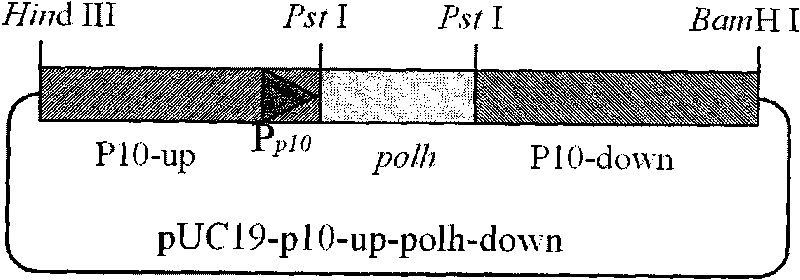Patents
Literature
230 results about "Culture bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A bacterial culture is a cultivated colony of bacteria grown in a lab for a variety of purposes, ranging from patient diagnosis to scientific research.
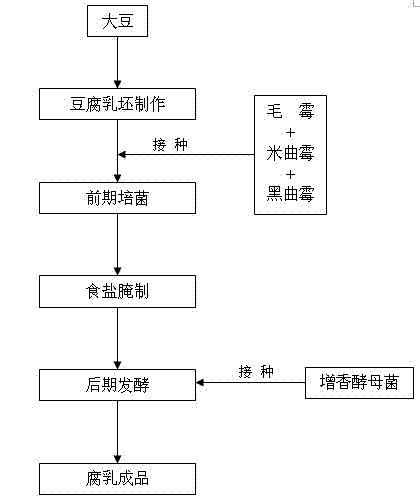
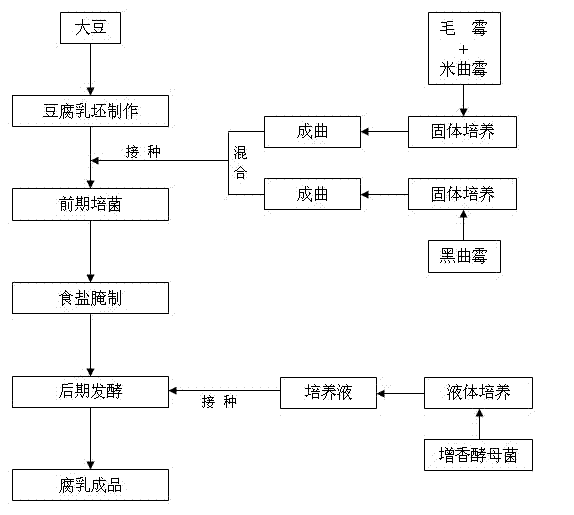
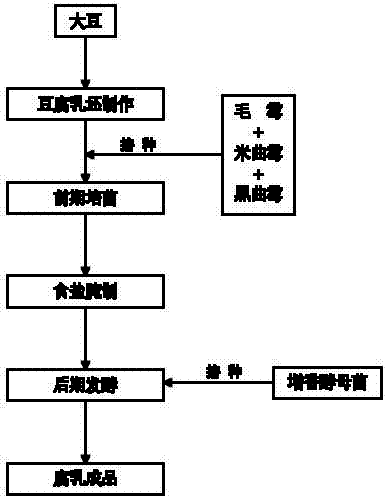
Method for producing fermented bean curd through multi-strain mixed fermentation
ActiveCN102197847APromote decompositionRich flavorCheese manufactureFood scienceYeastAspergillus oryzae
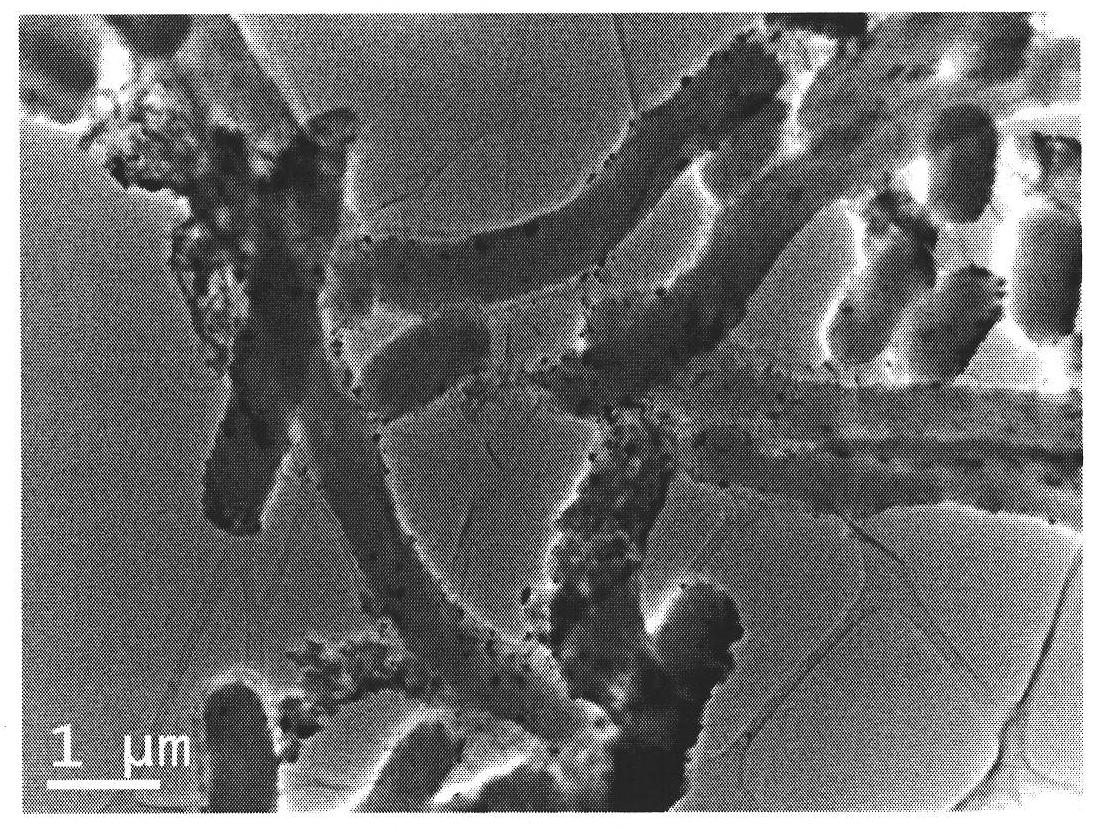
The invention discloses a method for producing fermented bean curd through multi-strain mixed fermentation. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing raw fermented bean curd, namely preparing the raw fermented bean curd from soybean; (2) culturing bacteria at the early stage, namely inoculating mixed strains comprising mucor, Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus niger into the raw fermented bean curd to culture bacteria at the early stage to obtain the fermented bean curd blanks; (3) pickling by using salt, namely placing the fermented bean curd blanks obtained in the step (2) into a rubber box, scattering salt layer by layer, and pickling with the salt to prepare salty blanks; (4) fermenting at the later stage, namely placing the pickled fermented bean curd salty blanks into a bottle, inoculating flavor-increasing yeast into wine liquid of semifinished products, and fermenting at the later stage; and (5) obtaining the fermented bean curd. By the method, the flavor of the fermented bean curd products can be enriched and the fermenting period of the fermented bean curd is shortened.
Owner:GUANGDONG CHUBANG FOOD
Method for recovering cement-based material crack by means of microorganism, culture fluid and repair nutrient fluid
ActiveCN101302484AImprove volume stabilityIncreased durabilityBacteriaBuilding repairsCulture fluidNutrient solution
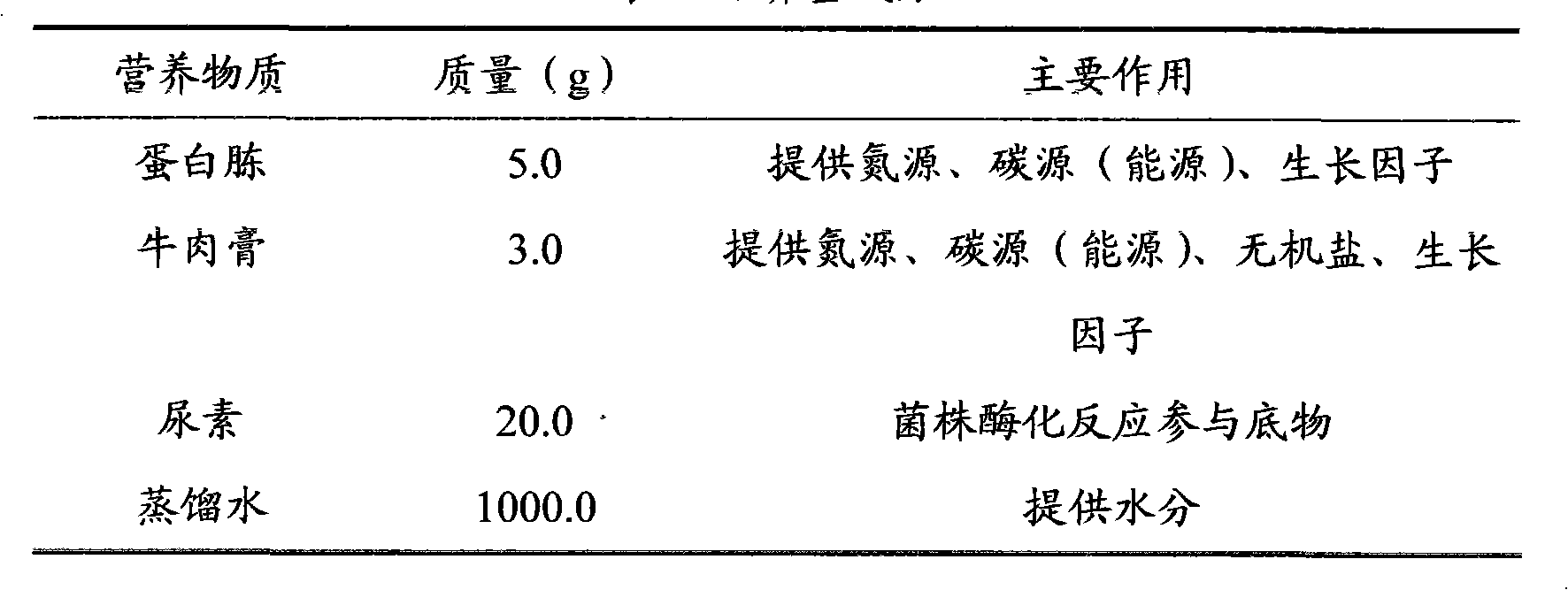
The invention discloses a method for repairing cement-based material cracks, as well as a culture solution and a repair nutrient solution. The method for repairing cement-based material cracks by through microorganisms comprises the following steps that: a Bacillus pasteurii strain is inoculate onto a culture medium provided with a urea-containing substrate; shake cultivation is carried out at a temperature of between 25 and 37 DEG C, and then a culture bacteria solution is taken out and centrifuged and has supernatant fluid removed; strain cells are collected through the culture solution; the concentration of the strain cells is controlled in a range of between 2x10<9> and 1x10<11> cell / ml; standard sand, urea and Ca(NO3)2.4H2O mixture are added to each milliliter of strain cell solution obtained through collection, mixed, stirred into slurry and injected into cement stone cracks; the frequency of the repair nutrient solution injection is not less than two times; finally, maintenance is carried out. In the culture solution, each liter of culture solution contains 4 to 6 g of peptone, 2 to 4 g of beef extract and 20 to 60 g of urea. The method fully utilizes microbial resources in nature; CO3<2-> decomposed out through microbial enzyme can chelate Ca<2+> in a substrate so as to be mineralized and deposit calcium carbonate, and is close in the combination with the substrate and good in stability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
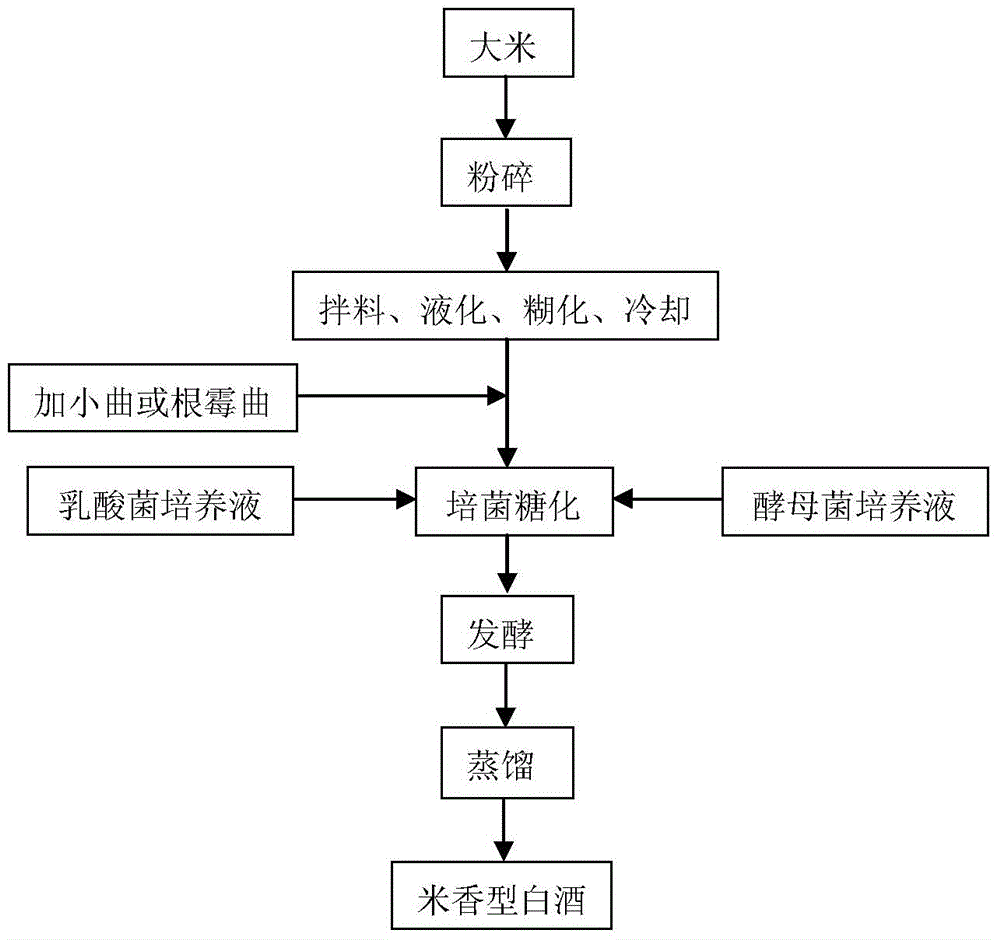
Method for producing rice-flavor liquor based on liquid fermentation
ActiveCN104450399ARealize production mechanizationReduce labor intensityMicroorganism based processesAlcoholic beverage preparationRhizopusFood flavor
The invention discloses a method for producing rice-flavor liquor based on liquid fermentation, belonging to the technical field of liquor brewing. The method comprises the steps of crushing raw materials, liquefying gelatinization, culture saccharification, fermentation and distilling, wherein the step of culture saccharification is carried out under the state of tiny oxygen consumption and comprises cooling a saccharification liquid, adding glucoamylase, and subsequently adding xiaoqu yeast powder or rhizopus yeast, a lactobacillus culture solution and a microzyme culture solution. According to the method, mechanical production of xiaoqu liquor is achieved by cooking liquefaction of starchy grains and then liquid state culture saccharification, and therefore the defect of unstable quality caused by such factors as climate, environment during saccharification of culture bacteria is improved; simultaneously liquor brewing yeasts which are purely cultured and can produce high yield of esters and appropriately low yield of higher alcohols, lactobacillus and a part of commercial enzyme preparations are subjected to synergistic saccharification with conventional saccharification fermentation agents, thereby partially purifying the fermentation system, making up the deficiency of the conventional saccharification fermentation agents and greatly increasing the content of ester substances in rice-flavor liquor; and controlling the content of higher alcohols can remarkably improve the quality of the rice-flavor liquor.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Multielement compound microbe bacterial fertilizer
ActiveCN1970506AThe effect of increasing production is obviousPrecociousBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMarshCulture bacteria
The invention discloses a making method of polyvalent composite microbe fertilizer, which comprises the following steps: culturing bacteria under each fitful culture medium to prepare; allocating ferment culture medium; setting constant volume of ferment tank when the pH value is 7.4; sterilizing; weighing each 10% gel-shaped bacillus and blown-ball Azotobacter to inoculate at 30 deg.c with the ventilation quantity at 1: 0.5; stirring to culture for 12h; weighing 10% thin yellow streptomycete to culture for 10h under the same condition after detecting; culturing 7% huge bacillus and bacillus subtilis for 10h; culturing 10% brewery saccharomycete for 10h; weighing 30% composite bacteria of red coccus, capsula Rhodopseudomonas and marsh capsula Rhodopseudomonas and prunosus red coccus to culture at 30 deg.c for 10h without stirring; being first choice fertilizer to manufacture green pollution-free crop.
Owner:张丽华
Field effect transistor-based antibiotic medicine screening device and antibiotic medicine screening method
InactiveCN102435653AFilter fast cheapReproduce fastMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansManufacturing technologyScreening method
The invention relates to a field effect transistor-based antibiotic medicine screening device and an antibiotic medicine screening method. The field effect transistor-based antibiotic medicine screening device comprises a field effect transistor biochip, a minitype liquid storage tank and a set of electronic detection system. The semiconductor manufacturing technology is utilized to construct a source electrode, a drain electrode and a semiconductor channel between the source electrode and the drain electrode on a silicon substrate, and the channel is subjected to biofunctional modification. Polydimethylsiloxane is then used for constructing the minitype liquid storage tank for culturing bacteria on the channel of the chip, and finally, the source electrode and the drain electrode are connected with the signal detection system. The method can screen antibiotic medicines at high flux, and is an integrated, automated, rapid and cheap antibiotic medicine screening method.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Biological denitrifier and application thereof
ActiveCN101851595AHigh ammonia nitrogen removal capacityQuick conversionBacteriaWater contaminantsBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a biological denitrifier and application thereof. The biological denitrifier is a strain of bacillus subtilis, named bacillus subtilis CPU BS-1, and preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center in March, 17th, 2010 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.3668. The invention also discloses a method for culturing bacteria with denitrification biological activity and application thereof in degrading nitrogen in a water body.
Owner:南京曜动节能环保科技有限公司 +1
Whole-process autotrophic nitrogen removal method and device
InactiveCN103288213APromote rapid formationIncreased chance of collisionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNitrationTotal nitrogen
The invention discloses a whole-process autotrophic nitrogen removal method. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) inoculating anammox sludge into a reactor; 2) introducing nitrogen into the wastewater so as to reduce the DO (Dissolved Oxygen) concentration of wastewater to 0mg / L (milligram per liter) by filling nitrogen into the wastewater, and regulating the pH value of a water inflow barrel to reach 7 to 8; 3) gradually increasing the water inflow load by increasing the total nitrogen concentration of the wastewater and reducing the hydraulic retention time; 4) gradually increasing the DO concentration in the wastewater after a reaction is stable, thereby culturing bacteria capable of consuming oxygen in the reactor; 5) forming the oxygen-containing bacteria on the outer layer of the anammox sludge after performing the culturing acclimatization for half a month; 6) inoculating nitrosobacteria into the reactor and properly lowering the nitrate nitrogen concentration in the inflowing water while performing aeration to the reactor and controlling aeration quantity at the same time, thereby partially converting ammonia nitrogen entering the reactor into the nitrate nitrogen, i.e., the concentration (mg / L) ratio of the ammonia nitrogen to the nitrate nitrogen is 1:1 or so; regulating the pH value in the reactor to reach 7.5 to 7.7 by using a pH controller; 7) gradually increasing the water inflow load, thereby removing the nitrogen stably. The invention further discloses a device for realizing the whole-process autotrophic nitrogen removal method.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Standardized gastrodia elata planting technology
InactiveCN106258879AIncrease productionHigh and stable outputGrowth substratesCulture mediaGastrodiaCulture bacteria
The invention provides a standardized gastrodia elata planting technology, which comprises the following steps of culturing bacteria, selecting seeds, cultivating, pollinating and picking fruits, making a box pool, mixing the bacteria, sowing and harvesting. The standardized gastrodia elata planting technology provided by the invention adopts sexual propagation, and is high and stable in yield and more convenient to operate; local good varieties and nonlocal good varieties are utilized to be hybridized, and better seeds are obtained; the seeds are utilized to be planted, so that commercial gastrodiae and gastrodia seeds with higher yield and better varieties are obtained; a manner of completing sowing in the existing box pool, and then putting the box pool in an excavated sowing hole to complete planting is adopted, so that the operation is more convenient, more normalized and more standardized; a traditional manner of sowing in the field is changed, so that the labor intensity is reduced.
Owner:贵州省仁怀市曹家沟中药材种植专业合作社
Method for producing biodiesel oil and soil regulator using plant waste
InactiveCN101007957AEffective resourcesAbundant resourcesBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBiodieselHydrolysate
The invention relates to agricultural energy field, which in detail relates to a method for producing biodiesel and soil modifier with plant waste. The method comprises following steps: disintegrating plant waste, hydrolyzing with normal enzyme or acid and getting hydrolysate, fermentating with hydrolysate to culture bacteria producing fat; inoculating endotrophic bacteria or probiotics to hydrolytic waste; extracting fat from cultured bacteria, methyl esterification for extracted fat and getting biodiesel; mixing bacteria waste and straw hydrolytic waste inculated with endotrophic bacteria or probiotics and getting soil modifier. The invention maximizes efficent use of capital by making use of straw.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
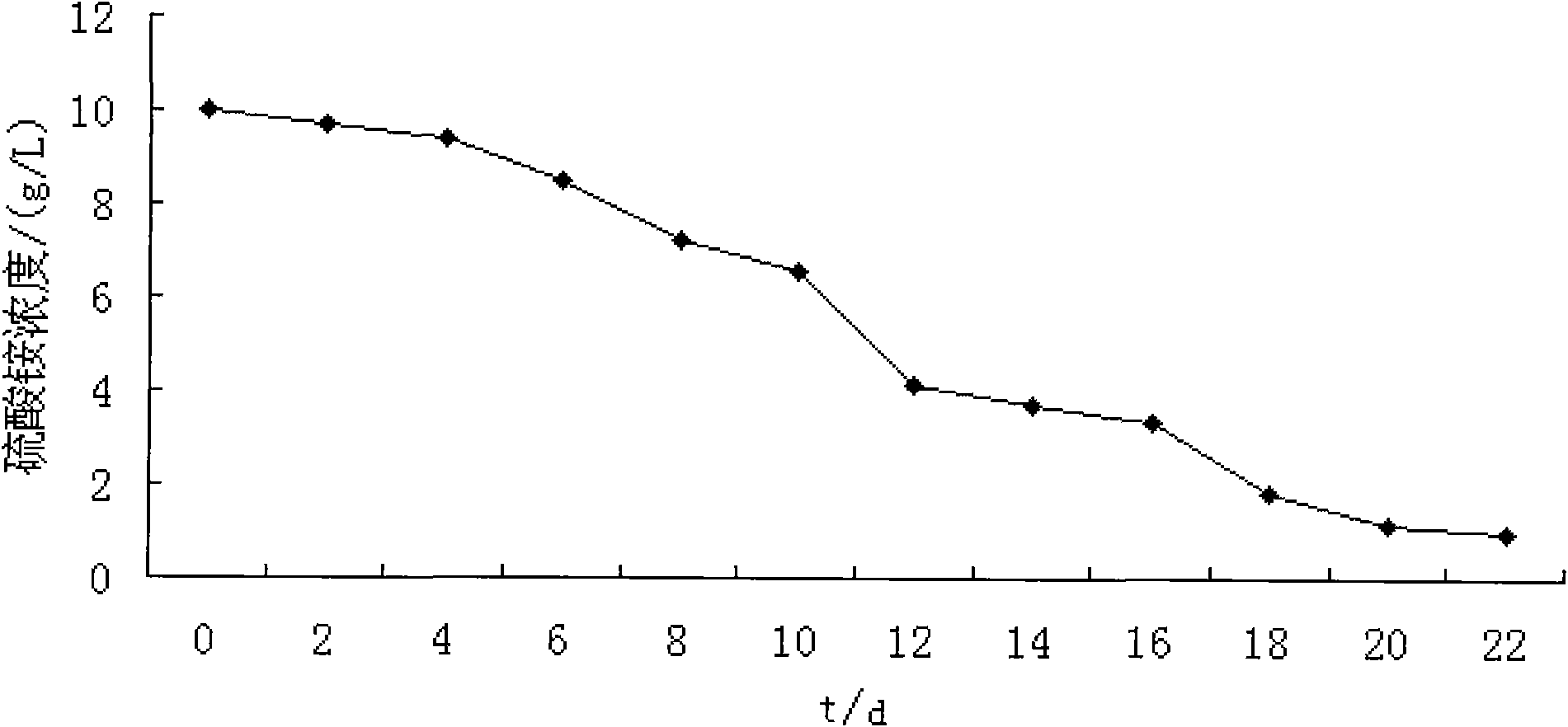
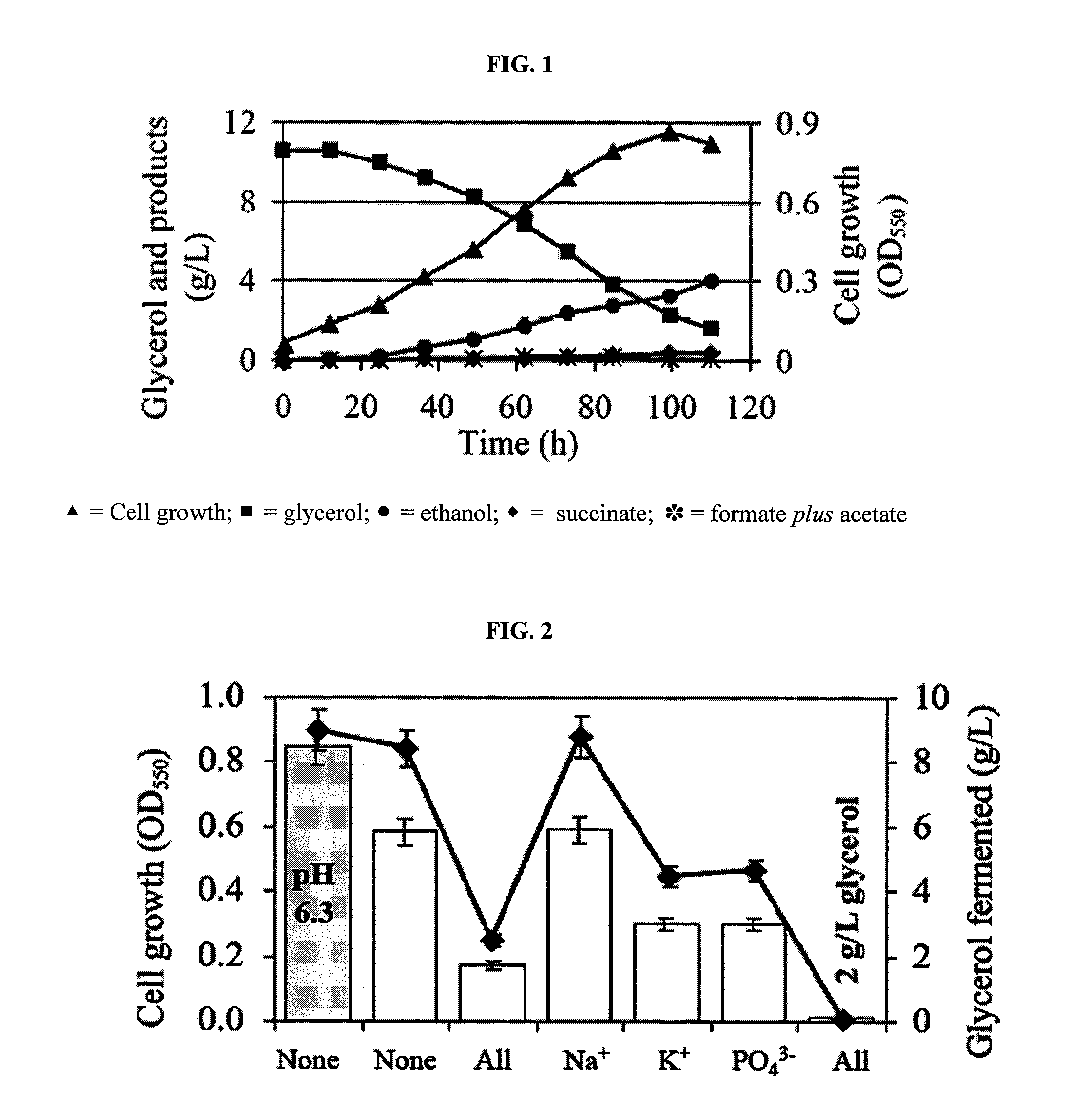
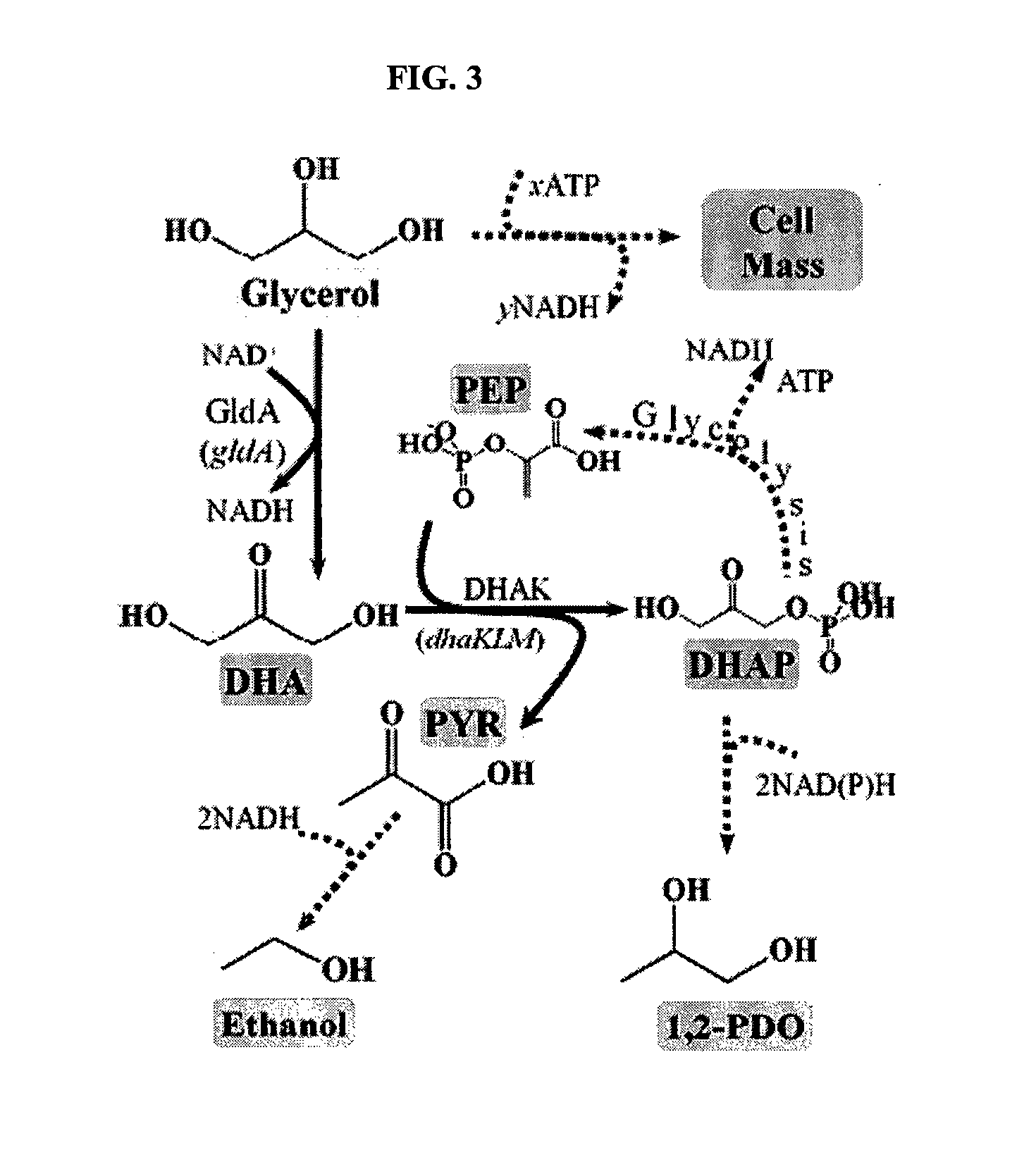
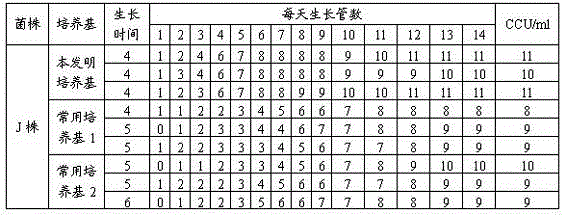
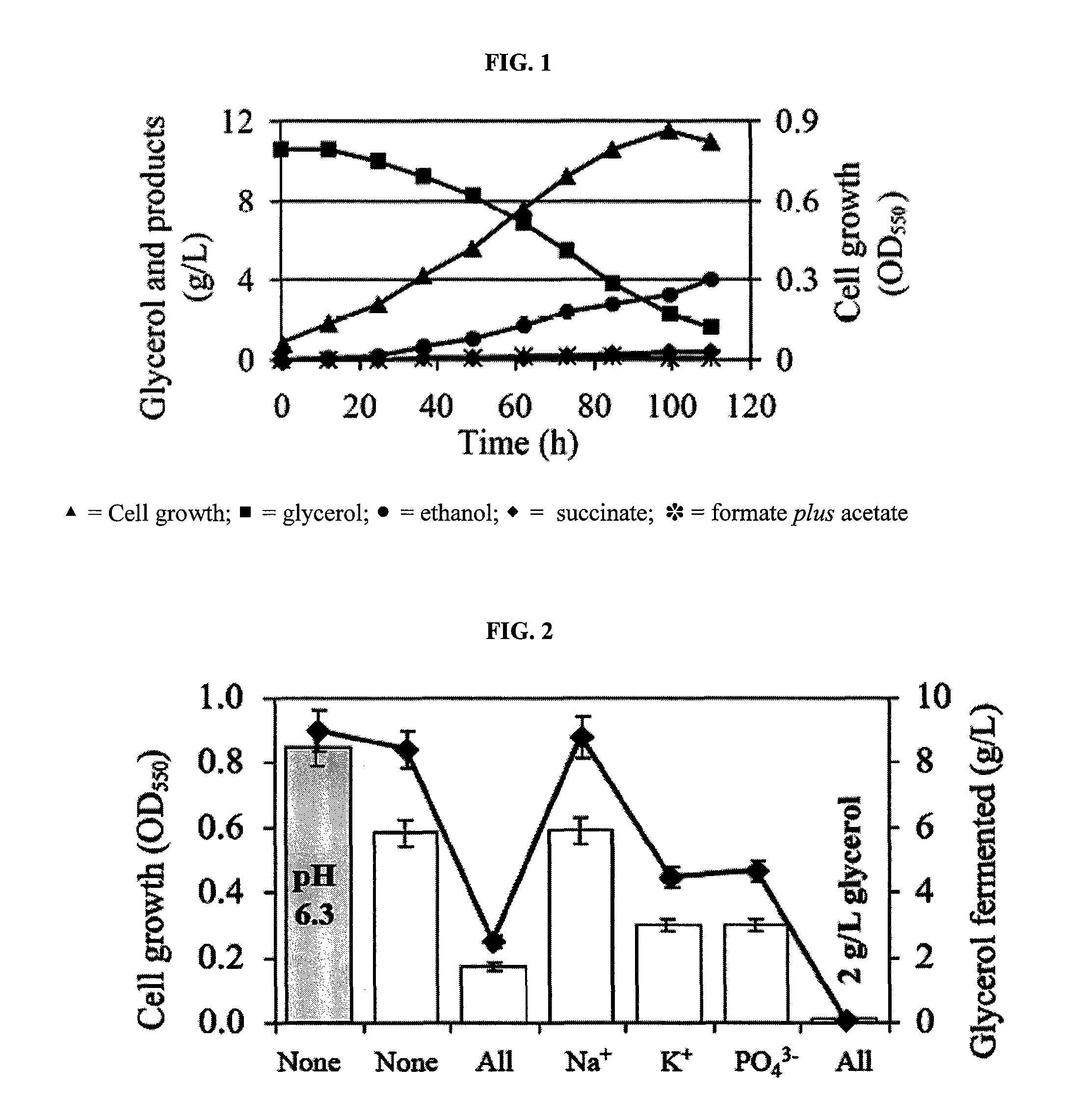
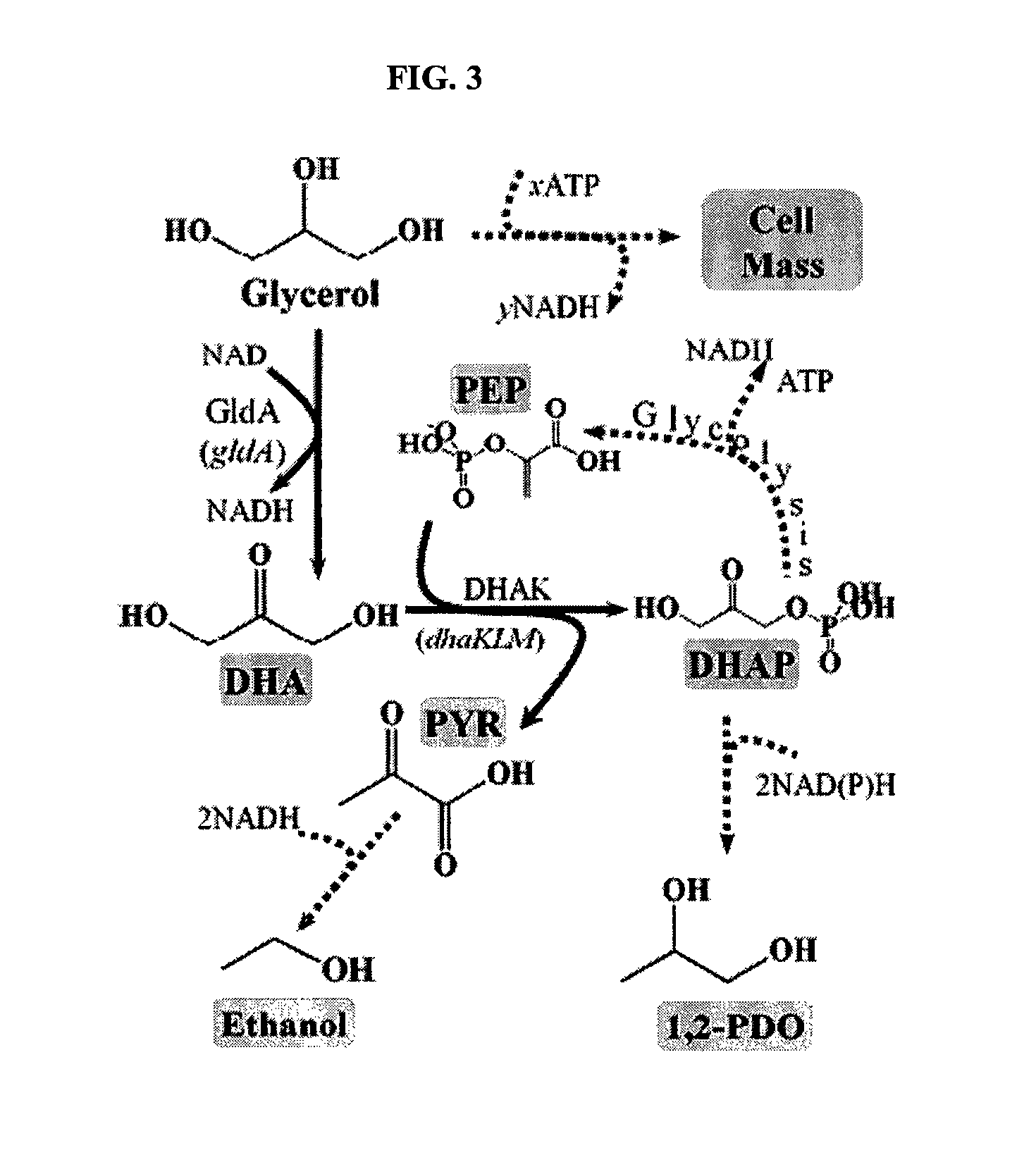
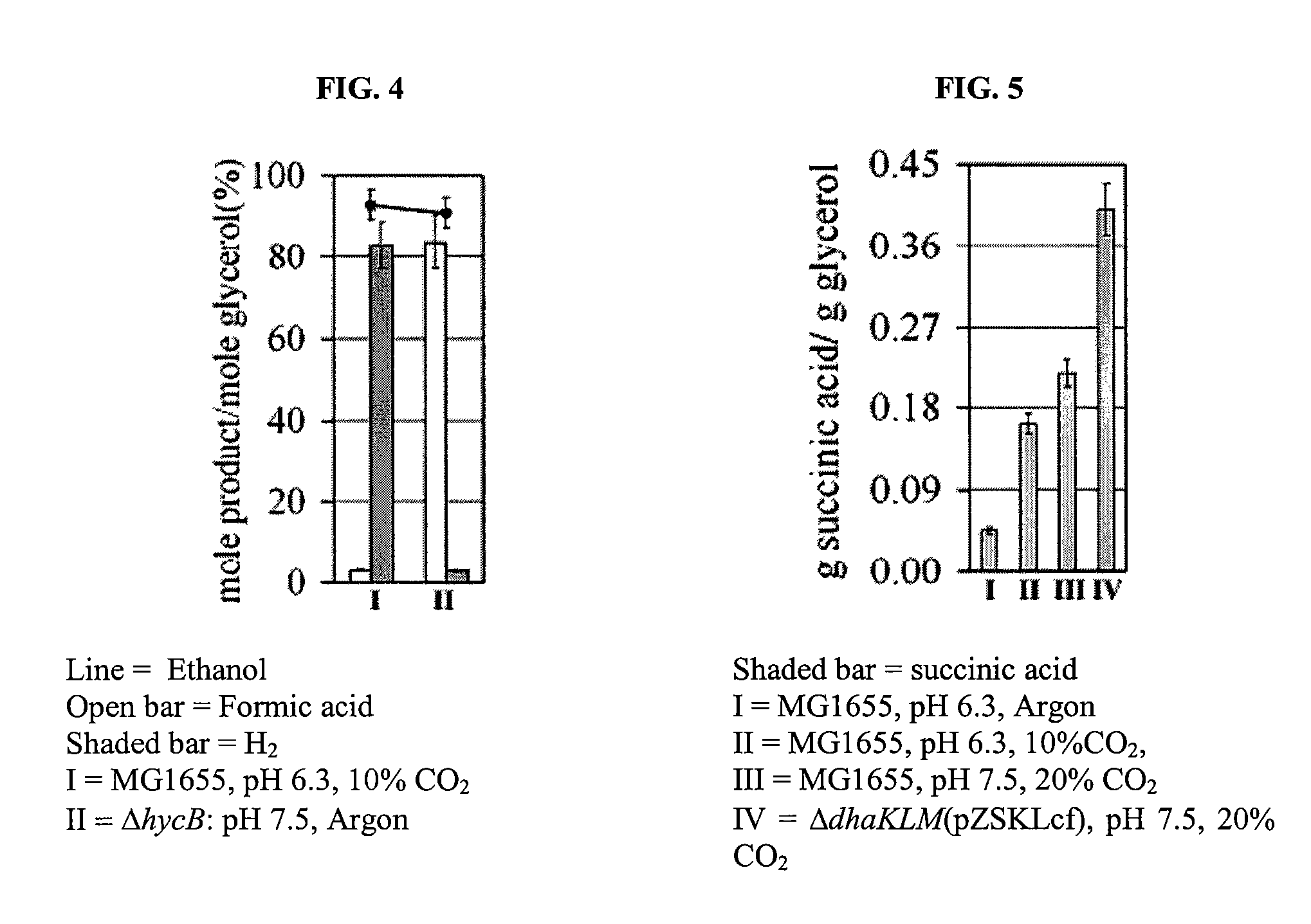
Anaerobic Fermentation of Glycerol
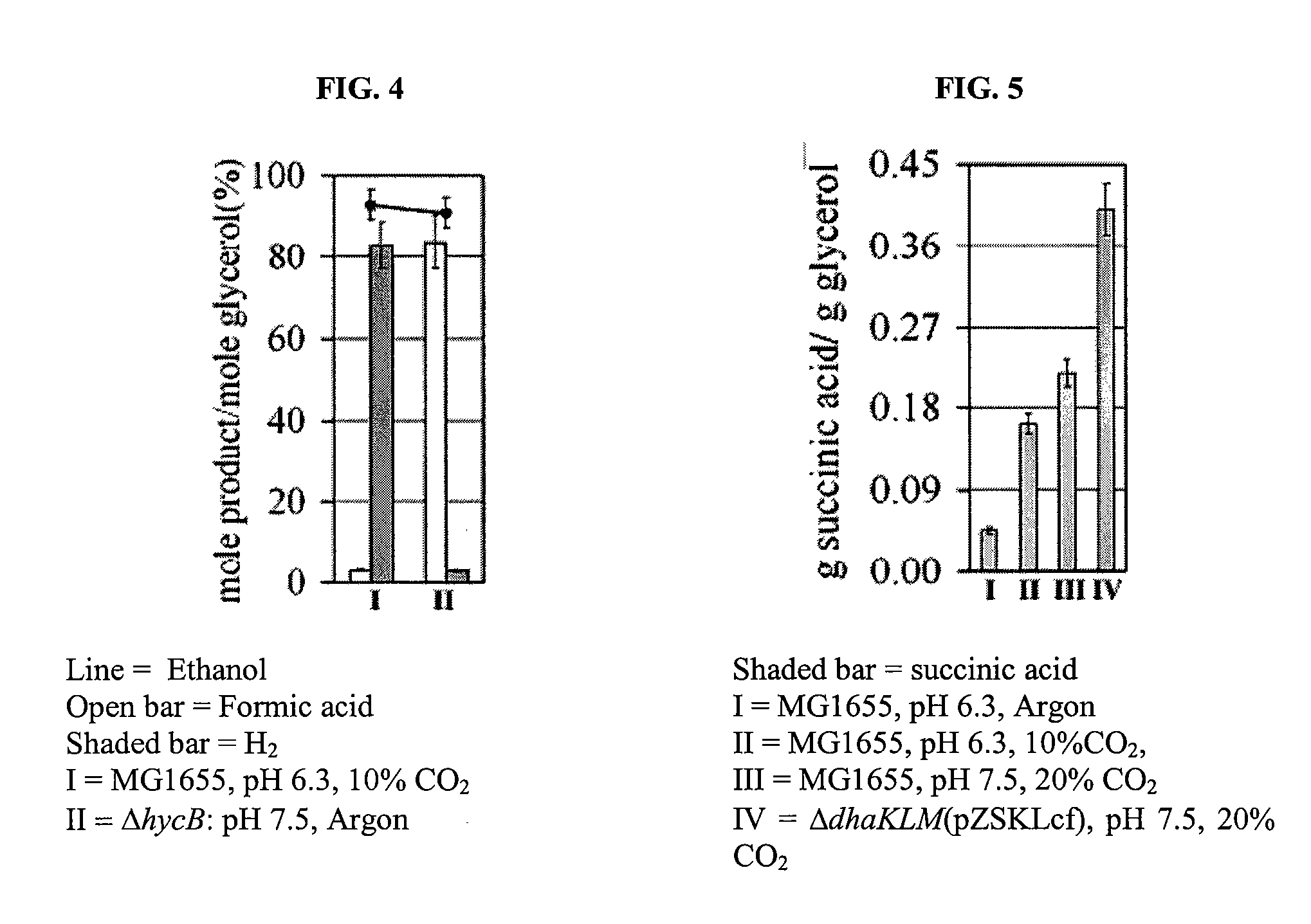
InactiveUS20090186392A1Reduce negative impactImprove filtering effectBiofuelsHybrid cell preparationHigh concentrationBacteroides
The invention relates to the development of appropriate cultivation conditions for a bacteria to grow anaerobically (fermentatively) on a glycerol substrate. The method requires culturing bacteria having a functional 1,2-propanediol pathway and a functional type II glycerol dehydrogenase-dihydroxyacetone kinase pathway in a culture medium containing high concentrations of glycerol, a neutral to mildly acidic pH, low levels of potassium and phosphate, and high levels of CO2, such that glycerol is thus converted into a desirable product, such as ethanol, —hydrogen, formate, succinate, or 1,2-propanediol.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Method of growing bacteria to deliver bioactive compounds to the intestine of ruminants
InactiveUS20080118472A1Solve the lack of resistanceReduce degradationBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesIntestinal structure
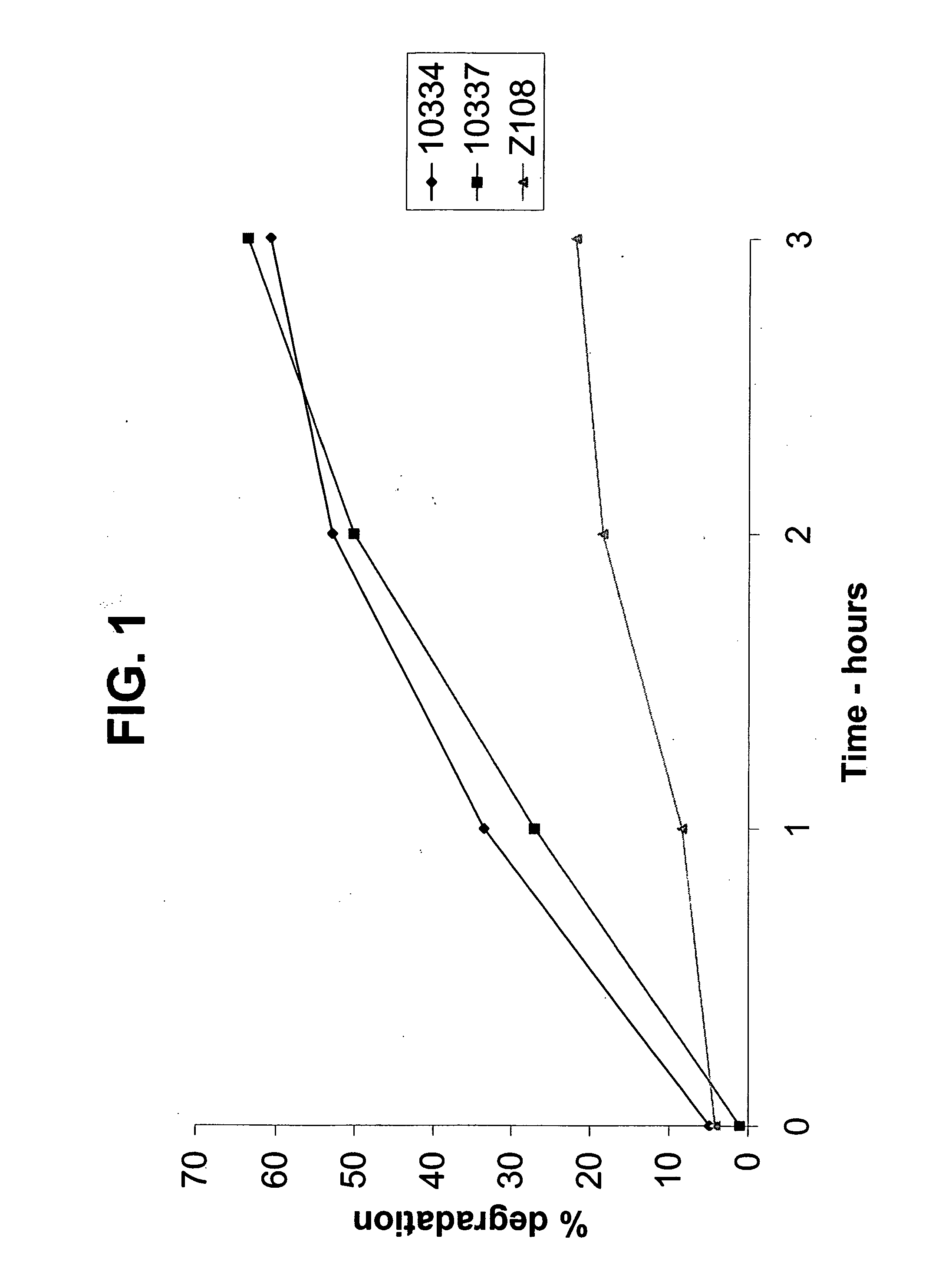
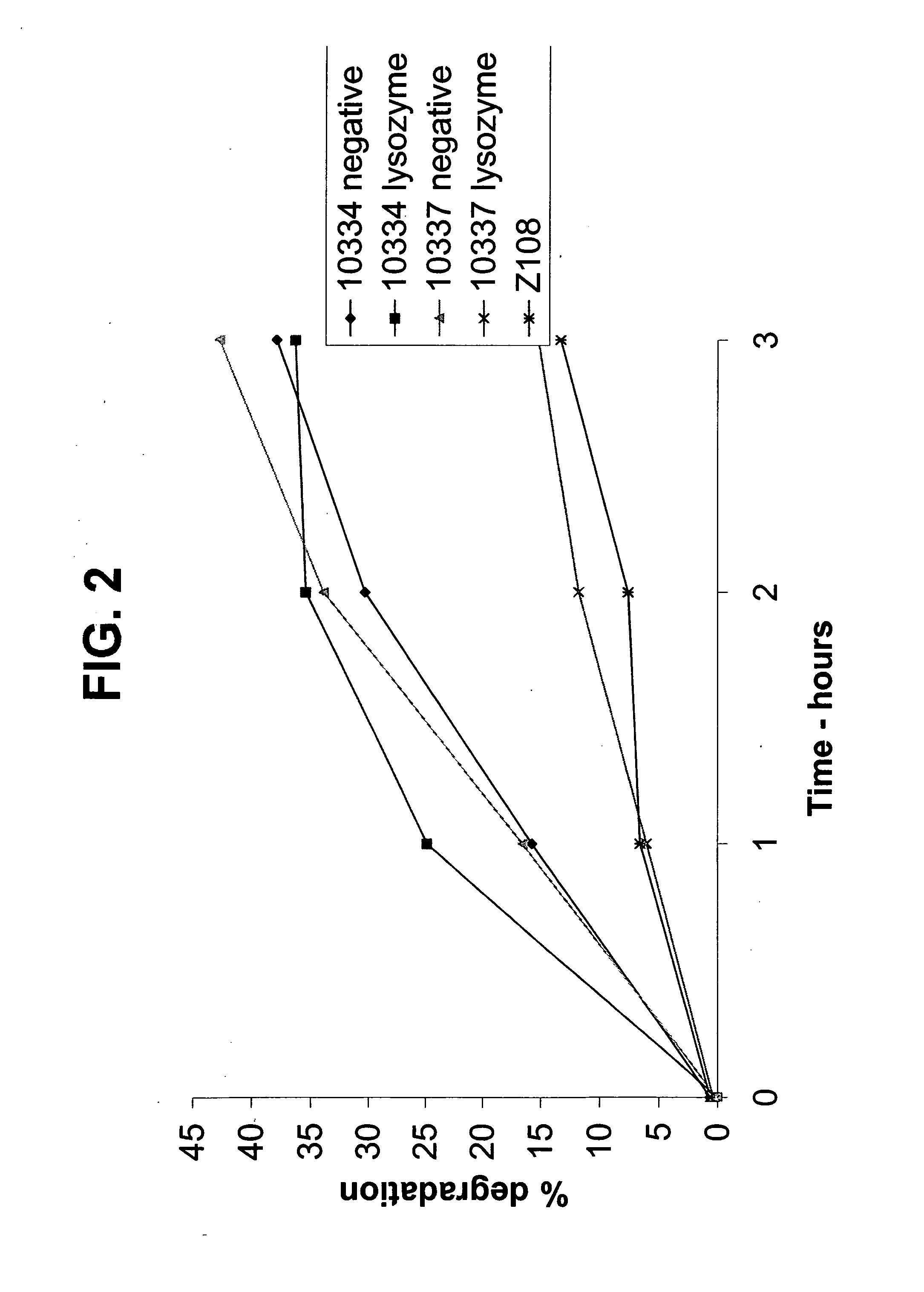
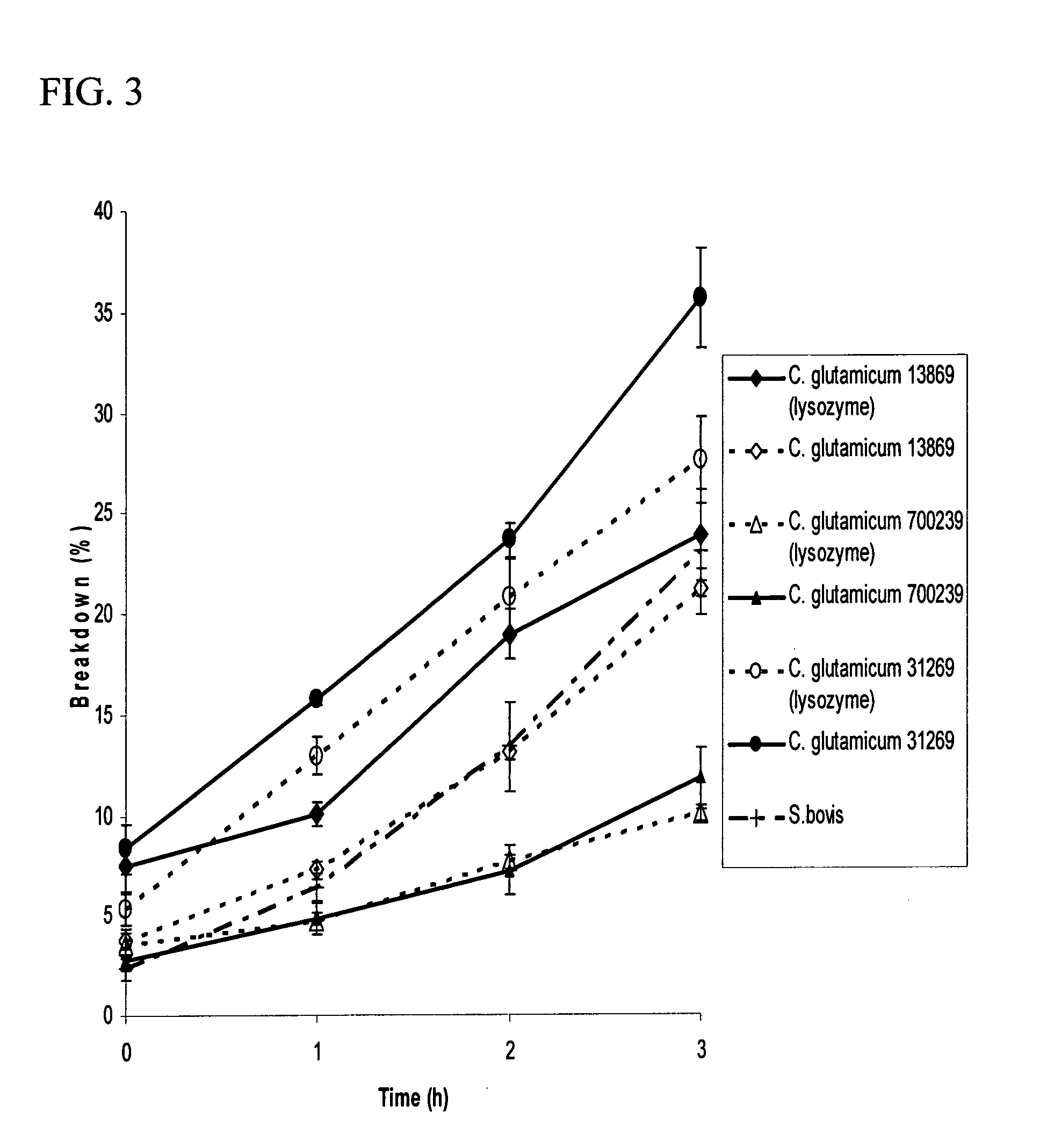
Methods for increasing the resistance to rumen inactivation of a cultured Gram positive bacteria strain useful for gastrointestinal delivery of bioactive compounds to ruminants, which includes the steps of growing a culture of the bacteria strain through at least one passage in a growth medium containing an amount of lysozyme effective to induce the growth of bacterial cell walls resistant to protozoal predation; and recovering the bacteria strain from the lysozyme-containing medium. Rumen-bypass feed supplements produced by the inventive method are also disclosed, as well as methods for supplementing the diet of a ruminant with the rumen bypass feed supplements and an in vitro method for evaluating the resistance of Gram positive bacteria strains to rumen inactivation in vivo.
Owner:SAGE BIOSCI
Bacterial cellulose culture method based on potato waste residue
ActiveCN102337311ASolve the reuse problemLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention relates to a bacterial cellulose culture method which concretely comprises the steps of: inoculating acetobacter xylinum strain in a culture medium for recovery; after recovery, inoculating 2-20% of acetobacter xylinum strain in the culture medium; culturing the inoculated acetobacter xylinum strain by a shaking bed for 2-3 days under the condition of 100-180 rpm; and transferring the obtained fermentation liquor into a shallow tray and culturing for 2-5 days in a static state to obtain bacterial cellulose, wherein the culture temperature is 26-31 DEG C, the culture ventilation amount is 0.3-0.6vvm, and the culture medium is potato culture solution. The culture method has the characteristics that: potato waste residue obtained after starch production is firstly taken as the raw material of the culture medium, is treated by a simplest method and then is used as the culture medium for culturing the bacterial cellulose; the culture medium is low in cost and high in yield; meanwhile, the problem of recycling the potato waste residue can be solved, and the culture time is short; and in addition, the invention provides an important condition for stably culturing the bacterial cellulose in a large scale.
Owner:BEIJING GUANLAN TECH
Serratia marcescens S-JS1 and application thereof
InactiveCN105331566AAvoid or reduce drug resistance problemsBiocideBacteriaMortality rateCulture bacteria
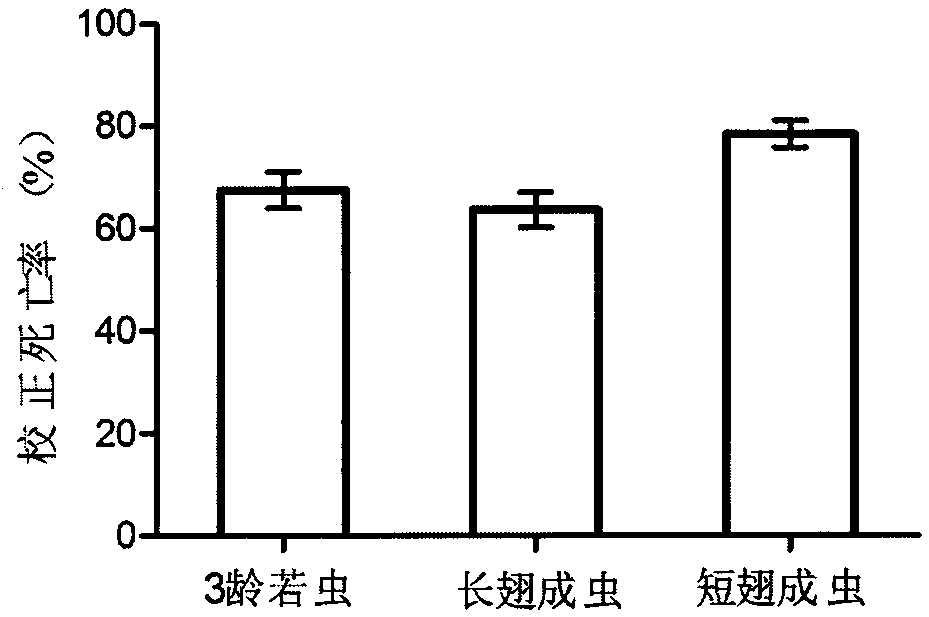
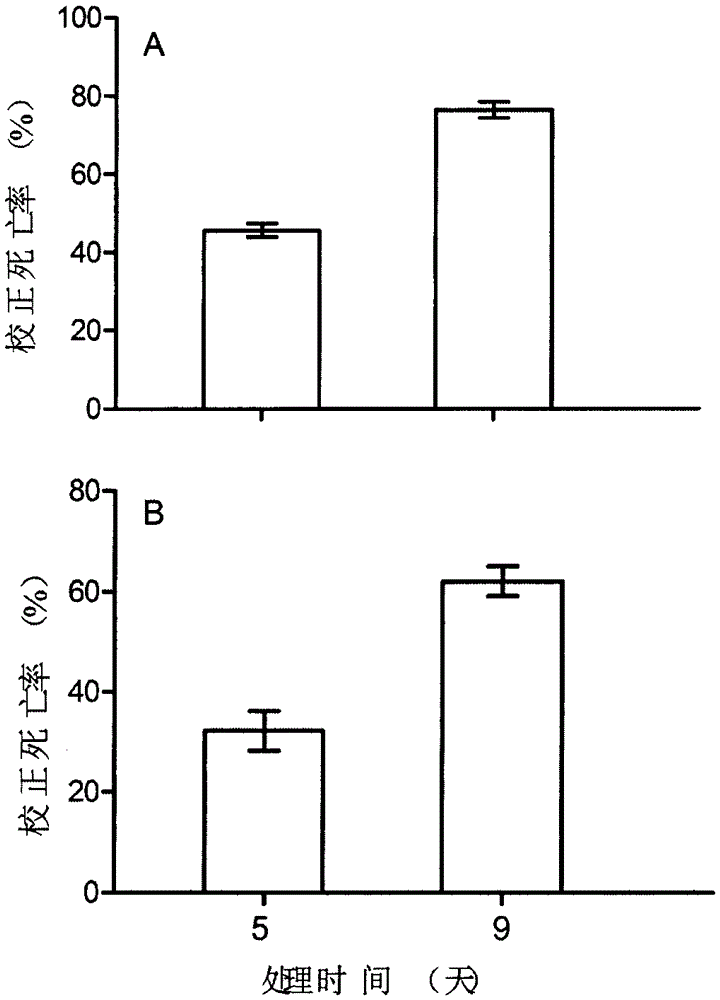
The invention relates to serratia marcescens S-JS1 and application of serratia marcescens S-JS1 in pest control. Serratia marcescens S-JS1 solid culture bacteria or bacterium suspension obtained through fermentation culture can both be applied to prevention and treatment of brown planthopper, beet armyworm and prodenia litura. After bacterium suspension of serratia marcescens S-JS1 is sprayed to brown planthopper, the result shows that the correcting death rates of third-instar nymphs, long-wing adult insects and short-wing adult insects of brown planthopper can reach 67.47%, 63.58% and 78.28% within 5 days respectively through the bacterium suspension with concentration of 8*109 cfu / ml; after 100 micro litters of the strain fermentation liquid with concentration of 108 cfu / ml are added to feed blocks (1*1*1 cm), the correcting death rates of third-instar nymphs of beet armyworm and prodenia litura are 45.64% and 32.20% respectively five days after the nymphs eat the feed blocks; the correcting death rates of third-instar nymphs of beet armyworm and prodenia litura are 76.36% and 62.06% respectively 9 days after the nymphs eat the feed blocks.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
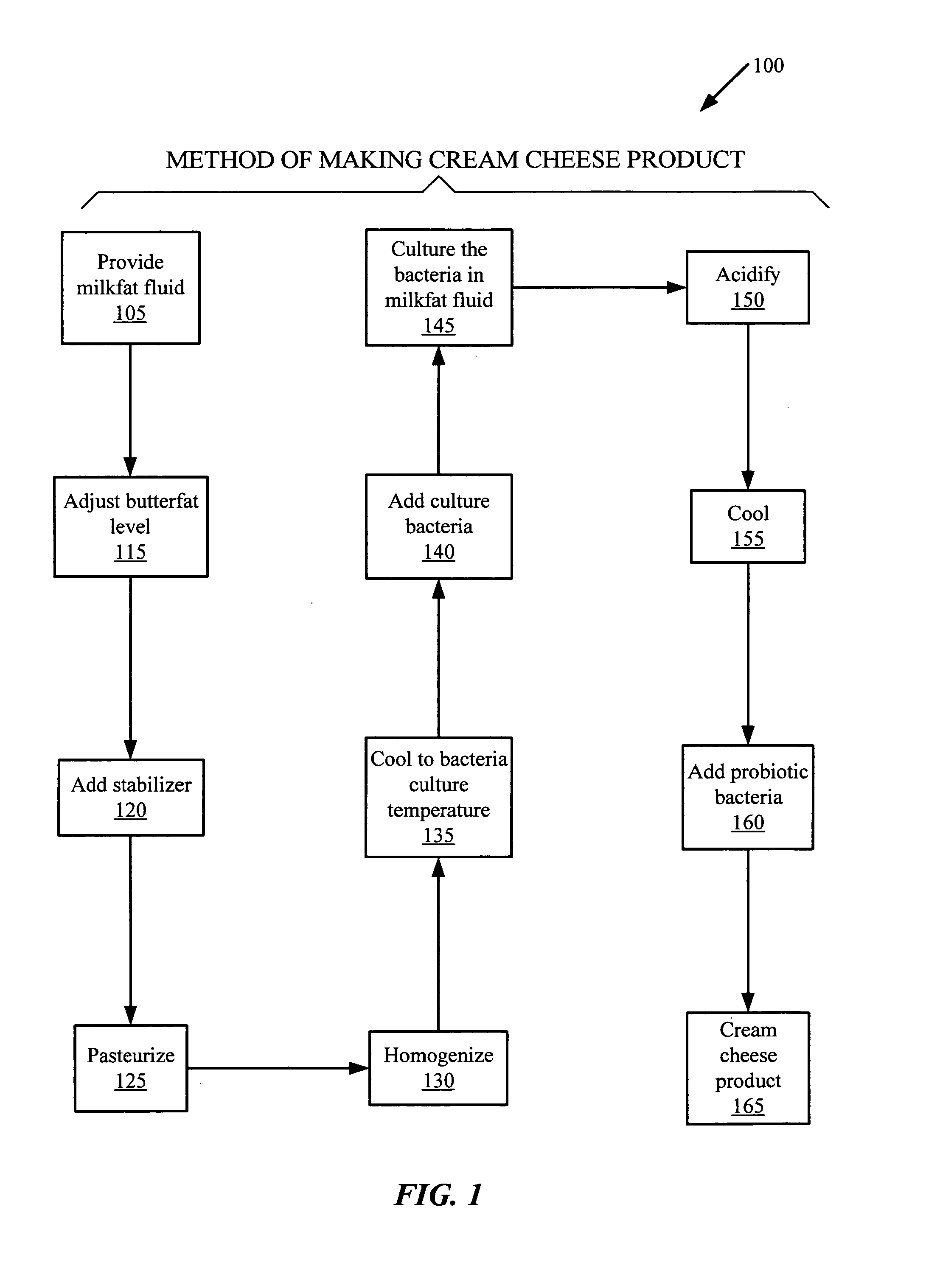
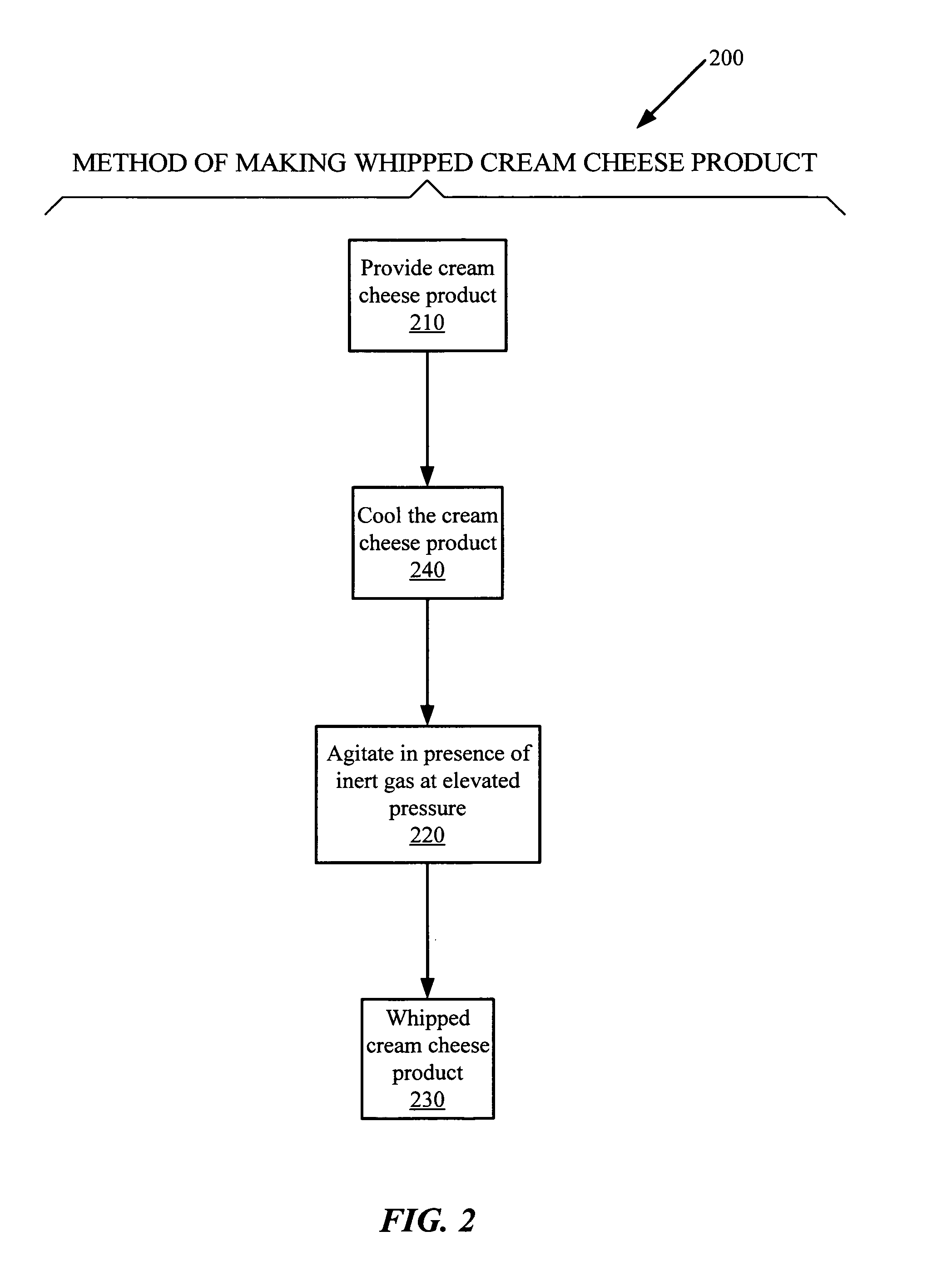
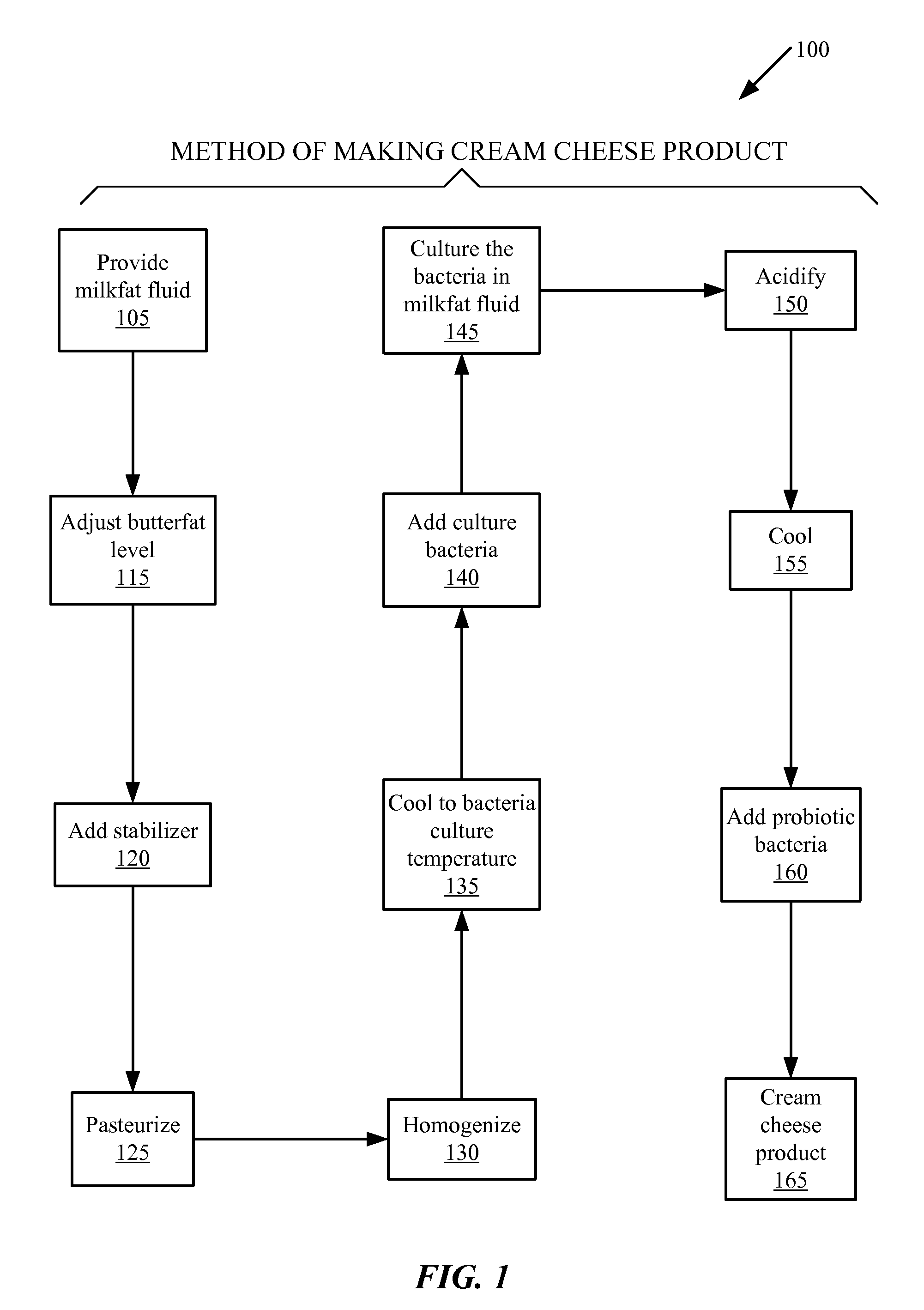
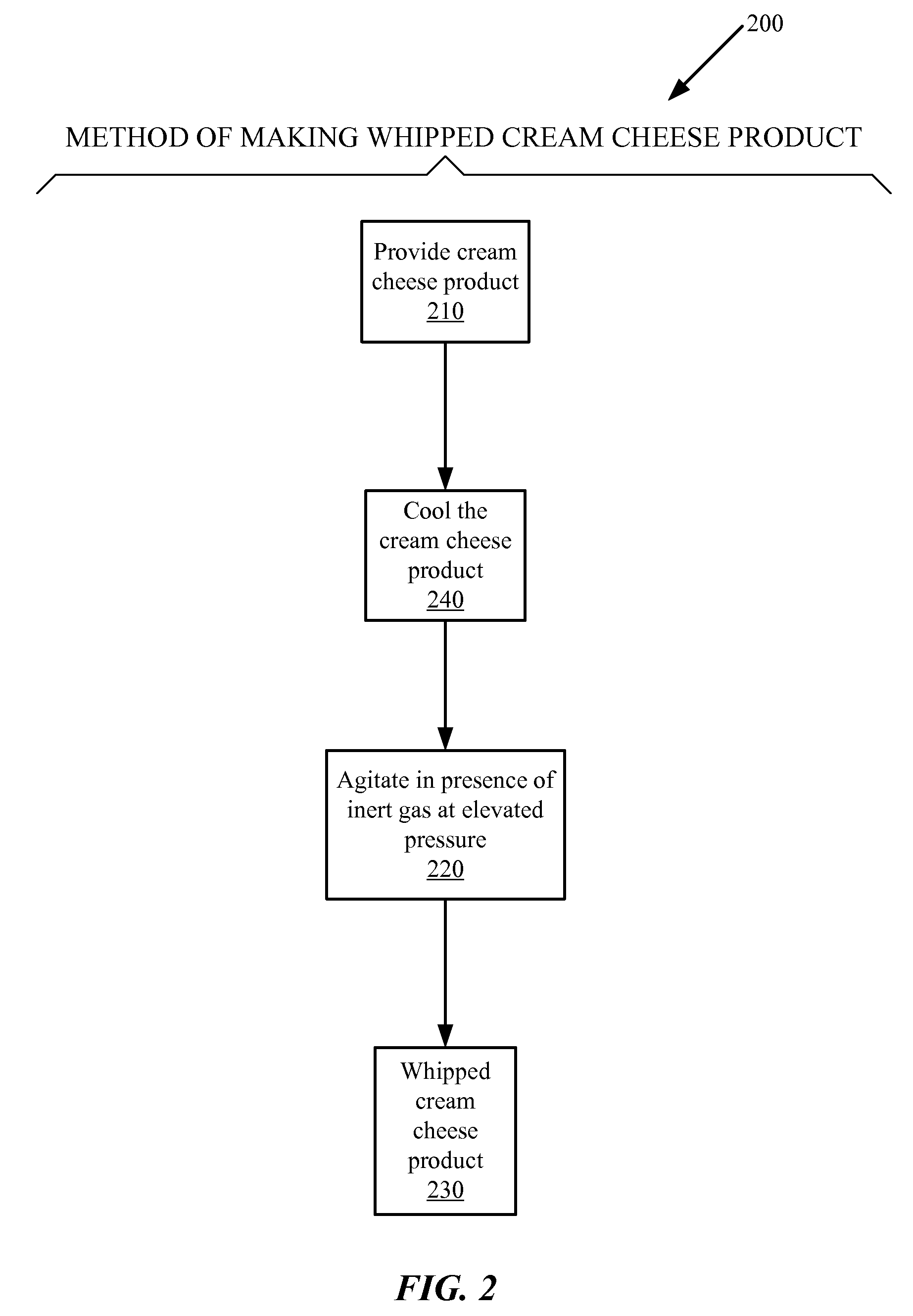
Cream cheese products and methods of making the same
Technique for making a cream cheese product comprising steps of: providing a milkfat fluid comprising butterfat; pasteurizing the milkfat fluid; homogenizing the milkfat fluid; and culturing bacteria in the milkfat fluid; producing a cream cheese product comprising live probiotic bacteria cultures. Cream cheese product comprising: between about 10% by weight and about 55% by weight of total butterfat; and a live probiotic bacteria culture.
Owner:FRLIN FOODS HLDG
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae culture medium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103555641AImprove enduranceReduce apoptosis rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMycoplasma culture
The invention discloses a mycoplasma hyopneumoniae culture medium and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of veterinary biological products. Each 1000 ml of phosphate buffer contains 20-50 g of PPLO (pleuropneumonia-like organism), 2-10 g of yeast powder, 3-15 g of glucose, 0.5-4 ml of 1% phenol red, 2-10 g of amino acid composition, 15-30 g of compound traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharide and 50-100 ml of pig serum. When culturing the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae culture medium disclosed by the invention can improve the tolerance of the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and reduce the apoptosis rate of the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae; the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae culture medium disclosed by the invention can increase the amount of culture bacteria of the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, the concentration of the culture bacteria liquid reaches 10<10-11> / ml, which is increased by more than 5-10 times compared with that of a common culture medium; the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae culture medium disclosed by the invention can inhibit the growth of other bacteria when culturing the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae so as to reduce the culture pollution risk of culturing the mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.
Owner:浙江美保龙生物技术有限公司
Anaerobic fermentation of glycerol
InactiveUS8129157B2Reduce negative impactImprove filtering effectBiofuelsHybrid cell preparationHigh concentrationFormate
The invention relates to the development of appropriate cultivation conditions for a bacteria to grow anaerobically (fermentatively) on a glycerol substrate. The method requires culturing bacteria having a functional 1,2-propanediol pathway and a functional type II glycerol dehydrogenase-dihydroxyacetone kinase pathway in a culture medium containing high concentrations of glycerol, a neutral to mildly acidic pH, low levels of potassium and phosphate, and high levels of CO2, such that glycerol is thus converted into a desirable product, such as ethanol, hydrogen, formate, succinate, or 1,2-propanediol.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Process for processing vegetable wrapped fermented bean curds
The invention relates to a process for processing vegetable wrapped fermented bean curds. The process comprises the following eight processes of: preparing straw, preparing seasonings, preparing vegetable leaves, preparing hawk-tea, preparing bean curd blanks, culturing bacteria, pickling the blanks and putting the blanks into a jar. The process has the advantages that the bacteria are cultured by the isolation of the straw, so that mycelia grow uniformly at the periphery of the bean curd blanks; the bean curd blanks are disinfected and flavored with distilled spirits, and after the seasonings are added into the bean curd blanks, the bean curd blanks are wrapped by the vegetable leaves, so that each bean curd blank is fermented to produce taste in independent space; after being put into the jar, the bean curd blanks are poured into the hawk-tea to be soaked, so that the fermented bean curds have the flavor of the hawk-tea, the quality guarantee period also can be prolonged, and oil which is used at present is replaced. The fermented bean curds produced by the process are fresh in mouthfeel, tender, tasty and refreshing and tasteful in aftertaste, and the fragrance of the fermentedbean curds is refreshing.
Owner:李慈燕
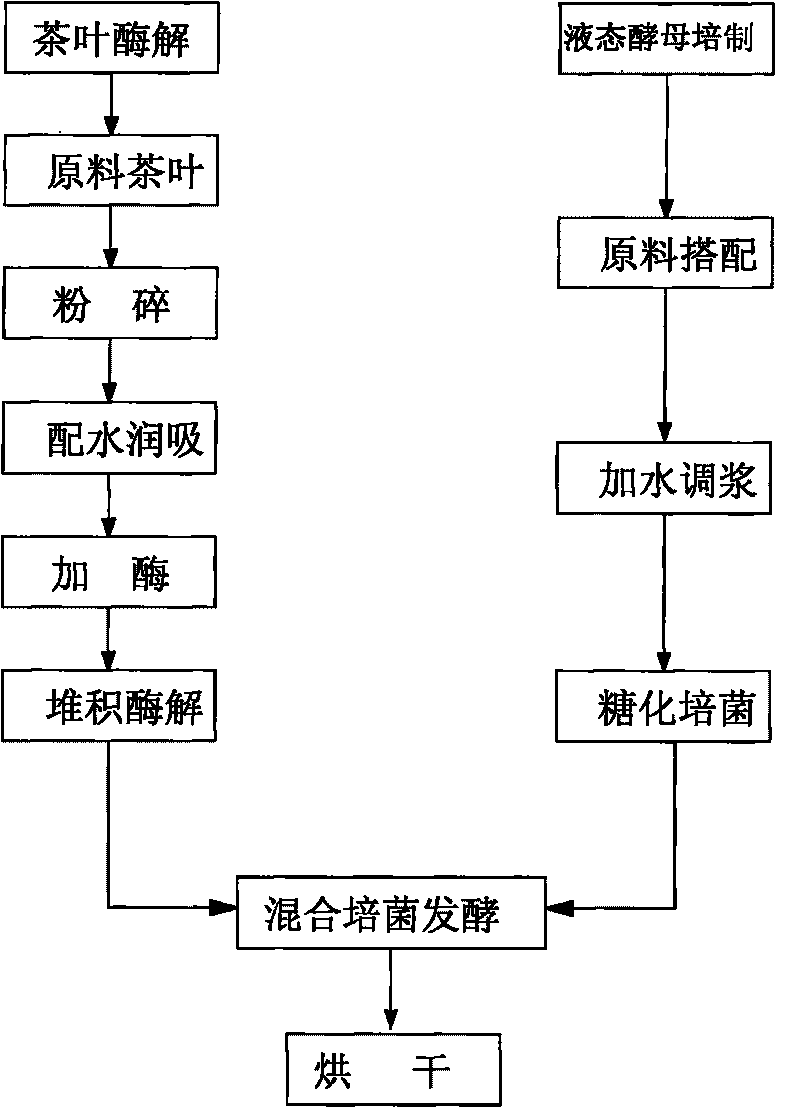
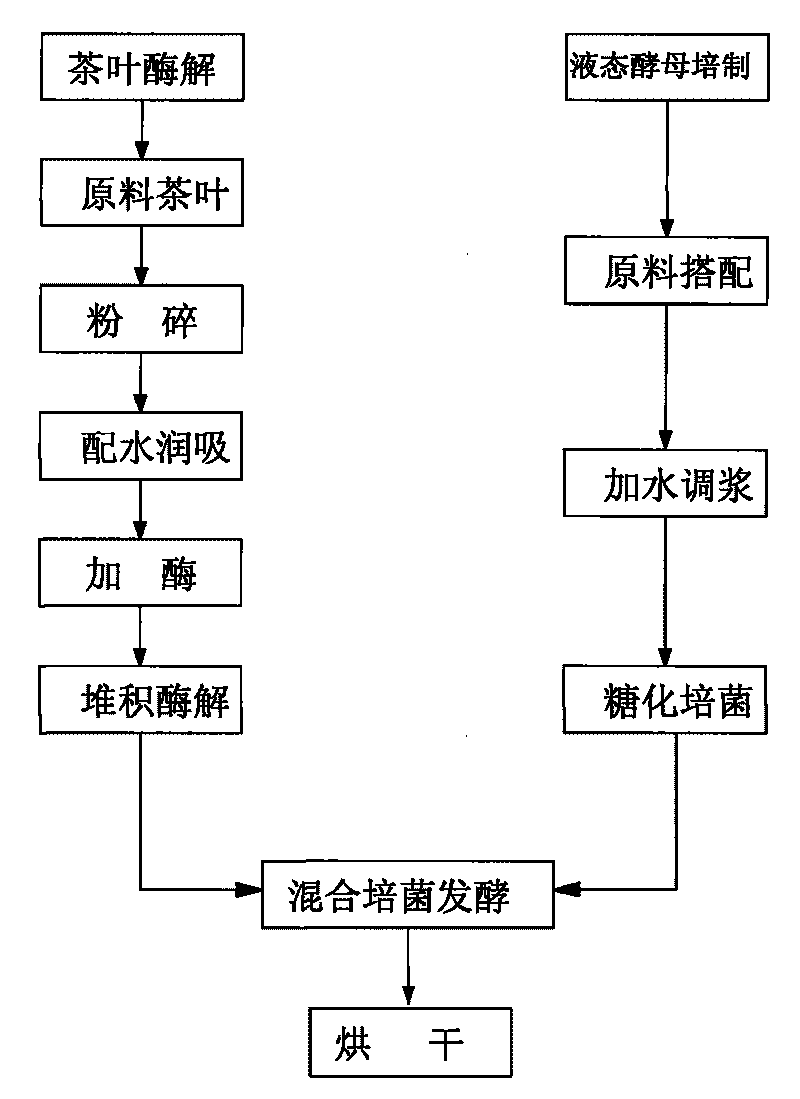
Tea organism mixed feed and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a tea organism mixed feed and a preparation method thereof. After catalyzing enzymolysis and saccharification, tea leaves used as substrate raw materials are matched with liquid yeast culture bacteria to ferment so as to obtain the tea organism mixed feed. The invention has simple process, and the feed prepared from the tea leaves instead of feeding grains is safe and sanitary and contains enriched micro-organism protein and natural tea leave trace elements.
Owner:胡宁华
In-situ environment microbe isolation method and soil source petroleum degrading microbe isolation and screening method
InactiveCN107118966AAchieve isolationAchieve bondageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobial fuel cell
Owner:李宜芳
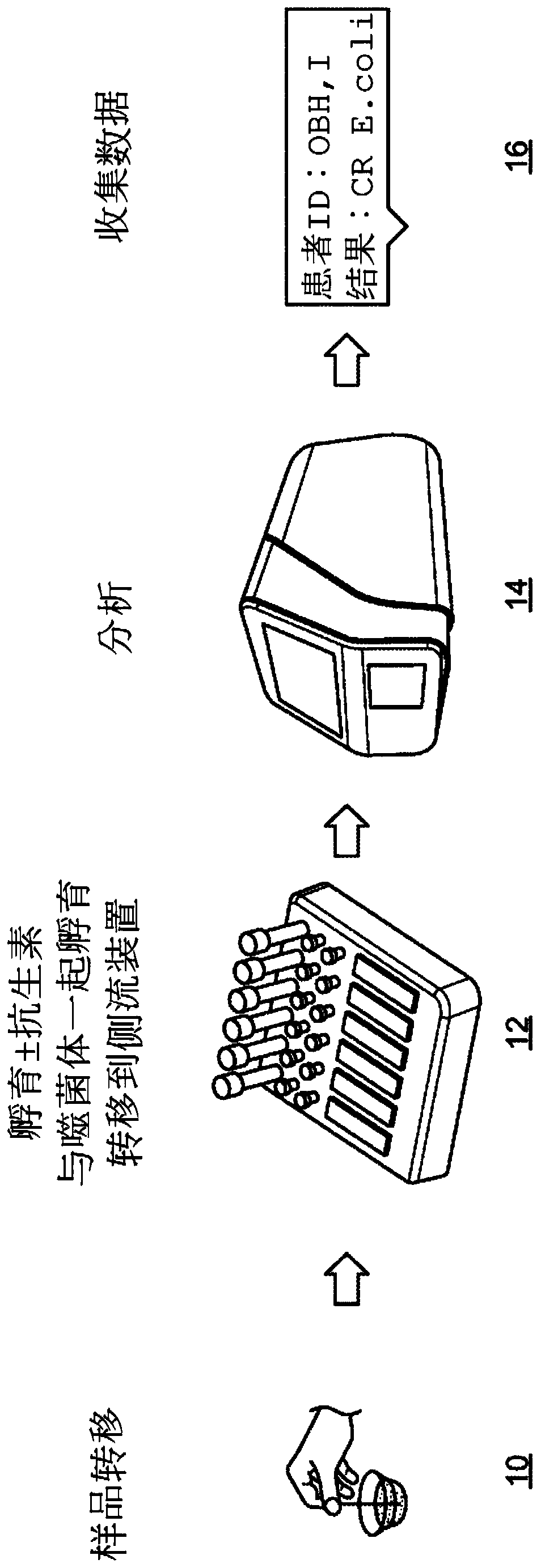
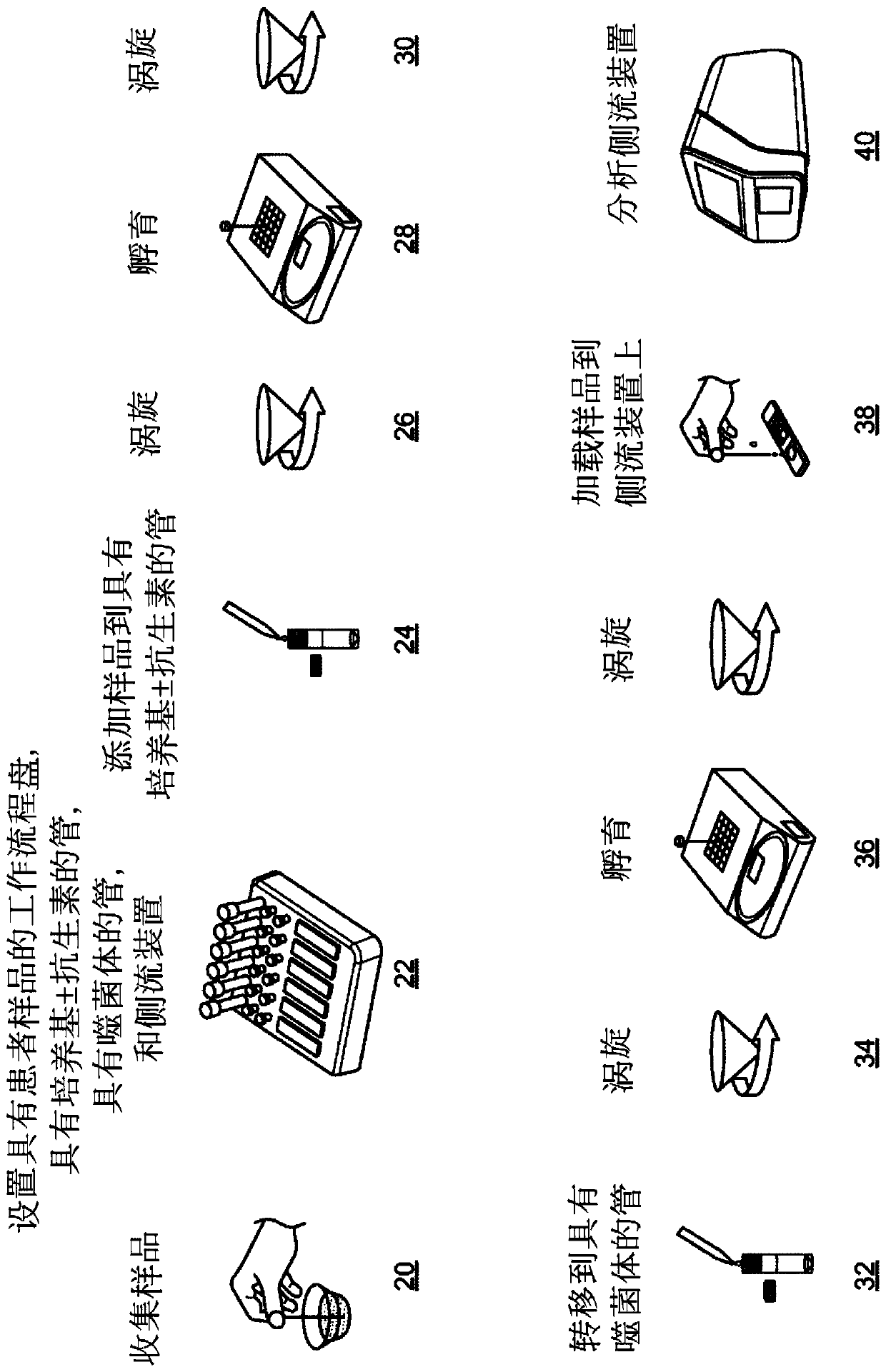
Phage-mediated immunoassay and methods for determining susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotic or probiotic agents
PendingCN111601897AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHeterologousImmune profiling
Methods for determining the susceptibility or resistance of bacteria to antibiotic agents are provided. In one embodiment, the methods include culturing the bacteria in the presence or absence or theantimicrobial agent to generate a primary culture which is then cultured in the presence or absence of transforming phages. The recombinant phages are specific to the bacteria and comprise a heterologous marker (e.g., a nucleic acid that is expressible as a detectable product such as an RNA or a protein). The susceptibility or resistance of the bacteria to the antimicrobial agent may be determinedby assaying the culture for the presence or absence of the heterologous marker, wherein a reduction in the level or activity of the marker in the culture compared to the level or activity of the marker in a comparative culture indicates that the bacteria is sensitive to the antibiotic agent.
Owner:QUIDEL +1
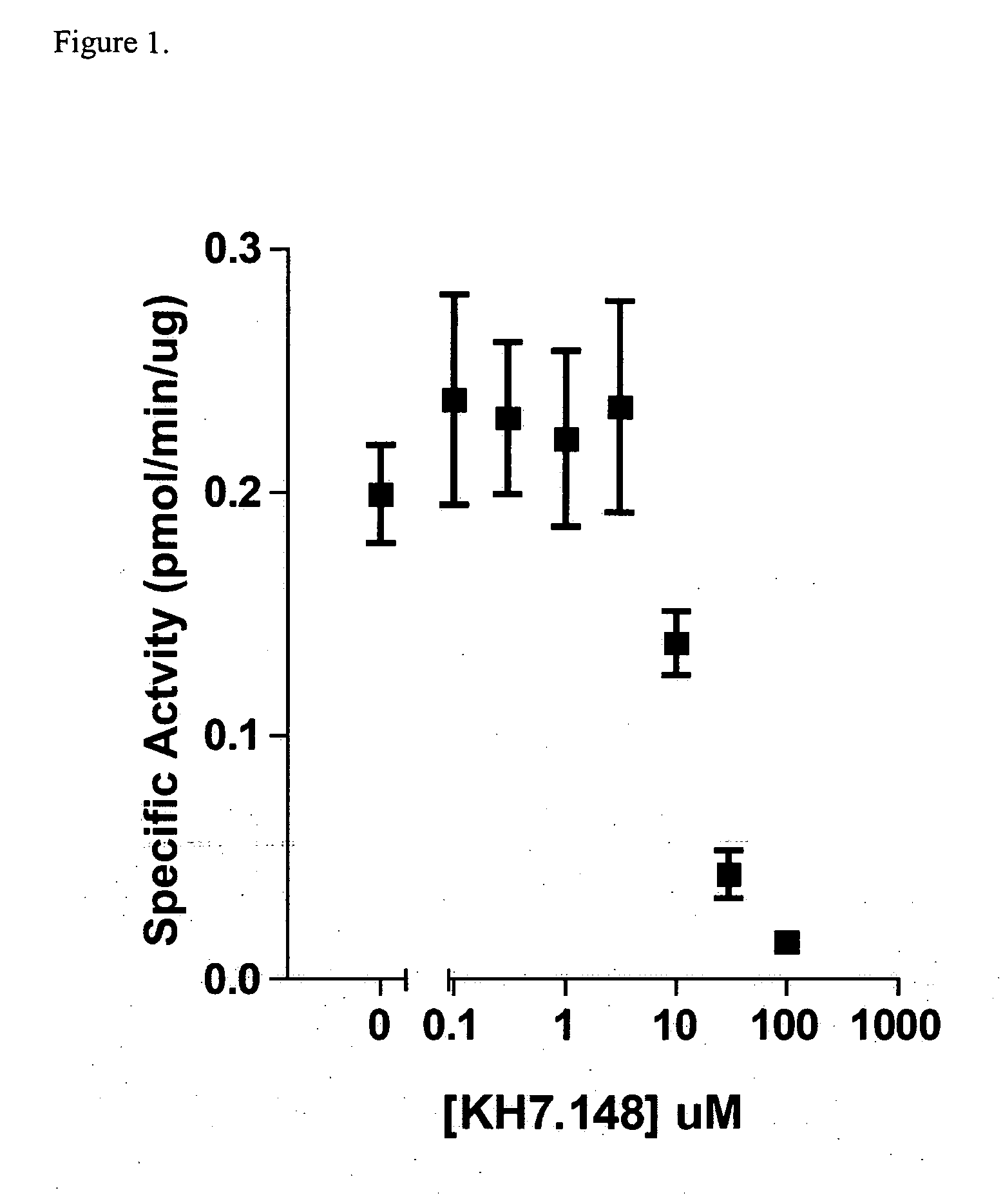
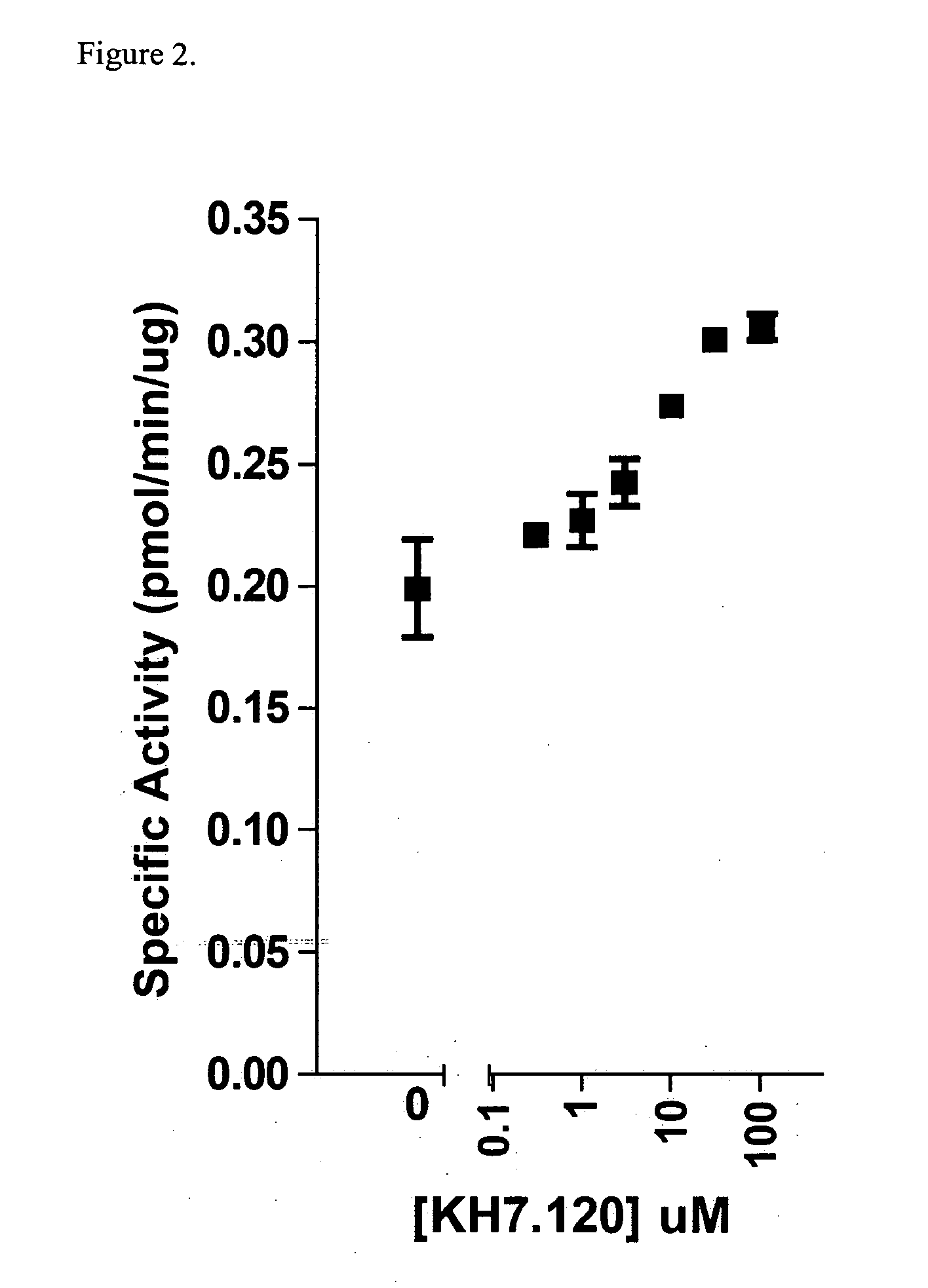
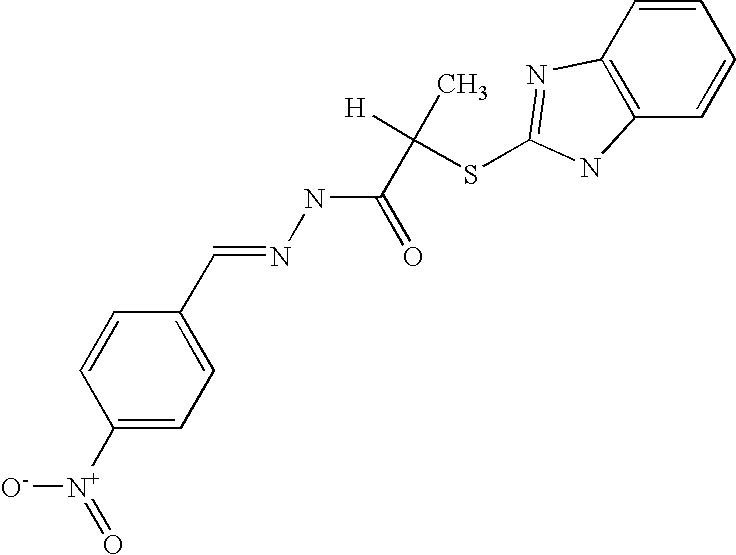
Adenylyl cyclases as novel targets for antibactrial interventions
InactiveUS20100168203A1Prevent diseaseSuppress gene expressionAntibacterial agentsBiocideCyclaseAdenylyl Cyclases
The present invention relates to a method of preventing or treating a disease caused by bacterial infection by administering an effective amount of a modulator of bacterial adenylyl cyclase. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions useful for preventing or treating a disease, with the compositions containing a therapeutically effective amount of a modulator of bacterial adenylyl cyclase. The invention also provides screening methods for identifying selective modulators of bacterial adenylyl cyclase that do not substantially modulate adenylyl cyclase of the subject. The invention also provides methods for culturing bacterial pathogens and methods for inducing the pathogenic state in vitro.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
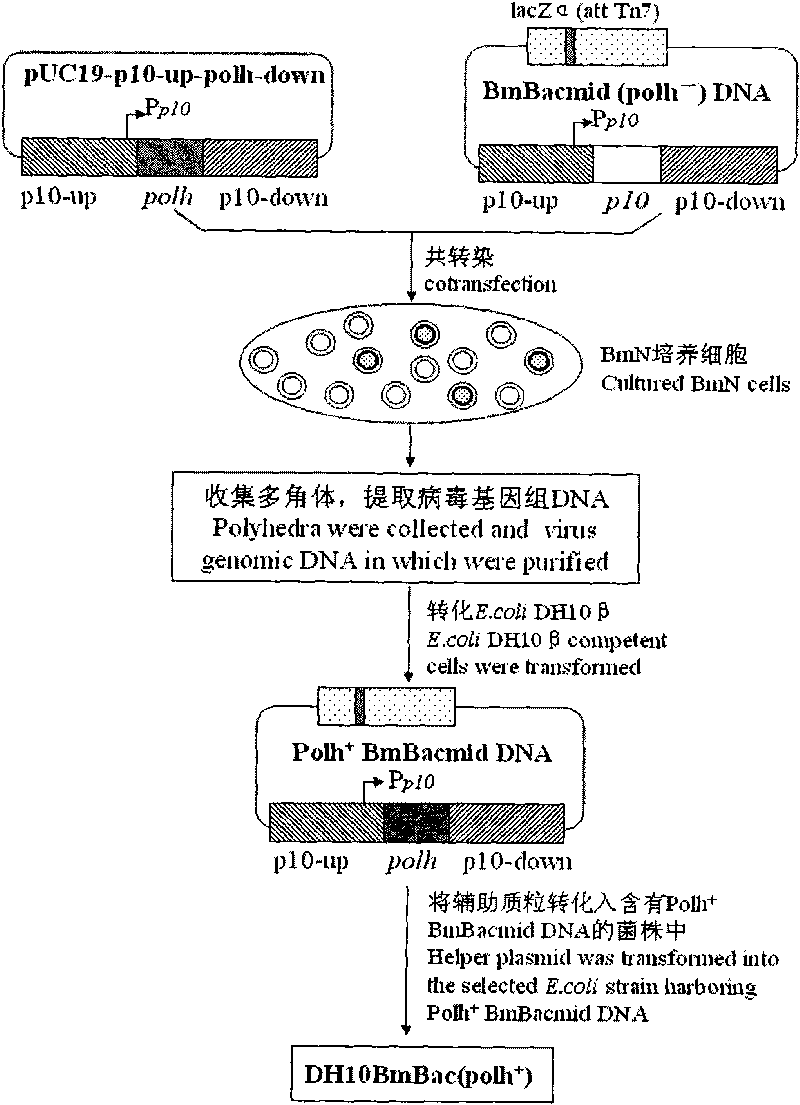
Building method of silkworm BmNPV Polh+Bac-to-Bac rhabdovirus expression system
The invention discloses a building method of a silkworm BmNPV Polh+Bac-to-Bac rhabdovirus expression system, comprising: taking silkworm wild type BmNPV genome DNA as the template; respectively taking P10-upF / P10-upB and P10-downF / P10-down B as a primer PCR for amplification to obtain p10-up and p10-down; after processed, inserting into BamHI-PstI-HindIII locus in pUC 19 to obtain recombinant plasmid pUC19-p10-up-down; using pUC-19-p10-up-polh-down, liposome lipofectin and MilliQ H2O to prepare DNA-Lipofectin mixed liquor; adding the mixed liquor into BmN cells for cultivating; collecting transfection cell supernatant; inoculating BmN cells, and recovering a polyhedral body; extracting virus DNA from the polyhedral body and electrically converting DH10 beta competent cells; screening locus ceruleus and cultivating; after cultivating PCR positive bacterial plaque, extracting macro-molecular DNA to transfect to the BmN cells; separating to obtain helper plasmids from DH10Bac culture bacteria of AcMNPV Bac-to-Bac; converting the helper plasmids into E.coli DH10 beta containg Ploh+BmBacmid; and screening the DH10 beta bacterial strain of the helper plasmid containg Ploh+BmBacmid. The invention can produce recombinant virus capable of infecting by eating with mouth, and recombinant virus does not need to infect by intracutaneous inoculation, thus improving the production efficiency of the silkworm rhabdovirus expression system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing ubiquinone by using sticky red rhodotorula
InactiveCN101619330ARaise the potentialMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismRhodotorula
The invention relates to a method for producing coenzyme Q10 by using rhodotorula gracilis, which belongs to the field of microorganism. The method comprises the following steps: culturing bacteria on a flat plate; preserving the bacteria at minus 80 DEG C after being washed by sterile water; and putting the activated bacteria into a fermentation culture medium to culture. The invention provides new high-potential candidate bacteria for fermenting and producing coenzyme Q10.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Cultivation method for producing Stropharia rugosoannulata by using cattle farm waste
InactiveCN105284426AEffective consumptionIncrease productionBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersMaterial typeEconomic benefits
The present invention discloses a cultivation method for producing Stropharia rugosoannulata by using cattle farm waste, and relates to a cultivation method of Stropharia rugosoannulata. The cultivation method solves the problems that few material types and high cost exist in planting of the existing Stropharia rugosoannulata in northern alpine areas and there is no suitable cultivation technical method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, cultivation material configuration and fermentation; secondly, pile turning; thirdly, bedding and material spreading; fourthly, seeding; fifthly, culturing bacteria management; sixthly, fruiting management; and seventhly, harvesting and management after harvesting. The cultivation method of the present invention configures cultivation materials suitable for growing in northern alpine areas, and avoids the problem of slow growth under low temperature; the adopted cultivation materials completely use the waste resource of northern agriculture and animal husbandry production by adding 20% of dried chips as raw materials; and the method is consistent with northern resource features, and turns waste into wealth, thereby reducing the production cost, improving the yield of Stropharia rugosoannulata, effectively eliminating animal farm waste, and reducing environmental pollution, so that the economic and ecological benefits are significant, the method is suitable for promotion, and the economic benefit is significant.
Owner:黑龙江生物科技职业学院 +1
Poultry and livestock intestinal ecological restoration microbial agent with virus and pathogenic bacteria-resisting functions and antibiotic-replacing effect and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a poultry and livestock intestinal ecological restoration microbial agent with virus and pathogenic bacteria-resisting functions and antibiotic-replacing effect and a preparation method thereof. The poultry and livestock intestinal ecological restoration microbial agent is prepared by mixing saccharomyces cerevisiae, candida utilis, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, rhodopseudomonas palustris, lactobacillus plantarum, and lactobacillus rhamnosus. The preparation method comprises the following steps of respectively inoculating each strain into a corresponding sterilization culture medium, activating, and preparing a first-level seed liquid; according to the neighboring and mutualism principle, during second-level and third-level fermenting, mixing and fermenting the saccharomyces cerevisiae and candida utilis, mixing and fermenting the bacillus subtilis and bacillus licheniformis, and mixing and fermenting the rhodopseudomonas palustris, lactobacillus plantarum and lactobacillus rhamnosus; mixing the three mixed and enlarged culture bacteria liquids according to the equal volume of 1:1:1, absorbing onto sterilizing wheat bran-rice bran, and performing solid fermenting and low-temperature drying, so as to obtain the solid microbial agent. The poultry and livestock intestinal ecological restoration microbial agent has the characteristics that the good properties of high density and high activity are realized; the probiotics microbial agent and the lemon and radix astragali seu hedysari water extracting liquid are compounded for first time; the usage amount is less, and the use method is simple and convenient.
Owner:道拓百旗(天津)房地产信息咨询有限责任公司
Antrodia cinnamomea cultivation method
InactiveCN104472226APromote growthImprovement quality is not highCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationCulture bacteriaYeast extract
The invention provides an antrodia cinnamomea cultivation method. The antrodia cinnamomea cultivation method comprises the following steps: 1) bacterium bag manufacturing: adding water into mulberry branch powder, performing enzymolysis, adding a compound enzyme preparation into the mulberry branch powder, stirring uniformly, fermenting, performing the enzymolysis at room temperature, adding glucose, peptone, a barley extract, a yeast extract and a curing agent in sequence after the enzymolysis is performed, and solidifying a mixed solution to prepare a cylinder culture medium; 2) inoculating and culturing bacteria: inoculating an antrodia cinnamomea strain to the cylinder culture medium in the step 1) under an aseptic condition, and transferring the cylinder culture medium into a constant-temperature bacterium culture room for culturing the bacteria. The antrodia cinnamomea cultivation method has the beneficial effects that the growth amount of antrodia cinnamomea mycelia or fruiting bodies of a unit culture medium are improved; moreover, the situations of infectious microbe pollution can be reduced; the prior art is greatly improved.
Owner:ZHISHENG TIANJIN BIOTECH
Bacterium composite nutrient
InactiveCN1966672ARapid cultivationRapid domesticationBacteriaBiological water/sewage treatmentBacteroidesSodium phosphates
The invention discloses a kind of complex bacterium nutritional agent, and characterized in that the components and their wt. % of the prepared bacterium nutritional agent is: corn flour 20-75, wheat bran 10-55, natrium carbonicum 5-10, ammonium carbonate or acid ammonium carbonate 5, kalium nitricum 1-5, ferrous sulfate 0.5-4, carbamide 0.5-5, magnesium sulfate 0.2-1, sodium phosphate 0.5-4, and vitamin as balance, the sum of the above percentages is 100%. The said complex bacterium nutritional agent is mainly used for culturing bacteria in wastewater management system to achieve required bacteria kinds and quantity for the normal running of the wastewater management system.
Owner:西安利能科技有限责任公司
Cream Cheese Products and Methods of Making the Same
Technique for making a cream cheese product comprising steps of: providing a milkfat fluid comprising butterfat; pasteurizing the milkfat fluid; homogenizing the milkfat fluid; and culturing bacteria in the milkfat fluid; producing a cream cheese product comprising live probiotic bacteria cultures. Cream cheese product comprising: between about 10% by weight and about 55% by weight of total butterfat; and a live probiotic bacteria culture.
Owner:FRLIN FOODS HLDG
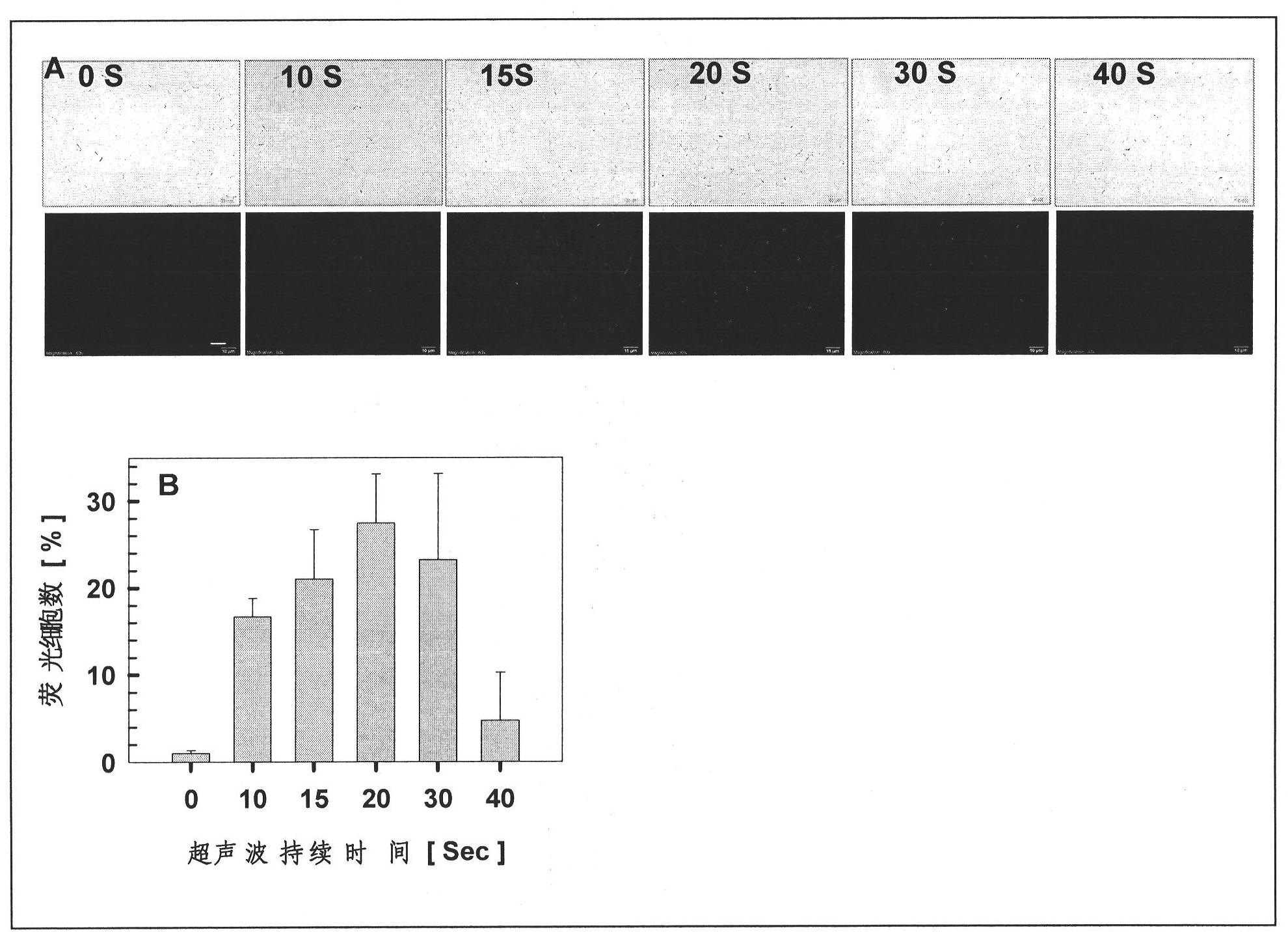
Ultrasonic-mediated microbial genetic transformation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101875947ANon-destructiveLow costMicroorganism based processesOther foreign material introduction processesProbe typeMicrobial genetics
The invention relates to a low-frequency ultrasonic-mediated method for transforming microbial, which comprises the following steps: (1) culturing bacteria to a logarithmic phase in a liquid culture medium; (2) adding a substrate to be transformed into a glass bottle containing the liquid culture medium in the step 1; (3) putting the glass bottle in the step 2 into the cavity of an ultrasonic instrument; (4) starting the ultrasonic instrument, wherein the frequency is 0.1-1000KHz, the power is 0.01-1000 Watts, non-probe type contact is adopted, the whole transformation process is carried out in the solution of a bioreactor, and ultrasonic waves are continuously adjustable or intermittent; and (5) recovering cells, transferring, and coating a panel. The invention can be used for operating a single cell and a single reactor, can realize high flux, has the advantages of simple operation and voluntary control, and can realize remote control.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
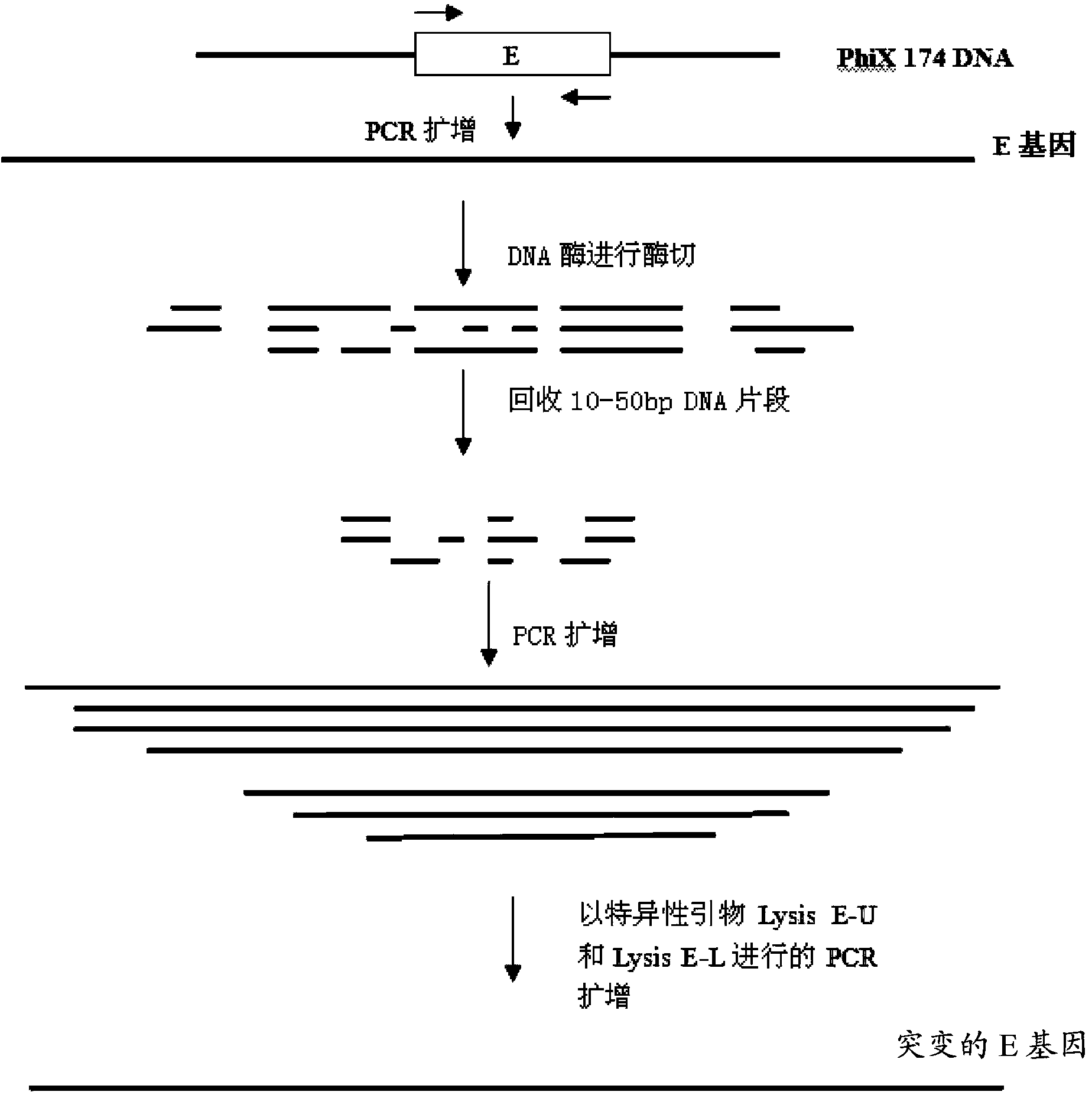
Mutant phage lysis gene E, lysis plasmid vector containing lysis gene and application in preparation of bacterial ghost vaccines
InactiveCN103451195ARepress transcriptionImprove cracking efficiencyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCulture bacteriaOrganism
The invention discloses a mutant phage lysis gene E, a lysis plasmid vector containing the lysis gene and an application in preparation of bacterial ghost vaccines. The mutant phage lysis gene E (Eprom) disclosed by the invention is obtained after mutation of a promoter region of the lysis gene E of a phage phiX174, the E gene after mutation can turn the temperature of culture bacteria from the existing 28 DEG C to 37 DEG C, the mutant phage lysis gene E further has higher lysis efficiency, higher starting induction concentration and large-scale production capacity, and the culture lysis efficiency of a fermentation tank is as high as 99.99997%. After the Eprom is connected with pBV220, the high-efficient lysis plasmid vector pBV-Eprom can be obtained. The pBV-Eprom is transformed into actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae to induce the gene expression of the Eprom so as to get a bacterial ghost of the actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Porcine transmissible pleuropneumonia bacterial ghost vaccines disclosed by the invention has good safety and immune protection efficacy and can stimulate organisms to produce high-titer antibodies and further provide good cross immunoprotection against attacks of different serotypes of actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae virulent strains.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com