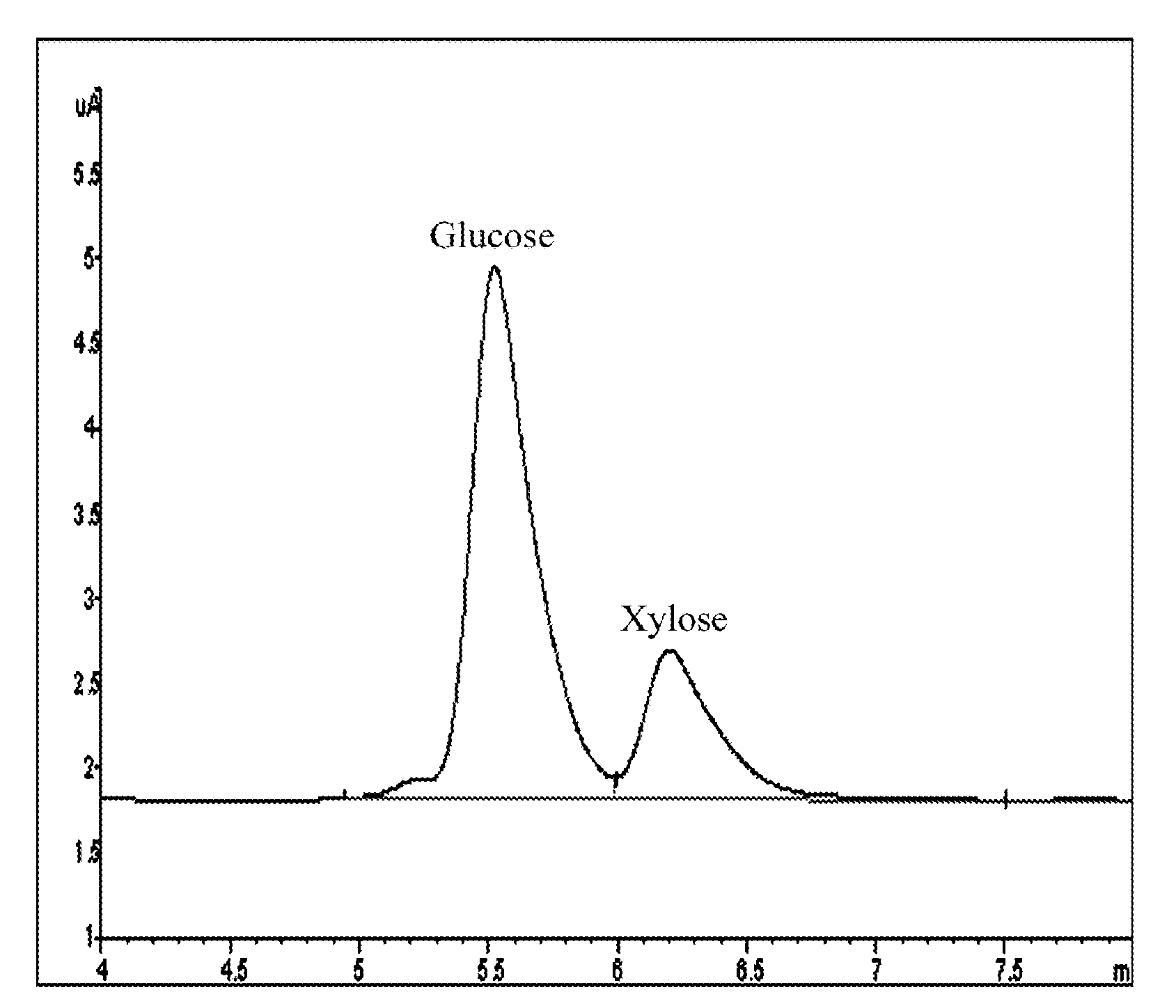
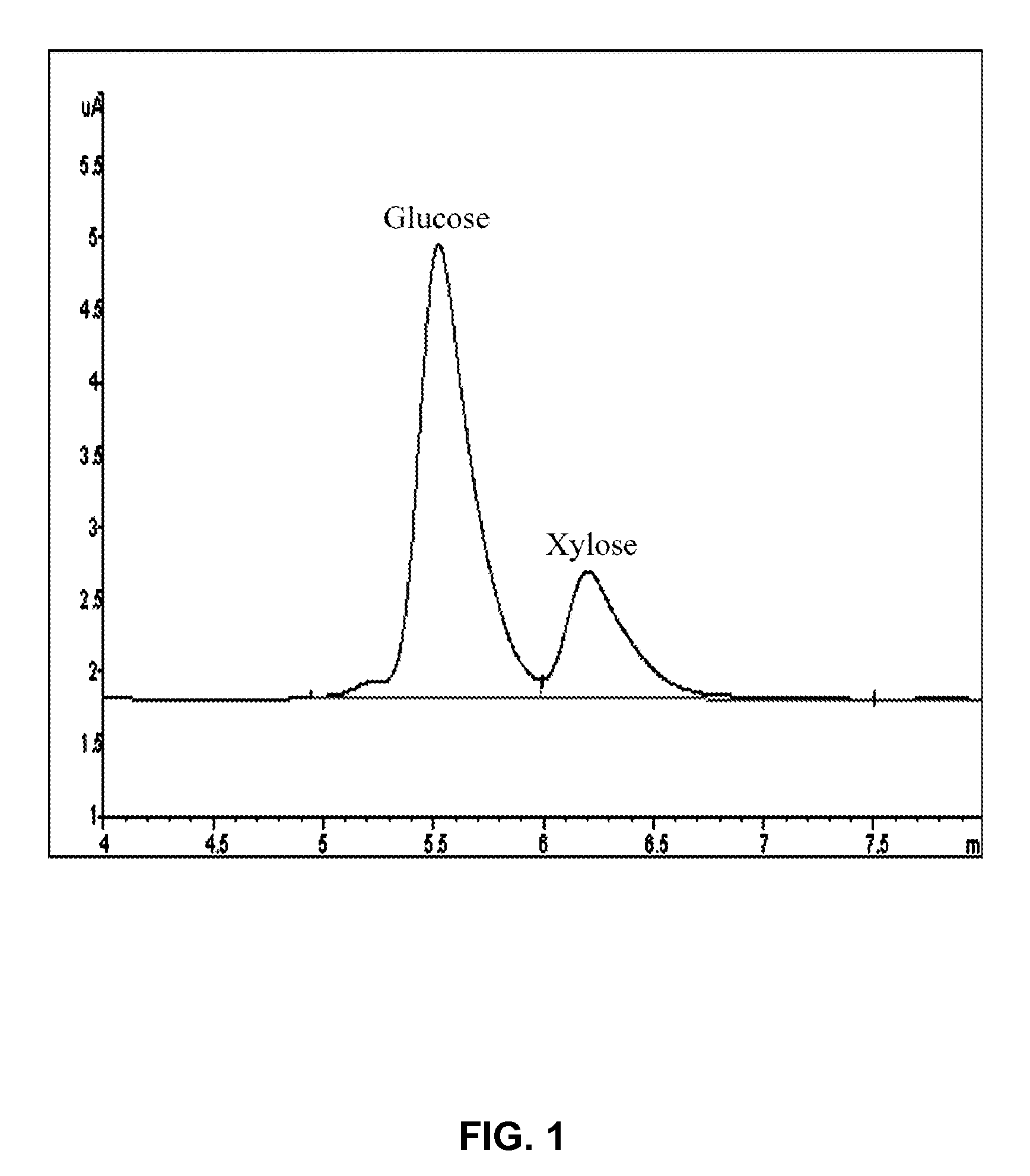
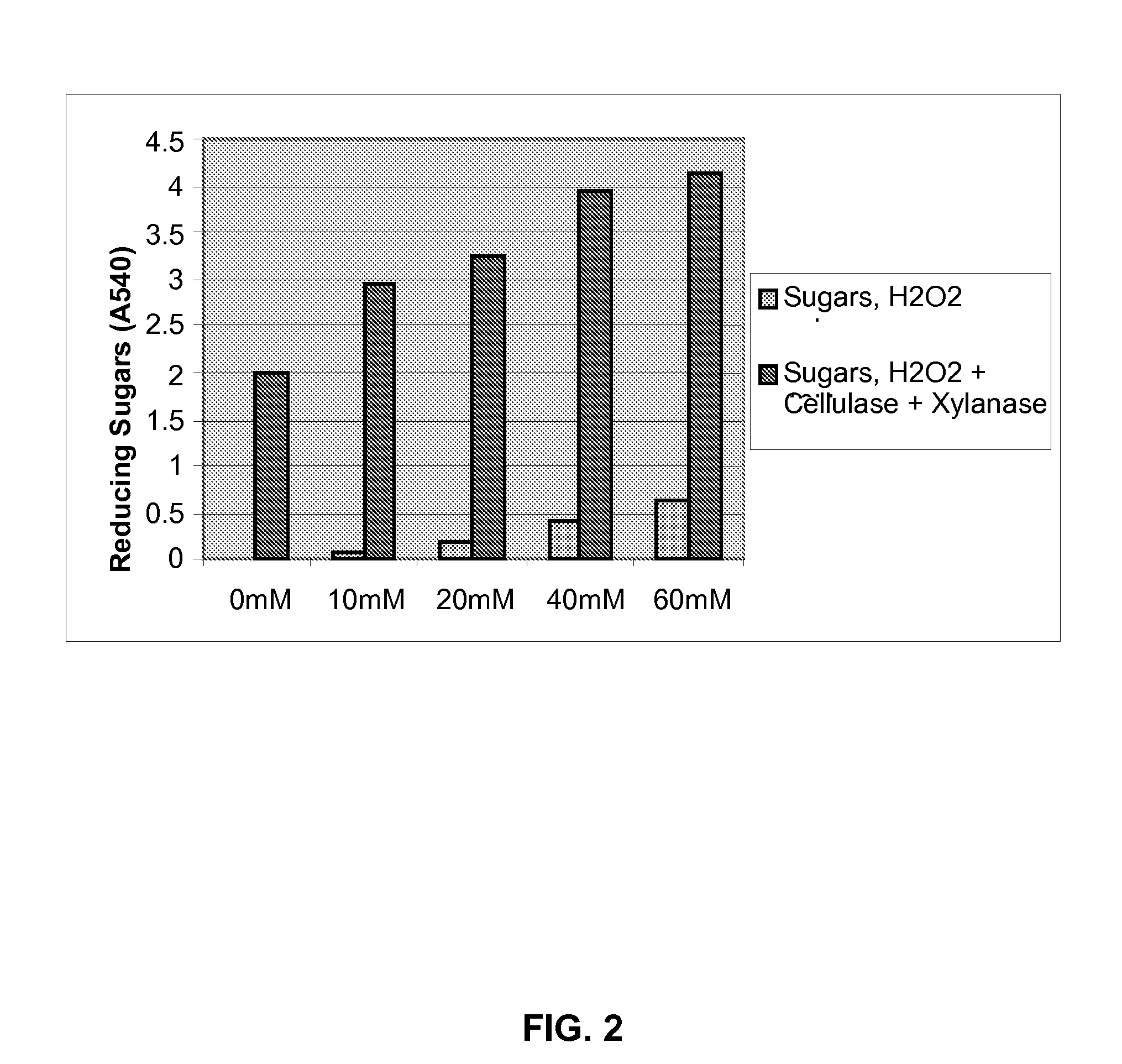
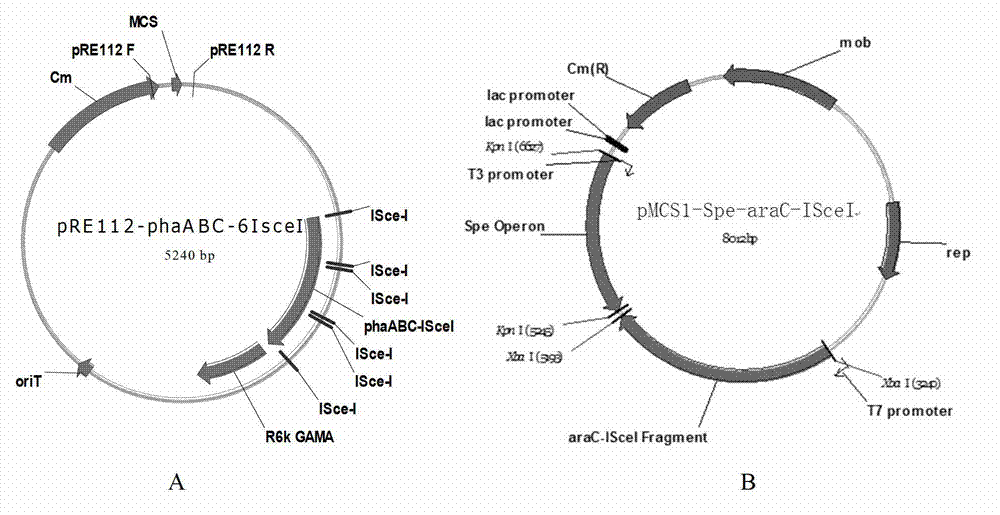
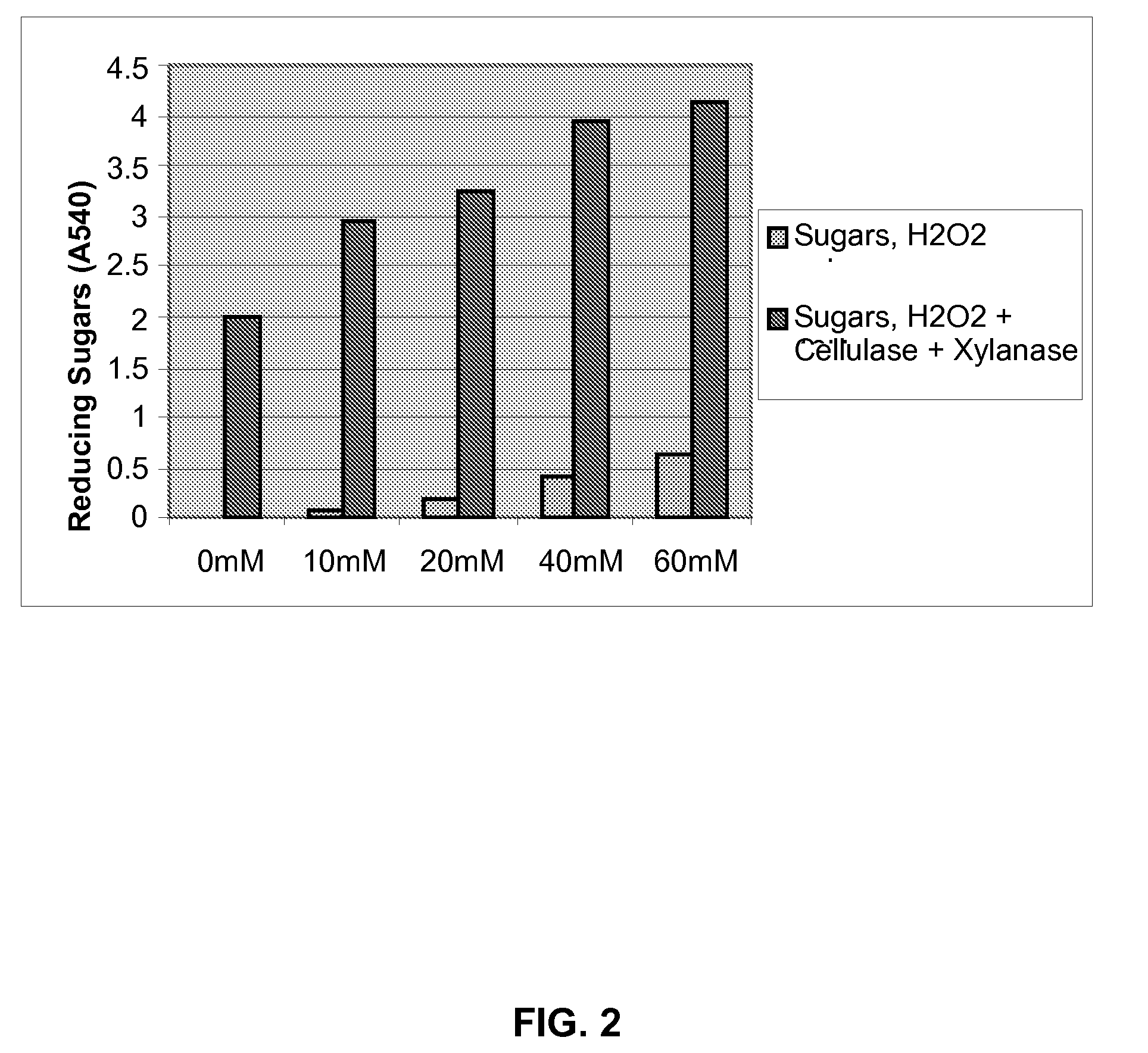
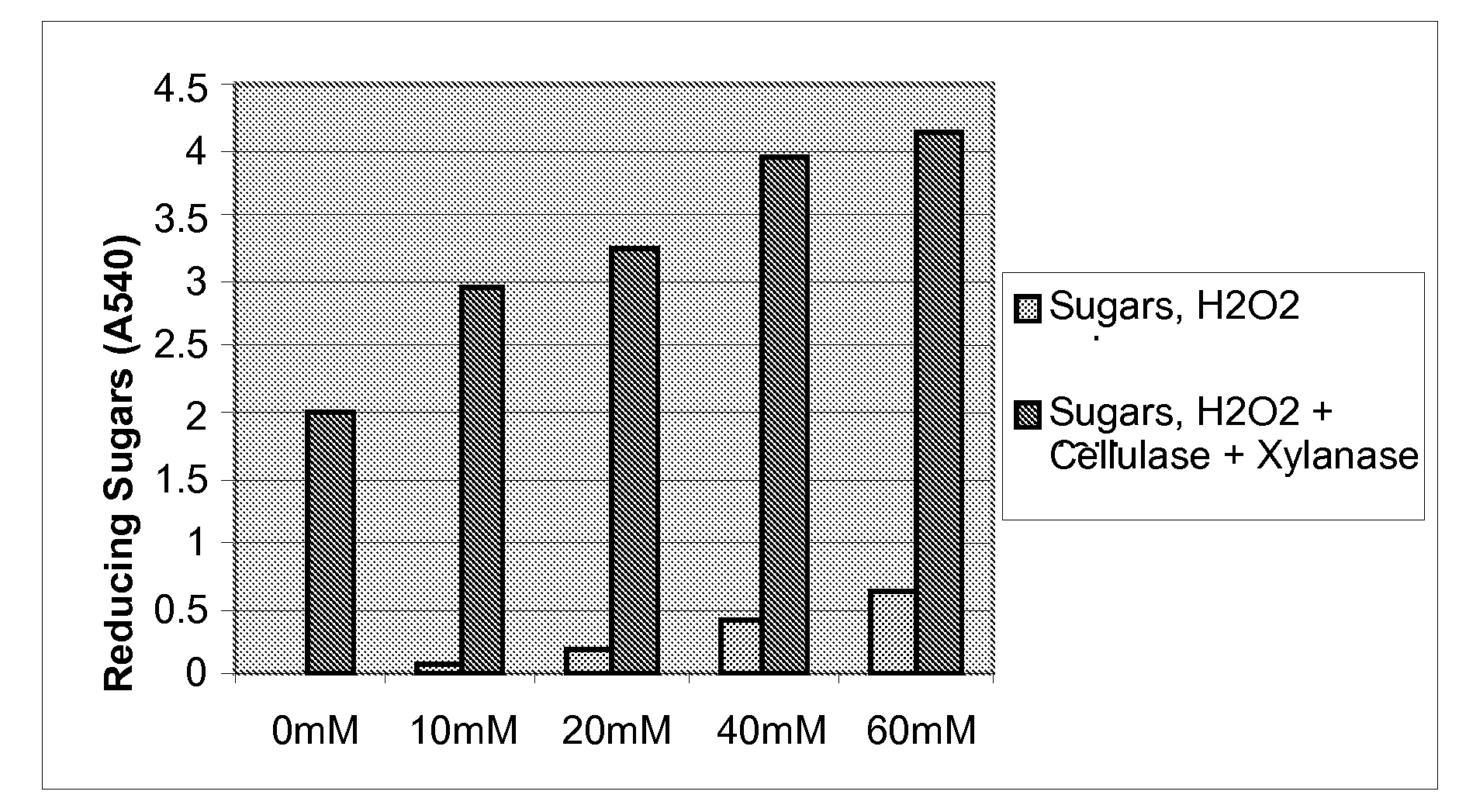
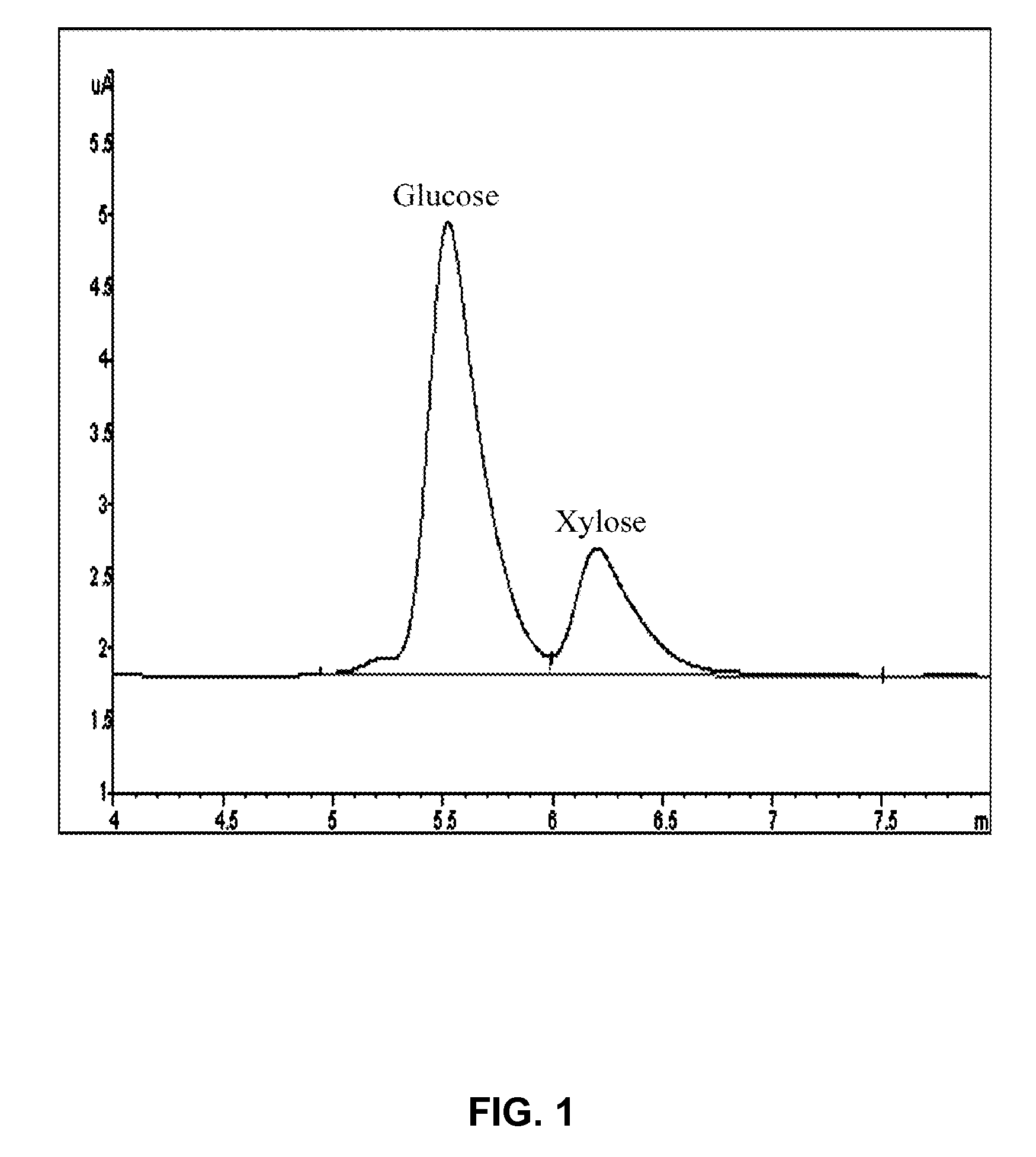
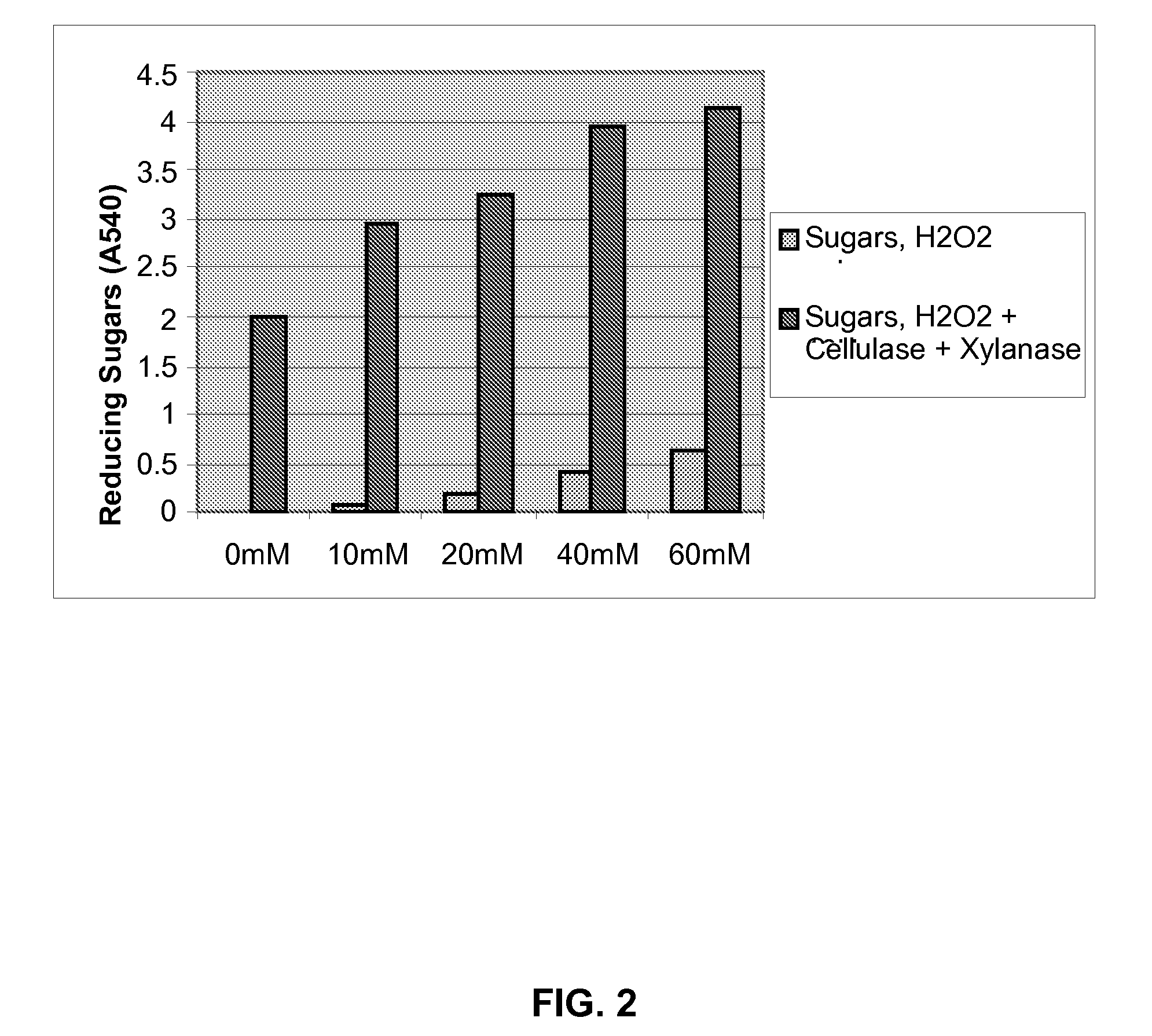
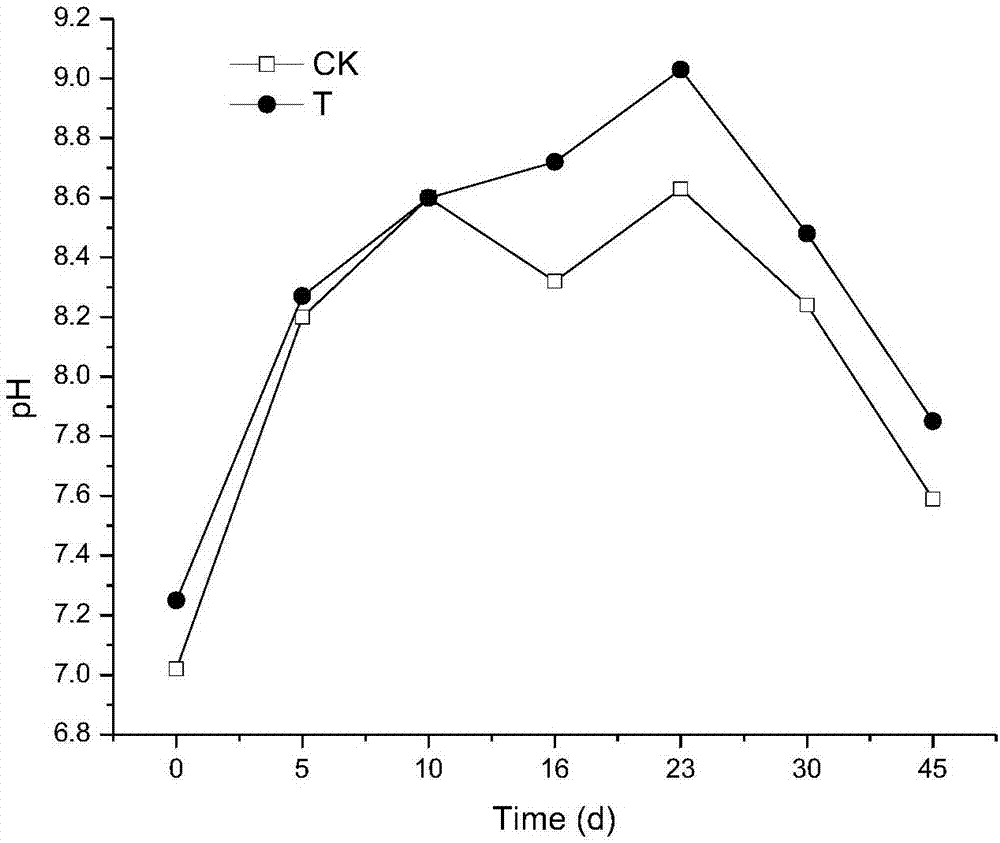
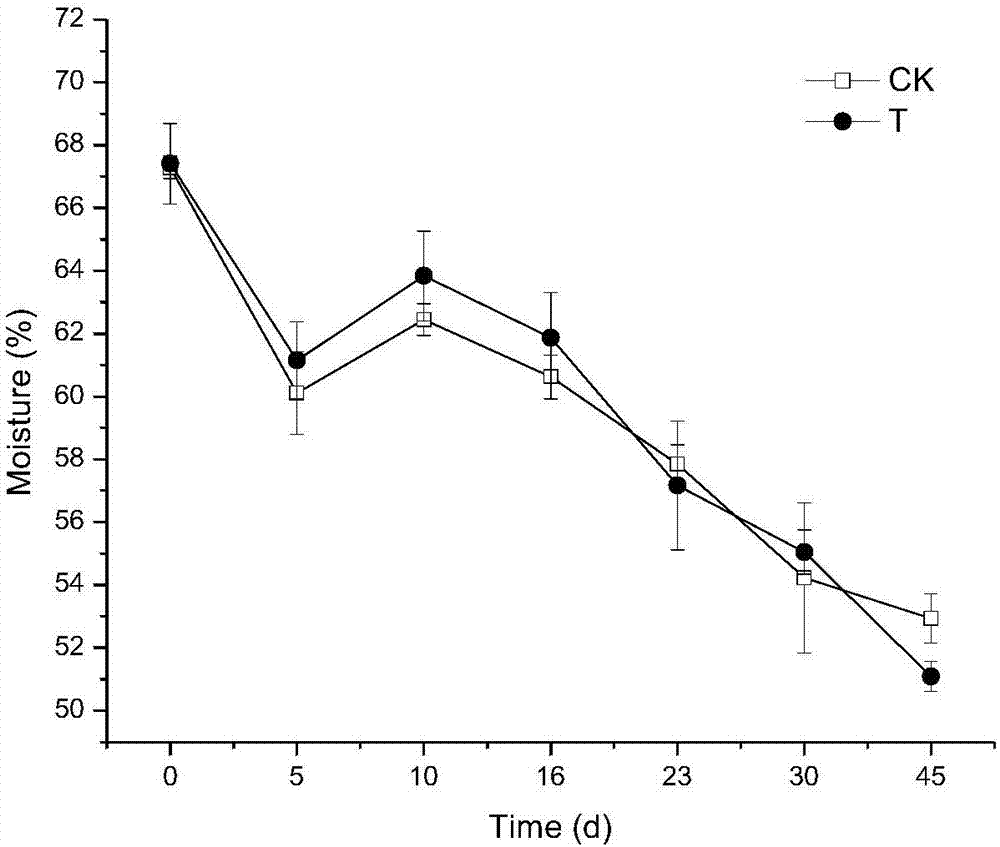
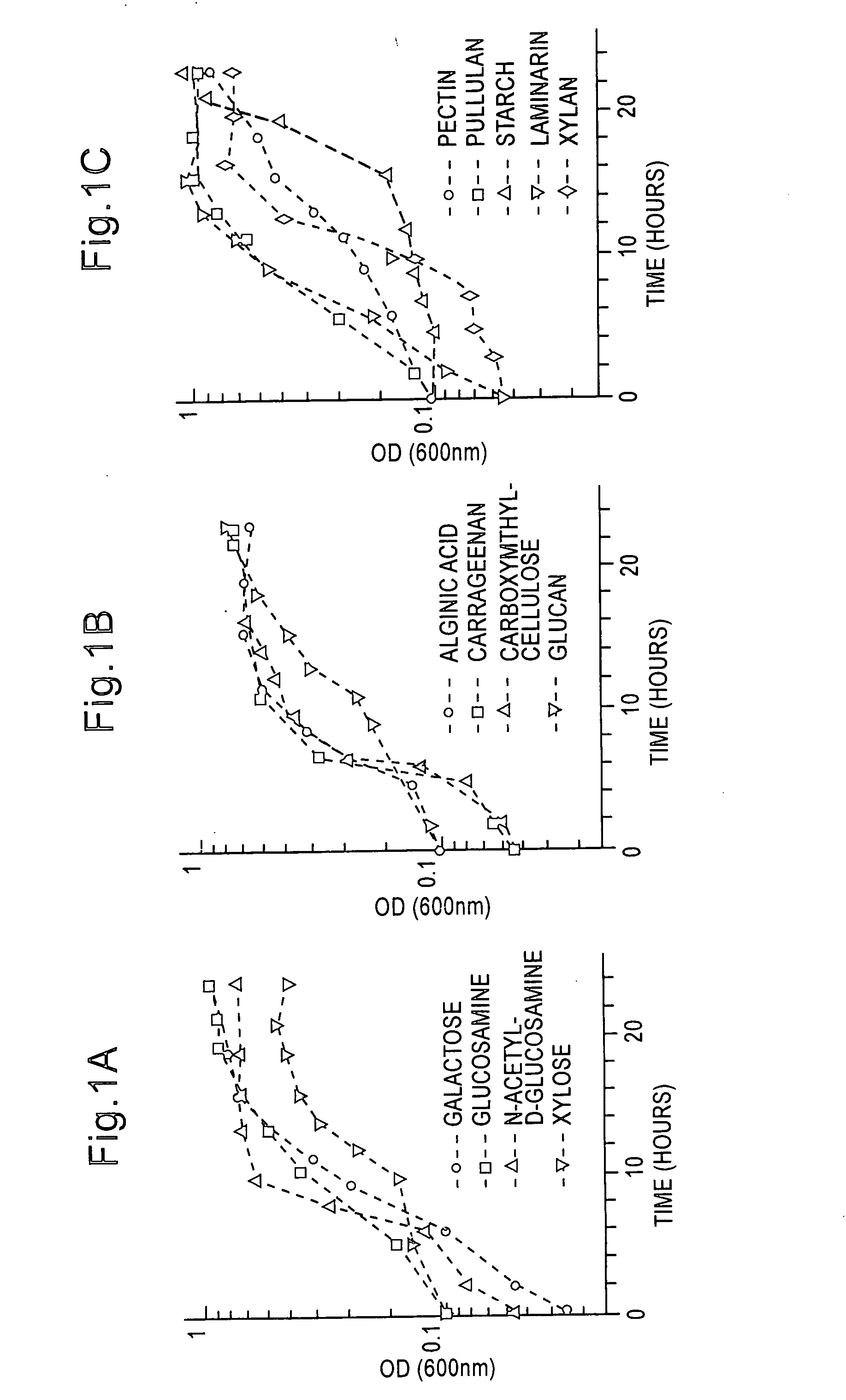
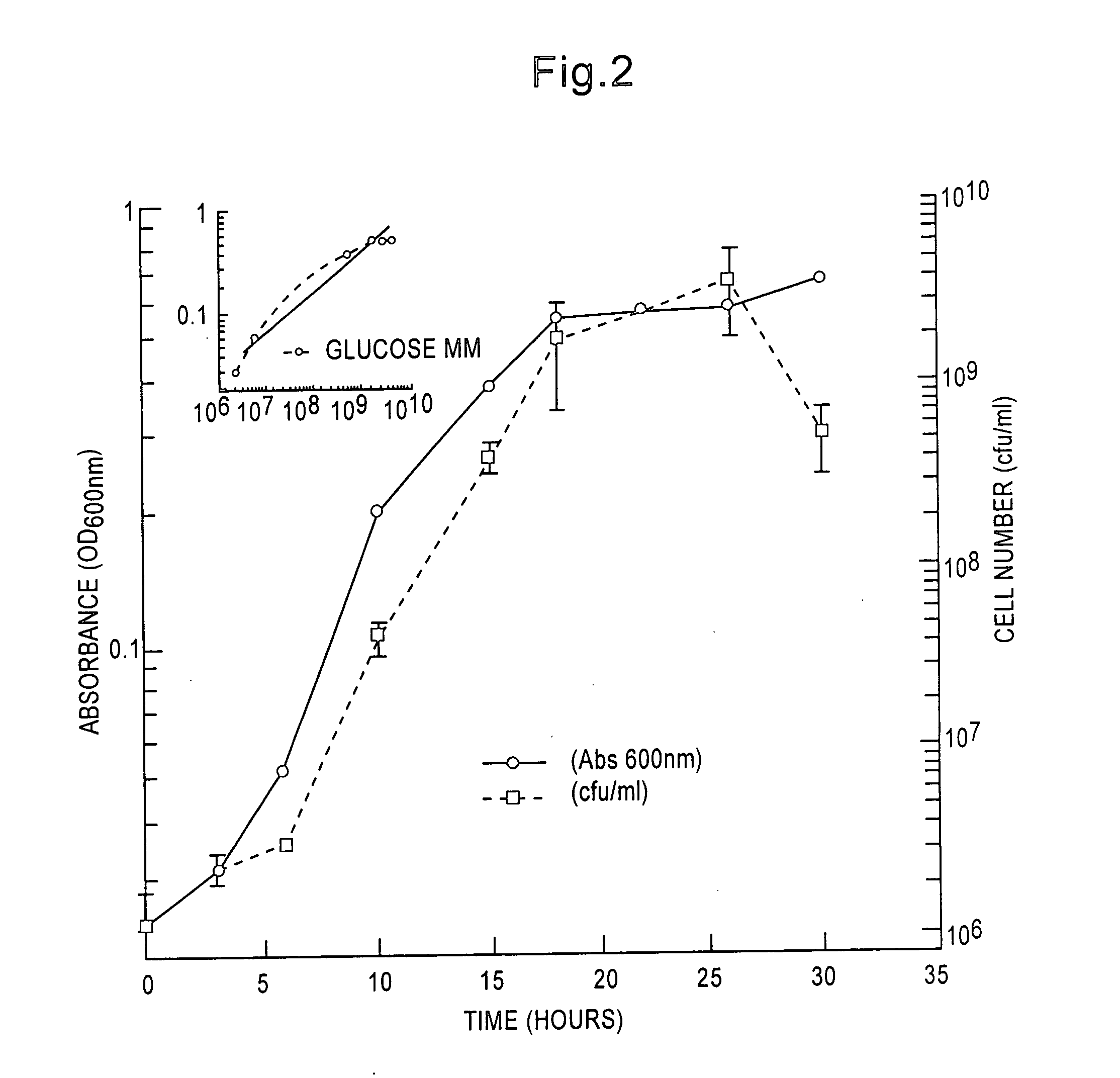
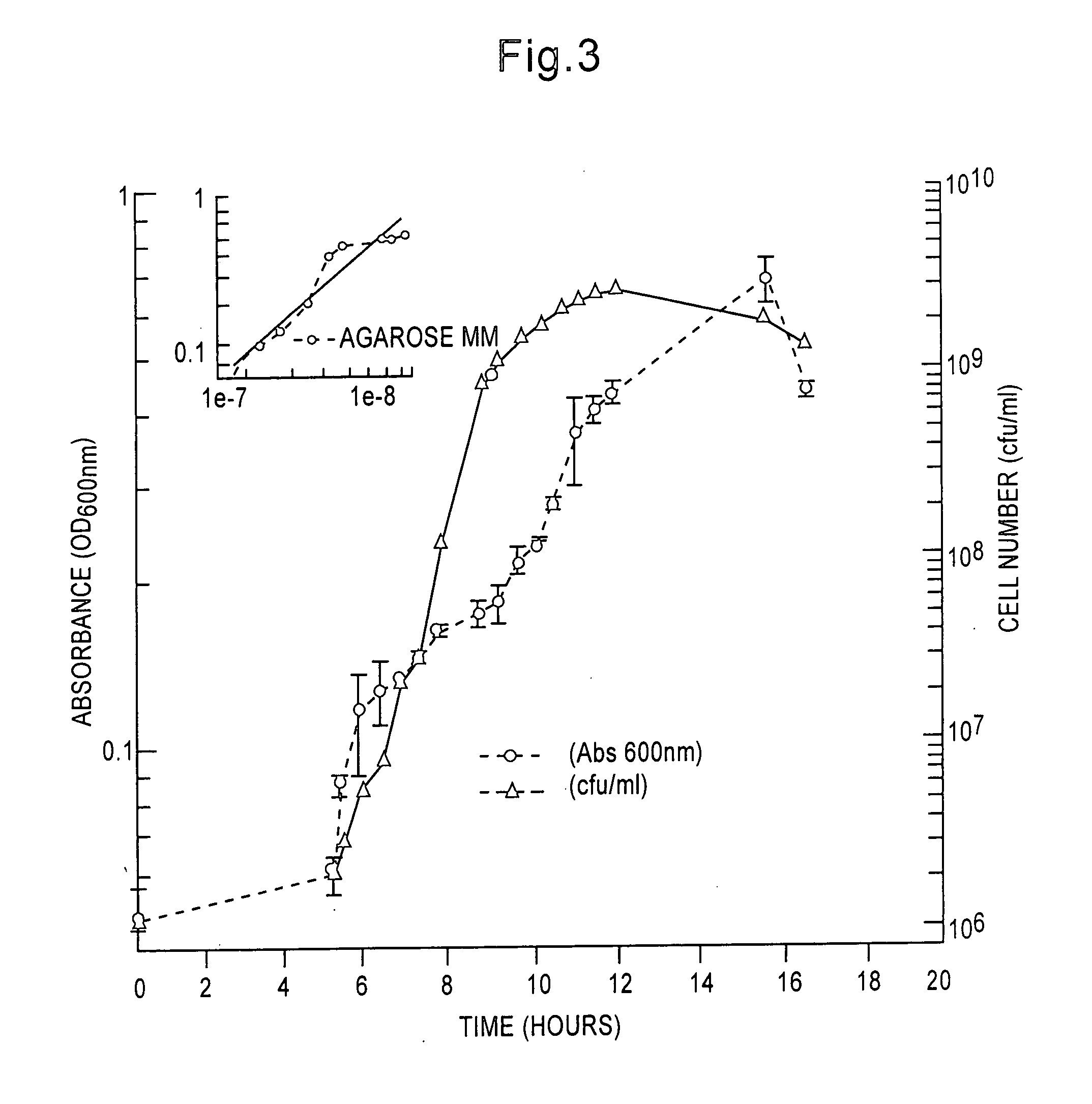
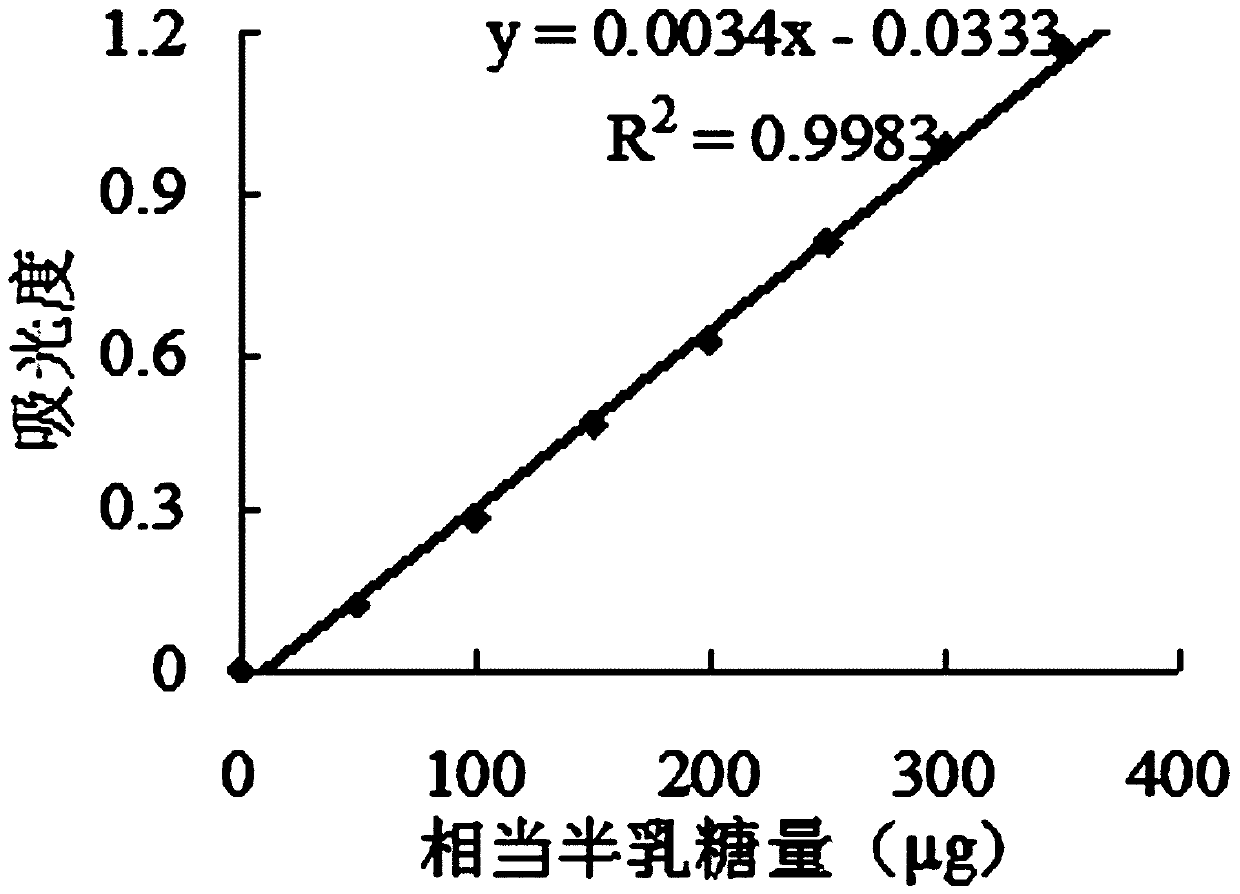
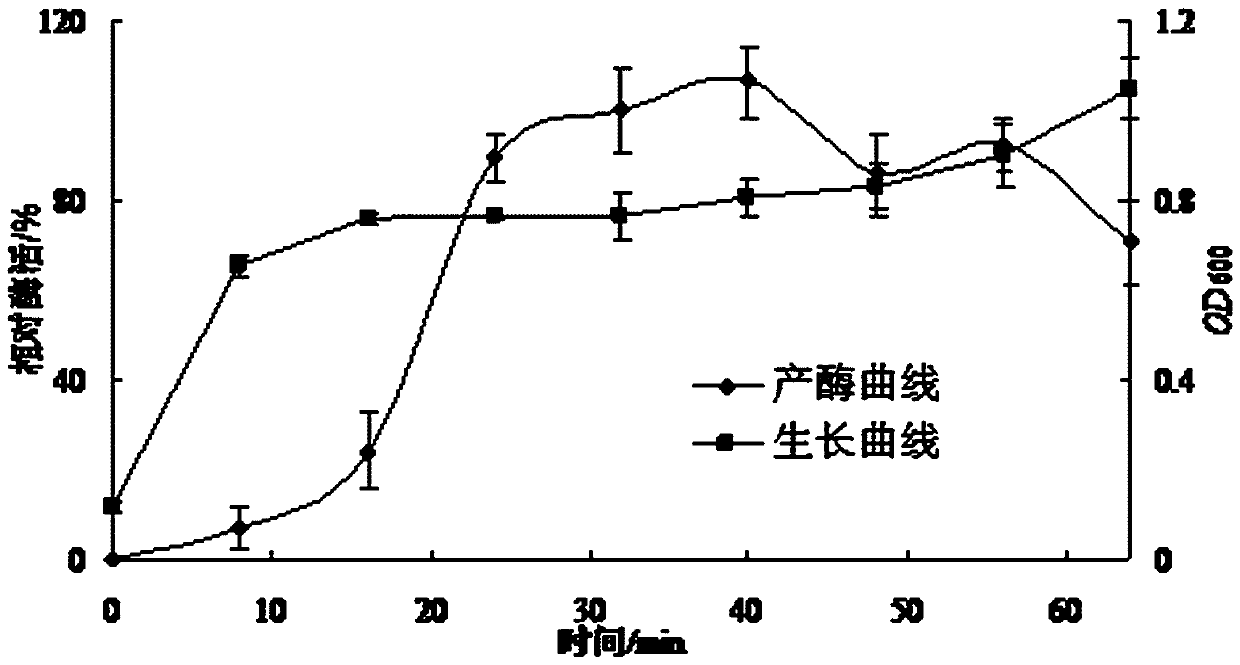
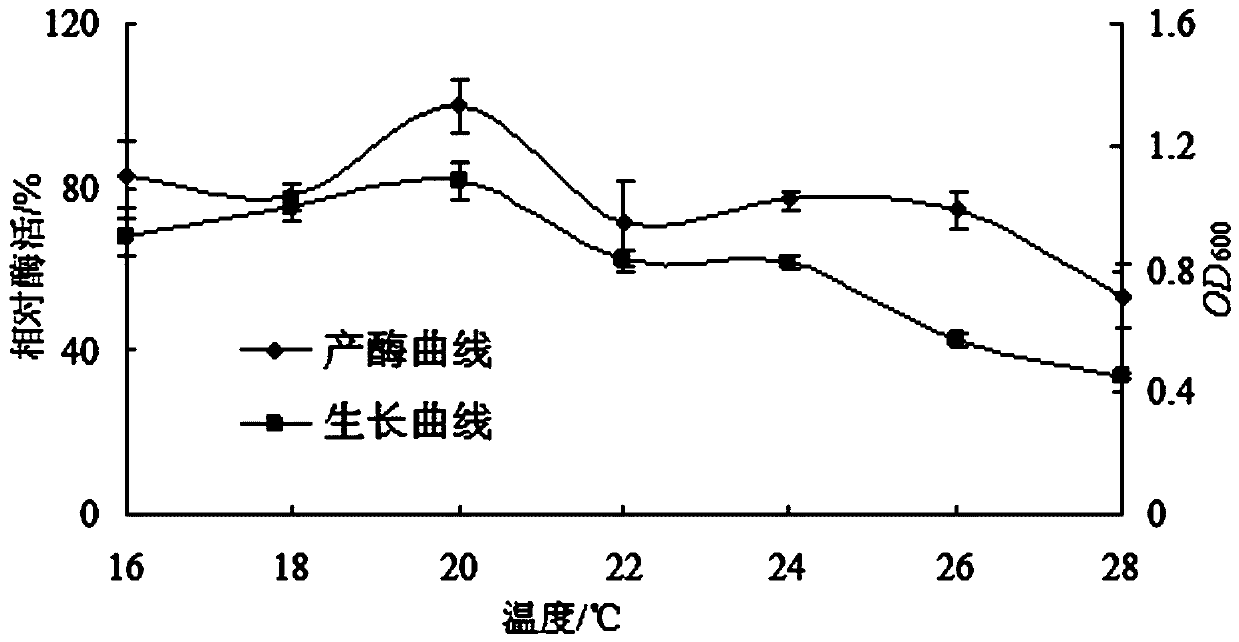
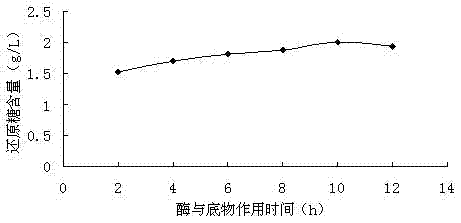
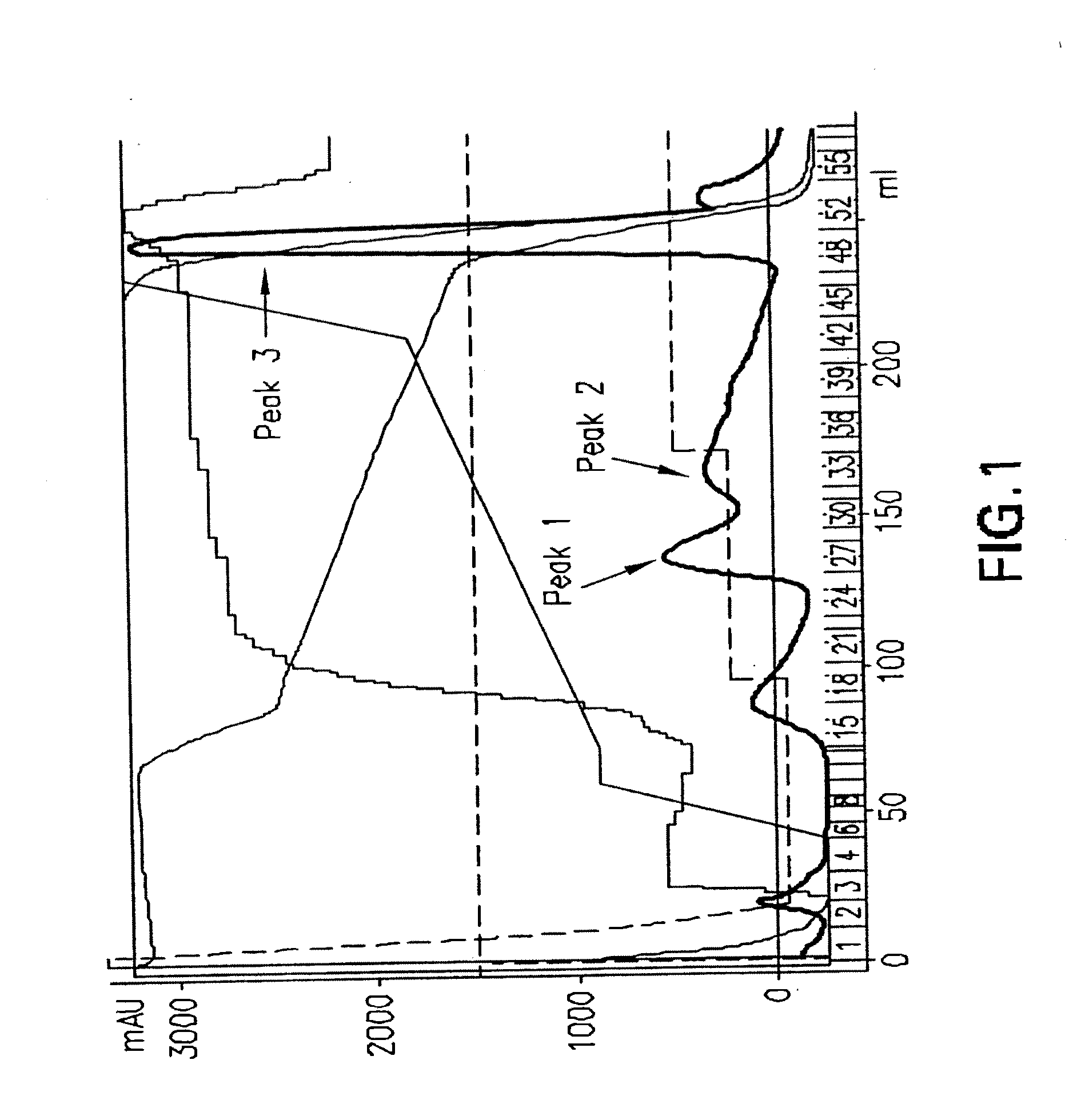
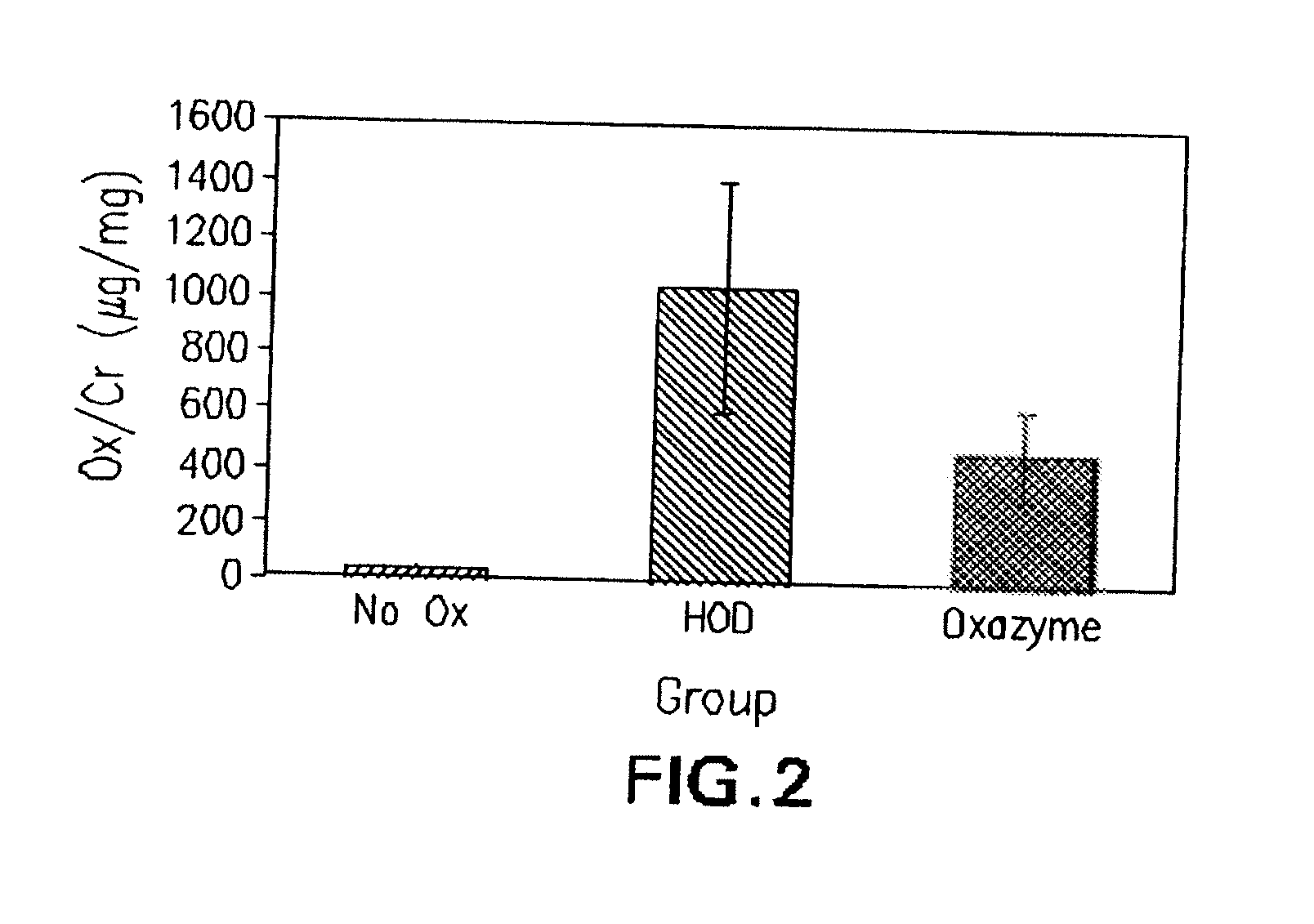
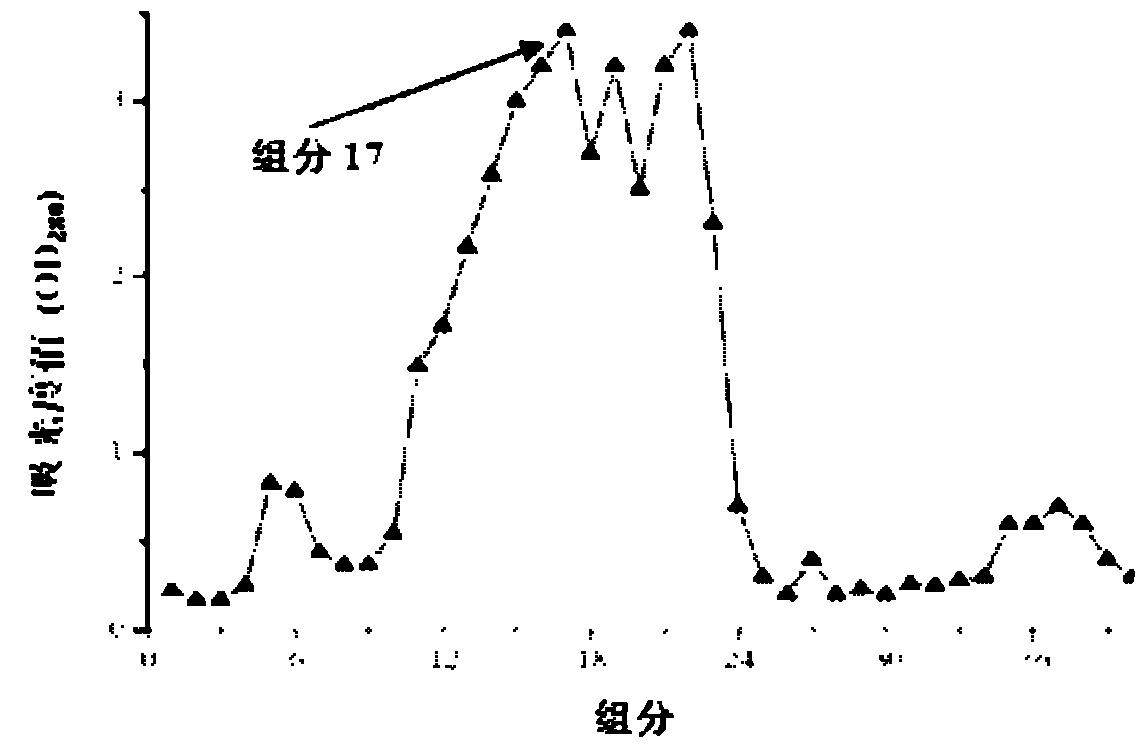
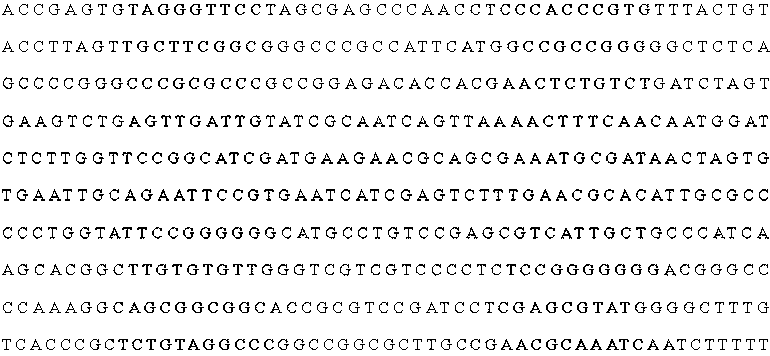Patents
Literature
257 results about "Degradative enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A degradative enzyme is an enzyme (in a broader sense a protein) which degrades biological molecules.
Commercial production of polysaccharide degrading enzymes in plants and methods of using same
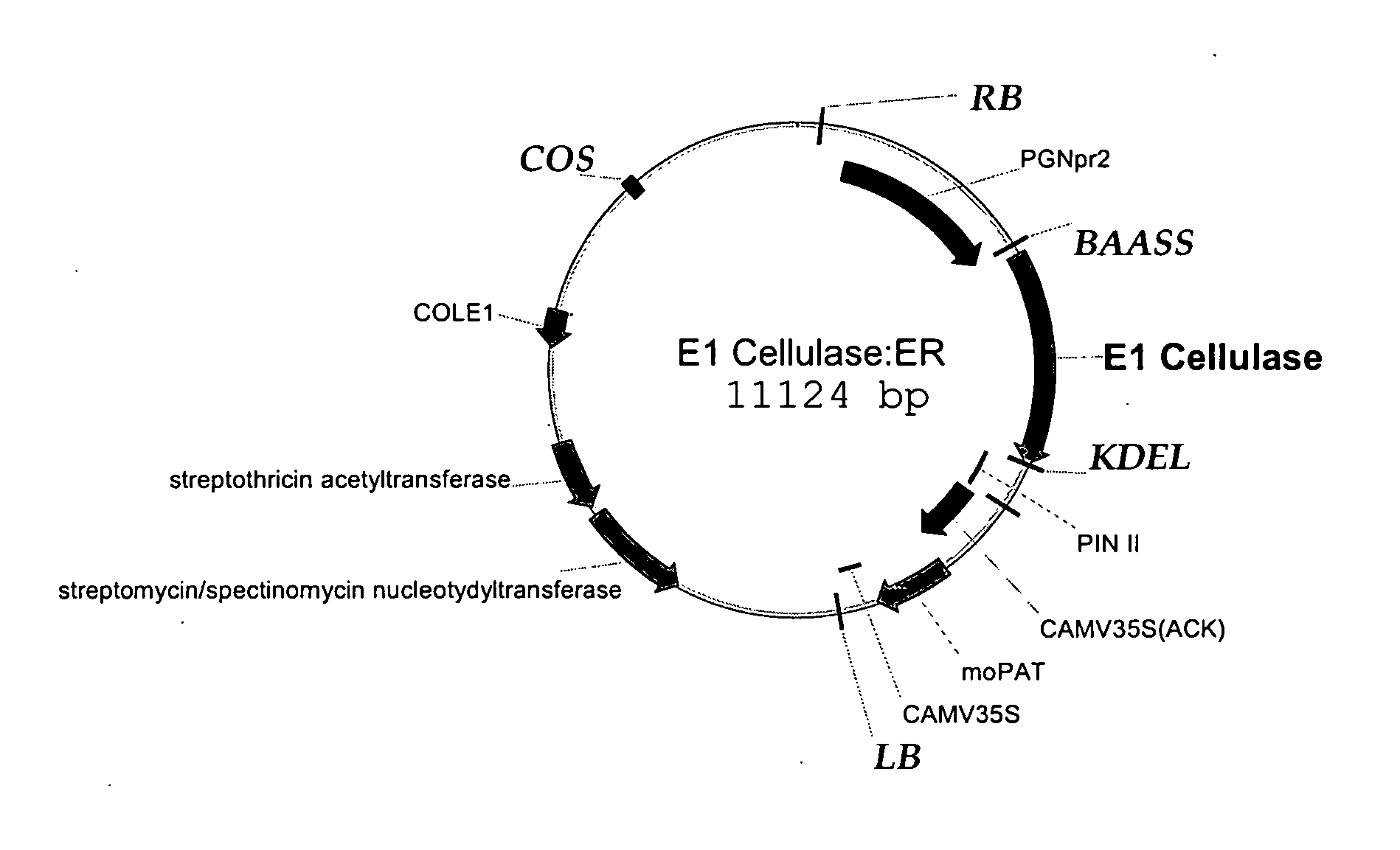
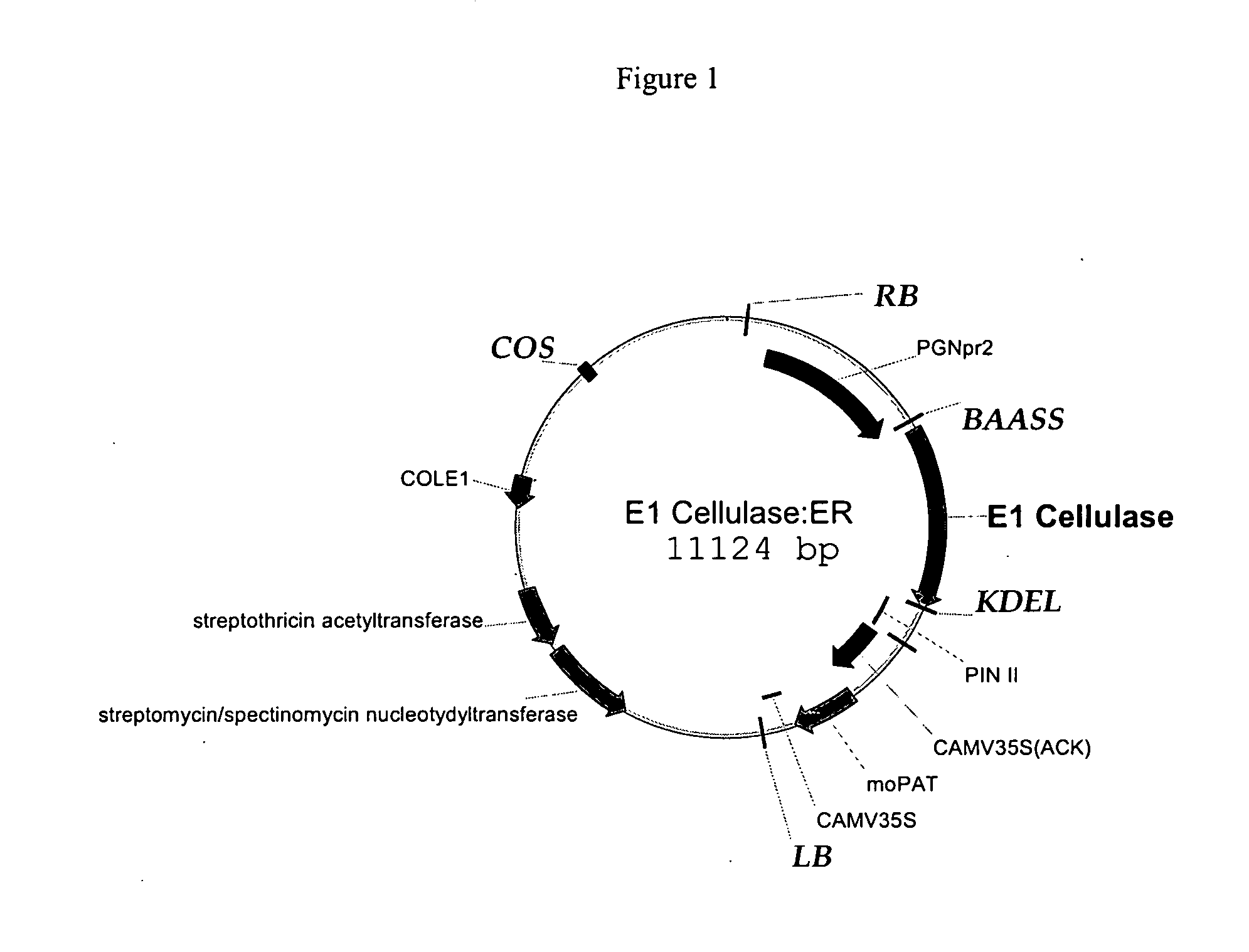
Expression of recombinant polysaccharide degrading enzymes in plants is described. In one embodiment, expression of the enzyme is preferentially directed to the seed of the plant. Expression may also be preferentially targeted to specific locations within the plant cell. Expression of cellulases in corn is shown. The result is the capacity to produce polysaccharide degrading enzymes in plants at commercially acceptable levels in a reliable manner. Methods of using same in production of ethanol is also described, including use of the plant-produced enzymes in the ethanol production process.
Owner:APPLIED BIOTECH INST
Method of degrading plastic and process for producing useful substance using the same
InactiveUS20060106120A1Lower water activityImprove the degradation problemFungiHydrolasesMicroorganismActive agent
A method of degrading a plastic in the presence of a biosurfactant; a method of degrading a plastic by contacting the plastic with a microorganism; a process for producing a useful substance from a plastic which comprises degrading the plastic by contacting the plastic with a microorganism and further converting the components of the thus degraded plastic with the use of a microorganism; a method of degrading a plastic by contacting the plastic with a microorganism in the coexistence of a biosurfactant and / or a plastic-degrading enzyme and thus degrading the plastic under the action of the microorganism; a transformant microorganism having been recombined with at least one DNA selected from among a DNA containing a gene encoding a surface active substance, a DNA containing a gene encoding a plastic-degrading enzyme and a DNA containing a gene encoding a useful substance; novel genes as described above; and proteins encoded thereby.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD +1
Small single-port arthroscopic lavage, directed tissue drying, biocompatible tissue scaffold and autologous regenerated cell placement delivery system
InactiveUS20150025311A1Increase chanceMore accurateCannulasSurgical needlesPort of entryDegradative enzyme
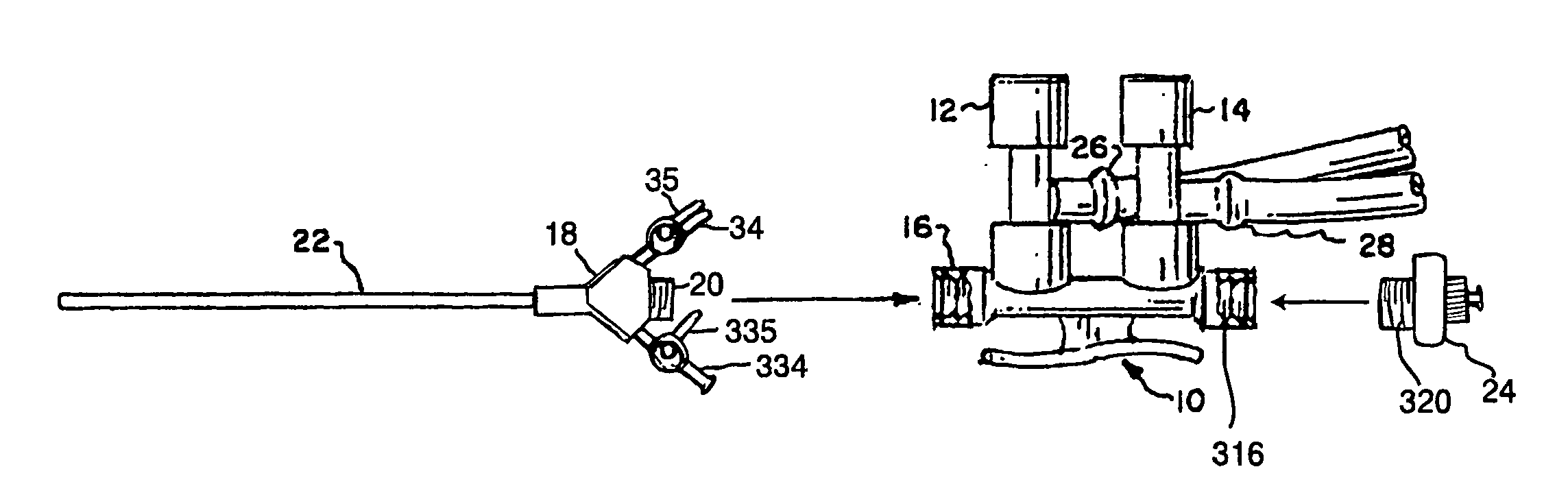
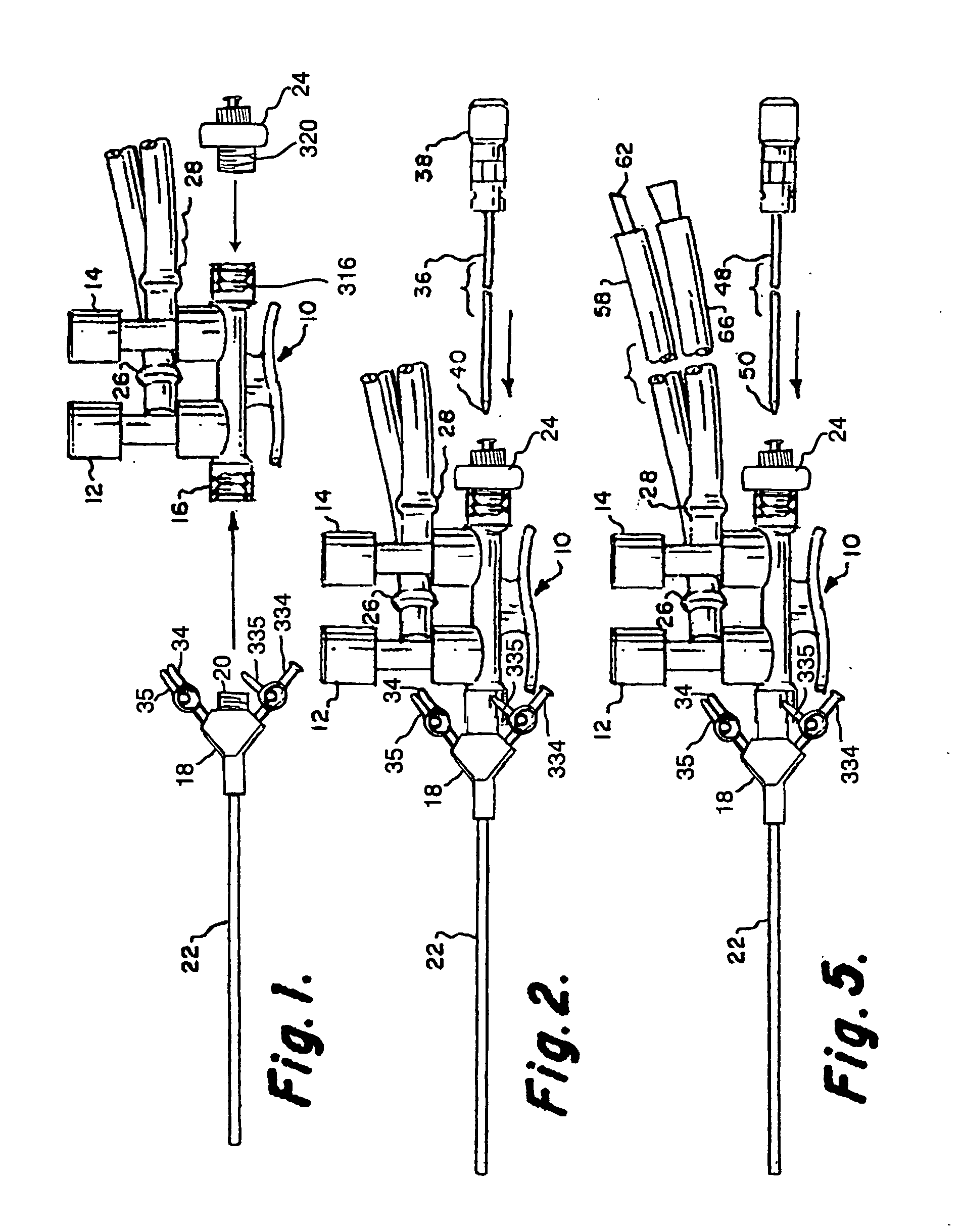
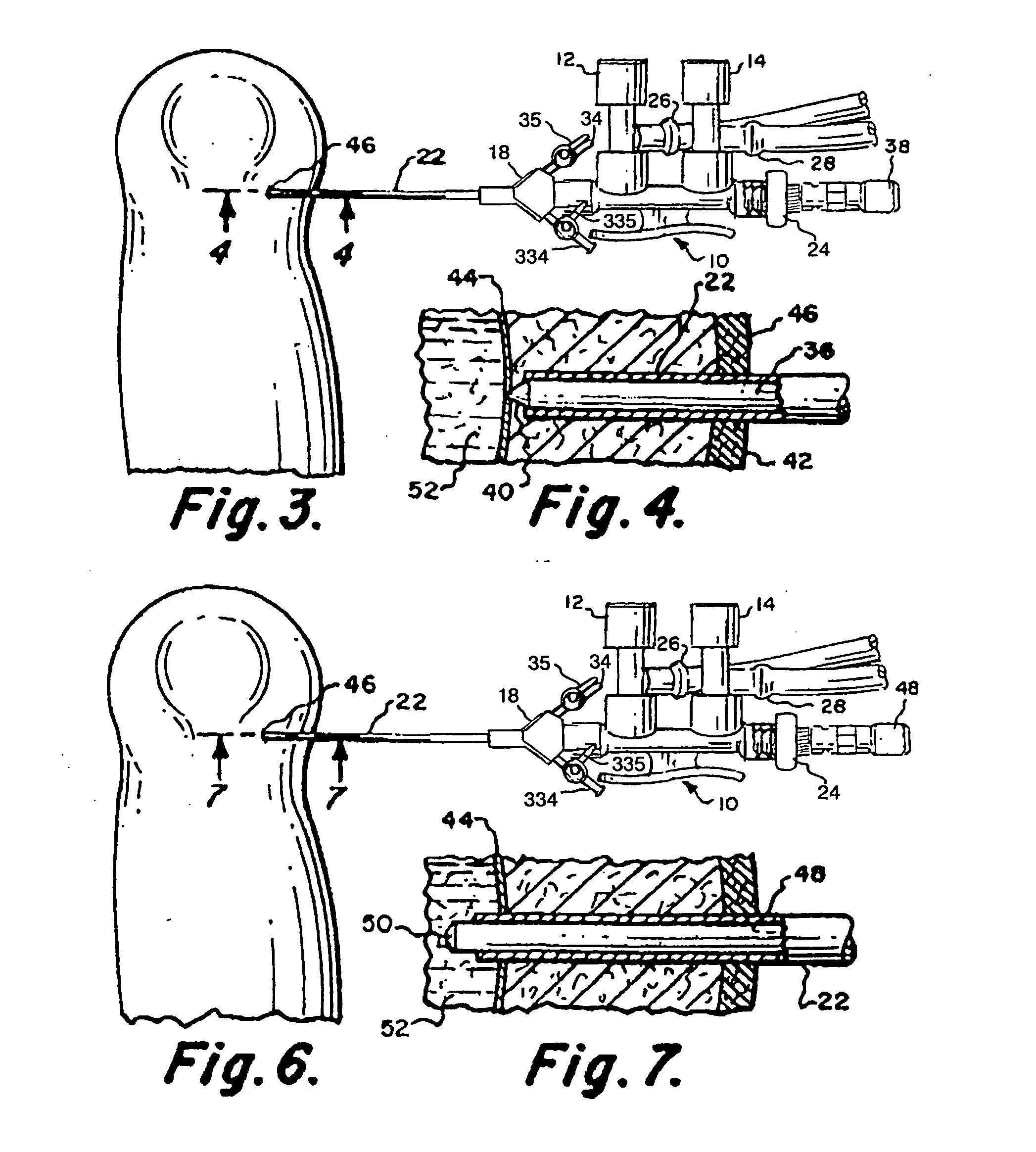
A system for performing arthroscopic lavage, directed tissue drying, and the accurate placement of a biocompatible tissue scaffold for the adherence of autologous regenerated cells through a small single port of entry into a joint compartment. The system is comprised of a handpiece having valves for irrigation and suctioning and a dual valve swivel cannula attached to the handpiece. The system includes a mobile cart, high resolution camera, light source, optical coupler, high-resolution monitor, an air compressor to power individually controlled irrigation pumps to deliver irrigation fluid to a handpiece and a vacuum suction console to collect fluid. The system also includes an insufflator to maintain distension immediately following the lavage and to dry tissue in preparation for directed tissue scaffold and regenerative cell placement. The delivery system achieves accurate biocompatible tissue scaffold placement to a specific tissue site or sites within the joint utilizing a small diameter arthroscope for direct visualization while inserting and advancing a grasping instrument or device through one of two valves located on the cannula. While holding the tissue scaffold in the jaws of the grasping device, it is advanced through the cannula lumen and extended beyond the distal tip and placed on the dried tissue site. Removing the grasping device, a catheter is then inserted and advanced through a cannula valve into the lumen and extended beyond the distal tip to the scaffold placed and prepared tissue site. A means of applying torque to the catheter tip further enhances the ability for accurate, exact placement of cells to a specific scaffold receptive tissue site. The cells are then injected into and through the catheter and applied under direct visualization to the scaffold. As comprised, the small single-port system allows a physician to perform the diagnosis, clean the joint space of debris and degradative enzymes using pressurized irrigation and suction, followed by a rapid conversion from a sterile saline fluid distension media to a dry gas CO2 distension media and directed tissue drying, and the accurate placement of a biocompatible tissue scaffold for the adherence and accurate placement of regenerated cells through a catheter to a specific tissue site within a joint.
Owner:KADAN JEFFREY S +1
Chitin oligose preparing process
InactiveCN1847267AImprove efficiencySimple process routeOligosaccharidesFermentationBiotechnologyDegradative enzyme
The present invention relates to chitin oligose preparing process, and is especially enzyme generating fermentation process to degrade chitin colloid for preparing bioactive chitin oligose. The preparation process has simple technological path, effective inhibition of further degradation of bioactive chitin oligose, reuse of degrading enzyme and other advantages, and is suitable for industrial production. The preparation process includes: culturing Aeromonascaviae strain to obtain fermented liquid, centrifugally separating the fermented liquid to obtain enzyme supernatant; preparing chitin colloid; compounding chitin colloid buffer solution in an enzyme reactor and adding abacterial enzyme liquid for enzymolysis to obtain enzymolyzed chitin oligose liquid; four stages of membrane separation to obtain concentrate and spray drying to obtain bioactive chitin oligose product.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
Methods to enhance the activity of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes
Methods for hydrolyzing lignocellulose are provided, comprising contacting the lignocellulose with at least one chemical treatment. Methods for pretreating a lignocellulosic material comprising contacting the material with at least one chemical are also provided. Methods for liberating a substance such as an enzyme, a pharmaceutical, or a nutraceutical from plant material are also provided. These methods are more efficient, more economical, and less toxic than current methods.
Owner:ATHENIX
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
ActiveCN102816729AGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnology3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
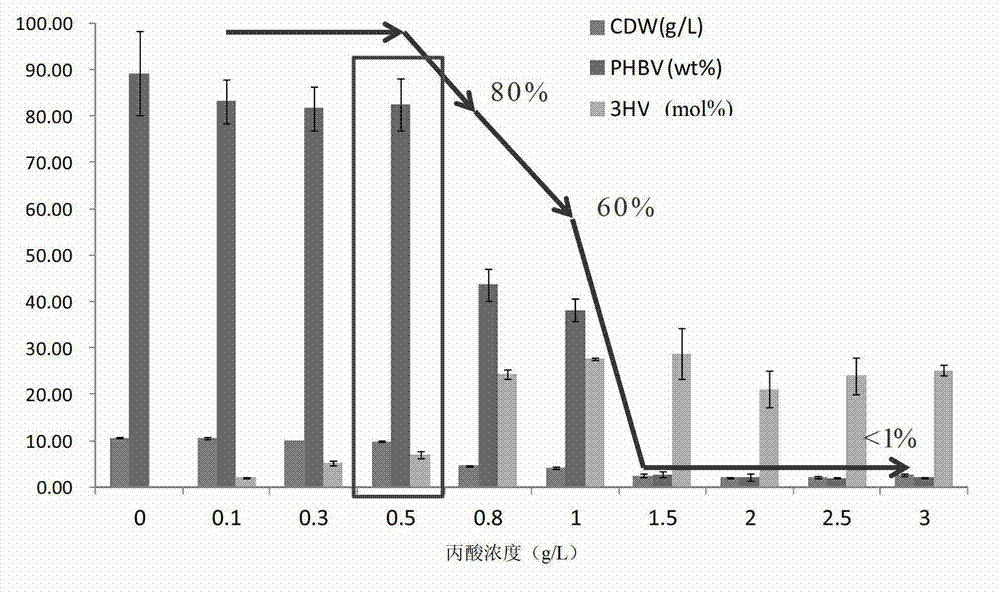
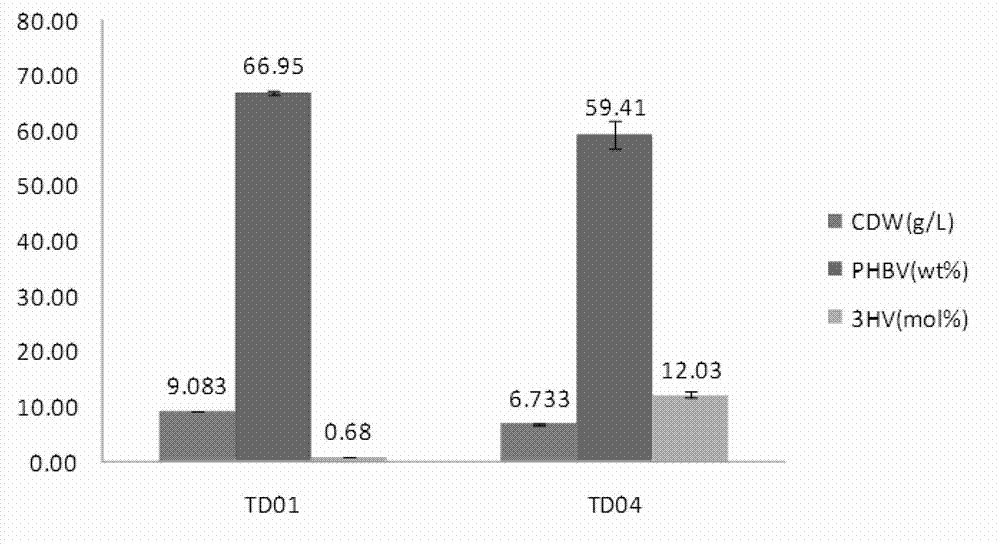
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
Methods to enhance the activity of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes
Methods for hydrolyzing lignocellulose are provided, comprising contacting the lignocellulose with at least one chemical treatment. Methods for pretreating a lignocellulosic material comprising contacting the material with at least one chemical are also provided. Methods for liberating a substance such as an enzyme, a pharmaceutical, or a nutraceutical from plant material are also provided. These methods are more efficient, more economical, and less toxic than current methods.
Owner:ATHENIX
Therapeutic pharmaceutical agent for diseases associated with decrease in function of gne protein, food composition, and food additive
InactiveUS20120264928A1Easily embodiedEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseFood additive
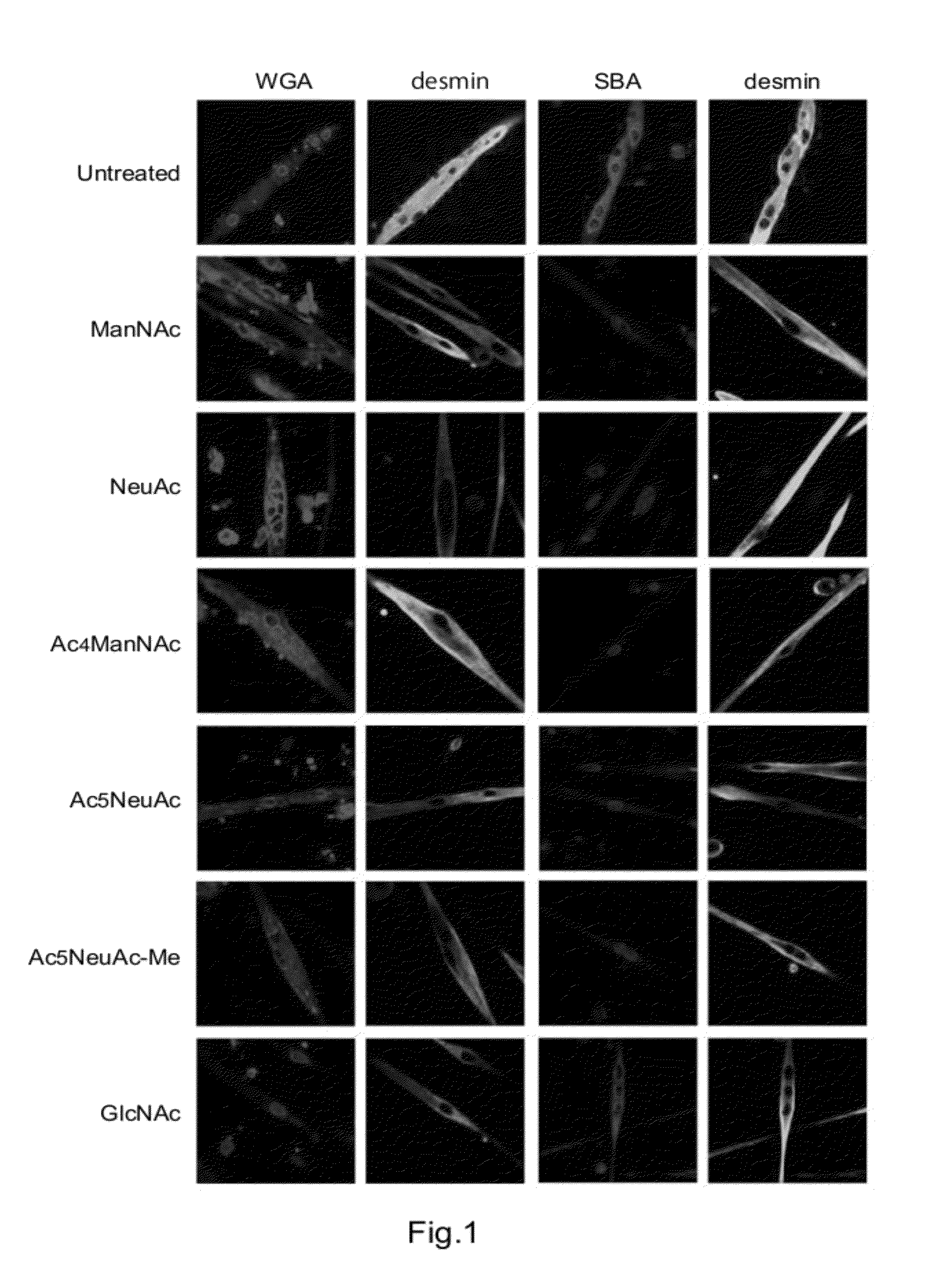
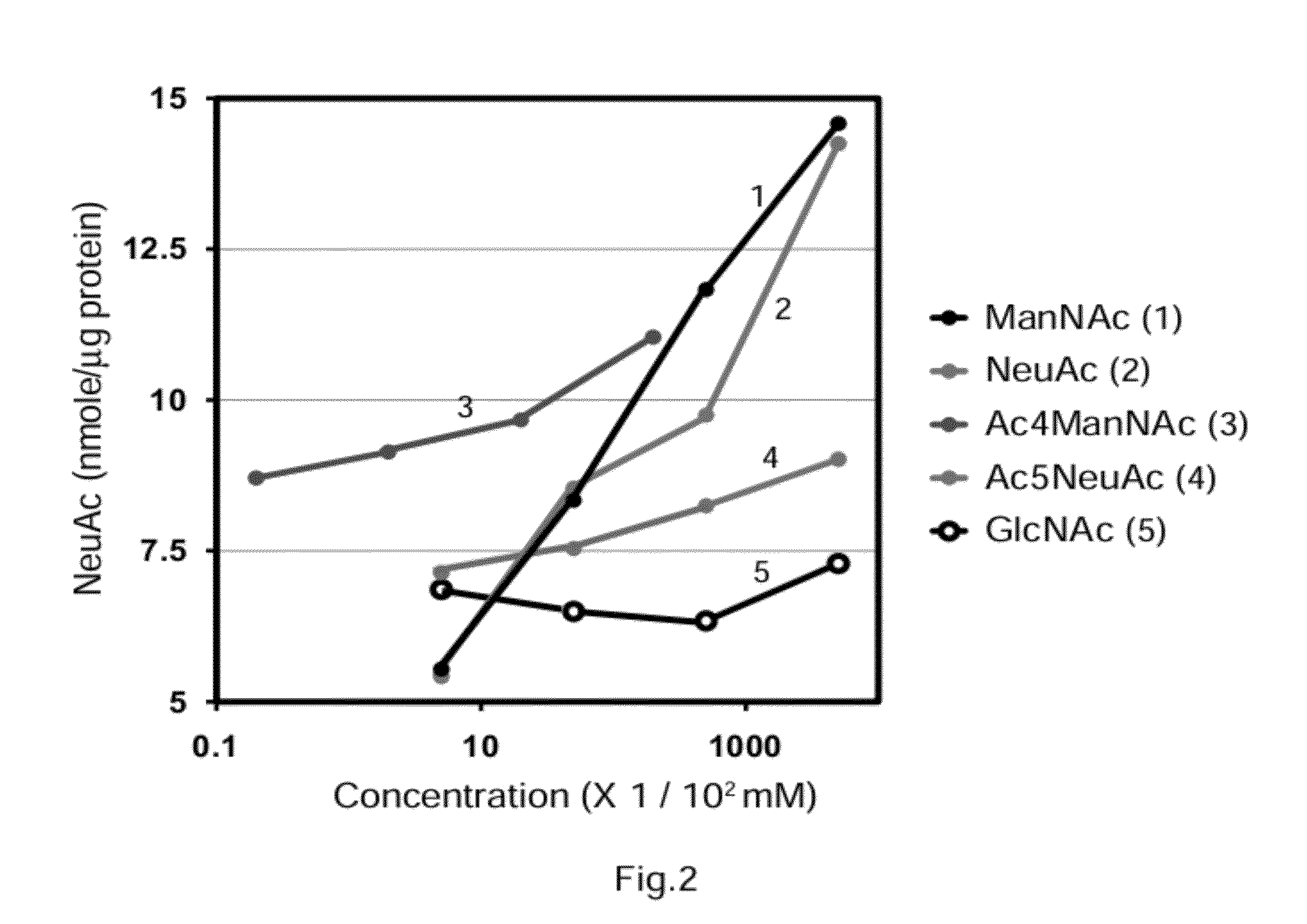
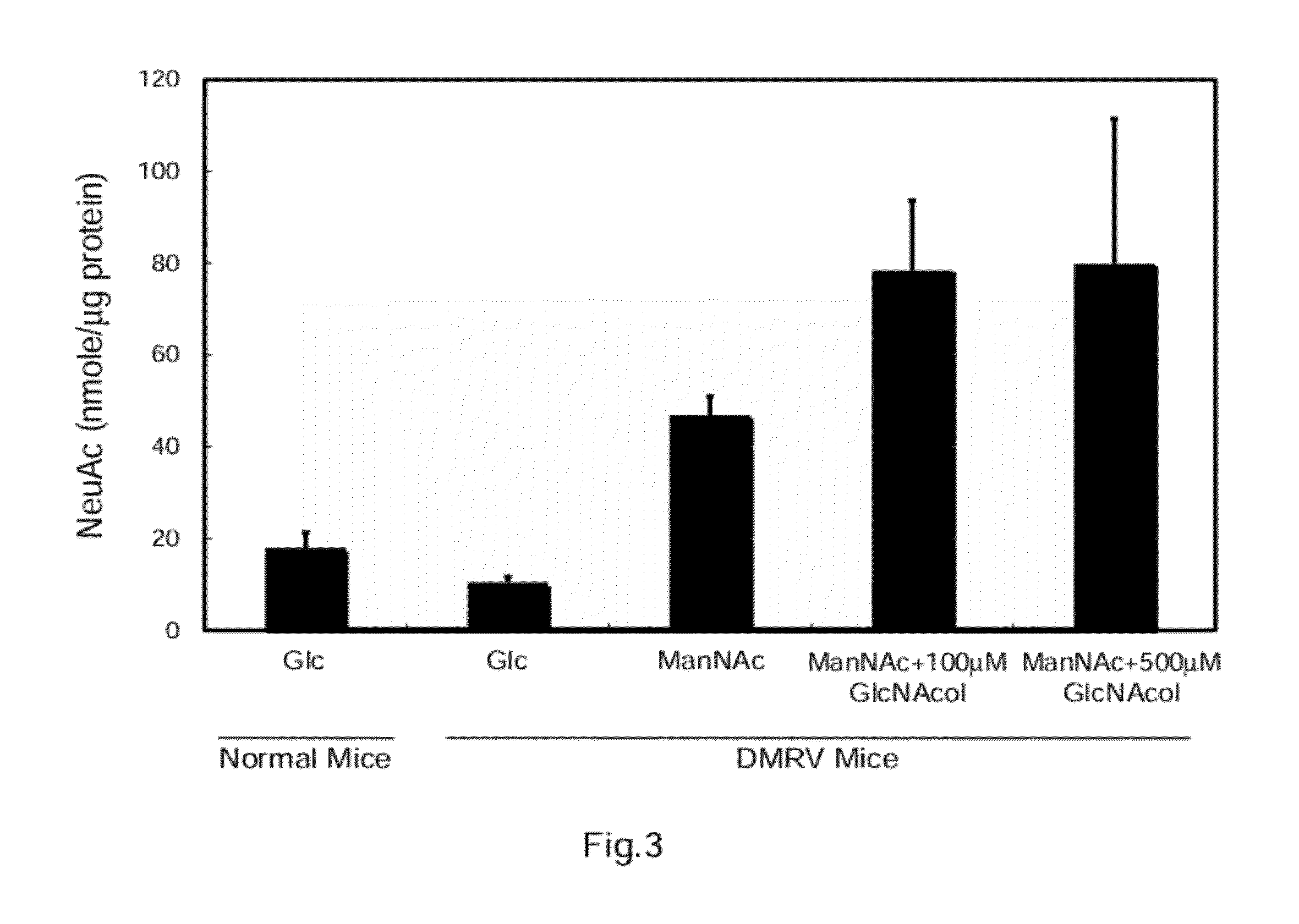
Disclosed are a therapeutic pharmaceutical agent for diseases associated with the decrease in the function of GNE protein, a food composition, and a food additive. The therapeutic pharmaceutical agent is characterized by comprising a compound capable of increasing the quantity of N-acetylneuraminic acid in cells. Examples of the compound to be contained in the therapeutic pharmaceutical agent include N-acetylneuraminic acid, an intermediate produced downstream from N-acetylmannosamine in an N-acetylneuraminic acid biosynthesis pathway, an N-acetylneuraminic acid derivative, an N-acetylmannosamine derivative, an N-acetylneuraminic acid-containing compound, an N-acetylneuraminic acid derivative-containing compound, an N-acetylmannosamine-containing compound, an N-acetylmannosamine derivative-containing compound, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for N-acetylneuraminic acid, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for N-acetylmannosamine, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for the intermediate, and others.
Owner:HEALTH SCI TECH TRANSFER CENT JAPAN HEALTH SCI FOUND
Method for preparing organic seaweed liquid fertilizer by fermentation and enzymolysis of microorganisms
The invention discloses a method for preparing organic seaweed liquid fertilizer by fermentation and enzymolysis of microorganisms and belongs to the field of fertilizer production. Seaweeds are degraded through a compound enzymolysis technology and a microorganism fermentation technology; a complicated enzyme system produced through microorganism fermentation and a compound enzyme including proteinase, cellulase, pectinase, polysaccharide degradation enzyme and the like are used for degrading the seaweeds step by step; seaweed cell walls are removed so that contents including alginic acid, polysaccharide, plant hormones and the like are sufficiently released; the decomposition of active substances including the alginic acid, plant growth promotion factors and the like is avoided under moderate technological condition; effective active components in the seaweeds are kept to the greatest extent. According to the method disclosed by the invention, energy saving, water saving, low carbonand environment protection are realized; the seaweed biological organic liquid fertilizer contains rich mineral substances and effective components including macro-elements, microelements and the likeneeded by the growth of plants; a soil structure can be improved to keep moisture and soil and the growth of root microorganisms of the plants is promoted; the yield of applied crops is remarkably improved and the fertilizer has a great market potential.
Owner:泰安达沃斯生物科技有限公司
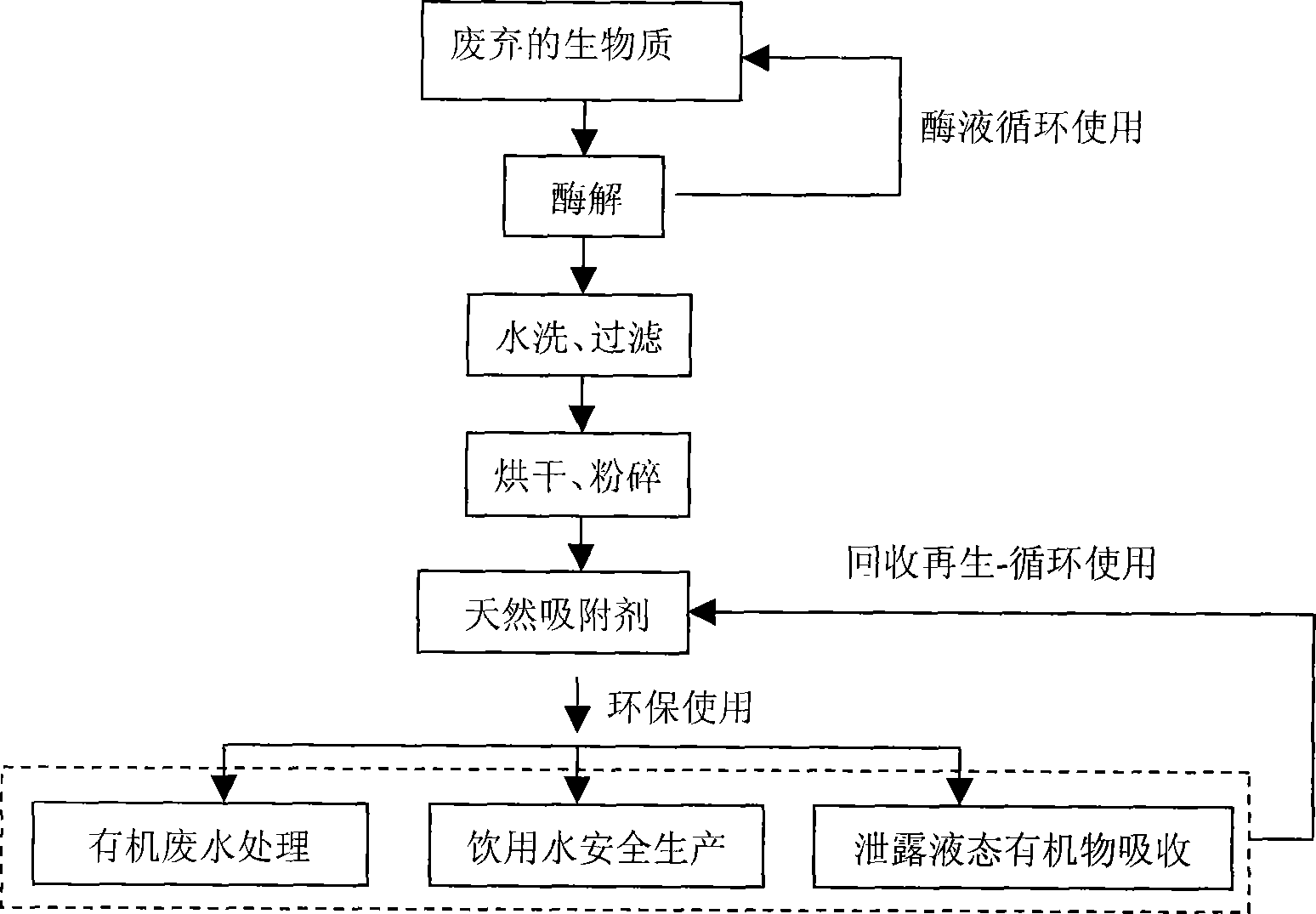
Method and use for preparing natural adsorption agent by zymolysis
InactiveCN101234335AEasy to prepareReduce manufacturing costOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionGramChemistry
The invention discloses a method and usage of preparing natural absorbent with enzymatic hydrolysis. Adding abandoned biomass and degrading enzyme solution into a fermentation reactor, and the pH value of the enzymolysis buffer solution is 3 to 6 under a enzymolysis temperature of 30-50 DEG C, and the natural absorbent is prepared through washing, filtering, drying and grinding after 1 to 10 days of stirring enzymolysis in 20 to 200r / min; the degradation enzyme is cellulose of 0.5 to 8mg / L, pectinase of 0.5 to 8mg / L or the mixing solution of the cellulose and the pectinase with a proportion of 1 to 1; 10 to 100mL degradation enzymes are added into every gram of abandoned biomass raw materials, which enables 2 to 20IU of active enzymes to be added into every gram of biomass raw material. The prepared natural absorbent are used for removing a micro amount of persistent organic pollutants in wastewater or drinking raw water and absorbing liquid organic pollutants leaked in accidents. The method and usage of preparing natural absorbent with enzymatic hydrolysis has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost and environmental protection; the absorbent has strong absorption power, large capacity without toxicity or harm.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Glucosidase/xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102041251AHigh activityReduce complexityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesChemical industryCellulose
The invention relates to a novel beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The coding sequence of amino acid of the RuGBGX2 contains 18-755th sites of an SEQ ID NO 2 sequence. The RuGBGX2 is sourced from the rumen microorganism of yak from China, a novel coding gene of the beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 is obtained by function screening and sequencing analysis on a rumen metagenome cosmid library and a subclone library. The beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme provided by the invention can be widely applied to the degradation of cellulose and the fields such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, medical industry and the like. By utilizing the difunctional enzyme RuGBGX2 to degrade wood fiber, the varieties of added enzymes can be reduced, and an enzymolysis process can be simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
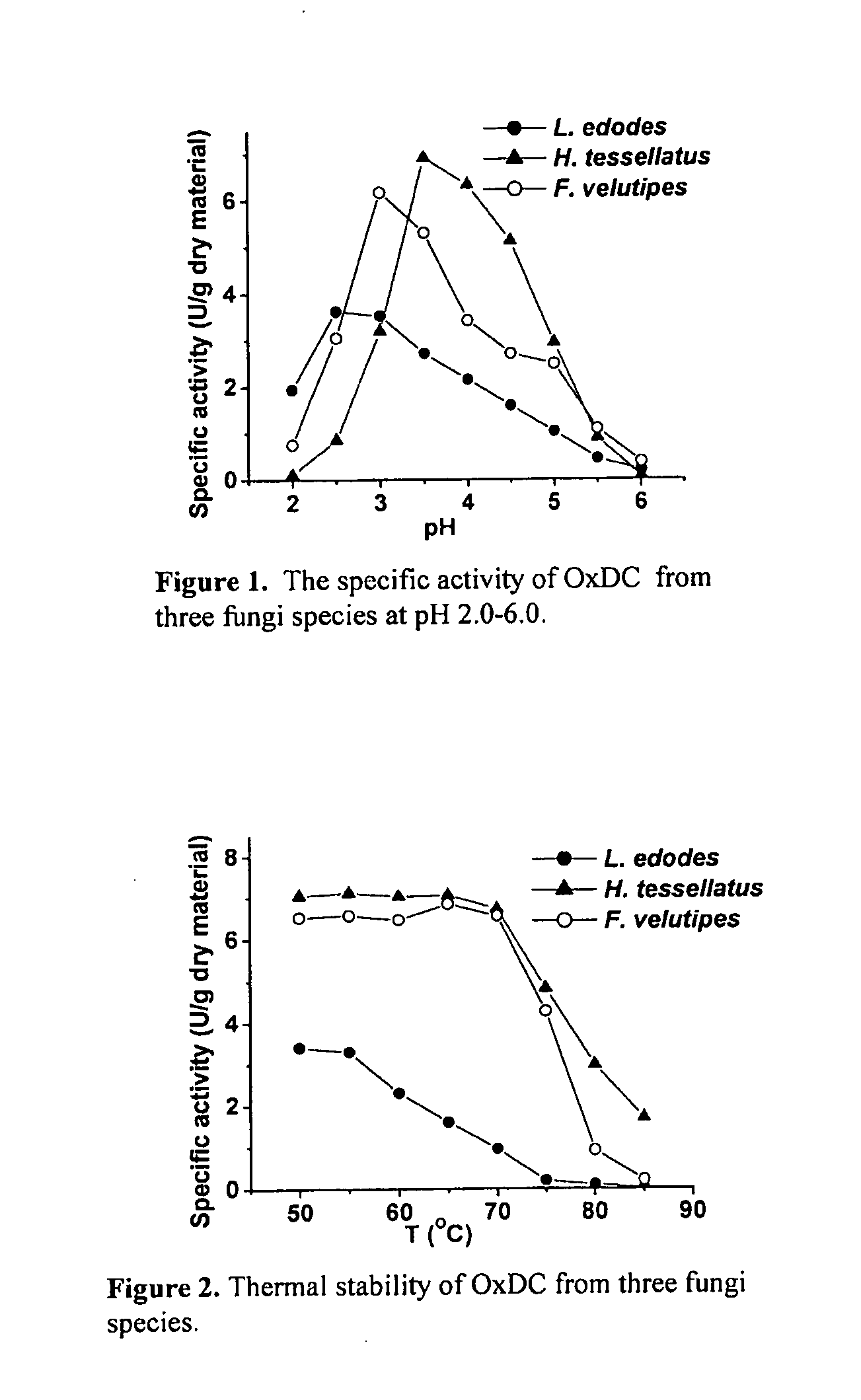
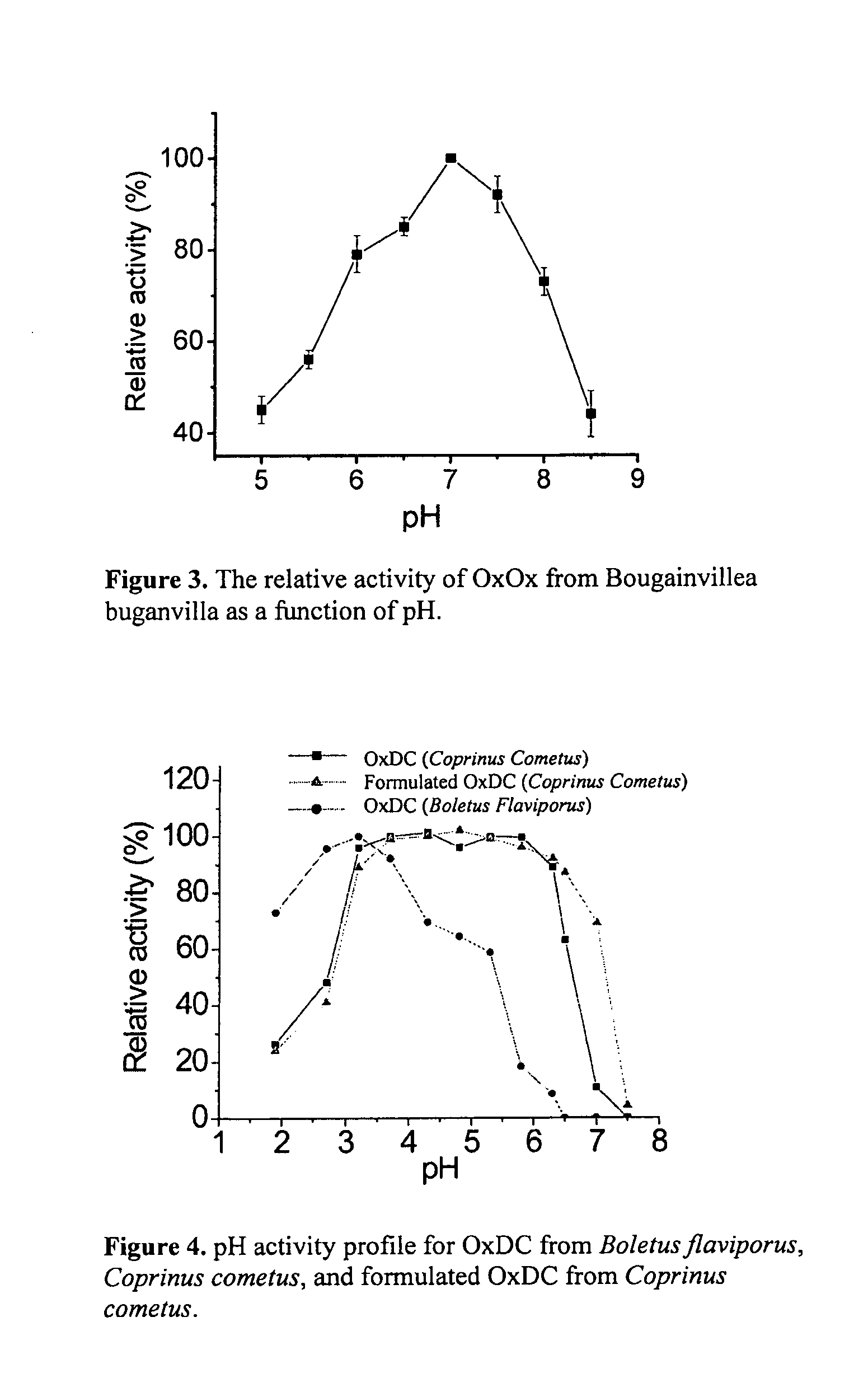
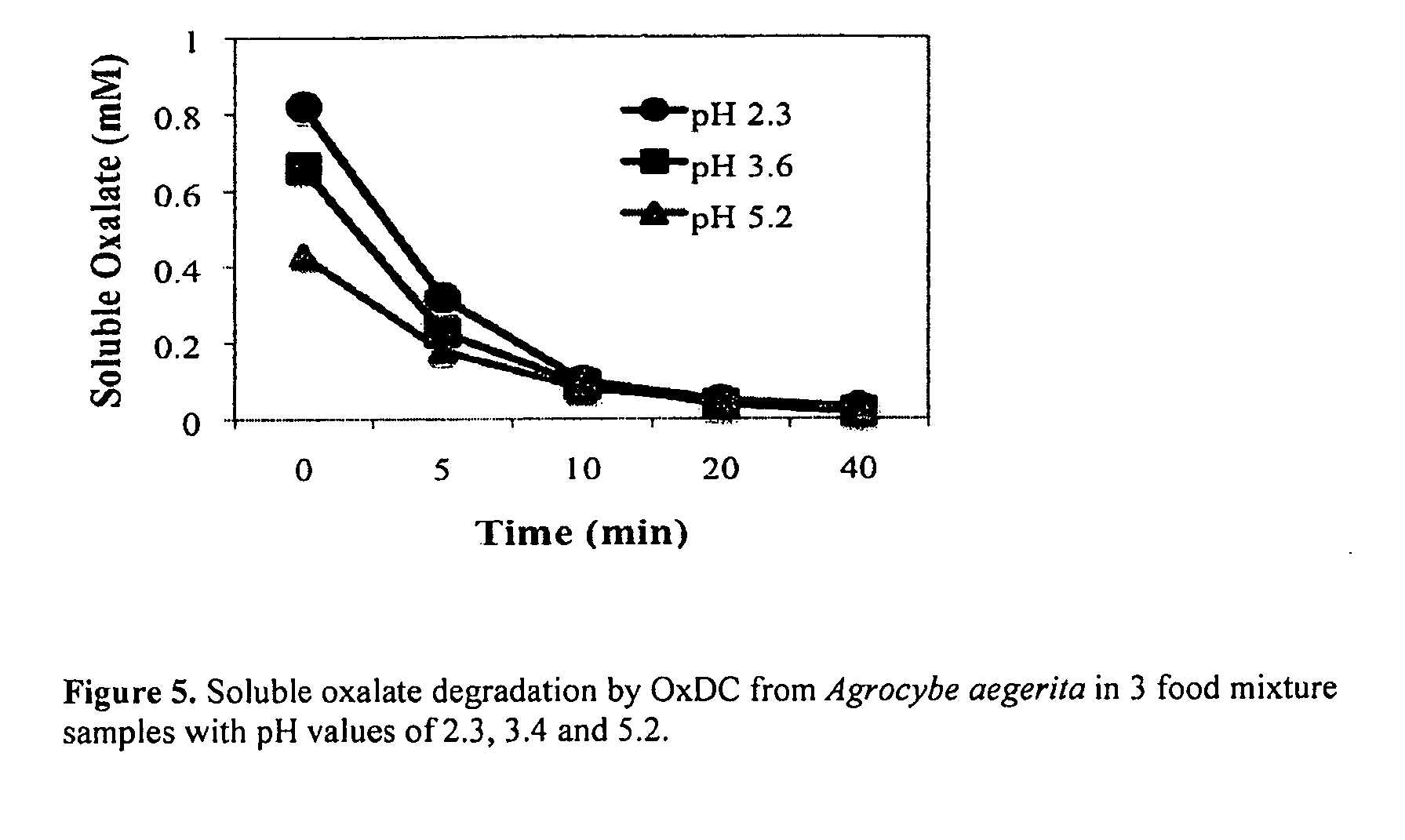
Methods and Compositions for Treating Oxalate-Related Conditions
ActiveUS20130108607A1Simple dryReduce amountNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsChemistryProtease
The subject invention relates in one aspect to an oxalate degrading composition, which includes at least one oxalate degrading enzyme. The composition includes an enriched insoluble component of fungal biosample, and the composition is effective to degrade oxalate at a pH of 1.9 or higher. The composition is protected from protease degradation such as pepsin, trypsin and chymotrypsin. The composition is capable of withstanding the conditions of the stomach, small intestines, and / or large intestines of a subject.
Owner:OXIDIEN PHARMACEUTICALS LLC
Bacillus cereus strain, pyrethroid pesticide degrading enzyme prepared using same and preparation method of pyrethroid pesticide degrading enzyme
The invention discloses a bacillus cereus strain, which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M209001. The invention also discloses a pyrethroid pesticide degrading enzyme prepared by using the bacillus cereus strain as an initial strain and a method for preparing the same. The strain is a bacillus cereus which is separated from the body of a tea plant and has high pyrethroid pesticide degradation efficiency. The intracellular crude enzyme of the strain has high efficiency in the degradation of pyrethroid pesticides such as cypermethrin, cyfluthrin and fenpropathrin, but low efficiency in the degradation of organophosphorus pesticides such as cygon, panaplate, methamidophos, chlorpyrifos and the like.
Owner:洪永聪 +2
Method for preparing regenerative silk fibroin and product and application thereof
InactiveCN102775465AEasy to prepareNot easy to inactivatePeptide preparation methodsOn/in organic carrierPolymer scienceDegradative enzyme
The invention discloses a method for preparing regenerative silk fibroin. The method includes adding a calcium alcohol solution into degumming silks, dissolving the degumming silks through water bath, centrifugally removing suspended impurities, and performing dialysis and drying to obtain the regenerative silk fibroin. The preparation method is simple, the dissolvability of the silk fibroin is good, the structure of the prepared regenerative silk fibroin is a beta-folding sheet layer, the irregular curl structure is decreased, the regenerative silk fibroin can be used as a carrier for immobilizing enzyme, and the enzyme can be immobilized on the regenerative silk fibroin, so that the enzyme can be prevented from being degraded by degeneration enzymes in an organism, and further the stability and the half-life period of the enzyme are improved.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Fumonisin degrading enzyme, coding gene, recombinant vector, cell, additive and application thereof
ActiveCN108251399AEfficient short-term degradationReduced pH requirementsHydrolasesAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyNo production
The invention relates to the biotechnology field, in particular to a fumonisin degrading enzyme, a coding gene, a recombinant vector, a cell, an additive and application thereof, and more specificallyrelates to the fumonisin degrading enzyme with a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2 or its mutant, the coding gene of the enzyme, the vector and cell containing the coding gene, the additive containing the enzyme and / or cell and / or the fermentation product thereof, application of the enzyme, the coding gene, the vector, the cell or the additive in degradation of fumonisins and / or other fungal toxins,as well as a method for degradation of fumonisin / or other fungal toxins. The enzyme provided by the invention has the advantages of: environmental friendliness, efficient and short time degradation offumonisins, and no production of harmful by-products. The enzyme can tolerate catalysis at high temperature up to 70DEG C, has low requirement for pH value and good stability, and also can degrade vomitoxin and T2 toxin to a certain degree.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
Compositions and methods related to therapeutic cell systems for tumor growth inhibition
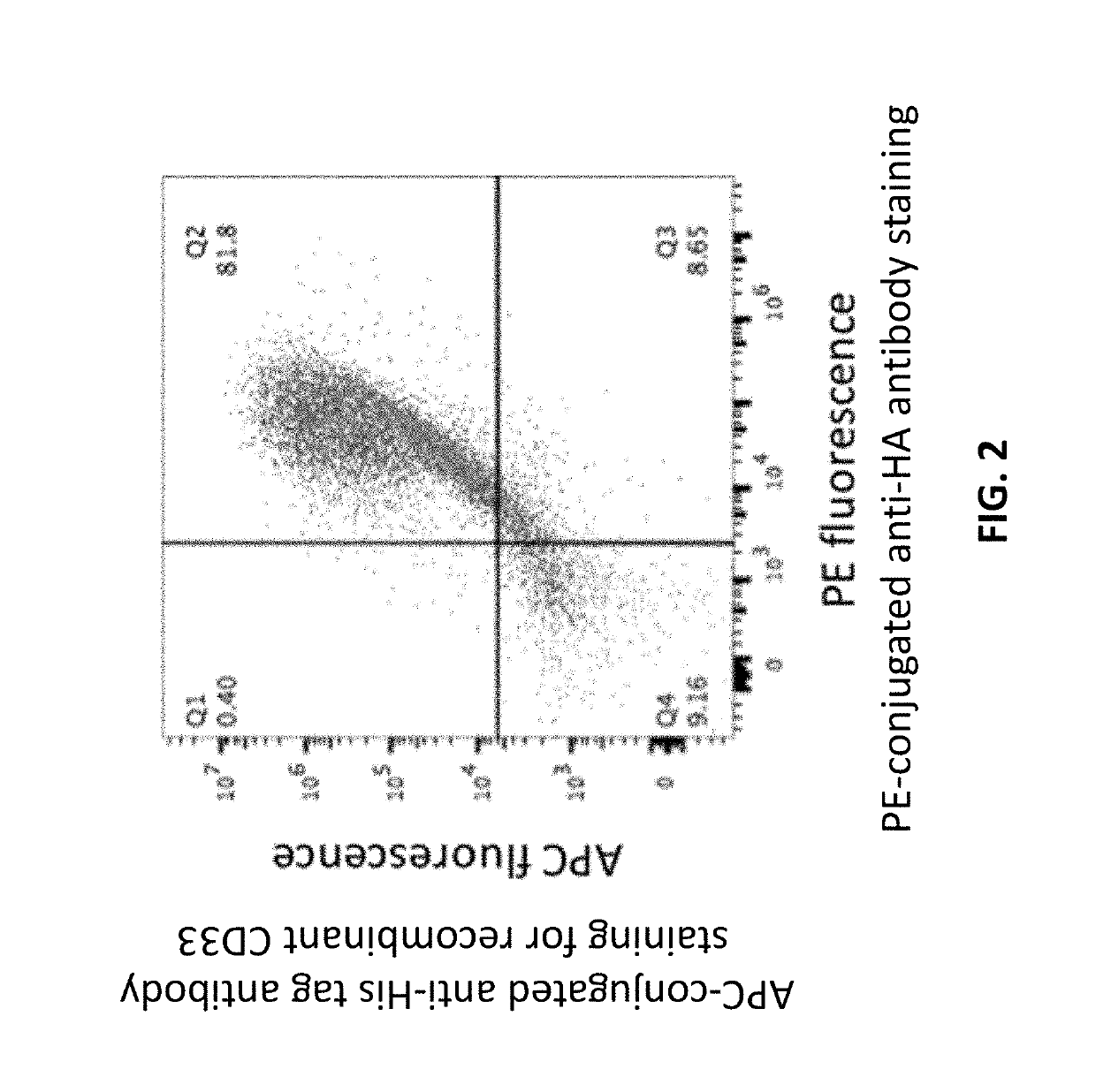
InactiveUS20190160102A1Impairing synthesisReduce concentrationHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCD33Degradative enzyme
The disclosure provides, e.g., enucleated erythroid cells comprising an amino acid degradative enzyme such as asparaginase and a targeting moiety such as an anti-CD33 antibody molecule. The cells may be used, e.g., to treat cancers such as AML.
Owner:RUBIUS THERAPEUTICS
Preparation method and application of petroleum degrading enzyme preparation
ActiveCN103484447AImprove degradation efficiencyFast degradationContaminated soil reclamationOn/in inorganic carrierDegradative enzymeEnzyme system
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a petroleum degrading enzyme preparation. The preparation method comprises the following preparation steps: performing cell breakage on microorganisms for degrading petroleum to prepare crude enzyme liquid; performing mixed adsorption on the crude enzyme liquid and a carrier; and separating and drying to prepare the petroleum degrading enzyme preparation, wherein the microorganisms for degrading the petroleum are acinetobacter calcoaceticus; the collection number of the strains is CGMCC No.3915; and the collection mechanism is Common Microorganism Center of China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The invention also comprises the application of the prepared petroleum degrading enzyme preparation to petroleum degradation. An enzyme system of the microorganisms with a petroleum degrading function is fixed by an adsorbent and then is used for degrading soil polluted by the petroleum, so that the degradation efficiency is obviously improved and is increased by 30 to 50 times compared with the microbial degradation speed, and the stability is improved by 15 to 20 times compared with that of the crude enzyme liquid.
Owner:ECOLOGY INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
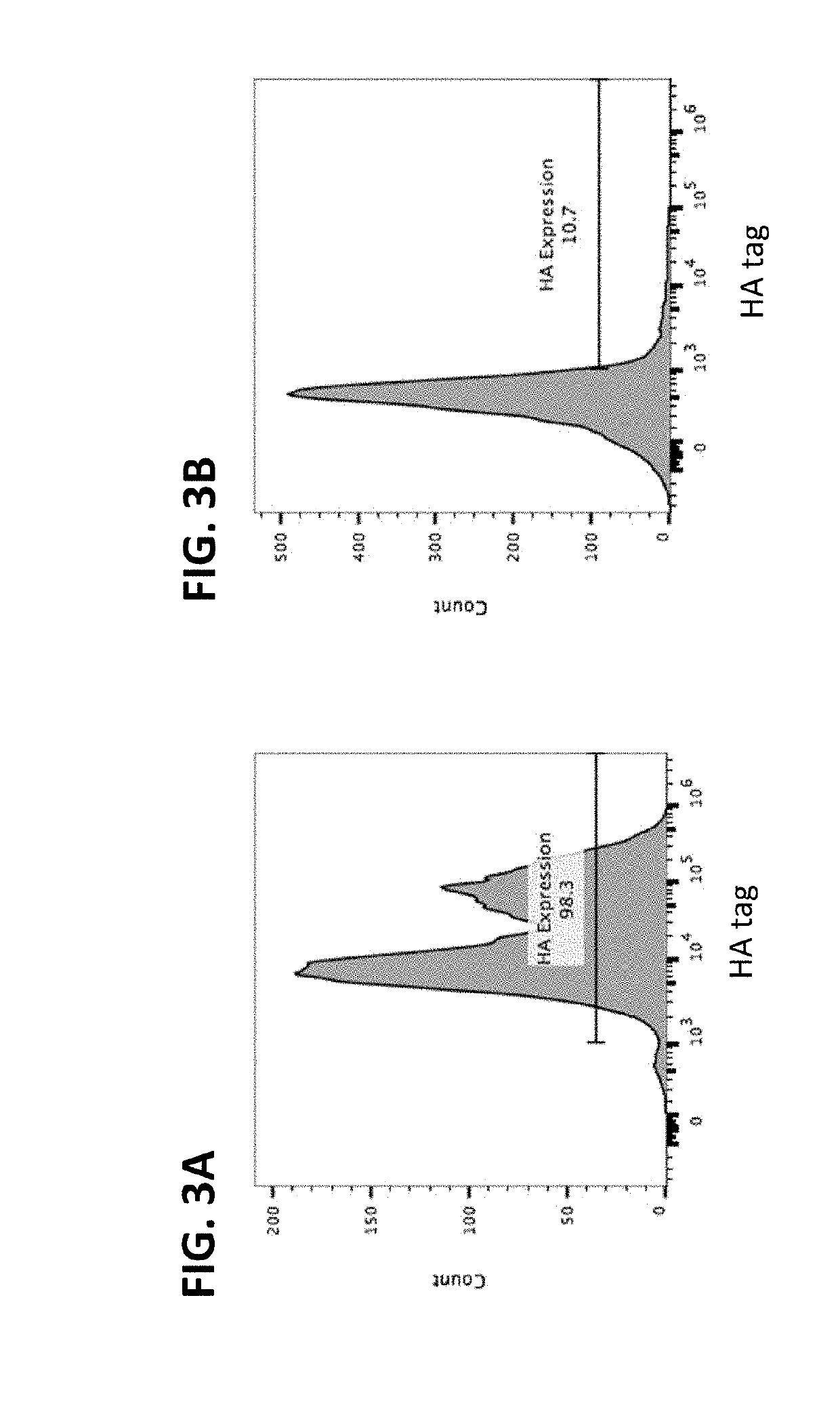
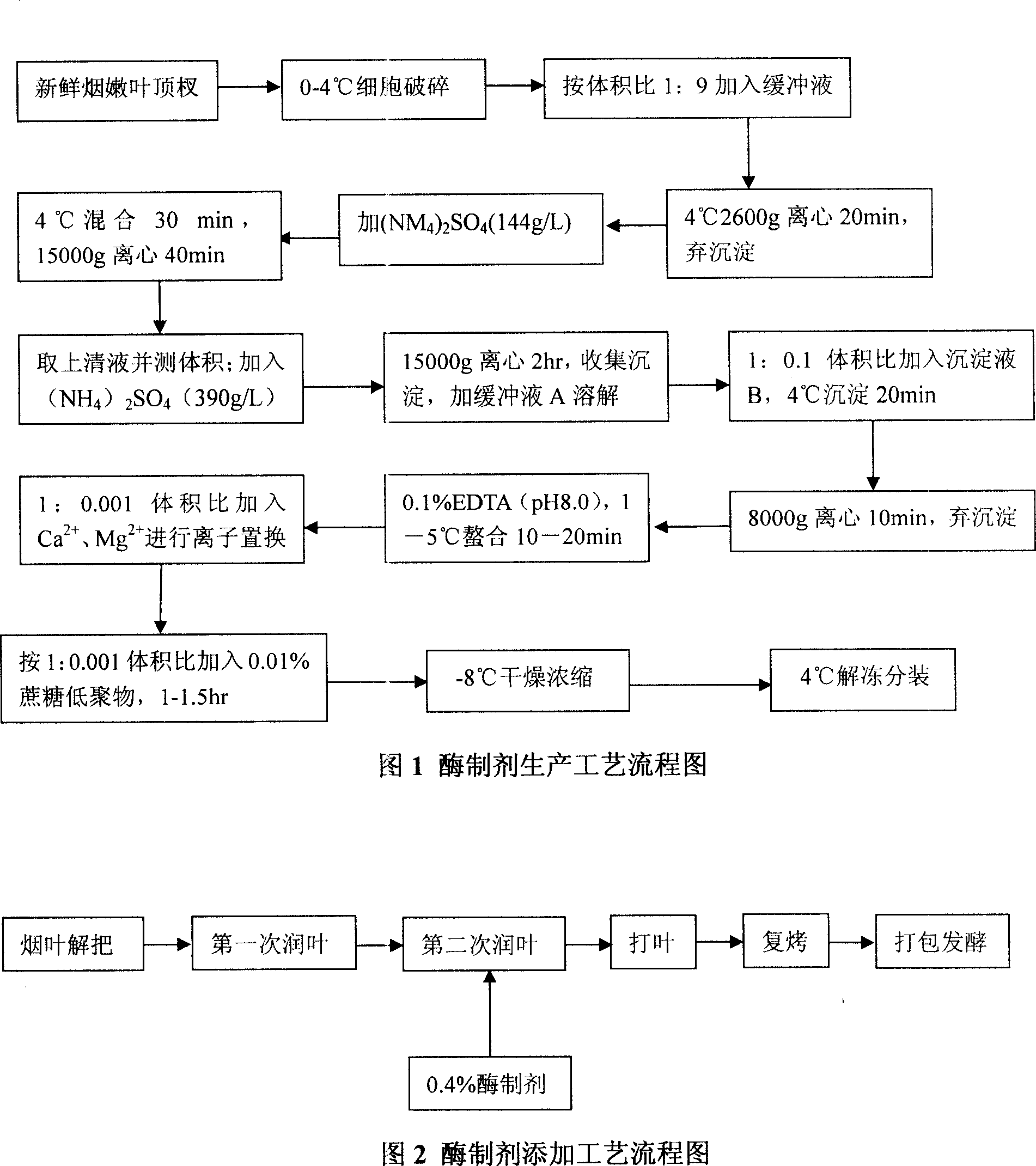
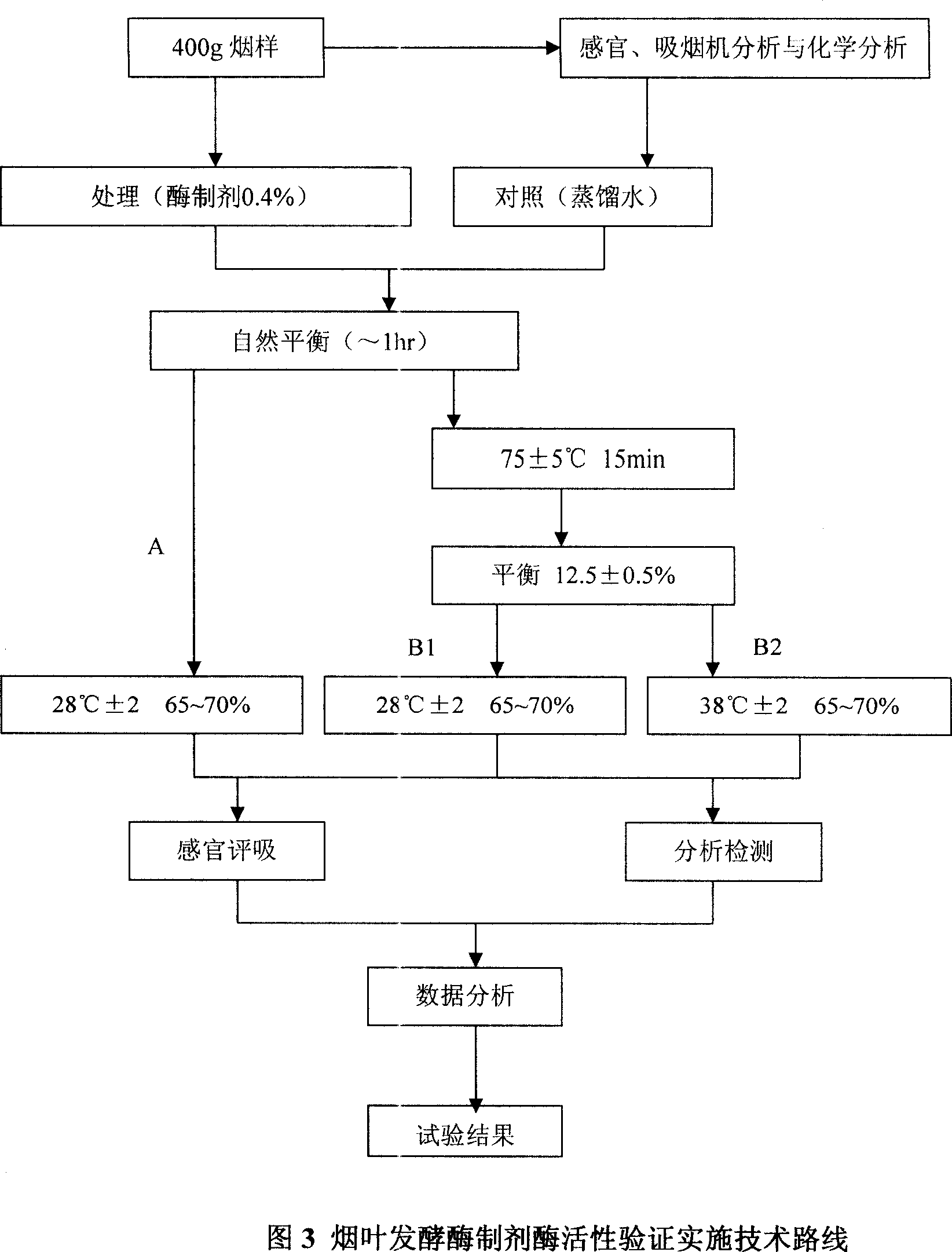
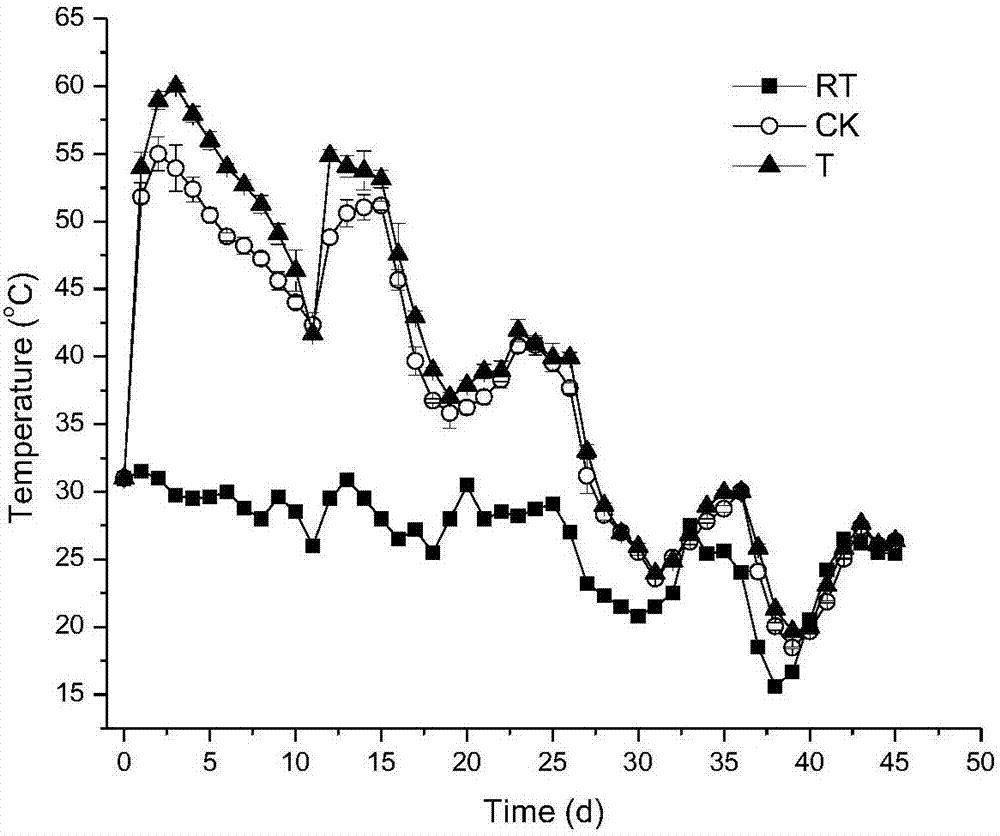
Method for producing tobacco leaf fermenting enzyme preparation
InactiveCN101144073AGood application effectIt has the characteristics of high temperature resistance of rebaking lineTobacco treatmentEnzymesBiotechnologySaccharum
The present invention relates to a novel tobacco leaf fermenting enzyme preparation production method which aims to solve the technical problems that how the quality of the tobacco leaf fermenting product is improved and how the reactivity protection of the tobacco leaf fermenting enzyme preparation is realized in the natural fermenting field of the tobacco leaf. The enzyme preparation consists of glucoseoxidase, chlorophyl oxidase, carotenoid oxidase, protease, and nicotine-degradation enzyme. Through the cell disruption of fresh leaves, (NH 4) 2 SO 4 is utilized to operate the second fractional precipitation to obtain crude enzyme fluid, an enzyme molecule adopts Ca 2 + and Mg 2 + to operate the metal ion exchange, to accomplish the molecule modification; a macro molecule combination modification is accomplished through adopting 0.01 percent of cane sugar low molecular polymer, thereby prolonging the half life period of an enzyme preparation, and obviously improving the high temperature resistant ability. The experimental result employed by the enzyme preparation indicates that the nicotine is decreased by 9.3 percent, the total nitrogen is decreased by 5.7 percent, the protein is decreased by 7.1 percent; cigarette smoke condensates are decreased by 8.4 percent, the tar content is decreased by 5.1 percent, cigarette smoke nicotine content is decreased by 28.0 percent, and the carbon is decreased monoxide by 1.6 percent. The enzyme preparation is employed when the tobacco is wet for the second time before defolat and redrying.
Owner:谢勇 +2
Geobacillus thermodenitrificans TB62 and application thereof in promoting compost maturity
ActiveCN107058177AFast growth and reproductionIncrease temperatureBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant growth-promoting bacteria development, and concretely relates togeobacillus thermodenitrificans TB62 and application thereof in promoting compost maturity. The geobacillus thermodenitrificans TB62 is named as Geobacillus thermodenitrificans in taxonomy, is preserved in Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms in January 05, 2017, and has the preservation No. CGMCC 13530. The geobacillus thermodenitrficans TB62 provided by the invention is firstly screened and separated from samples during a compost high temperature period, and is high in temperature resistant, fast in growth and propagation, and capable of producing lignocellulose-degrading enzyme; a microbial agent containing geobacillus thermodenitrificans TB62 can be beneficial to improving the compost temperature, accelerating organic matter degradation and water-dissolved organic matter (DOM) degradation, improving the content of Kjeldahl nitrogen, and promoting compost maturity; the geobacillus thermodenitrificans TB62 also has a function of biosurfactant production so as to be applicable for preparing a surface active agent.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Preparation and use of biofilm-degrading, multiple-specificity, hydrolytic enzyme mixtures
InactiveUS20050003503A1Improve efficiencyImprove hygieneBacteriaLens cleaning compositionsBiofilmDegradative enzyme
The present invention relates to isolated structures containing degradative enzymes produced from a marine organism. The enzymes produced are based on the carbon source upon which the marine organism is growing. The enzymes are found in structures that can be isolated such that the degradative enzymes are easily harvested.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Method for preparing t-carrageenase
The invention discloses a method for preparing t-carrageenase. A seed medium is inoculated with a strain Pseudoalteromonas carrageenovora ASY5 for producing carrageenase, the strain is transferred into a fermentation medium in an inoculation mode for induced enzyme production after activation culture, and t-carrageenase containing fermentation liquor is separated to obtain the t-carrageenase. T-carrageenan is adopted as an inductive agent for fermentation production of the t-carrageenase, a fermentation production technology of the t-carrageenase is established, and the method has good application value for industrial production of carrageenan degrading enzymes and carrageenan oligosaccharide.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
ª—- carrageenin catabolic enzymes , its preparing process and application
The invention is an enzyme, and its characteristic: it can degrade k-carrageenan to prepare oligo-carrageenan and degrade beta-1, 4-indican bond of k-carrageenan, therefore called k-carrageenan degrading enzyme, its molecular weight is 30,000Da. When preparing it, using 2216E culture medium to make shaking bottle culture on the sea Cytophaga sp at 28-35deg.C, then centrifugating the culture solution to obtain fermentation enzyme solution, ultrafiltering and concentrating the enzyme solution, then using 40-80% (NH4)2SO4 for salting-out and collecting protein deposit, and freeze-drying. It can effectively degrade k-carrageenan, be used to prepare oligo-carrageenan, and compared with chemical method, it has simple preparing coursee, high product yield, stable quality, and ensures the activity research and development of oligosaccharide, etc.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Recombinant bacillus amyloliquefaciens as well as construction method and application thereof
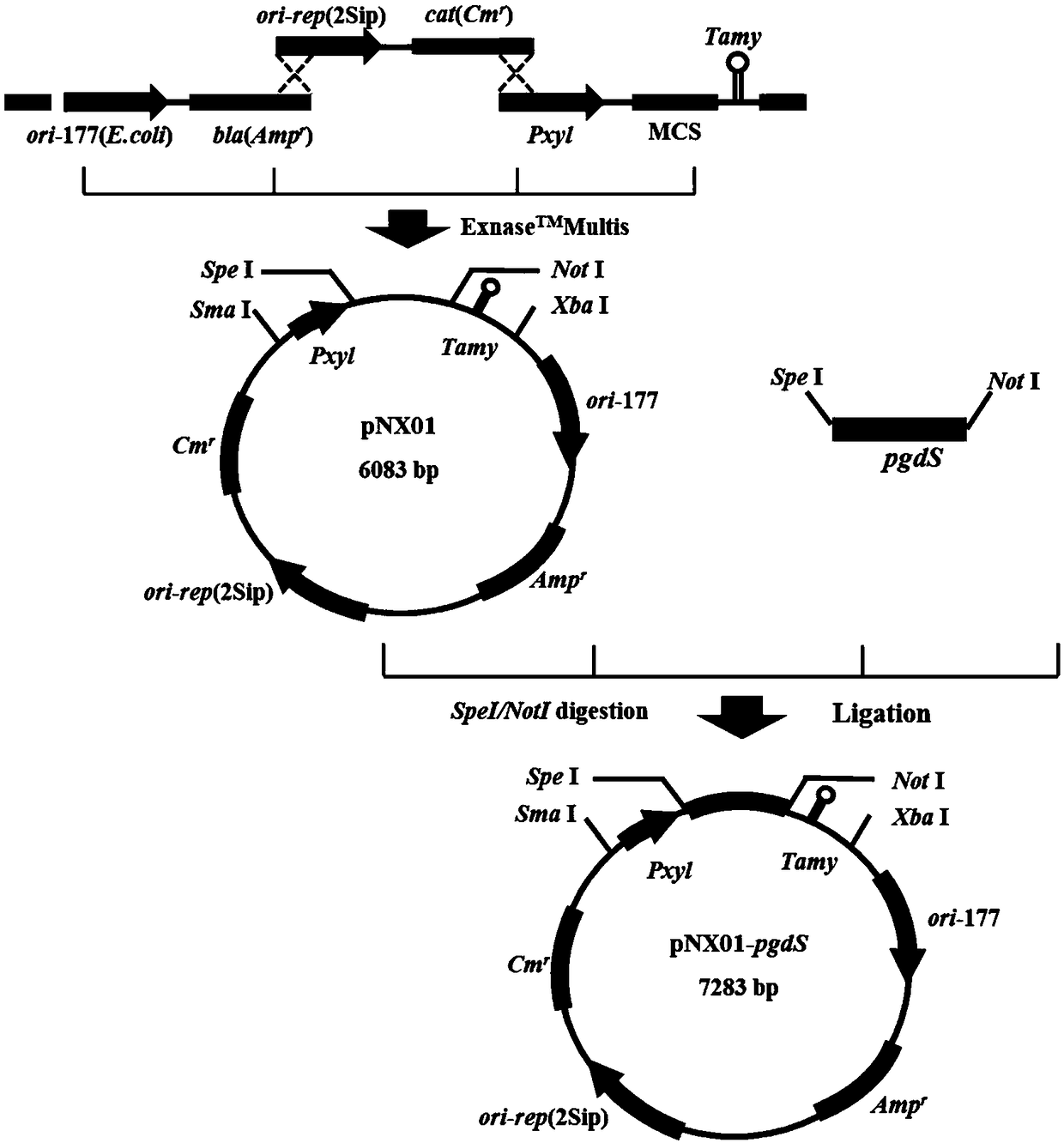
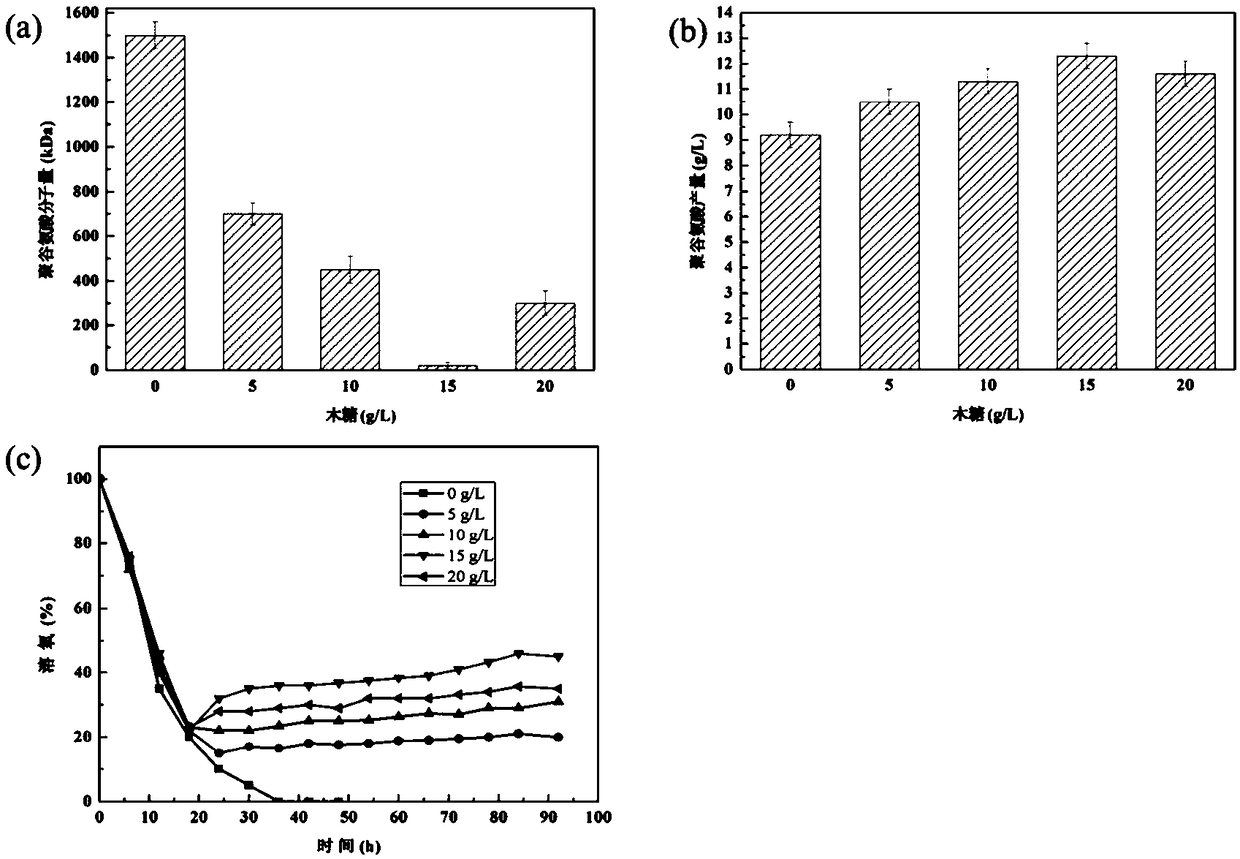
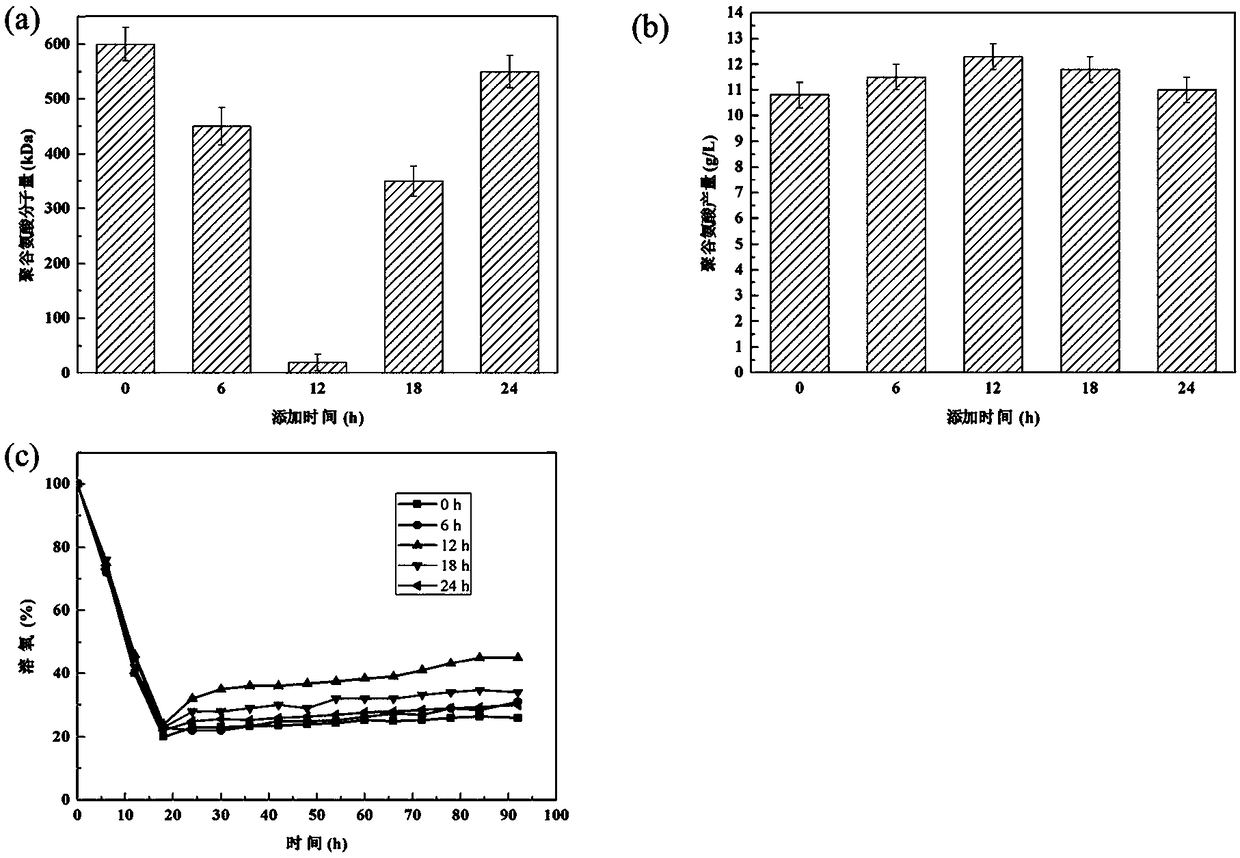
ActiveCN108624546AGreat application advantageIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a construction method of recombinant bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The method is characterized in that bacillus amyloliquefaciens in which indigenous plasmids are removed are used as host bacteria; a polyglutamate degrading enzyme gene pgdS is inserted between Spe I and Not I restriction enzyme cutting sites of a pNX01 carrier to obtain recombinant plasmids, and the recombinant plasmids are imported into the host bacteria to obtain the product. The invention further discloses the recombinant bacillus amyloliquefaciens constructed through the abovementioned construction method and application thereof in fermenting and producing of gamma-polyglutamic acid; the process of fermenting and producing gamma-PGA and the polyglutamic acid degrading enzyme process are coupled torealize the effect of directly obtaining two products of low-molecular weight gamma-PGA and polyglutamic acid degrading enzyme by one-step fermenting; the gamma-PGA is degraded through the polyglutamic acid degrading enzyme which is secreted to the outside of a cell during being the production of high polymer gamma-PGA. Therefore, the cumbersome operation of adding degrading enzyme from outside is avoided; the production technology is simplified; the low-molecule polyglutamic acid is synthesized by one-step fermenting.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Nucleotide sequence of encoded fucoidin glucoside hydrolase and application thereof
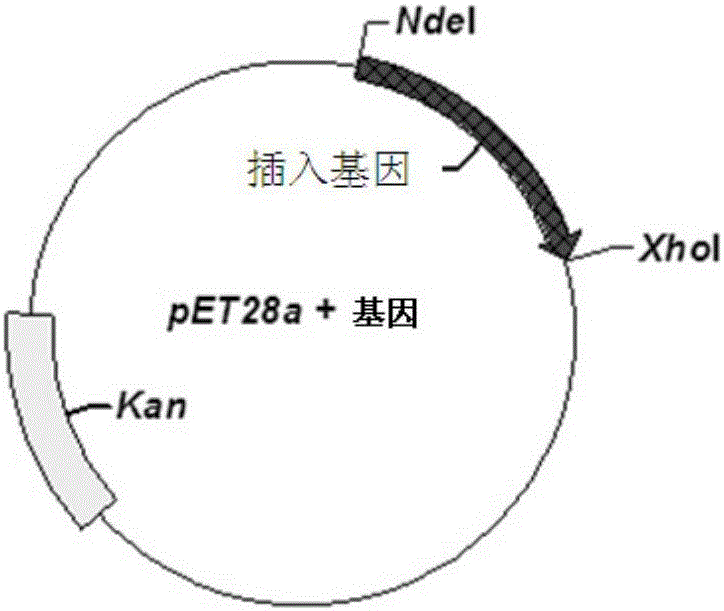
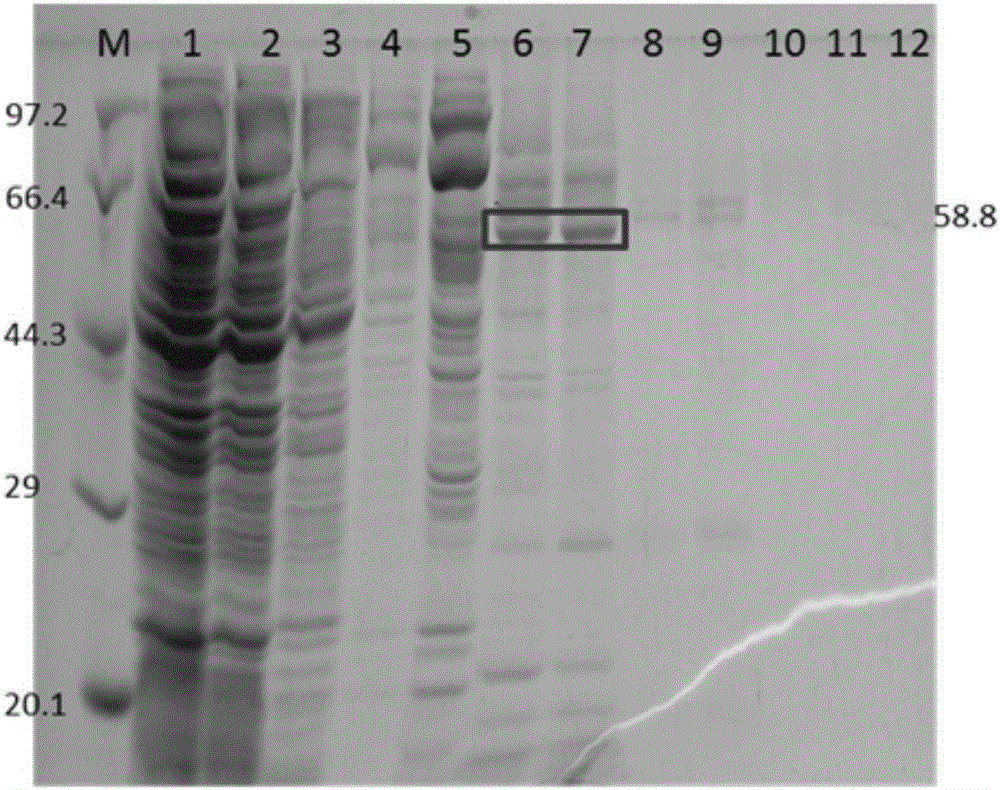
The invention relates to a nucleotide sequence of encoded fucoidin glucoside hydrolase and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO.1, encoded protein contains 529 amino acids, the nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO.2, and the predicted molecular mass of protein is 58.8 kDa. According to the nucleotide sequence and the application thereof, the gene GenBank No:AJ877239 of the encoded fucoidin hydrolase is subjected to codon optimization, 1599bp basic groups exist after optimization, and are loaded into a cloning vector pET28a, genes of the optimized fucoidin hydrolase can be expressed in escherichia coli BL21, glucoside hydrolase capable of efficiently and exclusively hydrolyzing fucoidin is obtained, and a biological degrading enzyme is provided for fucoidin hydrolysis.
Owner:SHANDONG JIEJING GROUP CORP
AFB1 degrading bacterium and degrading enzyme
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and discloses an AFB1 degrading bacterium and an AFB1 degrading enzyme. The degrading bacterium is aspergillusoryzane AOYIN2012Y8 with a collection number of CGMCC No.5817. The aspergillusoryzane AOYIN2012Y8 CGMCC No.5817 is inoculated into a PDA solid culture medium, and constant-temperature culturing is carried out under a temperature of 28-30 DEG C; collection is carried out when a lot of spores grows. The spores are scraped off by using an inoculation loop. The spore concentration is regulated to 1.0*10<8>CFU / mL by using normal saline containing 0.5-0.7% Tween 80. 5-7mL of the spore is inoculated to every 30g of a solid fermentation culture medium. Constant-temperature culturing is carried out for 5-7 days under a temperature of 28-30 DEG C, and collection is carried out. The solid fermentation culture medium is well mixed with normal saline, and the mixture is subjected to room-temperature soaking. The mixture is filtered and centrifuged; a supernatant is fetched and is subjected to salting-out, dialysis, and gel chromatographic separation; and concentrating and lyophilizing are carried out, such that the AFB1 degrading enzyme is obtained. The degrading enzyme provided by the invention has relatively high decomposing capability against AFB1, wherein a maximal degradation rate reaches 80.12%.
Owner:HENAN PUAI FEED GRP CO LTD +1
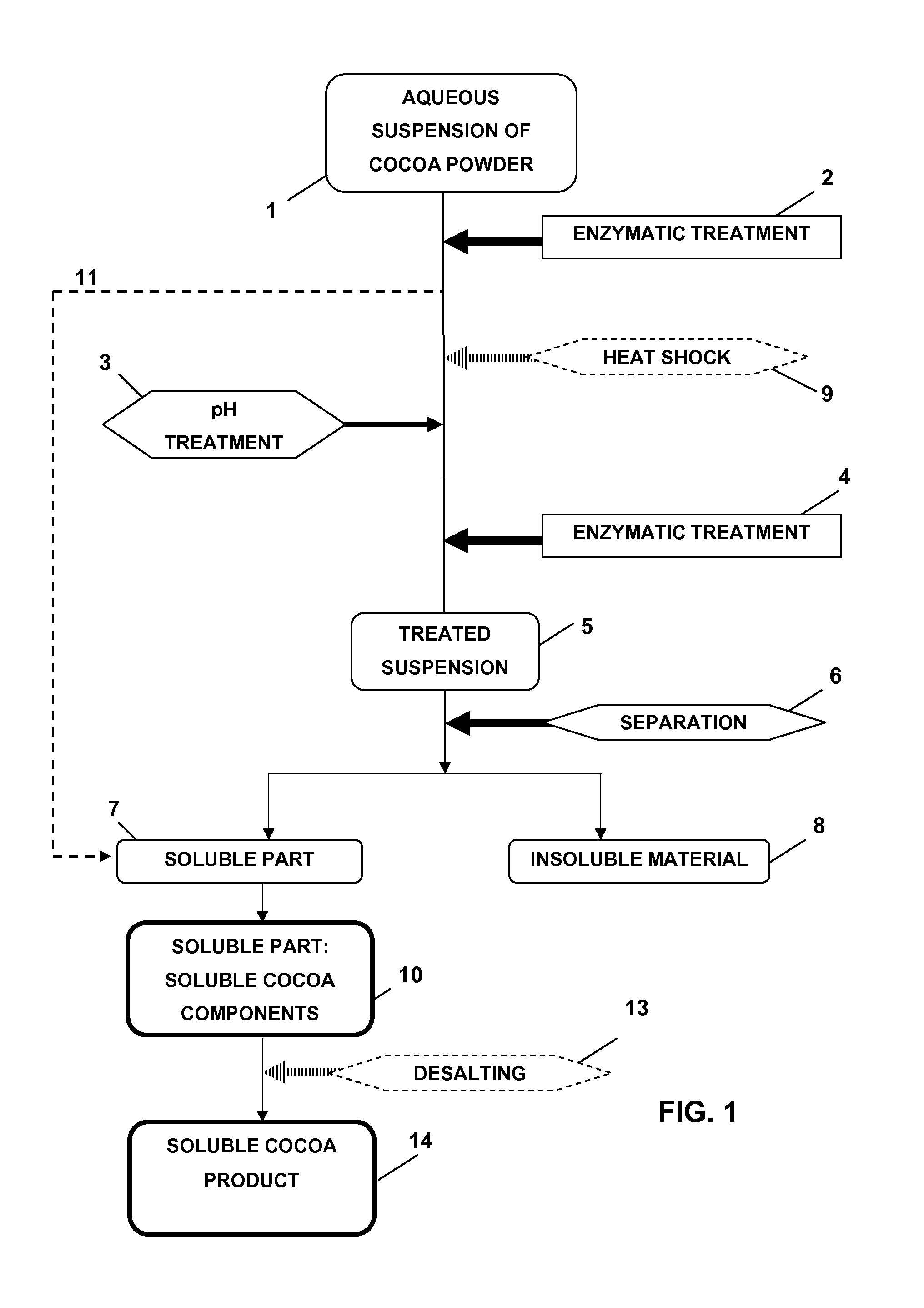
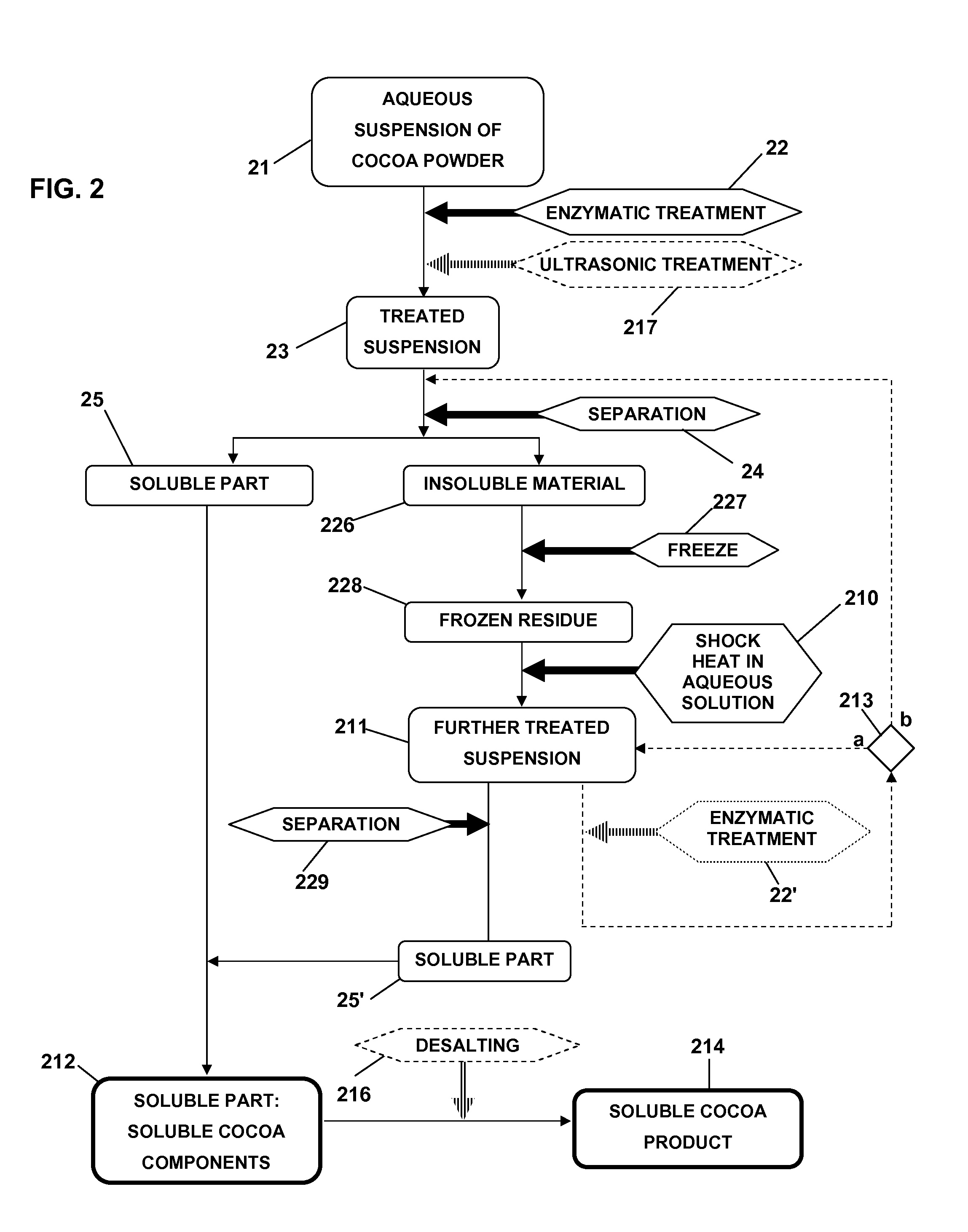
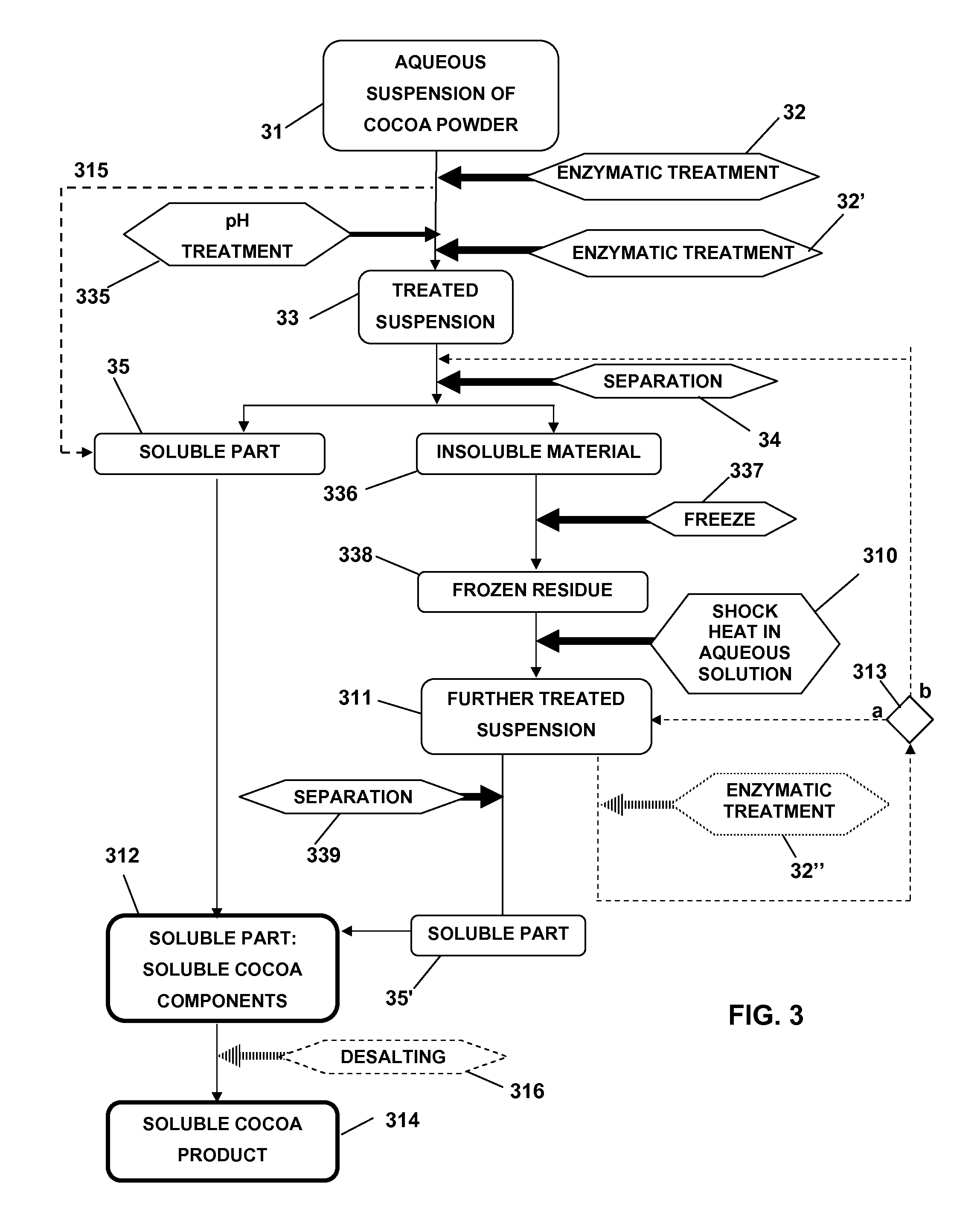
Method for producing a soluble cocoa product from cocoa powder
The present invention relates to a method for producing a soluble cocoa product from cocoa powder comprising the steps: a) preparing an aqueous suspension of cocoa powder (1), b) treating said suspension with one or more degrading enzymes (2), c) submitting (3) the suspension obtained in step b) to a pH treatment comprising treating said suspension for at least 2 hours at a suitable pH, a temperature of at 10 least 100° C., and a pressure which is at least 1 bar higher than the ambient pressure, d) optionally bringing the pH of the suspension obtained in step c) to a pH value corresponding with the pH of the suspension obtained in step a), e) treating (4) the suspension obtained in step c) or d) with one or more degrading enzymes, f) separating (6) the suspension (5) obtained in step e) into insoluble material (8) and a soluble part (7), and g) obtaining soluble cocoa components (10) from the soluble parts (7). The present invention further relates to cocoa products obtained by the present method and use thereof.
Owner:BARRY CALLEBAUT
Trichodermaviride used for producing cellulose degrading enzyme and its application in urban landscaping waste degradation
InactiveCN102559508AImprove hydrolysis effectSolve energy problemsFungiSolid waste disposalCellulose compoundsDegradative enzyme
The invention belongs to microbe technical field, and especially relates to a Trichodermaviride, and the invention also relates to an application of Trichodermaviride. The Trichodermaviride strain capable of producing cellulase with high-yield is Trichodermaviride in Trichoderma, the code number is M20, and the Trichodermaviride is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 2nd, April, 2011, the preservation number is CGMCC No.4732. The strain of the invention can be grown in a medium which takes a plurality of cellulose compounds as a sole carbon source, the cellulose compounds comprise carboxymethylcellulose sodium, microcrystalline cellulose, corn straw, cob, deciduous leaf, turf grass and the like. The Trichodermaviride of the invention can secrete a plurality of cellulose hydrolases, can be used for processing urban landscaping waste, can acquire high reducing sugar in short time, the obtained reducing sugar can be used for producing single cell protein and can be used for producing fuel ethanol, and the Trichodermaviride possesses important meaning for solving a series of problems of energy shortage and environmental pollution at present.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Purification and isolation of recombinant oxalate degrading enzymes and spray-dried particles containing oxalate degrading enzymes
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for the reduction of oxalate in humans, and methods for the purification and isolation of recombinant oxalate reducing enzyme proteins. The invention provides methods and compositions for the delivery of oxalate-reducing enzymes in particle compositions. The compositions of the present invention are suitable in methods of treatment or prevention of oxalate-related conditions.
Owner:OXTHERA INTPROP
Zearalenone (ZEN) toxin degrading enzyme for acinetobacter and coding gene and applications of ZEN toxin degrading enzyme
InactiveCN102618517APromote degradationTrue detox effectHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesActive siteZeranol
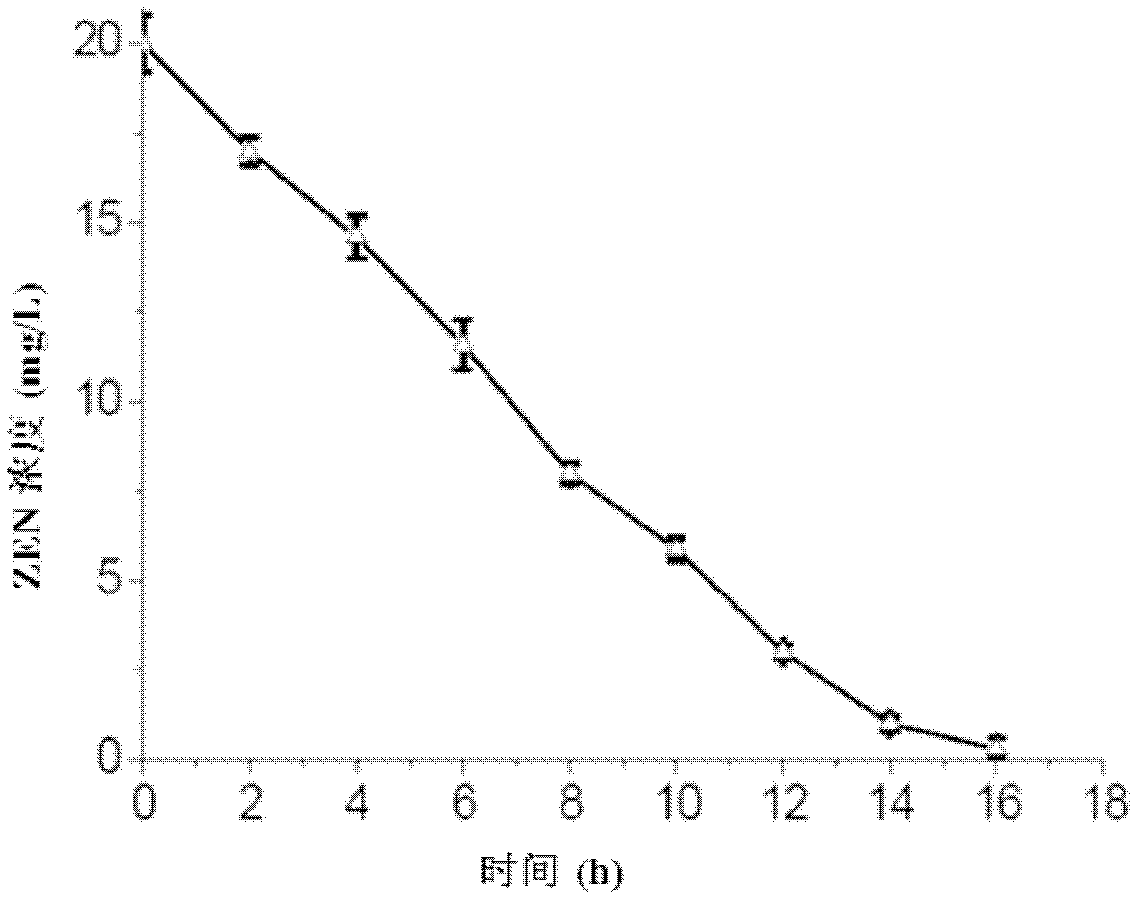
The invention discloses a zearalenone (ZEN) toxin degrading enzyme for acinetobacter and a coding gene and applications of the ZEN toxin degrading enzyme. The amino acid sequence of the ZEN toxin degrading enzyme for the acinetobacter is shown by SEQ ID NO.6. The sequence of the coding gene of the ZEN toxin degrading enzyme for the acinetobacter is shown by SEQ ID NO.5. The ZEN toxin degrading enzyme for the acinetobacter performs stronger degrading capacity on mycotoxin ZEN, is capable of degrading at least 90 percent of ZEN into a low-estrogen active product in 12h without generating high-estrogen active analogues, such as ZEN, zeranol and the like, and has a real detoxification effect. According to the invention, the coding sequence of the ZEN toxin degrading enzyme for acinetobacter sp.SM04 is determined, i.e. a Prx gene, and thereby, a foundation is laid for researching the active site of the enzyme and changing the Prx enzyme activity through site-specific mutagenesis in the future.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com