Method for detecting resistance of cotton plants to greensickness by molecular marker-assisted selection
A verticillium wilt and plant technology, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve the problems of large differences between years, poor disease resistance of bred varieties, inaccurate selection of progeny materials, etc., and achieve the effect of rapid detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
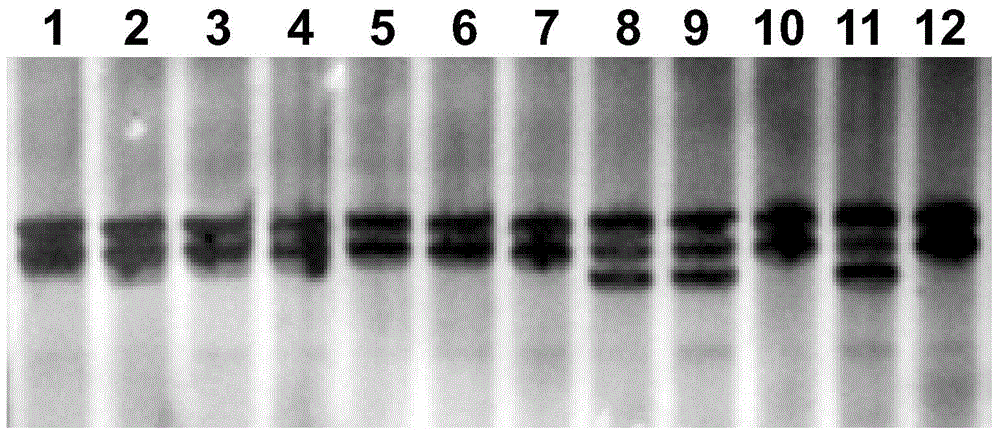
[0037] 1) Collect 31 kinds of cotton seed materials, according to the artificial seedbed disease in the literature (Zhang Xinghua, Cotton blight resistance, Verticillium wilt research progress and resistance identification method, Jiangxi Agricultural Journal, 2008,20(3):43-49) The results were listed in Table 1. Among them, 3 copies of disease-resistant germplasm were represented as "R" in the column of Verticillium wilt-resistant materials in Table 1; 28 copies of susceptible germplasm , which is indicated as "S" in the column of Verticillium dahliae-sensitive materials in Table 1.
[0038] (2) According to the method in the "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide", isolate the genomic DNA of each germplasm.
[0039] Using the genomic DNA of each germplasm as a template, the forward primer is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (5′-AAACAATAATAAACGAGTTGAATTA-3′) and the reverse primer is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 (5′-TTGTTTCATAATTTTAAAGTATGTA- 3′) for PCR amplification, the denaturation temperatu...
Embodiment 2
[0048] In this example, the cotton plants to be tested are the F2 generation seeds of Zhongzhimian 2 (GK44) selection line and Xin 59-4. The resistance to Verticillium wilt of the selected line Zhongzhimian 2 (GK44) and the F2 generation seeds of Xin 59-4 was not known in advance.
[0049] The tissue of the cotton plant that died of Verticillium dahliae was crushed, soaked in water of equal weight for 48 hours, and filtered to obtain the soaking solution containing the pathogenic bacteria of Verticillium dahliae.
[0050] Soak the F2 generation seeds of Zhongzhimian No. 2 (GK44) and Xin 59-4 in the above-mentioned soaking solution containing Verticillium dahliae pathogenic bacteria for 24 hours to obtain soaked seeds, wherein, relative to each part by weight seeds, the consumption of soaking liquid is 5 parts by weight.
[0051] The tissue of the cotton plant that died of Verticillium wilt was pulverized and mixed into the soil. The amount of the tissue of the cotton plant th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com