Patents
Literature
142 results about "Binding pocket" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
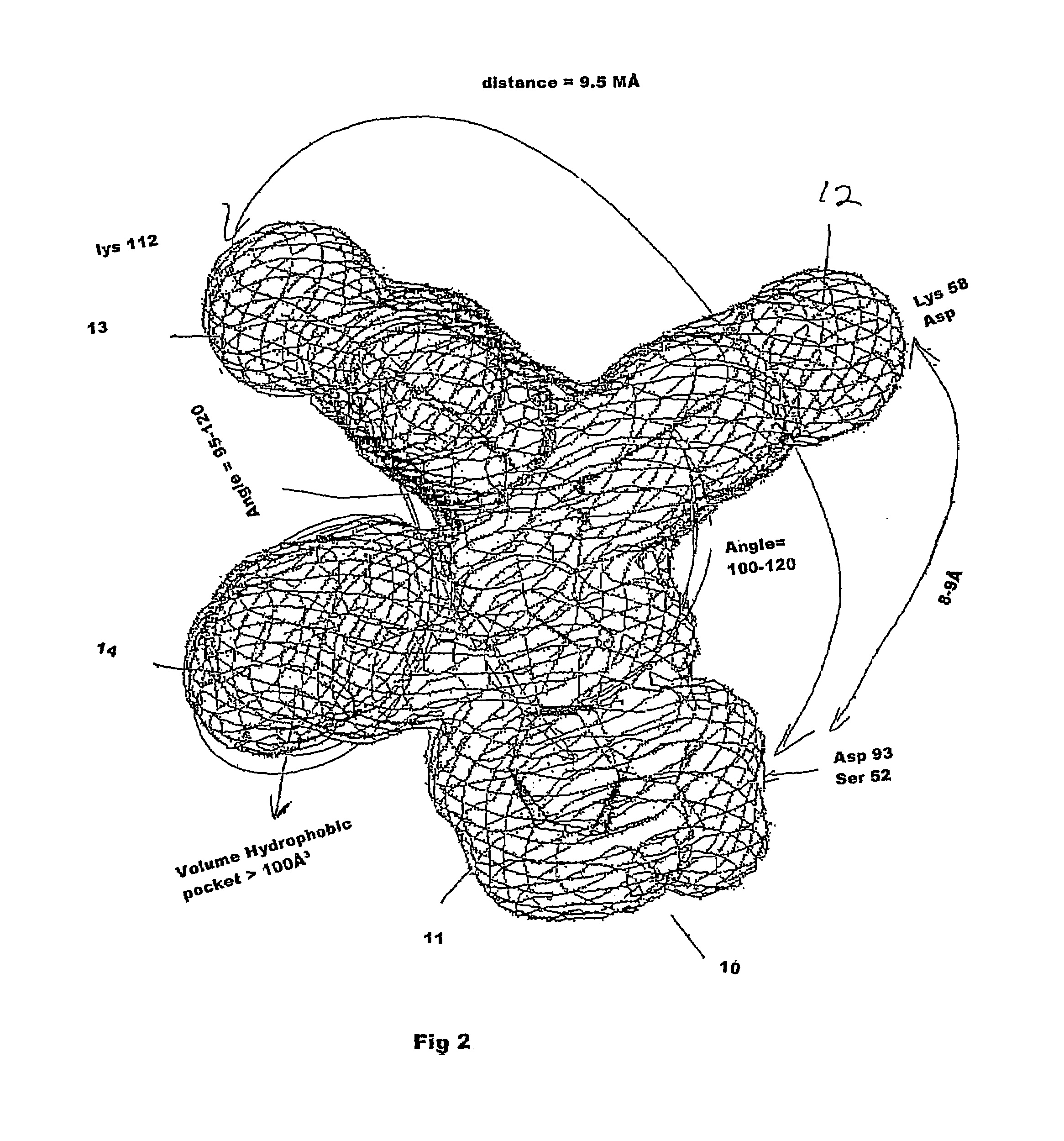
Binding pocket is a part of a receptor, adaptor/scaffold protein, or docking site for a medical drug. Binding pocket binds ligand or a knob-site of some binding partner (a good example is knob-hole interaction is between fibrin molecules in polymeric fibrin).
Variable domain library and uses
ActiveUS20050266000A1Generate efficientlyQuality improvementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
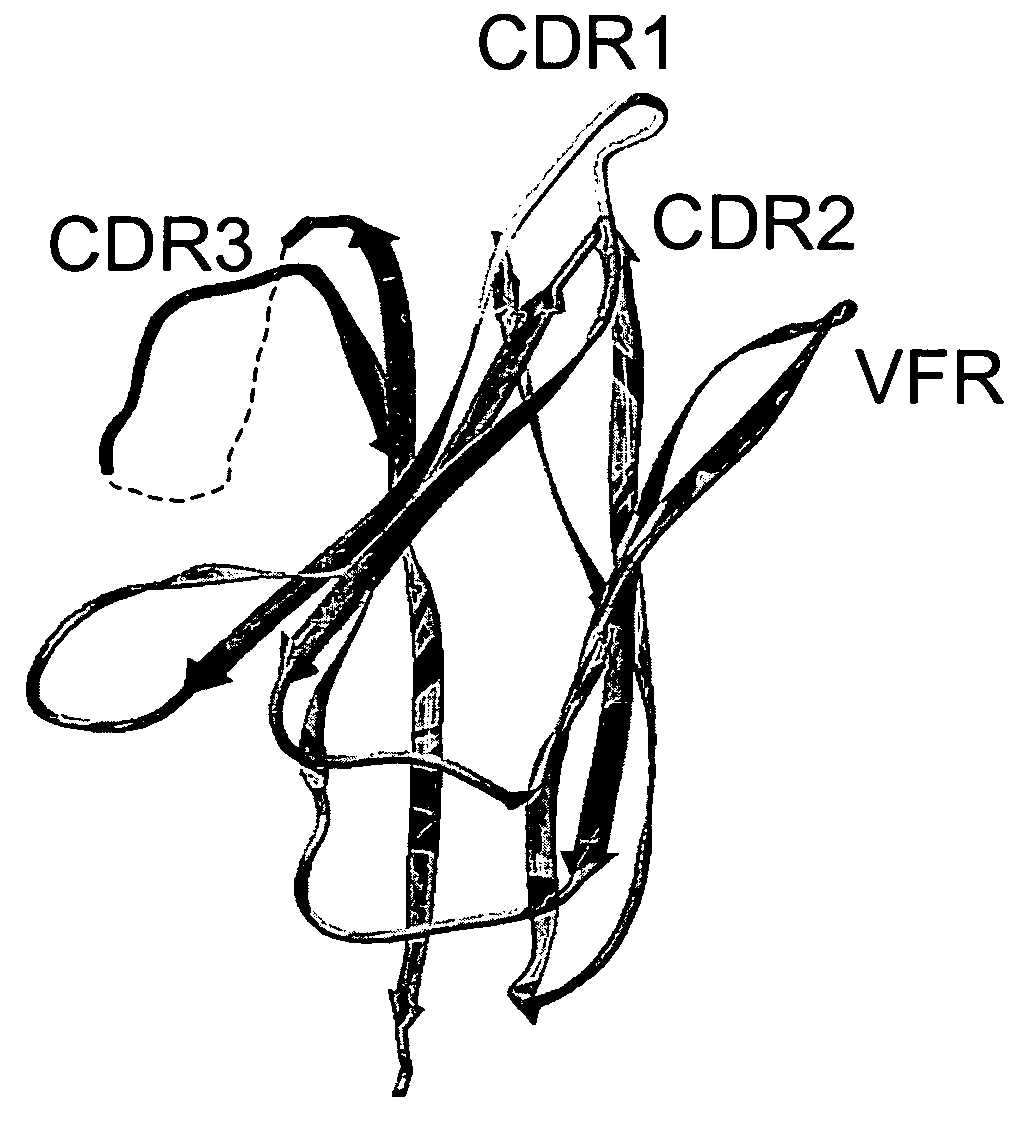
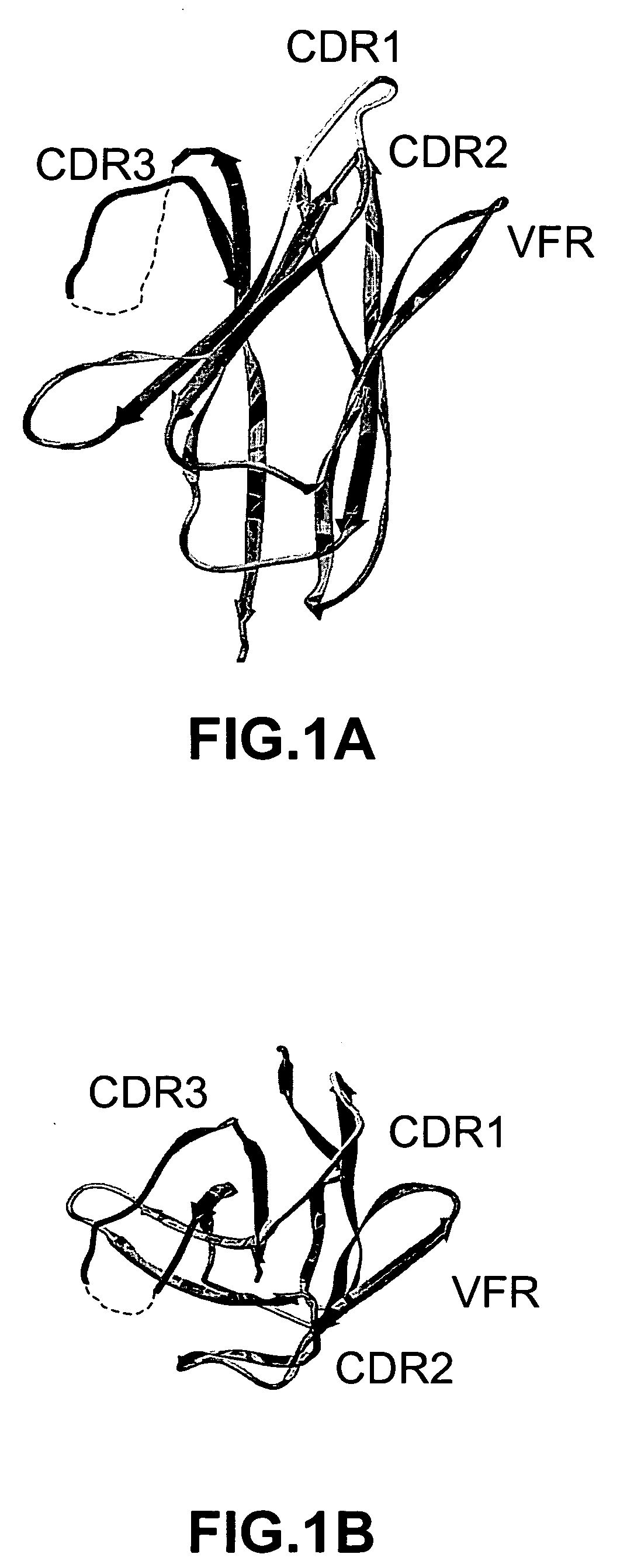
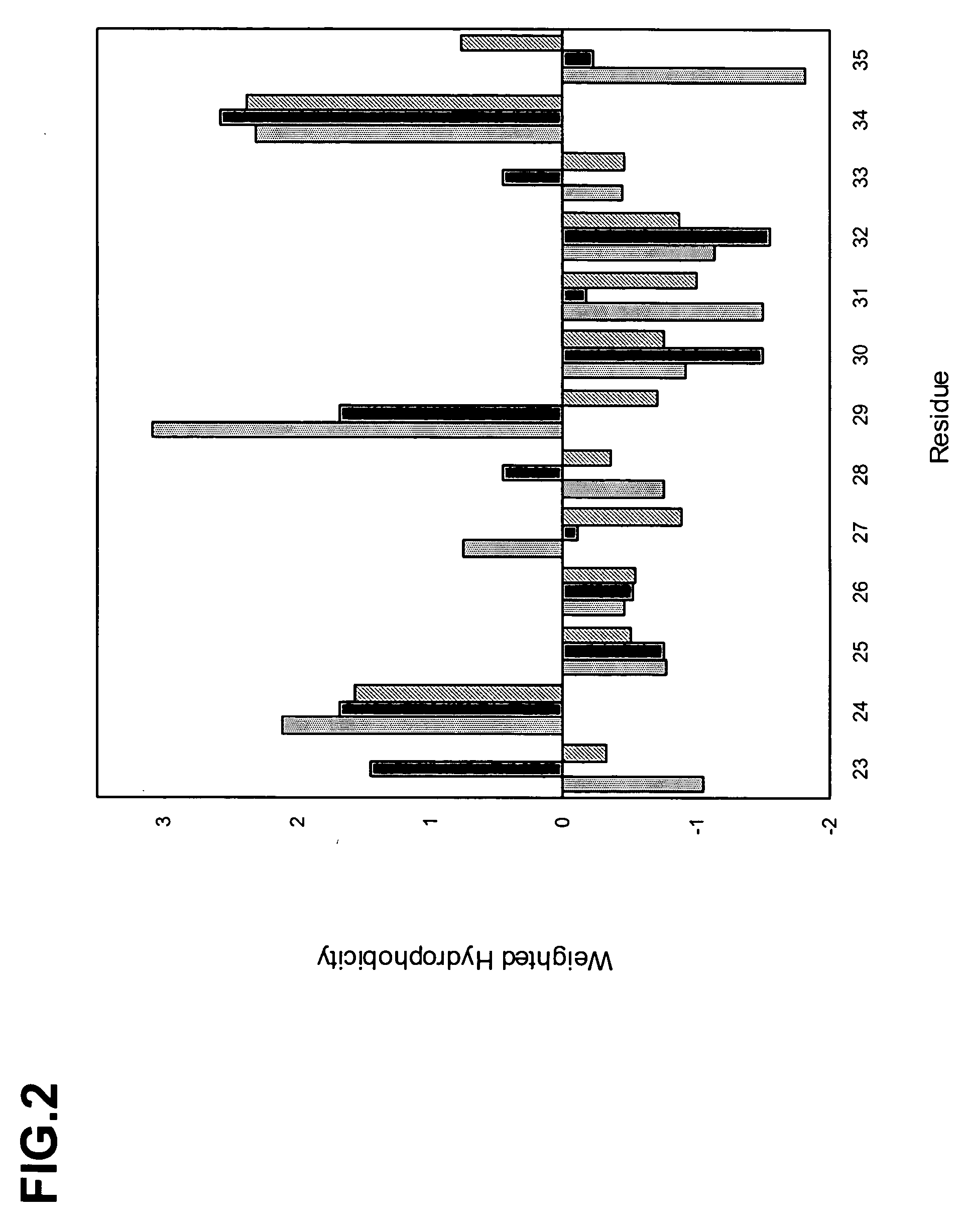
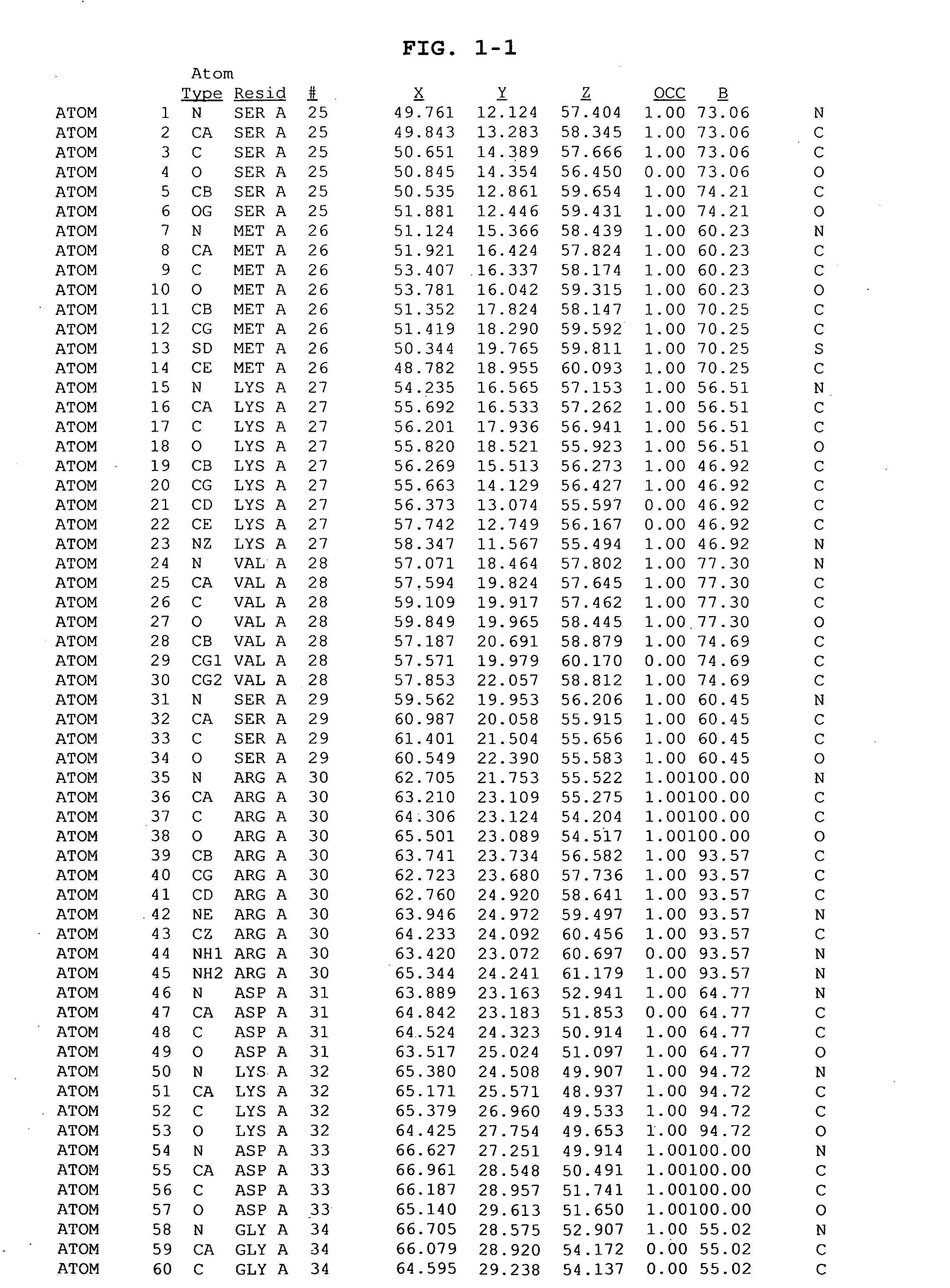
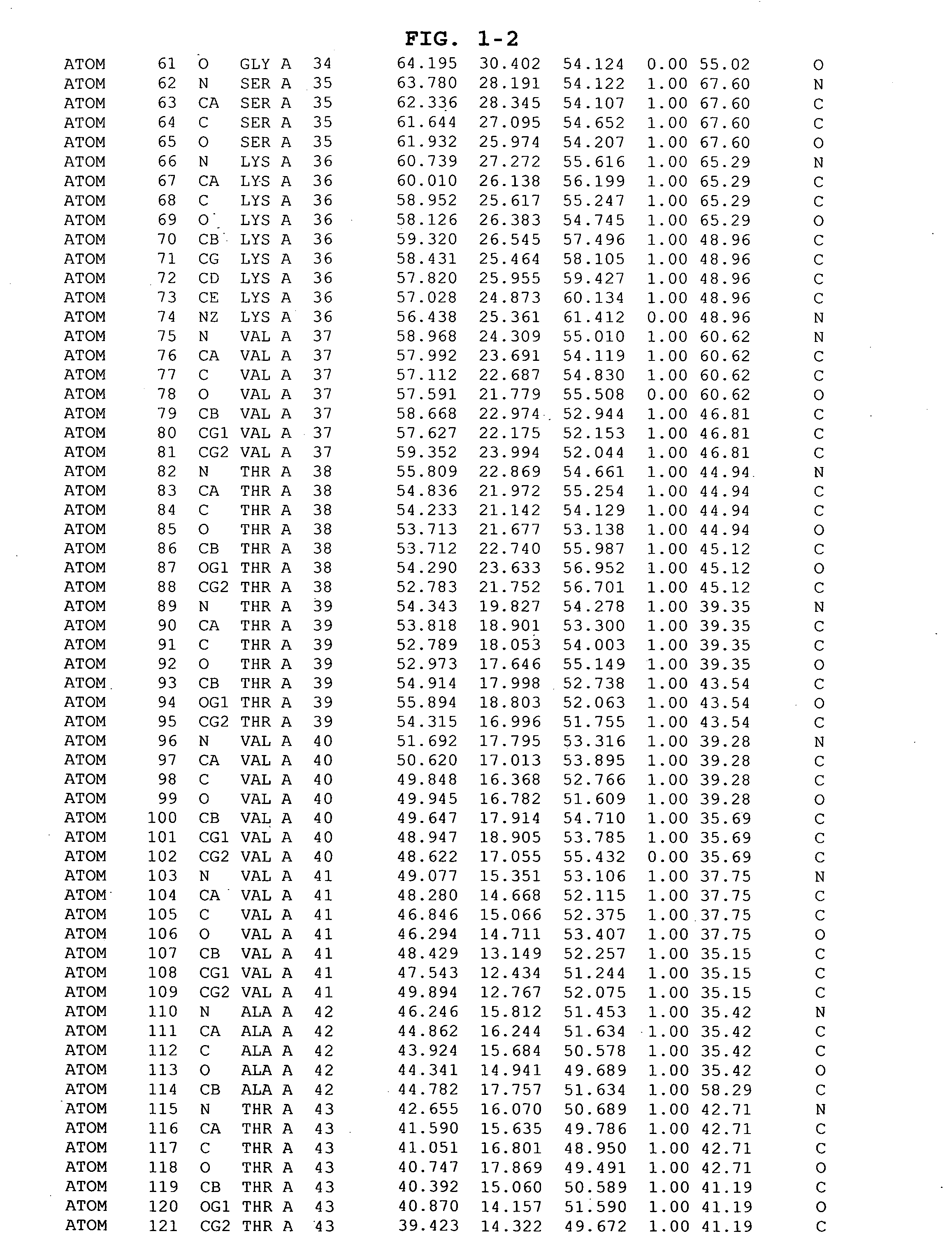
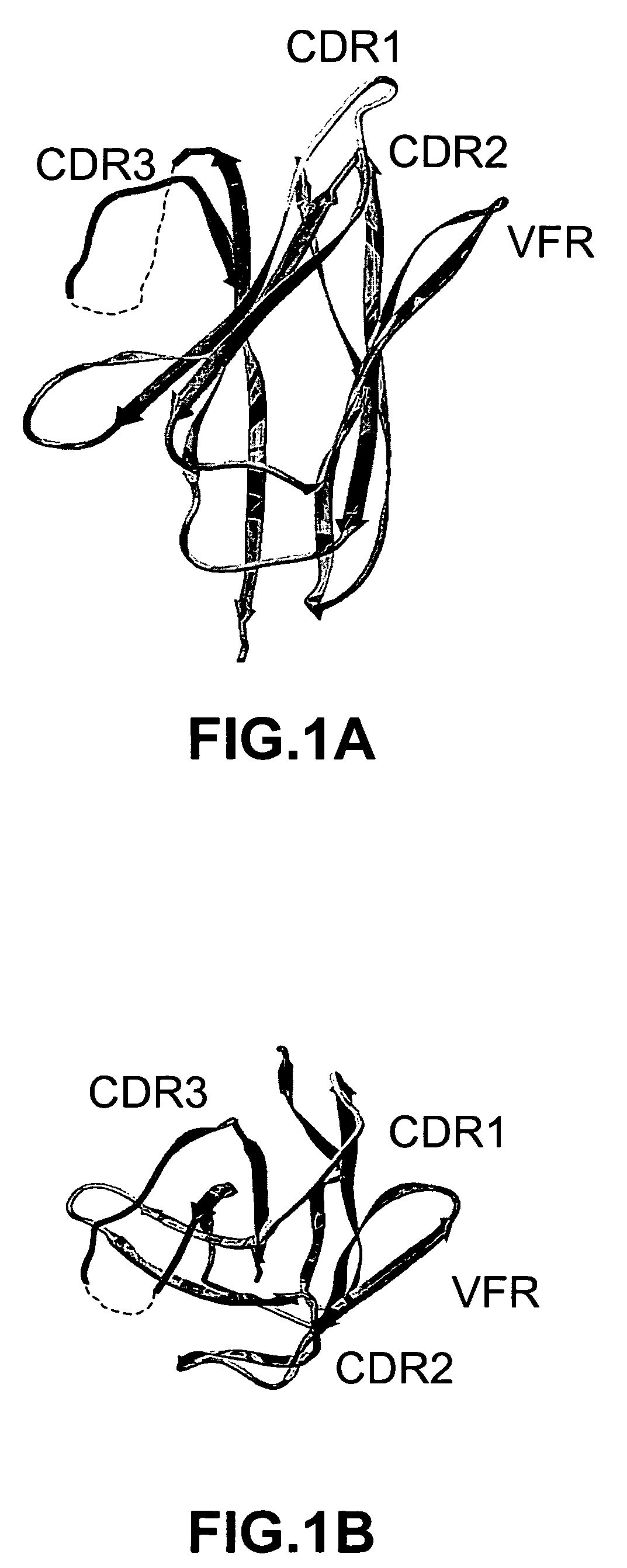
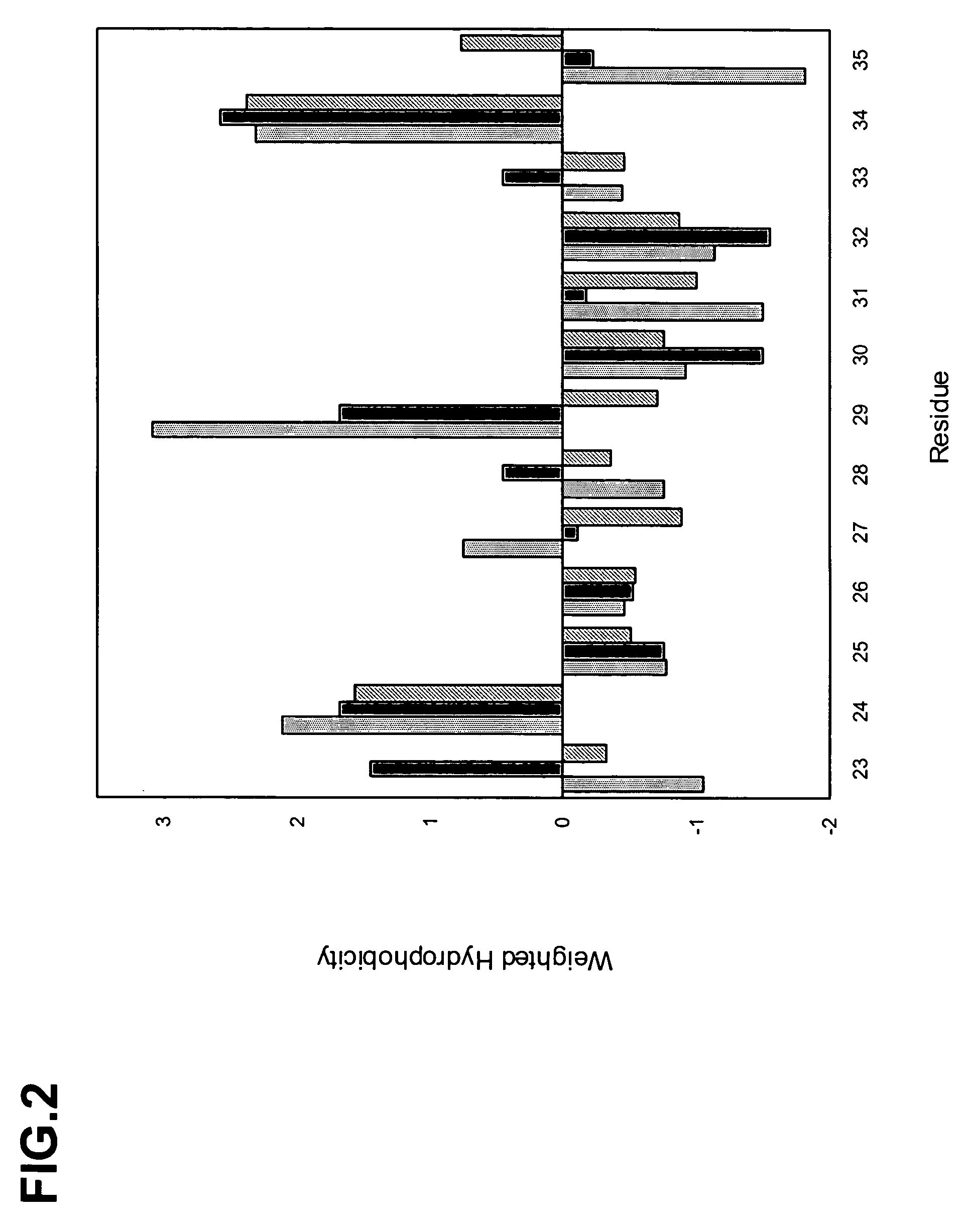
The invention provides polypeptides comprising a variant heavy chain variable framework domain (VFR). In some embodiments, the amino acids defining the VFR form a loop of an antigen binding pocket. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR. The polypeptide may optionally comprise one or more complementary determining regions (CDRs) of antibody variable domains. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR and one or more variant CDRs. Libraries of polypeptides that include a plurality of different antibody variable domains generated by creating diversity in a VFR, and optionally, one or more CDRs are provided and may be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides that can be used therapeutically or as reagents. The invention also provides fusion polypeptides, compositions, and methods for generating and using the polypeptides and libraries.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
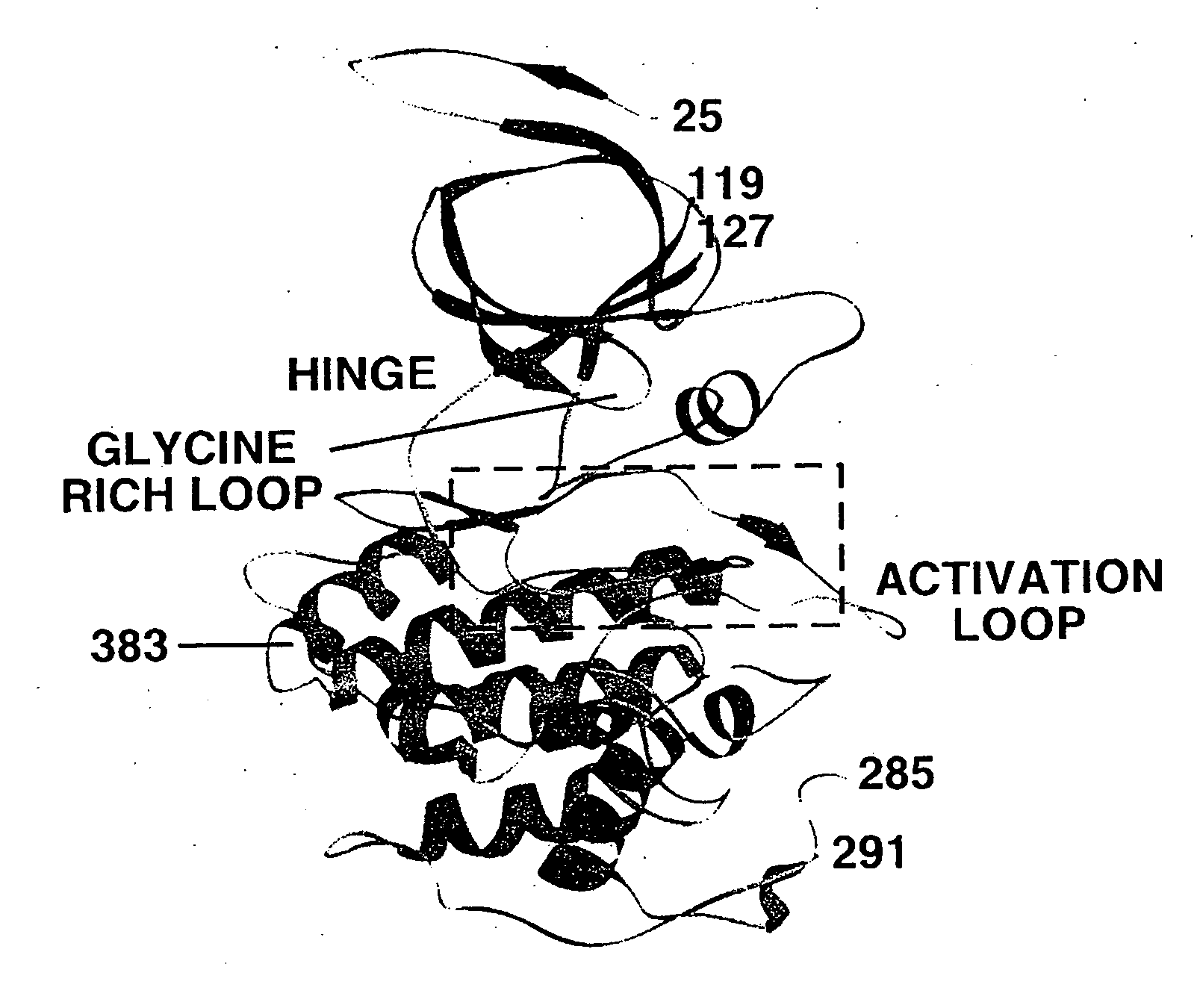
Inhibitors of GSK-3 and crystal structures of GSK-3beta protein and protein complexes
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Variable domain library and uses
ActiveUS7785903B2Generate efficientlyQuality improvementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
The invention provides polypeptides comprising a variant heavy chain variable framework domain (VFR). In some embodiments, the amino acids defining the VFR form a loop of an antigen binding pocket. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR. The polypeptide may optionally comprise one or more complementary determining regions (CDRs) of antibody variable domains. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR and one or more variant CDRs. Libraries of polypeptides that include a plurality of different antibody variable domains generated by creating diversity in a VFR, and optionally, one or more CDRs are provided and may be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides that can be used therapeutically or as reagents. The invention also provides fusion polypeptides, compositions, and methods for generating and using the polypeptides and libraries.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Crystal structure of aurora-2 protein and binding pockets thereof
The present invention provides crystalline molecules or molecular complexes which comprise binding pockets of Aurora-2 or its homologues. The invention also provides crystals comprising Aurora-2. The present invention also relates to a computer comprising a data storage medium encoded with the structural coordinates of Aurora-2 binding pockets and methods of using a computer to evaluate the ability of a compound to bind to the molecule or molecular complex. This invention also provides methods of using the structure coordinates to solve the structure of homologous proteins or protein complexes. In addition, this invention provides methods of using the structure coordinates to screen for and design compounds, including inhibitory compounds, that bind to Aurora-2 or homologues thereof.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Selective and dual-action p53/mdm2/mdm4 antagonists
A fragment-based strategy, involving “multicomponent reaction chemistry” (MCR), can identify novel chemotypes that disrupt the p53 / MDM2 or p53 / MDM4 complex employs. This approach uses high resolution structural information to delineate the region of a first protein or a ligand that is nestled within the binding pocket of a second target protein. The identified region is imported into a database containing MCR scaffolds to generate a virtual library of compounds, which subsequently are docked into the binding pocket of the target protein. Results from docking then are used to select compounds for synthesis and screening. A complementary, NMR-based methodology allows for screening the ability of compounds, selected using MCR, to disrupt the p53 / MDM2 or p53 / MDM4 complex.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
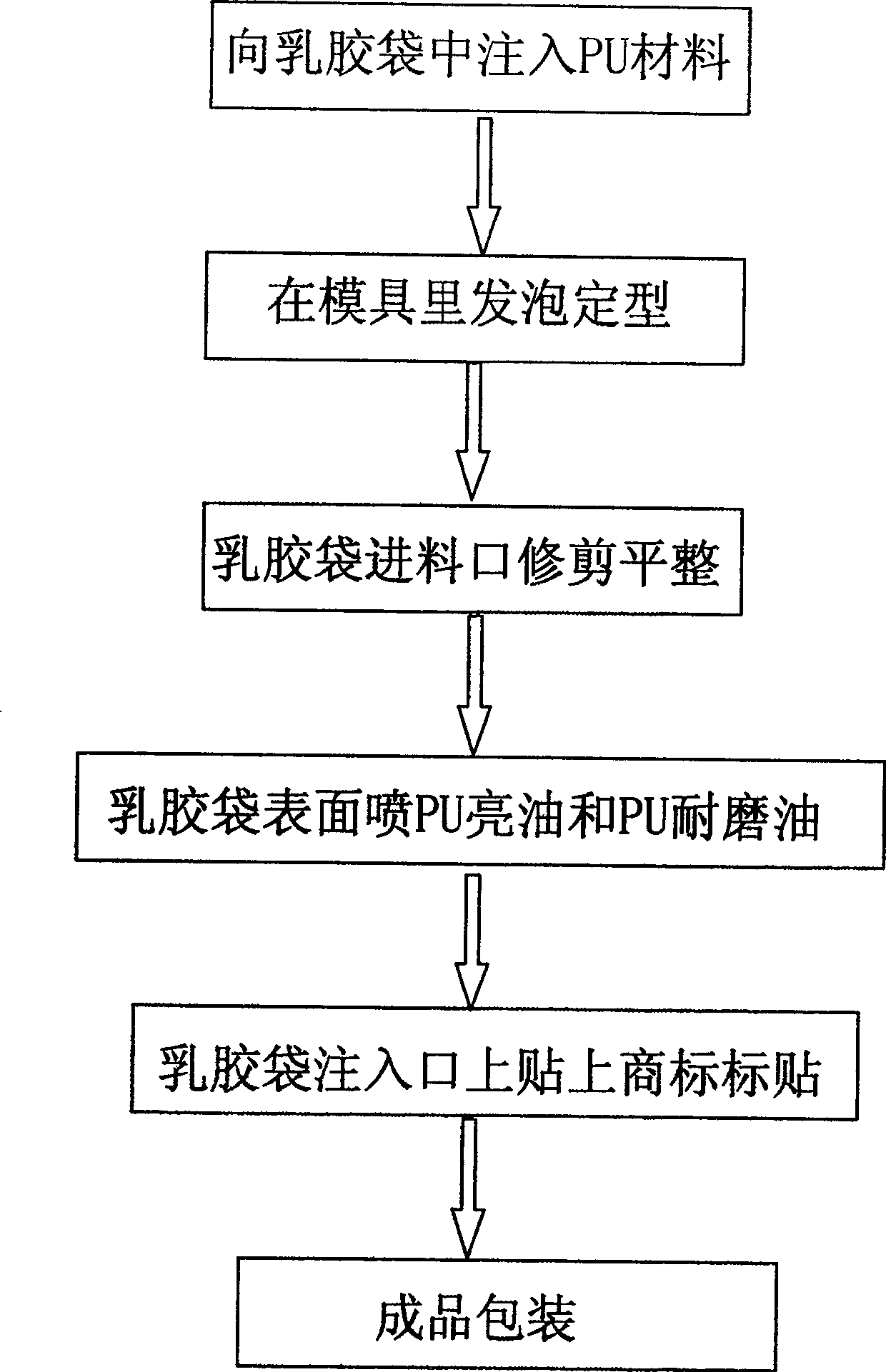
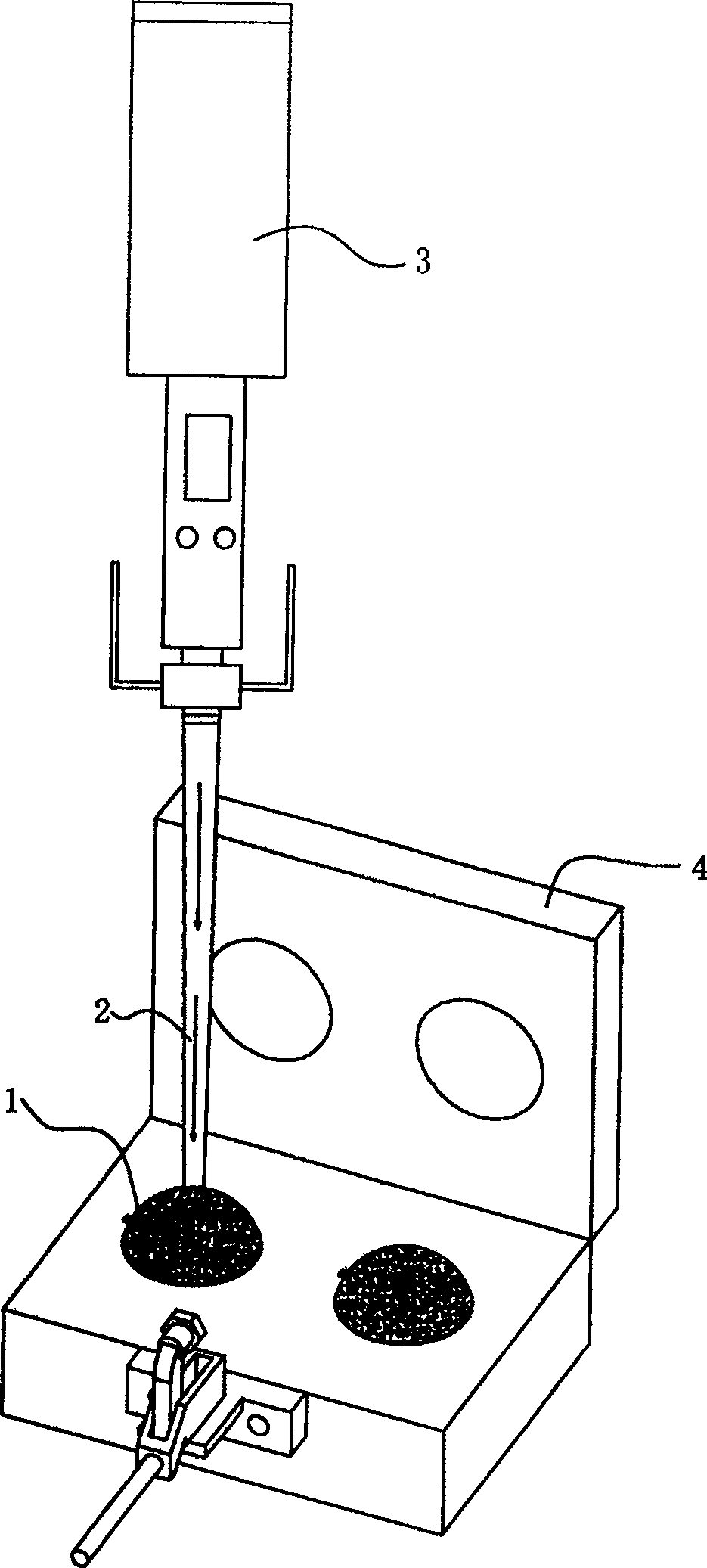
Solid spring ball and process for making same
InactiveCN100506327CIncrease brightnessImprove wear resistanceDomestic articlesSolid ballsState of artWear resistance
The invention discloses a solid elastic ball, which comprises a built-in foamed polyurethane ball center and a spherical latex bag wrapped on the outer wall of the polyurethane ball center. The outer wall of the latex bag is sprayed with polyurethane varnish and polyurethane wear-resistant oil. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing the solid elastic ball, which includes the following steps: a. inject polyurethane material into the spherical hollow latex bag; b. put the latex bag filled with solid polyurethane material into the mould, and foam and shape it; c. 1. Trim and level the feed port of the latex bag, and spray polyurethane varnish and wear-resistant oil on the spherical surface of the latex bag to finish the finished product. Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the advantages of: the combination degree of the center of the ball and the latex bag of the wrapping layer outside the center of the ball is greatly improved, the latex bag is evenly stressed, the sphere is not easy to deform, the outer wall of the latex bag has good integrity, and there is no foaming. Phenomena such as delamination and rough handle do not exist at all, which also improves the brightness and wear resistance of the ball, and facilitates the subsequent surface spraying process.
Owner:汪永国
Small molecule compositions for binding to hsp90
Structural differences in binding pockets of members of the HSP90 family can be exploited to achieve differential degradation of kinases and other signaling proteins through the use of designed small molecules which interact with the N-terminal binding pocket with an affinity which is greater than ADP and different from the ansamycin antibiotics for at least one species of the HSP90 family. Moreover, these small molecules can be designed to be soluble in aqueous media, thus providing a further advantage over the use of ansamycin antibiotics. Pharmaceutical compositions can be formulated containing a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a molecule that includes a binding moiety which binds to the N-terminal pocket of at least one member of the HSP90 family of proteins. Such binding moieties were found to have antiproliferative activity against tumor cells which are dependent on proteins requiring chaperones of the HSP90 family for their function. Different chemical species have different activity, however, allowing the selection of, for example Her2 degradation without degradation of Raf kinase. Thus, the binding moieties possess an inherent targeting capacity. In addition, the small molecules can be linked to targeting moieties to provide targeting of the activity to specific classes of cells. Thus, the invention further provides a method for treatment of diseases, including cancers, by administration of these compositions. Dimeric forms of the binding moieties may also be employed.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
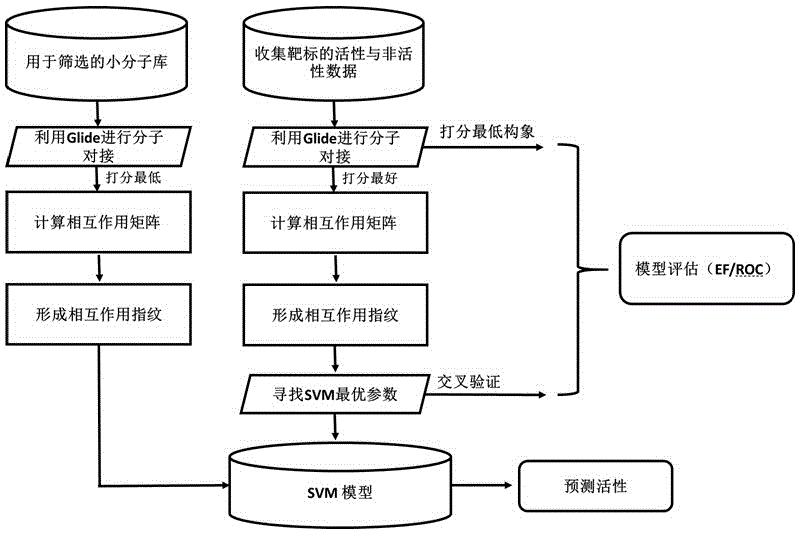
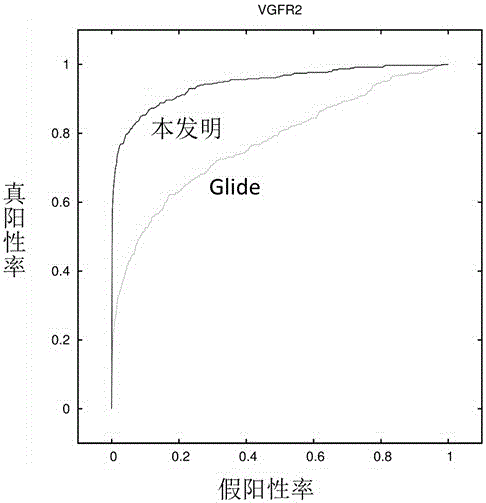
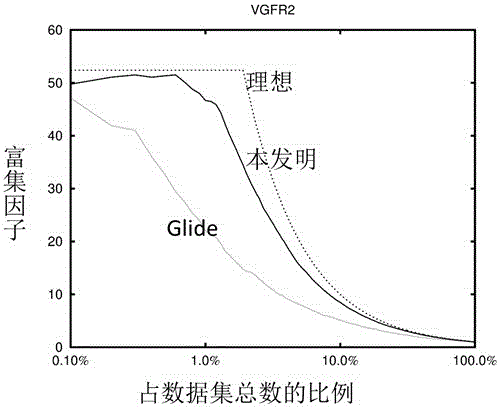
Drug target virtual screening method based on interactive fingerprints and machine learning
ActiveCN106446607AFully consider the specificityAvoid the pitfalls of underfittingBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsProtein targetBinding site
The invention relates to a drug target virtual screening method based on interactive fingerprints and machine learning. According to the method, based on traditional molecular docking, the interactive fingerprints of known active and non-active micromolecules and target protein are trained through machine learning to obtain a screening model of targets, and the obtained model is used for virtual screening. The specific targets are specifically trained, the specificity of each kind of targets is fully considered, and the defect of insufficient fitting of a traditional scoring function is avoided; interaction energy of each micromolecule and each residue in a binding pocket is calculated, so that effective binding sites or binding modes can be found; non-linear fitting is carried out through machine learning, and compared with linear fitting, the correlation or coupling effect between all the interaction energy can be better processed; by means of the method, enrichment of active molecules is better promoted.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
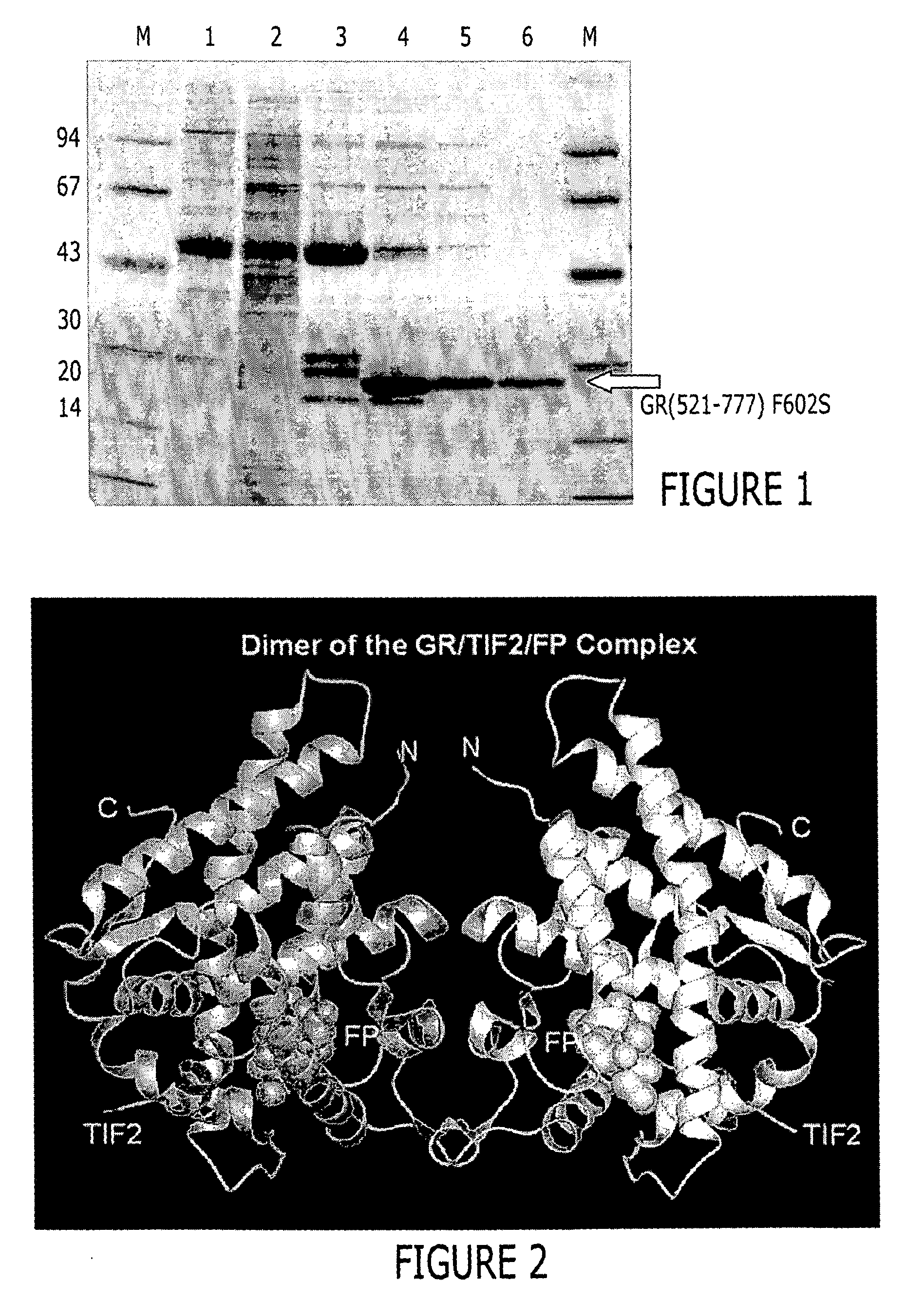
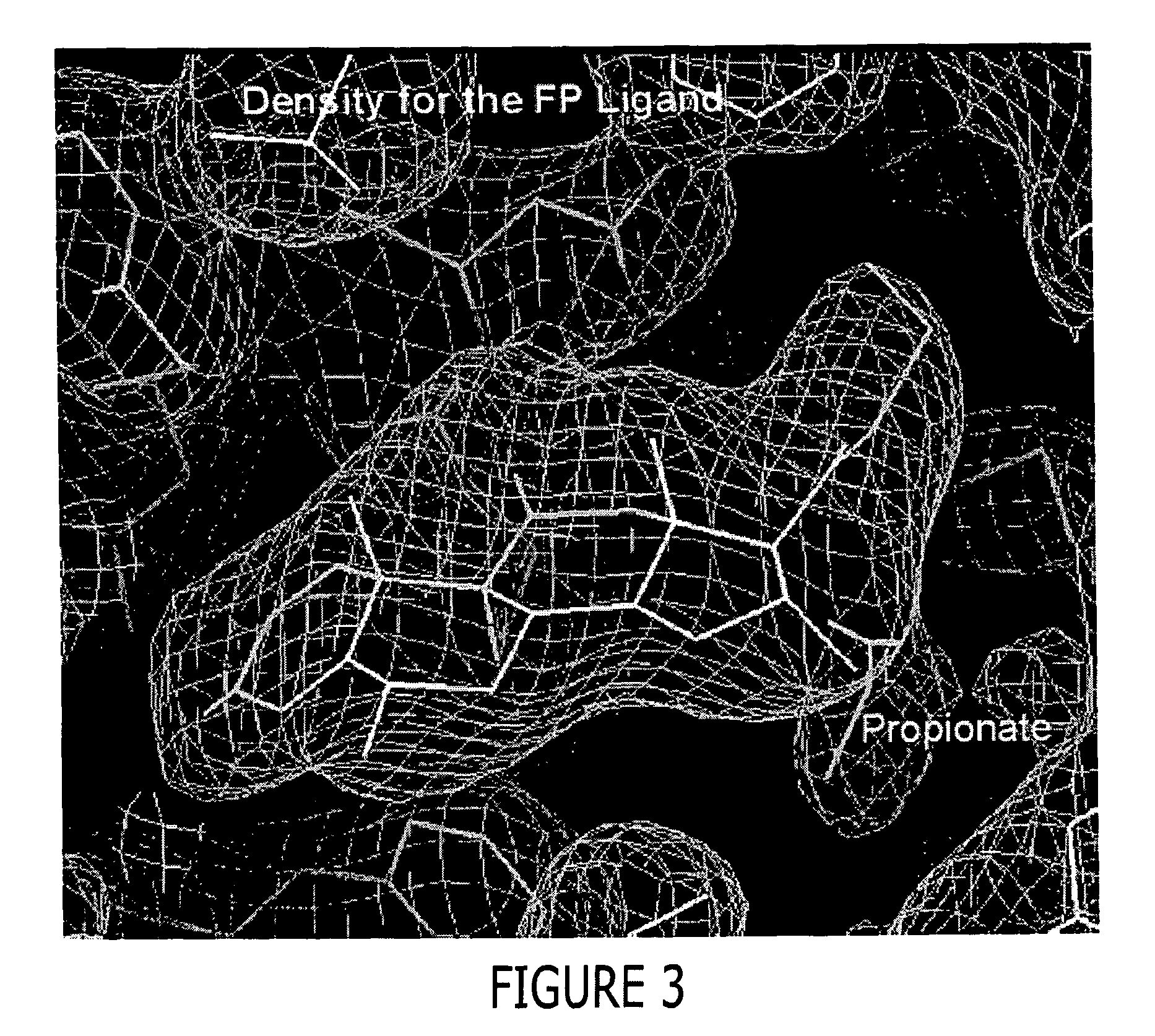
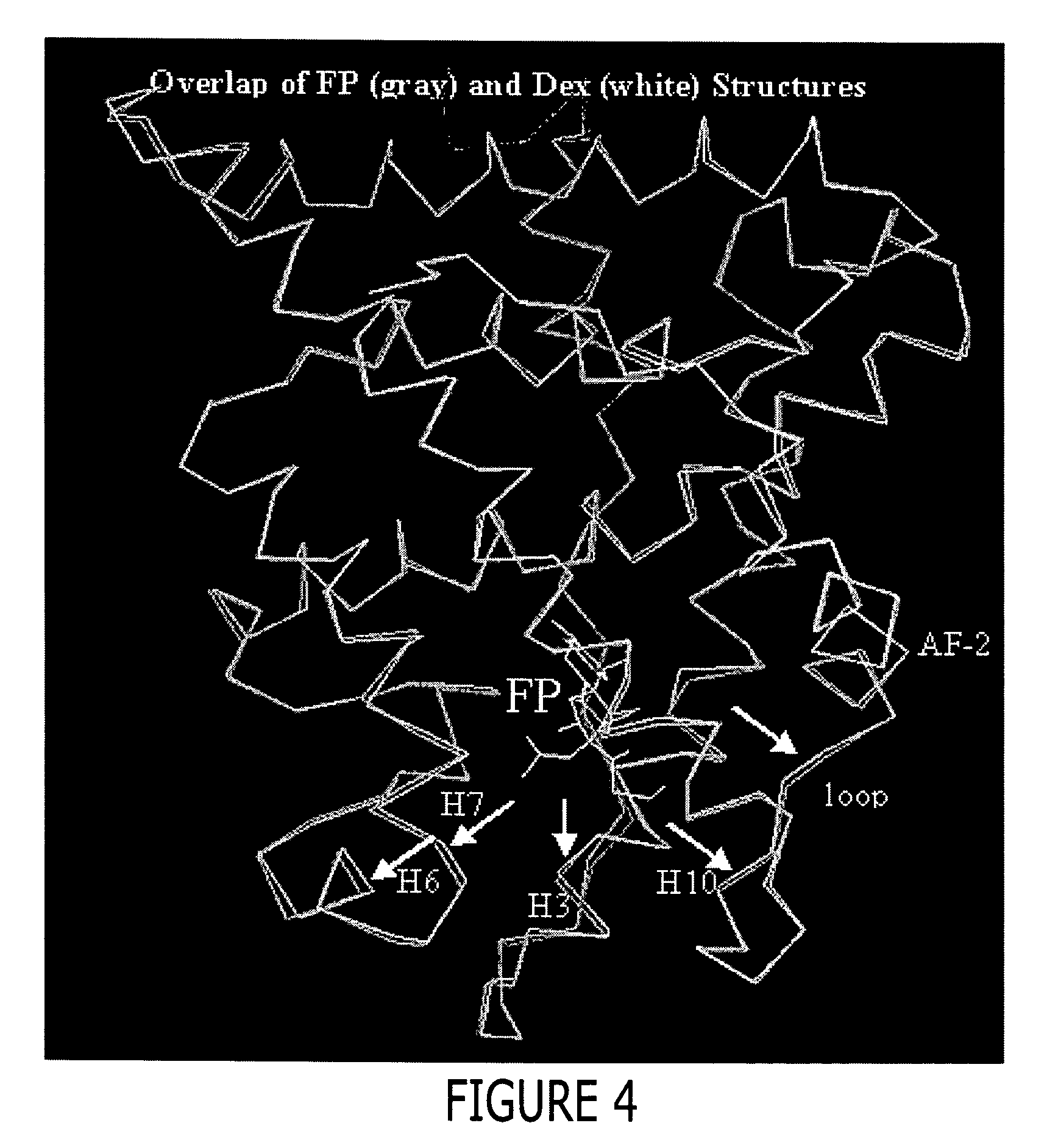
Structure of a glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain comprising an expanded binding pocket and methods employing same
InactiveUS20070020684A1Peptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisFluticasone propionatePR - Progesterone receptor
A solved three-dimensional crystal structure of a glucocorticord receptor (GR) α ligand binding domain polypeptide is disclosed, in the form of a crystalline glucocorticord receptor α ligand binding domain polypeptide in complex with the ligand fluticasone propionate (FP) and a peptide derived from the co-activator TIF2. The GR / FP / TIF2 structure includes an expanded binding pocket not seen in other GR structures. Methods of designing steroid and non-steroid modulators of the biological activity of GR and other nuclear receptors (NRs) are also disclosed. In another aspect of the present invention homology models of androgen receptor (AR), progesterone receptor (PR) and mineralcorticoid receptor (MR) are disclosed, as well as methods of forming homology models for other NRs. Methods of forming a soluble GR / FP / TIF2 complex are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
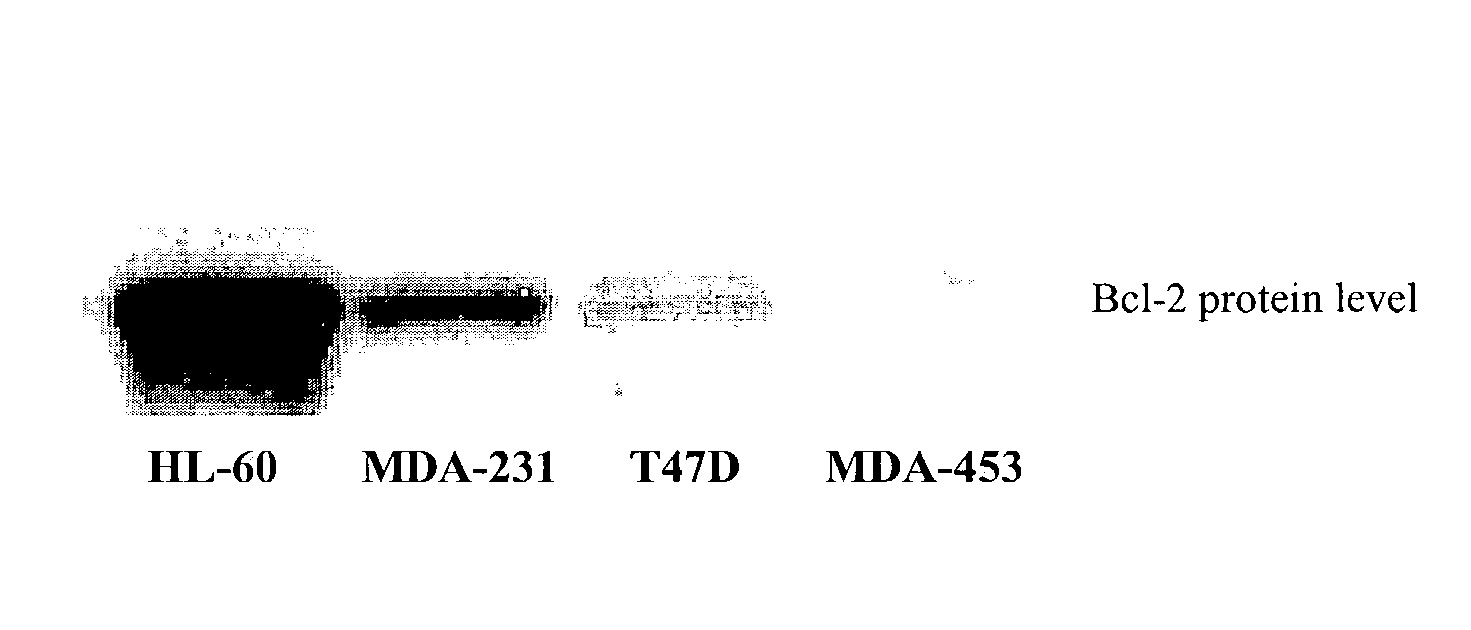
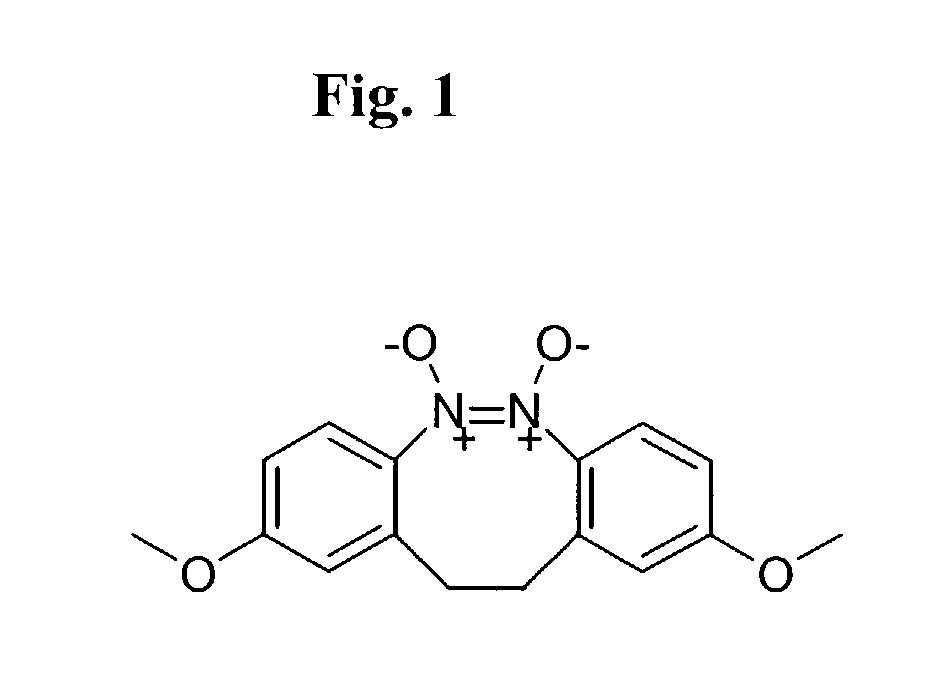
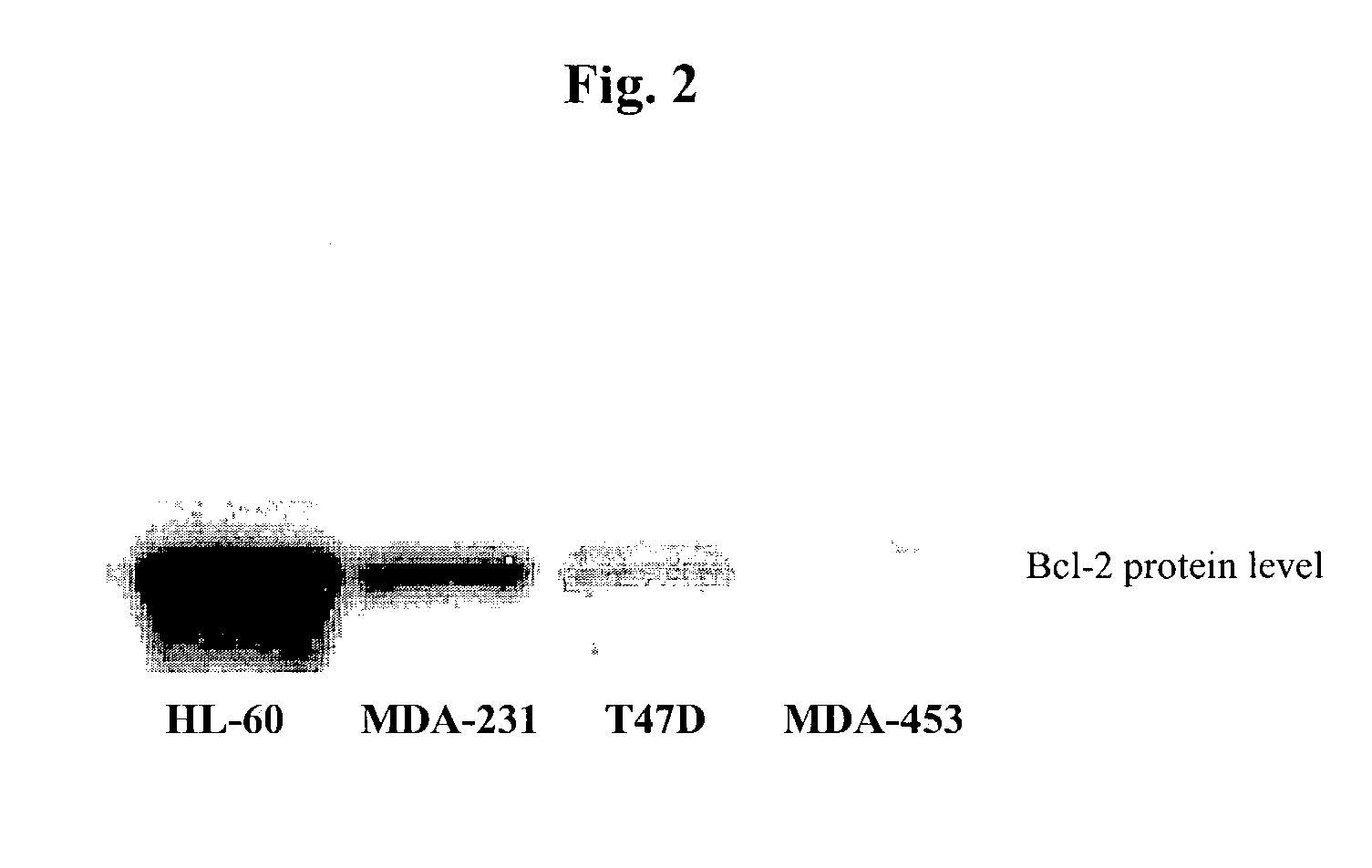
Small molecule inhibitors targeted at Bcl-2
InactiveUS7354928B2Effective treatmentReduce overexpressionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseCancer cell
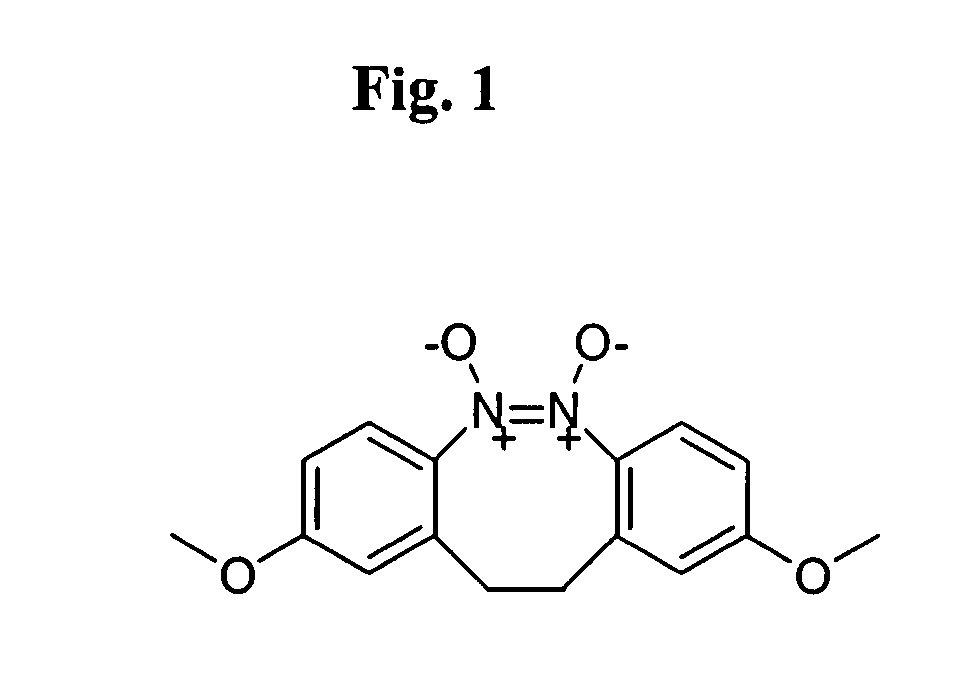
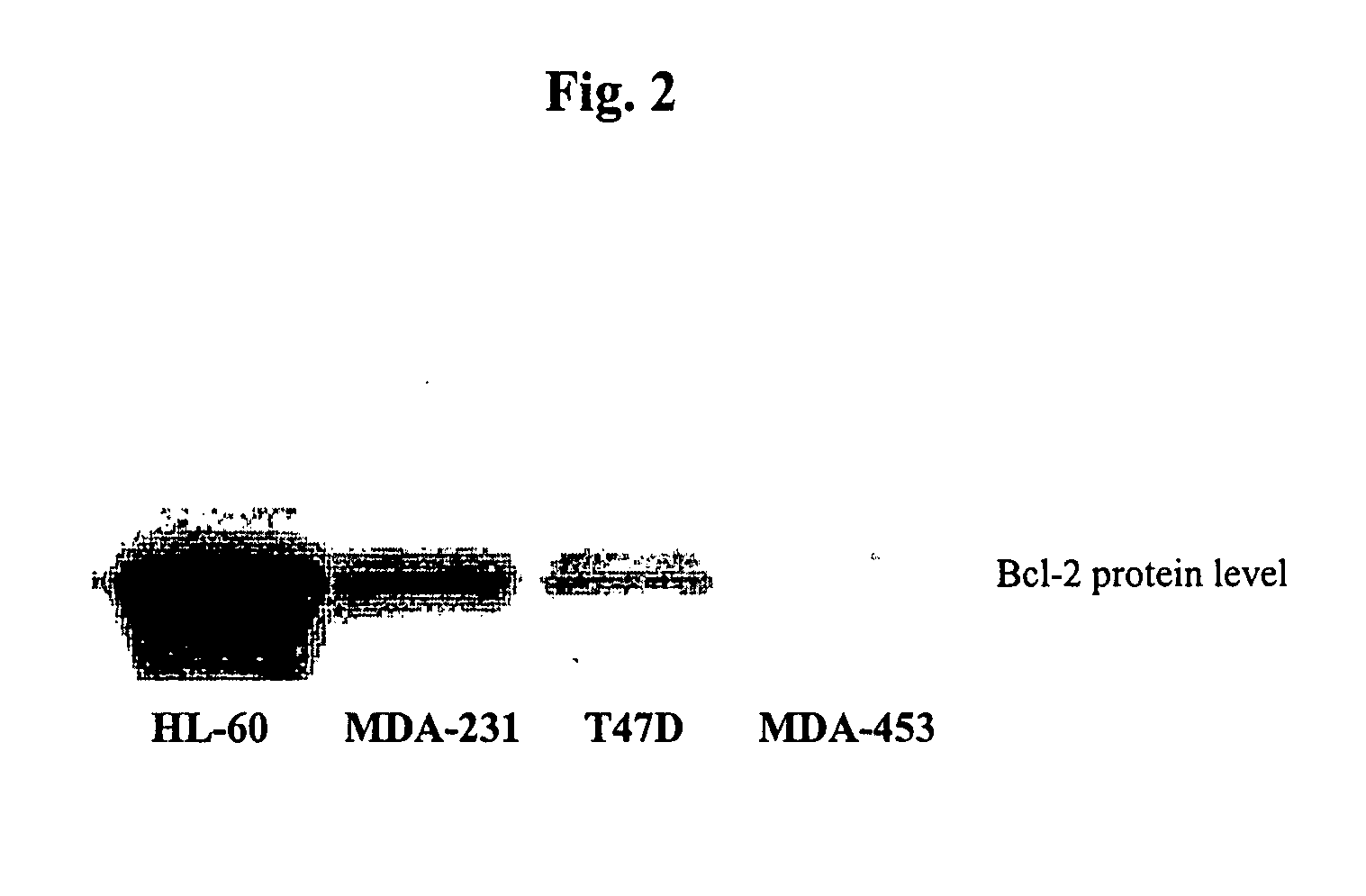
The present invention relates to small molecule antagonists of Bcl-2 family proteins such as Bcl-2 and / or Bcl-XL. In particular, the present invention provides non-peptide cell permeable small molecules (e.g., tricyclo-dibenzo-diazocine-dioxides) that bind to a pocket in Bcl-2 / Bcl-XL that block the anti-apoptotic function of these proteins in cancer cells and tumor tissues exhibiting Bcl-2 protein overexpression. In preferred embodiments, the small molecules of the present invention are active at the BH3 binding pocket of Bcl-2 family proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Mcl-1). The compositions and methods of the present invention are useful therapeutics for cancerous diseases either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic or other drugs.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV +1
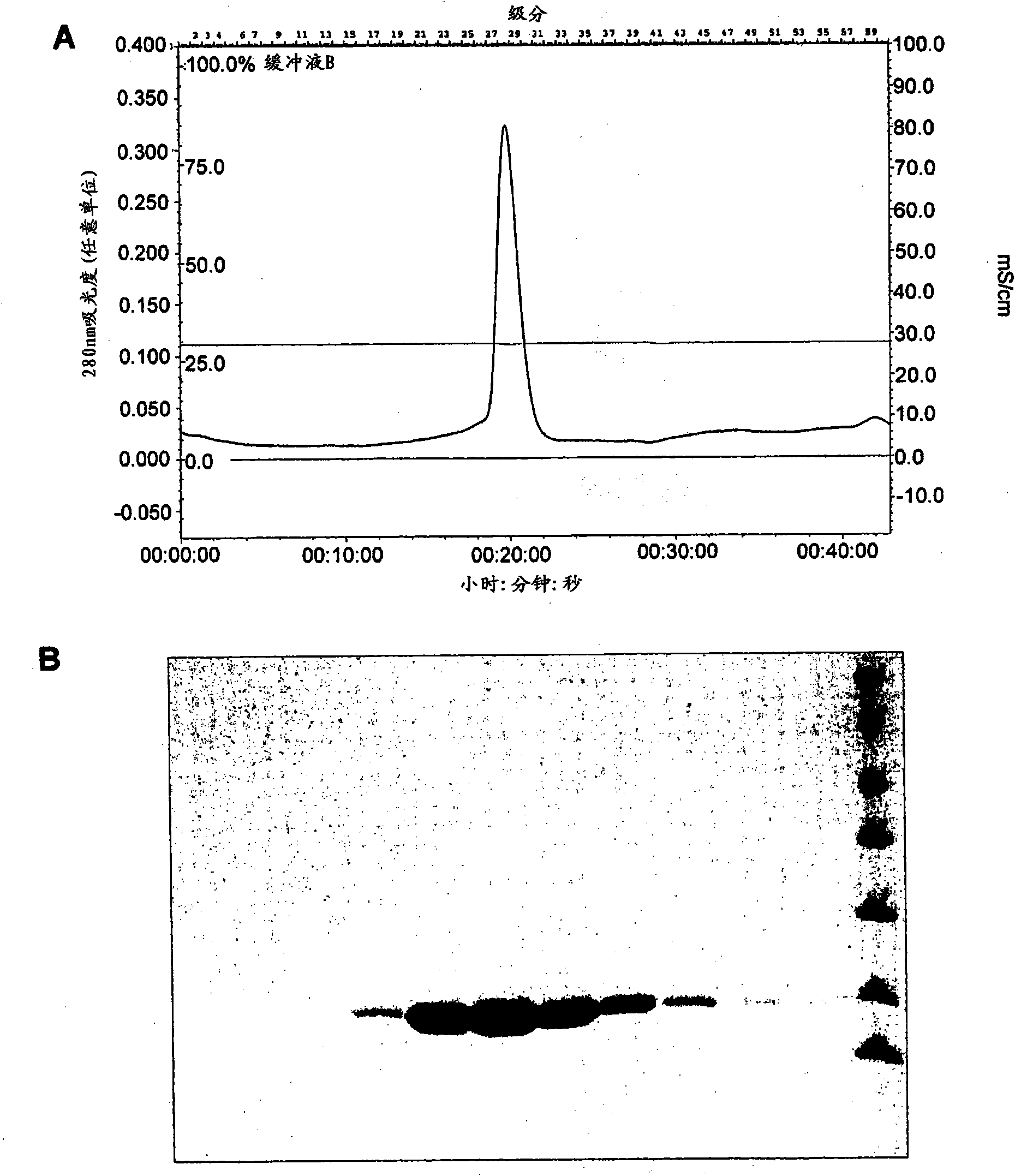
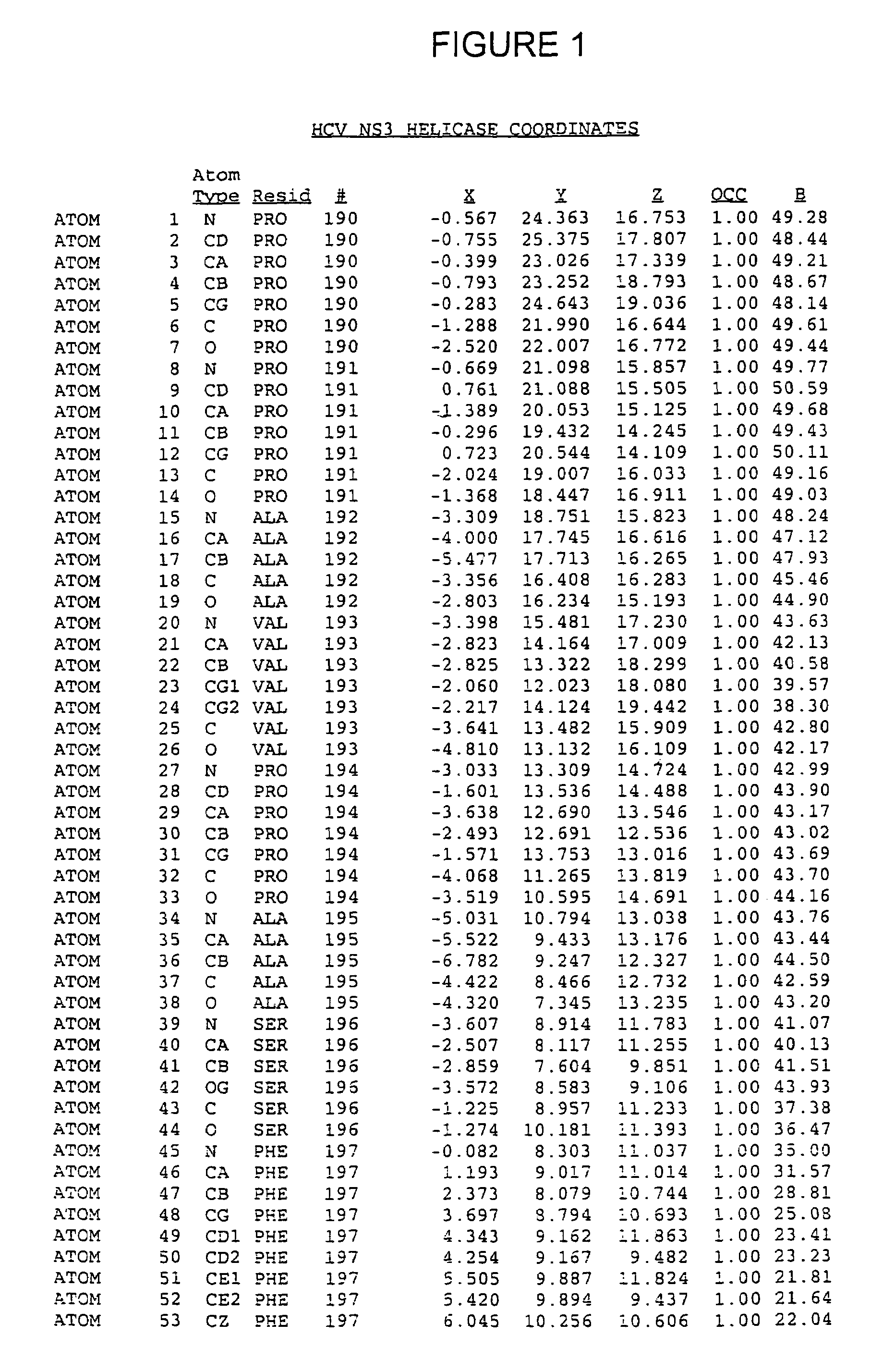
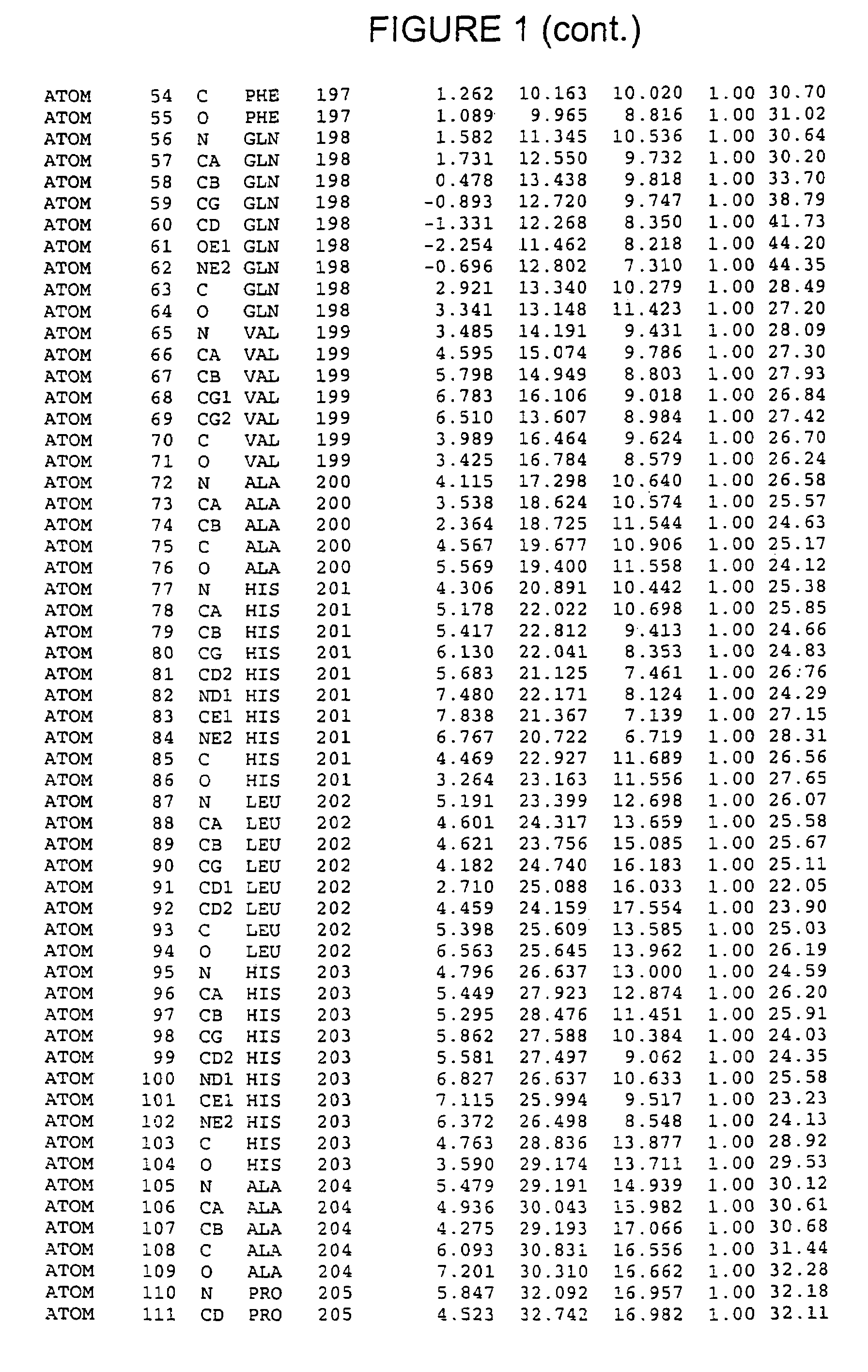
Crystals of hepatitis C virus helicase or fragments thereof comprising a helicase binding pocket
InactiveUS7438920B1SsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideDNA unwinding enzyme
The invention relates to the X-ray crystal structure of the hepatitis C virus helicase domain. More specifically, the invention relates to crystallized complexes of HCV helicase and an oligonucleotide, to crystallizable compositions of HCV helicase and an oligonucleotide and to methods of crystallizing an HCV helicase-oligonucleotide complex. The invention further relates to a computer programmed with the structure coordinates of the HCV helicase oligonucleotide binding pocket or the HCV helicase nucleotide triphosphate pocket wherein said computer is capable of displaying a three-dimensional representation of that binding pocket.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Inhibitors of GSK-3 and crystal structures of GSK-3β protein and protein complexes
The present invention relates to inhibitors of GSK-3 and methods for producing these inhibitors. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inhibitors and methods of utilizing those compositions in the treatment and prevention of various disorders, such as diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. In addition, the invention relates to molecules or molecular complexes which comprise binding pockets of GSK-3β or its homologues. The invention relates to a computer comprising a data storage medium encoded with the structure coordinates of such binding pockets. The invention also relates to methods of using the structure coordinates to solve the structure of homologous proteins or protein complexes. The invention relates to methods of using the structure coordinates to screen for and design compounds that bind to GSK-3β protein or homologues thereof. The invention also relates to crystallizable compositions and crystals comprising GSK-3β protein or GSK-3β protein complexes.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Hepatitis C Virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor binding pocket
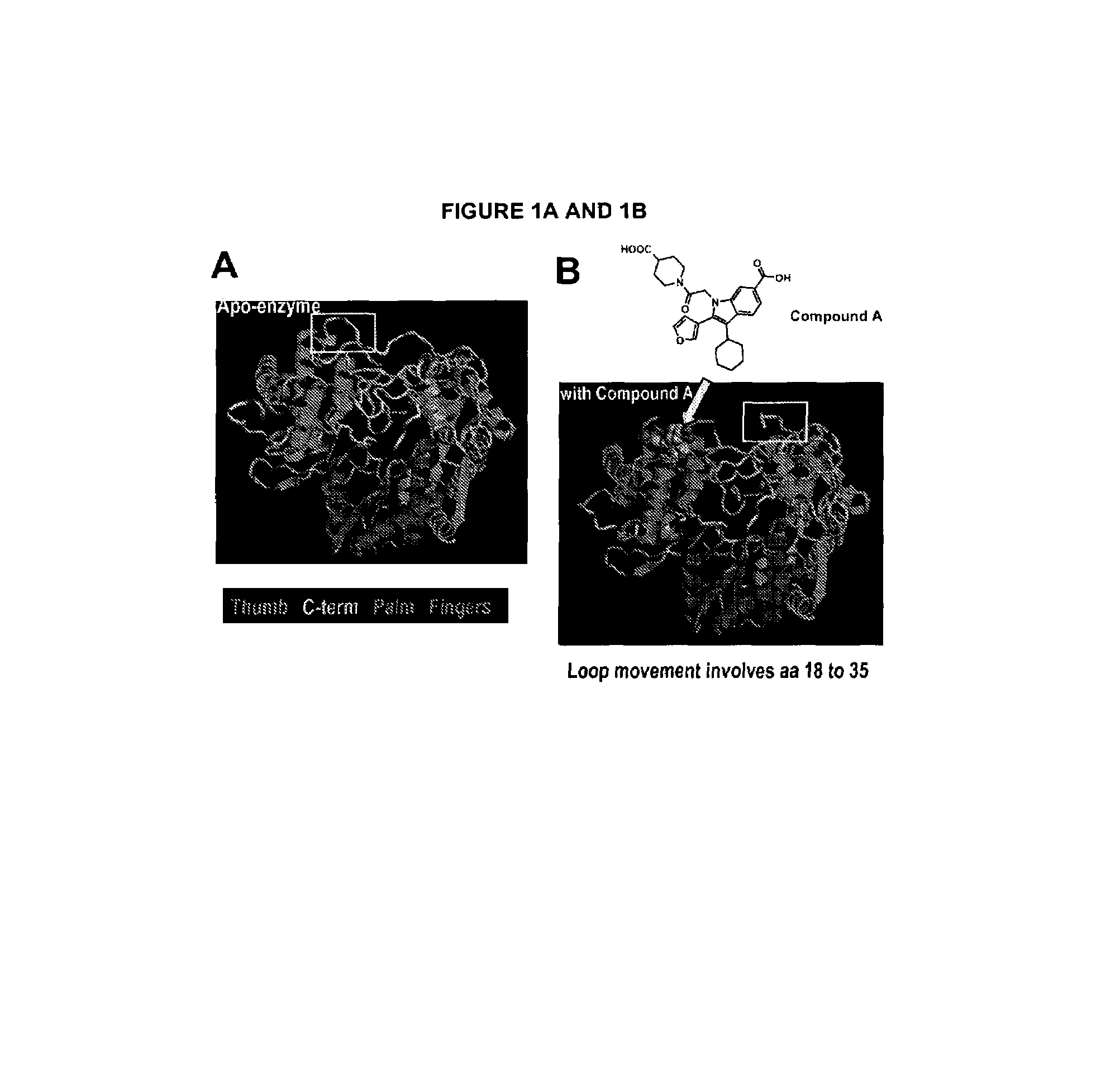
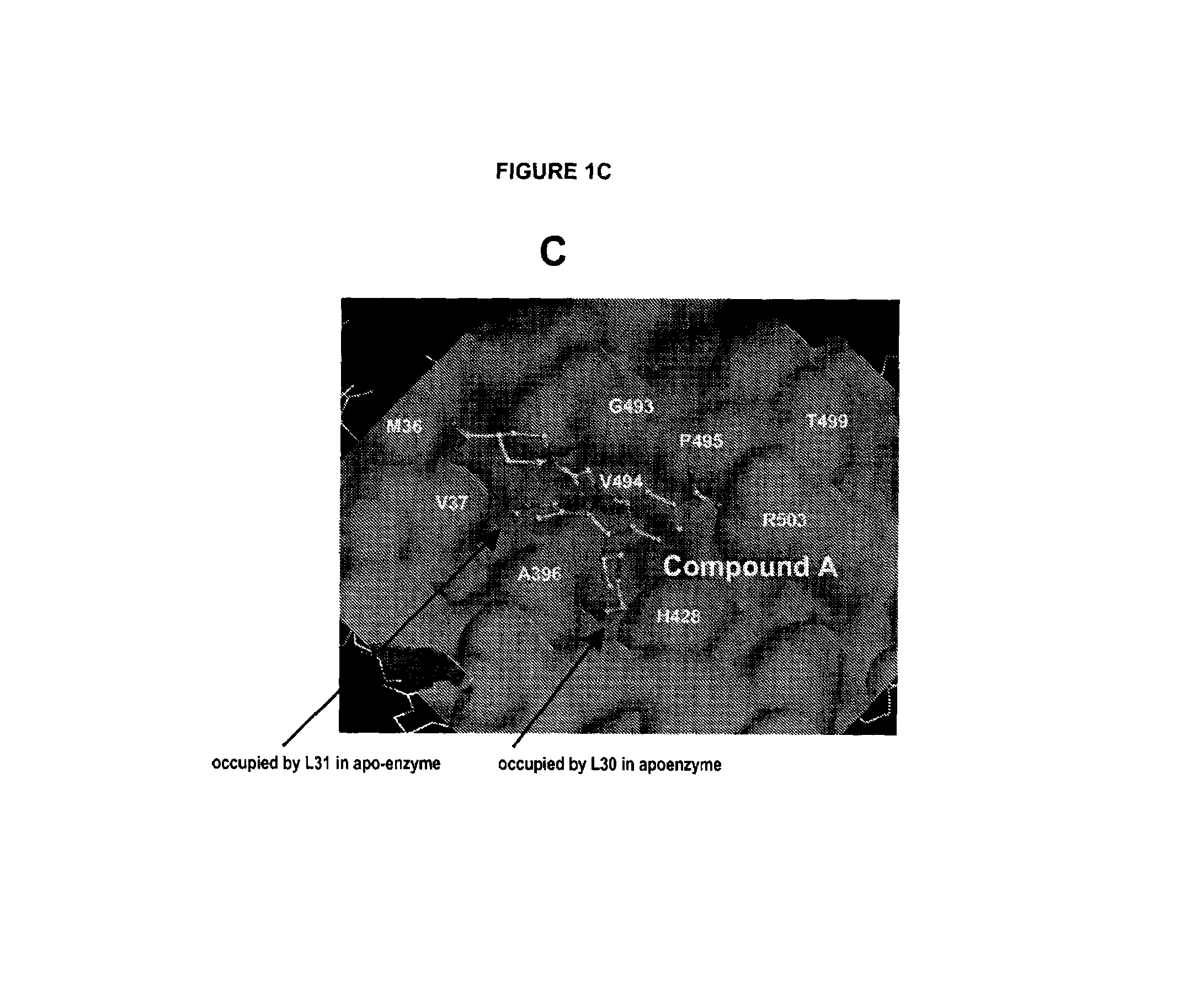
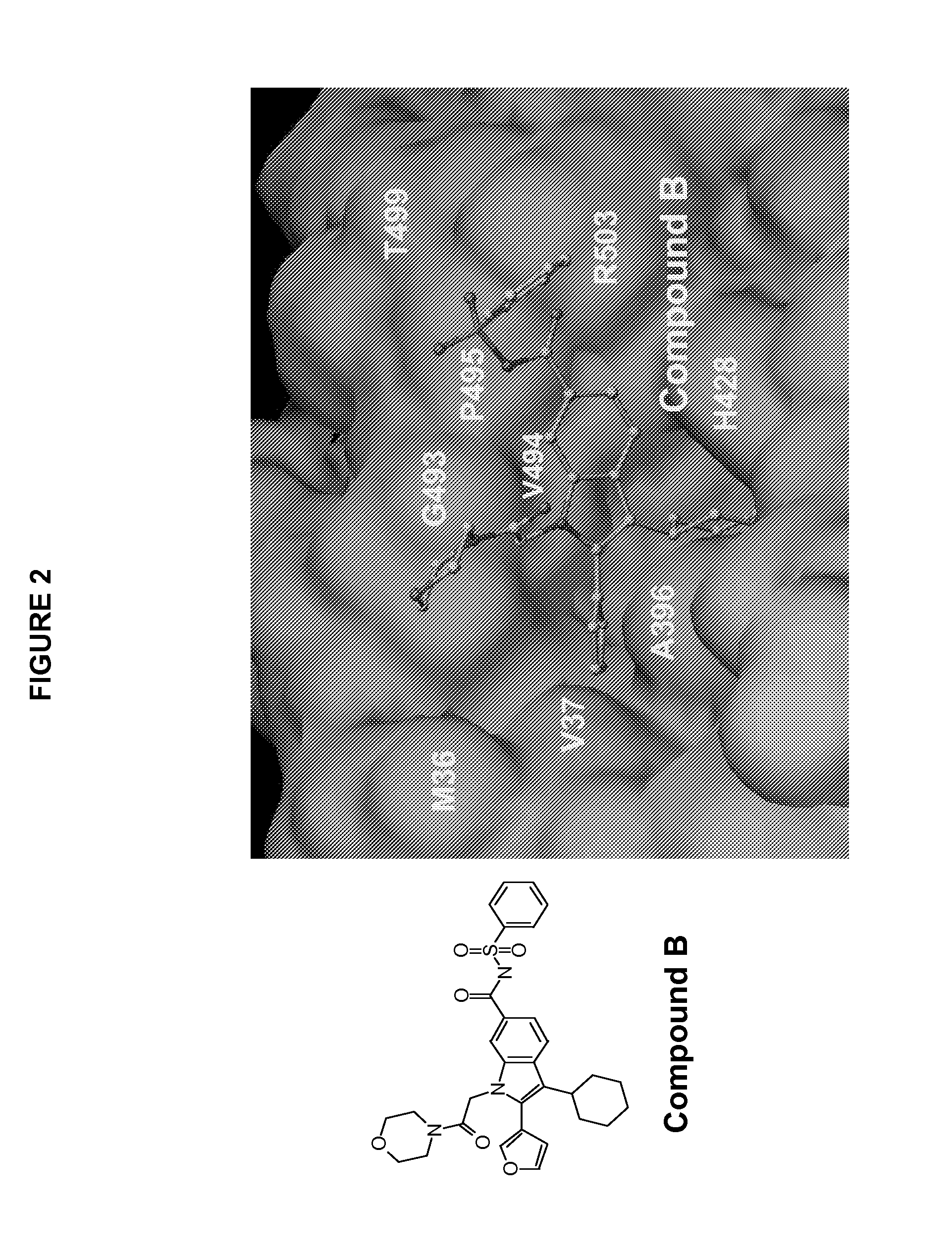
The HCV NS5B polymerase, when complexed with certain inhibitors, adopts a conformation in which the finger loop region defined by amino acid residues 18 to 35 is displaced to expose a binding pocket defined generally by amino acid residues 392, 393, 395, 396, 399, 424, 425, 428, 429, 492, 493, 494, 495, 496, 500 and 503. This newly exposed binding pocket defines a novel target in the search of further chemical entities which are capable of binding to HCV NS5B and modulating, or preferably inhibiting, the polymerase activity of HCV NS5B.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
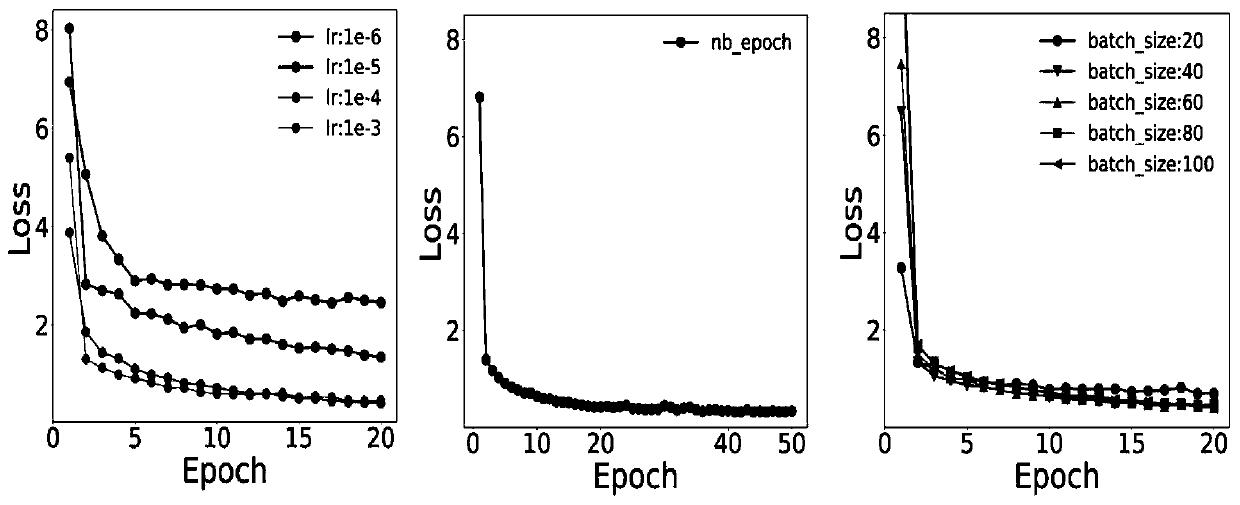
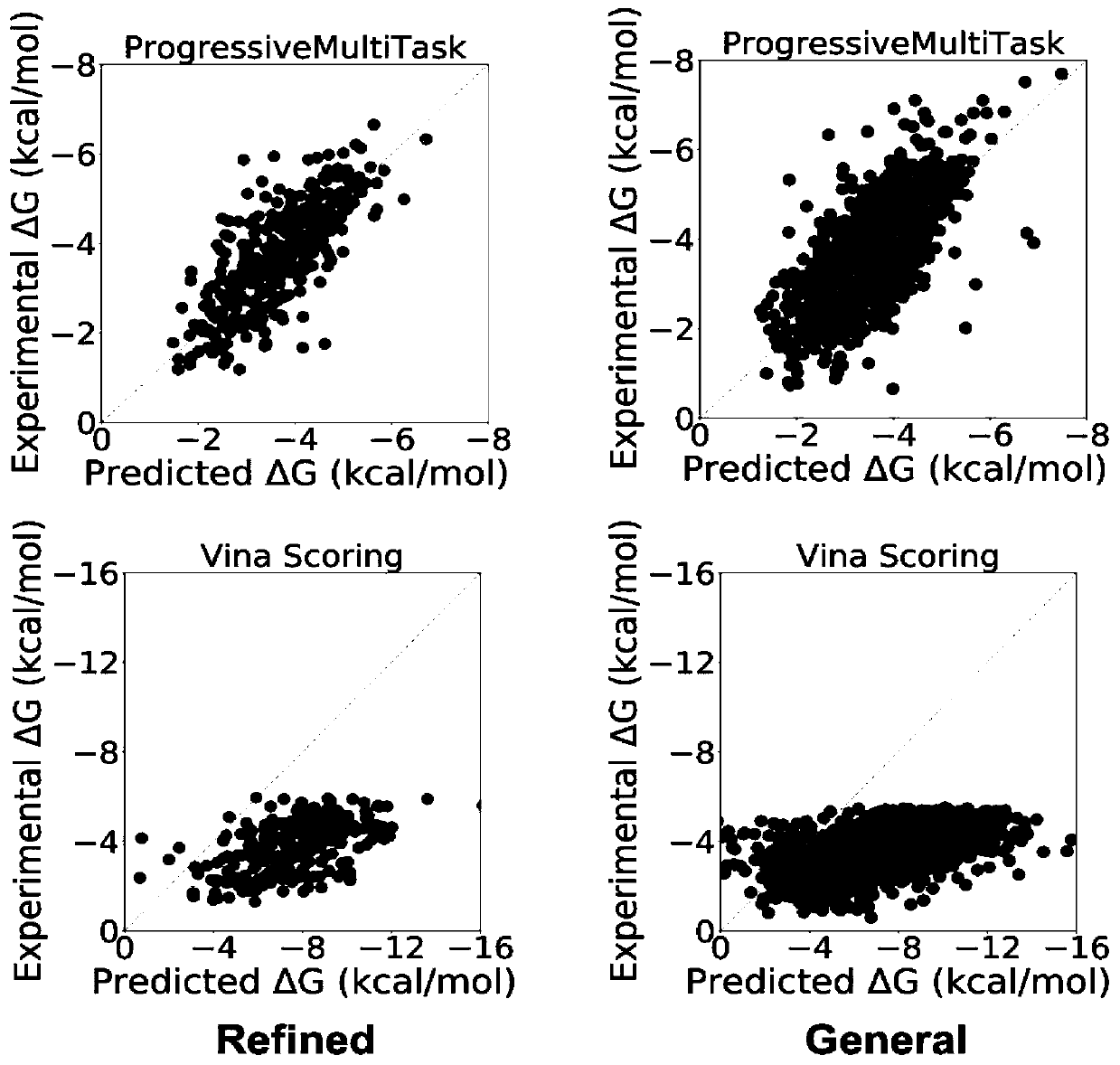
Method for predicting binding free energy of protein and ligand based on progressive neural network
ActiveCN110910951APrevent overfittingImprove generalization abilityProteomicsGenomicsAlgorithmTest set
The invention discloses a method for predicting the binding free energy of protein and ligand based on a progressive neural network, and belongs to the technical field of computer-aided drug design. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a pdb file from a PDBbind database, establishing local database, acquiring an amino acid molecule within 4.5 angstroms in the protein binding pocket by takingthe ligand molecule as a center, performing extended connectivity fingerprint calculation, carrying out SPLIF fingerprint calculation, searching for the number of salt bridges and hydrogen bonds between protein and ligand molecules, converting the structural information of the protein and the ligand into a one-dimensional tensor, and establishing a training set, a verification set and a test set;training the progressive neural network by using the training set; optimizing and searching hyper-parameters for prediction; through comparison with a molecular docking result, obtaining a higher Pearson correlation coefficient. According to the invention, the technical problem of how to convert a three-dimensional structure of protein and ligand molecules into tensors which are easy to calculateby a computer and input the tensors into the progressive neural network for training and optimization is solved, and the calculation rate and the prediction accuracy are greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
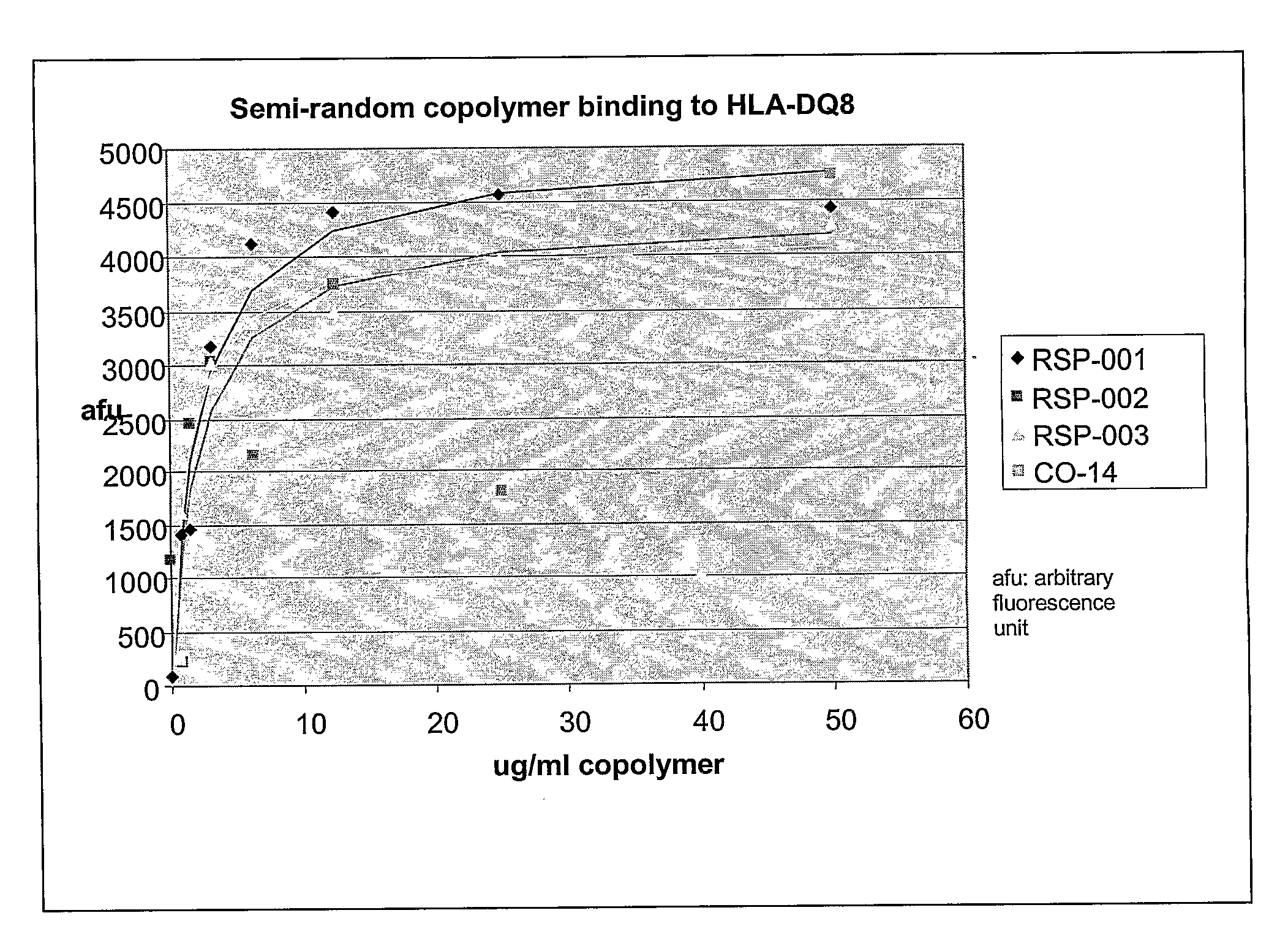
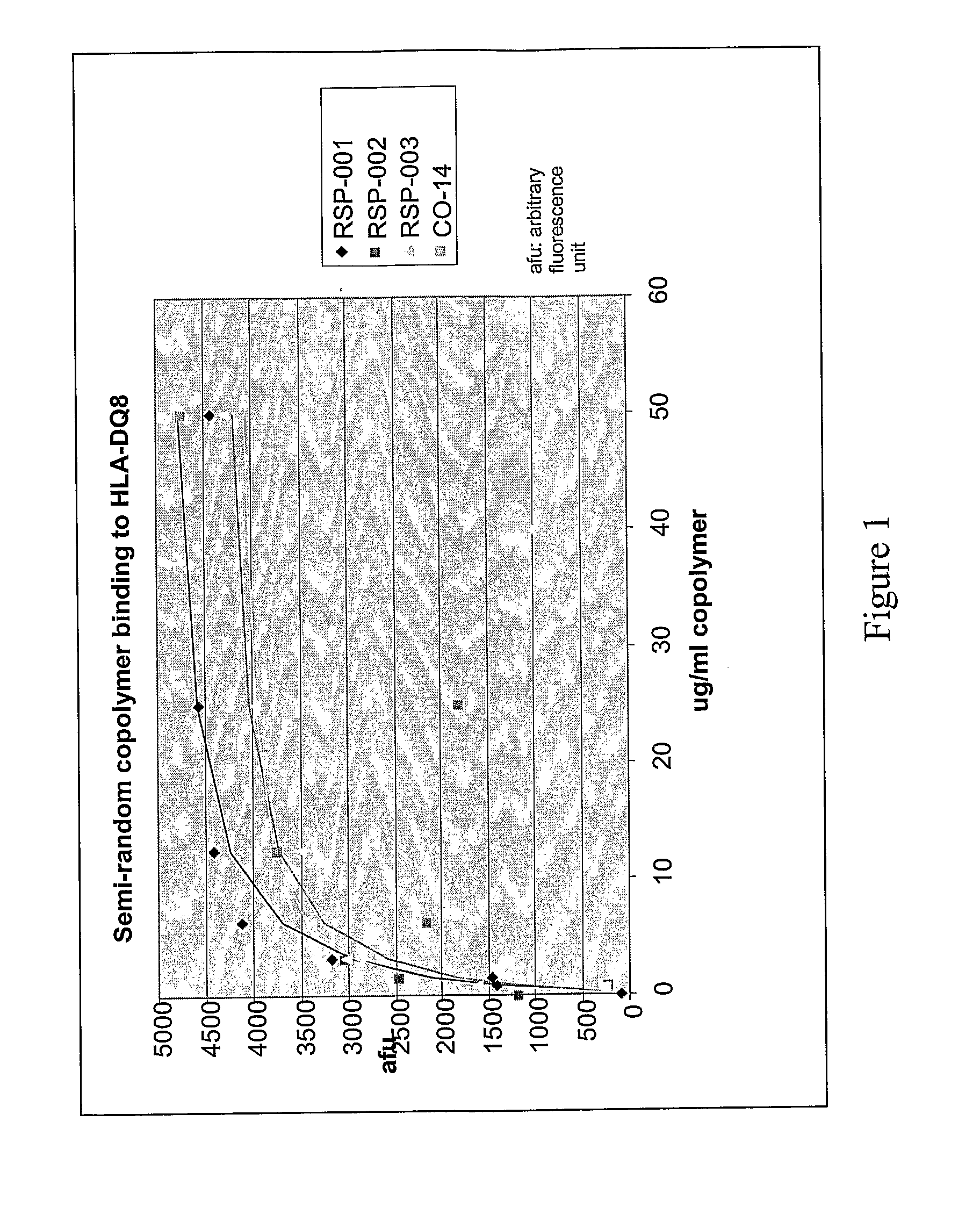
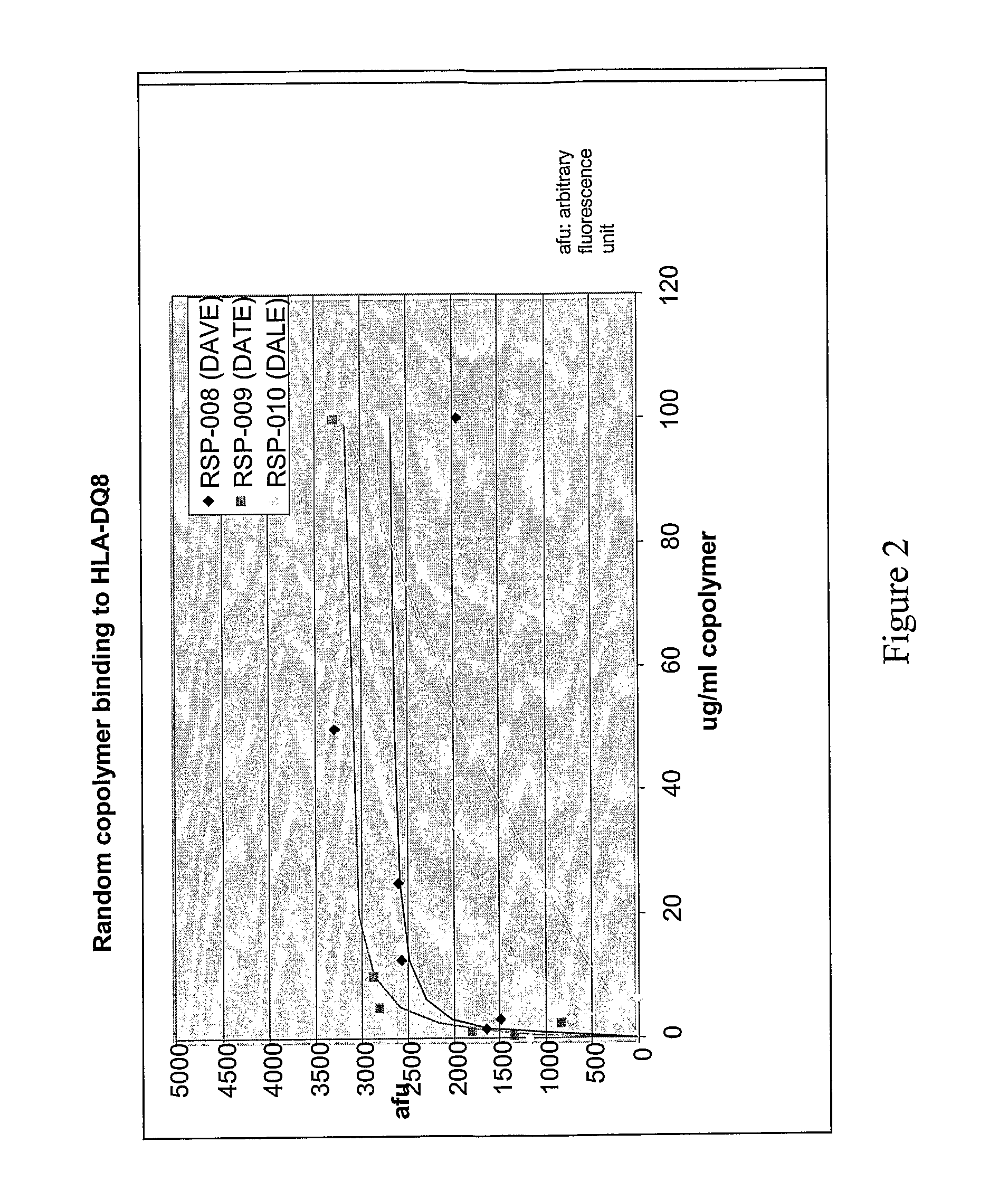
Methods and Compositions for Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases
InactiveUS20080194462A1Inhibit autoimmune responseEffective treatmentSenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides methods and compositions for treating autoimmune diseases and other unwanted immune reactions comprising administering a copolymer that binds to one or more HLA-DQ molecules and modulates DQ-restricted T cell responses. The copolymers are random copolymers of amino acids and copolymers comprising anchor residues to facilitate binding to the DQ binding pockets.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Spleen tyrosine kinase catalytic domain:crystal structure and binding pockets thereof
The present invention provides crystalline molecules and molecular complexes that comprise binding pockets of Sykcat and its homologues. The invention also provides crystals comprising the catalytic domain of Syk protein. The invention further provides a computer comprising a data storage medium encoded with the structure coordinates of Sykcat binding pockets and methods for using a computer to evaluate the ability of a chemical entity or compounds to bind to a crystalline molecule or molecular complex of the invention. This invention also provides methods of using the structure coordinates to solve the structure homologous proteins or protein complexes. The invention further provides methods of using the structure coordinates to screen for, design and optimize chemical entities or compounds, including inhibitory compounds, that bind to the catalytic domain of Syk or homologues thereof.
Owner:WILLIAMS DAVID +3
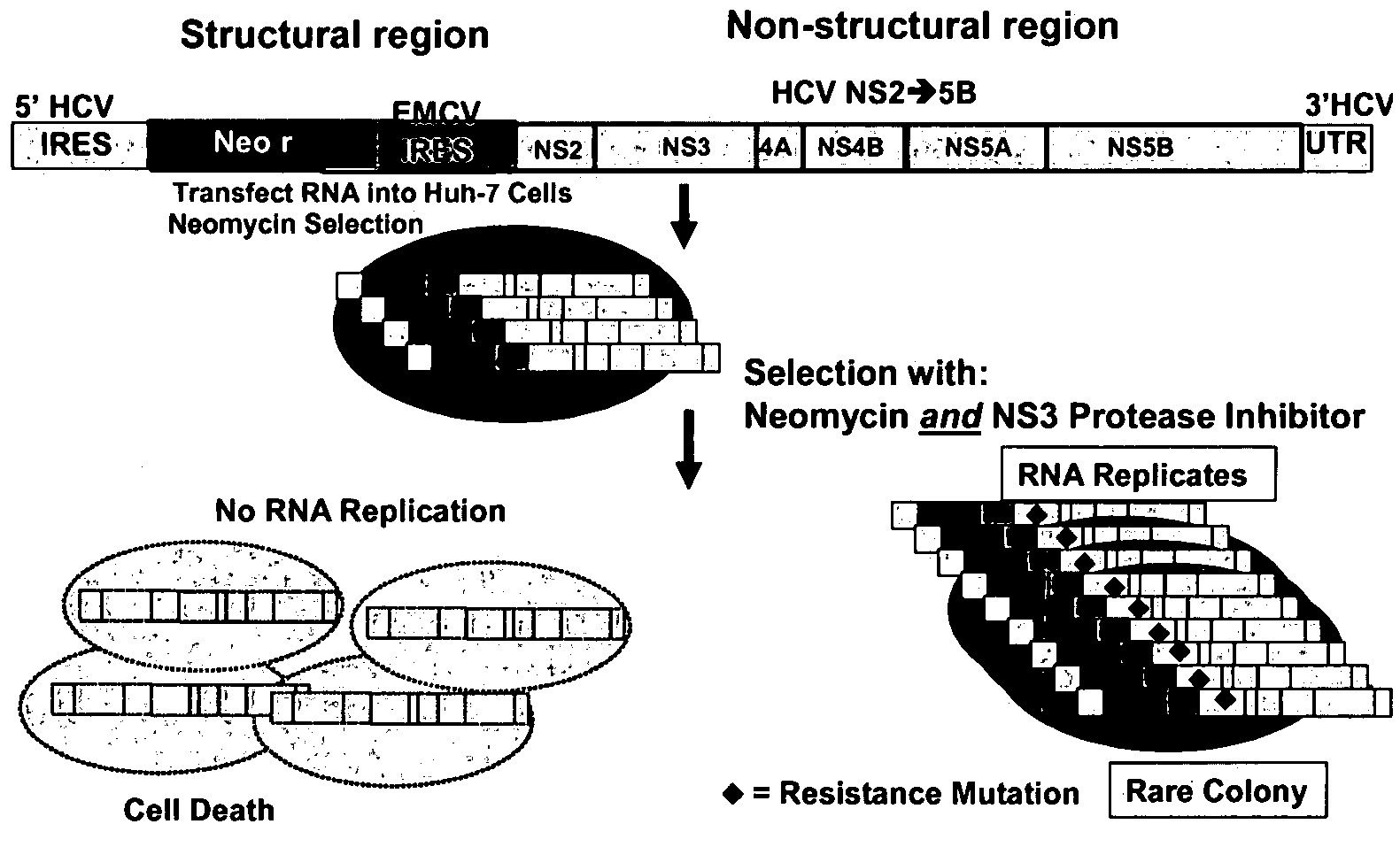
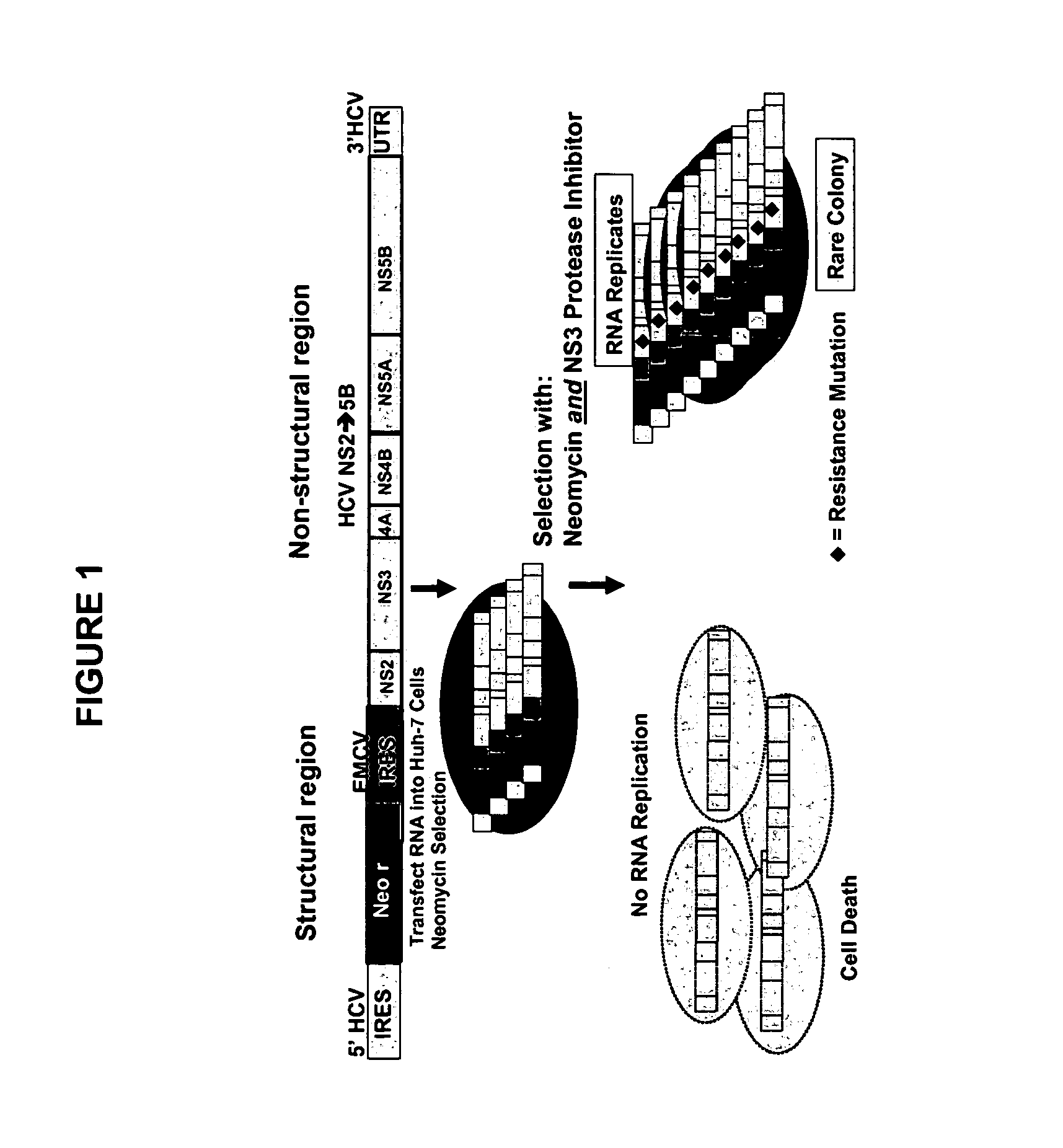
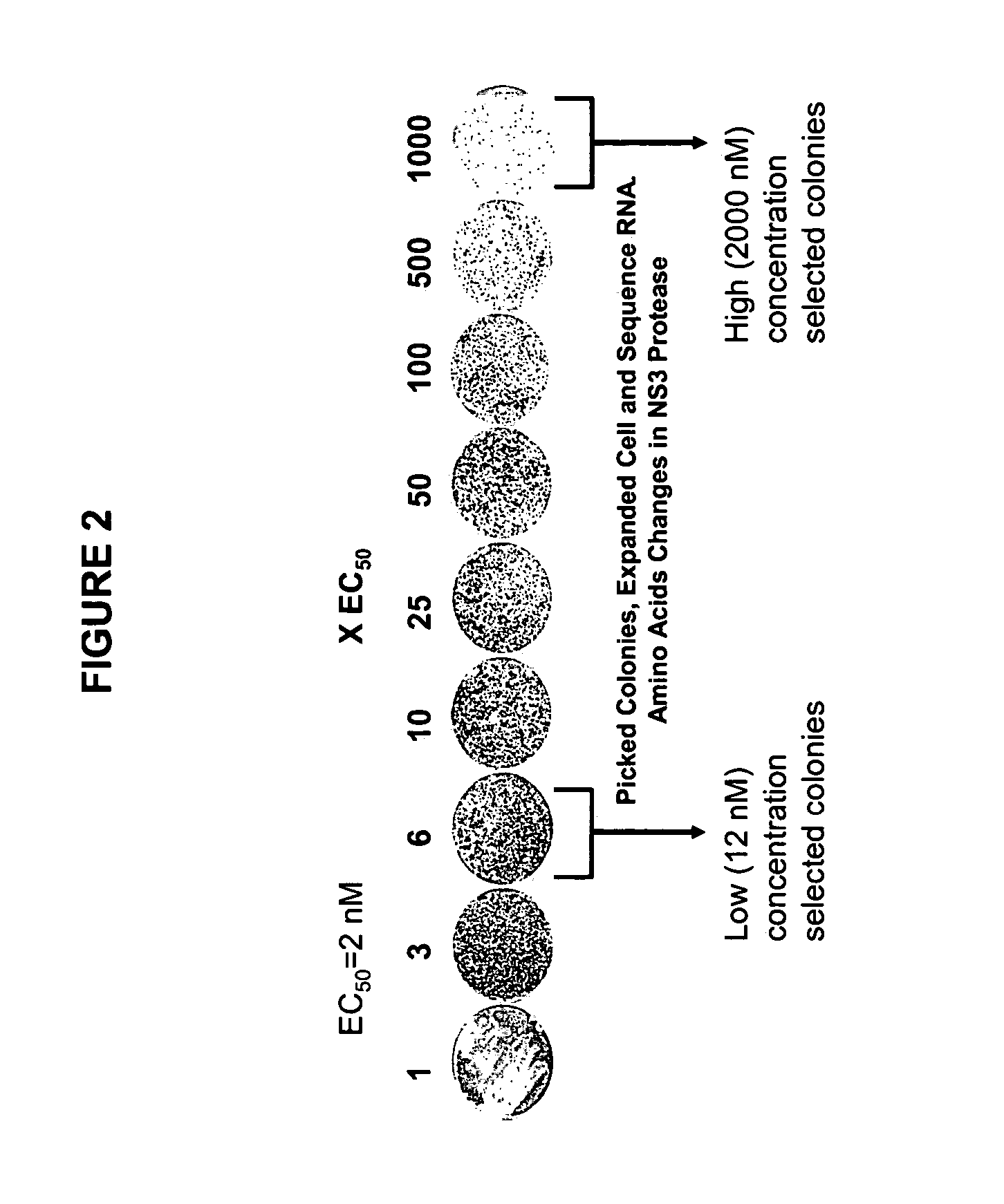
Inhibitor-resistant HCV NS3 protease
An inhibitor-resistant HCV NS3 protease is provided which is useful to screen for compounds having therapeutic value against drug resistant HCV strains. In particular, the inhibitor-resistant HCV NS3 protease comprises an amino acid sequence which is mutated in the substrate binding pocket thereof rendering the protease resistant to inhibitor. In a specific aspect of the present invention, at least one of the amino acids at position 155, 156 and 168 of the HCV NS3 protease is mutated to yield an inhibitor-resistant protease.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Small molecule inhibitors targeted at Bcl-2
InactiveUS20080058322A1Effective treatmentReduce overexpressionBiocideKetone active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
The present invention relates to small molecule antagonists of Bcl-2 family proteins such as Bcl-2 and / or Bcl-XL. In particular, the present invention provides non-peptide cell permeable small molecules (e.g., tricyclo-dibenzo-diazocine-dioxides) that bind to a pocket in Bcl-2 / Bcl-XL that block the anti-apoptotic function of these proteins in cancer cells and tumor tissues exhibiting Bcl-2 protein overexpression. In preferred embodiments, the small molecules of the present invention are active at the BH3 binding pocket of Bcl-2 family proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Mcl-1). The compositions and methods of the present invention are useful therapeutics for cancerous diseases either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic or other drugs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
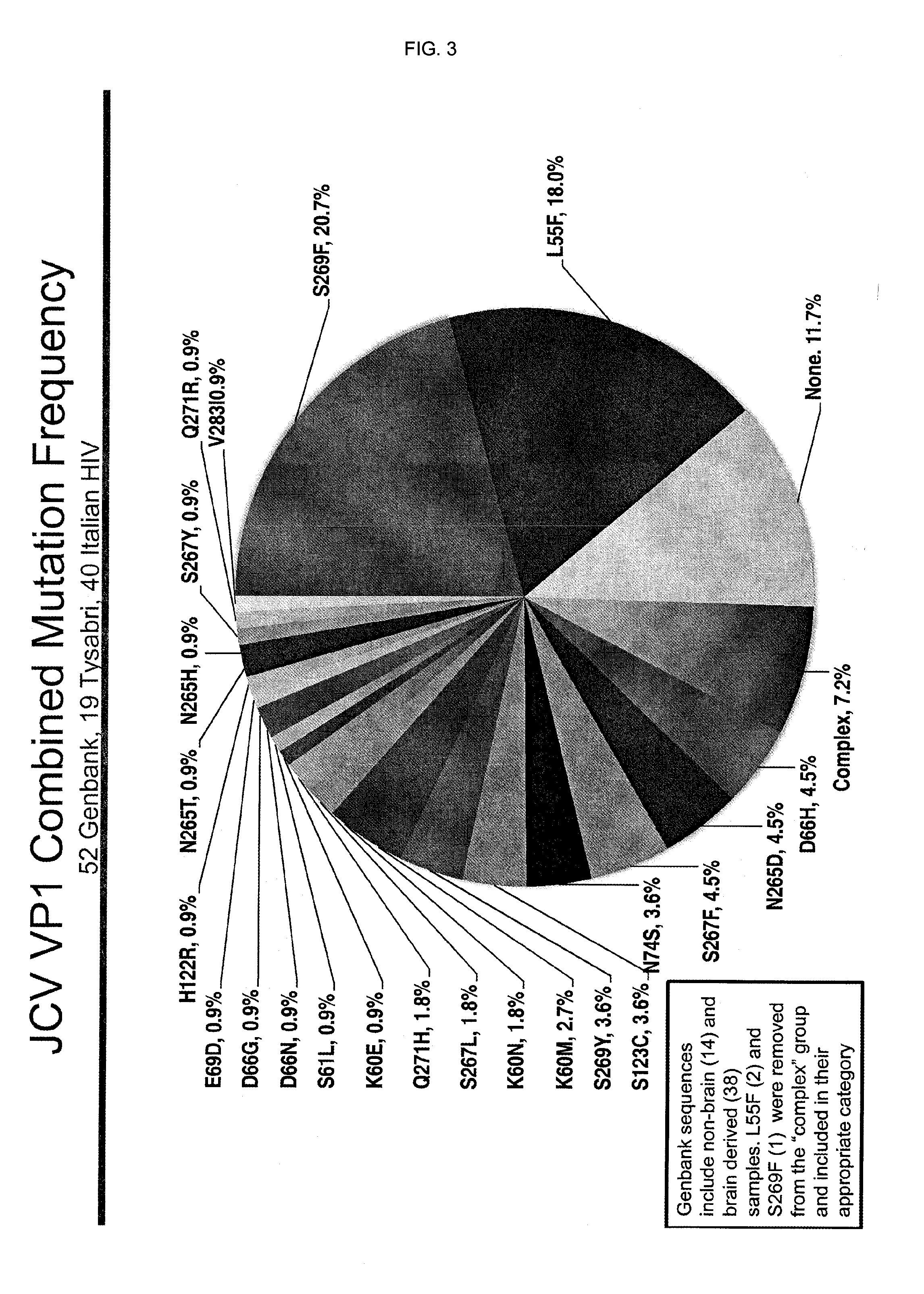
Jcv neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20150056188A1Reduce viral loadIncrease awarenessImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsAntibody SuppressionAntiendomysial antibodies
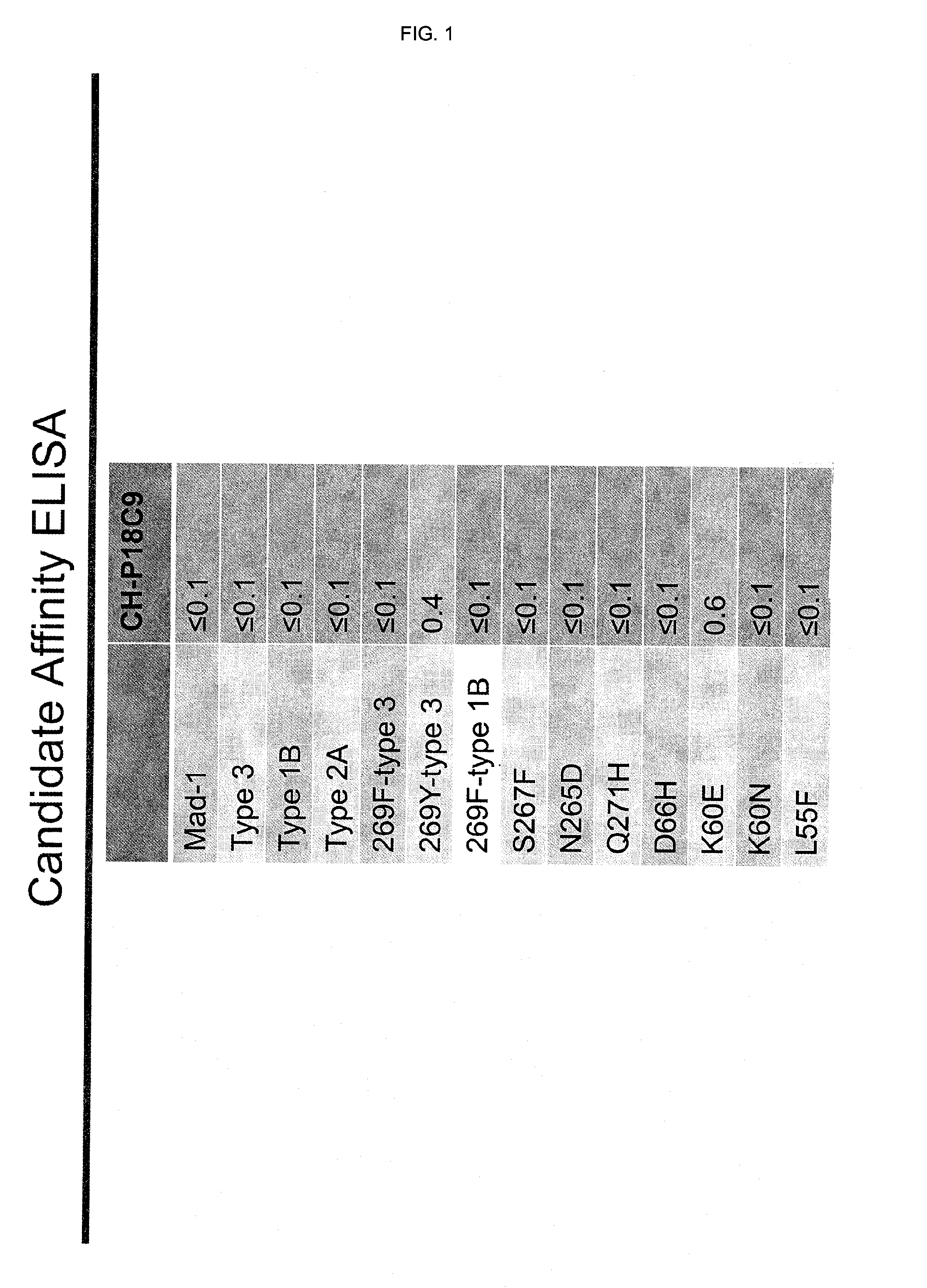
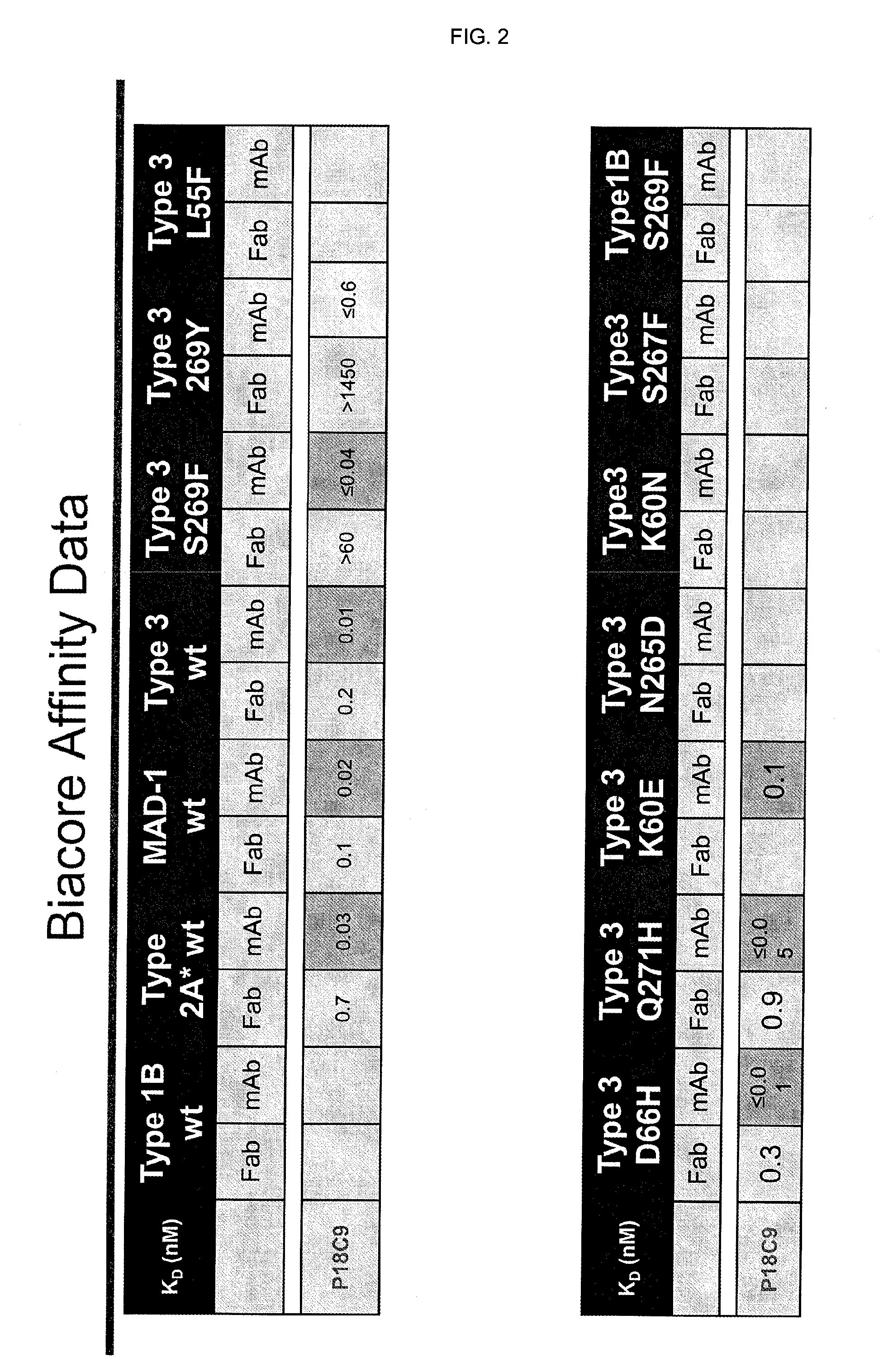
In one aspect, the disclosure provides neutralizing antibodies against JCV and methods for the treatment of PML. In some embodiments, aspects of the invention relate to an isolated JC-virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody against JCV capsid protein VPI (JCV-VP1). In some embodiments, the antibody suppresses infectivity of the JC-virus. In some embodiments, the antibody binds the sialic acid binding pocket of JCV-VPI. In some embodiments, the antibody binds JCV-VP 1 comprising one or more of the following mutations: S269F, S269Y, S267F, N265D, Q271 H, D66H, K60E, K60N and L55F.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Crystal structure of aurora-2 protein and binding pockets thereof
The present invention provides crystalline molecules or molecular complexes which comprise binding pockets of Aurora-2 or its homologues. The invention also provides crystals comprising Aurora-2. The present invention also relates to a computer comprising a data storage medium encoded with the structural coordinates of Aurora-2 binding pockets and methods of using a computer to evaluate the ability of a compound to bind to the molecule or molecular complex. This invention also provides methods of using the structure coordinates to solve the structure of homologous proteins or protein complexes. In addition, this invention provides methods of using the structure coordinates to screen for and design compounds, including inhibitory compounds, that bind to Aurora-2 or homologues thereof.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
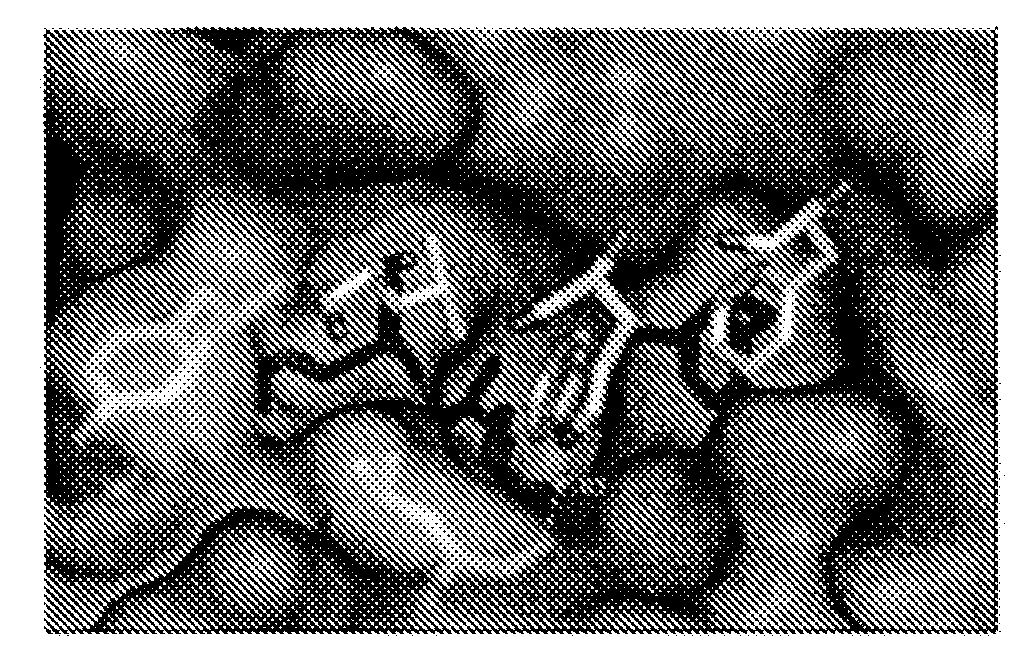
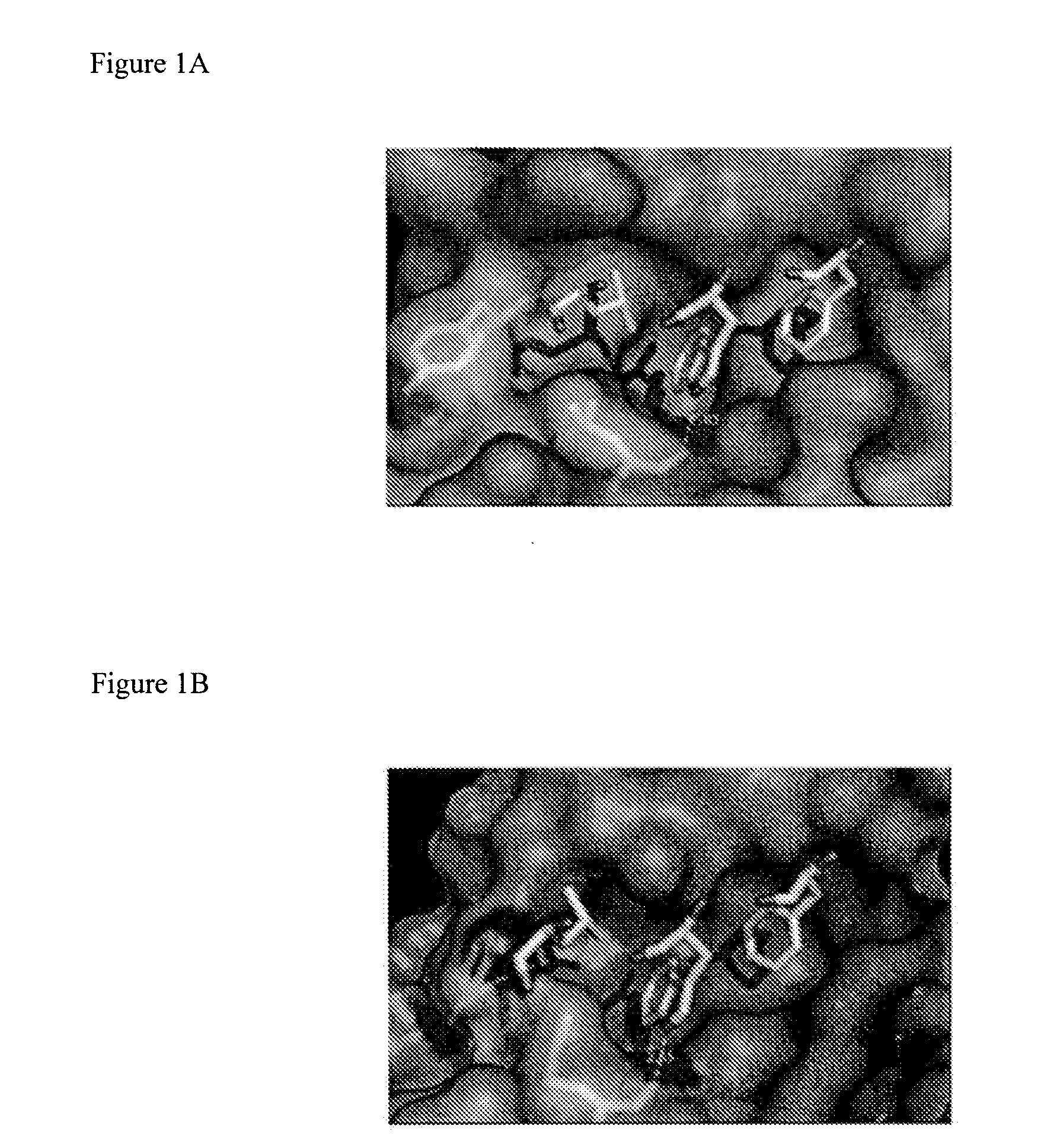
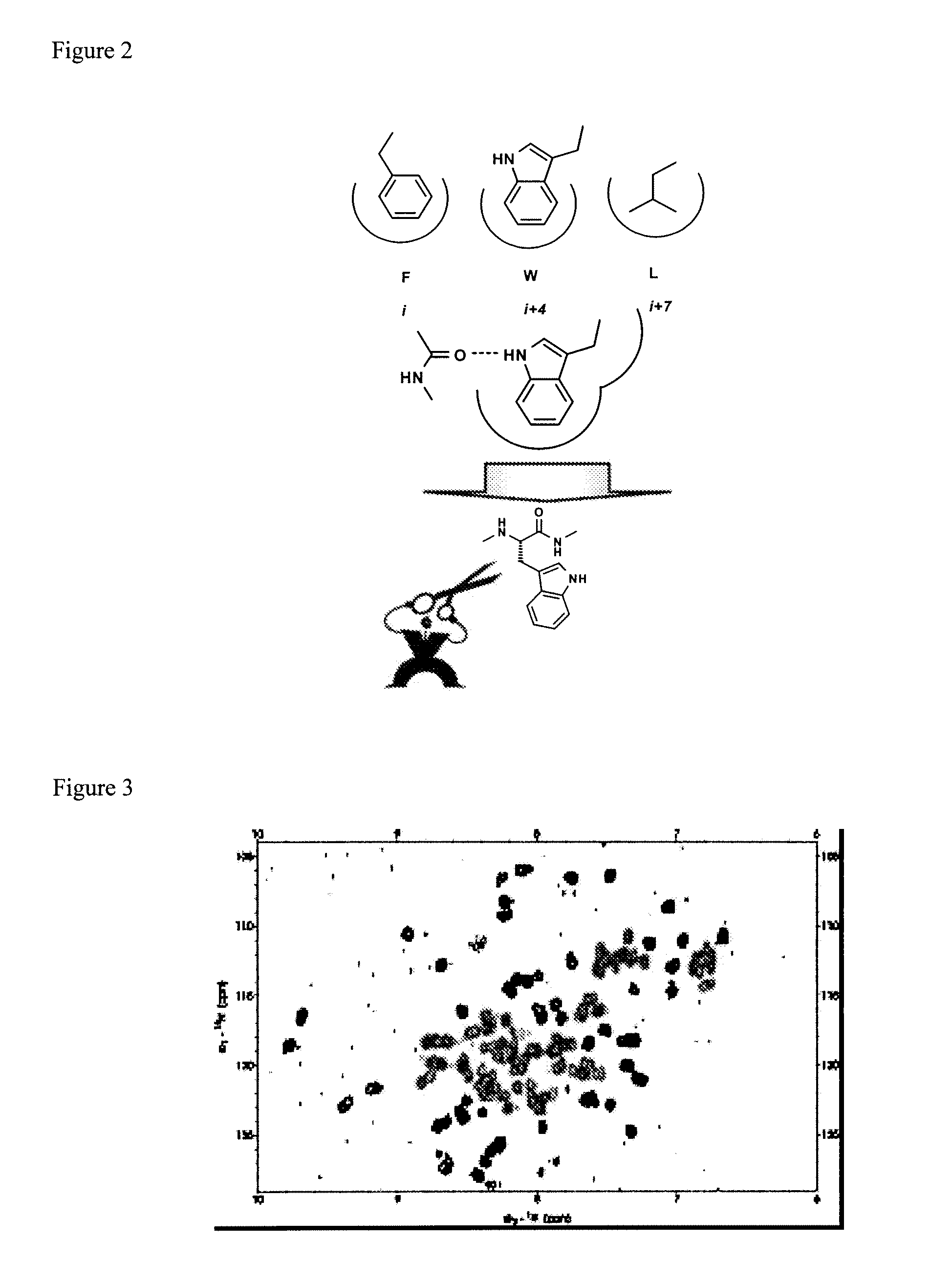
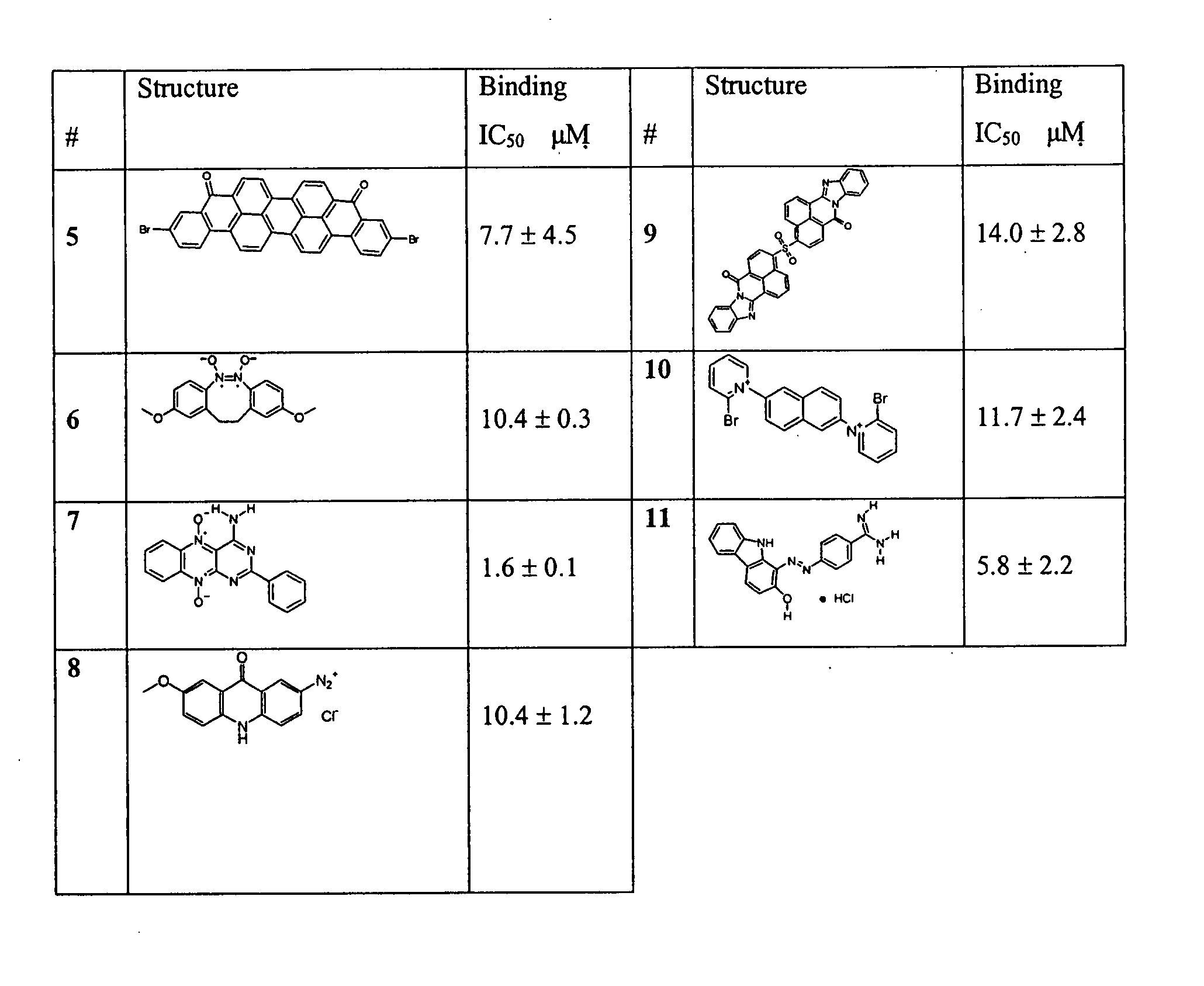
N- (hydrophobe-substituted) vancosaminyl [psi-[c(=nh) nh] tpg4] vancomycin and [psi-[ch2nh]tpg4] vancomycin
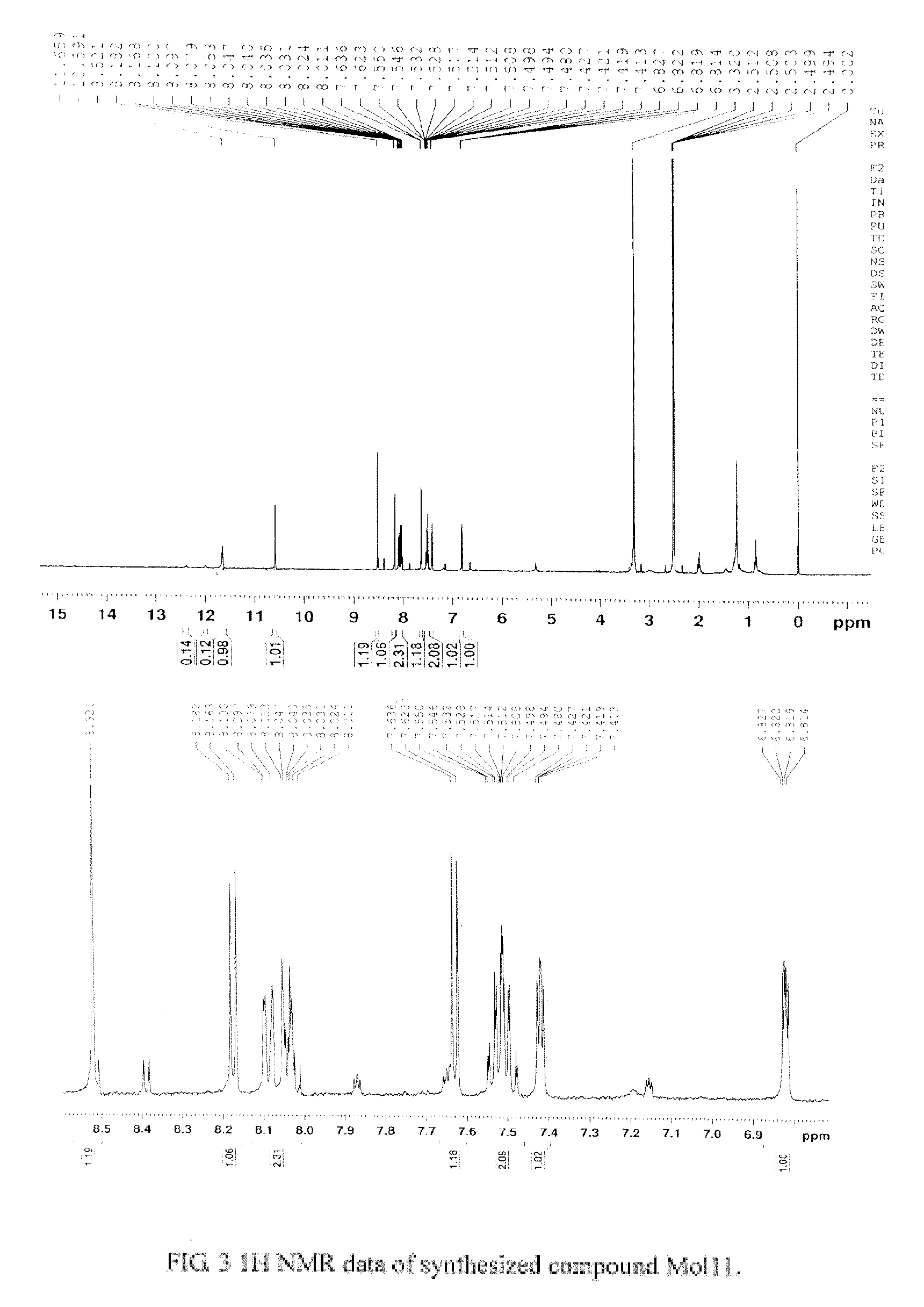
ActiveUS20170152291A1Improve effectivenessGood potencyAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsResistant bacteriaMechanism of action
The total synthesis and evaluation of key analogs of vancomycin containing single atom changes in the binding pocket are disclosed as well as their peripherally modified, N-(hydrophobe-substituted) derivatives exemplified by a N-4-(4′-chlorob-phenyl)-methyl derivative and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts are disclosed. Their evaluation indicates the combined pocket and peripherally modified analogs exhibit a remarkable spectrum of antimicrobial activity and truly impressive potencies against both vancomycin-sensitive and -resistant bacteria, and likely benefit from two independent and synergistic mechanisms of action. A pharmaceutical composition containing a contemplated compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt is disclosed, as is a method of treating a bacterial infection in a mammal by administering an antibacterial amount of a contemplated compound or its salt as above to an infected mammal in need of treatment.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Crystallization of IGF-1
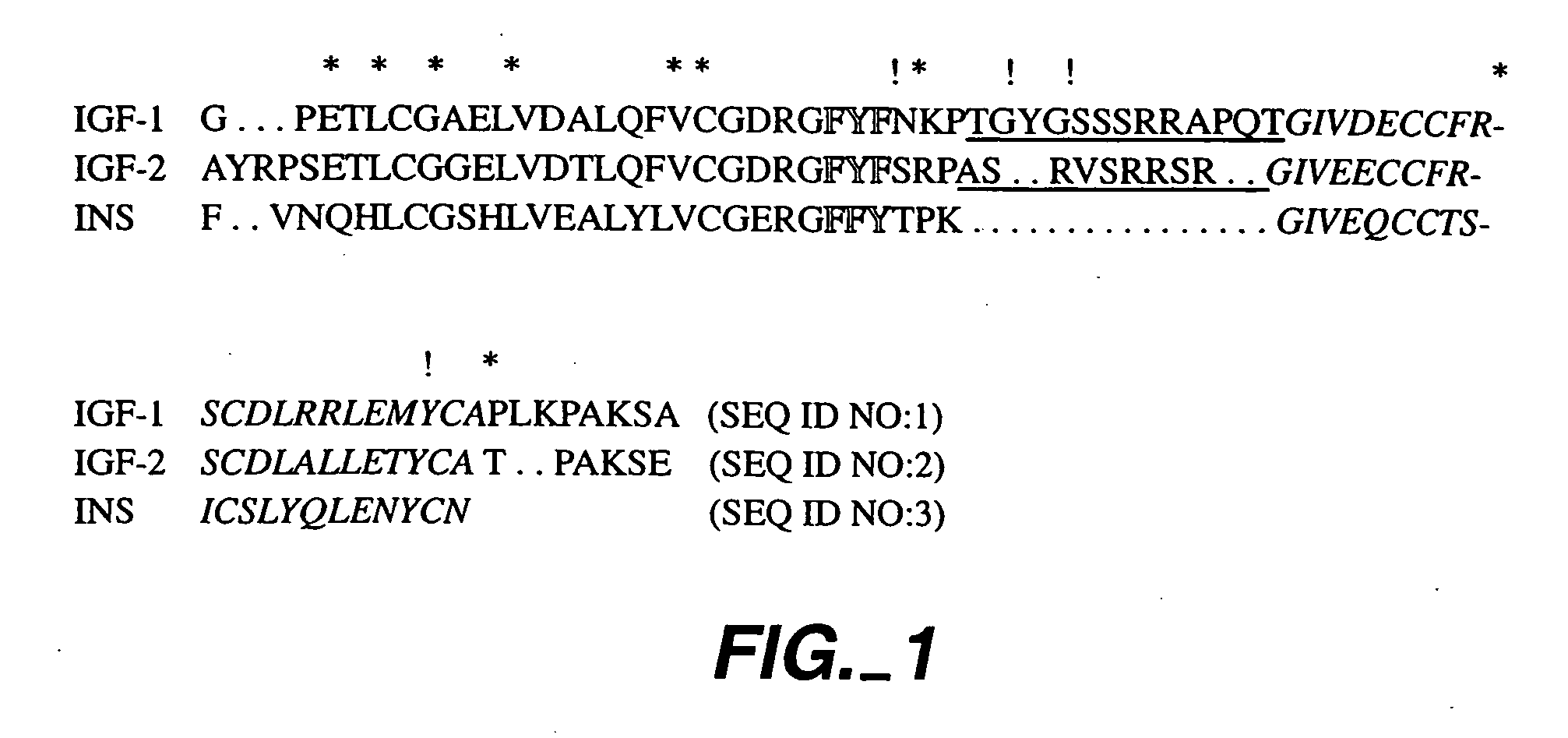
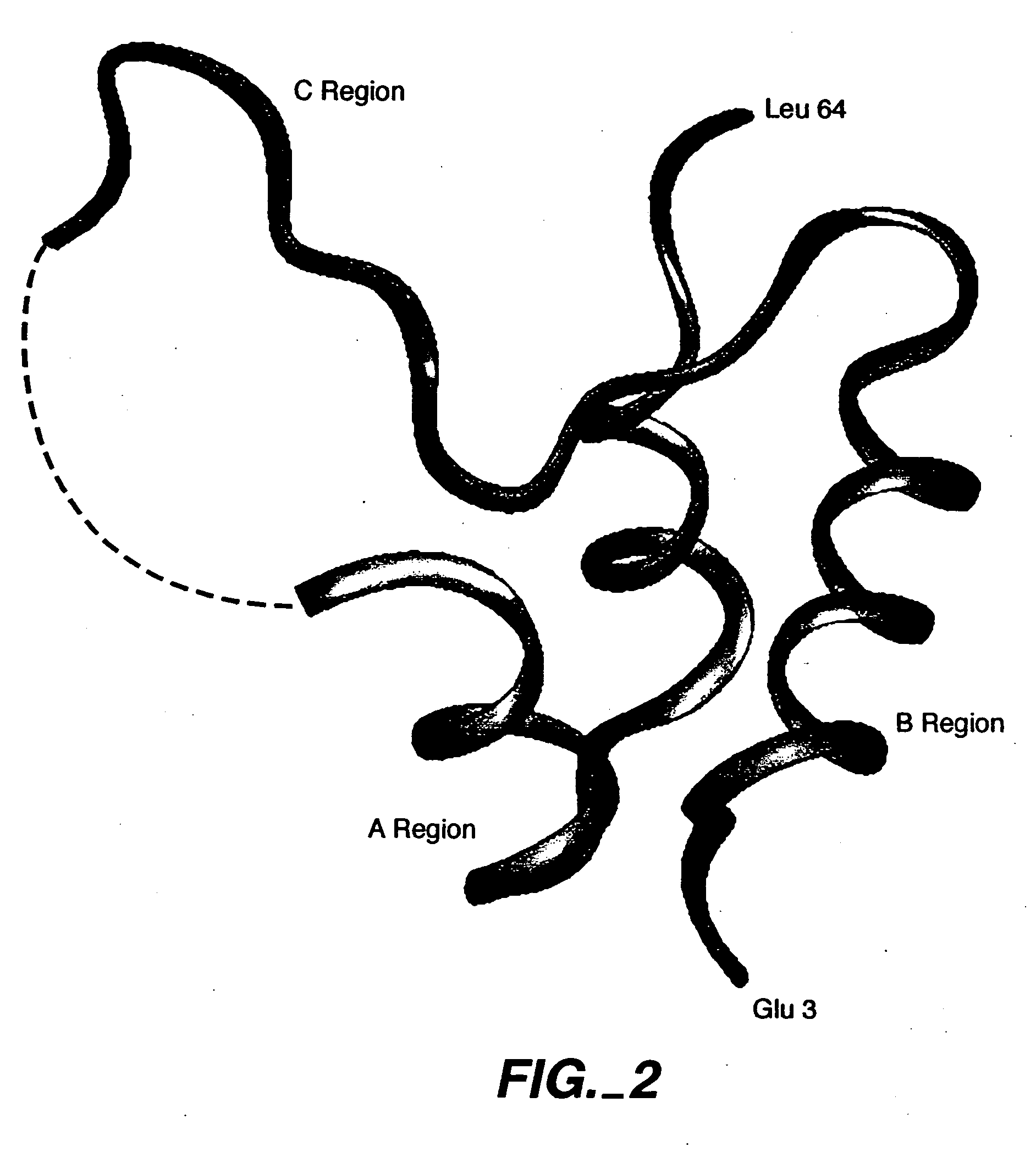
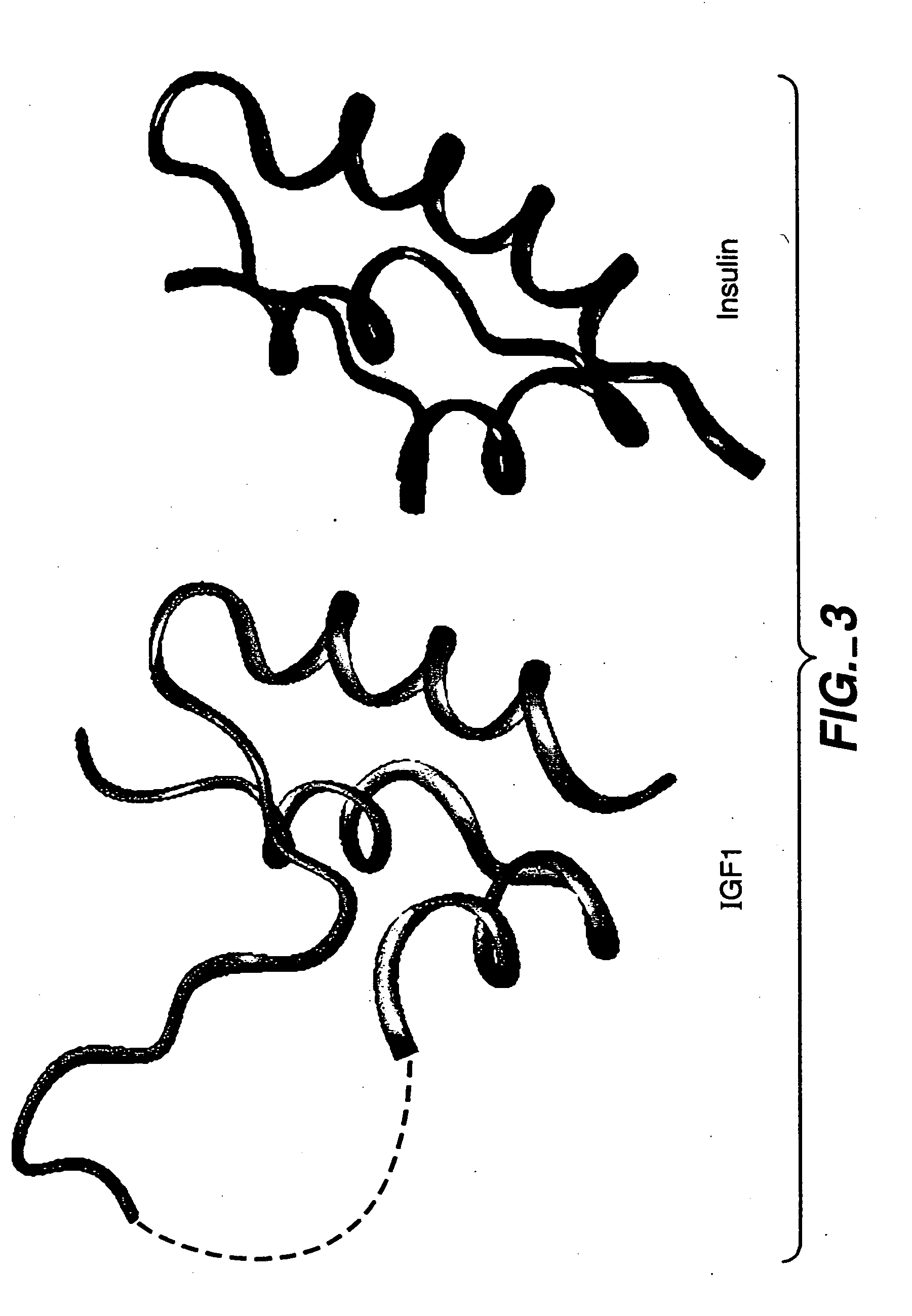
InactiveUS20050215477A1Inhibit bindingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyAgonist
Crystalline IGF-1 is provided along with a method for production thereof. Crystallizing IGF-1 comprises the steps of mixing an aqueous solution comprising IGF-1 with a reservoir solution comprising a precipitant to form a mixture; and crystallizing the mixture, optionally also recrystallizing and isolating the crystalline IGF-1. In addition, a method for identifying IGF-1 indirect agonists is provided using a detergent as a standard for the level of inhibition of binding of IGFBP-1 or IGFBP-3 to IGF-1 and / or using the coordinates of the binding pockets of IGF-1 to which a candidate indirect agonist binds for structure-based drug design.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and their application in preparation of l-phosphinothricin
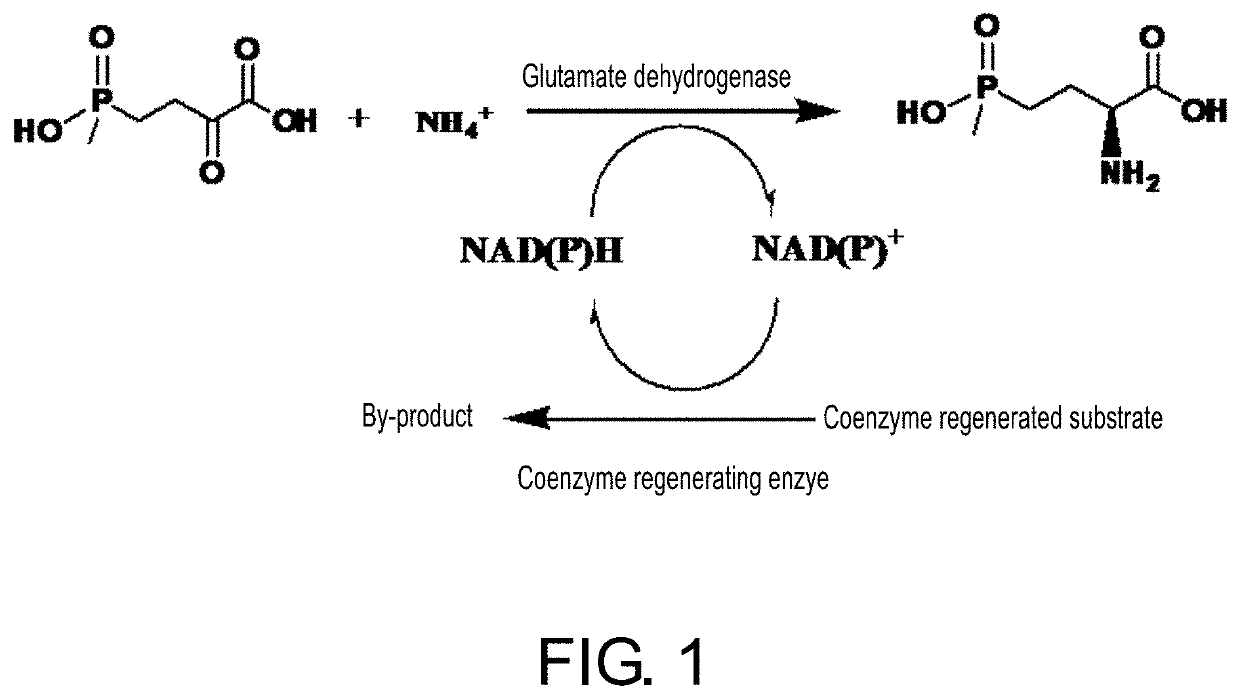
ActiveUS20200102546A1High catalytic activityLow glutamateOxidoreductasesFermentationValineAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The present invention relates to glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and their application in preparation of L-phosphinothricin. The amino acid sequences of the glutamate dehydrogenase mutants are as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1˜9, 11, 13, 15, 17˜19 and 22. By means of molecular engineering, mutating the specific alanine in glutamate dehydrogenase substrate-binding pocket into glycine and / or mutating the specific valine in glutamate dehydrogenase substrate-binding pocket into alanine, the present invention has obtained NADPH-specific glutamate dehydrogenase mutants with high enzyme activity in catalyzing the substrate 2-oxo-4-[(hydroxy)(methyl)phosphinoyl]butyric acid or its salt for L-phosphinothricin preparation or NADH-specific glutamate dehydrogenase mutants with catalytic activity toward PPO; this has significantly improved substrate conversion, and increased the product concentration of the L-phosphinothricin preparation process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
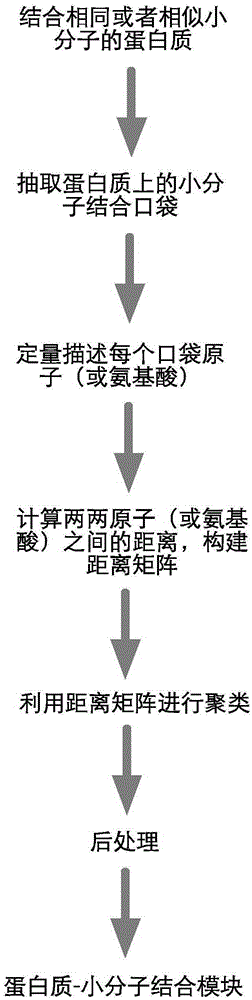
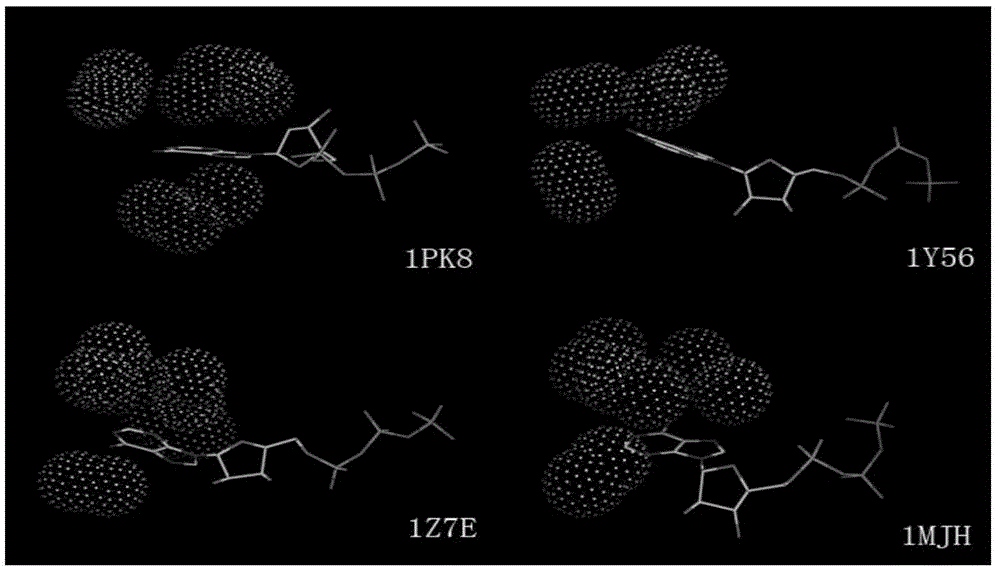
Method for extracting protein-micromolecule interaction module
The invention relates to a method for extracting a protein-micromolecule interaction module. The method specifically comprises: firstly, performing quantitative description on atoms (or amino acids) forming a micromolecular binding pocket on protein according to properties of the atoms (or amino acids); secondly, estimating the distance between the every two pocket atoms (or amino acids), and establishing a distance matrix; thirdly, extracting categories of the pocket atoms (or amino acids) with similar properties by utilizing a clustering algorithm; and finally, performing post-processing to obtain the protein-micromolecule interaction module. The method can be applied to multiple aspects of bioinformatics research, protein design, drug screening, micromolecular chemical synthesis and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Soluble fragments of influenza virus pb2 protein capable of binding rna-cap
Owner:EURO LAB FUER MOLEKULARBIOLOGIE EMBL
Crystal structure of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 and binding pockets thereof
The invention relates to crystalline molecules or molecular complexes that comprise binding pockets of mitogen activated protein kinase activated protein kinase 2 (MAPKAPK2) or its homologues. The invention also relates to crystals comprising MAPKAPK2. The present invention also relates to a computer comprising a data storage medium encoded with the structural coordinates of MAPKAPK2 binding pockets and methods of using a computer to evaluate the ability of a compound to bind to the molecule or molecular complex. This invention also relates to methods of using the structure coordinates to solve the structure of homologous proteins or protein complexes. In addition, this invention relates to methods of using the structure coordinates to screen for, design and optimize compounds, including agonists and antagonists, which bind to MAPKAPK2 or homologues thereof.
Owner:MENG WUYI +1
Crystallization of IGF-1
Crystalline IGF-1 is provided along with a method for production thereof. Crystallizing IGF-1 comprises the steps of mixing an aqueous solution comprising IGF-1 with a reservoir solution comprising a precipitant to form a mixture; and crystallizing the mixture, optionally also recrystallizing and isolating the crystalline IGF-1. In addition, a method for identifying IGF-1 indirect agonists is provided using a detergent as a standard for the level of inhibition of binding of IGFBP-1 or IGFBP-3 to IGF-1 and / or using the coordinates of the binding pockets of IGF-1 to which a candidate indirect agonist binds for structure-based drug design.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
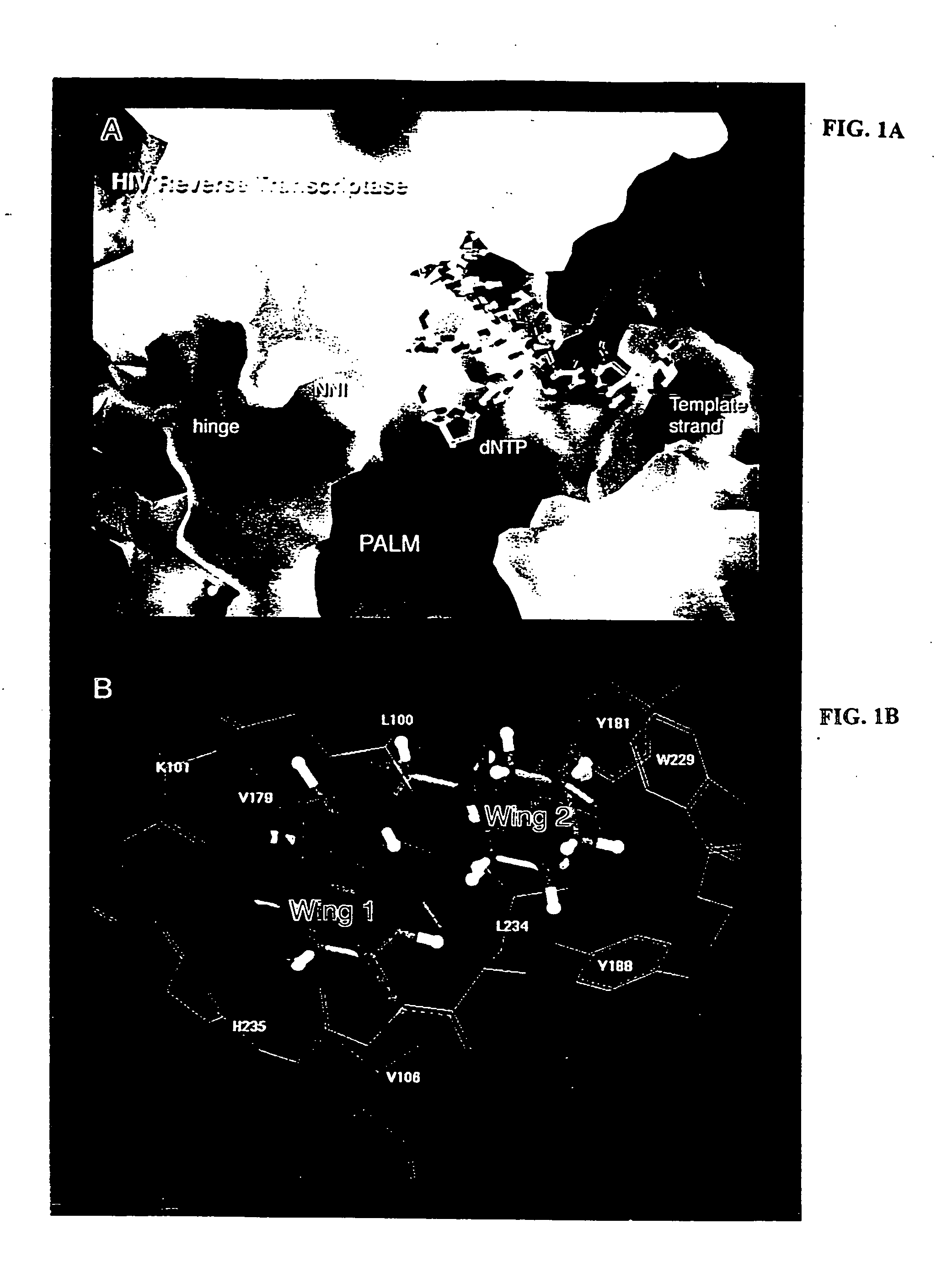
Nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase, composite binding pocket and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS20050153995A1Inhibition of RT activityPotent anti-HIV activityBiocideOrganic chemistryImmunodeficiency virusNon nucleoside inhibitor
Novel compounds that are potent inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase (RT) are described in the invention. Thes novel compounds also inhibit replication of a retrovirus, such as human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1). The novel compounds of the invention include analogs and derivatives of phenethylthiazolylthiourea (PETT), of dihydroalkoxybenzyloxopyrimidine (DABO), and of 1-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]-6-(phenylthio)thymine (HEPT). The invention additionally provides a composite HIV reverse-transcriptase (RT) nonnucleoside inhibitor (NNI) binding pocket constructed from a composite of multiple NNI-RT complexes The composite RT-NNI binding pocket provides a unique and useful tool for designing and identifying novel, potent inhibitors of reverse transcriptase.
Owner:PARKER HUGHES INST
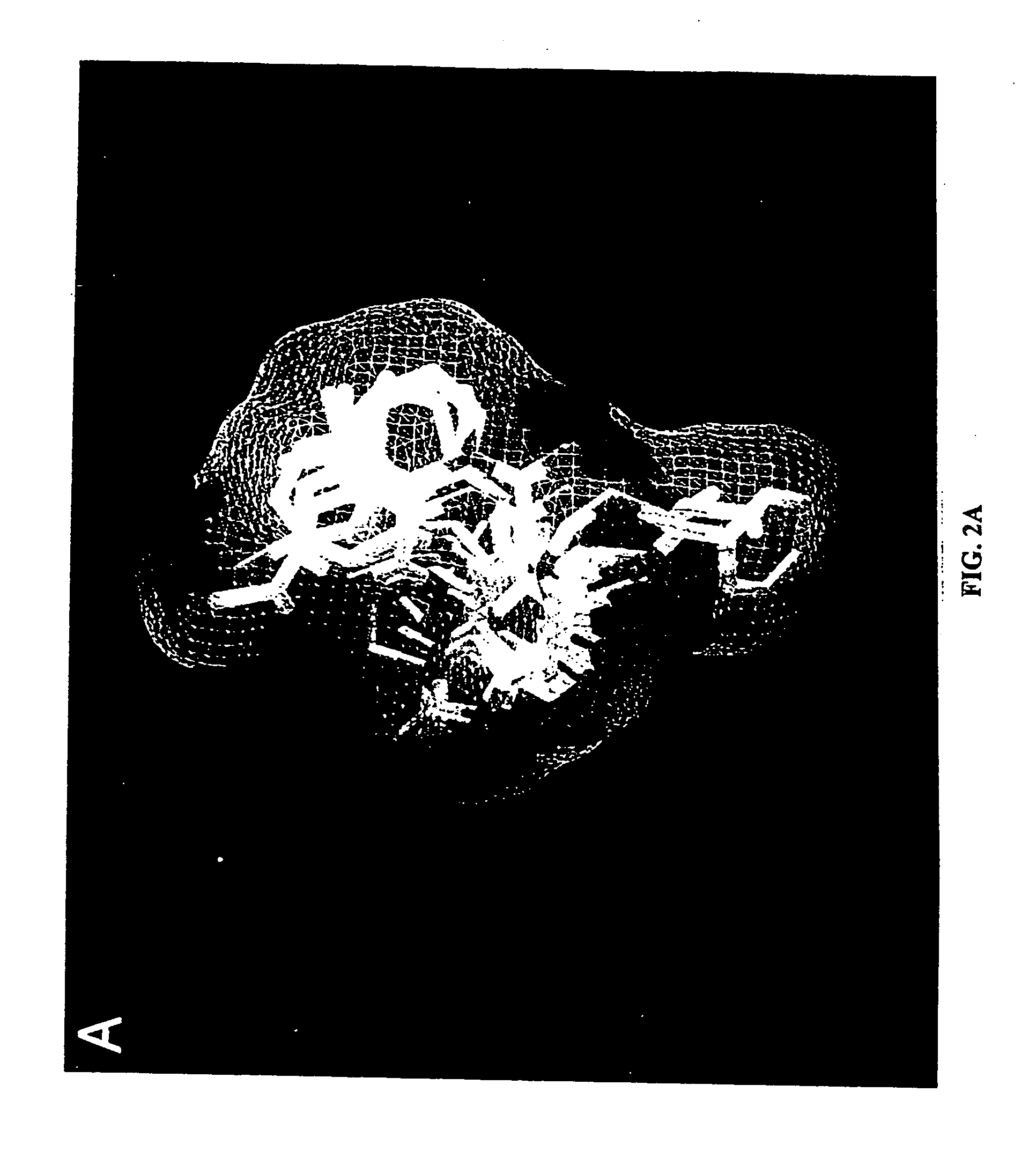
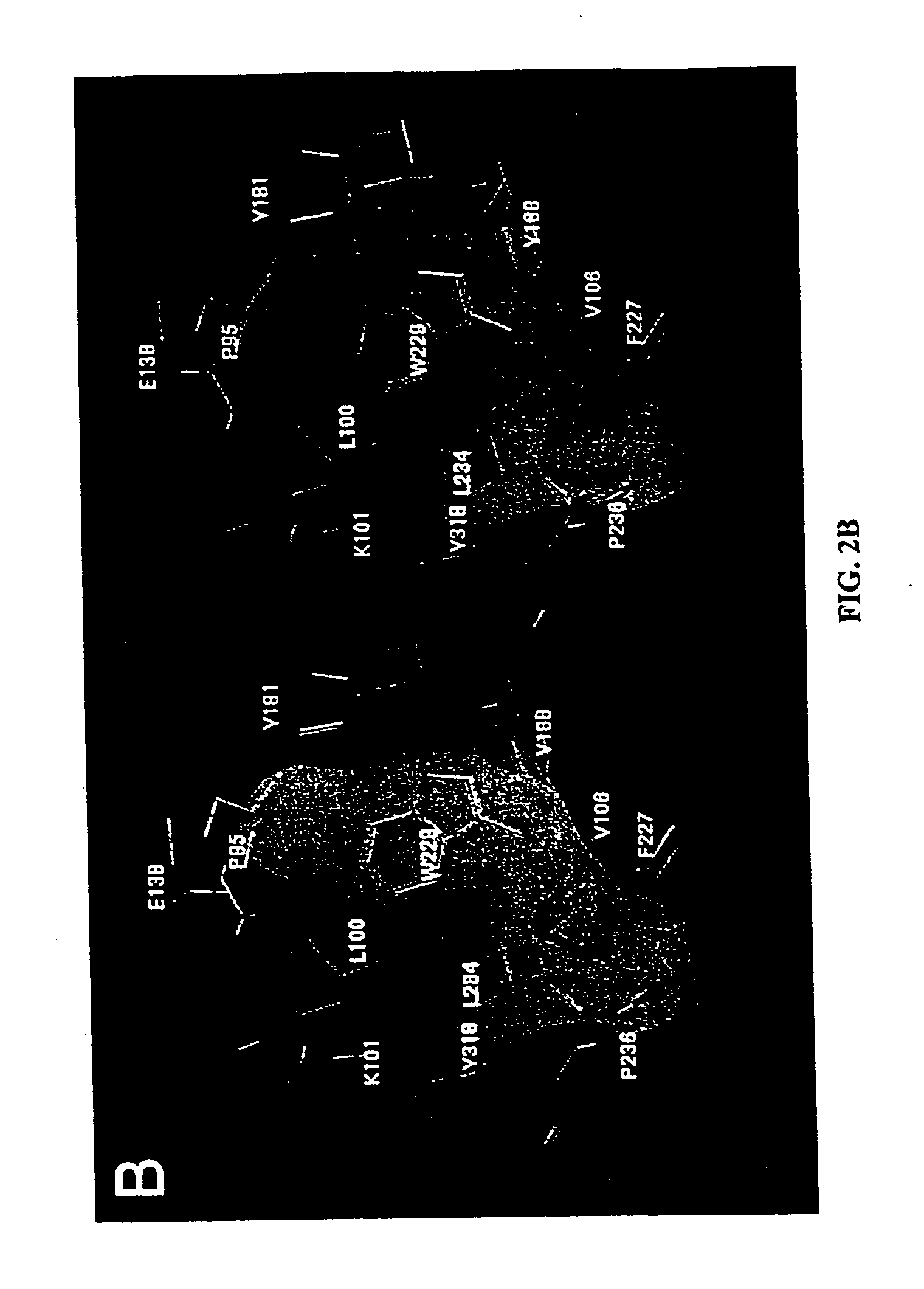
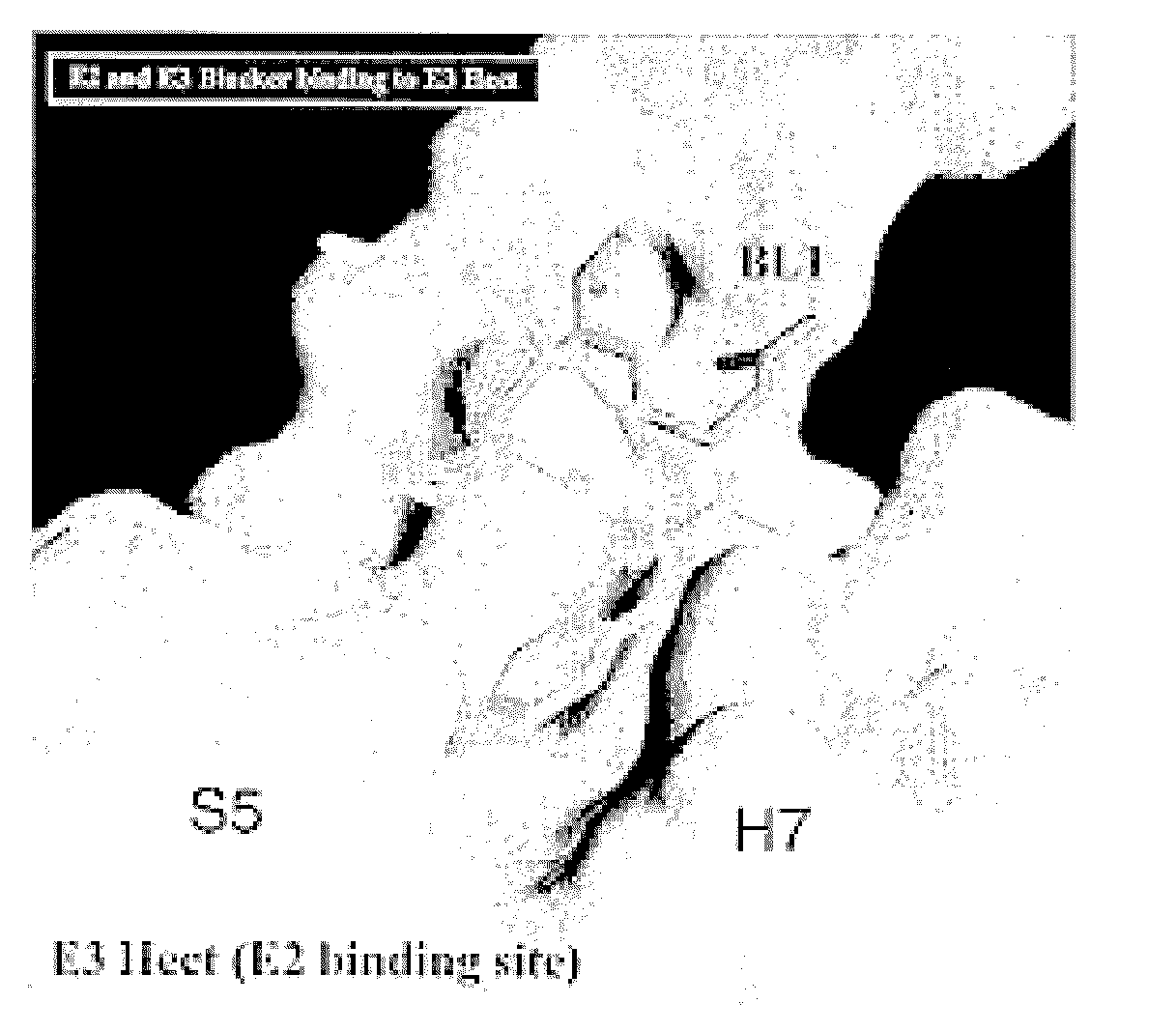
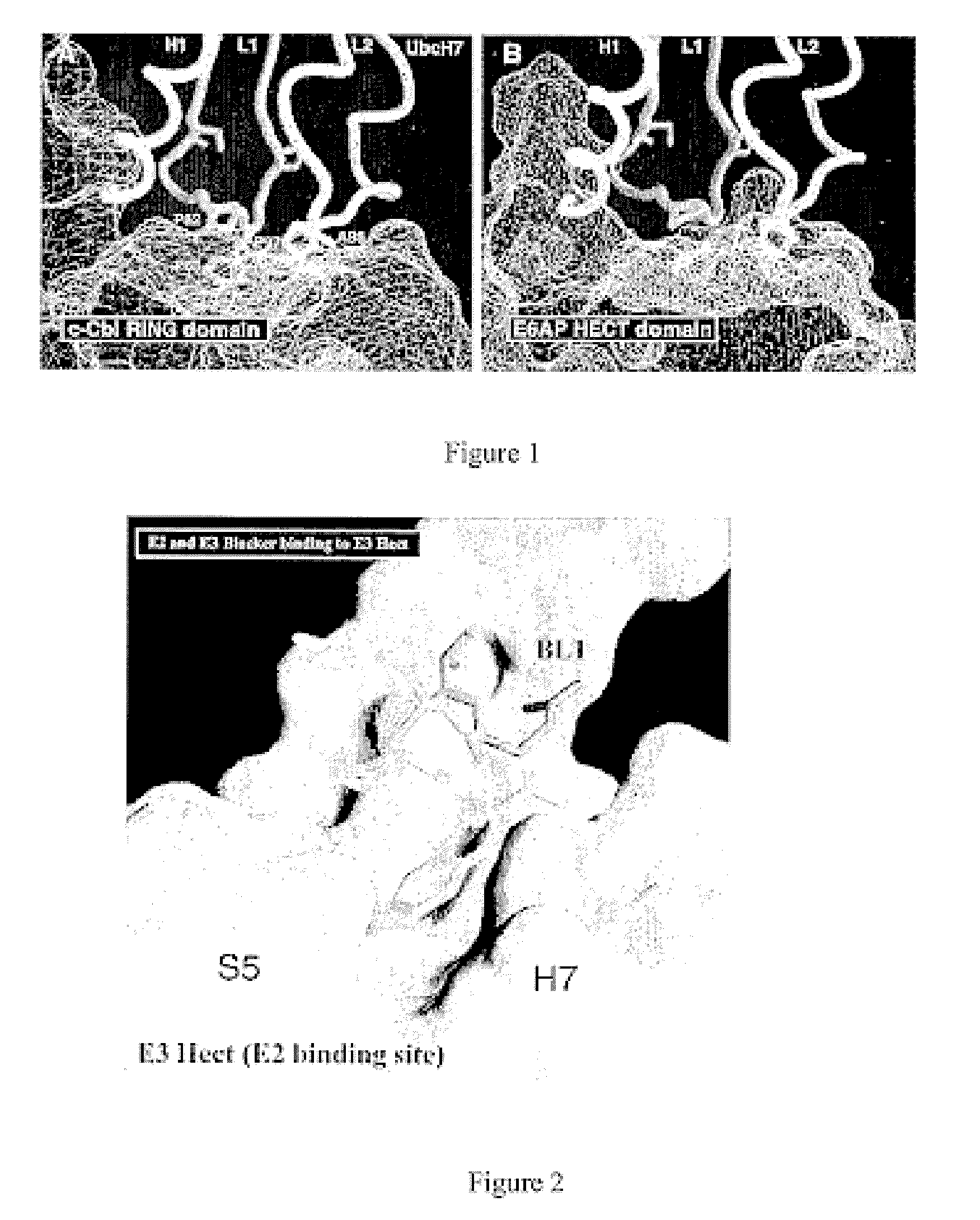
Inhibitors for disrupting the interaction of ubiquitination related enzymes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100189648A1Efficiently disruptedFormation is complexBiocideOrganic chemistryCrystallographyUbiquitin-Protein Ligases
A hydrophobic binding pocket on ubiquitin-protein ligase E3 is described, and used in designing the inhibitors disrupting ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 and E3 interaction. Four types of inhibitors designed by using the binding pocket are provided, which can be used for cancer treatment.
Owner:HUANG LAN +1
Crystal structure of tak1-tab1
The invention relates to molecules or molecular complexes which comprise binding pockets of TAK1 or its structural homologues. The invention relates to crystallizable compositions and crystals comprising TAK1. The present invention also relates to a data storage medium encoded with the structural coordinates of molecules and molecular complexes which comprise the TAK1 or TAK1-like ATP-binding pockets. The present invention also relates to a computer comprising such data storage material. The computer may generate a three-dimensional structure or graphical three-dimensional representation of such molecules or molecular complexes. This invention also relates to methods of using the structure coordinates to solve the structure of homologous proteins or protein complexes. In addition, this invention relates to methods of using the structure coordinates to screen for and design compounds, including inhibitory compounds, that bind to TAK1 or homologues thereof.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![N- (hydrophobe-substituted) vancosaminyl [psi-[c(=nh) nh] tpg4] vancomycin and [psi-[ch2nh]tpg4] vancomycin N- (hydrophobe-substituted) vancosaminyl [psi-[c(=nh) nh] tpg4] vancomycin and [psi-[ch2nh]tpg4] vancomycin](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/423abe5a-b7f6-4507-a2e3-18294d4a1f06/US20170152291A1-20170601-C00001.png)
![N- (hydrophobe-substituted) vancosaminyl [psi-[c(=nh) nh] tpg4] vancomycin and [psi-[ch2nh]tpg4] vancomycin N- (hydrophobe-substituted) vancosaminyl [psi-[c(=nh) nh] tpg4] vancomycin and [psi-[ch2nh]tpg4] vancomycin](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/423abe5a-b7f6-4507-a2e3-18294d4a1f06/US20170152291A1-20170601-C00002.png)
![N- (hydrophobe-substituted) vancosaminyl [psi-[c(=nh) nh] tpg4] vancomycin and [psi-[ch2nh]tpg4] vancomycin N- (hydrophobe-substituted) vancosaminyl [psi-[c(=nh) nh] tpg4] vancomycin and [psi-[ch2nh]tpg4] vancomycin](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/423abe5a-b7f6-4507-a2e3-18294d4a1f06/US20170152291A1-20170601-C00003.png)