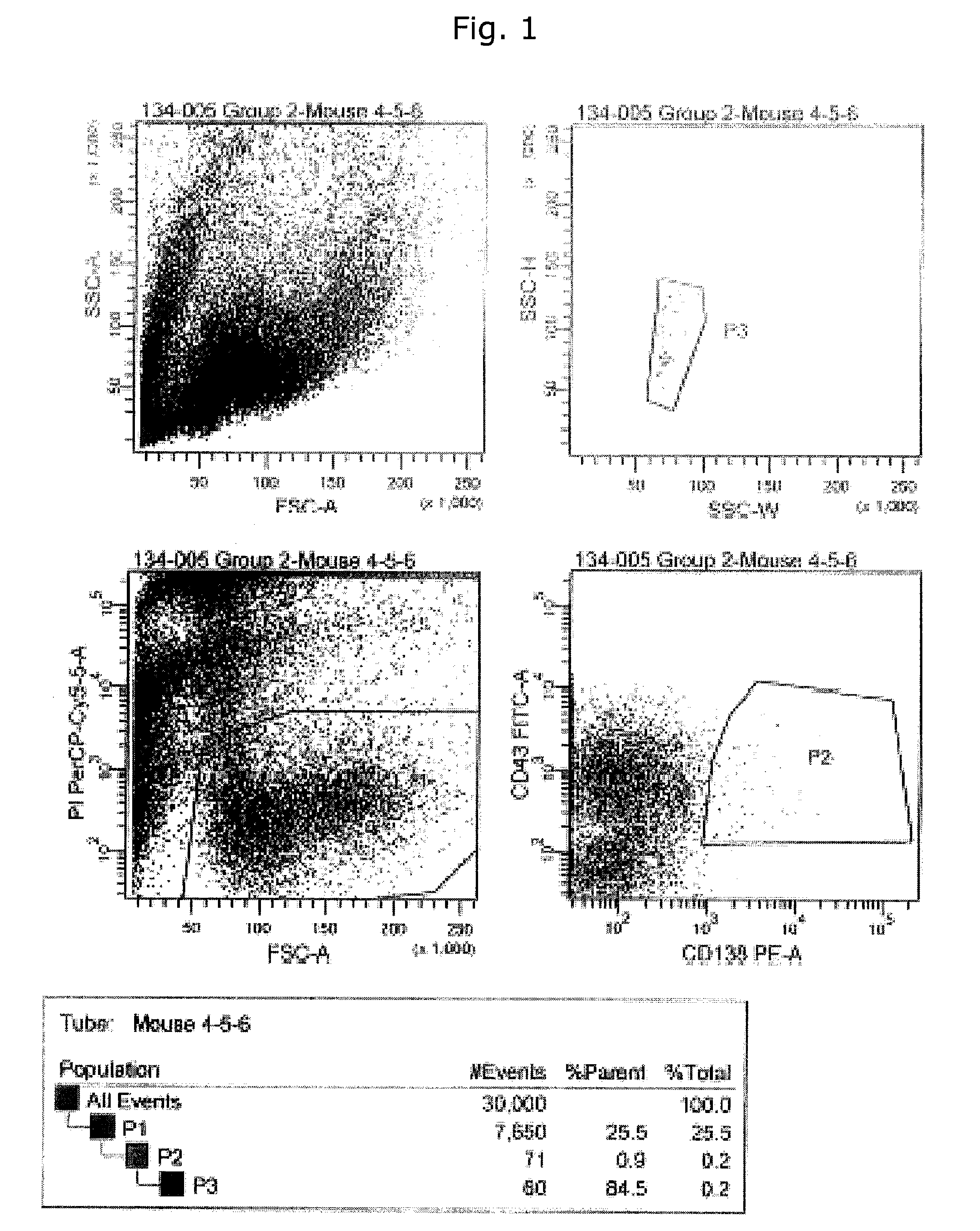
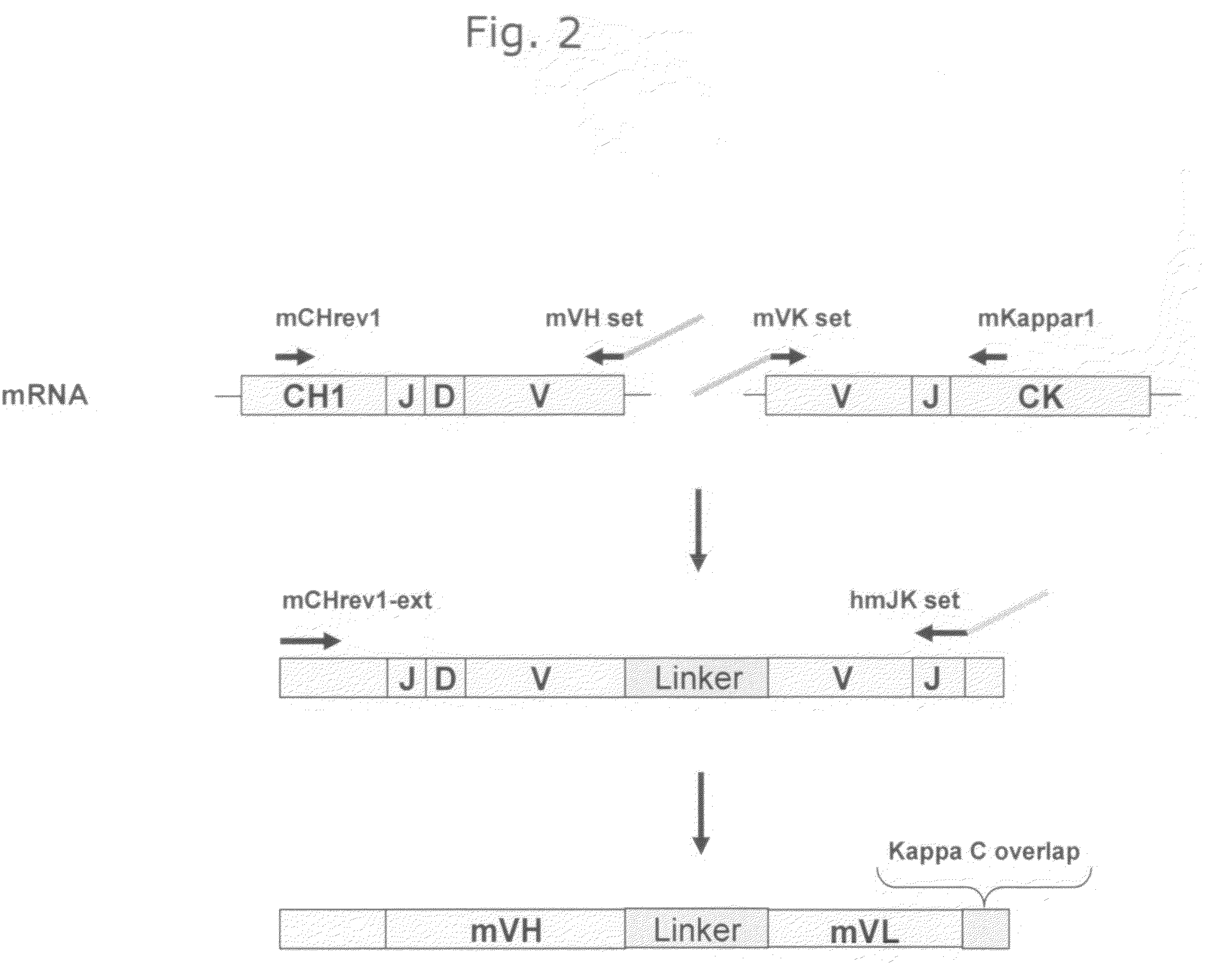
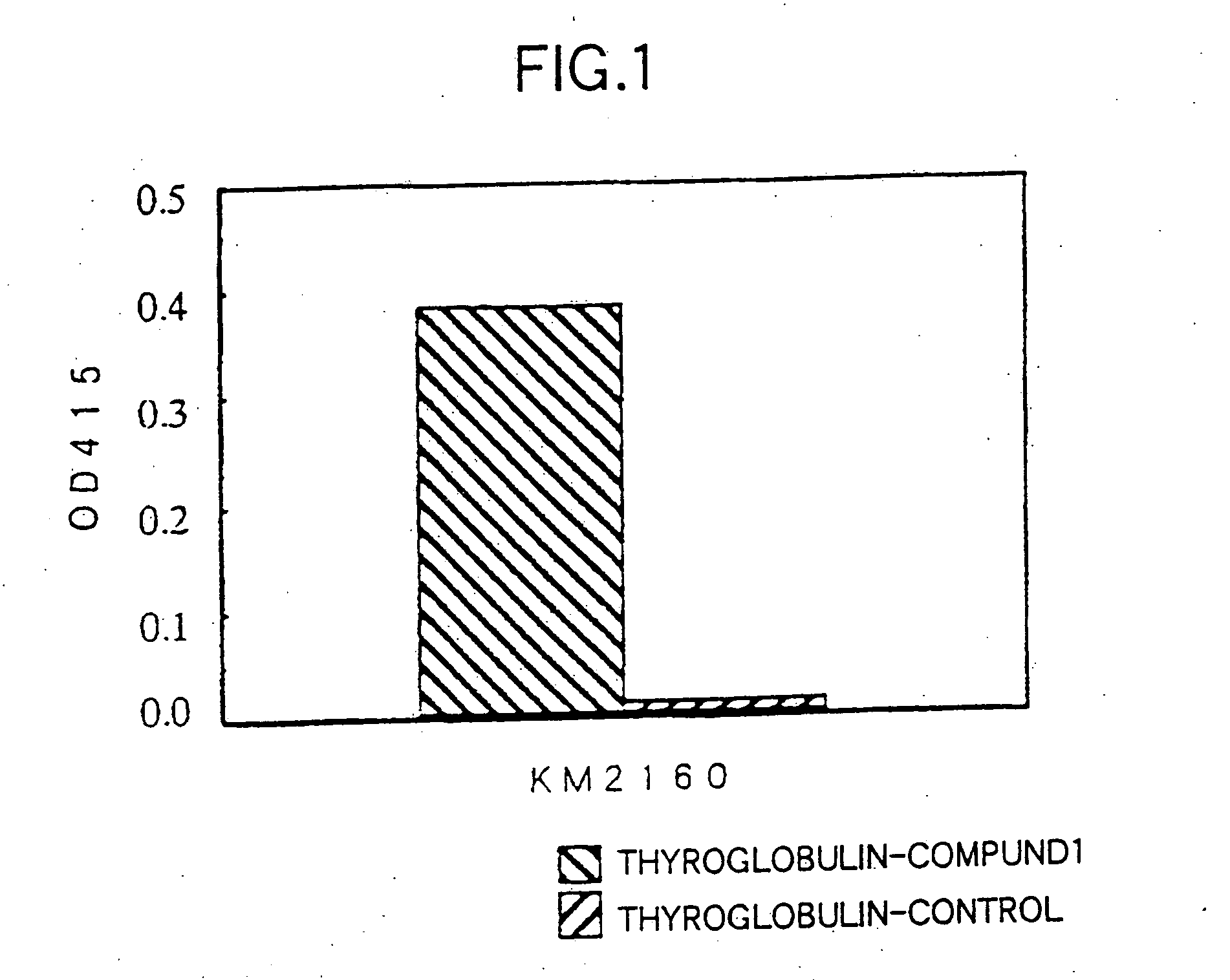
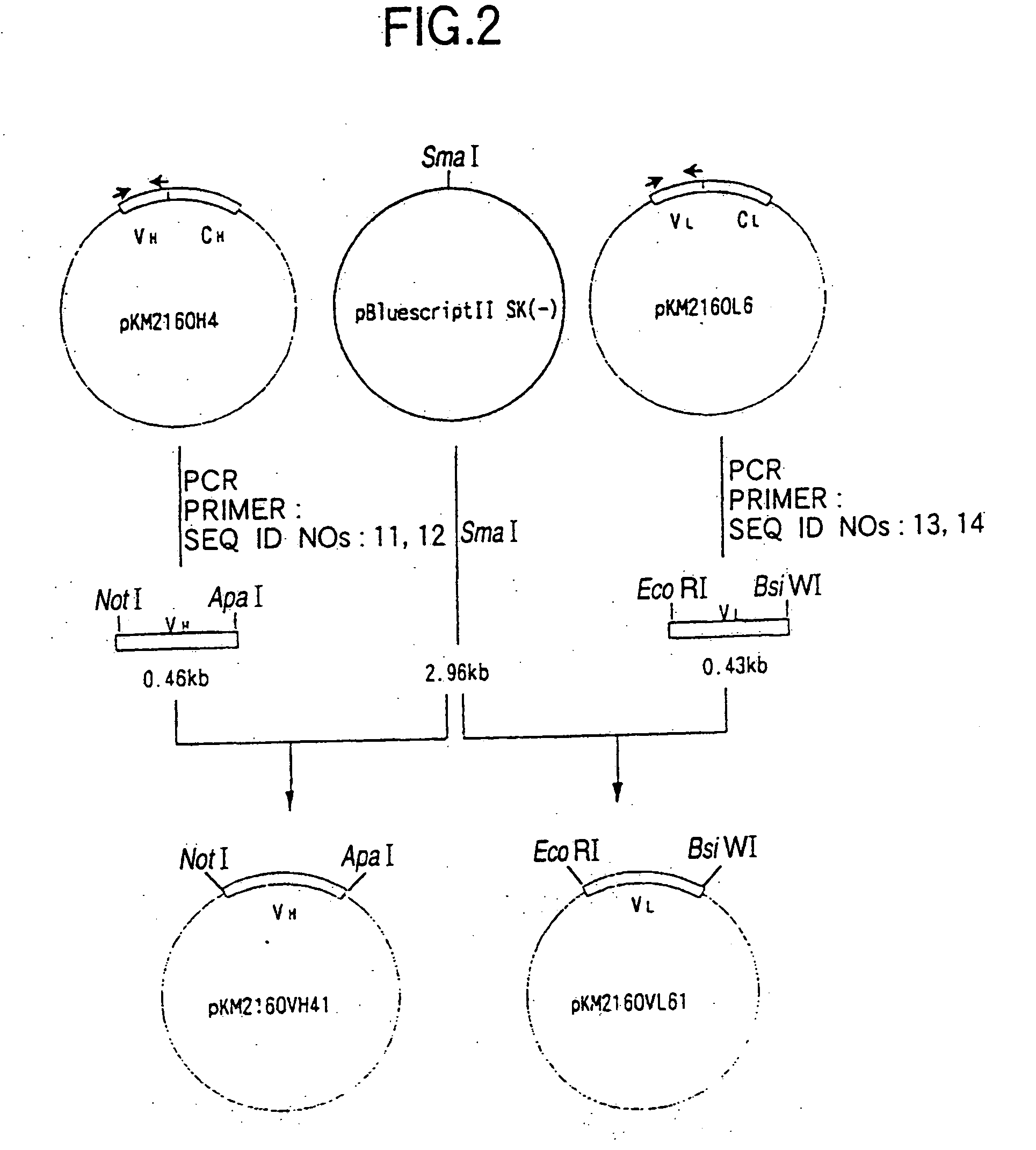
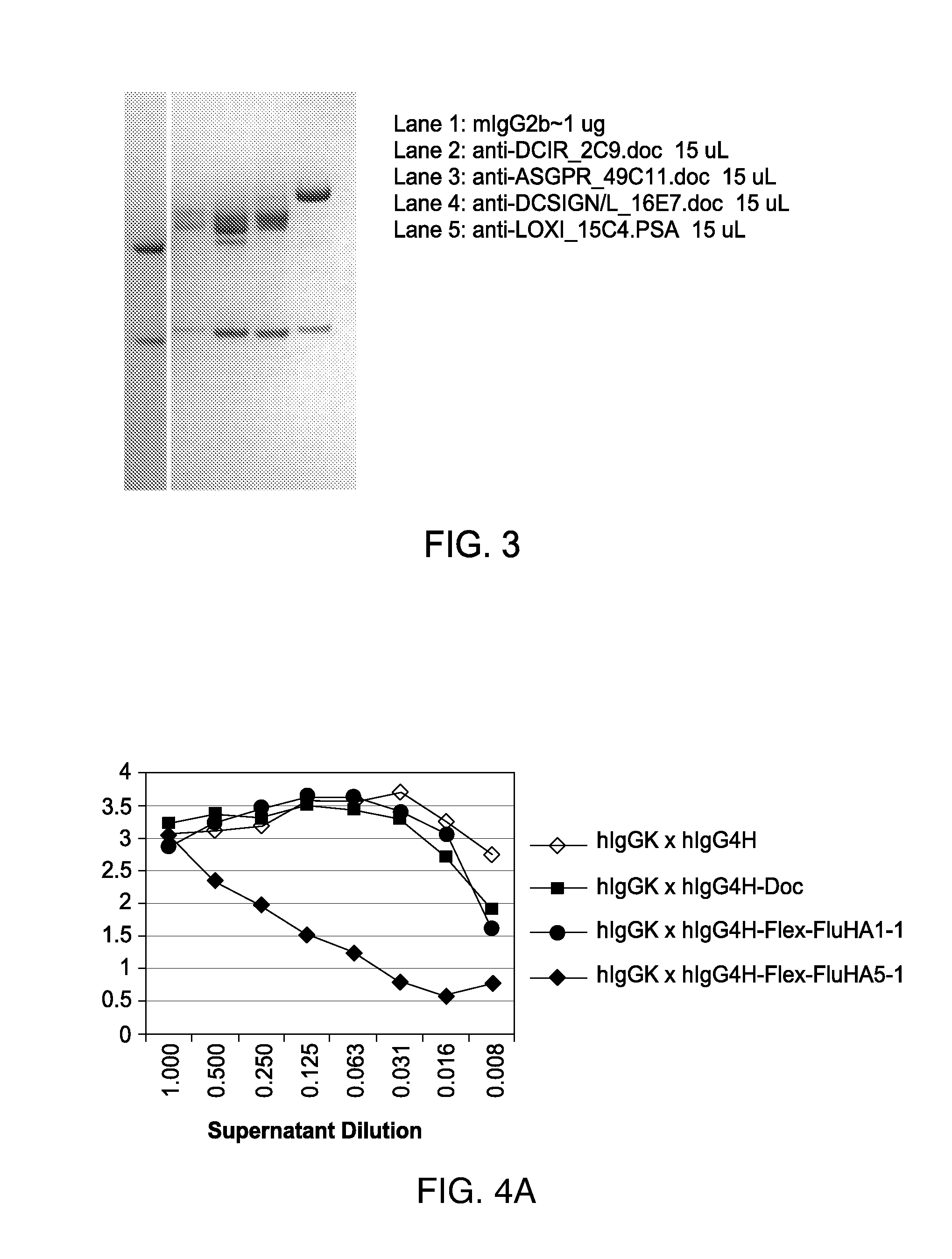
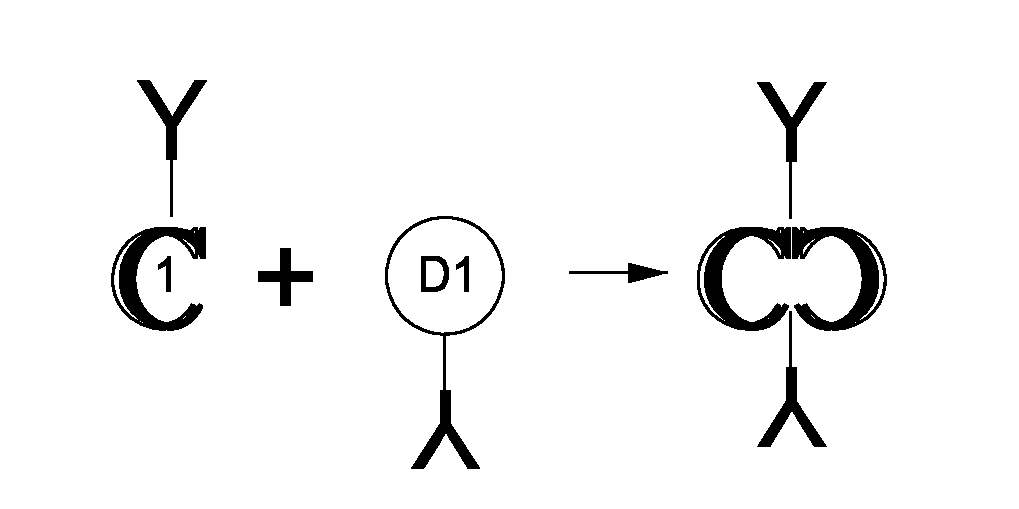Patents
Literature
376 results about "Recombinant antibodies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
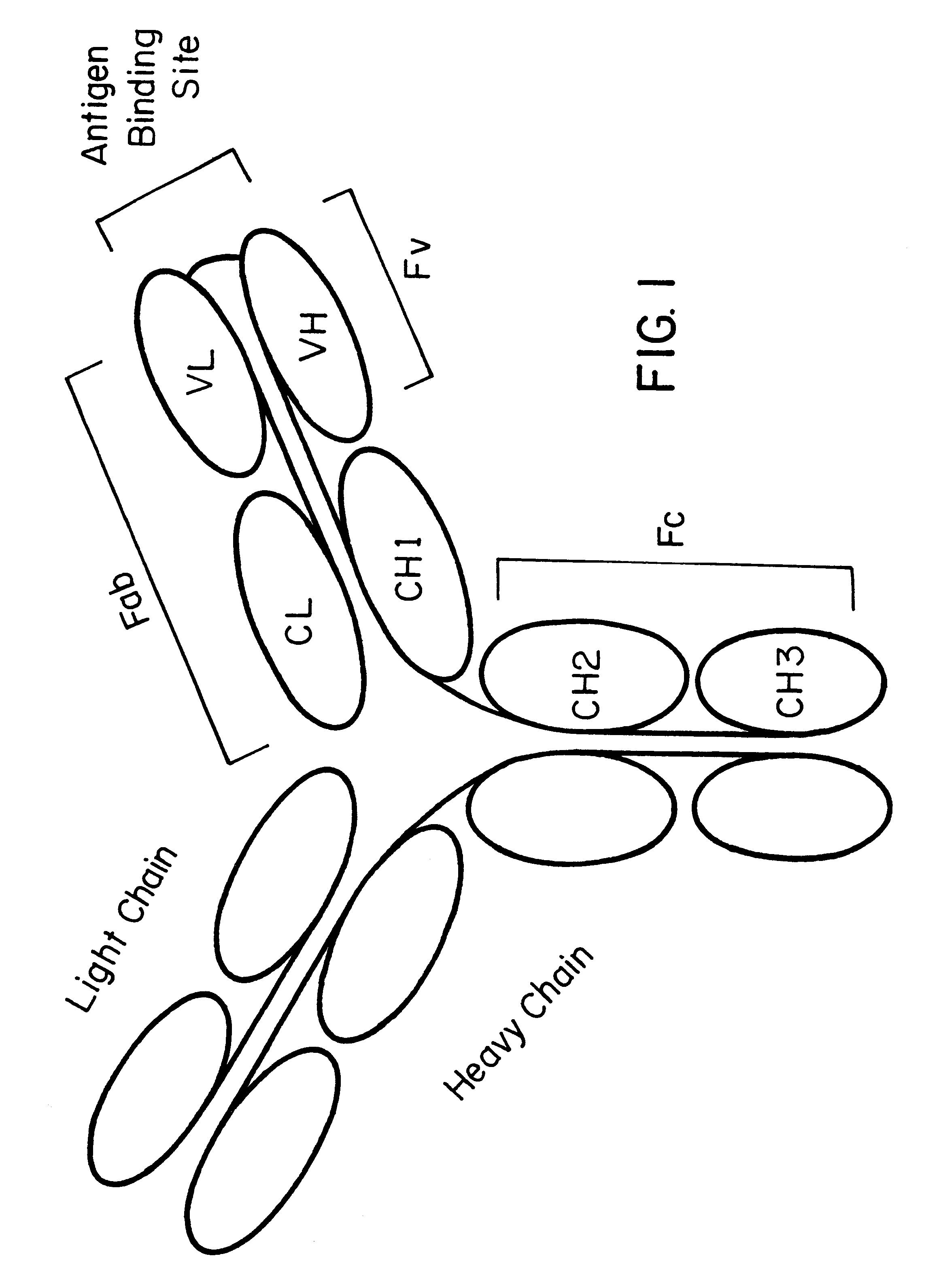
Recombinant antibodies are antibody fragments produced by using recombinant antibody coding genes. They mostly consist of a heavy and light chain of the variable region of immunoglobulin. Recombinant antibodies have many advantages in both medical and research applications, which make them a popular subject of exploration and new production against specific targets. The most commonly used form is the single chain variable fragment (scFv), which has shown the most promising traits exploitable in human medicine and research. In contrast to monoclonal antibodies produced by hybridoma technology, which may lose the capacity to produce the desired antibody over time or the antibody may undergo unwanted changes, which affect its functionality, recombinant antibodies produced in phage display maintain high standard of specificity and low immunogenicity.
Recombinant antibody composition
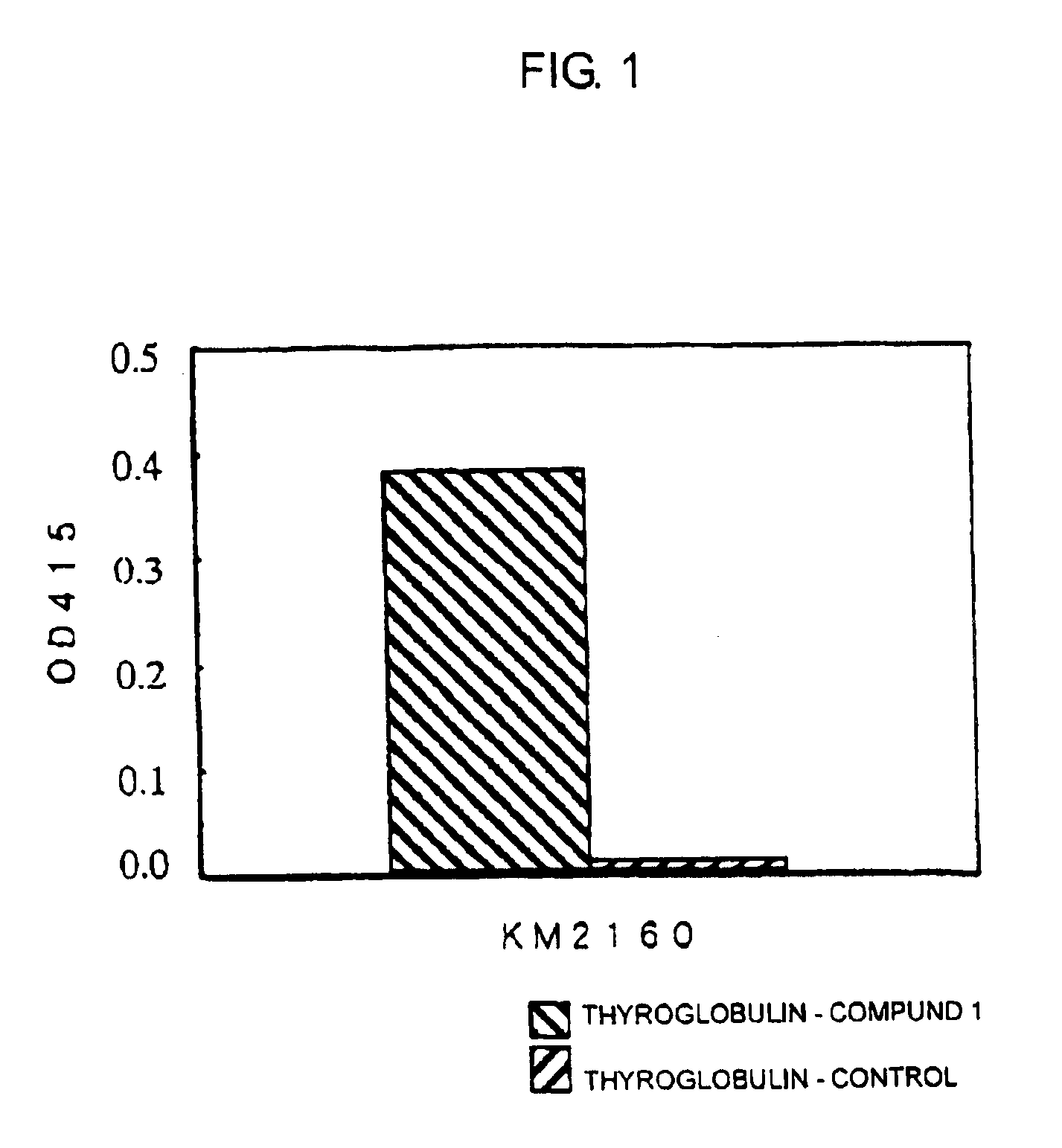
ActiveUS20070148165A1Enhanced effector functionGood treatment effectImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsA-DNABULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
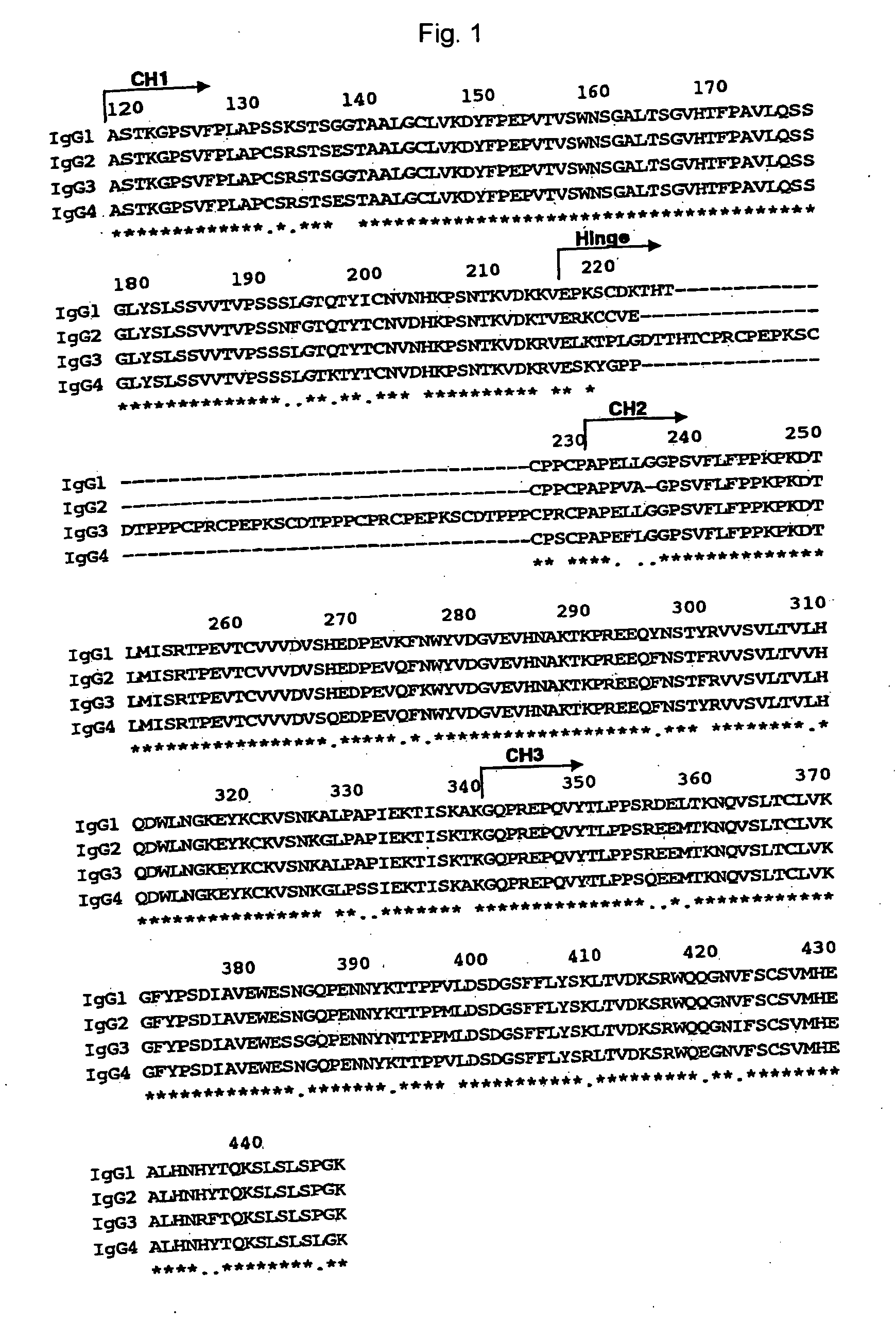
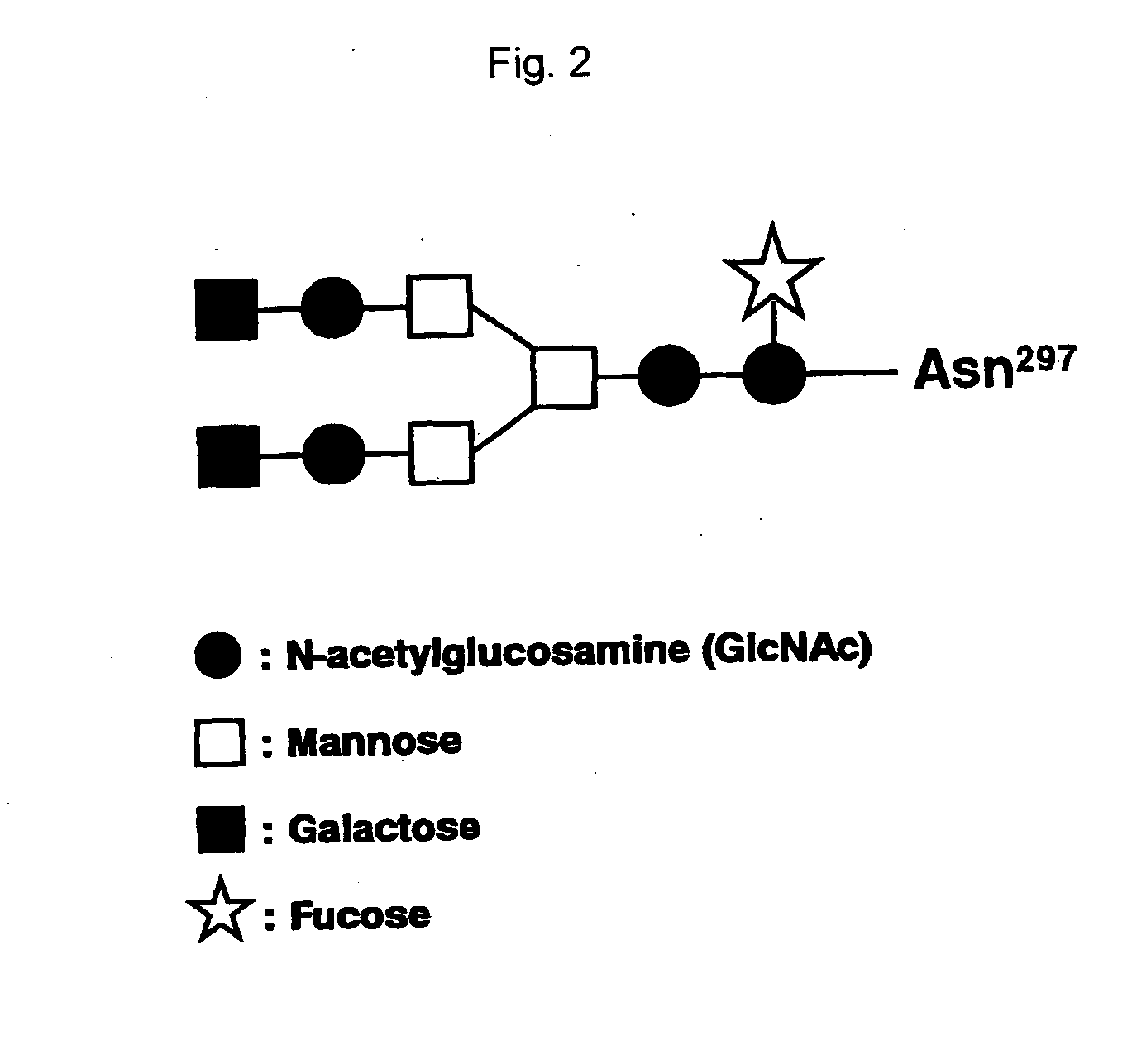
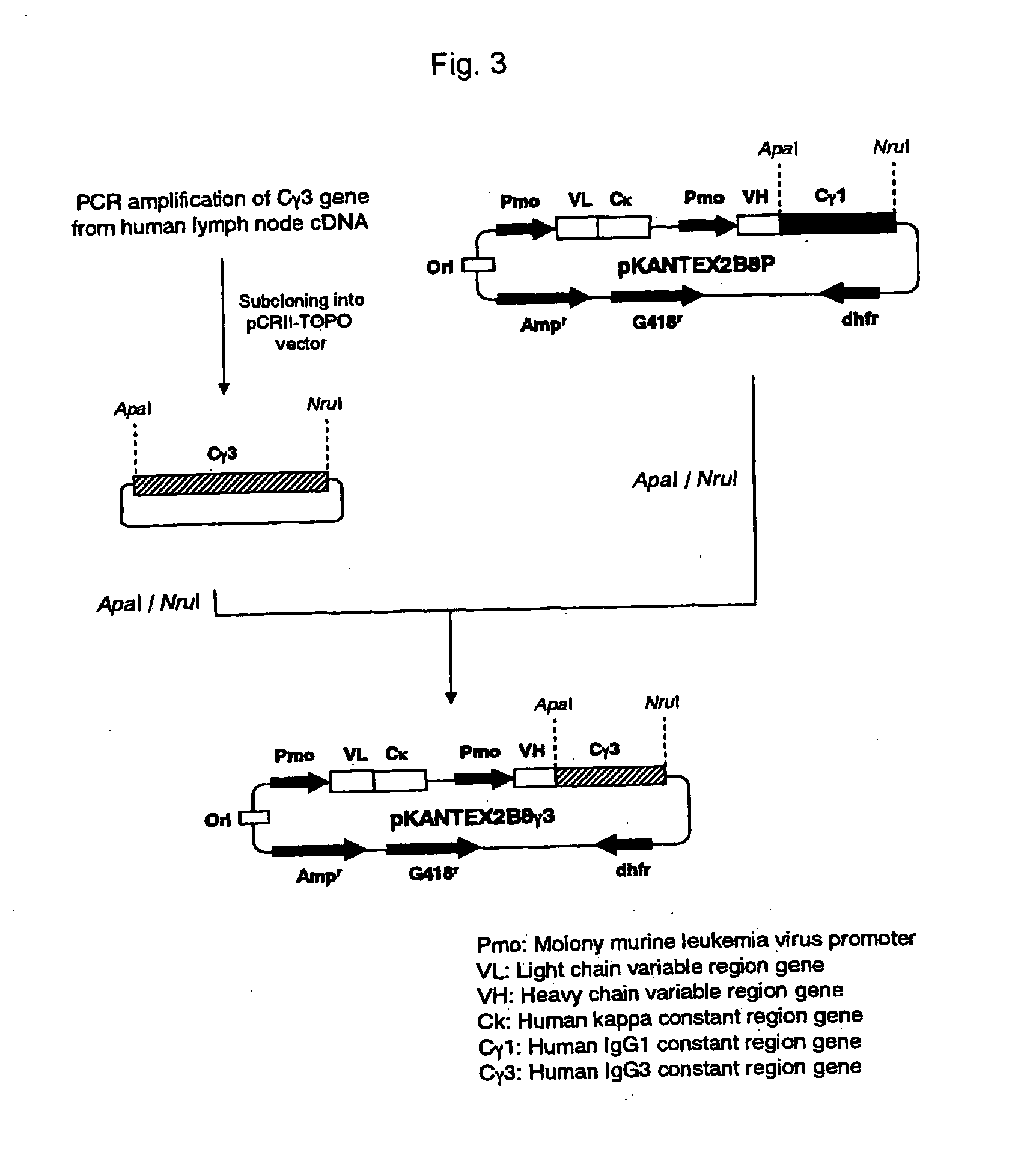
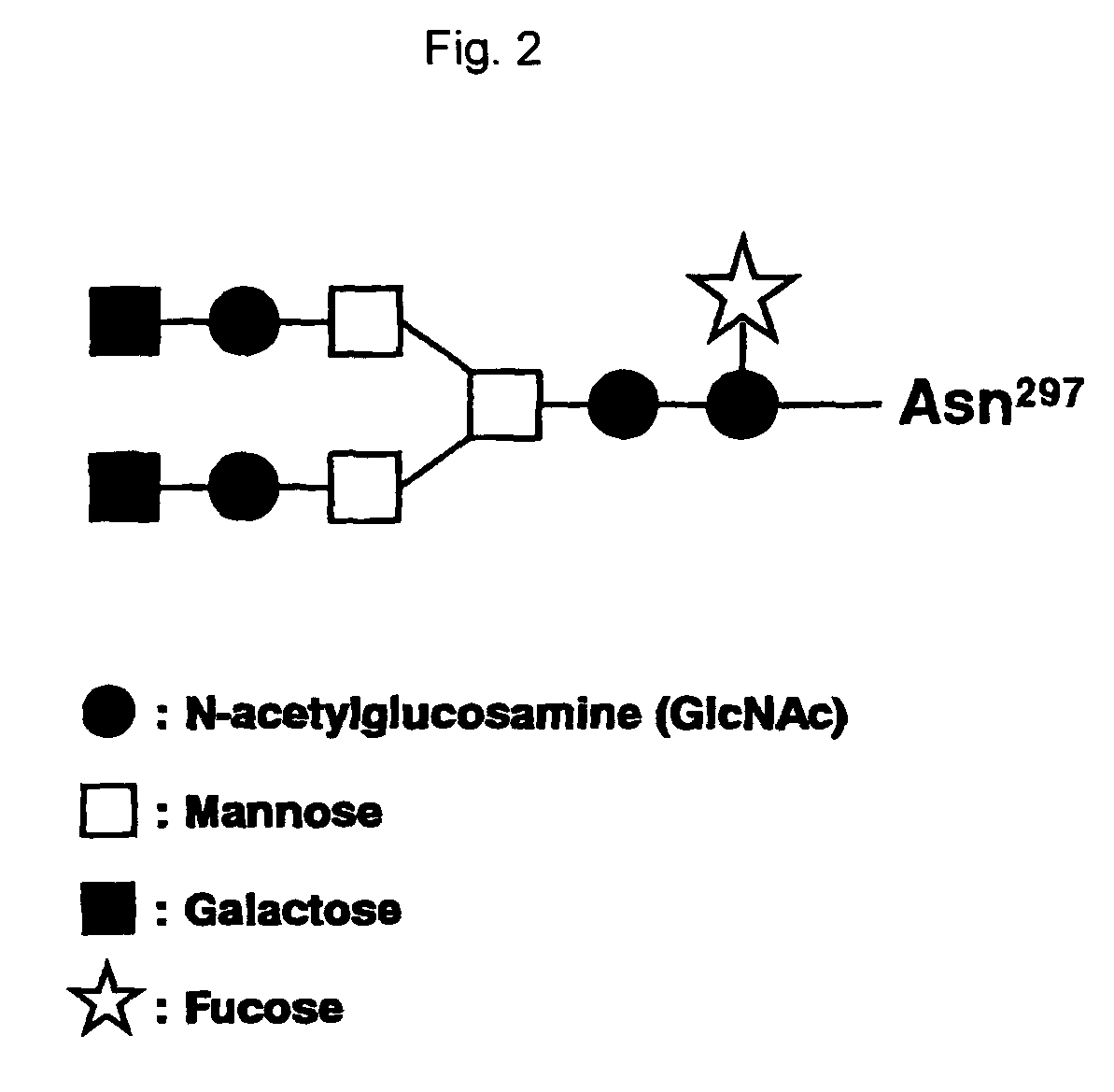
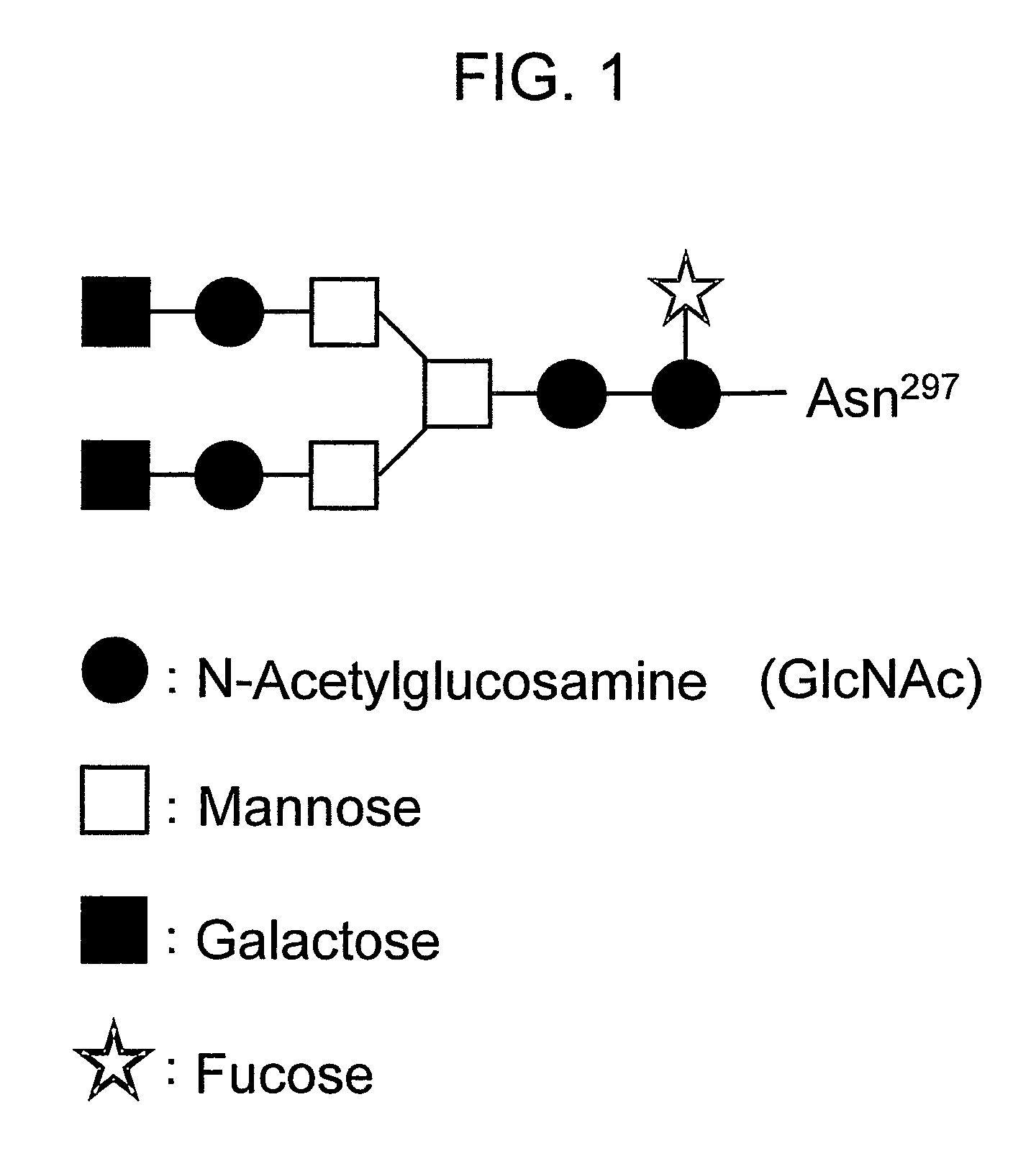
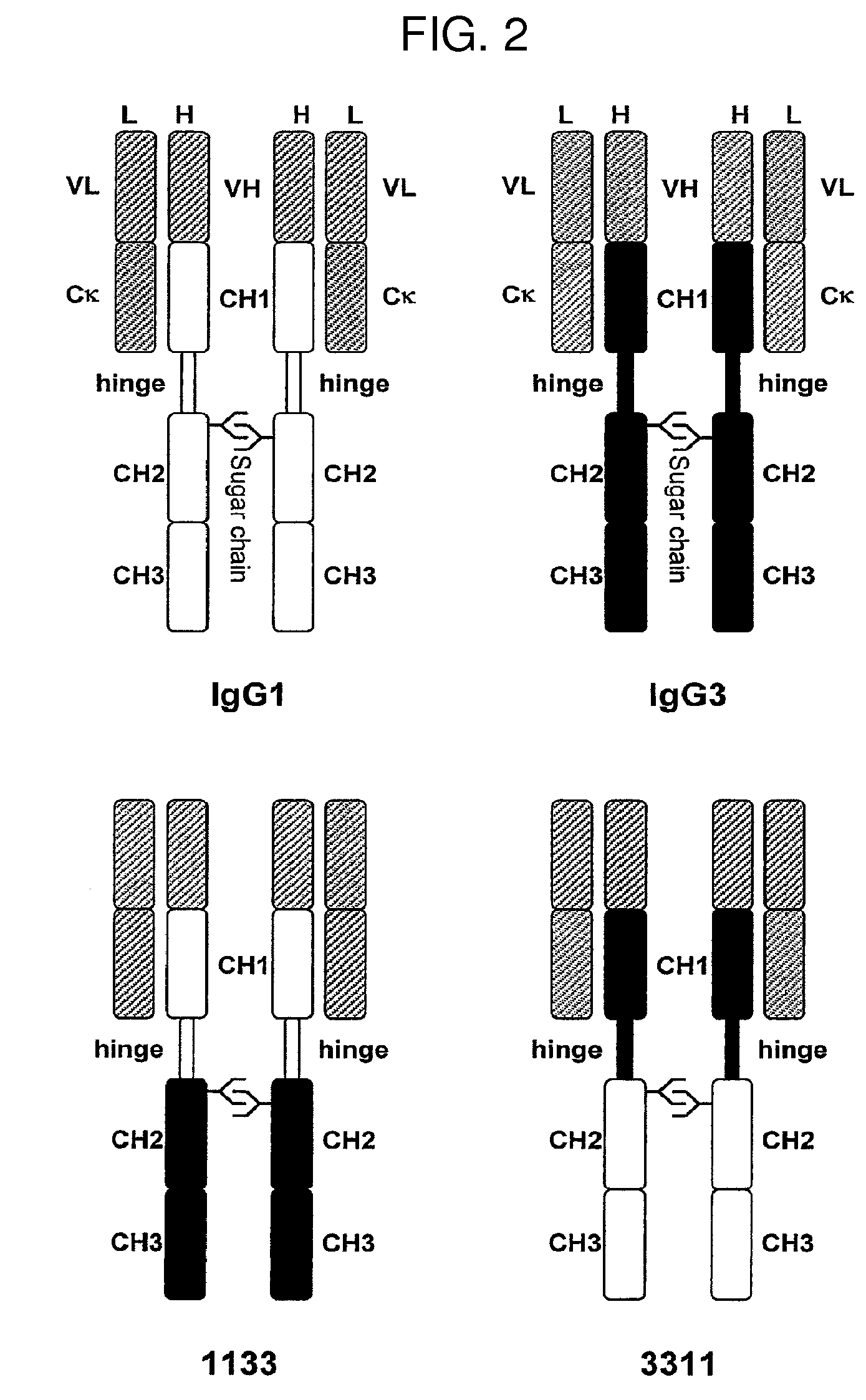
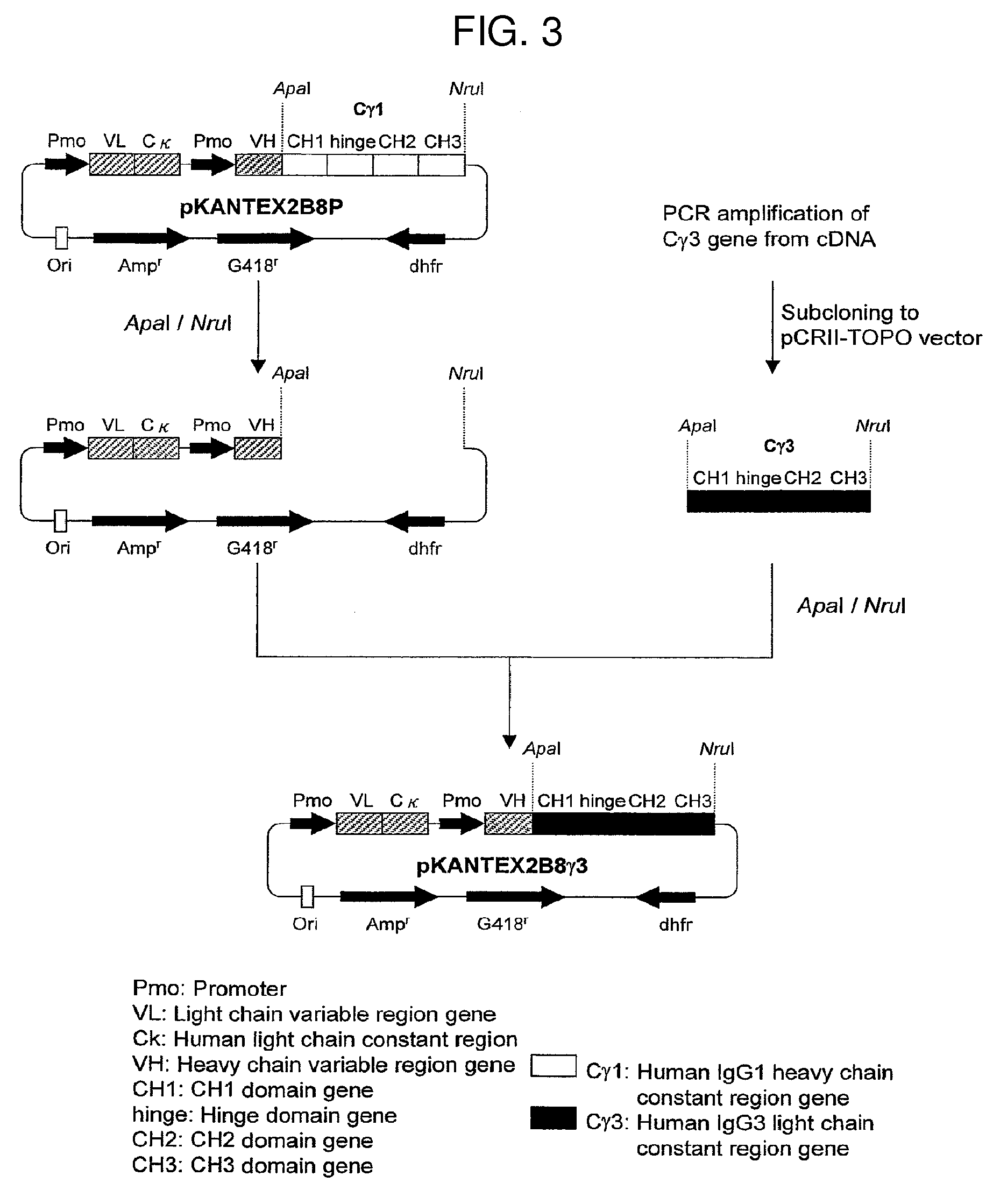
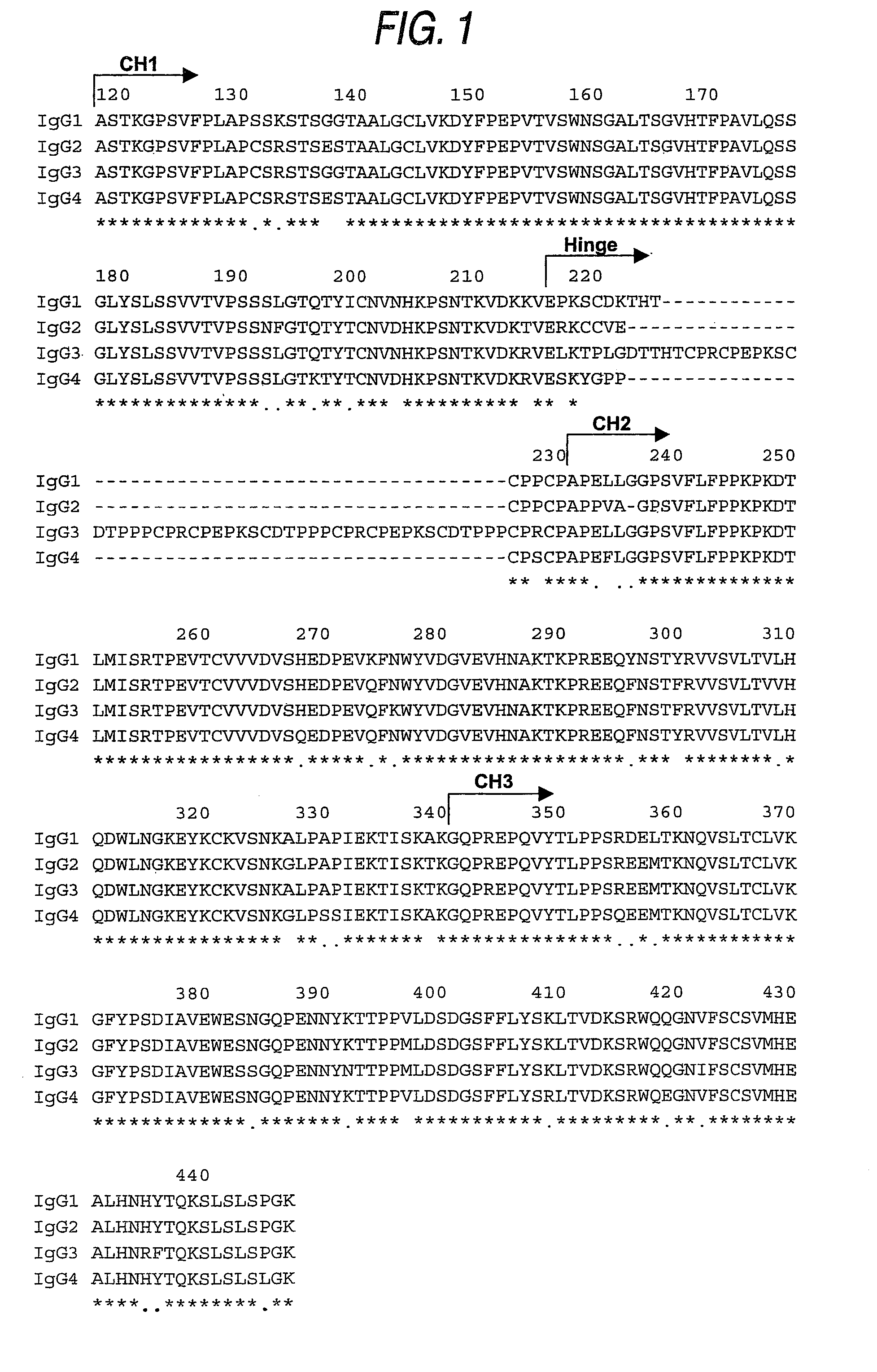
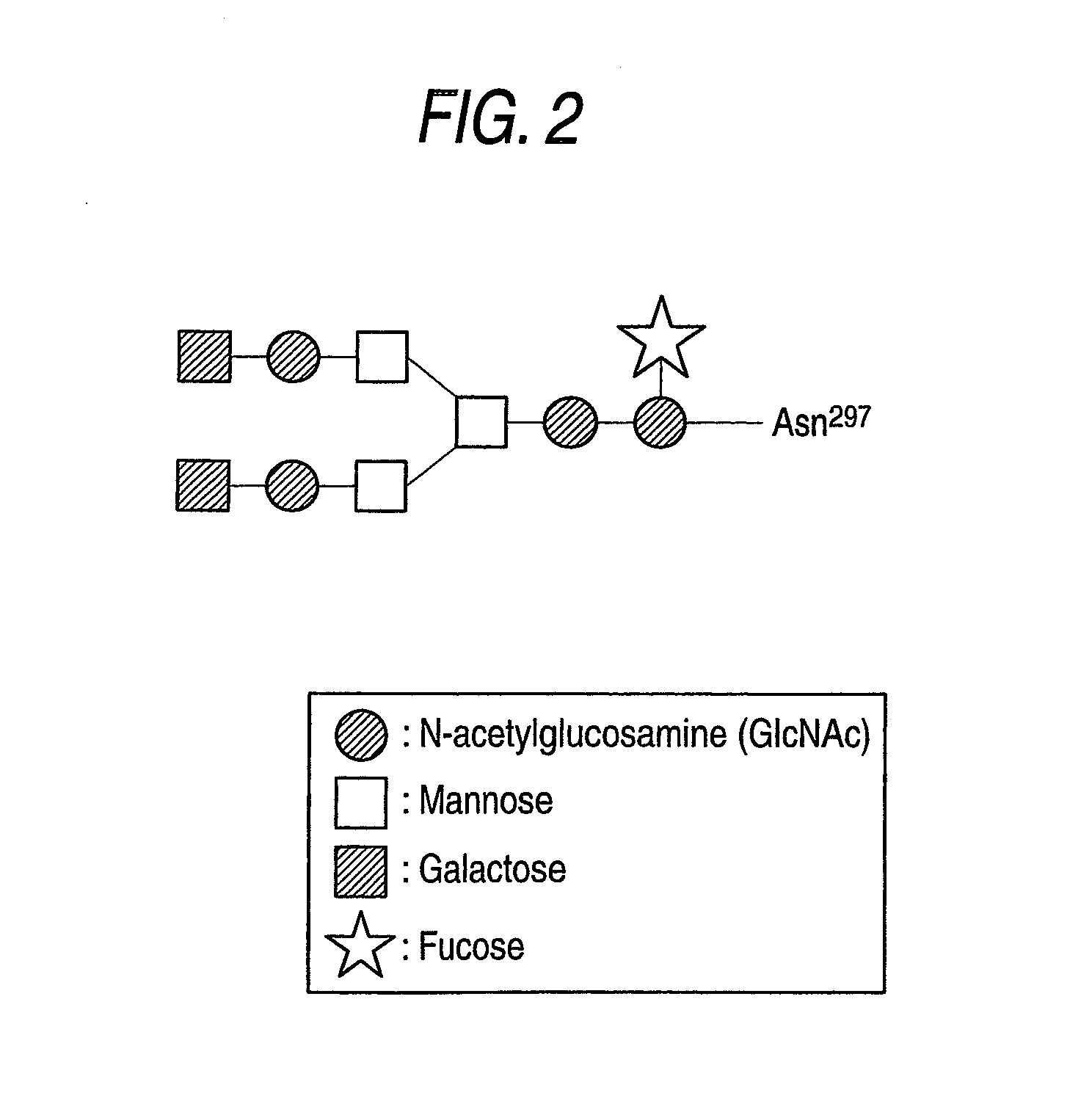
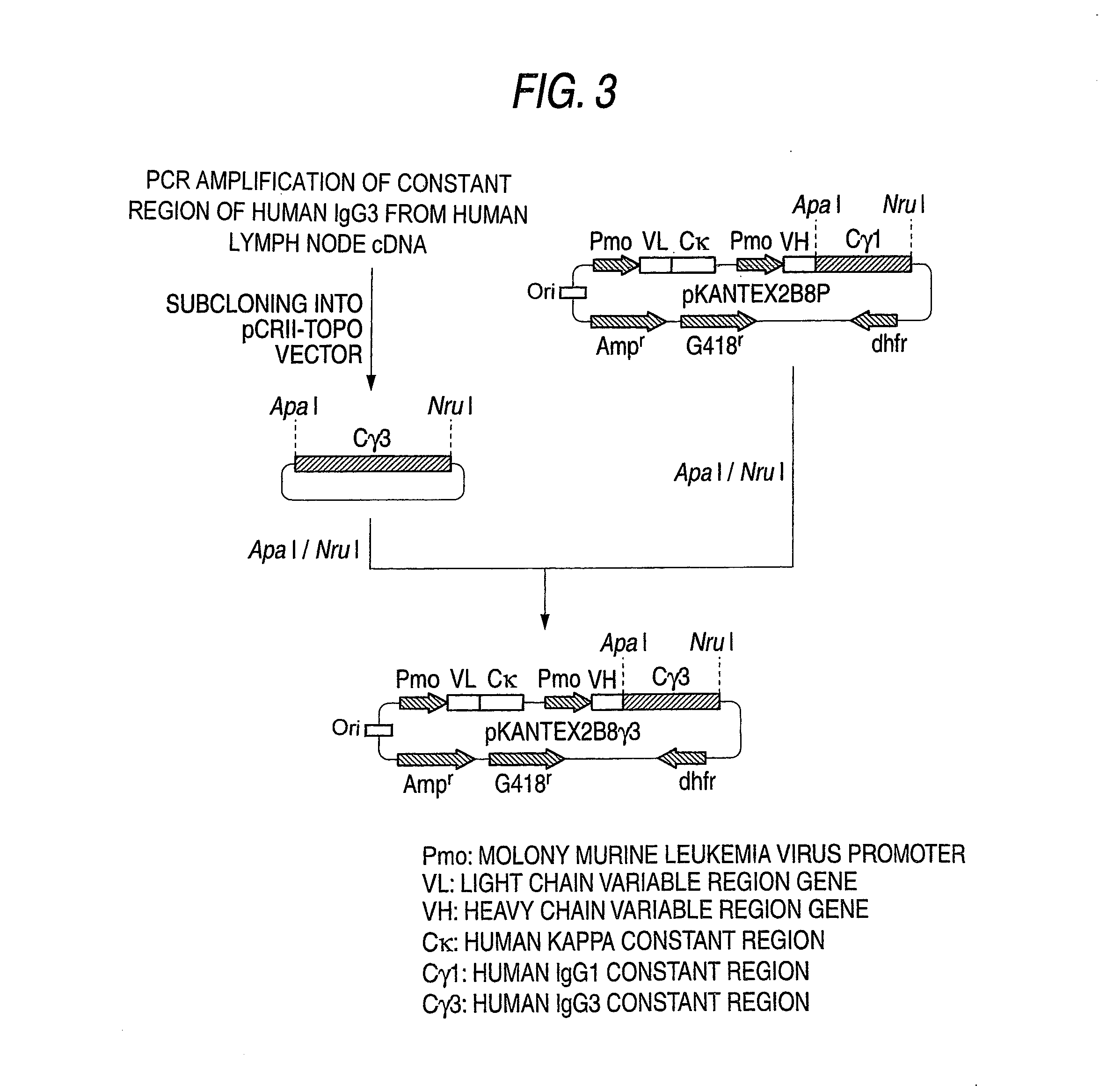
The present invention relates to a recombinant antibody composition having higher complement-dependent cytotoxic activity than a human IgG1 antibody and a human IgG3 antibody, wherein a polypeptide comprising a CH2 domain in the Fc region of a human IgG1 antibody is replaced by a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence which corresponds to the same position of a human IgG3 antibody indicated by the EU index as in Kabat, et al.; a DNA encoding the antibody molecule or a heavy chain constant region of the antibody molecule contained in the recombinant antibody composition; a transformant obtainable by introducing the recombinant vector into a host cell; a process for producing the recombinant antibody composition using the transformant; and a medicament comprising the recombinant antibody composition as an active ingredient.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Bivalent IgY antibody constructs for diagnostic and therapeutic applications
InactiveUS20070141049A1Improve the immunityIncrease contentImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsHeavy chainMammal
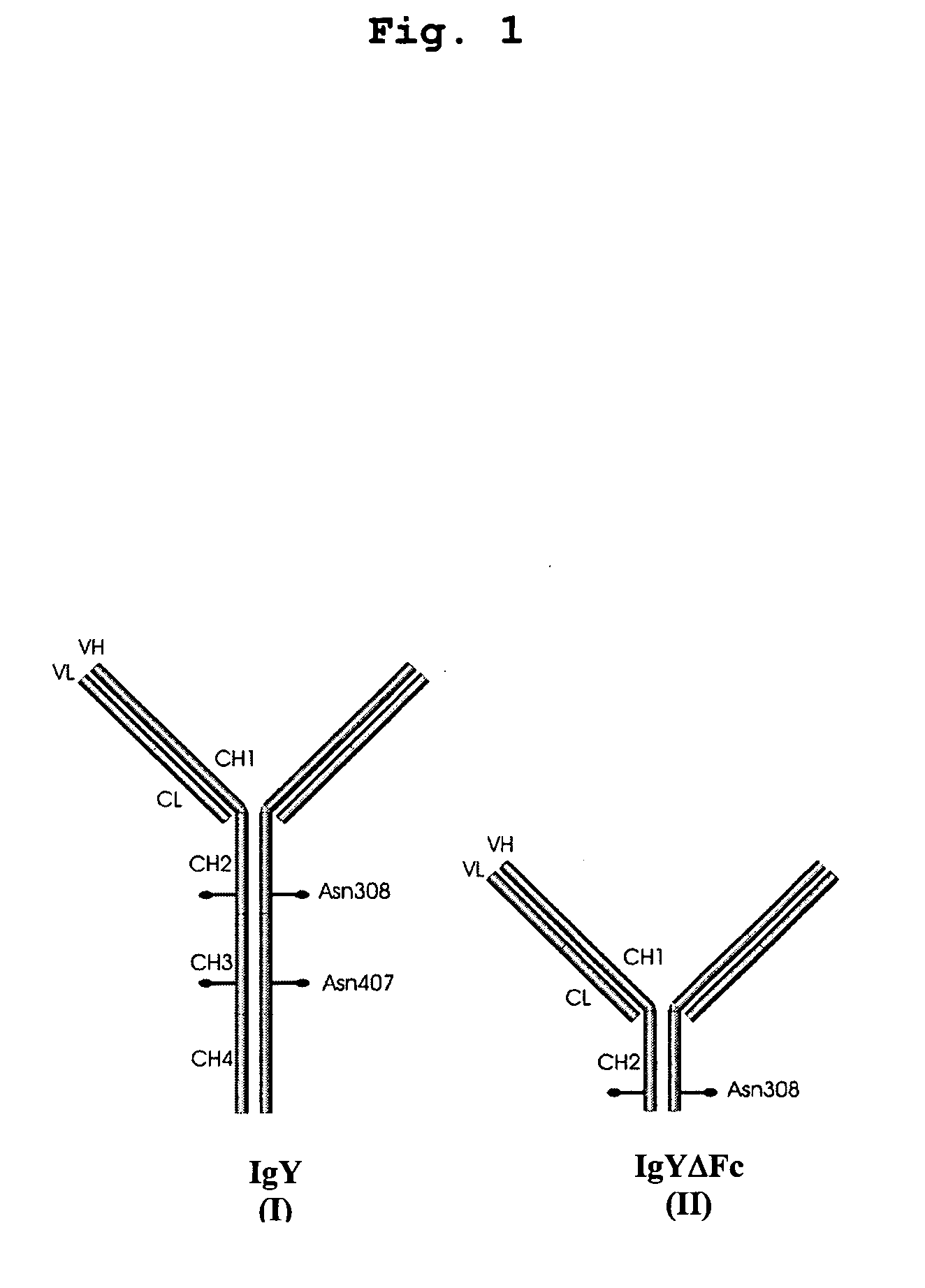
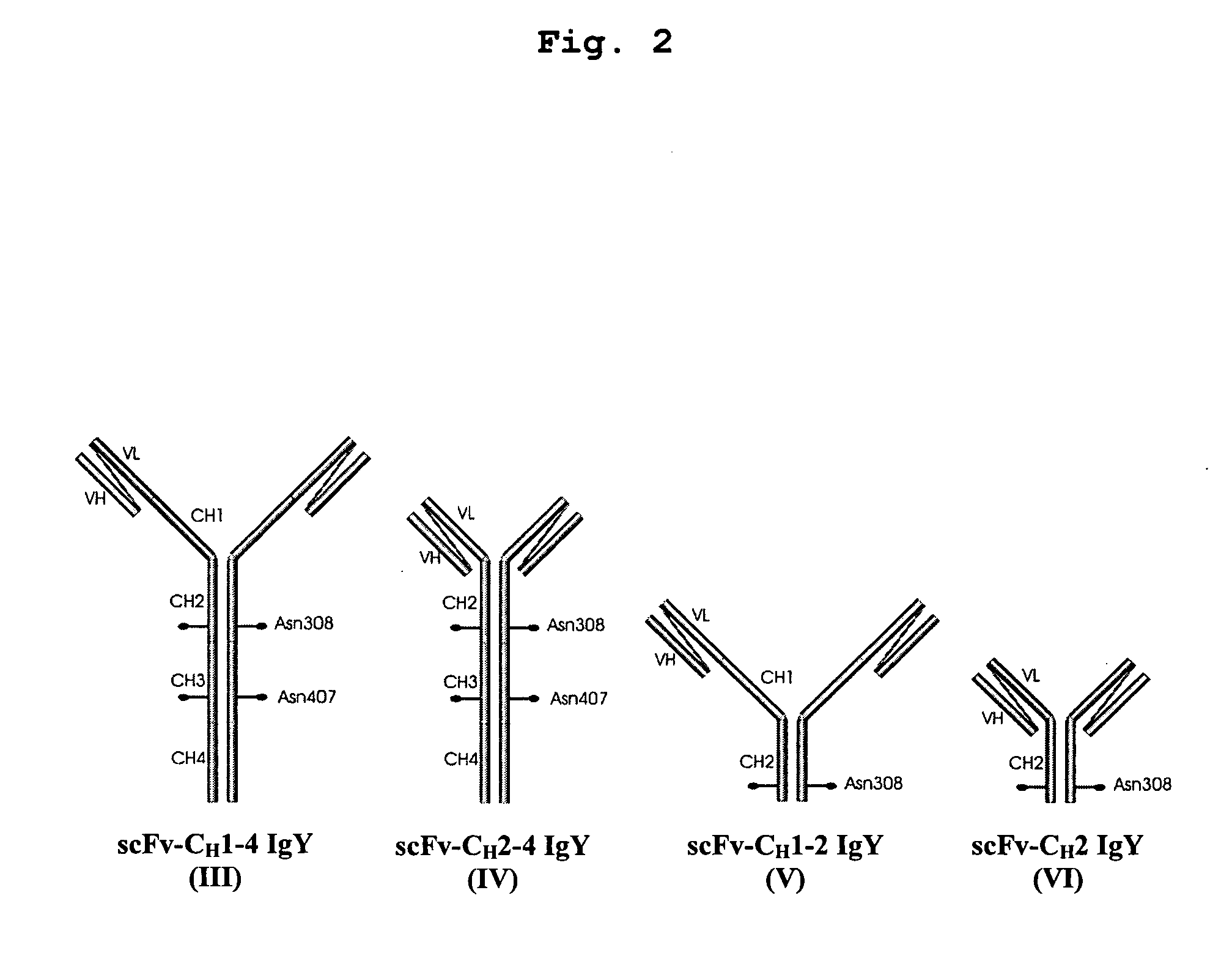
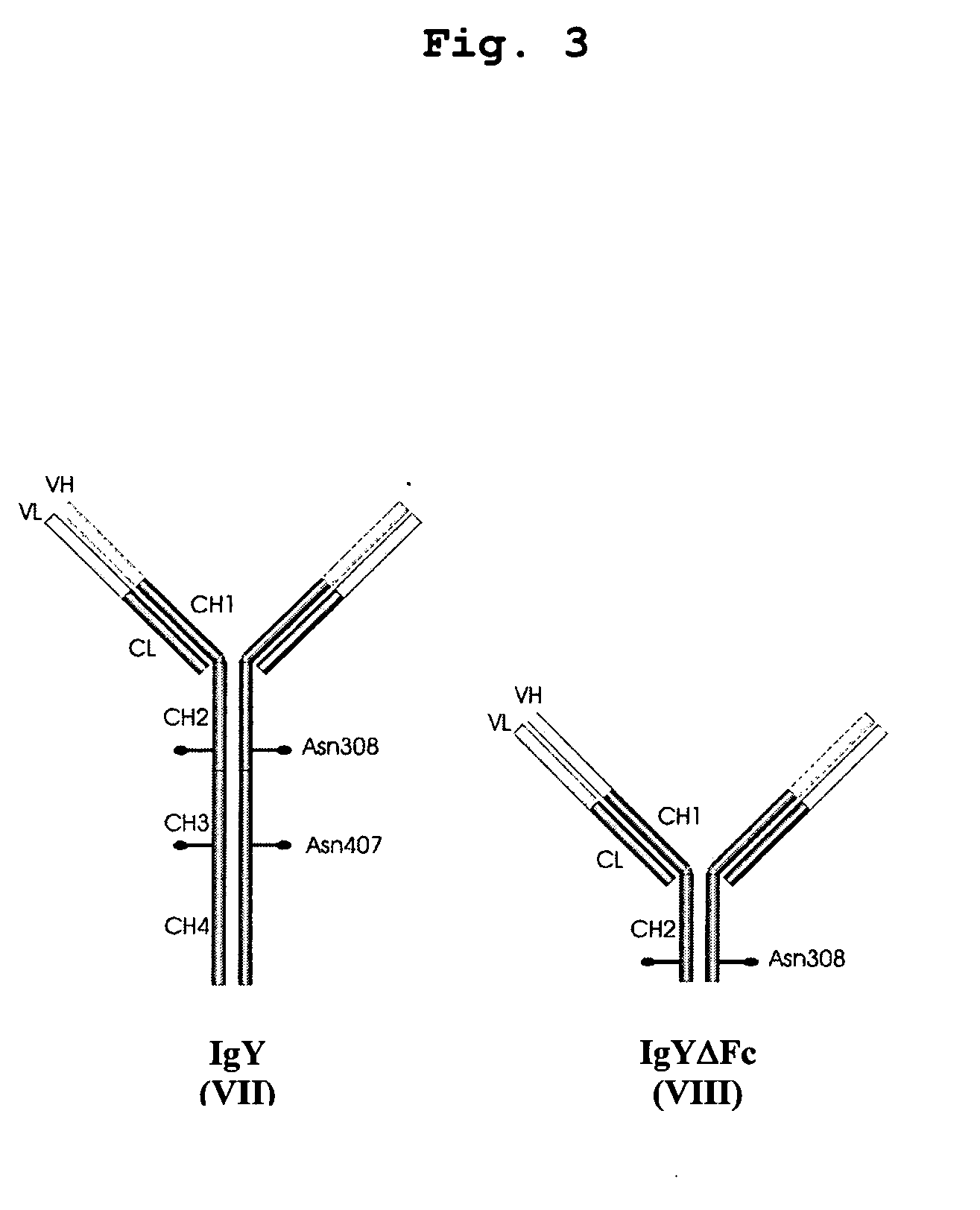
This invention relates to the field of recombinant antibody technology. It provides novel recombinant IgY antibody constructs for diagnostic and therapeutical applications. The bivalent antibody constructs display a heterotetrameric or homodimeric format stabilized by disulfide bonds. The constant heavy chain domains CH2-CH4 are partly or completely of avian origin, whereas the VH, VL, CL, and CH1 domains as well as the hinge region may be of avian origin or derived from any other species. The invention allows to combine the advantages of IgY antibodies with those of established mammalian monoclonal antibodies. IgY antibody constructs comprising nonglycosylated IgY constant heavy chain domains allow to reduce unwanted interactions with C-type lectins, e.g., in human sera. Furthermore, chimeric IgY antibody containing mammalian VH, VL, CL, and CH1 domains as well as a mammalian hinge region provide a higher molecular stability than IgY antibodies in acidic conditions and, thereby, are especially suited for peroral therapeutic applications.
Owner:PLS DESIGN
Methods for refolding of recombinant antibodies
ActiveUS20060194280A1Efficient and economic productionImproved pharmaceuticalImmunological disordersFermentationRecombinant antibodiesCoupling reagent
The present invention is generally directed to methods of producing an increase in the enrichment or recovery of preferred forms of IgG proteins. More particularly, the invention relates to subjecting preparations of such recombinant IgG proteins with a reduction / oxidation coupling reagent and optionally a chaotropic agent.
Owner:AMGEN INC
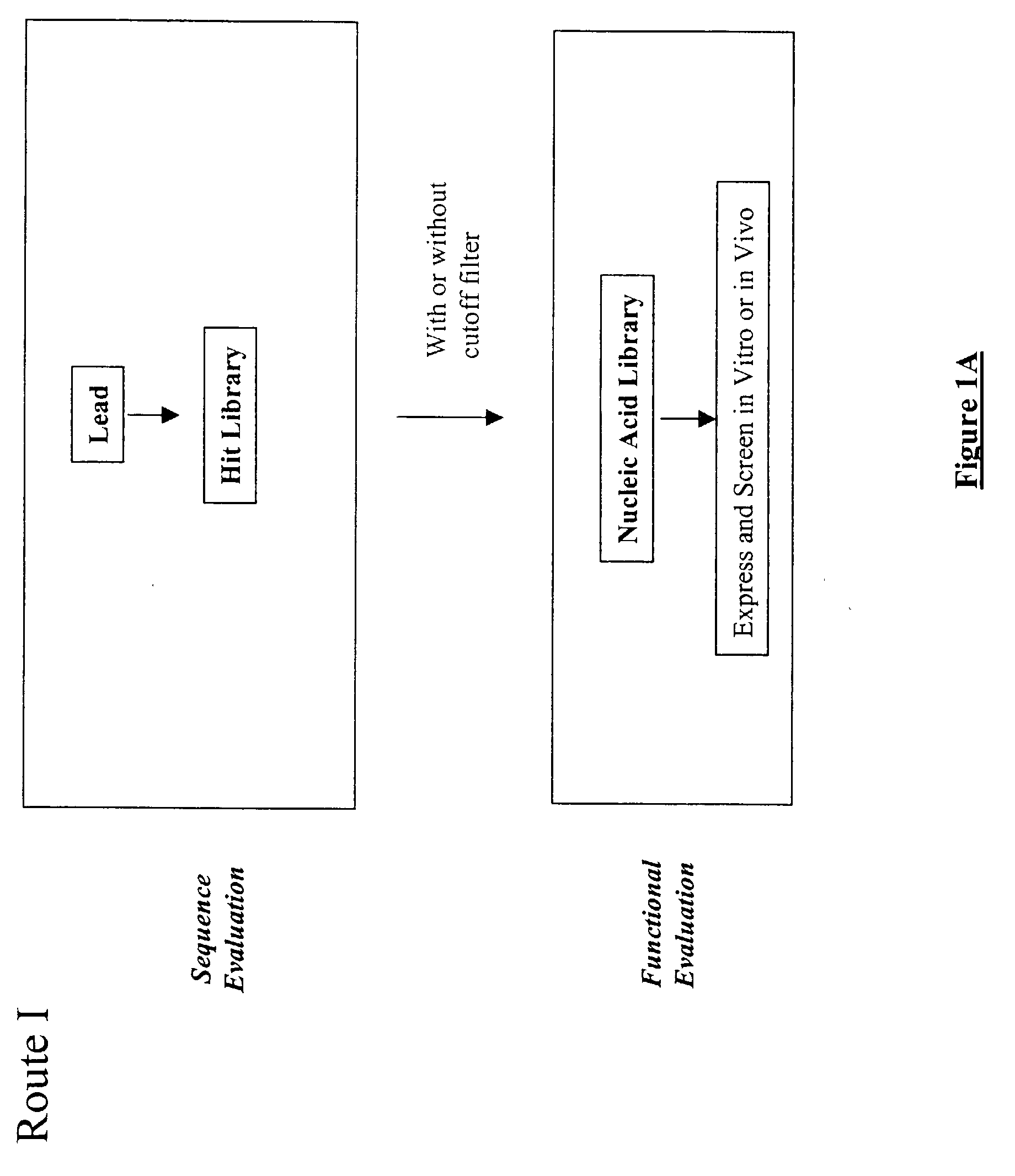
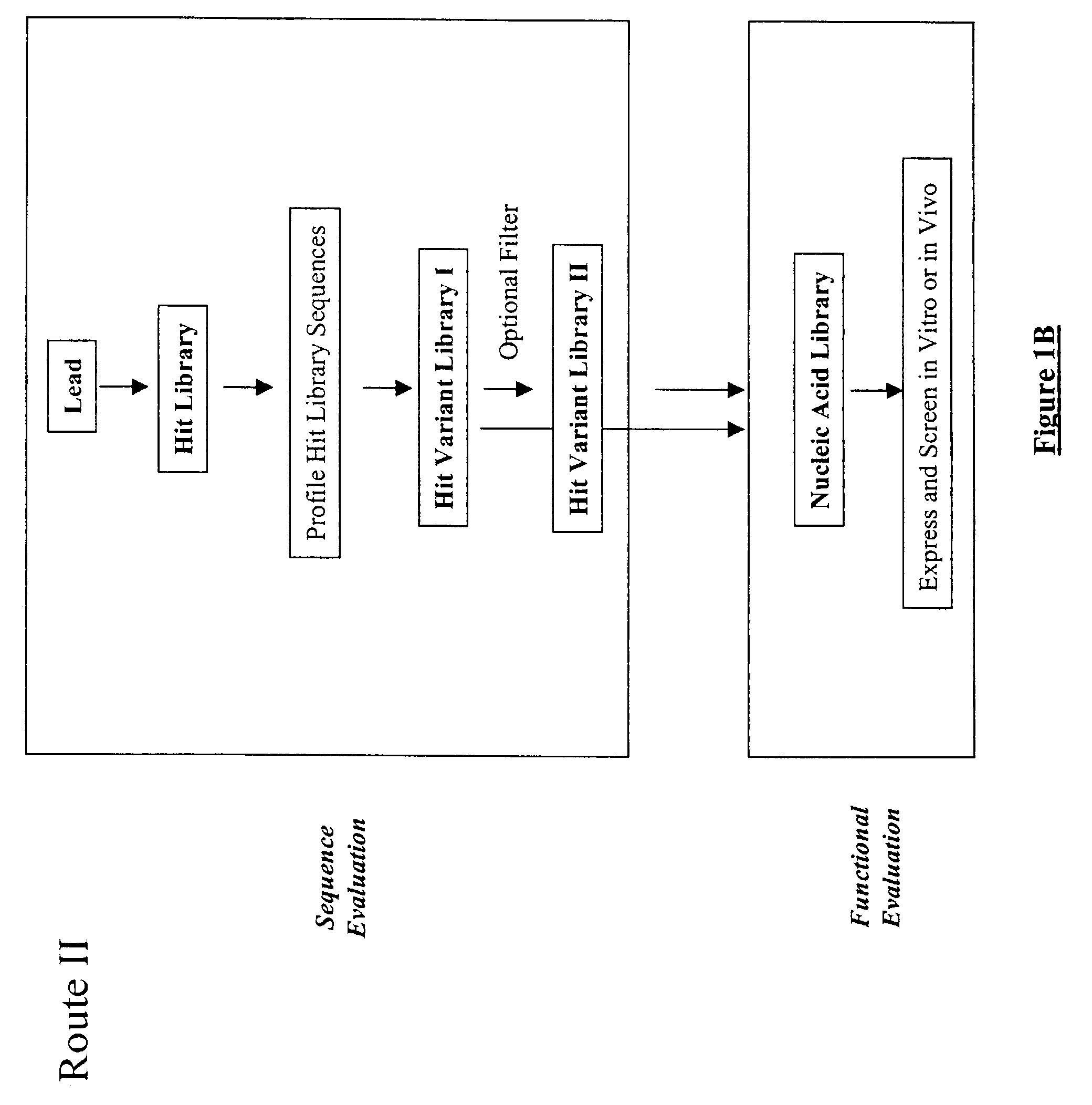
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
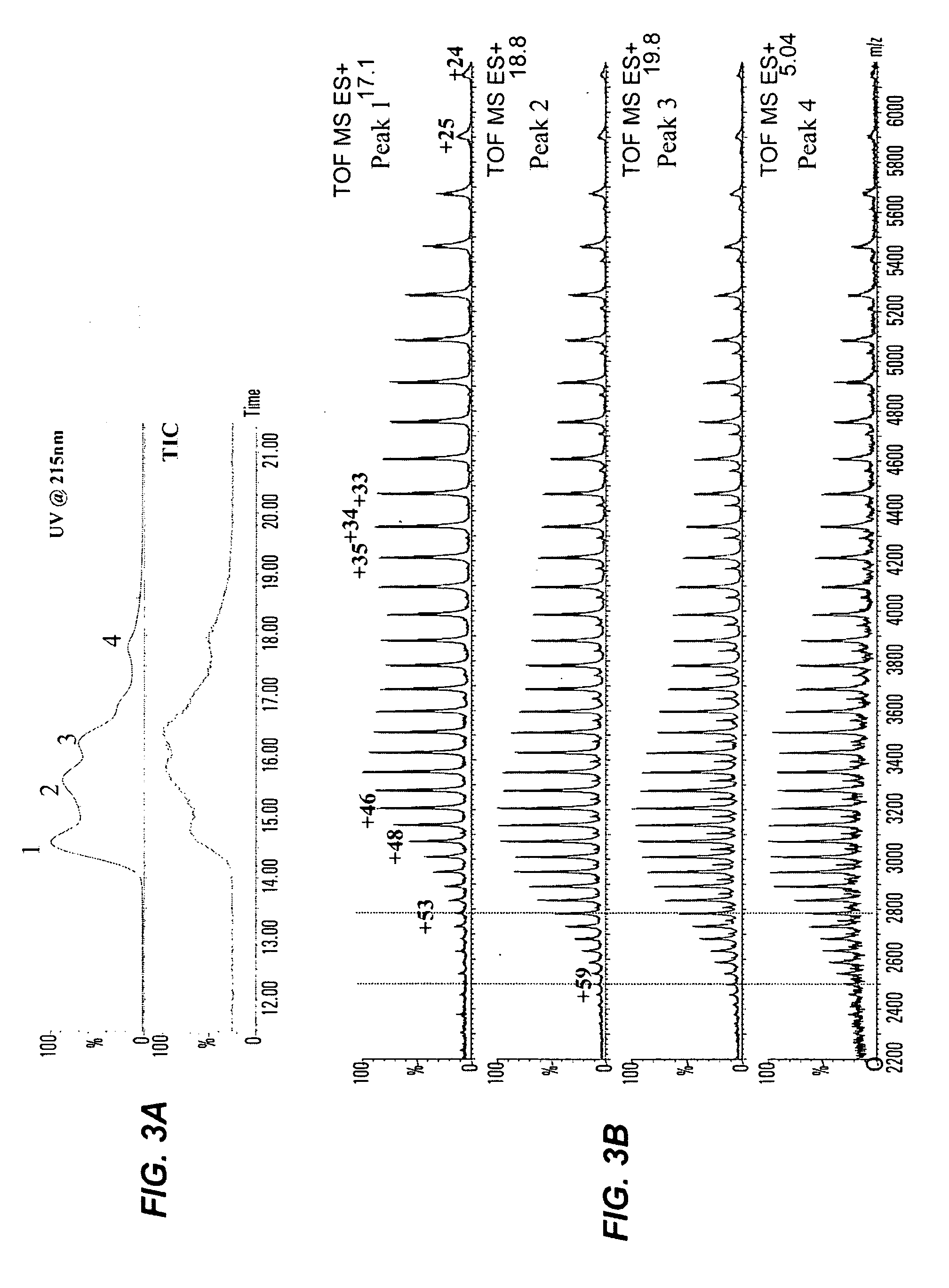
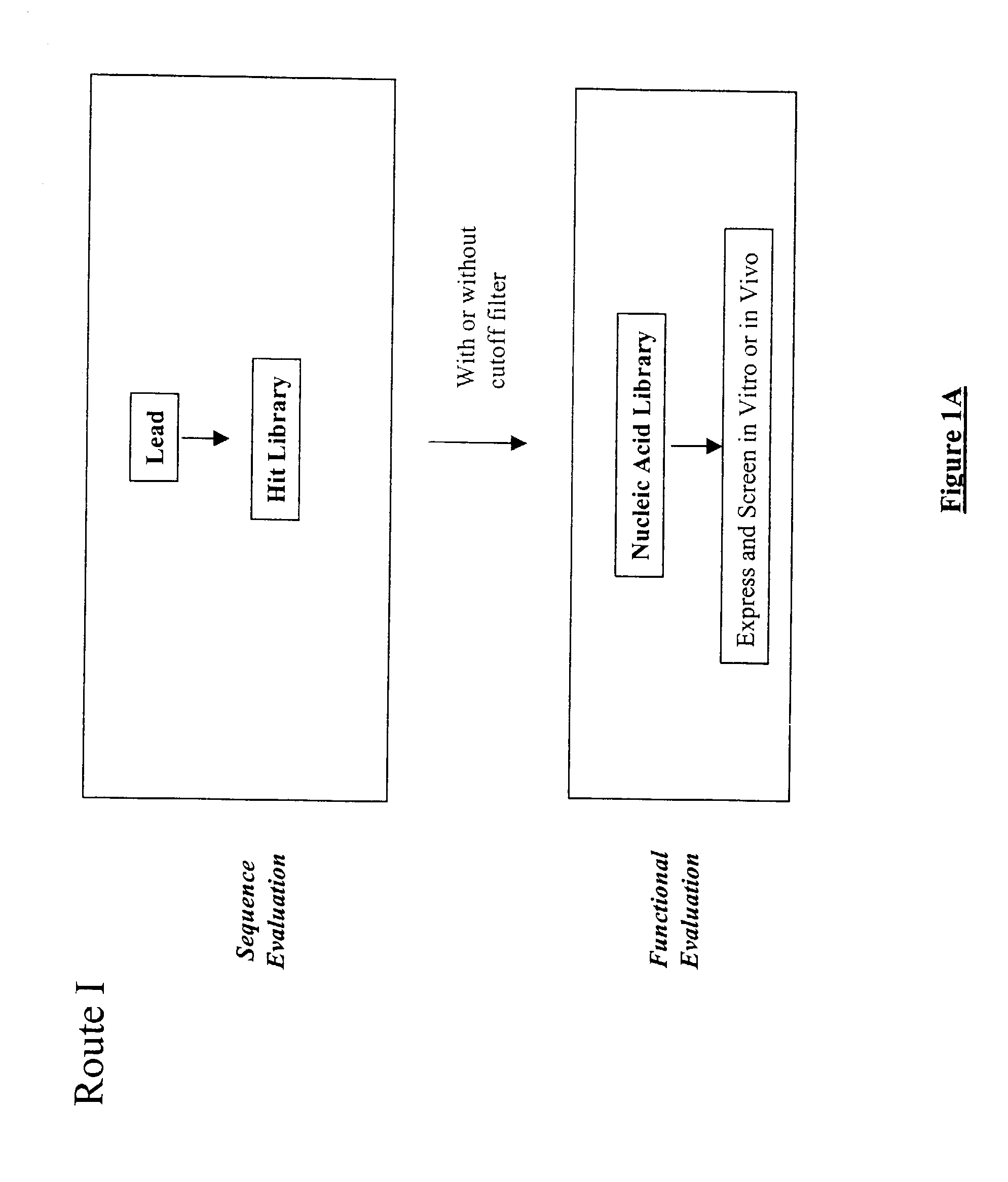
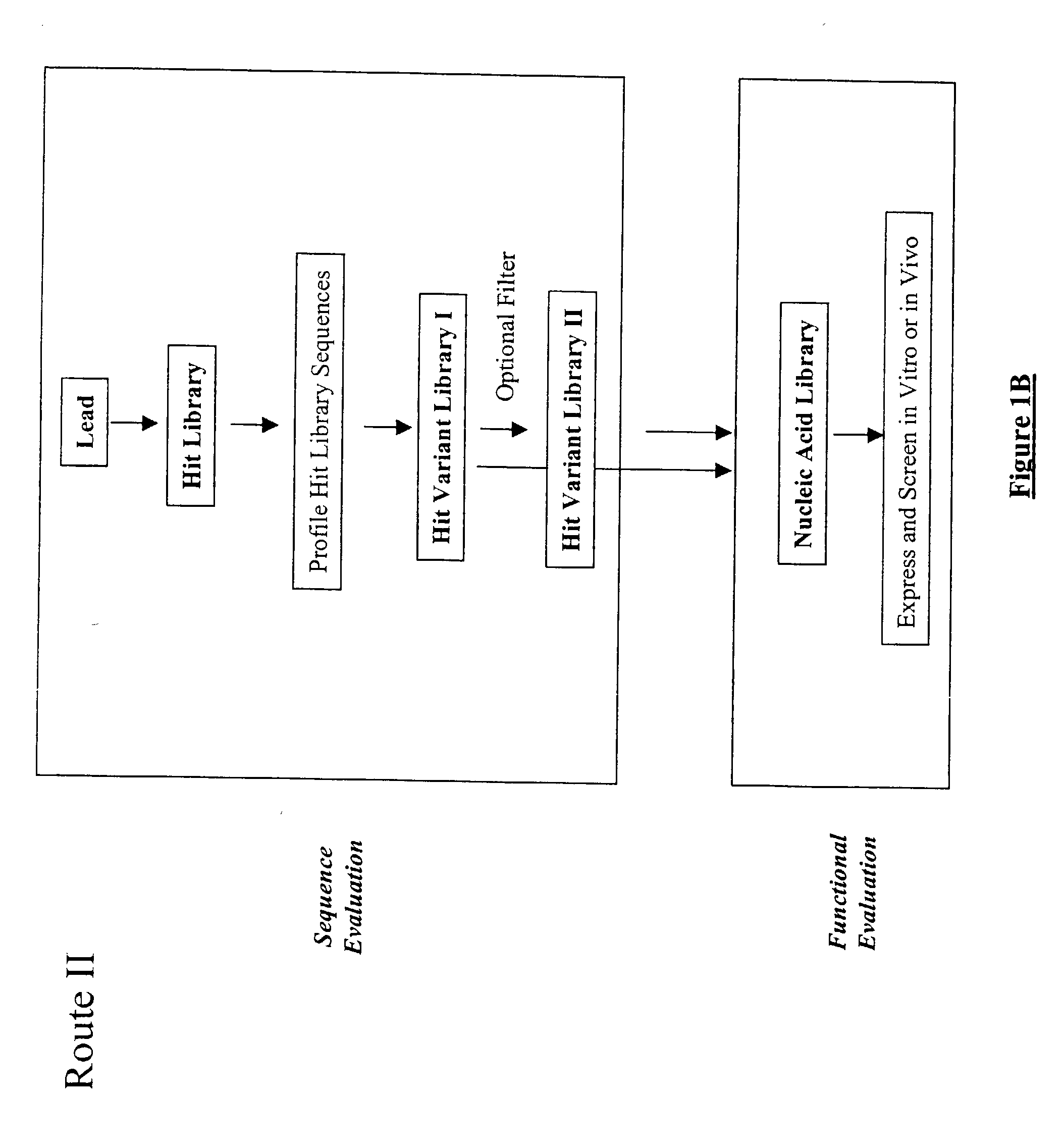
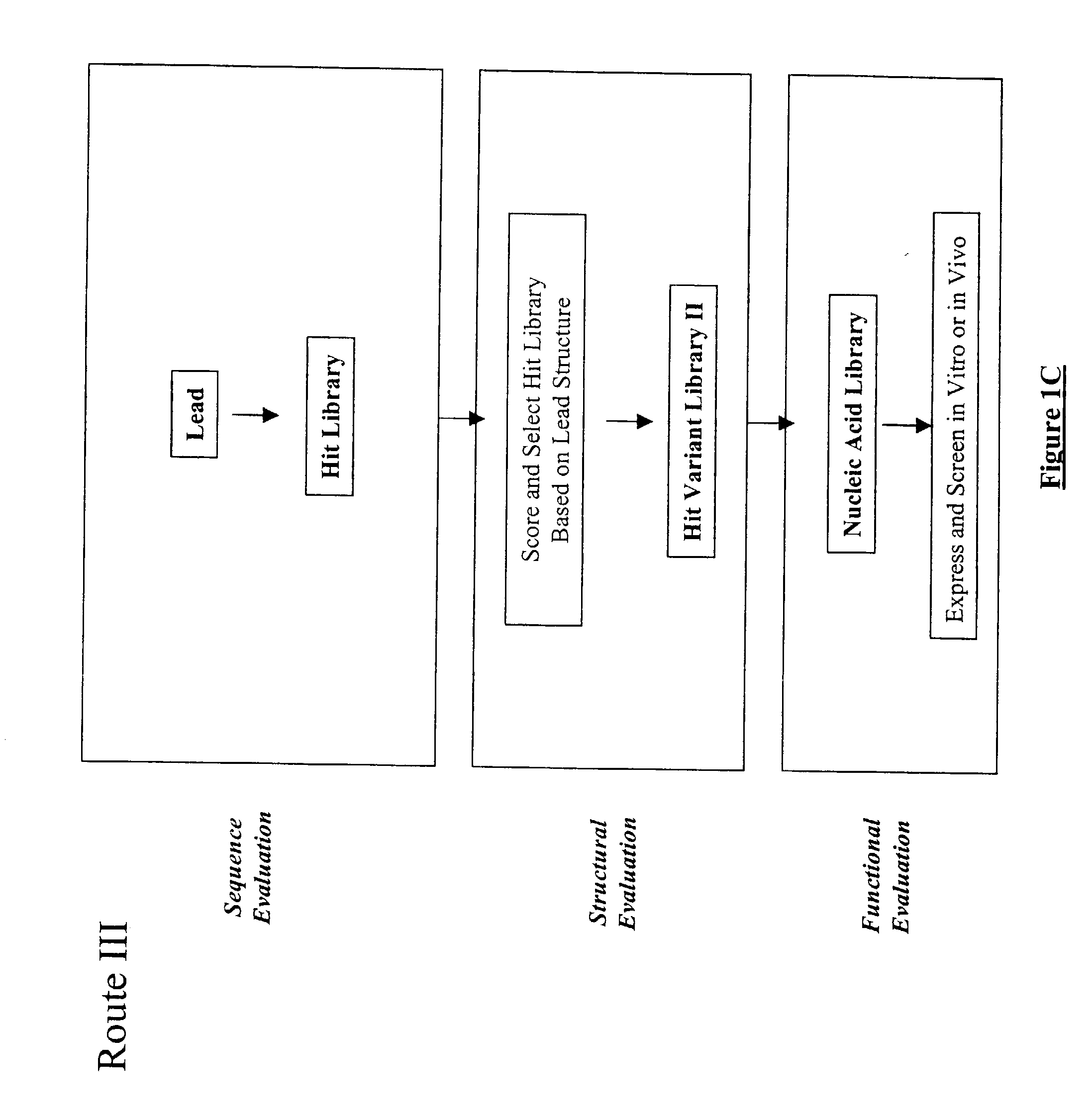
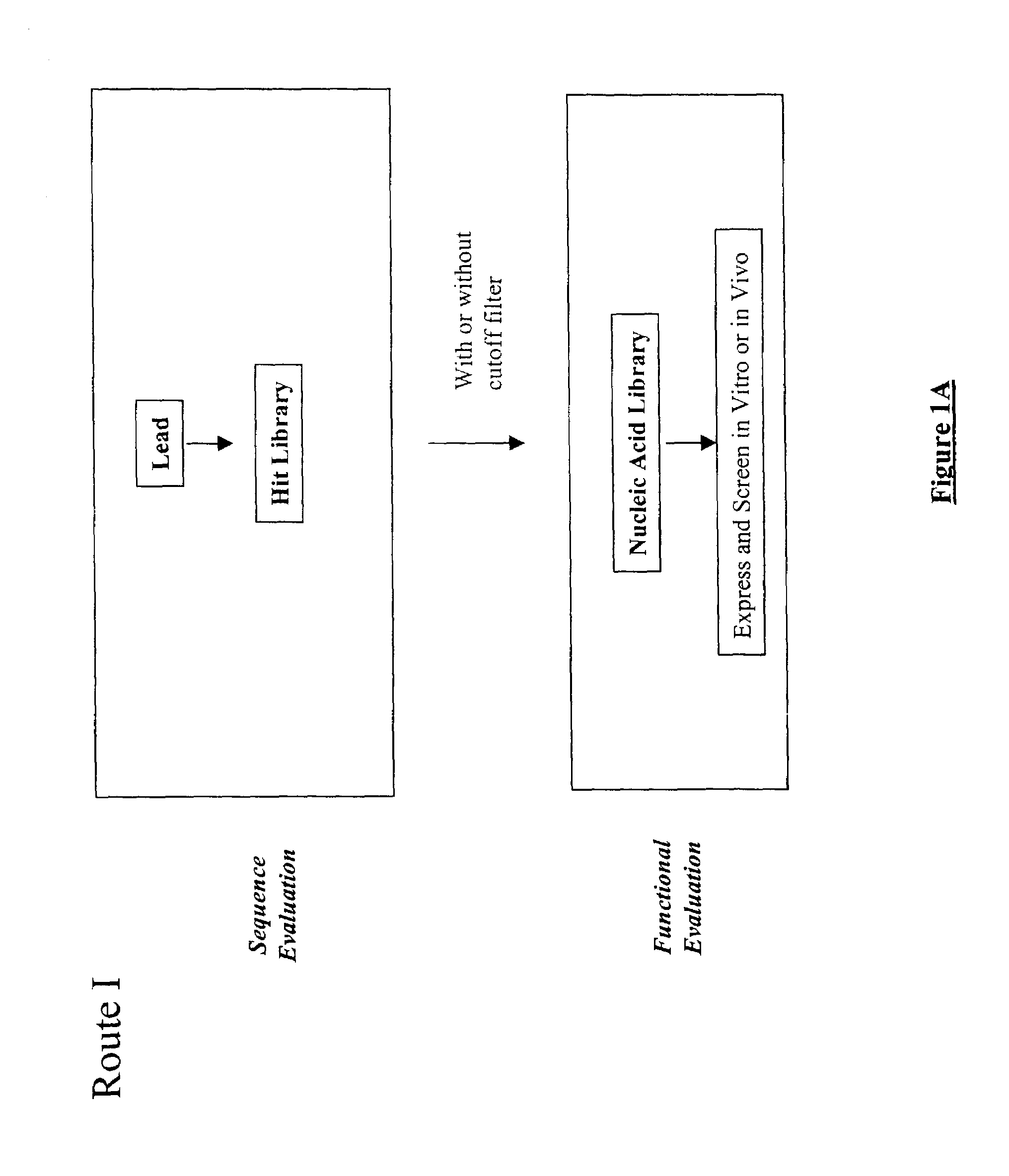
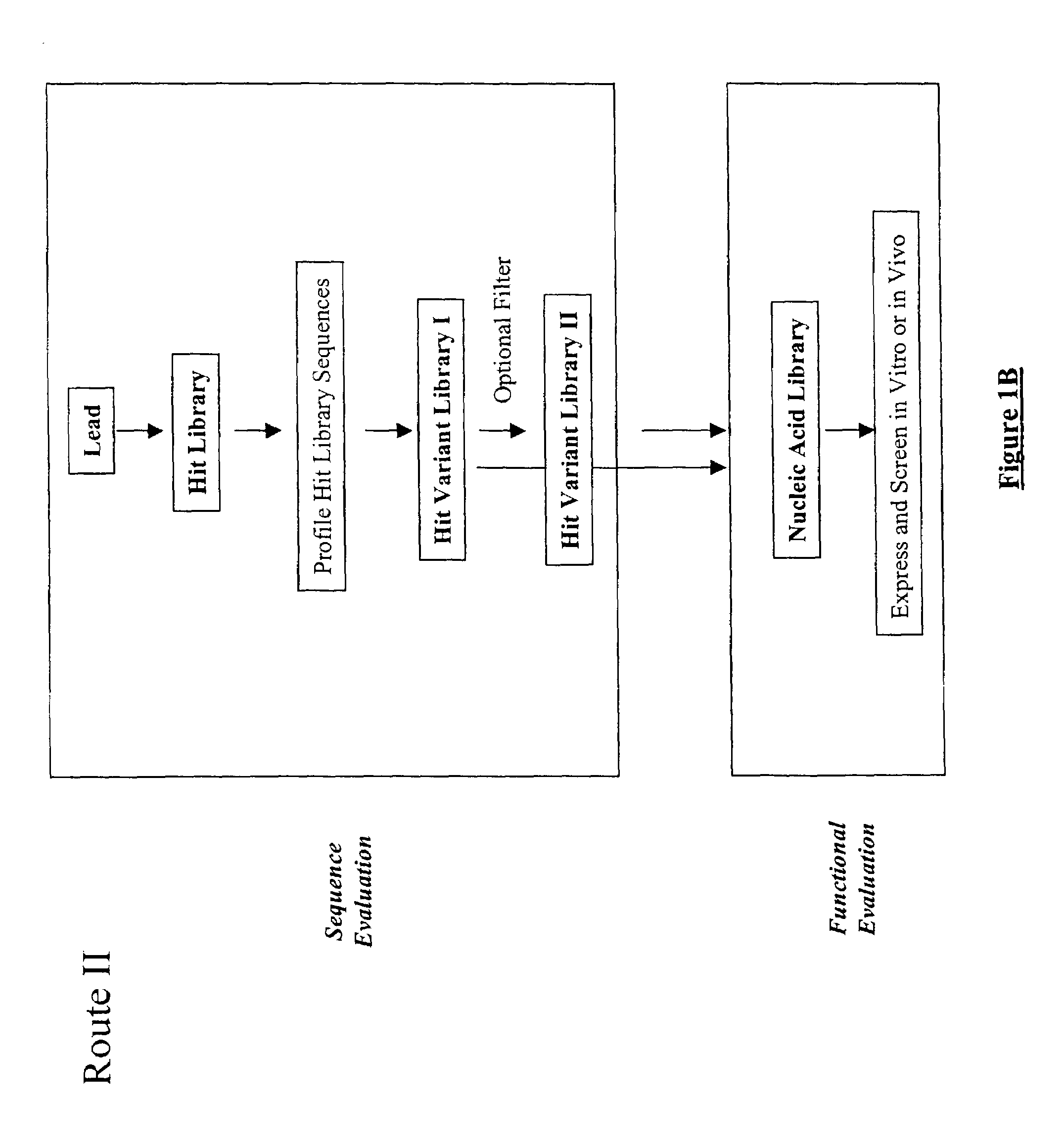
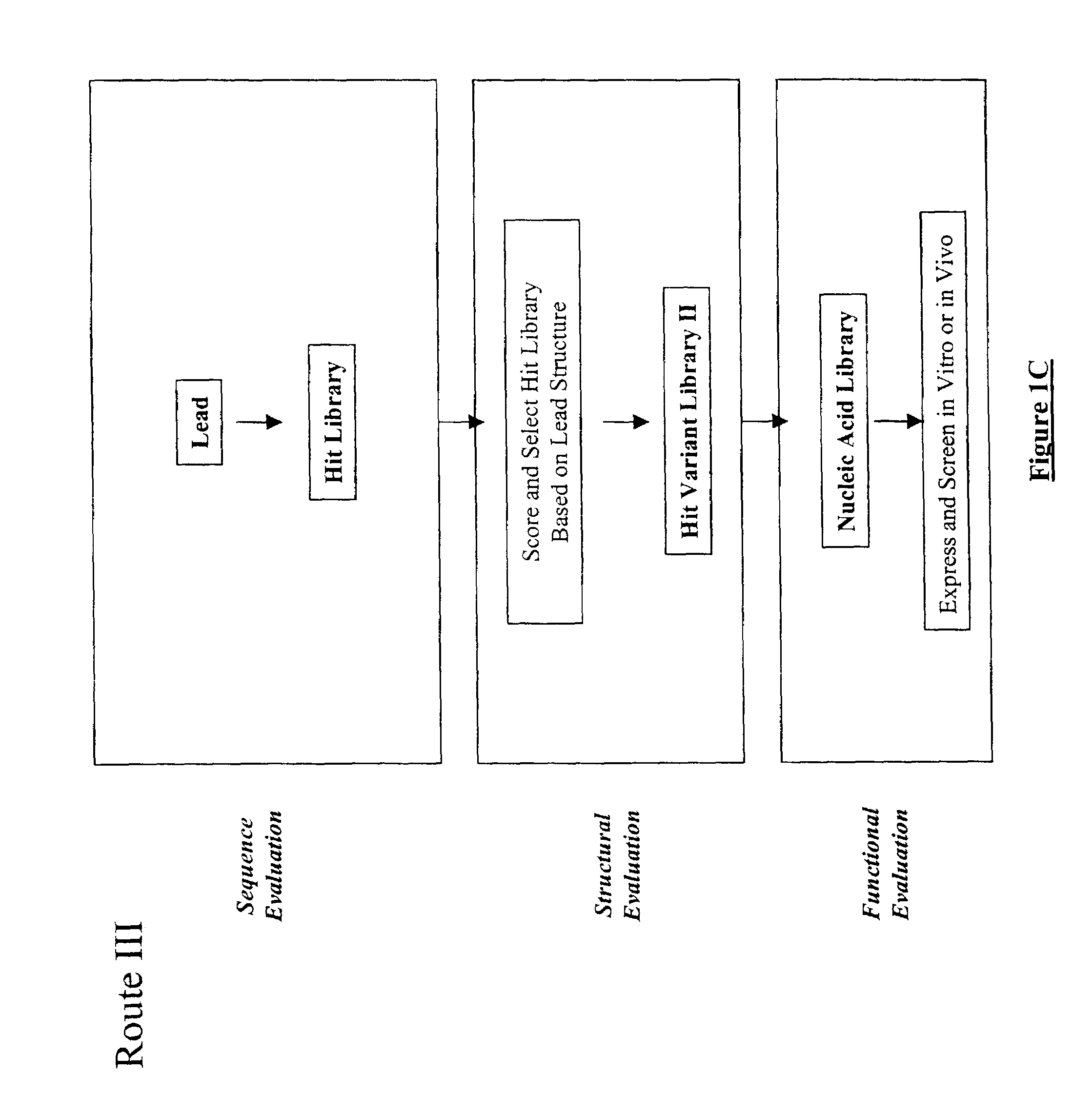
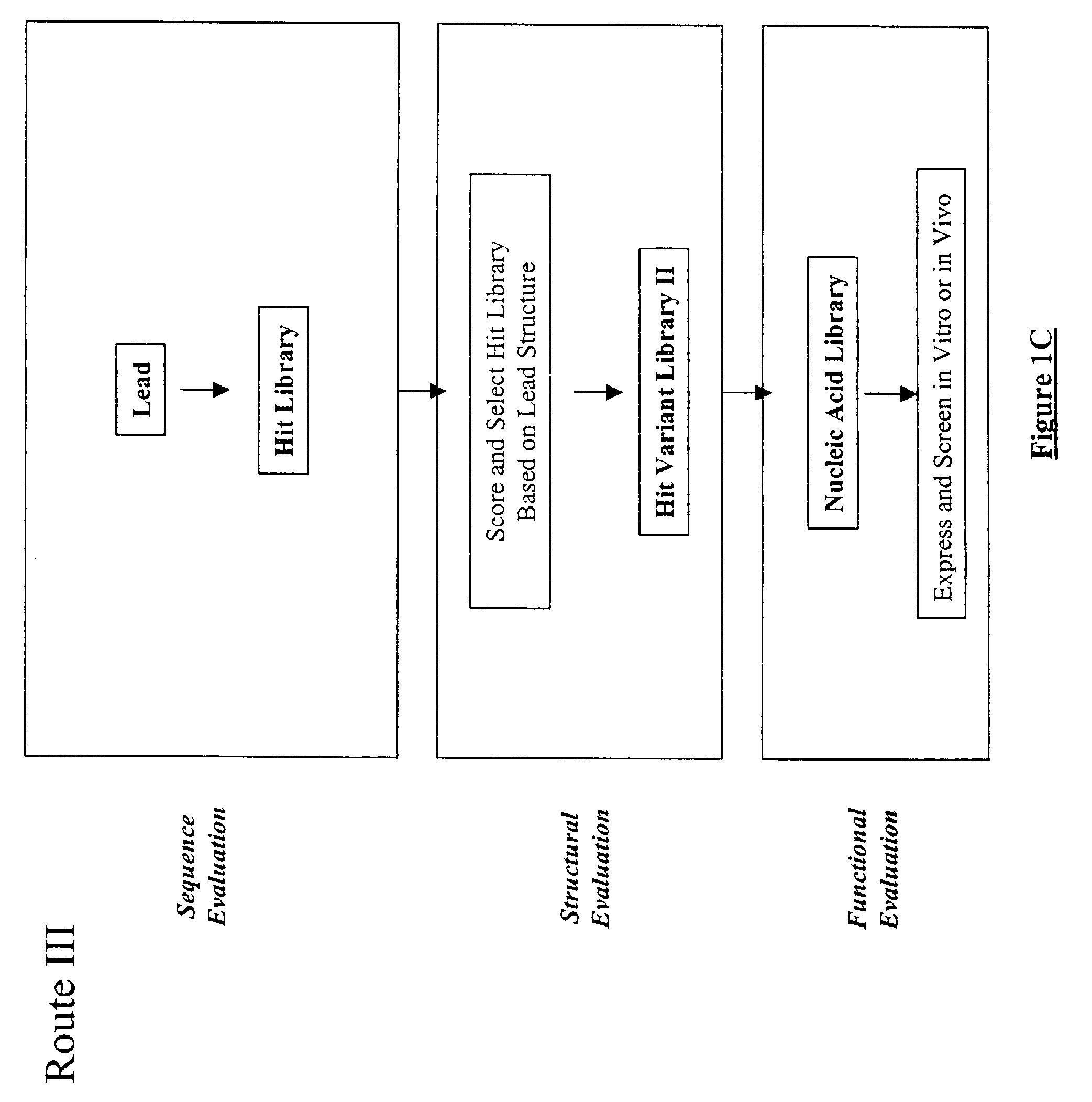
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
InactiveUS7117096B2High affinityImprove throughputPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein insertionIn vivo
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Isolating cells expressing secreted proteins
InactiveUS6919183B2Easy to detectImprove isolationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSecretory proteinCell sheet
A method for identifying and isolating cells which produce secreted proteins. This method is based upon a specific characteristic or the expression level of the secreted protein by transiently capturing the secreted protein on the surface of an individual cell, allowing selection of rare cell clones from a heterogeneous population. Also provided is the use of this method to generate cells which produce a desired level of secreted protein or secreted protein of a particular characteristic(s), and organisms which possess such cells. In particular, the method allows rapid isolation of high expression recombinant antibody-producing cell lines, or may be applied directly to rapid isolation of specific hybridomas, or to the isolation of antibody-producing transgenic animals. This method is applicable for any cell which secretes protein.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Recombinant antibodies and immunoconjugates targeted to CD-22 bearing cells and tumors
InactiveUS7541034B1Growth inhibitionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
Methods and compositions relating to recombinant anti-CD22 antibodies with high binding affinity, and immunoconjugates comprising the anti-CD22 antibody linked to a therapeutic agent such as a Pseudomonas exotoxin or a detectable label. The invention provides diagnostic methods, and means to inhibit the growth of malignant B cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICAN AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Recombinant antibody and antibody fragment
InactiveUS6989145B2Reduce in quantityHigh cytotoxic activitySenses disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseDiagnostic agent
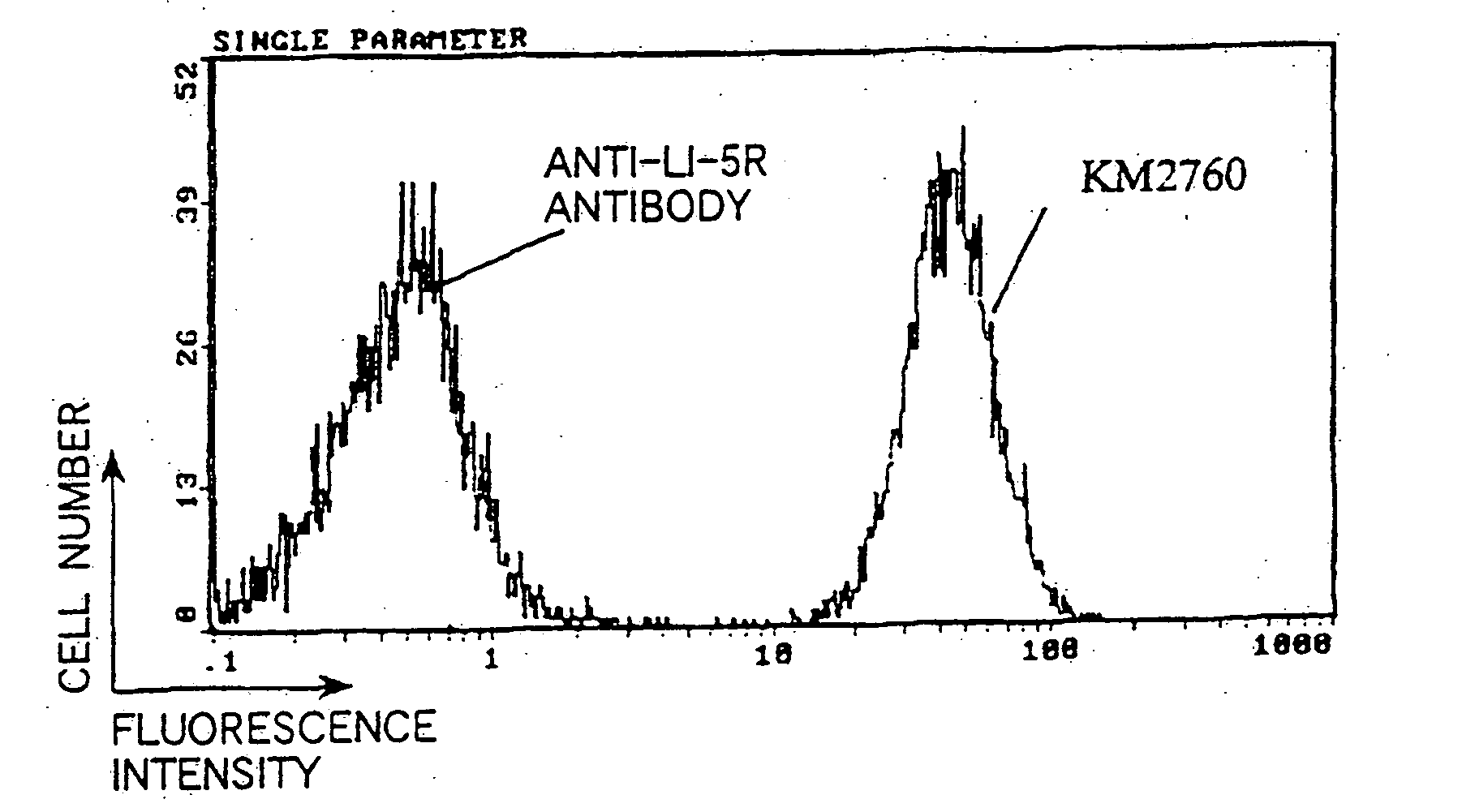
A recombinant antibody or the antibody fragment thereof which specifically reacts with an extracellular domain of human CCR4; a DNA which encodes the recombinant antibody or the antibody fragment thereof; a method for producing the recombinant antibody or the antibody fragment thereof; a method for immunologically detecting CCR4, a method for immunologically detecting a cell which expressed CCR4 on the cell surface, a method for depleting a cell which expresses CCR4 on the cell surface, and a method for inhibiting production of Th2 cytokine, which comprise using the recombinant antibody according or antibody fragment thereof; a therapeutic or diagnostic agent for Th2-mediated immune diseases; and a therapeutic or diagnostic agent for a blood cancer.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Recombinant antibody composition
ActiveUS7923538B2Enhanced effector functionGood treatment effectAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsA-DNAActive ingredient
The present invention relates to a recombinant antibody composition having higher complement-dependent cytotoxic activity than a human IgG1 antibody and a human IgG3 antibody, wherein a polypeptide comprising a CH2 domain in the Fc region of a human IgG1 antibody is replaced by a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence which corresponds to the same position of a human IgG3 antibody indicated by the EU index as in Kabat, et al.; a DNA encoding the antibody molecule or a heavy chain constant region of the antibody molecule contained in the recombinant antibody composition; a transformant obtainable by introducing the recombinant vector into a host cell; a process for producing the recombinant antibody composition using the transformant; and a medicament comprising the recombinant antibody composition as an active ingredient.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Increasing the production of recombinant antibodies in mammalian cells by site-directed mutagenesis
InactiveUS20060019342A1Improve expression levelHigh purification yieldAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHeavy chainMammal
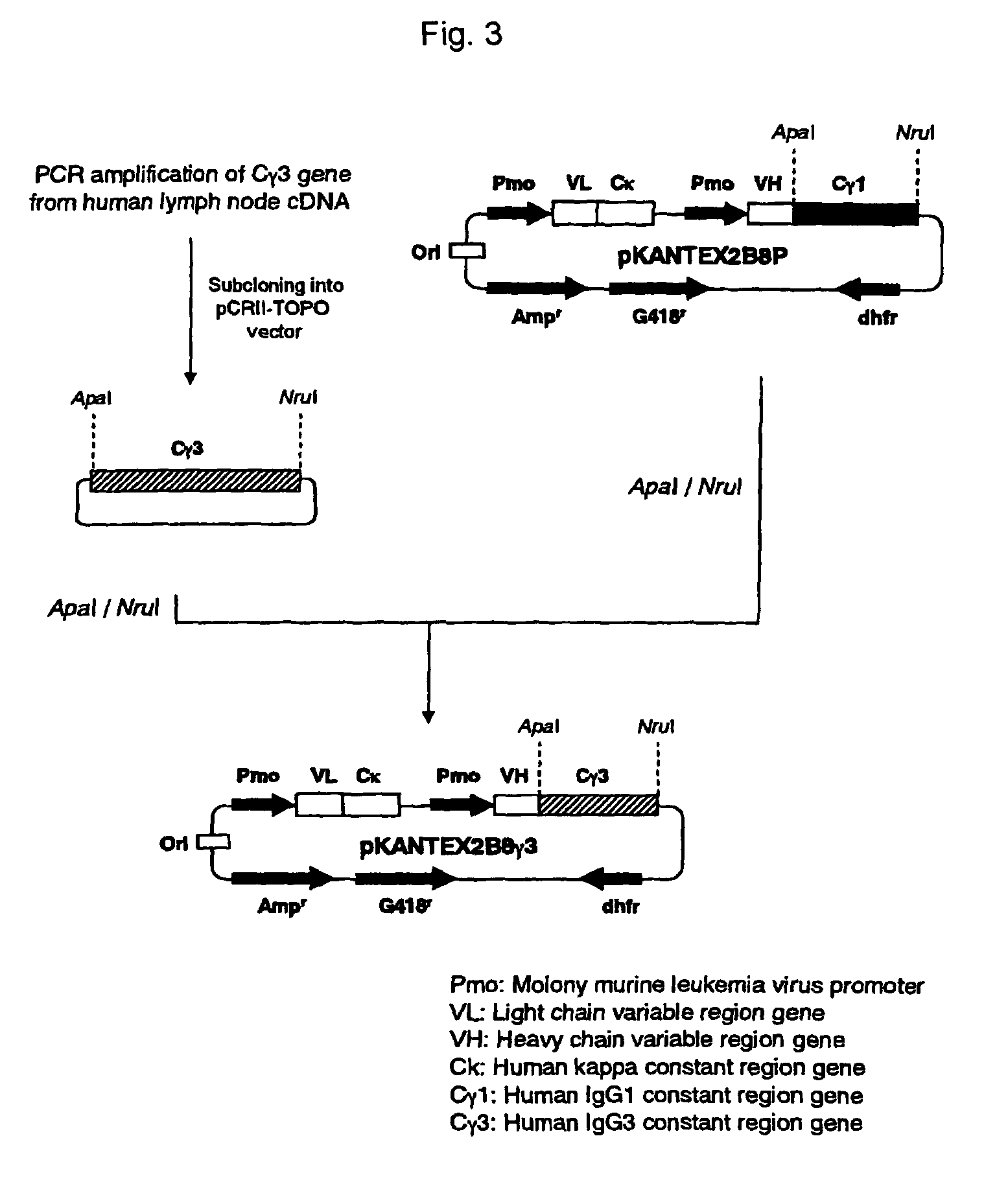
The present invention relates to a reliable, reproducible method for improving the producibility of an antibody. More specifically, this invention provides a method for modifying the heavy chain of an antibody to improve its producibility in eukaryotic cells. Additionally, the method of the invention may improve both antibody producibility and one or more antigen binding characteristics. The invention further provides modified antibodies which are better produced and which have either no change in their antigen binding characteristics or exhibit improved antigen binding characteristics.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
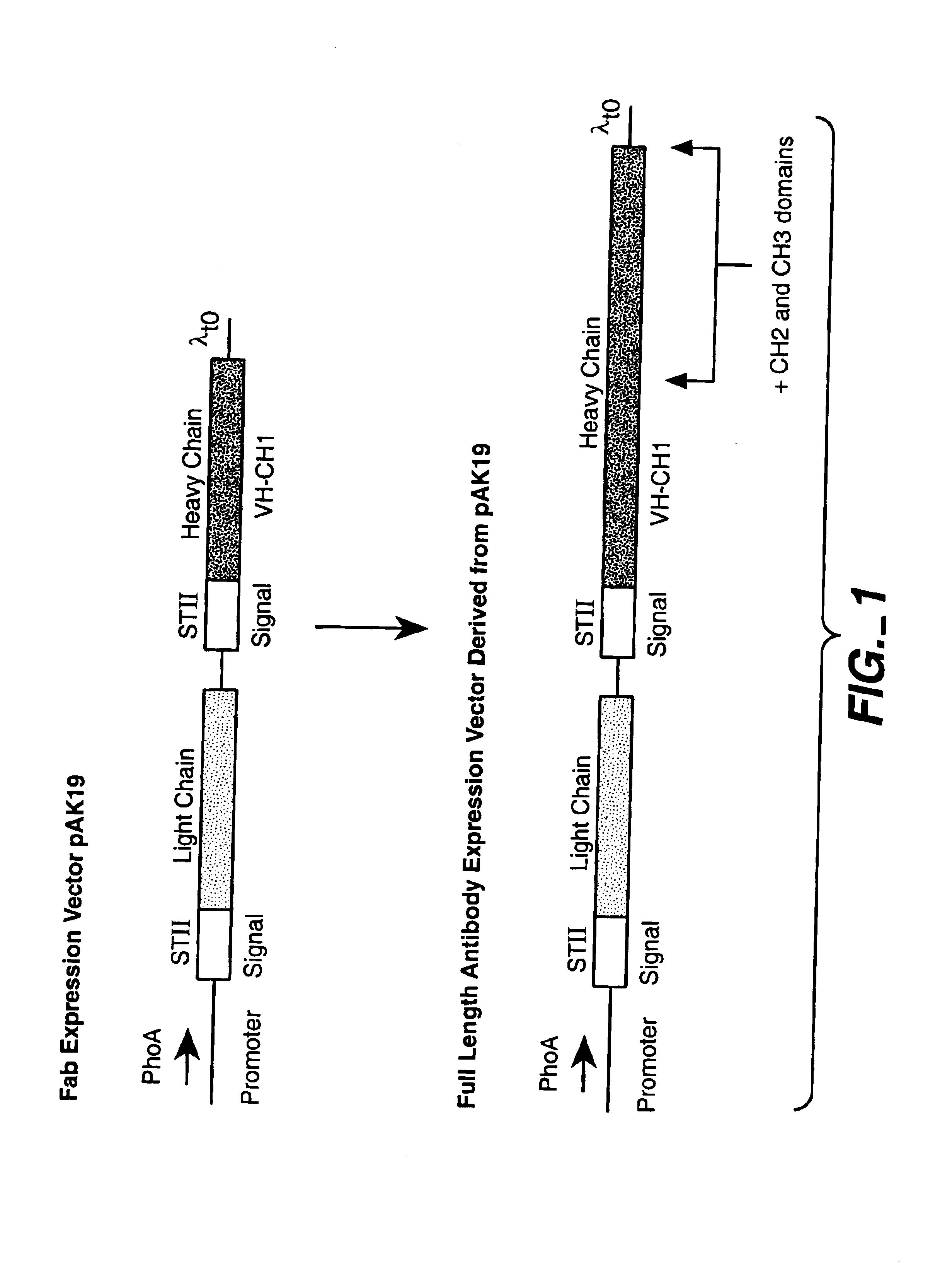
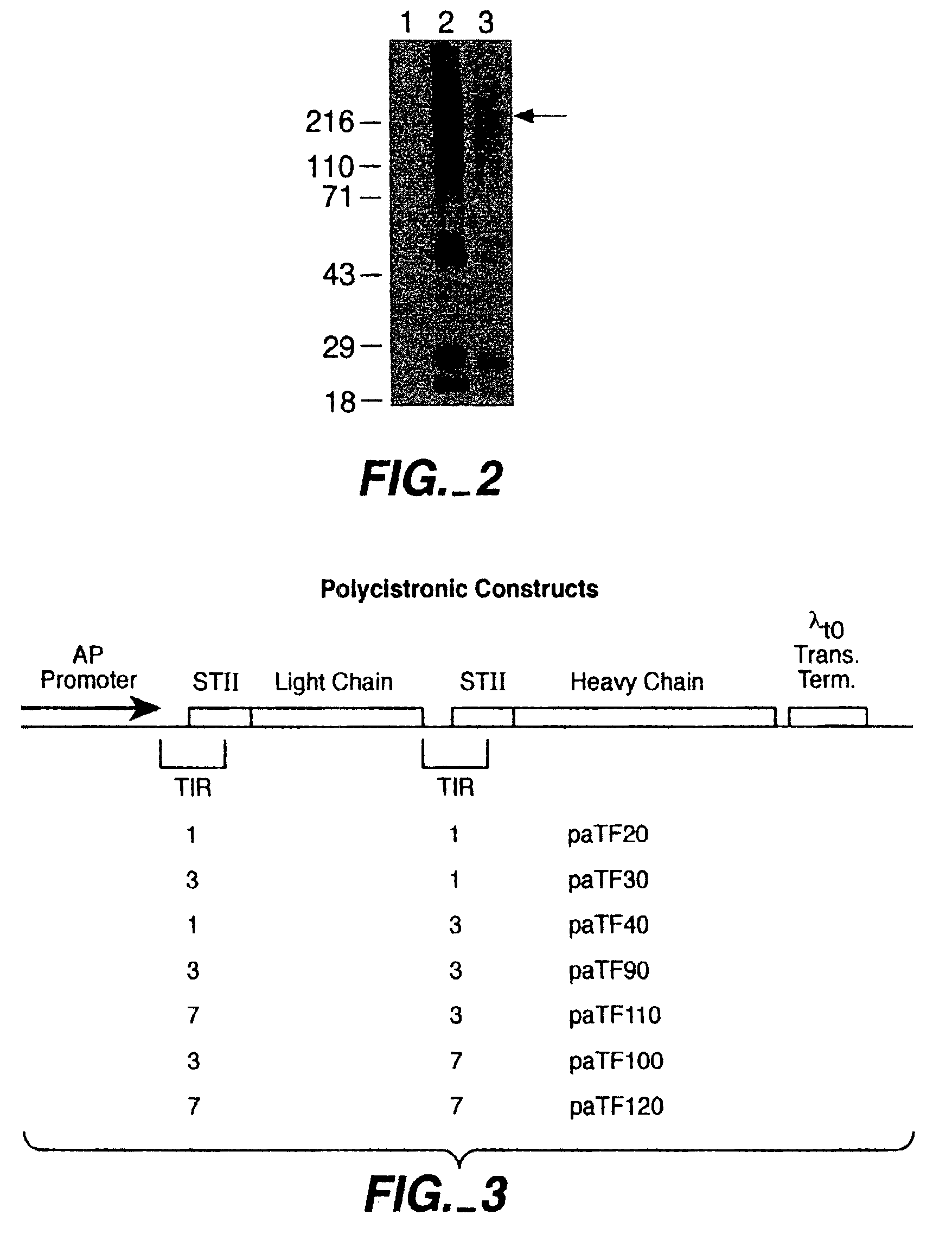
Separate-cistron contructs for secretion of aglycosylated antibodies from prokaryotes
InactiveUS6979556B2Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsSugar derivativesBiological studiesProkaryotic expression
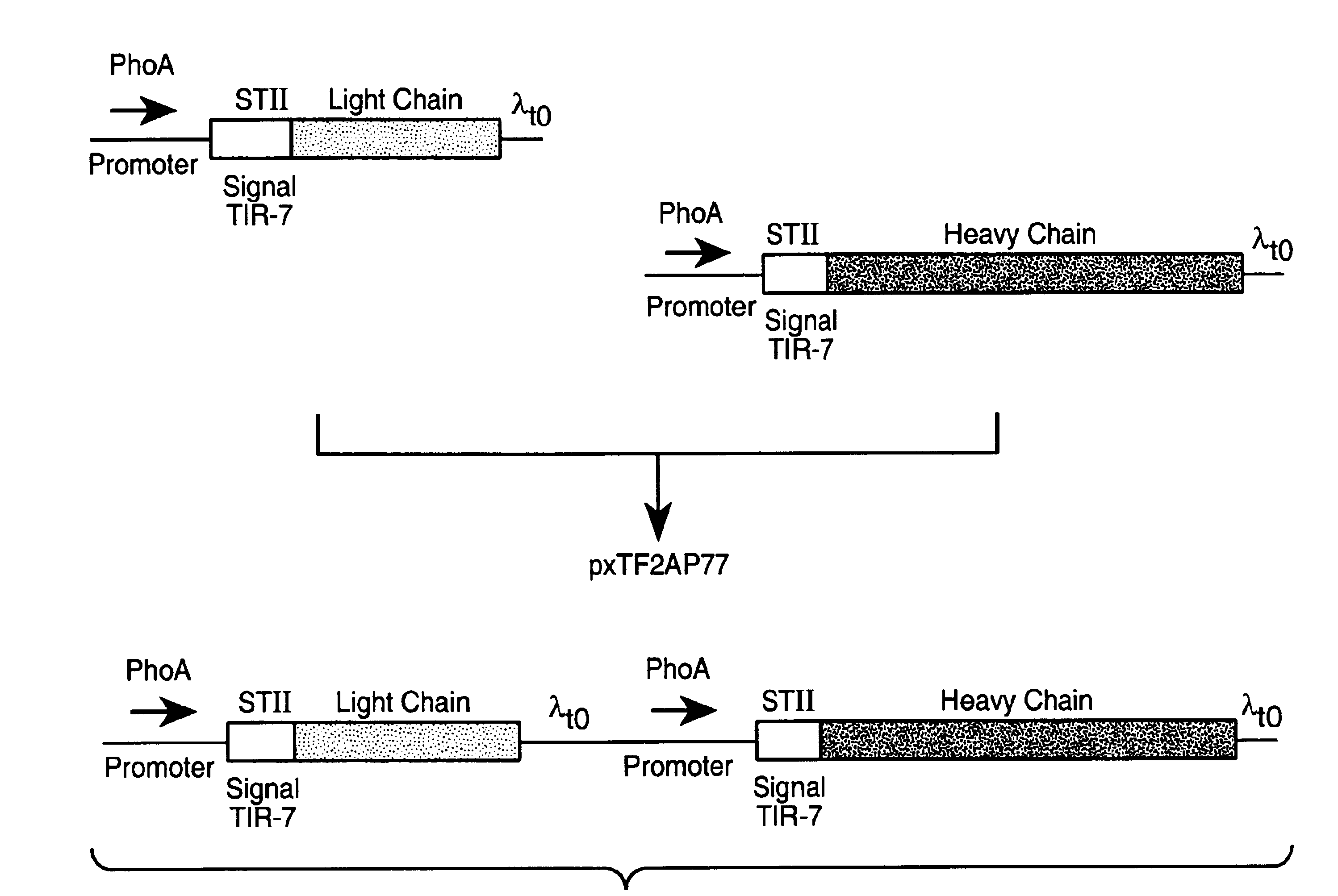
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improved expression and production of recombinant antibodies in prokaryotic expression systems. Particularly contemplated are prokaryotic expression and production of full length aglycosylated antibodies. The antibody products of the invention can be used in various aspects of biological research, diagnosis and medical treatment.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Generation and affinity maturation of antibody library in silico
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on the amino acid sequence of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library. The hit library of antibody sequences can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
System for isolating and identifying eukaryotic cells transfected with genes and vectors, host cells and methods thereof
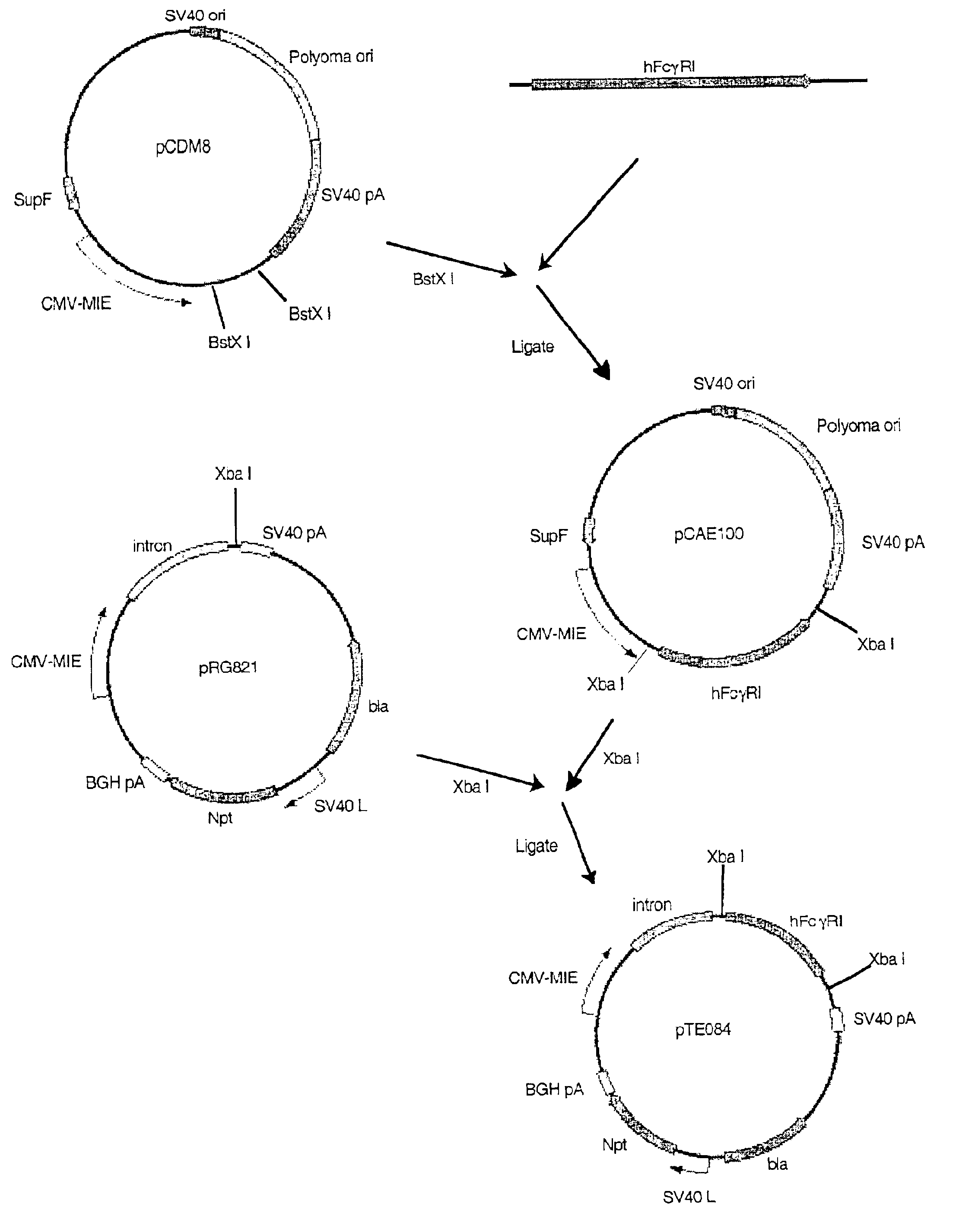
The present invention relates a novel expression system which allows the study of experimental genes of interest on cellular events soon after transfection. The expression system includes a vector which encodes for a recombinant antibody binding unit (rAb). The expression system enables identification and selection of transfected cells from culture to be carried out immediately, within hours, after the transfection
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
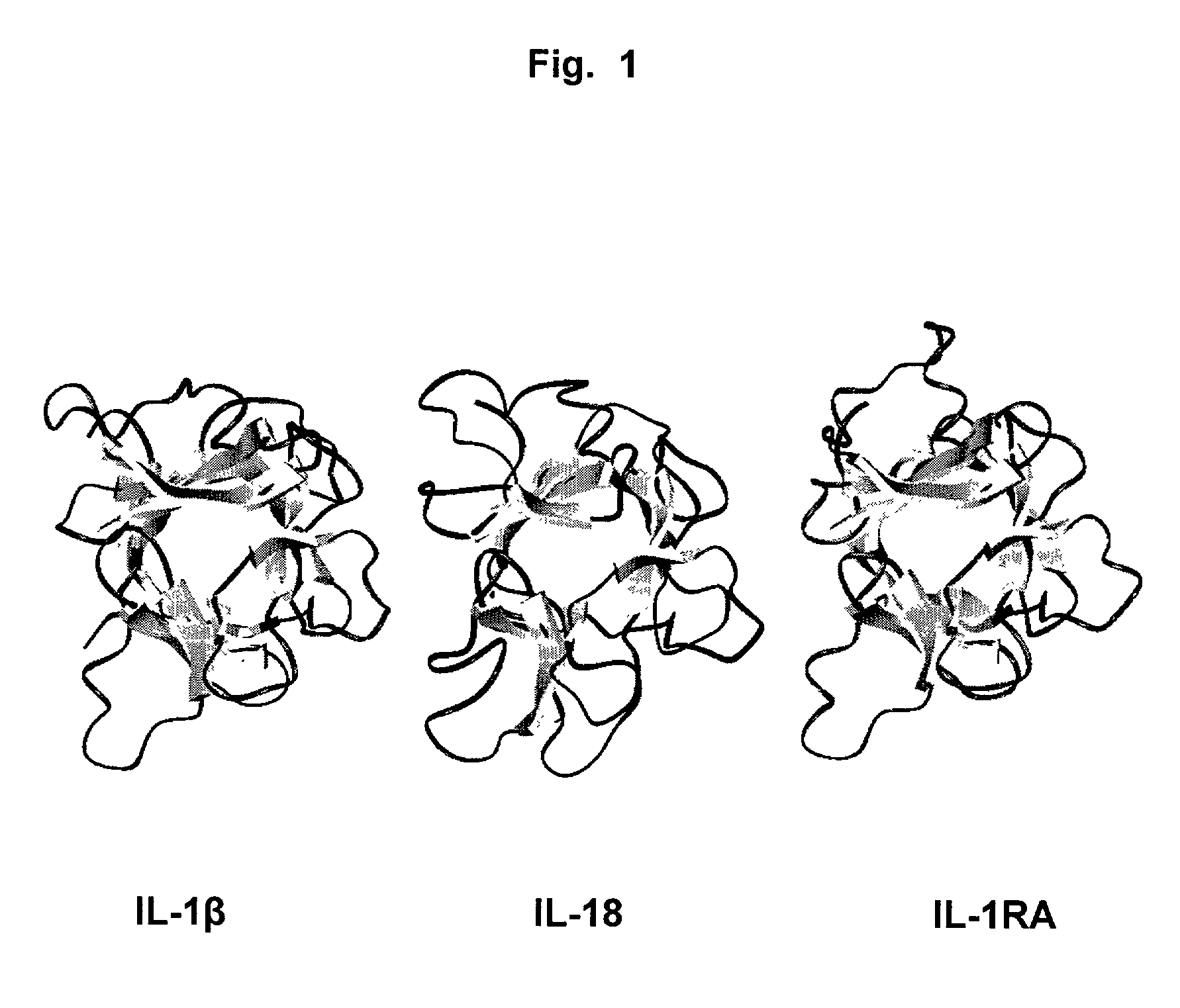
Dual specificity antibodies and methods of making and using
Antibodies having dual specificity for two different but structurally related antigens are provided. The antibodies can be, for example, entirely human antibodies, recombinant antibodies, or monoclonal antibodies. Preferred antibodies have dual specificity for IL-1α and IL-1β and neutralize IL-1α and IL-1β activity in vitro and in vivo. An antibody of the invention can be a full-length antibody or an antigen-binding portion thereof. Methods of making and methods of using the antibodies of the invention are also provided. The antibodies, or antibody portions, of the invention are useful for detecting two different but structurally related antigens (e.g., IL-1α and IL-1β ) and for inhibiting the activity of the antigens, e.g., in a human subject suffering from a disorder in which IL-1α and / or IL-1β activity is detrimental.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Effector function enhanced recombinant antibody composition
ActiveUS7994290B2Enhanced effector functionGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsA-DNAActive ingredient
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
High potency recombinant antibodies and method for producing them
InactiveUS7700735B2Improve performanceIncreasing rate constantPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against virusesAntigenDisease
High potency antibodies, including immunologically active fragments thereof, having high kinetic association rate constants and optional high affinities are disclosed, along with methods for producing such antibodies. The high potency antibodies disclosed herein are of either the neutralizing or non-neutralizing type and have specificity for antigens displayed by microorganisms, especially viruses, as well as antigenic sites present on cancer cells and on various types of toxins, and the products of toxins. Processes for producing high potency neutralizing antibodies and increasing the potency of already existing neutralizing antibodies are also described. Methods of using said antibodies in the prevention and / or treatment of diseases, especially diseases induced or caused by viruses, are disclosed.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Recombinant anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody compositions
ActiveUS7887805B2Reduce exerciseReduction tendencyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationHuman cancerCancer cell
Owner:LES LAB SERVIER SA
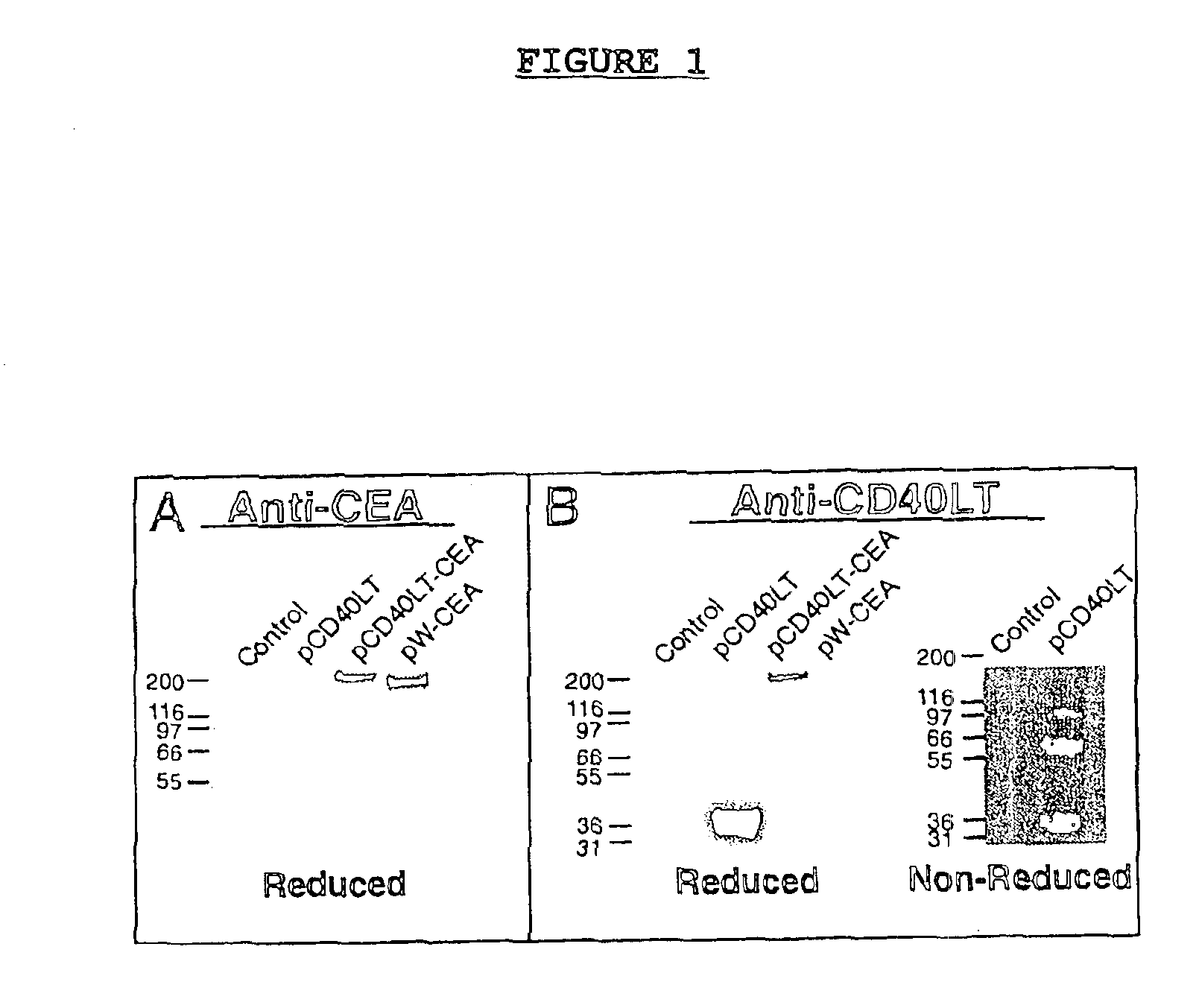
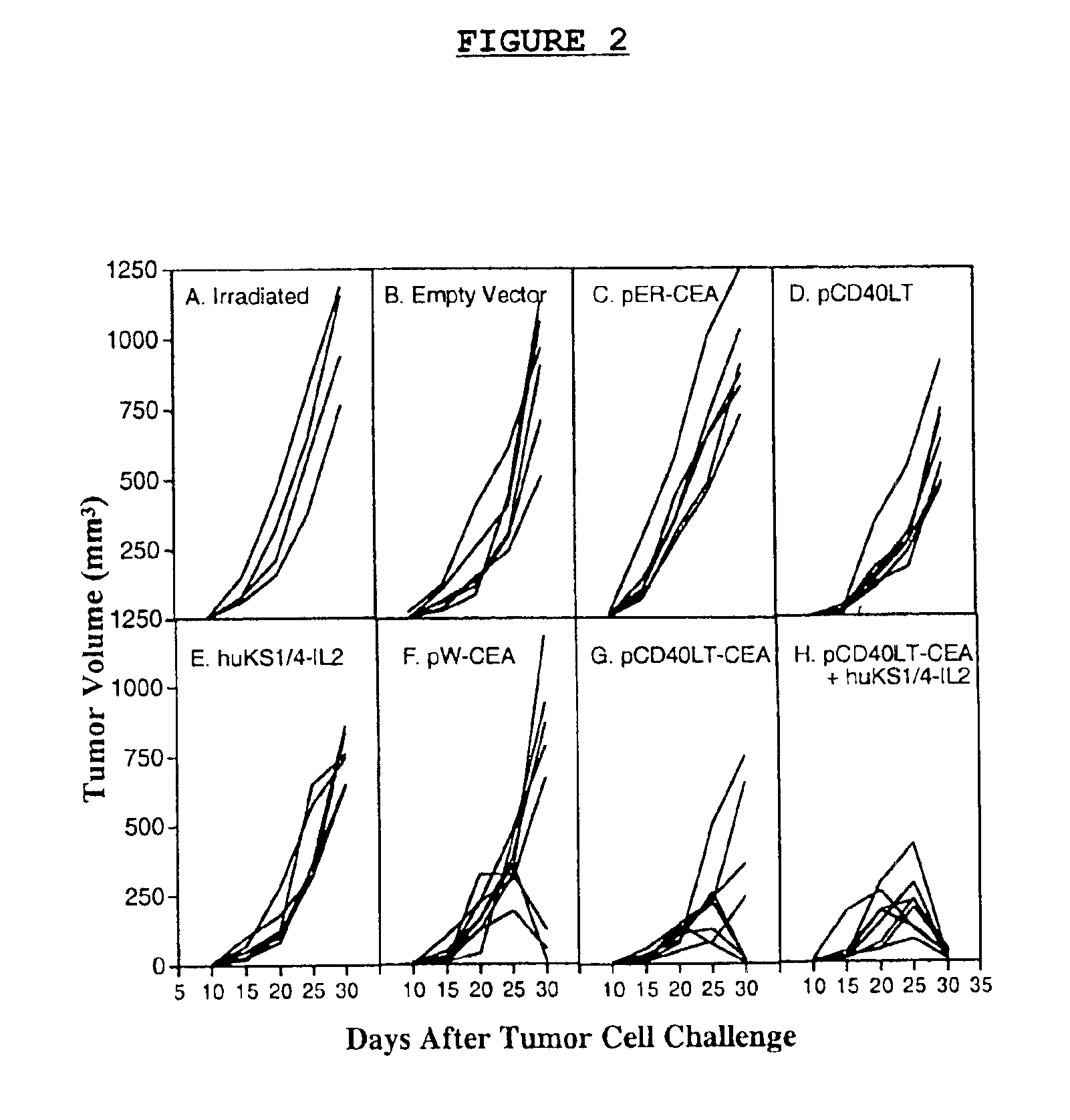
DNA vaccines encoding CEA and a CD40 ligand and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS6923958B2Enhance immune responseEffective immune responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLipofectamineMammal
A DNA vaccine effective for eliciting an immune response against cells that present a carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) comprises a DNA operably encoding a CEA and a DNA operably encoding a CD40 ligand, SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO: 2, respectively, or its homotrimer, CD40LT. The DNA vaccine can be incorporated in a delivery vector such as an attenuated live bacterium or virus, or a liposome carrier. In a method embodiment, the DNA vaccine is administered orally to a mammal, such as a human, to elicit an immune response against CEA presenting cells such as colon cancer cells. A preferred method embodiment includes the additional step of treating the mammal with recombinant antibody fusion protein huKS1 / 4-IL2 to enhance the immune response effectiveness of the vaccine.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Antibodies anti-c5 component of the complement system and their use
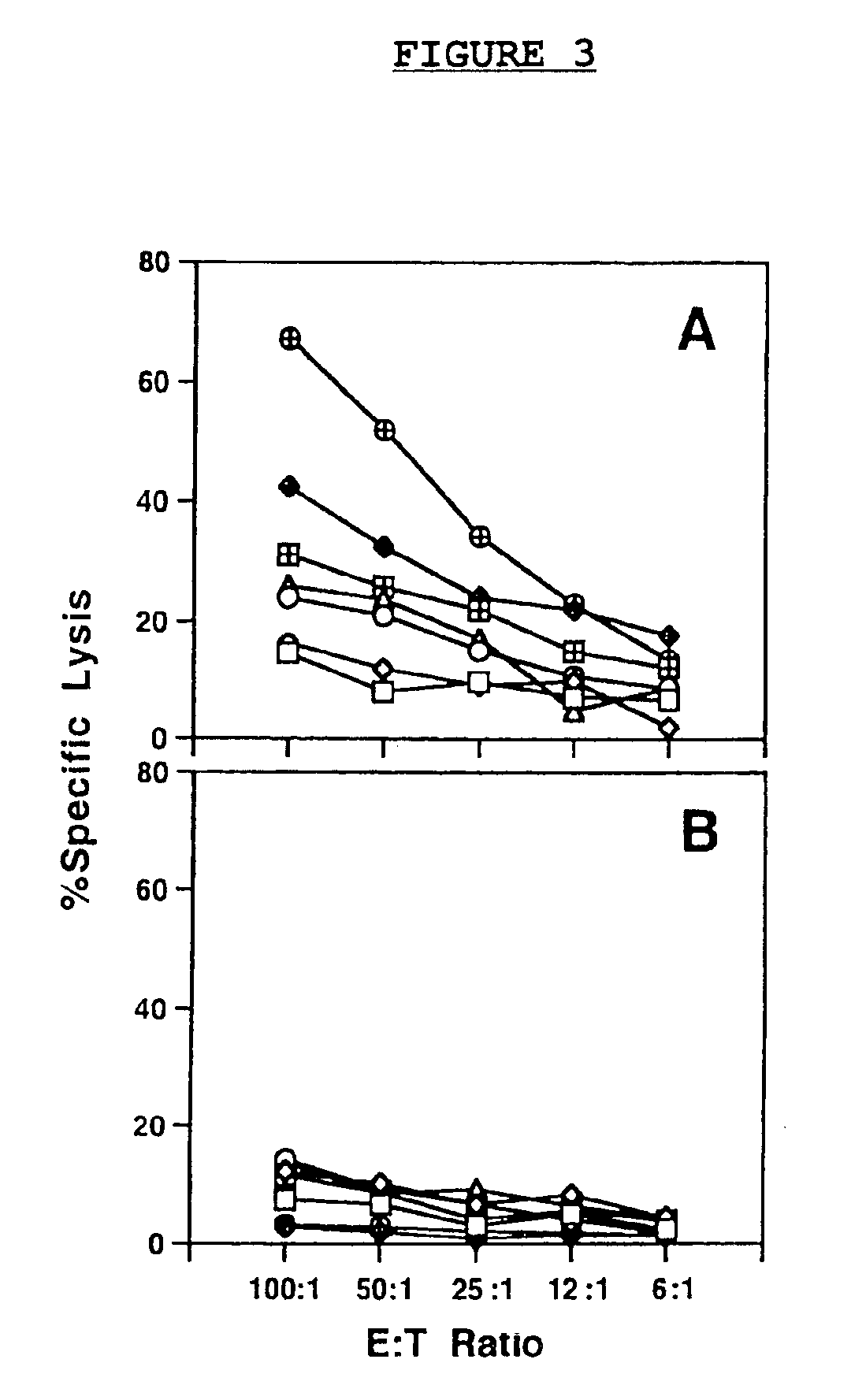
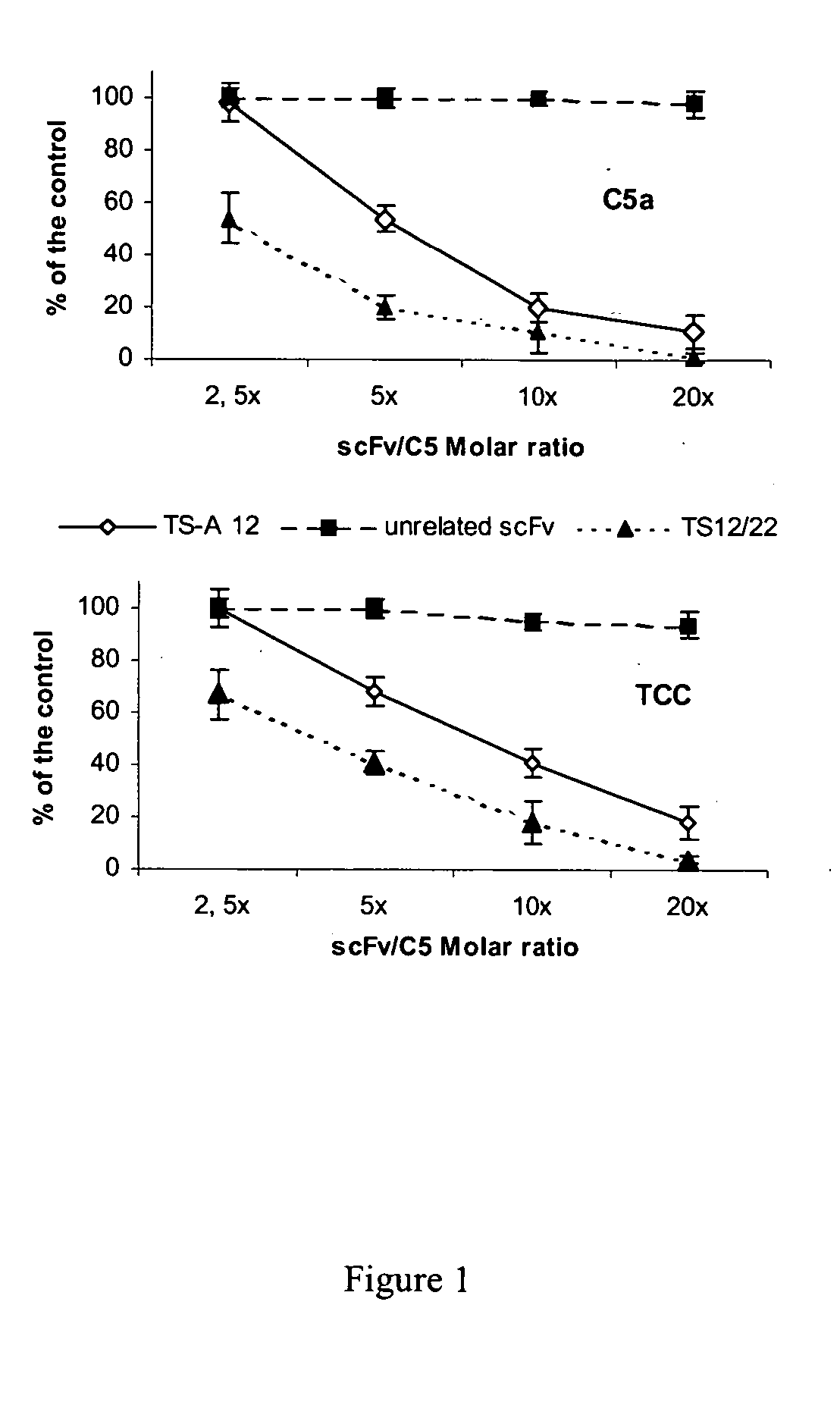
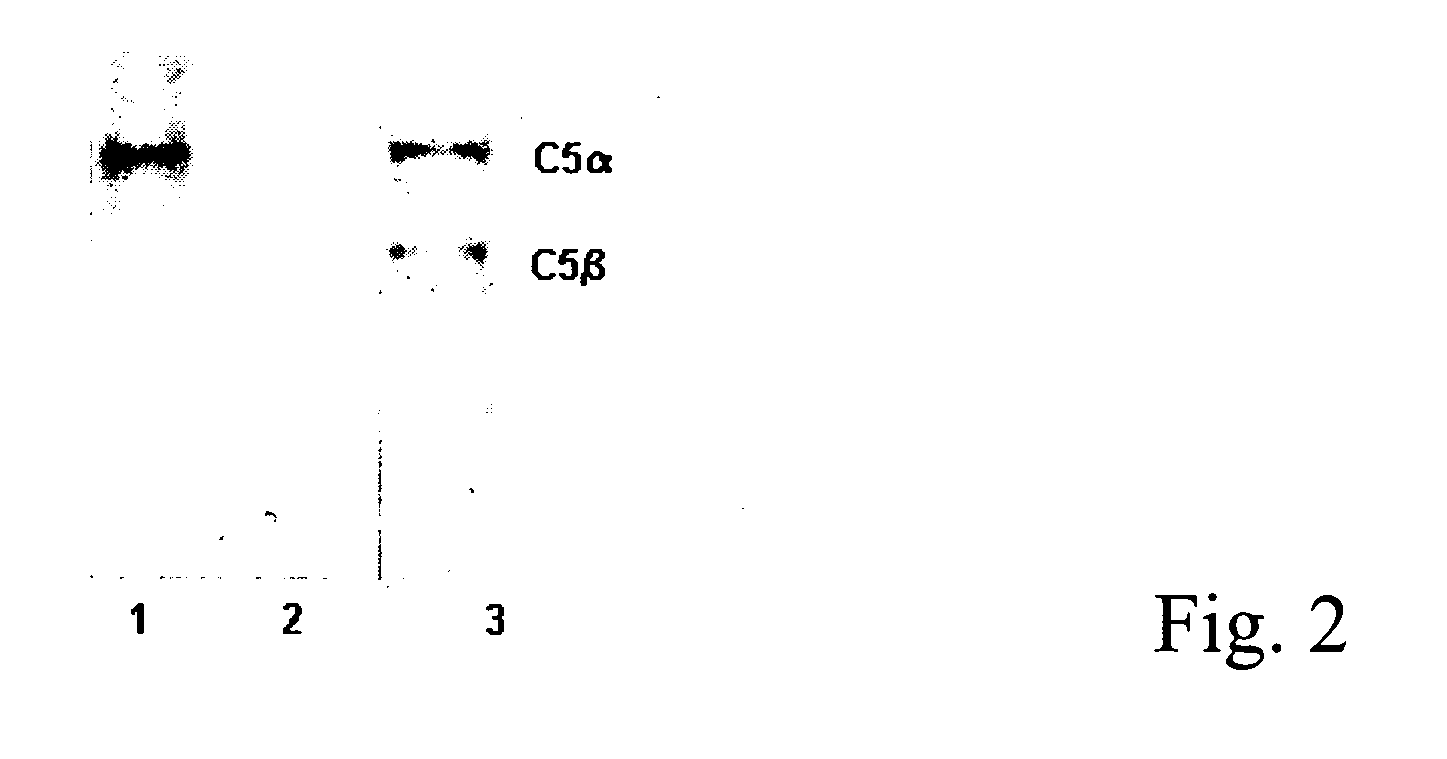
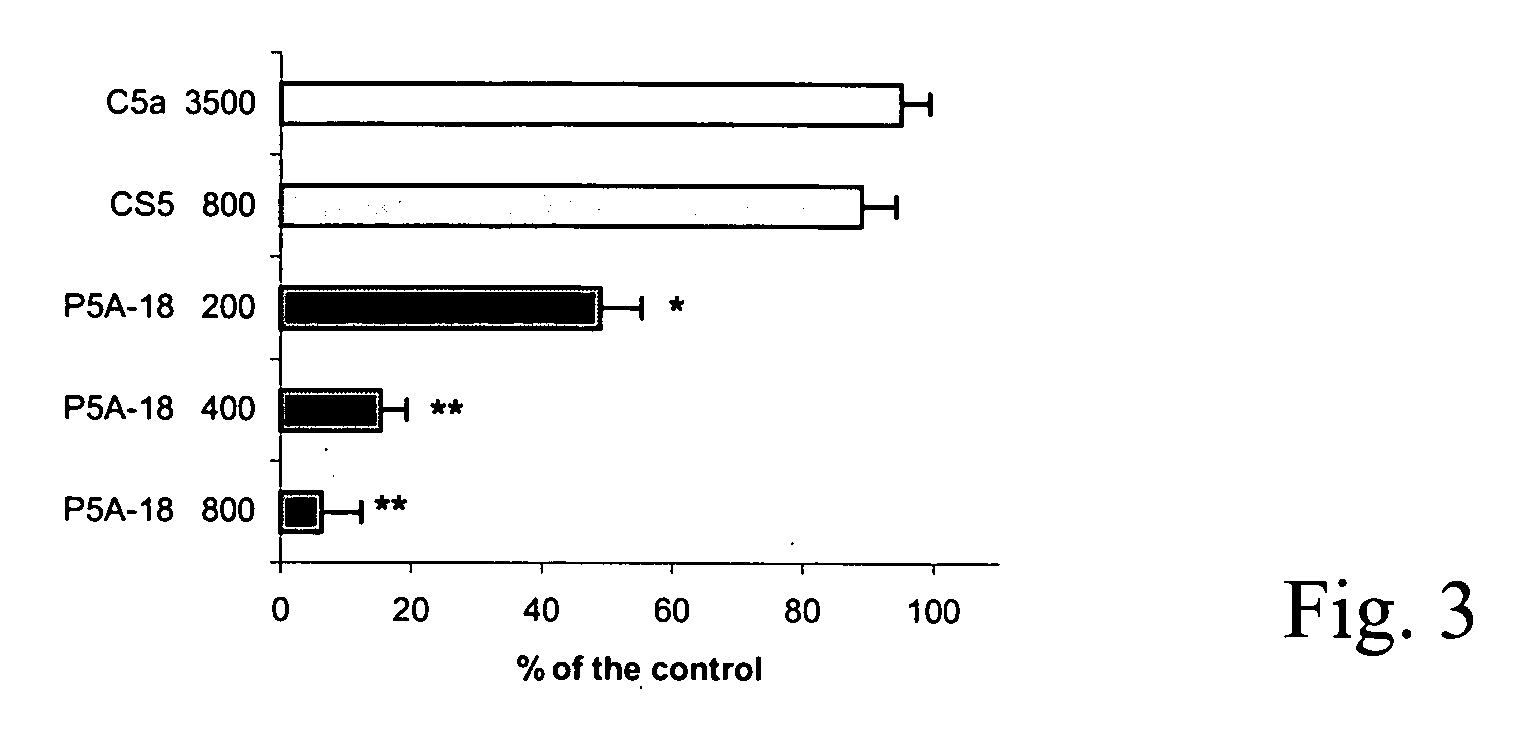
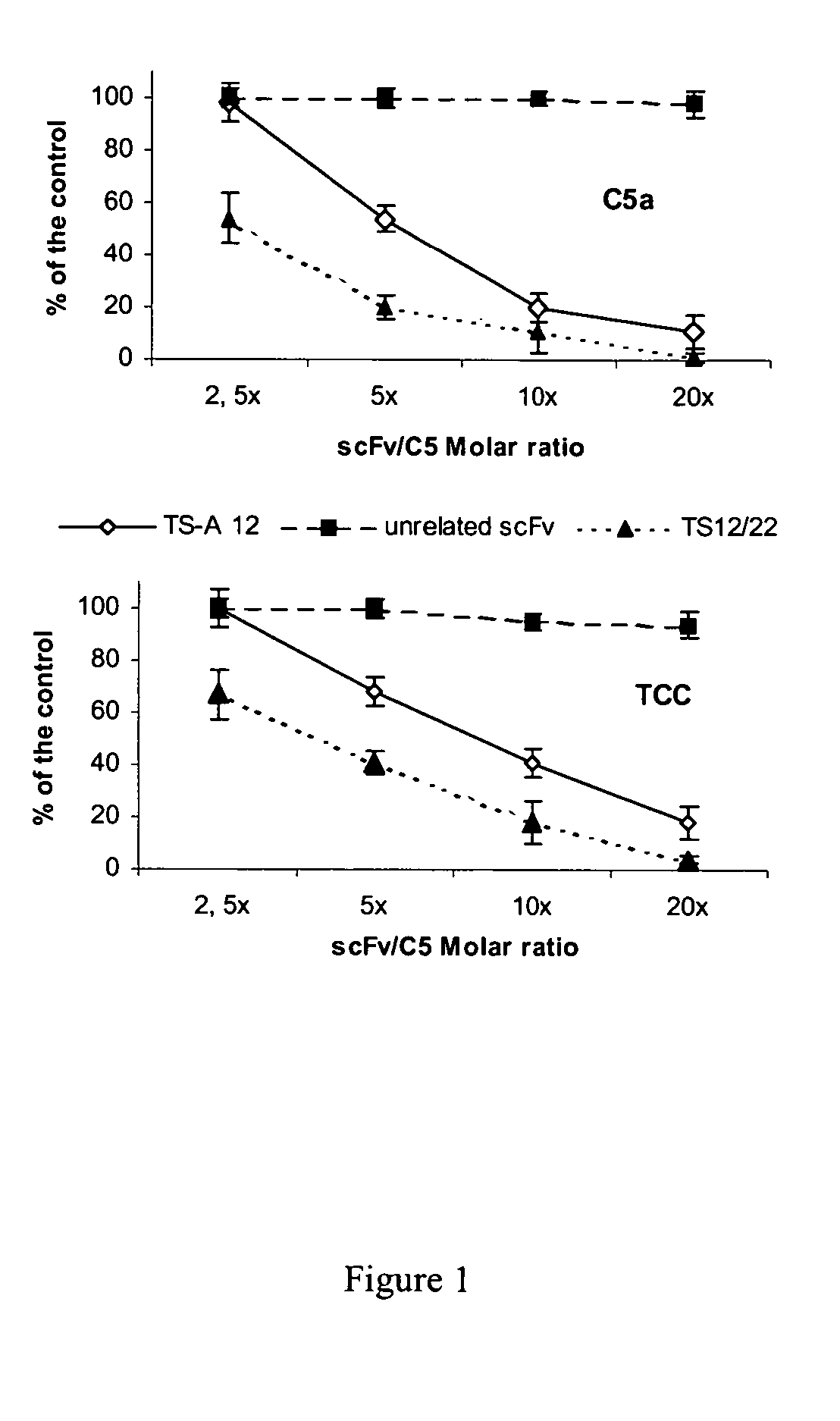
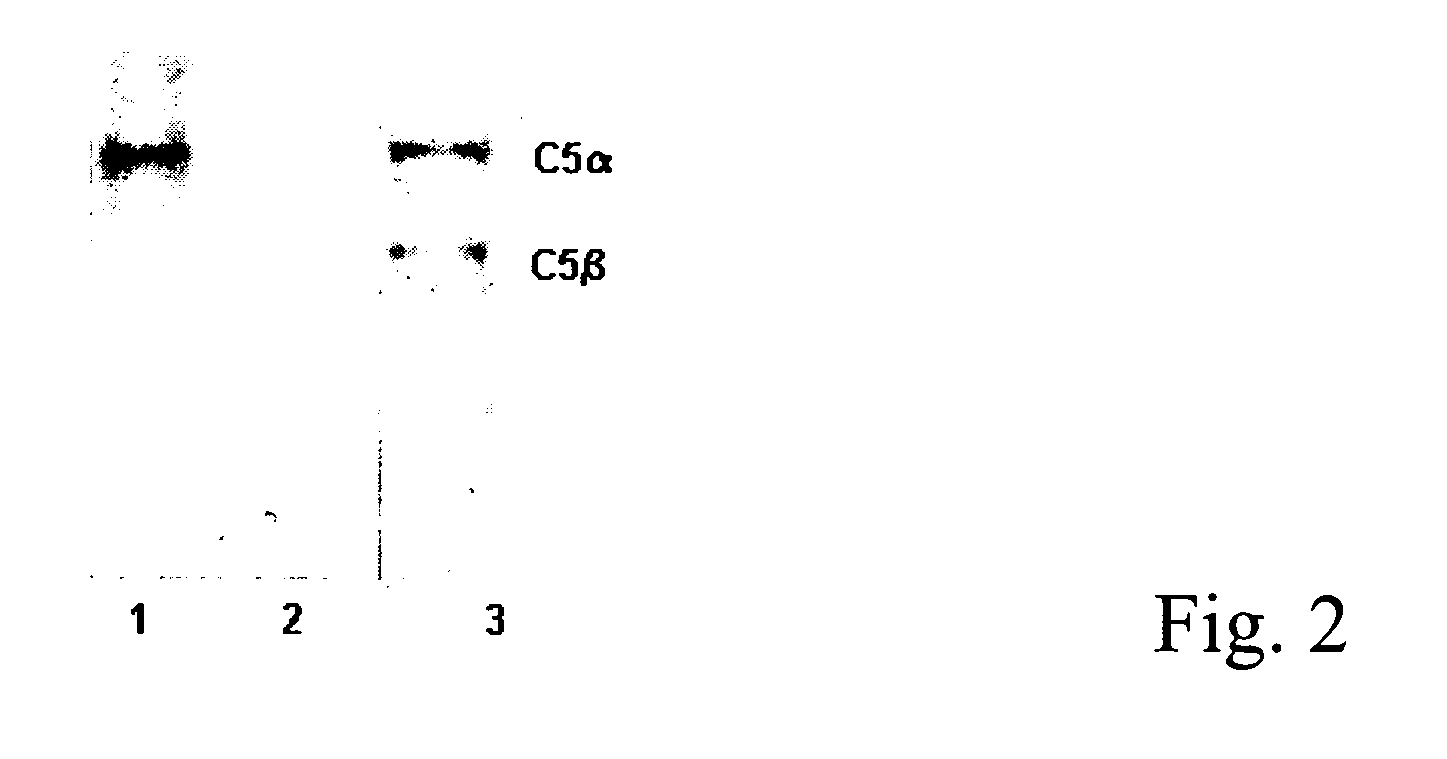
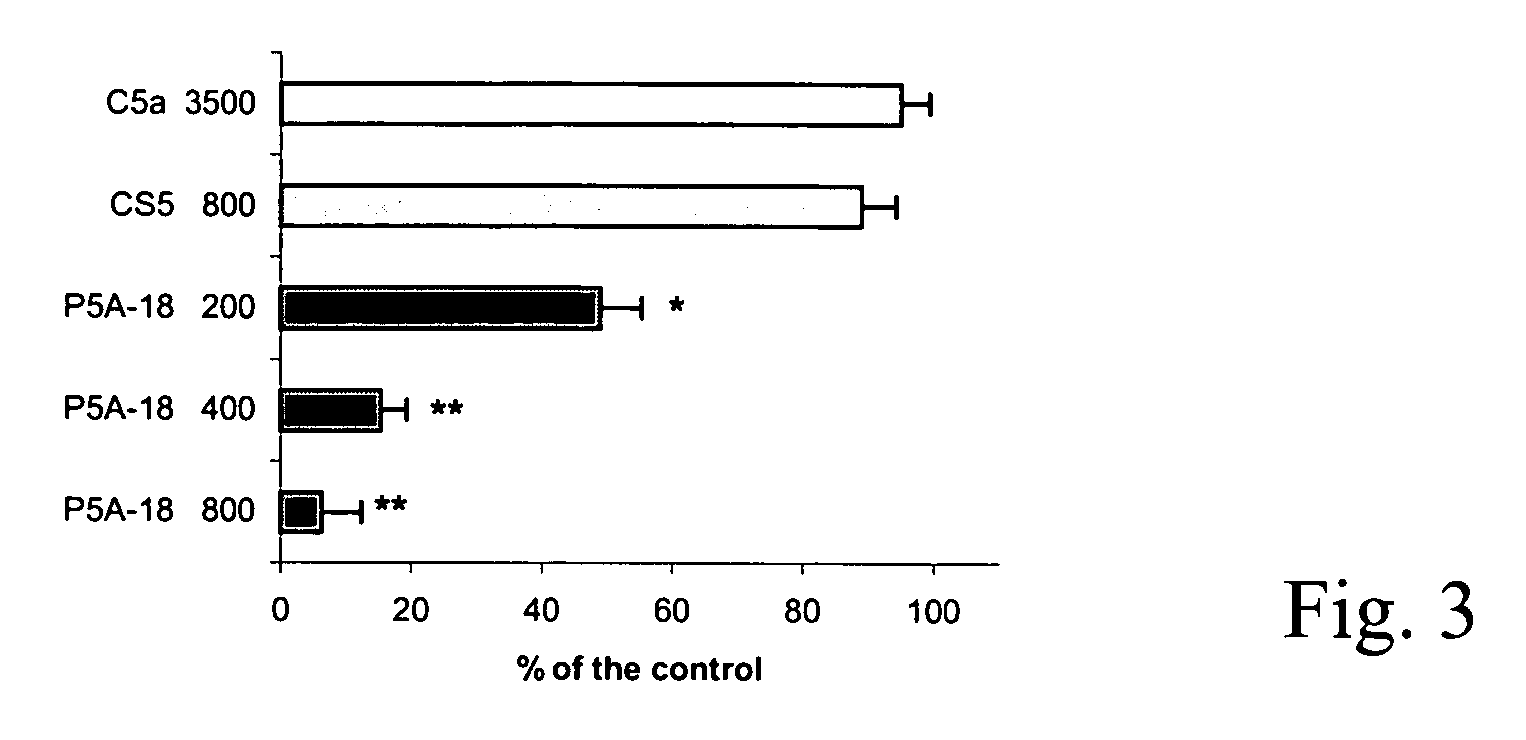
The present invention refers to recombinant antibodies of human origin specific for the C5 component of the activated complement and characterised by the ability to inhibit the conversion of the C5 alpha chain to C5a and C5b. Moreover the present invention refers to the nucleotide sequences coding for such antibodies and to the therapeutic use of both polypeptide and nucleotide sequences, in particular for the therapy of diseases involving tissue damage deriving from uncontrolled activation of the complement system.
Owner:ADIENNE SA
Anti-C5 alpha antibodies
InactiveUS7999081B2Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsNervous disorderDiseaseNucleotide
The present invention refers to recombinant antibodies of human origin specific for the C5 component of the activated complement and characterised by the ability to inhibit the conversion of the C5 alpha chain to C5a and C5b. Moreover the present invention refers to the nucleotide sequences coding for such antibodies and to the therapeutic use of both polypeptide and nucleotide sequences, in particular for the therapy of diseases involving tissue damage deriving from uncontrolled activation of the complement system.
Owner:ADIENNE SA
Stable and soluble antibodies inhibiting TNFalpha
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Methods for refolding of recombinant antibodies
ActiveUS7928205B2Promote formationImprove propertiesImmunological disordersFermentationCoupling reagentRecombinant antibodies
The present invention is generally directed to methods of producing an increase in the enrichment or recovery of preferred forms of IgG proteins. More particularly, the invention relates to subjecting preparations of such recombinant IgG proteins with a reduction / oxidation coupling reagent and optionally a chaotropic agent.
Owner:AMGEN INC
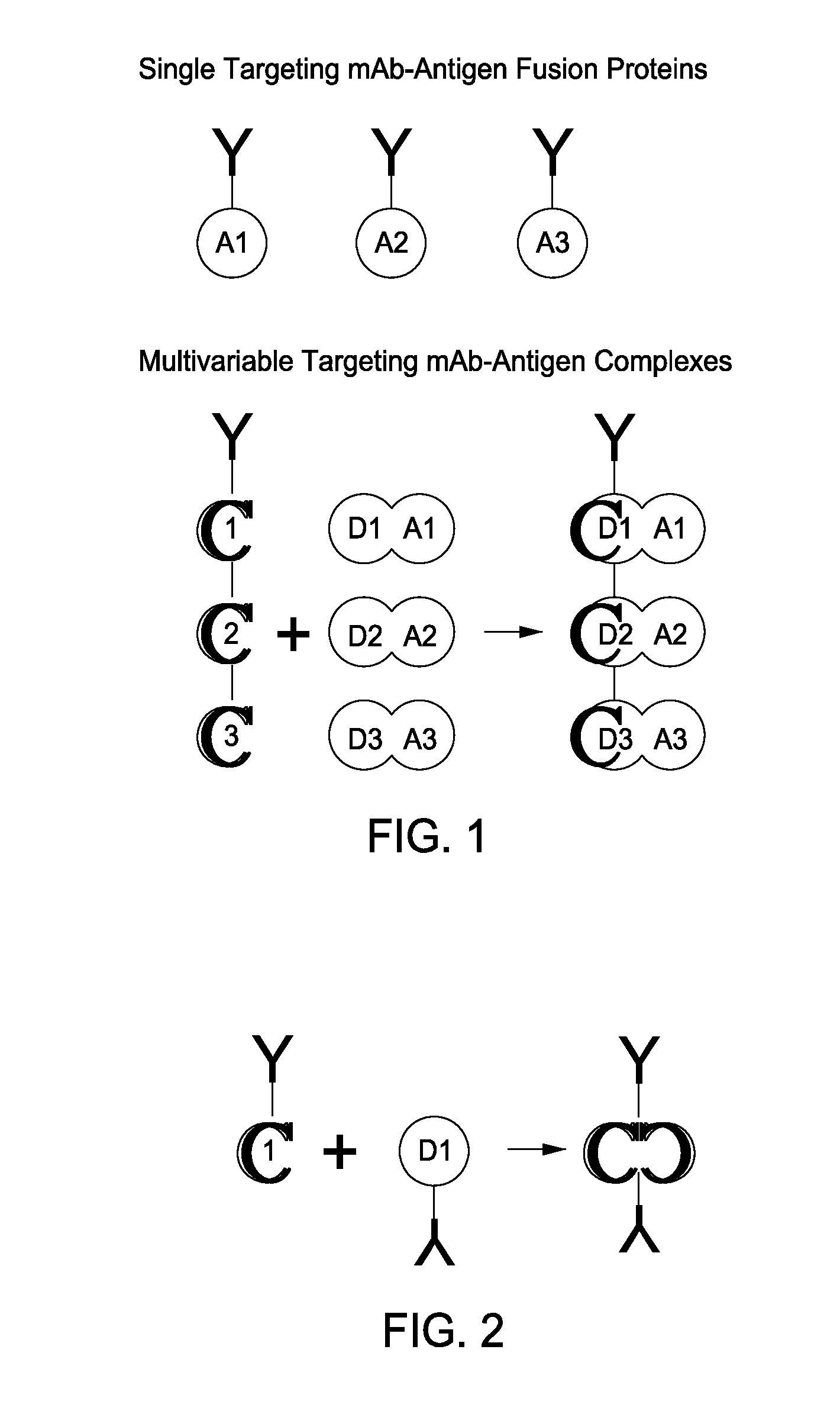
Multivariable Antigens Complexed with Targeting Humanized Monoclonal Antibody
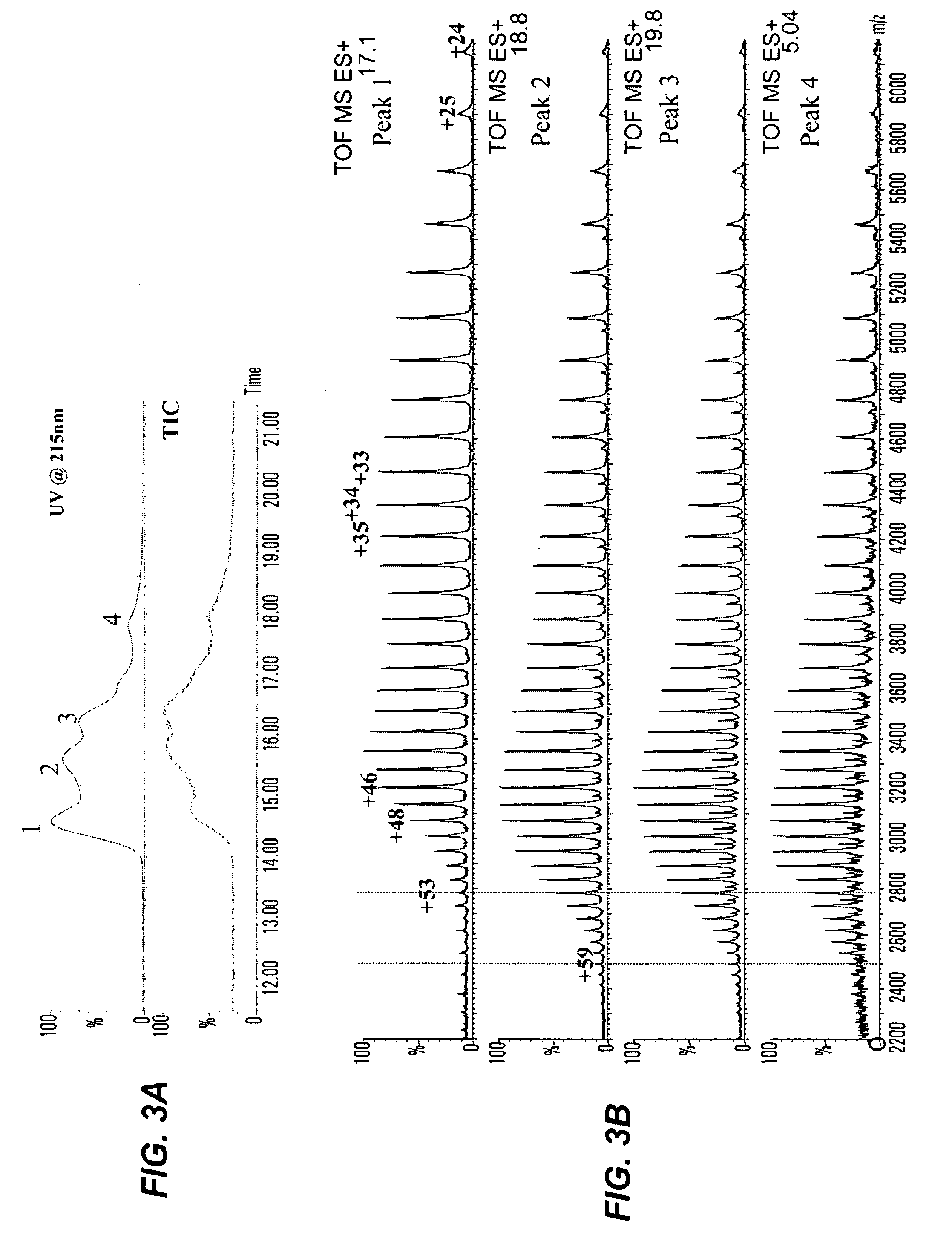
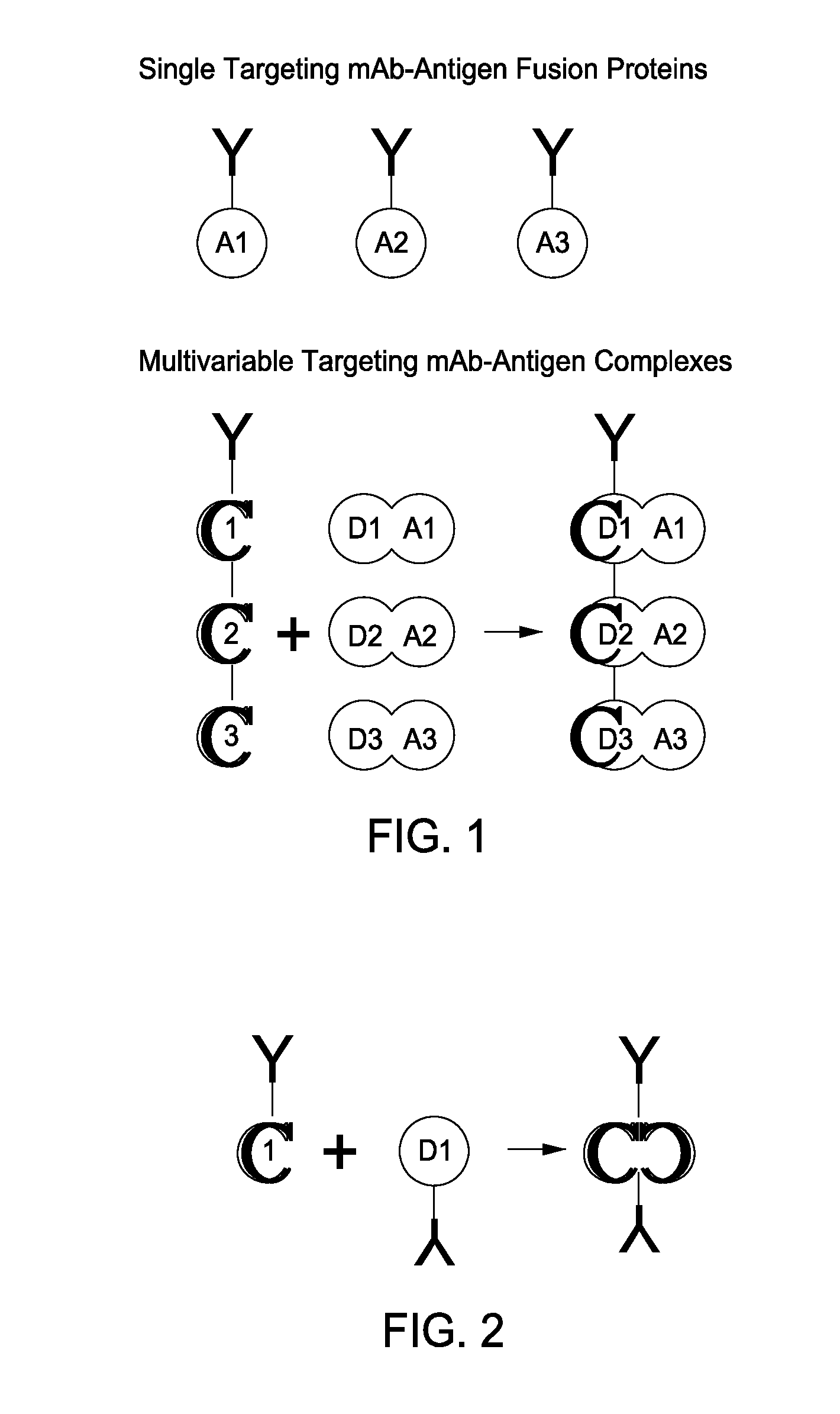
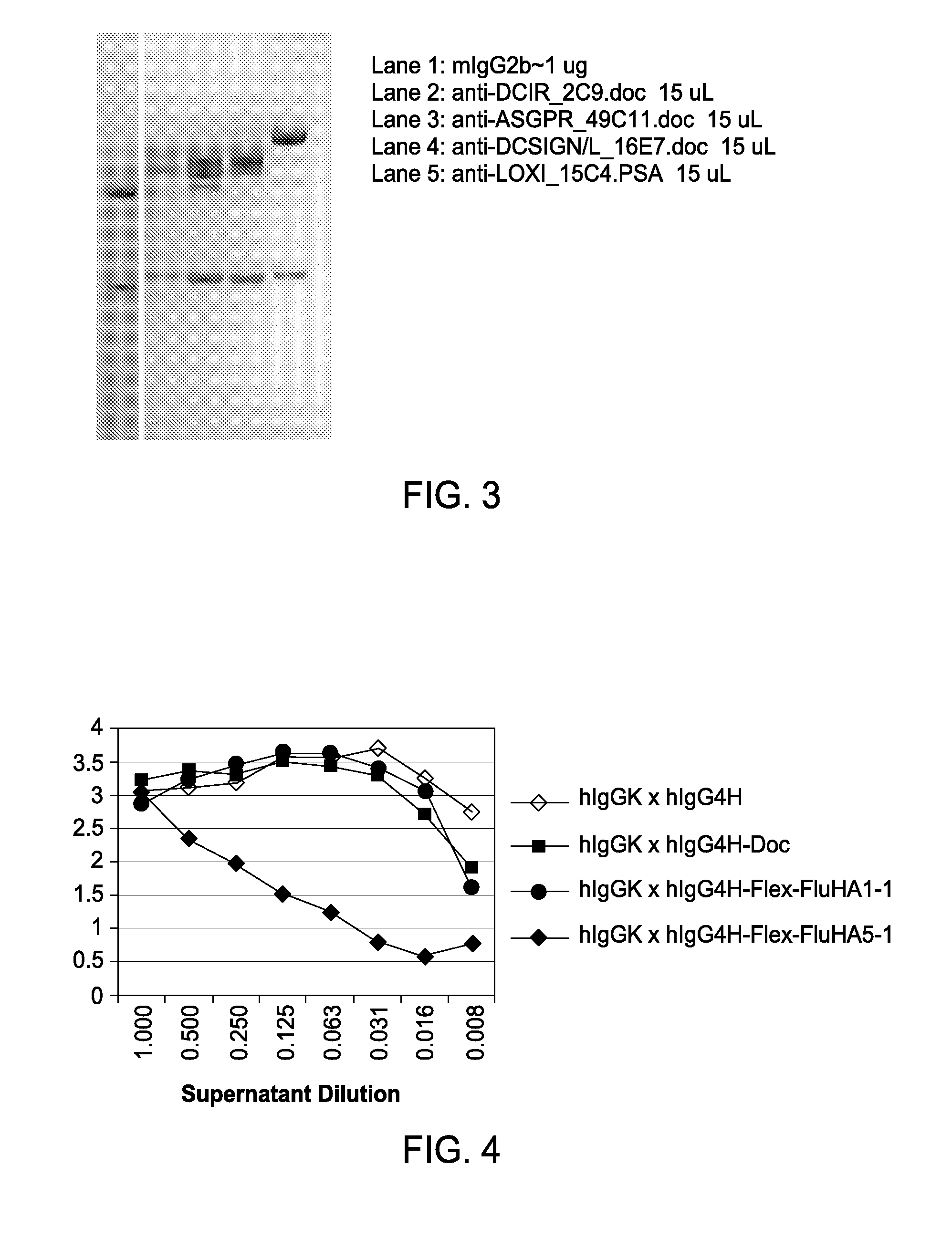
ActiveUS20080254044A1Effect be exertHigh affinityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenRecombinant antibodies
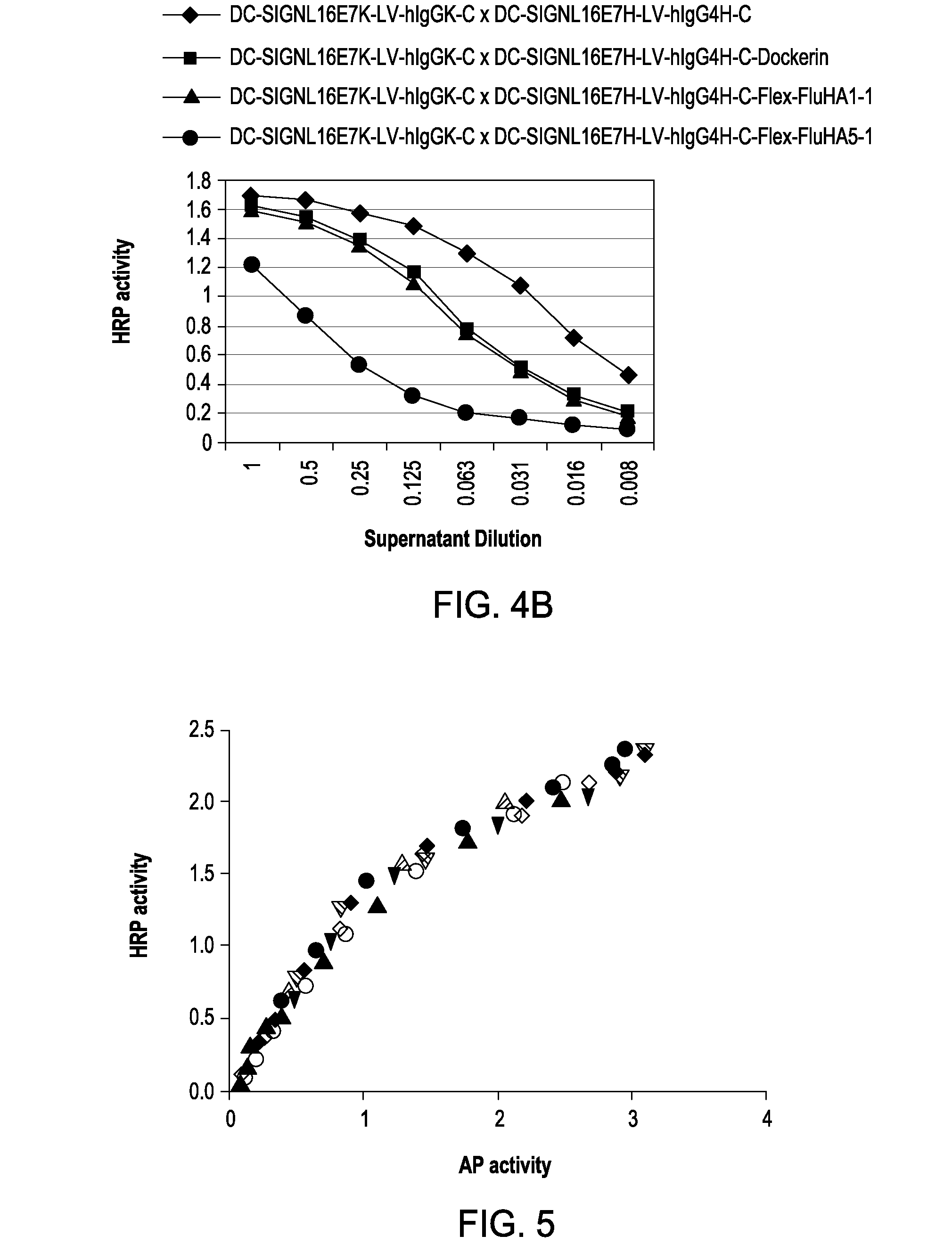
The present invention includes compositions and methods for designing, making and using modular recombinant antibodies or fragments thereof with one half of a cohesin-dockerin pair that permits the rapid assembly of multivariant antigen conjugates.
Owner:BAYLOR RES INST
Method for altering antibody light chain interactions
InactiveUS6485943B2Increase productionEasy to controlPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesHeavy chainAmino acid substitution
A method for recombinant antibody subunit dimerization including modifying at least one codon of a nucleic acid sequence to replace an amino acid occurring naturally in the antibody with a charged amino acid at a position in the interface segment of the light polypeptide variable region, the charged amino acid having a first polarity; and modifying at least one codon of the nucleic acid sequence to replace an amino acid occurring naturally in the antibody with a charged amino acid at a position in an interface segment of the heavy polypeptide variable region corresponding to a position in the light polypeptide variable region, the charged amino acid having a second polarity opposite the first polarity. Nucleic acid sequences which code for novel light chain proteins, the latter of which are used in conjunction with the inventive method, are also provided.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
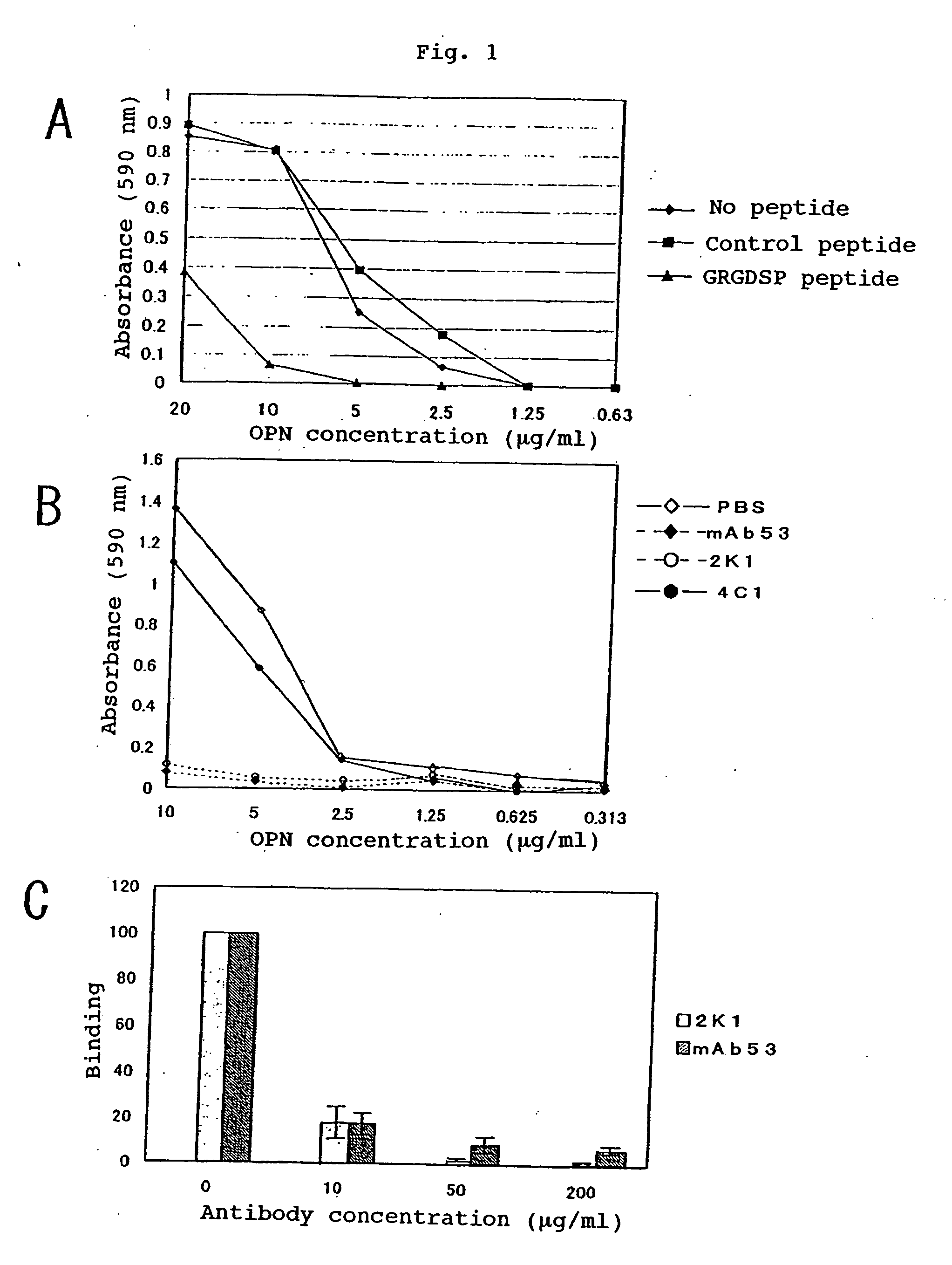
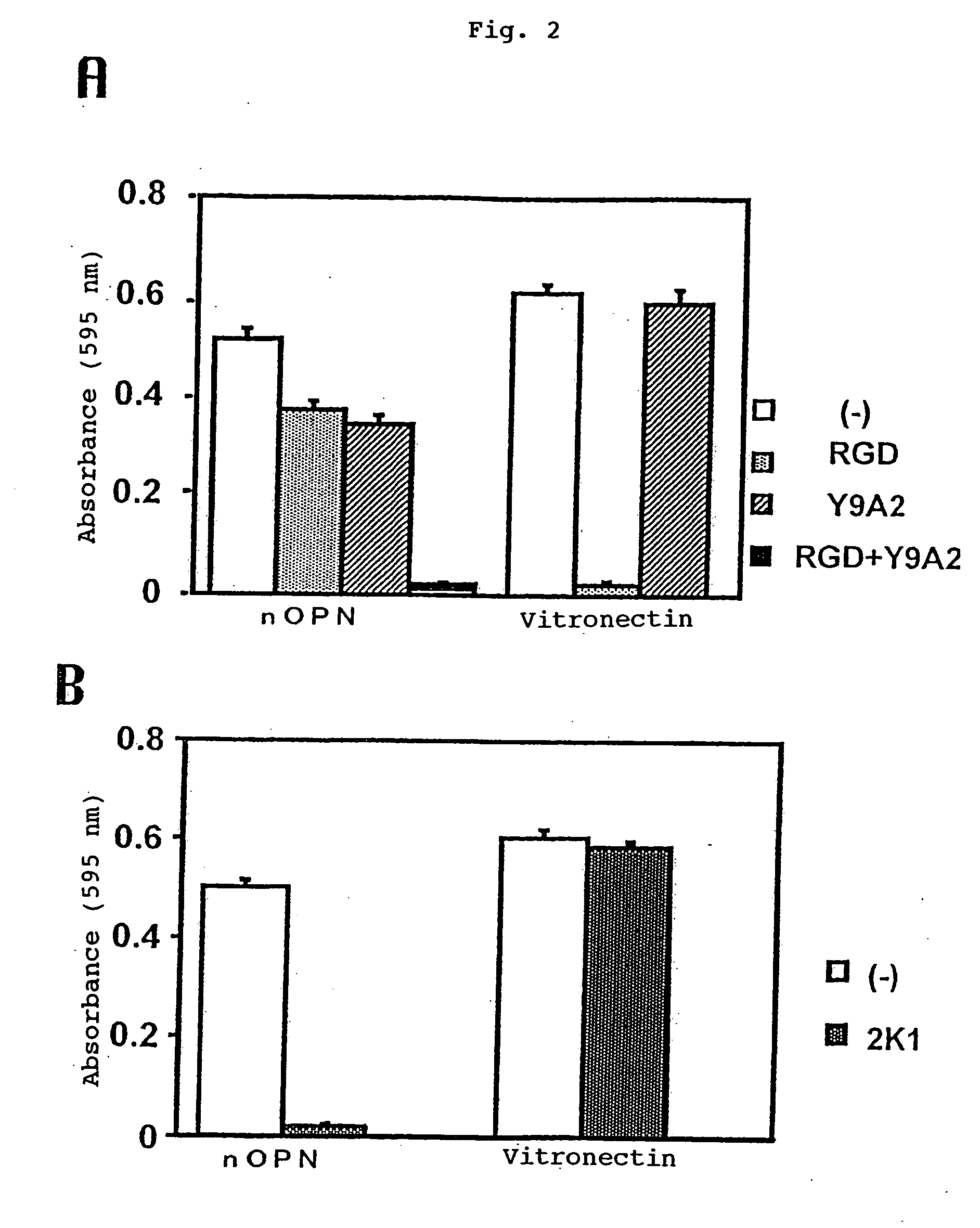
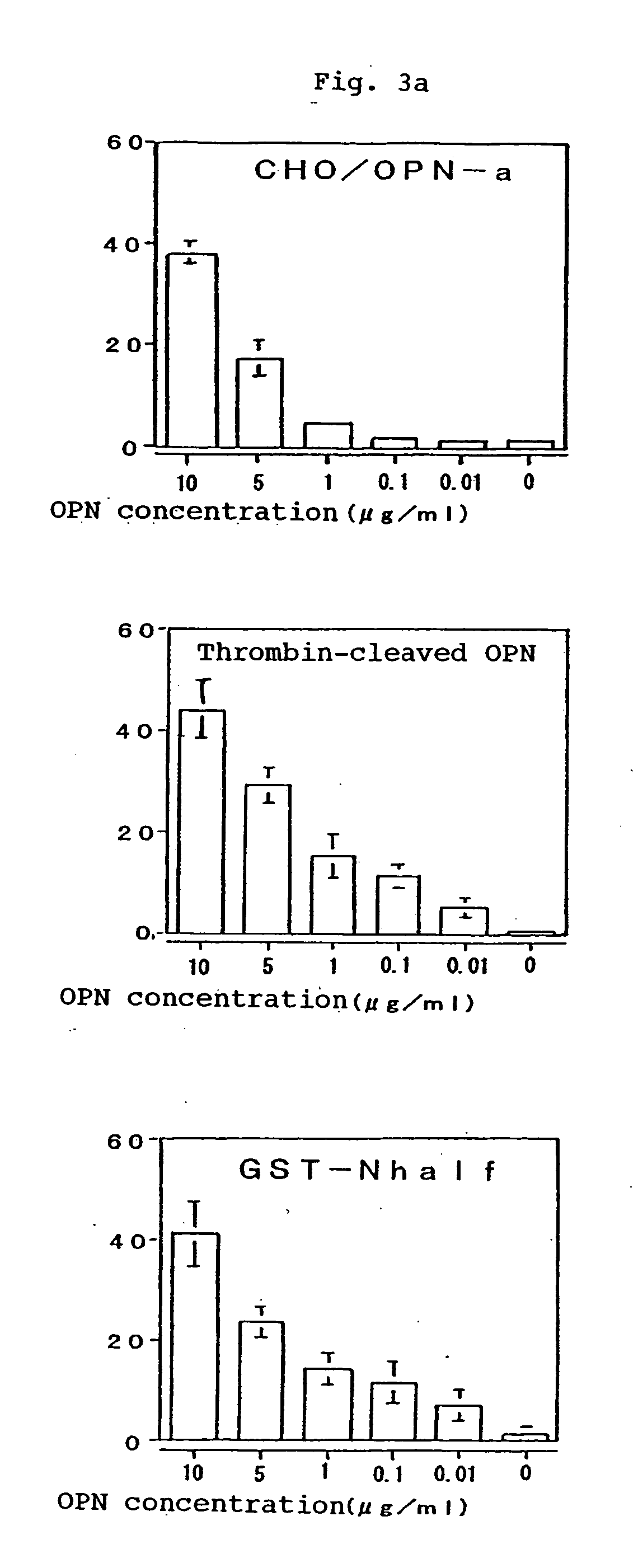
Recombinant anti-osteopontin antibody and use thereof
A recombinant antibody in which at least the constant regions in the heavy chain and the light chain have been converted into human-origin regions and which inhibits the binding of an integrin recognizing the RGD sequence to osteopontin or its fragment and inhibits the binding of an integrin recognizing the SVVYGLR sequence or a sequence corresponding thereto to osteopontin or its fragment. This antibody is useful as a remedy for autoimmune diseases and a remedy for rheumatism or rheumatoid arthritis. Thus, a method of treating autoimmune diseases, rheumatism or rheumatoid arthritis is provided. This osteopontin antibody is useful in a diagnostic for rheumatism and a method of diagnosing rheumatism too.
Owner:JURIDICAL FOUND THE CHEMO SERO THERAPEUTIC RES INST +1
Antibodies that bind IL-18 and methods of inhibiting IL-18 activity
InactiveUS7767207B2Inhibit hIL-1 activityInhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEpitopeAntigen binding
Antibodies that bind human interleukin-18 (hIL-18) are provided, in particular antibodies that bind epitope(s) of human IL-18. The antibodies can be, for example, entirely human antibodies, recombinant antibodies, or monoclonal antibodies. Preferred antibodies have high affinity for hIL-18 and neutralize hIL-18 activity in vitro and in vivo. An antibody of the invention can be a full-length antibody or an antigen-binding portion thereof. Method of making and method of using the antibodies of the invention are also provided. The antibodies, or antibody portions, of the invention are useful for detecting hIL-18 and for inhibiting hIL-18 activity, e.g., in a human subject suffering from a disorder in which hIL-18 activity is detrimental.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Medicine containing genetically modified antibody against chemokine receptor ccr4
ActiveUS20070020263A1Fear of possible side effect may aroseEliminate side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTreatment effectCC chemokine
A medicament having a higher therapeutic effect than that provided by administration of a recombinant antibody against human CC chemokine receptor 4 or an antibody fragment thereof or an agent alone is provided.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Genetically recombinant antibody composition capable of binding specifically to ganglioside gm2
InactiveUS20110236374A1High cytotoxic activityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticA-DNABULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to a genetically recombinant antibody composition which specifically binds to ganglioside GM2, which has higher complement-dependent cytotoxic activity than a human IgG1 antibody and a human IgG3 antibody, wherein a polypeptide comprising a CH2 domain in the Fc region of a human IgG1 antibody is replaced by a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence which corresponds to the same position of a human IgG3 antibody indicated by the EU index as in Kabat, et al.; a DNA encoding the antibody molecule or a heavy chain constant region of the antibody molecule contained in the recombinant antibody composition; a transformant obtainable by introducing the recombinant vector into a host cell; a process for producing the recombinant antibody composition using the transformant; and a medicament comprising the recombinant antibody composition as an active ingredient.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Method for treating Th2-mediated disease
InactiveUS20050187380A1Reduce in quantityHigh cytotoxic activitySenses disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiagnostic agentTh2 cytokines
A recombinant antibody or the antibody fragment thereof which specifically reacts with an extracellular domain of human CCR4; a DNA which encodes the recombinant antibody or the antibody fragment thereof; a method for producing the recombinant antibody or the antibody fragment thereof; a method for immunologically detecting CCR4, a method for immunologically detecting a cell which expressed CCR4 on the cell surface, a method for depleting a cell which expresses CCR4 on the cell surface, and a method for inhibiting production of Th2 cytokine, which comprise using the recombinant antibody according or antibody fragment thereof; a therapeutic or diagnostic agent for Th2-mediated immune diseases; and a therapeutic or diagnostic agent for a blood cancer.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com