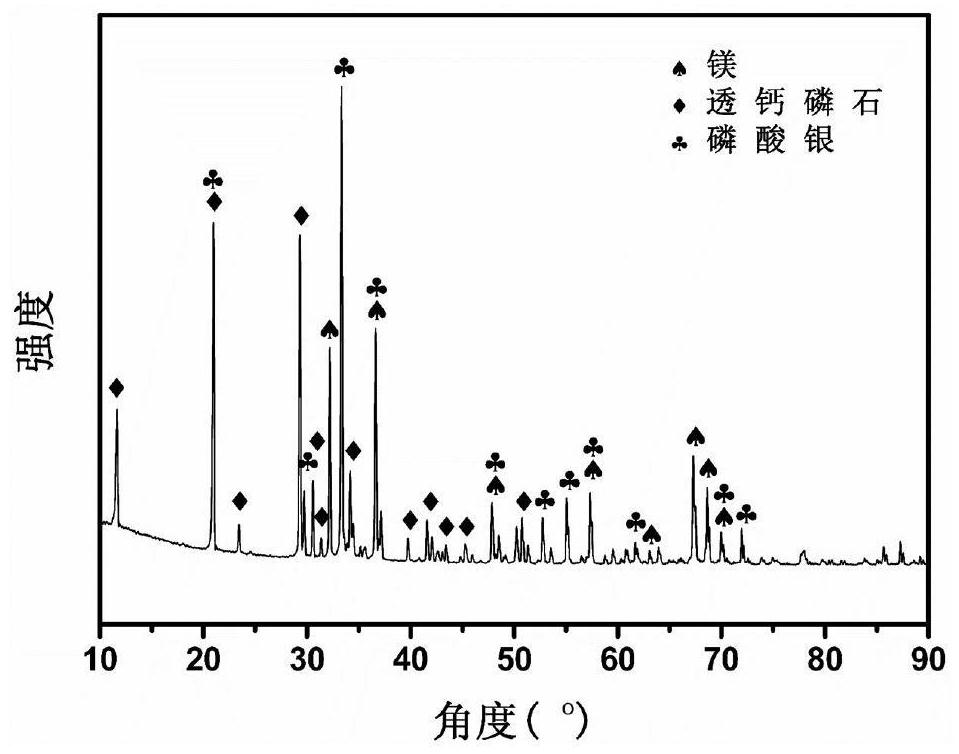
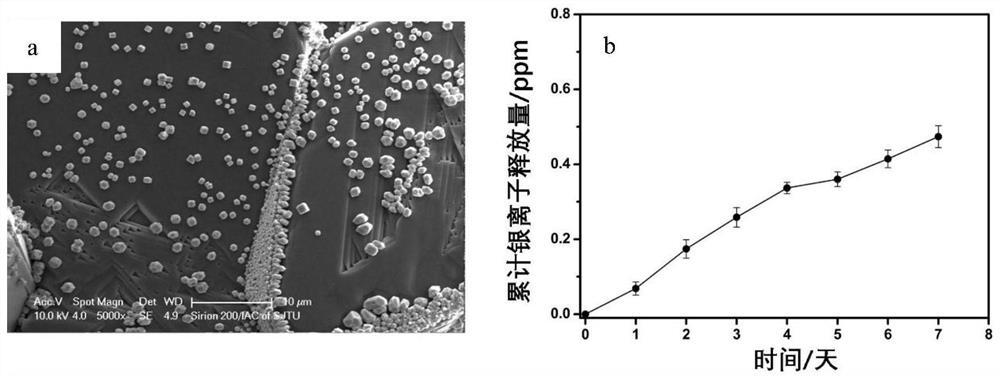
Patents
Literature
37 results about "DEPOSIT CALCIUM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bleaching composition
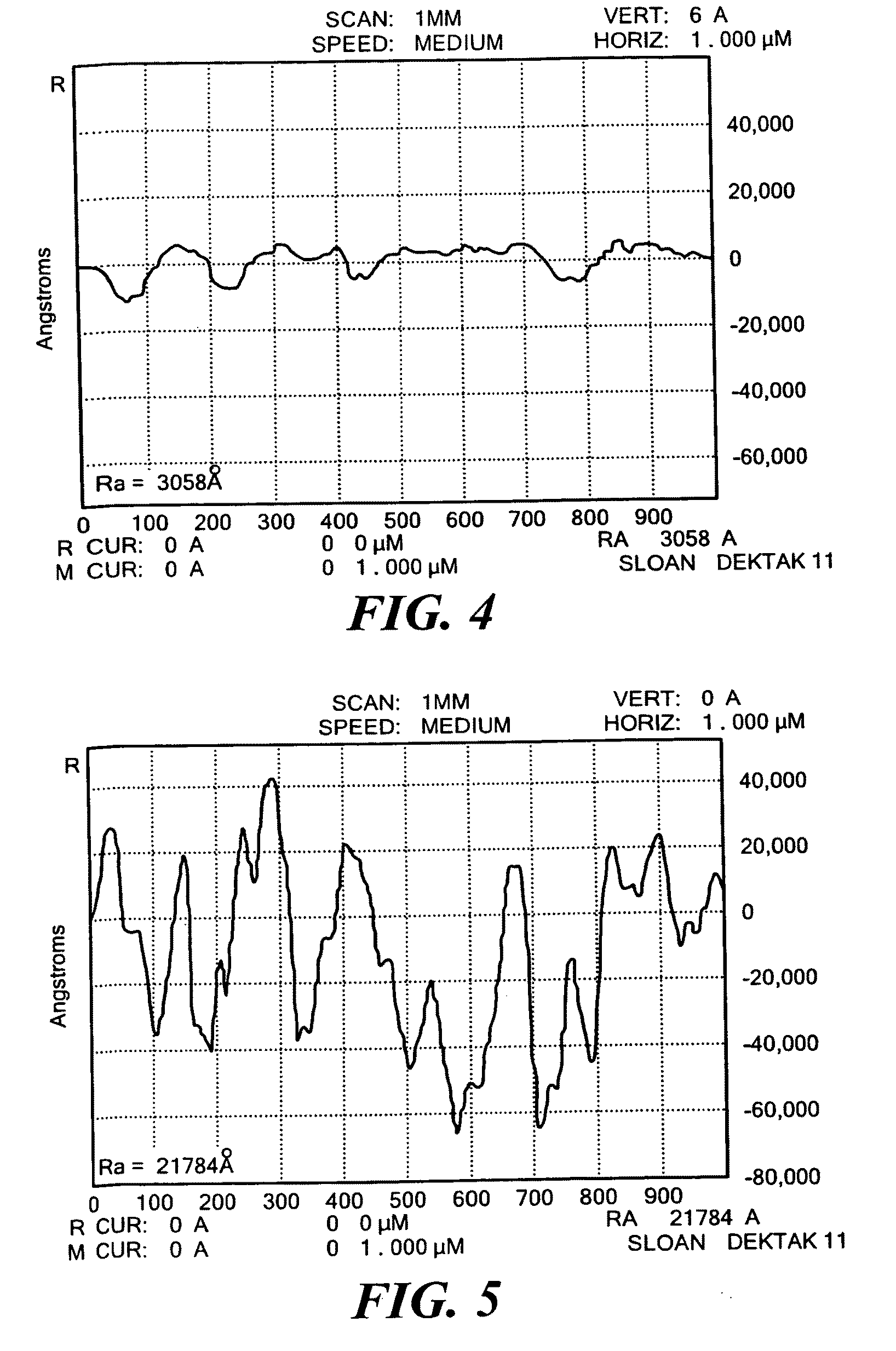
PCT No. PCT / US97 / 04957 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 24, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 24, 1999 PCT Filed Mar. 25, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 36989 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 9, 1997Bleach compositions comprising a percarbonate bleach and an amino tricarboxylic acid exhibit a reduced tendency to deposit calcium carbonate insolubles on substrates being bleached. Laundry compositions comprising percarbonate bleach and methyl glycine diacetic acid are provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for preparing galvanic deposit calcium phosphorus mineralized layer superfine fibre bone material
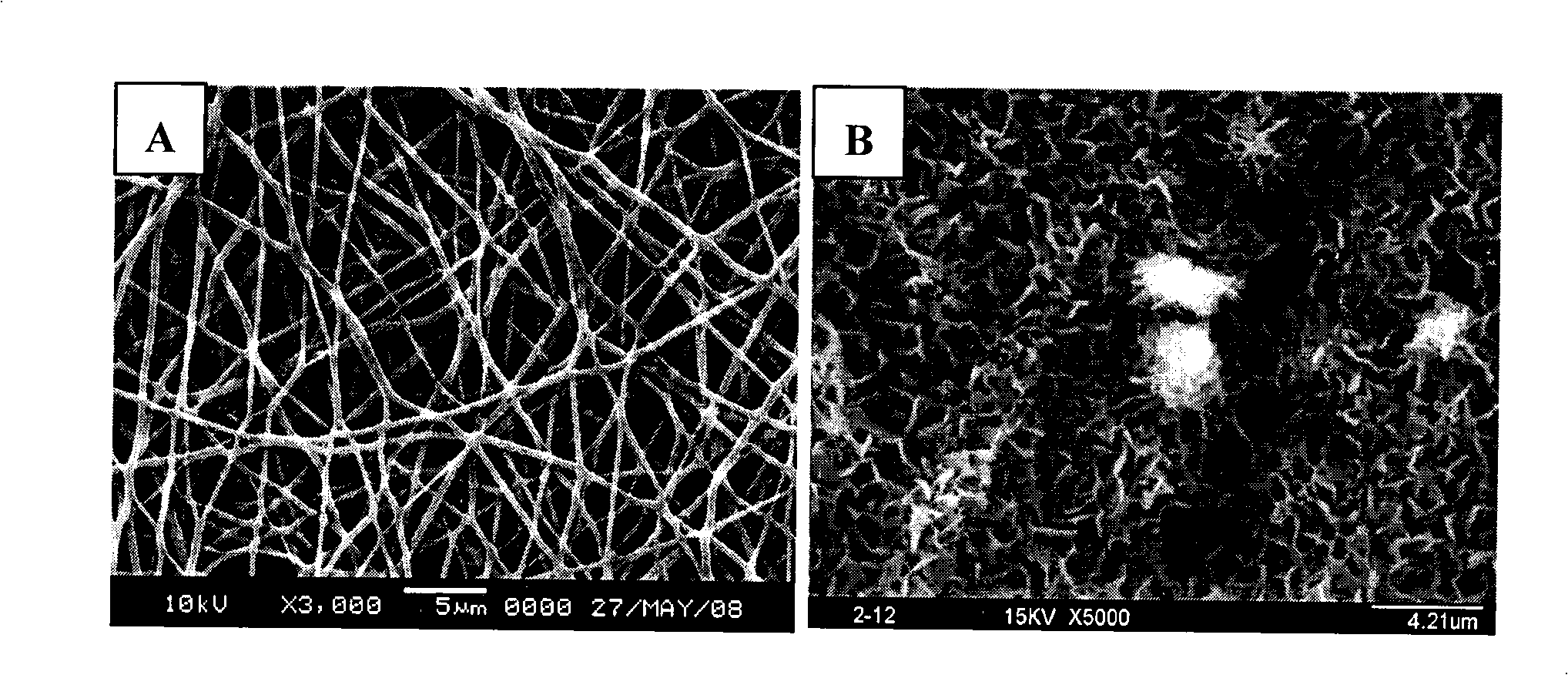
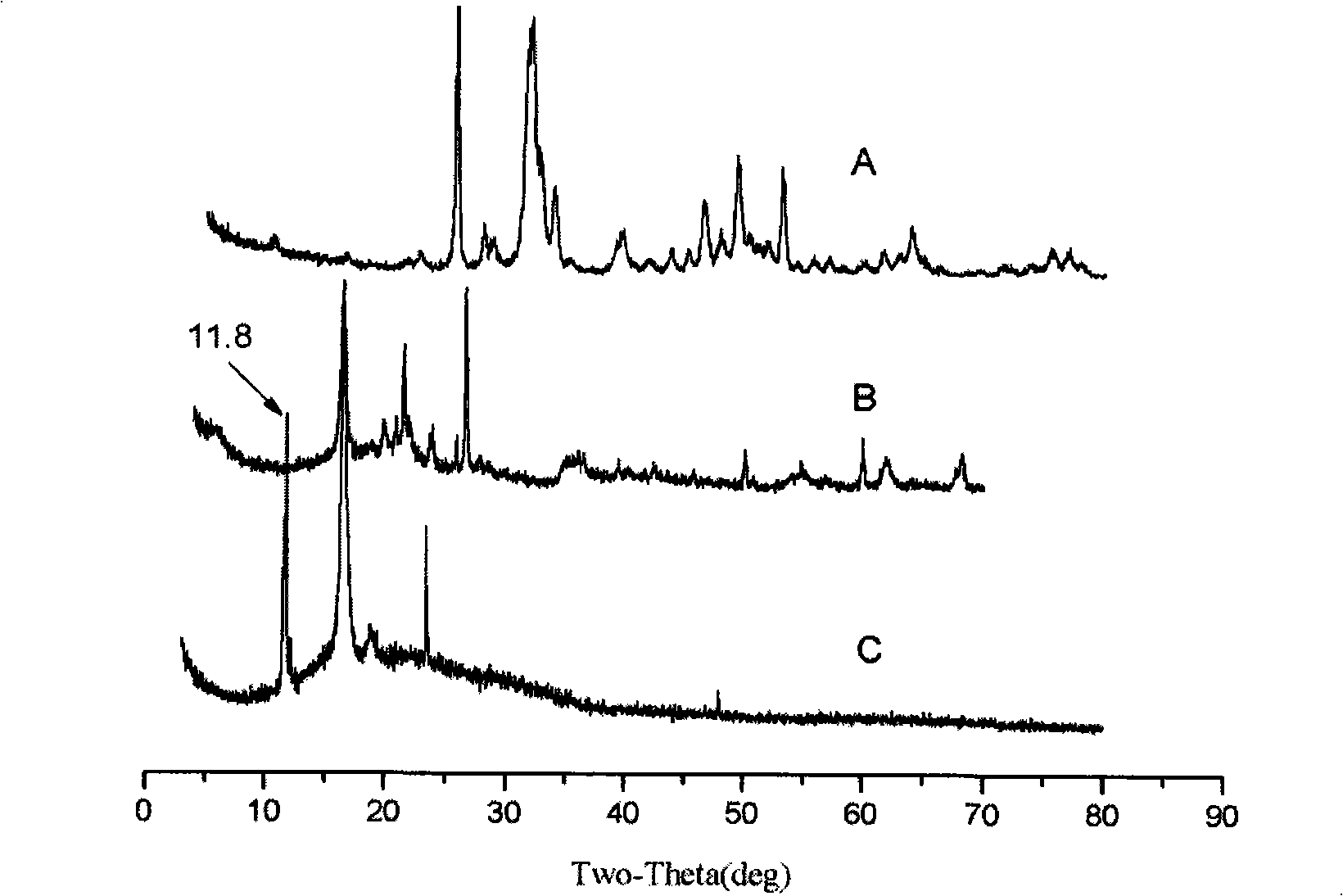
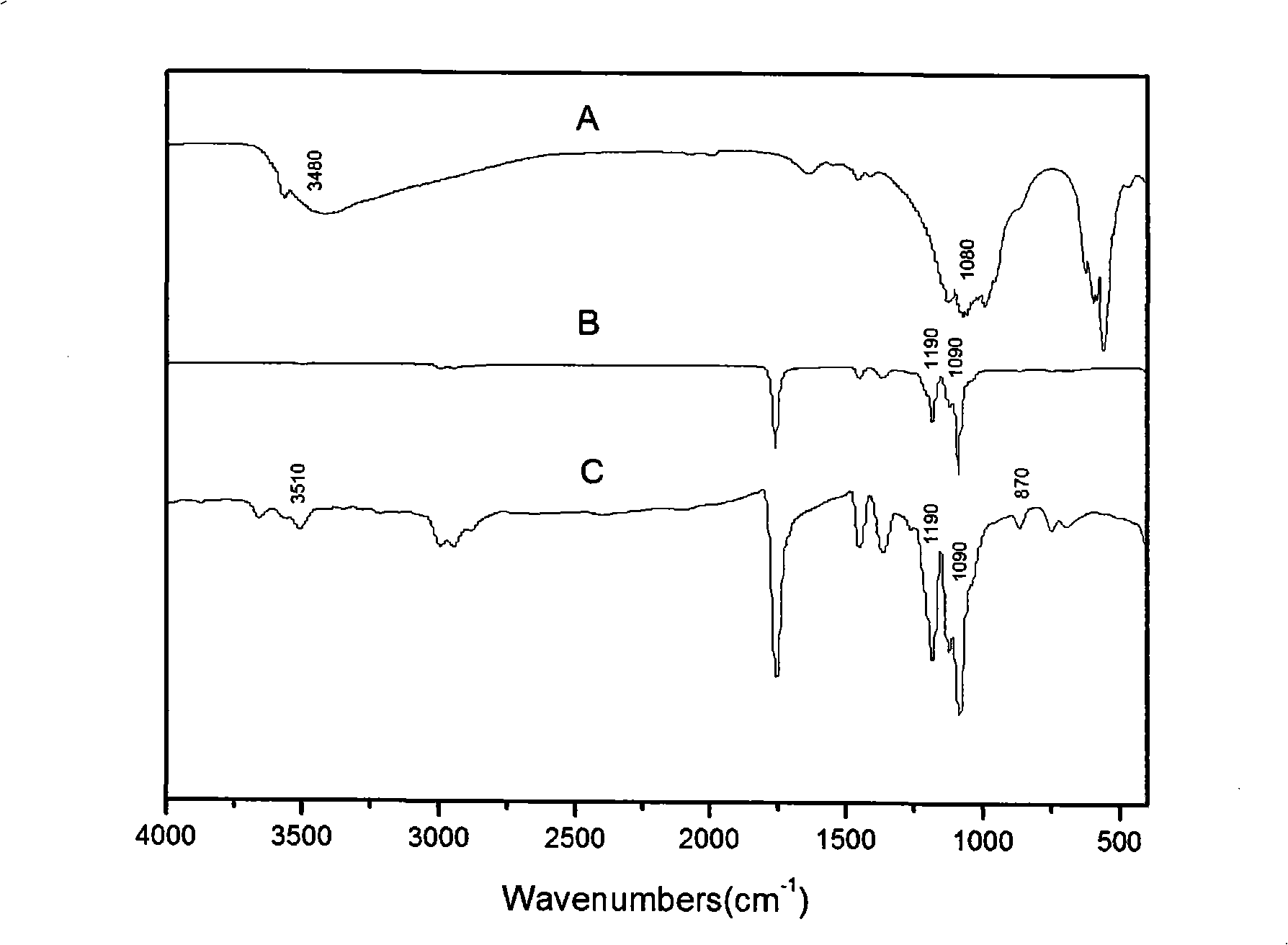
The invention relates to a method for preparing superfine fiber bone materials of an electrodeposition calcium phosphate mineralized layer, which comprises the following steps: firstly, high-polymer superfine fibers are prepared on the surface of a metal electrode by adoption of electrostatic spinning and taken as an electrochemical deposition template; a layer of bone salt ingredients which are rich in calcium and phosphor is deposited on the surface of the fibers by the constant-voltage or constant-current deposition technology; mineralized superfine fibers are soaked into 0.1 to 1.0 mol per liter of NaOH solution for 1 to 24 hours; mineralized electro spinning fibers are subjected to die stamping into blocks under the pressure of between 10 and 40 MPa; and the porous bone materials with a porosity between 50 and 90 percent and a pore diameter between 50 and 500 micrometers are processed by the salt particle leaching / gas foaming technology, and are used for bone defect restoration after freeze-drying sterilization. The porous bone materials prepared by the method have better biocompatibility; and the electrochemical deposition technology can prepare organic-inorganic composite materials with higher bone salt content within a shorter period; and the preparation time is short and the preparation conditions are mild.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
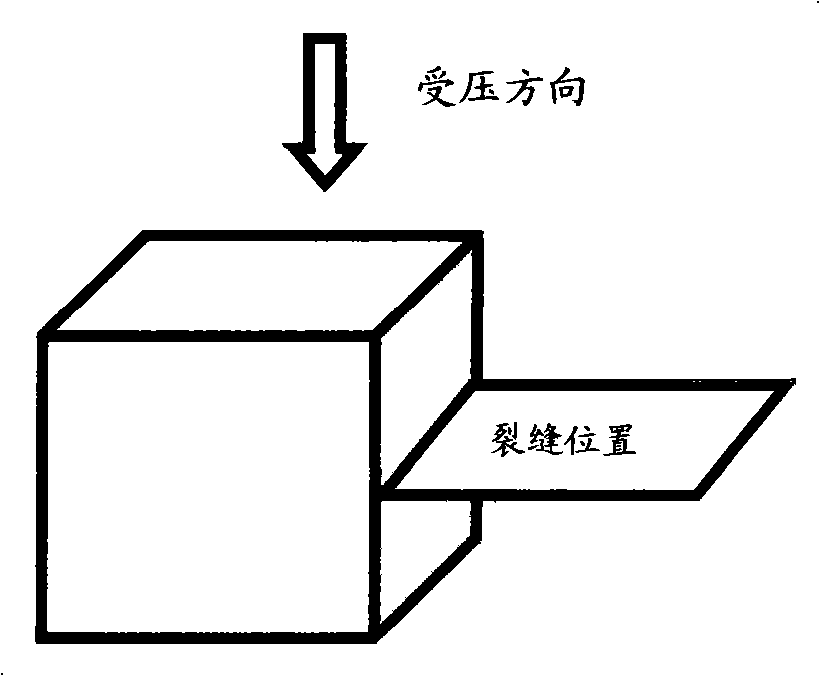
Method for recovering cement-based material crack by means of microorganism, culture fluid and repair nutrient fluid
ActiveCN101302484AImprove volume stabilityIncreased durabilityBacteriaBuilding repairsCulture fluidNutrient solution
The invention discloses a method for repairing cement-based material cracks, as well as a culture solution and a repair nutrient solution. The method for repairing cement-based material cracks by through microorganisms comprises the following steps that: a Bacillus pasteurii strain is inoculate onto a culture medium provided with a urea-containing substrate; shake cultivation is carried out at a temperature of between 25 and 37 DEG C, and then a culture bacteria solution is taken out and centrifuged and has supernatant fluid removed; strain cells are collected through the culture solution; the concentration of the strain cells is controlled in a range of between 2x10<9> and 1x10<11> cell / ml; standard sand, urea and Ca(NO3)2.4H2O mixture are added to each milliliter of strain cell solution obtained through collection, mixed, stirred into slurry and injected into cement stone cracks; the frequency of the repair nutrient solution injection is not less than two times; finally, maintenance is carried out. In the culture solution, each liter of culture solution contains 4 to 6 g of peptone, 2 to 4 g of beef extract and 20 to 60 g of urea. The method fully utilizes microbial resources in nature; CO3<2-> decomposed out through microbial enzyme can chelate Ca<2+> in a substrate so as to be mineralized and deposit calcium carbonate, and is close in the combination with the substrate and good in stability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
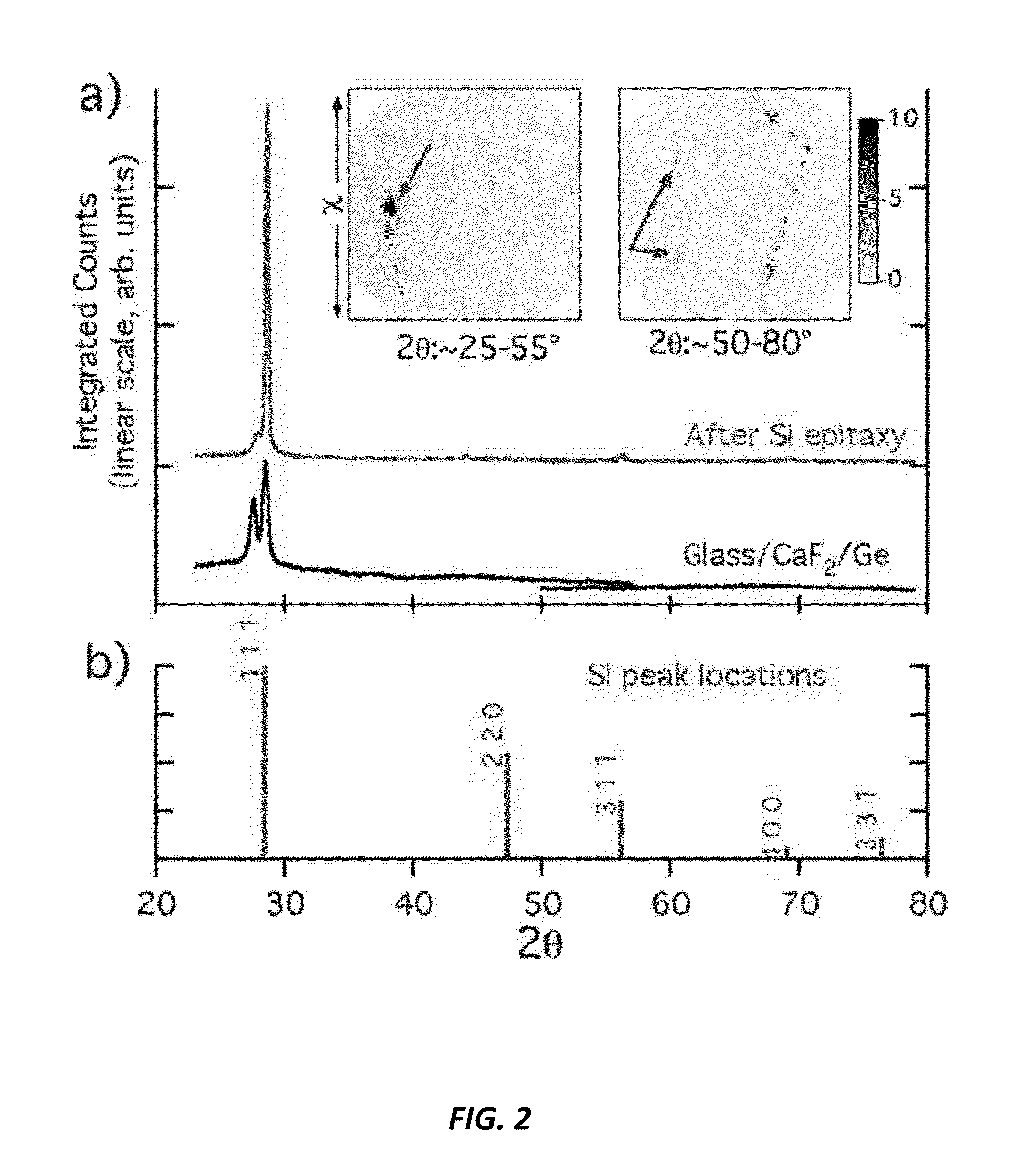
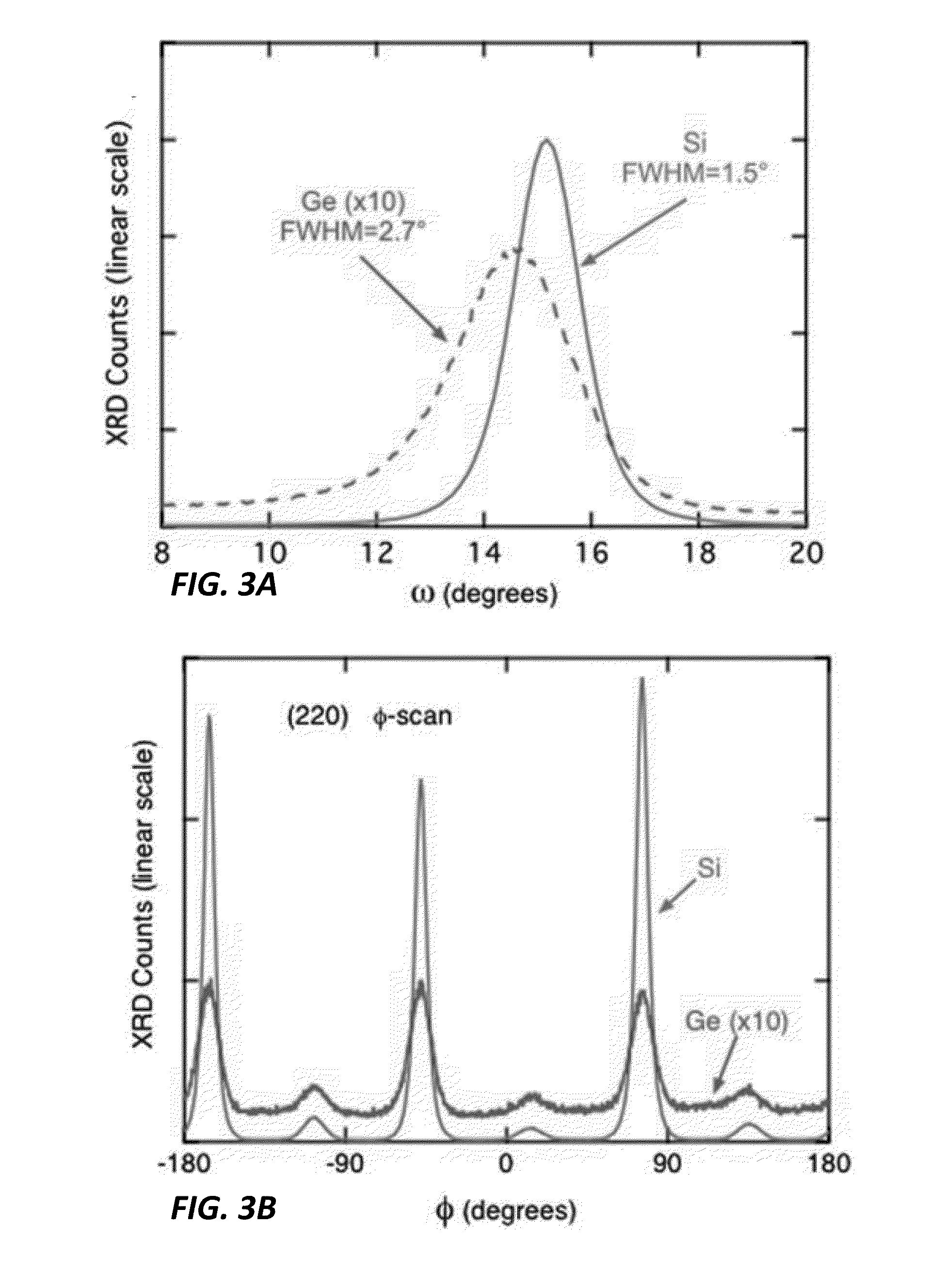
Depositing Calcium Fluoride Template Layers for Solar Cells
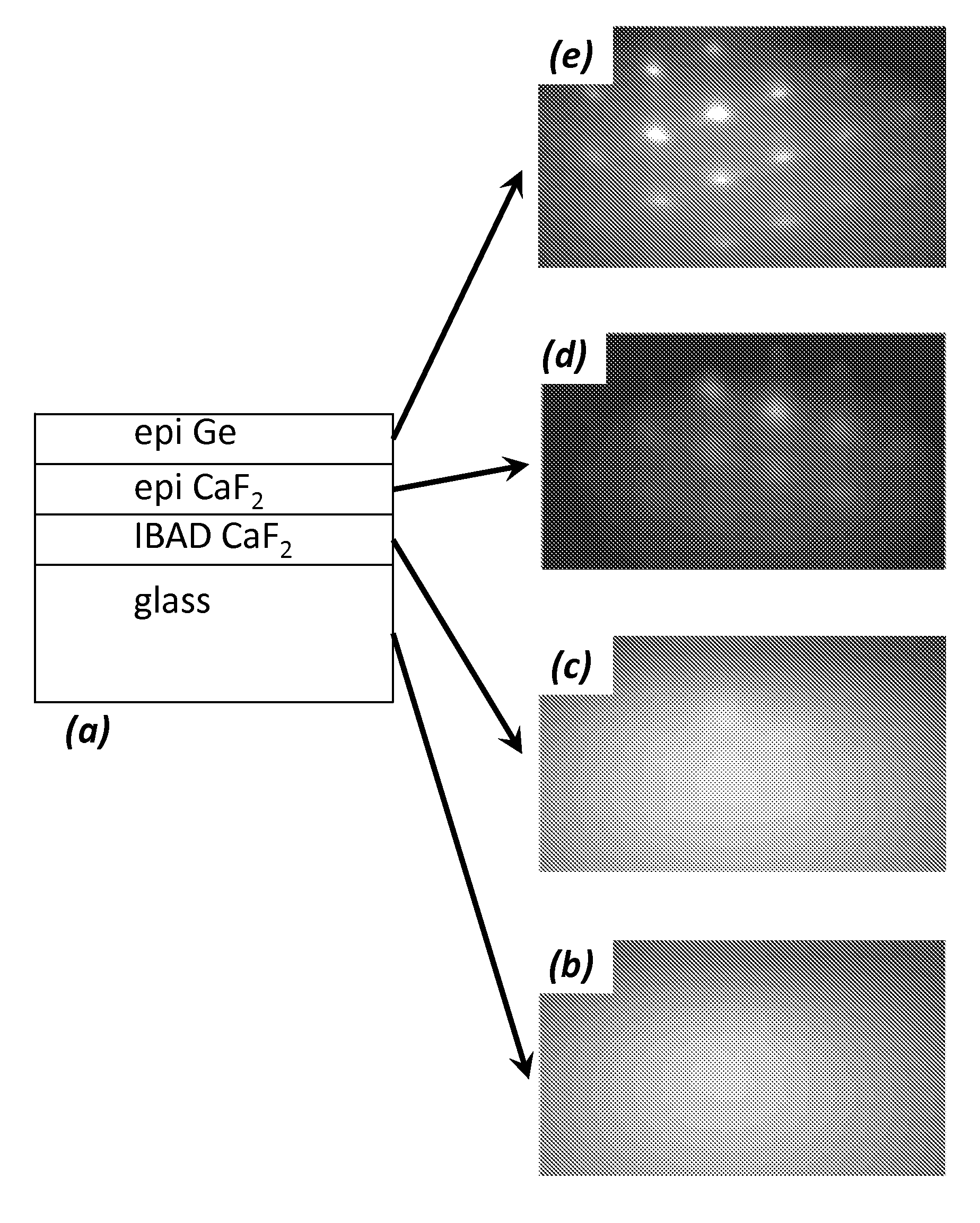
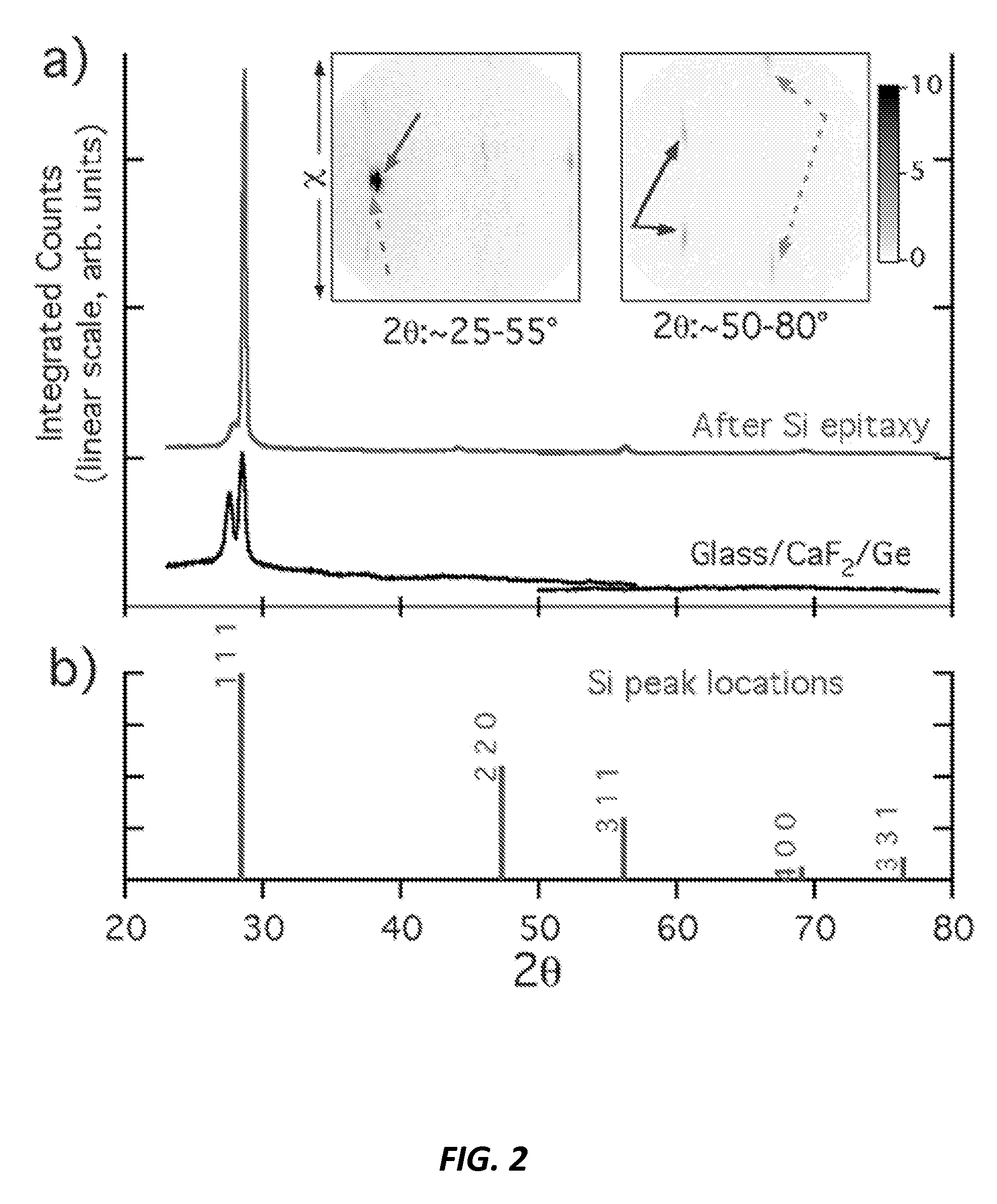
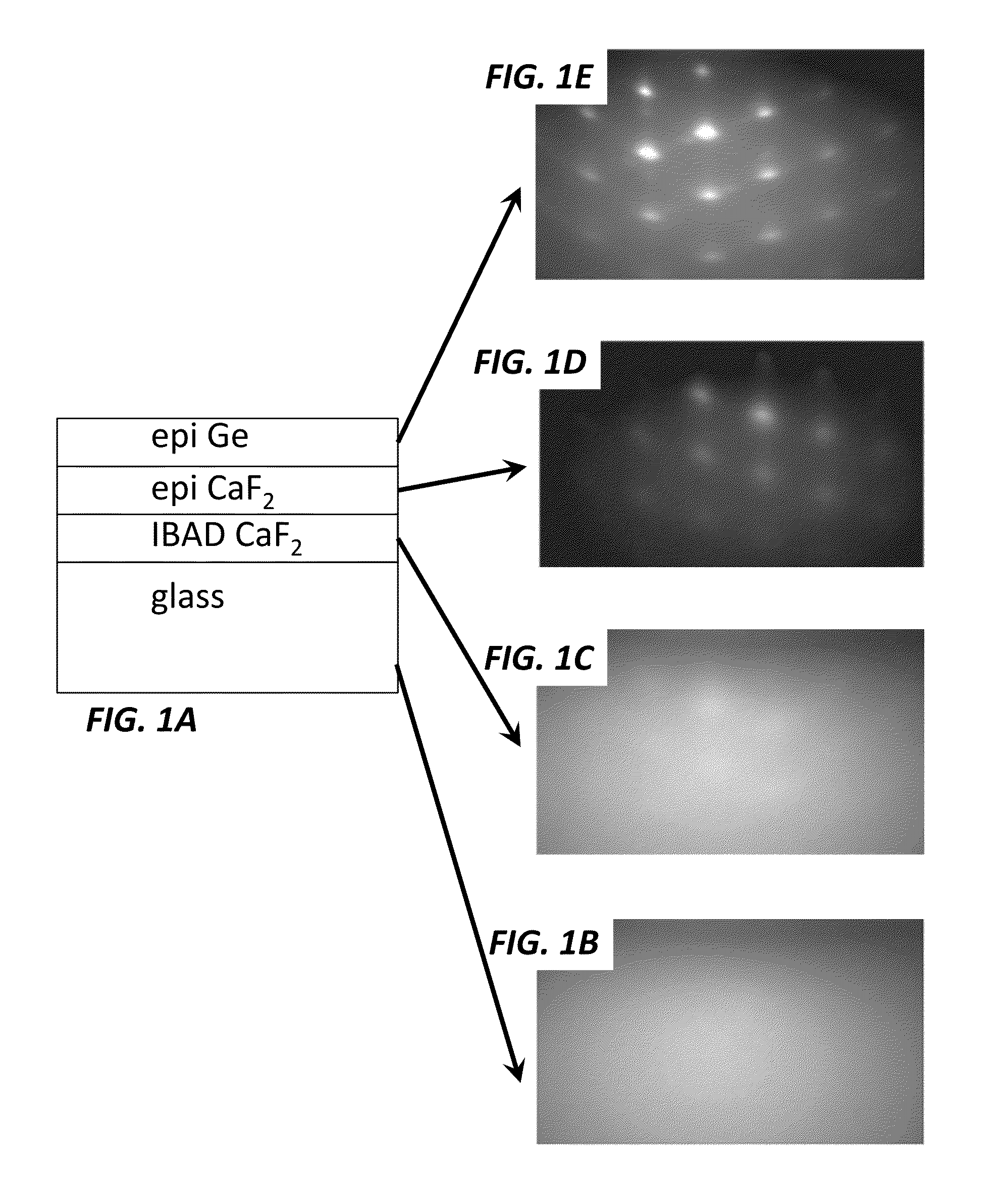
A biaxially textured crystalline layer formed on a substrate is provided. The biaxially textured crystalline layer includes an oriented CaF2 crystalline layer having crystalline grains oriented in both in-plane and out-of-plane directions, where the out-of-plane orientation is a (111) out-of-plane orientation. The oriented CaF2 crystalline layer is disposed for growth of a subsequent epitaxial layer and the CaF2 crystalline layer comprises an IBAD CaF2 layer. The biaxially textured CaF2 layer can be used in a photovoltaic cell, an electronic or optoelectronic device, an integrated circuit, an optical sensor, or a magnetic device.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Microorganism curing kit and calcareous sand in-site curing method
ActiveCN110438974APromote colonizationLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCalcium in biologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a microorganism curing kit and a calcareous sand in-site curing method, and belongs to the field of geological engineering and microorganism interdisciplines. The microorganismcuring kit is used for calcareous sand in-site curing and comprises a first component containing carboxylic acid, a second component containing microorganisms capable of generating urease, and a third component containing urea and a nutrient solution. The calcareous sand in-site curing method comprises the step that calcareous sand is partially dissolved by the first component. A calcium source can be efficiently obtained from sandy soil of an in-situ area or a nearby area of a calcareous sand soil body and then reacts with the microorganisms to deposit calcium carbonate, and the in-situ curing effect is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
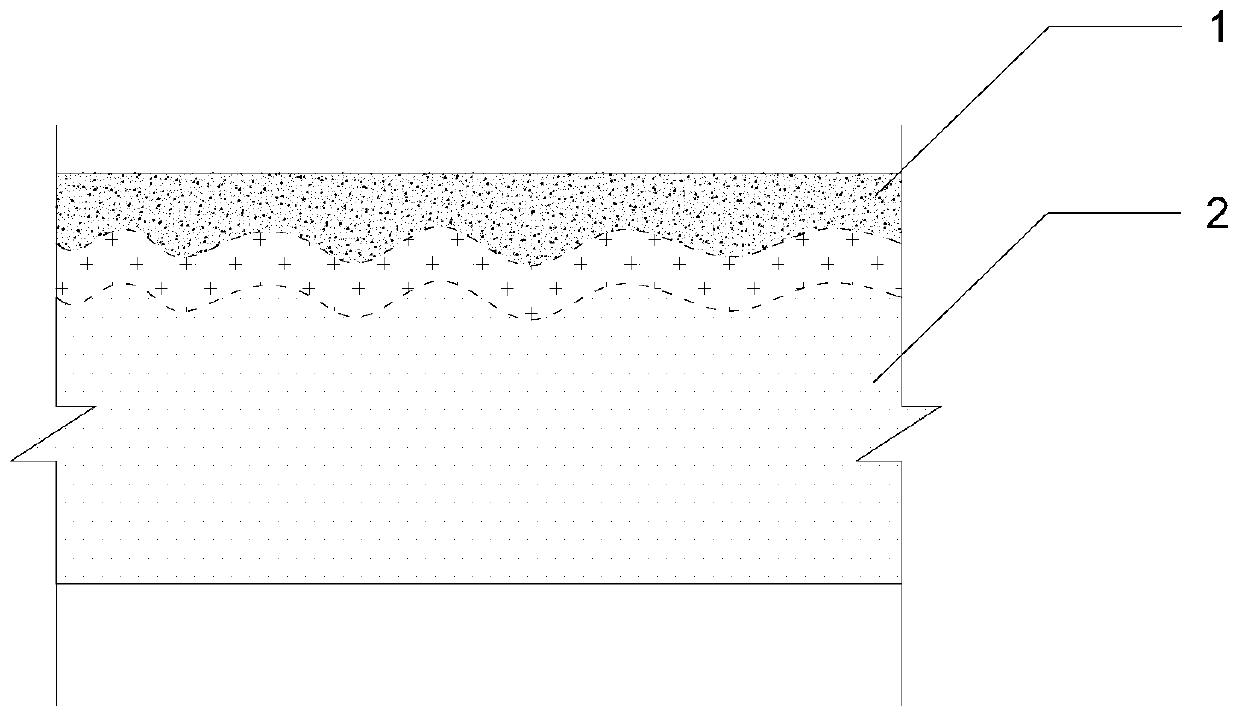
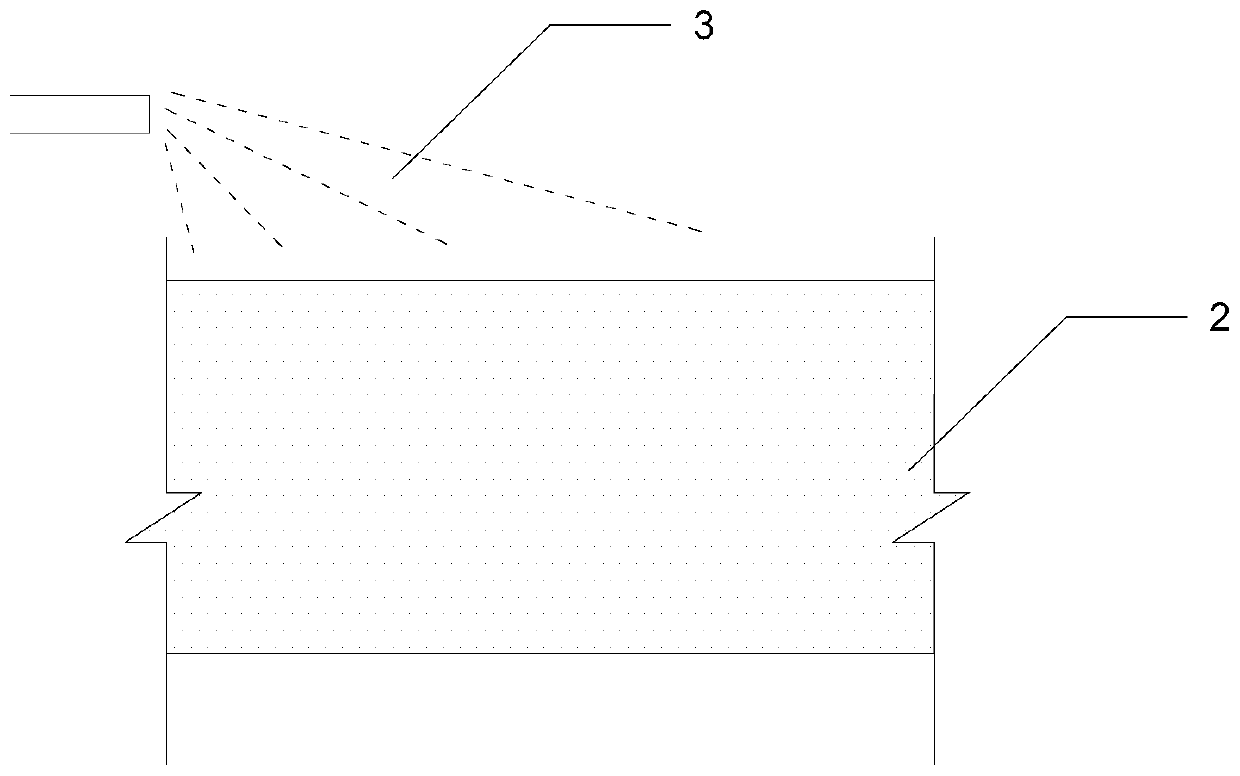
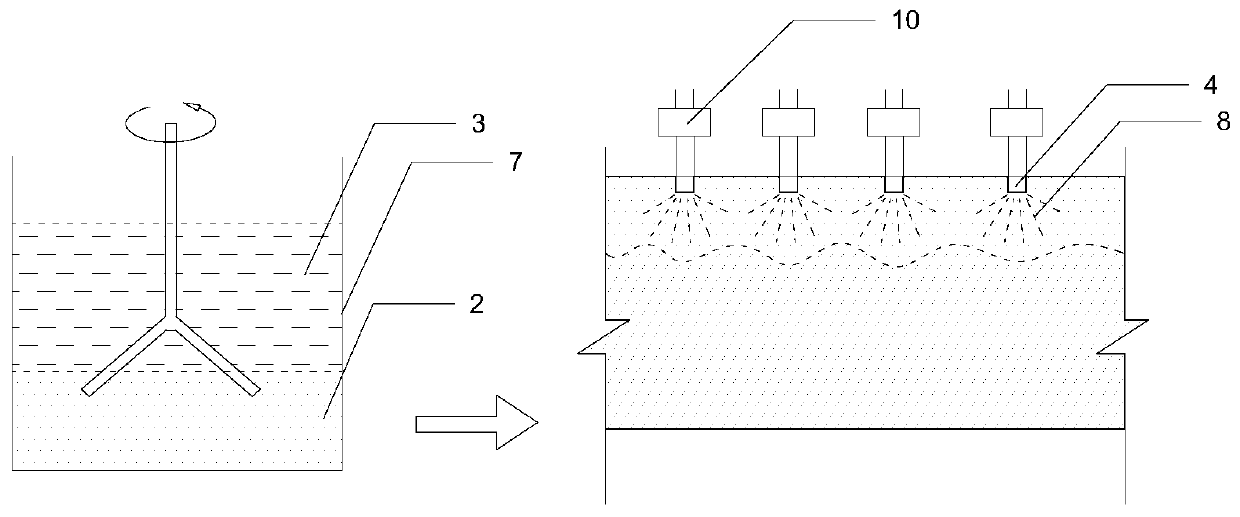
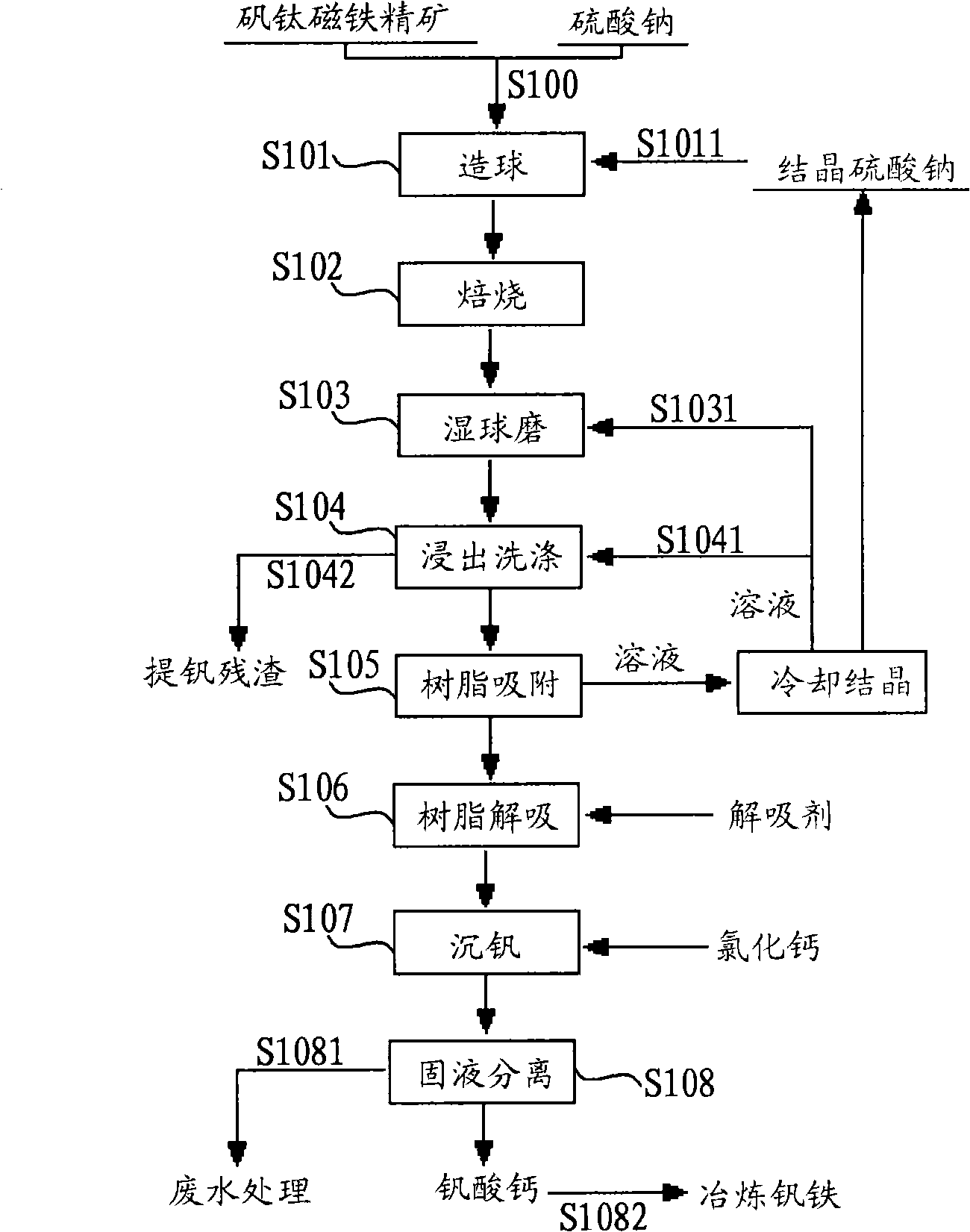
Method for directly extracting vanadium from vanadium titan magnetite concentrate
The invention provides a method for directly extracting vanadium from vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate. The method comprises the steps: a method for directly extracting vanadium from vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate comprises the steps: sodium sulfate is added into vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate, and pellet fabrication is carried out after the sodium sulfate and the vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate are mixed evenly; pellets which are obtained in pellet fabrication go through the high-temperature sodium oxide roasting; the roasted pellets are milled into powders and then are leached and washed by water; the leaching liquid is purified to collect vanadium to obtain vanadium solution; calcium chloride is added into the obtained vanadium solution to deposit calcium vanadate. The method can circularly utilize purified raffinate to avoid the generation of the waste water containing ammonia nitrogen, and can save the water and reduce the energy consumption.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +1
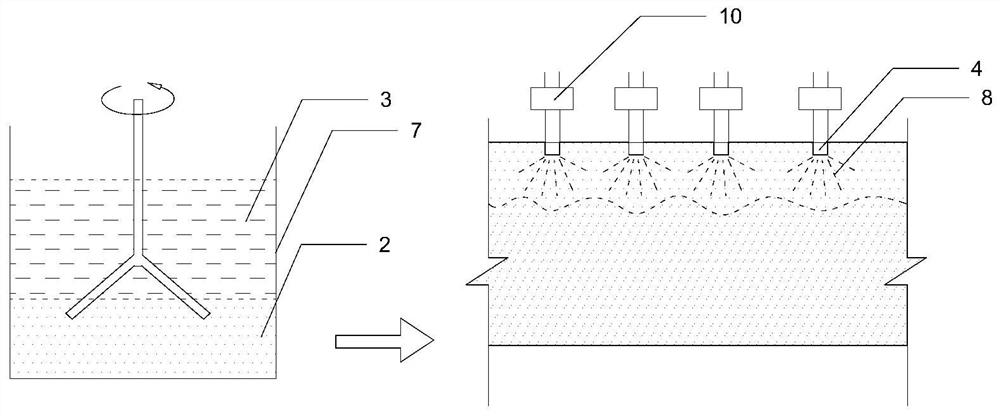
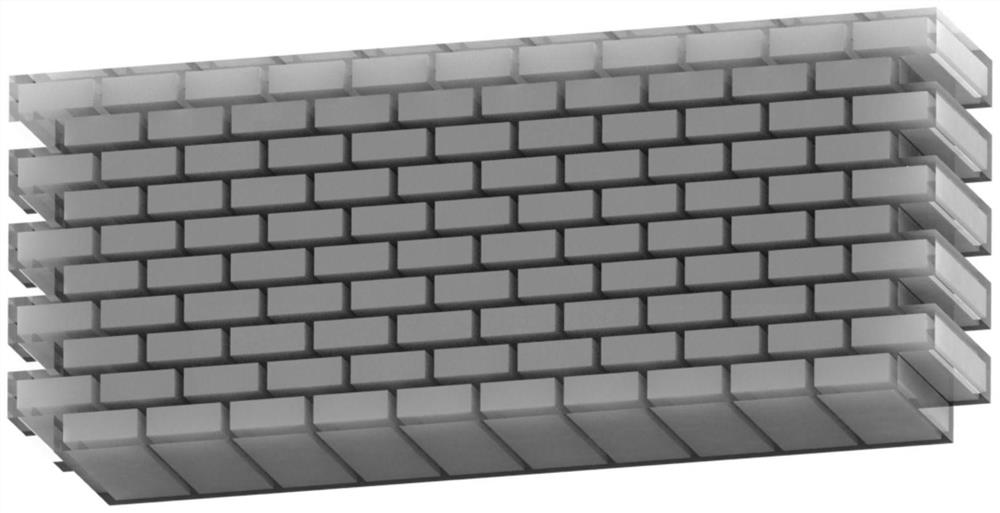
Preparation method of bionic shell material
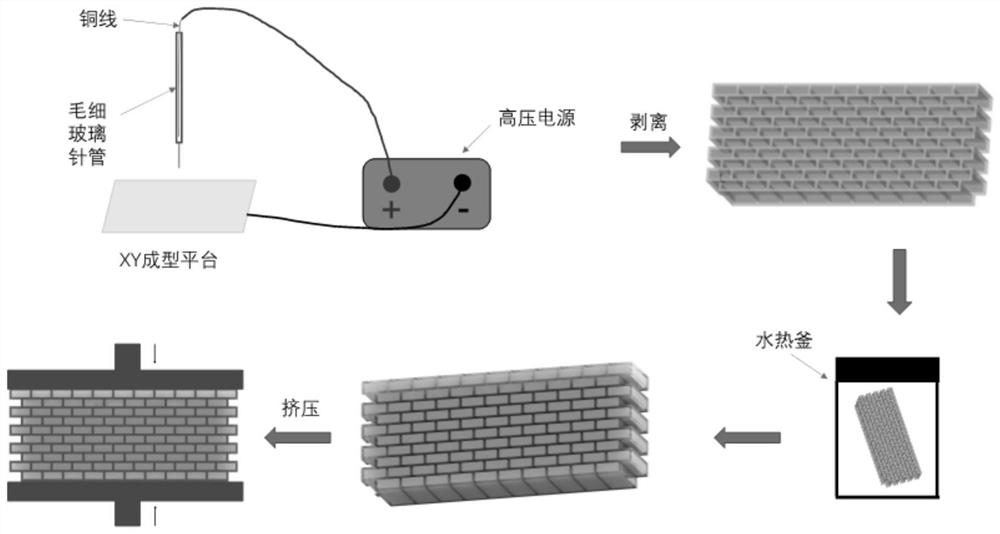
ActiveCN110126256AImprove uniformitySimple processCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicro nanoBrick
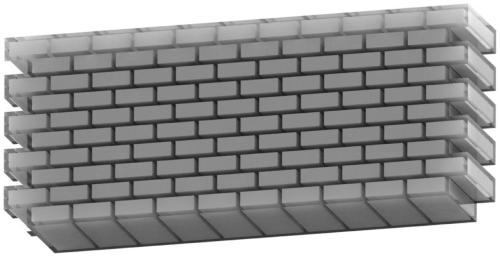
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bionic shell material, and belongs to the technical field of bionic structural mechanics materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) carrying out construction of brick-wall structure by using modeling software; (2) taking a photosensitive resin as a raw material, adding a diluent and a photoinitiator, and printing an organic framework of a shell structure by adopting micro-nano 3D printing equipment; (3) depositing calcium carbonate in the printed organic framework by adopting an in-situ precipitation method to obtainthe organic framework for depositing calcium carbonate; and (4) carrying out hot pressing on the organic framework deposited with the calcium carbonate by virtue of a hot pressing method to obtain the bionic shell material. The preparation method is simple in process, the prepared bionic shell material is good in uniformity, the strength and fracture toughness property of the prepared bionic shell material are close to that of the shell material, the bionic shell material has very practical value in the fields of mechanical engineering, aerospace, bullet-proof armor and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
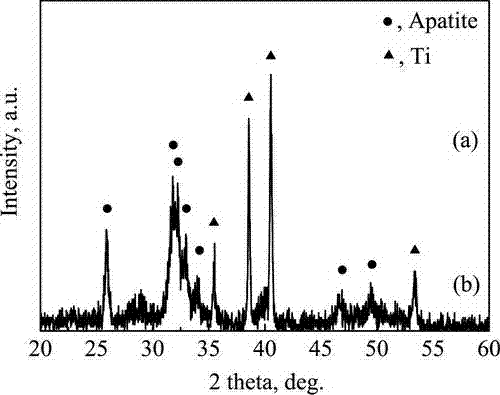
Bionic preparing method for depositing calcium and phosphor active layer on memory alloy of nickel and titanium for medical use
InactiveCN1557506AInhibition releasePromotes firm deposit growthCoatingsProsthesisShape-memory alloyBiological activation
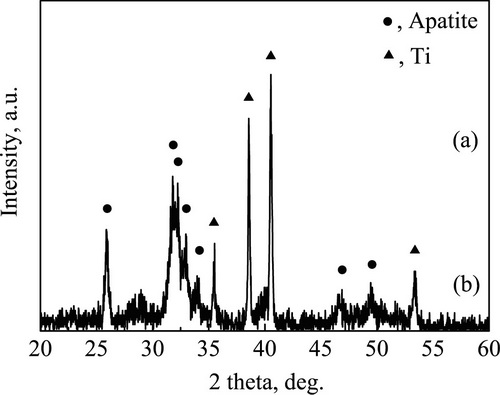
The present invention is the bionic process of preparing bioactive calcium phosphate layer on the surface of medical Ni-Ti memory alloy. The preparation process includes ultrasonic cleaning of medical Ni-Ti alloy with acetone, alcohol and distilled water successively; surface activation, and two-step bionic deposition of active calcium phosphate layer to form active calcium phosphate layer in two-layer structure on the surface of Ni-Ti alloy. The active calcium phosphate layer comprises transitional compact non-crystalline calcium phosphate layer of 1-10 micron thickness and porous octacalcium phosphate or surface bone-like crystalline apatite layer of 10-100 micron thickness. During the surface activation, boiling H2O2 aqua of 10-60 concentration is first used for treatment of 10-90 min, and NaOH aqua of 1-10 M concentration at 30-80 deg.c is then used for soaking after flushing for 6-48 hr.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
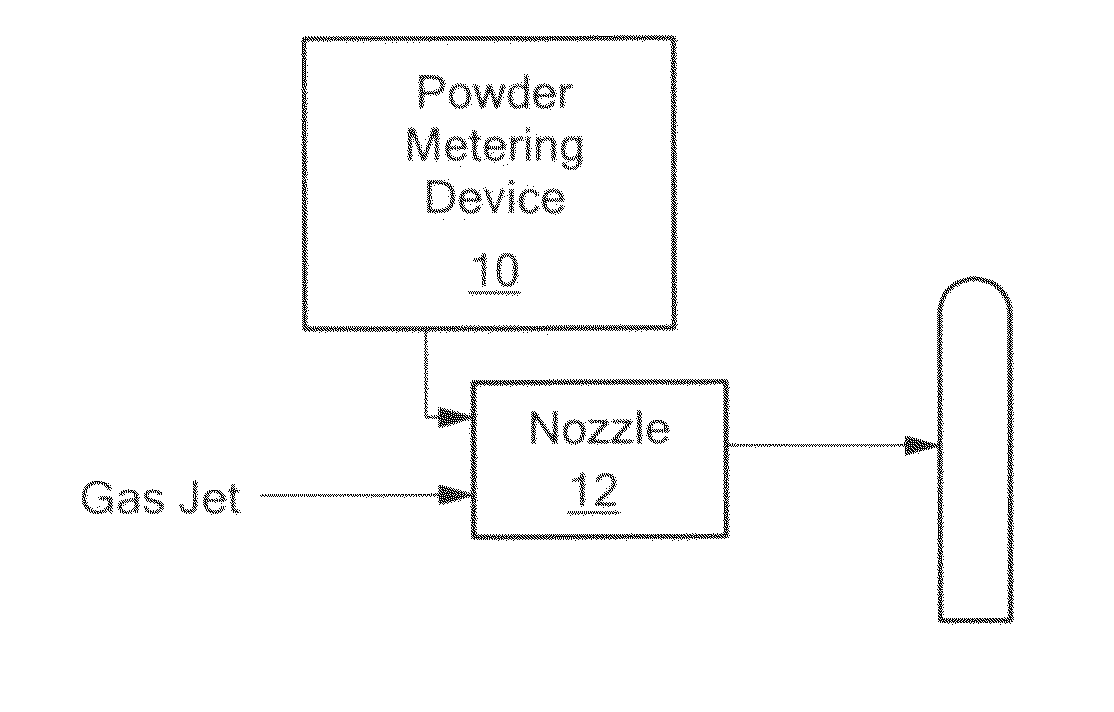
Process for depositing calcium phosphate therapeutic coatings with controlled release rates and a prosthesis coated via the process
InactiveUS20090010990A1Efficacy of the therapeutic agent is not adversely affectedBone implantPretreated surfacesDEPOSIT CALCIUMChemistry
Owner:SPIRE
Preparation method of carbonate hydroxyapatite/carbon nano tube composite coating material
InactiveCN101949046AUniform thicknessGood mechanical propertiesElectrophoretic coatingsProsthesisElectrophoretic depositionDEPOSIT CALCIUM
The invention relates to the fields of electrochemistry and materials and discloses a method for preparing a carbonate hydroxyapatite / carbon nano tube composite coating, which mainly comprises the following two steps: (1) depositing calcium carbonate powder or calcium carbonate-containing powder and carbon nano tubes on the surface of a metal matrix to obtain a calcium carbonate powder / carbon nano tube coating by electrophoretic deposition; and (2) treating the calcium carbonate powder / carbon nano tube coating with a phosphoric acid buffer solution, and converting the treated solution into the carbonate hydroxyapatite / carbon nano tube composite coating. The method is executed at normal temperature and pressure, has the advantages of simple process, low equipment investment and the like, and is suitable for preparing implants of various complicated shapes. The obtained composite coating has the fine bioactivity of the carbonate hydroxyapatite, and also can give full play to the favorable mechanical properties of the carbon nano tubes and the metal matrix.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
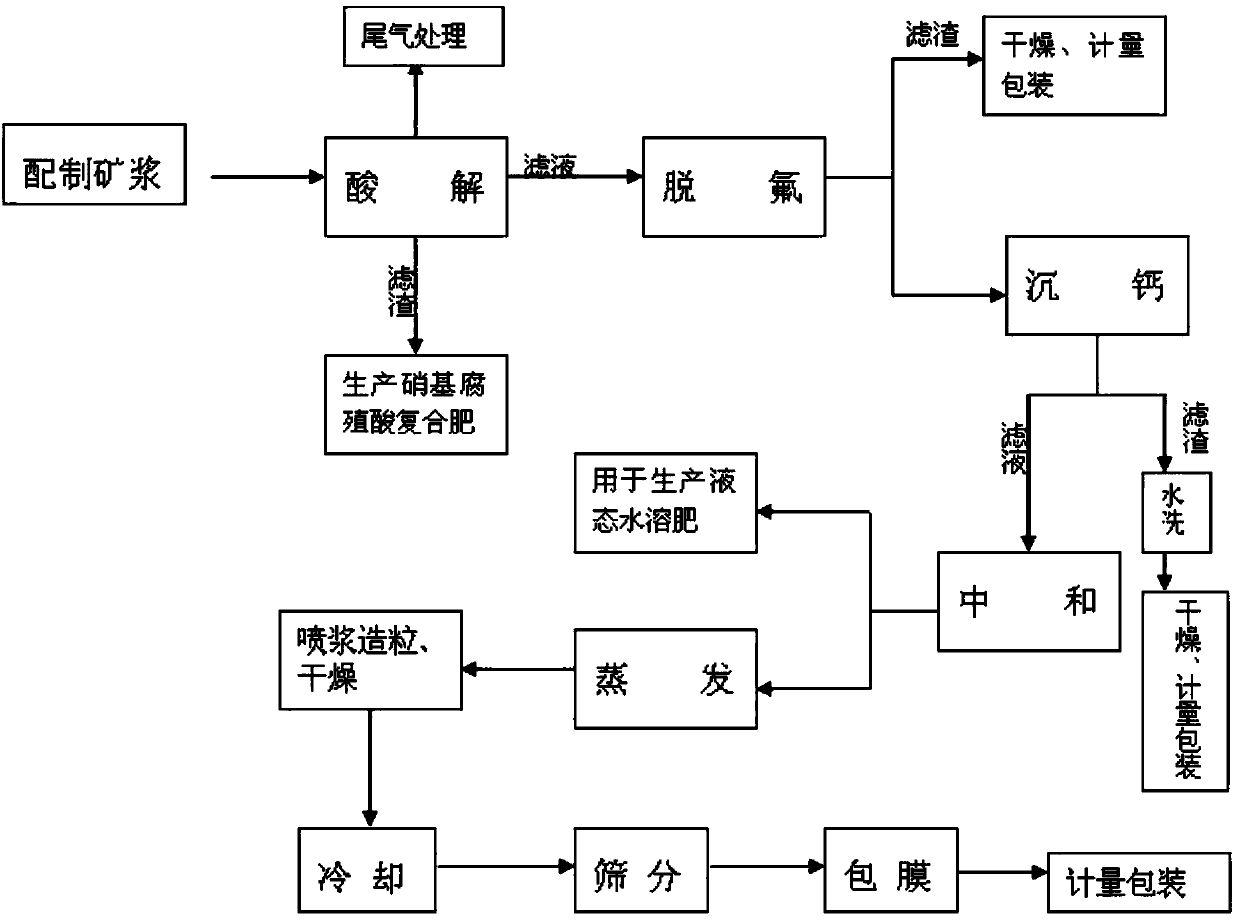
Method for co-production of chemical synthetic fertilizer by industrial calcium products
ActiveCN106517293ASimple product structureSimple structureCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesChemical synthesisNitrohumic acid
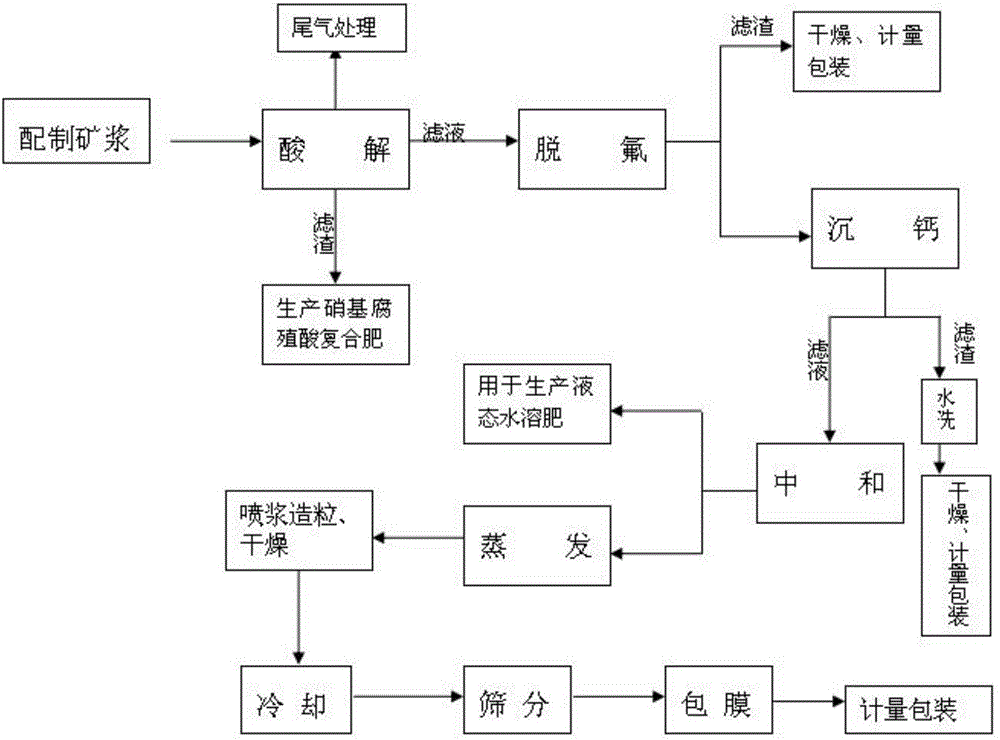
The invention relates to a method for co-production of a chemical synthetic fertilizer by industrial calcium products, and belongs to the field of production of agricultural fertilizers. The method comprises the following steps: preparing phosphorite powder into ore pulp by using a raw material slurry method, reacting the ore pulp with nitric acid, and filtering; feeding filter residues to a compound fertilizer workshop to produce a nitrohumic acid compound fertilizer; adding sodium nitrate in the filtrate to remove fluoride; centrifugally dehydrating; drying the filter residues to prepare sodium fluosilicate; adding ammonium sulfate, potassium sulphate or potassium carbonate in the filtrate to deposit calcium; then filtering; preparing the industrial calcium products from the filter residues; and neutralizing, concentrating, guniting, drying, cooling, enveloping, metering and packing the filtrate to obtain the chemical synthetic fertilizer.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAQIANG ECOLOGICAL FERTILIZER IND CO LTD
Depositing Calcium Fluoride Template Layers for Solar Cells
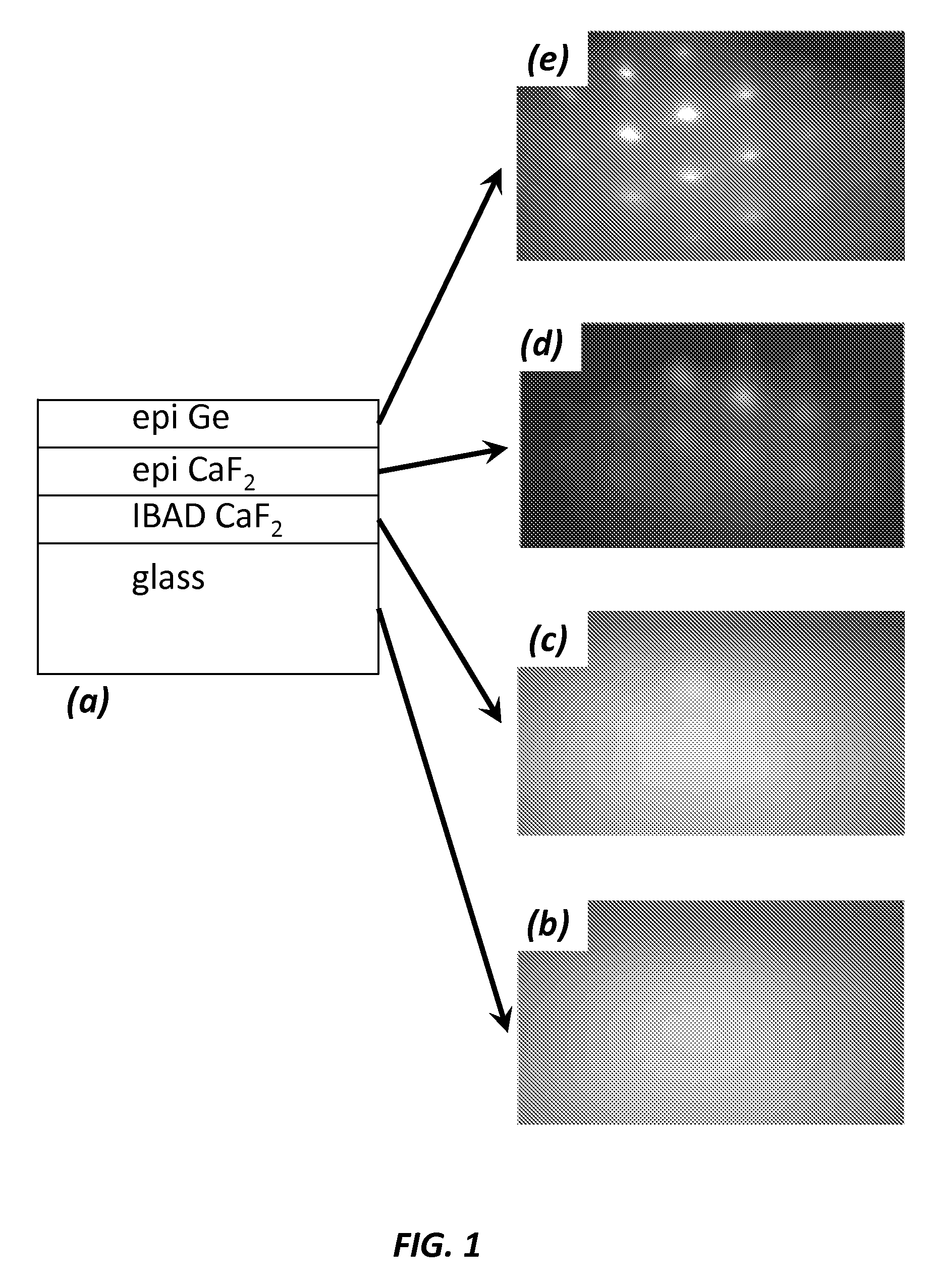
A biaxially textured crystalline layer formed on a substrate using ion beam assisted deposition (IBAD) is provided. The biaxially textured crystalline layer includes an oriented CaF2 crystalline layer having crystalline grains oriented in both in-plane and out-of-plane directions, where the out-of-plane orientation is a (111) out-of-plane orientation. The oriented CaF2 crystalline layer is disposed for growth of a subsequent epitaxial layer and the CaF2 crystalline layer is an IBAD CaF2 layer. The biaxially textured CaF2 layer can be used in a photovoltaic cell, an electronic or optoelectronic device, an integrated circuit, an optical sensor, or a magnetic device.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
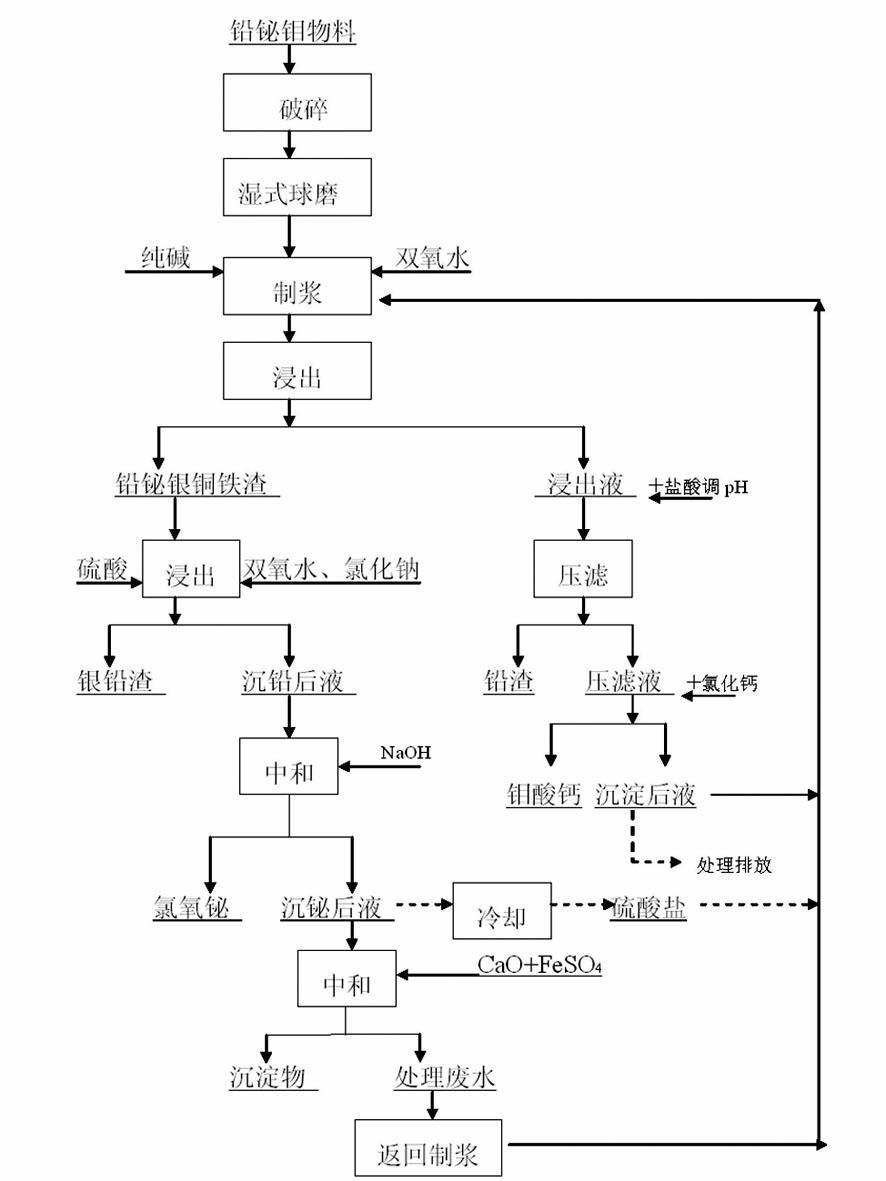
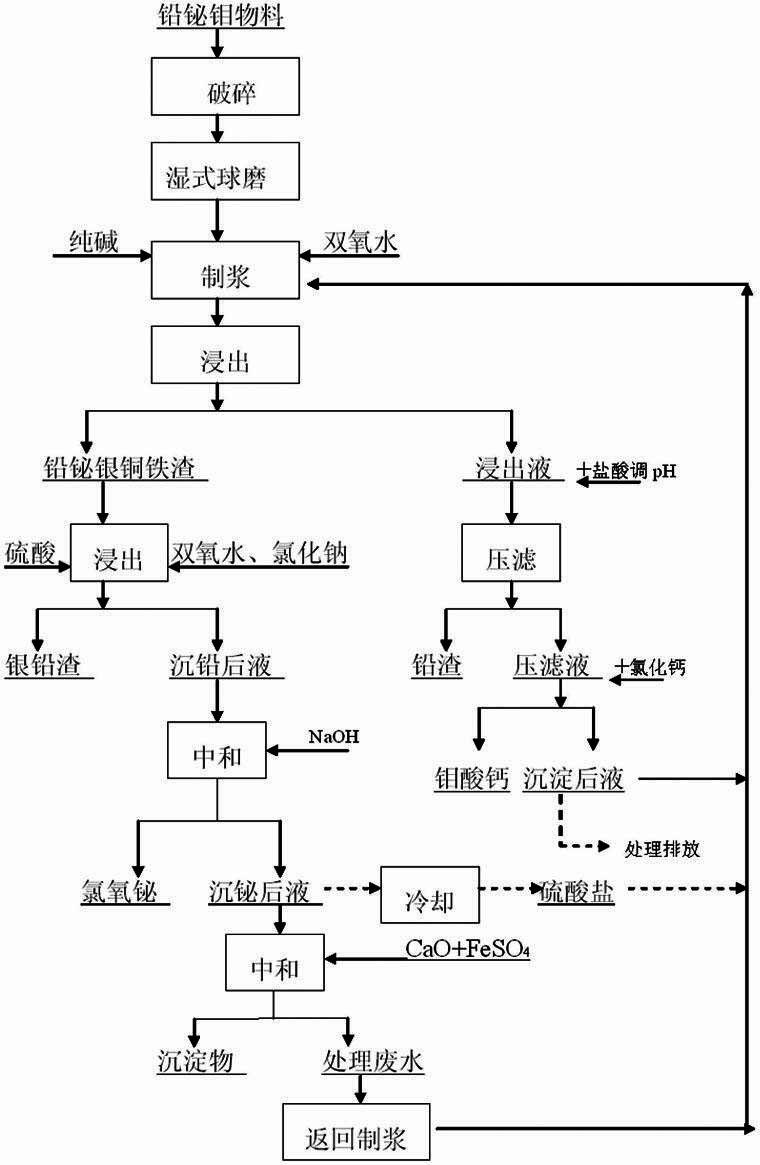
Wet separation technology for material containing lead, bismuth and molybdenum
InactiveCN102321804AHigh recovery rateIncrease added valueProcess efficiency improvementSlagSeparation technology
The invention relates to a wet separation technology for a material containing lead, bismuth and molybdenum, belonging to the technical field of nonferrous metallurgy. The material containing lead, bismuth and molybdenum provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly carrying out ball milling on the material containing lead, bismuth and molybdenum, pulping by adding pure alkaline and an oxidant, and leaching out a pulping material liquid by heating, so that molybdenum exists in a leaching liquid in the form of sodium molybdenum, and lead bismuth silver copper iron slag is formed for lead, bismuth, silver, copper and iron remaining in leached slag; dissolving lead by hydrochloric acid deposition part of leachate, forming lead slag, smelting and recycling by a lead fire method, then adding calcium chloride, and depositing calcium molybdate; leaching out the lead bismuth silver copper iron slag by sulfate, sodium chloride and hydrogen peroxide, and separating Pb in the form of silver and lead slag; and depositing the bismuth in the liquid after lead deposition through hydrolysis, thus the separation of lead, bismuth and molybdenum is realized. According to the invention, the metal recovery rate is high, the separation effect is good, the waste liquid is recycled, no waste slag is produced, and the technology is environmentally-friendly and safe.
Owner:HUNAN JINWANG BISMUTH
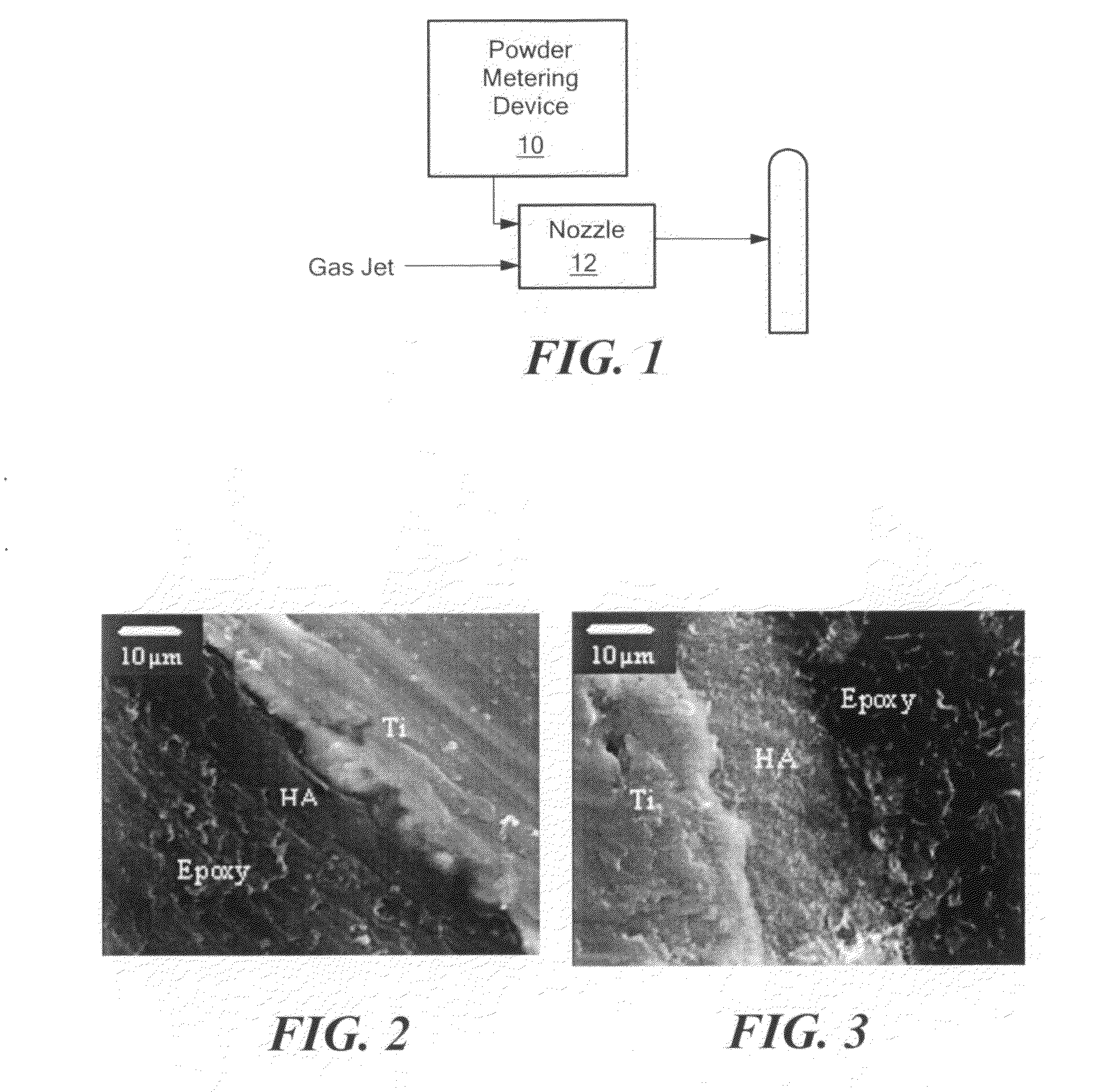
Formulation of calcium phosphate coating deposit solution for bone implantation material, and coating method
A solution for depositing calcium phosphate layer on bone implantation material is a deionized one containing calcium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium hydrogen carbonate. Its depositing process includes grinding and washing Ti matrix, surface treating in NaOH solution at 20-200 deg.C for 24-48 hr, washing, and depositing in said solution at 30-40 deg.C for 20-24 hr. Its advantage is short period.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Process for depositing calcium phosphate therapeutic coatings with different release rates and a prosthesis coated via the process
InactiveUS20110059149A1Promotes osteogenesisPromotes osteoconductionSurgeryVacuum evaporation coatingCalcium biphosphateOsseointegration
A method of coating a substrate including loading a calcium phosphate substance at a first crystallinity with a therapeutic agent; depositing the loaded calcium phosphate substance at the first crystallinity onto a least a portion of the substance; loading a calcium phosphate substance at a second, lower, crystallinity with a therapeutic agent; and depositing the loaded calcium phosphate substance at the second crystallinity onto the deposited loaded calcium phosphate substance at the first crystallinity to control and sustain a long-term osseointegration response and to control the release rate of the therapeutic substance from the calcium phosphate substance.
Owner:SPIRE
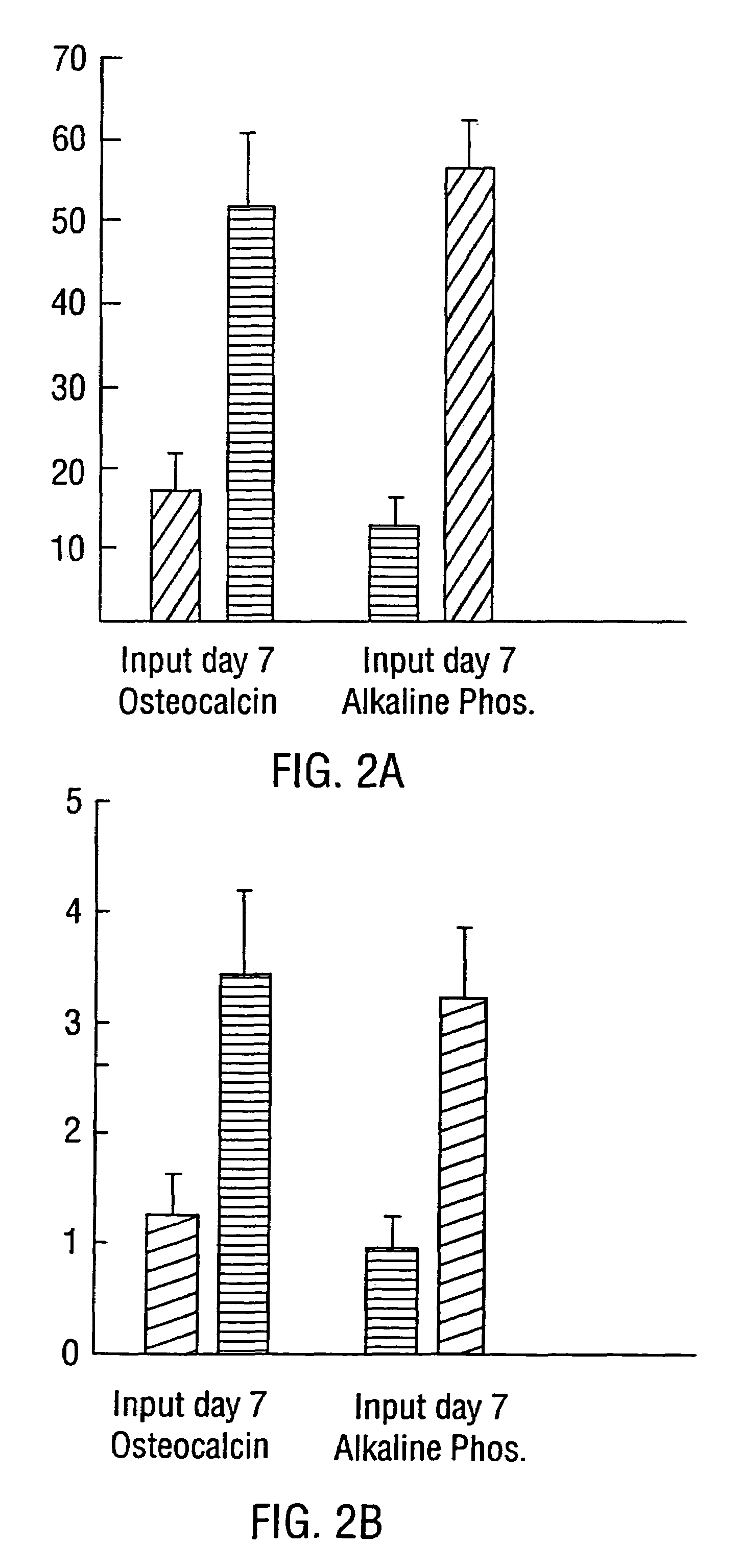
Bone precursor cells: compositions and methods
InactiveUS7498170B2Increased complexityIncrease in sizeDiagnosticsCulture processDiseaseHematopoietic cell
Disclosed are compositions of bone precursor cells and methods for their preparation and use. Bone precursor cells are cells which are not hematopoietic and which can differentiate into osteoblasts upon exposure to a bone growth factor and deposit calcium into the extracellular matrix. Such bone precursor cells are useful in the treatment of certain bone related disorders and diseases, such as osteoporosis, or in promoting fracture repair. In addition, methods of differentiating bone precursor cells into osteoblasts, and other diagnostic and even prognostic methods are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
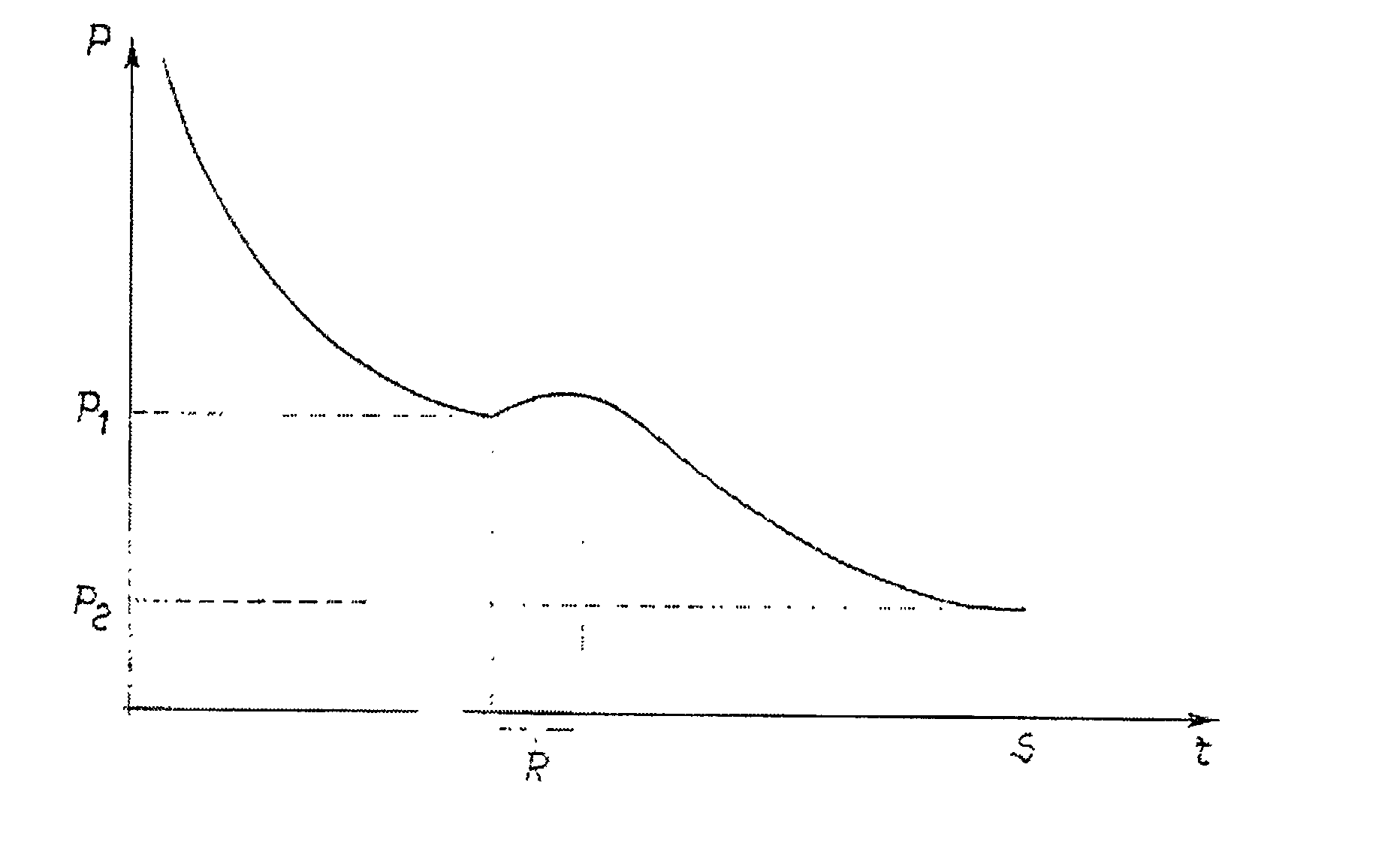
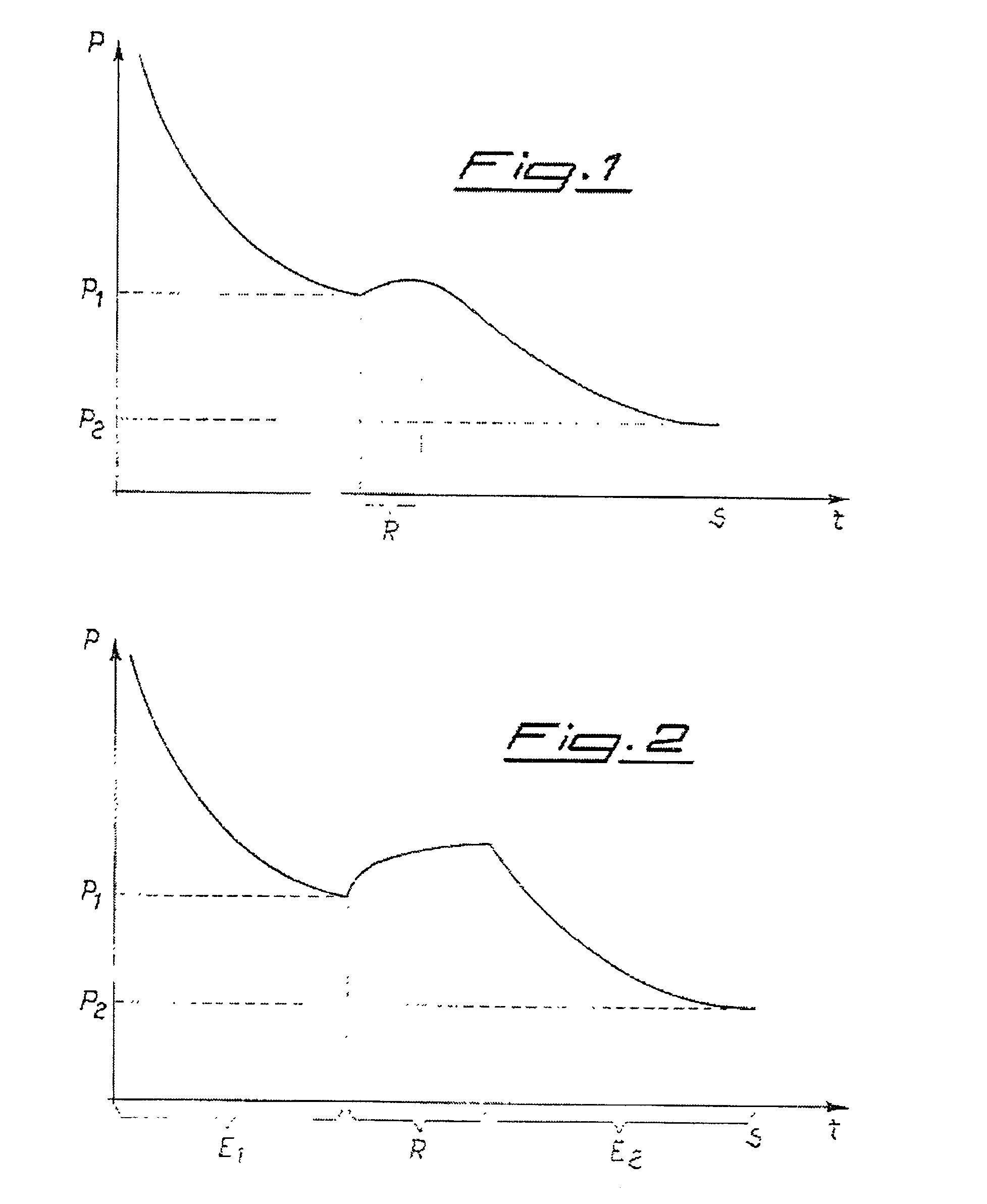
Process for depositing calcium getter thin films inside systems operating under vacuum
InactiveUS6851997B2Gas filling substance selectionTube/lamp vessel degassingEngineeringDEPOSIT CALCIUM
The present invention relates to a process for depositing a calcium getter thin film inside a system operating under vacuum. The process comprises the steps of introducing into the system under vacuum at least one evaporable getter device with an air-stable calcium compound. The system is evacuated until a pressure value P1 is reached. The system is then heated up to the calcium evaporation temperature of the stable compound. The system evacuation continues until a pressure value P2, which is lower than P1, is reached and the system is sealed. In a preferred embodiment, the heating step separates the two evacuation steps.
Owner:SAES GETTERS SPA
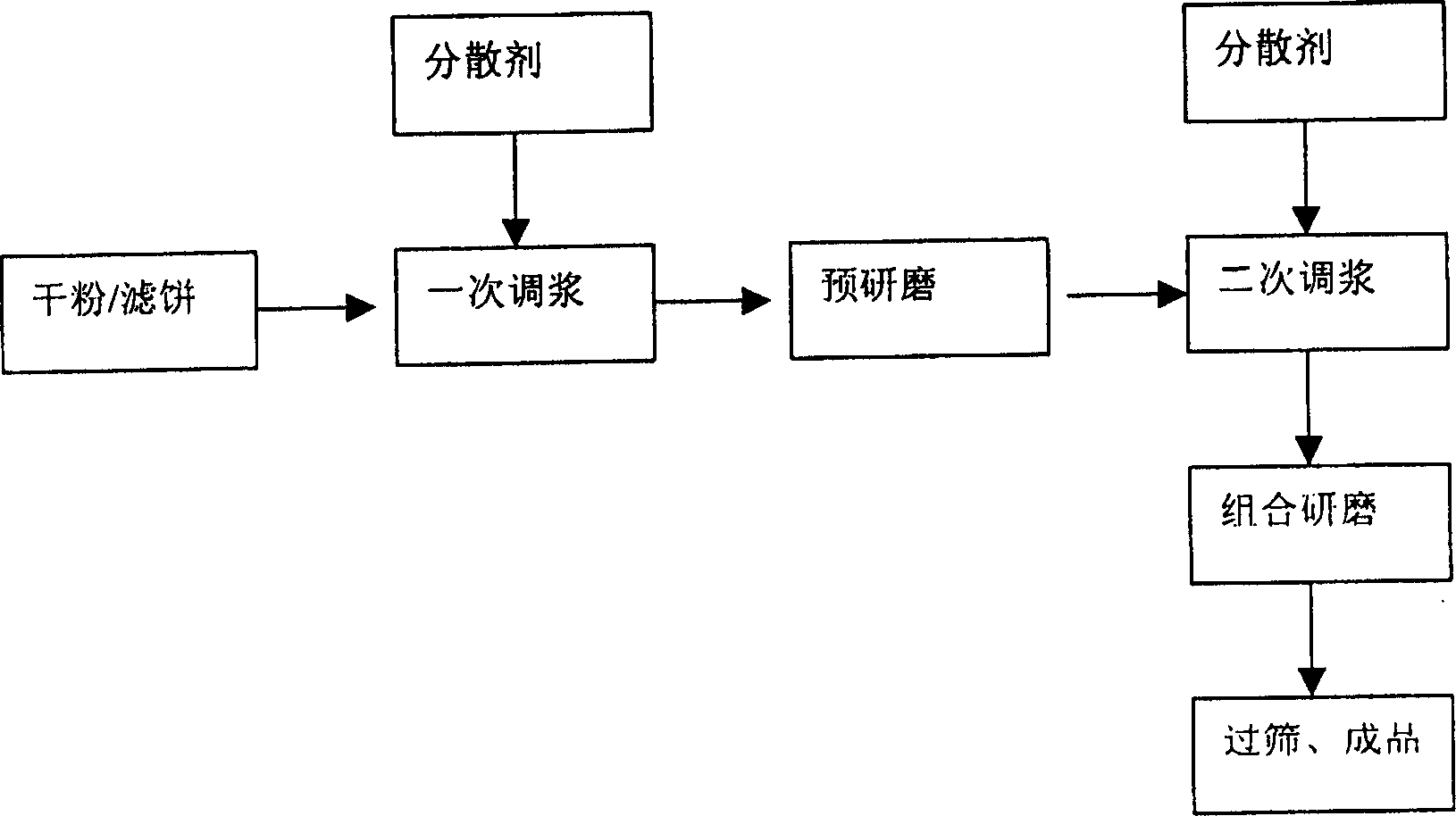
Method for preparing paper-making coating-grade deposited calcium carbonate pigment
InactiveCN1278939CSolve the problem of accumulation and agglomerationImprove the problem of accumulation and agglomerationCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCoatings with pigmentsCardboardPrecipitated calcium carbonate
The invention relates to a method for preparing a paper-making coating-grade precipitated calcium carbonate pigment, which is especially suitable for use as a coating pigment for high-grade coated paper, white cardboard, and light-weight (low-weight) coated paper, and belongs to the technical field of refining chemical raw materials . The present invention uses precipitated calcium carbonate dry powder as raw material, adds precipitated calcium carbonate to water in batches under high-speed dispersion conditions to adjust slurry, and obtains precipitated calcium carbonate with a solid content between 65% and 75% after multi-channel grinding. Papermaking coating grade precipitated calcium carbonate pigment with a ratio greater than 90% and a viscosity less than 300 centipoise (cps). The invention can effectively solve the agglomeration problem in the dispersion process of the precipitated calcium carbonate, improve the viscosity index of the precipitated calcium carbonate, and obtain high-concentration pigment for doctor blade coating.
Owner:LINCHENG RUIBANG CALCIUM CARBONATE
Method for recovering cement-based material crack by means of microorganism, culture fluid and repair nutrient fluid
ActiveCN101302484BAbundant resourcesImprove environmental friendlinessBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCulture fluidSlurry
The invention discloses a method for repairing cement-based material cracks, as well as a culture solution and a repair nutrient solution. The method for repairing cement-based material cracks by through microorganisms comprises the following steps that: a Bacillus pasteurii strain is inoculate onto a culture medium provided with a urea-containing substrate; shake cultivation is carried out at a temperature of between 25 and 37 DEG C, and then a culture bacteria solution is taken out and centrifuged and has supernatant fluid removed; strain cells are collected through the culture solution; the concentration of the strain cells is controlled in a range of between 2x10<9> and 1x10<11> cell / ml; standard sand, urea and Ca(NO3)2.4H2O mixture are added to each milliliter of strain cell solutionobtained through collection, mixed, stirred into slurry and injected into cement stone cracks; the frequency of the repair nutrient solution injection is not less than two times; finally, maintenanceis carried out. In the culture solution, each liter of culture solution contains 4 to 6 g of peptone, 2 to 4 g of beef extract and 20 to 60 g of urea. The method fully utilizes microbial resources innature; CO3<2-> decomposed out through microbial enzyme can chelate Ca<2+> in a substrate so as to be mineralized and deposit calcium carbonate, and is close in the combination with the substrate andgood in stability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A microbial solidification kit and method for in-situ solidification of calcareous sand
ActiveCN110438974BPromote colonizationLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a microbial solidification kit and a method for in-situ solidification of calcareous sand, belonging to the interdisciplinary field of geological engineering-microbiology. A microbial solidification kit of the present invention is used for in-situ solidification of calcareous sand, comprising: a first component containing carboxylic acid; a second component containing microorganisms capable of producing urease; a third component containing urea and nutrient solution components. The method for in-situ solidification of calcareous sand by microorganisms includes the step of partially dissolving the calcareous sand by using the above-mentioned first component. The present invention can efficiently obtain calcium source in the in-situ calcareous sandy soil or in the sandy soil in the nearby area, and then react with microorganisms to deposit calcium carbonate to realize the in-situ solidification effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
A kind of preparation method of bionic shell material
ActiveCN110126256BImprove uniformitySimple processCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAdditive manufacturing apparatusModeling softwareEngineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bionic shell material, and belongs to the technical field of bionic structural mechanics materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) carrying out construction of brick-wall structure by using modeling software; (2) taking a photosensitive resin as a raw material, adding a diluent and a photoinitiator, and printing an organic framework of a shell structure by adopting micro-nano 3D printing equipment; (3) depositing calcium carbonate in the printed organic framework by adopting an in-situ precipitation method to obtainthe organic framework for depositing calcium carbonate; and (4) carrying out hot pressing on the organic framework deposited with the calcium carbonate by virtue of a hot pressing method to obtain the bionic shell material. The preparation method is simple in process, the prepared bionic shell material is good in uniformity, the strength and fracture toughness property of the prepared bionic shell material are close to that of the shell material, the bionic shell material has very practical value in the fields of mechanical engineering, aerospace, bullet-proof armor and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of carbonate hydroxyapatite/carbon nano tube composite coating material
InactiveCN101949046BUniform thicknessImprove mechanical propertiesElectrophoretic coatingsProsthesisO-Phosphoric AcidElectrochemistry
The invention relates to the fields of electrochemistry and materials and discloses a method for preparing a carbonate hydroxyapatite / carbon nano tube composite coating, which mainly comprises the following two steps: (1) depositing calcium carbonate powder or calcium carbonate-containing powder and carbon nano tubes on the surface of a metal matrix to obtain a calcium carbonate powder / carbon nano tube coating by electrophoretic deposition; and (2) treating the calcium carbonate powder / carbon nano tube coating with a phosphoric acid buffer solution, and converting the treated solution into the carbonate hydroxyapatite / carbon nano tube composite coating. The method is executed at normal temperature and pressure, has the advantages of simple process, low equipment investment and the like, and is suitable for preparing implants of various complicated shapes. The obtained composite coating has the fine bioactivity of the carbonate hydroxyapatite, and also can give full play to the favorable mechanical properties of the carbon nano tubes and the metal matrix.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Teeth correcting wire with surface deposited calcium phosphorus biological ceramic and its preparation method
The present invention relates to an orthodontic wire for orthodontic treatment, in particular to an orthodontic wire with a calcium-phosphorous bioceramic coating on the surface with good biocompatibility and a preparation method thereof. The metal matrix of the orthodontic wire There is a layer of calcium phosphorus bioceramic coating with good biocompatibility on the surface. The calcium phosphorus bioceramic coating has a double-layer structure, that is, an amorphous bottom layer of calcium phosphate and bone-like phosphorous ash in contact with the metal matrix of the tooth correction wire. The surface layer of the stone crystal phase is composed of the calcium phosphate amorphous bottom layer with a thickness of 1-10 μm; the bone-like apatite crystal phase surface layer with a thickness of 10-50 μm. The preparation method is as follows: firstly process the tooth-orthopedic wire with nickel-titanium memory alloy or stainless steel; carry out surface activation treatment on the tooth-orthopedic wire, and then obtain a calcium phosphate amorphous bottom layer and A calcium-phosphorus bioceramic layer composed of bone-like apatite crystal phase surface layers in sequence.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Immortalized vascular adventital cell line
To provide an immortalized capillary pericyte line which maintains the original function / property of the cell line-deriving tissue, its establishment method, and the screening method for useful substance using the immortalized capillary pericyte line. Cerebral tissue of a transgenic rat carrying the large T antigen gene of SV40 thermo-sensitive mutant line tsA58 is homogenized and the resultant brain capillaries are treated with protease, thus obtained brain capillary cells are subcultured to establish an immortalized cell that expresses SV40 thermo-sensitive large T antigen, PDGF receptor β, and Angiopoietin-1. In addition, the immortalized vascular pericyte line has ability to deposit calcium on matrix by dense culture.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Immortalized vascular adventital cell line
To provide an immortalized capillary pericyte line which maintains the original function / property of the cell line-deriving tissue, its establishment method, and the screening method for useful substance using the immortalized capillary pericyte line. Cerebral tissue of a transgenic rat carrying the large T antigen gene of SV40 thermo-sensitive mutant line tsA58 is homogenized and the resultant brain capillaries are treated with protease, thus obtained brain capillary cells are subcultured to establish an immortalized cell that expresses SV40 thermo-sensitive large T antigen, PDGF receptor beta, and Angiopoietin-1. In addition, the immortalized vascular pericyte line has ability to deposit calcium on matrix by dense culture.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
A method for co-producing chemically synthesized fertilizer with industrial calcium products
ActiveCN106517293BSimple product structureSimple structureCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesFluosilicic acidChemical synthesisNitrohumic acid
The invention relates to a method for co-production of a chemical synthetic fertilizer by industrial calcium products, and belongs to the field of production of agricultural fertilizers. The method comprises the following steps: preparing phosphorite powder into ore pulp by using a raw material slurry method, reacting the ore pulp with nitric acid, and filtering; feeding filter residues to a compound fertilizer workshop to produce a nitrohumic acid compound fertilizer; adding sodium nitrate in the filtrate to remove fluoride; centrifugally dehydrating; drying the filter residues to prepare sodium fluosilicate; adding ammonium sulfate, potassium sulphate or potassium carbonate in the filtrate to deposit calcium; then filtering; preparing the industrial calcium products from the filter residues; and neutralizing, concentrating, guniting, drying, cooling, enveloping, metering and packing the filtrate to obtain the chemical synthetic fertilizer.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAQIANG ECOLOGICAL FERTILIZER IND CO LTD
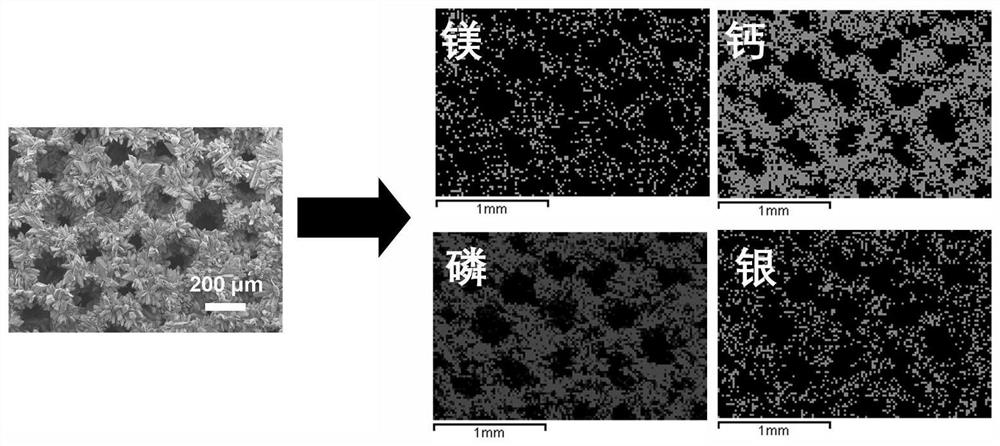
Antibacterial coating of magnesium-based tissue engineering material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108939155BSolve the problem of ineffective antibacterialAvoid infectionCoatingsProsthesisMg alloysDEPOSIT CALCIUM
The invention discloses a magnesium-based tissue engineering material antibacterial coating and a preparation method thereof. The coating includes a bioactive calcium-phosphorus coating and a nano-metal compound antibacterial coating on the surface of the porous magnesium and magnesium alloy materials from the inside to the outside; during preparation, the porous magnesium-based material is placed in a solution containing calcium phosphate salt Soaking, chemically depositing a bioactive calcium-phosphorus coating; then placing the porous magnesium-based material deposited on the calcium-phosphorus layer in a constant temperature and dynamic immersion reaction in a metal compound solution, and preparing the above-mentioned nanometer metal compound antibacterial coating on the surface of the outer layer of calcium-phosphorus layer, namely have to. The coating prepared by the invention not only significantly reduces the corrosion rate of the matrix porous magnesium and magnesium alloy, but also improves the surface biological activity of the matrix, can promote osteogenesis and angiogenesis, and has high-efficiency broad-spectrum antibacterial effect. The operation process is simple and easy, the prepared coating has strong binding force with the substrate, and the surface density and particle size of the nanometer metal compound carried can be adjusted.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOVATON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for dissolution reaction
InactiveUS7947229B2Easy to cleanConvenience to workGaseous chemical processesGas treatmentDissolution reactionSlurry
Owner:TAIHEIYO CEMENT CORP
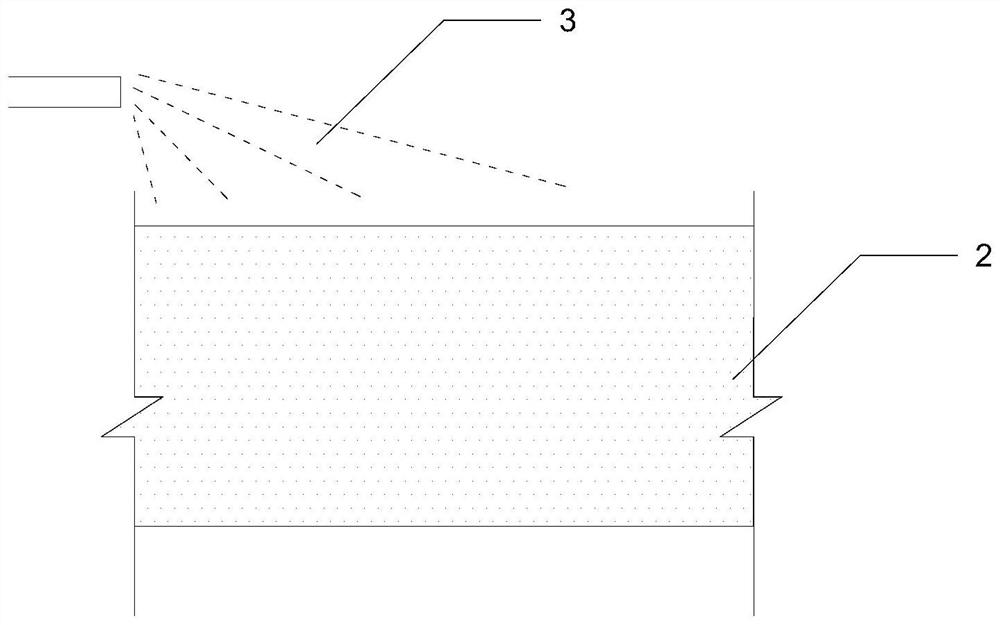
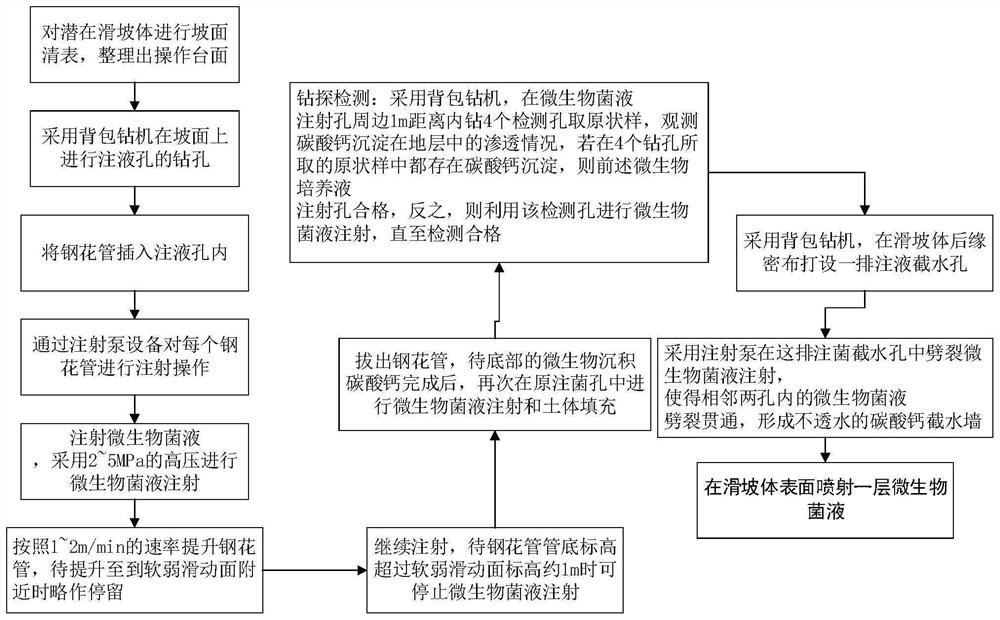
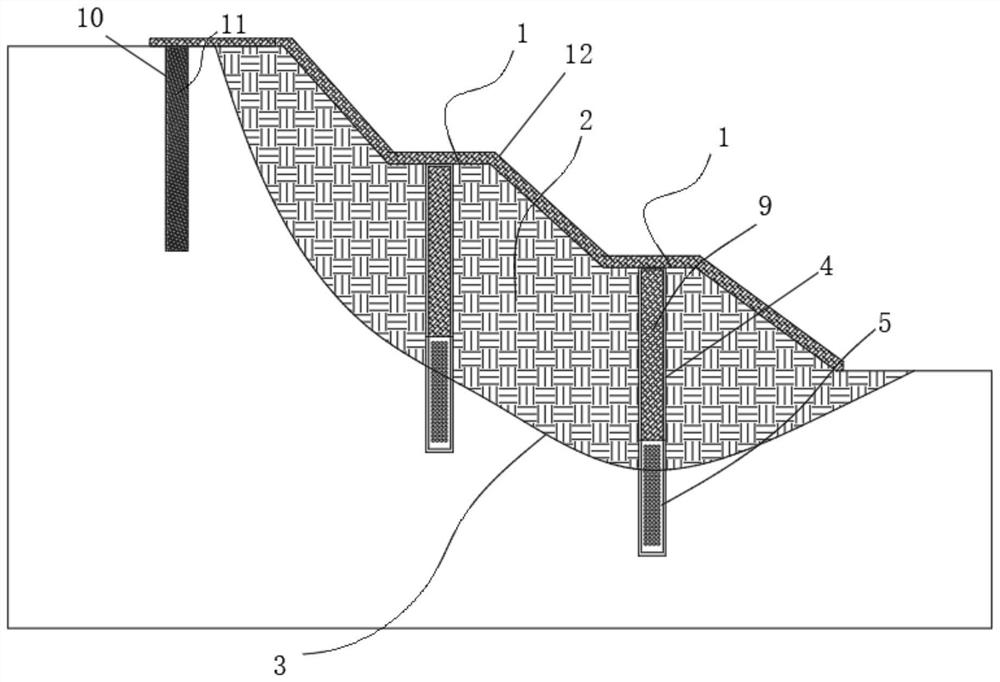
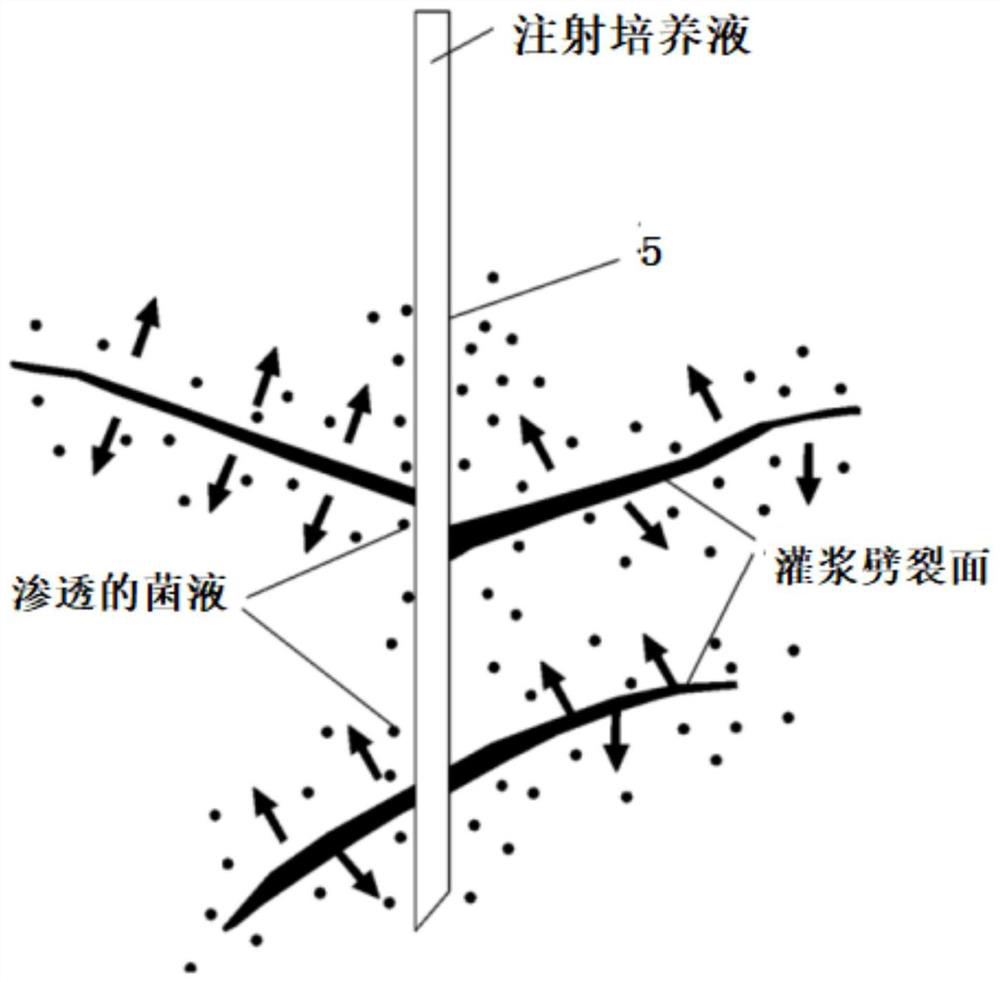
Construction method of high pressure spraying microbial bacteria liquid to deposit calcium carbonate to control landslide
Owner:FUJIAN GEOLOGICAL ENG SURVEY INST
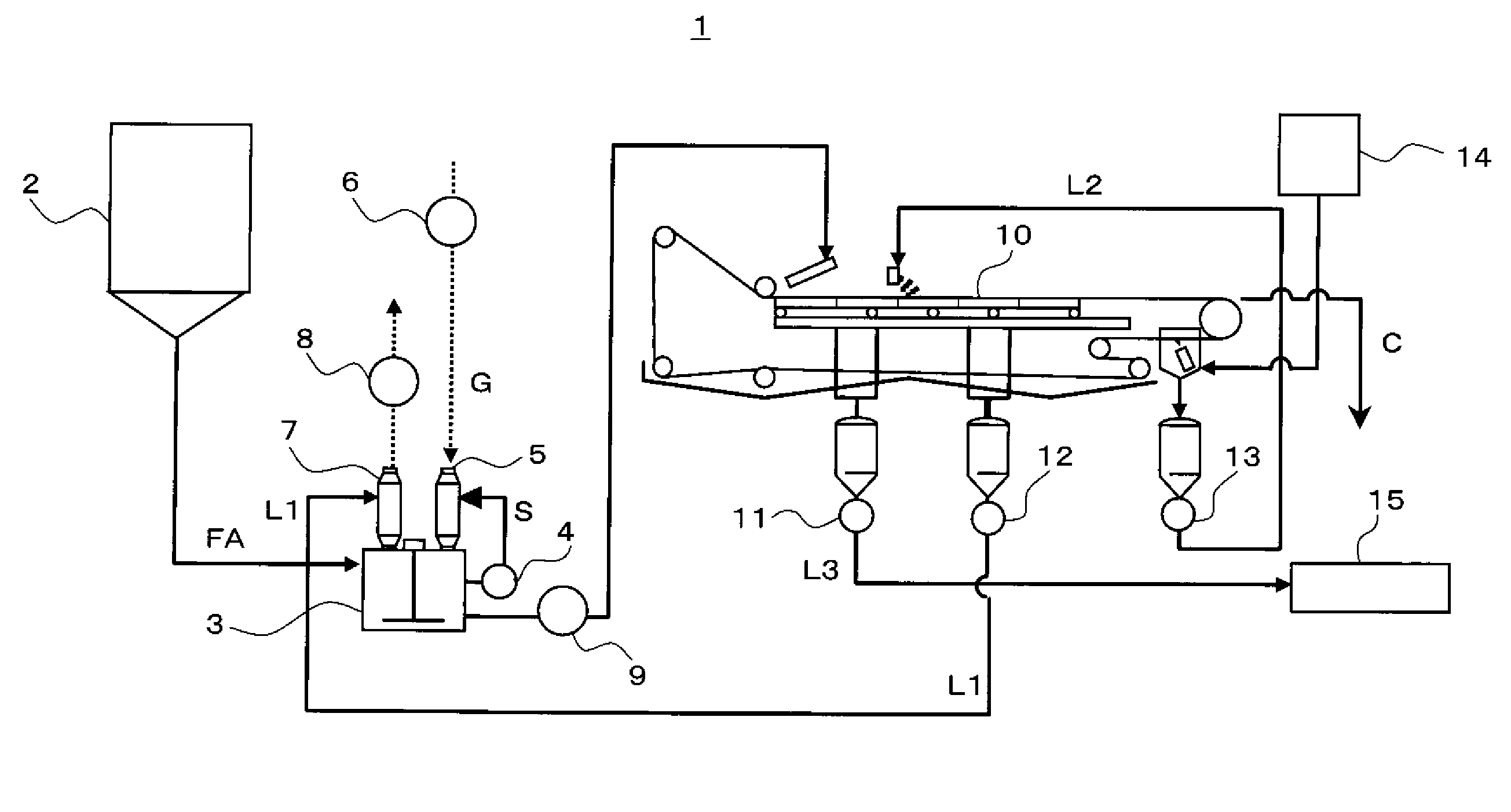
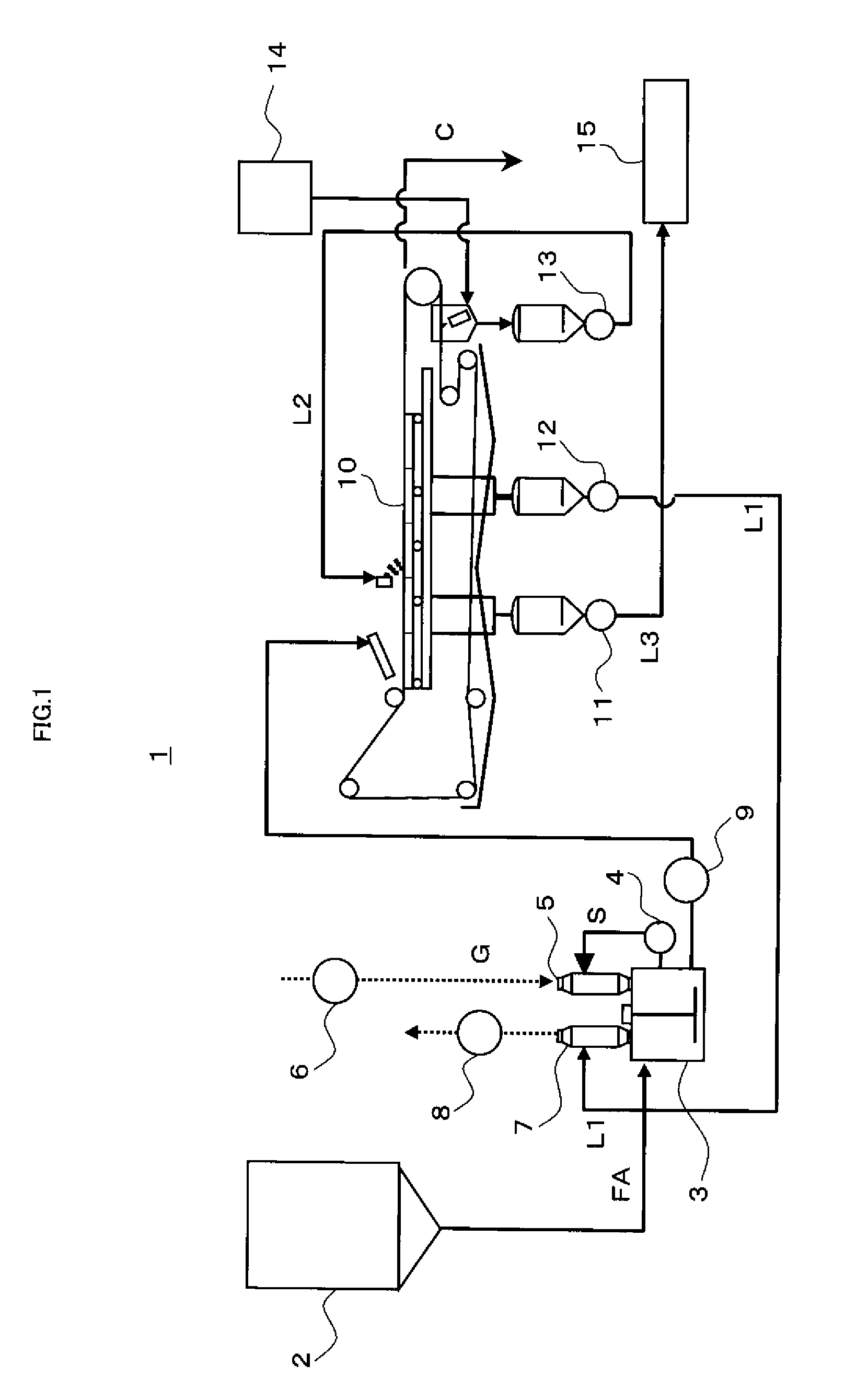
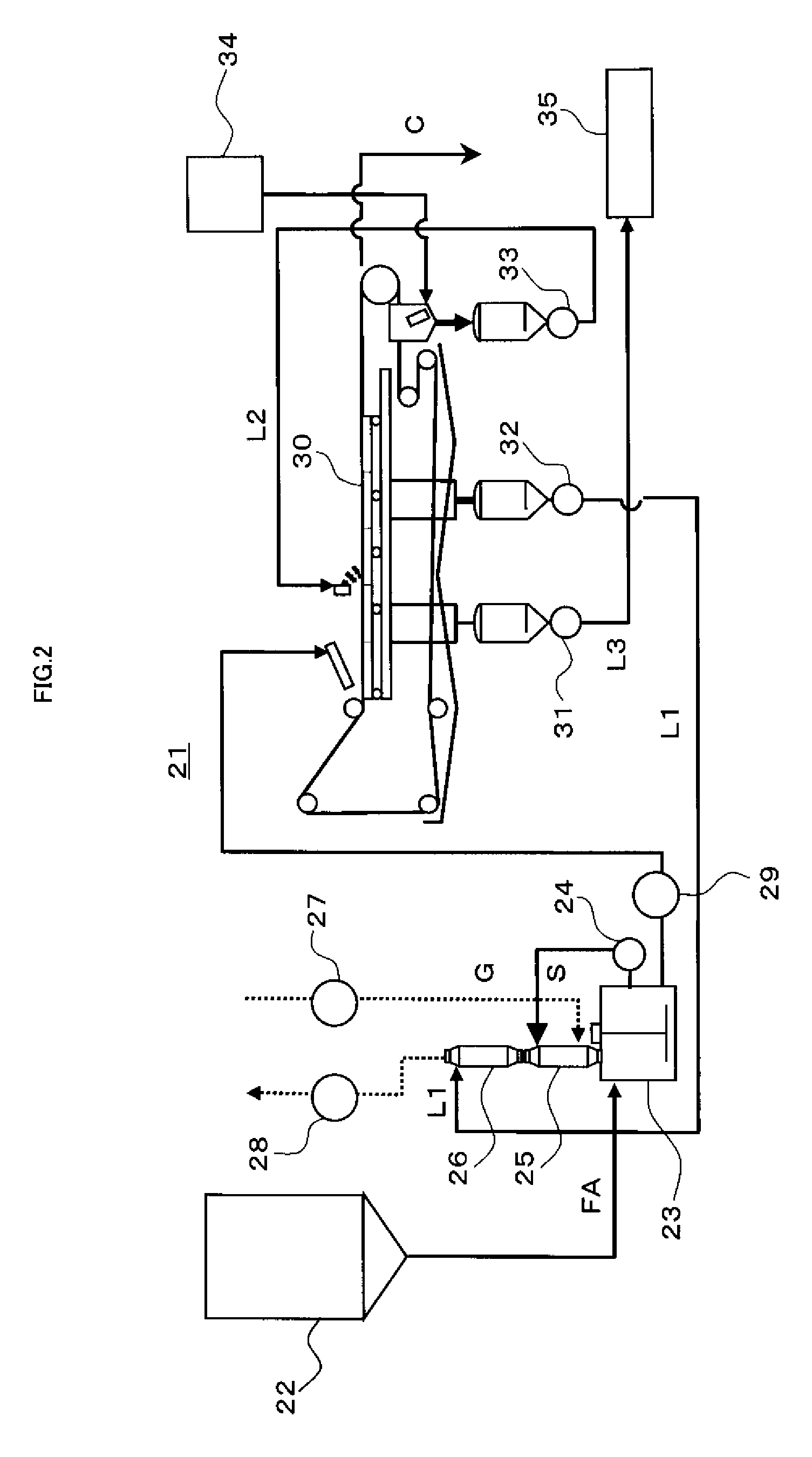
Apparatus and method for dissolution reaction
InactiveUS20100006008A1Easy to cleanConvenience to workGaseous chemical processesGas treatmentCounter flowDissolution reaction
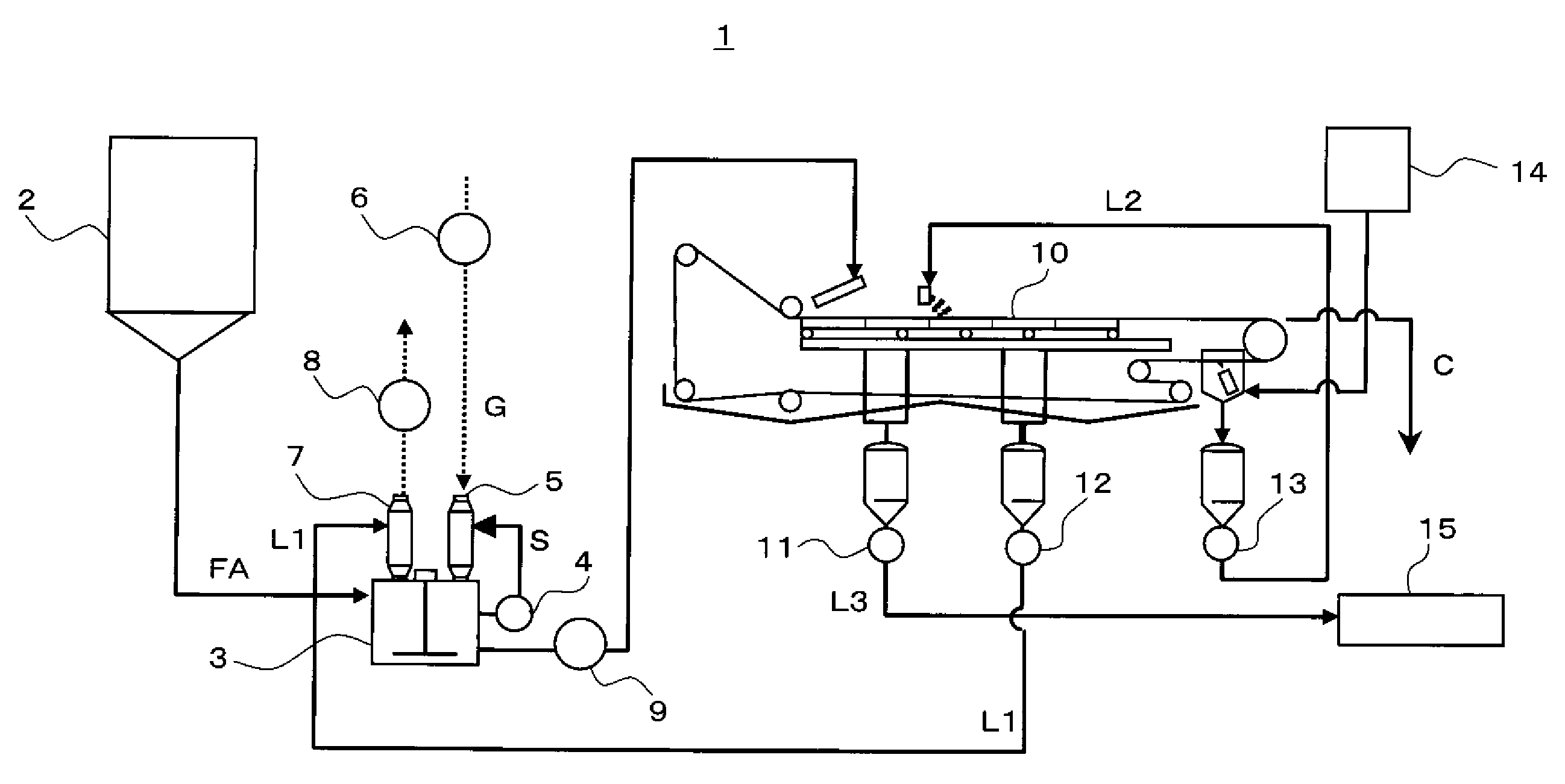
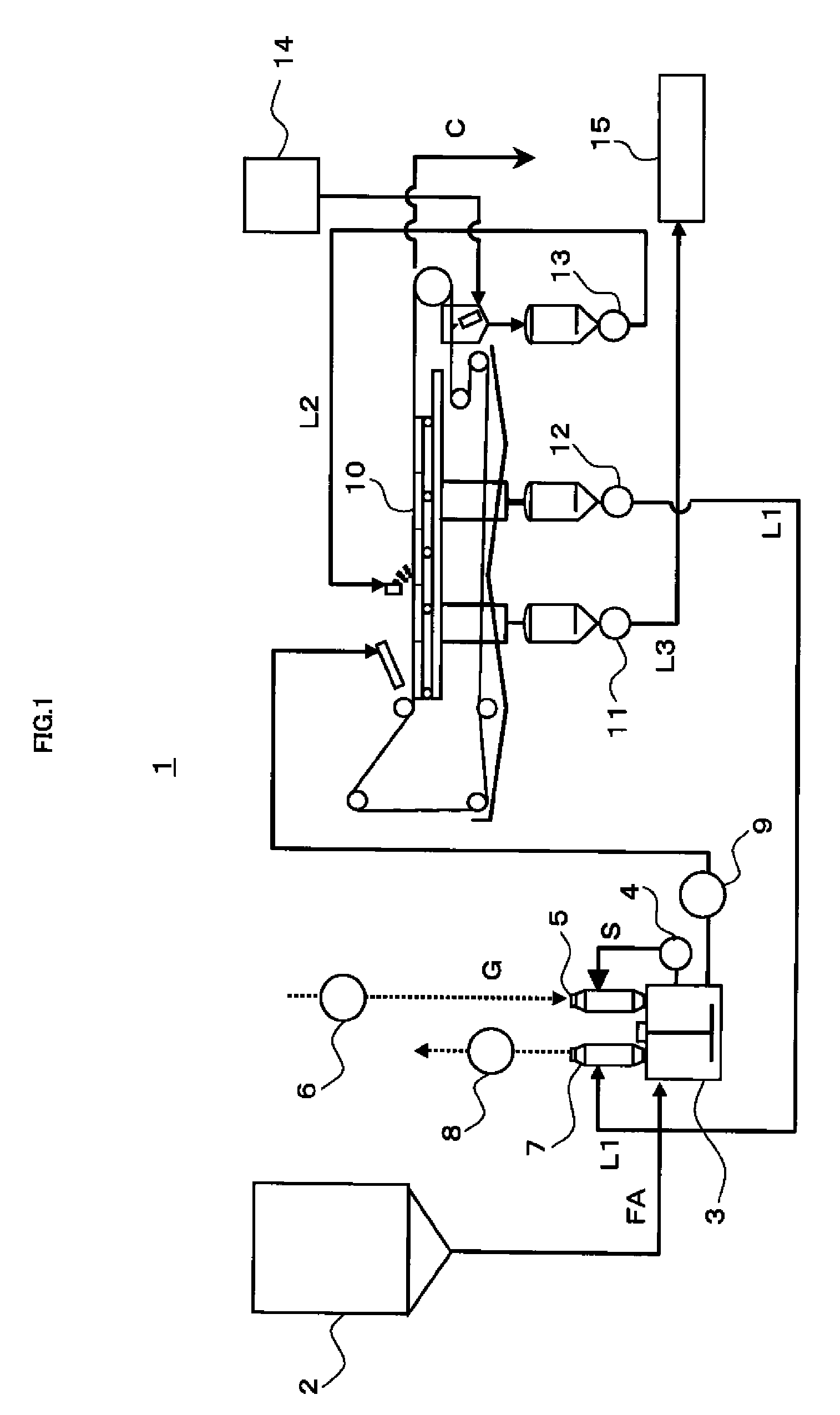
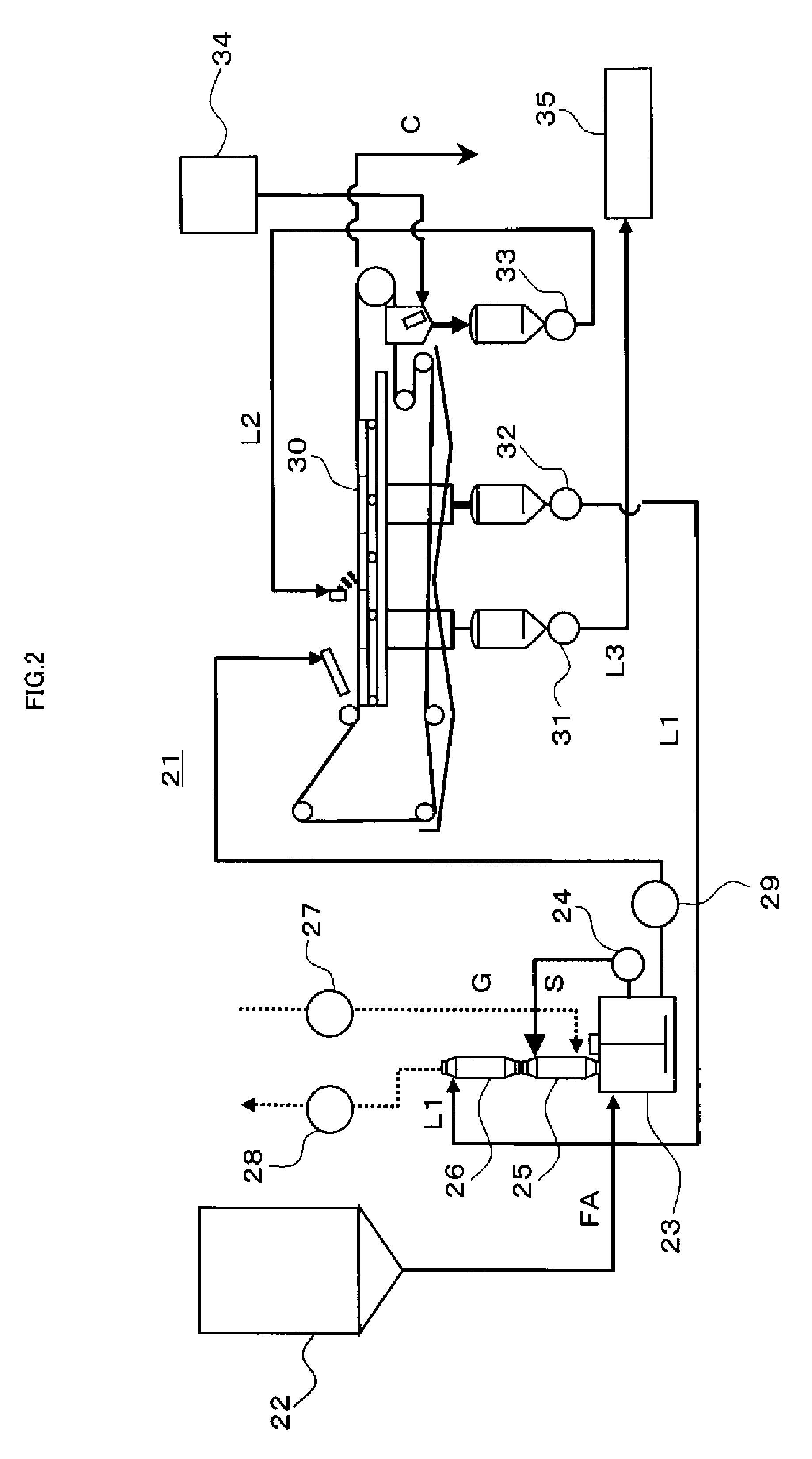
When fly ash is added to a cement kiln to materialize it after being desalinated by washing, scale is prevented from growing in a dissolution reaction apparatus depositing calcium-containing compounds dissolved in slurry, and the fly ash is effectively used as a cement material. A dissolution reaction apparatus according to the invention comprises: a dissolution tub 3 for dissolving powder material, a wet dust collector 5 for collecting powder material and mist while reacting slurry S in the dissolution tub 3 with gas G and returning the collected powder material and mist to the dissolution tub 3. A second wet dust collector 7 can be provided for collecting powder material and the like accompanying to the gas G discharged from the wet dust collector 5, and both the wet dust collectors 5, 7 can be vertical type and mounted independently with each other on the dissolution tub 3. The slurry S and the gas G can react with each other with parallel flow by feeding the slurry S and the gas G to an upper portion of the first wet dust collector 5, or the powder material and the like accompanying to the gas G may be collected with counter flow by feeding the gas G discharged from the dissolution tub 3 to a lower portion of the second wet dust collector 7.
Owner:TAIHEIYO CEMENT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com