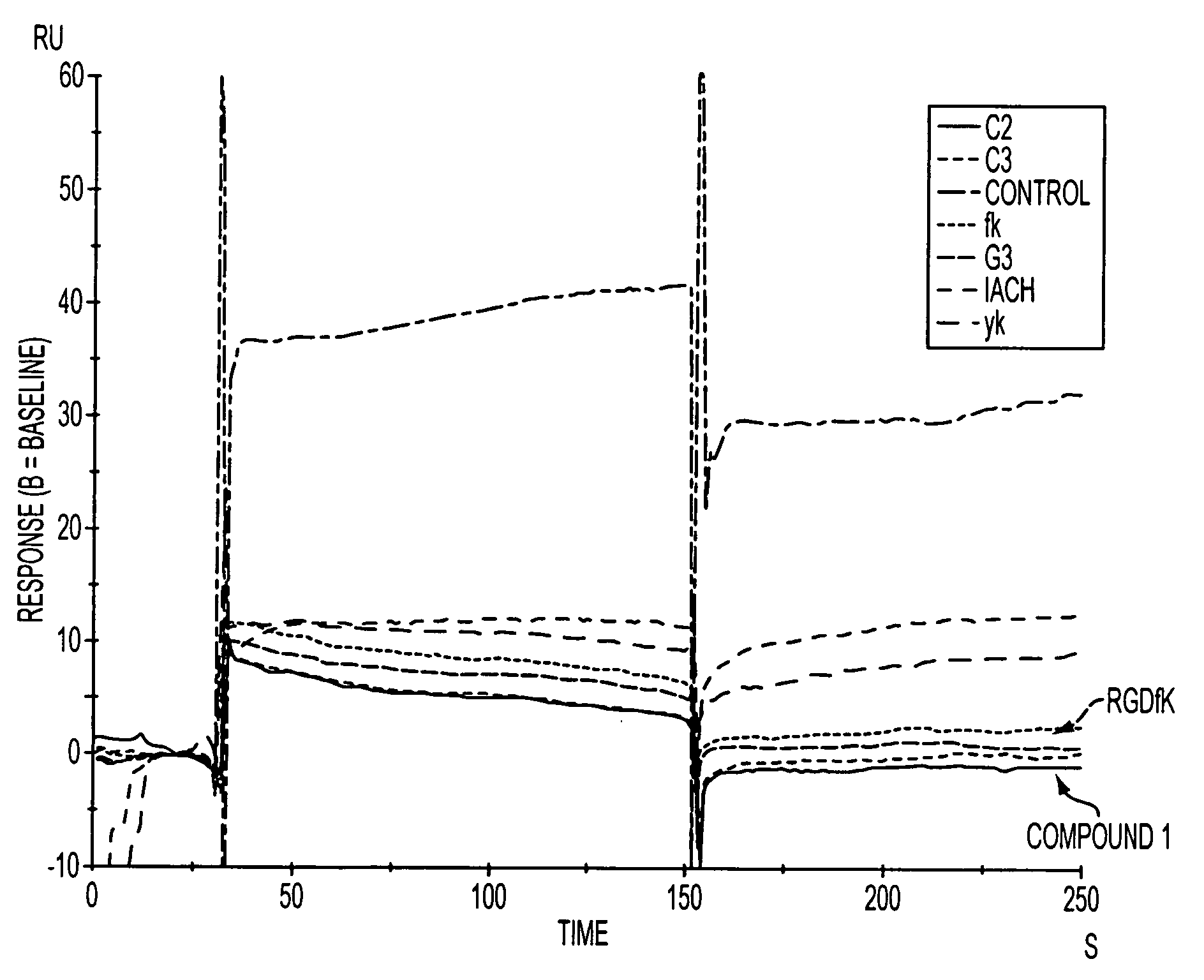
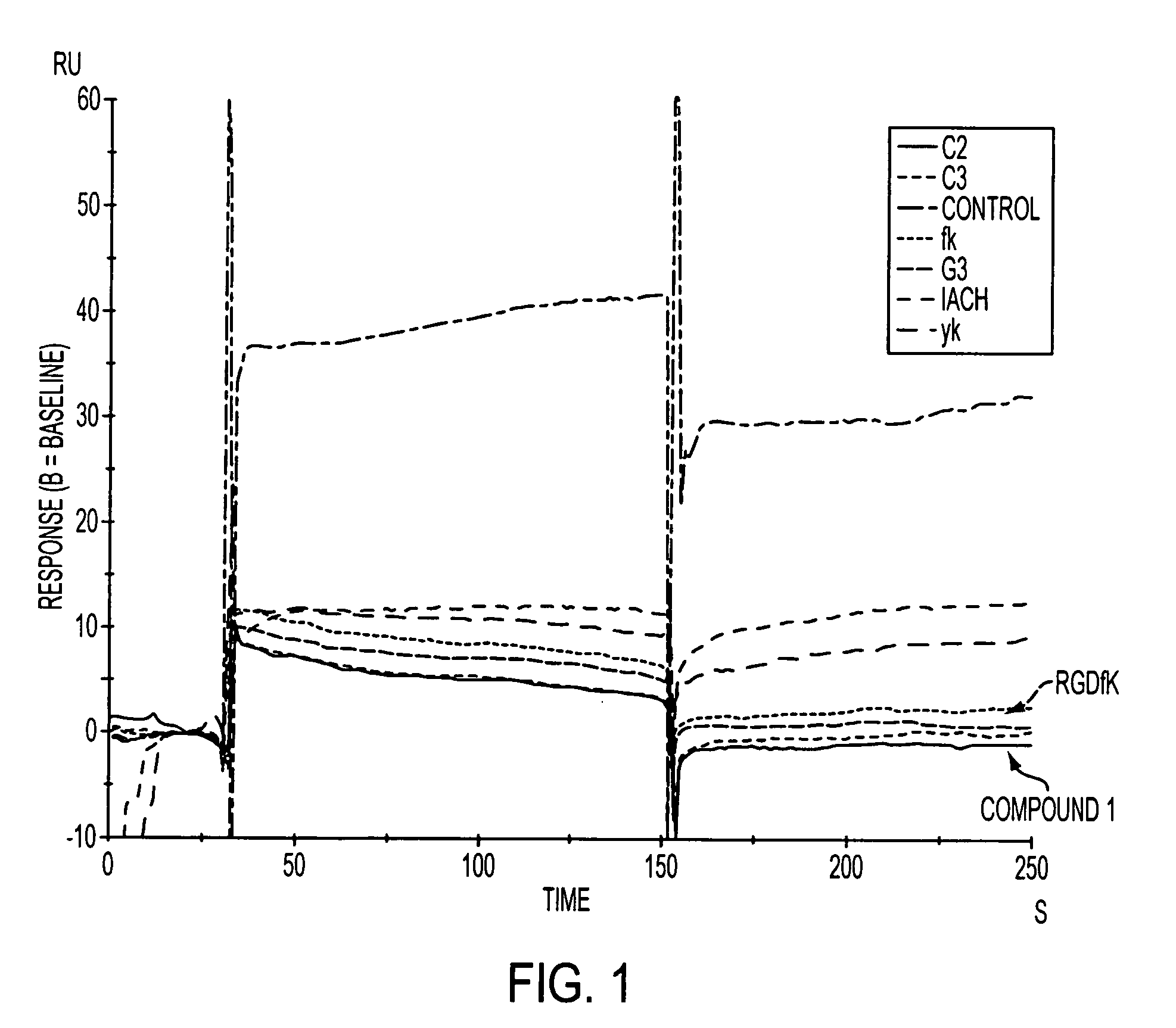
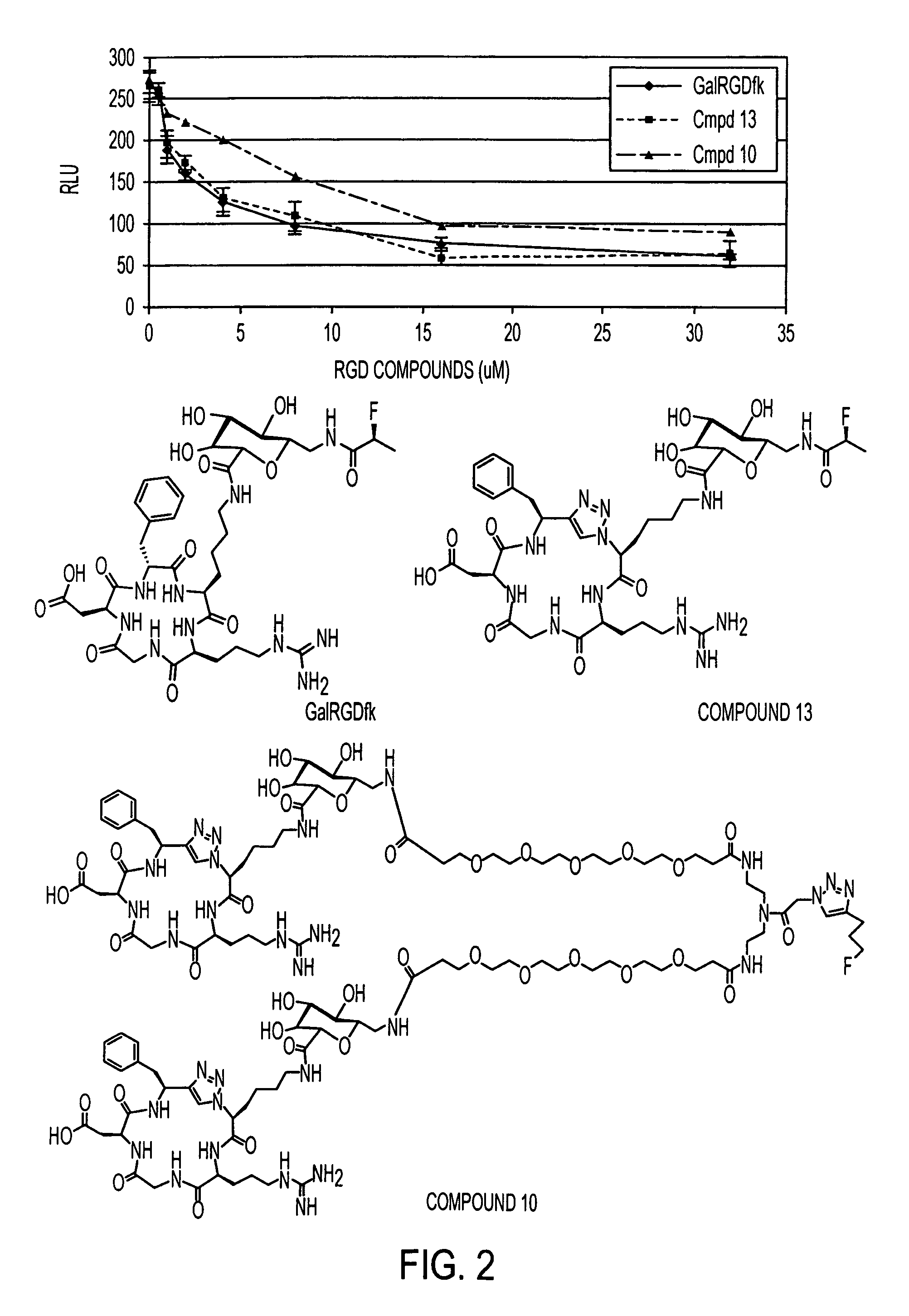
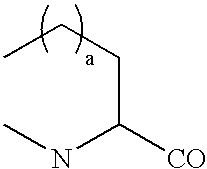
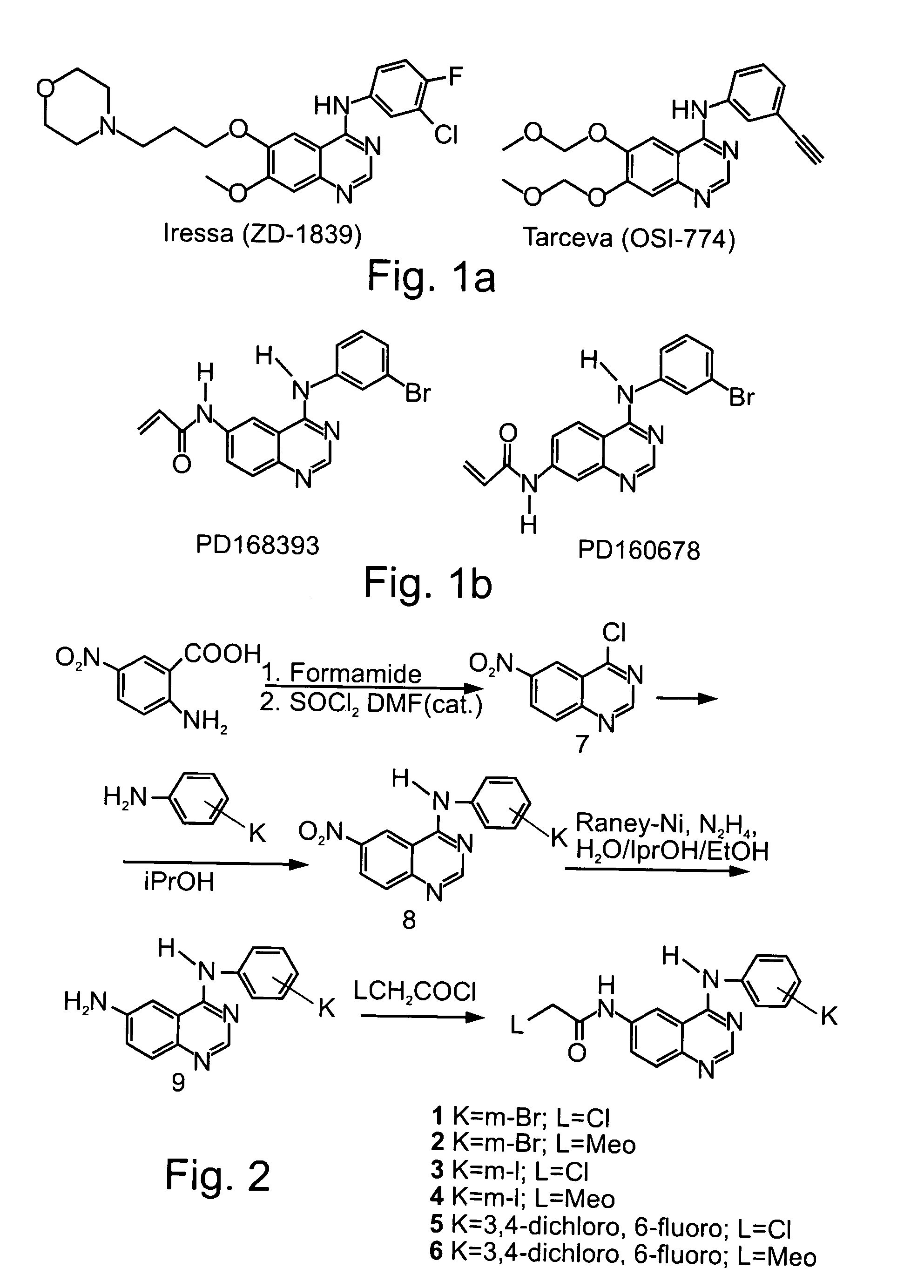
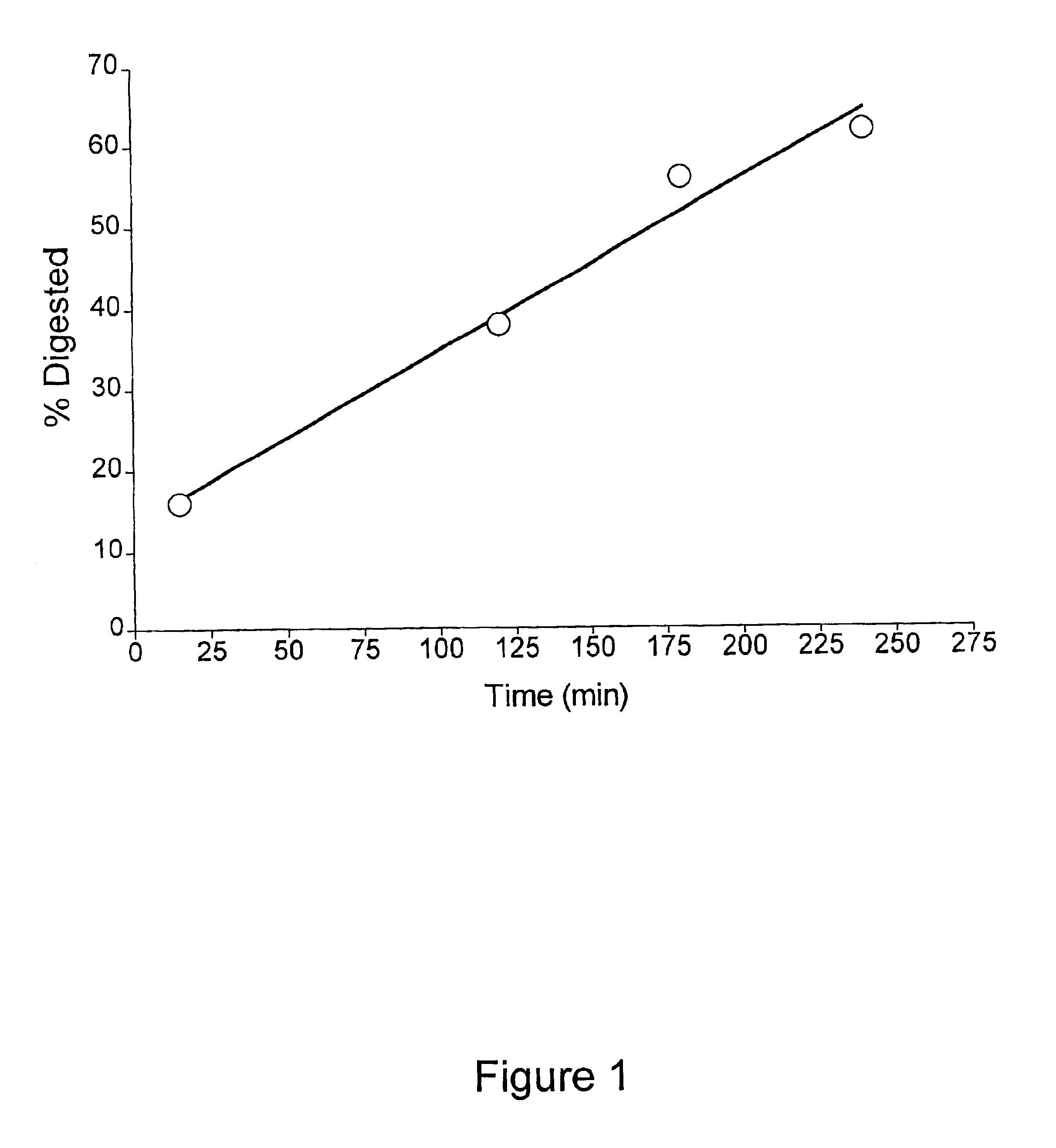
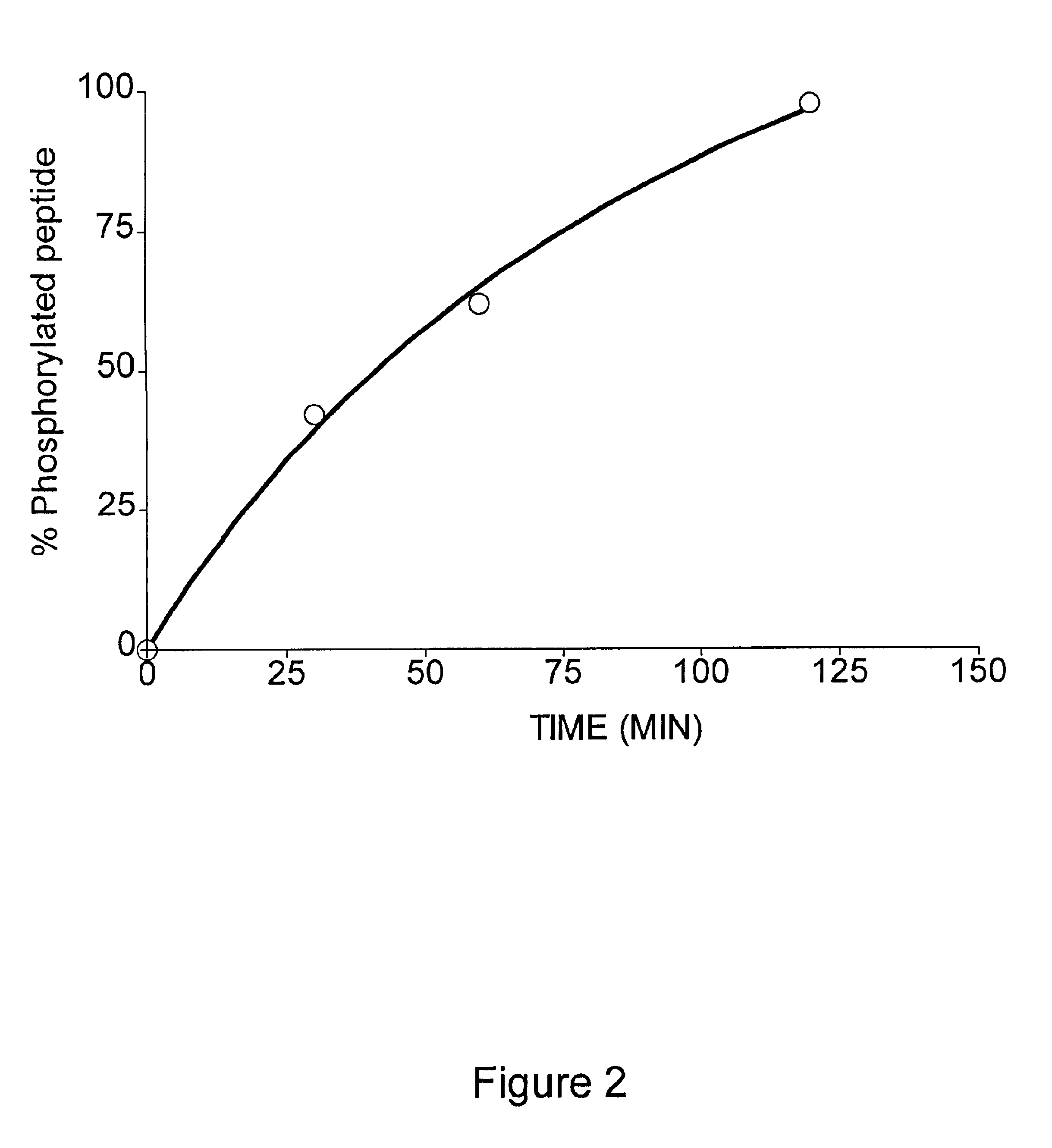
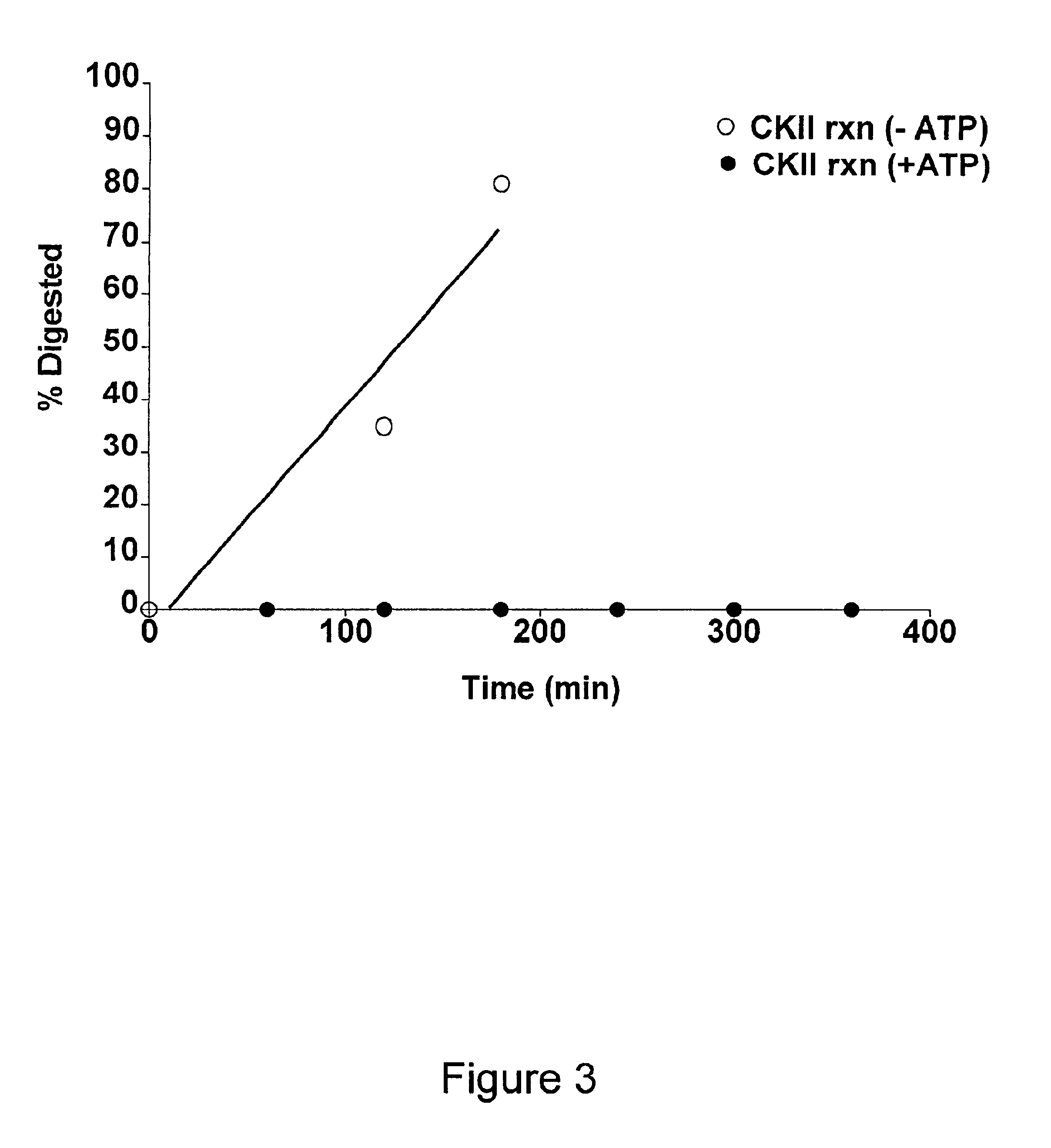
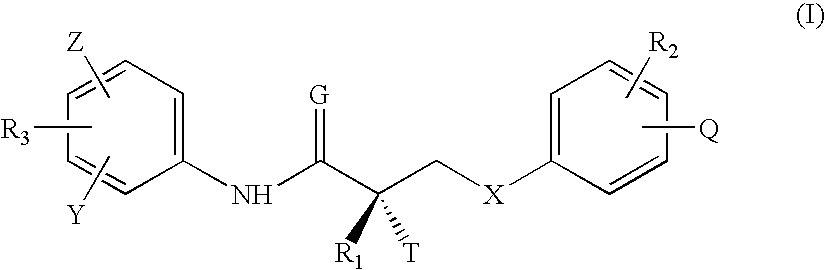
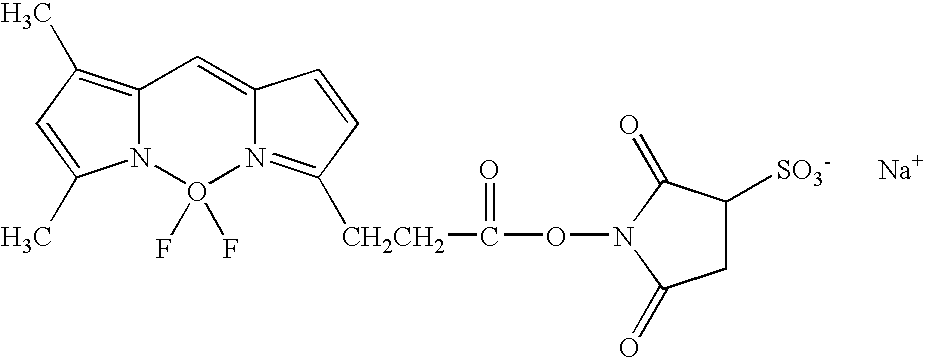
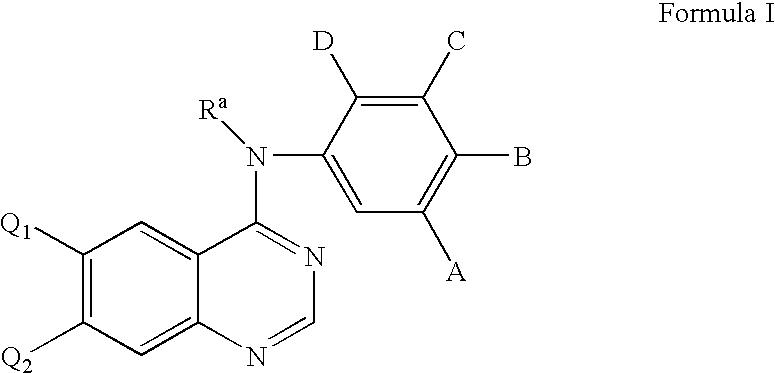
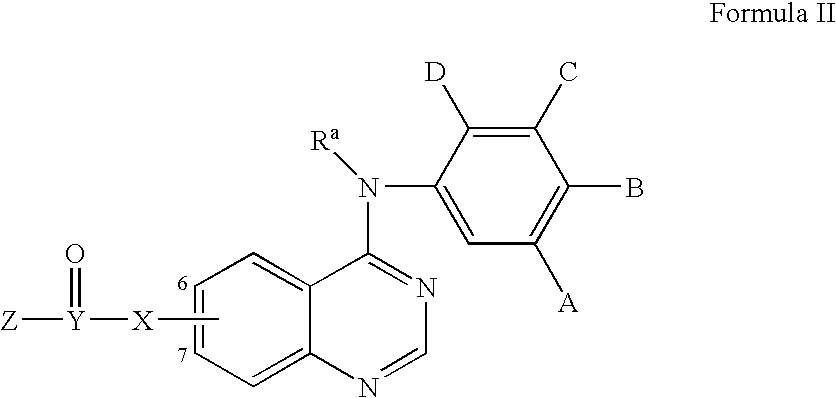
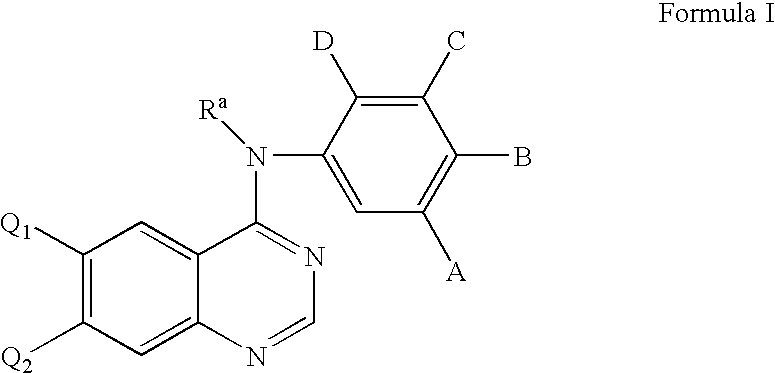
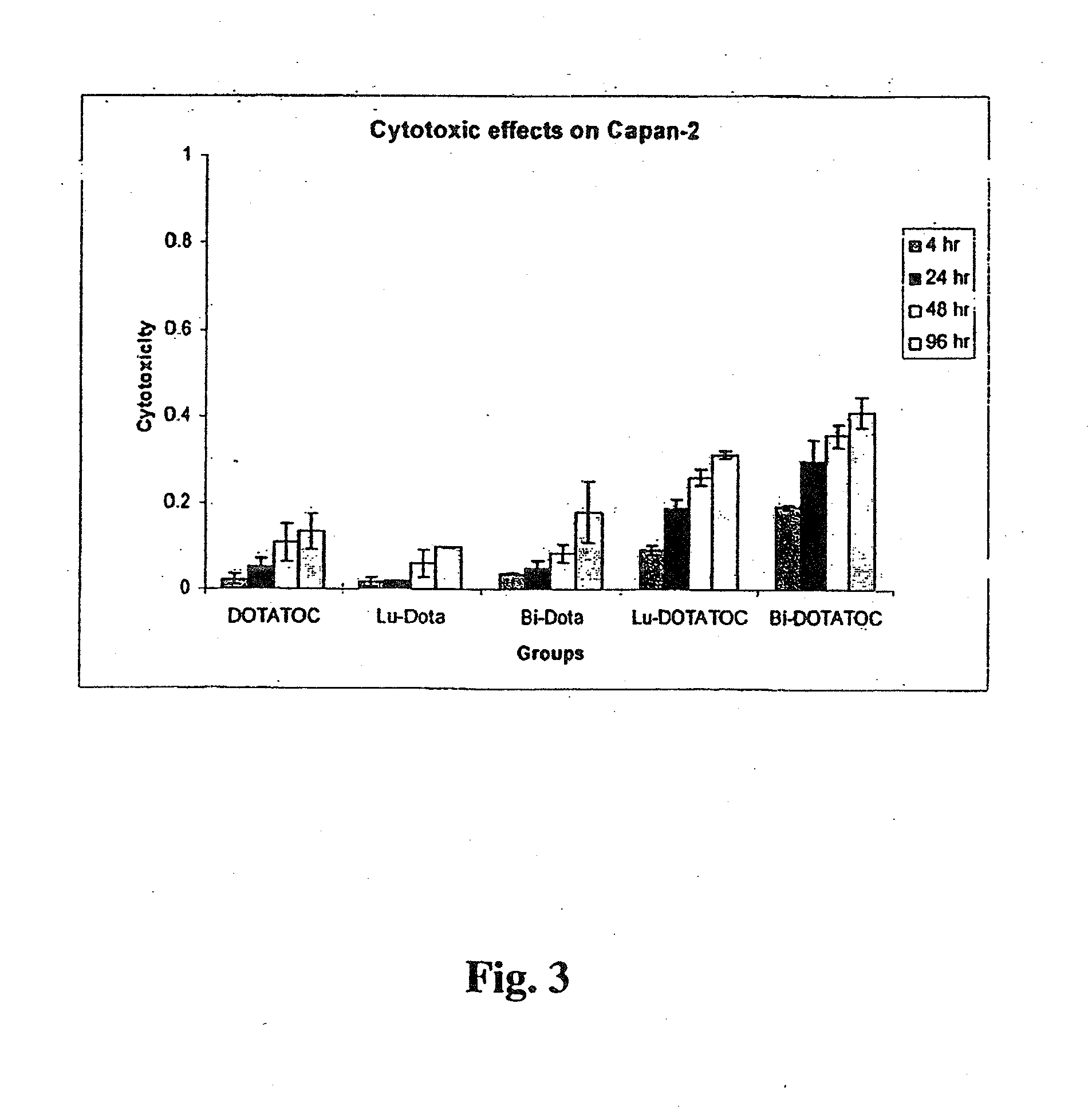
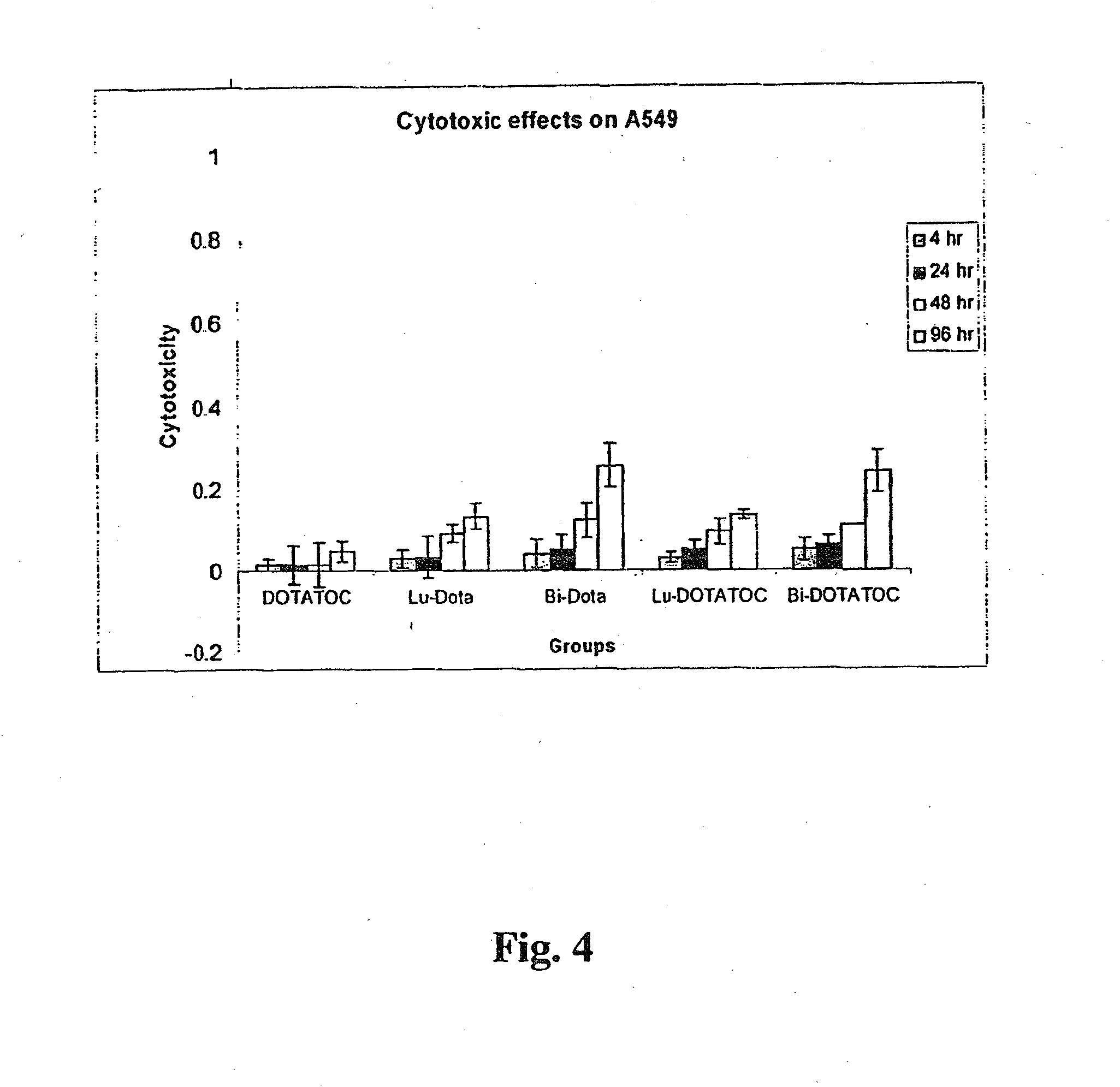
Patents
Literature
338 results about "Radioactive Label" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A substance containing a radioisotope that has an affinity for and binds to a chosen biologic substance of interest to enable quantification of biologic processes.
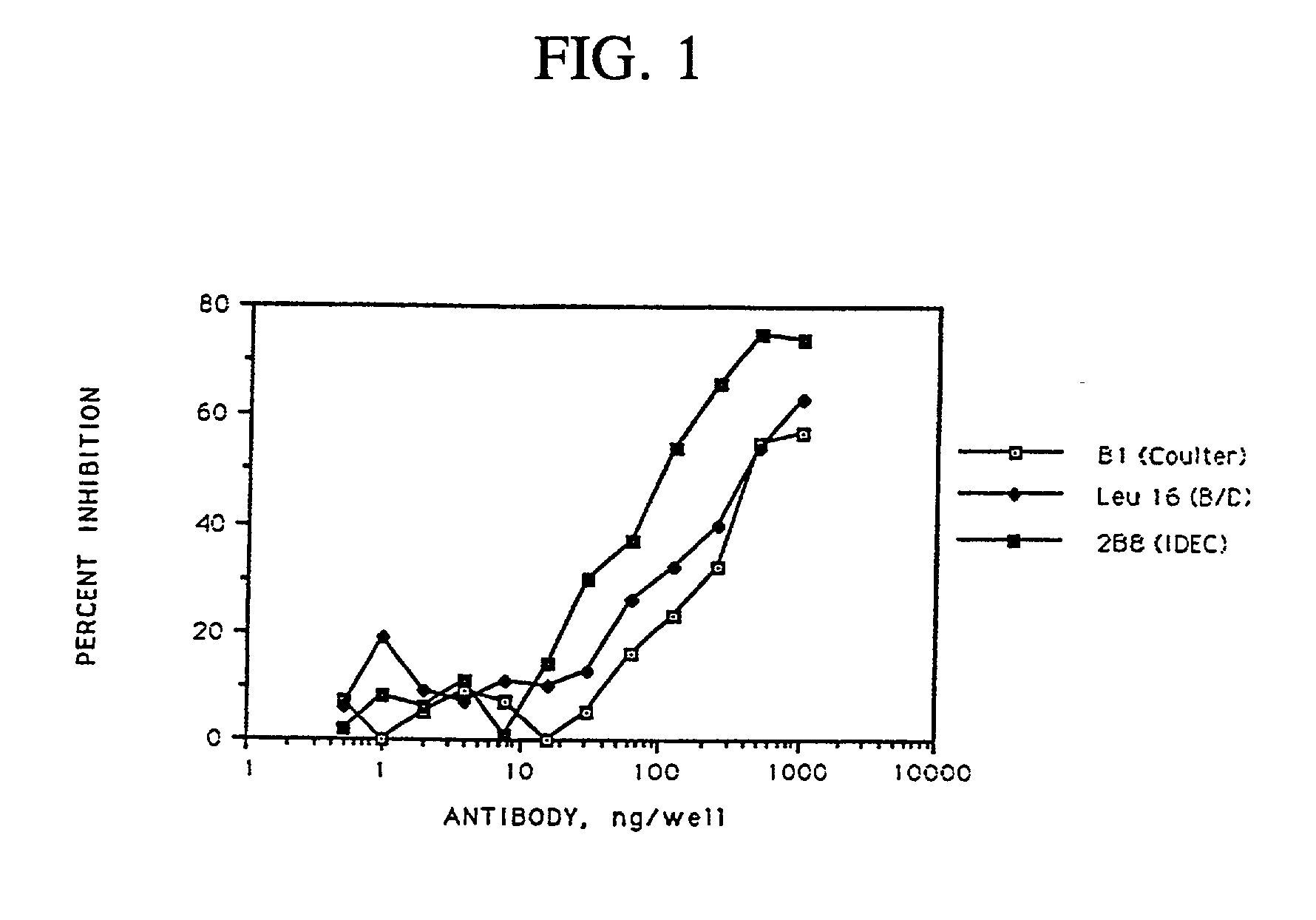
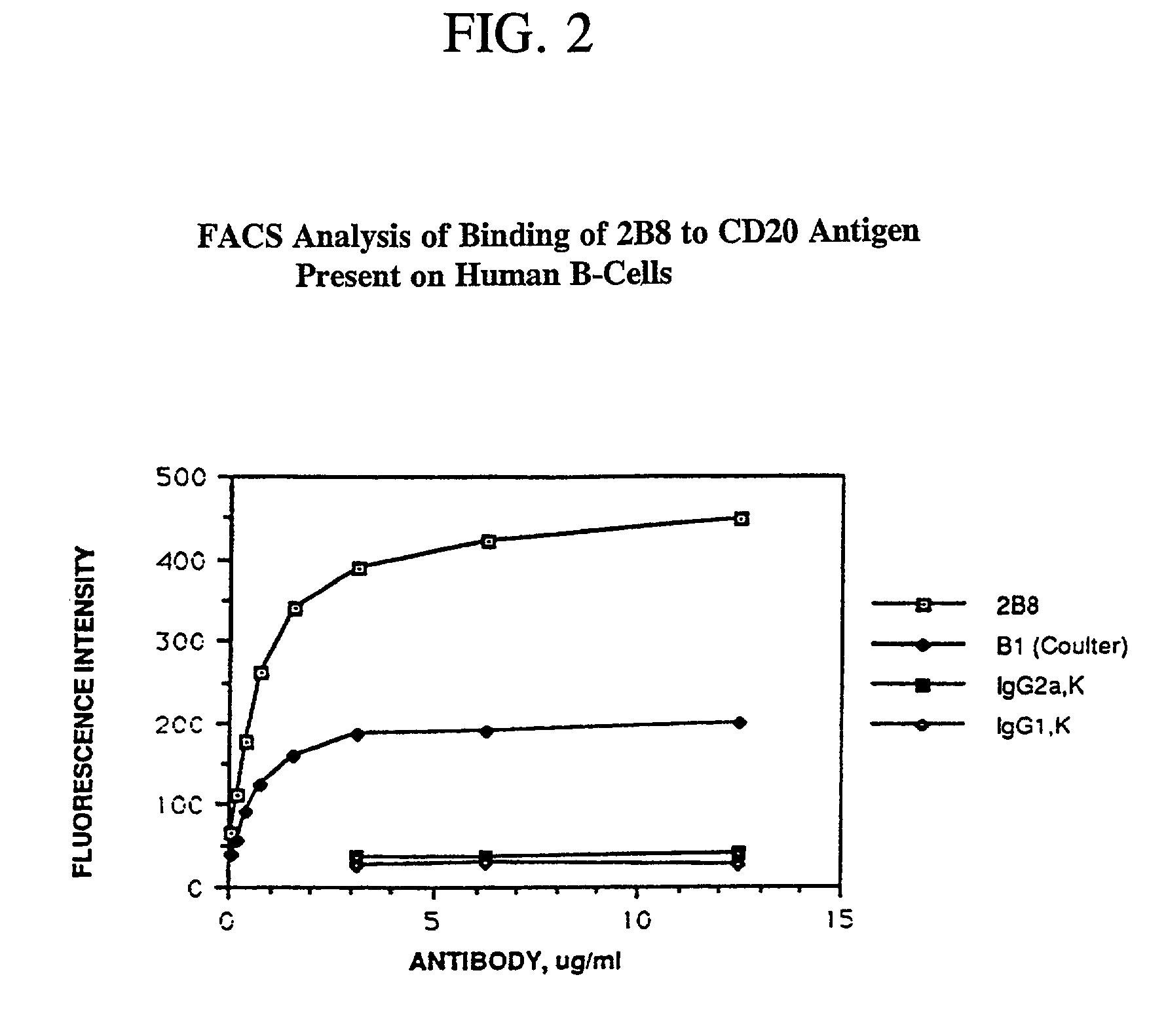
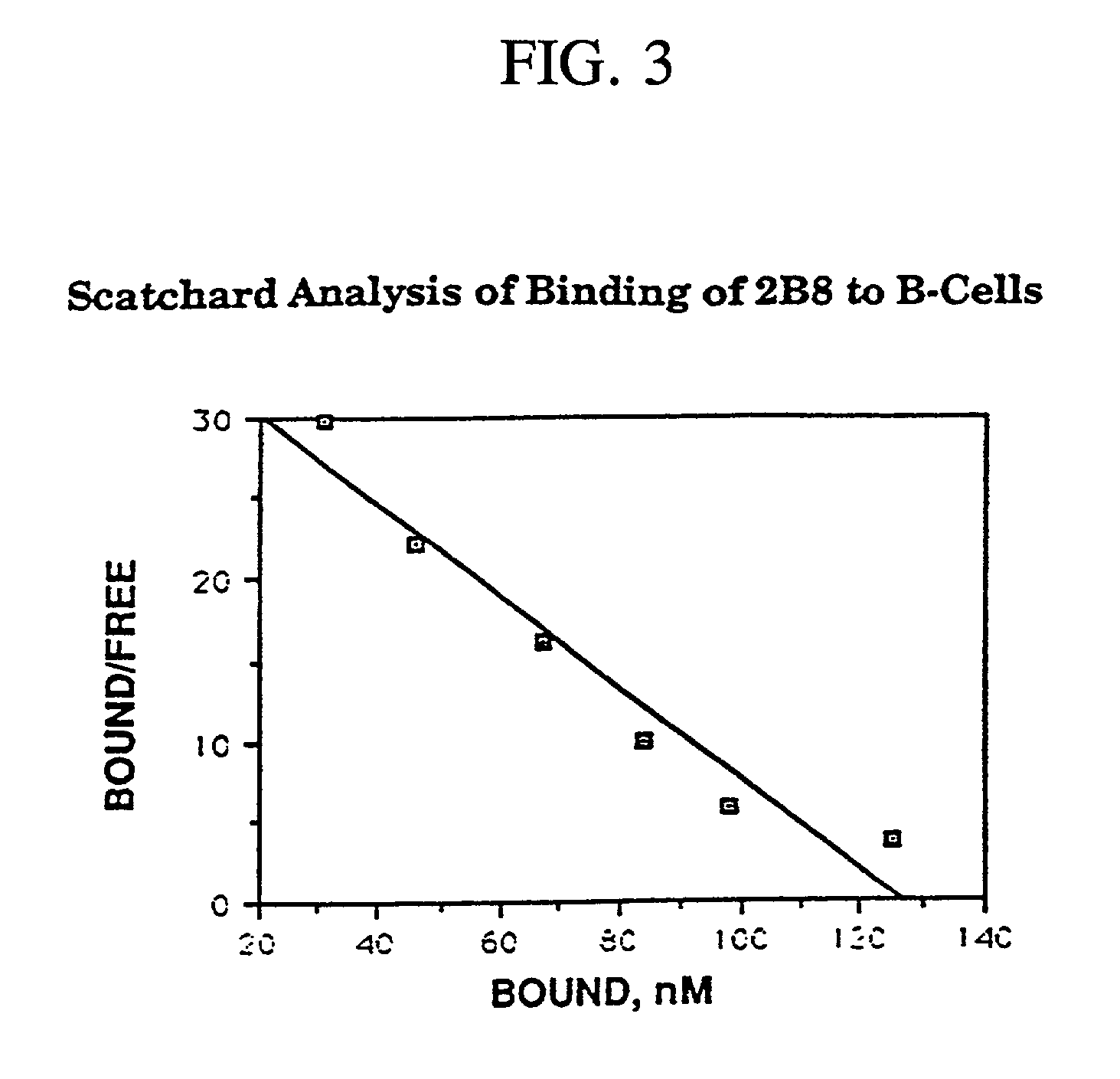
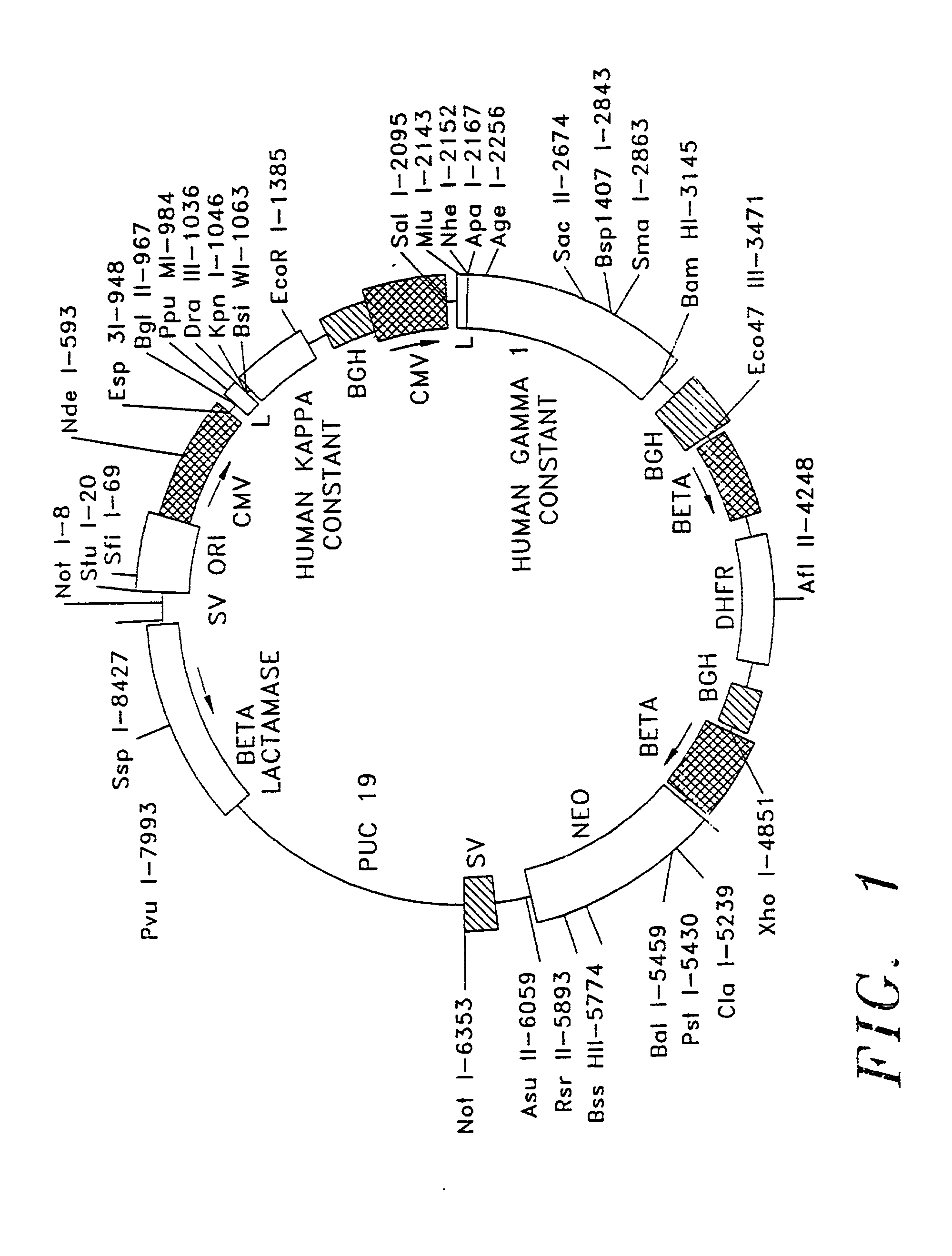
Radiolabeling kit and binding assay
InactiveUS20020102208A1No reduction in immunoreactivityNegligible lossIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDepsipeptidesTherapeutic antibodyAssay
Antibody binding assays and radiolabeling kits are disclosed for radiolabeling and testing therapeutic antibodies in the commercial setting. In particular, the kits are designed for making and evaluating radiolabeled anti-CD20 conjugates to be used for the treatment and imaging of B cell lymphoma tumors. All kit reagents are sterile and are designed to achieve a high level of antibody radiolabeling and product stability with results which are highly reproducible.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Therapeutic application of chimeric and radiolabelled antibodies to human B lymphocyte restricted differentiation antigen for treatment of B cell lymphoma
Disclosed herein are therapeutic treatment protocols designed for the treatment of B cell lymphoma. These protocols are based upon therapeutic strategies which include the use of administration of immunologically active mouse / human chimeric anti-CD20 antibodies, radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies, and cooperative strategies comprising the use of chimeric anti-CD20 antibodies and radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Heterodimers of glutamic acid
InactiveUS20080193381A1Group 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesUrea derivatives preparationHalogenStereochemistry
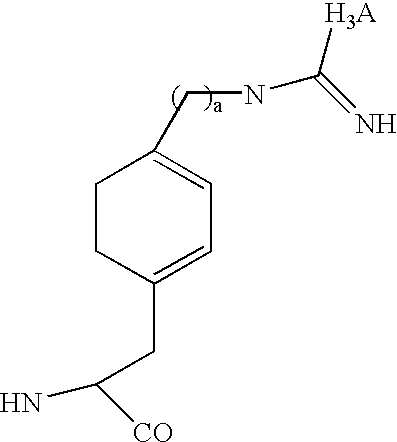
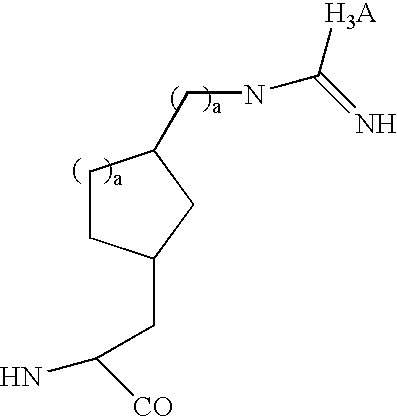
Compounds of Formula (Ia)wherein R is a C6-C12 substituted or unsubstituted aryl, a C6-C12 substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl, a C1-C6 substituted or unsubstituted alkyl or —NR′R′,Q is C(O), O, NR′, S, S(O)2, C(O)2 (CH2)pY is C(O), O, NR′, S, S(O)2, C(O)2 (CH2)p Z is H or C1-C4 alkyl,R′ is H, C(O), S(O)2, C(O)2, a C6-C12 substituted or unsubstituted aryl, a C6-C12 substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl or a C1-C6 substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, when substituted, aryl, heteroaryl and alkyl are substituted with halogen, C6-C12 heteroaryl, —NR′R′ or COOZ, which have diagnostic and therapeutic properties, such as the treatment and management of prostate cancer and other diseases related to NAALADase inhibition. Radiolabels can be incorporated into the structure through a variety of prosthetic groups attached at the X amino acid side chain via a carbon or hetero atom linkage.
Owner:MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMA
Radiolabeled irreversible inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and their use in radioimaging and radiotherapy
InactiveUS6562319B2BiocideOrganic chemistryPositron emission tomographyEpidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Radiolabeled irreversible inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and their use in radioimaging and radiotherapy
InactiveUS20020128553A1BiocideOrganic chemistryPositron emission tomographyEpidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
Radiolabeled epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) irreversible inhibitors and their use as biomarkers for medicinal radioimaging such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and as radiopharmaceuticals for radiotherapy are disclosed.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Fully-automated microfluidic system for the synthesis of radiolabeled biomarkers for positron emission tomography
InactiveUS20080233018A1Isotope introduction to sugar derivativesSugar derivativesChemical synthesisConfocal
The present application relates to microfluidic devices and related technologies, and to chemical processes using such devices. More specifically, the application discloses a fully automated synthesis of radioactive compounds for imaging, such as by positron emission tomography (PET), in a fast, efficient and compact manner. In particular, this application describe an automated, stand-alone, microfluidic instrument for the multi-step chemical synthesis of radiopharmaceuticals, such as probes for PET and a method of using such instruments.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Stereoselective Synthesis of Amino Acid Analogs for Tumor Imaging
InactiveUS20060292073A1Maximum service lifeOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid esters preparation1-amino-3-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acidCyclobutane
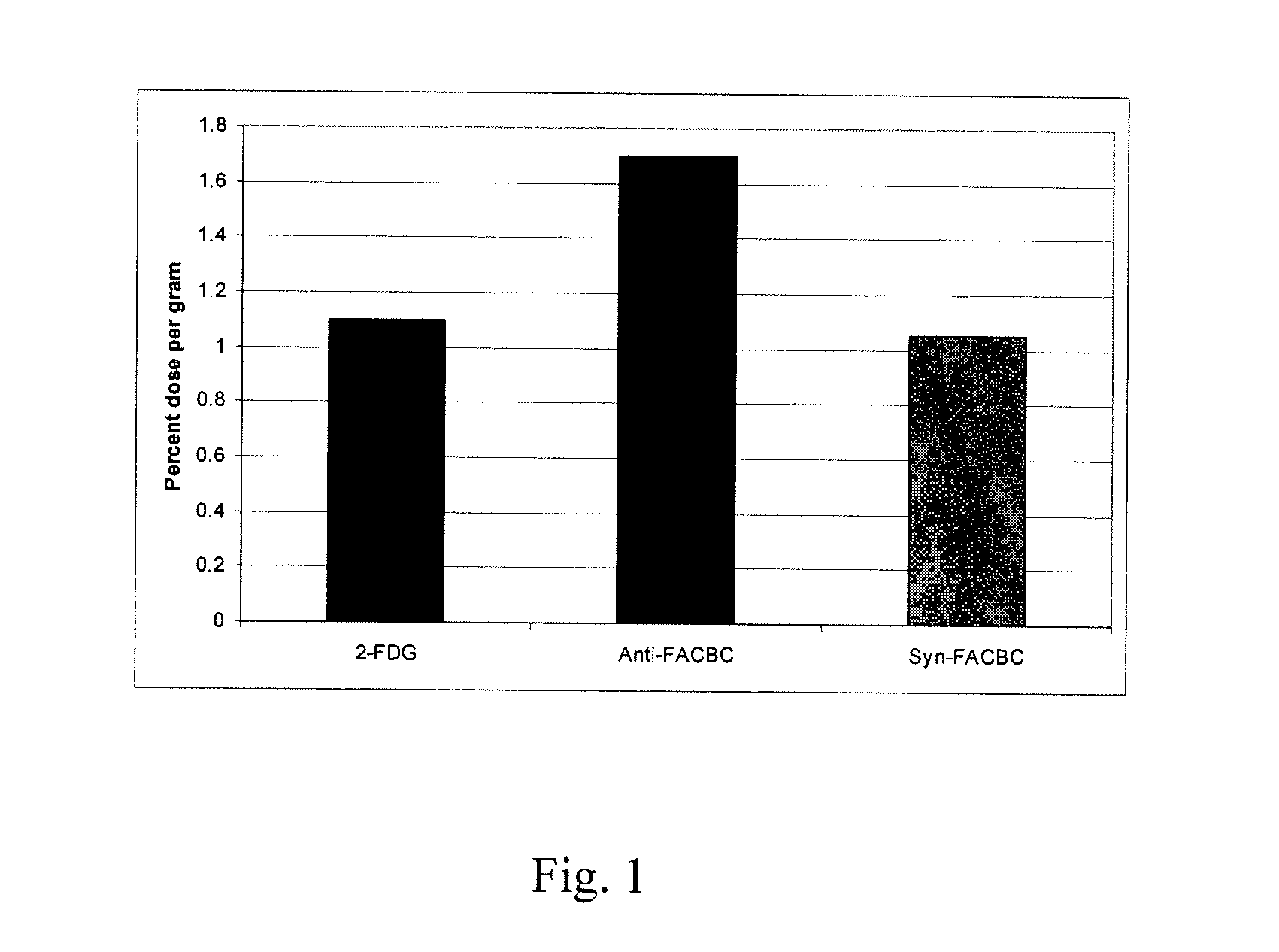
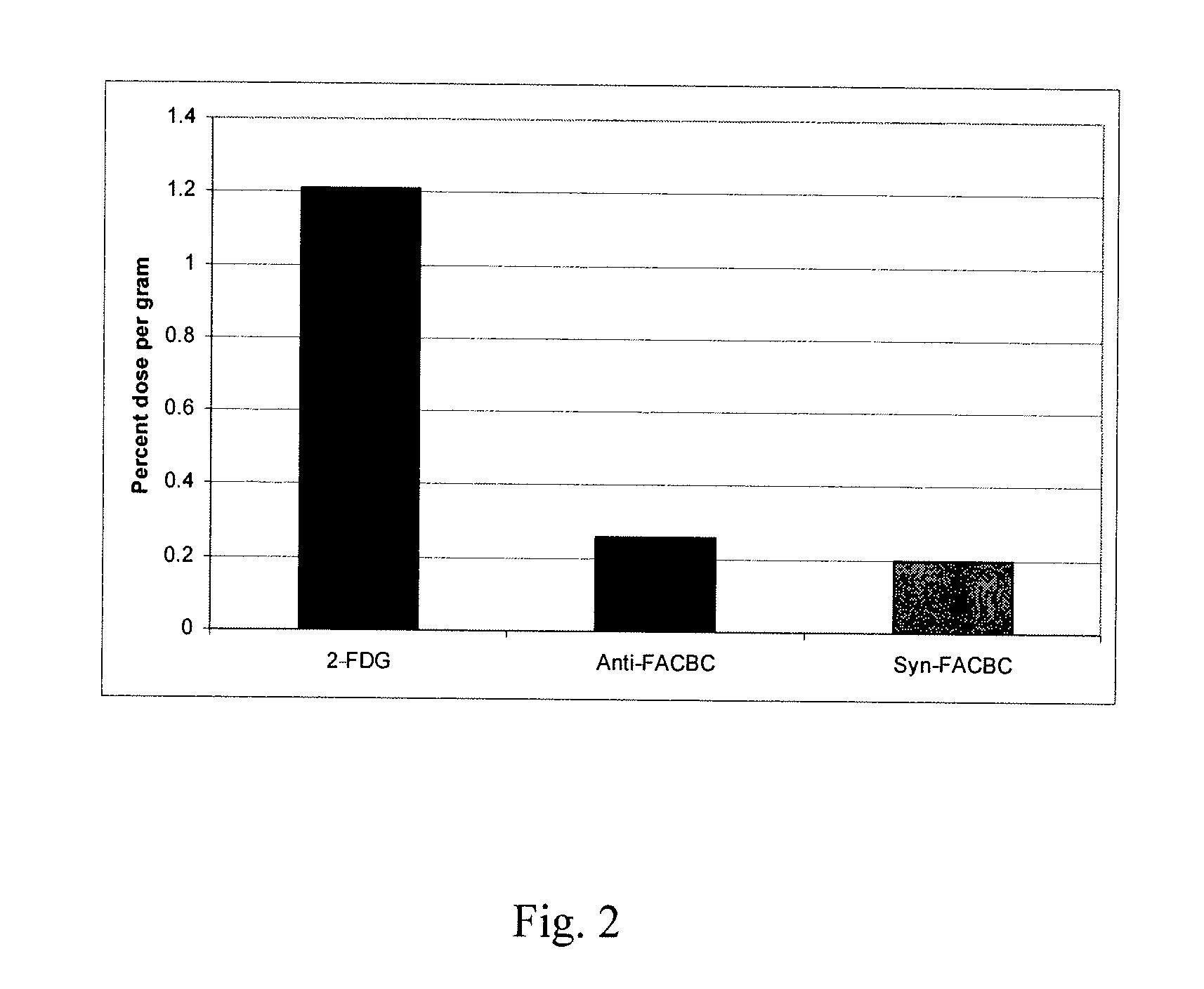
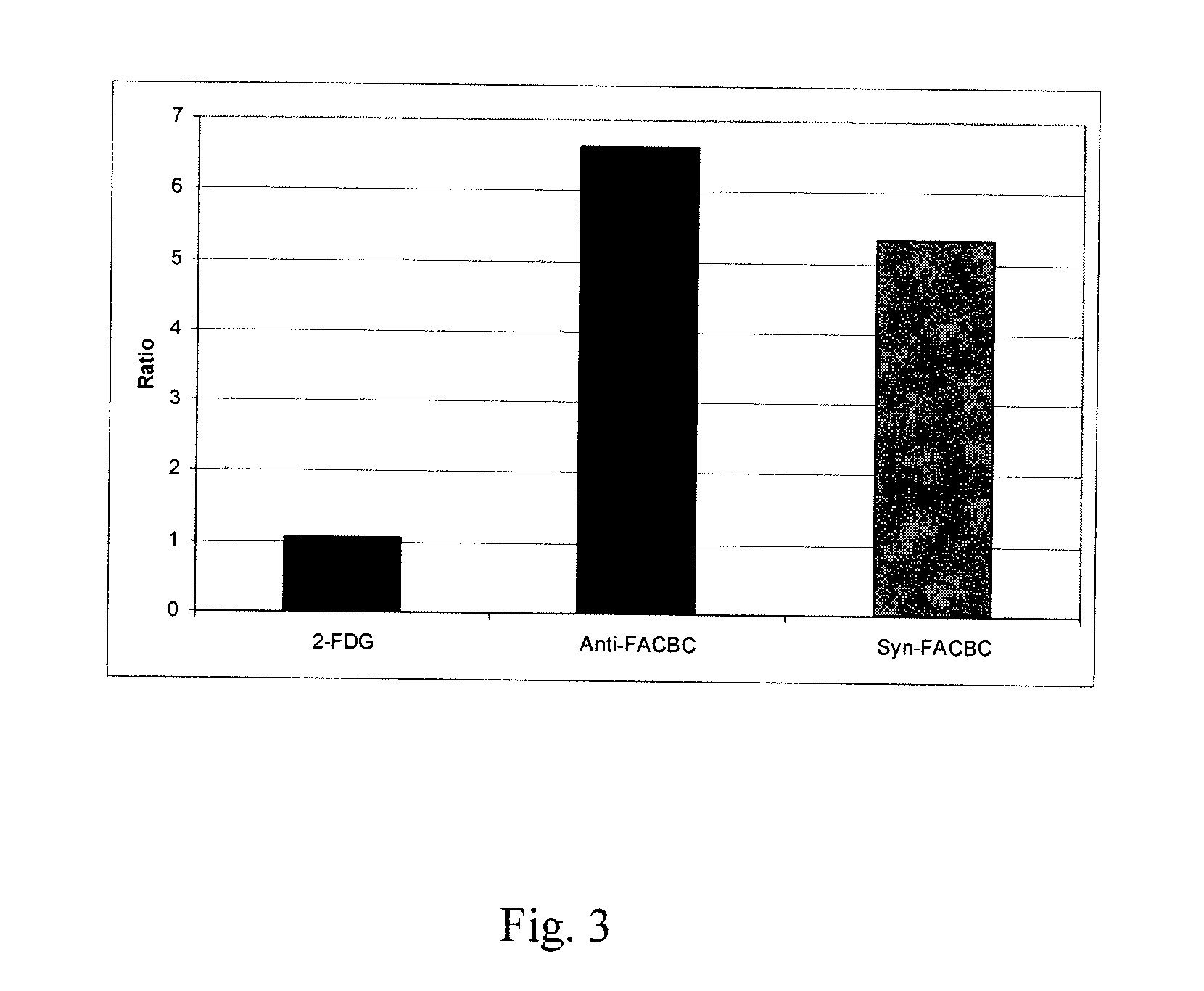
The radiolabeled non-natural amino acid 1-amino-3-cyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (ACBC) and its analogs are candidate tumor imaging agents useful for positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tomography due to their selective affinity for tumor cells. The present invention provides methods for stereo-selective synthesis of syn-ACBC analogs. The disclosed synthetic strategy is reliable and efficient and can be used to synthesize a gram quantity of various syn-isomers of the ACBC analogs, particularly, syn-[18F]-1-amino-3-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (FACBC) and syn-[123I]-1-amino-3-iodocyclobutane-1-carboxylic (IACBC) acid analogs.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Characterization of arteriosclerosis by optical imaging
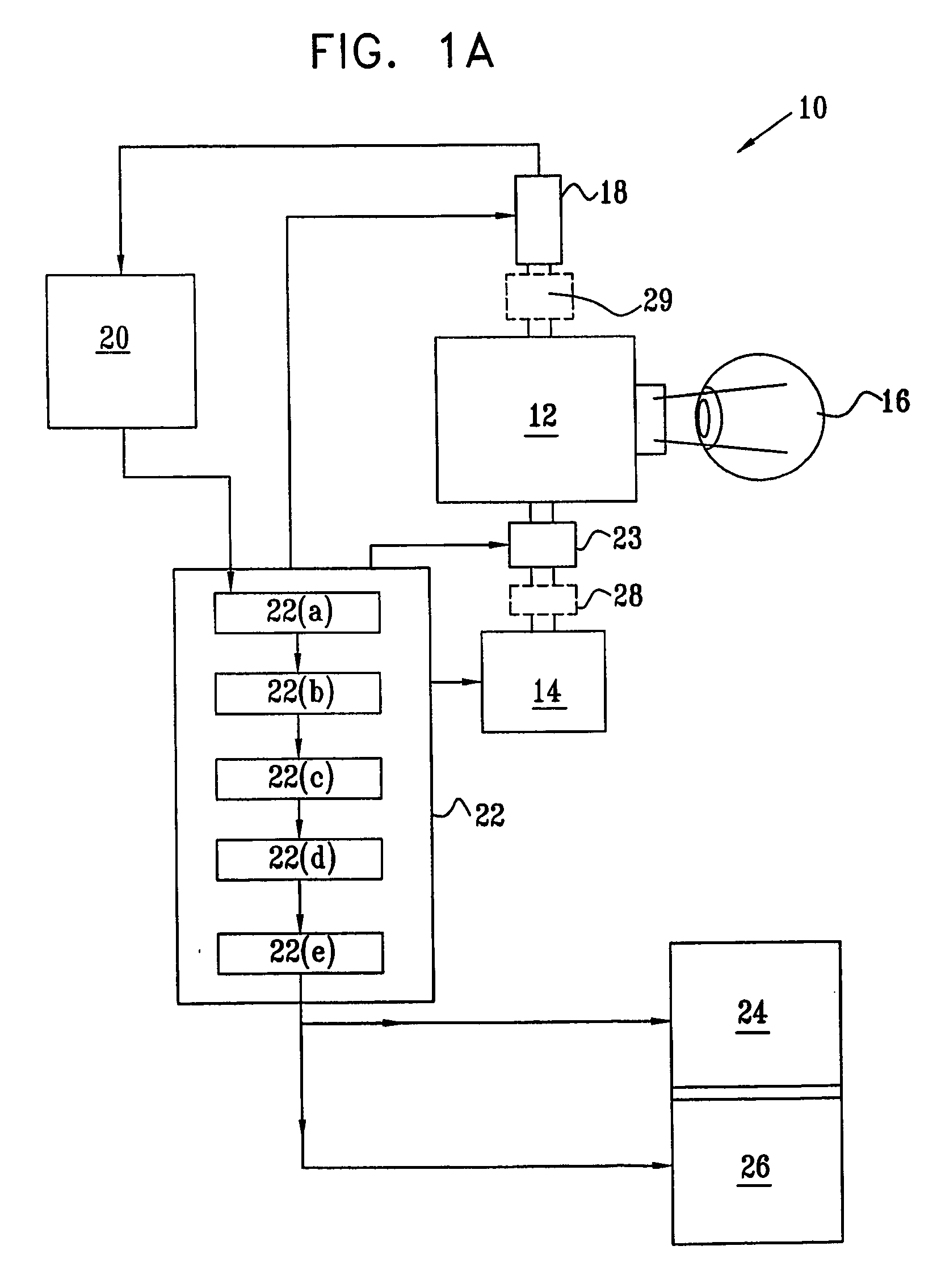
A method and system for detecting abnormalities in the properties of the walls of a subject's blood vessels by observing the characteristics of blood flow in vessels which are optically accessible, such as the retinal vasculature. A time sequenced series of images is taken, and the images are processed to eliminate the background and render erythrocyte motion visible. Information about the state of the inner wall of the blood vessel which has been imaged is obtained from the characteristics of this blood flow. This information can be extrapolated to provide information about the state of the blood vessels elsewhere in the subject. In addition, a system and method is described for detecting arteriosclerotic plaque on the walls of blood vessels by labeling the plaque with a molecular label having desired optical or radioactive properties, and directly imaging the plaque either in an optically accessible blood vessel, or by imaging radioactive label in the plaque in a blood vessel anywhere in the body.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
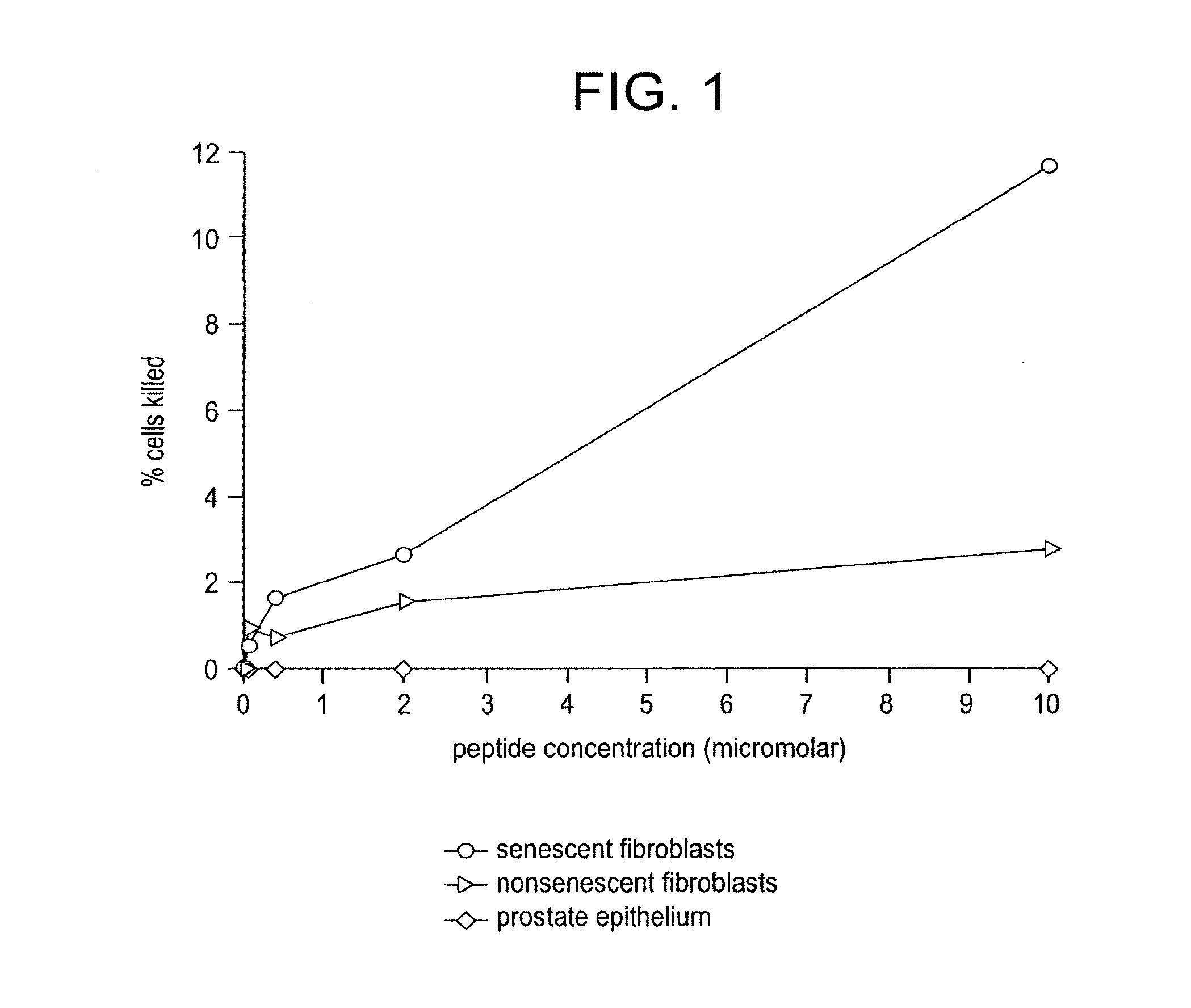
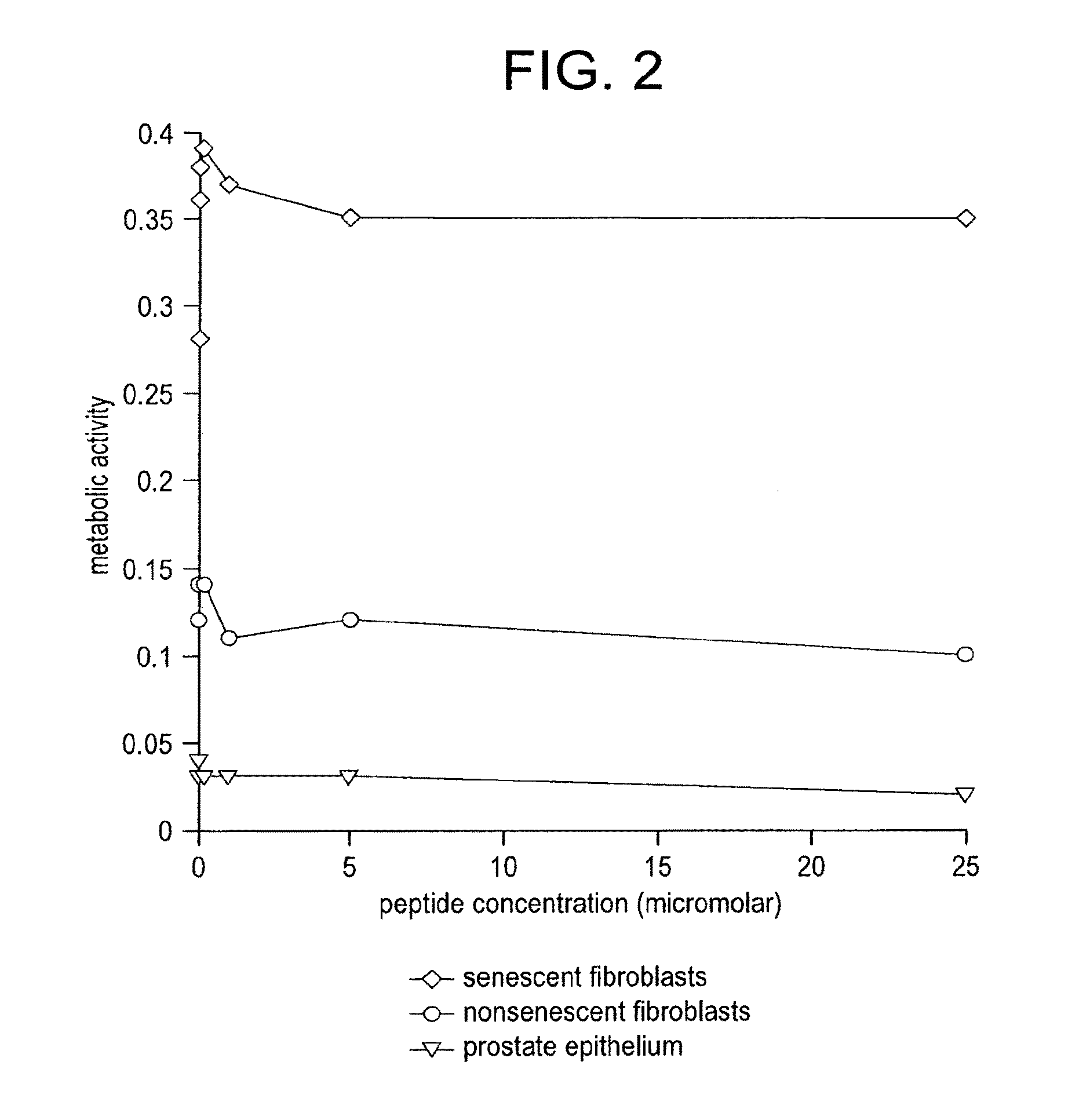
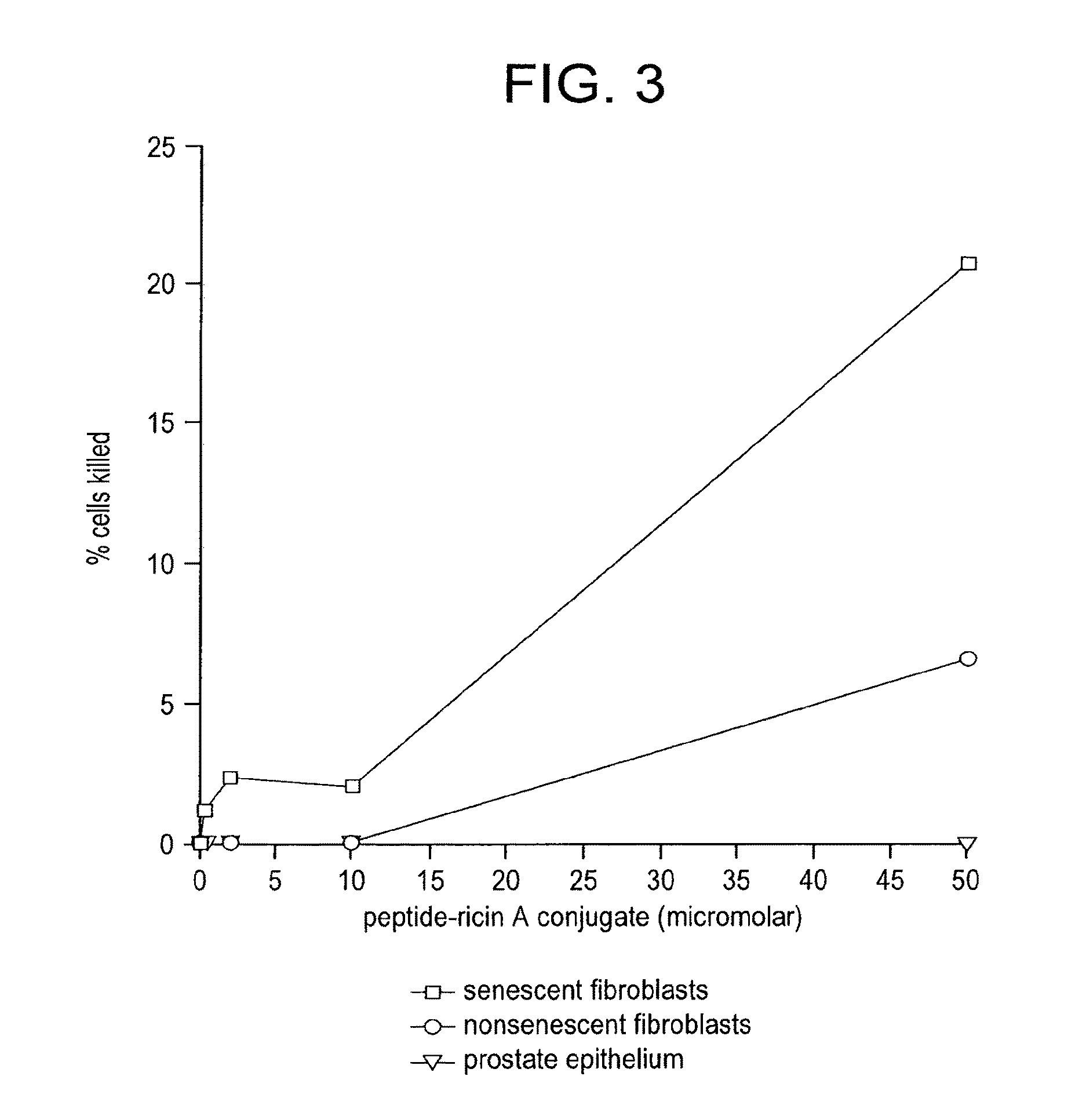
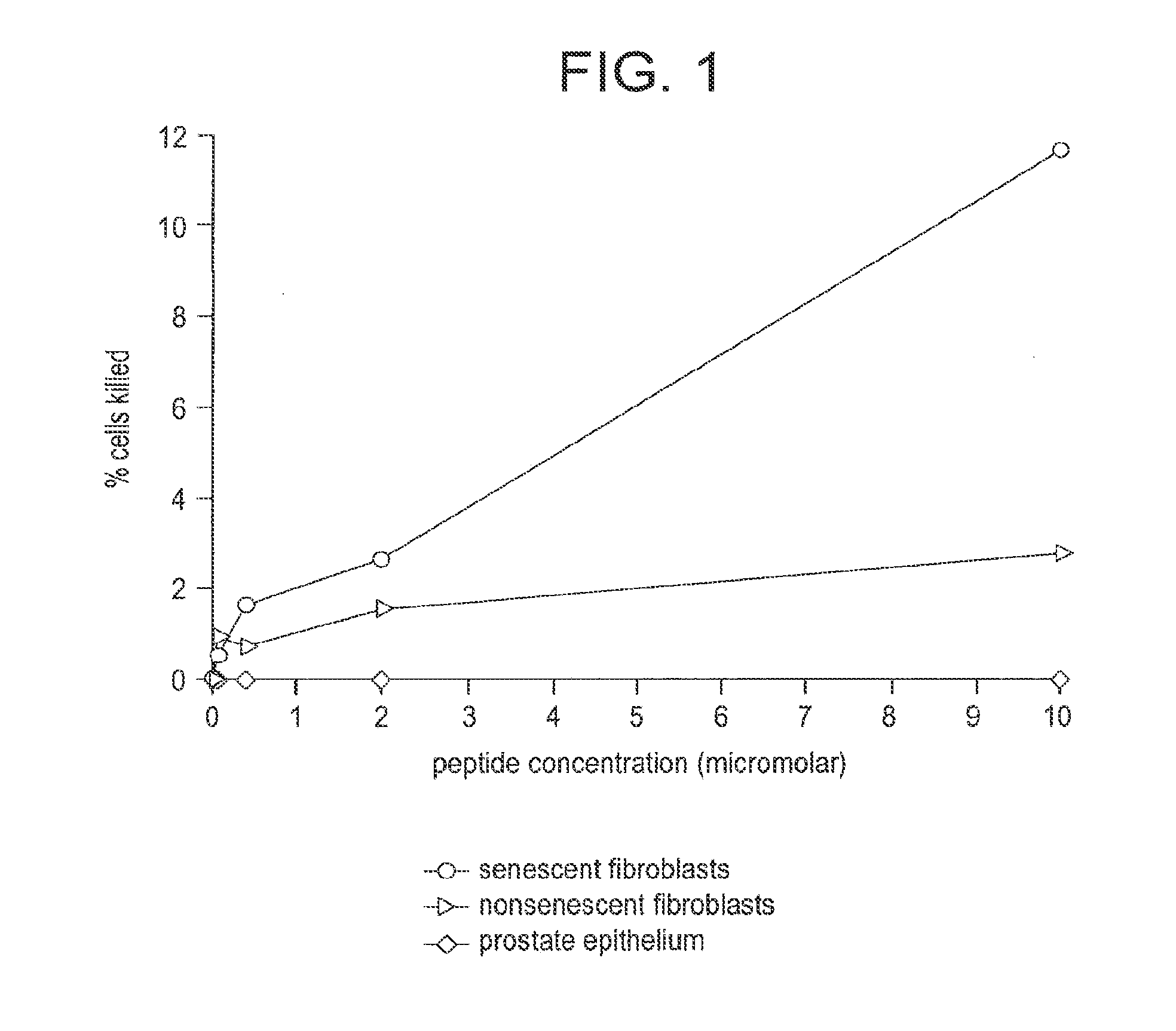
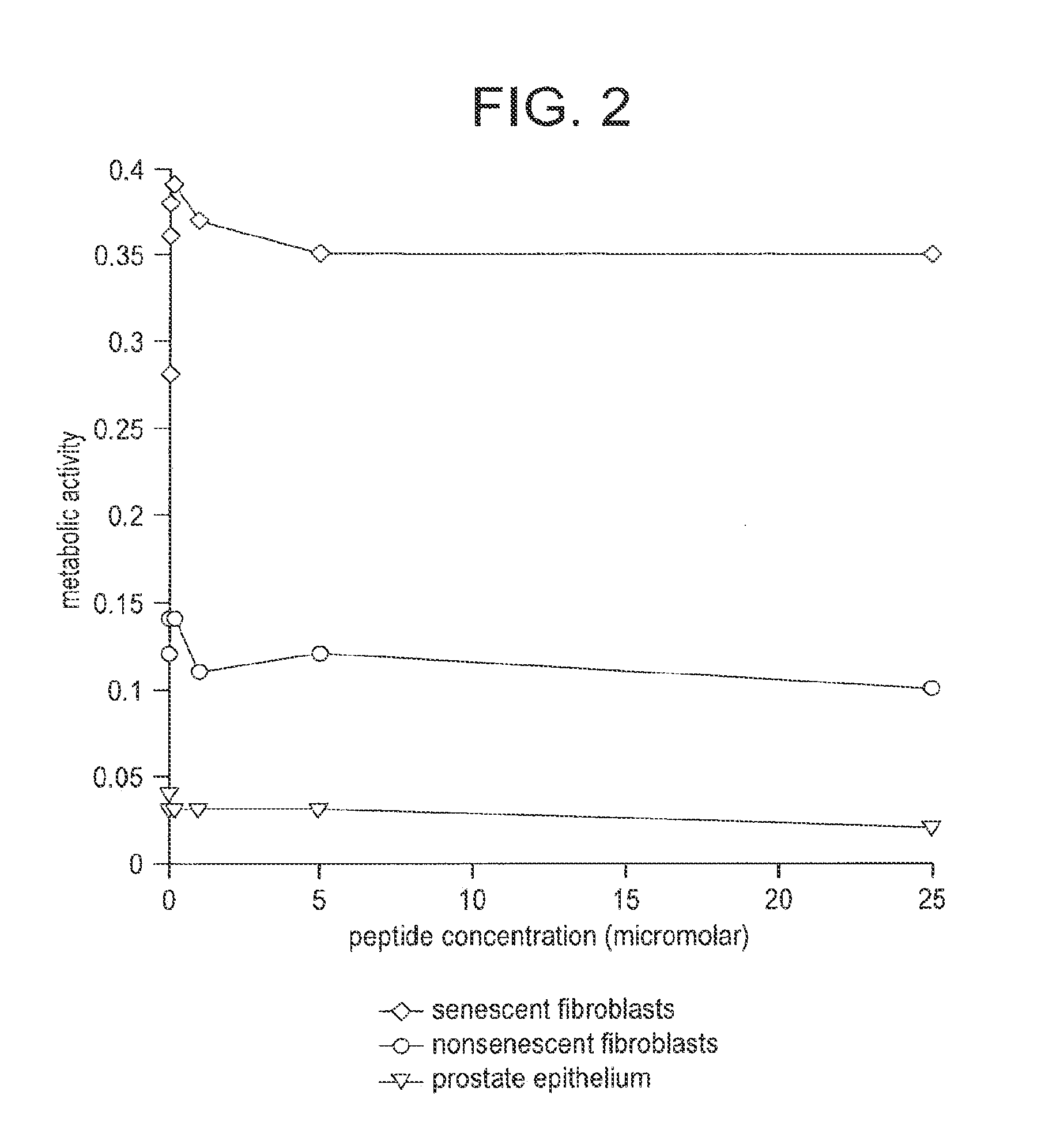
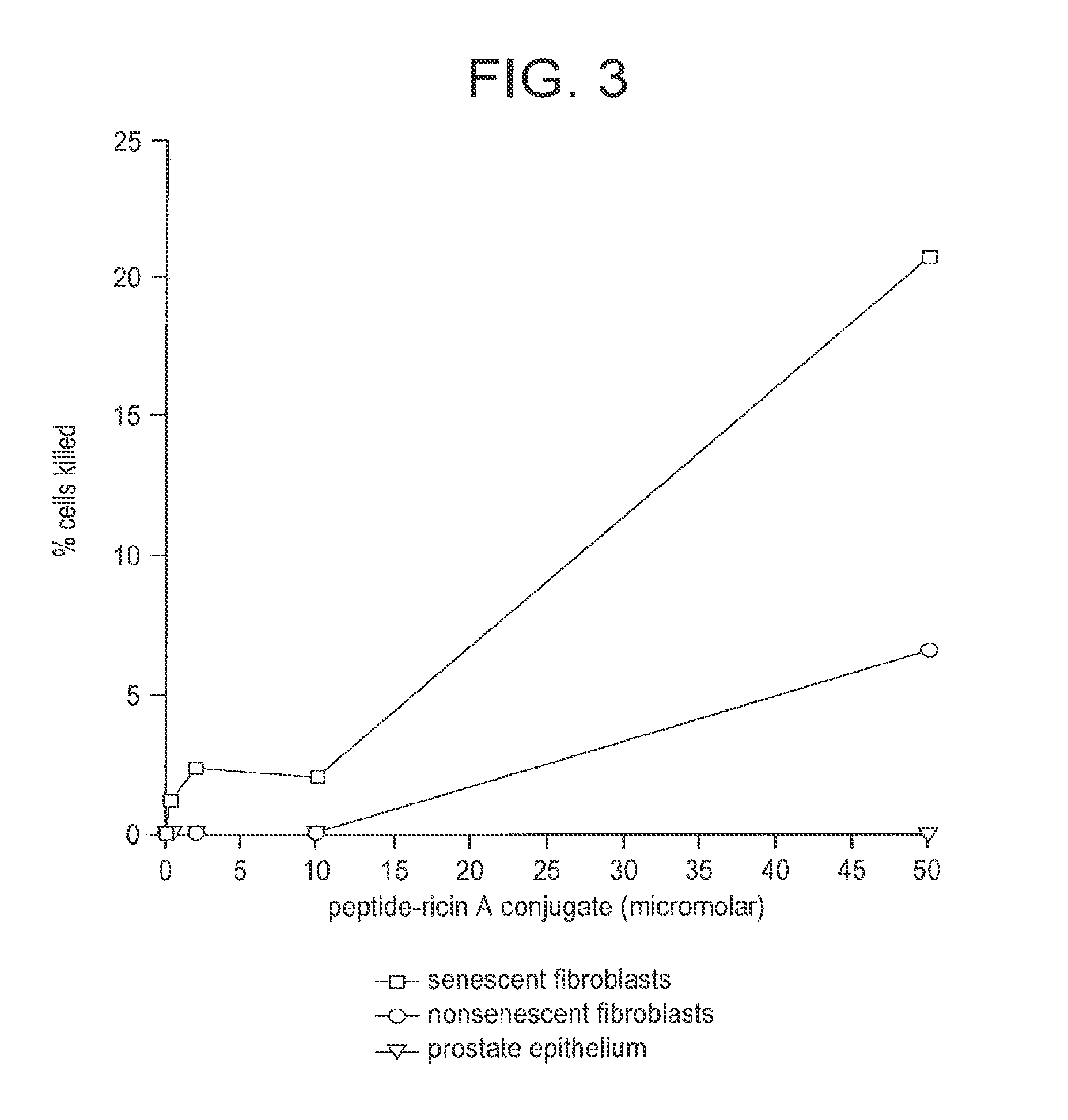
Compositions and methods for detecting or eliminating senescent cells to diagnose or treat disease
InactiveUS20120156134A1Reduce the numberShrink tumor sizeCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsCancer preventionNicotiana tabacum
Disclosed are agents (e.g., peptides, polypeptides, proteins, small molecules, antibodies, and antibody fragments that target senescent cells) and methods of their use for imaging senescent cells in vivo and for treating or preventing cancer, age-related disease, tobacco-related disease, or other diseases and disorders related to or caused by cellular senescence in a mammal. The methods include administering one or more of the agents of the invention to a mammal, e.g., a human. The agents, which specifically bind to senescent cells, can be labeled with a radioactive label or a therapeutic label, e.g., a cytotoxic agent.
Owner:UNITY BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
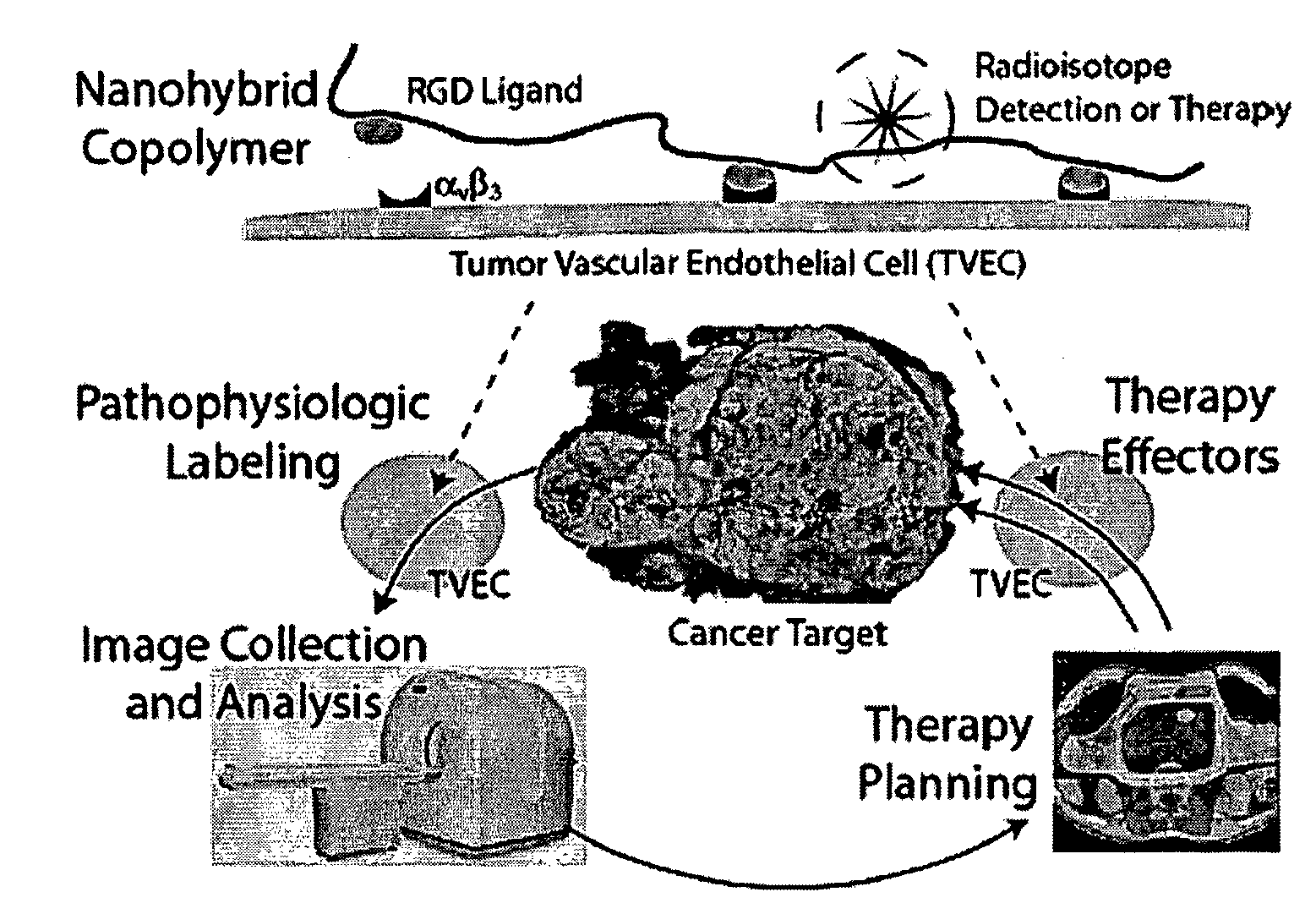
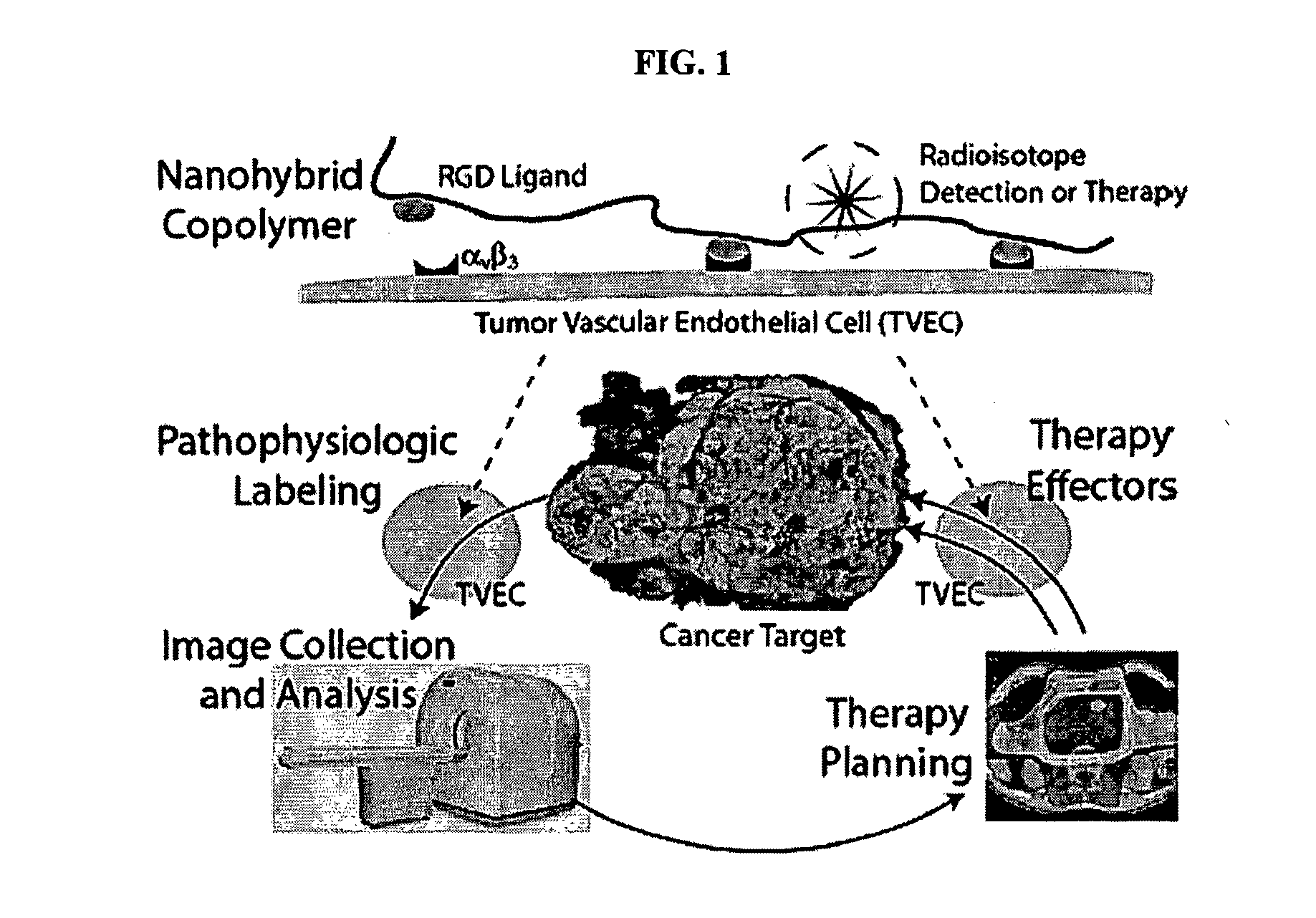
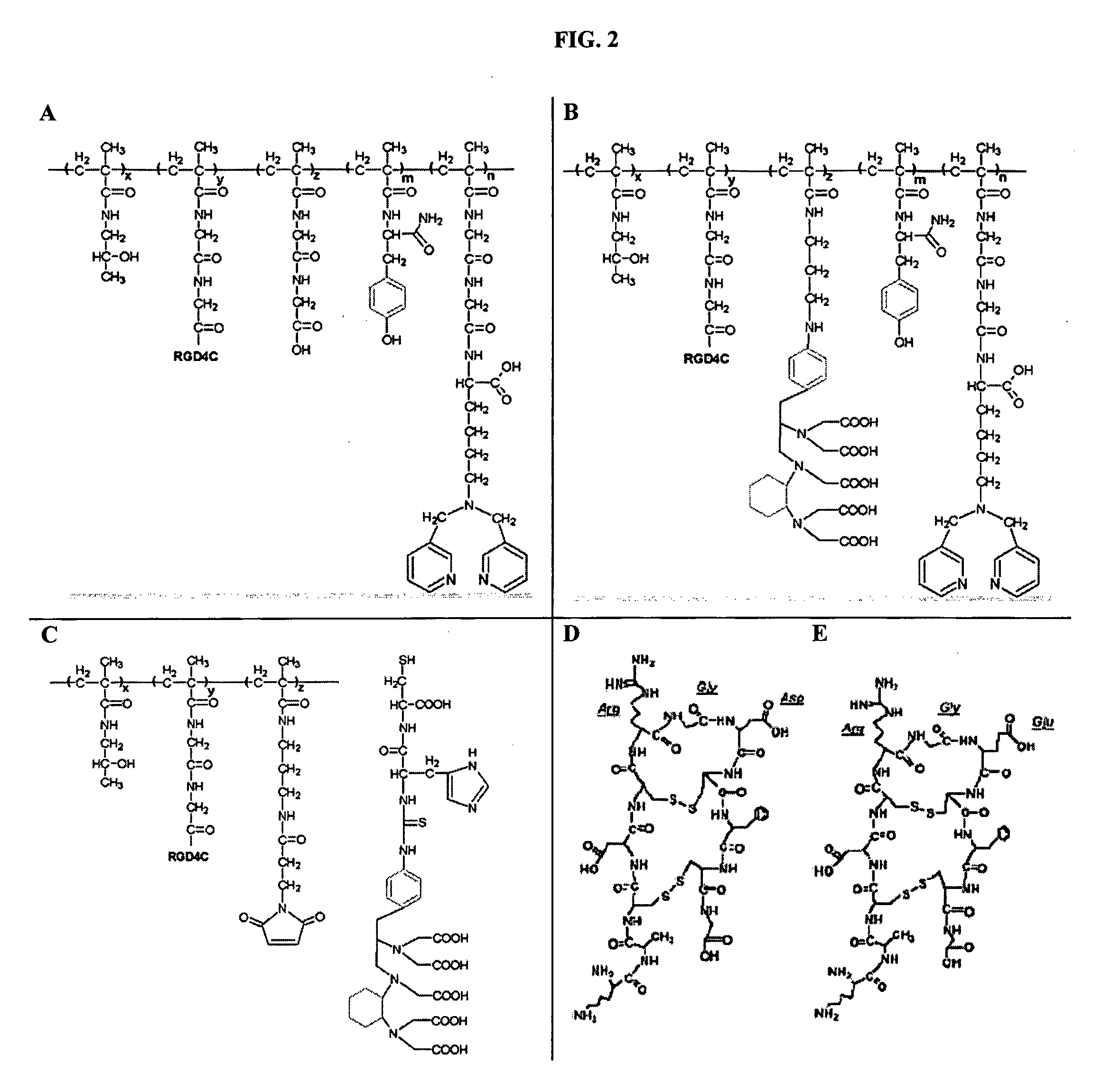
Radiolabeled Nanohybrids Targeting Solid Tumor Neovasculature and Method of Using Same
Nanohybrid polymer conjugates that provide a “platform” delivery system is disclosed. The delivery platform provides a multi-focused therapeutic regimen that may be tailored to combat a host of cancers, including advanced-stage, therapy-resistant tumors. The nanohybrids of the instant invention incorporate a configurable polymeric backbone, are multivalent (e.g., may incorporate several targeting ligands), and have the capacity to carry multiple classes of “payloads” (e.g., alpha-, beta-, gamma- and positron-emitting isotopes). The polymer conjugates comprise a single molecular species that can be useful not only in diagnostic assessment, but also in tailoring therapies to suit a variety of cancers.
Owner:ADVANCED NUCLIDE TECH LLC +1
Click chemistry-derived cyclic peptidomimetics as integrin markers
InactiveUS20080213175A1Good metabolic stabilityReduce decreaseAntibacterial agentsBiocideComputed tomographyClick chemistry
The present application is directed to radiolabeled cyclic peptidomimetics, pharmaceutical compositions comprising radiolabeled cyclic peptidomimetics, and methods of using the radiolabeled cyclic peptidomimetics. Such peptidomimetics can be used in imaging studies, such as Positron Emitting Tomography (PET) or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT).
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Radiolabeled peptides for the diagnosis and treatment of breast and prostate tumors and metastases of such tumors
InactiveUS20030224998A1Conveniently providedShort half-lifeCosmetic preparationsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBombesinReceptor
Compounds and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors, including breast and prostate tumors and metastases thereof using radiolabelled peptides that bind to GRP receptors. The peptides are Bombesin analogs wherein the first and optionally the third amino acid are modified.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
Modular and reconfigurable multi-stage high temperature microreactor cartridge apparatus and system for using same
InactiveUS20080181829A1Improve efficiencyIncrease speedGaseous chemical processesLiquid-gas reaction of thin-film typeMicroreactorGas phase
A microfluidic reactor cartridge having glass capillary tubing wound in a coil and surrounded by a ceramic housing capable use in high temperatures and method for using same. In another embodiment, the microfluidic cartridge is a serpentine reactor cartridge with a serpentine microreactor channel formed in a ceramic housing. The serpentine reactor cartridge has an inlet tube attached to its inlet port and an outlet tube attached to its outlet port. The inlet port is a macro / micro interface and the outlet port is a micro / macro interface useful in gas phase reactions where solids must be used to produce a reactant. The method for using a microfluidic reactor cartridge includes two phases, the first phase for producing a radioactive labeled gas such as methyl iodide and the second phase is a methylation reaction.
Owner:ADVION
Probes for In Vivo Targeting of Active Cysteine Proteases
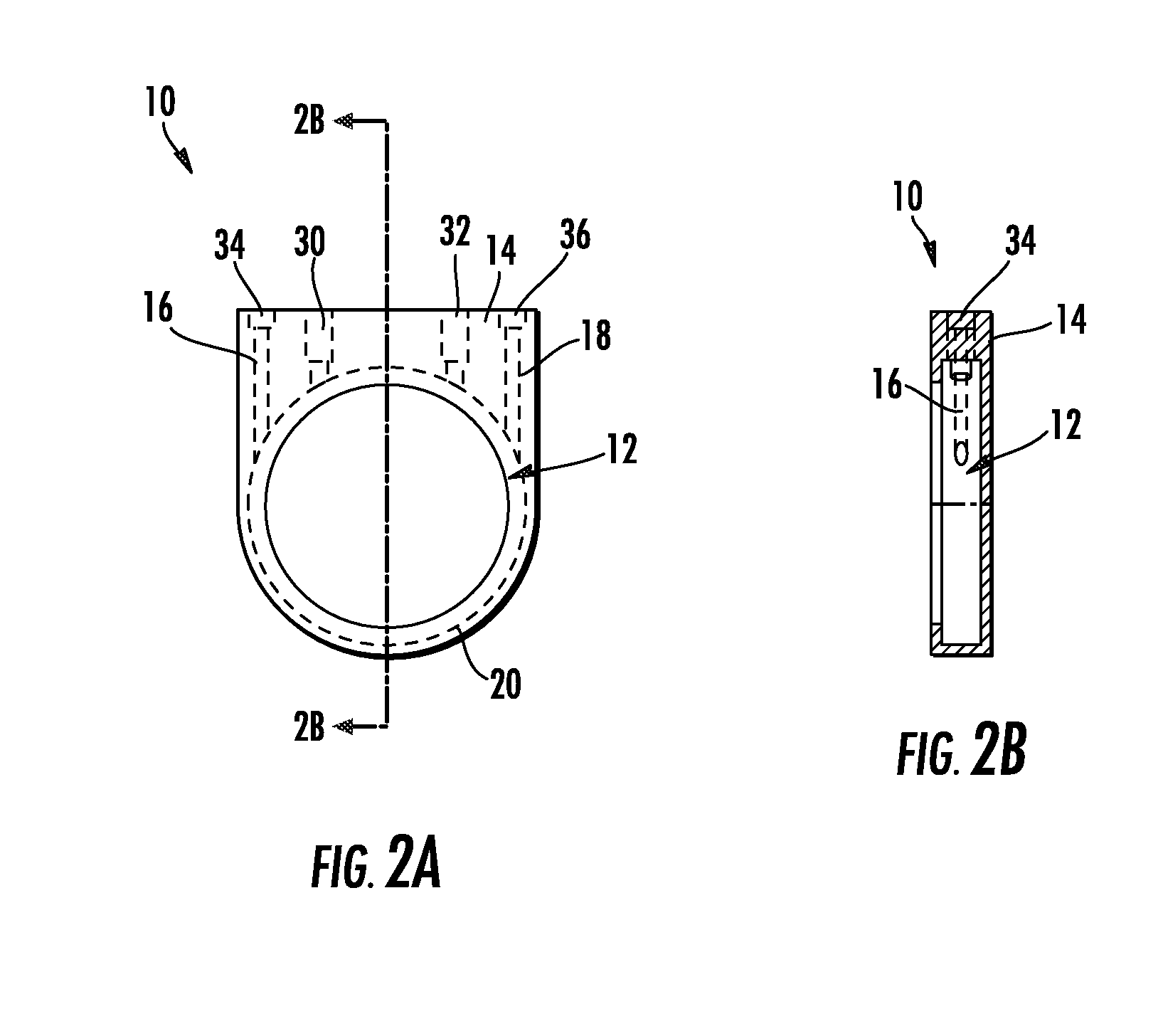
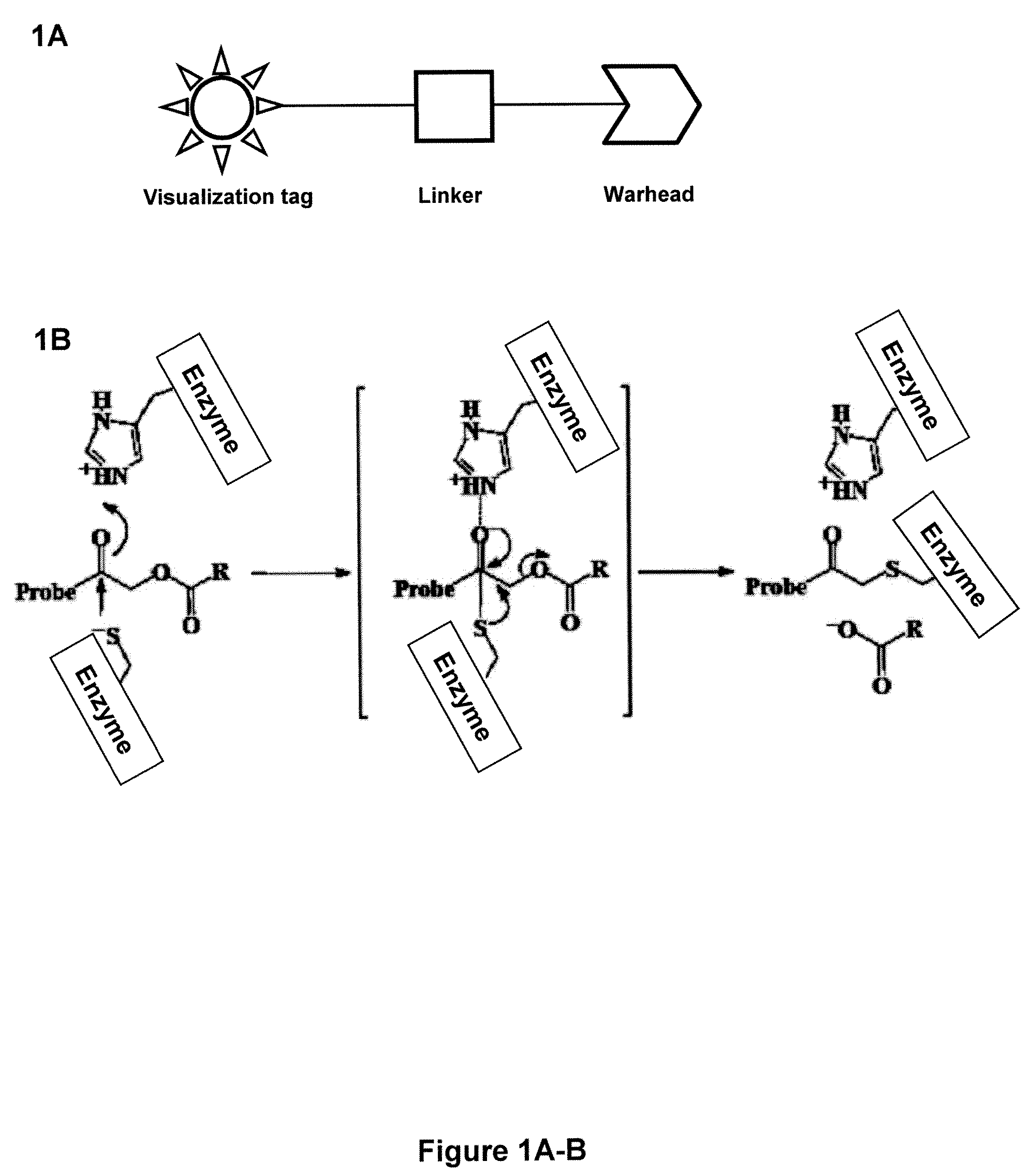
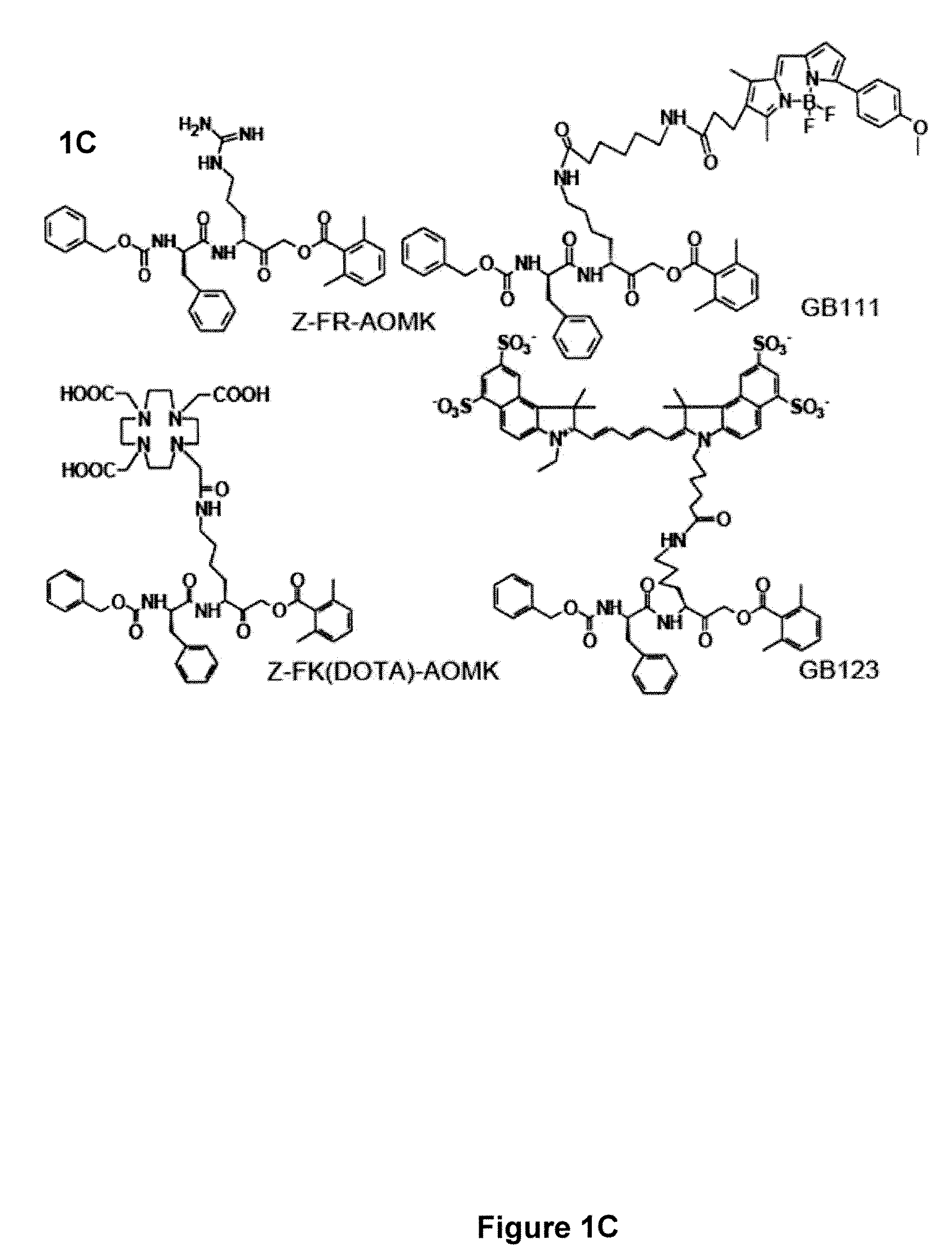
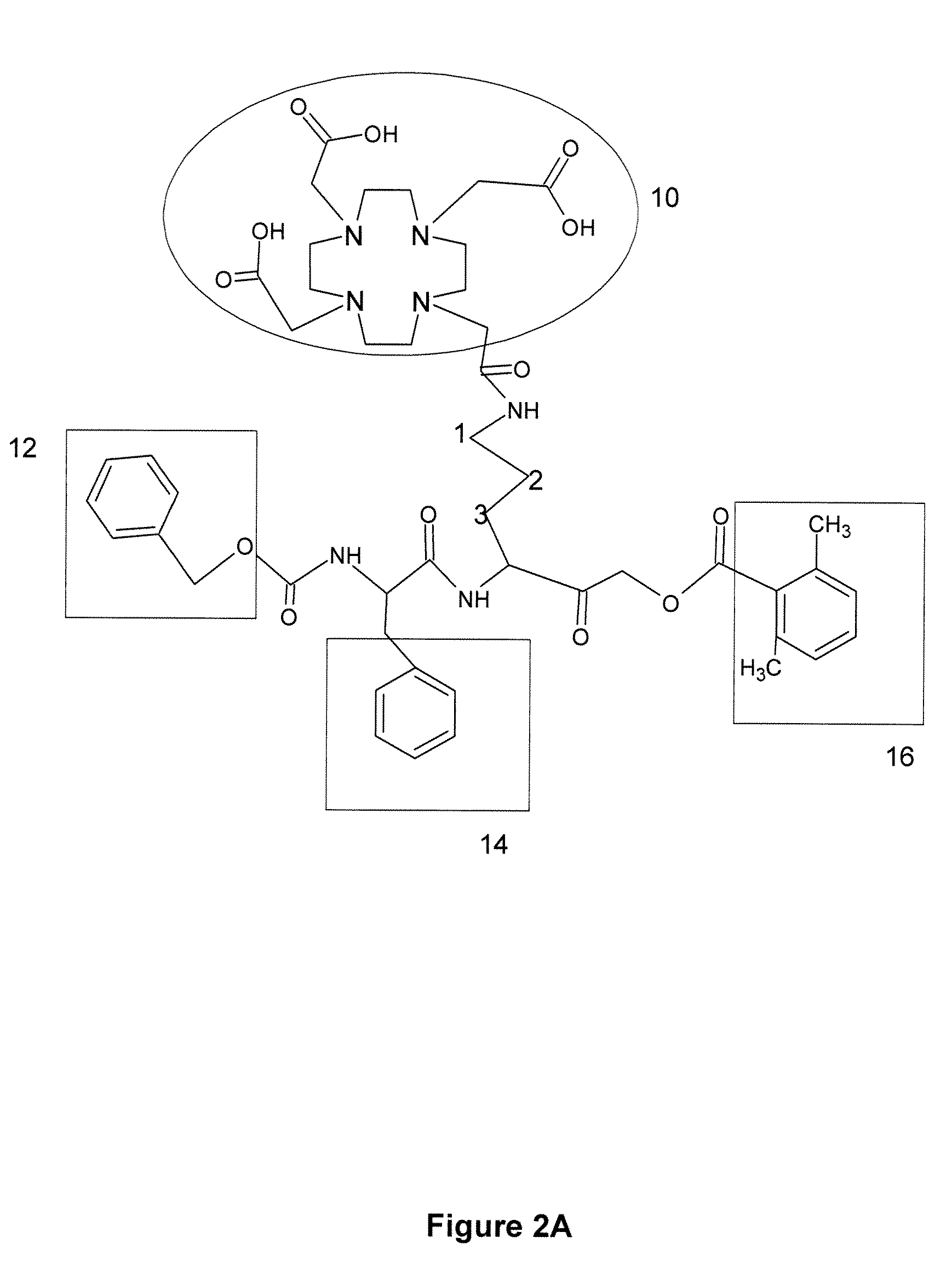
ActiveUS20090252677A1Stable labelingSufficient half-lifeRadioactive preparation carriersX-ray constrast preparationsActive enzymeHalf-life
Activity-based probes, which are specific for certain active cysteine proteases (caspase, cathepsin and legumain) and carry radioactive labels, are disclosed. The present probes comprise an acyloxymethyketone (AOMK) “warhead” that binds only to active enzyme. The probes further comprise peptide-like structure that targets the probe to a specific cysteine protease or protease family, and a radiolabel on the probe, which is bound to the targeted enzyme. It has been found that the present probes are stable in vivo and give specific target images distinguishable over background. The preferred probes are labeled with a positron-emitting agent such as 64Cu, 125I (SPECT) and 99mTc (PET). The probes show in vivo half-life and stability well suited for imaging.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Expression cloning processes for the discovery characterization, and isolation of genes encoding polypeptides with a predetermined property
InactiveUS6197502B1Protein production is suppressedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteRapid identification
The present invention is directed to a method for detection, characterization and isolation of nucleic acids encoding proteins of a desired property, such as a particular cellular localization. The invention further provides for rapid expression of such proteins or glycoproteins in mammalian cells and for facilitated purification of the novel secreted proteins or glycoproteins. Further, the invention provides for radioactive labelling of the novel proteins or glycoproteins, for rapid identification of sites of binding including animals and for rapid production of infective viral vectors for use in gene transfer.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
Novel irreversible inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and uses thereof for therapy and diagnosis
InactiveUS20060025430A1Improve bioavailabilityImprove biostabilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRadiation therapyPositron emission tomography
Novel epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) irreversible inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions including same and their use in the treatment of EGFR-TK related diseases or disorders are disclosed. Novel radiolabeled EGFR-TK irreversible inhibitors as their use as biomarkers for medicinal radioimaging such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and as radiopharmaceuticals for radiotherapy are further disclosed.
Owner:T K SIGNAL
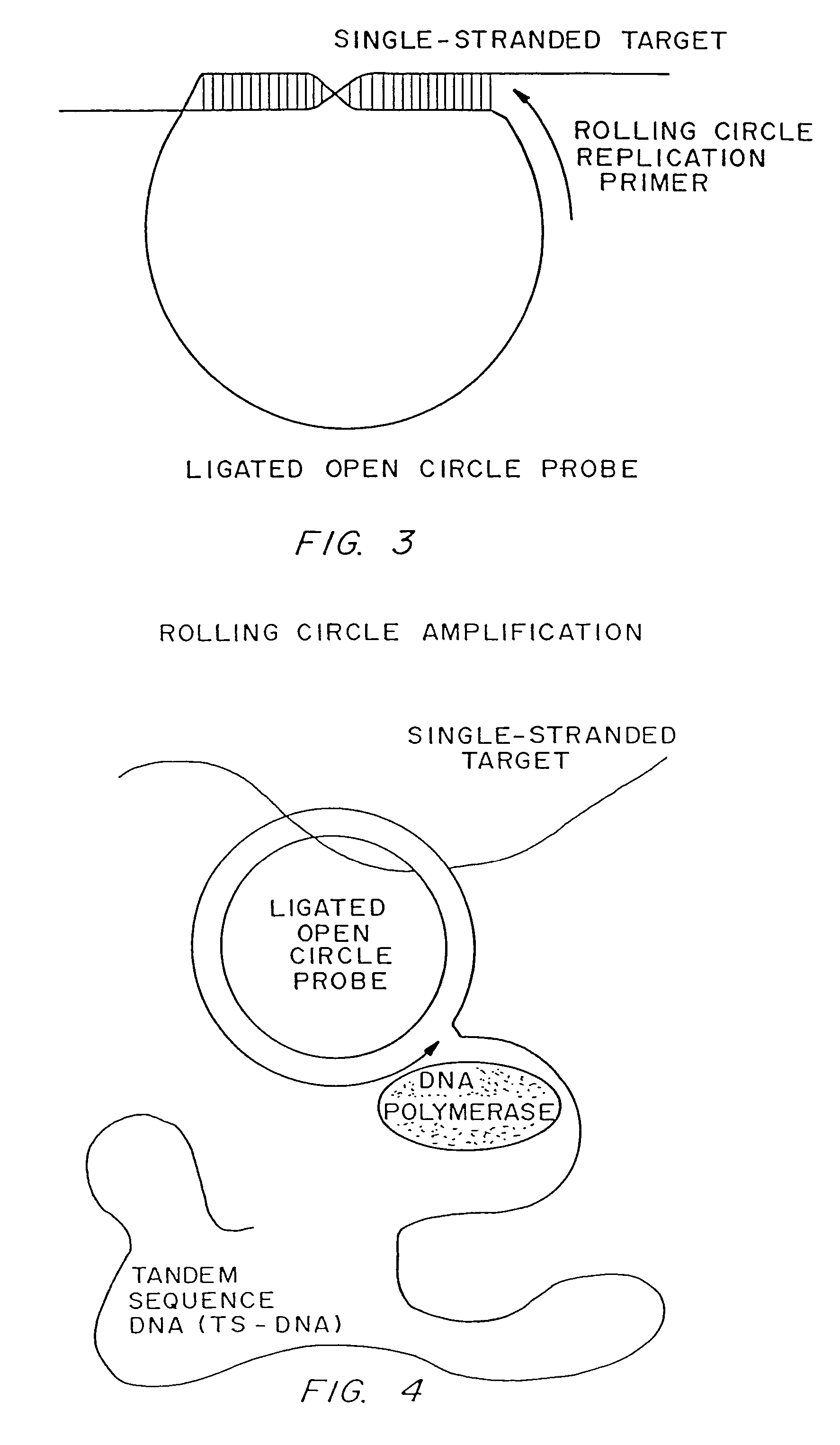
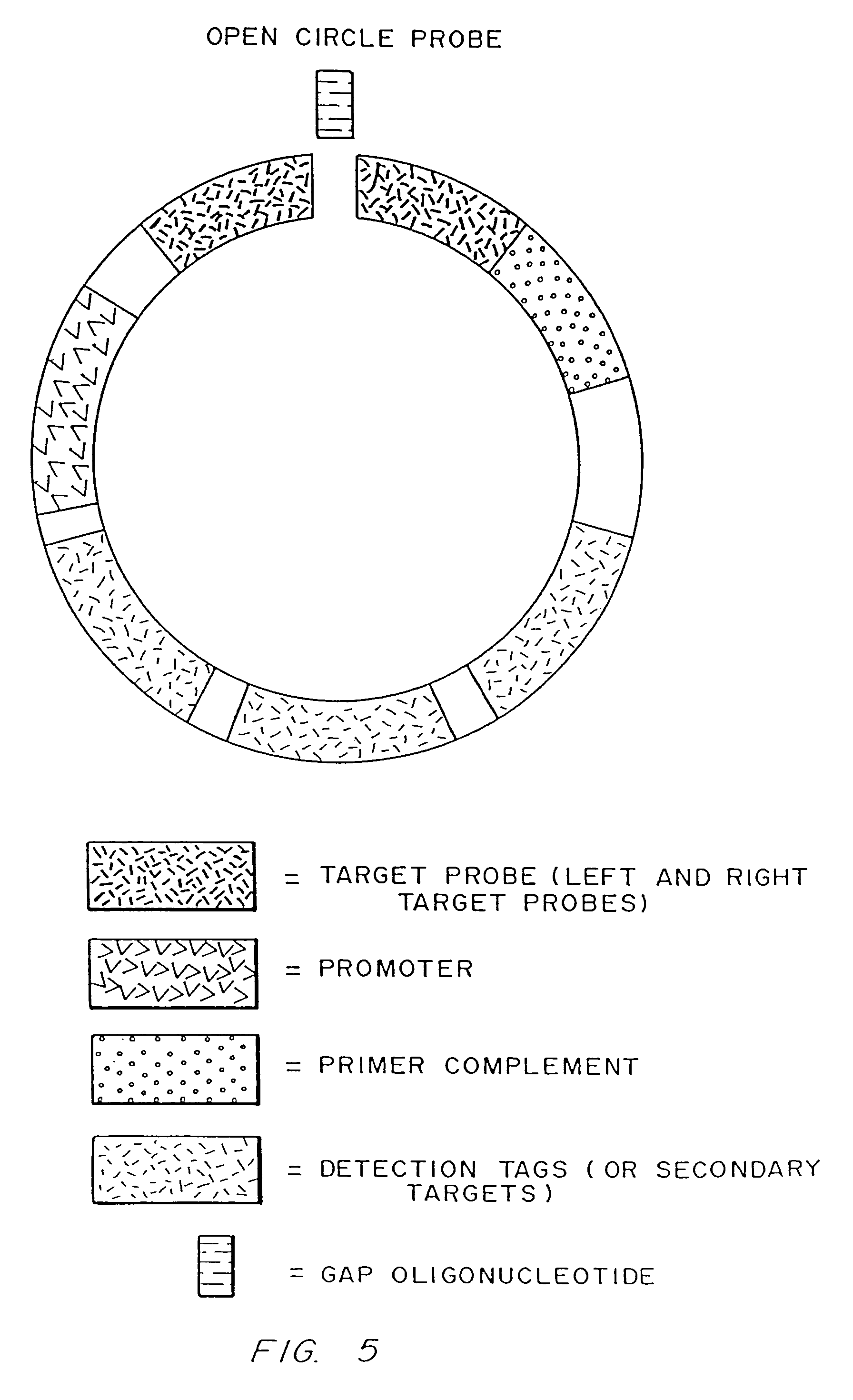
Rolling circle replication reporter systems
InactiveUS7618776B2Consistent outputAmplification less complicatedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMultiplexNucleotide
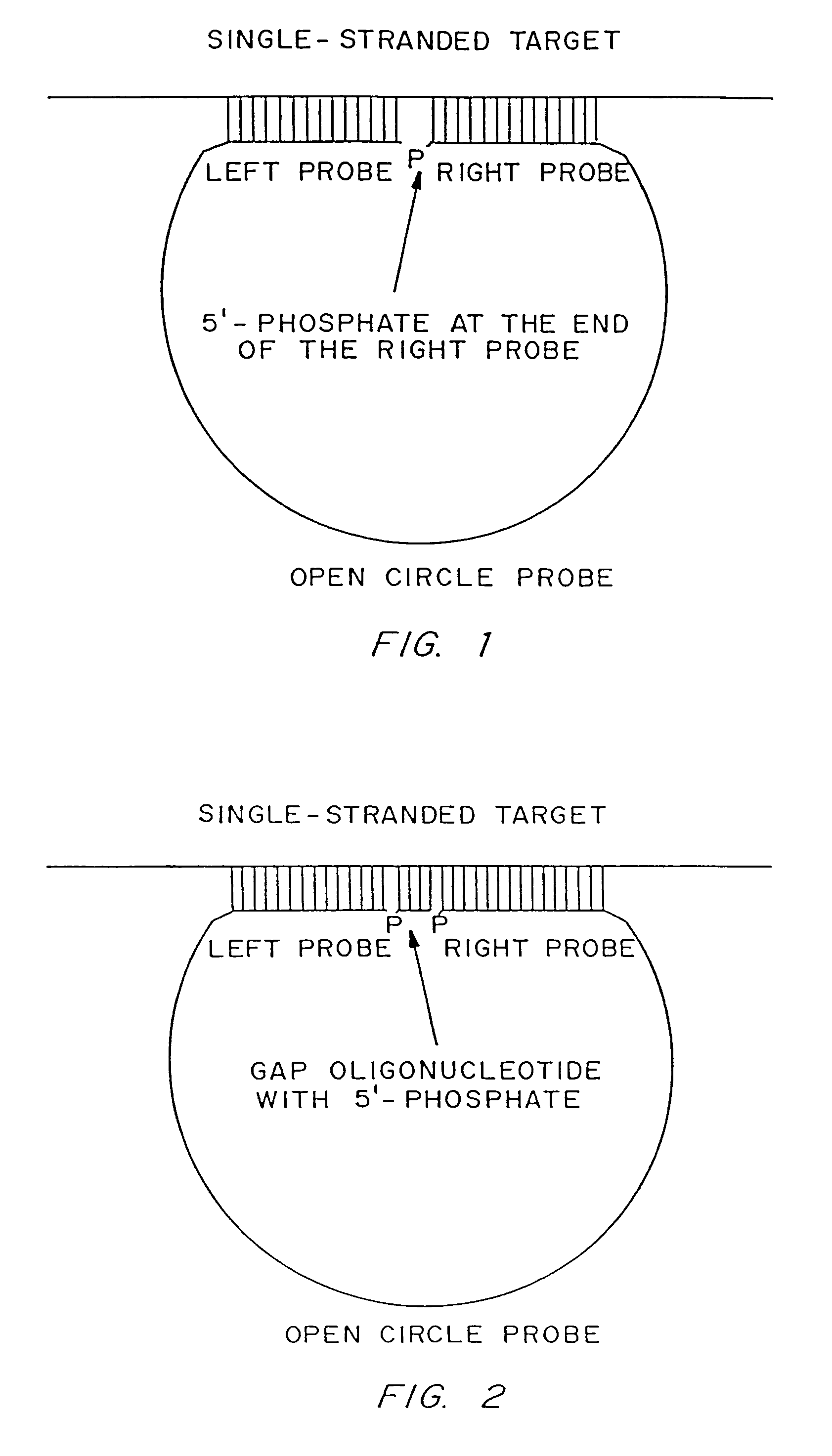
Disclosed are compositions and a method for of amplifying nucleic acid sequences useful for detecting the presence of molecules of interest. The method is useful for detecting specific nucleic acids in a sample with high specificity and sensitivity. The method also has an inherently low level of background signal. A preferred form of the method consists of a DNA ligation operation, an amplification operation, and a detection operation. The DNA ligation operation circularizes a specially designed nucleic acid probe molecule. This operation is dependent on hybridization of the probe to a target sequence and forms circular probe molecules in proportion to the amount of target sequence present in a sample. The amplification operation is rolling circle replication of the circularized probe. A single round of amplification using rolling circle replication results in a large amplification of the circularized probe sequences. Following rolling circle replication, the amplified probe sequences are detected and quantified using any of the conventional detection systems for nucleic acids such as detection of fluorescent labels, enzyme-linked detection systems, antibody-mediated label detection, and detection of radioactive labels. Because, the amplified product is directly proportional to the amount of target sequence present in a sample, quantitative measurements reliably represent the amount of a target sequence in a sample. Major advantages of this method are that the ligation step can be manipulated to obtain allelic discrimination, the DNA replication step is isothermal, and signals are strictly quantitative because the amplification reaction is linear and is catalyzed by a highly processive enzyme. In multiplex assays, the primer oligonucleotide used for the DNA polymerase reaction can be the same for all probes. Also described are modes of the method in which additional amplification is obtained using a cascade of strand displacement reactions.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Radiolabeled antibodies and peptides for treatment of tumors
InactiveUS20060039858A1Effective treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementRadioactive preparation carriersAbnormal tissue growthCellular component
This invention provides methods for imaging and / or treating a tumor in a subject which comprise administering to the subject an amount of a radiolabeled antibody and / or peptide effective to image and / or treat the tumor, where the radiolabeled antibody and / or peptide binds to a cellular component released by dying tumor cells. This invention also provides methods for imaging and / or treating melanin-containing melanomas or other melanin-containing tumors in a subject which comprise administering to the subject an amount of a radiolabeled anti-melanin antibody and / or peptide effective to image and / or treat the melanoma or tumor. The invention also provides compositions and methods of making compositions comprising radiolabeled antibodies and / or peptides for imaging and treating tumors, including melanin-containing melanomas.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
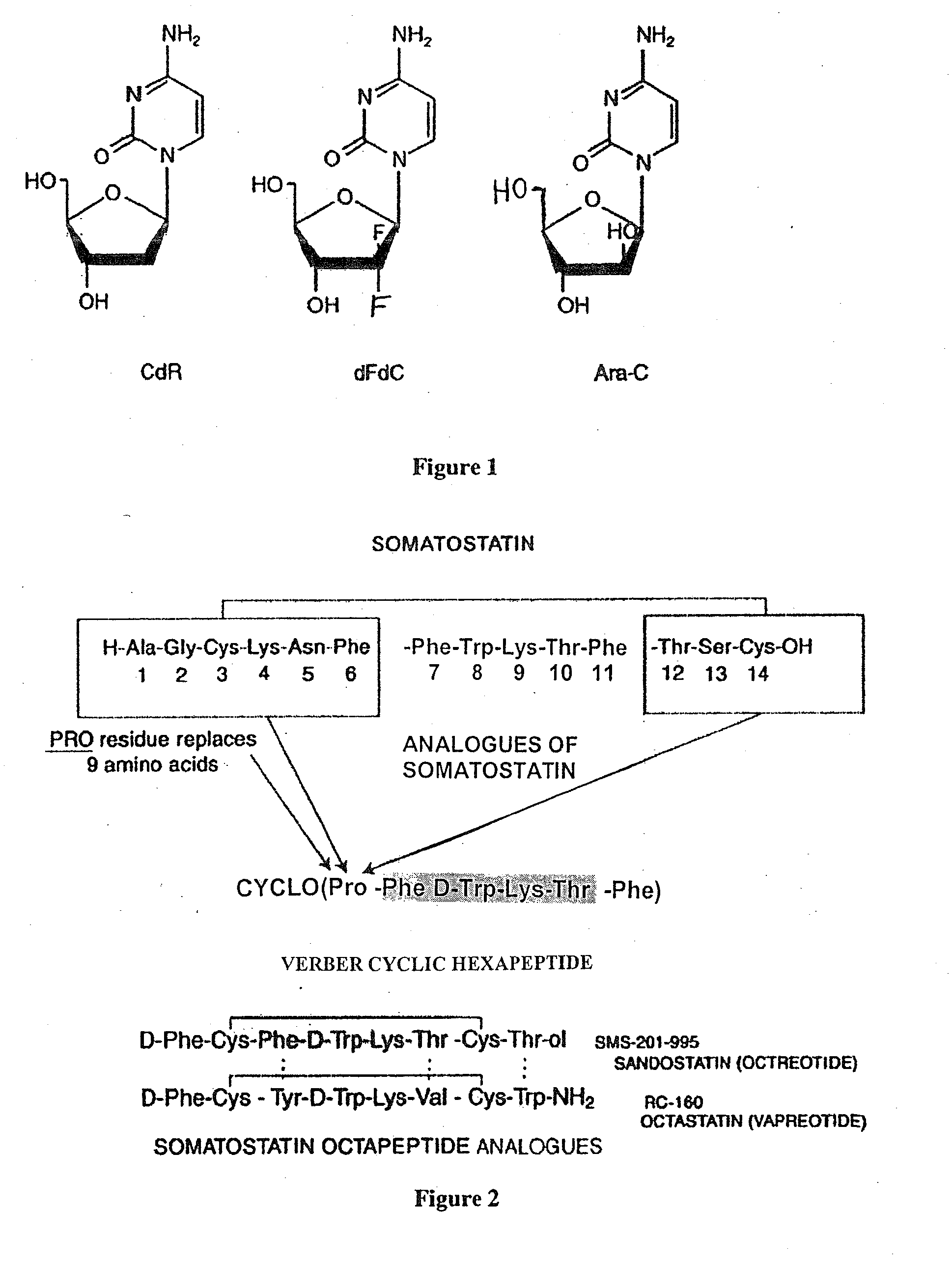
Anticancer therapy
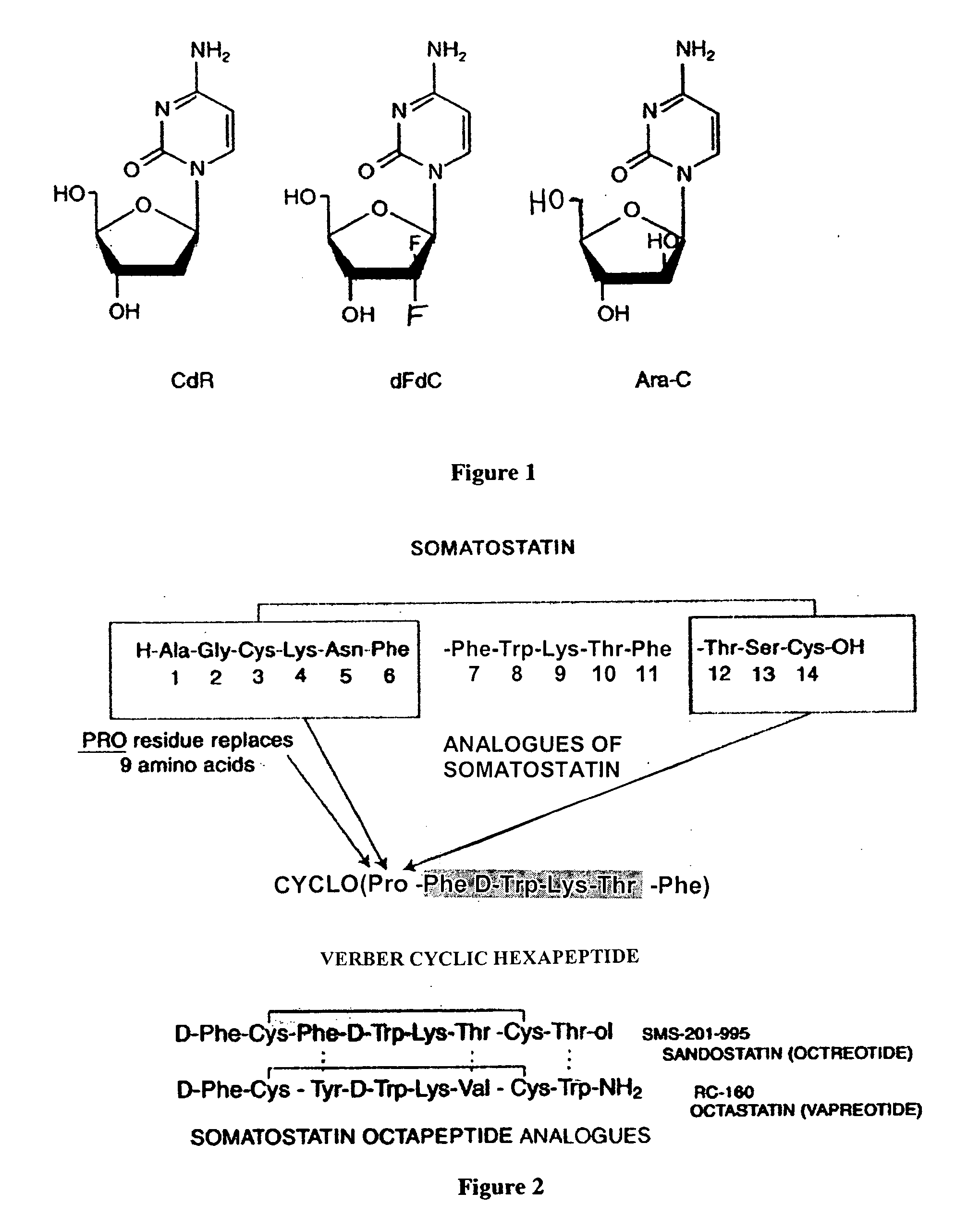
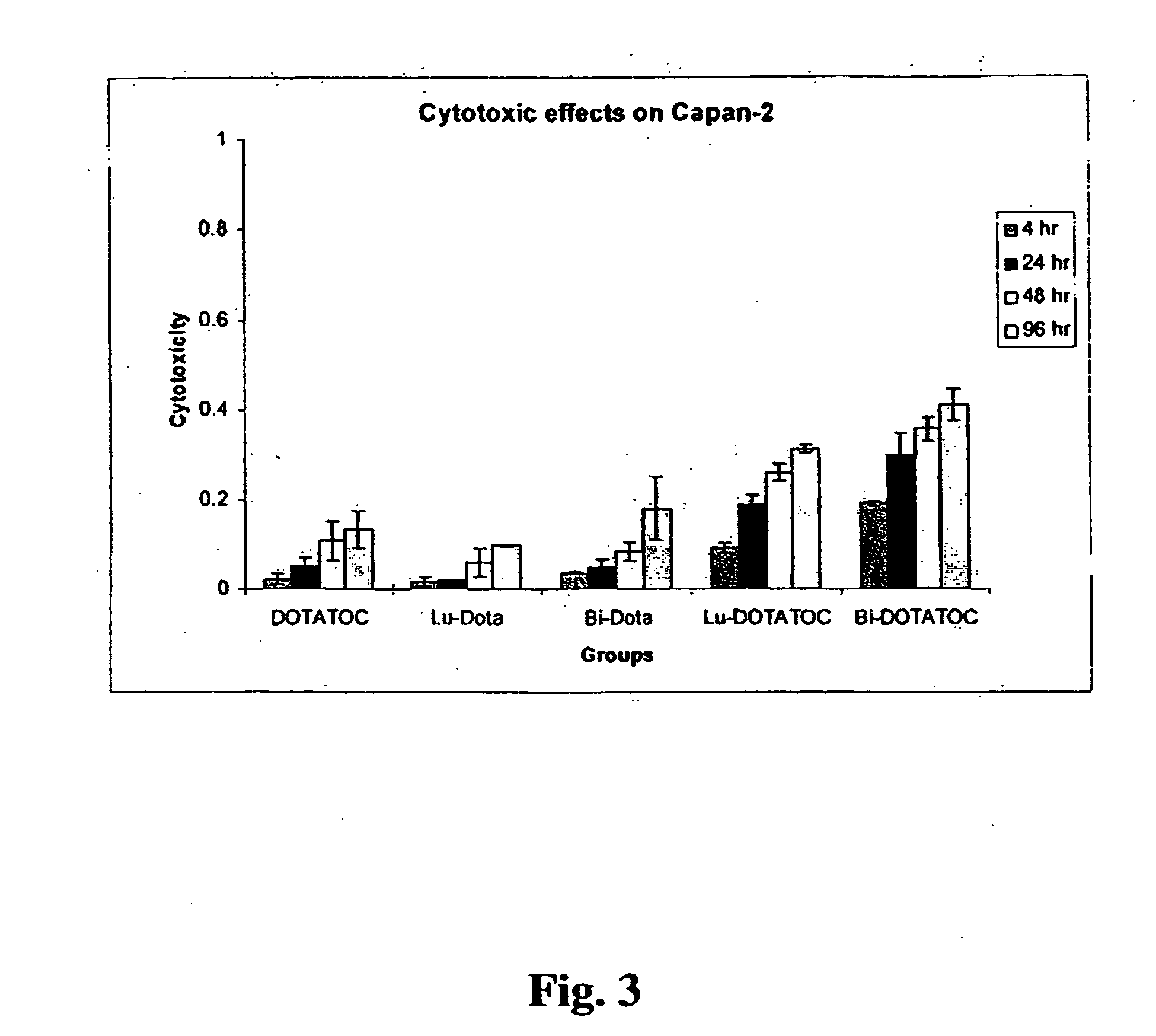
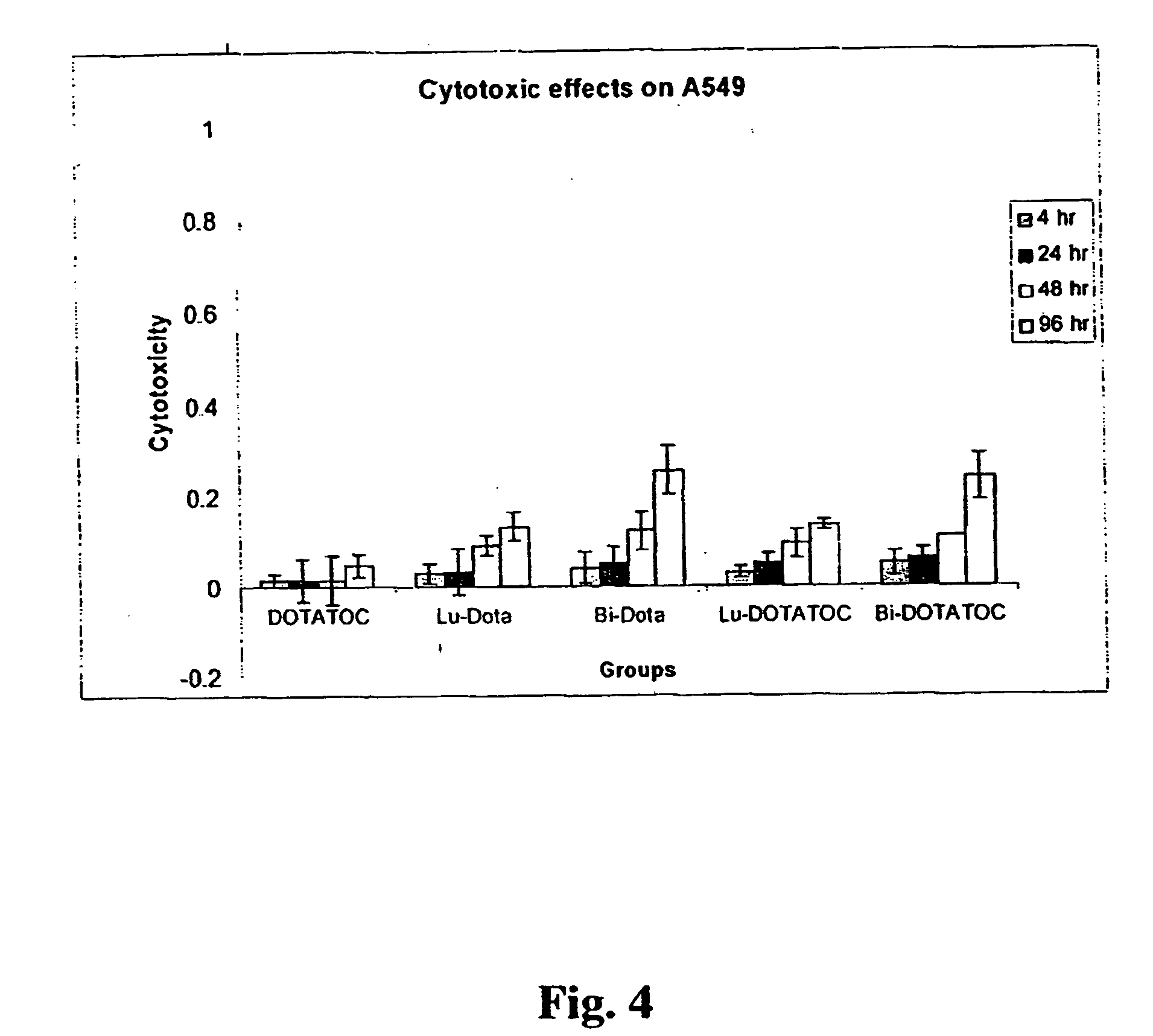
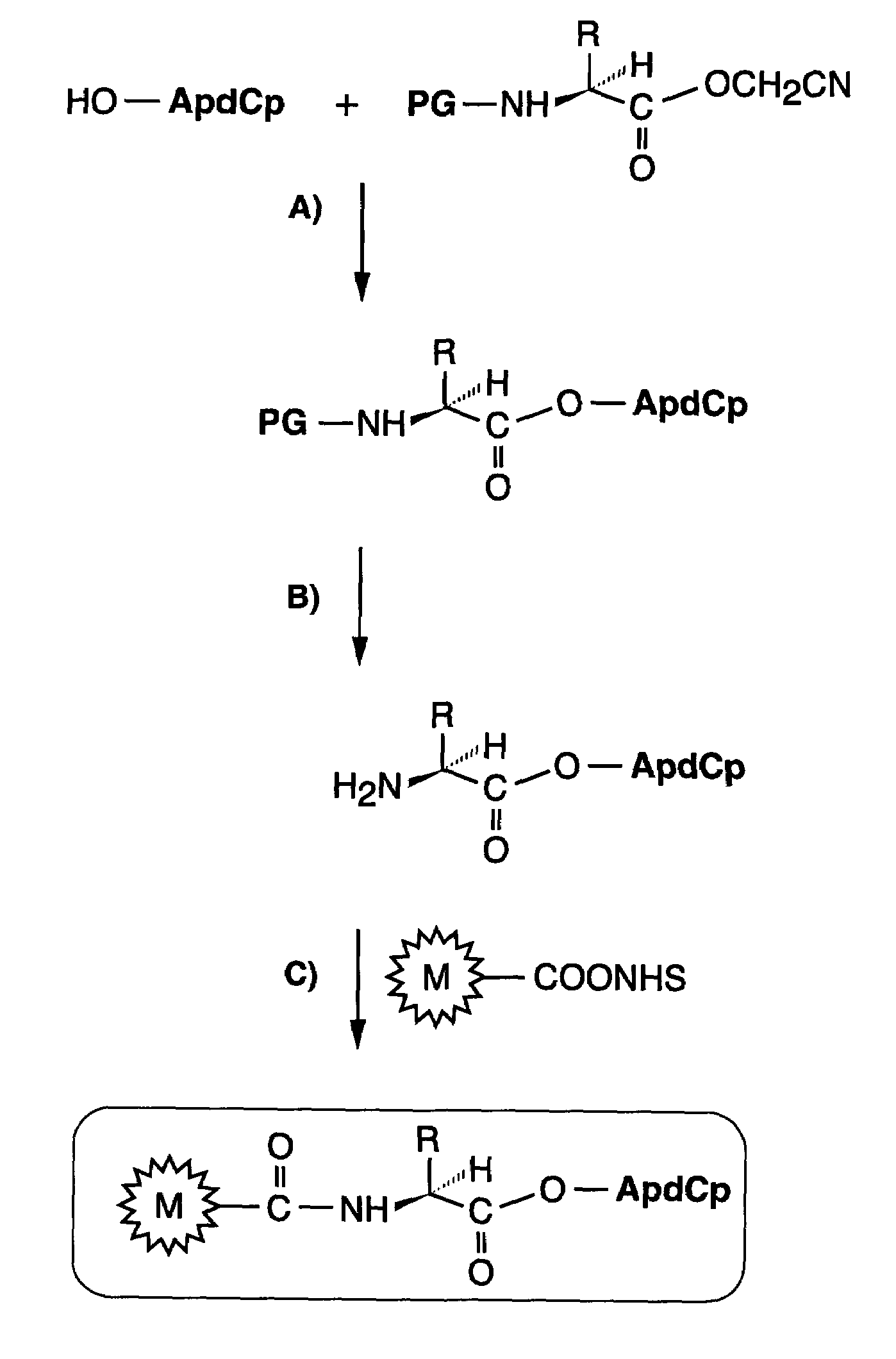
InactiveUS20070025910A1High expressionReduce the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSomatostatin analogCytotoxicity
A subject afflicted with a cancer or precancerous condition is treated by administering an agent that increases expression of somatostatin receptors, and a cytotoxic recognition ligand. In an alternative embodiment, somatostatin analogs, which are radiolabeled are used to treat cancer or precancerous conditions.
Owner:STC UNM
Methods for the preparation of chemically misaminoacylated tRNA via protective groups
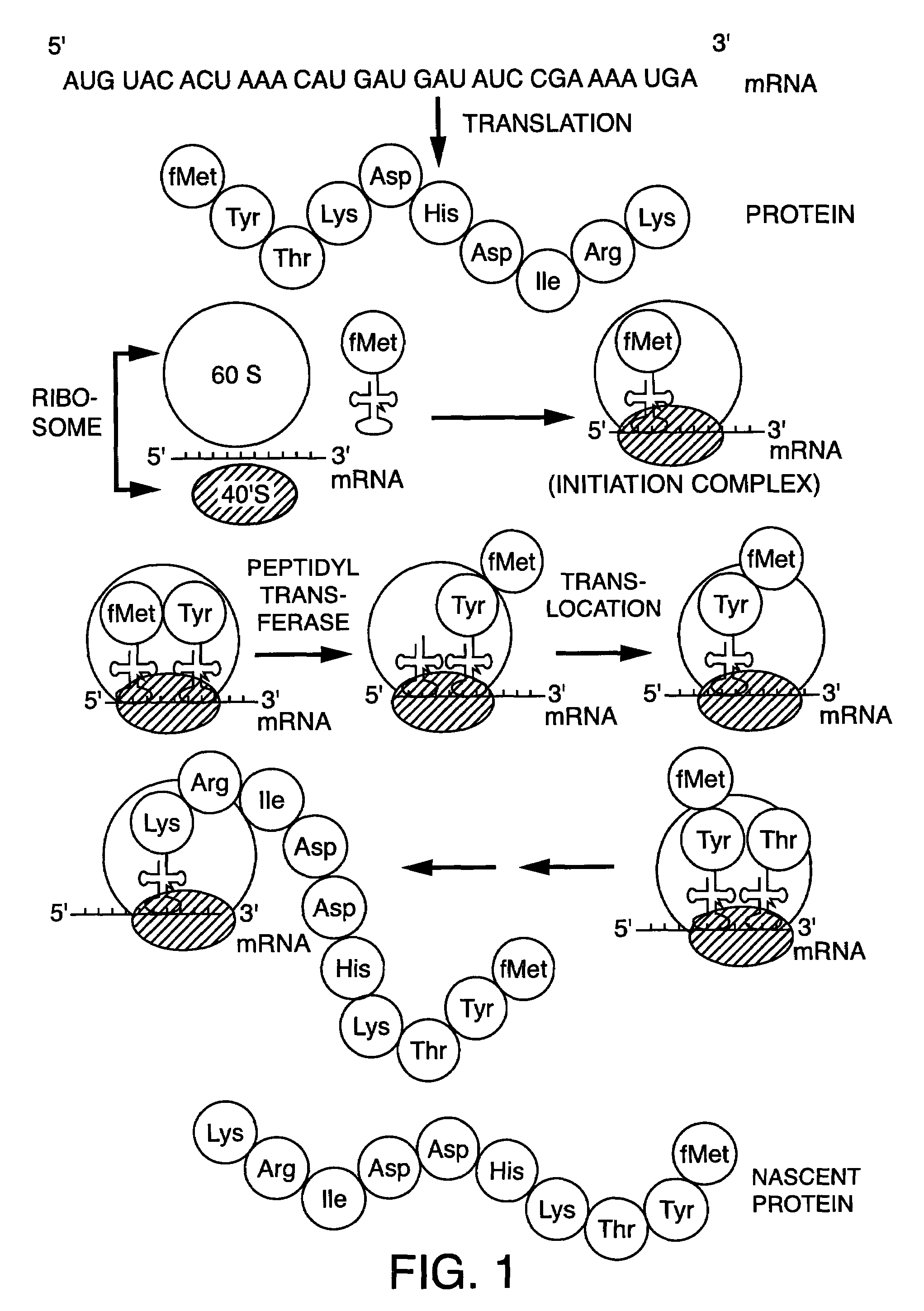
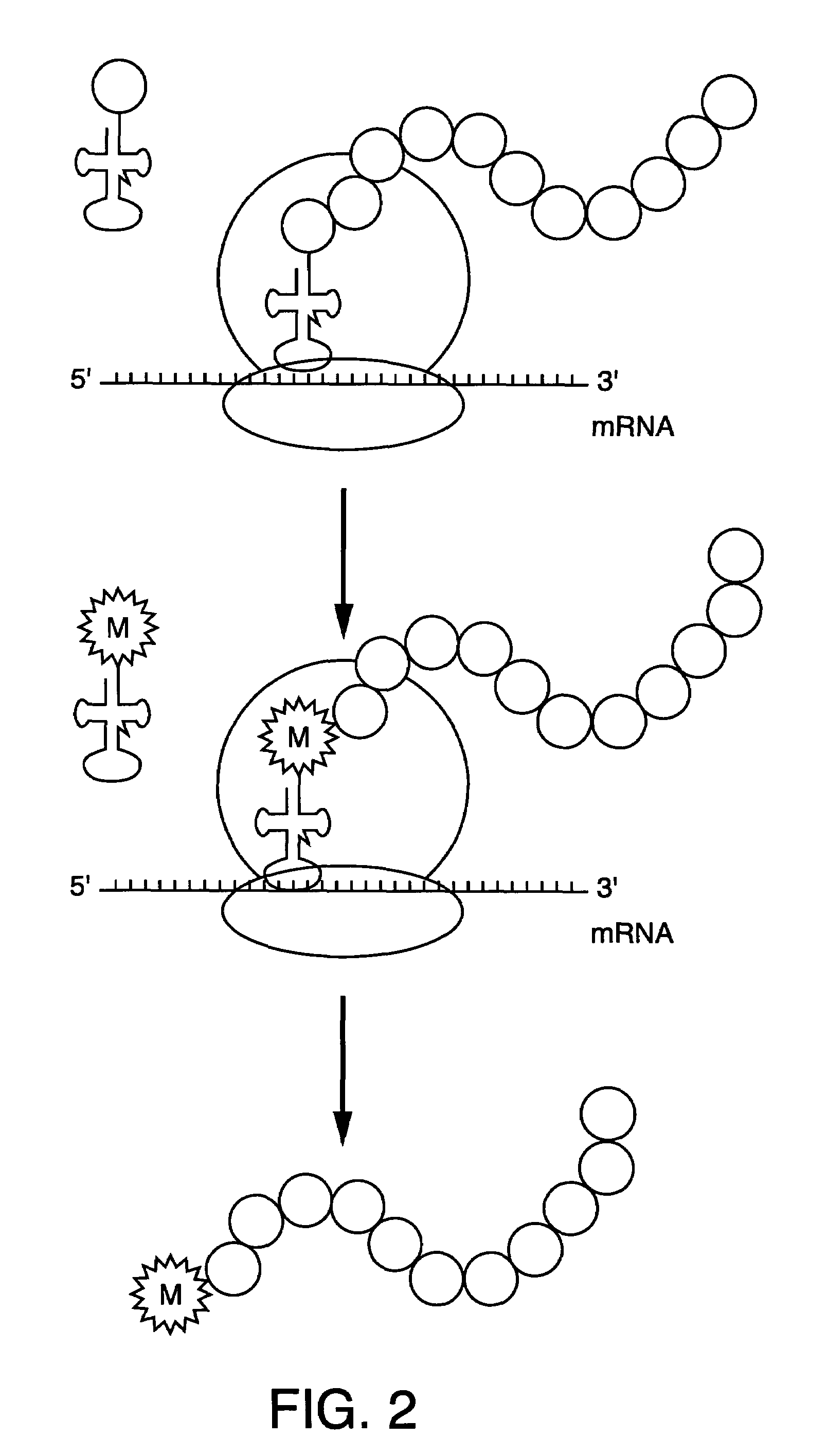
The present invention relates to methods for the preparation of chemically aminoacylated tRNAs for the purpose of introduction of markers into nascent proteins. The present invention also relates to methods for the non-radioactive labeling, detection, quantitation and isolation of nascent proteins translated in a cellular or cell-free translation system utilizing chemically aminoacylated tRNAs. tRNA molecules are misaminoacylated with non-radioactive markers which may be non-native amino acids, amino acid analogs or derivatives. Markers may comprise cleavable moieties, detectable labels, reporter properties wherein markers incorporated into protein can be distinguished from unincorporated markers, or coupling agents which facilitate the detection and isolation of nascent protein from other components of the translation system.
Owner:AMBERGEN
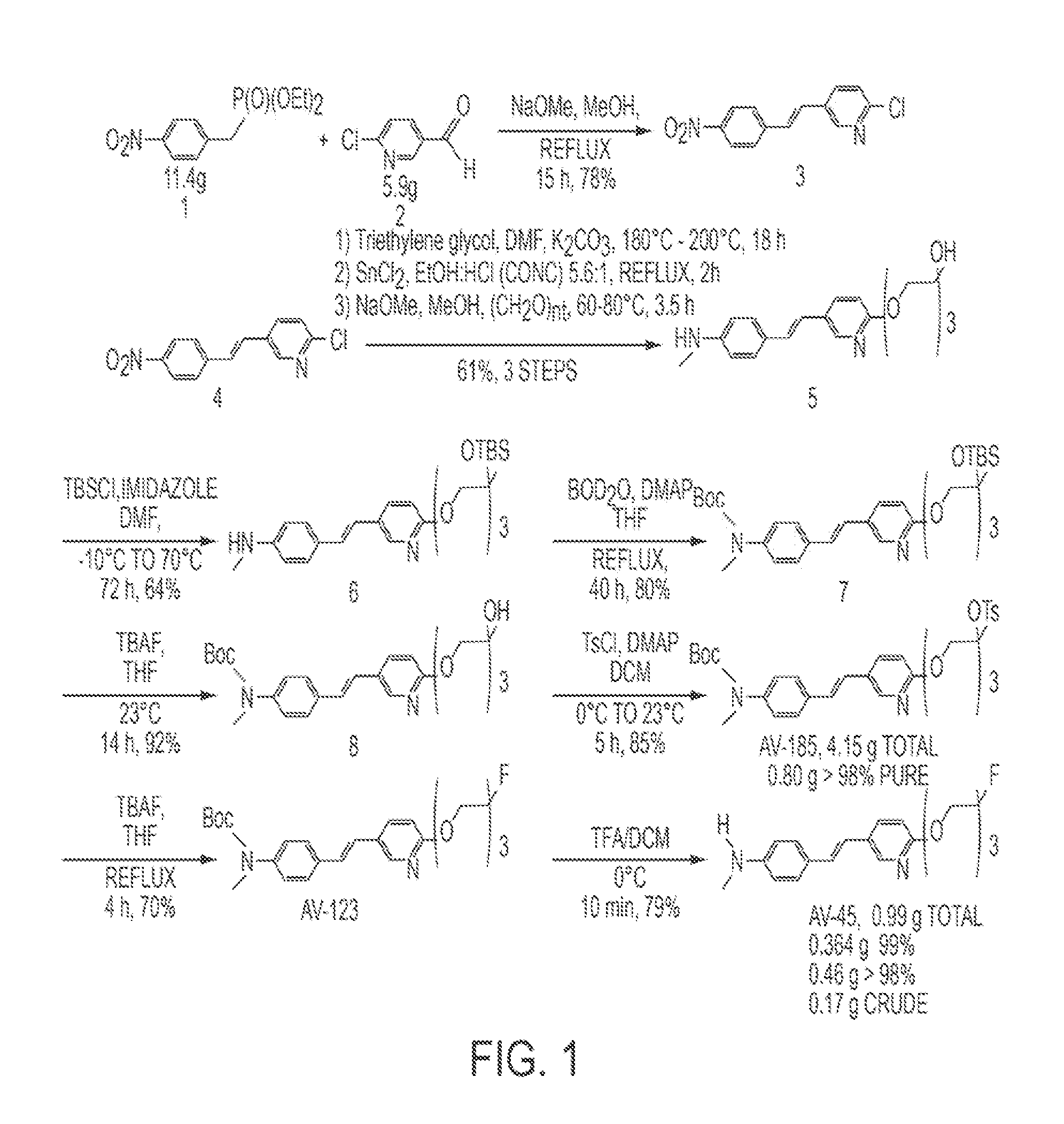
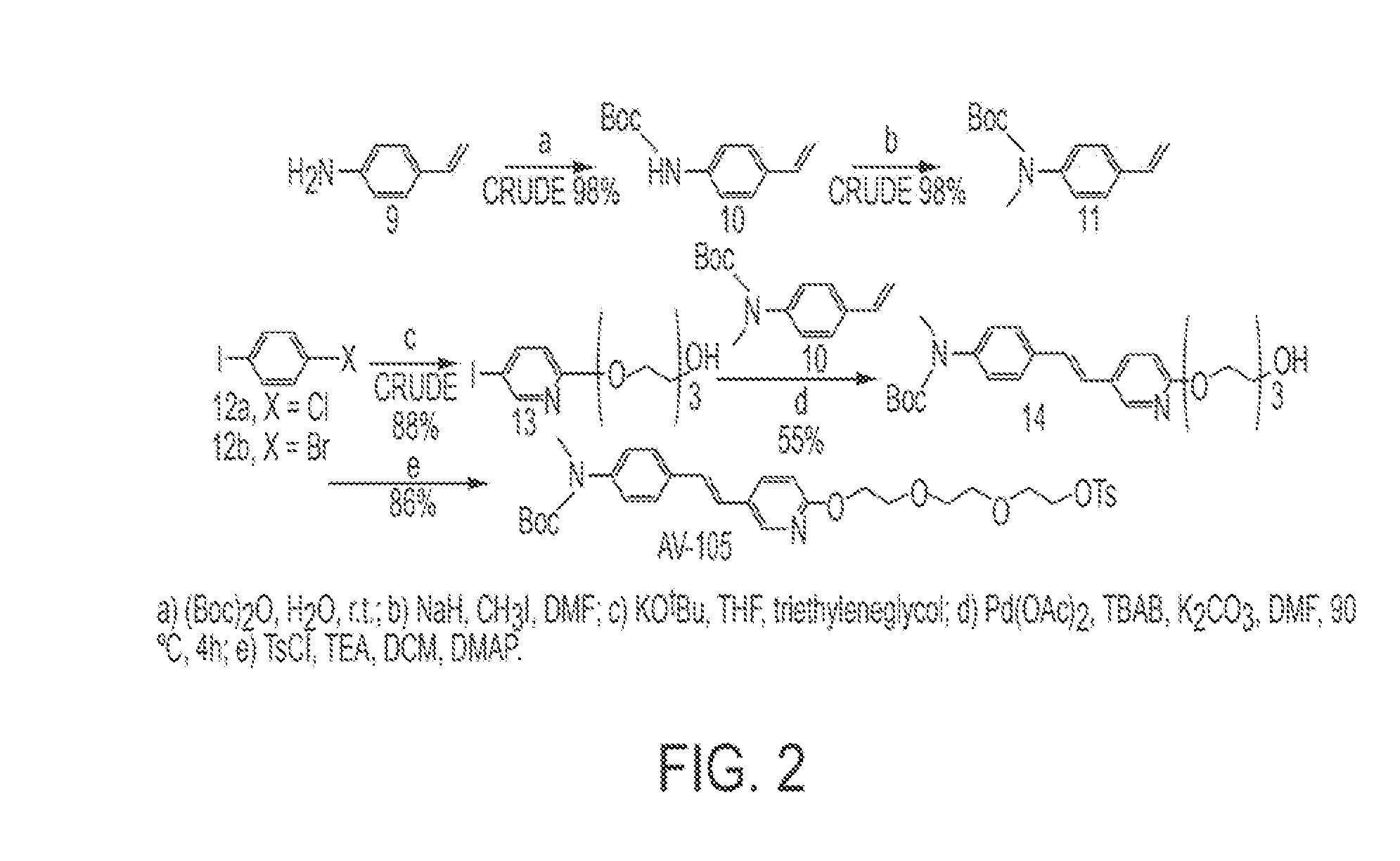
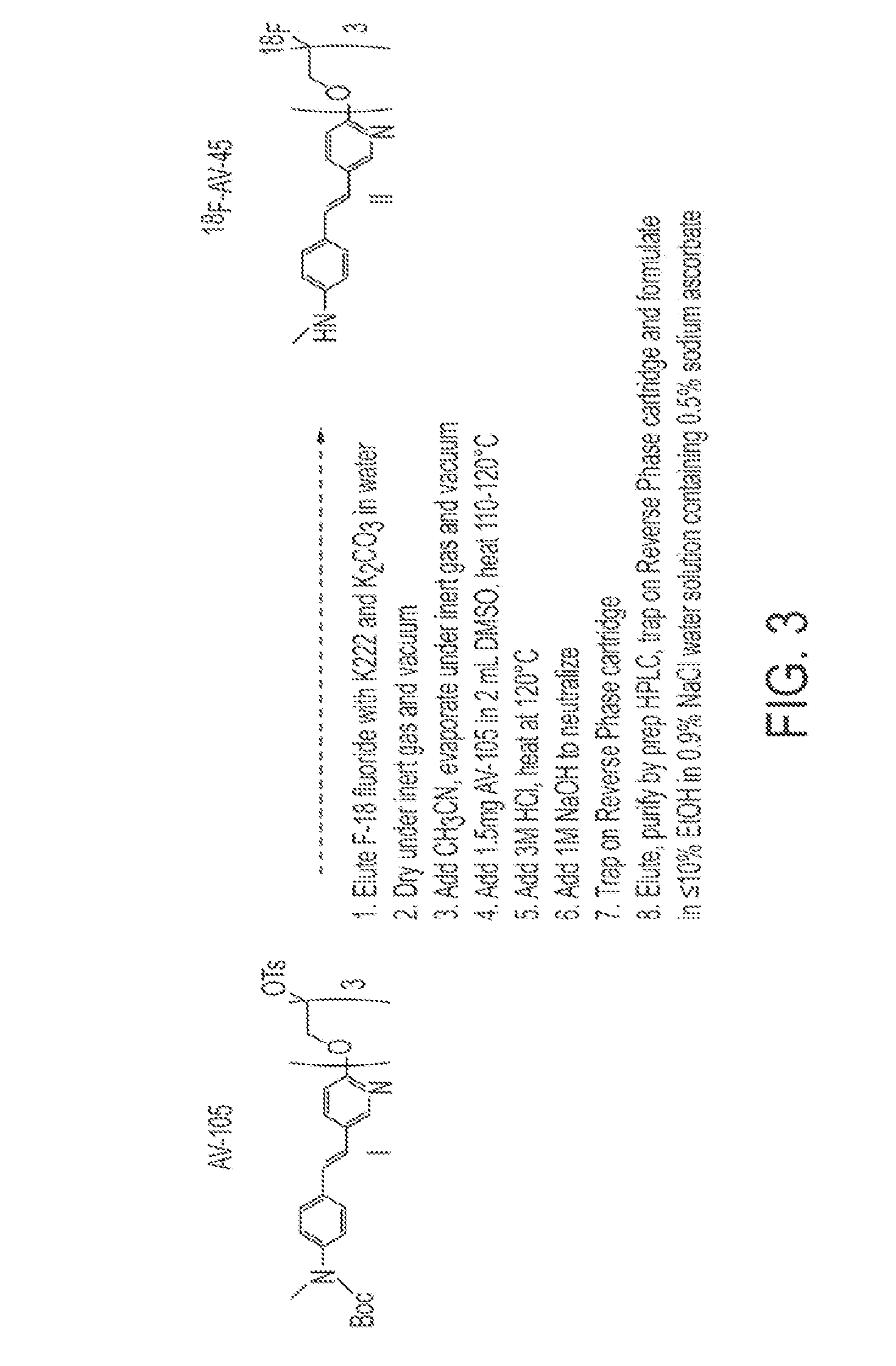
Synthesis of 18f-radiolabeled styrylpyridines from tosylate precursors and stable pharmaceutical compositions thereof
InactiveUS20100172836A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:AVID RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS
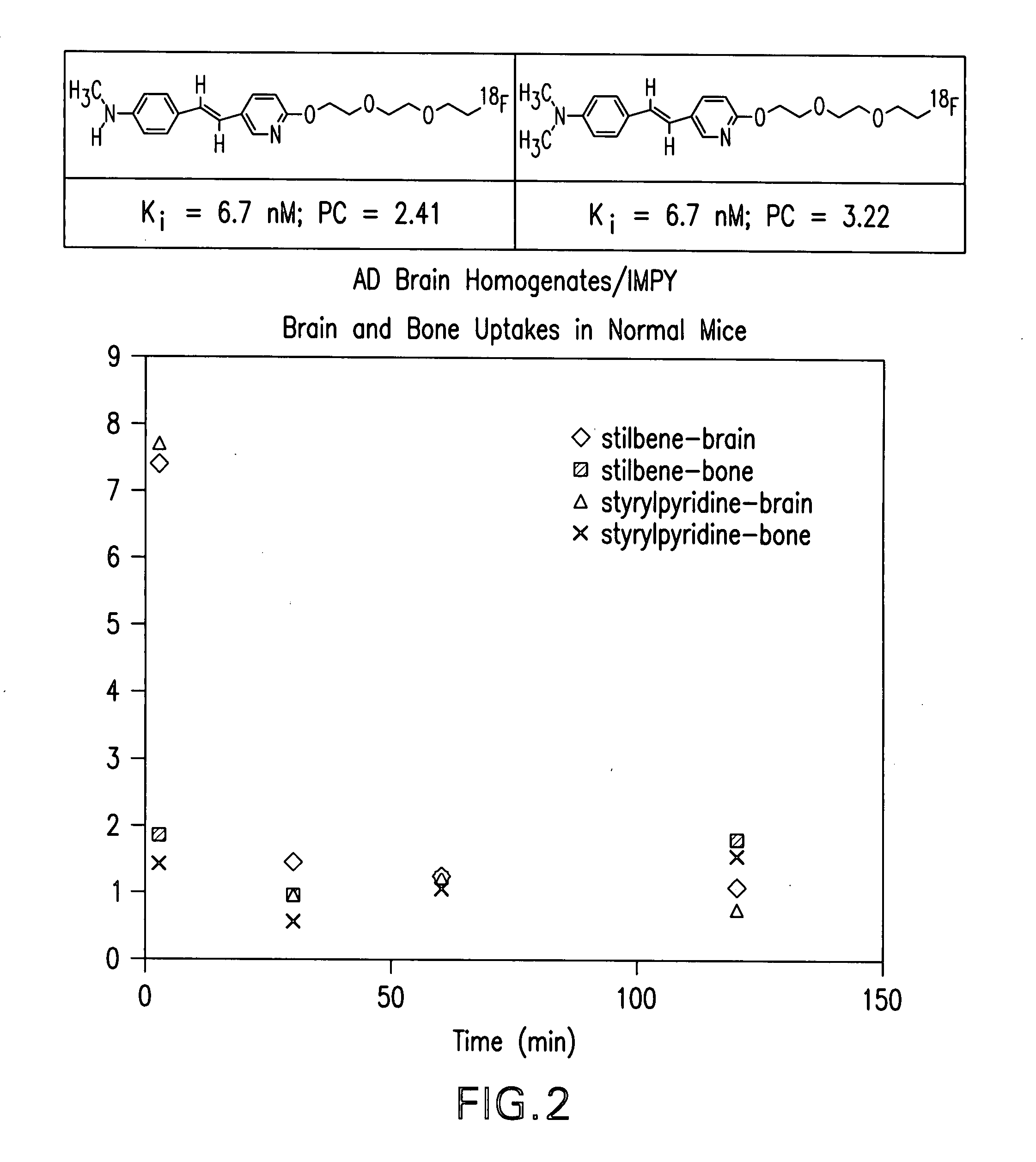
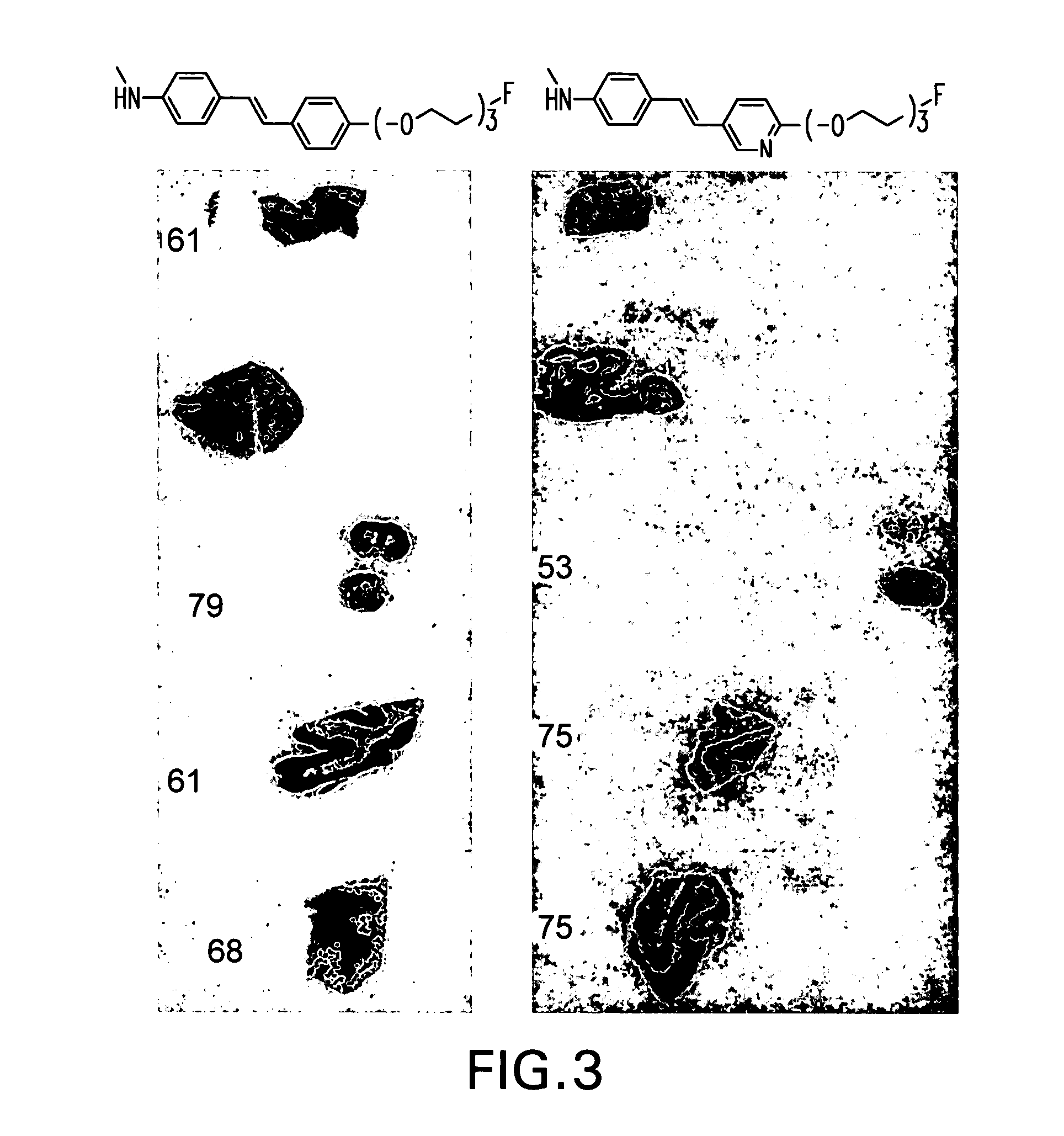
Stryrylpyridine derivates and theur use for binding and imaging amylod plaques
This invention relates to a method of imaging amyloid deposits and to styrylpyridine compounds, and methods of making radiolabeled styrylpyridine compounds useful in imaging amyloid deposits. This invention also relates to compounds, and methods of making compounds for inhibiting the aggregation of amyloid proteins to form amyloid deposits, and a method of delivering a therapeutic agent to amyloid deposits.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for measuring kinase activity
InactiveUS6942987B2Compound screeningApoptosis detectionKinase activityHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A method for determining the level of kinase activity or phosphatase activity in a sample without the use of antibodies or radioactive labels is disclosed. The method employs a fluorescently-labeled phosphorylatable reporter peptide that is capable of being cleaved by a protease only when the peptide is in an unphosphorylated state. A change in fluorescence characteristics is an indication that the peptide is cleaved and, therefore, in an unphosphorylated state. Thus, the level of protease cleavage, as measured by the fluorescence change, provides a direct measure of phosphatase activity whereas the level of kinase activity is inversely proportion to the level of protease cleavage. The method is particularly well suited to high throughput screening, for example, for screening compounds which modulate kinase or phosphatase activity.
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA DRUG DISCOVERY INC
Radiolabeled selective androgen receptor modulators and their use in prostate cancer imaging and therapy
InactiveUS20080193380A1Organic chemistryRadioactive preparation carriersSelective androgen receptor modulatorMedicine
Provided is a class of radiolabeled androgen receptor targeting agents (ARTA), useful for prostate cancer imaging and in treating or preventing prostate cancer. The agents define a new subclass of radiolabeled compounds, which are selective androgen receptor modulators (SARM), which demonstrate antiandrogenic activity of a nonsteroidal ligand for the androgen receptor, and / or which bind irreversibly to the androgen receptor. The present invention further provides methods for a) imaging of cancer in a subject, b) imaging an androgen receptor-containing tissue in a subject, c) in-vivo imaging in a subject, d) treating a subject suffering from prostate cancer, e) delaying the progression of prostate cancer in a subject suffering from prostate cancer, f) preventing the recurrence of prostate cancer in a subject suffering from prostate cancer, and g) treating the recurrence of prostate cancer in a subject suffering from prostate cancer, which comprise using the radiolabeled compounds of the present invention. The present invention further provides a method of producing the radiolabeled SARM compounds, and precursor compounds useful in the preparation of the radiolabeled SARM compounds.
Owner:DALTON JAMES T +3
Methods for the detection, analysis and isolation of nascent proteins
This invention relates to non-radioactive markers that facilitate the detection and analysis of nascent proteins translated within cellular or cell-free translation systems. Nascent proteins containing these markers can be rapidly and efficiently detected, isolated and analyzed without the handling and disposal problems associated with radioactive reagents. Preferred markers are dipyrrometheneboron difluoride (4,4-difluoro-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-s-indacene) dyes.
Owner:AMBERGEN
Radiolabeled irreversible inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and their use in radioimaging and radiotherapy
InactiveUS20040265228A1Organic active ingredientsRadiation applicationsSingle photon emission computerized tomographyComputed tomography
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT +1
Compositions and methods for detecting or eliminating senescent cells to diagnose or treat disease
InactiveUS20150151001A1Reduce the number of cellsReduce in quantityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCompounds screening/testingCancer preventionAge related disease
Disclosed are agents (e.g., peptides, polypeptides, proteins, small molecules, antibodies, and antibody fragments that target senescent cells) and methods of their use for imaging senescent cells in vivo and for treating or preventing cancer, age-related disease, tobacco-related disease, or other diseases and disorders related to or caused by cellular senescence in a mammal. The methods include administering one or more of the agents of the invention to a mammal, e.g., a human. The agents, which specifically bind to senescent cells, can be labeled with a radioactive label or a therapeutic label, e.g., a cytotoxic agent.
Owner:UNITY BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Anticancer therapy
ActiveUS20150196673A1High expressionReduce the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSomatostatin AnalogueSomatostatin receptor
A subject afflicted with a cancer or precancerous condition is treated by administering an agent that increases expression of somatostatin receptors, and a cytotoxic recognition ligand. In an alternative embodiment, somatostatin analogs, which are radiolabeled are used to treat cancer or precancerous conditions.
Owner:STC UNM
Methods for binding agents to b-amyloid plaques
A method for labeling structures, such as β-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, in vivo or in vitro, is provided and comprises contacting brain tissue with one or more compounds, preferably radiolabeled for detection by positron emission tomography (PET).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for the fluorescent detection of a DNA sequence in real time
InactiveUS6197499B1Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluorescenceX-ray
The present invention relates to a method of detecting a DNA sequence by means of a DNA:DNA hybrid in real time using fluorescence. The present invention eliminates the need to use radioactive probes to detect the DNA and eliminates the delay needed for autoradiographic exposure of the X-ray to the radioactive label.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com