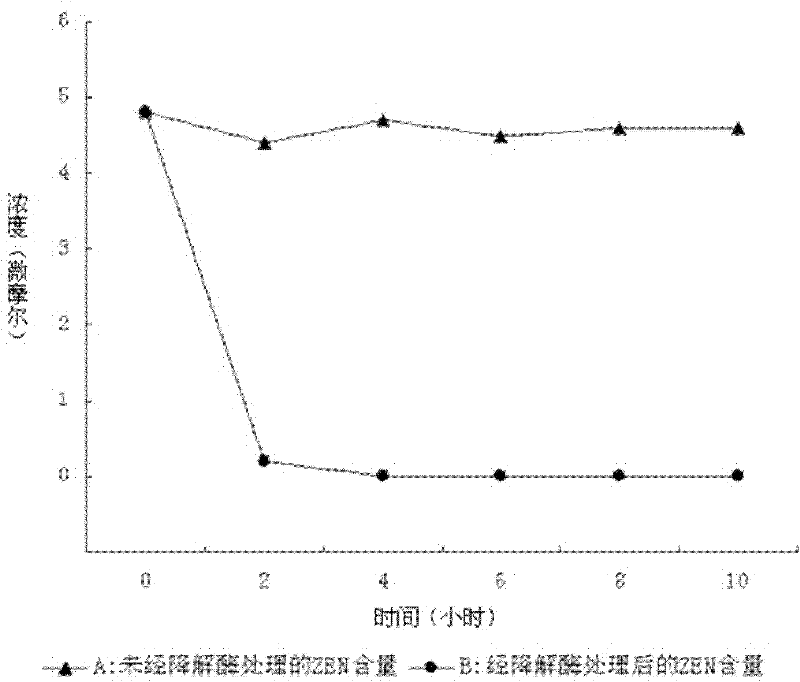
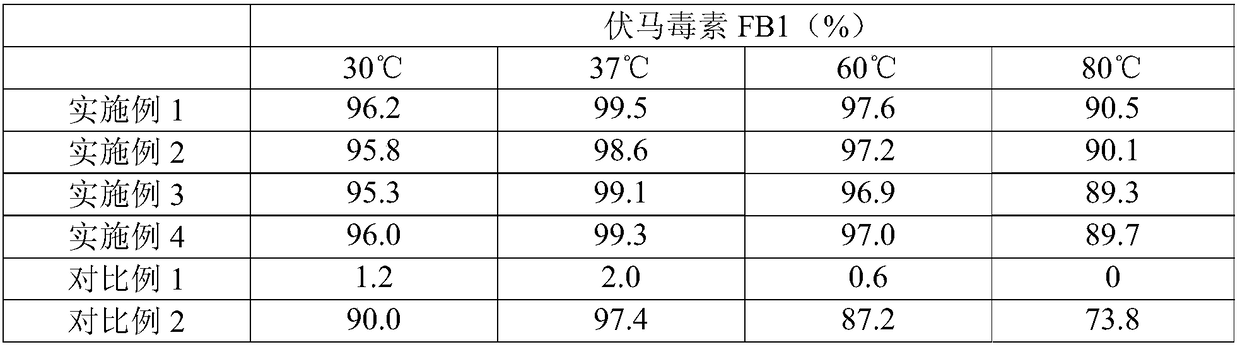
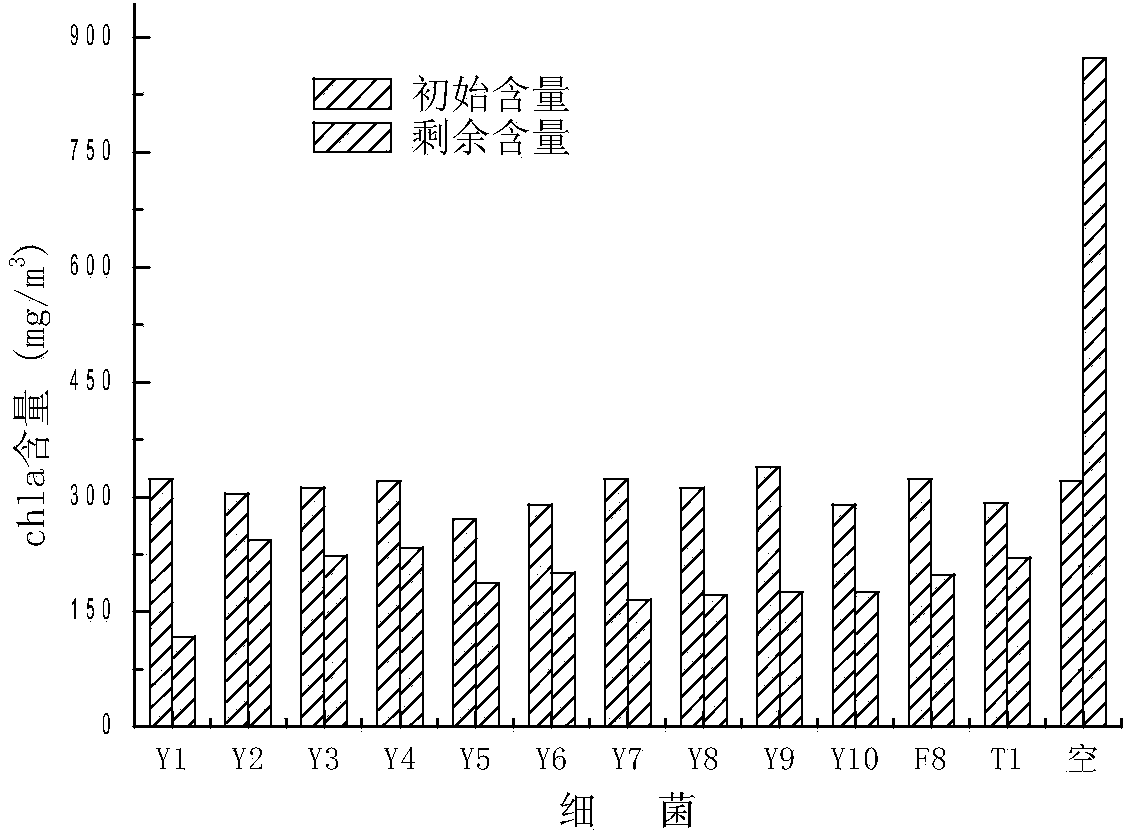
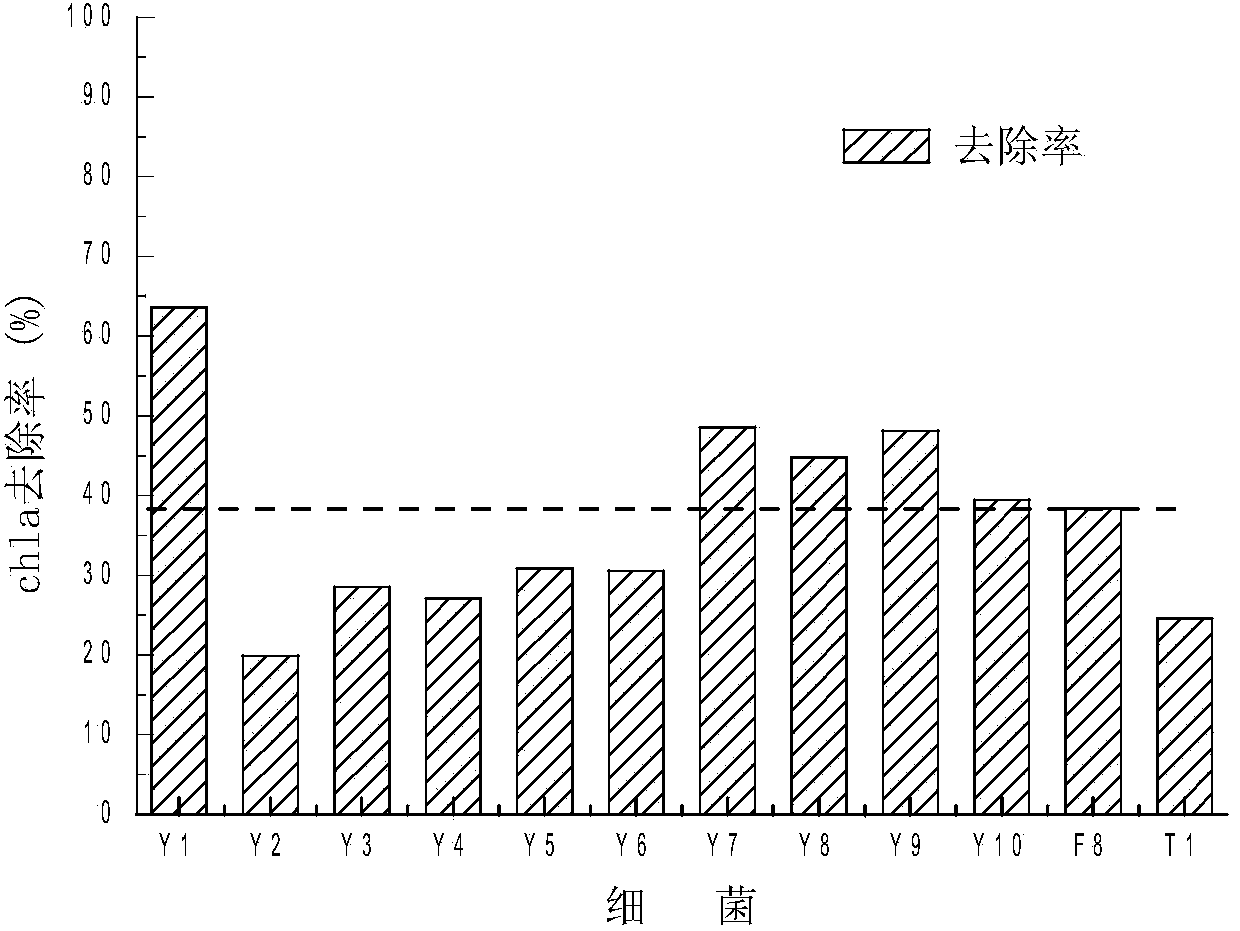
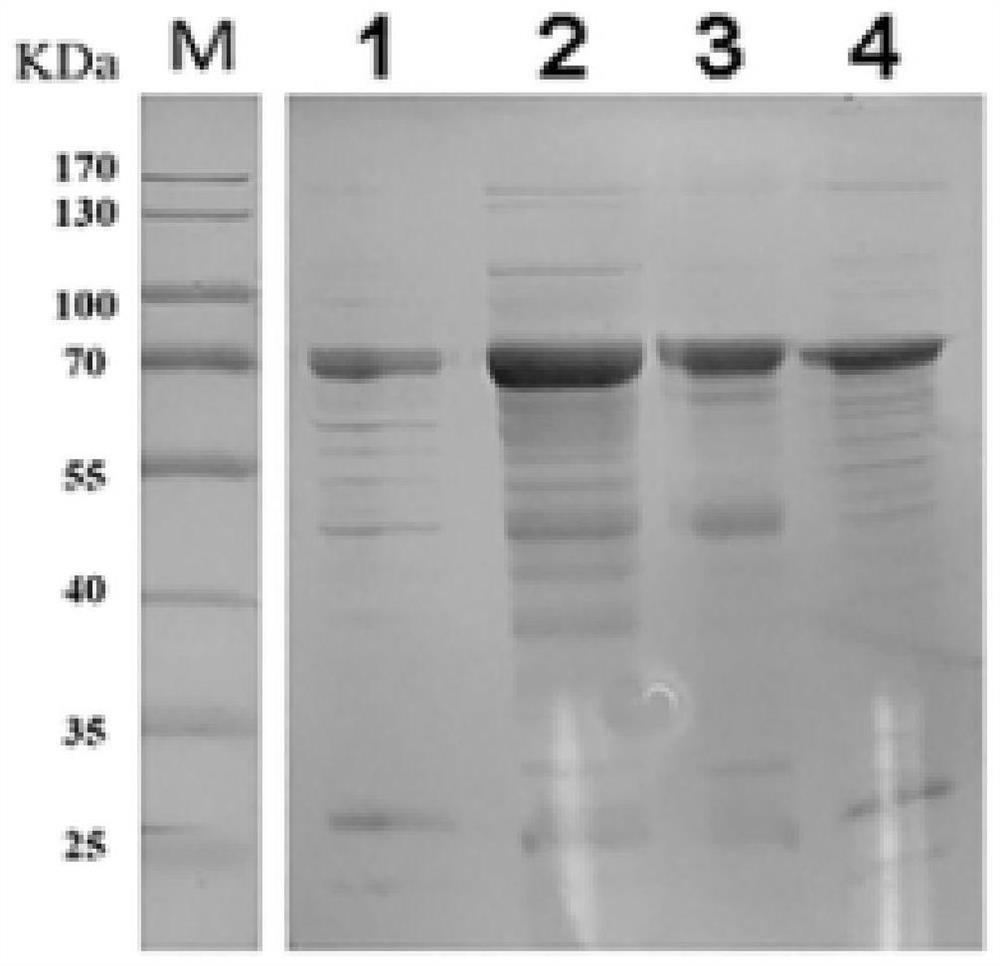
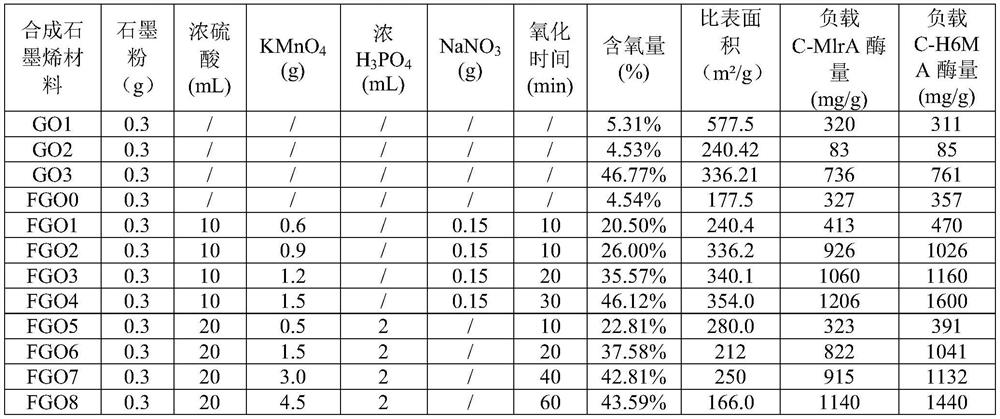
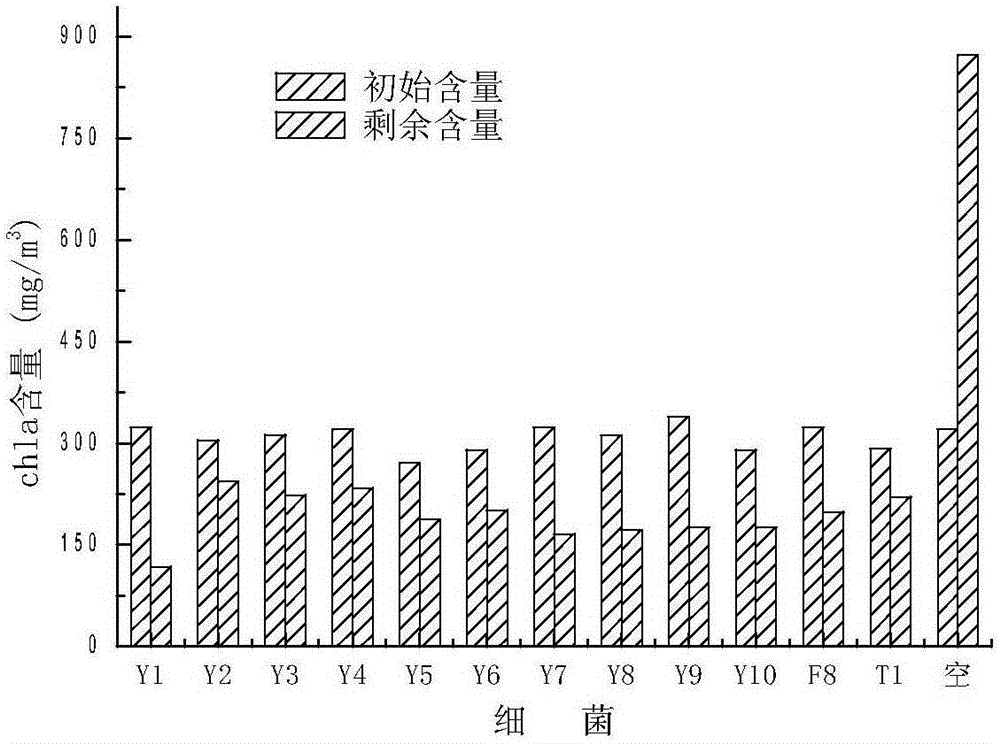
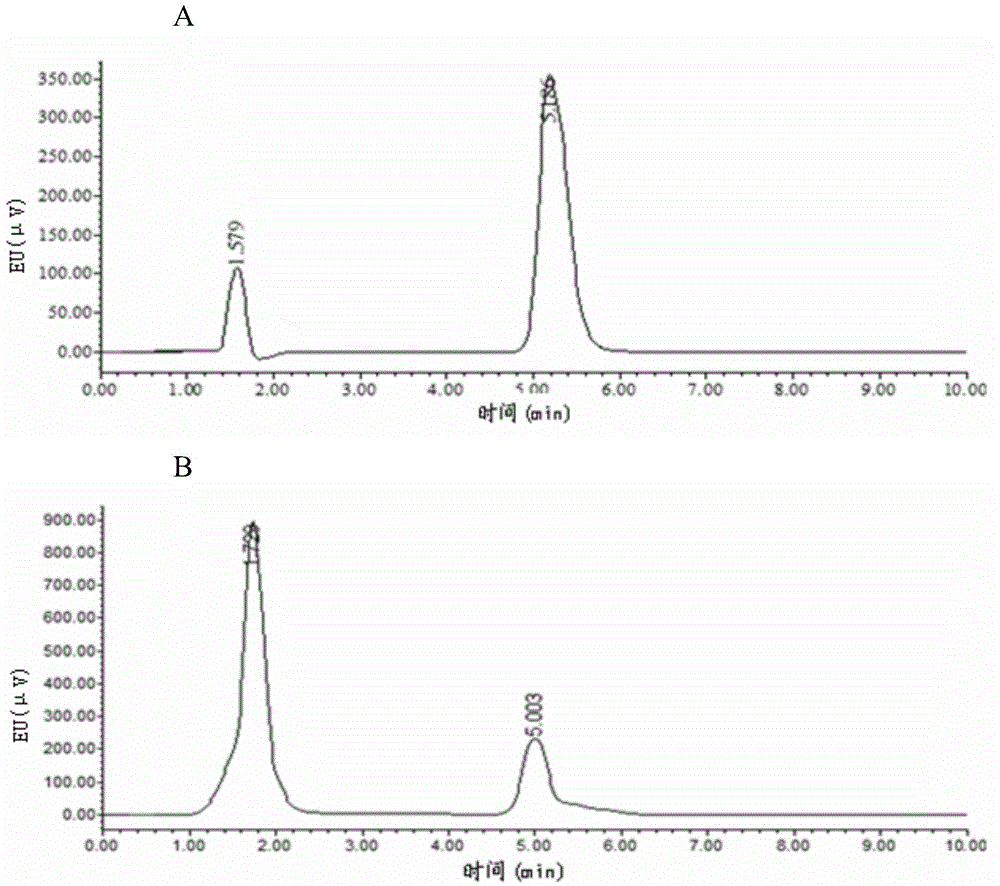
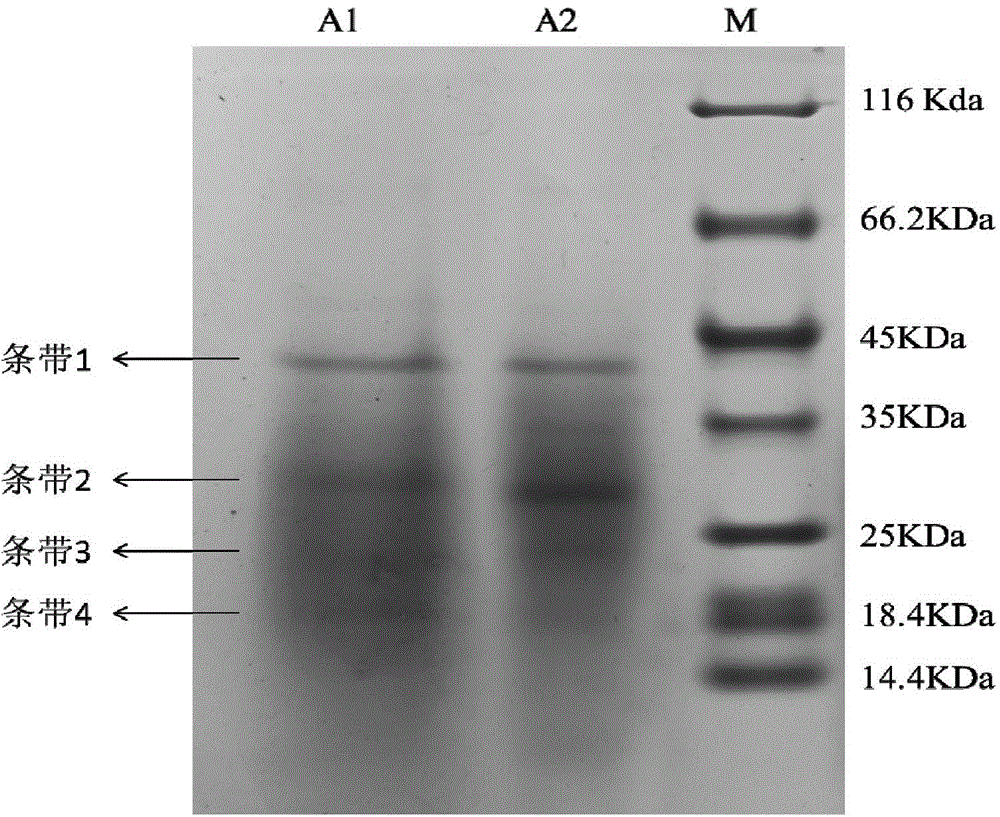
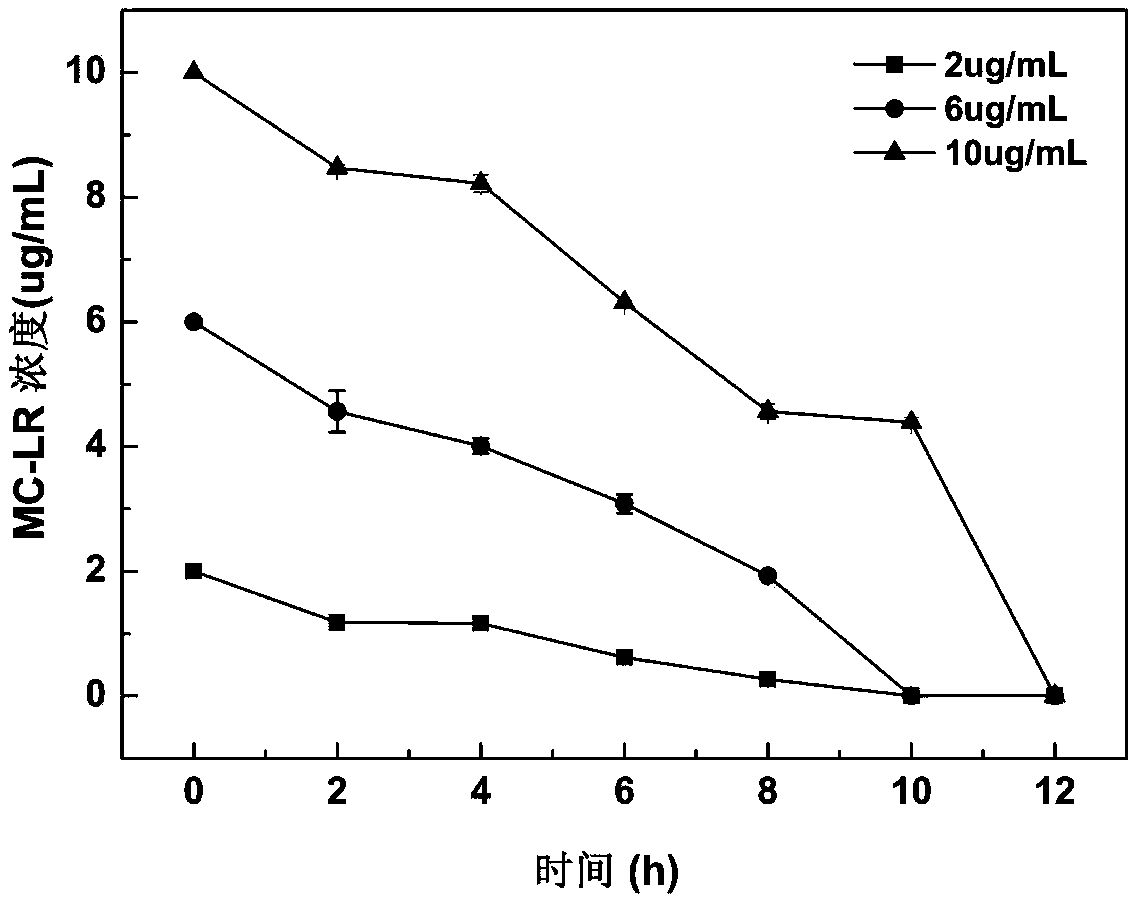
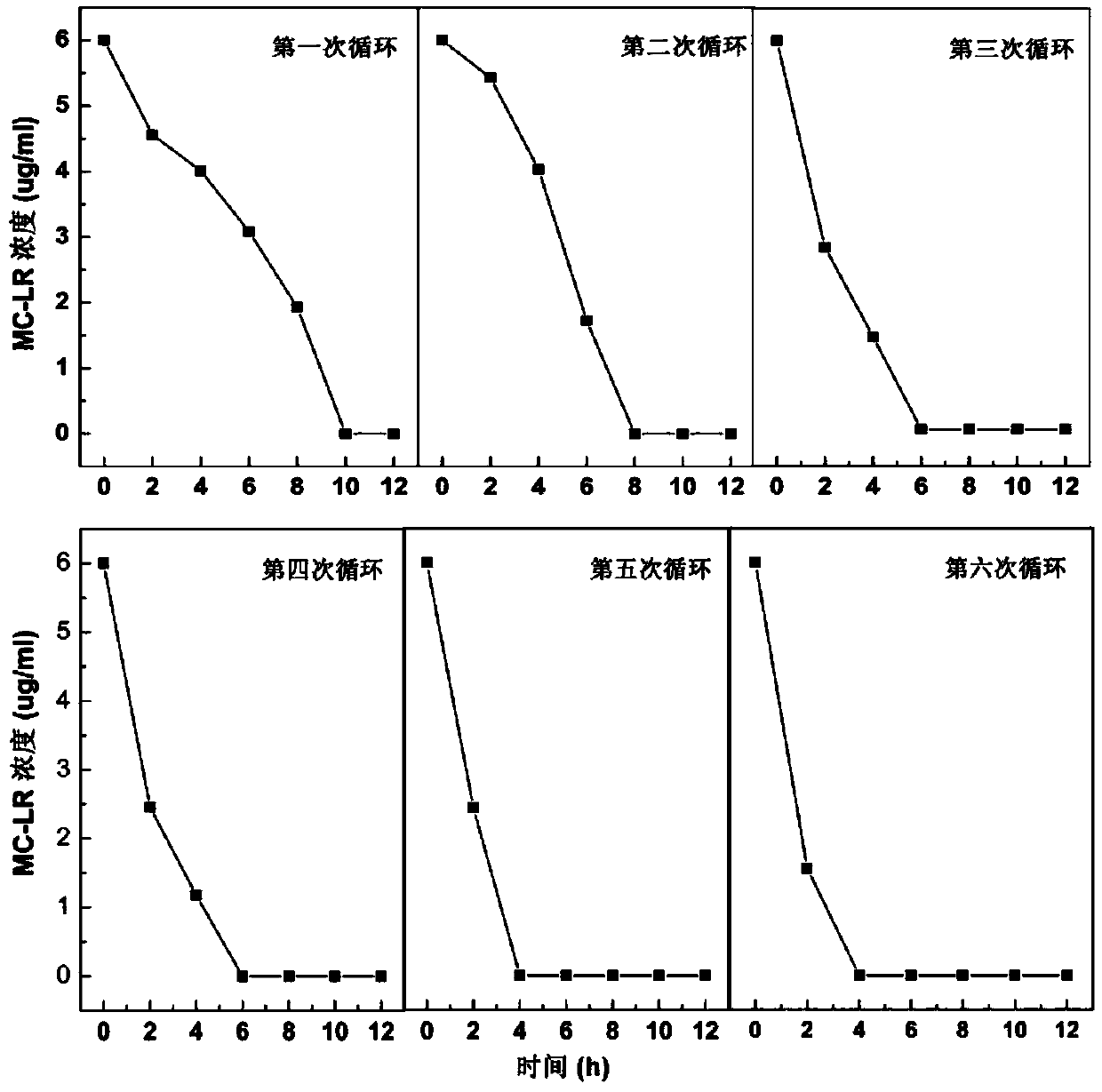
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Toxin degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The effects of storage conditions on viability of Clostridium difficile vegetative cells and spores and toxin activity in human faeces. ... On the basis of our results, we recommend that specimens should be stored at 4°C instead of −20°C to minimise toxin degradation.
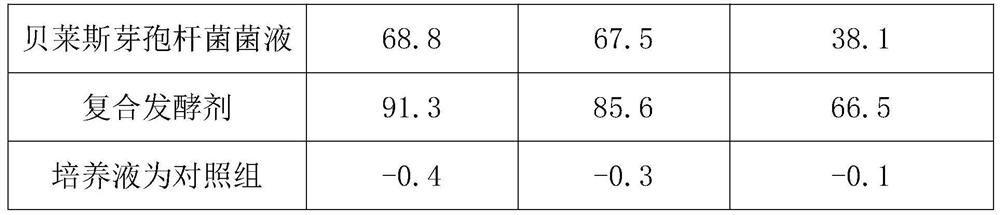
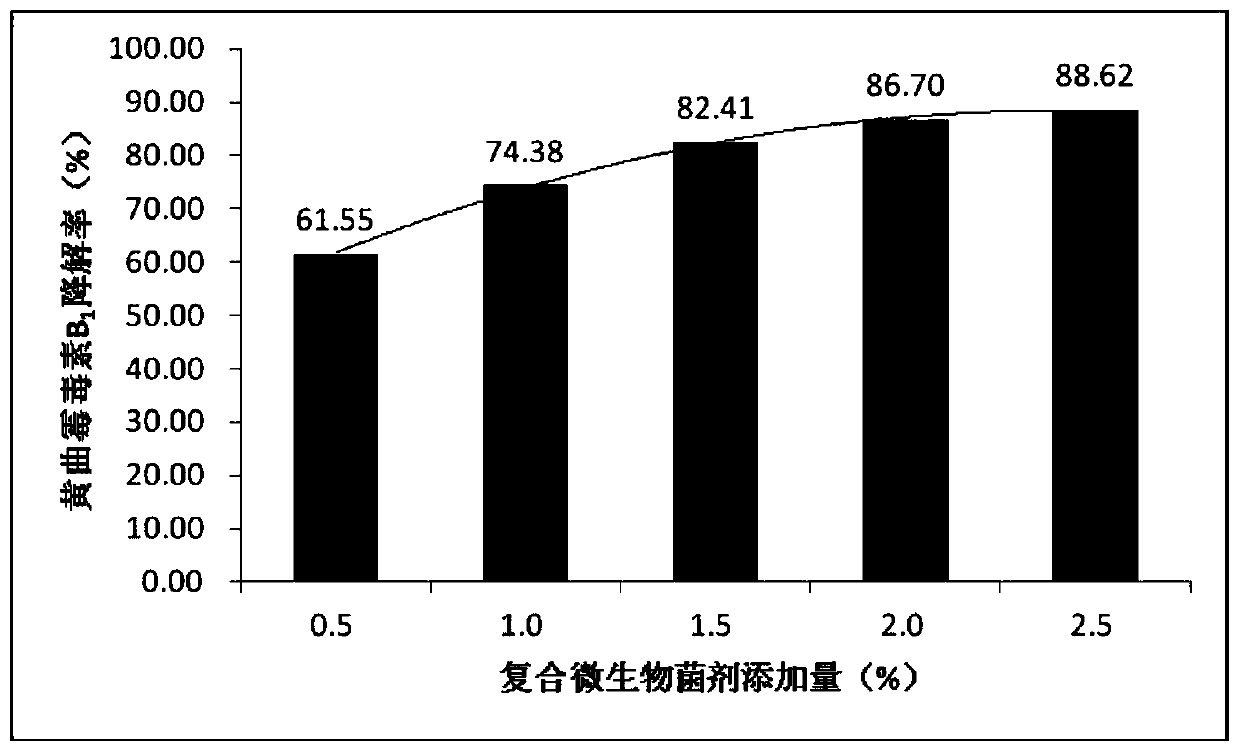
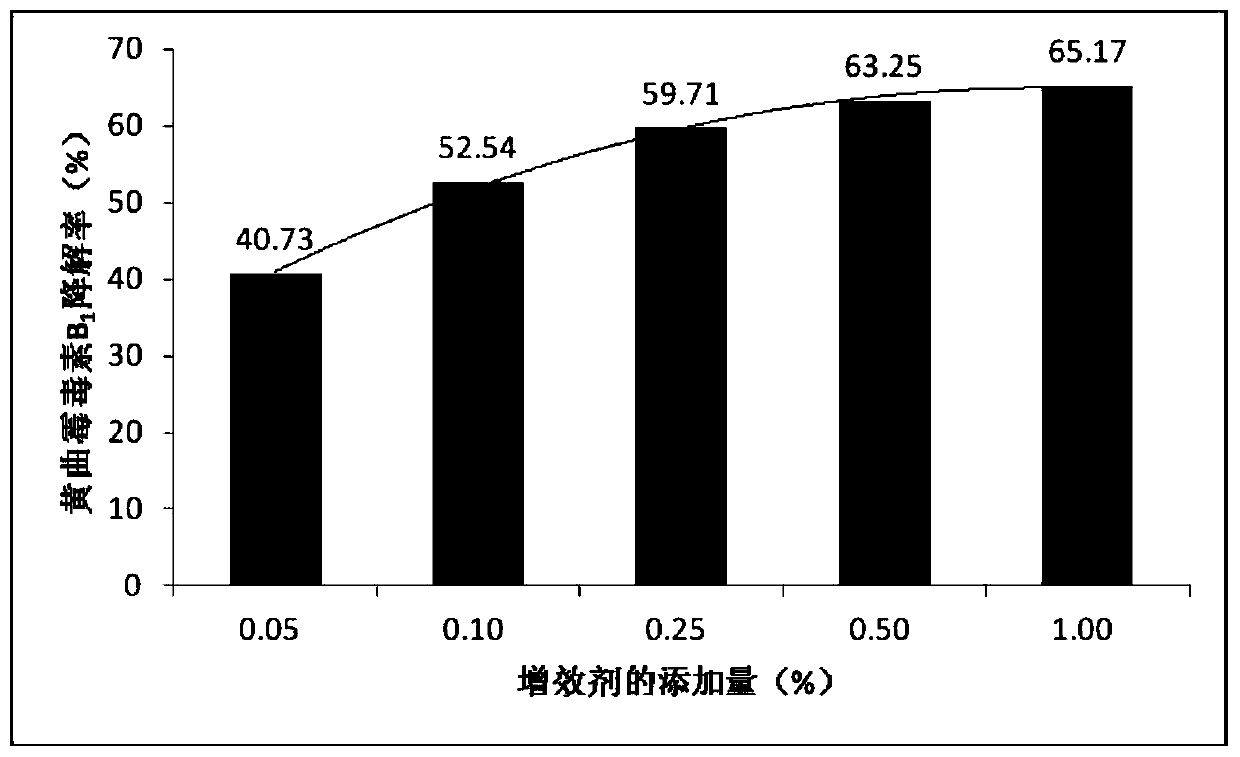
Bacillus velezensis for simultaneously degrading zearalenone and aflatoxin and application of Bacillus velezensis
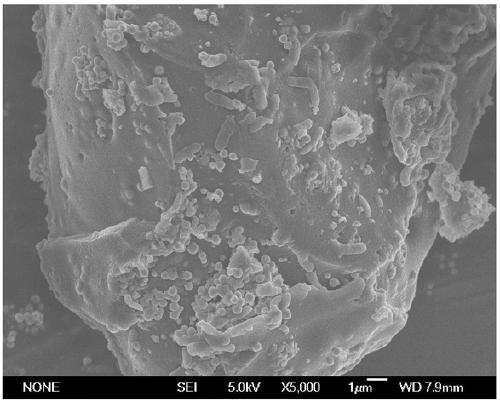
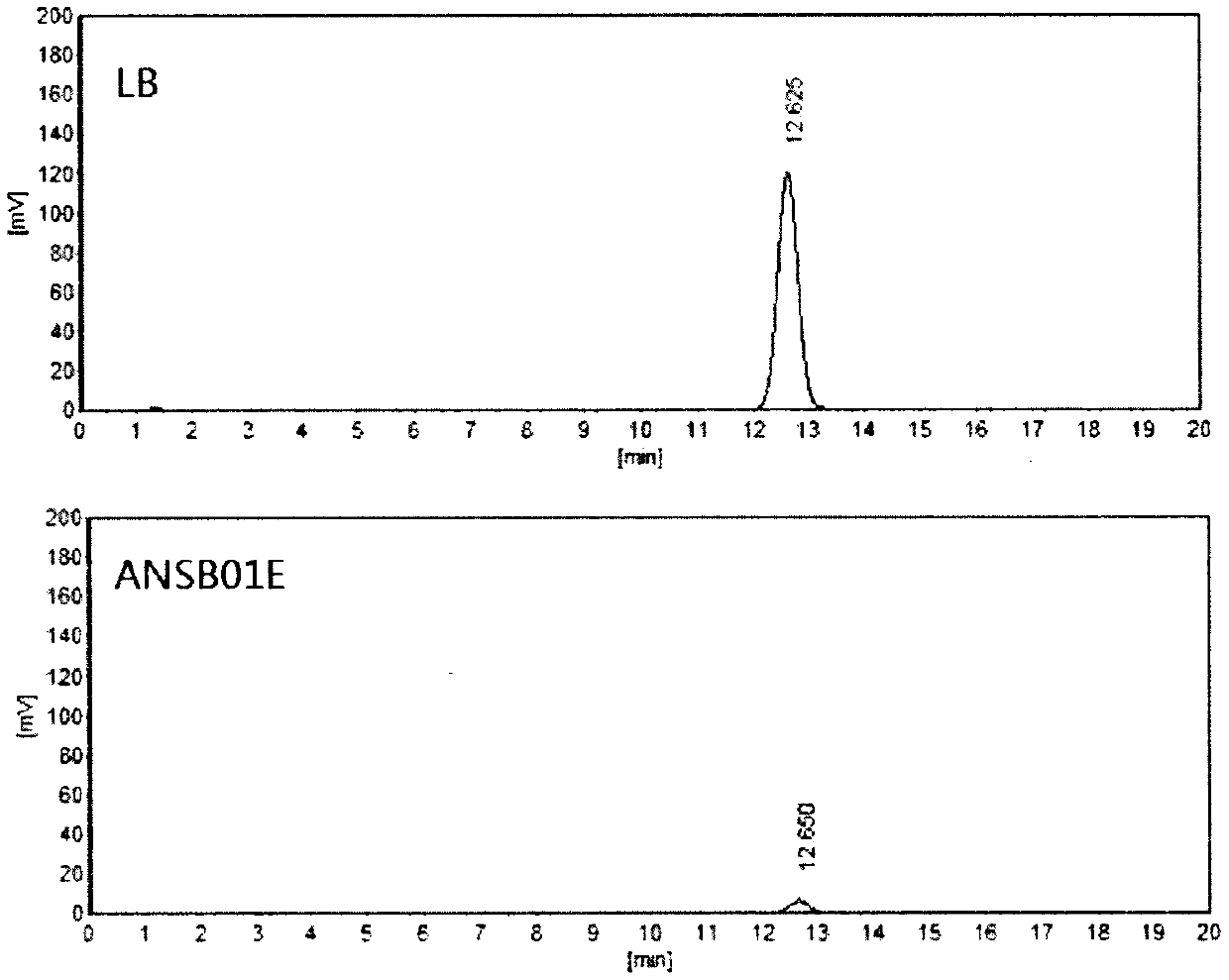
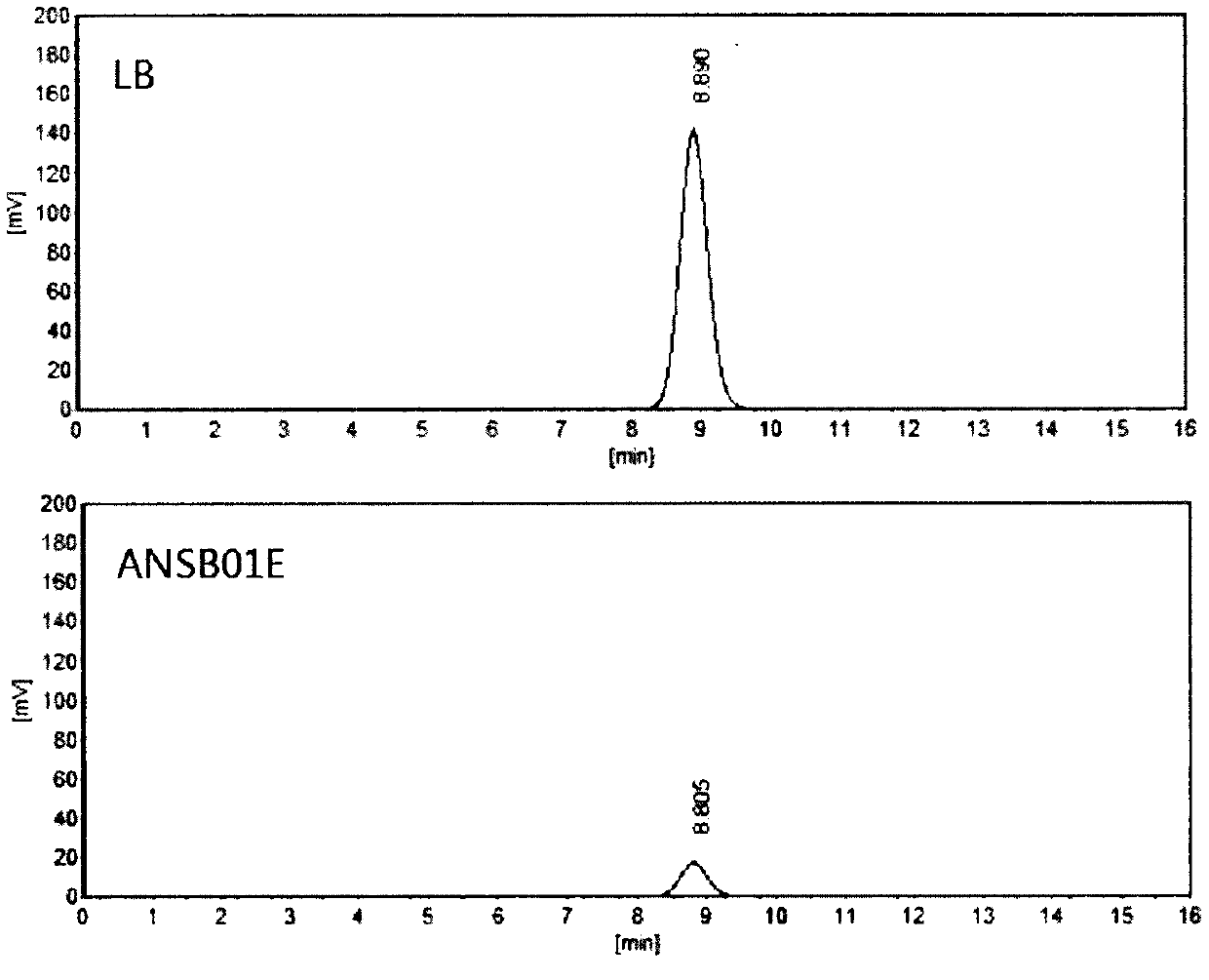
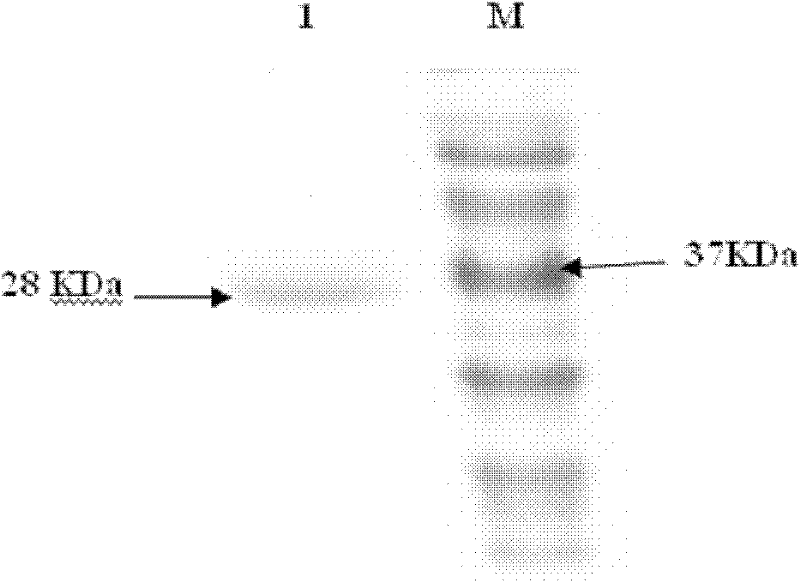
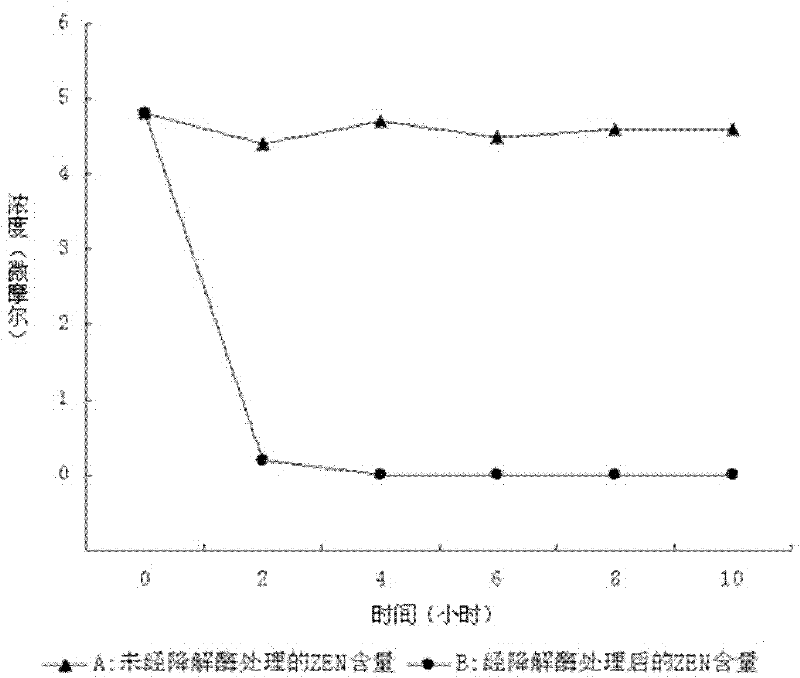
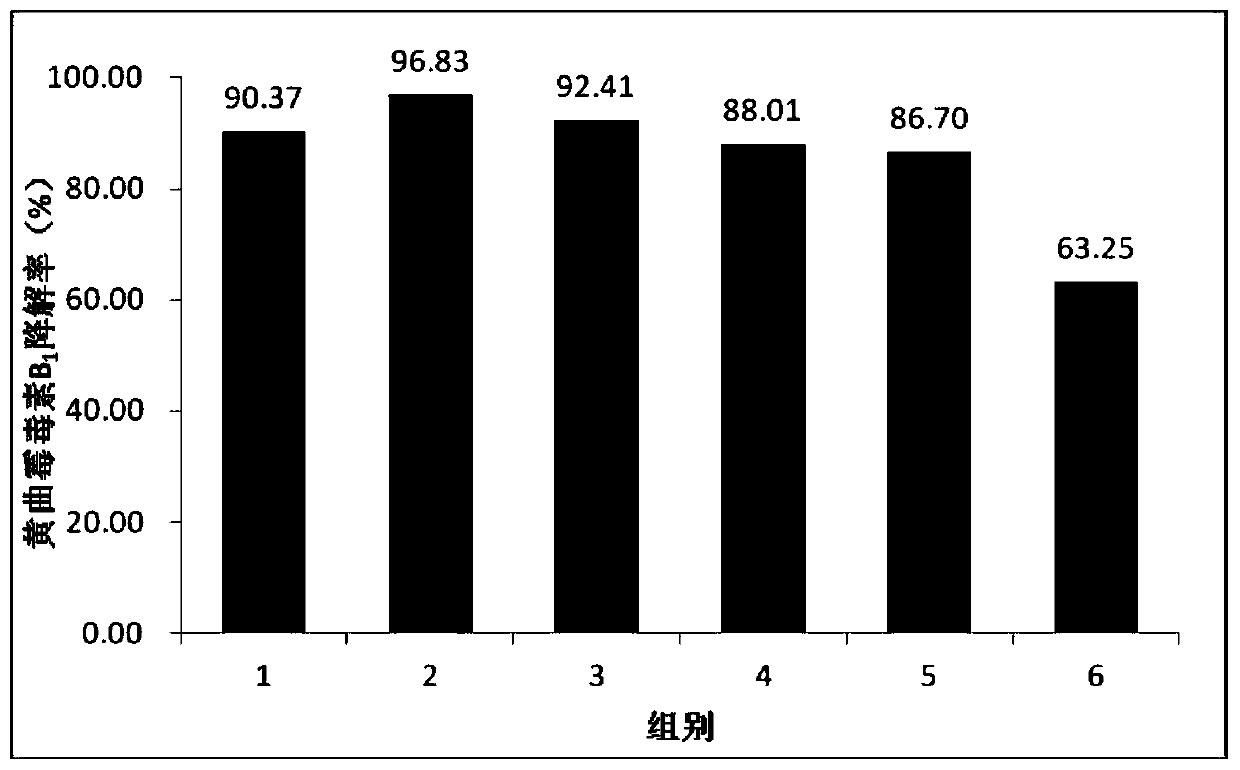
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural biologics and in particular relates to Bacillus velezensis ANSB01E CGMCC No. 17328 and application thereof. The Bacillus velezensis provided by the invention is capable of simultaneously and efficiently degrading zearalenone and aflatoxin, and degradation rates upon g zearalenone and aflatoxin are both up to 90% or greater 48 hours laterafter reactions. The Bacillus velezensis provided by the invention is high in toxin degradation efficiency, good in specificity, mild in action effect, free of damage to nutrient components in feedsand applicable to biological detoxification of mycotoxins in cereals, feeds and foods.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Zearalenone toxin degradation enzyme and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a zearalenone toxin gradation enzyme and a coding gene and application thereof. The enzyme is derived from Gliocladiumroseum and is protein in (a) or (b): (a) protein consisting of an amino acid residue sequence of SEQIDNO: 1 in a sequence table; and (b) protein which is derived from the SEQIDNO: 1, has a zearalenone degradation activity and is formed through carrying out substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residues on the amino acid residue sequence of SEQIDNO: 1 in the sequence table. The zearalenone toxin degradation enzyme has highly-efficient degradation effect on zearalenone (ZEN).
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
Fumonisin degrading enzyme, coding gene, recombinant vector, cell, additive and application thereof
ActiveCN108251399AEfficient short-term degradationReduced pH requirementsHydrolasesAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyNo production
The invention relates to the biotechnology field, in particular to a fumonisin degrading enzyme, a coding gene, a recombinant vector, a cell, an additive and application thereof, and more specificallyrelates to the fumonisin degrading enzyme with a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2 or its mutant, the coding gene of the enzyme, the vector and cell containing the coding gene, the additive containing the enzyme and / or cell and / or the fermentation product thereof, application of the enzyme, the coding gene, the vector, the cell or the additive in degradation of fumonisins and / or other fungal toxins,as well as a method for degradation of fumonisin / or other fungal toxins. The enzyme provided by the invention has the advantages of: environmental friendliness, efficient and short time degradation offumonisins, and no production of harmful by-products. The enzyme can tolerate catalysis at high temperature up to 70DEG C, has low requirement for pH value and good stability, and also can degrade vomitoxin and T2 toxin to a certain degree.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
Preparation method and application of immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria
ActiveCN103436518AImprove degradation rateImprove toleranceMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsFiberPhylum Cyanobacteria
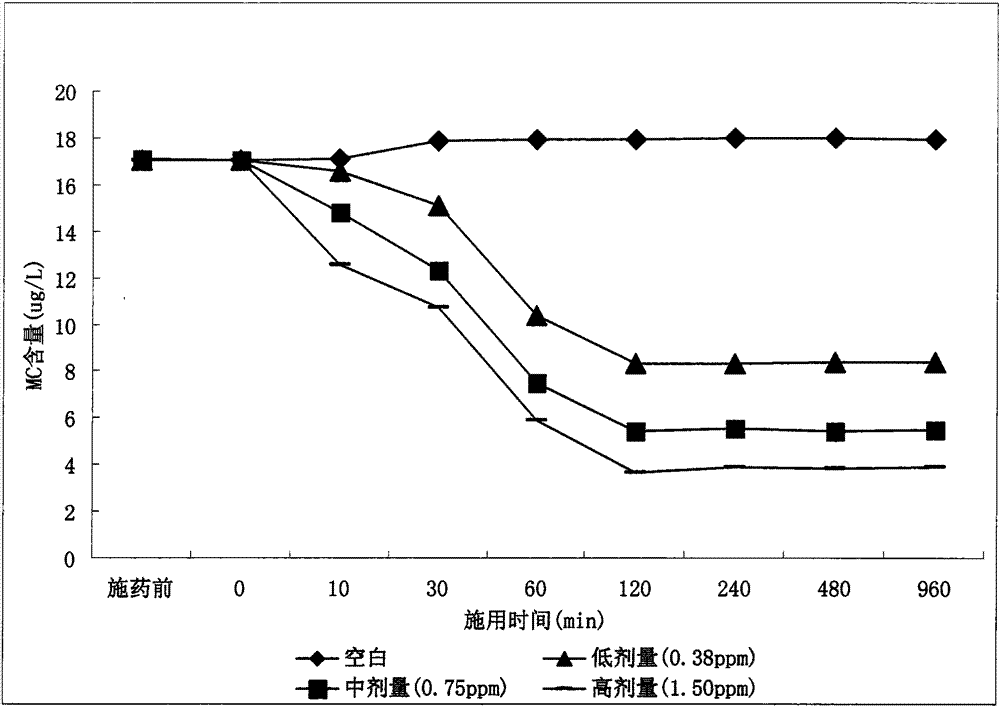
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria. The preparation method of the immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria comprises the steps: selecting activated carbon fibers as an immobilization material, after carrying out washing, boiling, hydrochloric acid soaking, drying and other pretreatment steps of the immobilization material, adding into an LB culture medium according to a certain specific value, then inoculating a bacterial strain for degrading microcystins (MCs), and carrying out immobilized culture to obtain the immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria. In the application of the immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria, while the activated carbon fibers adsorb algal toxins, the algal toxin degrading bacteria immobilized on the activated carbon fibers can degrade the algal toxins, can greatly shorten the time of degradation of the MCs, and simultaneously can biologically regenerate the activated carbon fibers. The bacterial strain for degrading the MCs has the MC-LR degradation rate of up to 91% or more, and is especially suitable for degradation of the MCs generated in a process of extracting phycobiliproteins from water-blooming cyanobacteria.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
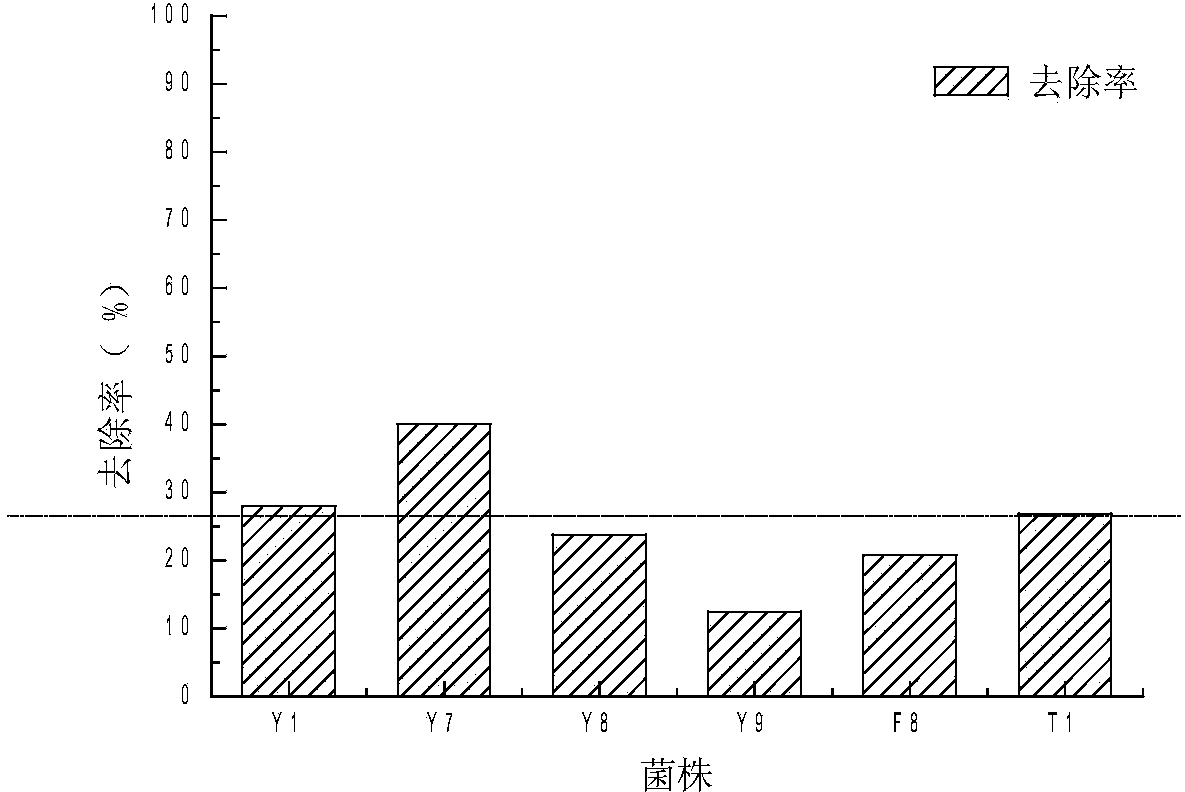
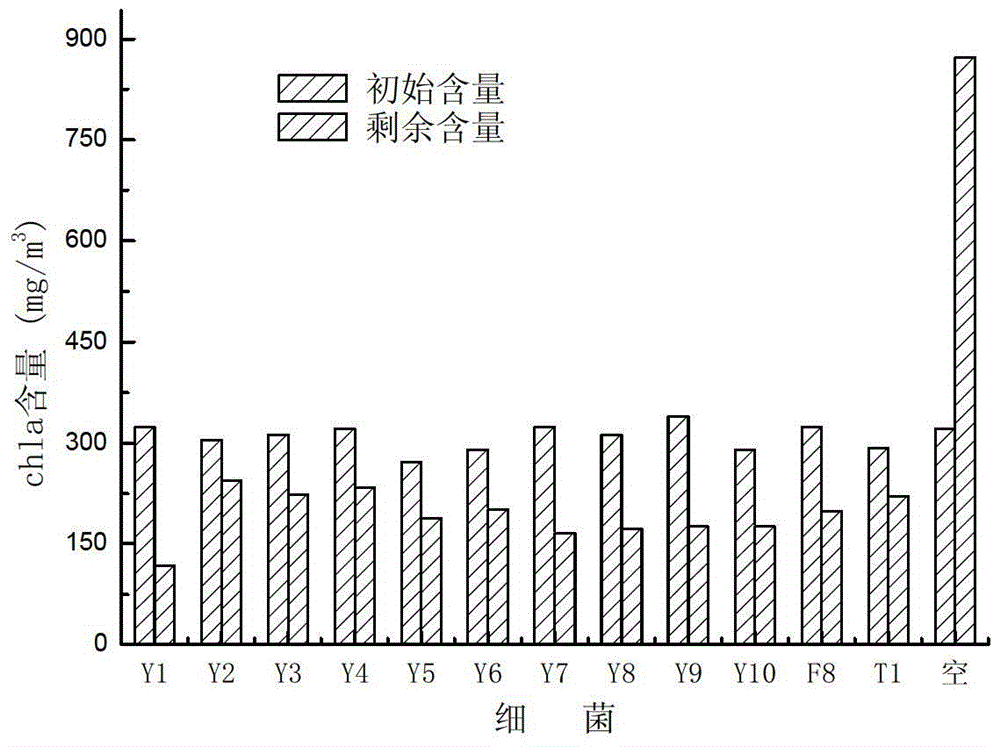
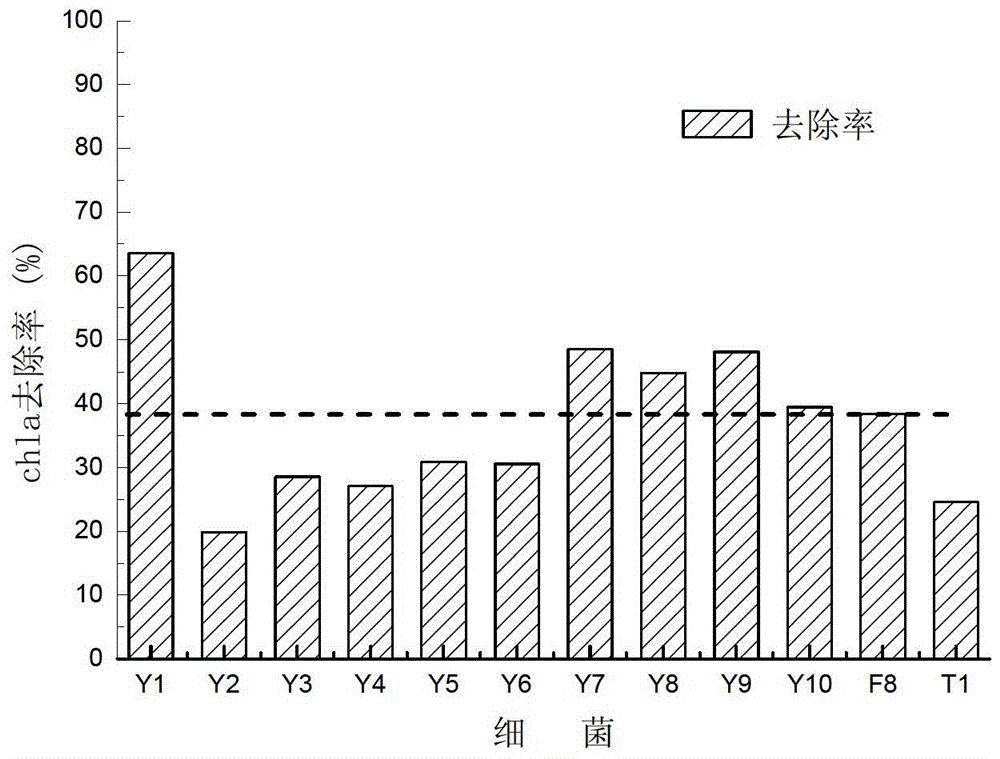
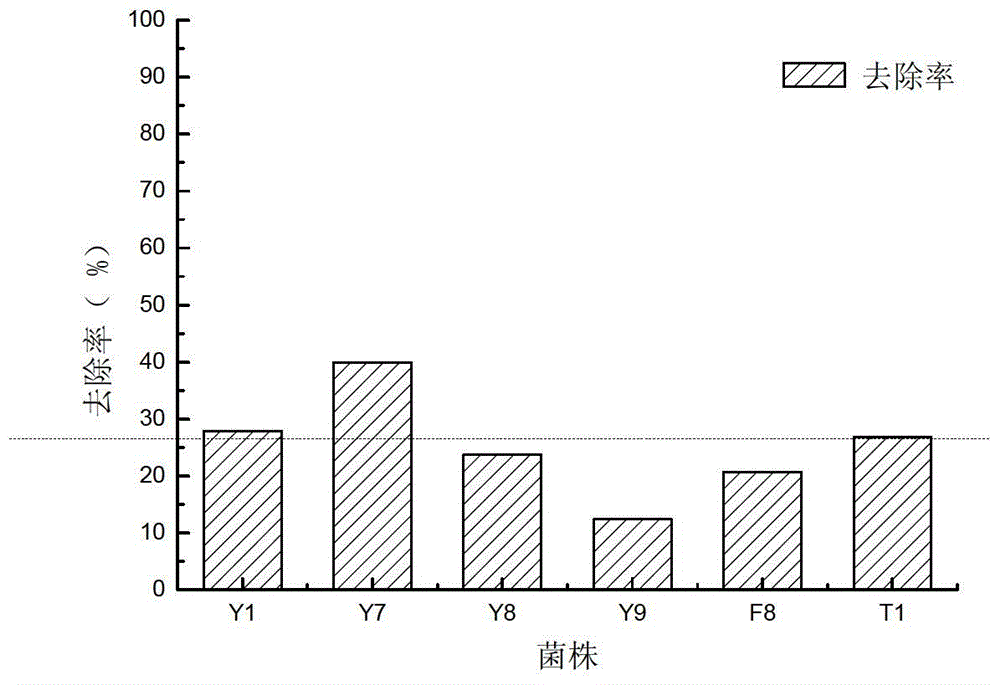
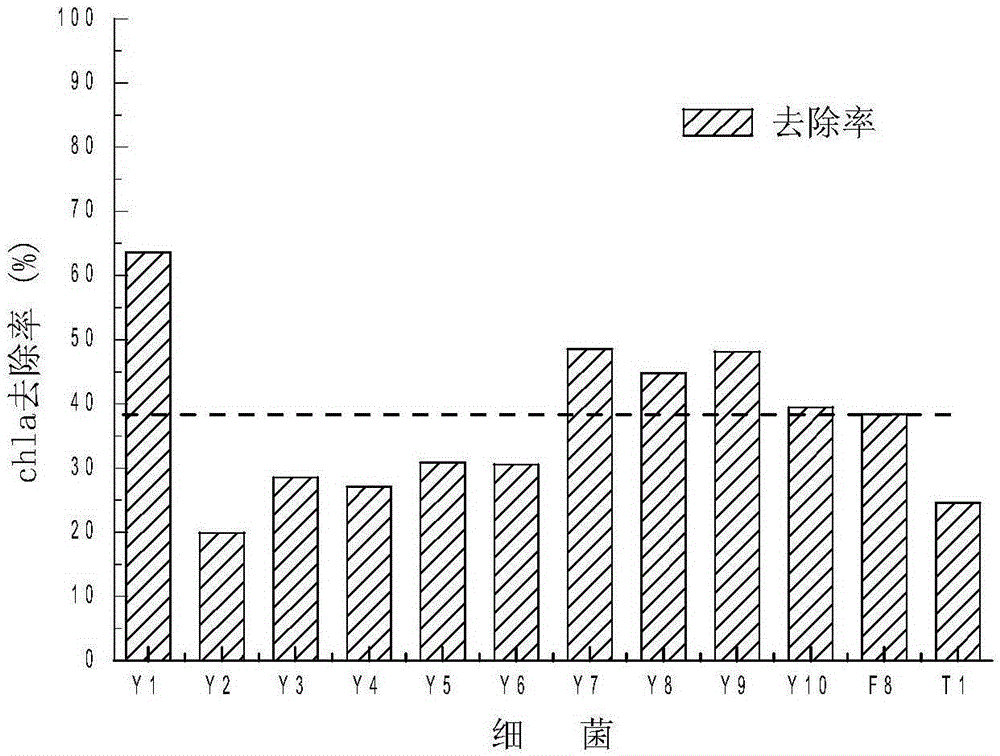
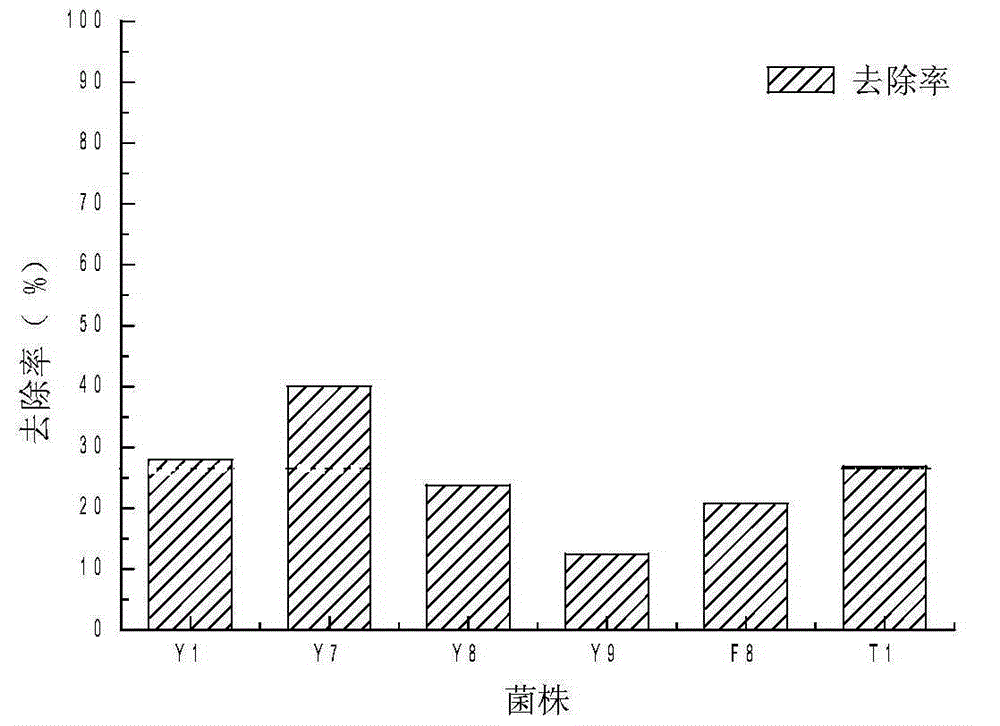
Alga lysing/algal toxin degradation double-effect engineering strain Y1 and construction method thereof
The invention discloses an alga lysing / algal toxin degradation double-effect engineering strain Y1 and a construction method thereof, belonging to the field of microbiology for treatment of blue-green algae. Fusion is performed on parent strains with alga lysing and algal toxin degradation functions by utilizing a protoplast fusion technology to construct the double-effect engineering strain with excellent traits of parents, namely Bacillussphaericus with the collection number of CGMCCNO. 7519. The alga lysing and the derived algal toxin pollution problem are synchronously solved. The protoplast fusion rate can achieve 31.97% under optimal conditions, and the double-effect engineering strain has certain guide effects on solving the problems of blue-green alga bloom and the derived MC-LR (microcystin-LR) pollution and constructing the engineering strain integrating the MC-LR degradation function and the alga lysing property into a whole by performing a protoplast fusion technology, thereby providing reference for achieving the effect on treating both the root course and the symptoms for solving the large-area blue-green alga bloom problem.
Owner:ANHUI HUANGHE WATER RESOURCE POLYTRON TECH INC
Immobilized algal toxin degrading enzyme as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104195129ALow costImprove degradation rateWater contaminantsOn/in inorganic carrierNanoparticleGraphene
The invention discloses a preparation method of an immobilized algal toxin degrading enzyme. The method comprises the following steps: (1) activating a graphene oxide with a carboxyl activator in the presence of a first solvent and then carrying out solid-liquid separation so as to obtain an activated graphene oxide; (2) contacting the activated graphene oxide obtained in the step (1) with functionalized ferroferric oxide nanoparticles in the presence of a second solvent and then carrying out solid-liquid separation so as to obtain a solid-phase carrier; and (3) loading an algal toxin degrading enzyme on the solid-phase carrier. The invention further provides the immobilized algal toxin degrading enzyme prepared by virtue of the method, and an application of the immobilized algal toxin degrading enzyme in algae toxin degradation. According to the method, the algal toxin degrading enzyme can be prepared into the immobilized algal toxin degrading enzyme in a low-cost manner, so that the reutilization frequency and the environmental tolerance of the algal toxin degrading enzyme are improved; and in addition, the reaction process of the algal toxin degrading enzyme can be strictly controlled, so that the degradation rate of algal toxin is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
A kind of algae-dissolving/algae toxin-degrading double-effect engineering bacteria y7 and its construction method
The invention provides a dual-effect engineering bacterium Y7 capable of lysing algae and degrading algal toxin and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the microbiological field of blue-green algae treatment. The dual-effect engineering bacterium Y7 capable of lysing algae and degrading microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is prepared based on a protoplast fusion technology in which the protoplast fusion rate can be up to 28.17% under optimal conditions. The dual-effect engineering bacterium Y7 provided by the invention is used for solving the problems of the outbreak of blue-green algae and the pollution of derived MC-LR, plays a guiding role in constructing a engineering bacterium integrating an MC-LR degradation function and algae-lysing property by virtue of an improved protoplast fusion technique and practical application and provides reference for solving the problem large-scale blue-green algae blooms fundamentally.
Owner:ANHUI HUANGHE WATER RESOURCE POLYTRON TECH INC
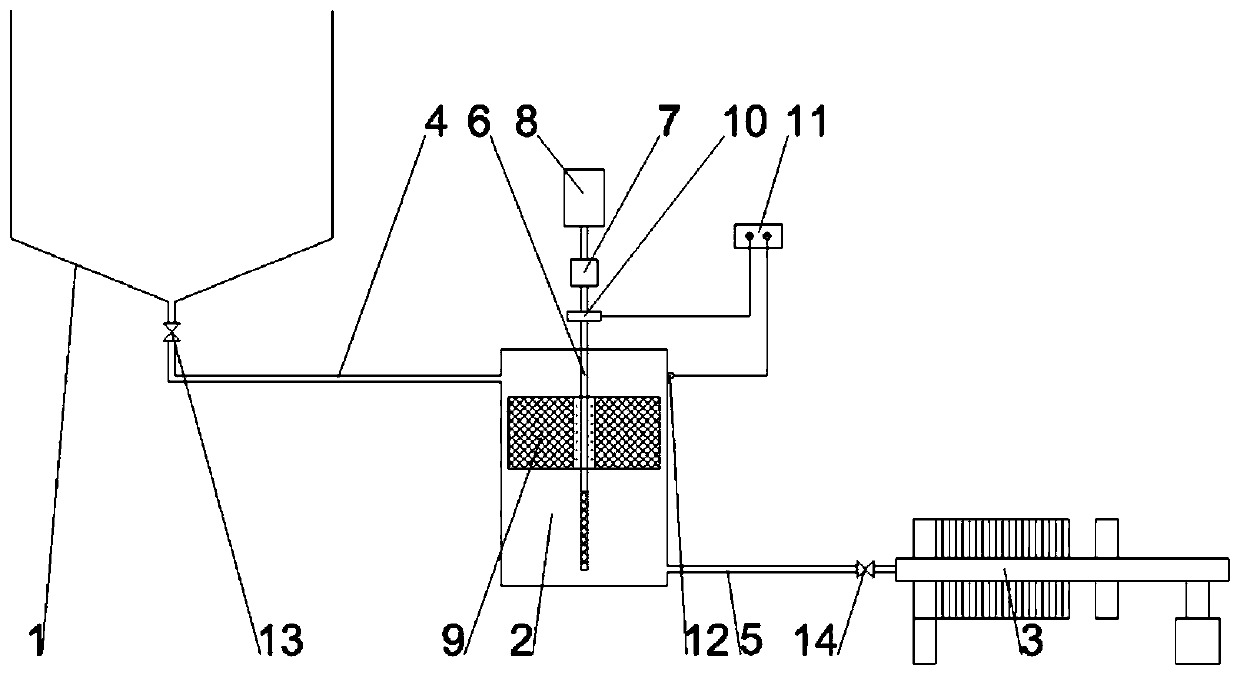
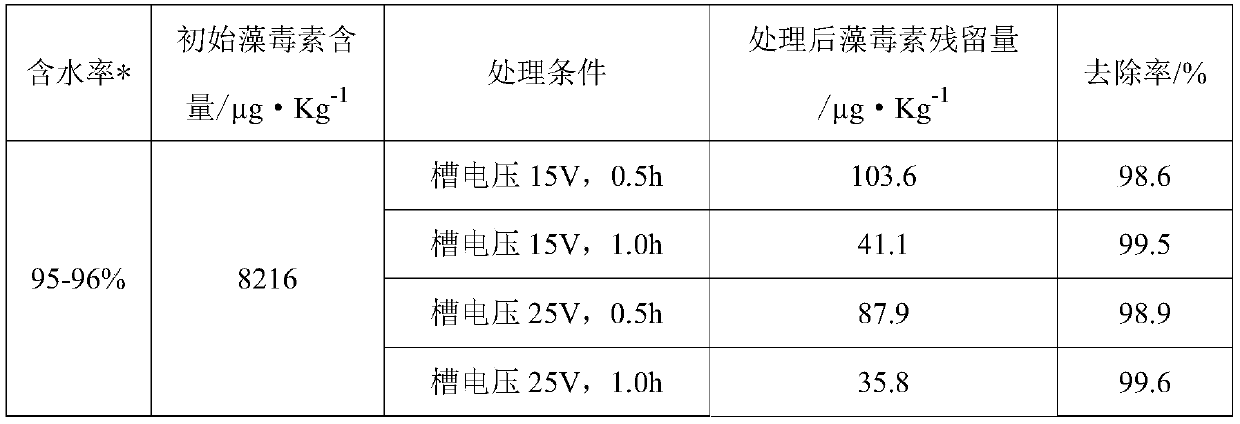
Method for electrochemical detoxification and deep dehydration of blue-green algae liquid
ActiveCN109912083AConducive to deep resource utilizationImprove degradation efficiencyMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processElectrochemical responseHigh pressure
The invention discloses a method for electrochemical detoxification and deep dehydration of a blue-green algae liquid. The method comprises the following steps: the blue-green algae liquid is put intoa primary sedimentation tank for preliminary standing and layering and flows into an electrochemical reactor; the cell voltage of the electrochemical reactor and the rotating speed of a stirrer are set, the electrochemical reactor and the stirring function of the electrochemical reactor are started, blue algae cells are subjected to wall breaking dehydration under the action of an electric fieldand mechanical stirring of an anode, algal toxins released by blue-green algae are continuously oxidized and degraded by hydroxyl radicals generated in the electrochemical reactor, and the processes of wall breaking dehydration and toxin removal of the blue-green algae are completed; the blue-green algae liquid flows into a high-pressure filter press device for deep dehydration, and finally blue algae mud cakes are obtained. According to the method, efficient dehydration of the blue-green algae and efficient degradation of the algal toxins are realized, the method is simple and controllable inoperation, the problems of algal toxin degradation, deep dehydration and inhibition of secondary pollution in the dehydration process in the blue-green algae recycling process are effectively solved,no chemical substances are added, and a solid foundation is laid for deep recycling of the blue-green algae.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Water purifier for purifying water environment of aquaculture
InactiveCN107572618AWith toxin degradation functionImprove stabilityWaste water treatment from animal husbandryWater/sewage treatmentAdhesiveMesoporous silica
The invention discloses a water purifier for purifying water environment of aquaculture. The water purifier is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of mesoporous silica SBA-15, 10-20 parts of poly-dimethyl-diallyl-ammonium chloride, 15-25 parts of activated carbon, 10-20 parts of Maya blue powder, 10-15 parts of polyhydroxybutyrate, 15-25 parts of micro / nano-bubble ozone water in concentration of 1.5-5.5mg.L-1, 12-18 parts of microbial flocculant, 5-10 parts of bios, 3-6 parts of toxin degradation agent, 15-25 parts of nanometer waterborne adhesive and 10-15 parts of aquaculture oxygen supplier. The water purifier provided by the invention has the characteristics of no pollution, no toxicity, high stability, high safety, high antibacterial efficiency, andthe like, has the function of degrading toxin and is capable of effectively reducing the damage of the toxicity generated in the water environment and in the purifying process of the common water purifier product to the aquatic products.
Owner:周爱民
Method for degrading fungal toxins in animal bodies through lactobacillus acidophilus
ActiveCN106259069AAchieve degradationClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffSaxitoxinLactobacillus acidophilus
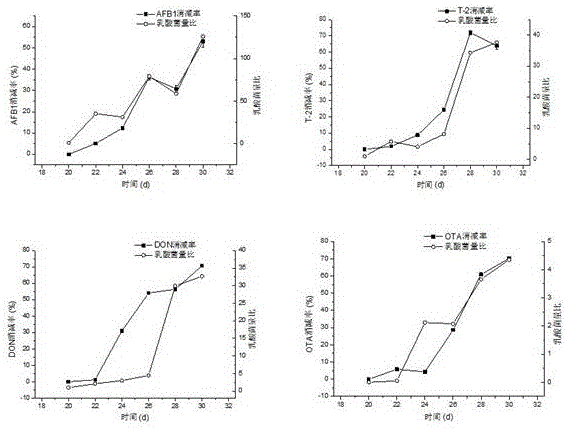
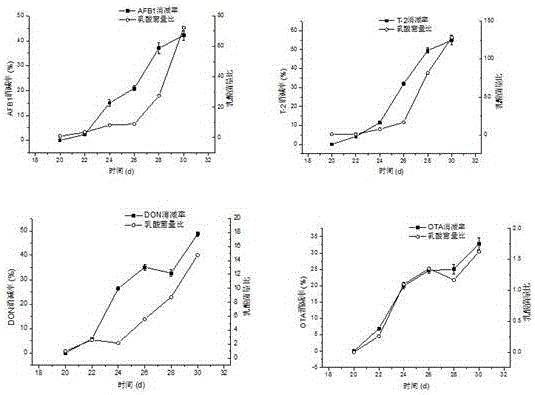
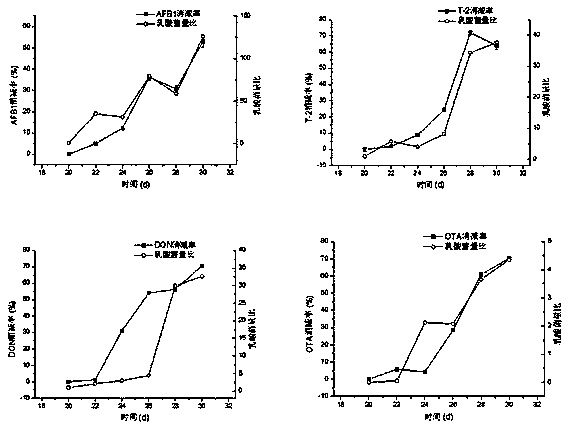
The invention belongs to the technical field of toxin degradation, and discloses application of lactobacillus acidophilus in degradation of fungal toxins in animal bodies. The fungal toxins comprise T-2 toxins, aflatoxin B1, deoxynivalenlo and ochratoxin; lactobacillus acidophilus liquid is uniformly sprayed to animal feed, litopenaeus vannamei and tilapia mossambica are fed with feed containing lactic acid bacteria and feed containing the T-2 toxins, the aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), the deoxynivalenlo (DON) and the ochratoxin (OTA) for ten days, and fungal toxin residues in the muscles of the litopenaeus vannamei and the tilapia mossambica are significantly reduced compared with a control group, wherein the T-2 content in the litopenaeus vannamei muscles is decreased by 63.86%+ / -1.32%, the AFB1 content in the litopenaeus vannamei muscles is decreased by 53.04%+ / -0.97%, the DON content in the litopenaeus vannamei muscles is decreased by 70.74%+ / -1.47%, the OTA content in the litopenaeus vannamei muscles is decreased by 70.24%+ / -1.22%, the T-2 content in the tilapia mossambica muscles is decreased by 54.93%+ / -2.52%, the AFB1 content in the tilapia mossambica muscles is decreased by 42.10%+ / -1.97%, the DON content in the tilapia mossambica muscles is decreased by 48.75%+ / -0.93%, and the OTA content in the tilapia mossambica muscles is decreased by 32.79%+ / -1.81%. Accordingly, the lactobacillus acidophilus is prepared into a feed additive, then the fungal toxins accumulated in the animal bodies can be degraded, and the practical application value is achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
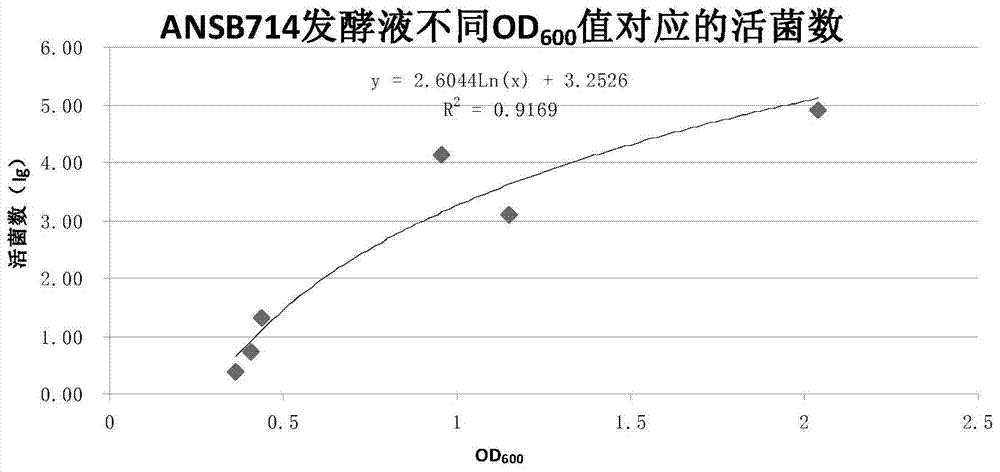
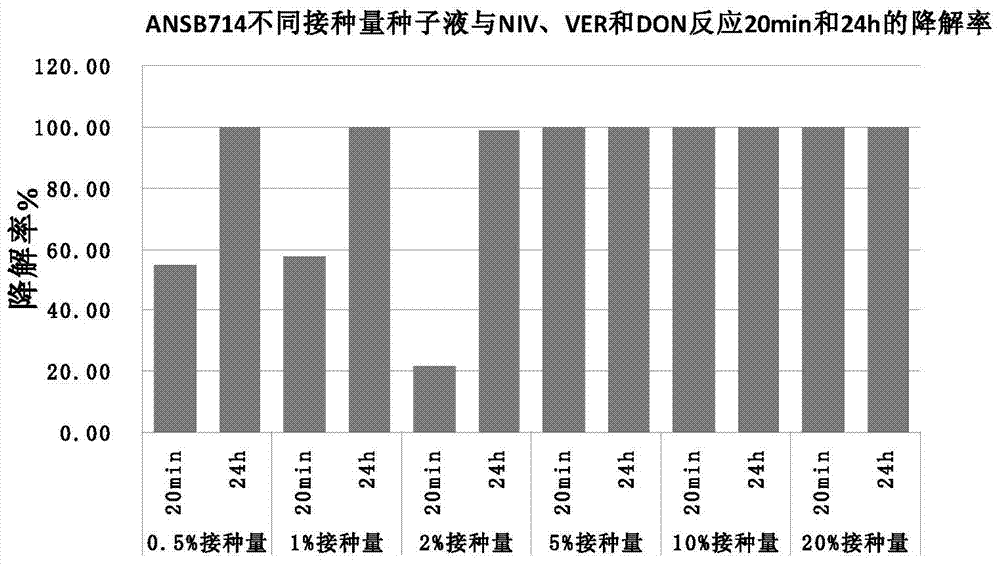
Trichothecene mycotoxin biodegradation agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104232517AEfficient degradationImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffAdditive ingredientDevosia sp.
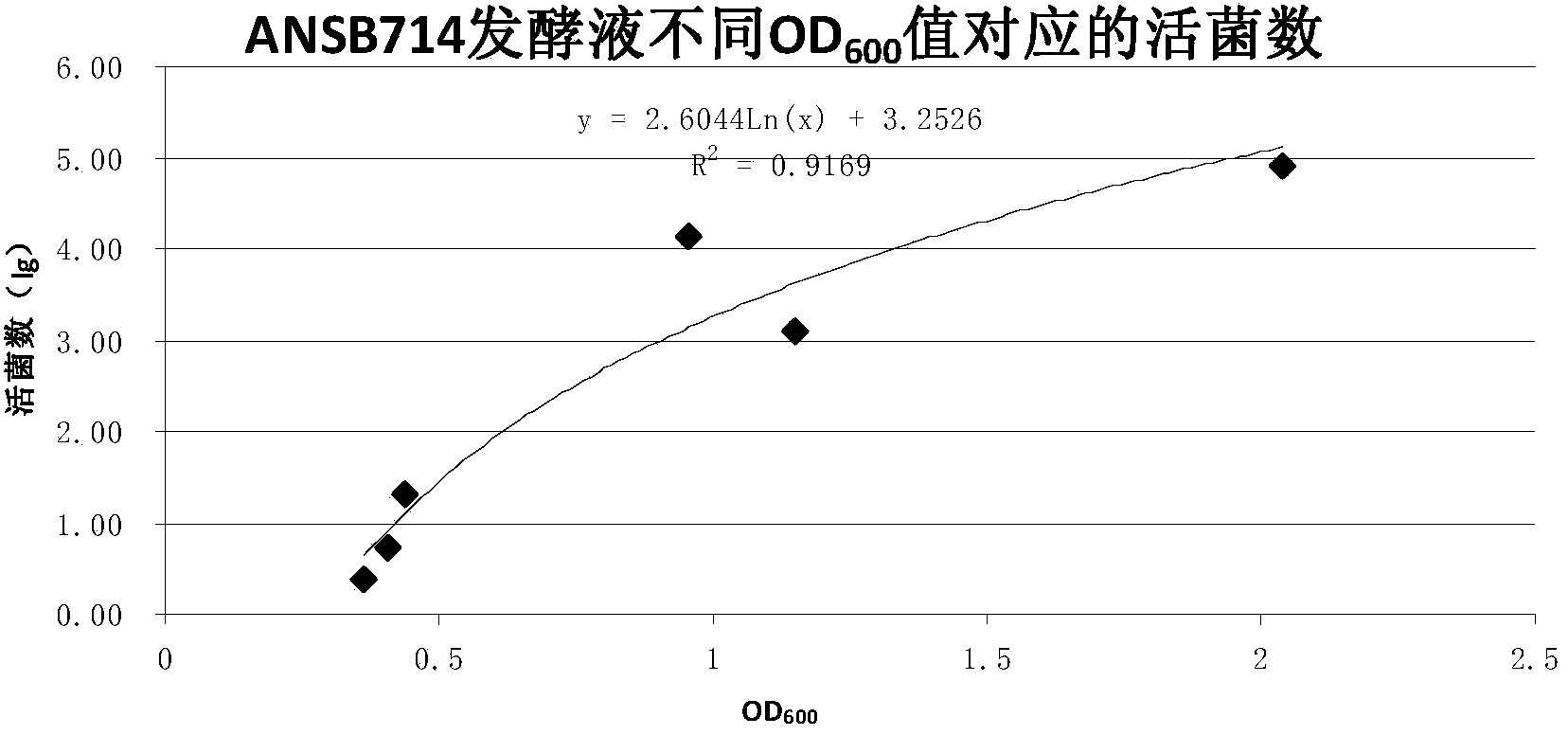
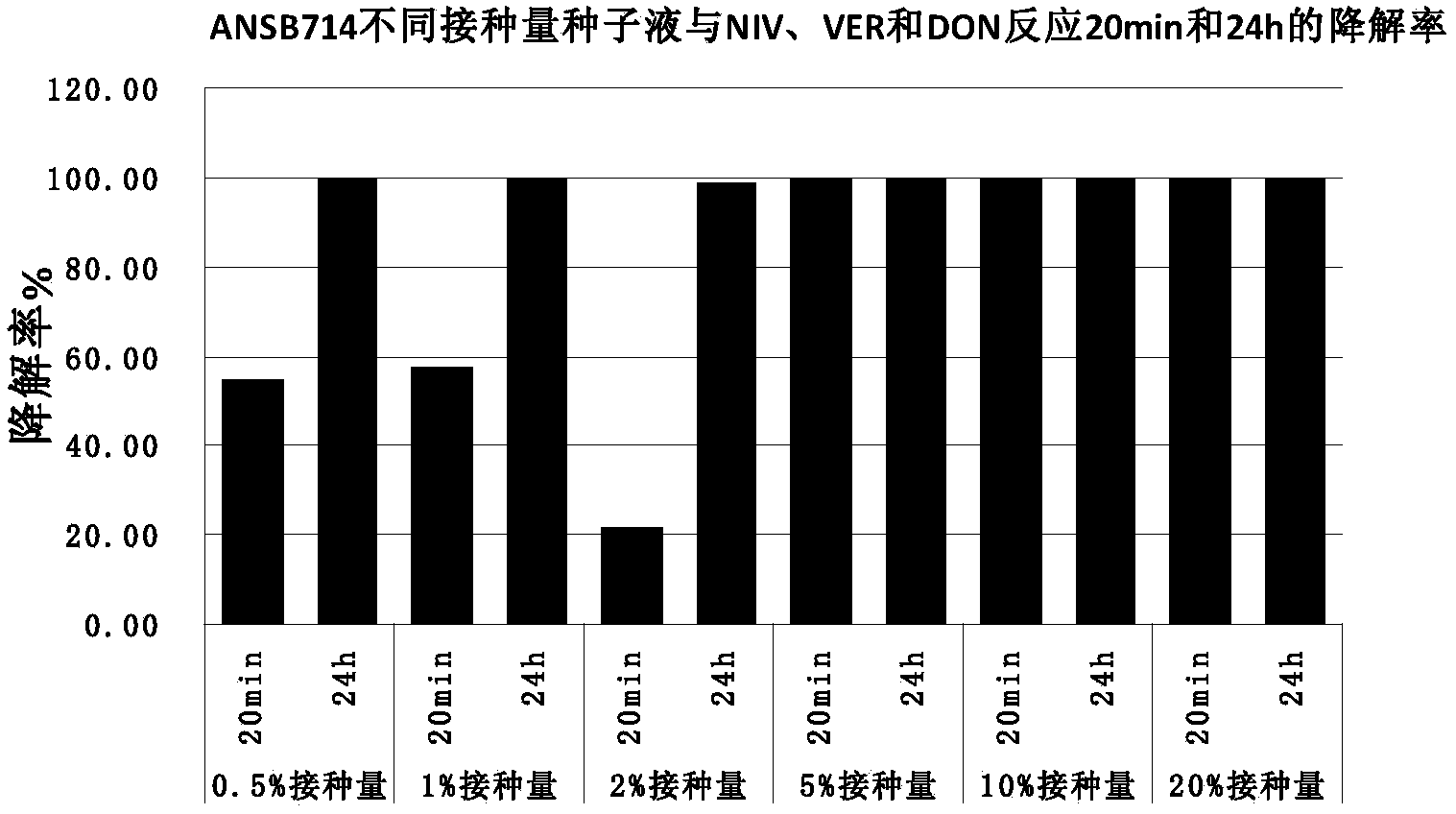
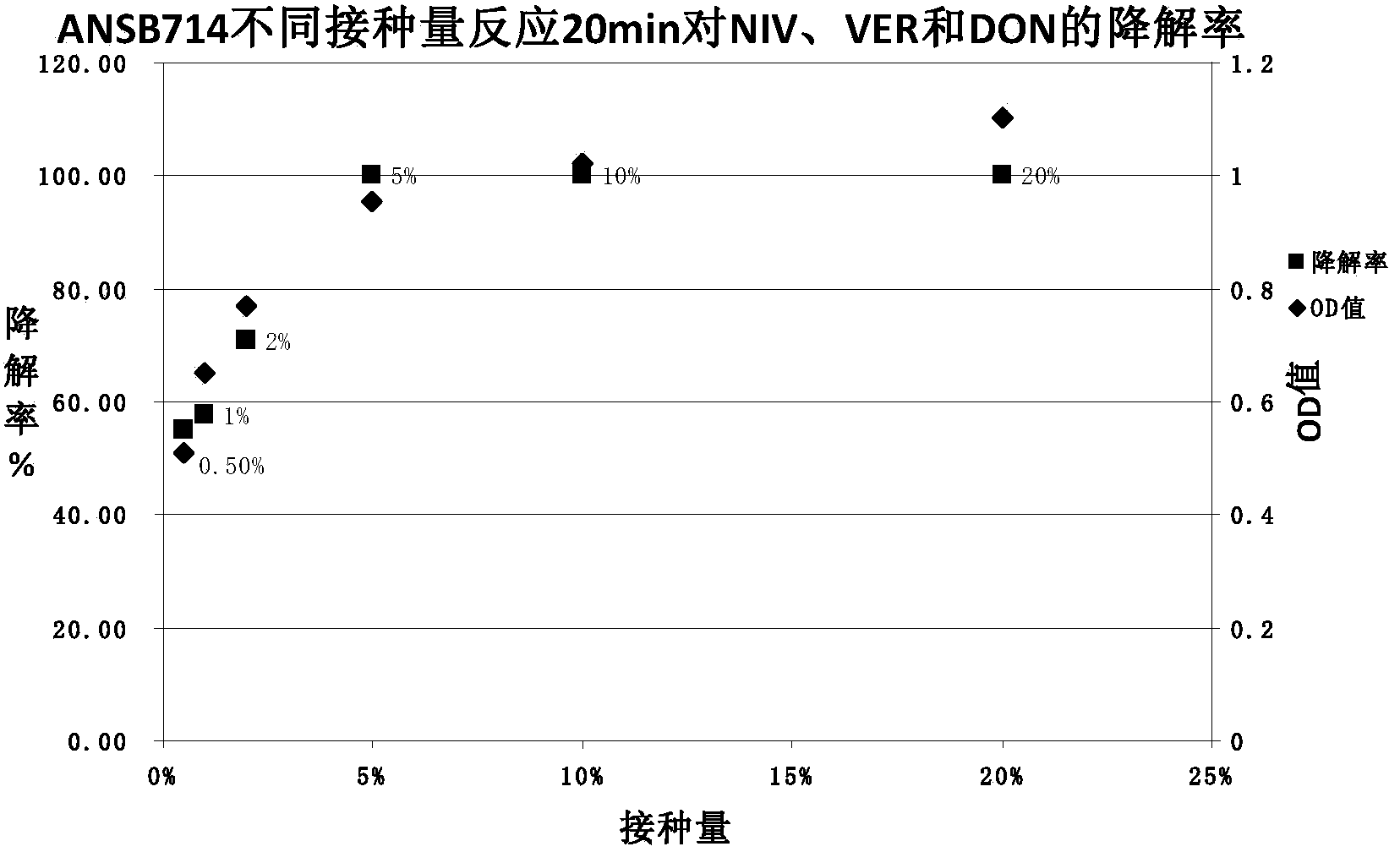
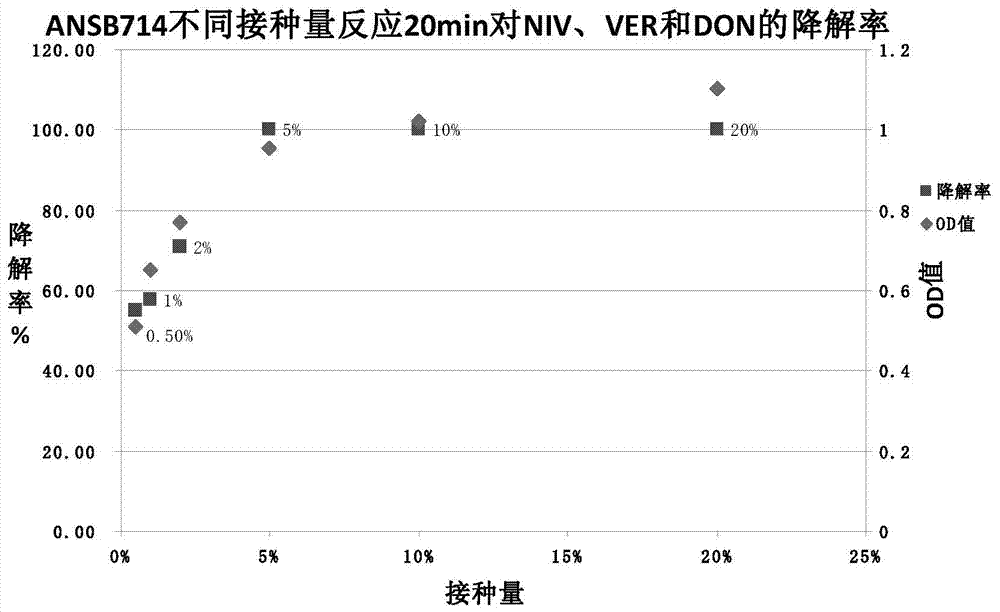
The invention provides a feed trichothecene mycotoxin biodegradation agent. Trichothecene mycotoxin comprises but is not limited to nivalenol, verrucarine and deoxynivalenol. By adopting the preparation method provided by the invention, a Devosia sp. ANSB714 for safely and efficiently degrading feed trichothecene mycotoxin is separated and screened out from a natural resource for the first time, and biological characteristics and toxin degradation characteristics of the bacterium are studied. The invention also provides a culture method of the bacterium, a method for preparing a biodegradation agent by using the bacterium, and a method for applying the biodegradation agent to degradation of the trichothecene mycotoxin in a feed. After the ANSB714 reacts with a moldy feed for 24 hours, the degradation rate of the trichothecene mycotoxin in the feed can reach 98%. The Devosia sp. ANSB714 in the invention has high activity, strong specificity and mild effect during degradation of the trichothecene mycotoxin, cannot damage nutritional ingredients in the feed, and improves the utilization ratio of the feed at the same time, so that the safety in production of animal husbandry is ensured and the economic benefit is improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Algal toxin degrading enzyme as well as composite material and application
The invention relates to the fields of biology, agriculture and fishery and environmental protection, and discloses an algal toxin degrading enzyme as well as a composite material and application, and the algal toxin degrading enzyme as shown in (a) or (b): (a) an algal toxin degrading enzyme consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4; (b) a protein which is derived from (a) by substituting, deleting or adding one or more amino acids to the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4, and has unchanged enzyme activity, or a protein which is as shown in the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4 and is connected with a tag at the amino terminal and / or carboxyl terminal of the SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4. The yield of the modified algal toxin degrading enzyme and the activity of enzyme degradation algal toxin are higher than those of the wild algal toxin degrading enzyme before modification, the yield and the enzyme activity are both improved, and the half-life period at 0 DEG C is long.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
A kind of alginolytic/algal toxin degradation double-effect engineering bacteria y1 and its construction method
The invention discloses an alga lysing / algal toxin degradation double-effect engineering strain Y1 and a construction method thereof, belonging to the field of microbiology for treatment of blue-green algae. Fusion is performed on parent strains with alga lysing and algal toxin degradation functions by utilizing a protoplast fusion technology to construct the double-effect engineering strain with excellent traits of parents, namely Bacillussphaericus with the collection number of CGMCCNO. 7519. The alga lysing and the derived algal toxin pollution problem are synchronously solved. The protoplast fusion rate can achieve 31.97% under optimal conditions, and the double-effect engineering strain has certain guide effects on solving the problems of blue-green alga bloom and the derived MC-LR (microcystin-LR) pollution and constructing the engineering strain integrating the MC-LR degradation function and the alga lysing property into a whole by performing a protoplast fusion technology, thereby providing reference for achieving the effect on treating both the root course and the symptoms for solving the large-area blue-green alga bloom problem.
Owner:ANHUI HUANGHE WATER RESOURCE POLYTRON TECH INC
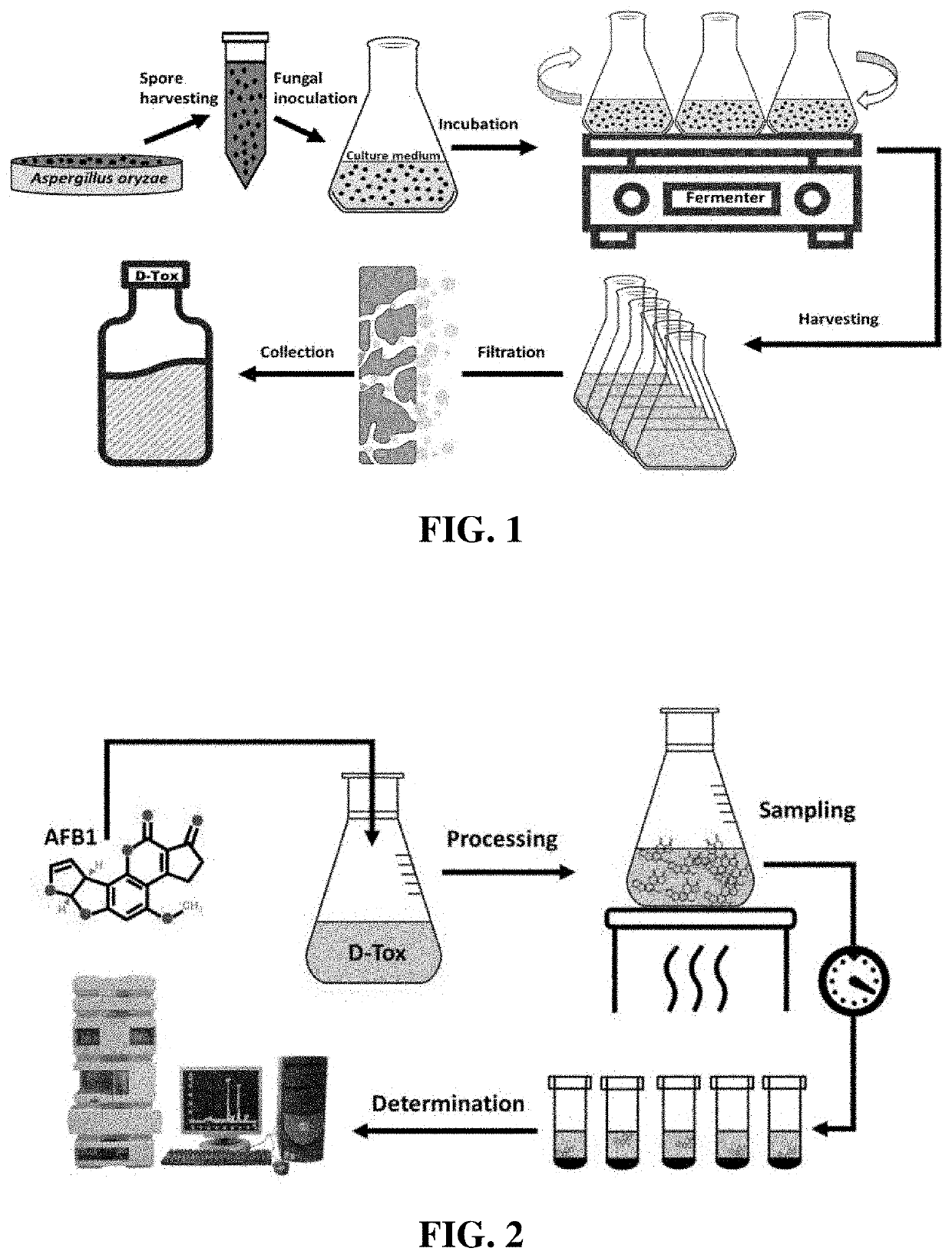
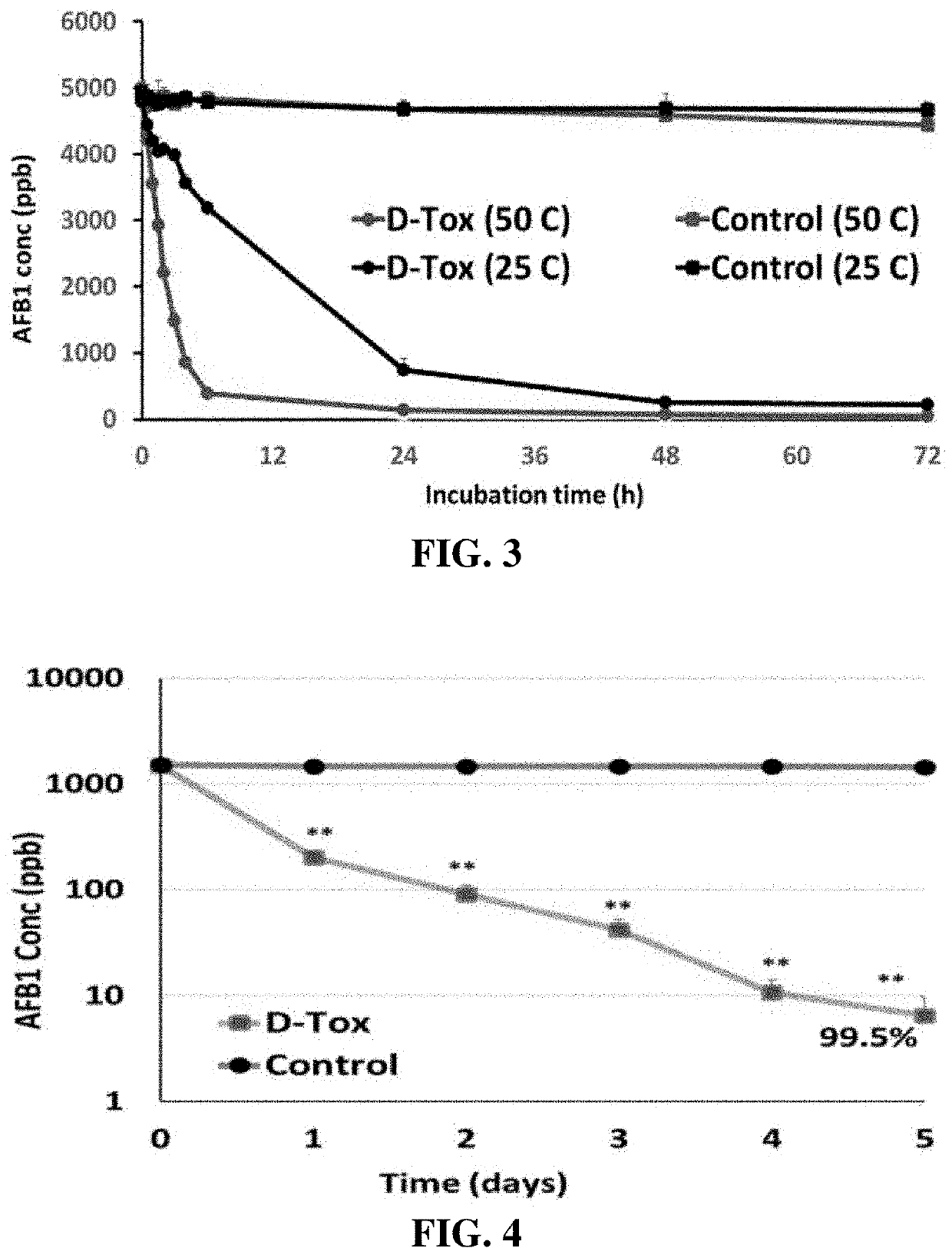
Composition for degradation of aflatoxin comprising aspergillus culture filtrate as effective component and uses thereof
InactiveUS20210139841A1Improve efficiencyReduce maintenanceFungiFood preservationFungal toxinAspergillus pseudonomius
A composition for degradation of aflatoxin includes Aspergillus culture filtrate as an effective component and uses thereof, and it is expected that, in the field of food products and animal feeds for which biodegradation of fungal toxin (in particular, aflatoxin) is required, the composition can be advantageously used as a novel material that can maintain the activity of degrading fungal toxin even at high temperatures.
Owner:SKYANGELBIO CORP
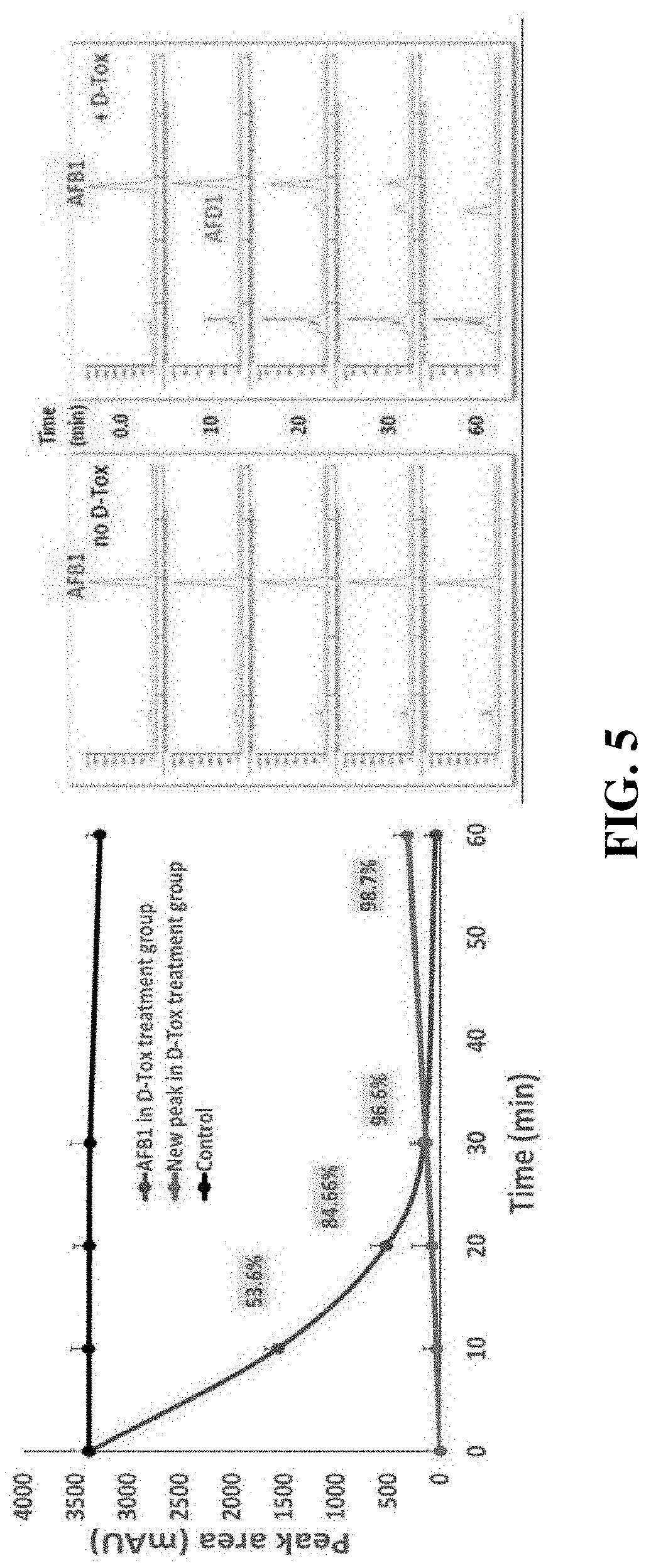
A Strain of Lactococcus lactis CAMT22361 Degrading t-2 Toxin
ActiveCN106085920BEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus lactisOrganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of toxin biological treatment, and specifically discloses a strain of Lactococcus lactis capable of degrading T-2 toxin ( Lactococcus lactis ) CAMT22361, the Lactococcus lactis Lactococcus lactis CAMT22361 was deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on May 13, 2015, and the deposit number is CCTCC NO: M 2015295. The Lactococcus lactis Lactococcus lactis The degradation rate of T-2 toxin can reach 61% after the fermentation broth of CAMT22361 reacts with T-2 toxin for 72 hours. When it is applied to remove T‑2 toxin in feed, the degradation rate can reach more than 50%. Lactococcus lactis of the present invention Lactococcus lactis CAMT22361 has the ability to efficiently and rapidly degrade T-2 toxin, and has a good application prospect in the treatment of T-2 toxin in biodegradable feed.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司
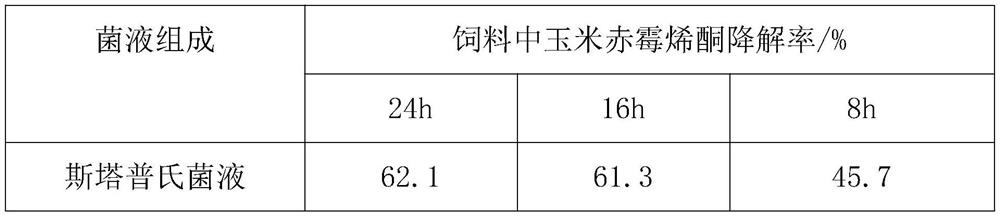
Microbial preparation for degrading zearalenone and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113322197APromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyToxin degradation
The invention relates to the technical field of toxin degradation, and particularly discloses a microbial preparation for degrading zearalenone and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that Starpa bacteria and bacillus velezensis are cultured respectively to obtain a Starpa bacterial solution and a bacillus velezensis solution, then the bacillus velezensis bacterial solution and the Starpa bacterial solution are mixed to obtain a compound bacteria bacterial solution, and finally the compound bacteria bacterial solution is put into a compound bacteria culture medium for mixed fermentation to obtain the microbial preparation. The microbial preparation has high degradation rate on zearalenone in the feed, and the fermentation inoculum is safe and environment-friendly, and can be directly added into the feed as a feed additive.
Owner:苏州优利莱生物科技有限公司
A kind of water algae toxin degrading factor
ActiveCN104056595BImprove adsorption capacityHas good adsorptionAluminium silicatesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSodium BentoniteAquatic animal
Owner:ZHONGHEFA BEIJING BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH DEV
A kind of fermentation agent for degrading aflatoxin, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108913627BNo toxic effectEfficient degradationFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformis[Candida] apicola
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Trichothecene toxin biodegradation agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104232517BImprove efficiencyStrong specificityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTrichotheceneBiological property
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Fumonisin degrading enzyme, coding gene, recombinant vector, cell, additive and application thereof
ActiveCN108251399BEfficient short-term degradationReduced pH requirementsHydrolasesAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyDegradative enzyme
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
A strain domestication method for improving the degradation efficiency of mycotoxin-degrading bacteria
ActiveCN108048385BImprove the degradation efficiency of degrading bacteriaImprove degradation efficiencyMicroorganism based processesMicrobiology processesMicroorganismMicrobiological Techniques
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Zen toxin-degrading enzyme oxa of Acinetobacter and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN103881986BHas ZEN degradation activityWith degradative activityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesFungal toxinNucleotide
The invention discloses a ZEN (zearalenone) toxin degrading enzyme Oxa of acinetobacter as well as a coding gene and application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the ZEN toxin degrading enzyme Oxa of acinetobacter is as shown in SEQ ID NO.6. A nucleotide sequence of the coding gene A4-Oxa of the ZEN toxin degrading enzyme Oxa of acinetobacter is as shown in SEQ ID NO.5. The ZEN toxin degrading enzyme Oxa of acinetobacter disclosed by the invention has stronger ability of degradation on mycotoxin zearalenone; the Oxa enzyme for prokaryotic recombinant expression can degrade over 30% of ZEN toxins within 12 hours. According to the invention, a non-peroxidase coding sequence, i.e., an A4-Oxa gene of Acinetobacter sp. SMO4-degreaded zearalenone toxin is determined, so that a foundation is laid for researching an active site of the enzyme and site-specific mutagenesis Oxa enzyme by a specific site in future.
Owner:河南亿万中元生物技术有限公司
Microbial magnetic chitosan nano material, preparation method thereof and application thereof in microcystic toxin degradation
ActiveCN109536481APreserve the degradation advantageRetention enrichmentMicroorganism based processesInorganic material magnetismMicrocystinToxin degradation
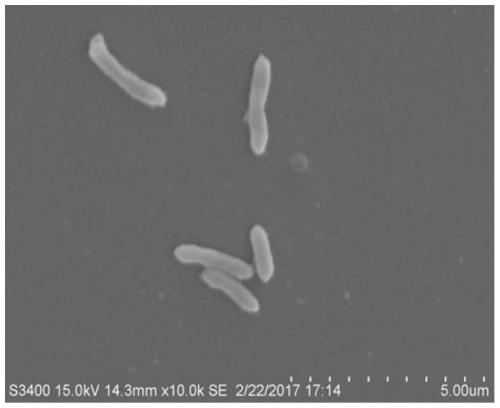
The present invention discloses a microbial magnetic chitosan nano material. The microbial magnetic chitosan nano material comprises a magnetic chitosan nano material and a Sphingopyxis sp. YF1 body immobilized and loaded on the magnetic chitosan nano material; the magnetic chitosan nano material is chitosan loaded with magnetic nano-Fe3O4 particles; and the Sphingopyxis sp. YF1 is preserved in the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee and has a preservation number of CGMCC No:16341. The present invention also discloses a preparation method and an application of the microbial magnetic chitosan nano material. The magnetic chitosan nano material is combined with the Sphingopyxis sp. YF1, a degradation effect is further improved, and after combining with the magnetic chitosan nano material, the bacterium body is not easily lost, good in the degradation effect and high in efficiency, and can also be recycled and reused.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
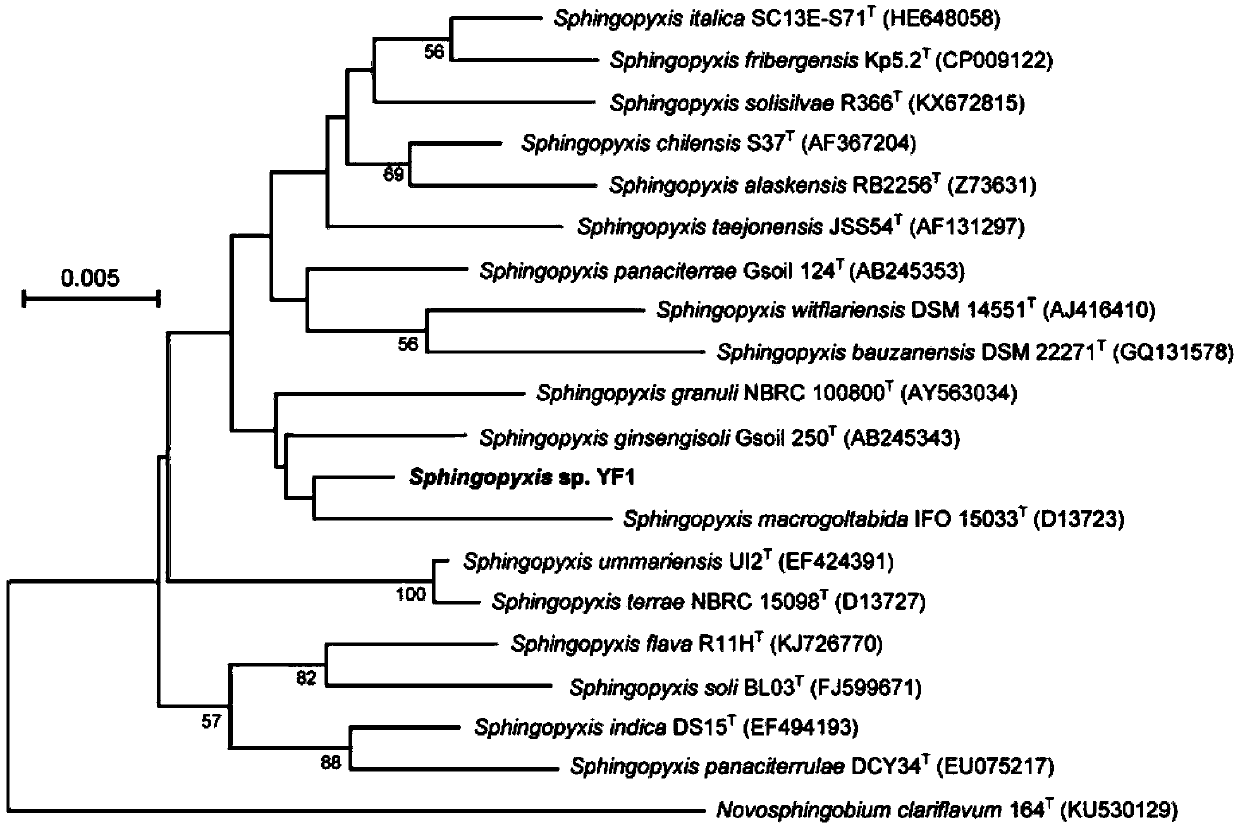
A novel Sphingosine strain and its application in the field of microcystin degradation and detoxification
ActiveCN109486717BStrong detoxificationCompletely degradedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrocystinMicroorganism
The invention discloses a new strain of Sphingopyxis sp., which is preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee. It is named Sphingopyxis sp. YF1 (Sphingopyxis sp. YF1), and the preservation number is CGMCC No: 16341, which was deposited on August 27, 2018. The strain has a strong degrading effect on microcystin, can be applied to control microcystin pollution, and also provides a new strain for the field of microcystin degradation. The invention also discloses the application of the sphingosine strain in the field of microcystin degradation and detoxification. The sphingosine YF1 is used to degrade and detoxify the microcystins, the degradation rate is high, and the microcystins can be completely degraded , can also remove the toxicity of microcystin and its degradation products, solve the problem that the current strains cannot completely remove the toxicity of microcystin, and have strong practical value and application value.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
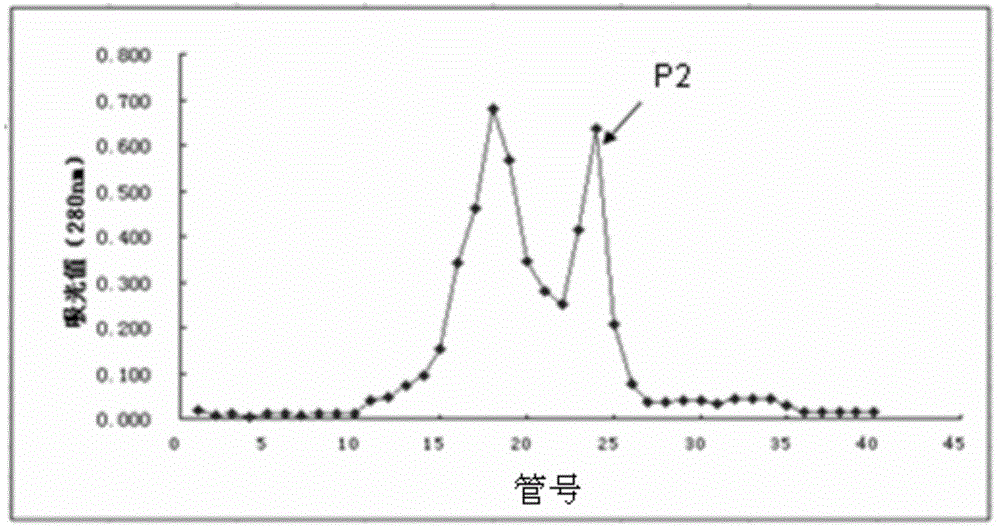
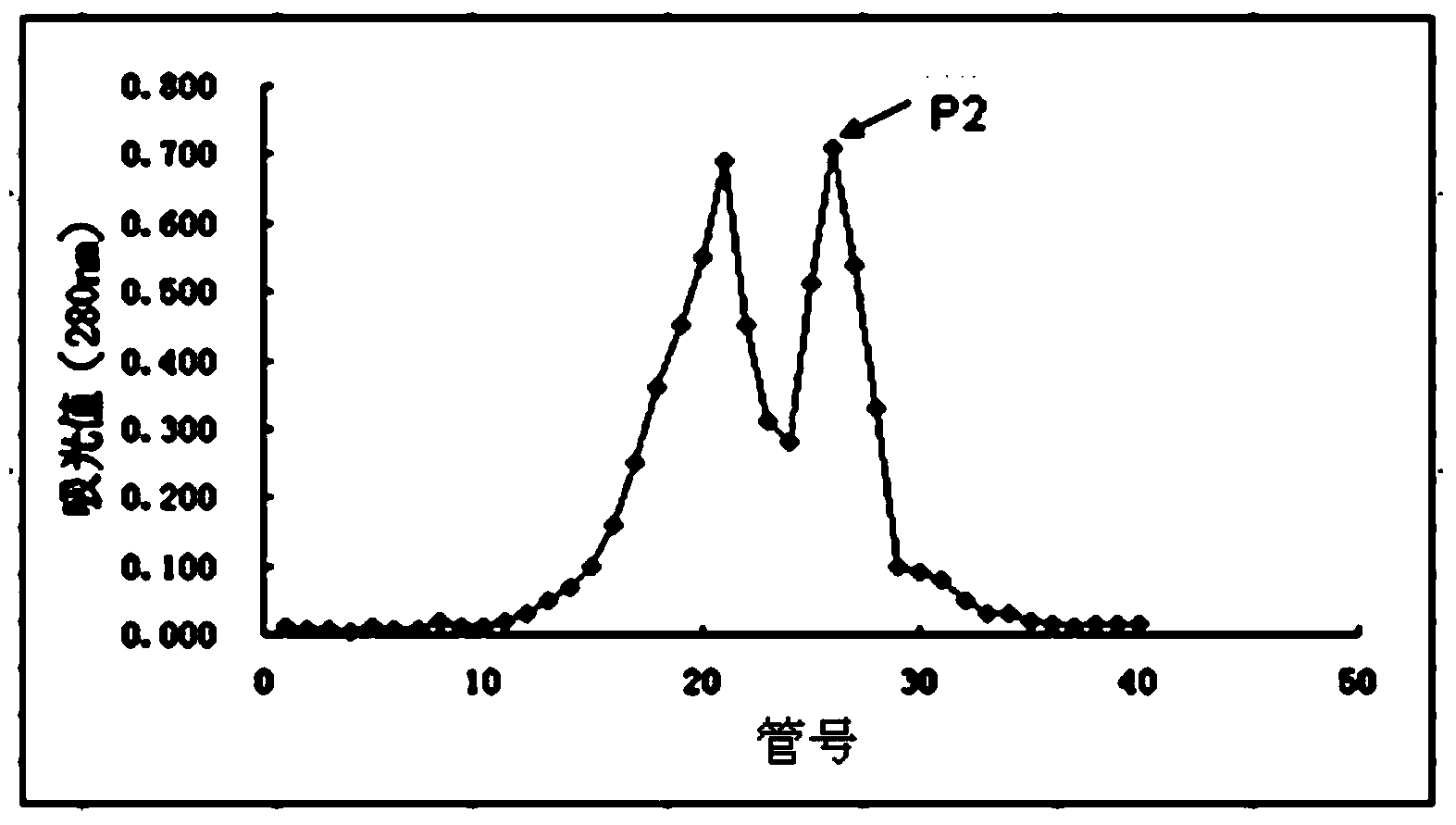
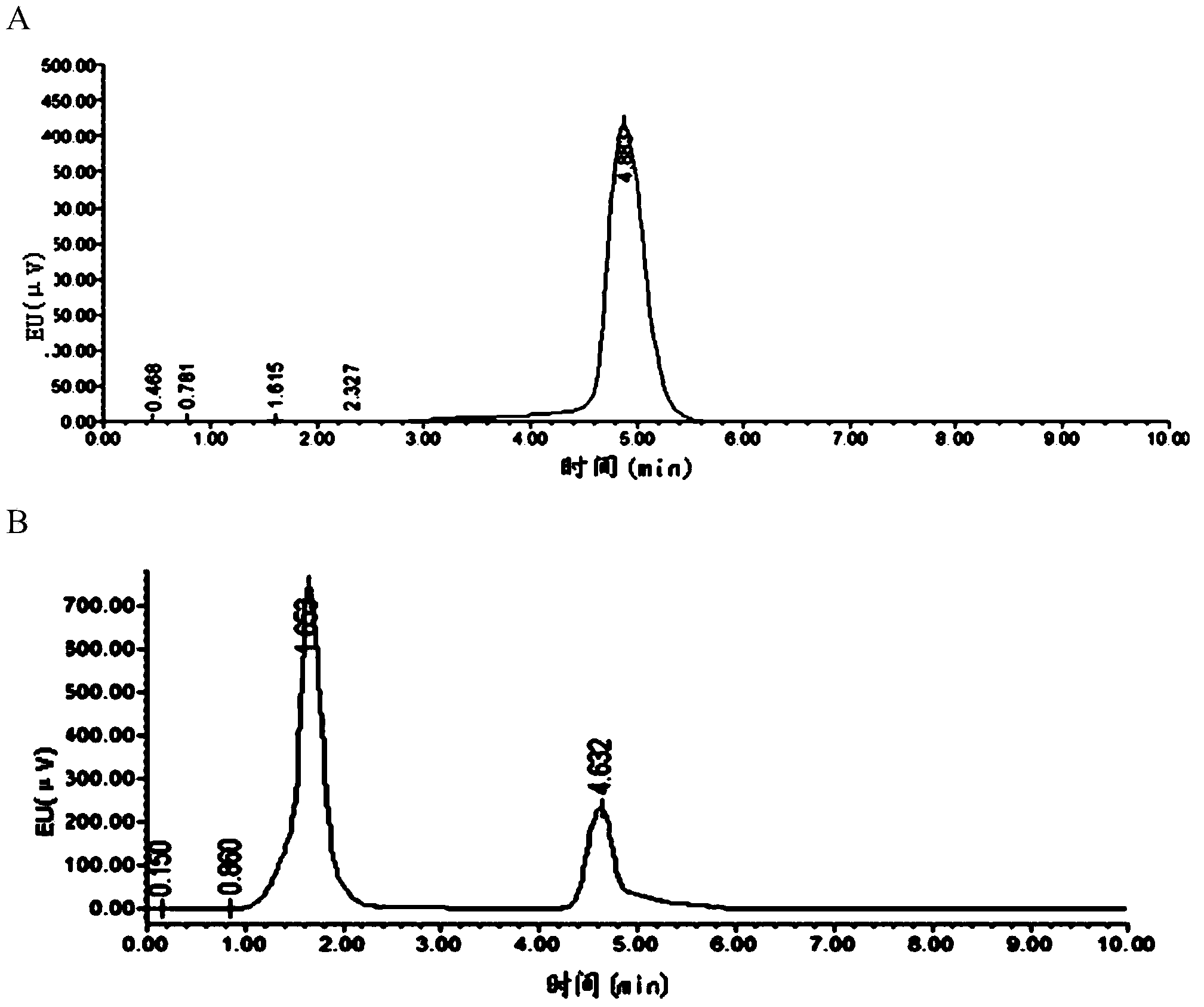
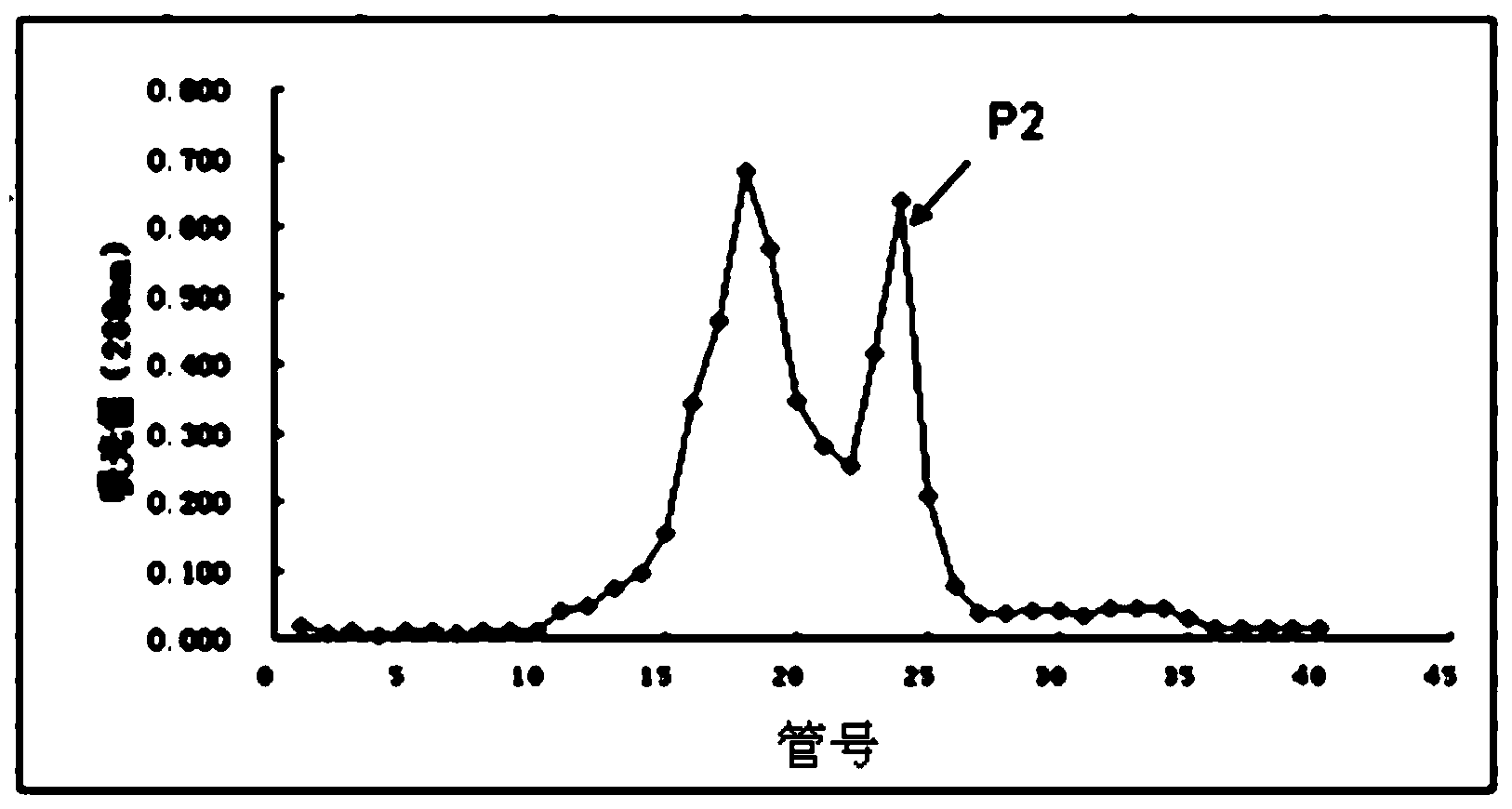
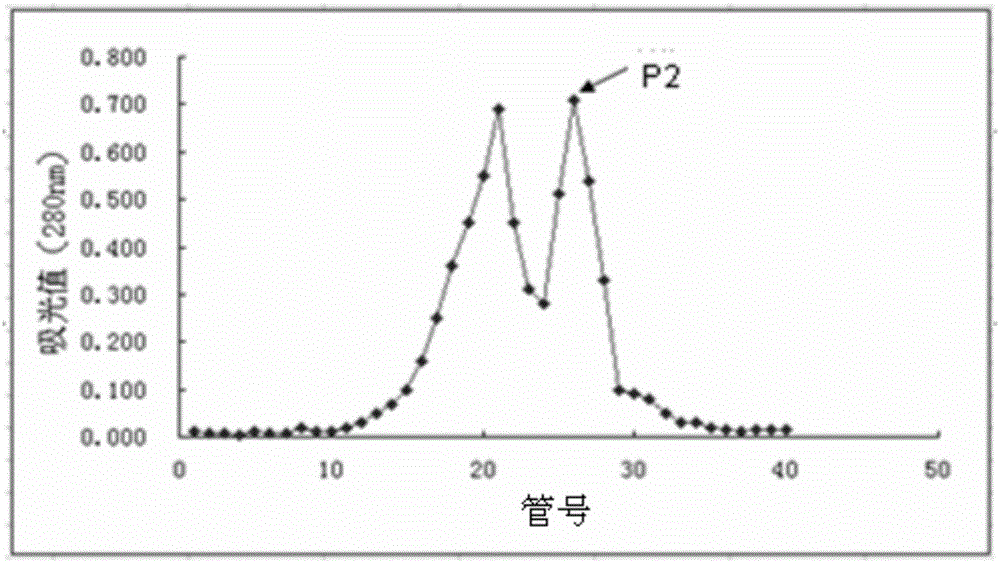
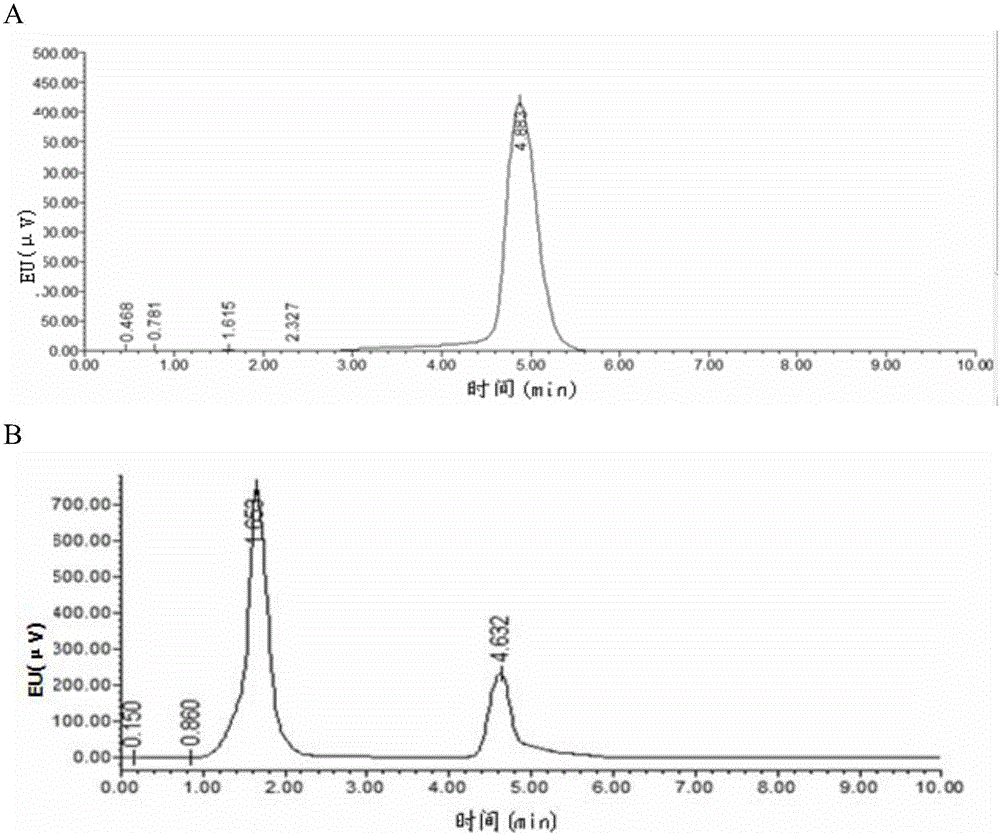
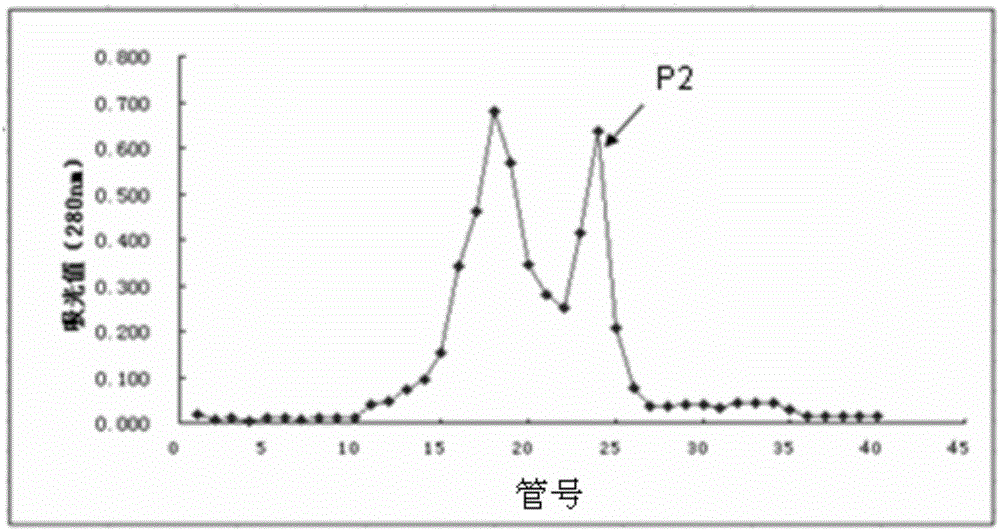
Separation method of components of non-peroxide enzyme capable of degrading zearalenone toxins
ActiveCN103881991APromote degradationHigh protein contentHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffGradient elutionToxin degradation
The invention discloses a separation method of components of a non-peroxide enzyme capable of degrading zearalenone toxins. The separation method comprises the following steps: firstly purifying acinetobacter crude enzyme by using an anionic sephadex column, and carrying out gradient elution by using 15-25mM of sodium phosphate buffer liquid; then purifying the acinetobacter crude enzyme by using a cationic sephadex column, and eluting by using 10-30mM of Tris-HCl buffer liquid; and purifying the acinetobacter crude enzyme by using the anionic sephadex column again, and carrying out gradient elution by using 15-25mM of sodium phosphate buffer liquid, thus obtaining the components of the non-peroxide enzyme capable of degrading the zearalenone toxins in the end. The obtained components of the non-peroxide enzyme capable of degrading the zearalenone toxins have relatively strong fungal zearalenone toxin degradation capability, are capable of degrading above 60% of ZEN within 12 hours without the synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and lay the foundation for the future research of the zearalenone toxin degradation property of non-peroxide enzyme and the application of the non-peroxide enzyme.
Owner:河南亿万中元生物技术有限公司
A kind of high-efficiency fermentation method of aflatoxin degrading bacteria
ActiveCN111154679BImprove filtration efficiencyReduce residual rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyAflatoxin degradation
The invention discloses a high-efficiency fermentation method of aflatoxin-degrading bacteria, which belongs to the field of biotechnology and includes the steps of seed liquid preparation, fermentation culture, adding oxygen-carrying agent, and measuring the content of aflatoxin; The method of adding dodecane as an oxygen-carrying agent in the fermentation system of toxin-degrading bacteria can improve the fermentation efficiency of the target strain, and the obtained fermentation product of the target strain can significantly reduce the residual rate of aflatoxin. The supernatant fermented for 20 hours Compared with the blank control group without oxygen carrier, the residual rate of aflatoxin was reduced by 24.41%, and the residual rate of aflatoxin was only 9.6%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A method for Lactobacillus acidophilus to degrade mycotoxins in animals
ActiveCN106259069BAchieve degradationClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffLactobacillus acidophilusFeed additive
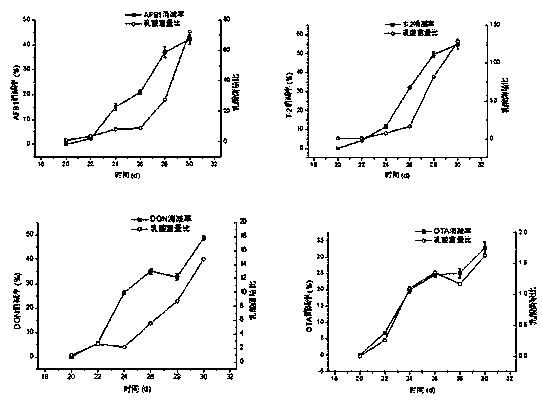
The invention belongs to the technical field of toxin degradation, and discloses the application of Lactobacillus acidophilus in degrading mycotoxins in animals, and the mycotoxins are T-2 toxin and aflatoxin B 1 , vomitoxin and ochratoxin; evenly spray the Lactobacillus acidophilus bacteria liquid into the animal feed, and after ten days feed the feed containing lactic acid bacteria and feed the feed containing T-2 toxin, (AFB 1 ), deoxynivalenol (DON), ochratoxin (OTA) toxins in Penaeus vannamei and tilapia, the mycotoxin residues in shrimp and tilapia muscles were significantly lower than those in the control group, among which T‑2 in shrimp muscle decreased by 63.86±1.32, AFB1 decreased by 53.04±0.97%, DON decreased by 70.74±1.47%, and OTA decreased by 70.24±1.22%. Tilapia muscle T‑2 decreased by 54.93±2.52%, AFB1 decreased by 42.18±1.97%, DON decreased by 48.75±0.93%, OTA decreased by 32.79±1.81%; the present invention makes Lactobacillus acidophilus into a feed additive to achieve degradation Mycotoxins accumulated in animals have practical application value.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
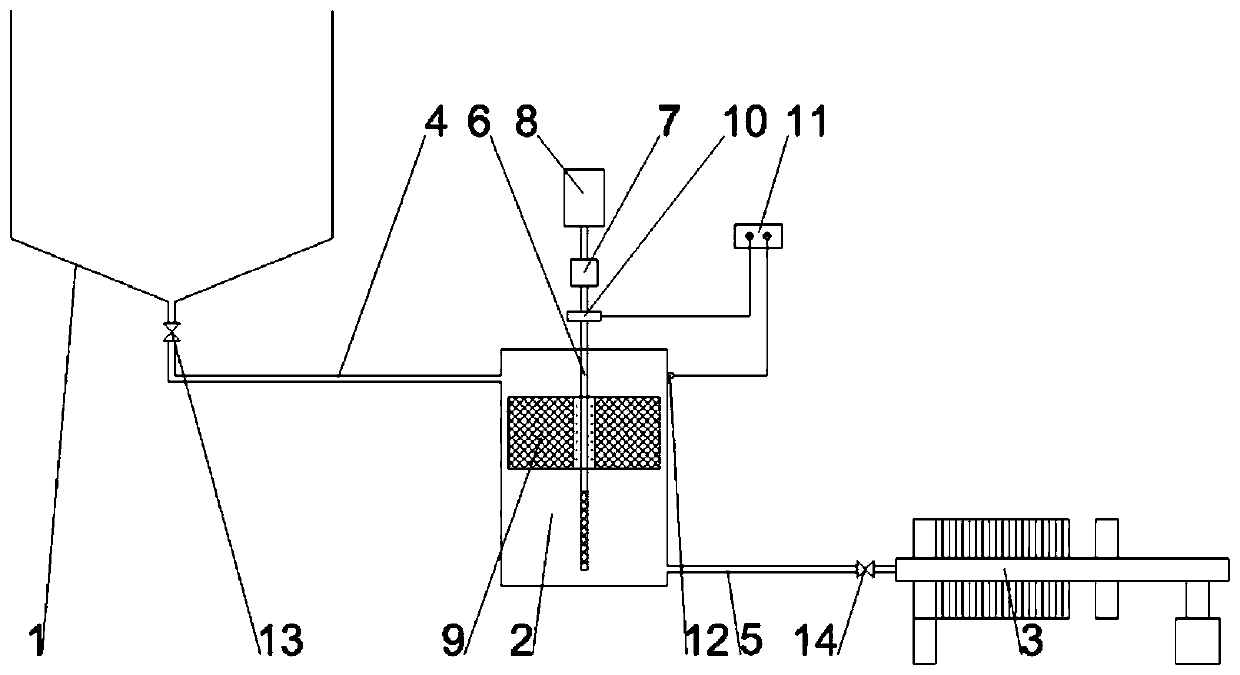
Apparatus for degrading environmental toxins
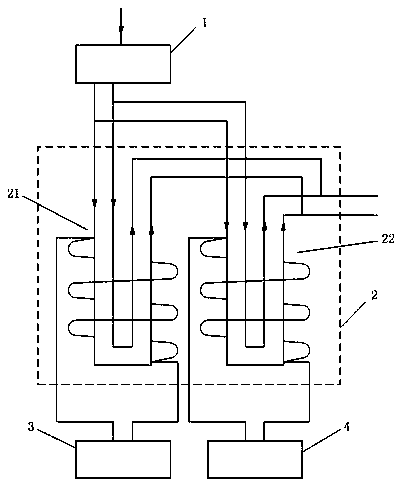
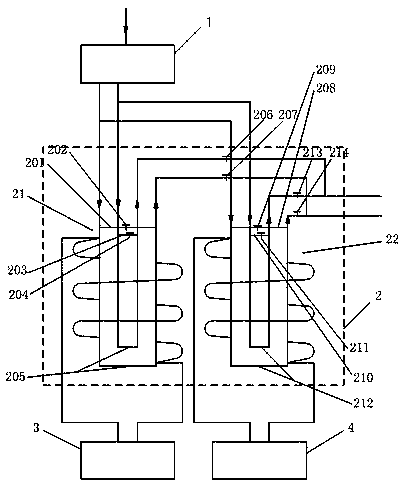
PendingCN110655153AIncrease the lengthImprove the efficiency of degradation treatmentWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsFrequency generationEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses an apparatus for degrading environmental toxins, and relates to the technical field of waste treatment. The apparatus comprises: a shunt valve device comprising an input pipeline and two or more output pipelines; a resonance degradation device comprising two or more environmental toxin degradation devices used for degrading environmental toxins; and two or more frequency generation devices, wherein every frequency generation device comprises a resonance coil and a control circuit, the resonance coils are wound outside pipelines of the environmental toxin degradation devices, and the control circuits are connected with the resonance coils and are used for generating sine waves with the frequency of 50-100 MHz and outputting the sine waves to the resonance coils. Theapparatus has a high degradation treatment efficiency.
Owner:航天国环技术集团有限公司
A method for separating non-peroxidase enzyme components capable of degrading zearalenone toxin
ActiveCN103881991BPromote degradationReduce concentrationHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffPeroxidaseGradient elution
The invention discloses a separation method of components of a non-peroxide enzyme capable of degrading zearalenone toxins. The separation method comprises the following steps: firstly purifying acinetobacter crude enzyme by using an anionic sephadex column, and carrying out gradient elution by using 15-25mM of sodium phosphate buffer liquid; then purifying the acinetobacter crude enzyme by using a cationic sephadex column, and eluting by using 10-30mM of Tris-HCl buffer liquid; and purifying the acinetobacter crude enzyme by using the anionic sephadex column again, and carrying out gradient elution by using 15-25mM of sodium phosphate buffer liquid, thus obtaining the components of the non-peroxide enzyme capable of degrading the zearalenone toxins in the end. The obtained components of the non-peroxide enzyme capable of degrading the zearalenone toxins have relatively strong fungal zearalenone toxin degradation capability, are capable of degrading above 60% of ZEN within 12 hours without the synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and lay the foundation for the future research of the zearalenone toxin degradation property of non-peroxide enzyme and the application of the non-peroxide enzyme.
Owner:河南亿万中元生物技术有限公司
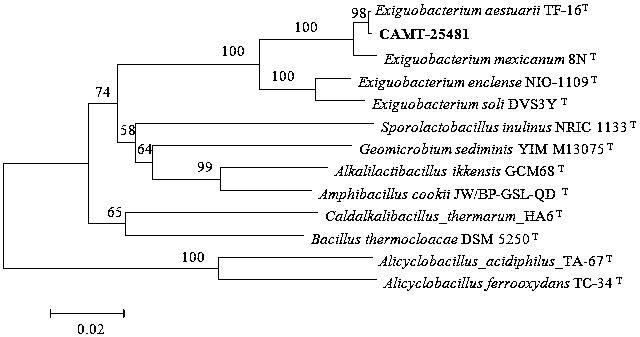
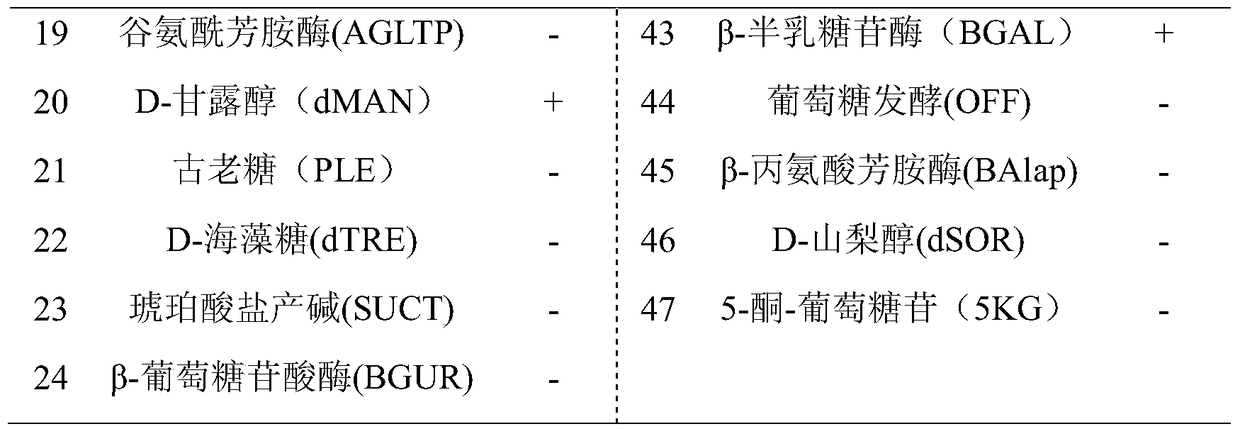
A kind of microbacterium in intertidal zone and its application
ActiveCN105349465BEfficient degradationEnsure food safetyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyToxin degradation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly discloses intertidal Exiguobacterium aestuarii and application thereof. The strain is the intertidal Exiguobacterium aestuarii CAMT25481, the strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on Oct.19th, 2015, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO. 11512. The degradation rate of the strain CAMT25481 to T-2 toxin can reach 73.80 percent to the maximum extent, the T-2 toxin can be effectively degraded, the significant problems that feed and raw material shrimps are polluted by the T-2 toxin and cannot be utilized, and environmental pollution is severe are solved, and a foundation is laid for ensuring the food safety of highly processed products of the raw material shrimps.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com