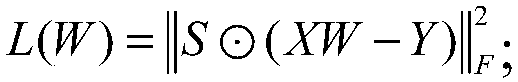Patents
Literature
225 results about "Virtual screening" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Virtual screening (VS) is a computational technique used in drug discovery to search libraries of small molecules in order to identify those structures which are most likely to bind to a drug target, typically a protein receptor or enzyme.
Application of N-(thiofuran-2) pyrazolo (1, 5-a) pyridine-3-formanides compounds for preparing antineoplastic
The invention searches the novel micromolecule inhibitor pyrazolo (1, 5-a) miazines compounds of cyclin-dependent kinase CDK9 (cyclin-dependent kinase) through the virtual screening of a computer, biometrically measures activity thereof, and validates interaction mechanism. The invention specifically comprises the following steps: the three-dimensional crystal conformation of the cyclin-dependent kinase family member CDK9 is obtained in a way of homology modeling; and micromolecule three-dimensional database is screened with DOCK (molecular docking). The invention uses a MTT tumor cell growth inhibition test to biometrically measures the activity of the selected compounds, researches the selected compounds pyrazolo (1, 5-a) miazines with high activety in a way of molecular mechanism, validates the inhibiting effect of the compounds to the activity of CDK9 kinase, and clarifies the interaction mechanism of the compounds for inhibiting the external activity and the molecule of various malignancies such as lung cancer, osteosarcoma, oophoroma, cervical carcinoma, breast cancer, etc.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Compound for targeted ubiquitinated degradation of Smad3
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Compounds and methods for the treatment of viral infections
High throughput and virtual screening methods are disclosed that can identify potential anti-viral agents. The virtual screening methods identify agents that interact with a viral nucleoprotein binding site. The high throughput methods identify compounds that inhibit viral infection by binding to viral nucleoprotein. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical formulations useful for treating or preventing viral infections, especially influenza A.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
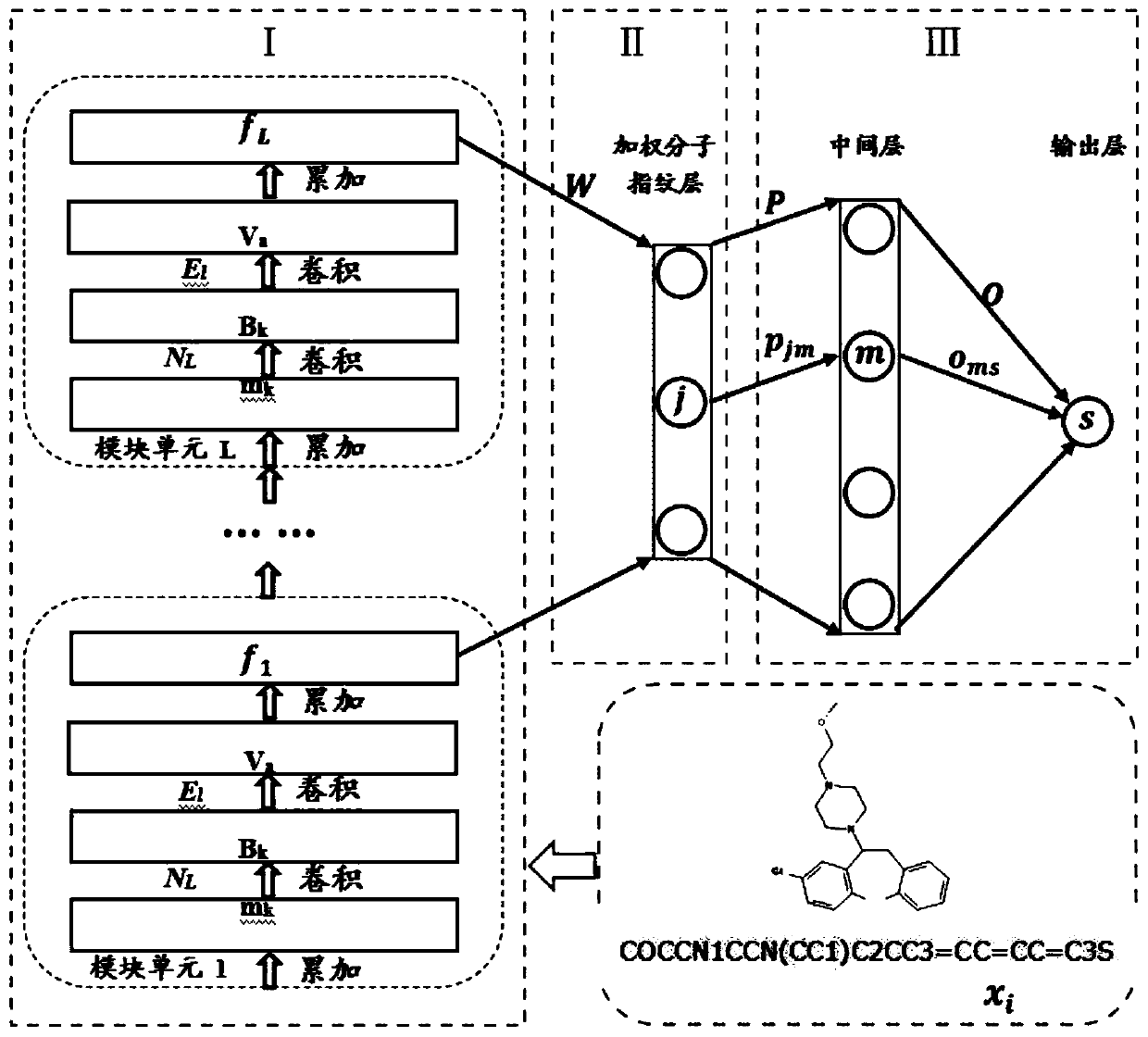
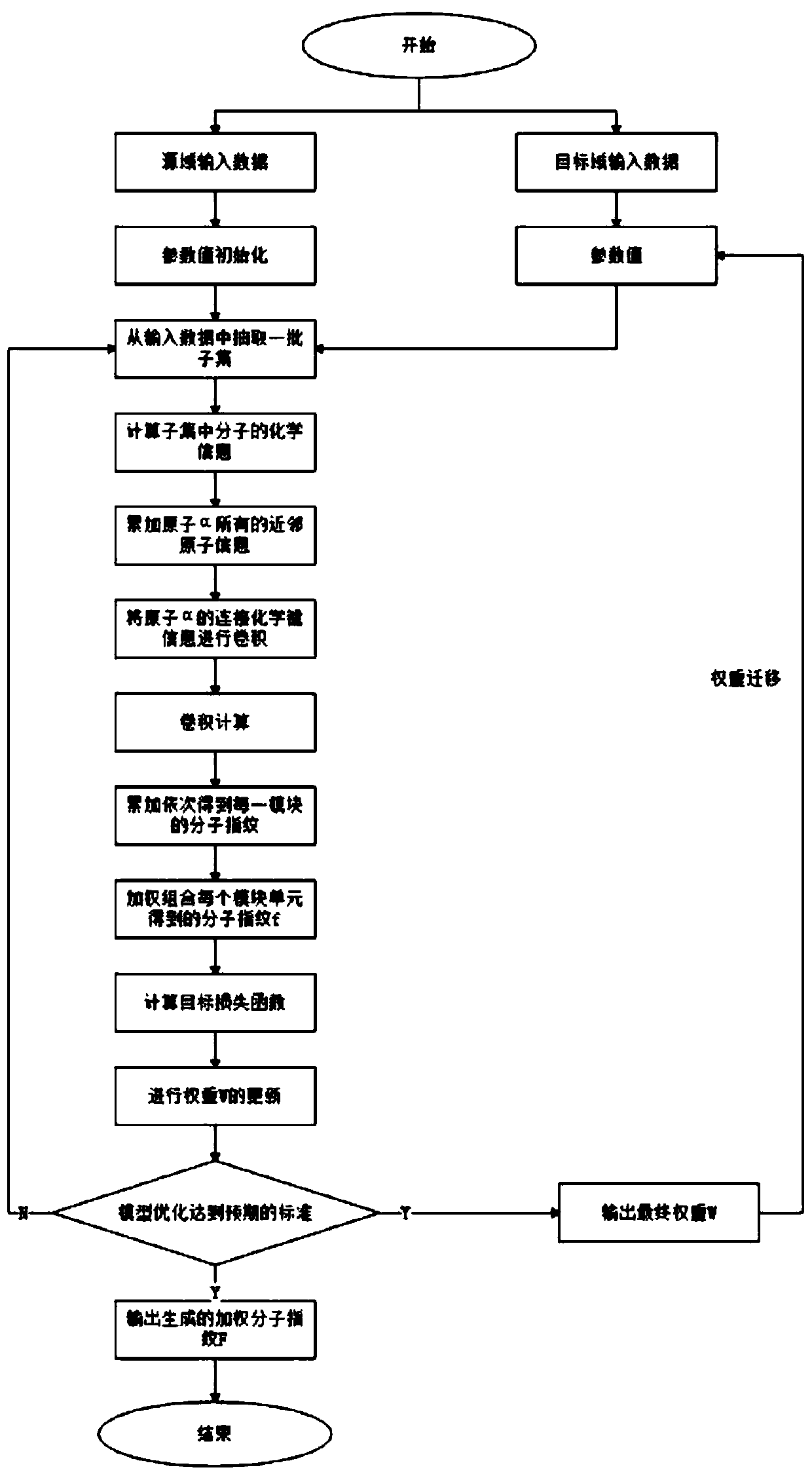
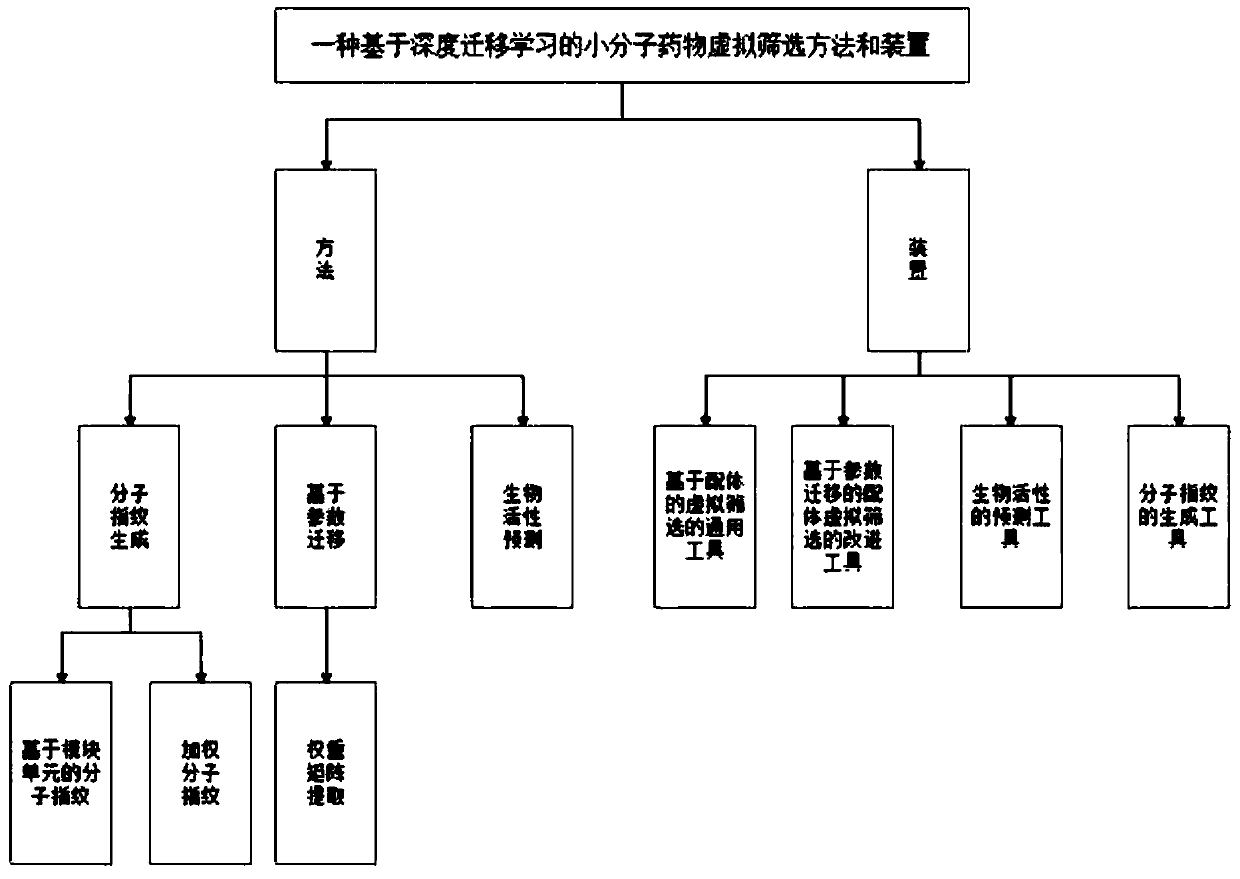
Small molecule drug virtual screening method based on deep migration learning and application thereof
ActiveCN110459274AImplement the buildMolecular designChemical machine learningDrug targetDrug biological activity
The invention discloses a small molecule drug virtual screening method based on deep migration learning and application thereof. A source domain is used as an input to be trained, converged and derived to obtain a weight matrix; a target domain is input into an improvement tool to serve as the initialization weight of the target domain; fine adjustment, training and convergence are conducted on the initialization weight and data in the target domain sequentially; a biological activity value of interaction of a lead compound and a drug target in the target domain is predicted, a target domain molecular fingerprint and a predicted value are obtained, and an evaluation index root mean square error and a correlation coefficient of a predicted result are output; the target domain is subjected to fine adjustment by repeating above steps, and the weight matrix of the source domain helps the target domain build a model. According to the small molecule drug virtual screening method and the application thereof, the effective virtual screening model can still be obtained under the condition that the information of a known active ligand sample is insufficient, and does not need to rely on a large number of data samples.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
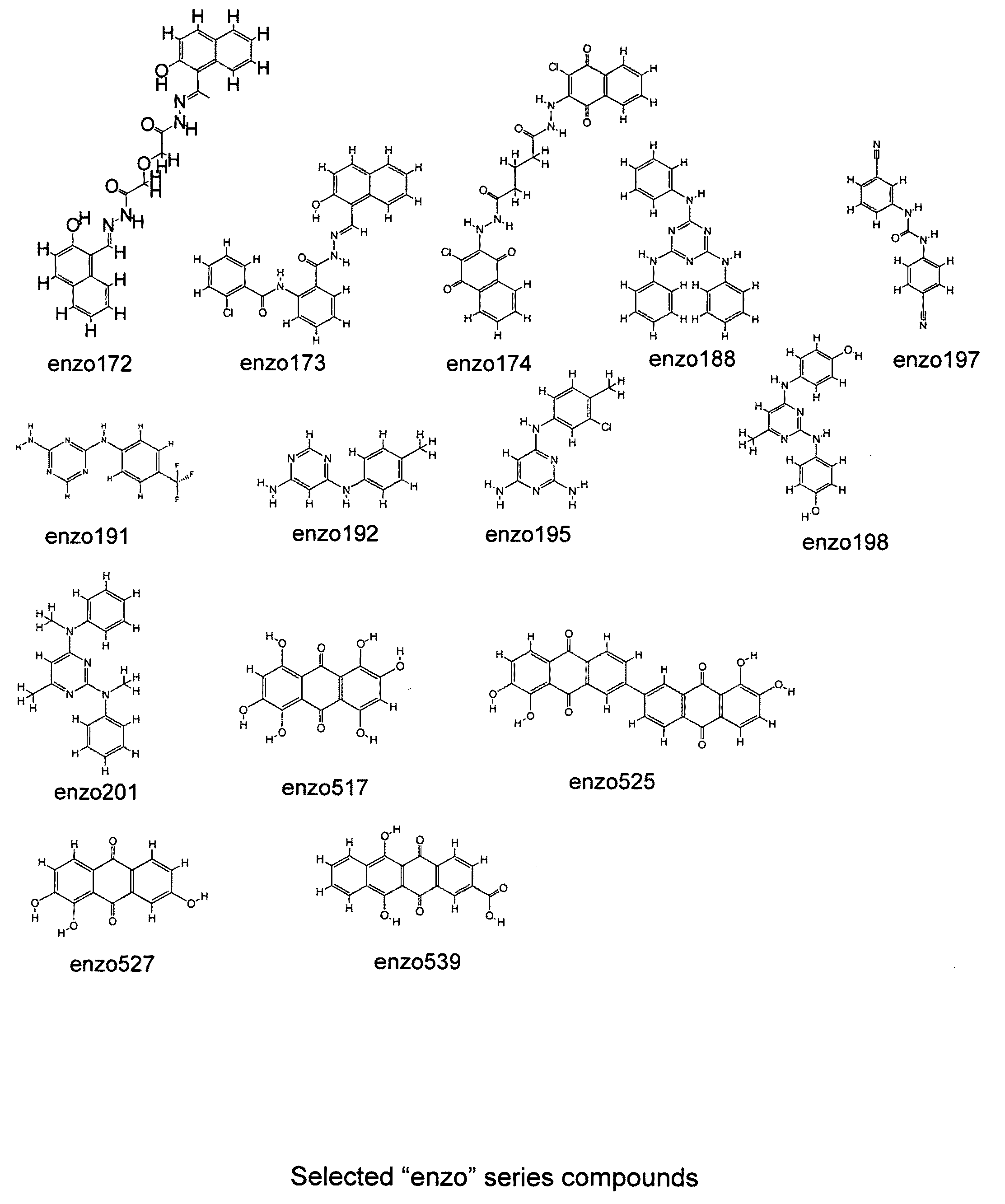
Compounds and assays for controlling Wnt activity
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
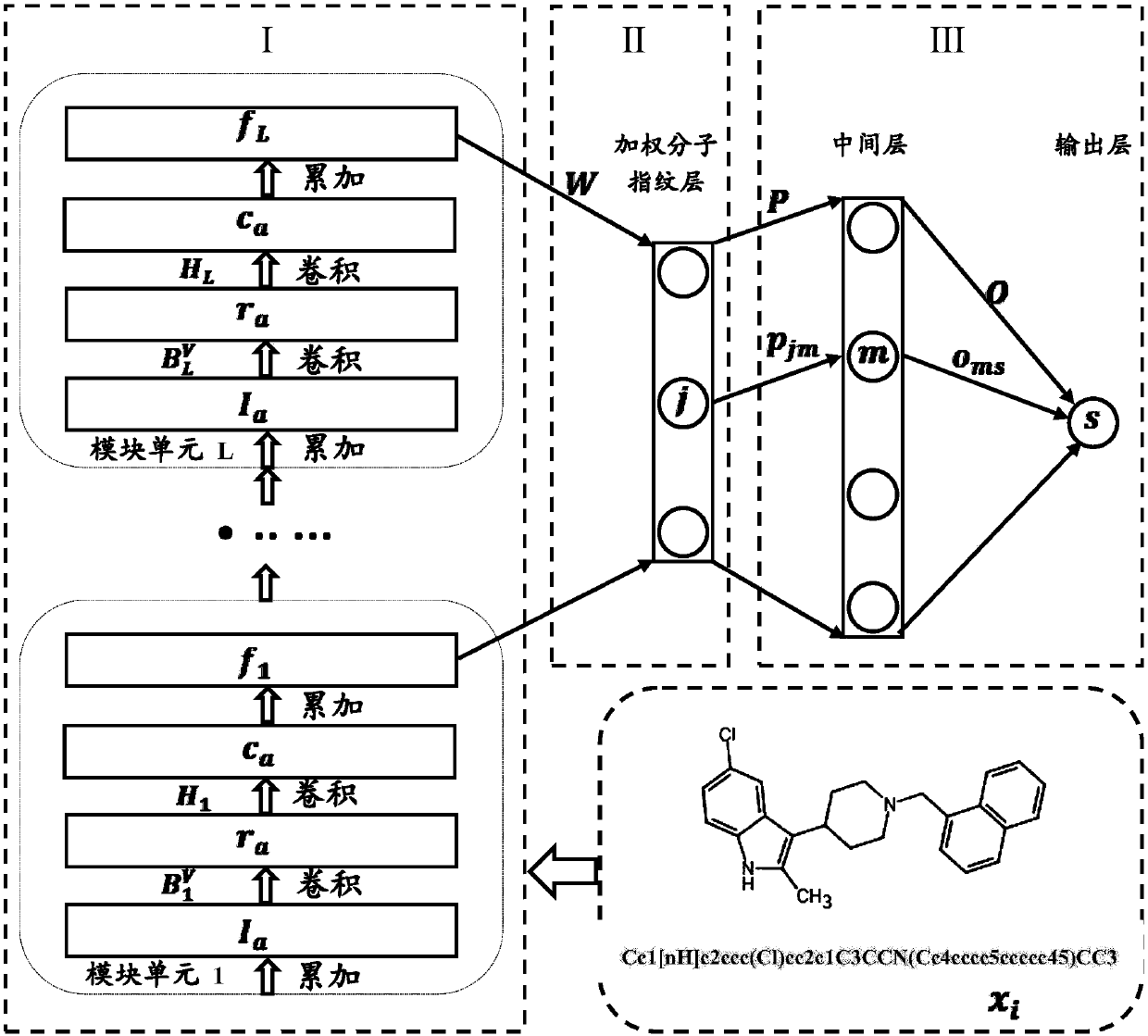
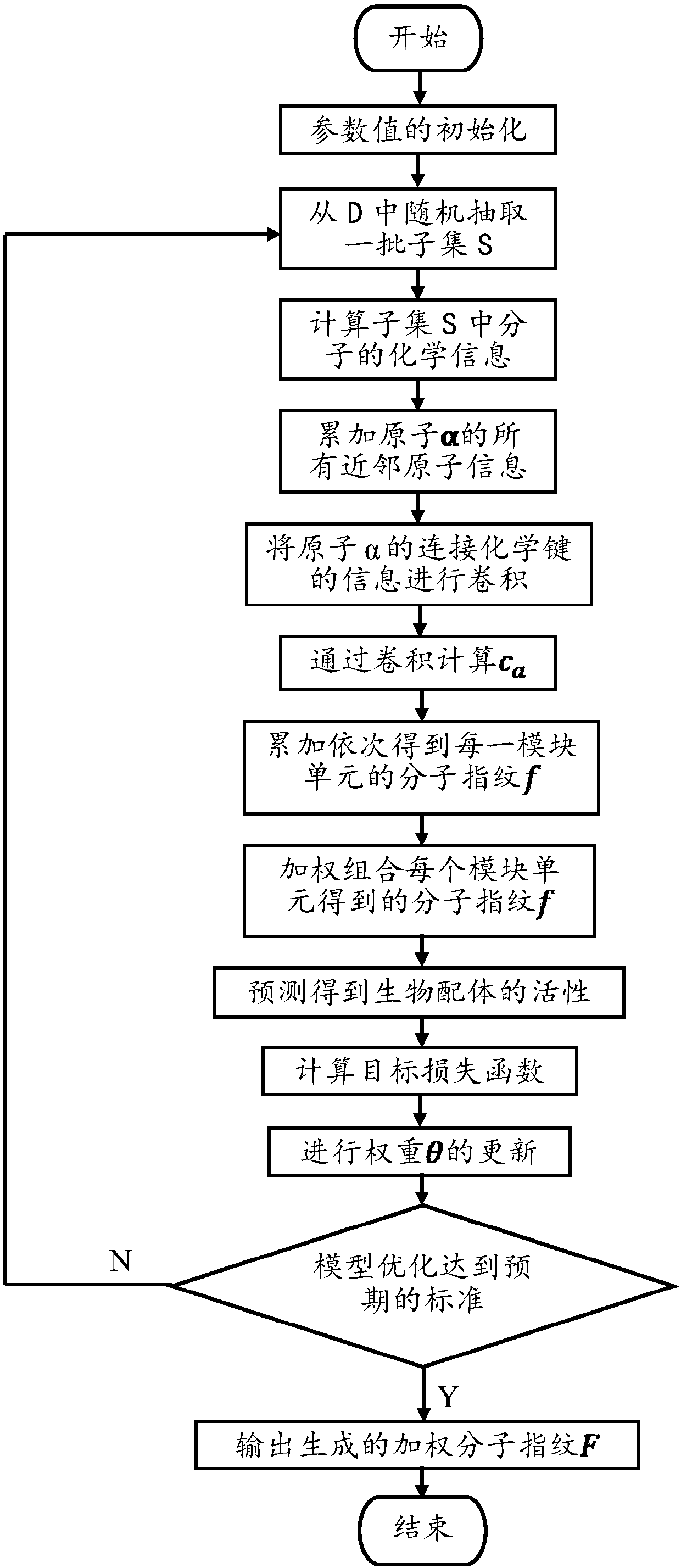
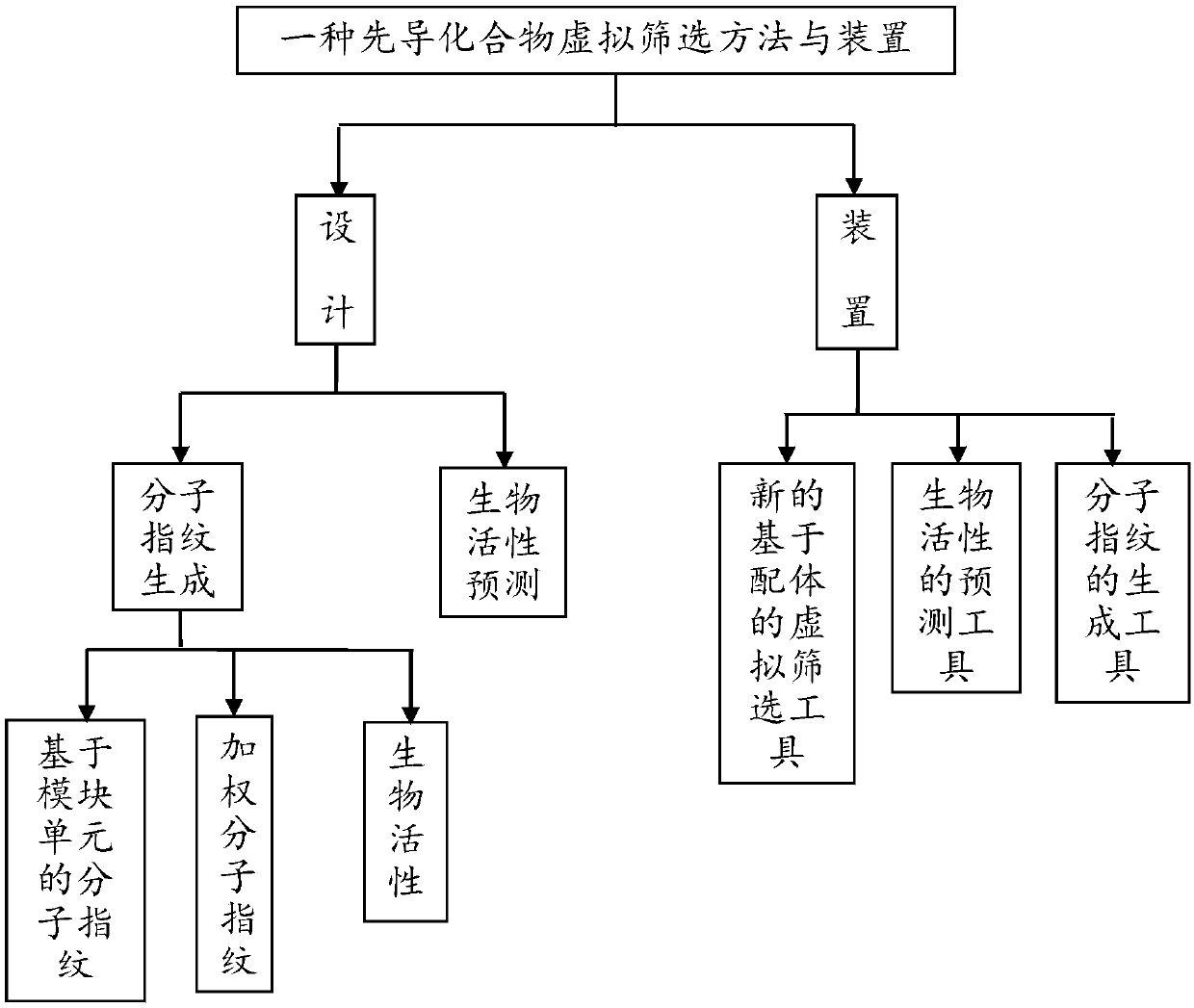
Lead compound virtual screening method and device
ActiveCN107862173AImprove performanceChemical property predictionChemical structure searchVirtual screeningMedicine
The invention discloses a lead compound virtual screening method and device. The method includes the steps of generation of molecular fingerprints of lead compounds on drug targets and bioactivity prediction of interaction between the lead compounds and the drug targets. The generation of the molecular fingerprints includes a molecular fingerprint part based on a module unit, a weighting molecularfingerprint part and a bioactivity part. During the bioactivity prediction, ligand molecular fingerprints and bioactivity values are utilized to serve as input of a random forest regression model, and a prediction model is constructed. Additionally, the device includes a universal tool for virtual screening on the basis of ligands, a prediction tool for the bioactivity generated when the lead compounds take effects on the drug targets, and a generation tool of the molecular fingerprints of the lead compounds on the drug targets. At present, molecular fingerprints which are excellent in performance and are used for the bioactivity prediction are often greater in length, and however, by adopting a designed deep learning algorithm, molecular fingerprints which are excellent in performance and smaller in length can be generated so that the best bioactivity prediction model of drug target ligands can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
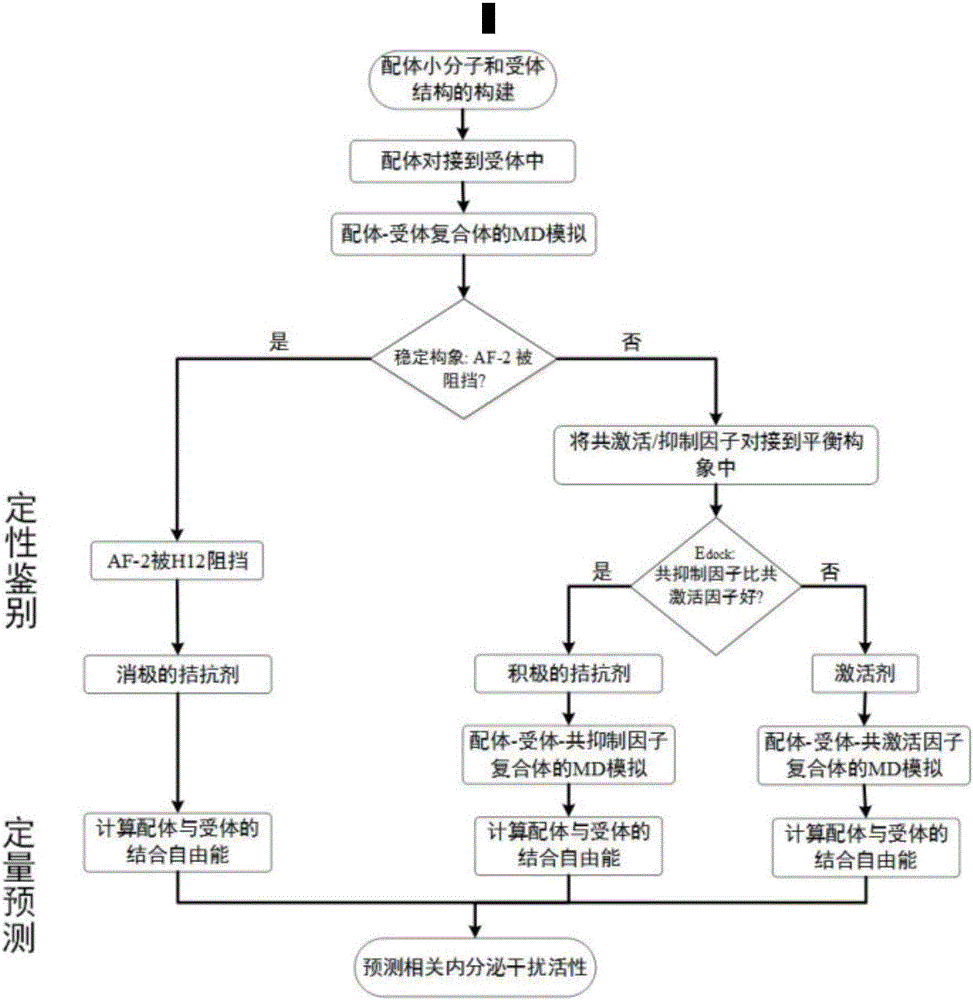
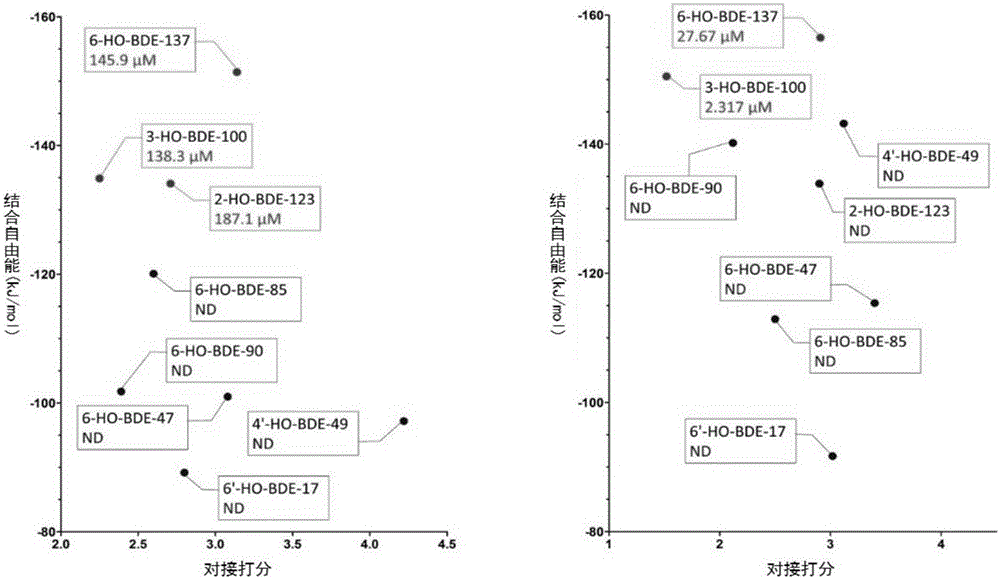
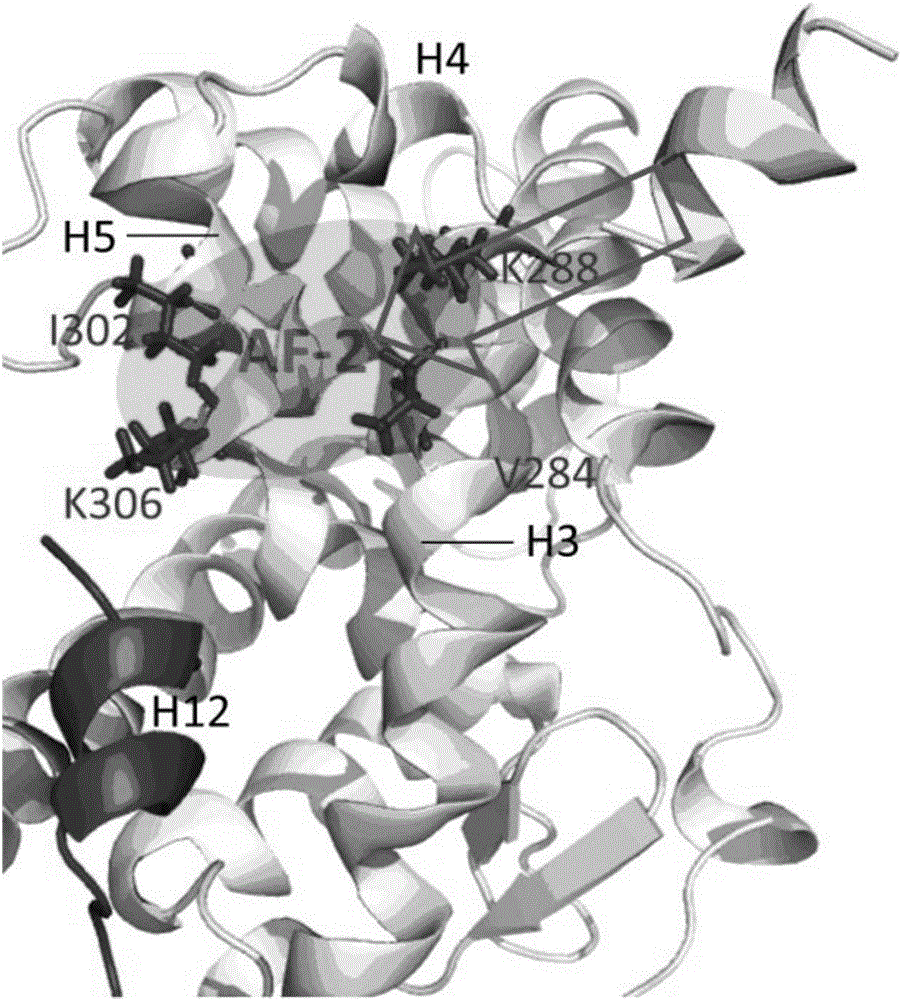
Molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruption substances
ActiveCN103324861ALow costSimple and fast operationSpecial data processing applicationsPerturbateurs endocriniensDrug biological activity
The invention discloses a molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruption substances, and belongs to the field of virtual screening and activity prediction of environmental suspicious endocrine disruption substances. The molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method includes the steps of carrying out butt joint on a receptor file obtained by the fact that optimization and testing or homology modeling are / is carried out on tested small molecules to form a compound, and then using a GROMACS software package to carry out molecular dynamics simulation. Motion trail analysis is carried out on a twelfth helix of a receptor, pollutants with the activity of the receptor are identified through a changing curve of root-mean-square deviation analysis of a space position along with time changes, within the required time, a corresponding helix is regarded to be located to a determined position when the curve tends to be stable, and the receptor has the biological activity. In addition, the located position is inspected to judge whether the activity is fitting or resistance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
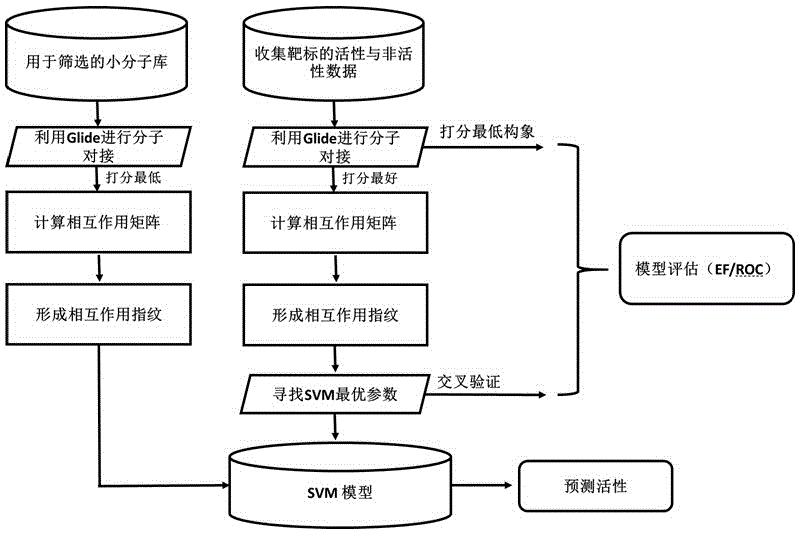
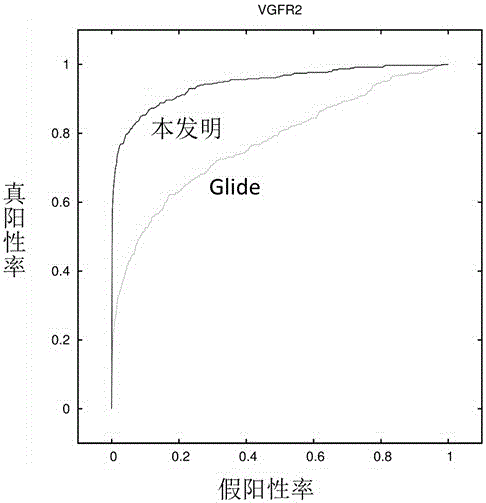
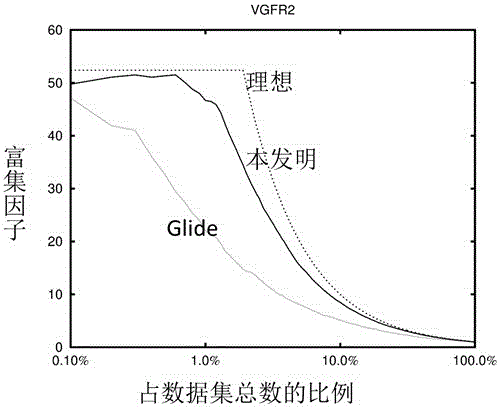
Drug target virtual screening method based on interactive fingerprints and machine learning
ActiveCN106446607AFully consider the specificityAvoid the pitfalls of underfittingBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsProtein targetBinding site
The invention relates to a drug target virtual screening method based on interactive fingerprints and machine learning. According to the method, based on traditional molecular docking, the interactive fingerprints of known active and non-active micromolecules and target protein are trained through machine learning to obtain a screening model of targets, and the obtained model is used for virtual screening. The specific targets are specifically trained, the specificity of each kind of targets is fully considered, and the defect of insufficient fitting of a traditional scoring function is avoided; interaction energy of each micromolecule and each residue in a binding pocket is calculated, so that effective binding sites or binding modes can be found; non-linear fitting is carried out through machine learning, and compared with linear fitting, the correlation or coupling effect between all the interaction energy can be better processed; by means of the method, enrichment of active molecules is better promoted.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
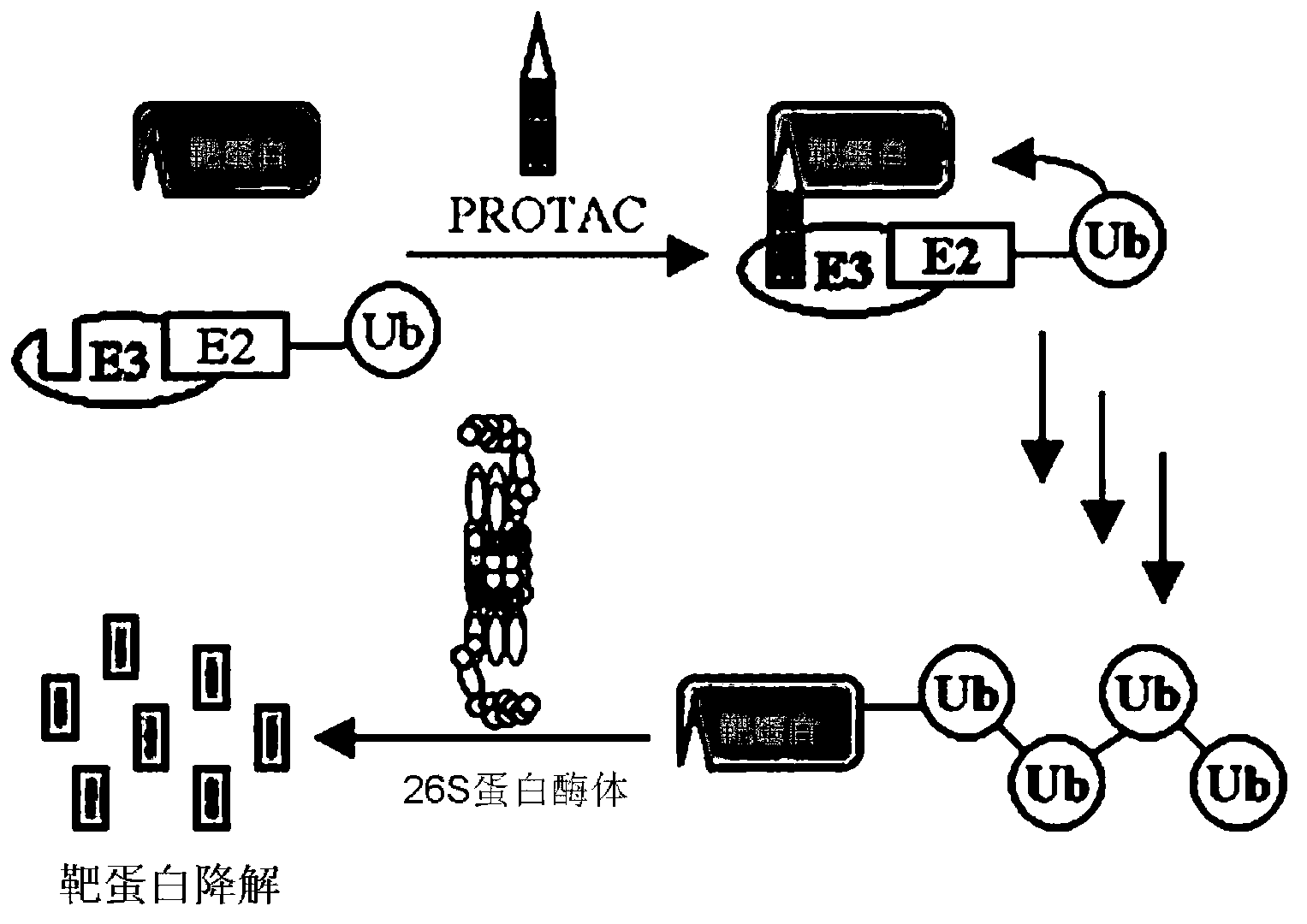
Universal construction method for protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound
InactiveCN103265635AReduce the numberImprove discovery efficiencyHybrid peptidesSpecial data processing applicationsChemical synthesisUniversal construction
The invention discloses a universal construction method for a protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound. The objective of the invention is to provide a method for adjusting the level of proteins by degrading the proteins through targeted ubiquitination. The construction method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) locating and analyzing a three-dimensional structure of a target protein and predicting active sites; 2) selecting a compound database; 3) virtually screening ligand compounds having high degrees of adaption to the target protein by using a computer; 4) acquiring the screened ligand compounds and screening an optimal ligand compound of the target protein through detection of interaction between micromolecules and the proteins; 5) constructing a protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound composed of the optimal ligand compound of the target protein, ubiquitin ligase E3 identification ligand and Linker connecting the optimal ligand compound of the target protein to the ubiquitin ligase E3 identification ligand by using a combination manner simulated by the computer; and 6) chemically synthesizing the protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound. With the method provided by the invention, the protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound can be rapidly and highly efficiently prepared, and specific degradation of intracellular target proteins is realized.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Compounds and assays for controlling Wnt activity
The present invention relates to the field of therapeutic methods to screen for compounds on the basis of their ability to influence Wnt activity. The screening process is applied to both a physical library of a series of compounds and a virtual library of compounds that affect Wnt activity. In one aspect, the virtual screening process could be carried out where a permutational library of small peptides is substituted for the small organic molecules. The inventive methods may be used to empirically test for effects on Wnt activity and may also be applied to any pair of proteins involved in protein-protein interactions.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
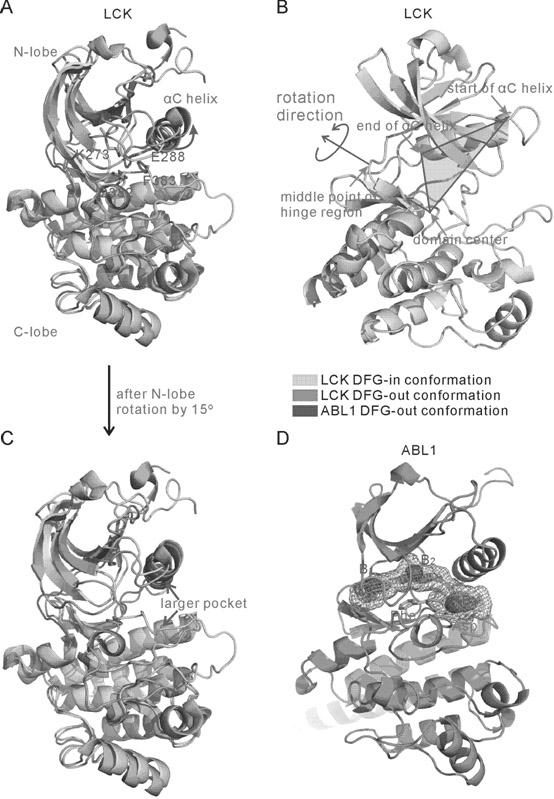
Method for screening compound with targeted action on inactive conformation of protein kinase
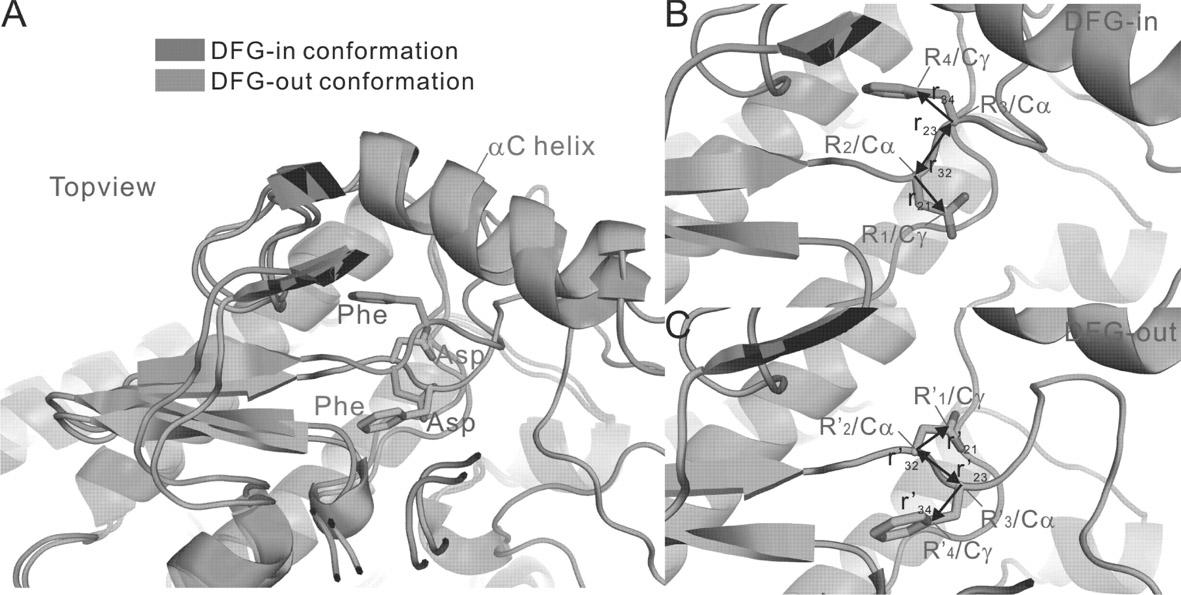
The invention belongs to the technical field of protein structure prediction and drug molecule virtual screening, specifically to a method for screening a compound with targeted action on an inactive conformation of a protein kinase. The method provided by the invention comprises a prediction method for the conformation of an active chain section of the protein kinase, wherein a corresponding DFG-out inactive conformation is generated from the DFG-in active conformation of the protein kinase; the method also comprises a selection method of a combined conformation after implementing butt joint of a II type inhibitor, and the selection method is used for selecting small molecules in conformation prediction and virtual screening. The method for screening a compound with targeted action on an inactive conformation of a protein kinase is already calculated and verified in the protein kinases of seven types of known inactive conformations, wherein the success rate is close to 96%. The method provided by the invention is already applied to the prediction of inactive conformation of PknB protein kinase of tubercle bacillus and the virtual screening of a possible II type inhibitor of PknB, and the bacteriostasis of two kinds of small molecules are already found according to bacteriostatic experiments.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
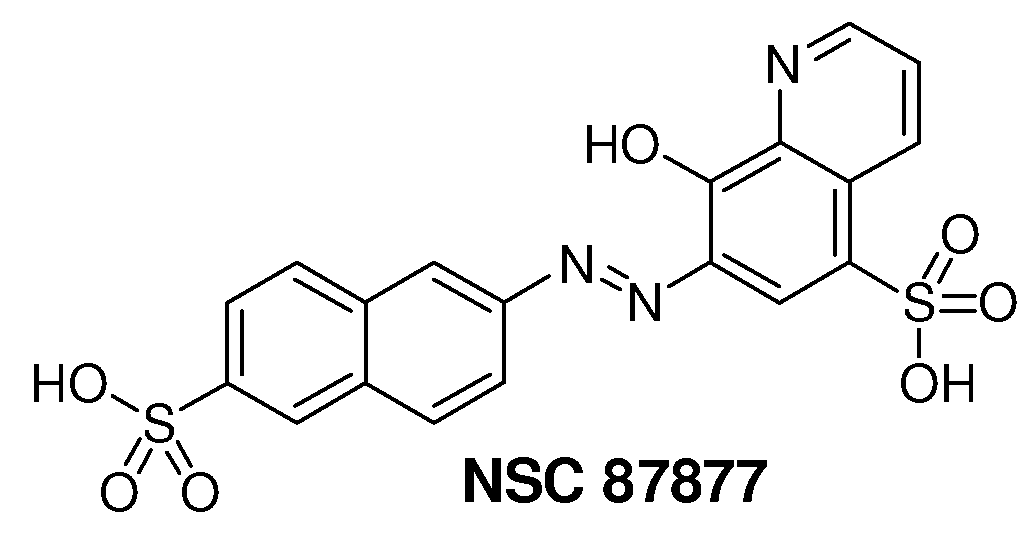
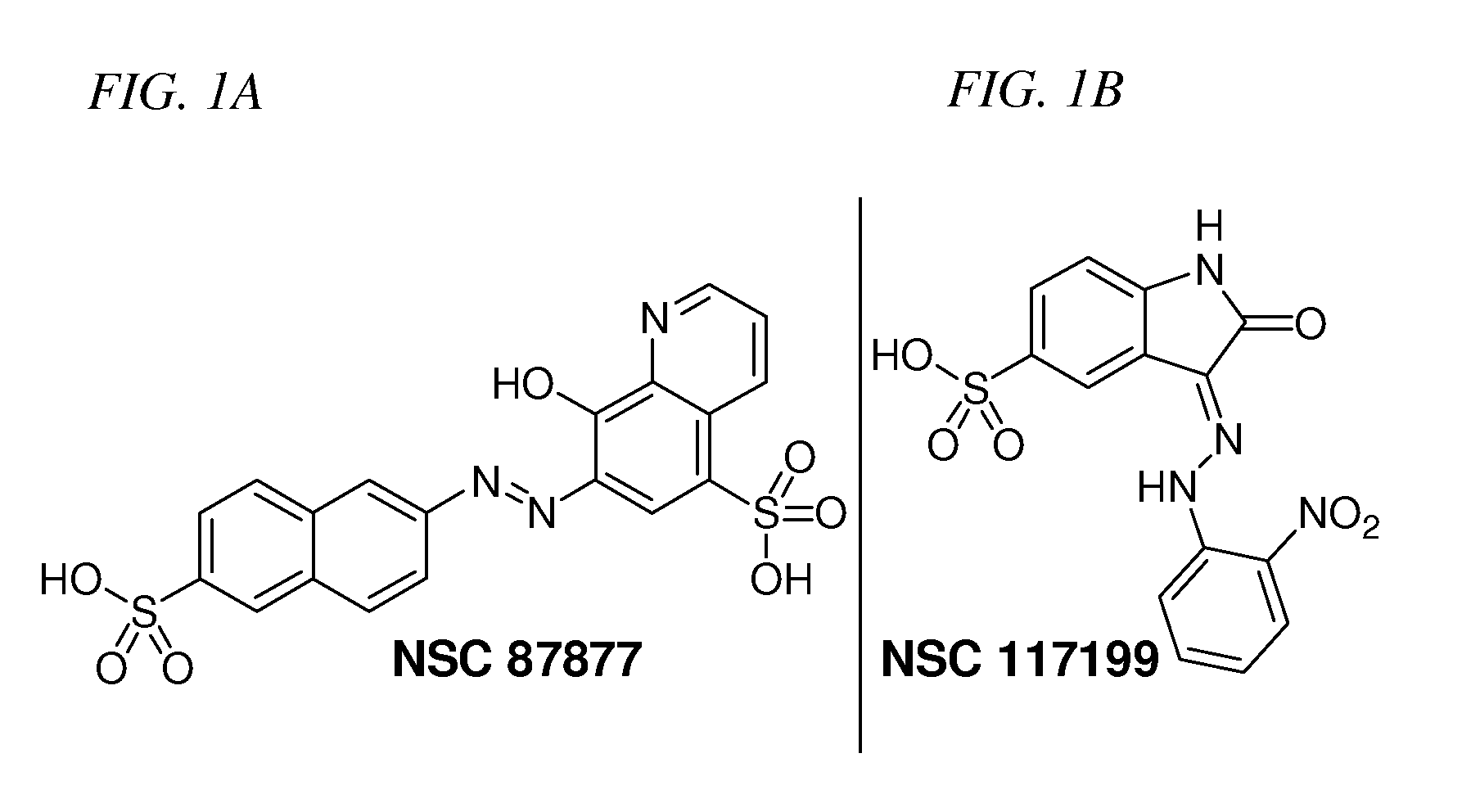
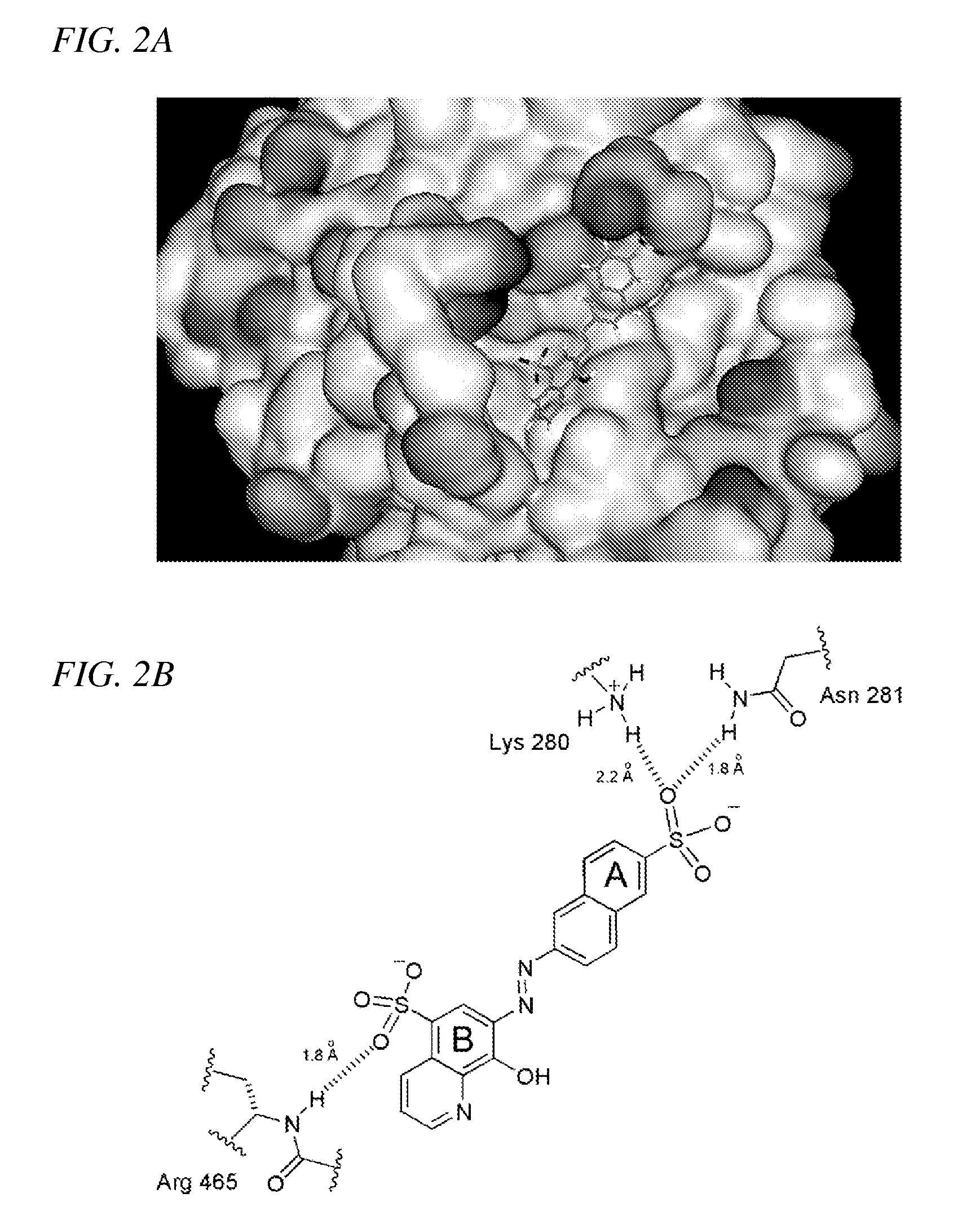
Inhibition of Shp2/PTPN11 Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase by NSC-87877, NSC-117199 and Their Analogs
Compounds and associated methods for inhibiting a protein tyrosine phosphatase. By a combination of experimental and virtual screenings of the NCI Diversity Set chemical library, NSC-87877 and NSC-117199 have been identified as Shp2 PTP inhibitors. Significantly, NSC-87877 is active in cell-based assays and has no detectable off-target effects in the EGF-stimulated Erk1 / 2 activation pathway. Additionally, a number of analogs of NSC-117199 have been produced. These analogs exhibit enhanced protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibition and are found to be potent and / or selective inhibitors of Shp1 and / or Shp2 protein tyrosine phosphatases.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT +1
Virtual screening method for compound pesticide effect matter base of traditional chinese medicine
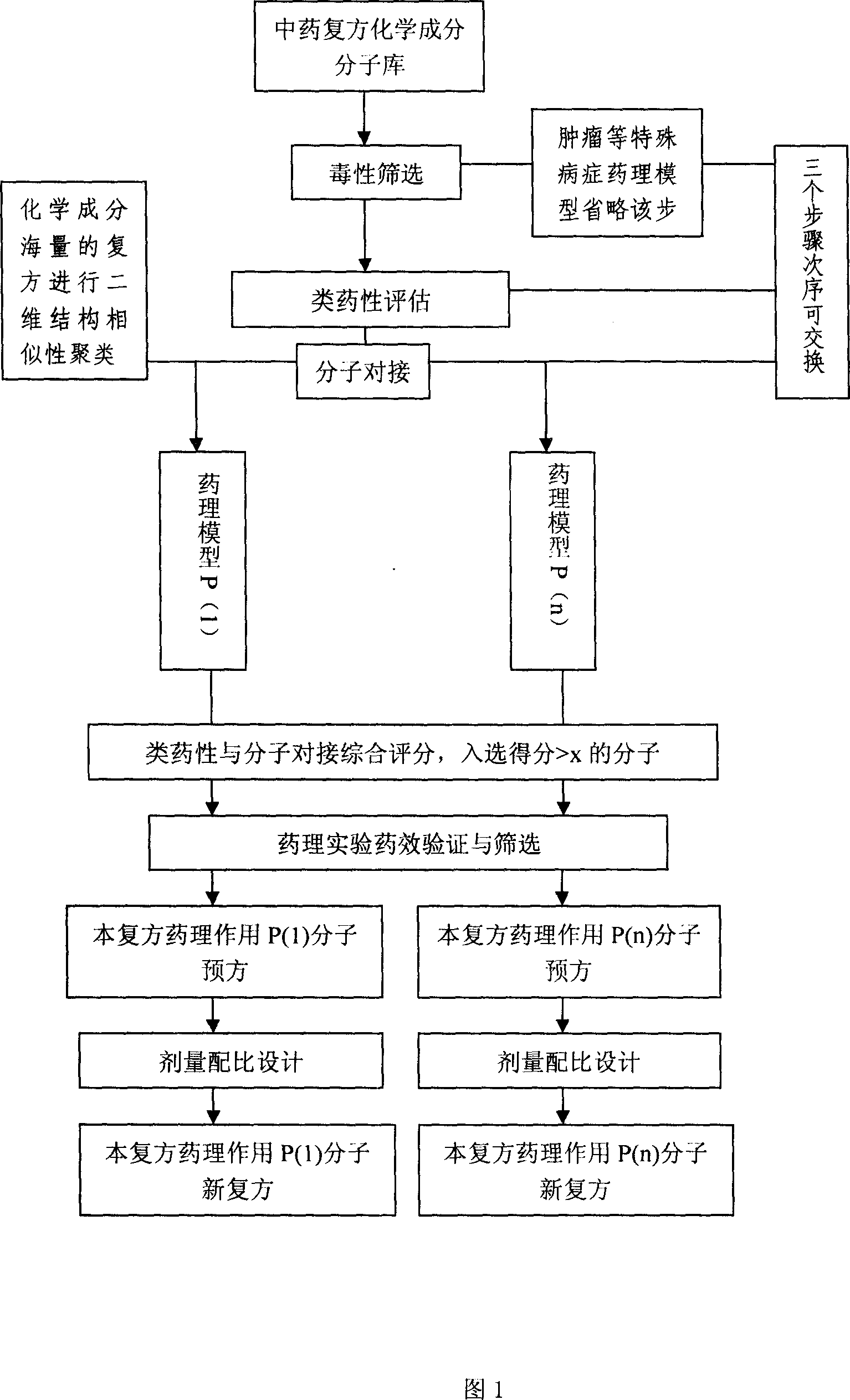
InactiveCN101089245AEconomic noveltyAbandon the shortcomings that are not conducive to poor compliance of preparationsLibrary screeningResearch ObjectAdditive ingredient
In this invention, first It is set that an object of study of a compound traditional Chinese medicine with its chemical compositions being clear about. The molecules of chemical constitutions of each ingredient of the Chinese medicine prescription are collected and reorganized, and setting a data base for chemical constitutions molecules of said Chinese medicine prescription. For the aim of pharmacodynamics effects of main therapeutical functions of the traditional Chinese medicine prescription with their clear therapeutical effects, clear mechanism and definited target spots, we search or set up the corresponding molecular target spots. Three procedures (without odor of priority) are: poisonousness sieving, analogous medicine properties estimation and molecular abutment decision to these molecular data base of the set pharmacodynamics models respectively. Finally we estimating all the molecules in the molecular data base, selecting-out the molecules with higher grading, to obtain the pharmacodynamics effect P(i) molecular pre-prescription, and then producing novel prescriptions.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
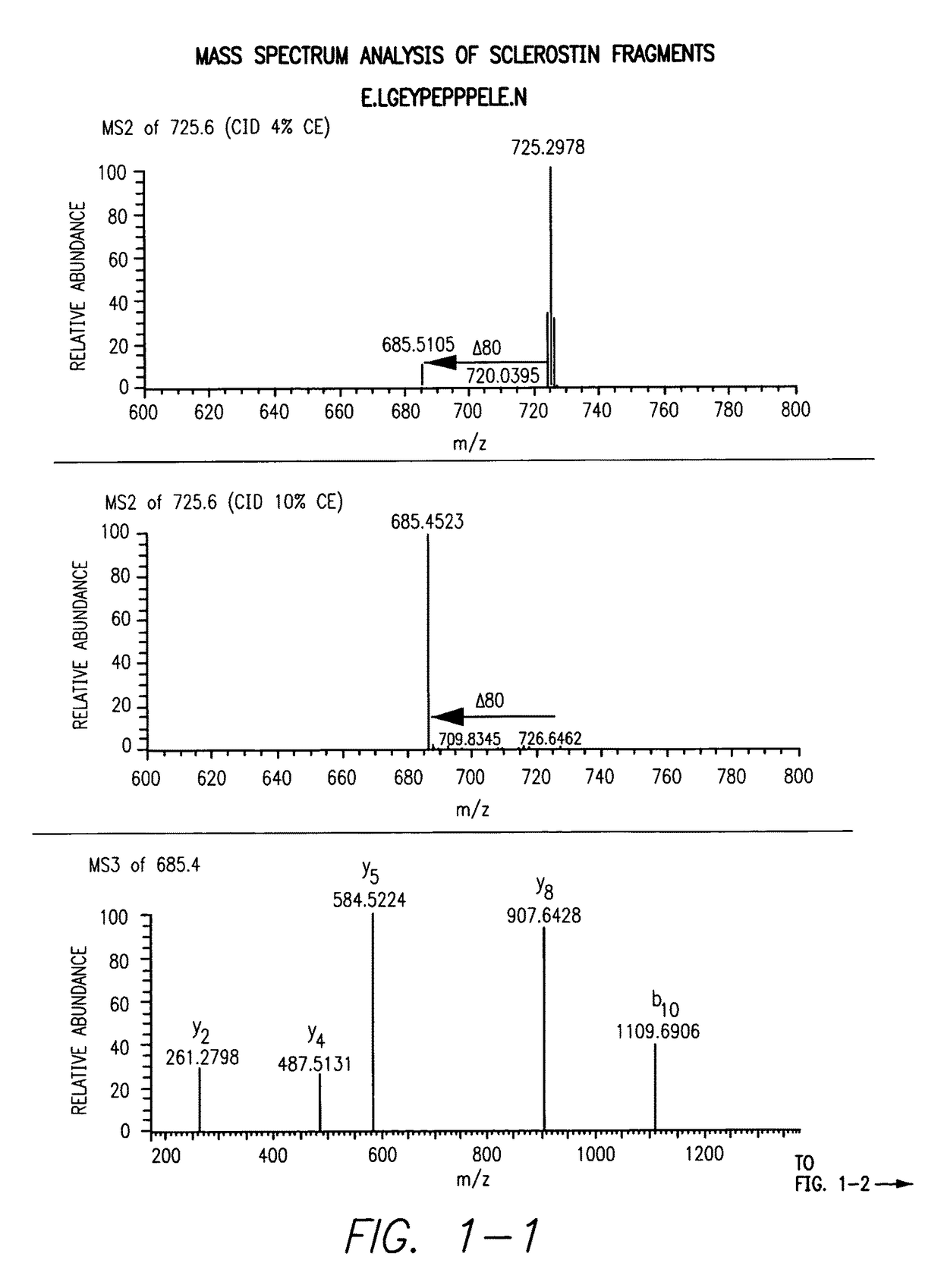
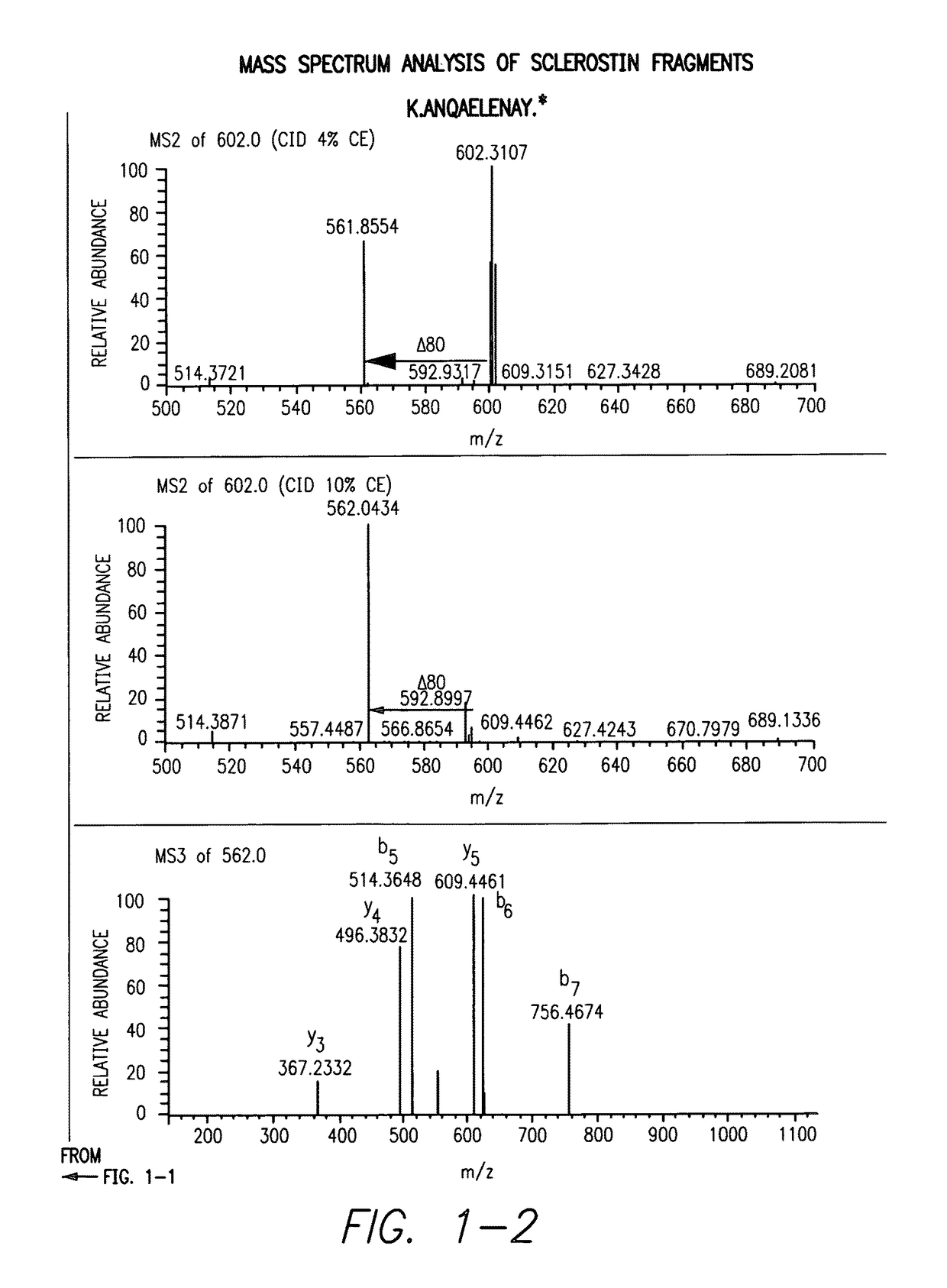
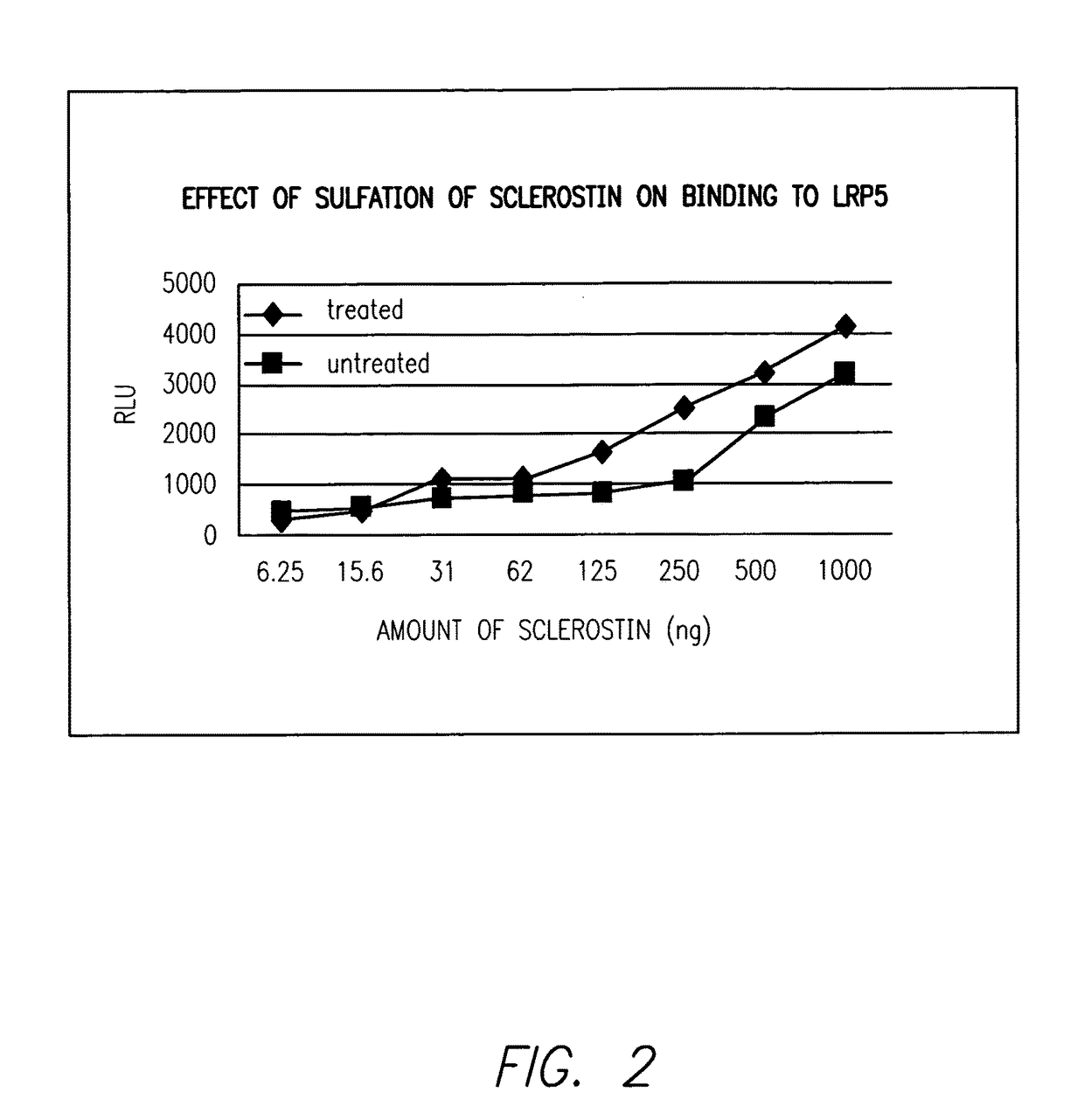
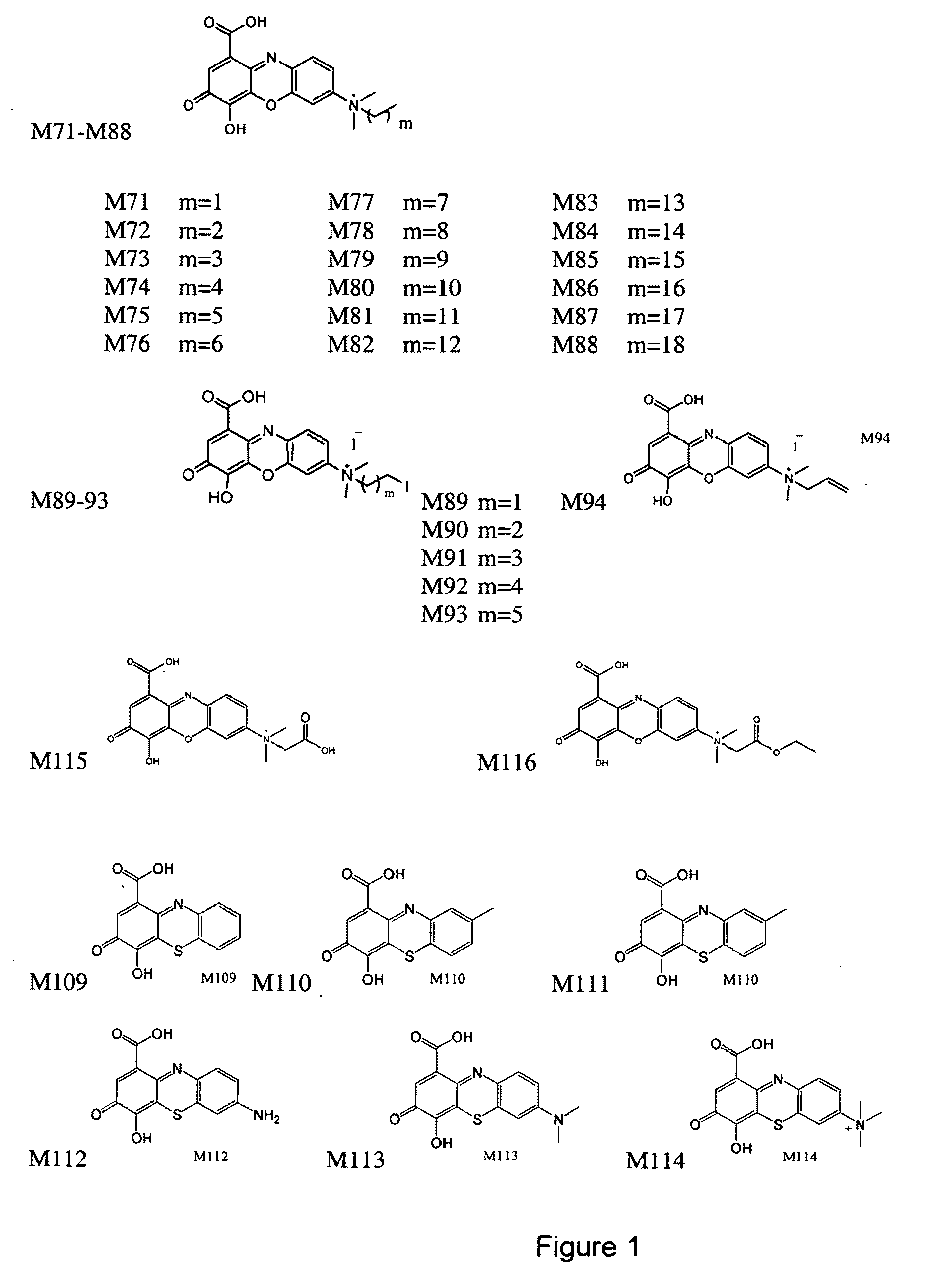
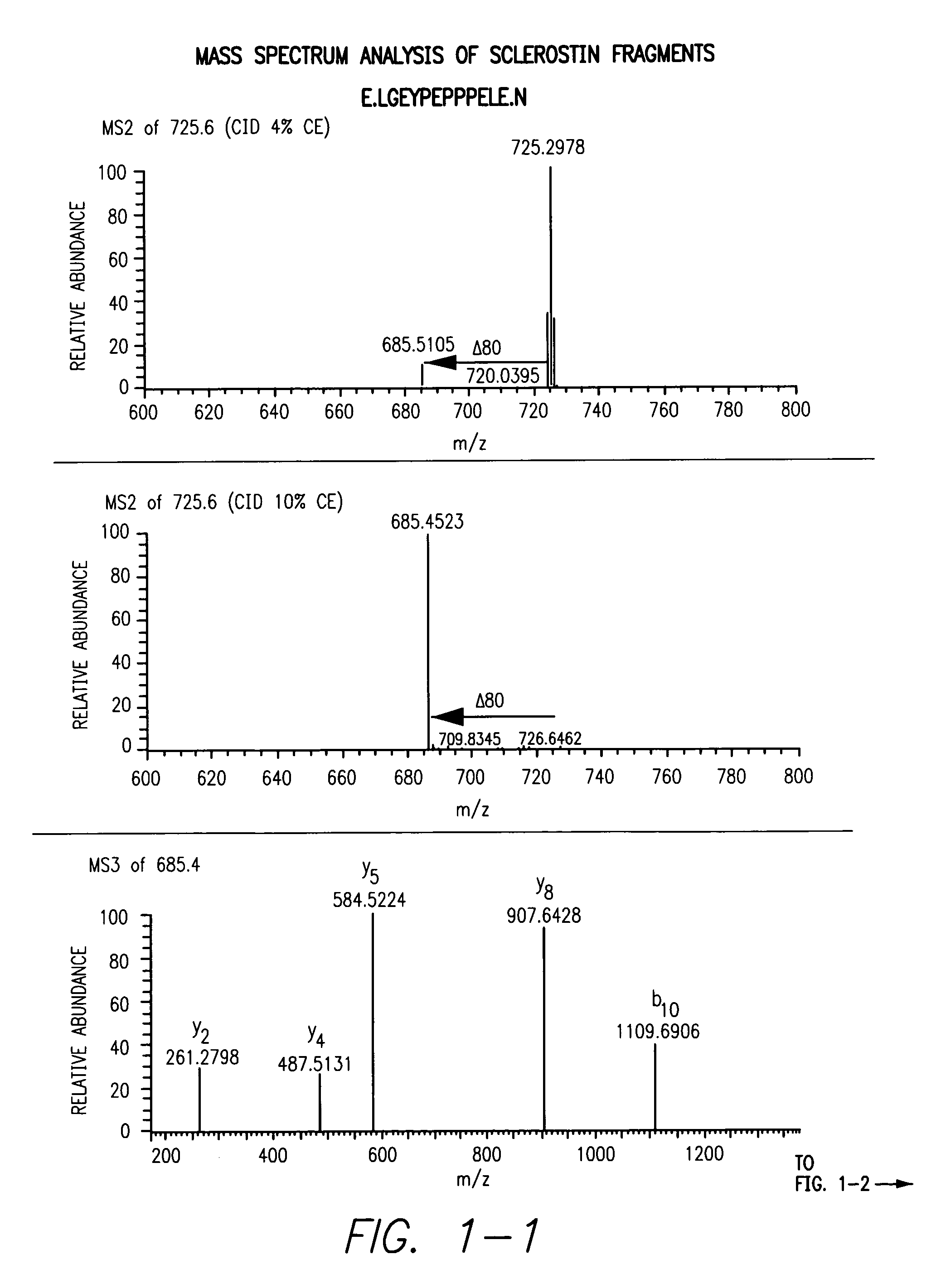
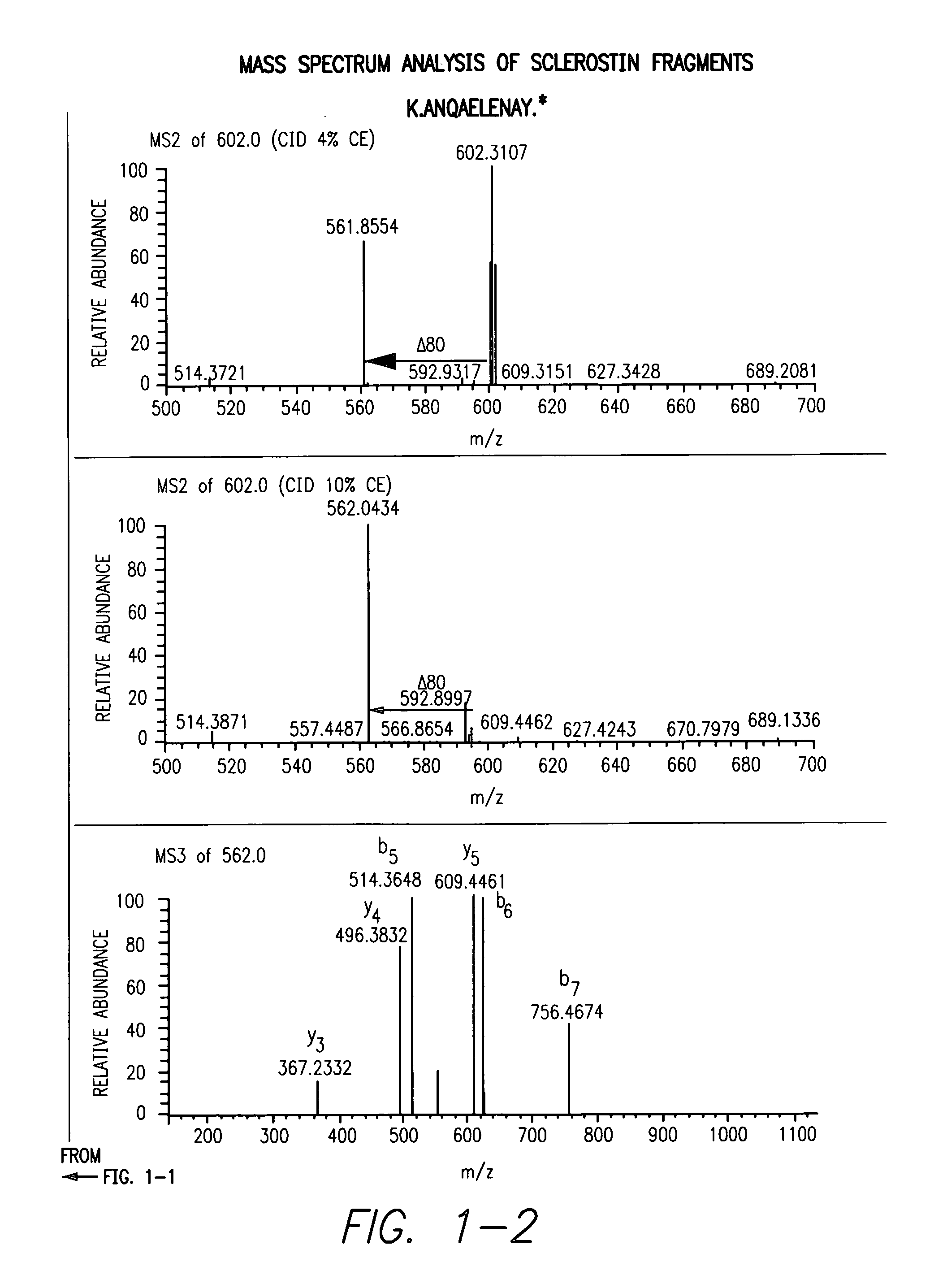
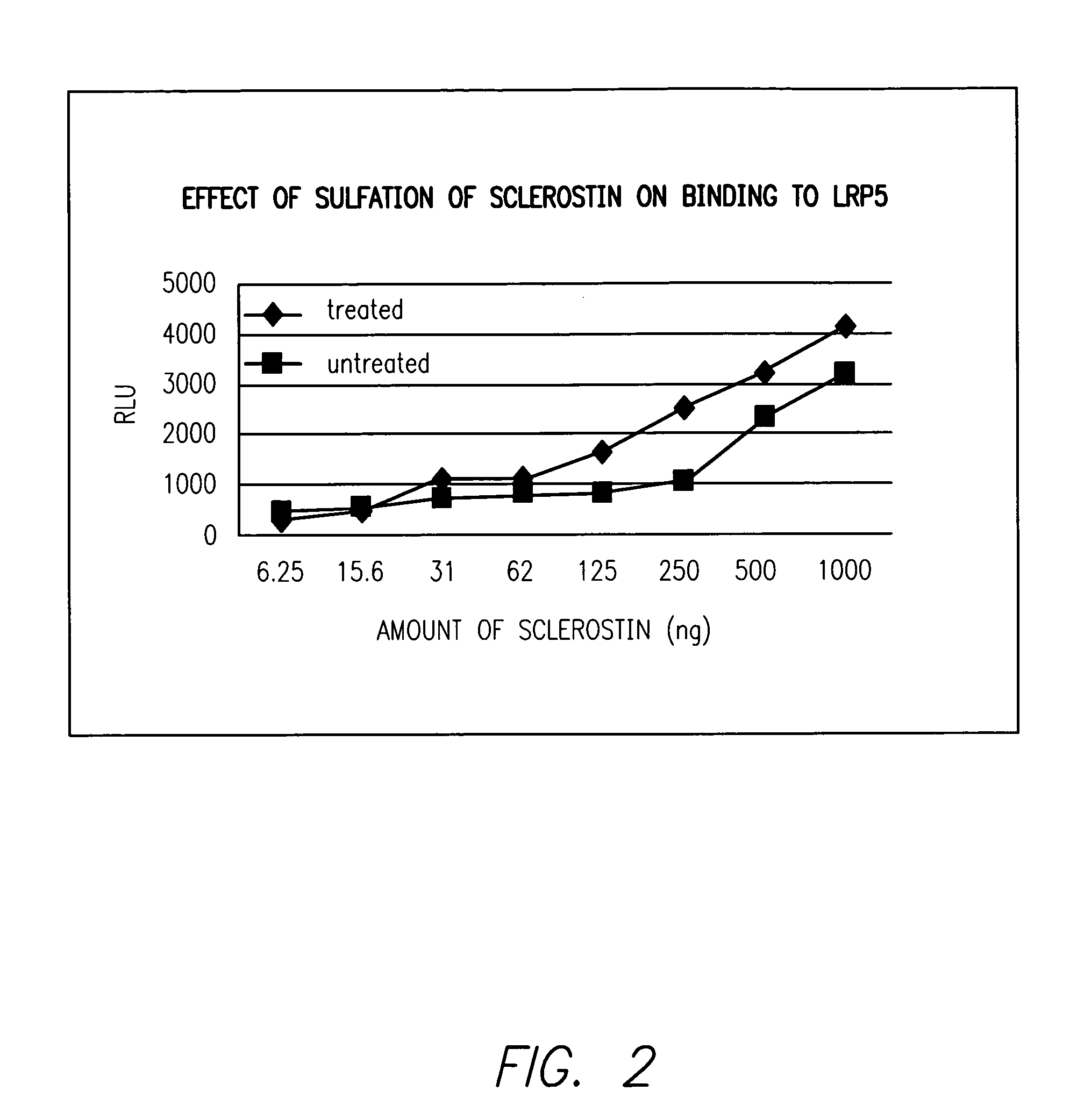
Sulfonated Sclerostin, antibodies, epitopes and methods for identification and use therefor
ActiveUS20110300159A1Reduce functionPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningEpitopeVirtual screening
Provided are antibodies that bind to: a sulfonated epitope of the protein Sclerostin, to Sclerostin portions comprising a sulfonated amino acid and to dimerized forms of Sclerostin. Further provided are compositions and peptides comprising a sulfonated epitope of sclerostin. Also provided by this invention are methods for production of such antibodies, both active and passive, and methods for identifying antibodies specific for sulfonation sites in Sclerostin and other antibodies which discriminate between sulfonated and unsulfonated forms of sclerostin. Physical and virtual screening processes are provided in this invention for identifying compounds whichh disrupt or inhibit sulfonation and the interaction between Sclerostin and binding partners. The antibodies and compositions of the present invention are useful in diagnostic and therapeutic applications directed to Sclerostin-related disorders.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
A screening method for anticancer drugs targeting cdk1
InactiveCN102270281AHas CDK1 inhibitory activityReduce in quantityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsStructure analysisVirtual screening
The invention discloses a method for screening novel anticancer drugs targeting CDK1, comprising the following steps: 1) acquisition, analysis and processing of the three-dimensional structure of CDK1 protein; 2) construction of a small molecule database; 3) computer virtual screening System establishment; 4) Biological activity screening. At the same time, five novel lead compounds with CDK1 inhibitory activity were determined by applying the present invention. The method for screening CDK1 inhibitors involved in the present invention quickly, economically and efficiently discovers novel anti-cancer lead compounds and shortens the drug research and development cycle.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Natural product active ingredient computation and recognition method based compound characteristic
InactiveCN101477597APredictableAvoid experimentationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsNatural productVirtual screening
The invention discloses a method with a strong discrimination power, which is used for calculating and recognizing active ingredient of a natural product on the basis of compound characteristics. The method is characterized in that whether a molecule has biological activity or not can be calculated and recognized in an extractive molecule of the natural product with a known structure by utilizing descriptors of compound characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: step A, a training set and a predicting set of natural product extractive molecules used for model building are structured; step B, molecular structure files of the training set and the predicting set are collected; step C, the descriptors of the compound characteristics can be figured out by utilizing the molecular structure files; step D, classification modeling can be performed on the training set by using a machine learning software according to the descriptors of the compound characteristics; and step E, the molecule of the predicting set has biological activity or not can be identified by the machine learning software with the combination of step D. The method of the invention has a good application prospect in high flux virtual screening and the study of synergistic effect of natural products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
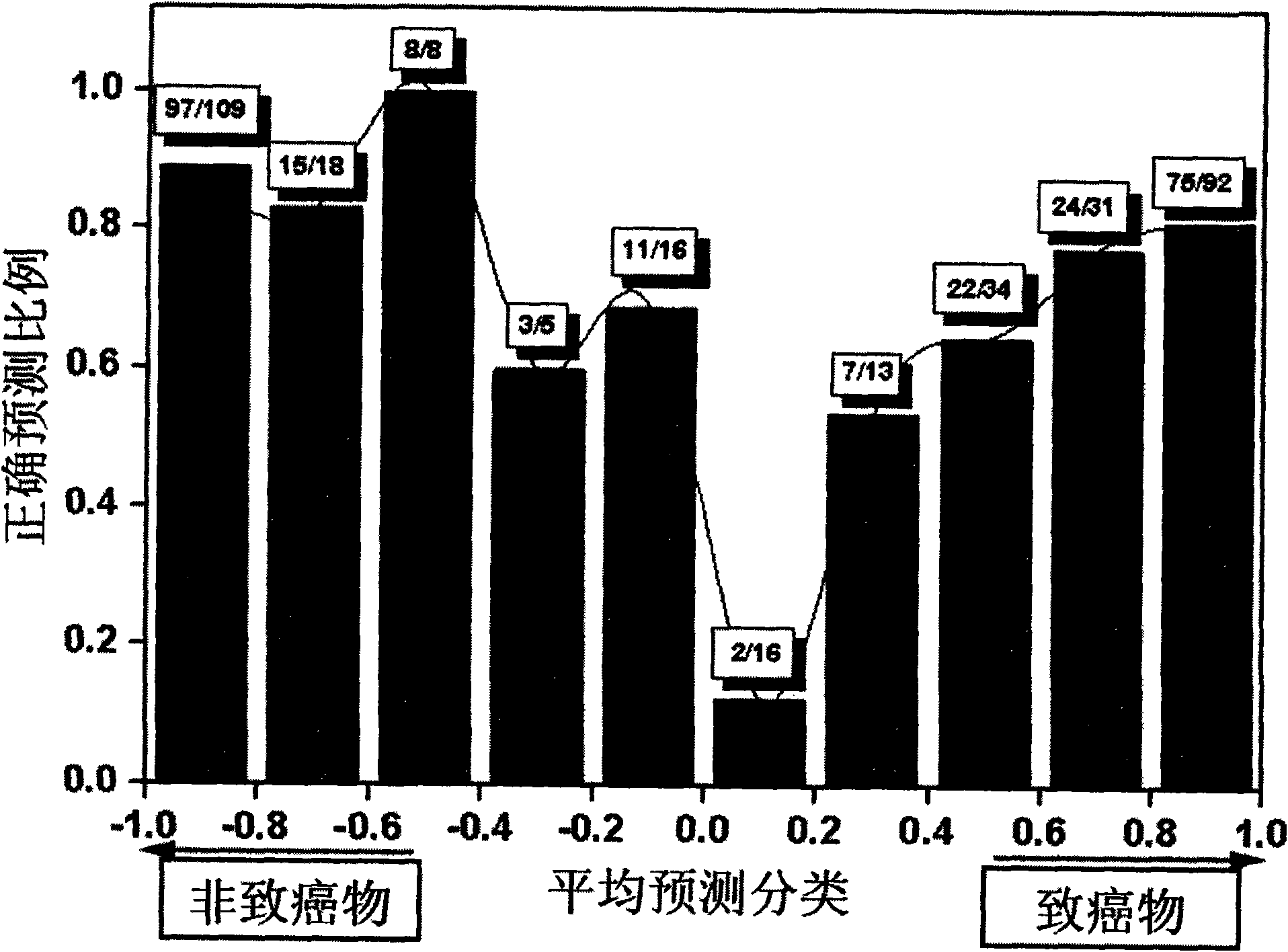
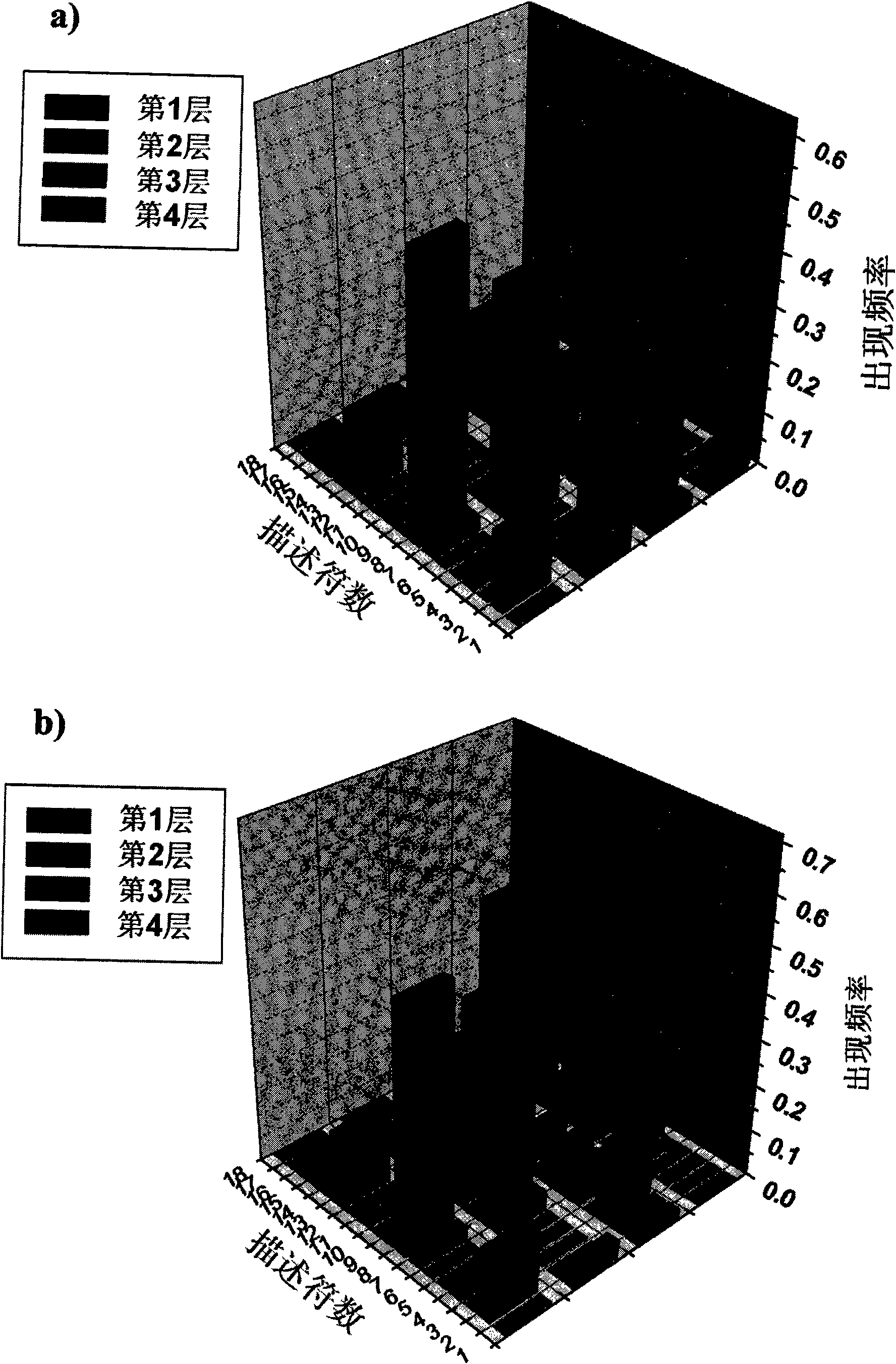
Method for predicting compound carcinogenic toxicity based on complex sampling and improved decision forest algorithm
InactiveCN101587510AEquilibrium predictive powerSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual screeningAlgorithm
The invention relates to a method for predicting compound carcinogenic toxicity based on complex sampling and an improved decision forest algorithm. The method is suitable for calculating carcinogenic toxicity evaluation and virtual selection on a compound according to an organic small molecular structure, and comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting a relative force field to molecules with the molecular structure to carry out optimization and charge calculation, carrying out complex sampling to the compound with centralized original training to be used for generating a training subset, and fixing various relative descriptors in composition calculation molecules of descriptors according to a complex sampling algorithm result; secondly, optimizing a descriptor pool by using a method based on relative matrix analysis and factor analysis; and finally, carrying out data mining on carcinogenic toxicity data and corresponding chemical characteristics thereof of training set molecules by using the improved decision forest method to obtain a classified prediction confidence interval, a carcinogenic toxicity prediction mold and a judgment rule. The method has favorable application prospect in high throughput virtual selection and calculating the carcinogenic toxicity evaluation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
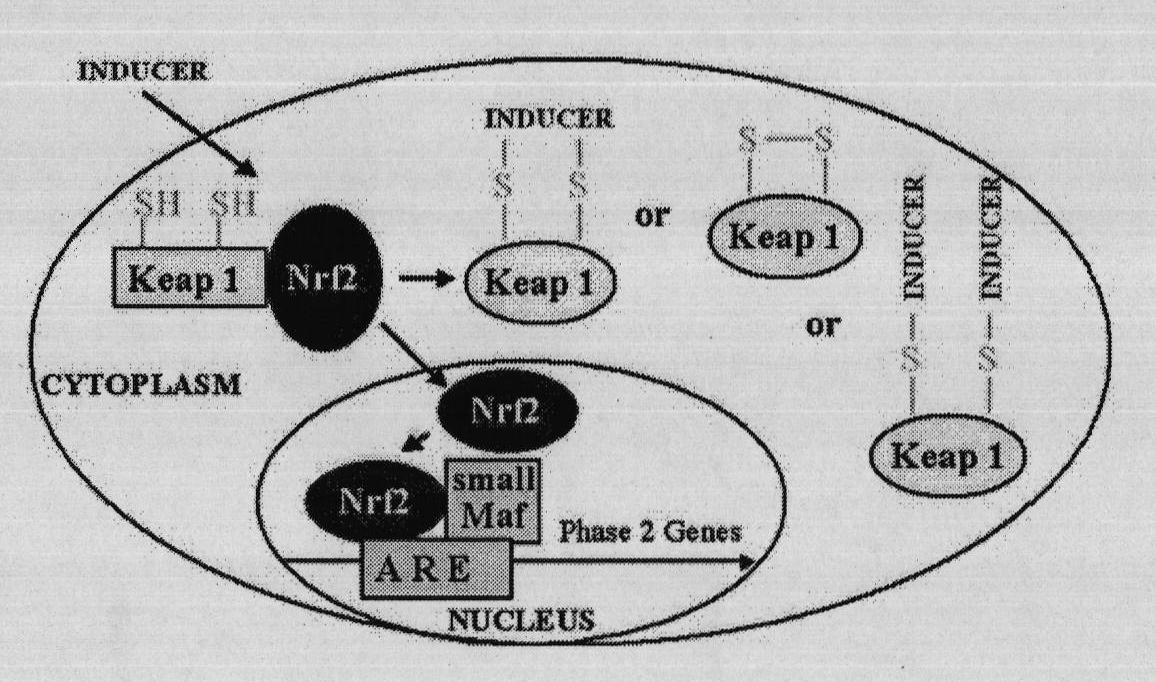
Virtual screening method for novel cancer-preventing or anti-cancer medicament by taking Keap1 as target point
InactiveCN101916330AHigh speedImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsMacromolecular dockingVirtual screening
The invention relates to a virtual screening method for a novel cancer-preventing or anti-cancer medicament by taking Keap1 as a target point. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) determining a PDB structural data of a Keap1 protein structure; 2) determining an active center according to an active cysteine residue site of the Keap1 by adopting molecular docking software, and setting active bags; 3) screening small molecule ligand; 4) establishing a small molecule ligand database for docking; 5) docking the small molecule ligand in the small molecule ligand database for docking and the active bags one to one according to the set active bags by using the molecular docking software; and 6) primarily determining a pilot medicament with chemical cancer-preventing or anti-cancer effect according to the sequencing of the docking results. The method can obtain a clue of an active compound in short time, and then screens the cancer-preventing or anti-cancer medicament by using animal horizontal screening or high-pass molecule platform screening so as to greatly improve the speed and the efficiency and shorten the research period of a new medicament.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting binding specificity between ligand and target and drug screening method
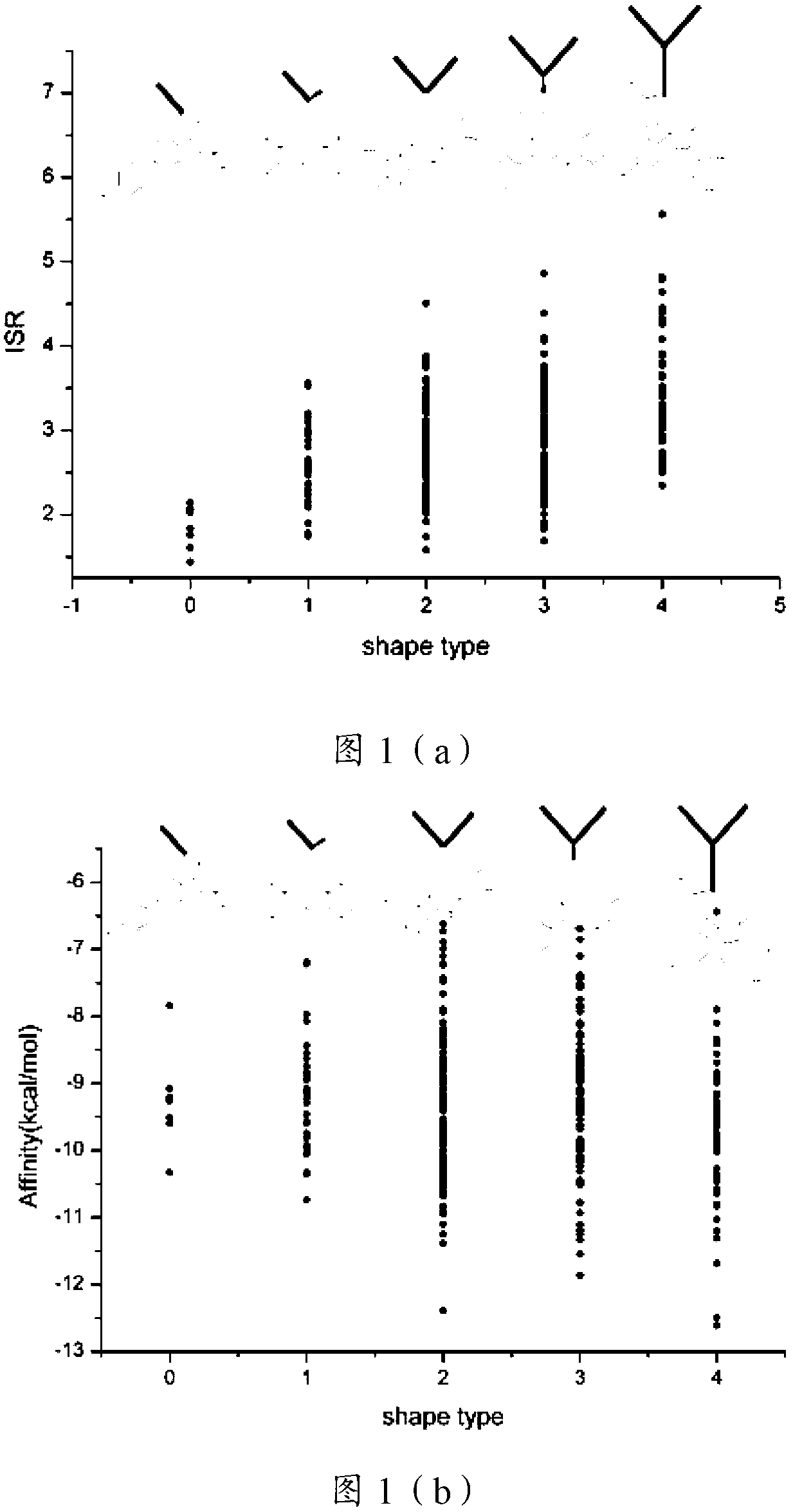
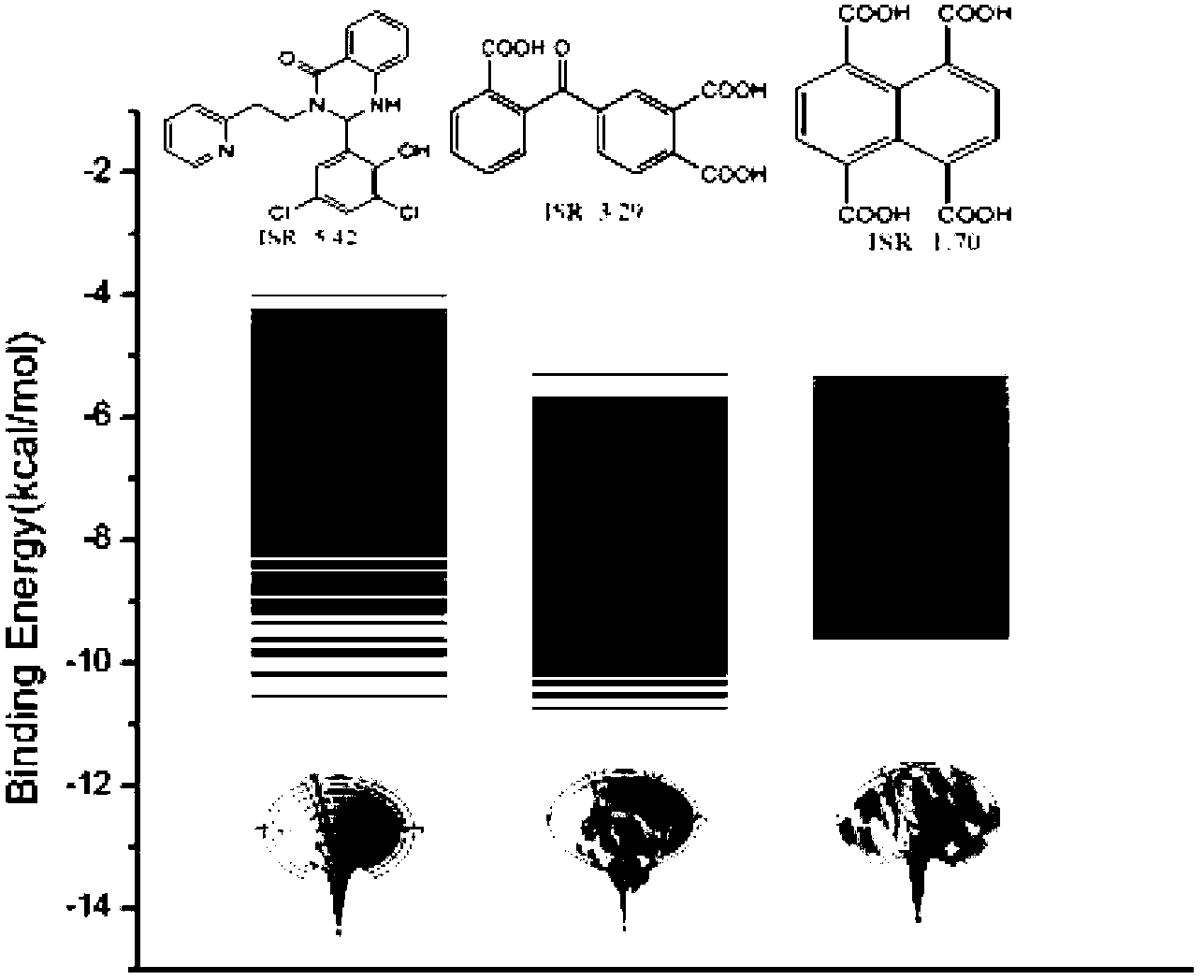
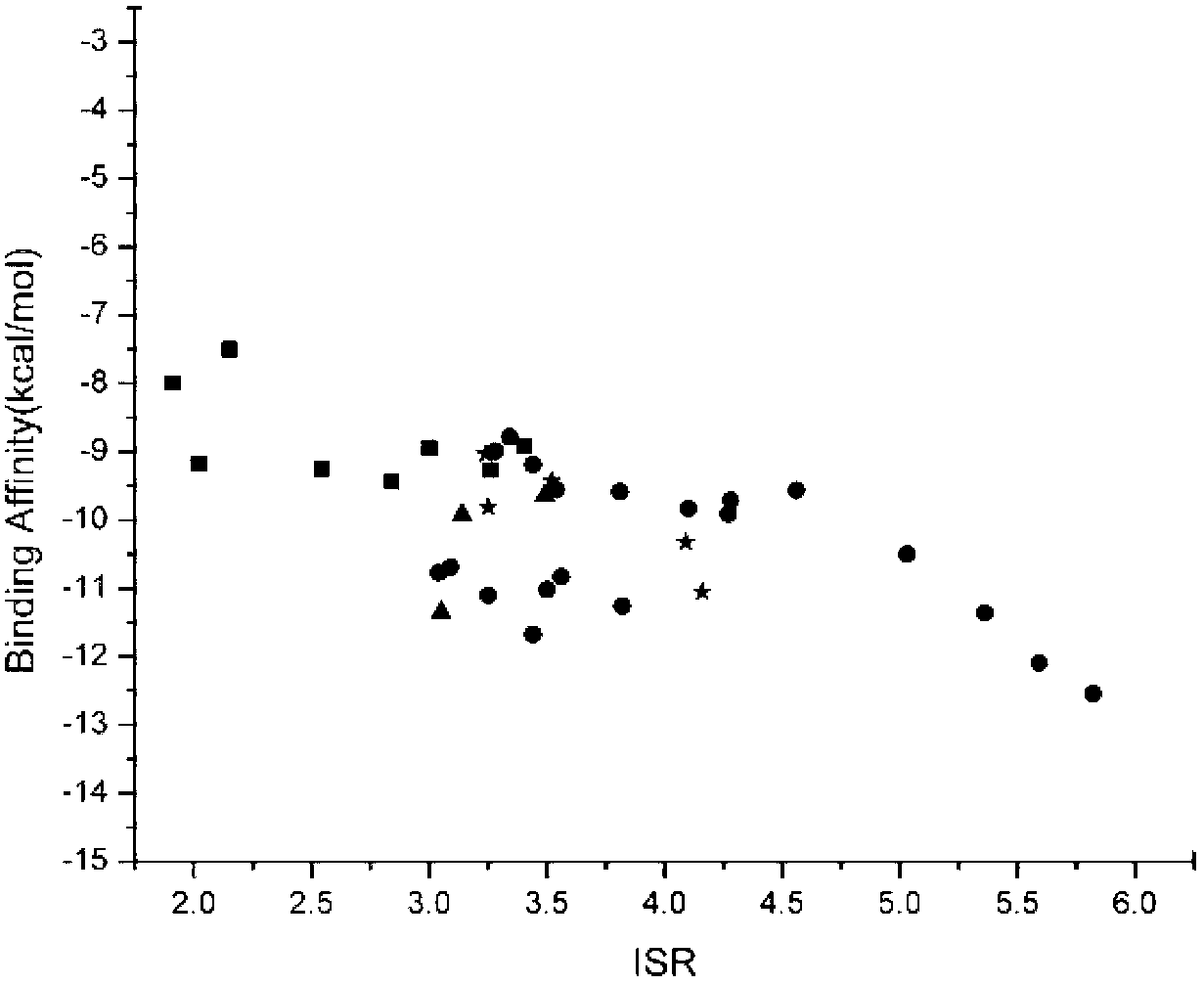
The present invention relates to the field of drug screening, and specifically relates to a method for detecting binding specificity between a ligand and a target and a drug screening method. The detection method includes: molecular docking through the ligand and the target, obtaining an energy spectrum of the ligand, introducing the ratio of intrinsic specificity, and thus determining the binding specificity between the ligand and the target. The detection method compared with conventional methods has the advantages of good specificity, high accuracy, fast speed and low cost. The invention provides a new detection method for structure-based virtual drug screening. Based on the detection method, a method of two-dimensional virtual drug screening directed at affinity and specificity is developed. At the same time, the detection method provides a new description characteristic for the side effect research of small molecule compounds, and provides guidance for chemical modification and transform of drug lead compounds. Relative to conventional mere affinity-concerning virtual drug screening, the specificity dimension is added to the method, so the chances of discovery of drug lead compounds are greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
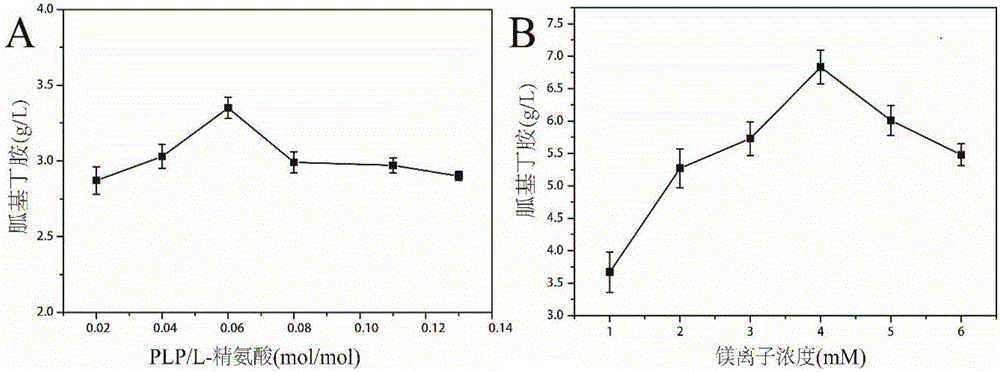
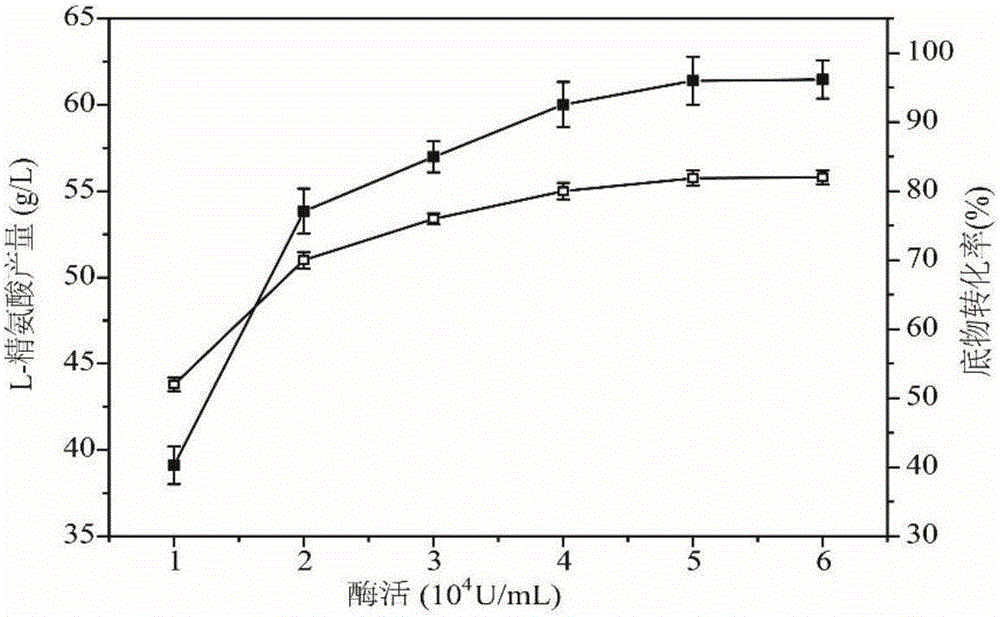
Arginine decarboxylase and application thereof
InactiveCN105861529AIncrease vitalityMeet the needs of industrial scale productionFermentationGenetic engineeringEscherichia coliArginine
The invention discloses arginine decarboxylase and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. Shewanella putrefaciens is cloned by adopting genome database mining and homologous sequence alignment and other virtual screening means and combining with a molecular biological means to obtain an arginine decarboxylase gene. The molecular biological means, process optimization and the like are adopted, the enzyme production capacity of arginine decarboxylase production strains is improved, and a platform for efficiently producing gamatine through biological catalysis is established by optimizing a catalytic system. Crude enzyme liquid obtained through fermentation is purified and then is converted, a reaction system is clear in composition, and extraction and purification of follow-up products are promoted. Under the condition of 37 DEG C, the decarboxylase has high activity, meanwhile is beneficial to the growth of escherichia coli of host cells, and at the temperature, the reaction speed is improved greatly, a conversion period should be 24 hours, the gamatine yield can be up to 61-71 g / L, and the conversion rate can be up to 68-82%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Virtual screening method of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor
ActiveCN108830041AReduce in quantityAvoid blindnessSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual screenIn vivo
The invention aims at disclosing a virtual screening method of an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, the virtual screening method and the application of screened compounds in pharmaceutical preparations forpreventing and / or treating 2-type diabetes. The method comprises the steps of 1, the obtaining, analyzing and treating of the three-dimensional structure of a large molecular protein; 2, the construction of a traditional Chinese medicine natural product library and the preparation of a small molecular compound; 3, the calibration of the prediction capability of a virtual screen model and the establishment of the screen model; 4, the virtual screening of the natural product library and the analyzing of a mutual impacting mechanism; 5, in vivo and in vitro biological activity verification of ascreening result. The method is used for screening and can be used for the discussing of a structure-activity relationship of compounds of the type, and the further modification of a structure based on a biological compound is guided.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
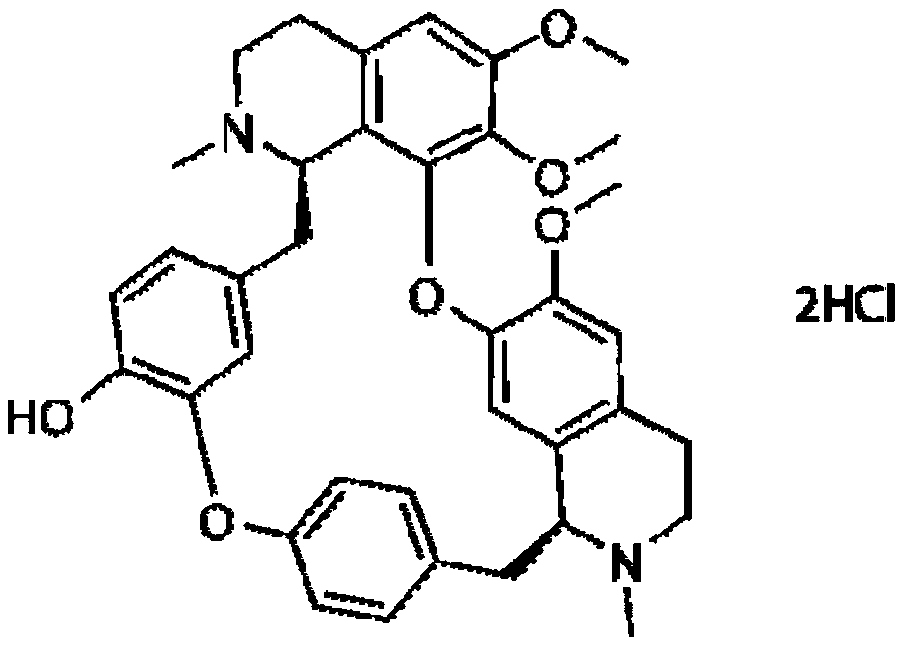
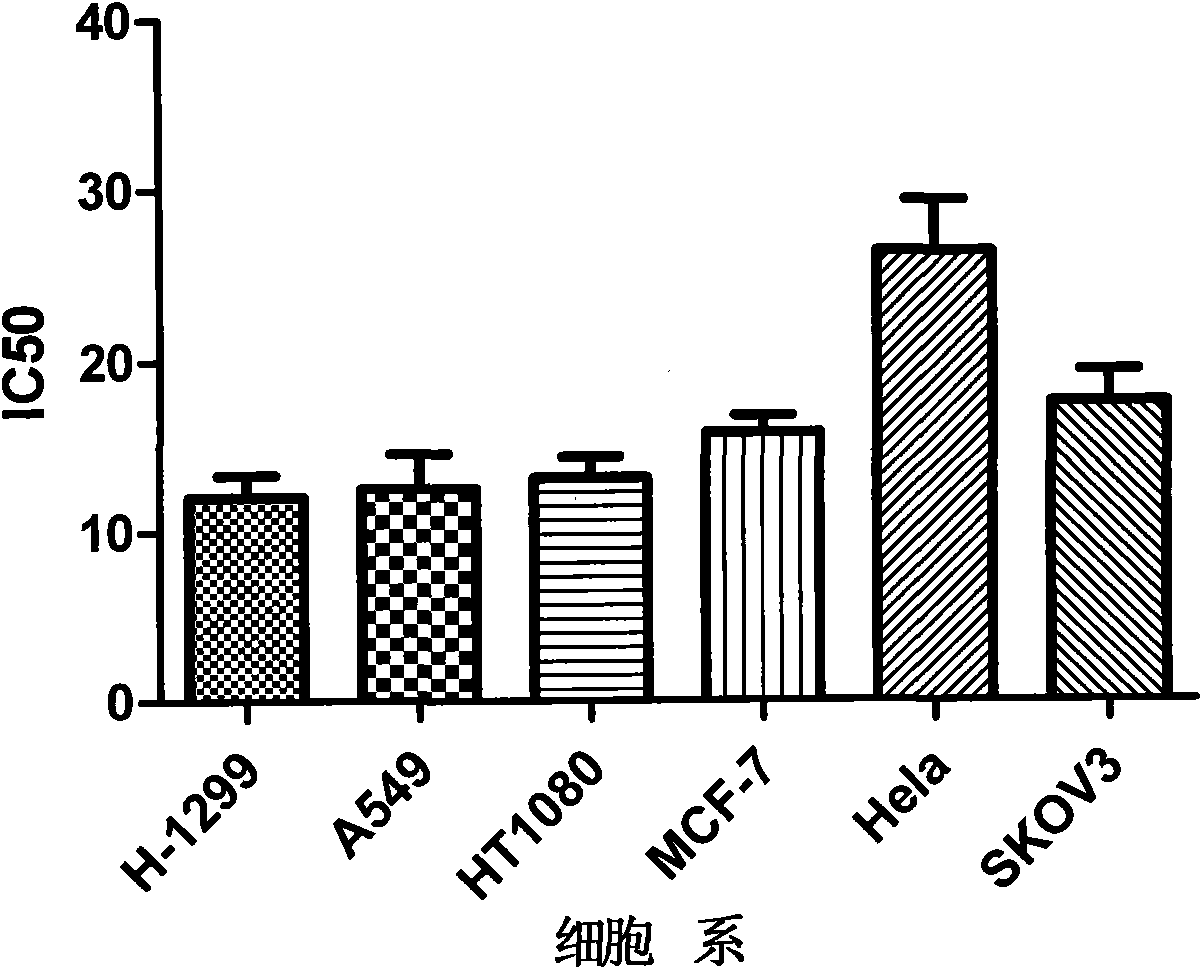
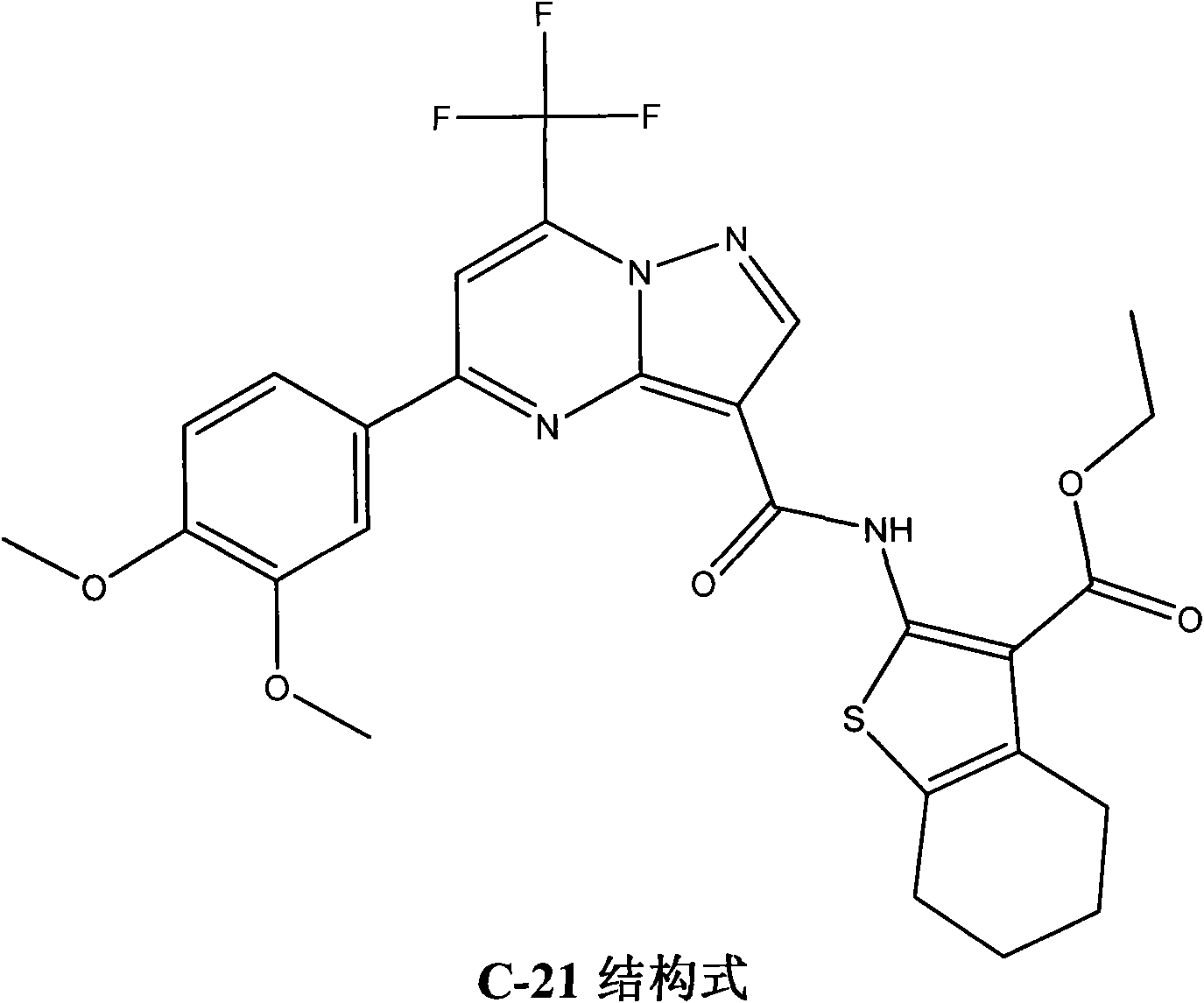
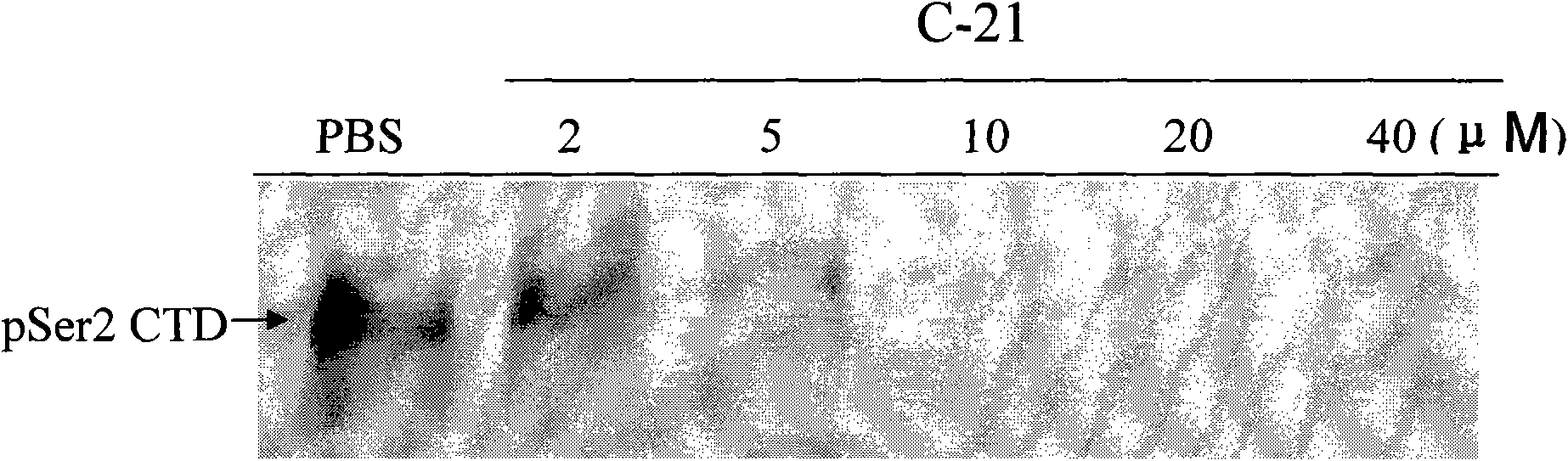
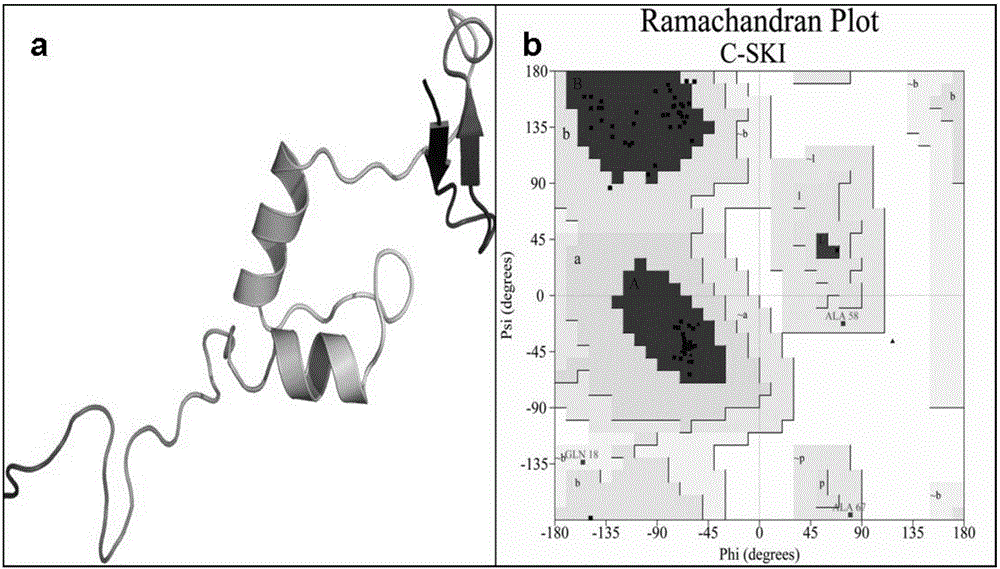
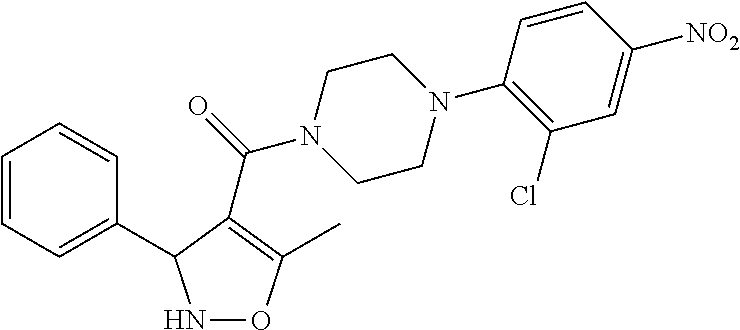
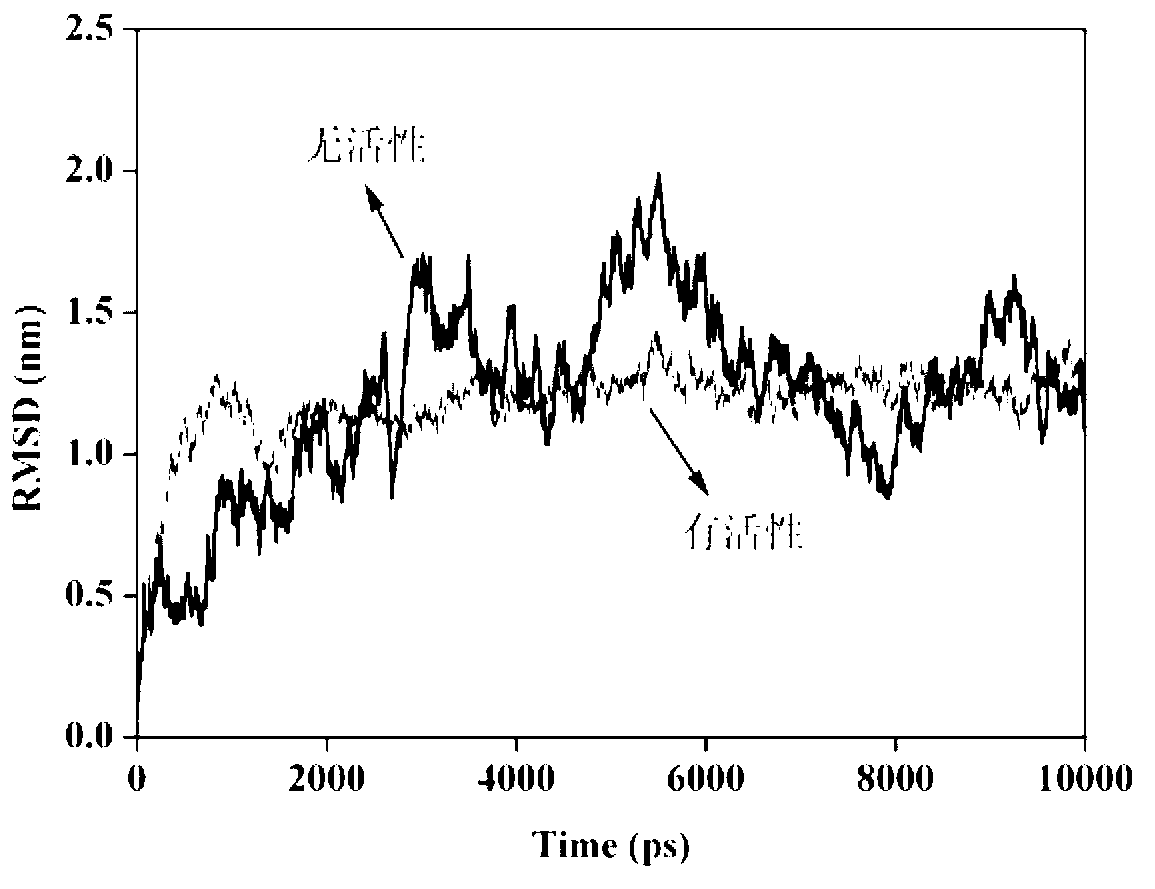
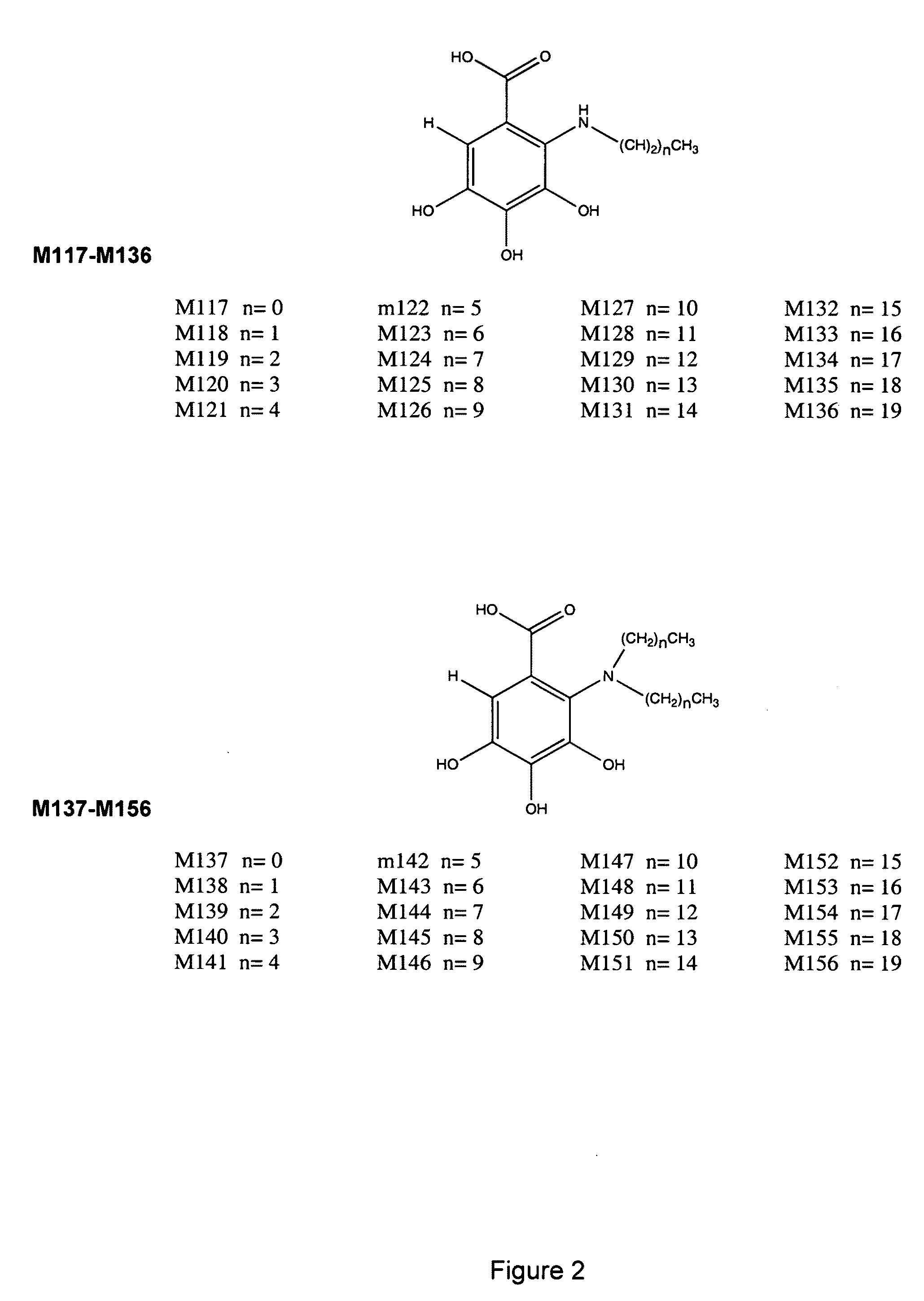
Use of 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives in preparation of drug for prevention or treatment on cerebral hemorrhage
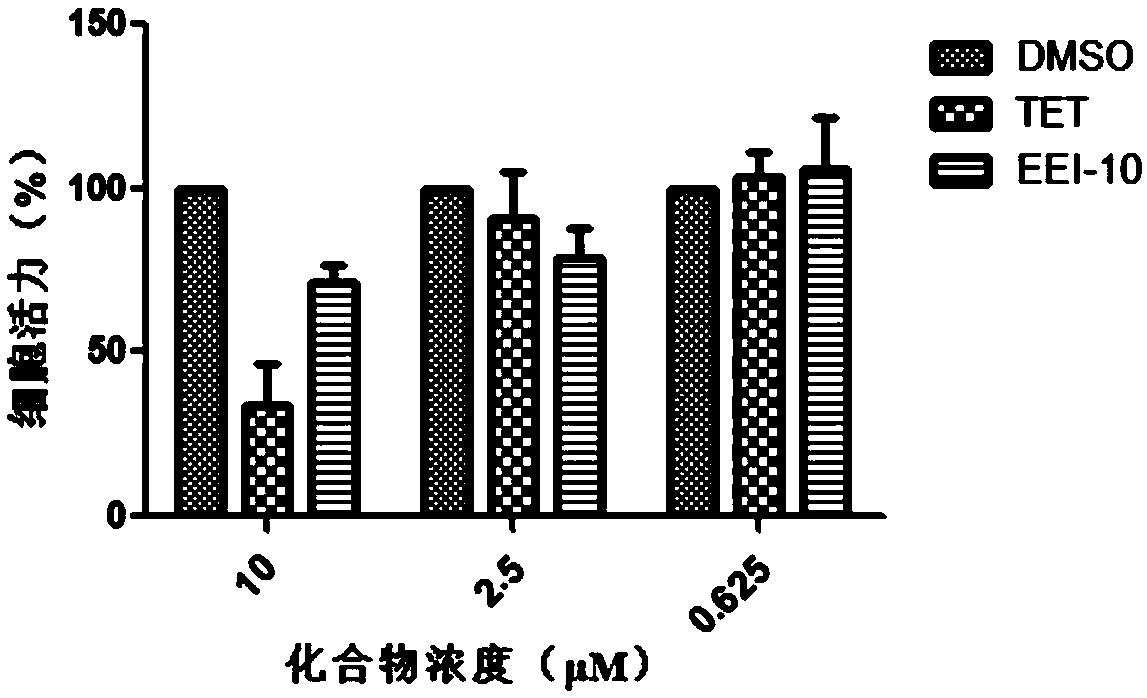
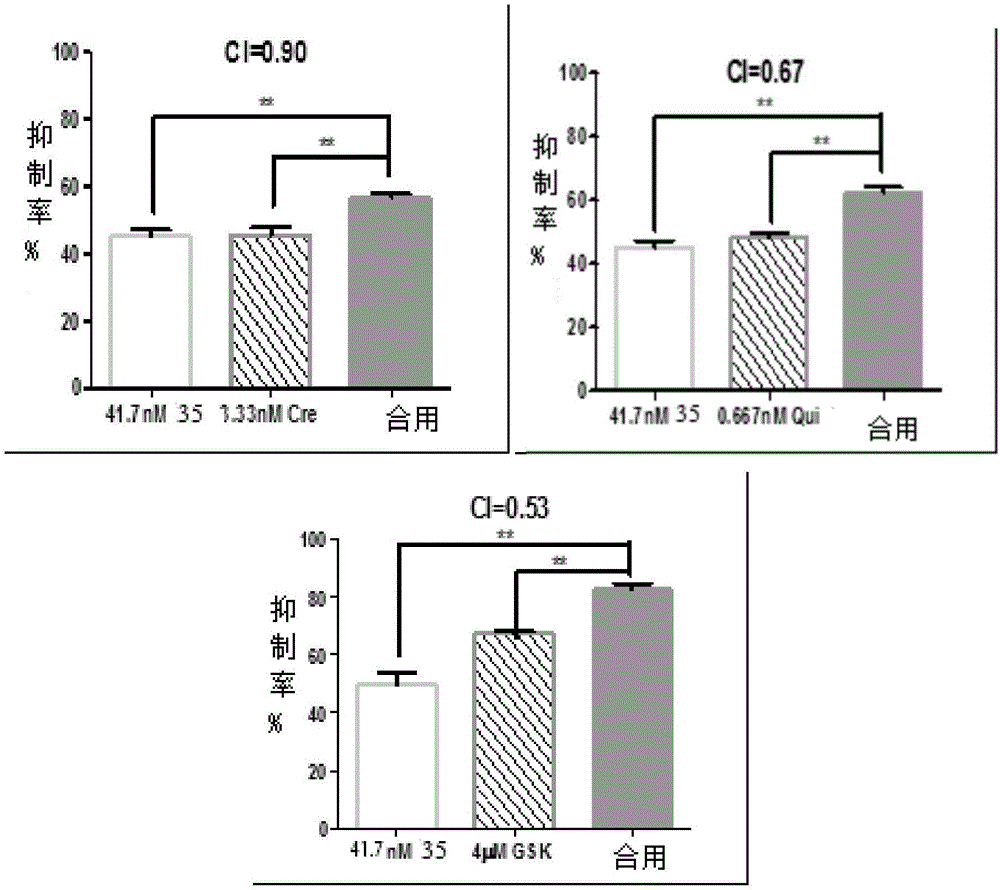
InactiveCN103193780AHas inhibitory activityStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTreatment effectVirtual screening
The invention discloses a use of 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives in preparation of a drug for prevention or treatment on cerebral hemorrhage. Through a self-created computer-assisted drug molecule design program and virtual screening, it is shown that the 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives have a ROCK1 protein inhibitory activity and can be used for treating cerebral hemorrhage. Through further biological activity detection of the screened 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound, it is shown that the screened 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound has an obvious ROCK1 protein inhibitory activity and has good prevention and treatment effects in an atorvastatin-induced zebra fish cerebral hemorrhage model.
Owner:深圳瀜新生物科技有限公司
Thyroid hormone disruptor virtual screening and interference activity quantitative calculating method based on nuclear receptor coregulator
ActiveCN105893759ALow costEasy to operateBiological material analysisProteomicsFactor iiScreening method
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Sulfonated sclerostin, antibodies, epitopes and methods for identification and use therefor
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
Method for screening small-molecule inhibitors by taking cathepsin D as target point
InactiveCN107346379AImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsBioinformaticsCathepsin KCathepsin O
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical chemistry, and relates to a drug screening method, in particular to a method for establishing a virtual screening model and an in vitro testing model of small-molecule inhibitors by taking cathepsin D as a target point. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring, analyzing and processing a three-dimensional structure of cathepsin D protein; (2) establishing and processing a small-molecule database; (3) establishing a computer virtual screening system; (4) applying the computer virtual screening system obtained in the step (3) to screen a small-molecule ligand library obtained in the step (2); (5) predicting absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADME-T). After the method for screening the cathepsin D inhibitors is adopted, six seedling compounds having cathepsin D inhibition activity are finally screened out; the method has the advantages of being rapid, economical and efficient, greatly increases the efficiency and provides a basis for finding the cathepsin D small-molecule inhibitors. The compounds, which are obtained by using the method and have the cathepsin D inhibition activity, can be further used for developing novel anti-cancer drugs.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Device and method to screen ligand molecular characteristics in drug design
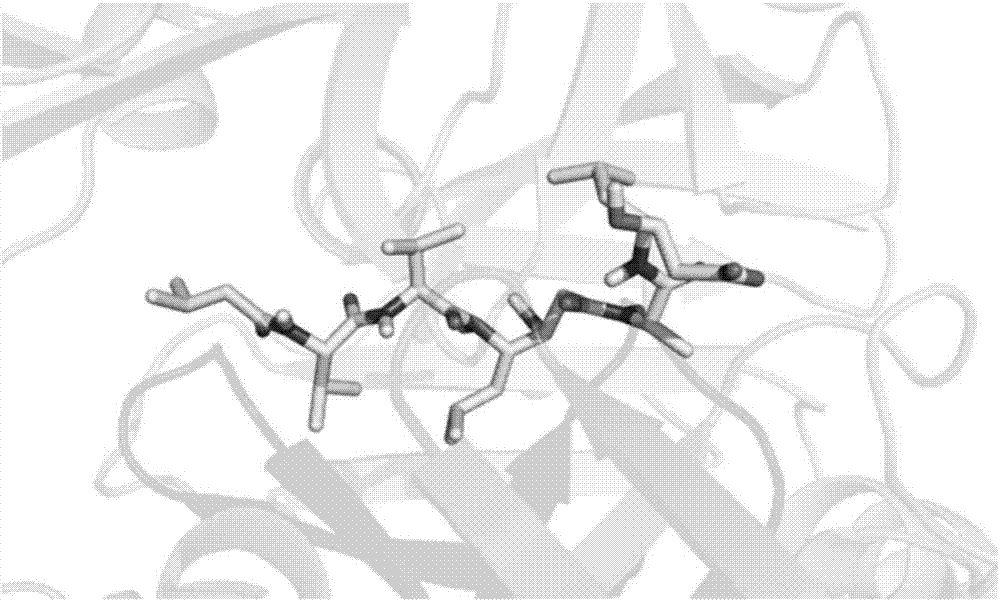
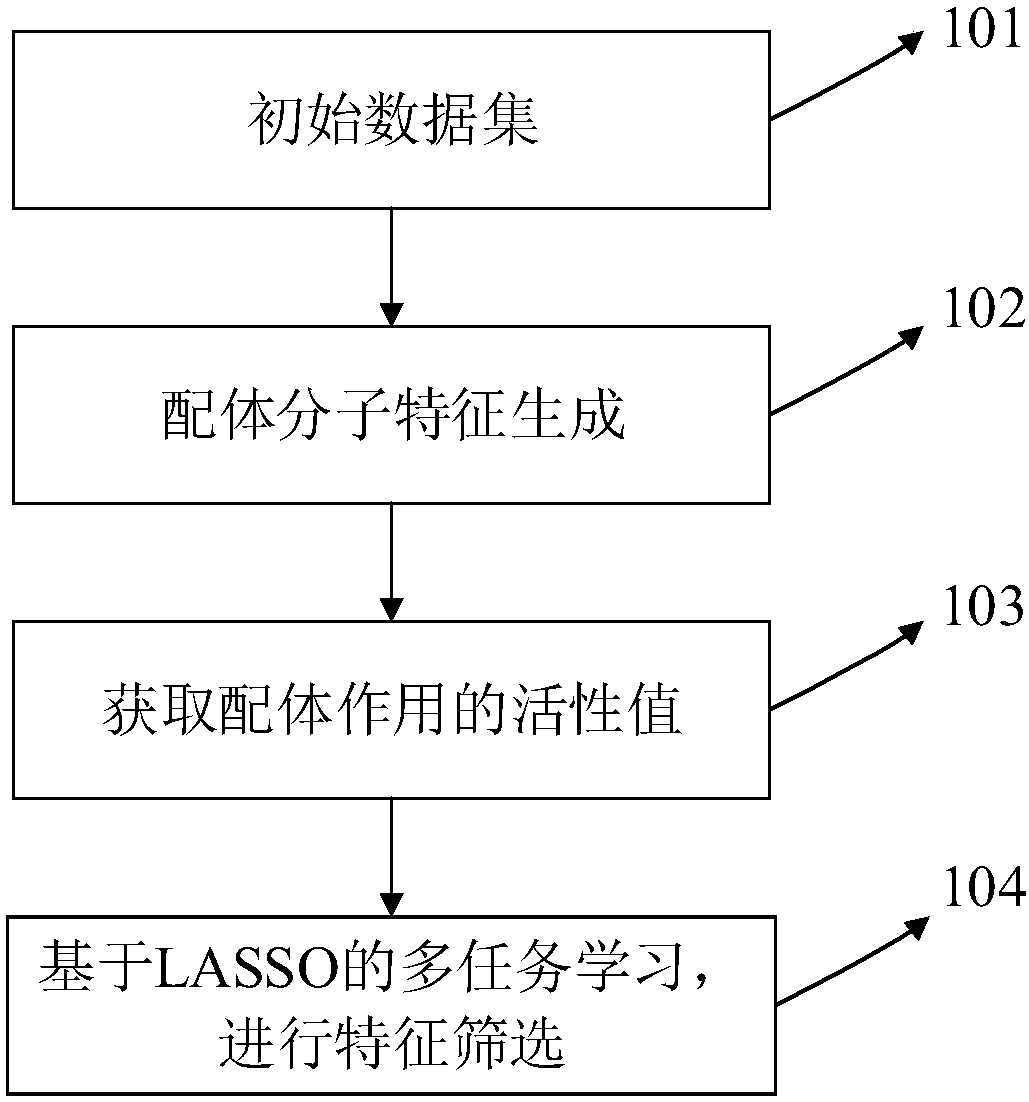
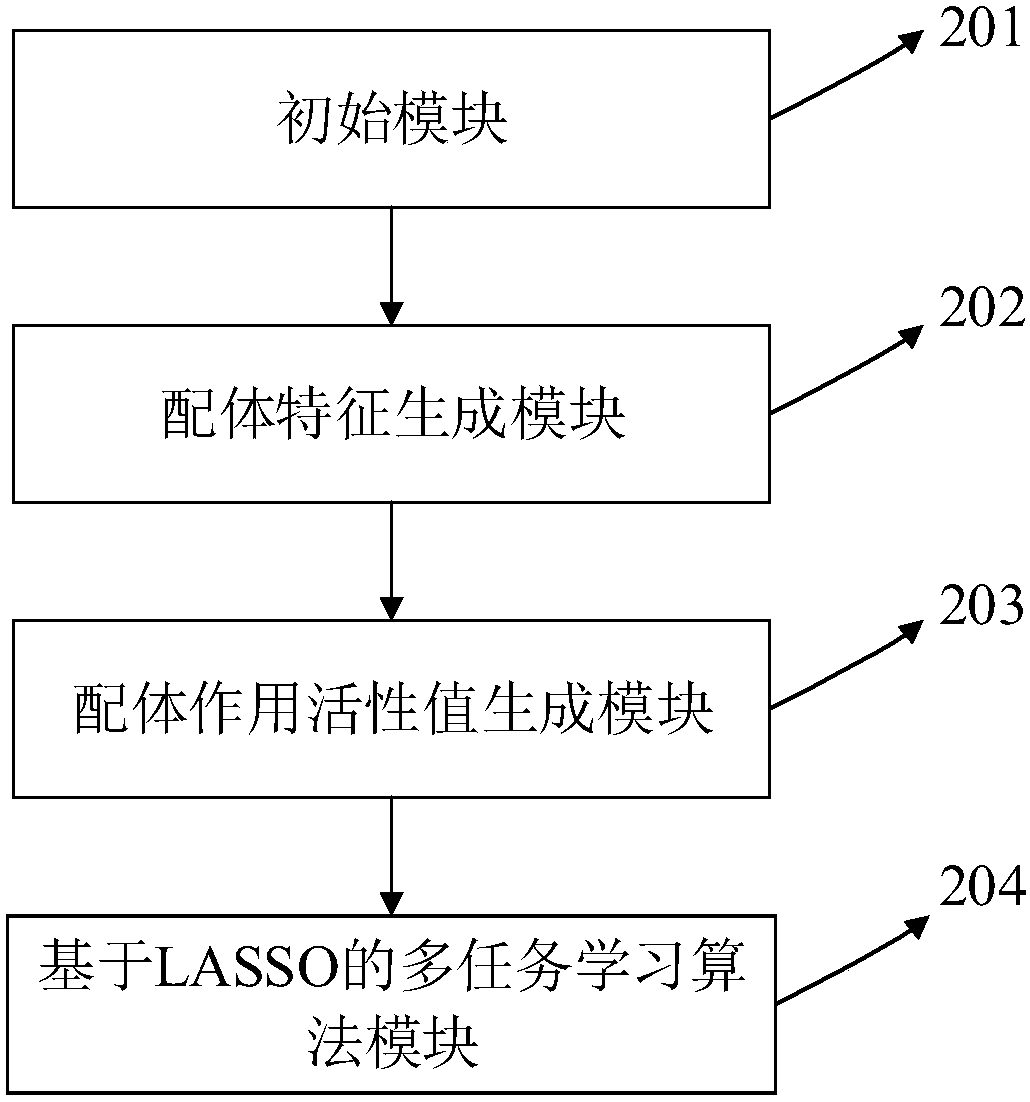
InactiveCN108399316ASolve problems that cannot exist in their natural stateFix build issuesMolecular designChemical machine learningScreening methodStudy methods
The invention discloses a ligand molecular characteristic screening method and device based on multitask learning for drug design. In drug molecular virtual screening based on ligands, few ligand molecules are discovered for important drug targets, and it is very difficult to establish a virtual screening model. A multitask learning method based on Lasso is utilized to acquire ligand molecular related characteristics through inter-task relevancy via robustness selection. The activity of ligand molecules is generally associated with few sub-structures; key factors that determine interactivity of a body and a ligand are quickly found, the problem with model construction when task sample quantity is low is solved, co-acting factors and independent acting factors are discovered; model robustness is improved; sub-structures associated with ligand activity are obtained, and characteristic screening is effectively performed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Application of berbamine dihydrochloride in preparing Ebola virus inhibitor
ActiveCN109125323AAchieve the effect of infectionEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsProtein targetVirtual screening
The invention discloses an application of berbamine dihydrochloride in preparing Ebola virus inhibitor. According to the invention, the envelope glycoprotein (EBOV-GPcl) of the Ebola virus in an activated state is taken as a target point, and an antiviral active compound which is capable of binding with the EBOV-GPcl is obtained through structure-based virtual screening, and the compound is the berbamine dihydrochloride. The berbamine dihydrochloride can specifically inhibit the entry of the Ebola recombinant virus by combining with the target protein EBOV-GPcl so as to achieve the effect of resisting Ebola virus infection. The semi-maximal effect concentration (EC50) of the berbamine dihydrochloride against the EBOV is 0.49 micrometer, indicating that the berbamine dihydrochloride has a strong inhibitory effect on the EBOV.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
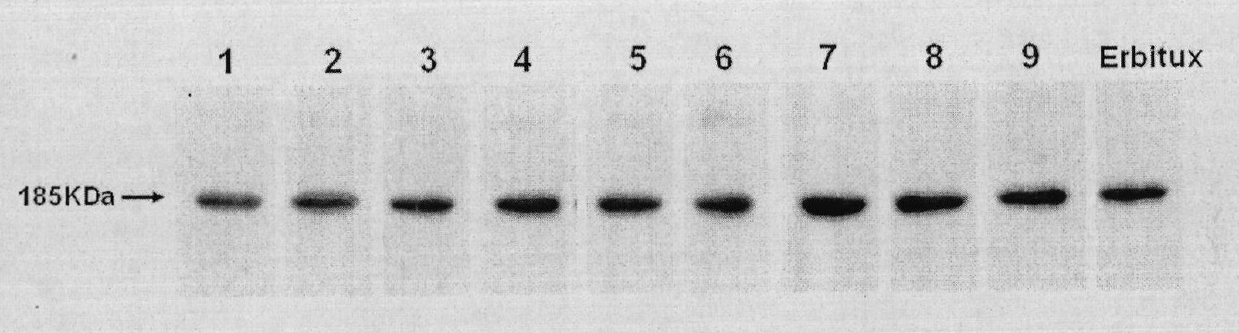
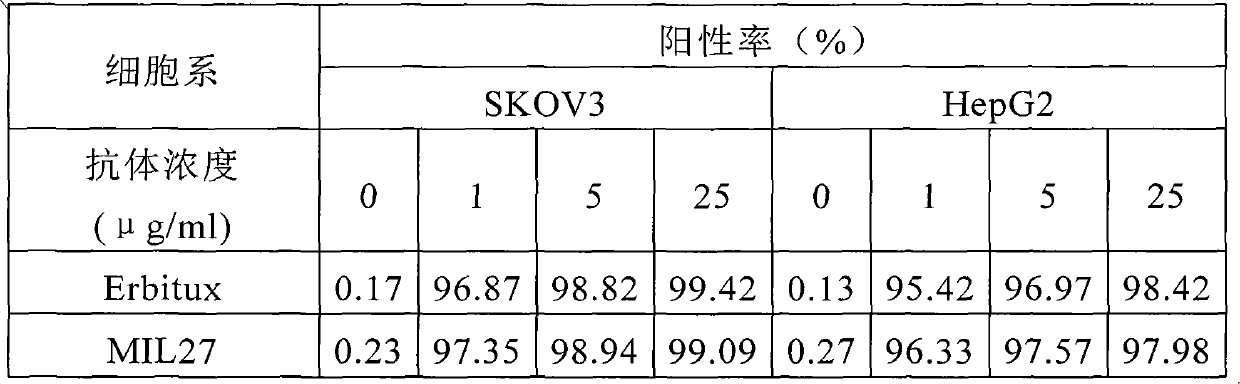
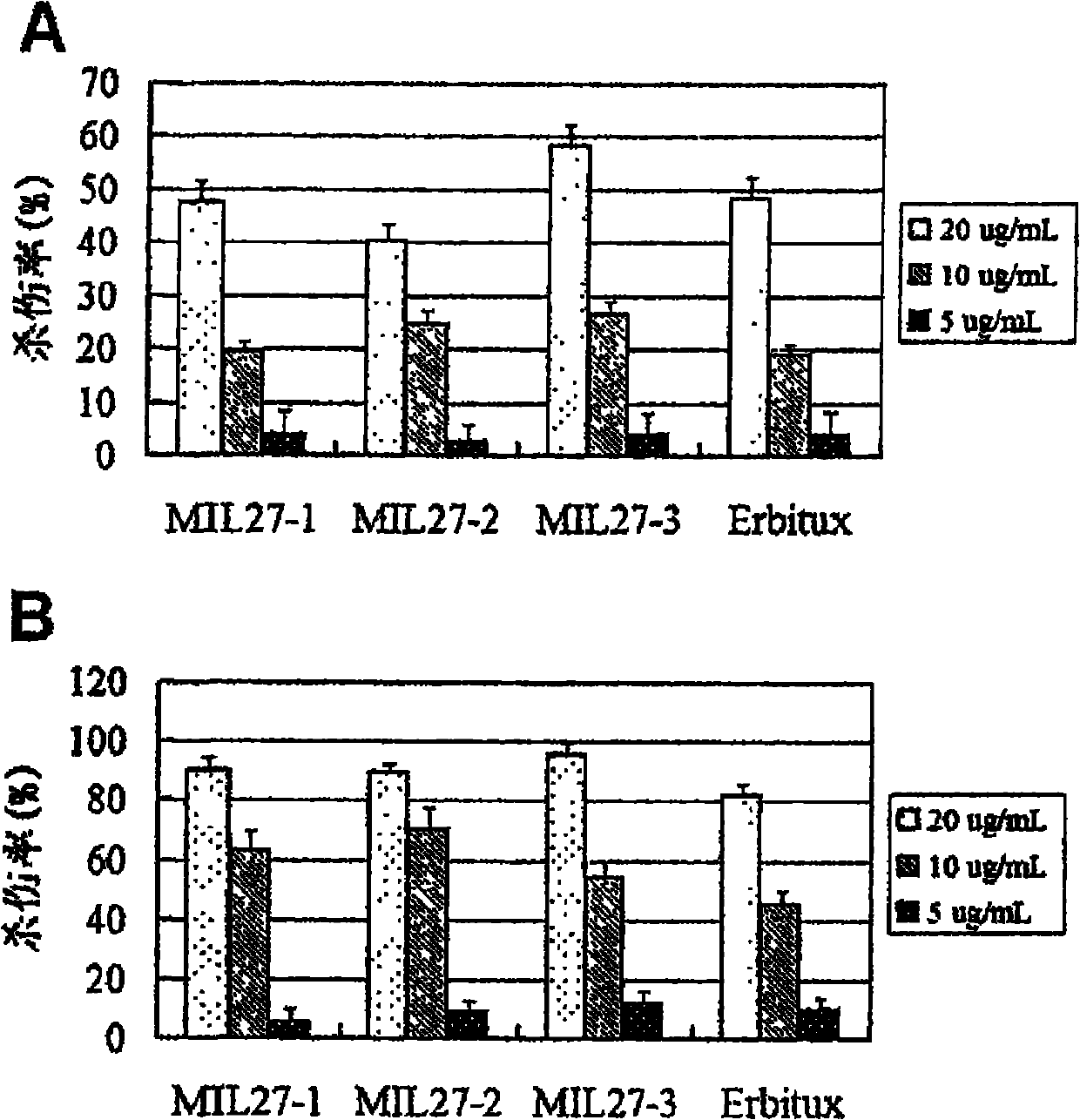
Preparation of novel anti-EGFR human source antibody MIL27 and application thereof
InactiveCN101948540AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCancer cellTumor cells
The invention discloses an anti-EGFR human source antibody MIL27 based on computer aided design and application thereof. The antibody can be used for obviously inhibiting and killing human cancer cell expressing EGFR. The invention is based on the interaction structure characteristic of EGFR protein extracellular region and functional antibody, computer virtual screening and design are adopted to obtain the anti-EGFR functional human source antibody MIL27, PCR method is applied to complete synthesis of antibody gene, eukaryotic expression vector is constructed, and MIL27 antibody capable of specifically identifying EGFR is expressed. The antibody MIL27 can effectively kill EGFR positive tumour cells, including blaster cancer cell and liver cancer cell. The antibody identifies EGFR new epitope, and competitive experiment verifies that the new epitope is different from EGFR epitope identified by Erbitux.
Owner:BEIJING MABWORKS BIOTECH +1
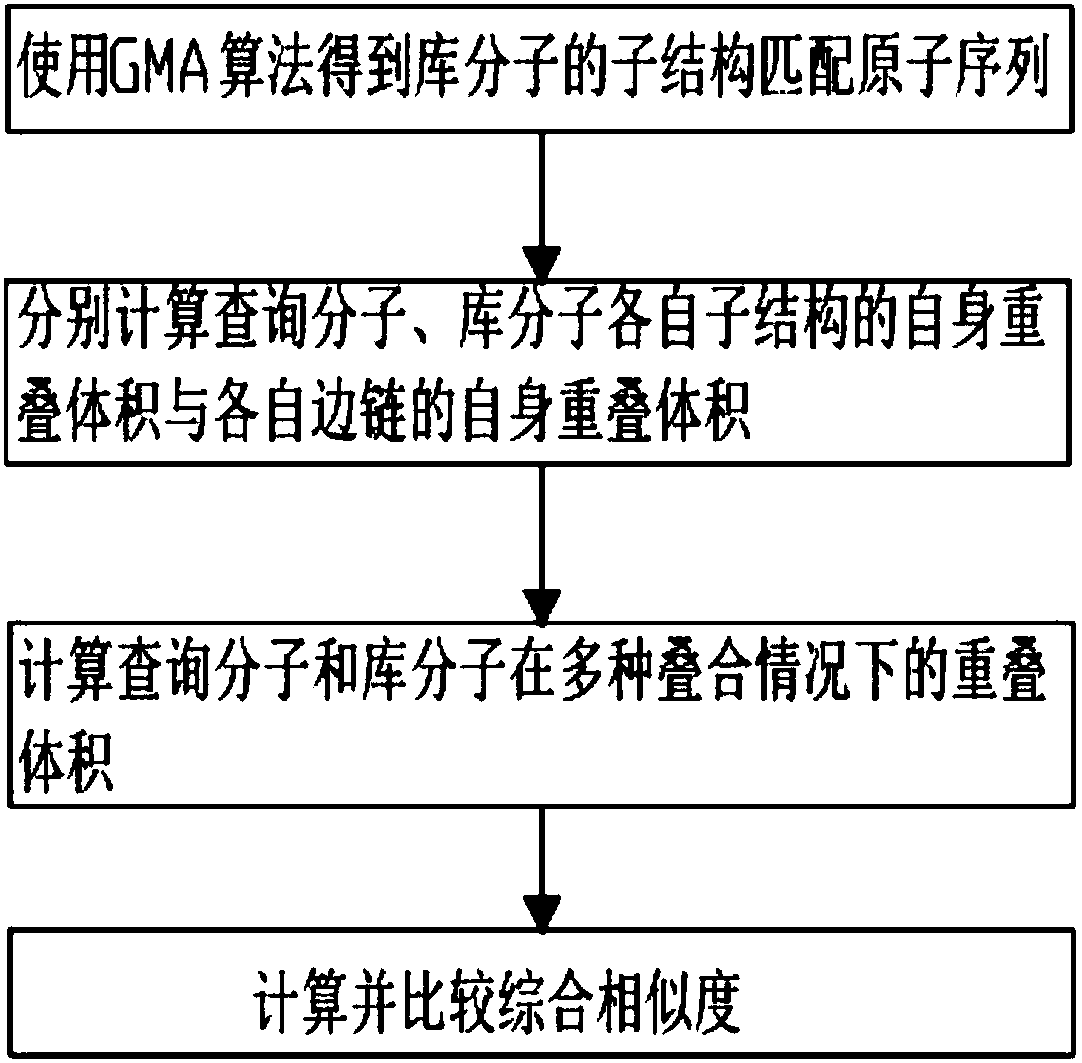
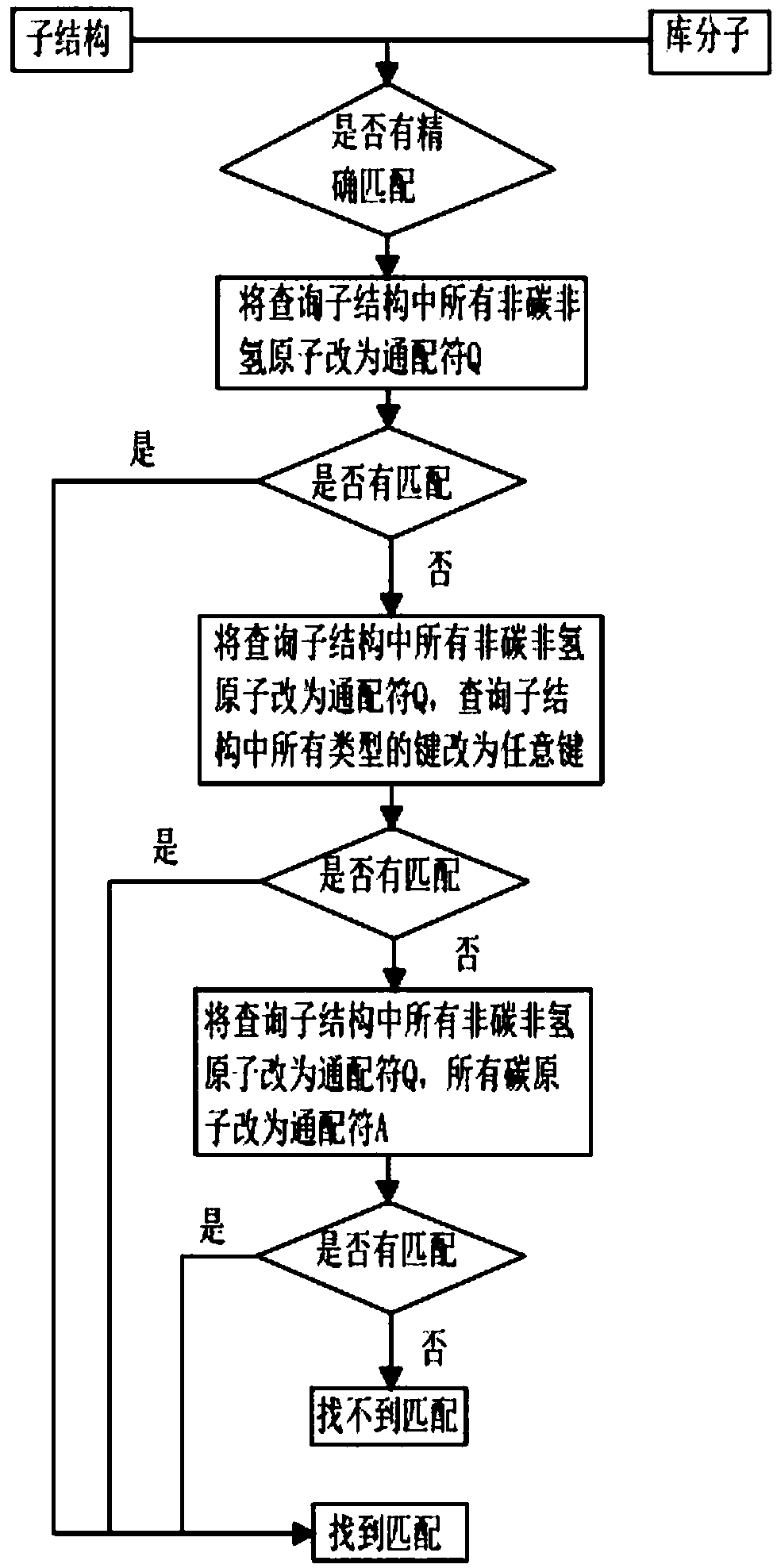
Three-dimensional substructure-based drug molecule comparison method
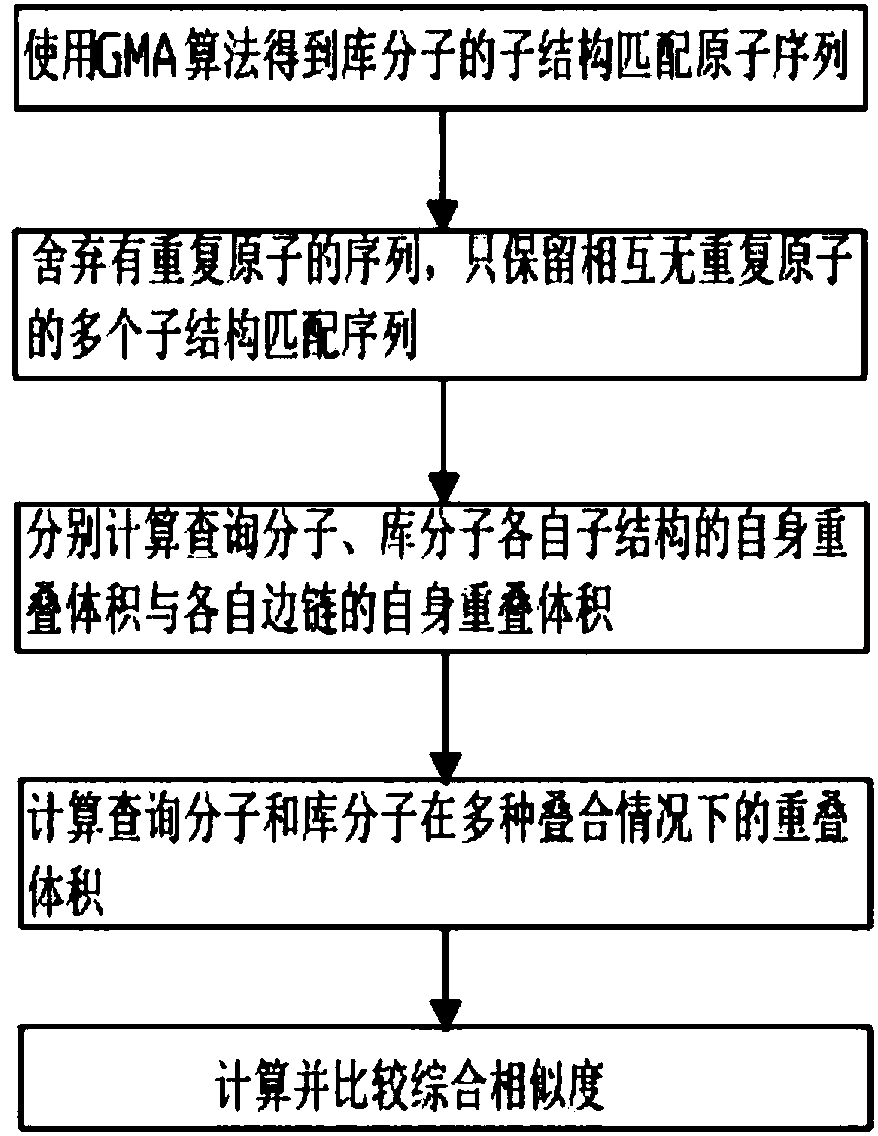
ActiveCN107657146AEasy to findIncrease flexibilityMolecular designChemical structure searchVirtual screeningSide chain
The invention discloses a three-dimensional substructure-based drug molecule comparison method, and relates to the technical fields of drug molecule design and screening. The method comprises the following steps: reading two-dimensional or three-dimensional structure information of a library molecule, and obtaining substructure matching atom sequences of the library molecule; reading three-dimensional structure information of a query molecule and the library molecule and related information of a query substructure, and respectively calculating self-overlapping volumes of respective substructures of the query molecule and the library molecule and self-overlapping volumes of respective side chains; calculating overlapping volumes of the query molecule and the library molecule in various overlapping cases; and respectively calculating a substructure similarity degree of the query molecule and the library molecule. The method can improve flexibility of molecule shape comparison, more facilitates discovery of lead compounds, and can be applied to virtual screening of drug molecules.
Owner:广州市爱菩新医药科技有限公司
2-polysubstituted aromatic ring-pyrimidine derivative and preparation and medical application
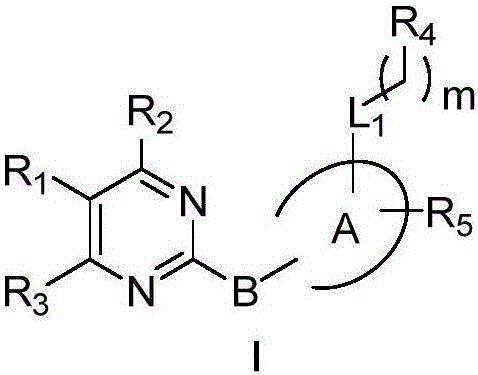
ActiveCN106588884AModerate to strong Chk1 kinase inhibitory activityStrong Chk1 kinase inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryVirtual screeningMolecular level
The invention provides a 2-polysubstituted aromatic ring-pyrimidine derivative, an optical isomer of the derivative or a medically acceptable salt or solvate of the derivative, and application of the compound, the optical isomer of the derivative or the medically acceptable salt or solvate of the derivative in preparing antineoplastic medicine. According to the 2-polysubstituted aromatic ring-pyrimidine derivative, by adopting N-substituted pyridine-2-minopyrimidine as a lead compound obtained based on virtual screening of a structure, a series of brand new small molecule Chk1 inhibitors are designed and synthesized, and a Chk1 kinase inhibitory activity test of a molecular level is conducted on the compound. Experiments prove that the compound is a Chk1 inhibitor with a strong antitumous effect, Chk1 kinase inhibitory activity and a prospect, and new cancer treating medicine, and can be used for treating solid tumor or leukemia related with human or animal cell proliferation. The 2-polysubstituted aromatic ring-pyrimidine derivative has a structure shown in the general formula I.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






![Use of 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives in preparation of drug for prevention or treatment on cerebral hemorrhage Use of 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives in preparation of drug for prevention or treatment on cerebral hemorrhage](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1246adbb-ecea-46bd-848a-27fc716d4400/HDA0000156784300000011.PNG)
![Use of 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives in preparation of drug for prevention or treatment on cerebral hemorrhage Use of 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives in preparation of drug for prevention or treatment on cerebral hemorrhage](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1246adbb-ecea-46bd-848a-27fc716d4400/HDA0000156784300000012.PNG)
![Use of 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives in preparation of drug for prevention or treatment on cerebral hemorrhage Use of 4,7-dihydrotetrazyl[1,5-alpha]pyrimidine compound and its derivatives in preparation of drug for prevention or treatment on cerebral hemorrhage](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1246adbb-ecea-46bd-848a-27fc716d4400/HDA0000156784300000021.PNG)