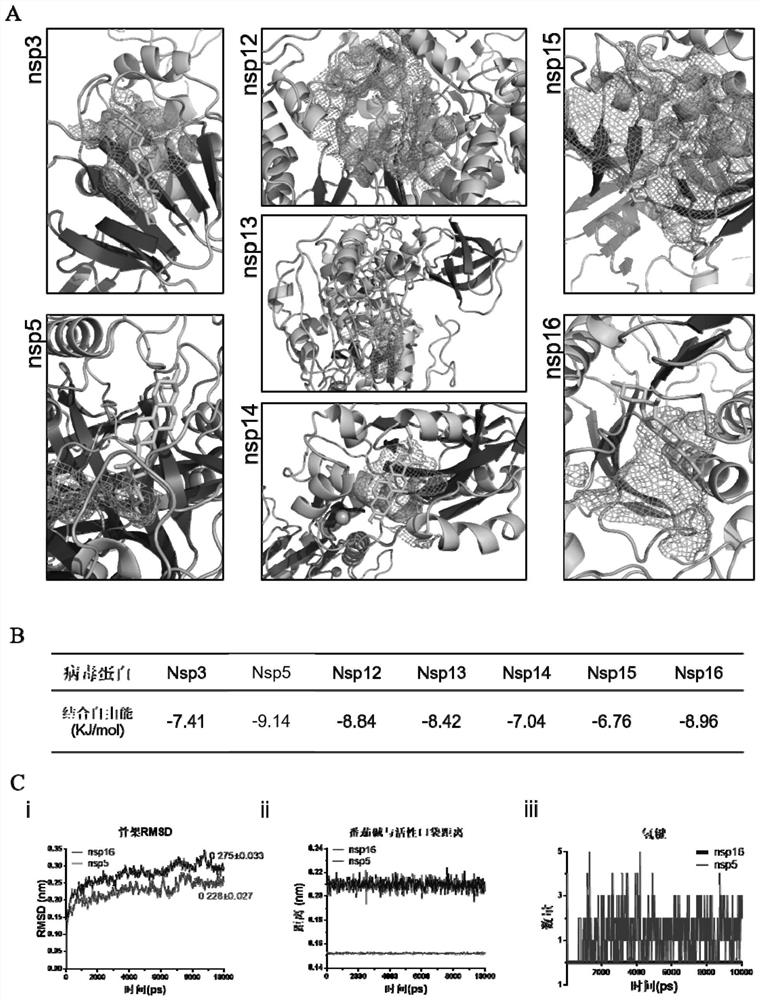
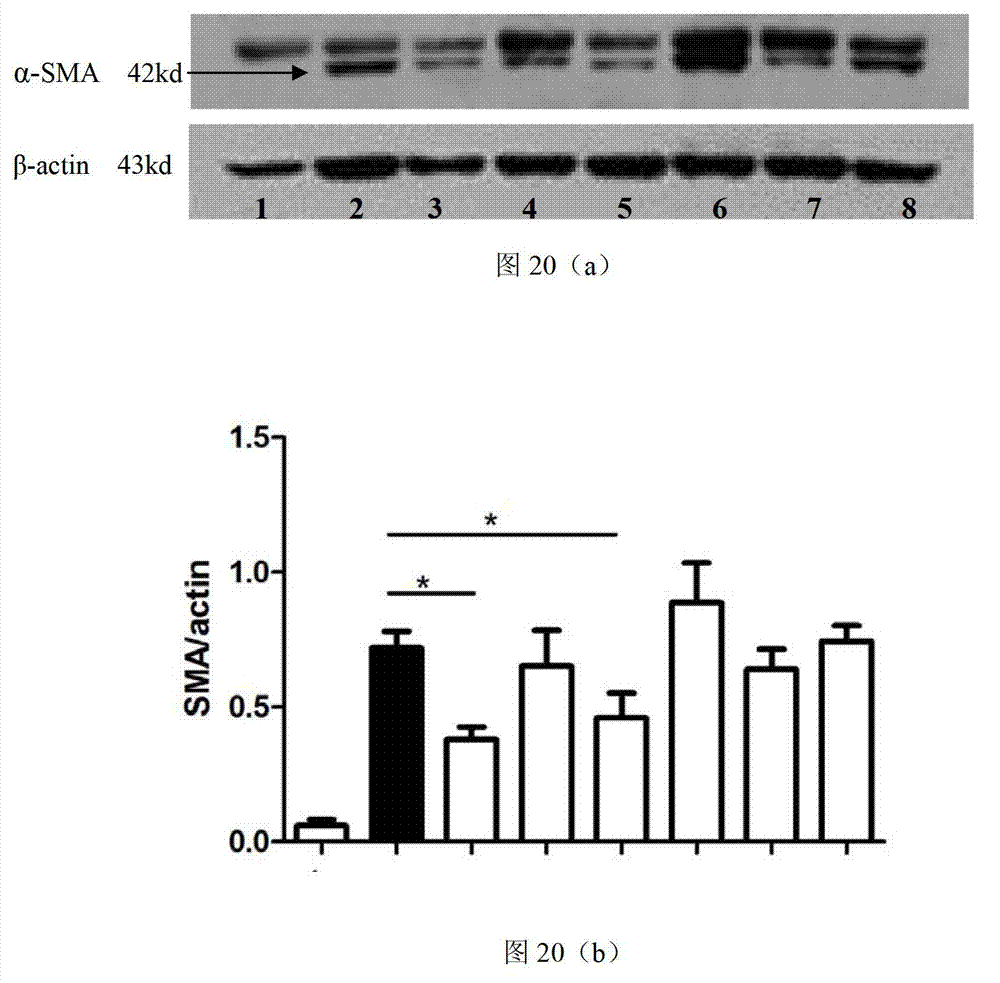
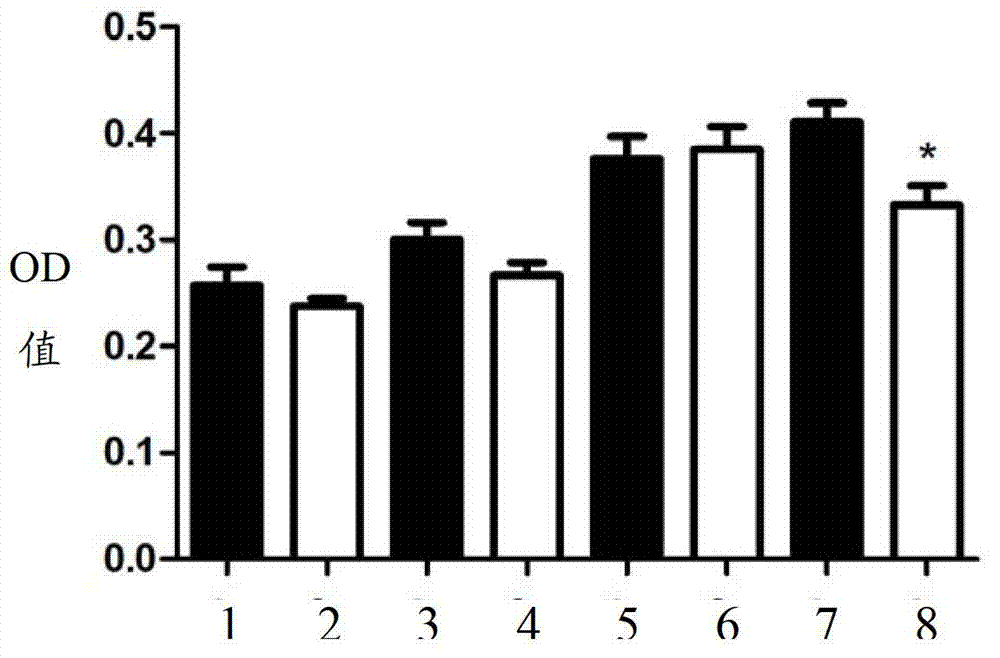
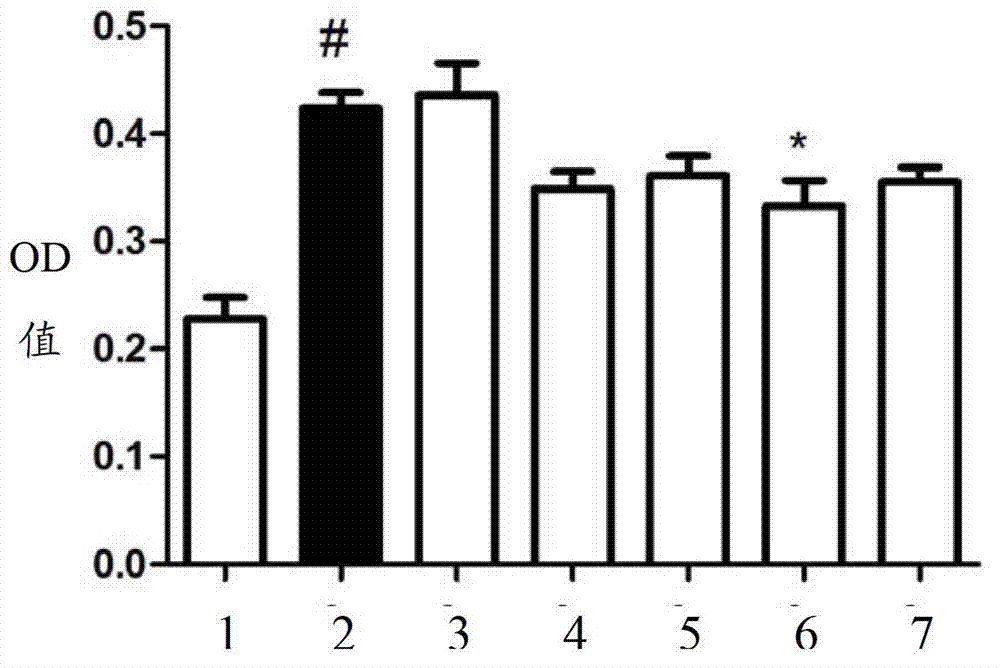
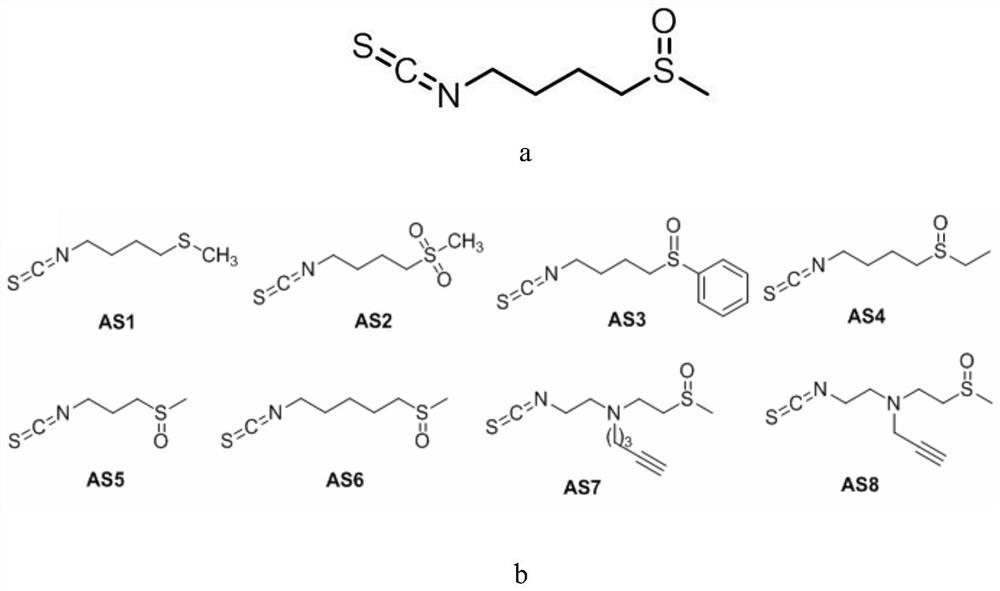
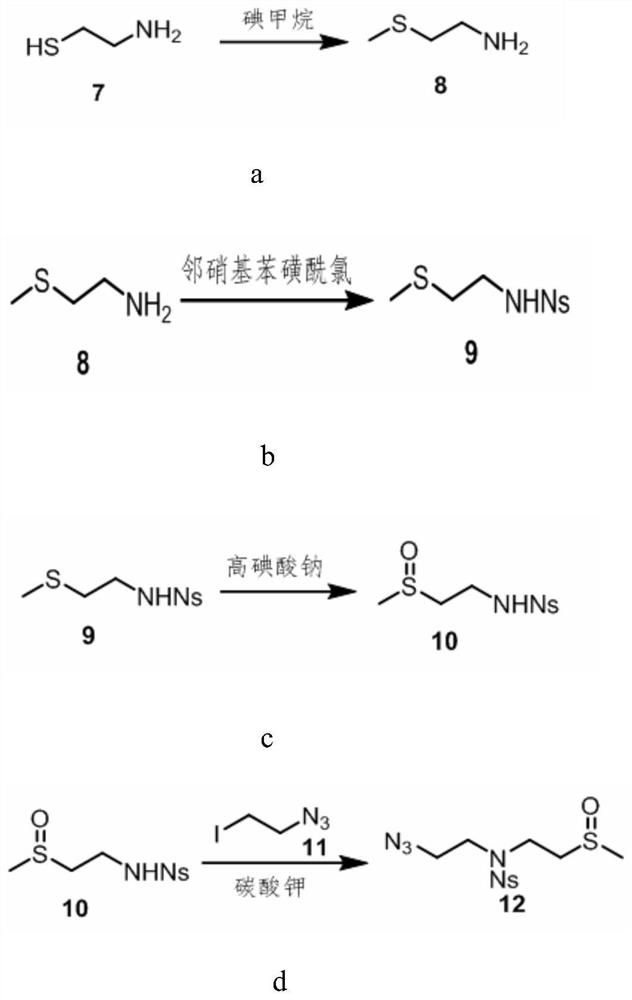
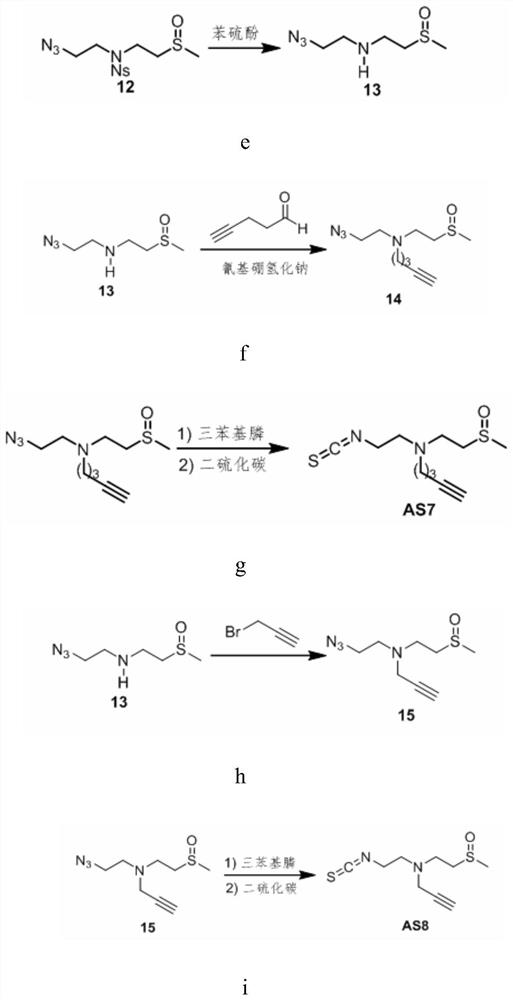
Patents
Literature
63results about How to "Repress transcription" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coronary artery medicinal-coating stent
InactiveCN1935274AIncrease cAMP contentInhibit biosynthesisStentsSurgeryPhosphorylcholinePercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention discloses a coronary artery medicine coating scaffold for inhibiting endometrial hyperplasia and preventing restenosis in the scaffold. It includes dilating scaffold base body and inner coating layer coated on the dilating scaffold base body, the above-mentioned inner coating layer is formed from medicine carrier and ligustrazine, their mass ratio is 3:1-1:3, the above-mentioned inner coating layer is one of methyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate copolymer, polylactic acid, polyglycollic acid, polymonoracemic lactic acid, polylactide-diglycolide polymer, phosphorylcholine, ethyl polyurethane inorganic micropore aluminium oxide and cellulose or their composite.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
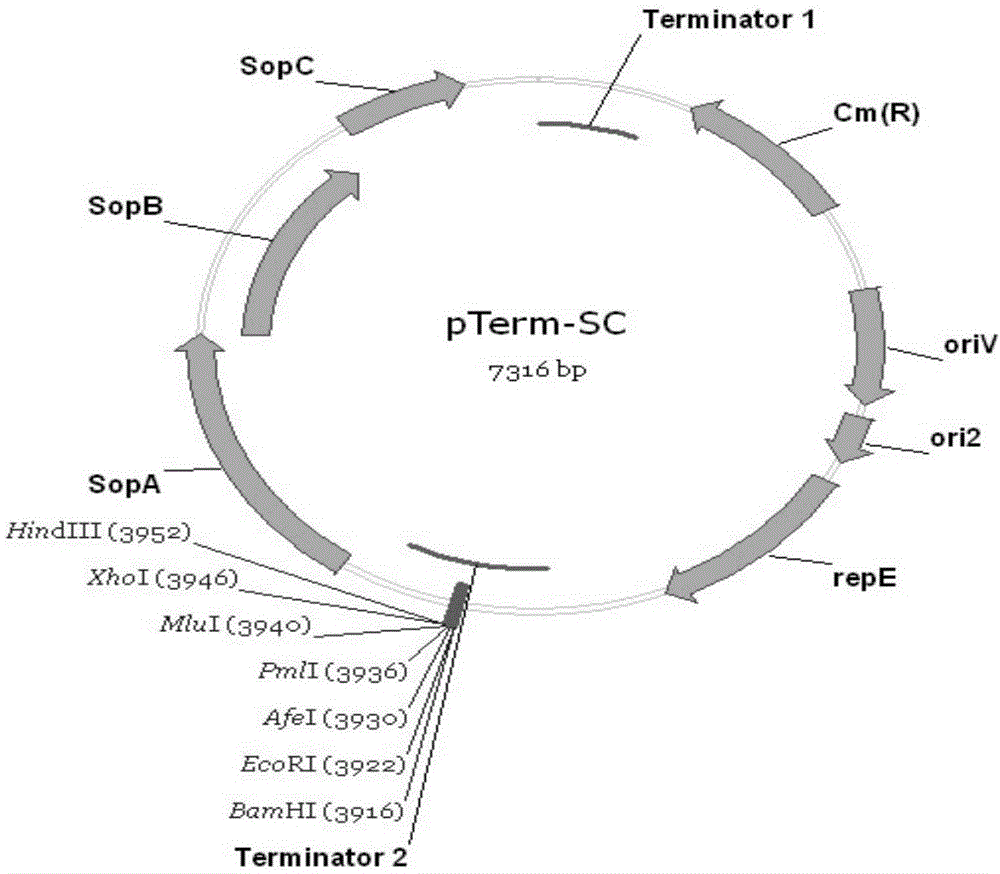
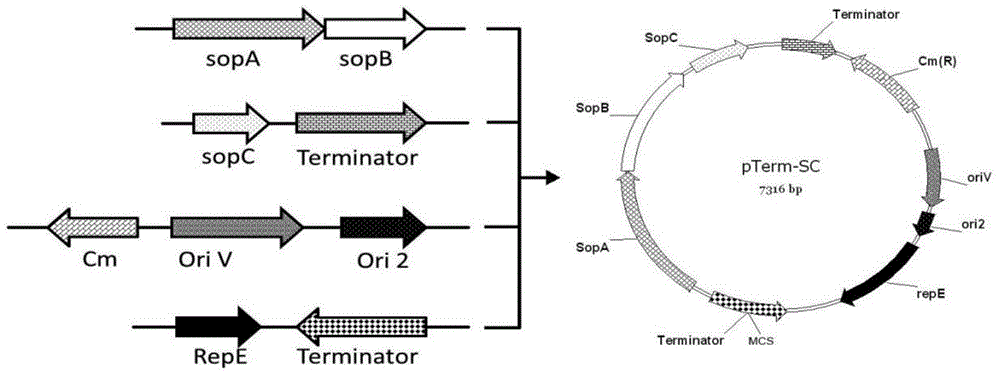
PTerm-SC plasmid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN104480130AEasy extractionTranscriptional repressionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YGene engineering
The invention relates to a pTerm-SC plasmid as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pTerm-SC plasmid comprises a repE gene, a sopA gene, a sopB gene, a sopC gene, an ori2 replicon, an oriV replicon, prokaryote transcription terminators and antibiotics resistance genes. The pTerm-SC plasmid has the characteristics of very low copy number, high volume and stability and the like, can be applied to gene engineering fields such as the cloning, the screening, sequencing and the genome construction of complex-structure genes including repetitive-sequence genes, instable genes and long-fragment genes and has important role in the high-efficiency and high-quality synthesis of genes.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
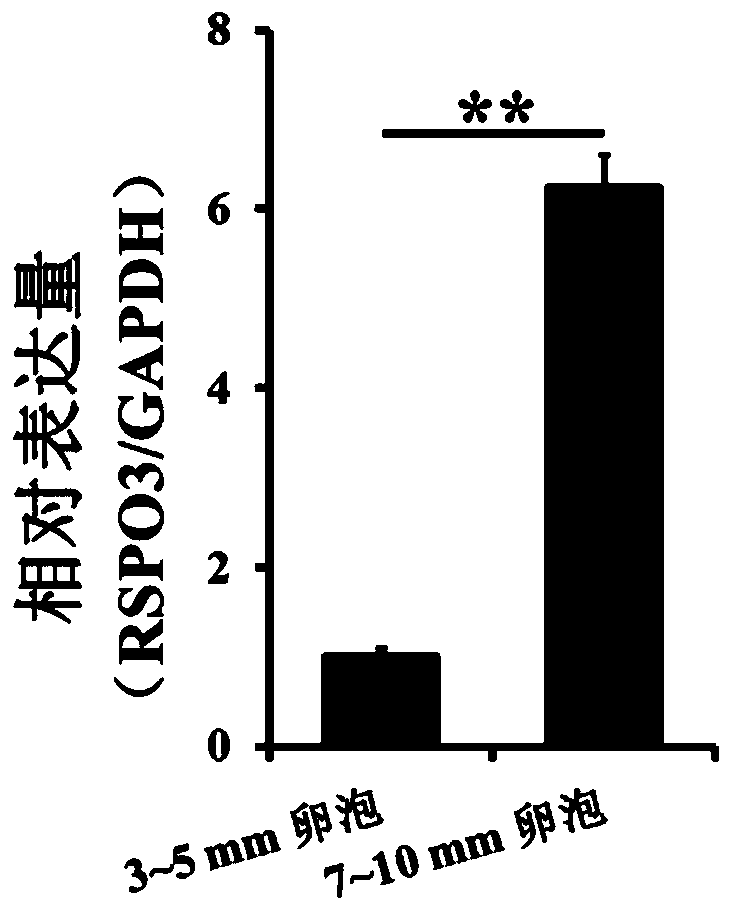
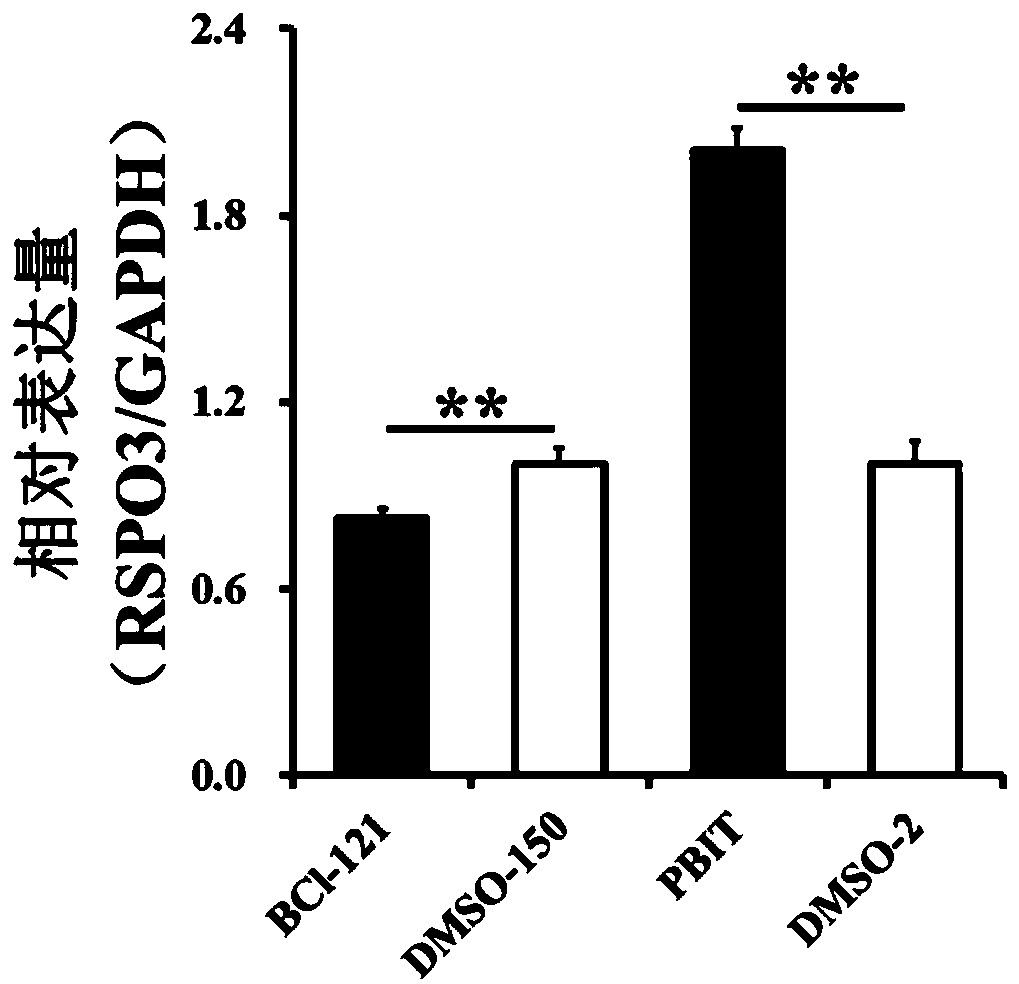
Application of RSPO3 gene in sow ovarian granulosa cells
ActiveCN110467663AReduce the degree of enrichmentPromote transcriptionArtificial cell constructsNucleic acid vectorH3K4me3Granulosa cell proliferation
The invention discloses an application of an RSPO3 gene in sow ovarian granulosa cells. Two kinds of follicles with diameters of 3-5 mm and 7-10 mm respectively are used as experimental materials, andthe relationship between H3K4me3 and the expression level of genes related to ovarian follicle development is studied by a sequencing technology. The enrichment degree of H3K4me3 in a promoter regionof the RSPO3 gene is found to be significantly different in the follicles with different size by ChIP-Seq; the expression quantity of the RSPO3 gene in the follicles with different size is found to be significantly different by qRT-PCR; promotion of the degree of the H3K4me3 is found to promote transcription of the RSPO3 gene by promoting or inhibiting the degree of H3K4me3 in the sow ovarian granulosa cells, and inhibition of the degree of H3K4me3 is found to inhibit transcription of the RSPO3 gene; the RSPO3 is found to promote the proliferation of the sow ovarian granulosa cells and inhibit the apoptosis of the cells through overexpression or interference of RSPO3.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
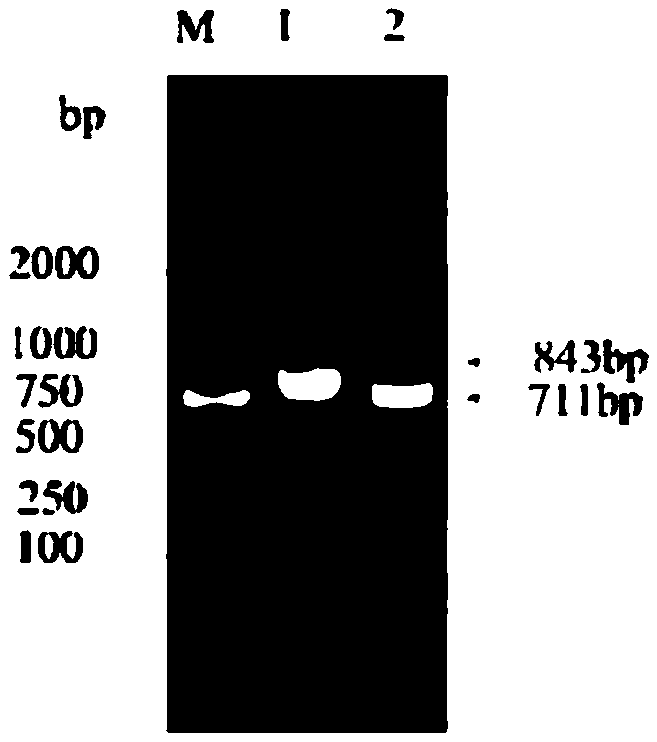
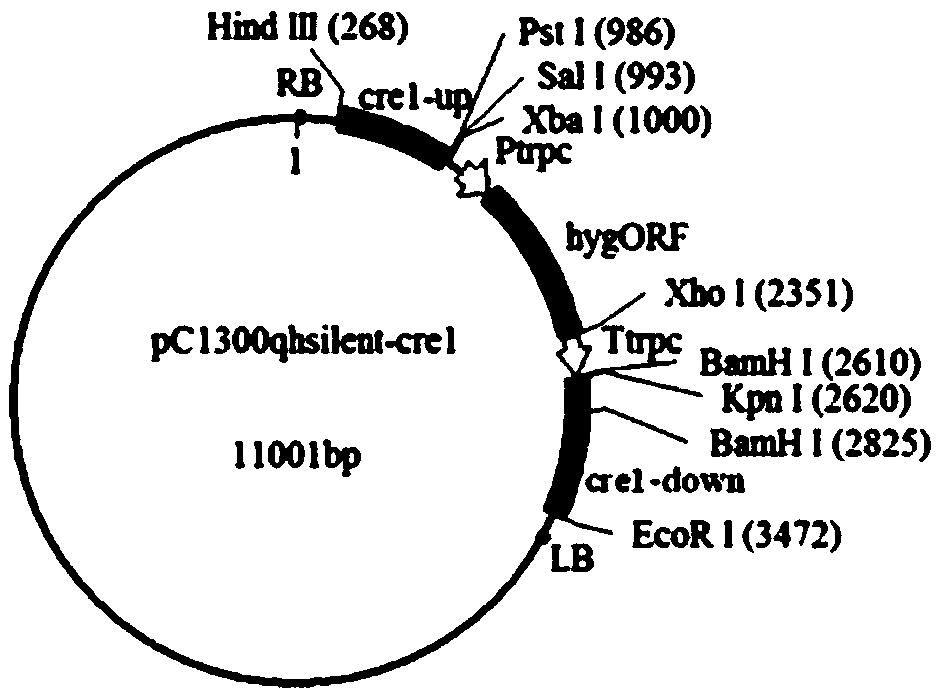
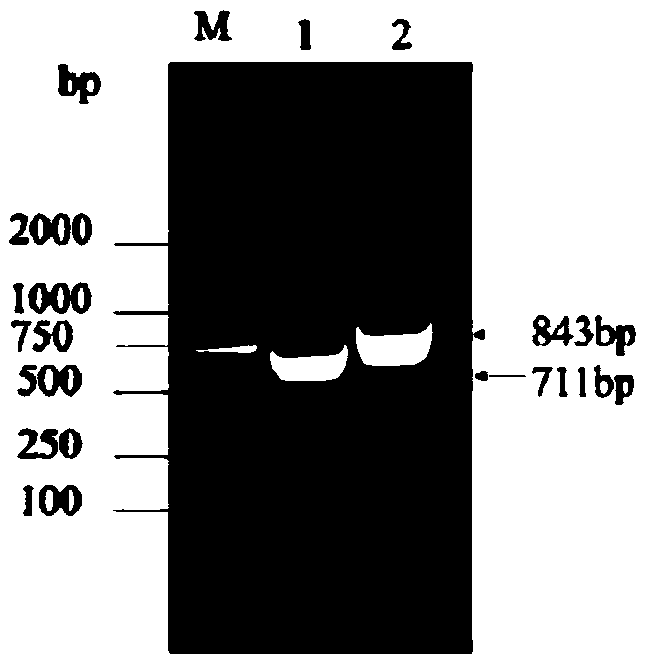
Application of improved ATMT (Agrobacterium Tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation) to construction of trichoderma atroviride T23 deltaCrel
ActiveCN105368866ARepress transcriptionInhibition of secretionFungiMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCarbon metabolism
The invention discloses an application of improved ATMT (Agrobacterium Tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation) to construction of trichoderma atroviride T23 deltaCrel. The application is characterized in that the genomic DNA of trichoderma atroviride T23 is taken as a template, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification is carried out on the Crel gene sequence, and thus upstream and downstream flanking sequences of the Crel gene are obtained; then leading in respectively to knock out upstream and downstream of plasmid pC1300qh, so as to form recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel; converting escherichia coli competence of the recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel, performing verification, screening positive clone, extracting recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel, leading in agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL1, and carrying out improved ATMT. By using the improved ATMT technique, a trichoderma atroviride carbon metabolism inhibiting factor CRE1-knocked-out mutant strain is successfully constructed; the T23 deltaCrel bacterial strain has the functions of promoting secretion and activity of degrading enzyme of cell walls of trichoderma spp., and indirectly improving the function of trichoderma spp. to antagonize pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
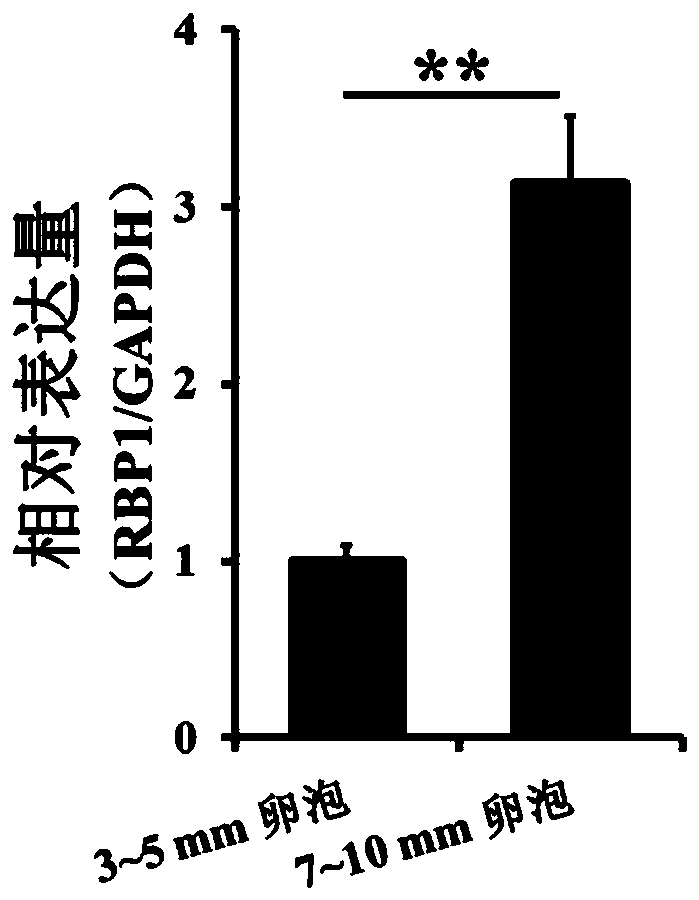
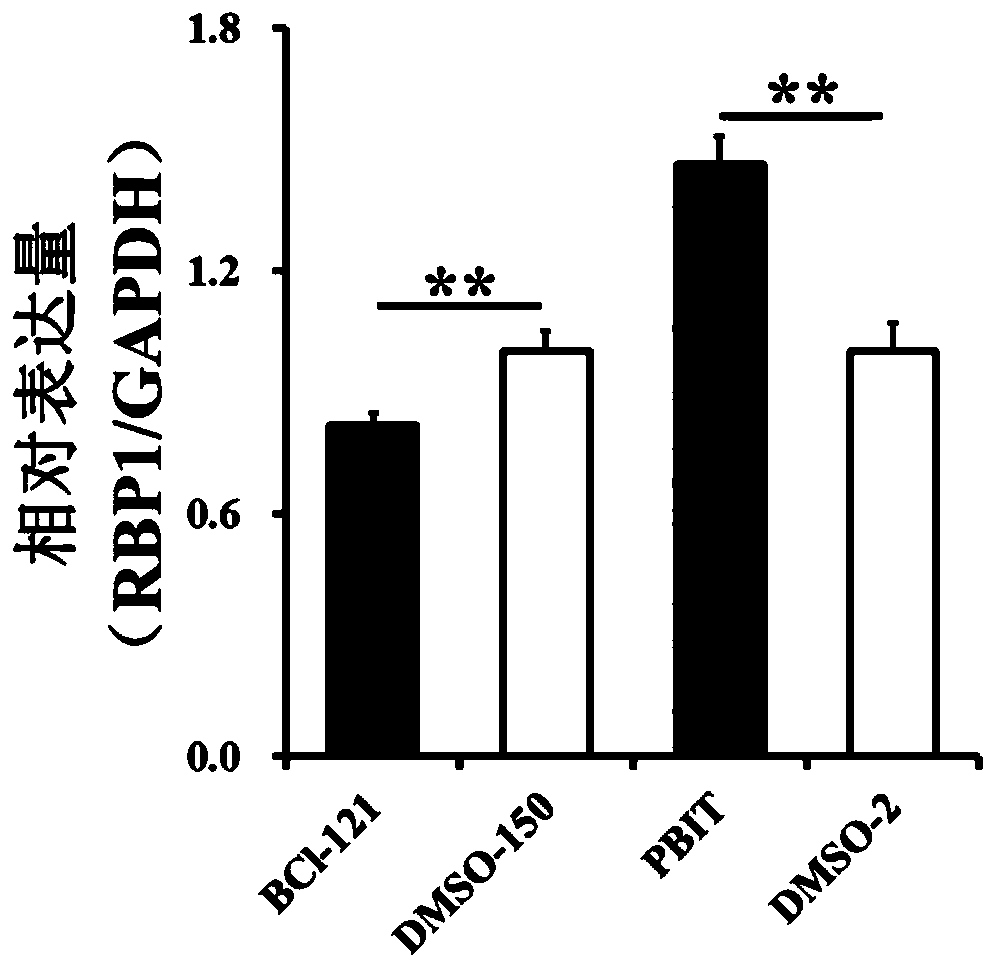
Application of RBP1 gene in sow ovarian granular cells
ActiveCN110373416AReduce the degree of enrichmentPromote proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorResearch ObjectGranular cell
The invention discloses application of a RBP1 gene in sow ovarian granular cells. RBP1 is taken as a research object, and a molecular and cell biological method is adopted to study the application ofthe RBP1 in sow ovarian granular cells. The molecular and cell biological method includes the following steps that through ChIP-Seq, it is found that the enrichment degree of H3K4me3 is different in RBP1 gene promoter regions in follicles different in size; through qRT-PCR, it is found that the expression quantity of the RBP1 gene in follicles different in size is different significantly. By promoting or inhibiting the enrichment degree of H3K4me3 in the sow ovarian granular cells, it is found that promotion of the enrichment degree of H3K4me3 can promote transcription of the RBP1 gene, and inhibition of the enrichment degree of H3K4me3 can inhibit transcription of the RBP1 gene; through RBP1 over-expression or interference with RBP1, it is found that RBP1 can promote proliferation of thesow ovarian granular cells and inhibit apoptosis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
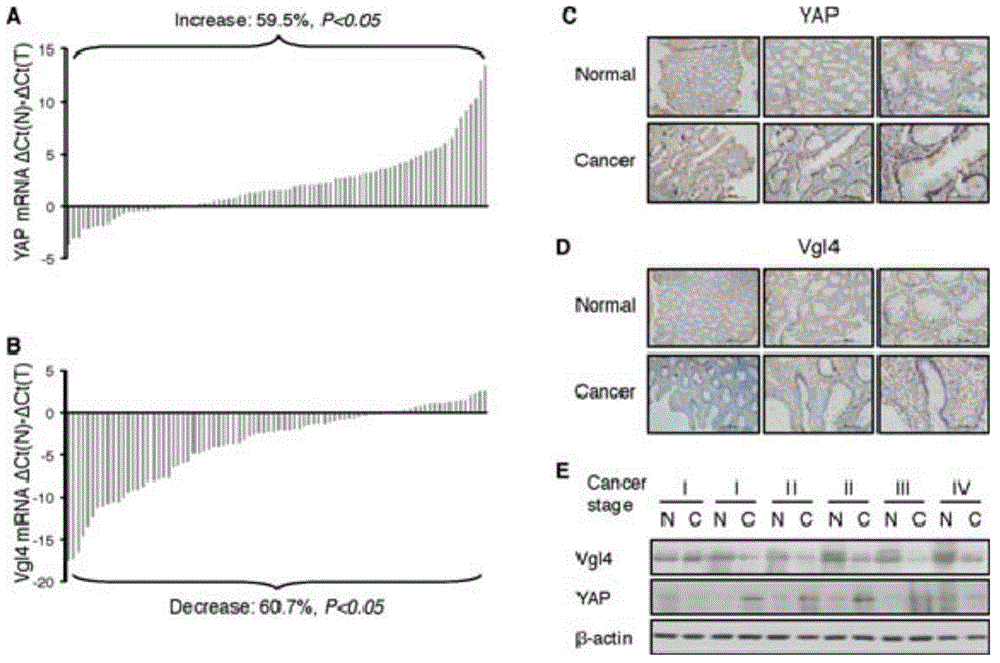
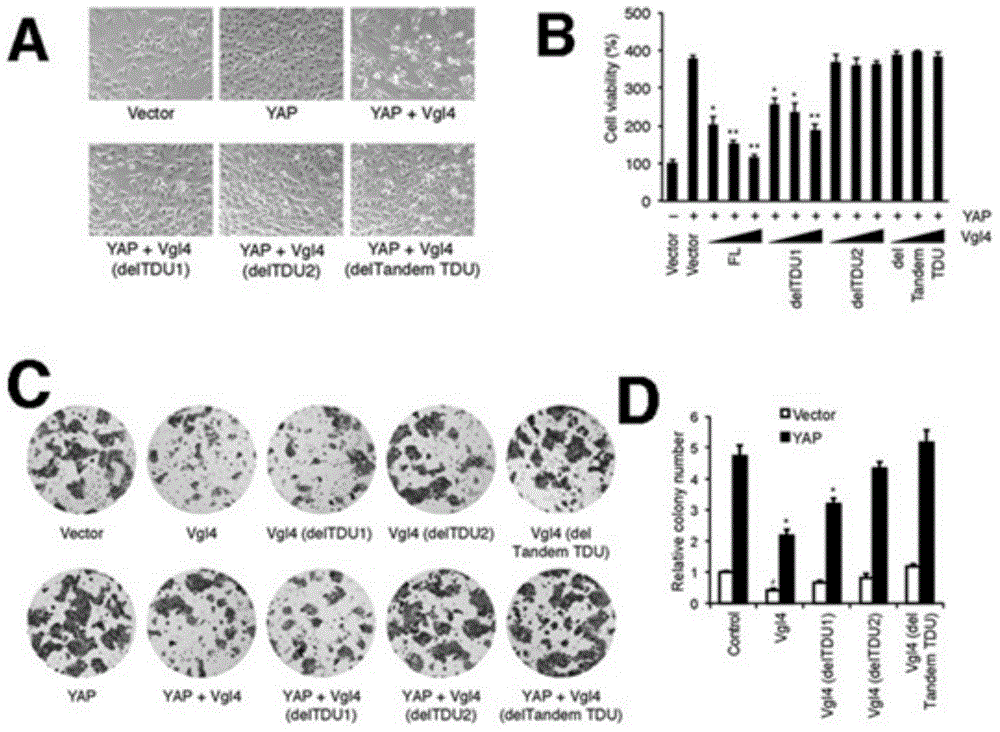
Application of VGLL4 gene in treatment of tumors and related medicament of VGLL4 gene
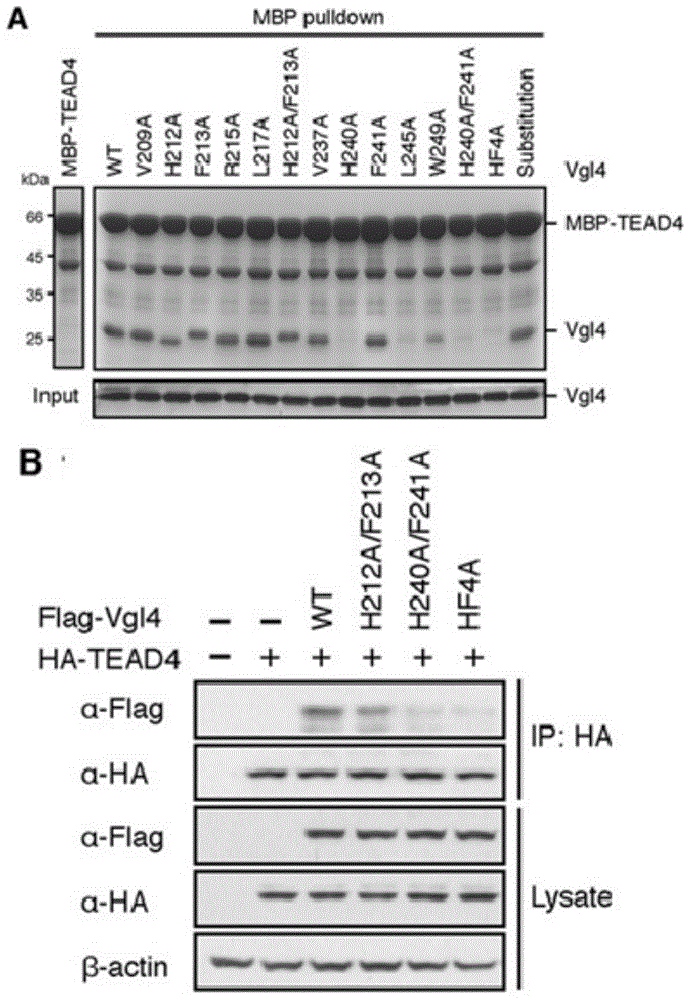
ActiveCN104548131AGrowth inhibitionNew Discovery Inhibits ProliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGrowth cellTEAD4
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to an application of a VGLL4 gene in treatment of tumors and a related medicament of the VGLL4 gene. The invention discloses a separated VGLL4 gene and a homologous sequence thereof, a VGLL4 protein and an application of related protein of the VGLL4 protein in preparation or screening of tumor treatment medicaments. Researches discover that VGLL4 can inhibit the transcription of a TEAD4 target gene CDX2 highly expressed in stomach cancer by inhibiting YAP-mediated TEAD4 transcriptional activation, thereby achieving the aim of inhibiting proliferation of cancer cells at last. The VGLL4 gene provided by the invention can be used for preparing medicaments for inhibiting the growth of tumor cells, developing anti-cancer medicaments and preparing medicaments for early diagnosis of cancer and medicaments for operation prognosis, so that the VGLL4 gene provides a new technical means for treating cancers, and has a great market value.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of oligochitosan in preparing medicine for preventing from formation of atherosclerosis
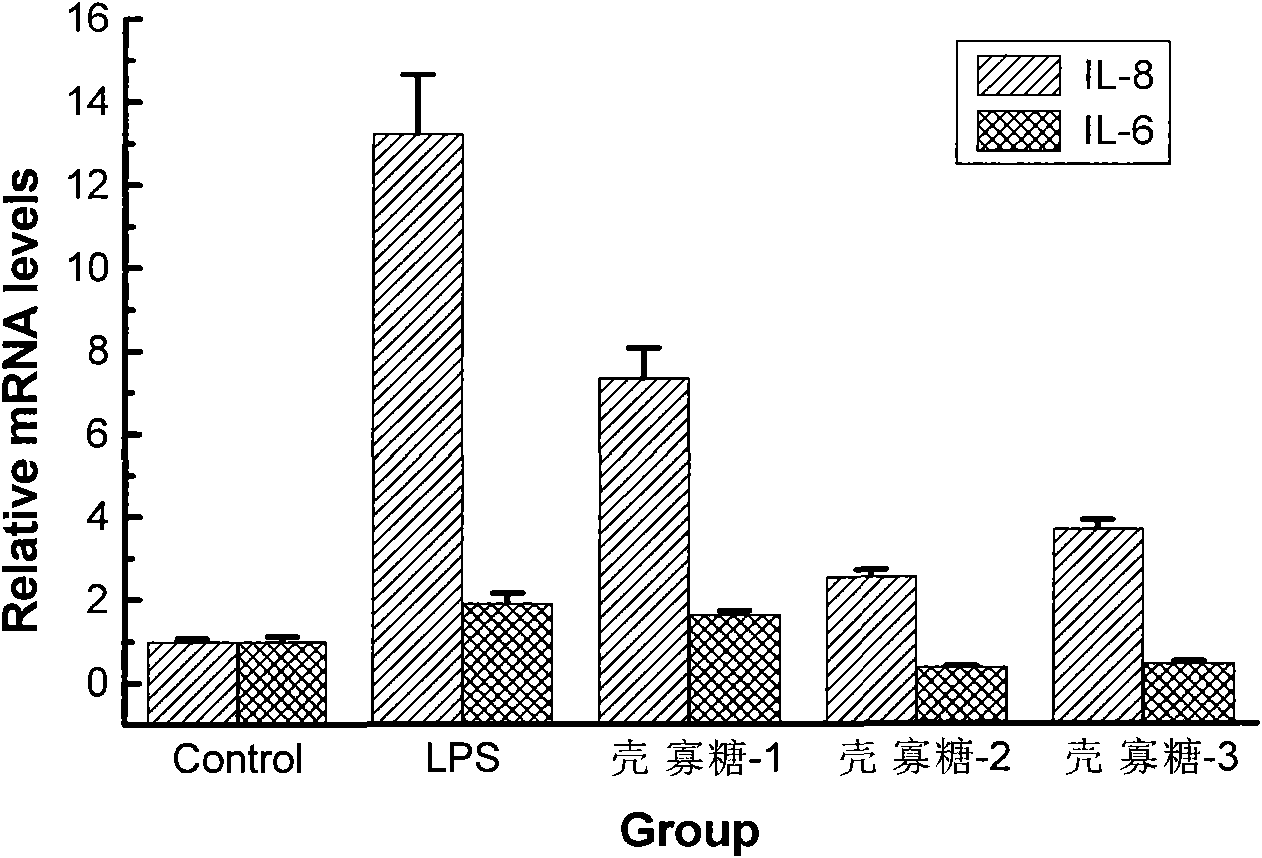
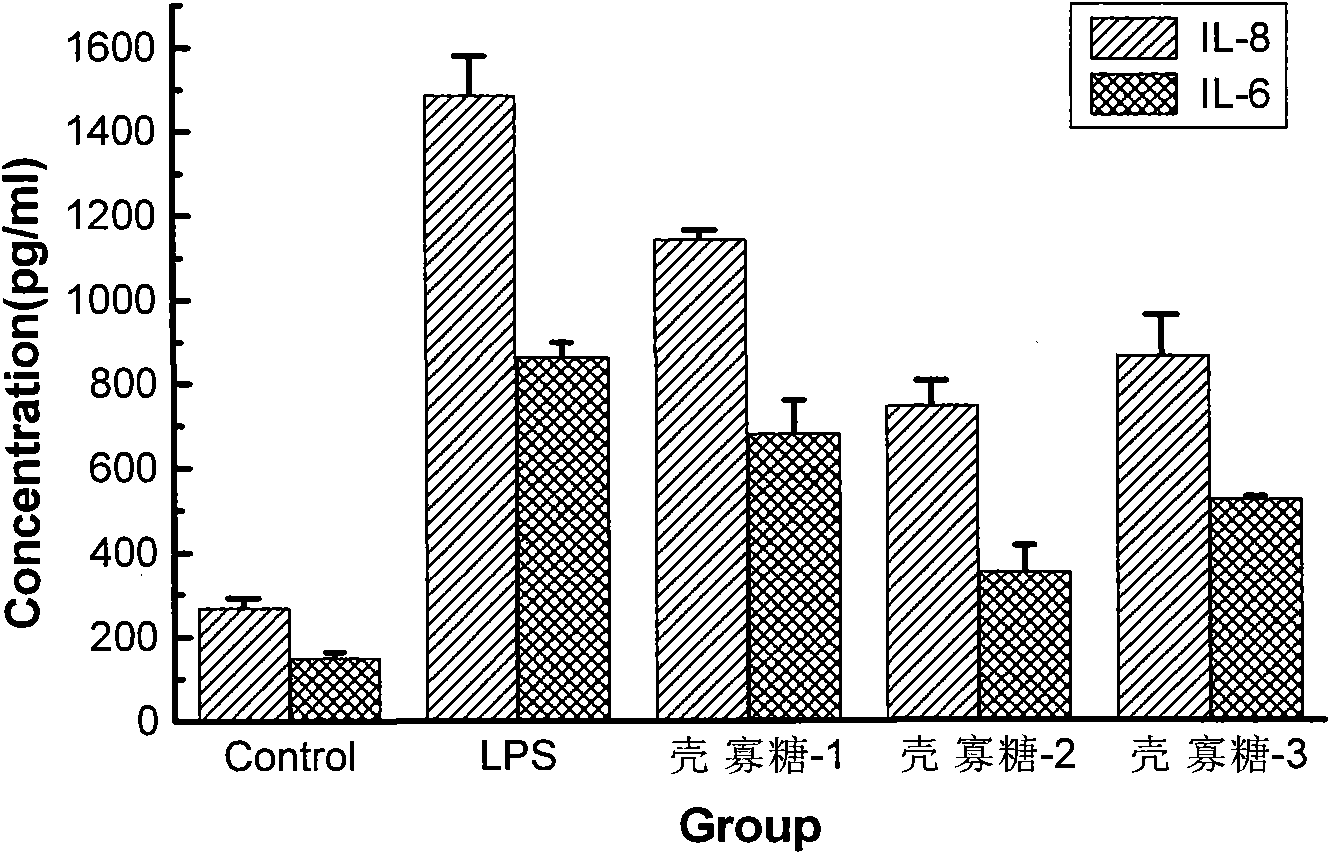
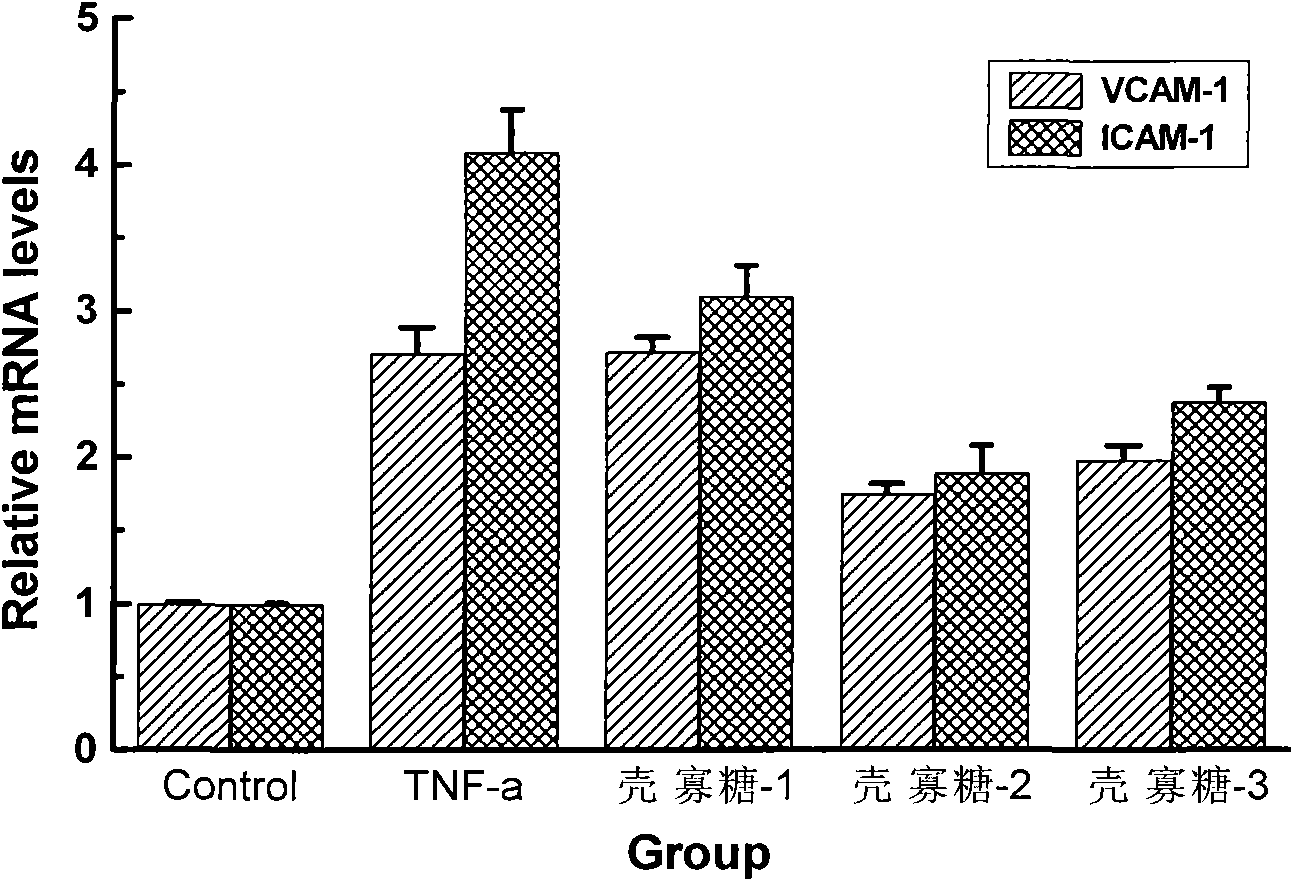
InactiveCN101849958APromote proliferationProtects against oxidative damageOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderVCAM-1Inflammatory factors
The invention relates to a medicine for curing atherosclerosis, in particular to application of oligochitosan in preparing a medicine for preventing from the formation of atherosclerosis. The application takes lipopolysaccharide (lipopolysaccharide) and humanized gene recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) as an induction factor, and takes human umbilical vein endothelial cell as a research object, thereby having the following results: (1) the oligochitosan can obviously restrain the expressions of IL-8, IL-6 and relevant inflammatory factors in the lipopolysaccharide-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell; (2) the oligochitosan can obviously restrain the expressions of membrane surface molecules VCAM-1. ICAM-1 and relevant adhesion molecules family members of the TNF-alpha-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell; and (3) the oligochitosan can obviously restrain the adhesion between the TNF-alpha-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell and the human mononuclear cell.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of double-response nano prodrug for cancer synergistic treatment
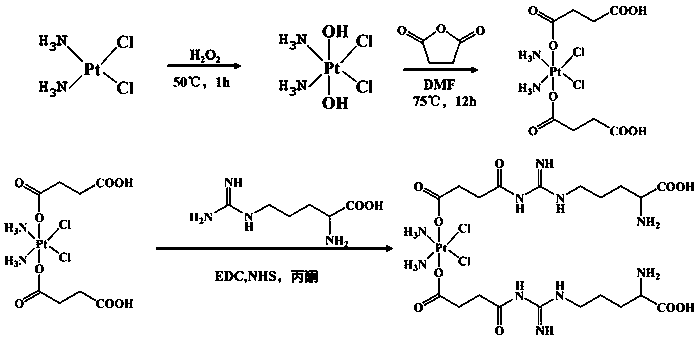
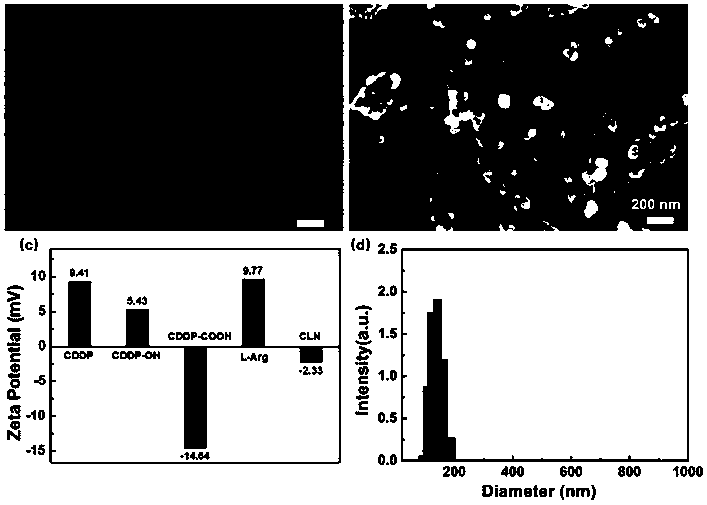
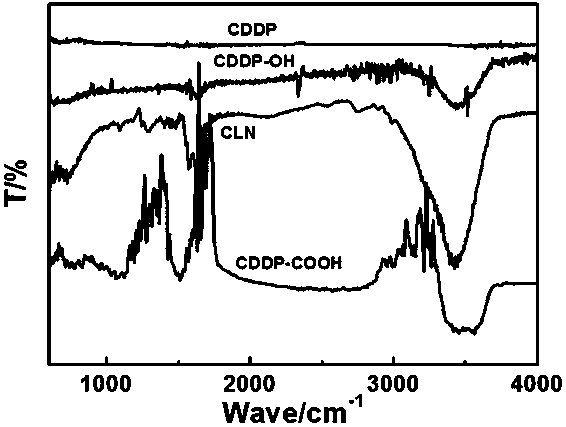
ActiveCN110898229ASimple methodRepress transcriptionInorganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCarboxyl radicalArginine
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-response nano prodrug for cancer synergistic treatment. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with cis-platinum as a precursor,performing carboxylation modification and then carboxyl activation on the cis-platinum; mixing the activated carboxyl cis-platinum with L-arginine; and forming a double-response nano prodrug with thecis-platinum / arginine composite structure through dehydration condensation of intermolecular carboxyl and amino. The method has advantages of being simple, green, and mild and being low in cost. Thecis-platinum can effectively inhibit DNA transcription to realize the effect of treating cancer; cis-platinum can promote H2O2 generation under the induction of NOX enzyme in vivo and the arginine serving as human amino acid can react with H2O2 to generate NO, so that tumor extinction is further induced. Therefore, the nano prodrug is expected to be developed into an efficient anticancer drug.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Dual inhibitors of AR and BET and use thereof
PendingCN110960528AHepatic drug enzyme metabolism stability is goodRepress transcriptionAntibacterial agentsIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsDiseaseMetabolite
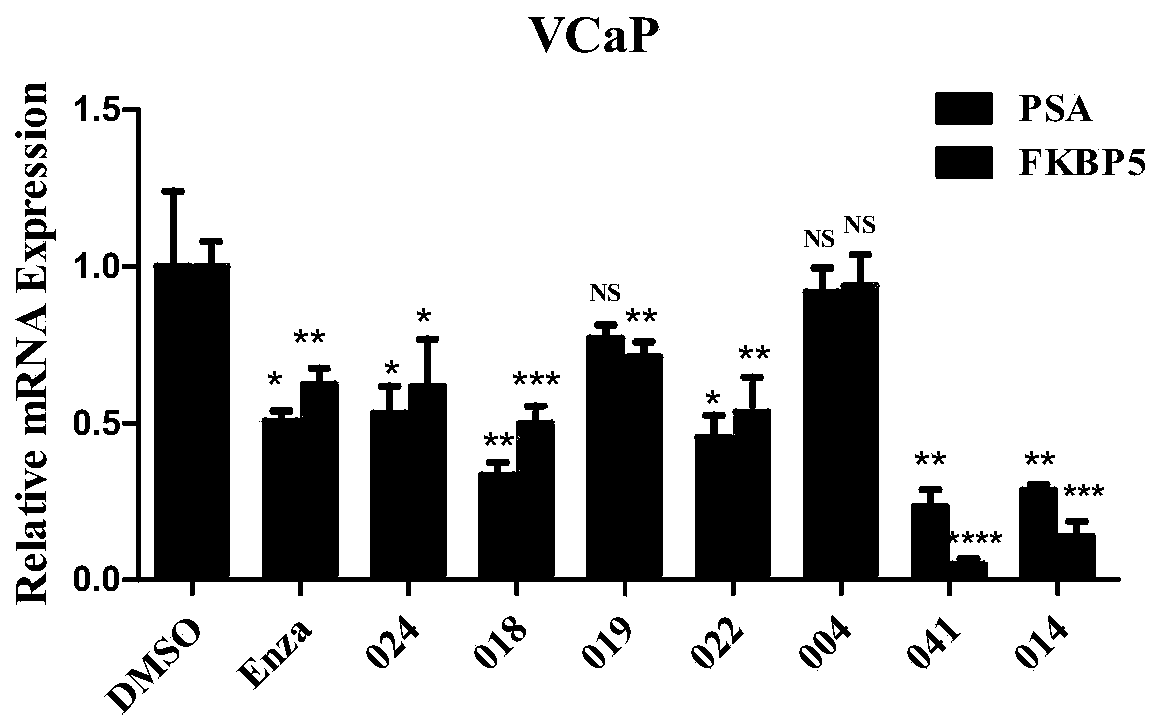
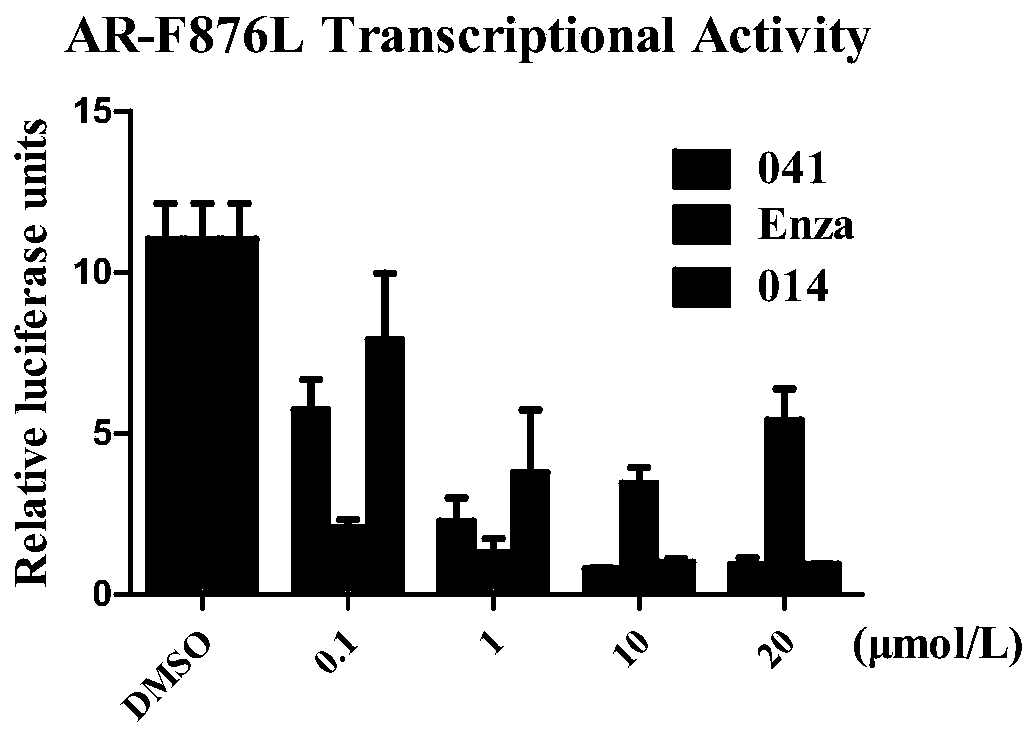
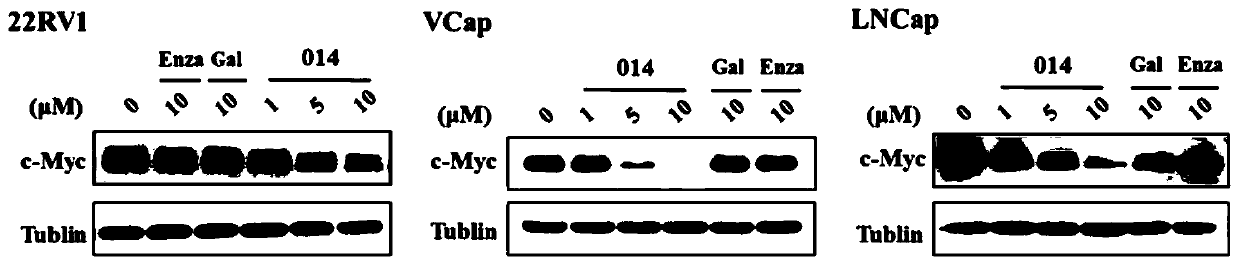
The present invention provides a polycyclic compound represented by formula (I) and a use in dual inhibitors of AR and BET. Specifically, the present invention provides the use of a compound represented by formula (I) or optical isomers, solvates, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs, tautomers, mesomers, racemates, enantiomers, diastereomers, mixture form, metabolites, metabolic precursorsor isotopic substitution form thereof in the preparation of dual inhibitors of AR and BET. Experimental results show that the compounds of the present invention can not only inhibit the transcriptionof PSA and FKBP5 downstream of AR, but also inhibit the transcriptional activity of AR-F876L mutants resistant to anthralin, and also downregulate the expression of BRD4 downstream protein c-Myc, andthe compounds have good binding affinity to AR and BET proteins. The experiment suggests that the compound of the present invention can inhibit the activity of AR and BET protein at the same time, and has a good application prospect in the preparation of medicine for preventing and / or treating diseases related to BET protein.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Application of lycopene in preparation of antiviral drugs
ActiveCN111920821AInhibits cysteine protease activityBroad-spectrum inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsAntiviral drugLycopene
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to application of lycopene in preparation of antiviral drugs. The lycopene has a new function of inhibiting cysteine protease activity, has a broad-spectrum inhibition effect on viruses containing 3CLpro, and can be used for research and development of antiviral drugs.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of hydrogen sulfide releasing agent in preparation of medicament for treating renal fibrosis disease
InactiveCN103040861APrevent proliferationRepress transcriptionUrinary disorderSulfur/selenium/tellurium inorganic active ingredientsDiseaseSodium hydrosulfide
The invention relates to the field of renal fibrosis disease treatment medicaments, in particular to an application of a hydrogen sulfide releasing agent in preparation of a medicament for treating renal fibrosis disease. According to the application of the hydrogen sulfide releasing agent in the preparation of the medicament for treating the renal fibrosis disease, the hydrogen sulfide releasing agent is sodium hydrosulfide or sodium sulfide. The sodium hydrosulfide or the sodium sulfide acts on renal fibroblasts, so that proliferation and differentiation of the renal interstitial fibroblasts are inhibited, deposition of renal interstitial collagen fibers is inhibited, the renal function is improved, further rise of serum creatinine and serum potassium levels is avoided, and the releasing agent has an effect of resisting renal fibrosis.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Antibacterial, worm-expelling and fresh-preserving cotton cloth
InactiveCN101725038ALife restrictionImprove biological activityVegetal fibresAgricultural scienceFood safety
The invention discloses antibacterial, worm-expelling and fresh-preserving cotton cloth which is prepared by the steps of: dipping the pure cotton cloth in pepper water with concentration of 1% for at least 10min, and then spraying molecular chitin or chitosan with the amount of 2.5g / sq.m on the cotton cloth after the cotton cloth is dried. The cotton cloth treated by the method is made into various packaging supplies with a sterilizing rate of 60%, a worm-expelling rate of 98% and a valid period of up to half a year. The packaging bag made of the antibacterial, worm-expelling and fresh-preserving pure cotton cloth is safe and non-toxic for packaging cereal products and dried fruits, good for people's health, simple and convenient to make, and worth popularizing.
Owner:李亚平
Novel pesticide for controlling plant bacterial diseases and preparation method of novel pesticide
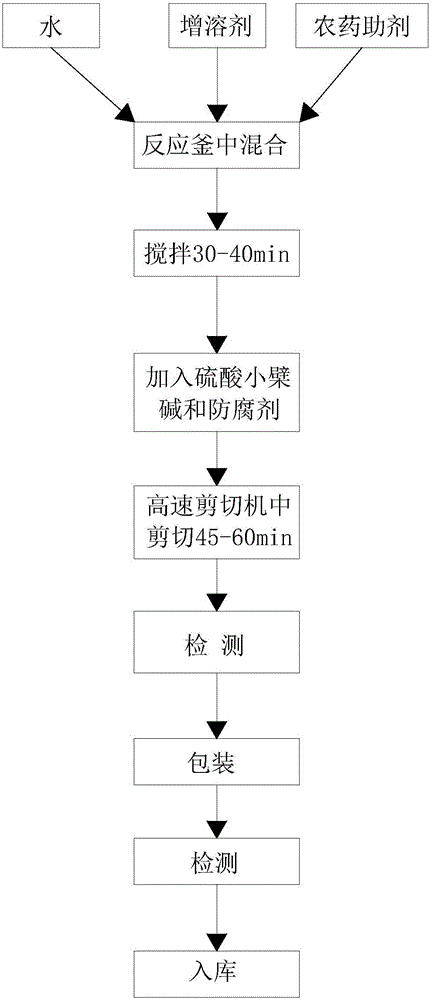
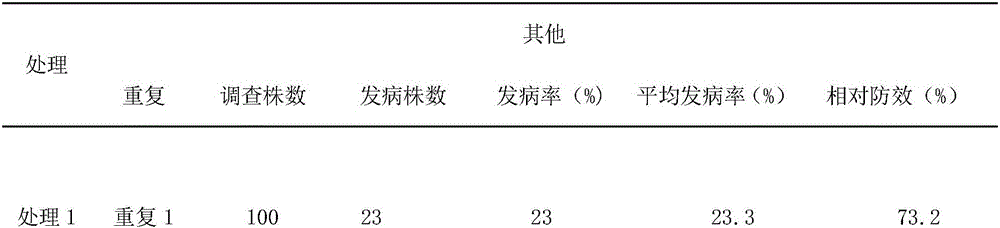
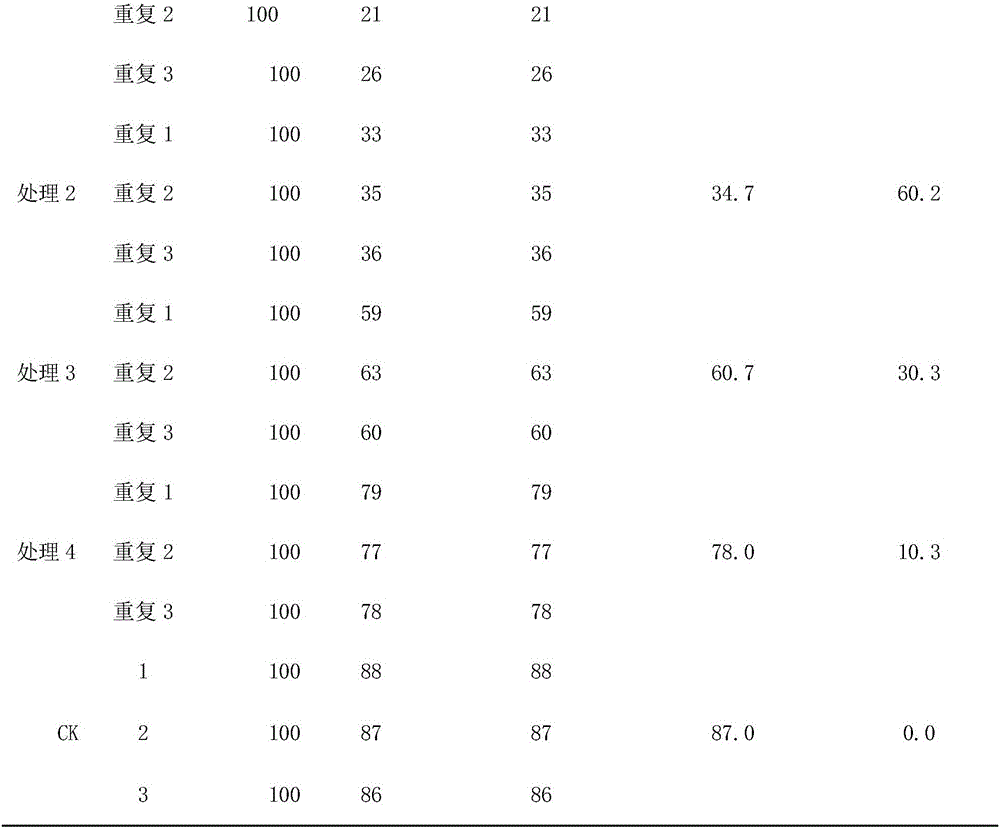
The invention discloses a novel pesticide for controlling plant bacterial diseases. The novel pesticide is prepared from raw materials in percentage by weight as follows: 1%-10% of berberine sulfate, 1%-10% of a solubilizer, 5%-15% of pesticide adjuvants and 0.1%-1% of a preservative, wherein berberine sulfate is chemically synthesized or extracted and purified from a traditional Chinese medicine, and the molecular formula is C20H18NO8S; the mole ratio of the solubilizer to berberine sulfate is 1:1-2; the novel pesticide for controlling plant bacterial diseases mainly contains 0.5%-1% of berberine sulfate and the balance of the solubilizer, the pesticide adjuvants and water; the novel pesticide adopts a form of a microemulsion, an aqueous solution or an emulsion in water. The application method of the novel pesticide comprises the following steps: the pesticide is diluted to 500-1,000 times solution, and the solution is used for root irrigation or sprayed to rhizome bases of tobacco plants after tobacco seedlings are transplanted for about 7-10 days, is applied once every 8-11 days and is continuously applied 3-4 times. The novel pesticide has wide antibacterial spectrum, does not produce drug resistance easily, is low-toxic for human and livestock, is residue-free and produces little pollution, and the control effect on the plant bacterial diseases such as tobacco bacterial wilt and the like is better than that of agricultural streptomycin.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +2
Organic selenium composition and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107213261AImprove immunityGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsFungi medical ingredientsCarcinogenCancer cell
The invention provides an organic selenium composition which comprises selenium-enriched edible fungus powder, wolfberries, honeysuckle and vitamin E. The organic selenium composition can be used as a food, can also be used as a medicine, can be taken for a long period of time, and is capable of improving the human immunity, preventing tumors, inhibiting growth of cancer cells and synthesis of DNA, RNA and protein, inhibiting oncogene transcription and interfering with metabolism of carcinogenic substances. The selenium-enriched edible fungus powder is matched with the wolfberries, the honeysuckle, the vitamin E and Jerusalem artichoke for use, so that the synergistic effects can be developed, the human immunity is enhanced, especially, the immunity of patients receiving tumor chemotherapy is enhanced, and the chemotherapy effect is strengthened.
Owner:吴庆旺
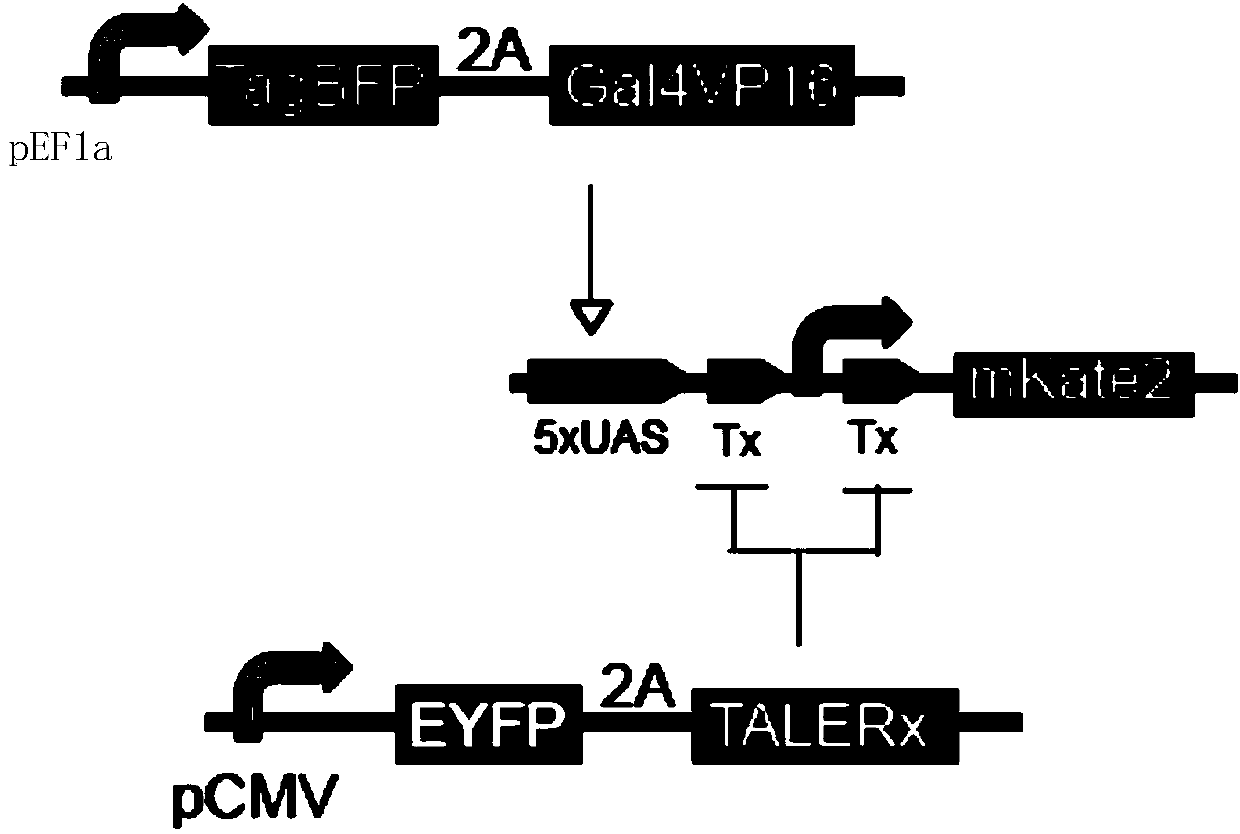
TALER protein for displaying transcription inhibiting action through steric hindrance and application thereof
ActiveCN104178506ARepress transcriptionMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria peptidesBiologyFunctional studies
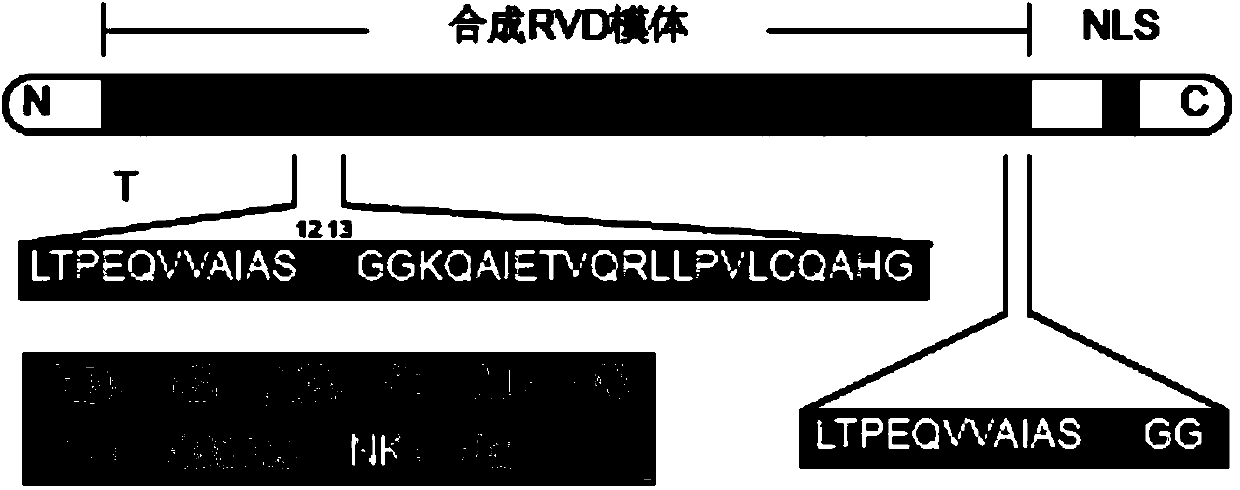
The invention discloses a TALER protein for displaying transcription inhibiting action through steric hindrance and application thereof. The invention protects application of the TALER protein in inactivating a target promoter. The upper stream and lower stream of the target promoter are respectively provided with at least one target spot of the TALER protein; or the upper stream of the target promoter is not provided with the target spot of the TALER protein, but the lower stream is provided with at least one target spot of the TALER protein. The invention also protects application of the TALER protein in inactivating the coding gene of the target protein. The expression of the coding gene of the target protein is started by the target promoter. The upper stream and lower stream of the target promoter are respectively provided with at least one target spot of the TALER protein; or the upper stream of the target promoter is not provided with the target spot of the TALER protein, but the lower stream is provided with at least one target spot of the TALER protein. The TALER protein has important value for regulation expression modes and function studies of proteins.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
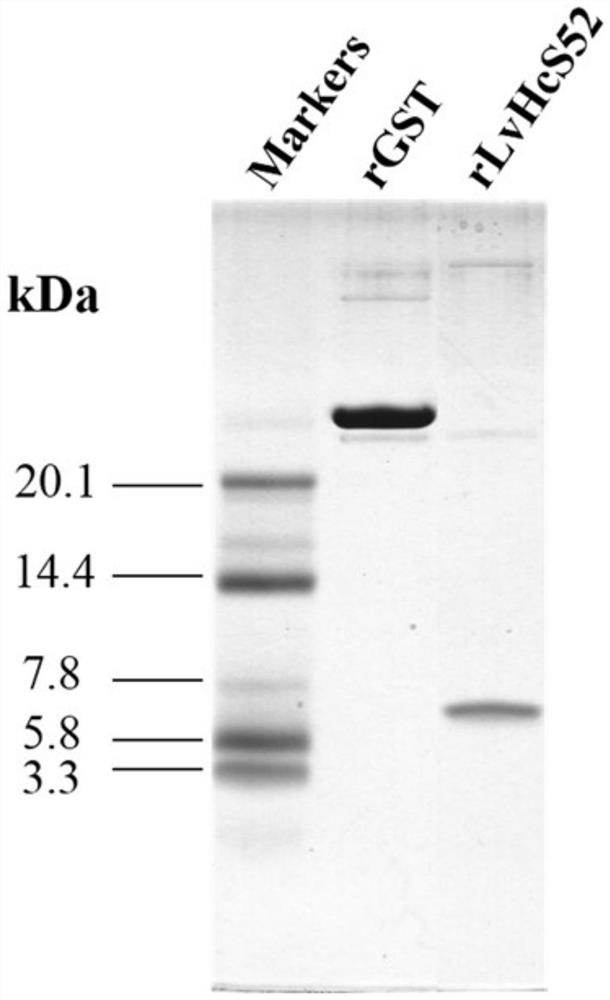
Anti-WSSV peptide LvHcS52 from blood blue protein of penaeus vannamei and application thereof
ActiveCN108976298APrevent proliferationRepress transcriptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsAntimicrobial peptidesLate gene
The invention relates to an anti-WSSV peptide LvHcS52 from blood blue protein of penaeus vannamei. The amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1; the coding gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:2; the short peptide LvHcS52 can obviously inhibit the WSSV immediate early gene wsv069 and late stage gene wsv421 transcription at both the animal level and the in vitro cell level; meanwhile, the WSSV proliferation can also be obviously inhibited in the body; the STAT signal path in the prawn blood cells can be activated; the transcription of the downstream antimicrobial peptide of the signal path can be triggered so that the anti-WSSV function is achieved. The anti-WSSV peptide LvHcS52 provided by the invention can be used as a preparation for inhibiting WSSV, and can be added into feed as additives so as to improve the anti-WSSV capability of the penaeus vannamei.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
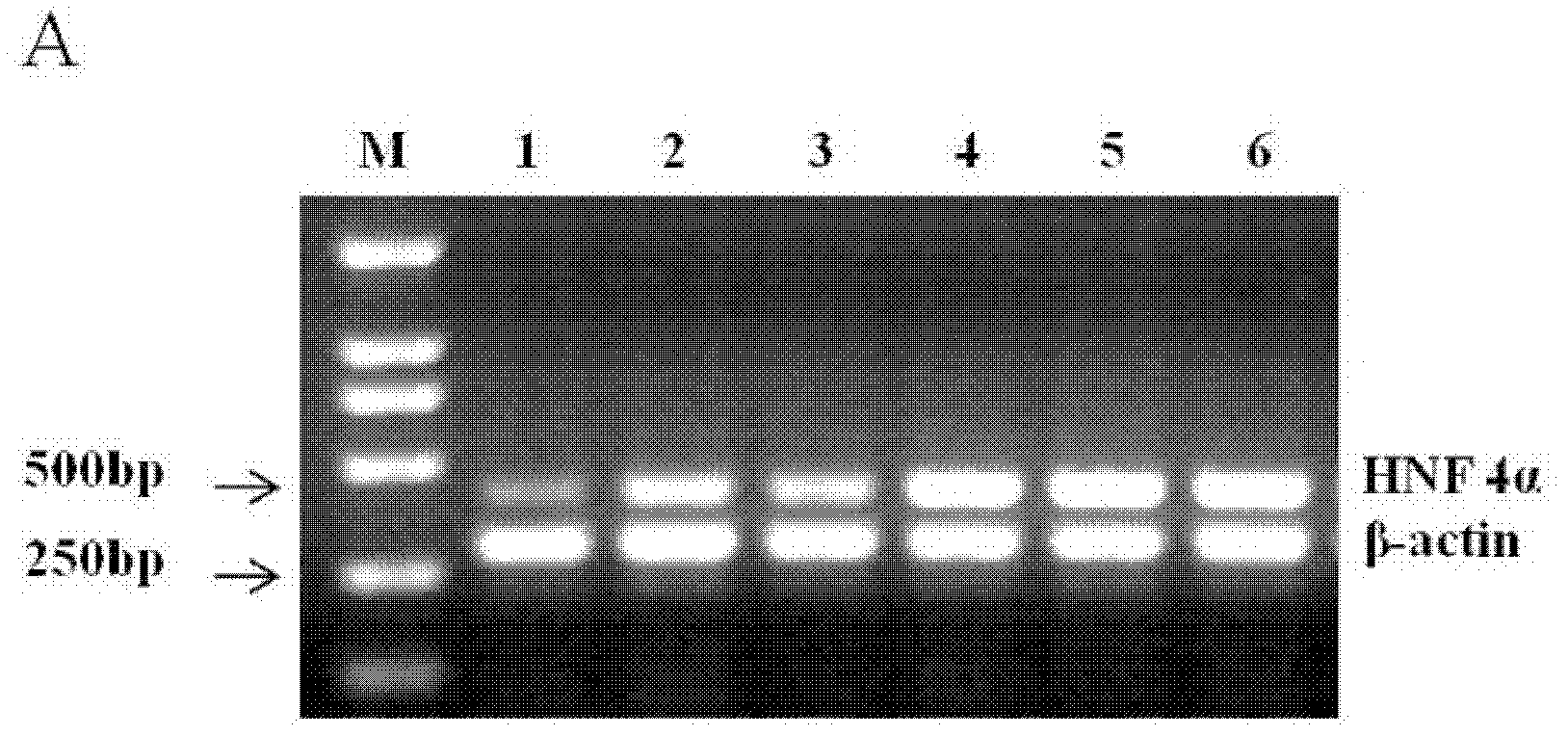
RNA interference sequence aiming at hepatocyte nuclear factor 4a and applications thereof
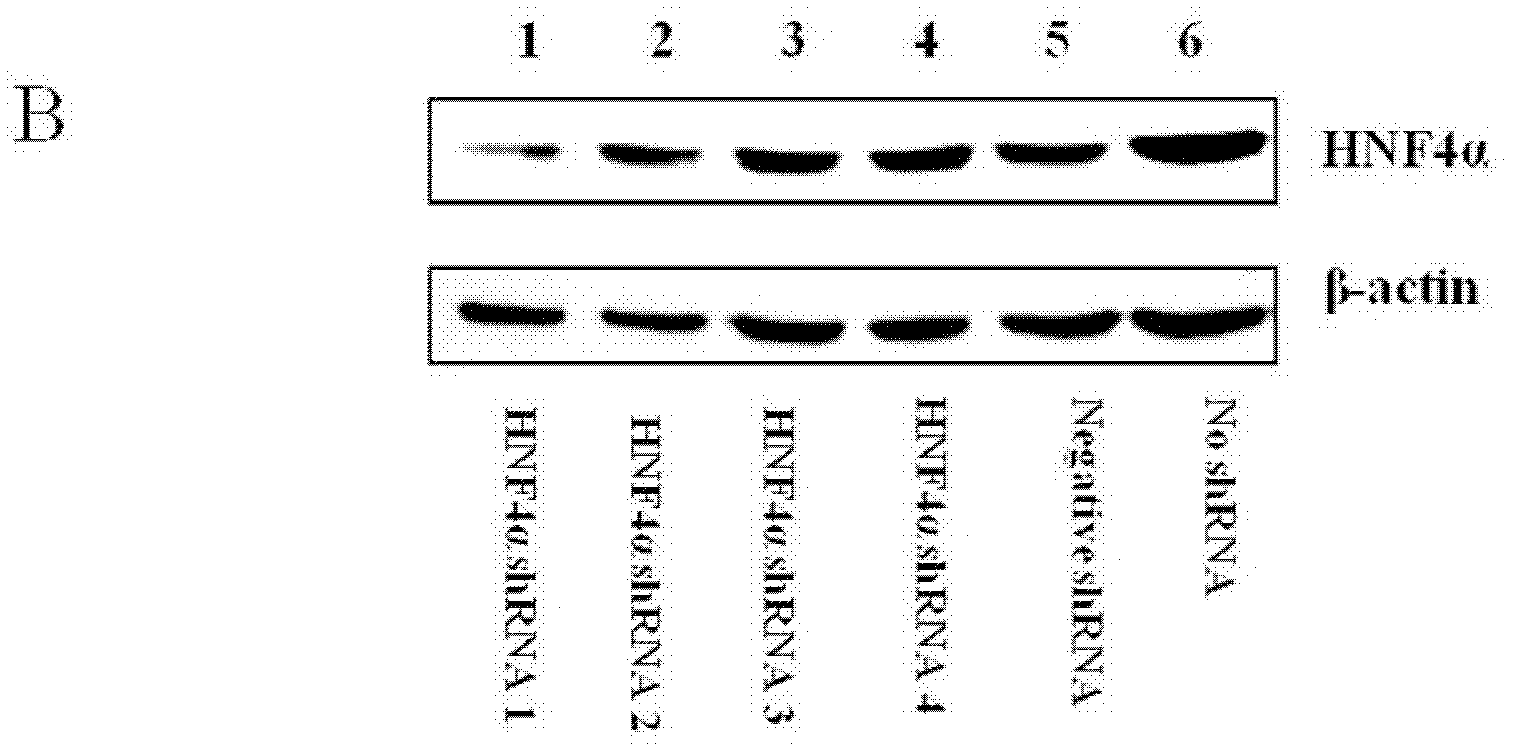
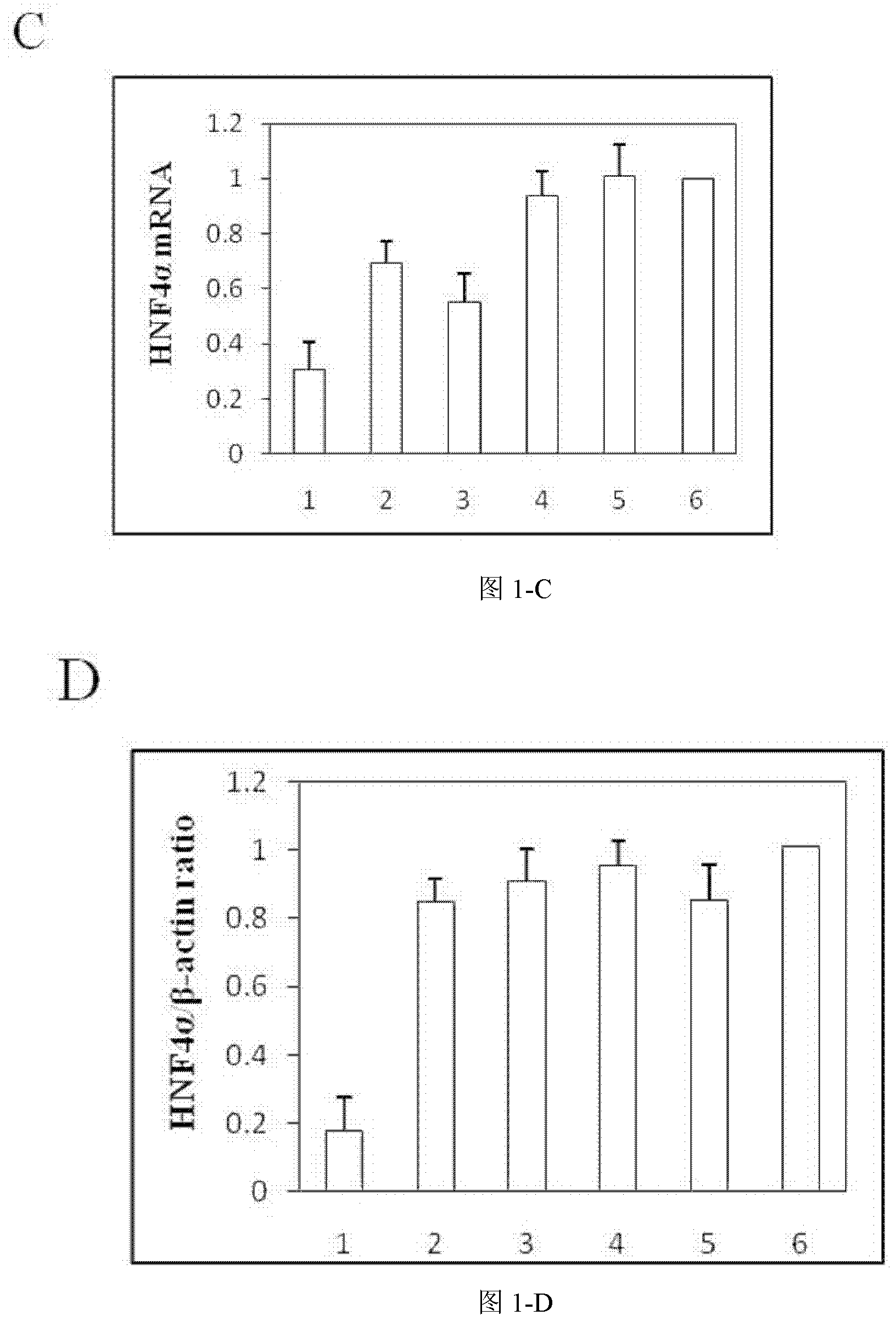
ActiveCN102304515ARepress transcriptionInhibition of replicationGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemSide effectHepatocyte nuclear factors
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Usage of human interferon in preparation of medicines for treatment or prevention of HPV (human paillomavirus) related diseases
InactiveCN102614497AGood antiviral effectInhibition of replicationPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseGenital Tract Infections
The invention relates to the medical field, and discloses the usage of human interferon in preparation of medicines for treatment or prevention of HPV (human paillomavirus) related diseases. According to clinical tests, human interferon has curative effects on HPV infection, and particularly has remarkable curative effects on simple type HPV infection and high-risk type HPV continuous genital tract infection. The usage of human interferon is significant to preventive treatment of HPV infection, particularly the simple type HPV infection, and prevention and reduction of cervical erosion and cervical cancers, and has bright clinical application prospect.
Owner:ZHAOKE PHARMA HEFEI
Application of Mad1 protein in regulation and control of fungal sporulation and germination and plant linolenic acid metabolic pathway
ActiveCN112390864AGrowth rate has no effectLow sporulationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses application of Mad1 protein in regulation and control of fungal sporulation and germination. Metarhizium anisopliae is used as a starting strain, a mad1 gene knockout strain (delta mad1) is obtained through a homologous recombination method, and the growth rate, sporulation and germination biological characteristics of a wild strain and the delta mad1 are measured. The wildstrain and delta mad1 spore suspensions are used for soaking the root of a peanut seedling to detect the transcription level of a linolenic acid metabolic pathway gene of the treated peanut root. Experimental results show that compared with the wild strain, the germination rate and sporulation quantity of the delta mad1 are remarkably reduced, the delta mad1 remarkably inhibits transcription of the linolenic acid metabolic pathway gene after acting on a plant, and thus the Mad1 can promote sporulation and germination of the Metarhizium anisopliae and up-regulate the transcription level of thelinolenic acid metabolic pathway gene. Theoretical support is provided for improvement and industrial production of fungal strains, and basic data are provided for Mad1 induced plant response to regulation and control of interaction between the Metarhizium anisopliae and the plant.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
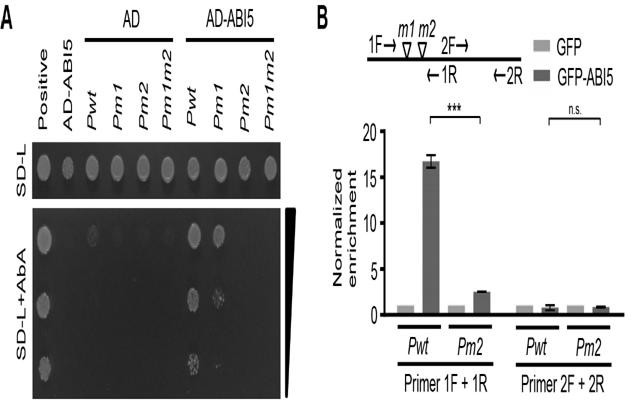
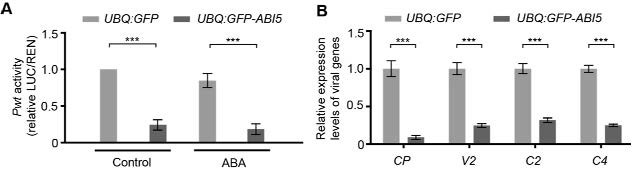
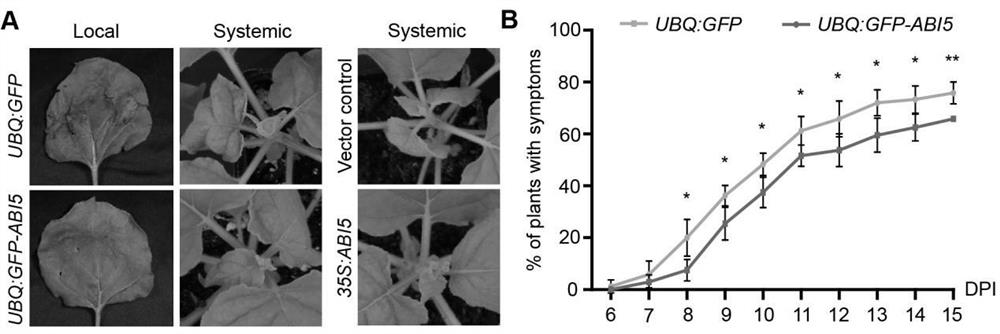
Method for inhibiting geminivirus infection by using arabidopsis ABI5 protein overexpression
ActiveCN114107321AEffect controlInhibition of transcriptional activityVectorsPlant peptidesPromoterArabidopsis sp.
The invention discloses a method for inhibiting geminivirus infection by overexpression of arabidopsis ABI5 protein, which inhibits transcription of geminivirus coding genes by overexpression of plant transcription factor ABI5 protein and combination of ABI5 protein and a promoter of geminivirus through specificity, and realizes improvement of virus resistance of plants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
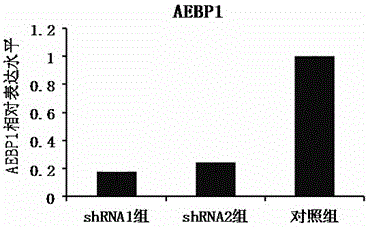
shRNA molecule capable of inhibiting expression of human AEBP1 gene
InactiveCN105950619AReduce expressionSpeed up the development processDNA/RNA fragmentationLentivirusSingle strand
The invention discloses a shRNA molecule capable of inhibiting expression of the human AEBP1 gene. According to the human AEBP1 gene (with a serial number of NM_001129.4) in Genbank, four shRNA molecules are designed and are synthesized targeted at the sequence of shRNA; two synthesized complementary single-stranded shRNA molecules are subjected to annealing to form a double-stranded shRNA molecule; and the double-stranded shRNA molecule is linked to a lentivirus vector to construct four lentivirus interference RNA plasmids. The shRNA plasmids are used for transfection of a Huh7 cell line containing AEBP1, and relative quantitative analysis is carried out on the AEBP1 gene through real-time quantitative PCR so as to evaluate inhibition effect on the expression of the AEBP1 gene. Results of relative quantitative analysis show that AEBP1-shRNA1 can inhibit transcription of 82.3% of AEBP1 and AEBP1-shRNA2 can inhibit transcription of 75.7% of AEBP1.
Owner:刘媛
Application of sulforaphane and derivatives thereof as bacterial effector protein transcription inhibitor
ActiveCN112568233ARepress transcriptionLower resistancePlant growth regulatorsBiocideMicroorganismBacterial effector protein
The invention discloses application of sulforaphane and derivatives thereof as a bacterial effector protein transcription inhibitor. The invention provides an application of sulforaphane and derivatives thereof in any one of application of the following 1) and 7): 1) prevention and treatment of pathogenic bacteria; 2) improvement of the resistance of plants to pathogenic bacteria; 3) inhibiting ofpathogenicity of pathogenic bacteria; 4) inhibiting of the function of a pathogenic bacterium III type secretion system; 5) inhibiting of the expression of effector protein related genes of a pathogenic bacterium type III secretion system; 6) inhibiting of the expression of a pathogenic bacteria transcription factor hrpL; and 7) using as a pathogenic bacteria effector protein transcription inhibitor. Experiments prove that the sulforaphane and the derivatives thereof can inhibit the function of a pathogenic bacteria type III secretion system by specifically inhibiting transcription of the pathogenic bacteria type III secretion system, can resist invasion of pathogenic bacteria without destroying interaction between plants and beneficial microorganisms, and have a wide application prospectin prevention and treatment of plant pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
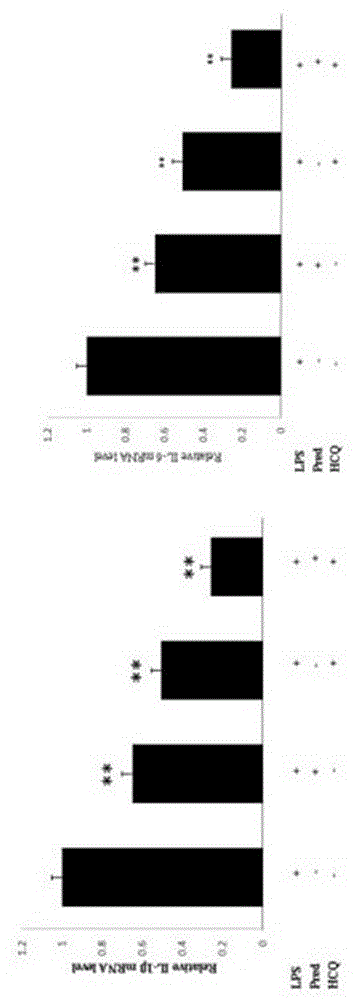
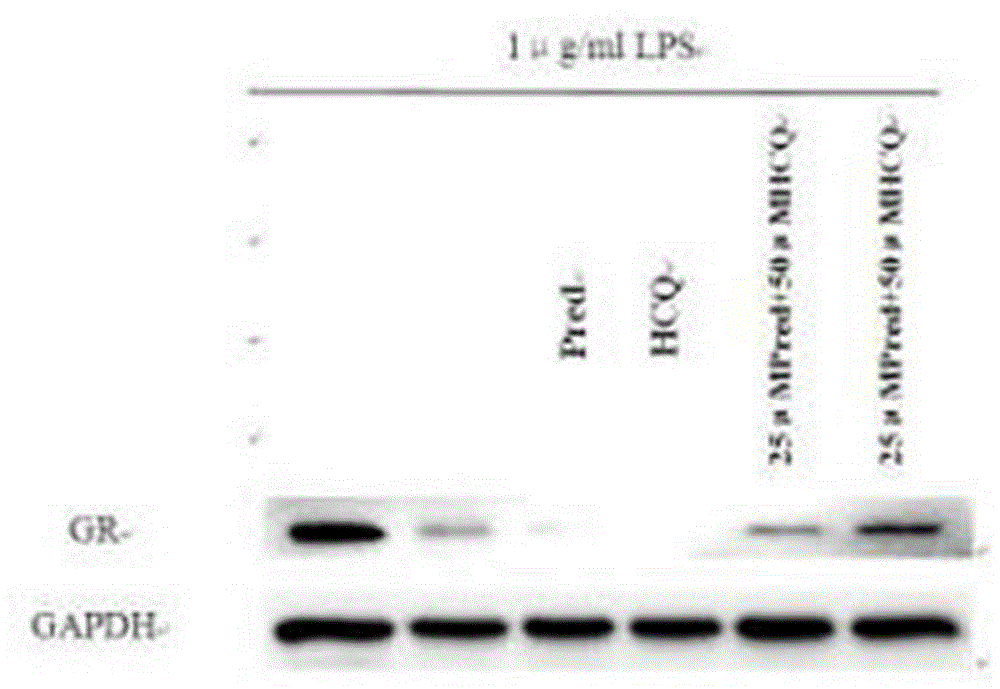
Application of prednisone and hydroxychloroquine to preparation of compound anti-inflammatory drug
InactiveCN103599109ARepress transcriptionReduce optical densityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticHydroxychloroquinePrednisone treatment
The invention discloses an application of prednisone and hydroxychloroquine to the preparation of a compound anti-inflammatory drug. The total dose of prednisone is 0.05-2mg / kg, and the total dose of hydroxychloroquine is 0.83-26.64mg / kg. The prednisone for a mouse, the dose of which is equivalent to half of the normal dose of the prednisone for an adult, is unobvious in anti-inflammatory effect in a dimethylbenzene caused mouse ear swelling test, and the prednisone with the dose has an obvious anti-inflammatory effect after being used together with the hydroxychloroquine. Cell and molecular biological tests prove that IL-1beta and IL-6 transcriptions induced by LPS (Lipopolysaccharide) can be remarkably inhibited by the combination of the hydroxychloroquine and the prednisone, and the inhibiting effect is stronger than the inhibiting effect of the prednisone or the hydroxychloroquine. The invention also develops a novel compound anti-inflammatory drug and lays the foundation for reducing the side treating effect of the prednisone and widening the application range of the prednisone.
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Nano silver durable antibacterial cloth permeated by semiconductor and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106319938AHigh antibacterial activityImprove antibacterial propertiesBiochemical treatment with wool-protecting/anti-moth agentsHigh pressureAtmospheric pressure
The invention discloses nano silver durable antibacterial cloth permeated by semiconductor and preparing method thereof. The invention applies the semiconductor permeation in the preparing of nano silver antibacterial solution and obtains nano silver antibacterial cloth from cloth through high pressure airless spray, squeezing and drying. The antibacterial cloth is obtained by semiconductor permeation. The invention comprises the steps of spraying the nano silver antibacterial solution with high pressure airless spray system, spraying with high pressure airless sprayer, evening up with pressure roller and drying. The invention can efficiently kill more than 650 kinds of bacterial, with sterilization rate reaching 99.9%. The invention also has good killing effect for white candida that is hard to be killed by general nano silver. As the invention improves the permeation and adhesive force and the washing resistance of nano silver antibacterial cloth enhances, the antibacterial effect is durable.
Owner:厦门博正科技有限公司
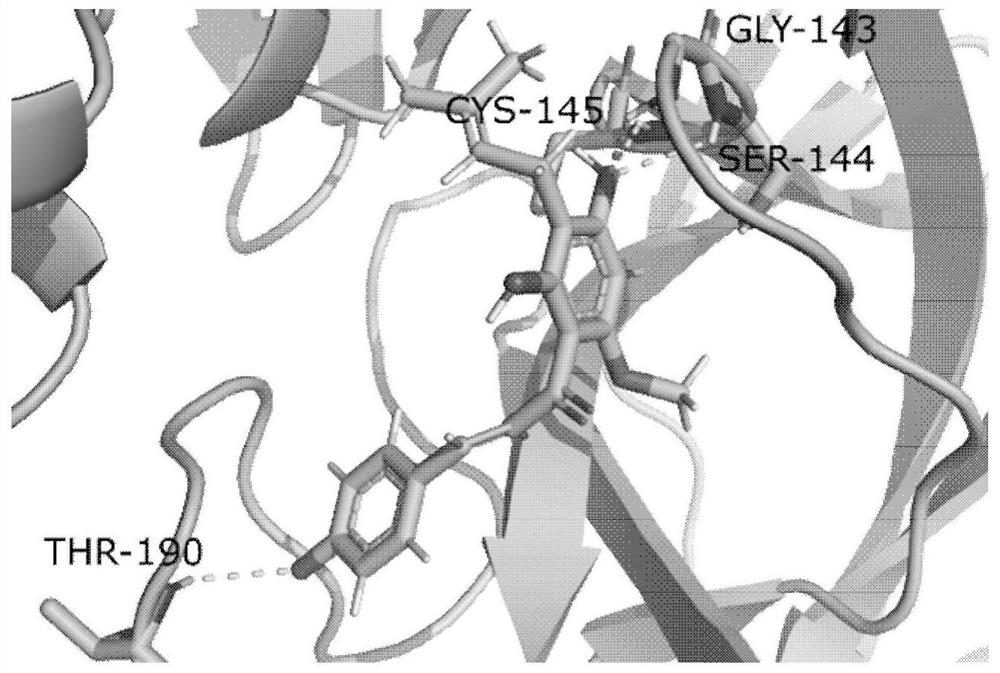
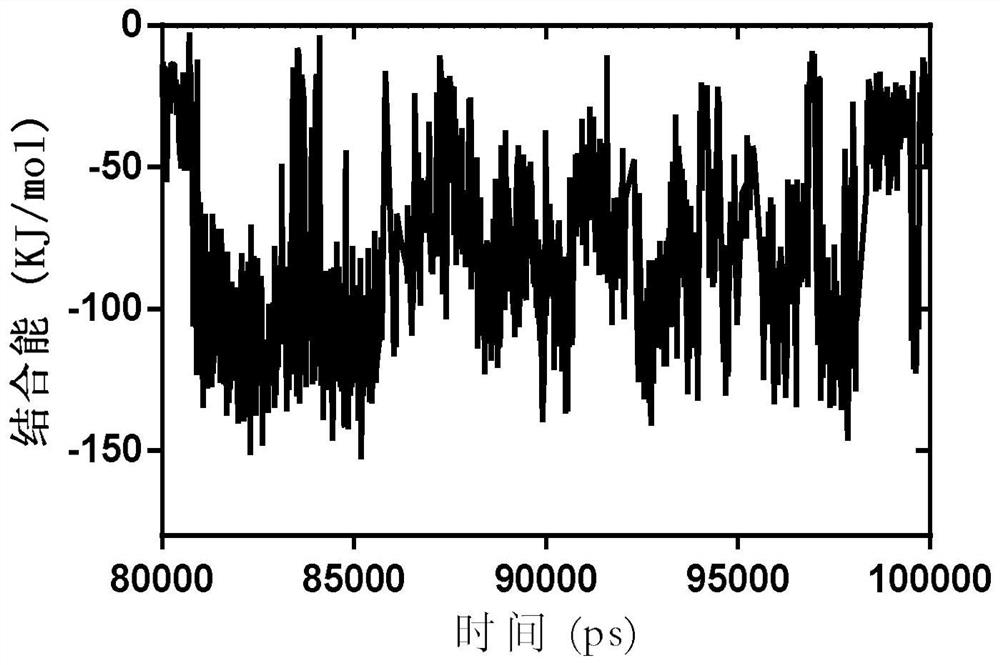
Application of xanthohumol in preparation of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor
InactiveCN112402402AStrong binding strengthInhibitory activityAntiviralsKetone active ingredientsLung InflammationsVirtual screening
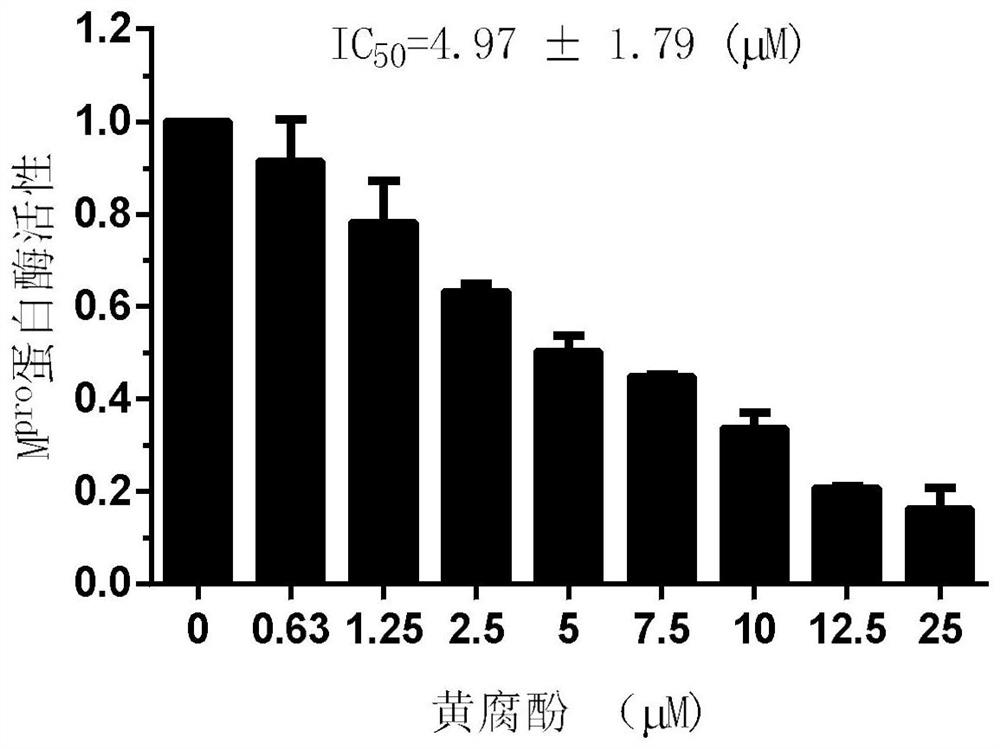
The invention provides application of xanthohumol in preparation of a SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor. The anti-virus active compound xanthohumol with high binding capacity with a Mpro protease is obtained through structure-based virtual screening by taking the Mpro protease, which causes lung inflammation, of the SARS-CoV-2 as a target point. The xanthohumol is bound with the target Mpro protease to inhibitthe activity of the Mpro protease, so that replication and transcription of viruses are inhibited, and the effect of resisting SARS-CoV-2 infection is achieved. The xanthohumol can be applied to preparation of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro protease inhibitor so as to be applied to preparation of a medicine for preventing and / or treating SARS-CoV-2 inflammation. The binding energy of the xanthohumol and theMpro protease is -63.427 KJ / mol, the IC50 of the xanthohumol to the Mpro protease is 4.97 + / - 1.79 [mu]M, and the inhibition constant Ki value is 2.14 [mu]M.
Owner:QINGDAO NAT LAB FOR MARINE SCI & TECH DEV CENT +1
Composition for treating testicular atrophy and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114377036APromote regenerationReduce contentCell dissociation methodsCulture processPlatelets bloodBlood plasma
The invention discloses a composition for treating testicular atrophy and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the field of medicines for treating testicular atrophy, in particular to a composition for treating testicular atrophy and a preparation method thereof. The invention aims to solve the problem of poor testicular atrophy treatment effect of the existing platelet-rich plasma. The composition comprises a platelet lysis buffer and a BMSCs exosome, and the volume ratio of the platelet lysis buffer to the BMSCs exosome is 1: 1. The platelet lysate sPL and the BMSCs exosome are prepared into the composition for promoting cell regeneration, and the composition is used for improving and treating testicular atrophy of rats. By taking activation and recovery of functions of spermatogonial stem cells as an entry point, a sPL preparation method capable of increasing secretion of three growth factors capable of promoting proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells, namely EGF, bFGF and IGF-1, and a BMSCs culture method for highly expressing miR-486-5p exosomes are found. The medicine is used for treating testicular atrophy.
Owner:天晴干细胞股份有限公司
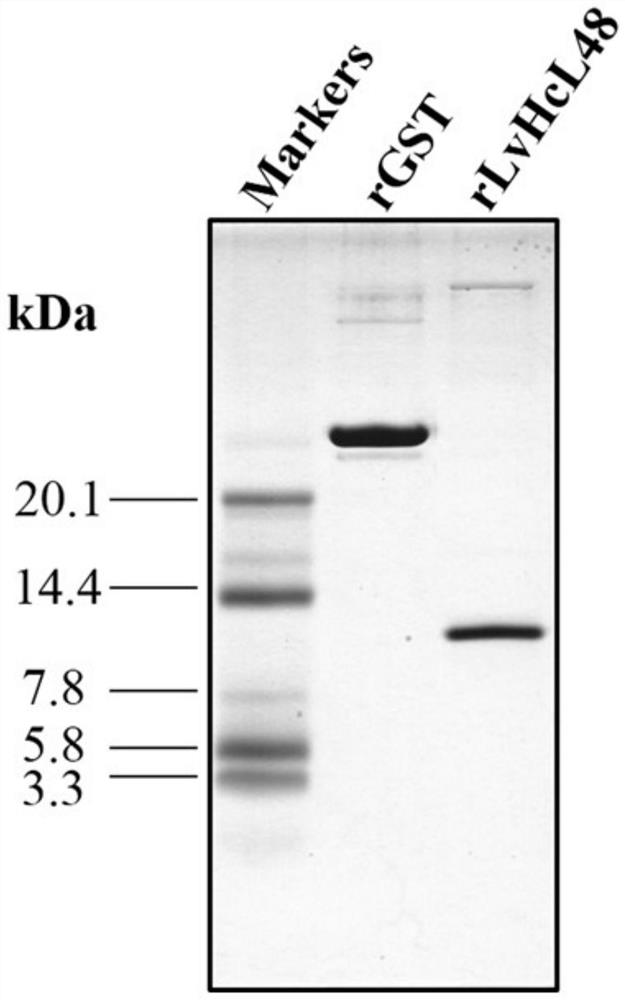
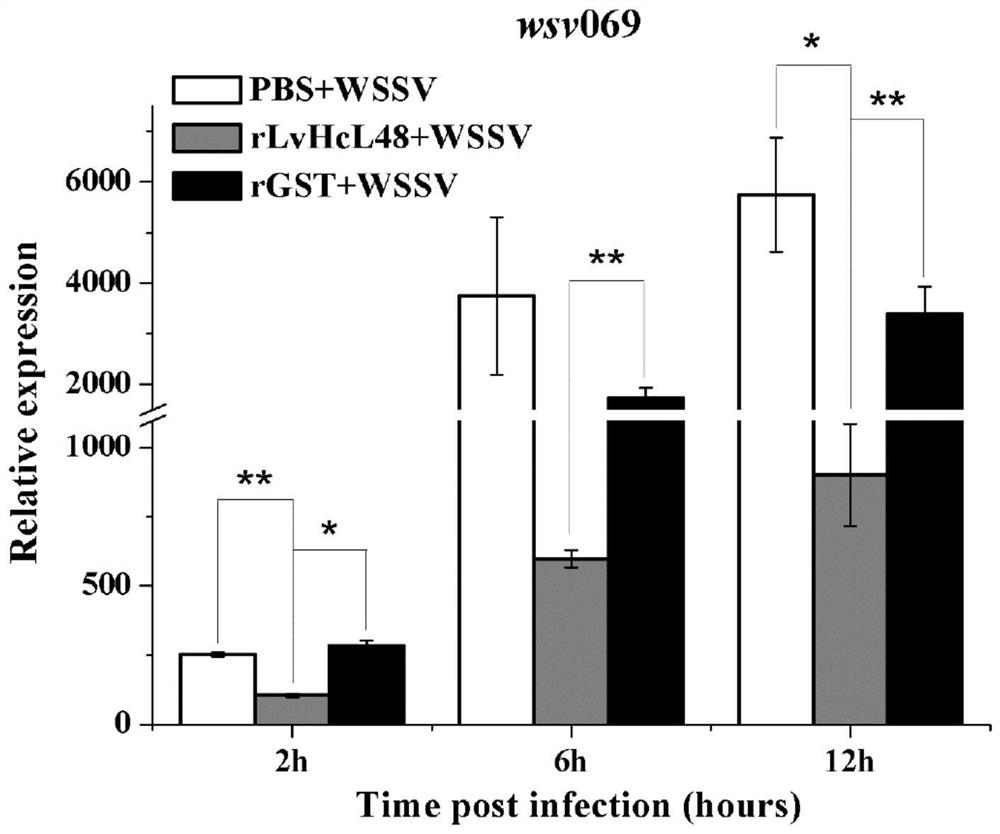
An anti-WSSV peptide lvhcl48 derived from hemocyanin of Litopenaeus vannamei and its application
ActiveCN108840925BPrevent proliferationRepress transcriptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsIn vivoLate gene
The invention relates to an anti-WSSV peptide LvHcL48 derived from Litopenaeus vannamei hemocyanin, the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the coding gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The short peptide LvHcL48 of the present invention can significantly inhibit the transcription of the very early gene wsv069 and the late gene wsv421 of WSSV no matter at the animal level or at the cell level in vitro, and can also significantly inhibit the proliferation of WSSV in vivo; The interaction between outer membrane protein VP28 may be the mechanism of its function. The anti-WSSV peptide LvHcL48 of the present invention can be used as a preparation for inhibiting WSSV, and can be added to feed as an additive in order to improve the anti-WSSV ability of prawns.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Application of two phenylethanoid glycoside compounds to preparation of antidiabetic drugs
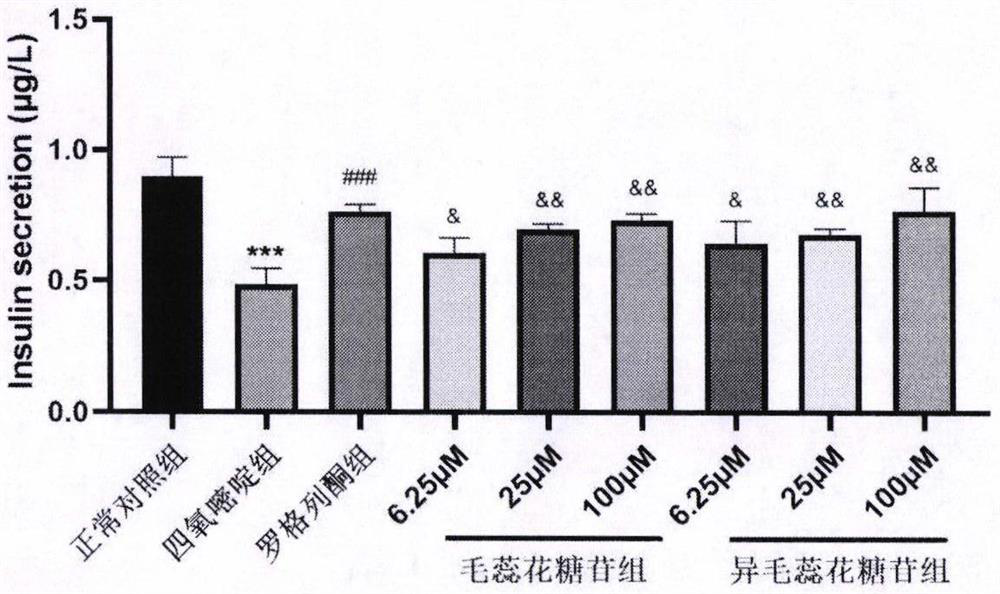
InactiveCN111803510AHigh activityImprove survival rateOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderPancreatic hormoneCaspase
The invention discloses an application of two phenylethanoid glycoside compounds, namely verbascoside and isoacteoside to preparation of antidiabetic drugs. Monomeric compounds of verbascoside and isoacteoside can be extracted from various plants, so that the source is wide, the toxicity is low, and the stability is good. An inventor proves by experiments that (1) the verbascoside and the isoacteoside can protect and repair an injury of an NIT-1 pancreatic beta-cell caused by alloxan, and promote insulin secretion of the injured pancreatic beta-cell in a dose-dependent manner; (2) a free radical injury of the pancreatic beta-cell caused by the alloxan can be reduced; and (3) the activity of the pancreatic cell can be enhanced, the survival rate of the cell is improved, and the mechanisms of the verbascoside and the isoacteoside can activate transcription of an apoptosis-inhibiting gene Bcl-2 mRNA and inhibit transcription of an apoptosis-promoting gene Bax mRNA and finally inhibit transcription of a Caspase-3 gene and expression of Caspase-3 and Bax proteins, thereby inhibiting apoptosis of the pancreatic cell injured by the alloxan. Therefore, the two phenylethanoid glycoside compounds, namely the verbascoside and the isoacteoside disclosed by the invention have potential value of being developed into antidiabetic candidate drugs.
Owner:内蒙古自治区中医医院
An anti-WSSV peptide lvhcs52 derived from hemocyanin of Litopenaeus vannamei and its application
ActiveCN108976298BPrevent proliferationRepress transcriptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsAntimikrobielle peptidePrawn
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Super-wear-resistant antiviral glaze, ceramic tile and preparation method of ceramic tile
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic tiles, and particularly relates to super wear-resistant antiviral glaze, a ceramic tile and a preparation method of the ceramic tile, and the glaze comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of potassium feldspar, 7-15 parts of calcined kaolin, 5-10 parts of quartz, 15-25 parts of dolomite, 5-10 parts of barium carbonate, 3-8 parts of wollastonite, 8-12 parts of corundum, 3-10 parts of zinc-aluminum phosphate and 2-5 parts of strontium phosphate. The ceramic tile disclosed by the invention has a very good antiviral effect and excellent wear resistance, and is high in pollution resistance.
Owner:FOSHAN CITY GANI CERAMICS CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com