In-situ environment microbe isolation method and soil source petroleum degrading microbe isolation and screening method
A technology of environmental microorganisms and separation methods, which is applied in the field of in-situ environmental microorganism separation, soil oil-degrading microorganism separation and screening, and can solve the problems of time-consuming, labor-intensive, different growth speeds of microorganisms, and environments that cannot provide material exchange.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
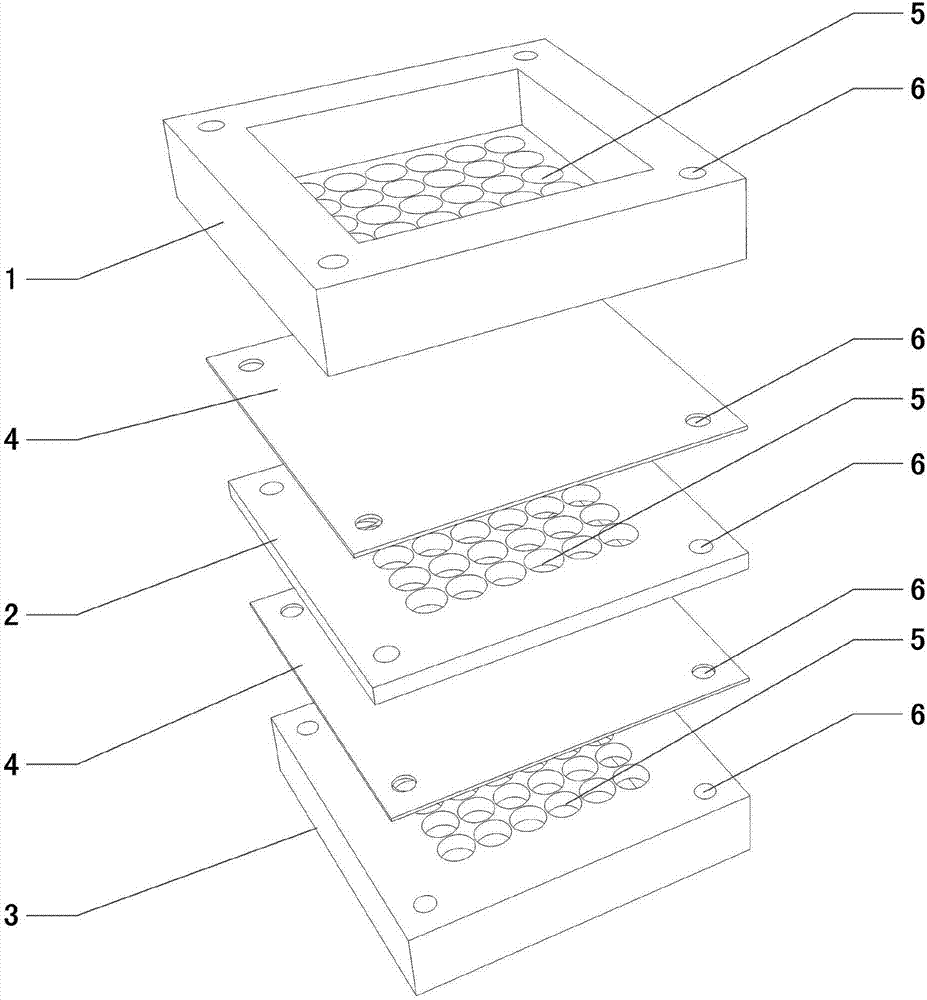
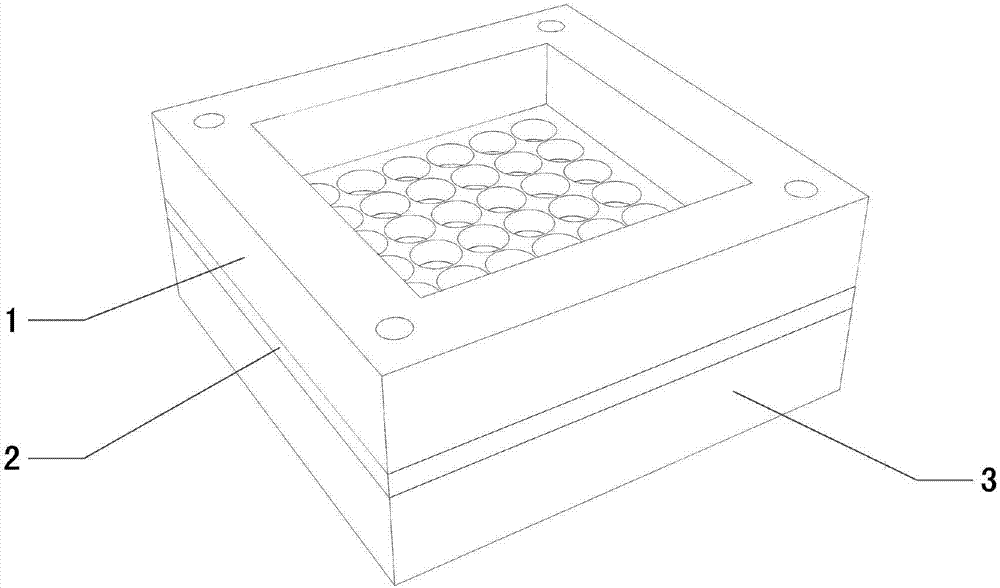
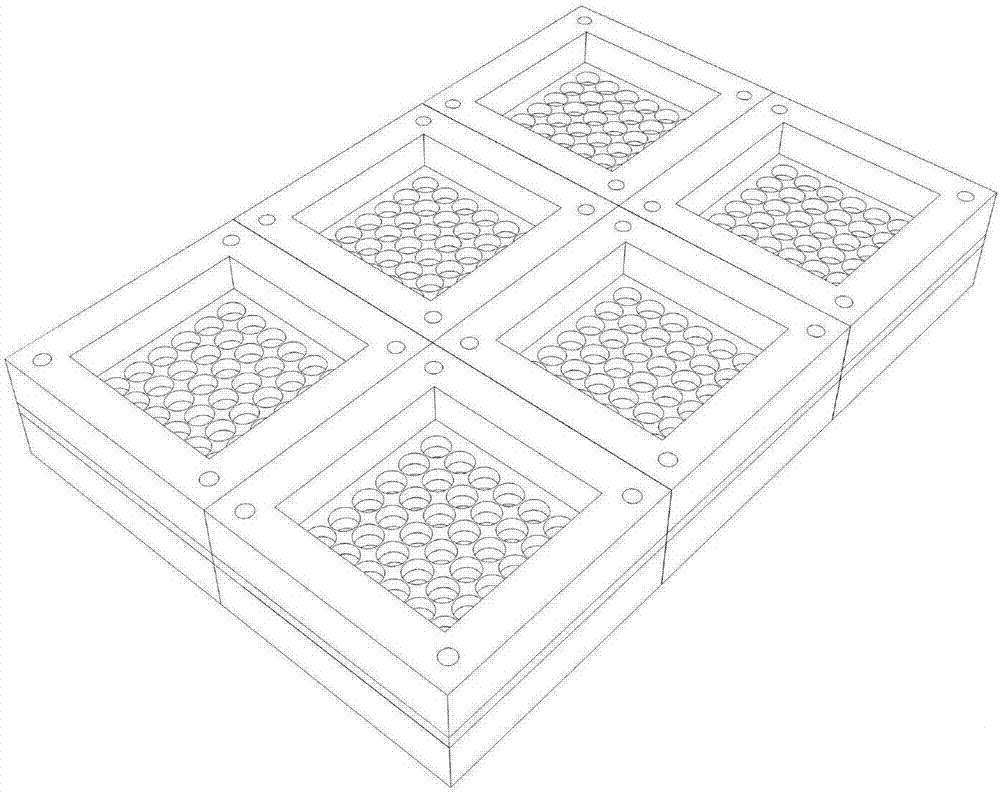
[0031] This embodiment mainly introduces the structural composition and working principle of an in-situ environmental microorganism cultivation device. Such as Figure 1 to 3 As shown, the present invention provides an in-situ environmental microorganism cultivation device, which includes an upper cover 1, a lower cover 3 and a splint 2. Preferably, the horizontal projection shapes of the upper cover plate 1, the lower cover plate 3, the splint 2 and the microporous filter membrane 4 are all squares of the same size, and the upper cover plate 1 and the lower cover plate 3 have a flat surface. The thickness of the edge on the other side is greater than the thickness at the position where the through hole is provided in the middle, which can effectively increase the strength of the edge, thereby improving the overall strength and reliability of the device.
[0032] The upper cover 1, the lower cover 3, and the splint 2 are provided with a plurality of longitudinal through holes 5 ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] This embodiment mainly introduces a method for separating microorganisms from petroleum produced liquid. For the petroleum produced fluid collected from Jilin Oilfield, the cultivation device described in Example 1 was used to separate functional microorganisms in situ. Proceed as follows:
[0039] 1. Prepare a solid medium containing 2% agar by taking an appropriate amount of extraction liquid;
[0040] 2. Take part of the petroleum produced fluid and record the microbial concentration with a hemocytometer (the actual measured concentration is about 7.6*10 7 Pcs / mL);
[0041] 3. Gradient dilution. Take part of the diluted solution and mix it into the 2% solid medium prepared in step 1 (cooled to about 45°C) to make the final concentration of bacteria 10 3 Pieces / mL (ie 1 piece / μL, so that there is only one cell in each well on average);
[0042] 4. Put the splint into the above-mentioned mixed culture medium and cool it until it solidifies; quickly take out the splint and le...
Embodiment 3
[0052] This embodiment mainly introduces a method for separating soil microorganisms using the culture device described in Embodiment 1. For soil samples collected near Weiming Lake of Peking University, a culture device was used to separate microorganisms in the soil samples in situ. Proceed as follows:
[0053] 1. Put 1g of soil into 10mL sterile water and shake for 10min to obtain soil extract;
[0054] 2. Take part of the soil extract and record the microbial concentration with a hemocytometer (the actual measured concentration is about 4.8*10 7 Pcs / mL);
[0055] 3. Gradient dilution. Take part of the dilution and mix it into 2% LB solid medium (cooled to about 45°C) to make the final concentration of bacteria 10 3 Pieces / mL (ie 1 piece / μL, so that there is only one cell in each well on average);
[0056] 4. Put the splint into the above-mentioned mixed bacteria culture medium and cool it until it solidifies; quickly take out the culture device and leave the small pieces of agar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com