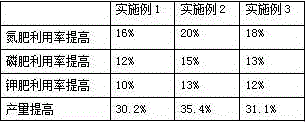
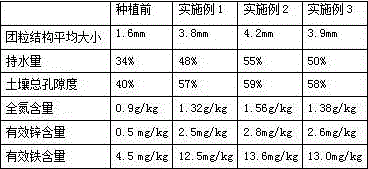
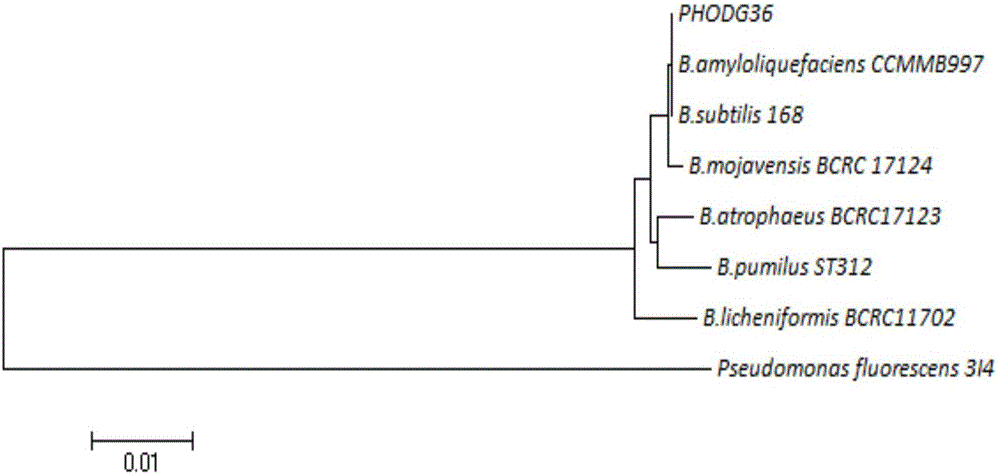
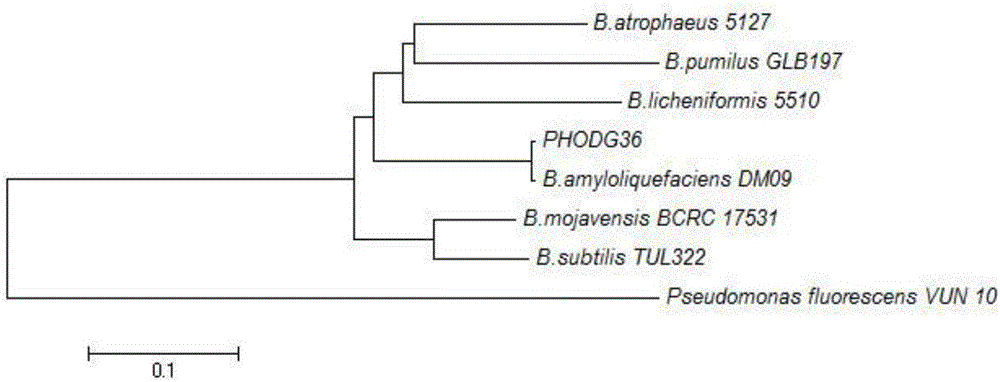
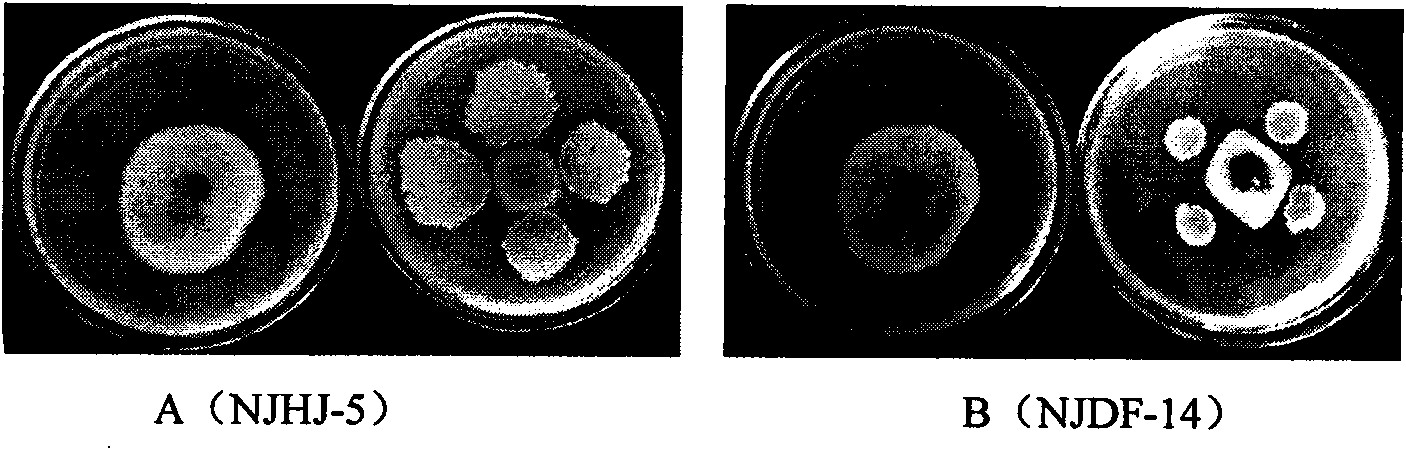Patents
Literature
576 results about "Verticillium wilt" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Verticillium wilt is a wilt disease affecting over 350 species of eudicot plants. It is caused by six species of Verticillium fungi: V. dahliae, V. albo-atrum, V. longisporum, V. nubilum, V. theobromae and V. tricorpus. (See, for example, Barbara, D.J. & Clewes, E. (2003). "Plant pathogenic Verticillium species: how many of them are there?" Molecular Plant Pathology 4(4).297-305. Blackwell Publishing.) Many economically important plants are susceptible including cotton, tomatoes, potatoes, oilseed rape, eggplants, peppers and ornamentals, as well as others in natural vegetation communities. Many eudicot species and cultivars are resistant to the disease and all monocots, gymnosperms and ferns are immune.
Composite bio-formulation for preventing crop diseases and application thereof
The invention discloses a composite bio-formulation for preventing crop diseases, comprising the following raw materials: trichoderma pseudokoningii fermenting liquid, bacillus subtilis fermenting liquid, water-soluble chitosan, sodium glutamate residue liquid and potassium humate, wherein the trichoderma pseudokoningii and the bacillus subtilis are high-effect strains which are obtained after being screened and processed, later the fermenting liquid of the trichoderma pseudokoningii and the bacillus subtilis is obtained through a submerged fermentation technique, and the composite bio-formulation for preventing crop diseases is obtained through combining. The composite bio-formulation for preventing crop diseases in the invention has obvious effects for preventing blight, verticillium, gray mold, phytoph-thora capsici leonian, downy mildew, powdery mildew, gray mold, fulvia fulva and so on, and can be especially used for preventing the blight and the verticillium which have large danger in agriculture. The invention is suitable for preventing the diseases and improving yields of various vegetables, melons, fruits and crops, such as tomatoes, chili peppers, eggplants, cucumbers, watermelons, apples, Chinese chives, cottons and so on.
Owner:山东靠山供应链管理有限公司
Bacillusamyloliquefaciens subsp Lh-1 and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of microbial control, in particular to bacillusamyloliquefaciens subsp Lh-1 and application thereof. With a preservation number of CGMCC No.8548, the bacillusamyloliquefaciens subsp Lh-1 is applied in control of Verticillium dahliae, erwinia carotovora, ralstonia solanacearum, valsa leucostoma, Valsa Mali Miyabe et Yamada, Phytophthora capsici and phytophthora infestans. According to the invention, the bacillusamyloliquefaciens subsp Lh-1 and pesticide and chitosan oligosaccharide with dual effects of fertilizer and pesticide are combined into an Lh-1 microecological agent, the viable count is small, the dosage is small, the production process is simple, the cost is low, and the Lh-1 microecological agent has the dual functions of disease prevention and growth promotion. Nursery test proves that reduce the disease incidence of crop is reduced, especially for control of Verticillium dahliae, the disease incidence drops to 6%, and the control effect is significant. In addition, the Lh-1 microecological agent is a biological strain preparation, is completely free of a series of problems caused by use of chemical pesticides, thus being conducive to pollution-free production of crops, and farmers can have no need for pesticide or reduce the dosage of chemical pesticide, thus greatly saving the expenditure.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE
Bacillus subtilis A16, preparation method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN101698829ASimple cultivation conditionsEasy to storeBiocidePlant growth regulatorsOysterColletotrichum musae
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis A16, which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) with CCTCC NO. 209105. The bacterial colony of the Bacillus subtilis A16 is oyster white on a beef extract peptone culture medium, has irregular shape and no luster, is not wet, has irregular edge, has diameter of 0.5-1cm, and has microfold surface, straight rod-shaped thallus and elliptic spore. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the bacillus subtilis A16. The bacillus subtilis A16 has broad bacteriostasis, can suppress exserohilum turcicum and helminthosporium maydis, has higher antagonism for exserohilum turcicum bacteria, helminthosporium maydis bacteria, maize curvularia leaf spot fungus, verticillium dahliae kleb, wheat scab pathogen, colletotrichum musae and banana vascular wilt bacteria, and has high prevention cure efficiency, and good safety and development application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bacillus subtilis 203 for highly effective preventing and curing banana wilt and application thereof
InactiveCN101186887AEnhanced inhibitory effectVarious modes of actionBiocideBacteriaFusarium oxysporumColletotrichum musae
The invention discloses bacillus subtils 203 for high effectively preventing banana wilt, and the preservation number of the bacillus subtils 203 is CCTCCM207094. The invention simultaneously discloses a process for preparation and usage. The bacillus subtils 203 are obtained after being selected by being cultured face to face on a plate and doing pot experiment, which which is capable of effectively preventing the growth of fusarium oxysporum and has wide antimicrobial spectrum. The invention is also capable of performing antagonistic action on various pathogenic fungi, such as cotton-wilt fusarium, verticillium wilt pathogen, fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum, fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici, curvulavia lunata or colletotrichum musae and the like, which is good in environmental security and good in prospect of development and application.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof
ActiveCN101643710AVitiligo wilt effect is remarkableGrow vigorouslyBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPhytotoxicityMicrobiology
The invention discloses a strain of bacillus subtilis and application thereof. The bacillus subtilis is Bs-03 CGMCC No. 3038 and can be used as a biological fertilizer and a biological pesticide whichcan prevent and control various diseases of plants. Experiments indicate that fermentation liquid of the bacillus subtilis Bs-03 CGMCC No. 3038 has significant effect on preventing and controlling verticillium dahliae in cotton, and cotton grows vigorously without causing phytotoxicity because of using the bacillus subtilis Bs-03 CGMCC No. 3038.
Owner:山东泰宝生物科技股份有限公司
Composite microbial inoculant for controlling plant continuous-cropping diseases and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a composite microbial inoculant for controlling plant continuous-cropping diseases, which comprises trichoderma harzianum, bacillus subtilis, and gliocladium roseum, and also comprises phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and potassium-solubilizing bacteria; the accession number of the trichoderma harzianum strain is CGMCC NO. 7861; the accession number of the bacillus subtilis strain is CGMCC NO. 7850; the accession number of the gliocladium roseum strain is CGMCC NO. 9008. The invention also provides a preparation method and an application of the composite microbial inoculant. Through the selection of high-efficient bacterial strains such as disease-preventing trichoderma, bacillus subtilis, gliocladium roseum, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and potassium-solubilizing bacteria, the composite microbial inoculant of the invention promotes the growth of crops, improves the utilization rate of fertilizers, enhances the stress resistance such as disease resistance and the like, improves the quality of crops, and can control diseases such as root rot, verticillium wilt, damping off, botrytis, epidemic diseases, powdery mildew, sclerotinia rot, seedling-stage damping off, and the like.
Owner:中农绿康(北京)生物技术有限公司
Pseudomonas aeruginosa D10, and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN101698828AAntagonisticSimple cultivation conditionsBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicrobiologyVerticillium wilt
The invention discloses a pseudomonas aeruginosa D10 which is preserved in China Typical Culture Preservation Center, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 209104. A colony on a beef paste peptone culture medium appears brown, round, glossy and wet, and has trim edges; the diameter of the colony is 0.2-0.5 cm; and the thallus is in a short bar shape and does not have gemma. The invention also discloses a preparation method and applications of the pseudomonas aeruginosa D10. The pseudomonas aeruginosa D10 of the invention can inhibit corn northern and southern leaf blight, has strong antergic functions on corn northern leaf blight, corn southern leaf blight, corn curvalaria leaf spot, cotton verticillium wilt, wheat fusarium graminearum, banana colletotrichum toilette and banana fusarium wilt, has the advantages of wide bacteriostatic range, high prevention efficiency and favorable environmental safety, and has favorable prospects for development and applications.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Antagonistic bacteria for preventing and eliminating greensickness of continuous cropping cotton and microbial organic fertilizer thereof
ActiveCN101671633ADo not use or reduce dosageConducive to pollution-free productionBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyContinuous cropping
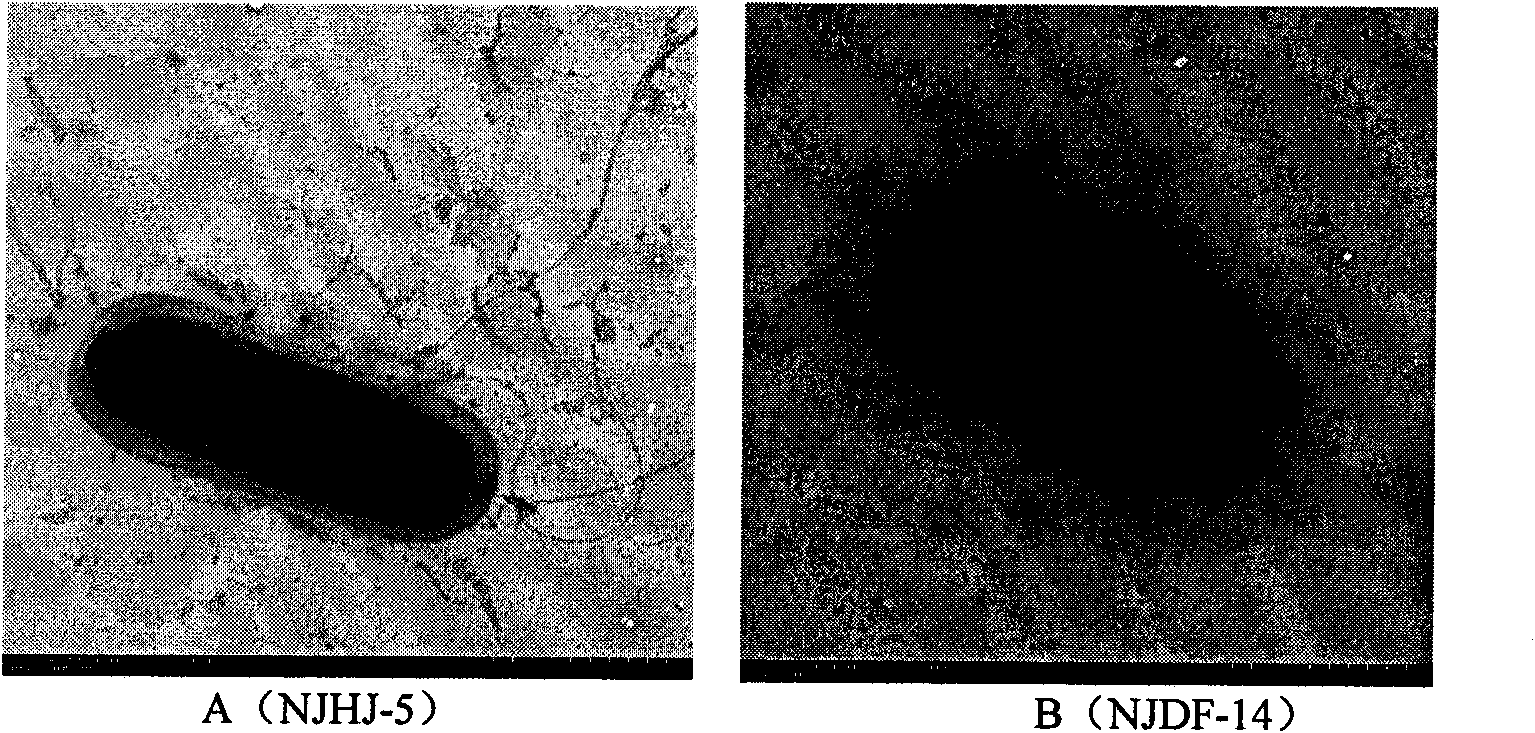
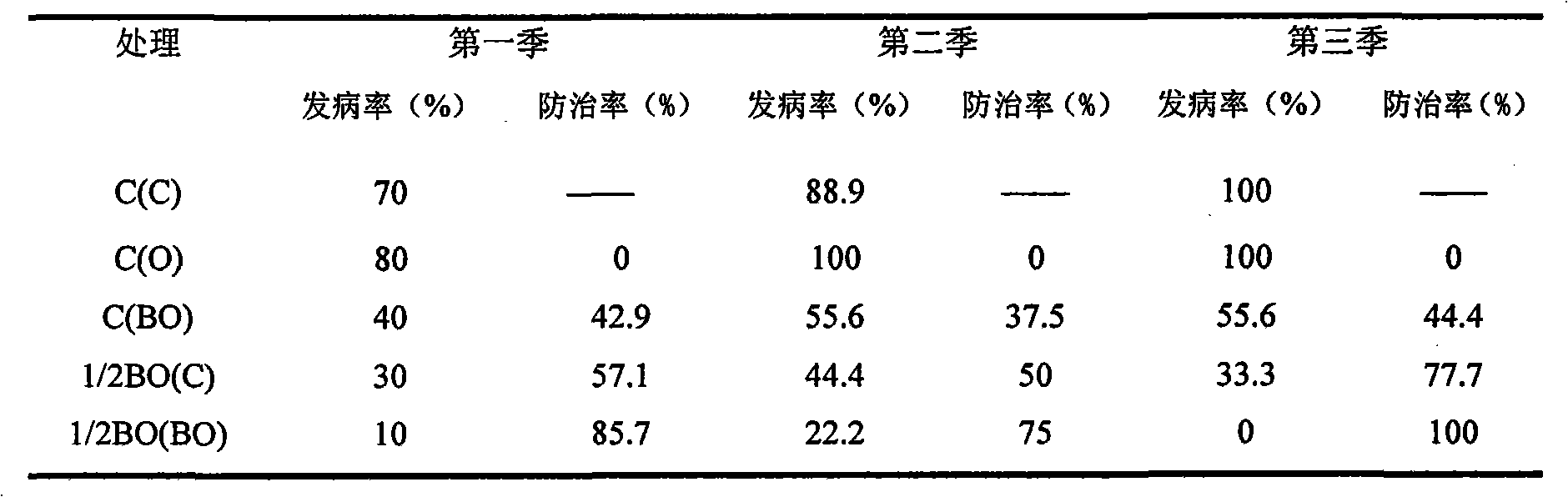
The invention relates to antagonistic bacteria for preventing and eliminating greensickness of continuous cropping cotton and a microbial organic fertilizer thereof, belonging to a technology of agricultural intensification production. In the invention, two antagonistic bacteria (bacillus subtilis NJHJ-5 and bacillus subtilis NJDF-14) having obvious antagonistic actions on pathogenic bacteria of the cotton greensickness are separated, and the microbial organic fertilizer is prepared by utilizing the antagonistic bacteria and organic composts, wherein the microbial organic fertilizer respectively contains more than 1*10<9> / g of the NJHJ-5 and the NJDF-14, the total-nitrogen content is 4-5 percent (more than 90 percent of the content is organic nitrogen), total nitrogen-phosphorus-potassiumnutrients are 6-10 percent, and the content of organic matters is 30-35 percent. Proved by experiments, after being fertilized into soil, the microbial organic fertilizer enables the antagonistic bacteria to quickly reproduce and form a dominant group in the soil. After the microbial organic fertilizer is continuously fertilized for three seasons, the prevention and cure rate of the cotton greensickness in the soil the original morbidity of which is higher than 60 percent can reach 100 percent.
Owner:河南省全元农业科技有限公司
Bacillus velezensis microbial agent and application thereof
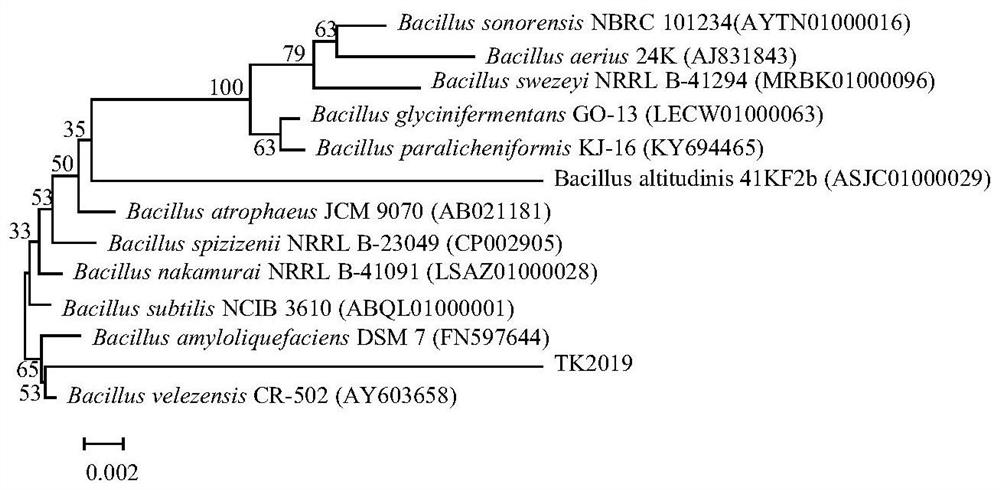
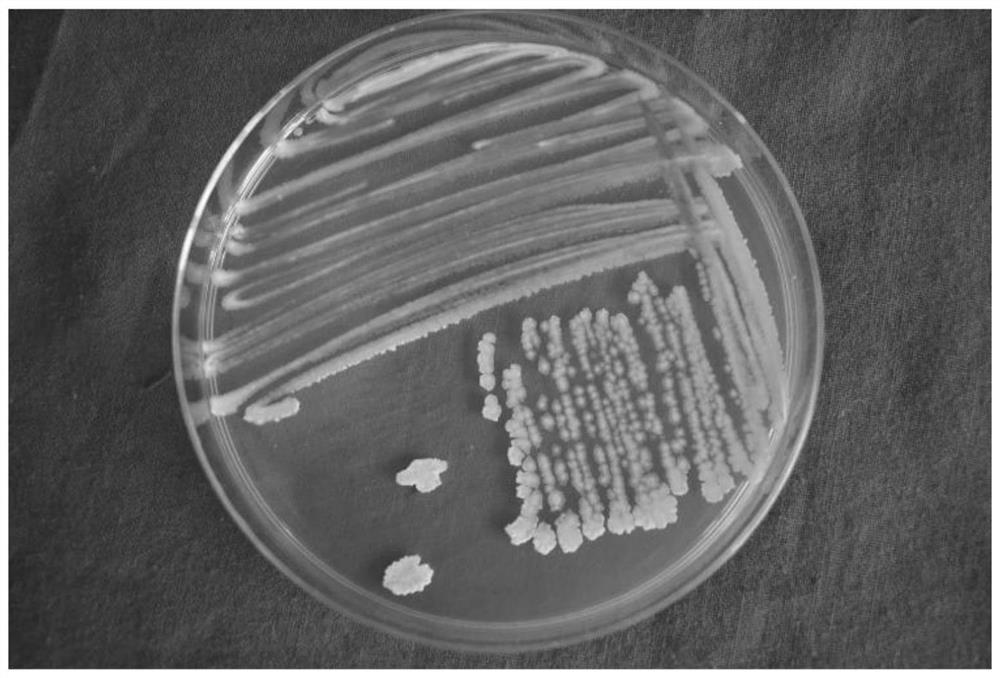
The invention discloses a bacillus velezensis TK2019 microbial agent and application thereof. The bacillus velezensis TK2019 is separated from rhizosphere soil of the cotton field of the 44 regiment in the Tumxuk city of Xinjiang, and the bacillus velezensis TK2019 microbial agent is used for preparing the bacillus velezensis TK2019. When the microbial agent is applied to prevention and treatmentof cotton verticillium wilt, cotton fusarium wilt, botrytis cinerea and red date black spots, the inhibition rate of the strain TK2019 on verticillium dahliae of cotton reaches 94.37 percent, the inhibition rate of the strain TK2019 on four tested pathogenic fungi is 84.83-93.73 percent, and the stock solution and 50-time diluted solution of the bacillus velezensis TK2019 microbial agent have thehighest prevention effects which are 92.86 percent and 91.97 percent respectively. Field tests prove that the prevention effect the TK2019 microbial agent on cotton verticillium wilt is 92.69 percent,which indicates that the Bacillus velezensis TK2019 and the microbial agent thereof provided by the invention have the advantages of high efficiency, wide bactericidal spectrum and the like and havewide values for expanding the application field of microbial strains.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Hybrid tomato variety 12n 808 rz
InactiveUS20150296729A1Strong ribbingMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal feeding stuffStemphyliumZoology
The present invention relates to a Solanum lycopersicum seed designated 12N 808 RZ, whereby a plant grown from such seed may exhibit resistance to Verticilium spp. (Va and Vd), resistance to Stemphylium spp., a very large fruit size of about 300-350 g, short to medium plant height, and very strong ribbing at the peduncle end. The present invention also relates to a Solanum lycopersicum plant produced by growing the 12N 808 RZ seed. The invention further relates to methods for producing the tomato cultivar, represented by tomato variety 12N 808 RZ.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Method for rapidly identifying resistance to verticillium wilt of eggplant
InactiveCN103355025ASame degree of root damageEnsure consistencySpore processesHorticultureSporeHigh survival rate
The invention provides a method for rapidly identifying resistance to verticillium wilt of eggplant. The method comprises the following steps of: accelerating germination and sowing of eggplant seeds, seedling culturing, preparation of a verticillium wilt spore suspension, treatment of pathogenic bacteria infection and incidence investigation. According to the invention, eggplant seedlings are infected with verticillium wilt in a manner of soaking and infecting seedling roots by a bacteria solution, and the eggplant seedlings are infected after being uniformly cultured in a substrate until achieving a state of one seedling with two leaves, so that the growth vigor and size of the eggplant seedlings are easy to control, and the consistency and reliability of an identification result are ensured. By adopting the appropriate verticillium wilt substrate and adjusting the concentration of the verticillium wilt suspension, the method has the advantages of good infection effect, high survival rate of the infected seedlings, uniform inoculation and rapid incidence. According to the invention, only different plants with consistent growth vigor need to be soaked in the bacteria solution after root cutting, so that the operation is simple and convenient, the seedling culture time is short, and the method is particularly suitable for identification of resistance to verticillium wilt of eggplant breeding materials in batches.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
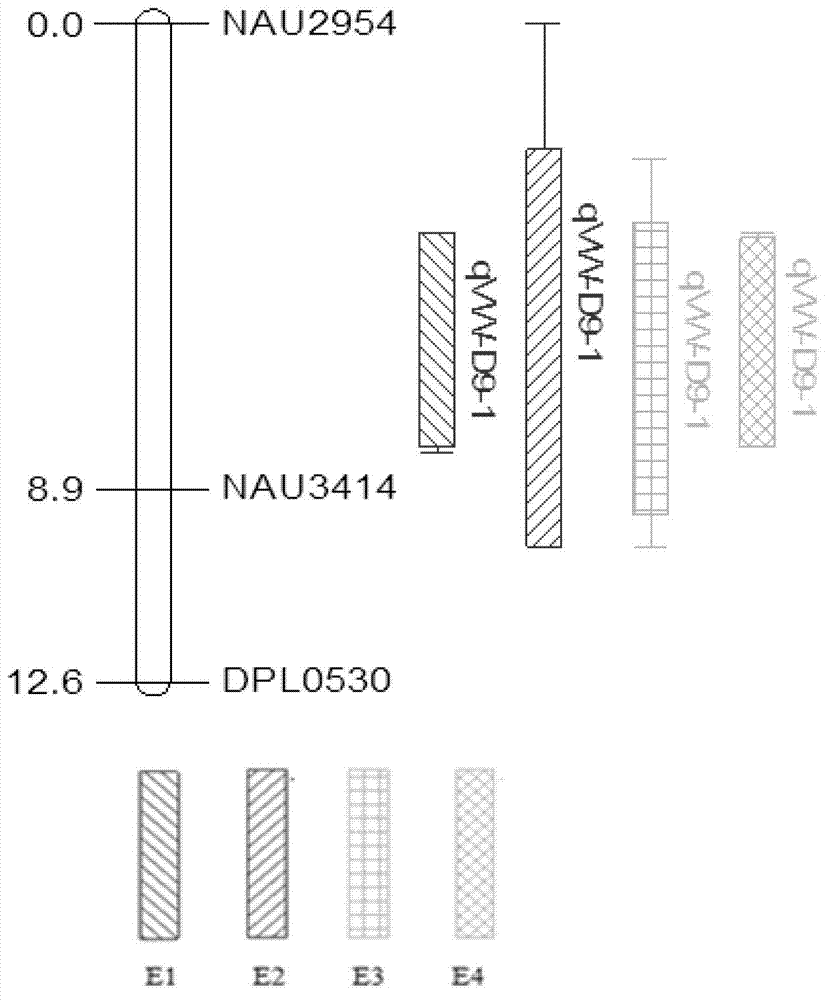
Cotton highly-verticillium wilt resistant major QTL (quantitative trait locus) and SSR molecular marker thereof
ActiveCN102925436AIncrease Verticillium wilt resistance levelStable resistance performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention discloses a cotton highly-verticillium wilt resistant major QTL (quantitative trait locus) and an SSR molecular marker thereof. The cotton highly-verticillium wilt resistant major QTL is located on the cotton D9 chromosome, 16.95-65.53% of phenotypic variation can be explained in the RIL (recombinant inbred line) colony from the highly-verticillium wilt resistant germplasm systems Prema and 86-1, and the following three SSR markers are in close linkage therewith: SSR / NAU2954209, SSR / NAU3414258 and SR / DPL0530220. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention is used for screening or identifying the verticillium wilt-resistant cotton variety. The invention is favorable for solving the problem of slow progress of the cotton verticillium wilt resistance breeding of the country, and is favorable for overcoming the defects of high cost, long time, low stability and the like of the existing breeding technology in verticillium wilt resistance identification; and the highly-verticillium wilt resistant cotton new variety breeding and seed industrialization progresses of the country are greatly accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Composite biological antimicrobial for preventing wilt and greensickness of cotton
InactiveCN101990907AHigh control rateGood control effectBiocideFungicidesActive componentCandida tropicalis
The invention relates to a composite biological antimicrobial for preventing wilt and greensickness of cotton. The active components of the composite biological antimicrobial comprise Candida tropicalis, streptomyces microflavus, Trichoderma viride and Bacillus subtilis. The composite biological antimicrobial for preventing wilt and greensickness of cotton can reduce the seedling death rate effectively, has obvious preventing and treating effect on wild and greensickness of cotton and provides the cotton output.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION & SOIL FERTILIZER HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting resistance of cotton plants to greensickness by molecular marker-assisted selection
ActiveCN103602743AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial resourcesVerticillium wilt
The invention provides a method for detecting the resistance of cotton plants to greensickness by molecular marker-assisted selection. The method comprises the following steps: (1), soaking seeds of cotton plants to be detected in a soaking solution; (2), planting the soaked seeds in a disease garden; (3), selecting a cotton plant capable of surviving in the disease garden as a preliminary screened cotton plant; and (4), respectively carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on genome DNA (Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) of the cotton plant by a first primer pair and a second primer pair to obtain a first amplification product and a second amplification product, wherein the first primer pair is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2, the second primer pair is shown as SEQ ID NO:3 and SEQ ID NO:4, and if the first amplification product has nucleic acid shown as SEQ ID NO:5 and the second amplification product has nucleic acid shown as SEQ ID NO:6, the cotton plant to be detected is a greensickness-resistant plant. According to the method, the resistance to greensickness is predicted, the cotton plants are screened to discard plants which do not show symptoms but are susceptible in a disease garden screening process, the waste of manpower and material resources is reduced, and the breeding efficiency is increased.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Biocontrol bacterium and application of biocontrol bacterium to preventing and controlling cotton blight and cotton greensickness
The invention discloses Streptomyces rochei 42561 which is preserved in the general microorganism center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM), with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.6556. The bacteriostatic and prophylactic actions of the biocontrol bacterium 42561 are comprehensively tested according to a cup-plate method, a mycelial growth rate inhibition method, a spore germination inhibition method, greenhouse pot culture and field tests; and the testing results show that the strain has a remarkable prevention effect on cotton blight and cotton greensickness, can be used as an effective biological pesticide preparation agent and has excellent application and development prospects.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Compound successive crop-resistance micro-ecological formulation special for cotton and special bacterial strain and use thereof
InactiveCN101352177AImprove qualityPile length increasedBiocideFungiContinuous croppingChlamydospore
The invention discloses a composite anti-continuous cropping microbial ecological agent specially used in cotton and the application thereof. The anti-continuous cropping microbial ecological agent of the invention takes bacillus subtilis KTB001 CGMCC No.2564 and trichoderma viride KTF001 CGMCC No.2562 as active ingredients, wherein, the content of the gemma of a fungus of the bacillus subtilis KTB001 CGMCC No.2564 is 50 hundred million cfu / g preparation; the content of chlamydospore of trichoderma viride KTF001 CGMCC No.2562 is 5 hundred million cfu / g preparation. The composite anti-continuous cropping microbial ecological agent of the invention can prevent and control cotton seedling diseases and verticillium wilt. Furthermore, the agent has the effectiveness of increasing cotton output, increasing cotton quality and enhancing cotton stress resistance, and the like, is beneficial to improving soil and reducing environmental pollution, and provides safeguard for producing cotton with excellent quality.
Owner:北京康泰正茂农业科技股份有限公司
Application of Bacillus methylotrophicus ZBL-1 in control of cotton verticillium wilt
ActiveCN105441366AStrong salt toleranceGood antibacterial effectBiocideBacteriaVerticillium speciesAgricultural science
The invention discloses an application of Bacillus methylotrophicus ZBL-1 in control of cotton verticillium wilt. The Bacillus methylotrophicus ZBL-1 with CGMCC No.11636 and higher inhibition effect on verticillium dahlia is obtained through separation, screening, breeding and domestication of soil samples collected in the cotton fields with severe diseases in Shihezi city and is obviously different from common Bacillus methylotrophicus strains, and meanwhile, the control effect of the screened strain ZBL-1 on the cotton verticillium wilt in indoor pot culture experiments is 73.0%; the control effect of the screened strain ZBL-1 in field plot experiments is 43.1%, and whether in development of a new biopesticide or biological control agent, the Bacillus methylotrophicus ZBL-1 as a biological control material for the cotton verticillium wilt has very good application prospect and has realistic significance and functions.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for preventing and curing tomato bacterial wilt and application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens
ActiveCN105950506AImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention relates to bacillus amyloliquefaciens W118. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens W118 is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 10, 2016, and the collection number is CGMCC No.12200. The invention further provides application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens W118 in prevention and cure of pathogenic bacteria of tomato bacterial wilt, cotton verticillium wilt, tomato early blight and cucumber corynespora cassiicola. Compared with the prior art, the bacillus amyloliquefaciens W118 and the application thereof have the advantages that the bacillus amyloliquefaciens W118 has a certain prevention and cure effect on the tomato bacterial wilt, and the highest prevention and cure rate can reach 59.2%; the highest prevention and cure rates for the cotton verticillium wilt, the tomato early blight and the cucumber corynespora cassiicola can reach 47.8%, 43.4% and 38.3% respectively.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compound bacterial manure used for prevention and control of cotton verticillium wilt and the preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a compound bacterial manure used for prevention and control of cotton verticillium wilt and the preparation method thereof. Materials of the compound bacterial manure consist of Streptomyces aburaviensis, Streptomyces tanashiensis, Brevibacillus agri, Bacillus clausii, Trichoderma citrinoviride, and potassium fulvic acid. Bacteria of the invention can make full use of the interspecific or intraspecific antibiosis, competition, hyperparasite, and bacteriolysis of microbes, and induce cotton to generate the disease resistance ability through secondary metabolite, thereby producing various antibiotic substances such as luteomycin and aburamycin to prevent the pathogenic bacteria of cotton verticillium wilt. The 5 strains used in the invention can be obtained through separation from soil directly; the strains can promote the growth of root, and secrete some secondary metabolites to plant roots while growing on the plant surface, inside the plant or in soil, thereby improving the plant's absorption of nutrients, and promoting the plant growth like fertilizers.
Owner:FOSHAN YANHUI BIOTECH CO LTD
Soil disinfection and soil remediation combined technology
InactiveCN105665434AGood prevention effectSignificant improvementBiocideContaminated soil reclamationDisinfectantCanker
The invention provides soil disinfection and soil remediation combined technology. The technology includes the steps of preparation before soil disinfection, soil disinfection and soil remediation. Before soil disinfection, the ploughing depth ranges from 40 cm to 50 cm, the ridge height ranges from 20 cm to 30 cm, and the height between each film and soil in the corresponding ridge ranges from 10 cm to 20 cm. An adopted soil disinfection agent comprises the following components of dithiocarbamic acid, sodium formate, nitrite 2-chloroisobutyl, borax, cyclodextrin, laminarin and phthalimide. An adopted soil remediation agent comprises the following components of microorganism bacterium powder, sodium alginate, 2-hydroxybenzoic acid-5-sodium sulfonate, beta-cyclodextrine, sodium caseinate, medical stone powder, EDTA-iron, corn protein peptide, polyglutamic acid, polyacrylamide and cortex pseudolaricis powder. The soil disinfection and soil remediation combined technology has remarkable effects on the root rot, canker, wilt, verticillium wilt, bacterial wilt and basal rot of plants and meanwhile has remarkable improvement effects on the soil properties.
Owner:WEIFANG XINYOUJI SOIL DISINFECTION PROFESSIONAL SERVICES COOP
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with inorganic phosphorus degrading and bacteria restraining effects and bacterial agent thereof
ActiveCN106399177AGood effect on degrading inorganic phosphorusGood antibacterial effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDiseasePlant disease
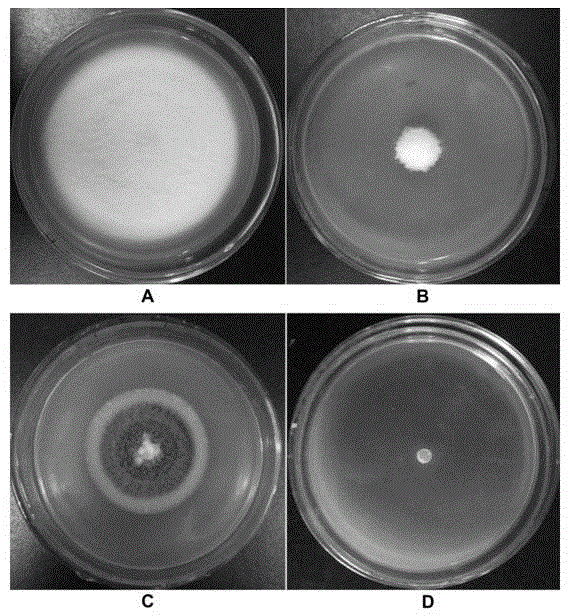
The invention discloses a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain PHODG36 which has been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.13041. The invention further discloses a microbial bacterial agent produced from the PHODG36, and discloses application of the PHODG36 to degradation of inorganic phosphorus, promotion of crop growth and prevention and treatment of cotton diseases. The strain PHODG36 has a good inorganic phosphorus degrading effect and high fertilizer efficiency; meanwhile, the strain is good in bacteria restraining effect and wide in antibacterial spectrum and has a quite good restraining effect on three pathogenic bacteria diseases of cotton verticillium wilt, wilt and damping off; in addition, a microbial bacterial manure is safe to human and livestock and is free of environment pollution problem; the bacterial agent is simple in method, low in cost and easy to use.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Cotton verticillium wilt resistant seedling stage identification method
InactiveCN102732596ARapid onsetSignificant incidenceFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseSpore
The invention belongs to the technical field of cotton disease resistance breeding and specifically relates to a cotton verticillium wilt resistant seedling stage identification method. The method provided by the invention comprises the following main steps of: firstly carrying out shaking culture on cotton verticillium wilt germ 6SY2-37 collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the collection number being CCTCC NO: M2011095 in a Czapek's liquid medium at the temperature of 25 DEG C for 5d, filtering by the use of gauze, counting by the use of a blood cell counting panel, preparing 5*106 spore / ml, pulling up seedling with a matrix when the water-planting cotton seedling grows to a stage of two leaves and one core, cutting 1cm of water root, dipping the root for 10s and inoculating, embedding wet soil into a plastic earthen bowl, inoculating pathogen, immediately watering to prevent the cotton seedling from fading, inoculating for 10 days and causing the disease. The method provided by the invention has advantages of high survival rate of the cotton seedling after inoculation, uniform inoculated pathogen, rapid morbidity, convenient operation and good stability of results. In addition, the method takes short time, requires short seedling growing time and is convenient to manage. Therefore, the method is suitable for cotton verticillium wilt resistance identification and pathogen pathogenicity differentiation determination of large-batch materials.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Breeding method of upland cotton hybrid
InactiveCN101401545AImprove high temperature resistanceLittle impact of high temperature weatherPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsDiseasePollination
The invention relates to a method for breeding an upland cotton intervarietal hybrid, and belongs to the technical field of plant breeding. Multi-parents are crossbred through mixed pollination, and filial generation excellent plants are crossbred through mixed pollination to breed female parent line 29-8. The male parent 203-16 line is selected and bred through multi-parent hybrid, excellent plant mixed pollination hybrid, and combination of techniques such as identification of verticillium wilt disease and verticillium wilt hybrid disease nursery, space-flight induction and so on. The female parent line 29-8 and the male parent 203-16 line are prepared into a hybrid Ning 2058. The hybrid Ning 2058 belongs to middle-early ripen variety, the growth season is about 120 days, the plant height is 98.60 cm, the node position number of fruit branch is 6.38, the fruit branch number of single plant is 11.96, the boll number of the single plant is 22.66, the boll number per mu is 65,900, the single boll weight is 6.95g, the seed index is 10.88g, the gin turnout is 41.17 percent, the pre-frost lint percentage is 89.23 percent, and the hybrid is suitable to be planted in various cotton areas in Tianjin City.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
BaciIllus polymyxa KN-03 and culturing method and use thereof
ActiveCN104611254APrevention of bacterial wiltPrevent Fusarium WiltBiocideBacteriaDiseaseSclerotinia
The invention discloses baciIllus polymyxa KN-03 capable of simultaneously preventing and treating various crop diseases, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2012077. The invention also discloses a culturing method and use of the baciIllus polymyxa. The baciIllus polymyxa can effectively simultaneously prevent and treat crop bacterial wilt, fusarium wilt, verticillium wilt, sclerotinia disease, take-all disease, early blight, gray mold and anthracnose, and has strong sporulation ability, the fermentation liquid spore number can reach 30 billion CFU / ml, at the same time, the baciIllus polymyxa KN-03 also has obvious growth promoting effect, and can significantly increase crop yield.
Owner:WUHAN KERNEL BIO-TECH CO LTD
Anti-Cotinus coggygria oxysporum strain and use thereof
The invention discloses an anti-Cotinus coggygria oxysporum strain and a use thereof. The anti-Cotinus coggygria oxysporum strain is Bacillus subtilis C-2-3-2 and has a microbial accession number of CGMCC NO. 9369. The Bacillus subtilis C-2-3-2 is separated from saline land soil, can prevent Verticillium wilt of Cotinus coggygria, and has good effects of inhibiting Cotinus coggygria oxysporum and fusarium oxysporum. The sterile filtrate of the Bacillus subtilis C-2-3-2 can obviously inhibit Cotinus coggygria oxysporum microsclerotia formation. The Bacillus subtilis C-2-3-2 is a biological control potential bacterial strain with high prevention effects, special prevention and treatment effects and environmental safety, and has a good development and application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Molecular marker for QTL/major gene related to verticillium wilt resistance of cotton
ActiveCN104313016AStable detectionImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceVerticillium wilt
The invention discloses an SSR marker interlocked with verticillium wilt resistance QTL / major gene loci qDI-5-1, qDI-5-2, qDI-5-3, qDI-5-4 and qDI-5-5 of cotton. The qDI-5-1, the qDI-5-2, the qDI-5-3, the qDI-5-4 and the qDI-5-5 are all located on a chromosome C5. By utilizing the SSR marker interlocked with verticillium wilt resistance major gene loci of cotton to carry out assistant selection, breeding efficiency of verticillium wilt resistance of cotton can be improved.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with inorganic phosphorus degrading and bacteria inhibiting functions and application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens
ActiveCN106399178AGood effect on degrading inorganic phosphorusGood antibacterial effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
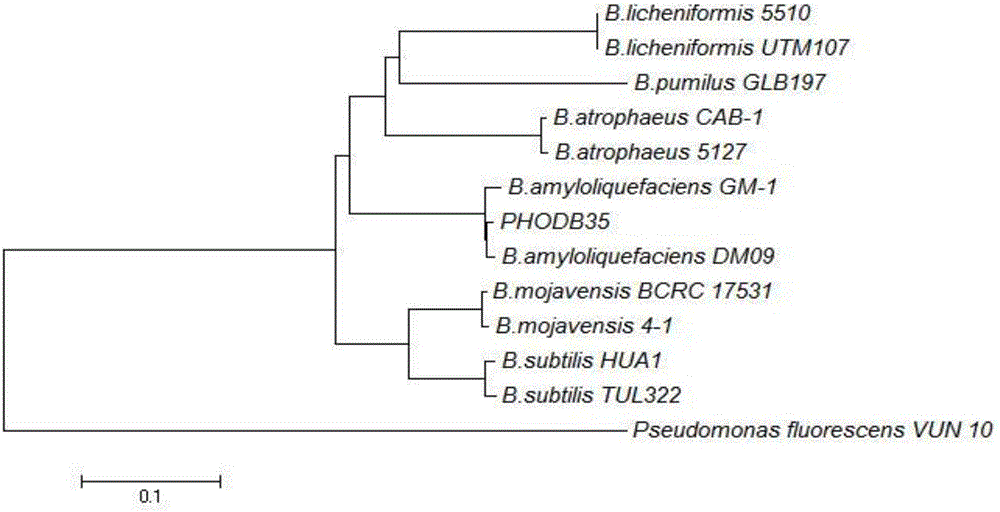
The invention discloses a PHODB35 bacteria strain of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and the bacteria strain is preserved in the common microorganism center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 13040. The invention further discloses a microorganism bacterium agent produced by the aid of the PHODB35 bacteria strain. The PHODB35 of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens is good in inorganic phosphorus degrading, good in fertilizer effect, good in bacterial inhibiting effect of three kinds of pathogenic bacteria of cotton verticillium wilt, wilt and fusarium patch and wide in antimicrobial spectrum; the bacillus amyloliquefaciens causes no pollution problem to safety of human and livestock; the bacillus amyloliquefaciens is simple in preparation method, low in cost and easy to use.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Bactericidal composition containing tetramycin and zhongshengmycin
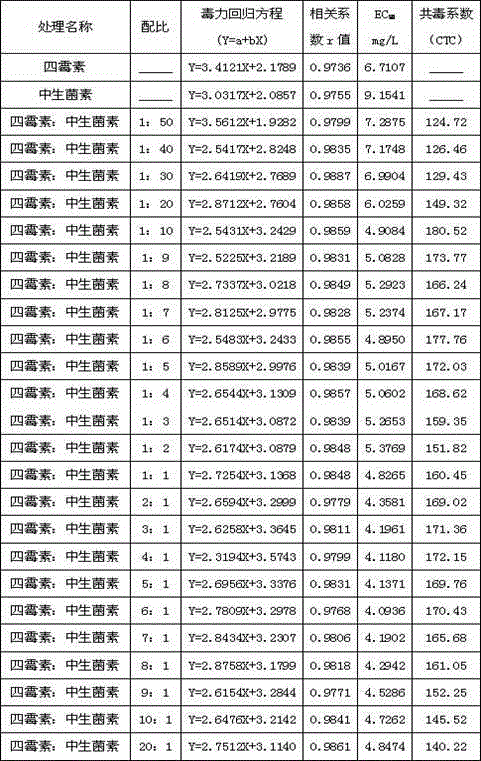
ActiveCN103598192ASynergistic effect is obviousDelay key drug resistanceBiocideFungicidesDiseaseExobasidium vexans
The invention provides a bactericidal composition containing tetramycin and zhongshengmycin. The bactericidal composition comprises compounded effective components consisting of tetramycin and zhongshengmycin, with the balance being auxiliary components. The mass ratio of tetramycin to zhongshengmycin in the composition is 1-50 50-1, and the mass fraction of tetramycin and zhongshengmycin in a preparation is 1 to 80%, with the balance being auxiliary components which are allowed to use and admitted in pesticides; dosage forms of the composition comprise missible oil, a suspending agent, a wettable powder, a water dispersible granule, an emulsion in water, a micro-emulsion, a granule and a micro capsule. The composition is mainly used for preventing and treating rot diseases of fruit trees, alternaria leaf spot, rice blast, soybean root rot, fusarium wilt of cucurbits, cotton verticillium wilt, rust diseases of jujube trees, white rot of grape, black spot of ginseng and pseudo-ginseng, Exobasidium vexans Massee of tea, forest rot, canker, gumming diseases, leaf cast, damping off of forest seedlings, soft rot bacteria of vegetable, Pseudomonas lachrymans, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, Physalospora piricola, Fusarium graminearum, etc.
Owner:HAILIR PESTICIDES & CHEM GRP
Bacillus licheniformis 201 for highly effective preventing and curing banana wilt and application thereof
InactiveCN101186885ASimple cultivation conditionsEasy to storeBiocideBacteriaBacillus licheniformisBeef extract
The invention discloses bacillus licheniformis 201 for high effectively preventing banana wilt, and the preservation number of the bacillus licheniformis 201 is CCTCCM207092. Bacterial colony on beef extract-peptone medium is greyish-white, round, flat and lackluster, the edge of the bacterial colony is in order, the diameter of the bacterial colony is generally 2 to 3 millimeters, bacteria are of straight rod shape, the size of the bacteria is 2.06* 0.70 micrometers, and spore is of elliptical shape. Simultaneously, the invention also discloses a process for preparation and usage. The bacillus licheniformis 201 is capable of strongly preventing fusarium oxysporum and has wide antimicrobial spectrum, which is capable of performing antagonistic action on various pathogenic fungi, such as fusarium oxysporum, fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum, fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici, gloeosporium musarum, colletotrichum gloeosporioides, maize curvularia leaf spot fungus, verticillium wilt pathogen, wheat scab pathogen and the like, furthermore, the invention is high effective in prevention, good in environmental security and good in the prospect of development and application.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bacillus licheniformis 201 and use thereof
InactiveCN101486978AAntagonisticEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a Bacillus licheniformis 201, which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection that is located in Wuhan University, Logosun, Wuchang, Wuhan, Hubei, and with CCTCC NO. of M207092. The invention simultaneously discloses a preparation method and applications of the Bacillus licheniformis 201, which has strong bacteriostasis of banana wilt fusarium, wide bacteriostasis spectrum and antagonism to various pathogenic fungi including banana wilt fusarium, watermelon wilt fusarium, tomato wilt fusarium, banana colletotrichum, gloeocystidium colletotrichum, corn leaf spot curvularia, cotton verticillium lecanii, gibberella zeae, and the like, and the Bacillus licheniformis 201 has high control efficiency, good environmental security and good development and application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com