Patents
Literature
228 results about "Microorganism resource" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
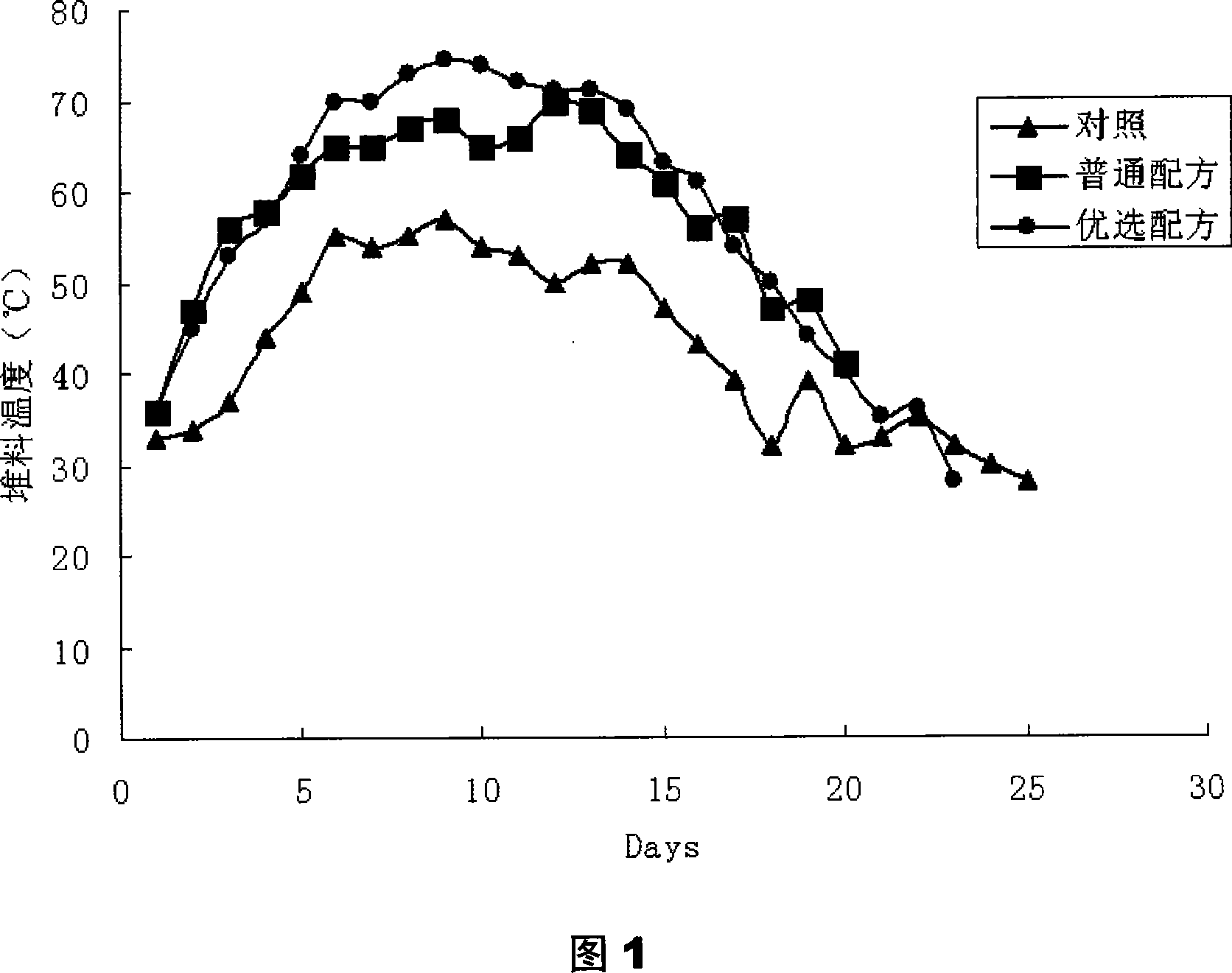
Agriculture castoff compost ternary microorganism composite microbial inoculum
ActiveCN101186879APromote degradationQuick conversionBio-organic fraction processingMicroorganismsMicroorganism resourceCompost
A composite biological agent with ternary microorganism for composting process of agricultural waste is composed of a composite biological agent I, a composite biological agent II, and a composite biological agent III, which is characterized in that the composite biological agent I is composed of bacillus, actinomycetes, microzyme and lactobacillus, the composite biological agent II is composed of trichoderma, ergillus, penicillium and trametes versicolor, and the composite biological agent III is composed of photosynthetic bacterium, azotobacter, phosphorus bacteria, and silicate bacterium. 30-60% composite biological agent I, 30-60% composite biological agent II, 10-20% composite biological agent III are mixed or applied to the process of composting process of agricultural waste in phases. Each component ratio and recruitment of biological agents can be both properly adjusted with different dung materials and dung purpose, thereby achieving purpose of using microorganism resources efficiently and raising fermentation efficiency.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation of calcium carbonate by microbe deposition
ActiveCN1778934AHigh purityHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganism resourceSediment
The invention presents a calcium carbonate preparation method by microbe sediment. Inoculating the Bacillus pasteurii on the substrate with urea, surging culture under 25-37 deg.C, controlling the beginning ph at 6.0-8.0, cultivating 24 hours, fetching the seed liquid, adding CaCl2 liquor, and getting the calcium carbonate after fetching, filtrating, drying the deposit. This invention can make a full use of the microbe of the nature, the resource is abundant, the technics is simple, the surrounding is cleansing, and the cost is low. The calcium carbonate preparing from the sediment has high pureness and productivity, it can be used as stuffing, repairing of the crack of building, and the cementation of regenerative concrete.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for recovering cement-based material crack by means of microorganism, culture fluid and repair nutrient fluid
ActiveCN101302484AImprove volume stabilityIncreased durabilityBacteriaBuilding repairsCulture fluidNutrient solution
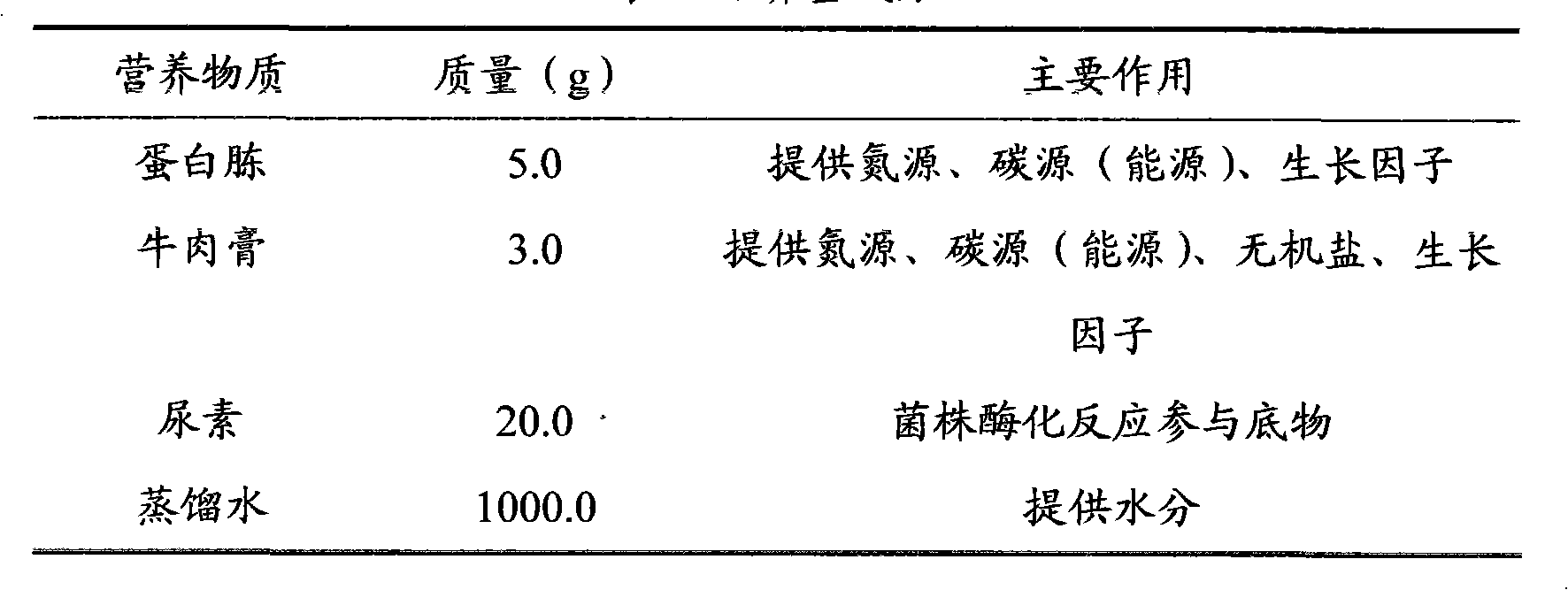
The invention discloses a method for repairing cement-based material cracks, as well as a culture solution and a repair nutrient solution. The method for repairing cement-based material cracks by through microorganisms comprises the following steps that: a Bacillus pasteurii strain is inoculate onto a culture medium provided with a urea-containing substrate; shake cultivation is carried out at a temperature of between 25 and 37 DEG C, and then a culture bacteria solution is taken out and centrifuged and has supernatant fluid removed; strain cells are collected through the culture solution; the concentration of the strain cells is controlled in a range of between 2x10<9> and 1x10<11> cell / ml; standard sand, urea and Ca(NO3)2.4H2O mixture are added to each milliliter of strain cell solution obtained through collection, mixed, stirred into slurry and injected into cement stone cracks; the frequency of the repair nutrient solution injection is not less than two times; finally, maintenance is carried out. In the culture solution, each liter of culture solution contains 4 to 6 g of peptone, 2 to 4 g of beef extract and 20 to 60 g of urea. The method fully utilizes microbial resources in nature; CO3<2-> decomposed out through microbial enzyme can chelate Ca<2+> in a substrate so as to be mineralized and deposit calcium carbonate, and is close in the combination with the substrate and good in stability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Bacillus aryabhattai J5 and application thereof
ActiveCN105985922APromote growthGood effectPlant growth regulatorsBiocideDiseaseBacillus aryabhattai
The invention belongs to the field of microbial resources, and particularly discloses a strain of Bacillus aryabhattai J5 and application thereof in promoting growth of corn. The Bacillus aryabhattai J5 is collected in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on October 15th, 2015 and is filed with the number of CGMCC NO.11508. The Bacillus aryabhattai J5 has functions of producing auxin, siderophore, ammonia and protease, dissolving phosphorus, resisting to salt, realizing antagonism, and the like. As the strain is capable of growing normally in a culture medium with salt content equal to 11%, the strain has good potential in eliminating soil salinization. As content of siderophore produced by the strain is up to 53.7%, the strain has effective disease-prevention property. By the strain, corn seed germination rate can be increased by 12.5%, and accordingly the strain has good growth promoting effect. By application of microbial inoculum prepared from the strain, corn yield is increased by 37.1%, and hundred-grain weight is increased by 35%. It is possible to develop the strain into microbial inoculum, and accordingly the strain has wide application prospect in terms of improving soil nutrient, eliminating salinization, promoting growth of plants, preventing diseases and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
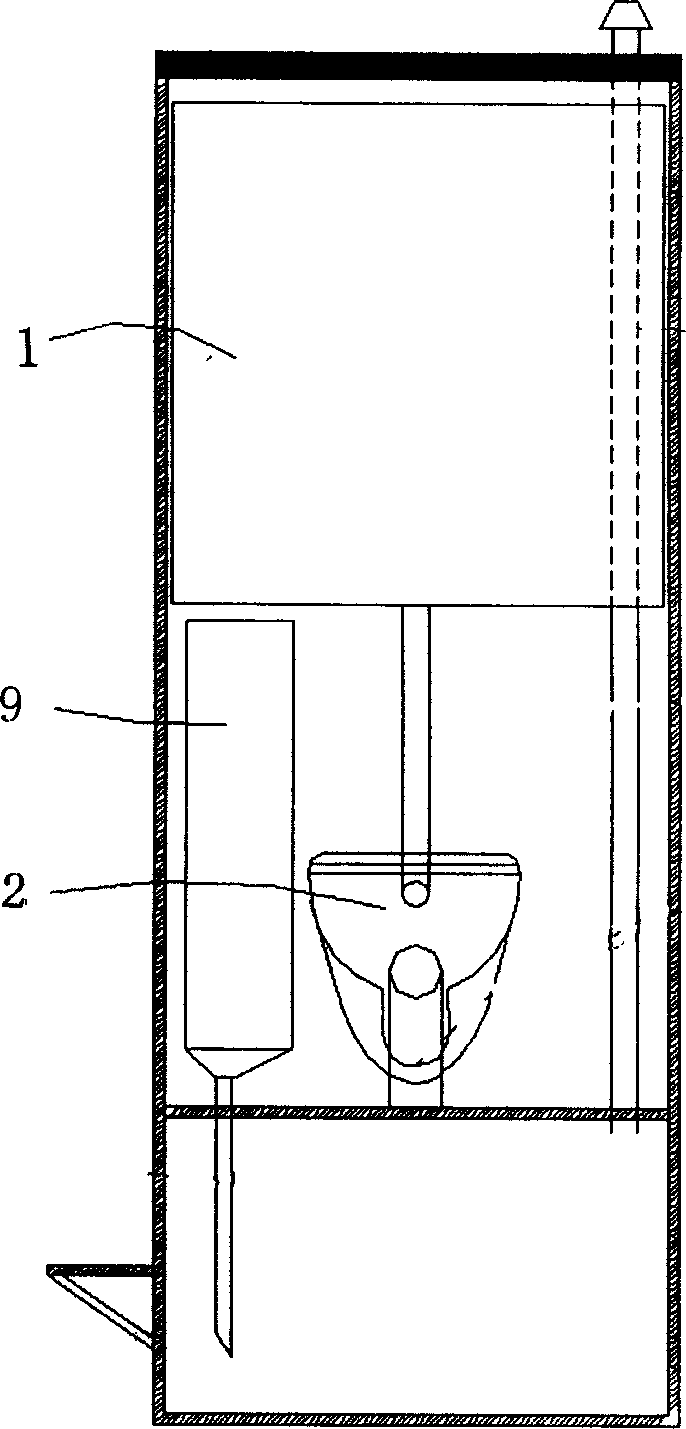
Circulating water flushing ecological toilet and sewage treatment method thereof
InactiveCN1594763AExpand conceptBroaden the field of applicationFlushing devicesLavatory sanitoryHuman wasteFeces
The invention discloses a circulating water flushing ecological toilet and sewage treatment method thereof. The high-position water tank orderly connects to the latrine, grinder-mixer, solid and liquid separator, anaerobic reacting device, facultative reacting device, aerobic reacting device and ozone disinfection device. The ozone disinfection device connects to the high-position water tank by water pump. The invention breaks the localization that the toilet depends on the water and the ecological toilet contaminant is treated elsewhere, conquers the secondary pollution of the transporting, collecting and packing materials for ecological no water toilet, improves the efficiency of the dejection treatment in situ and innocuous treatment degree, fully applies the abundant microbe resource in the dejection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for preparing calcium carbonate by using catalysis of microbial carbonic anhydrase
InactiveCN102121033AHigh purityAbundant resourcesMicroorganism based processesFermentationAtherion elymusFiltration
The invention provides a method for preparing calcium carbonate by using catalysis of microbial carbonic anhydrase, which comprises the following steps of: adding the carbonic anhydrase extracted from a microbial culture into a liquid system containing calcium ion and bicarbonate radical ion solution or a gas diffusion system containing calcium ion solution and releasing CO2 by using ammonium hydrogen carbonate solution, performing oscillating reaction at room temperature, controlling initial pH at 5 to 10, taking out the produced sediment, and performing filtration, washing and drying to obtain the calcium carbonate. The method makes full use of microbial resources and characteristics of specificity and high efficiency of enzyme catalytic reaction, prepares the calcium carbonate by accelerated deposition, and has the advantages of riche resources, simple process, clean environment, low cost, high efficiency, quickness and the like. The calcium carbonate prepared by deposition has high purity, is calcite crystal calcium carbonate, can be used as an industrial filler, and can also be used for repairing cracks of building engineering, buildings, stone landscapes and carved stone cultural relics.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
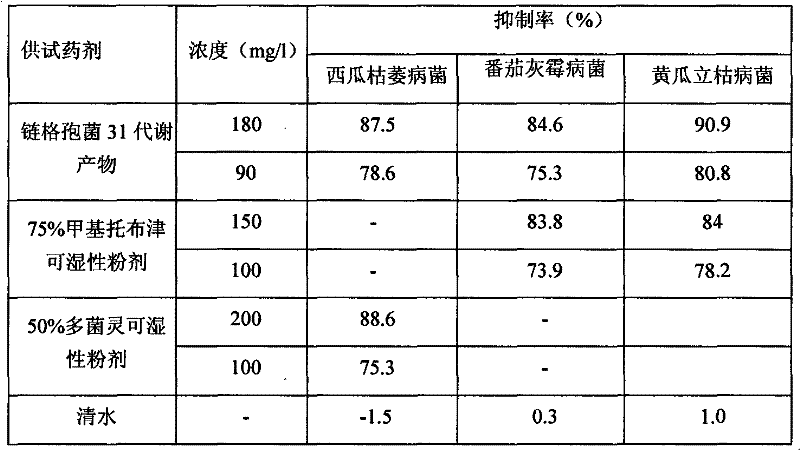
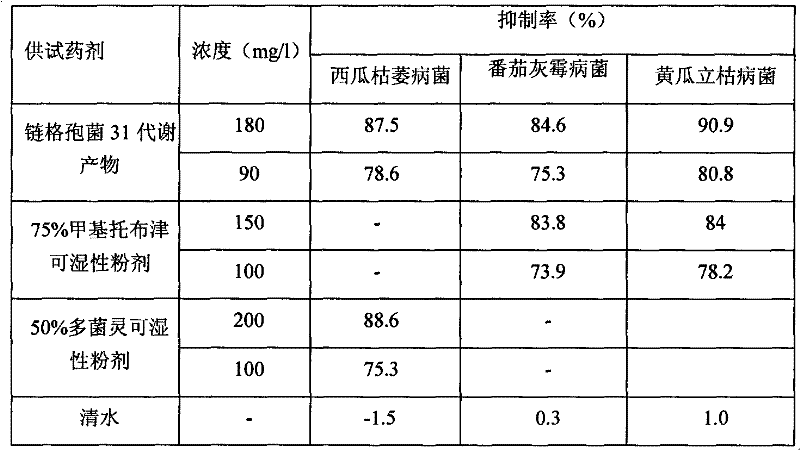
Application of alternaria alternate metabolic products in cucumber rhizoctonia solani prevention and control
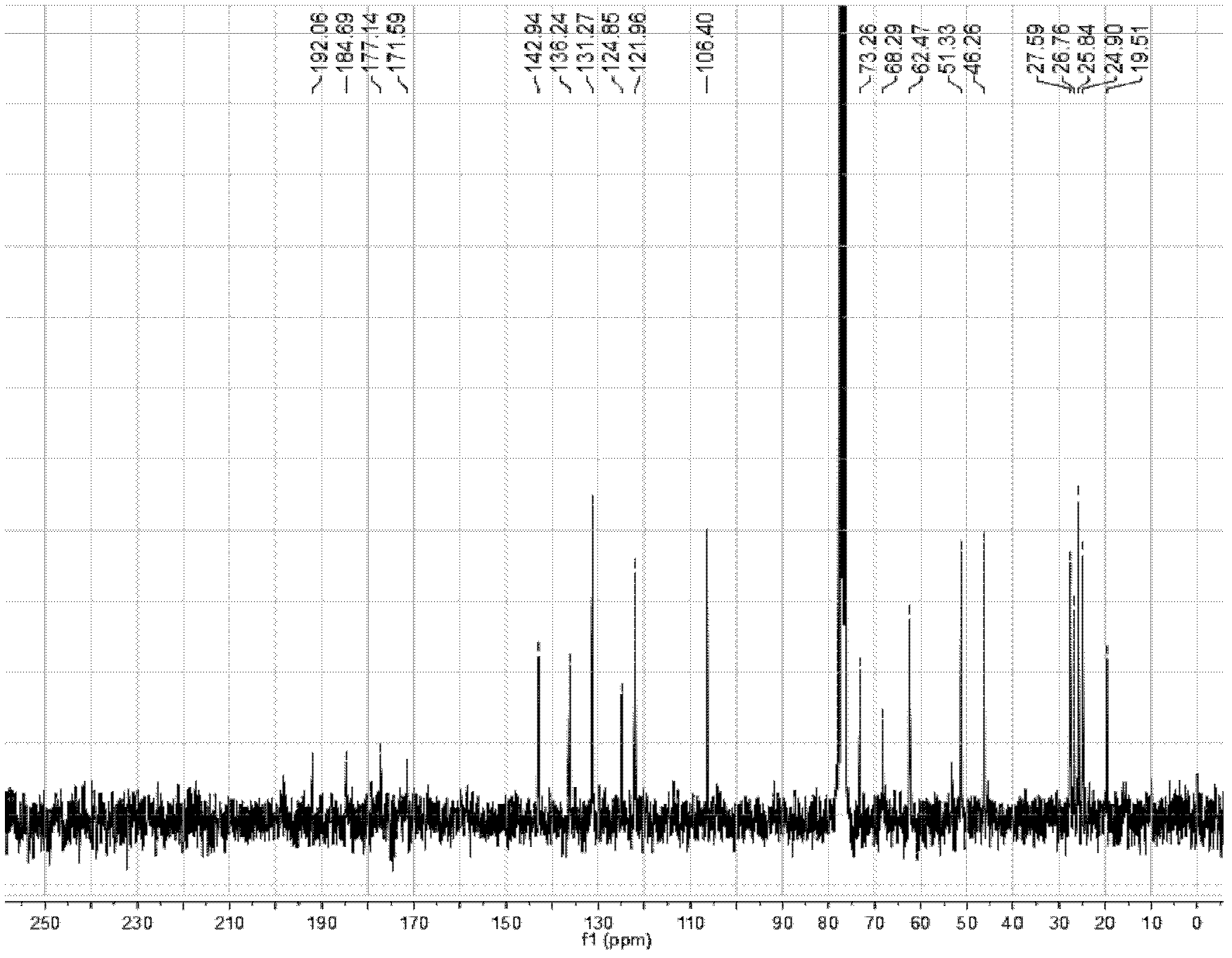
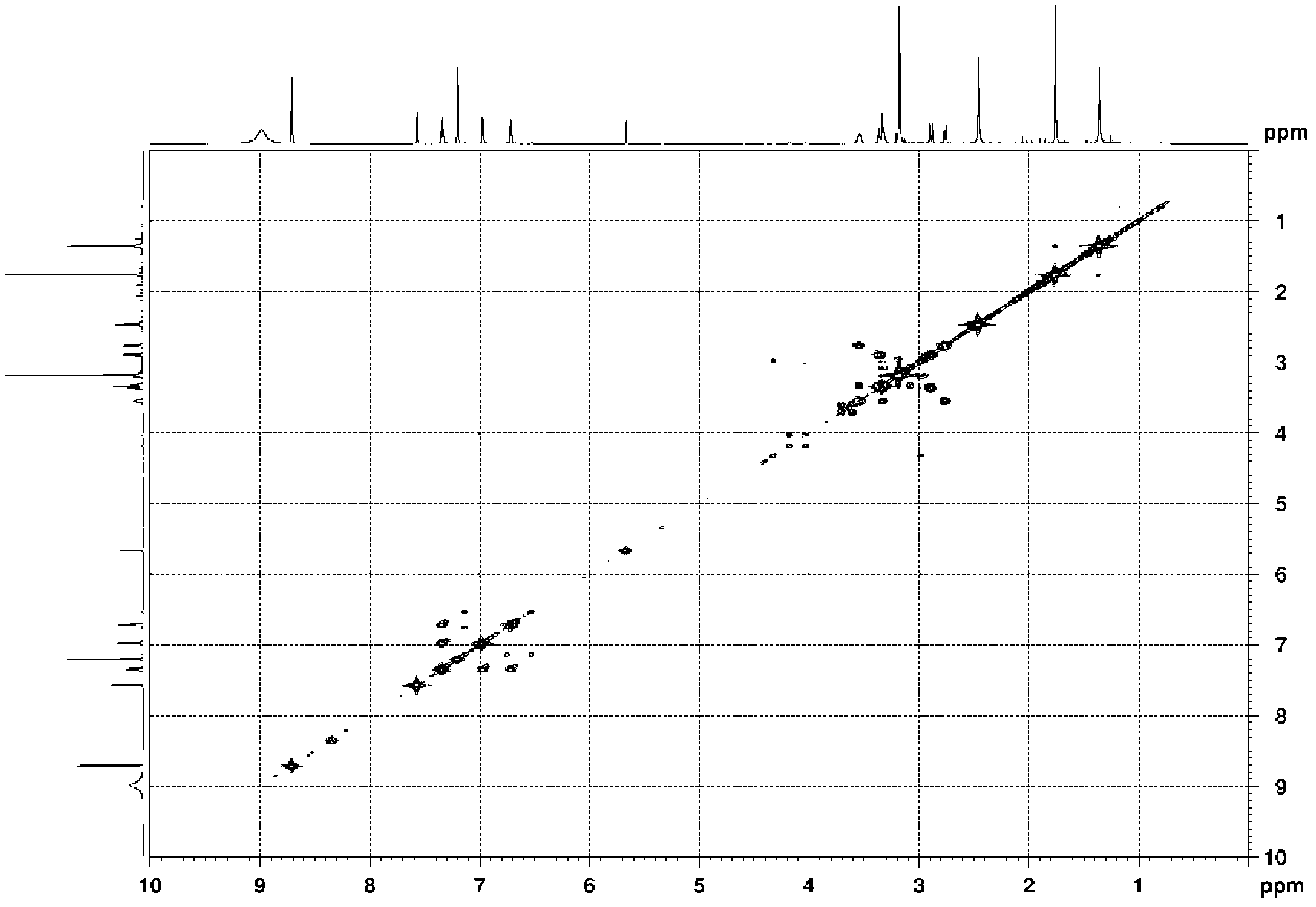
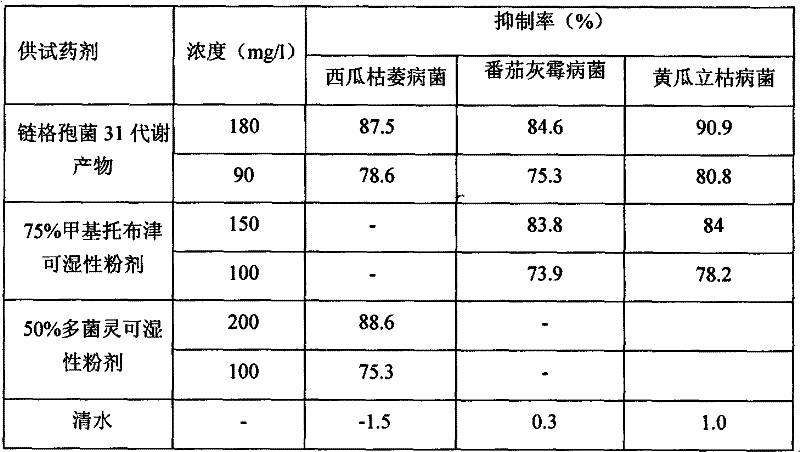
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to application of alternaria alternate metabolic products in cucumber rhizoctonia solani prevention and control. In the invention, endophytic fungus of camphor trees is separated from camphor tree living bodies collected from Tianmu mountain in Hangzhou, Zhejiang province by adopting endophytic fungus separation technology, and isnamed alternaria alternata 31 through microbial taxonomy identification, and the strain is stored in China General Microbiological Culture Collector Center (CGMCCC) on December 31, 2010, and the collection register number is CGMCC No.4508. The invention has a most obvious characteristic that the strain liquid can be fermented to produce active metabolic products which have inhibiting effect on pathogenic bacteria of plant fungus diseases such as Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium oxysporium, Botrytis cinerea and the like, thus alternaria alternate is an important microbial resource in agriculture.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
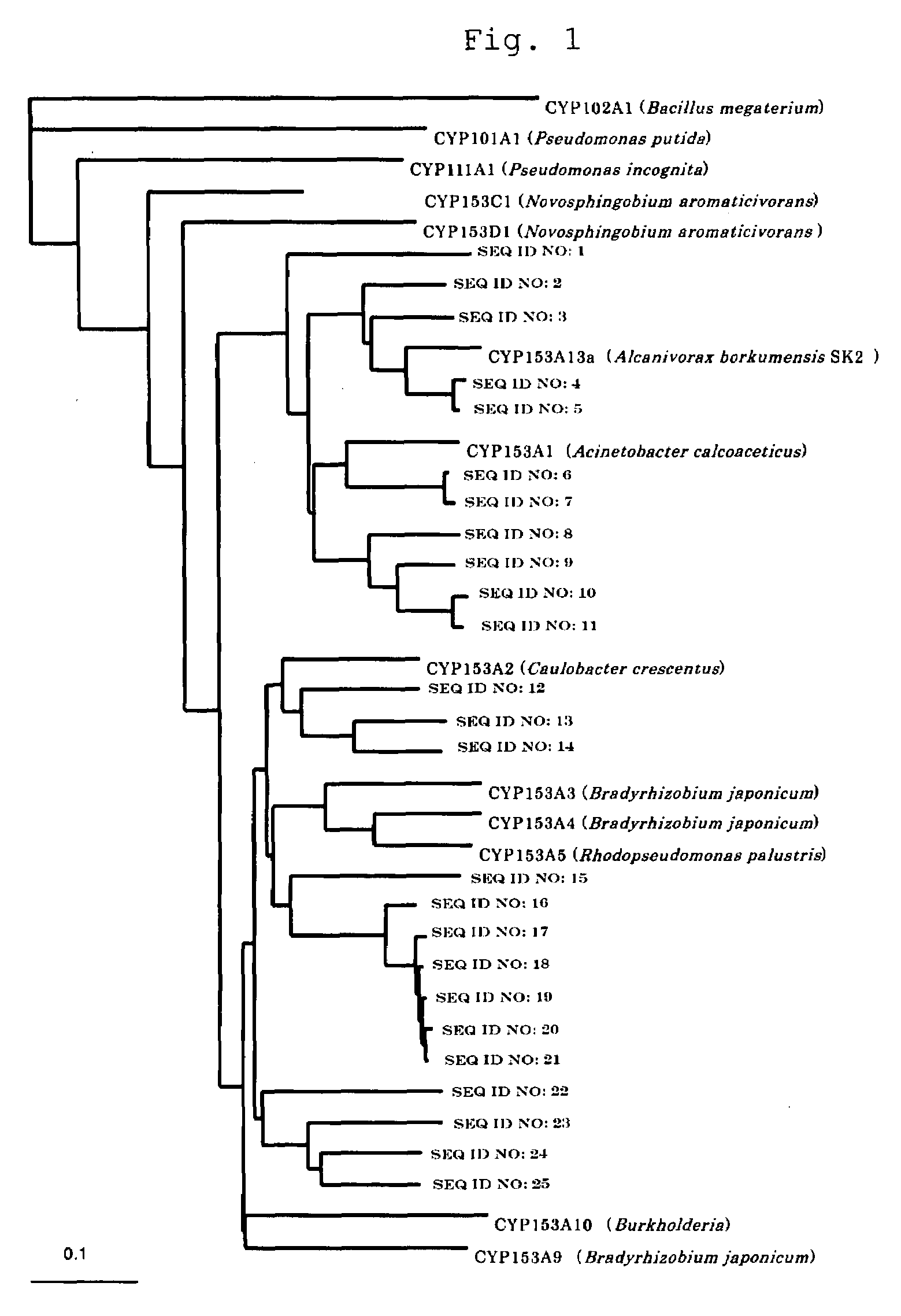
Method of Isolating P450 Gene
InactiveUS20080220419A1Effective isolationHigh throughput screeningAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganismsElectron transferMicroorganism resource
The present invention provides a method for preparing a hybrid gene. The method includes a step of amplifying a P450 gene fragment contained in a sample using primers designed on the basis of regions of a plurality of P450 in which amino acid sequences are highly conserved and a step of preparing the hybrid gene using the amplified fragments and a known P450 gene. The method includes no culturing step or a step of normalizing extracted DNAs and is useful in isolating a P450 gene from various microbial resources.The present invention further provides a fused cytochrome P450 monooxygenase containing a peptide which is linked to the C-terminus of a P450 protein with a linker portion disposed therebetween and which has the same function as that of a reductase domain contained in a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase originating from Rhodococcus sp. strain NCIMB 9784. This enables the construction of a high-efficiency electron transfer system useful for various P450 proteins and also enables the production of an active P450 monooxygenase.
Owner:KNC LAB
Sphingobium yanoikuyae and application thereof in degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
The invention discloses a Sphingobium yanoikuyae and an application thereof in degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. The Sphingobium yanoikuyae provided by the invention is named as LD29 with the strain collection number of CGMCC No.4400. The Sphingobium yanoikuyae LD 29 can grow and breed by respectively taking phenanthrene, anthracene, fluoranthene and pyrene as the only carbon source and energy source under the aerobic condition. In addition, the Sphingobium yanoikuyae LD 29 has a degrading effect on mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, especially on pentacyclic benzopyrene [alpha] in the mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. The Sphingobium yanoikuyae can be used for repairing soil and the water body polluted by the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is quick, convenient and environmentally-friendly, and can be used for reducing the content of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in the environment, thereby providing new microorganism resources for bioremediation for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution, and having an important value for environmental governance as well as considerable economic benefit and good social benefit.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing calcium carbonate by simultaneous mineralization of two microorganisms
InactiveCN108220380ARaise the pHNo pollution in the processMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganism resourceCalcium EDTA
The invention relates to a method for preparing calcium carbonate by simultaneous mineralization of two microorganisms. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding a culturesolution of the two cultured microorganisms to a mixed solution of calcium salt and urea, putting a reactor in an open mode to enable the solution to be exposed to the air to be subjected to mineralization reaction, taking out the precipitate after the reaction is completed, and washing and drying the precipitate to obtain a calcium carbonate product. The two microorganisms are respectively sporosarcina pasteurii belonging to a urease high-yield strain and bacillus pumilus belonging to a carbonic anhydrase high-yield strain. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the twostrains together participate in the mineralization process, the generation efficiency of calcium carbonate is increased, simultaneously, the pollution to the environment caused by generation of ammonia gas can be reduced, CO2 in the atmosphere can also be captured, and the advantages of the two strains are complementary so as to cooperatively promote the whole mineralization process; the microorganisms utilized in the method are rich in resources, efficient and single in enzyme catalysis reaction, simple in production process and low in cost; and furthermore, the obtained calcium carbonate product is higher in purity, has better cementing action and can be widely applied to the field of civil engineering.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Methylotroph bacillus and application thereof
ActiveCN107267412AAntagonisticOutstanding disease control effectBiocideBacteriaMethylotrophResource development
The invention discloses a methylotroph bacillus and application thereof to preparation of a plant pathogenic bacterium sterilization agent. The methylotroph bacillus CGMCC No.13541 has the antagonism effect on various phytopathogens such as botrytis cinereal, fusarium graminearum and rhizoctonia solani, and belongs to an environment-friendly antagonistic strain with the obvious plant disease prevention and control effect; the development and application prospects are good. Culture liquid obtained through culture by a beef extract liquid culture medium can be used for preventing and controlling plant diseases. The bacteriostasis rate on the botrytis cinereal is as high as 84 percent; the value is about 8 percent higher than that of ordinary biocontrol bacteria; the foundation is laid for the novel disease prevention microbe resource development and utilization. The resistance capability is high; the use range is wide; the growth speed is high; fast and great-amount multiplication can be realized; the popularization and application of a biological prevention and control preparation in the field are convenient.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
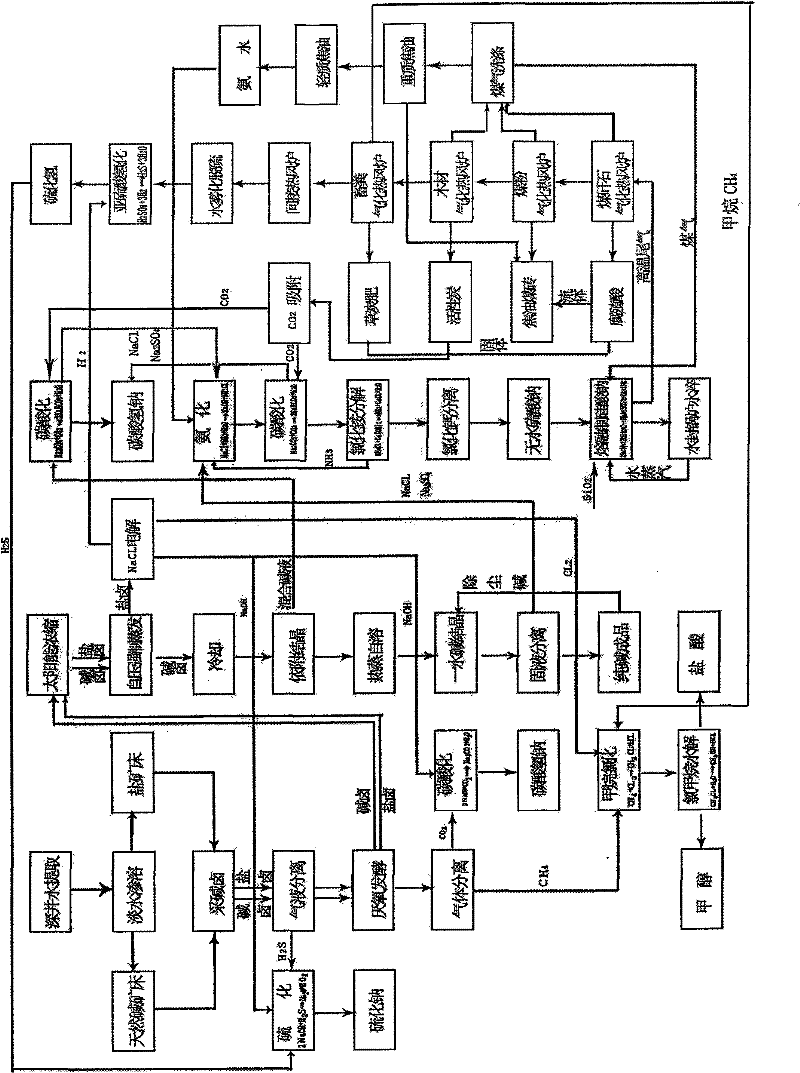
Large-scale joint alkali-making circulation process
InactiveCN102198952AAchieve associativityStrong complementarityBio-organic fraction processingElectrolysis componentsMicroorganism resourceEnergy conservation
The invention relates to a large-scale joint alkali-making circulation process. The process comprises the following steps: a. obtaining an alkali-making raw material by an infiltration alkali extraction method; b. obtaining hydrogen sulfide and methane by utilizing microbial resource in an alkali halide; c. evaporating and concentrating a thin alkali liquid by utilizing natural energy; d. obtaining various types of products by combining a natural alkaline method and a chemical combination method; e. obtaining subsidiary products by combing coal chemical industry deep processing and an alkali-making process; and f. obtaining series of products by combining an electrolytic process and a chemical combination method. The large-scale joint alkali-making circulation process has the beneficial effects that natural alkali waste resource and hidden resource are excavated for raw material supply, biological energy and natural energy are comprehensively utilized so as to realize energy utilization, potential of coal chemical industry deep processing is developed and an activated carbon purification technology is applied to low carbon economy so as to achieve the purposes of energy conservation and environmental friendliness so that technologies in various fields are tightly integrated with the alkali-making process, thus fundamentally realizing large-scale joint alkali-making circulation and greatly lowering the alkali-making cost.
Owner:崔怀奇 +2
Composite microbial fertilizer for controlling soil-borne disease and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105732195AImprove micro-ecological environmentIncrease diversityBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersBiosphereResource pool
The invention discloses a composite microbial fertilizer for controlling soil-borne disease and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial fertilizer for controlling soil-borne disease is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: waste livestock / fowl feather, rice bran, dry manure, weathered coal, biochar, a composite microbial inoculant, humic acid, bentonite, potassium sodium tartrate, citric acid, copper sulfate and ferrous sulfate. The composite microbial inoculant is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus mucilagimosus krassilm and Paenibacillus sabinae. The composite microbial fertilizer contains abundant various microbes, and the composite microbial inoculant is added to increase the beneficial bacterium content, so that the composite microbial fertilizer becomes a microbe resource pool. After being applied by drip irrigation and spraying, the composite microbial fertilizer can adjust the phytoedaphon structure, enhance the soil microbe diversity, improve the microecological environment of the soil and reduce the biosphere of the phytopathogen, thereby achieving the goal of controlling soil-borne disease.
Owner:GUANGXI WEILIDA BIOTECH CO LTD
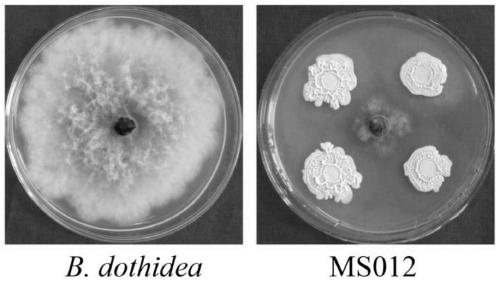
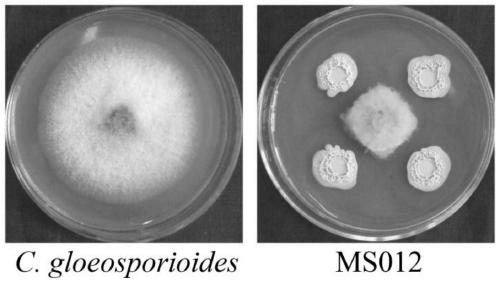
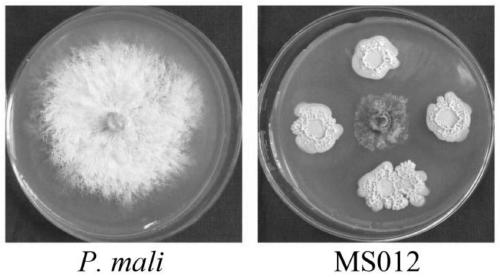
Bacillus velezensis having various disease preventive effects, application thereof and biocontrol inoculant
The invention relates to bacillus velezensis having various disease preventive effects, application thereof and a biocontrol inoculant and belongs to the technical field of plant disease and pest prevention and control. Bacillus velezensis MS012 having bacteriostatic activity is obtained by separating and screening from healthy branches of malus sieversii. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens has remarkableantagonistic effect on botryosphaeria dothidea, colletotrichum gloeosporioides, phomopsis mali, rhizoctonia cerealis, gaeumannomyces graminis, botrytis cinerea, fusarium graminerum, clivia stem basaldecay pathogen, nandina anthrax pathogen and erwinia amylovora and has broad spectra in bacteriostatic object, and a new microbial resource is provided for biocontrol on disease and pest of plants like apple trees.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Horned holly fungal endophyte-harzianum L
InactiveCN101037656AIncrease productionEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideFungiBiotechnologySeparation technology
The invention relates to microbe technique field, endophytic fungus of Chinese Holly of the invention collected from Chinese Holly living plant of Tianmu Mountain of Linan City is obtained by endophytic fungus microbe separation technology, named as Trichoderma harzianum Rifai stem L identified by microbial taxonomy stored by general microbilogy centre of China Forestry Culture Collection Center on date of august 14th 2006, registration number is CGMCC NO.1780. The most prominent feature is the stem can generate activated component seaquiterpenoids Trichothec-9-en-4-ol,12,13-epoxy-,acetate,(4beta)-(8CI,9CI) by fermentation for inhibiting phytopathogenic fungi bacteria, it is an important microbe resource in agriculture.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Array-type high-throughput microbe separating culturing apparatus
ActiveCN103865751ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnology researchTechnology research
The invention relates to an array-type high-throughput microbe separating culturing apparatus, and discloses a novel microbe separating culturing apparatus. The apparatus is capable of realizing high-throughput separation and culture of cultured and / or uncultured microbes in a laboratory, operation is simplified, and the apparatus has good compatibility with conventional laboratory equipment. The separating culturing apparatus is capable of simulating in-situ culturing of microbe by natural environment, and is capable of efficiently separating difficult-to cultured microbe ( or named uncultured microbe or unculturable microbe). The microbe separating culturing apparatus is applicable to separate and culture difficult-to cultured microbe from environment, also is applicable to research interacting relationship between microbe and microbe, between microbe and environment factors, and between microbe and nutrition factors, and also is applicable to fields such as microbe source investigation and research, environment and ecology relationship, natural medicine discovery, biological technology research and the like.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
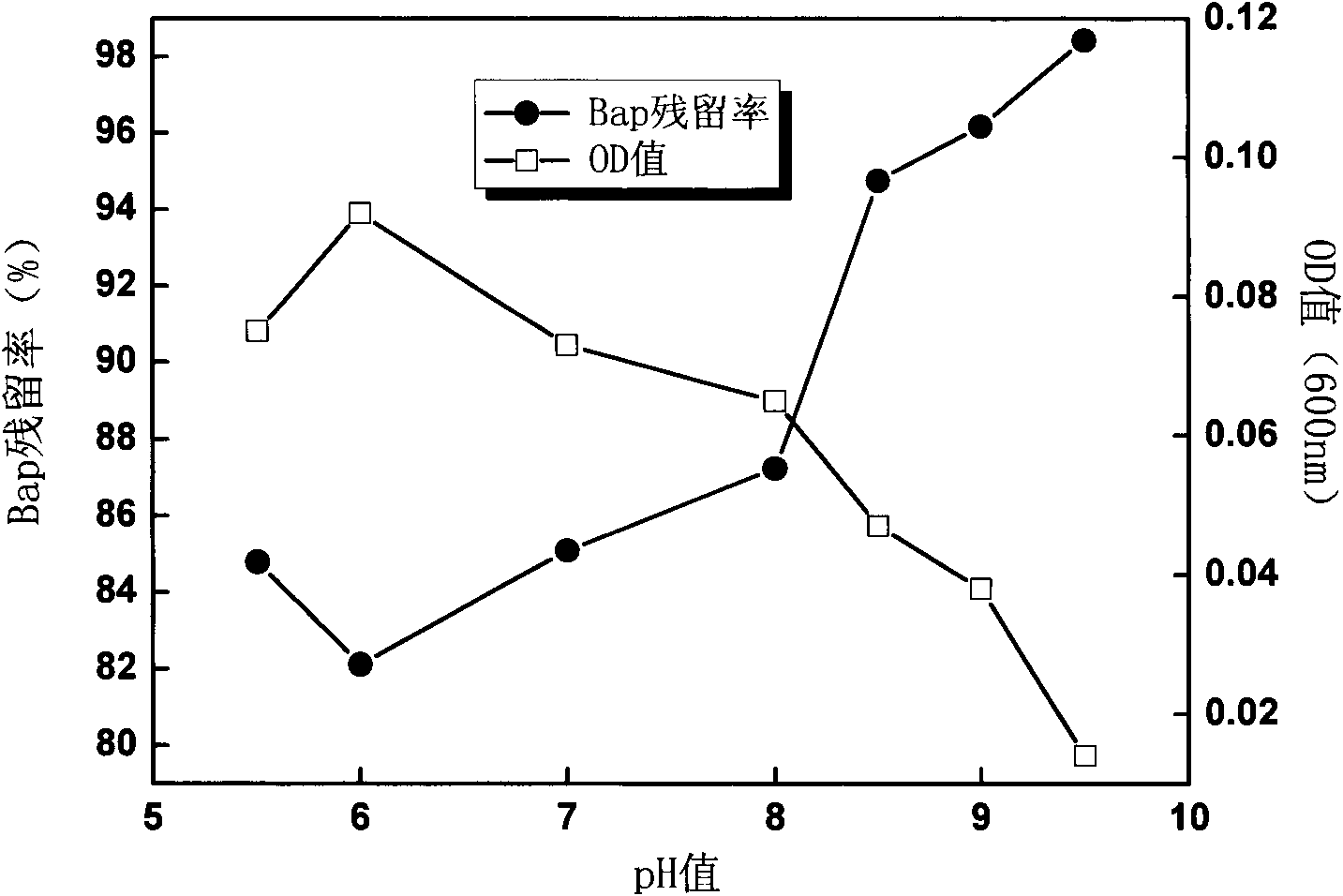
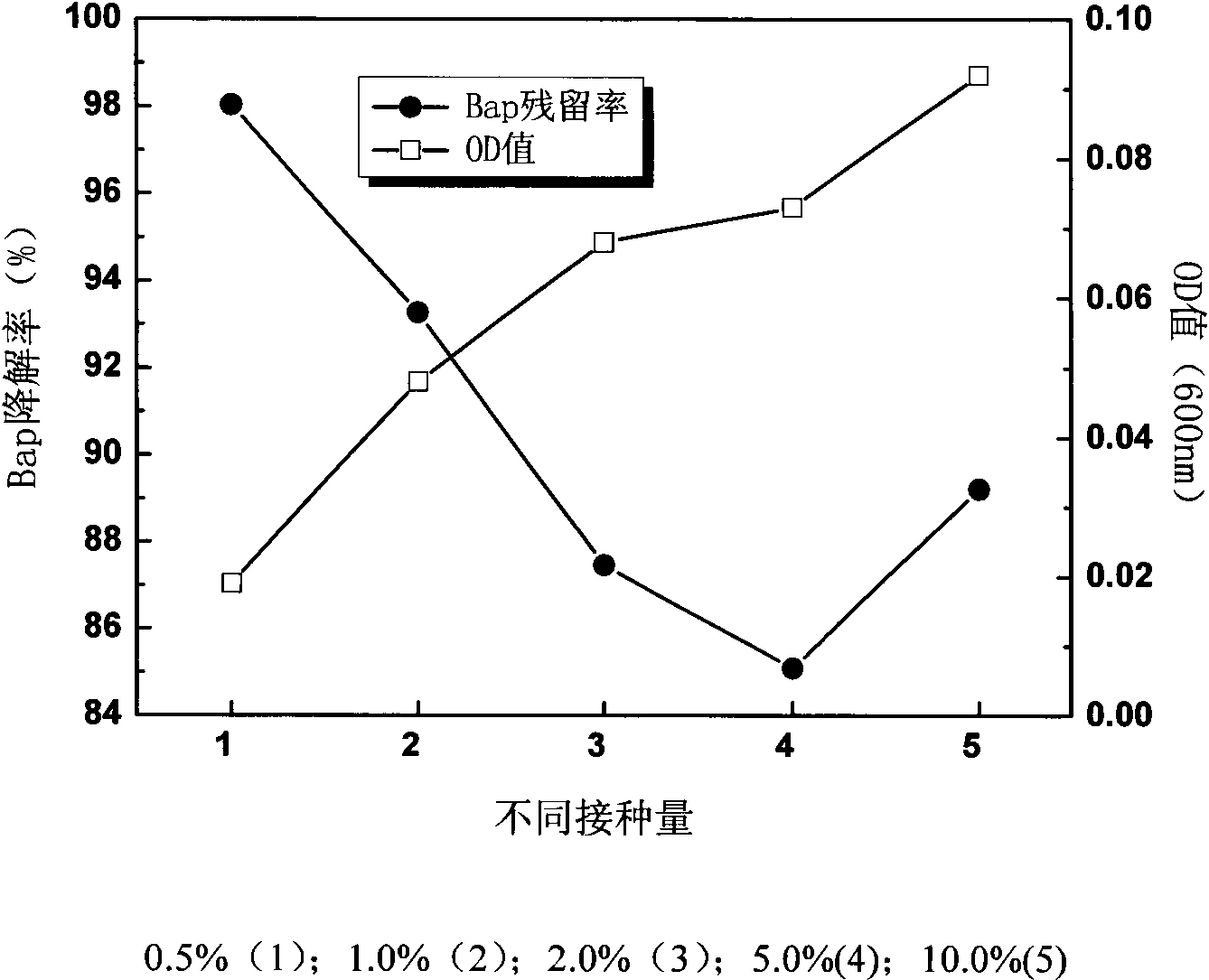
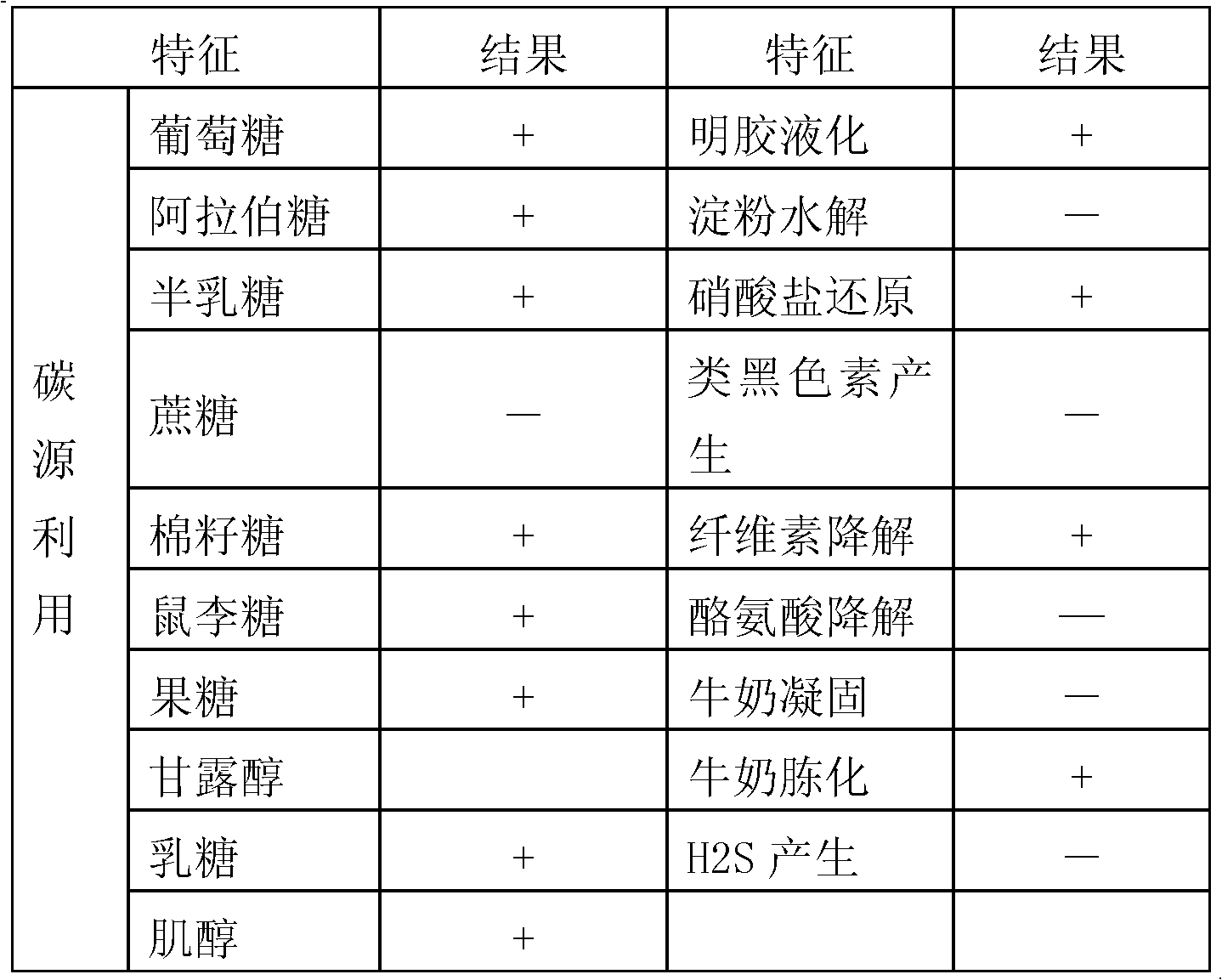
Acinetobacter sp.Bap30 capable of effectively degrading benzo(a)pyrene and application thereof
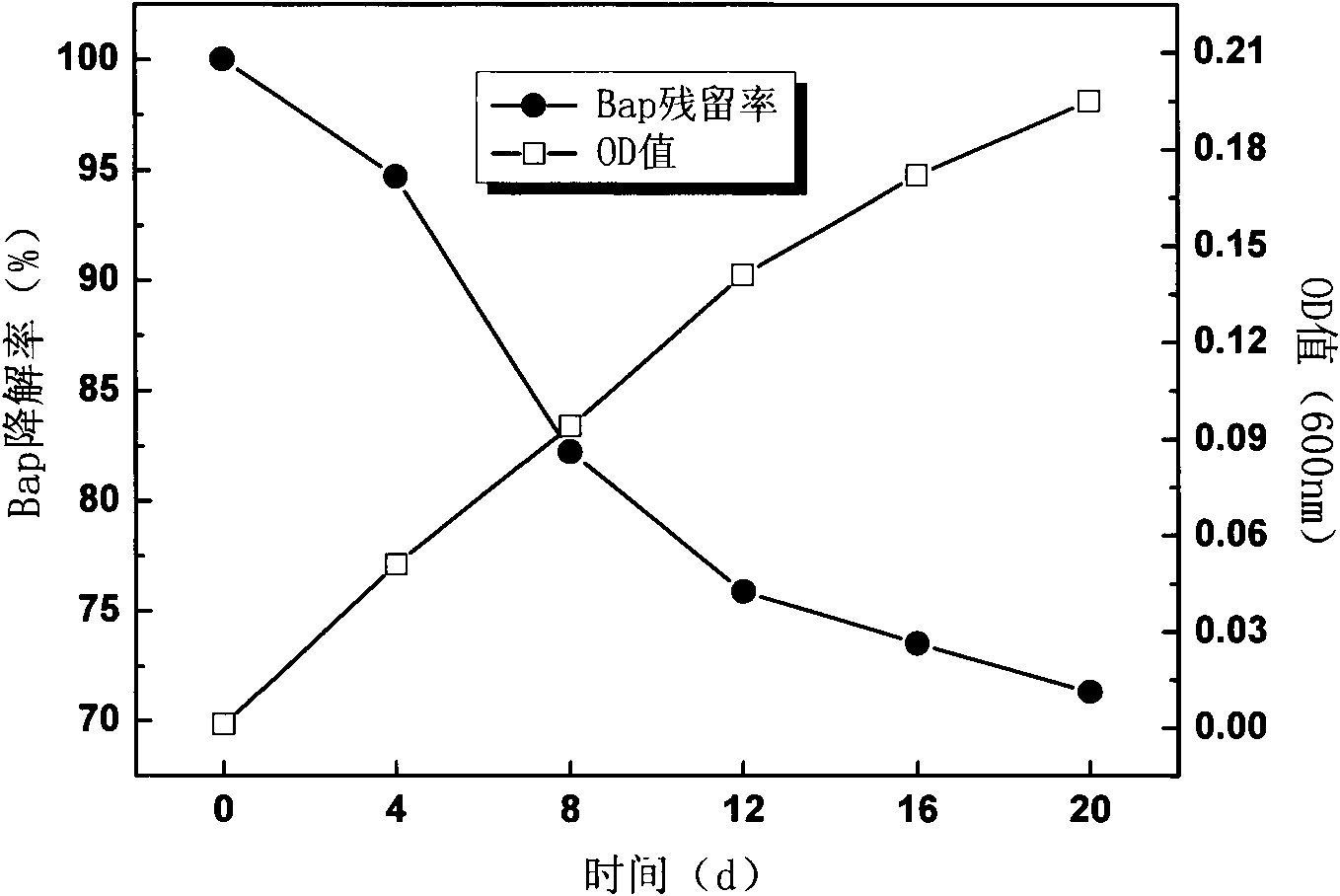
InactiveCN102174445AImprove degradation rateBacteriaWater contaminantsSaccharumMicroorganism resource
The invention discloses a bacterium for degrading benzo(a)pyrene and application thereof. The bacterium is acinetobacter sp.Bap30, CGMCC No.4586. The strain can grow with benzo(a)pyrene as the unique carbon source and energy, undergoes shake culture at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 20 days in the inorganic salt culture medium with benzo(a)pyrene concentration being 40mg / L and has degradation rate toward benzo(a)pyrene being 28.66%. The degradation rate of the strain toward benzo(a)pyrene can be effectively improved by adding defined amount of co-metabolic carbon sources, such as cane sugar and maltose. When another polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon phenanthrene is taken as a co-metabolic substrate and exists by being mixed with benzo(a)pyrene, the degradation rate of the strain toward benzo(a)pyrene can be improved to 48.87% and meanwhile, the strain can realize complete removal of phenanthrene. The strain provided by the invention can provide new microorganism resources for degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water environment or soil environment.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Streptomyces parvus strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a Streptomyces parvus strain and application thereof. The collection number of the Streptomyces parvus Yn168 is CGMCC No.4570. Through the experiment, the Streptomyces parvus Yn168 strain (CGMCC No.4570), which is derived from soil and has antiviral activity, is separated, has important instructive significance for screening and developing antiviral active substances from microorganism resources, and also lays an experimental basis for separation and purification research of antiviral active substances of the Streptomyces parvus Yn168.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Salt-tolerant aerobic denitrifying bacterium and application
The invention discloses a salt-tolerant aerobic denitrifying bacterium and an application thereof. The bacterium can be used for efficiently removing nitric nitrogen in high-salt wastewater, is namedas Pseudomonas sp. DN-23 and collected in a China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 21, 2018, and the collection number of the bacterium is CCTCC NO: M2018290. Acclimating, preliminary screening and secondary screening are performed to obtain the salt-tolerant aerobic denitrifying bacterium, and a new microorganism resource is provided. The screened Pseudomonas is acquired from leather wastewater and can grow well in a high-salt environment, and the nitric nitrogen in a water body can be effectively removed. The bacterium is applied to the treatment process of the high-salt wastewater,and has a wide prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Acinetobacter johnsonii AJ-3 strain and application thereof
ActiveCN103805546AHigh phosphorus removal rateBacteriaWater contaminantsMunicipal sewageWater organism
The invention belongs to the field of environmental microorganisms and in particular relates to separation and culture of an Acinetobacter johnsonii AJ-3 strain and application thereof in phosphorus removal in sewage and biological phosphorus removal in urban sewage treatment plants. The Acinetobacter johnsonii AJ-3 strain has a collection number of CCTCCM2014023, the collection place is China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the collection date is January, 16th 2014. The strain is an Acinetobacter johnsonii AJ-3 strain, is rapid in growth, high in adaptive capacity to environment and low in dissolved oxygen demands and can rapidly grow in a phosphorus-containing synthetic sewage liquid culture medium, the phosphorus is removed, the phosphorus removal efficiency is high and stable and reaches 55-60.1%, and secondary pollution is avoided. Therefore, the AJ-3 strain can be applied to phosphorus-containing sewage treatment, is an important microbial resource in a water organism phosphorus removal process and has wide application prospect.
Owner:威海海能海洋生物科技有限公司
Acid-resistant pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 and application thereof
ActiveCN108570433AAcid resistantEnhance disease preventionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAcid-fastNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides acid-resistant pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 and application thereof. According to the acid-resistant pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 and the application thereof, the bacterial strainof the pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 27th, 2016, and the biological preservation number of the pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 is CGMCC No.13205; the bacterial strain of the pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 has acid resistance, is good in disease prevention and plant growth promotion effects and high in stress resistance, hasthe antagonistic activity of pathogenic bacteria, is wide in soil acidity tolerance range and wide in antibacterial spectrum, and has application and development potential in prevention and treatmentof bacterial wilt, black shanks and brown spots; and meanwhile, under the general background that the acidification conditions in China is increasingly severe, the research on the bacterial strain ofthe pseudomonas protegens CLP-6 has reference significance in prevention and treatment of plant diseases under various soil qualities, a microbial resource is provided for green prevention and control over the bacterial wilt, the black shanks and the brown spots in acid soil, and secondary metabolites of microorganisms are excavated, so that an important foundation can be laid for the biocontrolefficacy on the bacterial wilt, the black shanks and the brown spots in the acid soil.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Eucommia ulmoides endogenous bacillus pumilus and application thereof
ActiveCN104789509AGrowth inhibitionGood inhibitory effectPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBacteroidesTriticeae
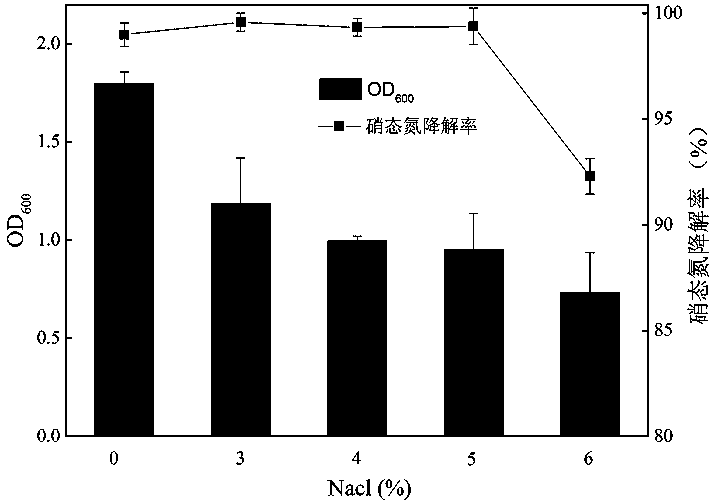
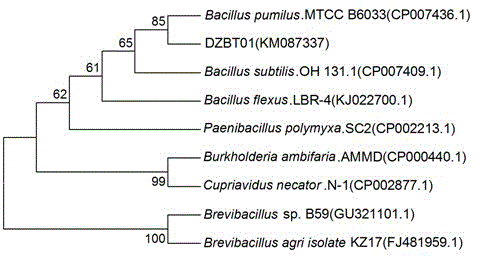
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes. The eucommia ulmoides endogenous bacteria are separated from eucommia ulmoides living plants by adopting an endogenous bacteria microbe separation technology. Through identification by microbial taxonomy, strain is named Bacillus pumilus DZBT01 and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection number is January 30, 2015, and the collection register number is CGMCC NO.10470. The strain disclosed by the invention has the characteristics that the strain can achieve an obvious effect of inhibiting plant pathogenic fungi. The invention discloses an application of the Bacillus pumilus DZBT01 in control of wheat sharp eyespot and an application of Bacillus pumilus in promotion of wheat growth. The Bacillus pumilus DZBT01 disclosed by the invention refers to eucommia ulmoides plant endogenous bacteria, is simple in culture conditions and easy to preserve and refers to an agriculturally important microbial resource.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of Alternaria alternata metabolic product in controlling watermelon fusarium oxysporum
InactiveCN102204571AEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideMicroorganism based processesSeparation technologyMicroorganism resource
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms. The camphor tree endophytic fungi disclosed by the invention is separated from a camphor tree plant living body collected in the Tianmu Mountain in Hangzhou city of Zhejiang province through use of an endophytic fungus microorganism separation technology and is called after Alternaria alternata 31 through microbial taxonomic identification; and the strain is preserved in the General Microorganism Centre of China Microorganism Strain Preservation Management Committee on December the 31st, 2010 and has a preservation registered number of CGMCC No.4508. The strain liquid is obviously characterized by generating an active metabolic product which has the inhibiting effect on plant fungus disease pathogens, such as cucumber rhizoctonia solani, watermelon fusarium oxysporium and tomato botrytis cinerea, and the like through fermenting and is an important microbial resource in agriculture.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Acinetobacter baumannii capable of efficiently degrading imazamox
ActiveCN102250789AEfficient degradationHas a repairing effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyAcinetobacter baumannii
The invention dislcoses acinetobacter baumannii capable of efficiently degrading imazamox, which relates to acinetobacter baumannii. The invention provides an acinetobacter baumannii strain, which is capable of efficiently degrading imazamox and provides theoretical and microbial resource foundations for the environmental modification and degradation mechanism research of an imazamox weedicide. The acinetobacter baumannii capable of efficiently degrading imazamox, disclosed by the invention, is acinetobacter baumannii IB5 which is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (Address: No.3, Yard 1, Beichen Road West, Chaoyang District, Beijing) with the collection number CGMCC No.4728 on April 1, 2011. The acinetobacter baumannii IB5 is capable of efficiently degrading imazamox.
Owner:海林市中农国泰生物科技有限公司
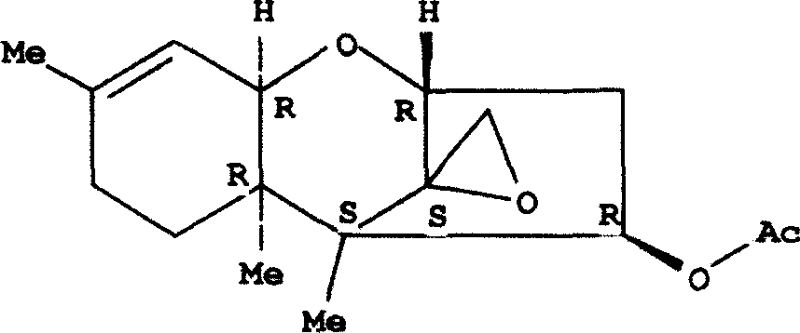
Cyclopiazonic acid compound, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN103183666AHigh insecticidal activityHigh cytotoxic activityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideMicroorganismGrowth plant
The invention relates to the fields of medicines and novel pesticides, in particular to a cyclopiazonic acid compound and preparation and application thereof. The cyclopiazonic acid compound is 3-hydroxyl speradine A as described in formula (I) in the specification. The compound is used as a pesticide, a plant growth regulator or an antineoplastic drug. According to the invention, the novel cyclopiazonic acid compound with hydroxyl substitution at position 3 is obtained from marine sponge-associated fungi. The preparation of the compound provided by the invention is simple and efficient, and the prepared compound has high purity. A strain referred to in the invention has a reference value for further development and utilization of marine microbial resources.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Liquid fertilizer capable of preventing soil-borne diseases and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN105110879AReduce dosageMake up for the lossFertilizer mixturesEcological environmentSodium potassium tartrate tetrahydrate
The invention discloses a liquid fertilizer capable of preventing soil-borne diseases. The liquid fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials, by weight, 36-40 parts of biogas residue mud, 5-7 parts of sodium potassium tartrate tetrahydrate, 6-8 parts of citric acid, 40-50 parts of corn germ meal, 15-19 parts of urea, 55-65 parts of dry chicken manure, 120-140 parts of waste livestock and poultry feathers, 6-7 parts of copper sulphate, 4-6 parts of ferrous sulphate, 4-5 parts of GM microbial preparations and a proper amount of water. Biogas residue mud, chicken manure and the like are employed in the raw materials of the liquid fertilizer and contain a lot of microbes with various kinds, the GM microbial preparations are added to raise the beneficial bacterium content, thus the liquid fertilizer becomes a microbe resource base, the soil microbial community structure can be adjusted after drip irrigation and spraying of the liquid fertilizer, the soil microbial diversity is raised, the soil micro-ecological environment is improved, the survival scope of plant pathogens is narrowed, and therefore the purpose of preventing soil-borne diseases is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI ZHONGYUE HEALTH TECH
Biological process oil extraction method for prolonging period of validity by use of microbe to drive oil
InactiveCN1447010ATimely and objective understanding of activity statusFluid removalMetaboliteEngineering
A microbial petroleum-recovering method for elongating its effective period features that the microbes and their metabolite in the liquid output from oil well are detected and analyzed to evaluate the activity of microbes and the nutritive liquid is supplemented in time according to evaluated result for increasing the activity of microbes.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biocontrol endophytic fungi-Alternaria alternata
InactiveCN102191184AEnhanced inhibitory effectFungiMicroorganism based processesDiseaseMicroorganism resource
The invention provides biocontrol endophytic fungi- Alternaria alternata and relates to the technical field of microorganisms. The endophytic fungi of camphor trees are separated from camphor tree living bodies collected from Tianmu Mountain in Hangzhou, Zhejiang by an endophytic fungi separation technique and are named as Alternaria alternata 31 according to microbial taxonomy identification. The biocontrol endophytic fungi-Alternaria alternata is collected in the General Microbiology Center of China Microorganism Strain Collection Management Committee, wherein the collection date is 2010.12.31 and the collection registered number is CGMCC No.4508. The biocontrol endophytic fungi-Alternaria alternata has the most remarkable characteristic that: the strain liquid is fermented to generate active metabolites which can inhibit plant fungi disease pathogenic bacteria such as rhizoctonia solani, fusarium oxysporium, botrytis cinerea and the like and is important microbial resources agriculturally.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for separating denitrification desulfurizing bacteria based on biodiversity information
InactiveCN104450592AEfficient Synchronized MetabolismImprove screening efficiencyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementThaueraSludge
The invention discloses a method for separating denitrification desulfurizing bacteria based on biodiversity information and relates to denitrification desulfurizing bacterium screening methods. The method comprises the steps of collecting sludge, conducting high-throughput sequencing on the sludge sample, analyzing the flora abundance fluctuation and space ecological distribution of the sludge sample, adopting different screening methods according to community composite and structure characteristics, conducting anaerobic culture on a target bacterial genus by means of an interlayer culture medium with different screening methods, selecting a single colony for isolated culture, and obtaining a single bacterial colony after repeated operation. Two kinds of denitrification desulfurizing bacterial strains, namely autotrophic denitrification desulfurizing bacteria which belong to Thiobacillus, and heterotrophic denitrification desulfurizing bacteria which belong to Thauera, Azoarcus, Arcobacter and Ochrobactrum are obtained through screening. Community structure information displayed by the strain screening result is consistent with that displayed by the high-throughput sequencing result, microbial resources are provided for improving biological treatment effectiveness of wastewater. Furthermore, the metabolic characteristics of the strains are identified.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
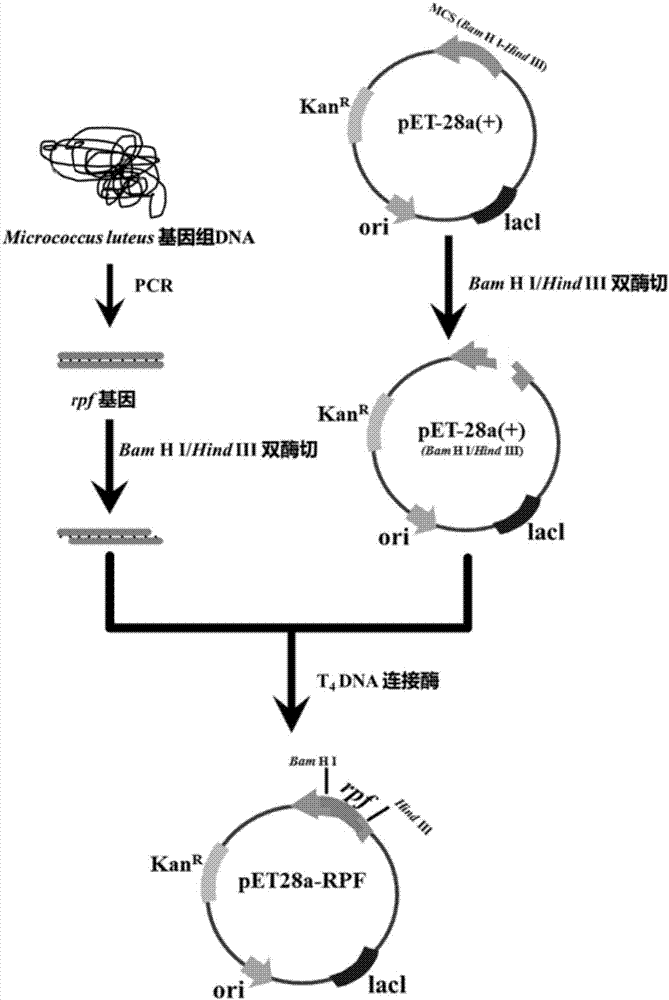
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing resuscitation promoting factors and application of genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN106967660APromote growthIncreased separation abundanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing resuscitation promoting factors and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The classified name of the genetically engineered bacterium for producing the resuscitation promoting factors is Escherichia Coli, the bacterial strain number is pET28a-RPF(WT), and the collection number is CGMCC No.13217. The genetically engineered bacterium is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Science, which is located at No.3 of first yard of Beicheng West Road of Chaoyang District of Beijing City, in October 31 of 2016. The genetically engineered bacterium has the advantages that growth of potential dormant bacteria in soil samples is promoted by RPF albumen made from the engineered bacterium, separation abundance is improved, and the genetically engineered bacterium can be applied to exploration and separation of microbial resources in a viable but non-culture (VBNC) state in environmental samples (soil, water, etc.).
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SCI RES & DESIGN INST OF ZHEJIANG PROVINCE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com