Patents
Literature
105results about How to "High-throughput screening" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
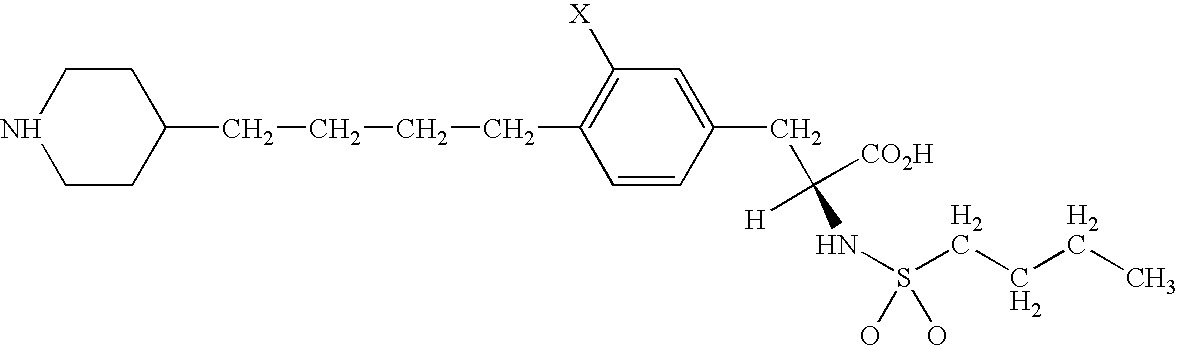
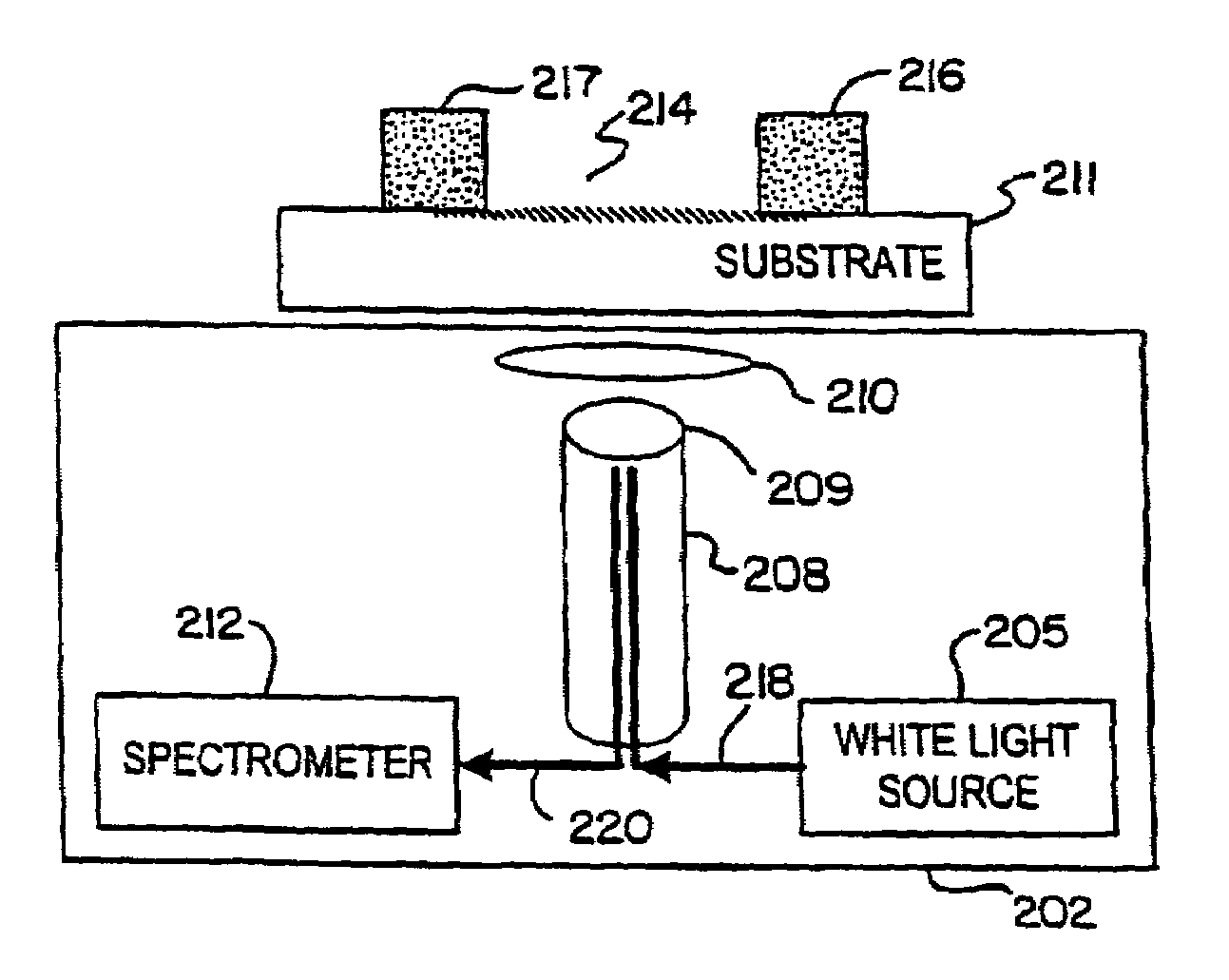
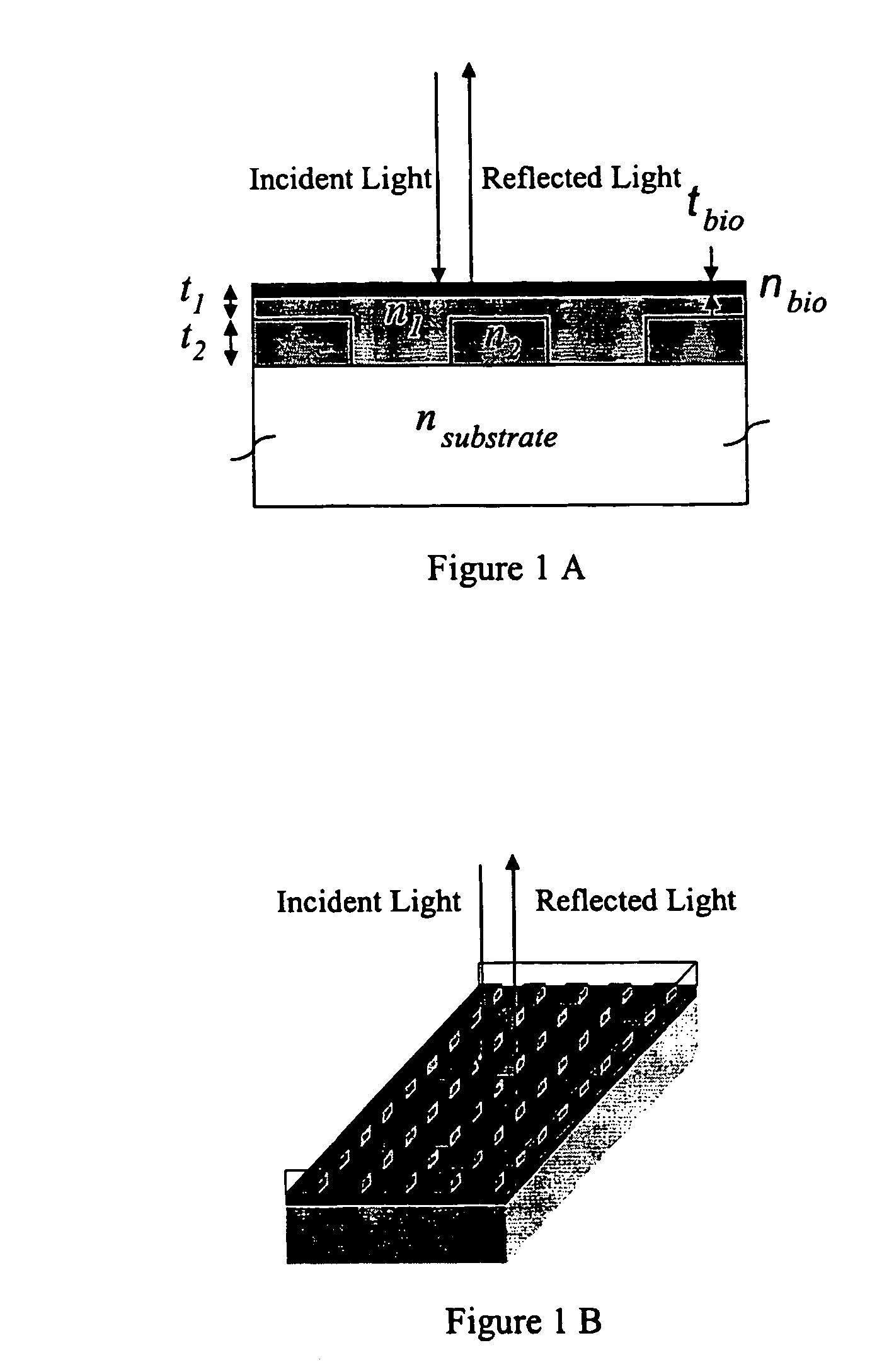
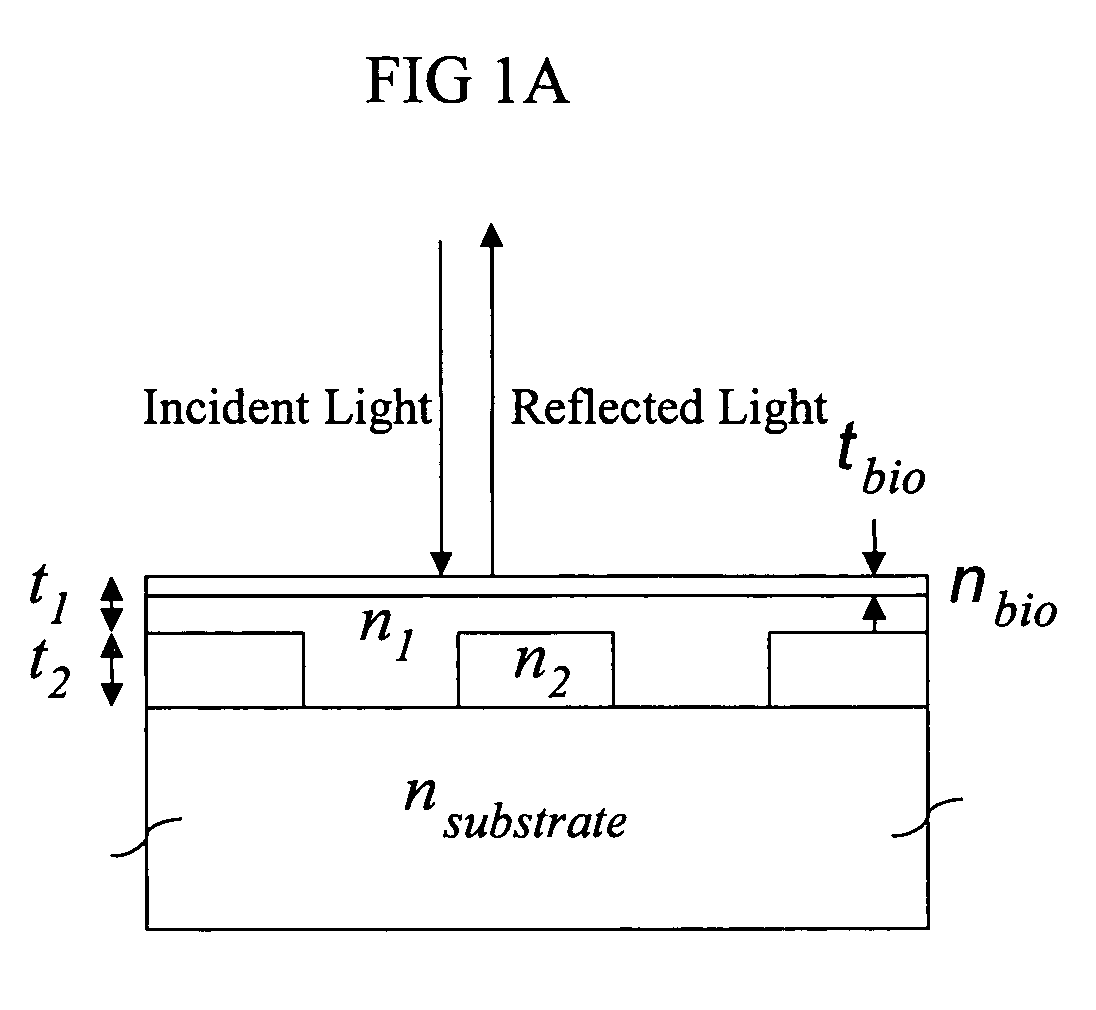
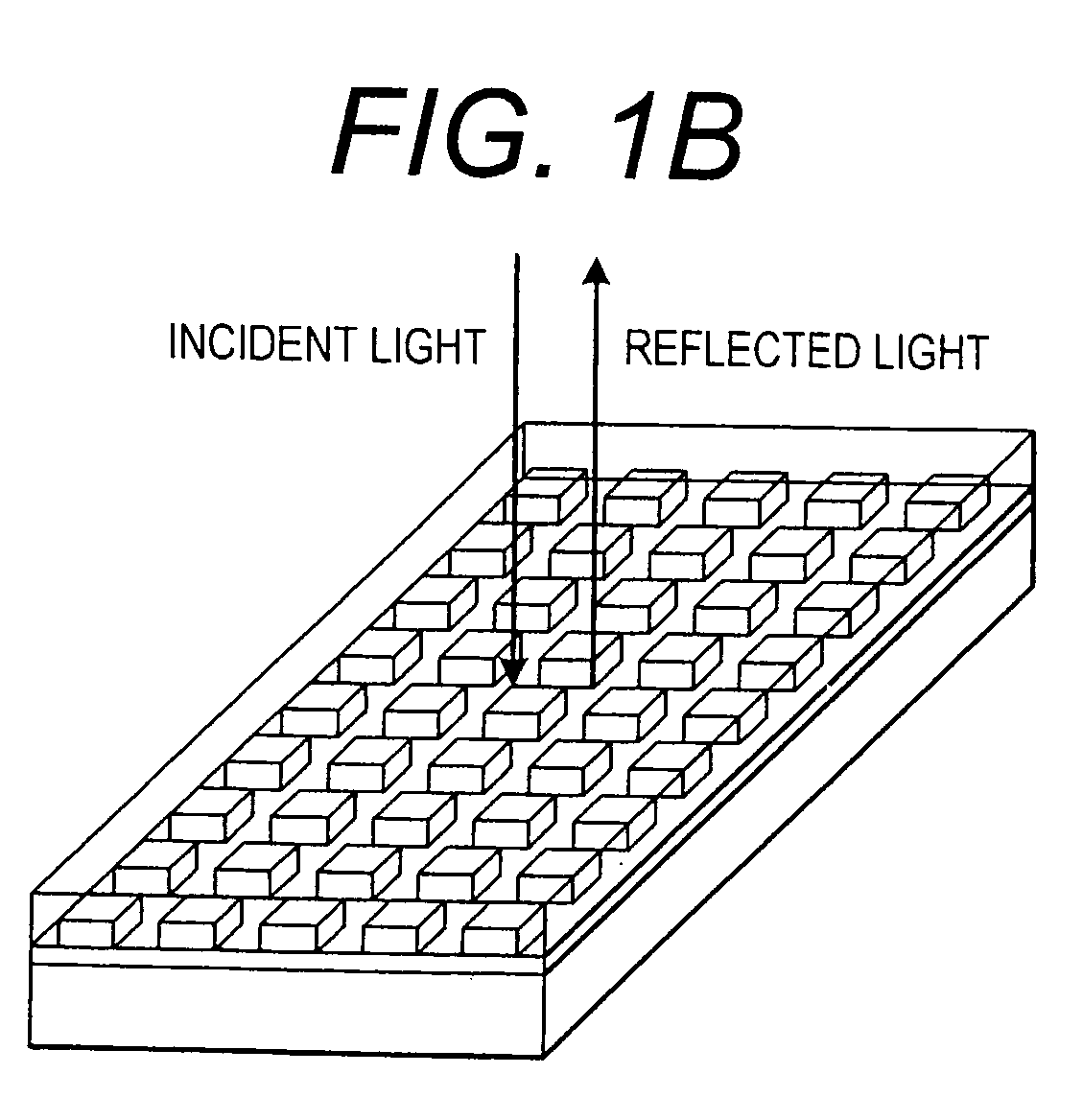
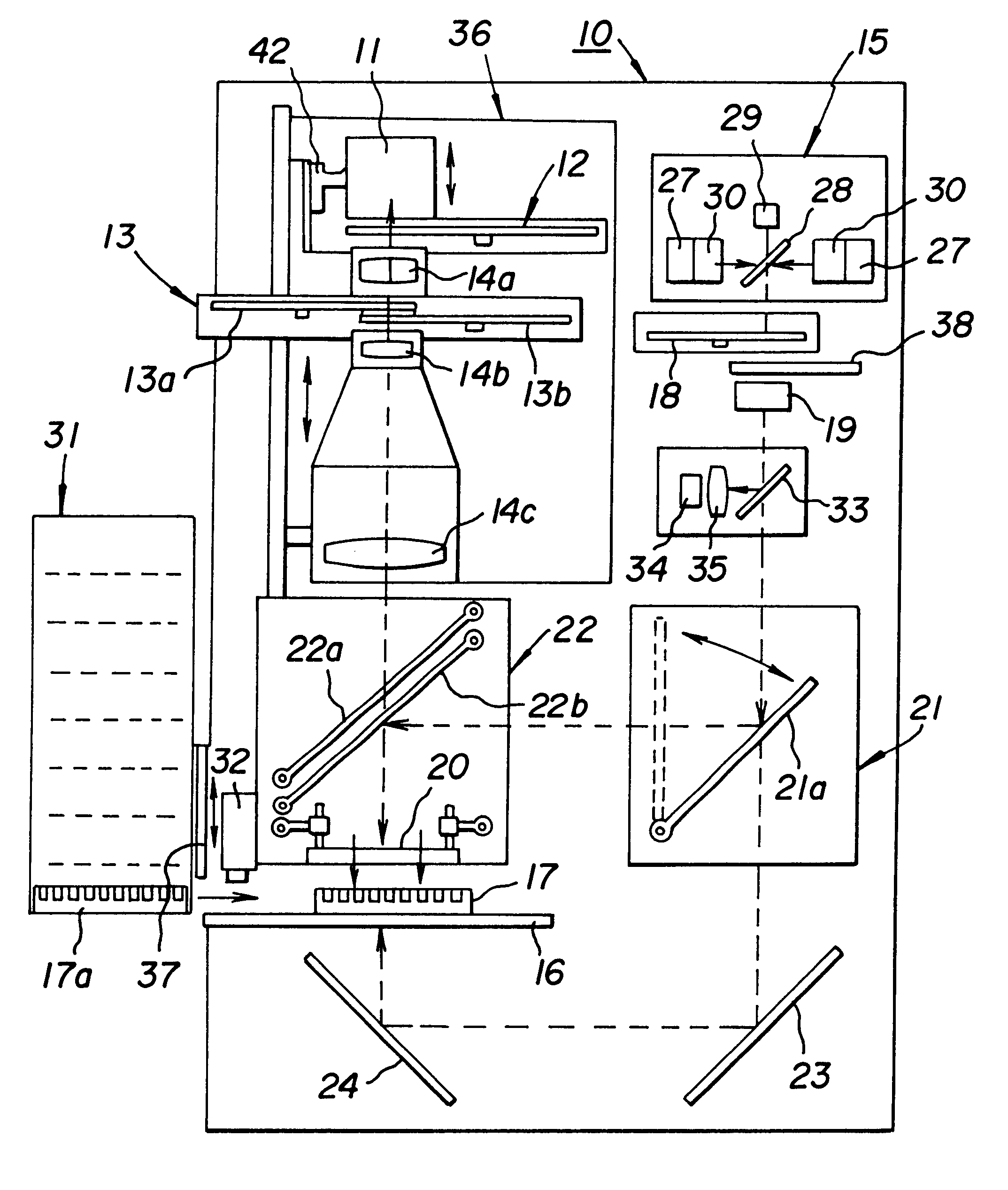
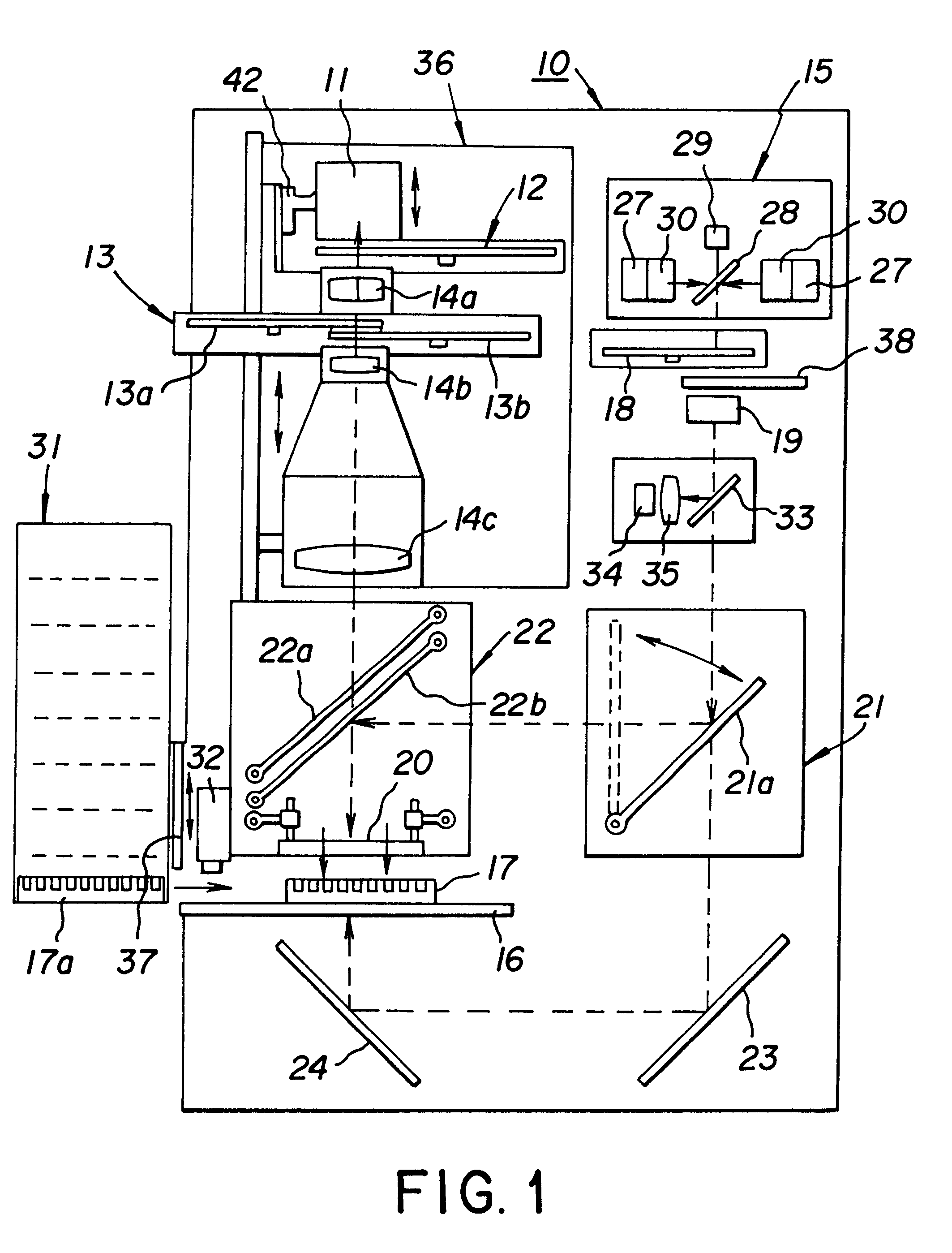
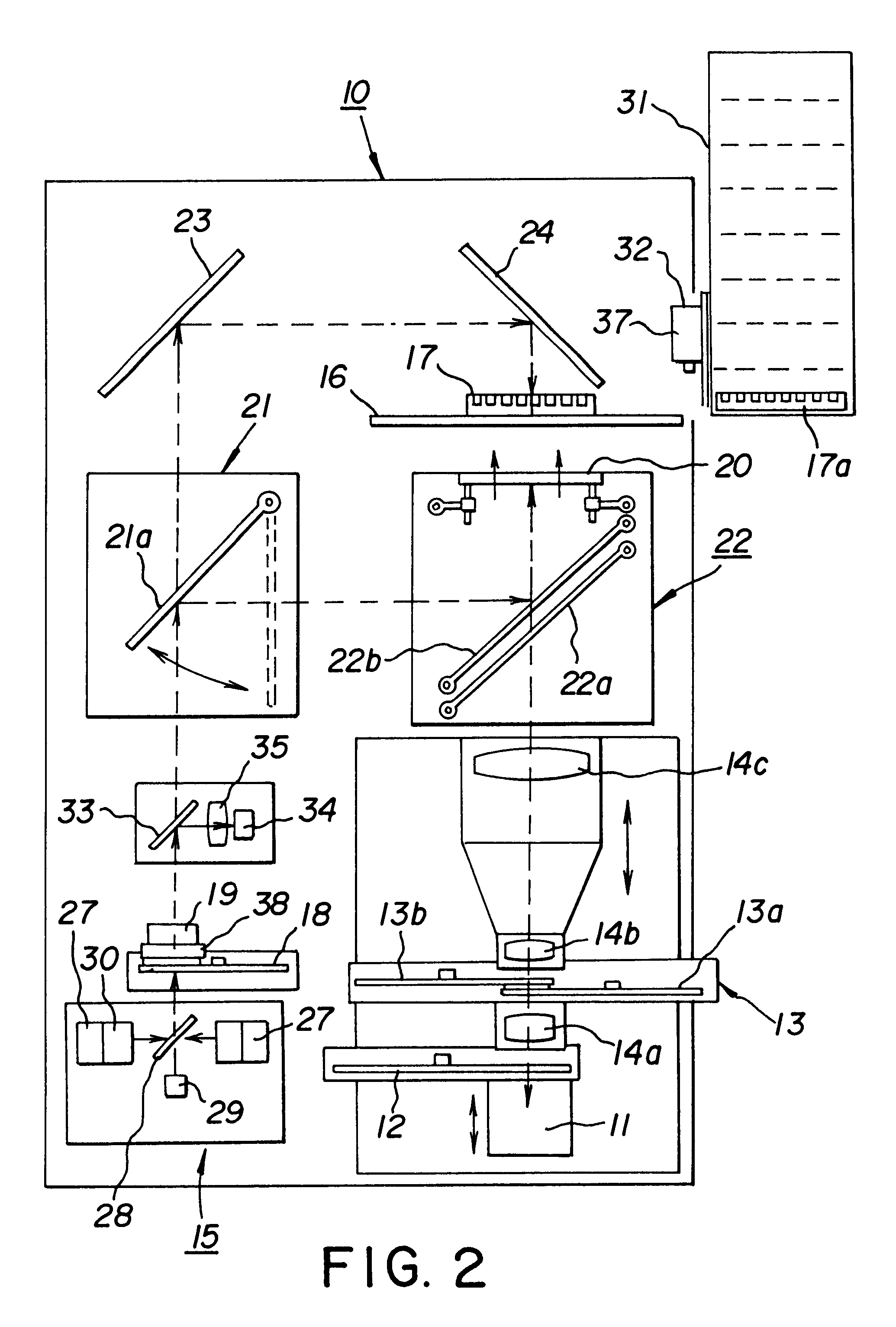
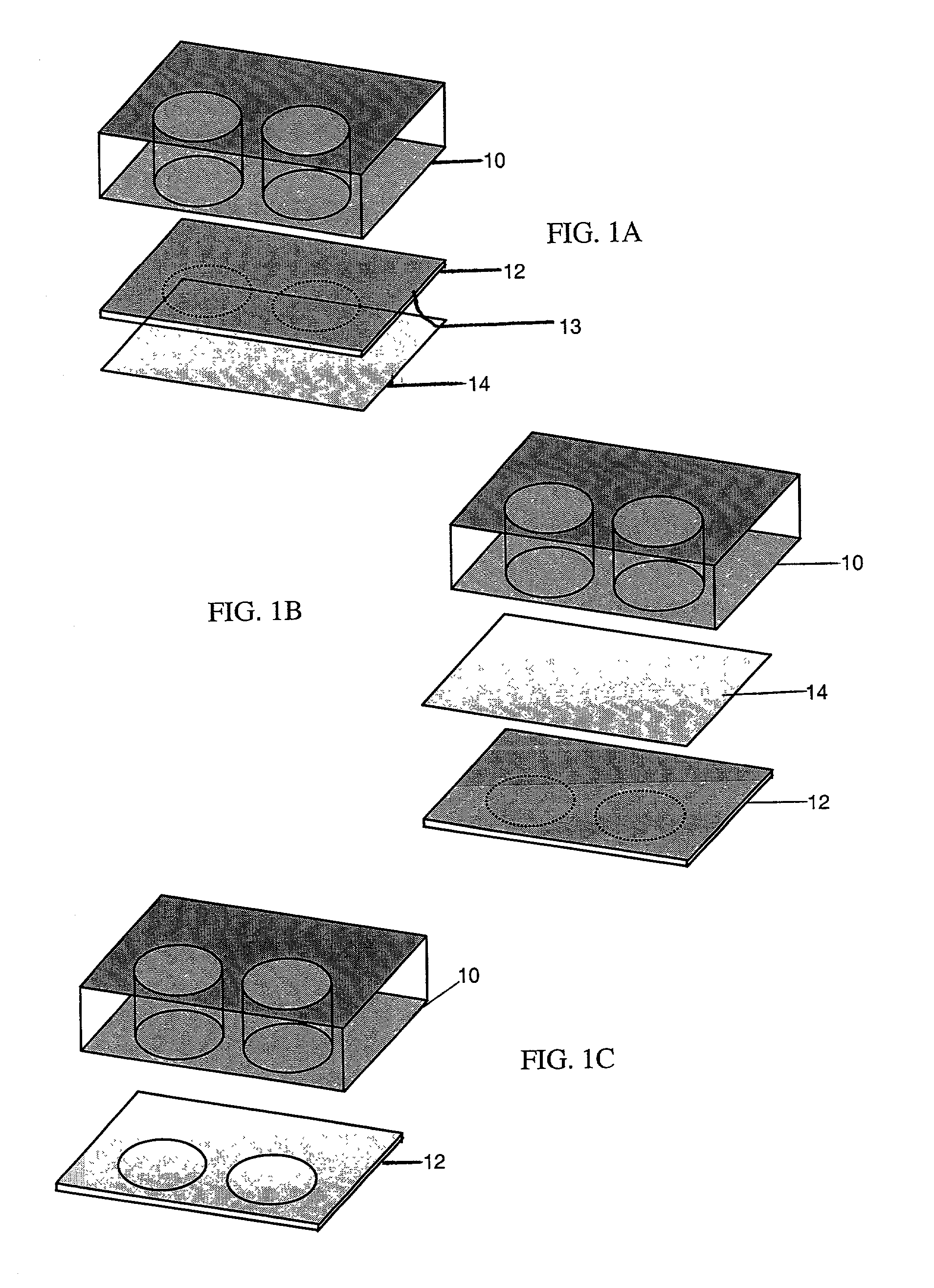
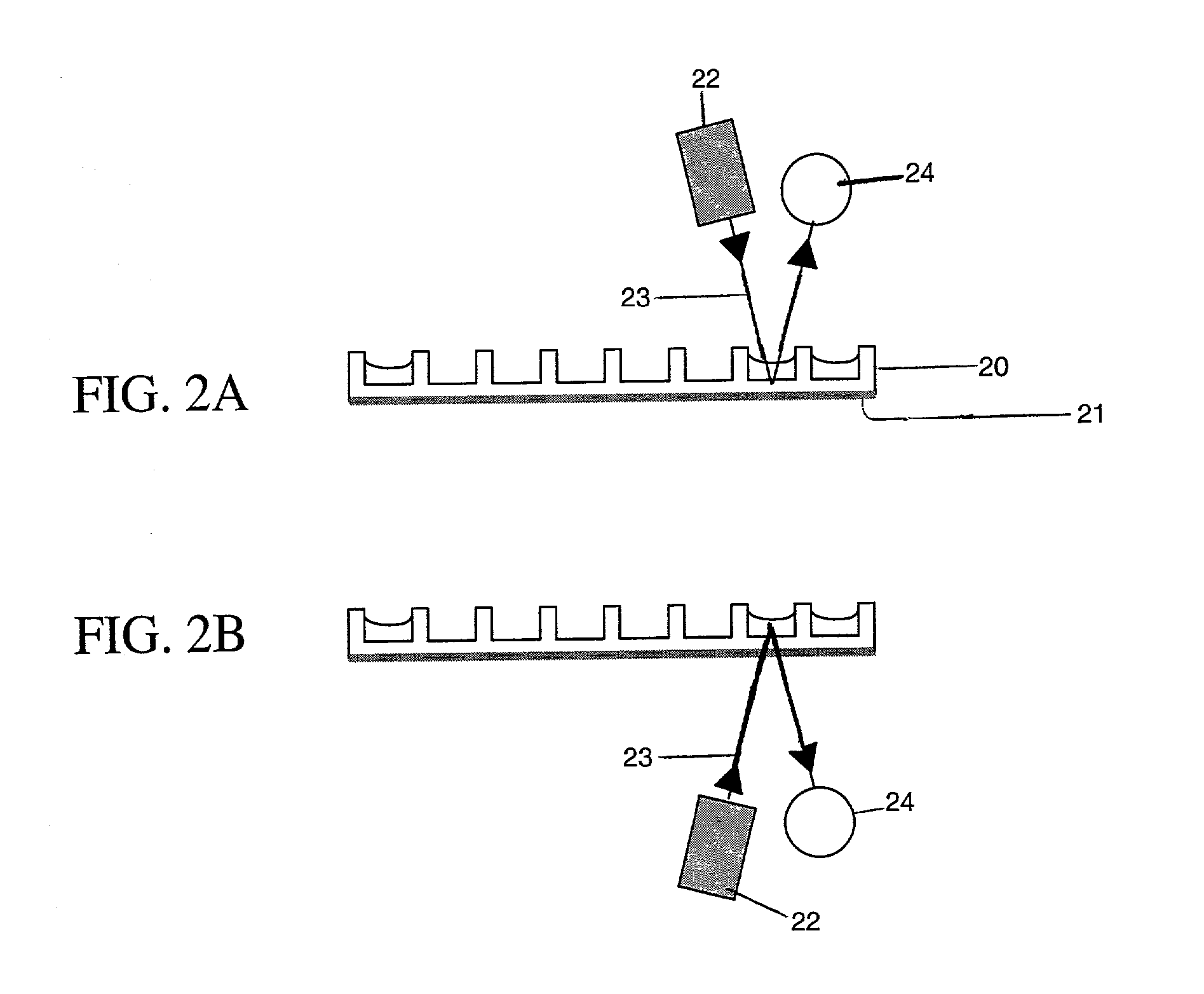
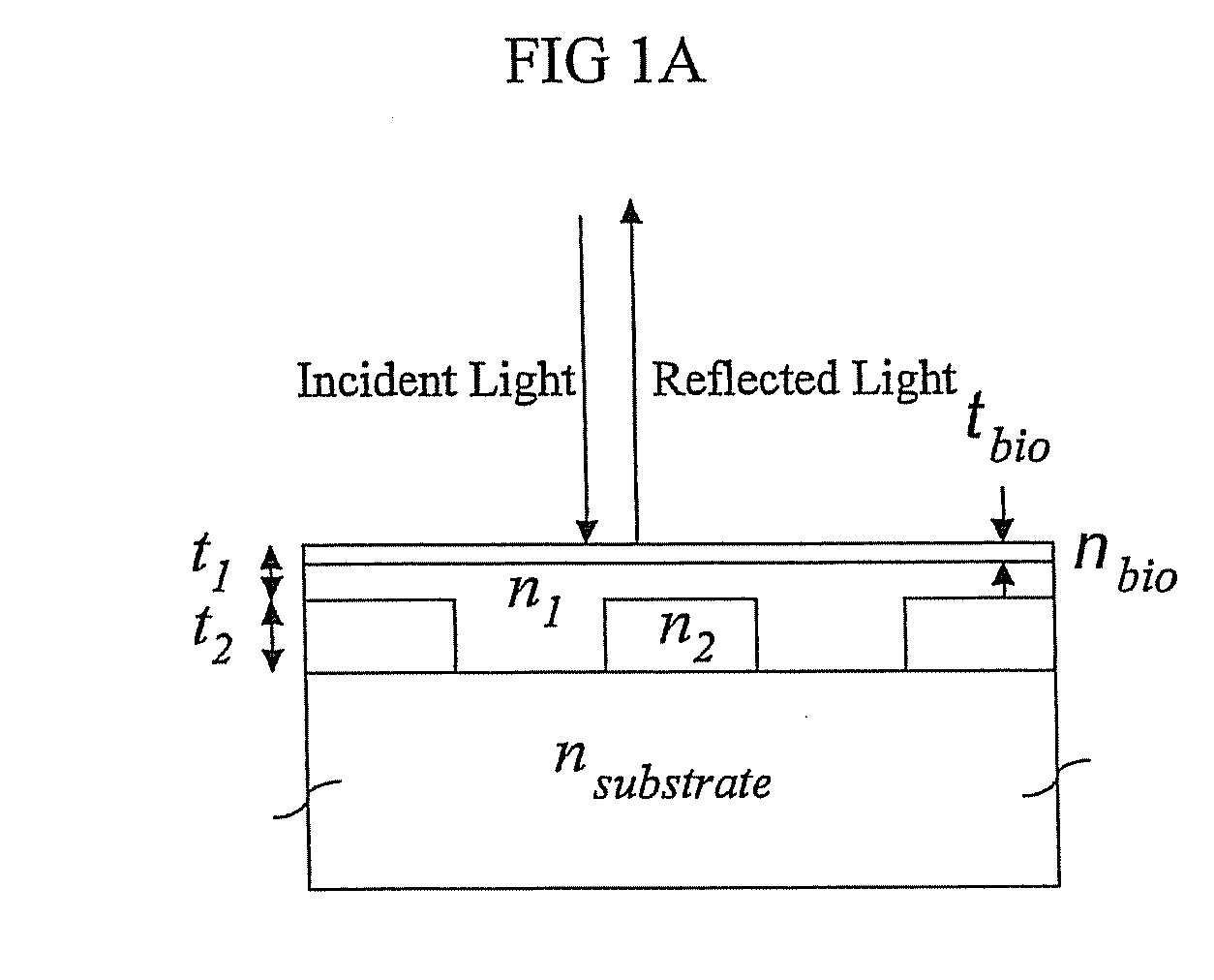
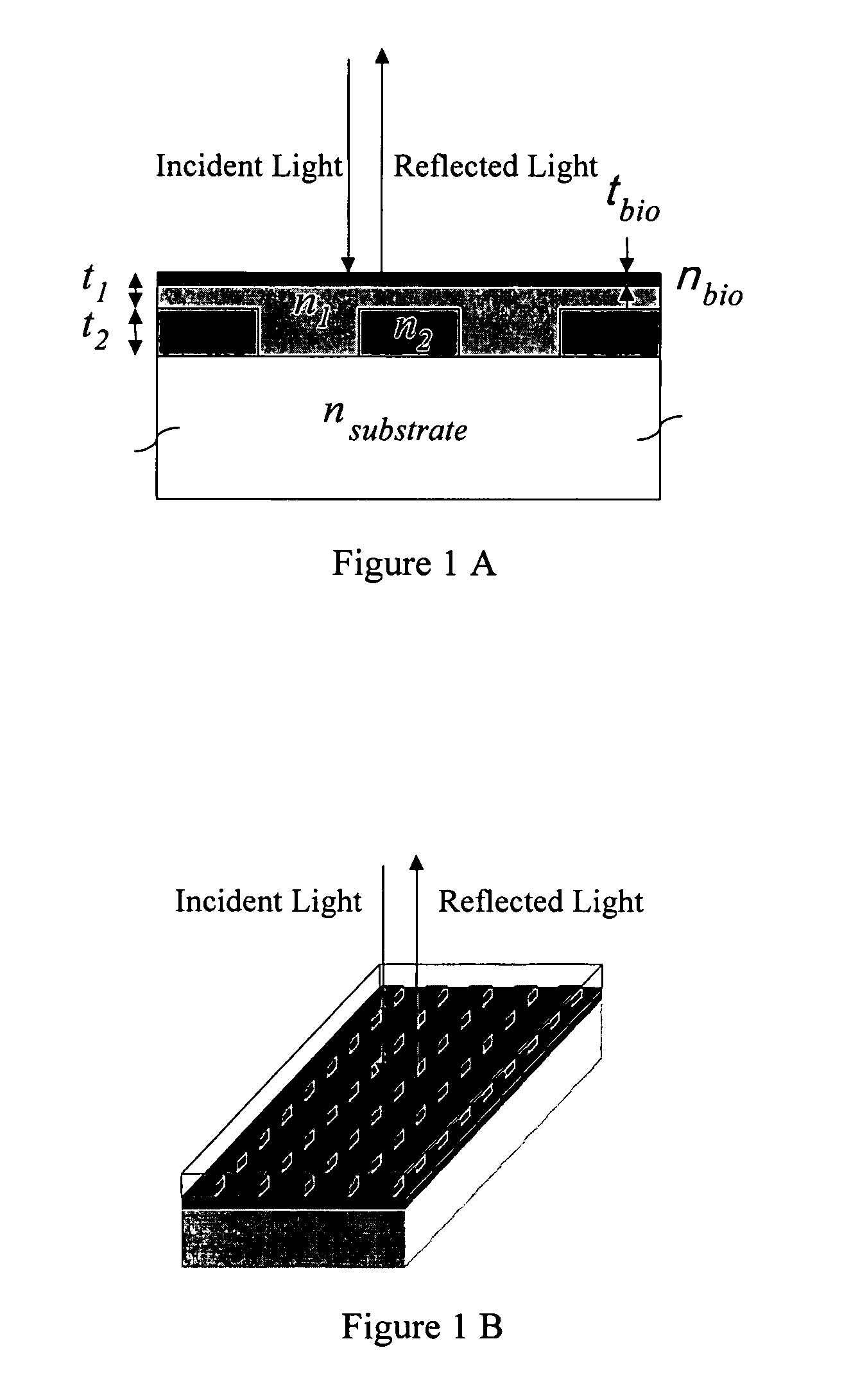
Method and instrument for detecting biomolecular interactions
InactiveUS7023544B2Inexpensively incorporatedHigh-throughput screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBeam splitterImaging spectrometer
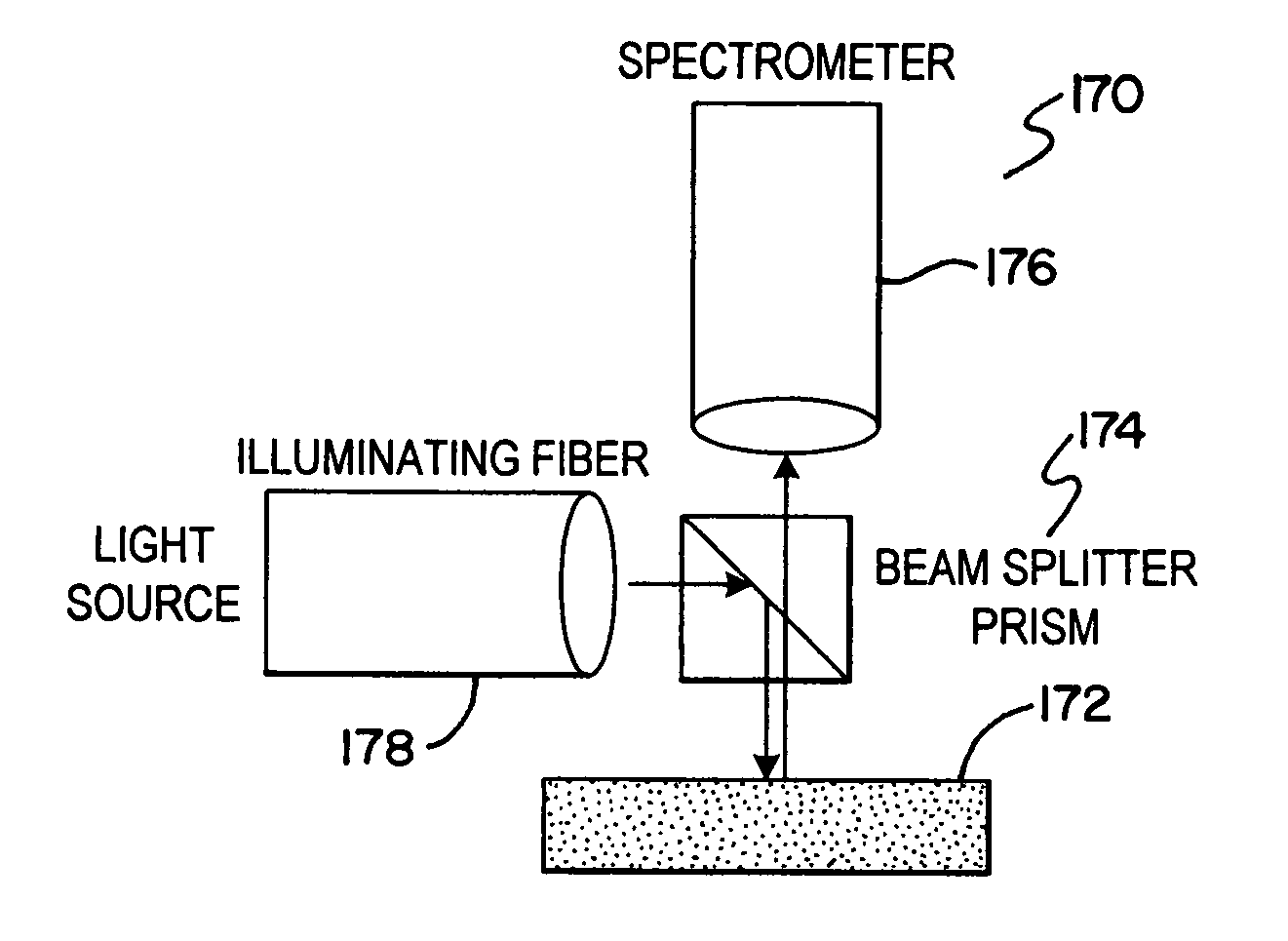
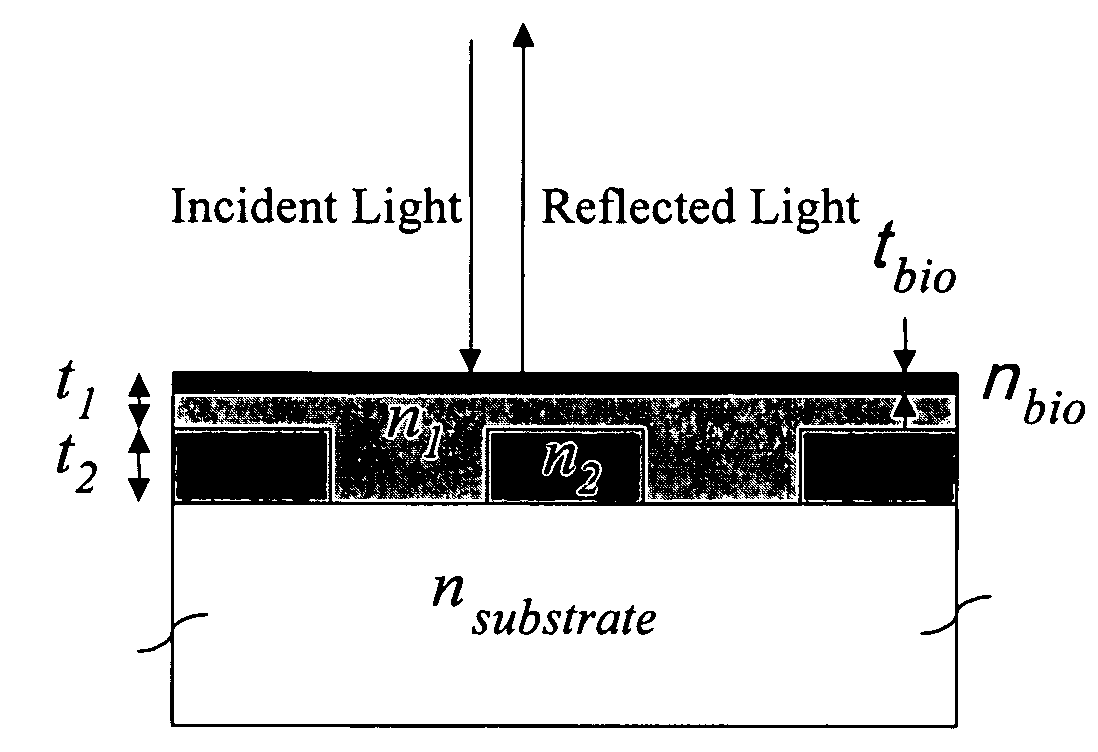
Method and apparatus for detecting biomolecular interactions. The use of labels is not required and the methods may be performed in a high-throughput manner. An instrument system for detecting a biochemical interaction on a biosensor. The system includes an array of detection locations comprises a light source for generating collimated white light. A beam splitter directs the collimated white light towards a surface of a sensor corresponding to the detector locations. A detection system includes an imaging spectrometer receiving the reflected light and generating an image of the reflected light.
Owner:X BODY
Rapid way to obtain high expression clones of mammalian cells using a methylcellulose and immunoprecipitation screening method
InactiveUS20050118652A1High throughput screeningImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsPeptide preparation methodsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsScreening method
The invention provides a genetic screening method for identifying a transfected cell expressing the polypeptide of interest. The methods allows for high throughput screening of recombinant cells for elevated levels of expression of the polypeptide of interest. The invention also provides capture media, formulations and methods of making and using thereof.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
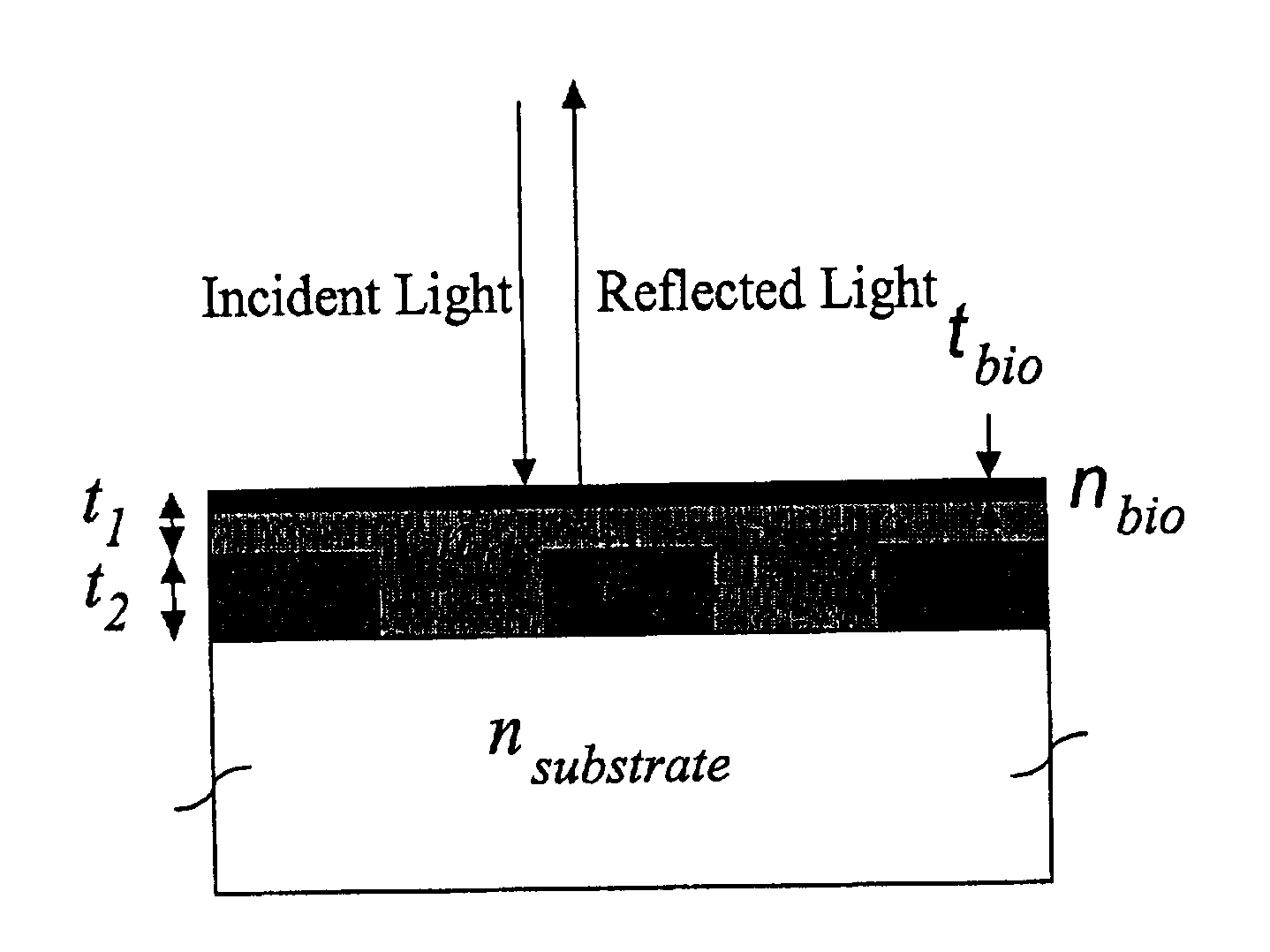
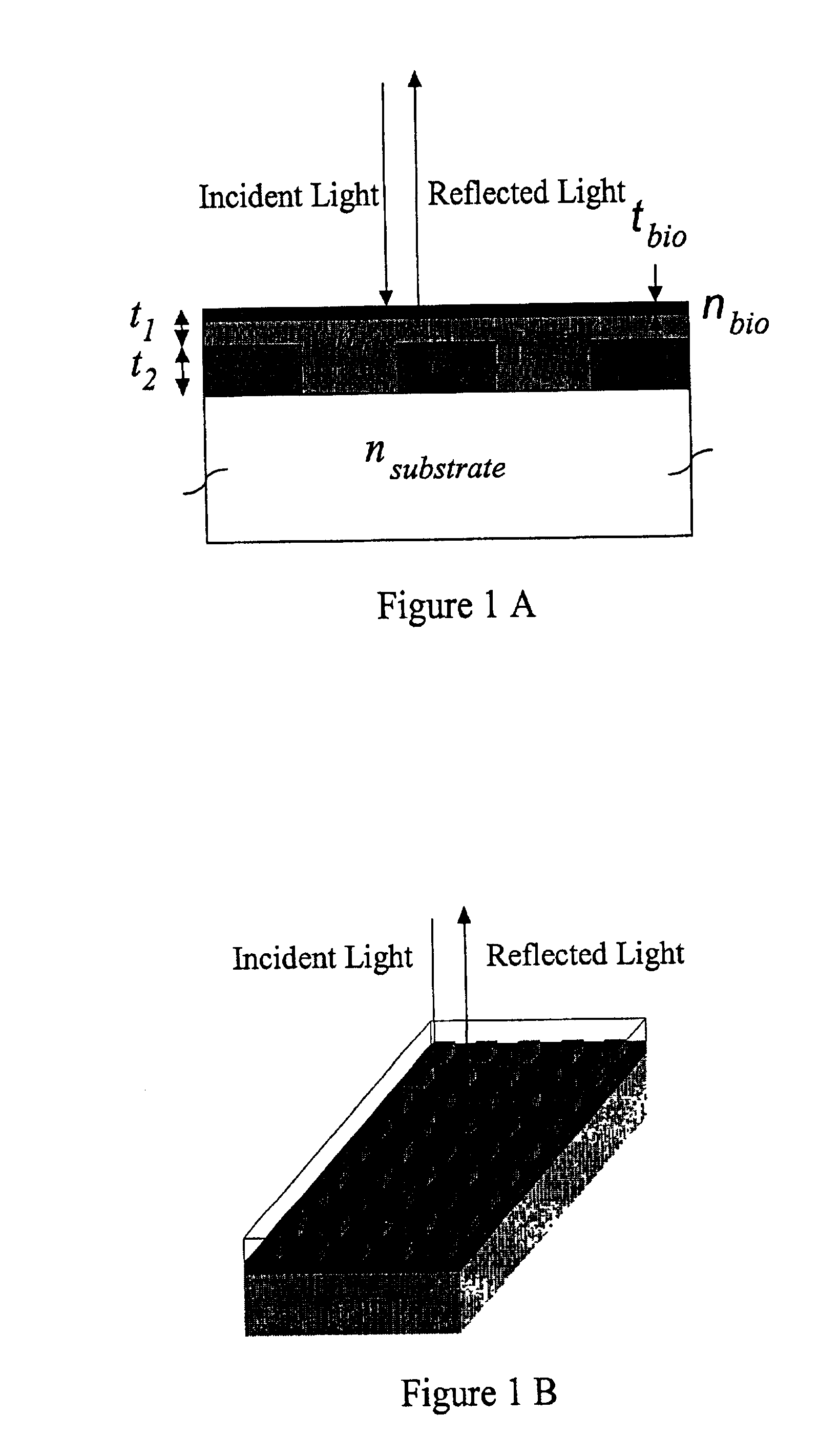
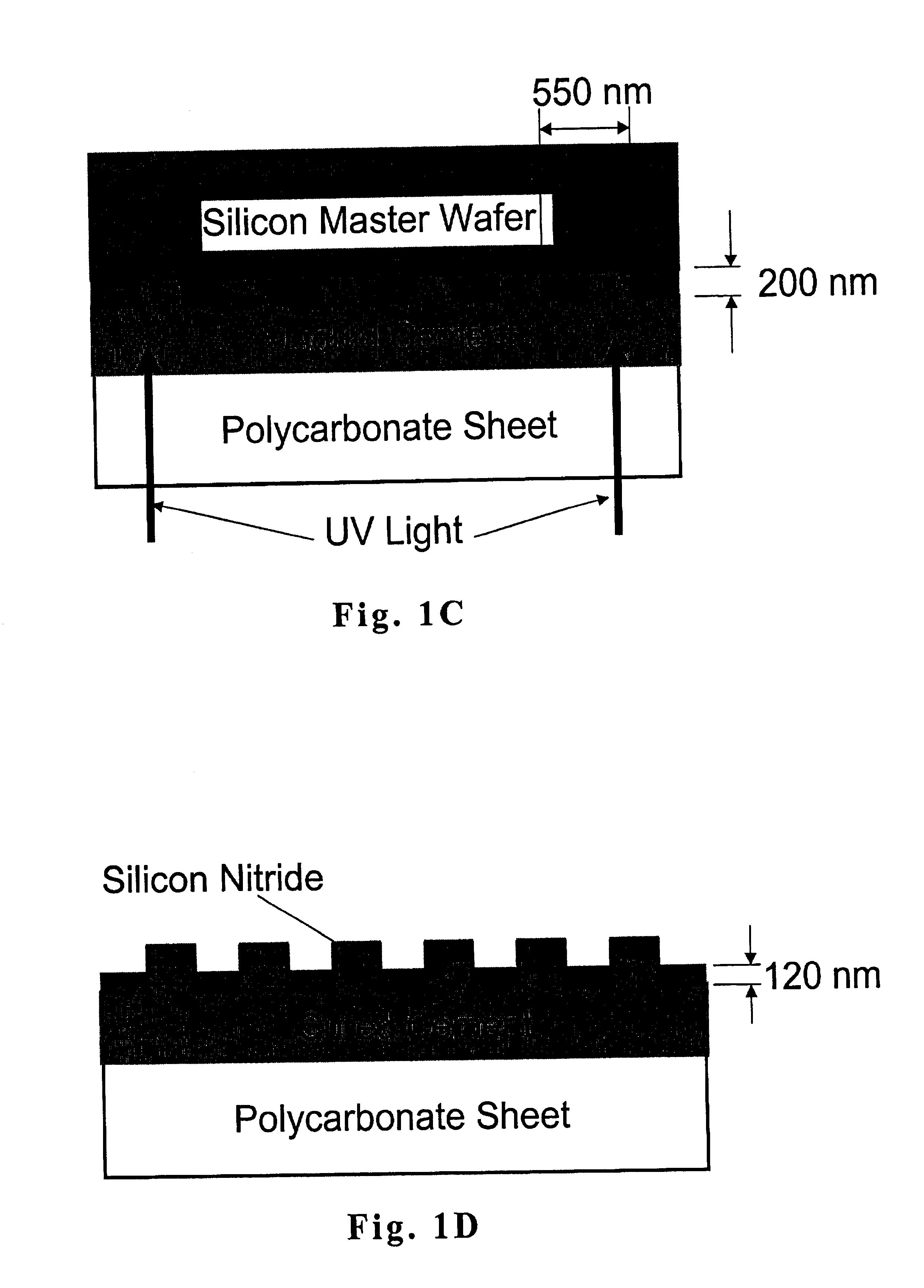
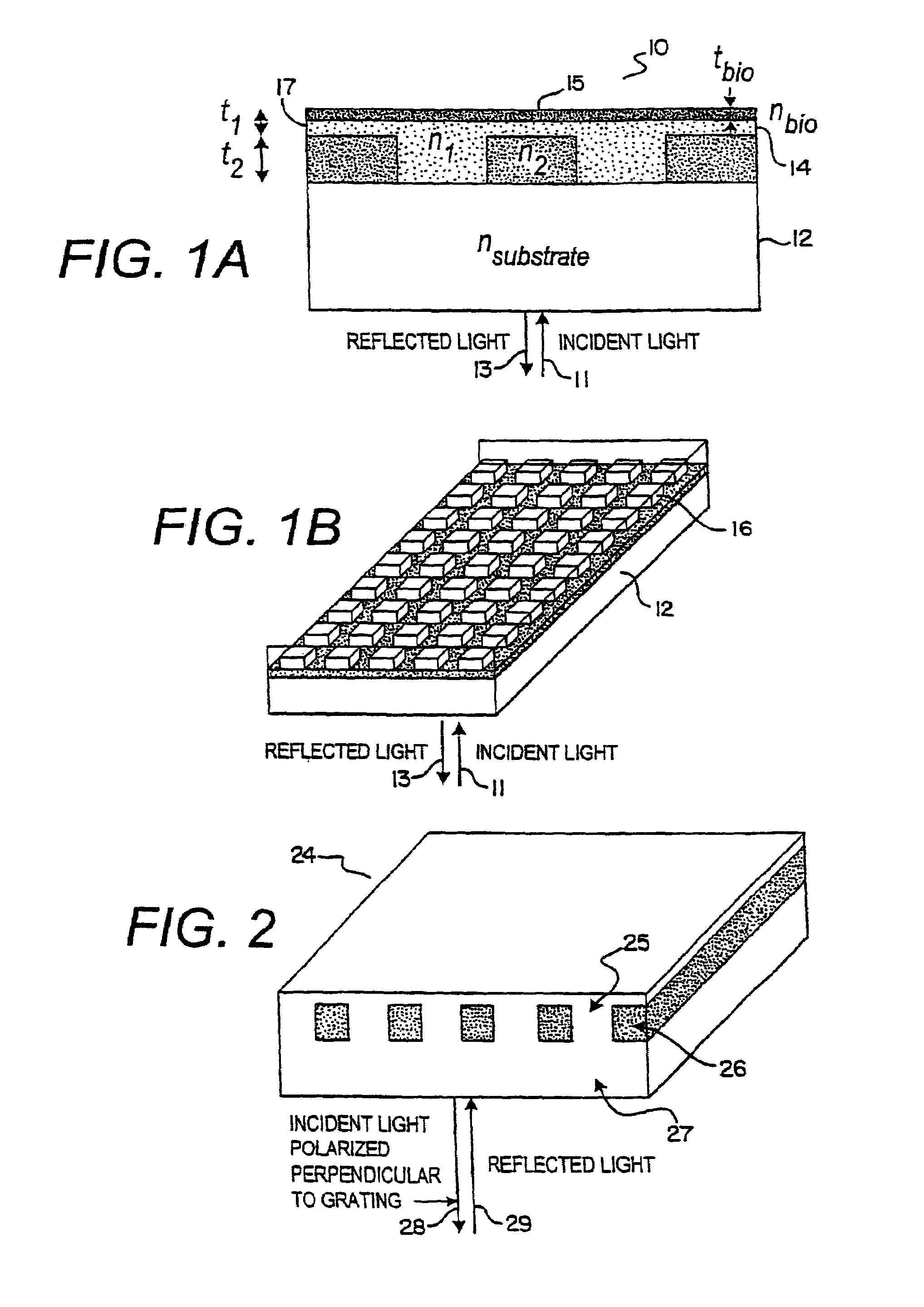
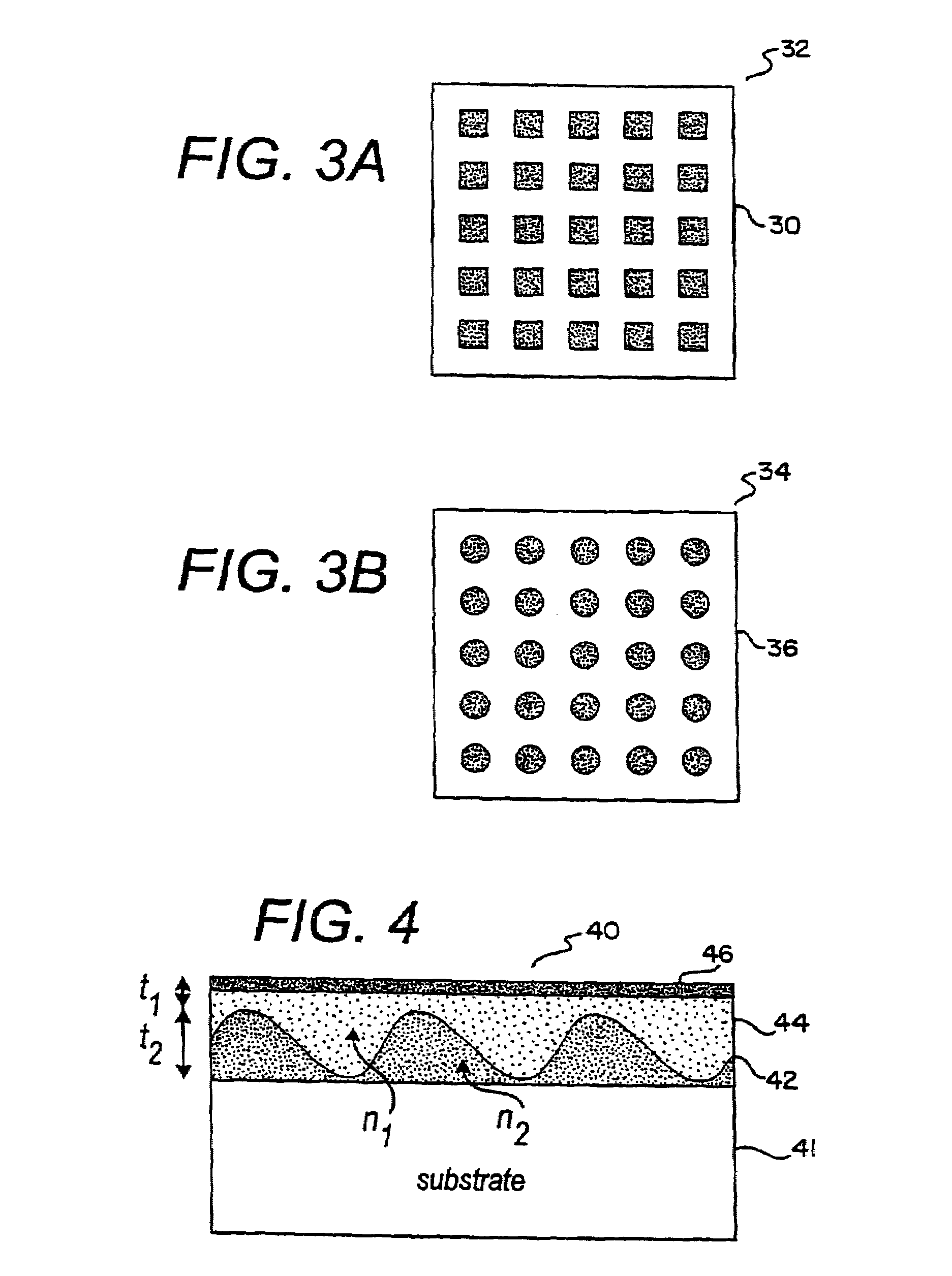
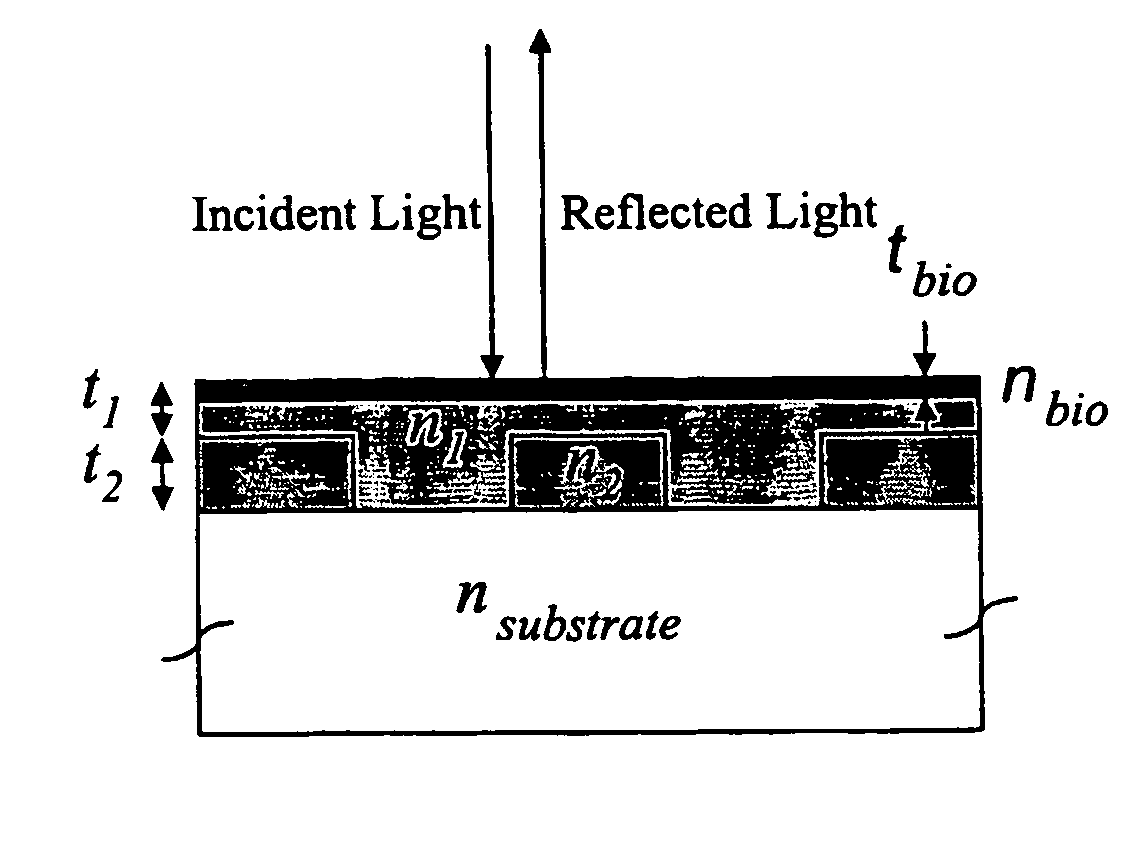
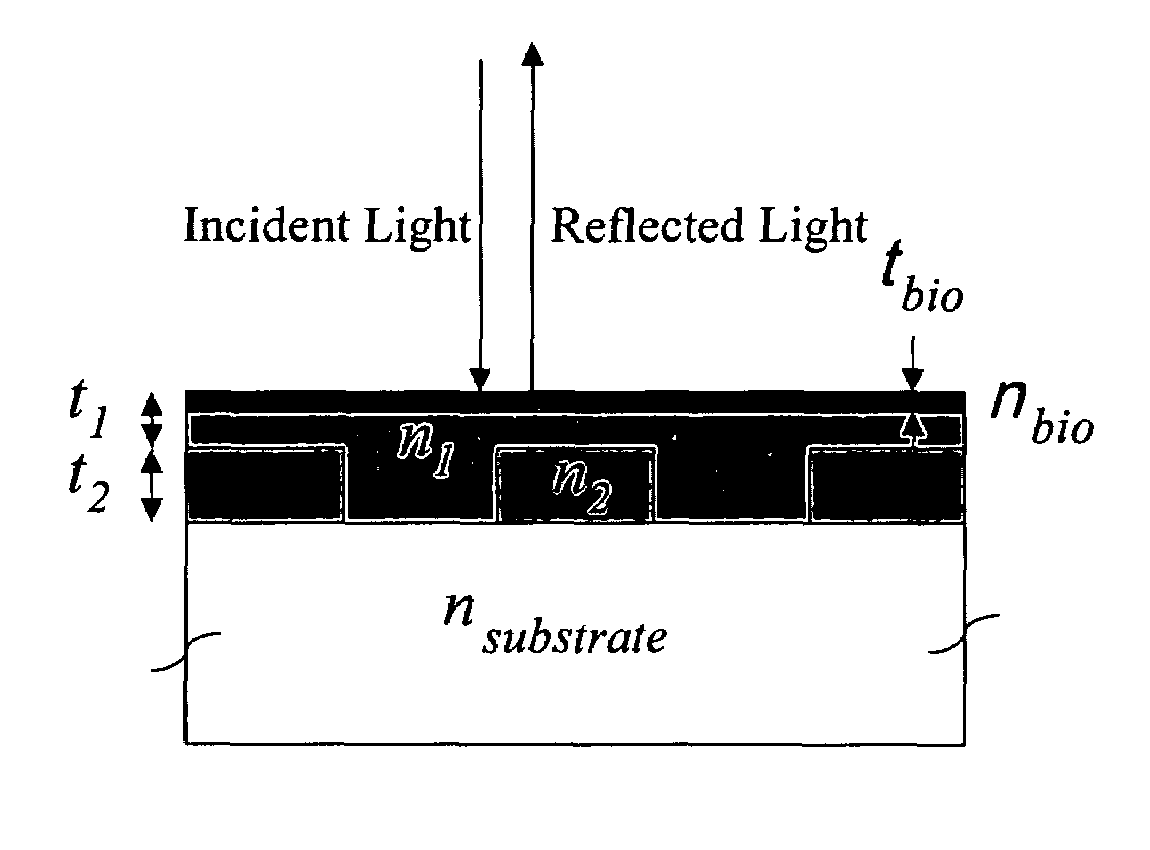
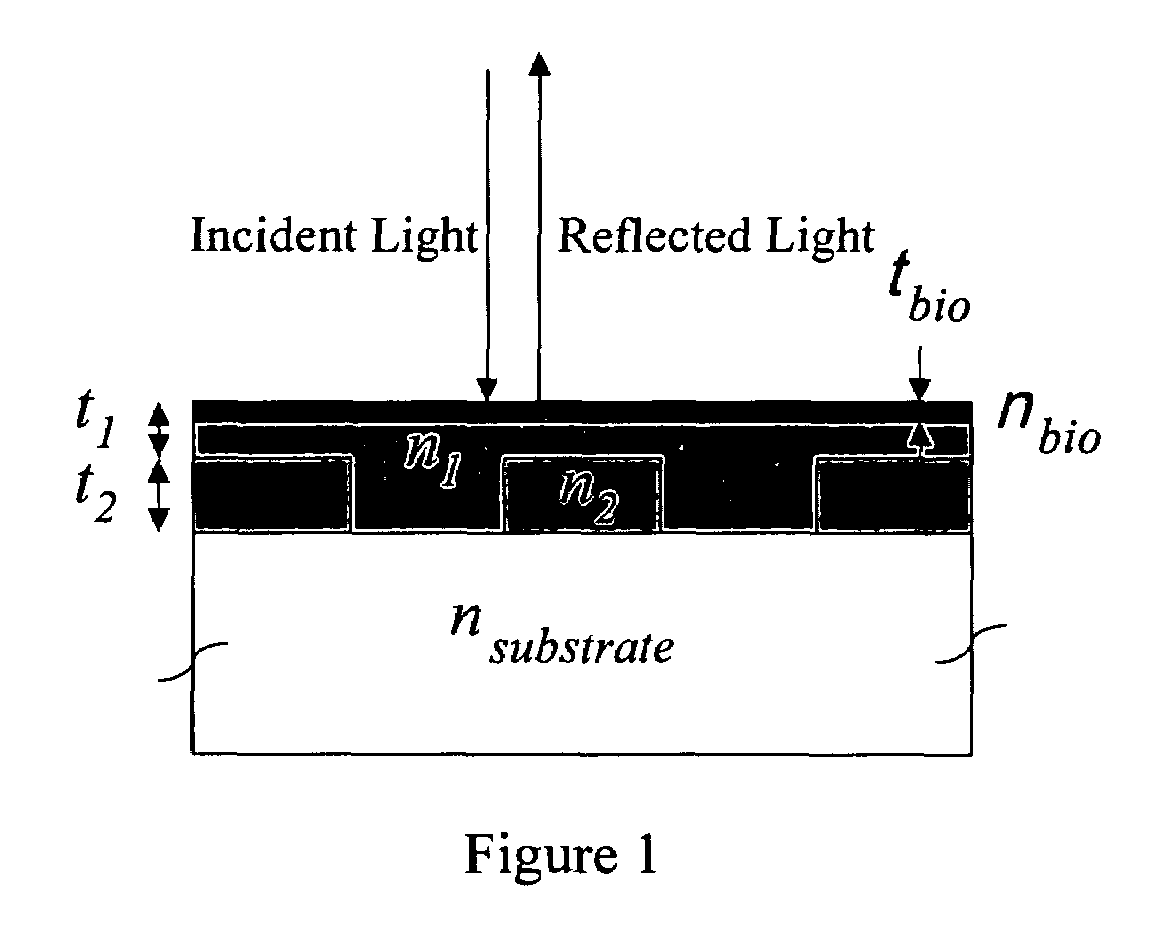
Optical detection of label-free biomolecular interactions using microreplicated plastic sensor elements
InactiveUS6951715B2Inexpensively incorporatedHigh-throughput screeningOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLabel freeNarrow band
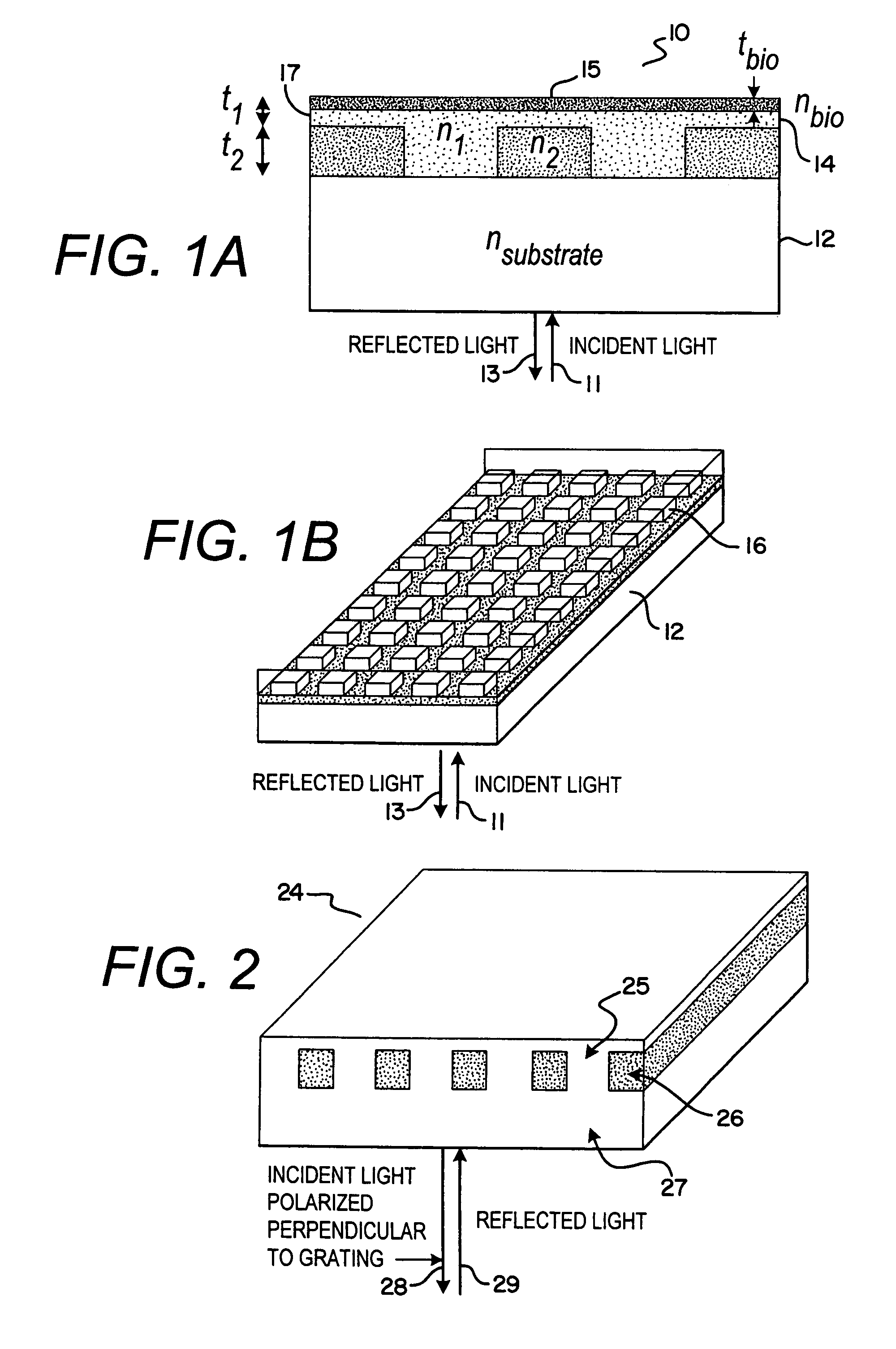
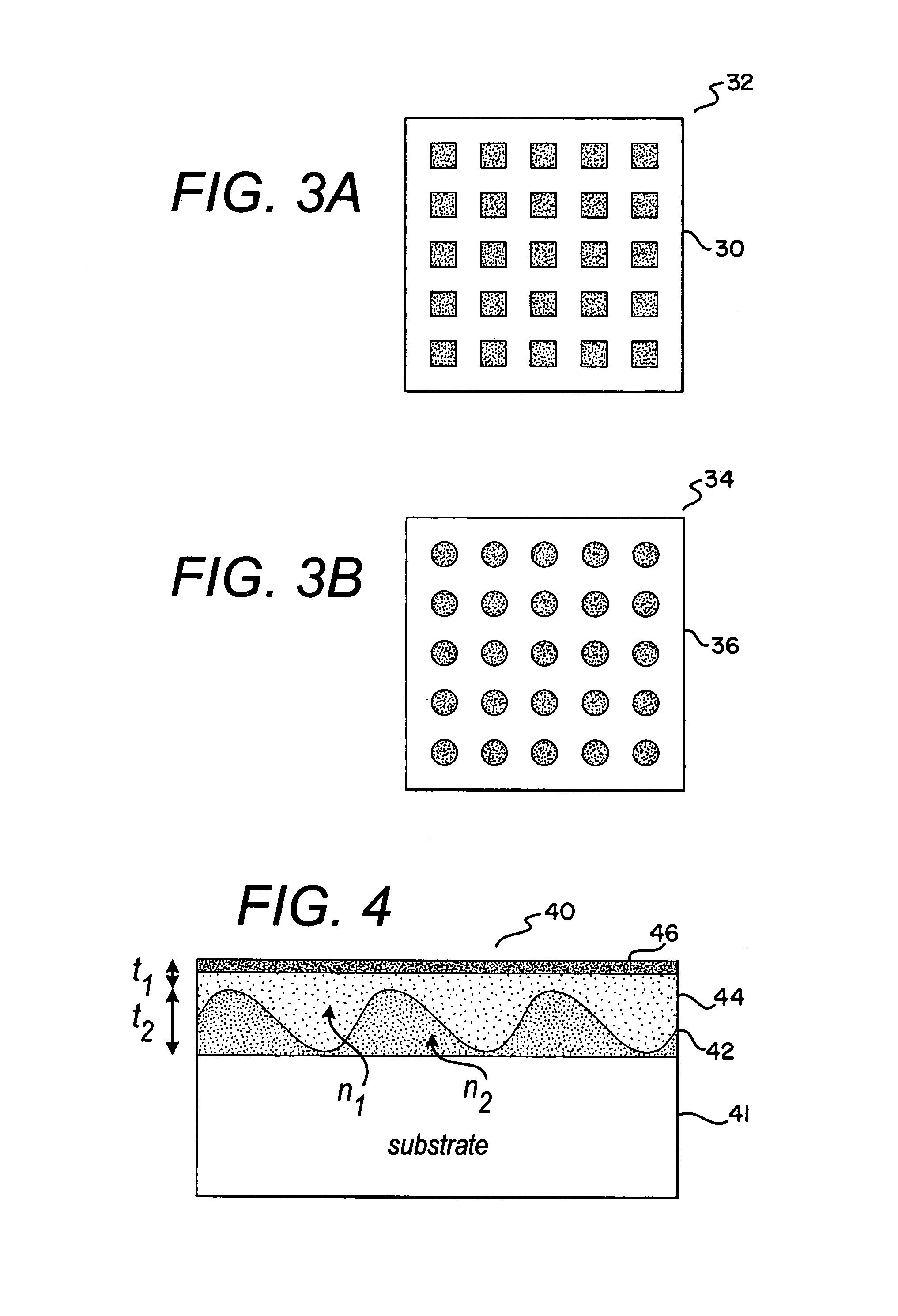
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting biomolecular interactions. The use of labels is not required and the methods can be performed in a high-throughput manner. The invention also provides optical devices useful as narrow band filters.
Owner:X BODY
Method and apparatus for detecting biomolecular interactions
InactiveUS7142296B2Inexpensively incorporatedHigh-throughput screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLength waveSpectrometer
Method and apparatus for detecting biomolecular interactions. The use of labels is not required and the methods may be performed in a high-throughput manner. An apparatus for detecting biochemical interactions occurring on the surface of a biosensor includes a light source. A first optical fiber is coupled to the light source and illuminates the biosensor. A second optical fiber detects a wavelength reflected from the biosensor. A spectrometer determines spectra of a reflected signal from the biosensor.
Owner:X BODY
Label-free high-throughput optical technique for detecting biomolecular interactions
InactiveUS7202076B2Inexpensively incorporatedHigh-throughput screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMolecular interactionsThroughput
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting biomolecular interactions. The use of labels is not required and the methods can be performed in a high-throughput manner. The invention also provides optical devices useful as narrow band filters.
Owner:X BODY
Assay for simultaneous genomic and proteomic analysis
InactiveUS20180208975A1High throughput screeningEfficient captureMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsAssay
The present invention is directed to a biochemical assay for simultaneous genomic and proteomic analysis.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
System and method for automatic color segmentation and minimum significant response for measurement of fractional localized intensity of cellular compartments
ActiveUS20070016373A1Improve throughputInteraction is complexBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementSystems approachesComputer science
A system, a method, and a programmed device for measurement of translocational activity among cellular compartments process magnified images of cellular material exposed to an agent by segmenting and compartmentalizing the images and then measuring fractional localized intensity of two or more components in the segmented, compartmentalized image. The measured fractional localized intensities are compared to determine translocation of cellular material among the measured components caused by the agent.
Owner:VALA SCI
Assay plates, methods and systems having one or more etched features
InactiveUS20100022416A1High throughput screeningIncrease contentResistance/reactance/impedenceDecorative surface effectsEngineeringNanoporous
Owner:LIFE BIOSCI
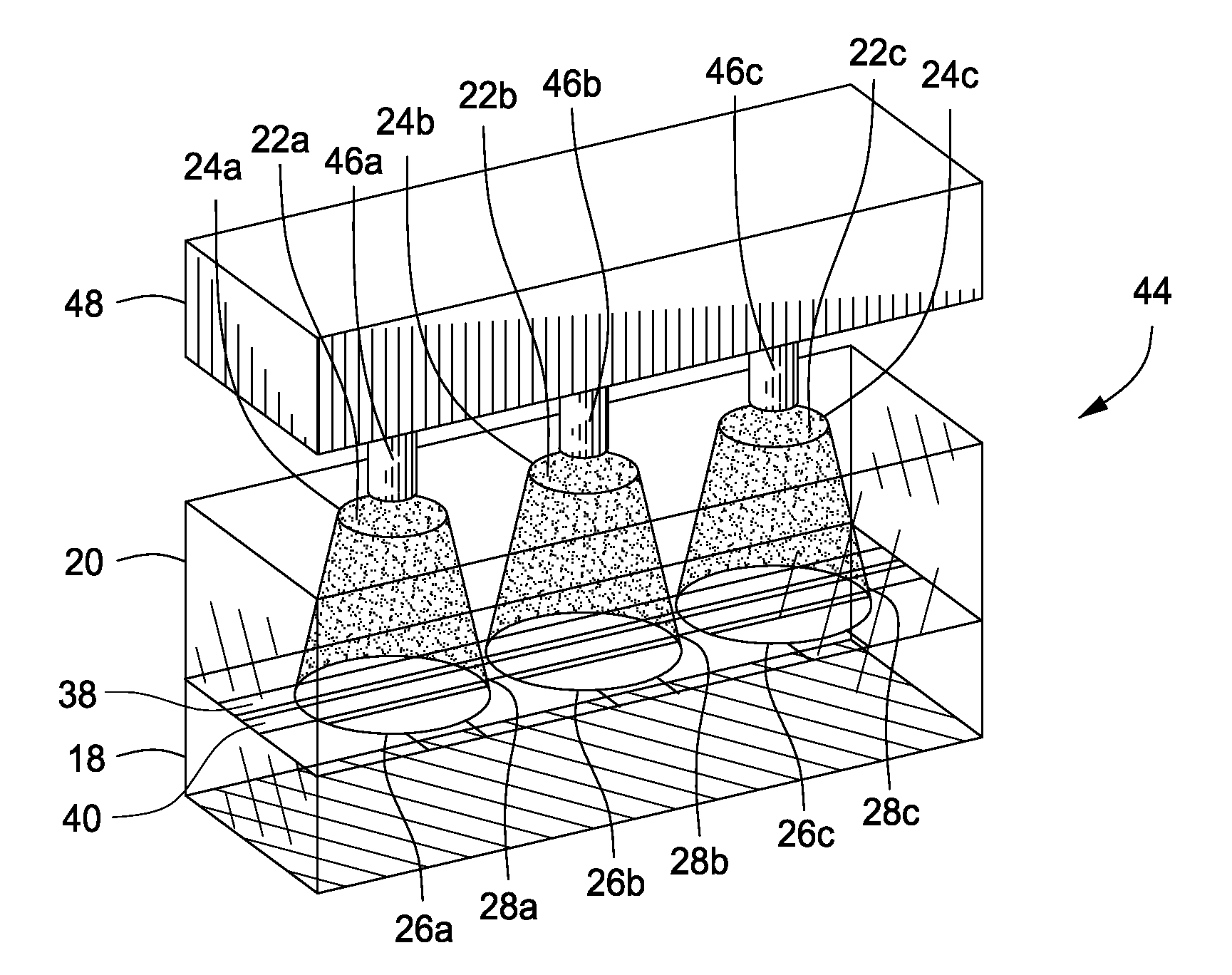
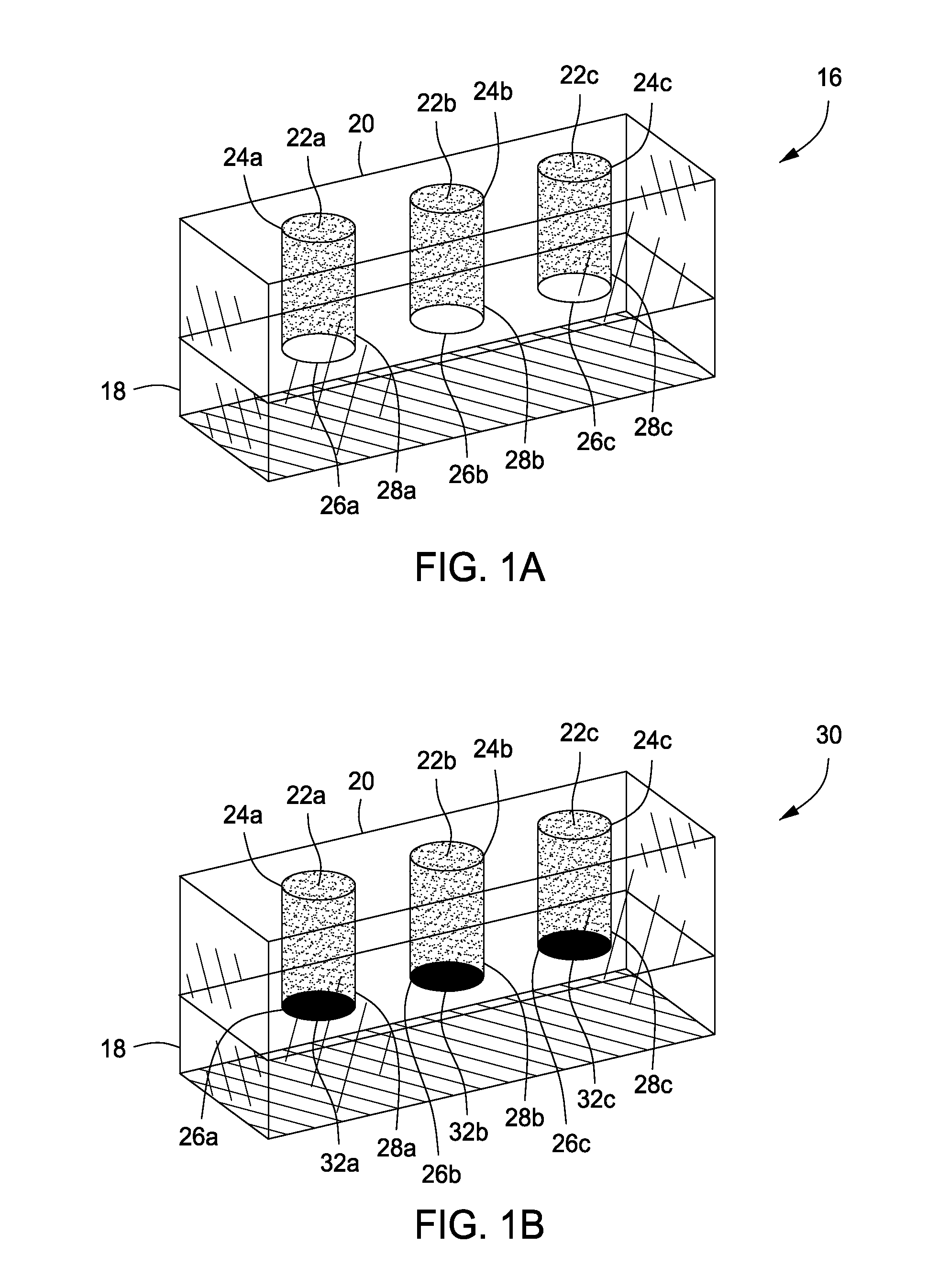
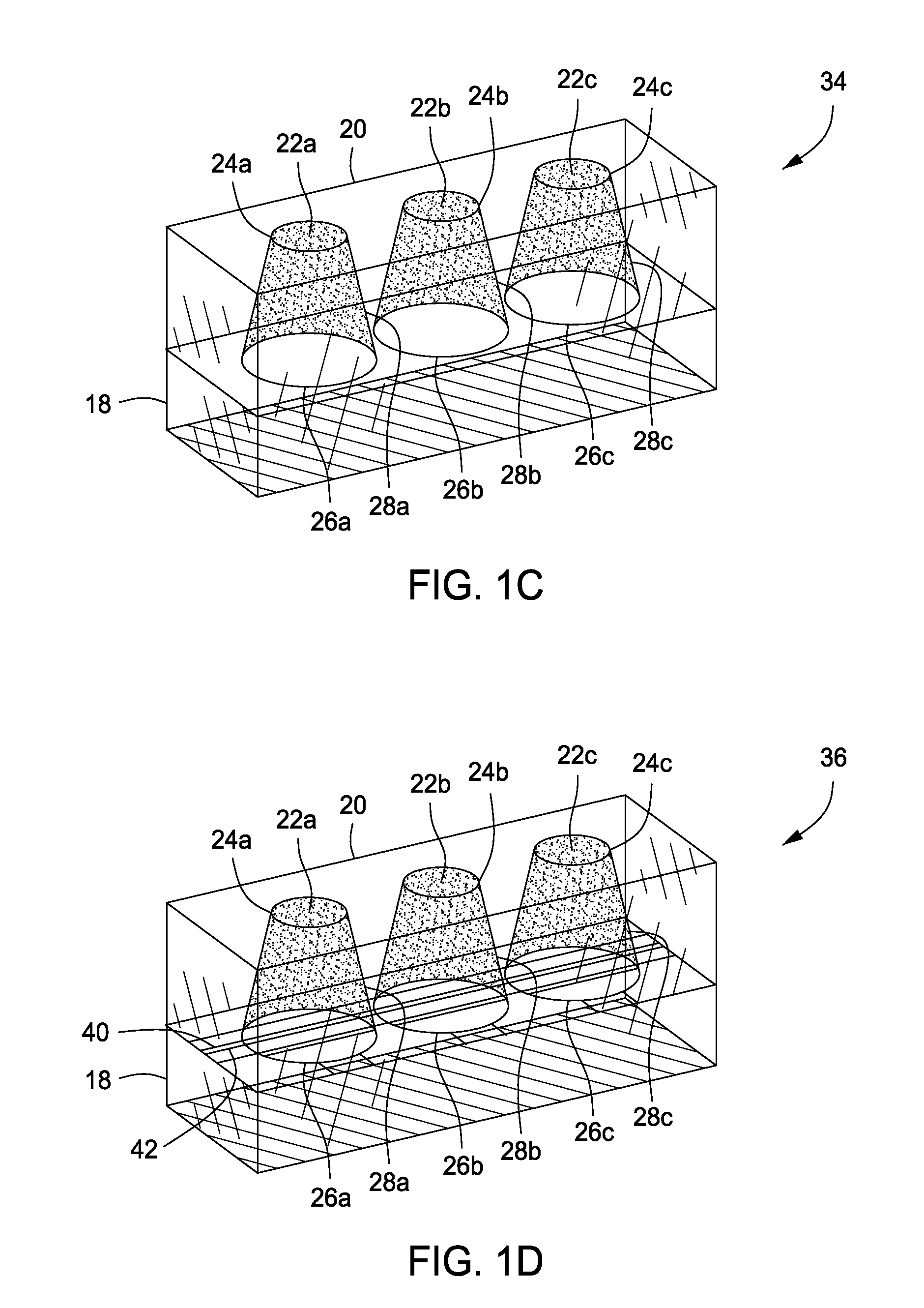
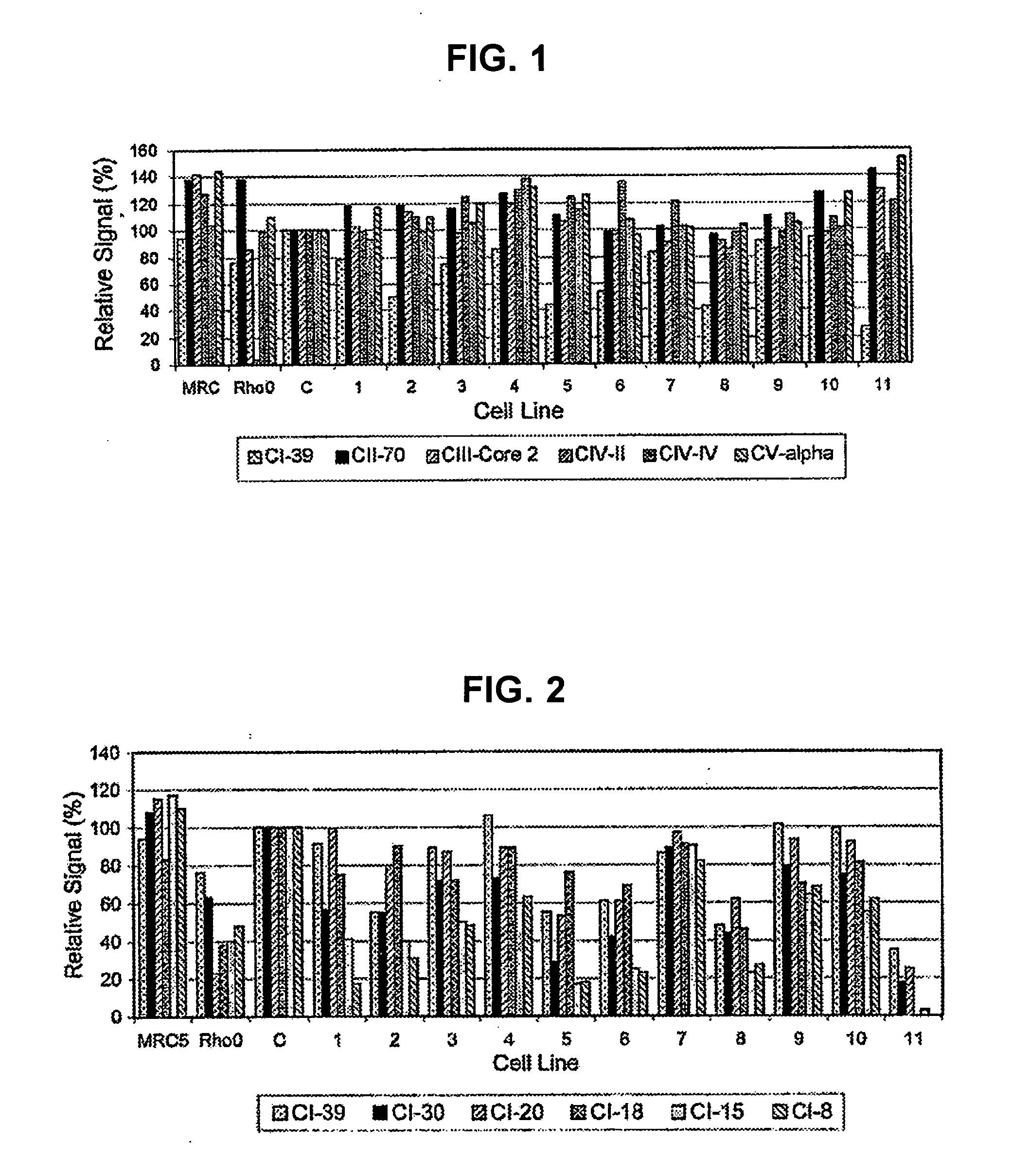
Immunocapture of mitochondrial protein complexes
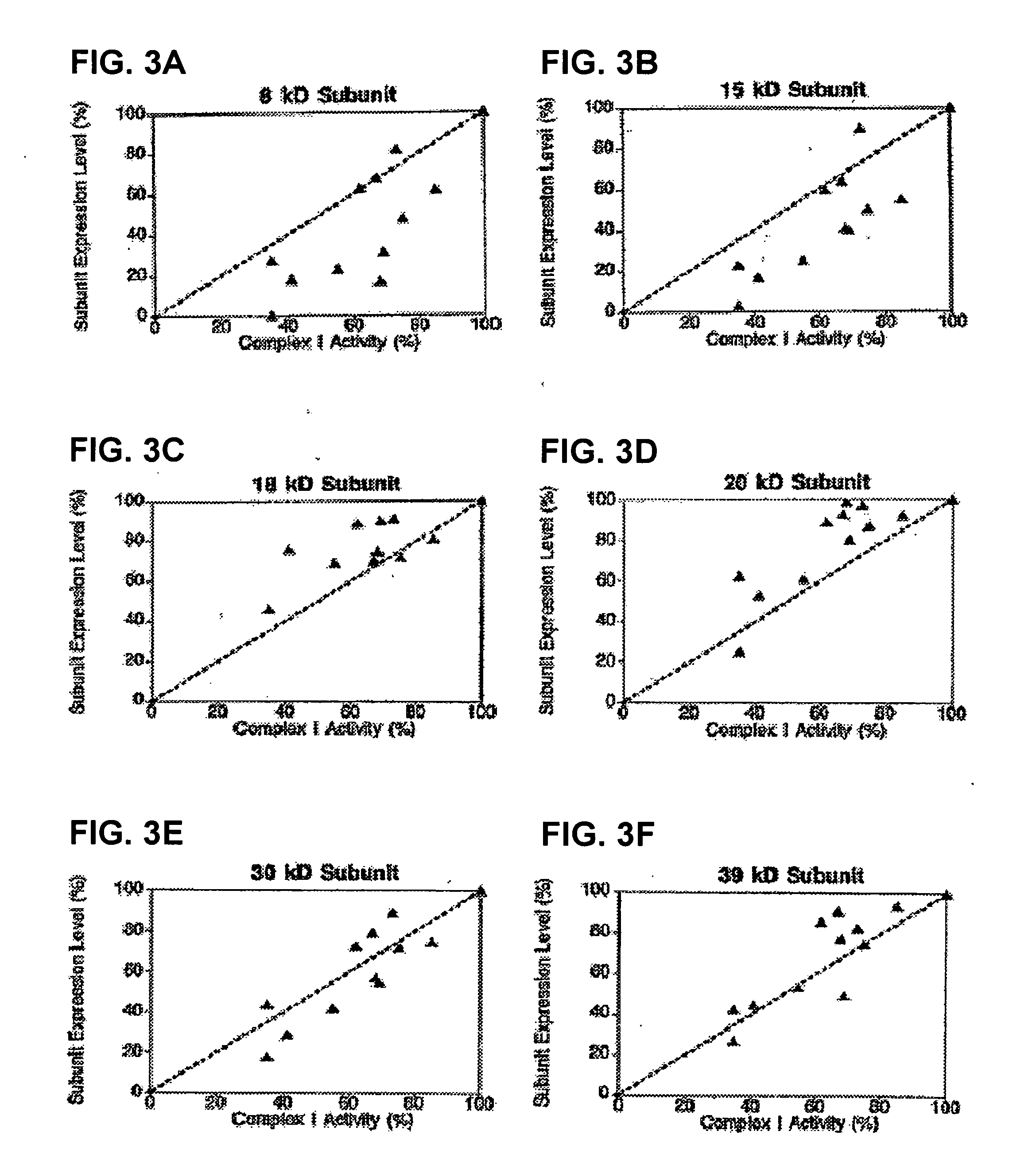
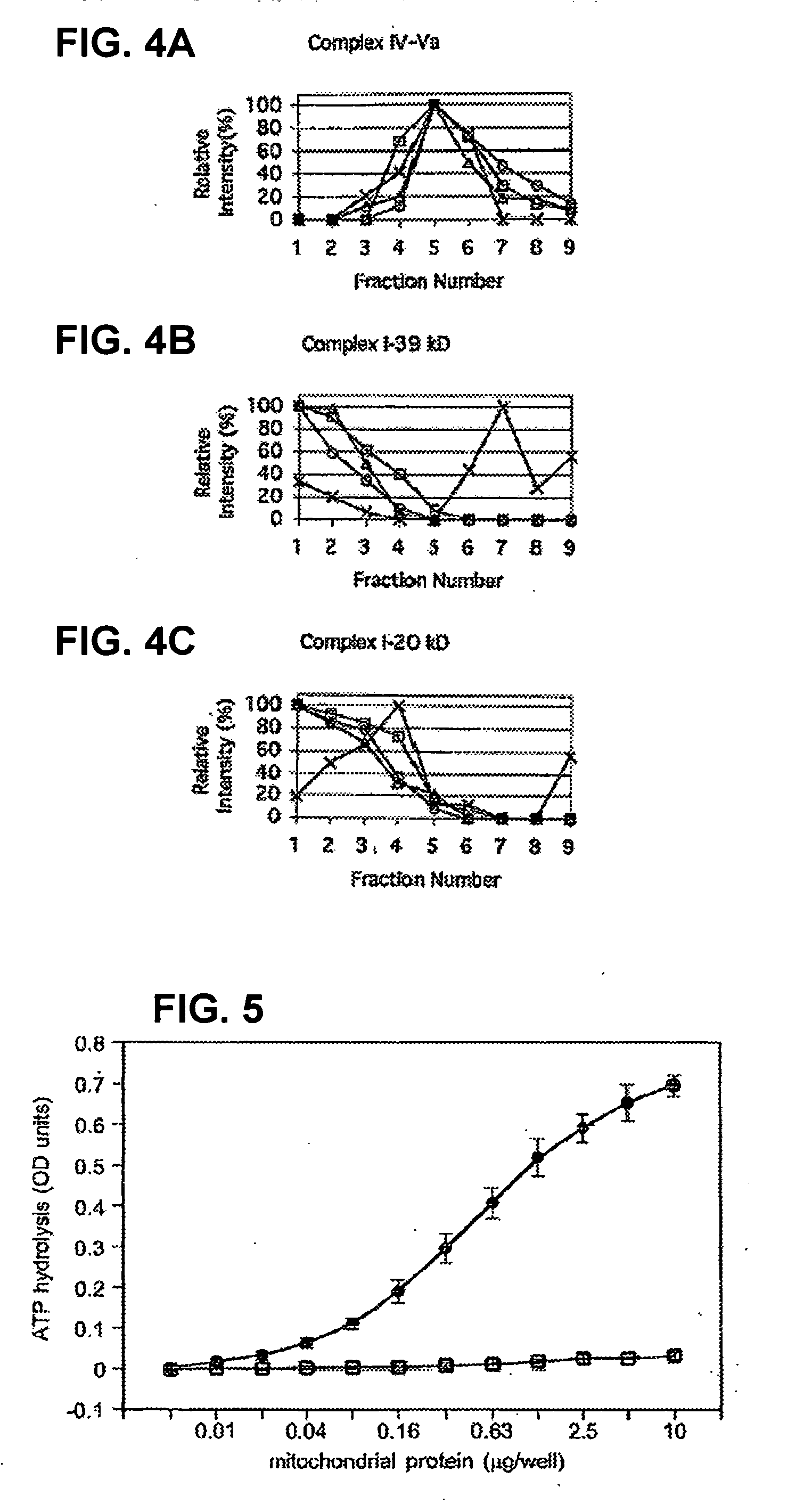
InactiveUS20050153381A1High-throughput screeningPrevent or treat mitochondrial disordersAnimal cellsCompound screeningDiseasePhosphorylation
Provided herein is a library of monoclonal antibodies specific for native proteins and native protein complexes of the oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) system (for example, Complex I, II, III, IV, or V, or any protein subunit of any of such complexes). Hybridomas expressing such antibodies and antibodies that competitively inhibit the binding of any such antibody (e.g., antibodies that bind the same or a sterically overlapping epitope) are also contemplated. Methods of using, and kits including, the disclosed antibodies are also provided. Antibodies, methods and kits described herein address a need in the art by providing immunological reagents and assays useful, at least, for detecting mitochondrial diseases associated with deficiencies or alterations in OXPHOS Complexes I, II, III, IV and / or V.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +1
Label-free high-throughput optical technique for detecting biomolecular interactions
InactiveUS20060030033A1Inexpensively incorporatedHigh-throughput screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh fluxLight filter
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting biomolecular interactions. The use of labels is not required and the methods can be performed in a high-throughput manner. The invention also provides optical devices useful as narrow band filters.
Owner:IGT +1
Transdermal assay with magnetic clamp
InactiveUS20030068614A1High-throughput screeningMinimize cytotoxicityCompound screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAssayMedicine
The transdermal assay apparatus includes first, second, and third members. The first member has one or more sample surfaces, each of which is configured to receive a sample thereon. The second member defines one or more reservoirs, each of which has an opening on a surface of the second member. Each sample surface is substantially the same size as each opening. The transdermal assay apparatus also includes a magnetic clamp configured to clamp a tissue specimen between the sample surface and the opening. The magnetic clamp preferably includes a magnet having a strength that is selected based on the clamping force required between the first member and the second member. The invention also provides a method for using a transdermal assay apparatus.
Owner:TRANSFORM PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Sample imaging device
InactiveUS6377346B1Short measurement timeMeasurement timeRadiation pyrometryPhotometryPulsed modeRotating disc
An imaging device for biochemical or medical samples, the pulse mode light source of which incorporates flash lamps and a rotating mirror in an inclined position, the said mirror reflecting the light emitted by each flash lamp in turn along the same optical path to the sample. The flash lamps are switched on alternately in phases and synchronised with the rotating mirror and the emission light chopper, which comprises two rotating discs. The turning mirror directs the light at the sample from above and / or below, in which case a double-acting transparent scattering plate can be used.
Owner:WALLAC
Detection of reactions and metabolic changes with fluorscent materials
InactiveUS20030012692A1High throughput screeningImprove throughputCompound screeningAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSurface reactionHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A system, method and device for the detection of reactions between analytes, (e.g., DNA, biomolecules, or cells) and a second compound are disclosed. The present invention includes a coating of a fluorescent material having a fluorescence that changes with temperature. The fluorescent material is associated with a substrate, and can be used for any type of surface reaction that requires determination of temperature conditions at an interface between the surface and the reaction analyte subject to assay. The substrate may be, for example, a microarray chip or microplate, preferably suitable for use in high-throughput screening of biomolecules or cells. Substrates containing the fluorescent material also can be used to compensate for temperature variations in refractive index in optical sensors.
Owner:CORNING INC
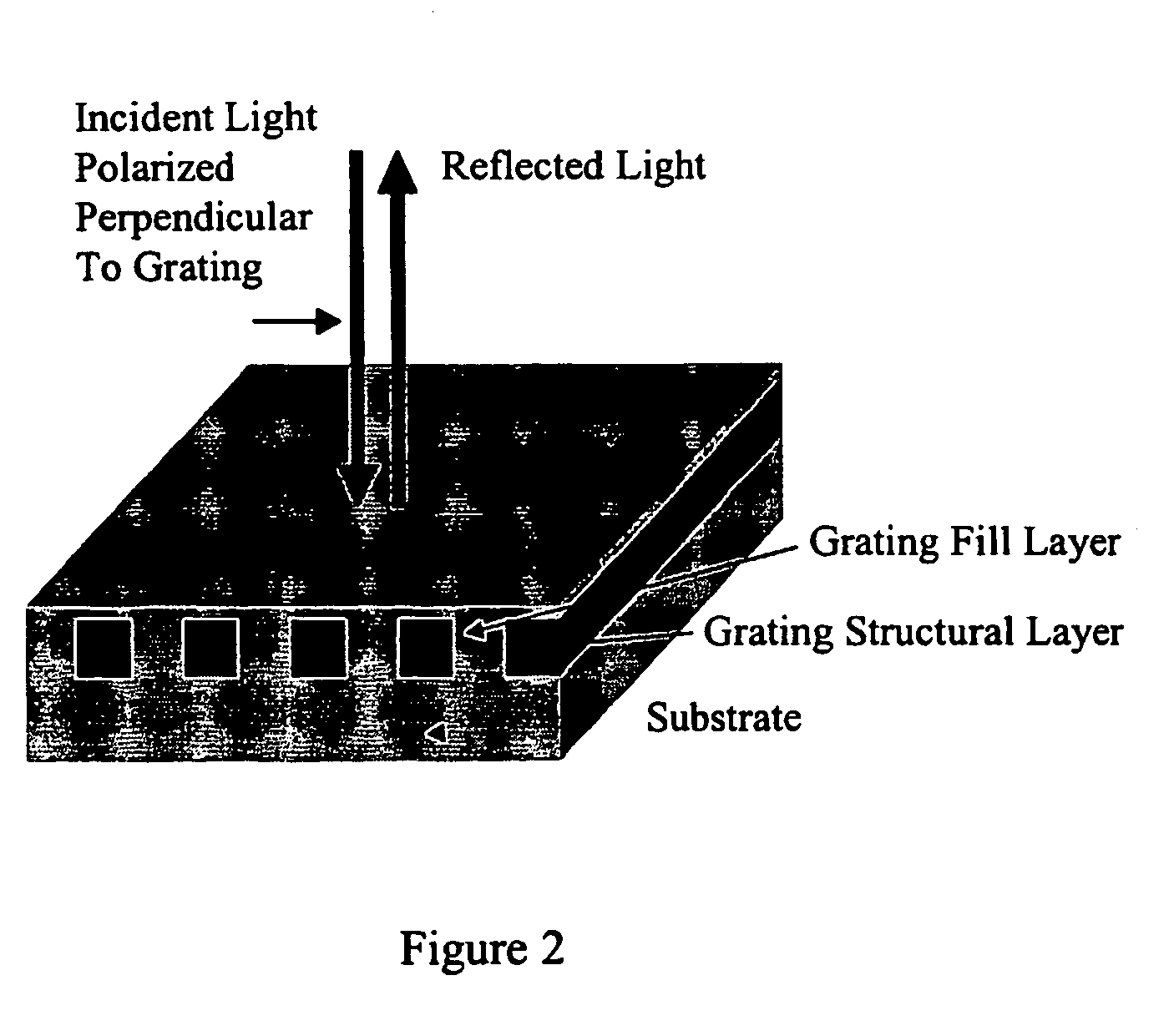
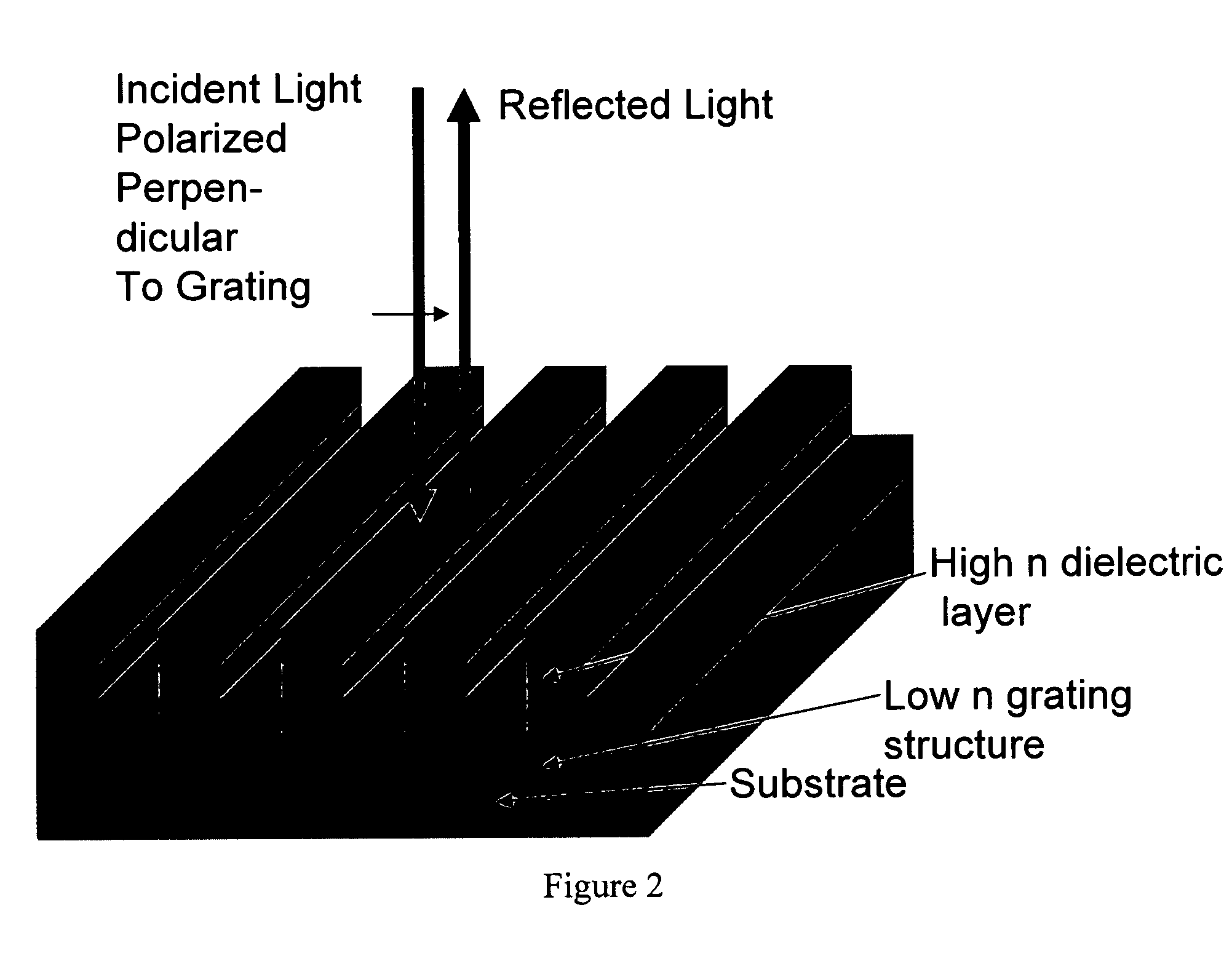
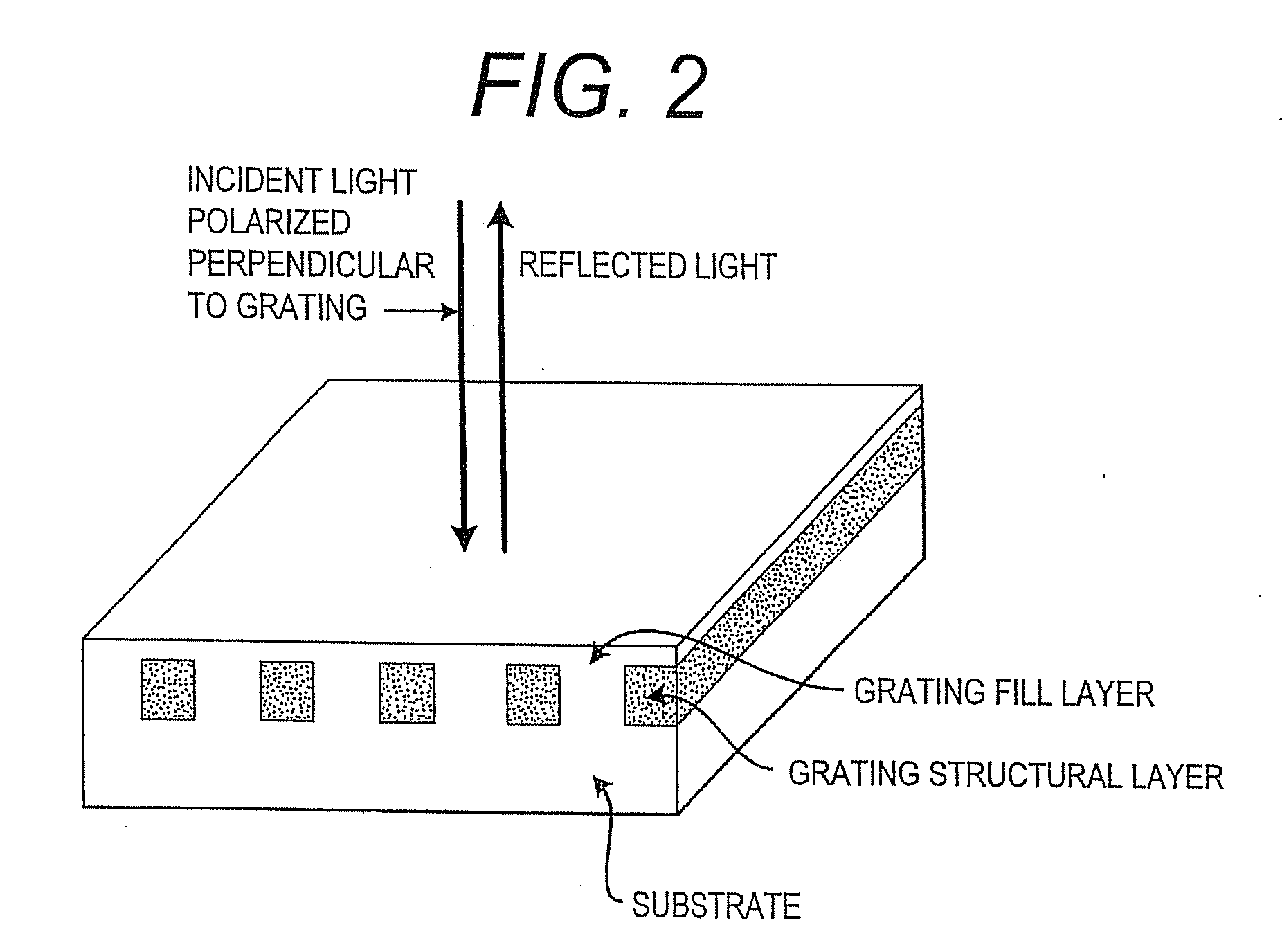
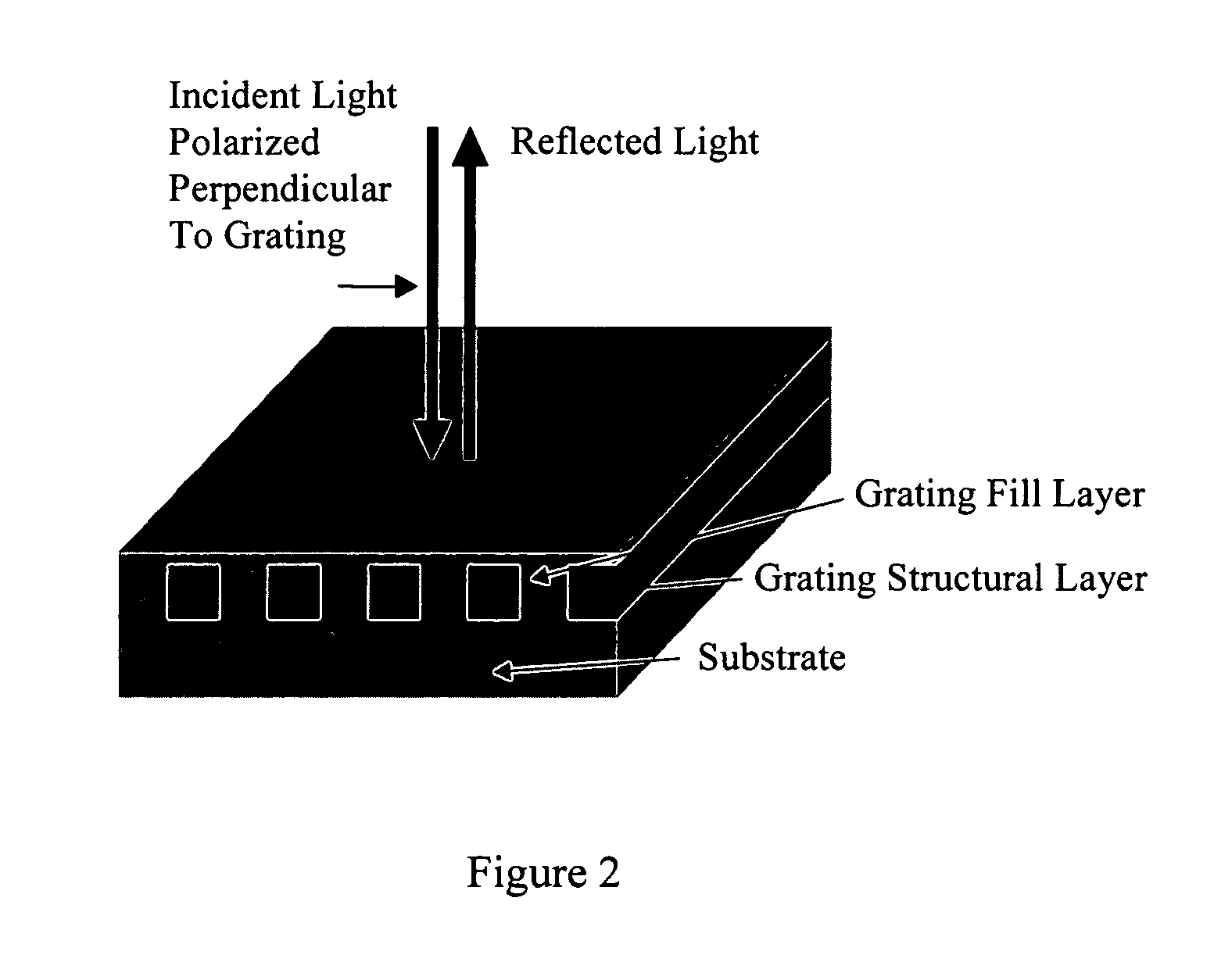
Guided mode resonant filter biosensor using a linear grating surface structure
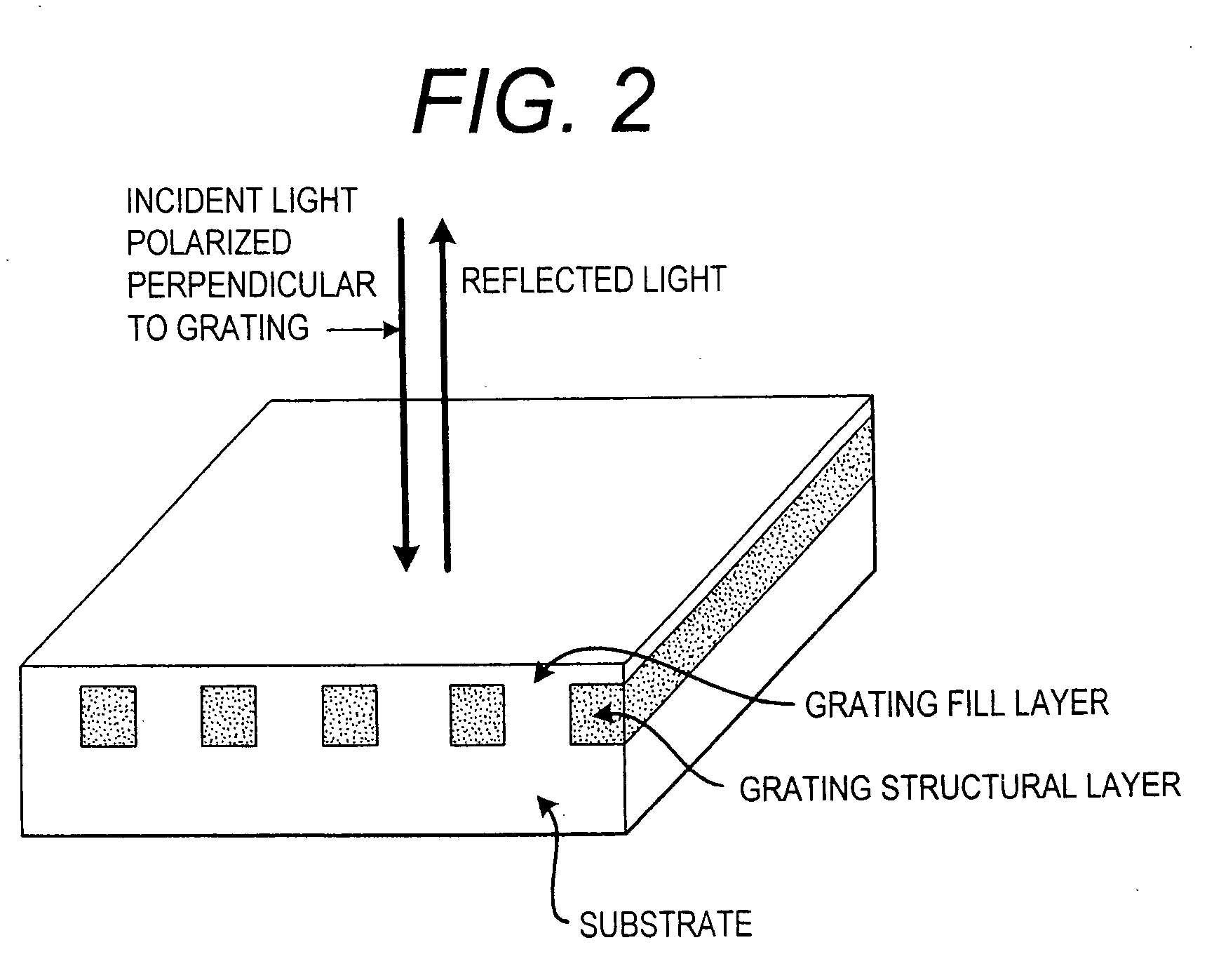
InactiveUS7371562B2Inexpensively incorporatedHigh-throughput screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGratingResonant filter
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting biomolecular interactions. The use of labels is not required and the methods can be performed in a high-throughput manner. The invention also provides optical devices useful as narrow band filters.
Owner:X BODY
Optical Detection of Label-Free Biomolecular Interactions Using Microreplicated Plastic Sensor Elements
InactiveUS20090264314A1Inexpensively incorporatedHigh-throughput screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesMolecular interactionsThroughput
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting biomolecular interactions. The use of labels is not required and the methods can be performed in a high-throughput manner. The invention also provides optical devices useful as narrow band filters.
Owner:X BODY
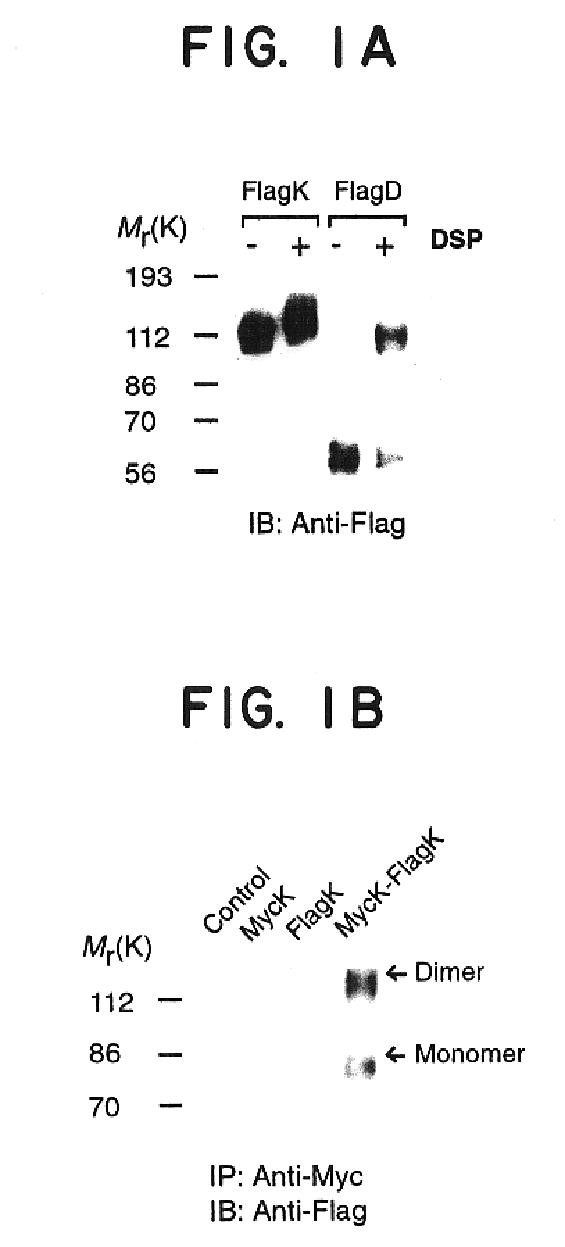
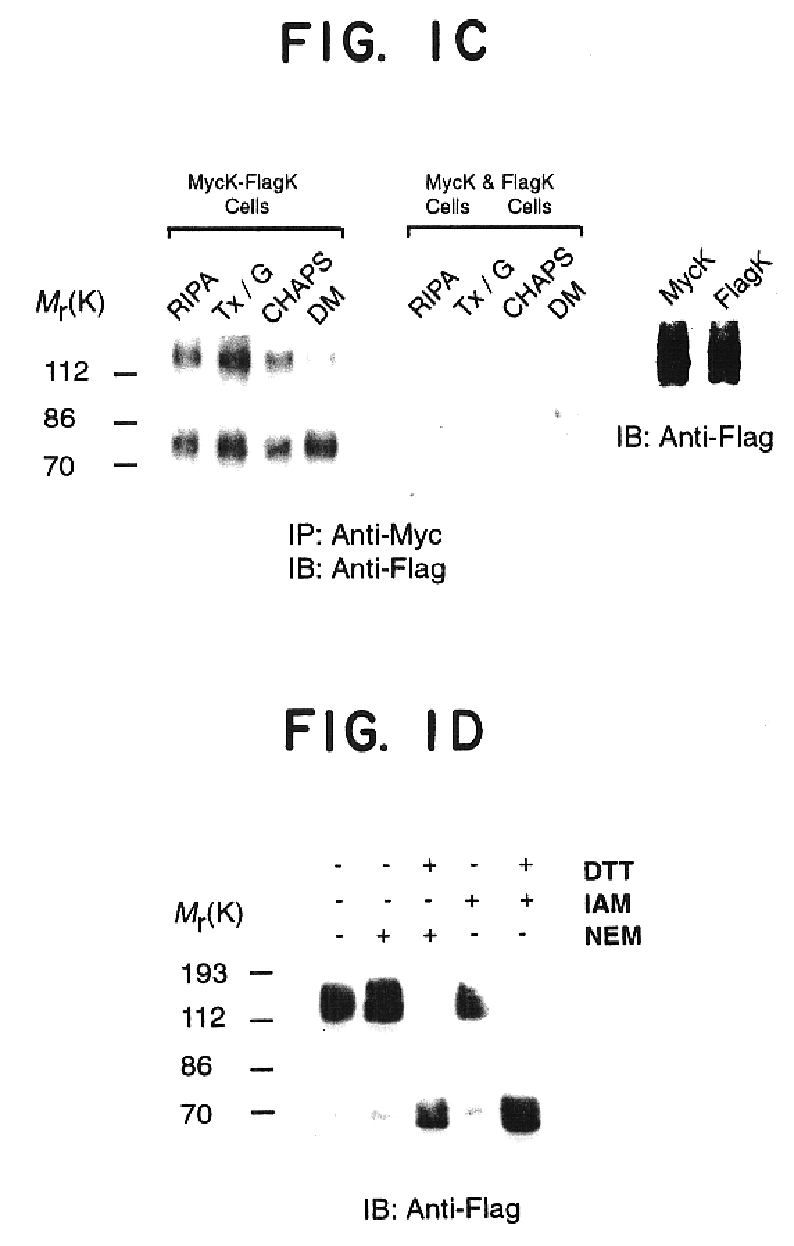
Heterodimeric opioid G-protein coupled receptors
InactiveUS6855807B1Effective treatmentAccurate identificationBacteriaBiological material analysisMu Opiate ReceptorHigh-throughput screening
Opioid receptors form functional heterodimers with each other and with other G-protein coupled receptors, such as dopamine receptors, adrenergic receptors, or chemokine receptors. These receptors can be exploited for high throughput screening of compounds to identify heterodimer opioid receptor modulators (agonists and antagonists). The invention also relates to identification of novel heterodimer receptor ligands and synergistic compositions, which can provide strategies for analgesia, narcotic addiction, hypertension, HIV infection, and immune system function.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
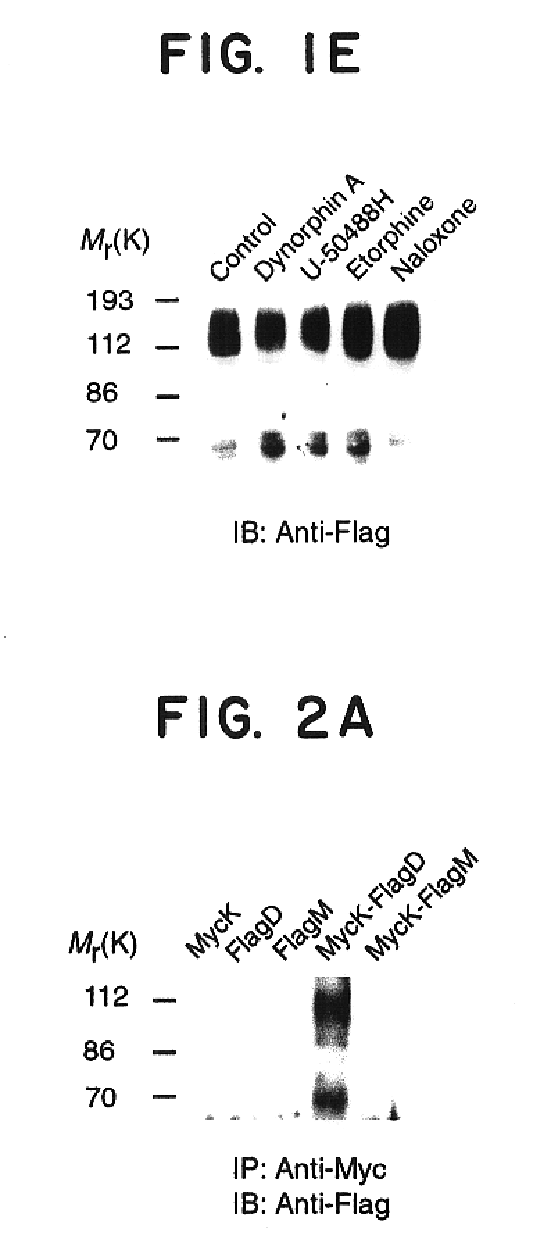
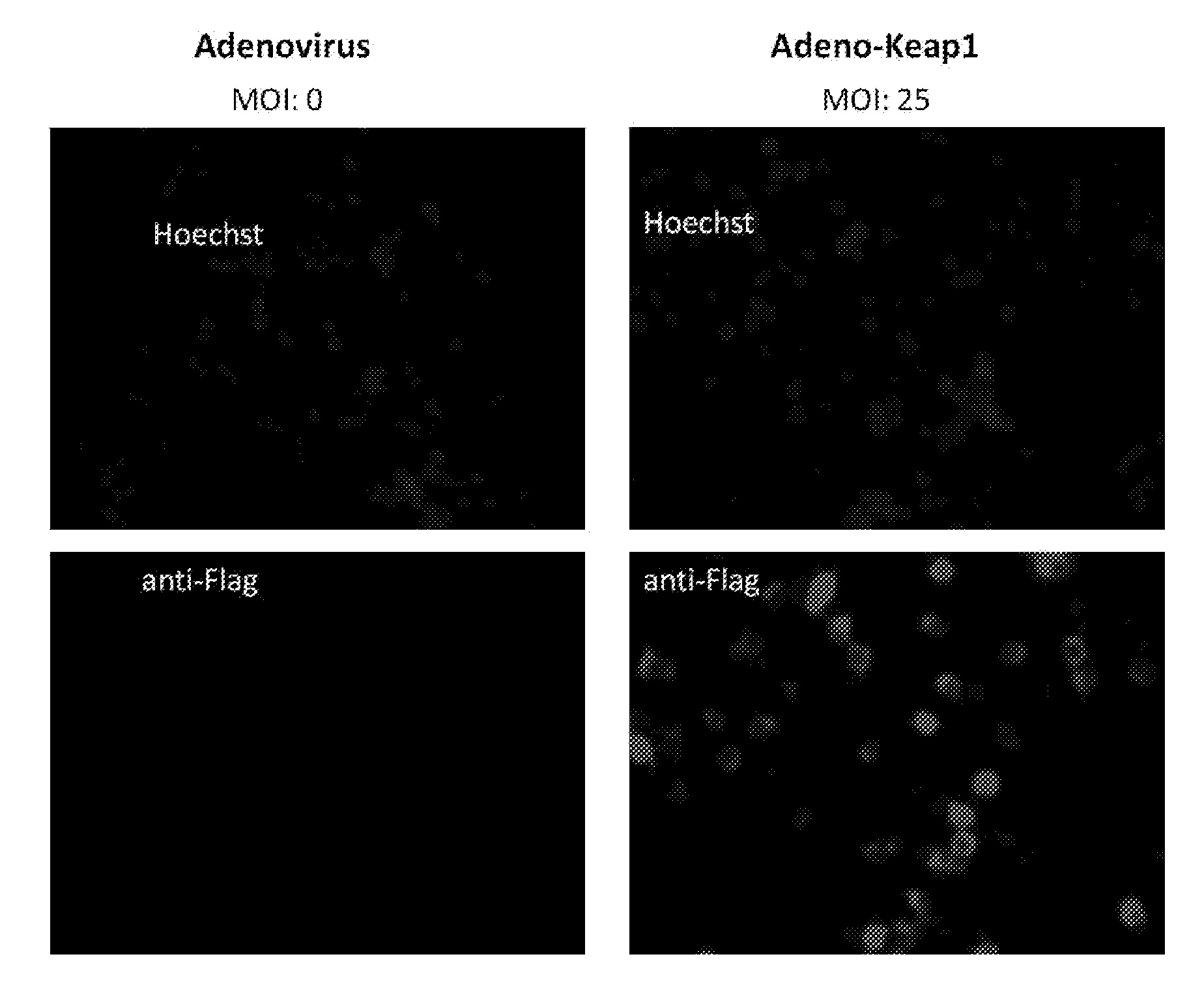
Reporter system for high throughput screening of compounds and uses thereof
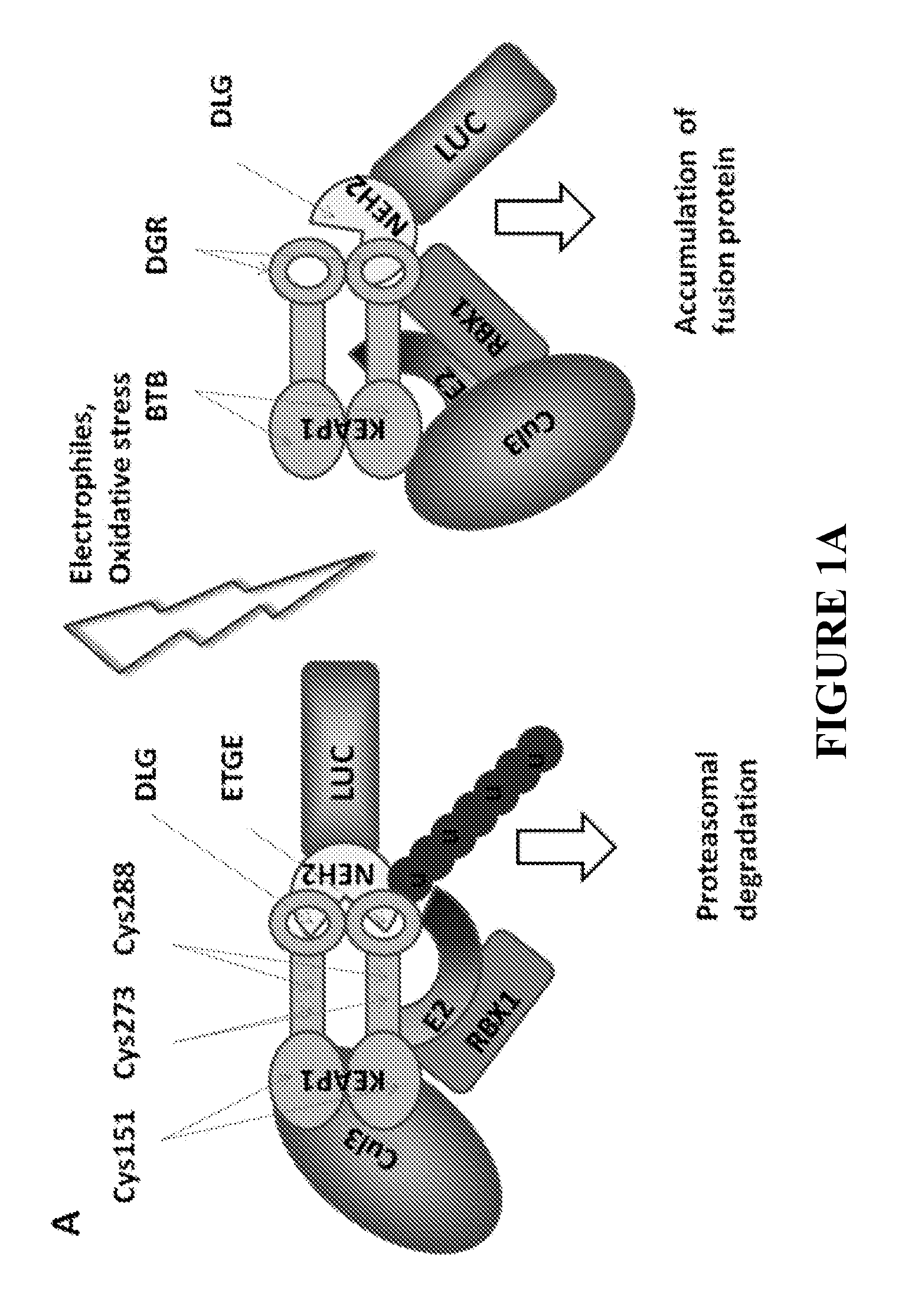
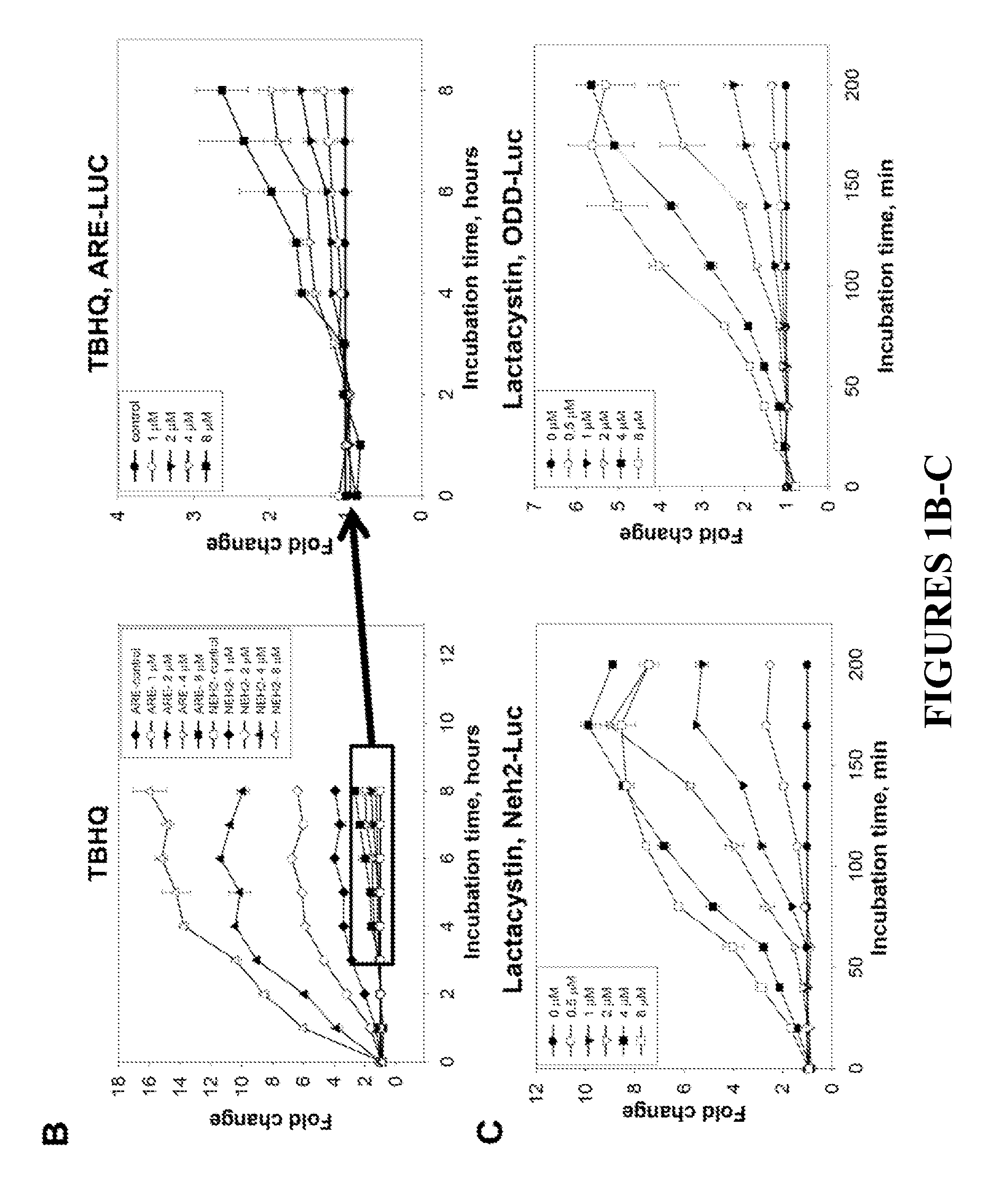
ActiveUS20130005666A1High throughput screeningImprove throughputOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNrf2 activation
The NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a key transcriptional regulator of antioxidant defense and detoxification. To directly monitor stabilization of Nrf2 we fused its Neh2 domain, responsible for the interaction with its nucleocytoplasmic regulator, Keap1, to firefly luciferase (Neh2-luciferase). It is shown herein that Neh2 domain is sufficient for recognition, ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Neh2-luciferase fusion protein. The novel Neh2-luc reporter system allows direct monitoring of the adaptive response to redox stress and classification of drugs based on the time-course of reporter activation. The novel reporter was used to screen a library of compounds to identify activators of Nrf2. The most robust and yet non toxic Nrf2 activators found—nordihydroguaiaretic acid, fisetin, and gedunin-induced astrocyte-dependent neuroprotection from oxidative stress via an Nrf2-dependent mechanism.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
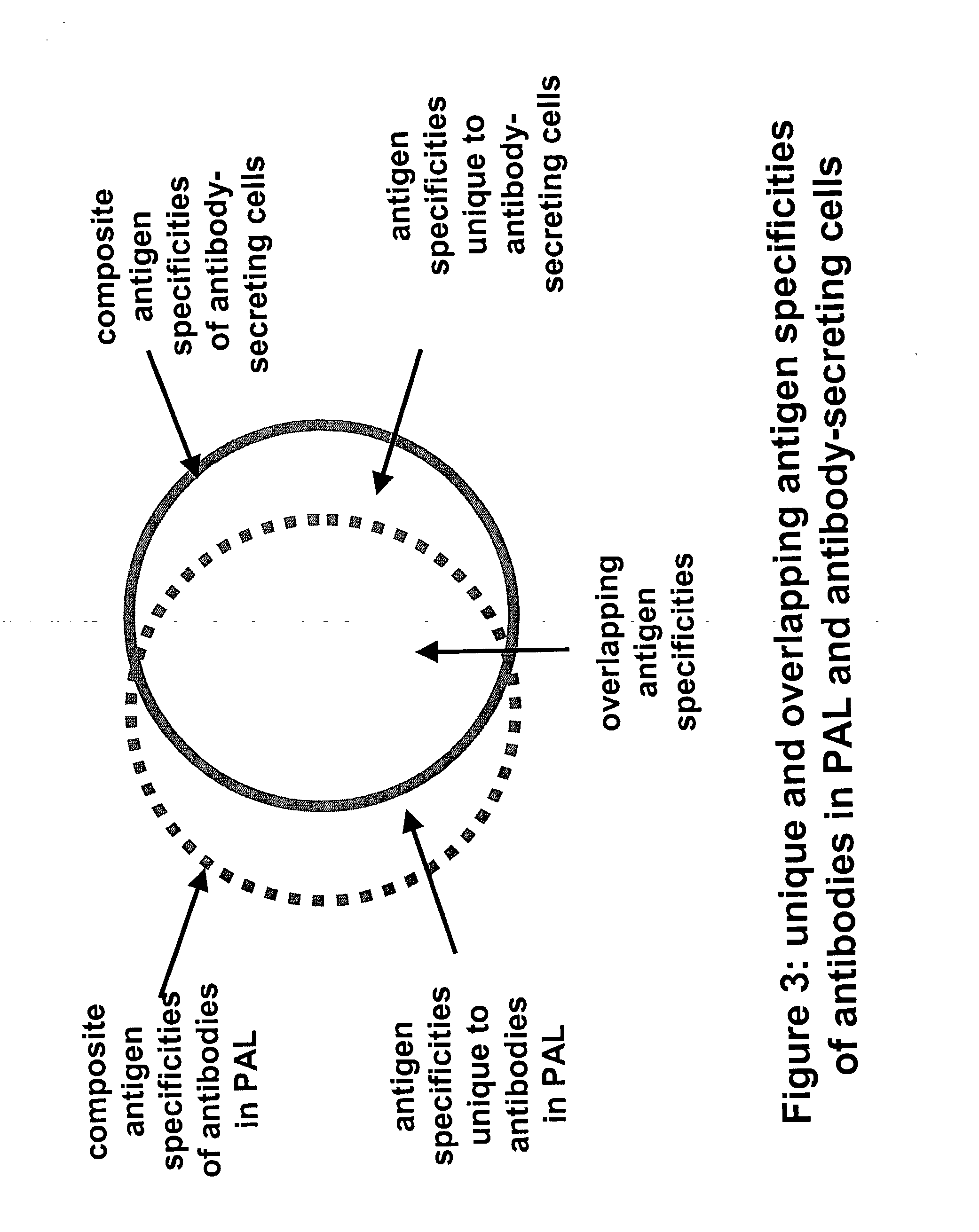
Methods for screening antibody-producing cells on heterogeneous antigen substrates
InactiveUS20060073095A1Reduce complexityShorten the timeAnimal cellsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsEpitopeMonoclonal antibody
Methods and compounds are disclosed that relate to screening and selection of monoclonal antibodies specific for antigens in heterogeneous antigen mixtures. Antibody-secreting cells such as hybridomas are modified to make them capable of directly binding antigens by capturing their secreted antibody products onto their surface membranes in appropriate binding density and orientation. Selectivity of binding to novel or desired antigens is achieved by first reacting the antigen mixtures affixed to a solid substrate with a polyclonal antibody library that prevents access to the majority of antigens or epitopes other than those that are novel or desired.
Owner:KESSLER STEVEN
Electrical field stimulation of eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20050164161A1High throughput screeningEfficient methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningIonElectric field
Methods of identifying activators and inhibitors of voltage-gated ion channels are provided in which the methods employ electrical field stimulation of the cells in order to manipulate the open / close state transition of the voltage-gated ion channels. This allows for more convenient, more precise experimental manipulation of these transitions, and, coupled with efficient methods of detecting the result of ion flux through the channels, provides methods that are especially suitable for high throughput screening.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Method of Isolating P450 Gene
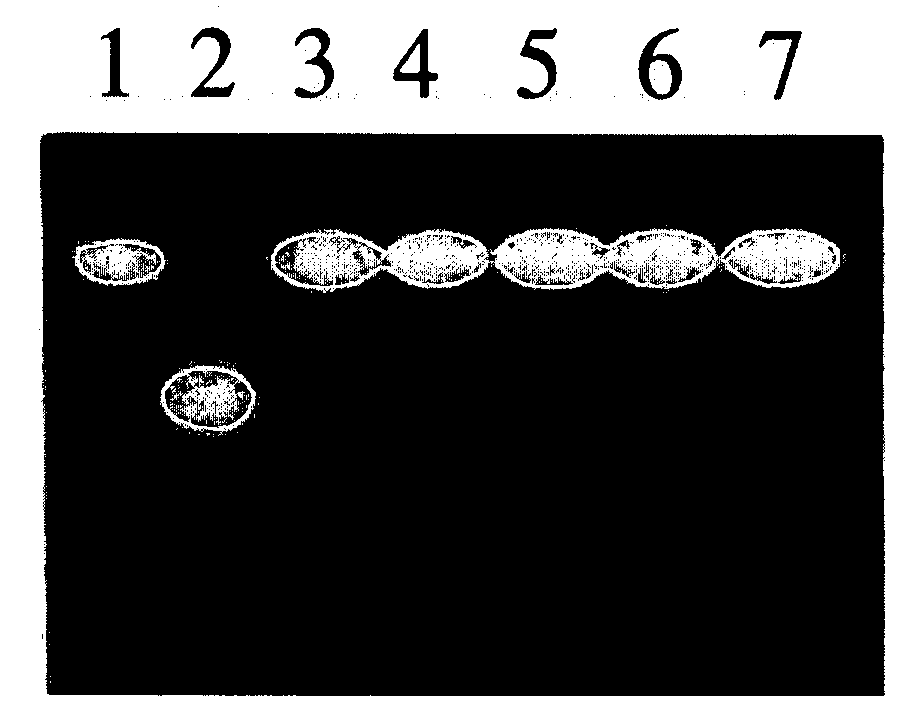
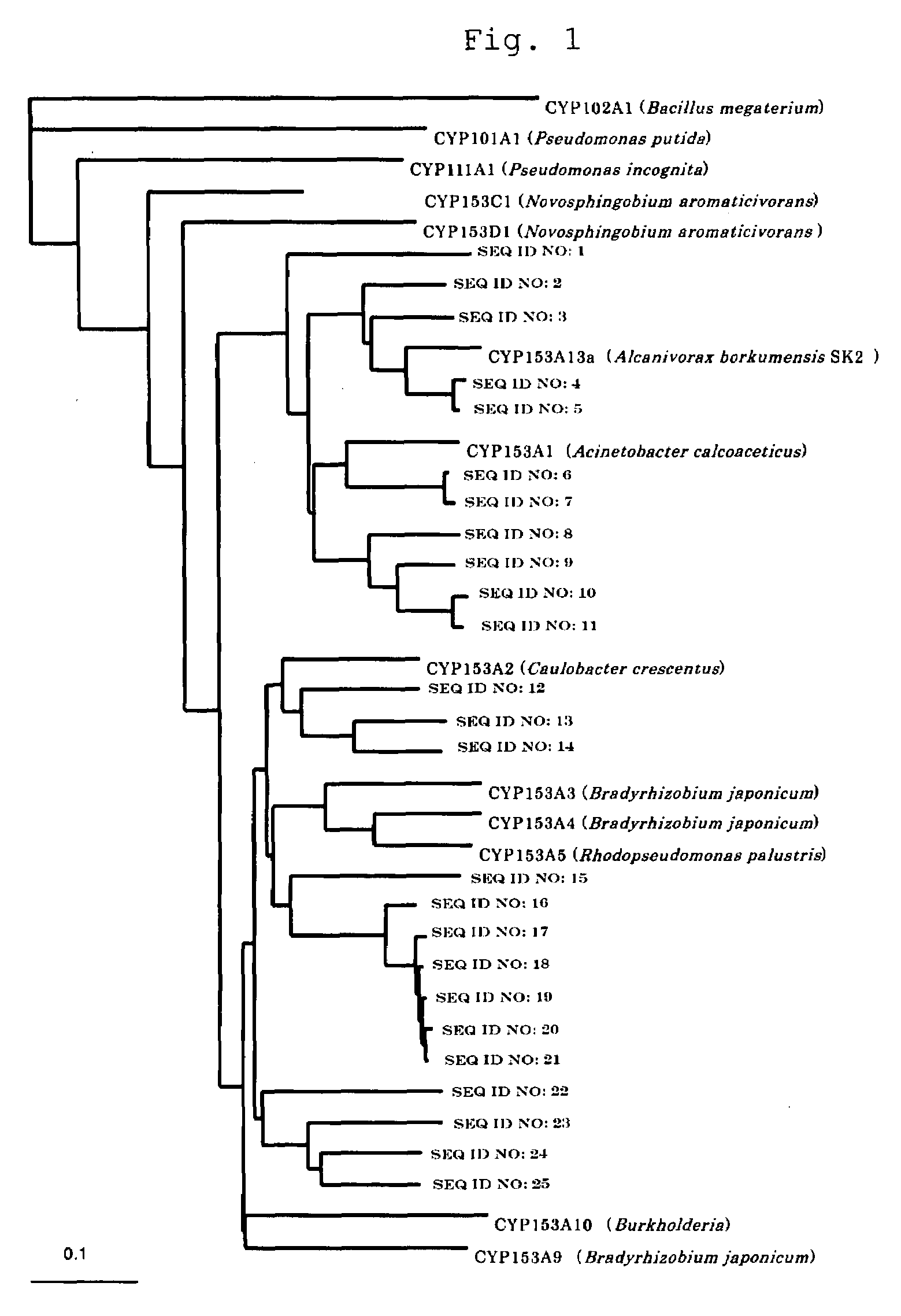
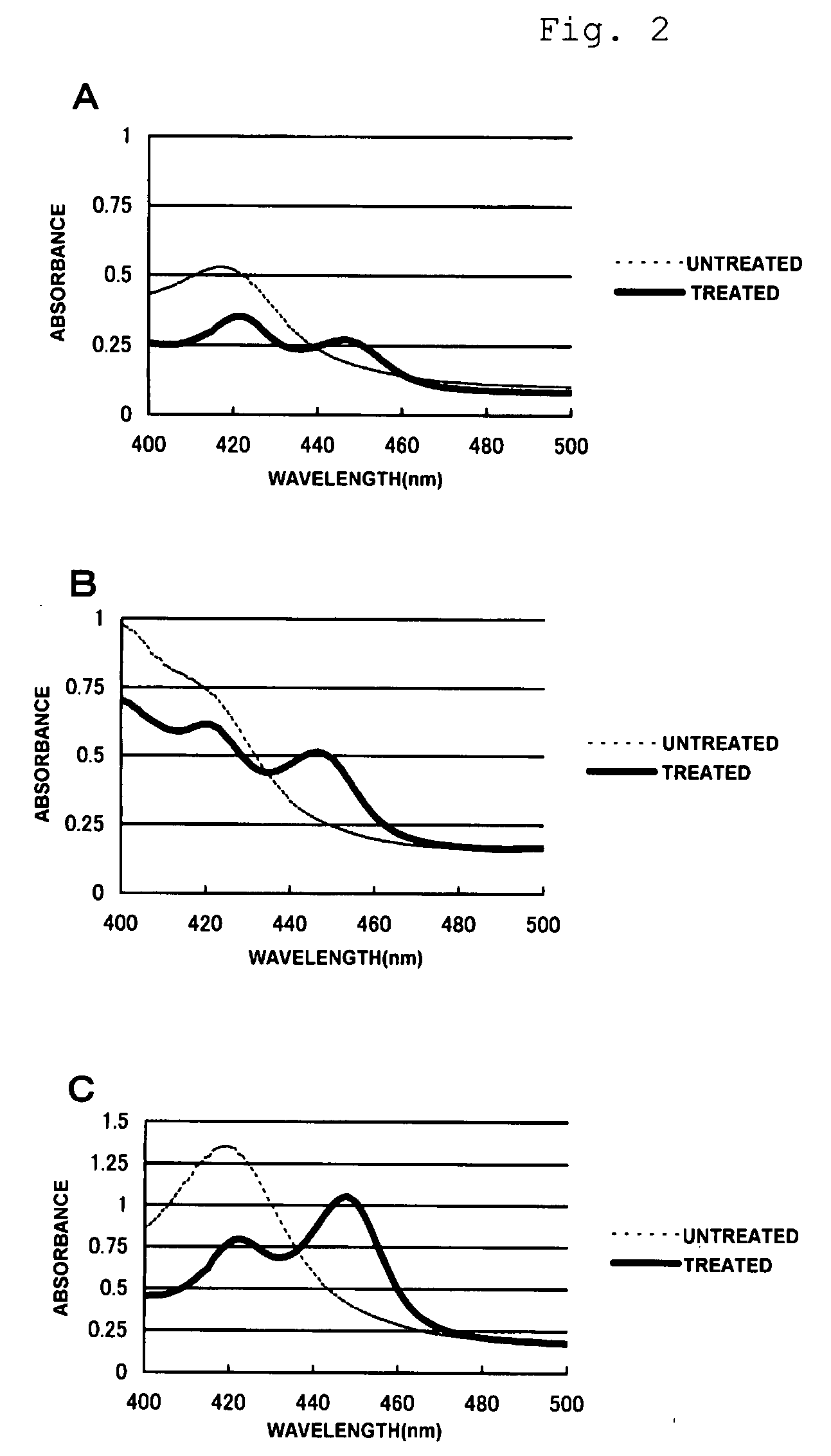
InactiveUS20080220419A1Effective isolationHigh throughput screeningAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganismsElectron transferMicroorganism resource
The present invention provides a method for preparing a hybrid gene. The method includes a step of amplifying a P450 gene fragment contained in a sample using primers designed on the basis of regions of a plurality of P450 in which amino acid sequences are highly conserved and a step of preparing the hybrid gene using the amplified fragments and a known P450 gene. The method includes no culturing step or a step of normalizing extracted DNAs and is useful in isolating a P450 gene from various microbial resources.The present invention further provides a fused cytochrome P450 monooxygenase containing a peptide which is linked to the C-terminus of a P450 protein with a linker portion disposed therebetween and which has the same function as that of a reductase domain contained in a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase originating from Rhodococcus sp. strain NCIMB 9784. This enables the construction of a high-efficiency electron transfer system useful for various P450 proteins and also enables the production of an active P450 monooxygenase.
Owner:KNC LAB
Optical detection of label-free biomolecular interactions using microreplicated plastic sensor elements
InactiveUS7575939B2Inexpensively incorporatedHigh-throughput screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMolecular interactionsThroughput
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting biomolecular interactions. The use of labels is not required and the methods can be performed in a high-throughput manner. The invention also provides optical devices useful as narrow band filters.
Owner:X BODY
Microfluidic protein crystallography
InactiveUS7244402B2High throughput screeningImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein crystallizationBiology
The use of microfluidic structures enables high throughput screening of protein crystallization. In one embodiment, an integrated combinatoric mixing chip allows for precise metering of reagents to rapidly create a large number of potential crystallization conditions, with possible crystal formations observed on chip. In an alternative embodiment, the microfluidic structures may be utilized to explore phase space conditions of a particular protein crystallizing agent combination, thereby identifying promising conditions and allowing for subsequent focused attempts to obtain crystal growth.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Label-free sensor
InactiveUS20100237885A1Cost reductionInstant and quick and rapid and sensitive detectionResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementFluorescenceLabel free
A label-free sensor is disclosed. The label-free sensor comprises a substrate, a first electrode formed on the substrate, a second electrode formed on the substrate and spaced away from the first electrode, and a semiconductor layer formed on the substrate and is in contact with the first electrode and the second electrode, wherein the semiconductor layer has a plurality of probe groups, which are bonded to the semiconductor layer by functionalization, for sensing a coupling-specific substance, which has bonding specificity with the probe groups. The semiconductor layer of the label-free sensor of the present invention is bonded with probe groups, and the detection of detected object is performed in instant, quick, rapid, and sensitive manner by measuring variation in electric current, thereby avoiding the use of the fluorescent reading equipment for reading fluorescent signals.
Owner:NATIONAL CHIAO TUNG UNIVERSITY
Novel high-throughput screening method of drug for bioactive protein
InactiveUS20060177813A1Safe and quick meanQuality improvementCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsWheat germ
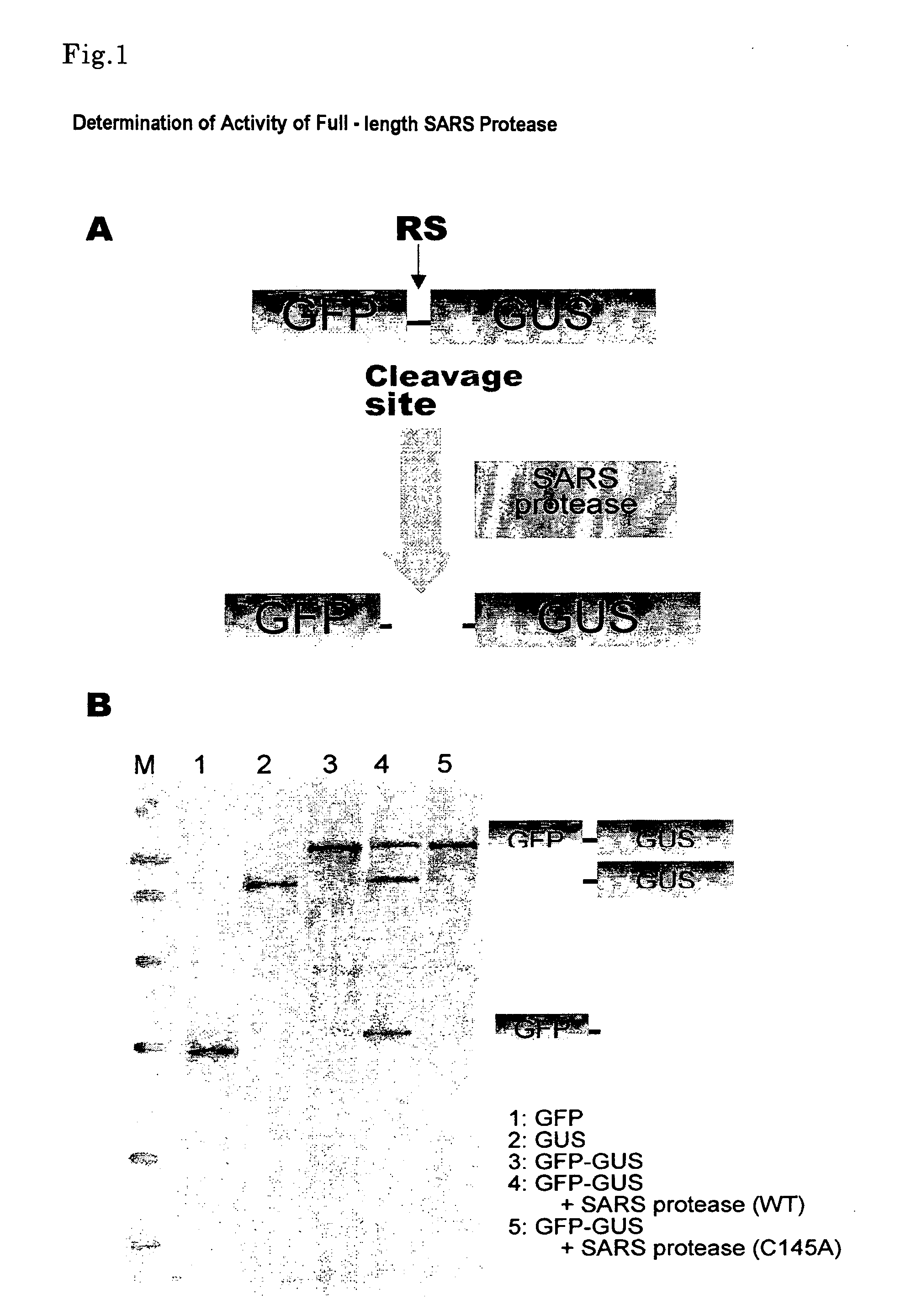
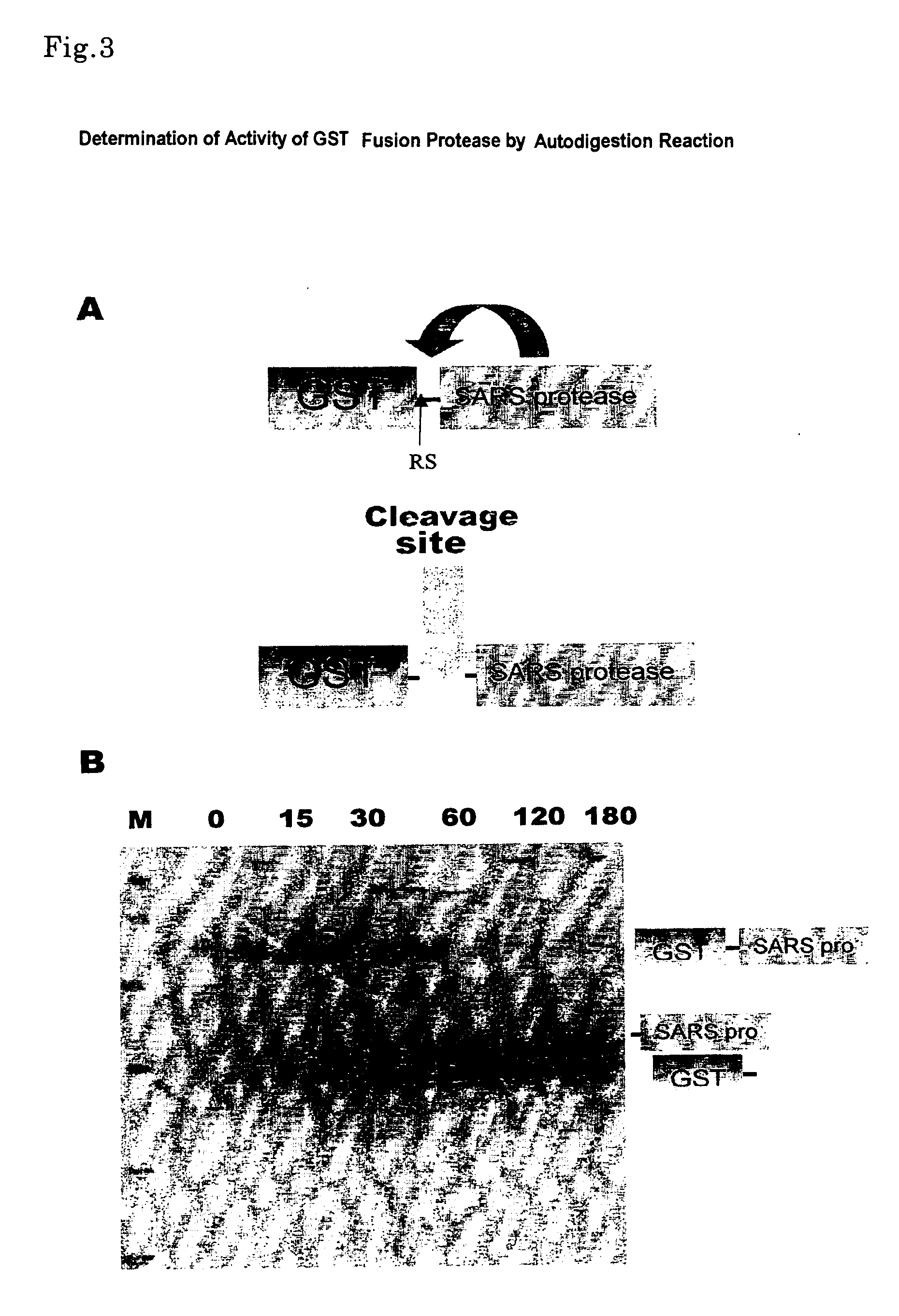
The present invention is intended to provide a safe and quick means for screening a drug to a bioactive protein, in particular, an inhibitor, using a cell-free protein synthesis system with the use of a wheat embryo extract solution. The present inventors have strenuously studied to solve the matters above and finally completed the present invention by, in a system with the use of a wheat embryo, among cell-free protein synthesis means, constructing a synthesis system of a bioactive protein while sustaining its activities, and constructing a system for screening an inhibitor candidate to SARS 3CLpro, as an example using the synthesis system.
Owner:CELLFREE SCI
Method of producing short hairpin library
InactiveUS20070141594A1Improve synthesis abilityEfficient processingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideGenetics
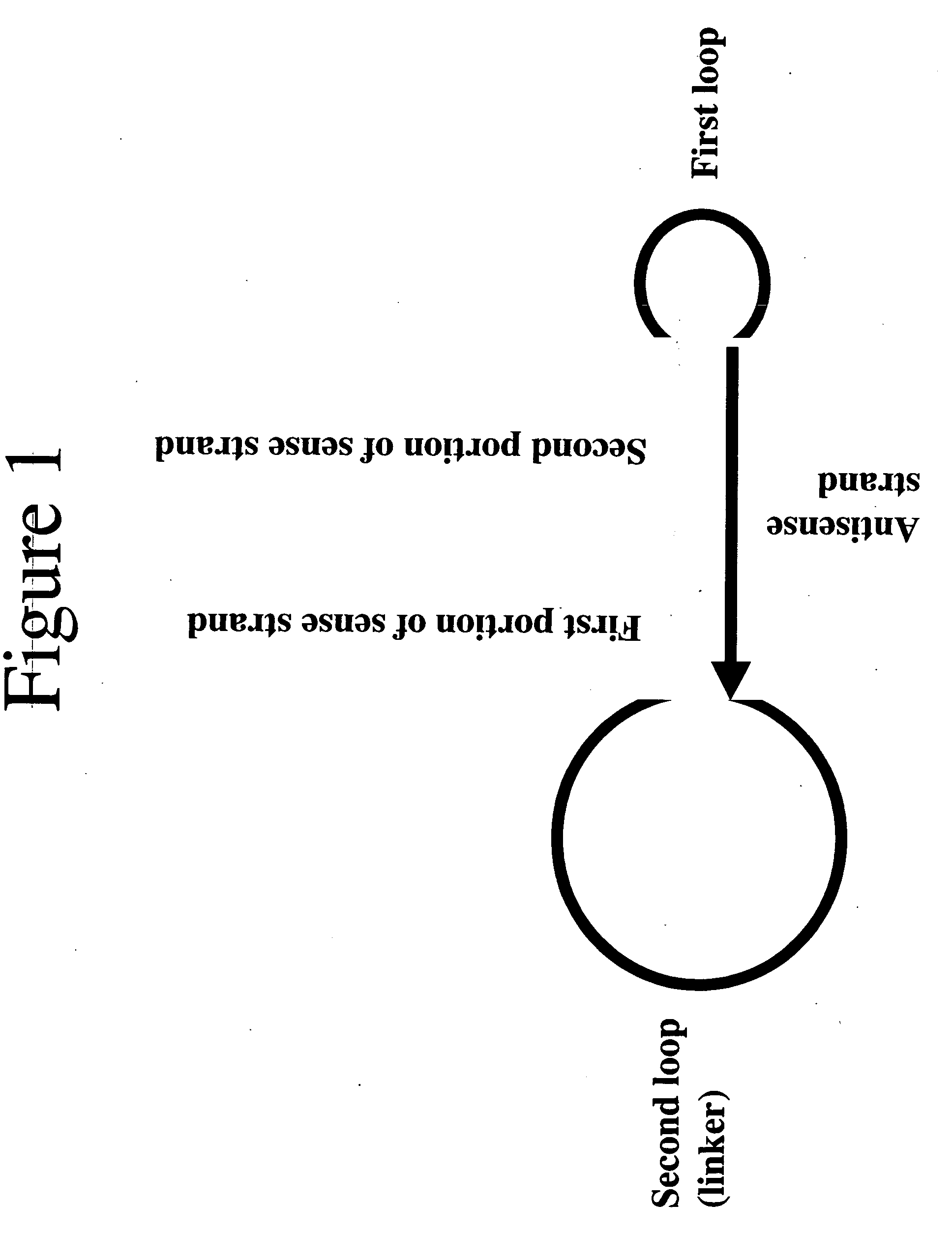
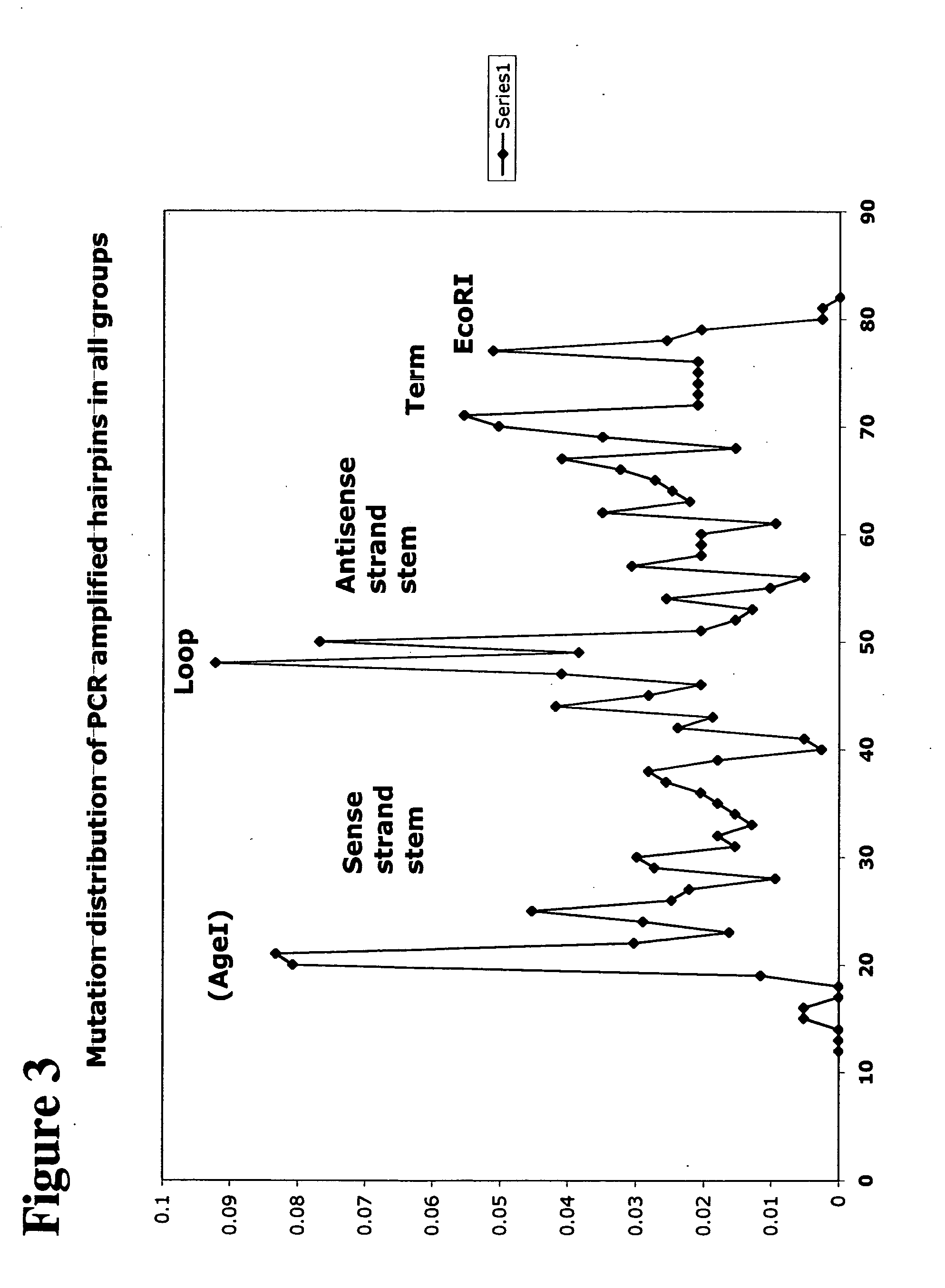
Described herein is a method of cloning synthetic oligos (including in situ synthesized oligos) into an (one or more) expression vector for library (e.g., shRNA library) production. The oligos are synthesized with one portion of the first stem of the hairpin, followed by a first loop sequence, the complete second stem, a second loop sequence, and finished with the remaining portion of the first stem of the hairpin. The two portions of the first stem anneal to the second stem, juxtaposing the 5′ end close to the 3′ end of the oligo. The methods described herein selected for hairpins with perfectly base-paired stems. After annealing, a ligase is added to the annealed oligos and the base-paired hairpins are preferentially annealed, and ligated, creating closed circular oligos. The now circularized hairpins served as templates for rolling circle amplification using a polymerase with high processivity. One or more primers complementary to the two strands of the amplified double stranded circular hairpins initiate the rolling circle amplification in the presence of a polymerase. Using primers (e.g., a sense and antisense primer), the rolling circle amplification yields double stranded hairpin sequences. These can be digested (e.g., using restriction enzymes) to produce a double-stranded hairpin fragment encoding a single hairpin. The fragment can be cloned into an appropriately digested vector for a variety of uses including expression.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Method And Device For Evaluation Of Pharmaceutical Compositions
InactiveUS20070205155A1Accurate assessmentRapid assessmentDialysisLaboratory glasswaresOrganic fluidAqueous solution
A membrane-permeation test for evaluating pharmaceutical compositions is described. The method comprises the following steps: (1) providing a microporous membrane having a plurality of pores, the membrane having a feed side and a permeate side, wherein the feed side of the membrane is in fluid communication with the feed solution, and wherein the permeate side of the membrane is in fluid communication with a permeate solution; (2) administering a pharmaceutical composition to an aqueous solution to form a feed solution; and (3) measuring the concentration of drug in the permeate solution; wherein the feed side of the membrane is hydrophilic, and / or wherein the permeate solution comprises an organic fluid.
Owner:BEND RES
Urethane hapten composition and artificial antigen composition, and preparation methods and application thereof
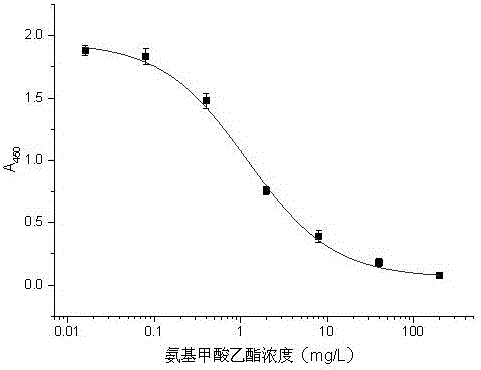
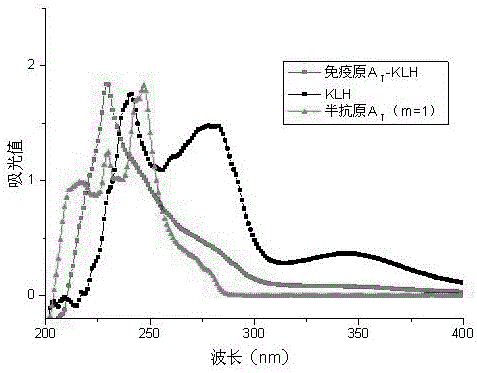
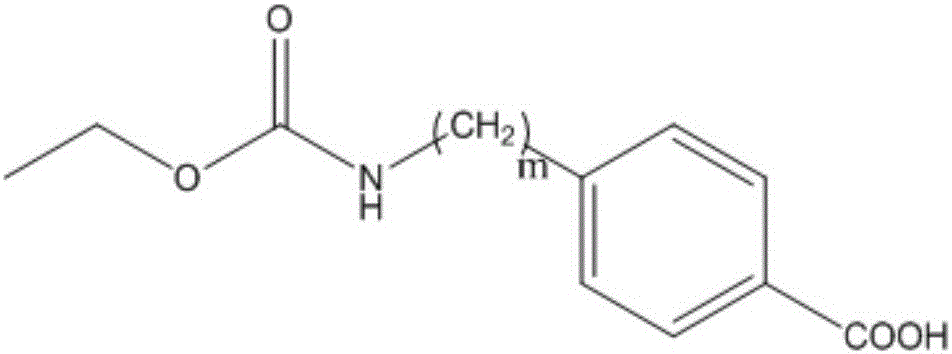
ActiveCN106366021AHigh throughput screeningHigh molecular weightCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationHigh fluxEthyl ester
The invention discloses a urethane hapten composition and artificial antigen composition, and preparation methods and application thereof. The urethane artificial antigen composition has molecular structures as shown in a formula (III) and a formula (IV). Antiserum prepared from artificial antigen provided by the invention has titer of up to 1.25*10<5>, a lowest detection limit of 0.16 mg / L and IC50 of 1.19 mg / L; a prepared antibody has high specificity, high sensitivity and high accuracy; and an immunoassay method for detecting urethane can be established to realize high-flux screening of urethane in food, improve detection efficiency and reduce detection cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
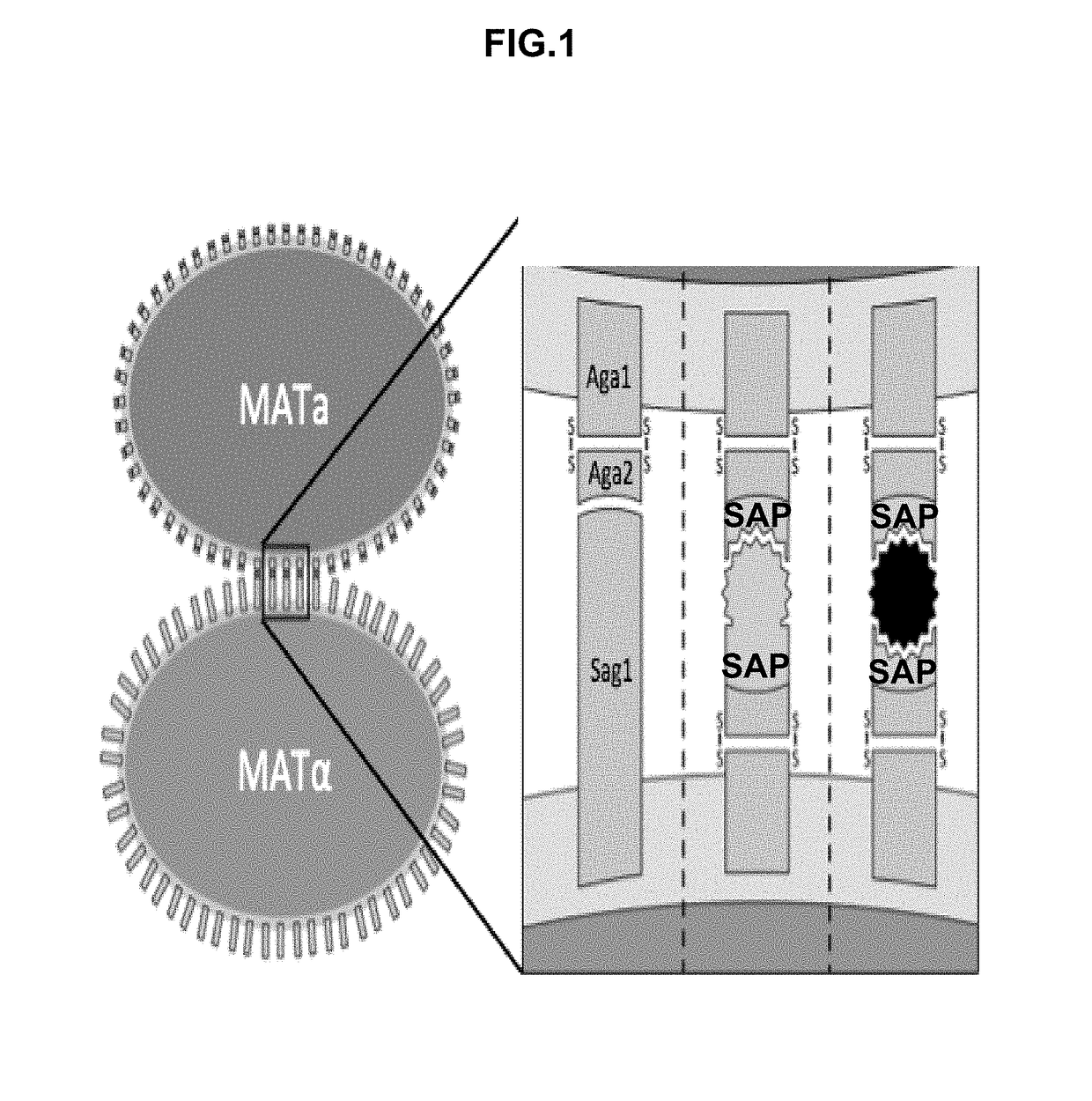
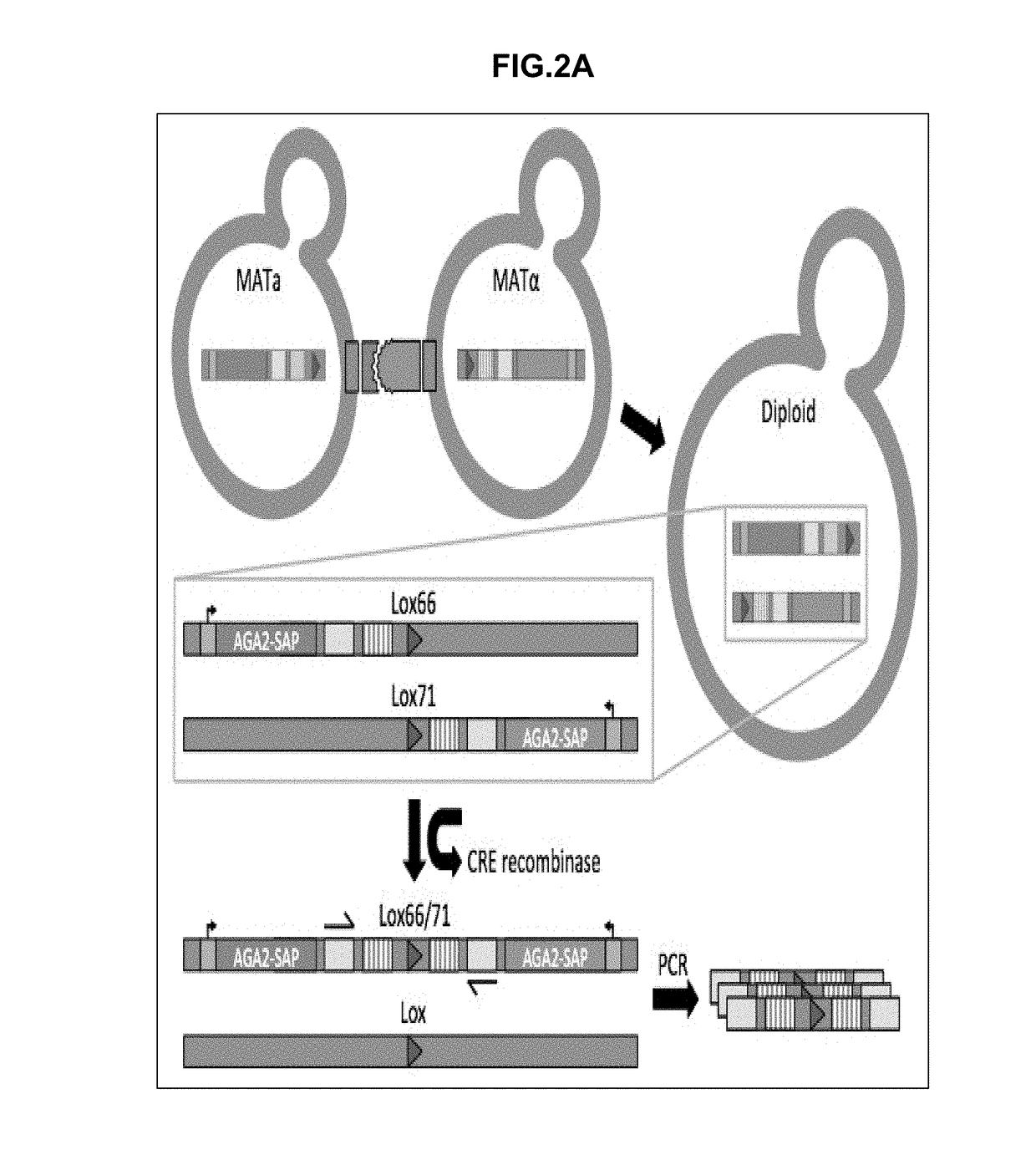
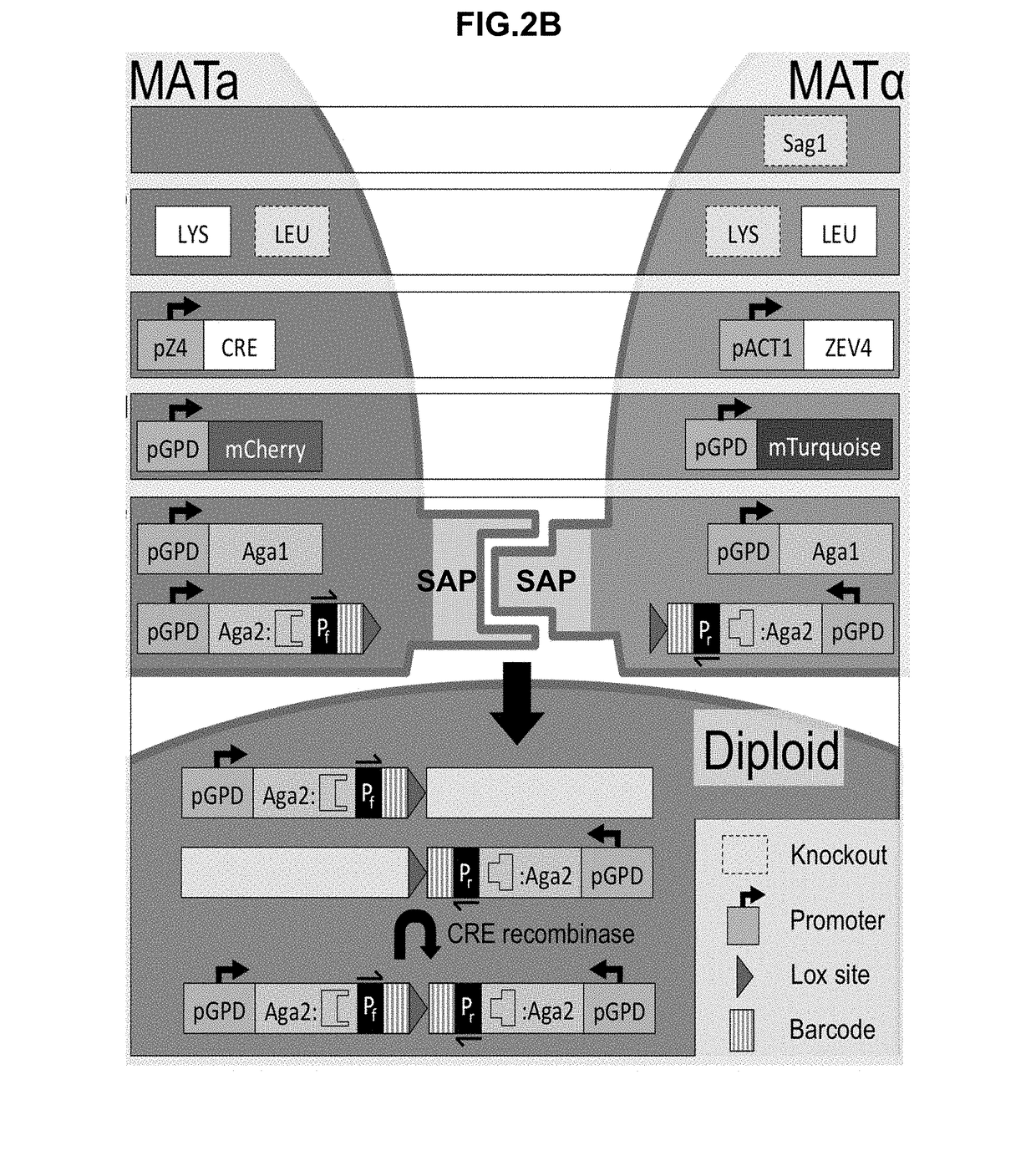
Synthetic yeast agglutination
InactiveUS20170205421A1High throughput screeningHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein protein interaction networkAgglutination
The present invention provides methods and compositions that can be applied to screening protein-protein interaction networks, screening drug candidates that modulate protein-protein interactions for on- and off-target effects, detecting extracellular targets for which no native S. cerevisiae receptor exists, and re-engineering yeast agglutination in order to answer biological questions about yeast speciation and ecological dynamics
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Fluorescent probes for ribosomes and method of use
InactiveUS20050118624A1High-throughput screeningSilicon organic compoundsCompound screeningFluorescence50S
Fluorescent probes that have binding affinity to ribosomes. The fluorescent probes are useful tools for identifying small molecules that bind to the 50S or 30S subunits of the bacterial and other ribosomes and serve as novel ribosome inhibitors. These probes are also useful for determining the interactions between a specific ligand and the ribosome.
Owner:CUMBRE
Iap binding peptides and assays for identifying compounds that bind iap
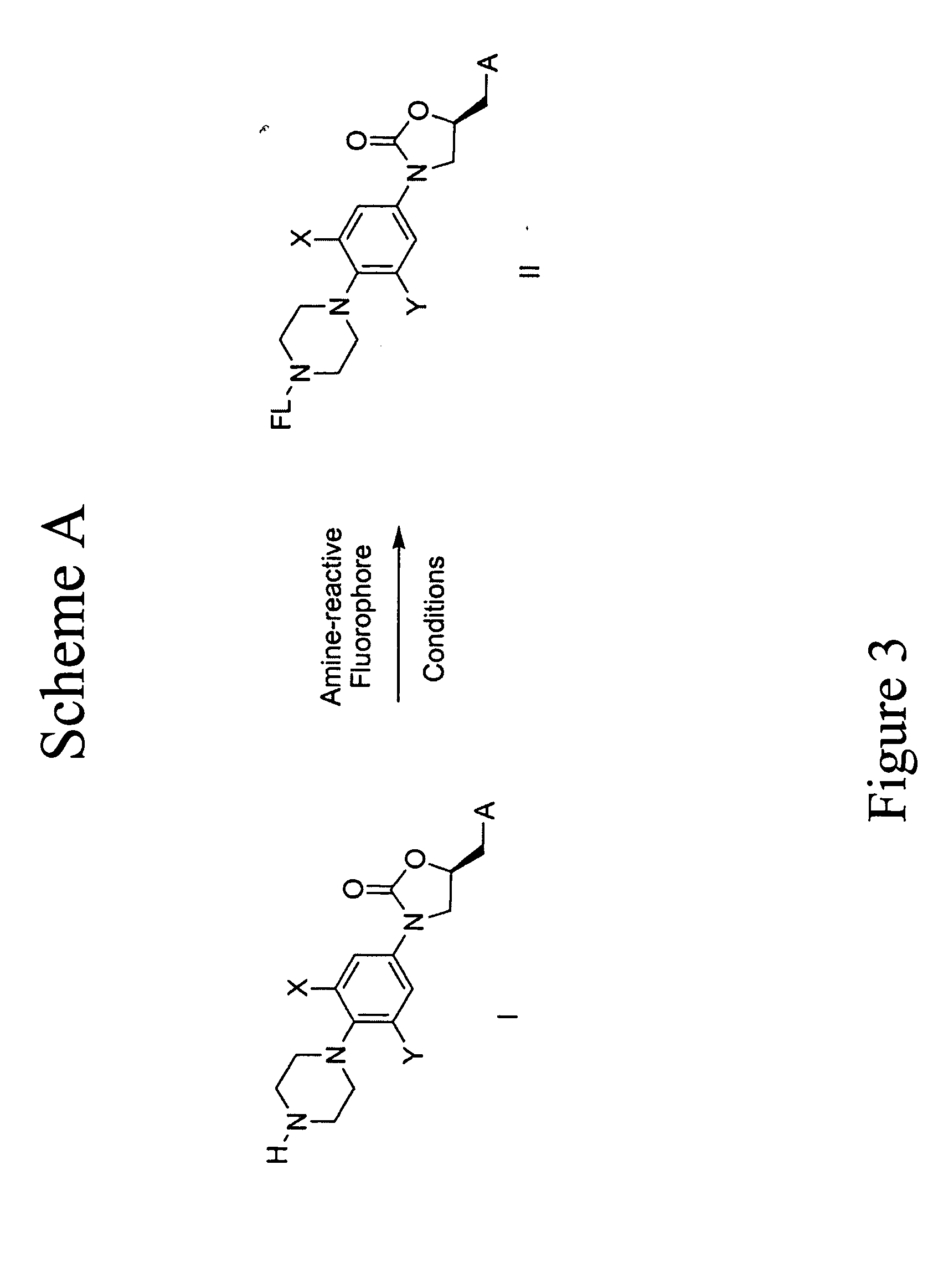
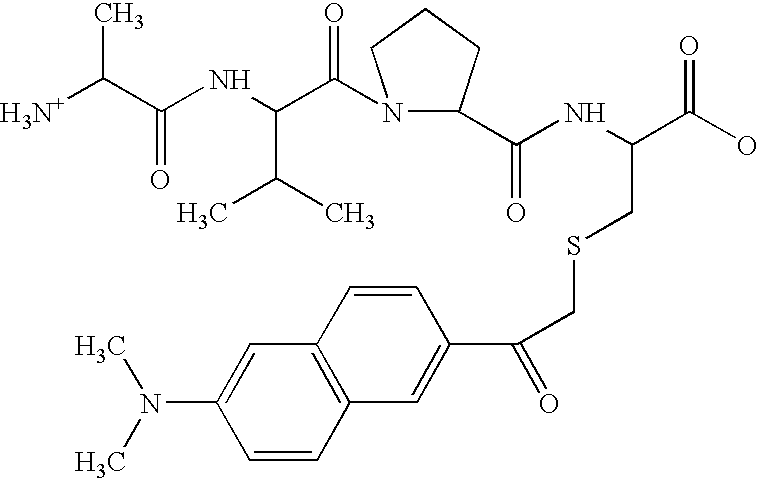
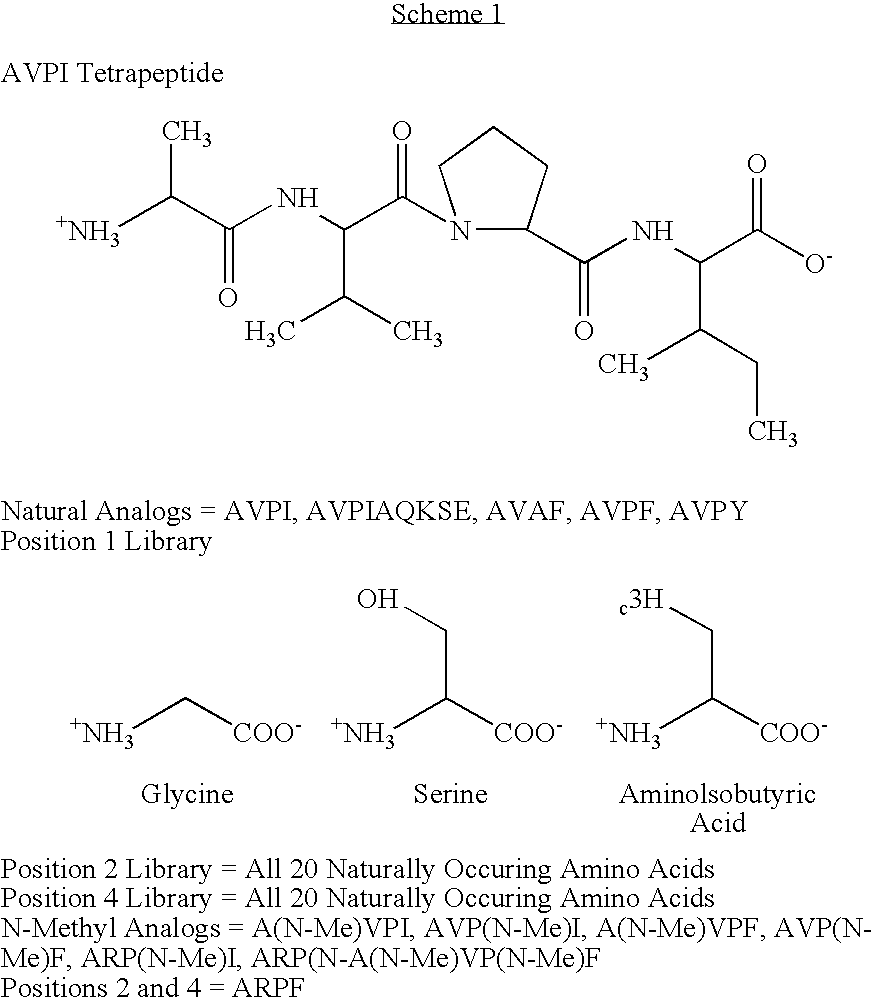
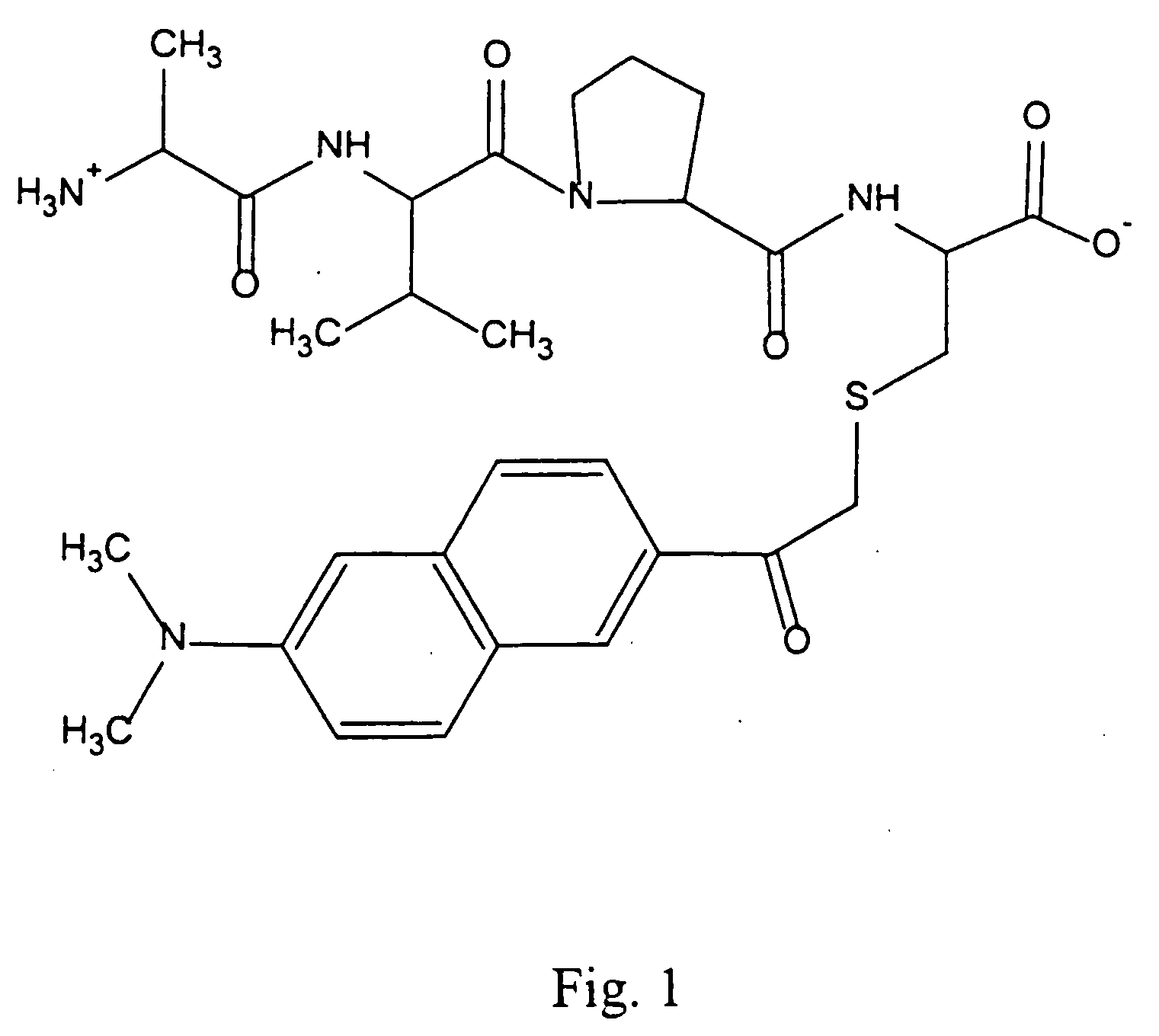
InactiveUS20050176649A1Relieving IAP-mediated suppressionHigh throughput screeningDipeptide ingredientsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorInhibitor of apoptosisBinding peptide
Assays are disclosed for identifying peptides and peptidomimetics for promoting apotosis in cells, through a pathway involving the Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins (IAPs), exemplified by XIAP, and the mitochondrial protein Smac / DIABOLO (hereinafter Smac) and homologs thereof. Also disclosed are IAP-binding peptides and peptidomimetics identified through the use of the assay.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com