Patents
Literature
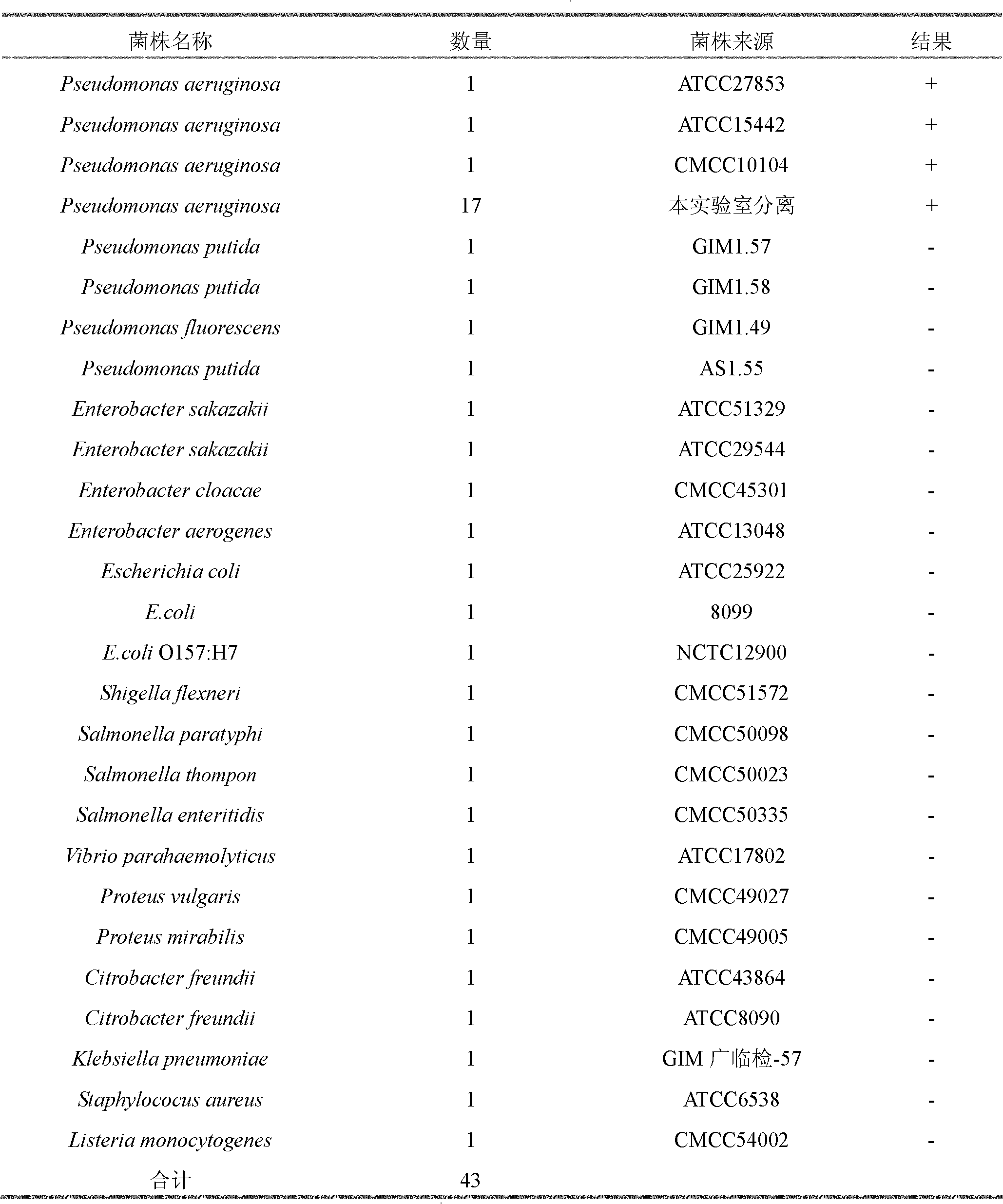
592 results about "Pseudomona aeruginosa" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences relating to Pseudomonas aeruginosa for diagnostics and therapeutics
The invention provides isolated polypeptide and nucleic acid sequences derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa that are useful in diagnosis and therapy of pathological conditions; antibodies against the polypeptides; and methods for the production of the polypeptides. The invention also provides methods for the detection, prevention and treatment of pathological conditions resulting from bacterial infection.
Owner:OSCIENT PHARMA
Nanosilver-containing antibacterial and antifungal granules and methods for preparing and using the same
The present invention relates to nanosilver-containing antibacterial and antifungal granules ("NAGs"). The NAGs have longlasting inhibitory effect on a broad-spectrum of bacteria and fungi, which include, but are not limited to, Escherichia coli, Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Chlamydia trachomatis, Providencia stuartii, Vibrio vulnificus, Pneumobacillus, Nitrate-negative bacillus, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, Bacillus cloacae, Bacillus allantoides, Morgan's bacillus (Salmonella morgani), Pseudomonas maltophila, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus foecalis alkaligenes, Streptococcus hemolyticus B, Citrobacter, and Salmonella paratyphi C. The NAGs contain ground stalk marrow of the plant Juncus effuses L. which has been dispersed with nanosilver particles. The nanosilver particles are about 1-100 mn in diameter. Each of the nanosilver particles contain a metallic silver core which is surrounded by silver oxide. The present invention also provides a process for making the NAGs. The NAGs can be used in a variety of healthcare and industrial products. Examples of the healthcare products include, but are not limited to, ointments or lotions to treat skin trauma, soaking solutions or cleansing solutions for dental or women hygiene, medications for treating gastrointestinal bacteria infections, sexual related diseases, and eye diseases. Examples of industrial products include, but are not limited to, food preservatives, water disinfectants, paper disinfectants, construction filling materials (to prevent mold formation).
Owner:LEGEND WIN FINANCE
Recombinant bacteriophage and methods for their use
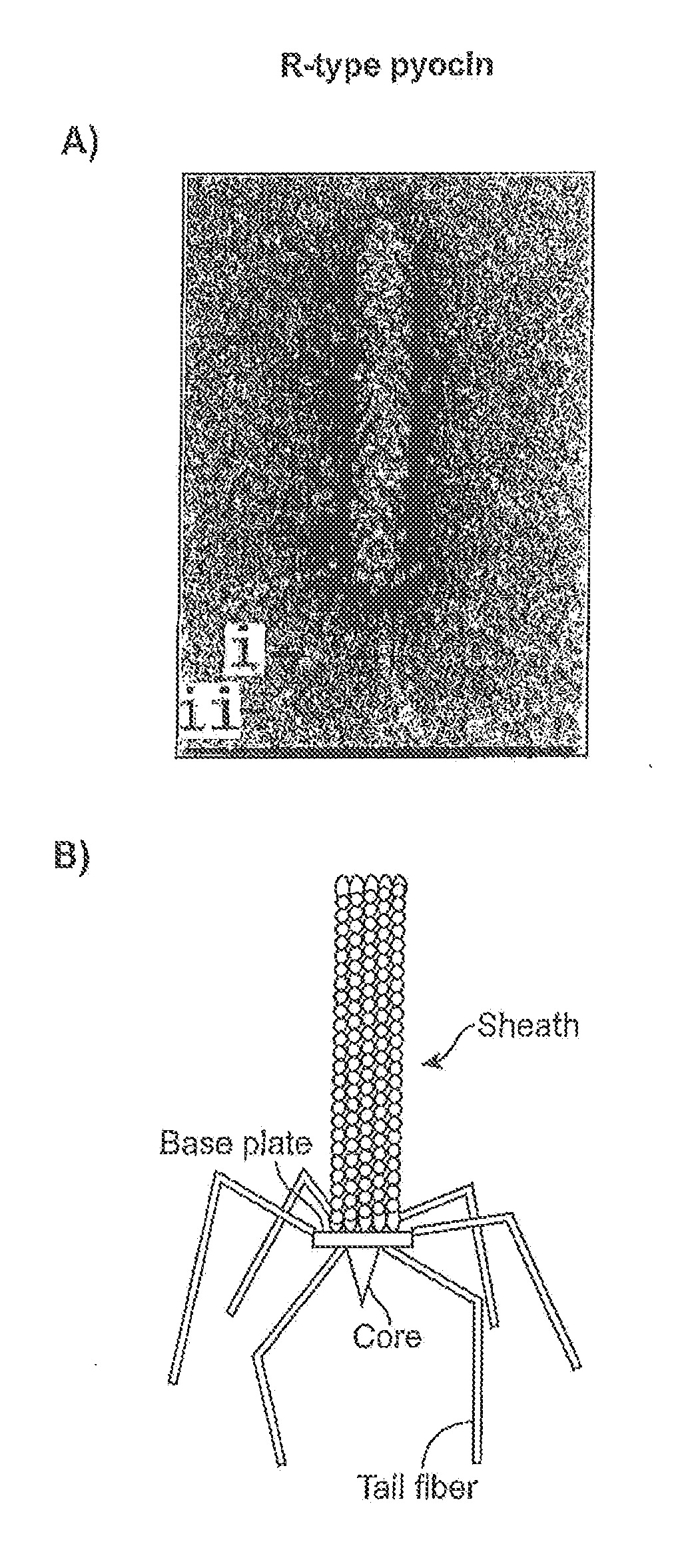
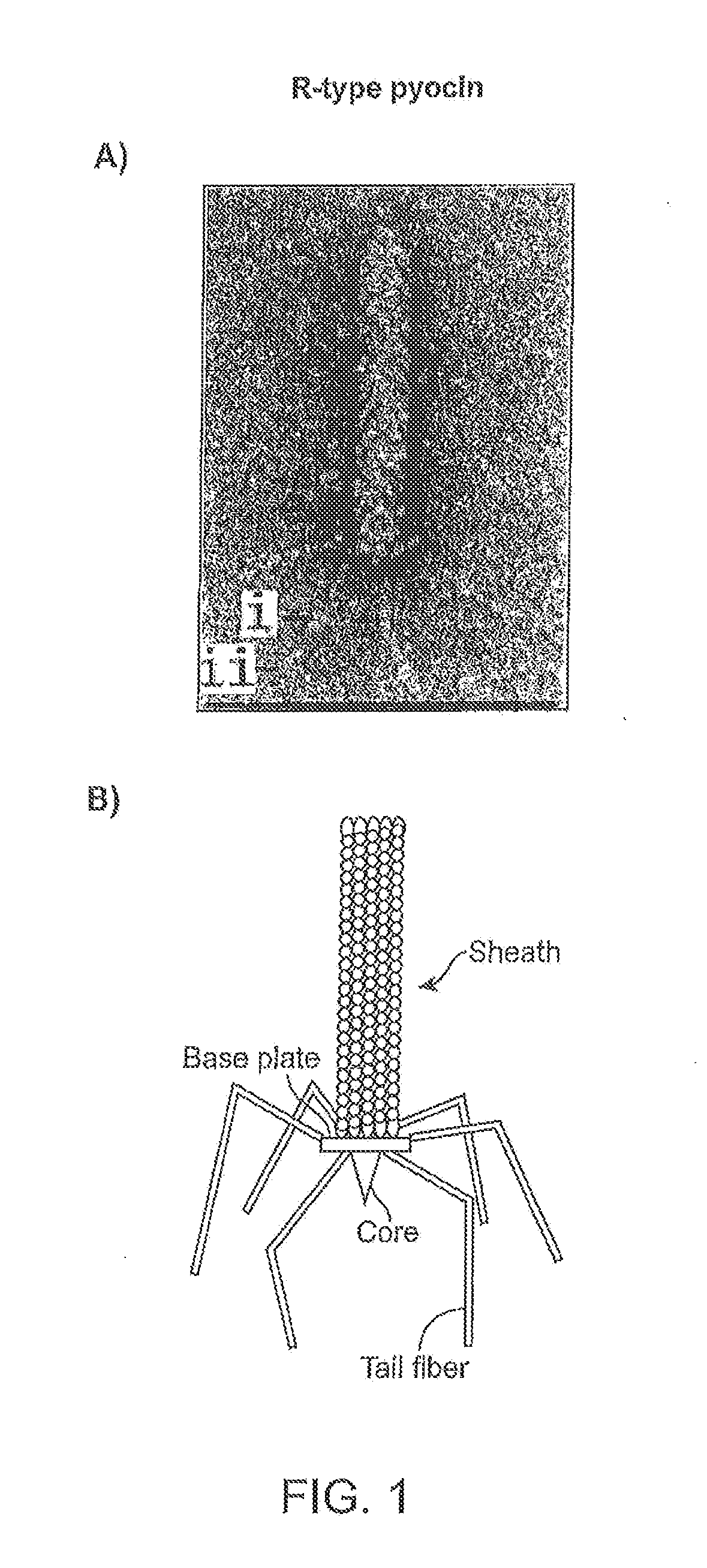
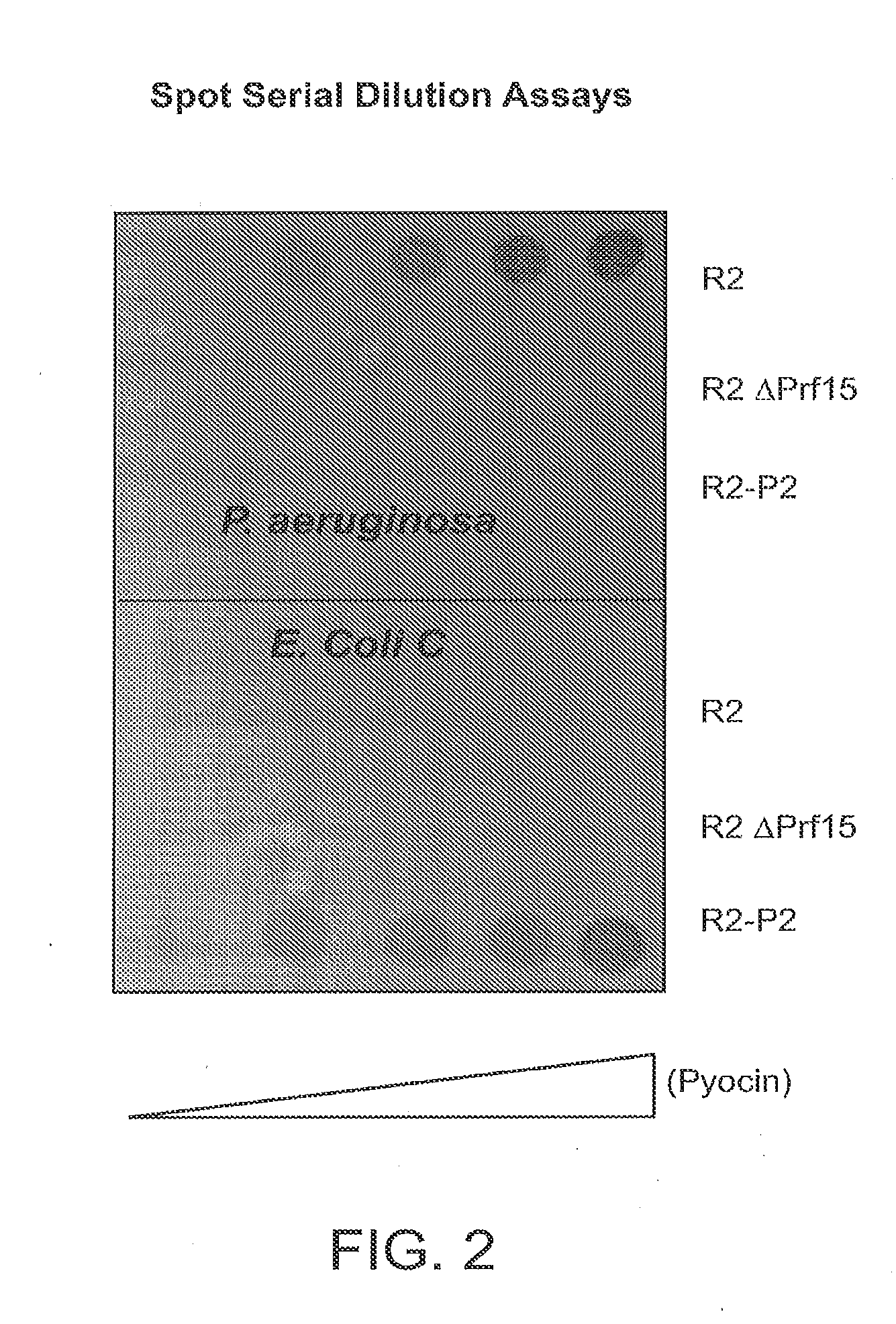
Modified forms of naturally occurring bacteriocins, such as the R-type pyocins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, are disclosed as are methods for producing them in GRAS organisms. The bacteriocins are modified at the ends of their tail fibers in a region responsible for binding specificity and affinity to their cognate binding partners, or receptors, such as those on the surface of bacteria. Methods for the use of the modified bacteriocins, such as to bind receptors, including virulence or fitness factors, on the surfaces of bacteria, are also described.
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Antibodies to the PcrV Antigen of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
InactiveUS20090191186A1Avoid cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsPseudomona aeruginosaHigh affinity antibody
The current invention provides high-affinity antibodies to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PcrV protein that have reduced immunogenicity when administered to treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
Phage therapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
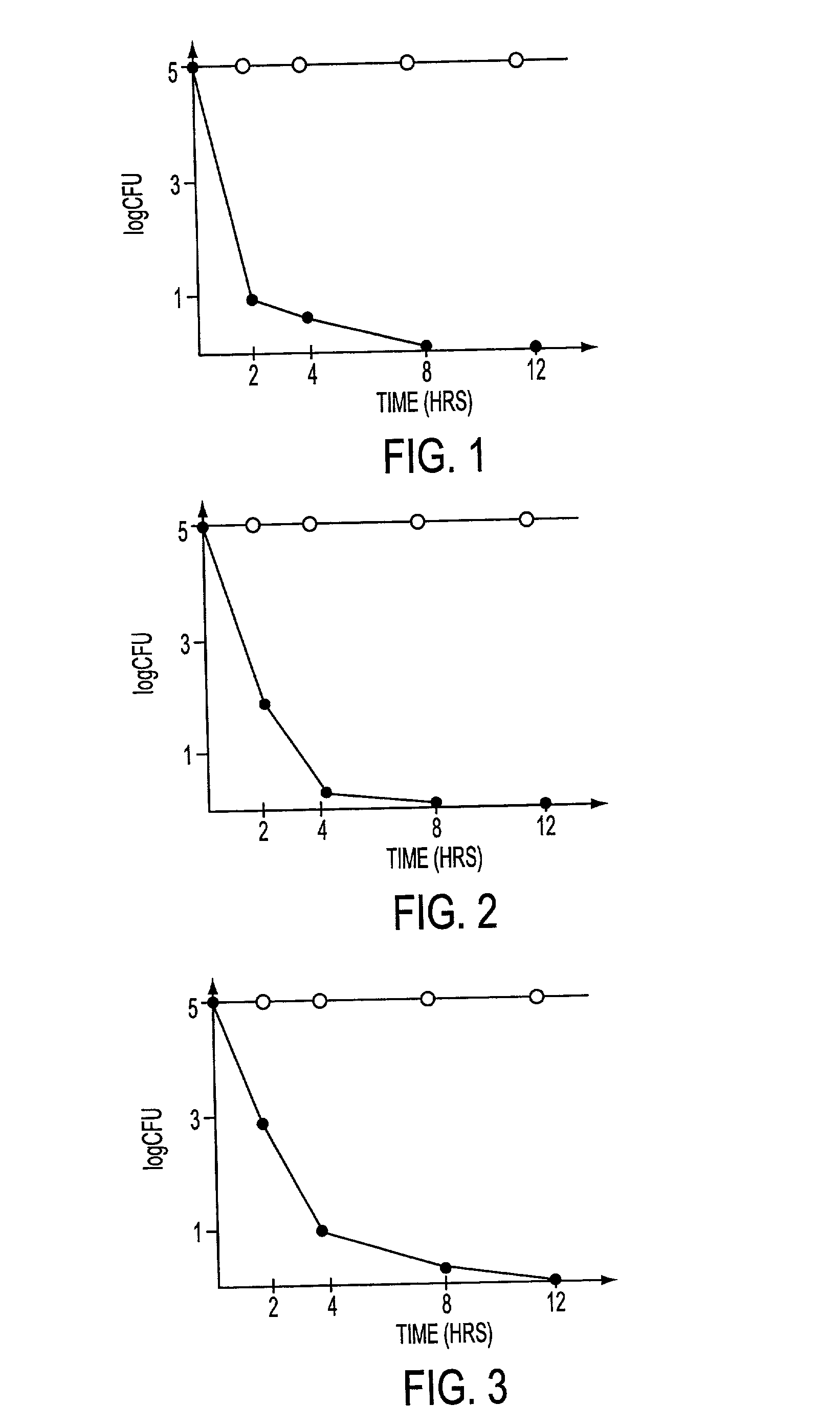
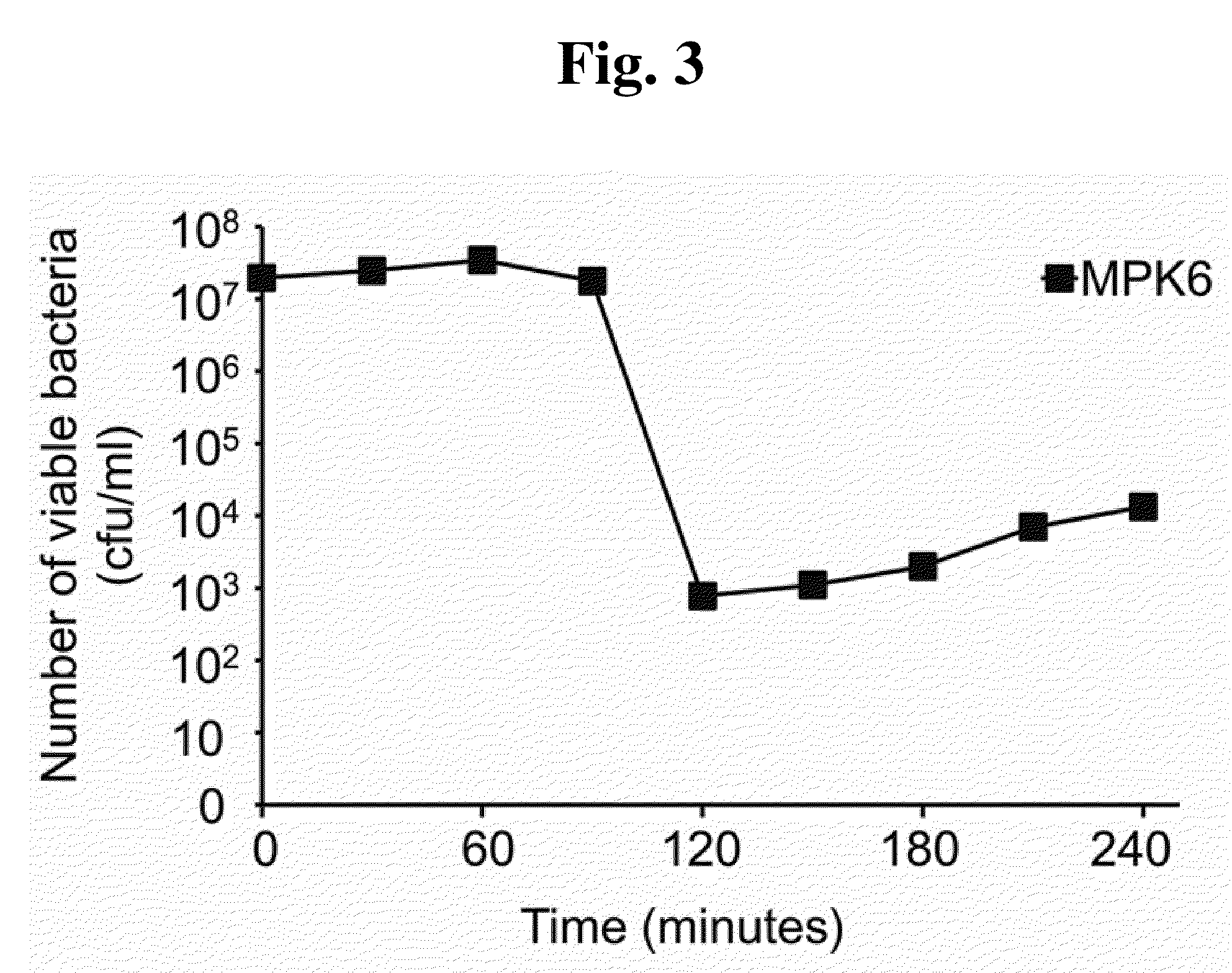
This invention relates to a bacteriophage MPK6 (deposit number: KCCM 11044P) having a lytic activity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or a progeny bacteriophage thereof having a RFLP (Restriction fragment length polymorphism) DNA profile substantially equivalent to the bacteriophage MPK6. The present invention provides a bacteriophage MPK6 or a progeny bacteriophage thereof capable of treating a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection disease, and suggests an anti-bacterial activity of MPK6 and its progeny bacteriophage using a mammalian and non-mammalian infection model. According to the present invention, the present bacteriophage MPK6 or progeny bacteriophage thereof represents very effective efficacy on treatment of P. aeruginosa-induced peritonitis-sepsis.
Owner:IND UNIV COOP FOUND SOGANG UNIV
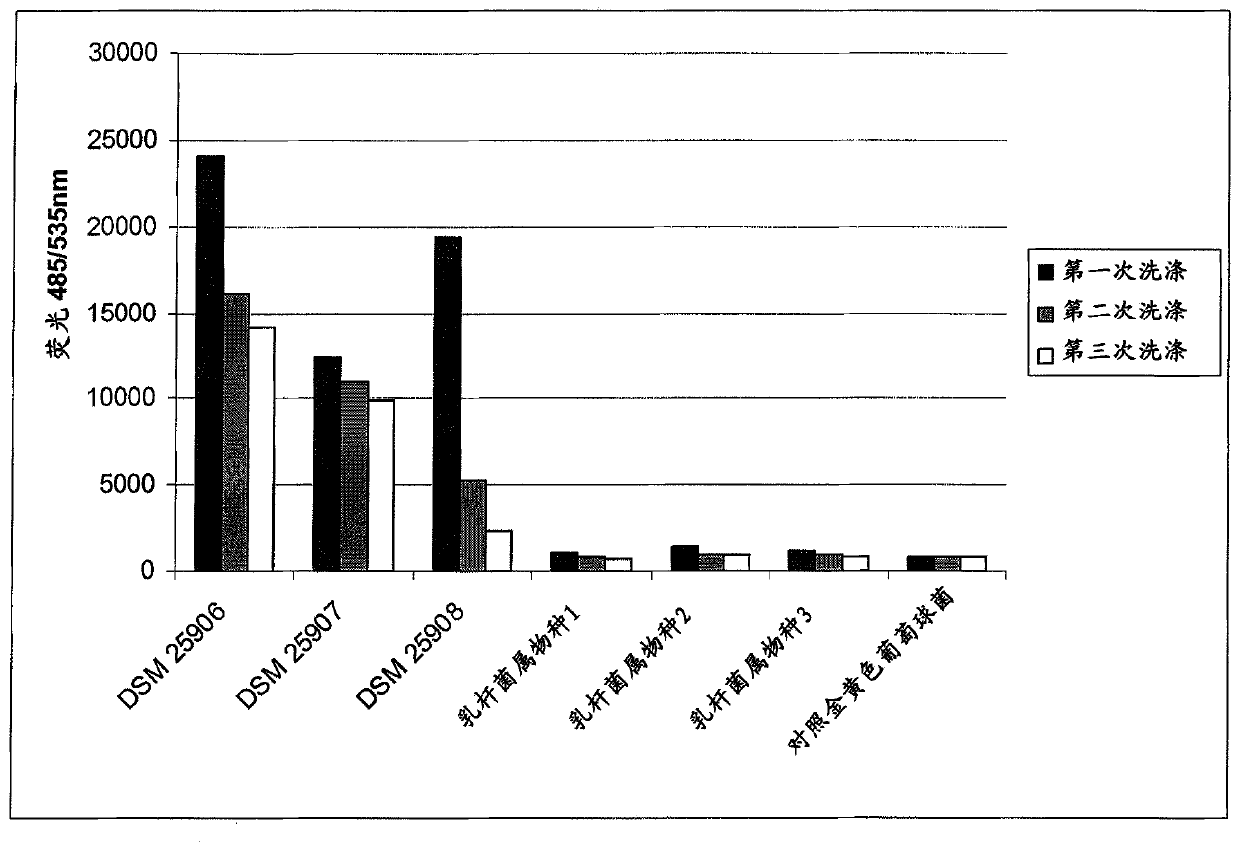
Novel lactic acid bacteria and compositions containing them
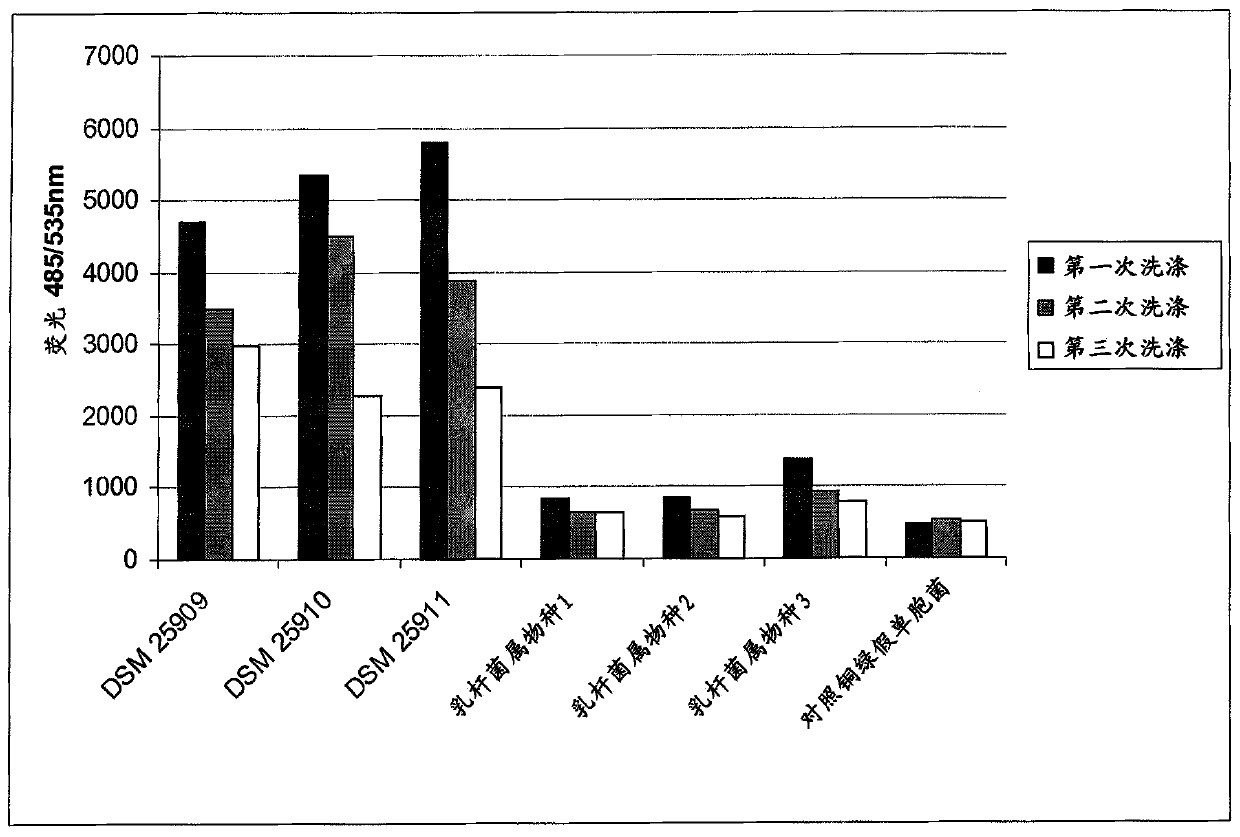
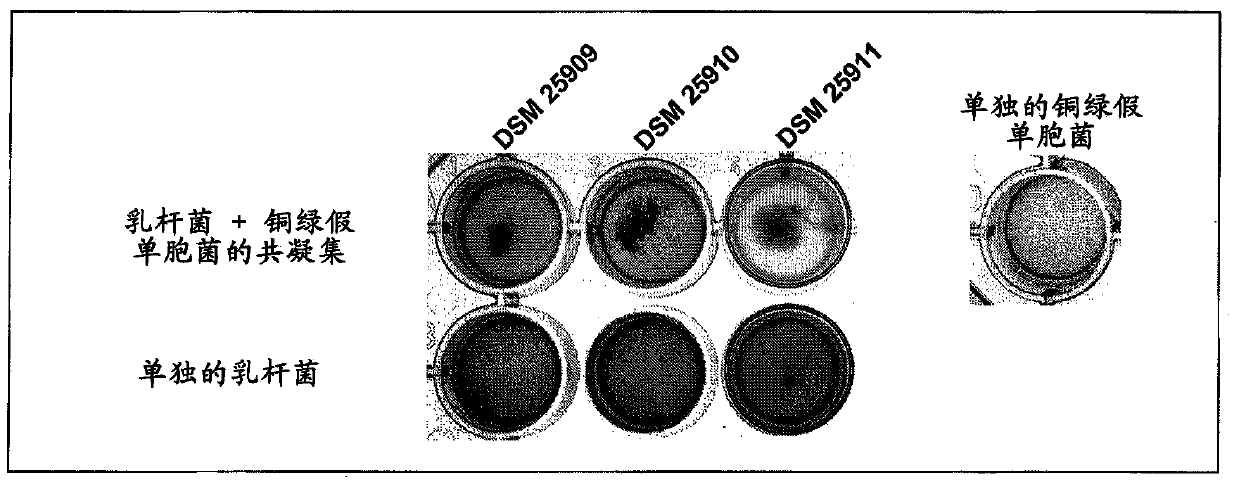
The invention relates to a microorganism, of the order of lactic acid bacteria or analog, fragment, derivative, mutant or combination thereof. Said microorganism, or analog, fragment, derivative, mutants or combination thereof can be co-aggregated with at least Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:ORGANOBALANCE MEDICAL AG
Solid microbial preparation for petroleum pollutant and oil product degradation, preparation and use
InactiveCN101486980AHigh activityPromote growthBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismPetroleum product
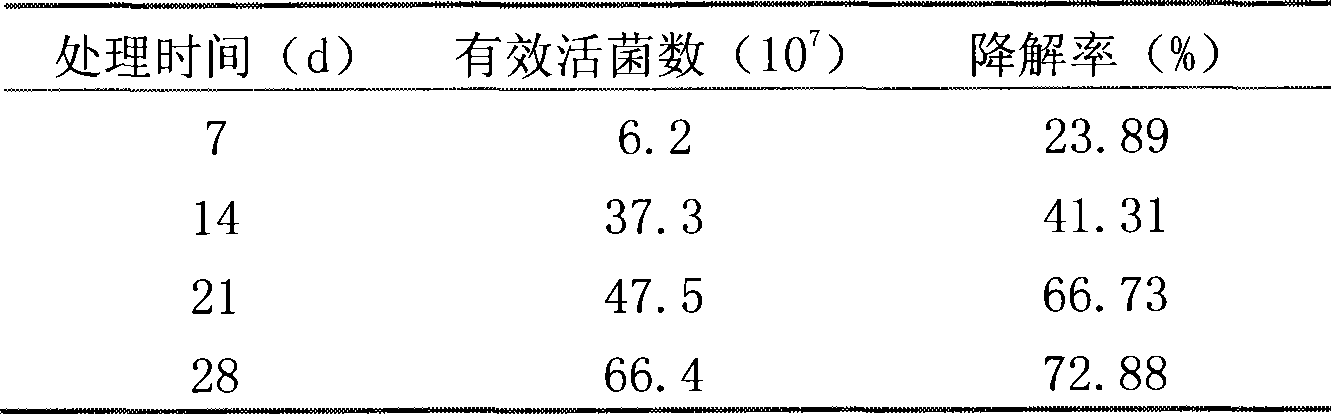
The invention discloses a solid microbial inoculum that is used for decomposing petroleum pollutants and petroleum products, and a preparation method and applications of the solid microbial inoculum; and the invention belongs to the technical field of biological reparation in the emergency processing of accidents including petroleum pollution of soils and petroleum product leakage. The solid microbial inoculum is prepared by mixing a pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria fermented fluid, turfy soil and bran with proportion by weight: 0.1-1:1:0.2-0.5, and the effective living bacteria number of pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria inside the pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria fermented fluid is 10 to 10 in each milliliter. The solid microbial inoculum has the advantages of high liveness in soil and quick growth, does not cause secondary environmental pollution, and can be used in the biological reparation on the spot of accidents including petroleum pollution of soils and petroleum product leakage.
Owner:于洋
Pseudomonas aeruginosa D10, and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN101698828AAntagonisticSimple cultivation conditionsBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicrobiologyVerticillium wilt
The invention discloses a pseudomonas aeruginosa D10 which is preserved in China Typical Culture Preservation Center, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 209104. A colony on a beef paste peptone culture medium appears brown, round, glossy and wet, and has trim edges; the diameter of the colony is 0.2-0.5 cm; and the thallus is in a short bar shape and does not have gemma. The invention also discloses a preparation method and applications of the pseudomonas aeruginosa D10. The pseudomonas aeruginosa D10 of the invention can inhibit corn northern and southern leaf blight, has strong antergic functions on corn northern leaf blight, corn southern leaf blight, corn curvalaria leaf spot, cotton verticillium wilt, wheat fusarium graminearum, banana colletotrichum toilette and banana fusarium wilt, has the advantages of wide bacteriostatic range, high prevention efficiency and favorable environmental safety, and has favorable prospects for development and applications.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain separating, purifying and domesticating method and use
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain TBPY, which is screened from tribromophenol(TBP)-polluted sludge and purified. The purified strain is domesticated by a pressure type domesticating method with gradually increased TBP concentration in an organic salt culture medium, and the domesticated strain can be used for the biological control of waste water containing persistent organic pollutants such as phenol, pyrocatechol, resorcinol, benzoic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillin, 4-chlorophenol, 2,4-dichlorophenol, trichlorophenol and tribromophenol and has high research and application values.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Strong emulsibility microbe wax cleaning and preventing bacterial agent and application thereof
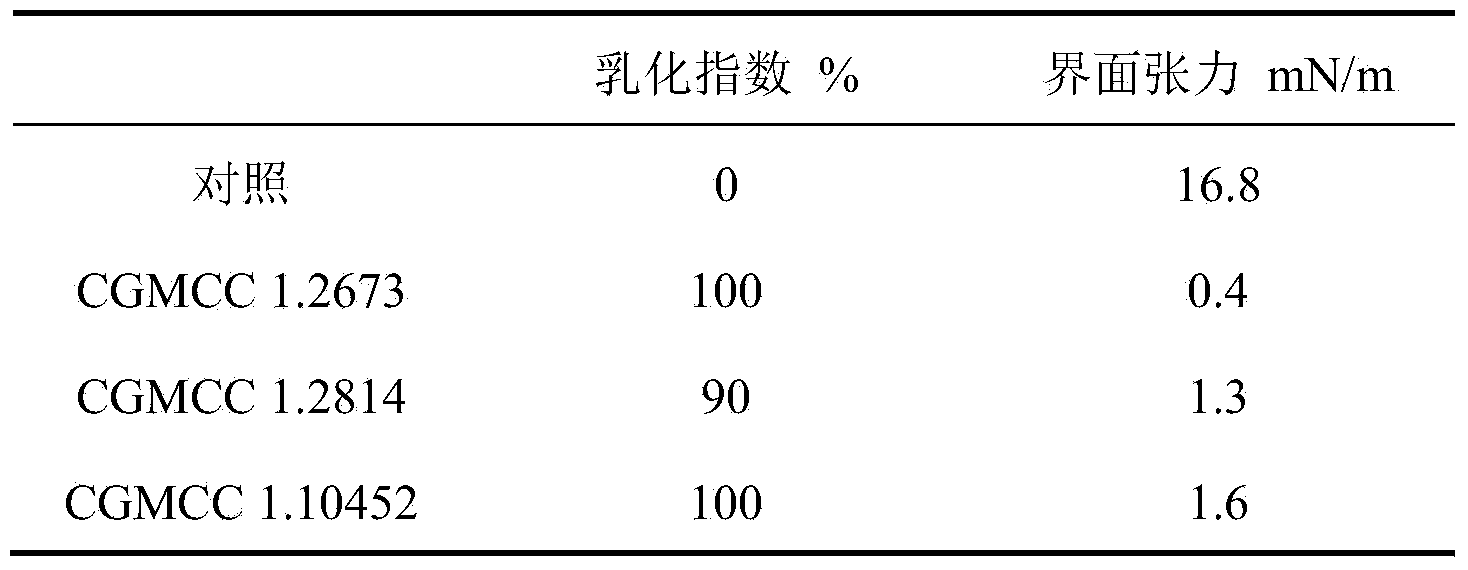
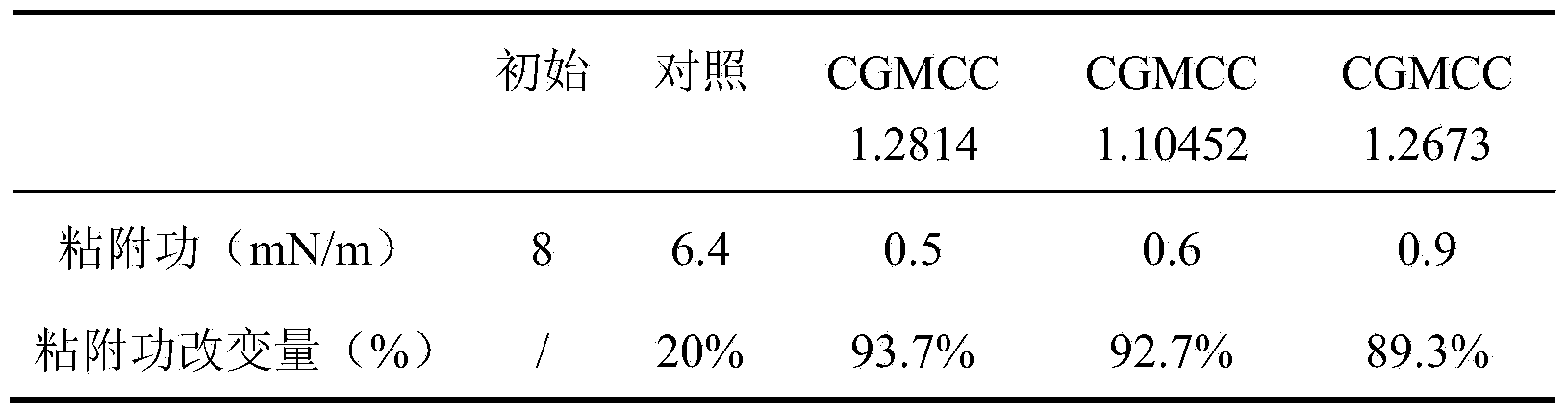
ActiveCN104109516AStrong emulsifying abilityReduce interfacial tensionCleaning apparatusFluid removalInhibition zoneOil production
The invention discloses a strong emulsibility microbe wax cleaning and preventing bacterial agent and an application, which belongs to the oil field chemical technology field. The wax cleaning and preventing bacterial agent mainly comprises pseudomonas aeruginosa and geobacillus sp, has strong emulsification capability, and is capable of dispersing crude oil, promoting crude oil to flow, changing adherence force of borehole wall, preventing the accumulation of wax crystal on the borehole wall, and playing the paraffin inhibition and wax cleaning effects. By increasing the initial application amount of the bacteria liquid and prolong the well closing time, a stable paraffin inhibition zone can be formed due to adhesion of bacteria on borehole wall, near wellbore formation can be cleaned, and the paraffin inhibition and oil increase effects can be increased. After on-site enforcement, the well cleaning and chemical paraffin inhibition works can not be carried out in recent half year in the test wells, so that the wax cleaning and preventing bacterial agent has good paraffin inhibition effect in the well. The oil production is increased by about 30% daily, pump efficiency is increased about 10%, the surface tension of the output liquid is decreased to 20-25%, and the crude oil condensation point is decreased by 1-3 DEG C.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and application thereof in degrading zearalenone
ActiveCN103981134AEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyPseudomonas cerasi
The invention discloses pseudomonas aeruginosa and an application thereof in degrading zearalenone. The preservation number of the pseudomonas aeruginosa is CGMCC No.8727. As a biologic material for degrading zearalenone, the pseudomonas aeruginosa is good in application prospect in no matter developing a novel biologic degrading bacterium agent or a biologic degrading bacterium-free preparation.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Food-originated pathogenic bactenium quick detection gene chip and its application
InactiveCN1536090AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFood poisoningBeta-hemolytic streptococcus
The present invention provides a gene chip for quickly detecting pathogens from food source, discloses the preparation method of said gene chip and provides 26 oligonucleotide probe sequences for detection. Said gene chip can quickly, accurately and high-effectively detect and identify the class of the pathogens in food, and its detection range includes staphylococcus aureus, Shiga's bacillus, salmonella, colibacillus 0157, bacillus proteus, mononuclear hyperplastic listerella, enterocolitis yersinia, aeruginous pseudomonads, vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio cholerae, bacillus cereus, beta hemolytic streptococcus, coconut fermentation pseudomonads, boticin, vibrio jejuni and bacillus perfringens, etc.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Inhibition and Dispersion of Bacterial Biofilms with 2-Aminobenzimidazole Derivatives
InactiveUS20130136782A1Reducing bacterial virulenceIncreased susceptibilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideControlled release2-aminobenzimidazole
Compounds described herein inhibit biofilm formation or disperse pre-formed biofilms of Gram-negative bacteria. Biofilm-inhibitory compounds can be encapsulated or contained in a polymer matrix for controlled release. Coatings, films, multilayer films, hydrogels, microspheres and nanospheres as well as pharmaceutical compositions and disinfecting compositions containing biofilm-inhibitory compounds are also provided. Methods for inhibiting formation of biofilms or dispersing already formed biofilms are provided. Methods for treating infections of gram-negative bacteria which form biofilms, particularly those of Pseudomonas and more particularly P. aeruginosa.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
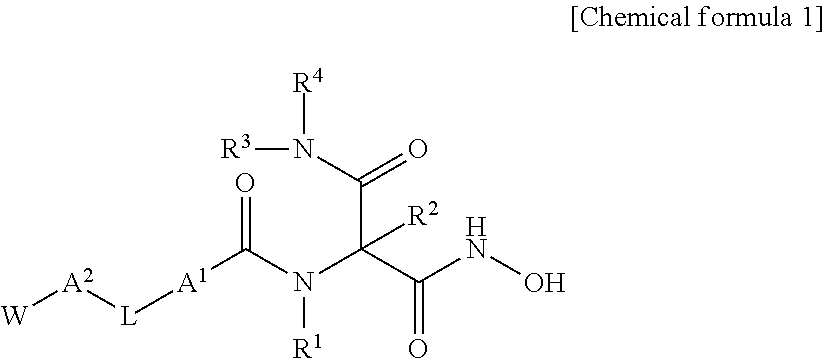
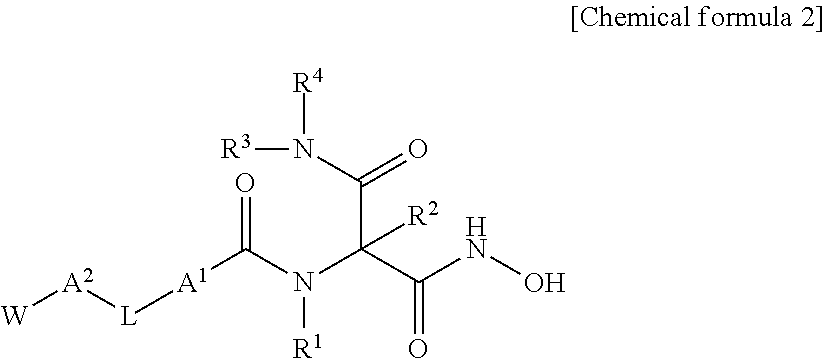
Novel hydroxamic acid derivative
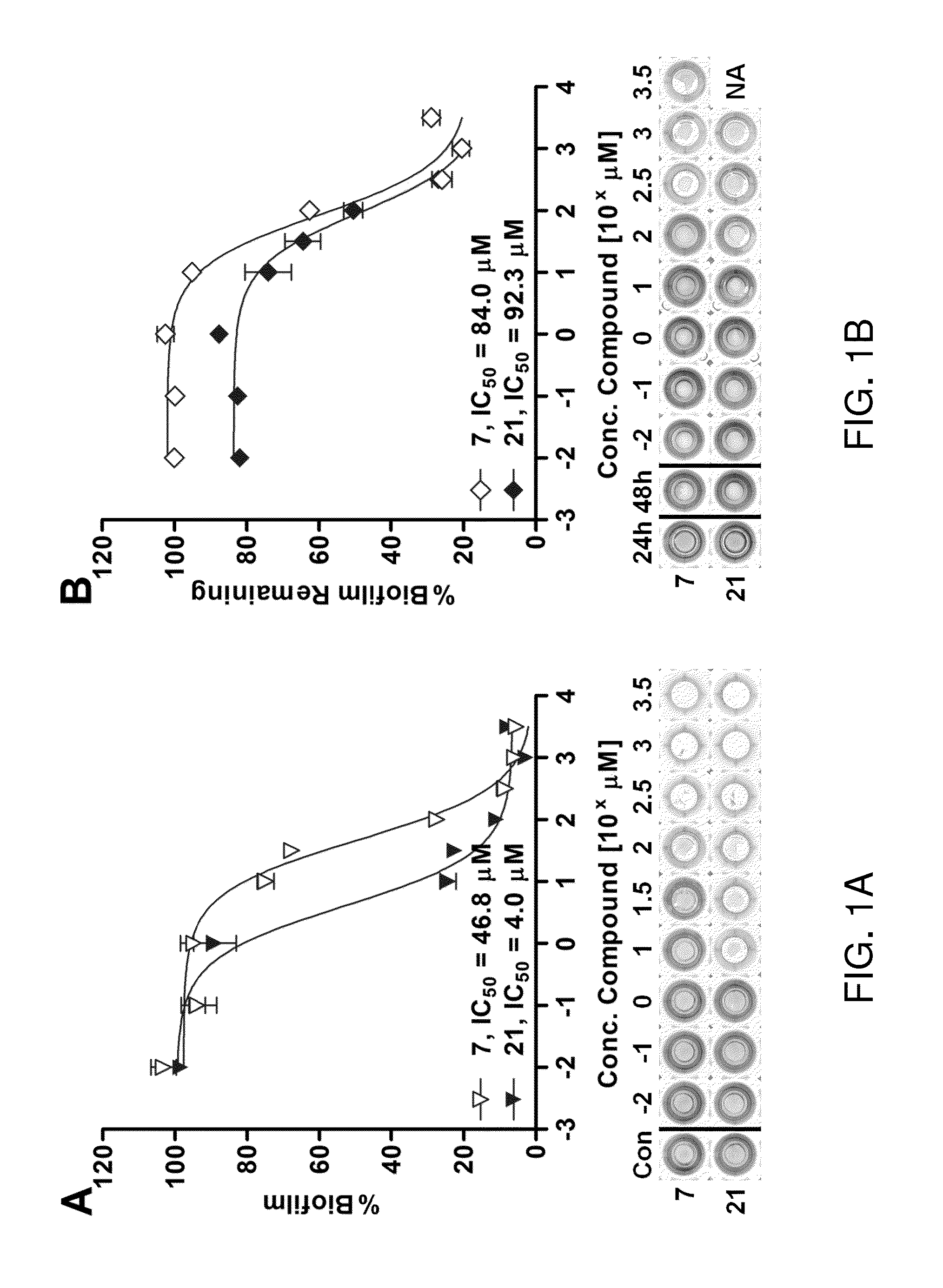
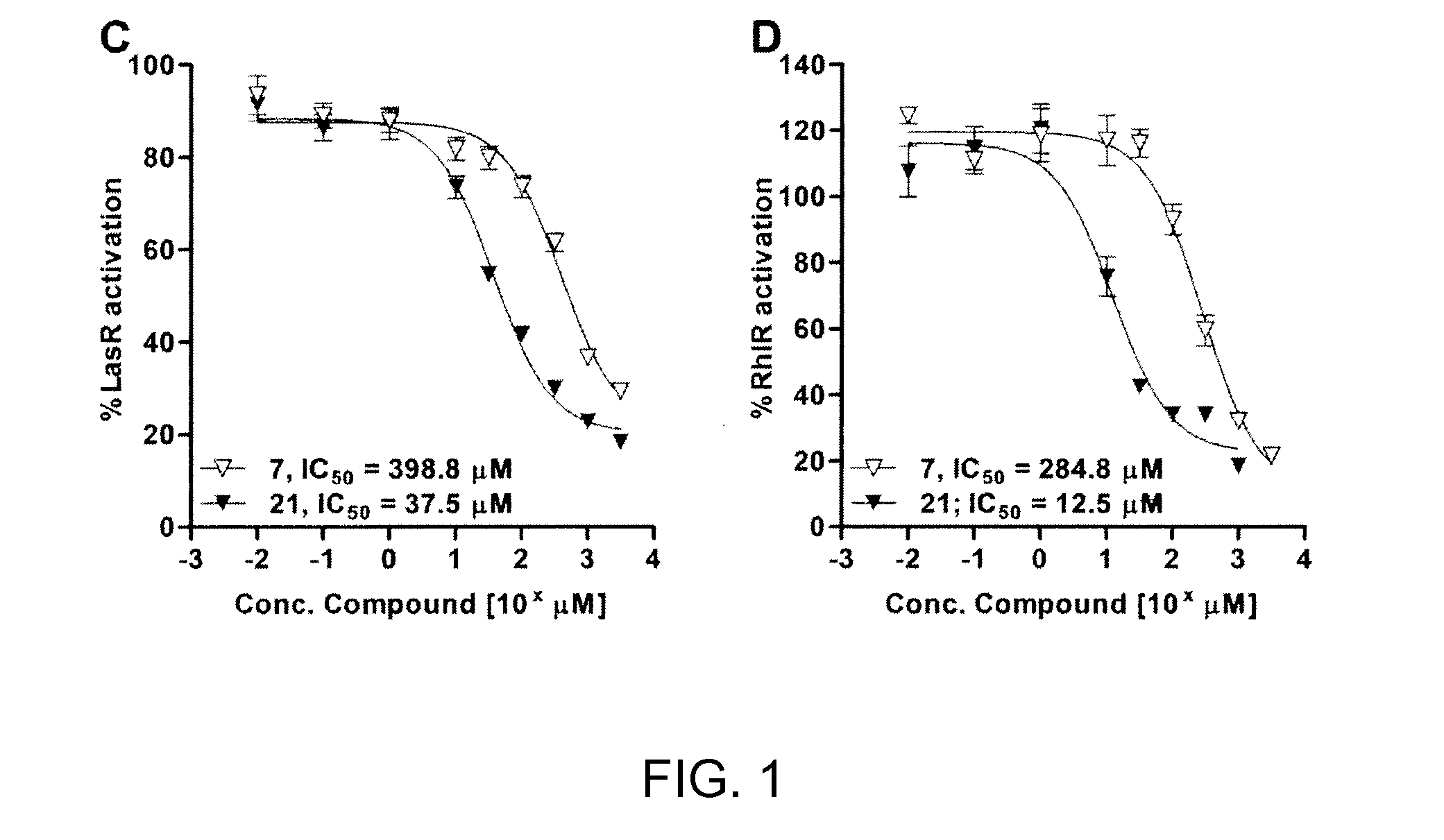
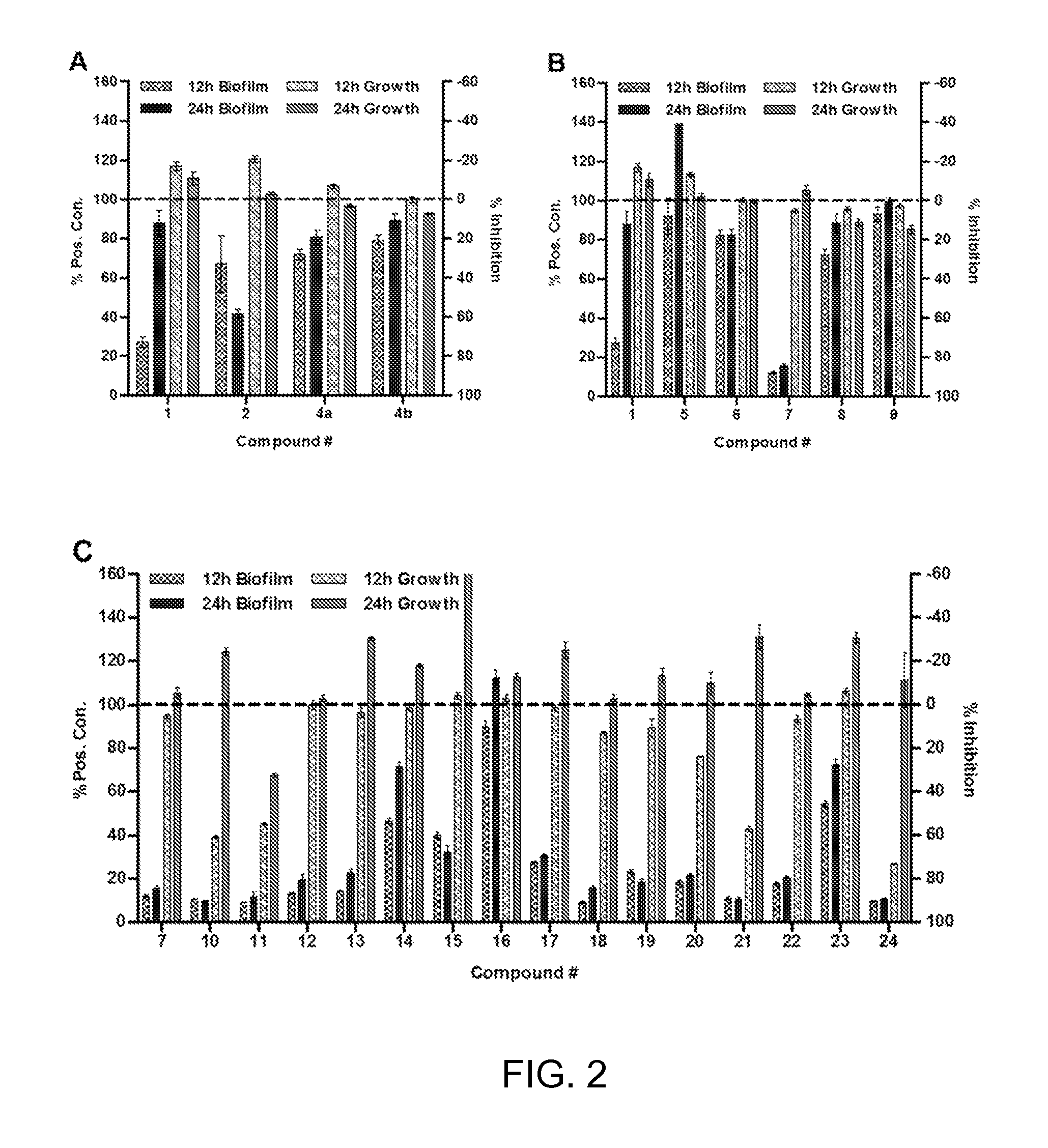
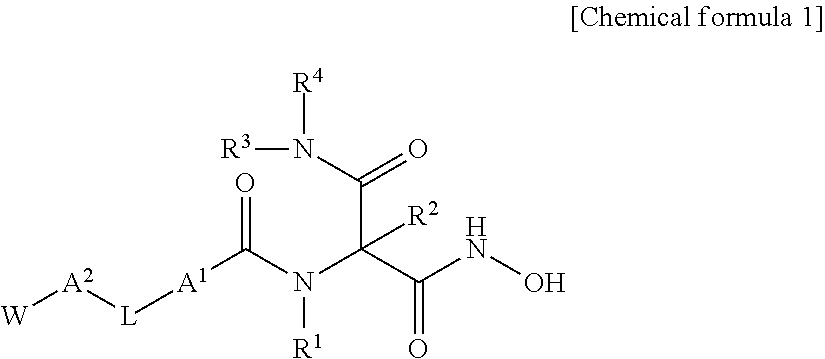
ActiveUS20130072677A1Strong LpxC-inhibiting actionHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsResistant bacteriaHydroxamic acid
Provided is a novel compound which is useful as a pharmaceutical composition by inhibiting an LpxC activity, thereby exhibiting potent antimicrobial activity against gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its drug resistant bacteria. Provided is a hydroxamic acid derivative represented by the following general formula [1] or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
Owner:TAISHO PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
Kitchen garbage bio-drying and stabilizing microbial agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111662853AReduce moisture contentIncrease the low calorific valueBacteriaClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and particularly relates to a kitchen garbage bio-drying and stabilizing microbial agent as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. According to the technical scheme, pseudomonas aeruginosa is conserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) with the conservation number being CGMCC No.17868.By means of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, microbial composition including starch degrading bacteria, protein degrading bacteria, cellulose degrading bacteria, oil degrading bacteria and deodorization bacteria is provided; and the oil degrading bacteria comprise pseudomonas aeruginosa. The microbial composition can treat kitchen garbage in a targeted manner and achieve the purposes of dewatering, drying, reduction and recycling of the kitchen waste.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Biological agent for reducing specific nitrosamine content which tobacco has, preparation method and use
InactiveCN1579260AReduce TSNA contentReduced or almost eliminatedTobacco treatmentAntibody medical ingredientsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a biology preparation for reducing nitrosamine content in tobacco, and the manufacturing method and application, which belongs to biology technology field. The fungus Pseudomonas aeruginosa KenLXP30 product in the invention is preserved in normal microbe centre of china microbe preservation management committee in Jul 28 2003, the preserving number is CCTCC NO.0985. The invention picks out a fungus KenLXP30 in large amount of tobacco inner bacteria which can eliminates the amino nitrous acid content in tobacco, produces the biology preparation which can reduce the hard of tobacco. The preparation can reduce the amino nitrous acid content in white rib tobacco prominently, and it has good application value in tobacco industry.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
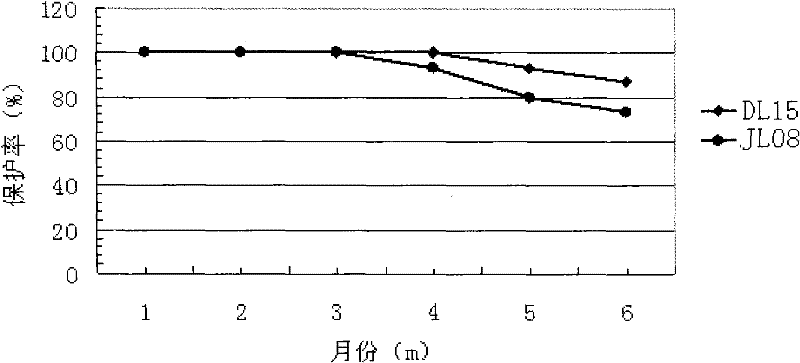
Mink hemorrhagic pneumonia bivalent inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, disclosing two pseudomonas aeruginosa virulent strains and a mink hemorrhagic pneumonia divalent inactivated vaccine prepared from the two strains. The pseudomonas aeruginosa virulent strains are inoculated in a culture medium to be amplified and cultured by ventilation; after the obtained cultured object is inactivated, the products are mixed at the ratio of 1-2:1; and adjuvant is added to prepare the mink hemorrhagic pneumonia divalent inactivated vaccine. The divalent inactivated vaccine disclosed by the invention has good immunity effect on mink hemorrhagic pneumonia, at least five-month protection periods can be obtained, the protection ratio is above 80%, the mink hemorrhagic pneumonia can be prevented, and the vaccine has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS +1
Compound bacterial agent for purifying black and odorous water body and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106148246ADegraded ammonia nitrogen contentDegradation of phosphate contentFungiBacteriaNitrifying bacteriaBacillus subtilis
The invention provides a compound bacterial agent for purifying a black and odorous water body and a preparation method thereof. The compound bacterial agent comprises the following components: actinomycetes, bacillus subtilis, nitrifying bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, candida utilis and pseudomonas aeruginosa in a weight ratio of 2:2:2:1:1:1. The invention has the following advantages: the COD content, ammonia nitrogen content and phosphate salt in the black and odorous water body can be effectively reduced, and the odor of the black and odorous water body can be eliminated; and meanwhile, by adding the ammonia nitrogen removal strain, the transparency of the water body can be gradually improved.
Owner:BIOLAND ENVIRONMENTAL TECH GRP CORP
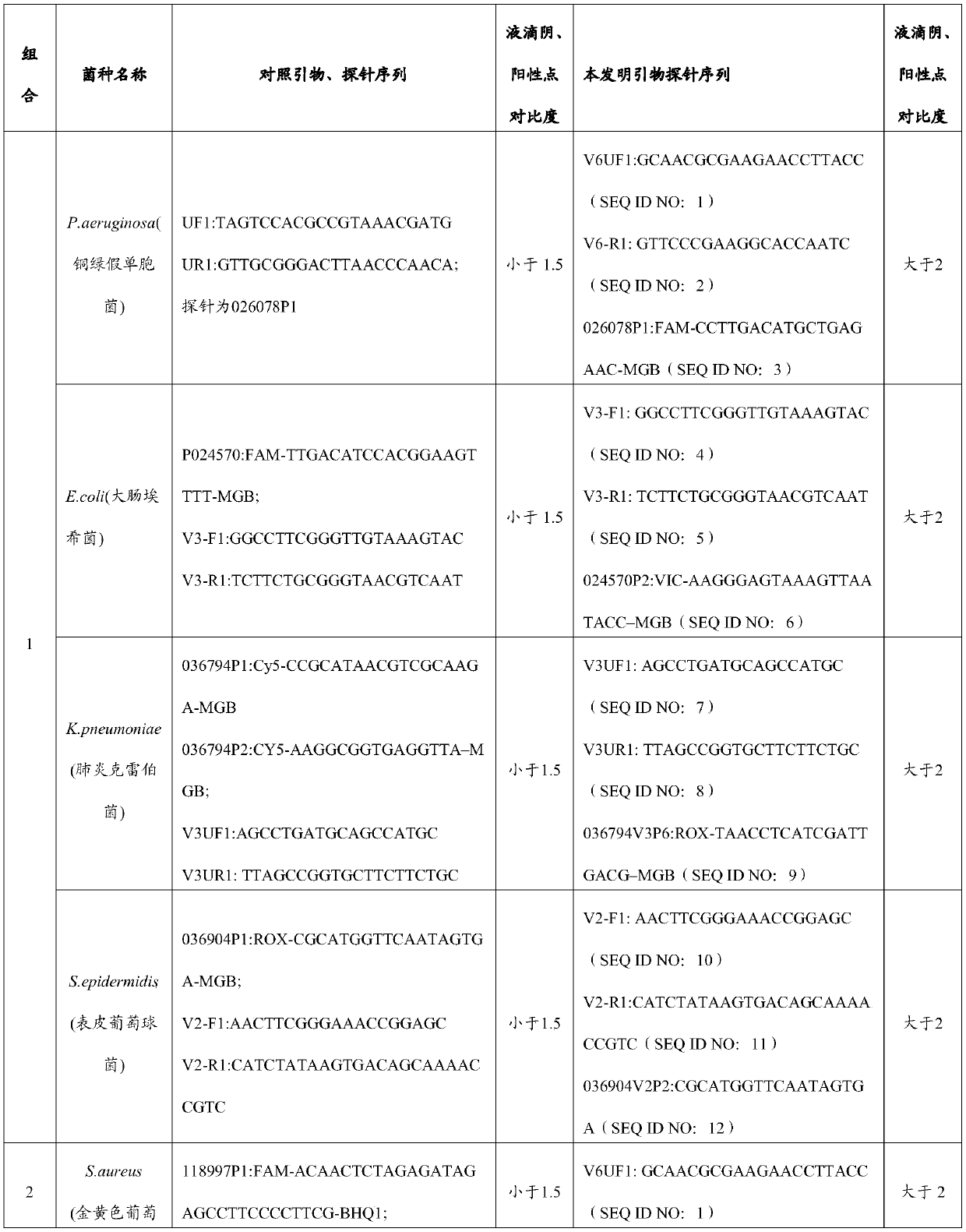
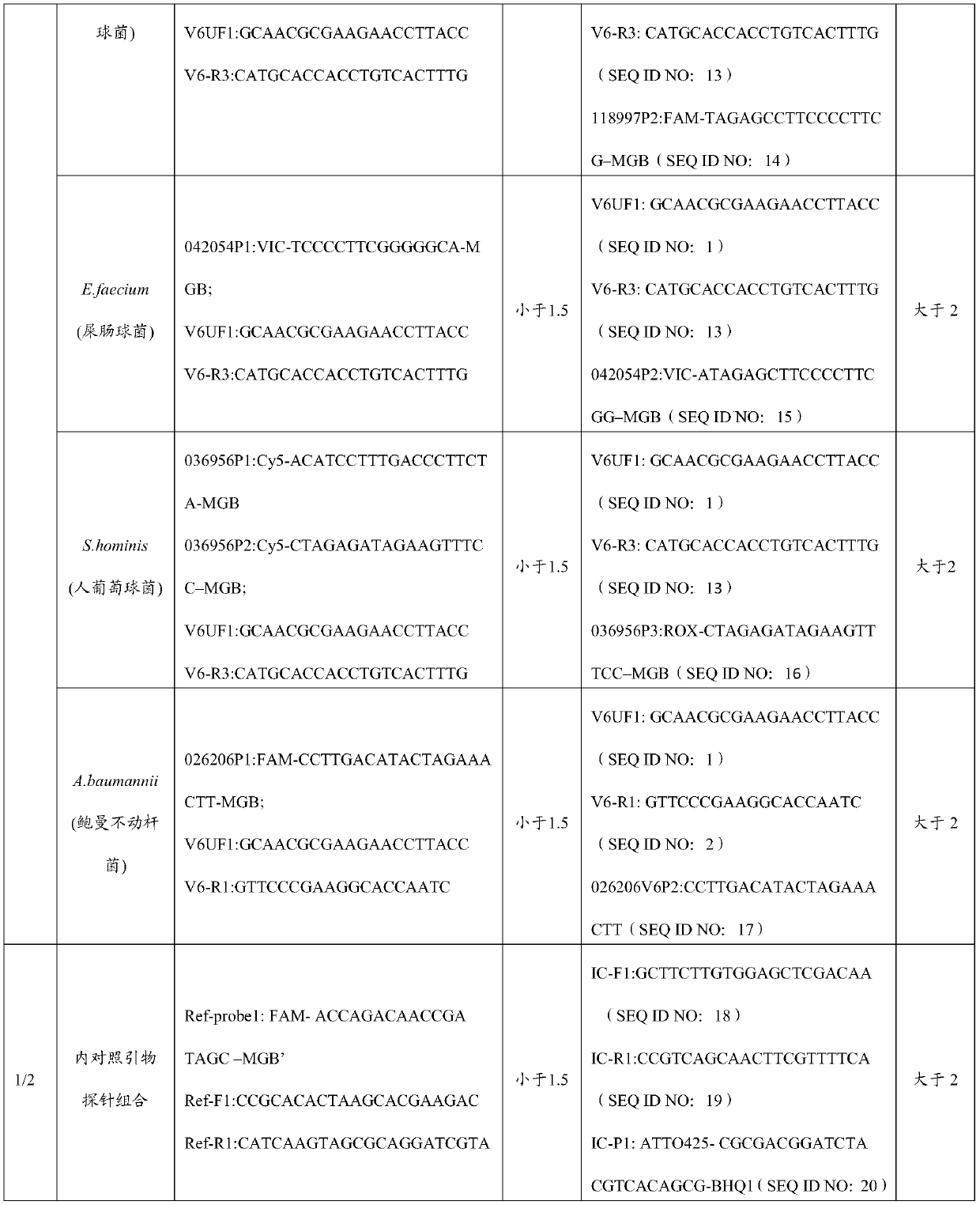
Primer and probe combination and kit for detecting human pathogenic bacteria
PendingCN110564824AShorten identification timeImprove positive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInfected patientTreatment effect
The invention relates to the technical field of medical detection, and in particular, relates to a primer and probe combination and a kit for detecting human pathogenic bacteria. The kit comprises theprimer and probe combination for detecting pseudomonas aeruginosa, escherichia coli, klebsiella pneumoniae, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus aureus, enterococcus faecium, human staphylococcus and acinetobacter baumannii. According to the kit, the primer and probe combination is adopted, multiple digital PCR is combined, the pathogenic bacteria types and the target nucleic acid copy number in the detection range can be rapidly and accurately identified, the detection method has high sensitivity, and positive detection of low-copy nucleic acid fragments of pathogenic bacteria is guaranteed; meanwhile, the variety of the pathogenic bacteria or the change of the copy number of the target nucleic acid fragment in the body of a pathogenic bacteria infected patient can be dynamically monitored, the treatment effect is assisted and evaluated in time, and reference is provided for optimization of a doctor clinical scheme.
Owner:PILOT GENE TECH HANGZHOU CO LTD
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection primer pair of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, detection method and detection kit
ActiveCN102134601AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific detectionElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) detection primer pair of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a detection method and a detection kit. Aiming at the ecfX gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the invention designs and screens a set of specific detection primer pair, a detection kit containing the detection primer pair and an LAMP detection method utilizing the detection kit. The detection method is adopted to detect a sample to be detected, specially for drinking water to confirm whether the sample contains the special gene segment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and further confirm whether the sample contains Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The detection kit and detection method disclosed by the invention have high sensitivity and specificity and short detection time, and the wholeprocess from sample processing to result reporting is only 24h; and the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifier and electrophoresis meter are not adopted, the operation process is simple and the method and kit are especially suitable for the self-checking of grassroots detection institutions and drinking water processing enterprises.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY +1
Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage lyase and application
ActiveCN107058265ABroad antibacterial spectrumImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaFood preservationBacteroidesBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to pseudomonas aeruginosa phage lyase and application. The artificial pseudomonas aeruginosa phage lyase has nucleic acid sequences 1 and 2 and amino acid sequences 3 and 4; a gene engineering technology is utilized and polycation nonapeptide and hydrophobic pentapeptide are added at an N end of previous Gram-negative bacterium phage lyase and are developed to obtain artificial lyase capable of efficiently killing pseudomonas aeruginosa, pseudomonas putida, bacillus licheniformis and bacillus subtilis. The lyase and a derivative thereof can be independently used or can be coordinated with a surfactant and can be used for specifically deactivating the pseudomonas aeruginosa and bacillus; the lyase can be used for removing and inhibiting a biological coating film formed by microorganisms, and an enzyme preparation source which is safe and has no toxic or side effect is provided for preventing and controlling infection of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, the bacillus licheniformis and the bacillus subtilis at present and controlling biological coating film pollution caused by bacteria including the bacillus licheniformis and the bacillus subtilis and the like in foods.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
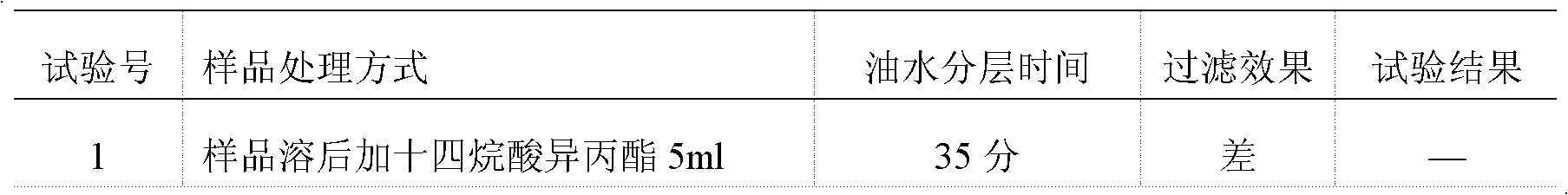
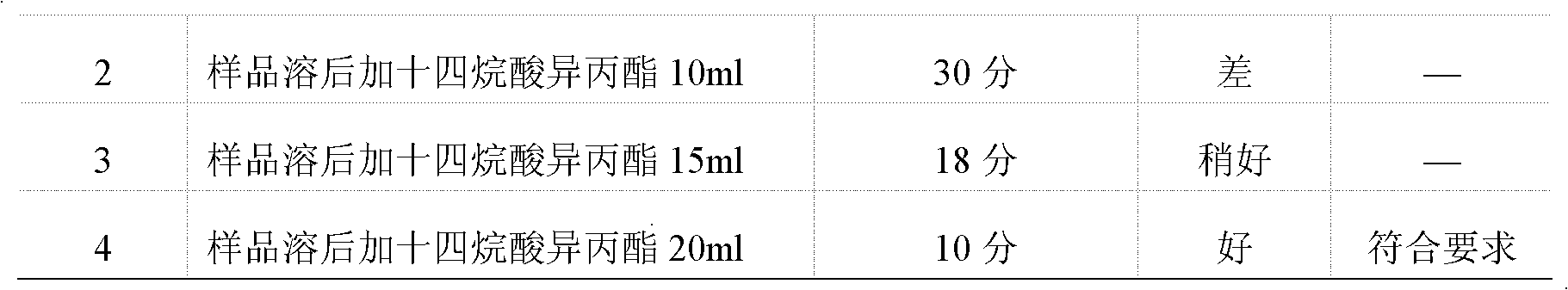
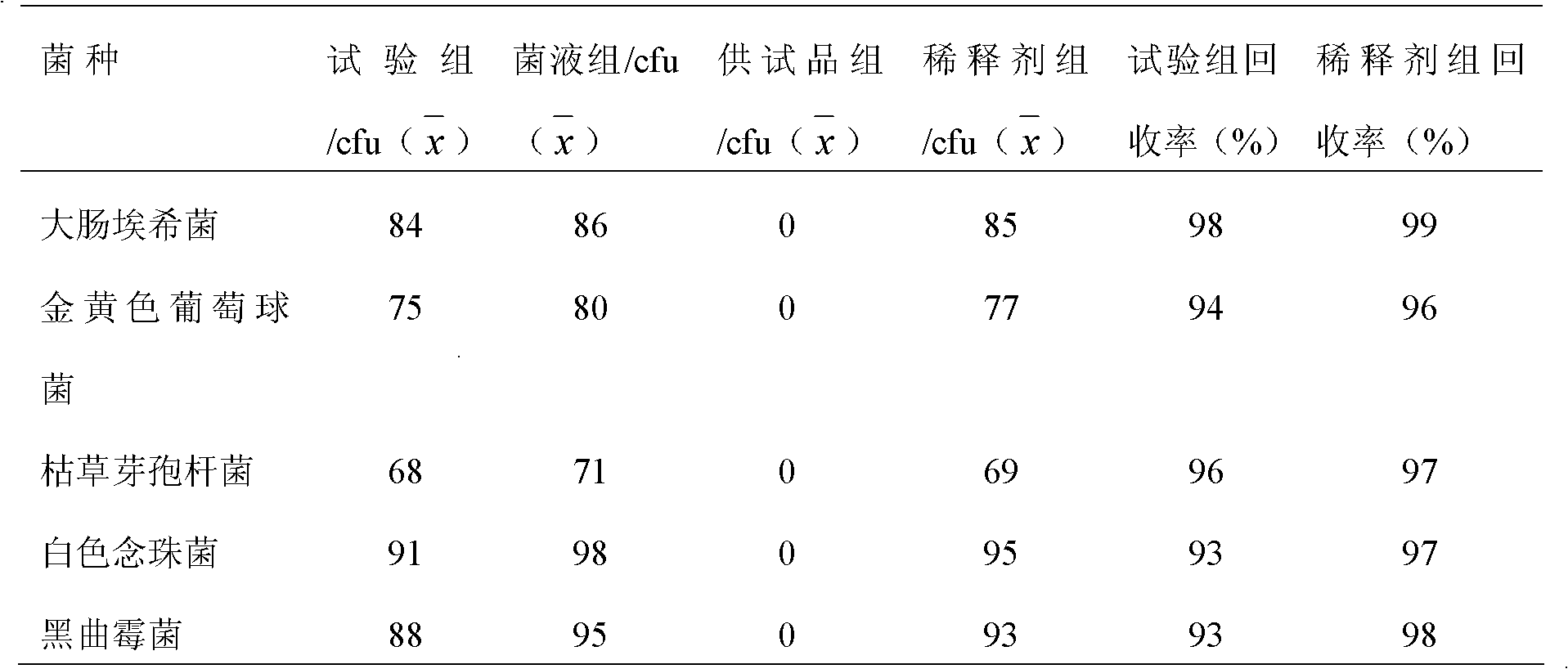
Microbial limit detection method of miconazole nitrate suppository
InactiveCN102586393AGood antibacterial effectPromote stratificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFiltrationStaphyloccocus aureus
The invention discloses a microbial limit detection method of miconazole nitrate suppository. The method comprises dissolving sample with sodium chloride-peptone buffer solution (pH 7.0) containing 10 vol% polysorbate 80 (Tween 80), adding 20ml of isopropyl myristate, and washing with aqueous solution containing 0.1 vol% polysorbate 80 and 0.1 wt% peptone. Membrane filtration method is adopted for bacteria, mildew, yeast, Staphyloccocus aureus and Monilia albican, with recovery rate all above 70%. Culture medium dilution method is adopted to detect Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. The addition of isopropyl myristate can accelerate fat / water layer separation, shorten experiment time, stabilize flow rate, reduce test cost, and achieve strong operability.
Owner:SHAANXI INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
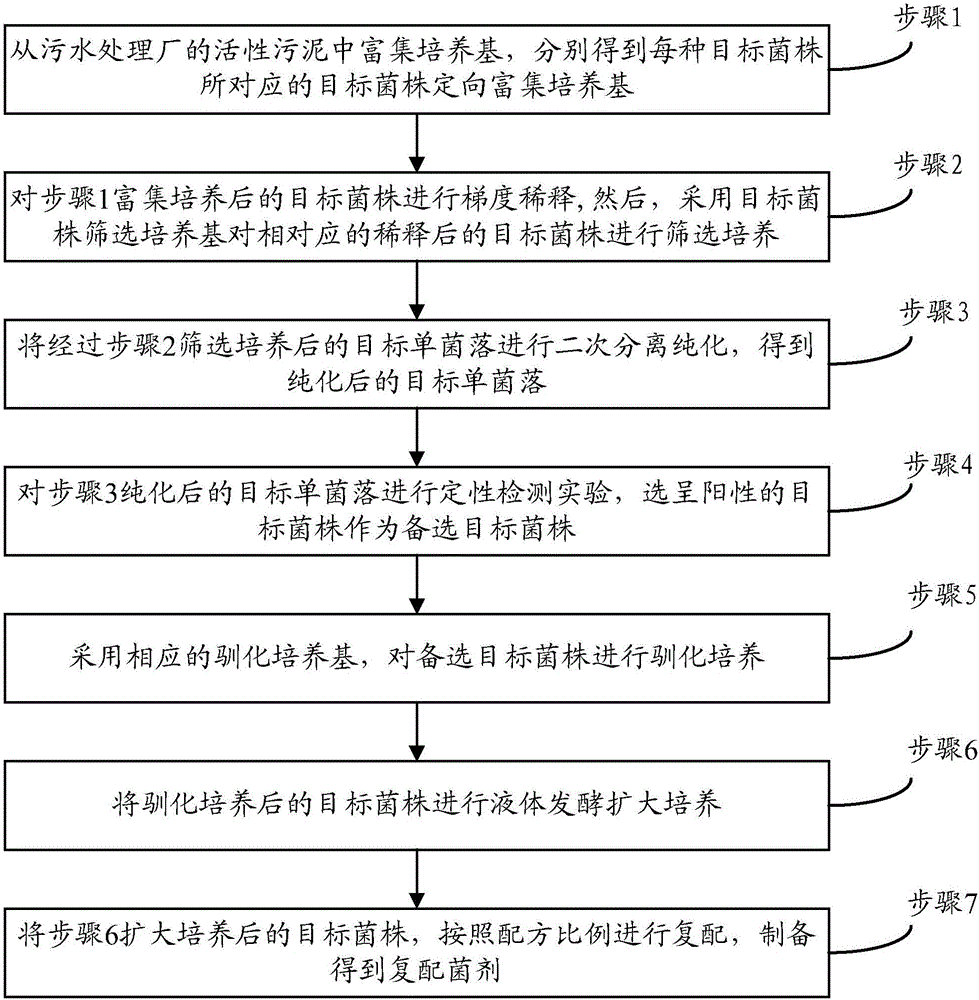
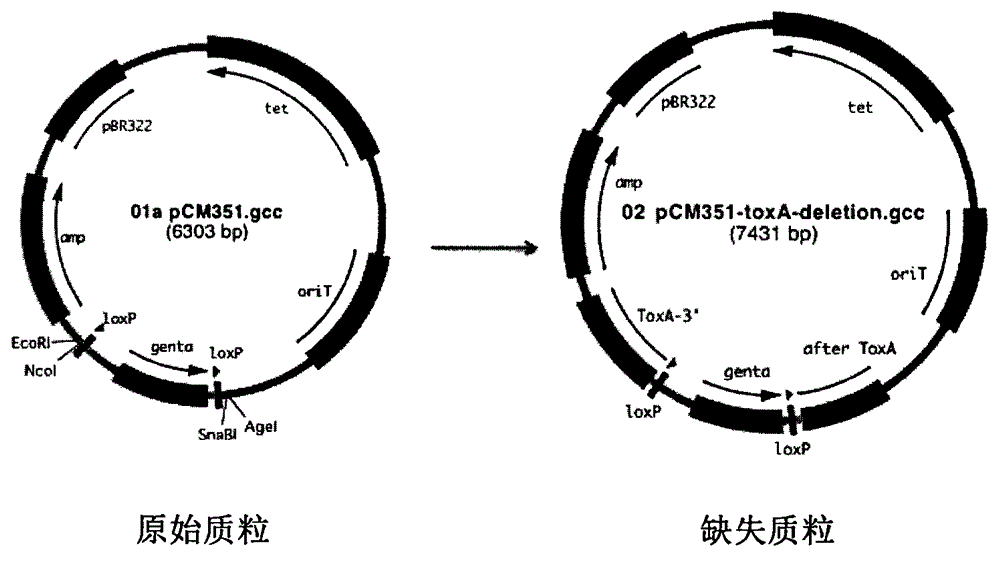
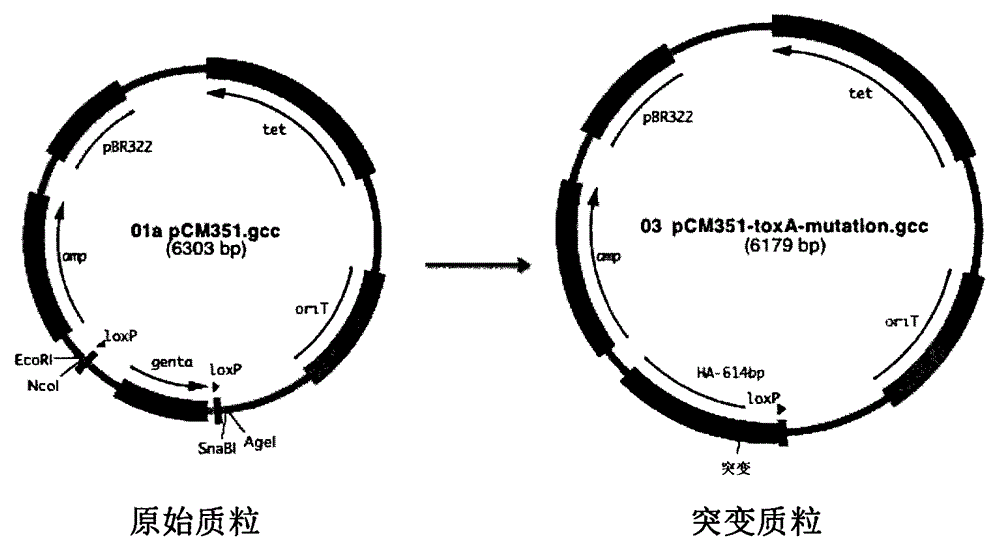
Construction method and application of pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant strain
The invention relates to a pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant strain genetic engineering mutant strain, in particular to a pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant strain exotoxin A attenuated strain, and further relates to a preparation method of the mutant strain and application of the mutant strain or the attenuated strain in preparing vaccines or adjuvant therapy drugs.
Owner:BENHEALTH BIOPHARMACEUTIC SHENZHEN CO LTD
Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage endolysins, and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108410840AGood water solubilityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliProtein
The invention discloses pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage endolysins, and a coding gene and application thereof. The invention provides a protein which is as shown in (a) or (b) as below: (a) the protein which is as shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table and consists of an amino acid sequence; (b) the protein which is obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence which is as shown in the sequence 1 in the sequence table, has a function of cracking gram-negative bacteria and is deviated from the sequence 1 in the sequencetable. The protein provided by the invention can crack a plurality of gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia cepacia and Salmonella typhimurium. The protein and a surfactant EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) act synergistically to achieve a stronger inhibiting effect on the gram-negative bacteria. A foundation is laid for researching and developing a new antibacterial preparation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
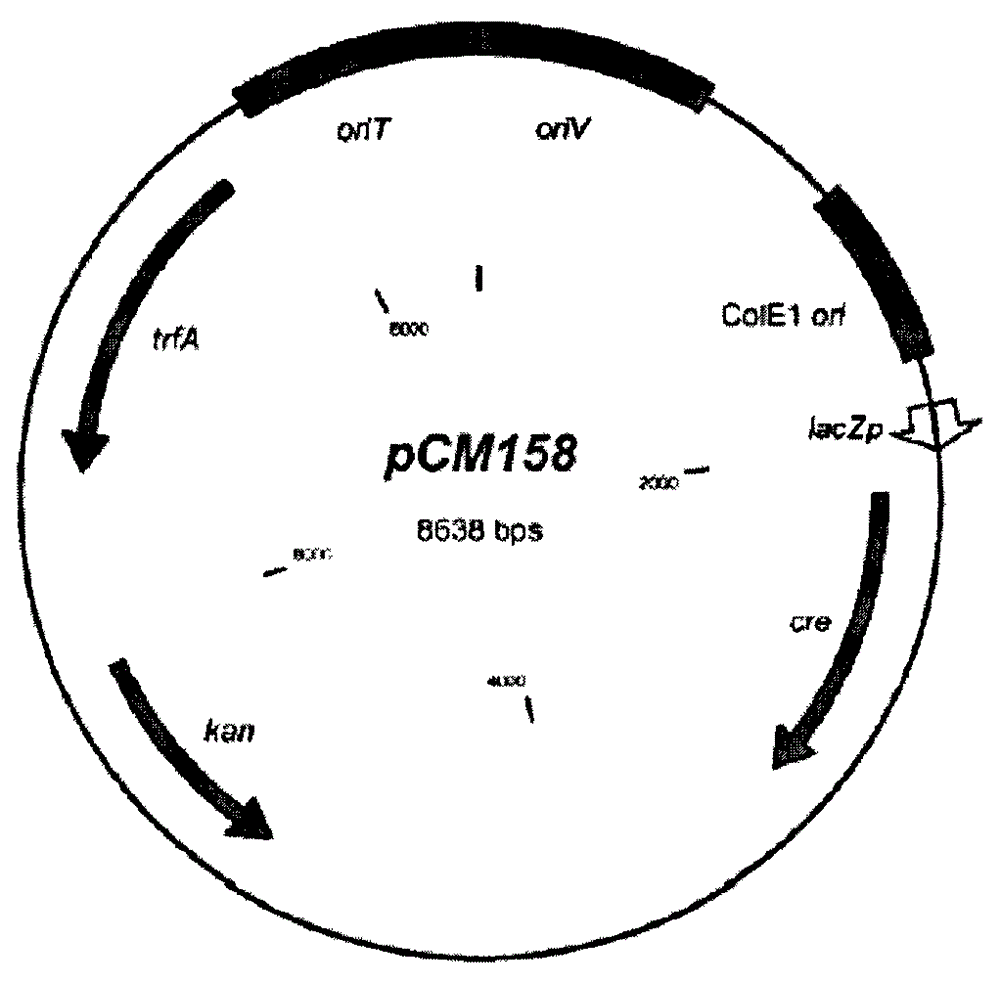
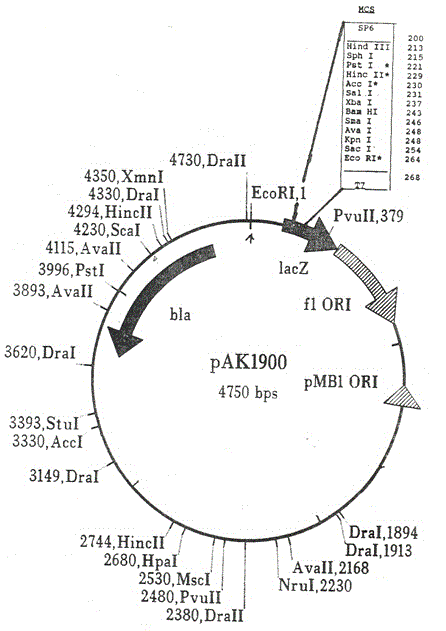
Genetic recombinant method of pseudomonas aeruginosa for high-yield producing rhamnolipid
ActiveCN104830889AReduce manufacturing costHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
A genetic recombinant method of pseudomonas aeruginosa for high-yield producing rhamnolipid includes following steps: (1) designing a primer for amplifying RhlAB gene according to the RhlAB gene sequence of rhamnolipid synthetase; (2) with chromosome of wild pseudomonas aeruginosa producing rhamnolipid as a template, performing PCR amplification to the RhlAB gene and performing rubber cutting purification to target genes through a purification kit; (3) performing enzyme digestion to the purified RhlAB gene to introduce the purified RhlAB gene into an escherichia coli-pseudomonas aeruginosa shuttle expression vector pAK1900 to obtain new plasmid pAK1900-AB; (4) introducing the constructed shuttle expression vector pAK1900-AB into a recipient bacterium pseudomonas aeruginosa competent cell through a heat-shock conversion method, coating a carboxyl-benzyl resistance plate with the competent cell and performing PCR verification to the constructed engineering bacteria; and (5) performing fermentation in a shake flask and measuring the yield of the rhamnolipid in a sulfuric acid-anthranone manner. The method can greatly reduce the production cost of the rhamnolipid, provides basis for industrial application of the rhamnolipid and can promote high-yield production of the rhamnolipid.
Owner:XIAN HAIGE BIOTECH RES INST CO LTD +1
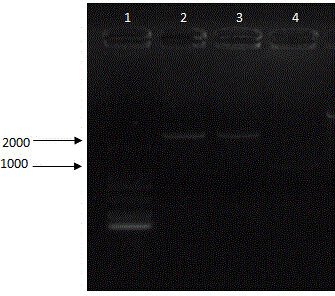
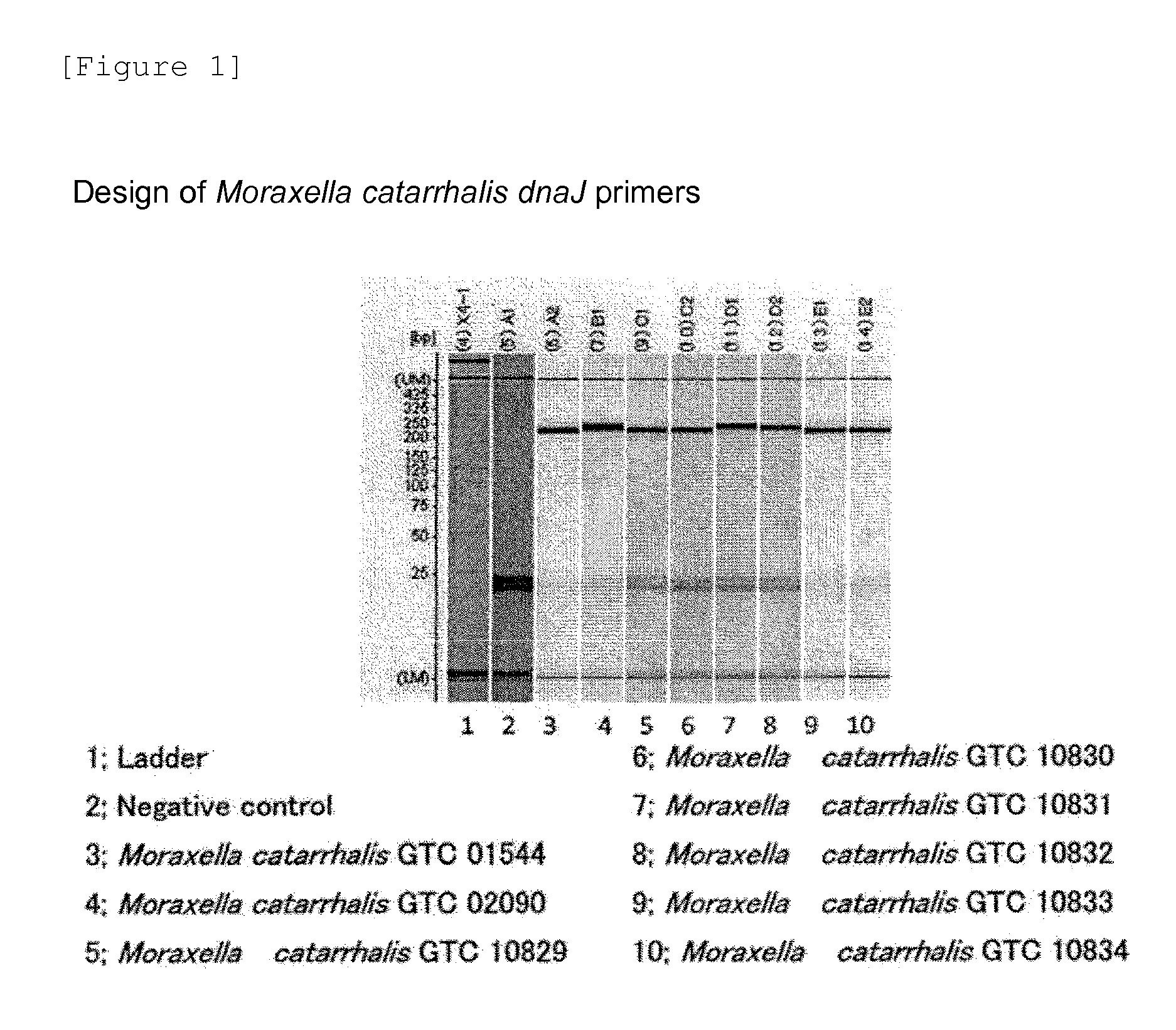
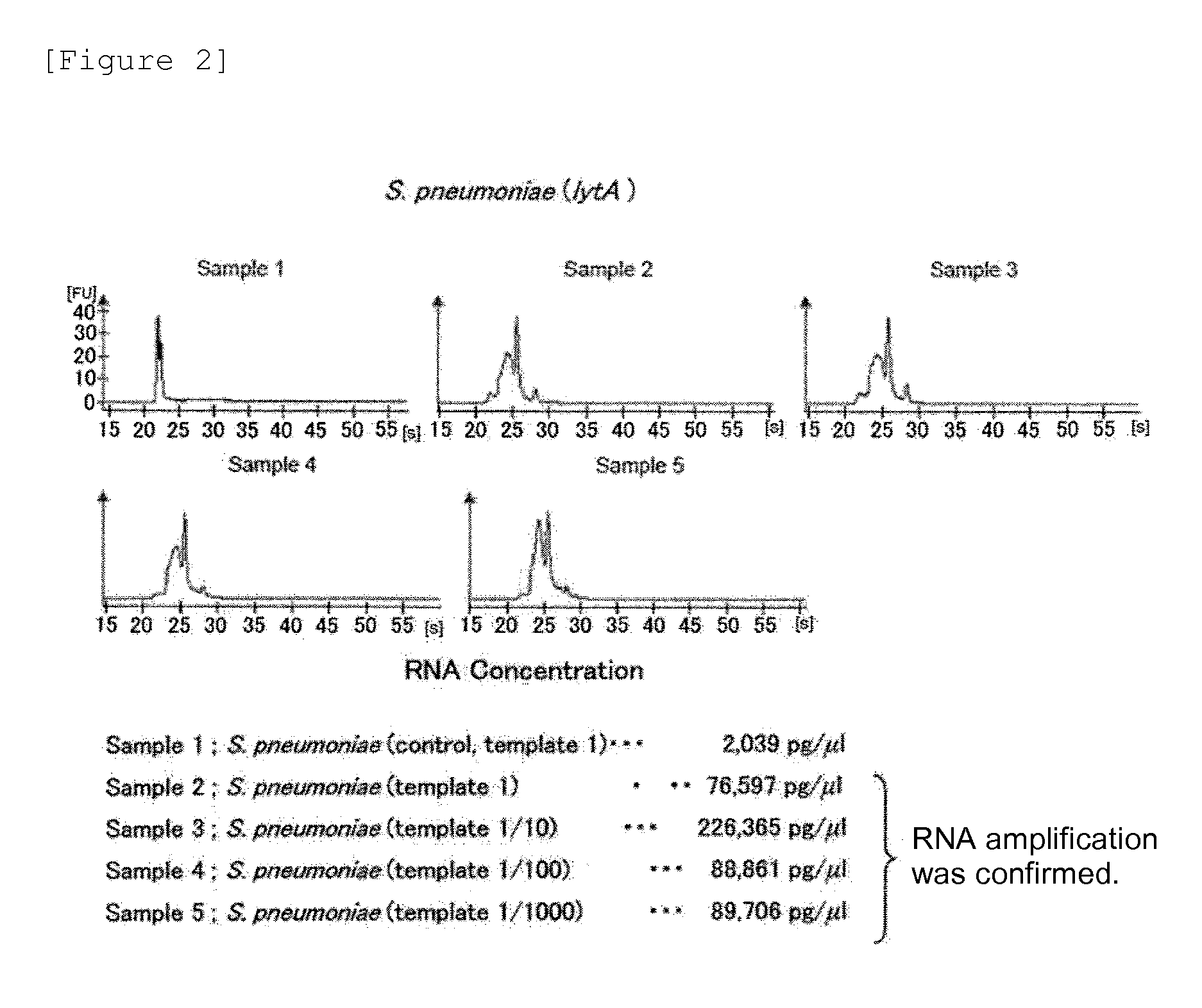
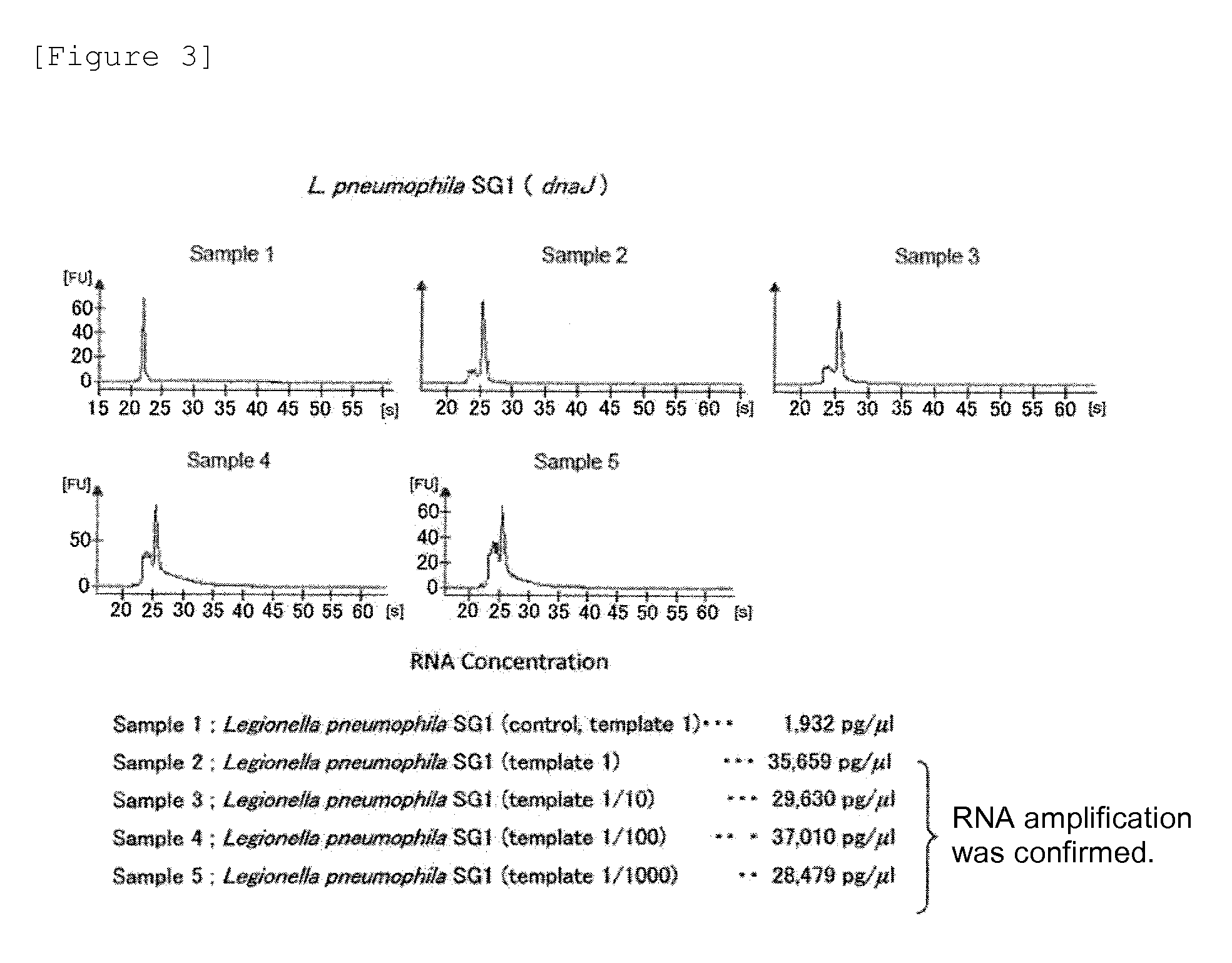
Method for detecting pneumonia causative bacteria using nucleic acid chromatography
InactiveUS20130023443A1Quick and accurate identificationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
Provided are a method and a kit for accurately and rapidly detecting ten types of targeting pneumonia bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Moraxella catarrhalis, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and Staphylococcus aureus. A set of primer pairs directed to their respective target regions contained in the DnaJ gene, etc., of the ten types of pneumonia causative bacteria is designed for the ten bacterial strains and used to amplify gene products. A set of bacterial strain-specific probe pairs is further designed for the ten bacterial strains such that the probe pairs hybridize with the amplification products via sequences in the respective target regions differing from the sequences hybridized by the set of primer pairs. A first probe-bound labeled high molecular carrier in which plural types of first probes for the pneumonia bacteria are bound to a labeled high molecular carrier and a solid-phase second probe-carrying developing support are used as the set of probe pairs to perform nucleic acid chromatography.
Owner:YAMAGUCHI TECH LICENSING ORG
A strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its isolation method and application
InactiveCN102296037AIncreased degradation rateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationHuminIn situ bioremediation
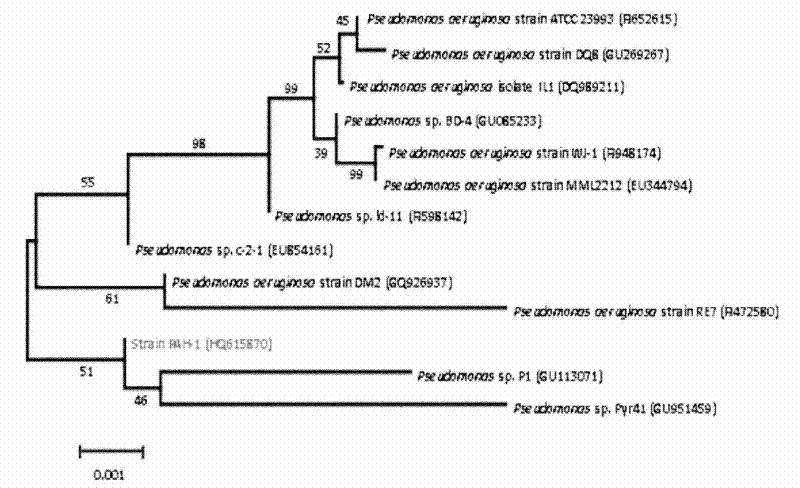
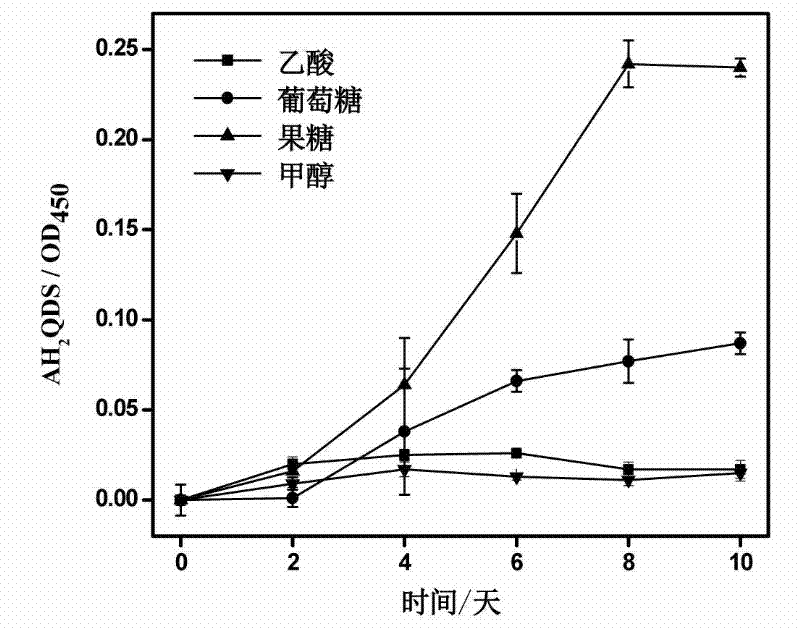
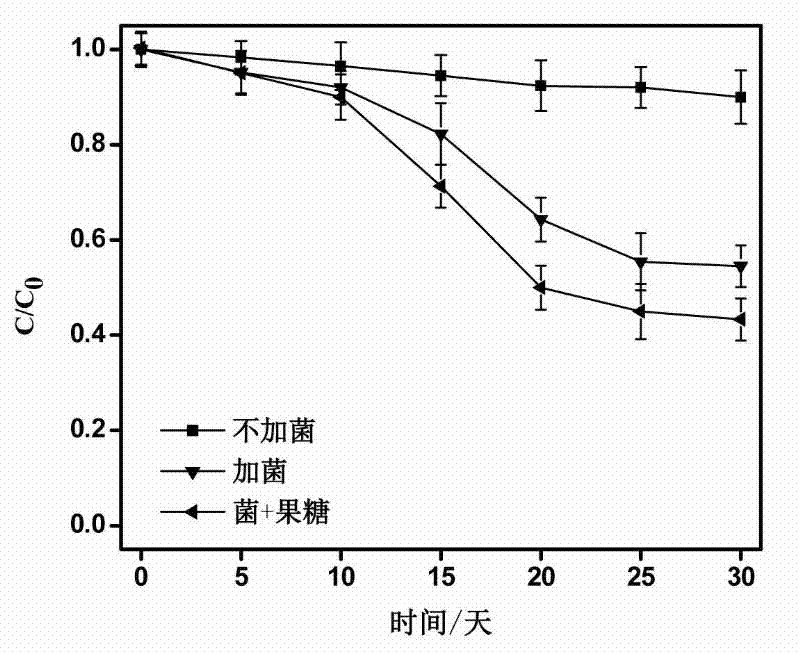
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAH-1 capable of degrading PAHs, and its preservation number is CGMCC No.4773. Pseudomonas aeruginosa of the present invention can use humus as an electron acceptor under anaerobic conditions to oxidize and degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and can significantly improve the degradation rate of phenanthrene under glucose or fructose and phenanthrene co-metabolism conditions, and can be widely used in mild In situ bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
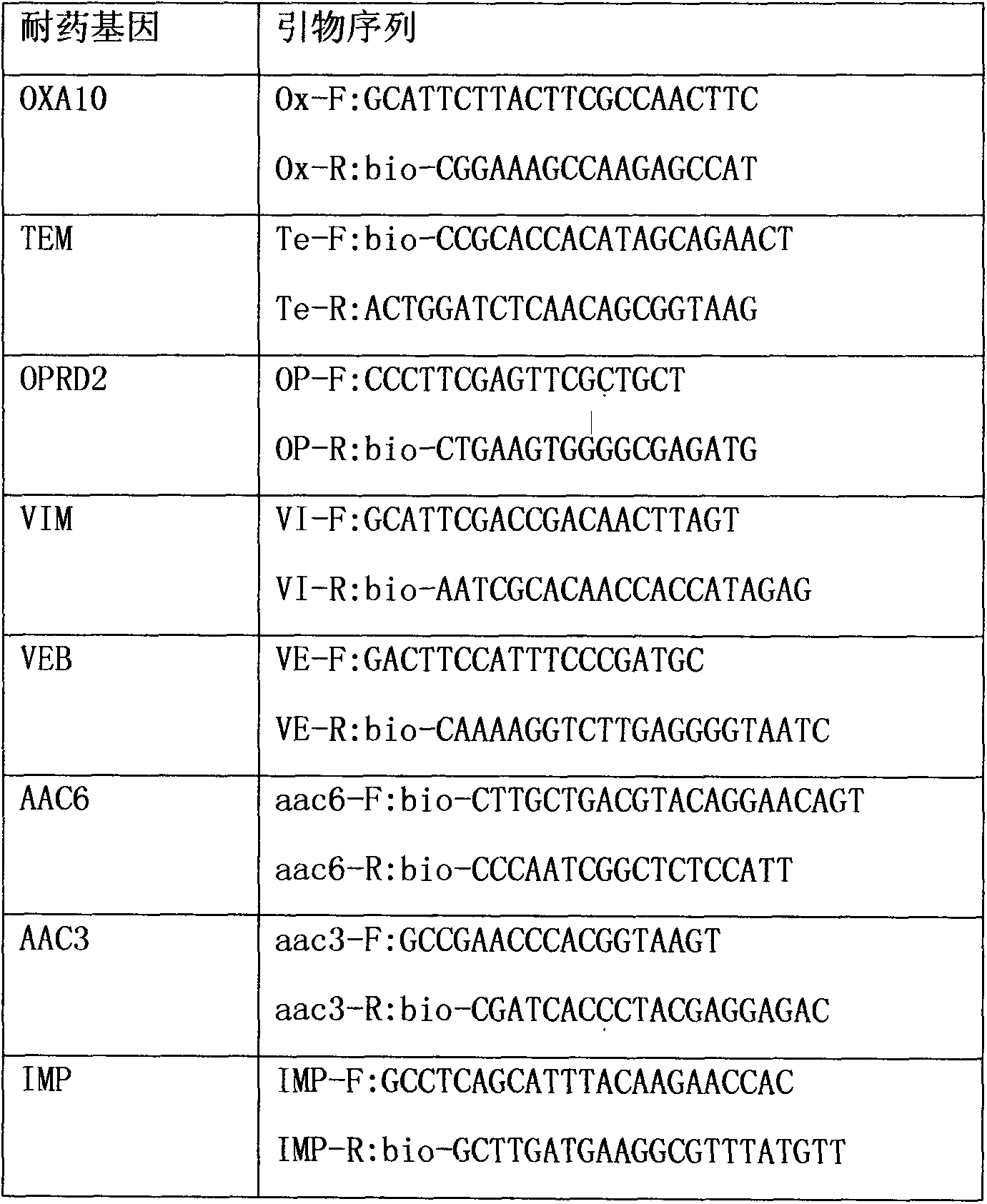
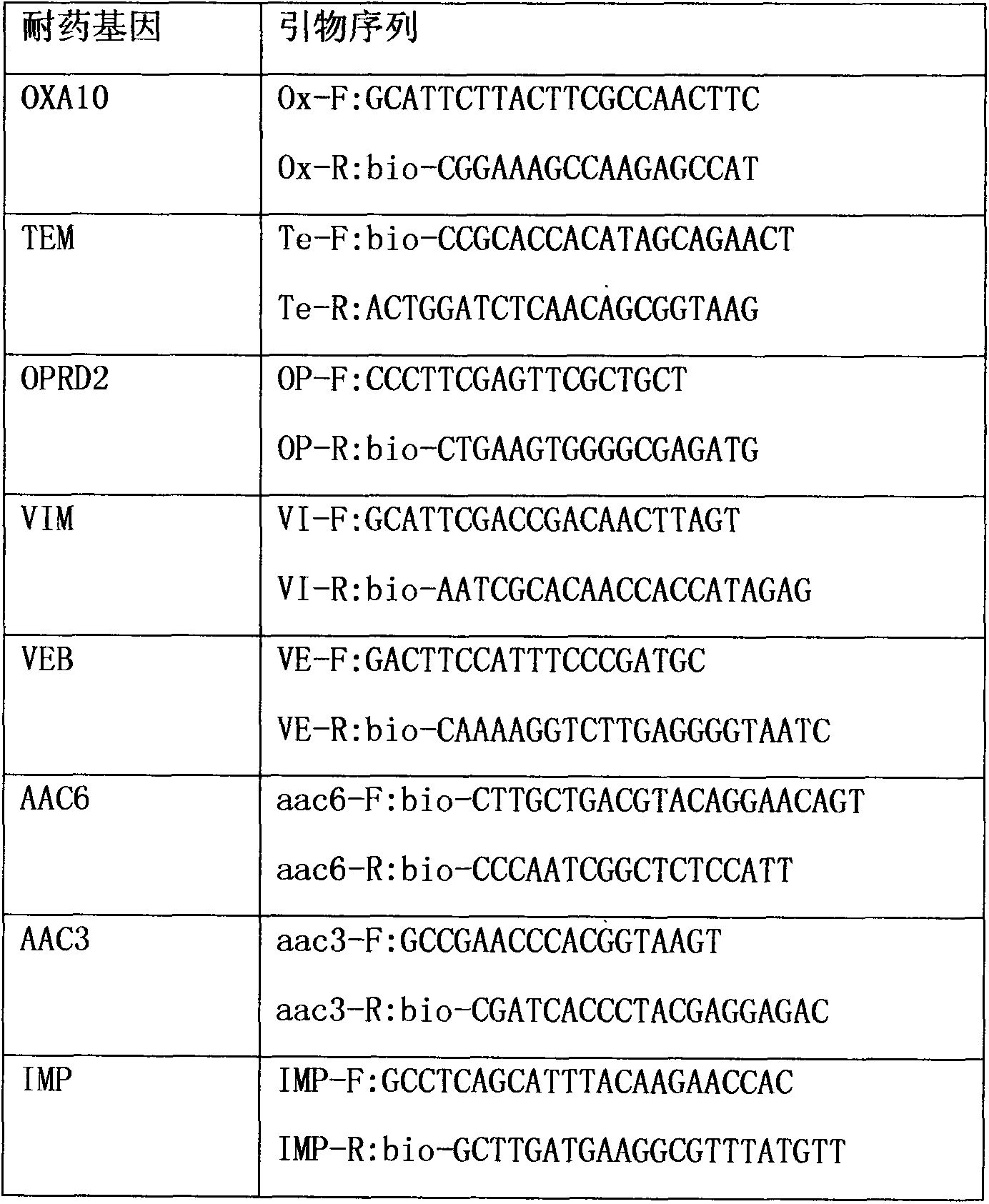
Liquid-chip detection kit for multiple drug-resistant genes of pseudomonas aeruginosa
InactiveCN104313166AStrong specificityHigh detection throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexMicrosphere
The invention discloses a liquid-chip detection kit for multiple drug-resistant genes of pseudomonas aeruginosa. The eight multiple drug-resistant genes of the pseudomonas aeruginosa are OPRD2, TEM, OXA10, AAC3, AAC6, VIM, VEB and IMP. The kit comprises a nucleic-acid amplification component and a hybridization component, wherein the nucleic-acid amplification component comprises the following specific components: premixed liquid, primer mixed liquid, polymerase, a positive quality control product and a negative quality control product; and the hybridization component comprises the following specific components: microsphere hybridization liquid, quality control microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin. The liquid-chip detection kit disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the multiple drug-resistant genes of the pseudomonas aeruginosa can be detected simultaneously, and the drug resistance of the pseudomonas aeruginosa can be rapidly and accurately detected, so that the need of clinical treatment is met; and simultaneously, the kit has the beneficial effects of high specificity, combined screening, high detection flux and more convenience in promotion and application.
Owner:中国人民解放军济南军区第四〇一医院
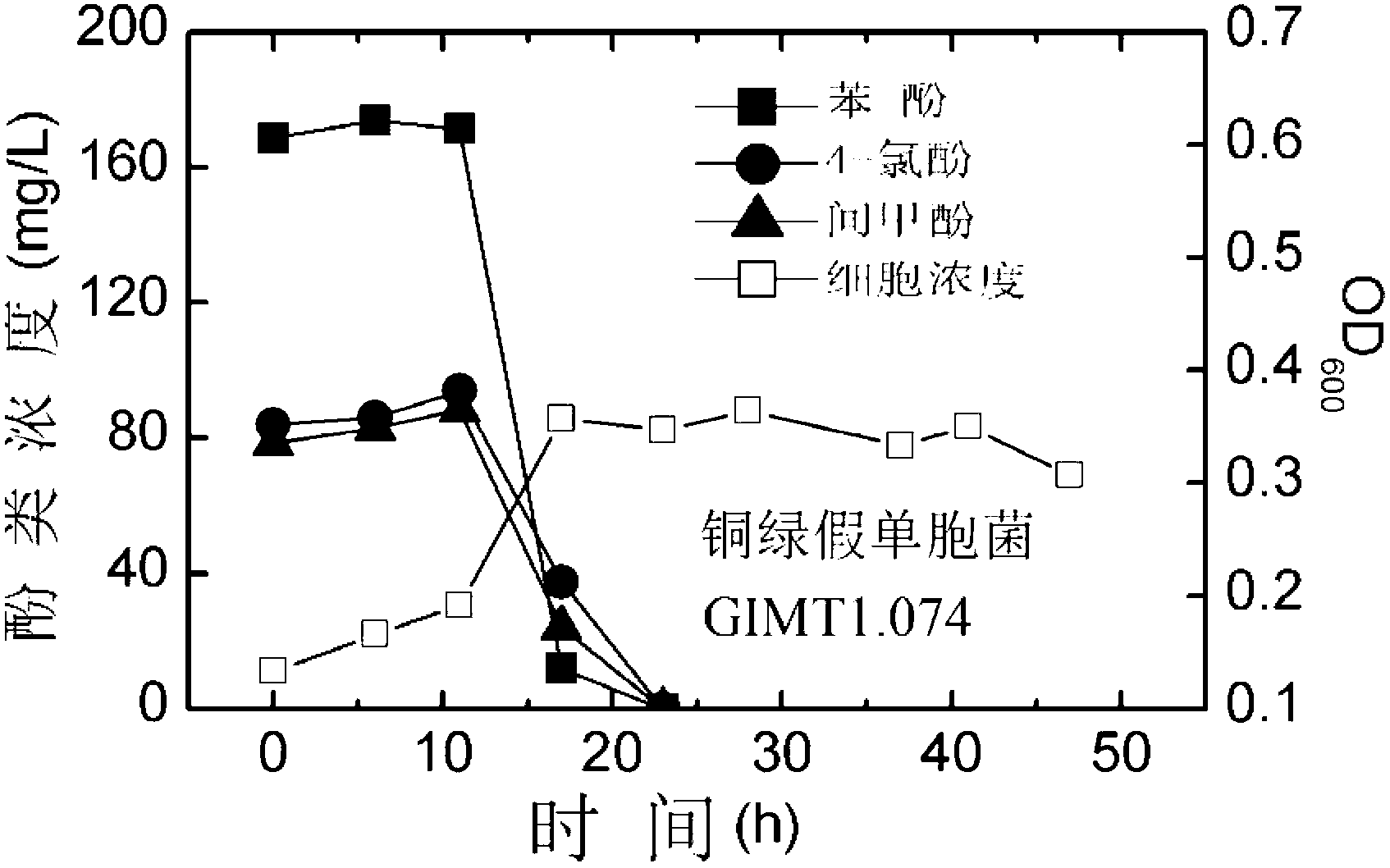
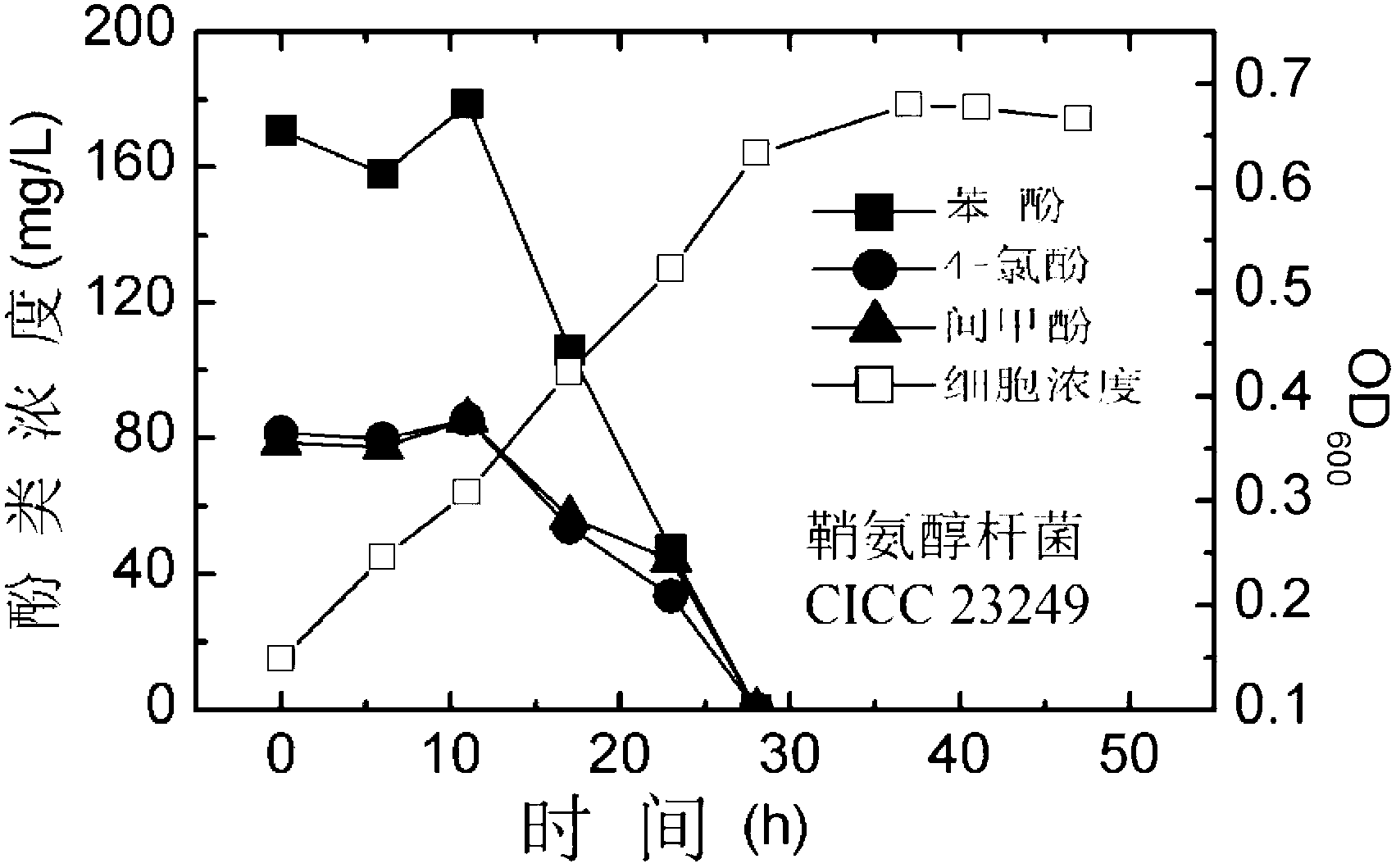
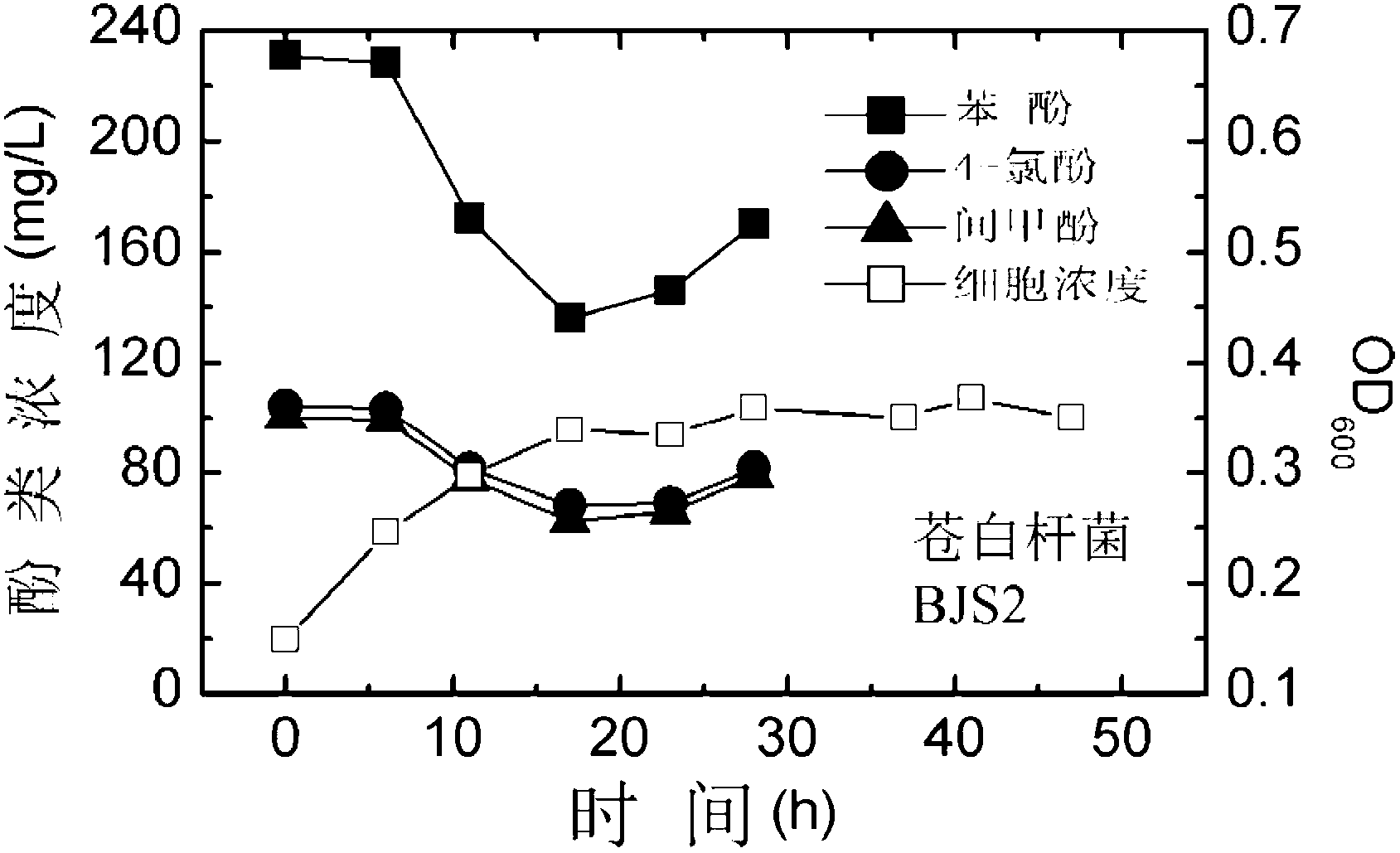
Synergistic effect of multiple bacterial strains on degradation of polyphenol pollutants and research method thereof
InactiveCN103060419APromote degradationImprove degradation efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStudy methodsBacterial strain
The invention relates to a synergistic effect of multiple bacterial strains on degradation of polyphenol pollutants and a research method thereof. According to the invention, a bacterial suspension is prepared from one or a mixture of two or three selected from the group consisting of pseudomonas aeruginosa GIMT1.074, sphingobacterium multivorum CICC 23249 and ochrobactrum sp. BJS2; then the bacterial suspension is inoculated to inorganic a salt medium containing phenol, meta-cresol and 4-chlorophenol with different concentrations for culture; parts of a culture solution are taken out at different time intervals to measure concentrations of phenol, meta-cresol and 4-chlorophenol in the culture solution so as to determine degradation rates at different times, and cell concentrations in the culture solution are measured to investigate growth conditions of different cells. According to research on synergistic degradation effects of the three phenol degrading bacteria, a mixed bacterial strain has superior capability in degradation of mixed phenolic pollutants and has much better degradation efficiency and effects compared to every individual bacterial strain; moreover, biomass of the mixed bacterial strain is increased to two times of the biomass of an original optimal bacterial strain, i.e., the pseudomonas aeruginosa GIMT1.074.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
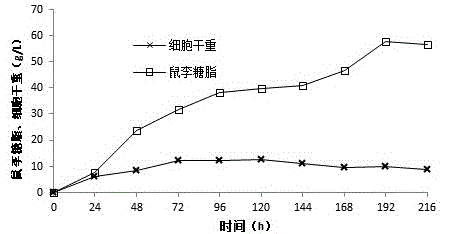
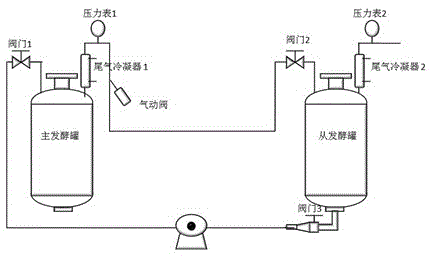
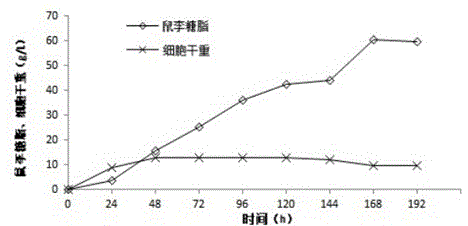
Pseudomonas aeruginosa for producing rhamnolipid biosurfactant with palm oil and application thereof
ActiveCN105420137AImprove fermentation yieldImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRhamnolipid
Rhamnolipid is an anionic surfactant which is free of toxicity and pollution, biodegradable, high in selectivity and specificity and excellent in surface activity and has unique application prospects in multiple industrial fields such as medicine, food, cosmetics and environment protection. The invention provides Pseudomonas aeruginosa TIB-R02 CGMCC No.9376 with the high rhamnolipid yield and the high conversion rate through screening. Related fermentation equipment is transformed according to the fermentation characteristic of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and a series connection fermentation experiment of 300L fermentation tanks is realized. According to the production state of the producing strain and the characteristic of the equipment, the production process of producing rhamnolipid in a fermented mode through Pseudomonas aeruginosa TIB-R02 CGMCC No.9376 is developed, and while the rhamnolipid yield is high, the liquid leakage problem caused by surface activity brought by a great deal of rhamnolipid can be controlled. By using the equipment and the fermentation process, when palm oil with the concentration of 75 g / L serves as a carbon source, the rhamnolipid yield reaches 60.6 g / l, and the conversion rate reaches 80% or more. Therefore, the strain and the production process have good industrial application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com