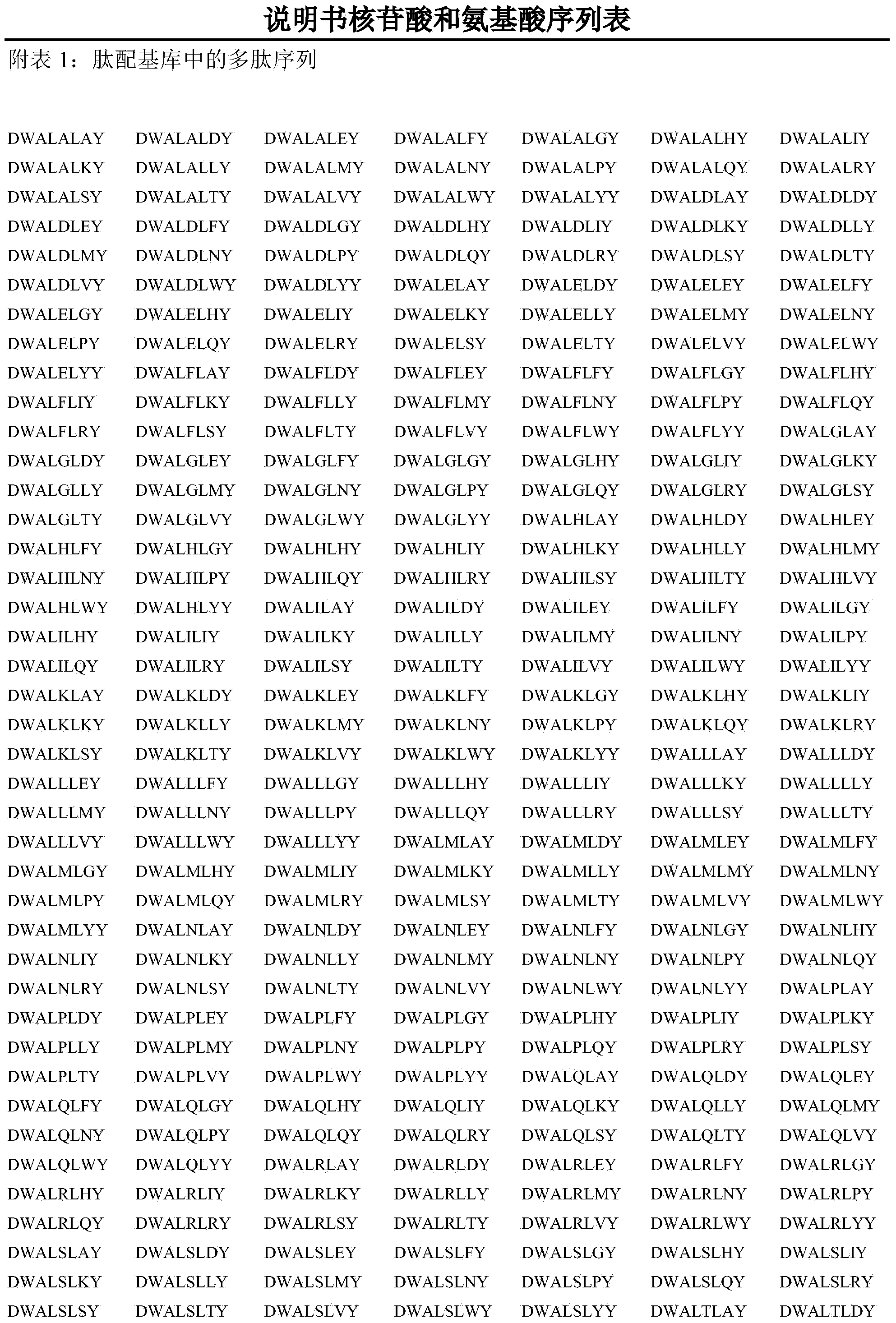Patents
Literature
84 results about "Macromolecular docking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
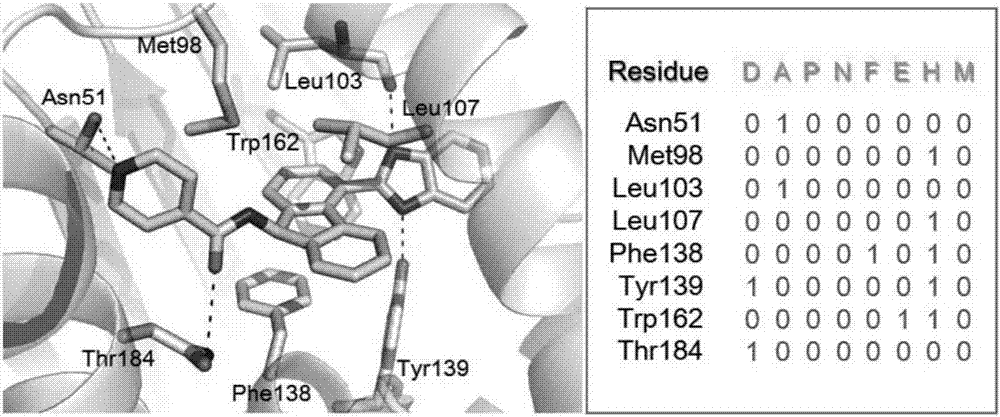
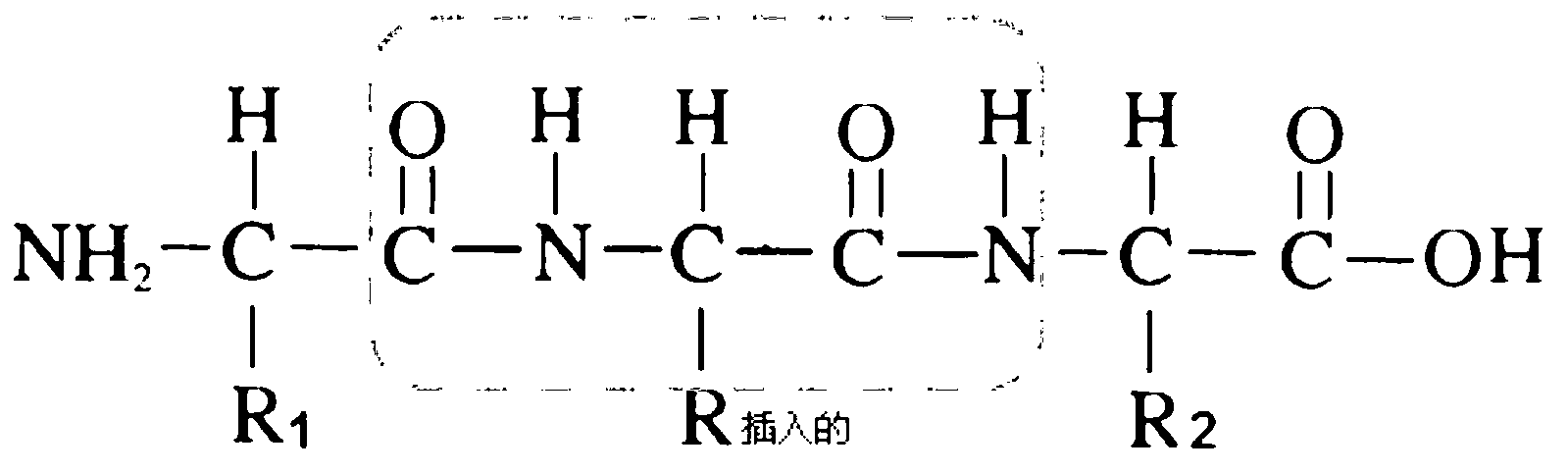
Macromolecular docking is the computational modelling of the quaternary structure of complexes formed by two or more interacting biological macromolecules. Protein–protein complexes are the most commonly attempted targets of such modelling, followed by protein–nucleic acid complexes.
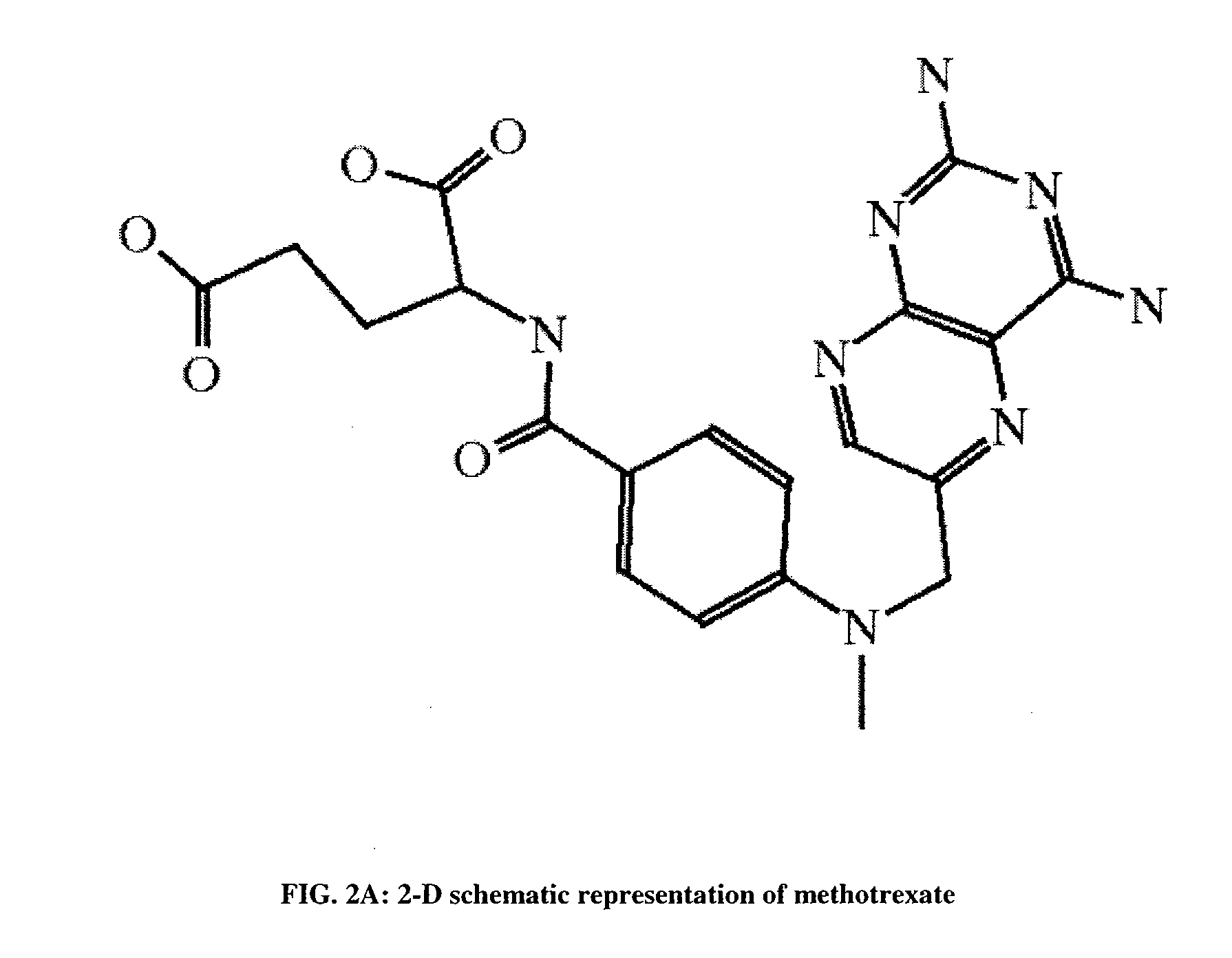
Application of N-(thiofuran-2) pyrazolo (1, 5-a) pyridine-3-formanides compounds for preparing antineoplastic
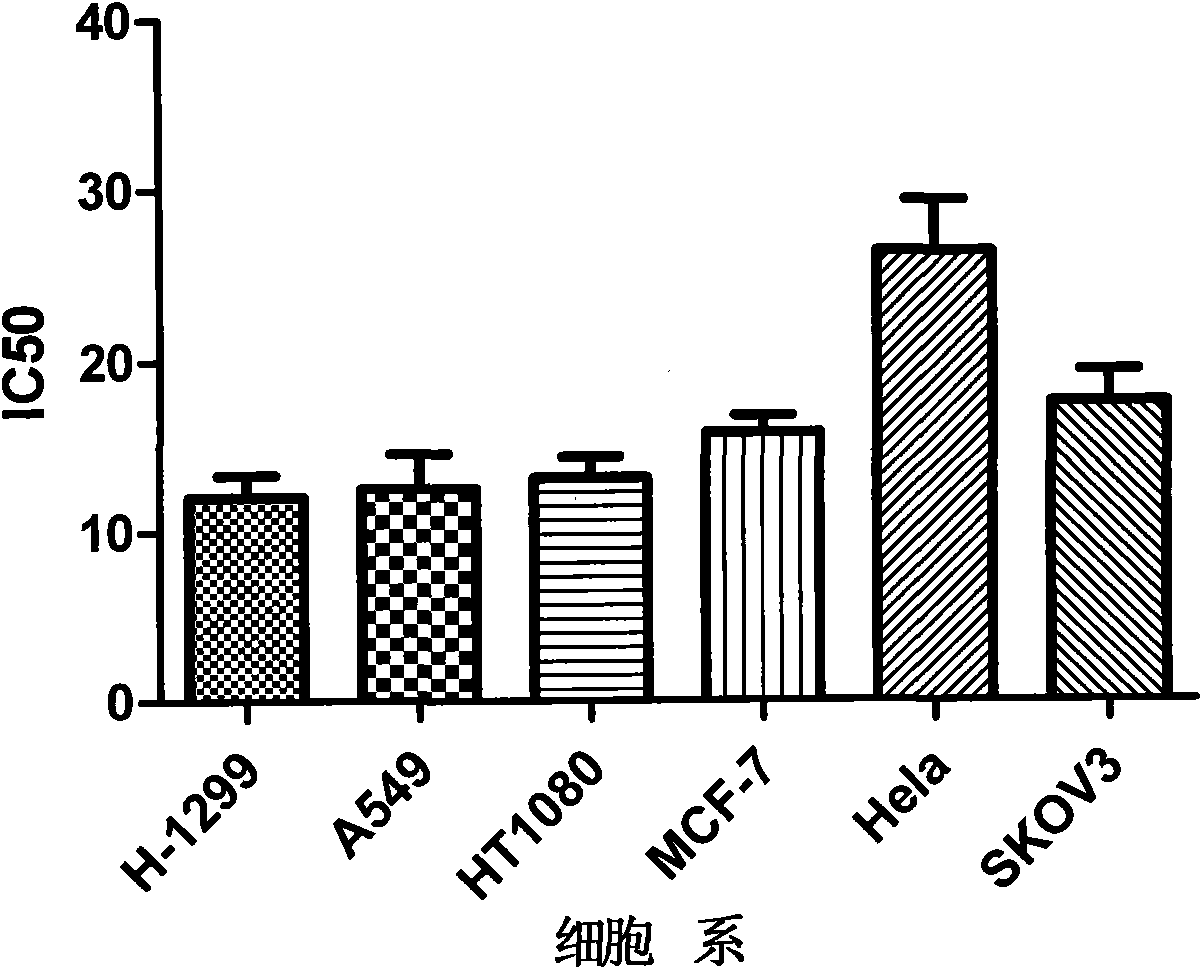
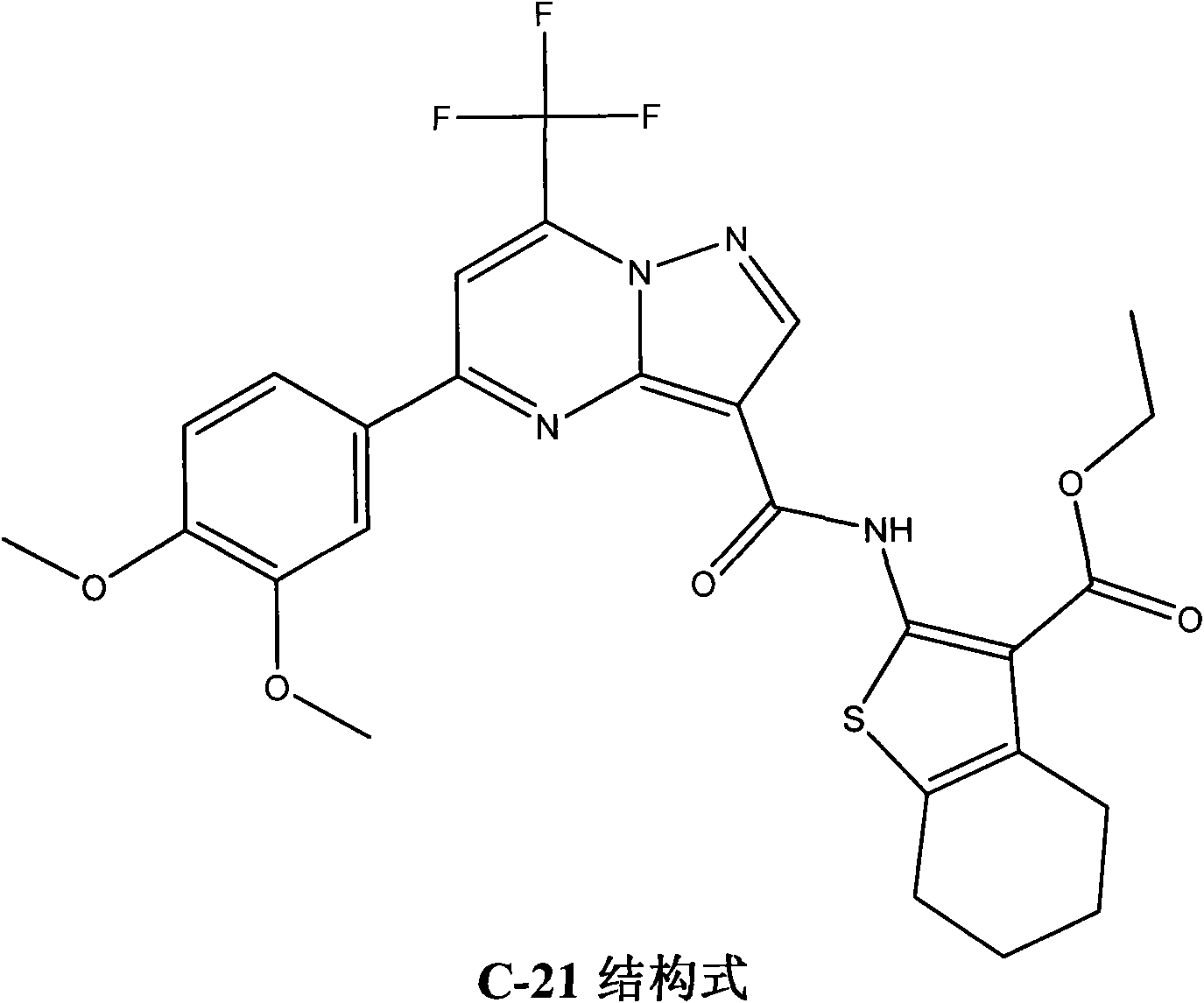
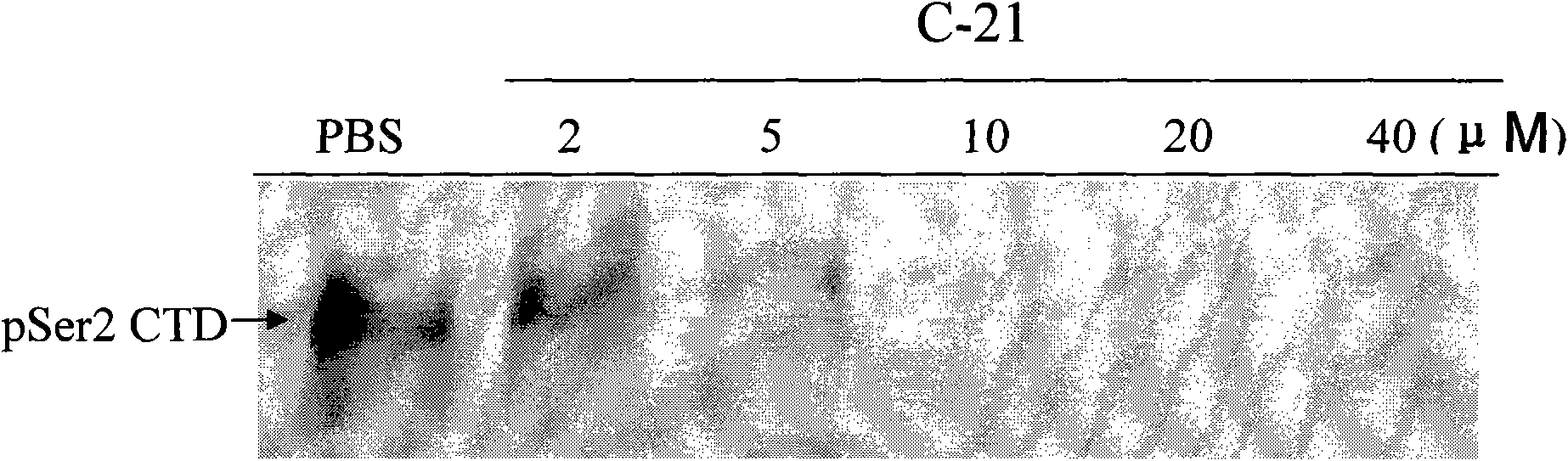
The invention searches the novel micromolecule inhibitor pyrazolo (1, 5-a) miazines compounds of cyclin-dependent kinase CDK9 (cyclin-dependent kinase) through the virtual screening of a computer, biometrically measures activity thereof, and validates interaction mechanism. The invention specifically comprises the following steps: the three-dimensional crystal conformation of the cyclin-dependent kinase family member CDK9 is obtained in a way of homology modeling; and micromolecule three-dimensional database is screened with DOCK (molecular docking). The invention uses a MTT tumor cell growth inhibition test to biometrically measures the activity of the selected compounds, researches the selected compounds pyrazolo (1, 5-a) miazines with high activety in a way of molecular mechanism, validates the inhibiting effect of the compounds to the activity of CDK9 kinase, and clarifies the interaction mechanism of the compounds for inhibiting the external activity and the molecule of various malignancies such as lung cancer, osteosarcoma, oophoroma, cervical carcinoma, breast cancer, etc.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
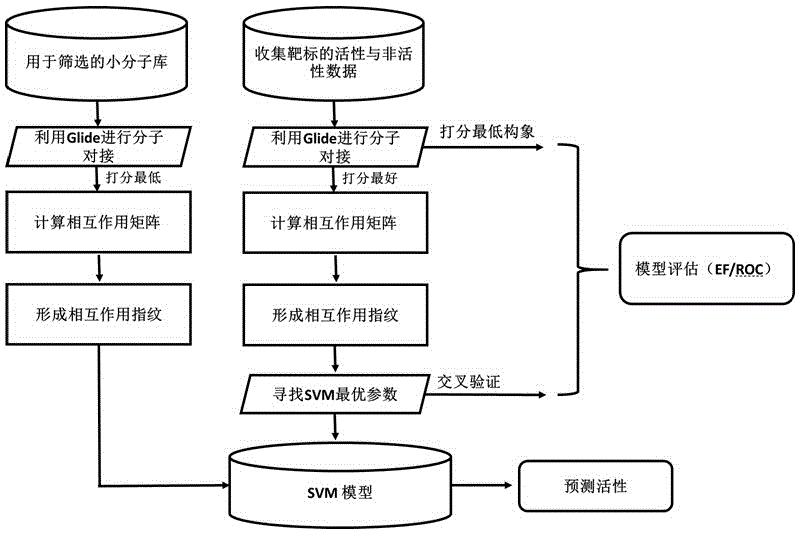
Drug target virtual screening method based on interactive fingerprints and machine learning
ActiveCN106446607AFully consider the specificityAvoid the pitfalls of underfittingBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsProtein targetBinding site
The invention relates to a drug target virtual screening method based on interactive fingerprints and machine learning. According to the method, based on traditional molecular docking, the interactive fingerprints of known active and non-active micromolecules and target protein are trained through machine learning to obtain a screening model of targets, and the obtained model is used for virtual screening. The specific targets are specifically trained, the specificity of each kind of targets is fully considered, and the defect of insufficient fitting of a traditional scoring function is avoided; interaction energy of each micromolecule and each residue in a binding pocket is calculated, so that effective binding sites or binding modes can be found; non-linear fitting is carried out through machine learning, and compared with linear fitting, the correlation or coupling effect between all the interaction energy can be better processed; by means of the method, enrichment of active molecules is better promoted.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Protein-ligand interaction fingerprint spectrum-based drug target prediction method
InactiveCN107038348AImprove forecast accuracyOvercome the disadvantage of low prediction success rateBiostatisticsProteomicsMacromolecular dockingCrystal structure
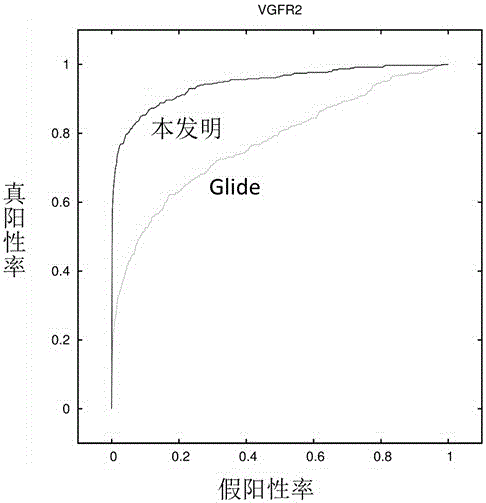
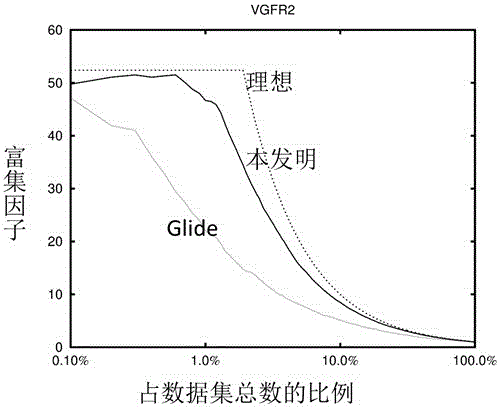
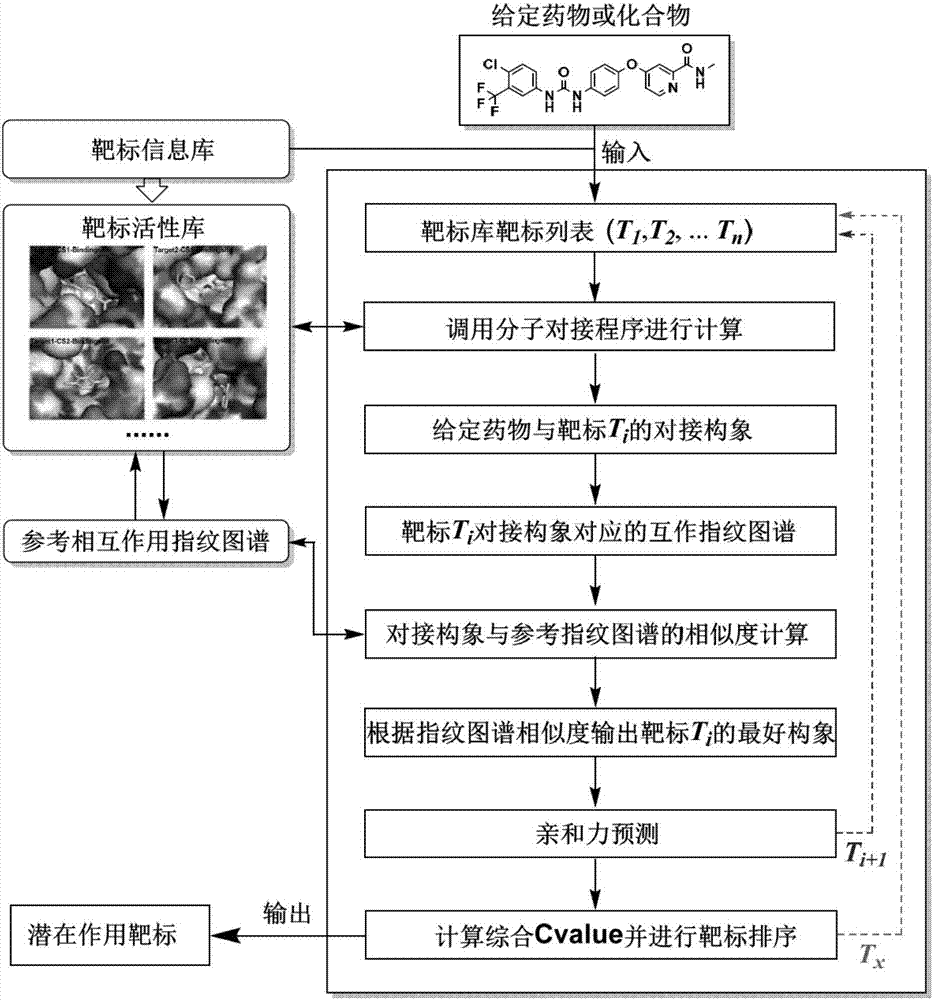
The invention discloses a protein-ligand interaction fingerprint spectrum-based drug target prediction method. The method comprises the steps of collecting a large amount of diversified target and ligand complex crystal structures; building a reference protein-ligand interaction fingerprint spectrum model; predicting a possible combination mode of a to-be-tested drug and each target by molecular docking; building a drug and target interaction fingerprint spectrum model; and calculating the similarity between a fingerprint spectrum and the reference interaction fingerprint spectrum model, and the affinities of the drug and targets, sorting the targets of a target library by integrating docking scoring, the fingerprint spectrum similarity and the affinities, and outputting a potential target of the drug. According to the method, drug and target interaction modes are sorted and predicted by adopting an interaction fingerprint spectrum method, so that the shortcoming of relatively low success rate of predicting the drug and target interaction modes due to the molecular docking is overcome; and the targets are sorted by adopting a comprehensive index Cvalue, and the advantages of various methods are brought into play, so that the prediction accuracy of the drug target is radically improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Novel affinity ligand polypeptide library of immunoglobulin G constructed based on protein A affinity model and application of design method
The invention discloses a novel affinity ligand polypeptide library of immunoglobulin G (IgG) constructed based on a protein A affinity model and an application of a design method. According to a molecular mechanics / Poisson-Boltzmann solvent-accessible surface area method, a key residue of protein A with a higher affinity interaction with human IgG is analyzed and obtained based on the available human IgG-protein A compound structure; the simplified protein A affinity model is constructed; the affinity polypeptide molecule library of the IgG is constructed based on the simplified protein A affinity model. On the basis of the peptide library, an amino acid type represented by X is ascertained by further utilizing an amino acid location method. Then, candidate polypeptides are screened gradually by applying molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation means. Finally, polypeptide affinity ligand capable of effectively separating and purifying the IgG is ascertained through an affinity chromatography experimental method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
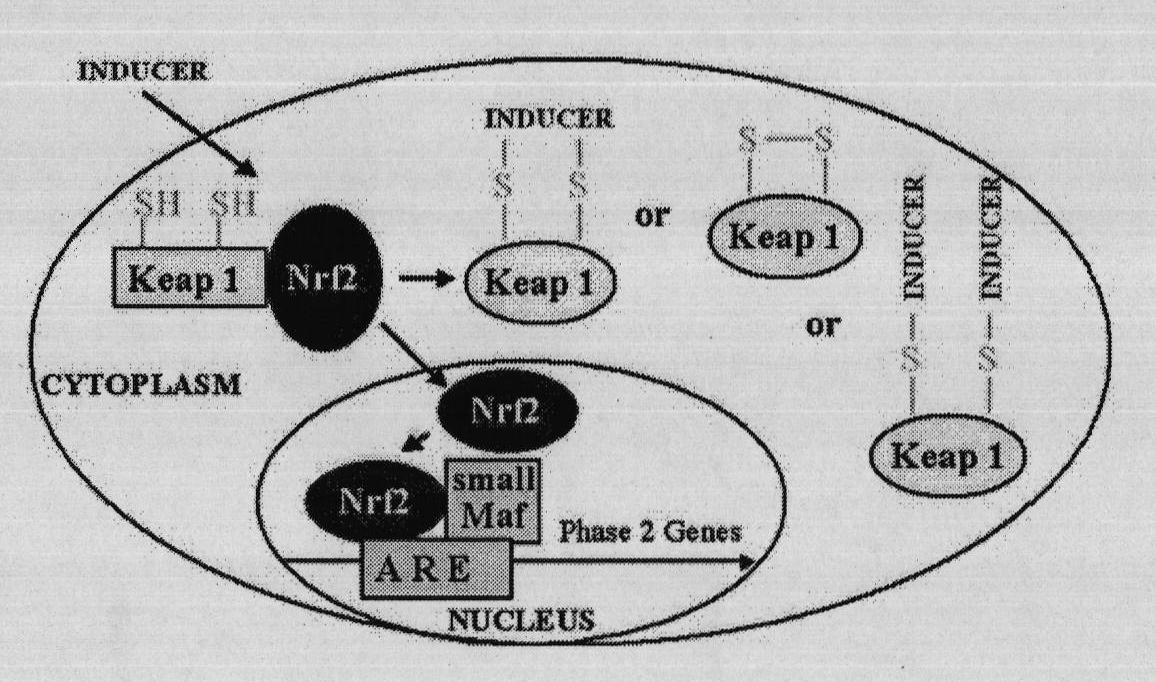
Virtual screening method for novel cancer-preventing or anti-cancer medicament by taking Keap1 as target point
InactiveCN101916330AHigh speedImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsMacromolecular dockingVirtual screening
The invention relates to a virtual screening method for a novel cancer-preventing or anti-cancer medicament by taking Keap1 as a target point. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) determining a PDB structural data of a Keap1 protein structure; 2) determining an active center according to an active cysteine residue site of the Keap1 by adopting molecular docking software, and setting active bags; 3) screening small molecule ligand; 4) establishing a small molecule ligand database for docking; 5) docking the small molecule ligand in the small molecule ligand database for docking and the active bags one to one according to the set active bags by using the molecular docking software; and 6) primarily determining a pilot medicament with chemical cancer-preventing or anti-cancer effect according to the sequencing of the docking results. The method can obtain a clue of an active compound in short time, and then screens the cancer-preventing or anti-cancer medicament by using animal horizontal screening or high-pass molecule platform screening so as to greatly improve the speed and the efficiency and shorten the research period of a new medicament.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting binding specificity between ligand and target and drug screening method
The present invention relates to the field of drug screening, and specifically relates to a method for detecting binding specificity between a ligand and a target and a drug screening method. The detection method includes: molecular docking through the ligand and the target, obtaining an energy spectrum of the ligand, introducing the ratio of intrinsic specificity, and thus determining the binding specificity between the ligand and the target. The detection method compared with conventional methods has the advantages of good specificity, high accuracy, fast speed and low cost. The invention provides a new detection method for structure-based virtual drug screening. Based on the detection method, a method of two-dimensional virtual drug screening directed at affinity and specificity is developed. At the same time, the detection method provides a new description characteristic for the side effect research of small molecule compounds, and provides guidance for chemical modification and transform of drug lead compounds. Relative to conventional mere affinity-concerning virtual drug screening, the specificity dimension is added to the method, so the chances of discovery of drug lead compounds are greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for calculating and simulating protein-protein docking
InactiveCN102314560AMeet needsImprove screening efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsMacromolecular dockingProtein-protein complex
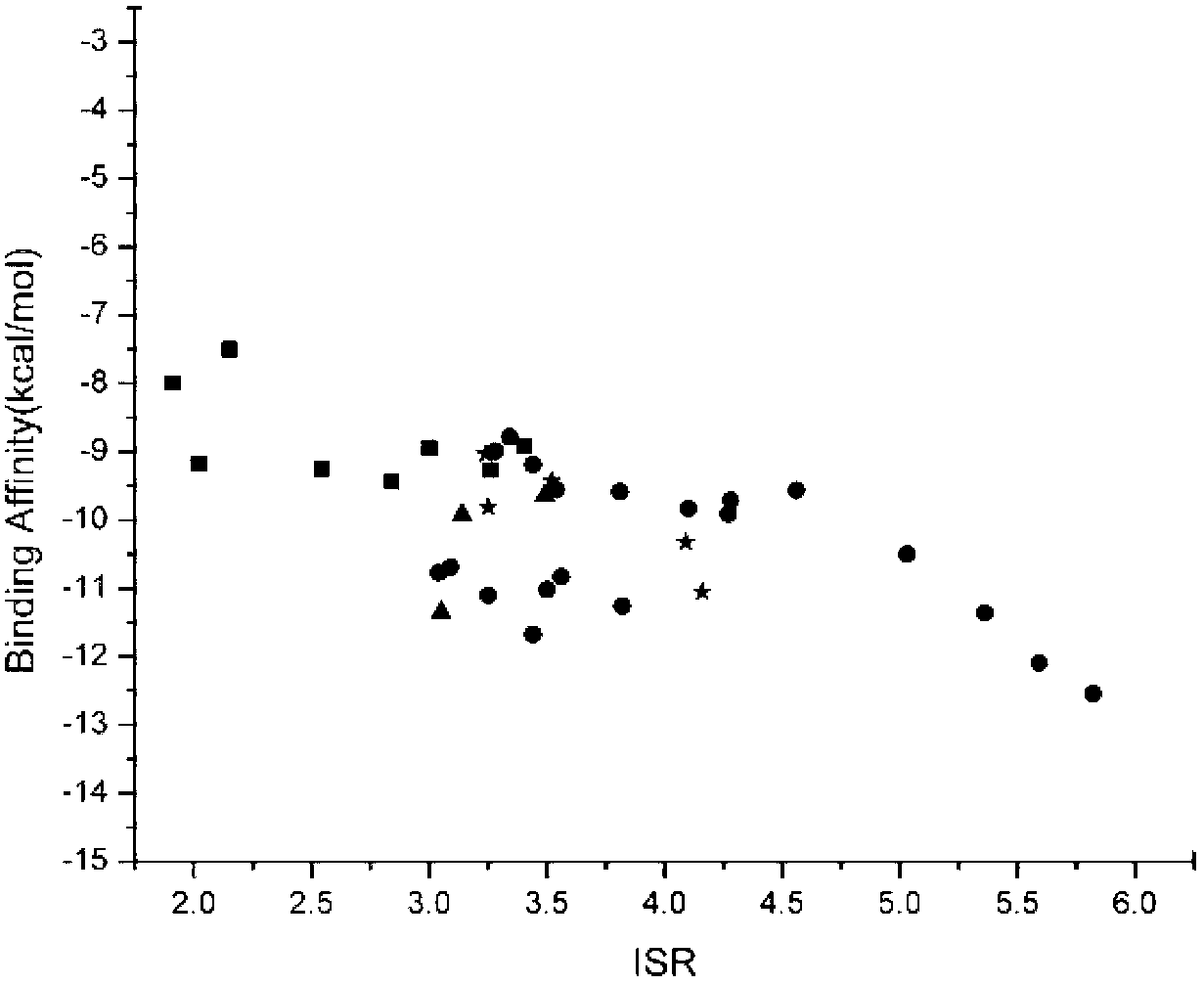
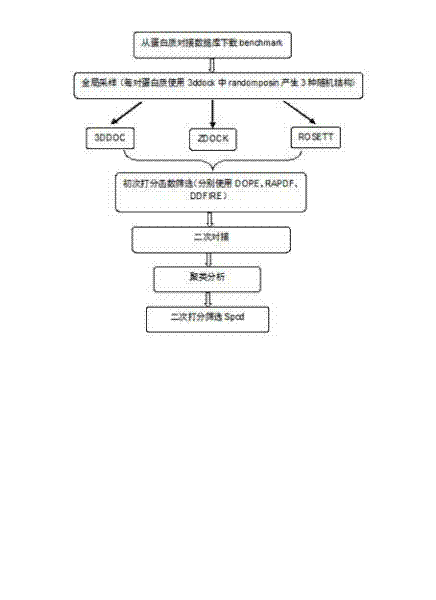
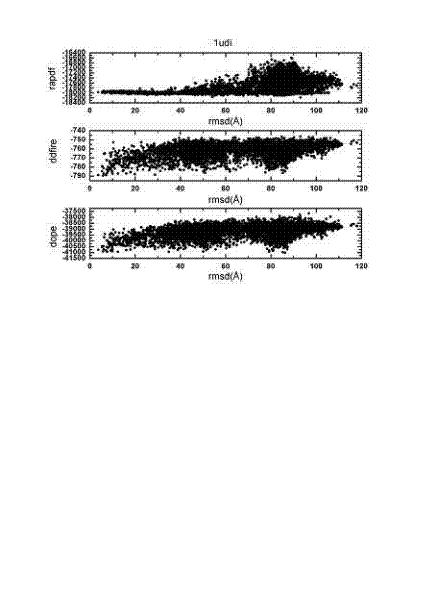
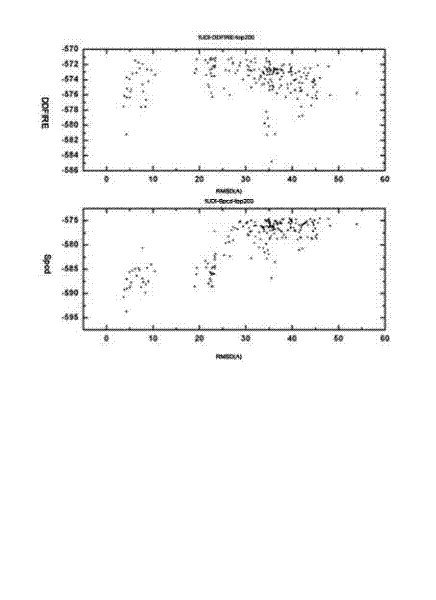
The invention relates to a method for calculating and simulating protein-protein docking, which mainly comprises the following steps: downloading a protein docking benchmark database; carrying out global sampling by using macromolecular docking software, i.e. 3DDOCK, ZDOCK and ROSETTA; screening protein compounds which are obtained through sampling by using scoring functions, i.e. DOPE, RAPDF and DDFIRE, so as to filter off most of the protein compounds; carrying out second molecular docking on compounds which are obtained through screening, i.e. second sampling; clustering protein compounds which are obtained through the second sampling, and carrying out second-round screening by using the designed scoring function, i.e. Spcd, after the protein compounds are clustered; and screening more target compounds through a method of combining different docking software, multi-round docking and multiple scoring. The designed scoring function, i.e. the Spcd, can distinguish compounds in a closely-natural bonding mode from compounds in a wrong bonding mode with high efficiency, thus more target molecular compounds can be obtained, which is the most outstanding advantage of the method provided by the invention.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
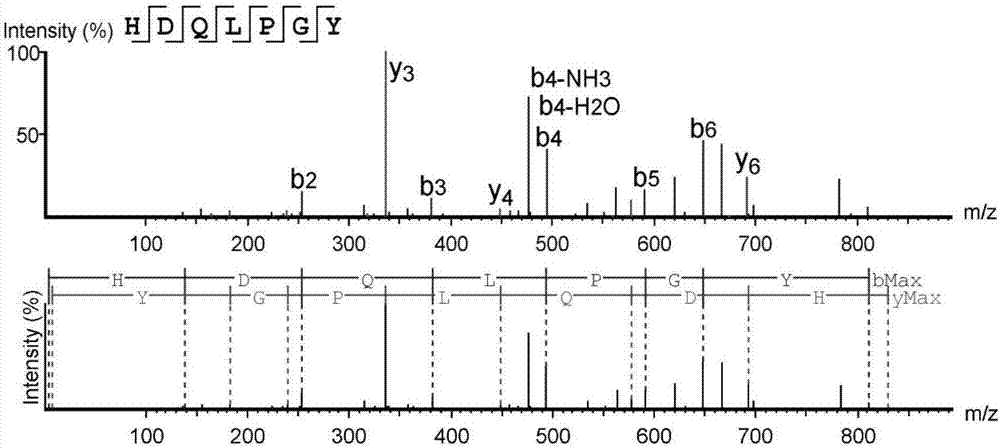
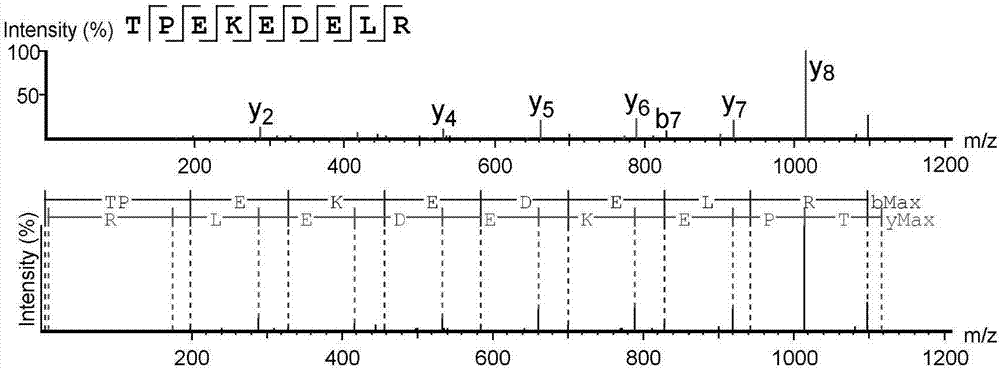
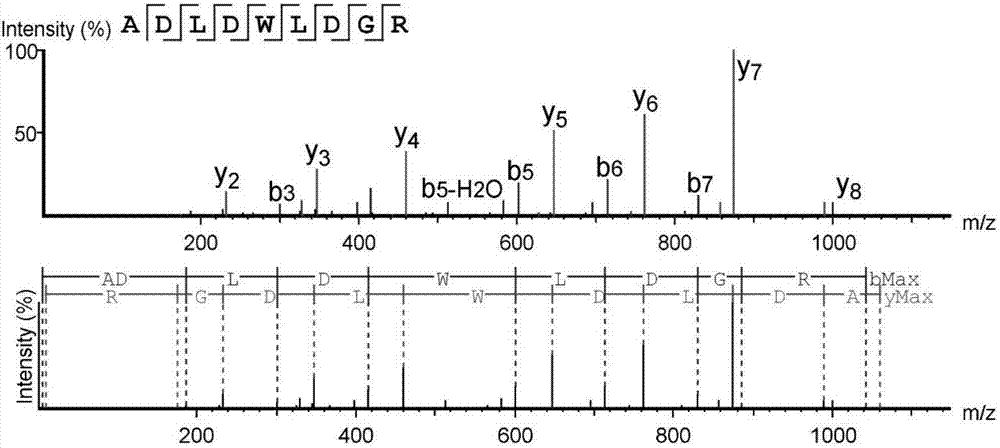
High-throughput active peptide screening method based on tandem mass spectrum and molecular docking
InactiveCN107132360AQuick searchEasy to operateBiological testingProtein targetHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to the field of medicine, and discloses a high-throughput screening method for active polypeptides based on tandem mass spectrometry and molecular docking. The invention uses modern biochemical technology to extract and prepare mixed polypeptides from marine molluscs, fish and other animals. After preliminary activity separation, the active site / component group is determined, and the amino acid sequence of all polypeptides in the active site / component group is identified by LC-MS / MS method. In the molecular docking software, all polypeptide sequences are homologously modeled, and then imported Molecular docking software docks with the target protein, analyzes the binding rate of the polypeptide and the target protein, and evaluates its inhibitory / activating activity, and screens the confirmed active polypeptide through solid-phase synthesis combined with in vitro activity evaluation to verify the accuracy of the screening. The invention has the advantages of fast and efficient search for marine active polypeptides, strong operability and important application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
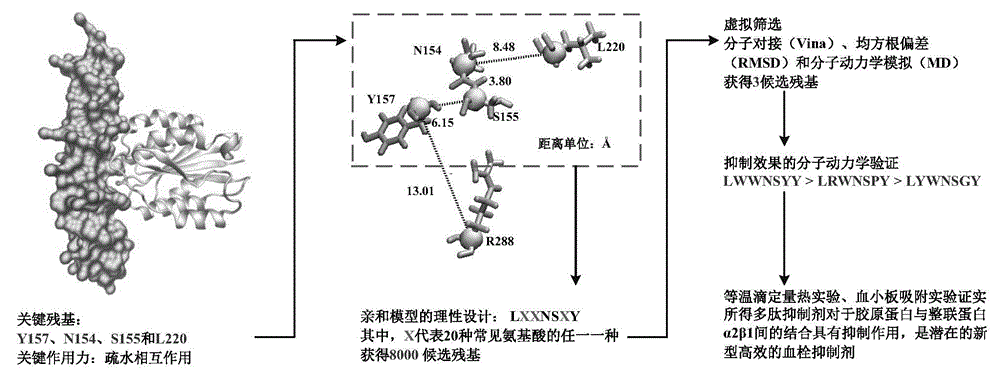
Collagen-integrin alpha2beta1 interacted polypeptide inhibitors and screening method thereof
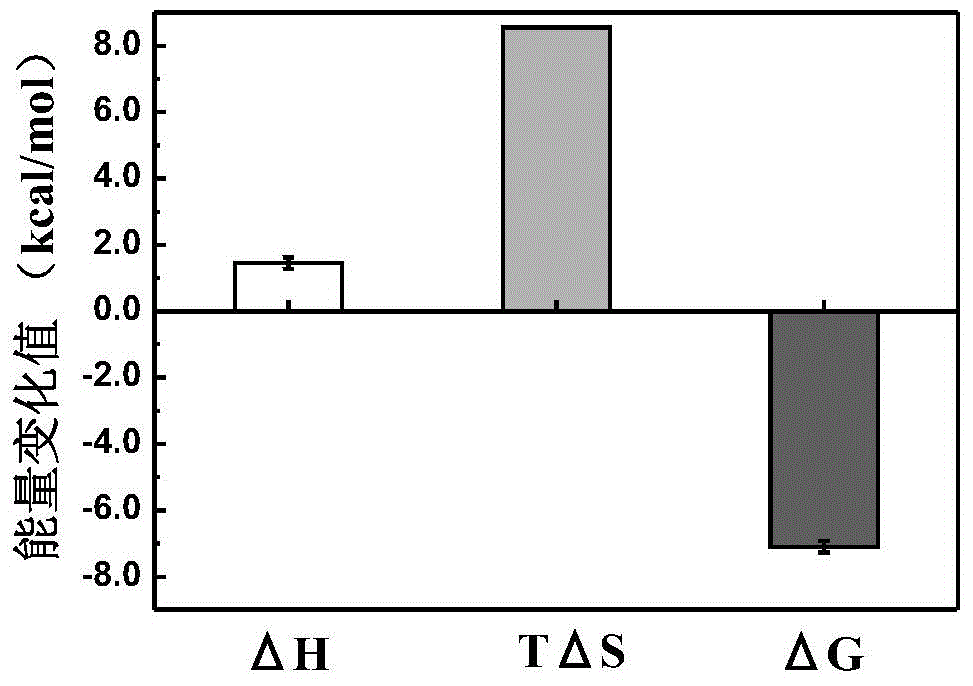
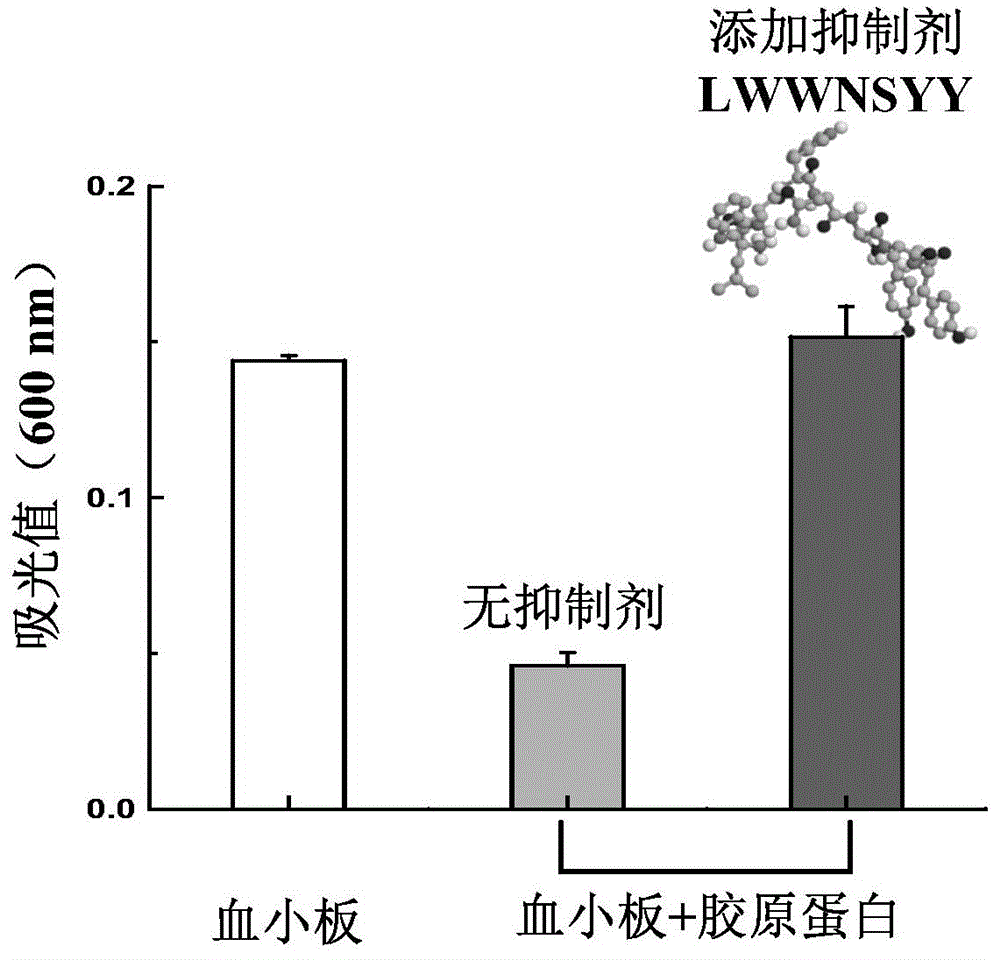
The invention discloses collagen-integrin alpha2beta1 interacted polypeptide inhibitors and a screening method thereof. The collagen-integrin alpha2beta1 interacted polypeptide inhibitors provided for the first time are LWWNSYY, LRWNSPY and LYWNSGY. According to a molecular mechanics-Poisson-Boltzmann solvent accessible surface area analysis method, the interaction between collagen short peptide and integrin alpha2beta1 on the surface of blood platelet is analyzed, so as to obtain a key residue with affinity interaction; therefore, a collagen-integrin alpha2beta1 interacted polypeptide inhibitor library can be constructed, the polypeptide inhibitors having high affinity to collagen can be obtained by screening polypeptides through molecular docking, root mean square deviation comparison and molecular dynamic simulation. Isothermal titration calorimetry experiments and blood platelet adsorption experiments proved that the obtained polypeptide inhibitors can inhibit the bonding between the collagen and integrin alpha2beta1, thus being potential high-efficiency thrombus inhibitors.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Metabolite-peptide-aptamer rapid screening method based on molecular docking technology
ActiveCN108197429AAddressing Limiting Factors for Broad ApplicationNo damageProteomicsGenomicsScreening proceduresAptamer
The invention discloses a metabolite-peptide-aptamer rapid screening method based on the molecular docking simulating computation technology. The metabolite-peptide-aptamer rapid screening method includes the steps that (1) a target metabolite is determined; (2) a potential polypeptide library is obtained, wherein binding force exists between the potential polypeptide library and the target metabolite; (3) the potential polypeptide library and the target metabolite are subjected to molecular docking forecasting. The metabolite-peptide-aptamer rapid screening method is high in speed and wide intarget range, a large quantity of manpower and material resources are not required, harm to experimenter bodies is avoided, and limiting factors of wide application of current peptide aptamer are avoided. According to the metabolite-peptide-aptamer rapid screening method based on the molecular docking simulating computation technology, the peptide-aptamer screening procedure can be simplified, the library capacity is increased to a greatest degree, the metabolite peptide aptamer with the suitable specificity and affinity is thus conveniently screened out, and the metabolite-peptide-aptamer rapid screening method is used for designing such as kit and sensor detection, and is applied to detection of the field such as nutriology, biology and clinical diagnosis.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
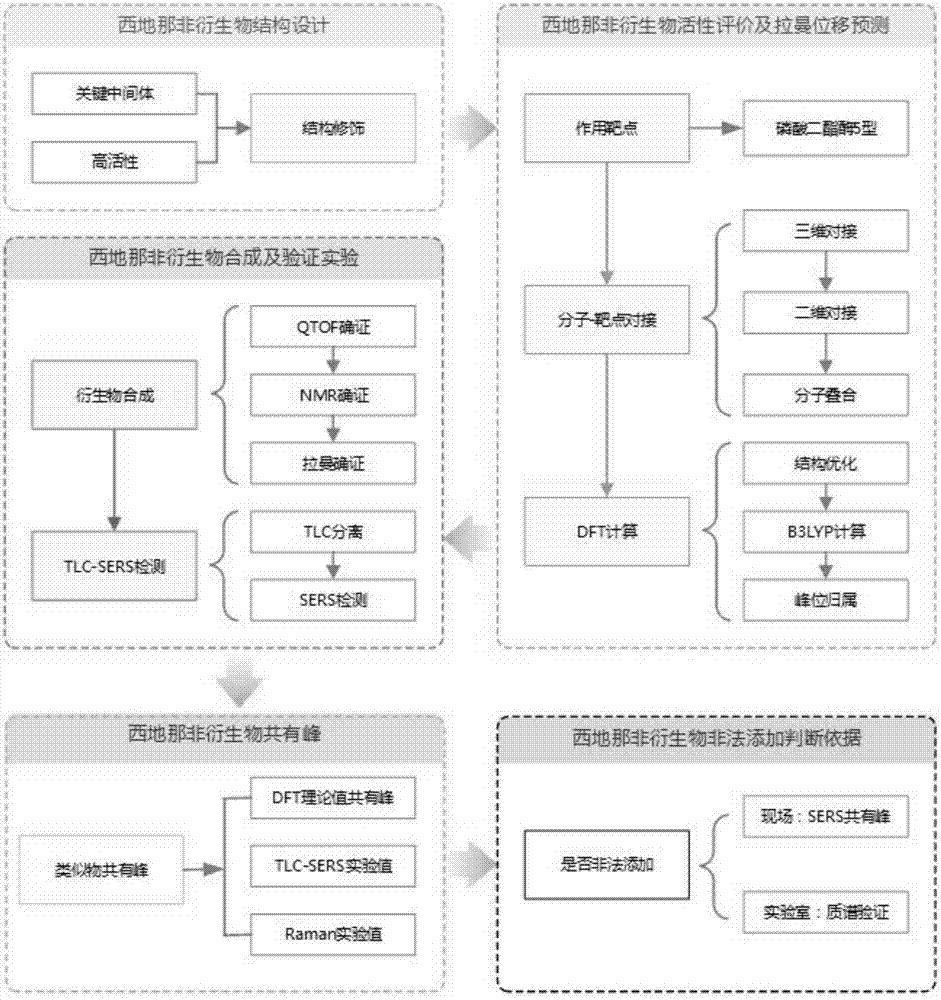
Method of quickly analyzing illegal addition of sildenafil analogue in yang-reinforcing health care products
InactiveCN107505305ARapid discriminant testReduce experiment costComponent separationRaman scatteringMacromolecular dockingMedicine
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine analysis, and particularly provides a method of quickly analyzing illegal addition of a sildenafil analogue in yang-reinforcing health care products and a method of screening quick detection conditions for the sildenafil analogue. The method, through molecular docking, generally considers the intensity of interactions between a ligand (micro-molecules) and an acceptor (bio-macro-molecules), thereby finding compounds which have potential pharmacological activity and may be added as an illegal additive; furthermore, with combination of density functional theory, a theoretical Raman peak position is calculated, and theoretical shared peaks, which are obtained after data handling, are deeply developed; the results are used as an evidence for quickly determining illegally added sildenafil compounds in the health care products in on-site detection. The method is free of an artificially synthesized reference substance, has wide application range and low experiment cost, has simple operation, is quick, is suitable for on-site quick detection, and supplies stronger evidence to identification for the illegally added derivatives in the health care foods.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Method for screening chitinase OfChtI inhibitor
ActiveCN107832577AEasy to prepareHigh activityMolecular designChemical structure searchMacromolecular dockingChitinase
The invention provides a method for screening a chitinase OfChtI inhibitor. The method comprises the steps that firstly, according to a pesticide-similar performance rule, micromolecular compounds which accord with the condition are screened out from an SPECS library, and a first database is established; a three-dimensional structure of OfChtI and a ligand eutectic crystal is acquired from a Protein Data Bank, compared and analyzed, and an active pocket is determined; then, according to mutual application and analysis, a pharmacophore model based on a receptor is established, the first database is screened, and a second database is established; then, by using a molecular docking program, micromolecular compounds in the second database are docked and graded, and a third database is established; finally, by using a framework analysis model in software, compounds in the third database are subjected to framework classification, and the chitinase OfChtI inhibitor with the structure is obtained, wherein the structure is shown in the formula (I). Through research, it is indicated that the chitinase OfChtI inhibitor has good inhibitory activity on chitinase OfChtI.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A molecular docking algorithm method based on quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm
InactiveCN109255427ASimple stepsFew control parametersChemoinformaticsBiomolecular computersMacromolecular dockingComputer science
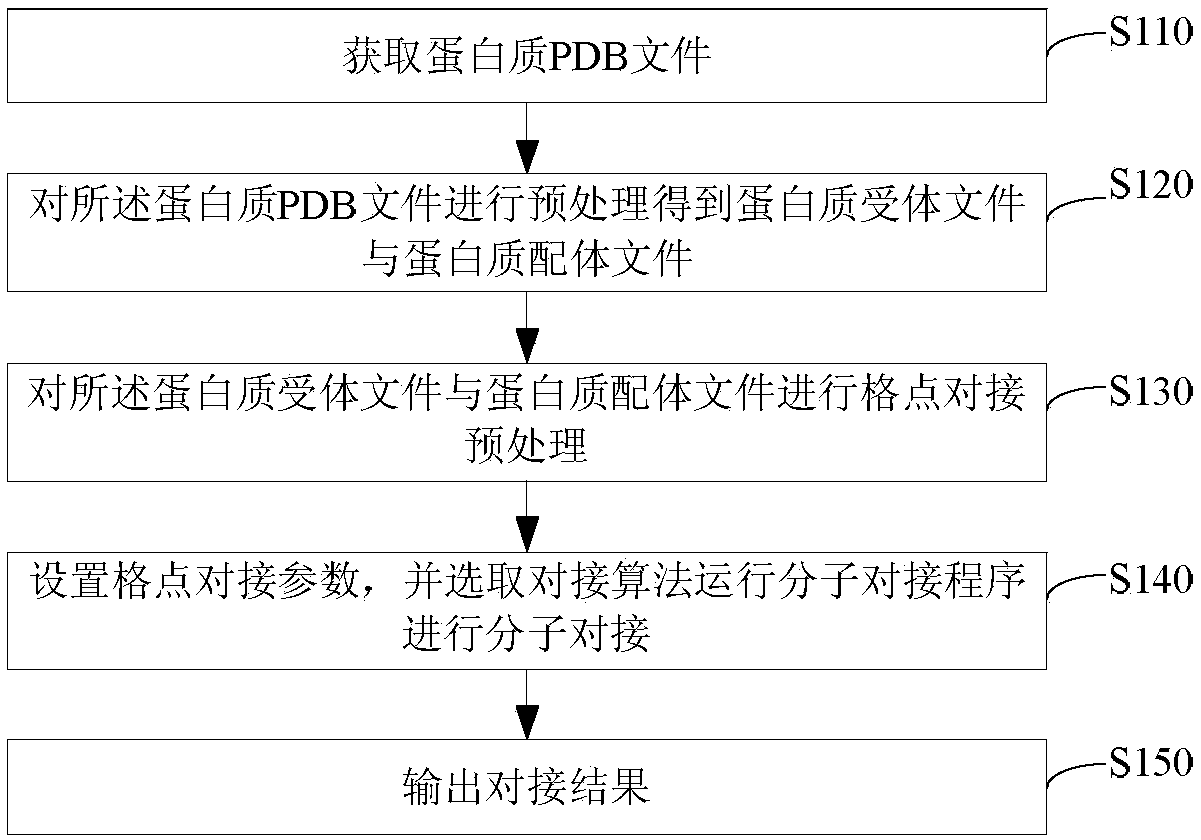
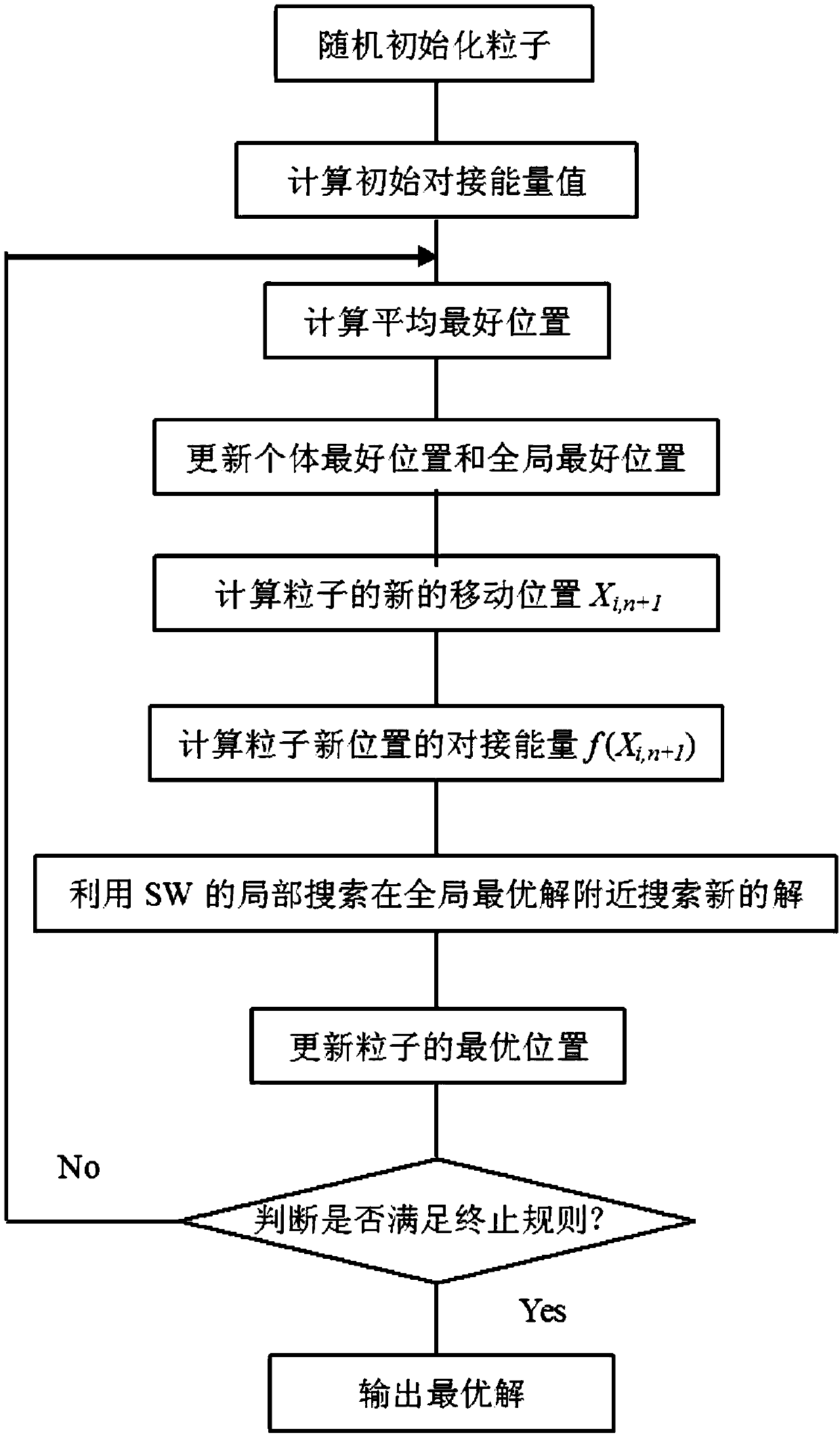
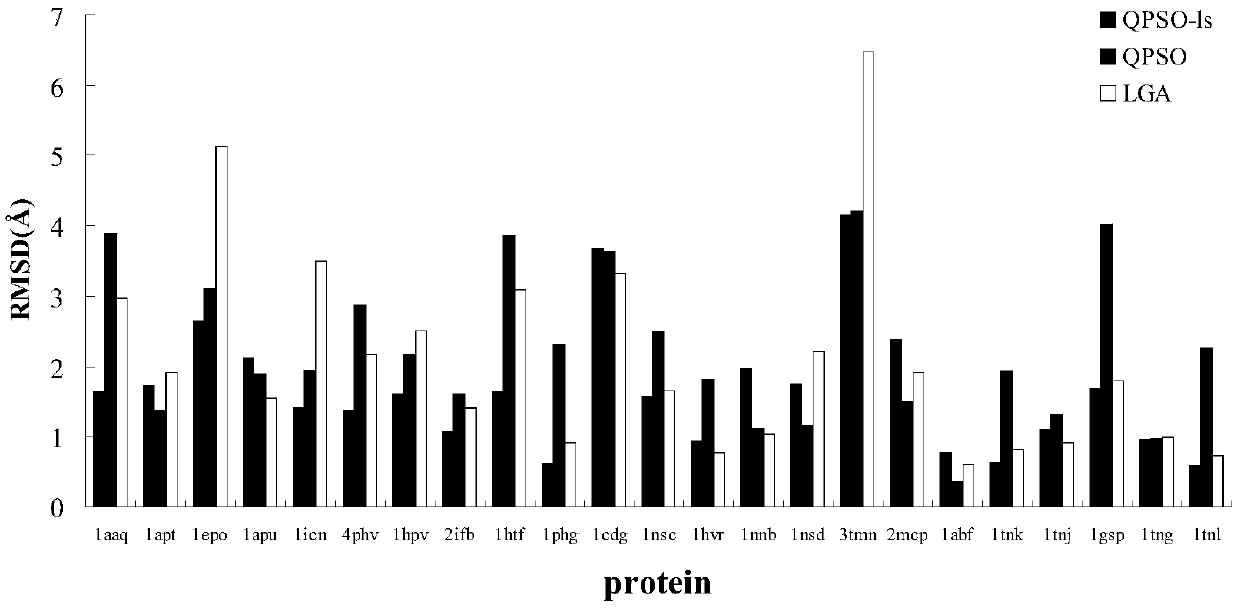
The invention relates to the technical field of computer application, in particular to a molecular docking calculation method based on a quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm, wherein, the molecular docking calculation method based on the quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm comprises the following steps: obtaining a protein PDB file; preprocessing the protein PDB file to obtain aprotein receptor file and a protein ligand file; performing lattice docking pretreatment on the protein receptor file and the protein ligand file; setting lattice docking parameters and selecting docking algorithm to run molecular docking program for molecular docking; outputting docking results. The molecular docking calculation method based on the quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm provided by the invention has the advantages of simple steps, few control parameters and easy solution.
Owner:WUXI CITY COLLEGE OF VOCATIONAL TECH
Computer medicine screening method based on BFGS algorithm
PendingCN110459263ASmall molecular weightPotential for oral administrationInstrumentsMolecular structuresData setMacromolecular docking
The invention discloses a computer medicine screening method based on a BFGS algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of 1) database establishment, wherein a data set cluster composed of 30,000-40,000 marine micromolecules is subjected to searching loop matching to form a micromolecule library with the similarity of 0-1; 2) database pre-processing, wherein micromolecule conformations, with the similarity of 1, in the micromolecule library obtained in step 1) are deleted; 3) molecular docking, wherein ligands are placed at active loci of a receptor, so that multiple ligands and one receptor are in molecular docking; 4) searching for conformations, wherein the BFGS algorithm is used for searching for the conformations, and when newly-generated conformations are identical to initial conformations or preset difference values of the newly-generated conformations and the initial conformations are smaller than or equal to 0.0001, searching for the conformations is stopped. According to the computer medicine screening method, by optimizing the algorithm, the time of searching for the low-energy conformations of the ligands and the receptor which are combined at the active loci of the receptor in the algorithm is shortened, and the effect and efficiency of virtual screening of a micromolecule database based on the method are improved.
Owner:QINGDAO NAT LAB FOR MARINE SCI & TECH DEV CENT +1
Novel affinity peptide ligand of murine polyoma capsomere as well as designing and screening method thereof
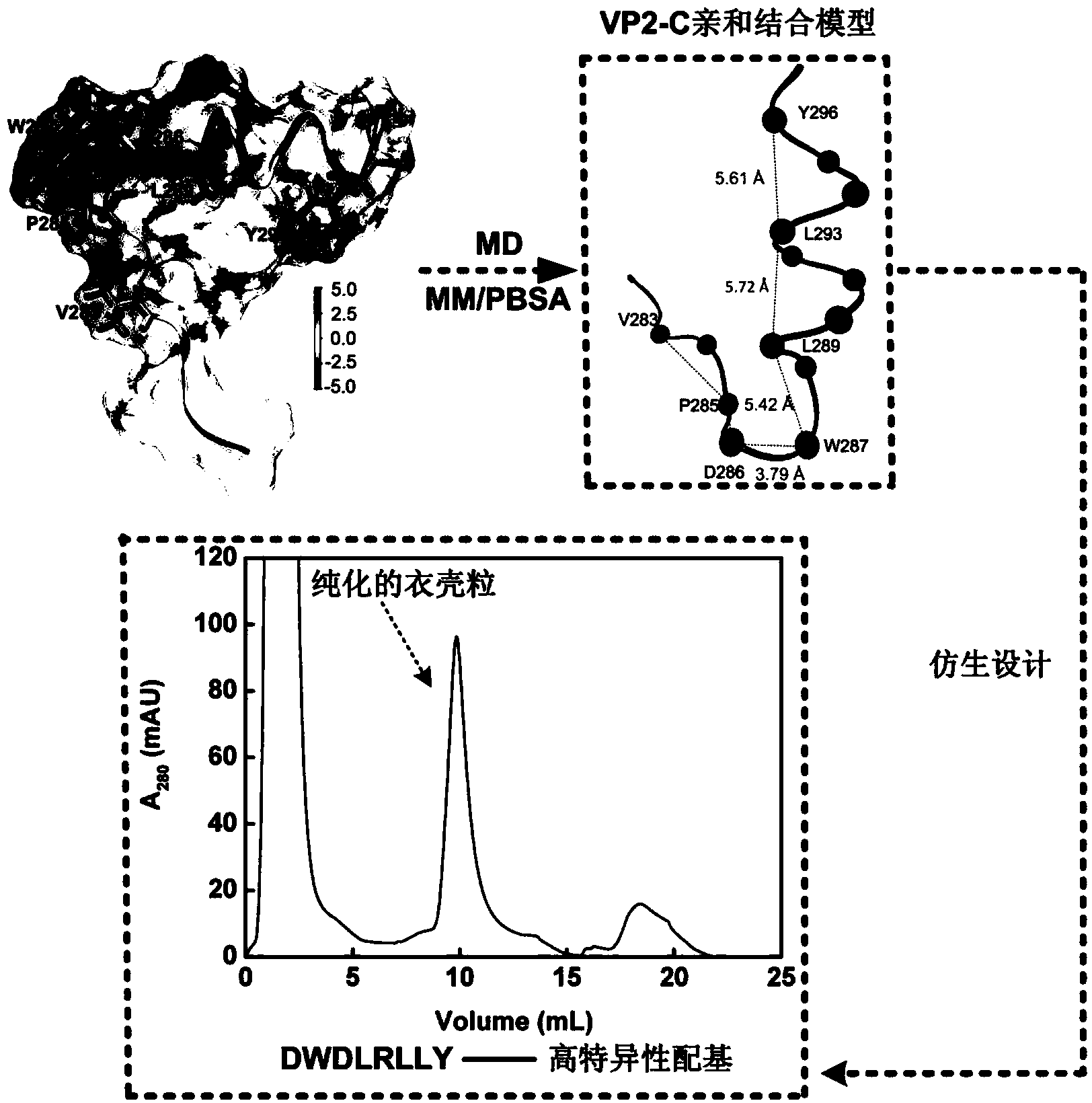
The invention discloses a novel affinity peptide ligand of murine polyoma capsomere as well as a designing and screening method thereof. Based on a compound of natural existing capsomere and a minor capsid structure protein VP2-C, a bionic designing process of the affinity peptide ligand of the capsomere is constructed. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, resolving intermolecular interactions in the compound by utilizing a molecular dynamics simulation combined Poisson-Boltzmann solvent accessible surface area (MM / PBSA) method; determining a hot spot residue ligand of the VP2-C and a simplified affinity model of the hot spot residue ligand so as to construct an affinity peptide ligand bank of the capsomere; screening the high-affinity peptide ligands in manners of molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation by virtue of the MM / PBSA method. The affinity chromatography experiment proves that the obtained affinity peptide ligand DWDLRLLY which ranks the first during the screening process can be used for effectively separating and purifying the capsomere by one step from an escherichia coli cracking supernatant, thereby having wide application prospect in preparation of virus-like particles.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and apparatus for analysis of molecular configurations and combinations
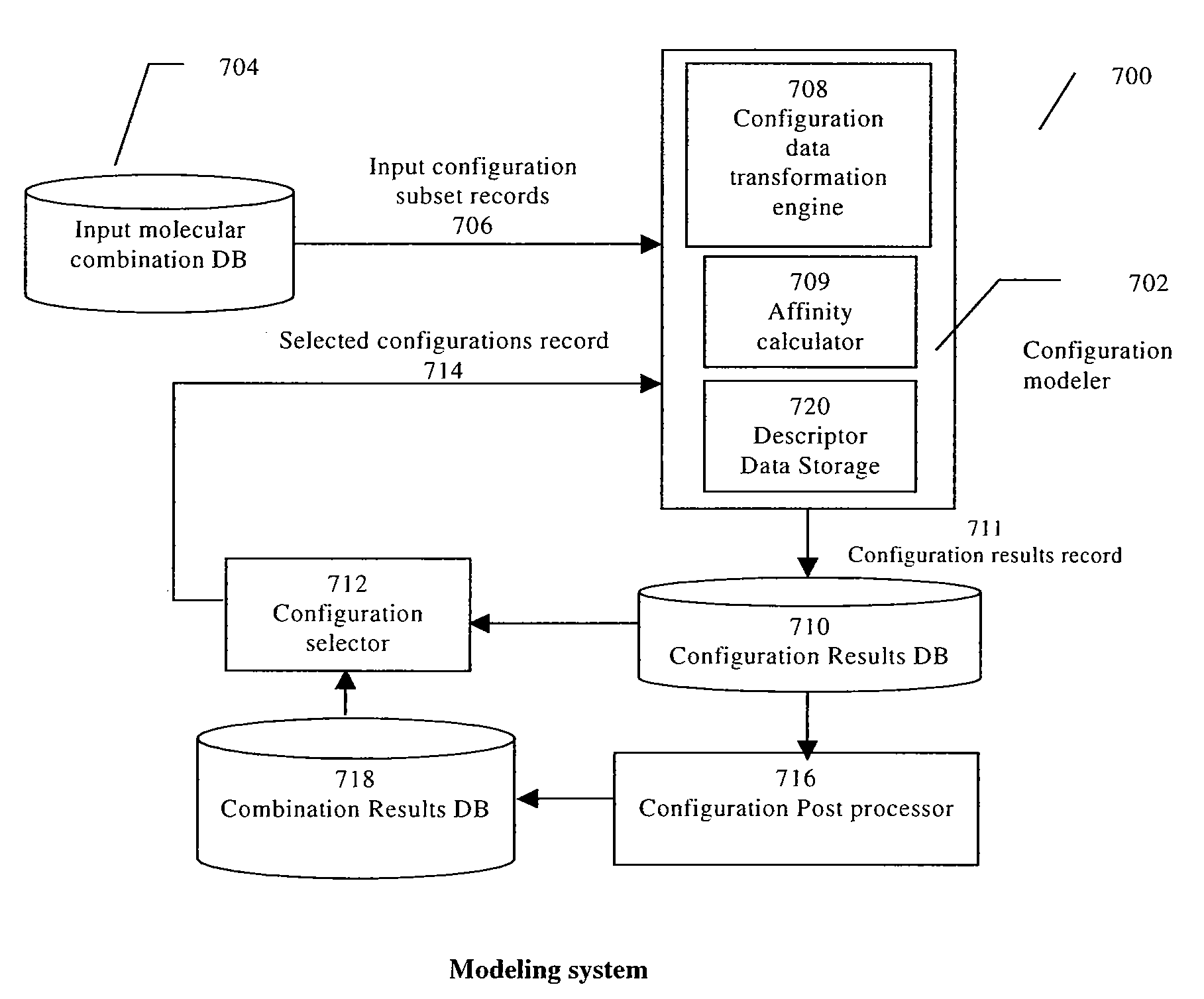
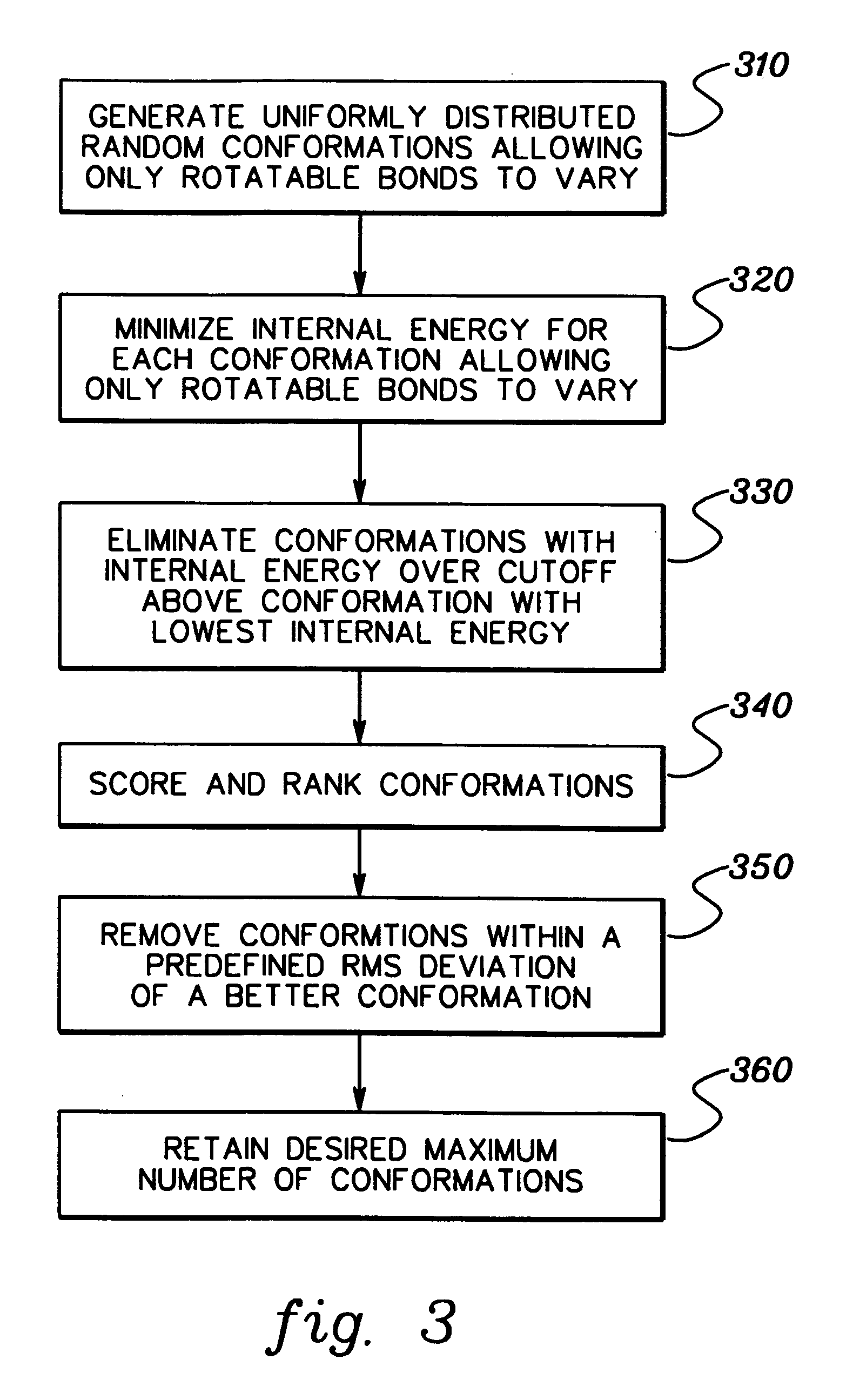
InactiveUS8036867B2Chemical property predictionAnalogue computers for chemical processesBond energyMacromolecular docking
Computing units are determined for performing molecular docking calculations in parallel with the number of computing units and the width of the data paths allocated by relative complexity of operations. Data can be expected to arrive at downstream computing units as it is needed, leading to higher utilization of computing units. Computing units are hardware components that are specific to a calculation performed. For molecular docking calculations, functions of molecular subsets or of combinations of molecular subsets are calculated. Determinations include fit between molecular subsets, affinity or energy of “fit” between molecular subsets, etc. Affinity might include inter-atomic energy, bond energy, energy of atoms immersed in a field, etc. The calculations could be used to simulate and / or estimate likelihoods of molecular interactions.
Owner:VERSEON INT CORP
Tripeptides with ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitory activity
ActiveCN108997477AReduce in quantityShorten the timePeptidesSolubilityHigh-performance liquid chromatography
The invention mainly relates to tripeptides with ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitory activity. The tripeptides have the peptide sequences of WGK and FQK in sequence and belong to the technical field of biology. According to the tripeptides, by virtue of an online database, the potential activity, water solubility and ADMET (acyclic diene metathesis) (absorption, metabolism and toxicity)property of an active peptide are predicted through virtual enzymolysis on proteins, multi-round screening is performed through molecular docking and the like, and the in vitro ACE inhibitory activity is verified by adopting an HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography), so as to obtain two types of tripeptides with the ACE inhibitory activity. The two types of active peptides are short in sequence, are safe and are easily obtained.
Owner:BOHAI UNIV
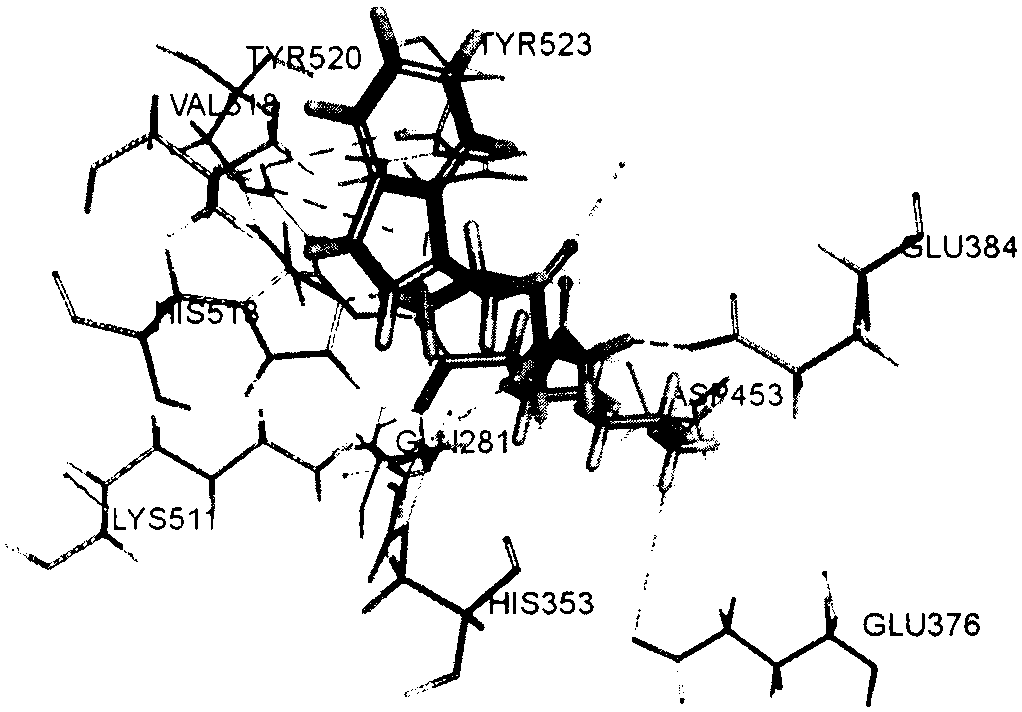
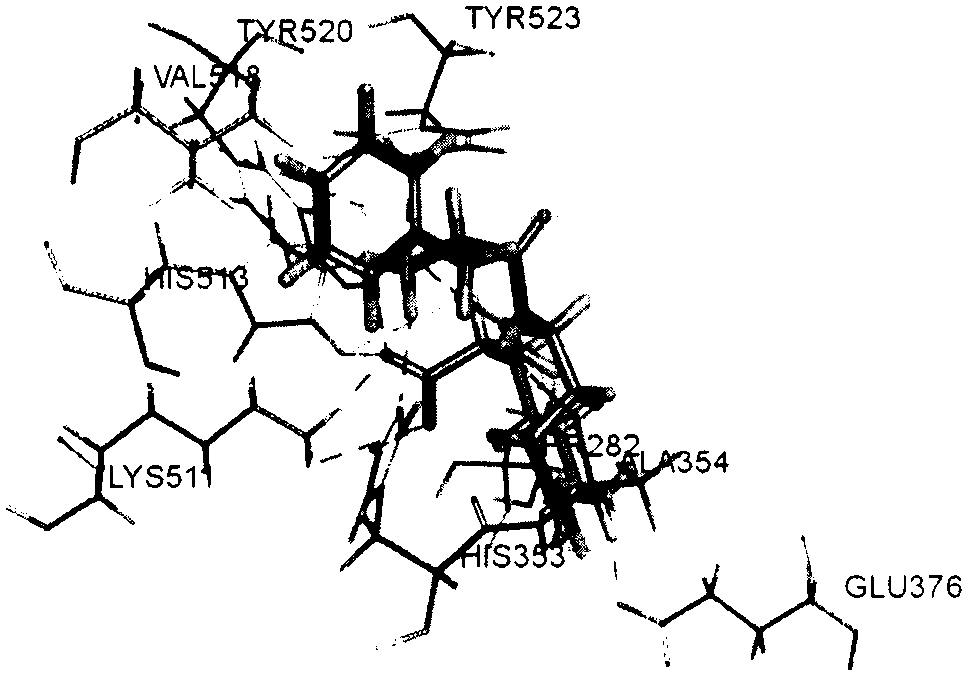
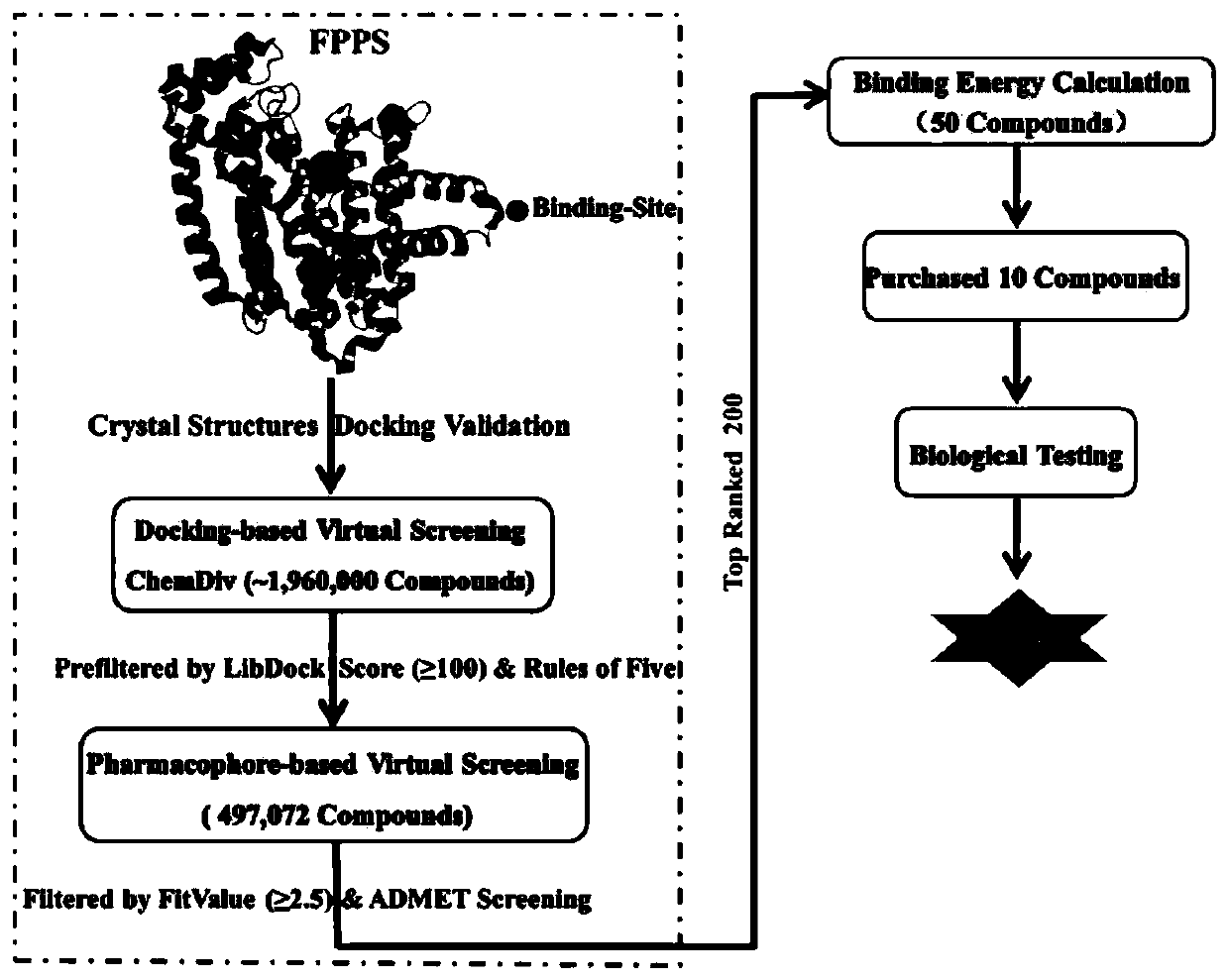
Screening method and application of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase FPPS inhibitor
ActiveCN110289054AReduce blindnessImprove hit rateChemical property predictionMolecular designData setScreening method
The invention provides a screening method of a farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPPS) inhibitor. The screening method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing an FPPS template; (2) preparing a data set; 3) performing virtual screening based on molecular docking; 4) performing virtual screening based on the pharmacophore model; 5) calculating binding energy; 6) integrating the docking scores in the steps 3), 4) and 5), the pharmacophore model FitValue value and the binding energy to obtain the FPPS inhibitor; and 7) carrying out FPPS enzyme activity inhibition experiment on the FPPS inhibitor obtained by virtual screening, and determining the FPPS inhibitor with the structure shown in the formula I. The method gives full play to the advantages of theoretical screening, reduces the blindness of drug synthesis, effectively improves the hit rate of positive drugs, saves manpower, material resources and financial resources, and realizes the new use value of old drugs. The invention further provides application of the FPPS inhibitor obtained through screening in preparation of drugs for treating colon cancer.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
Method for virtually screening cholesterol degrading medicine with 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR24) being target point
ActiveCN106909785AImprove bindingFast and effective concentrationMolecular entity identificationMolecular designCholesterol reductaseSmall molecule ligand
The invention relates to a method for virtually screening cholesterol degrading medicine with 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR24) being a target point. The method includes the steps that 1, the molecular structure of DHCR24 is determined; 2, molecular docking software is adopted, the active center of macromolecular docking of the medicine is determined according to a combined pocket which is formed after desmosterol and DHCR24 are docked, and an active pocket is set; 3, a macromolecular ligand databse used for docking is arranged; 4, according to the set active pocket, by the utilization of the molecular docking software, macromolecular ligands in the macromolecular ligand database used for docking and the active pocket are docked in sequence; 5, results which are screened after primary docking are accurately docked, and the candidate medicine having the effect of cholesterol degrading are determined. By the adoption of the method, within short time, the macromolecular candidate medicine which has the effect of competitive restraining of DHCR24 and is developed into the novel cholesterol degrading medicine is obtained, in this way, the research and development efficiency is greatly improved, and the research period of new medicine is shortened.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for predicting and modeling Anti-psychotic activity using virtual screening model
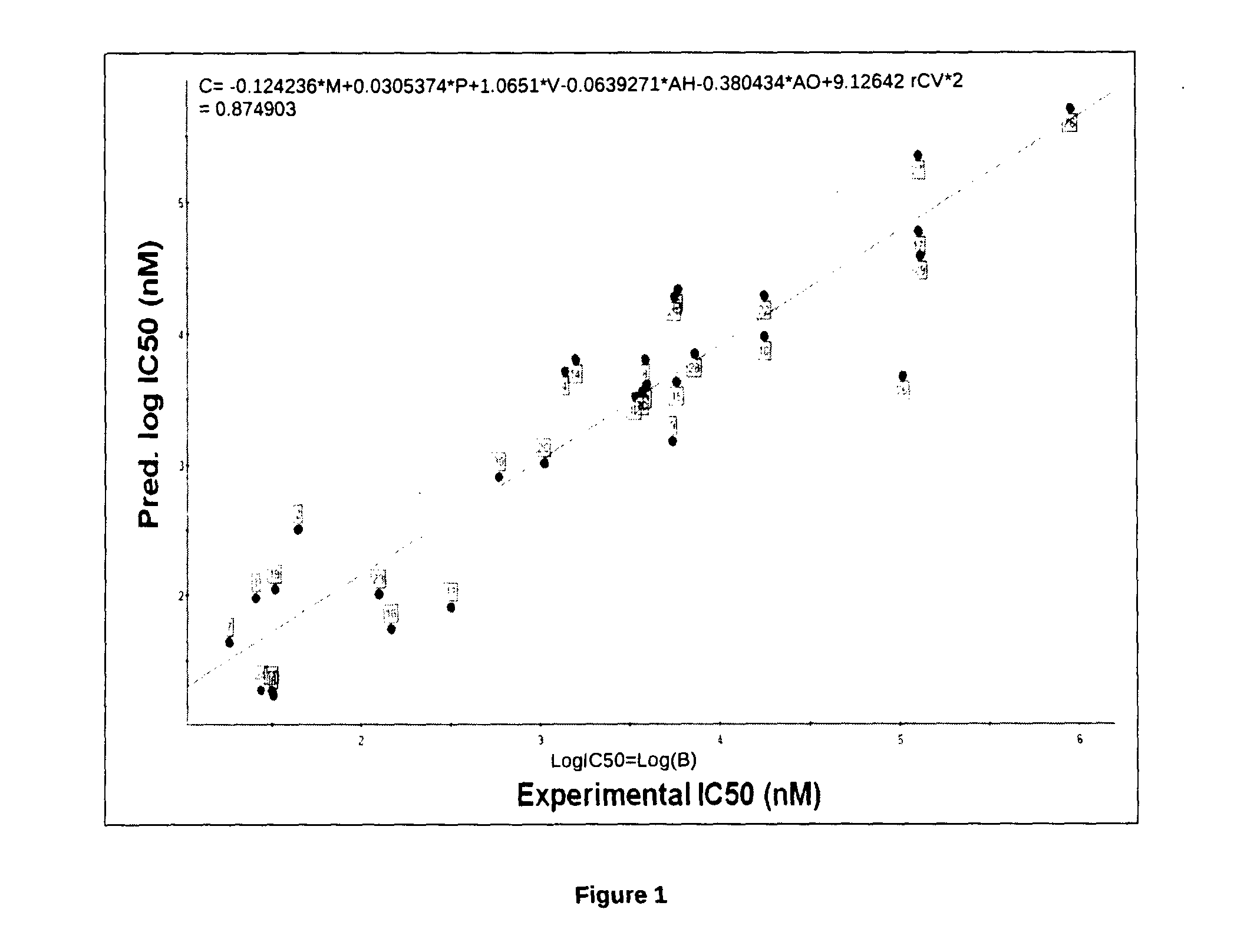
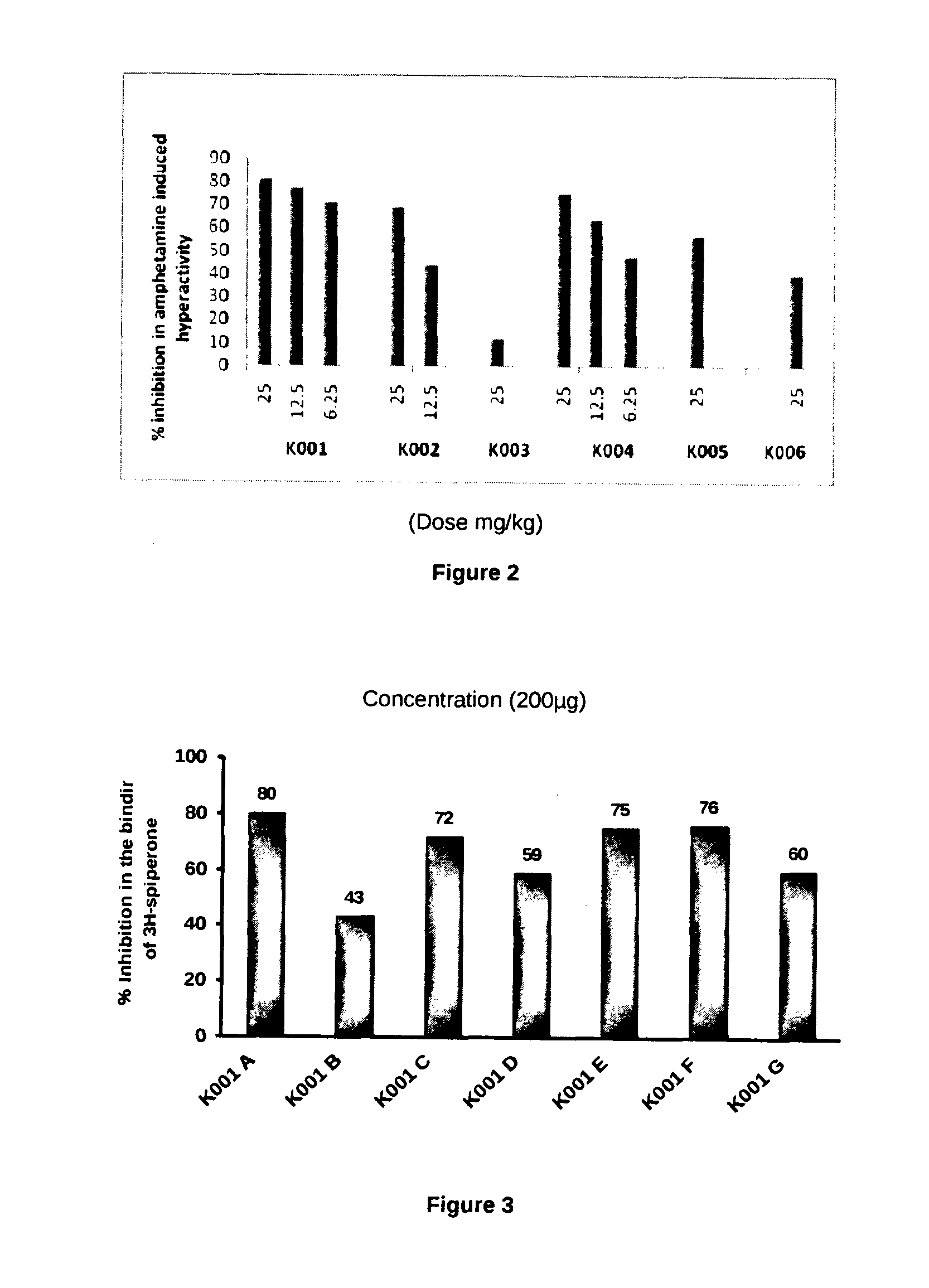
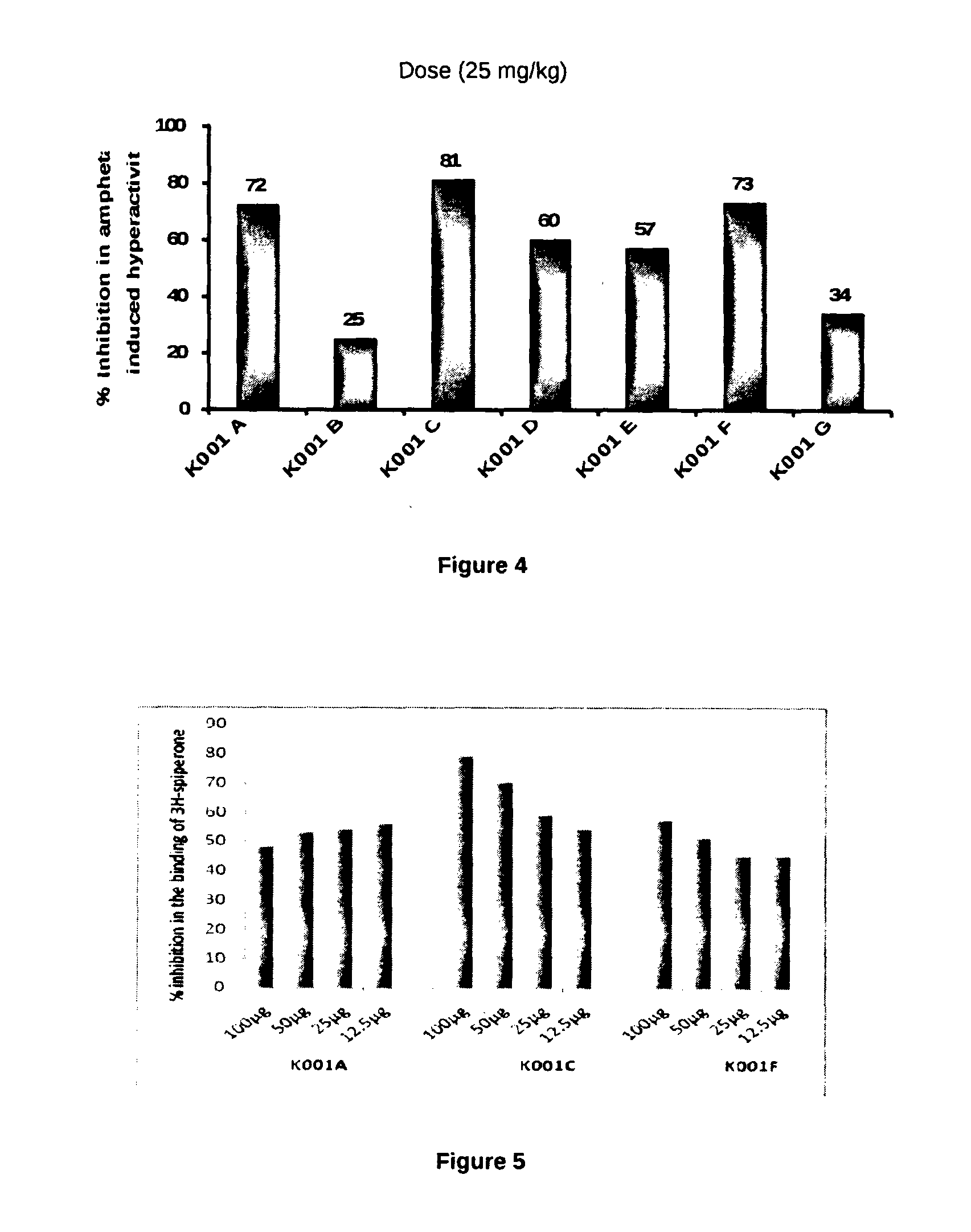
InactiveUS20130184462A1Effective controlChemical property predictionOrganic chemistryStrong bindingDrug discovery
The present invention relates to the development of a virtual screening model for predicting antipsychotic activity using quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR), molecular docking, oral bioavailability, ADME and Toxicity studies. The present invention also relates to the development of QSAR model using forward stepwise method of multiple linear regression with leave-one-out validation approach. QSAR model showed activity-descriptors relationship correlating measure (r2) 0.87 (87%) and predictive accuracy of 81% (rCV2=0.81). The present invention specifically showed strong binding affinity of the untested (unknown) novel compounds against anti-psychotic targets viz., Dopamine D2 and Serotonin (5HT2A) receptors through molecular docking approach. Theoretical results were in accord with the in vitro and in vivo experimental data. The present invention further showed compliance of Lipinski's rule of five for oral bioavailability and toxicity risk assessment for all the active Yohimbine derivatives. Therefore, use of developed virtual screening model will definitely facilitate the screening of more effective antipsychotic leads / drugs with improved antipsychotic activity and also reduced the drug discovery cost and duration.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Screening method of TTR (transthyretin) small-molecule inhibitors
InactiveCN103425859AImprove reliabilityShorten the development and research cycleSpecial data processing applicationsDiseasePharmacophore
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Molecular docking technique for screening of combinatorial libraries
InactiveUS20070078605A1Take advantageSignificant burdenMolecular designLibrary screeningMacromolecular dockingMedicine
Owner:DILLER DAVID J +1
Method for simultaneously realizing docking by multiple molecules
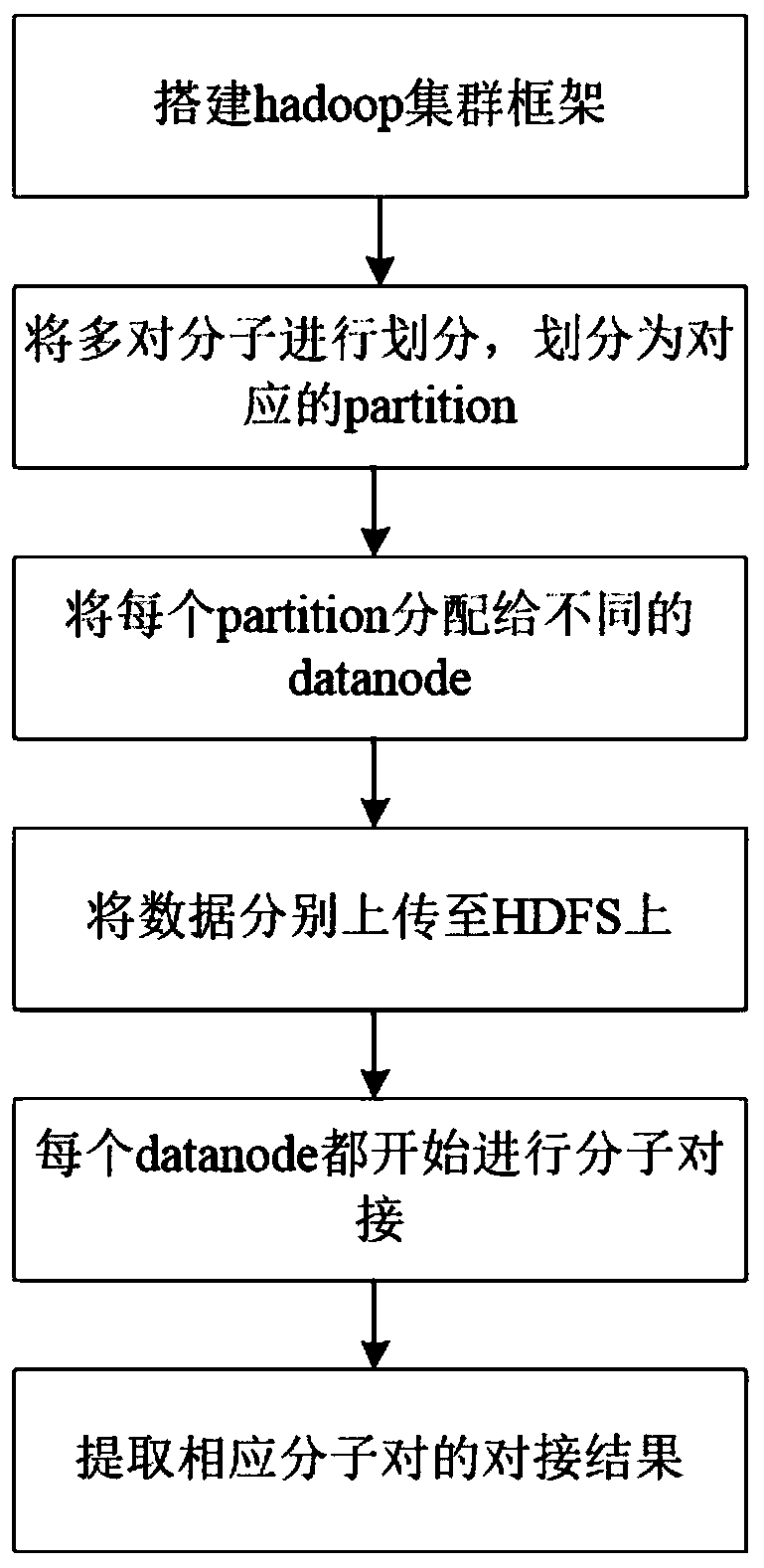
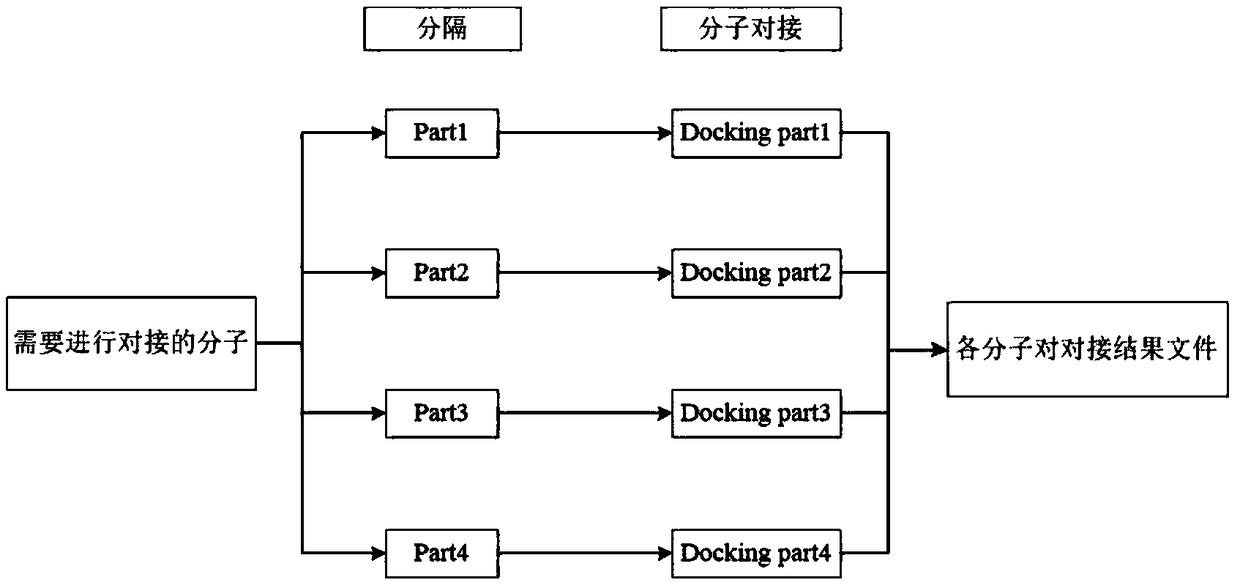
InactiveCN108763851AEasy to operateReduce computing costSpecial data processing applicationsMacromolecular dockingComputer science
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously realizing docking by multiple molecules, and belongs to the technical field of medicine screening. The multiple molecules simultaneously realize docking for making preparation for parallel computing; through parallel computing, the simultaneous docking on a plurality of pairs of molecules can be performed; Hadoop is used as a parallel computing framework; a corresponding cluster is built according to the Hadoop and is used for molecular docking; each pair of molecules requiring the docking are respectively stored onto different computers; each pair of separated molecules are subjected to molecular docking; and docking results in different equipment are summarized. The simultaneous docking on multiple molecules can be realized; the Hadoopis used as the parallel computing framework; the simultaneous docking of the multiple molecules is realized; the operation is simple; and the huge computing cost can be reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
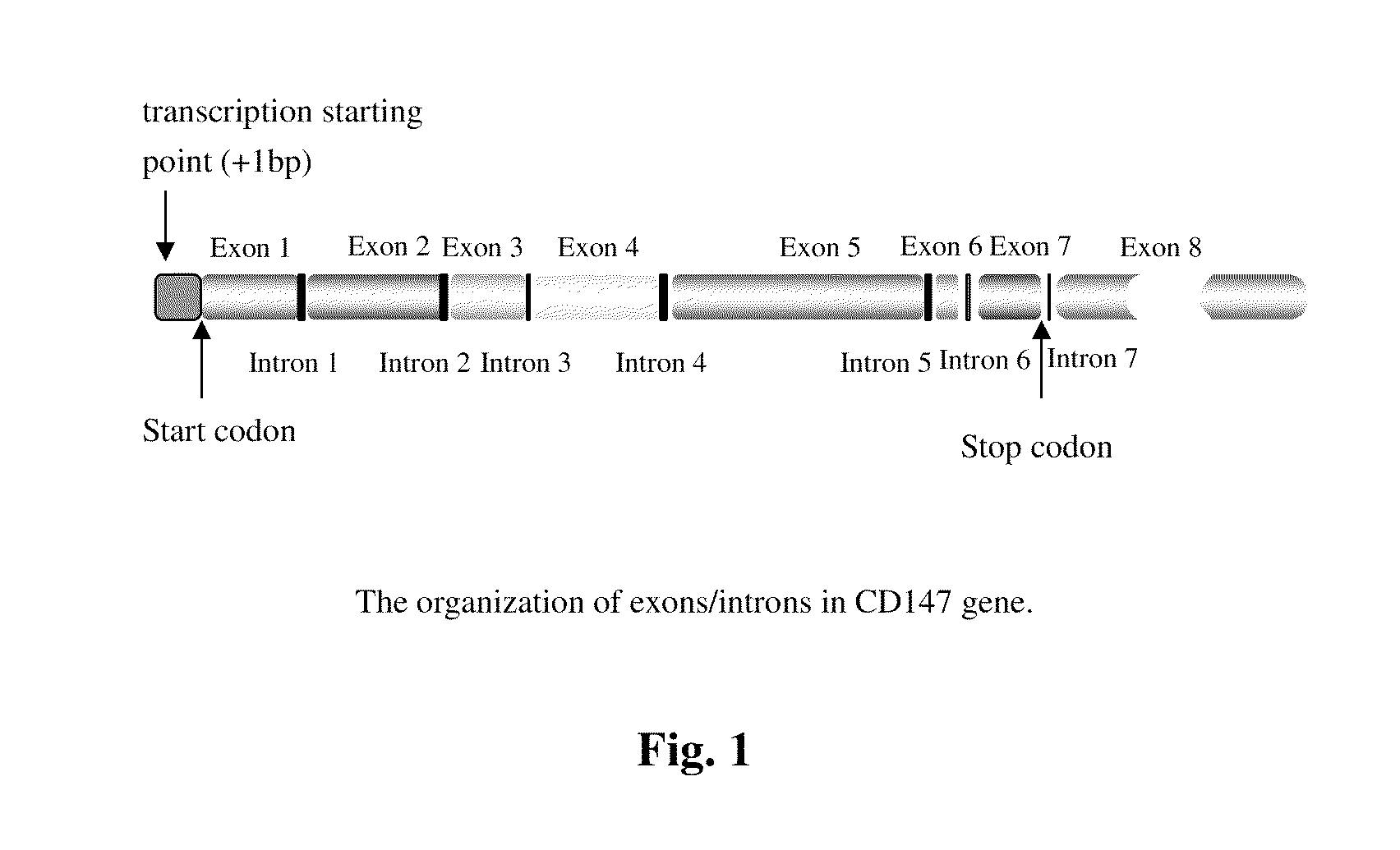
Crystal structure of cd147 extracellular region and use thereof
ActiveUS20100248974A1Affect activityInhibitory activityCompound screeningFrom normal temperature solutionsMacromolecular dockingReactive site
A crystal, a preparation method and 3D structure of CD147 extracellular region are provided. Such 3D structure is useful in the determination of the active site of CD147 extracellular region by computer modeling or molecular docking method. The crystal and / or 3D structure are useful in a structure-based drug design and the selection of an antibody, a ligand or an interacting molecule of CD 147 extracellular region.
Owner:CHEN ZHINAN
Realization method for using computer to assist in screening small molecule compound target aptamer
ActiveCN105678112AHigh affinityQuick filterMolecular designBiostatisticsMacromolecular dockingVirtual screening
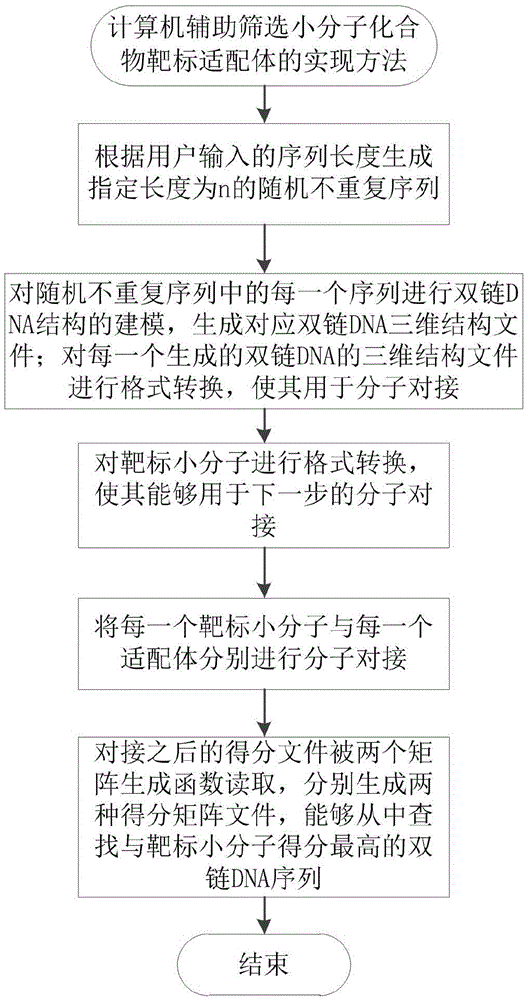
The invention relates to a realization method for using a computer to assist in screening a small molecule compound target aptamer. The realization method is realized by a reverse virtual screening algorithm based on a molecular docking technology, and comprises the following steps: according to the length of a sequence inputted by a user, generating a random unrepeated sequence with a designated length of n; carrying out double-chain DNA structure modeling on each sequence in the random unrepeated sequence to generate a corresponding double-chain DNA three-dimensional structure file; carrying out format conversion on each generated double-chain DNA three-dimensional structure file, enabling the formed converted files to be used for molecular docking; carrying out format conversion on small targeted molecules, enabling the molecules to be used for molecular docking in the next step; respectively carrying out molecular docking on each small targeted molecule and each aptamer; after docking, reading the score files by two matrix generating functions, and then respectively generating two score matrix files. The realization method, disclosed by the invention, solves the defects that the SELEX technology is long in screening time, high in laboring strength and screening cost, low in screening variety, high in risk of injuring a human body, and low in success rate.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Structure prediction method of voltage-gating sodium ion channel
ActiveCN107247885AStructural prediction methods are reliableReliable methodMolecular designSequence analysisMacromolecular dockingVoltage
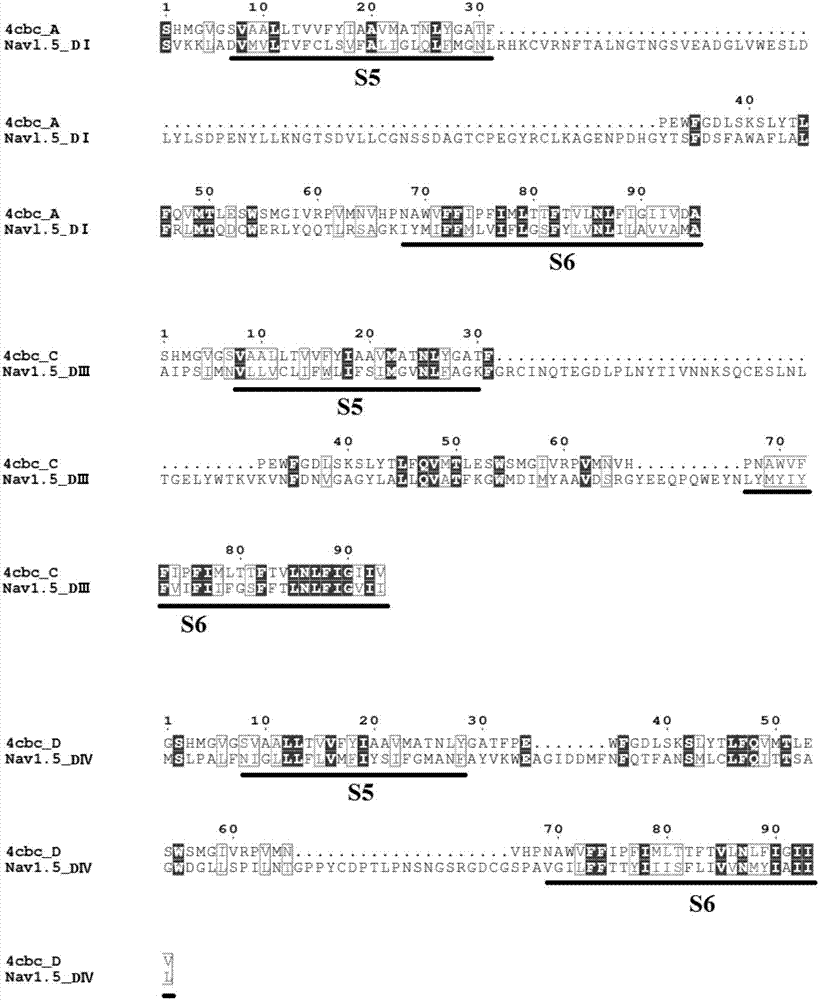
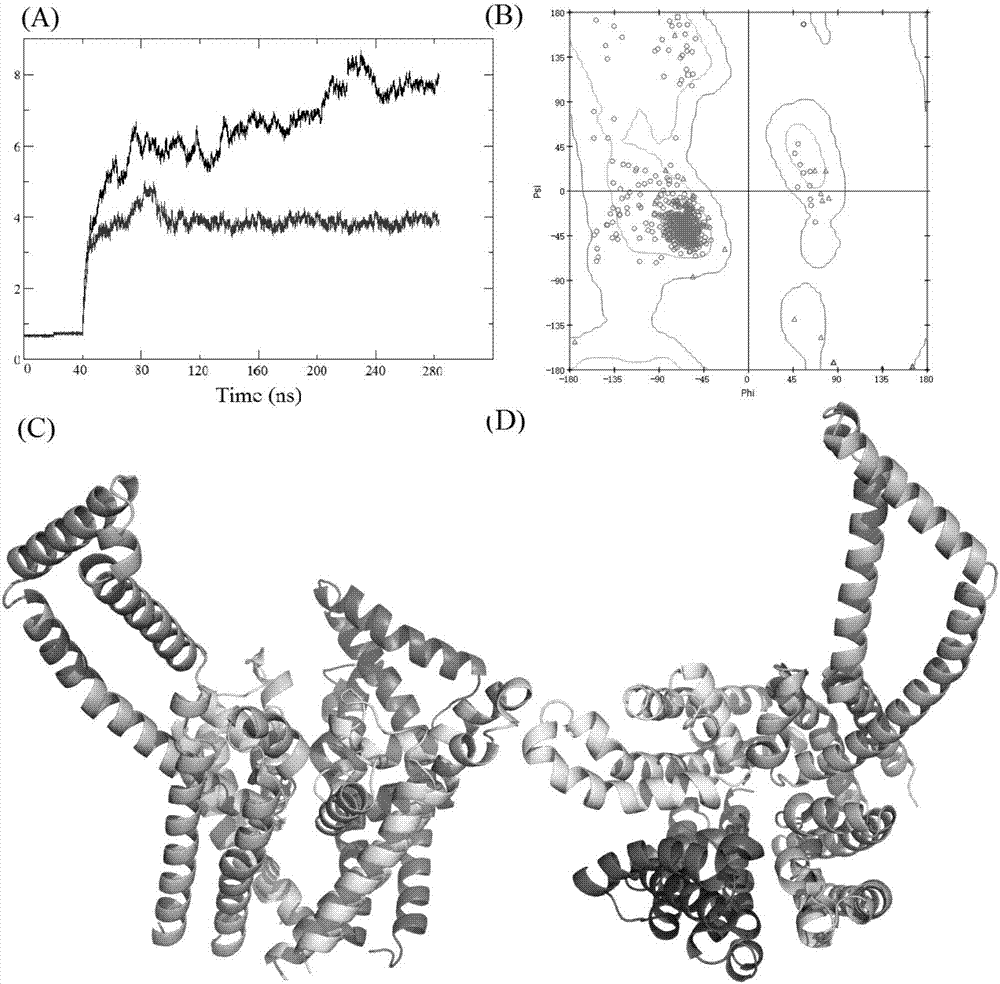
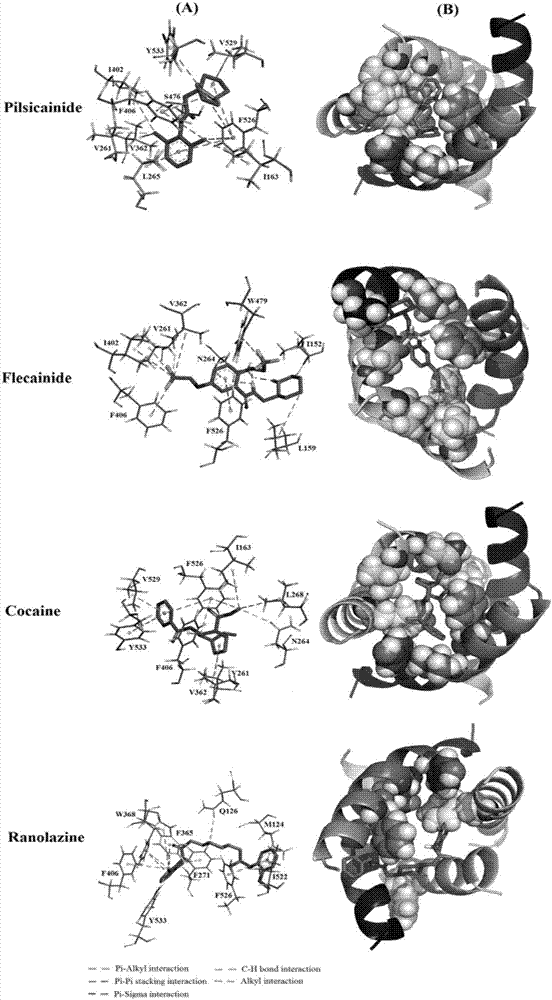
The invention discloses a structure prediction method of a voltage-gating sodium ion channel, and particularly relates to a structure modeling method of constructing the eukaryotic voltage-gating sodium ion channel Nav1.5 pore structural domain open state based on a template. The method includes the steps that a rosetta membrane protein homology modeling method is used for obtaining a germ sodium ion channel template of a crystal tripolar structure, and four subunit structures of the Nav1.5 pore structural domain are constructed and composed preliminarily; sorting is carried out according to the grading condition of all construction models, the structure with the maximum score is selected as the initial structure of all the structural domains; the four constructed subunit structures are compared to four 4CBC subunits, and the assembled overall structure is optimized; based on structure data and test data of existing local anesthetics drugs, molecular docking is carried out on the optimized structures, screening and evaluating strategies are set according to the existing experiment data to determine the reliability of model construction.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for distinguishing activities of complete agonist, partial agonist and antagonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
ActiveCN110426512AReduce usageReduce workloadMolecular designPeptide preparation methodsPharmacophoreReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing the activities of a complete agonist, a partial agonist and an antagonist of a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. The method comprises: modeling of the receptor and a ligand; molecular docking; simulation of conventional molecular dynamics; simulation of well-tempered meta-dynamic molecular dynamics; and construction of a pharmacophore. The method disclosed by the invention can quickly distinguish the activities of the PPARs gamma of different structural compounds, so that use of chemical drugs and cells in a conventional toxicity experiment process in a laboratory is greatly reduced, the workload in the laboratory is relieved, and expenses on the laboratory are saved; therefore, the activities of the PPARs gamma of the compounds are distinguished before QSAR (quantitative structure-activity relationship) modeling, and a QSAR model result is closer to an actual model; and a traditional QSAR is used more widely.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
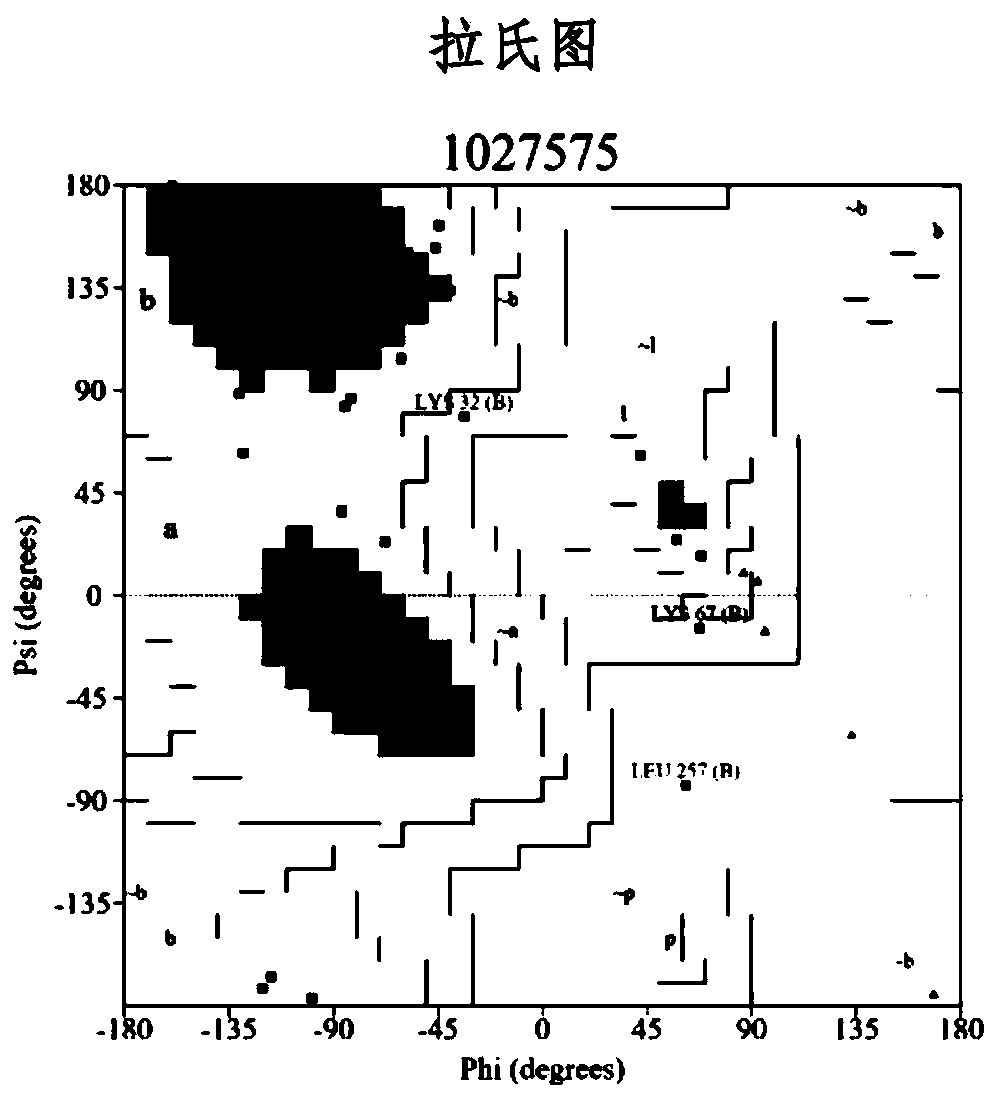
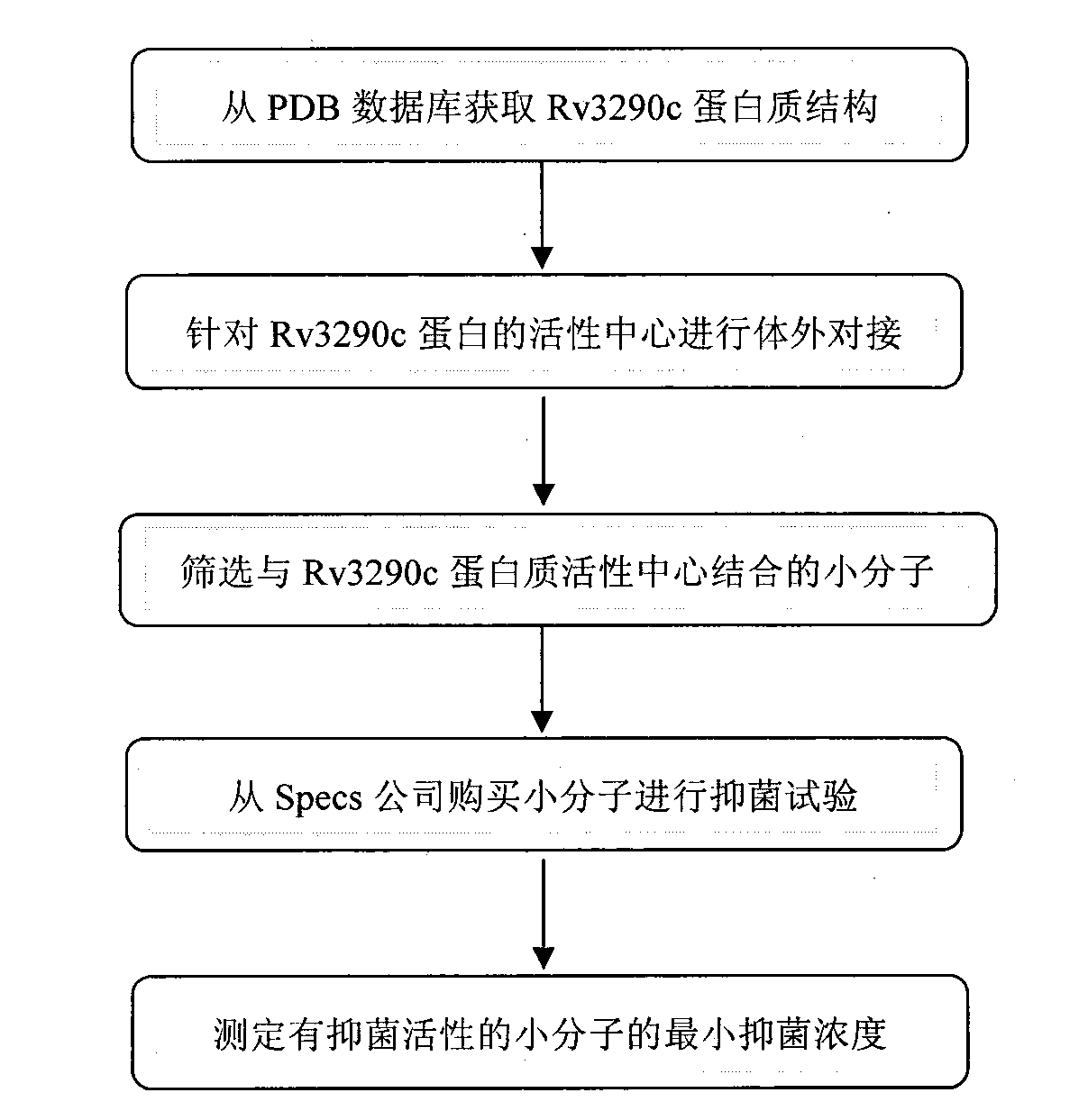
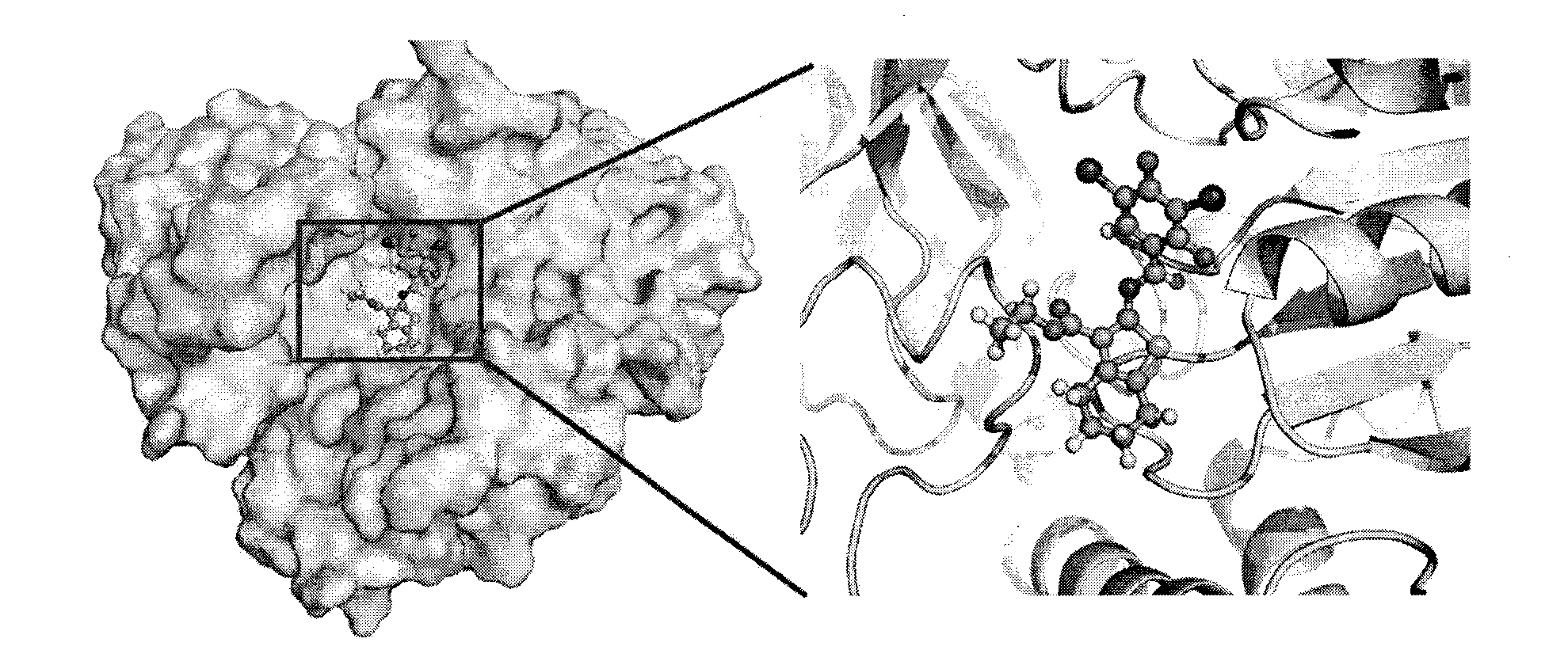
Target gene Rv3290c for screening antituberculous inhibitor and application
InactiveCN103122365AImprove hit rateReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesNucleotideBinding site
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical molecular biology, and in particular relates to application of mycobacterium tuberculosis gene Rv3290c used for screening an antituberculous inhibitor target. The gene is characterized in that the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in the sequence table SEQ. ID NO:1, and the sequence of protein coded with the gene is shown in the SEQ. ID NO:2. Through a virtual screening method, aiming at activity center of a natural substratge of Rv3290c, 20 small molecular compounds with high affinity to the combining sites of the natural substratge of Rv3290c are screened from a small molecular compound database by operating a molecular docking program, so that a bacteriostatic compound (benzothiophene compound 14#) is obtained. The compound is named ethyl-2-[(3, 5-dibromo-2, 4-dihydroxyl benzyl) amino]-4,5,6,7-tetrahuydro-benzothiophene-3-carboxylic acid. The bacteriostatic effect of the compound in mycobacterium tuberculosis is evaluated.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
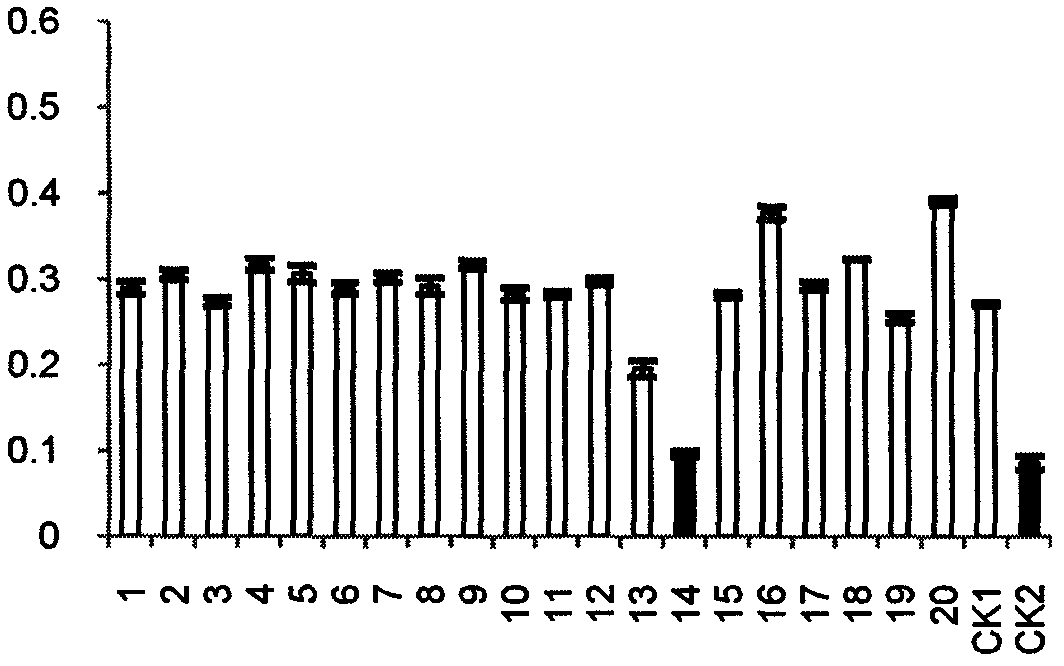
Screening method for inhibiting angiogenesis targets through celecoxib
The invention belongs to the field of treating tumor diseases, and particularly relates to a screening method for inhibiting angiogenesis targets through celecoxib. According to the method, by selecting protein expressed by 84 genes on a blood vessel formation polymerase chain reaction chip as a potential receptor protein database (PDB), the PDB and a UniProt database are used for screening 54 receptor protein structures, MGLTools is used for processing the receptor protein structures, after a molecular docking box is constructed, Autodock_vina is used as a molecular docking tool to calculatethe free energy of the binding site of the celecoxib and each protein receptor, and the protein receptors with the binding site free energy smaller than 9.0 kcal / mol are selected as potential targets.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
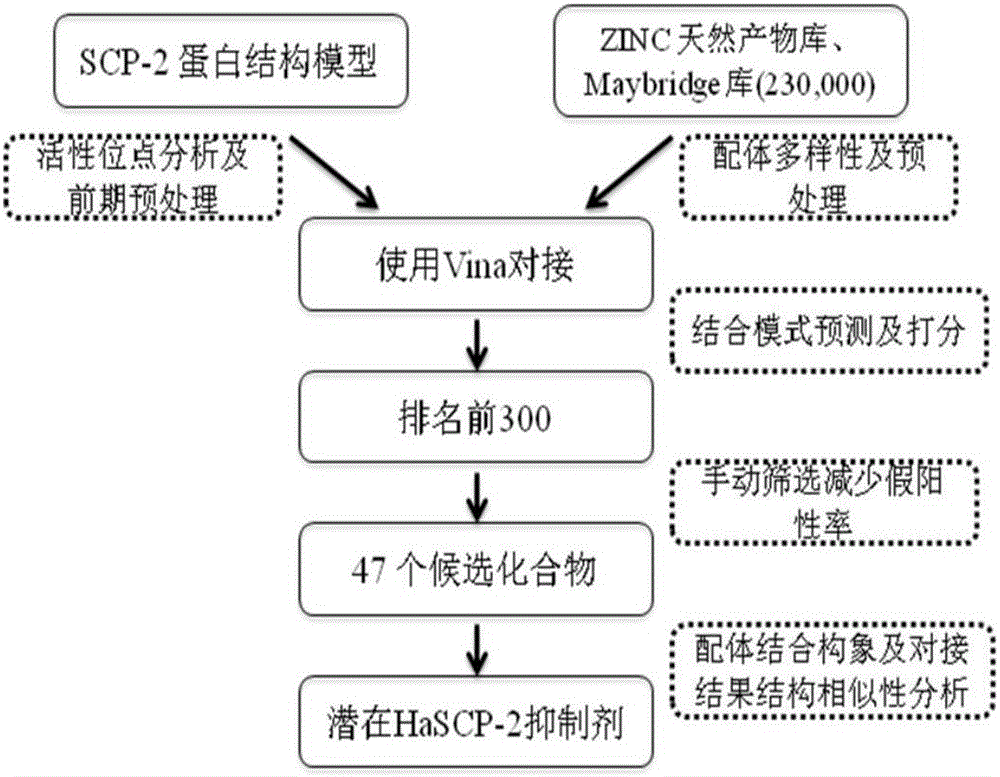
Cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 inhibitor and virtual screening method thereof
InactiveCN106106481AShorten screening timeImprove screening efficiencyChemical property predictionBiocideAgricultural scienceOrder Lepidoptera
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biotechnologies, and relates to establishment of a cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP-2) small-molecule inhibitor virtual screening method. The method comprises the following steps: according to structural data of cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP-2), analyzing a key amino acid residue so as to confirm a binding pocket; screening, scoring and calculating binding free energy by using molecular docking software; performing structure clustering and visual analysis on an obtained compound, thereby obtaining a small-molecule inhibitor for SCP-2 protein. The small-molecule inhibitor can be applied to screening, study and development of novel environmental-friendly pesticides for multiple agricultural pests of lepidoptera as the main target.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com