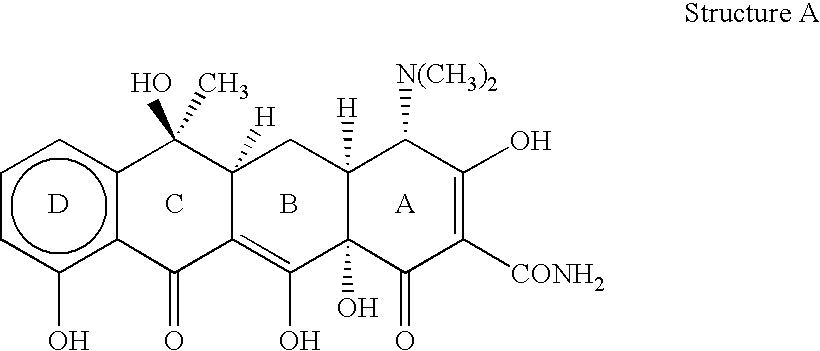
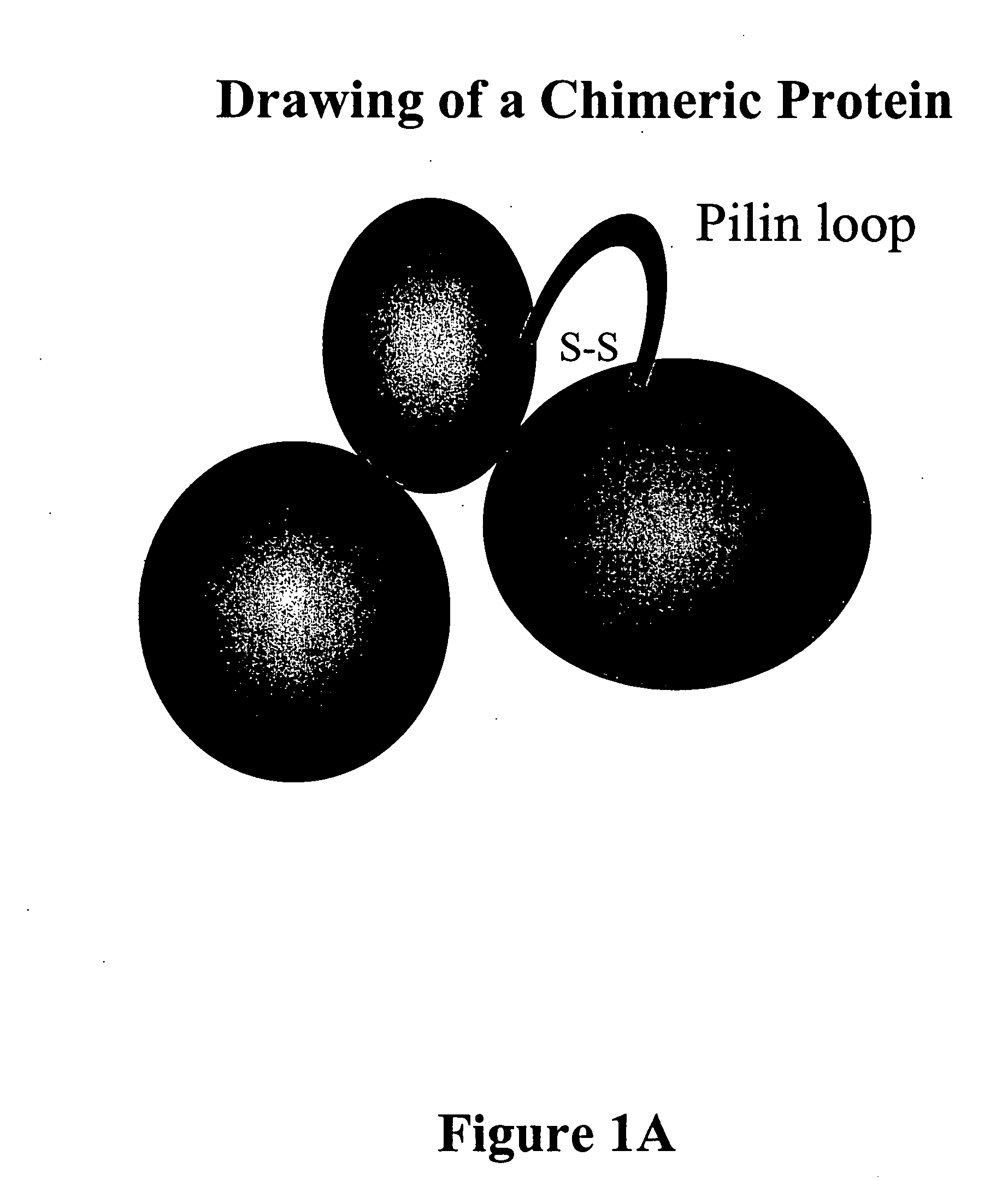Patents
Literature
182 results about "Exotoxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, similar to endotoxins, may be released during lysis of the cell. Gram negative pathogens may secrete outer membrane vesicles containing lipopolysaccharide endotoxin and some virulence proteins in the bounding membrane along with some other toxins as intra-vesicular contents, thus adding a previously unforeseen dimension to the well-known eukaryote process of membrane vesicle trafficking, which is quite active at the host-pathogen interface.
Fusion antigen used as vaccine
ActiveUS7335361B2SsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPseudomonas tolaasiiReticulum cell
The present invention mainly provides a fusion antigen specific for a target cell comprising a ligand moiety which is capable of reacting, recognizing or binding to the receptors on the target cell, a Pseudomonas exotoxin A translocation domain II, an antigenic moiety, and a carboxyl terminal moiety which permits combination of the fusion antigen to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane of the target cell. A method of immunizing an animal using the fusion antigen is also provided.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
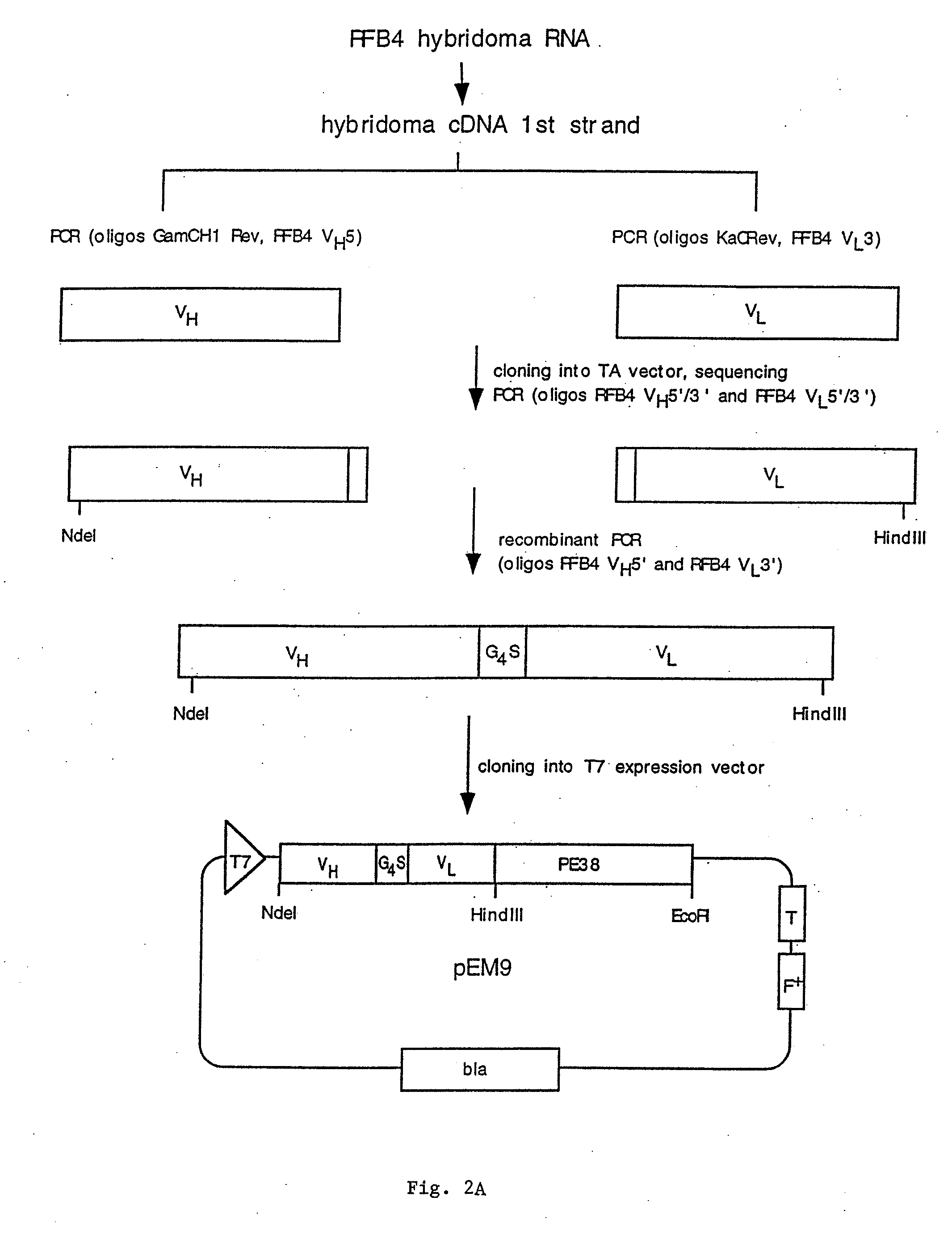
Mutated anti-cd22 antibodies and immunoconjugates
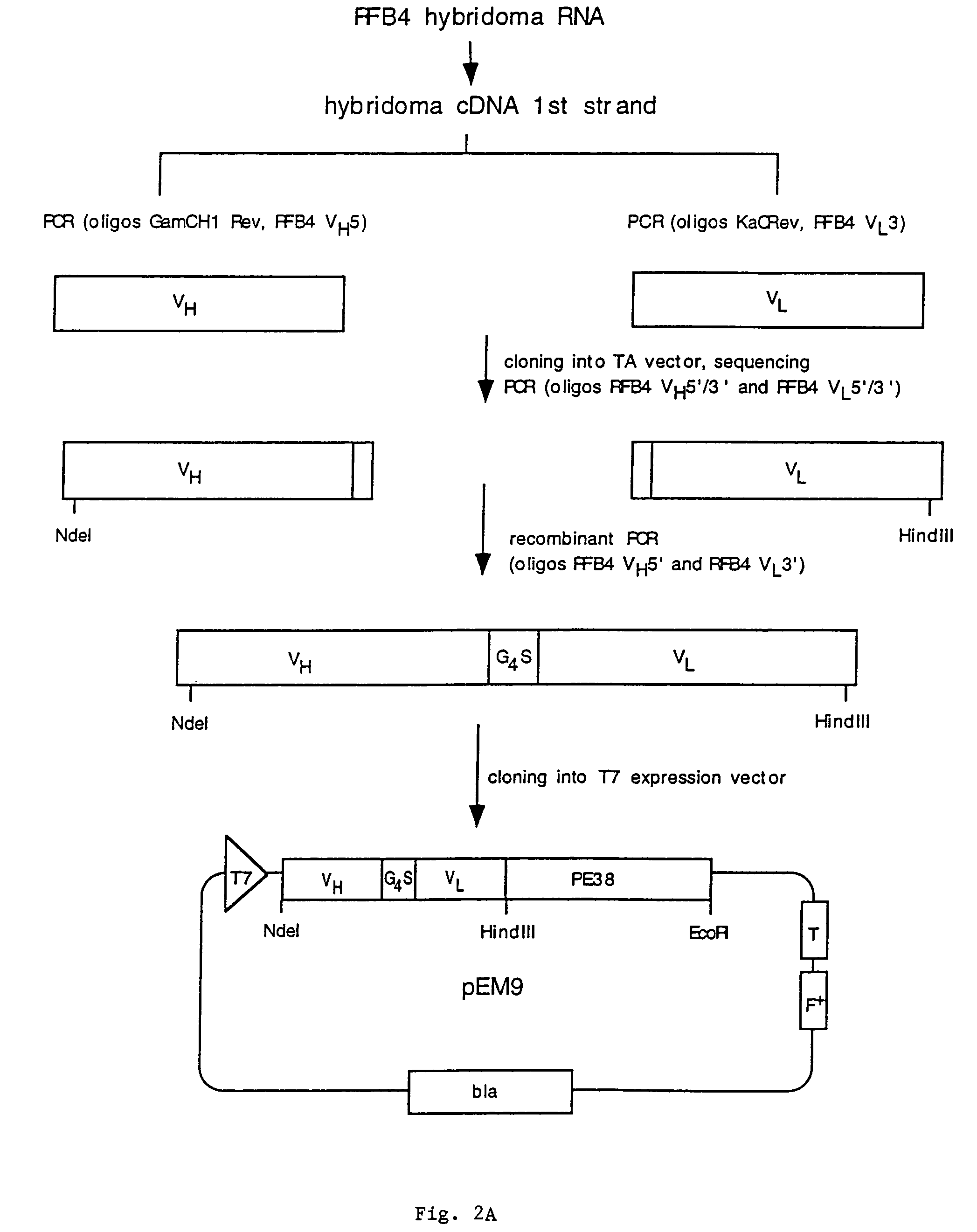
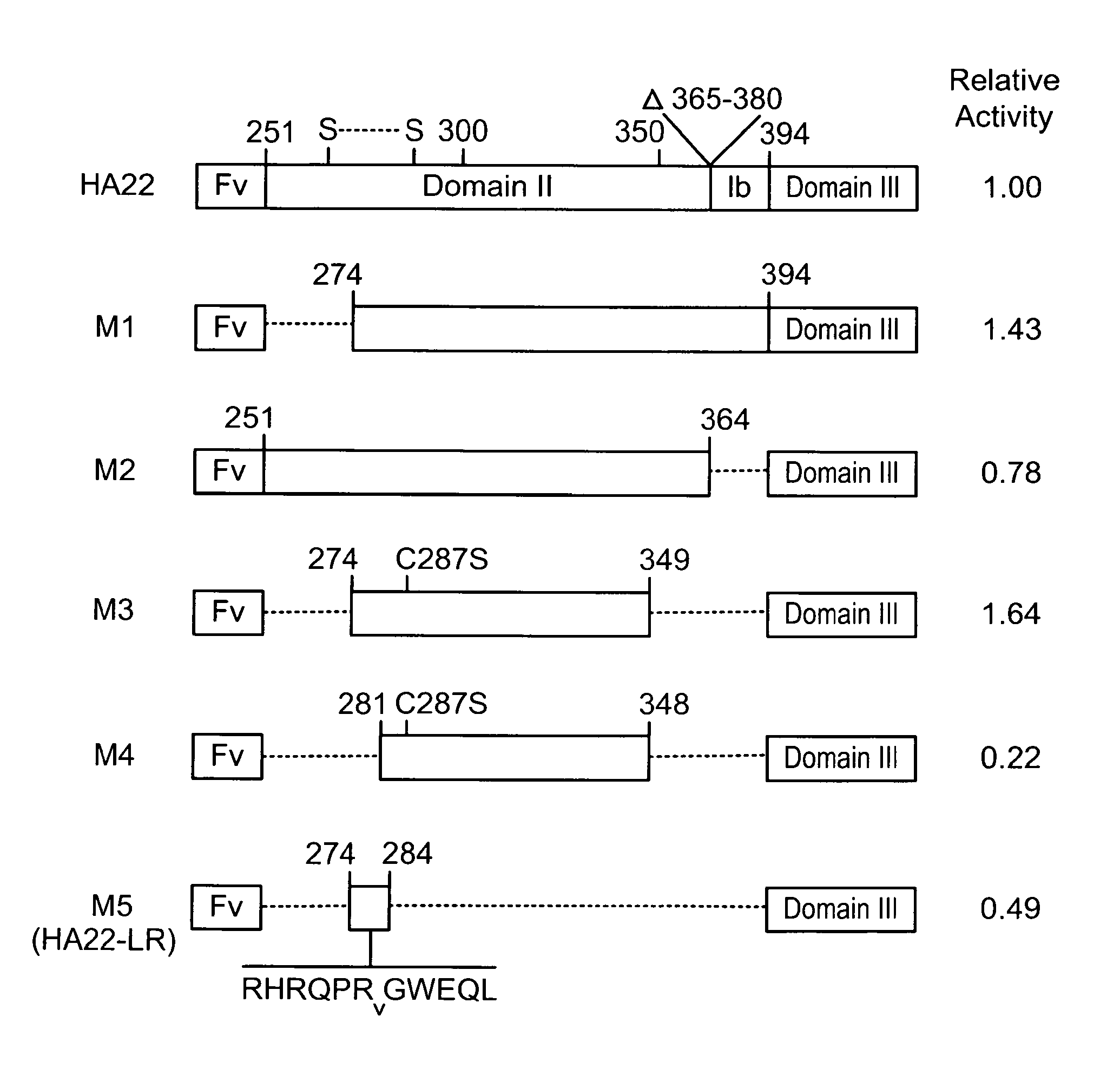
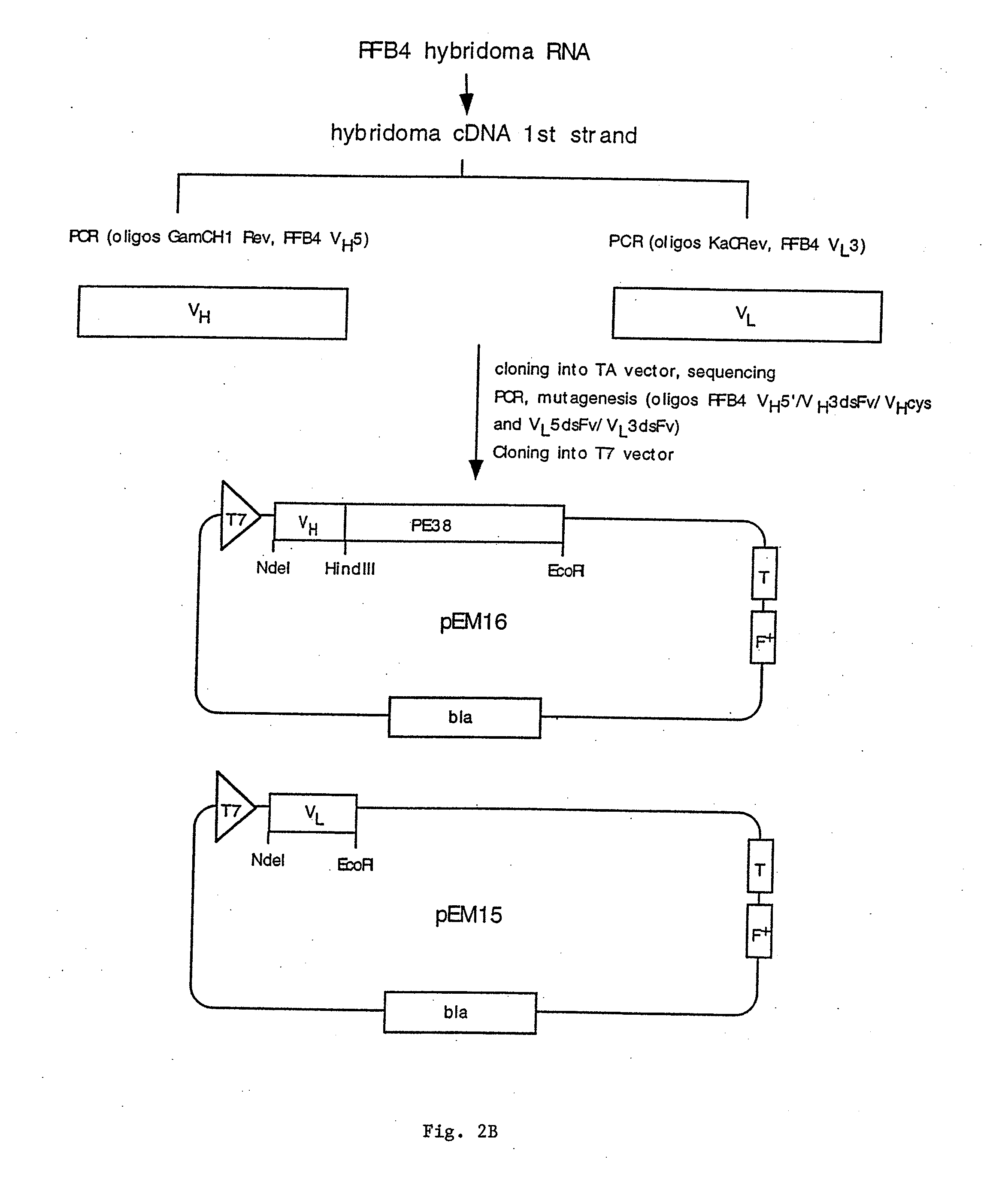
Recombinant immunotoxins are fusion proteins composed of the Fv domains of antibodies fused to bacterial or plant toxins. RFB4 (Fv)-PE38 is an immunotoxin that targets CD22 expressed on B cells and B cell malignancies. The present invention provides antibodies and antibody fragments that have improved ability to bind the CD22 antigen compared to RFB4. Immunotoxins made with the antibodies and antibody fragments of the invention have improved cytotoxicity to CD22-expressing cancer cells. Compositions that incorporate these antibodies into chimeric immunotoxin molecules that can be used in medicaments and methods for inhibiting the growth and proliferation of such cancers. Additionally, the invention provides a method of increasing the cytotoxicity of forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (“PE”) with the mutation of a single amino acid, as well as compositions of such mutated PEs, nucleic acids encoding them, and methods for using the mutated PEs.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Recombinant antibodies and immunoconjugates targeted to CD-22 bearing cells and tumors
InactiveUS7541034B1Growth inhibitionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
Methods and compositions relating to recombinant anti-CD22 antibodies with high binding affinity, and immunoconjugates comprising the anti-CD22 antibody linked to a therapeutic agent such as a Pseudomonas exotoxin or a detectable label. The invention provides diagnostic methods, and means to inhibit the growth of malignant B cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICAN AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
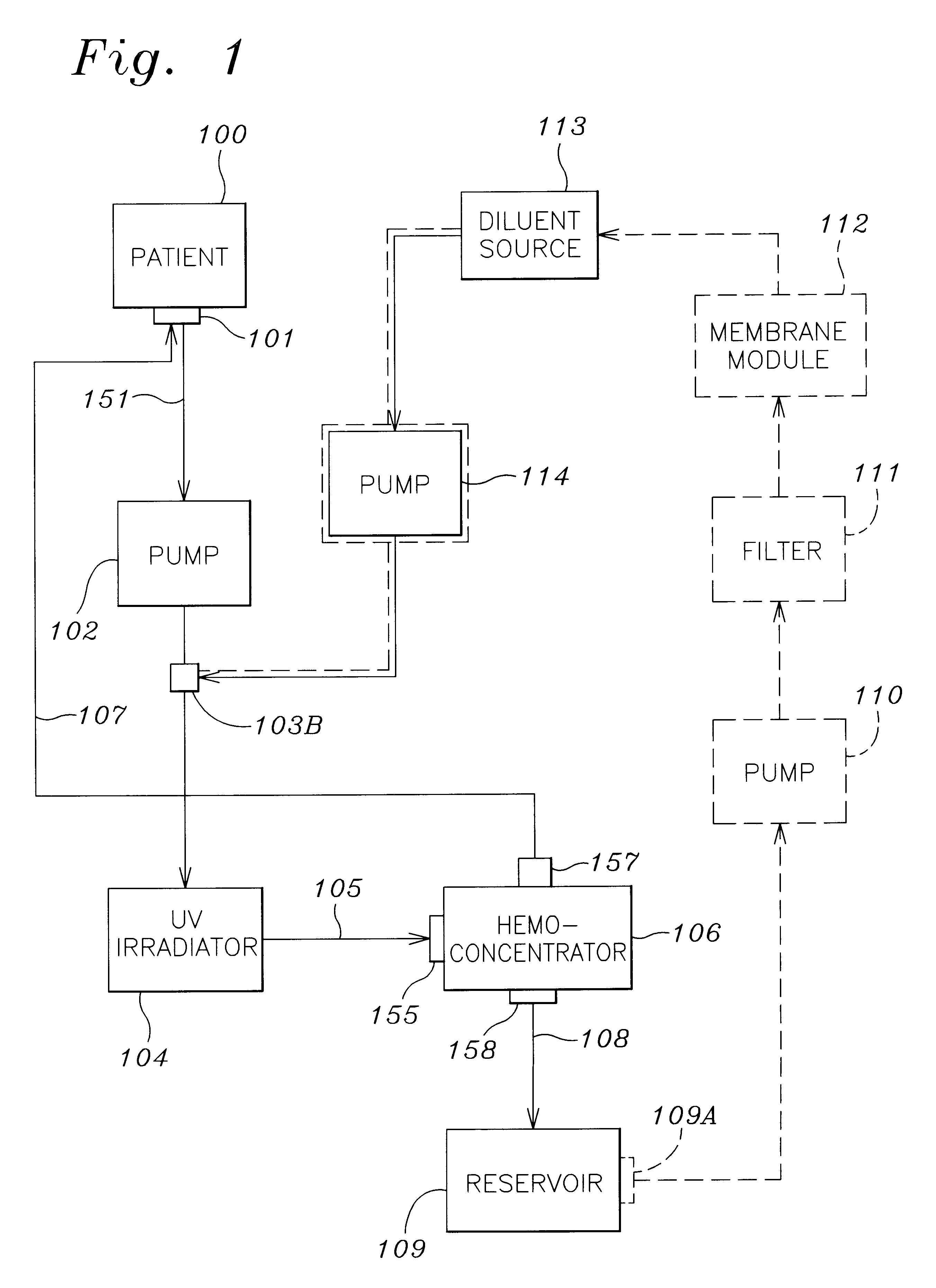
Septicemia prevention and treatment system
InactiveUS6193681B1Electrolysis componentsOther blood circulation devicesStaphylococcus cohniiFiltration
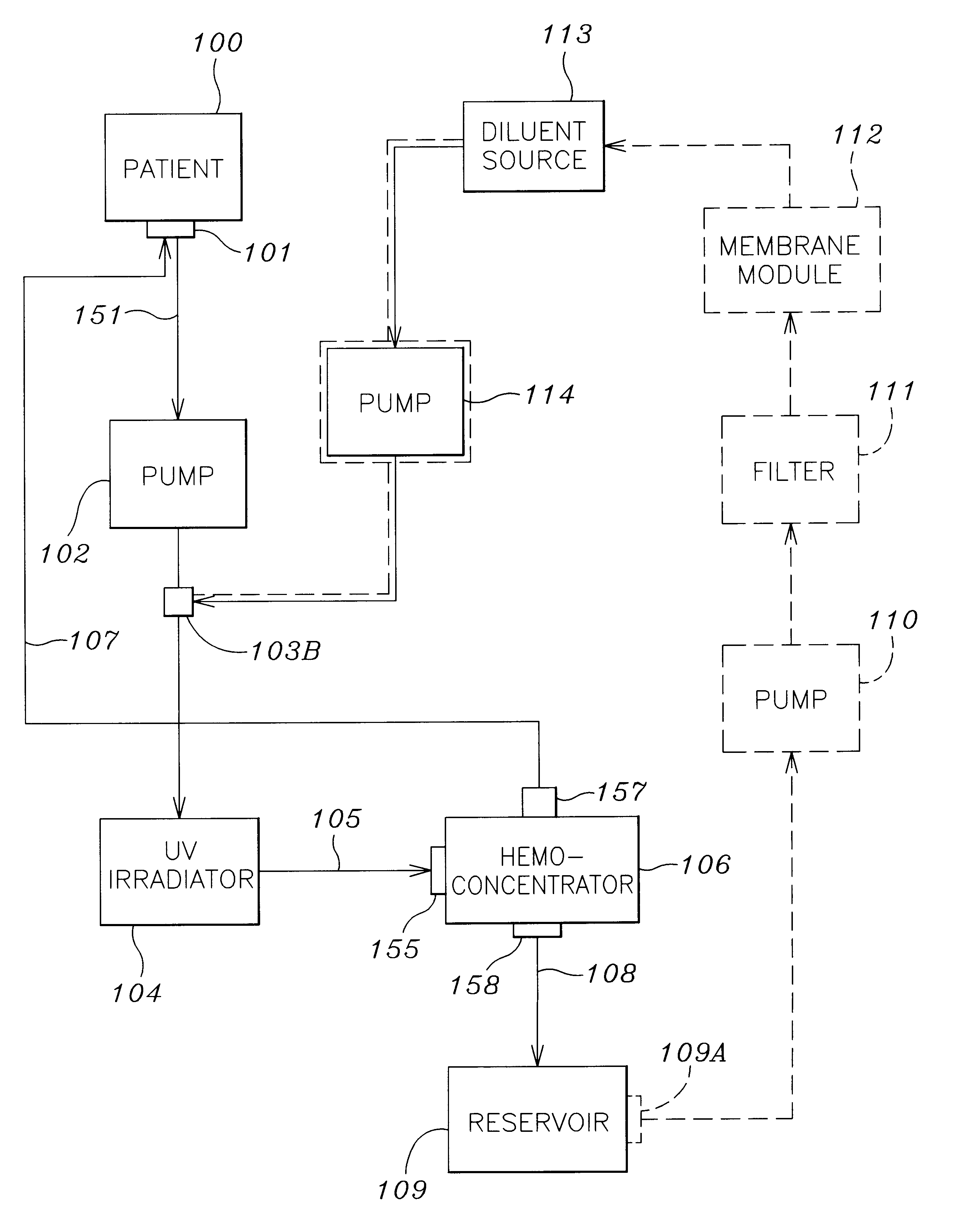
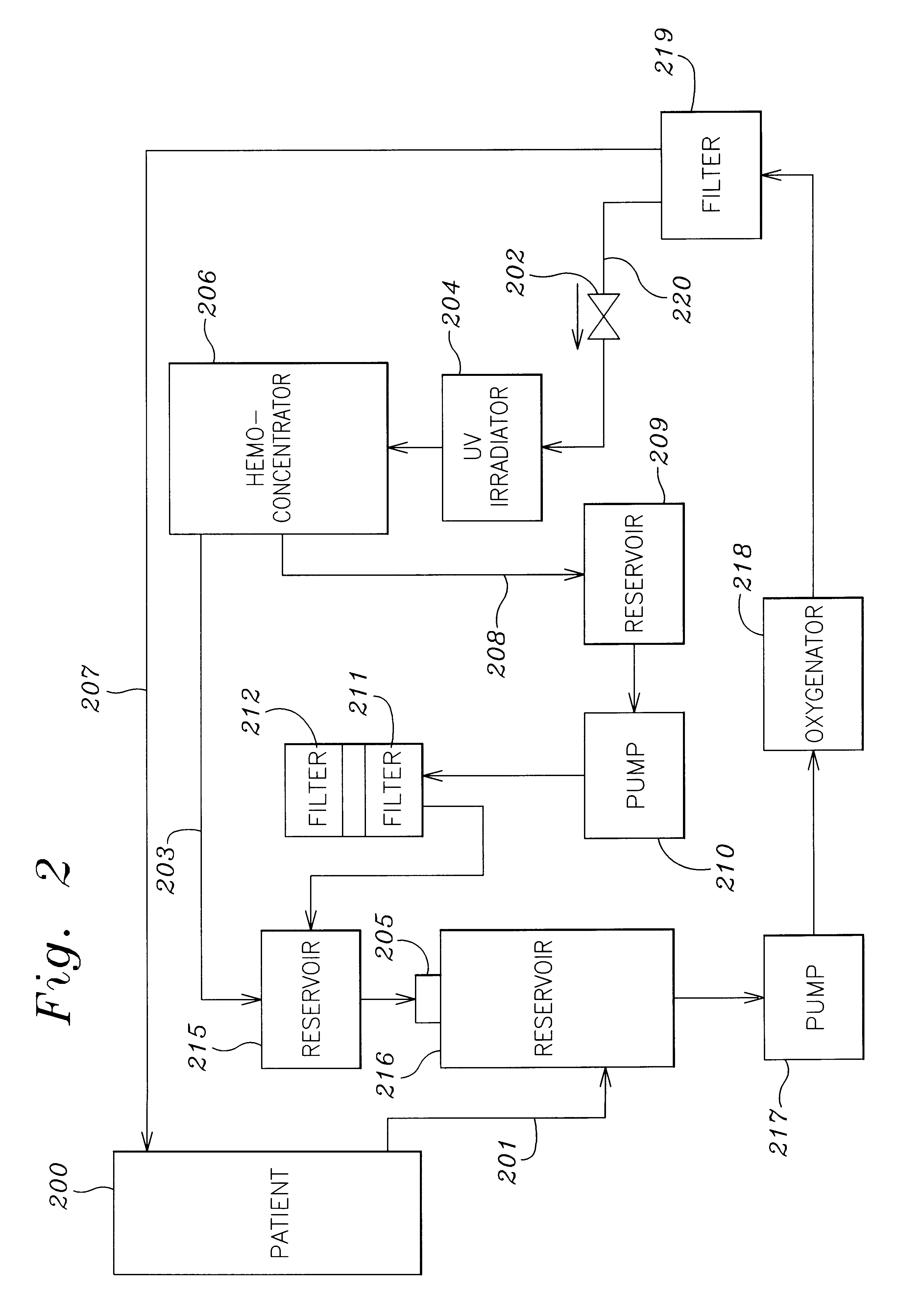
A method and apparatus for preventing and treating septicemia in patient blood. The extracorporeal system includes an anti-microbial device to kill at least 99% of bloodborne microorganisms, a hemoconcentrator / filtration unit to remove approximately 90% of target molecules from the patient blood and a filter unit to remove target molecules from patient blood from the sieved plasma filtrate. Target molecules are produced by microorganisms as well as the patient's cells and include endotoxins from gram negative bacteria, exotoxins from gram negative and gram positive bacteria, as well as RAP protein mediator from Staphylococcus aureus, and cell mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin 1-beta, complement proteins C3a and C5a, and brandykinin.
Owner:HEMAVATION
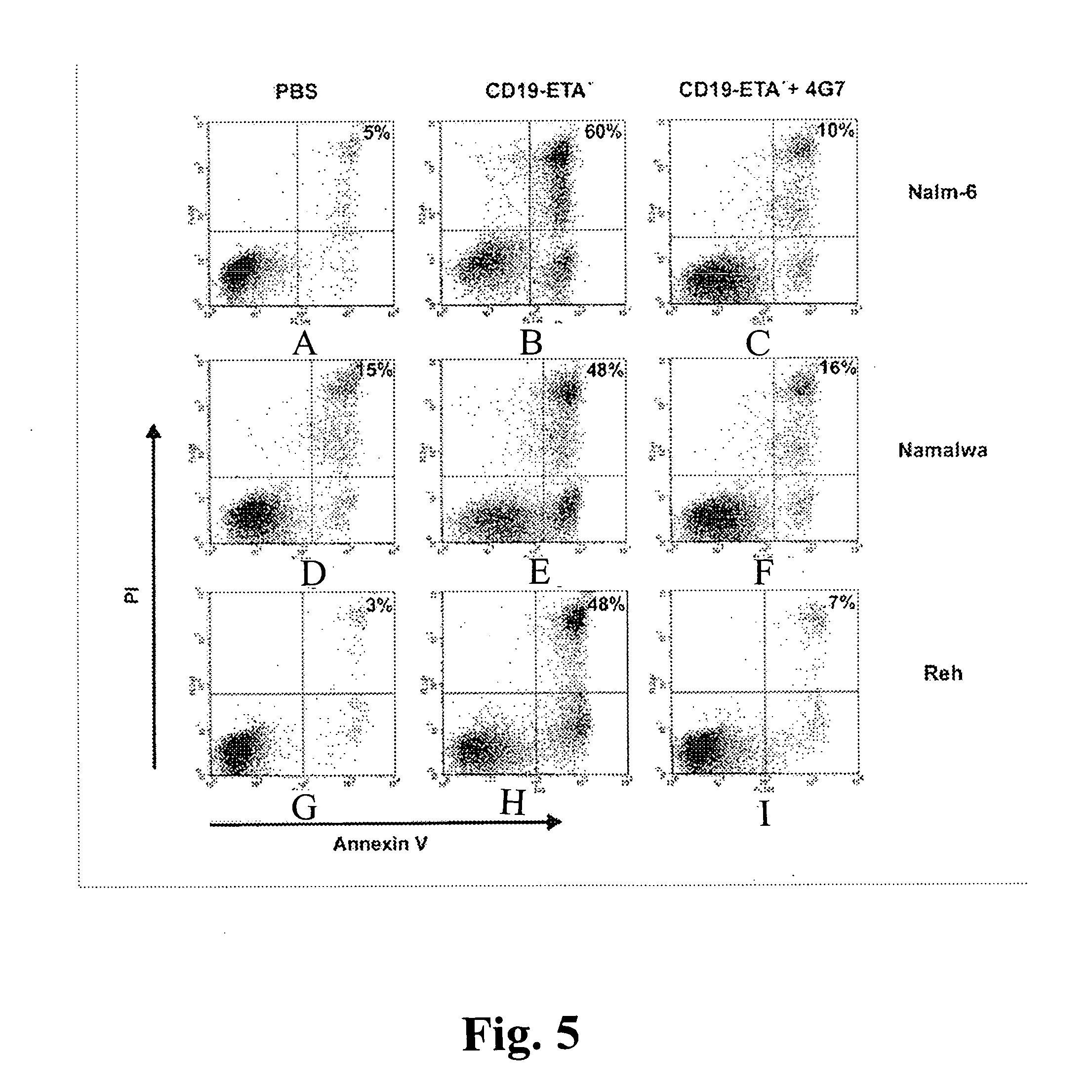
CD19-specific immunotoxin and treatment method
InactiveUS20070178103A1Easy to transportResistant to extracellular cleavagePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHybrid immunoglobulinsAutoimmune conditionBacterial exotoxin
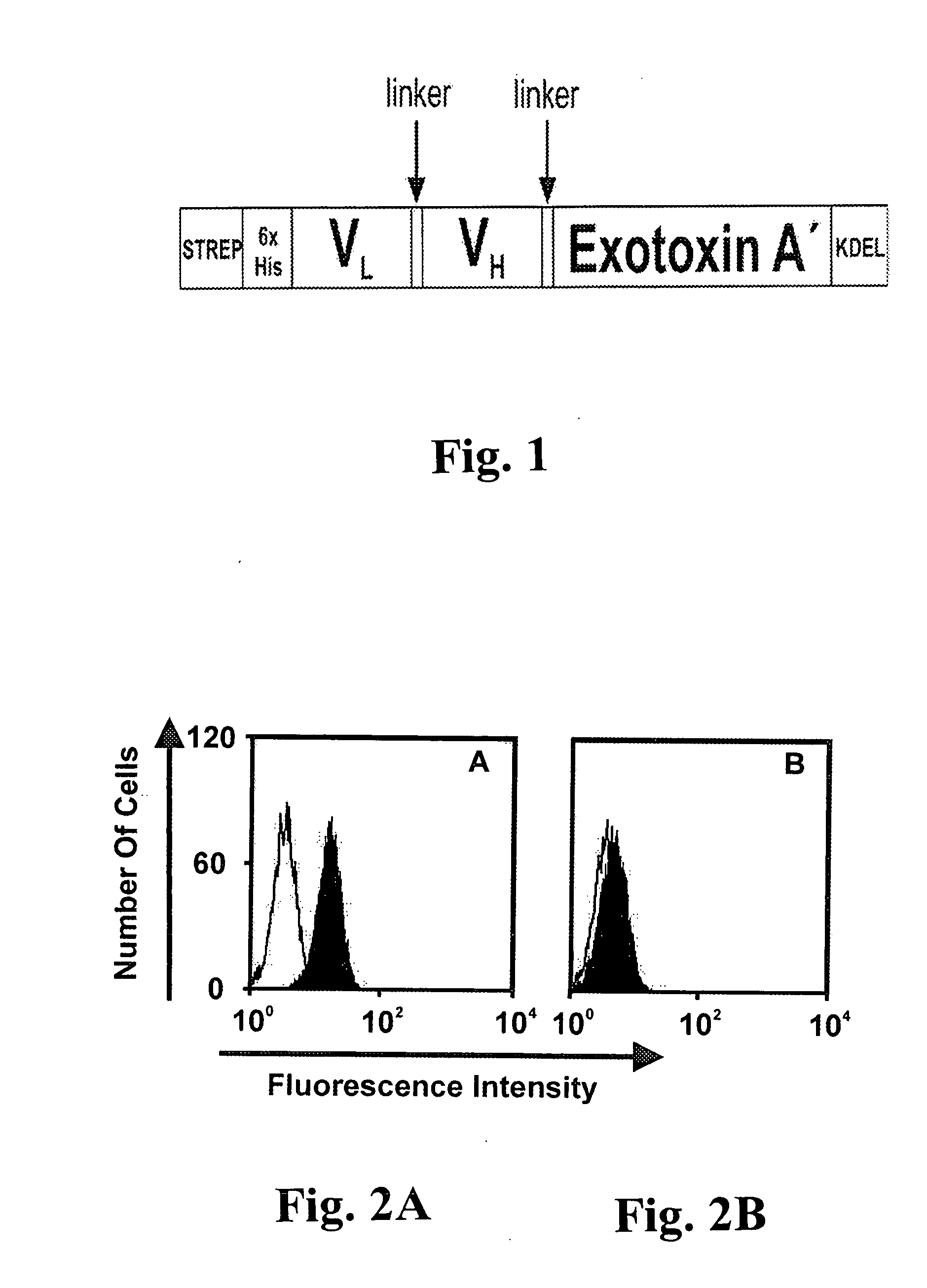
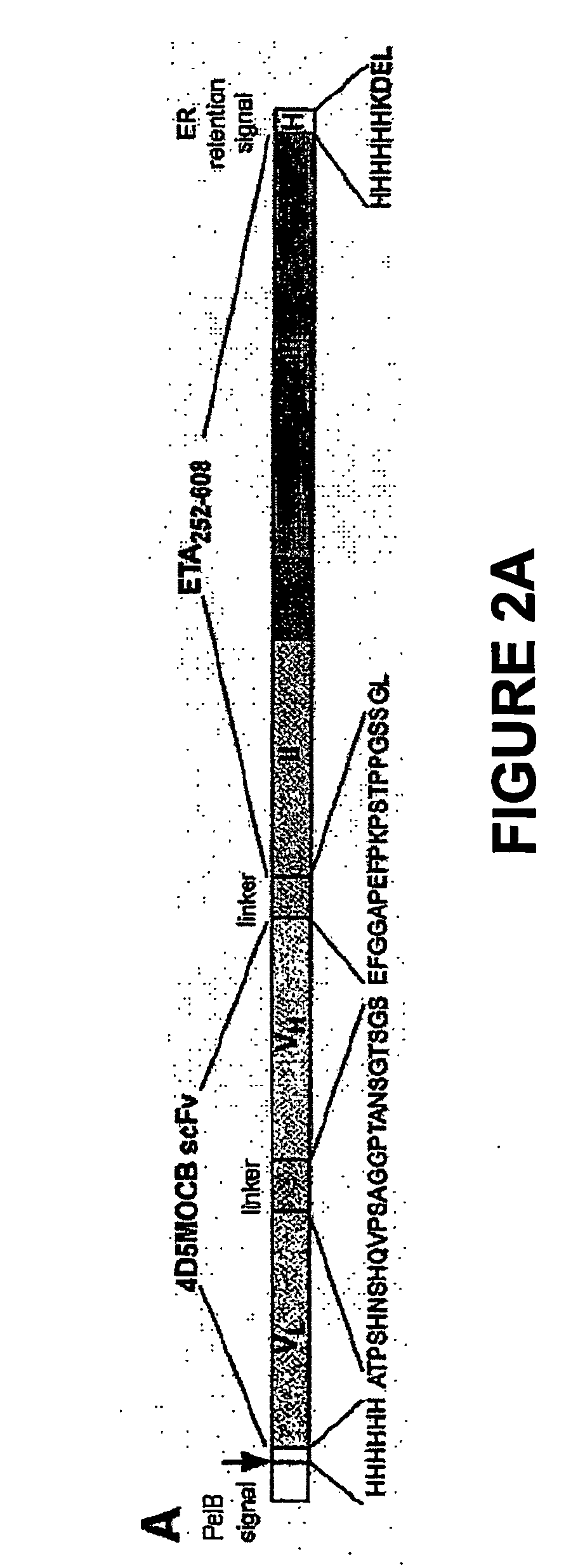
An immunotoxin for use in, and a method for treating a subject having a cancer associated with malignant B-lineage cells or an autoimmune condition, are disclosed. The immunotoxin includes (a) an anti-CD19 antibody lacking an Fc fragment, (b) a modified exotoxin A protein having both Domains II and III, but lacking Domain I, and (c) a peptide linker joining the C-terminal end of the antibody to the N-terminal end of the modified exotoxin A protein. The linker is substantially resistant to extracellular cleavage. The modified exotoxin A protein may be further modified to include a C-terminal KDEL sequence (SEQ ID NO: 6) that promotes transport of the protein to the endoplasmic reticulum of cells that have taken up the immunotoxin.
Owner:FRIEDRICH ALEXANDER UNIV ERLANGEN NURNBERG
Modified pseudomonas exotoxin a
ActiveUS20150099707A1Increased serum half-lifeOptimize treatment planOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
The invention provides a Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising an amino acid sequence having a substitution of one or more B-cell and / or T-cell epitopes. The invention further provides related chimeric molecules, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions. Methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal, methods of inhibiting the growth of a target cell, methods of producing the PE, and methods of producing the chimeric molecule are further provided by the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Mutated anti-cd22 antibodies and immunoconjugates
ActiveUS7982011B2Immunoglobulin superfamilyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesCancer cell
Recombinant immunotoxins are fusion proteins composed of the Fv domains of antibodies fused to bacterial or plant toxins. RFB4 (Fv)-PE38 is an immunotoxin that targets CD22 expressed on B cells and B cell malignancies. The present invention provides antibodies and antibody fragments that have improved ability to bind the CD22 antigen compared to RFB4. Immunotoxins made with the antibodies and antibody fragments of the invention have improved cytotoxicity to CD22-expressing cancer cells. Compositions that incorporate these antibodies into chimeric immunotoxin molecules that can be used in medicaments and methods for inhibiting the growth and proliferation of such cancers. Additionally, the invention provides a method of increasing the cytotoxicity of forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (“PE”) with the mutation of a single amino acid, as well as compositions of such mutated PEs, nucleic acids encoding them, and methods for using the mutated PEs.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
High level expression of recombinant toxin proteins
ActiveUS20110287443A1High yieldQuality improvementAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteria peptidesBacteroidesHigh level expression
The present invention relates to the field of recombinant toxin protein production in bacterial hosts. In particular, the present invention relates to production processes for obtaining high levels of a recombinant CRM197, Diphtheria Toxin, Pertussis Toxin, Tetanus Toxoid Fragment C, Cholera Toxin B, Cholera holotoxin, and Pseudomonas Exotoxin A, from a bacterial host.
Owner:PFENEX
Dry formulation for transcutaneous immunization
A transcutaneous immunization system delivers antigen to immune cells through the skin, and induces an immune response in an animal or human. For example, a skin-active adjuvant (e.g., an ADP-ribosylating exotoxin) can be used to induce an antigen-specific immune response (e.g., humoral and / or cellular effectors) after transcutaneous application of a dry formulation containing antigen and adjuvant to skin of the animal or human. The dry formulation may be a powder or a unit-dose patch. Use of adjuvant is not required if the antigen is sufficiently antigenic. Transcutaneous immunization may be induced with or without penetration enhancement.
Owner:IOMAI CORP
Immunotoxins and uses thereof
The invention provides novel recombinant immunotoxins comprising domain III of cholix toxin and exotoxin from Vibrio cholerae. The present invention further provides methods for using the compositions of the present invention to (i) induce apoptosis in a cell bearing one or more surface markers (ii) inhibit unwanted growth, hyperproliferation or survival of a cell bearing one or more cell surface markers, (iii) treat a condition, such as a cancer, (iv) provide therapy for a mammal having developed antibodies to Pseudomonas exotoxin A, and (v) provide therapy for a mammal having developed a disease caused by the presence of cells bearing one or more cell surface marker.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods for treating cancer using an immunotoxin
InactiveUS20070196366A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSingle-Chain AntibodiesCancer cell
The present invention relates to methods for preventing or treating head and neck squamous cell cancer and bladder cancer using an immunotoxin comprising (a) a ligand that binds to a protein on the cancer cell attached to; (b) a toxin that is cytotoxic to the cancer cell. In a specific embodiment, the invention is directed to the prevention or treatment of head and neck squamous cell cancer or bladder cancer using VB4-845, which is a recombinant immunotoxin comprising a humanized, MOC31-derived, single-chain antibody fragment that is fused to a truncated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin A. Also encompassed by the invention are combination therapy methods, including the use of reduced dosages of chemotherapeutic agents, for the prevention or treatment of cancer. Also encompassed by the invention are formulations and methods for direct administration of the recombinant immunotoxin to the carcinoma, for the prevention or treatment of cancer.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Apparatus and method for down-regulating immune system mediators in blood
InactiveUS20070190050A1Reducing free radicals in a patient's bloodReduce concentrationSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionInterleukin 6White blood cell
A method and apparatus for preventing and treating septicemia in patient blood is provided. The extracorporeal system includes an antimicrobial device to inactivate at least 99% of bloodborne microorganisms, a hemoconcentrator / filtration unit to remove approximately 50-75% of target molecules from the patient blood and a filter unit to remove target molecules from patient blood from the sieved plasma filtrate. Target molecules are produced by microorganisms, as well as by the patient's cells. These molecules include endotoxins from Gram negative bacteria, exotoxins from Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, as well as RAP protein mediator from Staphylococcus aureus, and cell mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin 1-beta, interleukin 6, complement proteins C3a and C5a, and bradykinin.
Owner:HEMAVATION
Deletions in domain II of pseudomonas exotoxin a that remove immunogenic epitopes
ActiveUS8871906B2Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
The invention provides mutated, cytotoxic forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising a furin cleavage sequence conjugated or fused directly to residues 395-613 of PE or variants of that sequence. These minimal forms of PE are smaller than previous cytotoxic forms of PE, reduce non-specific toxicity, and reduce immunogenicity due to domain II or domain Ib of PE. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding said PEs, chimeric molecules containing them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
High level expression of recombinant toxin proteins
The present invention relates to the field of recombinant toxin protein production in bacterial hosts. In particular, the present invention relates to production processes for obtaining high levels of a recombinant CRM197, Diphtheria Toxin, Pertussis Toxin, Tetanus Toxoid Fragment C, Cholera Toxin B, Cholera holotoxin, and Pseudomonas Exotoxin A, from a bacterial host.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Use of non-antibacterial tetracycline analogs and formulations thereof for the treatment of bacterial exotoxins
The invention relates to methods for protecting and / or treating a mammal at risk of acquiring a condition associated with bacteria that produce a calmodulin exotoxin, a metalloproteinase exotoxin, or both, by administering a non-antibacterial tetracycline formulation.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Fusion antigen used as vaccine
InactiveUS7595054B2SsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsBacterial exotoxinReticulum cell
Fusion antigen used as vaccine. The invention relates to a fusion antigen specific for a target cell. The fusion antigen contains a ligand moiety, a Pseudomonas exotoxin A translocation domain II, an antigenic moiety, and a carboxyl terminal moiety. The ligand moiety is capable of reacting, recognizing or binding to receptors on the target cell. The carboxyl terminal moiety permits retention and processing of the fusion antigen in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane of the target cell. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of inducing an immune response using the same are also disclosed.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Recombinant antibodies and immunoconjugates targeted to cd-22 bearing cells and tumors
InactiveUS20090305411A1BacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
Methods and compositions relating to anti-CD22 antibodies with high binding affinity, and immunoconjugates comprising the anti-CD22 antibody linked to a therapeutic agent such as a Pseudomonas exotoxin or a detectable label. The invention provides diagnostic methods, and means to inhibit the growth of malignant B cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods for Treating Cancer Using an Immunotoxin
ActiveUS20100249039A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBladder cancerSingle-Chain Antibodies
The present invention relates to methods for preventing or treating head and neck squamous cell cancer and bladder cancer using an immunotoxin comprising (a) a ligand that binds to a protein on the cancer cell attached to; (b) a toxin that is cytotoxic to the cancer cell. In a specific embodiment, the invention is directed to the prevention or treatment of head and neck squamous cell cancer or bladder cancer using VB4-845, which is a recombinant immunotoxin comprising a humanized, MOC31-derived, single-chain antibody fragment that is fused to a truncated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin A. Also encompassed by the invention are combination therapy methods, including the use of reduced dosages of chemotherapeutic agents, for the prevention or treatment of cancer. Also encompassed by the invention are formulations and methods for direct administration of the recombinant immunotoxin to the carcinoma, for the prevention or treatment of cancer.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Deletions in domain ii of pseudomonas exotoxin a that remove immunogenic epitopes
ActiveUS20100215656A1Maintain immunogenicitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
The invention provides mutated, cytotoxic forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising a furin cleavage sequence conjugated or fused directly to residues 395-613 of PE or variants of that sequence. These minimal forms of PE are smaller than previous cytotoxic forms of PE, reduce non-specific toxicity, and reduce immunogenicity due to domain II or domain Ib of PE. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding said PEs, chimeric molecules containing them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Chimeric protein comprising non-toxic pseudomonas exotoxin and type IV pilin sequences
InactiveUS20070003578A1Reduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin ABacterial exotoxin
The invention provides chimeric proteins comprising a non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A sequence and a Type IV pilin loop sequence, wherein the Type IV loop sequence is inserted within the non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A. The invention also provides polynucleotides encoding the chimeric proteins, and compositions comprising the polynucleotides or the chimeric proteins. The invention also provides methods for using the chimeric proteins, polynucleotides and compositions of the invention.
Owner:THE GOV OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEP OF HEALTH & HUAMN SERVICES
Superior molecular vaccine linking the translocation domain of a bacterial toxin to an antigen
ActiveUS8128922B2Enhance vaccine potencyFacilitate its translocationOrganic active ingredientsVirusesBacteroidesCD8
Nucleic acids encoding a chimeric or fusion polypeptide which polypeptide comprises a first domain comprising a translocation polypeptide; and a second domain comprising at least one antigenic peptide are disclosed. The preferred translocation polypeptide is a bacterial toxin translocation polypeptide, such as domain II of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A (ETA(dII)). Such nucleic acids, expression vectors thereof, and cells expressing these vectors are used as vaccine compositions in a method for enhancing an antigen specific immune response, a method of increasing the numbers of CD8+ CTLs specific for a selected desired antigen in a subject, or a method of inhibiting the growth of a tumor in a subject.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method to detect hemolytic streptococcus and optoelectrically determine results
InactiveUS20110045515A1Suppresses rogue protein modificationHigh detection sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpectral emissionHemolytic streptococcus
A reagent is provided for the detection of an exotoxin protein produced by a betahemolytic streptococcus bacteria suspected of being present in a host biological fluid collected from a subject. A kit is provided that is readily usable by an unskilled user and merely requires that an element of the kit be contacted with a biological sample and that element is then subjected to electromagnetic spectral energy. The incident electromagnetic spectral energy then reacts with the exotoxin protein indicator and can be reliably measured by an electromagnetic spectral emission. The emission is measured by a reporting module and is displayed to the user in a form recognized by the user's sensory systems; sight, sound, etc. or a combination thereof.
Owner:MOSHER LEROY E +1
Broad-spectrum in-vivo effective superantigen toxin antagonists based on the interaction between CD28 and the superantigen and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050191296A1Facilitates the binding of a B7-2 ligandEliciting protective immunity against toxic shockCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenBacterial exotoxin
Disclosed are methods and compositions for the inhibition of modulation of T cell costimulatory pathway by a pathogenic agent, particularly, the inhibition of activation of a T cell costimulatory pathway, preferably, the CD28 / B7 pathway, by a pyrogenic exotoxin. The method of the invention is based on the inhibition of the direct interaction of a superantigen with a specific site within the dimer interface of a CD28 family member, using immunomodulatory peptides. Further disclosed are specific antagonist immunomodulatory peptides comprising an amino acid sequence derived from a dimer interface of a T cell co-stimulatory pathway member, or peptides which comprise an amino acid sequence which specifically binds to an amino acid sequence within the dimer interface of a T cell co-stimulatory pathway member. Compositions comprising said peptides and methods for the treatment of immune-related disorders are also disclosed. Also disclosed is the use of the CD28 molecule or any fragment thereof comprising the sAg binding site in a method of screening for a test substance which specifically binds to the CD28 molecule and is capable of antagonizing pyrogenic exotoxin-mediated activation of Th1 lymphocytes.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Fusion antigen used as vaccine
InactiveUS20080206271A1SsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas tolaasiiReticulum cell
Fusion antigen used as vaccine. The invention relates to a fusion antigen specific for a target cell. The fusion antigen contains a ligand moiety, a Pseudomonas exotoxin A translocation domain II, an antigenic moiety, and a carboxyl terminal moiety. The ligand moiety is capable of reacting, recognizing or binding to receptors on the target cell. The carboxyl terminal moiety permits retention and processing of the fusion antigen in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane of the target cell. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of inducing an immune response using the same are also disclosed.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Fusion protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus as PRRS vaccine
ActiveUS20080008722A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AAllergy
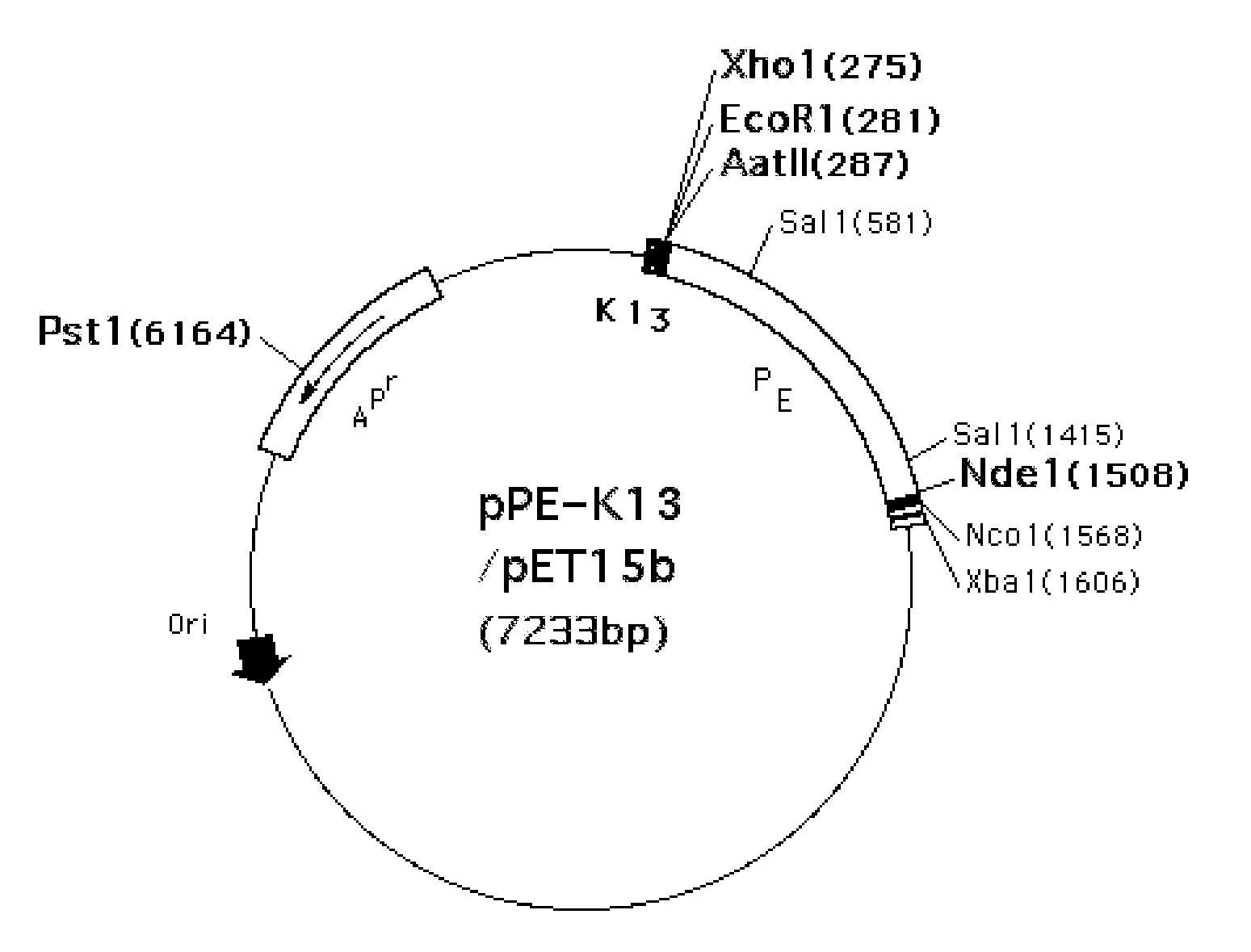
The present invention provides a PRRSV subunit vaccine comprising a fusion protein having neutralization titers evoked, PE-PQGAB-K3, which comprises a chimeric polypeptide containing N-terminal portions of PRRSV ORF5 and ORF6 structure proteins; a portion of Pseudomonas exotoxin A binding and translocation domain; and a carboxyl terminal domain containing KDEL-KDEL-KDEL(K3) sequence. Less inflammation of PE-PQGAB-K3 vaccine group in their lungs post being PRRSV-challenged indicates that PQGAB without an antigen-specific allergy effect. Importantly, PE-PQGAB-K3 vaccine presents a good protection against PRRSV infection than control groups in pig challenged experiment.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Pseudomonas exotoxin A-like chimeric immunogens
InactiveUS8092809B2Eliminate needAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeGenus Pseudomonas
This invention provides Pseudomonas exotoxin A-like chimeric immunogens that include a non-native epitope in the Ib domain of Pseudomonas exotoxin. Methods of eliciting an immune response using these immunogens also are provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Construction method and application of pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant strain
The invention relates to a pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant strain genetic engineering mutant strain, in particular to a pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant strain exotoxin A attenuated strain, and further relates to a preparation method of the mutant strain and application of the mutant strain or the attenuated strain in preparing vaccines or adjuvant therapy drugs.
Owner:BENHEALTH BIOPHARMACEUTIC SHENZHEN CO LTD
Modified Pseudomonas exotoxin A
ActiveUS9388222B2Eliminate side effectsIncreased serum half-lifeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologyAmino acid
The invention provides a Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising an amino acid sequence having a substitution of one or more B-cell and / or T-cell epitopes. The invention further provides related chimeric molecules, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions. Methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal, methods of inhibiting the growth of a target cell, methods of producing the PE, and methods of producing the chimeric molecule are further provided by the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
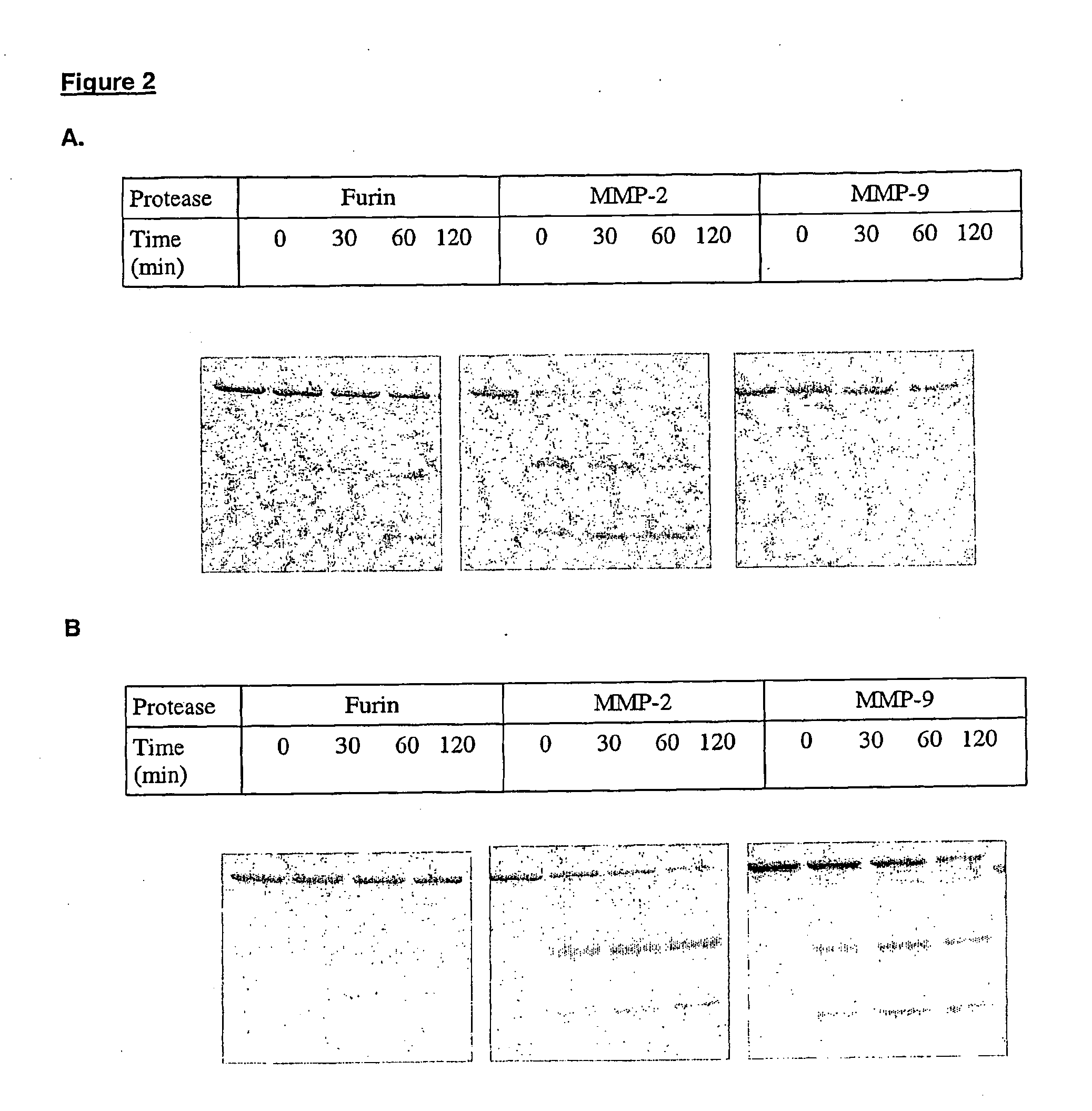
Methods for treating cancer using an immuno-toxin comprising an exotoxin a moiety having a furin cleavage site replaced with a cancer associated protease site cleaved by mmp-2 or mmp-9
The present invention provides a modified toxin having an ETA moiety that has the furin site replaced with a cancer-associated protease site. The present invention also provides modified immunotoxins having a ligand that binds to a cancer cell attached to an ETA moiety that has the furin site replaced with a cancer-associated protease site. Also provided are a method of inhibiting or destroying mammalian cancer cells using the immunotoxins of the invention and pharmaceutical compositions for treating human cancer.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com