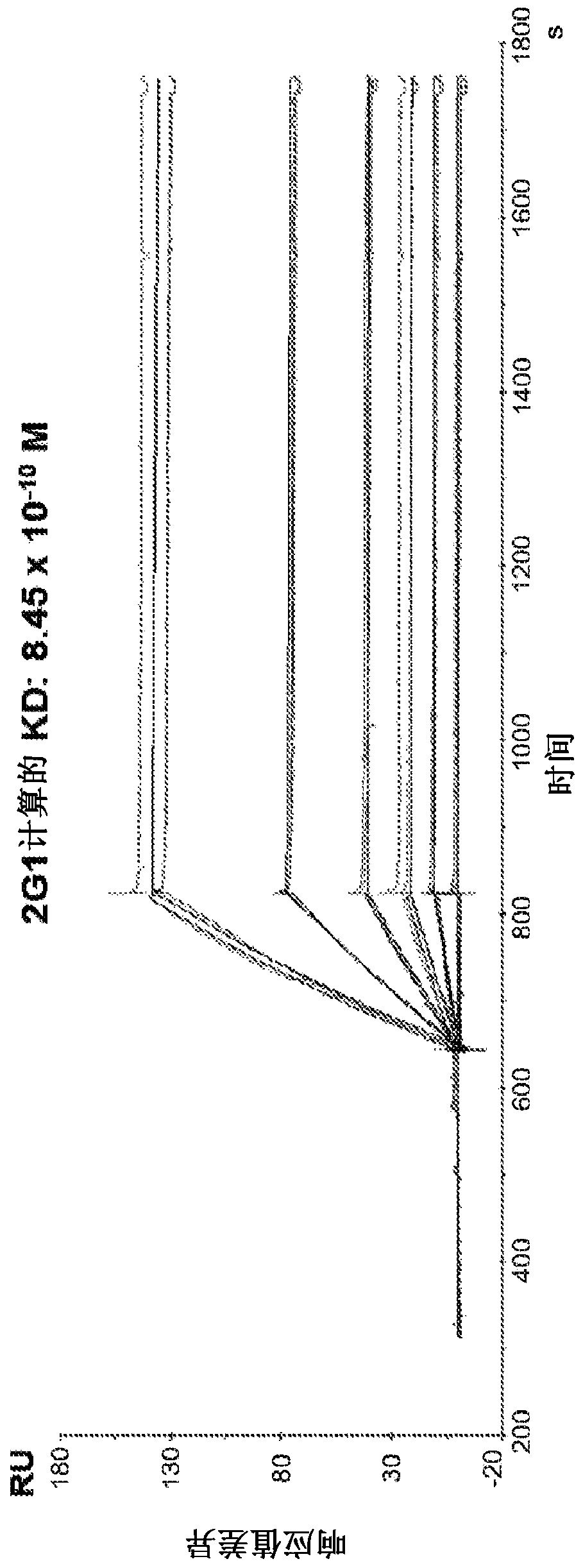
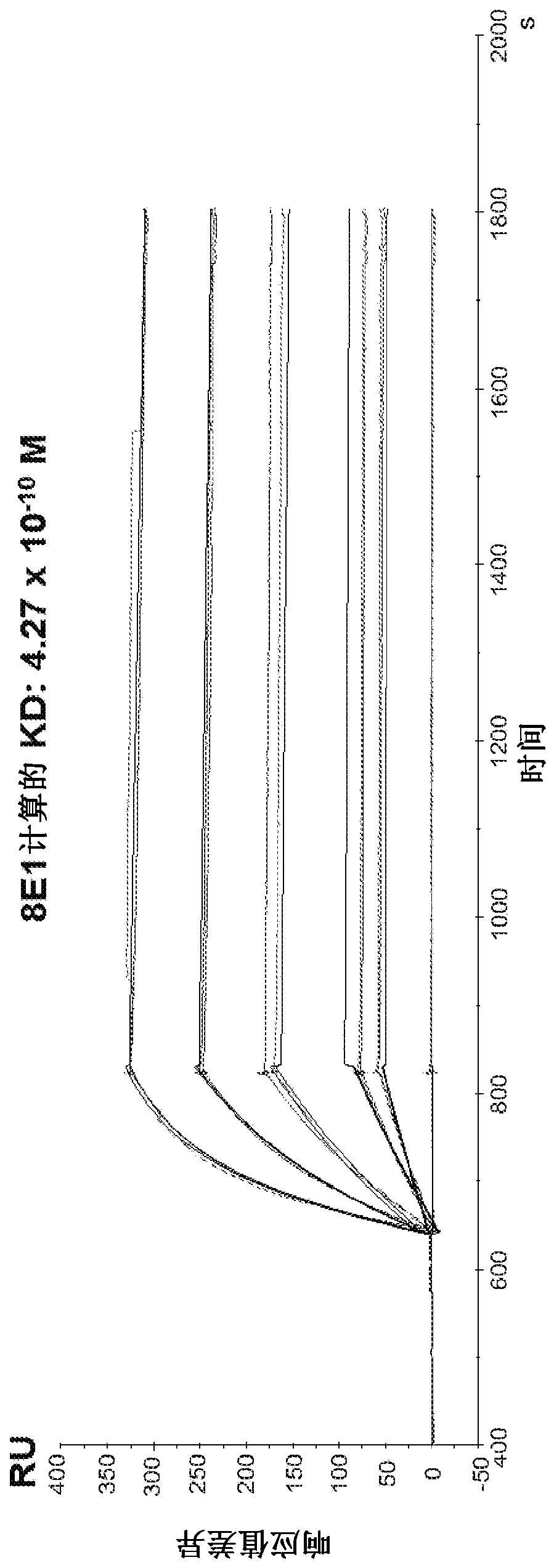
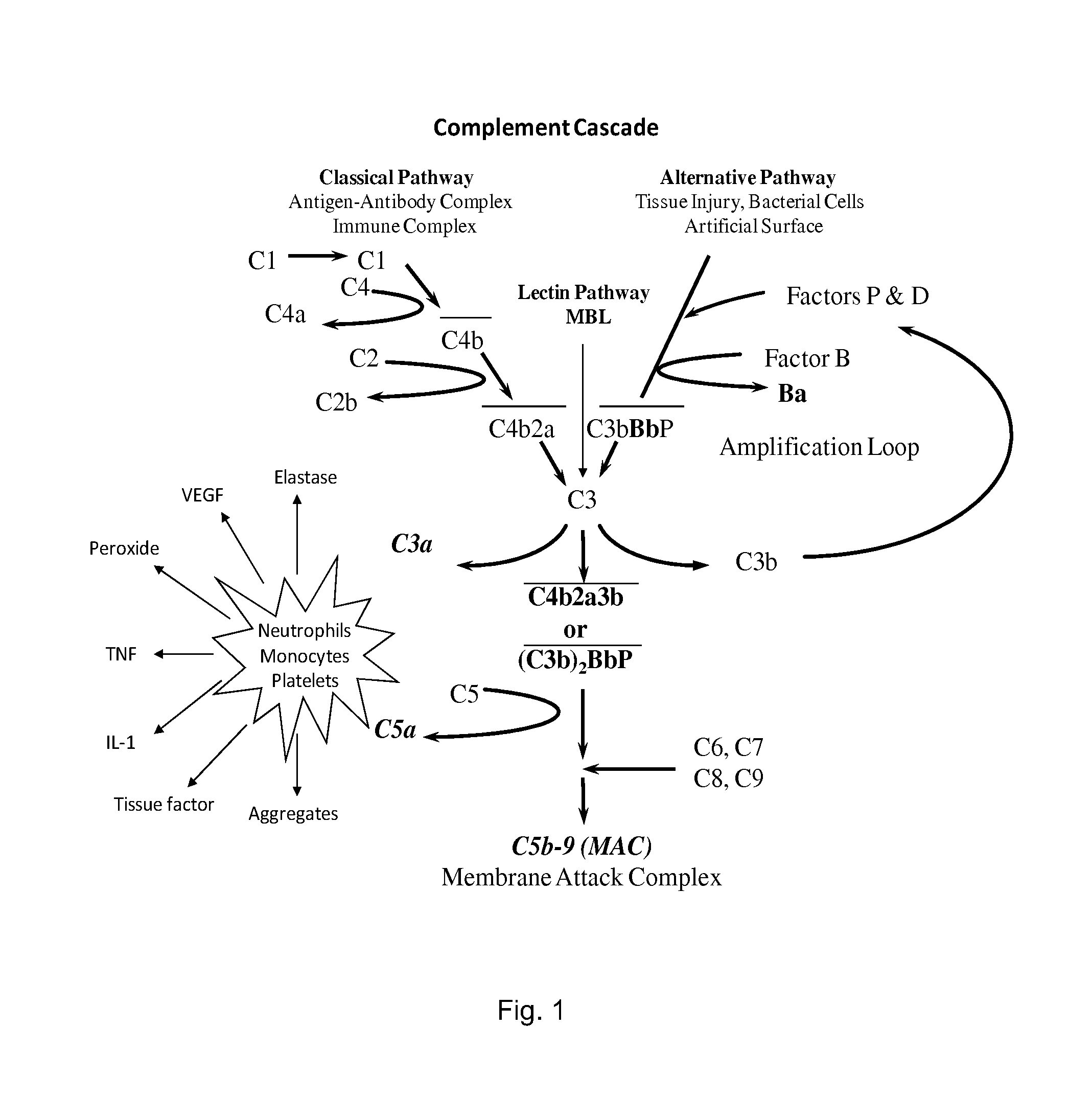
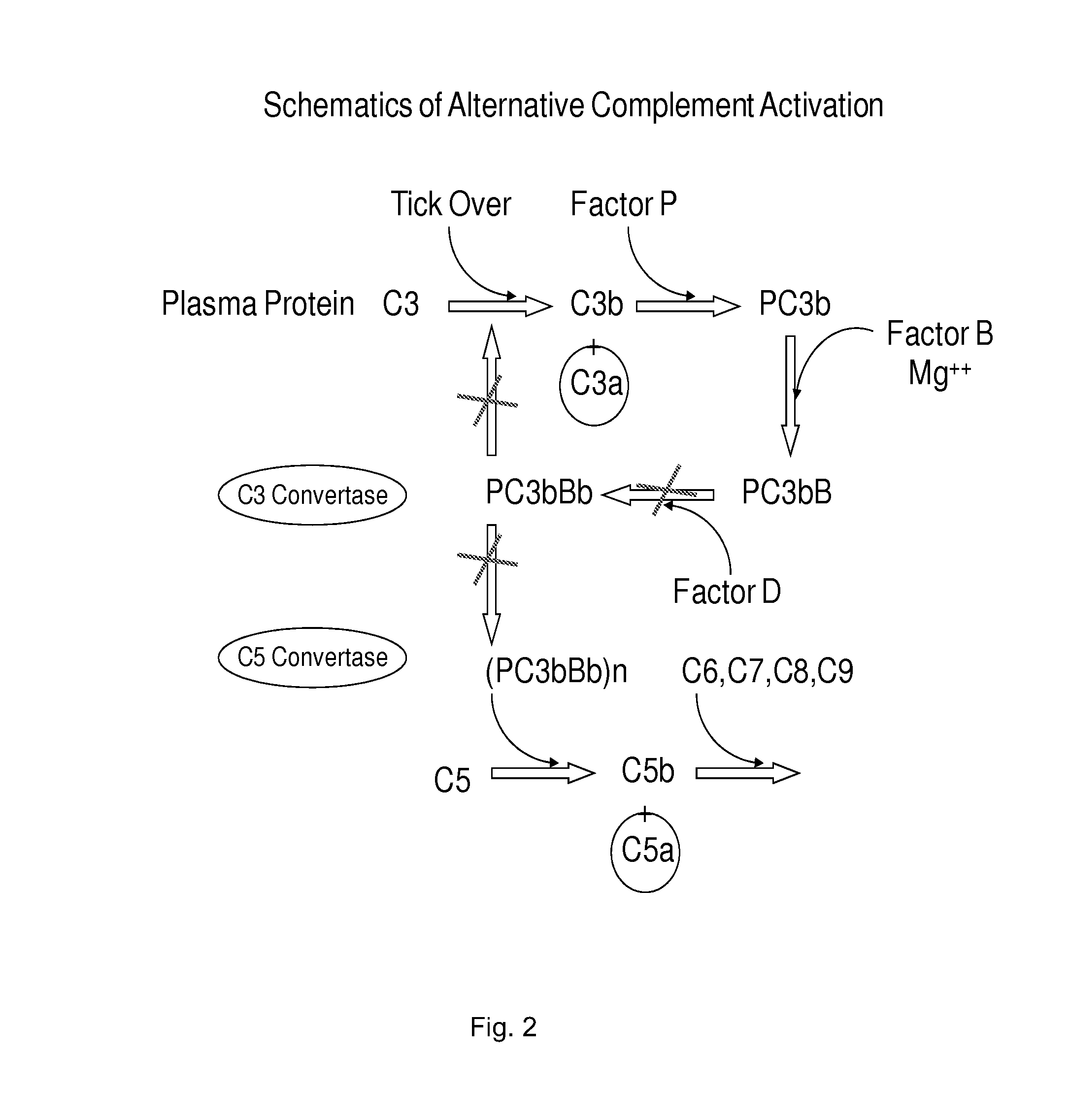
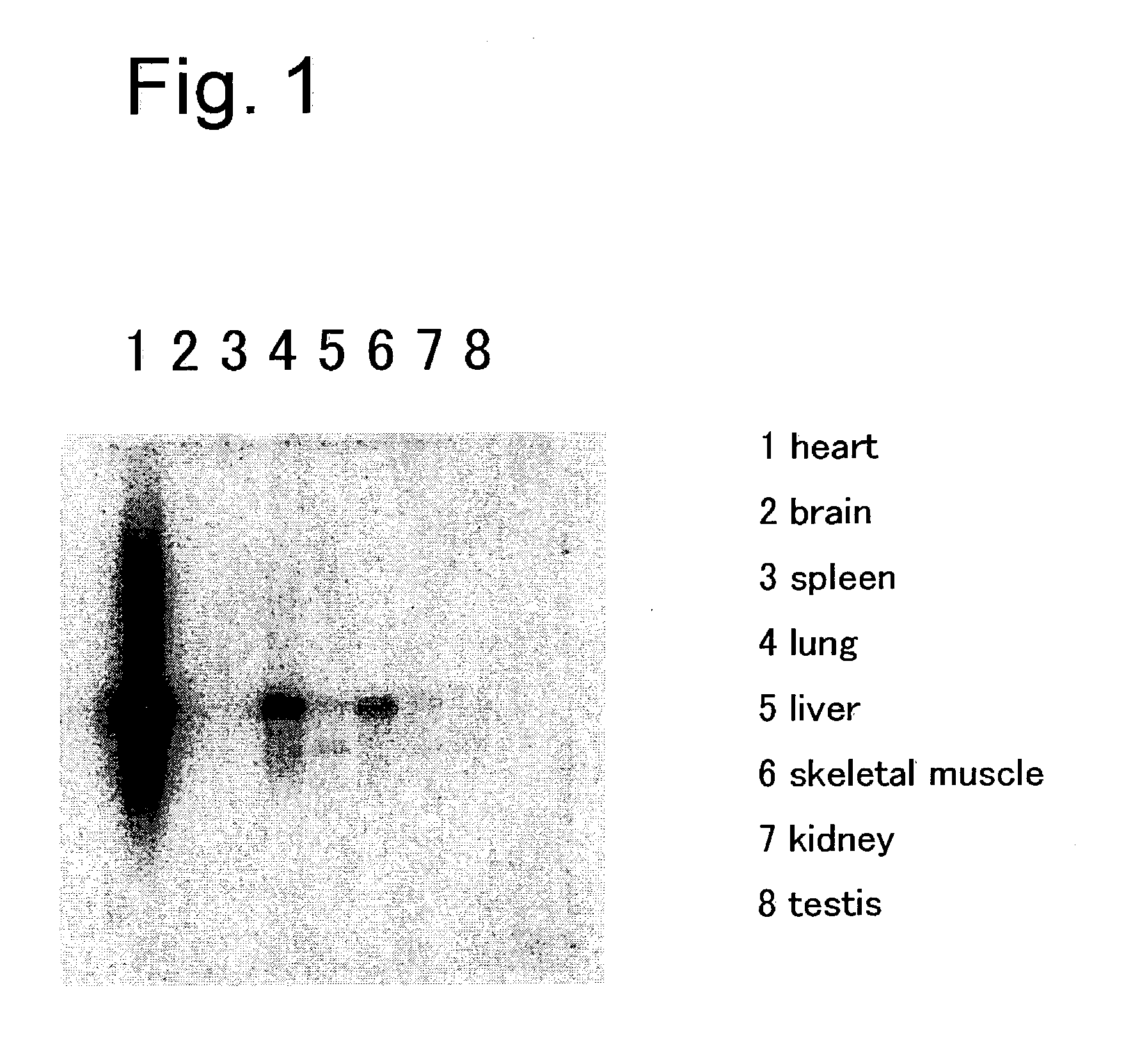
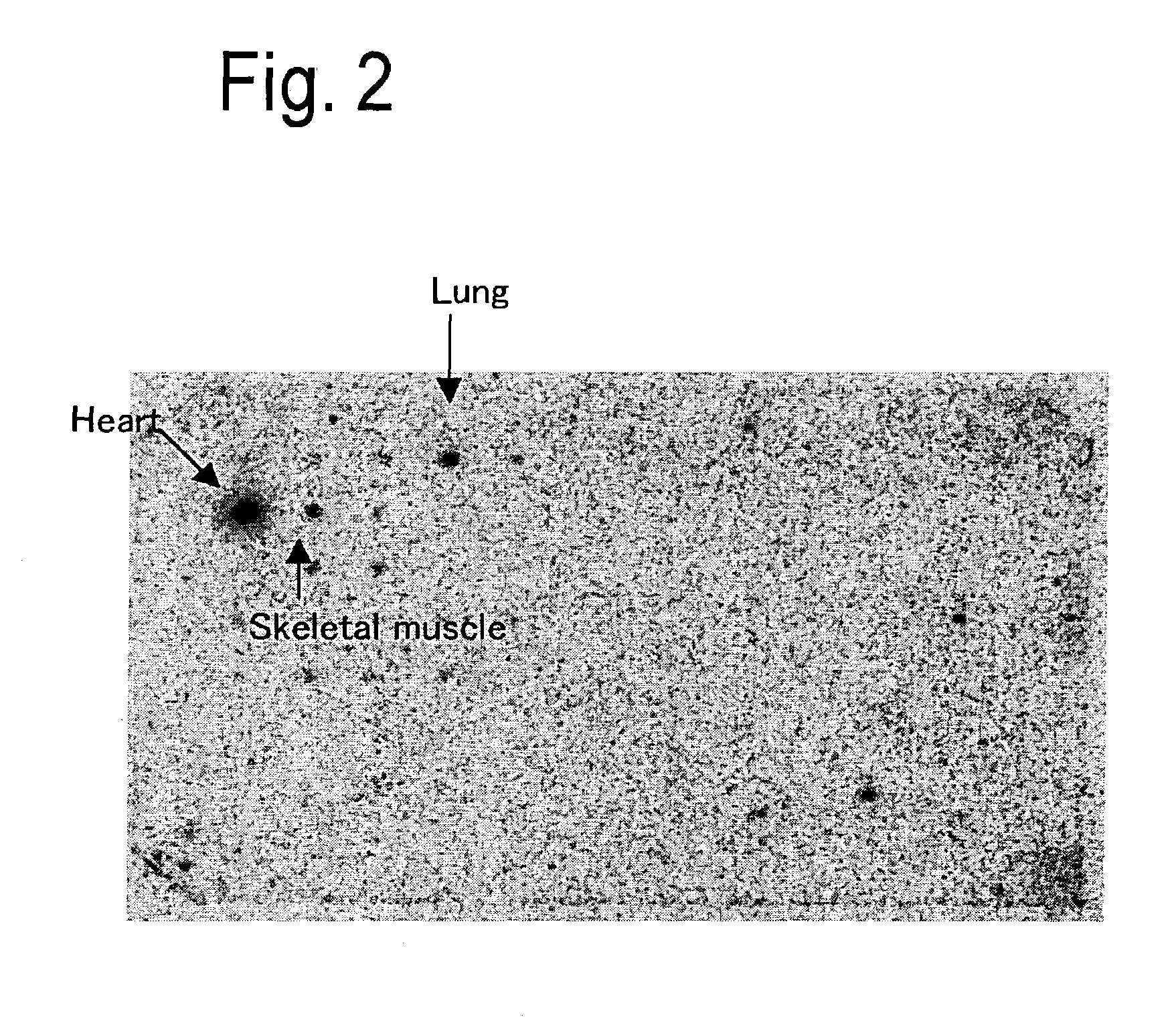
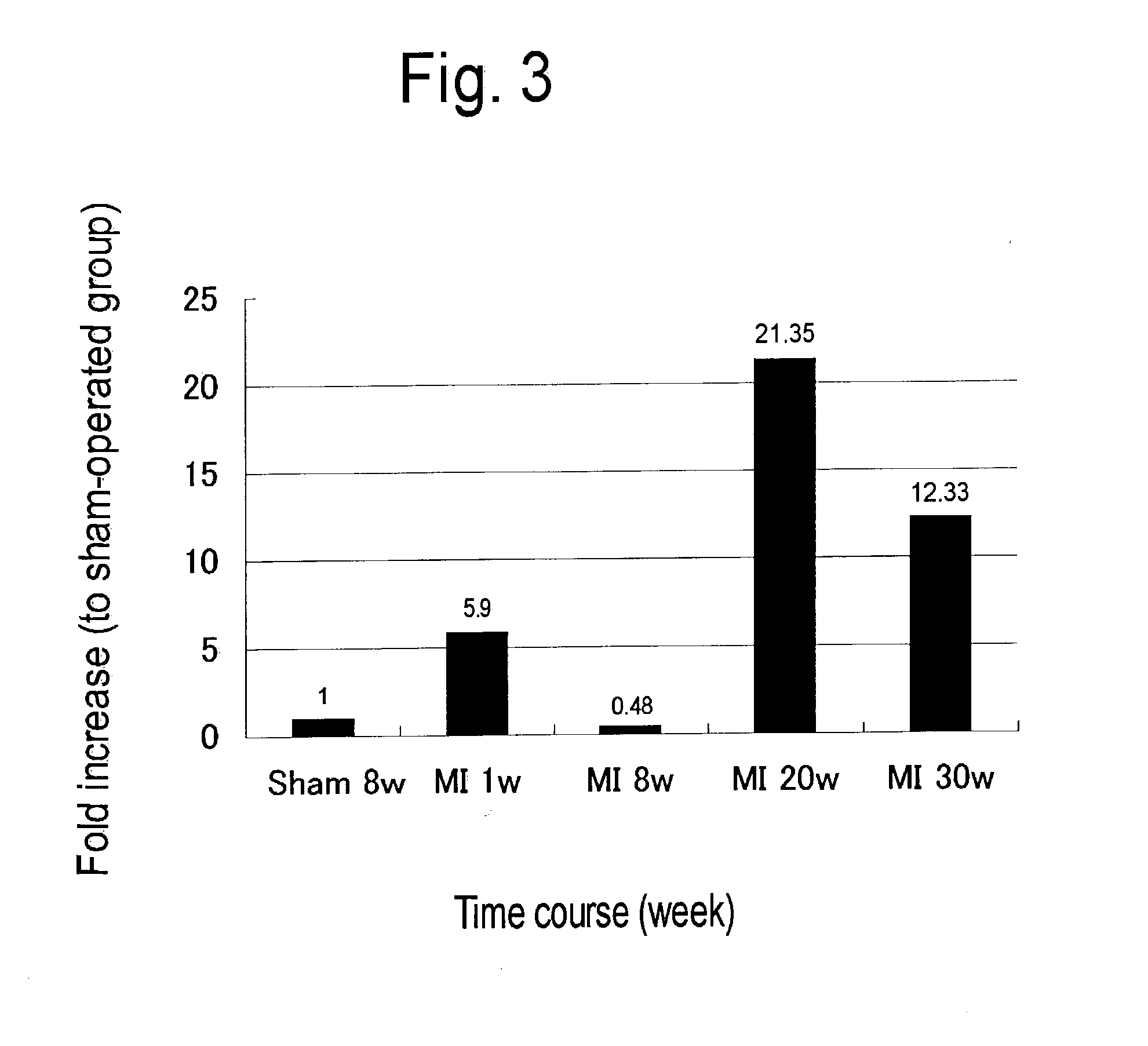
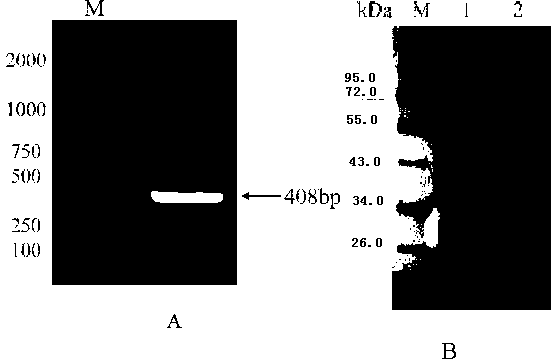
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Antibody Suppression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Monoclonal antibodies against prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) lacking in fucosyl residues
ActiveUS7875278B2Inhibit cell growthStrong cytotoxicityAnimal cellsAntibody ingredientsAntigenFucosylation
The invention pertains to anti-PSMA antibodies that lack fucosyl residues. The antibodies of the invention exhibit increased antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity as compared to the fucosylated form of the antibodies. The invention also provides host cells that express the anti-PSMA antibodies that lack fucosyl residues, wherein the host cells are deficient for a fucosyl transferase. Methods of using the antibodies to inhibit the growth of PSMA+ cells, such as tumor cells, are also provided.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC +1
Methods to identify growth differentiation factor (GDF) receptors
InactiveUS20040077053A1Compound screeningOrganic active ingredientsGrowth differentiation factor-9Agonist
The present invention provides receptors for the growth differentiation factor (GDF) family of growth factors and methods of identifying such receptors. Also included are methods of identifying antibodies which bind to the receptors, peptide fragments of the receptor which inhibit GDF binding, GDF receptor-binding agents capable of blocking GDF binding to the receptor. The receptors of the invention allow the identification of antagonists or agonists useful for agricultural and human therapeutic purposes.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Anti-pacap antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20160304604A1Good analgesic effectCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderNeurophysinsAntigen binding
The present invention is directed to antagonistic antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof having binding specificity for PACAP. These antibodies inhibit, block or neutralize at least one biological effect associated with PACAP, e.g., vasodilation. In exemplary embodiments these antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof may comprise specific VH, VL, and CDR polypeptides described herein. In some embodiments these antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof bind to and / or compete for binding to specific epitope(s) on human PACAP. The invention is further directed to using these antagonistic anti-PACAP antibodies, and binding fragments thereof, for the diagnosis, assessment, and treatment of diseases and disorders associated with PACAP and conditions where antagonism of PACAP-related activities, such as vasodilation, mast cell degranulation, and / or neuronal activation, are therapeutically beneficial, e.g., headache and migraine indications.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
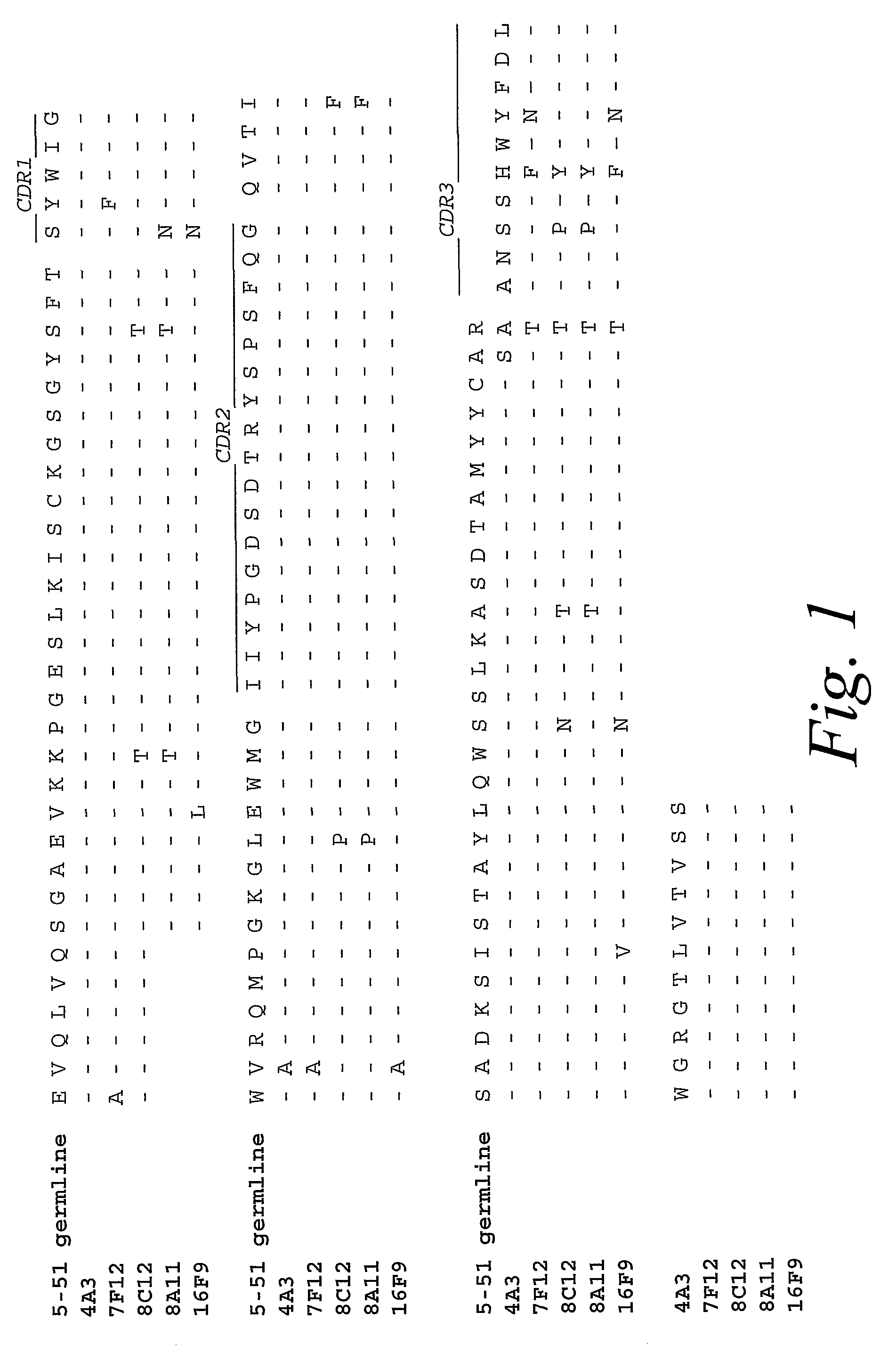
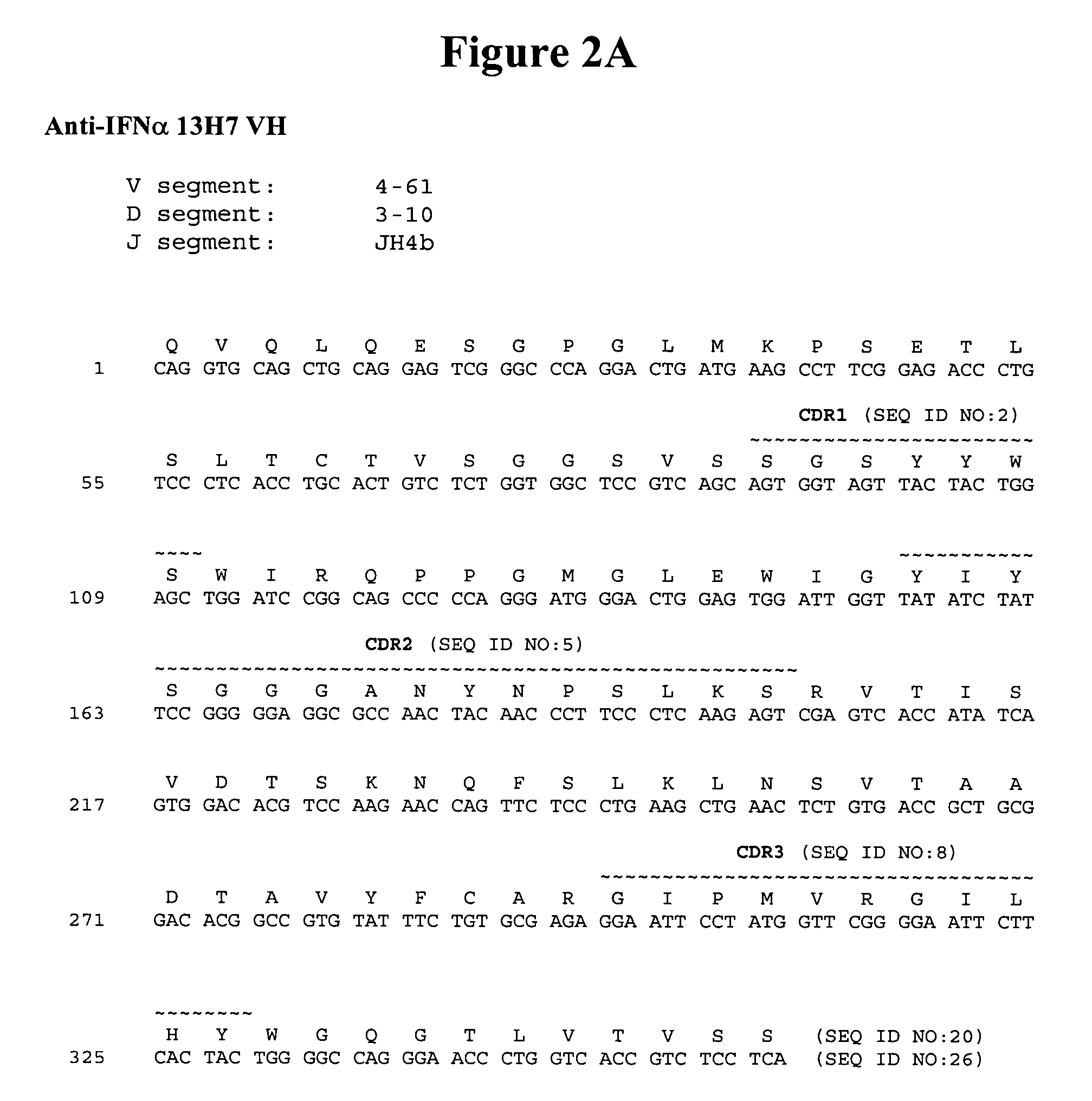
Anti-interferon alpha antibodies
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
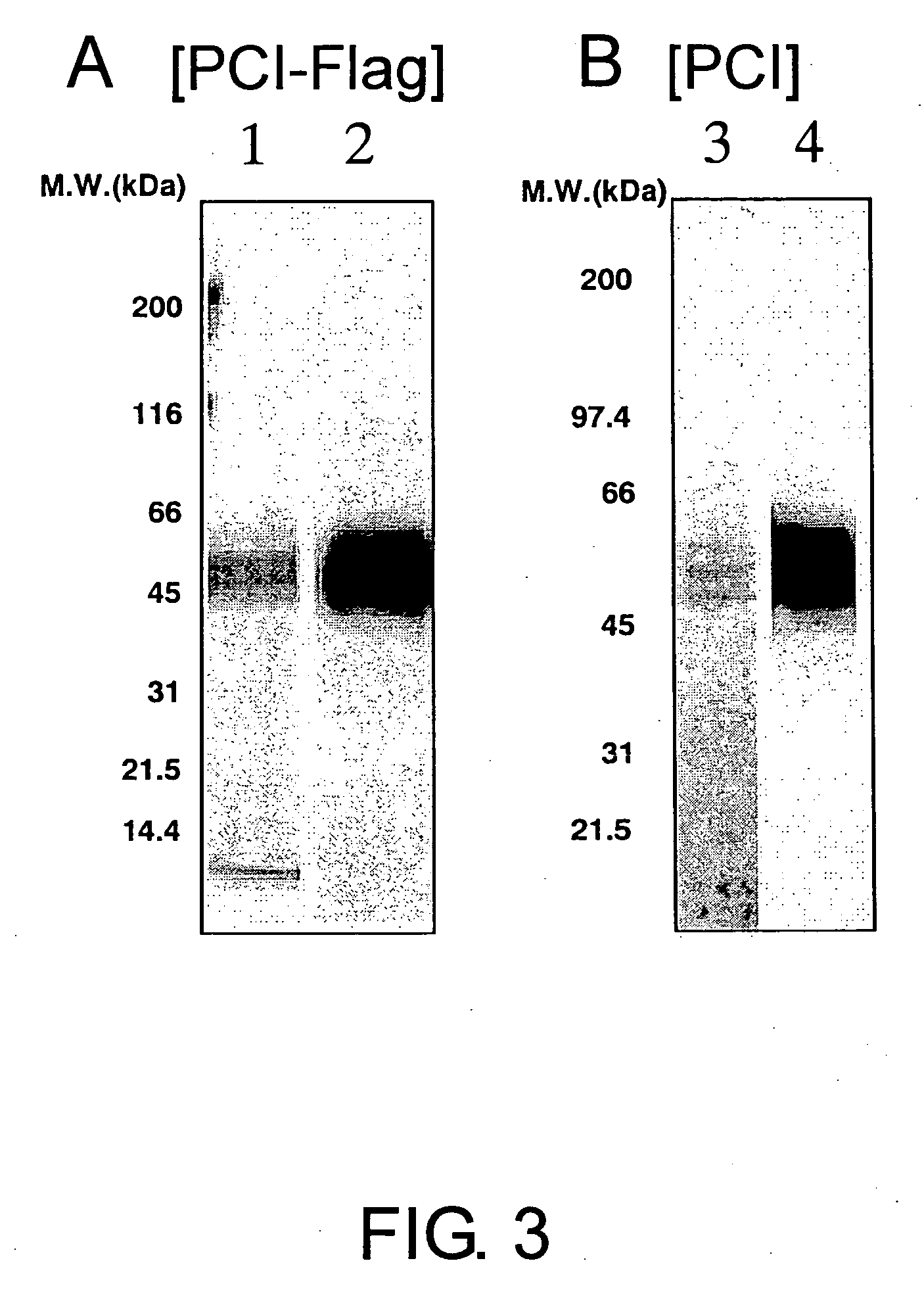
Anti-pci neutralizing antibody
InactiveUS20060167230A1Increase productionHigh activityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticProtein C inhibitorTherapeutic effect
The present invention provides anti-PCI antibodies having Protein C inhibitor (PCI)-neutralizing activity, and the uses thereof. Through the generation and screening of anti-PCI antibodies, the inventors successfully isolated anti-PCI antibodies which inhibit PCI's inhibitory effect on the production and activity of activated Protein C (aPC). The antibodies of the present invention suppress PCI's inhibitory effect on aPC production and / or the aPC inactivation by PCI, and thus can be used to maintain aPC activity and sustain the effects of aPC physiological activities, such as suppression of the activation of blood coagulation system and anti-inflammatory functions. The present invention also provides uses of the antibodies of the present invention in treating diseases such as thrombosis and sepsis using aPC. In treatments by aPC administration, the therapeutic effect of aPC can be sustained by administering an antibody of the present invention. The antibodies of the present invention can be used in the treatment and prevention of diseases such as thrombosis and sepsis.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
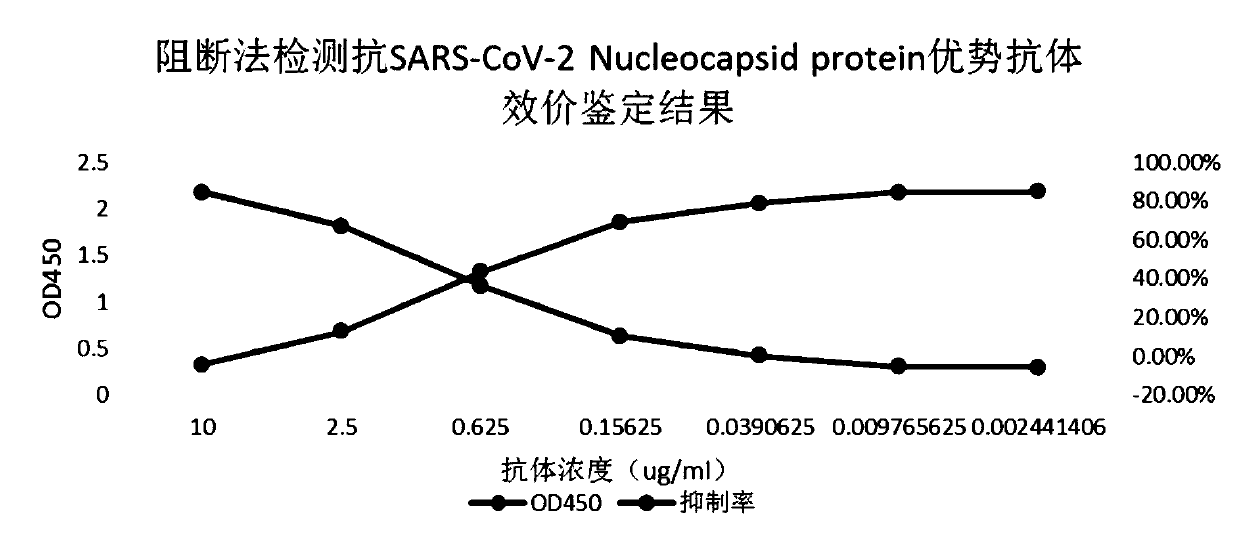
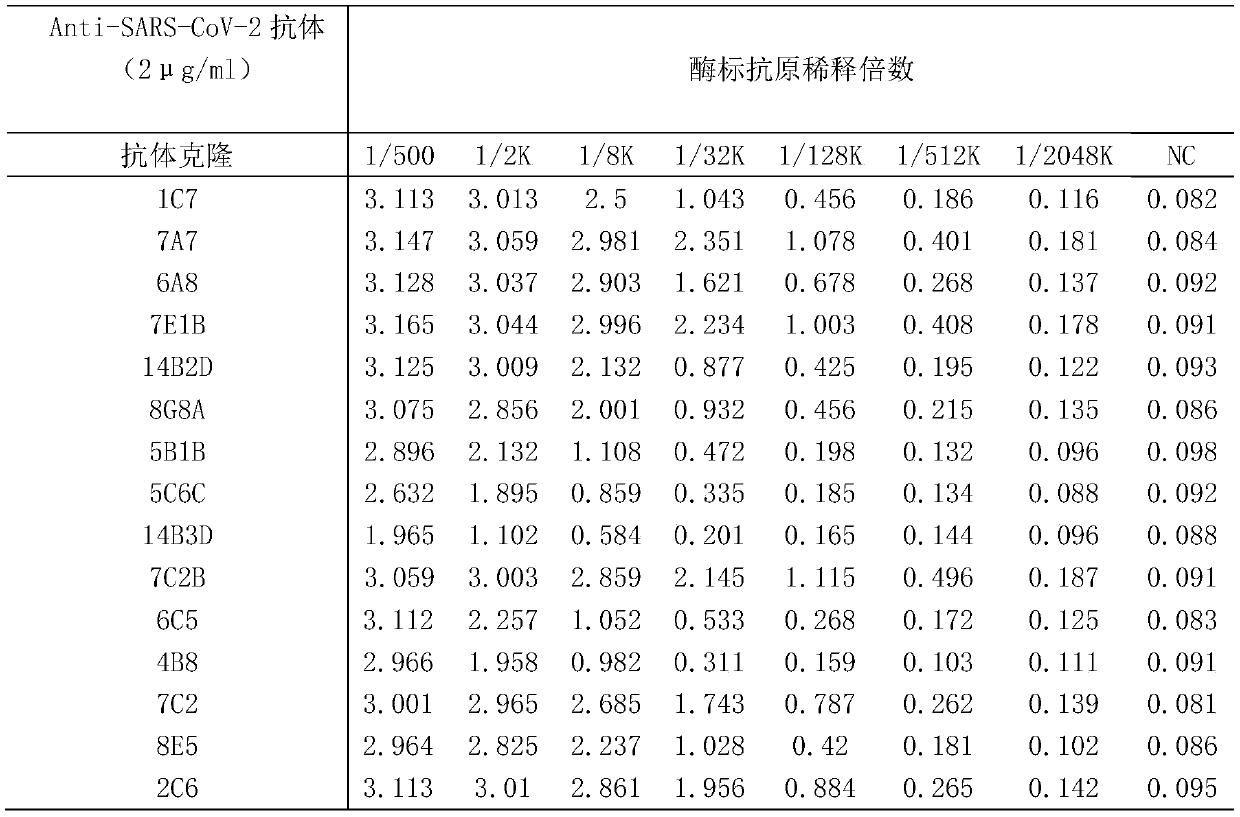
SARS-CoV-2 antibody detection method
PendingCN111474345AQuick checkEasy to detectBiological material analysisAntibody SuppressionAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses an SARS-CoV-2 antibody detection method. The SARS-CoV-2 antibody detection method comprises the following steps: carrying out horseradish peroxidase labeling on recombinant SARS-CoV-2Nucleocapsid protein, meanwhile, selecting an anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody or a dominant antibody to coat the enzyme-linked plate and sealing; according to a competitive ELISA principle, simultaneously adding a to-be-detected sample and an enzyme-labeled antigen into a test hole of an enzyme-linked plate, performing incubation at room temperature, thoroughly washing the plate, then adding a substrate TMB, performing color development in a dark place, finally, terminating the reaction, measuring a light absorption value at 450 nm, and evaluating the titer of the antibody in the sample by calculating the antibody inhibition rate. According to the method disclosed by the invention, relatively conservative N protein in SARS-CoV-2 and a specific antibody of the N protein are selected as rawmaterials. Compared with a traditional antibody detection method, the detection of the Anti-SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody is completed more quickly, more conveniently and more sensitively, and the method has specificity, sensitivity, accuracy and precision and has important application prospect and value.
Owner:BEIJING BIOSYNTHESIS BIOTECH
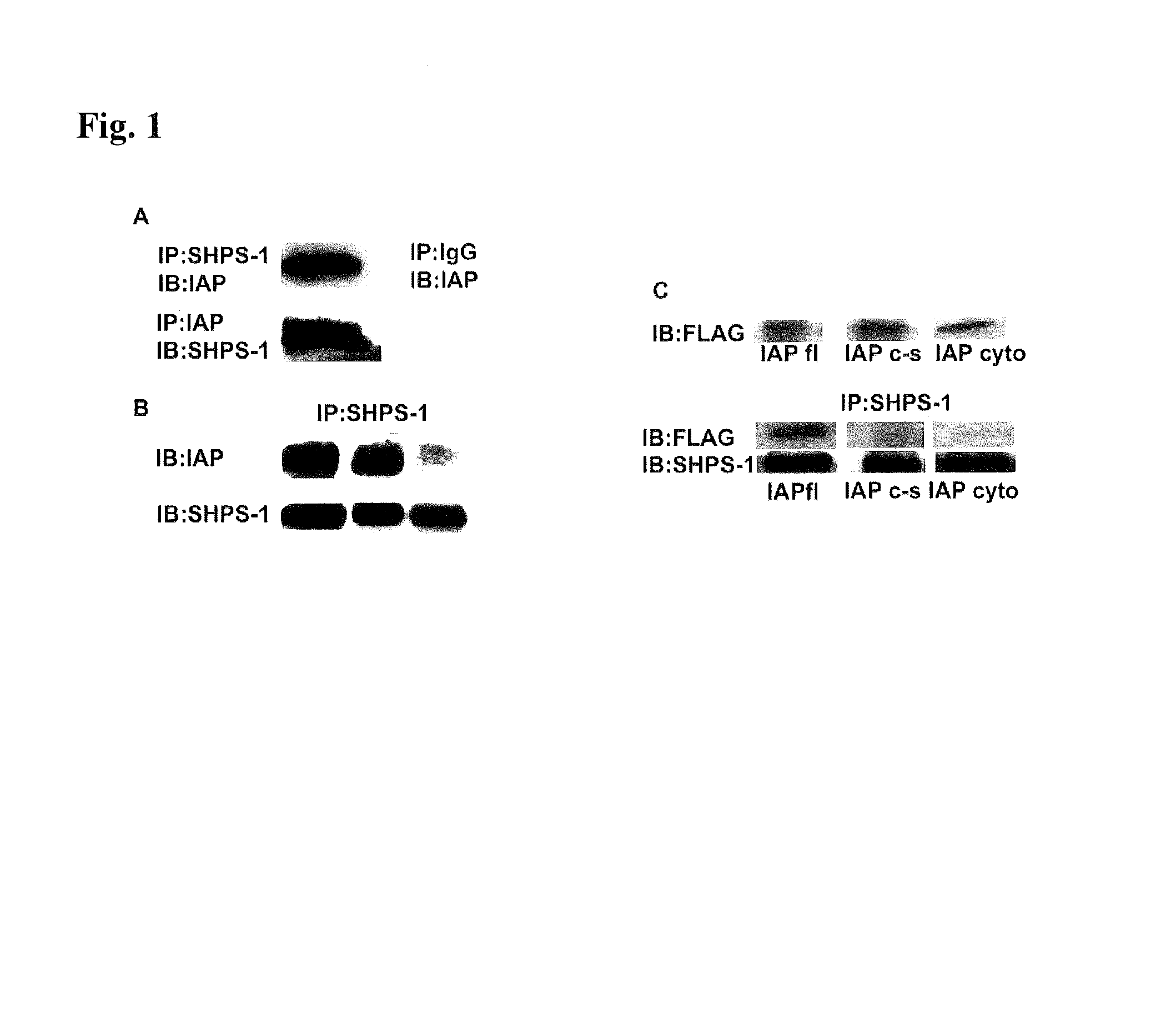
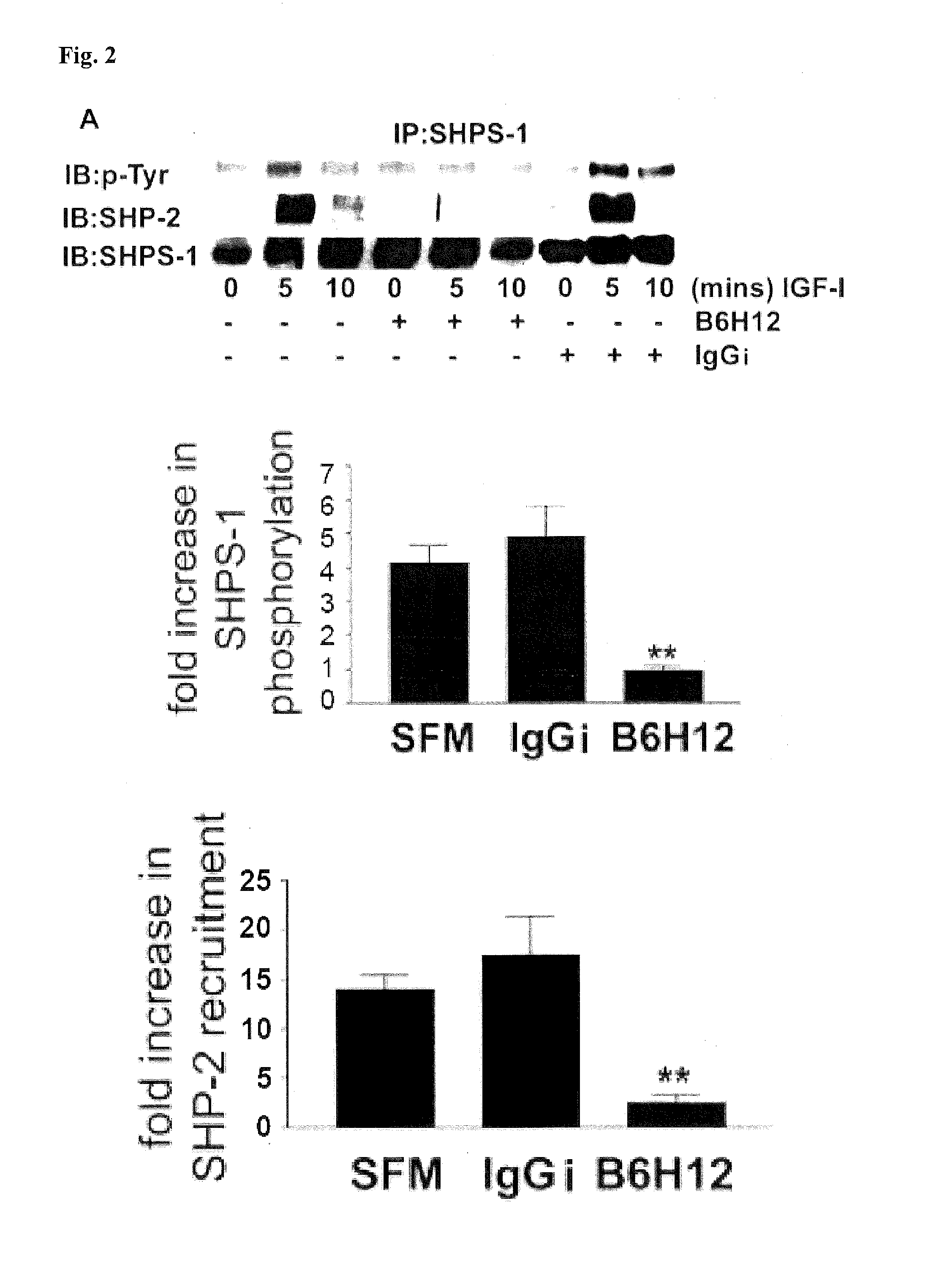
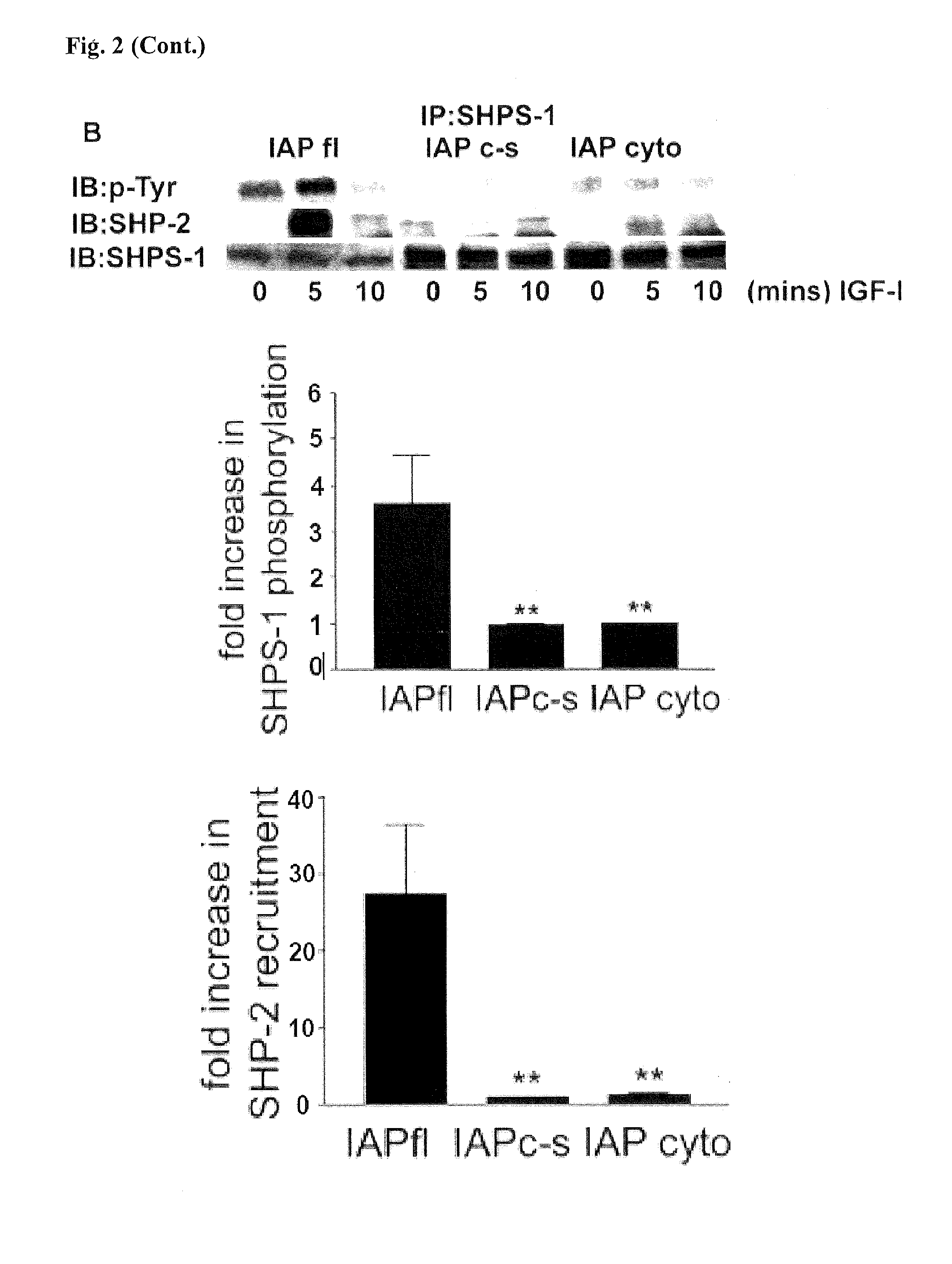
Methods for inhibiting diabetic retinopathy with an antibody against integrin associated protein (IAP)
InactiveUS8613922B2Senses disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiabetic retinopathyInsulin-like growth factor
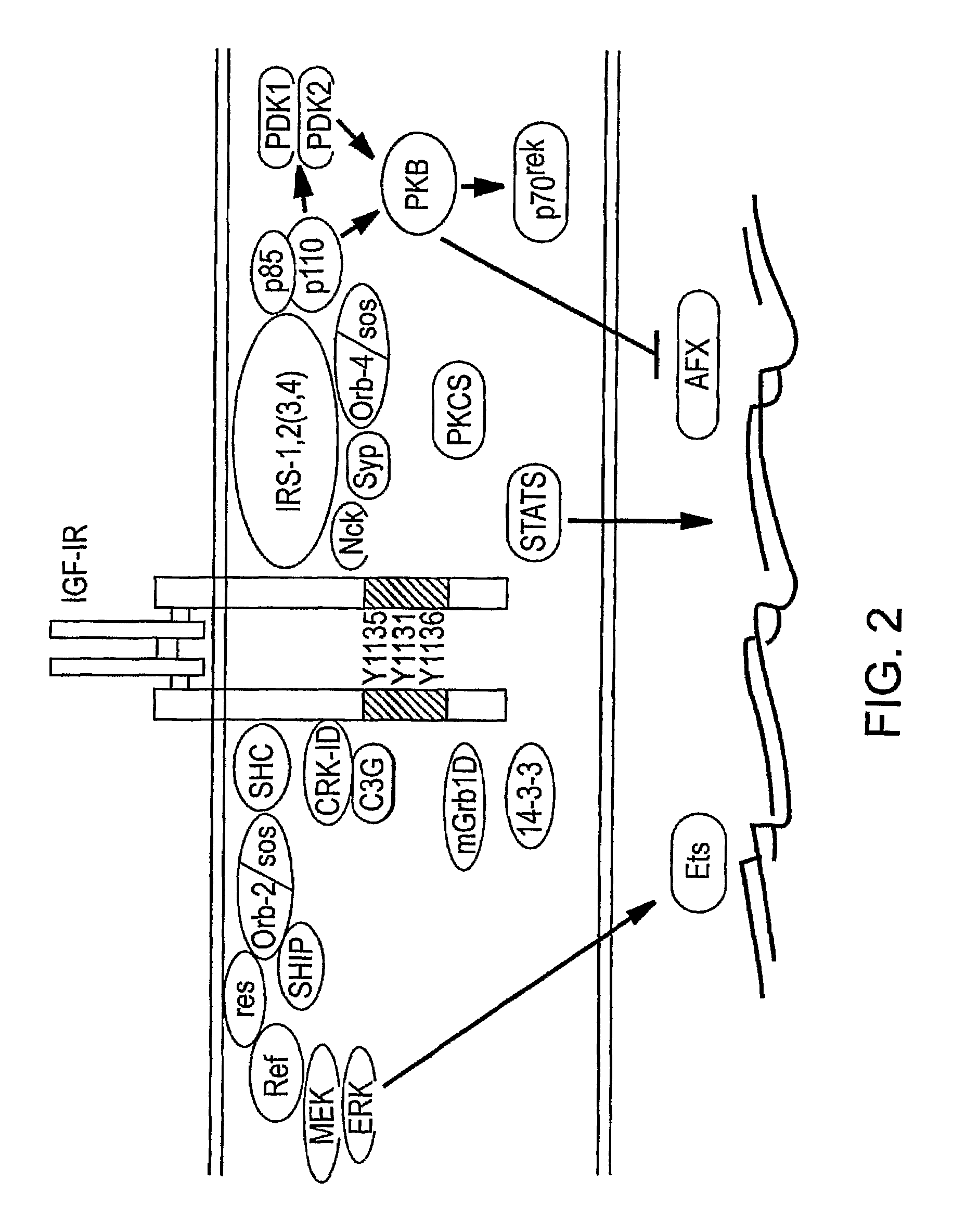
A method of inhibiting cellular activation by insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in a subject in need thereof (e.g., a subject afflicted with cancer, atherosclerosis, diabetic retinopathy or other disease) comprises administering an antagonist that inhibits the binding of IAP to SHPS-1 to the subject in an amount effective to inhibit cellular activation by IGF-1. Compounds and compositions for carrying out such methods are also described.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
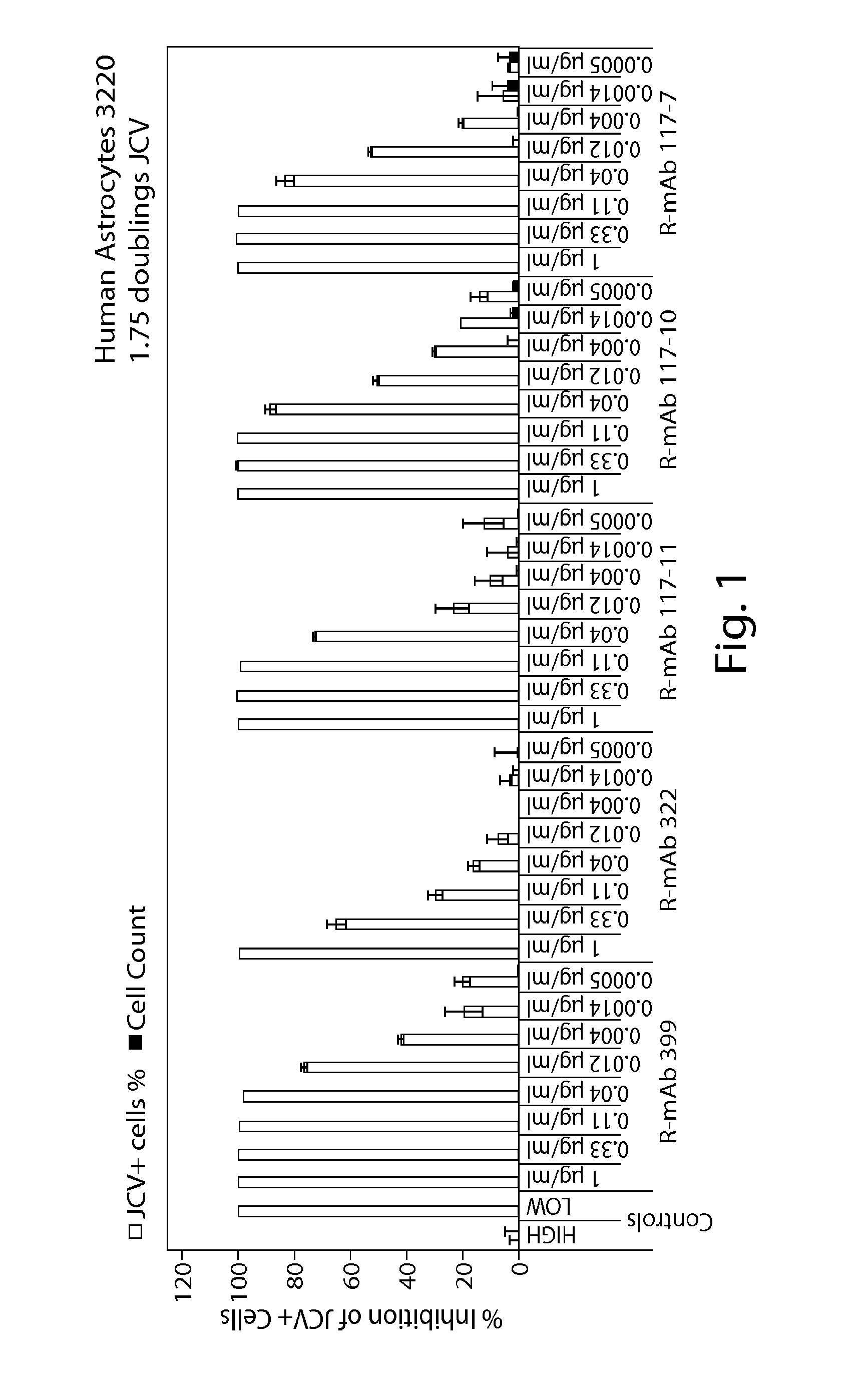
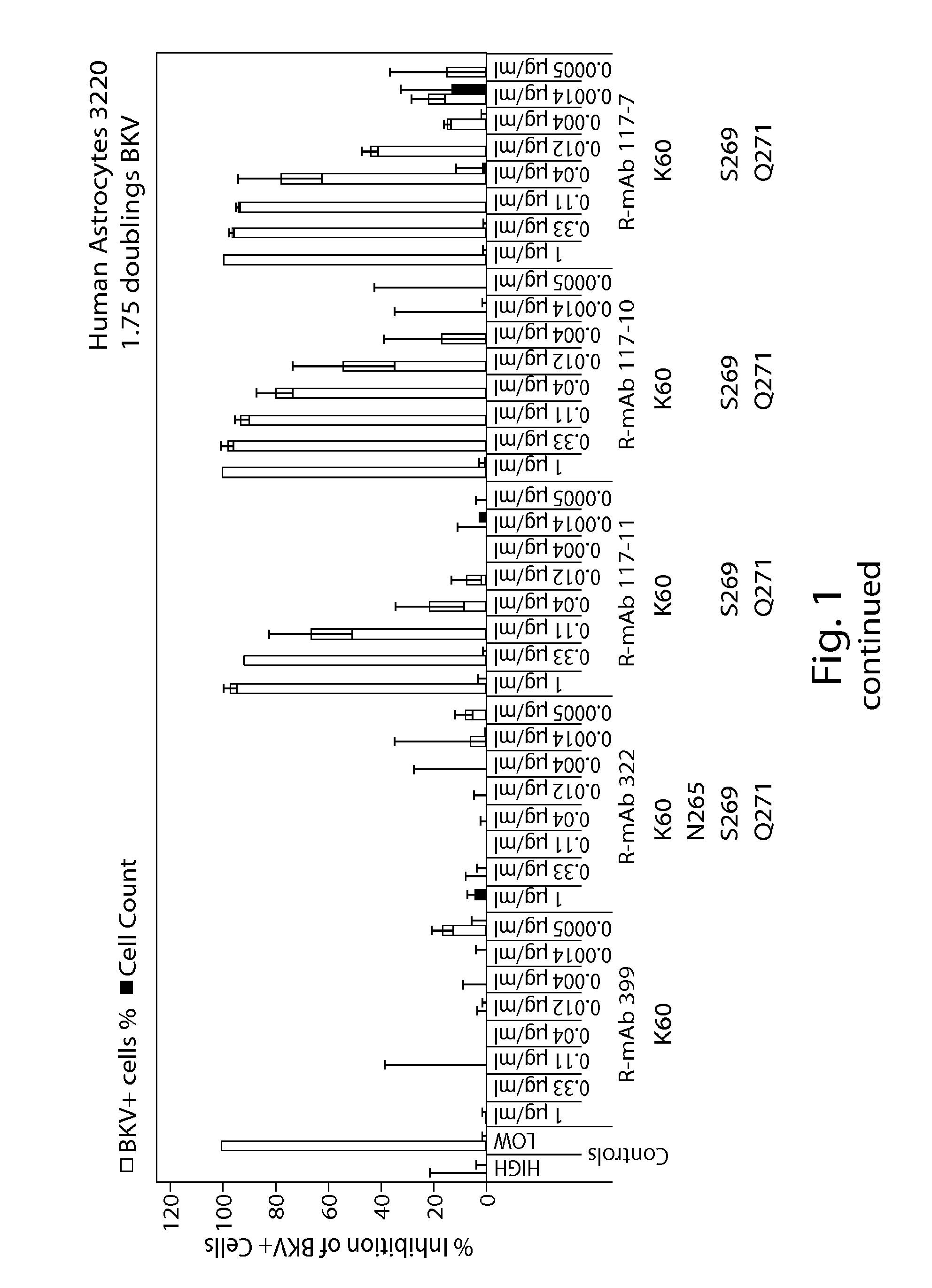
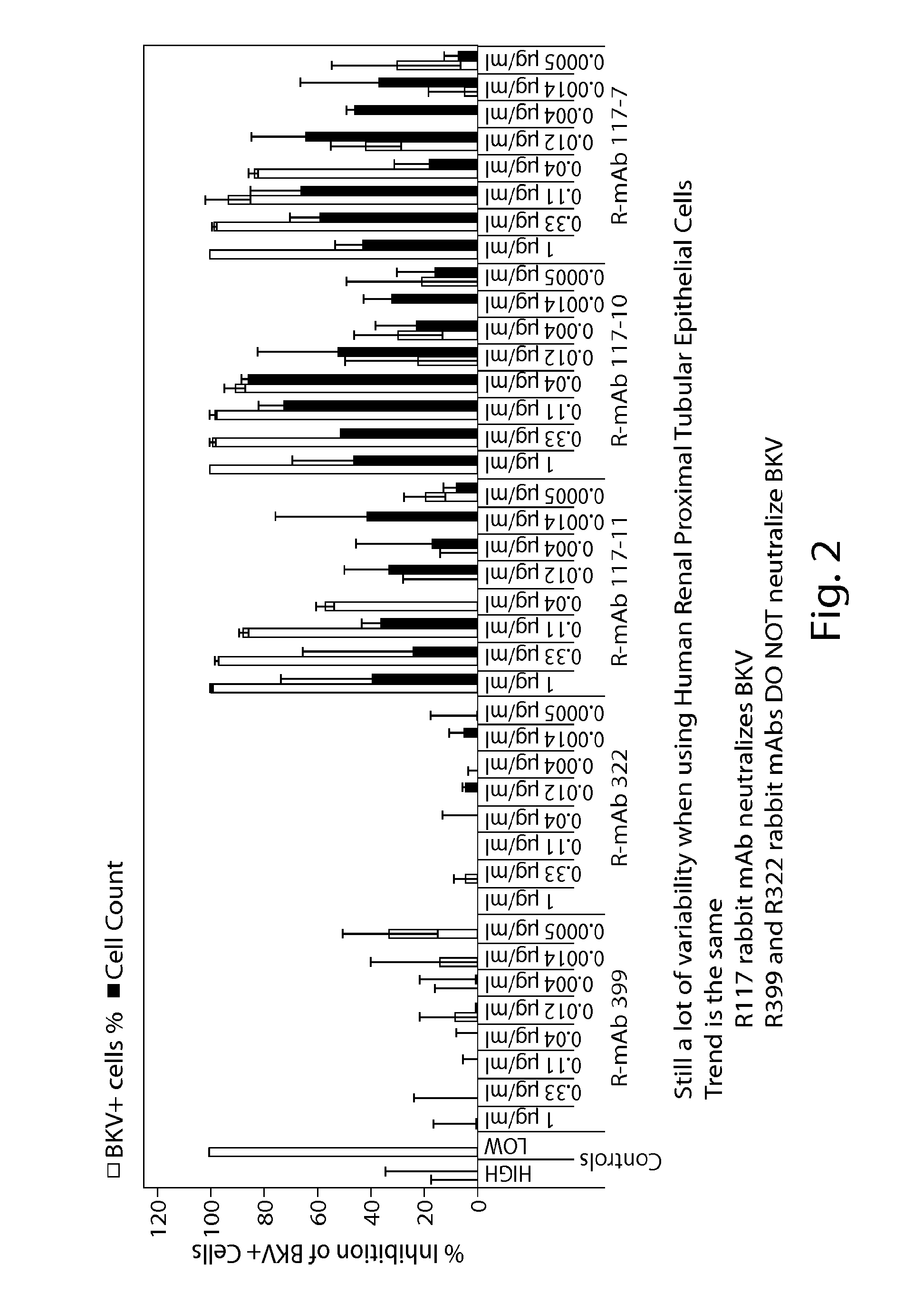
Jcv neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20150056188A1Reduce viral loadIncrease awarenessImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsAntibody SuppressionAntiendomysial antibodies
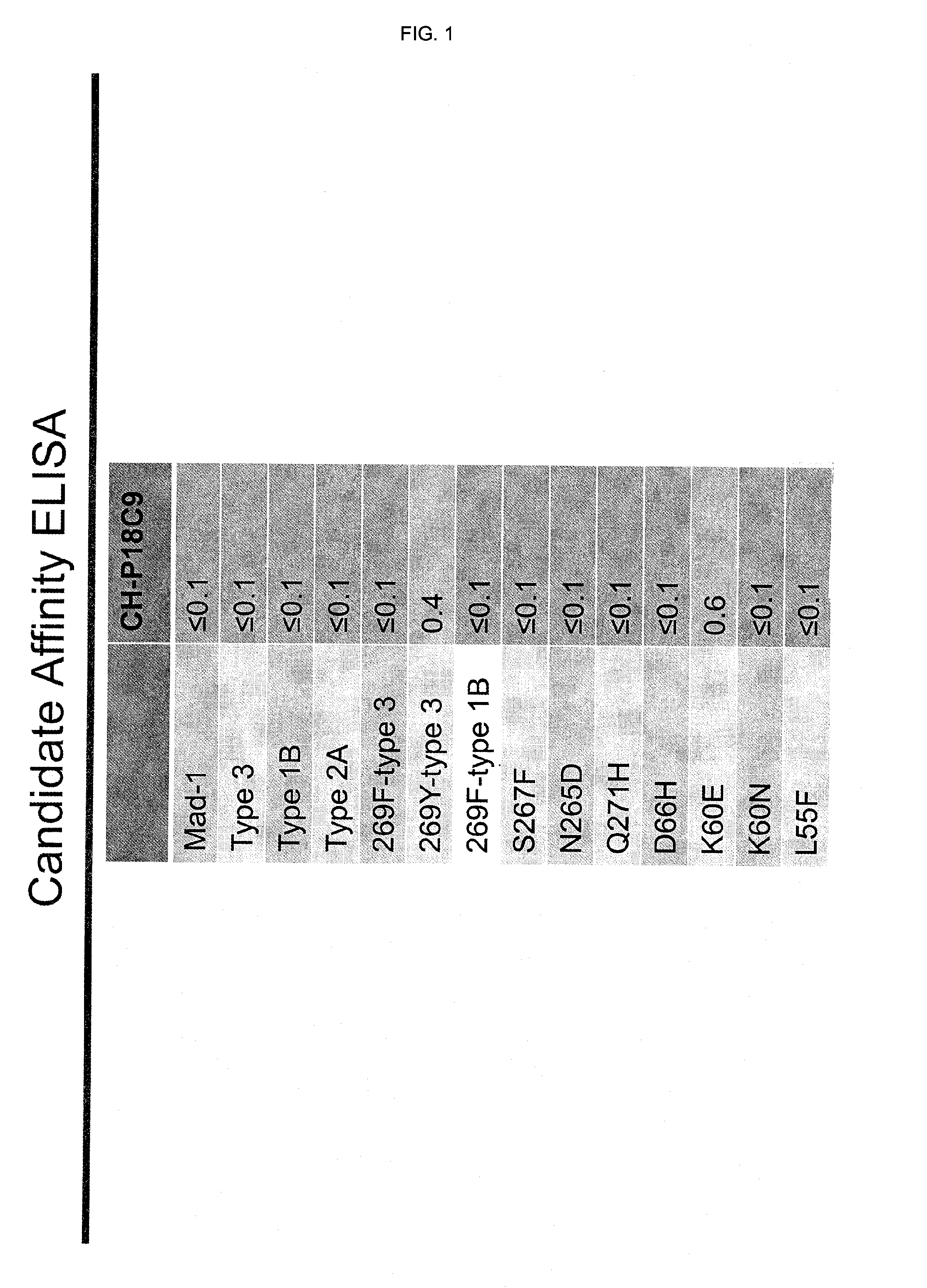
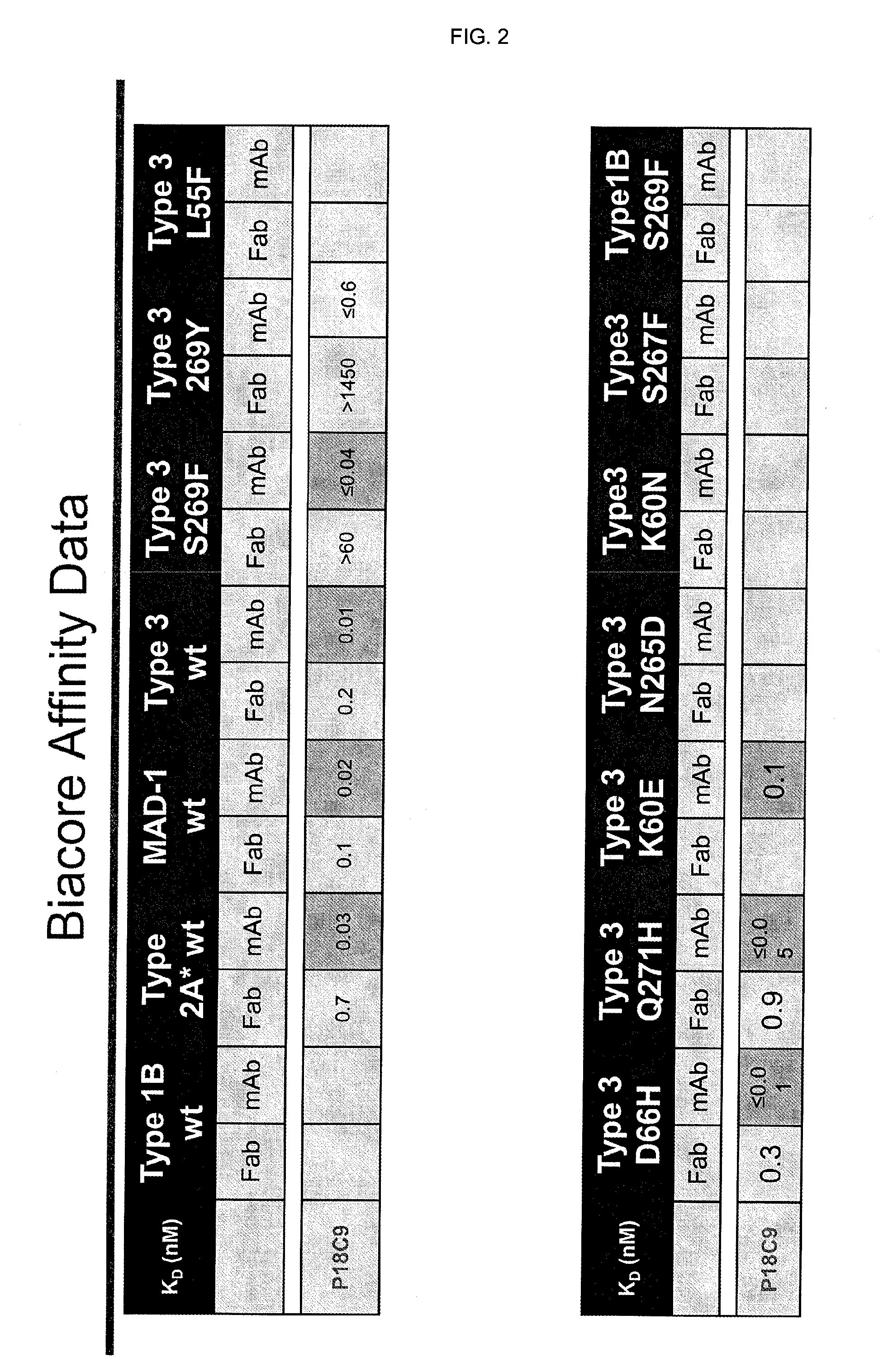
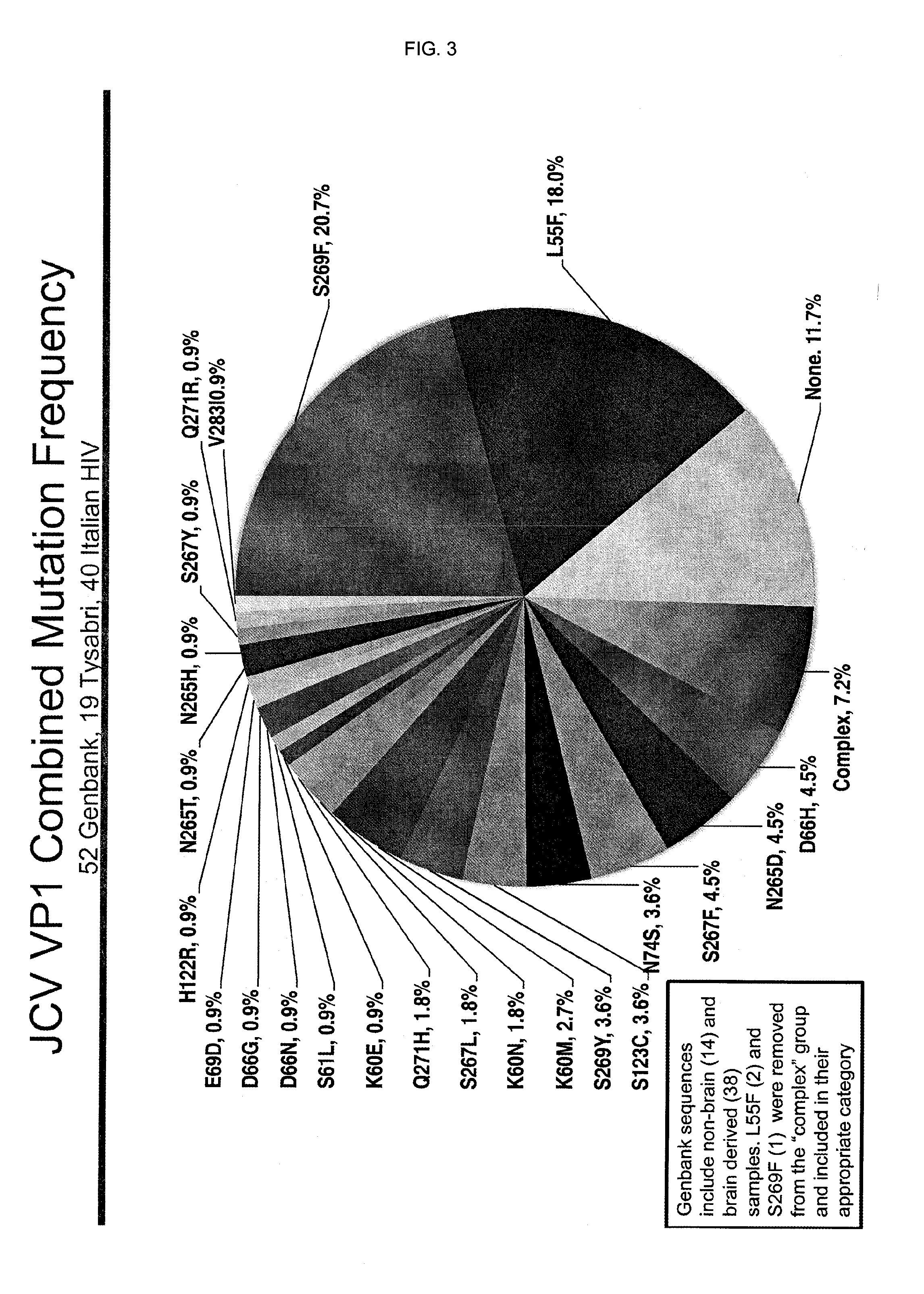
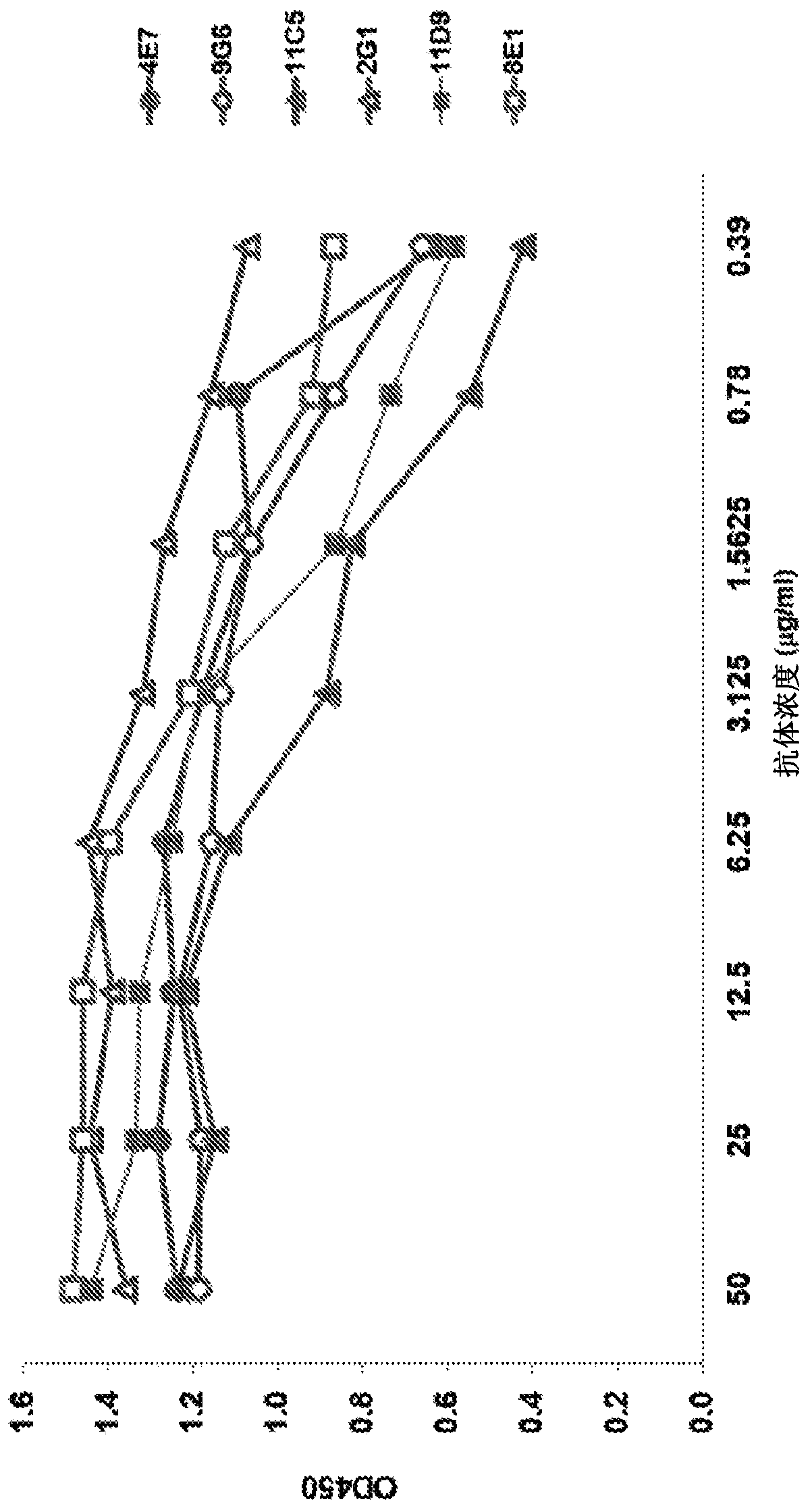
In one aspect, the disclosure provides neutralizing antibodies against JCV and methods for the treatment of PML. In some embodiments, aspects of the invention relate to an isolated JC-virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody against JCV capsid protein VPI (JCV-VP1). In some embodiments, the antibody suppresses infectivity of the JC-virus. In some embodiments, the antibody binds the sialic acid binding pocket of JCV-VPI. In some embodiments, the antibody binds JCV-VP 1 comprising one or more of the following mutations: S269F, S269Y, S267F, N265D, Q271 H, D66H, K60E, K60N and L55F.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Anti-c5 antibodies and uses thereof
PendingCN110603054AHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody SuppressionDisease
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
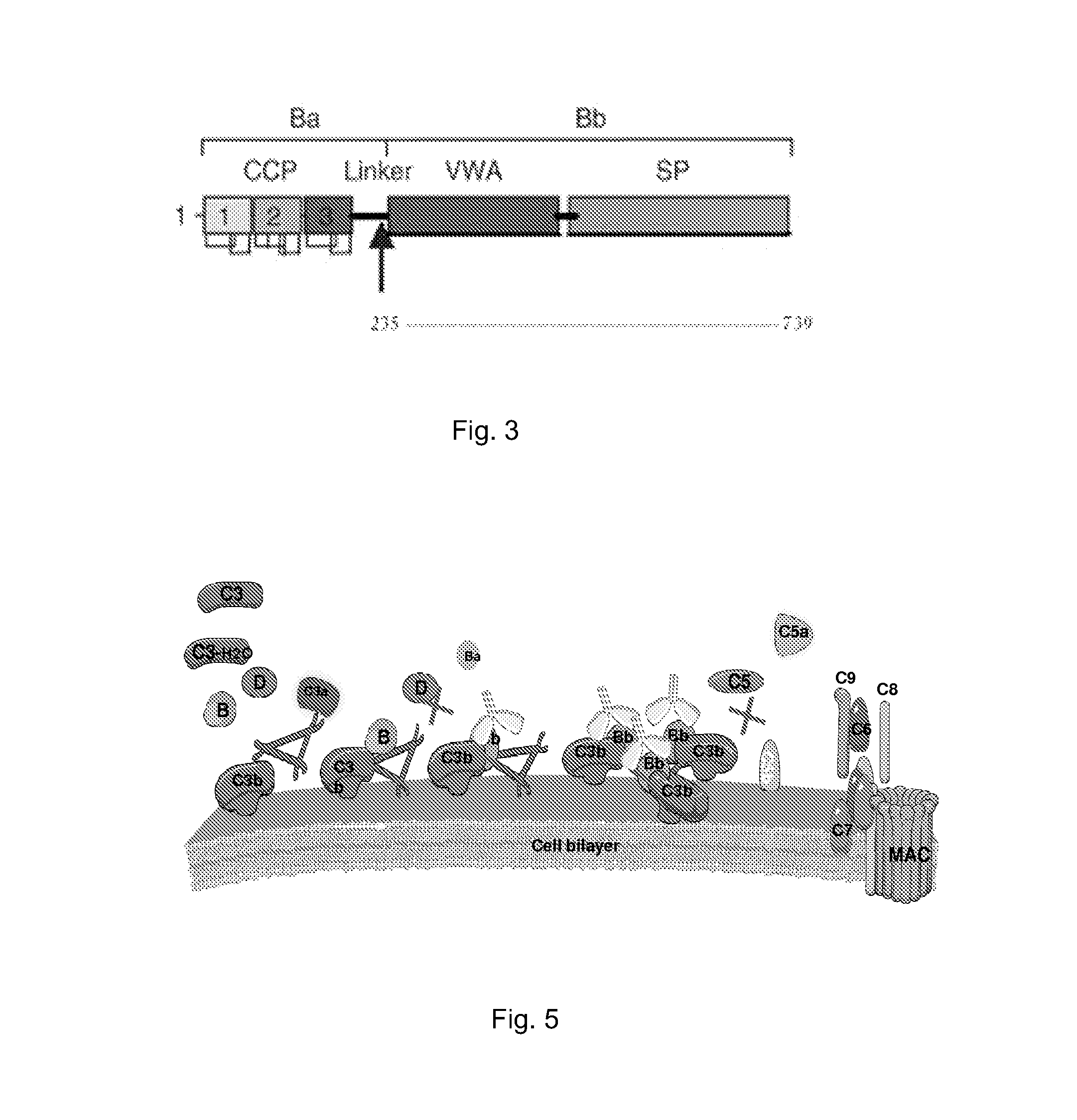
Method of inhibiting complement activation with factor Bb specific antibodies
ActiveUS8981060B2Lower Level RequirementsImprove the level ofNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPlateletNeutrophil granulocyte
A process of inhibiting the adverse effects of alternative complement pathway activation products in a subject includes administering to the subject an amount of anti-factor Bb antibody effective to selectively inhibit formation of an alternative complement pathway activation products C3a, C5a, and C5b-9, and activation of neutrophils, monocytes, and platelets.
Owner:NOVELMED THERAPEUTICS
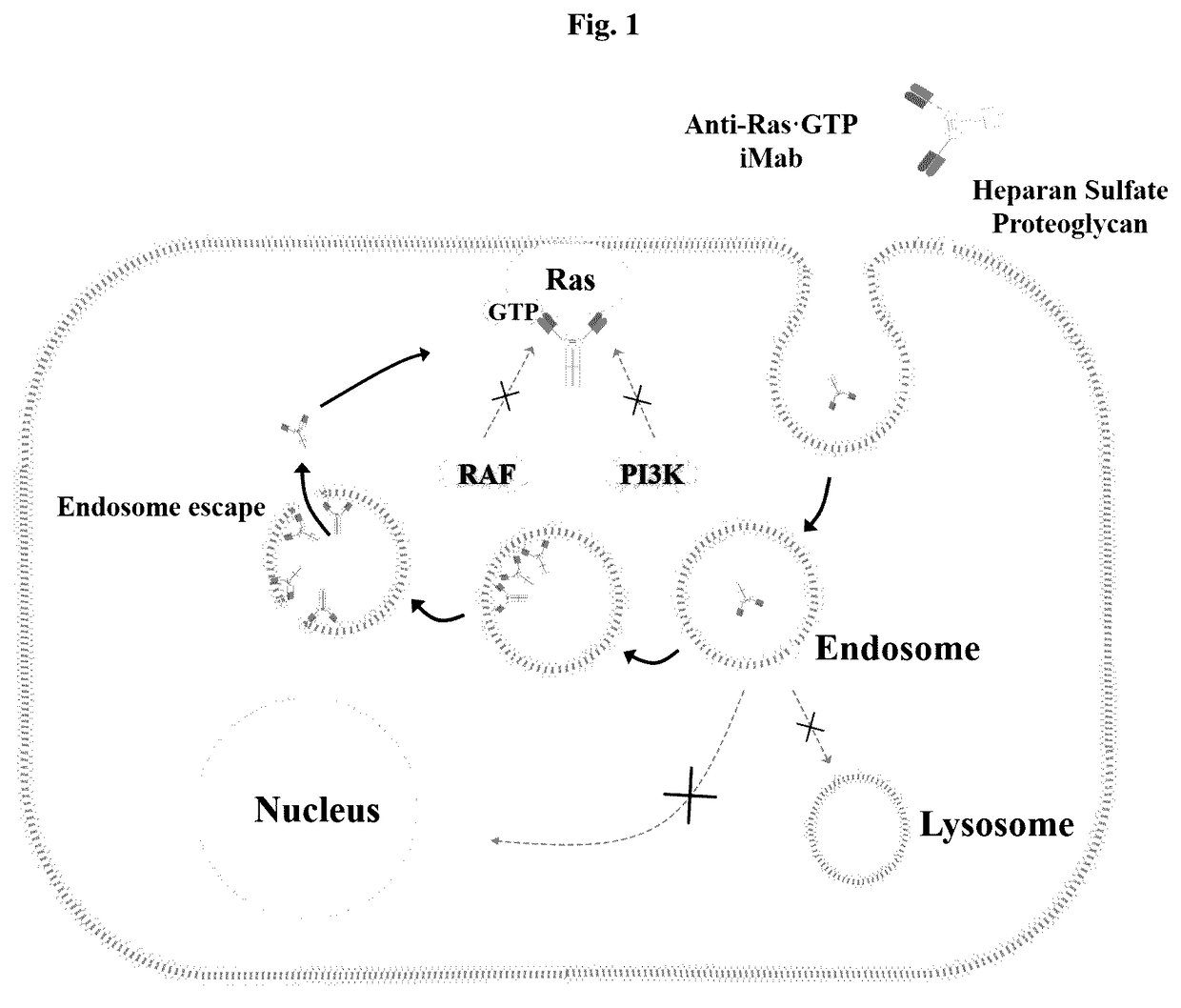
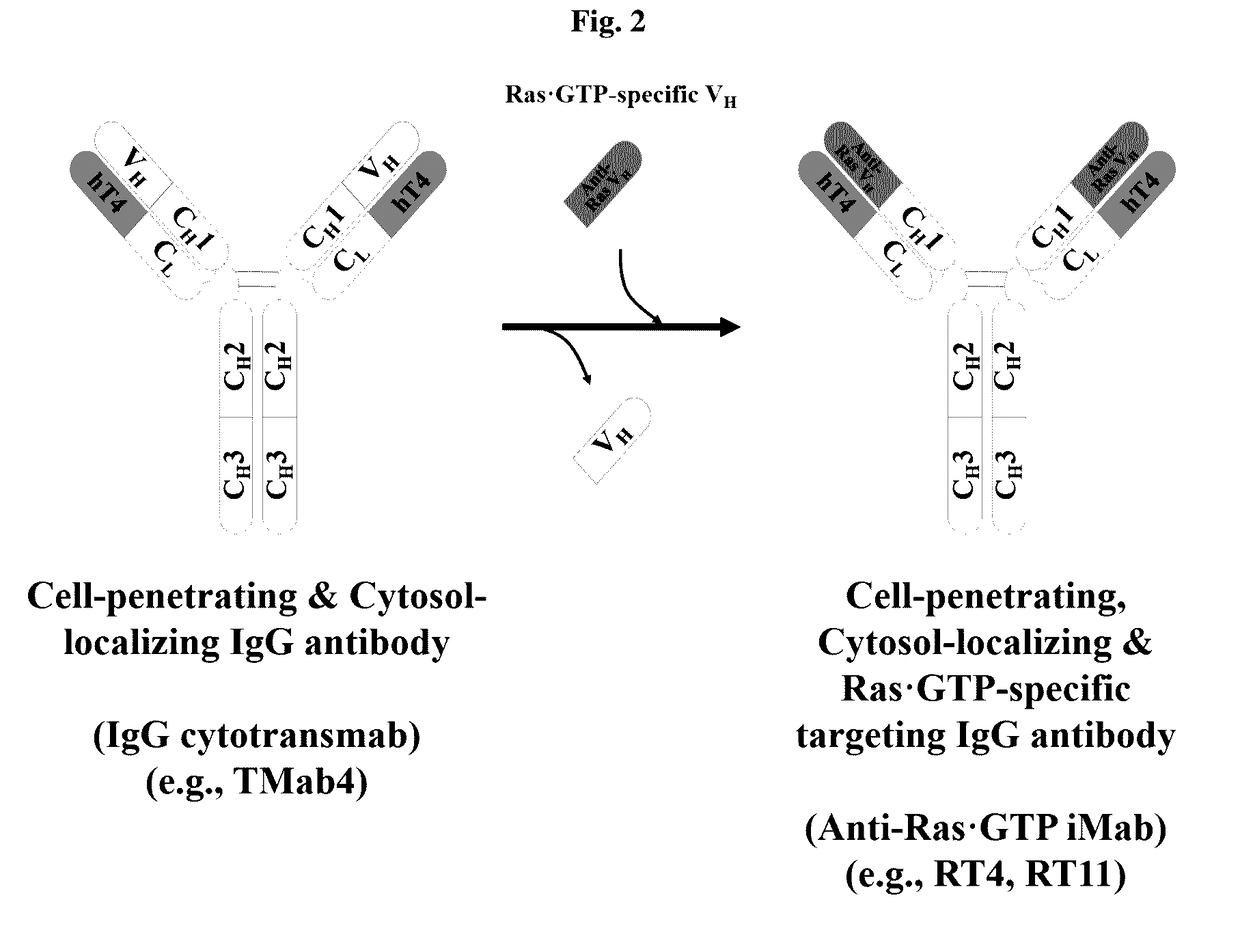
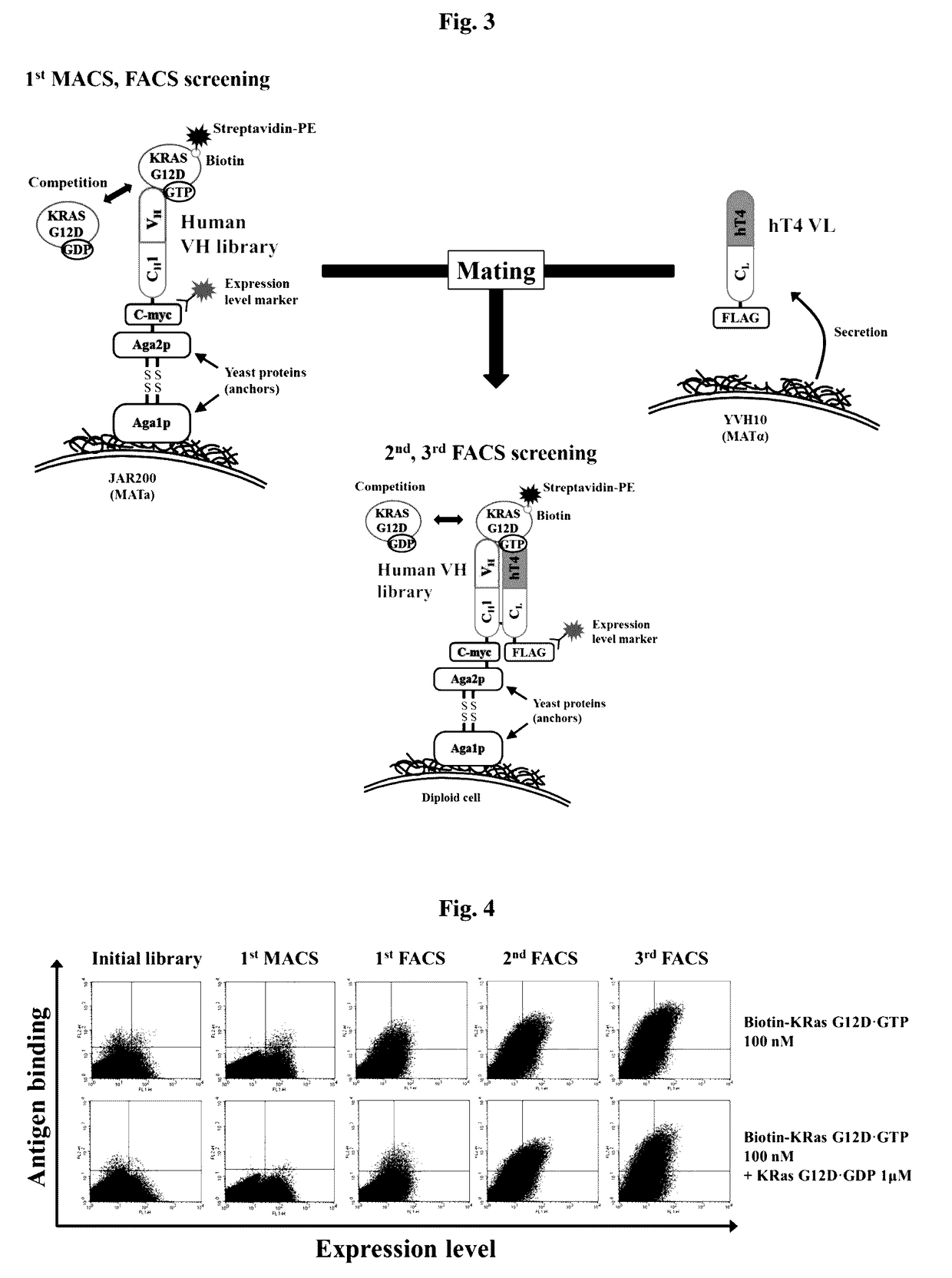
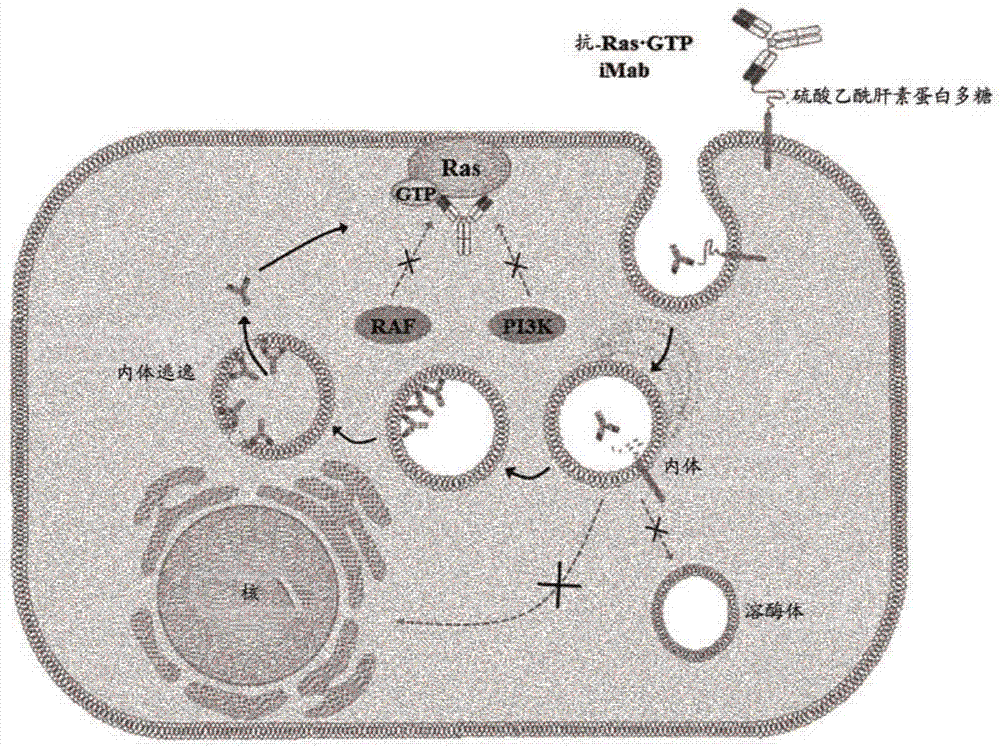
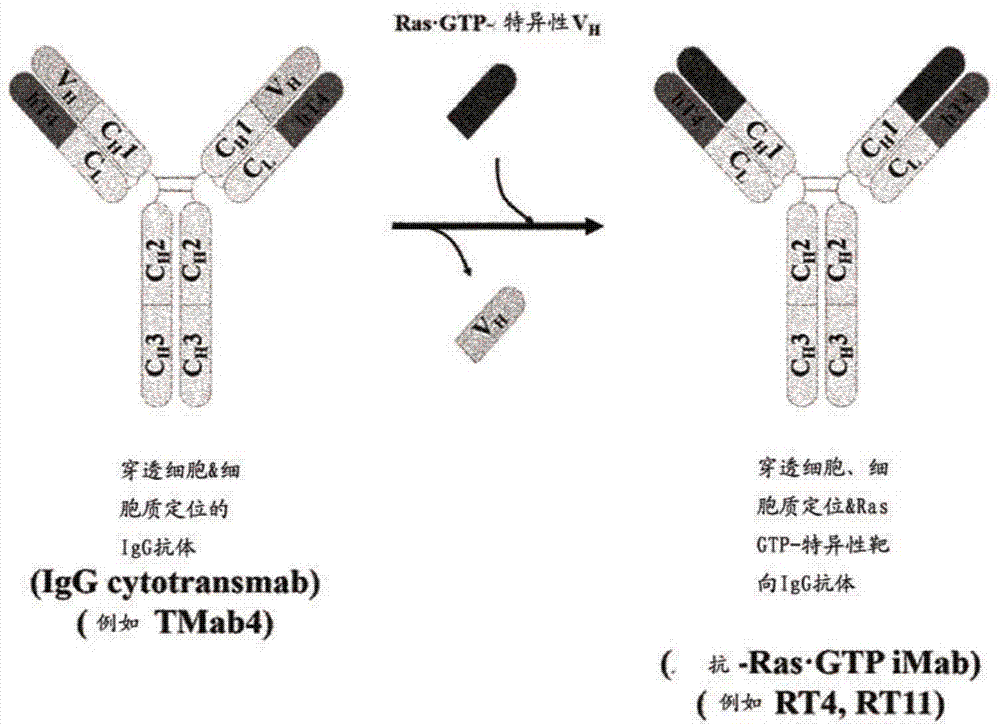
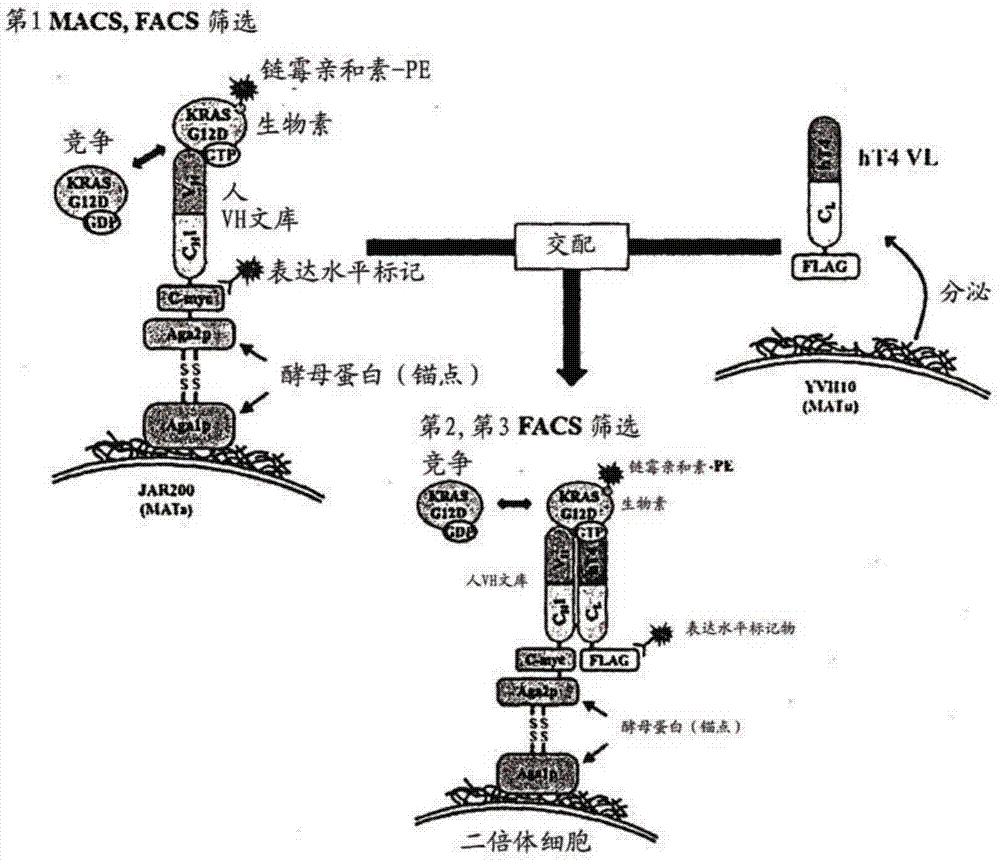
Method for inhibiting intracellular activated ras using intact immunoglobulin-type antibody having cytosol-penetrating ability and use thereof
ActiveUS20170158777A1Inhibitory activityNo cytotoxicityCompound screeningHybrid immunoglobulinsDiseaseCytoplasm
The present invention relates to a method for inhibiting intracellular activated RAS using an intact immunoglobulin-type antibody having the ability to penetrate the cytosol. The present invention also relates to a heavy-chain variable region (VH) which induces an intact immunoglobulin-type antibody to actively penetrate the cytosol of living cells through endocytosis and endosomal escape and to bind to activated RAS in the cytosol, and to an antibody comprising the same. The present invention also relates to a method of inhibiting the growth of cancer or tumor cells and a method of treating cancer or tumor, by use of the antibody. The present invention also relates to a method for screening a heavy-chain variable region that binds specifically to RAS in the cytosol. The present invention also relates to a biologically active molecule fused to the antibody and selected from the group consisting of peptides, proteins, small-molecule drugs, nanoparticles and liposomes. The present invention also relates to a composition for prevention, treatment or diagnosis of cancer, comprising: the antibody; or a biological active molecule fused to the antibody and selected from the group consisting of peptides, proteins, small-molecule drugs, nanoparticles and liposomes. The present invention also relates to a polynucleotide that encodes the light-chain variable region and the antibody.According to the present invention, the method for inhibiting intracellular activated RAS using an intact immunoglobulin-type antibody having the ability to penetrate the cytosol is achieved by allowing the antibody to penetrate living cells and to specifically recognize activated (GTP-bound) RAS in the cytosol. Thus, the antibody can target activated (GTP-bound) RAS in the cytosol of living cells and inhibit the activity of the RAS.Furthermore, the antibody light-chain variable region according to the present invention and an antibody comprising the same is able to penetrate living cells and localize in the cytosol, without having to use a special external protein delivery system. Particularly, the antibody light-chain variable region according to the present invention can easily interact with various human heavy-chain variable regions (VHs) and has the ability to penetrate the cytosol and remain in the cytosol, and an intact IgG-type monoclonal antibody comprising the light-chain variable region can penetrate cells and localize in the cytosol, and shows no cytotoxicity non-specific for target cells.The antibody heavy-chain variable region according to the present invention and an antibody comprising the same can selectively inhibit mutations of the major drug resistance-related factor RAS of conventional various tumor therapeutic agents, and can exhibit synergistic anticancer activity with conventional therapeutic agents. In addition, the cytosol-penetrating, intact immunoglobulin-type antibody according to the present invention can penetrate cells and remain in the cytosol, without affecting the high specificity and affinity of a human antibody heavy-chain variable region (VH) for antigens, and thus can localize in the cytosol which is currently classified as a target in disease treatment based on small-molecule drugs, and at the same time, can exhibit high effects on the treatment and diagnosis of tumor and disease-related factors that show structurally complex interactions through a wide and flat surface between protein and protein.
Owner:ORUM THERAPEUTICS INC
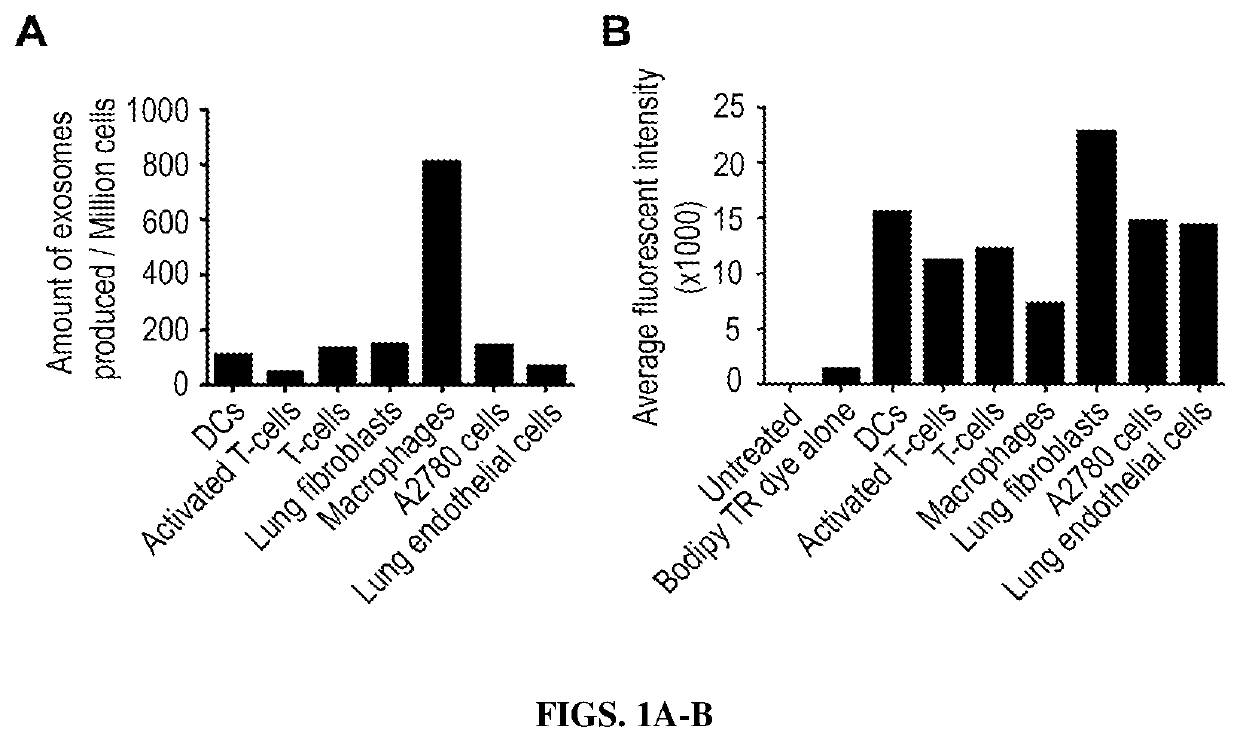
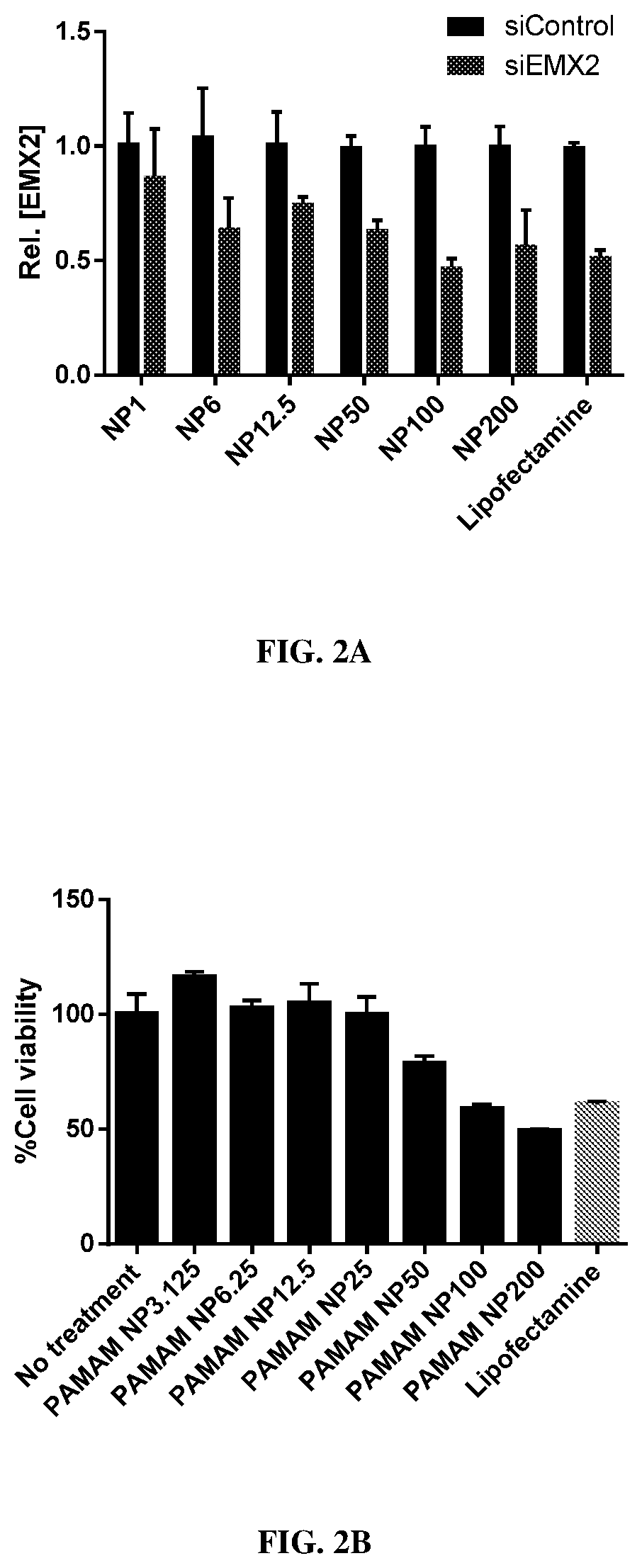
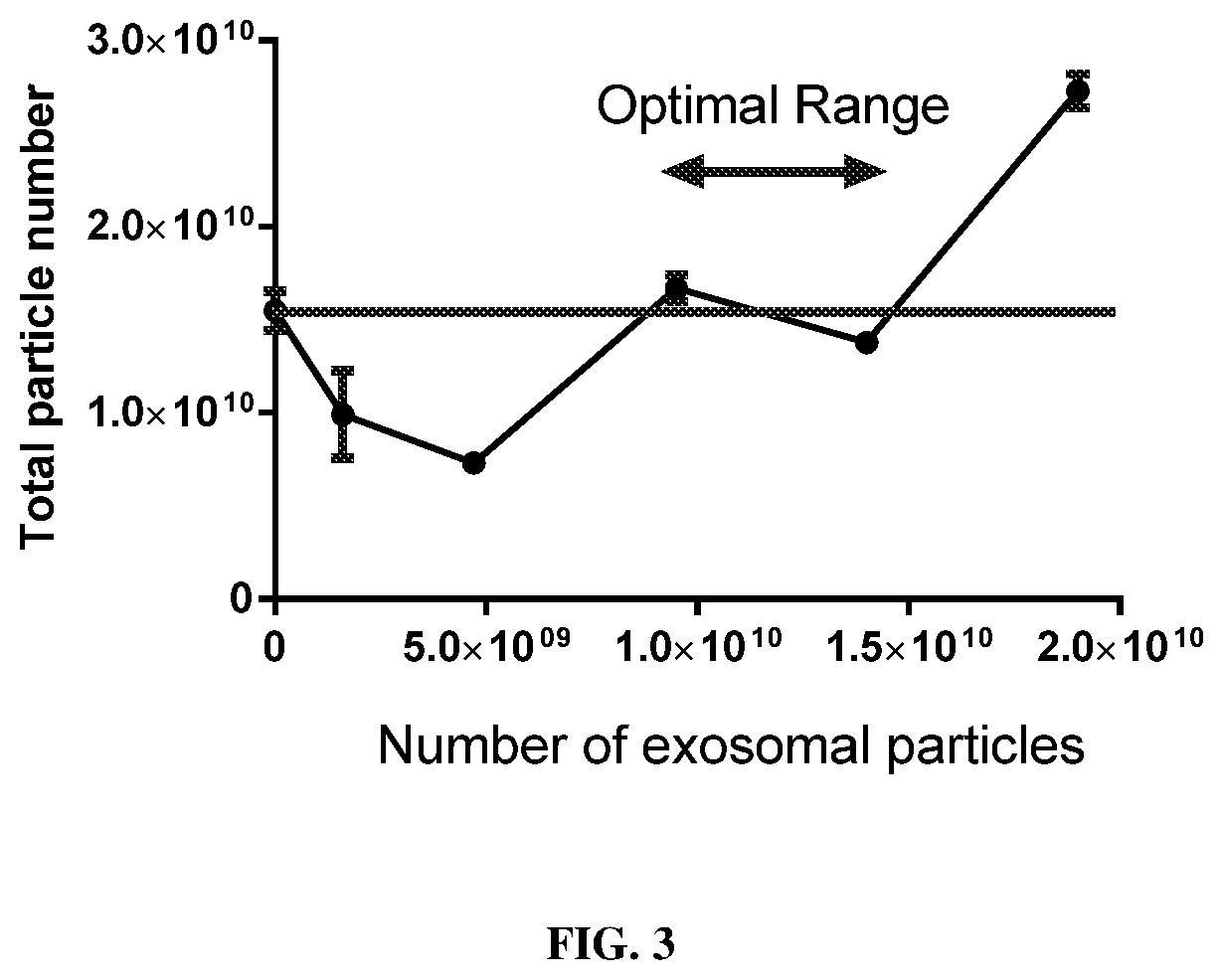
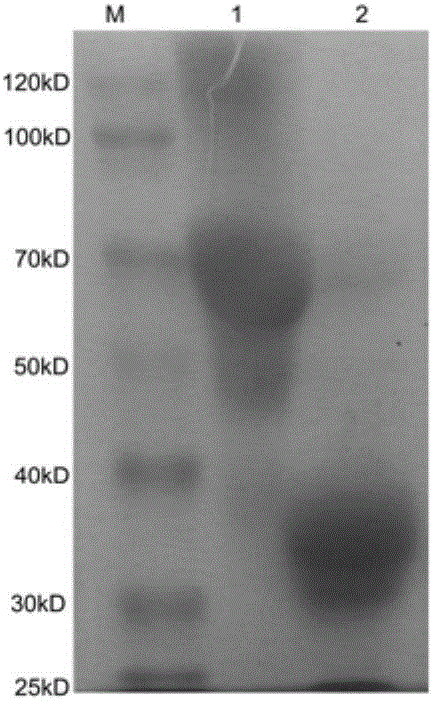
Hybrid exosomal-polymeric (HEXPO) nano-platform for delivery of rnai therapeutics
PendingUS20200069594A1Improve efficiencyEfficient deliverySpecial deliveryMicroencapsulation basedAntibody SuppressionAntiendomysial antibodies
Provided herein are lipid-based nanoparticles (e.g., exosomes) having (a) a core comprising a cationic polymer and a therapeutic agent (e.g., a therapeutic protein, an antibody, an inhibitory RNA, and / or a small molecule drug) and (b) a lipid coating comprising an exosomes-derived membrane. Furthermore, the present invention provides methods of producing such nanoparticles as well as methods for use of such lipid-based nanoparticles in therapy.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
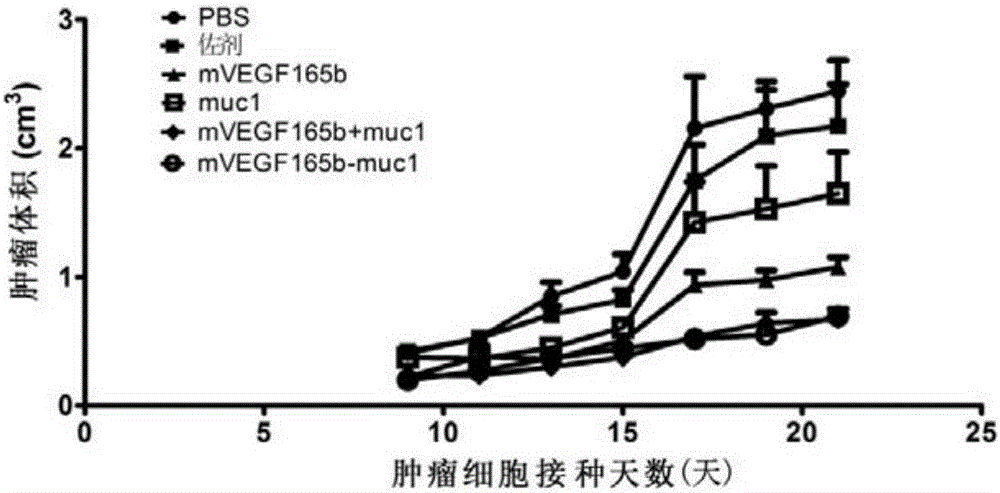
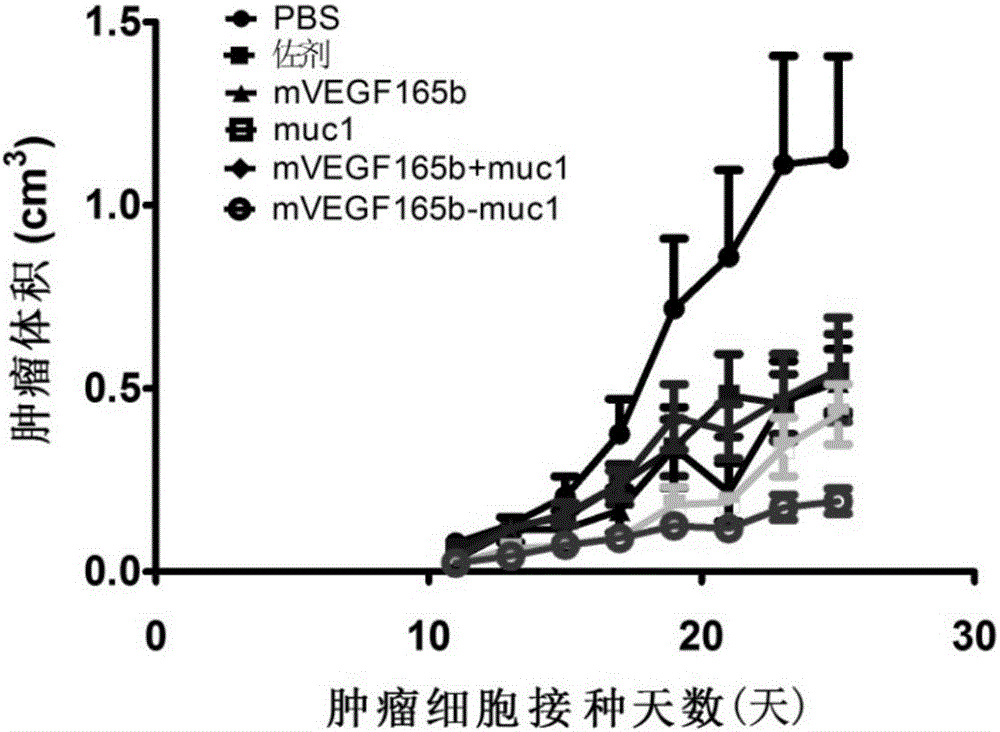
Antitumor vaccine, encoding gene, expression vector, expression engineering bacteria and application of targeted VEGF and mucin1
ActiveCN106279435AAffinity chromatography is convenientAffinity Chromatography ExpressFungiTumor rejection antigen precursorsTumor vesselMutant
The invention discloses an antitumor vaccine, an encoding gene, an expression vector, an expression engineering bacteria and application of targeted VEGF and mucin1, and belongs to the technical field of biology. An antitumor vaccine fusion protein adopts VEGF165, VEGF165b or corresponding modified VEGF mutants as an epitope vector, at least one section of epitope peptide of tumor related antigen mucin1 is connected to an end N or an end C of the vector to form the antitumor vaccine having a double target effect. The VEGF in the vaccine can be used as the epitope vector to improve the antigenicity of the mucin1 epitope connected with the VEGF, the over-expressed mucin1 tumor cells are killed, the VEGF can also be used as an antigen to produce an antibody for VEGF so as to inhibit the generation of tumor vessels and cut off the nutrient supply of the tumor. Meanwhile, the epitope vector has a heparin-binding domain which can be bond with heparin sepharose, thereby facilitating the subsequent protein purification.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
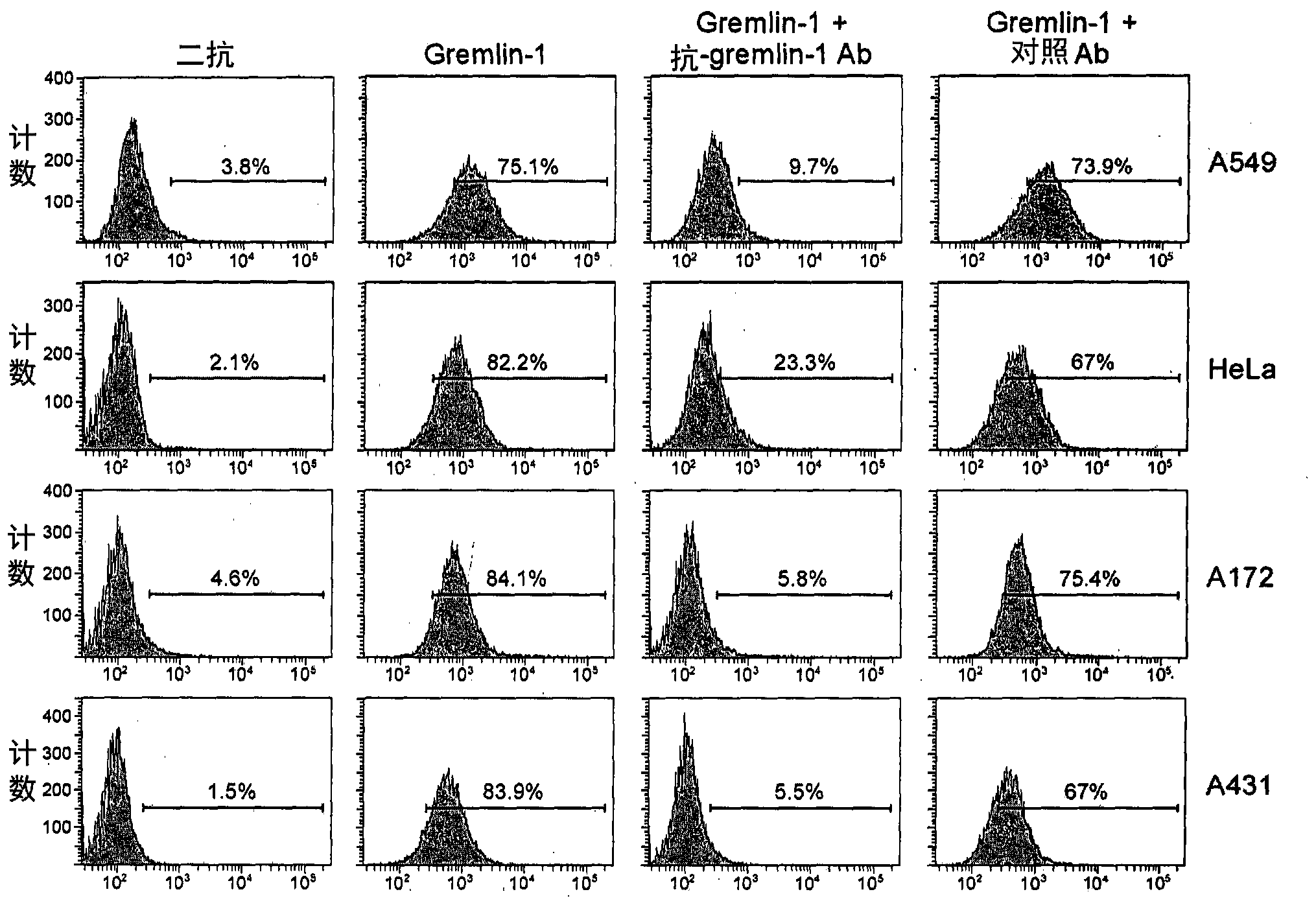
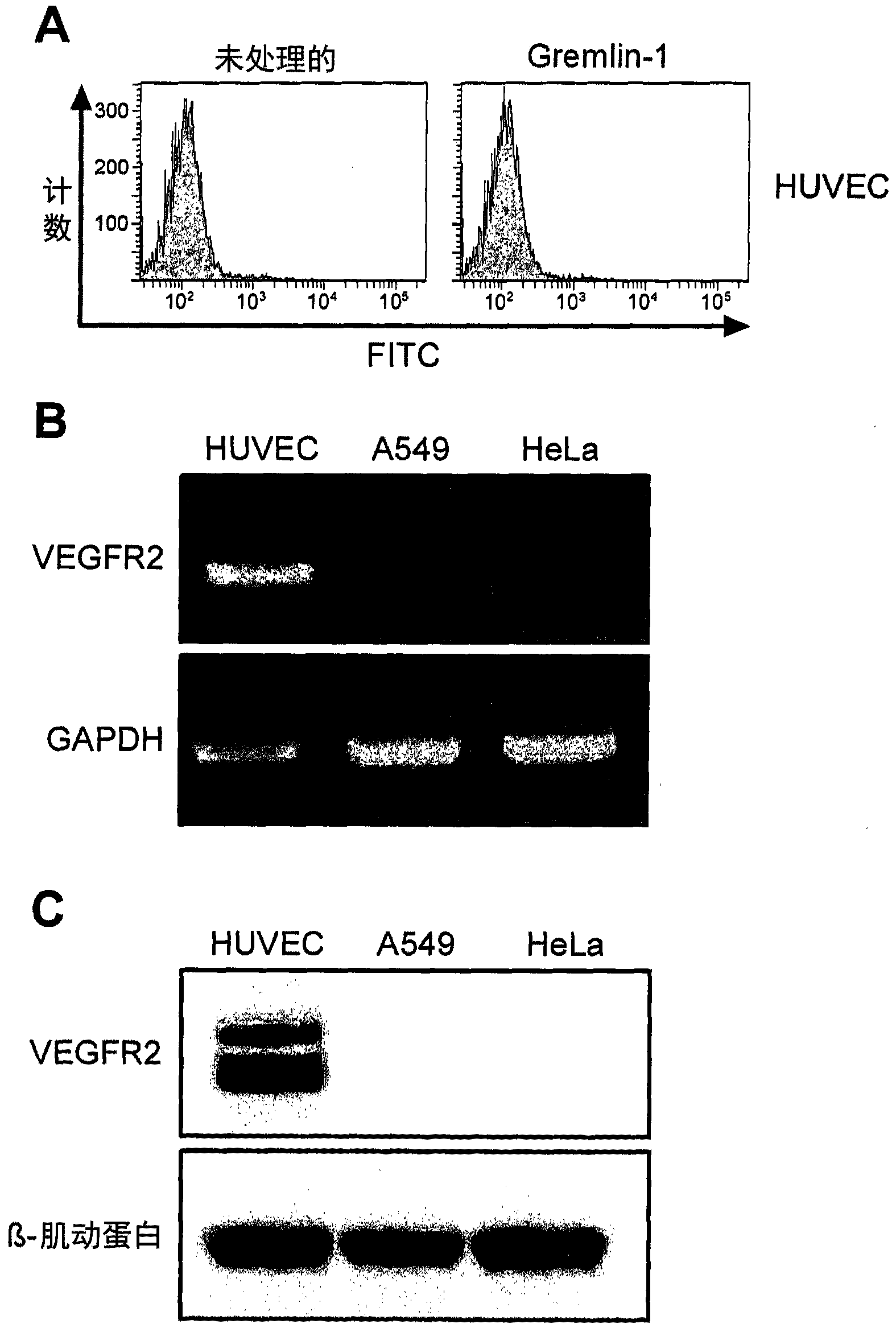
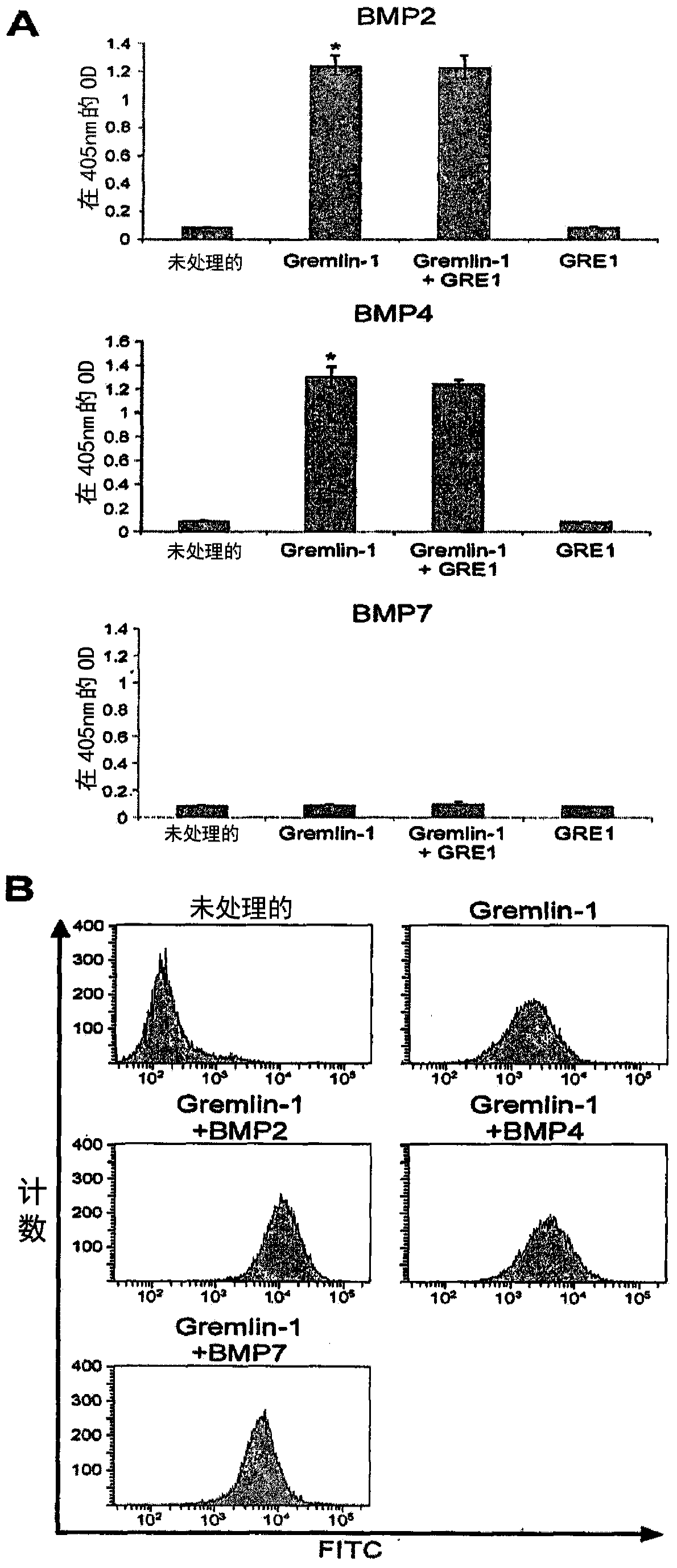
Gremlin-1 antibody
ActiveCN104321342AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticNervous disorderAntipyreticCell invasionAntibody
The present invention relates to a Gremlin-1 antibody that inhibits Gremlin-1 in a manner independent of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) or vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2), thus providing the effect of treating cancer. The antibody of the present invention inhibits cell migration, cell invasion and cell proliferation which are dependent on Gremlin-1, and therefore, can be effectively used in treating cancer or immune disease.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
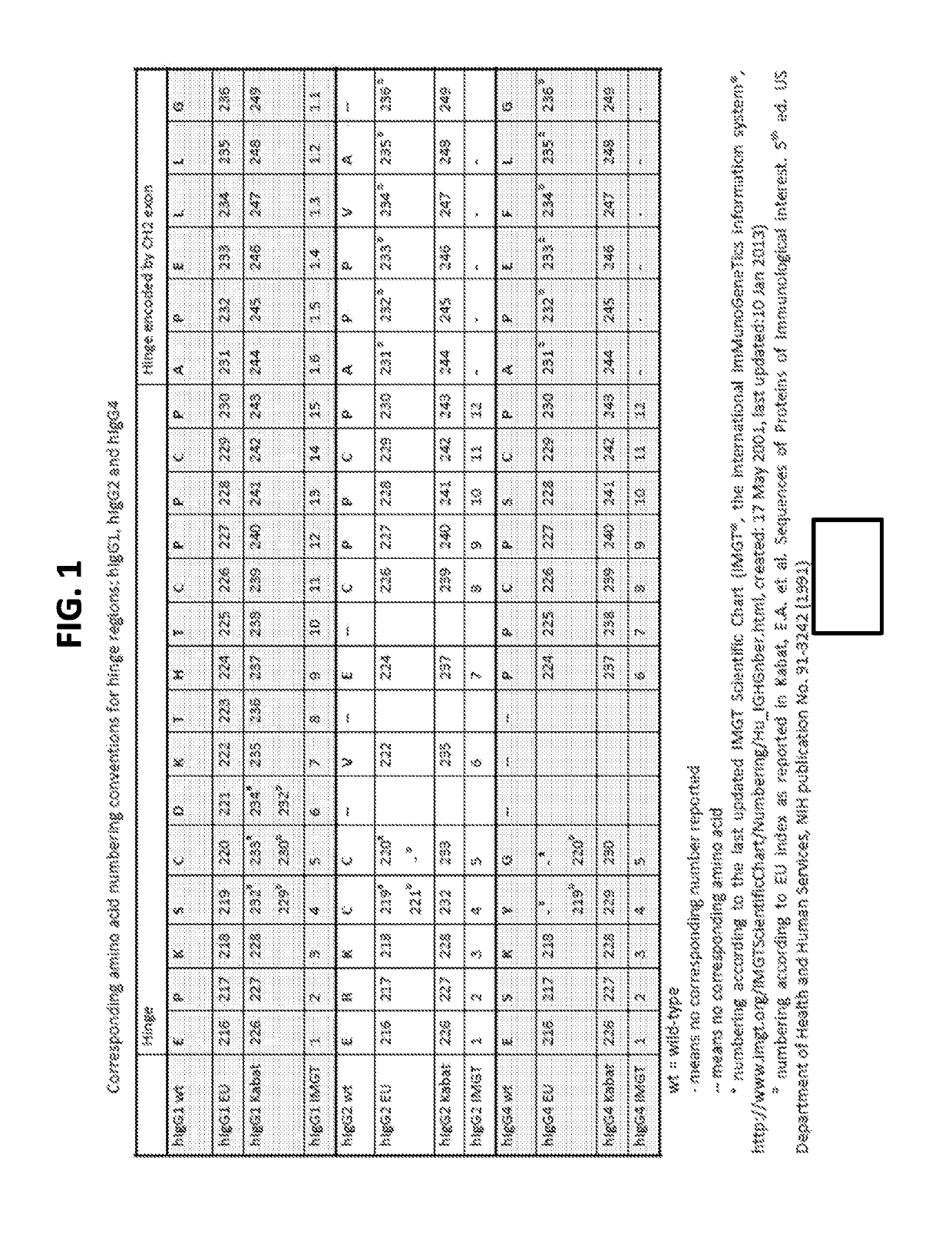
Heavy chain constant regions with reduced binding to Fc gamma receptors
ActiveUS10556952B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody SuppressionGlycine
The invention provides antibody heavy chain constant regions with a hinge region modified to reduce binding to Fcγ receptors. The modification occurs within positions 233-236 by replacement of natural residues by glycine(s) and / or deletion(s). Such modifications can reduce binding of an antibody bearing such a constant region to Fcγ receptors to background levels. The constant regions can be incorporated into any format of antibody or Fc fusion protein. Such antibodies or fusion proteins can be used in methods of treatment, particularly those in which the mechanisms of action of the antibody or Fc fusion protein is not primarily or at all dependent on effector functions, as is the case when an antibody inhibits a receptor-ligand interaction or agonizes a receptor.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Pd-1 antibodies and uses thereof
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to human PD-1 with high affinity. Nucleic acid molecules encoding the antibodies of the invention, expression vectors, hostcells and methods for expressing the antibodies of the invention are also provided. The PD-1 antibodies of the present invention inhibit the binding of PD-L1 to PD-1, thereby modulating immune responses in general, and those mediated by TcR and CD28, in particular. The invention also provides methods for treating various diseases, including infectious diseases and cancer using the PD-1 antibodiesof the present invention.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHANGJIANG BIOTECH
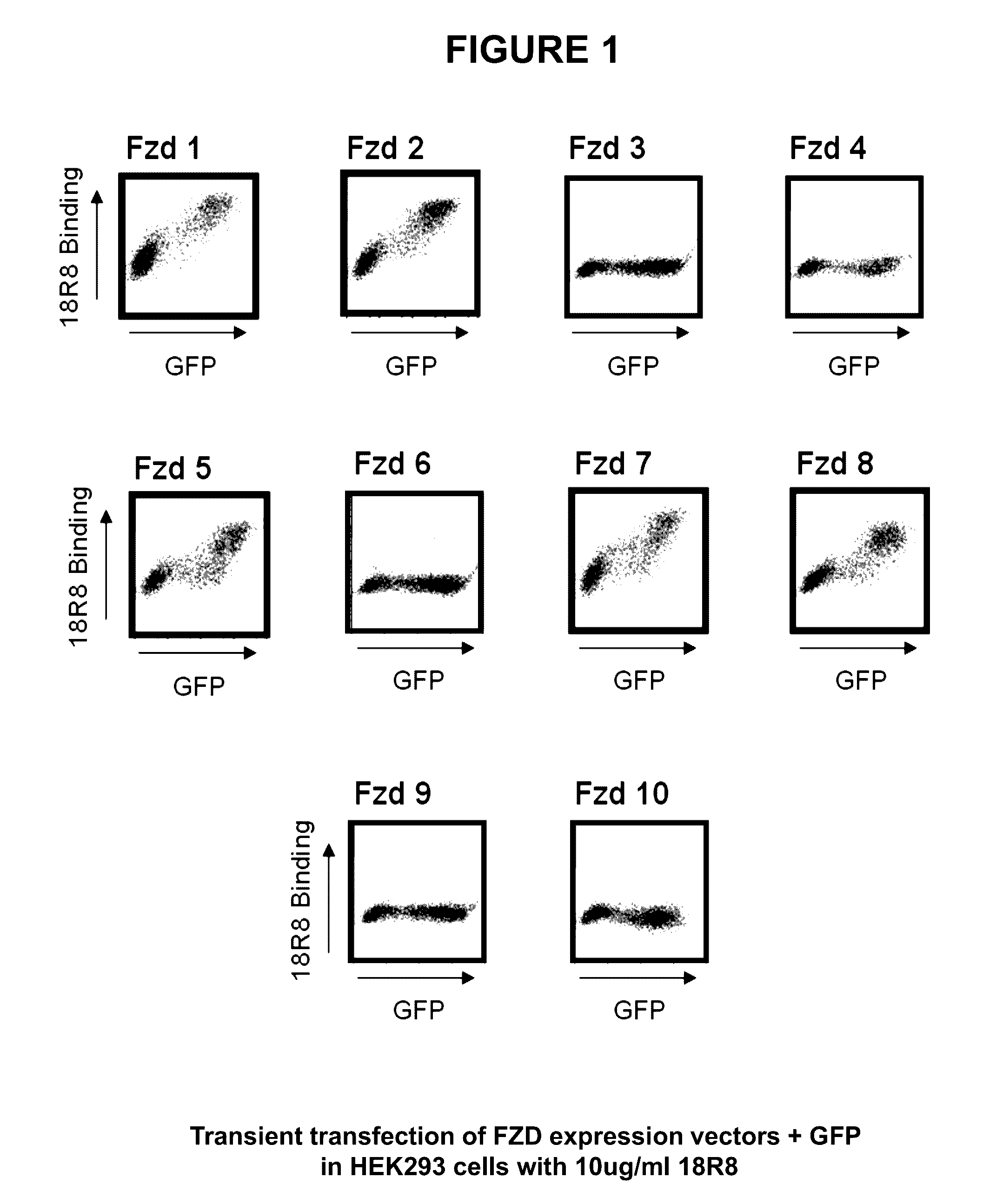
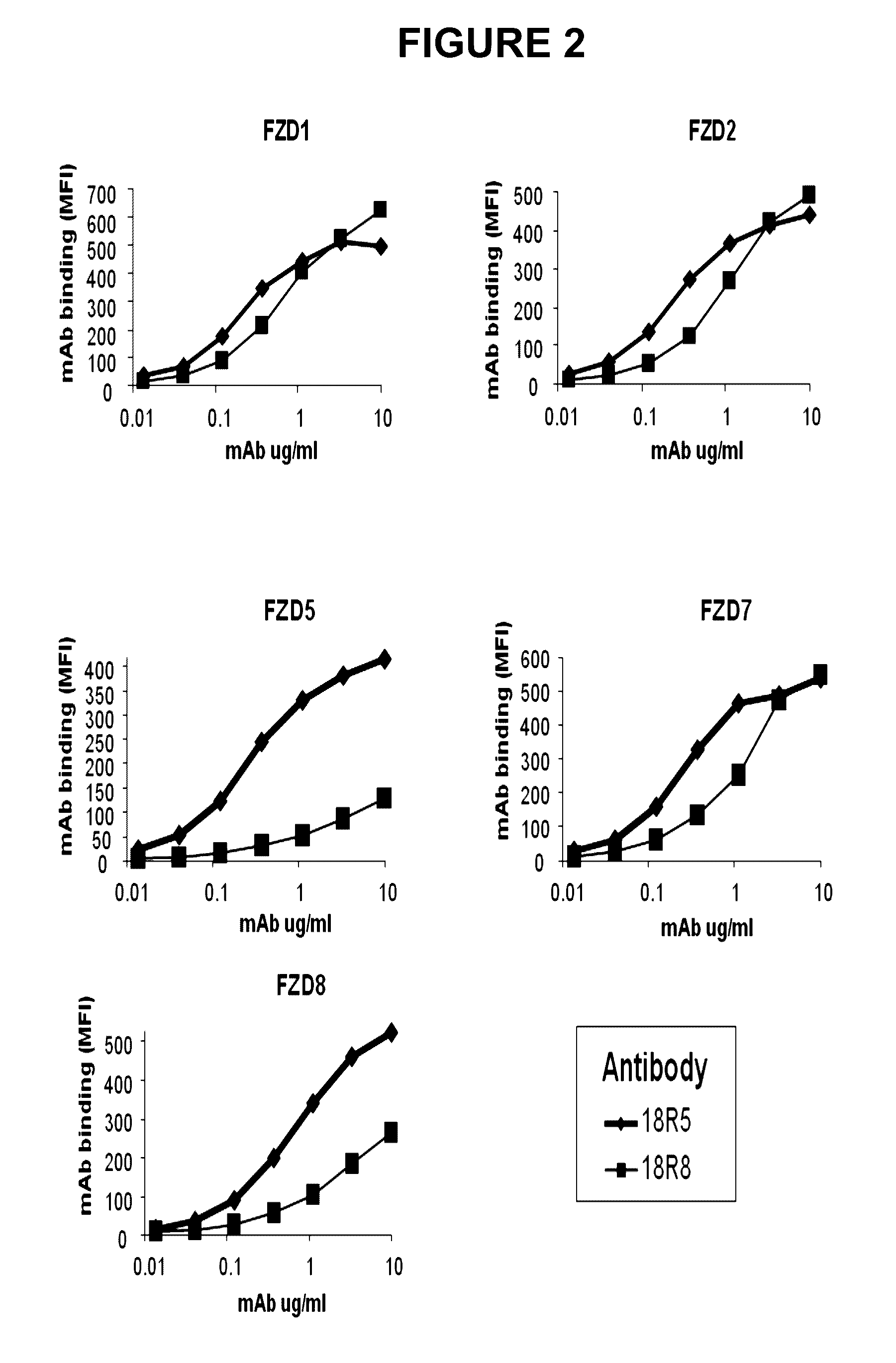
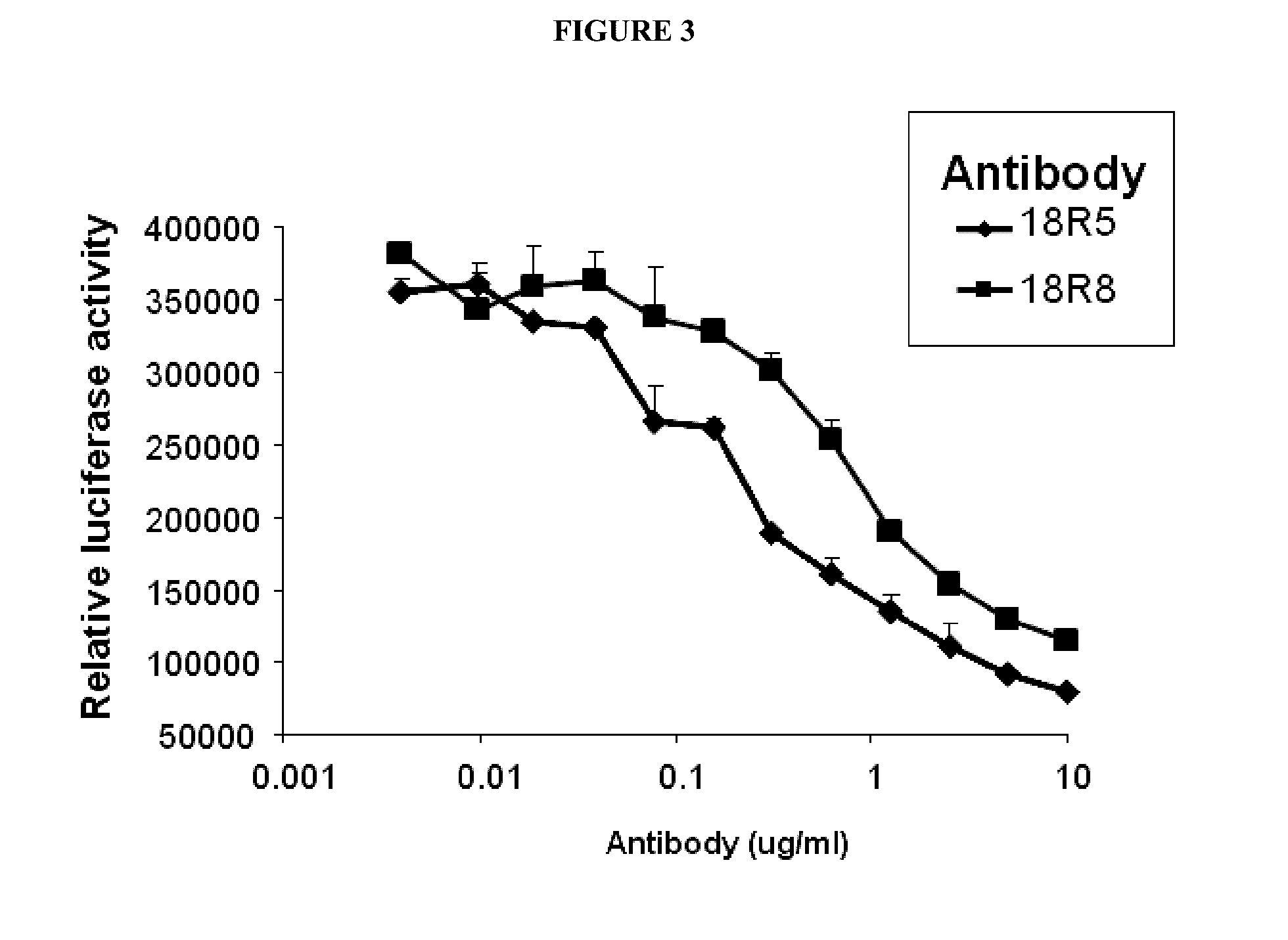
Antibodies against human FZD5 and FZD8
InactiveUS9573998B2Organic active ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody SuppressionAnticarcinogen
Owner:ONCOMED PHARMA
Inhibitors of autophosphorylation protein kinases
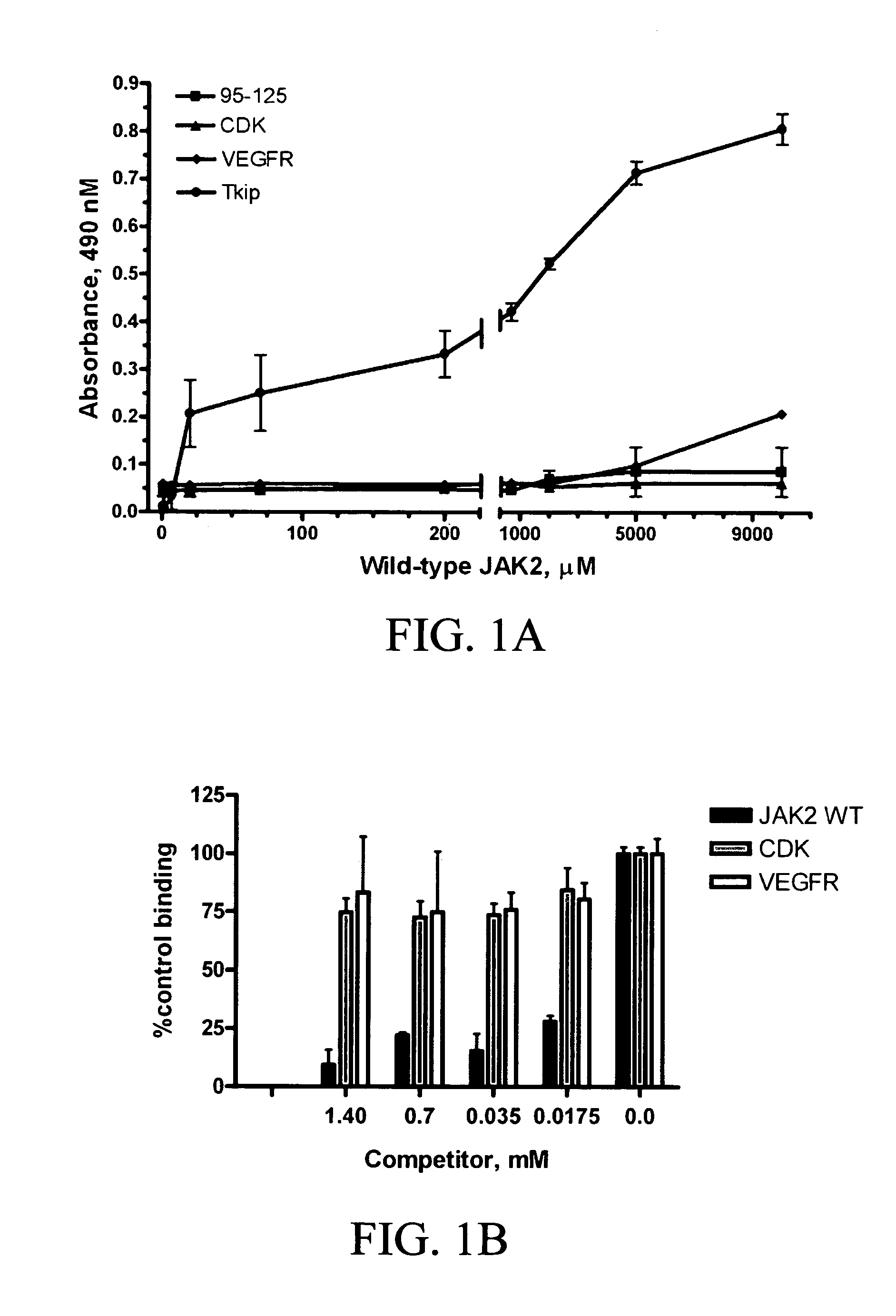
InactiveUS7189694B2Inhibit enzymatic functionShuts down functioning pathwayPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticADAMTS ProteinsTyrosine
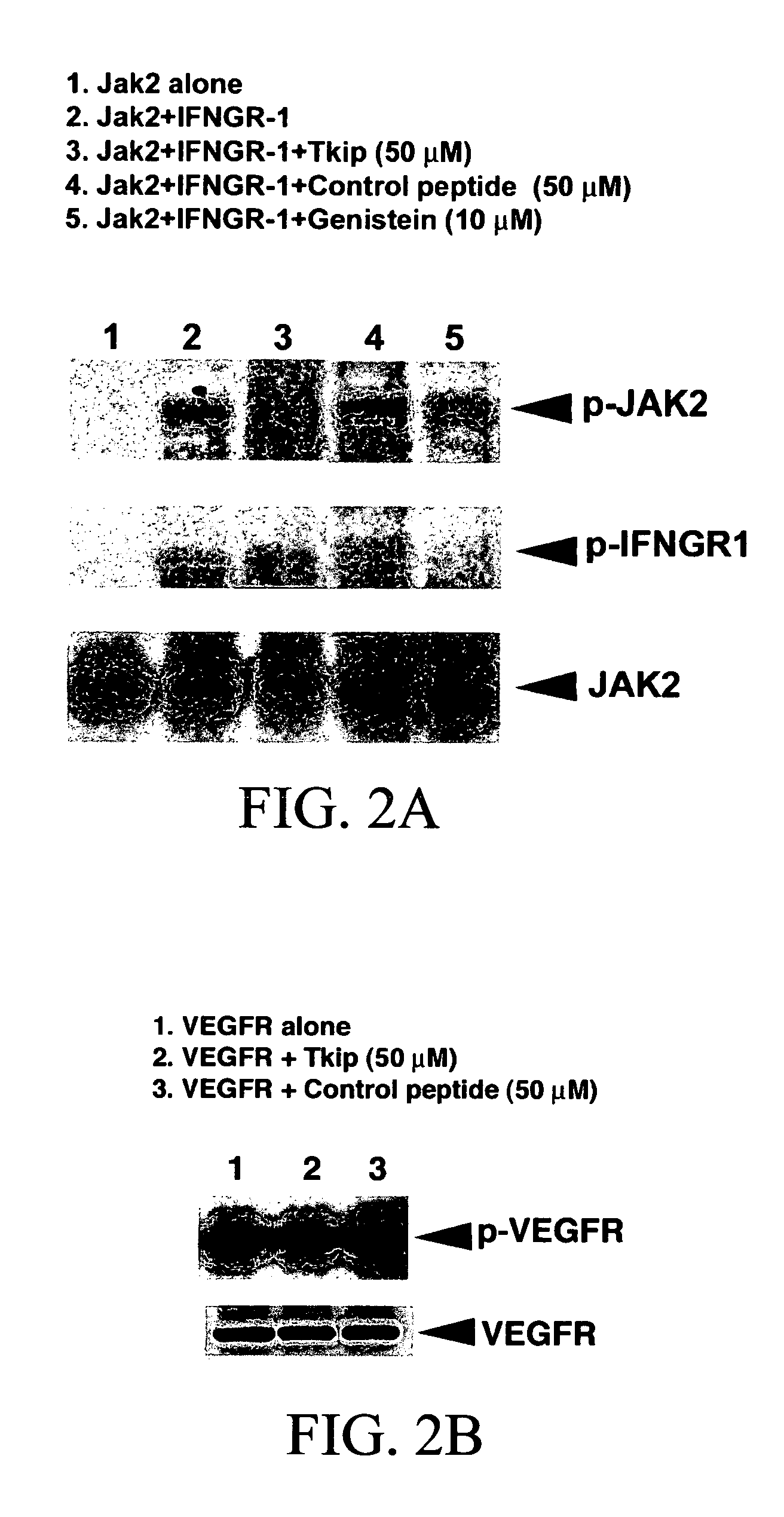
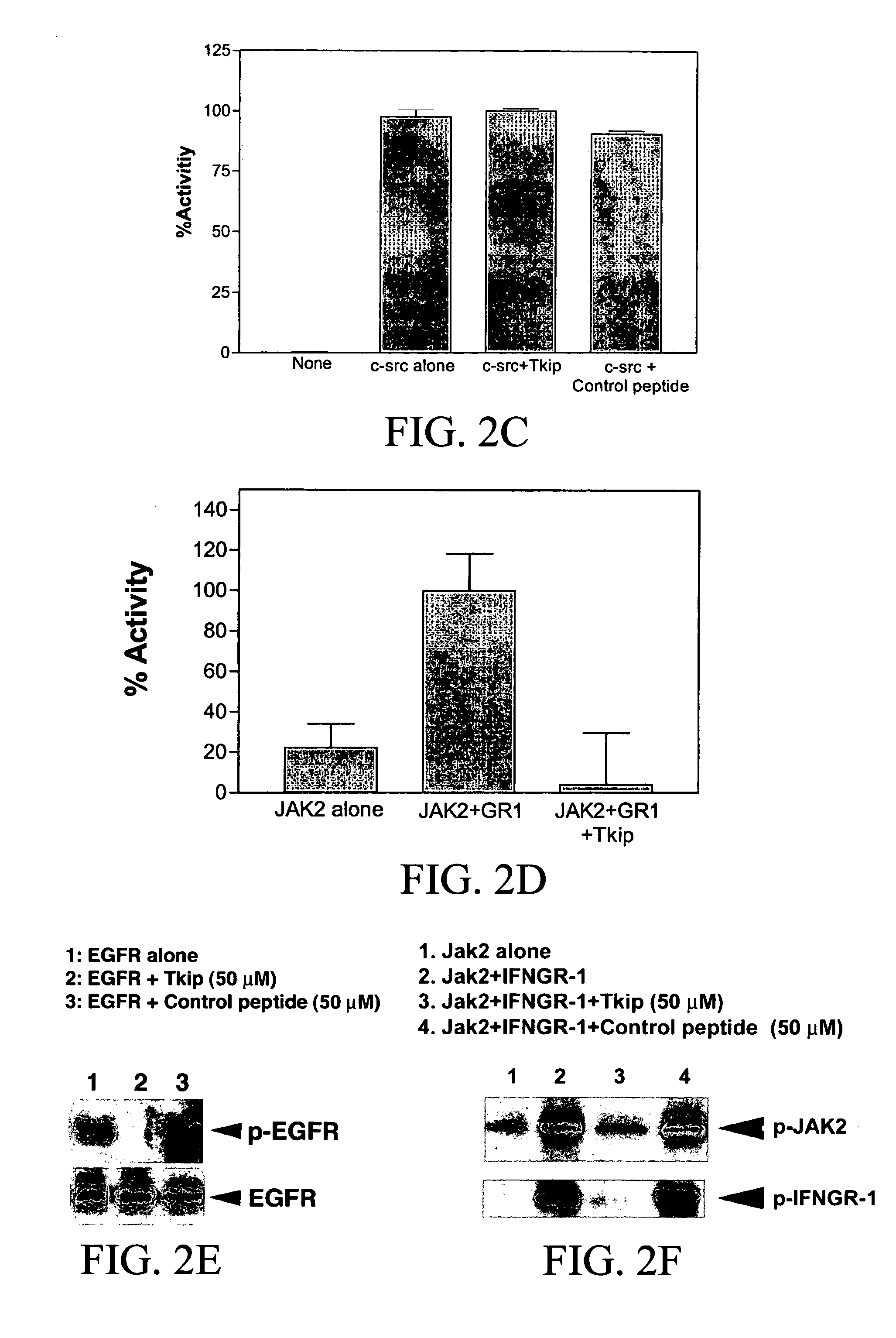
The subject invention concerns peptide molecules that specifically inhibit the enzymatic function of tyrosine kinases, including the JAK and EGF receptor (EGFR) family of kinases, to autophosphorylate, i.e., to transfer a phosphate group from ATP to an amino acid in the kinase. Phosphorylation of proteins is the most fundamental method for signal transduction among proteins in a cell. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation activities inhibits the enzyme's signaling and shuts down the functioning pathways originating from the enzyme. The JAK2 and EGFR tyrosine kinases are involved in both inflammatory disorders and cancer. In these disorders, the tyrosine kinases can often be activated in an uncontrolled fashion. The subject application also concerns antibodies that bind to a tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation site. The subject invention also concerns pharmaceutically acceptable formulations of the subject peptides and antibodies, and methods for treating inflammatory and oncological disorders by inhibiting tyrosine kinase signaling in these situations by administering a peptide or antibody of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
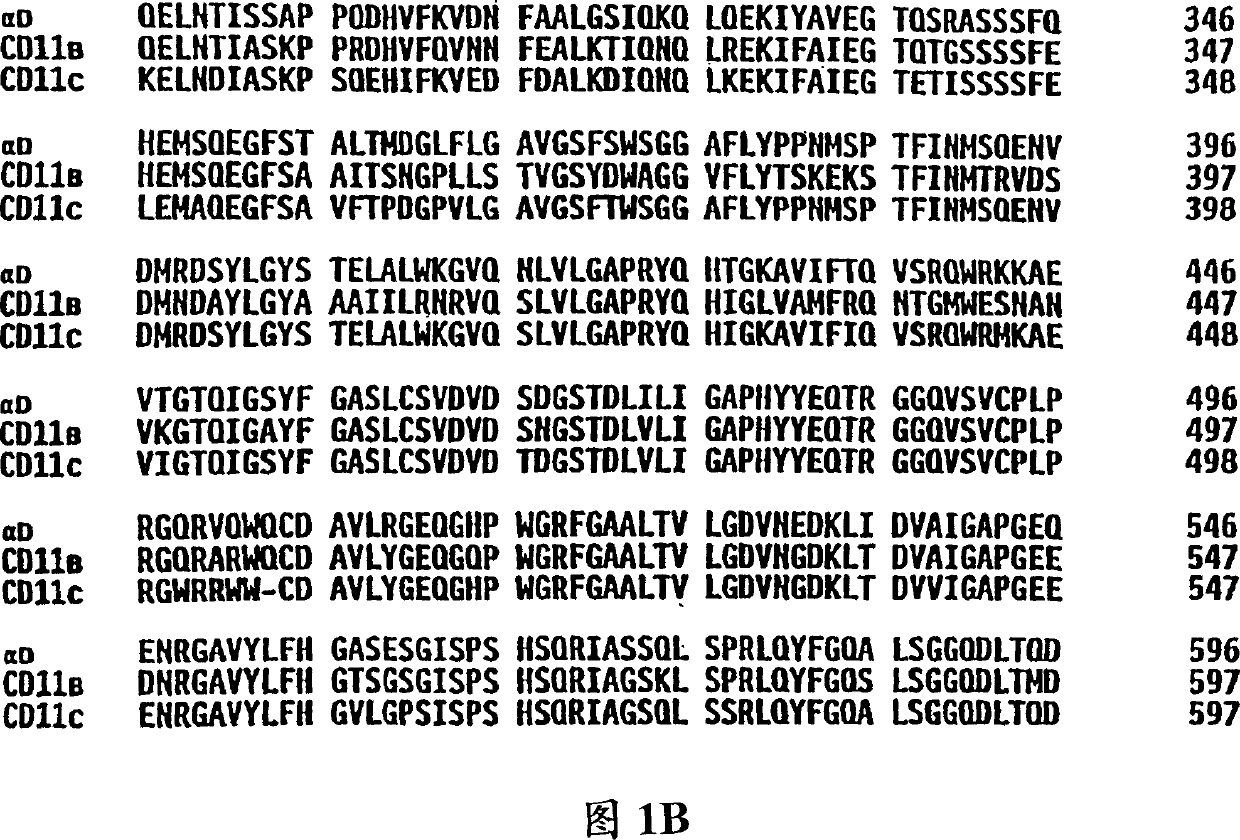
Method for inhibiting macrophage infiltration using monoconal anti-alpha-D-antibodies
Methods to inhibit inflammation and macrophage infiltration following spinal cord injury are disclosed along with methods to modulate TNFalpha release from cells expressing alphad are disclosed.
Owner:ICOS CORP
Jcv neutralizing antibodies
ActiveUS20150050271A1Reduce viral loadIncrease awarenessImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsMonoclonal antibodyNeutralizing antibody
In one aspect, the disclosure provides neutralizing antibodies against JCV and methods for the treatment of PML. In some embodiments, aspects of the invention relate to an isolated JC-vims neutralizing monoclonal antibody against JCV capsid protein VPI (JCV-VP1). In some embodiments, the antibody suppresses infectivity of the JC-vims. In some embodiments, the antibody binds the sialic acid binding pocket of JCV-VP1.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Malaria vaccine
InactiveUS20020160017A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPlasmodium merozoiteMalaria
A non-naturally occurring variant of a C-terminal fragment of a Plasmodium merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1) wherein said variant has (i) a reduced affinity, compared with a naturally occurring Plasmodium MSP-119, for at least one first antibody capable of blocking the binding of a second antibody, which second antibody inhibits the proteolytic cleavage of Plasmodium MSP-142 and (ii) substantially the same affinity for at least one third antibody compared with said naturally occurring Plasmodium MSP-119. which third antibody inhibits the proteolytic cleavage of Plasmodium MSP-142 is provided for use in an anti-malarial vaccine.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Red blood cells covalently bound with polymers
InactiveUS20020141976A1Preserve functionPreserve viabilityBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseBlood plasma
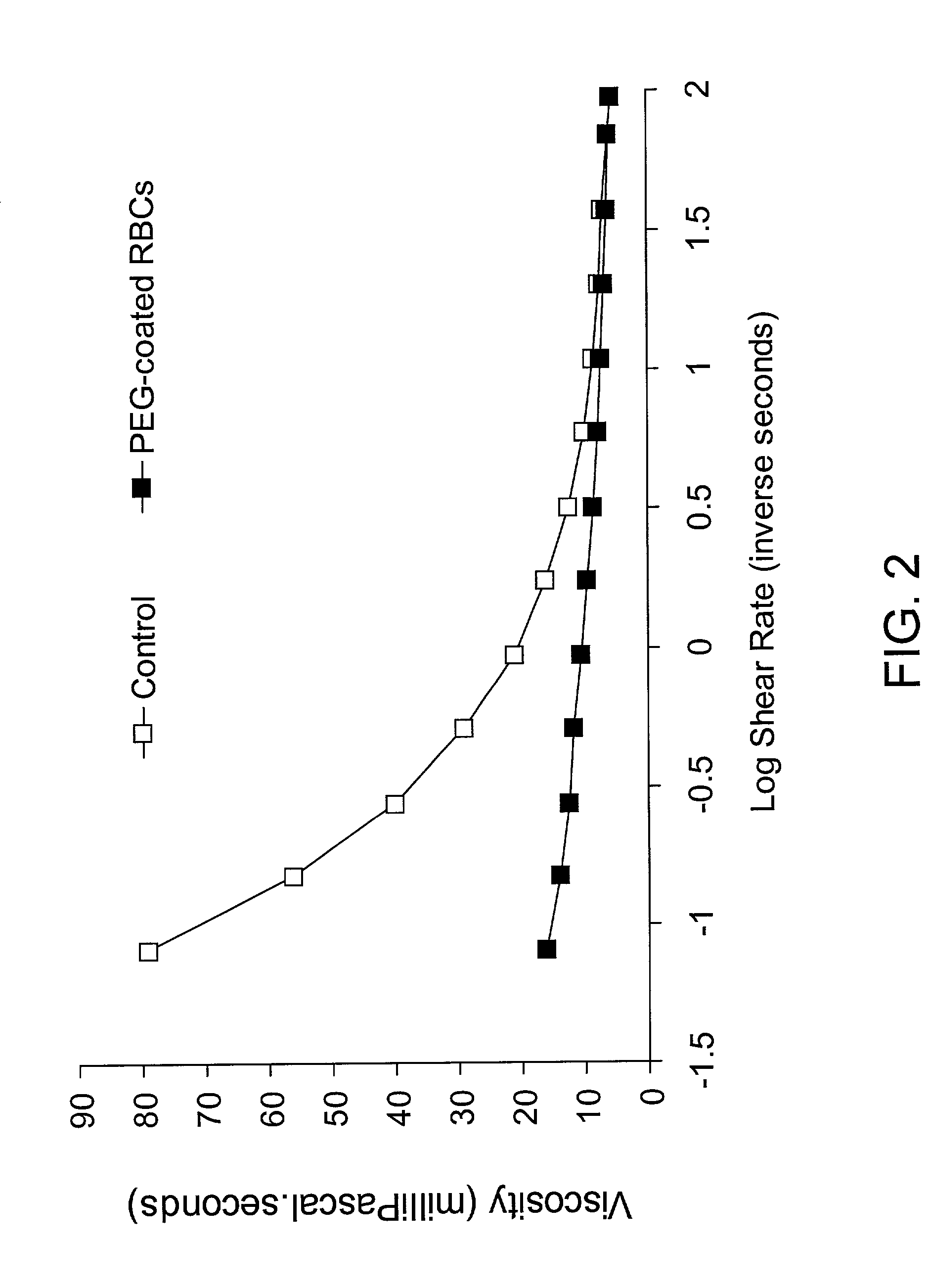
Living cells modified at their surface with specially selected polymers are disclosed. A simple method to covalently attach specially selected PEG derivatives to the surface of RBC in aqueous media under mild conditions is a preferred example. The selected PEG-modification dramatically reduced aggregation and low shear viscosity of RBC resuspended in autologous plasma, and inhibited RBC agglutination by blood group-specific antibodies. The morphology and deformability of the PEG-treated cells were unaltered. The PEG coating of the RBC surface is applicable to the treatment of a variety of diseases characterized by vaso-occlusion or impaired blood flow, e.g., myocardial infarction, shock, and sickle cell disease.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Recombinant phage peculiar smell removal vaccine for boars
ActiveCN102335422AOvercoming the disadvantage of weak immunogenicityImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesAntibody SuppressionT7 phage
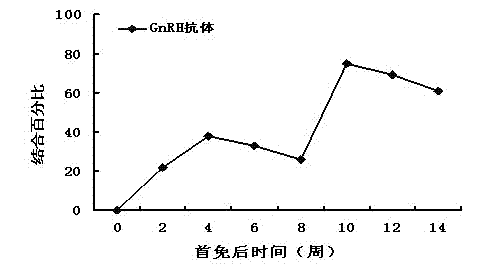
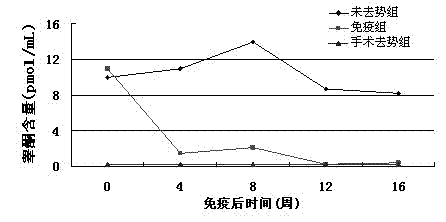
The invention provides a recombinant phage peculiar smellremoval vaccine for boars. In the vaccine, recombinant T7 phage is used as an antigen; gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) protein shown as SEQ ID No:2 in amino acid sequences is expressed on the surface of the recombinant T7 phage; and the GnRH protein is expressed by inserting three copied GnRH genes into the downstream of a P10B gene of the T7 phage. The recombinant phage peculiar smell removal vaccine has the advantages that: (1) the recombinant phage vaccine prepared from a T7 phage carrier can overcome the defect of poor immunogenicity of a GnRH peptide hormone, improve immunogenicity effectively, stimulate organisms to generate an antibody with a higher level and inhibit the development of testicles of the boars; (2) the T7phage is easy to cultivate and purify, and has multiple advantages when used for producing genetic engineering vaccines, so the recombinant phage peculiar smell removal vaccine is convenient to produce in large scale and low in cost; and (3) an immunological method is more humanistic, so the conventional castration method is replaced, and the requirements of modern large-scale feeding and management are met.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Use of diseases-associated gene
InactiveUS20030108951A1Low toxicEfficient activationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseHeart disease
The present invention relates to a method of screening a drug by using a disease-associated gene product, an antibody to the disease-associated gene product, an antisense DNA that suppresses the expression of the disease-associated gene, etc. A compound regulating the activity of a protein having an amino acid sequence which is the same or substantially the same amino acid sequence as the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1, or its salt, a neutralizing antibody regulating the activity of the above protein, an antisense DNA, etc. can regulate the expression of the protein having an amino acid sequence which is the same or substantially the same amino acid sequence as the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 and, therefore, are usable as preventive / therapeutic agents for diseases, e.g., heart diseases, etc.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Molecular marker for eimeria tenella sensitive strain and drug-resistant strain and application of molecular marker
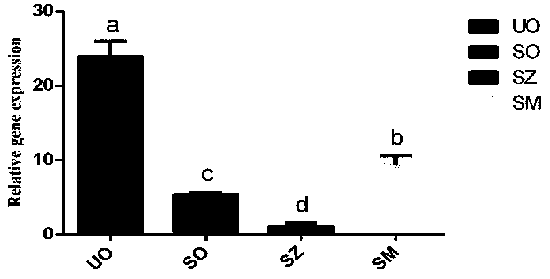
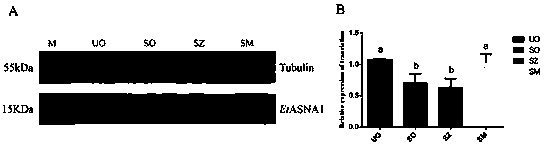
ActiveCN111518788AInhibitionFully resistantHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody SuppressionATPase
The invention provides a molecular marker for an eimeria tenella sensitive strain and a drug-resistant strain and application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker is ATPase (EtASNA1) homologous with eimeria tenella ASNA1. The invention finds that the transcription and protein expression of mRNA of a diclazuril drug-resistant strain and a maduramycin drug-resistant strain are obviously higher than that of the sensitive strain; and the influence of drug stimulation on the EtASNA1 transcription level is detected through an in-vitro culture experiment and an in-vivo experiment, and the invention finds that addition of drugs can cause up-regulation of expression. An antibody inhibition test detects that the EtASNA1 participates in invasion of host cells by polypides. Research results show that the EtASNA1 may participate in invasion, growth and development of eimeria tenella, may be closely related to formation of drug resistance of the eimeria tenella, and may play an important role in resisting drugs.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for suppressing ras activated in cell by using antibody having cytoplasm penetration capacity and complete immunoglobulin form, and use for same
InactiveCN106999575AInhibitory activityDid not show cytotoxicityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAntibody SuppressionIntravenous gammaglobulin
The present invention relates to a method for suppressing RAS activated in a cell by using an antibody having cytoplasm penetration capacity and complete immunoglobulin form. In addition, the present invention relates to a heavy chain variable region (VH) that induces bonding, with RAS activated in a cytoplasm, by means of the active penetration, by an antibody having complete immunoglobulin form, of the cytoplasm of a living cell by endocytosis and endosomal escape, and an antibody comprising same. Also, the present invention relates to a method for treating cancer or tumors or for inhibiting the growth of cancer or tumor cells by using the antibody. The present invention also relates to a method for screening a heavy chain variable region that specifically bonds to RAS in a cytoplasm. The present invention also relates to a bioactive molecule fused to the antibody. The present invention also relates to a composition for preventing, treating or diagnosing cancer, comprising the antibody or the bioactive molecule fused to same. The present invention also relates to a polynucleotide that codes a light chain variable region and the antibody.
Owner:ORUM THERAPEUTICS INC
Inhibition ELISA method for detecting foot-and-mouth disease virus antibody and application
ActiveCN112881710ASolve operational problemsFix stability issuesBiological testingImmunoassaysAntibody SuppressionDisease
The invention relates to an inhibition ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method for detecting a foot-and-mouth disease virus antibody and application, and belongs to the technical field of biotechnology. The inhibition ELISA method comprises the following steps of: directly diluting negative and positive serum and detected serum on an ELISA plate coated with a captured antibody, and then adding an equal amount of virus antigen diluted to a working concentration, at the same time, setting at least four-hole virus antigen control (serum diluent with the same volume is added in advance), inhibiting virus antigens from being combined with captured antibodies on an ELISA plate by foot-and-mouth disease type specific antibodies in the detected serum and negative and positive serum, referring to a liquid phase blocking ELISA method for judgment, taking 50% of the average value of OD values of virus antigen control holes as a critical value of 50% inhibition of the virus antigens, thus successfully establishing the inhibition ELISA method for detecting the foot-and-mouth disease antibody.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
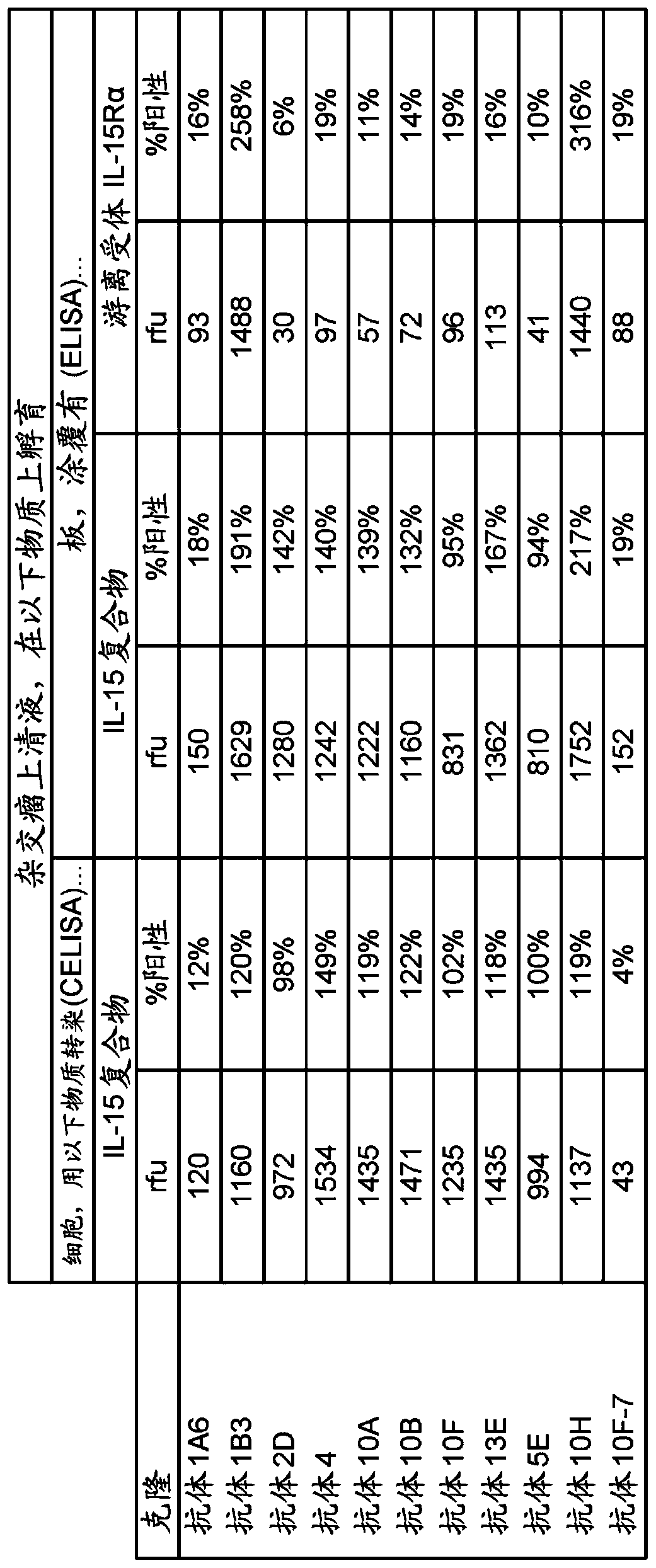
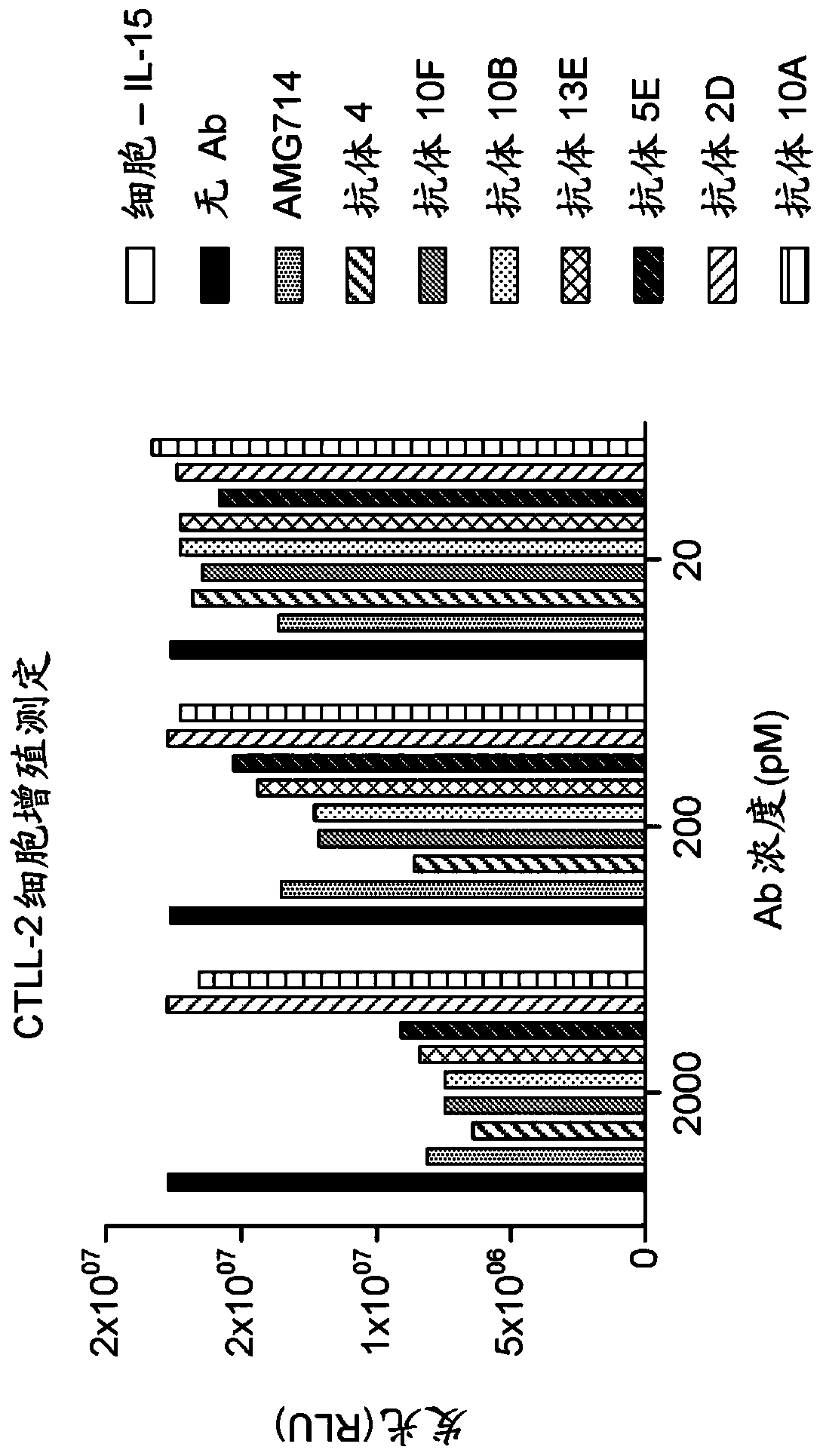
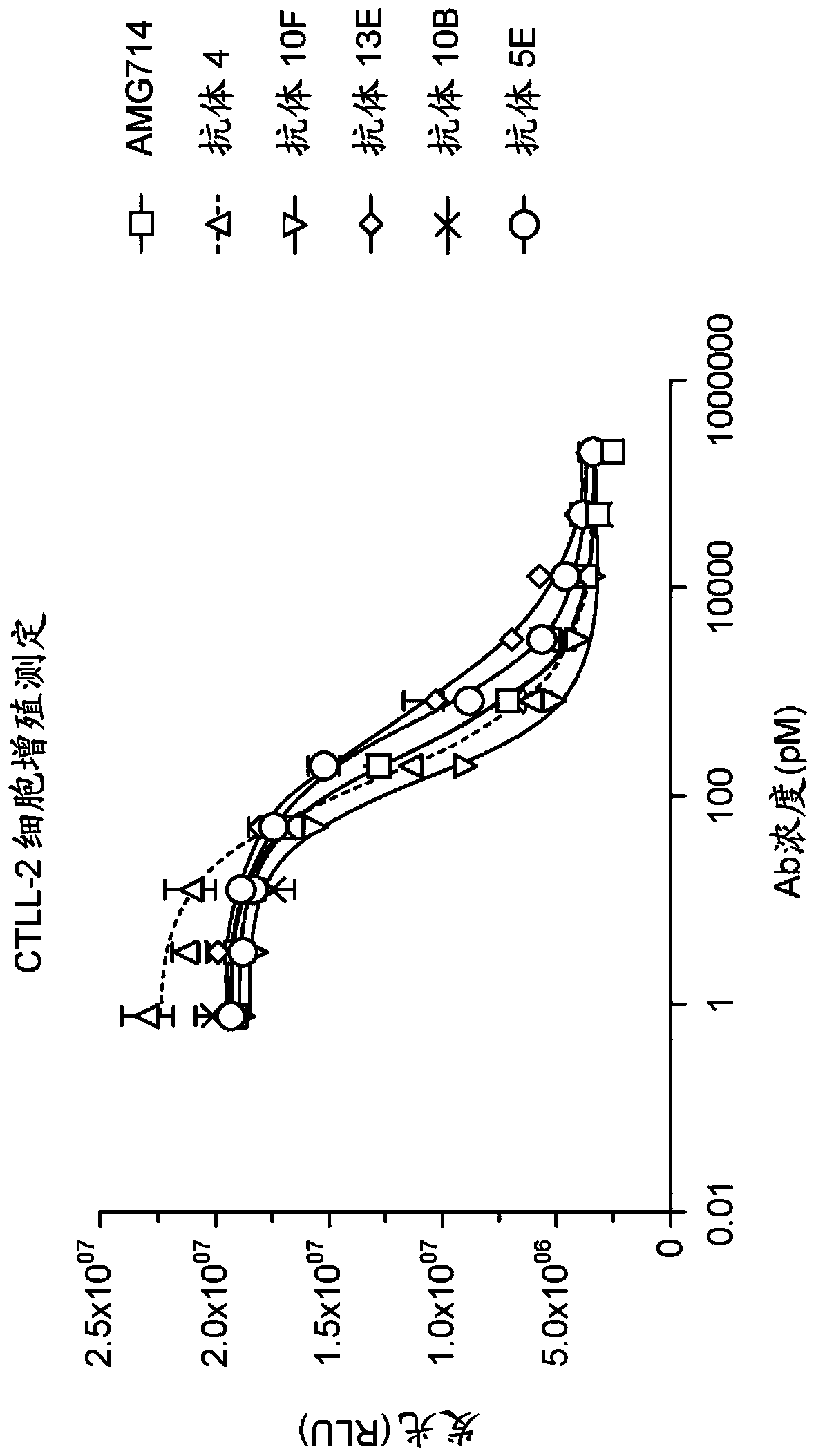
Antibodies that specifically bind to human il-15 and uses thereof
Recombinant antibodies that specifically bind to IL-15 as well as a complex of IL-15 and the IL-15 Receptor-alpha are provided. The antibodies inhibit immune cell proliferation, and are capable of usein the treatment of any autoimmune or inflammatory disease or condition where IL-15 is dysregulated, including Celiac disease.
Owner:赛福伦有限责任公司
Humanized anti-IL-1R3 antibodies
ActiveUS11203642B2Slow catabolismLong half-lifeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntibody SuppressionDisease
The present disclosure relates to humanized antibodies that specifically bind to IL-1R3 or a fragment or derivative thereof or a polypeptide that contains at least a portion of said antibody that is sufficient to confer IL-1R3 binding specificity. Said antibodies inhibit IL-1R3 induced NFkB activity. They also inhibit IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-33, and / or IL-36 stimulated NFkB activity. The disclosure further relates to use of said humanized antibody in the treatment of an IL-1R3 mediated disease such as cancer. The disclosure finally encompasses a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a therapeutically effective amount of the antibody according to the invention. The pharmaceutical composition can be used in treating a IL-1R3 mediated disease such as cancer.
Owner:SANOFI BIOTECH SAS
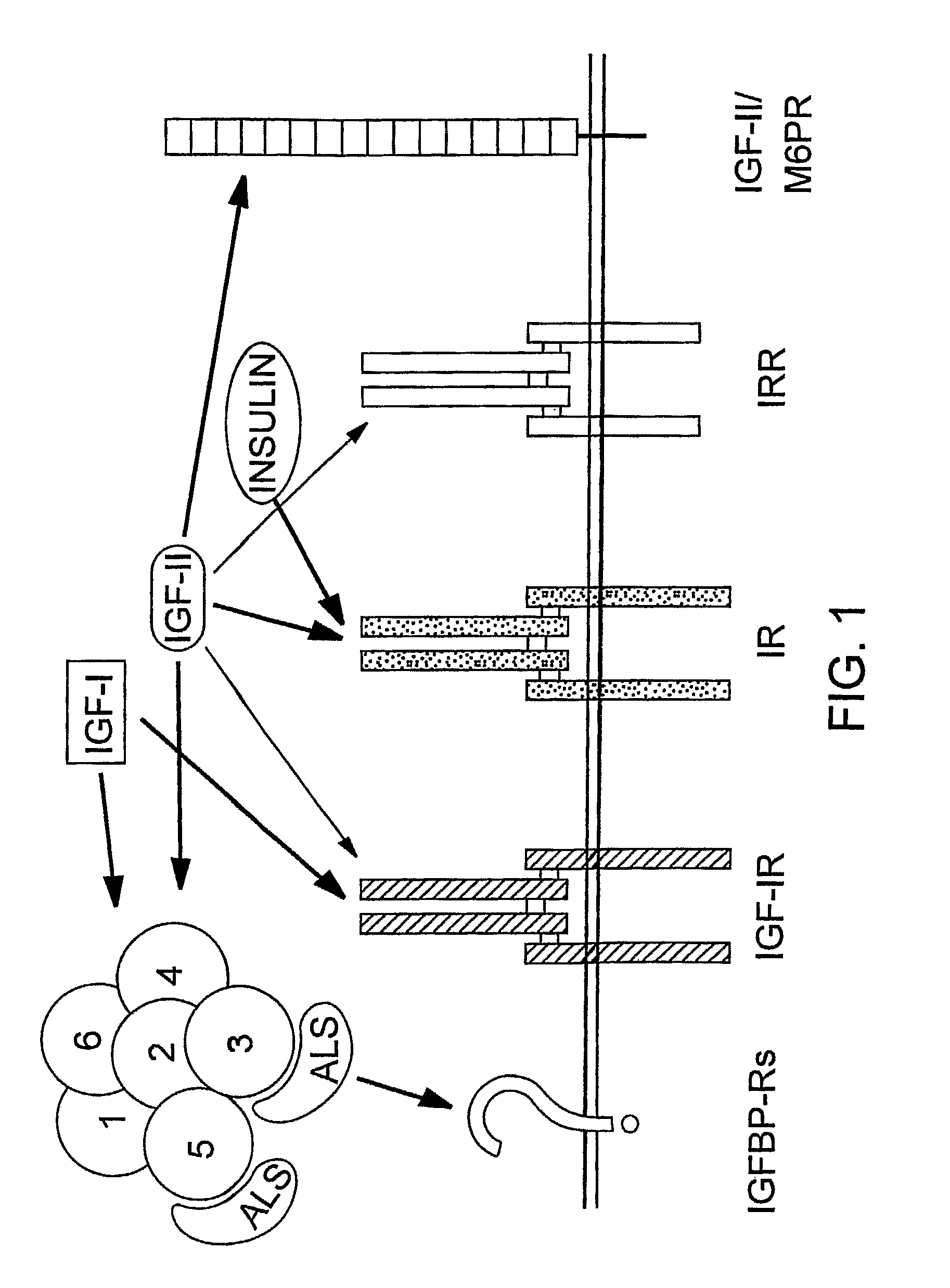
Human monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind IGF-II
InactiveUS7824681B2Immunoglobulins against growth factorsDrug compositionsInsulin-like growth factorAntibody Suppression
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com