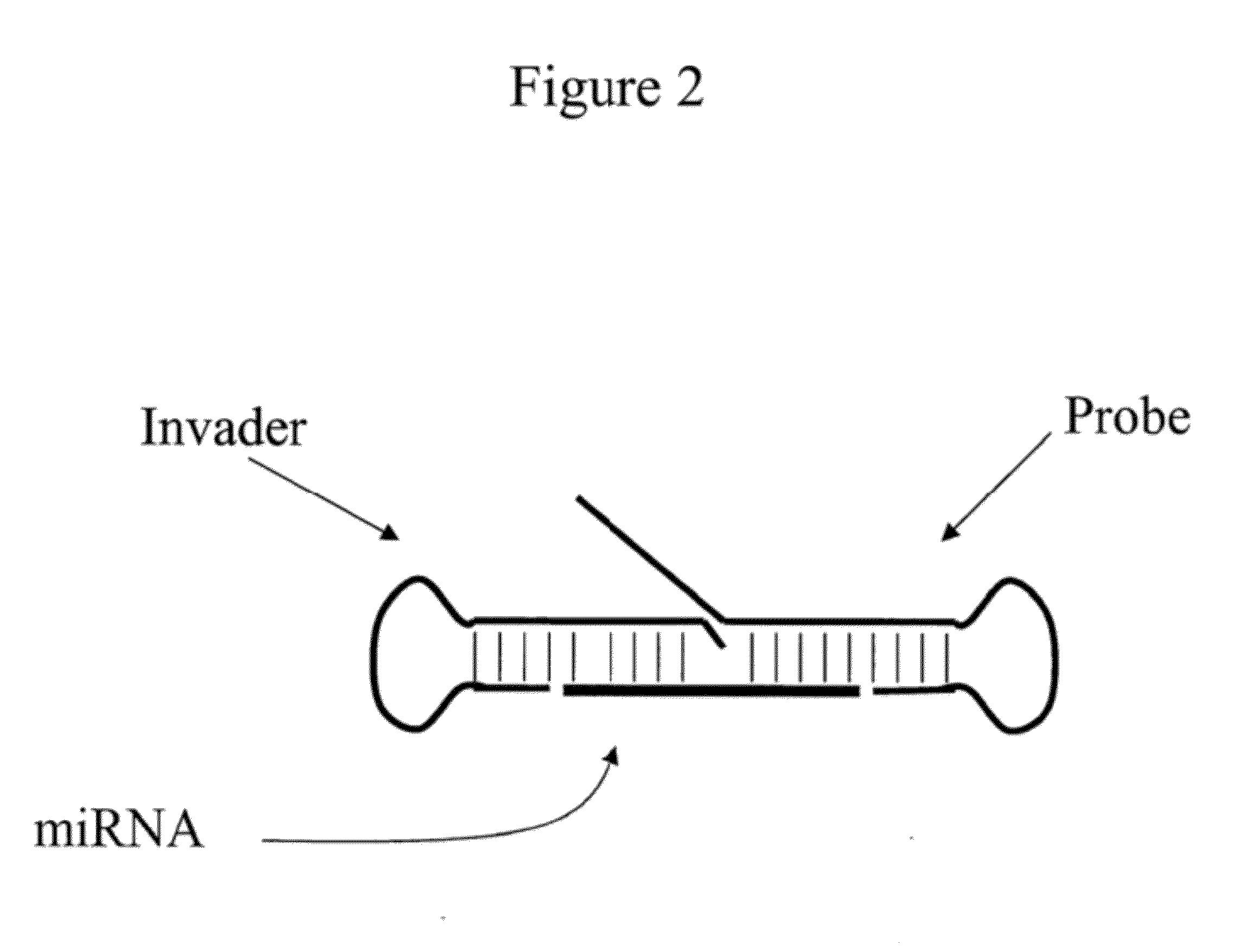
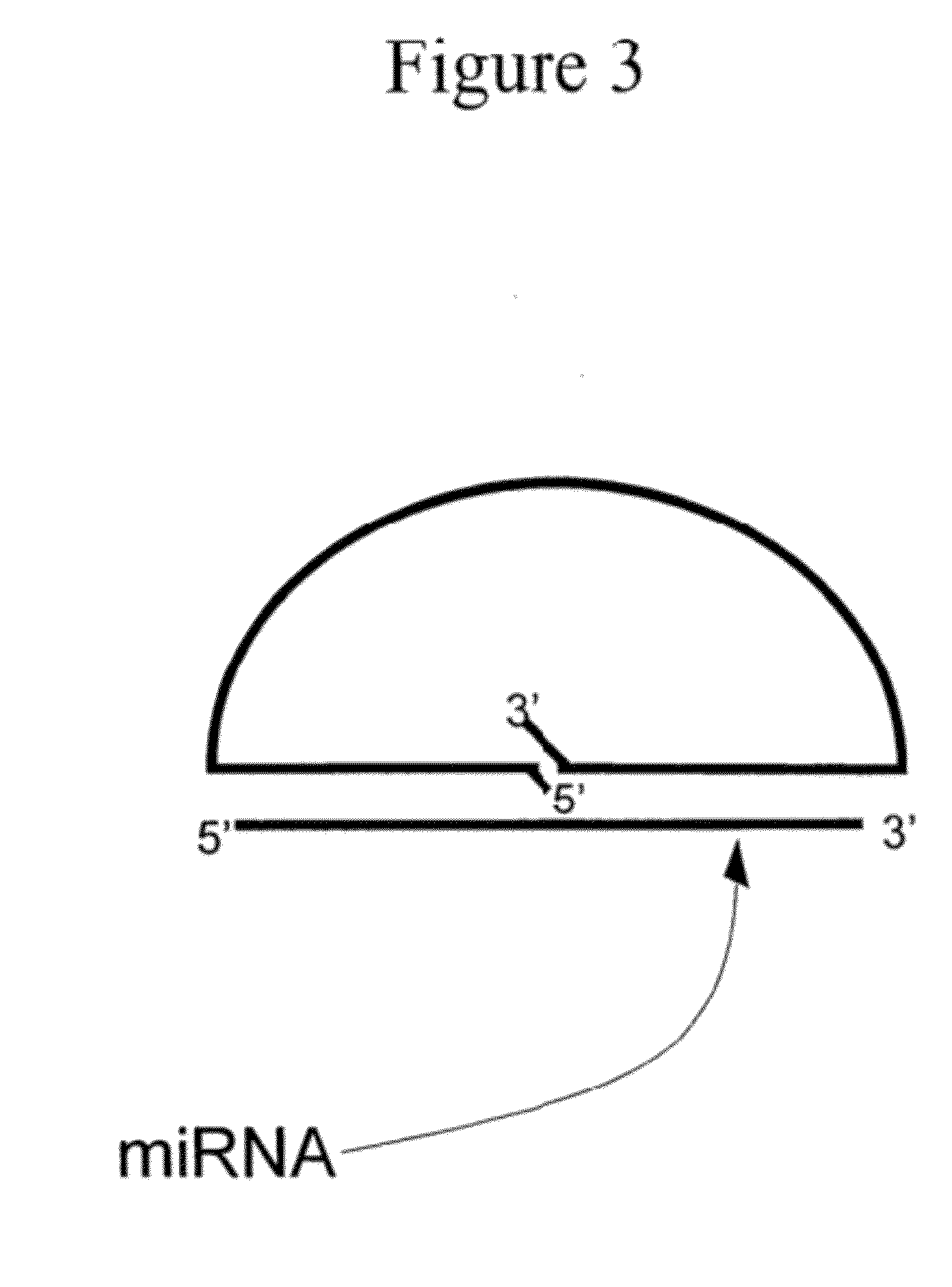
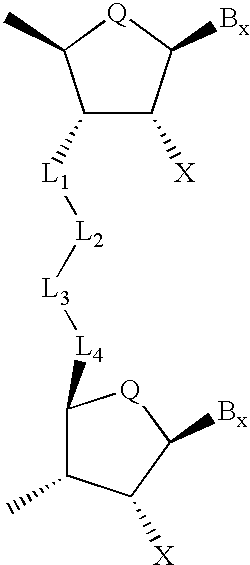Patents
Literature
246 results about "Rna expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
RNA expression profiling of biological models to identify which genes are expressed and which pathways are active in biological systems under different conditions is central to unraveling how genes control biology.
Solution-based methods for RNA expression profiling
The present invention is directed to novel high-throughput, low-cost, and flexible solution-based methods for RNA expression profiling, including expression of microRNAs and mRNAs.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
DECREASING GENE EXPRESSION IN A MAMMALIAN SUBJECT IN VIVO VIA AAV-MEDIATED RNAi EXPRESSION CASSETTE TRANSFER
InactiveUS20050019927A1High efficacyStrong specificityVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsDecreased ConcentrationIn vivo
Decreasing the expression of genes in a mammalian subject has multiple applications ranging from cancer therapy to anti-infective therapy or treatment of autosomal dominant genetic disorders. Yet, there is still a lack of efficient technologies to achieve that goal in mammalian subjects in vivo. The present invention relates to methods for decreasing gene expression by administering to a mammalian subject a recombinant adeno-associated viral vector in vivo with said vector comprising an RNA interference (RNAi) expression cassette whose RNA expression products directly or indirectly lead to a decrease in expression of the corresponding RNAi target gene. Upon successful transduction with the recombinant adeno-associated viral vector, the RNA expression products of the RNAi expression cassette will decrease the cellular concentration of the mRNA transcripts of the RNAi target gene, thus resulting in decreased concentration of the protein encoded by the RNAi target gene.
Owner:HILDINGER MARKUS +1
Human Cancer micro-RNA Expression Profiles Predictive of Chemo-Response
InactiveUS20130059015A1High likelihood of effectivenessHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideHuman cancerRna expression
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
Enhanced biodistribution of oligomers
This invention relates generally to oligomers useful for modulating expression and / or activity of RNAs or genes. More particularly, the invention relates to single stranded, double stranded, partially double stranded and hairpin structured chemically modified oligomers that have a broad biodistribution profile for inhibiting RNA expression in a plurality of cells, tissues, or organs, and to methods of making and using the modified oligomers.
Owner:GROOVE BIOPHARMA CORP
Compositions and methods for micro-rna expression profiling of cancer stem cells
InactiveUS20120053224A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementControl cellRna expression
The present invention relates compositions and methods for microRNA expression profiling of cancer stem cells. In particular, the invention relates to a method for identifying and / or diagnosing one or more cancer stem cells, the method comprising identifying from a plurality of nucleic acid molecules, each encoding a microRNA sequence, one or more nucleic acid molecules are differentially expressed in the cancer stem cells and in one or more control cells, wherein the one or more differentially expressed nucleic acid molecules together represent a nucleic acid expression signature that is indicative for the presence of cancer stem cells. The invention further relates to a corresponding diagnostic kit of molecular markers, namely the nucleic acid expression signature. Finally, the invention is directed to a method using such nucleic acid expression signatures for preventing the proliferation and / or self-renewal of such cancer stem cells as well as to a corresponding pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:UNIV REGENSBURG
Method for stimulating an immune response
InactiveUS6977073B1Stimulating directed immune responseStimulate immune responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsAbnormal tissue growthHematopoietic cell
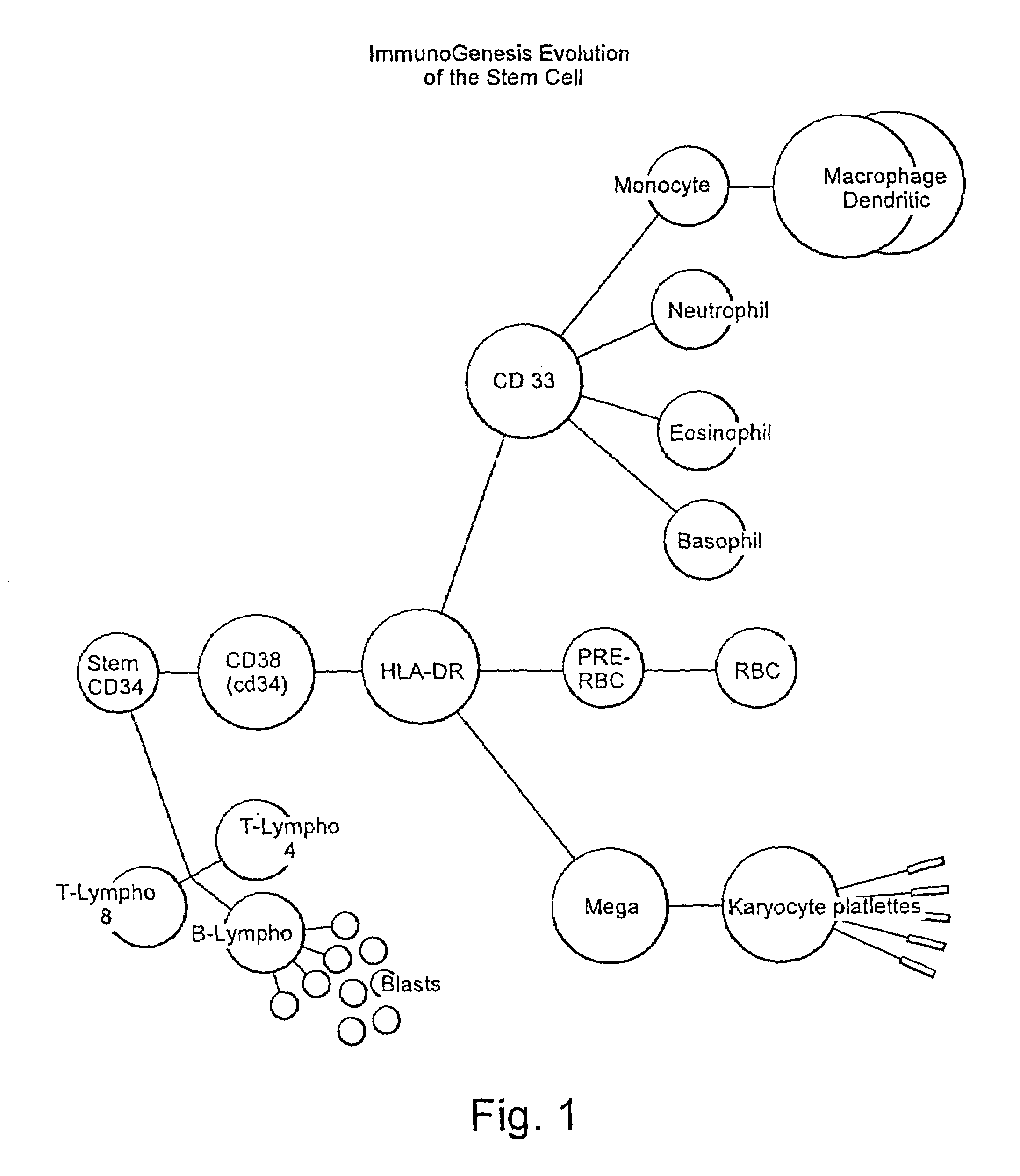
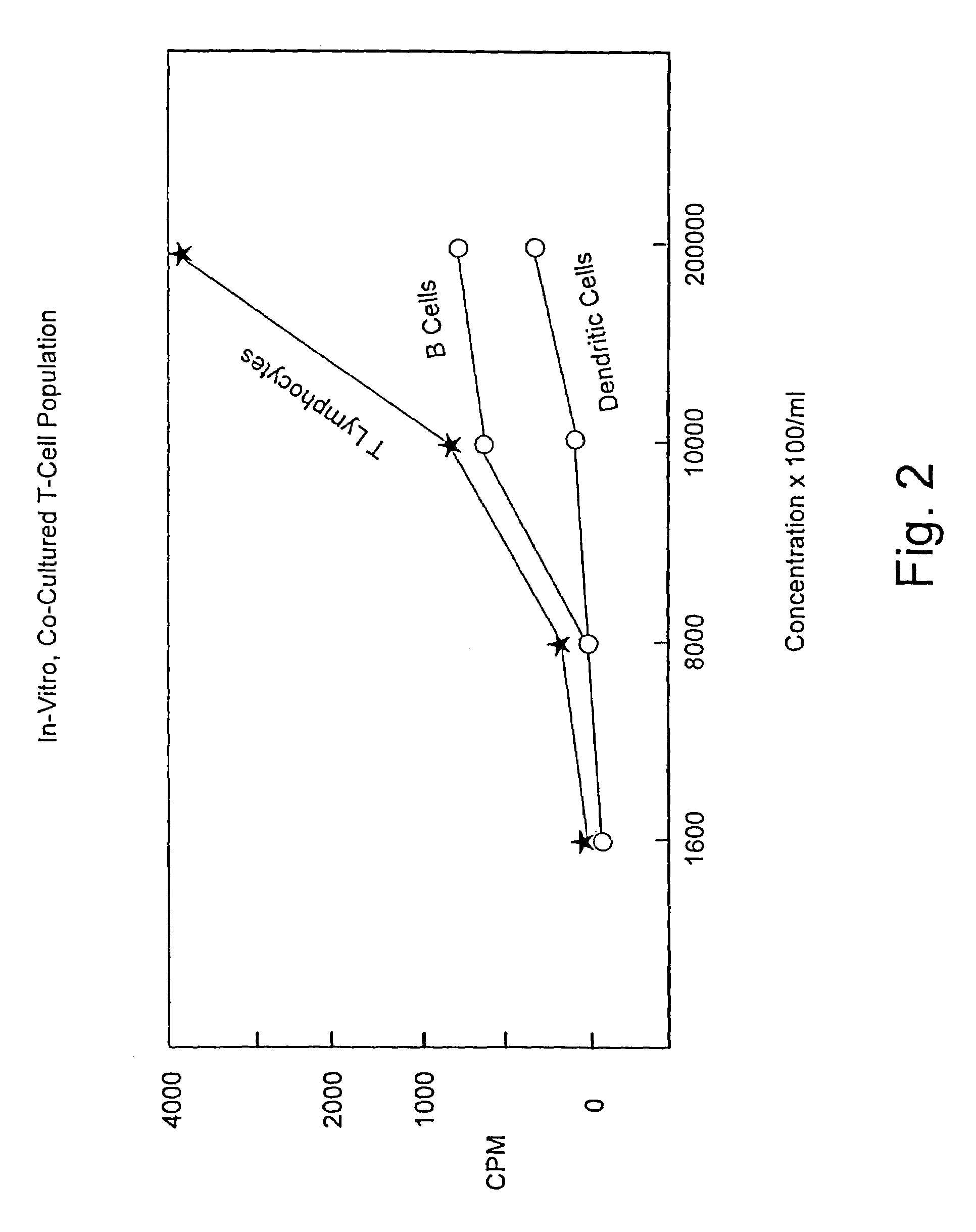
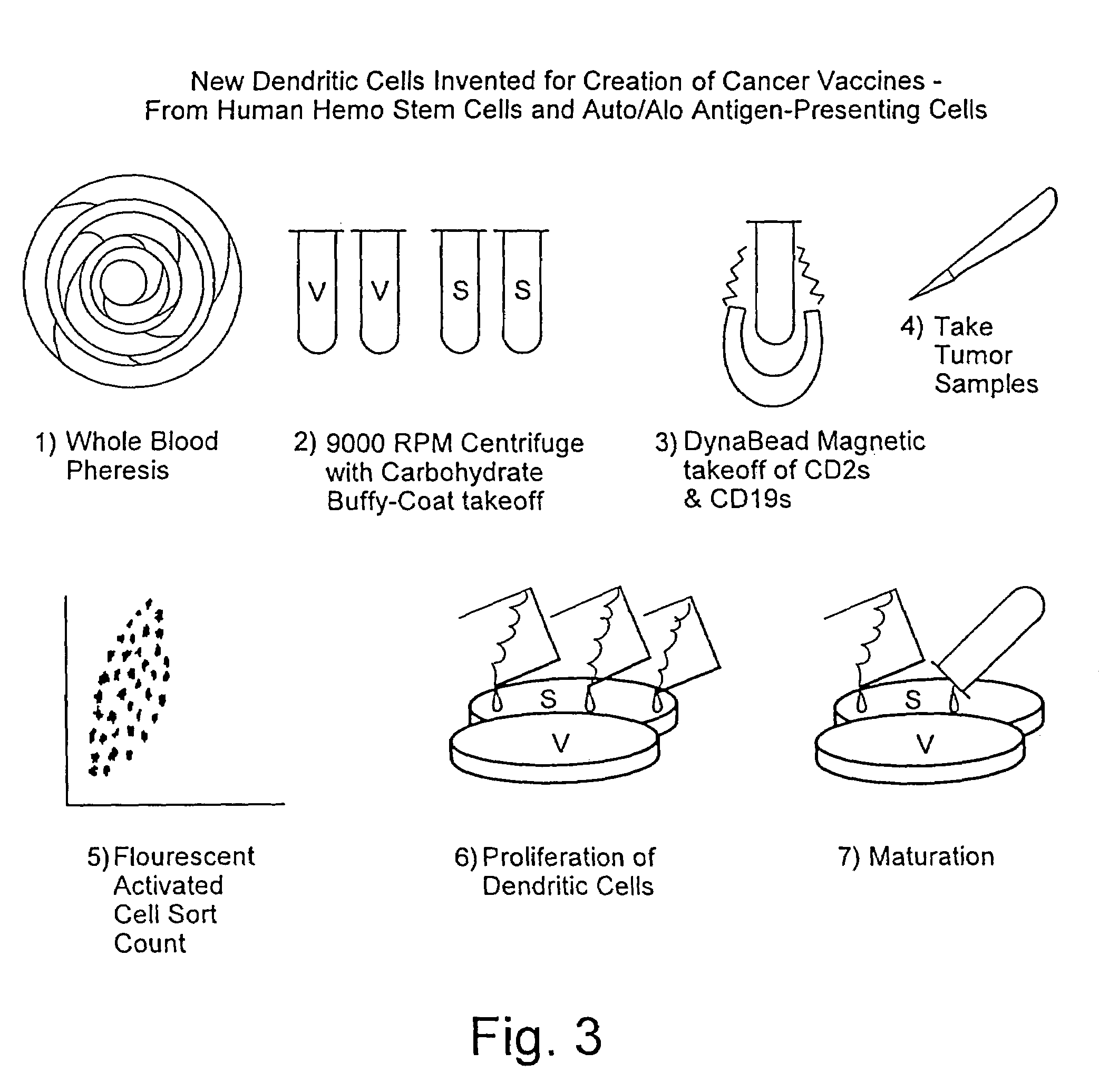
A method is described whereby dendritic cells derived from the CD34+ and CD 34−hematopoietic cell lineages are directed to become programmable antigen presenting cells. The programmed cells may be pulsed with tumor cell RNA or tumor cell RNA expression products. The protocol provides for directing the maturation of dendritic cells to become antigen presenting cells. The protocol further provides for isolating tumor cell RNA from biopsy material that has been prepared in paraffin block storage. The directed dendritic cell is provided with a plurality of tumor markers by using tumor RNA in toto, the poly A+RNA fraction or the expression product of such RNA. Once activated the dendritic cells are incubated with T4 and T8 lymphocytes to stimulate and sensitize the T lymphocytes which upon introduction either into a donor host or a nondonor recipient will provide immune response protection.
Owner:CEZAYIRLI CEM
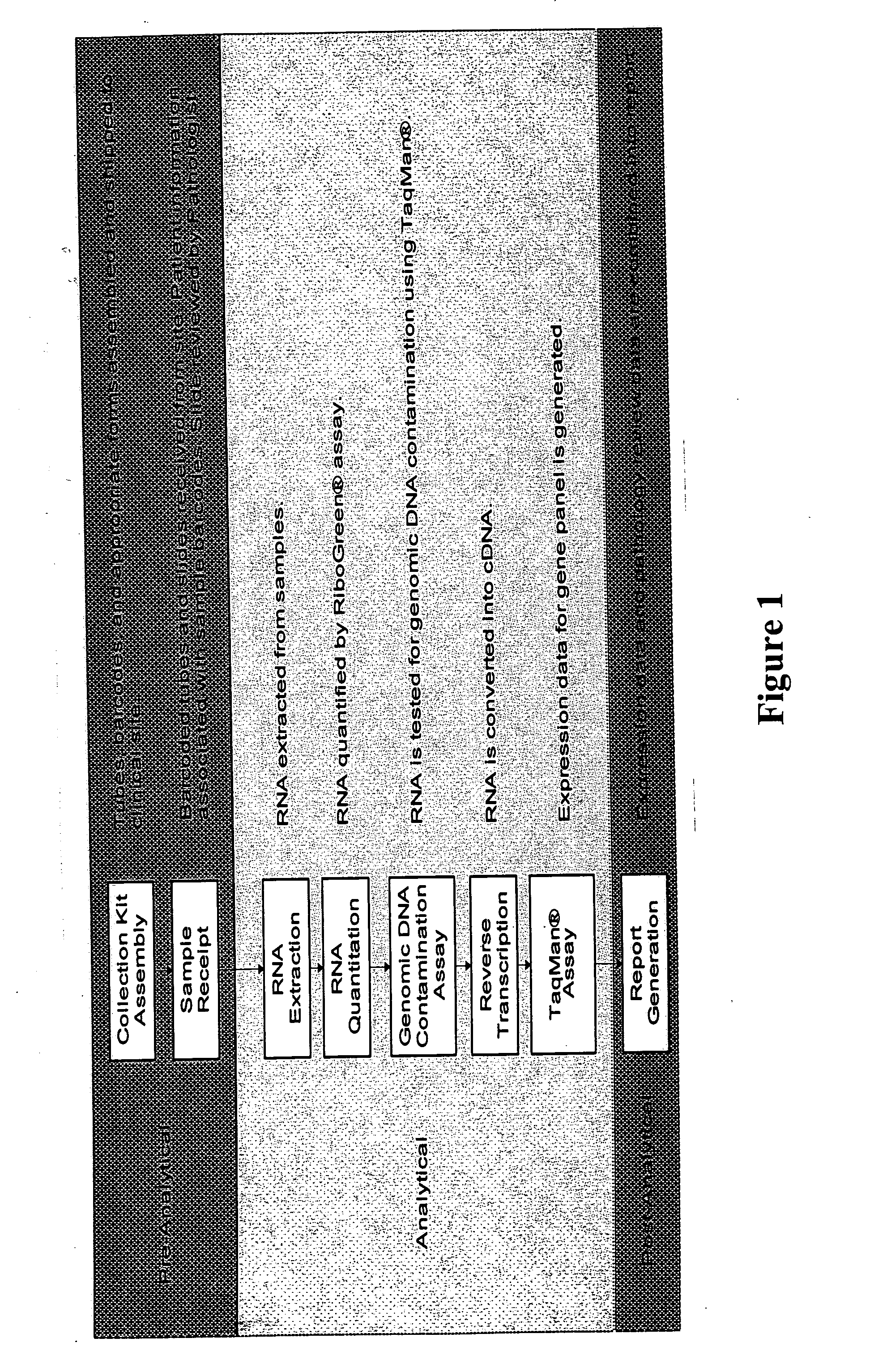
qRT-PCR assay system for gene expression profiling
InactiveUS20050095634A1High precisionSensitive highMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMulti analytePcr assay
The invention concerns an integrated, qRT-PCR-based system for analyzing and reporting RNA expression profiles of biological samples. In particular, the invention concerns a fully optimized and integrated multiplex, multi-analyte method for expression profiling of RNA in biological samples, including fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples. The gene expression profiles obtained can be used for the clinical diagnosis, classification and prognosis of various pathological conditions, including cancer.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Heteroatomic oligonucleoside linkages
InactiveUS6087482AEnhanced cellular uptakeImprove propertiesGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSugar derivativesRna expressionOligonucleotide
PCT No. PCT / US94 / 03536 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 18, 1995 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 18, 1995 PCT Filed Mar. 30, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO94 / 22886 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 13, 1994Oligonucleotide-mimicking macromolecules that have improved nuclease resistance are provided. Replacement of the normal phosphorodiester inter-sugar linkages found in natural oligonucleotides with four atom linking groups provide unique compounds that are useful in regulating RNA expression and in therapeutics. Methods of synthesis and use also are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
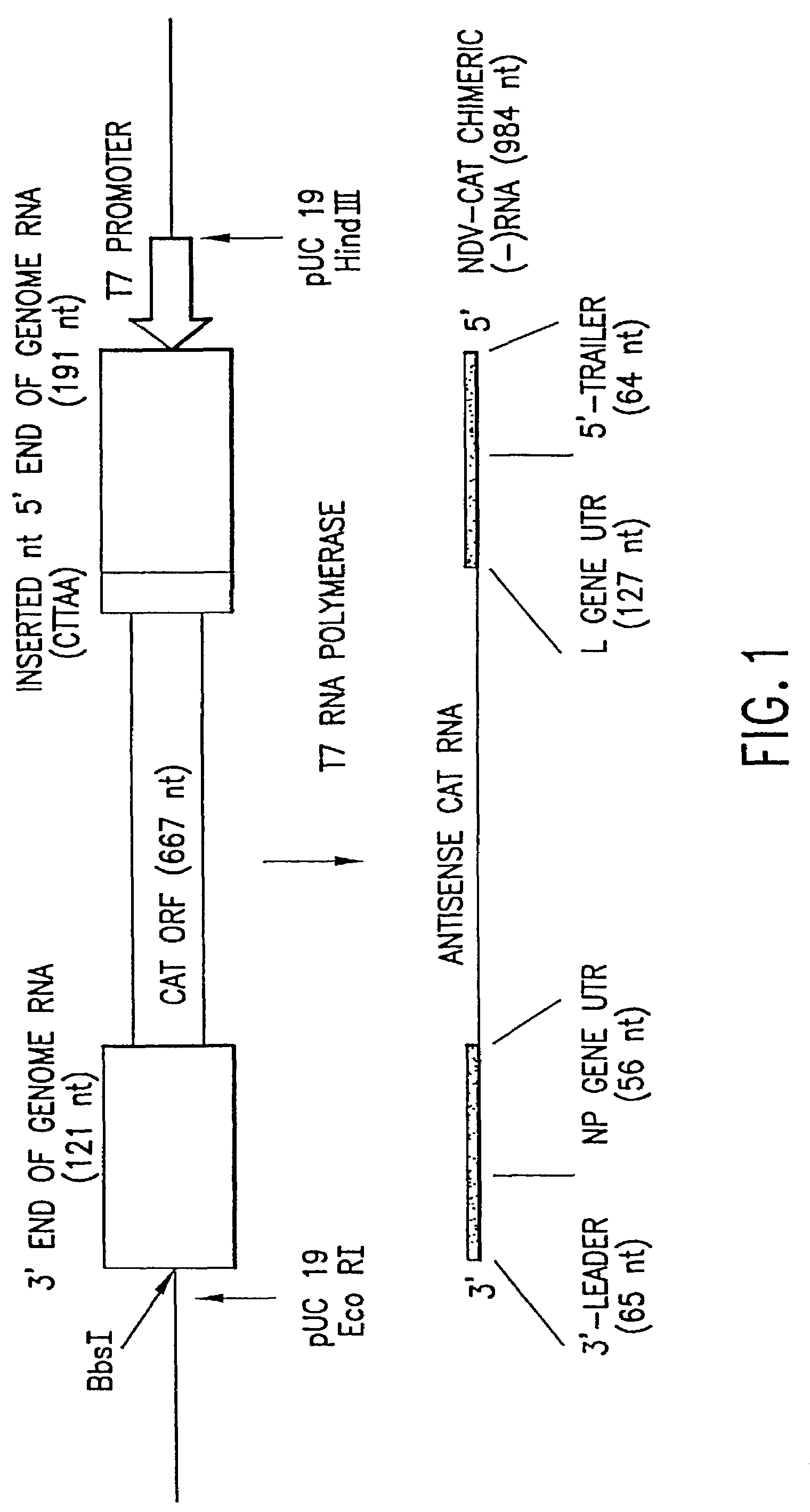
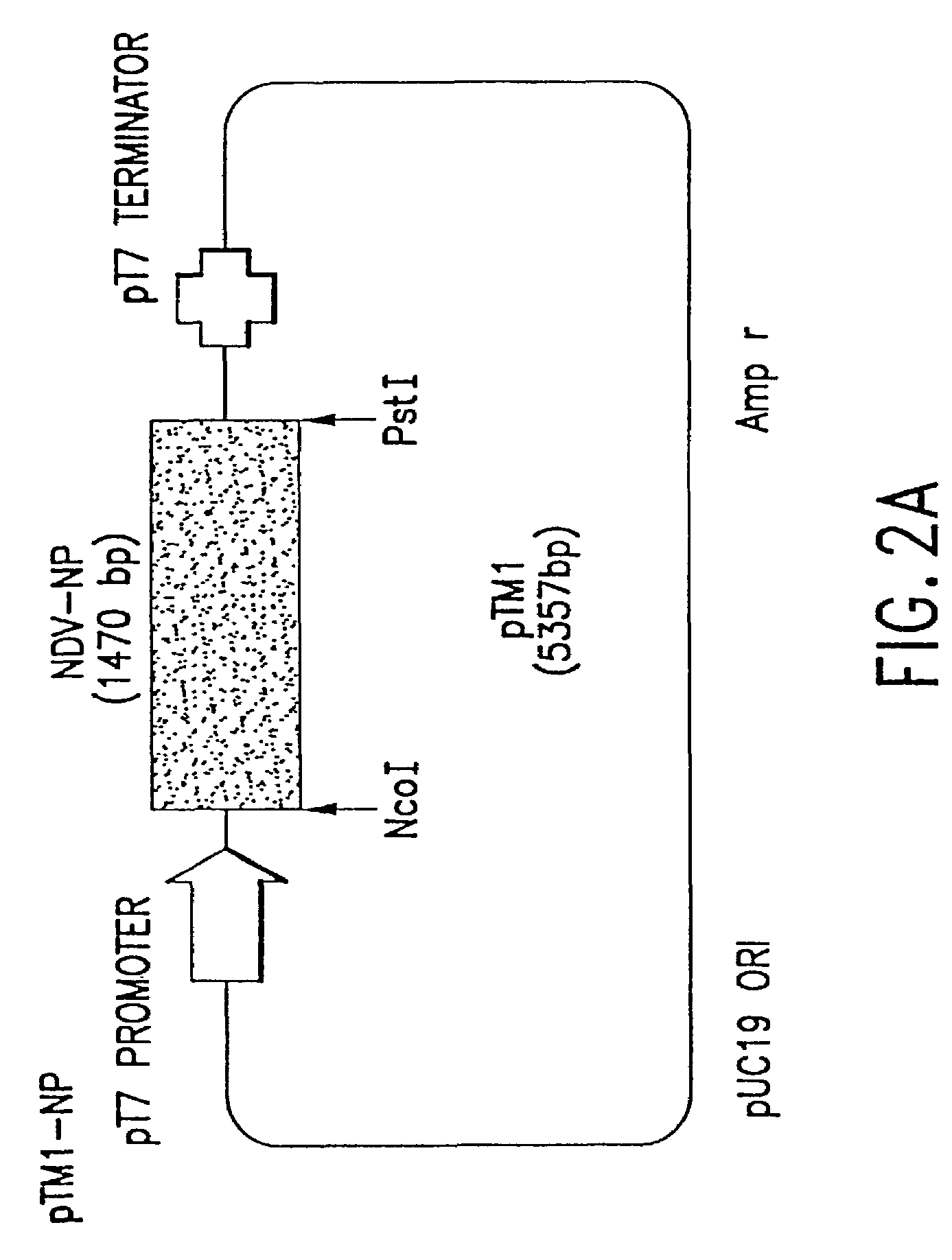
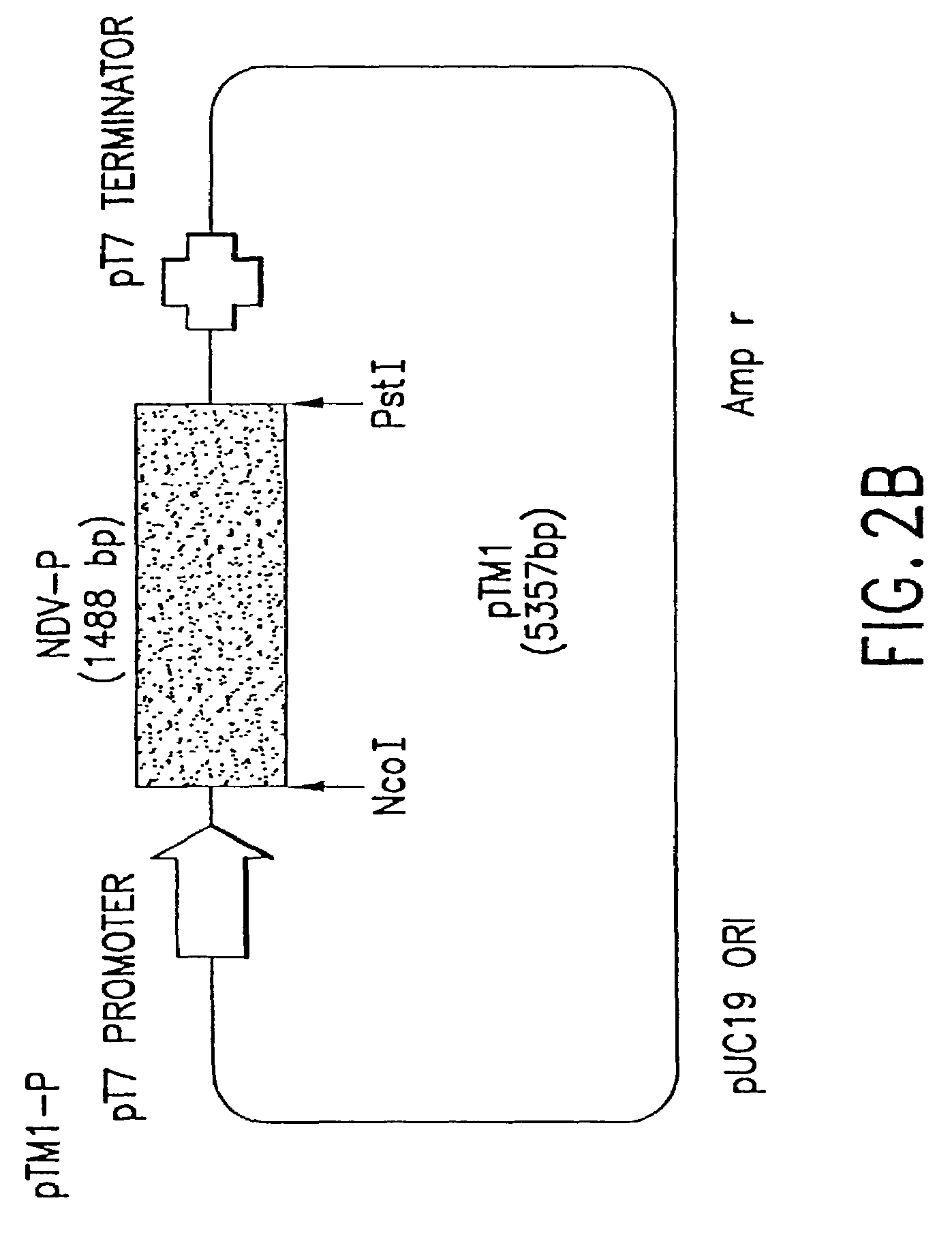
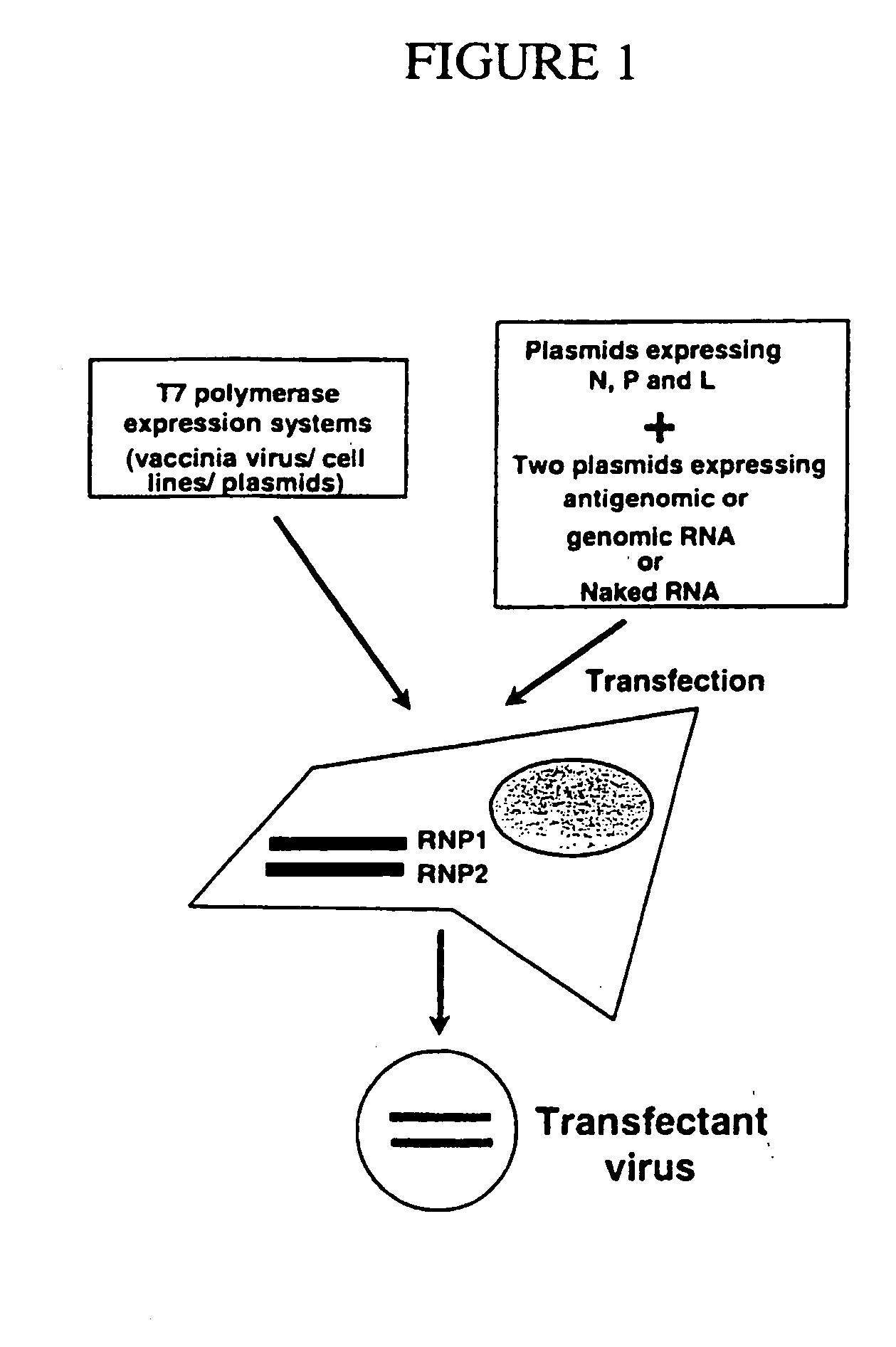
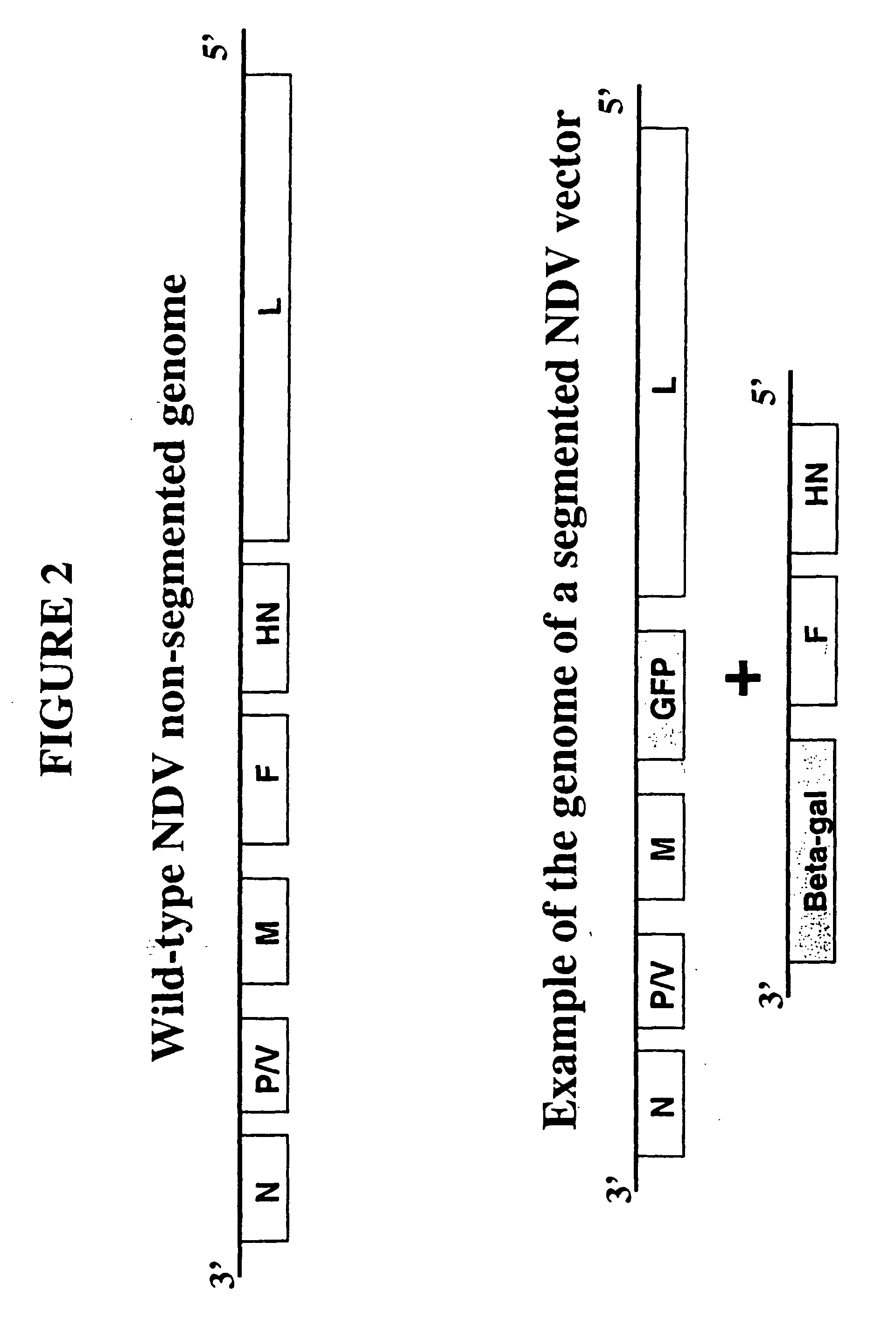
Recombinant Newcastle disease virus RNA expression systems and vaccines
This invention relates to genetically engineered Newcastle disease viruses and viral vectors which express heterologous genes or mutated Newcastle disease viral genes or a combination of viral genes derived from different strains of Newcastle disease virus. The invention relates to the construction and use of recombinant negative strand NDV viral RNA templates which may be used with viral RNA-directed RNA polymerase to express heterologous gene products in appropriate host cells and / or to rescue the heterologous gene in virus particles. In a specific embodiment of the invention, the heterologous gene product is a peptide or protein derived from the genome of a human immunodeficiency virus. The RNA templates of the present invention may be prepared by transcription of appropriate DNA sequences using any DNA-directed RNA polymerase such as bacteriophage T7, T3, SP6 polymerase, or eukaryotic polymerase I.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
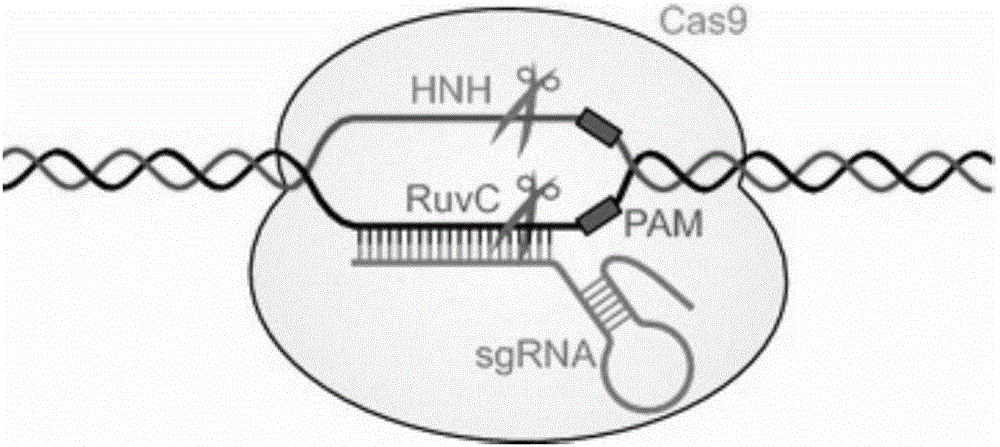
Establishment method of caffeine synthetase CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing vector
InactiveCN105821075ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme digestionGolden Gate Cloning
The invention relates to an establishment method of a caffeine synthetase CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing vector. The method comprises the following steps: designing two target sequences T1 and T2 on the basis of tea tree caffeine synthetase genes; respectively establishing sgRNA expression cassettes of the target sequences T1 and T2; and carrying out enzyme digestion-coupling reaction on a double-element expression vector pYLCRISPR / Cas9P35S-H, the T1sgRNA expression cassette and the T2sgRNA expression cassette so that the T1sgRNA expression cassette and the T2sgRNA expression cassette are connected and inserted into the double-element expression vector, thereby obtaining the CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing vector. By taking the tea tree caffeine synthetase as the example, conventional PCR (polymerase chain reaction), Overlapping PCR and Golden Gate Cloning techniques are combined to establish the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing vector comprising the tea tree caffeine synthetase double targets, thereby laying a solid foundation for application of the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technique in tea trees, and providing technical supports for the establishment of CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing vectors of other plants.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Compositions and methods for micro-rna expression profiling of colorectal cancer
ActiveUS20110281756A1Reliable discriminationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementControl cellRna expression
The present invention relates compositions and methods for microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling of colorectal cancer. In particular, the invention relates to a diagnostic kit of molecular markers for identifying one or more mammalian target cells exhibiting or having a predisposition to develop colorectal cancer, the kit comprising a plurality of nucleic acid molecules, each nucleic acid molecule encoding a miRNA sequence, wherein one or more of the plurality of nucleic acid molecules are differentially expressed in the target cells and in one or more control cells, and wherein the one or more differentially expressed nucleic acid molecules together represent a nucleic acid expression signature that is indicative for the presence of or the predisposition to develop colorectal cancer. The invention further relates to corresponding methods using such nucleic acid expression signatures for identifying one or more mammalian target cells exhibiting or having a predisposition to develop colorectal cancer as well as for preventing or treating such a condition. Finally, the invention is directed to a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention and / or treatment of colorectal cancer.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
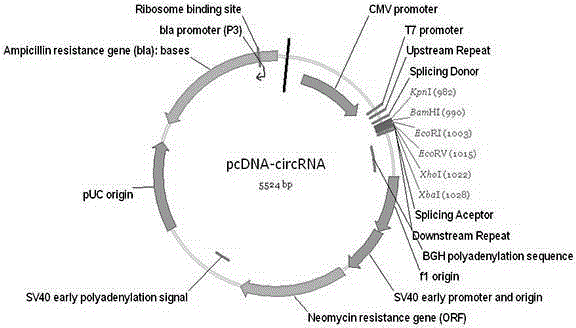
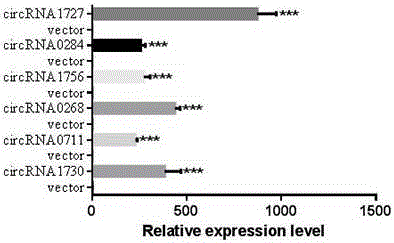
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence used for circular RNA (ribonucleic acid) expression, expression vector and applications of DNA sequence and expression vector
ActiveCN105176981AGood expression vectorSimple and fast operationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseRna expression
The invention provides a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence used for circular RNA (ribonucleic acid) expression and a vector containing the DNA sequence used for circular RNA expression. The vector is inserted in a eukaryotic expression vector, a lentiviral vector, an adenovirus vector or a retroviral vector to form a series of special expression vectors for circRNA. The DNA sequence and the corresponding expression vector have the best effects, are simple and convenient to operate and are stable in results and efficient in expression (the circRNA expression level is increased by more than a hundredfold). The sequence and the corresponding vector can be widely applied to expression of various circRNA, provide a powerful research tool for the functions and mechanisms of circRNA and provide theoretical support for research and development of further determination of circRNA molecules as novel markers and disease treatment targets.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FOREVERGEN HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Recombinant negative strand virus rna expression systems and vaccines
ActiveUS20050221489A1Improving immunogenicityAttenuated phenotypeSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsHeterologousNegative strand
The present invention relates to recombinant RNA virus templates derived from and applicable to negative strand naturally non-segmented viruses, including the families Bornaviridae, Filoviridae, and Paramyxoviridae, and methods for generating such recombinant RNA virus templates, wherein the templates are RNA generated from two or more recombinant RNA molecules. The invention relates to the use of segmented recombinant RNA virus templates for naturally non-segmented RNA viruses to express heterologous gene products in appropriate host cell systems and / or to construct recombinant viruses taken from that family and that express, package, and / or present the heterologous gene product. The invention includes the expression products and recombinant and chimeric viruses thus prepared and vaccine and therapeutic formulations comprising the recombinant RNA viruses.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Long chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) gene and application method thereof
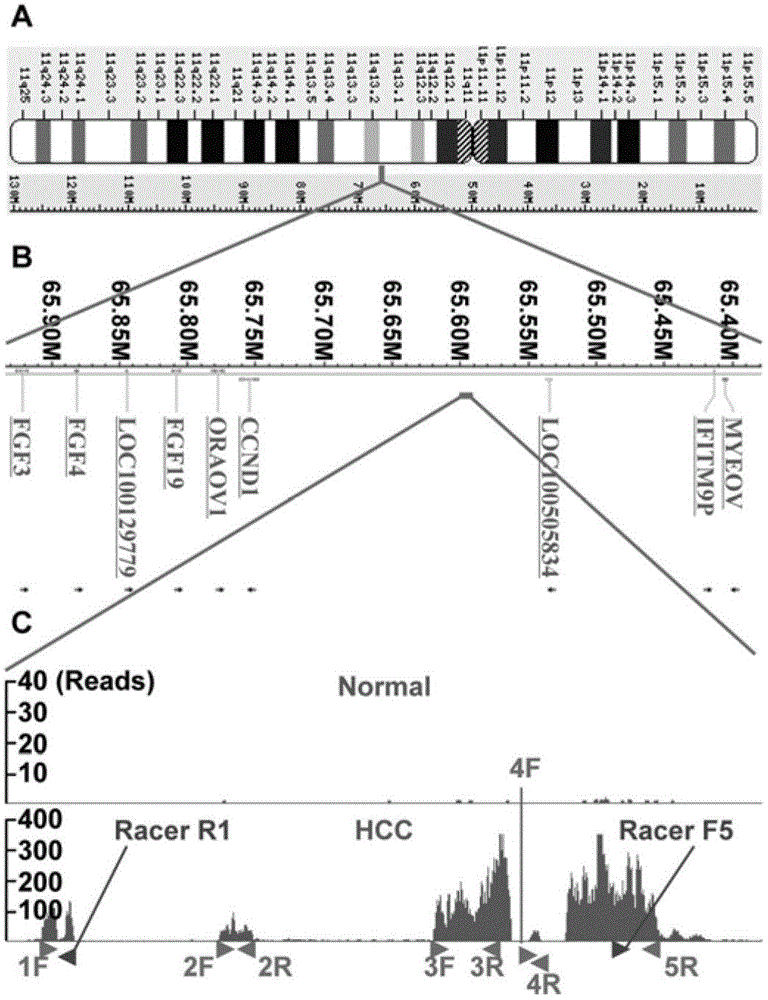
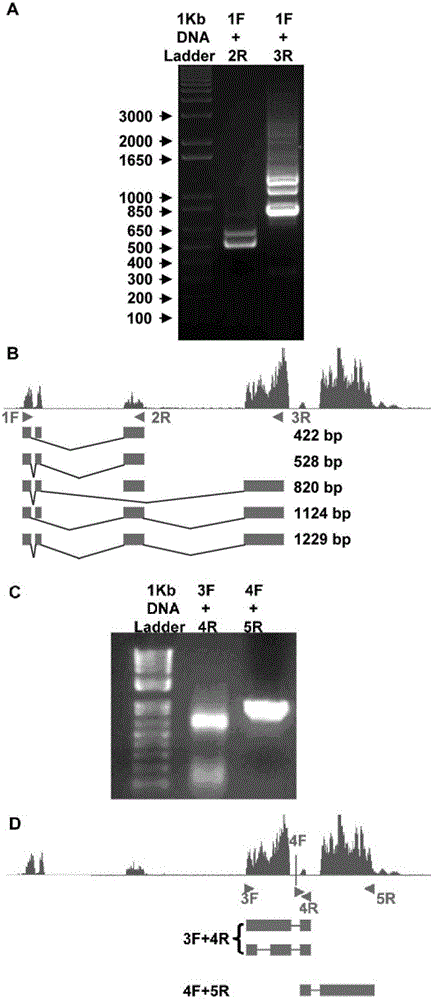
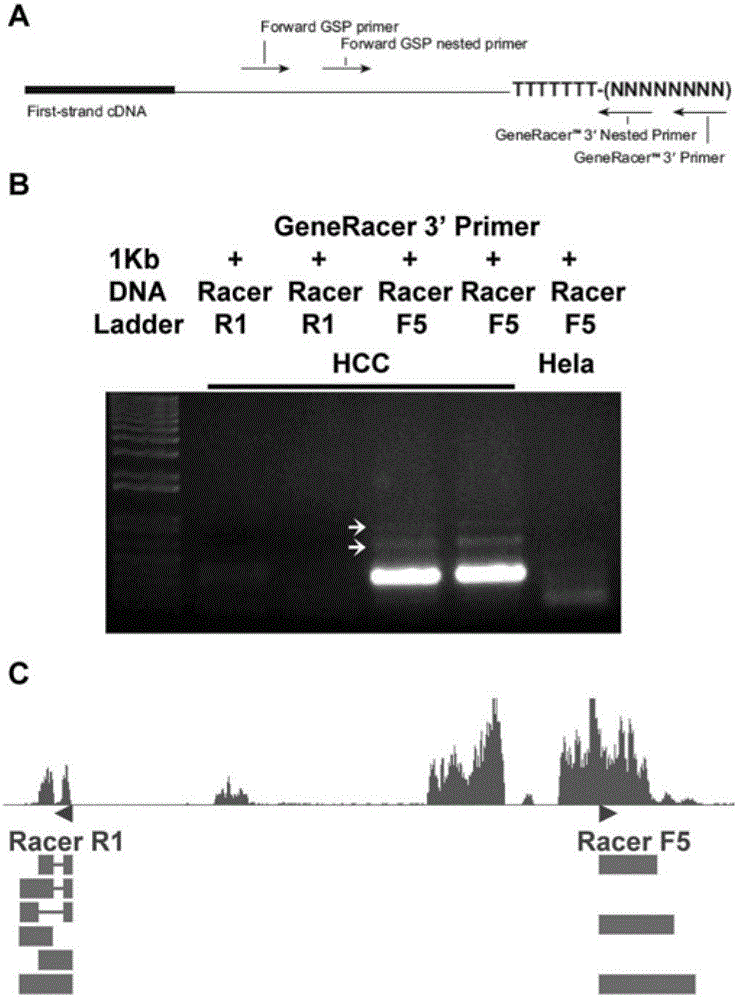
ActiveCN103146693ADeep meaningFar-reaching promotionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExpression vectorRNA interference
The invention relates to a newly cloned full-length sequence of a long chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) gene and an application method thereof. The gene can be detected in a separation sample by methods including a hybrid method or an amplification method; and the gene can be used as a tumor marker, in particular a marker of liver cancer. According to the gene sequence, a real-time quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer and an in situ hybridization probe are designed and synthesized; and by detecting the expression level of the long chain non-coding RNA in a liver cancer clinical case sample, expression of the long chain non-coding RNA in liver cancer is up-regulated remarkably, and prognosis of patients with liver caner with high expression of long chain non-coding RNA is poorer. According to the gene sequence, a RNA eukaryotic expression vector in a short hairpin structure for closing the expression of the long chain non-coding RNA by RNA interference is designed and synthesized; and the expression of the long chain non-coding RN in a liver cancer cell line A is inhibited successfully by using the vector.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
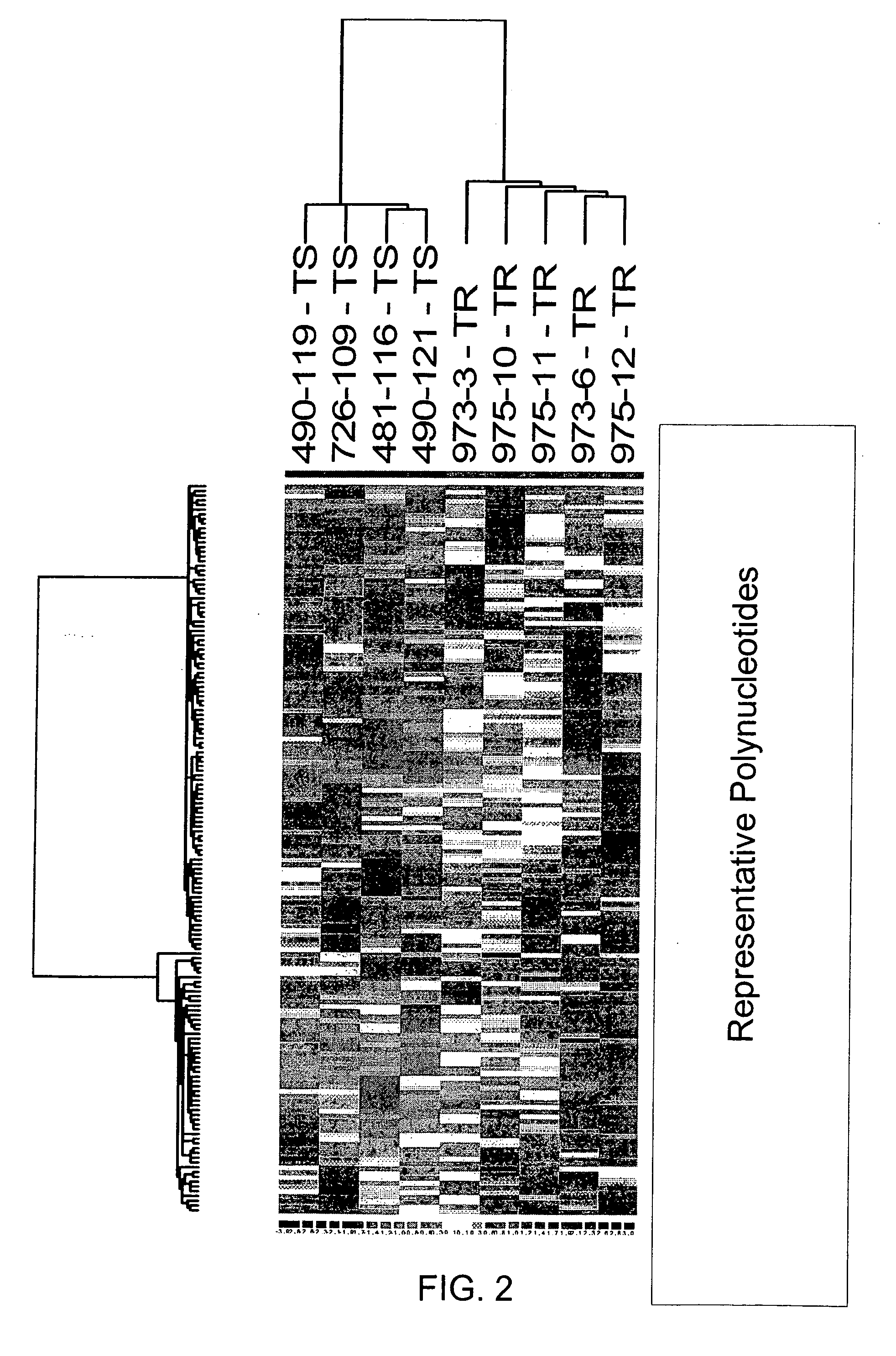
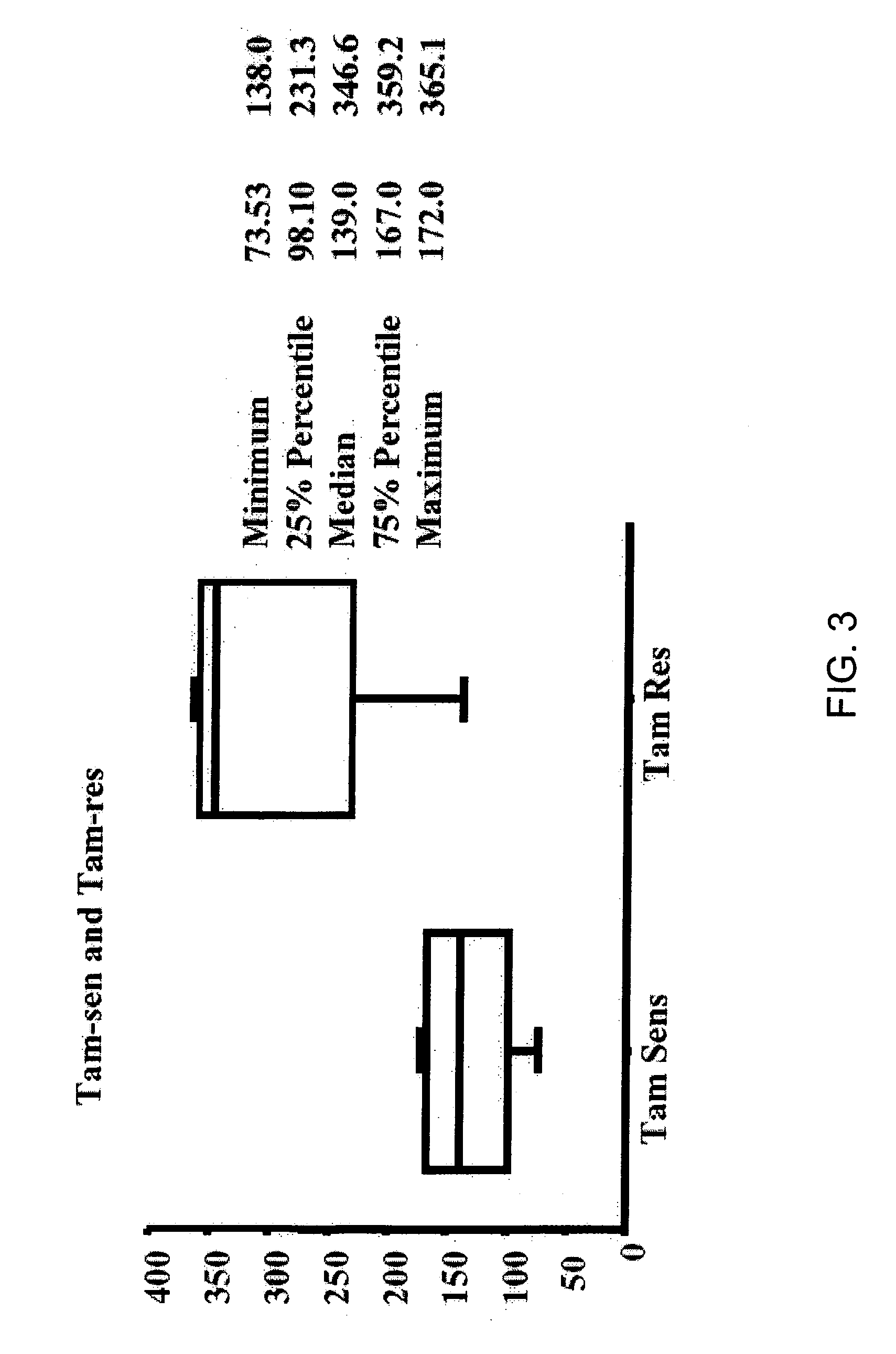
RNA expression profile predicting response to tamoxifen in breast cancer patients
InactiveUS20060246470A1Improve understandingAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDUSP6Rna expression
The present invention regards predicting a response to a therapy using RNA expression profiling. In particular, a resistance to a chemotherapy, such as tamoxifen, is predicted by comparing expressed genes in a patient on the therapy to a patient sensitive to the chemotherapy. In further embodiments, there is an RNA expression profile indicative of tamoxifen resistance in an individual. In additional embodiments, the RNA expression profile comprises DUSP6 EBP50, and / or RhoGDIa.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
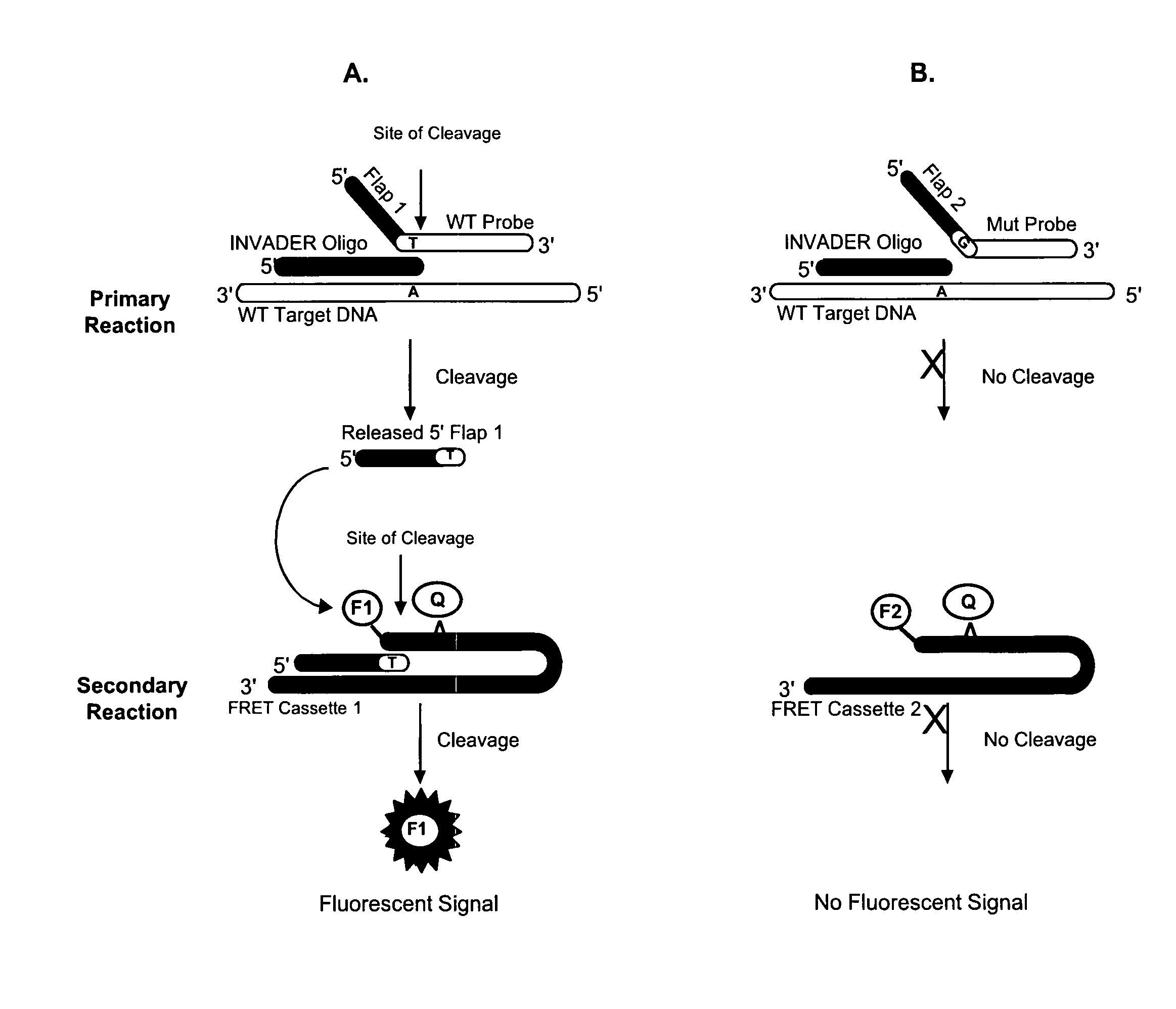
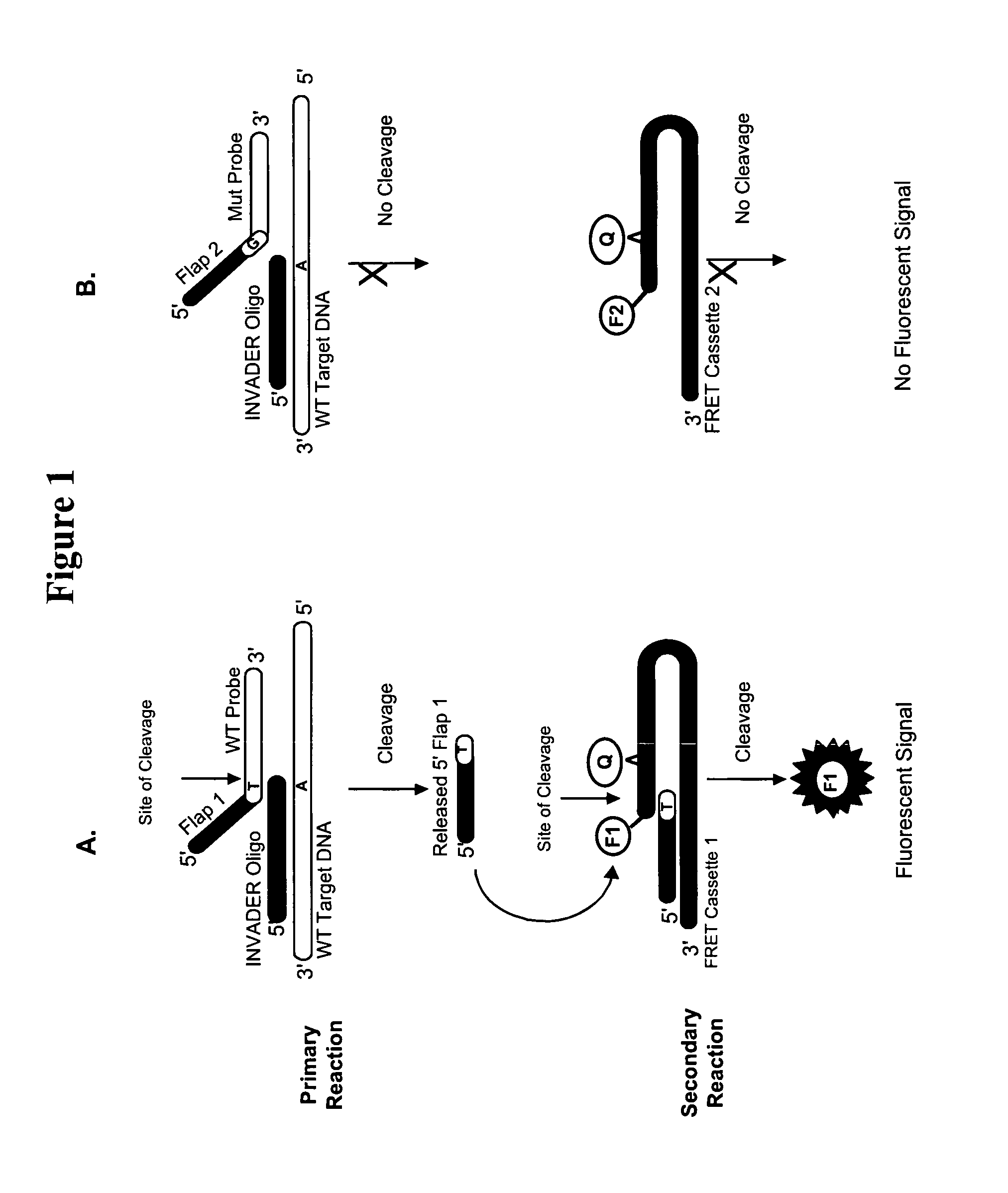
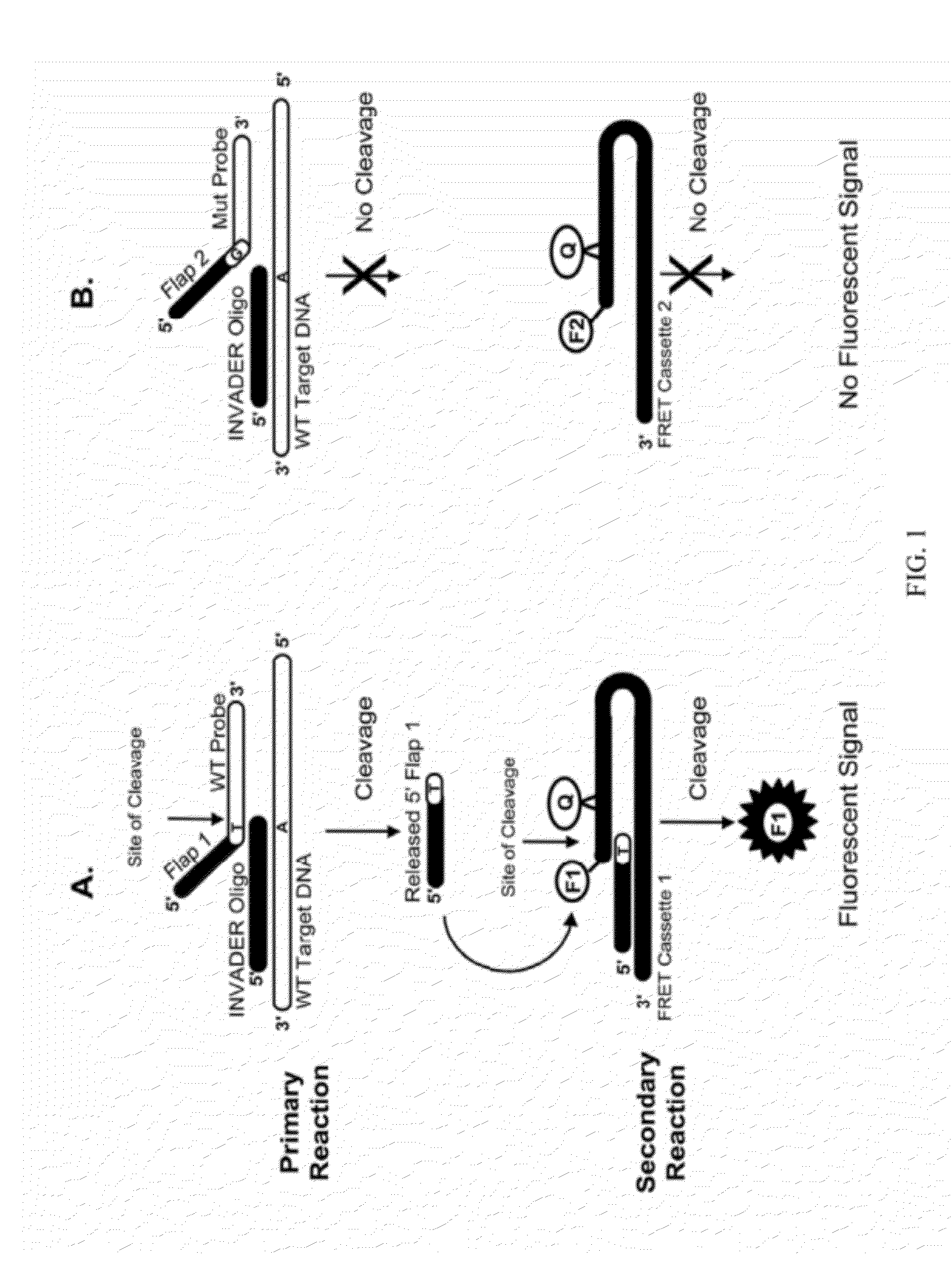
Detection of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20080131890A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRna expressionSmall interfering RNA
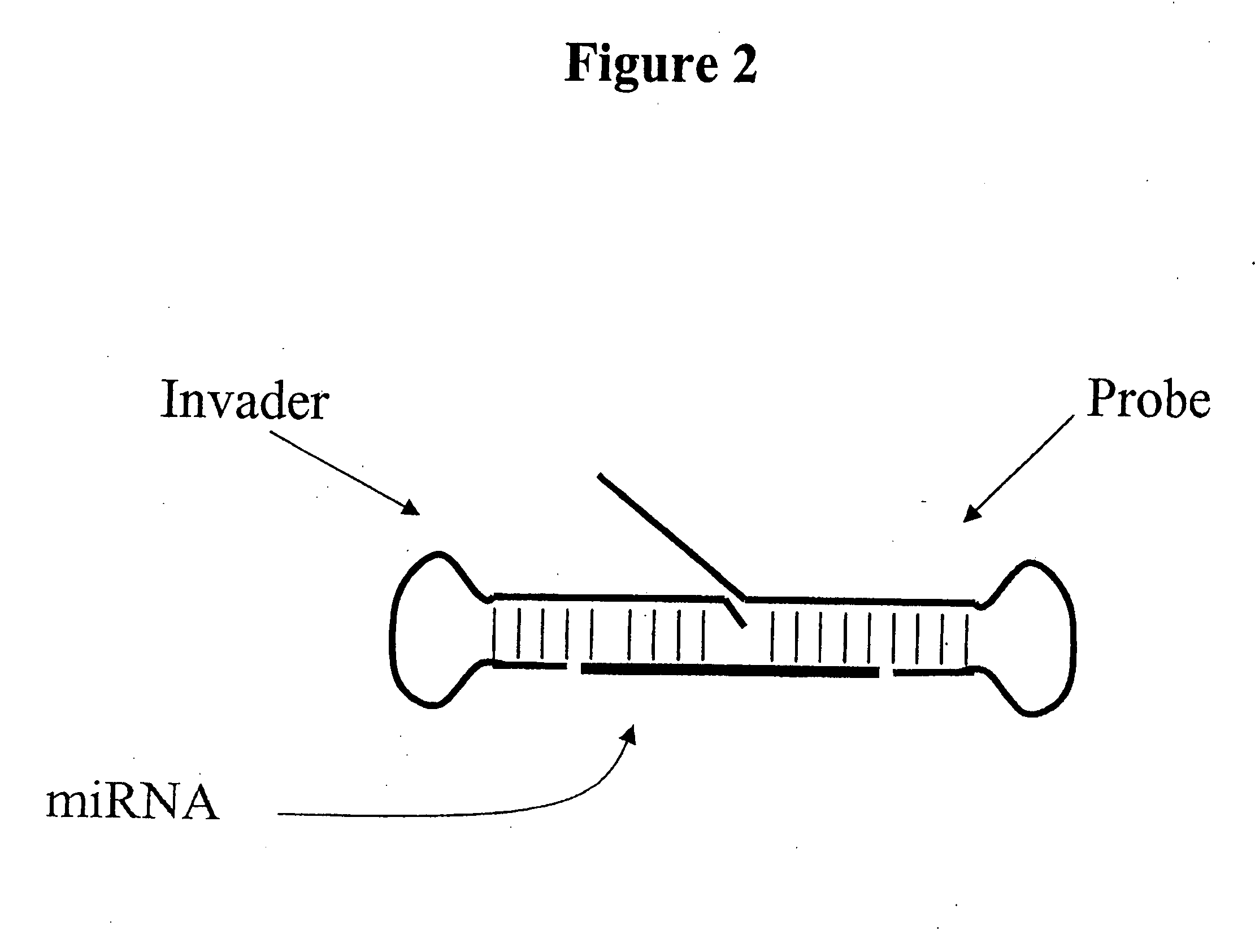
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of small nucleic acid molecules (e.g., RNA (e.g., small RNAs such as micro RNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)) and other short nucleic acid molecules). More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for the detection and quantification of RNA expression. The present invention further provides for the detection of miRNA and siRNA variants.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Method of analysis allowing avoidance of surgery
ActiveUS20170275702A1Prevent removalAvoid surgeryMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisDNA methylationCervix
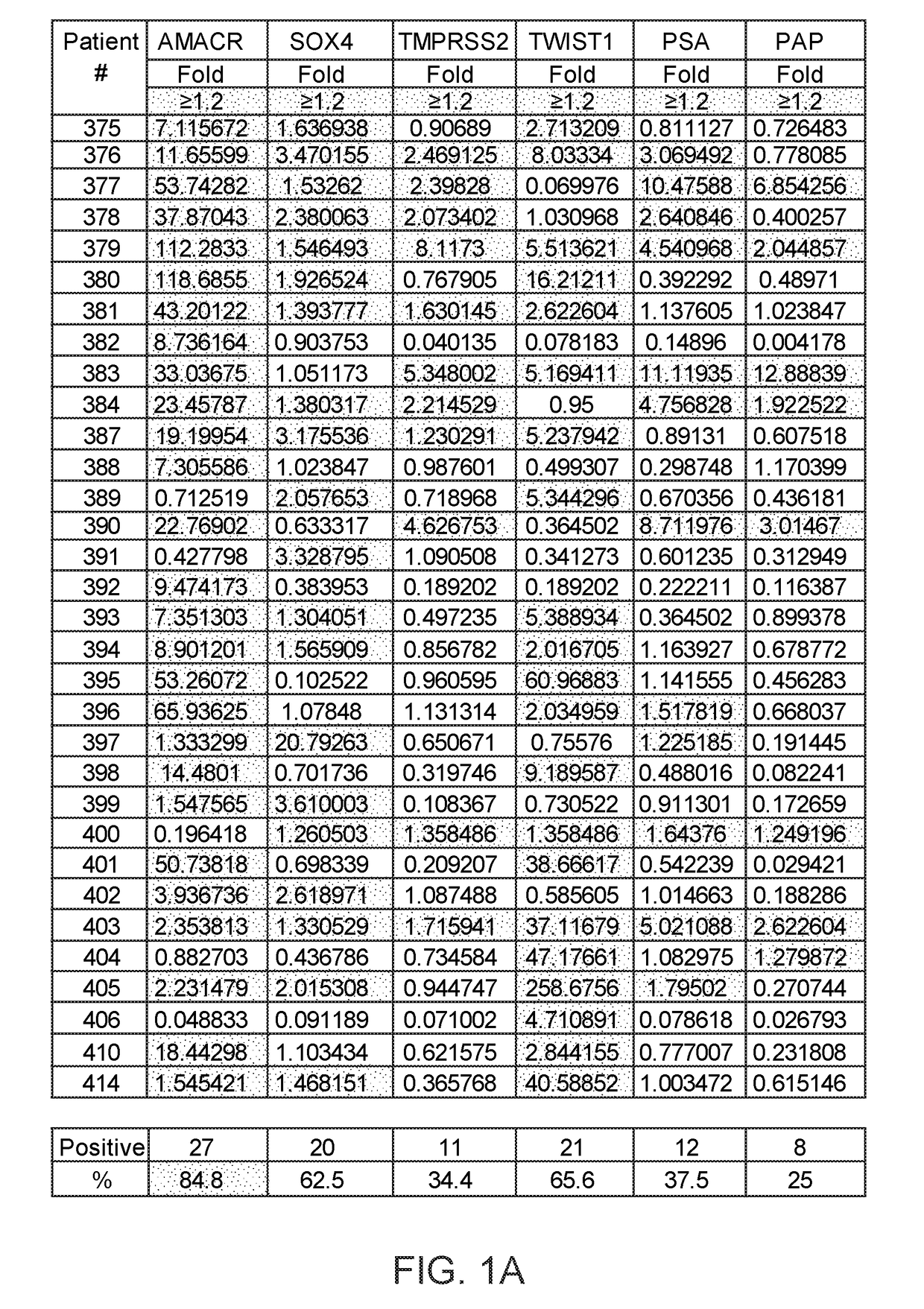
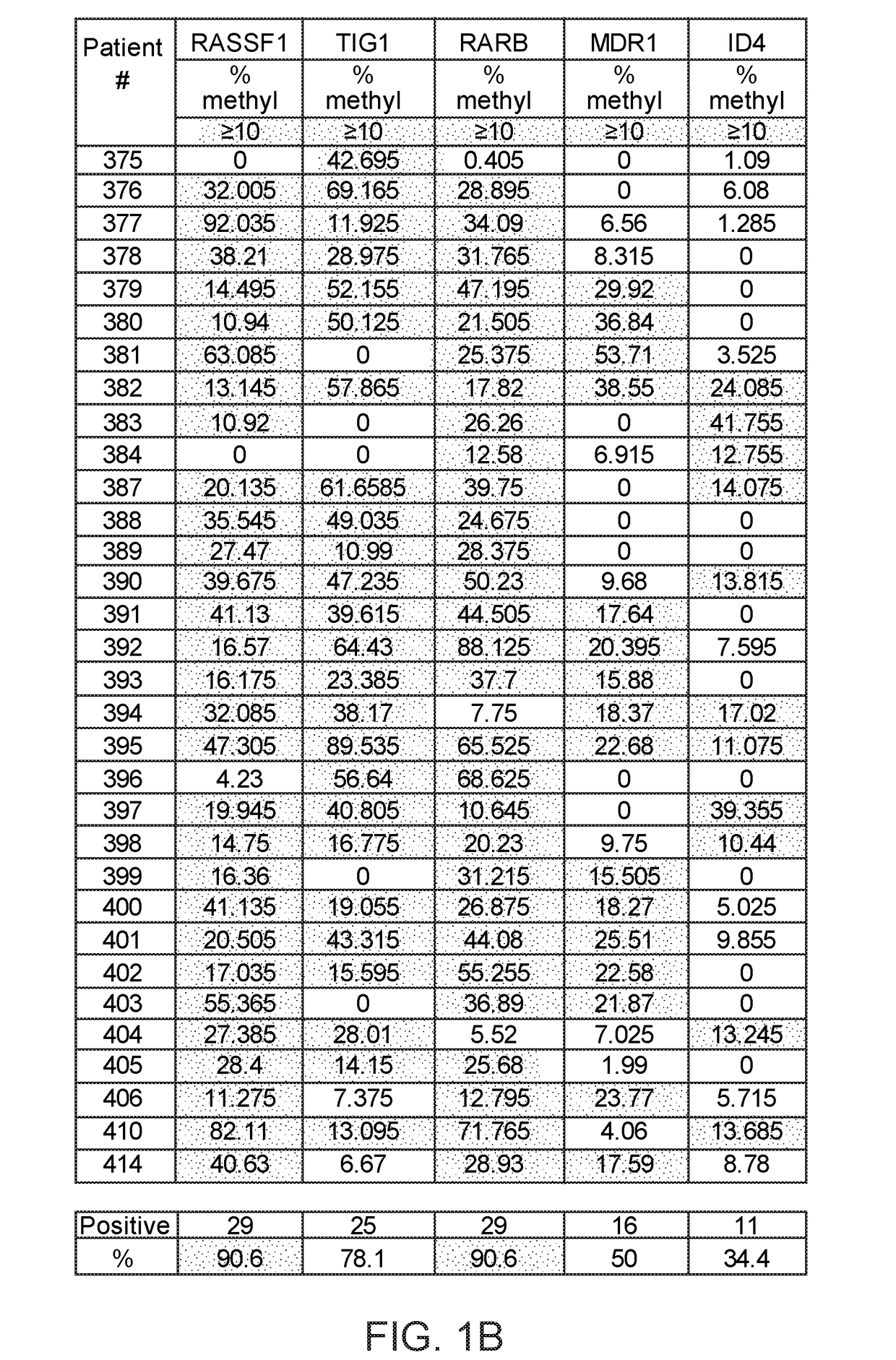
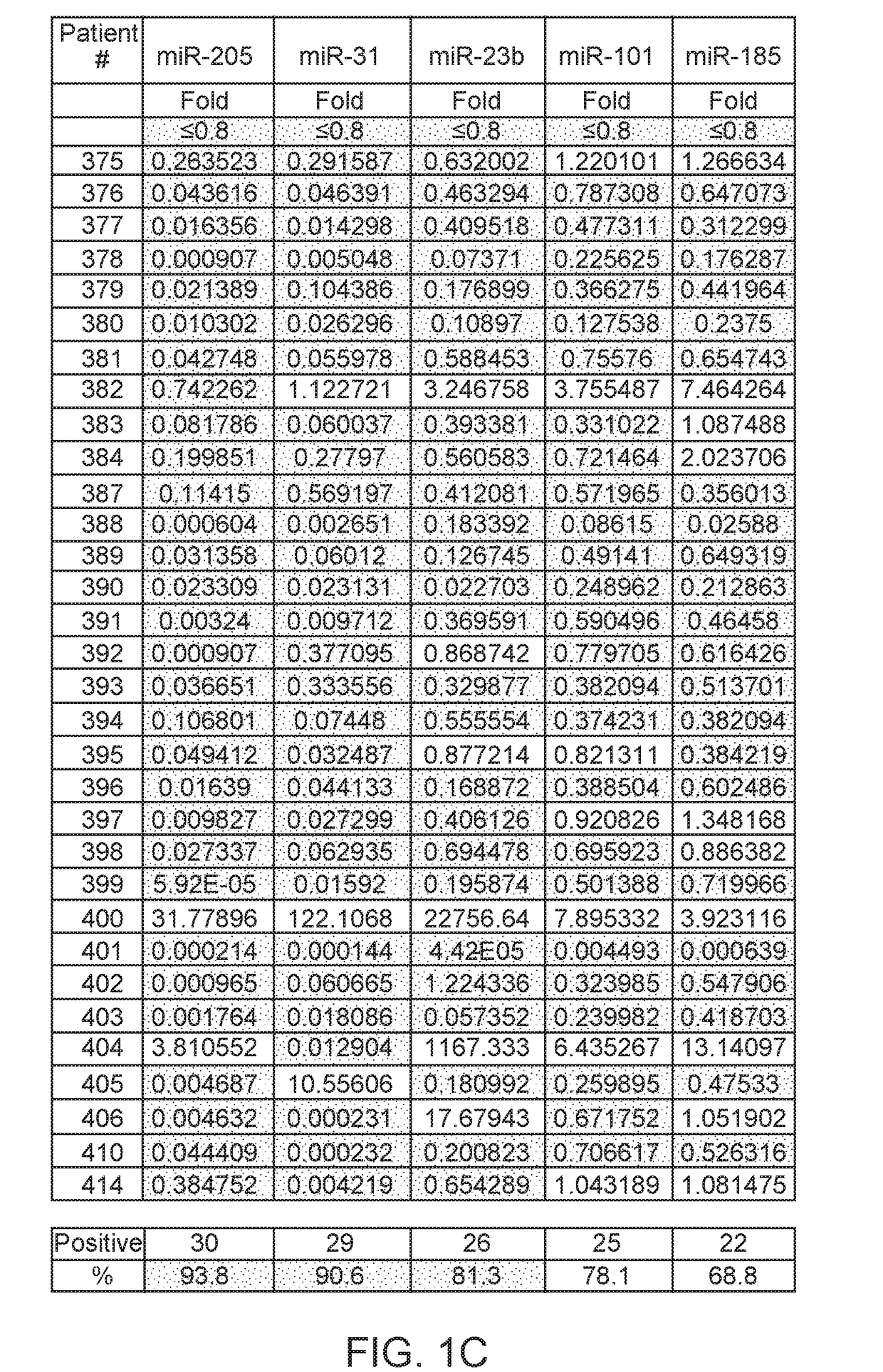
A multi-gene-based assay for analysis of the following: (a) oncogene expression; (b) DNA methylation of tumor suppressor genes; (c) non-coding RNA expression (microRNA profiling); and (d) long non-coding RNA expression in cancer samples is disclosed. The assay method and device for conducting the assay are applicable to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of various cancers such as lung, breast, colorectal, prostate, liver, bladder; kidney, cervix, pancreatic, gastric, brain, oral, endometrium, and ovary. The assay methods allow avoidance of surgery to remove cancerous tissue.
Owner:GENEVERIFY INC
Particle-based multiplex assay system with three or more assay reporters
InactiveUS20060177850A1Increase the number ofImprove abilitiesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsReference sampleDiscriminator
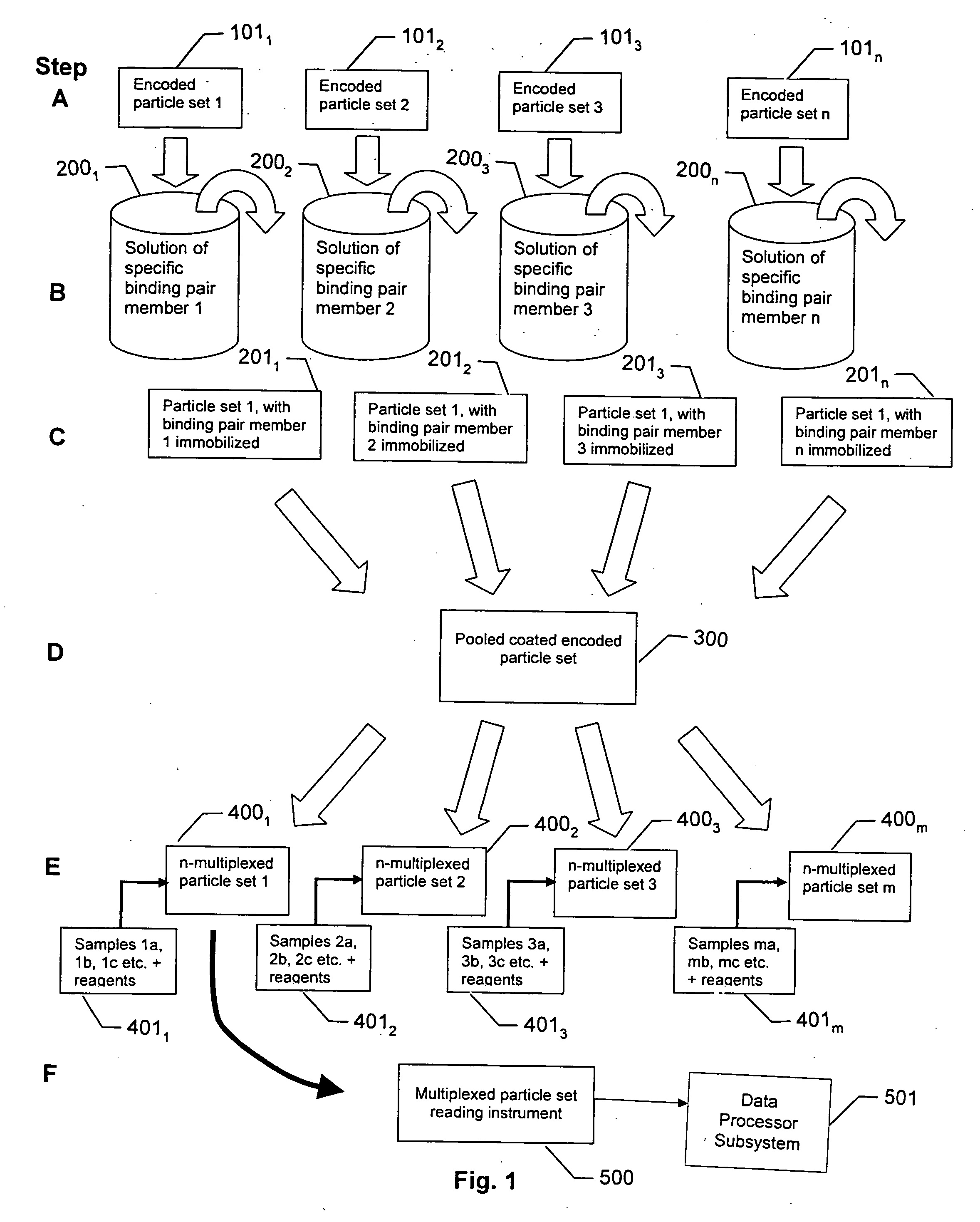
A system and method for developing and utilizing particle-based n-multiplexed assays that include three or more reporters utilizes n particle sets that are associated with particle identification images or labels (IDs) that differ between sets. The encoded particles for a given set are coated with a specific binding member, or in the case of the sandwich assay with coupled capture and detector binding pair members, to form particle types. The sets of particle types are then pooled, and aliquots of the particle types are removed to assay vessels. Next, samples with three or four reporter molecules are supplied to the respective vessels. After one or more incubation periods, the particles are supplied to a reader system, which determines the particle IDs to identify the particle types and also detects the reporter signals. The reader system includes multiple excitation lasers that excite the various reporters in sequence or in parallel, to supply associated signals to one or more detectors. Emission filters and wavelength discriminators are included such that a given detector receives at a given time the signals associated with a single assay binding label. The system further develops greater capacity sandwich assays by assigning subsets of capture and detector antibody pairings to the three or four reporters, respectively. The system performs greater numbers of differential RNA expressions based on the use of the three or more reporters, with one or more reporters assigned to the reference sample and the other reporters assigned to respective test samples. The system and method are also capable of performing greater numbers of SNPs utilizing primer extension reactions, by assigning different color reporters to the respective nucleotides or terminators.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Treatment of cancer by inhibiting BRAF expression
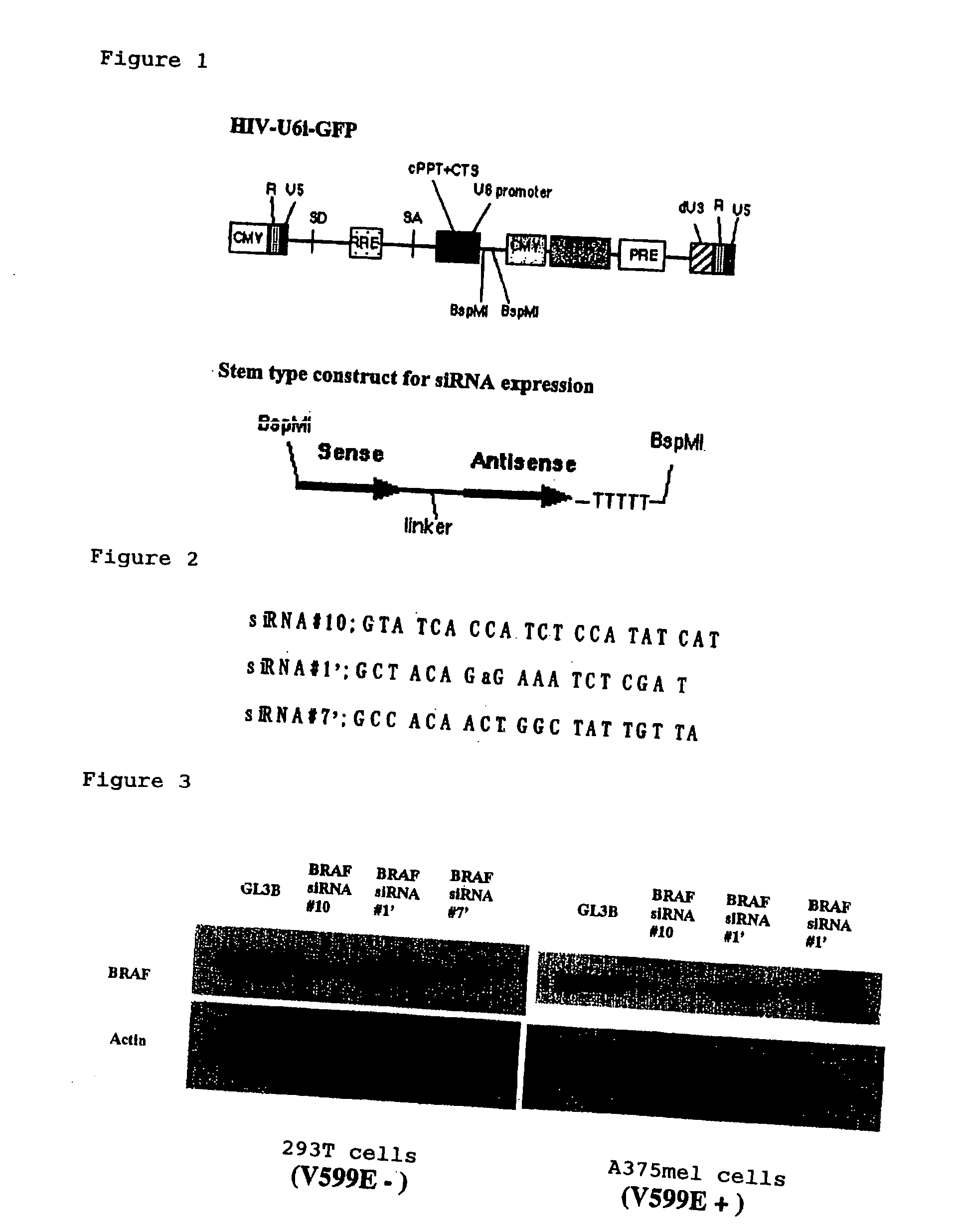
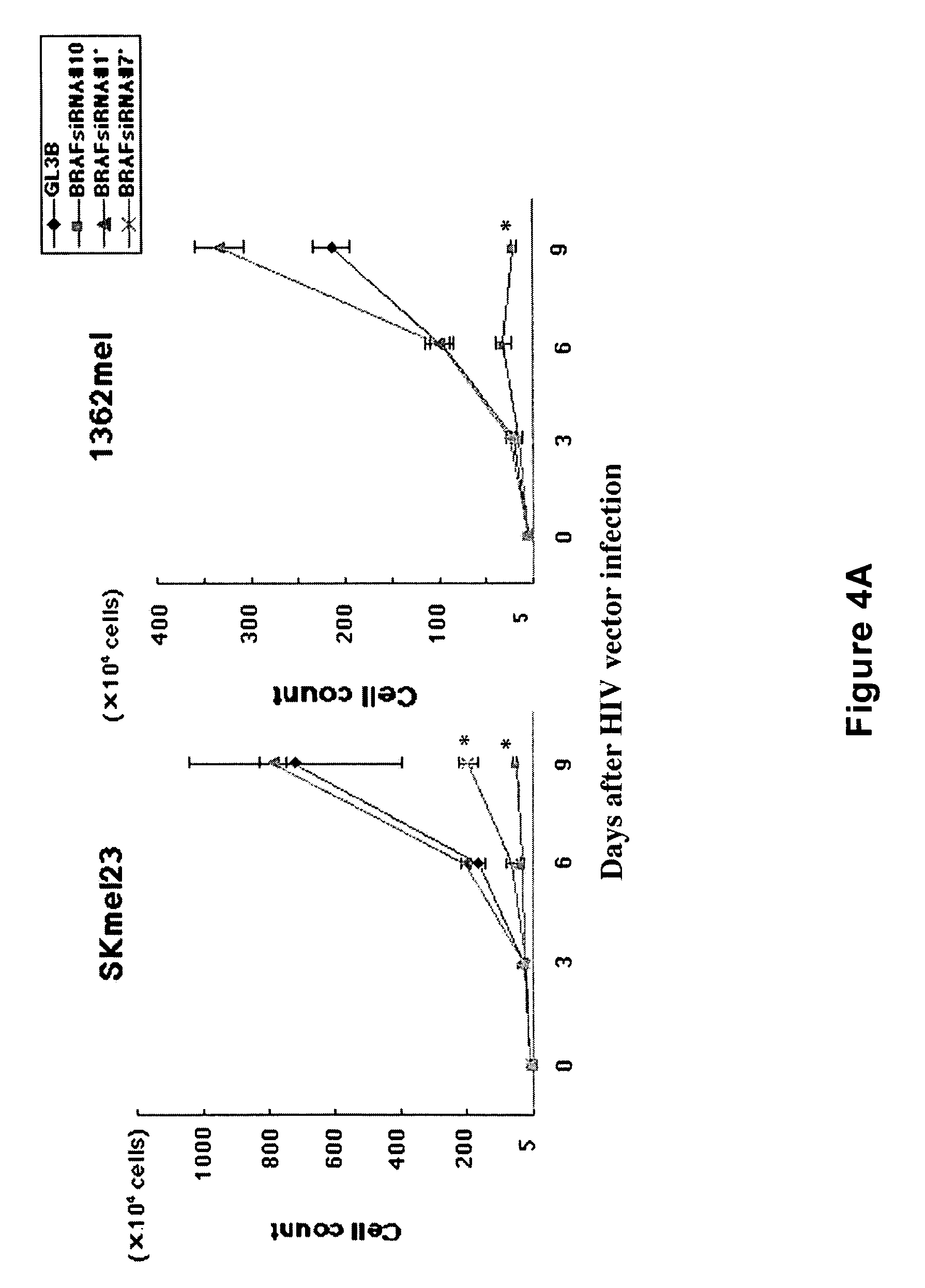
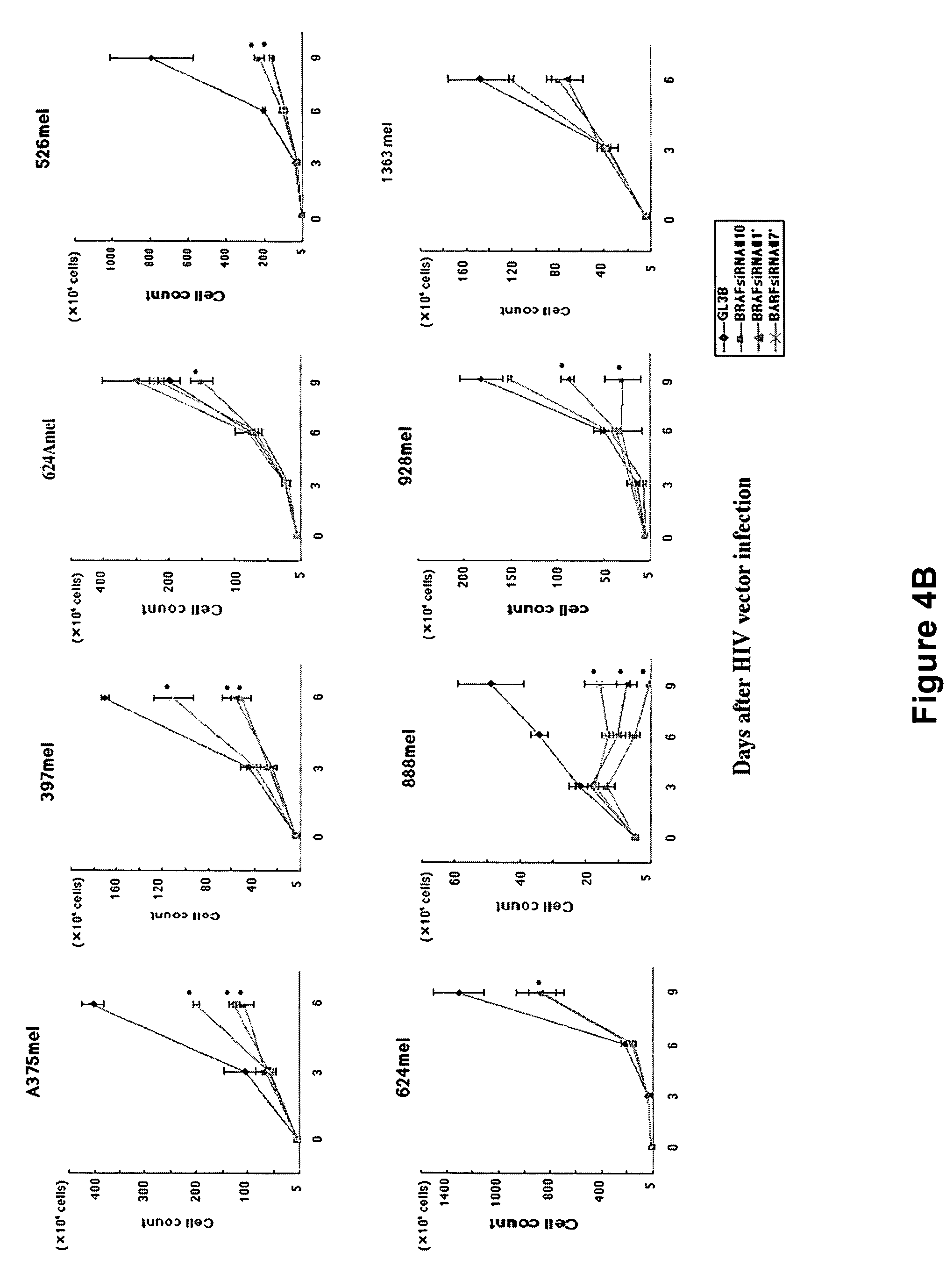
InactiveUS20050019918A1Strong growth inhibitory effectImprove securitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeRna expression
The present invention relates to a therapeutic method using RNAi directed at BRAF, of which the point mutation, especially V599E, occurs frequently in melanomas. RNAi specific for the mutated BRAF will provide a specific therapeutic intervention for cancers such as malignant melanoma. Several target sequences for RNAi were selected in the protein coding region of the BRAF mRNA. The short hairpin RNA expression cassette was constructed on the lentiviral vector. One recombinant viral vector for the mutated BRAF V599E and two other vectors sites for wild type BRAF were constructed to infect various malignant melanoma cell lines, and the effects on the growth inhibition and the signaling of MAPK pathway were examined. The inhibitory effect on the invasion ability of malignant melanoma cell line and in vivo growth of a malignant melanoma cell line were examined.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
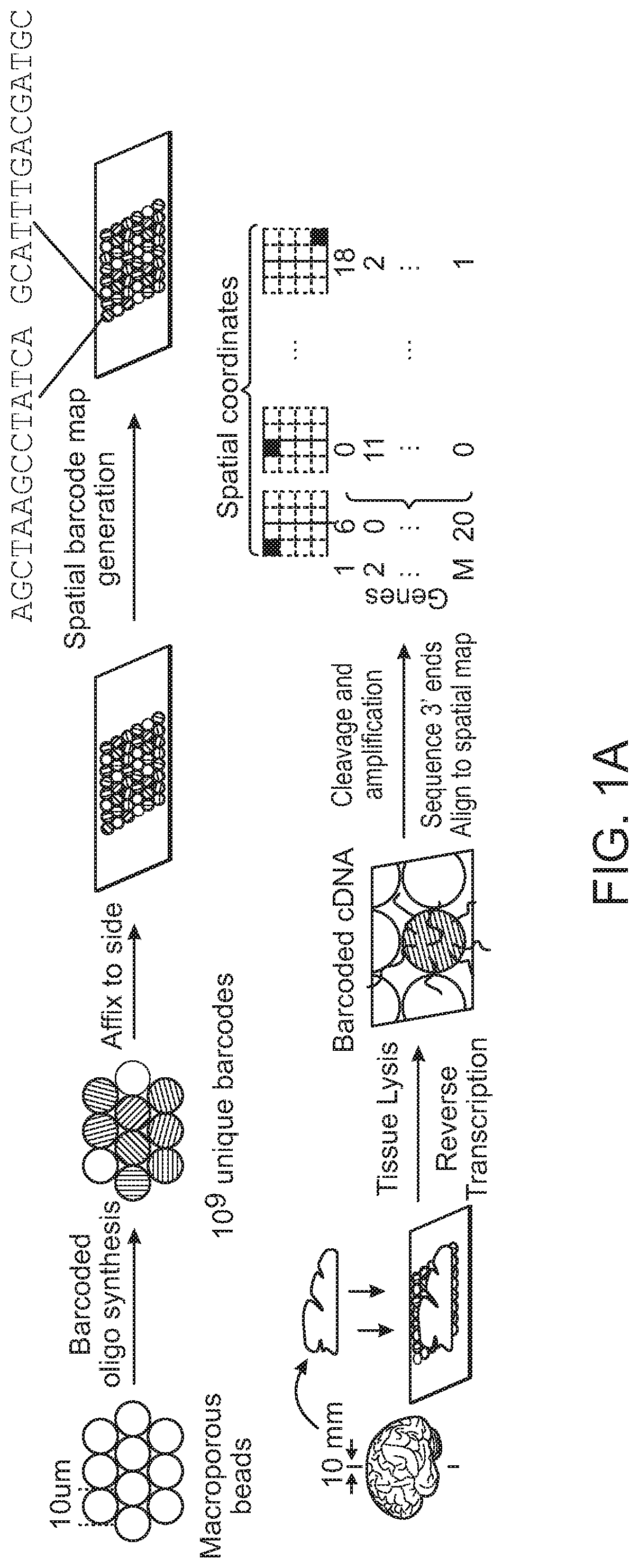
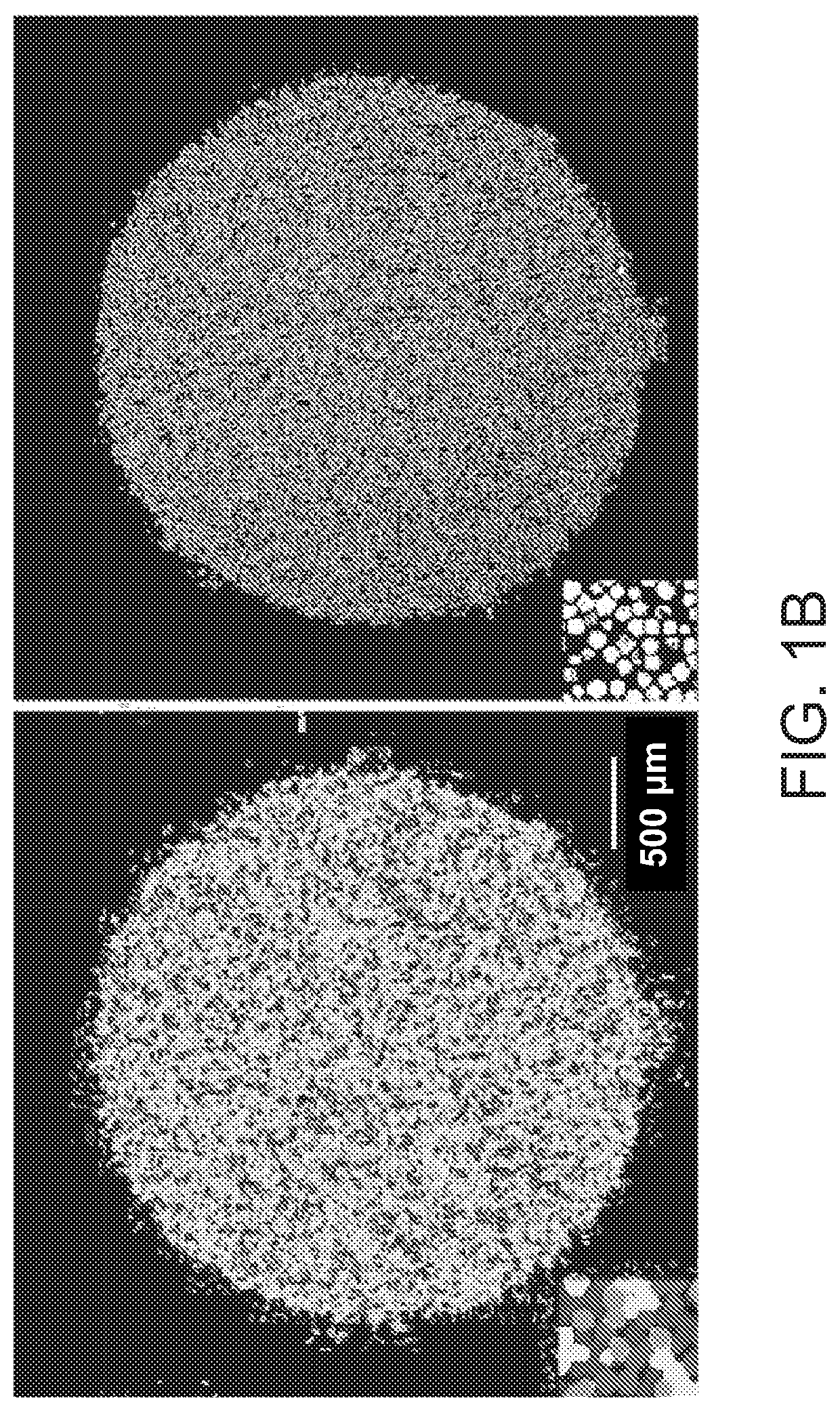
High-resolution spatial macromolecule abundance assessment
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods for assessing relative macromolecule abundance (e.g., RNA expression levels) in a spatially-defined manner across a tissue sample, specifically providing deep transcriptomic coverage at high-resolution across multiple locations assessed across the tissue sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Backbone plasmid carrier for genetic engineering and application thereof
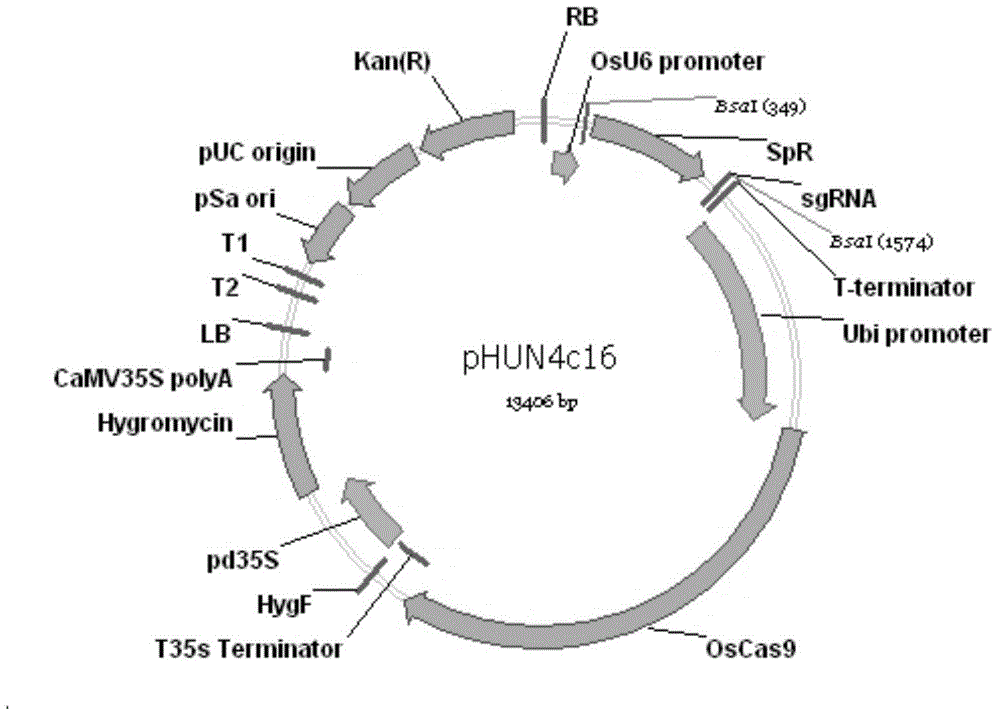
The invention discloses a backbone plasmid carrier for genetic engineering. In the backbone plasmid carrier, a guide RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) expression frame and a Cas9 nuclease expression frame are positioned in one same double-element carrier; the guide RNA expression frame sequentially consists of a rice U6 promoter, a spectinomycin resistance gene, an artificially synthesized sgRNA backbone sequence and a Poly-T terminator; the Cas9 nuclease expression frame sequentially consists of a ZmUBI promoter, a rice preference codon modified Cas9 coded sequence and a 35s terminator. The invention further discloses a recombinant carrier which is established by using the plasmid carrier and contains a target sequence, and an application of the recombinant carrier in rice gene targeting.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Backbone modified oligonucleotide analogues
InactiveUS20030045705A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesImprove propertiesEsterified saccharide compoundsCompounds screening/testingOligomerRna expression
Therapeutic oligonucleotide analogues which have improved nuclease resistance and improved cellular uptake are provided. Replacement of the normal phosphorodiester inter-sugar linkages found in natural oligomers with four atom linking groups forms unique di- and poly-nucleosides and nucleotides useful in regulating RNA expression and in therapeutics. Methods of synthesis and use are also disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Detection of Small Nucleic Acids
InactiveUS20120149018A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRna expressionSmall interfering RNA
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the detection and characterization of interfering RNAs such as micro RNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and other short nucleic acid molecules. More particularly, the present invention relates to improved methods for the detection and quantitation of interfering RNA expression. The present invention further provides for the detection of variants and types of miRNAs and siRNAs.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Backbone modified oligonucleotide analogues
InactiveUS6900301B2Improve stabilitySequencing is facilitatedCompounds screening/testingEsterified saccharide compoundsOligomerRna expression
Therapeutic oligonucleotide analogues which have improved nuclease resistance and improved cellular uptake are provided. Replacement of the normal phosphorodiester inter-sugar linkages found in natural oligomers with four atom linking groups forms unique di- and poly-nucleosides and nucleotides useful in regulating RNA expression and in therapeutics. Methods of synthesis and use are also disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
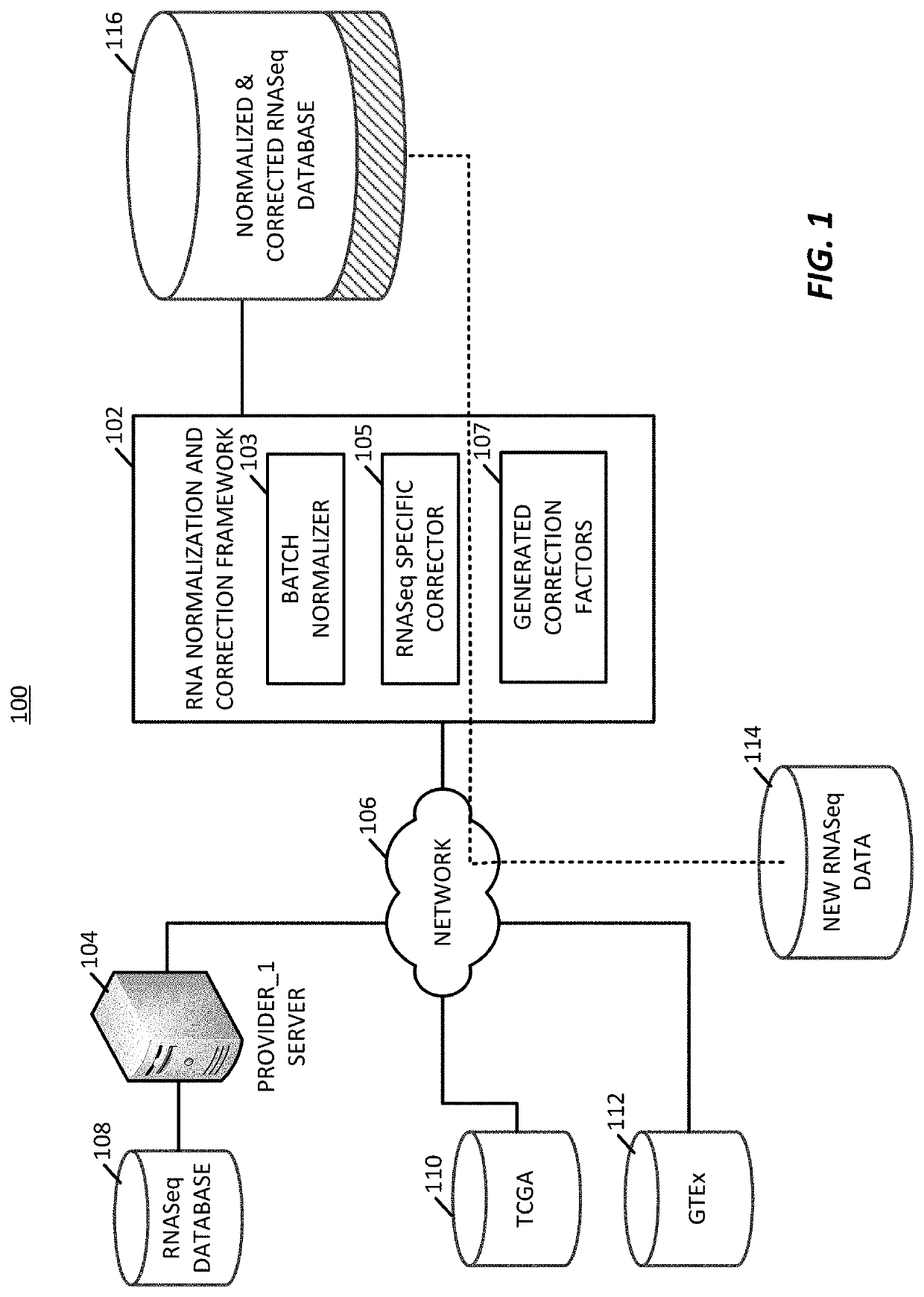
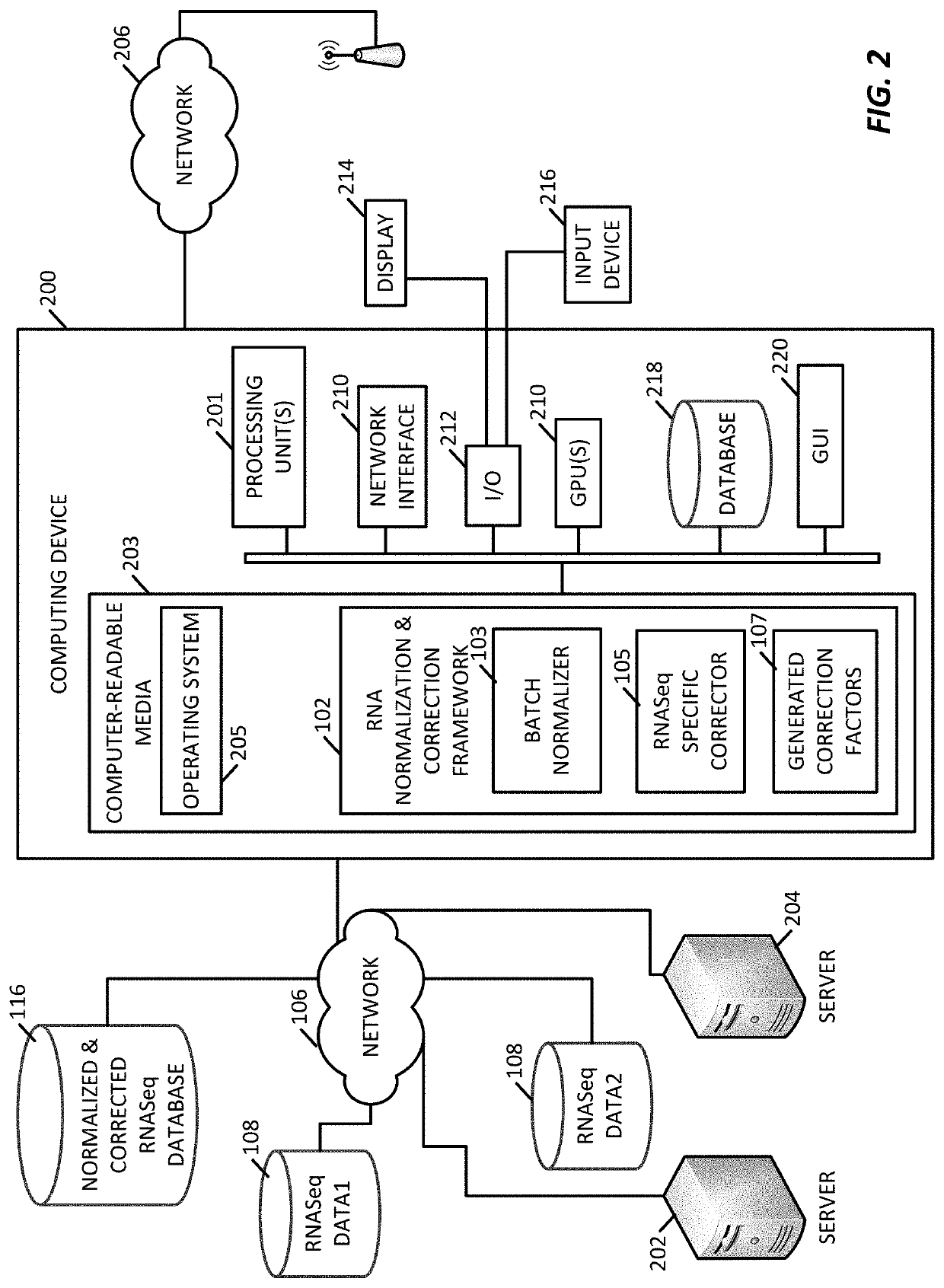
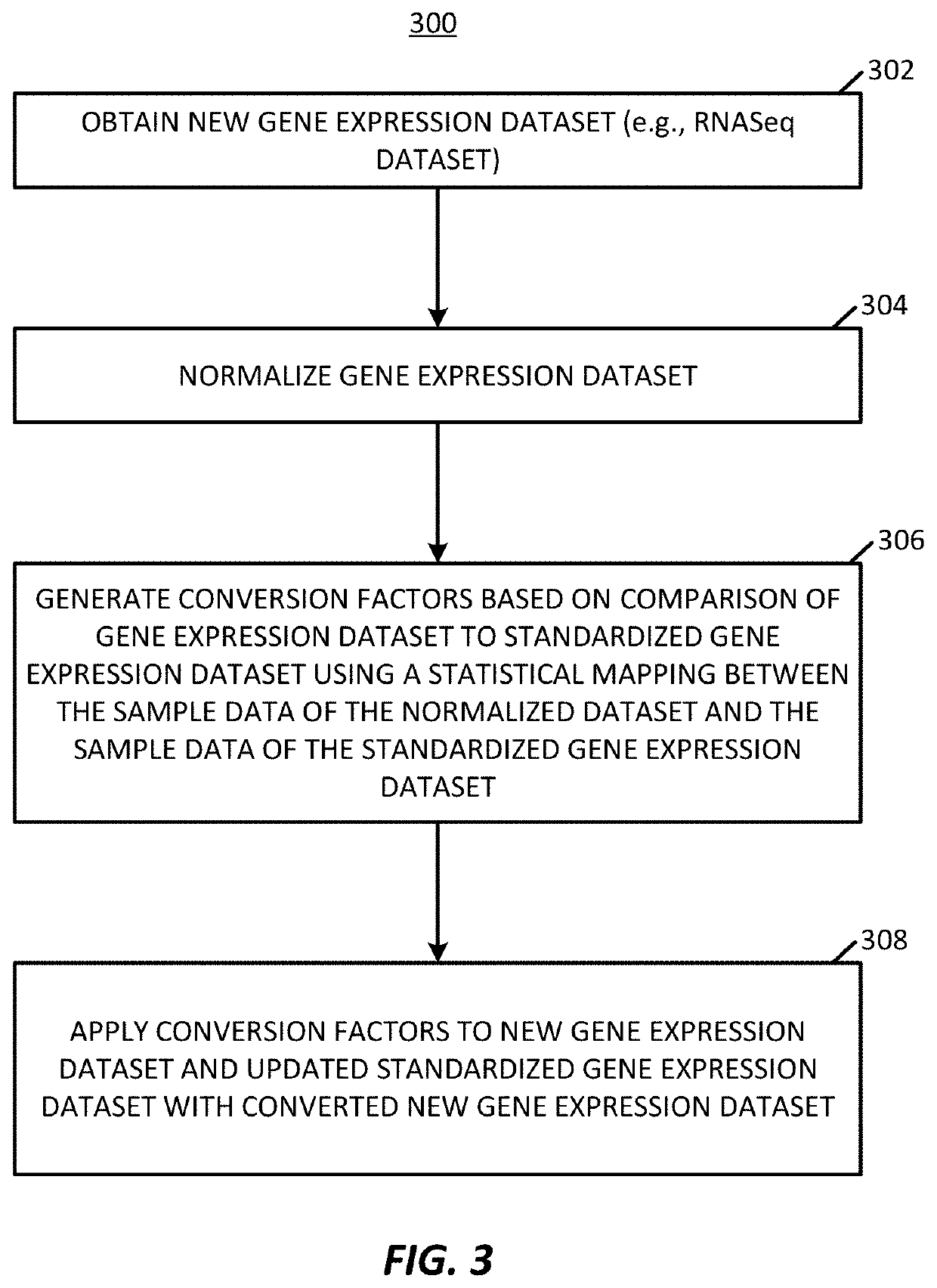
Methods of normalizing and correcting RNA expression data
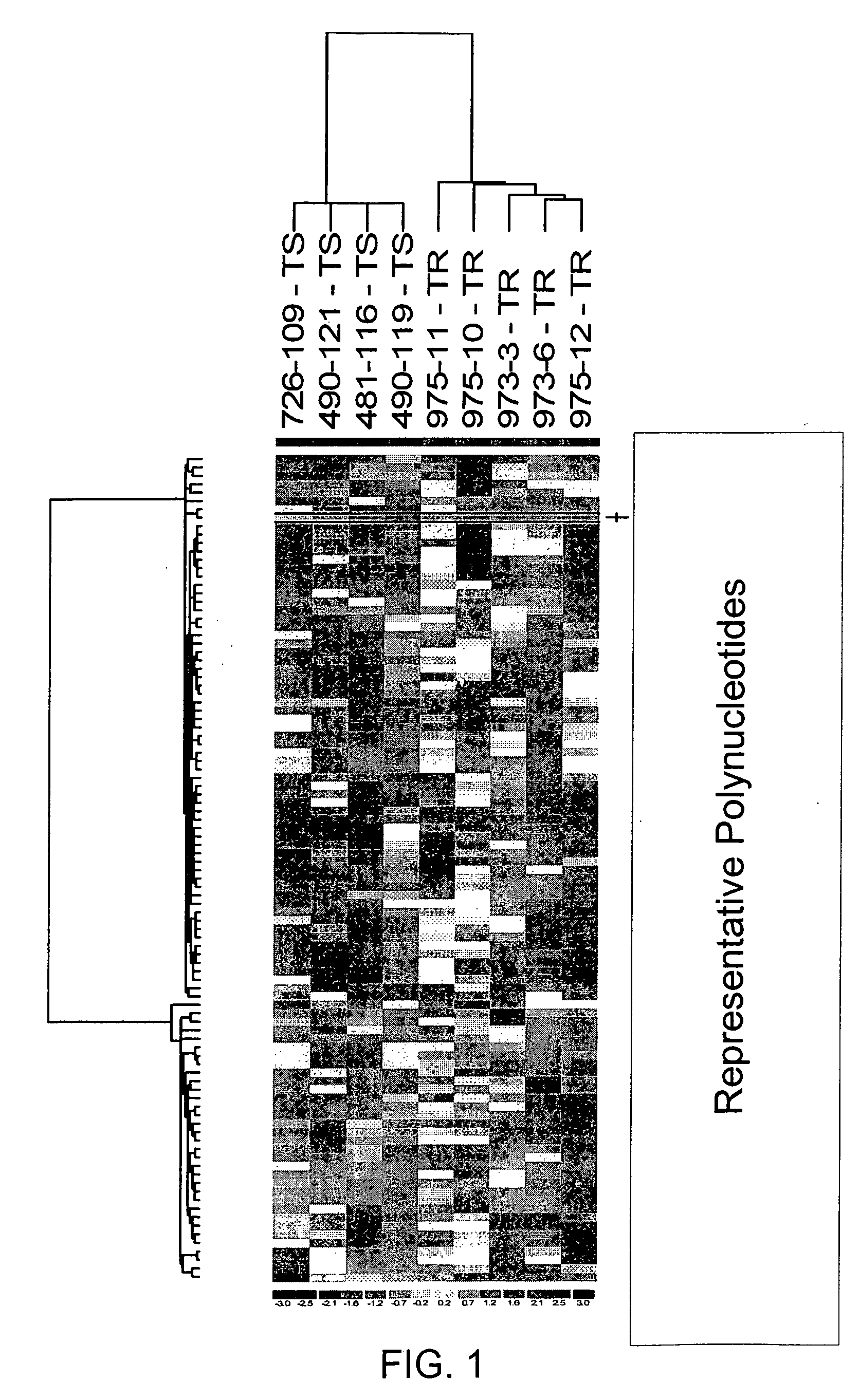
PendingUS20200098448A1Accurate analysisShorten speedDigital data information retrievalBiostatisticsData setCollection system
A platform to perform normalization and correction on gene expression datasets and combines different datasets into a standard dataset using a framework configured to continuously incorporate new gene expression data. The framework determines a series of conversion factors that are used to on-board new gene expression datasets, such as unpaired datasets, where these conversion factors are able to correct for variations in data type, variations in gene expressions, and variations in collection systems.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS INC
Micro-RNA expression profiling and targeting in peripheral blood in lung cancer
InactiveCN101918594AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRna expressionTreatment of lung cancer
A method for the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of lung cancer by detecting at least one microRNA in peripheral blood is disclosed.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Self-Processing Rna Expression Cassette
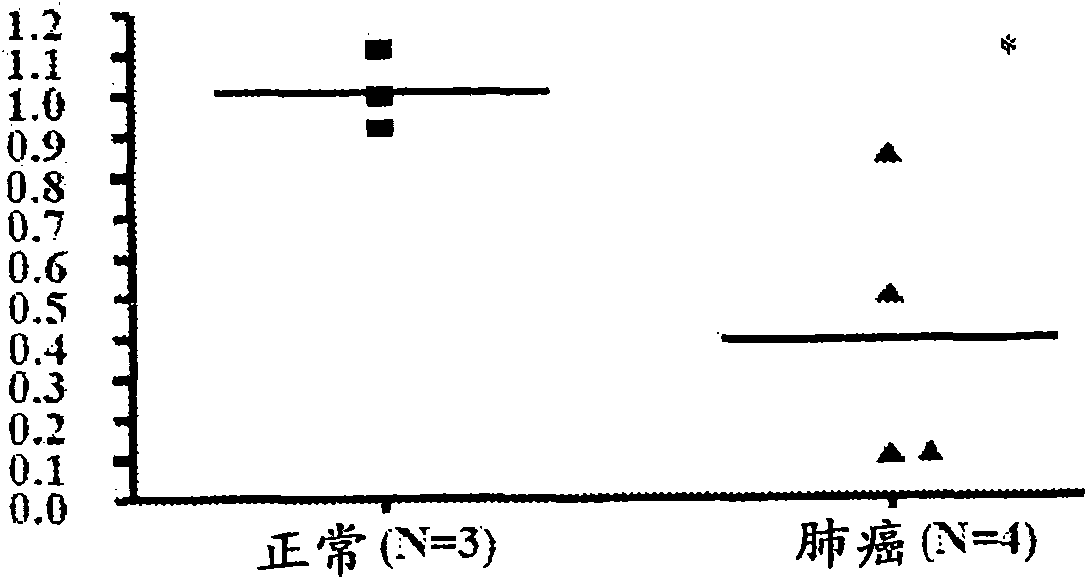
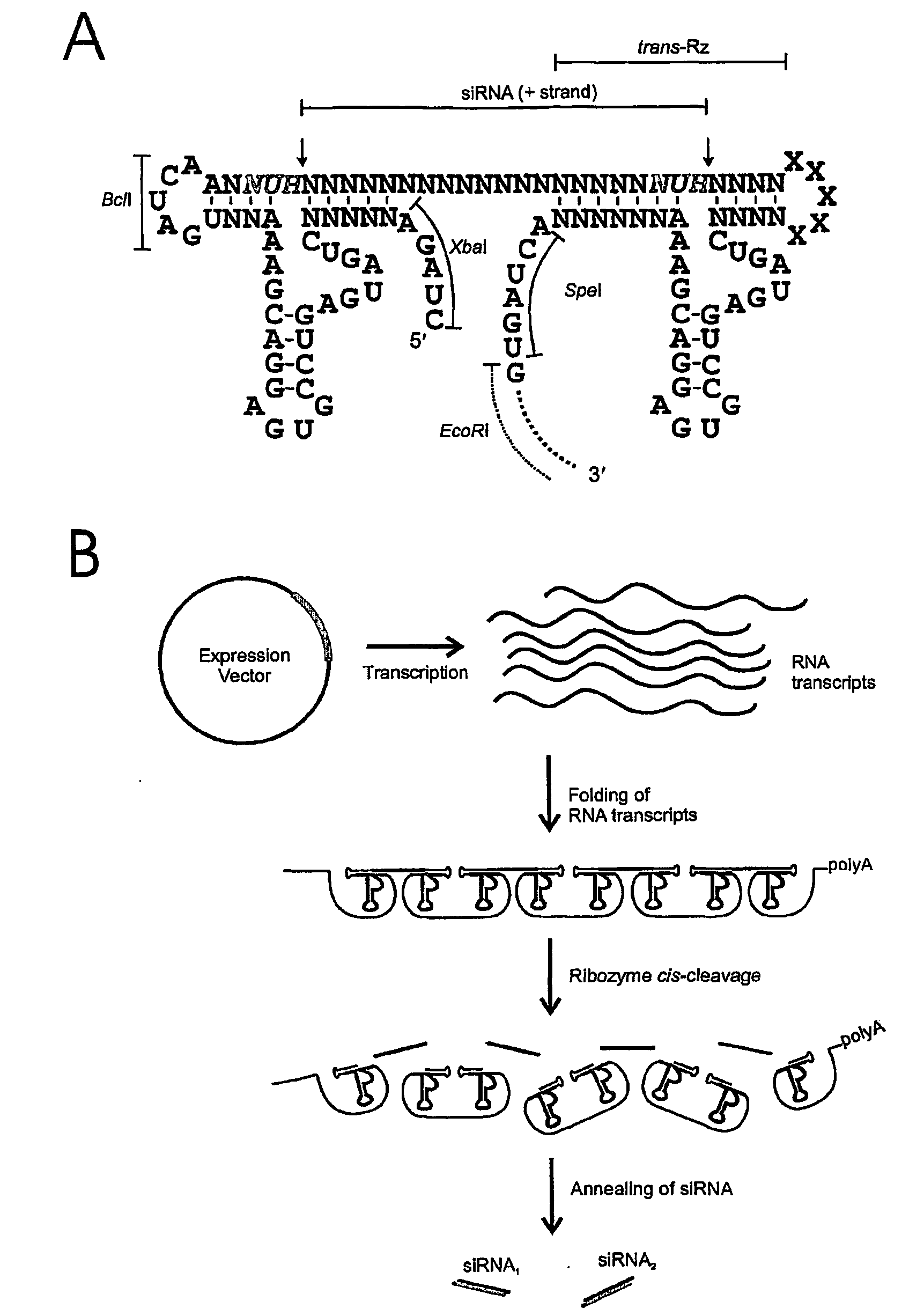
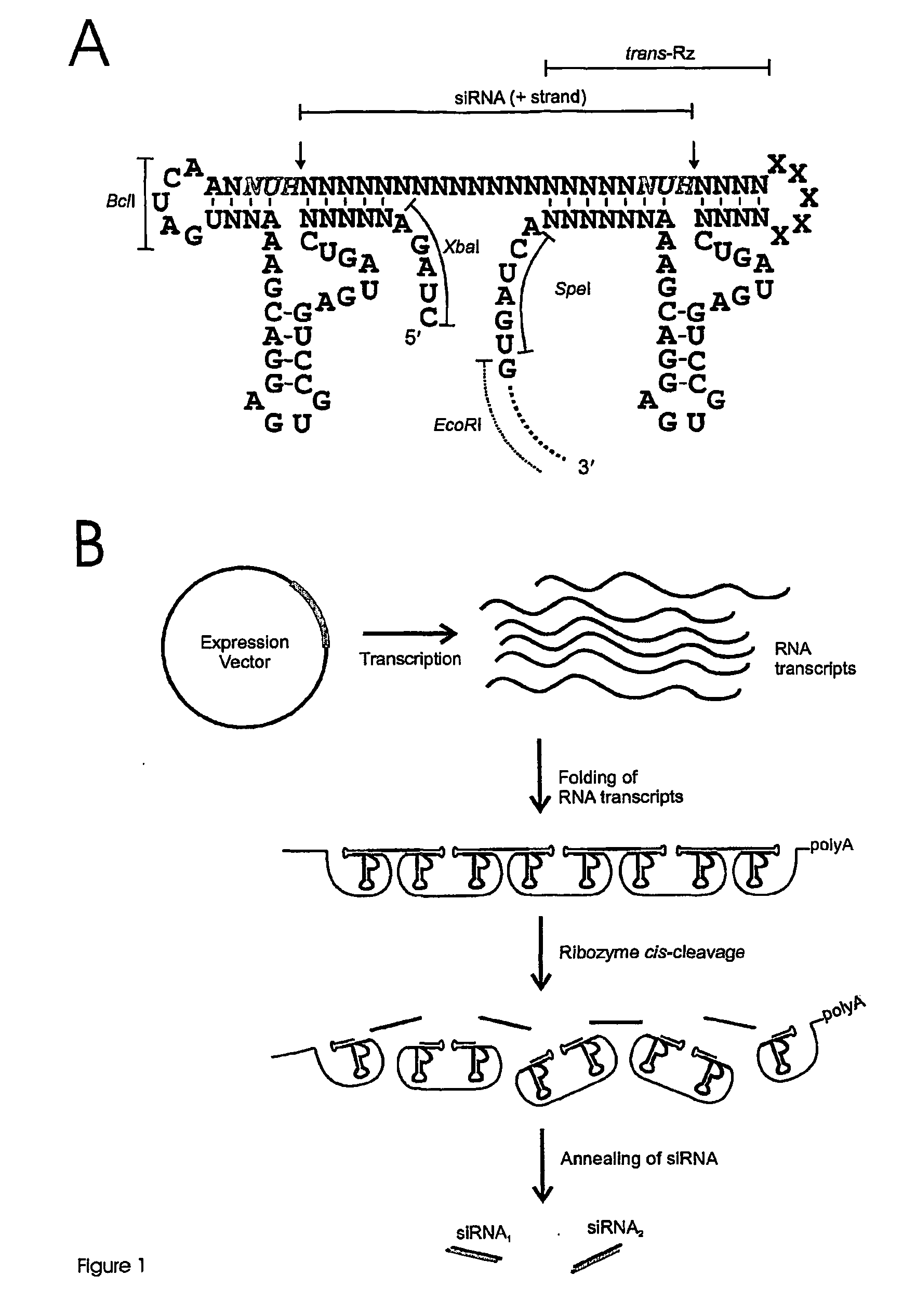
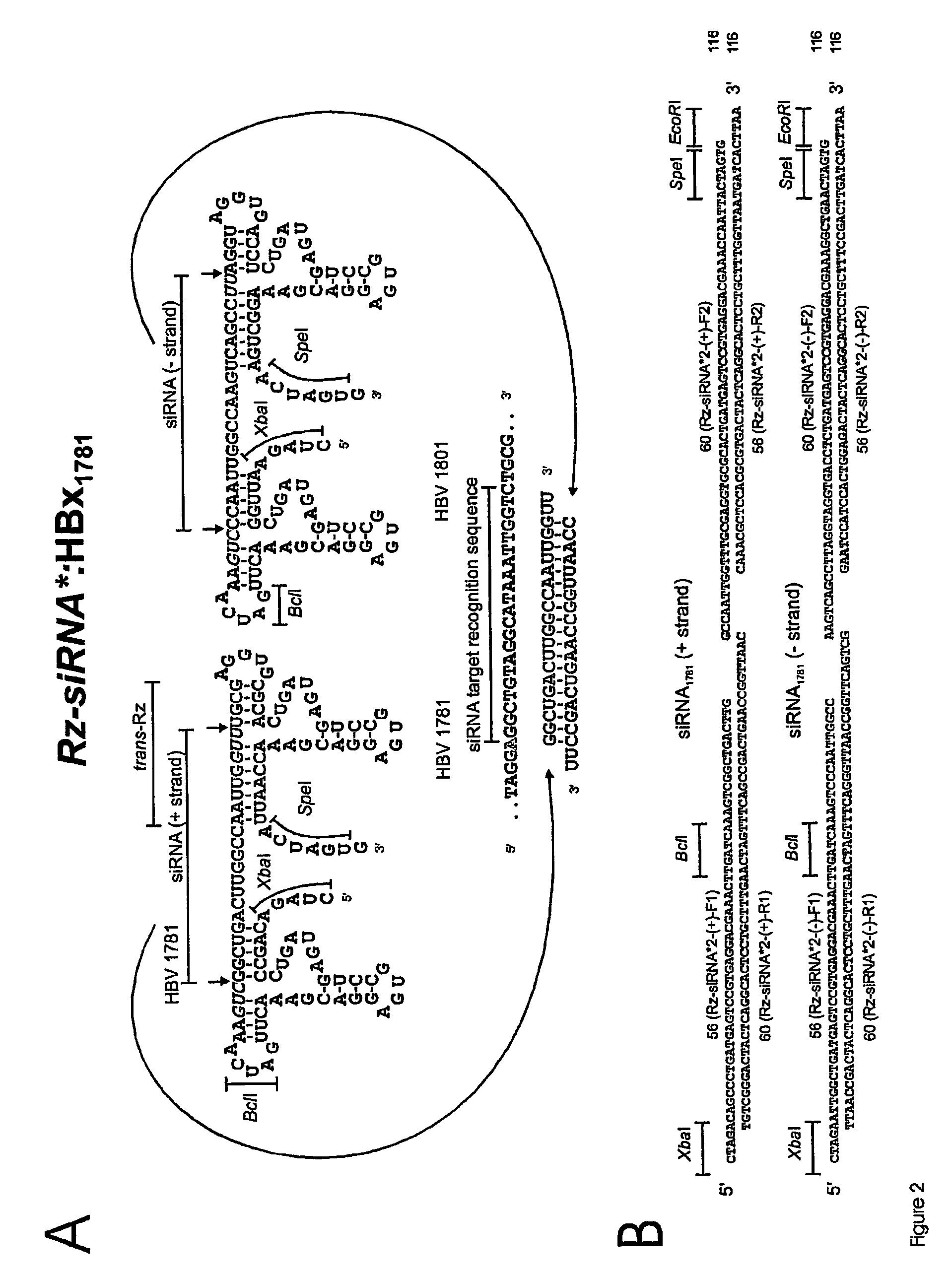
InactiveUS20080207539A1Reduce gene transcriptionPreserve their longevitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsHBxRna expression
The invention provides a self-processing RNA expression cassette which includes at least one pair of processing units, an RNAi effecter sequence of predetermined length that regulates target gene expression which is flanked by said pair of processing units; and at least one pair of cognate ribozyme cis-cleavage target sites located 5′ and 3′ of the RNAi effecter sequence. The self-processing RNA expression cassette is able to express in vivo and in vitro and the RNAi effecter sequence includes at least one target recognition sequence derived from the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) X gene (HBx).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
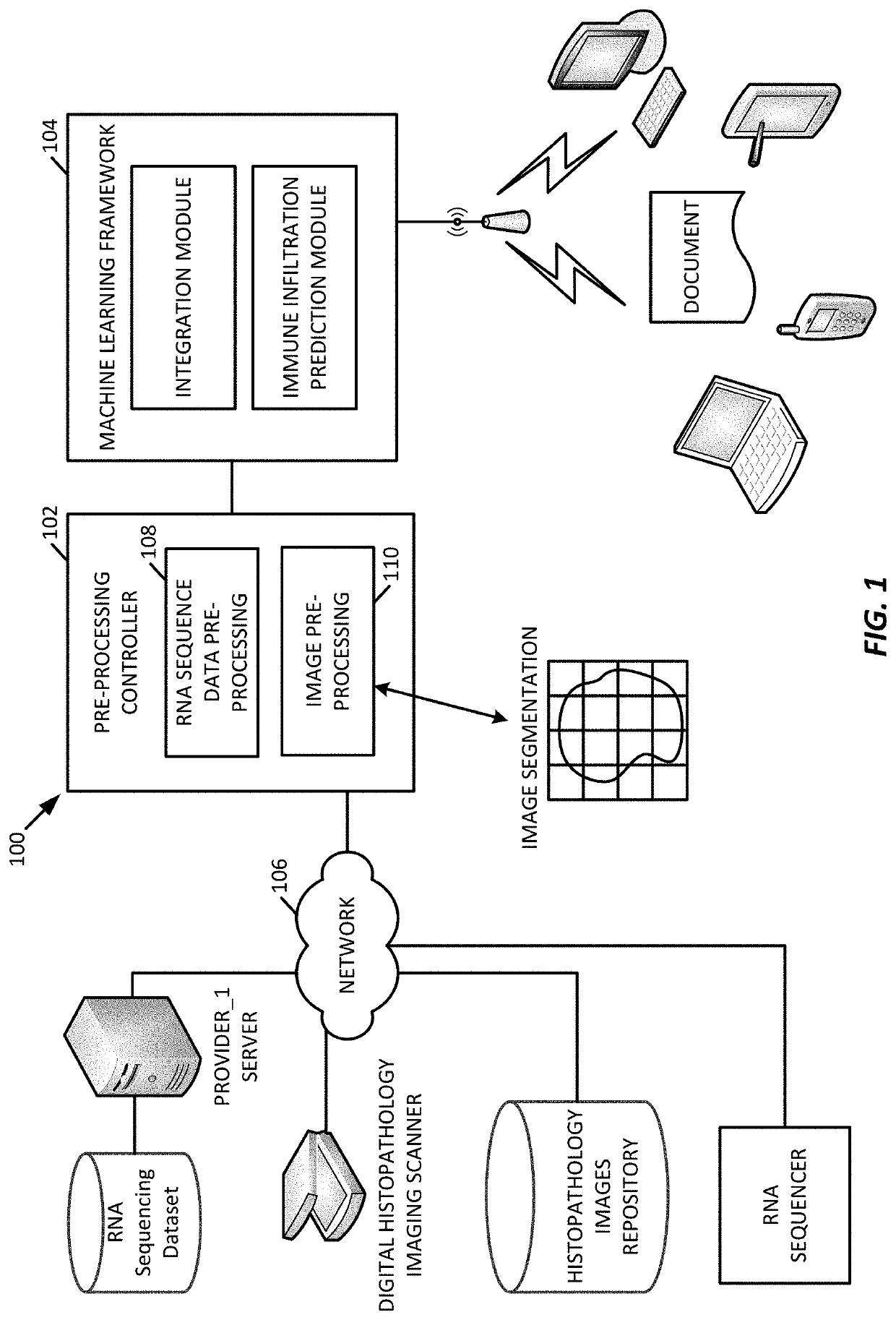
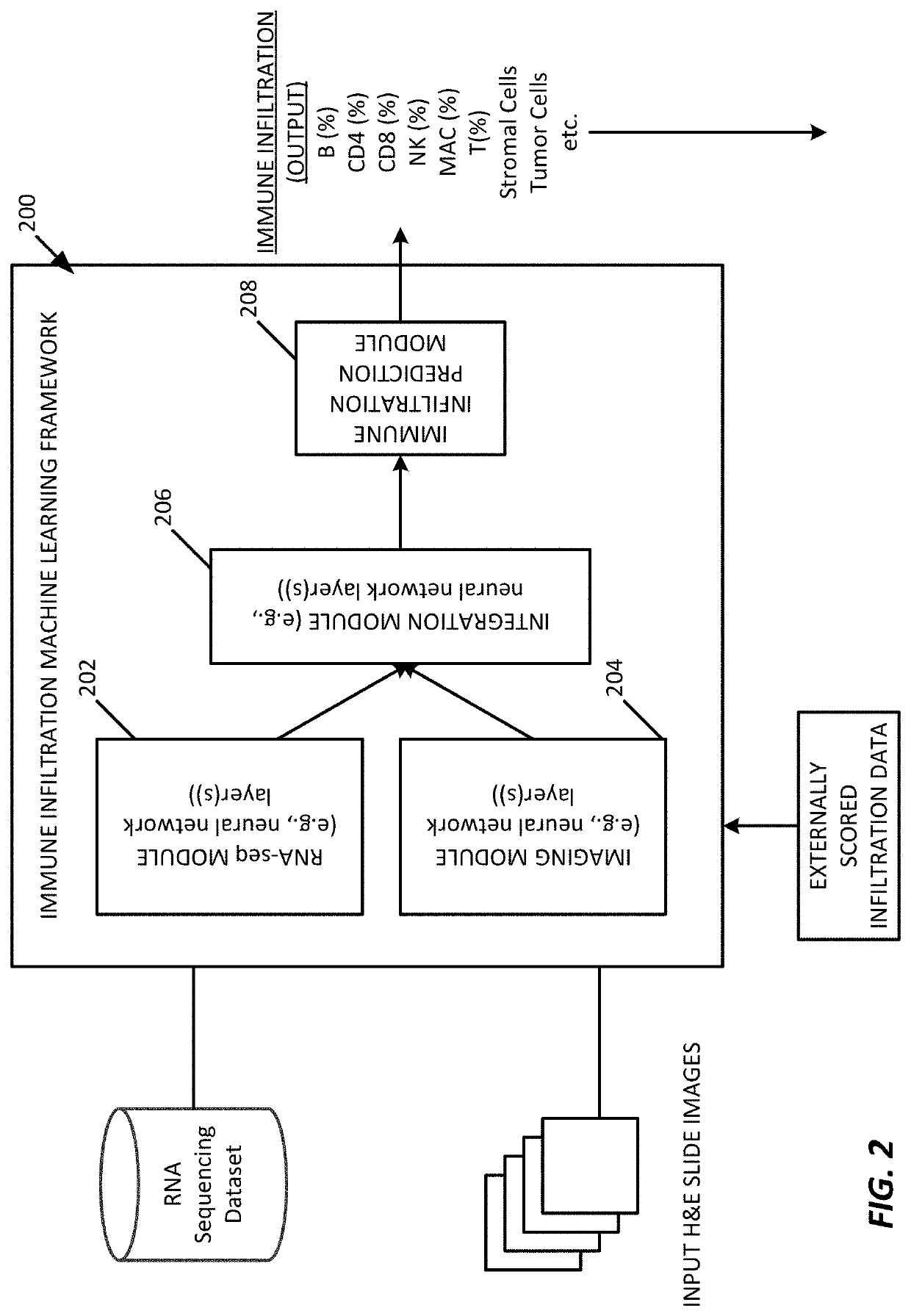
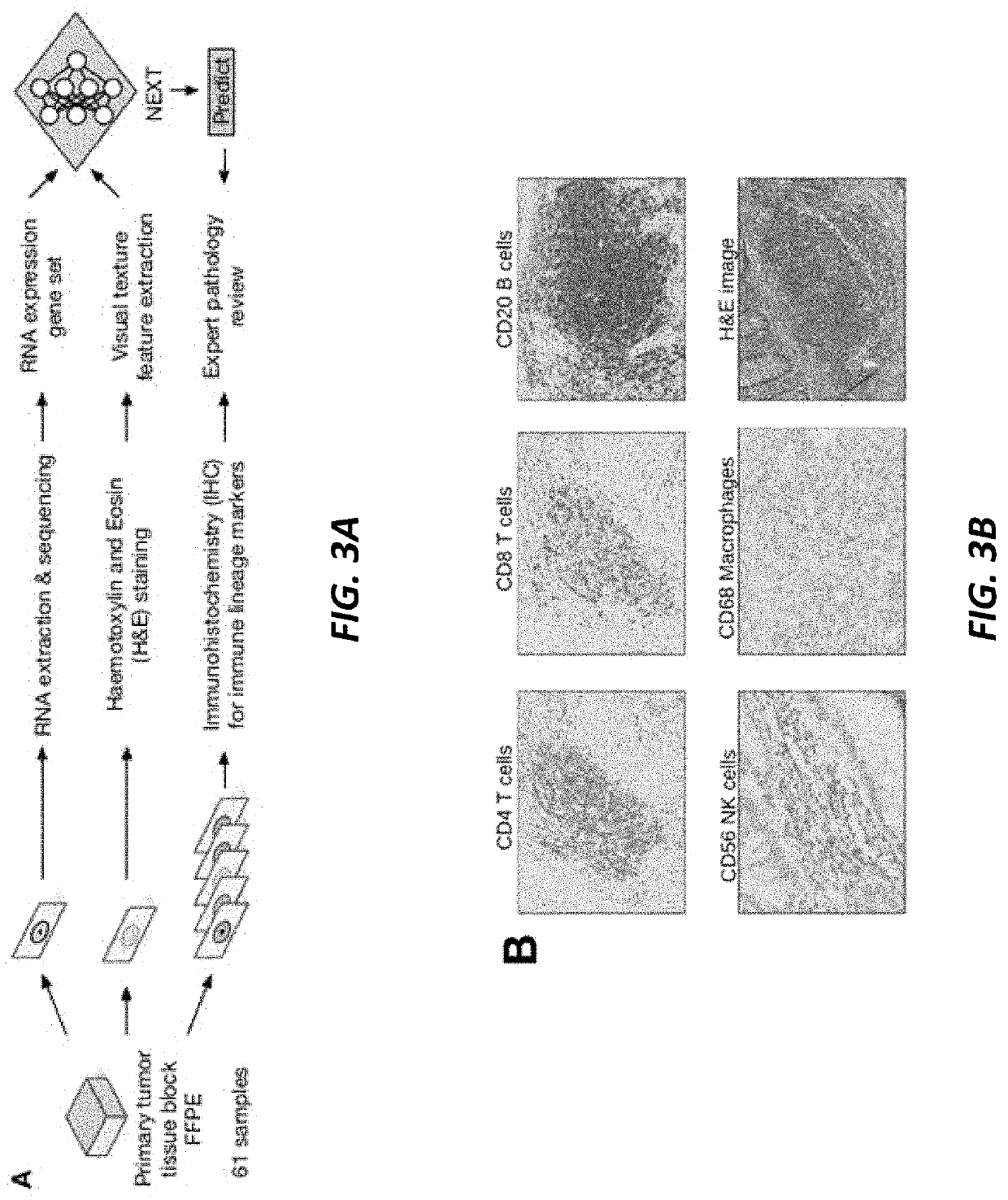
Multi-modal approach to predicting immune infiltration based on integrated RNA expression and imaging features
Multi-modal approaches to predict tumor immune infiltration are based on integrating gene expression data and imaging features in a neural network-based framework. This framework is configured to estimate percent composition, and thus immune infiltration score, of a patient tumor biopsy sample. Multi-modal approaches may also be used to predict cell composition beyond immune cells via integrated multi-layer neural network frameworks.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS INC
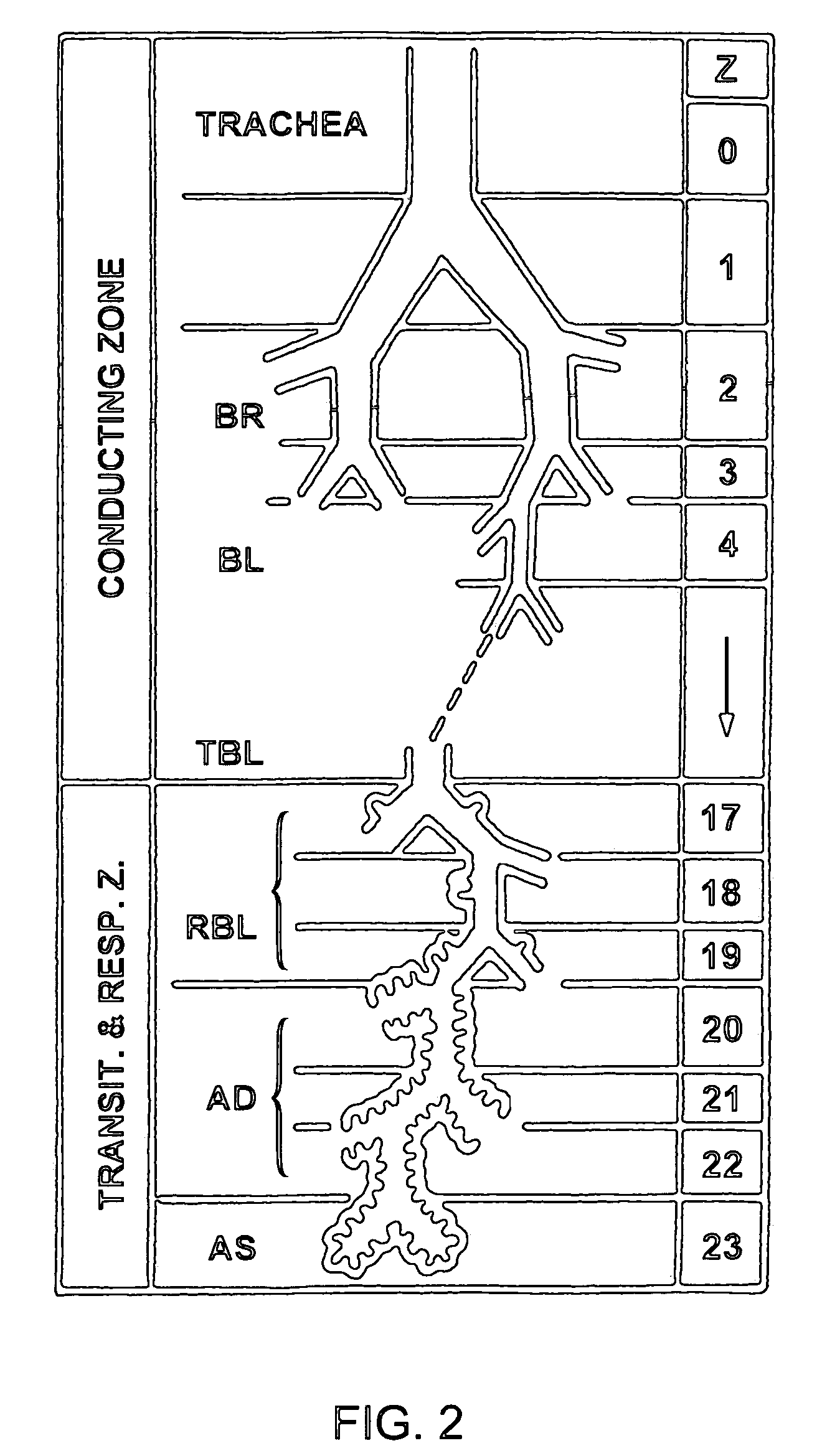
Methods of delivering aerosolized polynucleotides to the respiratory tract
Methods and devices for delivering aerosolized formulations containing polynucleotides to specified regions within a subject's respiratory tract are disclosed. The methods find use in the delivery of ribozymes, antisense polynucleotides, and DNA and RNA expression vectors into airway epithelial cells, alveoli, pulmonary macrophages and other cells in the respiratory tract (including the oropharynx, nose, nasopharynx). These methods may be used for optimization of transfection efficiency and expression in vivo, and for in vivo expression, for example for generating an immune response, or inducing immunological tolerance.
Owner:ARADIGM
Triple minRNA for resisting virus infection of aids and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103184224APrevent escapeHigh infection efficiencyAntiviralsFermentationPol genesRna expression
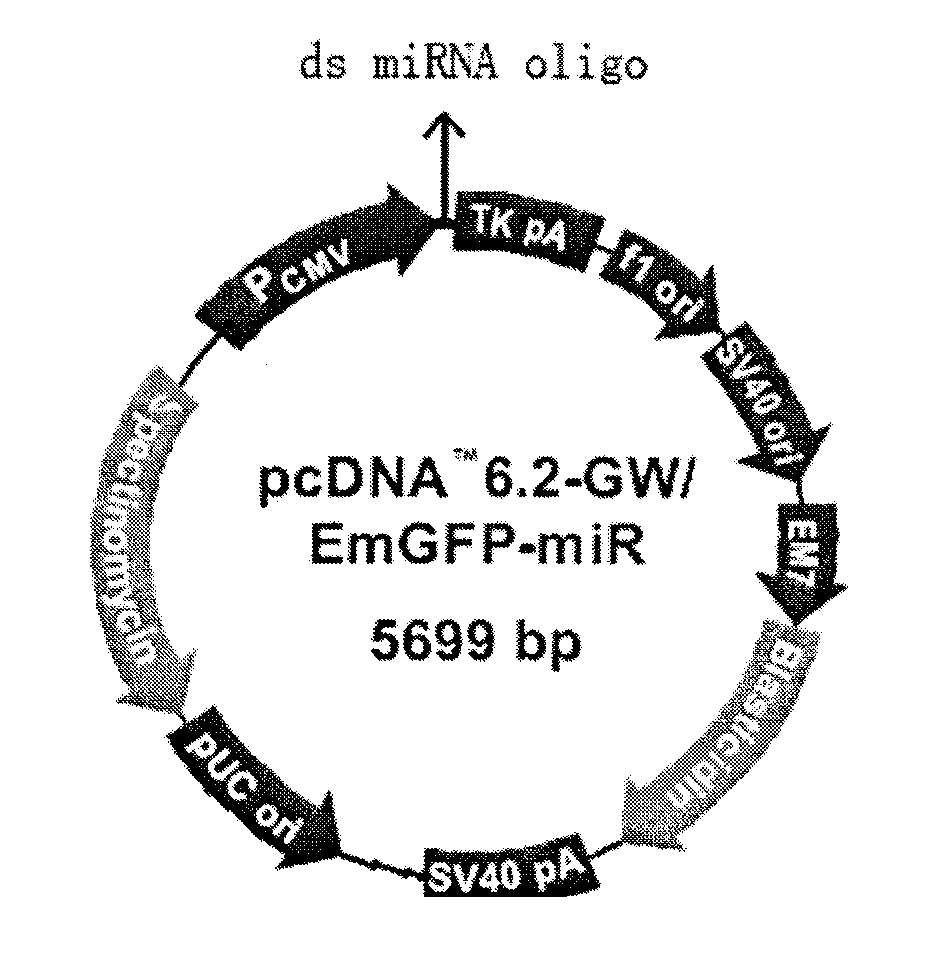
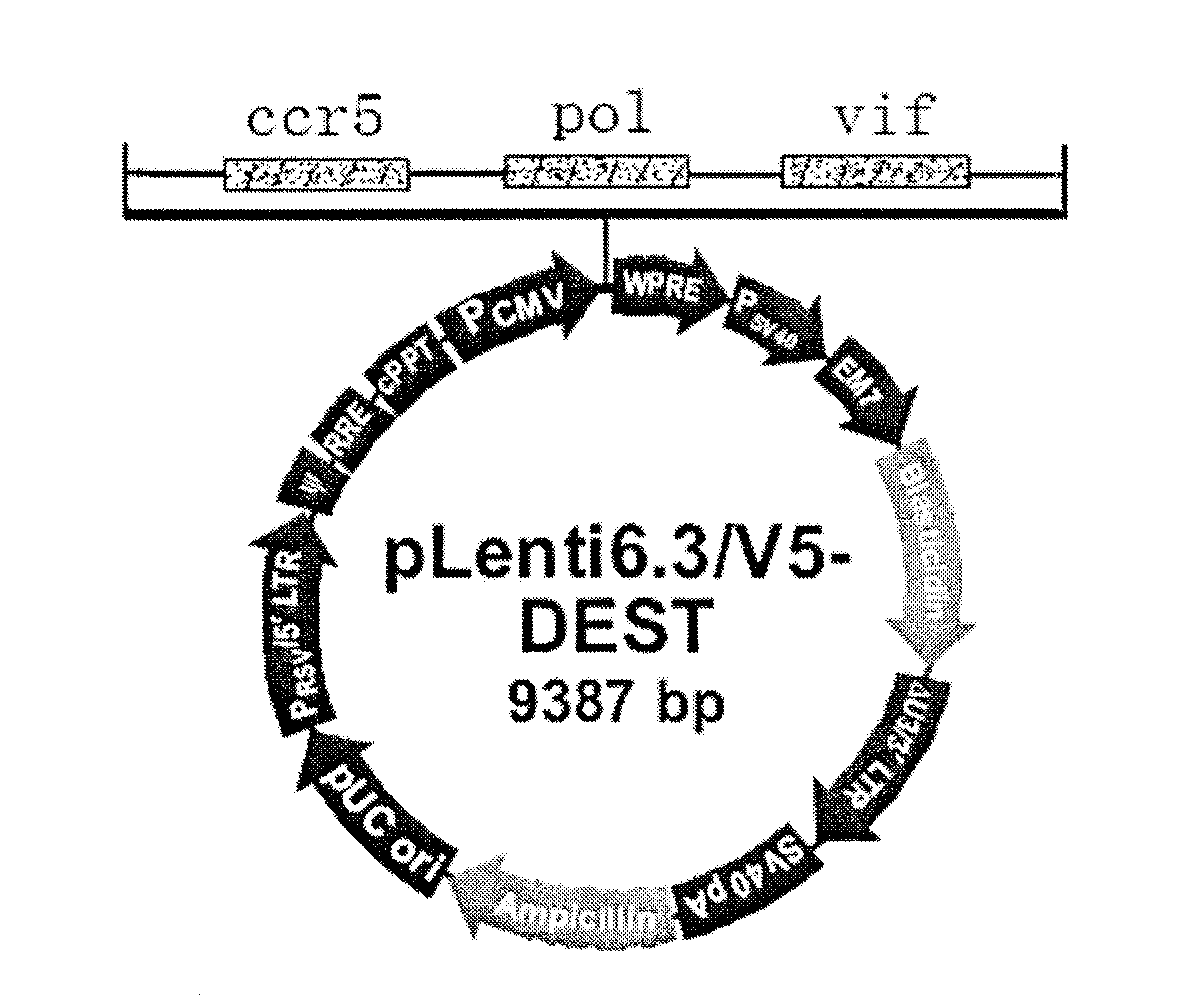
The invention discloses a triple minRNA for resisting virus infection of aids and the construction method thereof. The sequences of the triple minRNA are respectively designed according to gene sequences of ccr5, pol and vif and combined to be miRNA oligomeric and single strand DNA, then double-strand DNA is formed through annealing, then double-strand DNA is respectively inserted into the expression vector of pcDNA<TM> 6.2-GW / EmGFPmiR of miRNA to built the mi RNA expression plasmid, and the jamming effect of mi RNA expression plasmid to target gene can be detected through a Qpcr method. A miRNA string with the best gene interference effect to ccr5, vif and pol is inserted into a carrier of pcDNA 6.2 <TM>-GW / EmGFP, so as to obtain a series-wound interference vector of pcDNA6.2<TM>-GW / EmGFP-ccr5-pol-vif, and then the miR-ccr5-pol-vif in the series-wound interference vector is transferred to a lentiviral vector pLenti6.3 / V5-DEST so as to construct pLenti6.3 / V5-DEST miR-ccr5-pol-vif. The recombinant lentiviral vector can product three miRNA at the same time to cause interference effects to gene ccr5, gene pol and gene vif, so as to prevent the gene ccr5, the gene pol and the gene vif from expressing corresponding protein. Therefore, the effect of controlling Hiv infection and replication can be achieved.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com