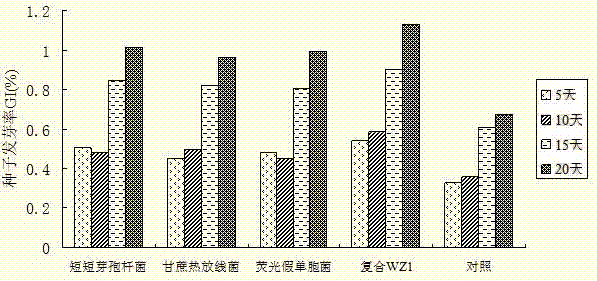
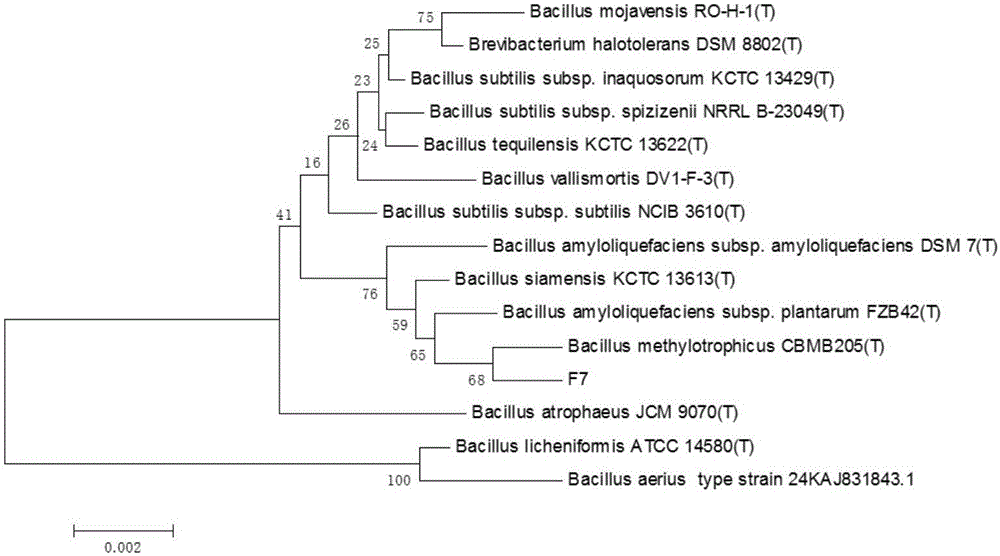
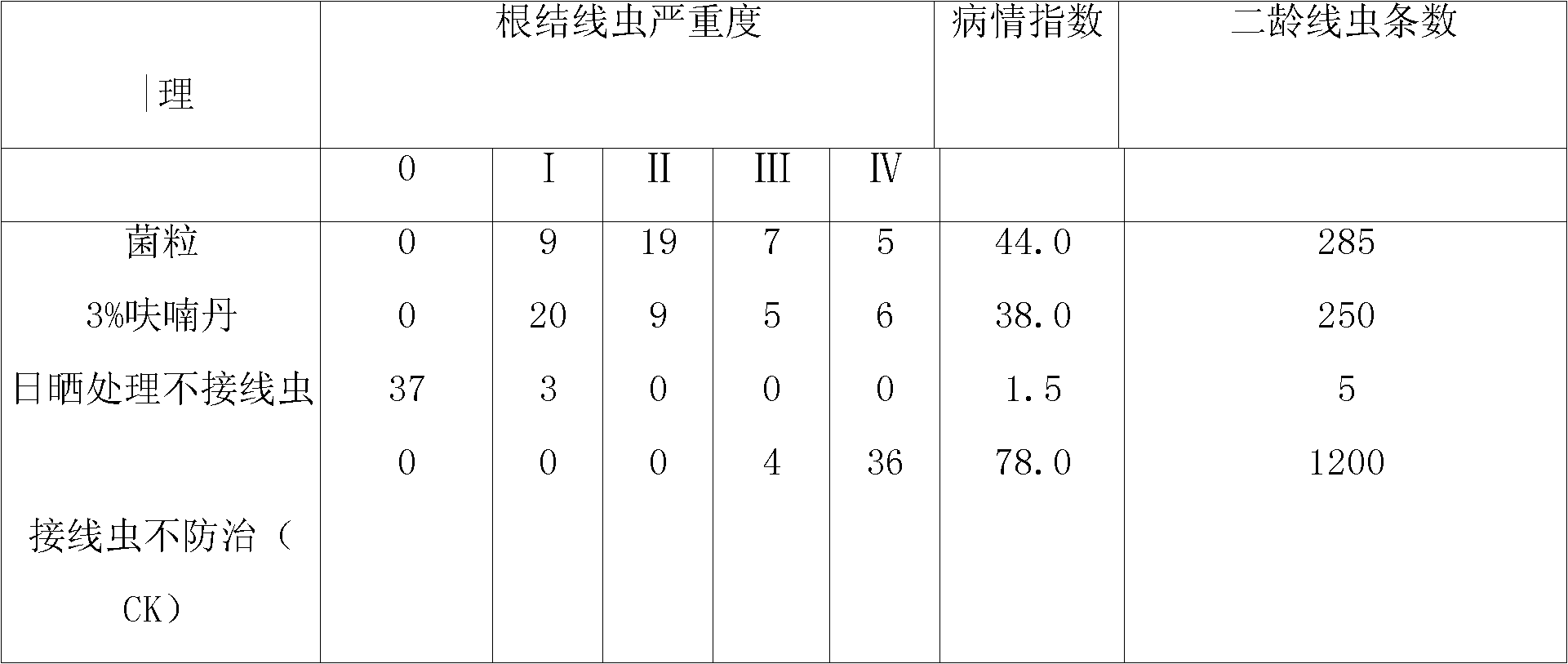
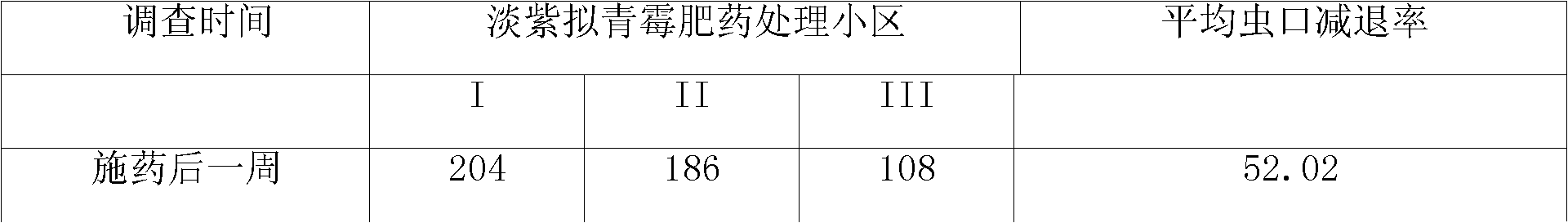
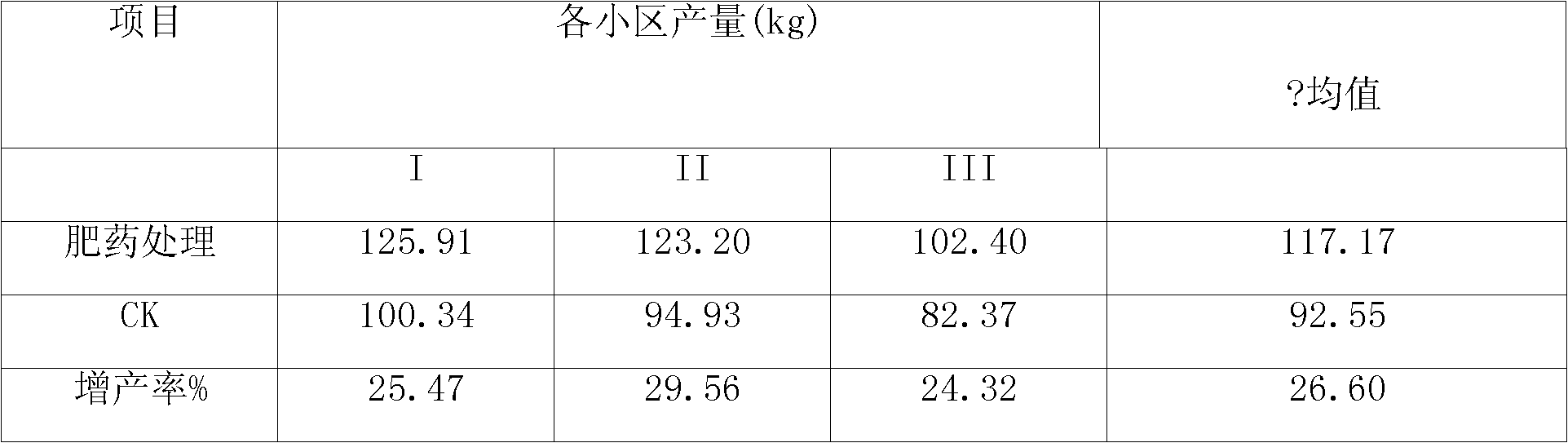
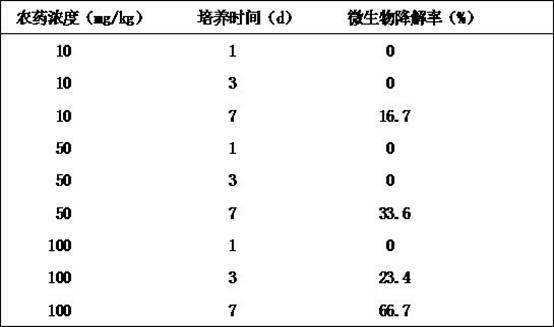
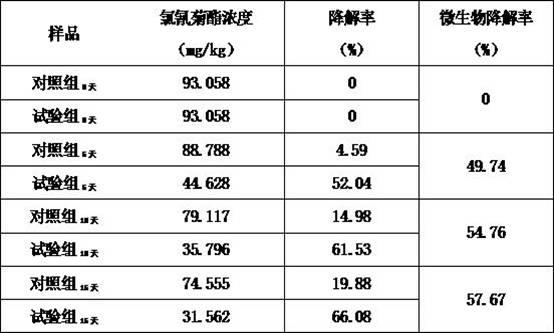
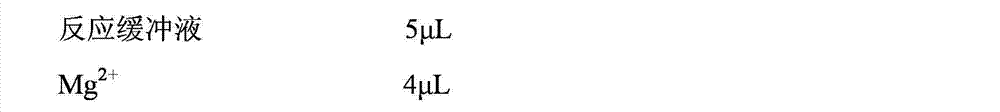Patents
Literature
565 results about "Agricultural biotechnology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agricultural biotechnology, also known as agritech, is an area of agricultural science involving the use of scientific tools and techniques, including genetic engineering, molecular markers, molecular diagnostics, vaccines, and tissue culture, to modify living organisms: plants, animals, and microorganisms. Crop biotechnology is one aspect of agricultural biotechnology which has been greatly developed upon in recent times. Desired trait are exported from a particular species of Crop to an entirely different species. These transgene crops possess desirable characteristics in terms of flavor, color of flowers, growth rate, size of harvested products and resistance to diseases and pests.
Bacillus velezensis for simultaneously degrading zearalenone and aflatoxin and application of Bacillus velezensis
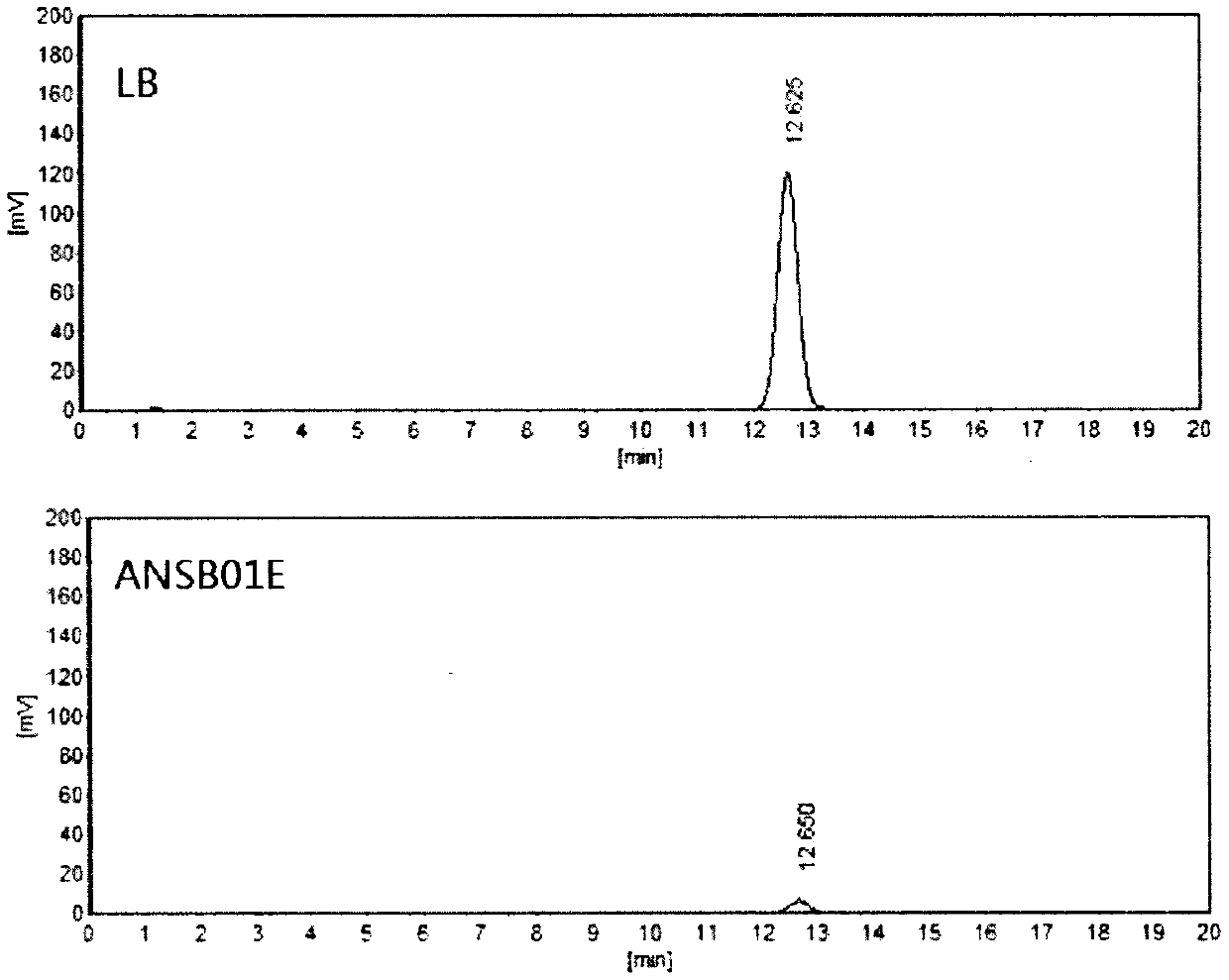
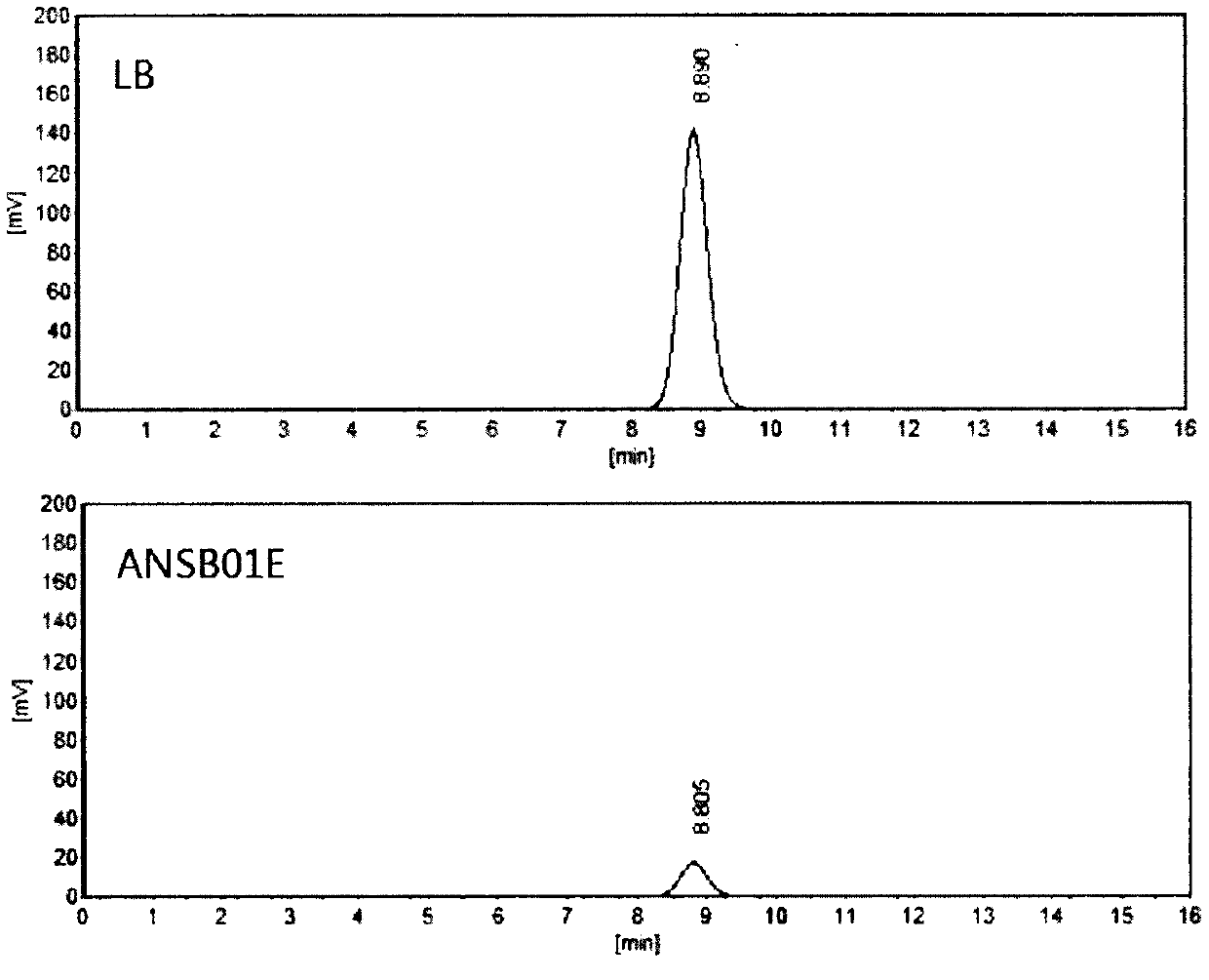
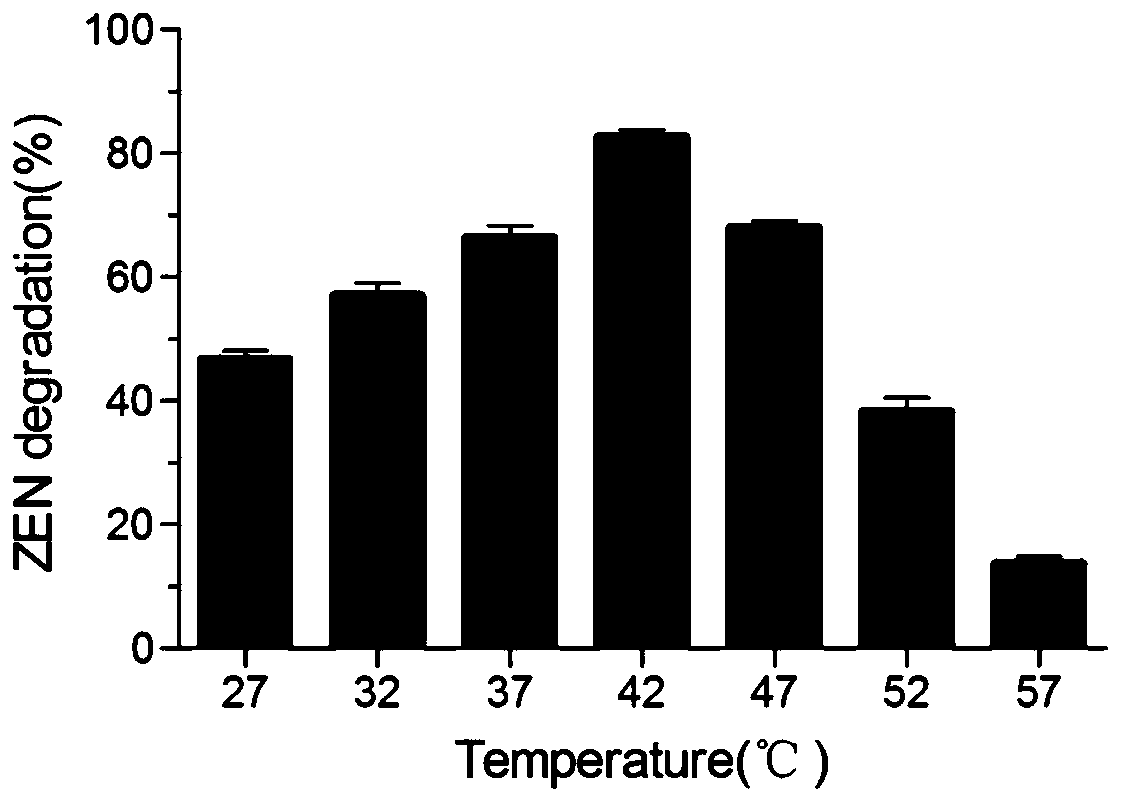
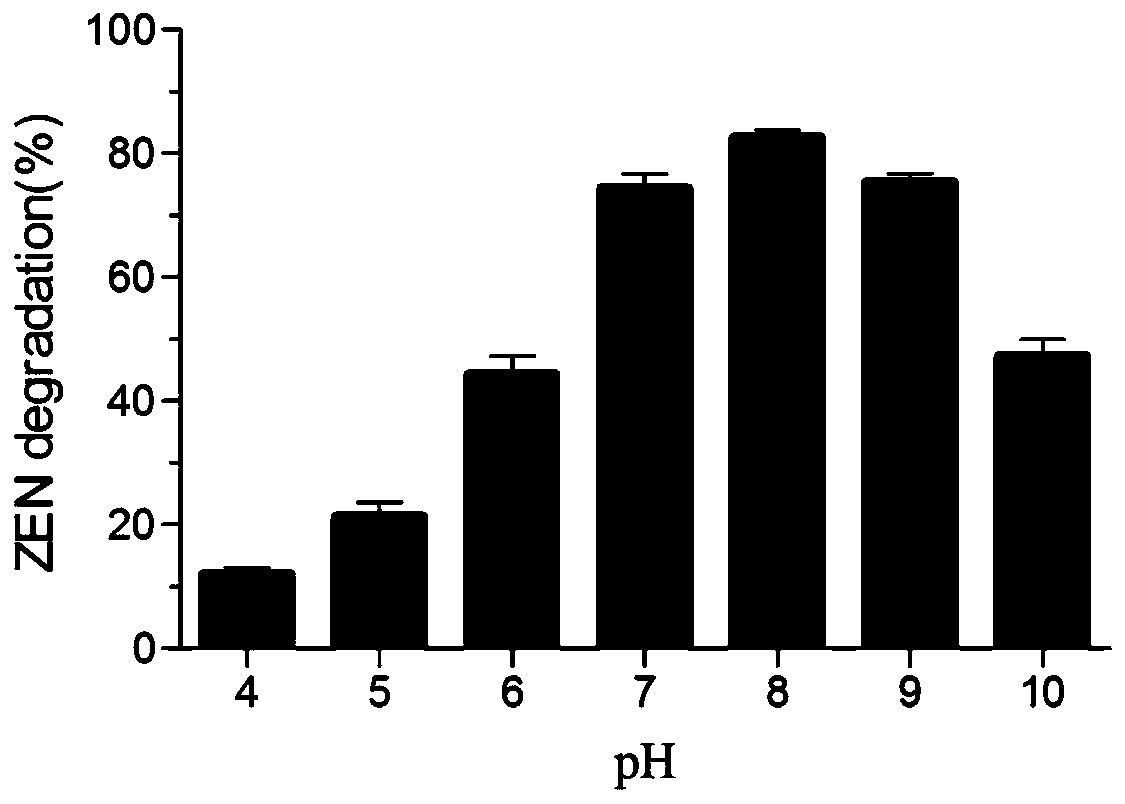
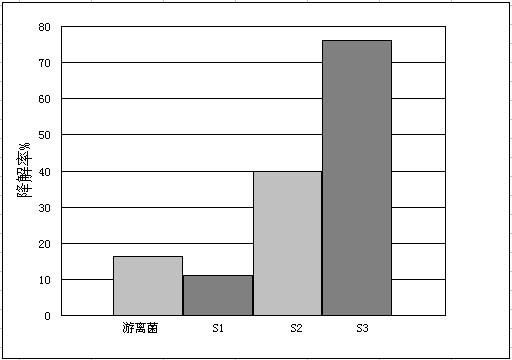
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural biologics and in particular relates to Bacillus velezensis ANSB01E CGMCC No. 17328 and application thereof. The Bacillus velezensis provided by the invention is capable of simultaneously and efficiently degrading zearalenone and aflatoxin, and degradation rates upon g zearalenone and aflatoxin are both up to 90% or greater 48 hours laterafter reactions. The Bacillus velezensis provided by the invention is high in toxin degradation efficiency, good in specificity, mild in action effect, free of damage to nutrient components in feedsand applicable to biological detoxification of mycotoxins in cereals, feeds and foods.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Composite bacterial preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102199562AImprove decomposition abilityPromote degradationBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyDecomposition
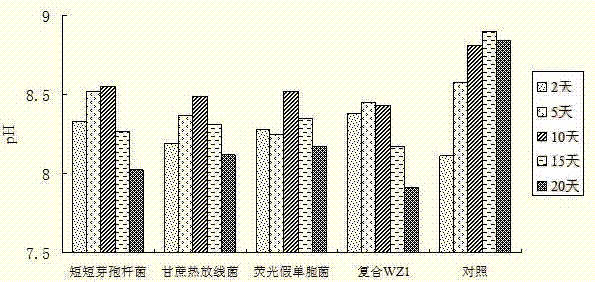
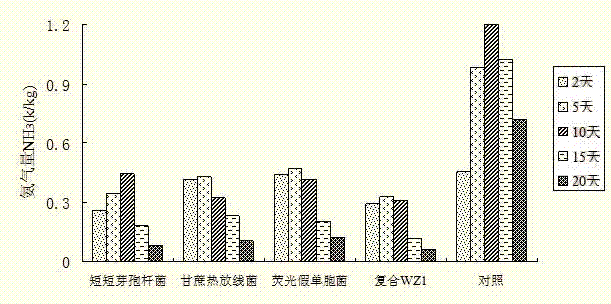
The invention discloses a composite bacterial preparation as well as a preparation method and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of agricultural biochemistry. The composite bacterial preparation comprises the following components in parts by volume: 10-40 parts of brevibacillus brives fermentation bacterial liquid, 10-40 parts of pseudomonas fluorescens fermentation bacterial liquid and 15-45 parts of sugarcane thermophilic actinomyces, wherein the bacterial count in each mol of fermentation liquid is 0.4-0.7 billion. The strains of brevibacillus brives, pseudomonas fluorescens and sugarcane thermophilic actinomyce are separated from rabbit dung and fungi residues; and fermentation bacterial liquids of the separated strains are mixed according to a proper proportion to form the composite bacterial preparation. The composite bacterial preparation disclosed by the invention can be used for accelerating the degradation of organic materials and reducing the conversion of organic nitrogen into gaseous nitrogen, so that the composite bacterial preparation can present stronger ammonia-suppressing and decomposing capabilities in the fermentation process of pig manurecompost; and a smaller amount of ammonia gas is released while thorough decomposition of pig manure is accelerated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Bacillus methylotrophicus F7 and application thereof
PendingCN106754489AStrong antagonistic effectGood biological control effectPlant growth regulatorsBiocideRalstonia solanacearumPlant growth
The invention discloses bacillus methylotrophicus F7 and an application thereof. The invention aims at providing a strain which has a plurality of beneficial properties, namely producing siderophore, cellulase and protease, producing auxin, producing ammonia and the like; the strain not only can be used for effectively inhibiting various pathogenic bacteria such as ralstonia solanacearum, fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense, colletotrichum gloeosporioides, fusarium oxysporum f.sp cucumerinum but also can promote plant growth. In accordance with the technical scheme, the bacillus methylotrophicus F7 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on February 1, 2016, with preservation number of CGMCC No.12124; in addition, five surfactin homologs, six fengycin homologs and three iturin homologs, which have an antibacterial effect, are extracted from fermentation liquid of the bacillus methylotrophicus F7; and the bacillus methylotrophicus F7 belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bacillus atrophaeus strain DPPG-28 and application in crop disease control
InactiveCN104531545AImprove germination rateIncreased fresh weightBiocideBacteriaDry weightDrip irrigation
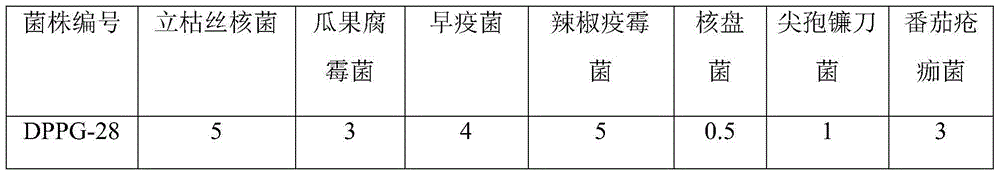
The invention discloses a bacillus atrophaeus strain DPPG-28 and an application in crop disease control, and belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The strain is separated from soil of drip irrigation fields with damping off in tomato processing production areas, and has an accession number of CGMCC No. 9394. The strain can be used for biological control of crop pathogens such as rhizoctonia solani, pythium aphanidermatum, alternaria solani, phytophthora capsici, tomato scab fungi, and the like; the control effects on tomato damping off, capsicum early blight, and cotton damping off reach respectively 74.17%, 66.83%, and 70.12%; the strain can significantly improve the crop germination rate, plant height, fresh weight, and dry weight at the seedling stage. The strain of the invention has high-efficient wide-spectrum germicidal activity, and has wide application prospects in biocontrol agents.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Rhodococcus ruber XS-2 strain and biological microbial inoculant, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105820982AGrowth inhibitionReduce pollutionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationSerratia salinariaMicrobiology
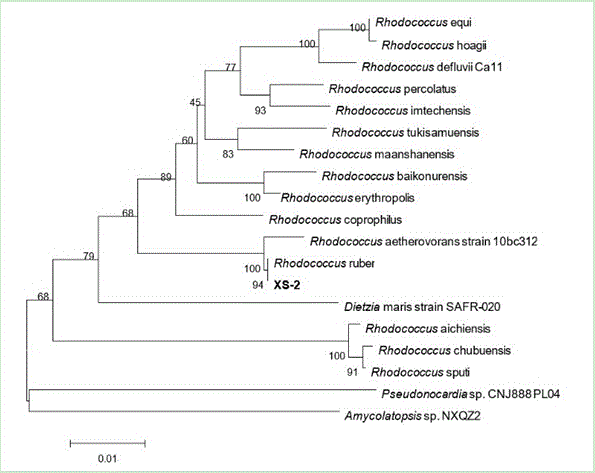
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology, and particularly discloses a Rhodococcus ruber XS-2 strain of which the collection number is CGMCC No.11562. The Rhodococcus ruber XS-2 strain has the function of degrading chemical pesticides. The invention also discloses a microbial preparation containing the Rhodococcus ruber and a preparation method thereof. The microbial preparation is compounded from the Rhodococcus ruber, Serratieae Bacillus subtilis and Brevibacillus brevis. The microbial preparation has the functions of restoring pesticide-polluted soil, preventing diseases and promoting growth, has high environmental safety, and has favorable development and application prospects.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF SCI +1
Breeding technology of konjak testtube taro
InactiveCN1493186AReduce the high demands of transplant managementImprove survival rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePlant TubersPaclobutrazol
A test tube technique for reproducing the konjak features that the paclobutrazol is added to the culture medium MS+NAA5-1 mg / L used for rooting the tissue culture seedlings of konjak, they are cultured at temp higher than 20 deg.C, under light radiation (1000 LX) for 20-25 days to form small bulb, when the weight of small bulb reeches 2-4 g they are cultured at lower than 15 deg.C in dark environment, after cultured in flask for 10-15 day they are sprouted and then transplanted in seedbed, and they are cultured at higher than 20 deg.C, while the fertilizer is proportionally and periodically applied.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
Liquid composite microorganism fertilizer and its preparation method
ActiveCN1911870APromote growthImprove stress resistanceFungiBacteriaDipotassium hydrogen phosphateManganese
The process of preparing liquid compound microbial fertilizer belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The preparation process includes inoculating beer yeast, plant lactobacillus and Bacillus lacticus separately to produce liquid bacteria seeds in conical flasks; mixing potato, brown sugar, glucose, peptone, magnesium sulfate, manganese sulfate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate and sodium chloride in certain weight proportion; dissolving the mixture and heat treatment to sterilize; inoculating beer yeast, plant lactobacillus and Bacillus lacticus successively; gathering after pH value is lowered to 3.5-4.5; and abacterial packing. The liquid compound microbial fertilizer is acid brown liquid with live bacteria content over 1 billion / ml, and may be used as microbial soil improver and as foliage fertilizer to promote plant growth and raise plant resistance.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Phosphate dissolving bacterium and acquisition method thereof
InactiveCN104774784AExtended backendRich genetic resourcesBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateBiological organism
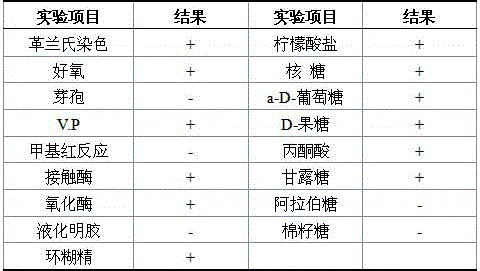
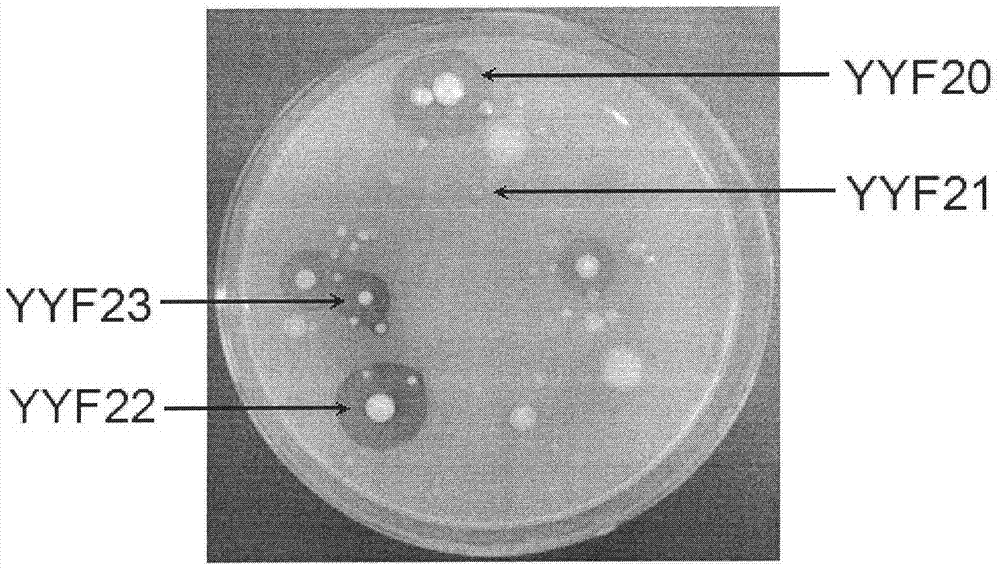
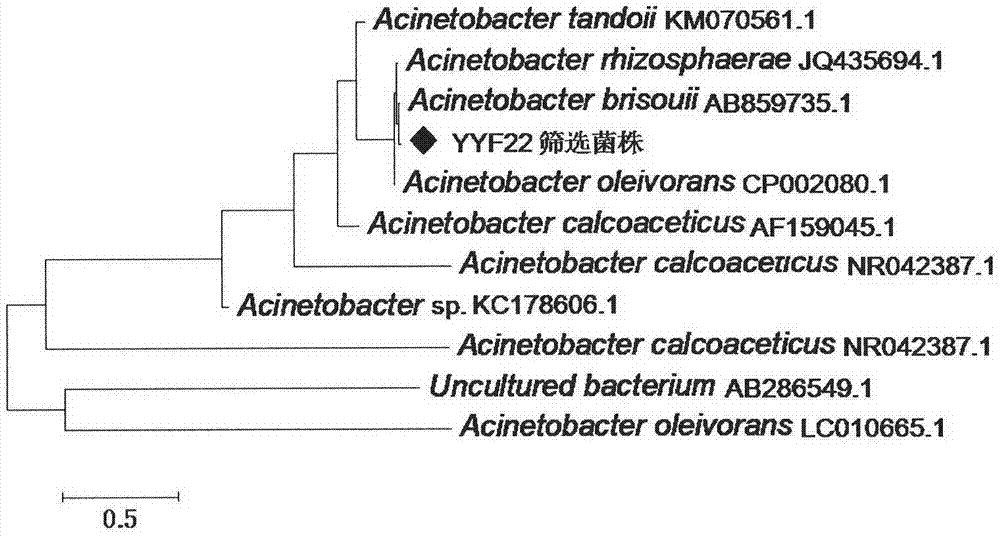
The invention provides a phosphate dissolving bacterium and an acquisition method thereof, belonging to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The phosphate dissolving bacterium and the acquisition method thereof can enrich the genetic resource of wild phosphate dissolving bacteria and enlarge a backup library for whole-genome breeding of phosphate dissolving bacteria. The phosphate dissolving bacterium provided by the invention is named as YYF22 and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with an accession number of CCTCC No: M2015043. The colony characteristics of the phosphate dissolving bacterium are as follows: the YYF22 strain is coccobacillus with a length of 1.2 to 2.9 [mu]m and a width of 0.4 to 1.5 [mu]m; the phosphate dissolving bacterium is normally arrayed in pairs and may independently exist; the phosphate dissolving bacteria sometimes adhere to from a filose shape or chain shape; the phosphate dissolving bacterium is free of flagellum, has a capsule, and cannot move; and on an LB flat, the colony of the bacterium has a neat edge, a moist surface and low bulges, and is glossy and cream yellow.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
China rose salt-resistance strain vitro quick-screening method
InactiveCN101422132AImprove salt toleranceGood repeatabilityCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsSalt resistanceAgricultural science
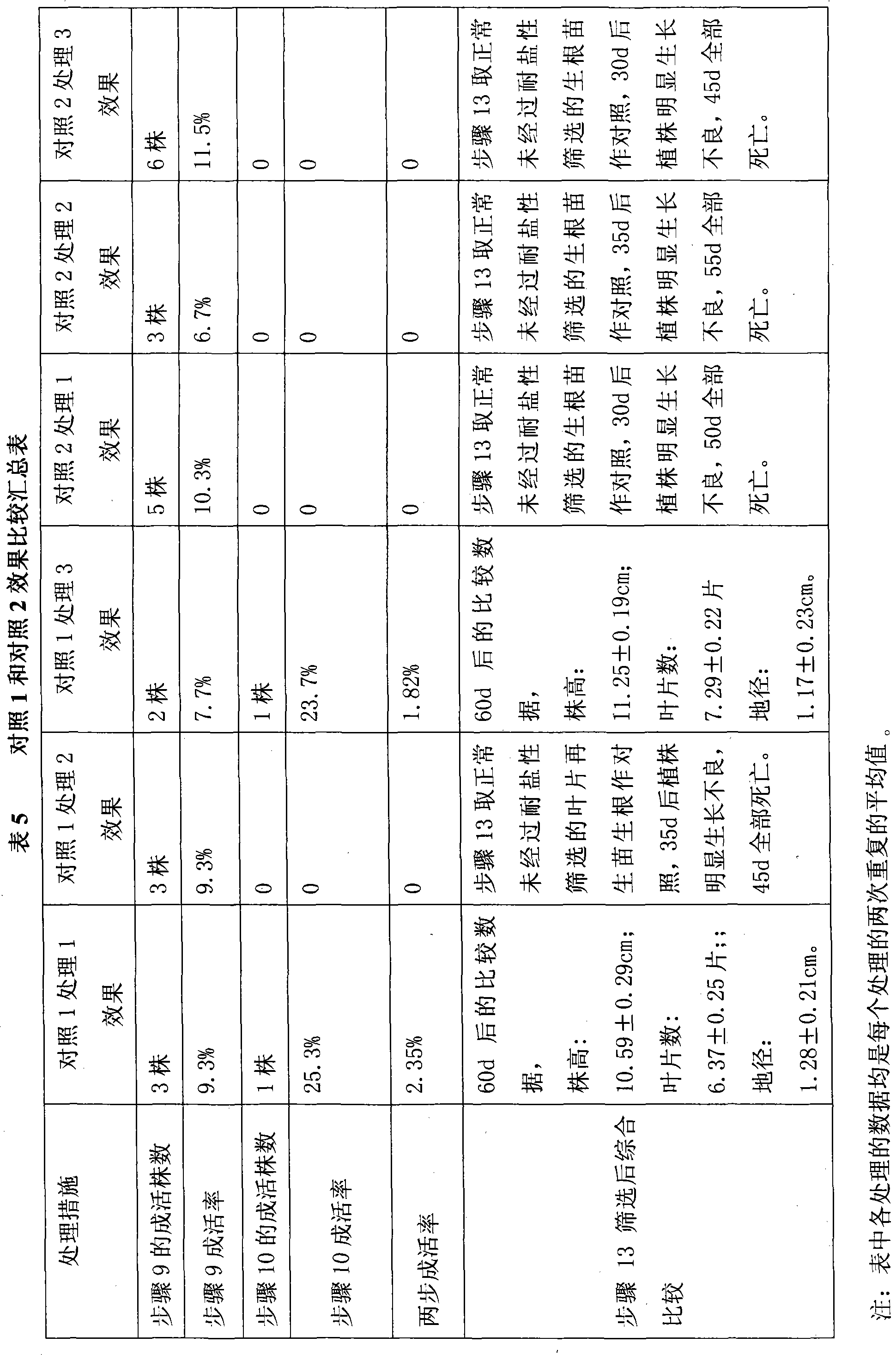
The invention discloses an excised quick screening method for the salt-resistant strains of a China rose, which belongs to the field of agriculture biotechnology. The invention consists of 13 steps of the selecting and sterilizing of an initial explant, sprout inducing, propagation culture, the continuous subculture of propagated seedlings, the direct regeneration of vanes, the indirection regeneration of vanes, physical mutagenesis, mutagenesis resuming and culturing, the excised quick screening of the salt-resistant strains, the quick propagation and re-screening of the salt-resistant strains, resuming and culturing and seedling strengthening, rootage and transplanting. In the invention, the callus or the directly regenerated adventitious bud of the vane of the China rose is used as a processing material to mainly research the four key procedures of the excised screening technology, the subculture propagation, the seedling strengthening and the rootage culturing of the salt-resistant strains; the method has good repetitiveness, can effectively eliminate false positive strains, and obtain the salt-resistant strains with stable heredity; and the average total surviving rate of the salt-resistant screening thereof achieves about 18 percent which is improved by about 16 percent than comparison 1 and is improved about 18 percent than comparison 2; and the salt-resistant screening efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARD & DETECTION TECH YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for horizontal transfection of exogenesis endosymbiosis bacterium to bemisia tabaci gennadius
InactiveCN101220377AOvercoming the problem of easy slidingOvercome the disadvantage of sticking to adultsMicroinjection basedInfection rateEndosymbiotic bacteria
The invention relates to a method for the horizontal transfection of bemisia tabaci of the exogenous endosymbiotic bacteria, which pertains to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The preparation method includes: the purification of the exogenous endosymbiotic bacteria Wolbachia, the collection and fixation of a bemisia tabaci receptor, the horizontal transfection of the exogenous endosymbiotic bacteria Wolbachia to the bemisia tabaci receptor, the collection and fixation of an injection individual and the detection of the endosymbiotic bacteria. The invention is simple and quick, which can successfully transfect the exogenous endosymbiotic bacteria to a bemisia tabaci individual, and a bemisia tabaci offspring has higher infection rate.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Ribosomal protein L9-B based on gene-silencing technology and dsRNA thereof
InactiveCN102220339AResistance to degradationLower synthesis costFermentationPlant genotype modificationRibosomal proteinPest control
Belonging to the field of agricultural biotechnology, the invention relates to a laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment. By a laboratory improved dsRNA feeding method, the invention, from laodelphax striatellus, screens out the laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Ribosomal protein L9-B which can lead to laodelphax striatellus death and has sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.1. Feeding laodelphax striatellus with the dsRNA of the gene fragment provided in the invention can have good lethal effect, thus providing sequence and data bases for establishing new strategies of pest control with RNA interference technology.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of paecilomyces lilacinus biological fertilizer
InactiveCN101671210APromote growthOutstanding disease control effectBiocideBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyPesticide residue
The invention provides a preparation method of paecilomyces lilacinus biological fertilizer, belonging to the technical field of agrobiomechanics, and solving the problems in the prior art. The preparation method comprises the steps of: taking the paecilomyces lilacinus as bacterial strain, inoculating triangular flask liquid bacterial strain, and fermenting with czapek-dox medium to prepare liquid bacterial strain for production; taking decomposed or semi-decomposed fermenting bed padding materials in a culturing farm as basic medium, matching with accessorial carbon source and water, inoculating the liquid bacterial strain, and fermenting in a ventilation way in the depth layer of a solid fermenting pond to prepare paecilomyces lilacinus solid fermentation culture material; and drying the paecilomyces lilacinus solid fermentation culture material and grinding. The invention takes high-effective eelworm biocontrol bacteria paecilomyces lilacinus as the bacterial strain, takes the decomposed or semi-decomposed fermenting bed padding materials in the culturing farm as main raw materials, and ferments to prepare the paecilomyces lilacinus biological fertilizer to be taken as soil microorganism fertilizer which can prevent and cure the parasitic eelworm and various plant pathogenic bacteria, promote the plant growth, and reduce the pesticide residue in the soil.
Owner:福建省农业科学院农业生物资源研究所
Zearalenone degrading enzyme fusion protein and coding gene thereof and application thereof
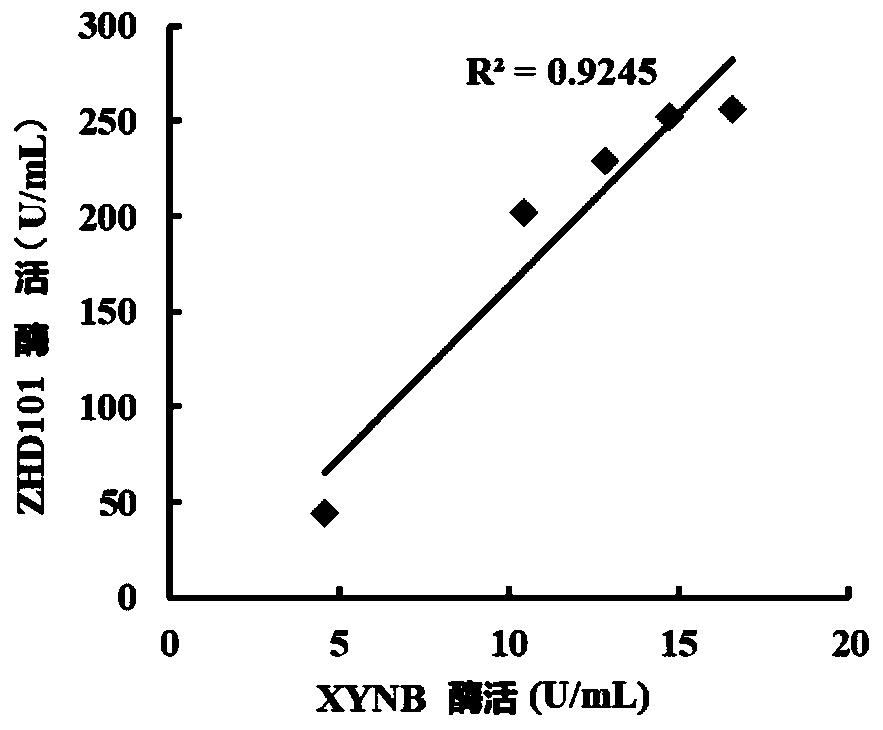
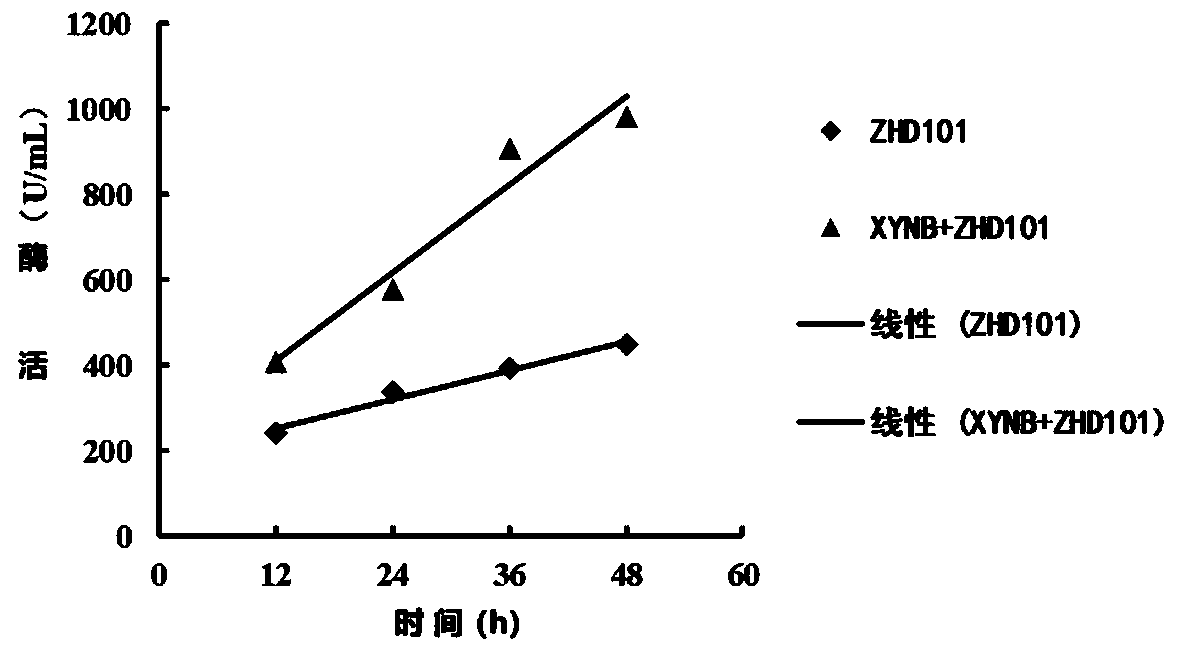
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology, and particularly relates to a zearalenone degrading enzyme fusion protein and a coding gene thereof and application thereof. The zearalenone degrading enzyme fusion protein is composed of a zearalenone degrading enzyme ZHD101 and xylanase XYNB, and an amino acid sequence of the zearalenone degrading enzyme ZHD101 is as shown in SEQID No. 1, and an amino acid sequence of the xylanase XYNB is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. According to the zearalenone degrading enzyme fusion protein and the coding gene thereof and the application thereof, the expression level of the zearalenone degrading enzyme is greatly increased, and the enzyme activity is 2.2 times that of ZHD101 expressed alone.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment
InactiveCN102220339BSignificant lethal effectResistance to degradationFermentationPlant genotype modificationRibosomal proteinPest control
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
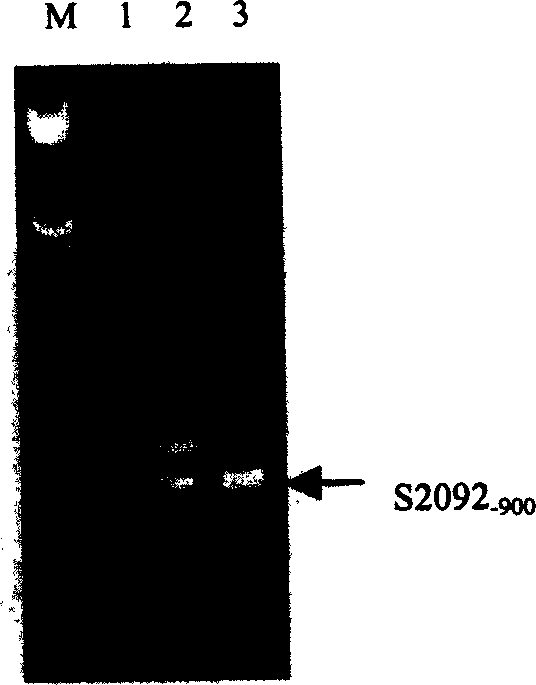
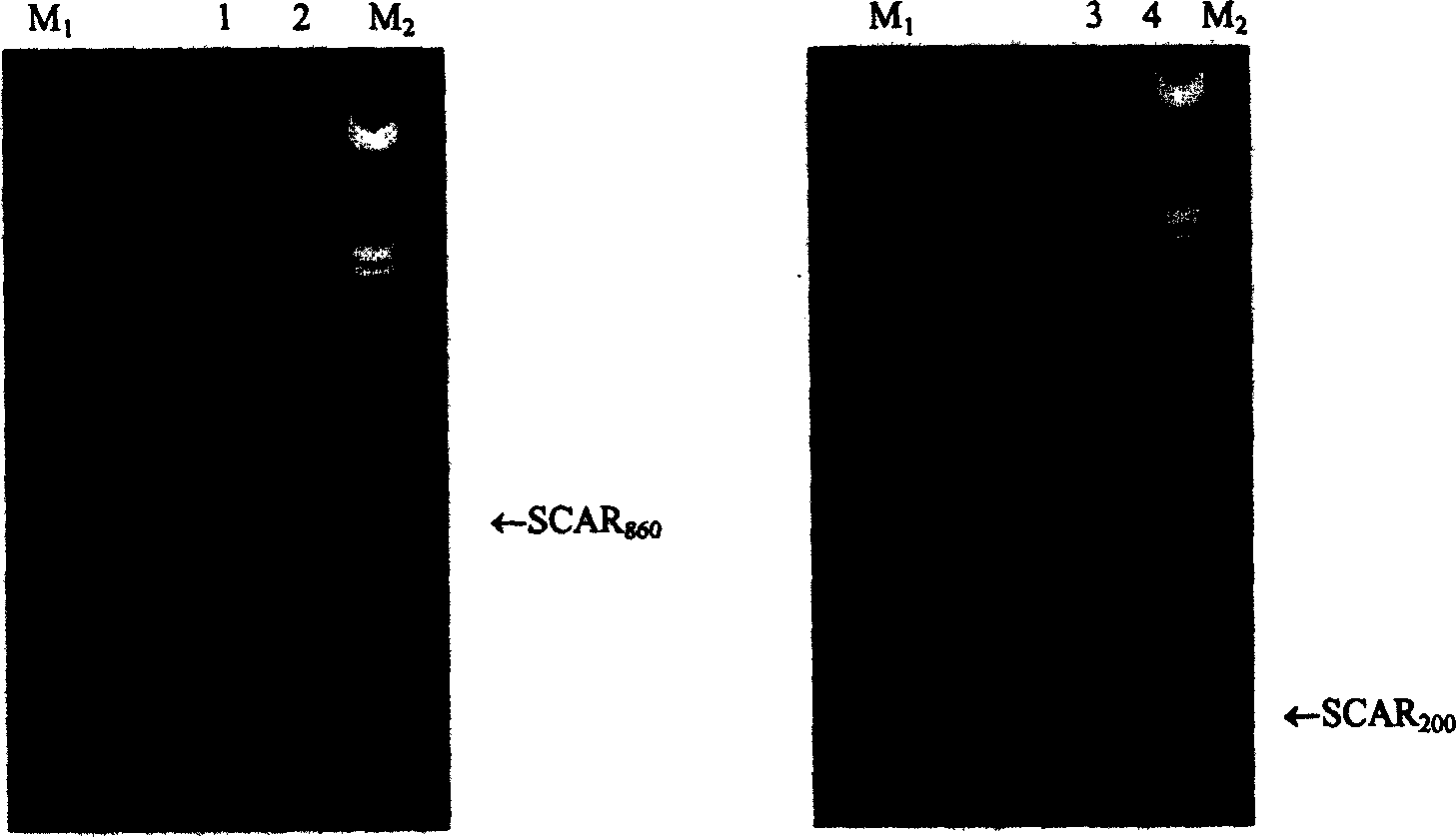
SCAR molecule marker closely linked with wheat anti powdery mildew gene
InactiveCN1556218AOvercoming shortcomings such as long time periodPurposeful aggregationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural biotechnologyTriticeae
A molecular marker SCAR associated with the wheat gene resisting powdery mildew features that the RAPD molecular marking method is used to mark the resistances of wheat parents and their hybrid descendant 'Brock / 015 / / Jing411' and screen from them. The 10bp oligonucleoside is used as random primer to obtain new molecular marker S2092 900, which is then transformed to stable SCAR markers: SCAR860 and SCAR200.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
Pseudomonas putida SRPG-396 and salt-dissolving and growth-promoting application thereof
InactiveCN104531546AMitigate the hazards of salt stressImprove germination ratePlant growth regulatorsBiocideEcological environmentDry weight
The invention relates to pseudomonas putida SRPG-396 and salt-dissolving and growth-promoting application thereof, and belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The accession number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No. 9397. The bacterial strain has the functions of dissolving inorganic phosphorus, and secreting auximone and siderophore, can improve the absorption of elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, iron, and the like by crops, reduce the absorption of sodium, has good salt resistance, can effectively relieve salt stress of crops caused by salinized soil and promote growth of crops under salt stress. When compared with a control, the bacterial strain can significantly improve the germination rate, dry weight, and plant height of crops such as cotton, tomatoes, capsicum and the like under salt stress. The bacterial strain of the invention has the advantages of stable functions, strong environment adaptability, and ecological environment friendliness, can be prepared into products such as microbial agents, biological fertilizers, and the like, has great development potential for industrial products, and has good application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Culture medium for in-vitro induced regeneration plants of double-haploid stems of potatoes
InactiveCN102870682ASolve the key technical problems of low regeneration rateImprove seedling ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEthylenediamineSucrose
The invention discloses a culture medium for in-vitro induced regeneration plants of double-haploid stems of potatoes, which belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnologies. The culture medium comprises the following compositions: potassium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, monopotassium phosphate, magnesium sulfate, calcium chloride, potassium iodide, boric acid, manganese sulfate, zinc sulfate, sodium molybdate, copper sulfate, cobalt chloride, ferrous sulfate, disodium ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, nicotinic acid, pyridoxine hydrochloride, glycine, glutamine, casein hydrolysate, yeast extracts, sucrose, 6-benzylaminopurine, naphthalene acetic acid, kinetin, zeatin and heteroauxin beilining. The culture medium is applied to the induction and culturing of double-haploid stem regenerated seedlings of potatoes, the test effect is good, the initiating rate is increased by 76%, and the seedling rate is as high as 80.5%. The regeneration rate of double-haploid stems of potatoes is significantly increased, thereby laying a foundation for the establishment of a genetic transformation system; and the culturing mode adopts a one-step seedling method, so that the pollution probability is reduced.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Production process for fermenting biocontrol trichoderma by using Chinese herbal medicine dregs
InactiveCN101748070AImprove protectionReduce pollutionBiocideFungiAdditive ingredientChinese traditional
The invention relates to a method for fermenting biocontrol trichoderma spores by using Chinese herbal medicine dregs as main culture substrate materials, belonging to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The biocontrol trichoderma has obvious effect on controlling various plant diseases, and the development of the production process for improving spore yield, shortening fermentation time and reducing fermentation cost is favorable for preparing the biocontrol trichoderma into preparations. The technical essential of the invention is to use the Chinese herbal medicine dregs as main raw materials to manually ferment and culture biocontrol trichoderma such as trichoderma viride, trichoderma harzimum and the like, and the production process comprises the steps of strain culture, preparation of fermentation substrates, inoculation, spore culture and the like. The invention is mainly characterized in that the raw materials used as culture substrate materials are obtained by selecting waste Chinese herbal medicine dregs through a proper formula after medicinal components are extracted in the process of preparing Chinese traditional medicines in a Chinese traditional medicine factory to be used for fermenting and culturing the biocontrol trichoderma. The method has simple process, easy acquisition of raw materials and low cost. The biocontrol trichoderma spore microbial inoculum produced by the method has better storage resistance and biocontrol activity.
Owner:텐진인스티튜트오브플랜트프로텍션
Method for preventing and treating bemisa babaci by utilizing RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) interference technology
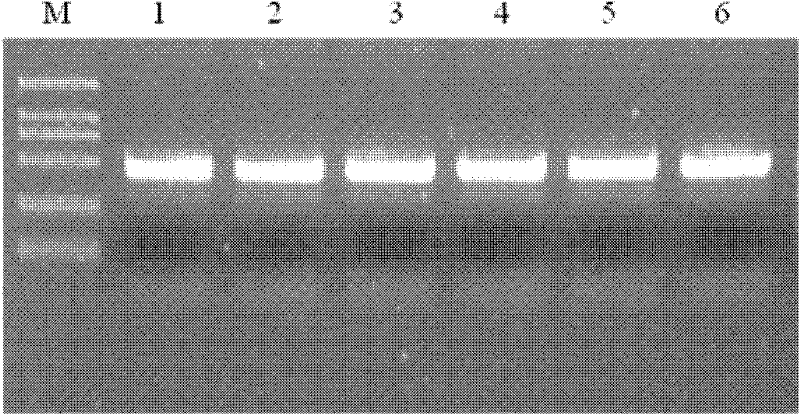
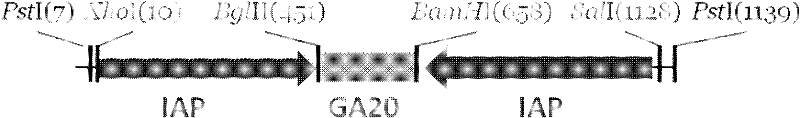
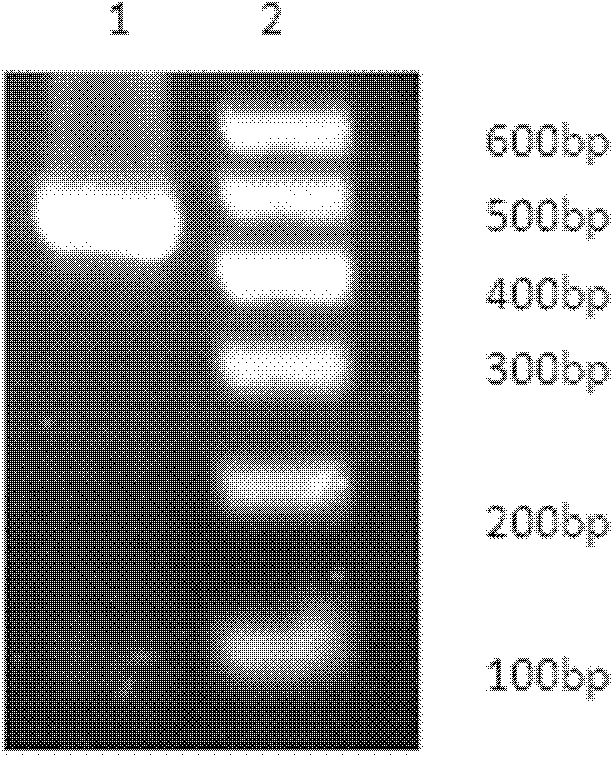
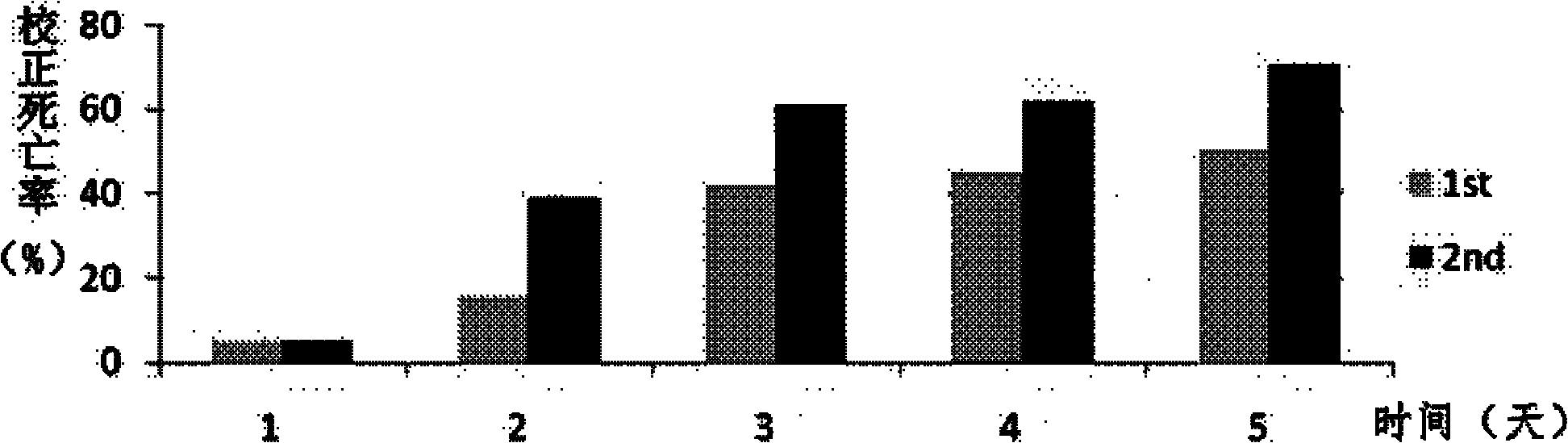
InactiveCN102212522AEasy to controlIn line with habitsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsInhibitor of apoptosisComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention provides a method for preventing and treating bemisa babaci by utilizing an RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) interference (RNAi) technology, belonging to the technical field of agriculture and biology. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting a target sequence IAP (Inhibitor Of Apoptosis Protein) gene of RNAi according to a gene sequence of the bemisa babaci and designing a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification primer of the target sequence; (2) extracting the RNA of the bemisa babaci and carrying out transcription to obtain a cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid); then carrying out PCR amplification on the cDNA and purifying to prepare a target gene; (3) inserting the target gene into an expression vector to prepare the expression vector containing the target gene; (4) and transforming the expression vector containing the target gene into a crop to obtain a transgenic crop for preventing and treating bemisa babaci; and planting the crop. The method provided by the invention has important guiding value and theoretical significance on researching the gene function of the bemisa babaci by utilizing the RNAi technology, preventing and treating the bemisa babaci by utilizing the RNAi technology, and preventing and treating the bemisa babaci by utilizing the transgenic crop.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Gene silencing technique based Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Alpha1-tubulin and dsRNA thereof
InactiveCN102220344ASignificant lethal effectResistance to degradationFermentationPlant genotype modificationMortality rateGene silencing
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural and biological technology and relates to a gene silencing technique based Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Alpha1-tubulin and a dsRNA thereof. The invention is to screen the Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Alpha1-tubulin, which can lead to the death of Laodelphax striatellus after interference and has a sequence representedby SEQ ID No.1, from Laodelphax striatellus by using a laboratory improved dsRNA feeding method. When the dsRNA of the gene fragment is used for feeding Laodelphax striatellus, the adjusted mortalityof the Laodelphax striatellus may reach 70 percent, and a sequence basis and a data basis are provided for the construction of a new policy of controlling pests by using RNA interference technology.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker method for avirulence gene of rice blast
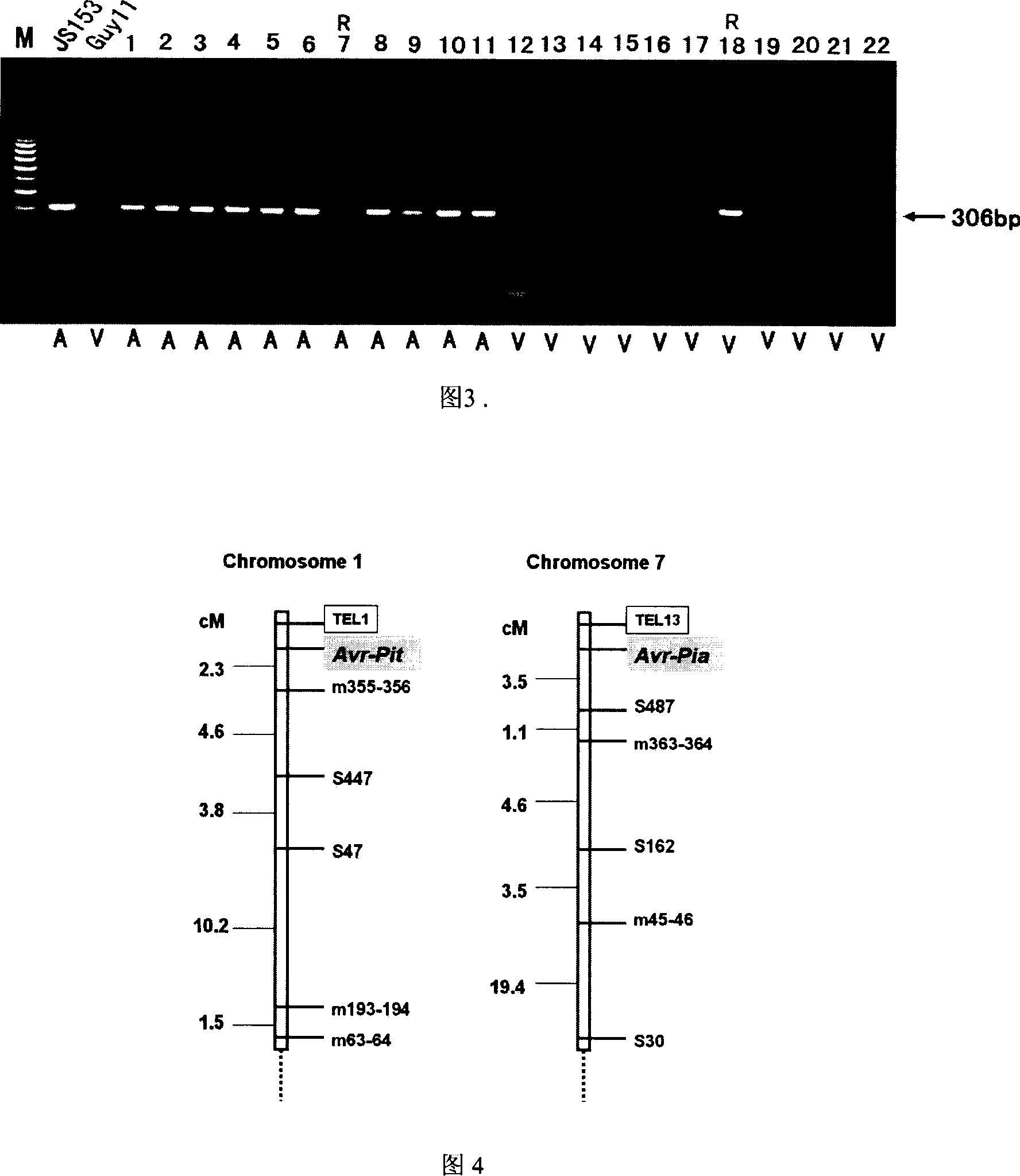
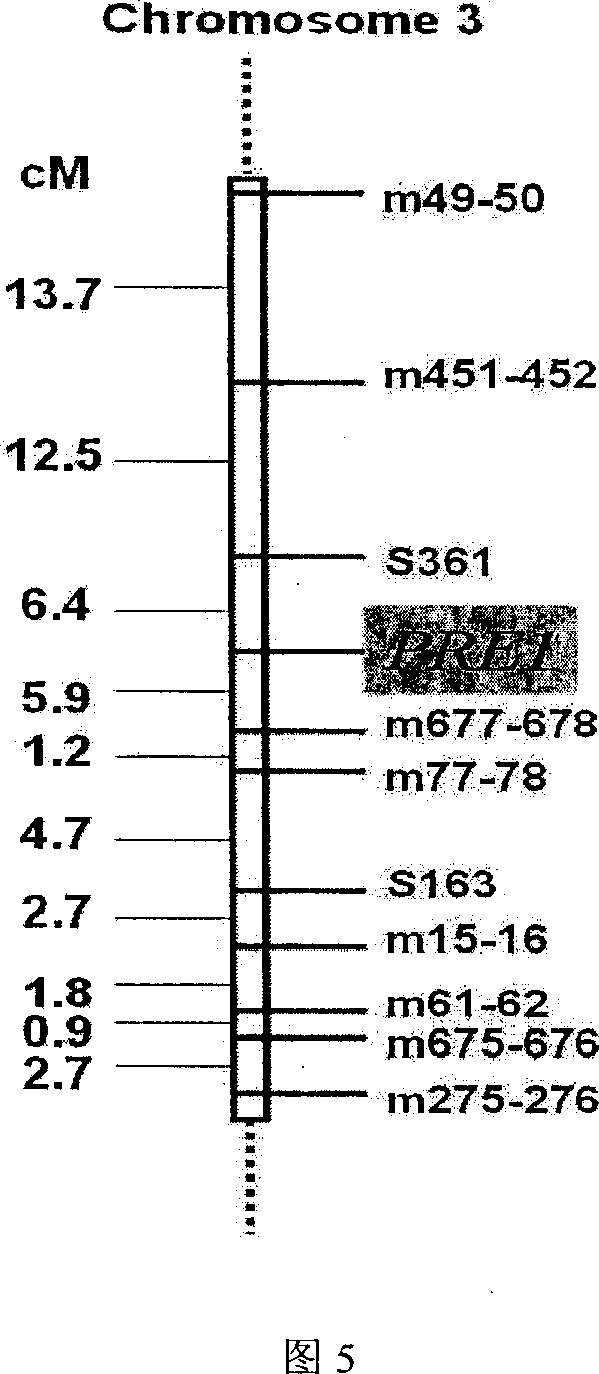
InactiveCN1952177AReveal Toxic ComponentsReveal featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPyricularia griseaParental strain
The invention of molecular labeling method of Pyricularia grisea avirulent gene belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The molecular labeling technology includes performing molecular labeling to avirulent gene though assessment from two parental strains and filial generation groups of Pyricularia grisea. M355-356 labeled by SSR near NO. 1 chromosome telomere links with avirulent gene Avr-Pit with a genetic distance of 2.3cm; S487 labeled by RAPD located near NO. 7 chromosome telomere links with avirulent gene Avr-Pia with a genetic distance of 3.5cm; S361 labeled by m677-678 and RAPD located at middle of N0. 3 chromosome telomere links with Pyricularia grisea specified avirulent gene PRE1 with genetic distances of 5.9cm and 6.4. The invention can not only make use of the nontoxic gene marker as gene probe, but also set foundations for further clone of the gene through physical mapping.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly extracting DNA from plant leaves
The invention discloses a method for quickly extracting DNA from plant leaves, and relates to a method for quickly extracting beet total DNA by using leaf tissues. The method comprises the following steps: directly grinding leaves in a grinding pestle centrifuge tube, performing high-temperature water bath treatment by using an extracting buffer solution, and adding a separation medium to perform high-speed centrifugation. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in step, less in required tissue sample, less in toxic chemical reagent, low in cost, short in operation time and good in experimental effect. The obtained DNA can be directly used for PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification of nucleoplasm gene fragments, and applied to molecular biology tests of molecular markers, fingerprint spectrums and the like, so that a DNA nucleic acid base material is provided for agricultural biotechnology molecular breeding and researches in the field of molecular biology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multi-seedling autogenic relay growth method for seeds of amorphophallus muelleri
The invention relates to a multi-seedling autogenic relay growth method for seeds of amorphophallus muelleri, and belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The multi-seedling autogenic relay growth method includes 1, processing the seeds; 2, soaking the seeds in solution containing 3% of potassium permanganate by 30 minutes to bactericide the seeds; 3, soaking the seeds in cold water for three days; 4, soaking the seeds in thiourea with the concentration of 0.1-3% or mixed liquid containing 400ppm GA3, 33ppm IBA and 33ppm 6-BA for 12 hours; and 5, breaking dormancy of the seeds and sowing the seeds. In the procedure for breaking the dormancy of the seeds and sowing the seeds for breeding seed bulbs, the moisture content of soil keeps 25-45% after the seeds are sown in the soil. As shown by test results, a germination rate of the seeds can reach 95% at least after seed dormancy breaking, an emergence rate of the seeds reaches 90% at least, the maximum weight of harvested seed bulbs of the amorphophallus muelleri is 710g, and the average weight of the harvested seed bulbs of the amorphophallus muelleri is 500g. The multi-seedling relay growth method has the advantages that a procedure is simple, and operation is convenient; by combining dormancy breaking with a germination accelerating and seedling raising mode, the germination speed and the germination rate of the seeds of the amorphophallus muelleri can be effectively increased, and the germination uniformity of the seeds of the amorphophallus muelleri can be effectively improved; and the quality of spouts is improved, the amorphophallus muelleri production period is shortened, and the method can be efficiently applied to large-scale production for commercial amorphophallus muelleri or seed bulbs in amorphophallus muelleri plantation.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV +1
Preparation method of biological bacterial fertilizer for improving stress resistance of plants
InactiveCN102863262AReduce diseaseImprove drought resistanceBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationBiotechnologyEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a preparation method of biological bacteria fertilizer for improving stress resistance of plants, which belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology; and the preparation method is characterized in that the biological bacteria fertilizer consists of following components by weight percent that: 5 to 10 percent of biological bacteria strain, 20 to 30 percent of animal excrement, 40 to 50 percent of pool mud, 10 to 15 percent of decomposed coal and water in balance. The preparation method comprises following steps that the raw materials are adequately stirred and mixed according to the proportion and placed inside a fermentation pond to be thermo-modulated and fermented for 30 days, after the fermentation is completed, the material is crushed and filtered by a 100-mesh coarse sieve to obtain the powder preparation, and the prepared preparation is placed inside a packaging bag with a moistening function, so that the bagged solid bacteria fertilizer product is formed. The preparation method has characteristics of simplicity, convenience in obtaining of raw materials, low cost and good economic benefit.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly reproducing new pteris fern seedlings by using prothallium reproduction approaches
ActiveCN102715092ASame biological ageGrow neatlyCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsSporophyteSeedling
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology and relates to a method for rapidly reproducing new pteris fern seedlings by using prothallium reproduction approaches. The method comprises the steps of prothallium culture process, multiplication culture process, sporophyte induction process, rooting induction process, and transplant and manage process. The technological process is simple; by reproduction in the form of prothallium, a great amount of prothallium can be obtained; by the processes of multiplication, sporophyte induction, sporophyte rooting and transplant, a great number of seedlings capable of being used for production and culture can be obtained; the obtained seedlings are at the same physiological age and grow uniformly; and the method is suitable for industrial seedling raising and scale culture.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Gene silencing technique based Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Tubulin and dsRNA thereof
InactiveCN102220340AResistance to degradationLower synthesis costFermentationPlant genotype modificationMortality rateGene silencing
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural and biological technology and relates to a Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment thereof. The invention is to screen the Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Tubulin, which can lead to the death of Laodelphax striatellus after interference and has a sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1, from Laodelphax striatellus by using a laboratory improved dsRNA feeding method. When the dsRNA of the gene fragment is used for feeding Laodelphax striatellus, the maximum adjusted mortality of the Laodelphax striatellus may reach 67.4 percent, and a sequence basis and a data basis are provided for the construction of a new policy of controlling pests by using RNA interference technology.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
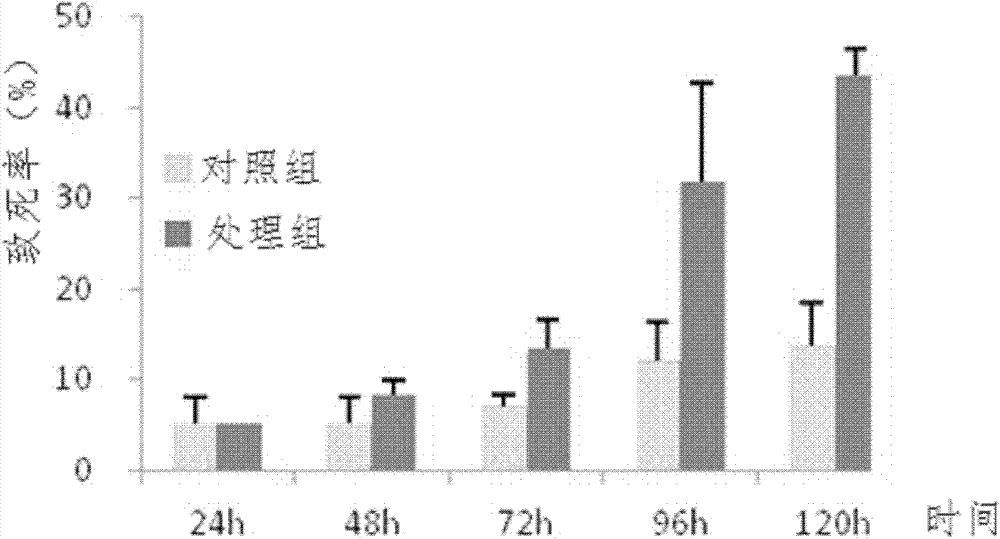
Dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP and application of dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP in mycotoxin detoxification
ActiveCN111073867AImprove degradation efficiencyHigh catalytic efficiencyOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringMycotoxinAgricultural biotechnology
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology, and specifically relates to a dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP as well as an encoding genes and application thereof; and the dyedecolorizing peroxidase BsDyP disclosed by the invention has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 or SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention further discloses a gene encoding the dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP; and the gene encoding the dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP has a DNA sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 3 or SEQ ID NO. 4. The invention still further discloses a preparation method of the dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP as well as application of the dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP in mycotoxin detoxification, and a preparation method of a mycotoxin biodegradation agent by using the dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP as well as application of the prepared mycotoxin biodegradation agent. Thus, the dye decolorizing peroxidase BsDyP disclosed by the invention has great application prospect in the field of mycotoxin detoxification.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for exsomatizing screening grassiness salt resistsomatic mutation body
ActiveCN101161055AImprove selection efficiencySpeed up the processHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCallithamnion granulatumPennisetum purpureum
The invention relates to an screening method in vitro of elephant grass salt-tolerant somatic mutant belongs to a field of agricultural biotechnology. The process is: granular callus is transferred into proliferation medium with 16g / L NaCl, into differentiation medium with 16g / L NaCl after 45 days, and into rooting medium with no NaCl after 35 days to get regeneration plant; pot salt-tolerance identification of the regeneration plant is applied after tidal flat field comprehensive agronomic characters evaluation and grass-production measurement to get plants of which the fresh grass yield is higher than a control by 23.8% in tidal flat field with pH8.67-9.01; the fresh grass increment of the first time and the second tiome of cutting for the clonal progeny of the plants is higher than the control by 9.2% and 7.4% respectively in 1 / 2Hoagland nutrient solution with 8.25g / L sea-salt; therefore, the salt-tolerant somatic mutant of good comprehensive agronomic characters and significantly high salt-tolerance is selected. The invention has the advantages of simple-operation, short-cycle, and high selection efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of microorganism immobilization particles for removing residual pesticide in soil
InactiveCN102653754ALow priceLow costContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganism based processesMineral particlesEdaphic
The invention discloses a preparation method of microorganism immobilization particles for removing residual pesticide in soil, belonging to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing the environment-friendly mineral particles and the plant waste dried at constant temperature to constant weight into particles, and mixing the particles proportionally to obtain a carrier; sufficiently mixing the liquid of the microorganism strain and the carrier according to the volume-to-weight ratio ml:g of (1:0.1)-(1:0.5); uniformly stirring by taking glutaraldehyde as a cross-linking agent and standing at 4 DEGE C for 2-6 hours, and performing cross-linking to obtain immobilization particles; and washing the immobilization particles with distilled water and drying to obtain the microorganism particles. According to the invention, the carrier material is low in cost, widely available and non-toxic to organisms, has good air permeability and does not cause secondary pollution to the soil; and the carrier and the immobilization technology thereof can be applied to the immobilization of the microorganisms of multiple strains such as fusobacterium and the like, and the microorganism immobilization particles are directly spread into the soil without damaging the original soil structure.
Owner:中华人民共和国沈阳出入境检验检疫局 +1
Method for producing polypeptide enramycin with zymotechnics
InactiveCN101245362AHigh potencyAchieve high density cultureMicroorganism based processesFermentationAntibiotic YBacterial strain
The invention relates to a method for producing polypeptide antibiotics enramycin by the fermentation method, which pertains to the fields of agricultural biotechnology, industrial biotechnology and the fermentation engineering. The method is as follows: (1) slant culture: a Streptomyces sp.NJWGY3665 bacterial strain is inoculated in a glucose nutrient culture medium to carry out the slant culture, the culture temperature is 28 to 37 DEG C and the culture time is 2 to 6 days; (2) seed culture: a spore which is cultured on a slant is produced into a single-spore suspension by using sterile water, which is also inoculated in a seed culture medium for culture, the temperature is 28 to 32 DEG C, the rotational speed is 200rpm and the culture lasts for 2 to 6 days; (3) fermentation culture: the seed liquid is inoculated in a fermentation culture medium for culture, the temperature is controlled at 28 to 37 DEG C, the pH is controlled at 6.0 to 9.0, the rotational speed is 180 to 220rpm, the fermentation lasts for 5 to 9 days, so as to obtain the Streptomyces sp., methanol or ethanol is used for the extraction and separation of mycelium through the method of centrifugal separation, then the resin method is adopted for carrying out refining, so as to obtain the peptide antibiotics enramycin.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com