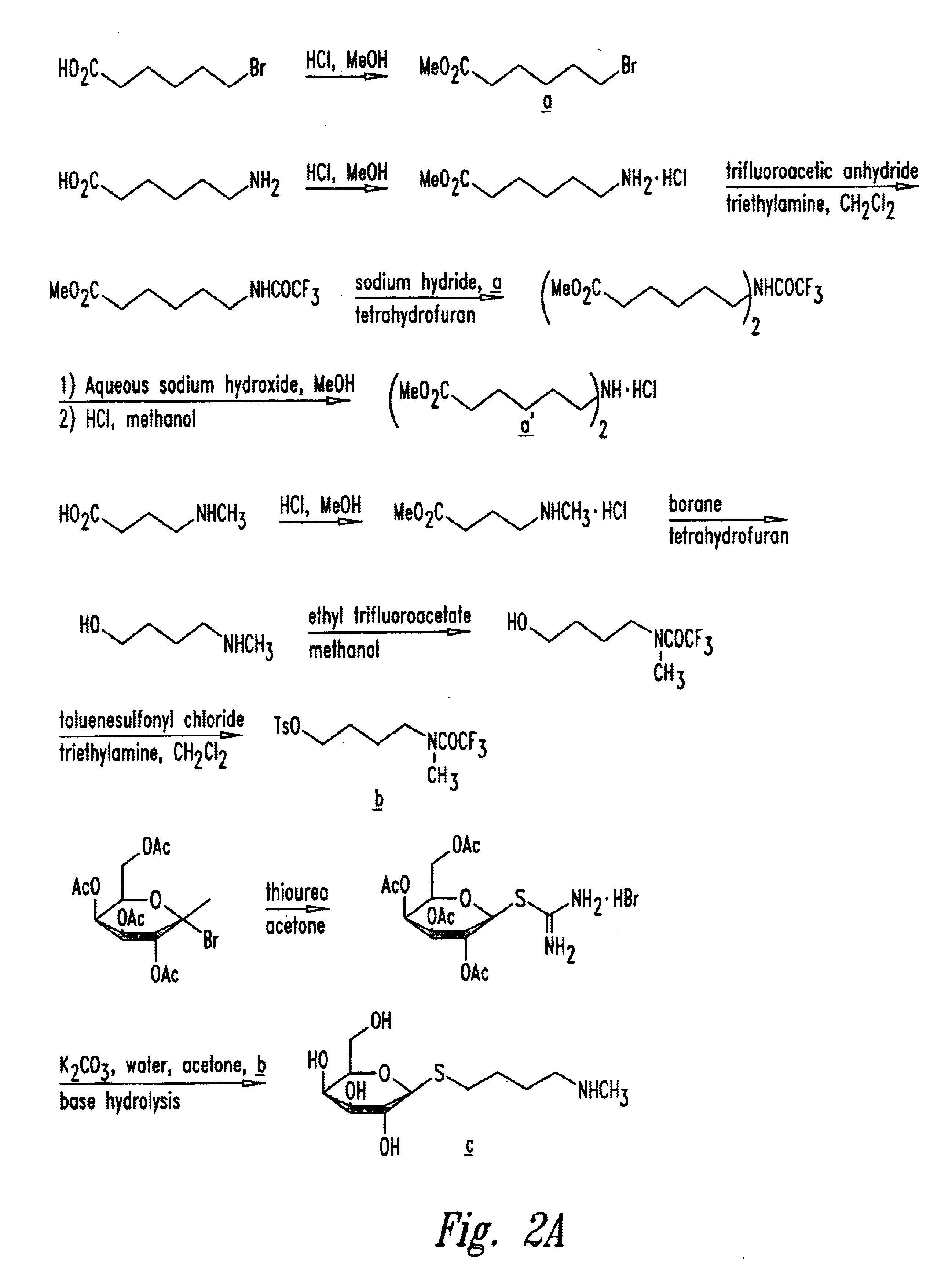
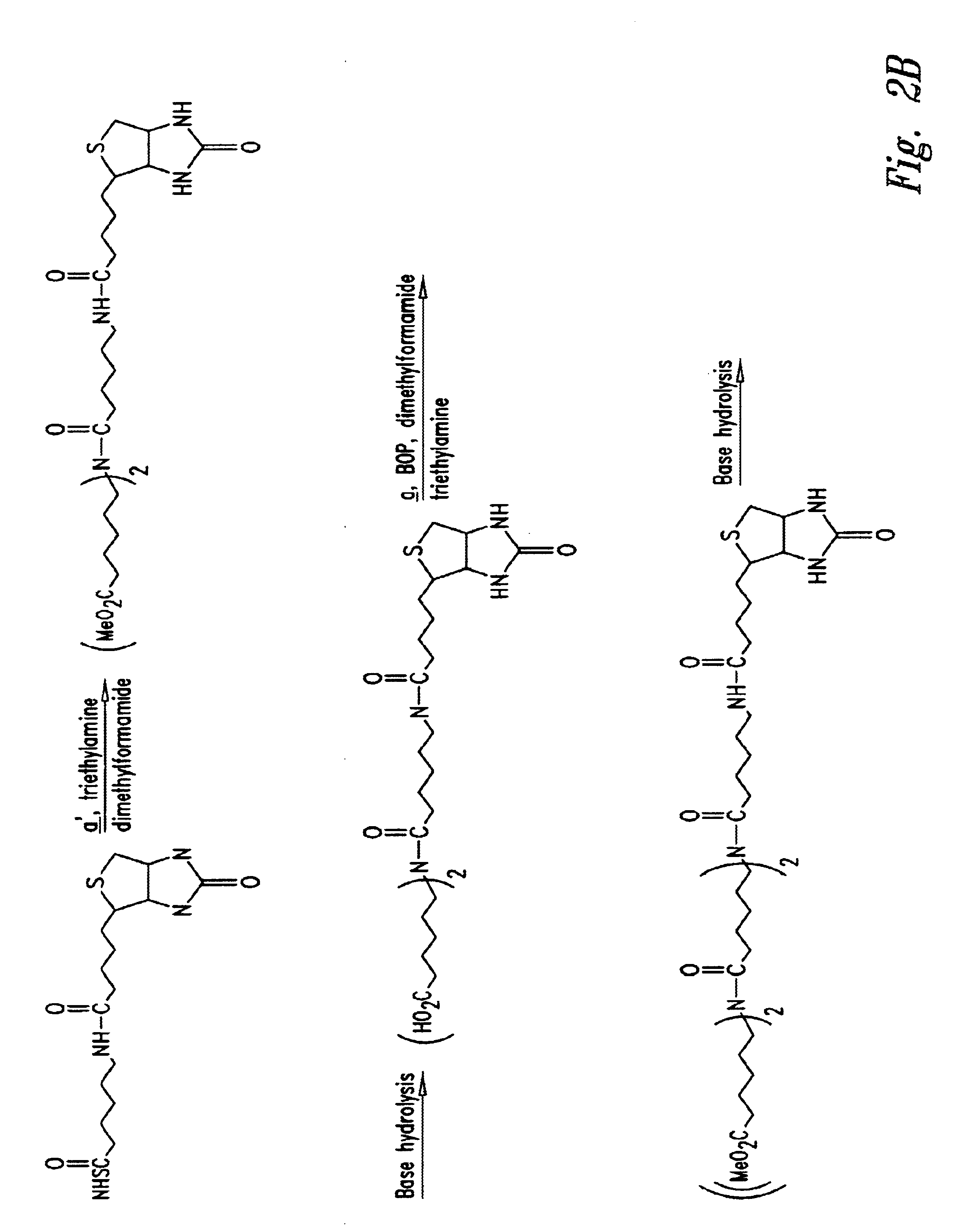
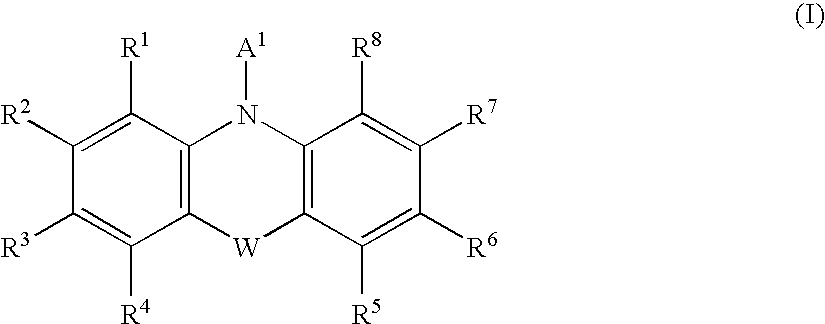
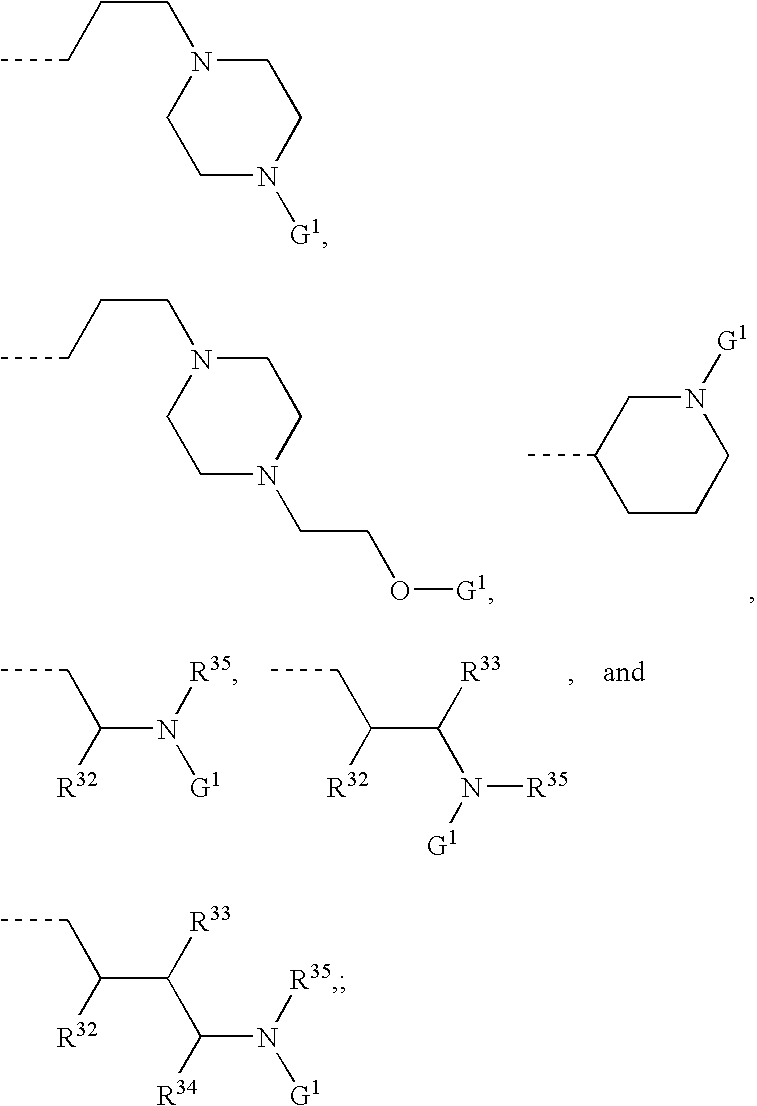
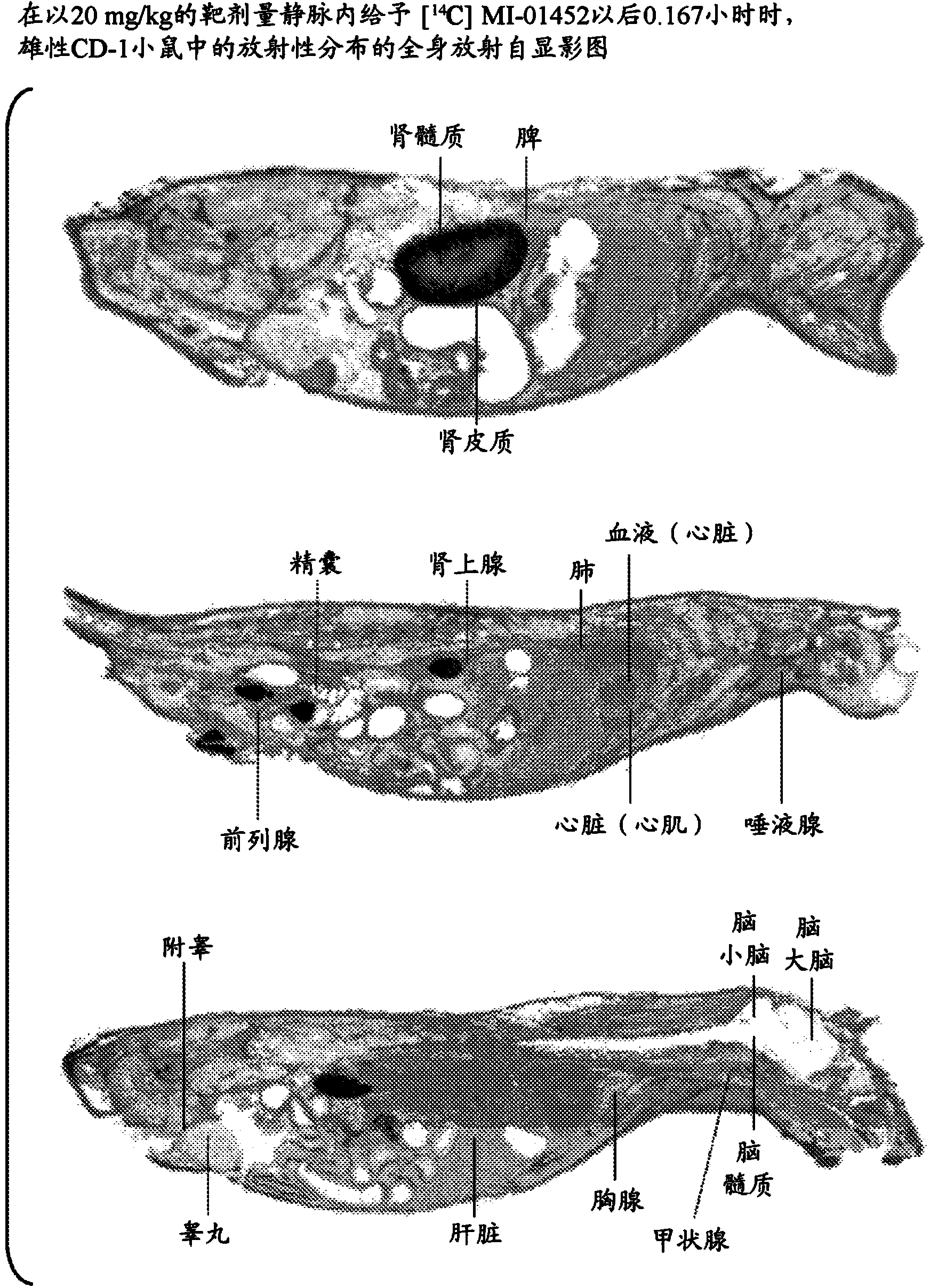
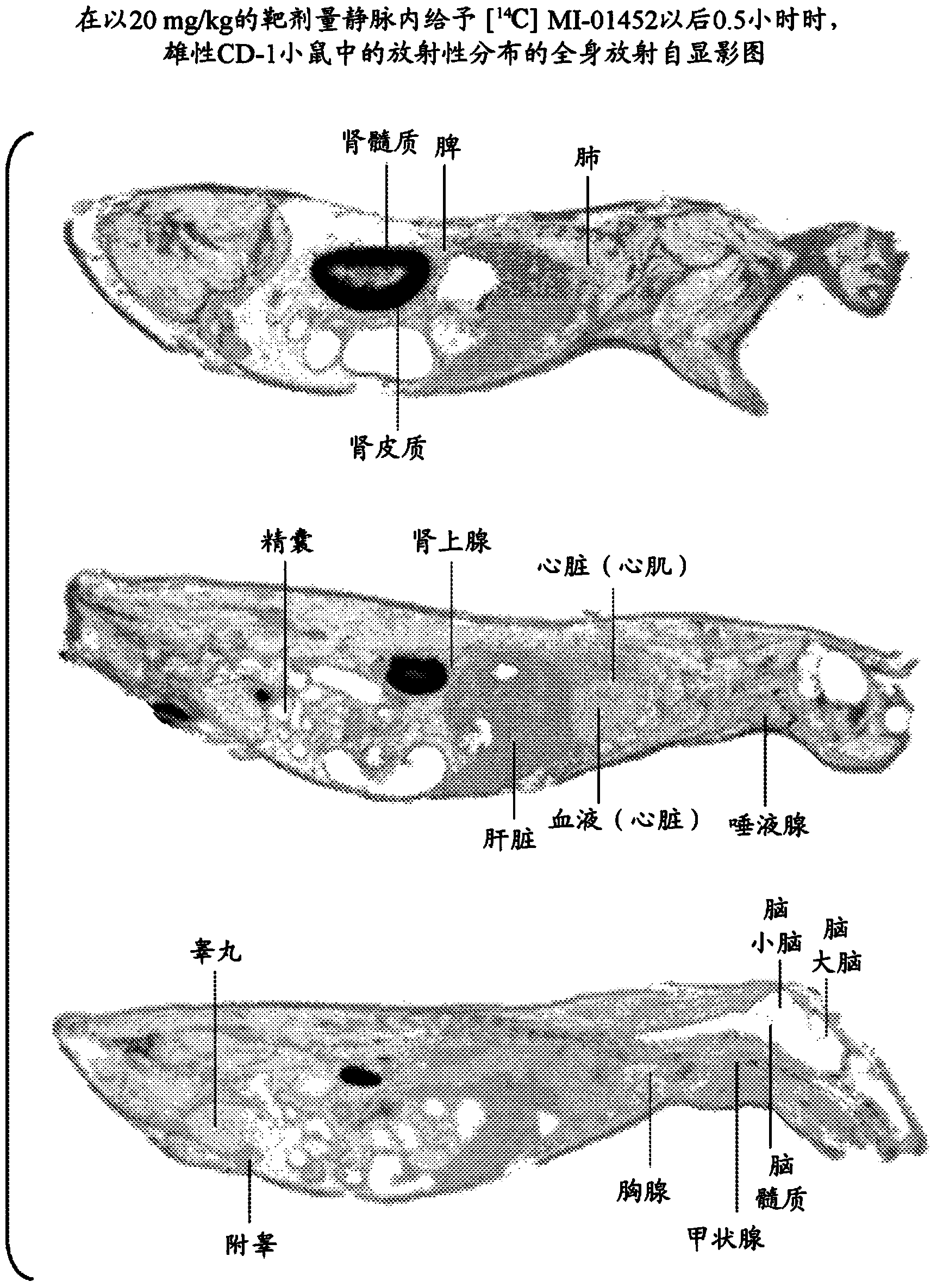
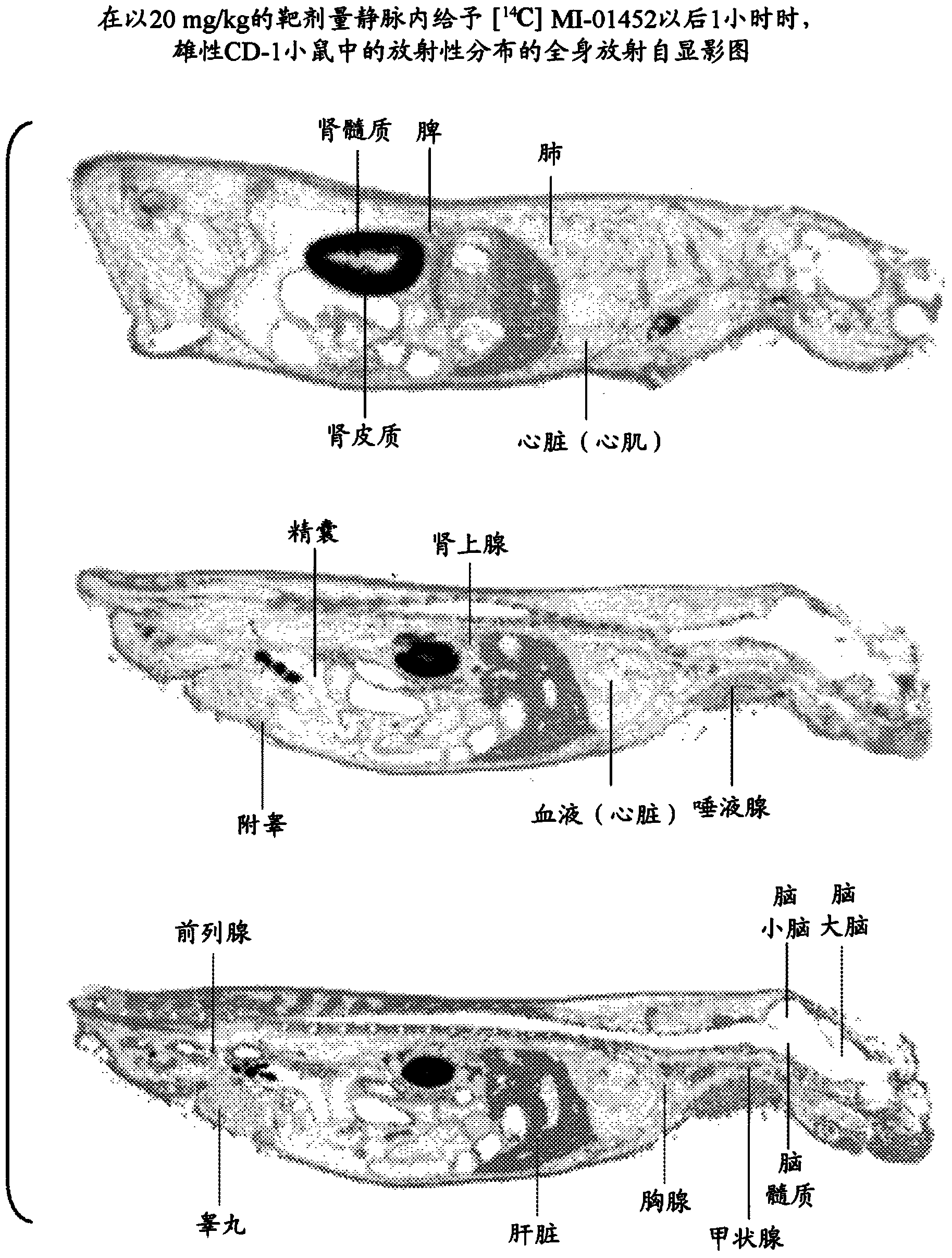
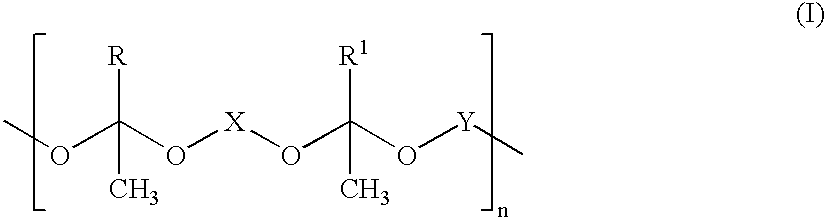
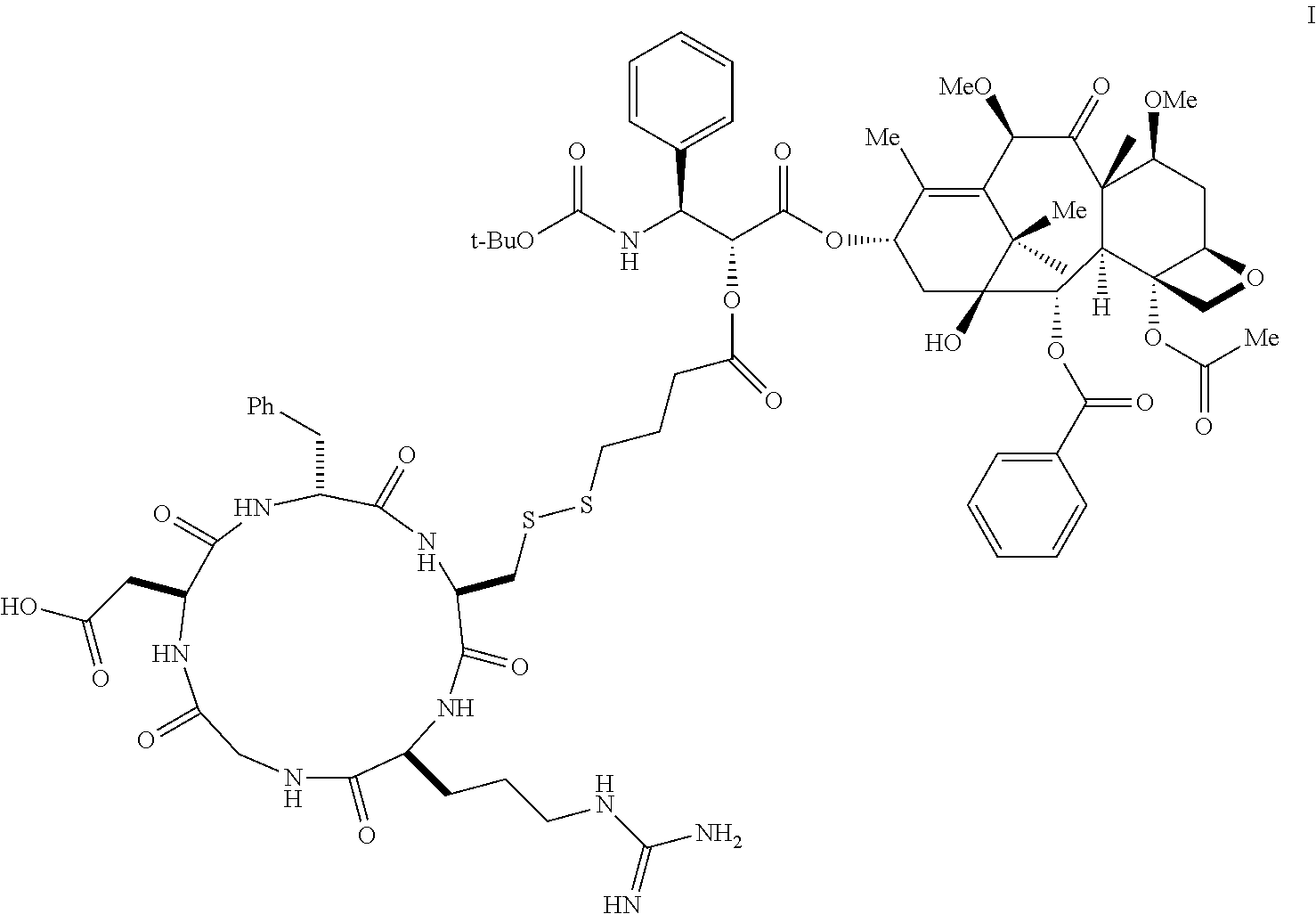
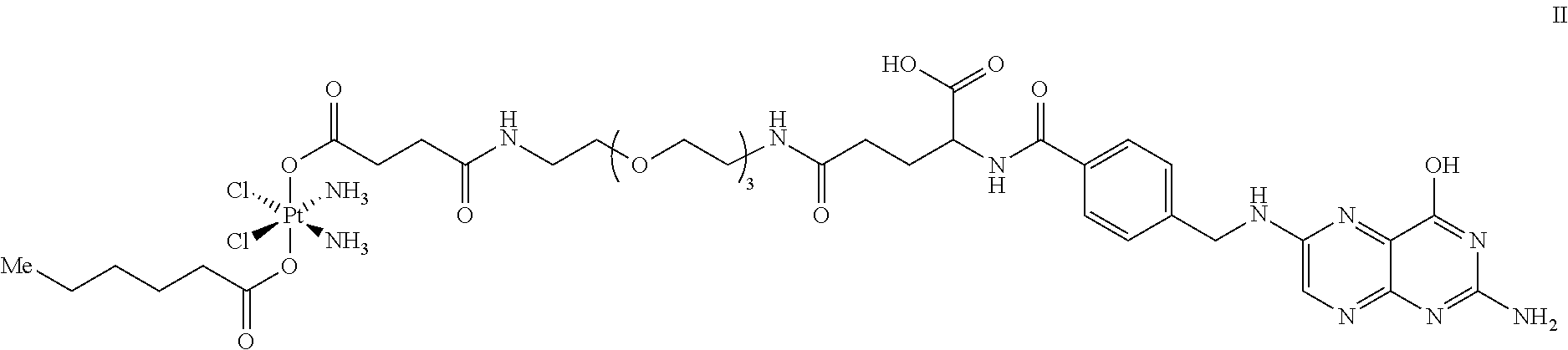
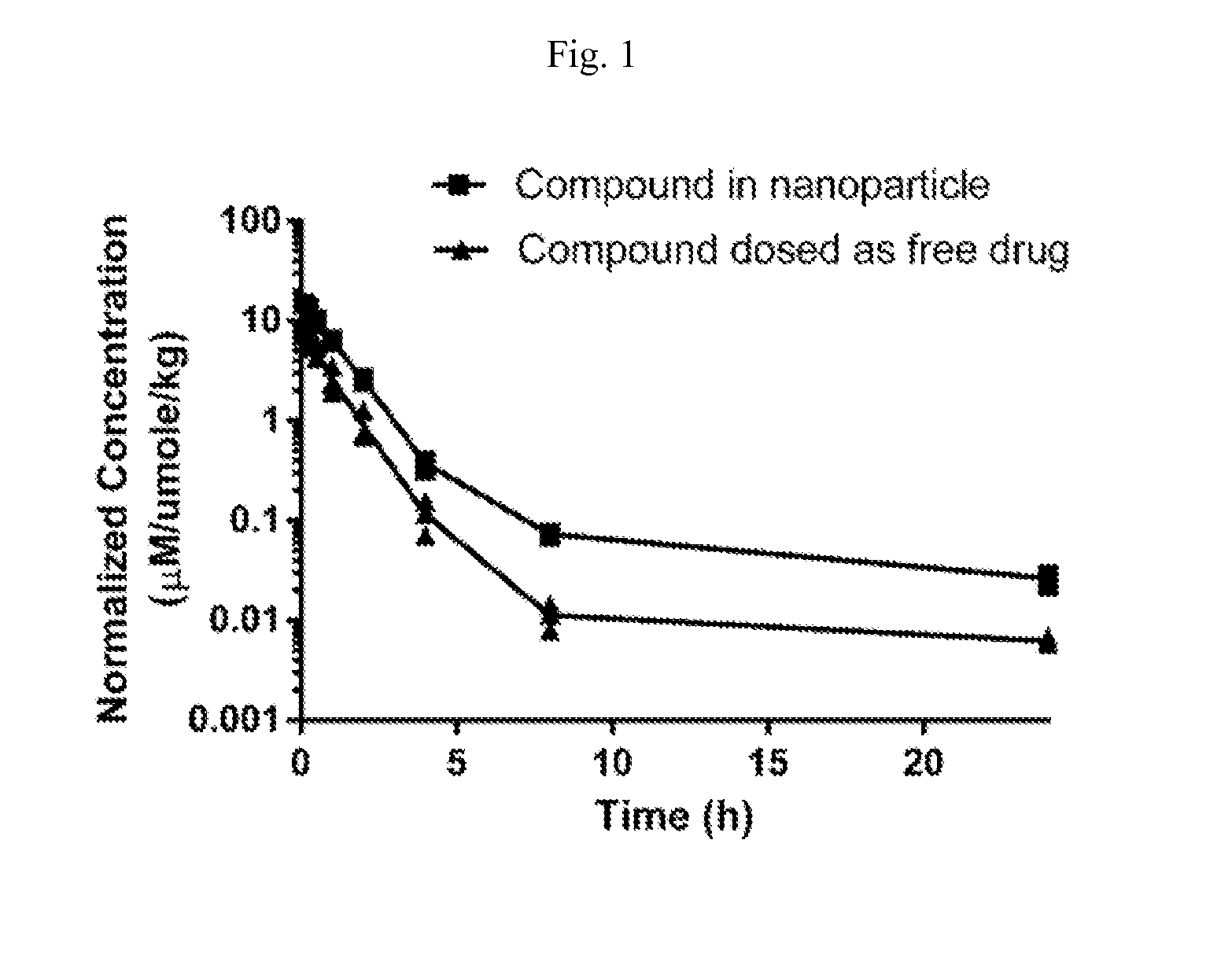
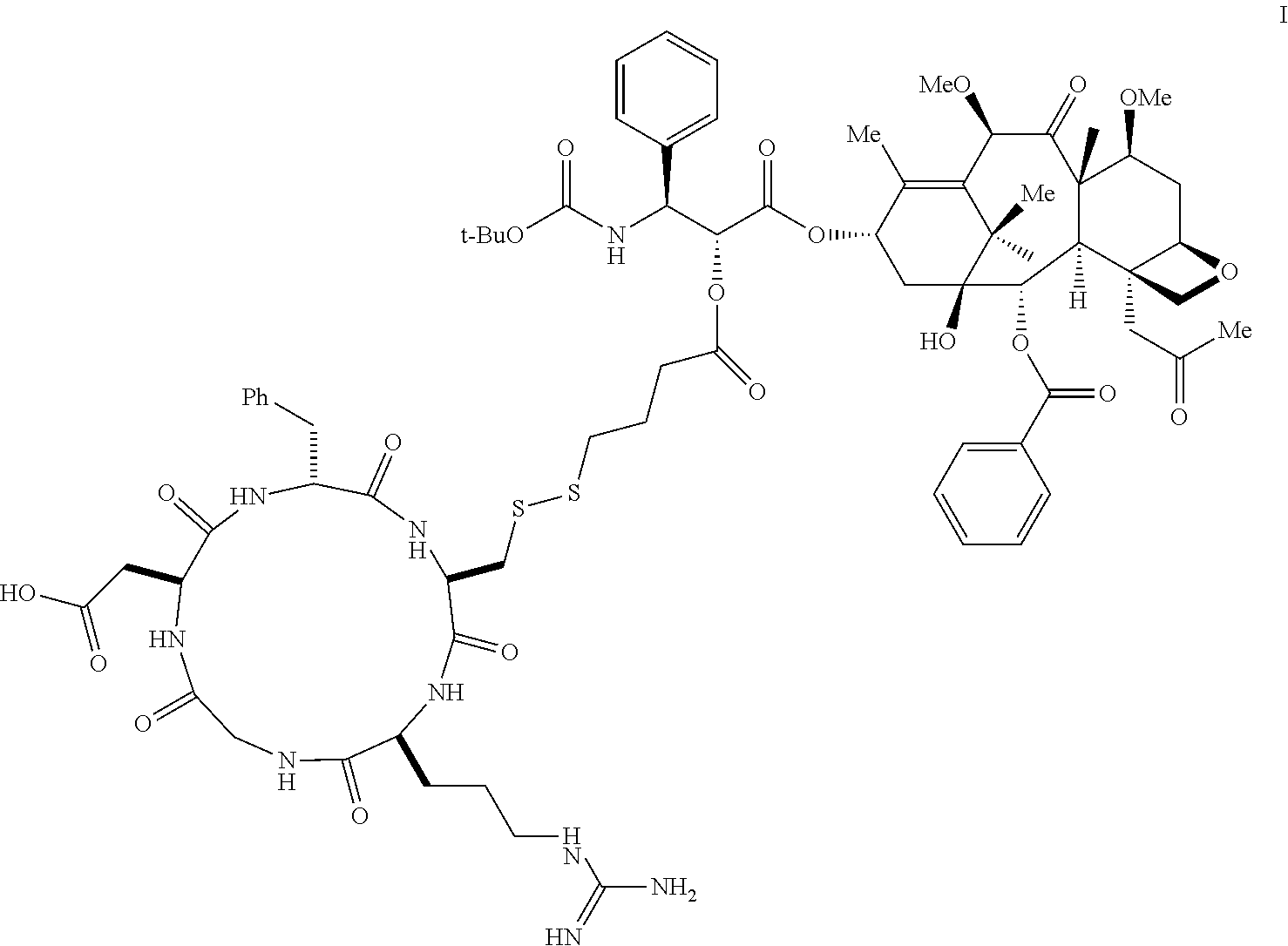
Patents
Literature
122 results about "Biodistribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
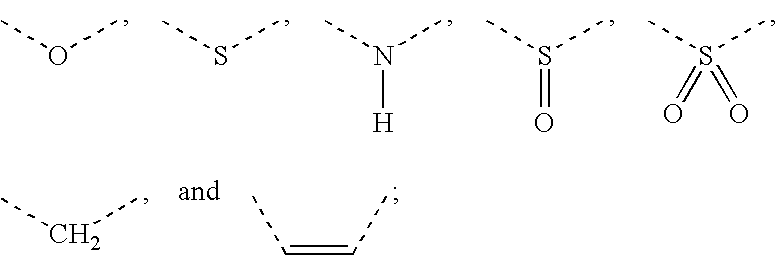
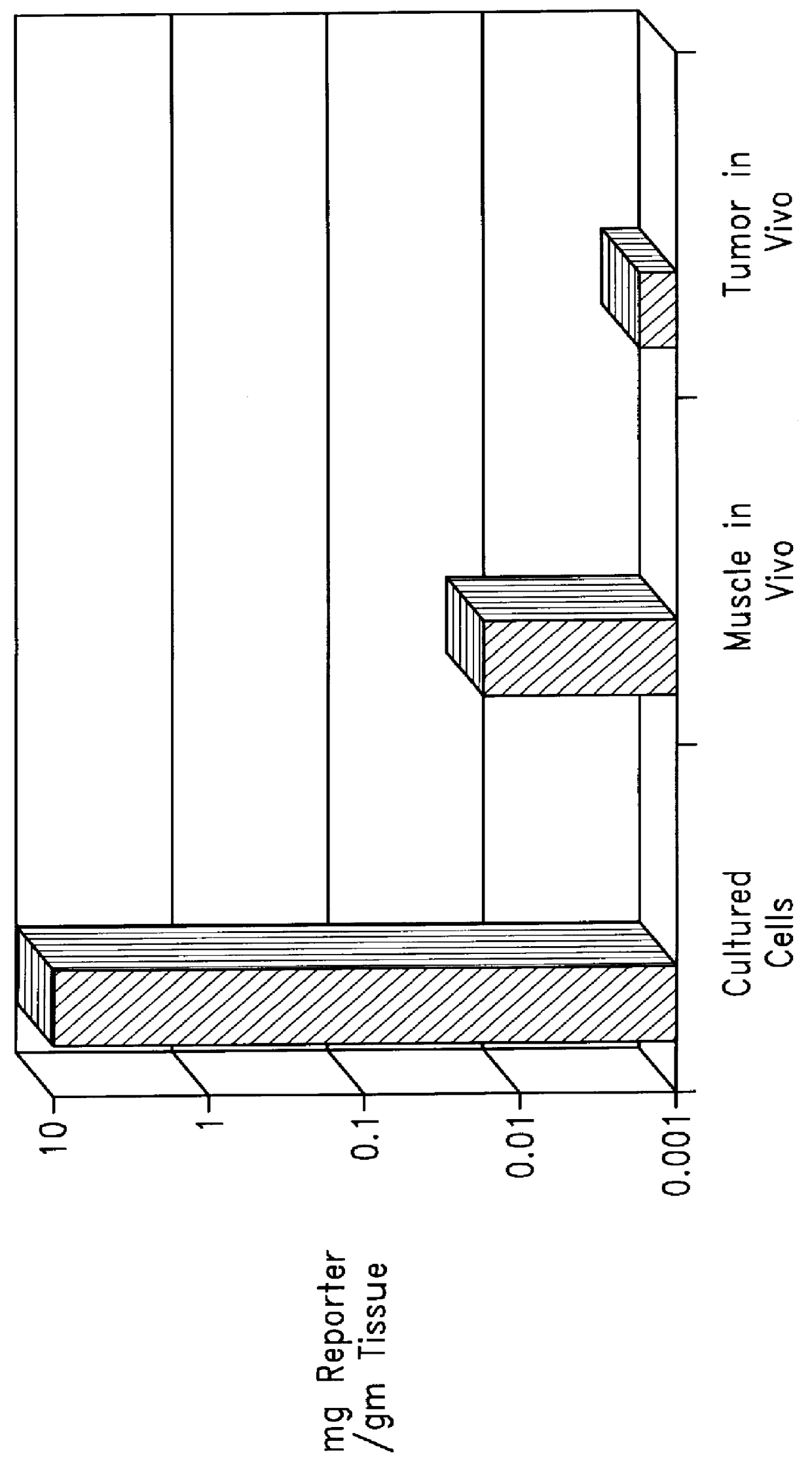
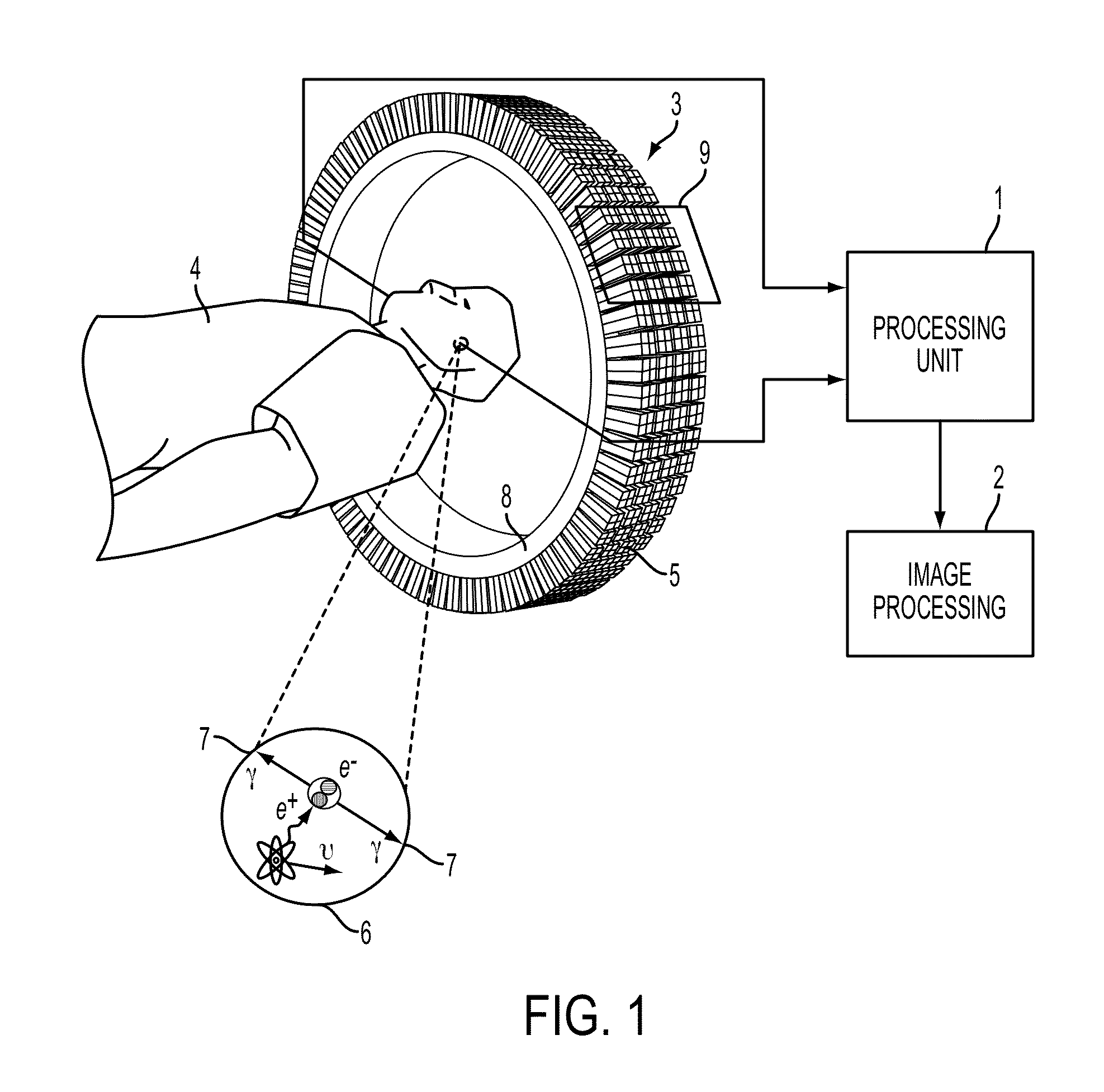
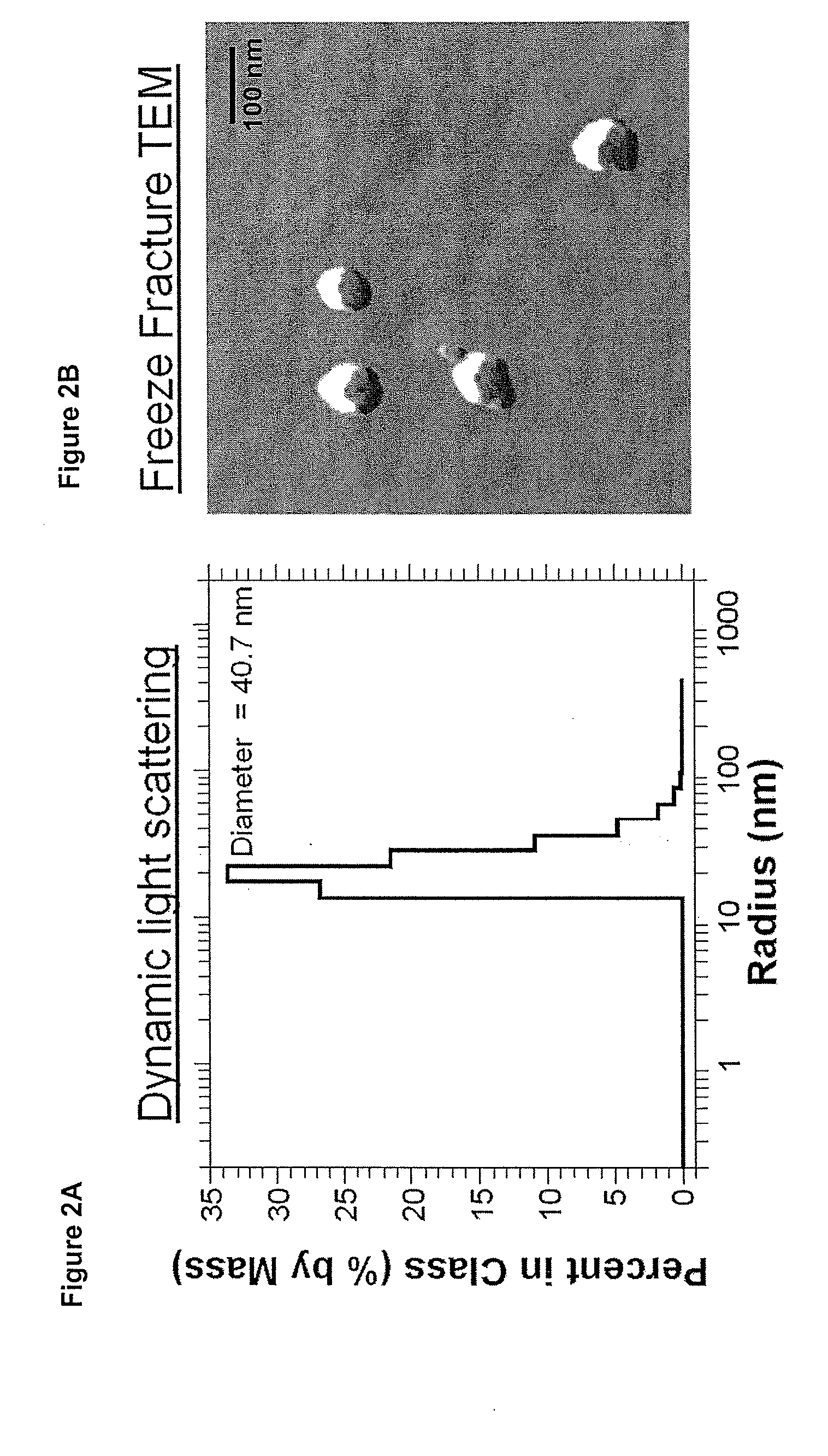
Biodistribution is a method of tracking where compounds of interest travel in an experimental animal or human subject. For example, in the development of new compounds for PET (positron emission tomography) scanning, a radioactive isotope is chemically joined with a peptide (subunit of a protein). This particular class of isotopes emits positrons (which are antimatter particles, equal in mass to the electron, but with a positive charge). When ejected from the nucleus, positrons encounter an electron, and undergo annihilation which produces two gamma rays travelling in opposite directions. These gamma rays can be measured, and when compared to a standard, quantified.
Compositions for the delivery of therapeutic agents and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060051405A1Improve stabilityPromote accumulationSpecial deliveryMicroencapsulation basedLipid formationMedicine
The present invention provides drug delivery vehicles comprising polytheylyene-lipid conjugates (PEG-lipid), wherein the circulation lifetime and biodistribution of the drug delivery vehicles are regulated by the PEG-lipid. More particularly, the present invention provides liposomes, SNALP and SPLP comprising such PEG-lipid conjugates, and methods of using such compositions to selectively target a tumor site or other tissue of interest (e.g., liver, lung, spleen, etc.).
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Cluster clearing agents
InactiveUS6908903B1Rapid and efficient complexationImprove efficiencyBiocideNanomedicineClearing AgentHepatic clearance
Cluster clearing agents (CCAs) and the use thereof are discussed. CCAs are composed of a hepatic clearance directing moiety which directs the biodistribution of a CCA-containing construct to hepatic clearance; and a binding moiety which mediates binding of the CCA to a compound for which rapid hepatic clearance is desired.
Owner:ALETHEON PHARMA
Formulations, conjugates, and combinations of drugs for the treatment of neoplasms
InactiveUS20050080075A1Reduce generationInhibiting passage across the blood-brain barrierOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNeoplasmBiodistribution
The invention provides formulations and structural modifications for phenothiazine compounds which result in altered biodistributions, thereby reducing the occurrence of adverse reactions associated with this class of drug.
Owner:COMBINATORX
Compositions and methods for enhanced biostability and altered biodistribution of oligonucleotides in mammals
InactiveUS6753423B1Improve biostabilityBiodistribution can be alteredOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalBiodistribution
The invention is directed to oligonucleotides and oligonucleosides functionalized to include lipophilic moieties and having improved biostability and altered biodistribution in mammals. In one embodiment, such lipophilic oligonucleotide conjugates are used in a method of targeting antisense oligonucleotides to hepatic tissues and thereby preferentially modulating gene expression in the liver and associated tissues of a mammal.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Enhanced biodistribution of oligomers
This invention relates generally to oligomers useful for modulating expression and / or activity of RNAs or genes. More particularly, the invention relates to single stranded, double stranded, partially double stranded and hairpin structured chemically modified oligomers that have a broad biodistribution profile for inhibiting RNA expression in a plurality of cells, tissues, or organs, and to methods of making and using the modified oligomers.
Owner:GROOVE BIOPHARMA CORP
Degradable polyacetal polymers
InactiveUS20020082362A1Microbiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDrugBiodistribution
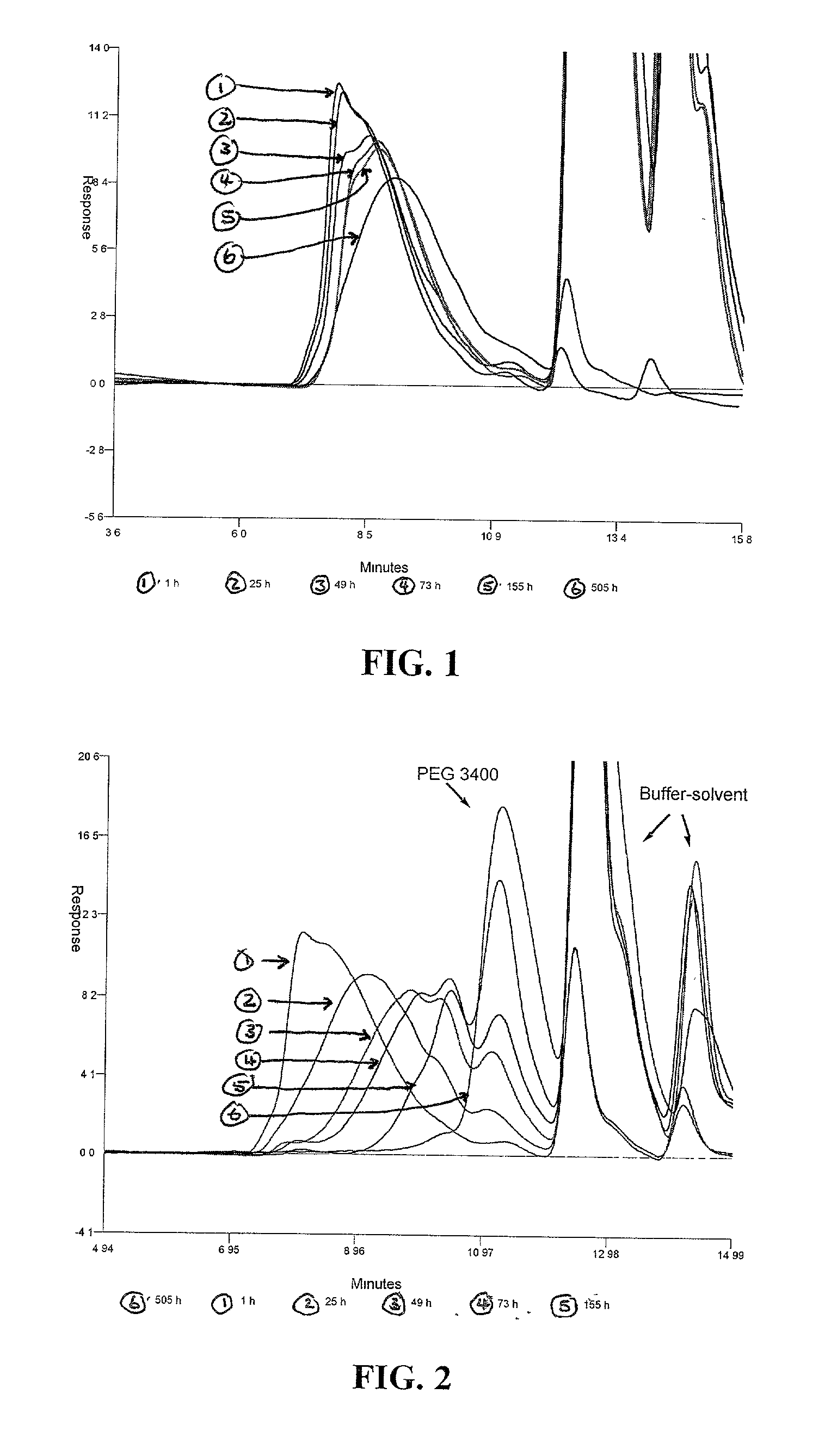
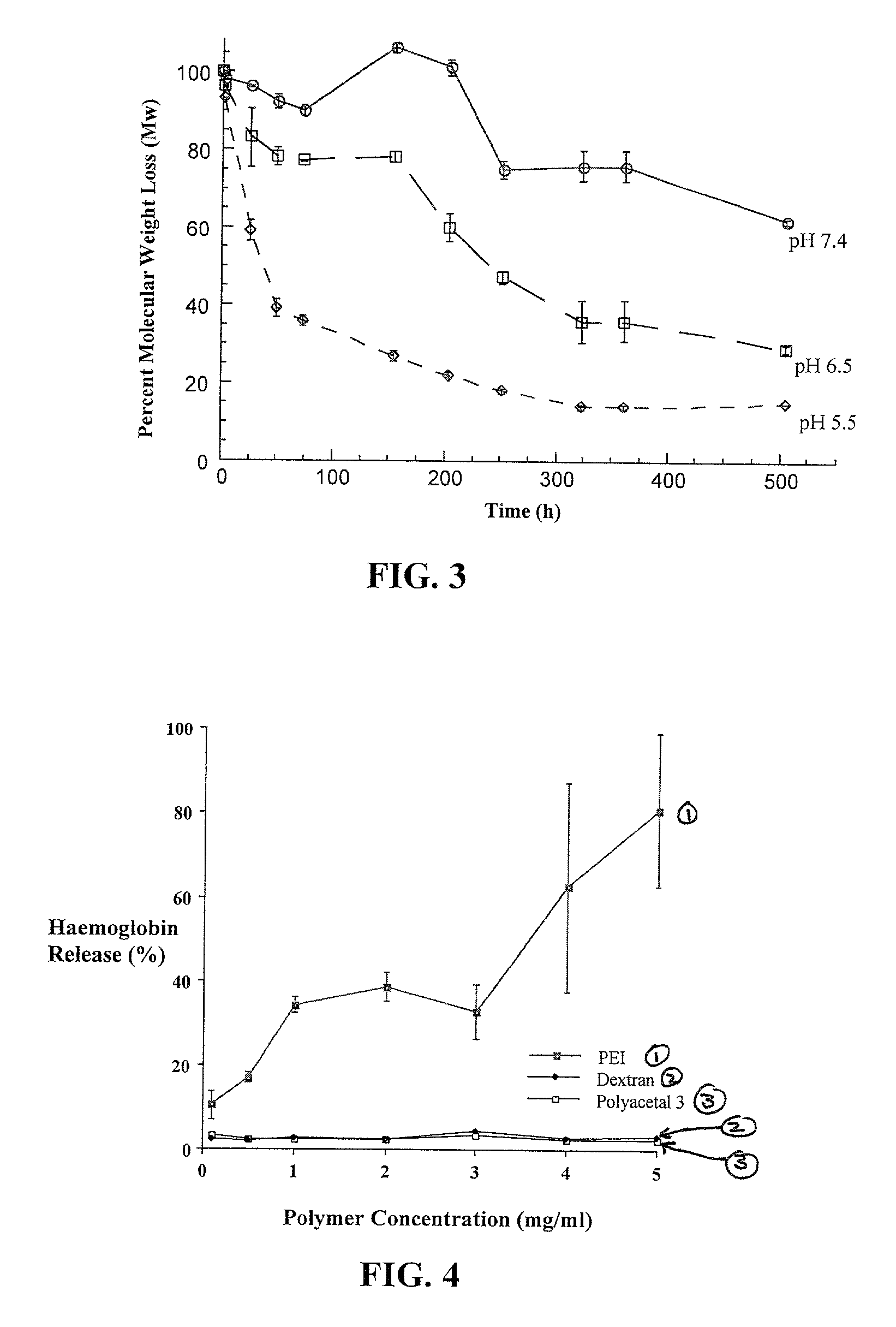
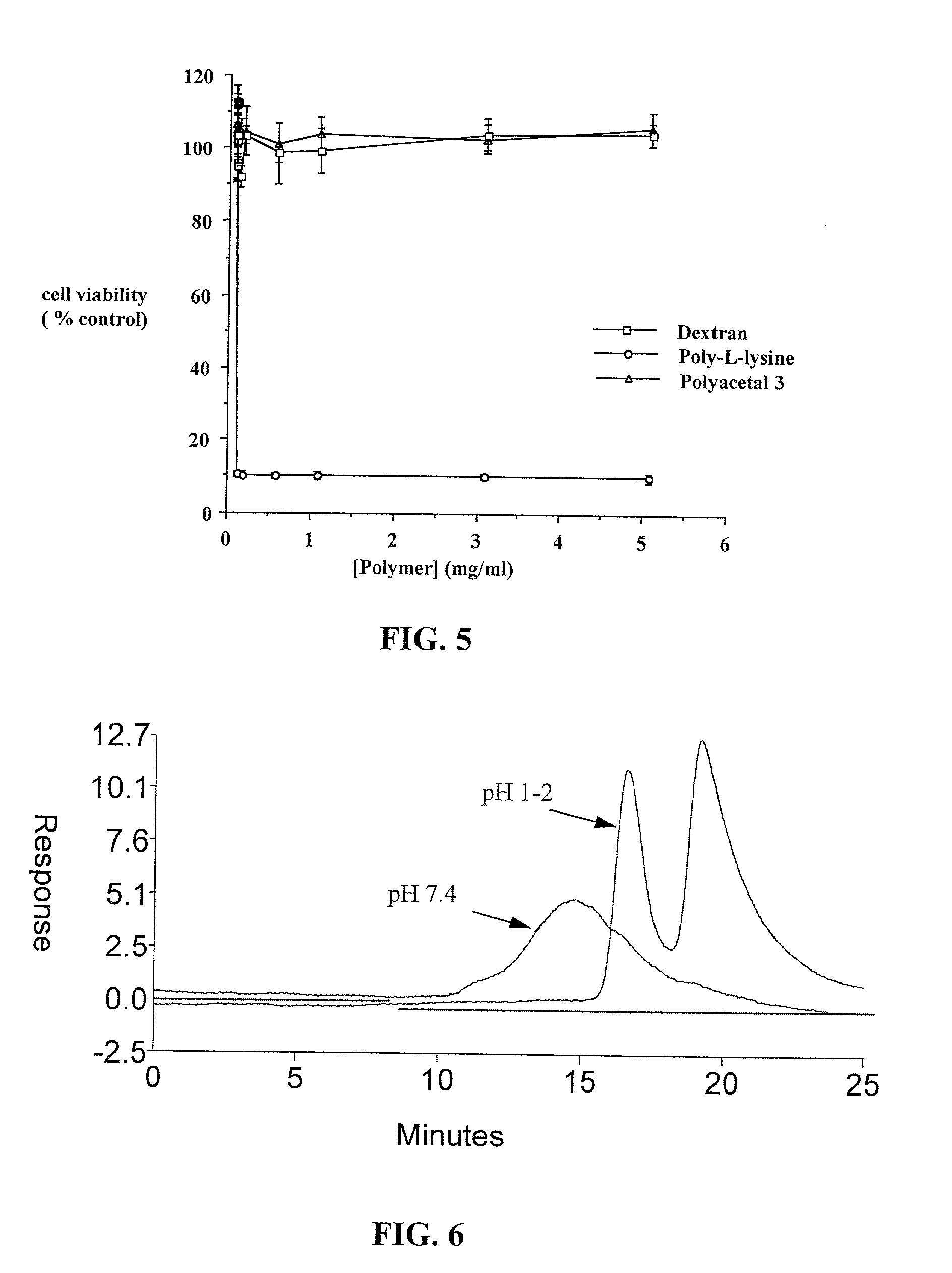
Degradable polyacetal polymers and functionalized degradable polyacetal polymers have properties favorable for use in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. The degradable polyacetal polymers are relatively stable at physiological pH with favorable biodistribution profiles, and degrade readily in low pH conditions. Conjugates of the polymers with drugs, especially anticancer drugs, and methods of treatment of cancer.
Owner:HERON THERAPEUTICS
Drug Delivery Formulations For Targeted Delivery
The size and location of microsphere uptake / delivery are important determinants of the final biodistribution of oral microsphere systems. Formulations, kits, methods of administering the formulations, and using the kits are described herein. The formulations are oral dosage formulations. In one embodiment, the formulations contain microparticles and / or nanoparticles having a homogenous size range selected to optimize uptake in a specific region of the GI tract and target drug delivery to specific organs. In some embodiments, the dosage formulation contains an enteric coating and / or a magnetic material. In a preferred embodiment, the formulation contains a magnetic material and an active agent to be delivered, optionally the active agent is in the form of micro- or nano-particles. In some embodiments metallomucoadhesive materials and / or magnetic materials are employed as magnetic and / or mucoadhesive sources. Formulations containing magnetic materials can be localized using the kits and methods disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the method includes orally administering the formulation and applying an extracorporeal magnet to a site on the outside surface of the patient's body in an area that closely apposes the location in the gastrointestinal tract to which delivery of the formulation is desired. The extracorporeal magnet is applied for a suitable time period to allow for the drug to be released from the formulation and / or to allow for the formulation to adhere to the site. Both magnetic and mucoadhesive forces may be utilized to site-direct and retain the dosage form in the region of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract most suitable for the desired delivery.
Owner:PEROSPHERE INC
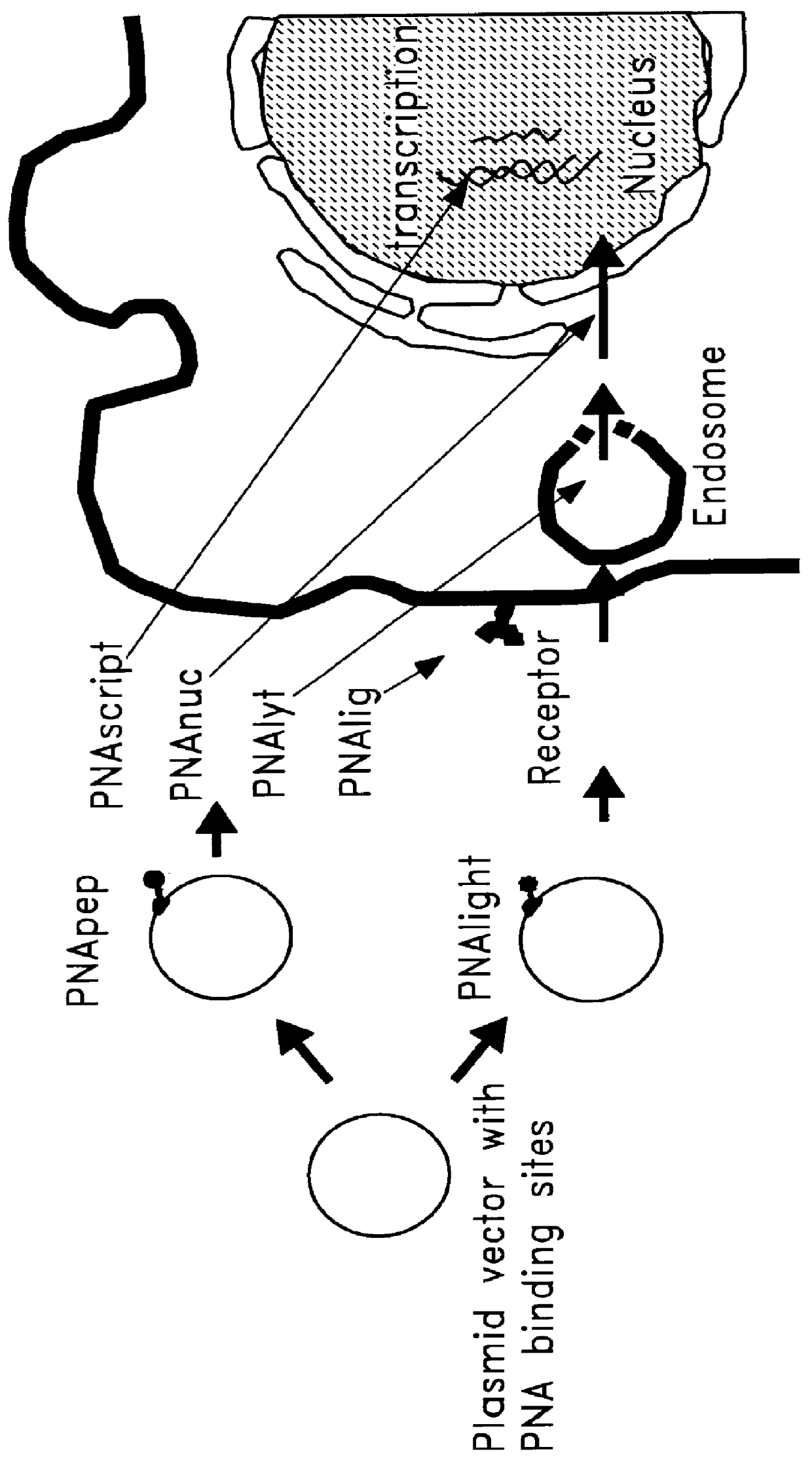
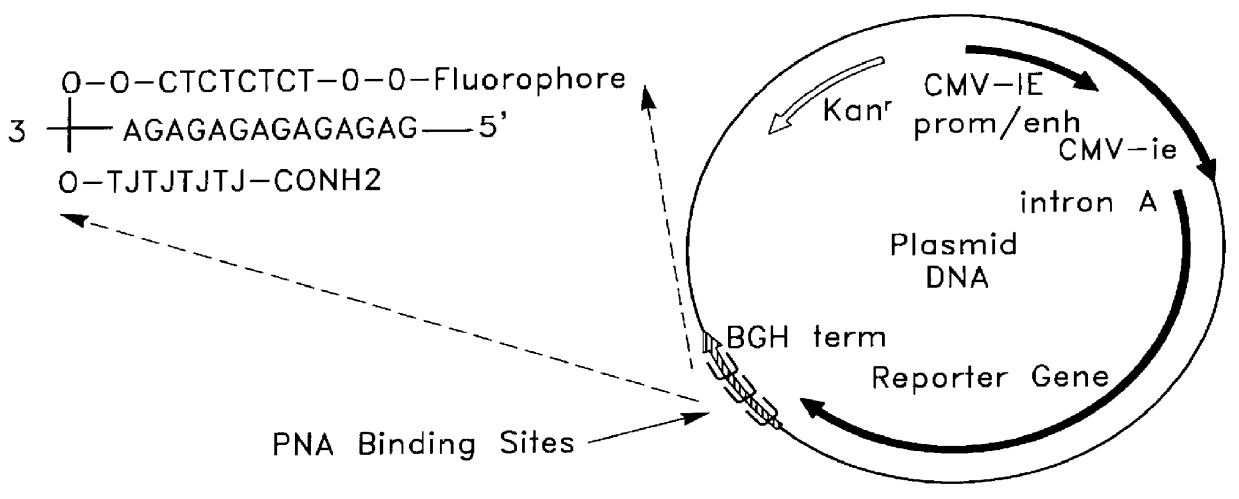
Chemical modification of DNA using peptide nucleic acid conjugates
InactiveUS6165720AReduce deliveryHigh transfection efficiencyFungiBacteriaEukaryotic plasmidsBiological activation
Complexes comprising a nucleic acid molecule and a conjugated peptide nucleic acid (PNA). The PNA may be labeled or conjugated to a protein, peptide, carbohydrate moiety or receptor ligand. These complexes are used to transfect cells to monitoring plasmid biodistribution, promote nuclear localization, induce transcriptional activation, lyse the endosomal compartment and facilitate transfection. These complexes increase the efficiency of expression of a particular gene.
Owner:GENE THERAPY SYST +1
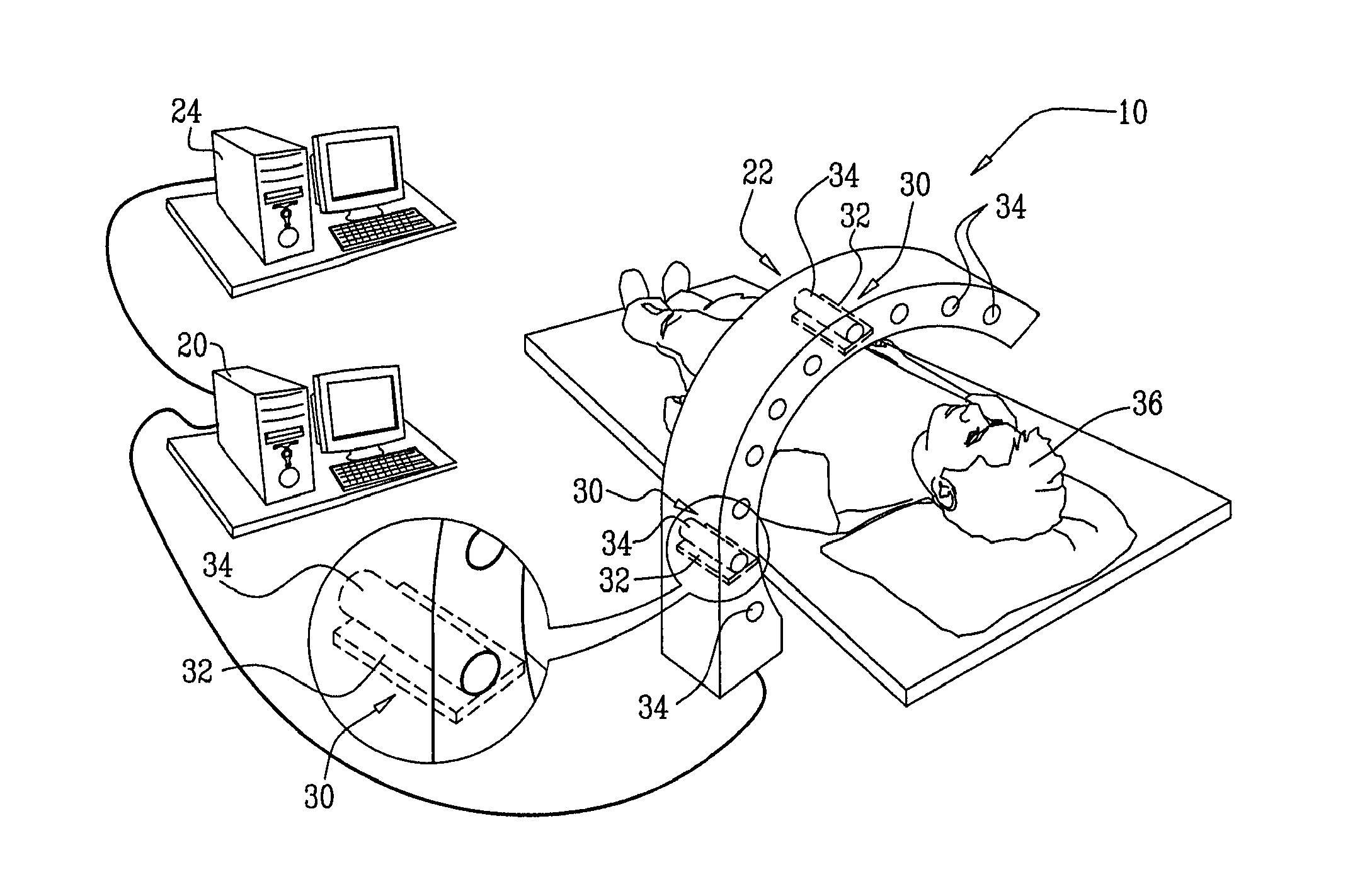
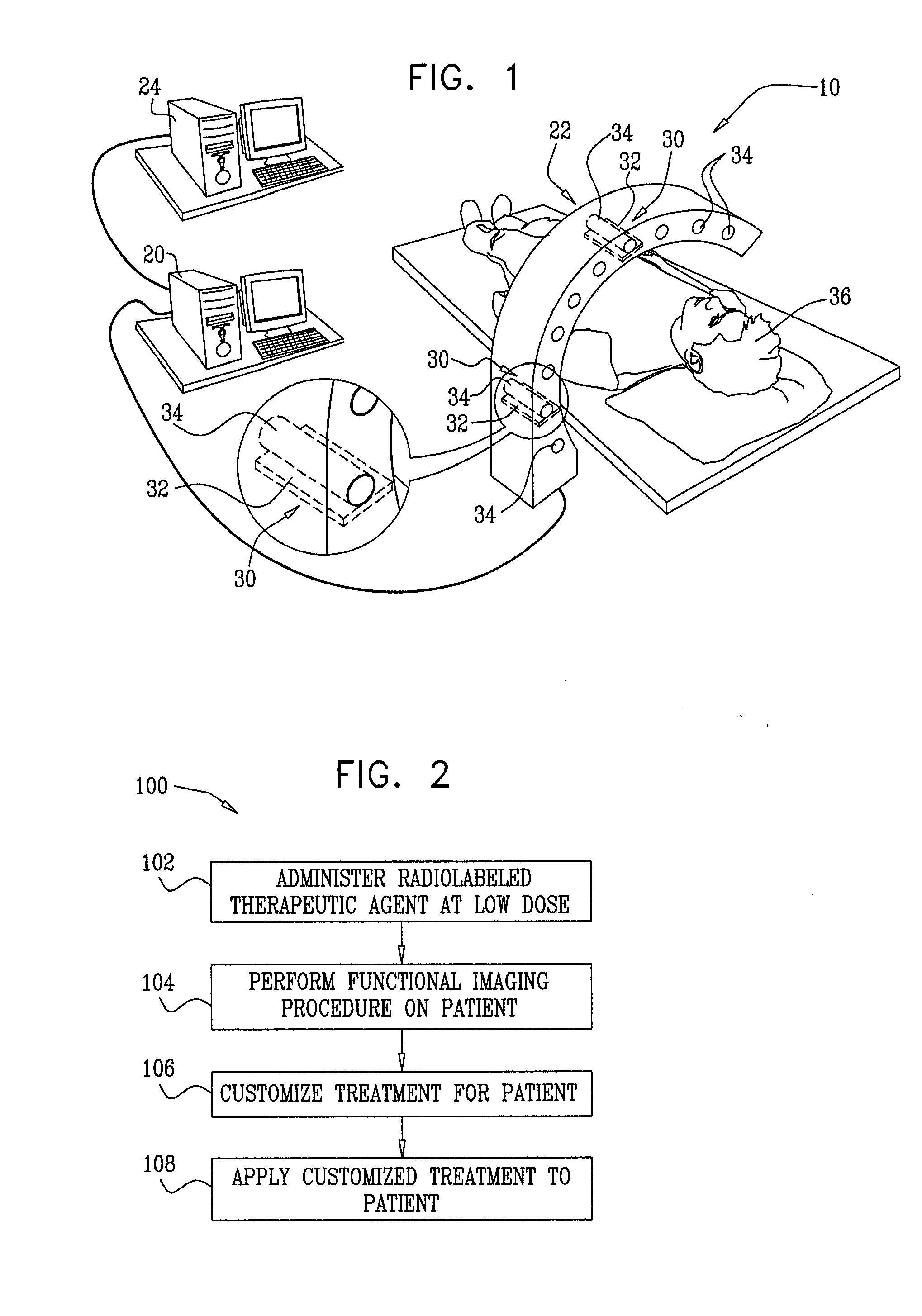
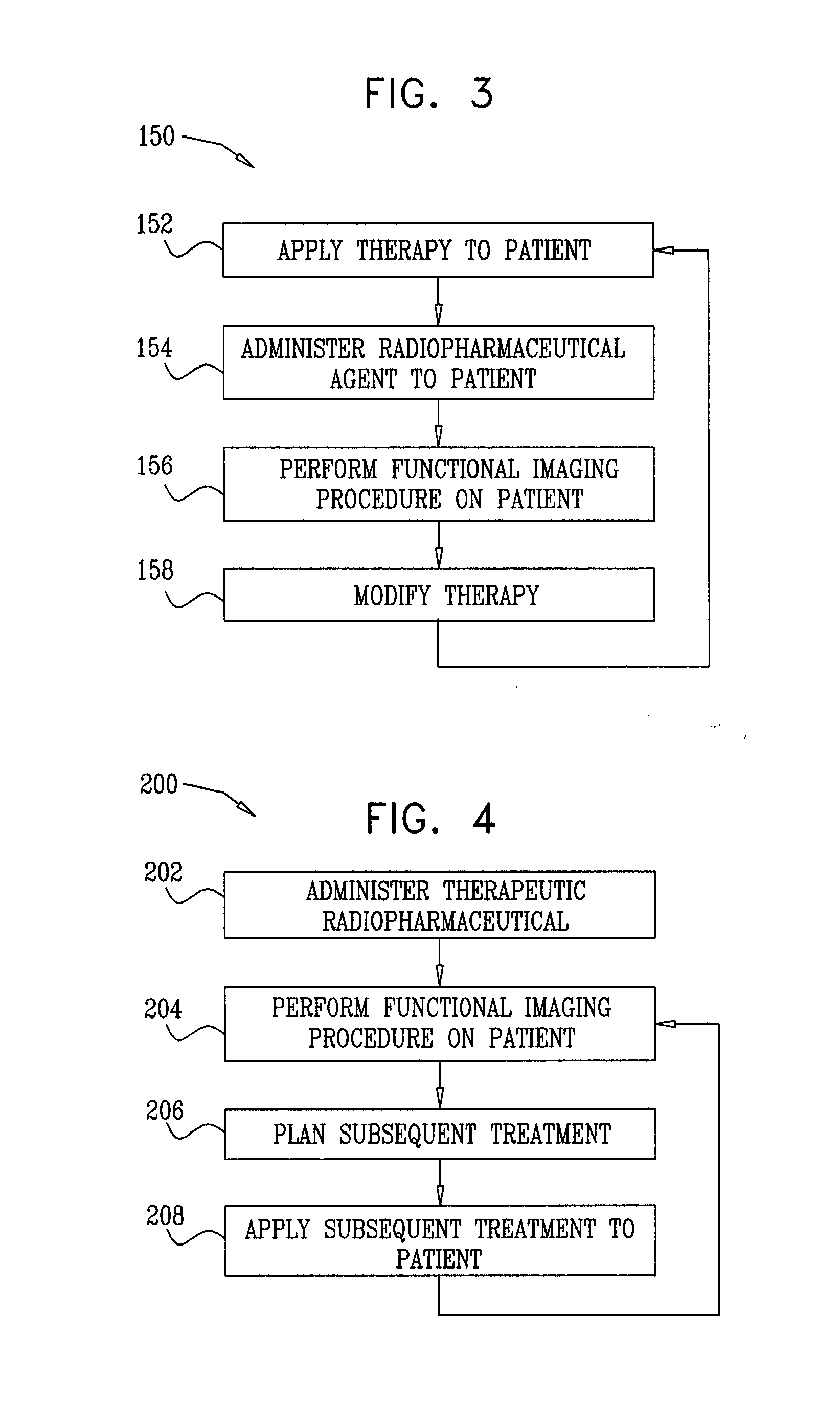
Radiopharmaceuticals For Diagnosis And Therapy
ActiveUS20070265230A1Maximize effectivenessConvenient treatmentCompounds screening/testingBiocideRadiology markerHuman patient
A method for treating a human patient is provided, including administering a radiolabeled form of a therapeutic agent to the patient at a first substantially non-therapeutically-effective dose, wherein pharmacological activity of the therapeutic agent is not due to radioactivity of the therapeutic agent. The method also includes determining information related to a biodistribution of the radiolabeled form of the therapeutic agent in the patient by performing a radioimaging procedure on the patient. Responsively to the information, a decision is made whether or not to treat the patient by administering the therapeutic agent to the patient. If the decision is made to treat the patient, the patient is treated by administering the therapeutic agent to the patient at a second therapeutically-effective dose. If the decision is made not to treat the patient, treatment of the patient with the therapeutic agent is withheld. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
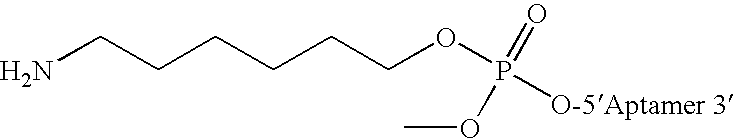
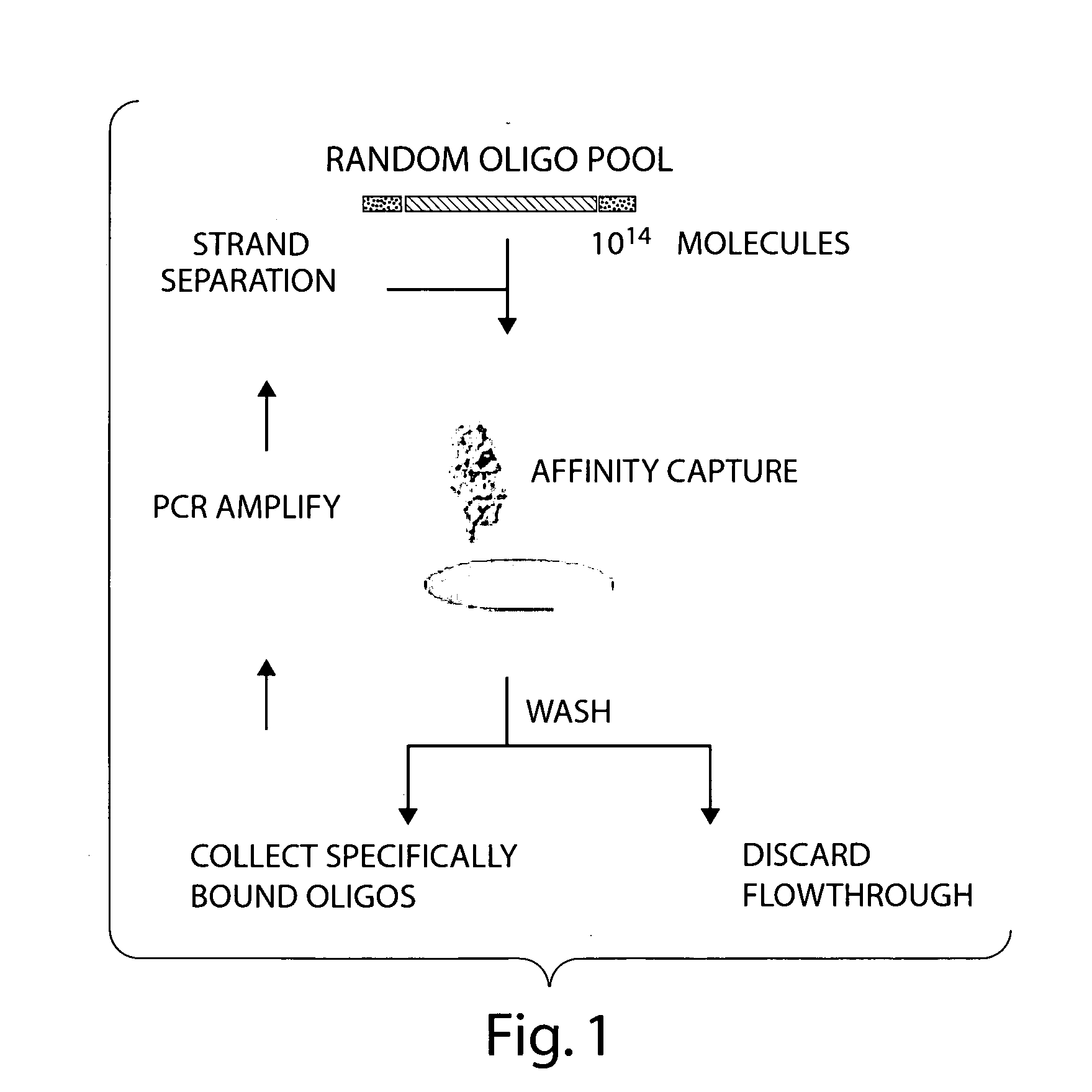
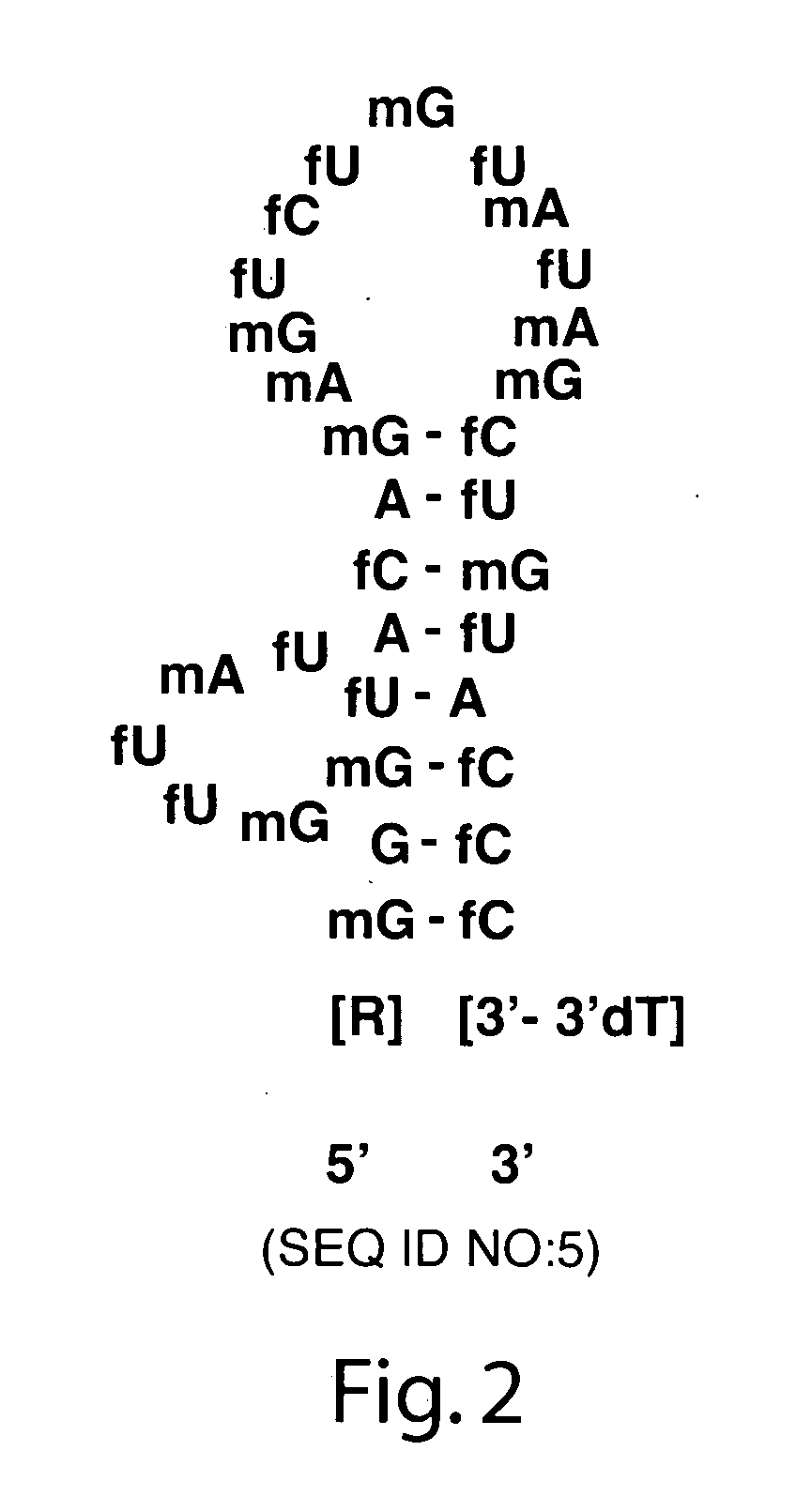
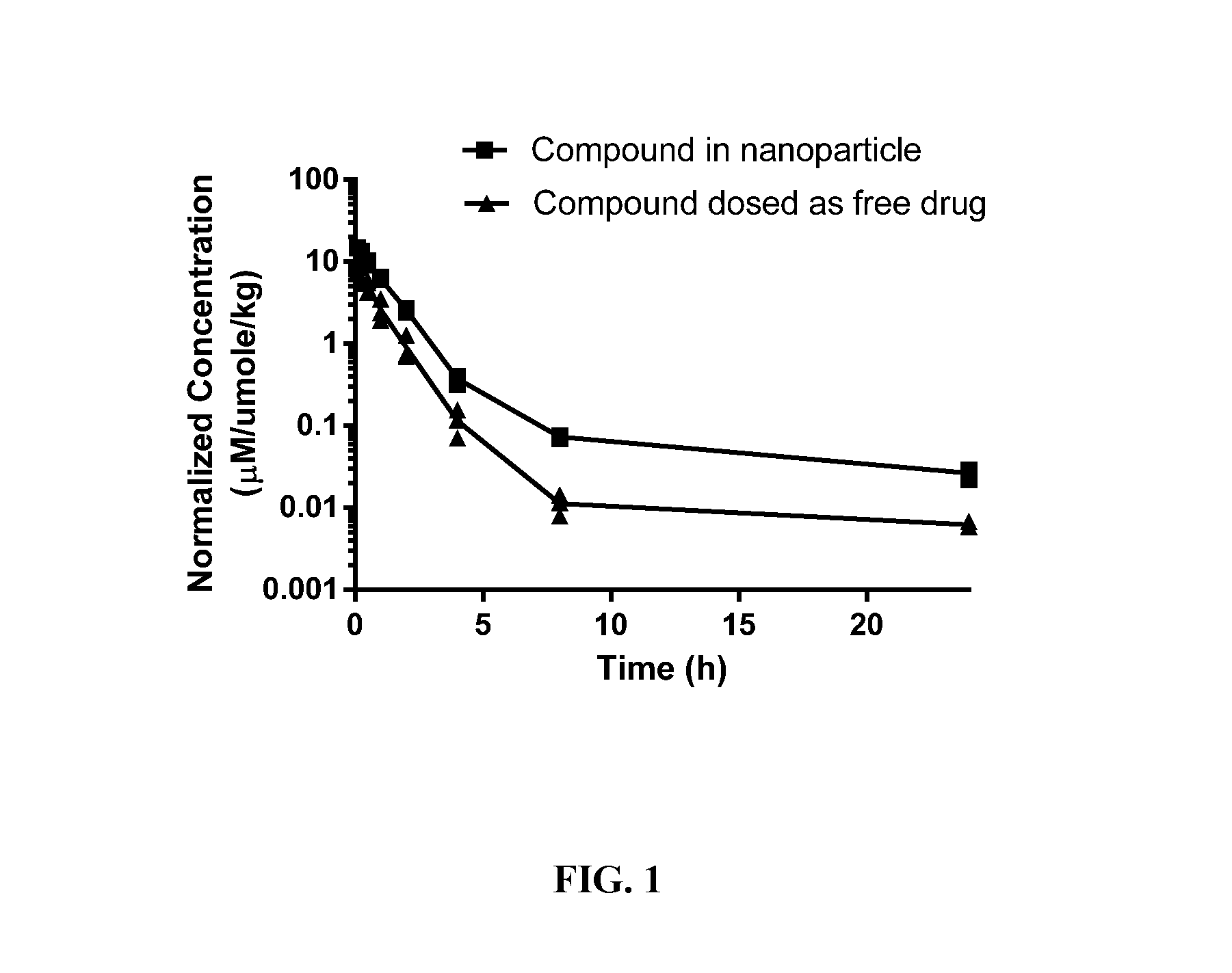
Controlled modulation of the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of aptamer therapeutics
InactiveUS20060030535A1Reduce distributionReduce ratePowder deliveryActivity regulationControl mannerBiodistribution
Materials and methods are provided to modulate, in a controlled manner, the pharmacokinetic and biodistribution properties of nucleic acid aptamers, and to enhance their safety and efficacy properties as therapeutic agents.
Owner:ARCHEMIX CORP
Targeted Conjugates Encapsulated in Particles and Formulations Thereof
InactiveUS20140187501A1Improve permeabilityImprove retention effectOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiagnostic agentActive agent
Particles, including nanoparticles and microparticles, and pharmaceutical formulations thereof, containing conjugates of an active agent such as a therapeutic, prophylactic, or diagnostic agent attached to a targeting moiety via a linker have been designed which can provide improved temporospatial delivery of the active agent and / or improved biodistribution. Methods of making the conjugates, the particles, and the formulations thereof are provided. Methods of administering the formulations to a subject in need thereof are provided, for example, to treat or prevent cancer or infectious diseases.
Owner:TVA (ABC) LLC
Sstr-targeted conjugates encapsulated in particles and formulations thereof
InactiveUS20160074526A1Improved biodistributionImprove permeabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiagnostic agentMedicine
Particles, including nanoparticles and microparticles, and pharmaceutical formulations thereof, containing conjugates of an active agent such as a therapeutic, prophylactic, or diagnostic agent attached to a targeting moiety via a linker have been designed which can provide improved temporospatial delivery of the active agent and / or improved biodistribution. Methods of making the conjugates, the particles, and the formulations thereof are provided. Methods of administering the formulations to a subject in need thereof are provided, for example, to treat or prevent cancer or infectious diseases.
Owner:TVA (ABC) LLC
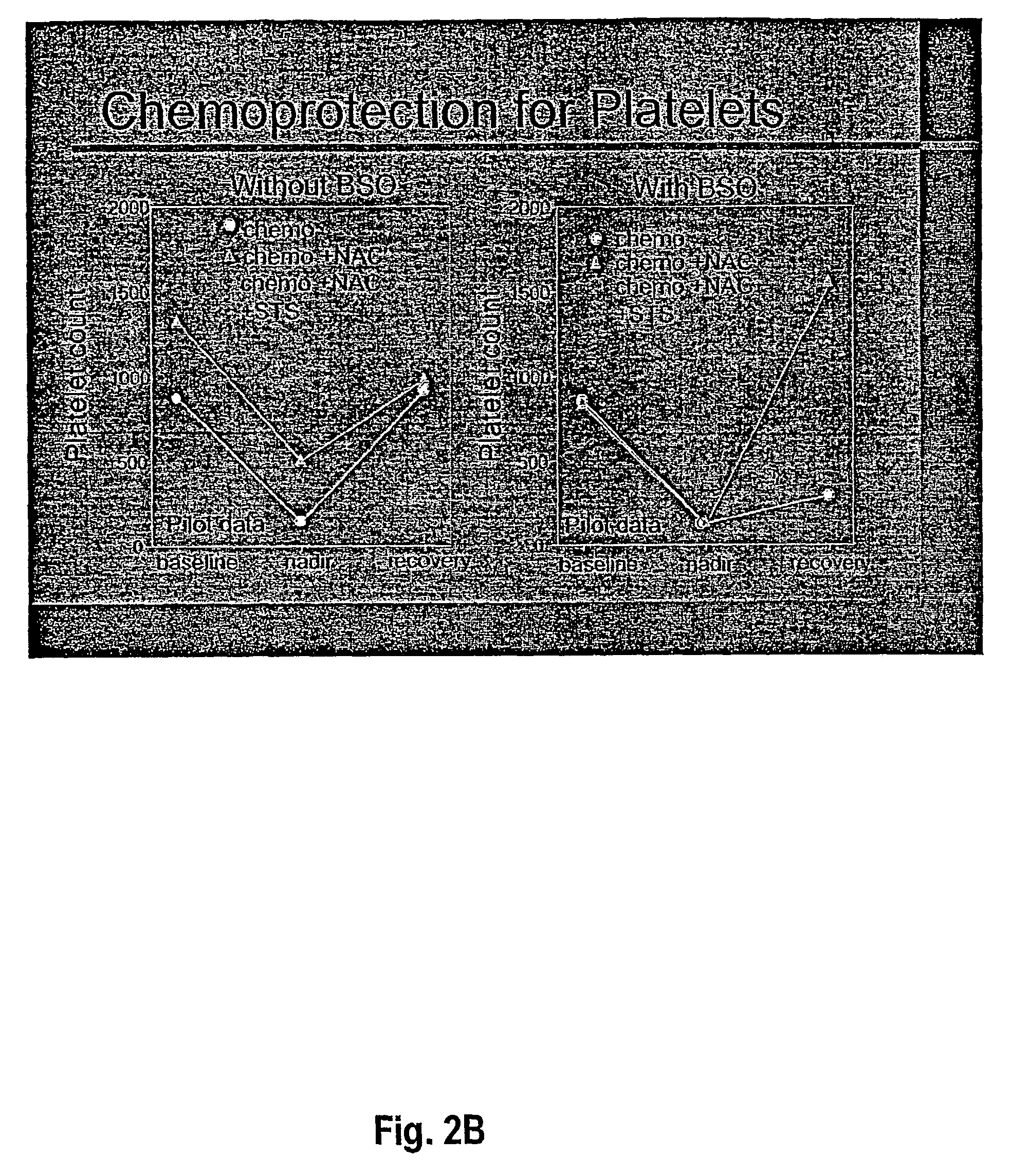
Administration of a thiol-based chemoprotectant compound
InactiveUS20060177523A1Treat and mitigate side effectProtect from harmBiocideDipeptide ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthSide effect
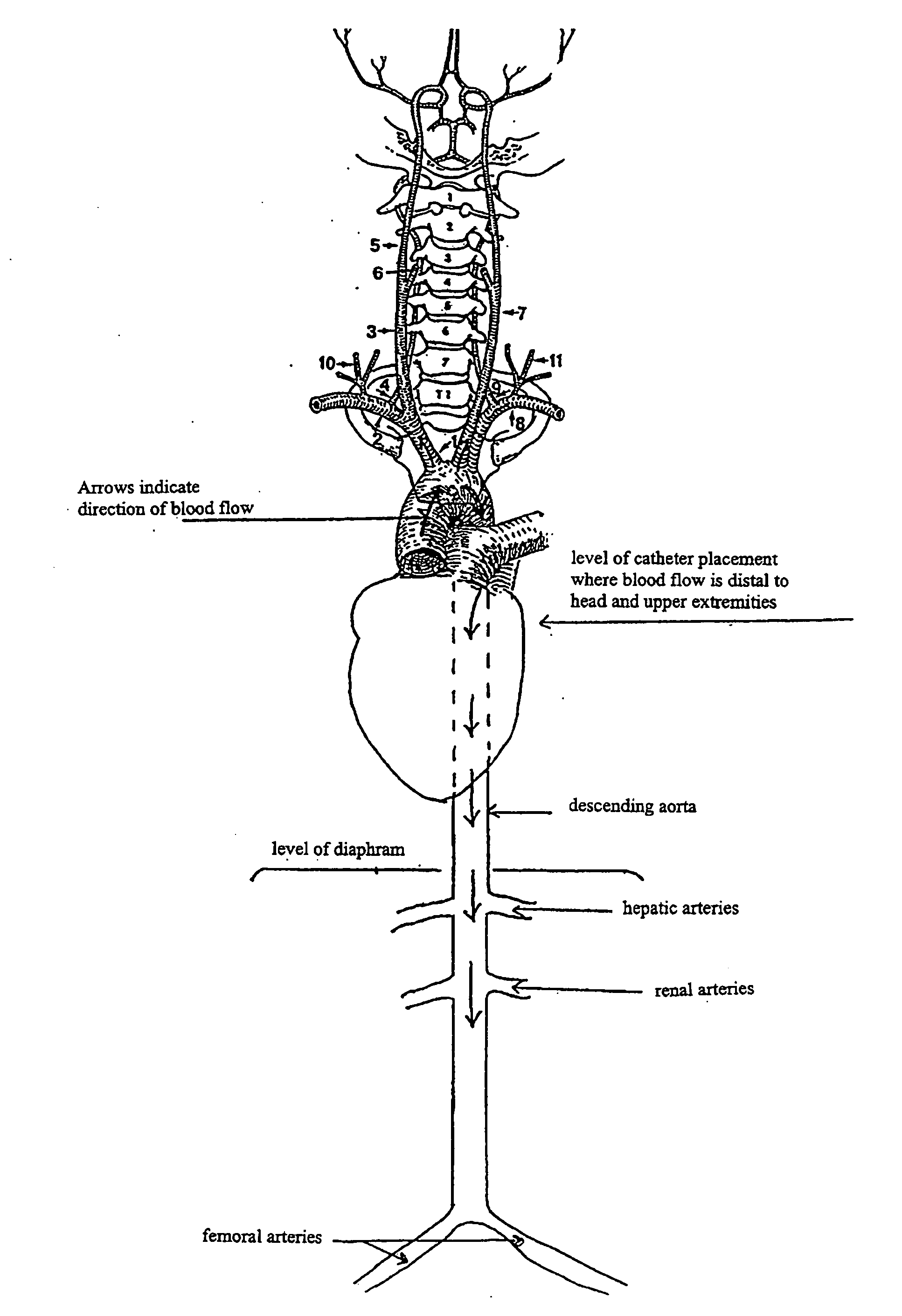
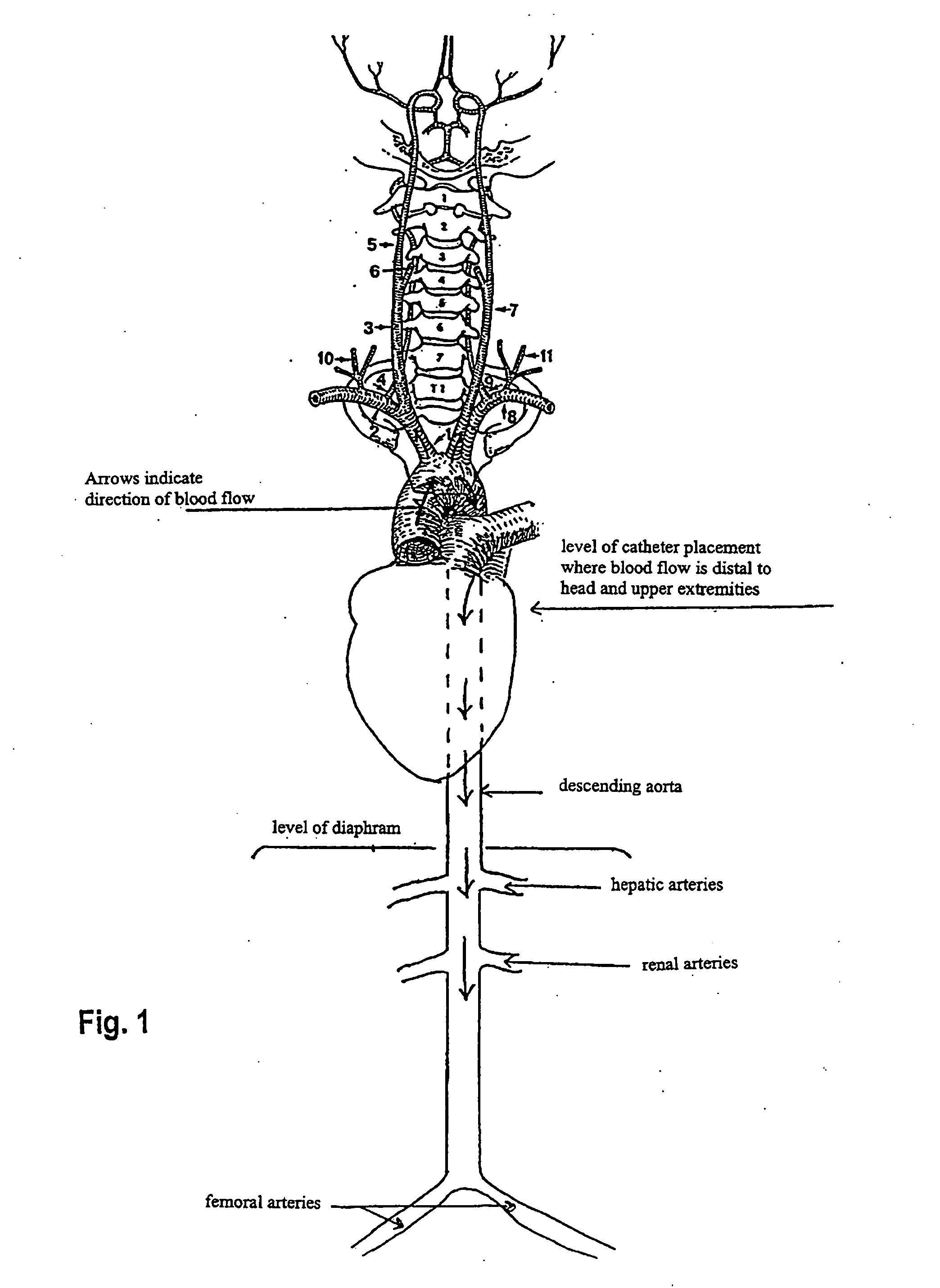
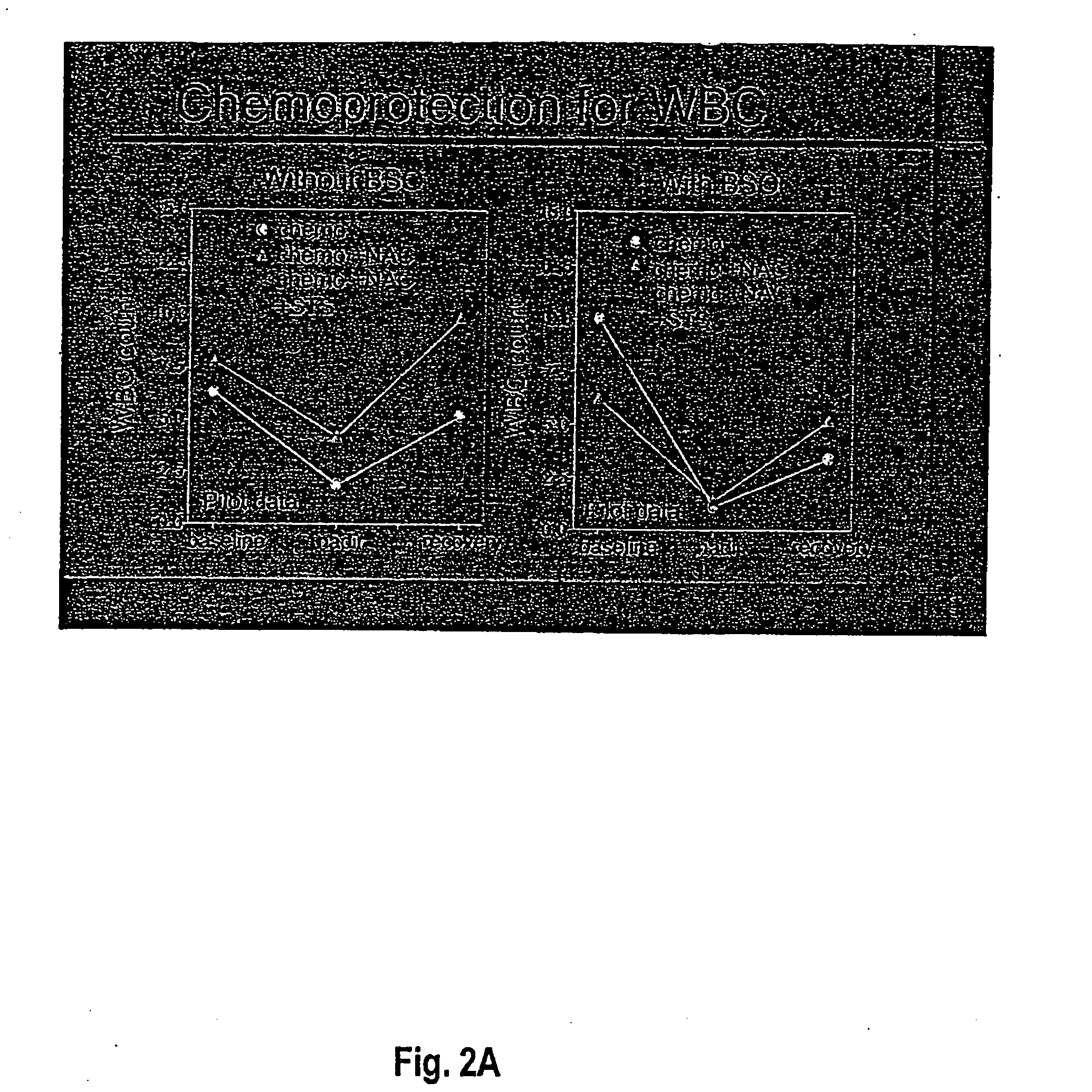
A method of administration of a thiol-based chemoprotectant agent including NAC (N-acetylcysteine) and STS (sodium thiosulfate) that markedly affects biodistribution and protects against injury from diagnostic or therapeutic intra-arterial procedures. A method for treating or mitigating the side effects of cytotoxic cancer therapy for tumors located in the head or neck and brain tumors. The thiol-based chemoprotectant agent is administered intra-arterially with rapid and first pass uptake in organs and tissues other than the liver.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +1
Degradable polyacetal polymers
InactiveUS7220414B2Microbiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsBiodistributionOrganic chemistry
Degradable polyacetal polymers and functionalized degradable polyacetal polymers have properties favorable for use in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. The degradable polyacetal polymers are relatively stable at physiological pH with favorable biodistribution profiles, and degrade readily in low pH conditions. Conjugates of the polymers with drugs, especially anticancer drugs, and methods of treatment of cancer.
Owner:HERON THERAPEUTICS
Vehicles for Controlled Delivery of Different Pharmaceutical Agents
ActiveUS20150064265A1Facilitate different rate of releaseAdvantageous biodistributionOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryChemical compositionMedicine
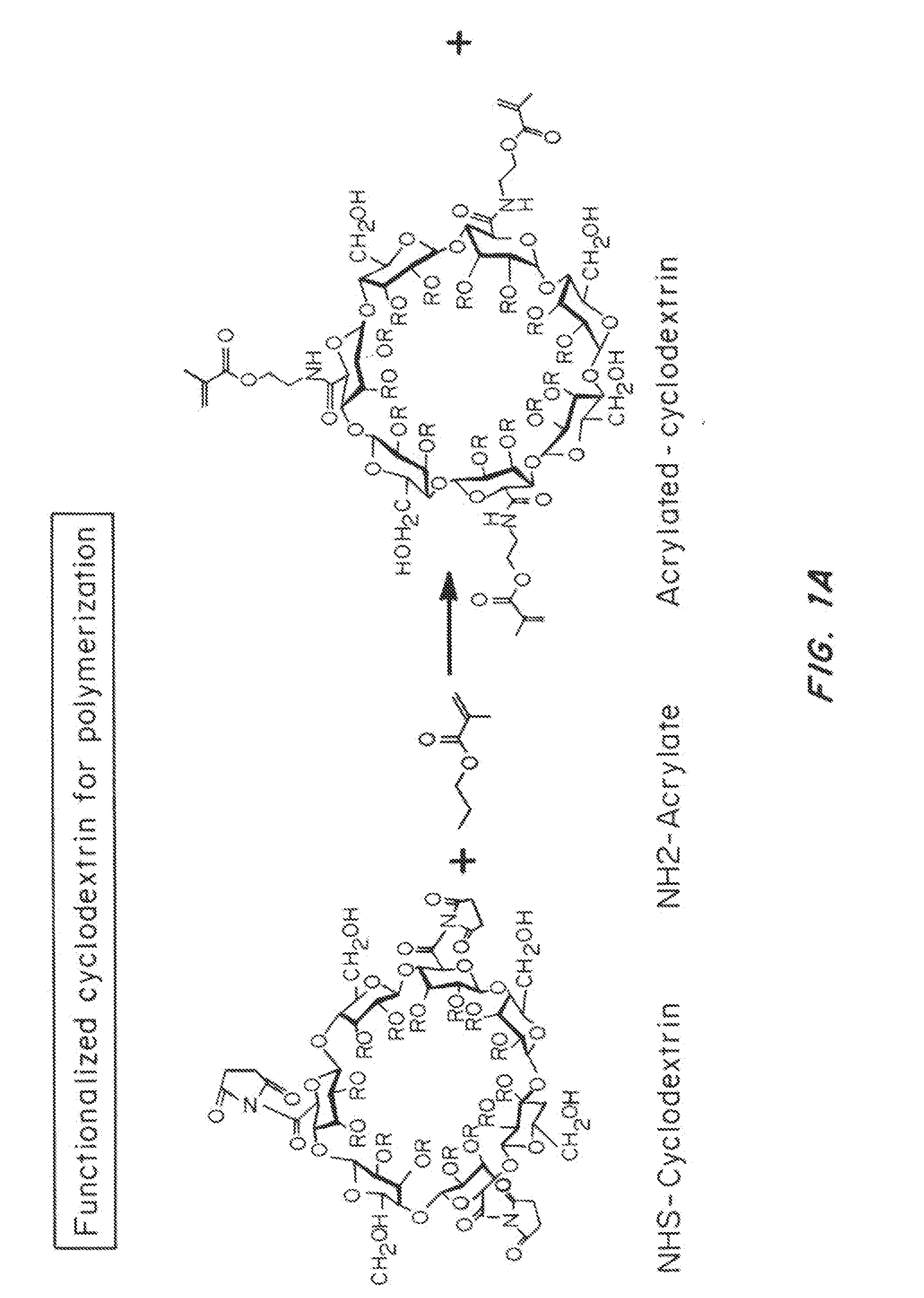
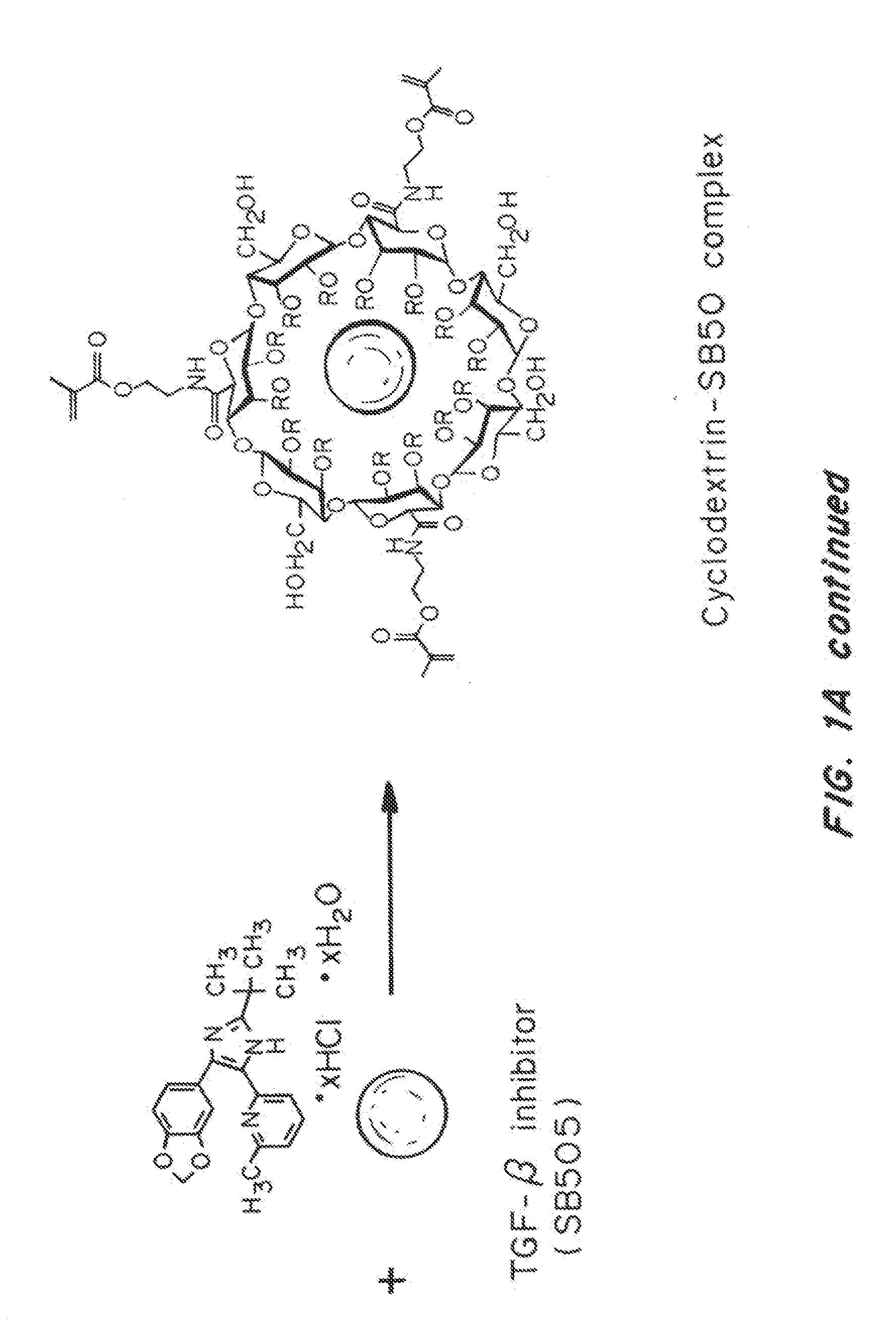
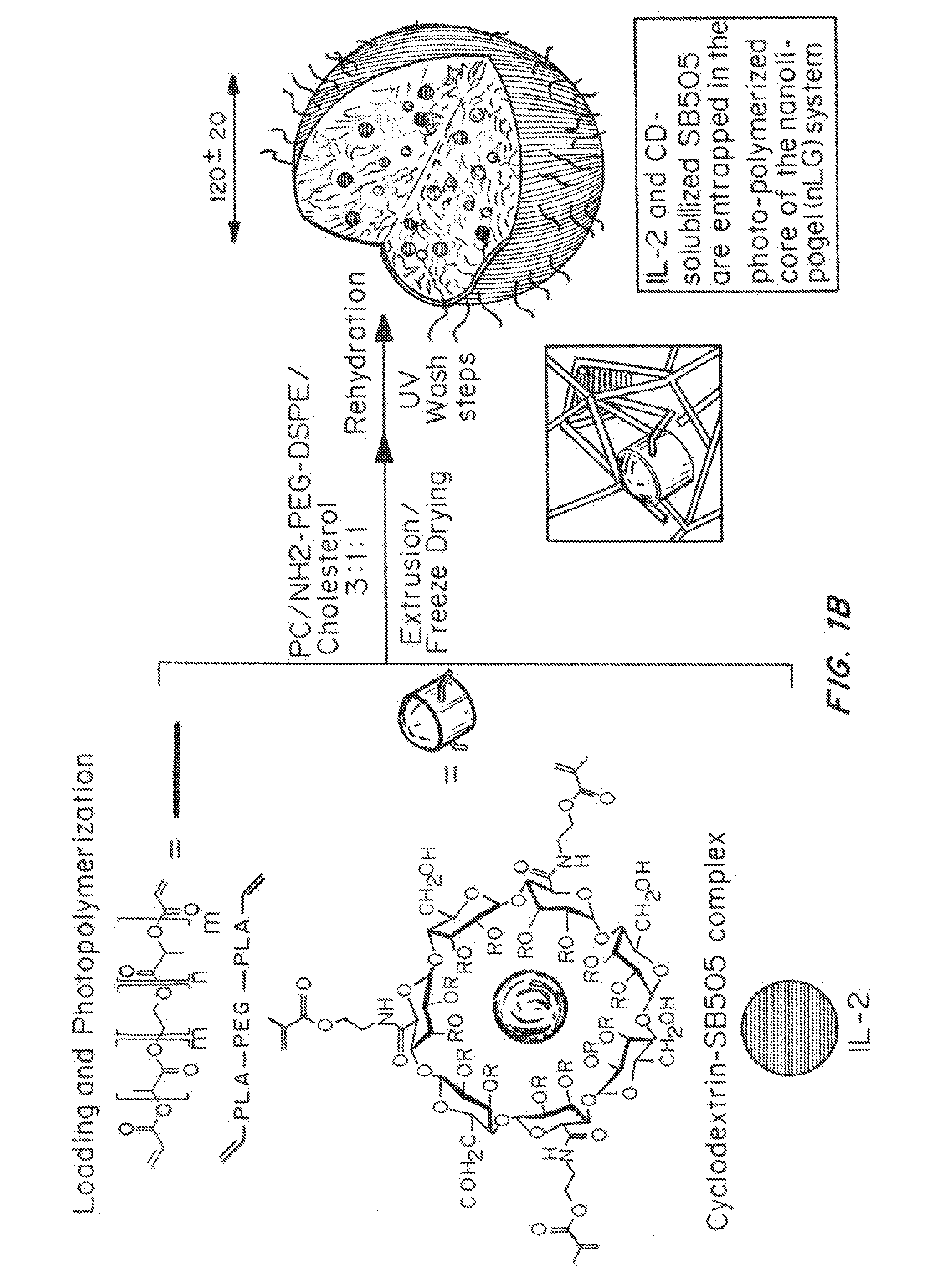
A “nanolipogel” is a delivery vehicle including one or more lipid layer surrounding a hydrogel core, which may include an absorbent such as a cyclodextrin or ion-exchange resin. Nanolipogels can be constructed so as to incorporate a variety of different chemical entities that can subsequently be released in a controlled fashion. These different incorporated chemical entities can differ dramatically with respect to size and composition. Nanolipogels have been constructed to contain co-encapsulated proteins as well as small hydrophobic drugs within the interior of the lipid bilayer. Agents incorporated within nanolipogels can be released into the milieu in a controlled fashion, for example, nanolipogels provide a means of achieving simultaneous sustained release of agents that differ widely in chemical composition and molecular weight. Additionally, nanolipogels can favorably modulate biodistribution.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Microbubble compositions and methods for oligonucleotide delivery
InactiveUS7115583B2Low effective doseHigh indexUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAntibacterial agentsMedicineBiodistribution
The invention relates to a new and improved pharmaceutical composition and method for delivery of therapeutic agents. The methods and composition of the invention can be used with several therapeutic agents and can achieve site specific delivery of a therapeutic or diagnostic substance. This can allow for lower doses and for improved efficacy with drugs which traditionally reach targeted sites and can result in improved utility for agents such as oligonucleotides and polynucleotides which are plagued with problems with biodistribution.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
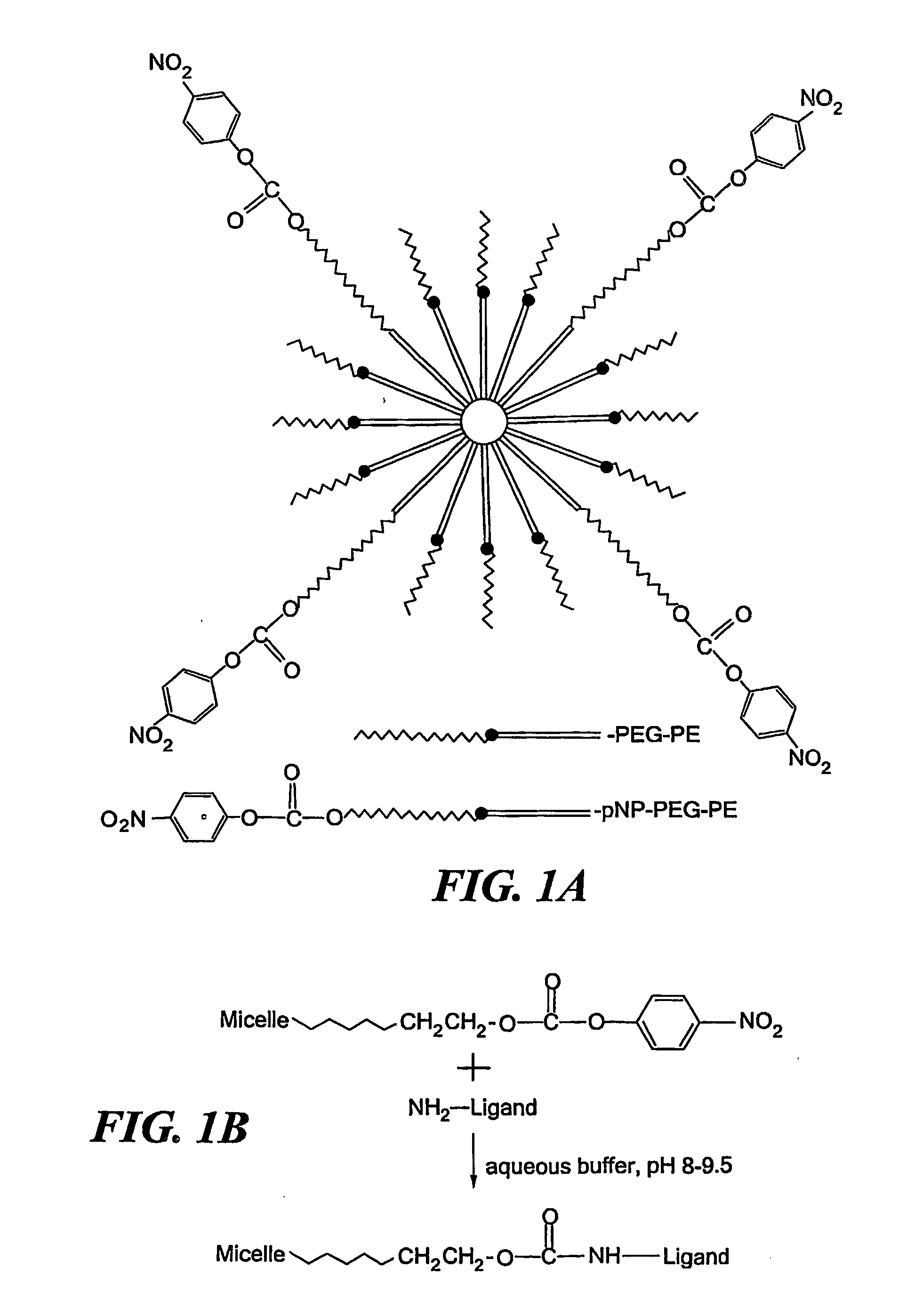
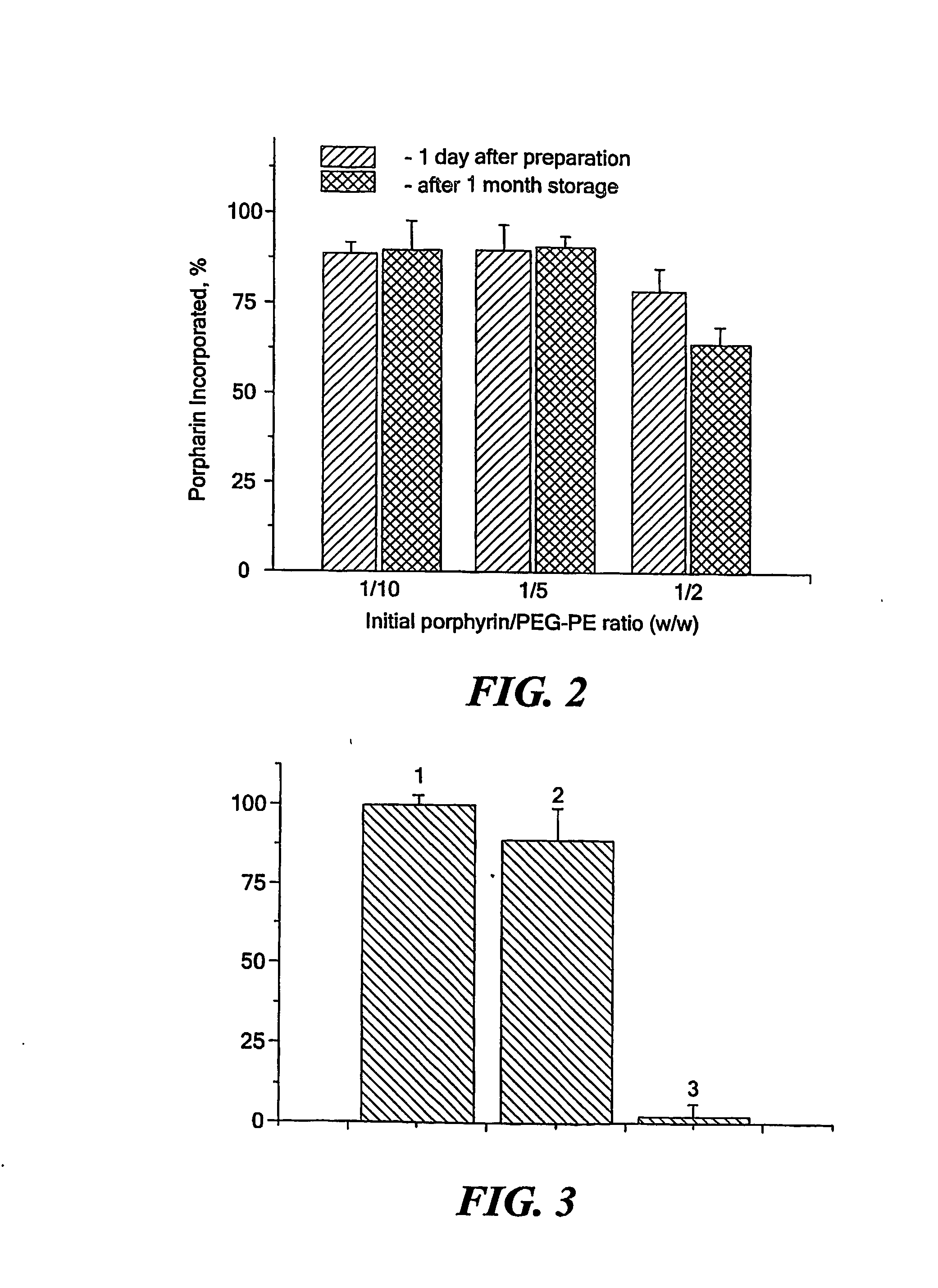
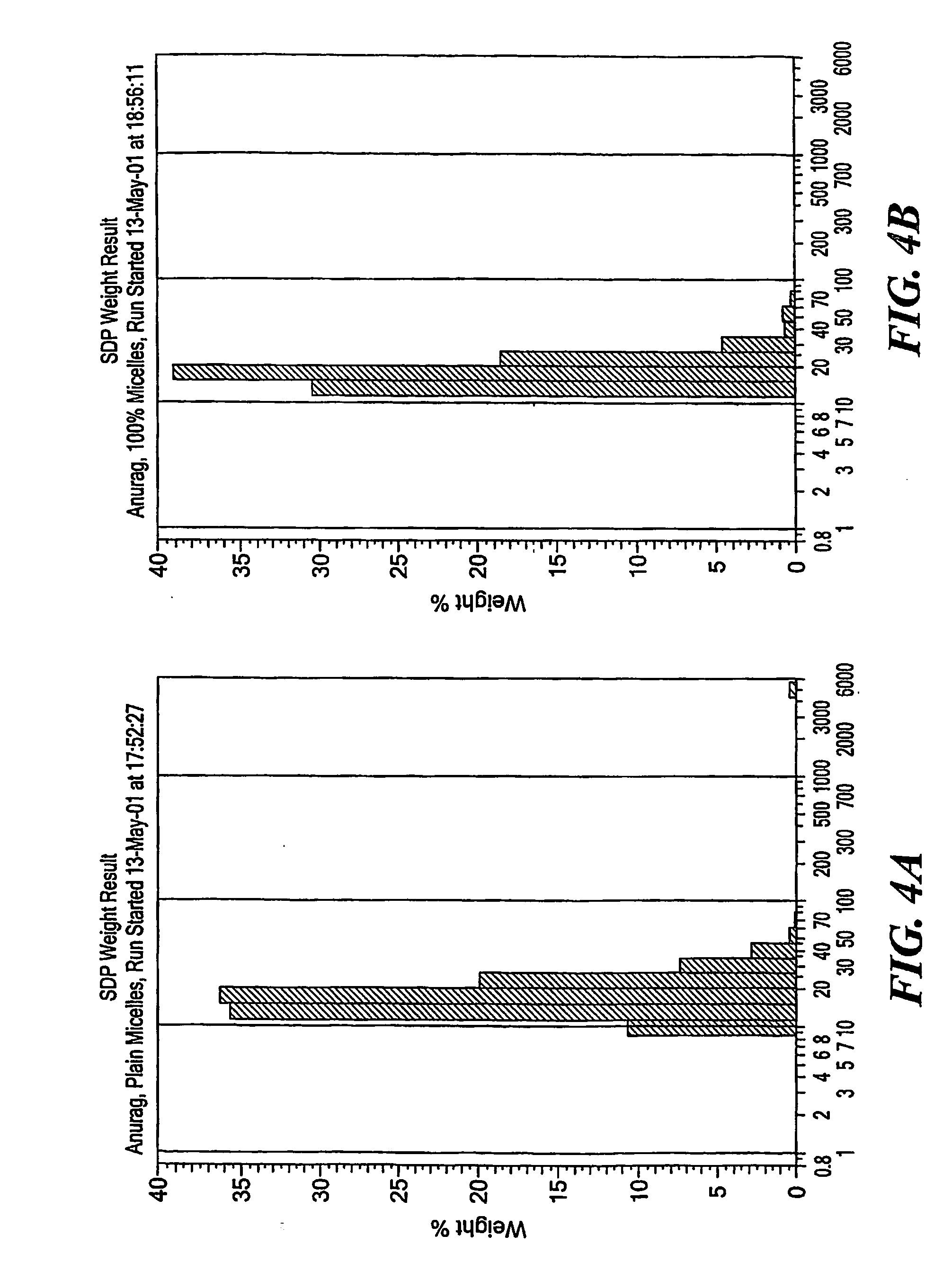
Micelle delivery system loaded with a pharmaceutical agent
InactiveUS20060216342A1Process stabilityGood curative effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthLipid formation
The invention is directed to an improved drug delivery system that includes a micelle, comprising polyethylene glycol and a lipid component, and a pharmaceutical agent dispersed in the lipid component. The delivery system may also include a targeting ligand. The micelle delivery system of the invention is capable of stabilizing, inter alia, poorly soluble pharmaceutical agents and increasing their delivery efficacy. Appropriate pharmaceutical agents useful in the system of the invention include anti-inflammatory agents, agents for photodynamic therapy, anti-tumor agents, anti-neoplastic agents, anti-metastatic agents, and imaging agents, as well as hydrophobized derivatives thereof. Specifically, the pharmaceutical agent can be porphyrin, chlorine-6-trimethyl ester, tamoxifen, paclitaxel, 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea, camptothecin, ellipticine, rhodamine, dequalinium, diphenylhexatriene, vitamin K3, diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid, or a functional derivative thereof. The micelles in the system of the invention have low critical micellar concentration and high kinetic stability, which provides great advantages in biodistribution, for example, accumulation at the site of a tumor.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
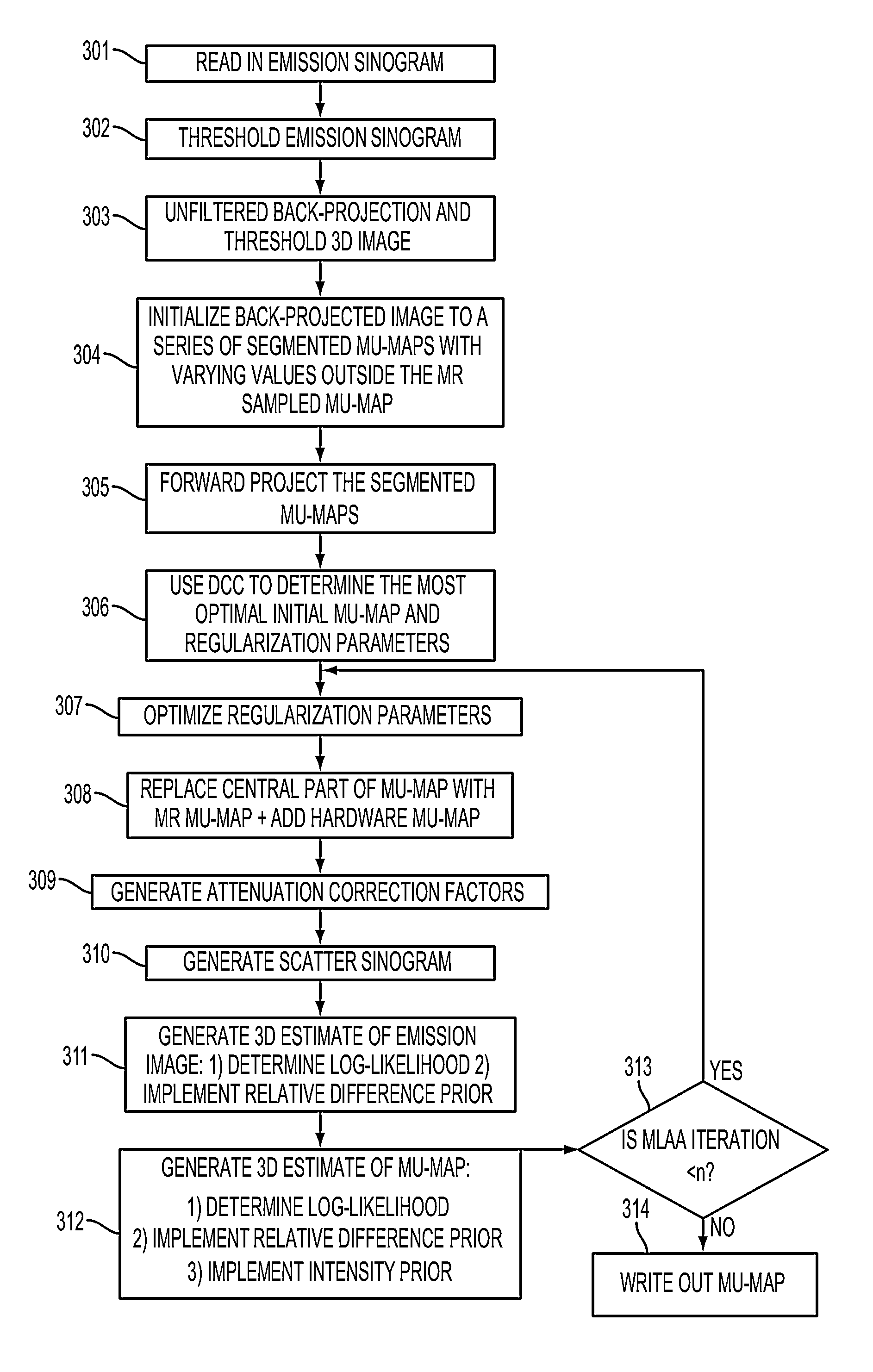
Generating Attenuation Correction Maps for Combined Modality Imaging Studies and Improving Generated Attenuation Correction Maps Using MLAA and DCC Algorithms
ActiveUS20140056500A1Reduce noiseReduce the numberReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionWhole bodyCompanion animal
The DCC (Data Consistency Condition) algorithm is used in combination with MLAA (Maximum Likelihood reconstruction of Attenuation and Activity) to generate extended attenuation correction maps for nuclear medicine imaging studies. MLAA and DCC are complementary algorithms that can be used to determine the accuracy of the mu-map based on PET data. MLAA helps to estimate the mu-values based on the biodistribution of the tracer while DCC checks if the consistency conditions are met for a given mu-map. These methods are combined to get a better estimation of the mu-values. In gated MR / PET cardiac studies, the PET data is framed into multiple gates and a series of MR based mu-maps corresponding to each gate is generated. The PET data from all gates is combined. Once the extended mu-map is generated the central region is replaced with the MR based mu-map corresponding to that particular gate. On the other hand, in dynamic PET studies the uptake in the patient's arms reaches a steady state only after the tracer distributes throughout the body. Hence, for dynamic scans, the projection data of all frames is summed and used to generate the MLAA based extended mu-map for all frames.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Phosphorescent Molecules for Measuring Oxygen and Imaging Methods
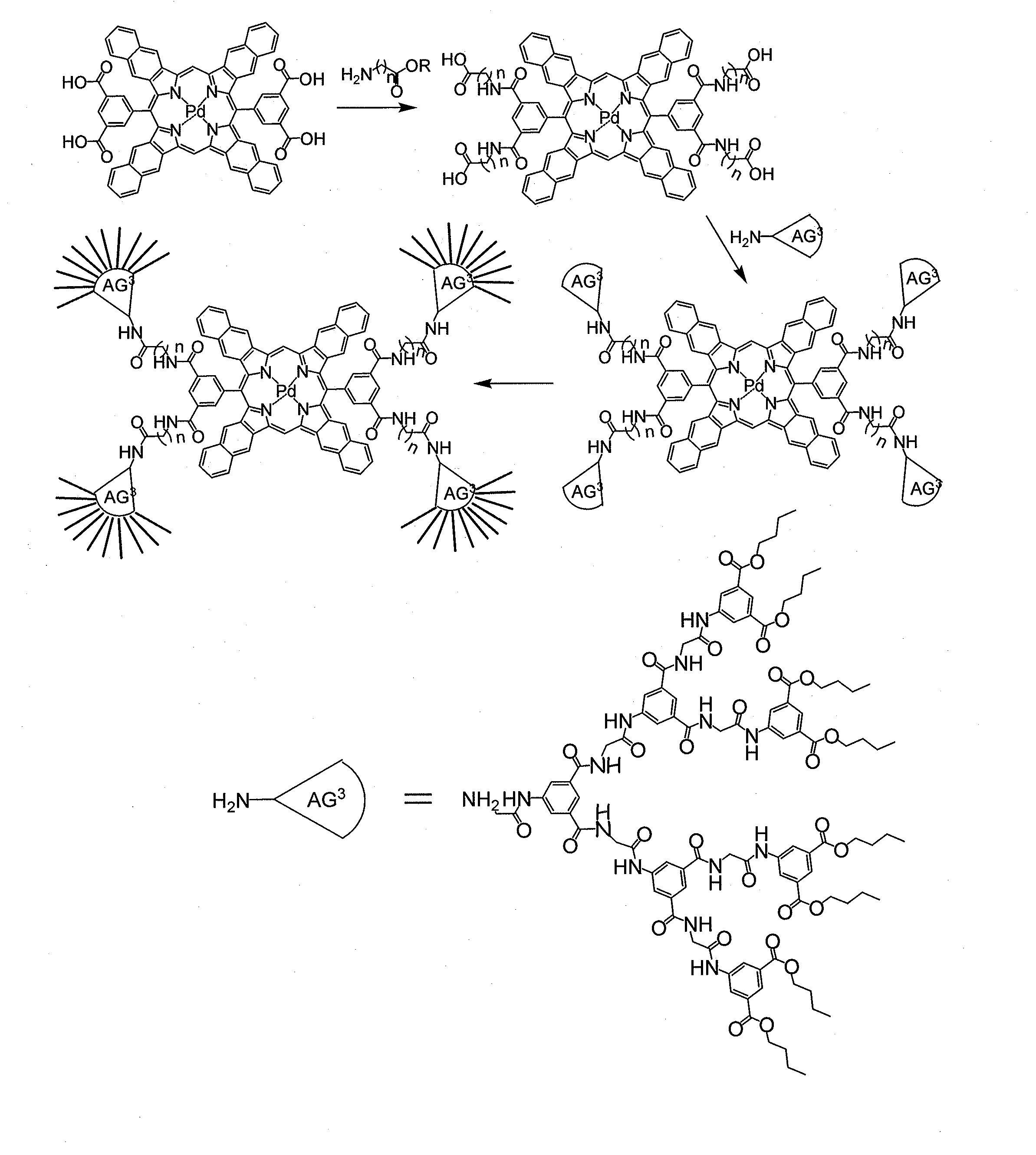
ActiveUS20130224874A1Simple structureImprove chemical structureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsBiological testingDendrimerSinglet oxygen
Oxygen levels in biological tissue or systems can be measured by the phosphorescence quenching method using phosphorescent porphyrin probes, also referred to as a dendritic oxygen probes, with controllable quenching parameters and defined biodistributions. Provided are a “next generation” of oxygen sensors with substantially improved phosphorescence emission for better imaging capabilities, ease of use, increasing the quantum efficiency (phosphorescence intensity) and extending their range of applicability including constructing a class of oxygen sensors for making measurements in organic media. In addition, provided are methods for synthesizing new porphyrin constructs in which the porphyrin is made less flexible and more planar, changing with decrease internal quenching, and thereby increasing the phosphorescence emission used for oxygen sensing. Additional methods are provided for structurally modifying the dendrimer used to encapsulate the porphyrin phosphor to provide internal quenching of singlet oxygen molecules formed during oxygen measurements.
Owner:OXYGEN ENTERPRISES
Methods and compositions for modulating drug-polymer architecture, pharmacokinetics and biodistribution
Drug-polymer chemotherapeutics are provided having improved therapeutic efficacy and reduced dose-limiting toxicity. Methods are also provided for modulating the architecture, pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of drug-polymers and for reducing the dependence of transition temperature on concentration for drug-polymers.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
System, method, computer-readable medium, and use for planning combined therapy
InactiveUS20100081857A1Possible to predictAvoid side effectsUltrasound therapyIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBiodistributionSystems approaches
A system and method for planning a necrosis-inducing therapy and subsequent administration of a necrosis-targeting agent are described. The system takes into account the effect of necrosis-induction therapy as a basis for the biodistribution estimate of the necrosis-targeting agent. This interaction between the different calculation steps is essential for an accurate planning result. A computer-readable medium and use are also provided.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Echo-scintigraphic probe for medical applications and relevant diagnostic method
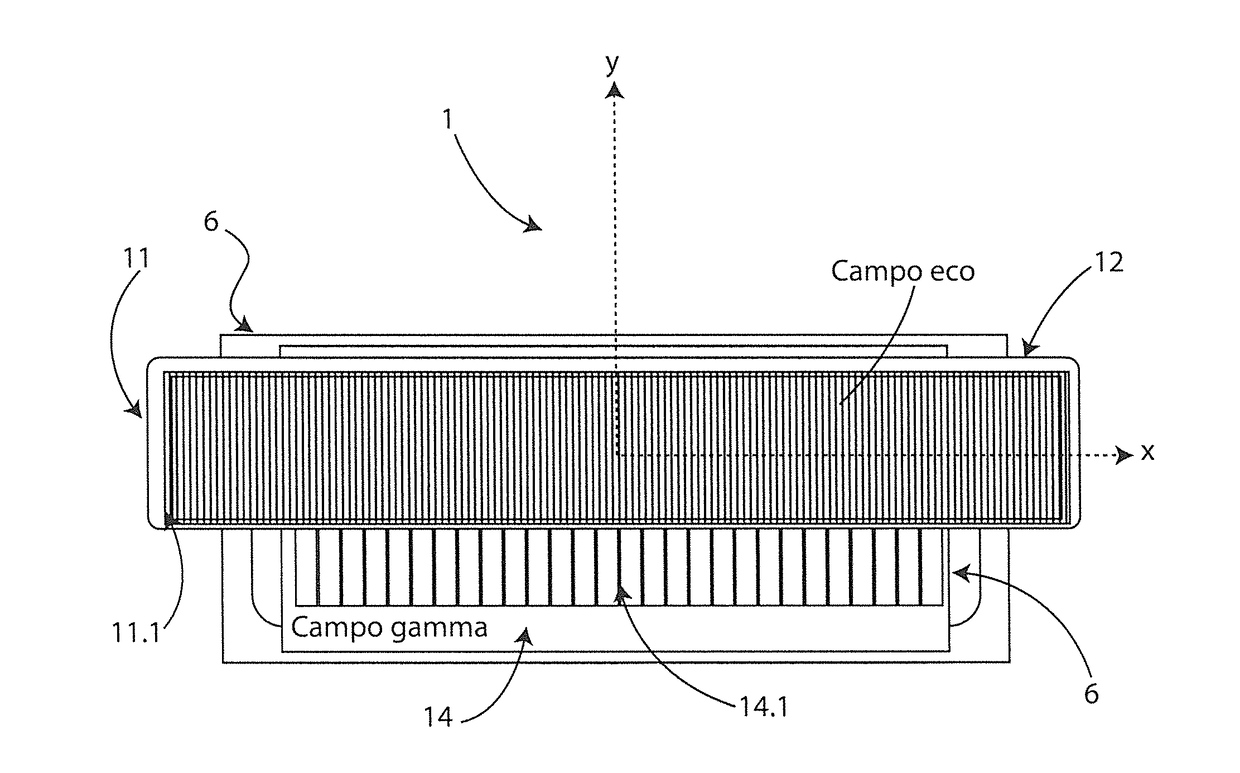
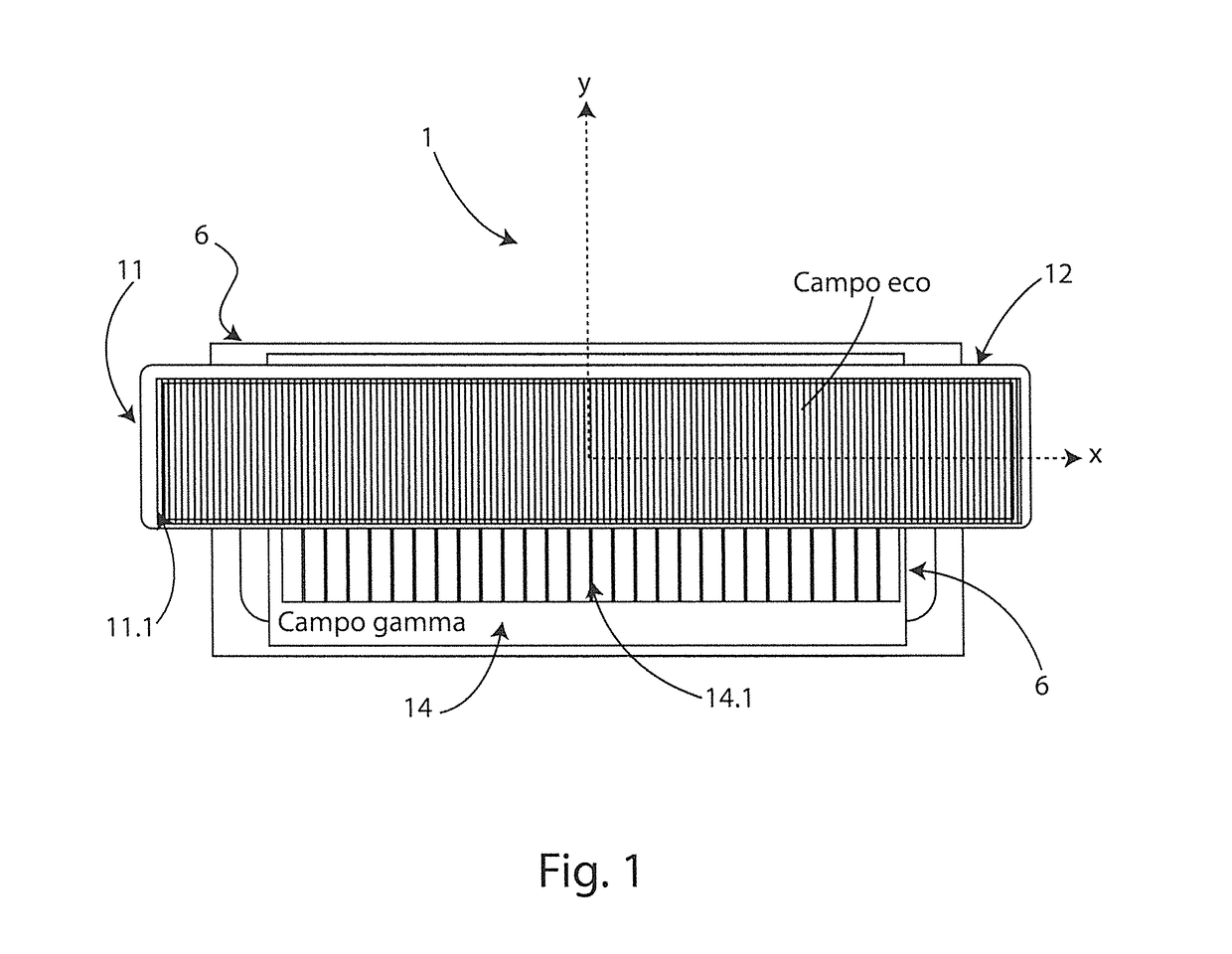
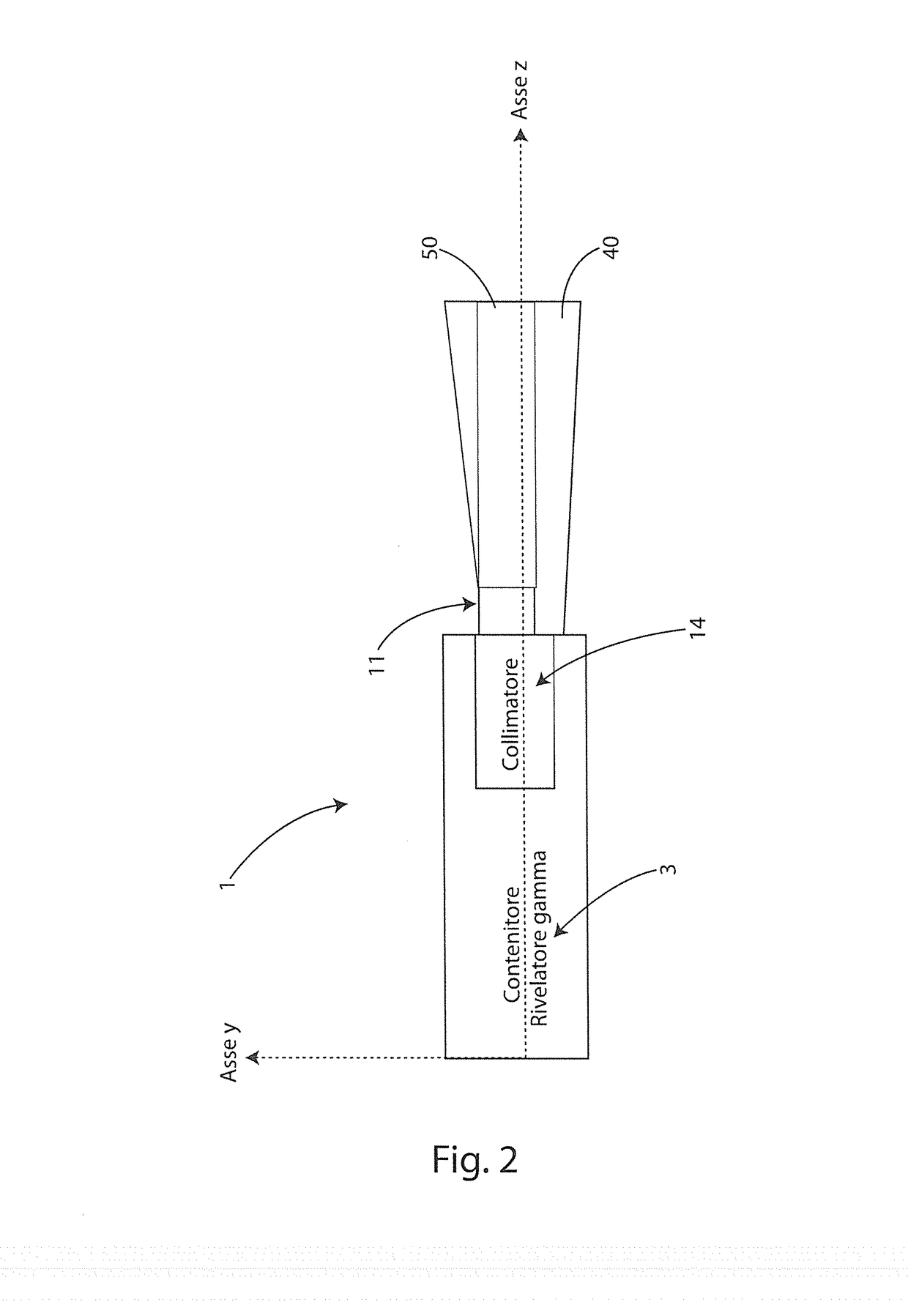
ActiveUS20170079609A1Easy to implementMinimum realization costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsRadioactive tracerRadioactive Label
An echo-scintigraphic probe for medical applications and the method of merging images. It is constituted by the union of an ultrasound probe suitably integrated, both in geometric terms, and in terms of image processing, with a scintigraphic probe or gamma camera (3). With a single application of said probe, one is able to provide a double image of the object under examination. The ultrasound probe is housed in the head, above the plane of the collimator and kept projecting to favor the direct contact with the body part of the patient to be examined. The collimator is able to obtain images of the biodistribution of a radiolabelled drug by radiation with frontal incidence, maintaining the characteristics of the ultrasound probe. The probe is applicable to both clinical diagnosis and intraoperative diagnosis of cancer with the use of radio tracers. A guided diagnostic method is disclosed that realizes a functional integration of a pair of ultrasound and scintigraphic images concurrently obtained by the echo-scintigraphic probe.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA
Administration of a thiol-based chemoprotectant compound
InactiveUS7022315B2Avoid problemsTreat and mitigate side effectCosmetic preparationsBiocideSide effectWilms' tumor
A method of administration of a thiol-based chemoprotectant agent including NAC (N-acetylcysteine) and STS (sodium thiosulfate) that markedly affects biodistribution and protects against injury from diagnostic or therapeutic intra-arterial procedures. A method for treating or mitigating the side effects of cytotoxic cancer therapy for tumors located in the head or neck and brain tumors. The thiol-based chemoprotectant agent is administered intra-arterially with rapid and first pass uptake in organs and tissues other than the liver.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US THE +1
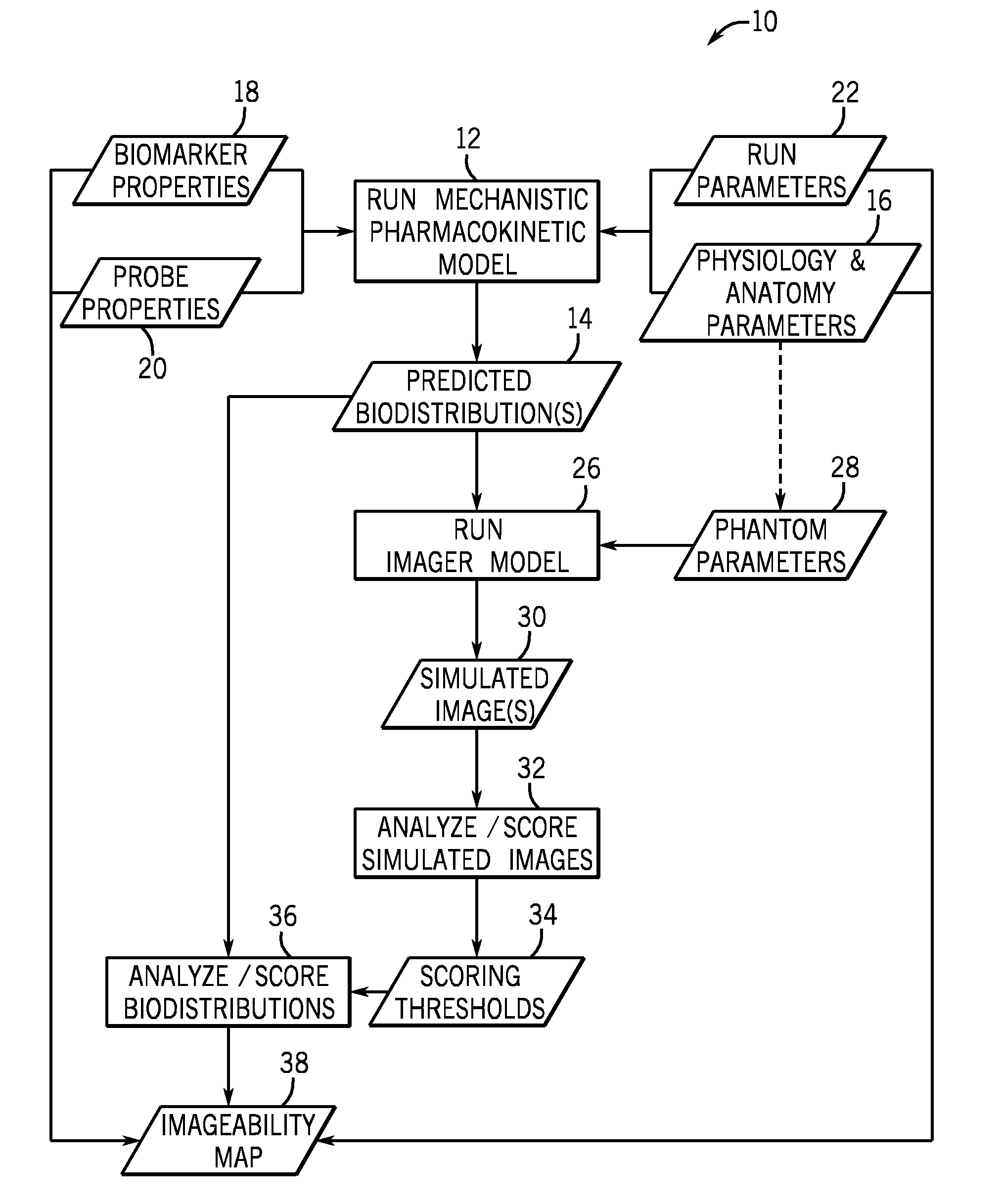
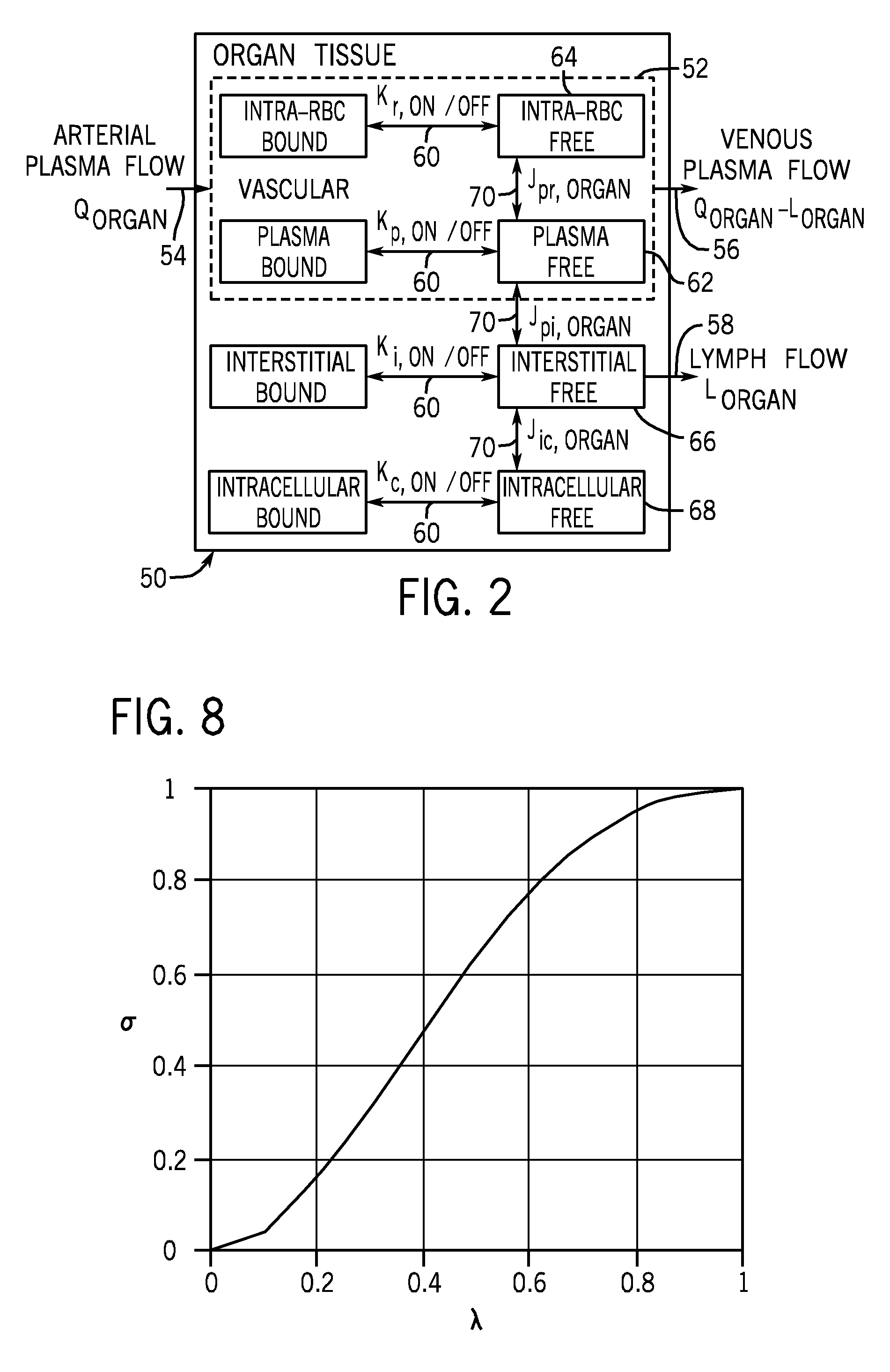
Method and apparatus for assessing feasibility of probes and biomarkers
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
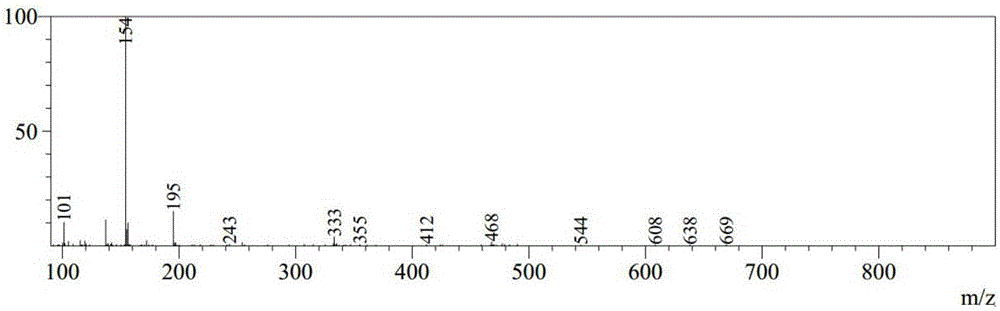
Novel 18F labeled amino acid derivatives, preparation method and application thereof in tumor imaging
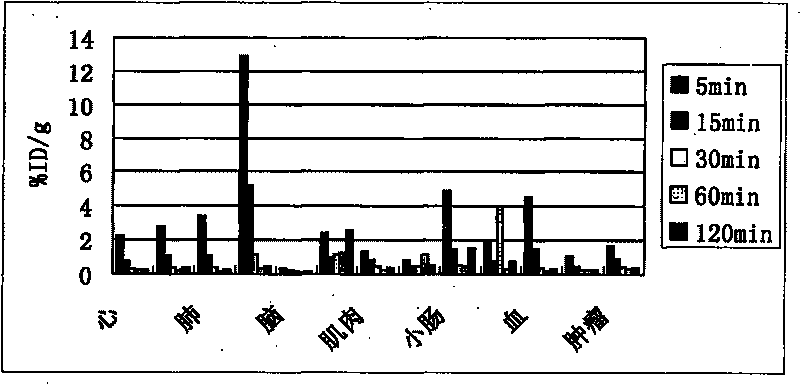
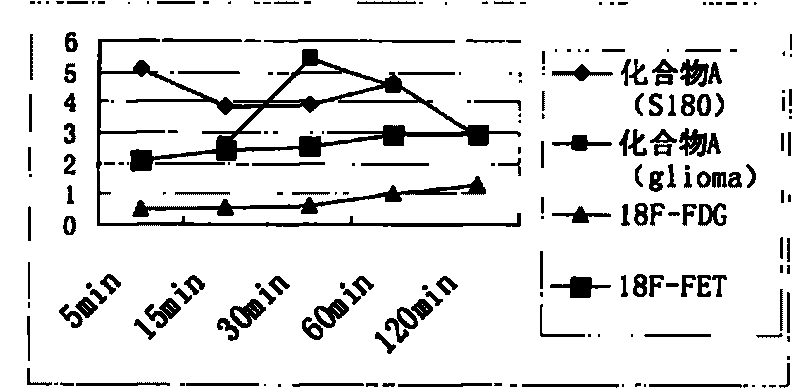
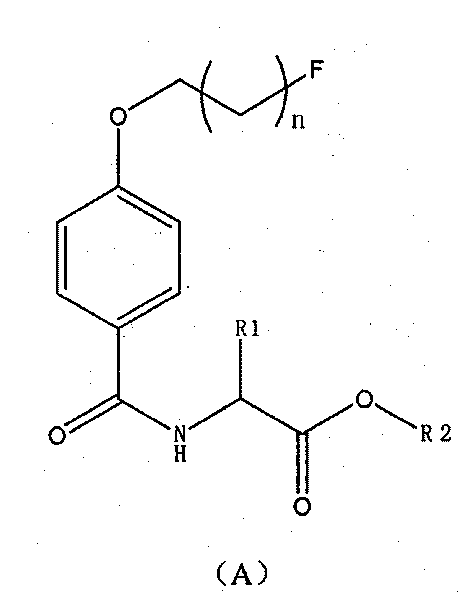
InactiveCN101723849AEasy to markEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationRadioactive preparation carriersAbnormal tissue growthImaging agent
The invention discloses novel radioactive 18F labeled amino acid derivatives, which are used in research on tumor positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. The derivatives are characterized in that one end of the derivatives is provided with F substituted alkoxy benzoyl structure, and the other end of the derivatives is provided with alpha-amino acid structure; substituent R1 is positioned on an alpha site of carboxyl group and is hydrogen, methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group, isopropyl group, butyl group, methylthio-ethyl group, methyl acetate group or propionate carbomethoxy group; R2 is methoxy group; and n is a number between 1 and 5. The R1 is hydrogen, methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group, isopropyl group, butyl group, methylthio-ethyl group, methyl acetate group or propionate carbomethoxy group; the R2 is hydrogen; and the n is a number between 1 and 5. Compounds improve fat solubility. Different amino acid structures are introduced into the structure, and F in the structure is 19F and 18F. Compared with the prior art, the 18F labeled amino acid derivatives provided by the invention have better discrimination degree of biological distribution, the potential of being used as a tumor imaging agent (particularly a brain tumor imaging agent), as well as the characteristics of simple preparation and high labeling rate. The R1 is hydrogen, methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group, isopropyl group, butyl group, methylthio-ethyl group, methyl acetate group or propionate carbomethoxy group; the R2 is methoxy group; and the n is a number between 1 and 5. The R1 is hydrogen, methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group, isopropyl group, butyl group, methylthio-ethyl group, methyl acetate group or propionate carbomethoxy group; the R2 is hydrogen; and the n is a number between 1 and 5.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
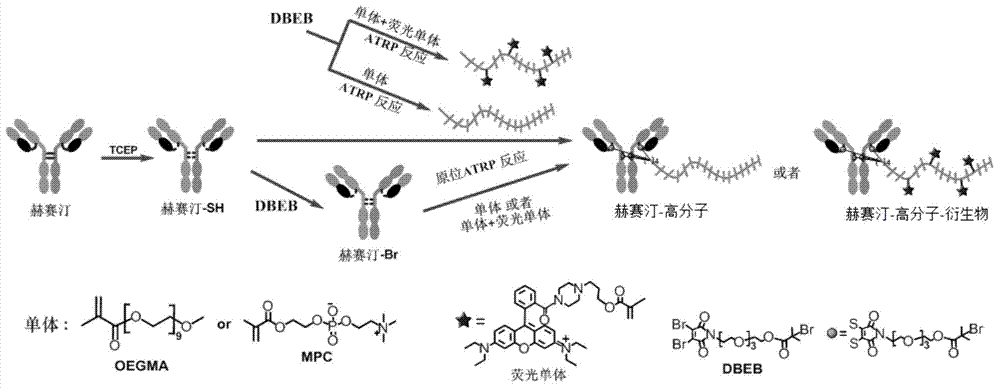
Antibody-polymer combined body and fluorescent derivative thereof and preparation method of antibody-polymer combined body and fluorescent derivative
ActiveCN104288777ARetain activitySimple stepsAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsSolubilityVaccine Immunogenicity
The invention discloses an antibody-polymer combined body and a fluorescent derivative thereof and a preparation method of the antibody-polymer combined body and the fluorescent derivative. The antibody comprises at least one disulfide bond or free sulfydryl; the polymer is combined to the antibody through connection to the disulfide bond or free sulfydryl of the antibody; according to the method, a specific site of the antibody is modified; a polymer and a fluorescent derivative thereof grow in situ; or a polymer and a fluorescent derivative thereof are prepared in advance; and the antibody-polymer combined body and the fluorescent derivative thereof are prepared in a manner of specific site coupling of the antibody. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, convenient and efficient; the prepared product not only reserves the original biological activity of the antibody, but also improves the water solubility, stability, pharmacokinetics, distribution of organisms and treatment efficacy; the immunogenicity is reduced; in addition, compared with an antibody-fluorescence indicator prepared by the traditional method, the antibody-polymer fluorescent derivative prepared by the method has stronger fluorescence signal and detection signal strength.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
GSH (glutathione) response based diagnosis and treatment integrated organic molecular probe and production method thereof
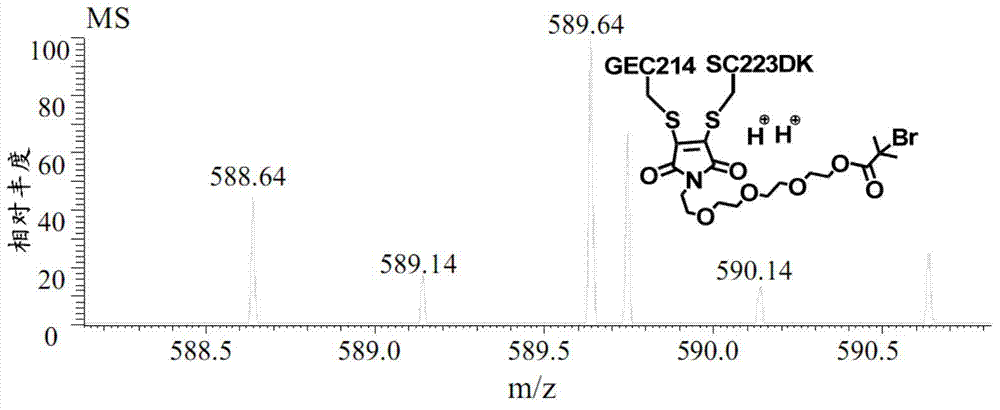
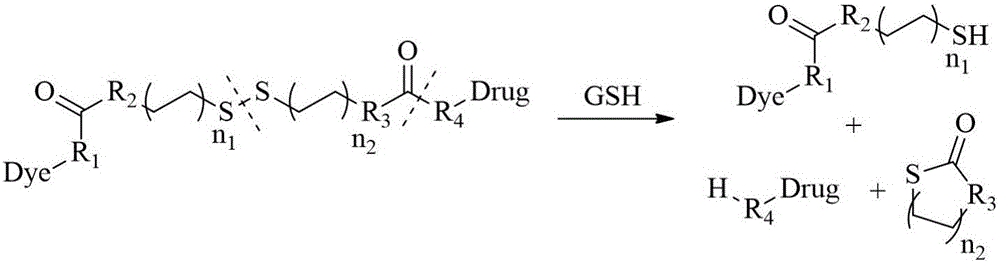
InactiveCN106188191AMonitoring biodistributionThe reaction steps are simpleOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSide effectFluorescence
The invention discloses a GSH (glutathione) response based diagnosis and treatment integrated organic molecular probe and a production method thereof. The diagnosis and treatment integrated molecular imaging probe of the class is structured on the basis of near-infrared fluorescent dyes and tumor microenviroment, disulfide bonds in the probe can be cut off through oxidation reduction of the GSH, active drugs are released, and the purpose of monitoring transferring and releasing of the drugs is achieved. The synthetic process is relatively simple and rapid, the active drugs are released rapidly, action period is short, side effect on normal cells is small, tremendous utilization potential is achieved, reaction step is simple, operation process is clear, the molecular imaging probe and anticancer prodrugs are integrated, target detection on cancers can be realized while effect of targeted cancer treatment can be achieved through the reasonably designed structure, meanwhile biological distribution of the prodrugs in biological bodies and releasing and enriching process of the active drugs can be monitored, and great significance in studying of action mechanism of the drugs, resistance mechanisms of the cancers and the like is achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
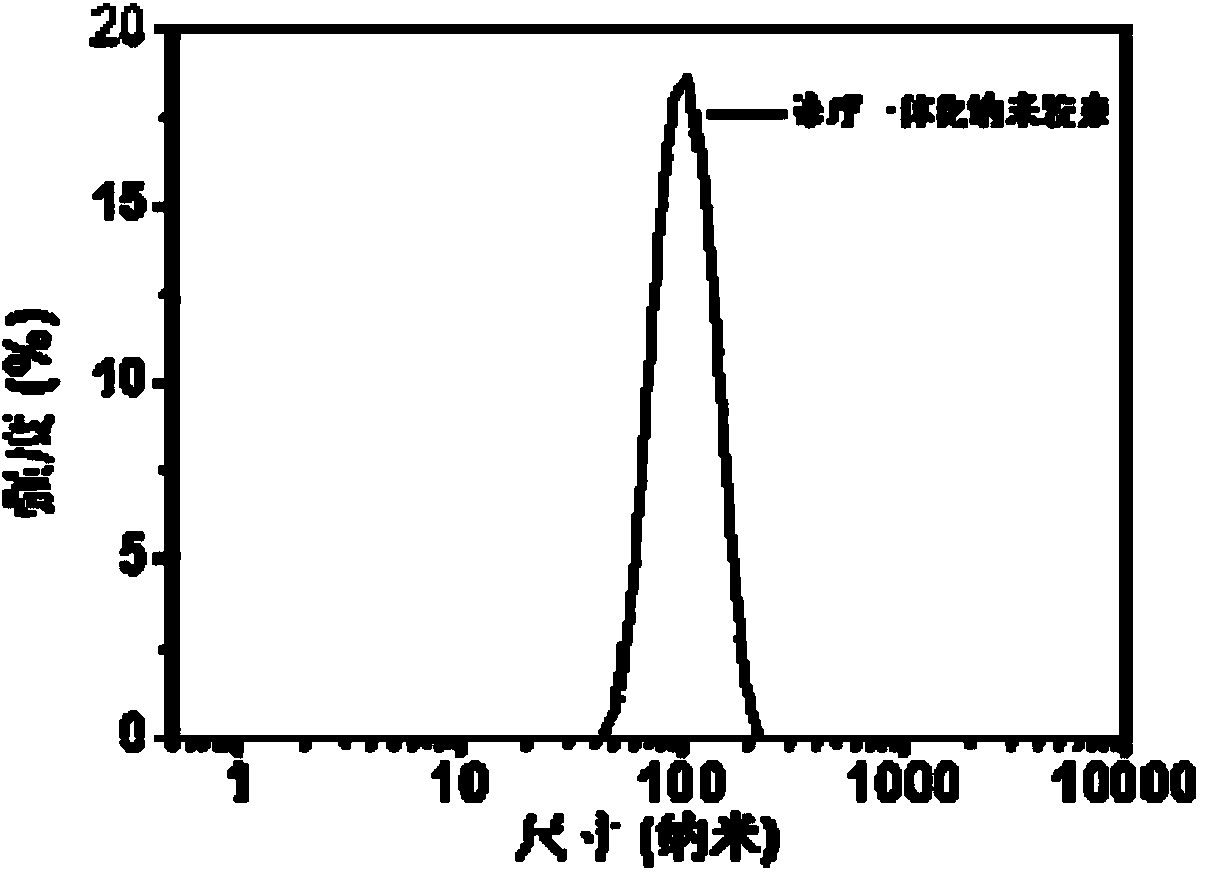
Nano-micelle capable of realizing integration of diagnosis and treatment, as well as preparation method and application of nano-micelle
ActiveCN104174036AAchieve enrichmentEffective treatmentKetone active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseAggregation-induced emission
The invention discloses a nano-micelle. The nano-micelle comprises an AIE (aggregation-induced emission) dye, an active pharmaceutical ingredient and an amphipathic carrier in a mass ratio of 1 to 1 to (5-10). The invention further discloses a preparation method of the nano-micelle and application of the nano-micelle in preparing tumor diagnosing and / or treating agents. The nano-micelle is capable of realizing integration of diagnosis and treatment, is used for in-vivo non-invasive fluorescence imaging, diagnosis and disease treatment, and can be well gathered on a tumor site by sufficiently utilizing the EPR effect of a tumor, so that the active pharmaceutical ingredient carried by the nano-micelle can be enriched on the tumor site to play a role in effectively treating the tumor; furthermore, an AIE red-light dye is high in luminous efficiency, is not easy to quench, is capable of well reflecting the situation of delivery and biological distribution of the active pharmaceutical ingredient in a body, and can be used for diagnosing tumors.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
A system, method, computer-readable medium, and use for planning combined therapy
InactiveCN101563041AGood curative effectConvenient treatmentUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsBiodistributionBiology
A system and method for planning a necrosis-inducing therapy and subsequent administration of a necrosis-targeting agent are described. The system takes into account the effect of necrosis-induction therapy as a basis for the biodistribution estimate of the necrosis- targeting agent. This interaction between the different calculation steps is essential for an accurate planning result. A computer-readable medium and use are also provided.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
RNAi CONJUGATES, PARTICLES AND FORMULATIONS THEREOF
Particles, including nanoparticles and microparticles, and pharmaceutical formulations thereof, comprising conjugates of an RNAi agent attached to a targeting moiety via a linker have been designed which can provide improved temporospatial delivery of the RNAi agent and / or improved biodistribution. Methods of making the conjugates, the particles, and the formulations thereof are provided. Methods of administering the formulations to a subject in need thereof are provided, for example, to treat or prevent cancer or infectious diseases.
Owner:TVA (ABC) LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com