Patents
Literature
141results about How to "Maximum service life" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
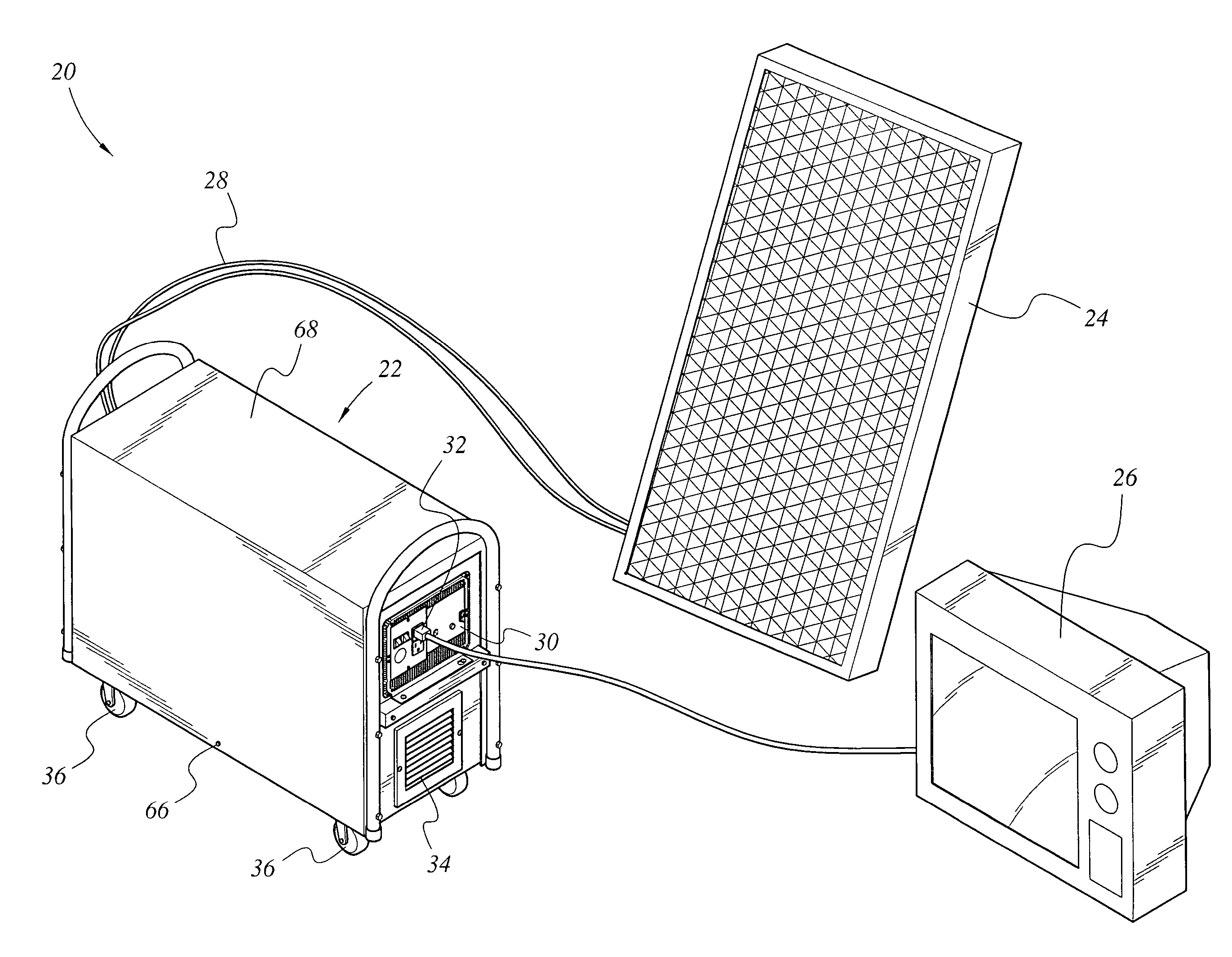
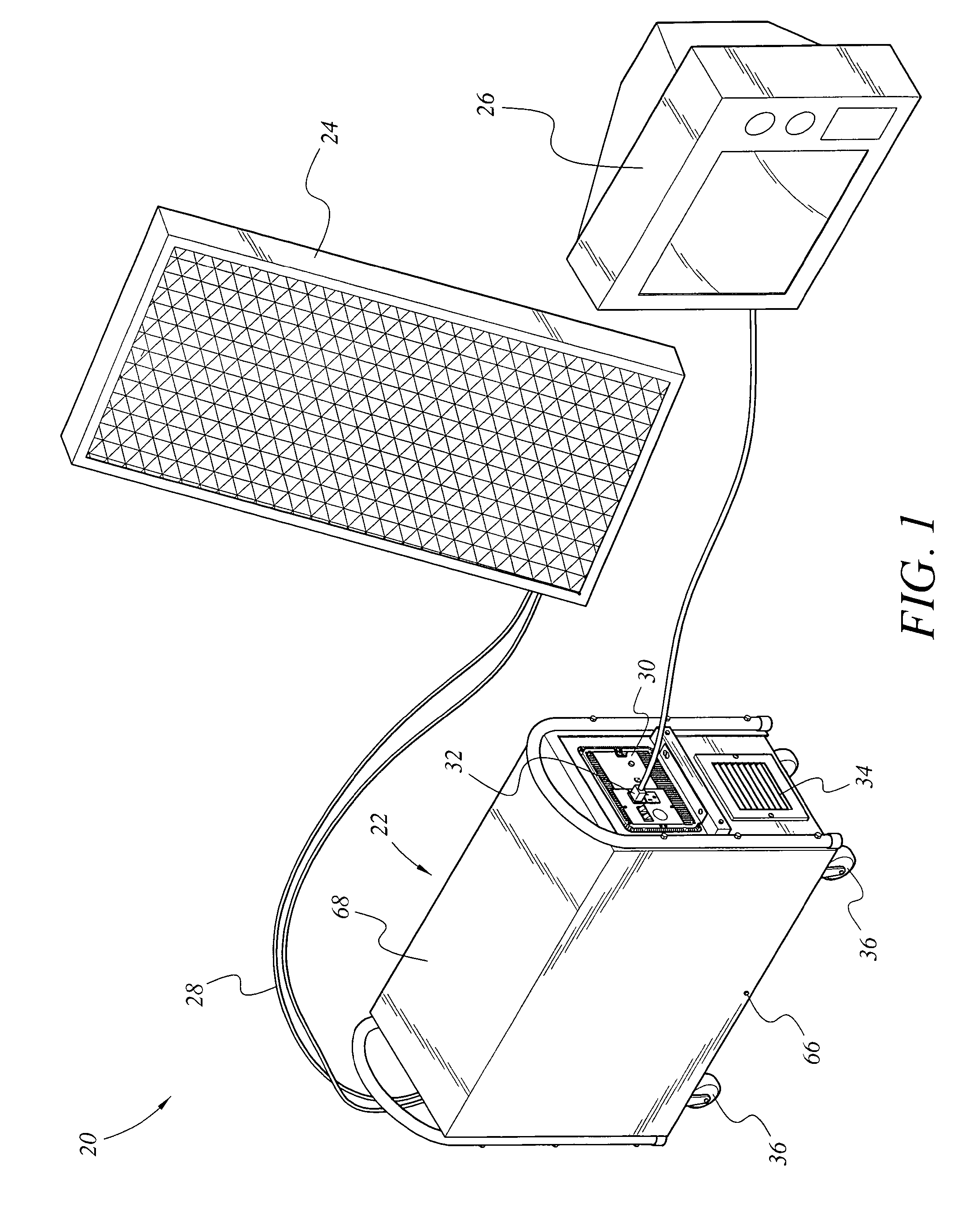
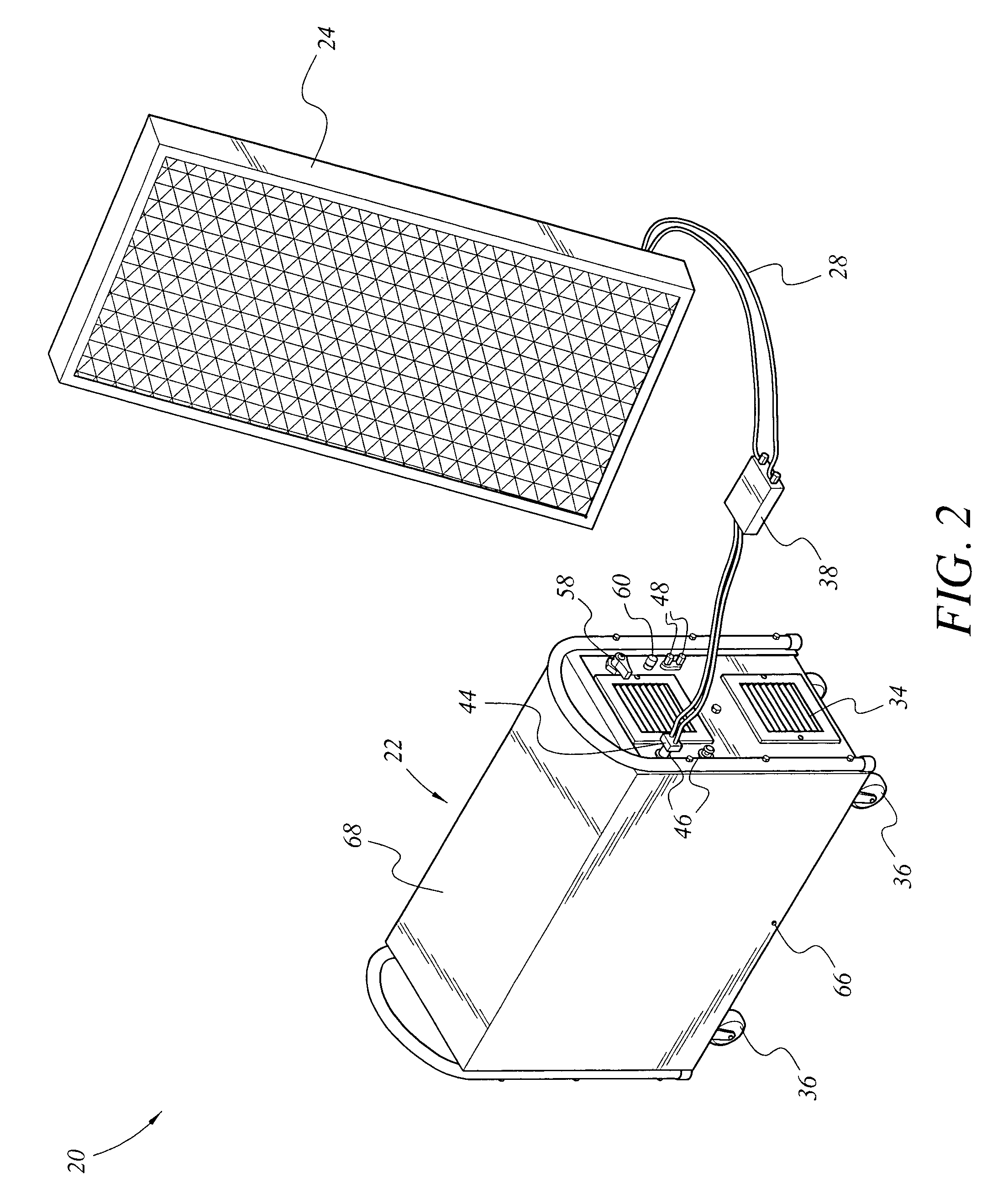
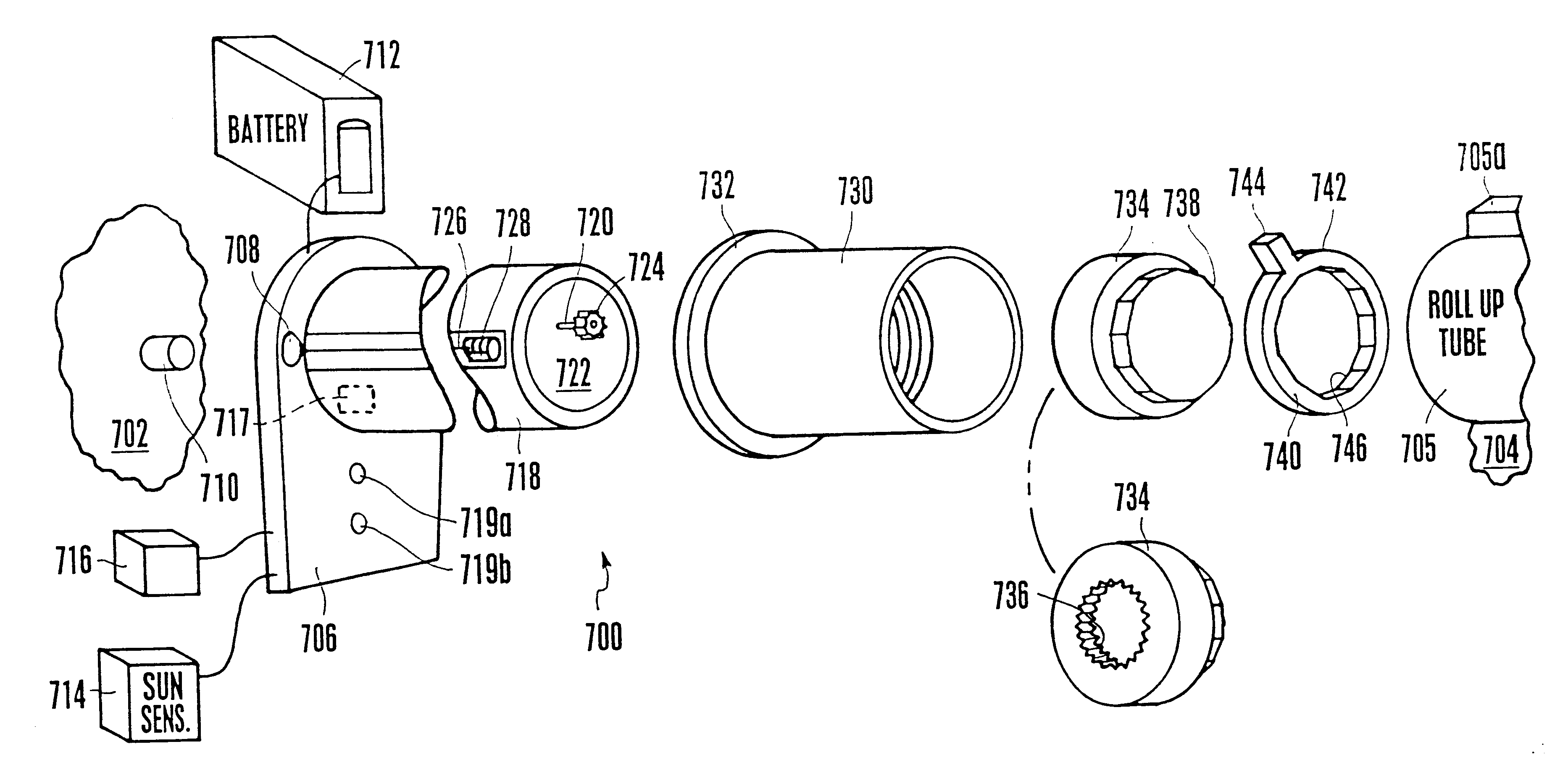
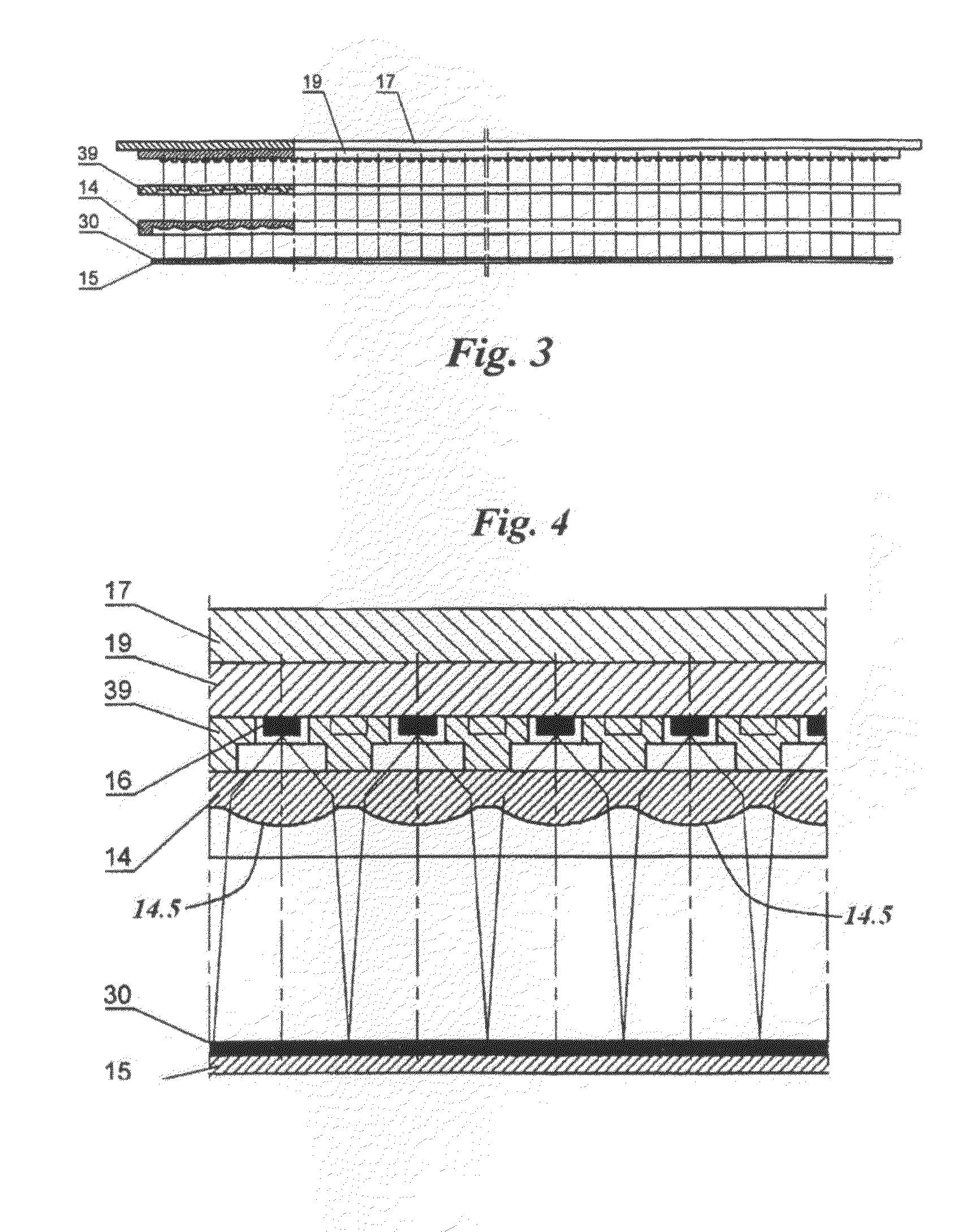
Portable solar energy system
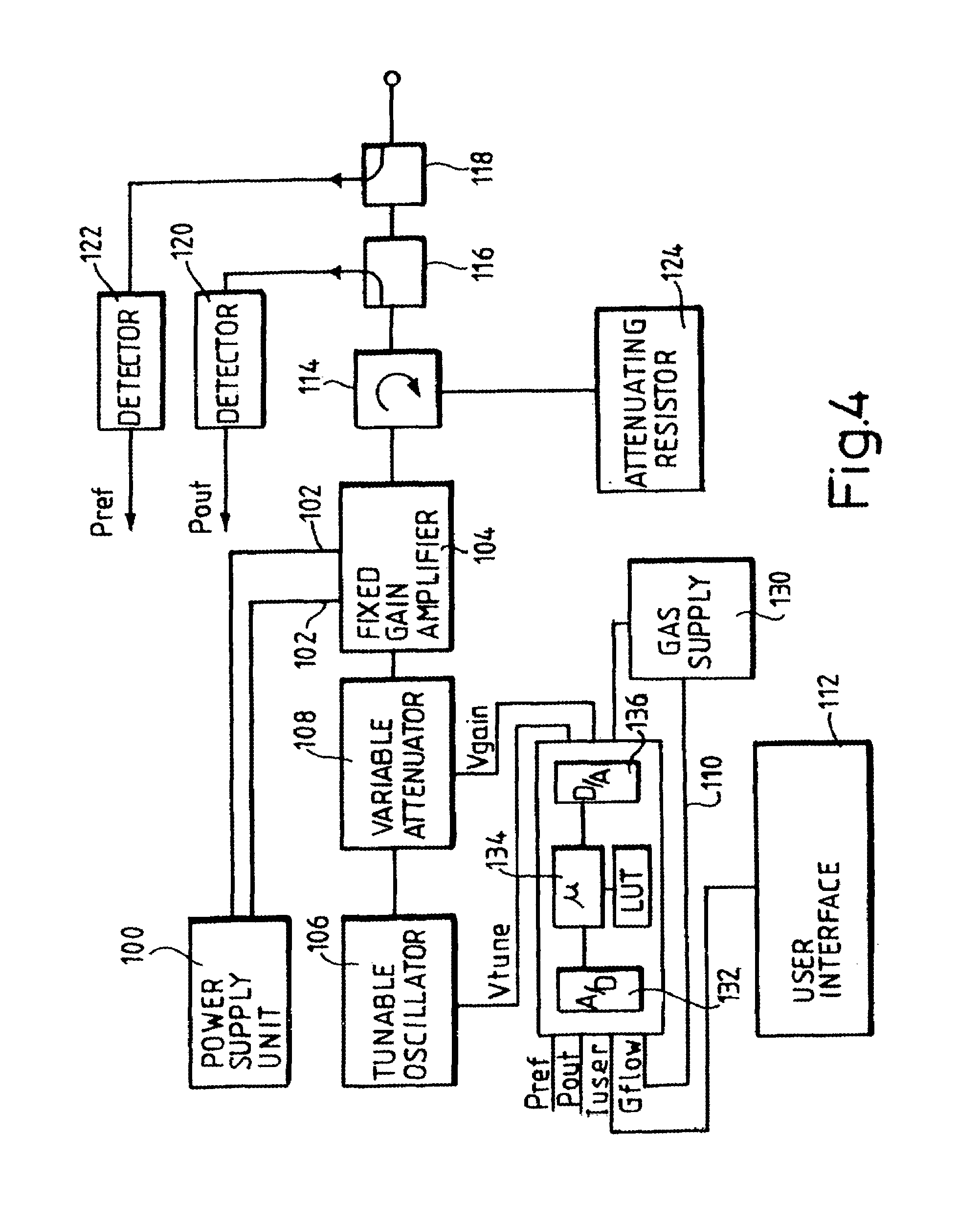
ActiveUS7388348B2Convenient charging statusMaximum service lifeSubstation/switching arrangement detailsDigital data processing detailsGlass fiberStored energy
The portable solar energy system stores electrical energy generated by a solar panel, which is made of an array of photovoltaic cells, in a dc storage battery, and upon demand converts the dc voltage of the battery to an ac output suitable for supplying conventional electrical appliances. The battery is a sealed lead-acid type and may be an Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) battery. The system includes an energy storage and converting unit, which houses the battery and a dc-to-ac inverter. The inverter converts the stored energy of the battery, supplied at a low dc voltage, into the ac voltage and current required for supplying conventional appliances. A charge controller manages the flow of current from the solar panel to optimize the state of charge of the battery and to maximize the useful life of the battery. Additional circuitry monitors the discharge level of the battery to limit deep discharging.
Owner:GODMAN POWER GRP INC
Filter element and method
InactiveUS20090044702A1Life of element can be lengthenedIncrease capacityCombination devicesNon-fibrous pulp additionMultiple formsParticulates
A filter element having multiple formed layers of filtration media is disclosed. The media are layered so as to form a pore size gradient. The filter element is capable of removing both solid and liquid particulates from a moving fluid stream. The filter element has high strength and compressibility. The layers can be supported on a porous or perforate support to provide mechanical stability during filtering operations. The filtration media layers can be formed into various filter element forms such as panels, cartridges, inserts, and the like.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
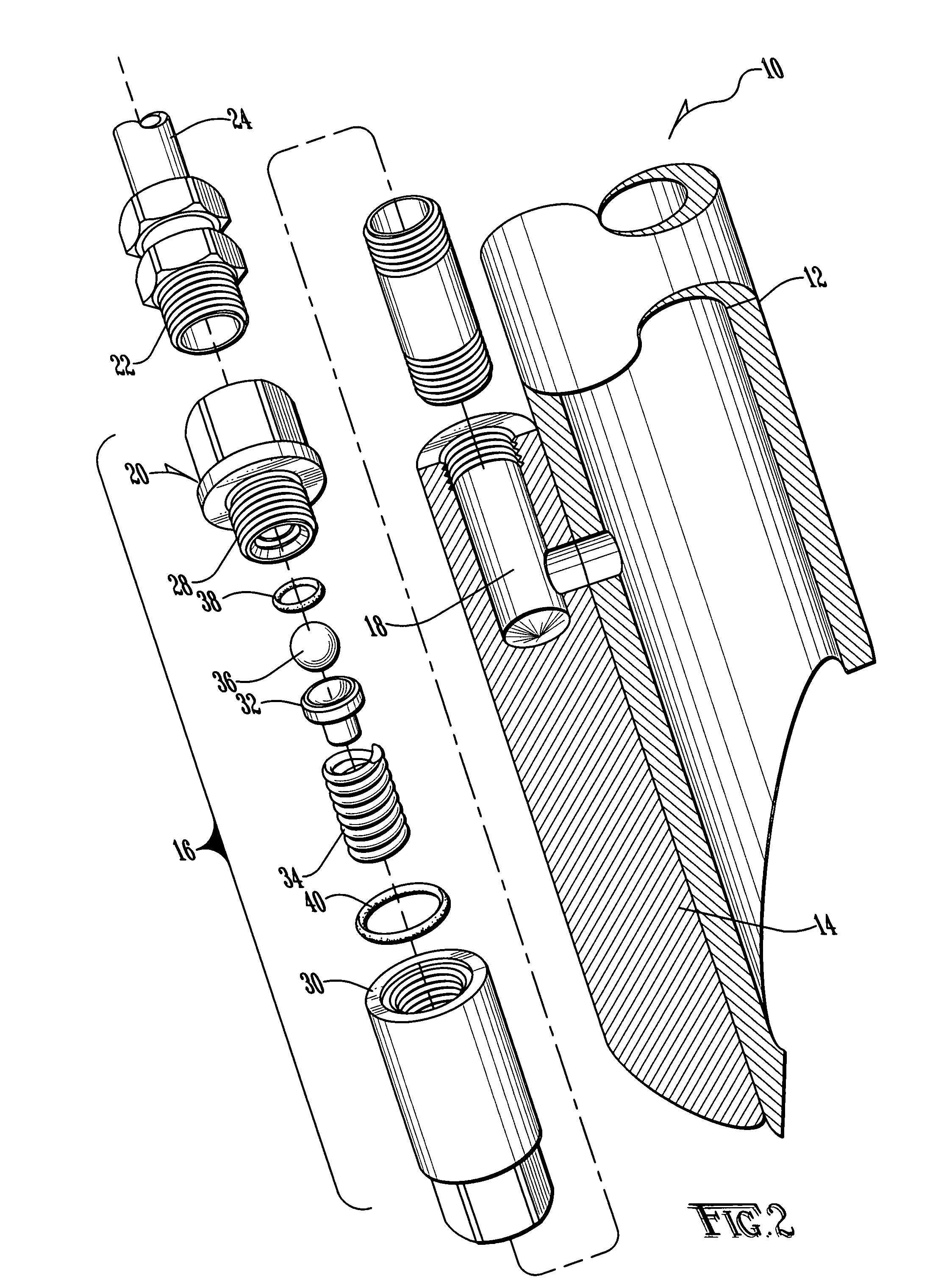
High pressure rotary shaft sealing mechanism
InactiveUS6227547B1Large dynamic runout and lateral offset of the shaftSignificant changeEngine sealsLeakage preventionRotational axisEngineering
A laterally translatable pressure staged rotary shaft sealing mechanism having a seal housing with a shaft passage therein being exposed to a fluid pressure P1 and with a rotary shaft being located within the shaft passage. At least one annular laterally translatable seal carrier is provided. First and second annular resilient sealing elements are supported in axially spaced relation by the annular seal carriers and have sealing relation with the rotary shaft. The seal housing and at least one seal carrier define a first pressure staging chamber exposed to the first annular resilient sealing element and a second pressure staging chamber located between and exposed to the first and second annular resilient sealing elements. A first fluid is circulated to the first pressure chamber at a pressure P1, and a second staging pressure fluid is circulated to the second pressure chamber at a fraction of pressure P1 to achieve pressure staging, cooling of the seals. Seal placement provides hydraulic force balancing of the annular seal carriers.
Owner:KALSI ENG
Tissue resurfacing
InactiveUS7300436B2Easy to getRapid treatment at the tissue surfaceSurgical instruments for heatingProsthesisSkin treatmentsSkin surface
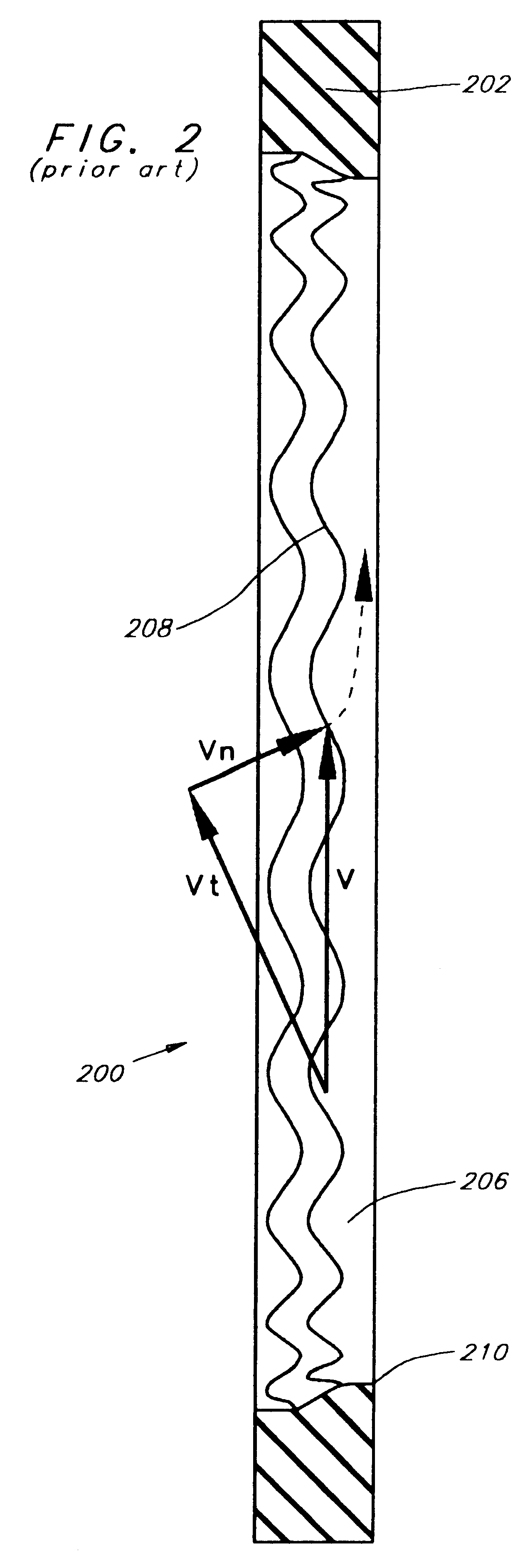
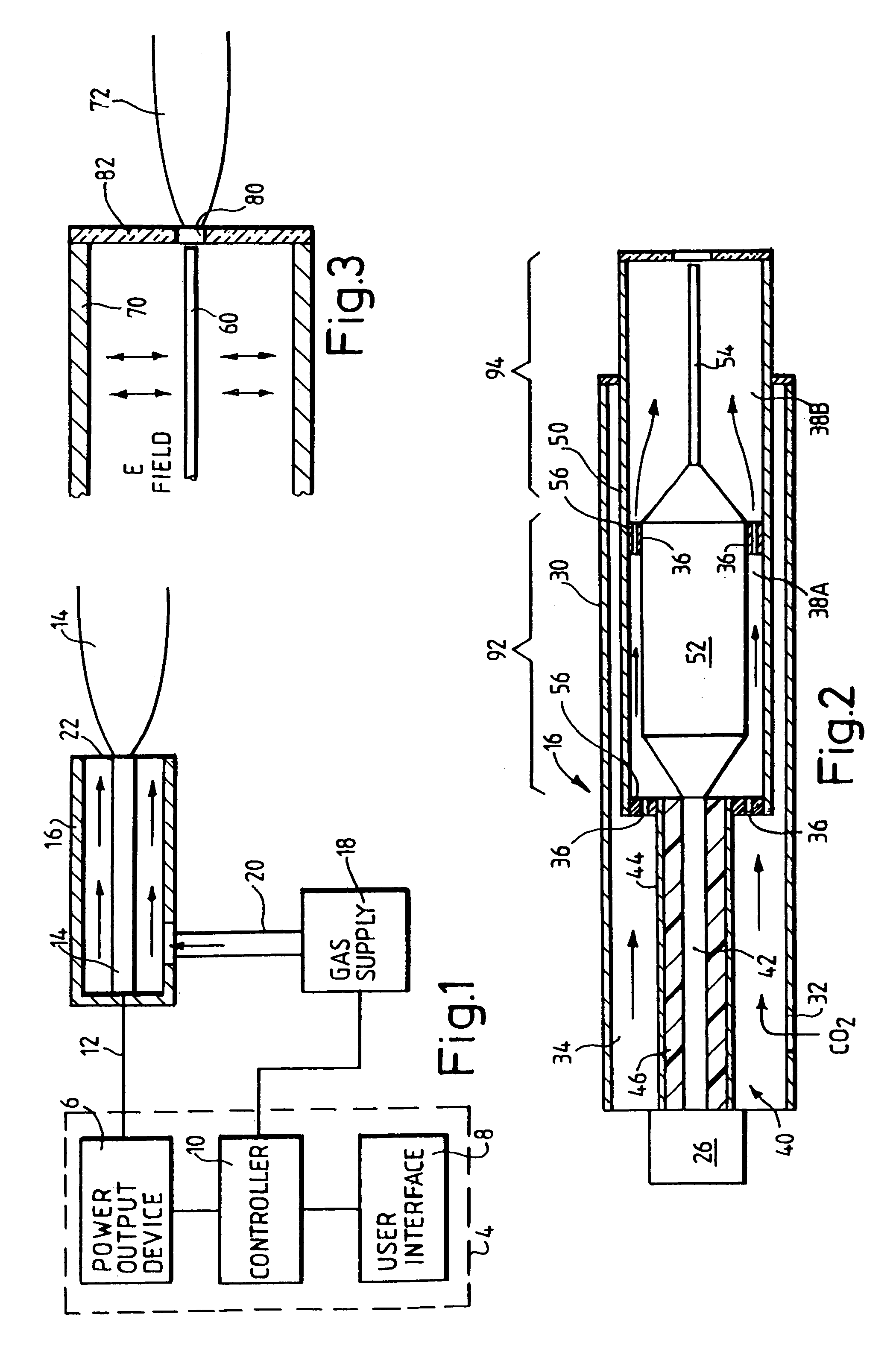
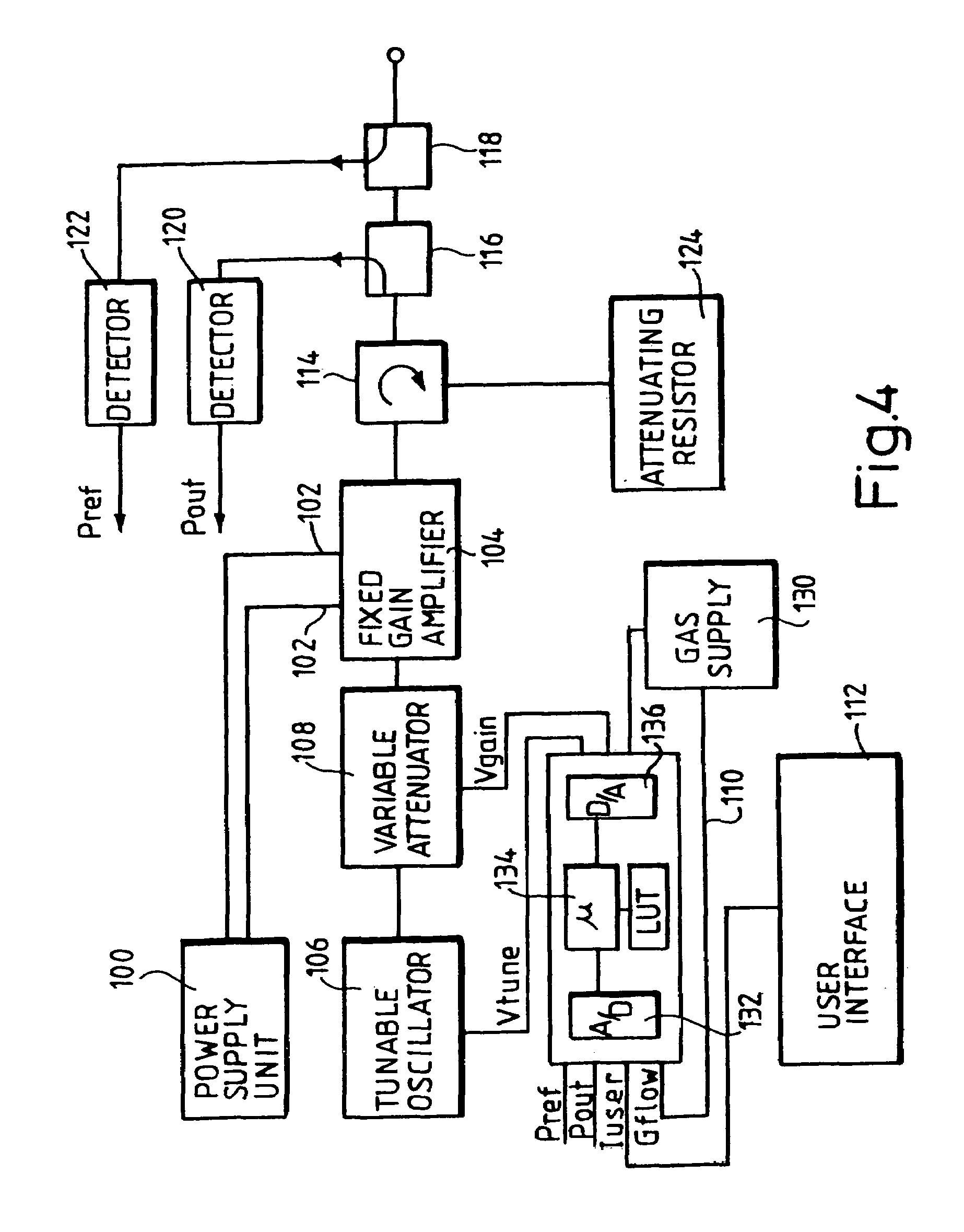
A method for skin treatment comprises the steps of delivering at least one pulse of radio frequency power to at least one electrode in order to create an electric field; passing gas through the electric field in order to form plasma from the gas; and applying the plasma to the surface of skin. The amount of radio frequency power may be relatively low such that the application of plasma causes denaturation of collagen within the collagen-containing tissue beneath the skin surface, which may promote the generation of new collagen within the collagen-containing tissue.
Owner:ENERGIST
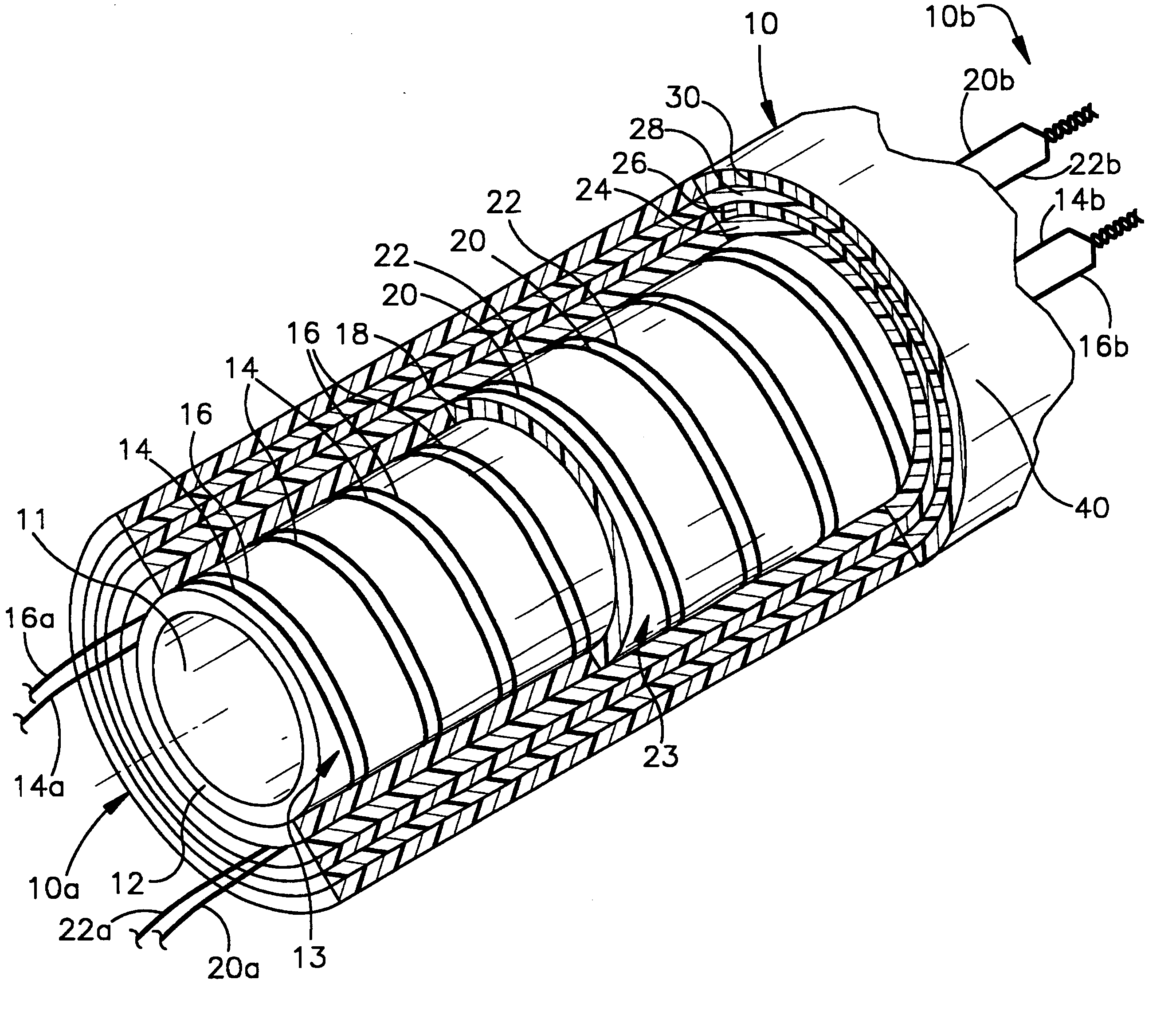
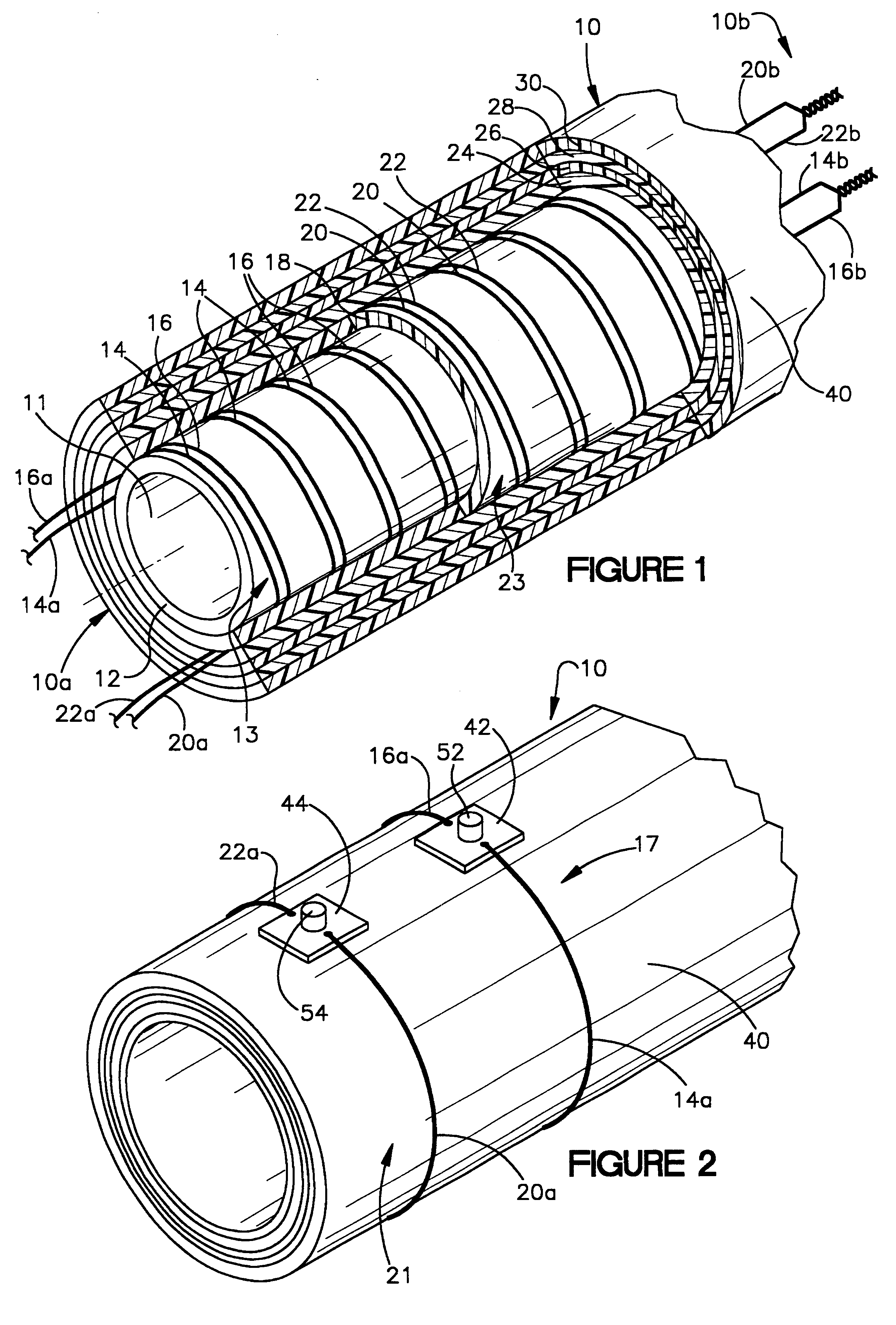
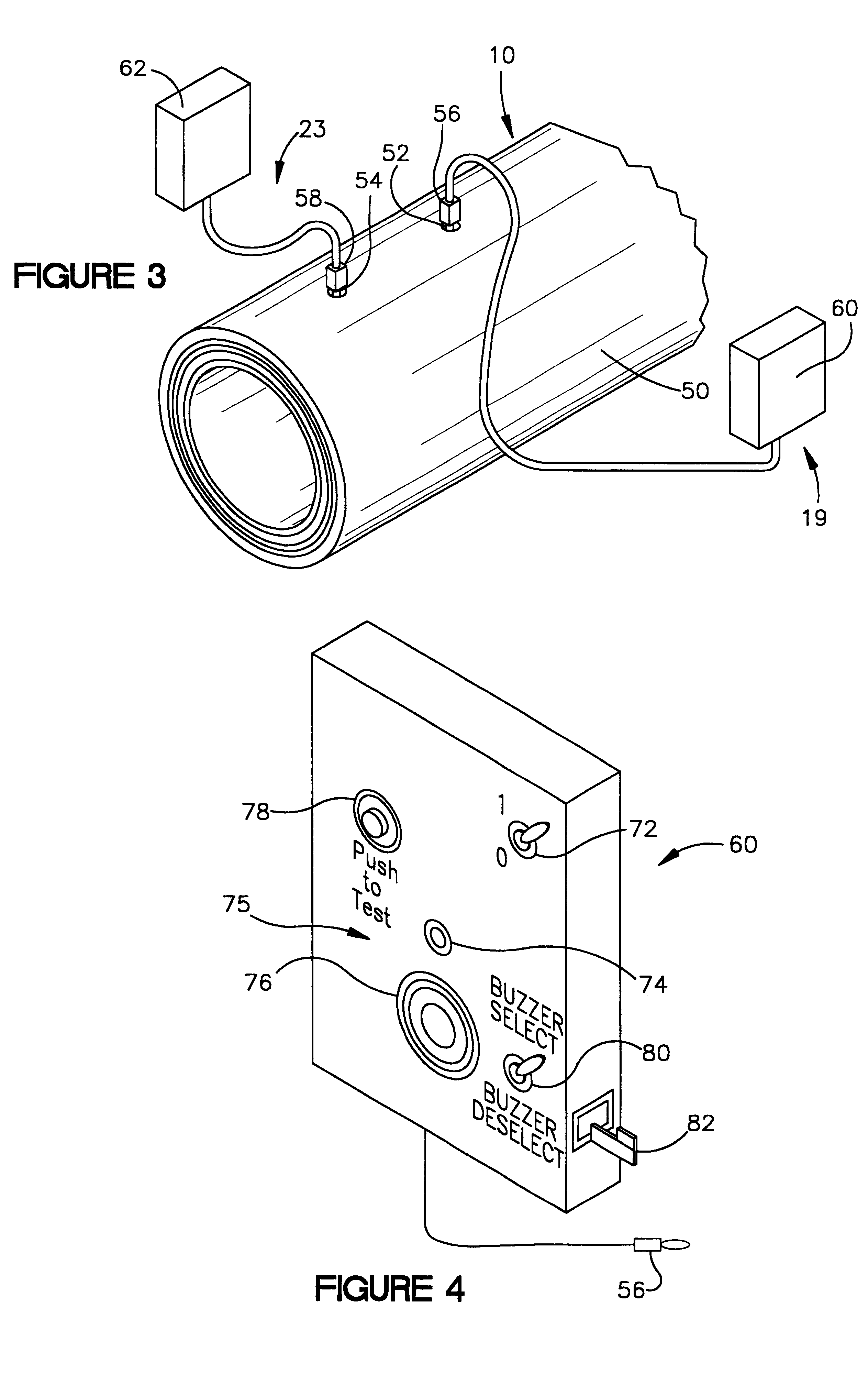
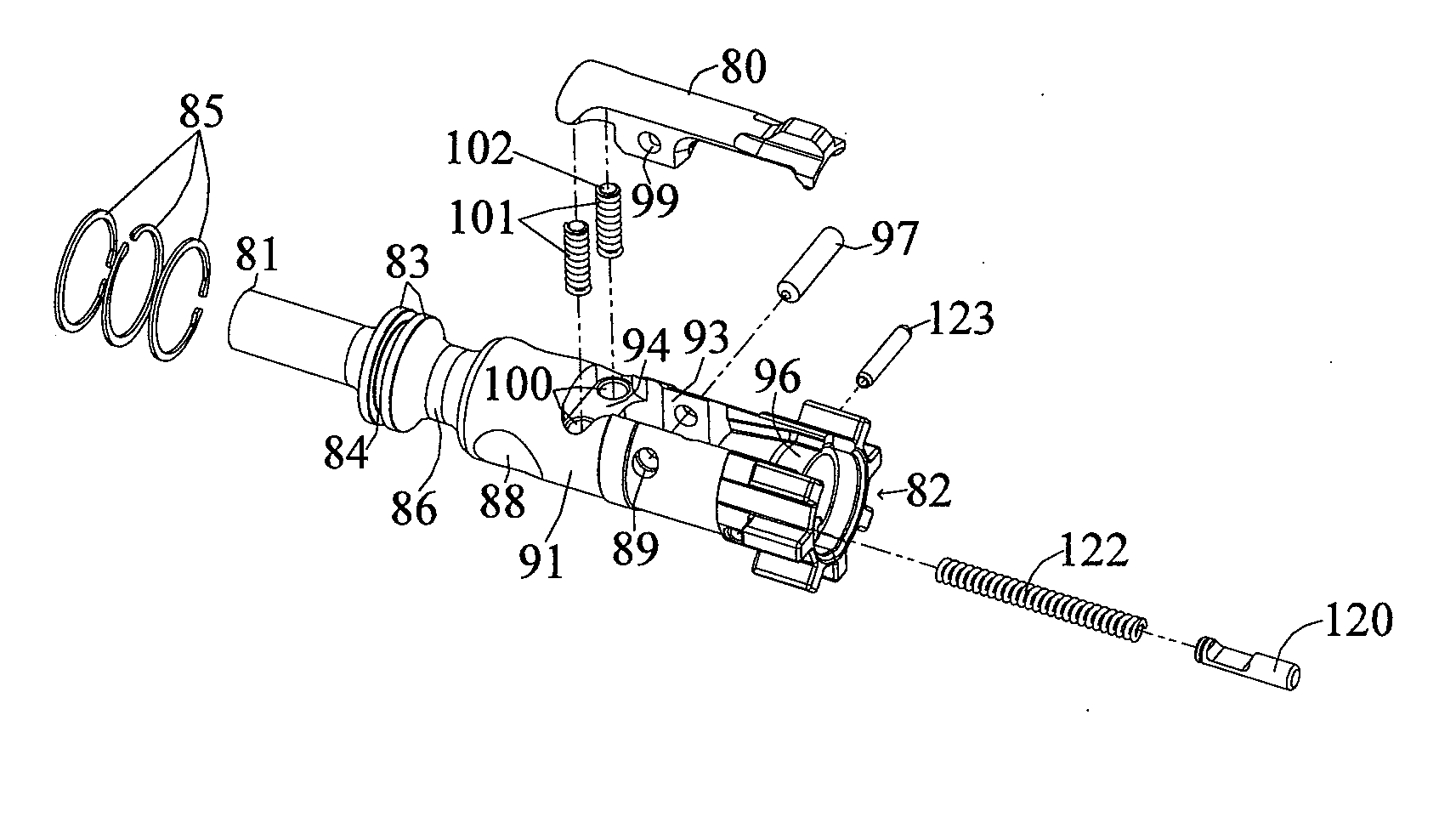
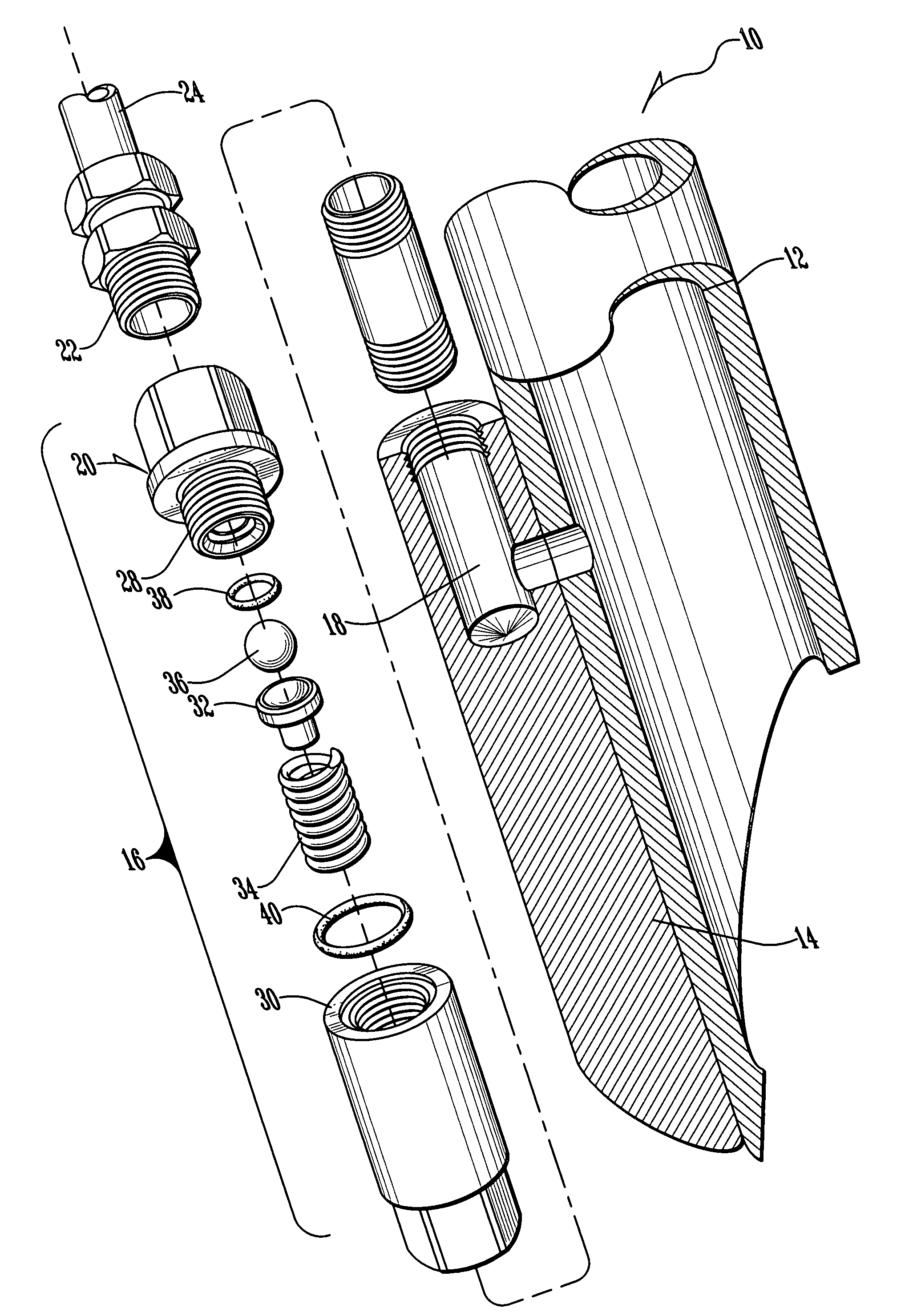
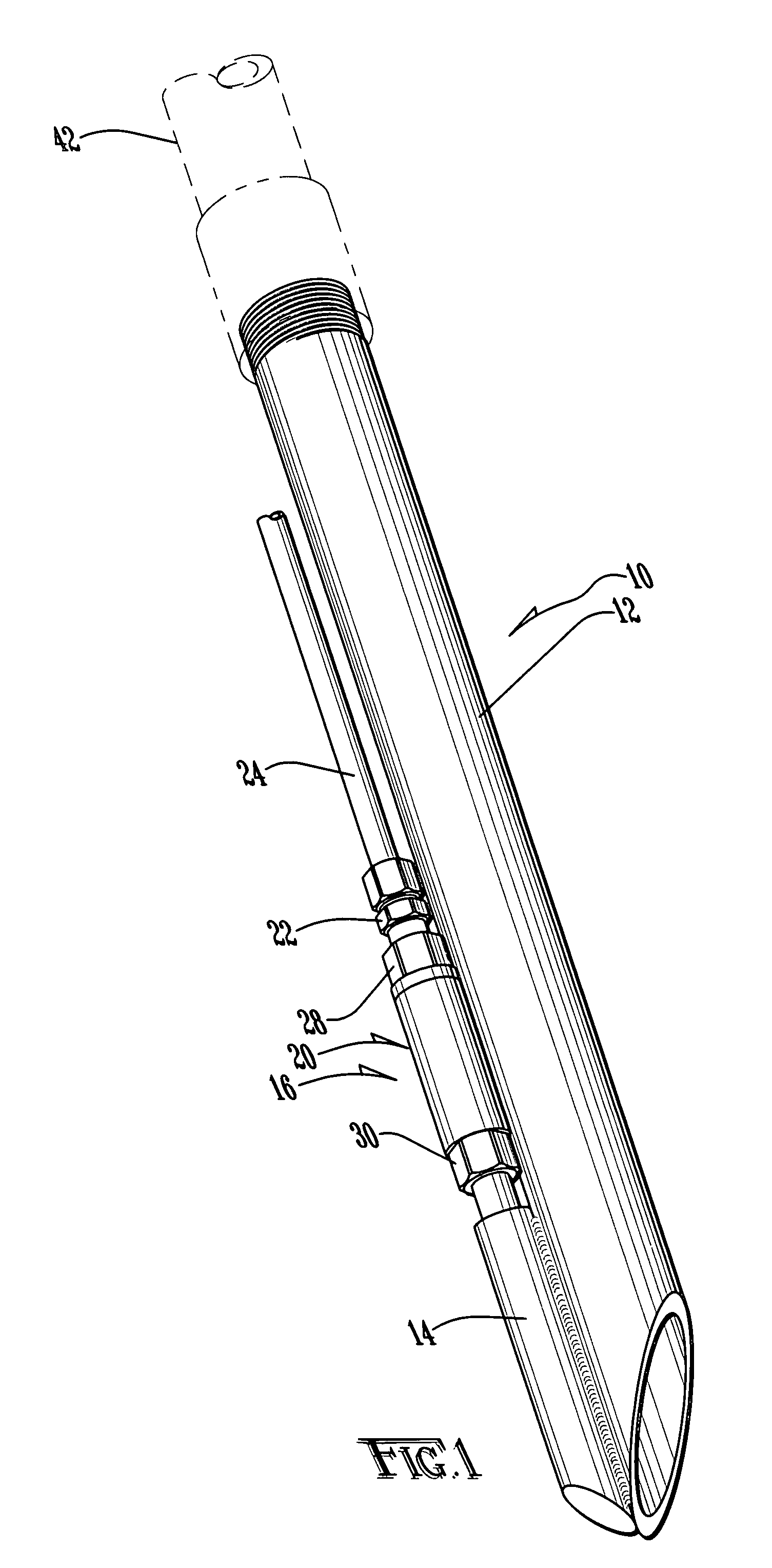
Abrasive material transport hose with wear detecting sensors
InactiveUS6386237B1Easy to replaceMaximum service lifePipe elementsFluid-tightness measurementEngineeringMaterial transport
The useful life of an abrasive material transport hose (10) can be maximized if the hose is repositioned at the first signs of internal wear. This is accomplished by disposing at least two wear sensing elements (17, 21), each at a specified distance from the inwardmost surface of the inner tube (12), and each monitoring a condition indicative of wear of the hose (10) at its specified distance from the inwardmost surface of the inner tube. When the innermost wear sensing element (17) implies wear, the hose can be repositioned to extend the useful life until the outermost wear sensing element (21) indicates wear requiring replacement of the hose.
Owner:CONTITECH USA INC
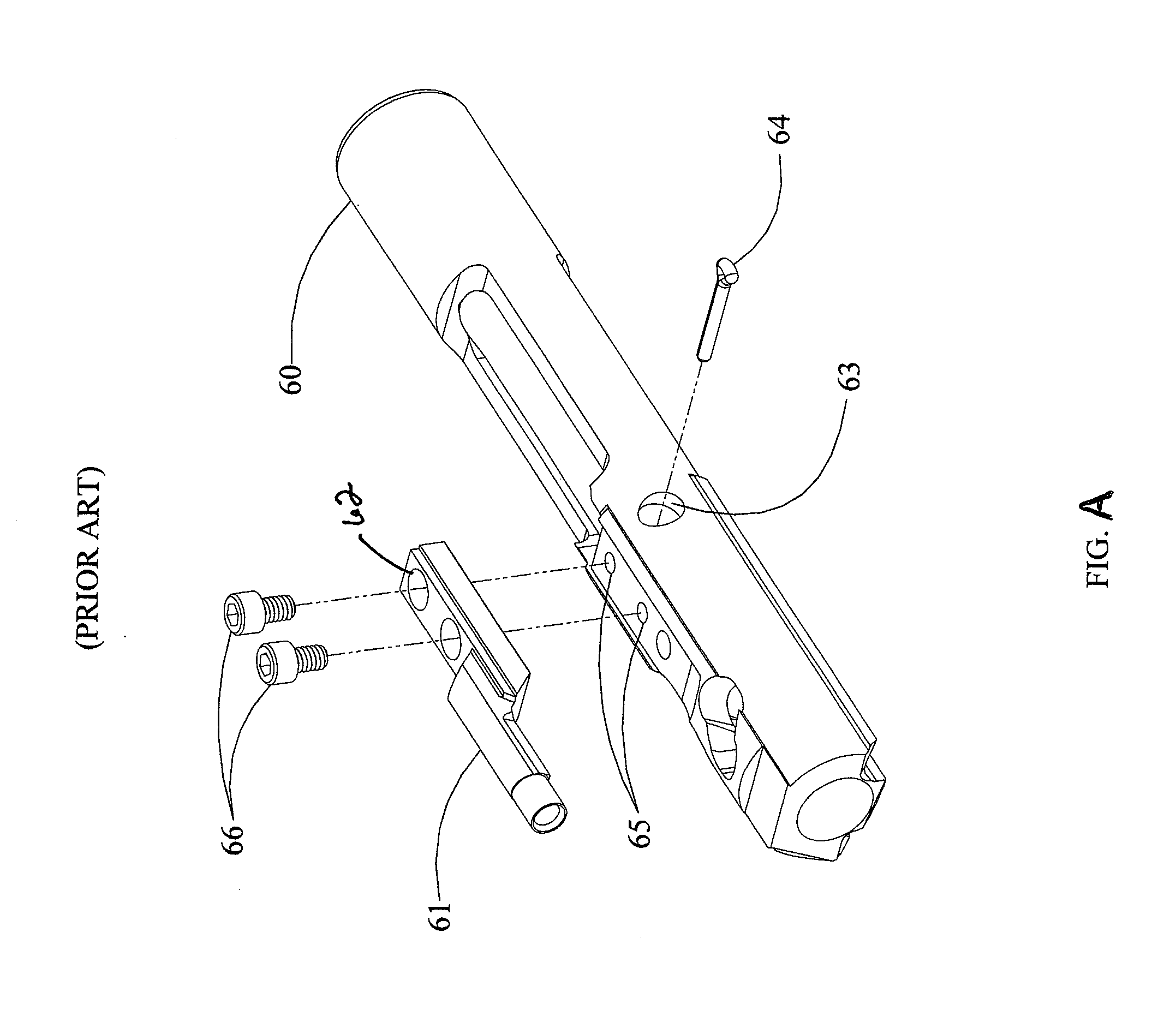
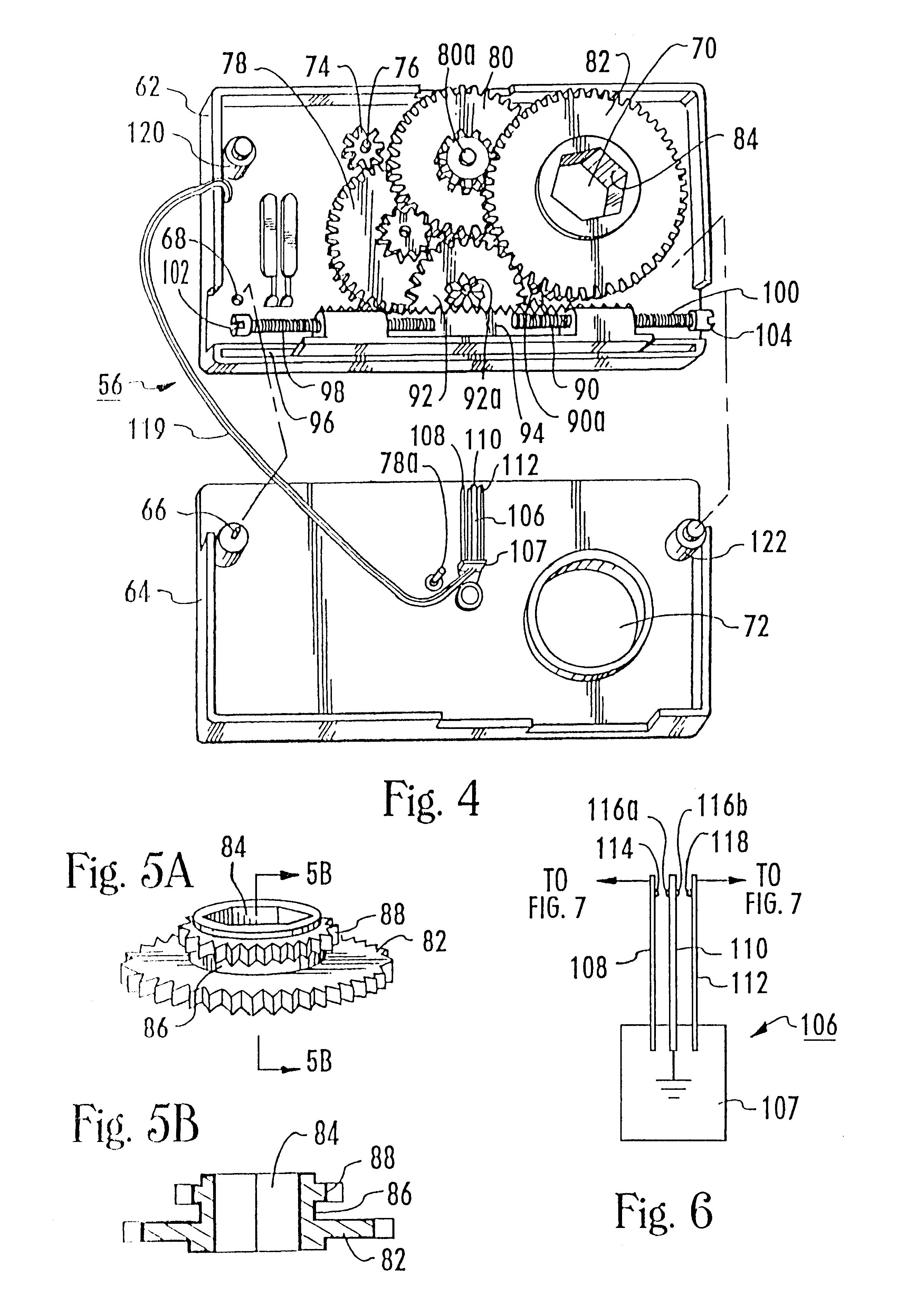
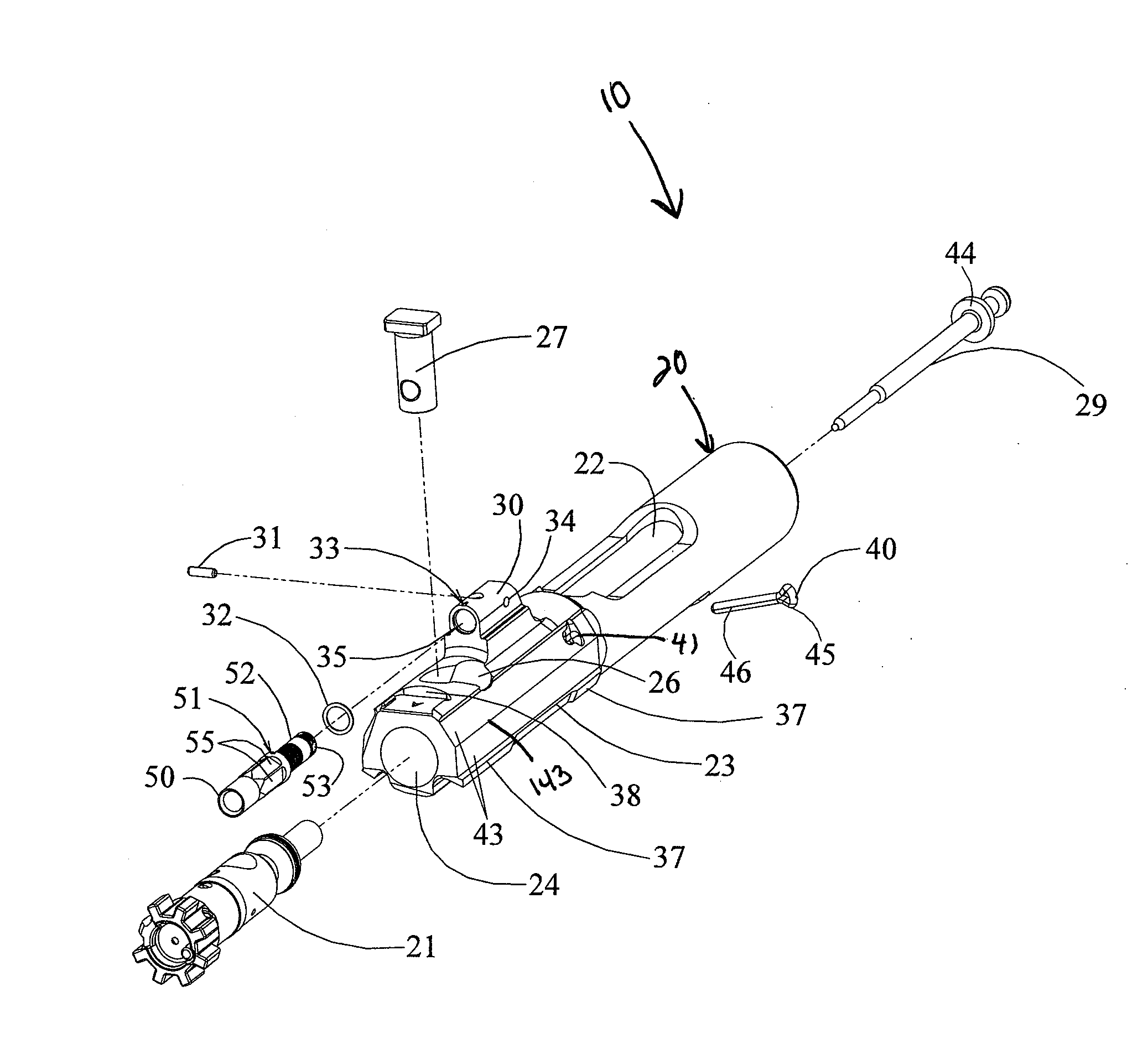
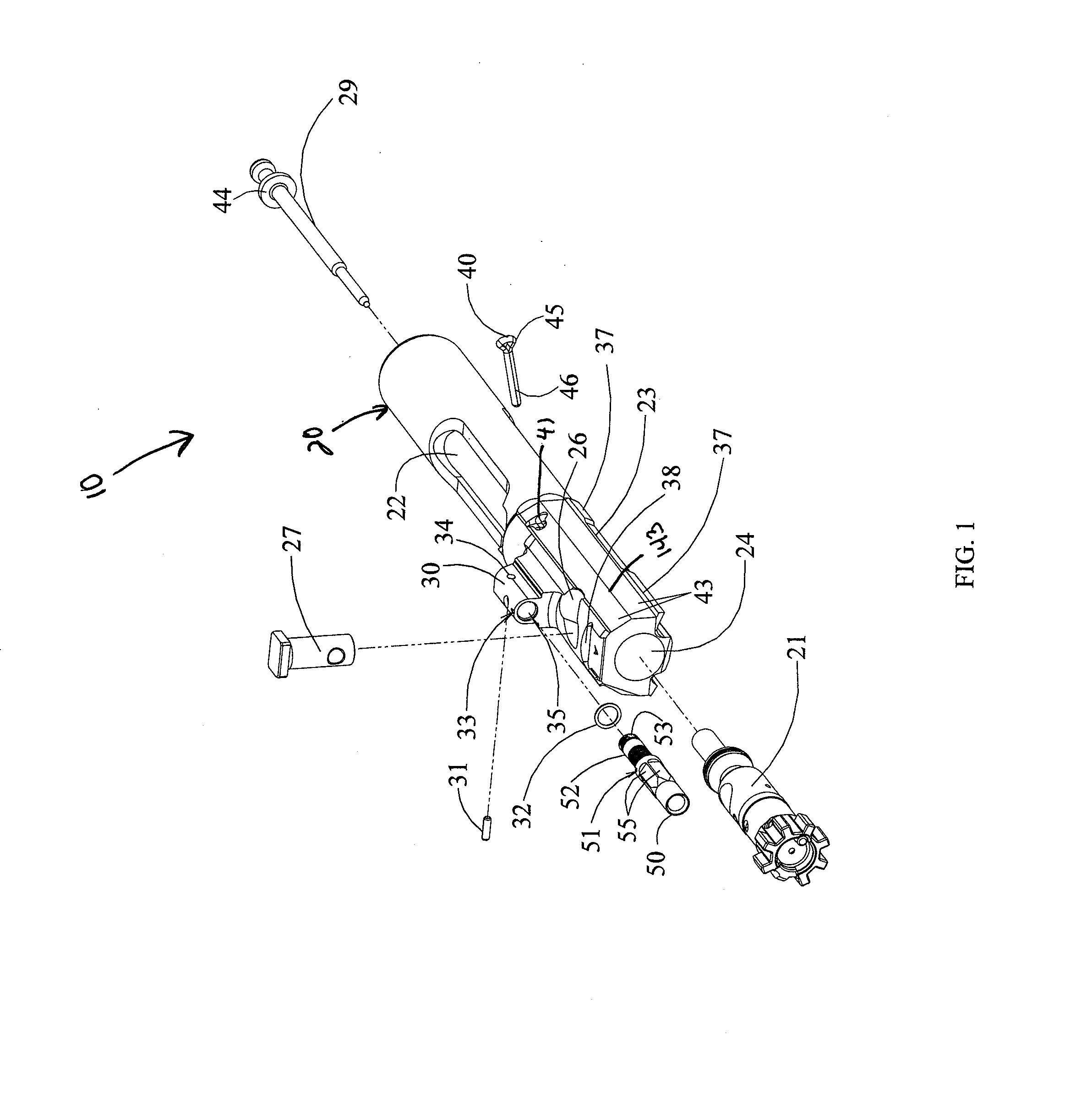
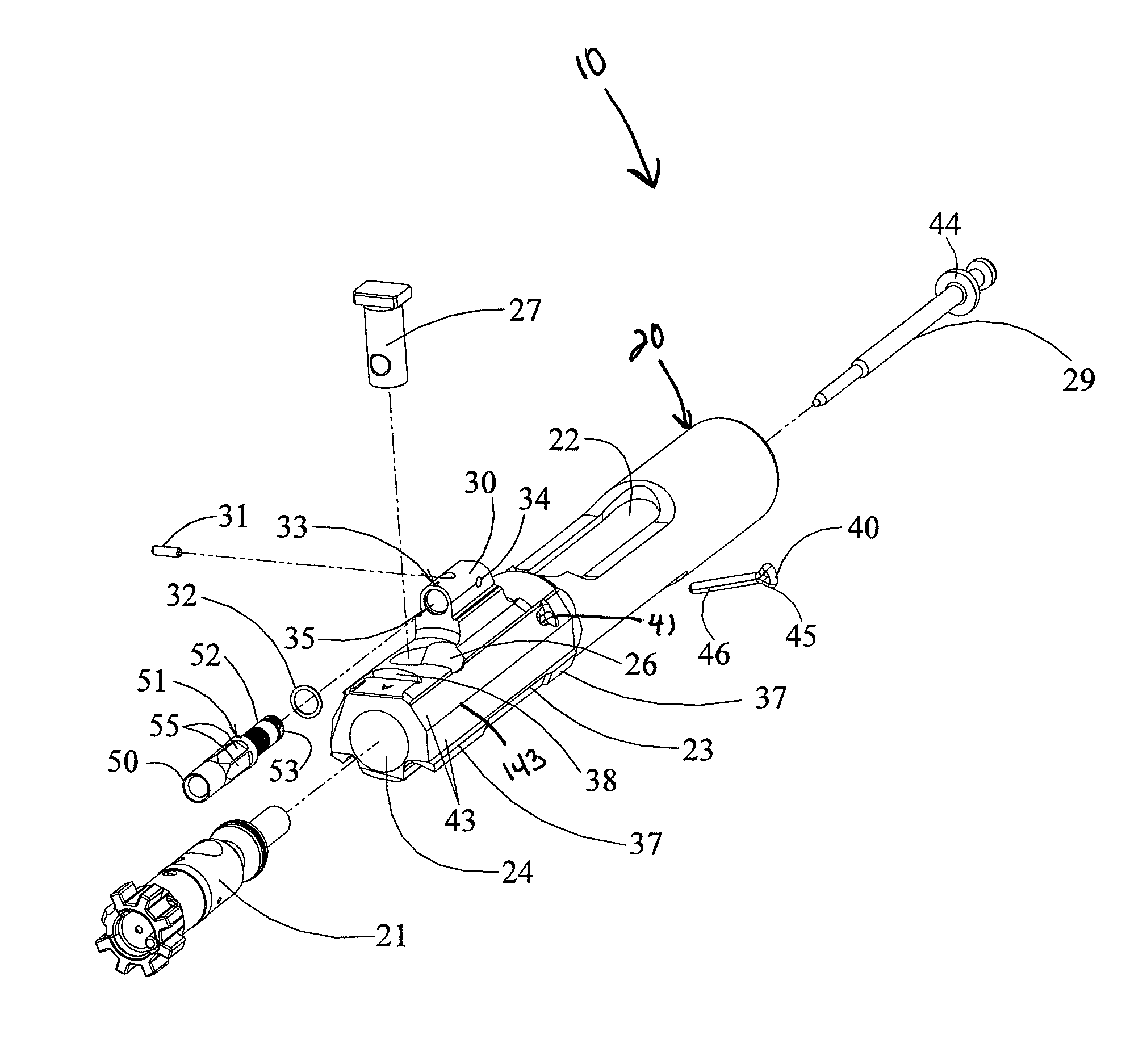
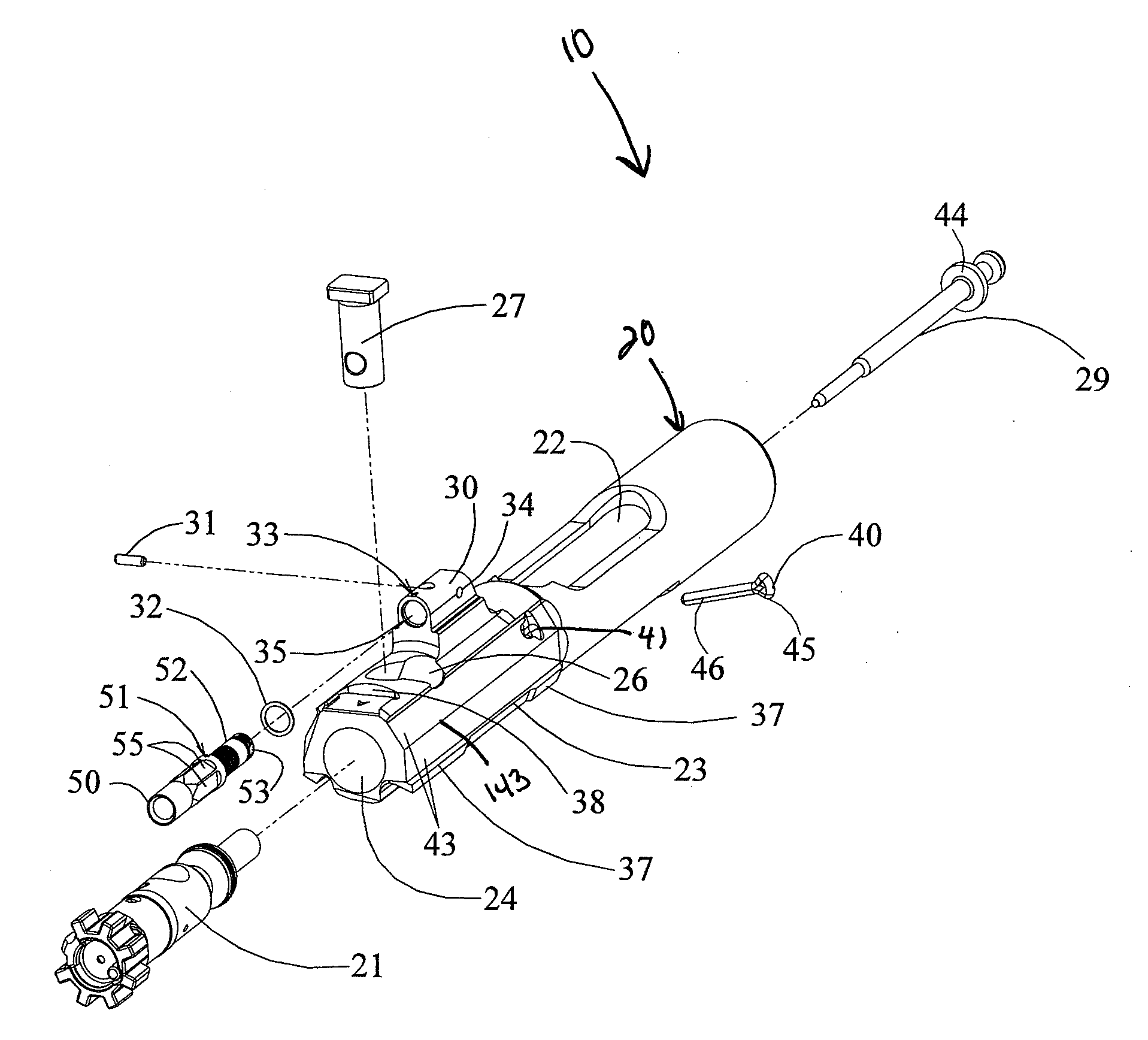
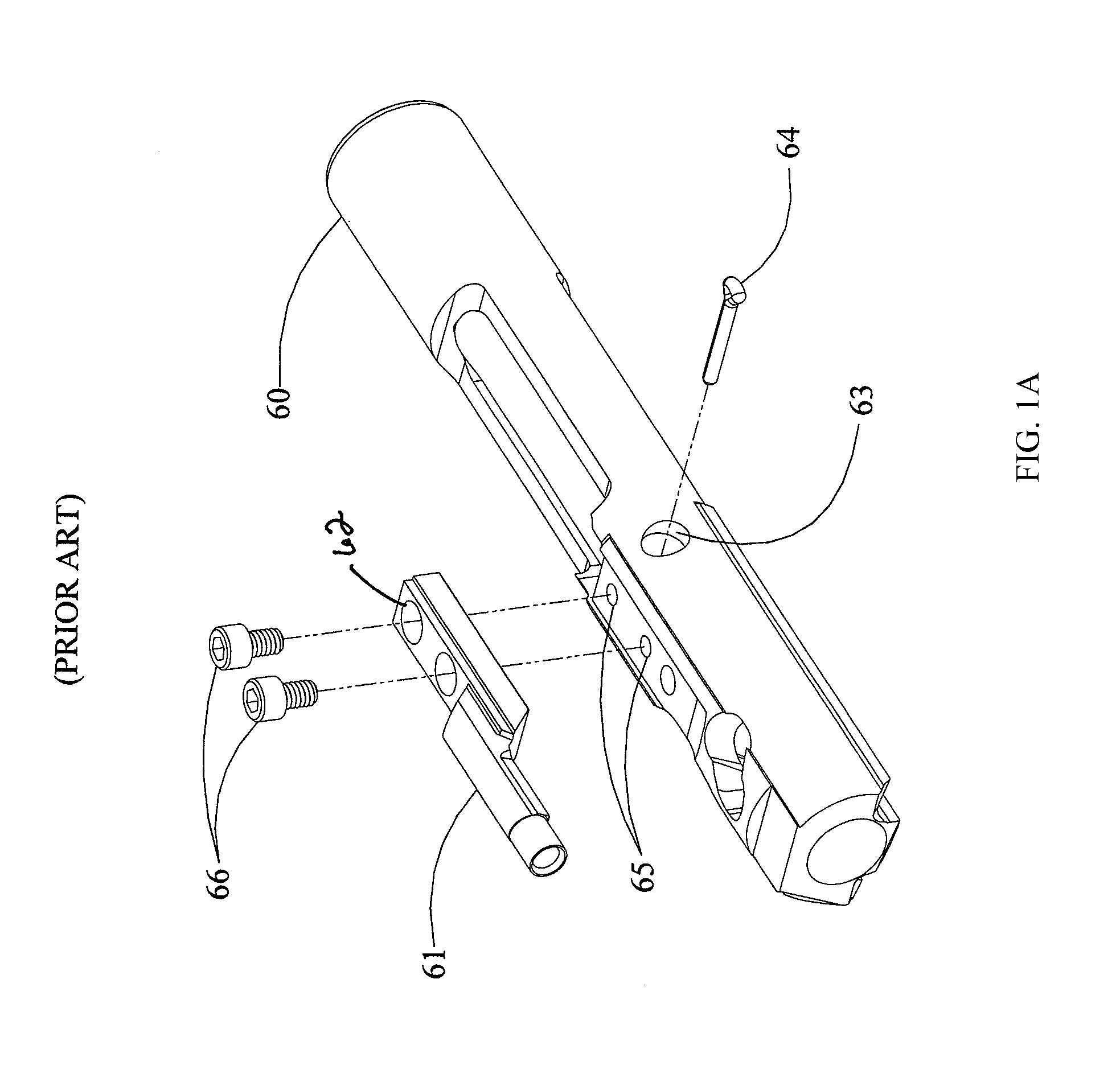
Bolt carrier and bolt for gas operated firearms
ActiveUS20140090283A1Prevent looseningMaximum service lifeCartridge extractorsBreech mechanismsSpray nozzleRetaining Pin
An improved bolt and bolt carrier with integral gas key having an extension nozzle threadedly secured and pinned to the gas key for use with a direct gas operated firearm is provided. The extension nozzle is designed to receive a portion of the host firearms gas operating system. The firing pin retaining pin is oriented so as to expose its widest profile to the firing pins annular flange, increasing its service life. The bolt has a plurality of lugs extending from its forward end and an extractor recess. The extractor recess is constructed to accommodate an enlarged extractor claw while not undercutting the bolt lugs adjacent thereto. The extractor engages approximately 57% more of a seated ammunition cartridges rim as compared to some prior art AR15 / M16 type extractors used with automatic firearms chambered in 6.8 SPC. The result is an improved bolt and bolt carrier which provides for increased operational reliability.
Owner:LWRC INTERNATIONAL
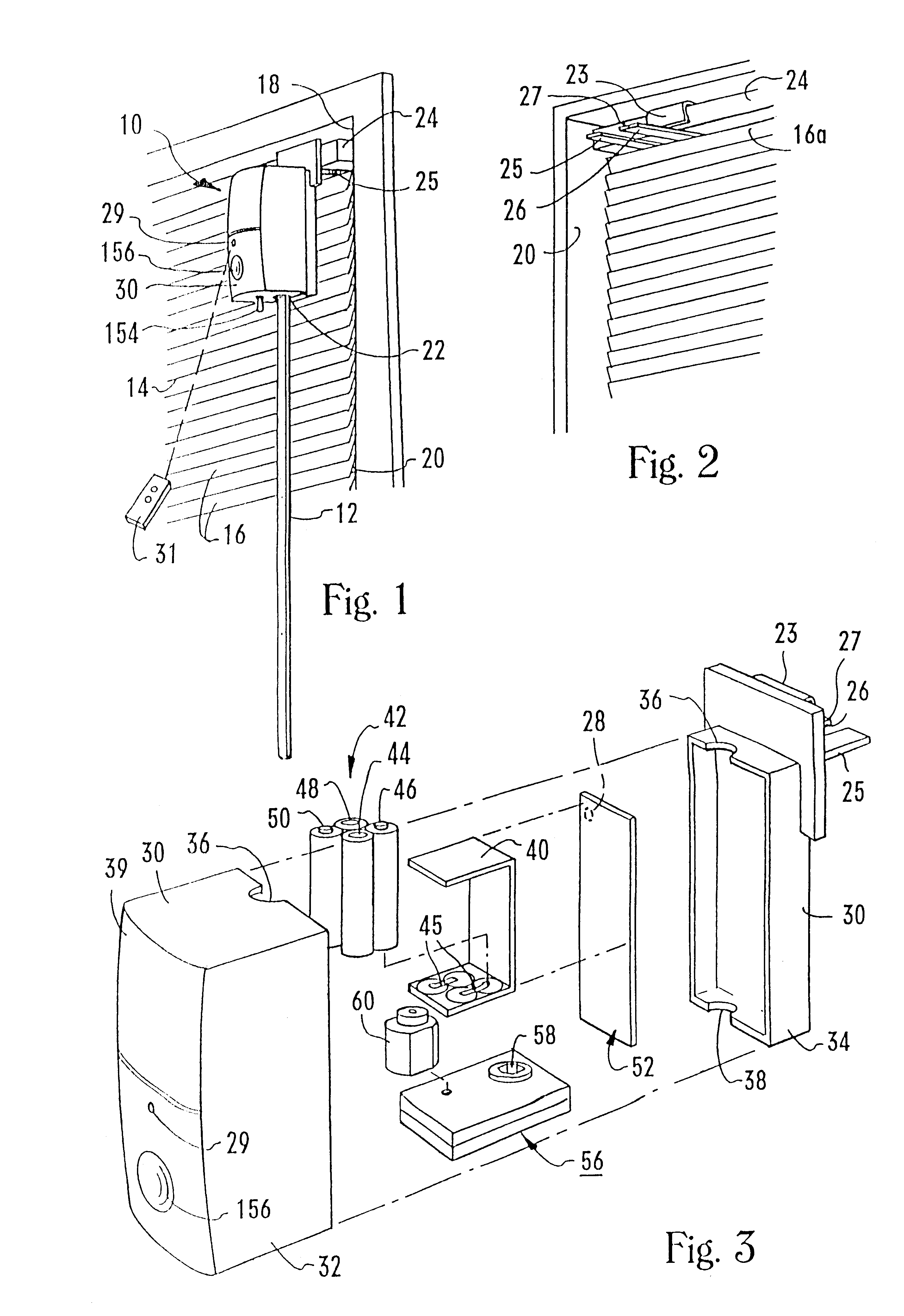
Head rail-mounted actuator for window coverings
InactiveUS6850017B1Save battery powerMaximum service lifeLight dependant control systemsDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical batteryWindow shutter
A mini-blind actuator has a motor and a housing that holds the motor and a dc battery. The rotor of the motor is coupled to the baton of the mini-blind for rotating the baton and thereby opening or closing the slats of the mini-blind. Alternatively, the rotor is coupled to the tilt rod of the blind to rotate the tilt rod and thereby open or close the slats of the mini-blind. A control signal generator generates a control signal for completing the electrical circuit between the battery and the motor. The control signal can be generated in response to a predetermined amount of daylight or in response to a user-generated remote command signal. The actuator can be used to rotate the slats of horizontal or vertical blinds, or the sections of a pleated shade. Or, the actuator can be used to rotate the hollow rotatable tube of a roll-up shade.
Owner:HARMONIC DESIGN INC FORMERLY SOMFY ACQUISITION
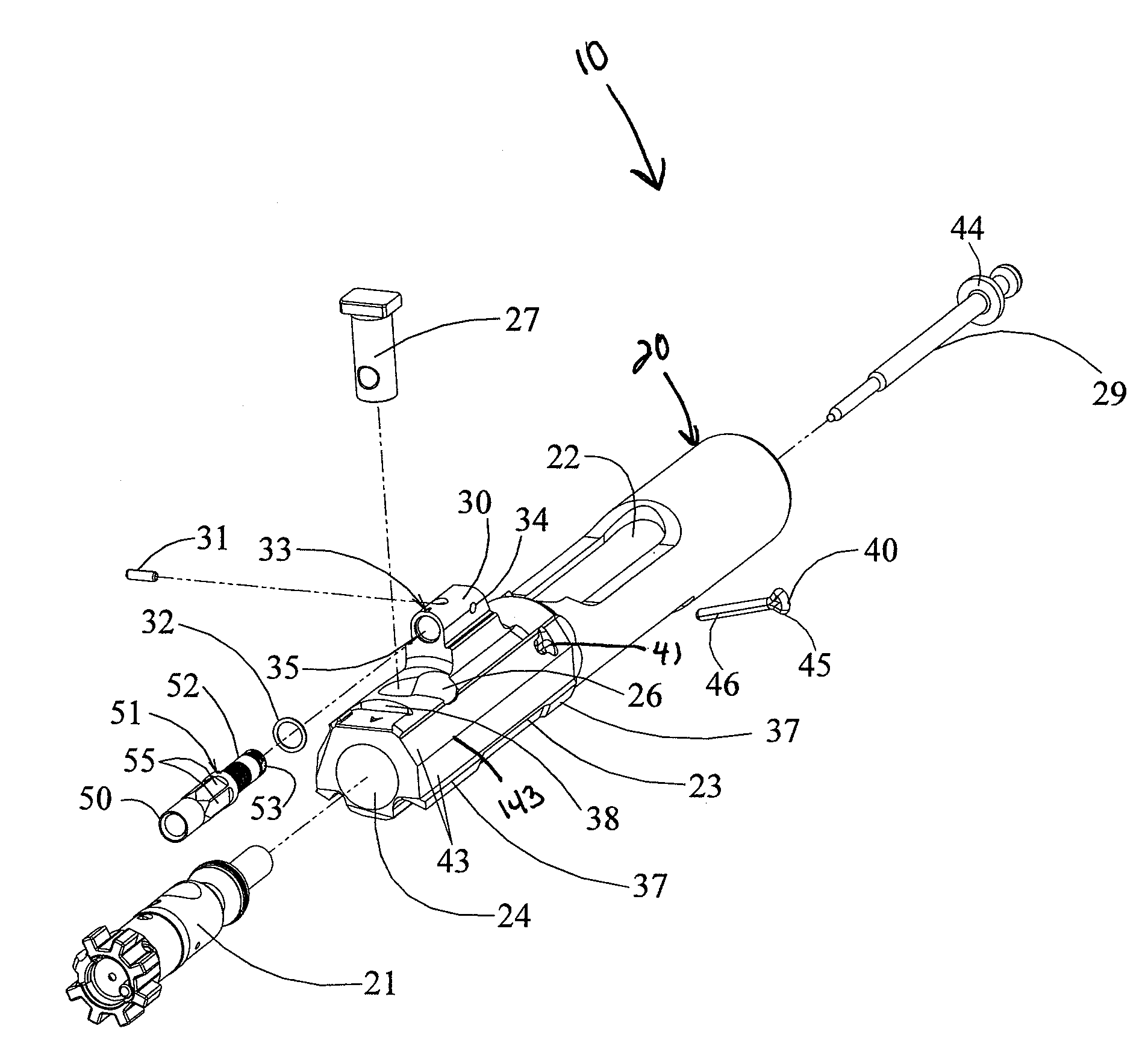
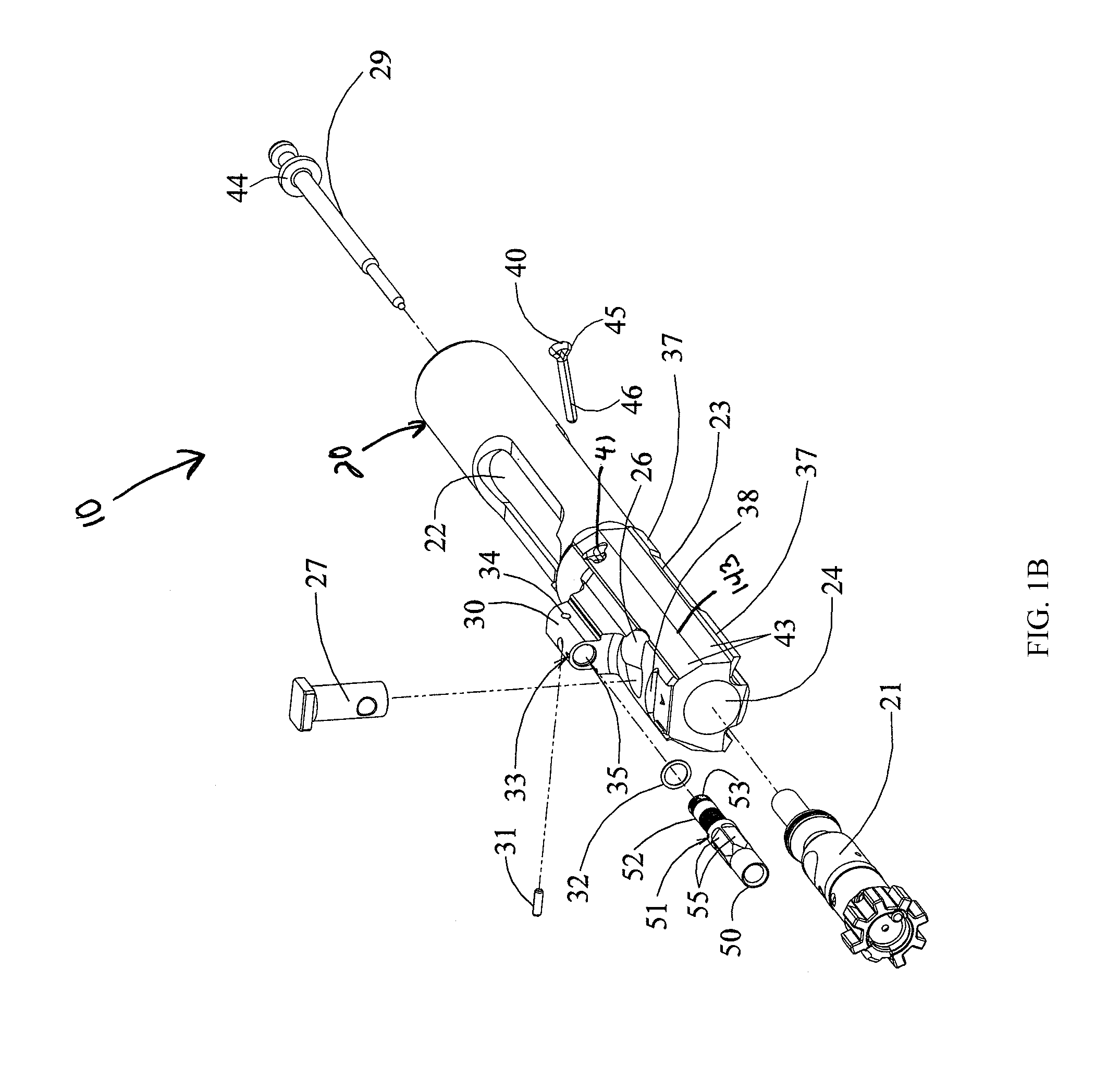
Bolt carrier and bolt for gas operated firearms
ActiveUS20140076144A1Improve safety and reliabilityReduce manufacturing costCartridge extractorsFiring/trigger mechanismsEngineeringRetaining Pin
An improved bolt and bolt carrier with integral gas key having an extension nozzle threadedly secured and pinned to the gas key for use with a direct gas operated firearm is provided. The extension nozzle is designed to receive a portion of the host firearm's gas operating system. The firing pin retaining pin is oriented so as to expose its widest profile to the firing pin's annular flange, increasing its service life. The bolt has a plurality of lugs extending from its forward end. The extractor recess is constructed so that the face of the bolt is round and the adjacent lugs fully supported. The extractor engages approximately 17% more of a seated ammunition cartridge's rim as compared to the prior art AR15 / M16 extractor. The result is an improved bolt and bolt carrier which provides for increased operational reliability.
Owner:LWRC INTERNATIONAL
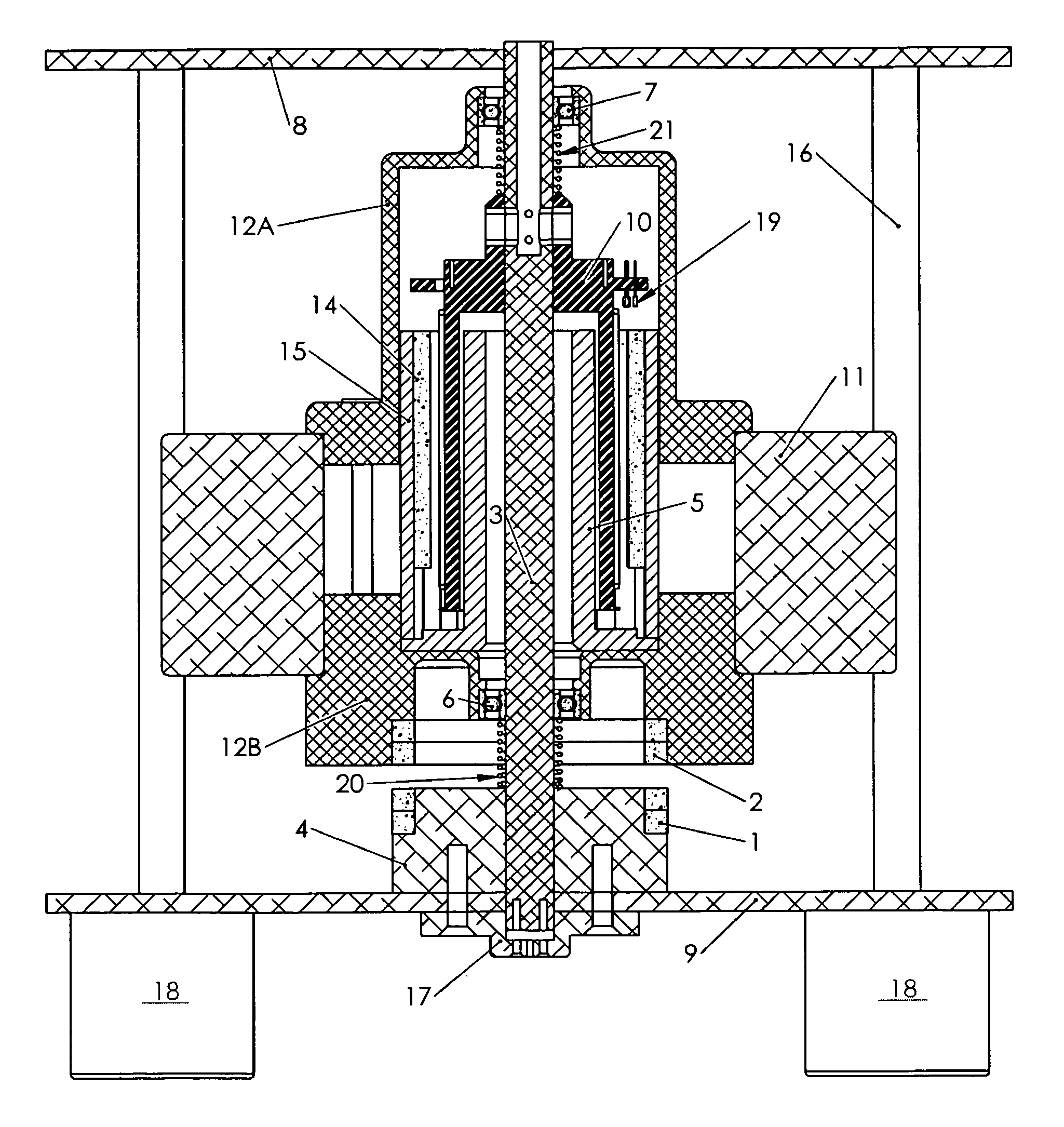
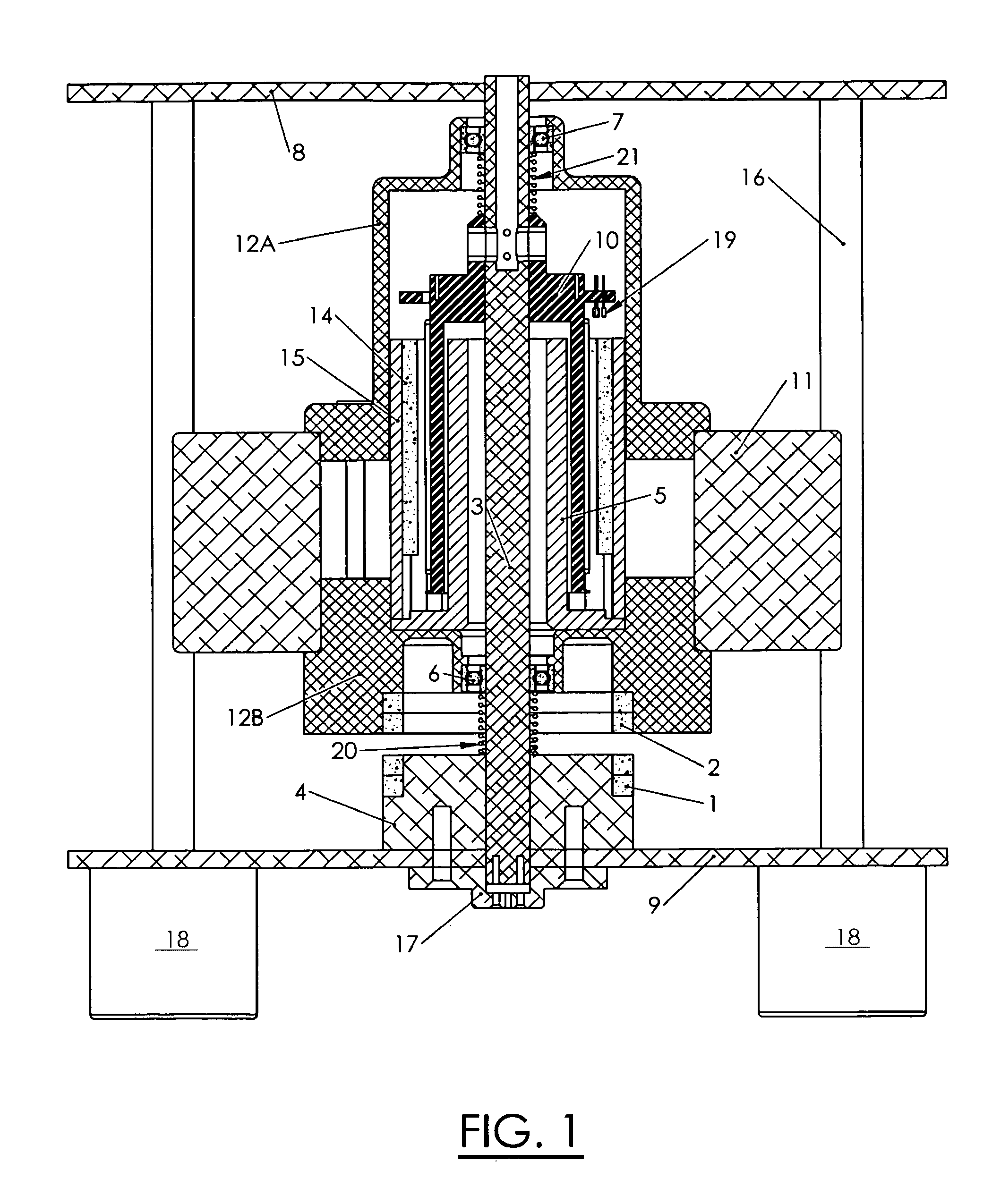
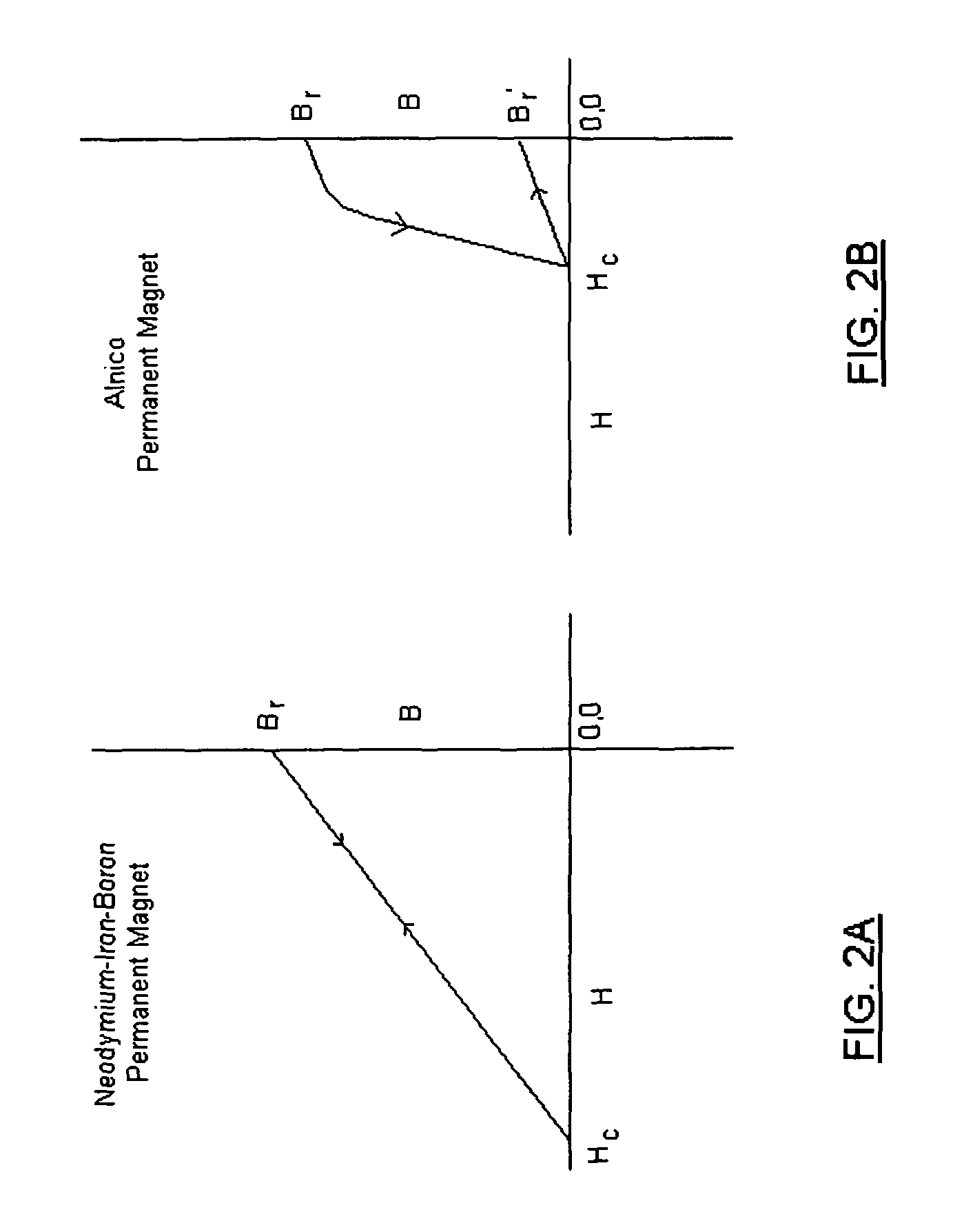
Low-Cost Minimal-Loss Flywheel Battery
InactiveUS20100283340A1Low-cost minimal-lossMinimize ball bearing radial thrustRolling contact bearingsControllers with pulse-train output signalBall bearingDc current
A low-cost minimal-loss zero-maintenance flywheel battery, to store electric power from a DC power source by conversion to kinetic energy, and regenerate electric power as needed. Its vertical spin-axis rotor assembly is supported axially by repelling annular permanent magnets, and is centered by ceramic ball bearings which have axial preload that prevents vibration and augments axial rotor support. A regenerative multi-pole permanent-magnet motor, controlled by its 2-phase stator current, and connected by power and signal conductors to power interface electronics, is integrated within the flywheel assembly, in a vacuum enclosure supported by a self-leveling structure. Sinusoidal 2-phase stator currents are controlled by high-frequency pulse-width-modulated H-bridge power electronics that draw and regenerate controlled DC current with minimal ripple, responsive to respective 2-phase rotation angle sensors, the DC power voltage, and other settings. The electronics includes logic and over-voltage protection to prevent otherwise possible damaging current and voltage.
Owner:FRADELLA RICHARD B
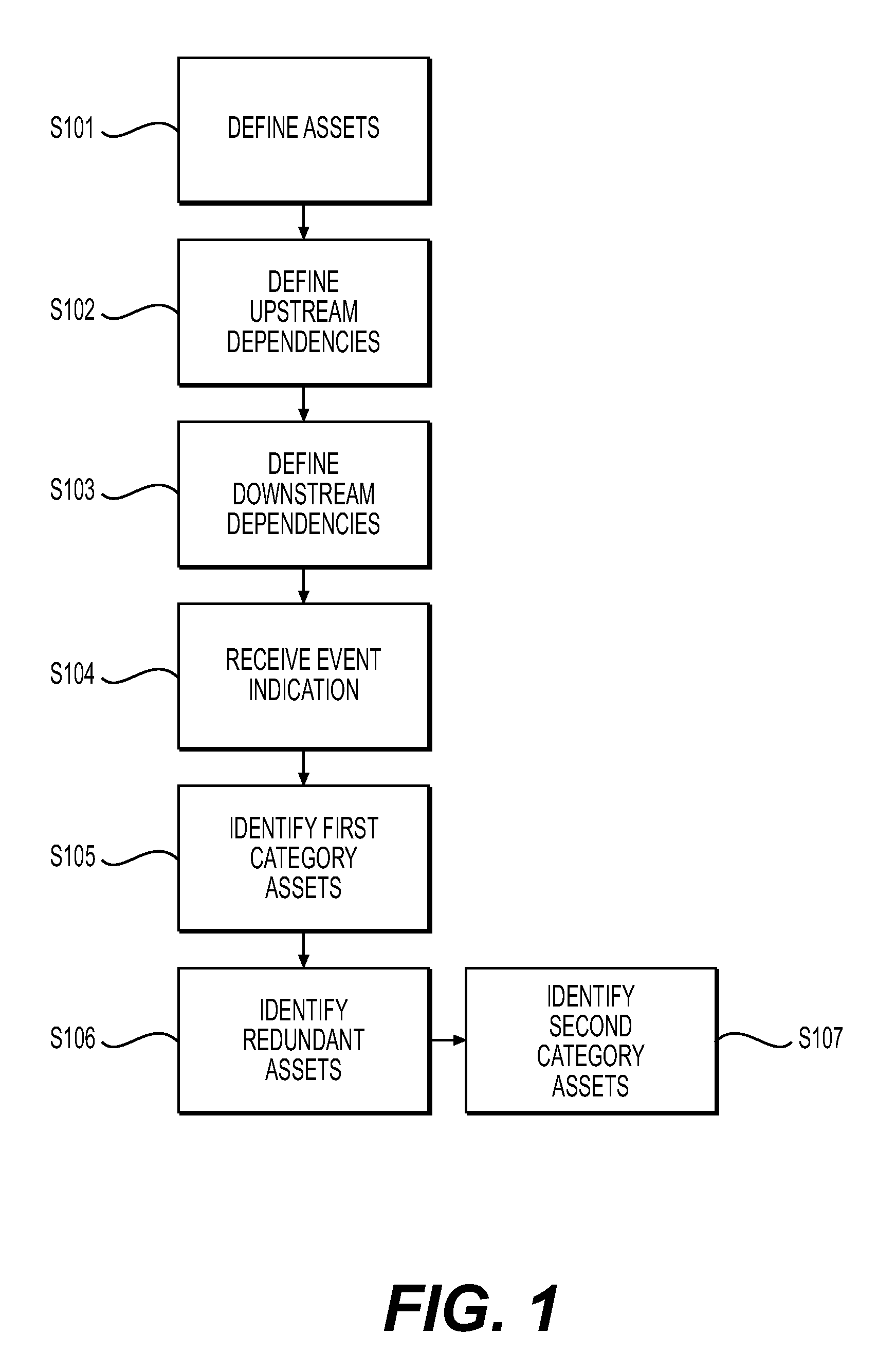
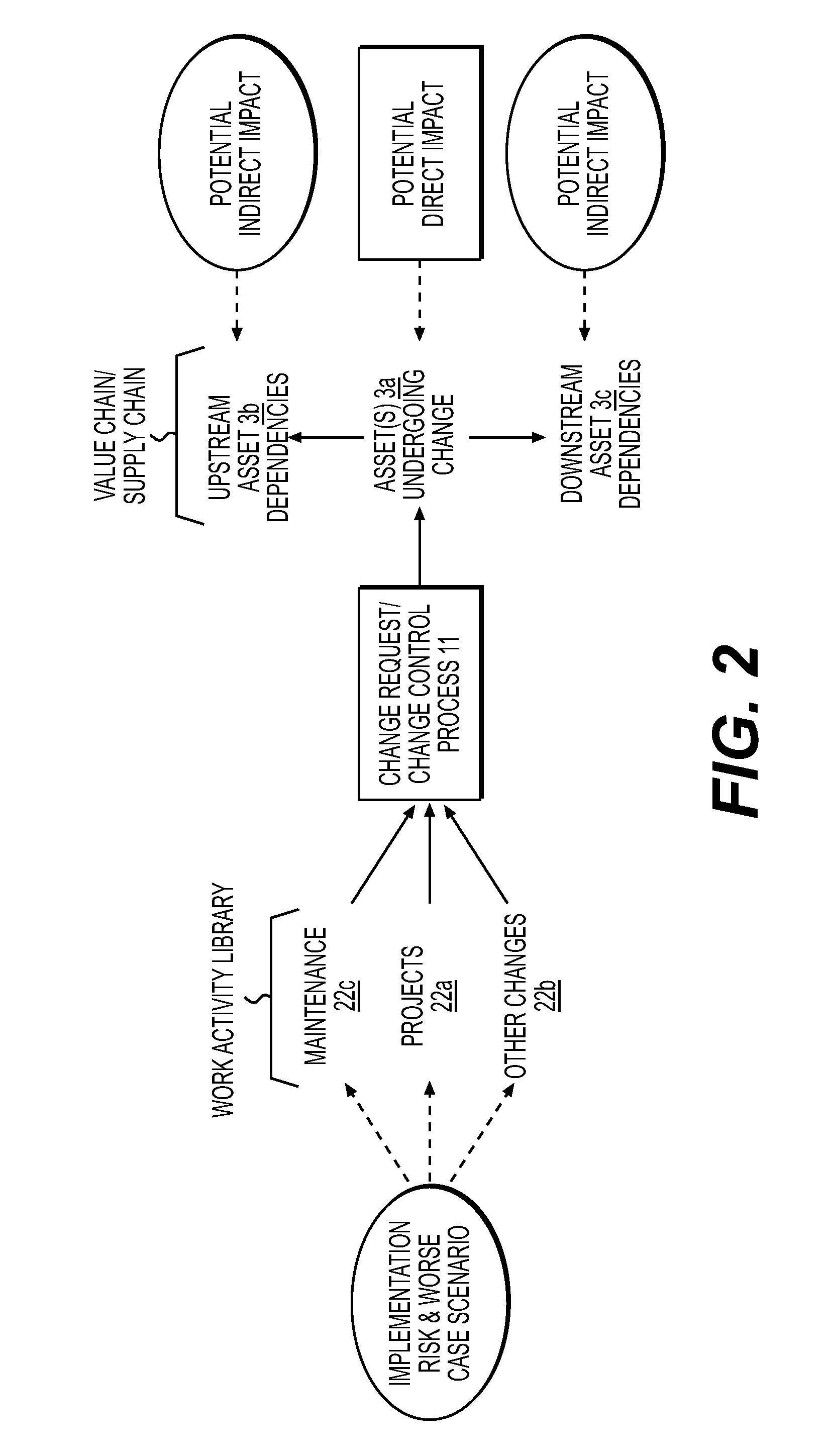
System and Method for Integrated Mission Critical Ecosystem Management
InactiveUS20150120359A1Effective and holistic decision makingReduce riskRelational databasesResourcesProgram planningEngineering
Owner:FULCRUM COLLABORATIONS
Tissue resurfacing
InactiveUS20110121735A1Minimize changesMaximum service lifeElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsEngineeringRadio frequency
In an electonic key associated with a device for skin treatment there is a housing and an integrated circuit, the integrated circuit is positioned within the housing, wherein the device for treating human tissue comprises a surgical instrument having a gas conduit terminating in a plasma exit nozzle, and an electrode associated with the conduit, and a radio frequency power generator coupled to the instrument electrode and arranged to deliver radio frequency power to the electrode in single or series of treatment pulses for creating a plasma from gas fed through the conduit, the pulses having durations in the range of from 2 ms to 100 ms.
Owner:KREOS CAPITAL III UK +1
Portable solar energy system
ActiveUS20070013340A1Maximize useful lifeOptimize state of chargeSubstation/switching arrangement detailsDigital data processing detailsState of chargeCharge controller
The portable solar energy system stores electrical energy generated by a solar panel, which is made of an array of photovoltaic cells, in a dc storage battery, and upon demand converts the dc voltage of the battery to an ac output suitable for supplying conventional electrical appliances. The battery is a sealed lead-acid type and may be an Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) battery. The system includes an energy storage and converting unit, which houses the battery and a dc-to-ac inverter. The inverter converts the stored energy of the battery, supplied at a low dc voltage, into the ac voltage and current required for supplying conventional appliances. A charge controller manages the flow of current from the solar panel to optimize the state of charge of the battery and to maximize the useful life of the battery. Additional circuitry monitors the discharge level of the battery to limit deep discharging.
Owner:GODMAN POWER GRP INC
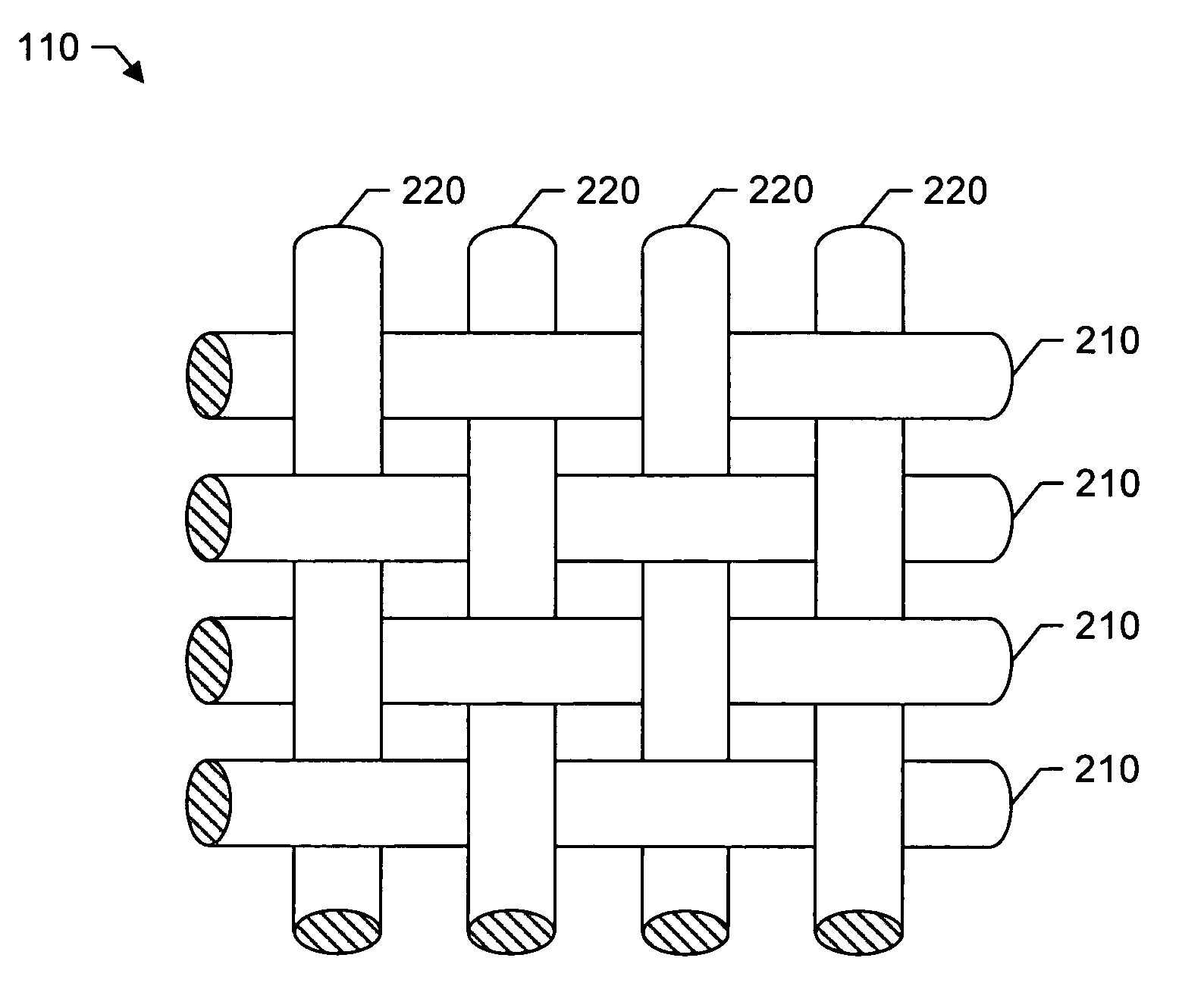
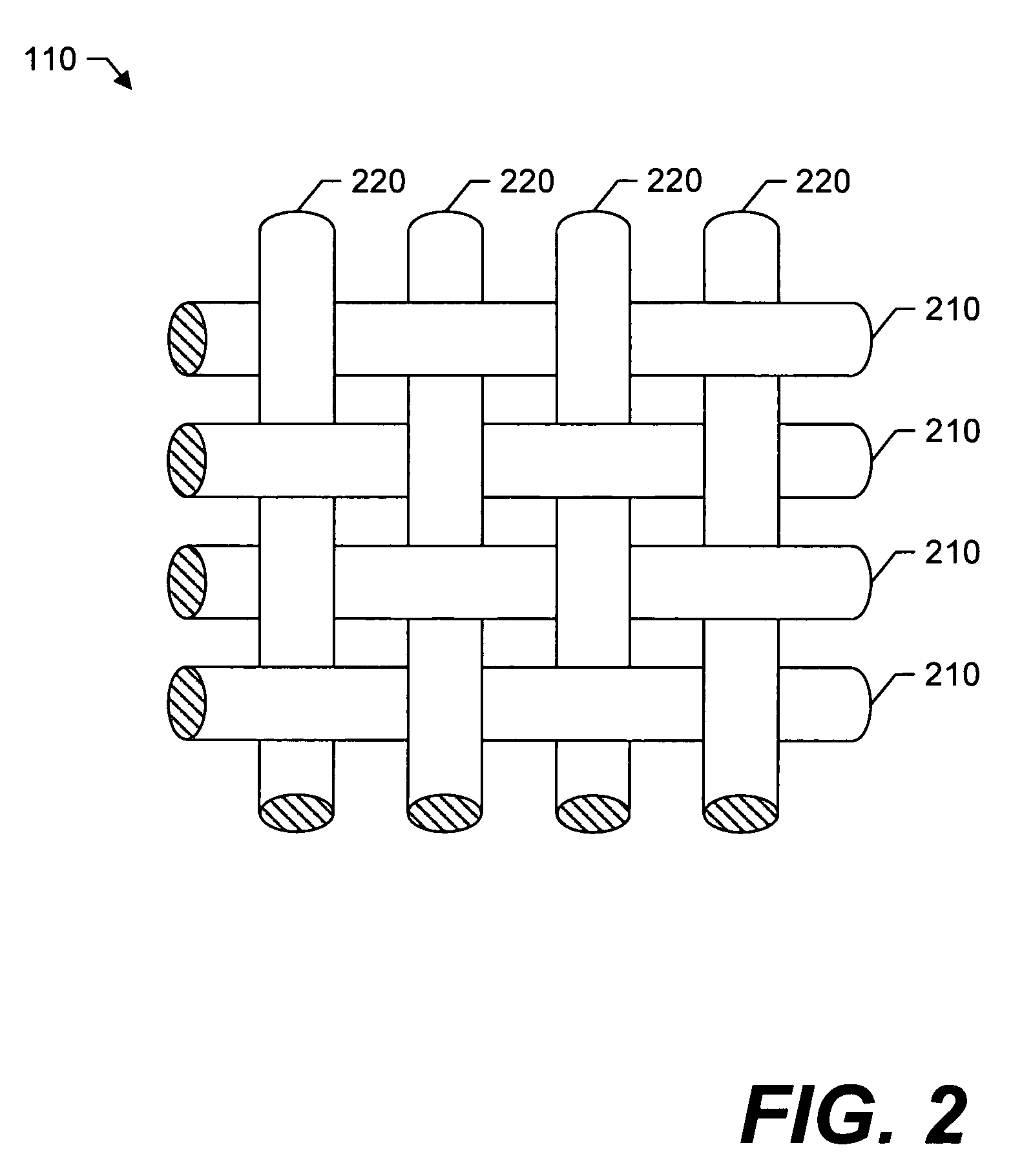
Polyester woven fabric sheeting
InactiveUS20070014967A1Desirable breaking strengthGood hygroscopicitySynthetic resin layered productsAbsorbent padsPolyesterFiber
A polyester woven sheeting material including a set of 100% polyester warp yarns and a set of 100% polyester weft yarns, wherein the warp and weft yarns are interlaced to form the sheeting material. The warp and weft yarns comprise of air-jet spun polyester fibers that wisk moisture away from an individual laying on the woven sheeting material and, therefore, provide a quick-drying, breathable woven sheeting material which simulates the absorbency characteristics of cotton yarns. The set of polyester warp yarns and the set of polyester weft yarns may be interlaced to form a ground fabric, where a set of polyester pile yarns may then be interlaced with the ground fabric so that the pile yarns extend outwardly (e.g., forming a plurality of loops) on the front side, back side, or both sides of the ground fabric.
Owner:1888 MILLS
Implantable infusion device with optimized peristaltic pump motor drive
InactiveUS7122026B2Maximum service lifeAvoid wastingPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesPeristaltic pumpPulse parameter
A medical device known as an implantable therapeutic substance delivery device is configured for implanting in humans to deliver a therapeutic substance such as pharmaceutical compositions, genetic materials, and biologics to treat a variety of medical conditions such as pain, spasticity, cancer, and many other conditions. The infusion device incorporates a stepper motor that controls the infusion flow rate during the service life of the device. The stepper motor is controlled by continuously varying electrical pulse parameters based on the continuously decreasing power source voltage during the service life of the substance delivery device. In particular the stepper motor electrical pulse parameters, especially duty cycle, are selected to efficiently compensate for decreasing battery voltage thereby optimizing the motor performance while maximizing the power source service life. The infusion device has a housing, a power source, a therapeutic substance reservoir, a therapeutic substance pump, and electronics. Many embodiments of the therapeutic substance delivery device with optimized pump motor drive and its methods of operation are possible.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Polyester woven fabric
InactiveUS20080057813A1Good hygroscopicityDesirable breaking strengthBed linenAbsorbent padsPolyesterFiber
A polyester garment material including a set of 100% polyester warp yarns and a set of 100% polyester weft yarns, wherein the warp and weft yarns are interlaced to form the garment material. The warp and weft yarns comprise of air-jet spun polyester fibers that wisk moisture away from an individual wearing the garment material and, therefore, provide a quick-drying, breathable garment material that simulates the absorbency characteristics of cotton yarns. The set of polyester warp yarns and the set of polyester weft yarns may be interlaced to form a ground fabric, where a set of polyester pile yarns may then be interlaced with the ground fabric so that the pile yarns extend outwardly (e.g., forming a plurality of loops) on the front side, back side, or both sides of the ground fabric.
Owner:1888 MILLS
Bolt carrier and bolt for gas operated firearms
ActiveUS8844424B2Improve safety and reliabilityReduce manufacturing costSafety arrangementCartridge extractorsSpray nozzleEngineering
An improved bolt and bolt carrier with integral gas key having an extension nozzle threadedly secured and pinned to the gas key for use with a direct gas operated firearm is provided. The extension nozzle is designed to receive a portion of the host firearms gas operating system. The firing pin retaining pin is oriented so as to expose its widest profile to the firing pins annular flange, increasing its service life. The bolt has a plurality of lugs extending from its forward end and an extractor recess. The extractor recess is constructed to accommodate an enlarged extractor claw while not undercutting the bolt lugs adjacent thereto. The extractor engages approximately 57% more of a seated ammunition cartridges rim as compared to some prior art AR15 / M16 type extractors used with automatic firearms chambered in 6.8 SPC. The result is an improved bolt and bolt carrier which provides for increased operational reliability.
Owner:LWRC INTERNATIONAL
Bolt carrier and bolt for gas operated firearms
ActiveUS20160116240A1Improve safety and reliabilityReduce manufacturing costCartridge extractorsBreech mechanismsSpray nozzleRetaining Pin
An improved bolt and bolt carrier with integral gas key having an extension nozzle threadedly secured and pinned to the gas key for use with a direct gas operated firearm is provided. The extension nozzle is designed to receive a portion of the host firearms gas operating system. The firing pin retaining pin is oriented so as to expose its widest profile to the firing pins annular flange, increasing its service life. The bolt has a plurality of lugs extending from its forward end and an extractor recess. The extractor recess is constructed to accommodate an enlarged extractor claw while not undercutting the bolt lugs adjacent thereto. The extractor engages approximately 57% more of a seated ammunition cartridges rim as compared to some prior art AR15 / M16 type extractors used with automatic firearms chambered in 6.8SPC. The result is an improved bolt and bolt carrier which provides for increased operational reliability.
Owner:LWRC INTERNATIONAL
Bolt carrier and bolt for gas operated firearms
ActiveUS8950312B2Improve safety and reliabilityReduce manufacturing costCartridge extractorsFiring/trigger mechanismsEngineeringScrew thread
An improved bolt and bolt carrier with integral gas key having an extension nozzle threadedly secured and pinned to the gas key for use with a direct gas operated firearm is provided. The extension nozzle is designed to receive a portion of the host firearm's gas operating system. The firing pin retaining pin is oriented so as to expose its widest profile to the firing pin's annular flange, increasing its service life. The bolt has a plurality of lugs extending from its forward end. The extractor recess is constructed so that the face of the bolt is round and the adjacent lugs fully supported. The extractor engages approximately 17% more of a seated ammunition cartridge's rim as compared to the prior art AR15 / M16 extractor. The result is an improved bolt and bolt carrier which provides for increased operational reliability.
Owner:LWRC INTERNATIONAL
Process and apparatus for the production of collimated UV rays for photolithographic transfer
InactiveUS20090244510A1Shorten the optical lengthSpeed up the processPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingPhysicsRadiation
The present invention provides an improved process and an apparatus for producing collimated UV radiation for exposing printed circuit boards. The process consists in shortening the optical length of the downstream optics by dividing the UV radiation over many radiation sources, and in distributing the UV radiation uniformly on the substrate by using a scanning slide.
Owner:RADOVE
Low-cost minimal-loss flywheel battery
InactiveUS8242649B2Axial force stabilityLow-cost minimal-lossRolling contact bearingsControllers with pulse-train output signalBall bearingDc current
A low-cost minimal-loss zero-maintenance flywheel battery, to store electric power from a DC power source by conversion to kinetic energy, and regenerate electric power as needed. Its vertical spin-axis rotor assembly is supported axially by repelling annular permanent magnets, and is centered by ceramic ball bearings which have axial preload that prevents vibration and augments axial rotor support. A regenerative multi-pole permanent-magnet motor, controlled by its 2-phase stator current, and connected by power and signal conductors to power interface electronics, is integrated within the flywheel assembly, in a vacuum enclosure supported by a self-leveling structure. Sinusoidal 2-phase stator currents are controlled by high-frequency pulse-width-modulated H-bridge power electronics that draw and regenerate controlled DC current with minimal ripple, responsive to respective 2-phase rotation angle sensors, the DC power voltage, and other settings. The electronics includes logic and over-voltage protection to prevent otherwise possible damaging current and voltage.
Owner:FRADELLA RICHARD B
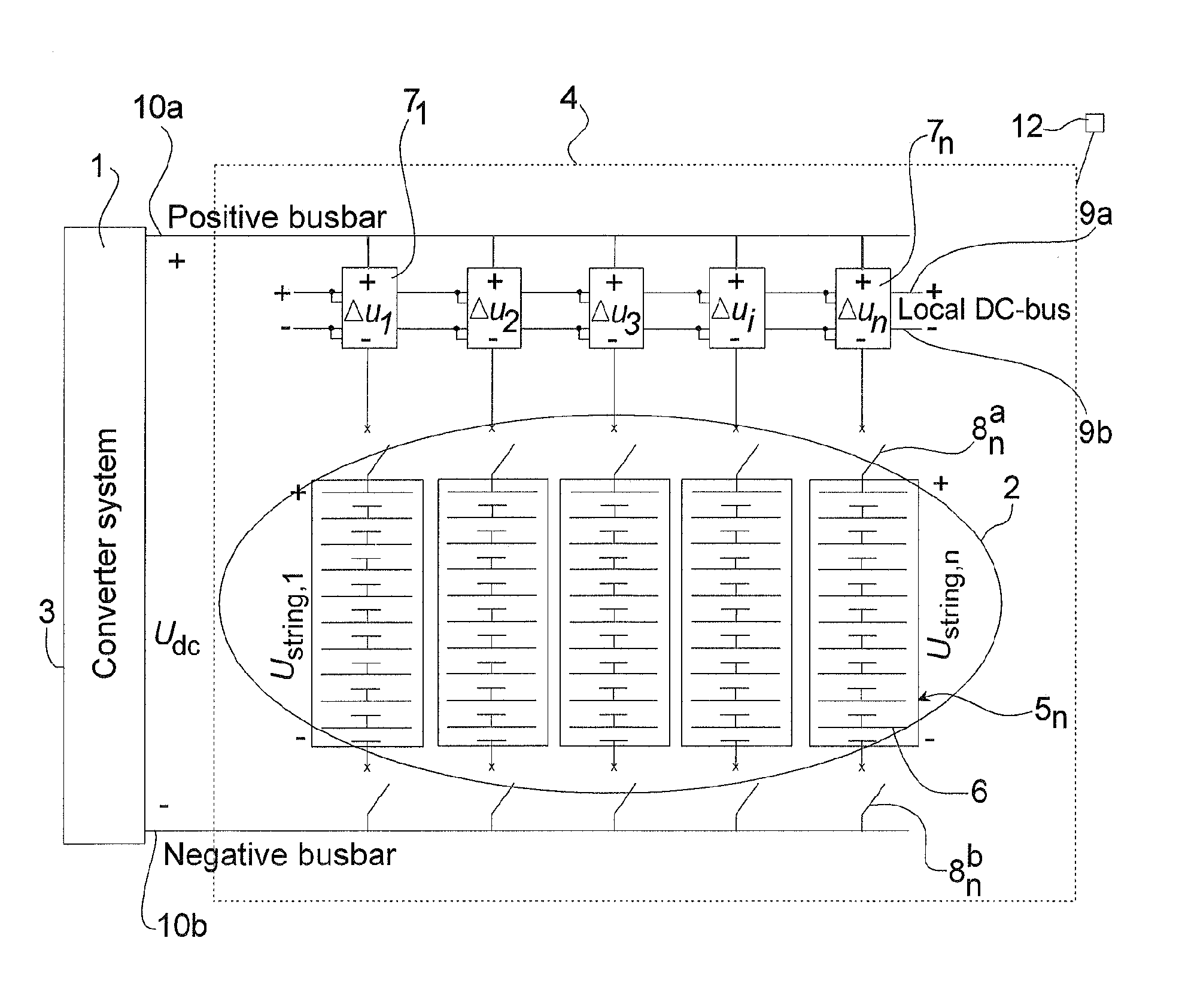
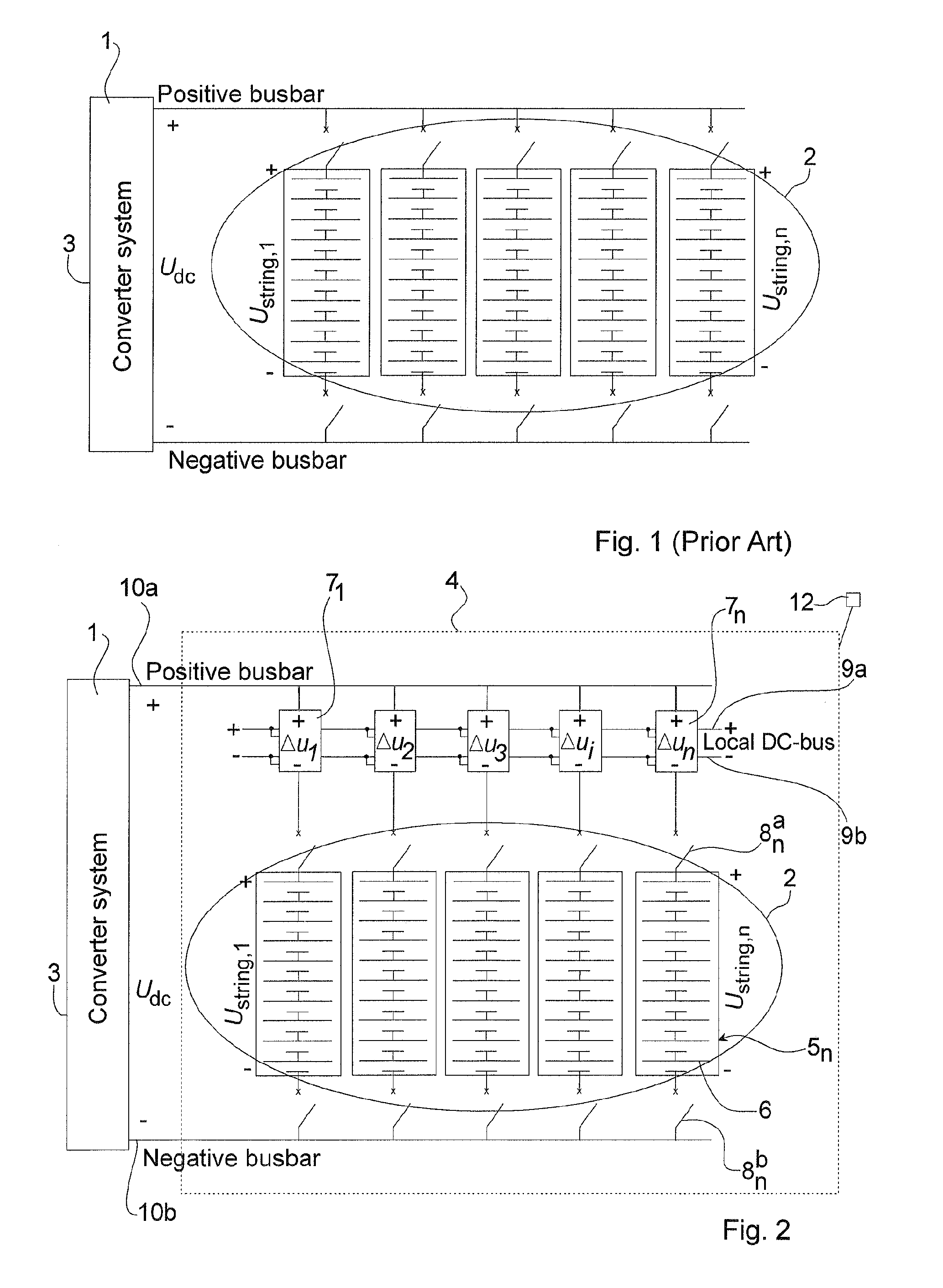
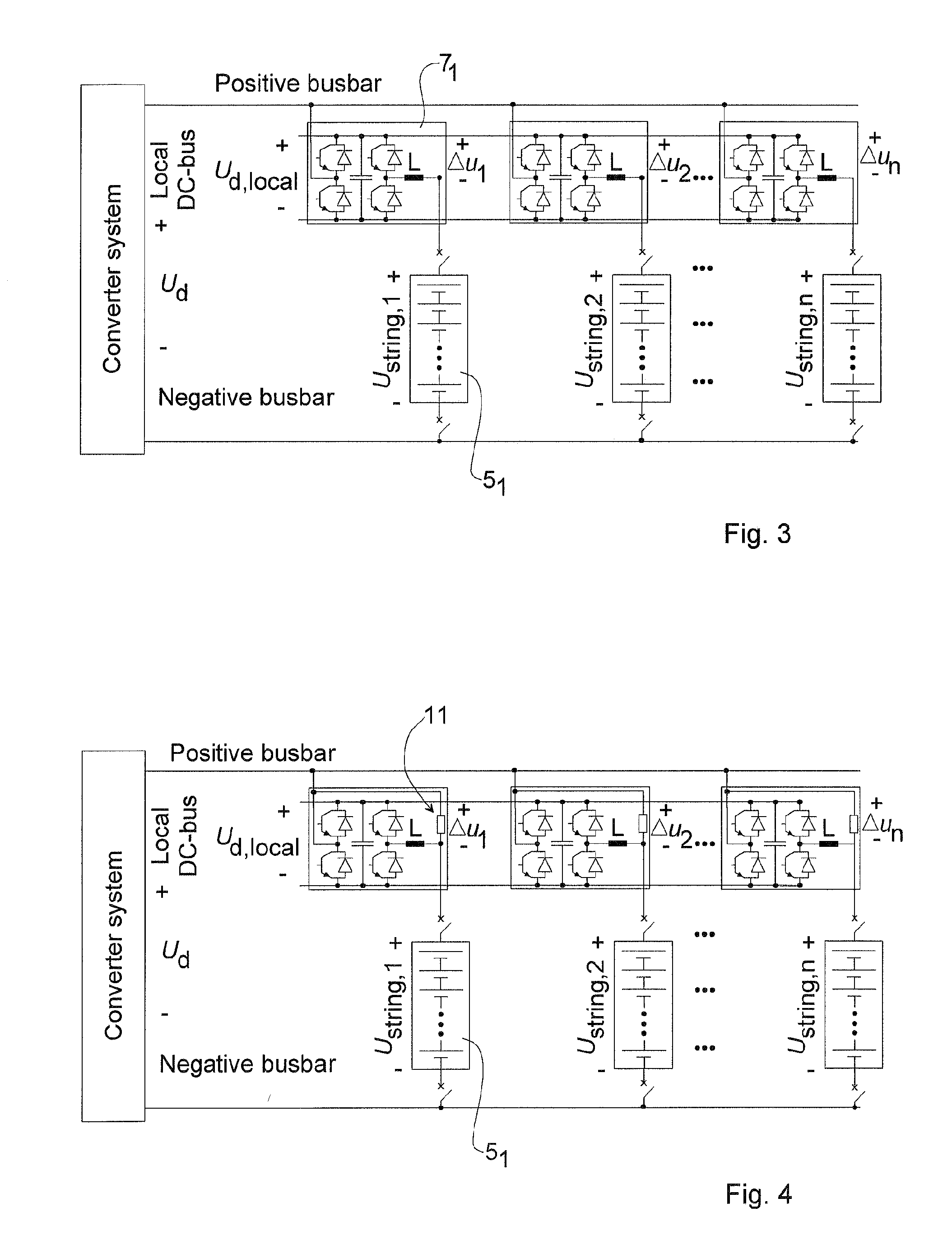
Battery Energy Source Arrangement And Voltage Source Converter System
ActiveUS20110089763A1Improved battery energy source arrangementExtended service lifeDc network circuit arrangementsFlexible AC transmissionElectrical batteryPower grid
The invention relates to power networks, and in particular to a battery energy source arrangement and voltage source converter system in such network. The battery energy source arrangement includes battery energy storage, having one or more parallel-connected battery strings and a mechanism for connecting a voltage of the battery strings to a load. The battery energy source arrangement further includes battery string voltage adapter devices connected in series with respective ones of the one or more battery strings wherein the battery string voltage adapter devices are designed to handle only a fraction of the voltage handled by the battery strings.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Multi-target coordinated operation optimization method of wind and photovoltaic storage electricity generation units
InactiveCN104022534AMaximum service lifeImprove operational efficiencyForecastingSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind drivenPower balancing
The invention discloses a multi-target coordinated operation optimization method of wind and photovoltaic storage electricity generation units and relates to the technical field of wind and solar storage electricity generation control. The method comprises the steps of determining output power models of the electricity generation units, wherein the output power models comprise the output power models of wind driven generators, the output power models of photovoltaic generators and the output power models of energy storage batteries; building multi-objective functions of the wind and photovoltaic storage electricity generation units, wherein the multi-objective functions comprise the electricity-generation-unit total-cost minimum objective functions and the renewable-energy-source loss-ratio minimum objective functions; setting constraint conditions of the multi-objective functions, wherein the constraint conditions comprise the power balance constraint conditions, the generator output constraint conditions and the energy-storage-battery capacity constraint conditions; solving the multi-objective functions through an improved multi-target universal gravitation search algorithm to obtain an active output value of each period of each electricity generation unit. On the basis that renewable energy sources are fully used, the longest service life of each storage battery is achieved, and therefore overall operating efficiency of the wind and photovoltaic storage electricity generation units is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +2
Polymer pelletizing indexing system
InactiveUS6217802B1Maximum service lifeAcceptable knife sharpnessMouldsConfectioneryEngineeringPolymer
A polymer pelletizing apparatus includes a device for automatically and electronically indexing (advancing) a set of pelletizer knives by a predetermined distance upon the expiration of a predetermined time period. This advancement is continued for the useful life of the pelletizer knives and is called the advancement cycle. The predetermined distance and predetermined time period are entered into a PLC. The PLC is connected to an external advancing device such that when the PLC determines that the predetermined time period has expired, the PLC causes the external advancing device to index or advance the pelletizer knives by a predetermined distance. This advancement cycle provides consistent wear of the pelletizer knives and accurately provides an estimate of the need for a knife change.
Owner:PELLETIZER KNIVES
Method for controlling the hybrid drive of a motor vehicle and control system
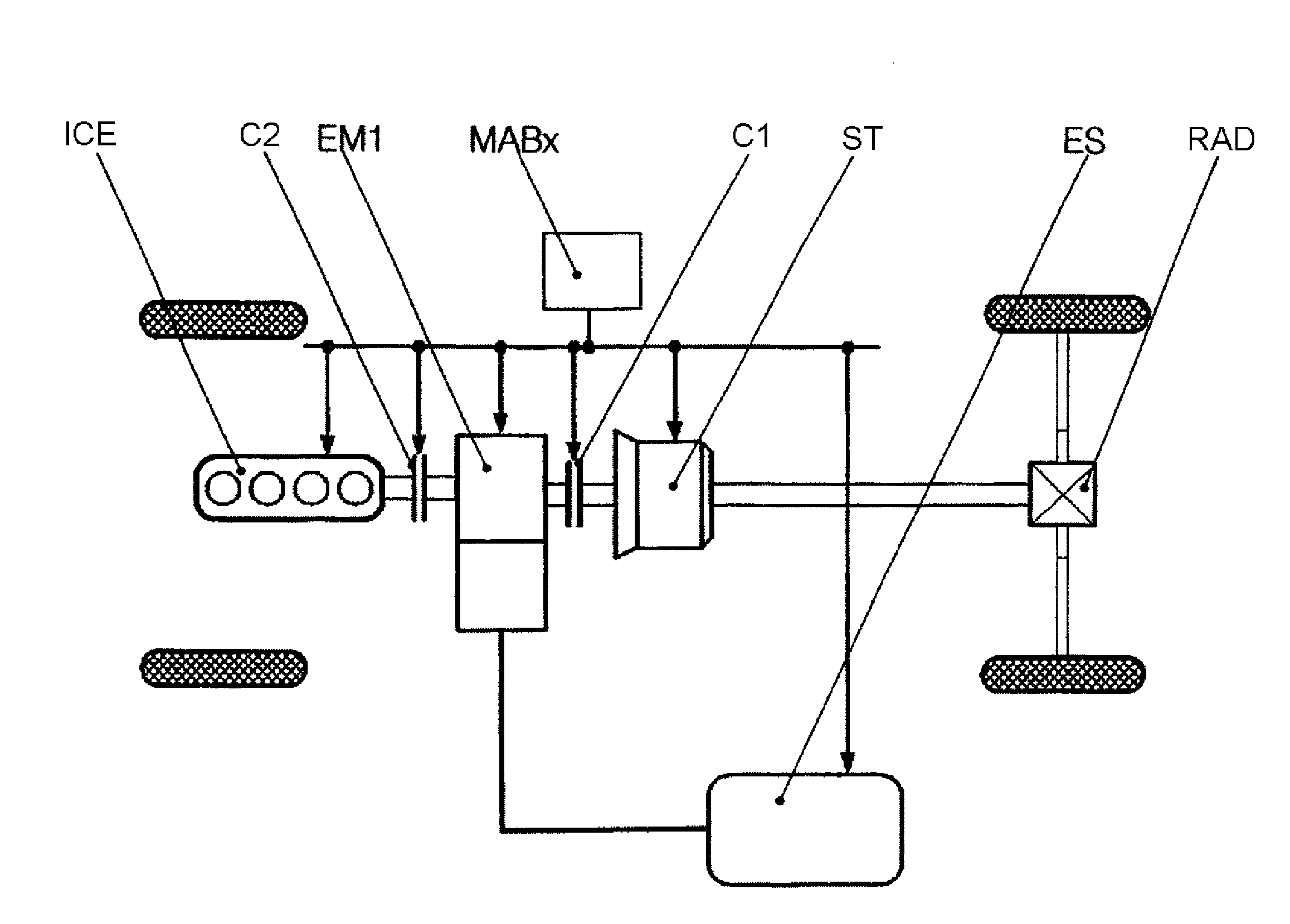
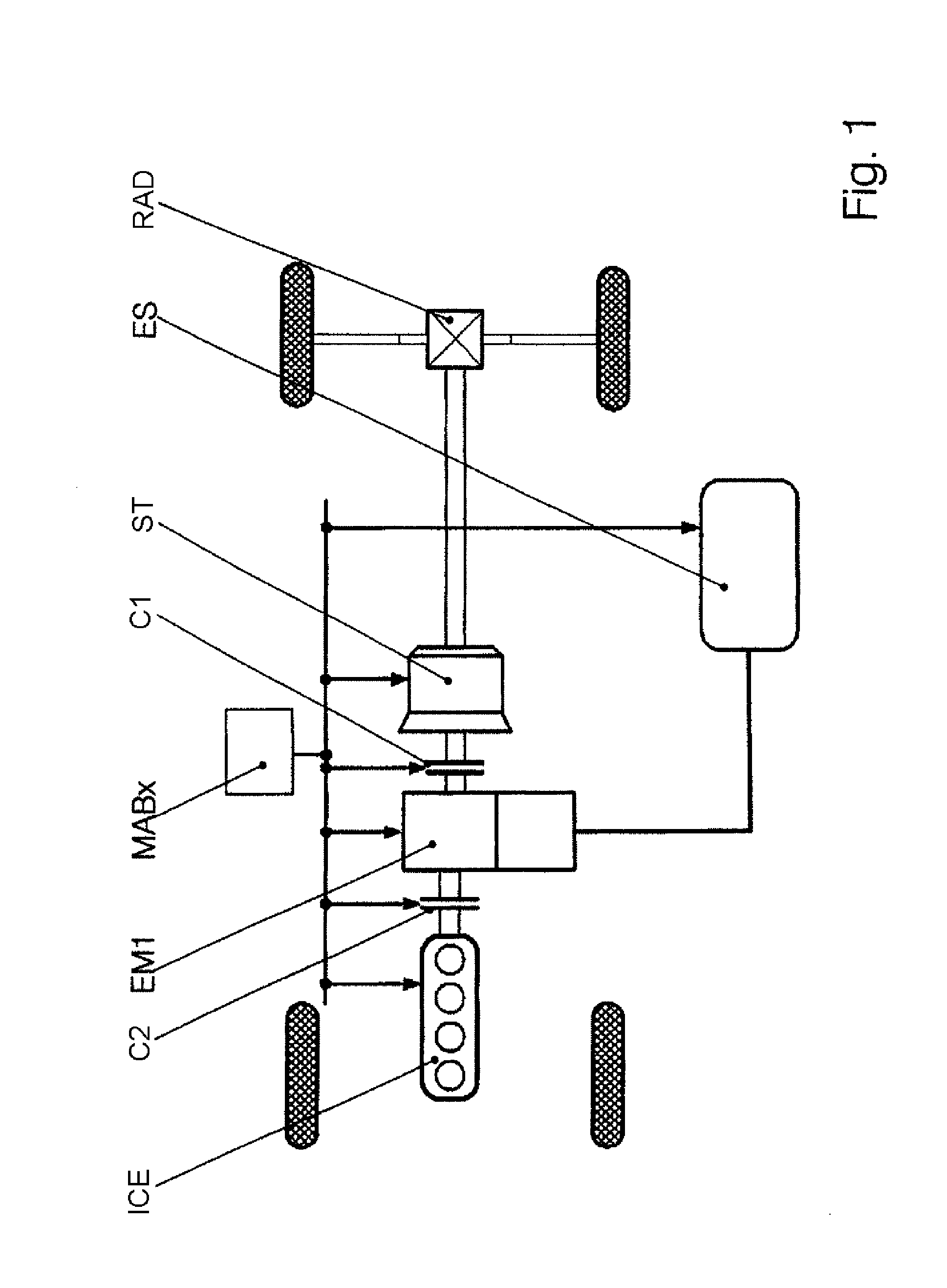
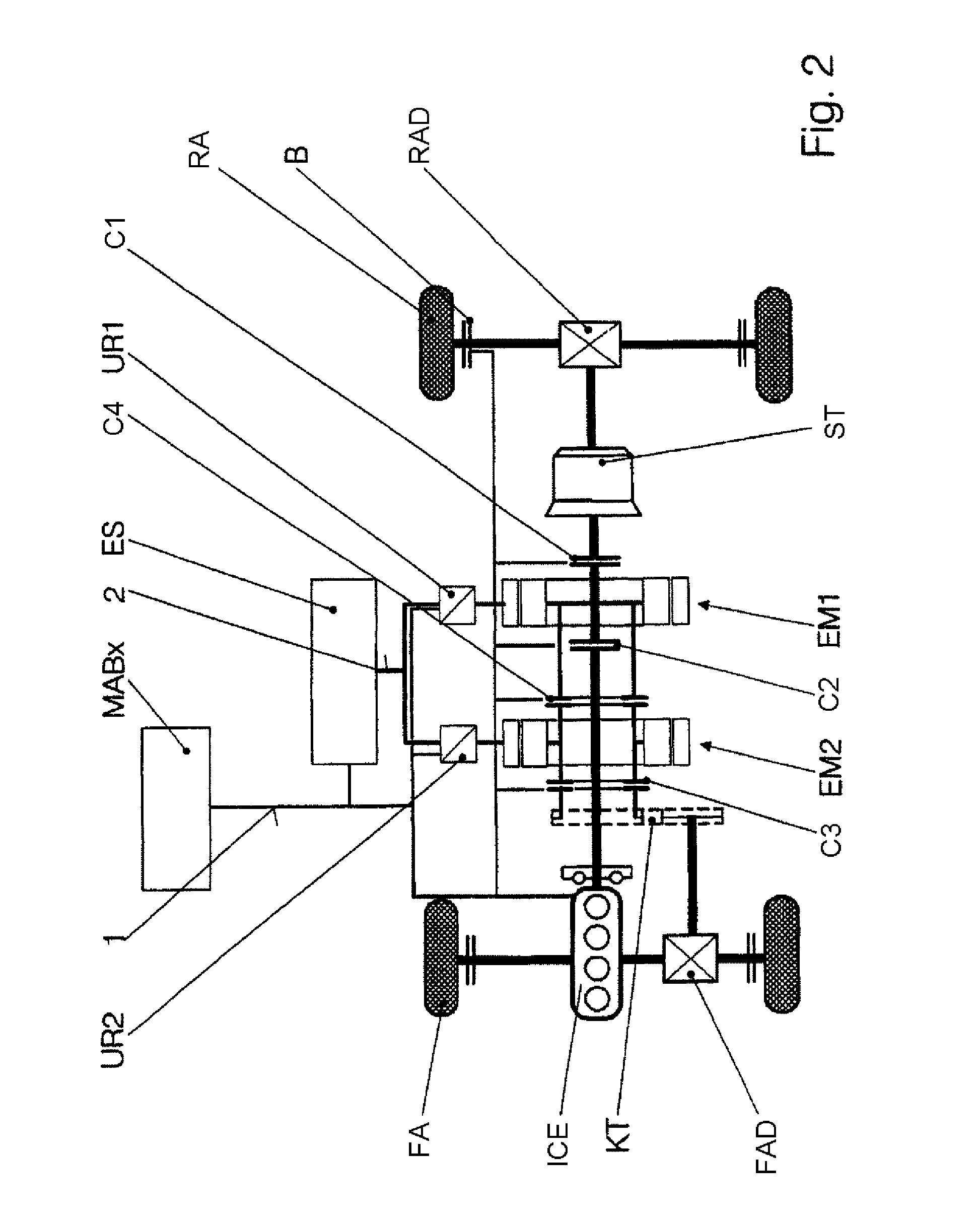
ActiveUS8249768B2Flexible controlEasy to adaptValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesOperating pointControl system
A method and an apparatus for controlling the hybrid drive of a motor vehicle having the following components: internal combustion engine (VKM), manual transmission (SG), at least one electrical machine (Emi), at least one clutch (Kj) and an energy storage device (ES), and at least one driven axle (HA; VA) are intended to provide maximum efficiency and service life of the components. To this end, a decision is made about which operating modes (AMK) are possible on the basis of a driver input (FW) and operating state, a division is made about which gears (Gj) are available for the possible operating modes (AMK), so that a larger number of modes (AMGK) are available for selection, operating points which correspond to the driver input are determined for all these modes (AMGK), taking into account the operating state and system state (SZA), the modes (AMGK) are assessed and the mode (AMGK*) which is assessed as being most expedient is selected.
Owner:MAGNA STEYR FAHRZEUGTECHN
Polyester woven fabric
ActiveUS20100015874A1Good hygroscopicityDesirable breaking strengthLayered productsBed linenPolyesterFiber
A polyester garment material including a set of 100% polyester warp yarns and a set of 100% polyester weft yarns, wherein the warp and weft yarns are interlaced to form the garment material. The warp and weft yarns comprise of air-jet spun polyester fibers that wisk moisture away from an individual wearing the garment material and, therefore, provide a quick-drying, breathable garment material that simulates the absorbency characteristics of cotton yarns. The set of polyester warp yarns and the set of polyester weft yarns may be interlaced to form a ground fabric, where a set of polyester pile yarns may then be interlaced with the ground fabric so that the pile yarns extend outwardly (e.g., forming a plurality of loops) on the front side, back side, or both sides of the ground fabric.
Owner:1888 MILLS
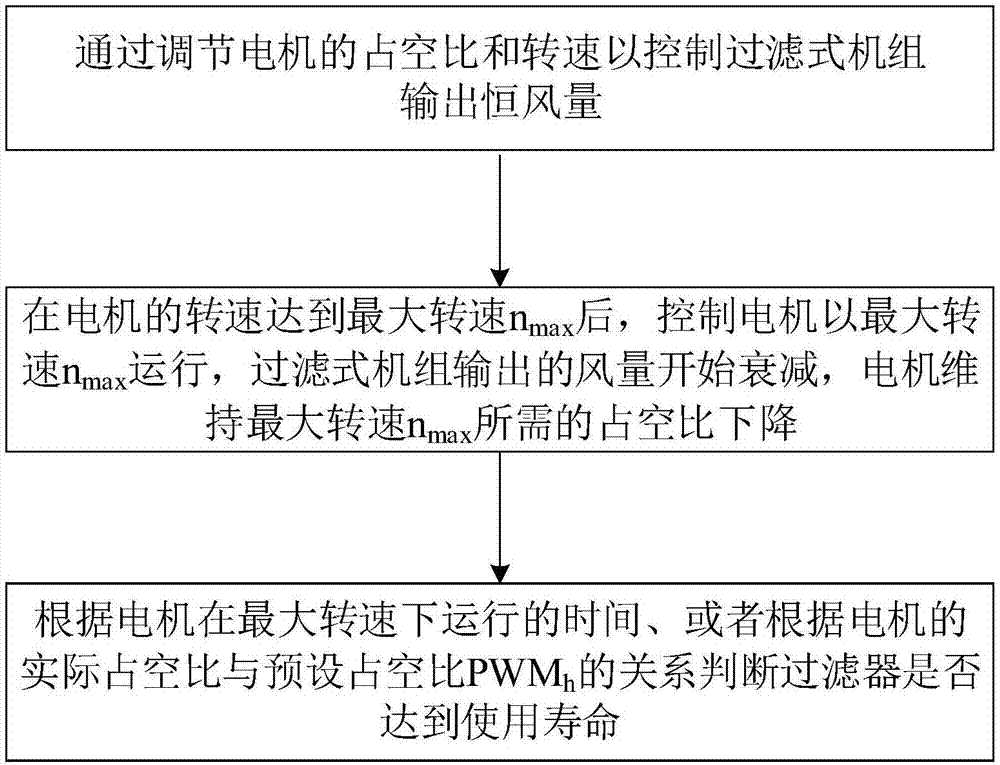
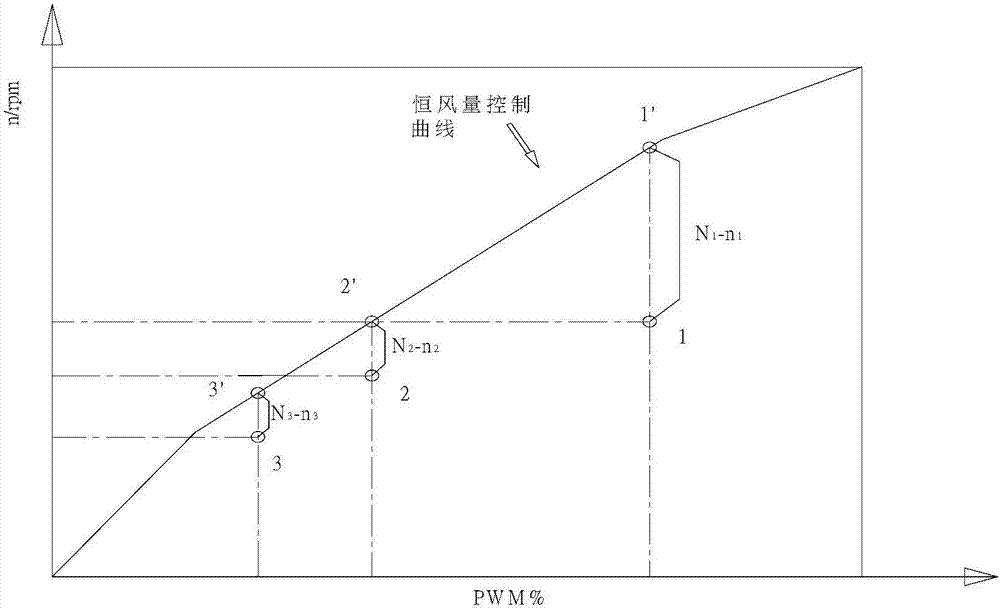
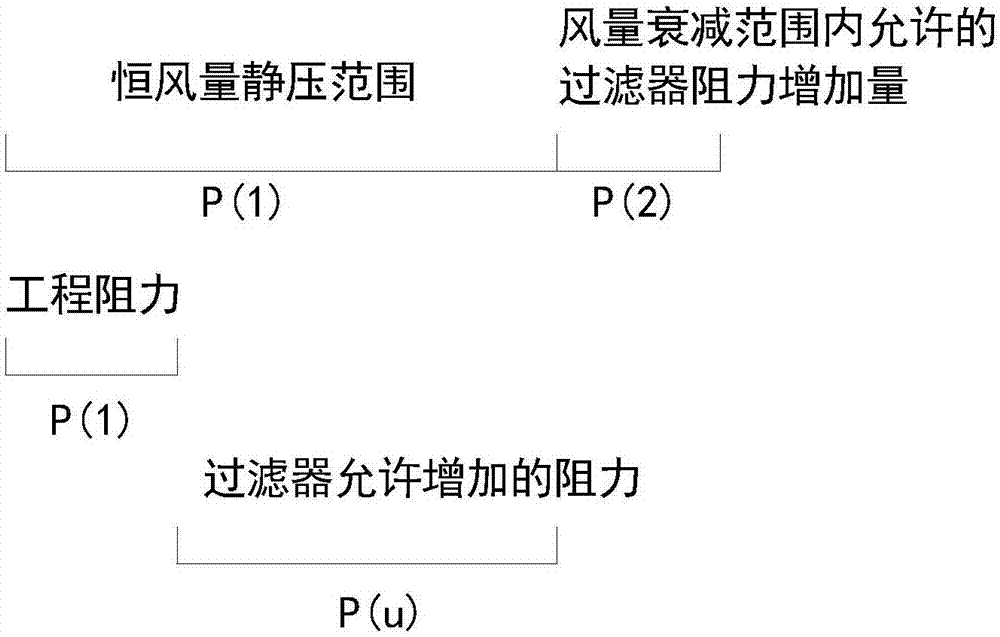
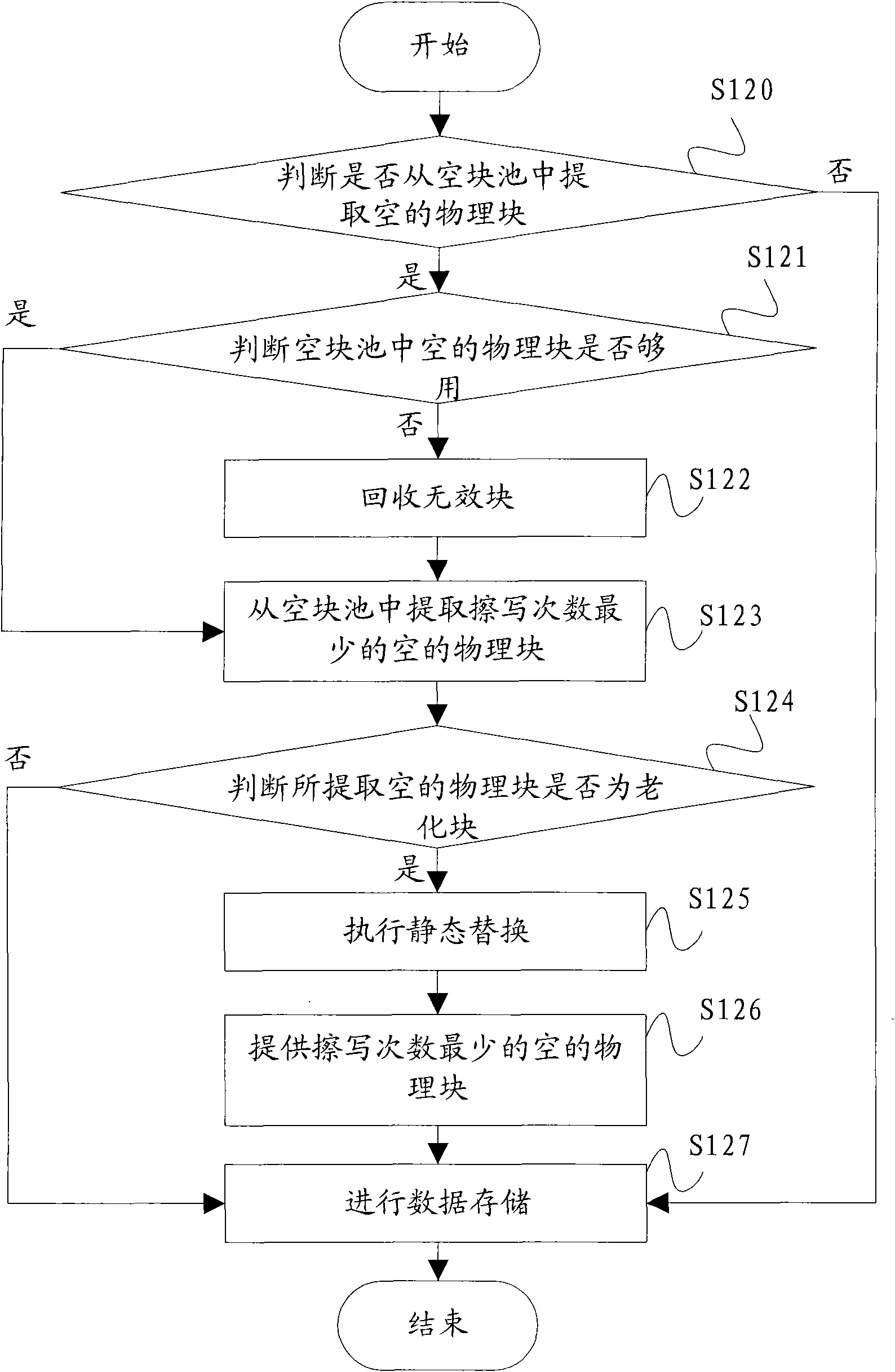
Service-life judging method for filter of filtration-type machine set and filtration-type machine set
InactiveCN107514740AMaximum service lifeAccurate service lifeSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusFiltrationControl theory
The invention discloses a service-life judging method for a filter of a filtration-type machine set and the filtration-type machine set. The filtration-type machine set comprises an air fan and the filter, and the air fan comprises a motor. The service-life judging method for the filter comprises the following steps that the output constant air amount of the filtration-type machine set is controlled by adjusting the duty ratio and the rotary speed of the motor; after the rotary speed of the motor reaches the maximum rotary speed nmax, the motor is controlled to operate at the maximum rotary speed nmax, the output air amount of the filtration-type machine set begins to be attenuated, the required duty ratio for the motor to maintain the maximum rotary speed nmax declines; and whether the filter reaches the service life or not is judged according to the operating time of the motor at the maximum rotary speed or according to the relation between the actual duty ratio and the preset duty ratio PWMh of the motor. By means of the service-life judging method for the filter of the filtration-type machine set and the filtration-type machine set, the service life of the filter can be accurately judged, the hardware cost does not need to be added, and it is guaranteed that the service life of the filter can reach the maximization.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Sprocket with wear limit indication
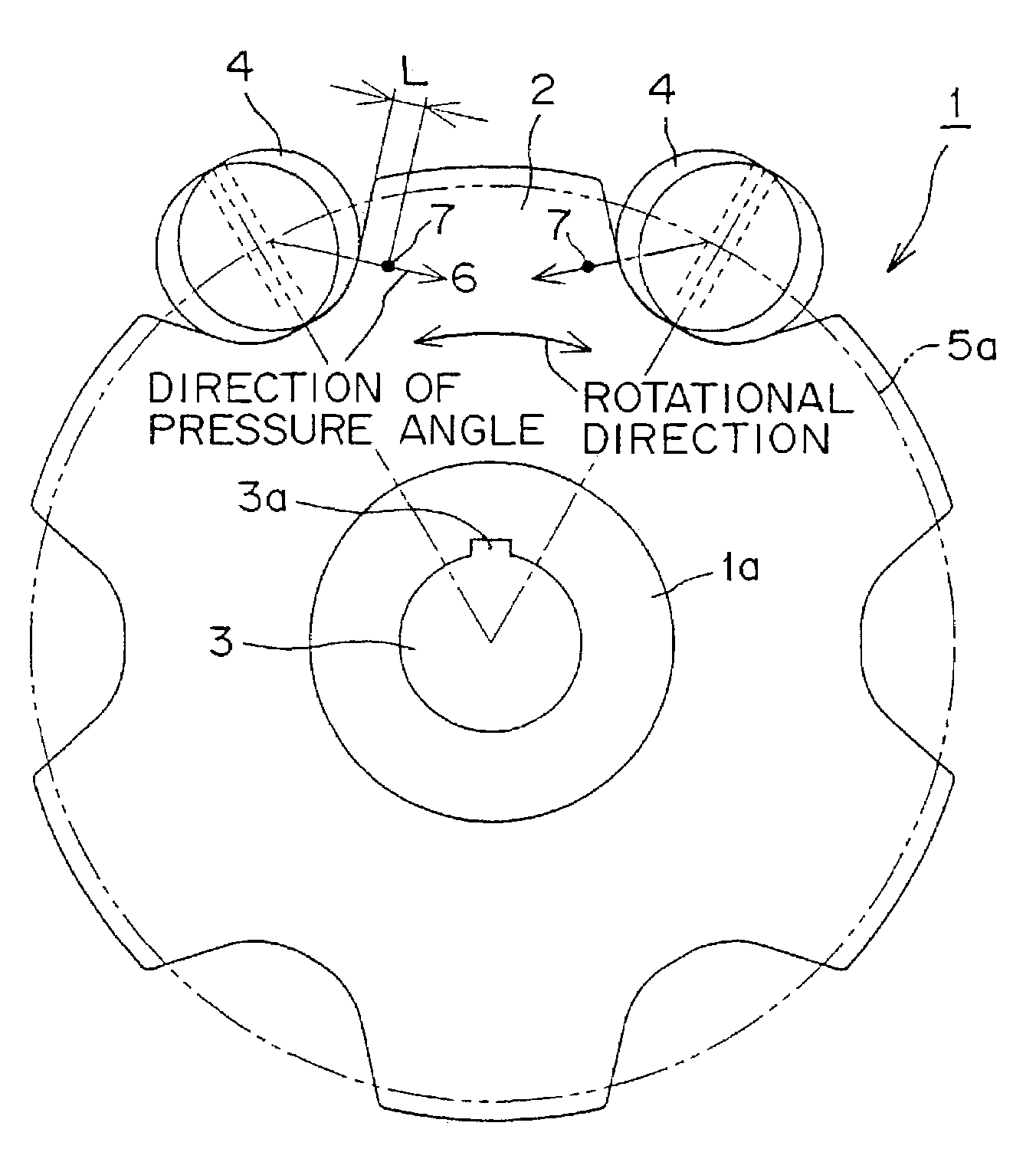
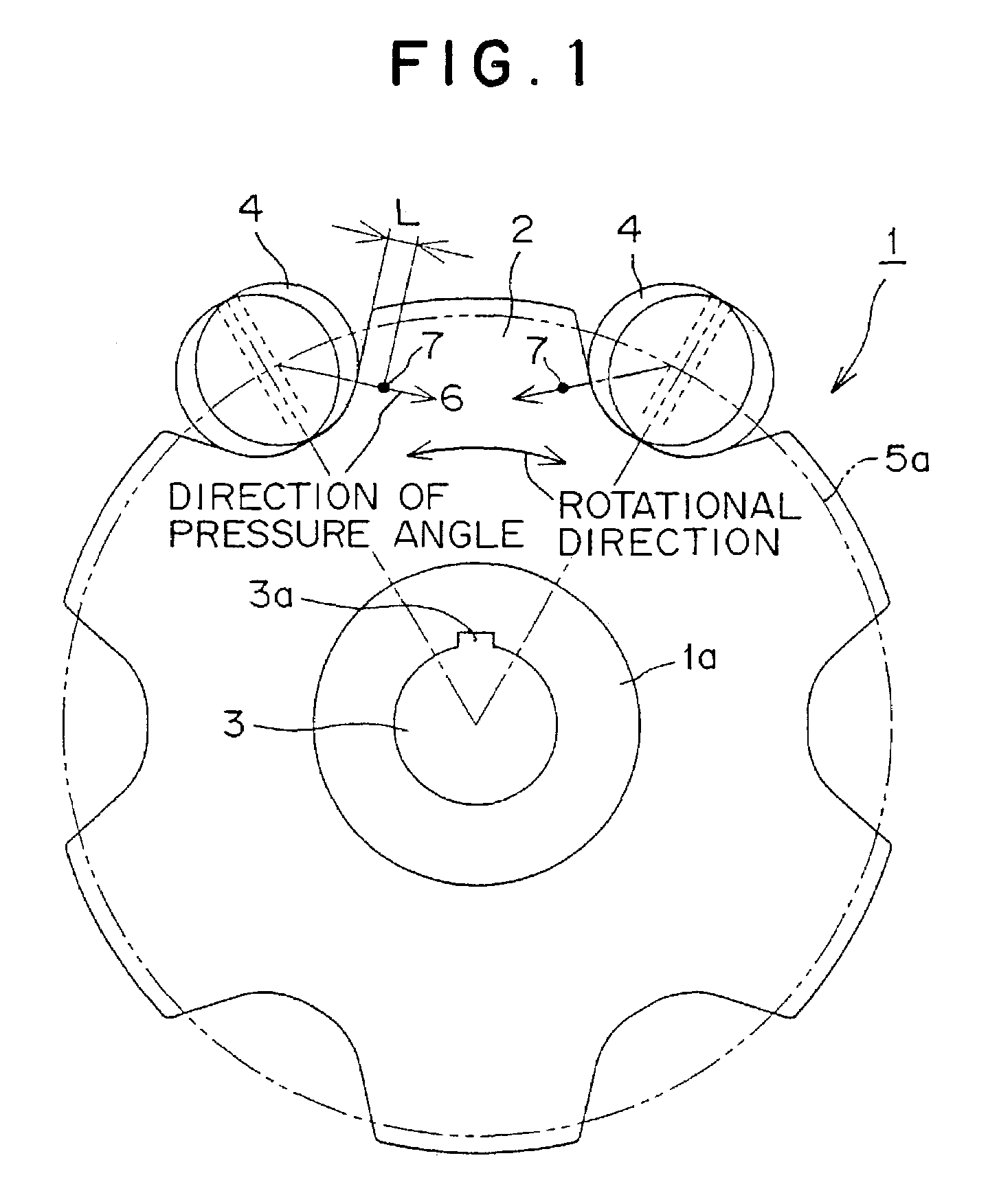
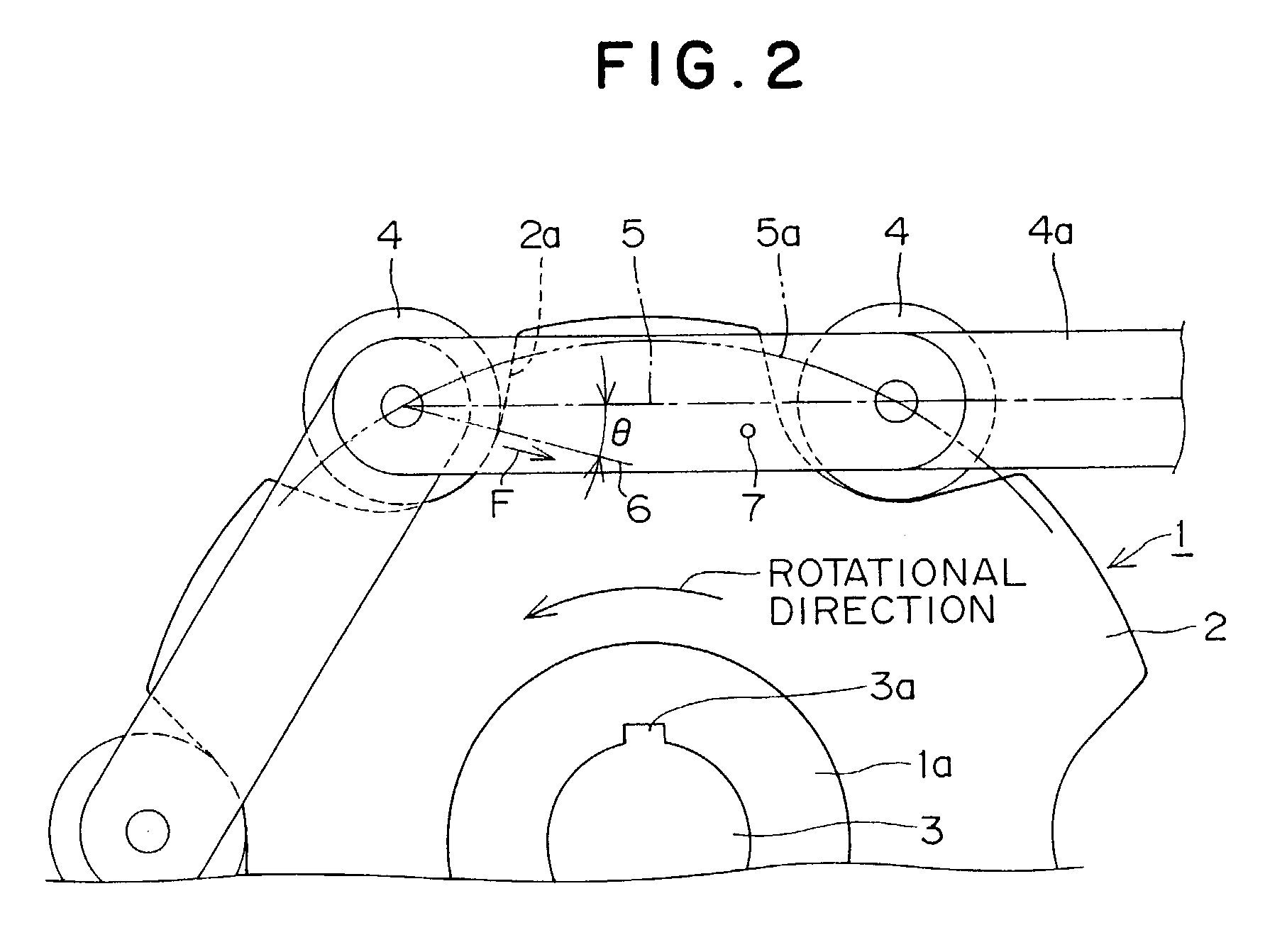
In a sprocket for use with a roller chain, a wear limit marker, having a different color from that of the base material of the sprocket, is provided on side surface of a sprocket tooth adjacent to a keyway. The wear limit marker is disposed on an imaginary line extending in the direction of the pressure angle, and is located in a hole or groove provided in a side surface of the sprocket tooth. The marker makes it possible to determine easily and reliably whether or not wear at the location at which wear of a sprocket tooth proceeds most rapidly is within a predetermined limit, and the location of the marker makes it possible to evaluate wear conditions even when the sprocket is installed in a machine.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO SPROCKET
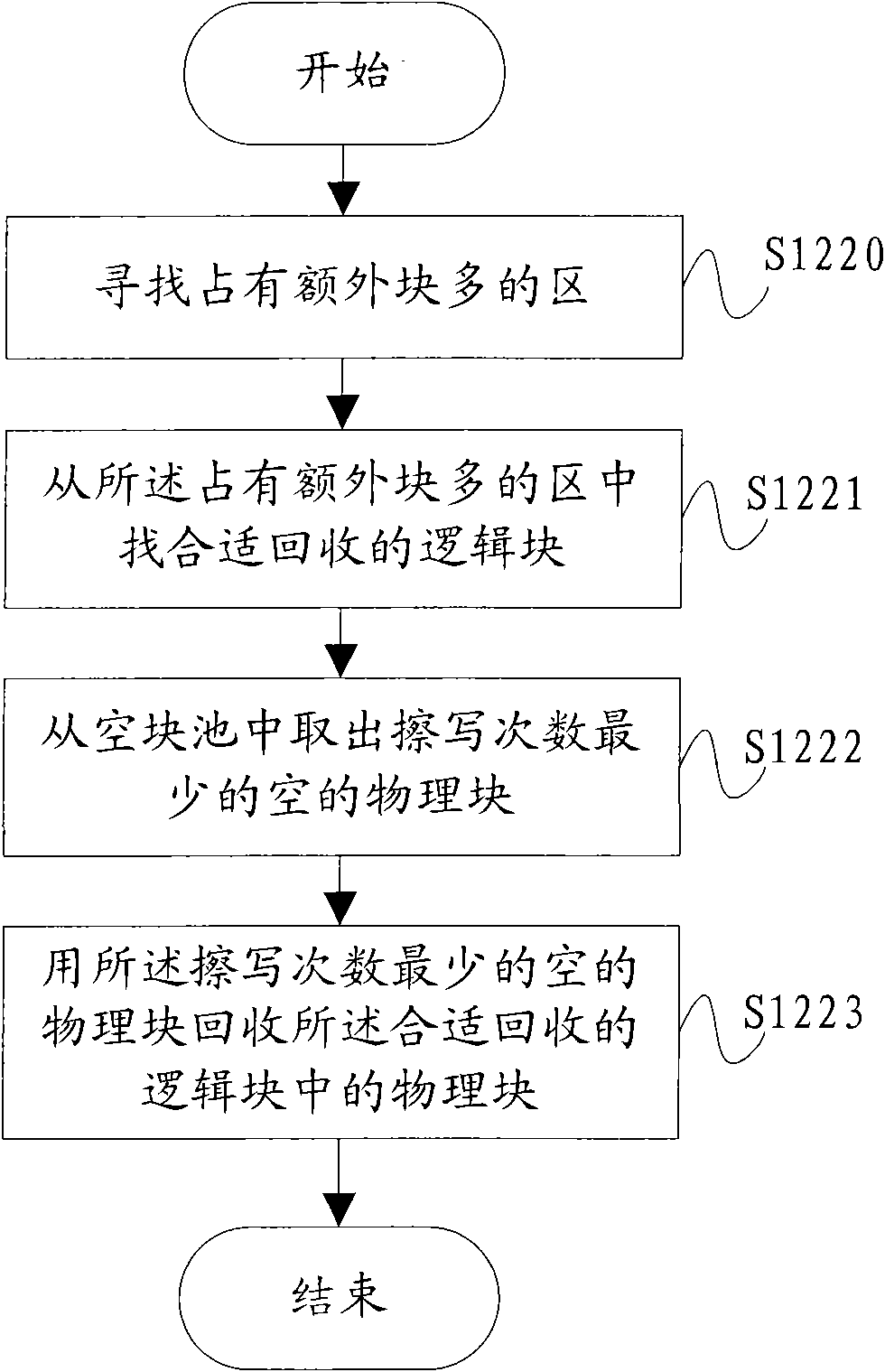
Method and device for protecting storage medium
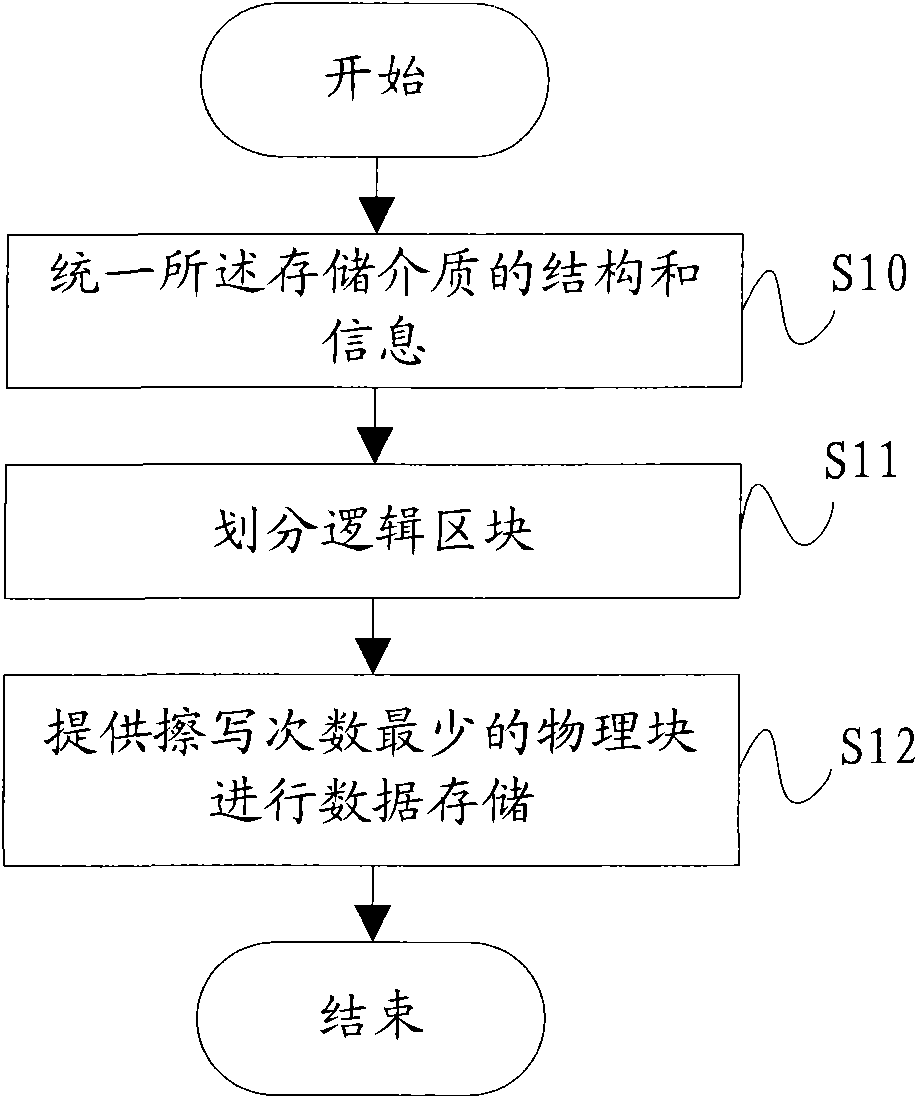
ActiveCN101571833AMaximum service lifeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareLogic block
Owner:NETAK TECH KO LTD
Apparatus and method for increasing well production
InactiveUS7909101B2Improve efficiencyEfficient drawingFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsHydrostatic pressureCheck valve
An apparatus and method for hydrocarbon recovery in a well for coal bed methane (CBM) recovery, tight sand gas extraction, and other gas extraction techniques provides for the formation of a hydrocarbon foam comprised of a fluid delivered into a downhole portion of the well and the hydrocarbon, maximizing water removal for gas recovery. The apparatus may include a check valve that feeds a nozzle to deliver or atomize the spray of fluid into the downhole portion of the well when the pressure applied to the fluid is sufficient to overcome a hydrostatic pressure in the downhole portion of the well and to deliver the fluid into the downhole portion of the well. The fluid is not sprayed directly into the formation, thereby protecting the formation from damage and recovering the fluid even in the case where water is not present. The capillary tube feeding the fluid to the check valve may be placed externally to the production tube to facilitate ease of cleaning and clearing of the production tube.
Owner:SIX DEGREES +2
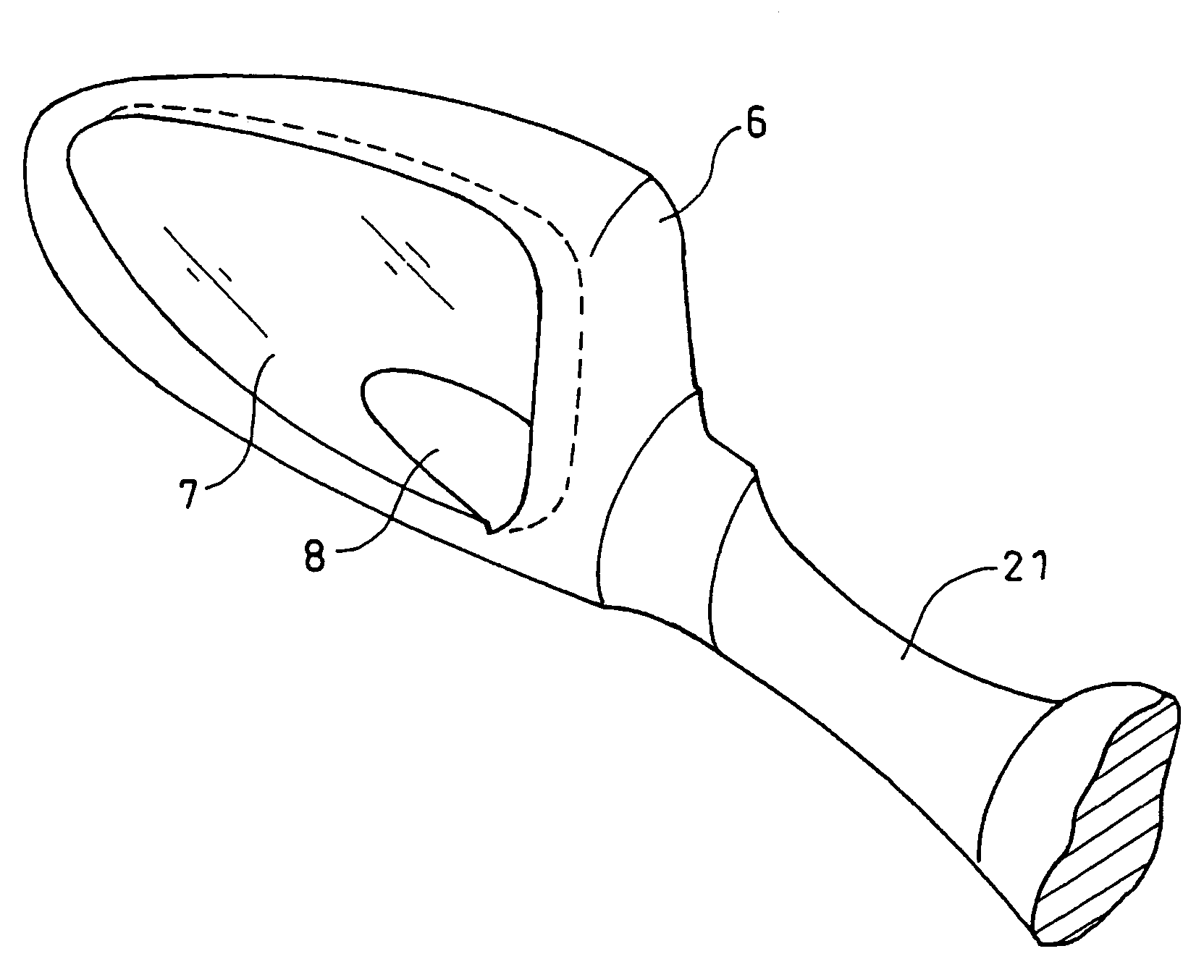
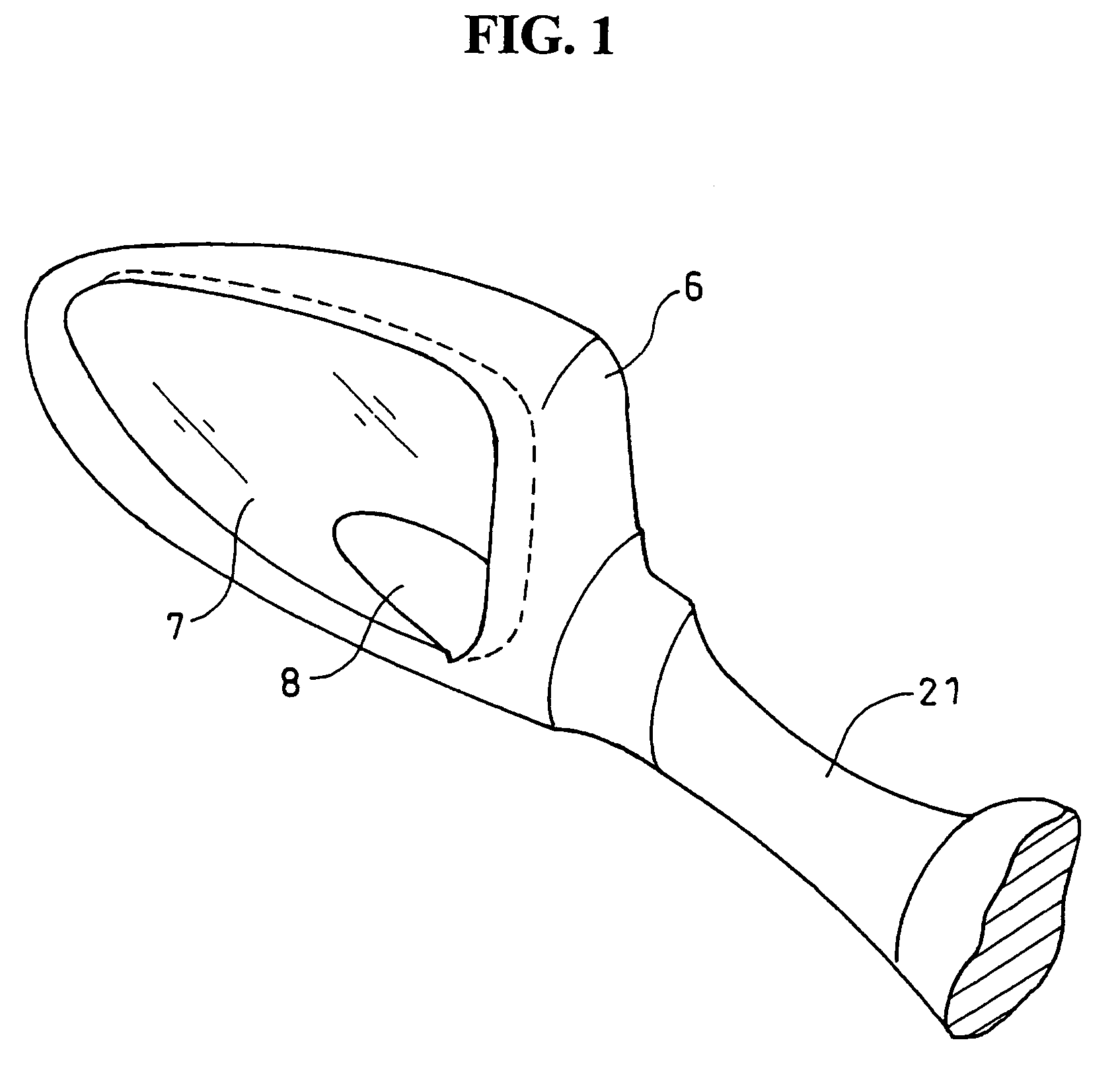
Rear view mirror assembly
InactiveUS7048420B2Extended service lifeIncrease awarenessLighting support devicesOptical signalWing mirrorLight-emitting diode
A turn indicator light and a position light are provided for a rear mirror assembly mounted in a vehicle body. A light body for the turn indicator light is a filament light bulb and a light body for the position light is a light emitting diode. Positioning the lights in the rear mirror permits the width of the vehicle to be more recognizable. The turn indicator light and the position light are provided with individual light bodies, respectively, for allowing independent service to be performed with respect to each light.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com