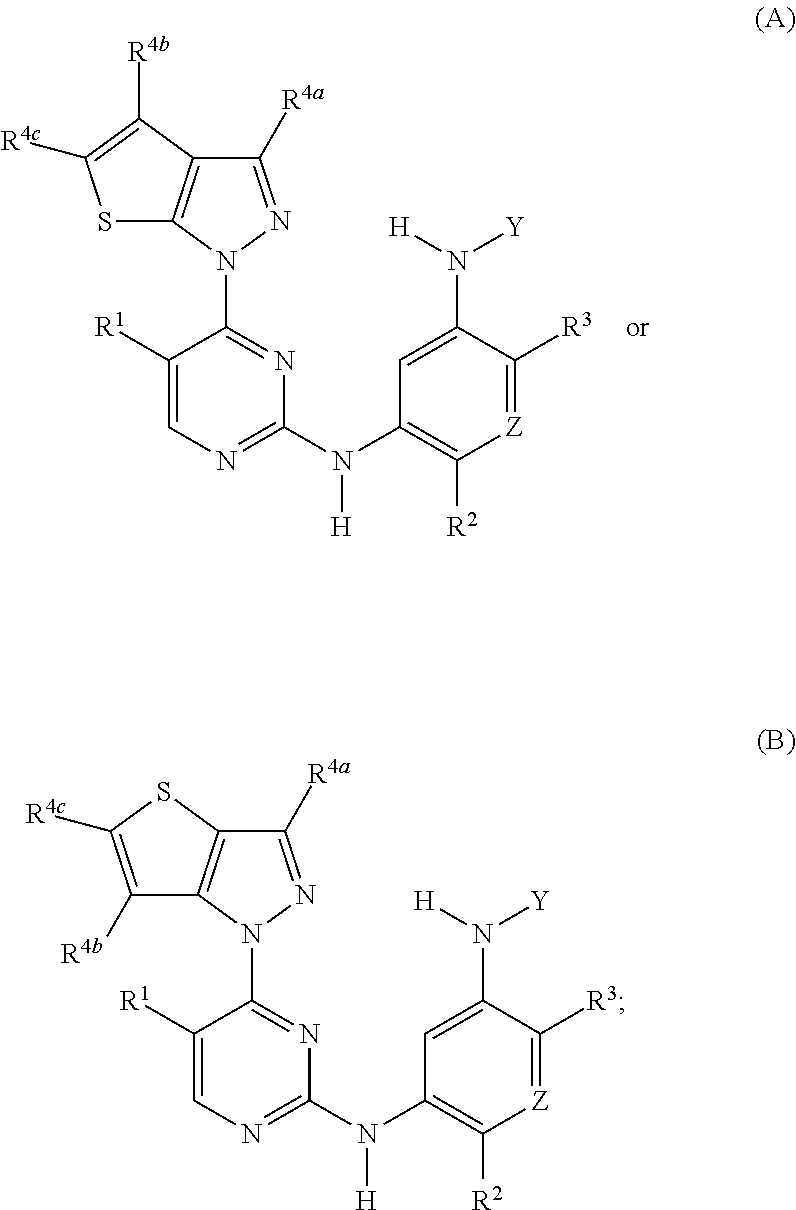
Selective inhibitors of clinically important mutants of the EGFR tyrosine kinase
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) or a subgeneric structure or species thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, solvate, and / or prodrug thereof, and methods and compositions for treating or ameliorating abnormal cell proliferative disorders, such as cancer, wherein A, R2, R3, R10, E1, E2, E3, Y, and Z are as defined herein.
Owner:CS PHARMATECH LTD +1
Compositions and methods for treating cancer
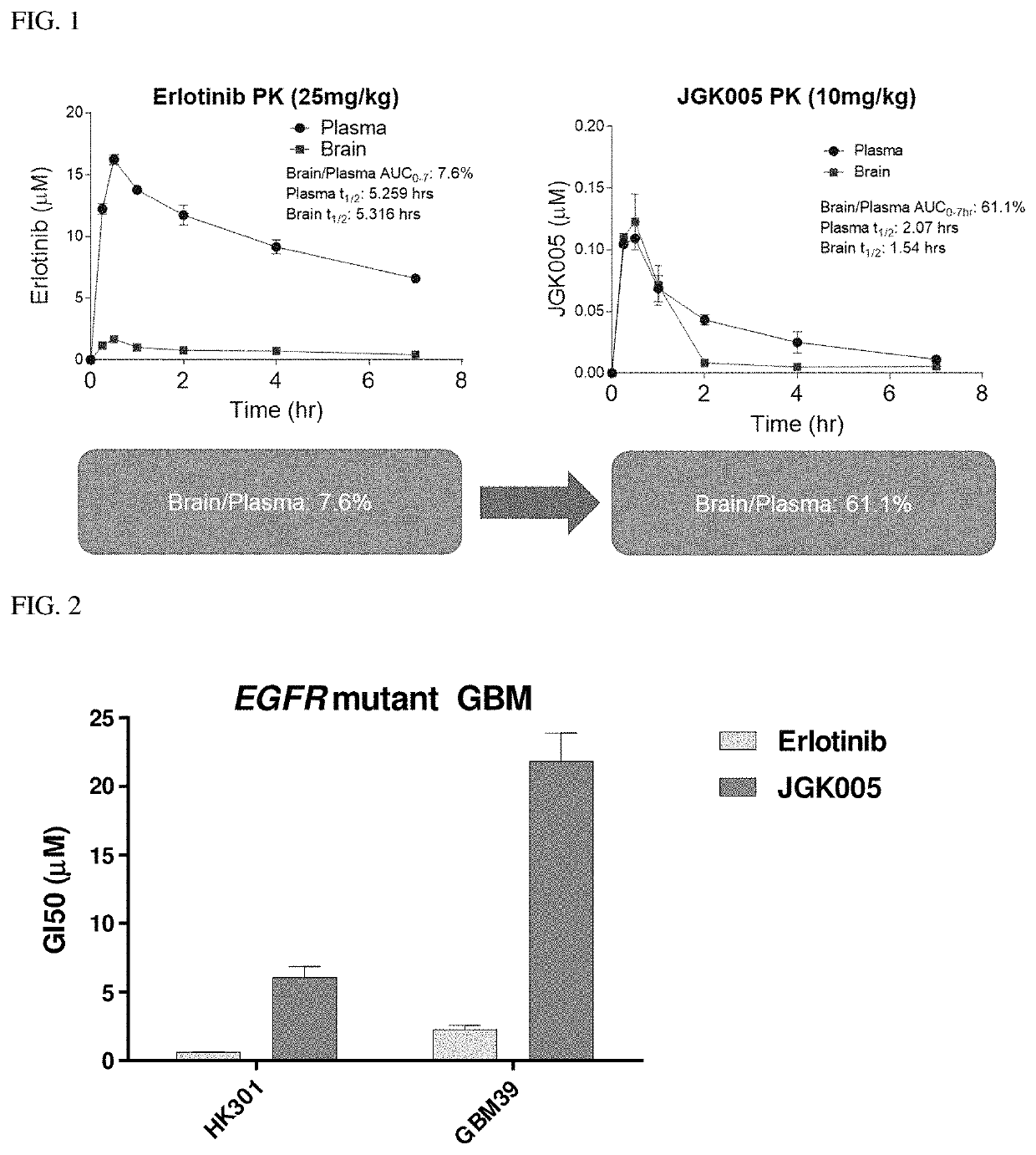
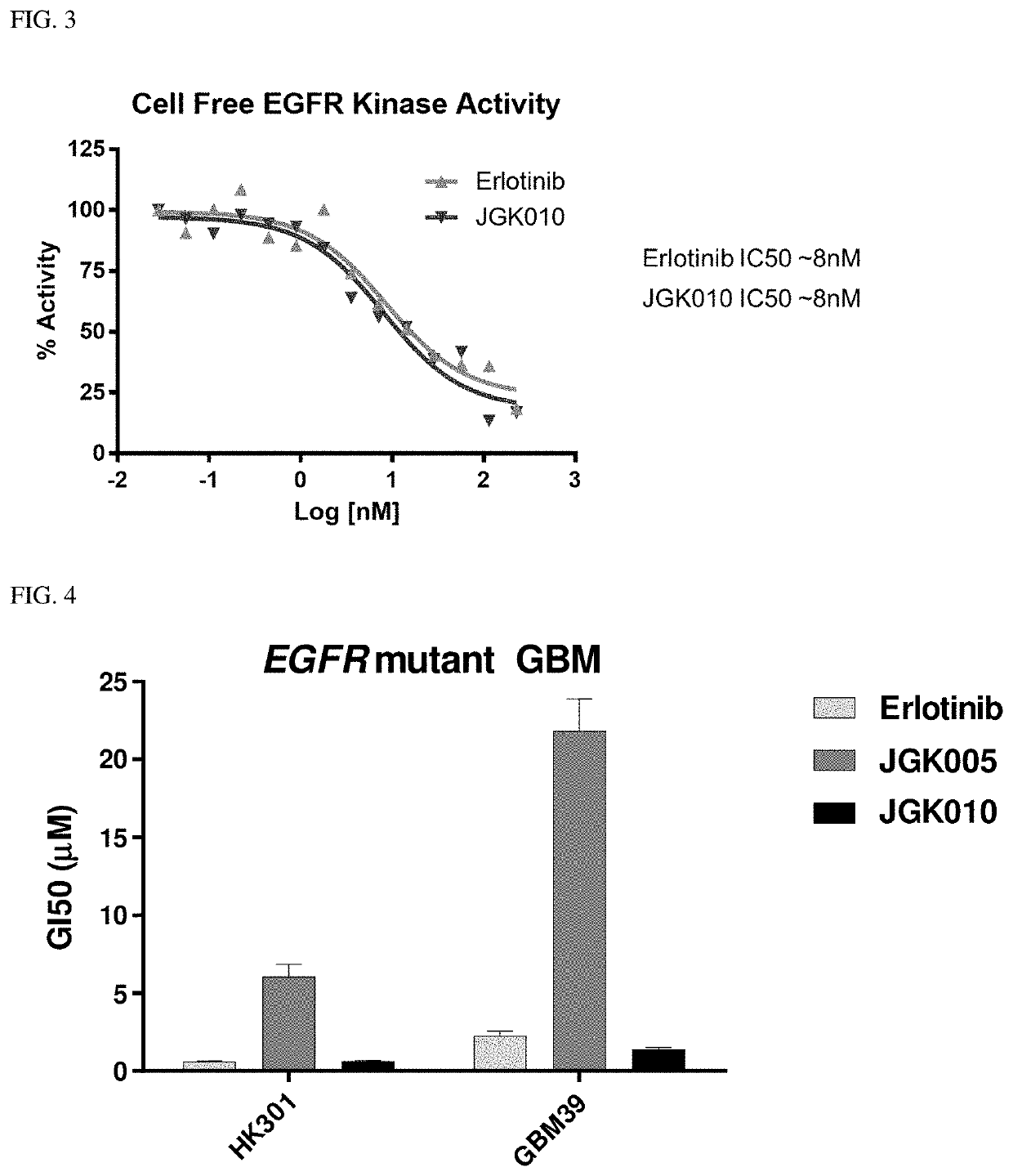
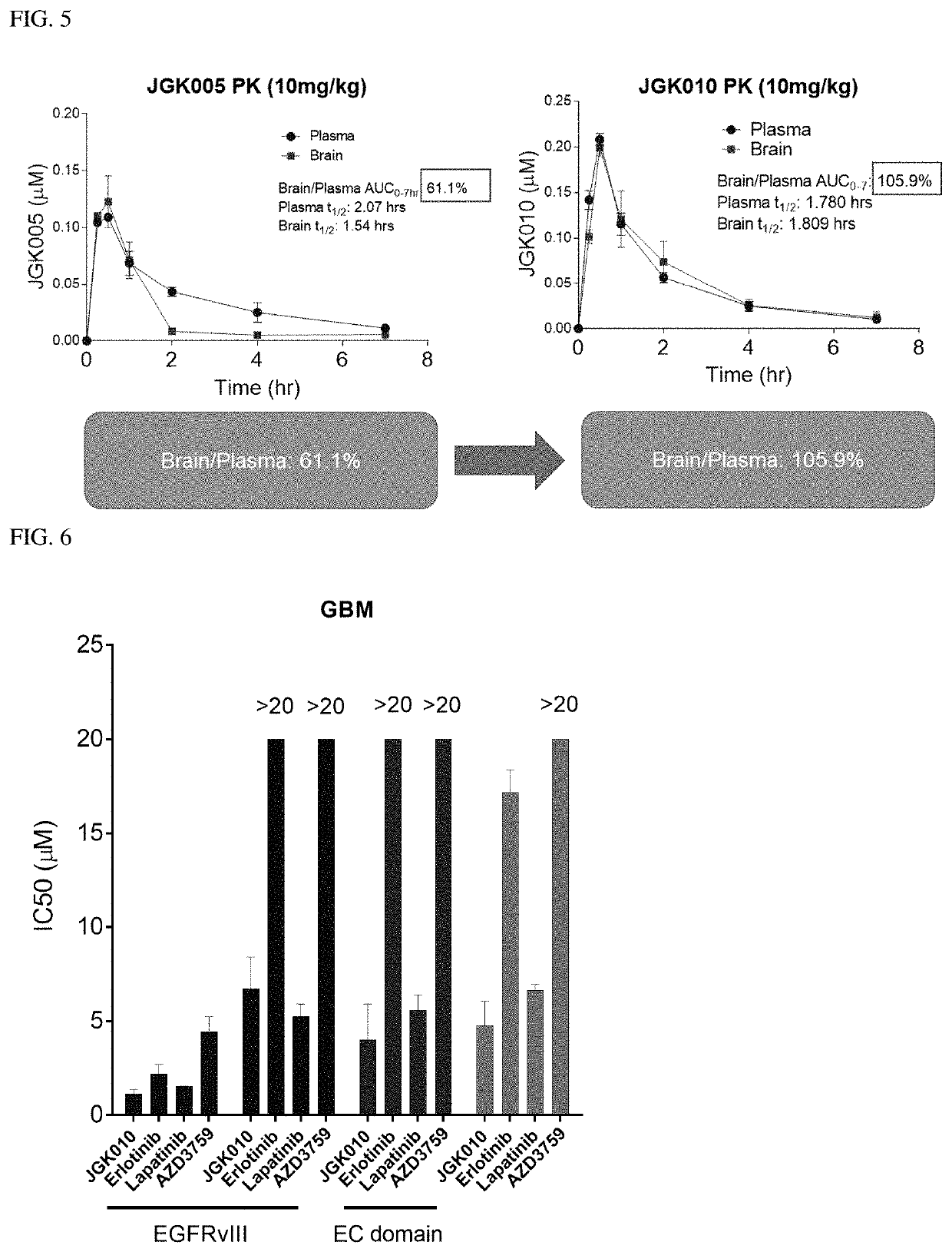
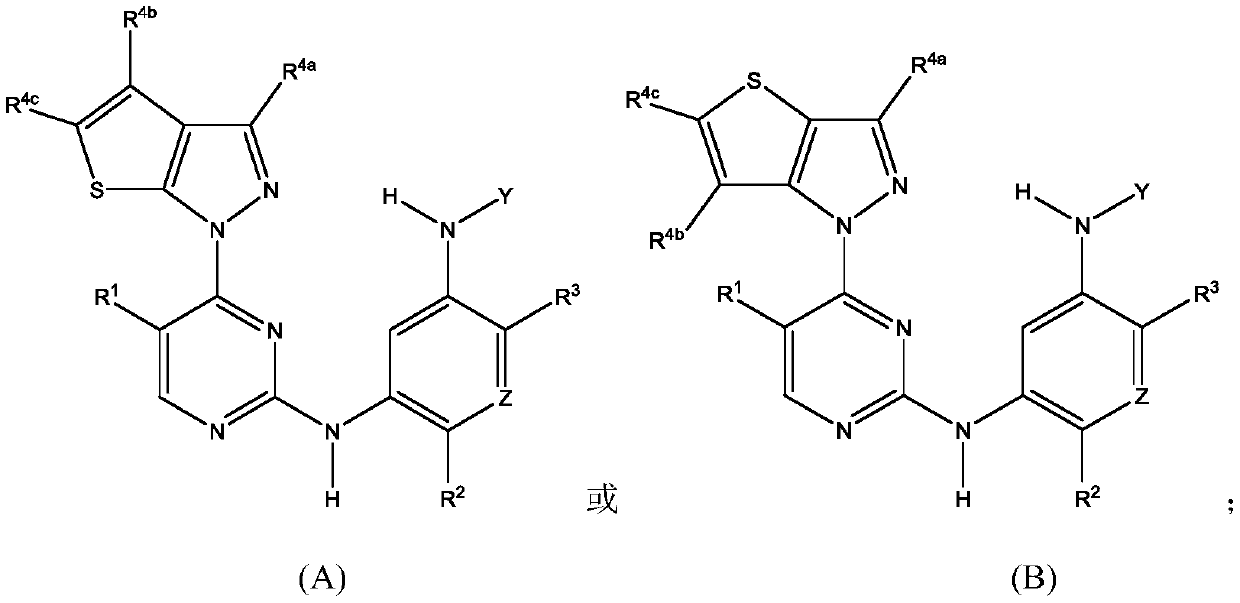
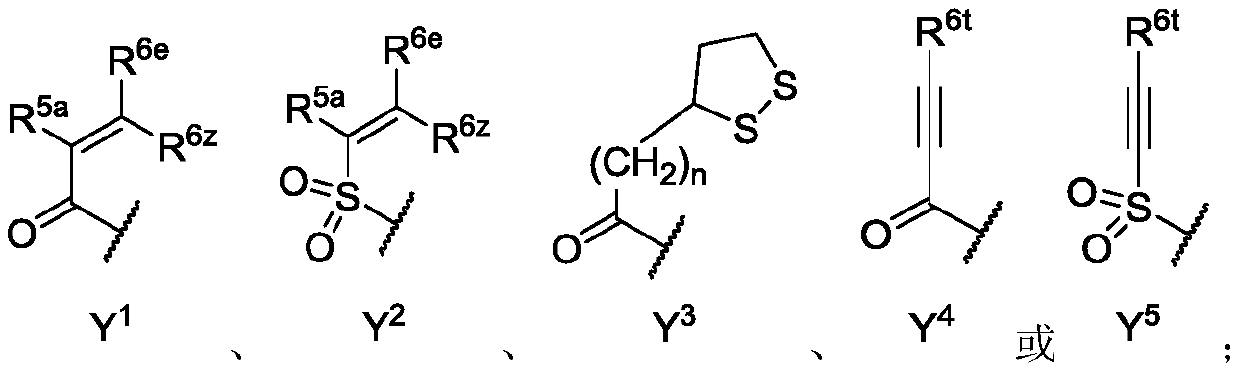
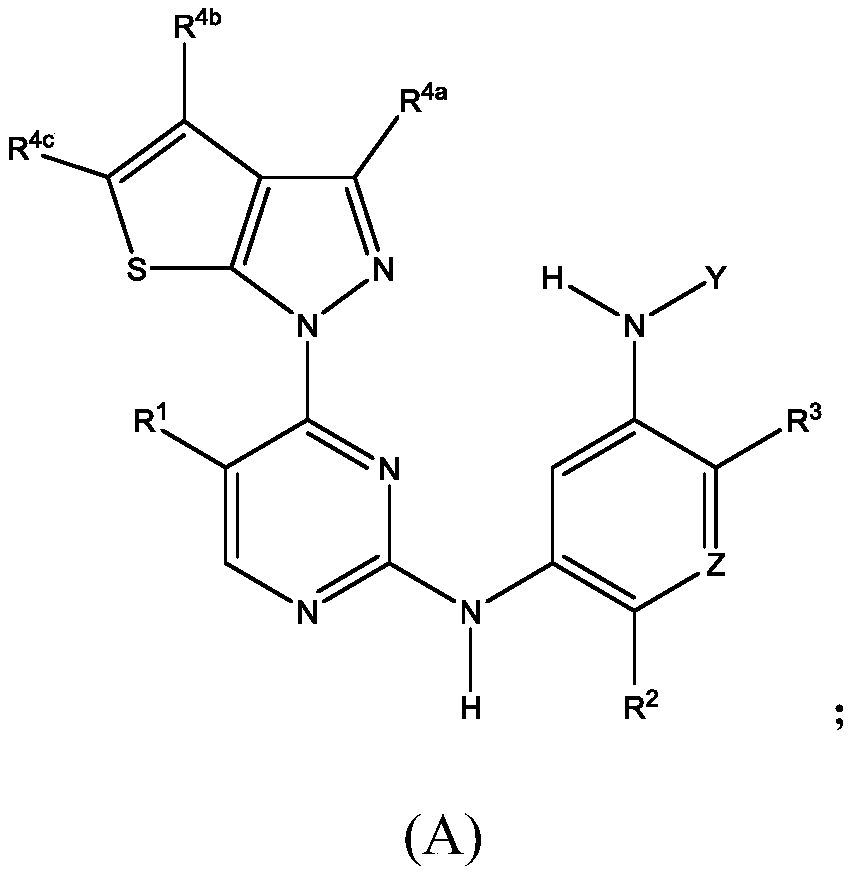
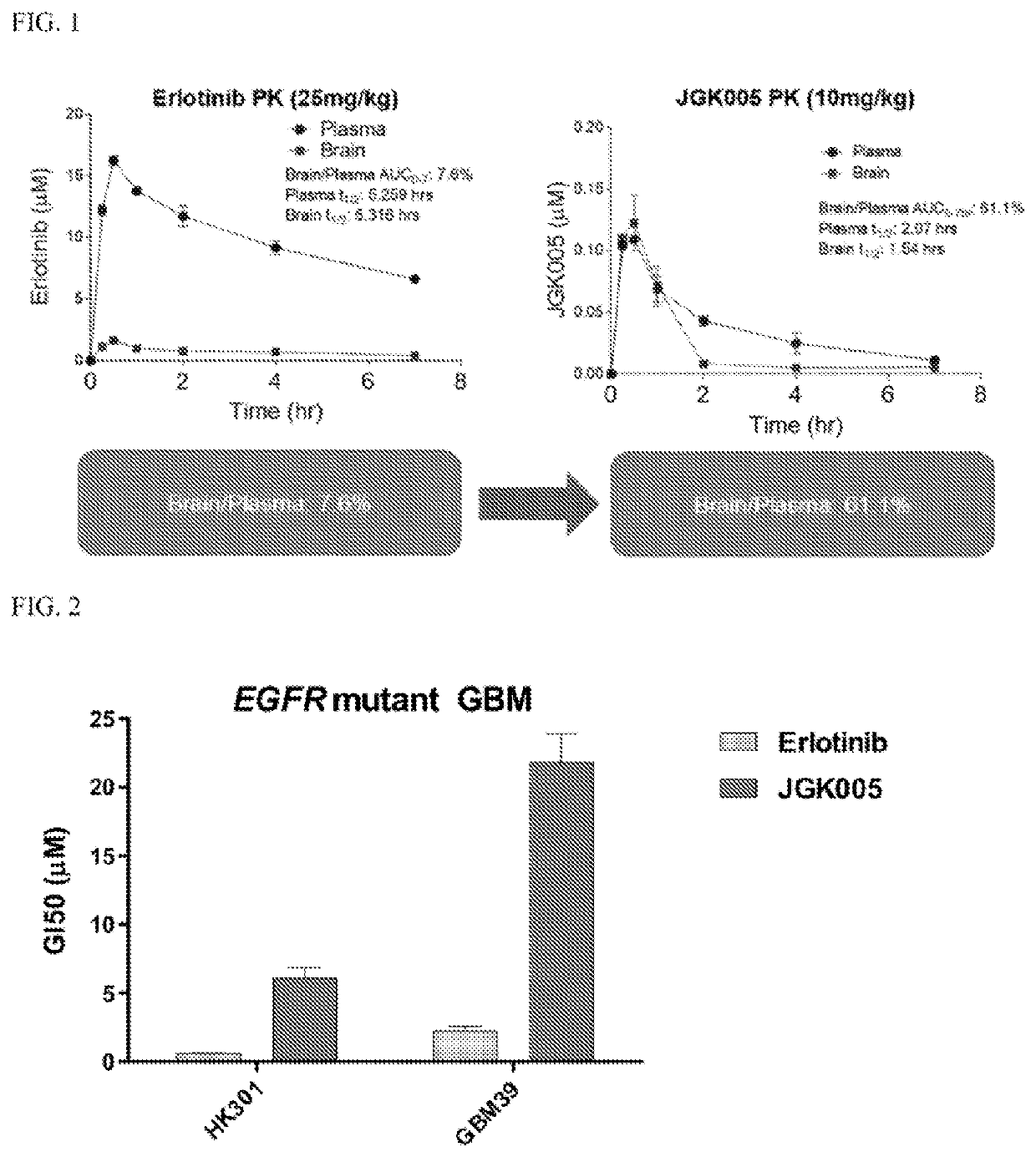
The present disclosure relates to compounds that are capable penetrating to the blood brain barrier to modulate the activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase. The disclosure further relates to methods of treating glioblastoma and other EGFR mediated cancers. The disclosure further relates to methods of treating glioblastoma and other EGFR mediated cancers that have been determined to have altered glucose metabolism in the presence of inhibitors. The present disclosure also provides methods of administering to a subject a glucose metabolism inhibitor and a cytoplasmic p53 stabilizer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
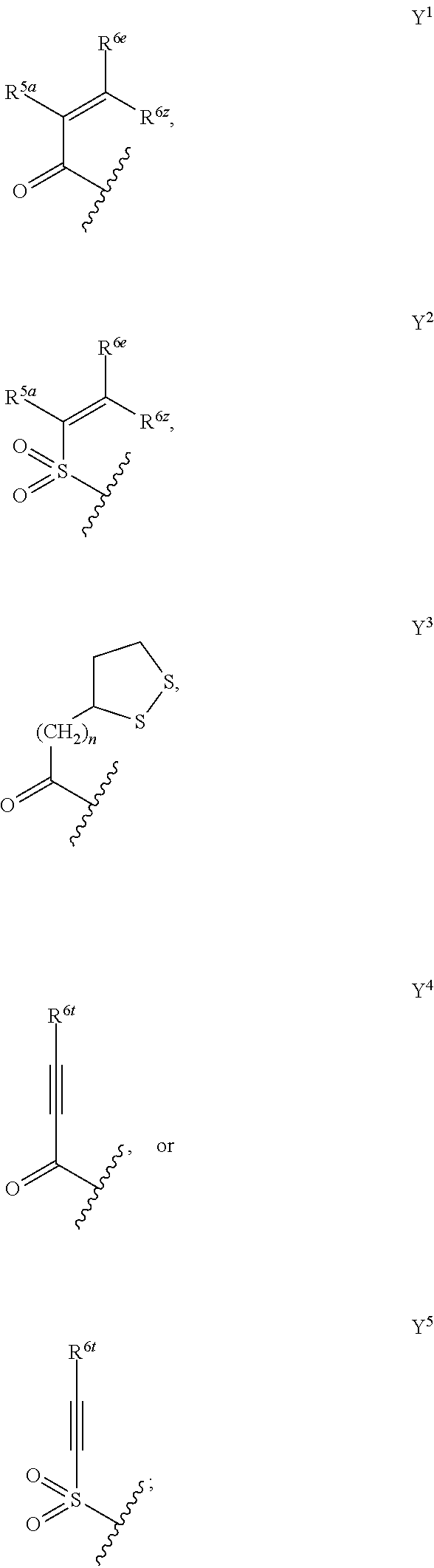
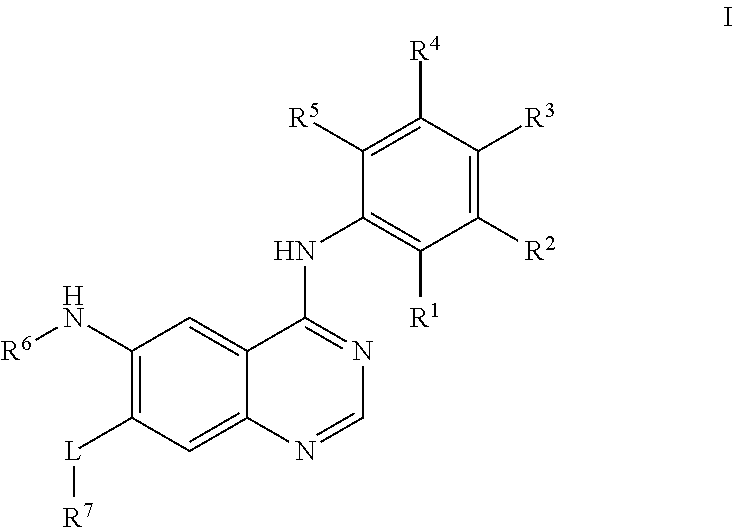
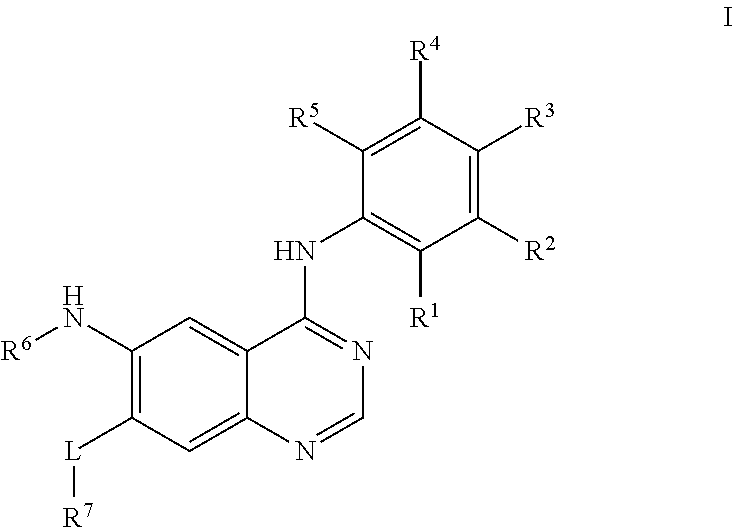
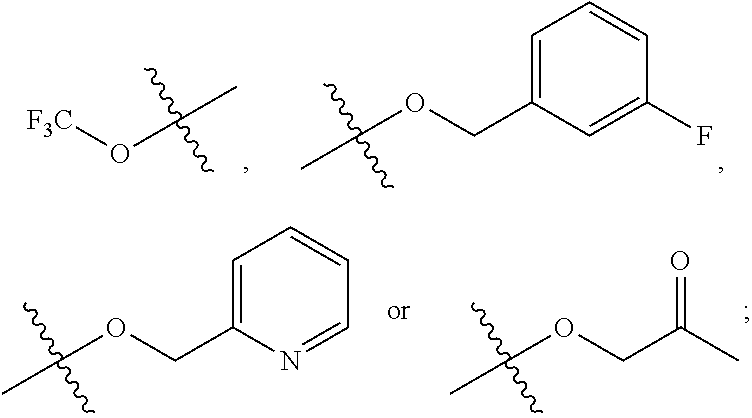
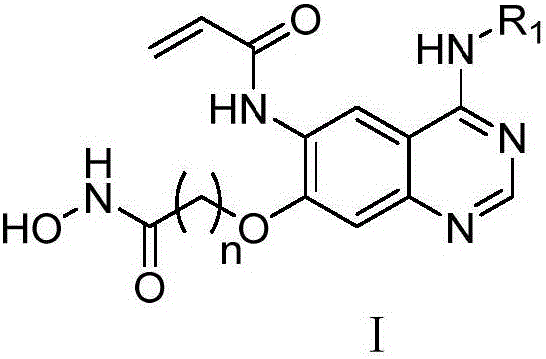
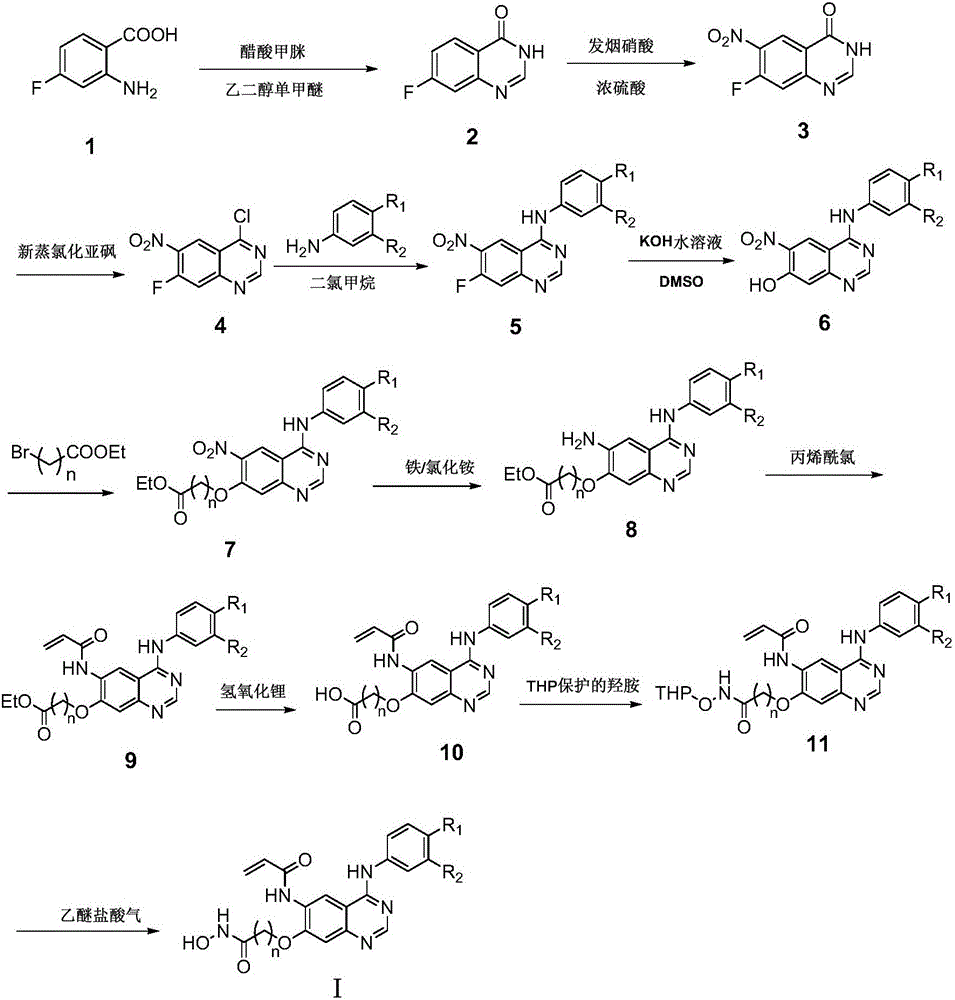
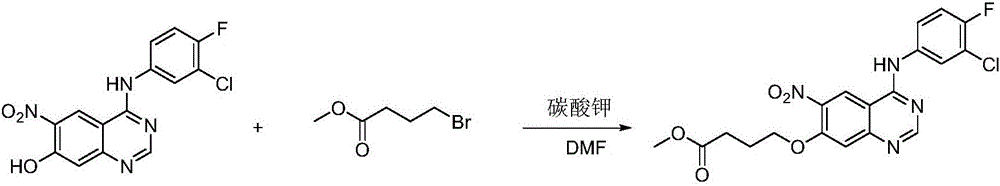
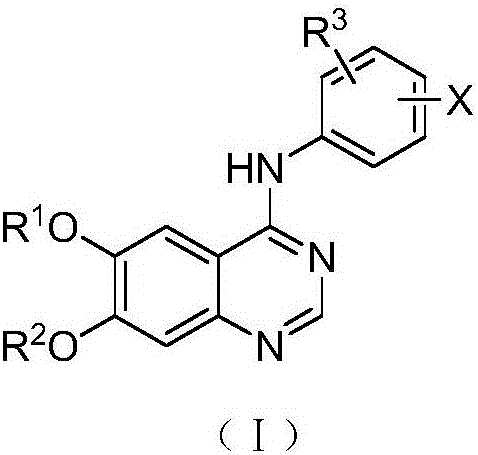
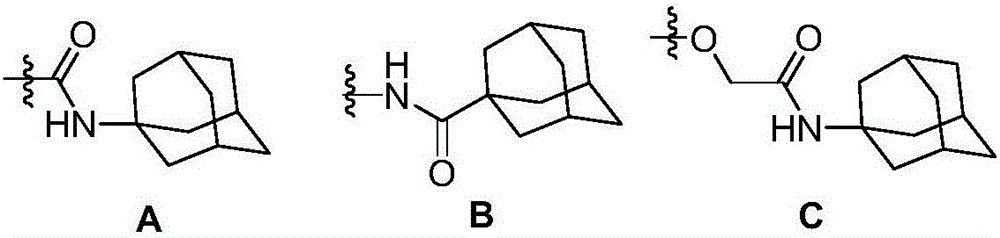
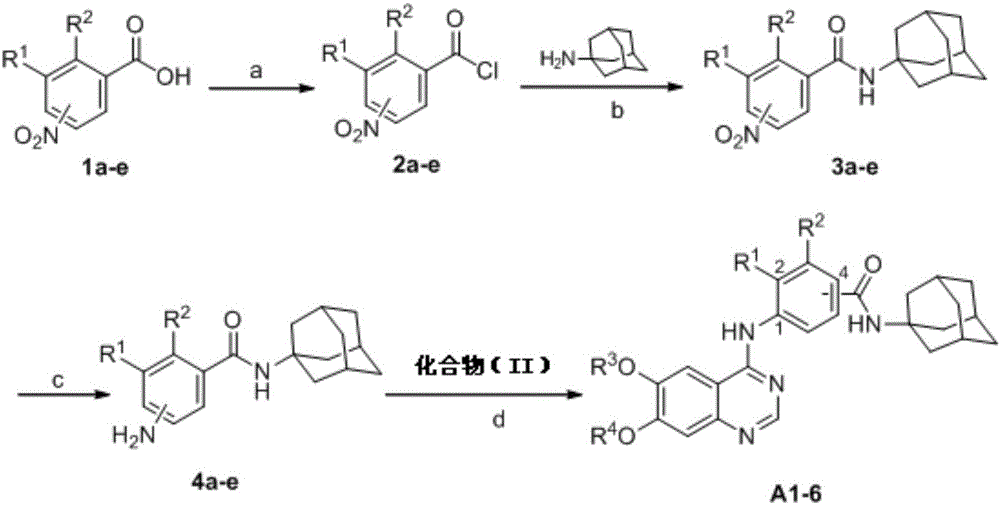
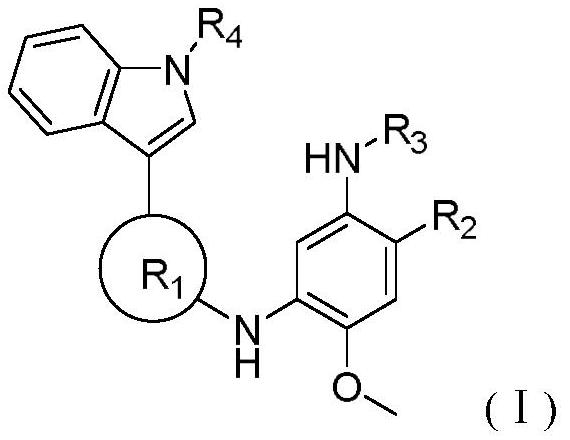
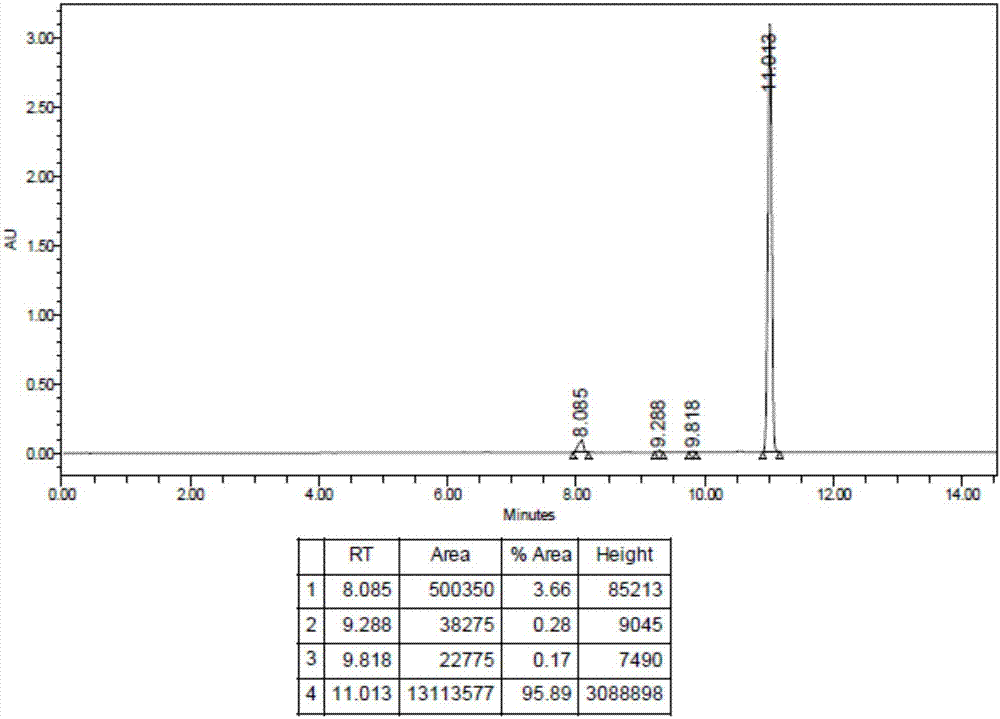
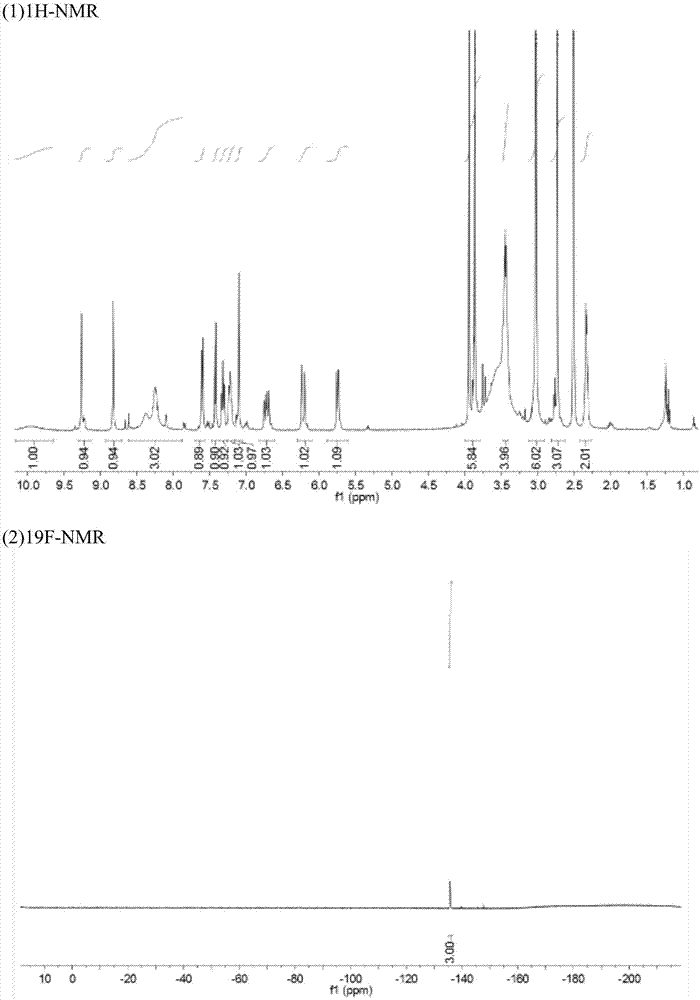
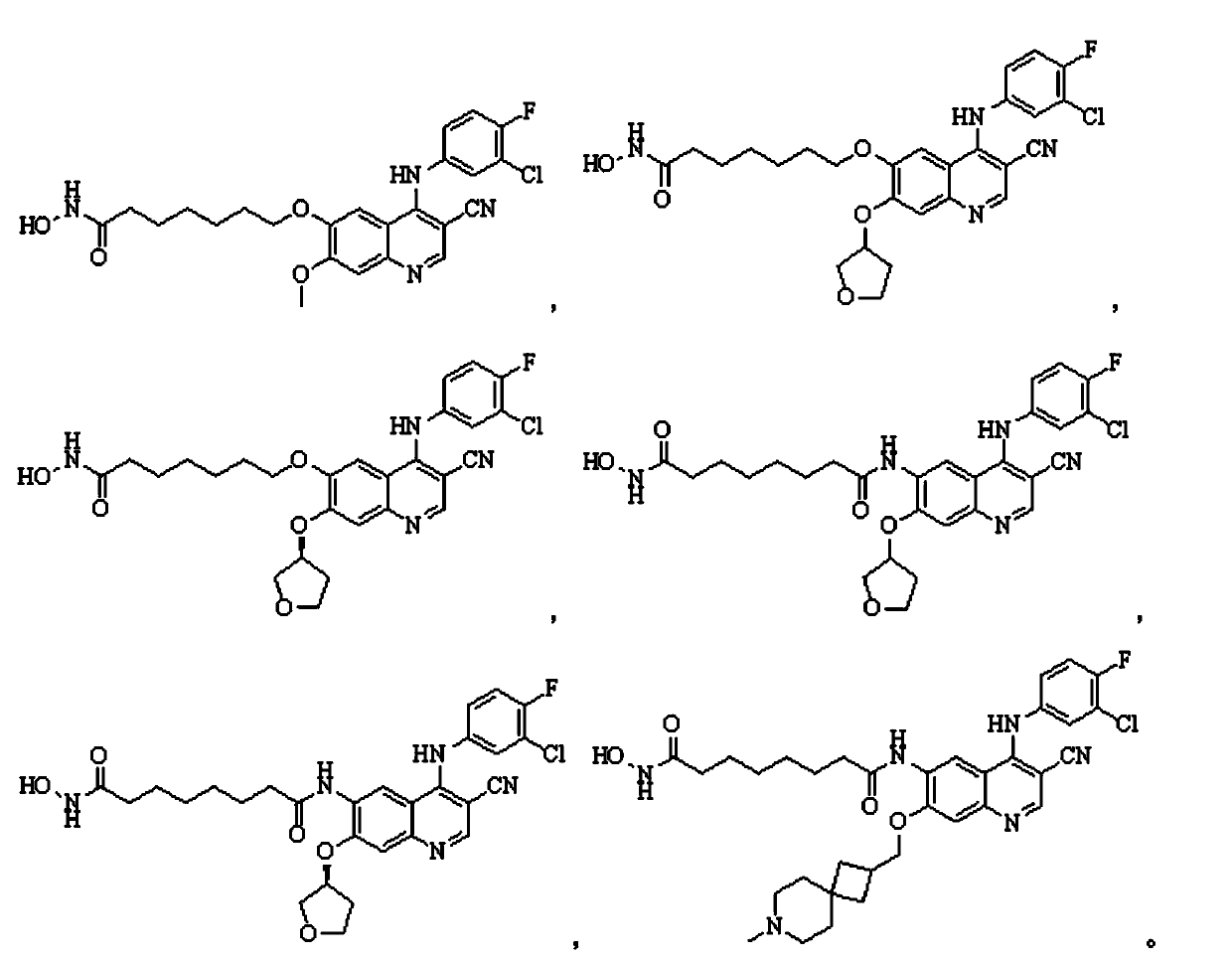
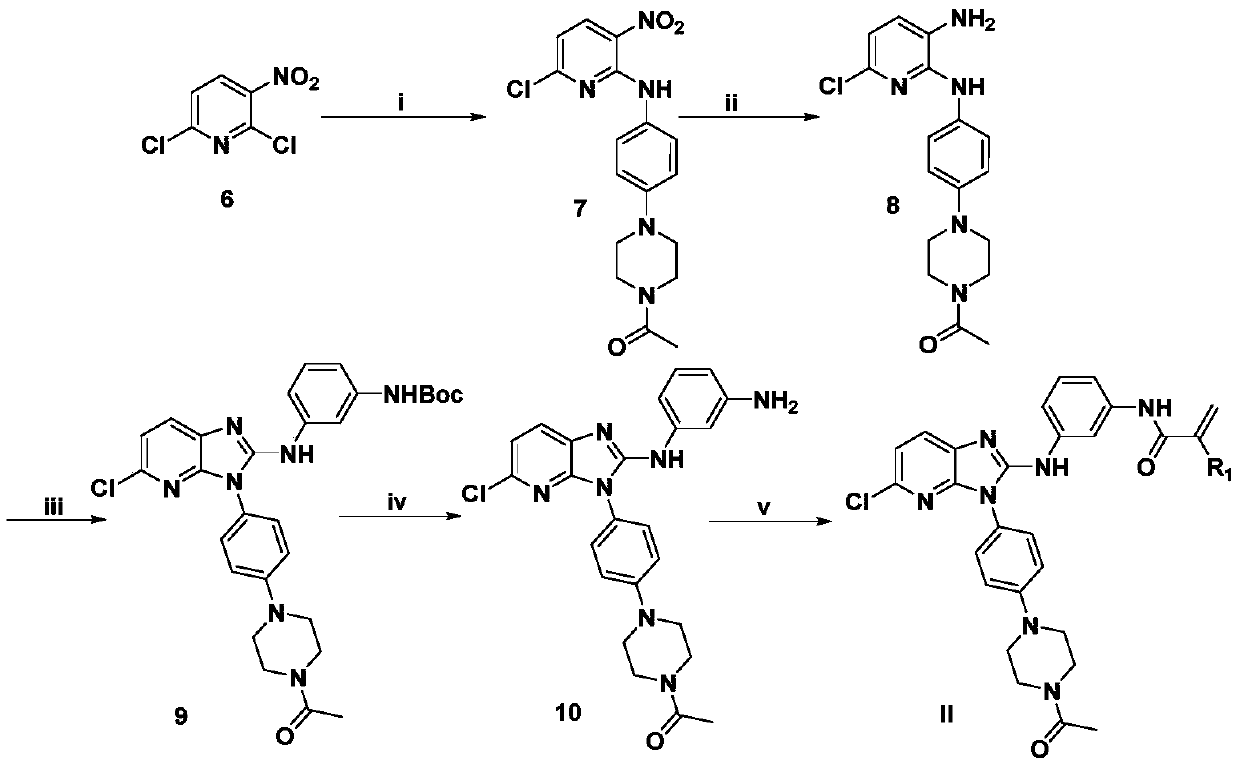
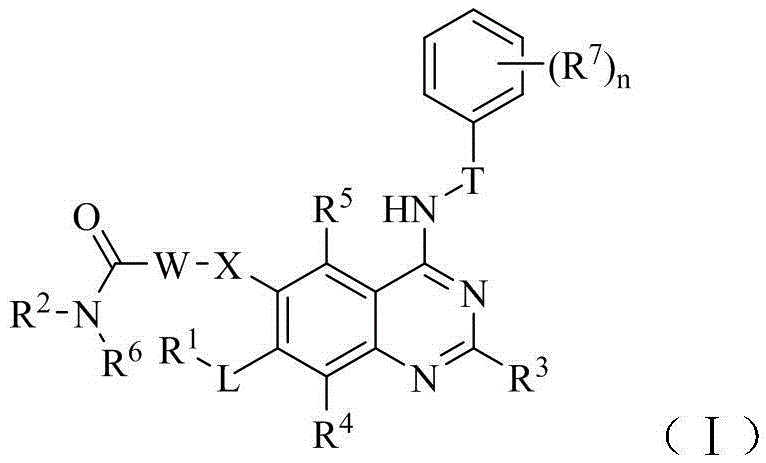
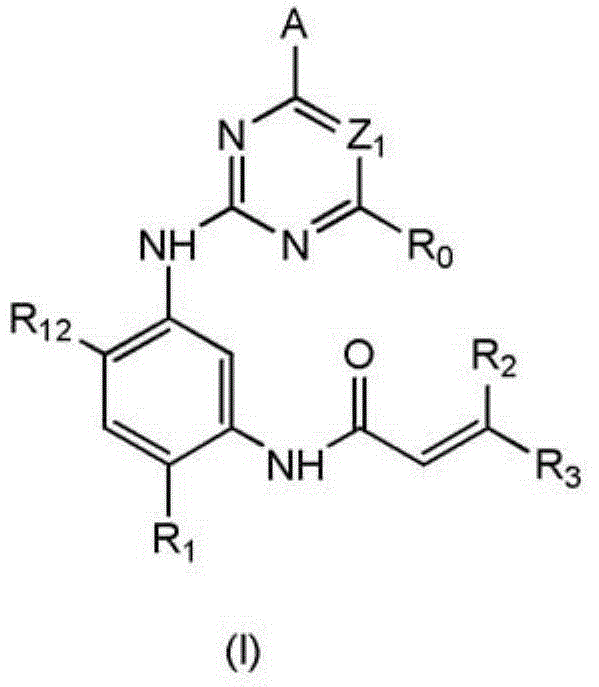
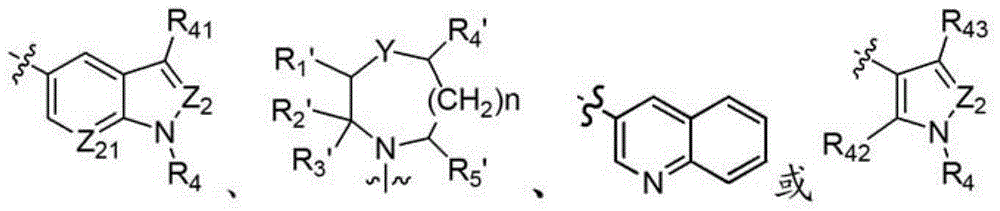
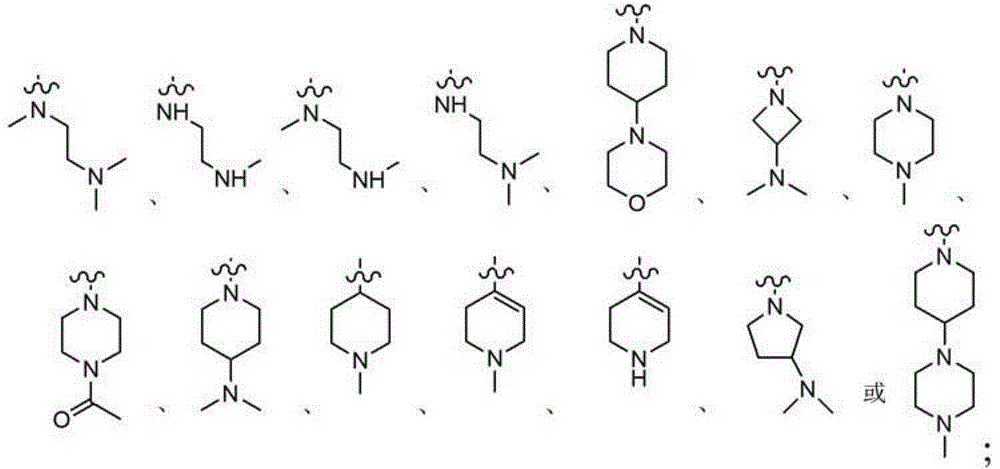
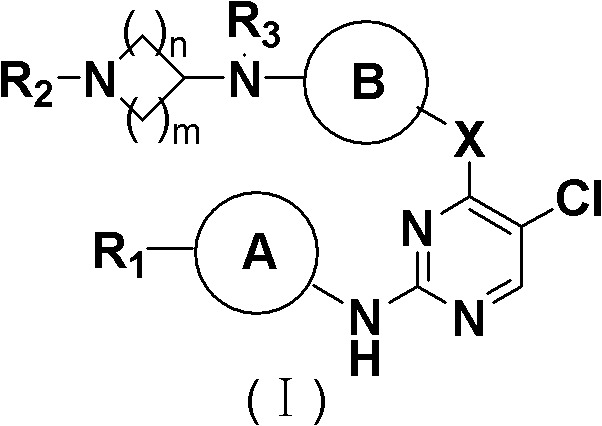
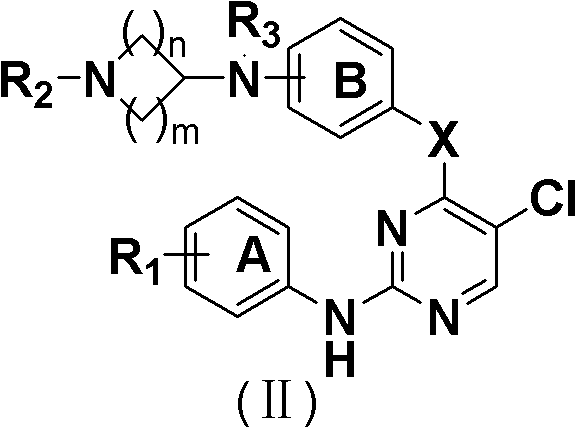
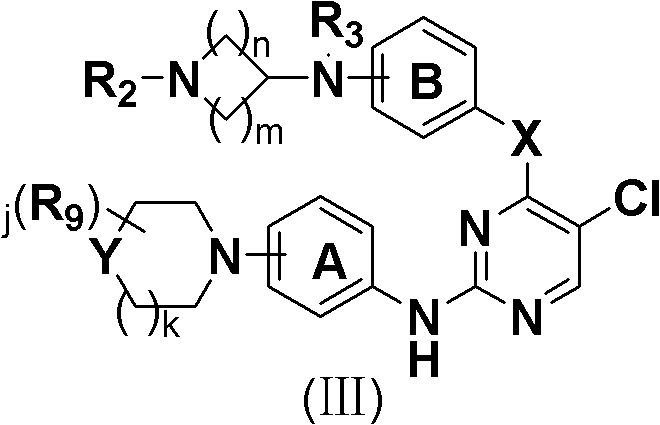
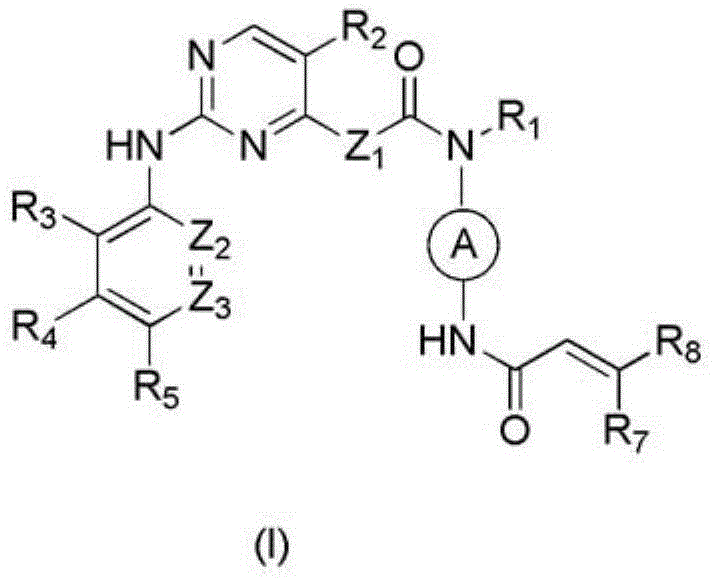
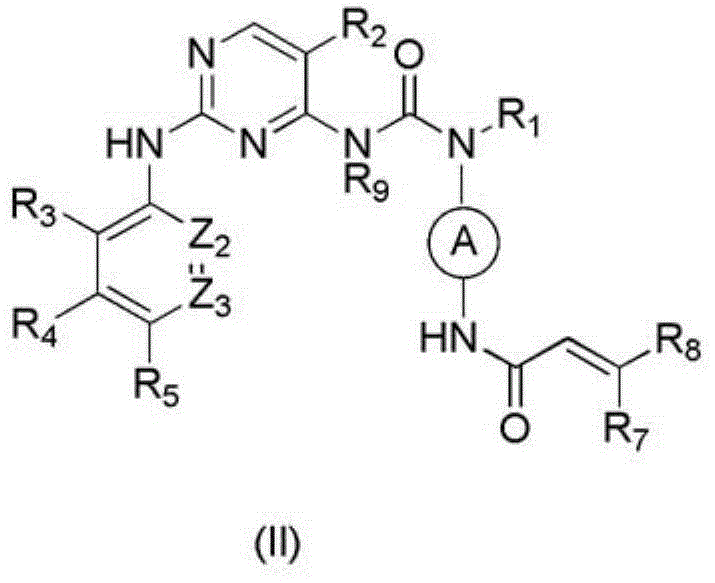
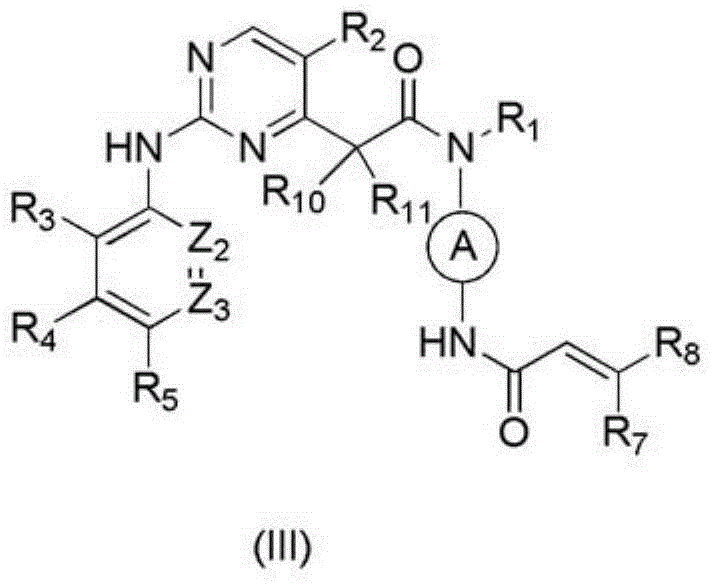
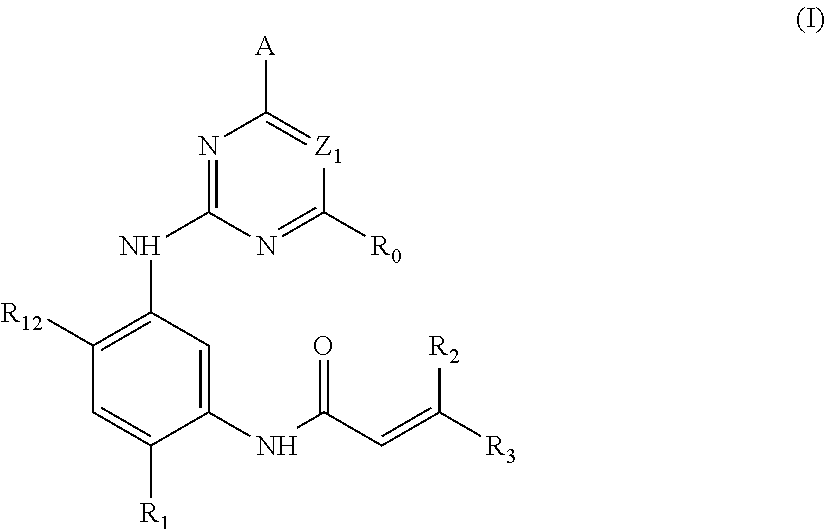
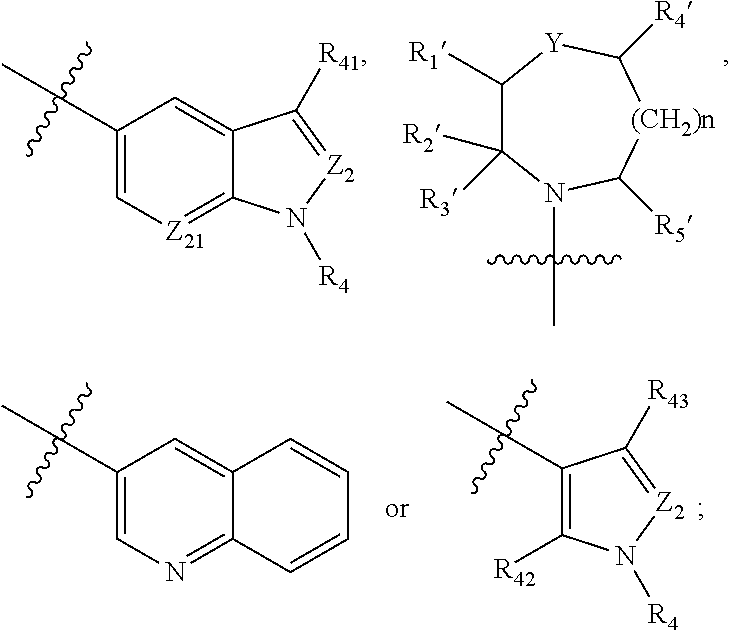
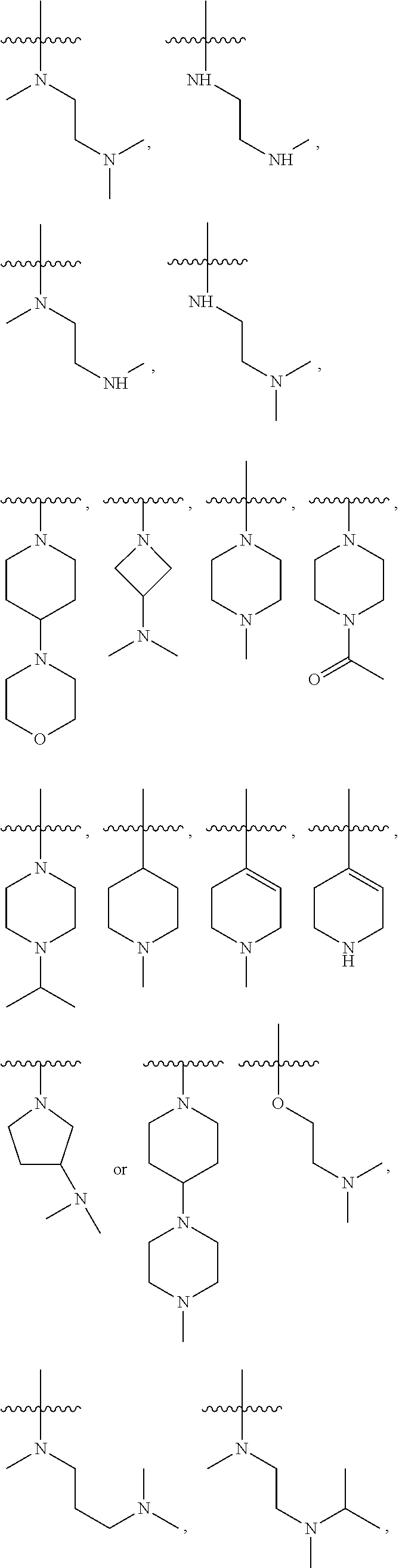
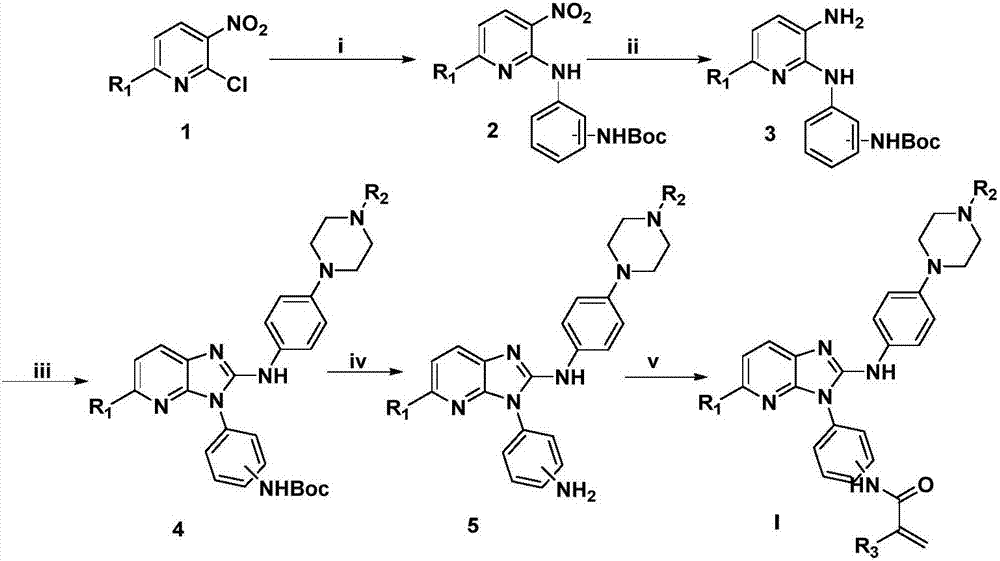
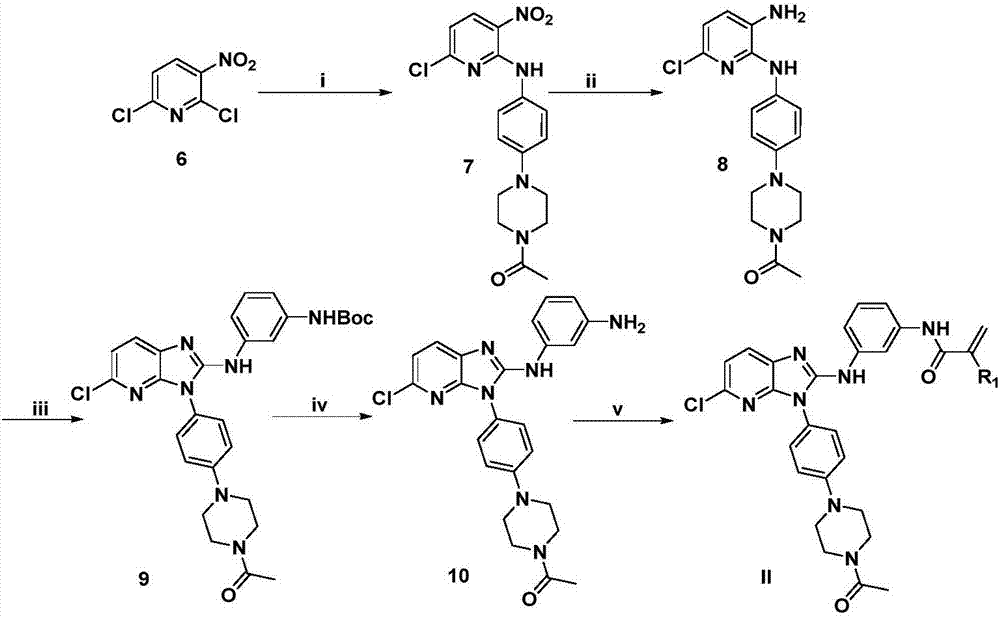
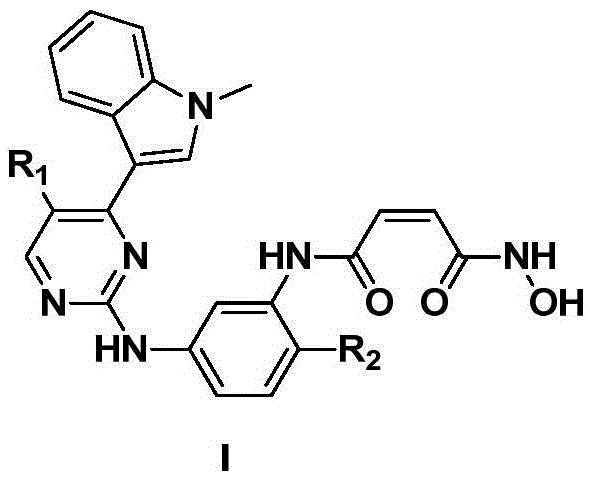
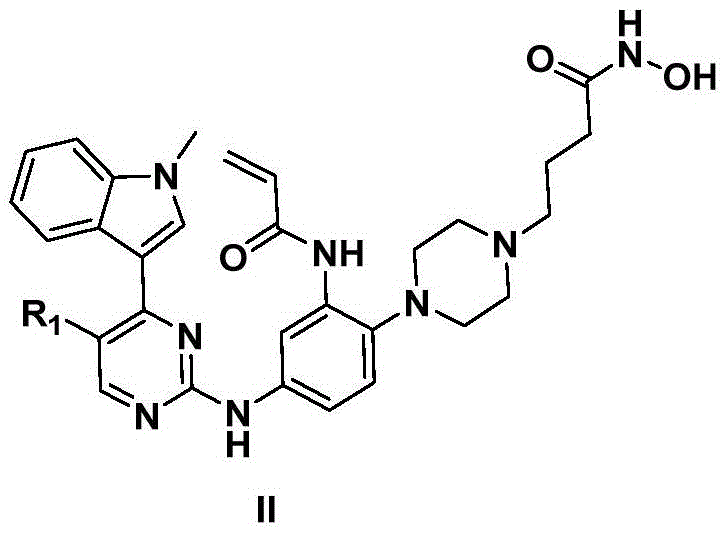
Derivative adopting pyridino-[2,3-d]pyridine as mother nucleus as well as preparation method and application thereof
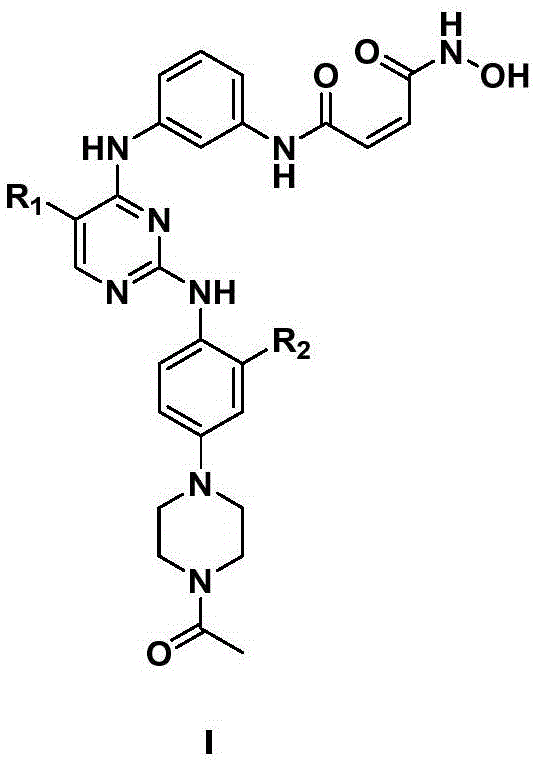
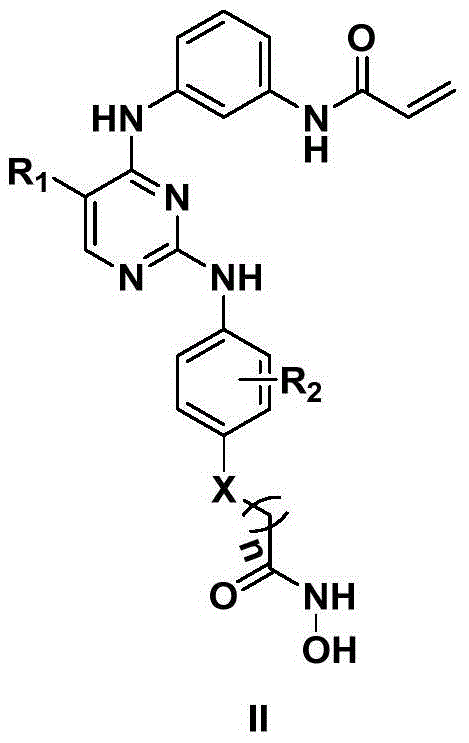
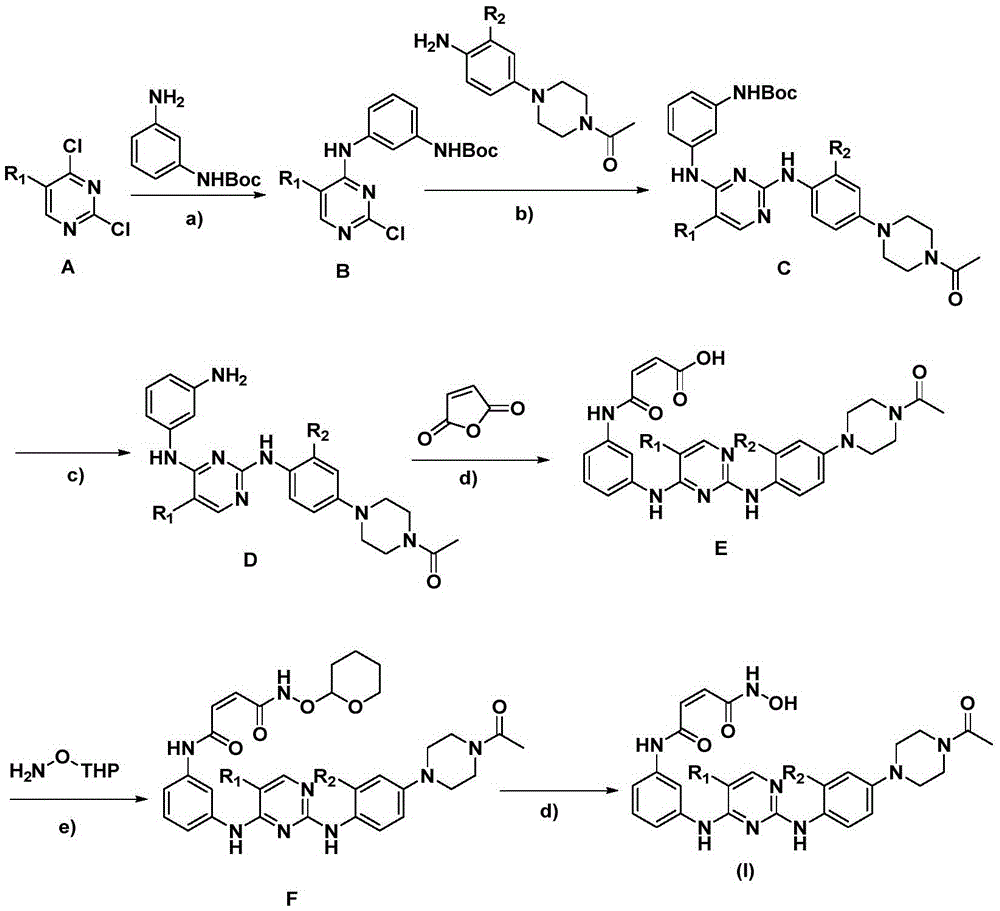
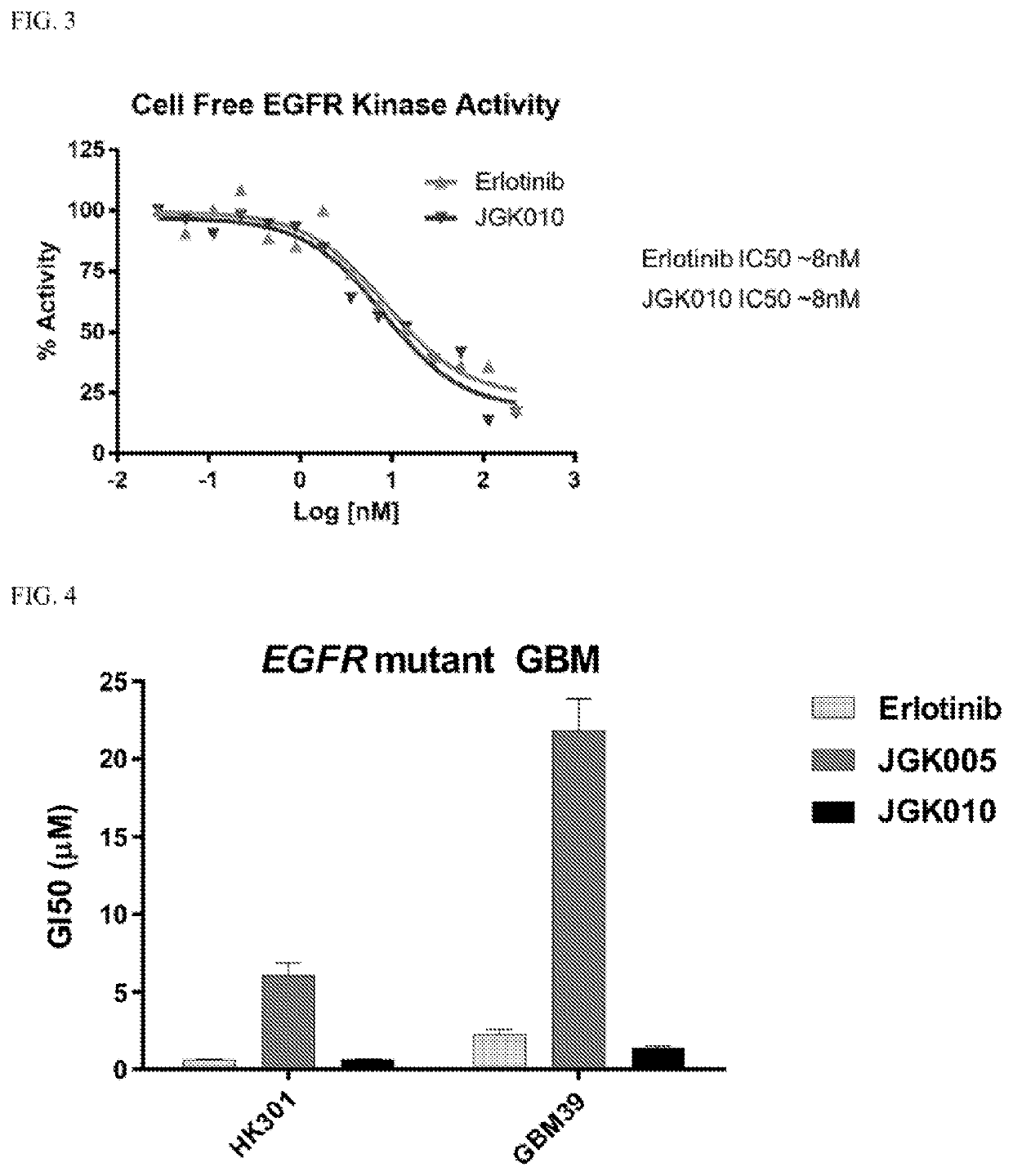
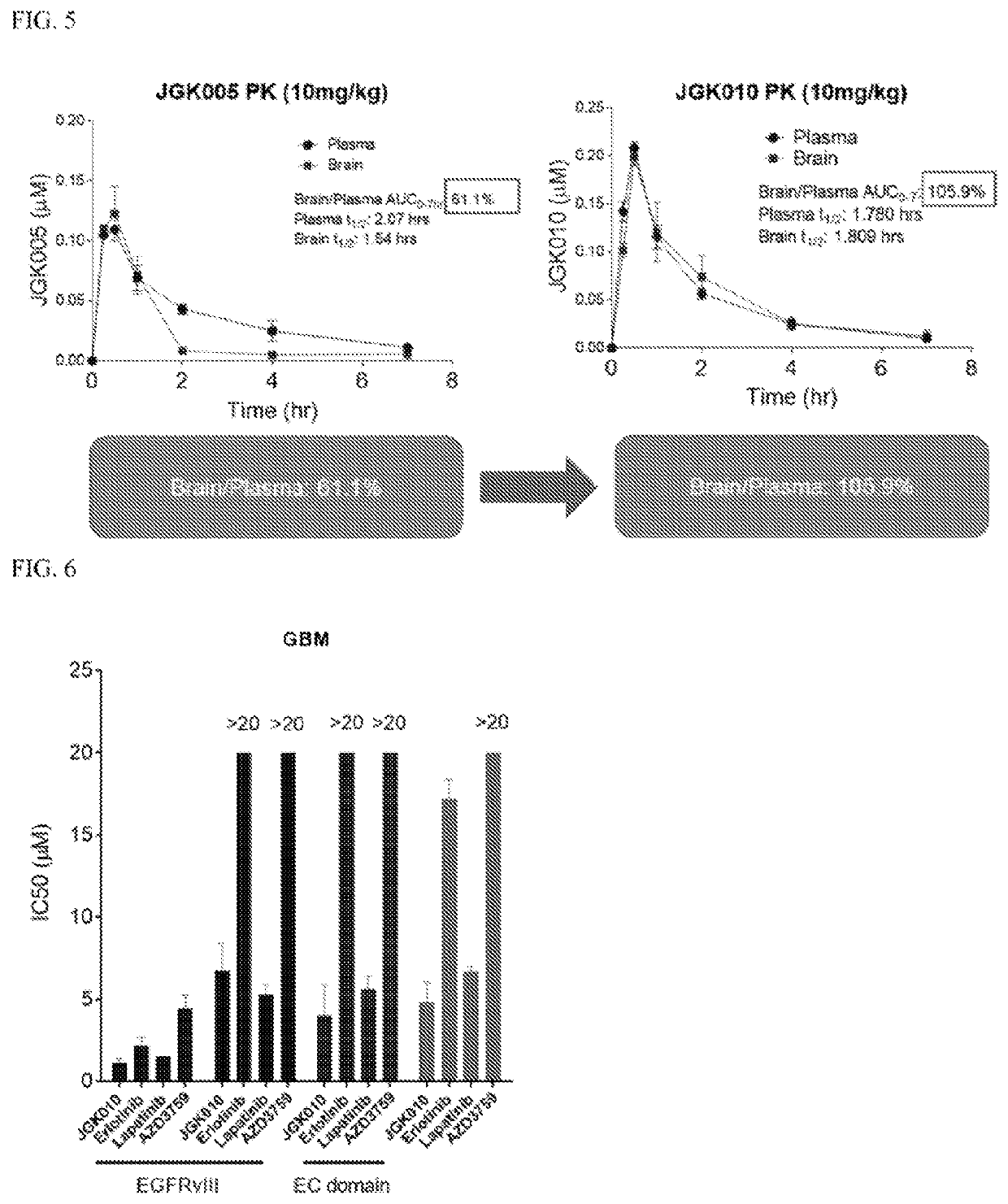
ActiveCN108558865AGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTherapeutic effectPyridine
The invention discloses a derivative adopting pyridine-[2,3-d] pyridine as a mother nucleus as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The derivative of the invention is a compound having an inhibition effect for tumor cells mutated for EGFR tyrosine kinase and can be used for treating, jointly treating or preventing various cancers. Particularly, the effect of the compound for treating the mutation type of del19, L858R and T790M of EGFR is significant.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Kit for quantitative detection of braf mutation
InactiveUS20130095491A1Accurately and quantitatively ratioEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBRAF Gene MutationBraf genes
The present invention relates to a method and assay kit for BRAF gene mutations which relates to the effect of molecule-targeting anti-tumor drug. Particularly, the present invention relates to a fluorescent quantitative PCR method and kit for detecting mutations at hotspots of BRAF gene, together with the use thereof. The present invention detects the mutations at specific sites of BRAF gene, and can predict the therapeutic efficacy of anti-EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, an anti-tumor drug. Therefore, the present invention can provide a guidance to individualized treatments for cancer patients.
Owner:BEIJING ACCB BIOTECH
Inhibitors of autophosphorylation protein kinases
InactiveUS7189694B2Inhibit enzymatic functionShuts down functioning pathwayPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticADAMTS ProteinsTyrosine
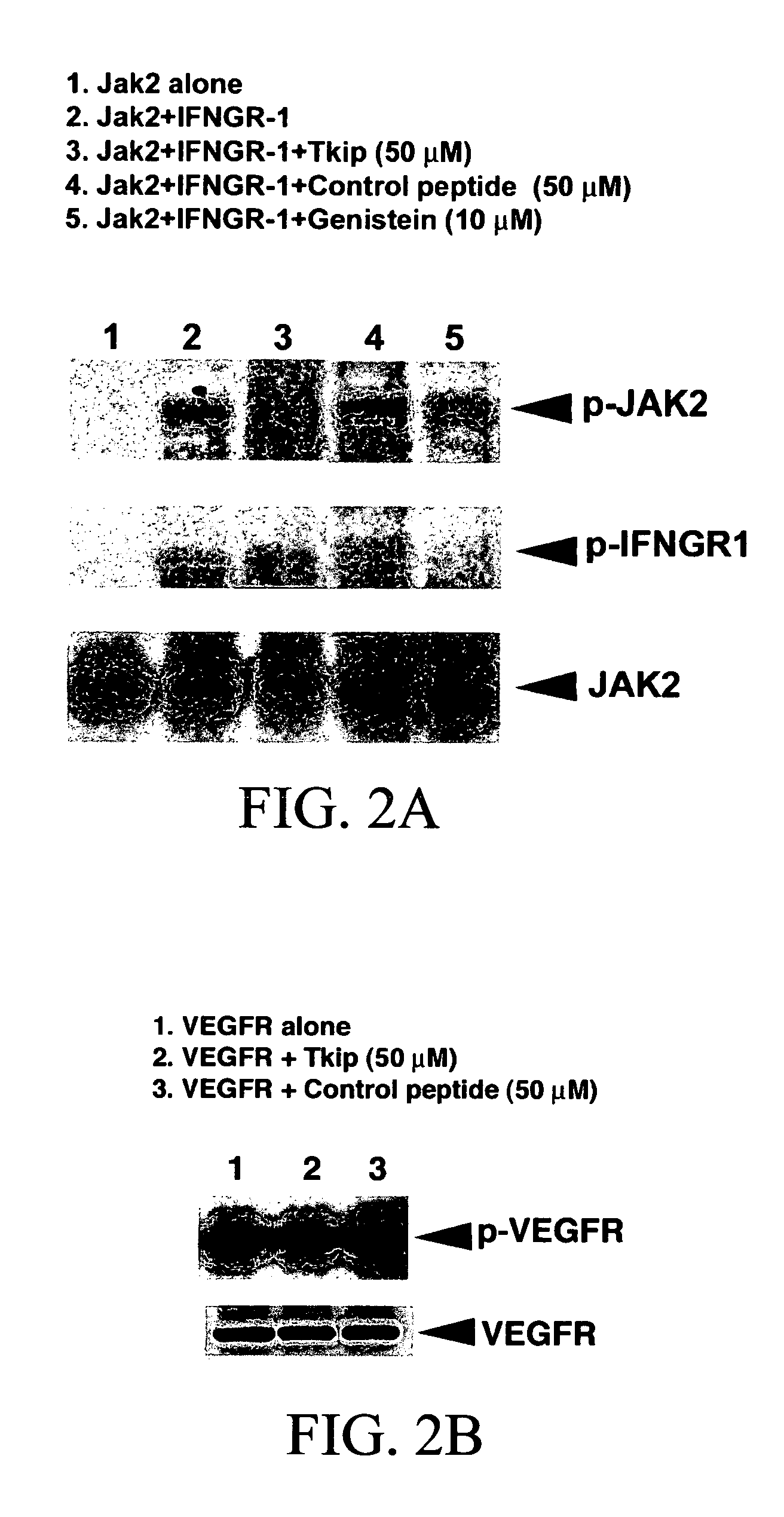
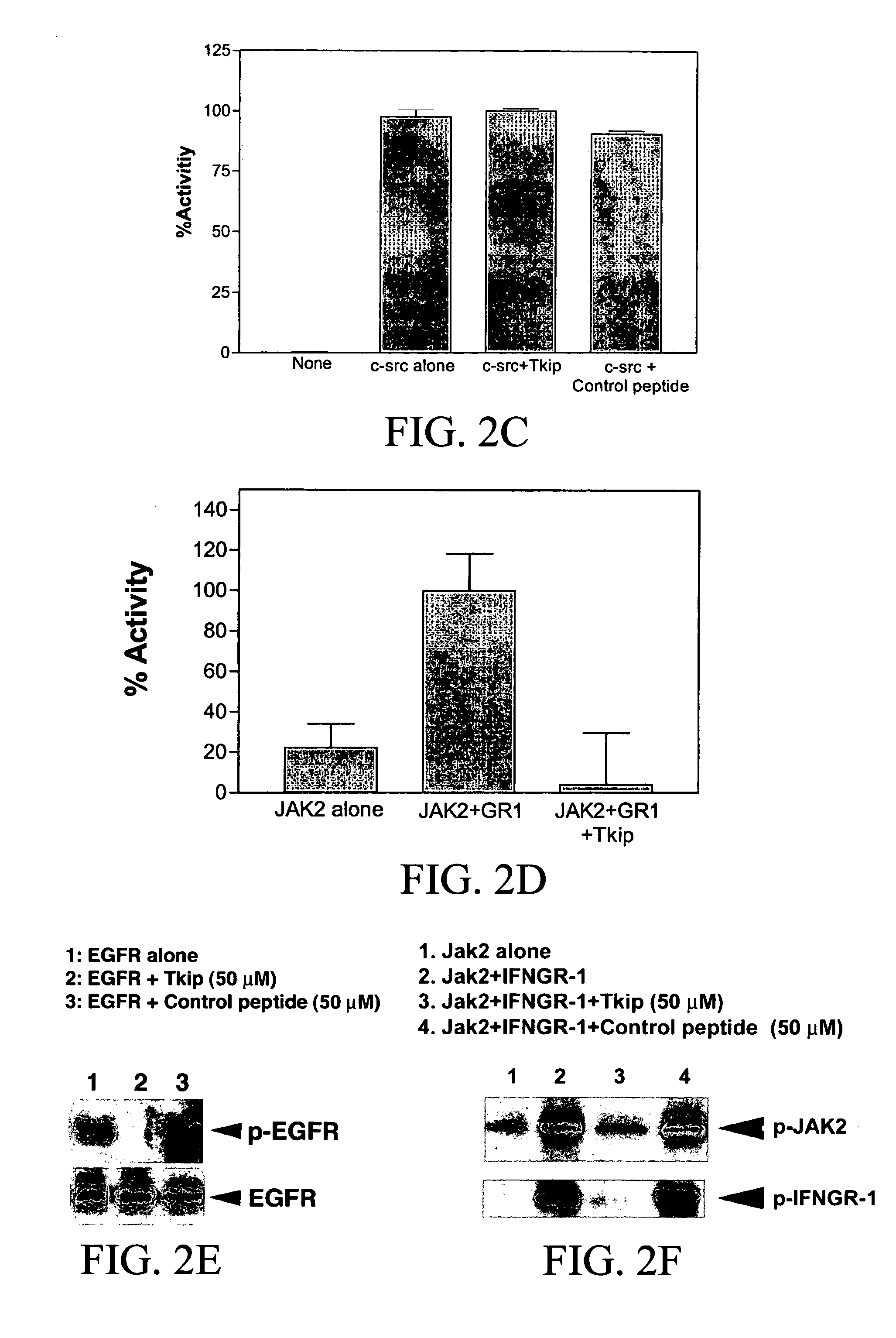
The subject invention concerns peptide molecules that specifically inhibit the enzymatic function of tyrosine kinases, including the JAK and EGF receptor (EGFR) family of kinases, to autophosphorylate, i.e., to transfer a phosphate group from ATP to an amino acid in the kinase. Phosphorylation of proteins is the most fundamental method for signal transduction among proteins in a cell. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation activities inhibits the enzyme's signaling and shuts down the functioning pathways originating from the enzyme. The JAK2 and EGFR tyrosine kinases are involved in both inflammatory disorders and cancer. In these disorders, the tyrosine kinases can often be activated in an uncontrolled fashion. The subject application also concerns antibodies that bind to a tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation site. The subject invention also concerns pharmaceutically acceptable formulations of the subject peptides and antibodies, and methods for treating inflammatory and oncological disorders by inhibiting tyrosine kinase signaling in these situations by administering a peptide or antibody of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Screening method for epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and inhibitors identified using same
InactiveCN102341708AInhibitory activityEasy to pickCompound screeningApoptosis detectionADAMTS ProteinsScreening method
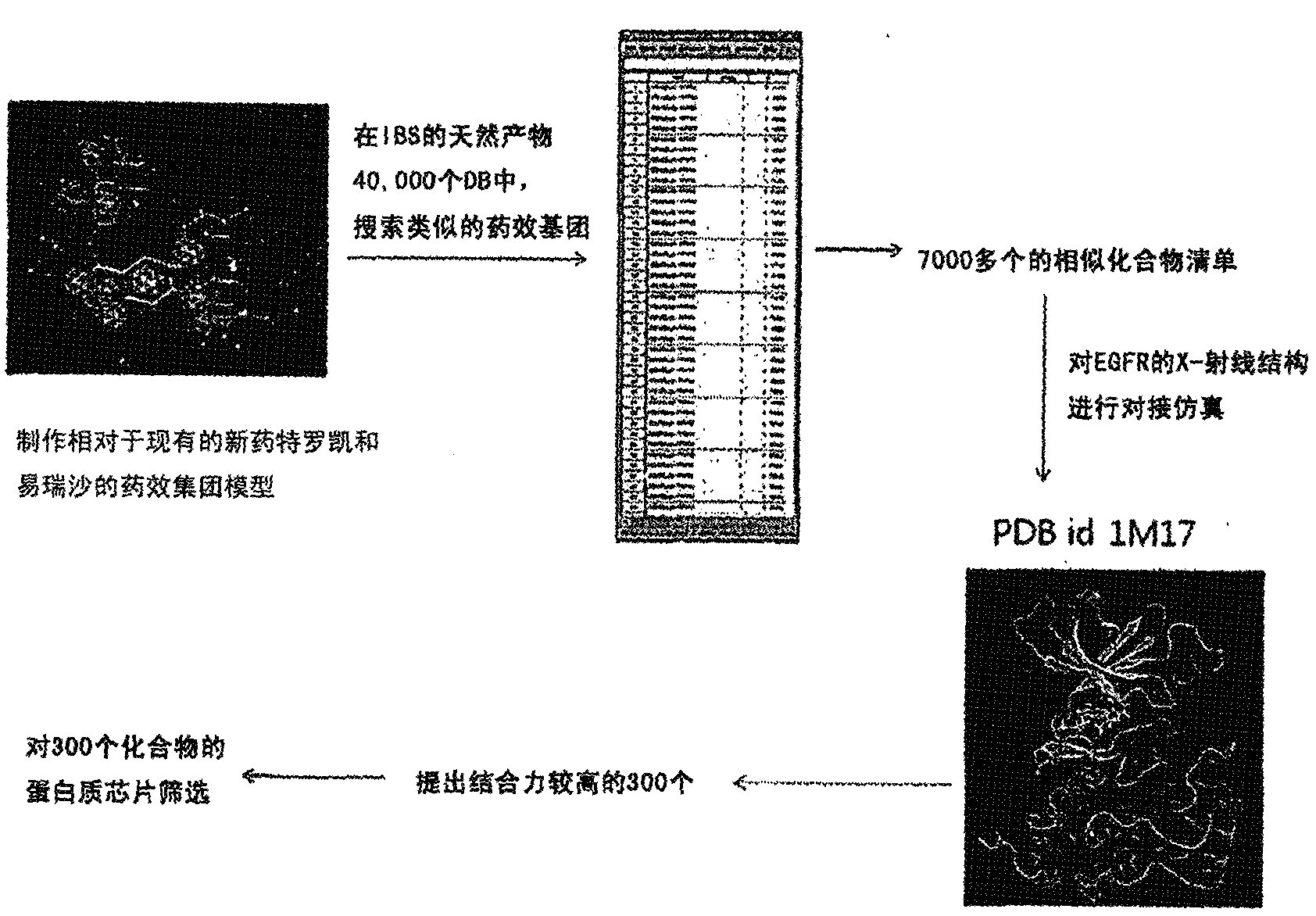
The present invention relates to a fast screening method for identifying large quantities of new substances which can effectively inhibit the activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase, and comprises attaching an EGFR tyrosine substrate, which is activated by reaction with EGFR tyrosine kinase, to a protein chip and reacting it with a compound pool consisting of EGFR tyrosine kinase, ATP, Mg2+ and a single candidate library, to provide superior and rapid screening for tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Owner:HOSEO UNIV ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Selective inhibitors of clinically important mutants of the EGFR tyrosine kinase
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) or a subgeneric structure or species thereof or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, solvate, and / or prodrug thereof and methods and compositions for treating or ameliorating abnormal cell proliferative disorders, such as cancer, wherein A, R2, R3, R10, E1, E2, E3, Y, and Z are as defined herein.
Owner:HIGH GREAT INVESTMENT LTD
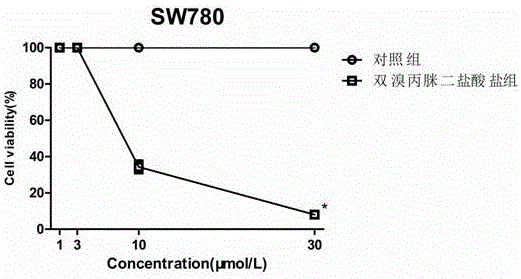
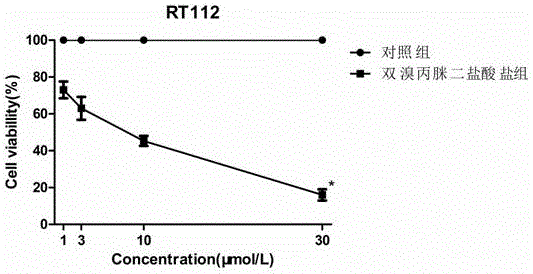
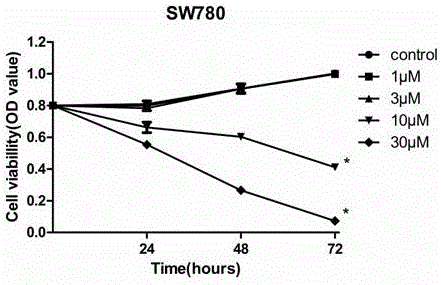
Application of dibrompropamidine dihydrochloride to preparation of medicine for inhibiting bladder cancer EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) target spot
InactiveCN106074473APromote apoptosisInhibition of survivalOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsApoptosisEgfr tyrosine kinase
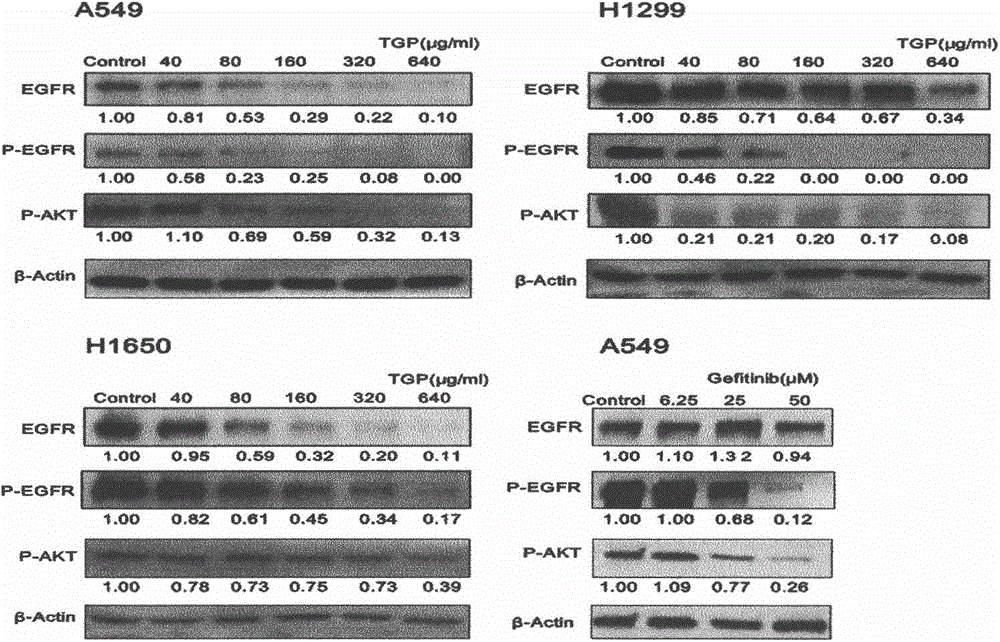
The invention provides application of dibrompropamidine dihydrochloride to the preparation of a medicine for inhibiting a bladder cancer EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) target spot and belongs to diamidine series compound medicines and application thereof. The dibrompropamidine dihydrochloride can be used for inhibiting IC50 of SW780and RT112 cell growth to be 5Mumol / L-8Mumol / L; and the concentration has positive correlation with effect of promoting SW780 and RT112 apoptosis and has inverse correlation with p-EGFR, p-AKT and p-ERK phosphorylation degrees. The invention takes the dibrompropamidine dihydrochloride as a medicine for inhibiting a tyrosine kinase structure domain of the human bladder cancer EGFR; and the utilization efficiency of a medicine is improved and a market prospect is wide.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +2
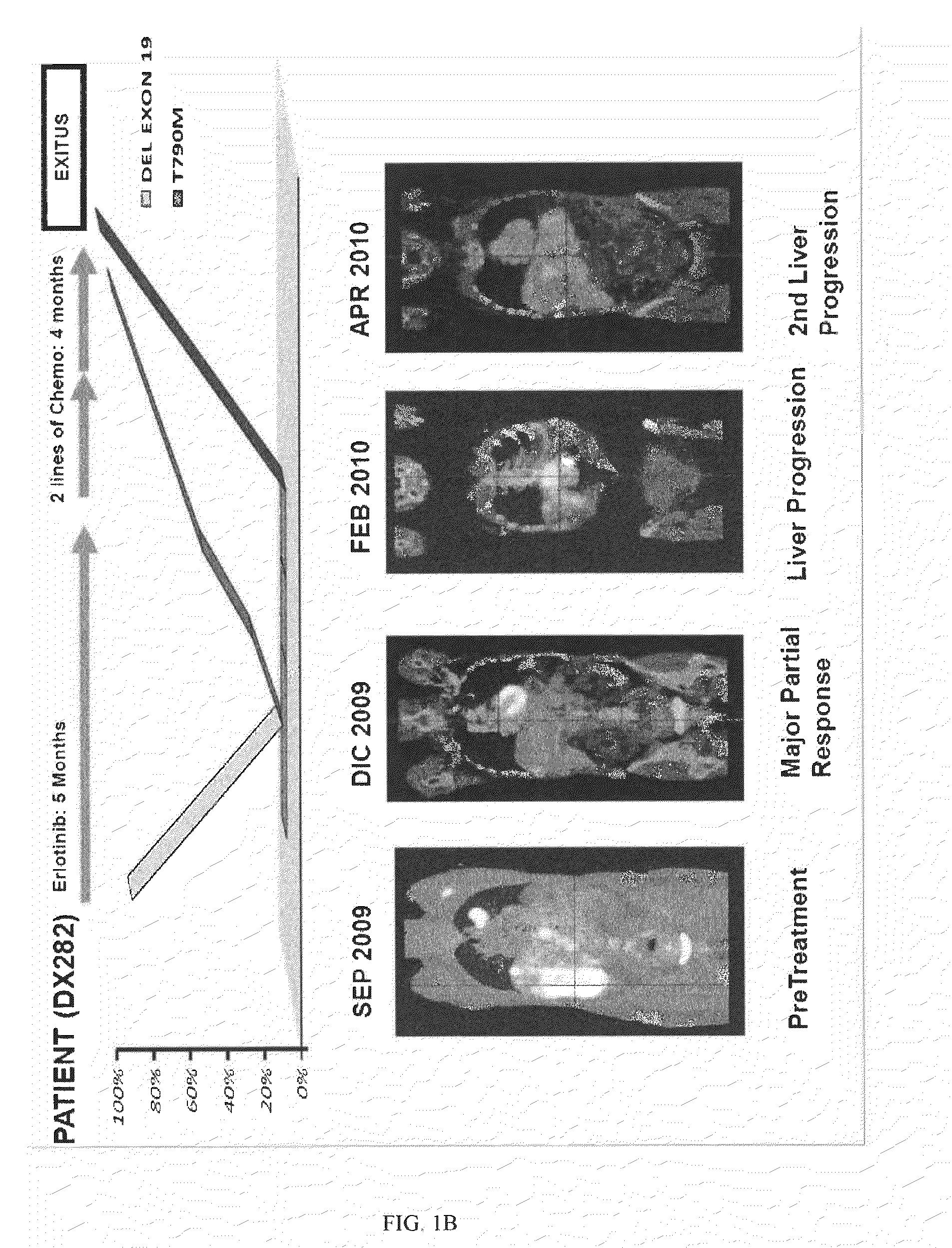
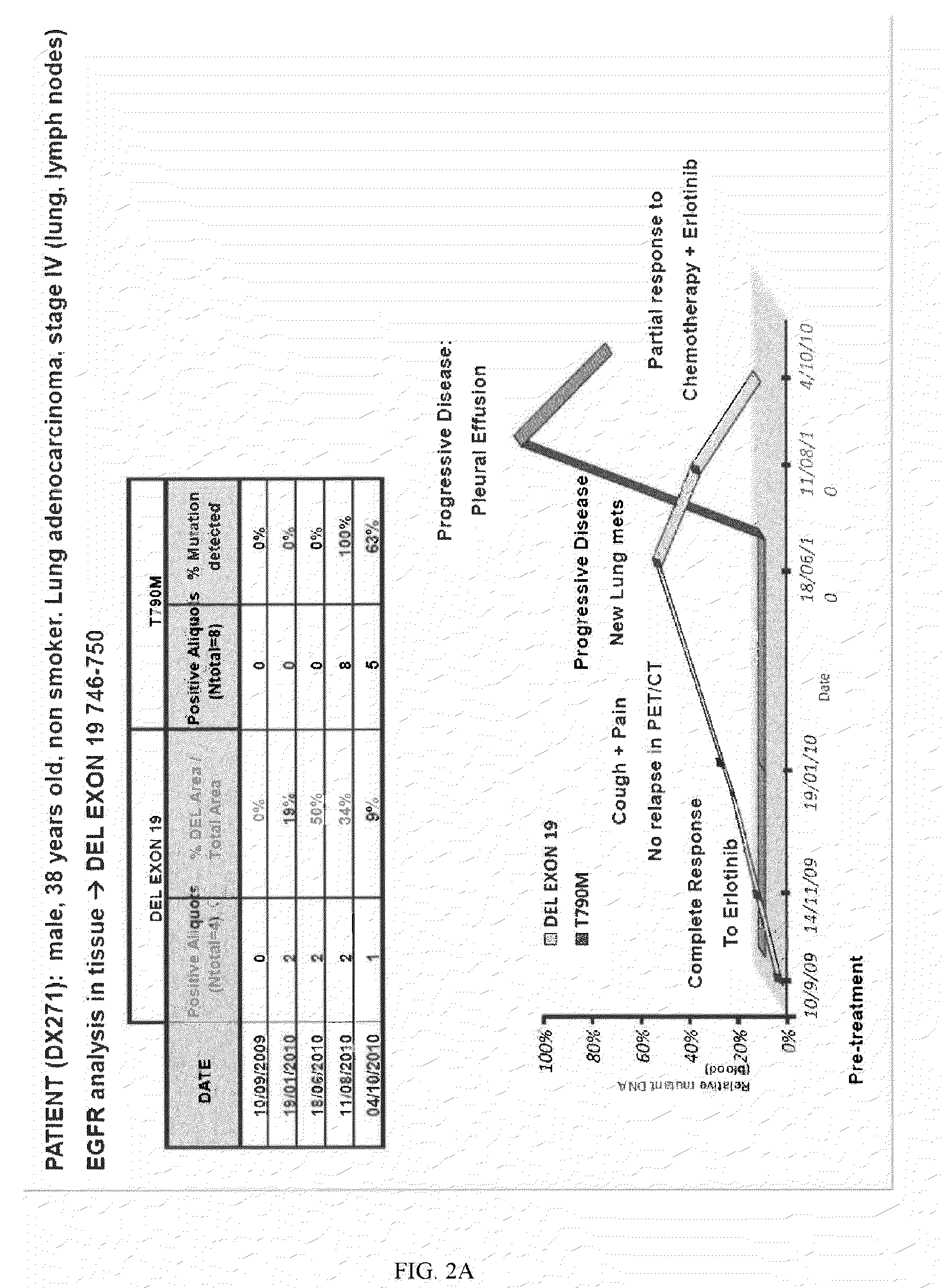
Molecular Biomarkers for Predicting Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Lung Cancer
The invention relates to methods for determining the clinical outcome of patients suffering lung cancer and being under treatment with an EGFR inhibitor. The methods are based on the detection of the presence of mutations in the EGFR gene conferring resistance to inhibitors of the EGFR tyrosine kinase activity, wherein the appearance of said mutations in the biofluid of the patient is indicative of a high probability that the patient suffers a relapse of the disease. The invention also provides therapeutic methods for said patients.
Owner:PANGAEA BIOTECH
Selective inhibitors of clinically important mutants of the EGFR tyrosine kinase
InactiveUS20200131176A1Selectively modulate activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTyrosinePharmaceutical medicine
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) or a subgeneric structure or species thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, solvate, and / or prodrug thereof, and methods and compositions for treating or ameliorating abnormal cell proliferative disorders, such as cancer, wherein A, R2, R3, R10, E1, E2, E3, Y, and Z are as defined herein.
Owner:CS PHARMATECH LTD
Quinazoline derivative, preparation method therefor, and pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
ActiveUS20170247339A1Improve anti-tumor effectDelay drug resistanceOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChemical structureWilms' tumor
Disclosed are a quinazoline derivative, a preparation method therefor, and a pharmaceutical composition and an application thereof. The present invention provides a compound represented by general formula I, a stereoisomer thereof and a pharmaceutical acceptable salt or a solvate thereof. The quinazoline derivative of the present invention has a unique chemical structure, is characterized by irreversibly inhibiting EGFR tyrosine kinase, has high biological activity, apparently improves the inhibiting effect on the EGFR tyrosine kinase, has quite strong tumor inhibiting effect on tumor cells and a transplantation tumor pathological model of animal tumors, and has good market developing prospects.
Owner:ARROMAX PHARMATECH
Quinazoline derivatives containing hydroxamic acid side chain as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN106187919AIncreased drug resistancePrevent desensitizationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHydroxylamineSide chain
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Adamantyl quinazoline compound, composition and application of adamantyl quinazoline compound and composition
The invention discloses an adamantyl quinazoline compound, a composition and application of the adamantyl quinazoline compound and the composition. The compound shown in a formula (I) and all possible isomers or pharmaceutically acceptable salts or hydrates or compositions are used to treat diseases caused by EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) tyrosine kinase, and are particularly used to treat non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, squamous-cell carcinoma, breast cancer and gastric carcinoma.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
4-methoxyphenyl-1, 3-diamine derivative containing 1-methyl-1H-indole structure and application of 4-methoxyphenyl-1, 3-diamine derivative
The invention discloses a 4-methoxyphenyl-1, 3-diamine derivative containing a 1-methyl-1H-indole structure and an application of the 4-methoxyphenyl-1, 3-diamine derivative containing the 1-methyl-1H-indole structure. The compound has a structural general formula as shown in (I). The 4-methoxyphenyl-1, 3-diamine derivative containing the 1-methyl-1H-indole structure and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the 4-methoxyphenyl-1, 3-diamine derivative are reversible inhibitors of EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) kinases, are compounds with inhibition effects on tumor cells with mutational EGFR tyrosine kinases, and can be used for treatment, combined treatment or prevention of various cancers.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
New application of total glucosides of paeony as EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) tyrosine kinase inhibitor
ActiveCN103550313AImprove securityReduce expressionAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsEGFR Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The invention belongs to the field of medicines and relates to a new application of total glucosides of paeony as an EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) tyrosine kinase inhibitor. The content of paeoniflorin (C23H28O11) in the total glucosides of paeony is not less than 34.6%. Compared with the traditional EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib, the total glucosides of paeony have the advantages that the total glucosides of paeony have high safety, can obviously reduce the expression quantity and activation quantity of EGFR tyrosine kinase, are low in price and have abundant resources, thereby providing a new choice for medicine development.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
EGFR-TK (epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase) inhibitor BF3-AZD9291 with antitumor activity as well as preparation method and application of EGFR-TK inhibitor BF3-AZD9291
InactiveCN107501240APrevent proliferationGood antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChemical structureTumor therapy
The invention discloses an EGFR-TK (epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase) inhibitor BF3-AZD9291 with antitumor activity as well as a preparation method and an application of the EGFR-TK inhibitor BF3-AZD9291, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. Brand-new EGFRTKI is obtained by optimizing and improving chemical structure of AZD9291 and named BF3-AZD9291 shown as formula I in the description. Research proves that the synthesized EGFR TKI BF3-AZD9291 can effectively inhibit drug resistance of tumor cells, has stronger drug resistance habitation effect on a mutant EGFR lung cancer cell line H1975T790M than AZD9291 and can be clinically applied as an antitumor agent accordingly. Besides, the invention discloses the preparation method of the EGFR-TK inhibitor BF3-AZD9291 with antitumor activity. With provision of the invention, an effective technological means for tumor treatment, especially treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
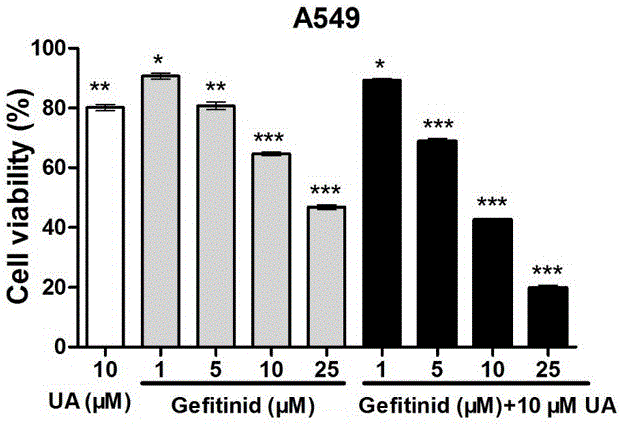
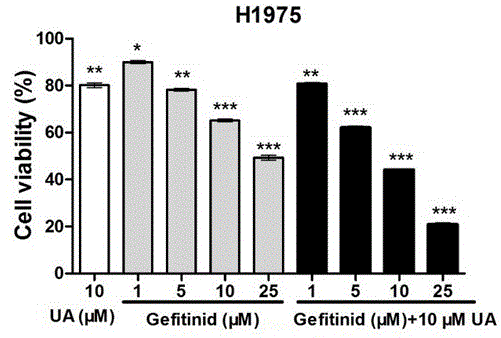
Low-dosage medicine composition containing EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) tyrosine kinase and application thereof in preparation of anti-tumor transfer medicines
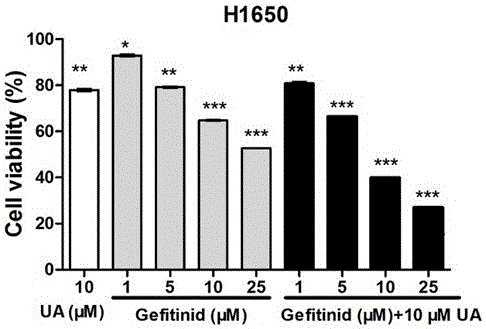
The invention relates to a low-dosage medicine composition containing EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) tyrosine kinase and an application thereof in preparation of anti-tumor transfer medicines. The low-dosage medicine composition with anti-tumor transfer function is characterized by comprising ursolic acid and gefitinib according to the weight ratio of 10:(1-5). The low-dosage medicine composition has the advantage that after the gefitinib with targeting function is jointly used together with the anti-tumor natural product of ursolic acid with high efficiency and low toxicity, the good anti-tumor transfer function on cancer cells is realized, and a safe and reliable novel candidate medicine is obtained.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
2,4-diarylamine pyrimidine derivatives containing hydroxamic acid fragments and preparation and application
InactiveCN105646371AStrong growth inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCarcinoma cell lineHydroxamic acid
The invention provides 2,4-diarylamine pyrimidine derivatives containing hydroxamic acid fragments shown in formulas I and II. 2,4-diarylamine pyrimidine containing carboxyl fragments is mainly used as a parent nucleus and is subjected to single-step condensation and related modification with hydroxylamine protected by THP to obtain a target compound. An experiment proves that the remarkable anti-proliferative effect is achieved for tumor cells (a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line H1975 and an overexpression EGFR human epidermal carcinoma cell line A431) related to EGFR tyrosine kinase activity on the cellular level, and a human cervical carcinoma cell line Hela, a human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell line KB, a human promyelocytic acute leukemia cell line HL60, a human hepatoma cell line HepG2, a human colon cancer cell line SW620 and other tumor cells related to the HDAC histone acetylase activity, and the corresponding medicine for resisting cancer cells can be prepared. The general structural formula is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compositions and methods for treating cancer
ActiveUS11377451B2Improve throughputLimit deliveryOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsGlioblastomaTyrosine
The present disclosure relates to compounds, compositions and methods for treating cancer, including compounds that are capable of penetrating the blood brain barrier to modulate the activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase. The disclosure further relates to methods of treating cancer in the brain, including glioblastoma and other EGFR mediated cancers. The disclosure further relates to methods of treating cancers such as glioblastoma and other EGFR mediated cancers that have been determined to have altered glucose metabolism in the presence of inhibitors. The present disclosure also provides methods of administering to a subject a glucose metabolism inhibitor and a cytoplasmic p53 stabilizer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Quinolyl EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor containing zinc binding group
InactiveCN103965106AGood antitumor activityDelay drug resistanceOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryEGFR Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsZinc binding
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicin and specifically relates to a quinolyl EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor containing a zinc binding group and a deuterated material, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or stereoisomer thereof. The inhibitor is represented by a general formula (I) which is described in the specification; and in the general formula (I), R1, R2, R2', R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, W, X, L, T and n are as defined in the specification. The invention further relates to a preparation method for the inhibitor, a medicinal preparation containing the inhibitor and application of the inhibitor in preparation of drugs used for treating and / or preventing tumors.
Owner:TONGHUA SIHUAN PHARM
2-aminoimidazopyridine derivatives and their preparation and application
ActiveCN107383004BEnhanced inhibitory effectGood antitumor activityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsCarcinoma cell lineCancer cell
The invention provides a 2-aminoimidazopyridine derivative shown as a formula I, a formula II, a formula III or a formula IV and further provides a preparation method and application of the 2-aminoimidazopyridine derivative. An experiment shows that the 2-aminoimidazopyridine derivative has a remarkable proliferation inhibition effect on tumor cells (including an over-expressed wild type EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) human epidermal carcinoma cell line A431 and a Gefitinib drug-resisting human lung adenocarcinoma cell line H1975) related to the activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase in the aspect of a cell level, especially has a relatively good inhibition effect on the drug-resisting cell line H1975, has relatively weak inhibition activity on a low-expression EGFR human colon cancer cell line SW620 and can be applied to preparation of corresponding anti-tumor cell medicines. A general formula is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Quinazoline-based egfr tyrosine kinase inhibitor containing a zinc-binding group
ActiveCN103965174BStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryEGFR Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsHuman epidermal growth factor receptor
Belonging to the technical field of medicine, the invention in particular relates to a zinc binding group-containing quinazolinyl EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) tyrosine kinase inhibitor shown as general formula (I), its deuterated compounds, pharmaceutically acceptable salts or stereoisomers, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, W, X, L, and T are defined as the specification. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the compounds, pharmaceutical preparations containing the compounds, and application of the compounds in preparation of drugs treating and / or preventing tumors. (formula I).
Owner:BEIJING AOHE DRUG RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Derivative adopting pyridino-[2,3-d]pyridine as mother nucleus as well as preparation method and application thereof Derivative adopting pyridino-[2,3-d]pyridine as mother nucleus as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/935891c1-0fdb-4b44-a9a8-6386ce8d6850/BDA0001619614220000021.png)
![Derivative adopting pyridino-[2,3-d]pyridine as mother nucleus as well as preparation method and application thereof Derivative adopting pyridino-[2,3-d]pyridine as mother nucleus as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/935891c1-0fdb-4b44-a9a8-6386ce8d6850/BDA0001619614220000023.png)
![Derivative adopting pyridino-[2,3-d]pyridine as mother nucleus as well as preparation method and application thereof Derivative adopting pyridino-[2,3-d]pyridine as mother nucleus as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/935891c1-0fdb-4b44-a9a8-6386ce8d6850/BDA0001619614220000031.png)