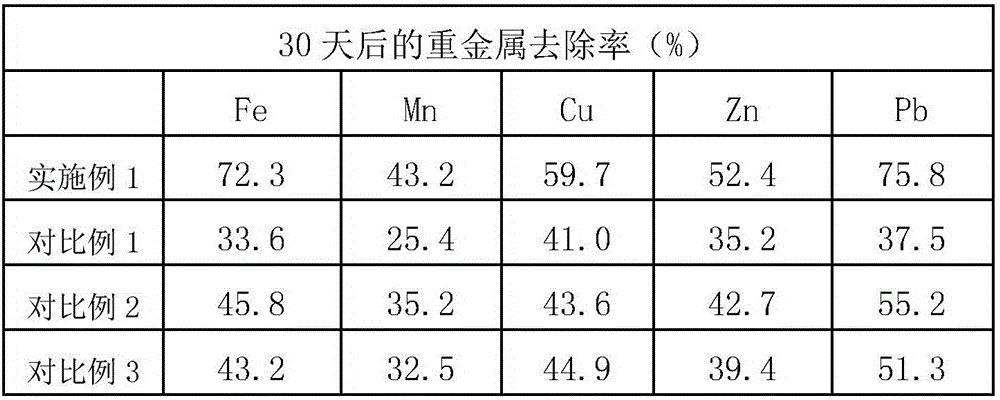
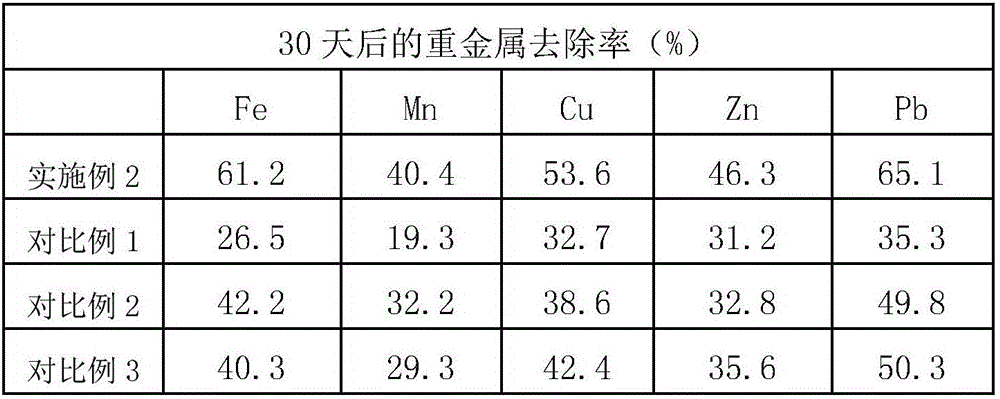
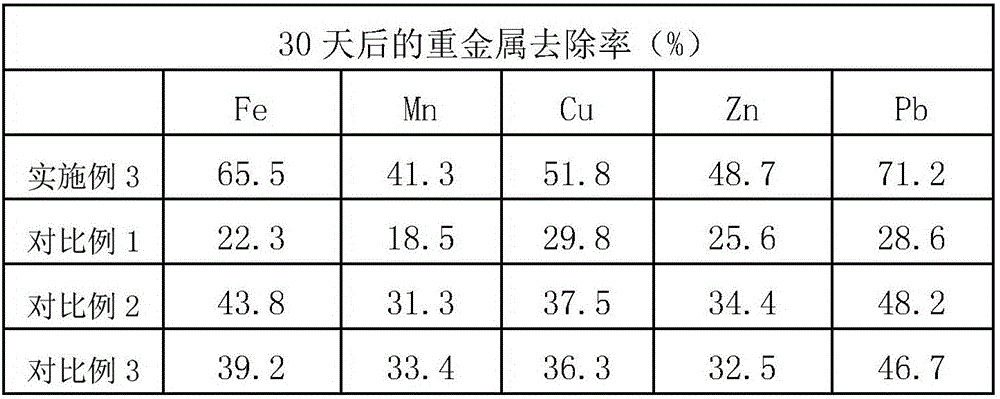
Patents
Literature
248 results about "Single-cell protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Single-cell proteins (SCP) or microbial proteins refer to edible unicellular microorganisms. The biomass or protein extract from pure or mixed cultures of algae, yeasts, fungi or bacteria may be used as an ingredient or a substitute for protein-rich foods, and is suitable for human consumption or as animal feeds. Industrial agriculture is marked by a high water footprint, high land use, biodiversity destruction, general environmental degradation and contributes to climate change by emission of a third of all greenhouse gases, production of SCP does not necessarily exhibit any of these serious drawbacks. As of today, SCP is commonly grown on agricultural waste products, and as such inherits the ecological footprint and water footprint of industrial agriculture. However, SCP may also be produced entirely independent of agricultural waste products through autotrophic growth. Thanks to the high diversity of microbial metabolism, autotrophic SCP provides several different modes of growth, versatile options of nutrients recycling, and a substantially increased efficiency compared to crops.
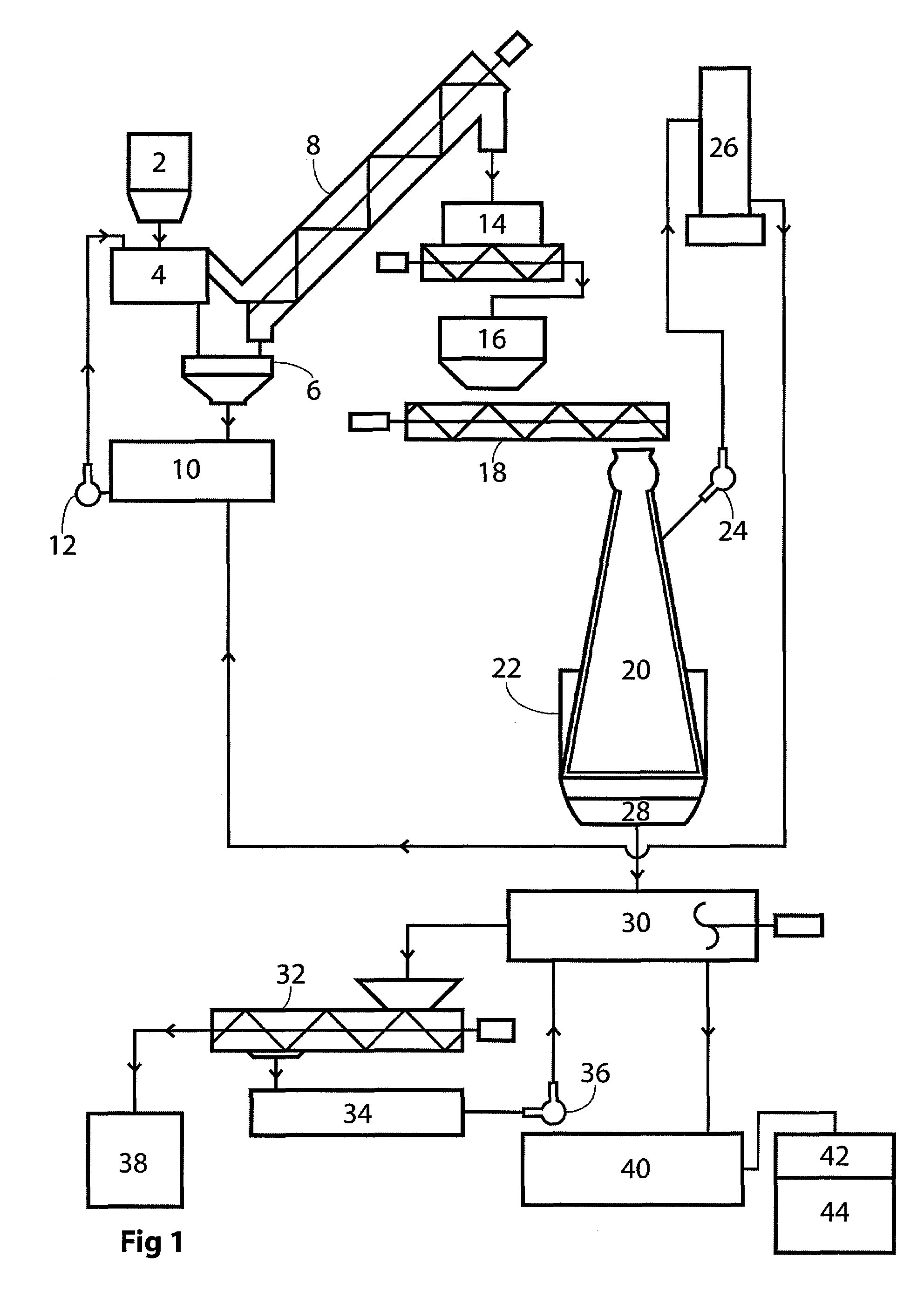
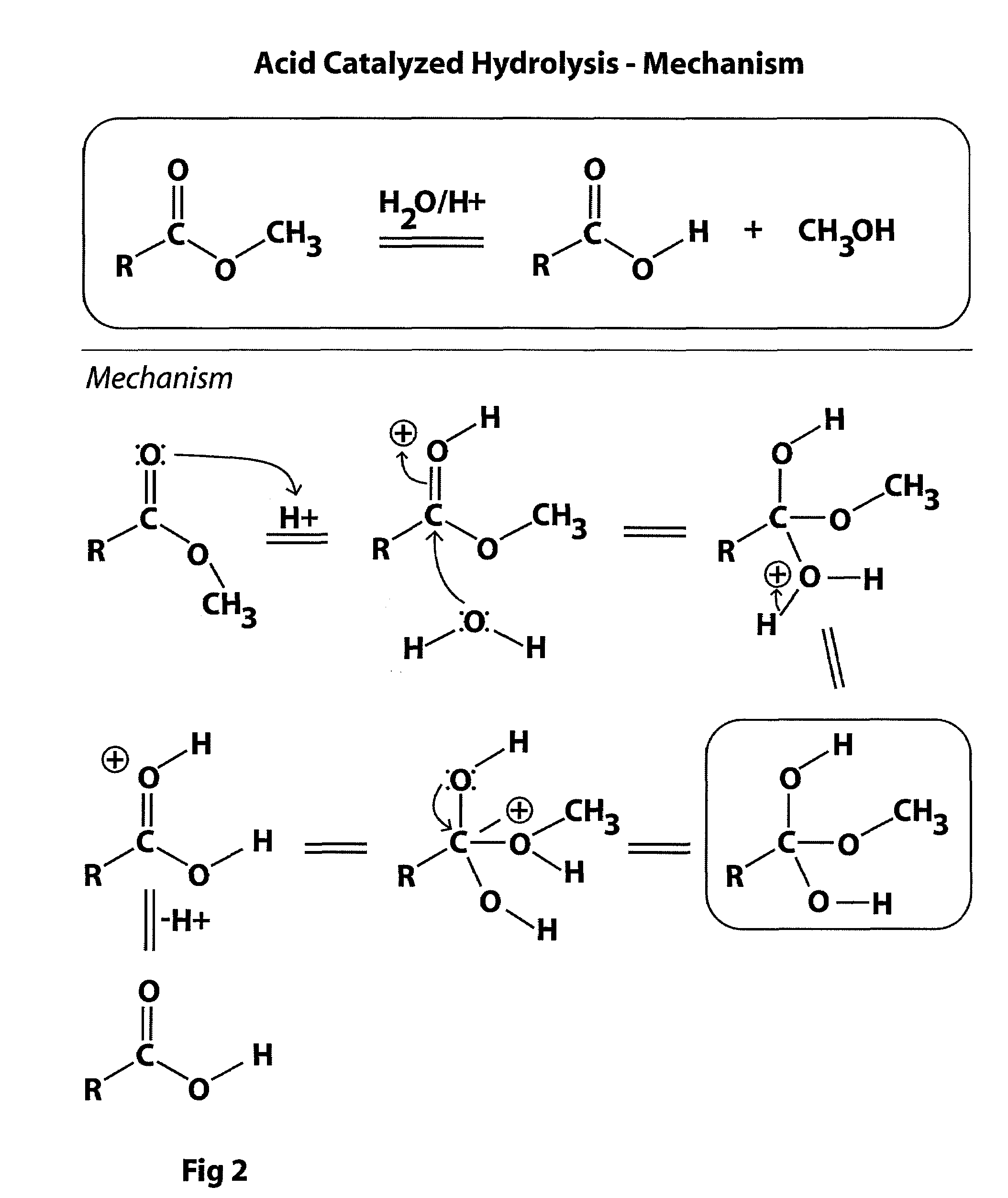
Method for producing pulp and lignin
InactiveUS20040244925A1Pretreatment with acid reacting compoundsPulp bleachingCellulosePtru catalyst
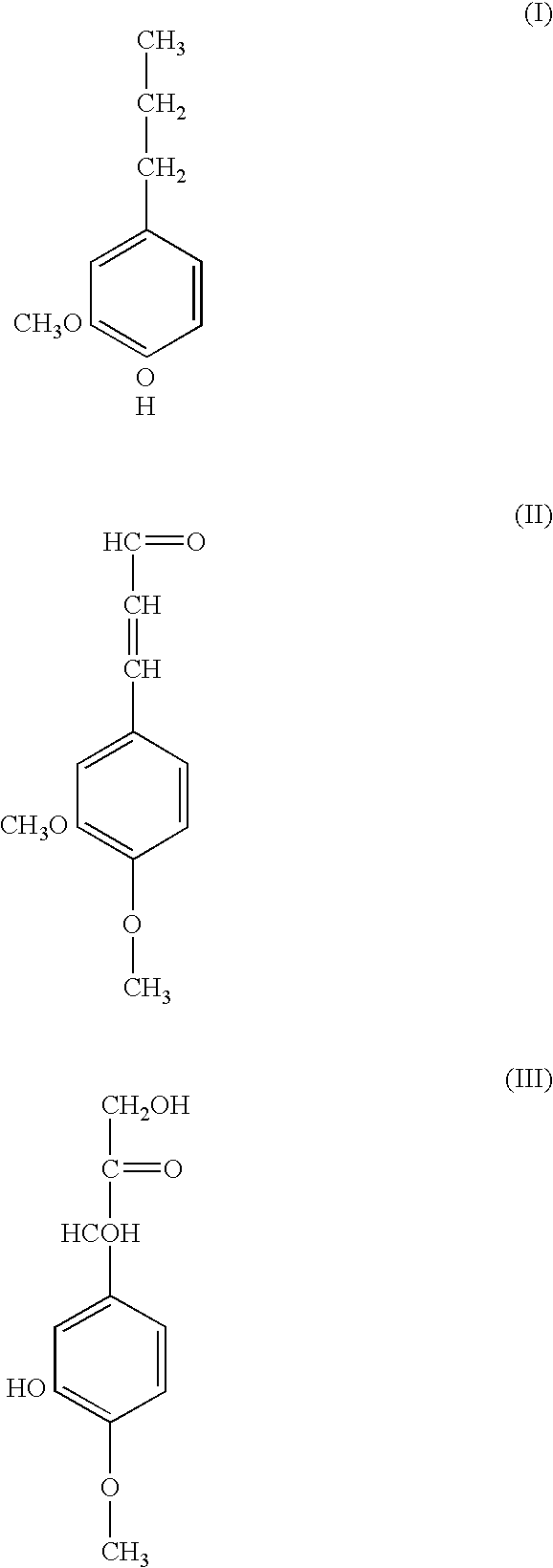
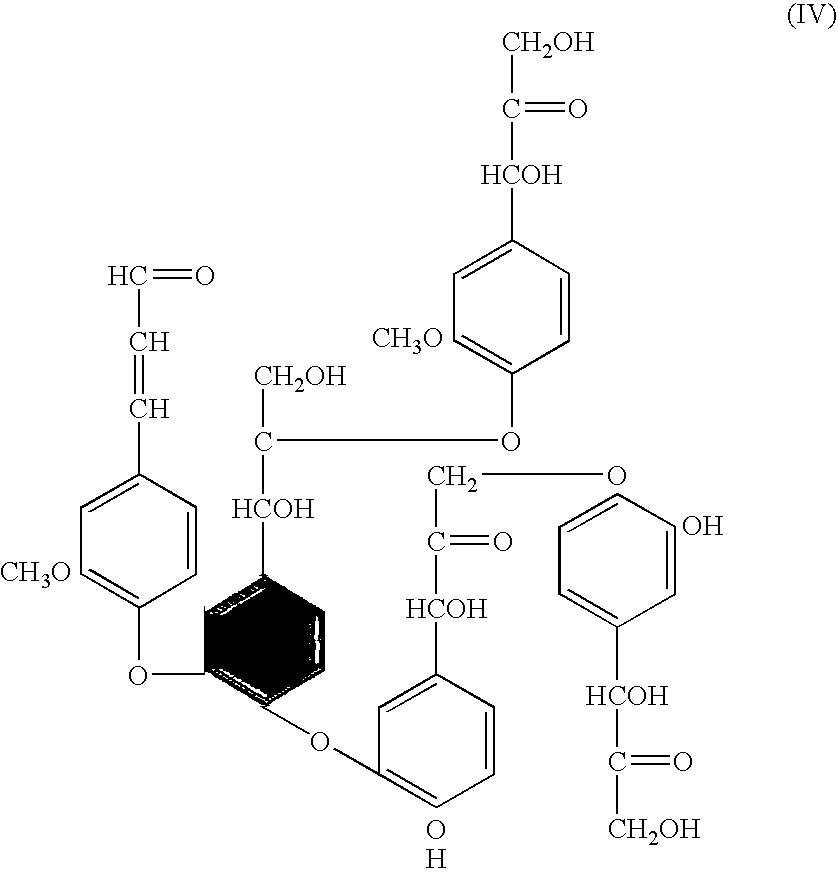
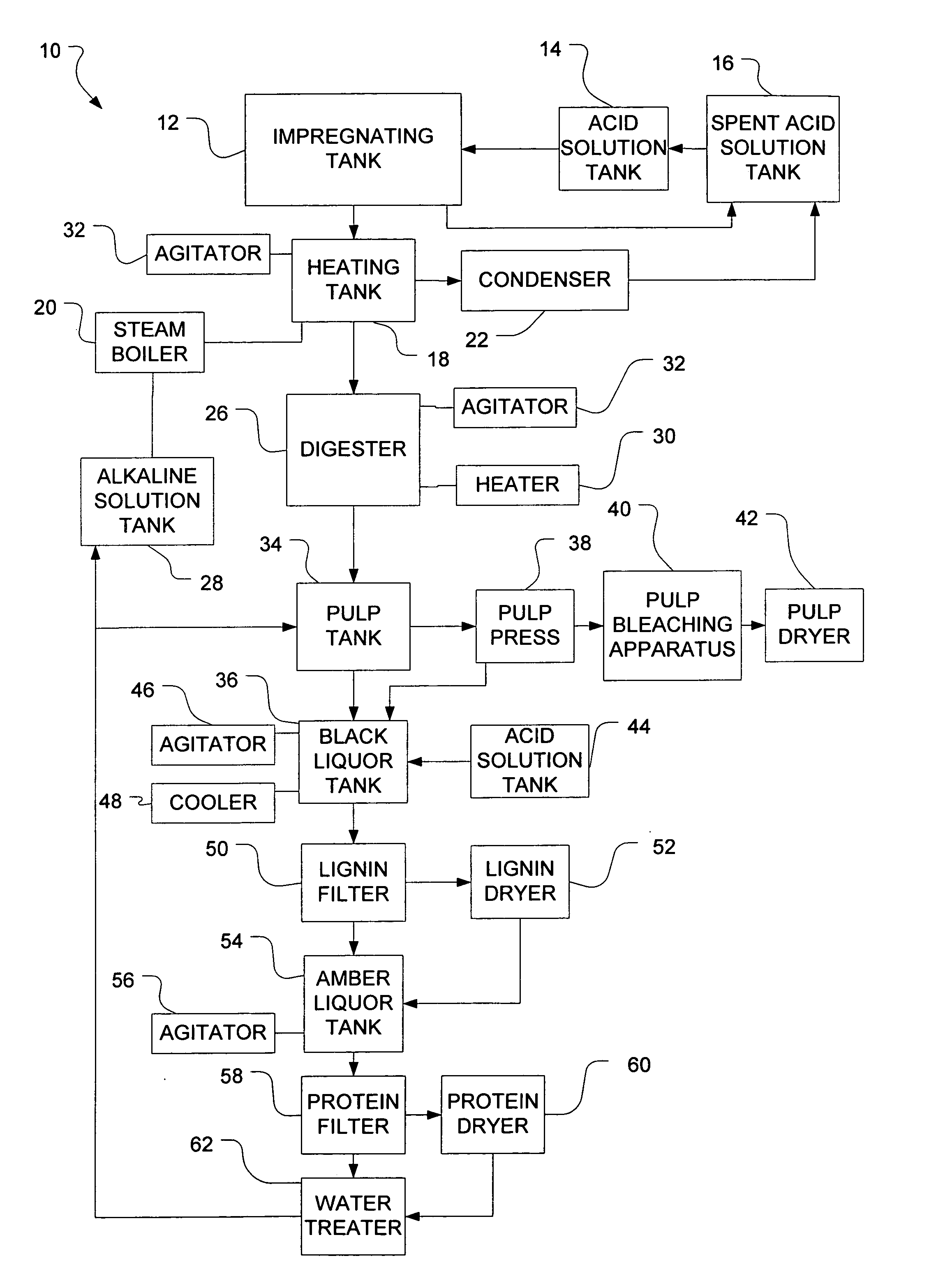
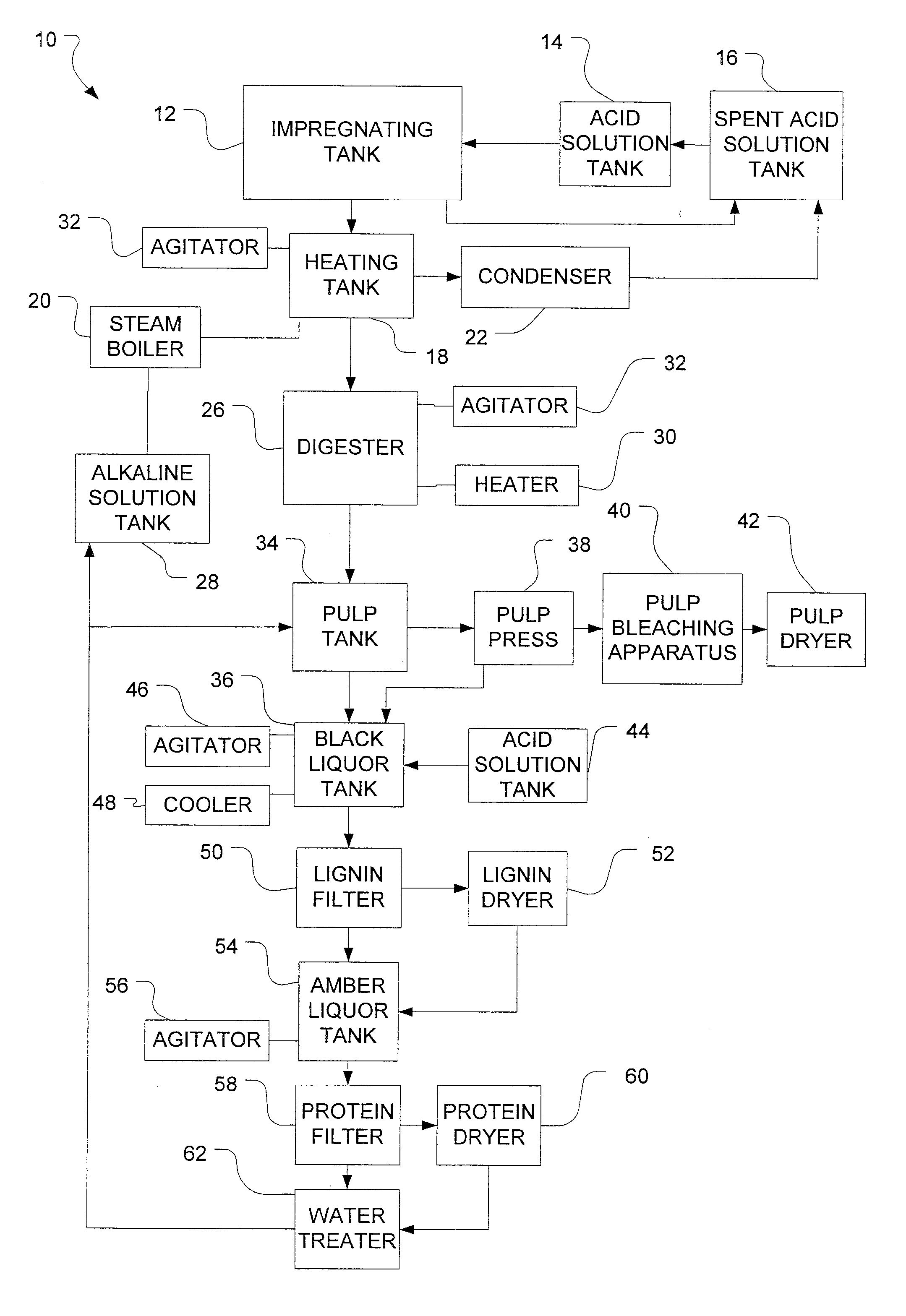
The invention provides for methods for producing pulp (comprising cellulose) and lignin from lignocellulosic material, such as wood chips. The methods involve acid catalyzed hydrolysis. Lignocellulosic material having a relatively high moisture concentration can be used as the starting material. The lignocellulosic material is impregnated with an acid (preferably nitric acid) and heated. During the heating lignin is depolymerized at relatively low temperatures, and the acid catalyst is distilled off. The acid catalyst can be collected and recycled after impregnation and heating. The lignocellulosic material is then digested in an alkaline solution under heat, dissolving the lignin and allowing the pulp to be removed. Acid is added to the black liquor to precipitate the lignin which is then removed. The resultant amber liquor can be further processed into other ancillary products such as alcohols and / or unicellular proteins.
Owner:PACIFIC PULP RESOURCES
Straw and pot ale mixed fermented feed and production method thereof
ActiveCN102113622AImprove degradation efficiencyHigh in nutrientsFood processingAnimal feeding stuffCelluloseSingle-cell protein
The invention discloses straw and pot ale mixed fermented feed and a production method thereof, and relates to the field of environmental science, in particular to the mixed fermented feed and the production method thereof. The production method comprises the following steps: (1) crushing straw, and then mixing pot ale; (2) preparing aerobic fermentation bacteria liquid, uniformly spraying the aerobic fermentation bacteria liquid into materials, adding compound trace elements, and fermenting; (3) preparing anaerobic fermentation bacteria liquid, appropriately adding according to the fermentation situation of the fermented materials, and fermenting; and (4) drying the fermented materials containing water, and then getting the straw and pot ale mixed feed. Aerobic bacteria used in the method are high-efficient cellulose and lignin degrading bacteria, thereby improving the degradation rate of cellulose and lignin, fully utilizing yeast and other microbes in the pot ale to produce single-cell proteins, improving the content of nutrition in the feed, enabling the protein content to be 13-20%, having certain bouquet and acid fragrance and improving the palatability of the feed. The fermentation process is simple to operate, the fermentation time is 7-9 days, and the production time of the feed is shortened.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Biofuel cell
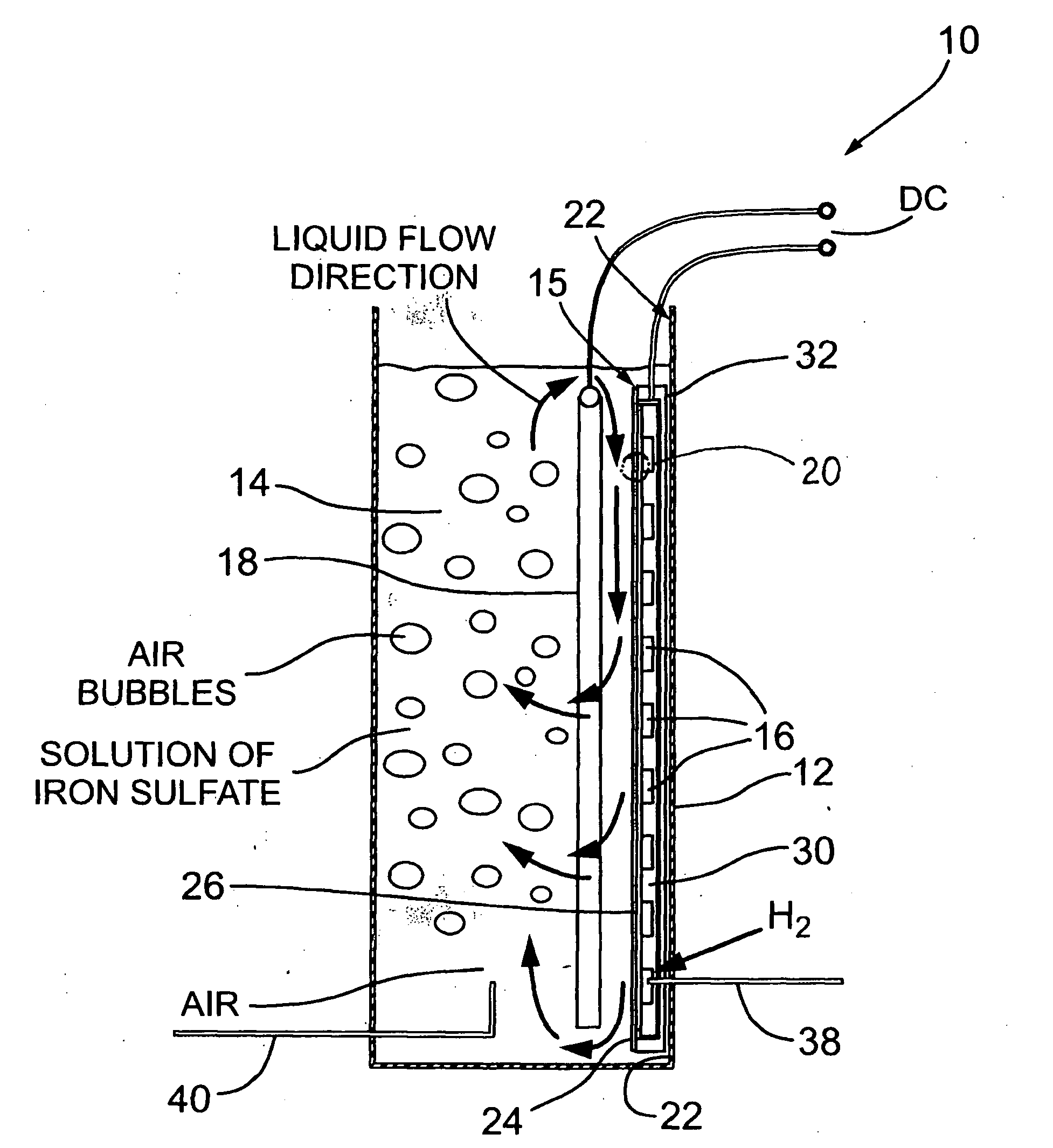
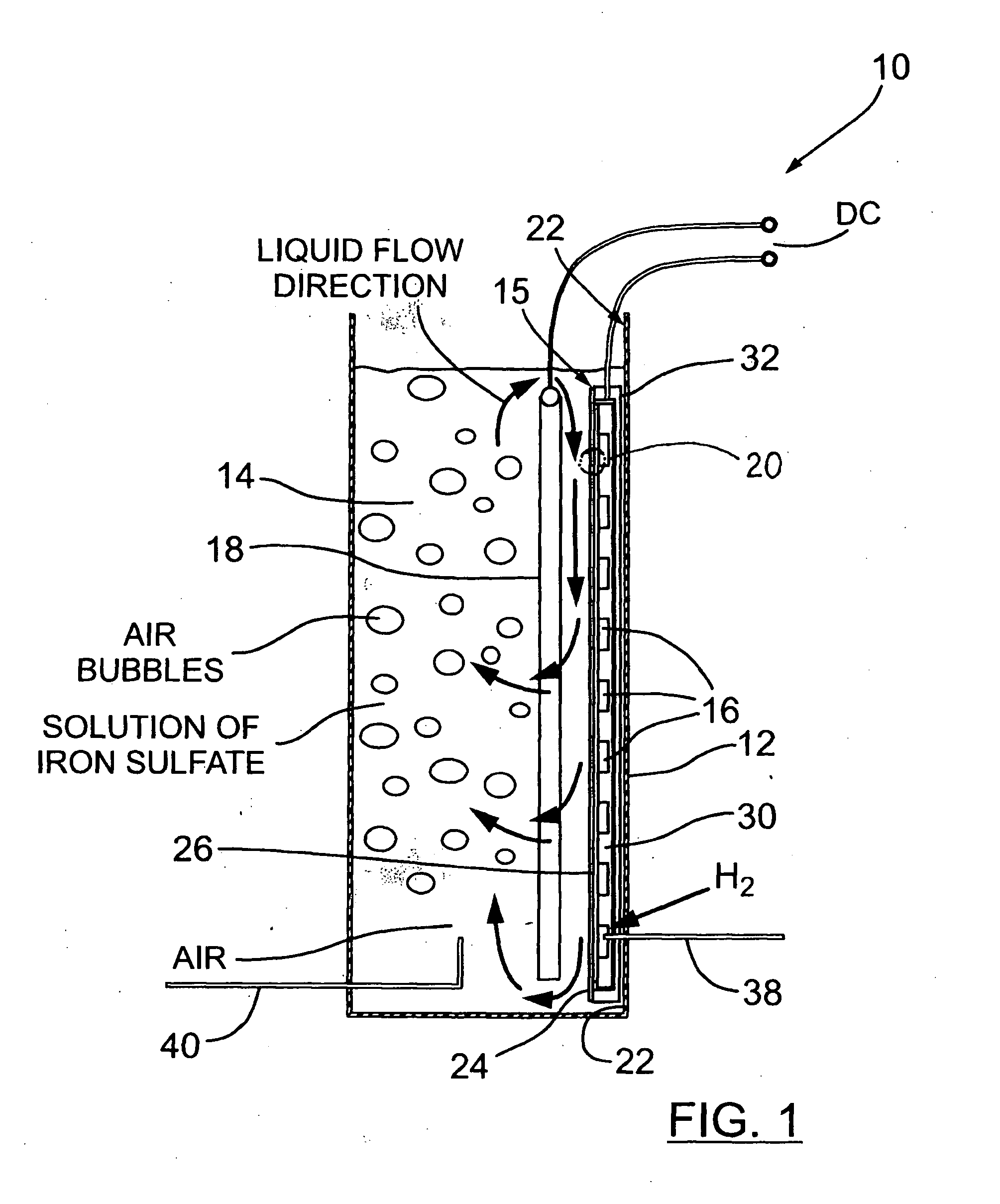
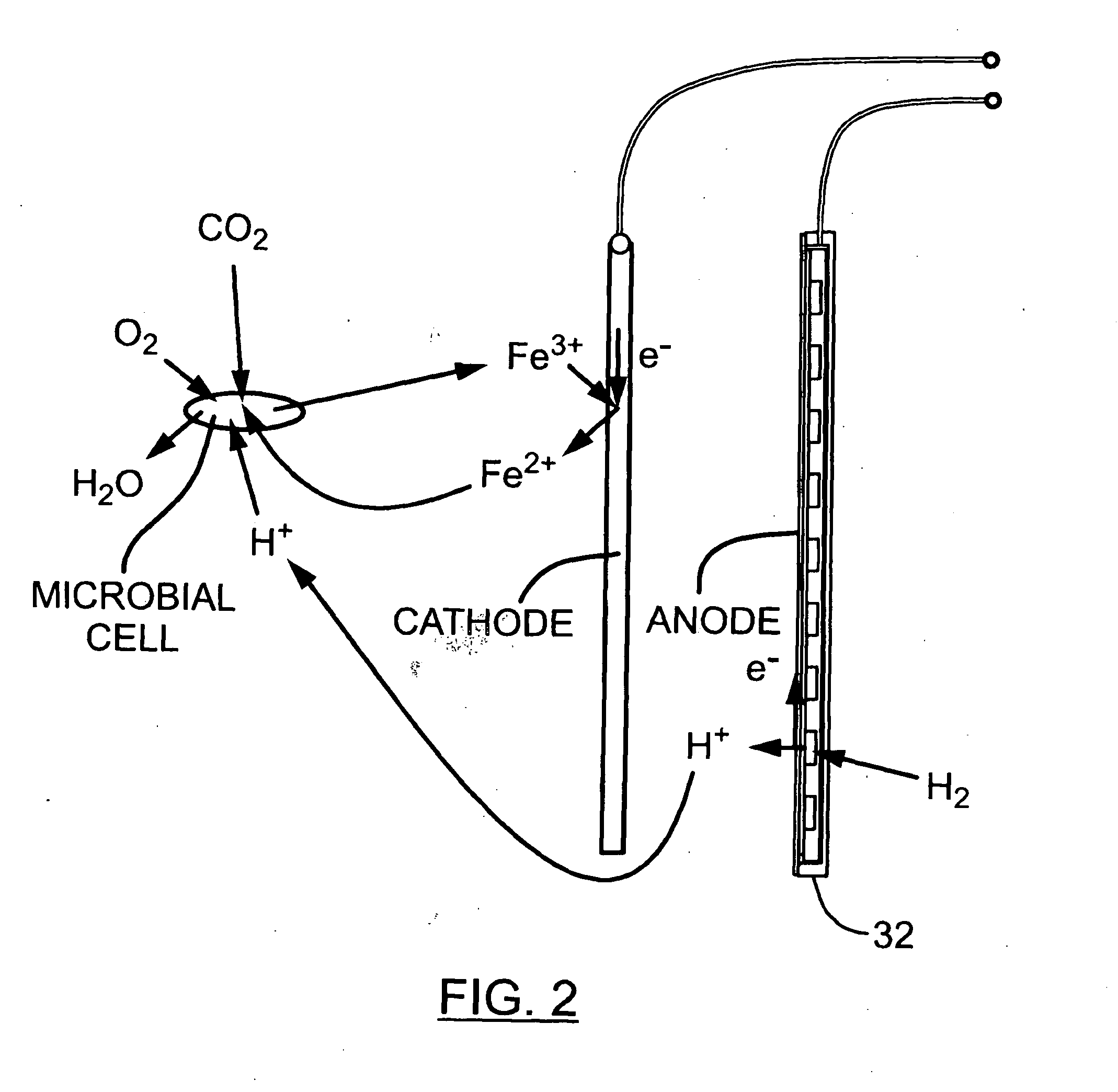
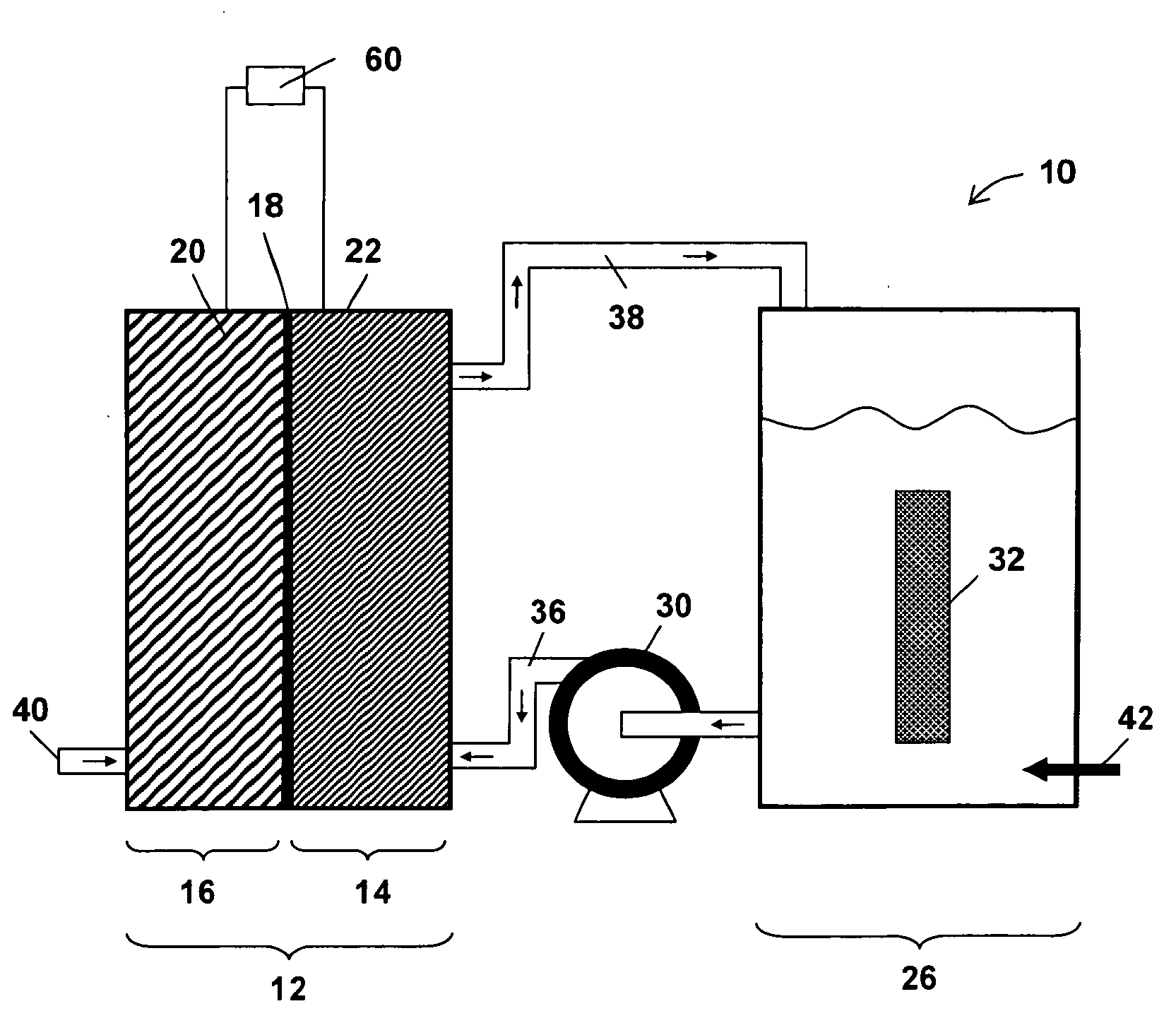
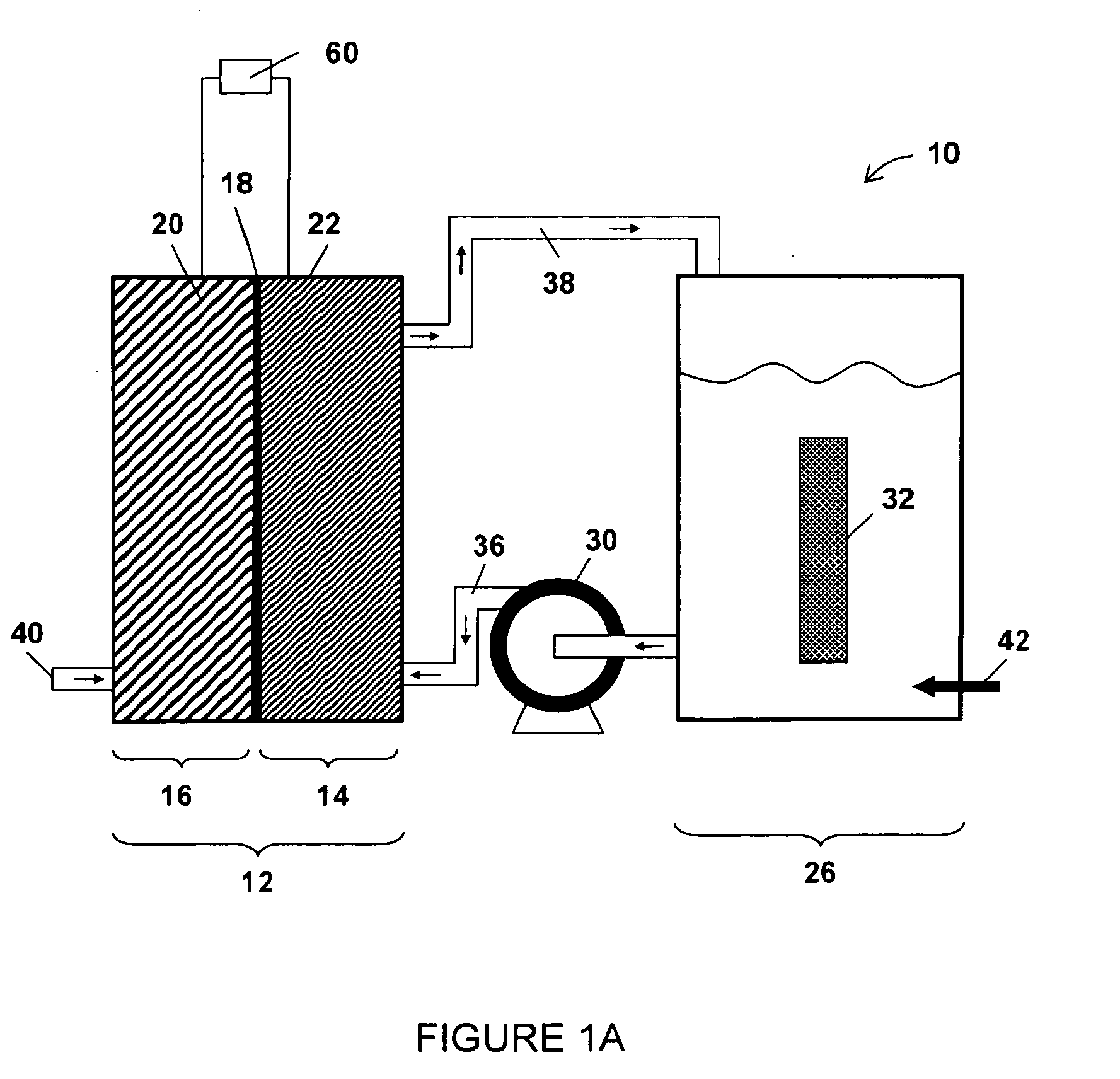
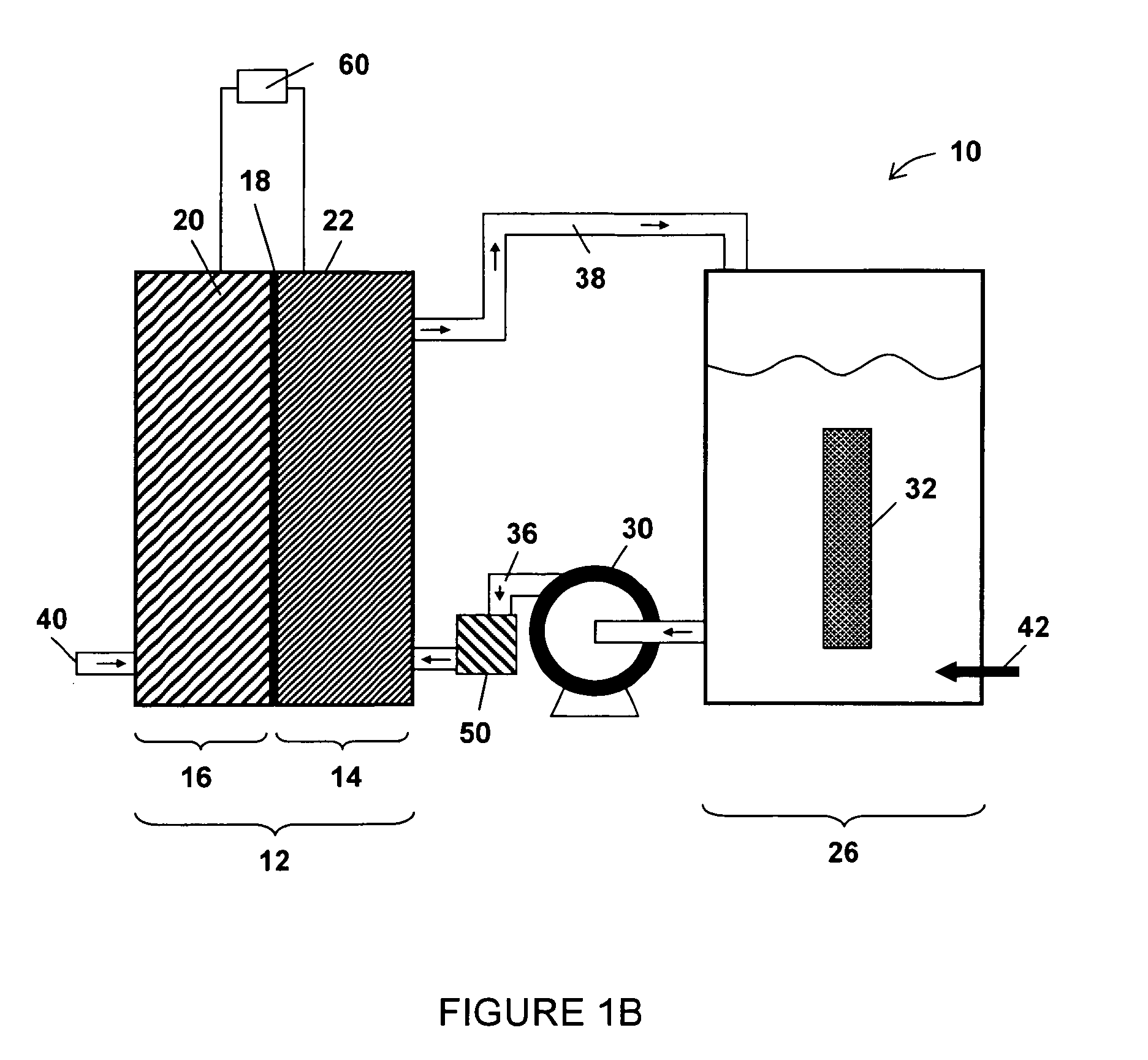
InactiveUS20060251959A1Promote growthElectrolyte holding meansRegenerative fuel cellsMicroorganismHydrogen
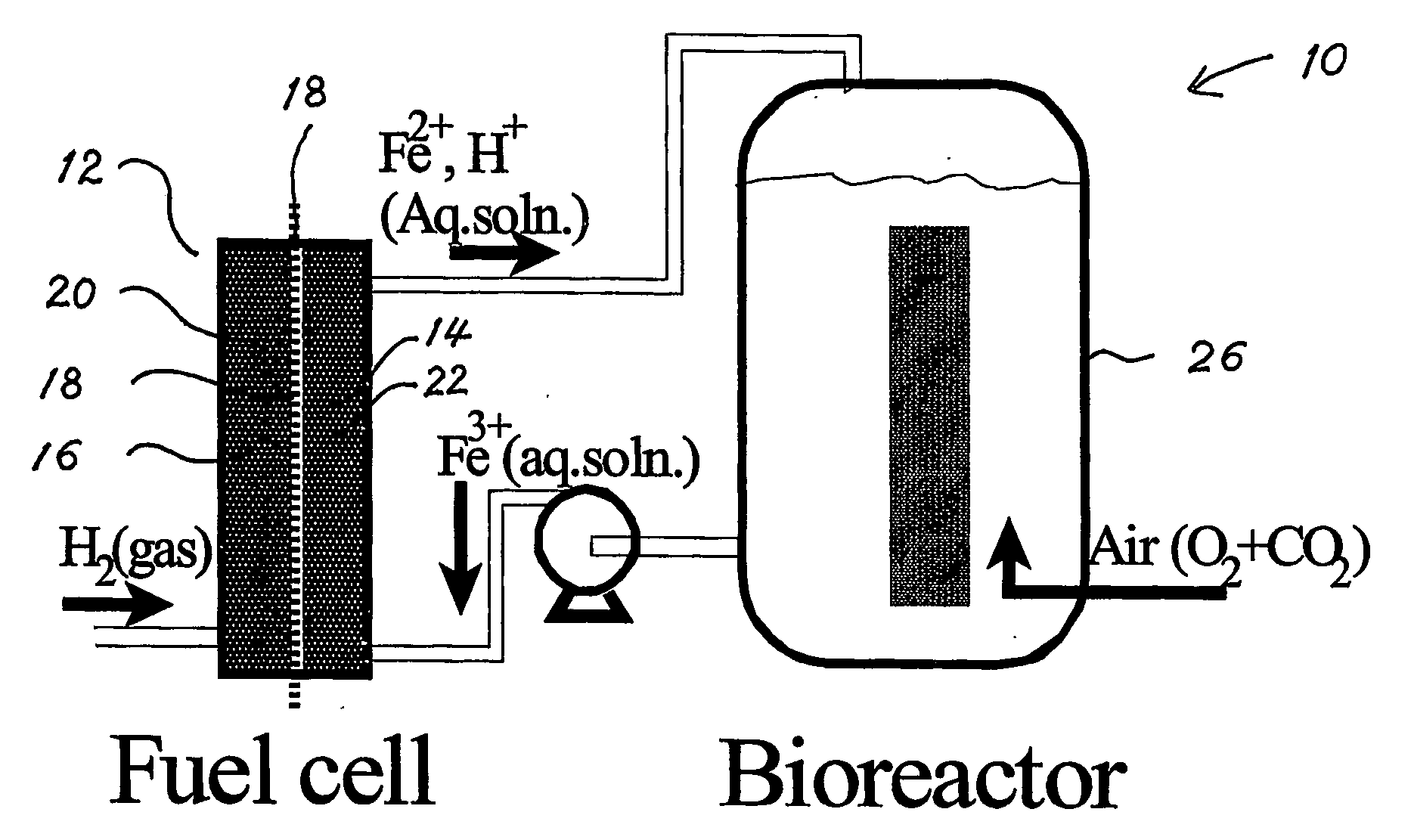
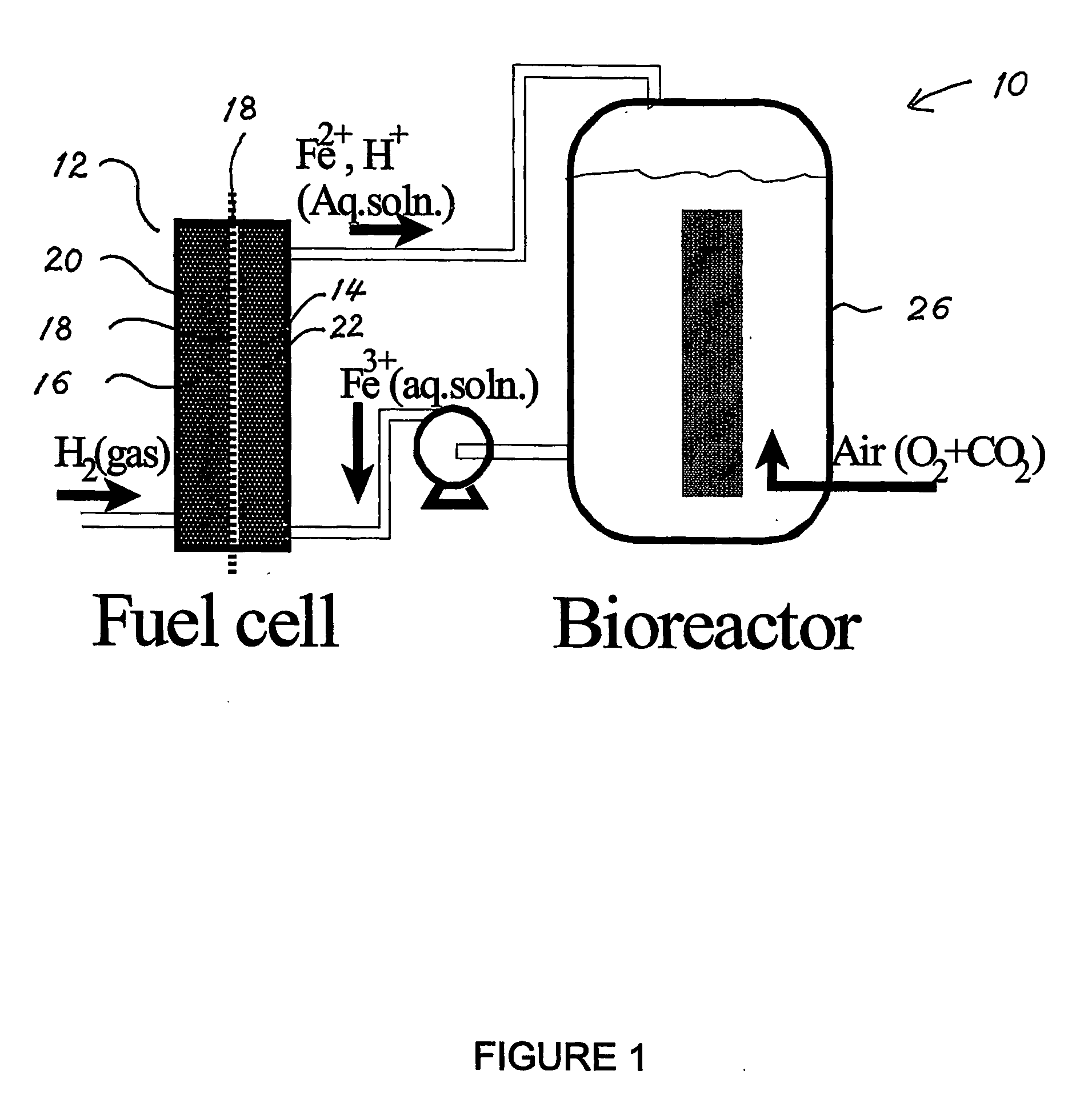
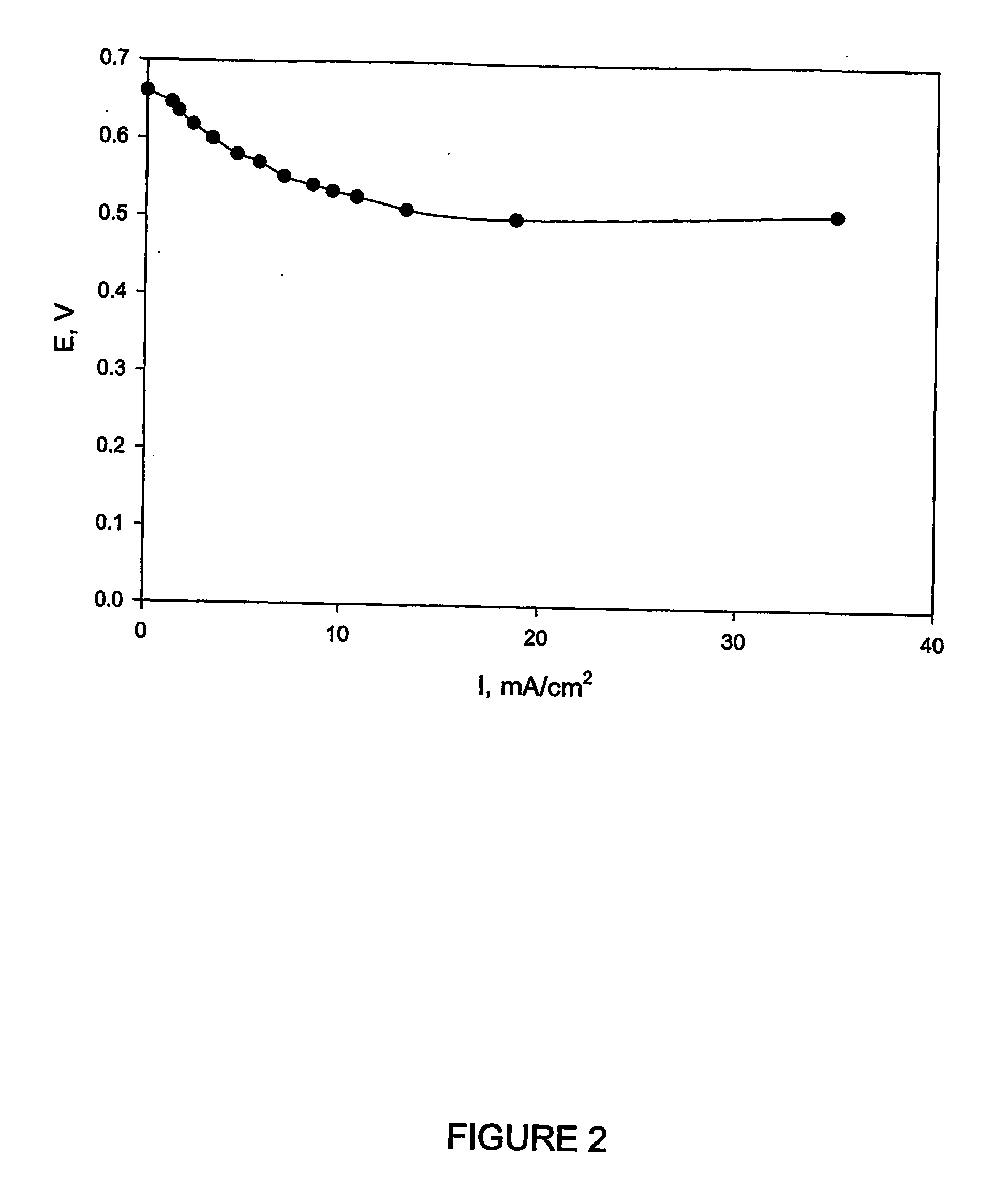
The present invention discloses a new type of biofuel cell, based on the microbial regeneration of the oxidant, ferric ions. The bio-fuel cell is based on the cathodic reduction of ferric to ferrous ions, coupled with the microbial regeneration of ferric ions by the oxidation of ferrous ions, with fuel (such as hydrogen) oxidation on the anode. The microbial regeneration of ferric ions is achieved by chemolithotrophic microorganisms such as Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans. Electrical generation is coupled with the consumption of carbon dioxide from atmosphere and its transformation into microbial cells, which can be used as a single-cell protein.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Lignocellulosic biomass conversion
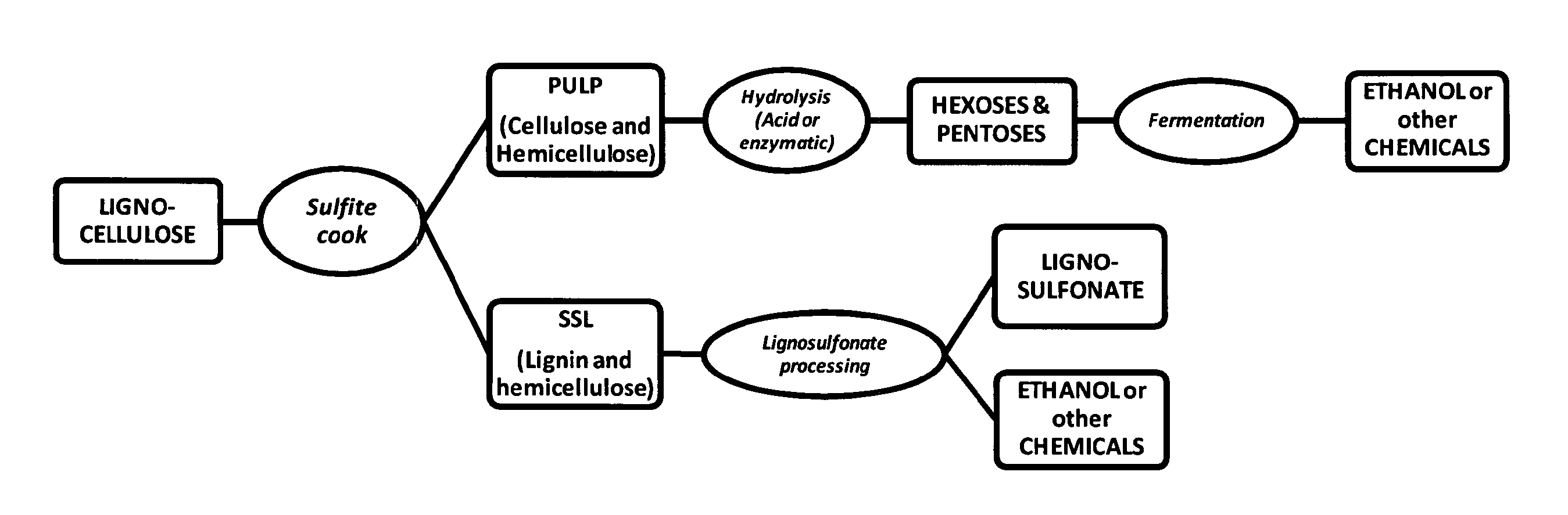
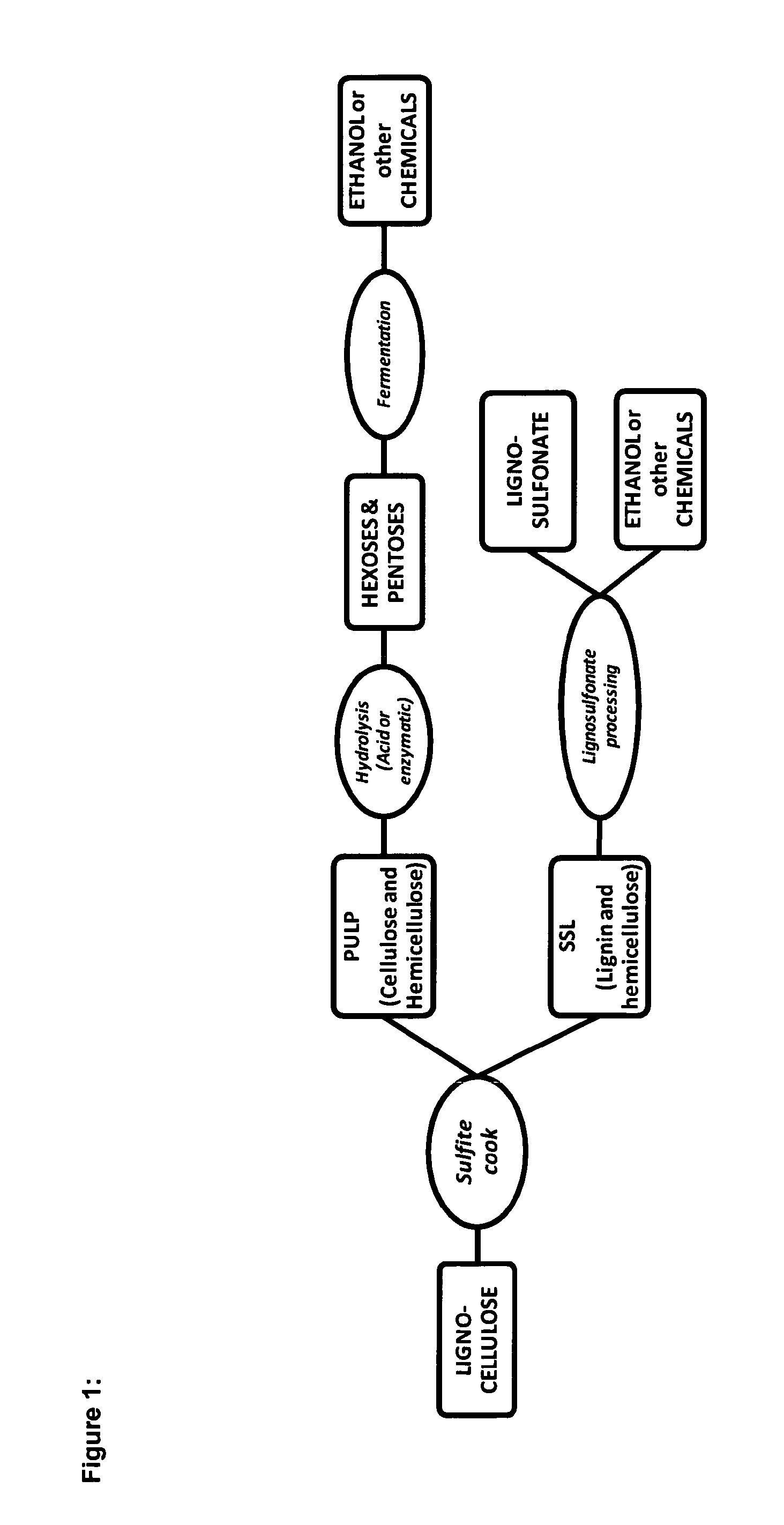
ActiveUS20110250638A1Easy to separateMaintain good propertiesSugar derivativesPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsCelluloseSingle-cell protein
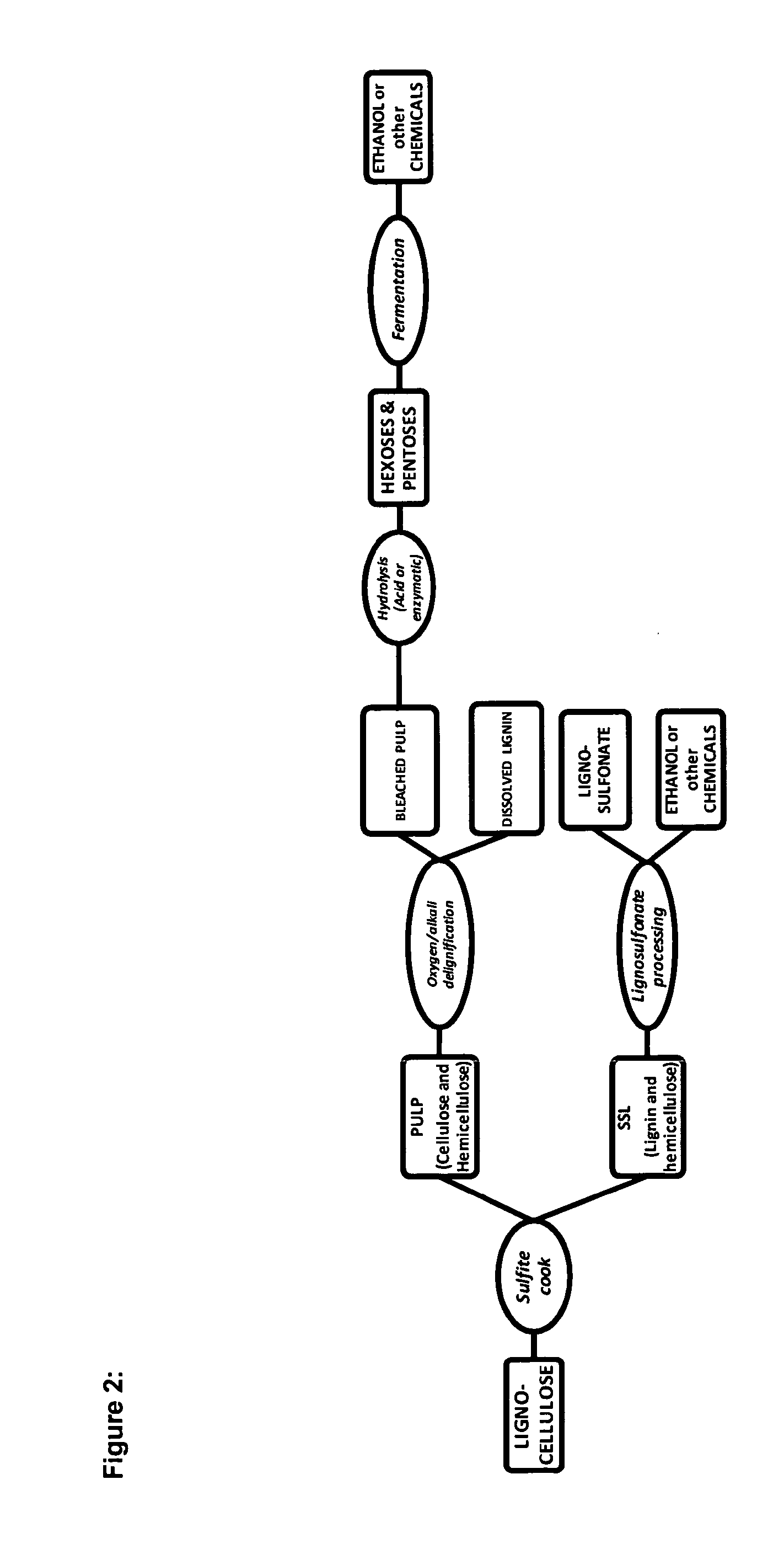
The present invention relates to a process for the production of second generation biofuels and / or sugar based chemicals—for example ethanol, butanol etc—and / or materials—for example plastics, single cell proteins etc.—together with sulfonated lignin from lignocellulosic biomass, in particular from lignocellulosic biomass comprising, among others, annual plants, agricultural waste, or wood. In particular, the present invention relates to a process for the production of sugar based chemicals, biofuels or materials together with sulfonated lignin from lignocellulosic biomass comprising the pretreatment of a lignocellulosic biomass in a sulfite cooking step.
Owner:BORREGAARD INDS
Gas-phase double-dynamic solid fermentation technology and fermentation apparatus
InactiveCN1434113ASimple structureImprove sealingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGas phaseEngineering
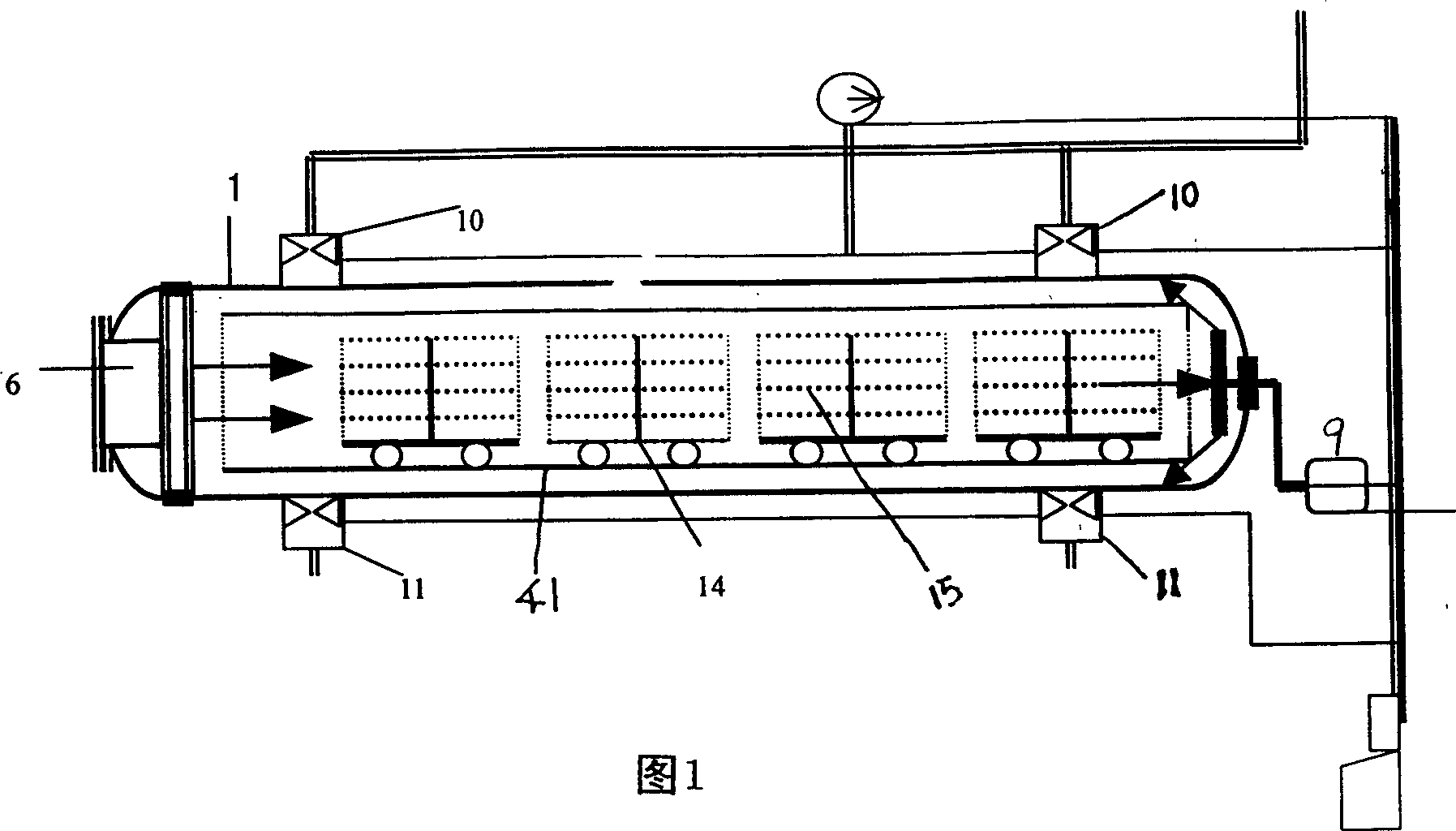
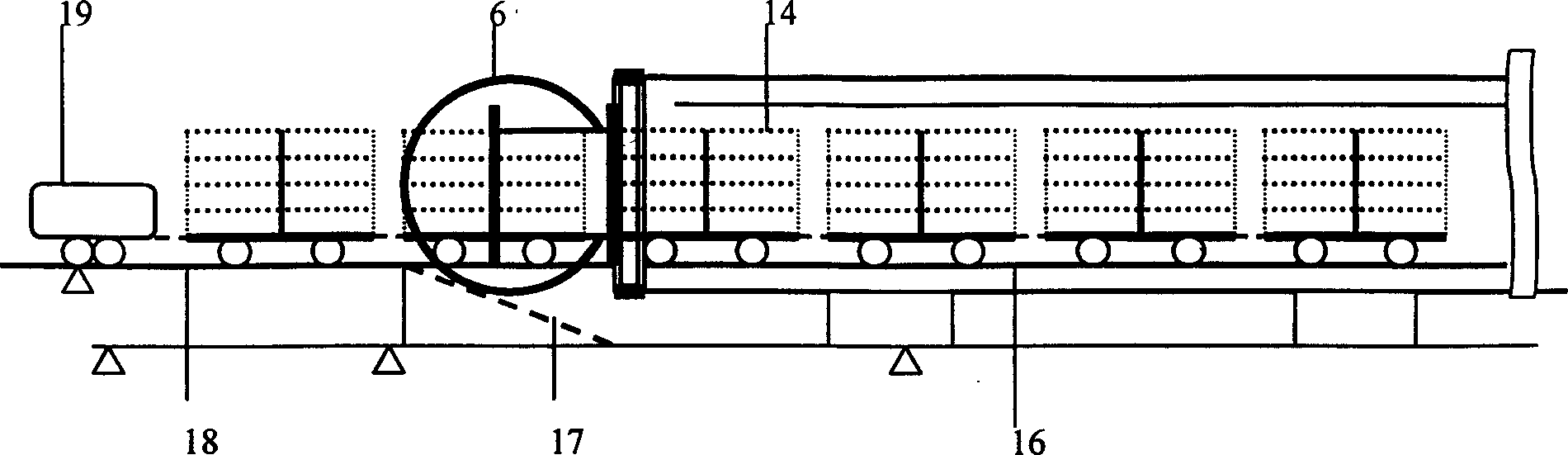
The present invention relates to a gas-phase double-dynamic solid fermentation techinque, and is characterized by that the solid material to be fermented is placed into a double-dynamic environment with pressure pulsatino and circular flowing air to make solid fermentation. Its fermentation equipment includes a horizontal cylindrical tank with a quickly-opening door, in the interior of the tank arectangular spacing cylinder which is formed from four partition boards and whose section is quadratic is axially placed, and in the space of partition board and tank wall a cooling calandria parallel to the partition board is arranged, and the vertical centre of the spacing cylinder is equipped with horizontally-arranged several groups of cooling calandria.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing pulp and lignin
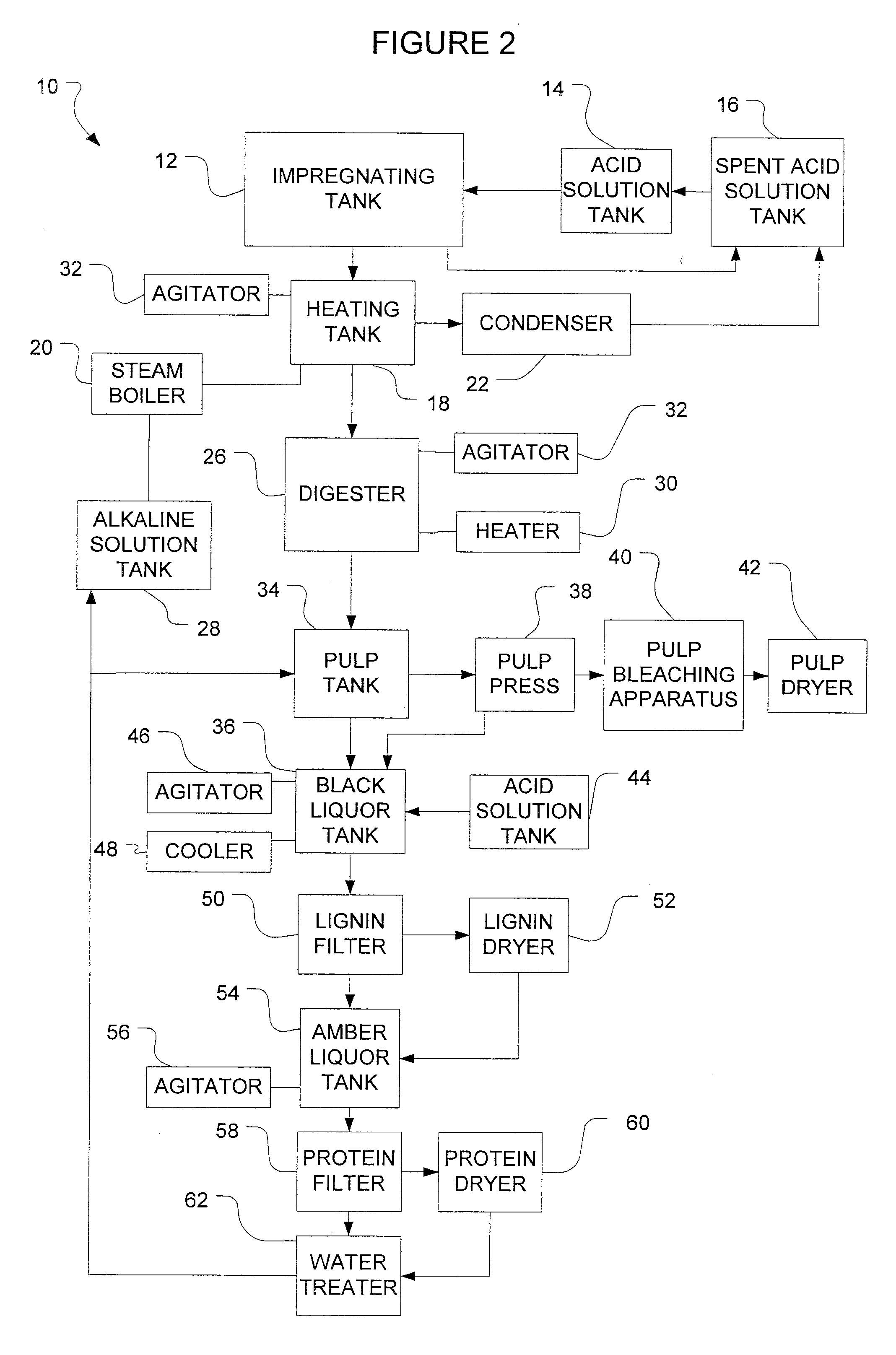
The invention provides for methods for producing pulp (comprising cellulose) and lignin from lignocellulosic material, such as wood chips. The methods involve acid catalyzed hydrolysis. Lignocellulosic material having a relatively high moisture concentration can be used as the starting material. The lignocellulosic material is impregnated with an acid (preferably nitric acid) and heated. During the heating lignin is depolymerized at relatively low temperatures, and the acid catalyst is distilled off. The acid catalyst can be collected and recycled after impregnation and heating. The lignocellulosic material is then digested in an alkaline solution under heat, dissolving the lignin and allowing the pulp to be removed. Acid is added to the black liquor to precipitate the lignin which is then removed. The resultant amber liquor can be further processed into other ancillary products such as alcohols and / or unicellular proteins.
Owner:PACIFIC PULP RESOURCES
Catalytic reactor process for the production of commercial grade pulp, native lignin and unicellular protein
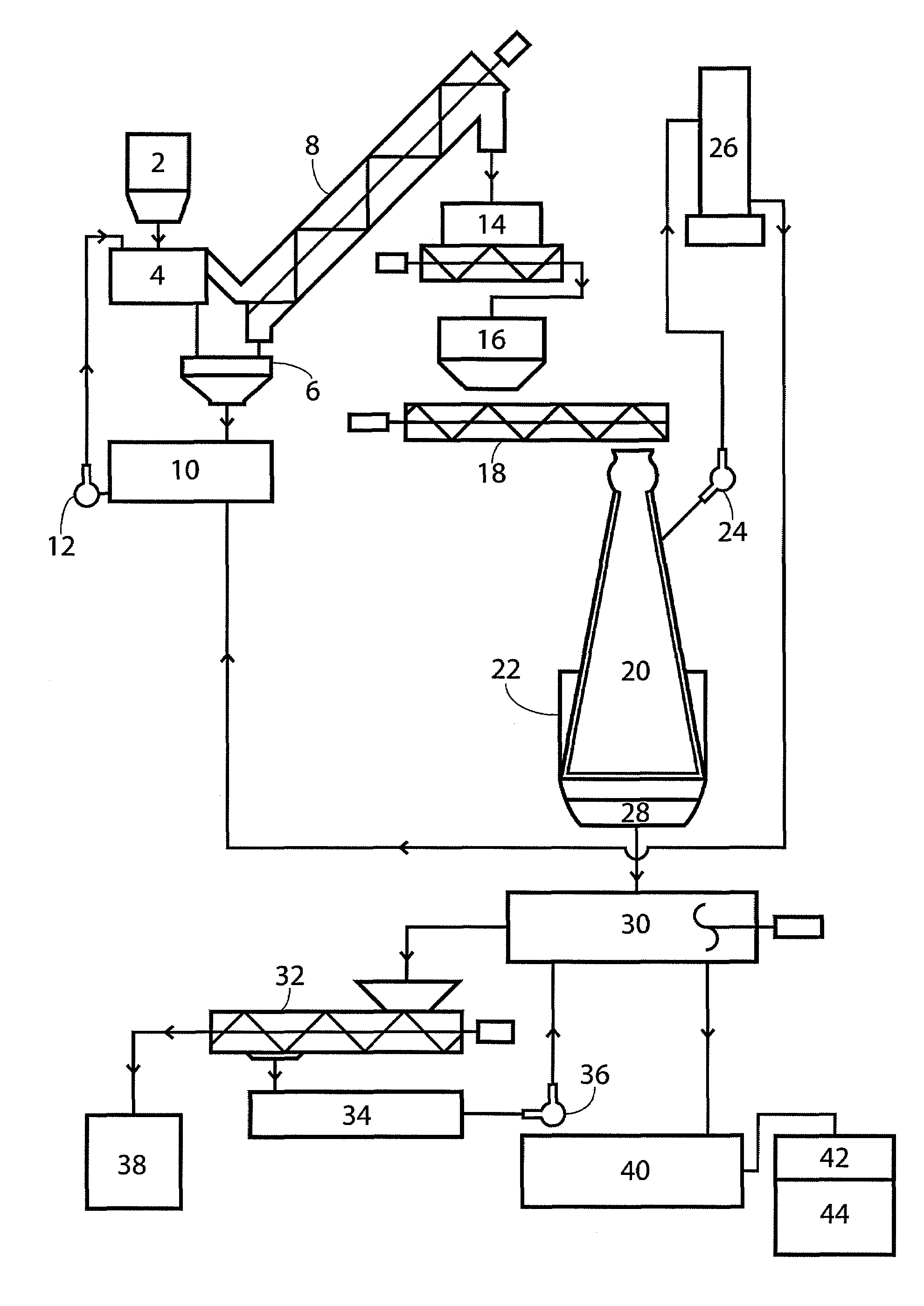
ActiveUS7396434B2Pulp liquor regenerationWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsCelluloseChemical solution
A continuous and batch system to produce cellulose, native lignin and unicellular protein from any form of vegetation in a closed process. The biomass is mixed in the impregnate solution of nitric acid and / or ammonium hydroxide and water. After a period of time at room temperature and atmospheric pressure the chemical solution is recycled. The biomass is moved to the reactor and heated. Evaporated impregnate is recovered via absorption tower and recycled back to chemical solution. The biomass is moved to an alkaline solution, then cooled to separate pulp from black liquor. The black liquor is pumped to a separation tank and is treated to precipitate lignin. The solution is filtered to separate sweet liquor and lignin. The lignin is dried and the sweet liquor is fermented to produce unicellular protein.
Owner:PURE LIGNIN ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
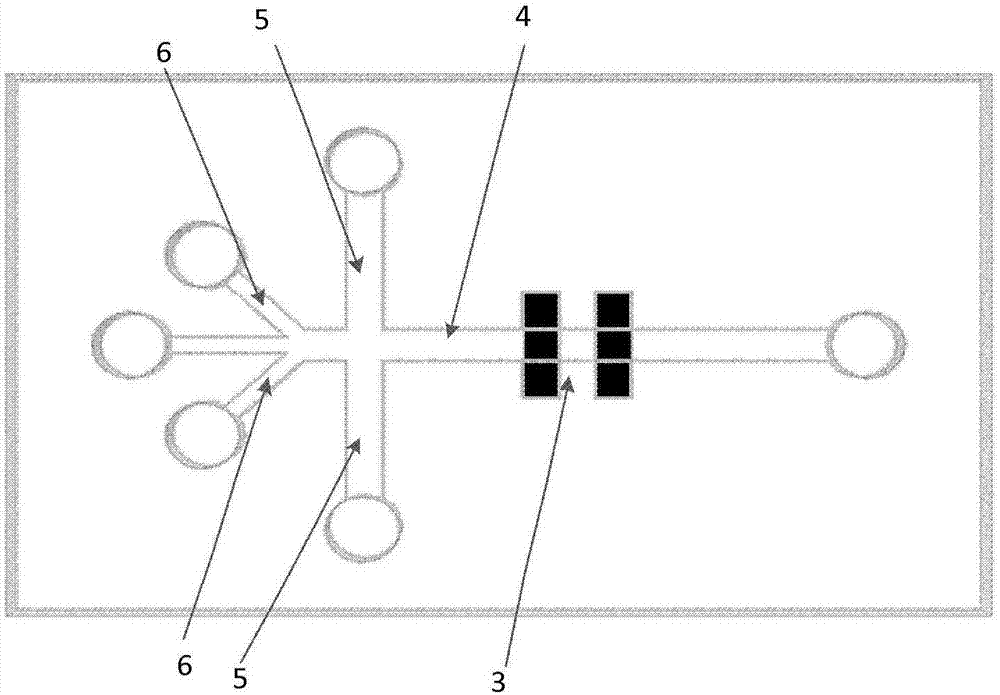
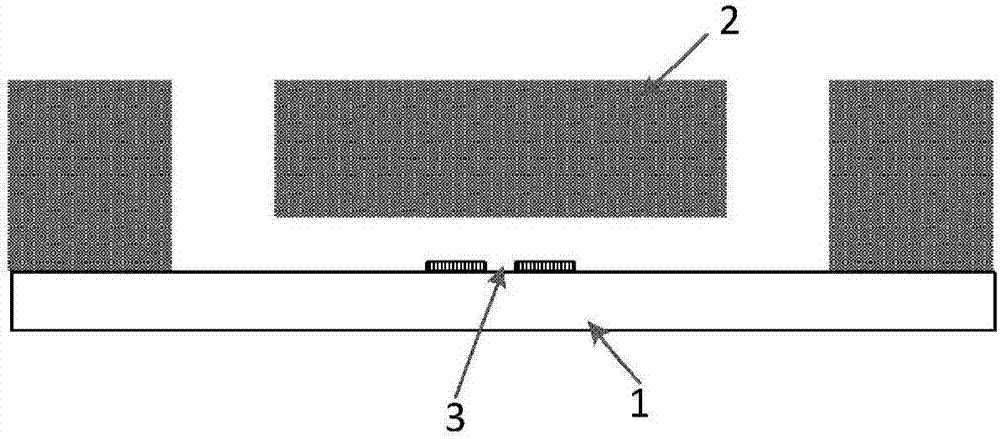
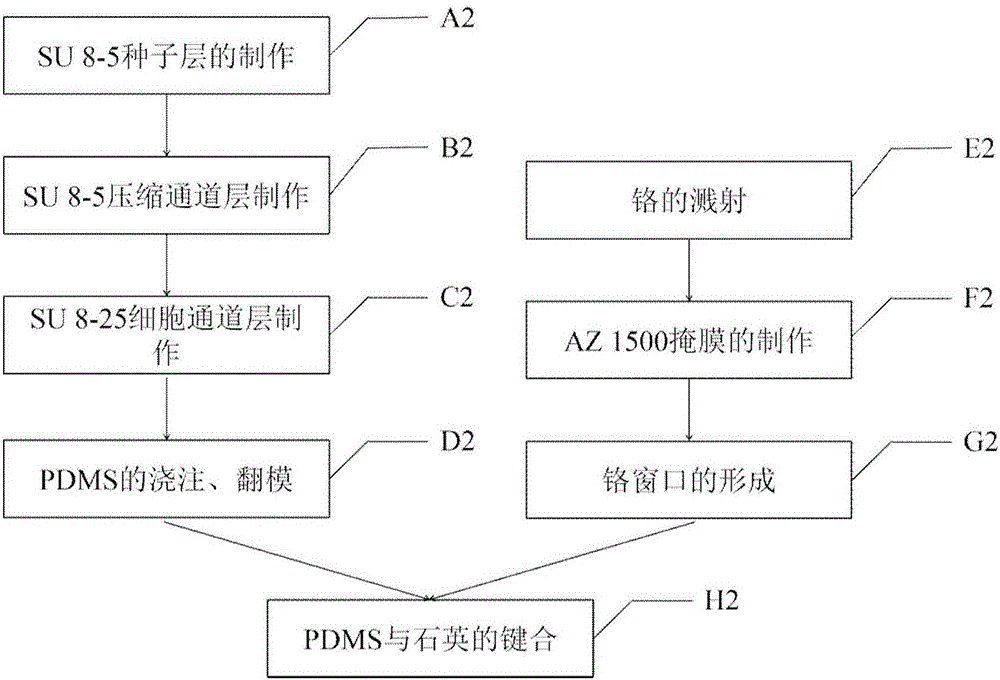
Microfluidic chip and single cell protein quantitative detection device and method
InactiveCN107064091ARealize high-throughput quantitative detectionAvoid the impact of test resultsLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingFluorescenceSingle-cell protein
The invention provides a microfluidic chip and a single cell protein quantitative detection device and method. The chip is composed of a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) layer and a quartz layer; a microfluidic chip technology is combined with a liquid drop formation technology, a fluorescence antibody preparation technology and a fluorescence detection technology and then high-throughput quantitative detection of proteins in single cells is realized; reliable device and method are provided for characterization of cell biological characteristics. By designing and manufacturing a fluorescence antibody pair and setting an optical filter, the detection precision can be effectively improved and detection errors are reduced. Equipment including an inverted fluorescent microscope, a photomultiplier and the like can be used in a traditional biological laboratory, so that the device and the method have strong adaptability and high portability and are convenient to realize.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Method for processing starch wastewater as well as product and application thereof
InactiveCN102815795ARealize resource processingHigh nutritional valueFungiAnimal feeding stuffRhizopusWastewater
The invention discloses a method for processing starch wastewater and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mould is inoculated in starch wastewater for fermentation; and (2) saccharomycete is inoculated in the product obtained by fermentation in step (1) and the fermentation is continued to obtain the product. The mould comprises one or several out of aspergillus niger, Taiwan rhizopus and aspergillus oryzae. The fermentation conditions are as follows: after mould is inoculated in starch wastewater, the fermentation is performed for 16 hours at the temperature of 29.5 DEG C; the fermentation is continued after saccharomycete is inoculated and pH of fermentation broth is 5.0. The method utilizes the mutualism effect among microorganism and adopts the mixed culture fermentation method to process starch wastewater. The method can not only remove the main pollutants in starch wastewater, but also acquire single cell protein with high feed value, thereby realizing recycling processing of starch wastewater.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES +1
Biofuel cell
The present invention discloses a new type of biofuel cell, based on the microbial regeneration of the oxidant, ferric ions. The bio-fuel cell is based on the cathodic reduction of ferric to ferrous ions, coupled with the microbial regeneration of ferric ions by the oxidation of ferrous ions, with fuel (such as hydrogen) oxidation on the anode. The microbial regeneration of ferric ions is achieved by chemolithotrophic microorganisms such as Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans. Electrical generation is coupled with the consumption of carbon dioxide from atmosphere and its transformation into microbial cells, which can be used as a single-cell protein.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Single-cell protein biological feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107668374APromote decompositionIncrease egg productionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyTrichoderma asperellum
The present invention relates to a single-cell protein biological feed and a preparation method thereof. Particularly, the single-cell protein biological feed is prepared from rhizoma atractylodis medicinal residues and prepared by a two-step fermentation method using shiraia bambusicola, and trichoderma asperellum and candida utilis. The feed has effects of improving an egg laying rate of layingchickens, enhancing immunity, etc.
Owner:长沙仲善新能源科技有限公司
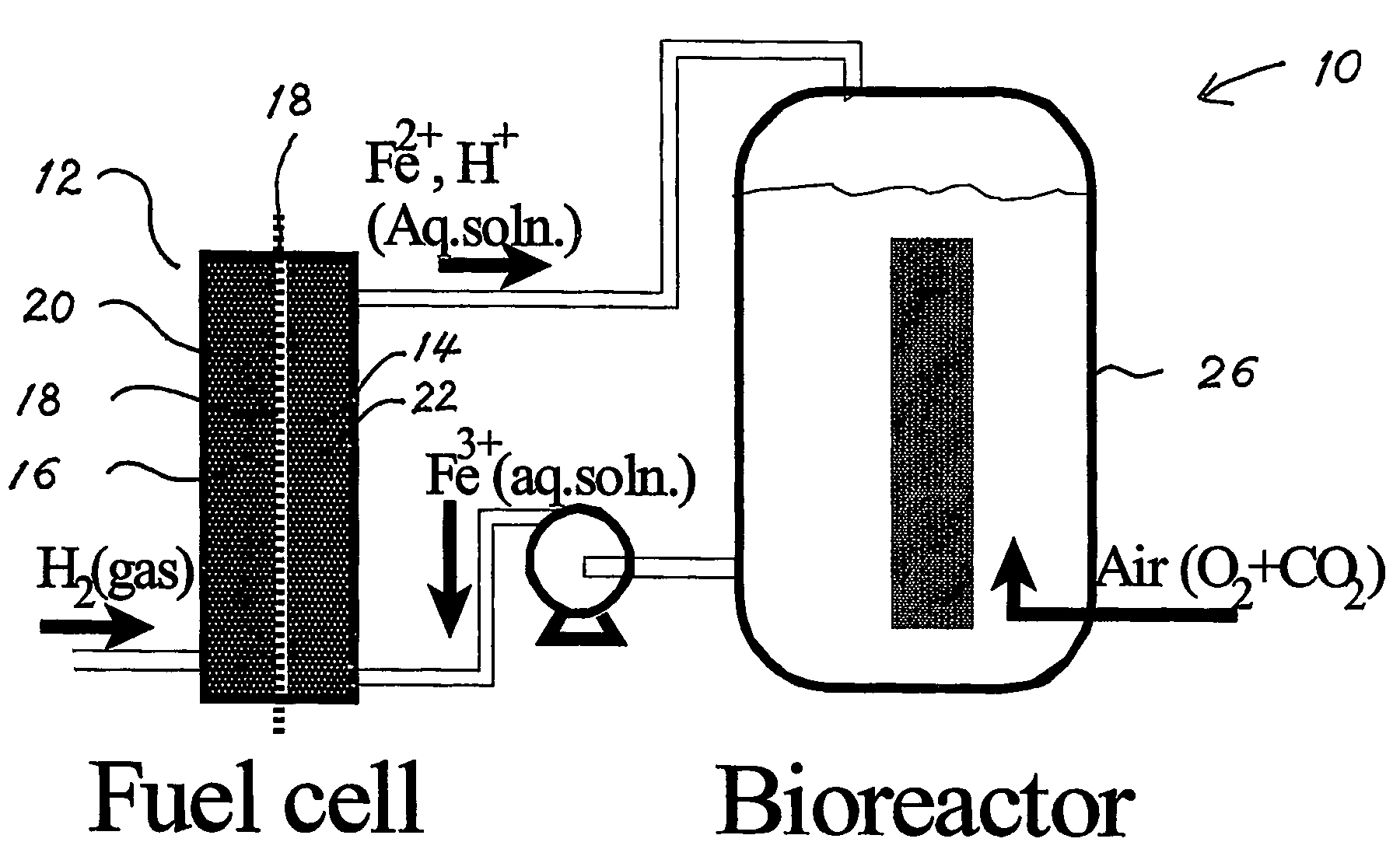
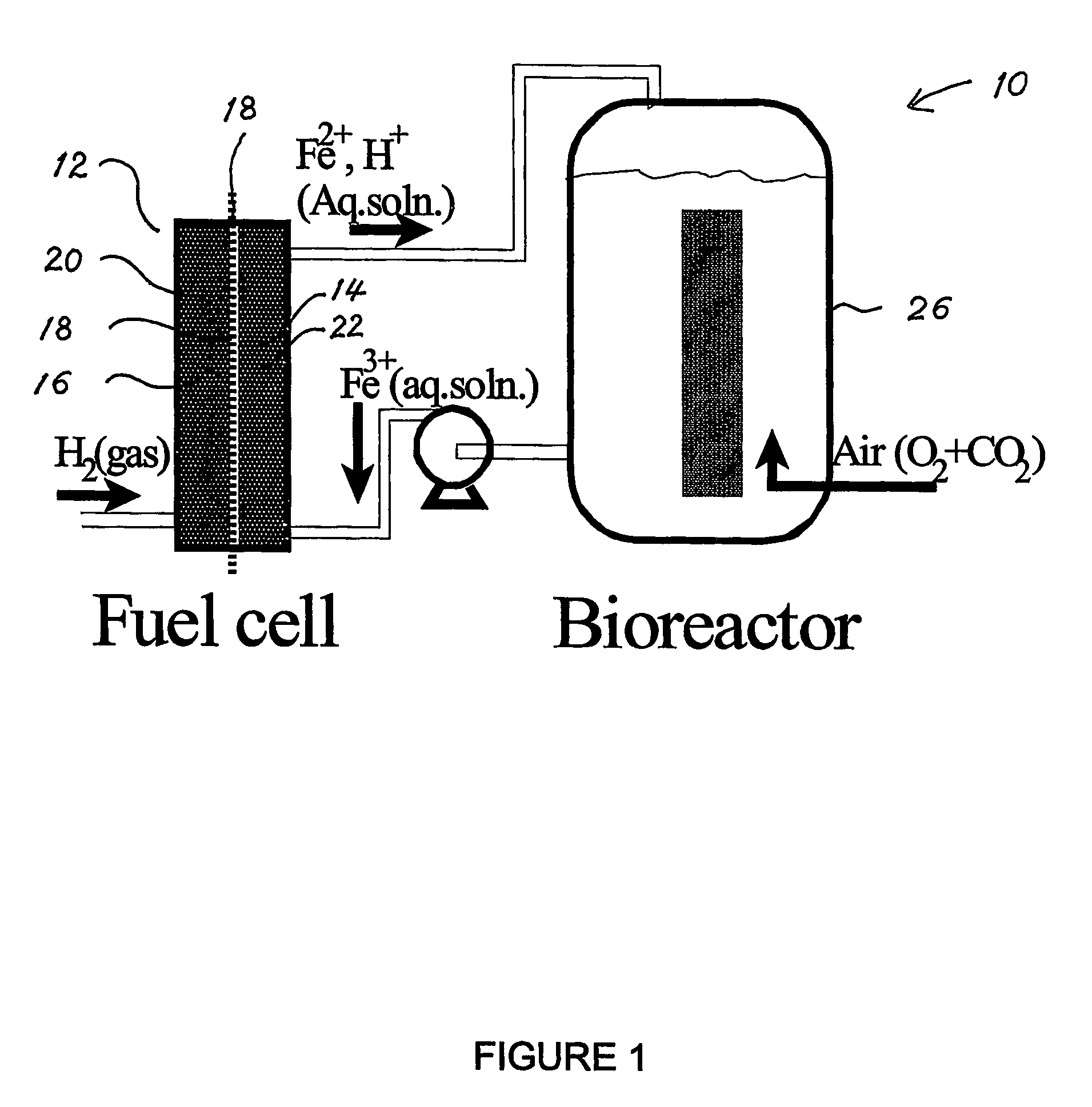
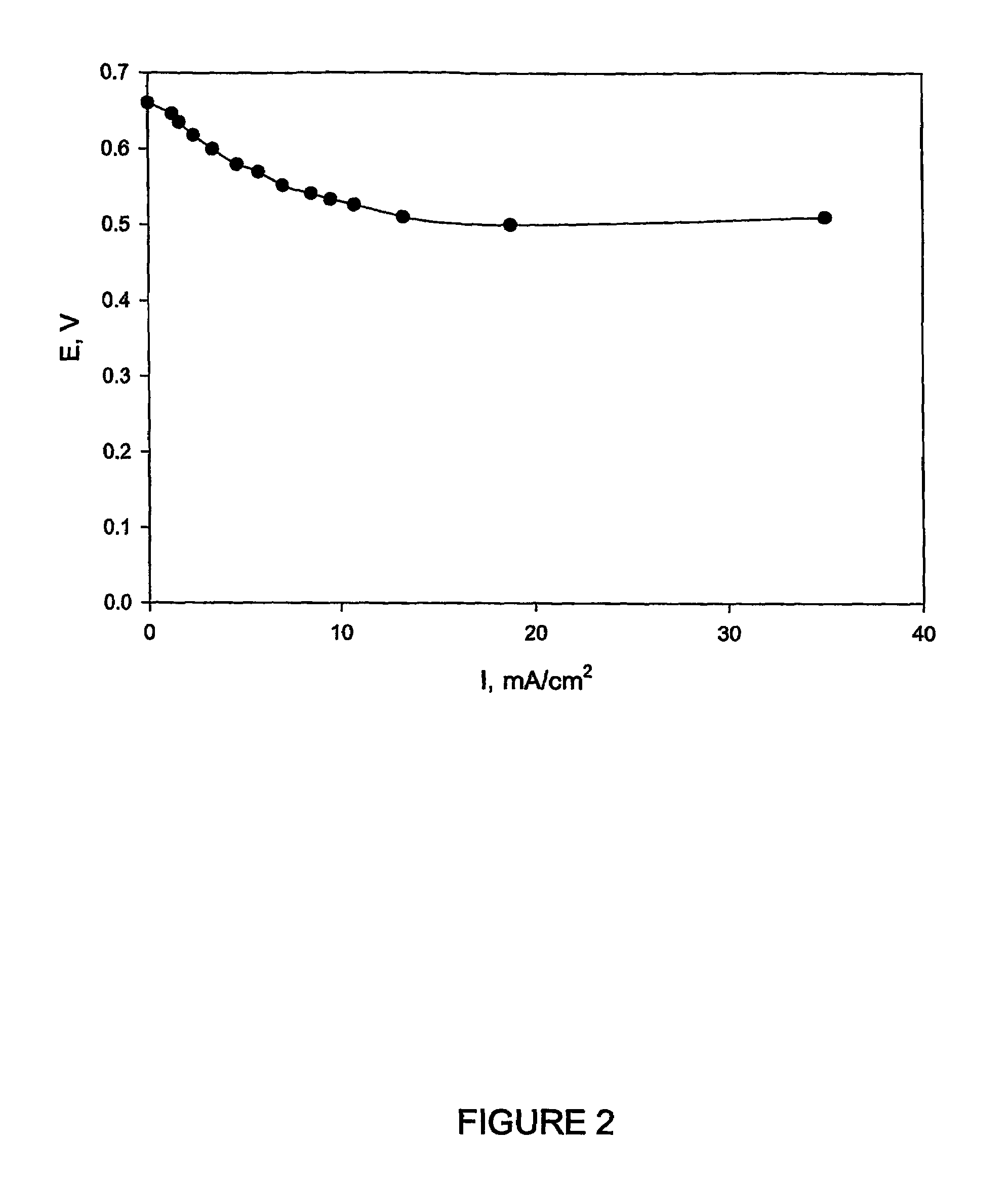
Fuel Cell Bioreactor
The present invention discloses a fuel cell bioreactor, based on the microbial regeneration of the oxidant, ferric ions and on the cathodic reduction of ferric to ferrous ions, coupled with the microbial regeneration of ferric ions by the oxidation of ferrous ions, with fuel (such as hydrogen) oxidation on the anode. The microbial regeneration of ferric ions is achieved by iron-oxidizing microorganisms such as Leptospirillum. Electrical generation is coupled with the consumption of carbon dioxide from atmosphere and its transformation into microbial cells, which can be used as a single-cell protein.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Method for preparing functional microbial preparation from lactic acid bacillus and yeast
InactiveCN101715877AGuaranteed high growthGuaranteed retentionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention relates to a method for preparing a functional microbial preparation from lactic acid bacillus and yeast, which is characterized in that: liquid of beneficial strains is adopted for culture; cell walls of the strains are collected centrifugally; a strain group is subjected to solid amplification culture; and a culture is added with the collected cell walls rich in polysaccharide. The method has the advantages that: high-concentration lactobacillus in the product can obviously improve the digestion and absorption of bred animals, and the generated metabolic products such as peptidogly can improve the immunity of the animals to pathogen; the high-concentration yeast in the product can improve rich single cell proteins required by the growth of the animals, and simultaneously the yeast cells are subjected to full wall breaking, and release a great amount of beta-1,3-glucan so as to obviously improve the immunity to Gram positive bacteria and Gram negative bacteria; and grain crops and common feeds are adopted as main raw materials for a culture medium, the production cost is reduced, and the method is easy to promote in animal breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENCHUANG BIOTECH RES INST
Compound enzyme for producing reducing sugar by degrading maize straws
InactiveCN101532004AHigh industrial application valueHigh glucoseHydrolasesFermentationPectinaseHigh energy
The invention provides a compound enzyme for producing reducing sugar by degrading maize straws. The compound enzyme is prepared from pectase, cellulose, hemicellulase, ligninolytic enzyme, amylase, prolease, lipase and chitosanase. Compared with the prior art, 1) the yield of the reducing sugar by degrading the maize straws has high yield, and the gross amount of the reducing sugar of straws per gram reaches over 480 mg, so the compound enzyme has wide application prospect in the fuel alcohol industry; 2) compared with sugar preparation by acid process, severe acid pollution is prevented to facilitate subsequent fermentation; and 3) compared with monomer cellulose or simple compound enzyme, the pretreatment of steam explosion with high energy consumption is not required, and the amount of the reducing sugar is increased by over 1 time; meanwhile, glucose and xylose in a degradation product have high content, side products are few so as to contribute to subsequent fermentation, the industrial application value of the maize straws is improved, and the compound enzyme can be applied to production of single cell protein and fuel alcohol.
Owner:ENZYME ENG INST SHAANXI PROVINCE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing single cell protein (SCP) feedstuff by using waste slag of citrus
InactiveCN101129159AFast growthImprove reproductive abilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSporeSlag
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of single cell protein (SCP) fodder through waste citrus slag, which comprises the following steps: culturing aspergillus niger at 28-32 deg. c for 4-6d; making the suspension to test the spore number to 107 -109 / mL during microscopy; culturing yeast at 25-32 deg. c for 1-2d; testing the number of yeast cell suspension at 108-1010 / mL; building up with number rate at 1: 1-1: 20; adding 106-108 / g fermenting material into waste modulated citrus slag; setting the bulk quality of suspension and fermenting material at 5-15%; switching the suspension into non-sterile material at 28-32 deg. c to stew and culture; stirring every 24h; fermenting 2-4d; fetching the material to place at 45-55 deg. c to dry; grinding; obtaining the product with little energy consumption, short period and low cost. The invention improves the protein content not less than 20% and cellulose degrading rate not less than 5%, which has good fodder taste without any pollution.
Owner:SICHUAN ACAD OF FOOD & FERMENTATION INDS
Comprehensive application method of salicornia bigelovii
The invention relates to a comprehensive application of salicornia bigelovii. The salicornia bigelovii comprises fresh vegetables and tender stems of plants; active substances are extracted after the salicornia bigelovii is pulped or dried and crushed; the active substances comprise components such as polysaccharide, ferulic acid, general flavone and the like; the residues of salicornia bigelovii after the active substances are extracted are inoculated with food-security microorganism aureobasidium pullulans for fermentation so as to produce fermented products rich in single-cell protein (SCP) and viscous pullulan which has been allowed by the FDA (food and drug administration) in Japan to be used as a food additive, the pullulan produced by self fermentation is utilized as a binding agent, infrared and microwave technologies are adopted to dewater, dry and form fermentation mud, and the fermented products are prepared into instant vegetable paper with rich nutrition, so that the variety of leisure foods is richened and the high-additional-value comprehensive utilization system of the salicornia bigelovii is constructed.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Single cell protein fodder and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN1449673AWide variety of sourcesLow priceFungiFood processingBiotechnologySingle-cell protein
The present invention relates to a kind of single cell protein feed and its production process. Its technical scheme is characterized by that it uses grain or by-product produced by milling engineering as solid culture medium, adds the corn steep liquor and lysine waste liquor, uses any one of zymophyte, candida, distillers' yeast, torula yeast and baidy enzyme or their any combination to make inoculation. Said invention is extensive in raw material source, and its cost is low, and the gross protein value of said feed is up to 35-55%, and it is easily absorbed by livestock and fowl.
Owner:JILIN HUANYU FODDER
Microbial agent for treating heavy metal polluted soil, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN106424125AImprove toleranceKeep aliveFungiContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismMicrobial agent
The present invention relates to a microbial agent for treating heavy metal polluted soil, a preparation method and applications thereof. The microbial agent comprises the following raw materials: rice husk, pig manure, chicken manure, soybean powder, single cell protein, a Mortierella alpina fermentation broth, a Trichoderma asperellum fermentation broth, and a Mucor circinelloides fermentation broth. According to the present invention, the microbial agent prepared by mixing Mortierella alpina, Trichoderma asperellum and Mucor circinelloides according to a certain ratio is firstly used, can be used in the complex and changing environment, and can provide effects in the poor soil environment, wherein the functional microbes provide high tolerance to heavy metals, and can maintain activity and perform efficient repair in the heavily heavy metal polluted soil.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
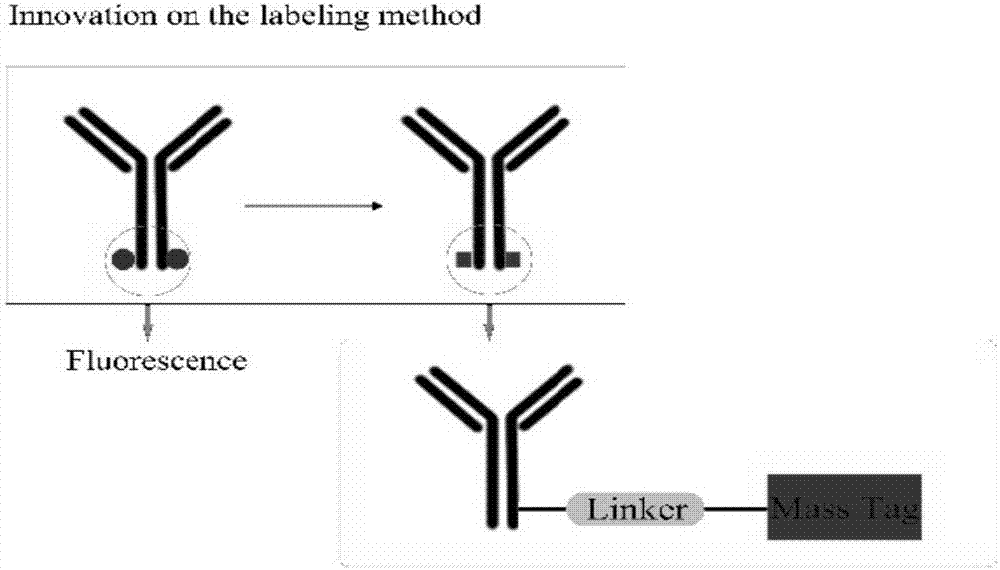
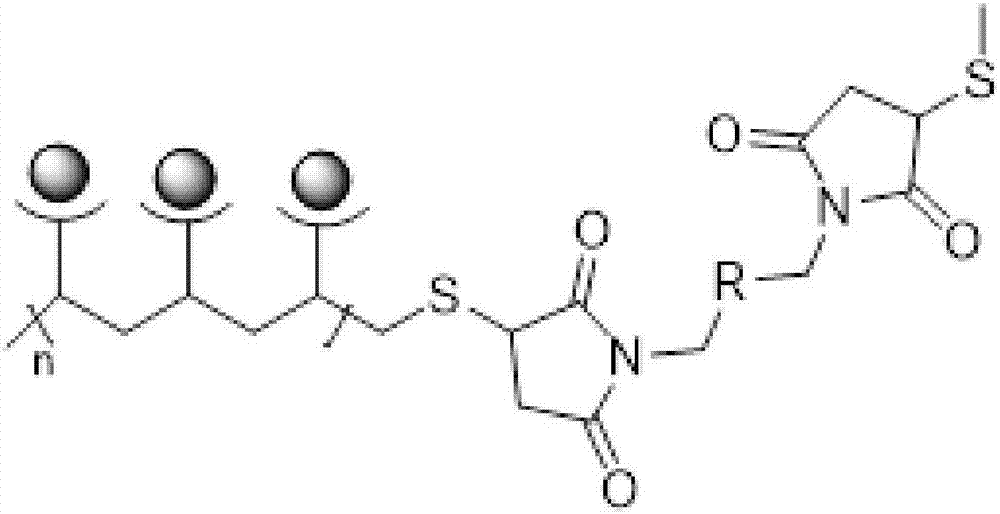
Single-cell protein detecting method for flow type combination ICP-MS on basis of metal isotope labels
InactiveCN107255722AImprove resolutionInnovativeIndividual particle analysisBiological testingMass spectrometryIsotope
The invention discloses a single-cell protein detection method based on metal isotope labeling flow cytometry combined with ICP-MS, and belongs to the technical field of flow cytometry single-cell protein detection. The present invention uses metal element tags to mark antibodies or dyes, which fundamentally solves the problem of fluorescent cross-color, uses the principle of mass spectrometry to perform multi-parameter quantitative detection of single cells, realizes the simultaneous measurement of dozens of parameters, and is applied to single-cell proteomics academic analysis. The fusion of the two experimental platforms of mass spectrometry and flow cytometry not only inherits the high-speed analysis characteristics of traditional flow cytometry, but also has the high-resolution capability of mass spectrometry detection. The metal tag elements that can be used in the present invention are rich in types, and the content in cells is extremely low. At the same time, metal elements are covalently coupled to antibodies through polychelates. The non-specific binding capacity of the product is extremely low, so the background of the signal is extremely low.
Owner:马鞍山普梅森细胞检测技术有限公司
Method for producing single-cell protein feed by utilizing bean product waste water
The invention provides a method for producing a single-cell protein feed by utilizing bean product waste water. A modern microorganism fermentation technology is adopted, and through the steps of high-speed strain liquid culture, deep layer liquid culture of the bean product waste water and the like, a great amount of yellow serofluid, bean soaking water, soybean whey waste water and the like generated in bean product production by utilizing a plurality of target microorganisms of mycete, fungi and bacteria are subjected to a deep layer liquid fermentation technology to produce a protein feed rich in single-cell protein and various biological metabolism enzymes, so that the requirement of increasing protein feeds can be met, and the method for producing the single-cell protein feed by utilizing bean product waste water is a novel technology which turns waste into wealth, and reduces the environment pollution caused by food processing waste water greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI QINGMEI GREEN FOOD
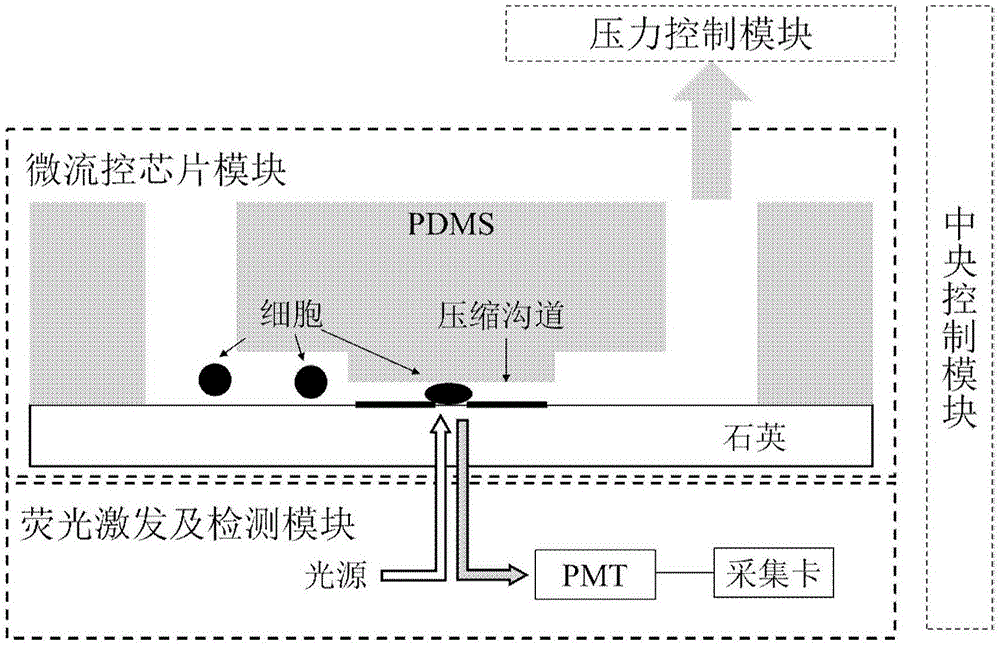
Single cell protein detection system and application thereof
ActiveCN106290279ARealize high-throughput (high-speed) quantitative acquisitionReliable methodLaboratory glasswaresFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh fluxFluorescence
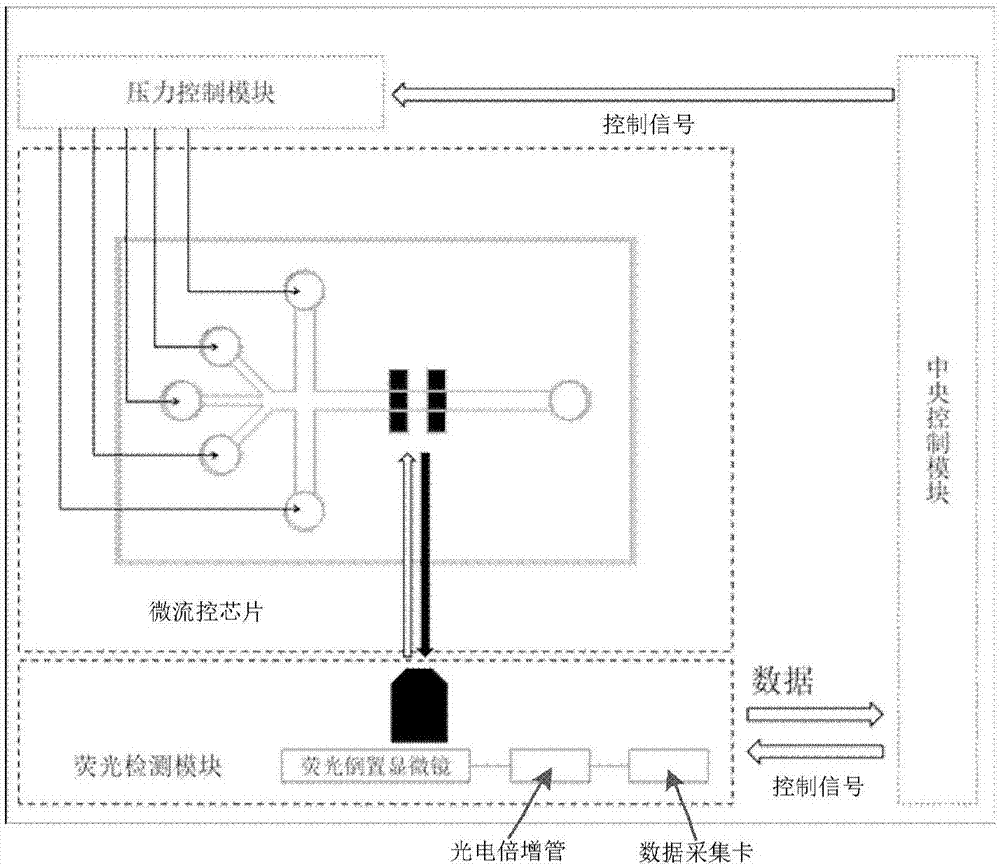
The invention relates to a single cell protein detection system, which comprises a micro-fluidic chip module, a fluorescence excitation and detection module and a pressure control module, wherein the micro-fluidic chip module comprises a transparent substrate and a compression passage formed on the substrate; the compression passage is configured to a state that the cross section area is smaller than the cross section area of cells to be tested, so that the cells deform under the pressure effect and pass through the compression passage in an extruding way; the fluorescence excitation and detection module is used for performing fluorescence detection on the cells entering the compression passage; the pressure control module is used for providing the pressure so that the cells deform and pass through the compression passage. The invention also provides a method for performing detection by using the system. The method provided by the invention can be used for quantificationally detecting the single cell protein at high flux.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bio-fuel cell system
The present invention discloses a new type of bio-fuel cell, based on the microbial regeneration of the oxidant, ferric ions. The bio-fuel cell is based on the cathodic reduction of ferric to ferrous ions, coupled with the microbial regeneration of ferric ions by the oxidation of ferrous ions, at a pH less than about 1.0, with fuel (such as hydrogen) oxidation on the anode electrode. The microbial regeneration of ferric ions is achieved by microorganisms such as Leptospirillum ferriphilum. Electrical generation is coupled with the consumption of carbon dioxide from atmosphere and its transformation into microbial cells, which can be used as a single-cell protein.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Paracoccus denitrificans and method for disposing single-cell protein through high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater
ActiveCN107760622AUnique metabolic functionAchieve fixationBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesSynechococcusMicroorganism
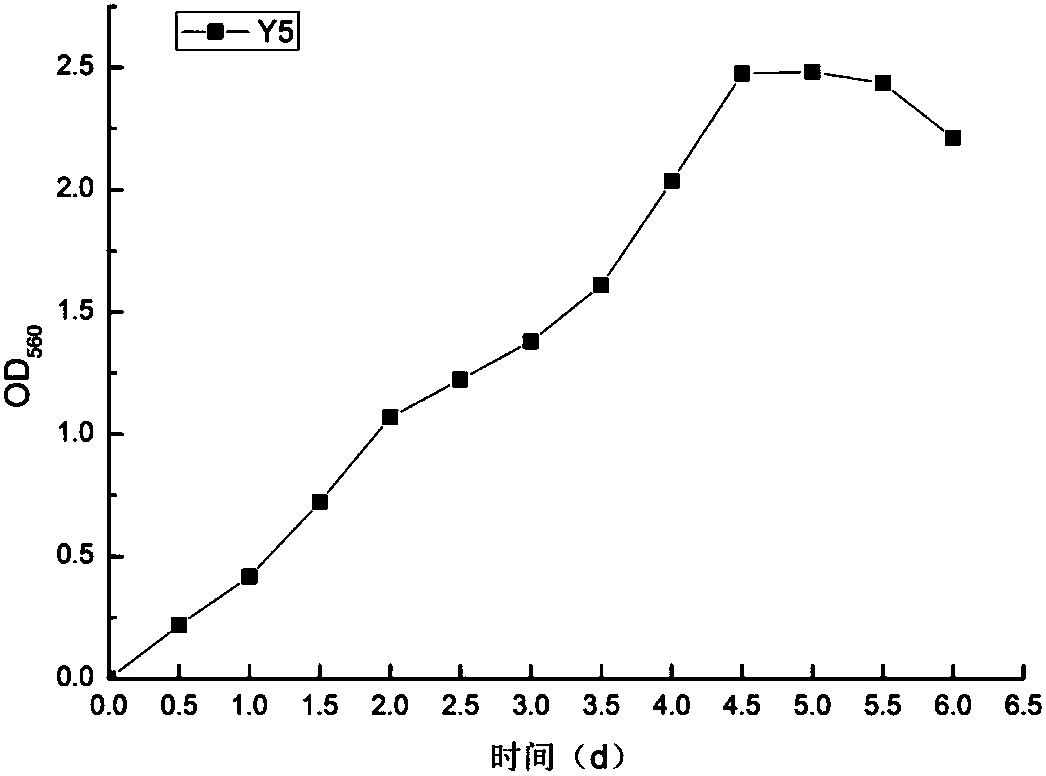
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and environment protection, and aims at providing paracoccus denitrificans and a method for disposing single-cell protein through high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater. The adopted technical scheme is as follows: the invention provides hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria, namely paracoccus denitrificans Y5, which is collected in General Microorganisms Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on May 12, 2017 (address: Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, No.1 yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, 100101), with preservation number CGMCC No. 14118. The paracoccus denitrificans Y5 provided by the invention can remove COD and ammonia nitrogen in high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater, fix production of single-cell protein (SCP) by CO2, and can remove stink of wastewater.
Owner:广州清源生物科技有限公司
Pichia pastoris for efficiently converting methanol to produce single cell protein and application of pichia pastoris
ActiveCN103045494AShorten fermentation timeIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesMycoproteinSingle-cell protein
The invention relates to pichia pastoris for efficiently converting methanol to produce single cell protein and an application of the pichia pastoris. The classification designation is pichia pastoris HGD-01. The pichia pastoris is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2012342. As the pichia pastoris strain is used for methanol protein production, the whole fermentation period is 70-84h, the fermentation time is shortened, and the yield of a single fermentation tank is increased to 140kg of dry weight of the mycoprotein per ton of fermentation liquid.
Owner:义马煤业集团煤生化高科技工程有限公司
Sample pretreatment method based on flow combination ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) single cell protein detection
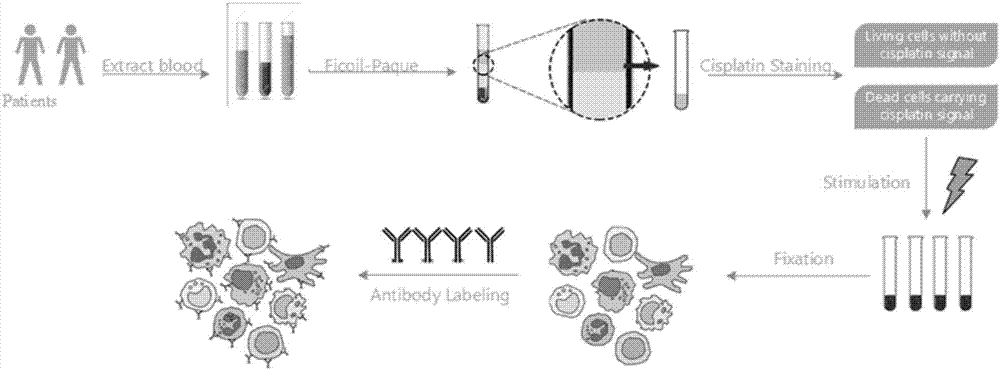
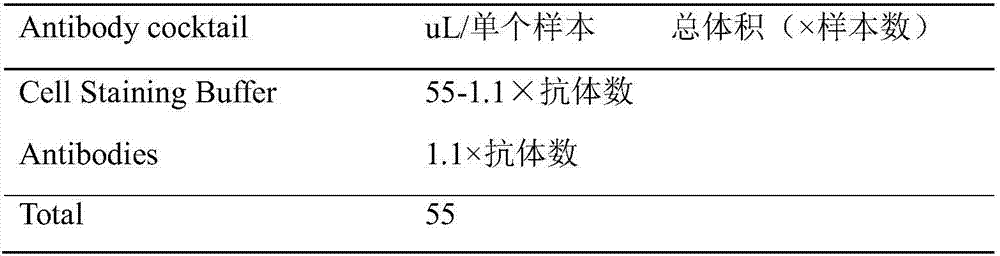
ActiveCN107314965AImpact AnalysisImpact statementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIndividual particle analysisPretreatment methodPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a sample pretreatment method based on flow combination ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) single cell protein detection, and belongs to the technical field of sample pretreatment of flow cytometry. The sample pretreatment method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting and transporting a whole blood sample; (2) performing PBMC (Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell) cell separation; (3) performing cell active dyeing; (4) performing cell stimulation; (5) performing cell immobilization; (6) performing surface antibody dyeing; (7) performing intracellular phosphorylated protein dyeing; (8) performing single cell labeling, and the like. With the combination of a metal element labeled antibody with cell surface antigen, labeled cells are mixed with beads as internal reference for standardization, dead cells and living cells are distinguished in the pretreatment process, then the situation that the testing result analysis and description are affected by too many dead cells is avoided, single cells are distinguished from cell dimmers, cell trimers or even cell multimers, and flow combination ICP-MS single cell protein detection requirements can be very well met.
Owner:马鞍山普梅森医学检验实验室有限公司
Method of extracting proteins from a cell
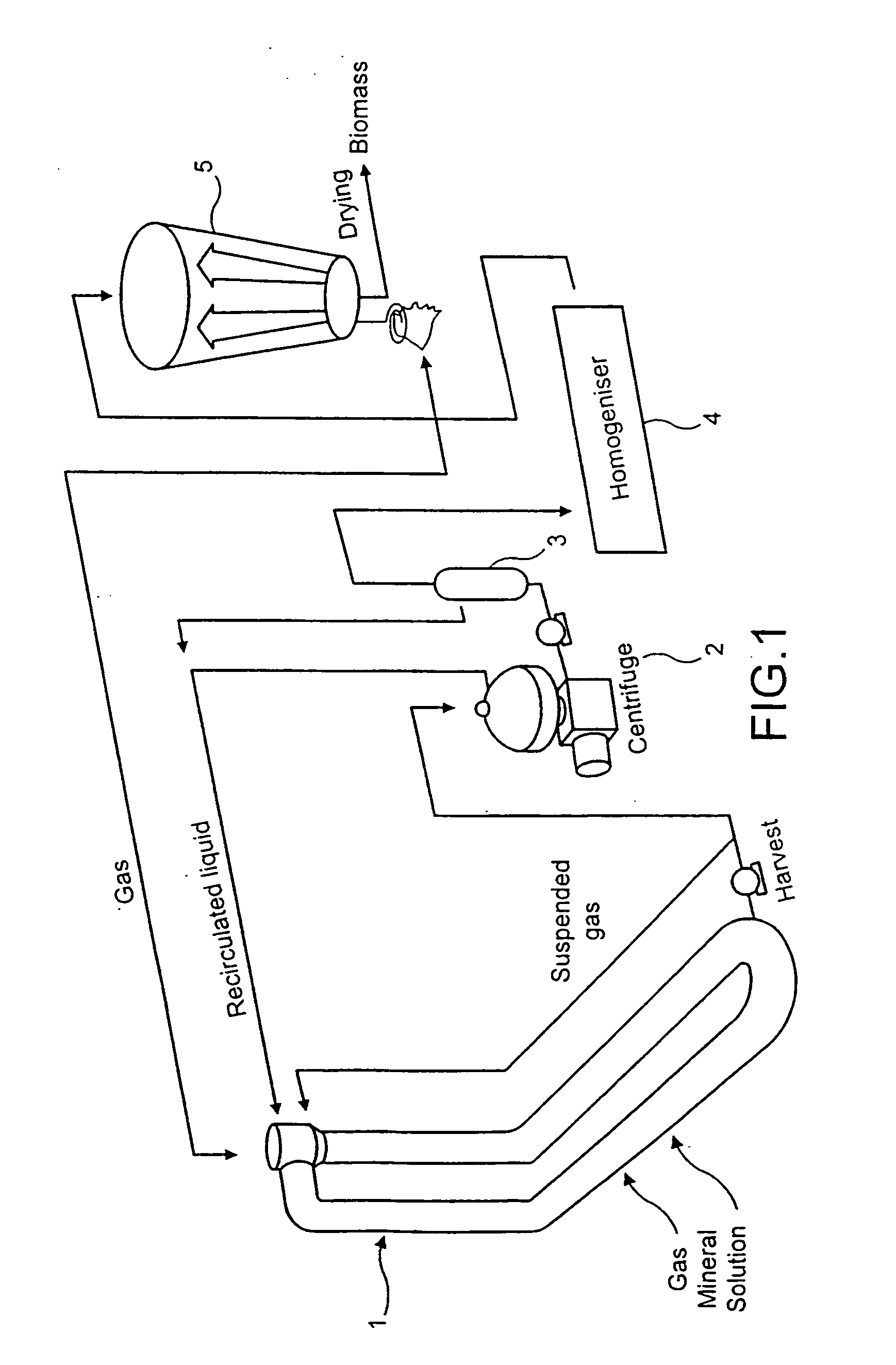
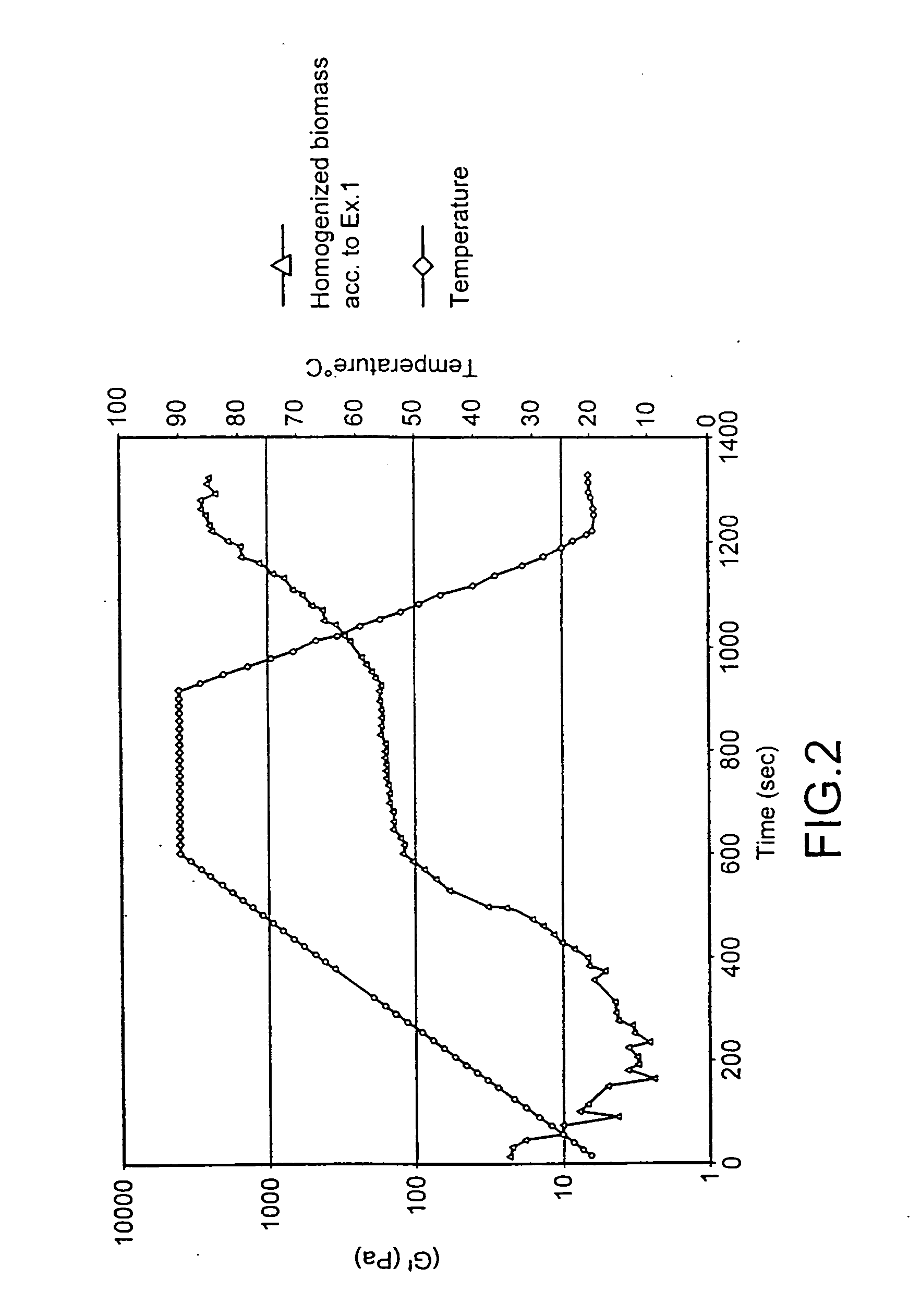
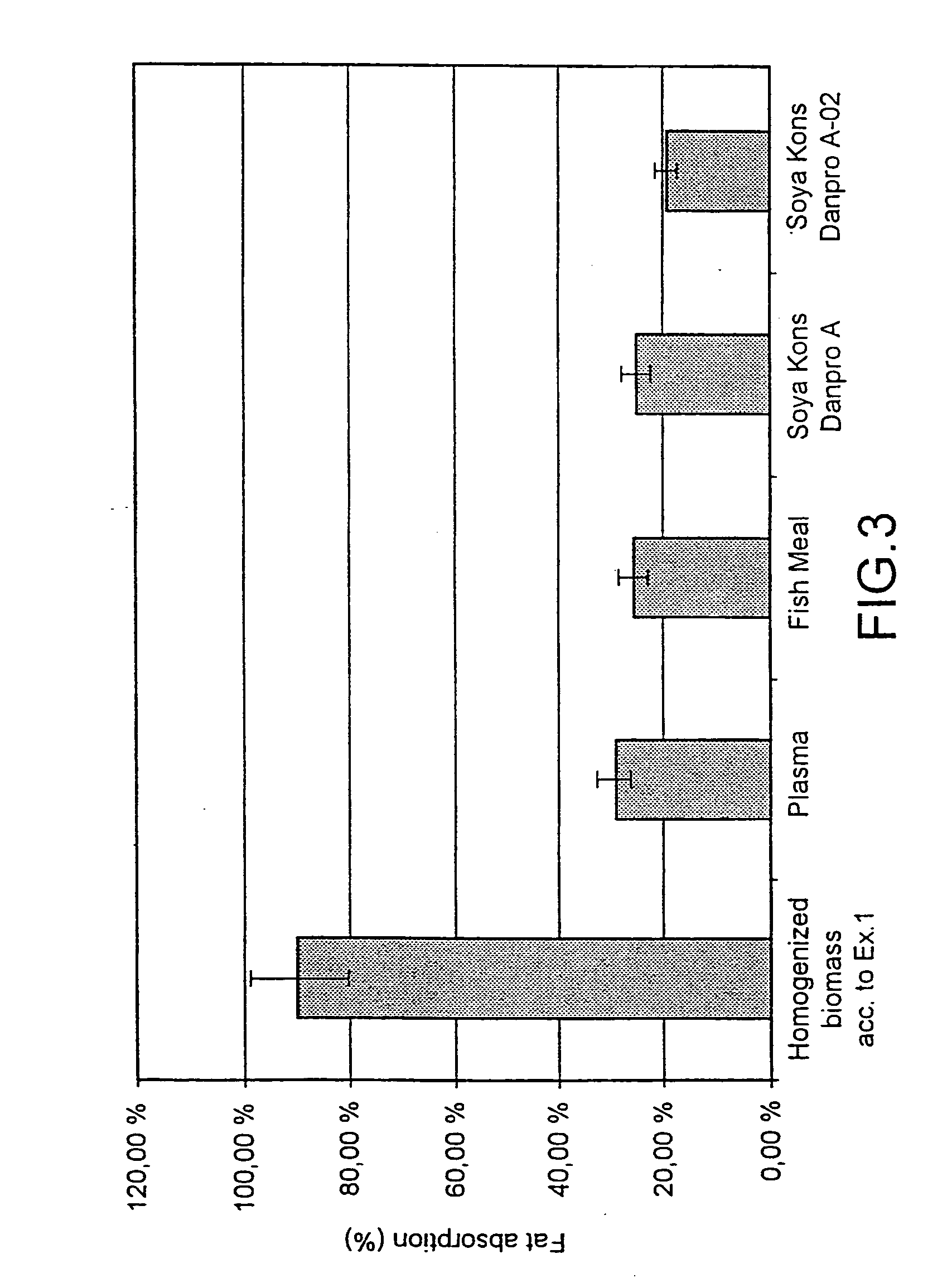
InactiveUS20070003602A1Improve propertiesImprove functional propertiesBacteriaFood homogenisationSlurrySingle-cell protein
The present invention provides a process for imparting improved functional properties to a single-cell protein material, said process comprising the step of homogenizing an aqueous slurry of the single-cell protein, e.g, a single-cell protein material derived from fermentation on natural gas. The resulting homogenized protein material has excellent functional properties and finds particular use in the preparation of food products, for example as a gelling agent or emulsifier.
Owner:EQUINOR ENERGY AS
Processing technology of single-cell protein from distilled spirit lees
InactiveCN104171265AIncrease supplyIncrease productionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a processing technology of a single-cell protein from distilled spirit lees and relates to the technical field of animal nutrition and microbial fermentation. A finished product is obtained by performing pretreatment on the distilled spirit lees, then reasonably combining the lees with various ingredients according to a formula of a solid-state culture medium, fully mixing, then inoculating, fermenting for 48h, then drying and finally packaging. The processing technology comprises the steps of pretreatment of the lees, preparation of the solid-state culture medium, inoculation, fermentation, drying, packaging and obtainment of the finished product. The pretreatment comprises the steps that the distilled spirit lees is aired till the water content is 55-65%, then 600-1000 units of glucoamylase is added in per 100g of the distilled spirit lees, and the pretreatment of the lees is performed for 1-2h under the conditions that the temperature is 50-60 DEG C and the pH is 4.0-5.2. The processing technology disclosed by the invention can develop the distilled spirit lees into a single-cell protein fodder by combining with a microbial fermentation technology on the basis of animal nutrition theory, thereby turning waste into treasure and exploring fodder resources; simultaneously, the processing technology disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of simple technology, low cost and no pollution.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for extracting ribonucleic acid and cell wall polysaccharides in single cell protein by using one-step method
InactiveCN101830998AHigh separation and extraction rateHigh puritySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationWater bathsDry weight
The invention discloses a method for extracting ribonucleic acid (RNA) and cell wall polysaccharides, in particular to a single cell protein prepared by using brewers' yeast. The method comprises the steps of: adding water with 10-30 percent of dry weight of the single cell protein and then fully mixing, freezing at a low speed, placing into an ultrasonic assisting water bath, repeatedly thawing and breaking cell walls; adding sodium chloride with weight ratio of 5-18 percent, rapidly cooling, and eccentrically separating to obtain supernate and cell wall polysaccharides precipitates; and washing the precipitates by using water and then drying to obtain dry products of the cell wall polysaccharides. The protein is precipitated at an isoelectric point PI4.2 in the supernate, the RNA is participated at an isoelectric point PI2.5, and the dry product of the RNA is obtained by the supernate. Because a mixture of amino acid is separated by adopting methods of repeatedly freezing and thawing for breaking the single cell protein and regulating the isoelectric points, the invention has the characteristics of high separation and extraction efficiency, high purity and simple and convenient method.
Owner:黄山市迎客松生物科技有限公司
Method for producing single-cell protein feed by means of fermentation of sweet potato residues
InactiveCN103271224AHigh in proteinPromote growthAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologySingle-cell protein
The invention discloses a method for producing single-cell protein feed by means of fermentation of sweet potato residues. The method comprises the following steps. (1) Activation and amplification culture of strains. Geotrichum candidum strains are activated by test-tube slant medium which is made from wort, agar and distilled water. Liquid strains are made by using a culture solution which is made from sweet potato slices, glucose and distilled water. (2) Material distribution and fermentation. Corn flour, urea, pectinase, cellulase and a certain amount of sterile water are added into fresh sweet potato residues and stirred. The liquid strains are then inoculated. The mixture are fermented for 20-120 h at the temperature of 25-30 DEG C, and dried and sterilized to obtain the single-cell protein feed. The single-cell protein feed has a protein content of 18-28% and is higher in protein content. The single-cell protein feed is nontoxic and harmless to human and animals. The single-cell protein feed can be used as feedstuffs of animals such as pigs, chickens or the like and has a wide market prospect.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
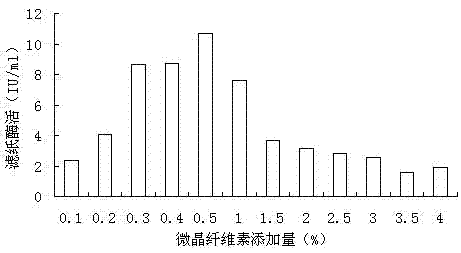
Trichodermaviride used for producing cellulose degrading enzyme and its application in urban landscaping waste degradation
InactiveCN102559508AImprove hydrolysis effectSolve energy problemsFungiSolid waste disposalCellulose compoundsDegradative enzyme
The invention belongs to microbe technical field, and especially relates to a Trichodermaviride, and the invention also relates to an application of Trichodermaviride. The Trichodermaviride strain capable of producing cellulase with high-yield is Trichodermaviride in Trichoderma, the code number is M20, and the Trichodermaviride is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 2nd, April, 2011, the preservation number is CGMCC No.4732. The strain of the invention can be grown in a medium which takes a plurality of cellulose compounds as a sole carbon source, the cellulose compounds comprise carboxymethylcellulose sodium, microcrystalline cellulose, corn straw, cob, deciduous leaf, turf grass and the like. The Trichodermaviride of the invention can secrete a plurality of cellulose hydrolases, can be used for processing urban landscaping waste, can acquire high reducing sugar in short time, the obtained reducing sugar can be used for producing single cell protein and can be used for producing fuel ethanol, and the Trichodermaviride possesses important meaning for solving a series of problems of energy shortage and environmental pollution at present.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com