Patents
Literature
1132 results about "High-Throughput Screening Methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-throughput screening. High-throughput screening (HTS) is a method for scientific experimentation especially used in drug discovery and relevant to the fields of biology and chemistry.
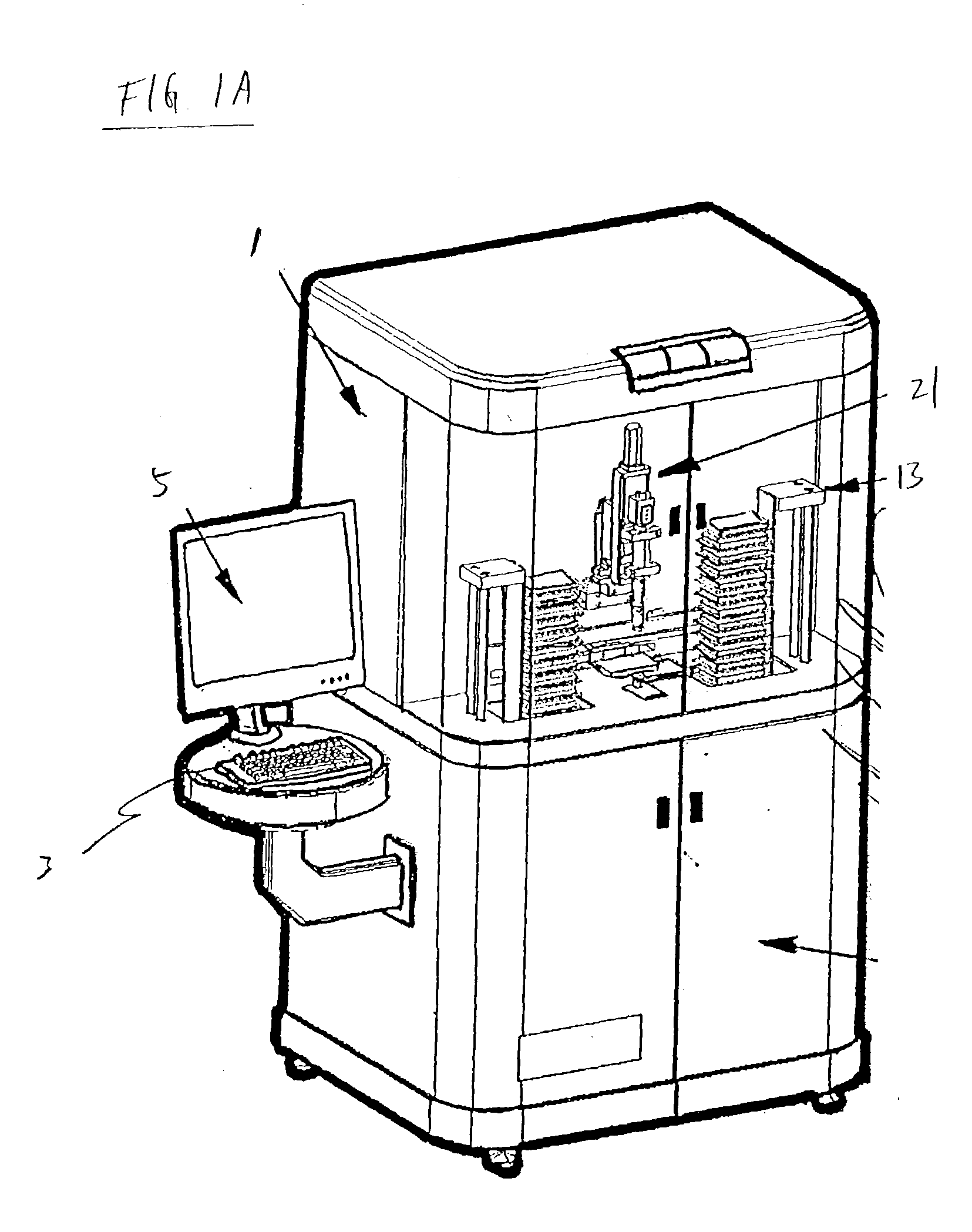
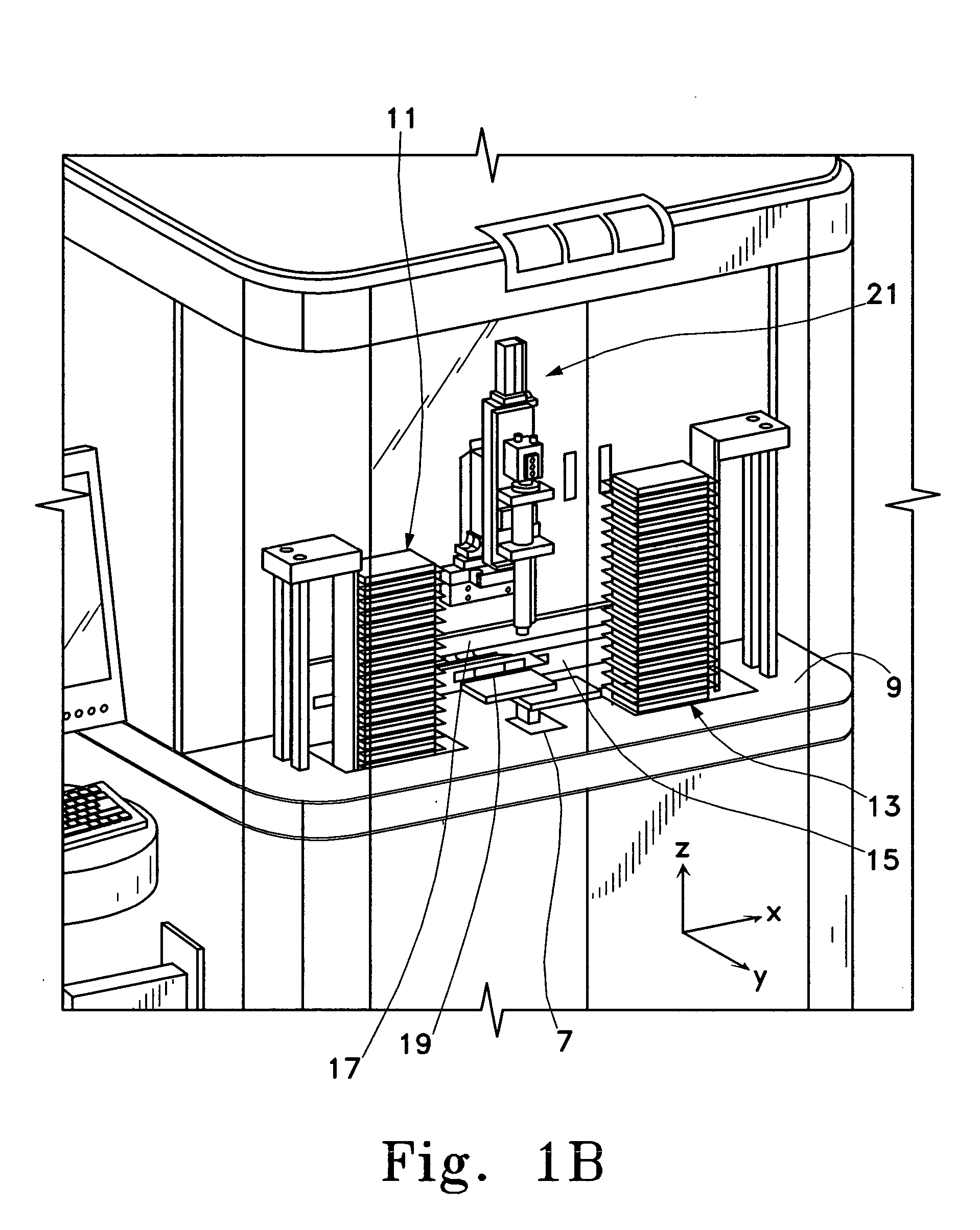
Miniaturized cell array methods and apparatus for cell-based screening
InactiveUS6103479AImprove throughputIncrease contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyTemporal informationHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
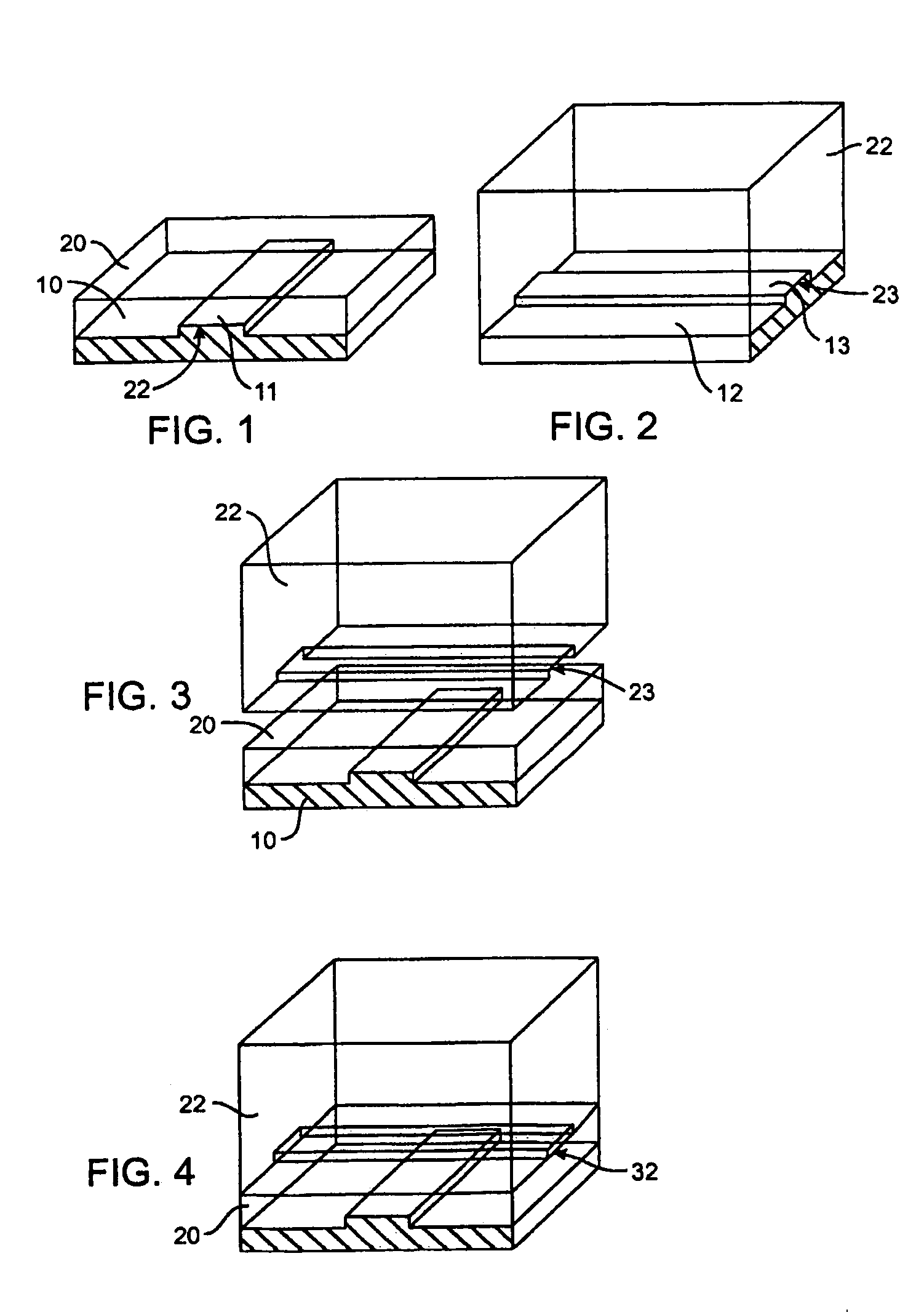
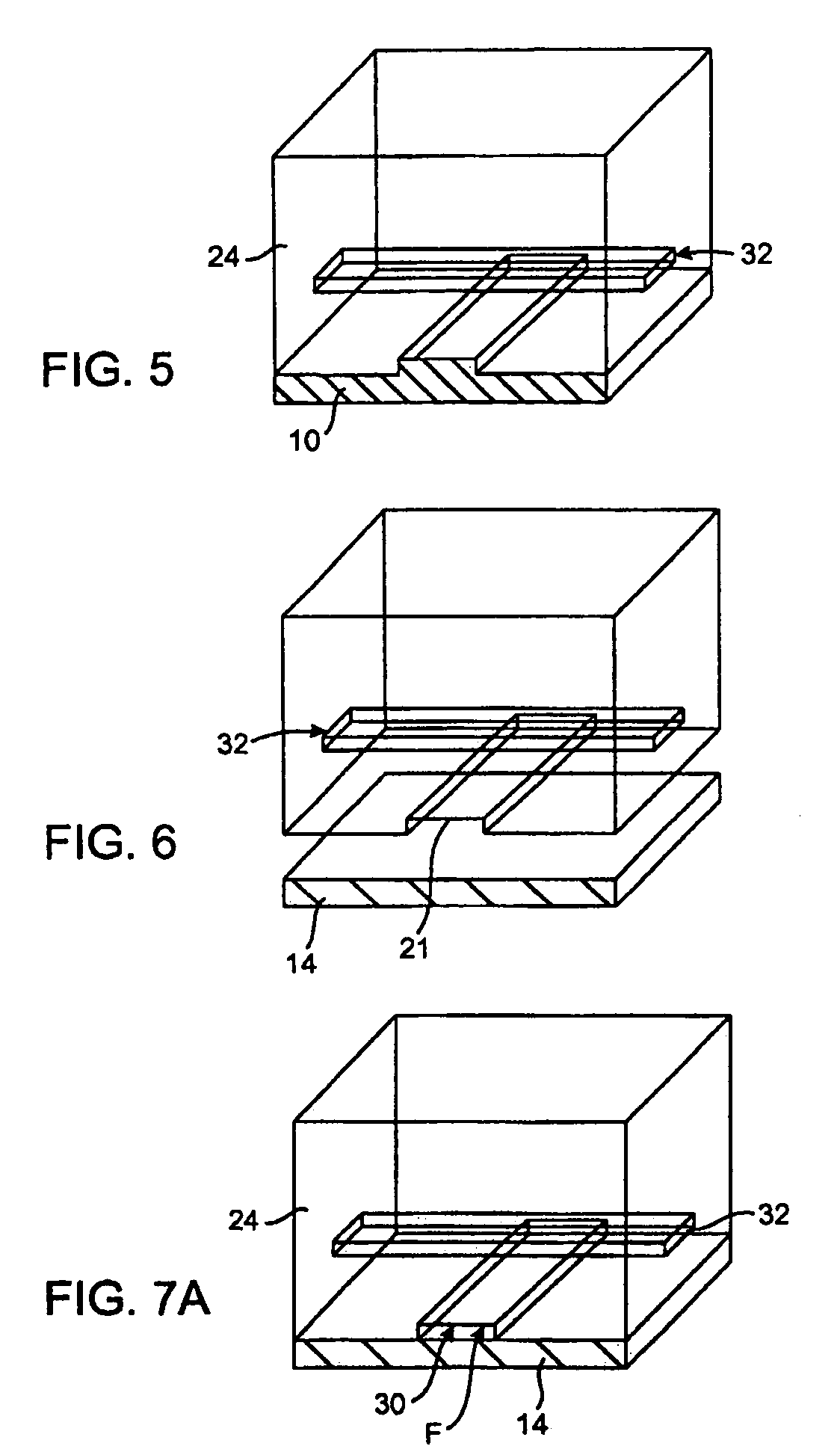
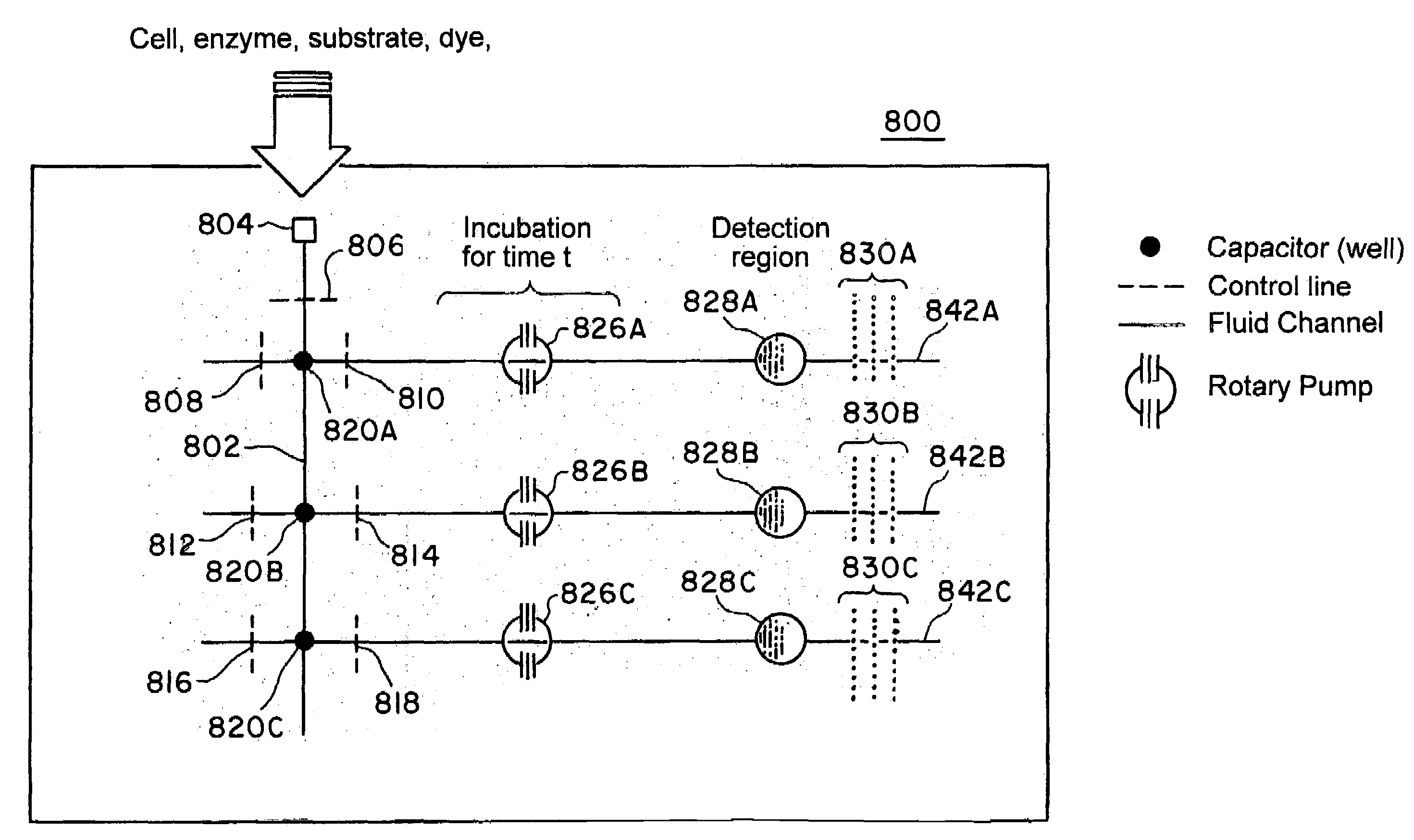
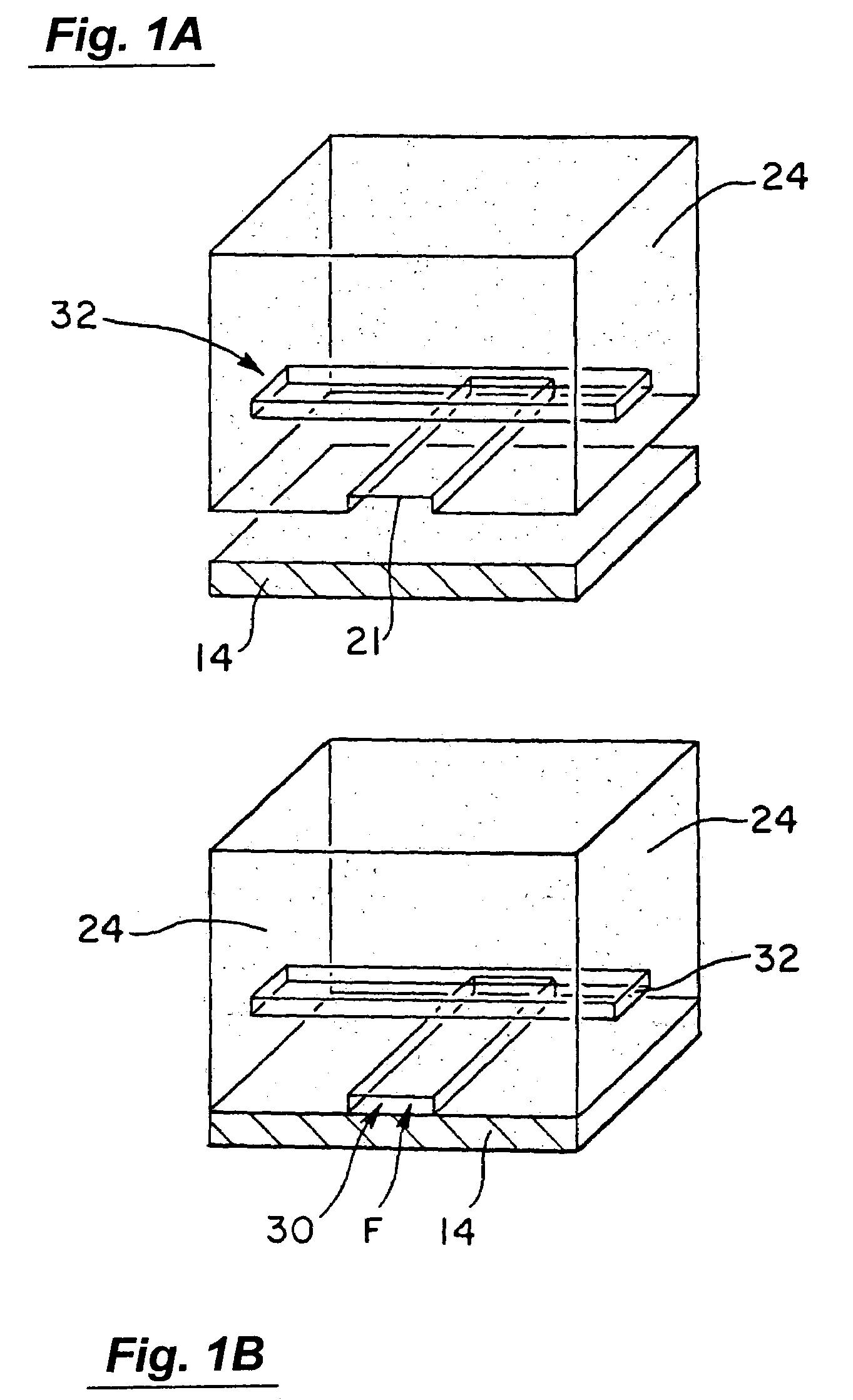
The present invention discloses devices and methods of performing high throughput screening of the physiological response of cells to biologically active compounds and methods of combining high-throughput with high-content spatial information at the cellular and subcellular level as well as temporal information about changes in physiological, biochemical and molecular activities. The present invention allows multiple types of cell interactions to be studied simultaneously by combining multicolor luminescence reading, microfluidic delivery, and environmental control of living cells in non-uniform micro-patterned arrays.
Owner:CELLOMICS
Combinatorial fabrication and high-throughput screening of optoelectronic devices
InactiveUS7247346B1Solid-state devicesSpecial surfacesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsComputer science
Methods and apparatus for the rapid and parallel synthesis of optoelectronic cell devices and for the high-throughput screening of such devices for useful properties are disclosed. The methods comprise the parallel synthesis of arrays of optoelectronic devices fabricated within an addressable sample-holding matrix. Each optoelectronic device is created and tested within an addressable sample-holder in the fabrication device.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Crystal growth devices and systems, and methods for using same
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Apparatus and methods for conducting assays and high throughput screening
The present invention provides microfluidic devices and methods for using the same. In particular, microfluidic devices of the present invention are useful in conducting a variety of assays and high throughput screening. Microfluidic devices of the present invention include elastomeric components and comprise a main flow channel; a plurality of branch flow channels; a plurality of control channels; and a plurality of valves. Preferably, each of the valves comprises one of the control channels and an elastomeric segment that is deflectable into or retractable from the main or branch flow channel upon which the valve operates in response to an actuation force applied to the control channel.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
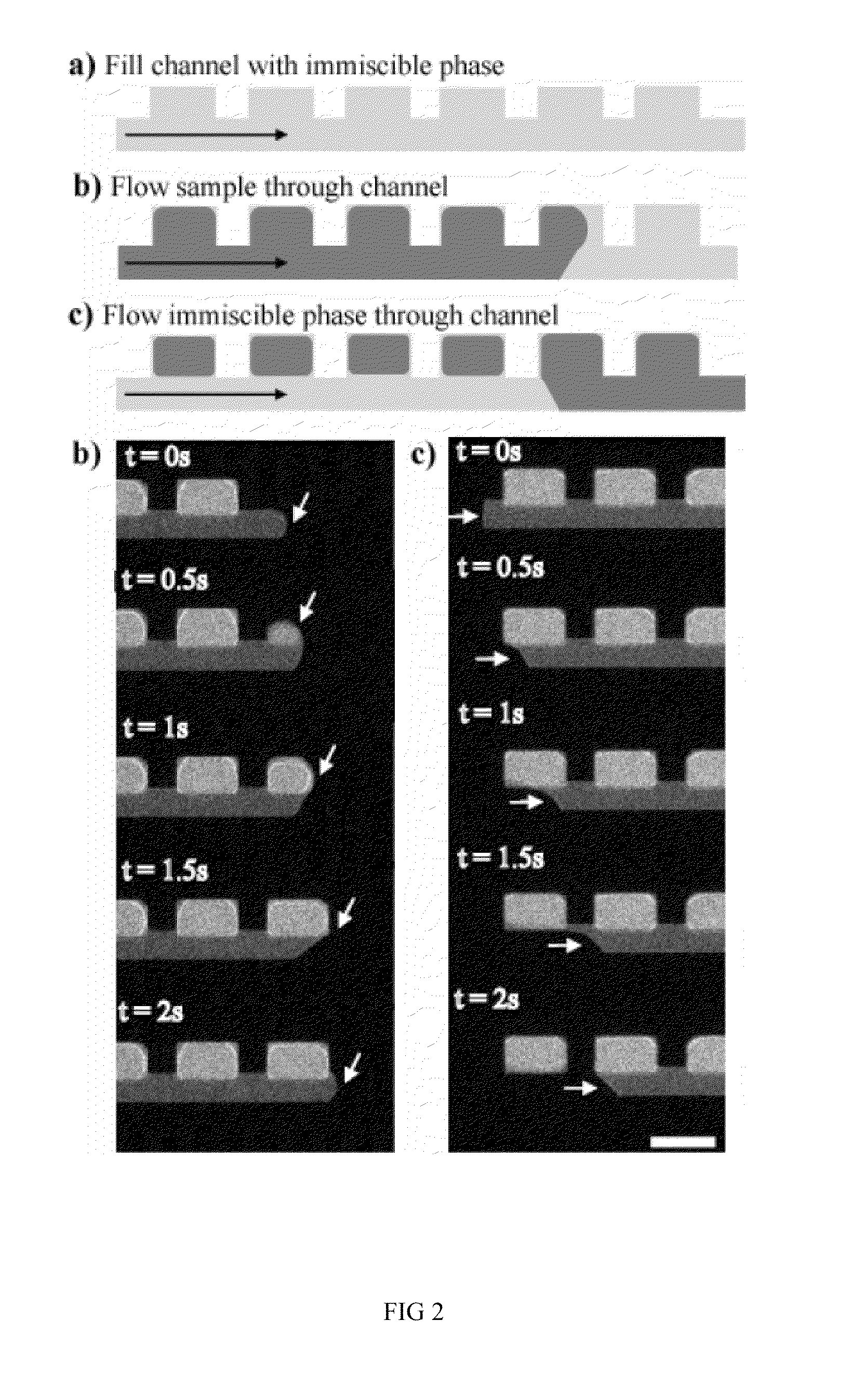
System and method for high throughput screening of droplets
InactiveUS20030119193A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh flux
A system and method for high throughput screening of fluid samples. A reduced pressure is applied, via an injection valve, to a sample aspiration tube. A first fluid and a second fluid are alternatively aspirated, via the sample aspiration tube, the first fluid for filling a sample loop with samples, the second fluid for flushing the sample aspiration tube. Excess fluid aspirated from the first fluid source and all fluid aspirated from the second fluid source is captured in an inline trap.
Owner:BIOCIUS LIFE SCI
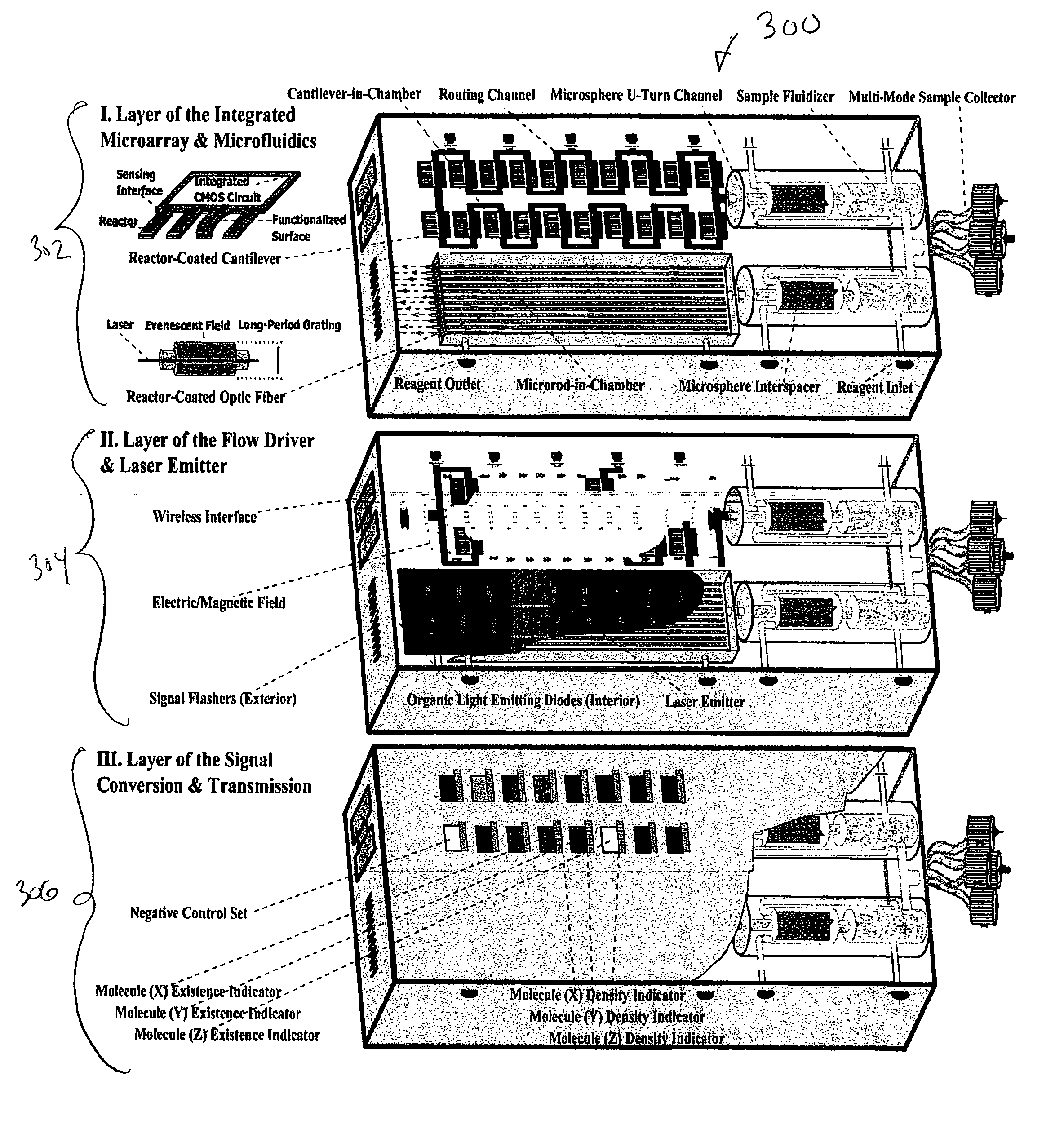
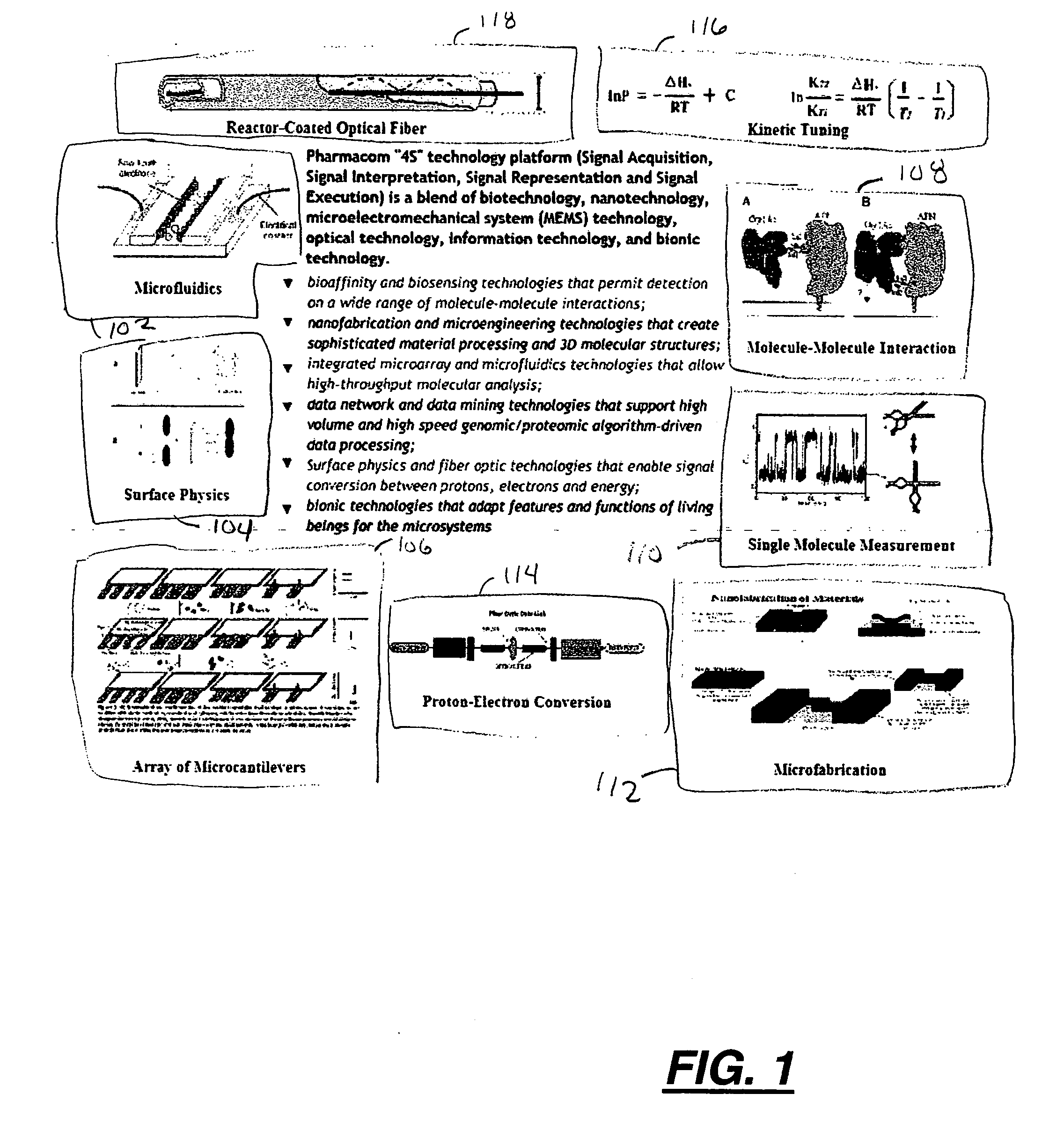
Microsystems that integrate three-dimensional microarray and multi-layer microfluidics for combinatorial detection of bioagent at single molecule level
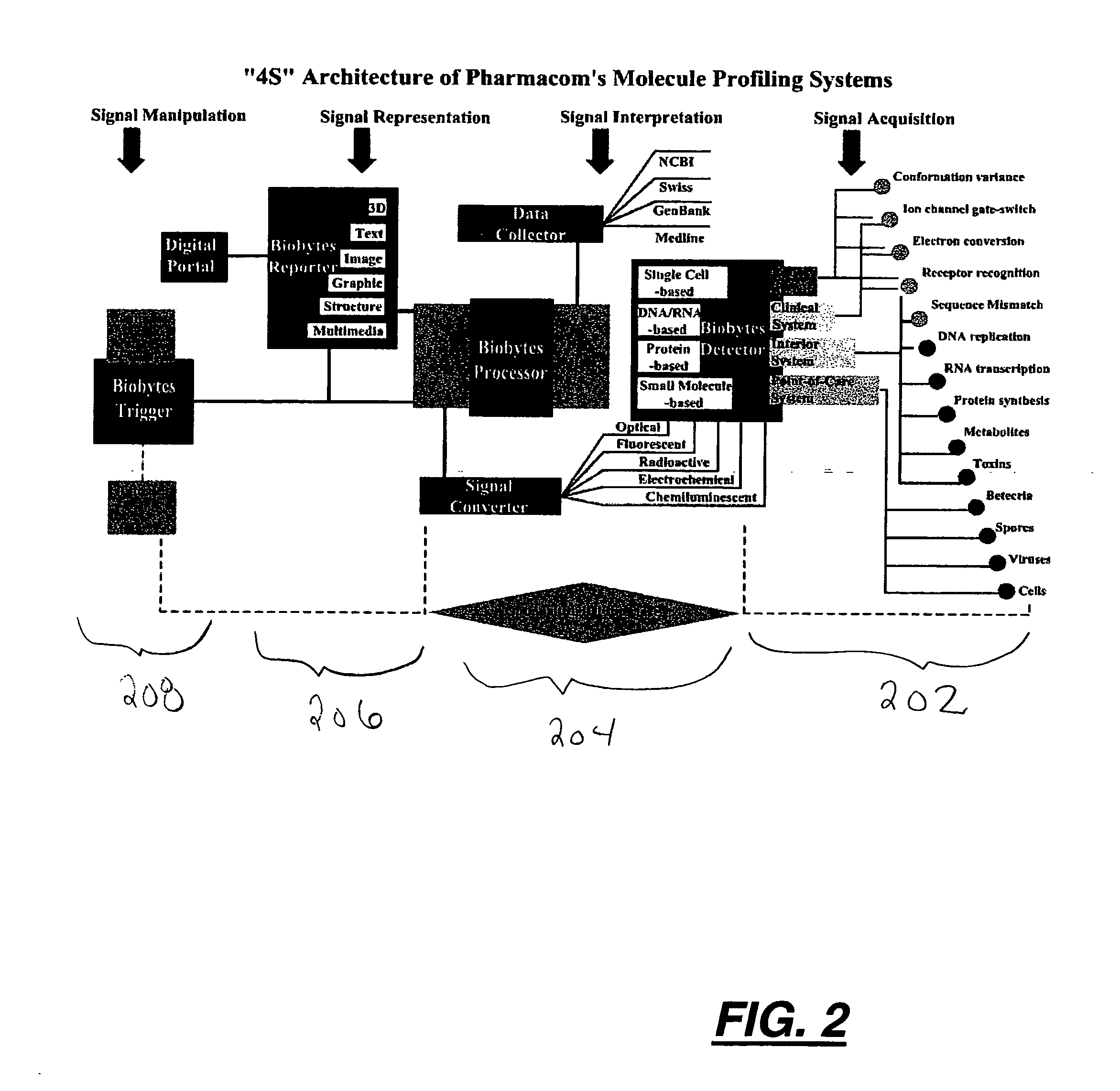
InactiveUS20070116607A1Reduce resultHigh detection sensitivityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesBiological bodyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Stand-alone microsystems adapted for performing combinatorial detection of bioagents at single molecule level wherein the microsystems are featured with three-dimensional microarray and multi-layer microfluidics to thereby provide high throughput screening and high content screening sufficient to allow for substantially real-time performance of the microsystem. Methods for detection of bioagents at a single molecule level or single organism level include providing a reconfigurable microsystem adapted for performing combinatorial detection of bioagents at a single molecule level and reconfiguring the reconfigurable microsystem for various environments.
Owner:PHARMACOM MICROELECTRONICS
Microfluidic reaction apparatus for high throughput screening
An SBS-formatted microfluidic device where the geometry of the plate defines an array of interrogation areas, and where each interrogation area encompasses at least one reaction site.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Fiber optic apparatus and use thereof in combinatorial material science
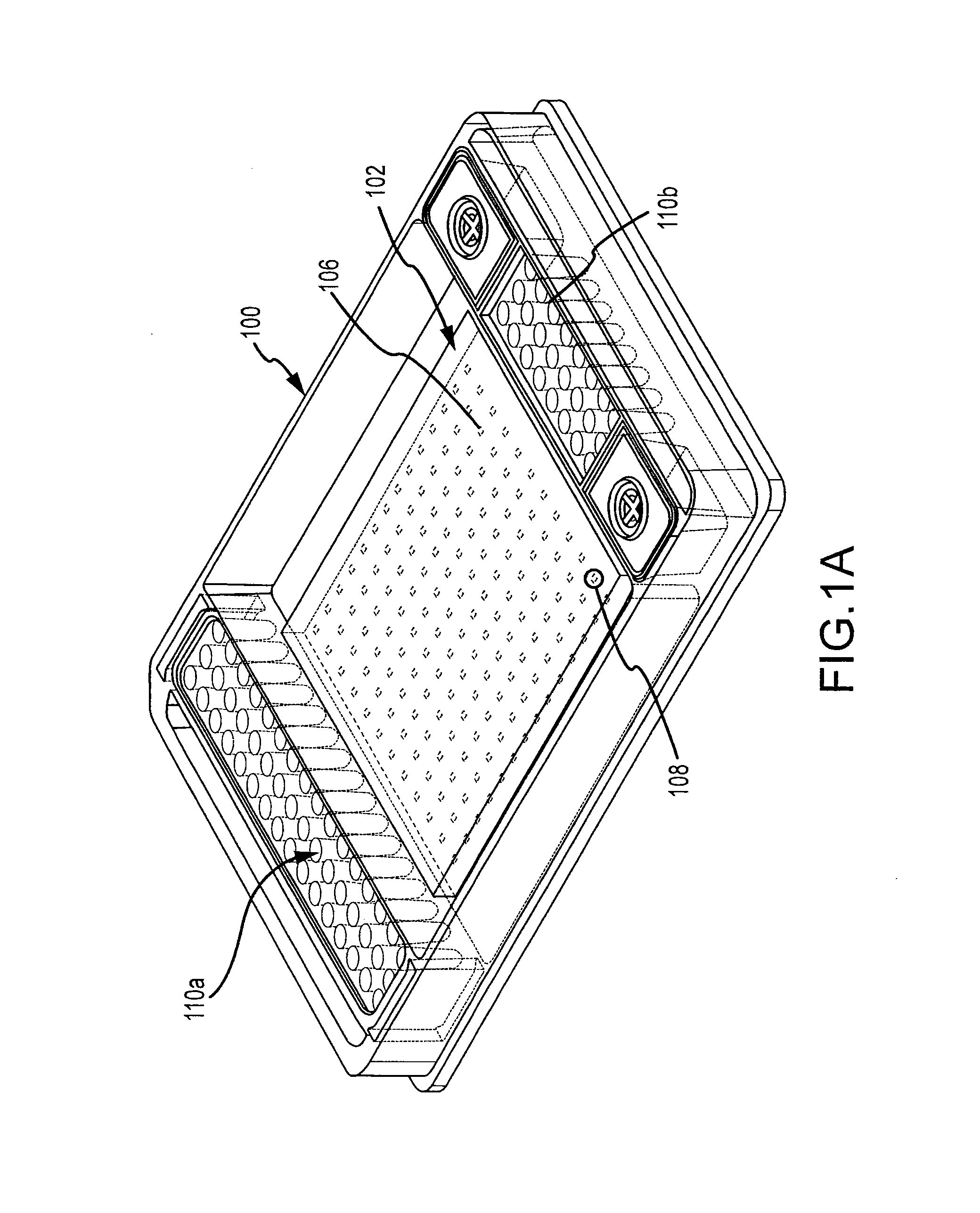
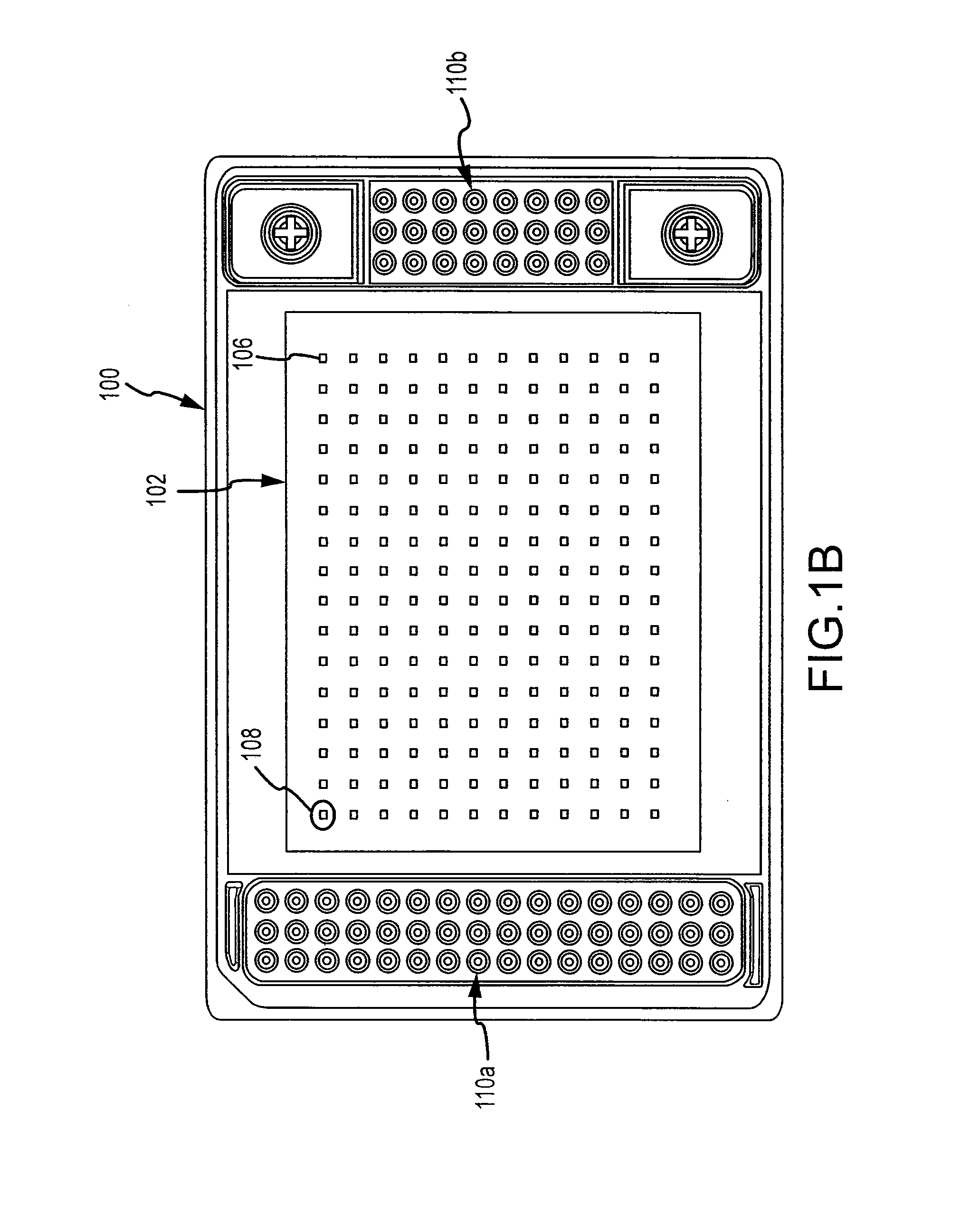
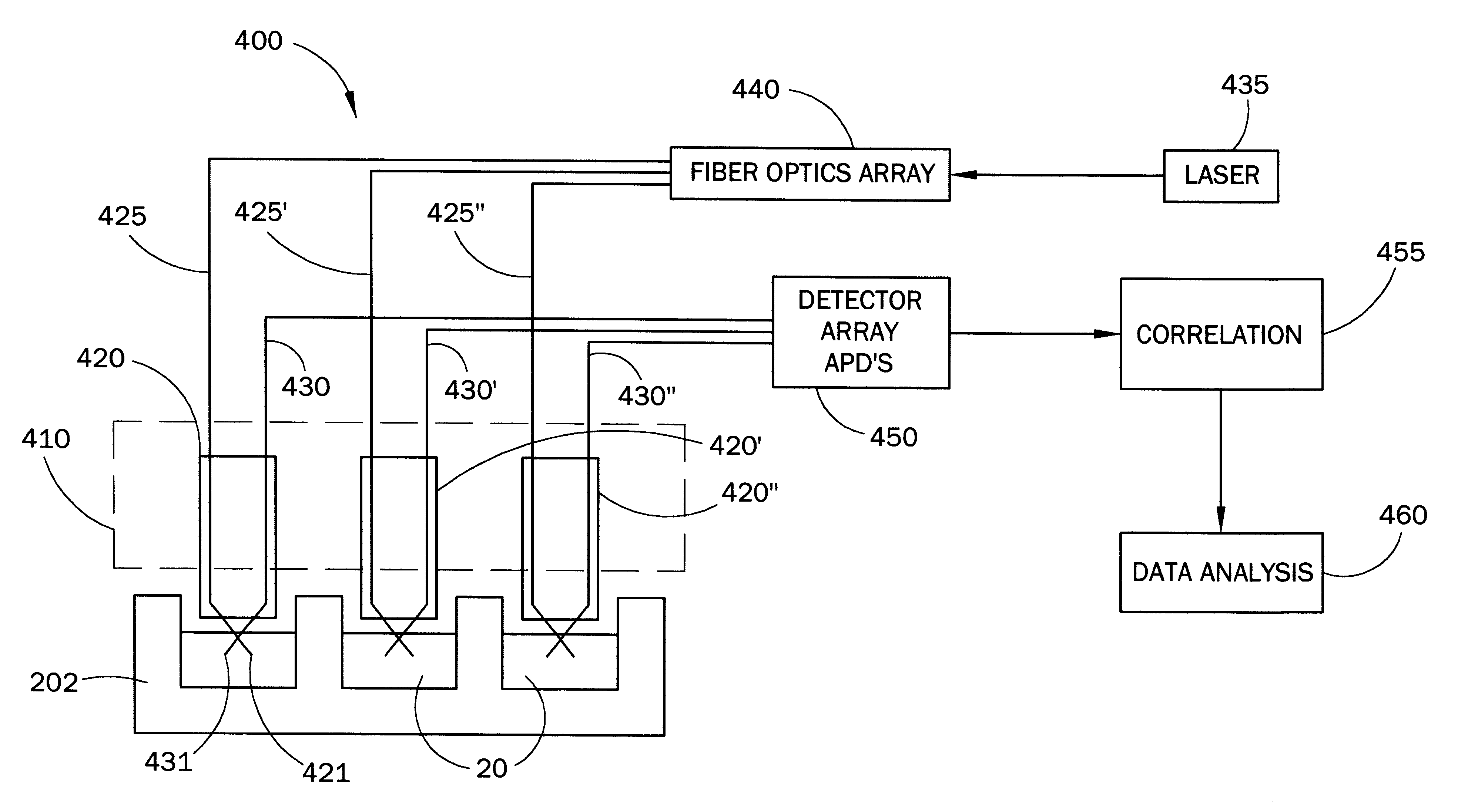
InactiveUS6519032B1Facilitate the discovery of commercially important polymericEffectively and efficiently characterizingSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationFiberHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Methods, systems and devices are described for rapid characterization and screening of liquid samples to determine properties (e.g., particle size, particle size distribution, molar mass and / or molar mass distribution) thereof with static light scattering and / or dynamic light scattering. The liquid samples can be solutions, emulsions, suspensions or dispersions. One method, includes providing a vessel containing a liquid sample having an exposed surface that defines a gas-liquid sample interface, and analyzing the sample by light scattering methods that include transmitting light through the gas-liquid sample interface into the sample, and detecting light scattered from the sample or from a component thereof. Additional methods are directed to characterizing a plurality of liquid samples or components thereof. The methods, systems, and devices have applications in high-throughput screening, and particularly, in combinatorial materials research and in industrial process control.
Owner:WYATT TECH
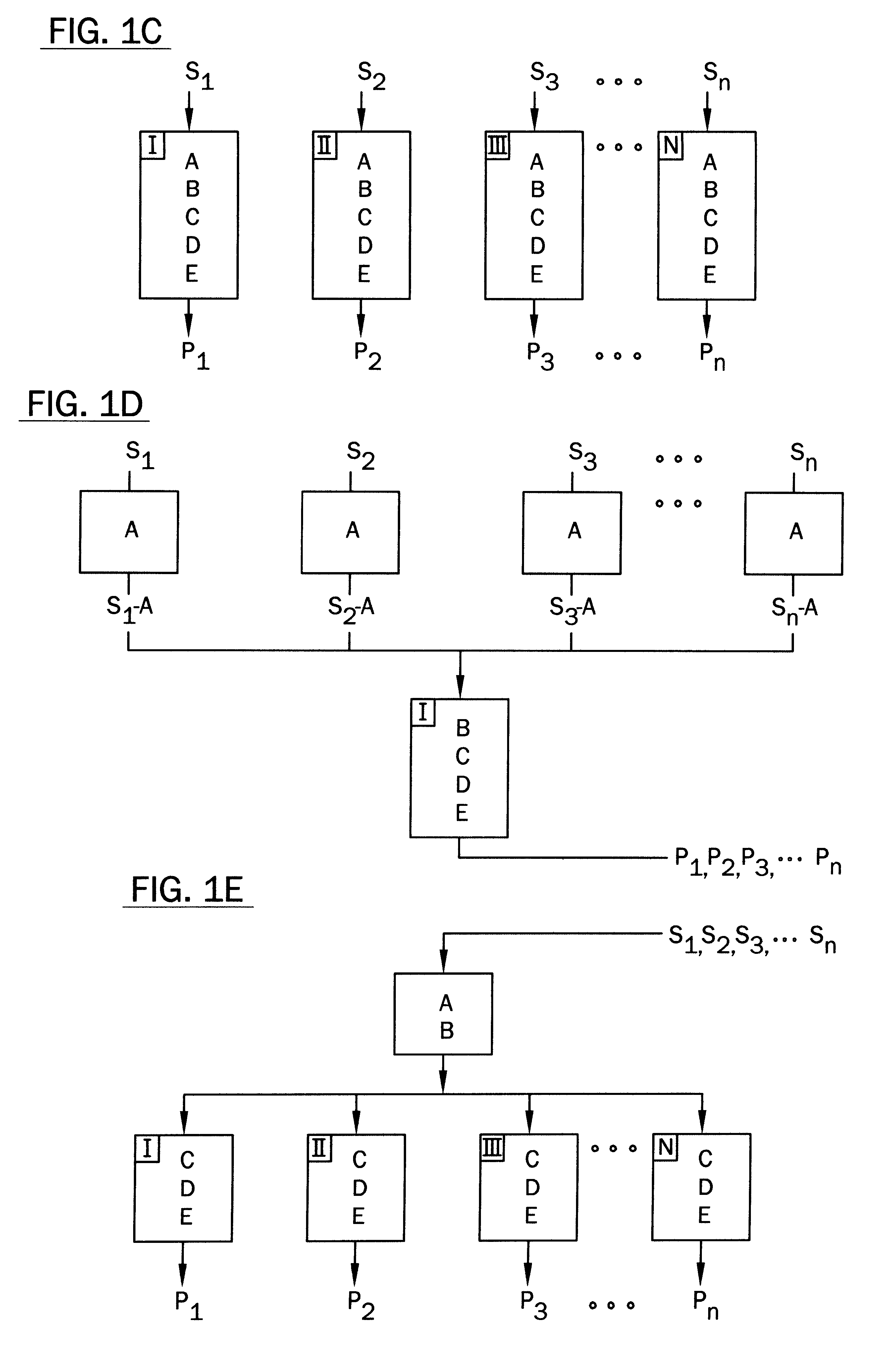
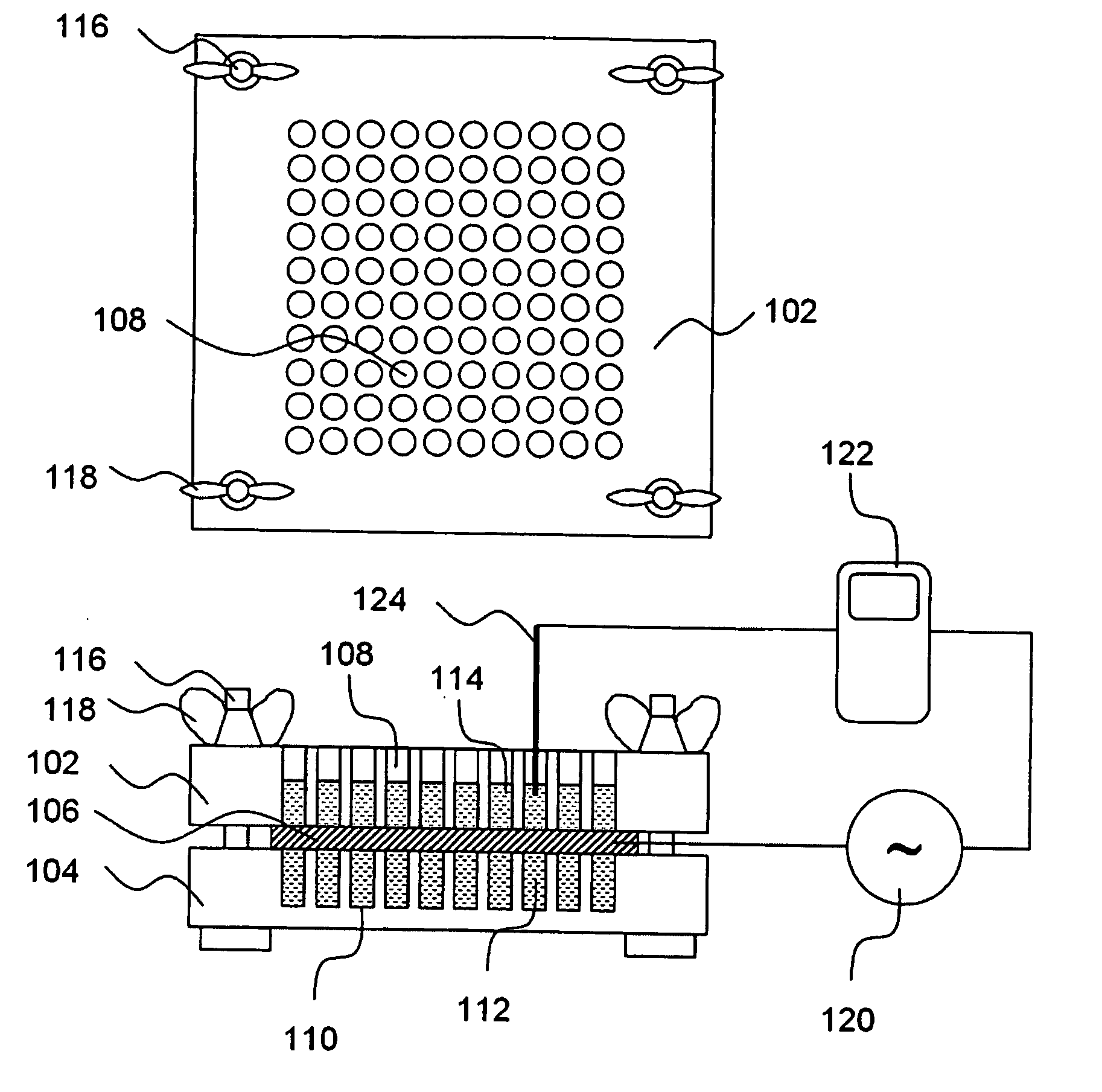
Penetration Enhancer Combinations for Transdermal Delivery
InactiveUS20070269379A1Easy to transportLess irritatingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsIrritation
A high throughput screening and isolation system identifies rare enhancer mixtures from a candidate pool of penetration enhancer combinations. The combinations are screened for high penetration but low irritation potential using a unique data mining method to find new potent and safe chemical penetration enhancer combinations. The members of a library of chemical penetration enhancer combinations are screened with a high throughput device to identify “hot spots”, particular combinations that show higher chemical penetration enhancement compared to neighboring compositions. The irritation potentials of the hot spot combinations are measured to identify combinations that also show low irritation potential. A active component, such as a drug, is then combined with the combination in a formulation which is tested for the ability of the drug to penetrate into or through skin. It is then assessed whether the formulation can deliver the quantity of drug required, and animal tests are conducted to confirm in vivo the ability of the chemical penetration enhancer combinations to facilitate transport of sufficient active molecules across the skin to achieve therapeutic levels of the active molecule in the animal's blood. The invention provides specific unique and rare mixtures of chemical penetration enhancers that enhance skin permeability to hydrophilic macromolecules by more than 50-fold without inducing skin irritation, such as combinations of sodium laurel ether sulfate and 1-phenyl piperazine, and combinations of N-lauryl sarcosine and Span 20 / sorbitan monolaurate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and methods for conducting assays and high throughput screening
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Screening for west nile virus antiviral therapy
InactiveUS20050058987A1Improve efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseVectorsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsImmunogenicity
The instant invention provides stable and novel lineage I WNV reverse genetics systems, and methods for making the reverse genetics systems, specifically, a fully-infectious lineage I WNV cDNA or replicon system engineered with one or more nucleotide sequences each encoding a reporter gene to be used in high throughput cell-based screening assays for the identification of novel antiflaviviral chemotherapeutics and / or vaccines effective to treat and / or immunize against infections by WNV and other emerging flaviviruses, such as, for example, JEV, SLEV, AV, KV, JV, CV, YV, TBEV, DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, DENV-4, YFV and MVEV. The present invention further provides methods of high throughput screening of antiflaviviral compounds or improved derivatives thereof using novel lineage I WNV reverse genetics systems and / or cell lines stably containing the reverse genetics systems. Also, the invention provides novel pharmaceutical compositions comprising an attenuated lineage I WNV that is less virulent but similarly immunogenic as the parent WNV and is capable of providing a protective immune response in a host.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
High throughput screening of mutagenized populations
InactiveUS20090170713A1Goal is achievedEfficient screeningSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsDNA
Efficient methods are disclosed for the high throughput identification of mutations in genes in members of mutagenized populations. The methods comprise DNA isolation, pooling, amplification, creation of libraries, high throughput sequencing of libraries, preferably by sequencing-by-synthesis technologies, identification of mutations and identification of the member of the population carrying the mutation and identification of the mutation.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Rapid way to obtain high expression clones of mammalian cells using a methylcellulose and immunoprecipitation screening method
InactiveUS20050118652A1High throughput screeningImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsPeptide preparation methodsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsScreening method
The invention provides a genetic screening method for identifying a transfected cell expressing the polypeptide of interest. The methods allows for high throughput screening of recombinant cells for elevated levels of expression of the polypeptide of interest. The invention also provides capture media, formulations and methods of making and using thereof.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Crystal growth devices and systems, and methods for using same
High throughput screening of crystallization of a target material is accomplished by simultaneously introducing a solution of the target material into a plurality of chambers of a microfabricated fluidic device. The microfabricated fluidic device is then manipulated to vary the solution condition in the chambers, thereby simultaneously providing a large number of crystallization environments. Control over changed solution conditions may result from a variety of techniques, including but not limited to metering volumes of crystallizing agent into the chamber by volume exclusion, by entrapment of volumes of crystallizing agent determined by the dimensions of the microfabricated structure, or by cross-channel injection of sample and crystallizing agent into an array of junctions defined by intersecting orthogonal flow channels.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Biochip for High-Throughput Screening of Circulating Tumor Cells
ActiveUS20080318324A1Reduce direct impactShorten speedLiquid separation auxillary apparatusLaboratory glasswaresRe entryHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Embodiments in accordance with the present invention relate to the use of effusive filtration to segregate tumor cells from a sample of bodily fluid. In one embodiment, fluid containing a cell is flowed down a channel having a filtration medium present along at least one side wall. The tumor cell is captured when the fluid passes through the filtration medium. Accumulated pressure on the captured tumor cell is reduced by allowing the fluid that has passed through the filtration medium to re-enter the channel. In a particular embodiment, the filtration medium may comprise side wall apertures having a width smaller than that of the cell, with downstream apertures allowing re-entry of the fluid into the channel.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Microfluidic protein crystallography
InactiveUS20050205005A1High throughput screeningImprove throughputValve arrangementsPeptide librariesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAgent Combination
The use of microfluidic structures enables high throughput screening of protein crystallization. In one embodiment, an integrated combinatoric mixing chip allows for precise metering of reagents to rapidly create a large number of potential crystallization conditions, with possible crystal formations observed on chip. In an alternative embodiment, the microfluidic structures may be utilized to explore phase space conditions of a particular protein crystallizing agent combination, thereby identifying promising conditions and allowing for subsequent focused attempts to obtain crystal growth.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for the discretization and manipulation of sample volumes
ActiveUS20100041046A1Easy to useEasy to implementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChannel geometryAssay
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods and apparatuses for the discretization and manipulation of sample volumes that is simple, robust, and versatile. It is a fluidic device that partitions a sample by exploiting the interplay between fluidic forces, interfacial tension, channel geometry, and the final stability of the formed droplet and / or discretized volume. These compartmentalized volumes allow for isolation of samples and partitioning into a localized array that can subsequently be manipulated and analyzed. The isolation of the discretized volumes along with the device's inherent portability render our invention versatile for use in many areas, including but not limited to PCR, digital PCR, biological assays for diagnostics and prognostics, cancer diagnosis and prognosis, high throughput screening, single molecule and single cell reactions or assays, the study crystallization and other statistical processes, protein crystallization, drug screening, environmental testing, and the coupling to a wide range of analytical detection techniques for biomedical assays and measurements. The minimal fluid interconnects and simple flow geometry makes the device easy to use and implement, economical to fabricate and operate, and robust in its operations.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
High throughput screening of crystallization of materials
InactiveUS7052545B2Sequential/parallel process reactionsFrom normal temperature solutionsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSize determination
High throughput screening of crystallization of a target material is accomplished by simultaneously introducing a solution of the target material into a plurality of chambers of a microfabricated fluidic device. The microfabricated fluidic device is then manipulated to vary the solution condition in the chambers, thereby simultaneously providing a large number of crystallization environments. Control over changed solution conditions may result from a variety of techniques, including but not limited to metering volumes of crystallizing agent into the chamber by volume exclusion, by entrapment of volumes of crystallizing agent determined by the dimensions of the microfabricated structure, or by cross-channel injection of sample and crystallizing agent into an array of junctions defined by intersecting orthogonal flow channels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
High throughput screening with parallel vibrational spectroscopy
InactiveUS20030175160A1Enhances signal developmentImprove performanceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsMeasurement device
Rapid spectrum assay of multiple samples with infrared light is made possible by devices and methods that increase total light throughput. Multiple wavelength scan with Fourier analysis is combined with large numbers of sample wells located within infrared light compatible solid materials. In particular, very large scale measurement devices and systems for their use are fabricated from lithography and other techniques used for semiconductor processing.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL HLDG
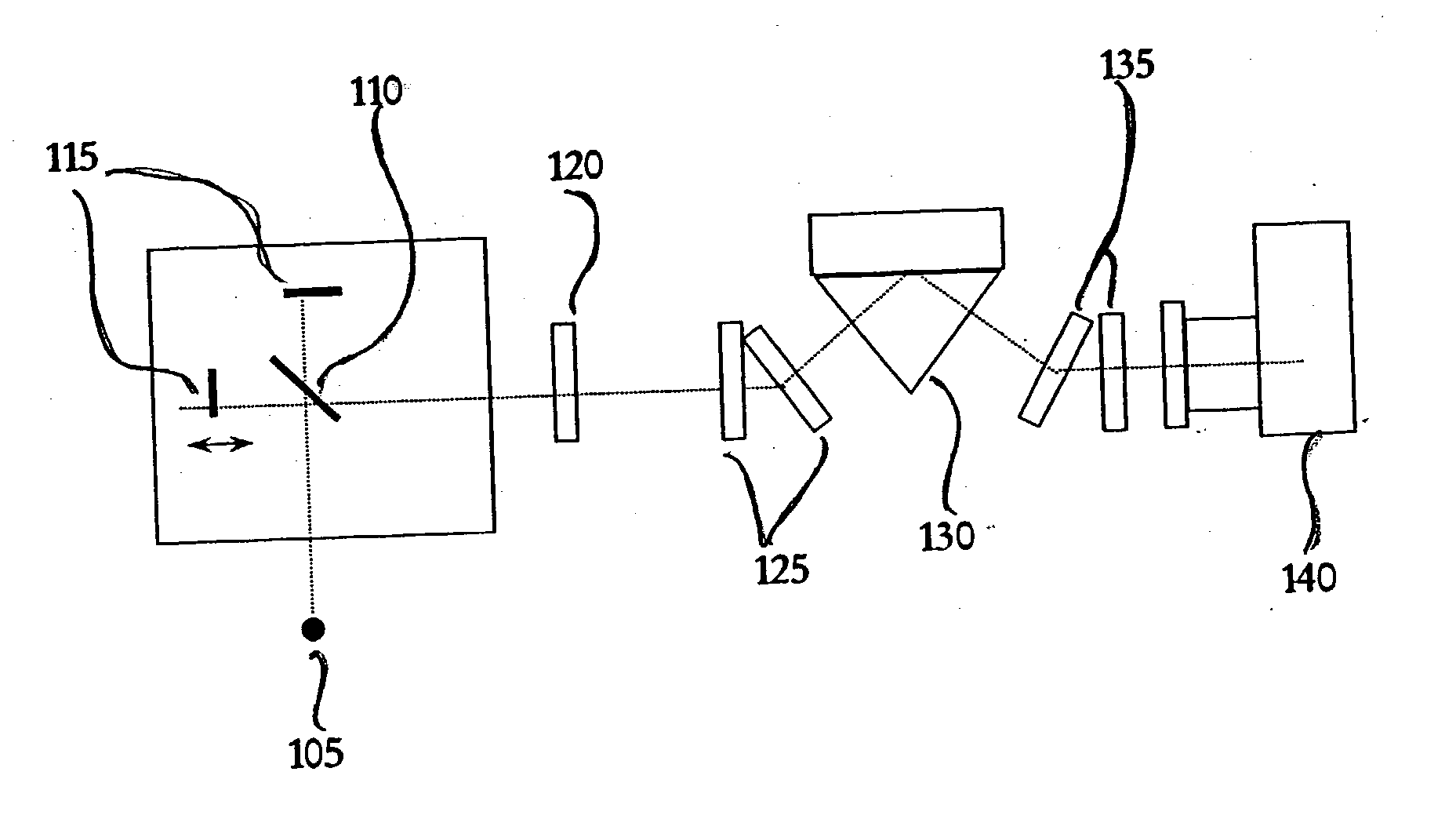
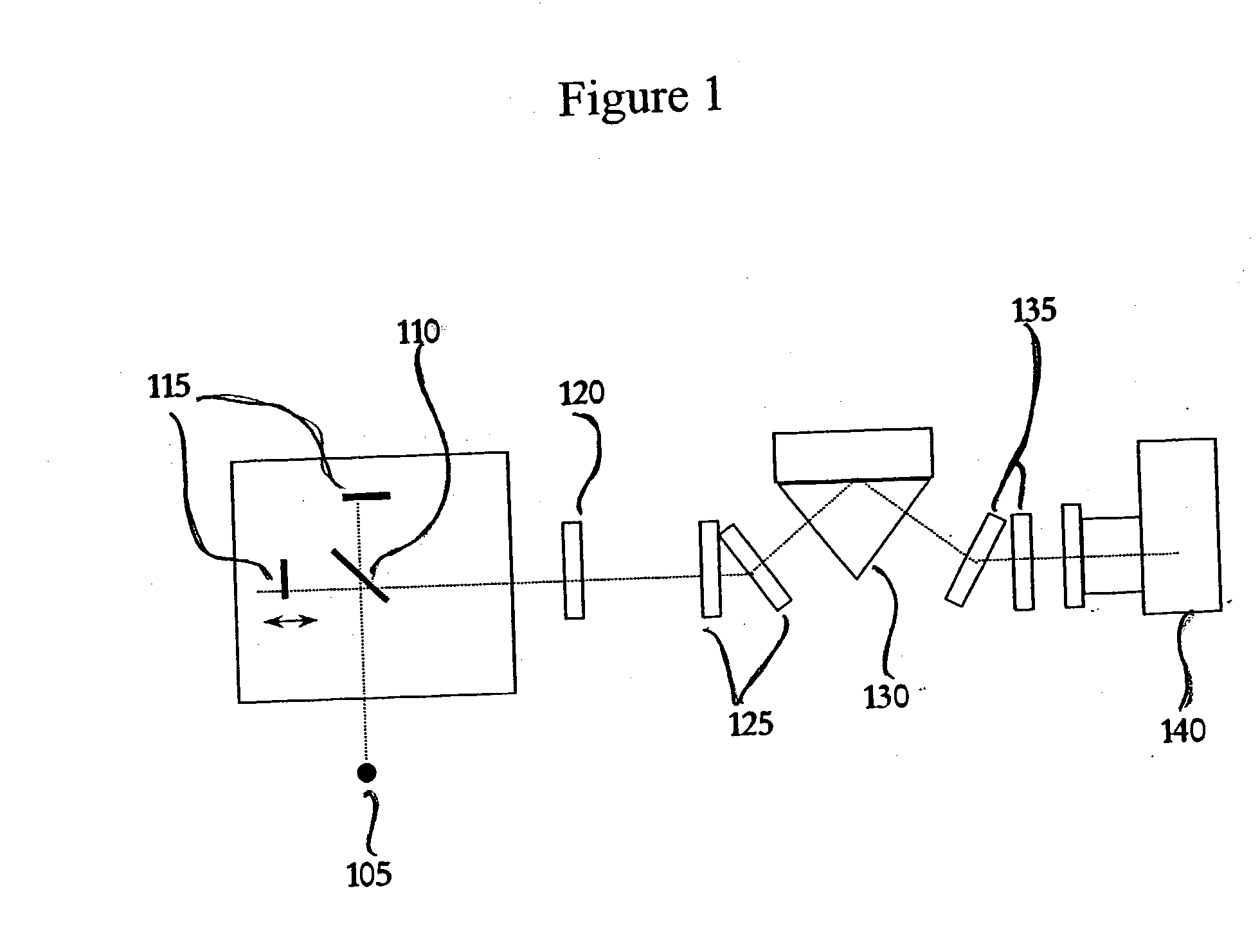
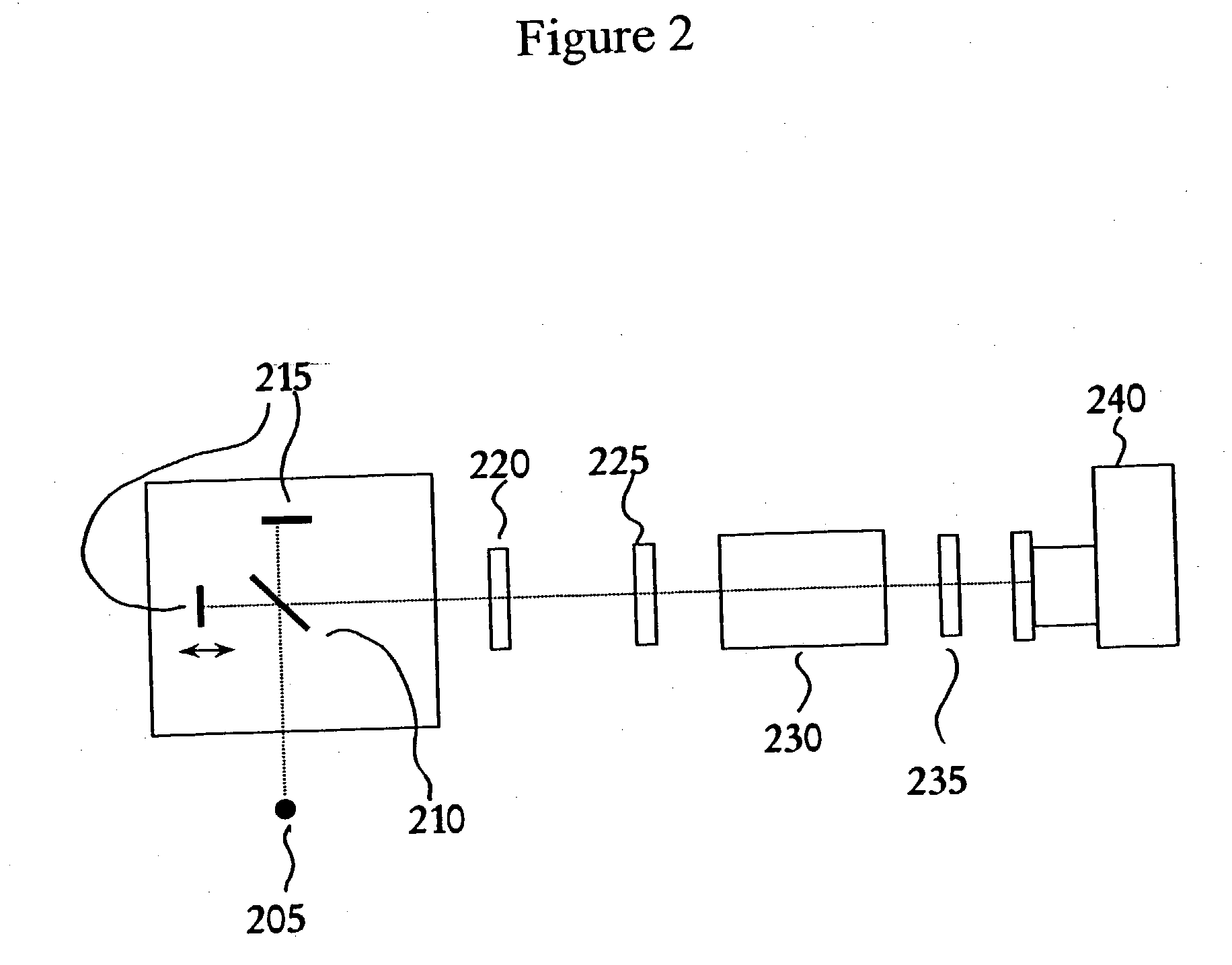
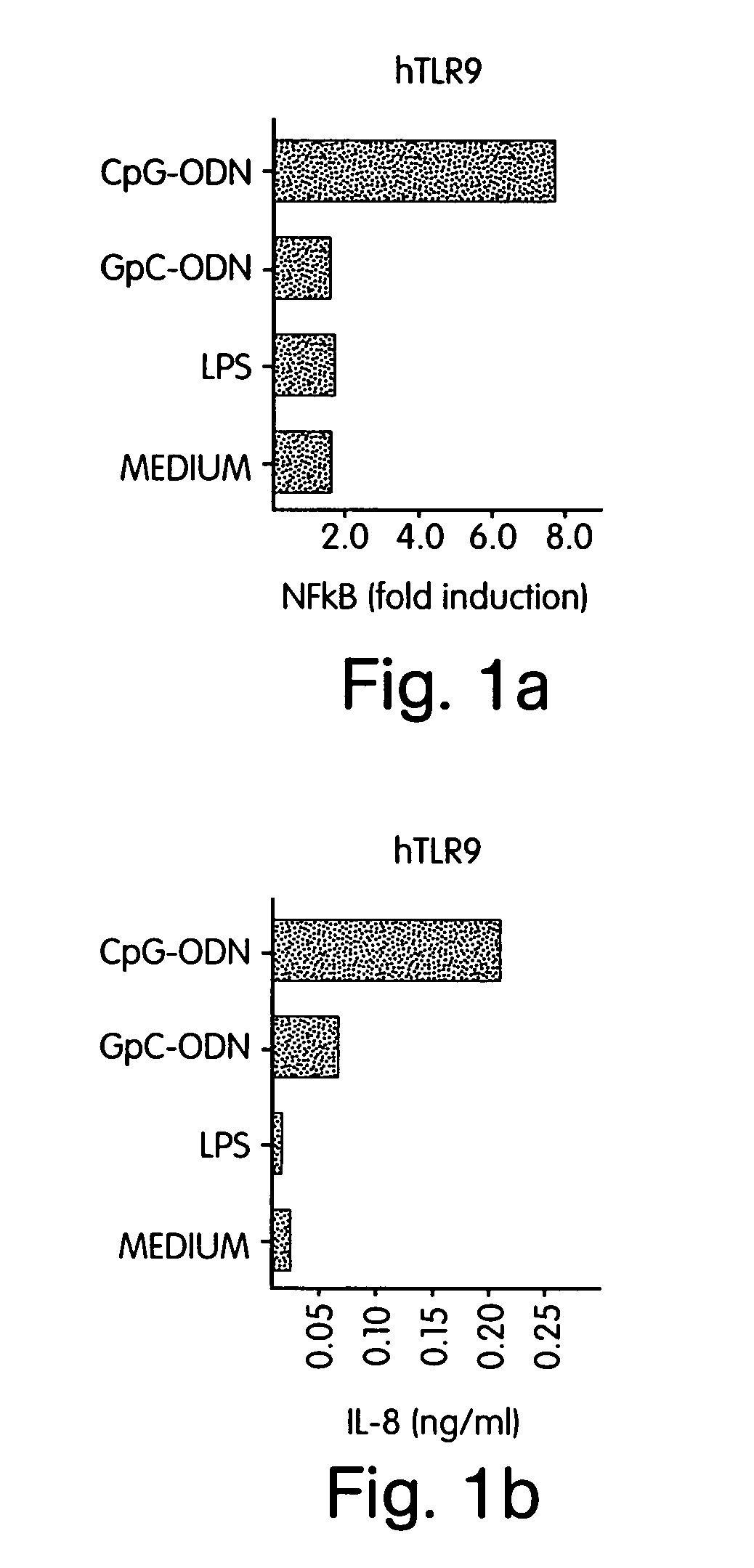
Process for high throughput screening of CpG-based immuno-agonist/antagonist
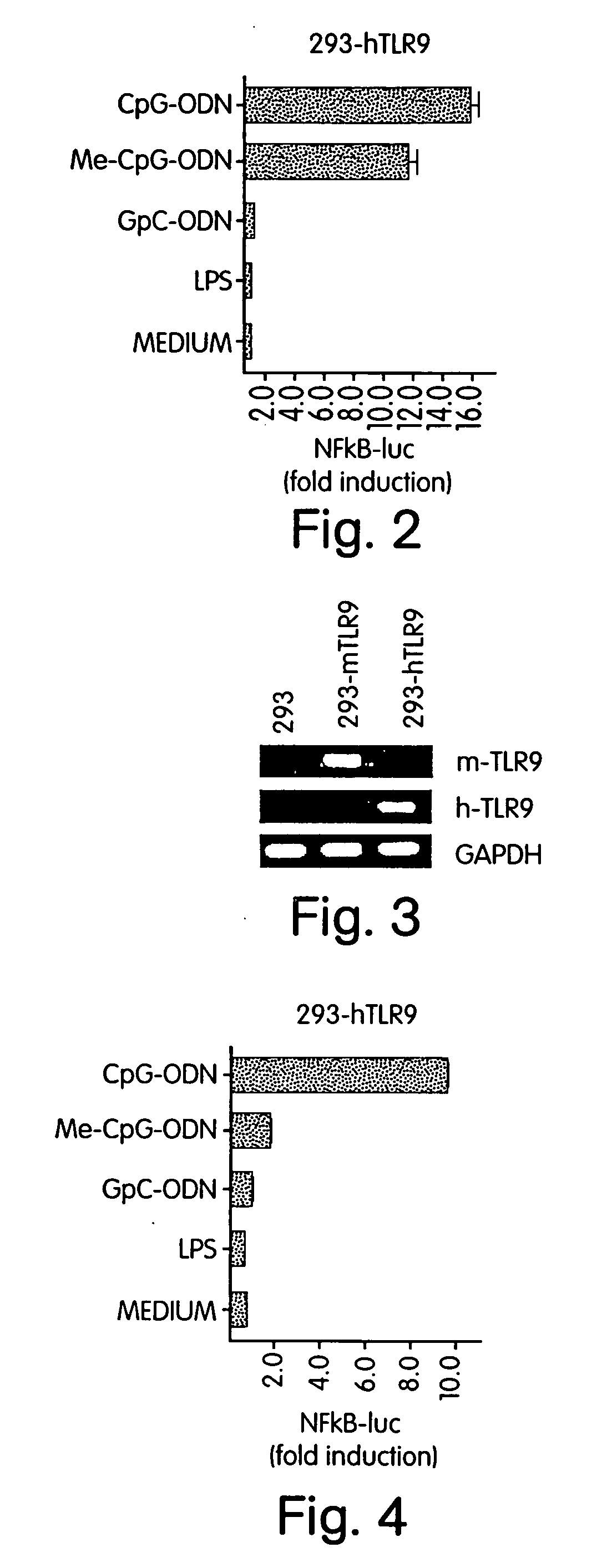
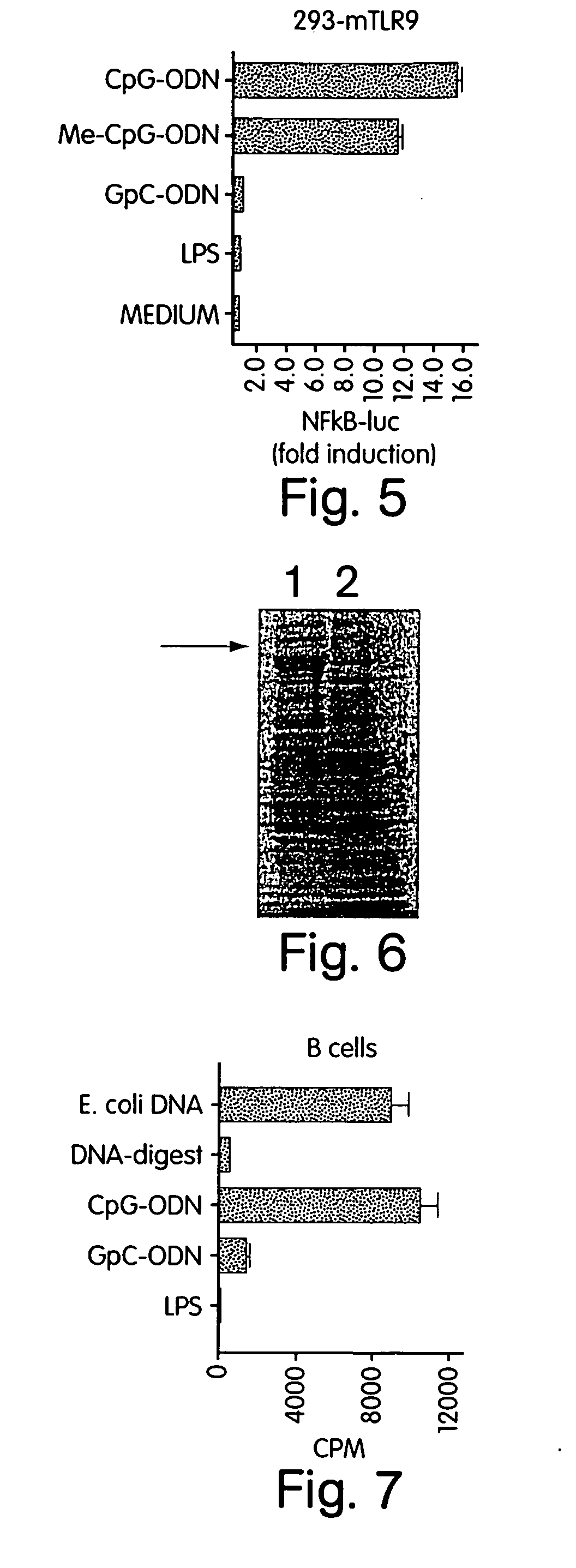
InactiveUS20050181422A1Reduces TLR signaling activityIncrease TLR signalingFungiBacteriaTLR8High-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention pertains to murine TLR9 and related TLR9s which include murine-specific amino acids, as well as nucleic acids which encode those polypeptides. The present invention also includes fragments and biologically functional variants of the murine TLR9. The invention further relates to methods of using such murine and non-murine TLR9 nucleic acids and polypeptides, especially in methods for screening for agonists and antagonists of immunostimulatory CpG nucleic acids. Also included are murine TLR9 inhibitors which inhibit murine TLR9 activity by inhibiting the expression or function of murine TLR9. In a further aspect the present invention pertains to murine TLR7 and murine TLR8, as well as related TLR7 and TLR8 molecules which include murine-specific amino acids, as well as nucleic acids which encode those polypeptides. The present invention also includes fragments and biologically functional variants of the murine TLR7 and TLR8. Methods are included for screening for ligands of TLR7 and TLR8, as well as for inhibitors and agonists and antagonists of signaling mediated by TLR7 and TLR8.
Owner:COLEY PHARMA GMBH
Methods and apparatuses for stretching polymers
InactiveUS20040166025A1Flow mixersTransportation and packagingHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsEngineering
The present invention provides structures and methods that allow polymers of any length, including nucleic acids containing entire genomes, to be stretched into a long, linear conformation for further analysis. The present invention also provides structures and methods for selecting and stretching polymers based on their lengths. Polymers are loaded into a device and run through the structures. Stretching is achieved by, e.g., applying shear forces as the polymer passes through the structures, placing obstacles in the path of the polymer, or a combination thereof. Since multiple molecules may be stretched in succession, extremely high throughput screening, e.g., screening of more than one molecule per second, is achieved.
Owner:PATHOGENETIX
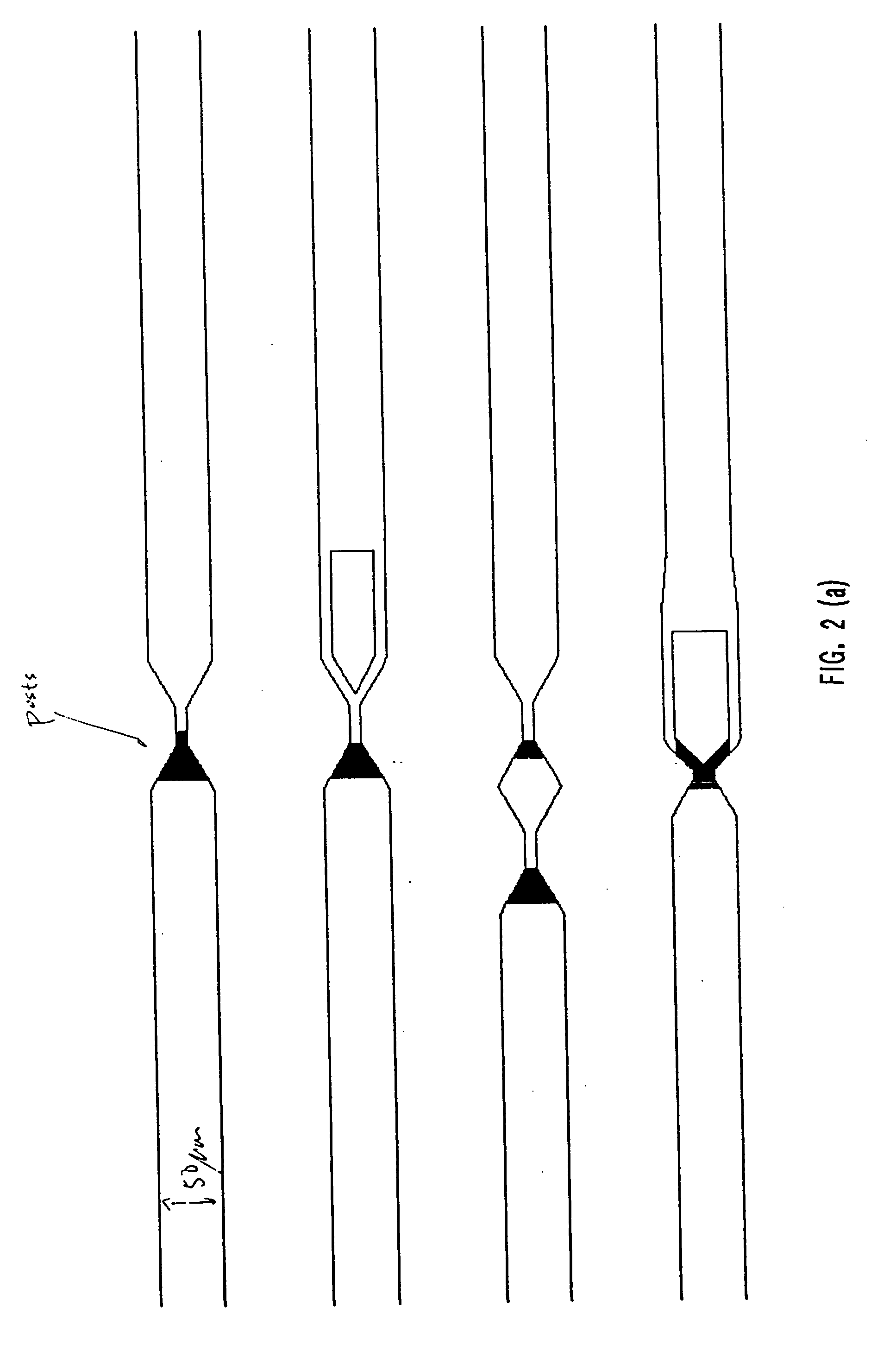
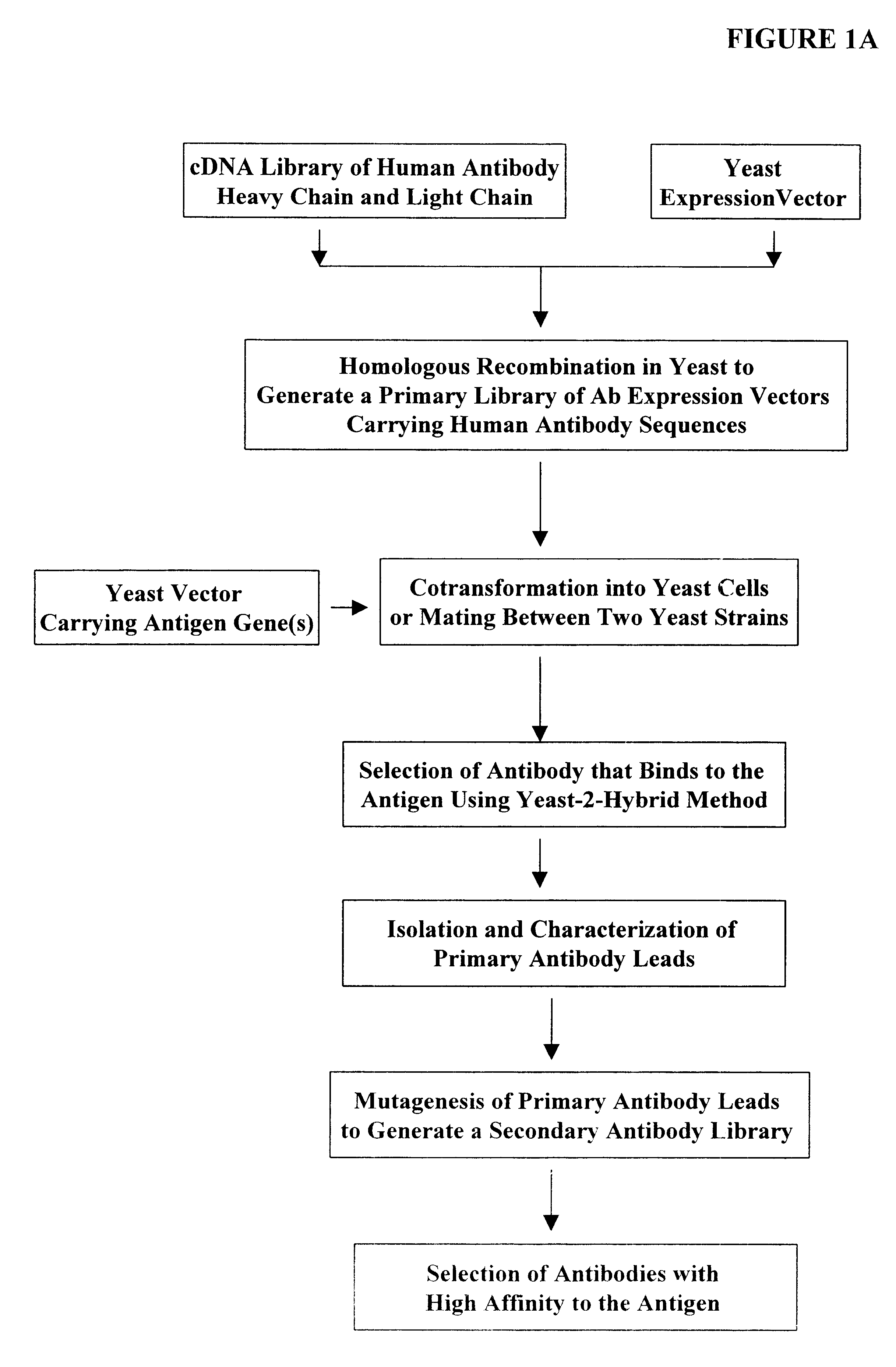
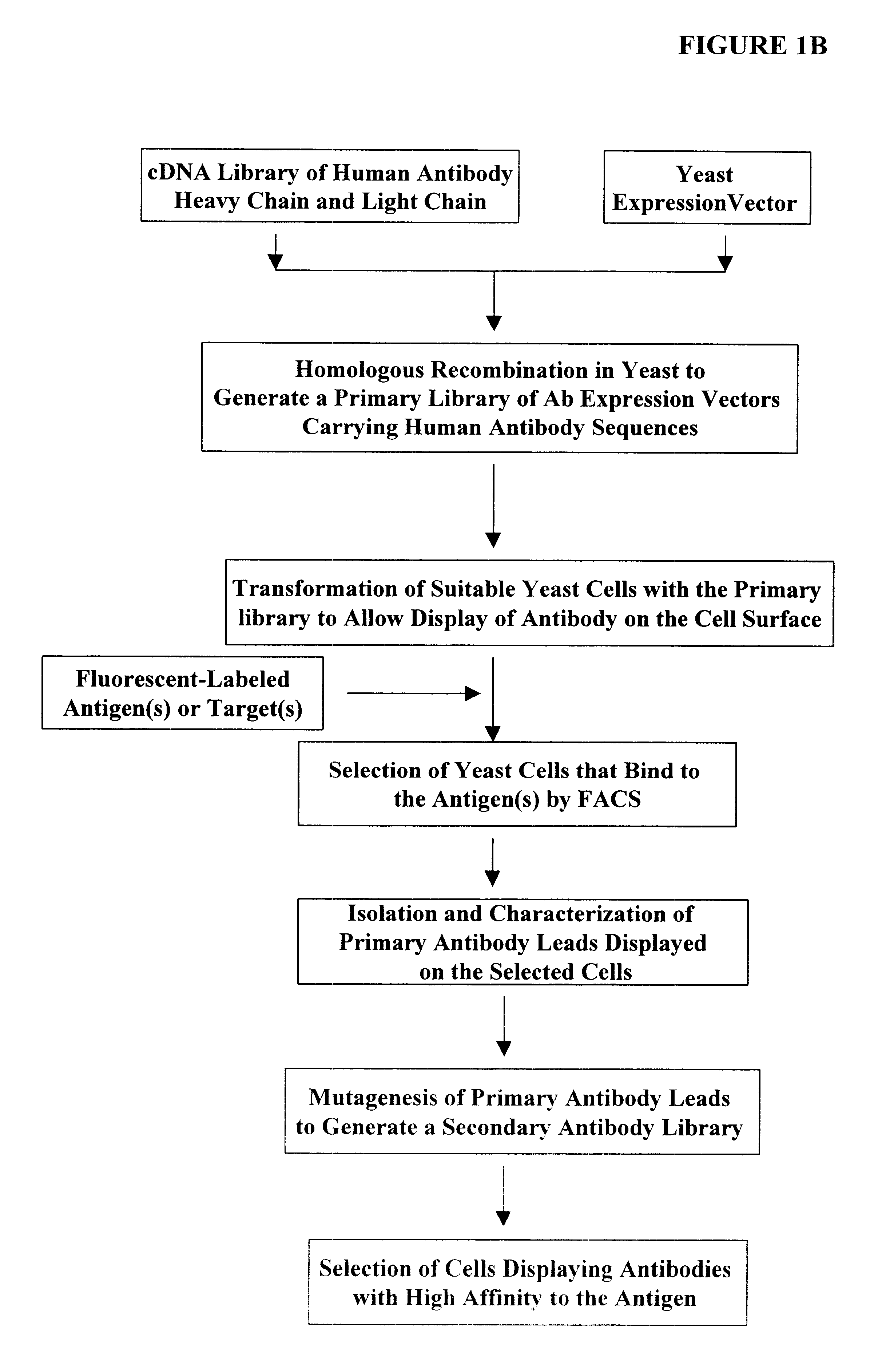
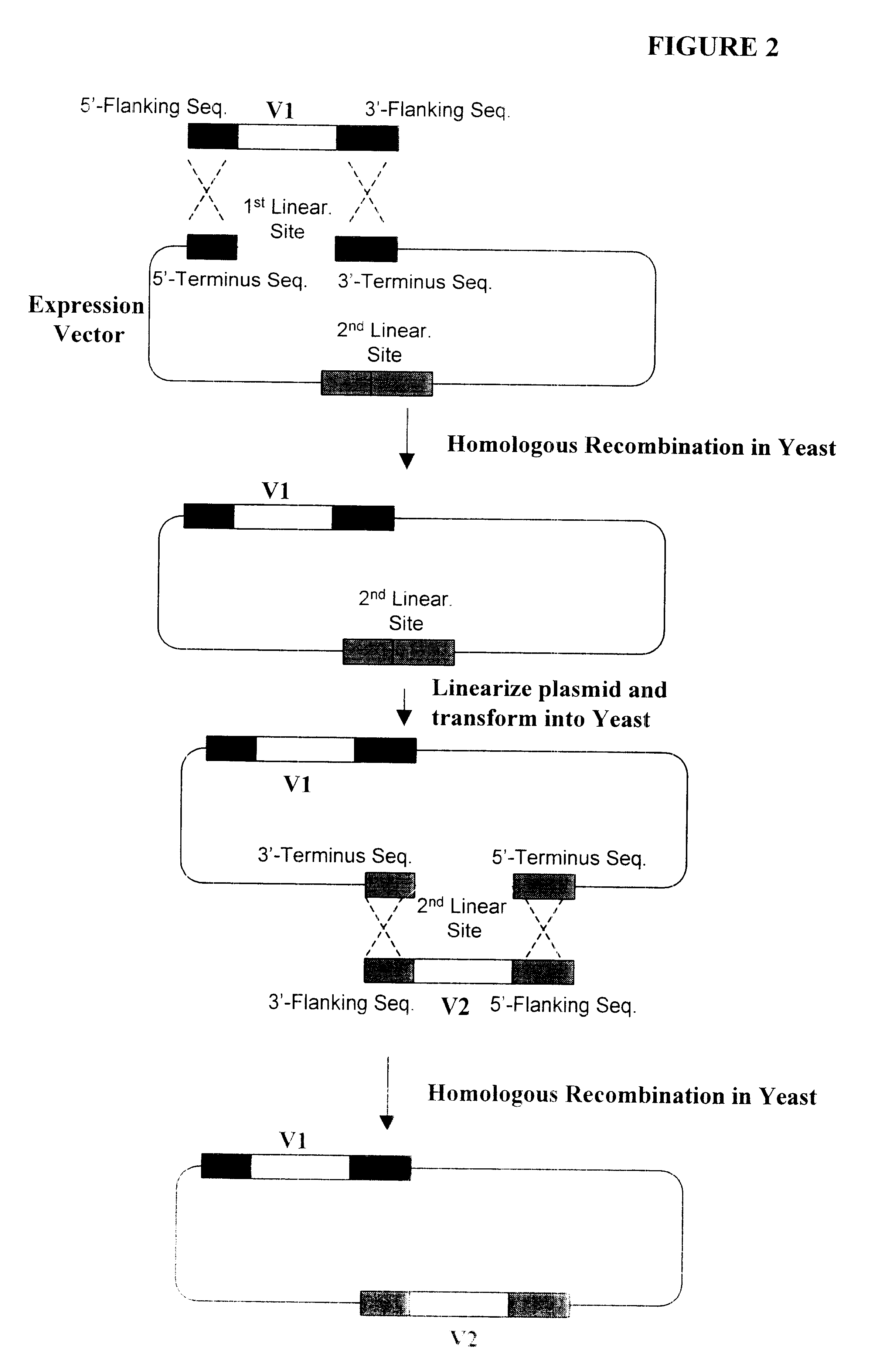
Assembly and screening of highly complex and fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6610472B1High affinityEasy to assembleFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNucleotide
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening a library of highly diverse protein complexes for their ability to bind to other proteins or oligonucleotide sequences. In one aspect of the invention, a library of expression vectors is provided for expressing the library of protein complexes. The library comprises a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first polypeptide subunit; and a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second polypeptide subunit. The first and second nucleotide sequences each independently varies within the library of expression vectors. In addition, the first and second polypeptide subunit are expressed as separate proteins which self-assemble to form a protein complex, such as a double-chain antibody fragment (dcFv or Fab) and a fully assembled antibody, in cells into which the library of expression vectors are introduced. The library of expression vectors can be efficiently generated in yeast cells through homologous recombination; and the encoded proteins complexes with high binding affinity to their target molecule can be selected by high throughput screening in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
High throughput screening of fatty acid composition
InactiveUS20070048872A1Process can be speededEasy to sampleBiological testingFatty-oils/fats productionHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAdemetionine
A method for the high throughput screening of fatty acid characteristics in seeds is provided. The method comprises feeding seeds individually to a sampling station; removing a sample from the seed in the sampling station; conveying the sample to a compartment in a sample tray; converting extracted oil from the sample in the sample tray to form a mixture of fatty acid methyl esters; and analyzing the mixture of fatty acid methyl esters from the sample to determine the fatty acid profile of the corresponding seed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Antifungal assay
InactiveUS6284480B1MicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntifungalHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention provides high throughput screening systems for identifying antifungal compounds. The method can be performed in plurality simultaneously with fluorescence or absorbance readouts.
Owner:CYTOKINETICS INC
Fiber optic apparatus and use thereof in combinatorial material science
InactiveUS20030142309A1Facilitate the discovery of commercially important polymericSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFiberHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Methods, systems and devices are described for rapid characterization and screening of liquid samples to determine properties (e.g., particle size, particle size distribution, molar mass and / or molar mass distribution) thereof with static light scattering and / or dynamic light scattering. The liquid samples can be solutions, emulsions, suspensions or dispersions. One method, includes providing a vessel containing a liquid sample having an exposed surface that defines a gas-liquid sample interface, and analyzing the sample by light scattering methods that include transmitting light through the gas-liquid sample interface into the sample, and detecting light scattered from the sample or from a component thereof. Additional methods are directed to characterizing a plurality of liquid samples or components thereof. The methods, systems, and devices have applications in high-throughput screening, and particularly, in combinatorial materials research and in industrial process control.
Owner:WYATT TECH
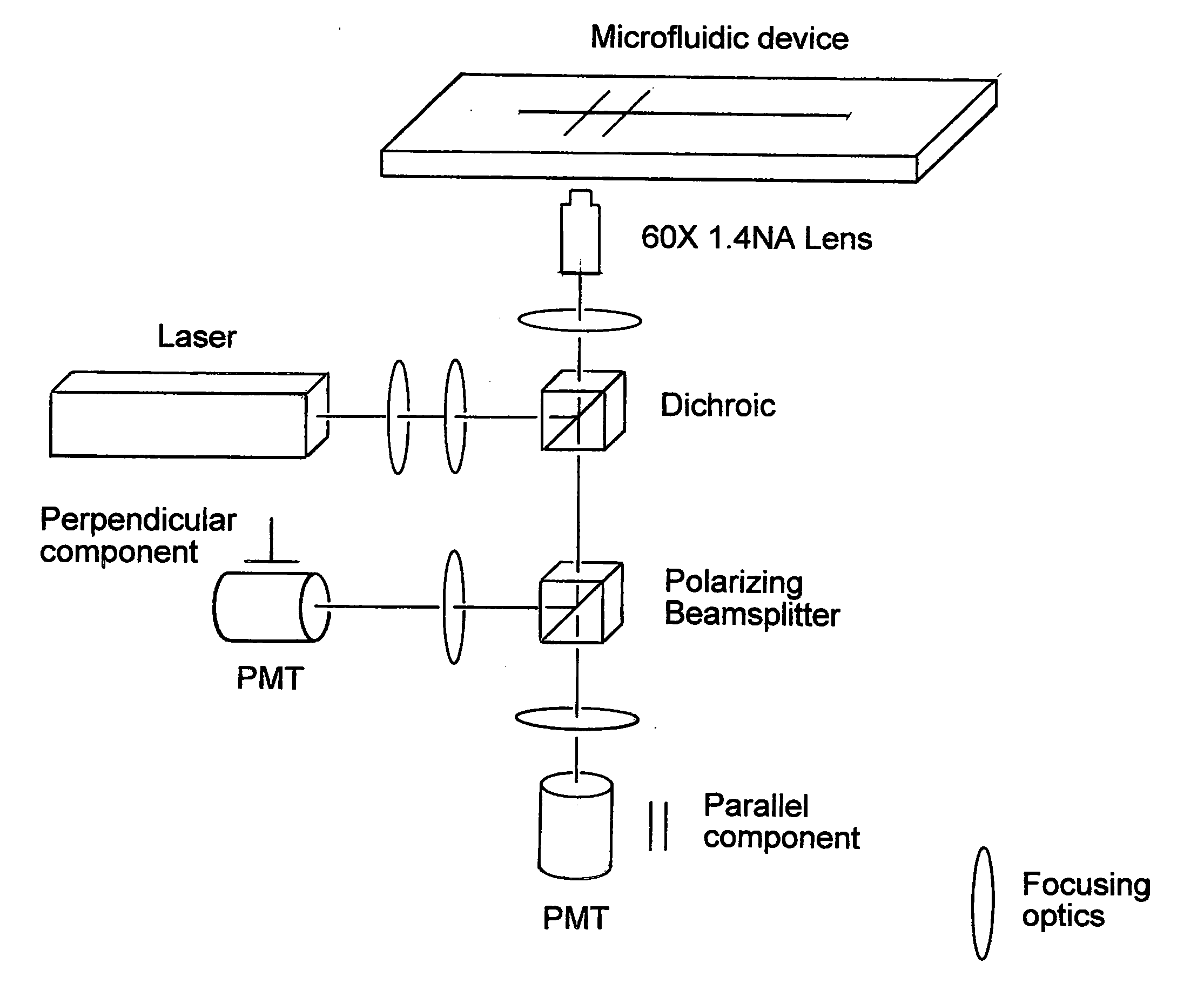
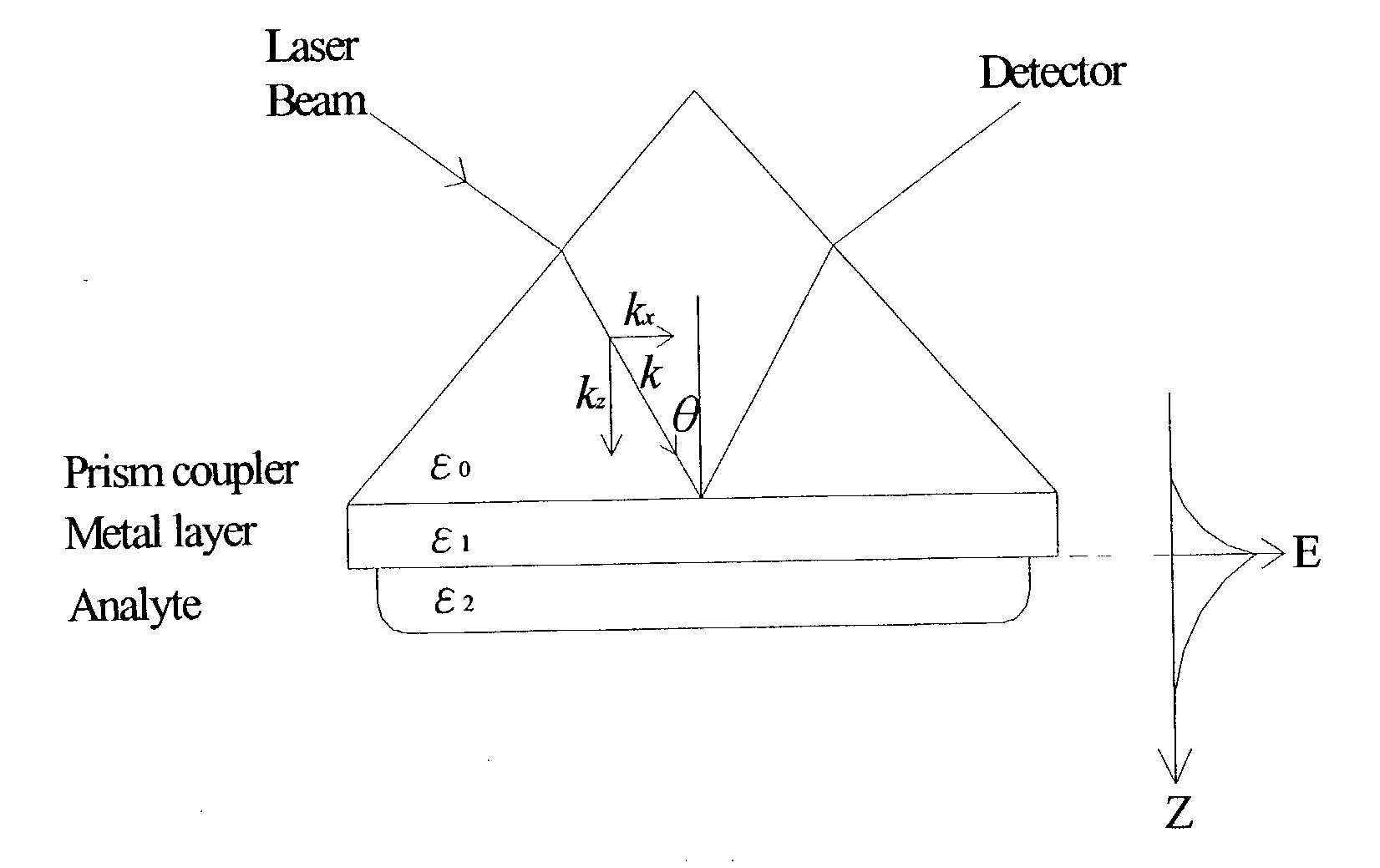
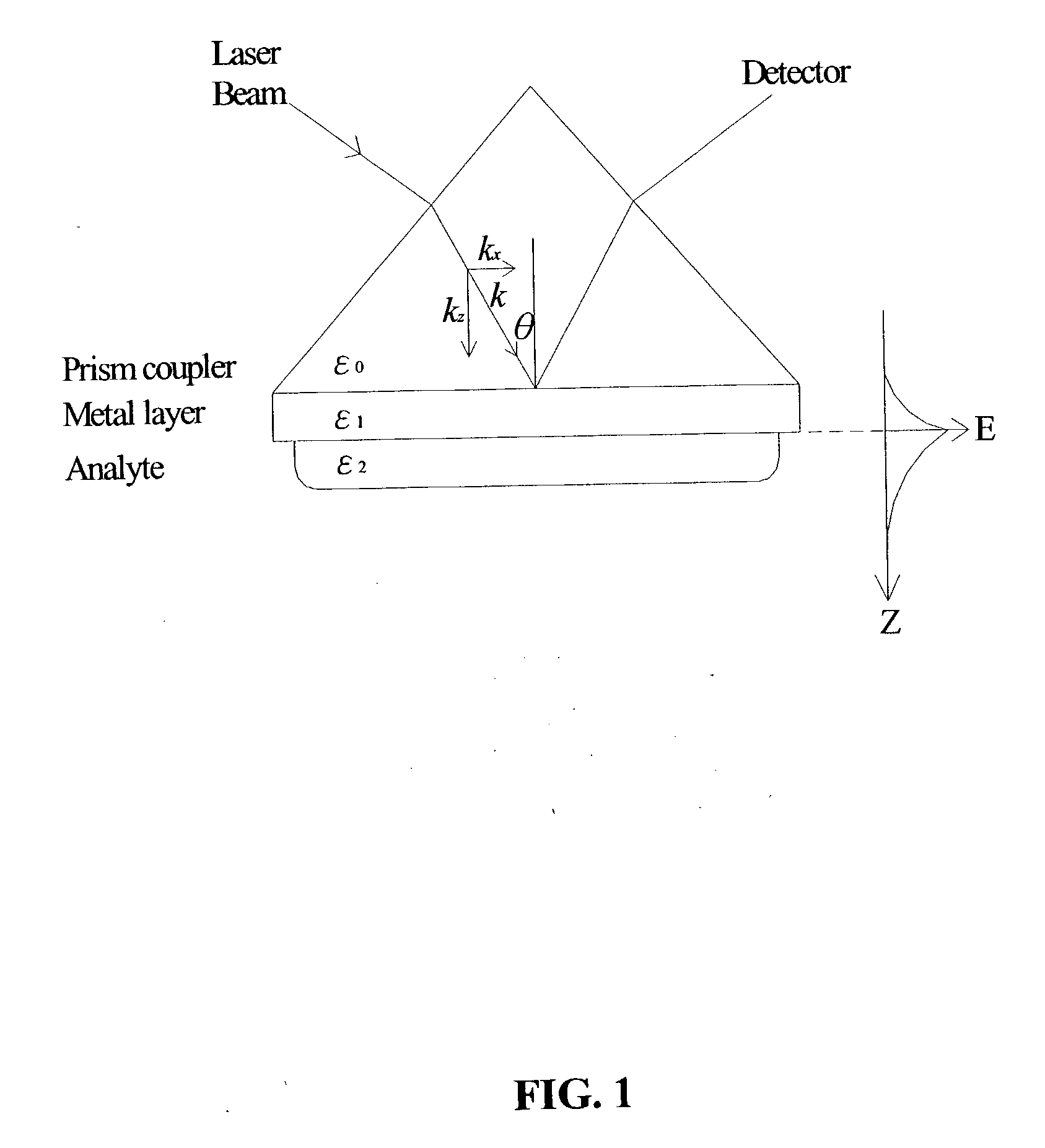
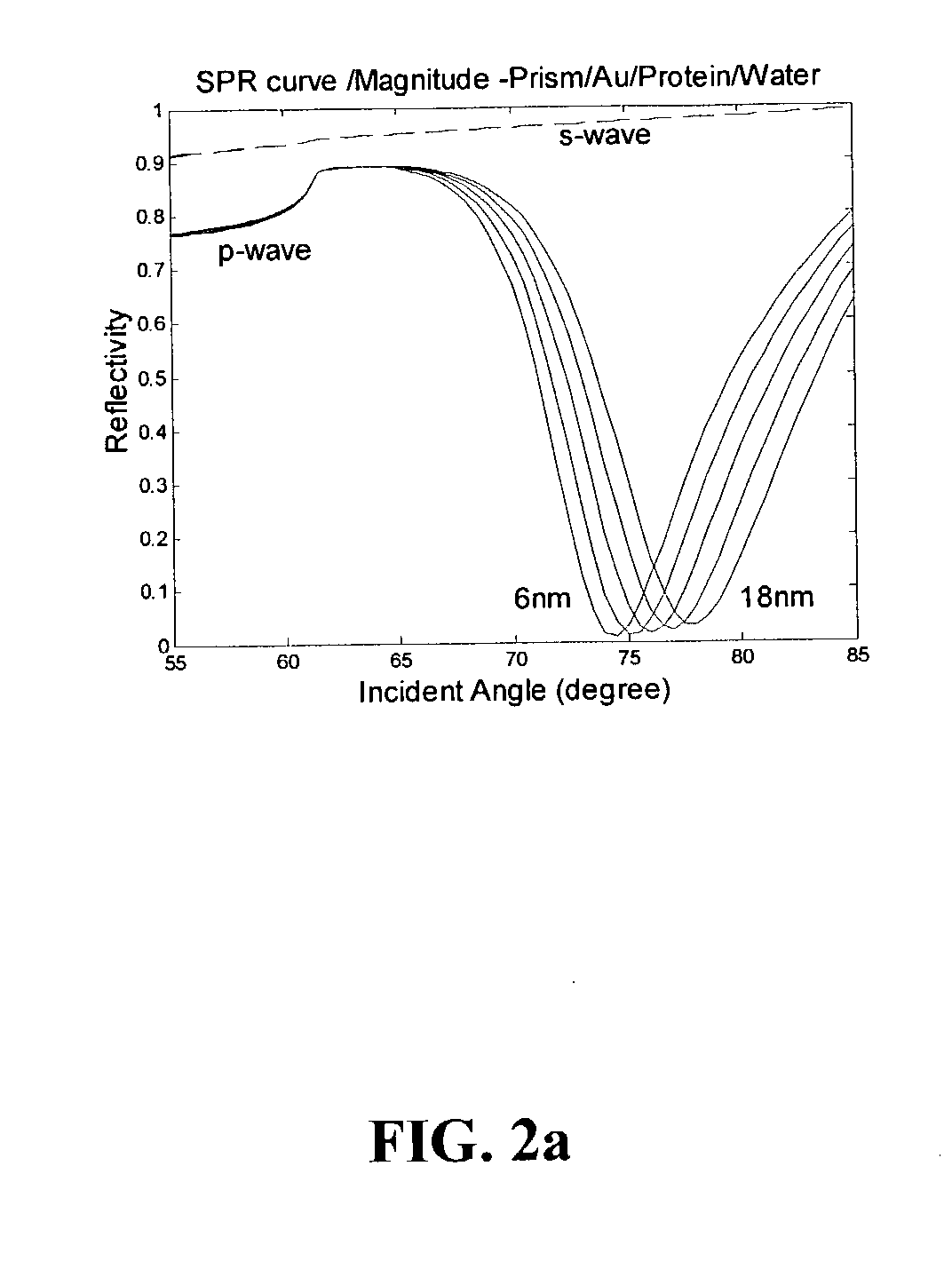
Surface plasmon resonance shifting interferometry imaging system for biomolecular interaction analysis
InactiveUS20030219809A1High resolutionHigh-throughput screening capabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementReal time analysisHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A novel surface plasmon resonance (SPR) imaging system based on modified Mach-Zehnder phase-shifting interferometry (PSI) measures the spatial phase variation of a resonantly reflected light during chemical or biological detection. The SPR microarray can diagnose the target analyte without additional labeling in the real-time analysis. Experimental results demonstrate that the detection limit of the SPR PSI imaging system is improved to about 1 pg / mm<2 >surface coverage of chemical or biological material for each individual spot over that of the conventional SPR imaging system. Therefore, the SPR PSI imaging system and its SPR microarray can provide the capability of real-time analysis, with high resolution and at high-throughput screening rates.
Owner:U VISION BIOTECH
High throughput screening of crystallization of materials
InactiveUS7195670B2From normal temperature solutionsFixed microstructural devicesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSize determination
High throughput screening of crystallization of a target material is accomplished by simultaneously introducing a solution of the target material into a plurality of chambers of a microfabricated fluidic device. The microfabricated fluidic device is then manipulated to vary the solution condition in the chambers, thereby simultaneously providing a large number of crystallization environments. Control over changed solution conditions may result from a variety of techniques, including but not limited to metering volumes of crystallizing agent into the chamber by volume exclusion, by entrapment of volumes of crystallizing agent determined by the dimensions of the microfabricated structure, or by cross-channel injection of sample and crystallizing agent into an array of junctions defined by intersecting orthogonal flow channels.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
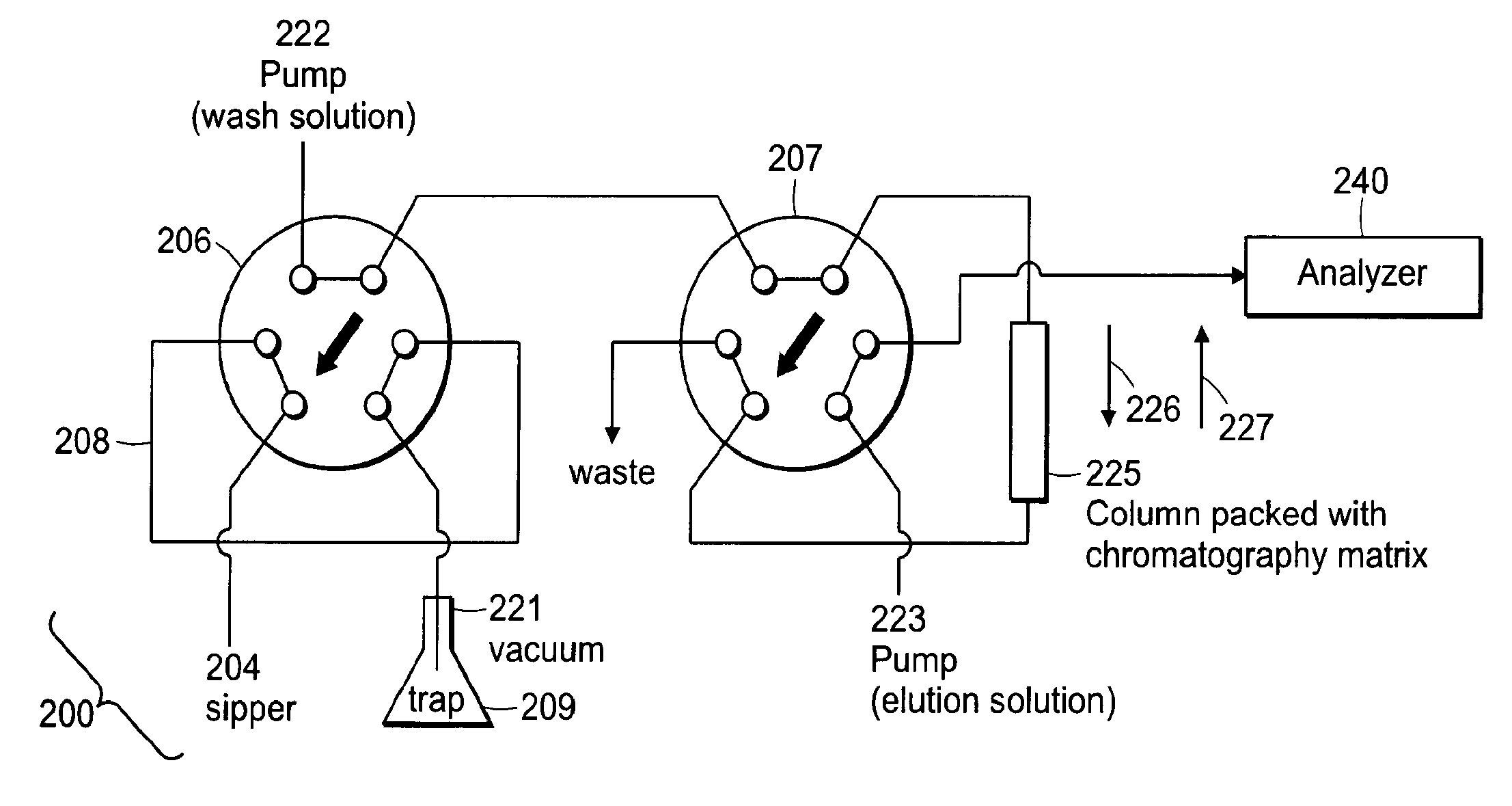
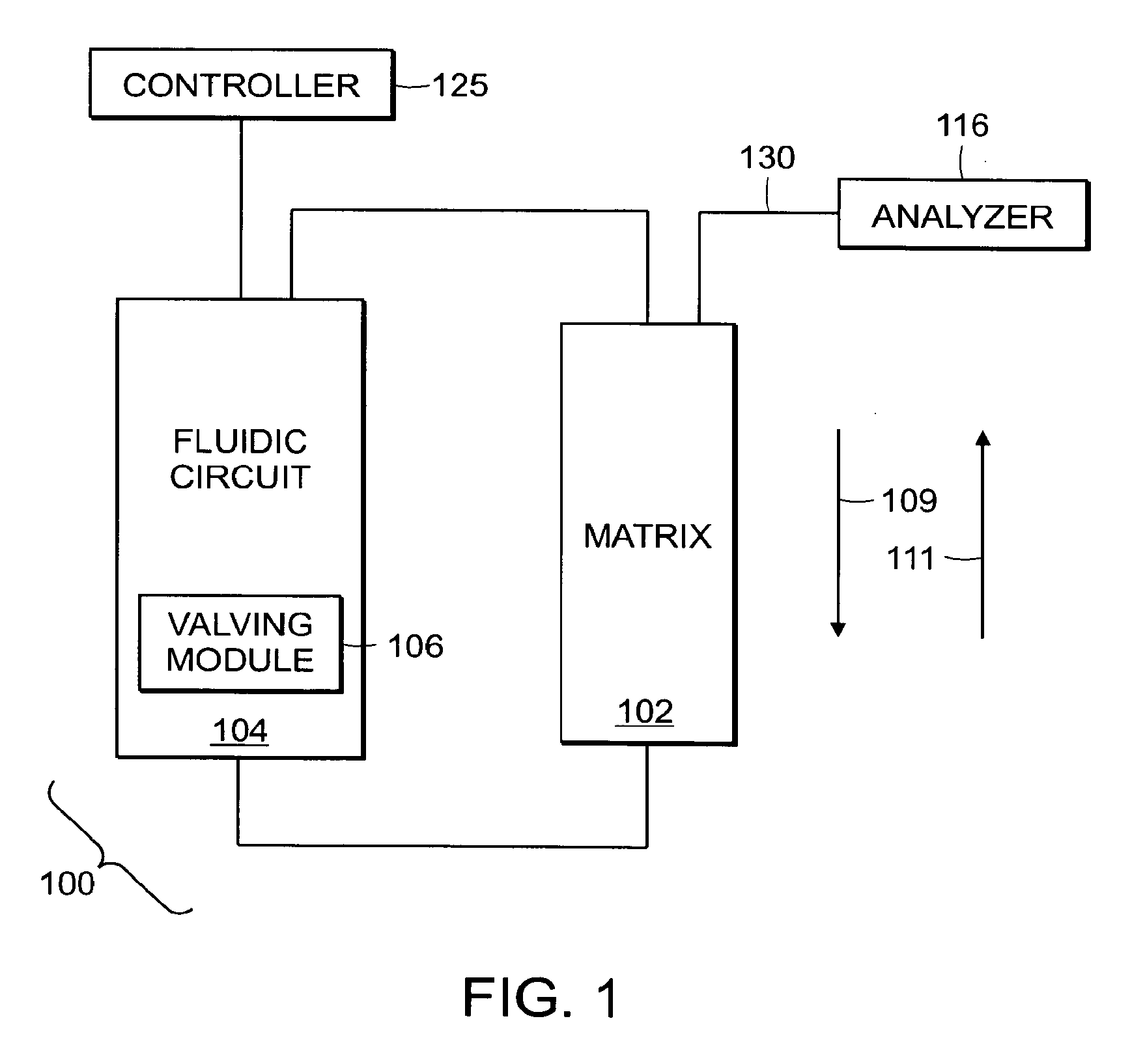
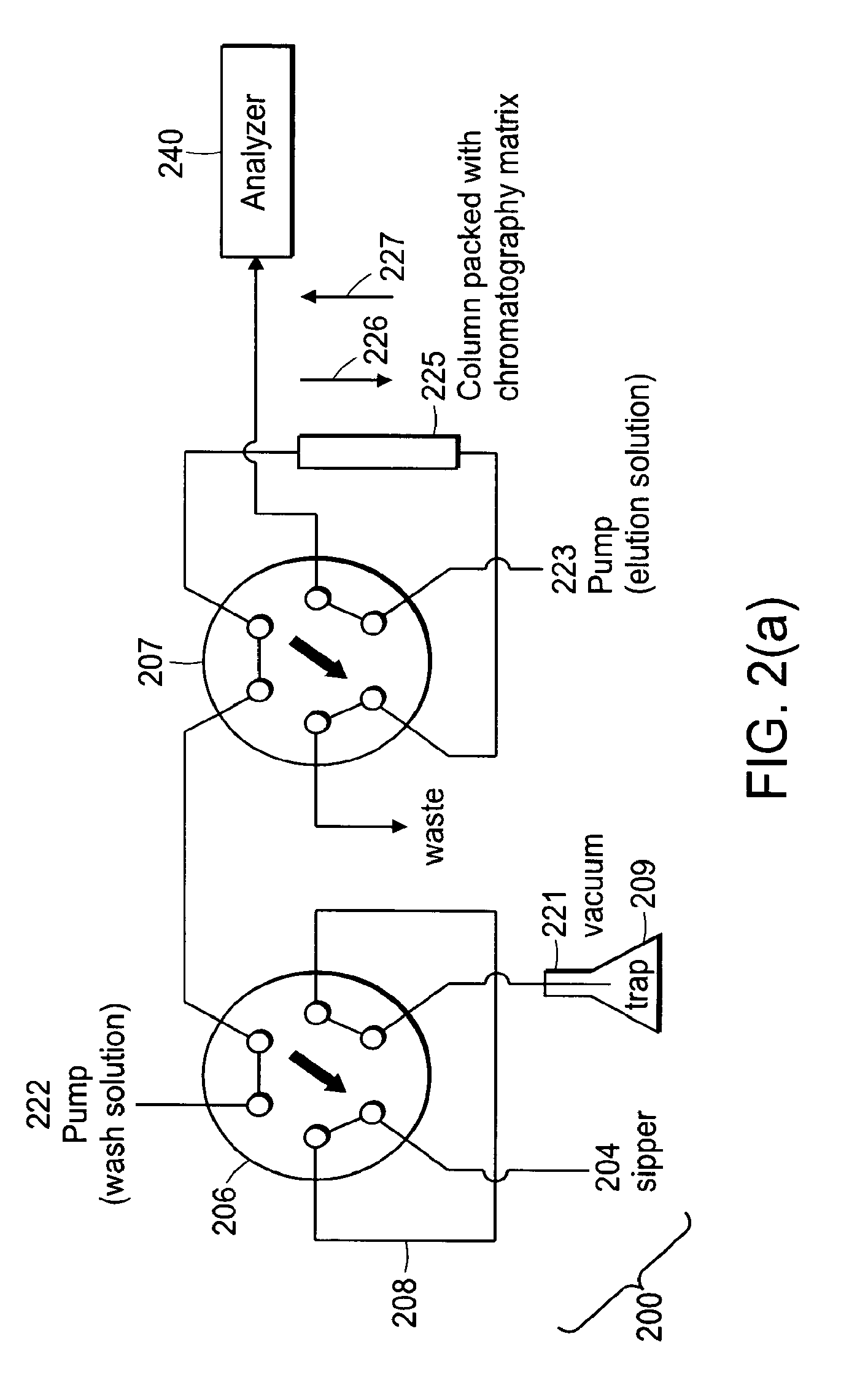
Systems and methods for high-throughput screening of fluidic samples
InactiveUS20100024527A1High throughput screeningFacilitate continuous flowIon-exchange process apparatusSequential/parallel process reactionsAnalyteHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Aspects of the invention provide systems and methods for high-throughput screening of fluidic samples. In some embodiments, two chromatography columns are utilized in series. The first chromatography column can have a high affinity for phosphorylated compounds while the second chromatography column has a high affinity for one or more analytes of interest.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Source and target management system for high throughput transfer of liquids
InactiveUS20040120855A1Spray nozzlesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPrecession
An apparatus for high-throughput screening and generation of chemical libraries. The apparatus comprises computer controlled mechanical displacement devices and storage queues capable of managing a large number of source well plates and target well plates. In one aspect of the invention, precession alignment mechanisms are provided for efficient transfer of liquid from source well plates to target well plates. The apparatus may be configured such that any source fluid in any of the source well plates may be transferred to any target location within any of the target well plates in any sequence defined by the user. The computer controller may track the location of all the source well plates and target well plates and allow user defined association of any source well with any target well in any order defined by the user, thus providing an effective platform for chemical and biochemical synthesis and screening.
Owner:LABCYTE
High throughput screening of crystallization of materials
InactiveUS20050229839A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsFrom normal temperature solutionsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSize determination
High throughput screening of crystallization of a target material is accomplished by simultaneously introducing a solution of the target material into a plurality of chambers of a microfabricated fluidic device. The microfabricated fluidic device is then manipulated to vary the solution condition in the chambers, thereby simultaneously providing a large number of crystallization environments. Control over changed solution conditions may result from a variety of techniques, including but not limited to metering volumes of crystallizing agent into the chamber by volume exclusion, by entrapment of volumes of crystallizing agent determined by the dimensions of the microfabricated structure, or by cross-channel injection of sample and crystallizing agent into an array of junctions defined by intersecting orthogonal flow channels.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com