Patents
Literature
429results about How to "Improve functional properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
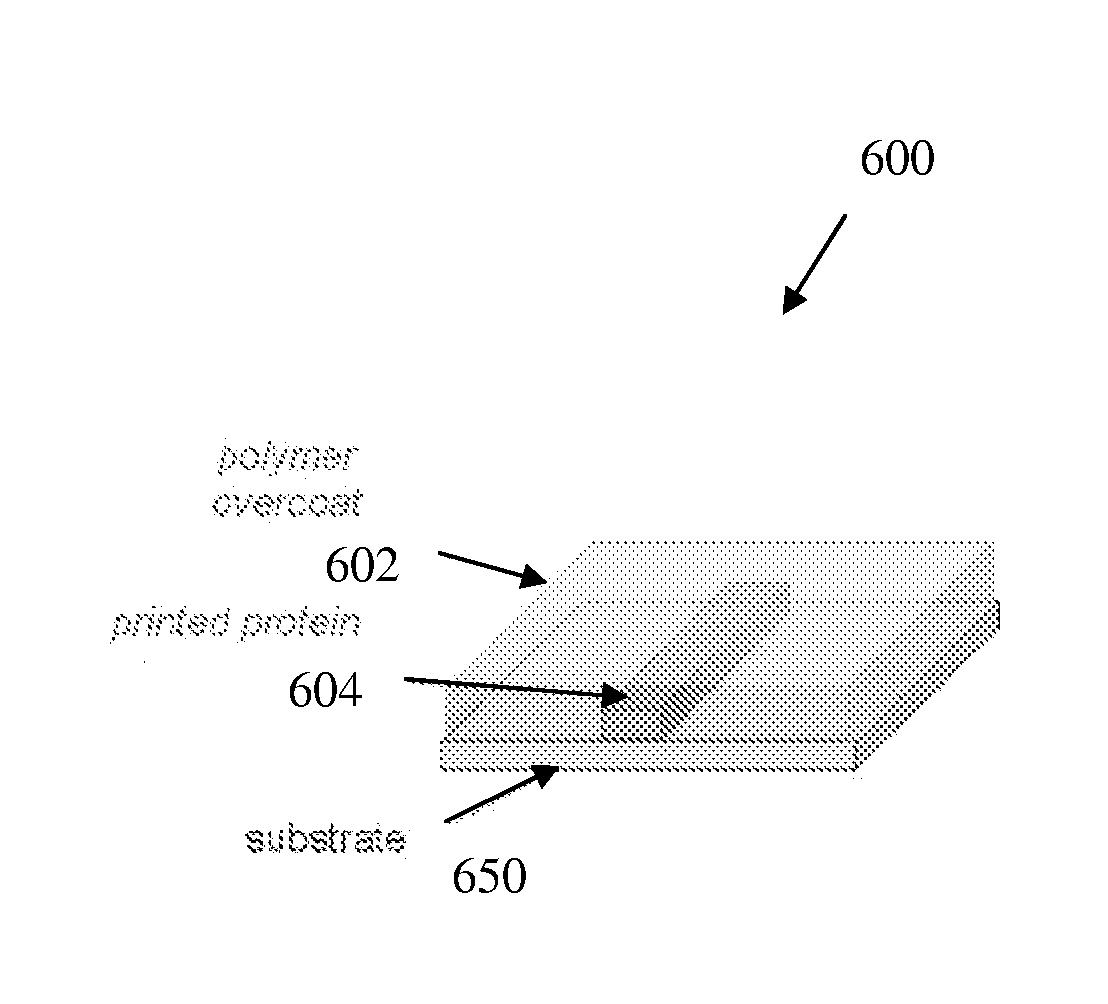
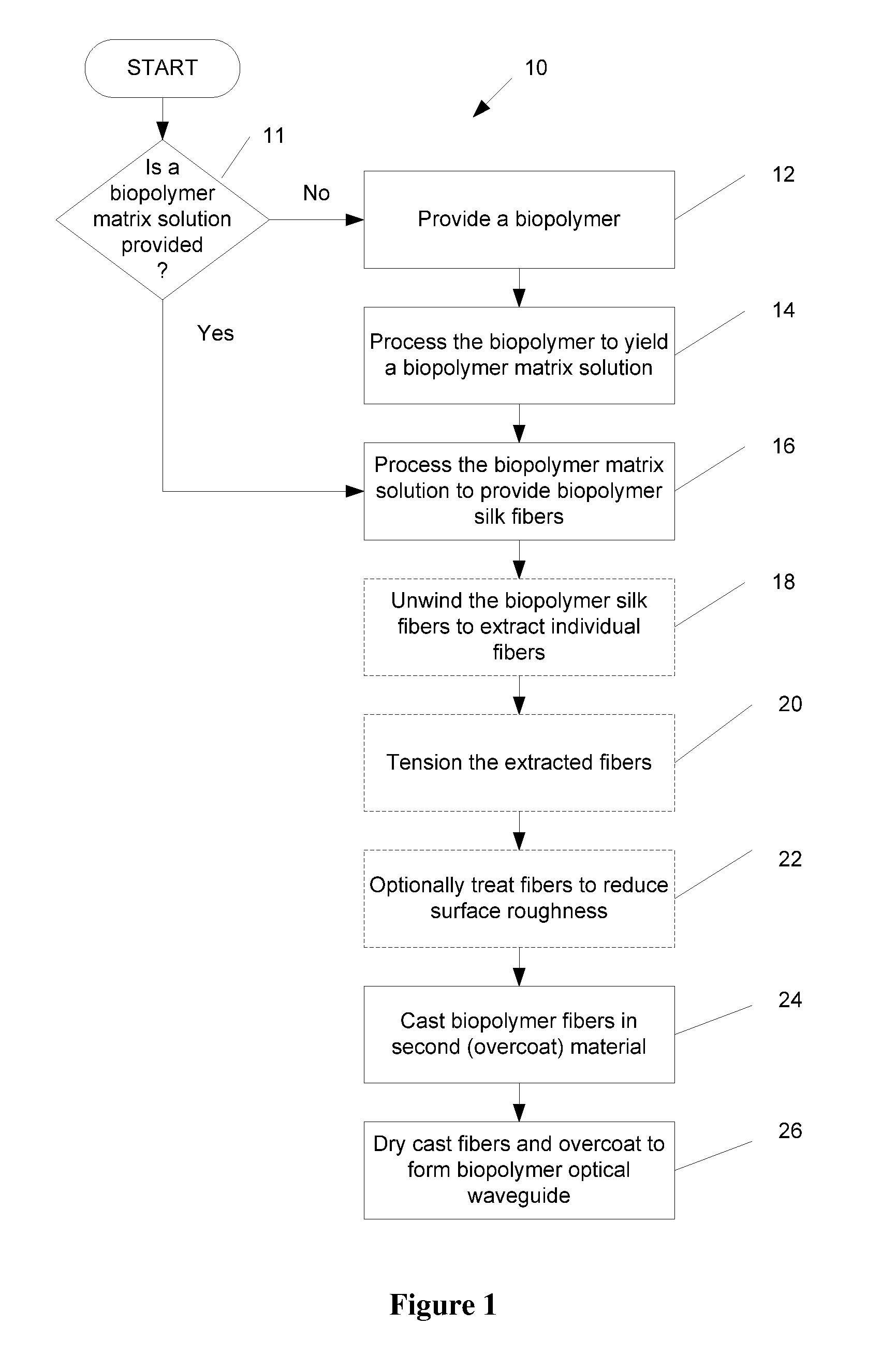
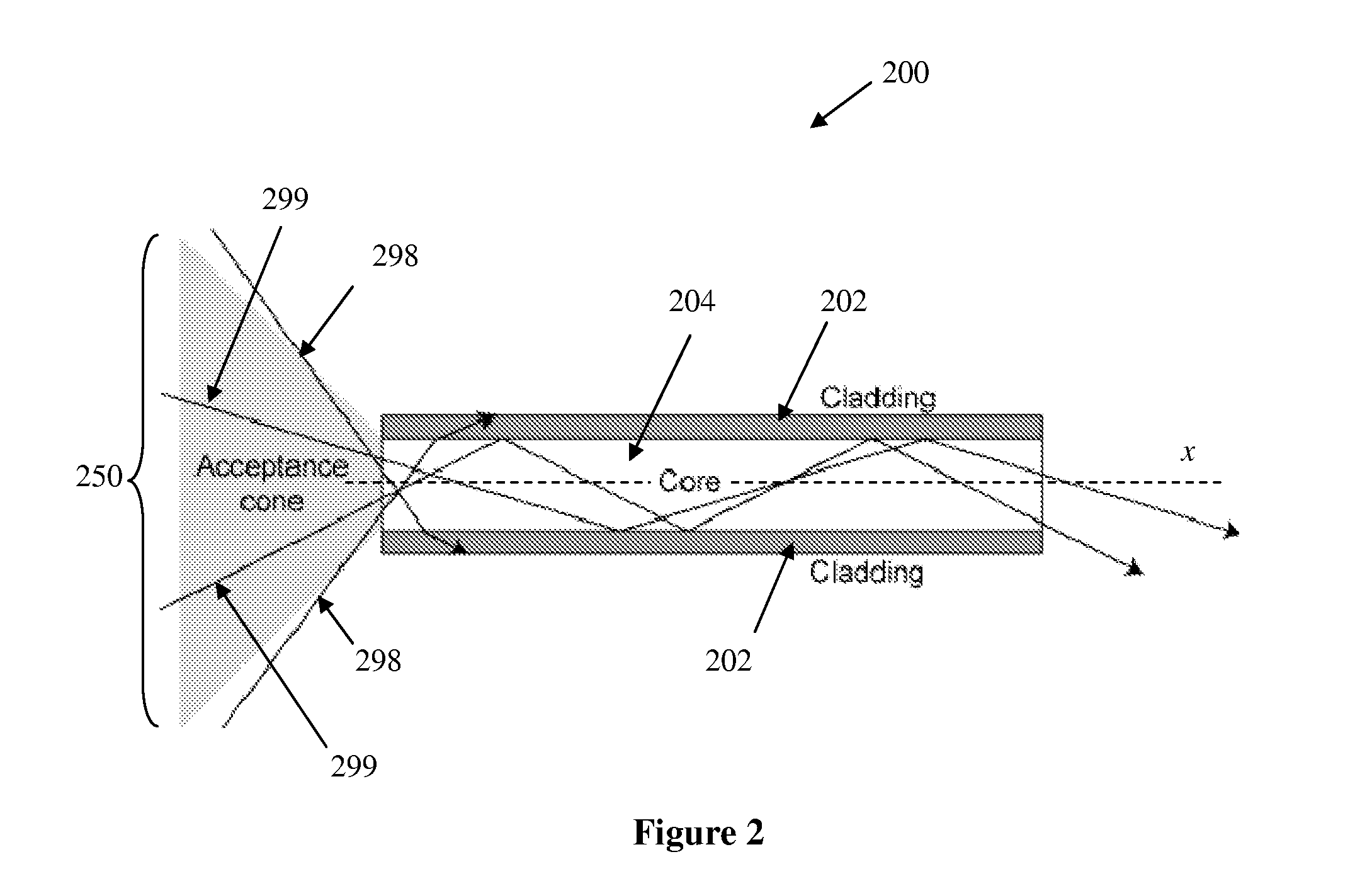
Biopolymer optical waveguide and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100063404A1Minimize negative impactImprove functional propertiesBiological material analysisMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentFiberBiopolymer
A method of manufacturing a biopolymer optical waveguide includes providing a biopolymer, unwinding the biopolymer progressively to extract individual biopolymer fibers, and putting the unwound fibers under tension. The tensioned fibers are then cast in a different polymer to form a biopolymer optical waveguide that guides light due to the difference in indices of refraction between the biopolymer and the different polymer. The optical fibers may be used in biomedical applications and can be inserted in the body as transmissive media. Printing techniques may be used to manufacture the biopolymer optical waveguides.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
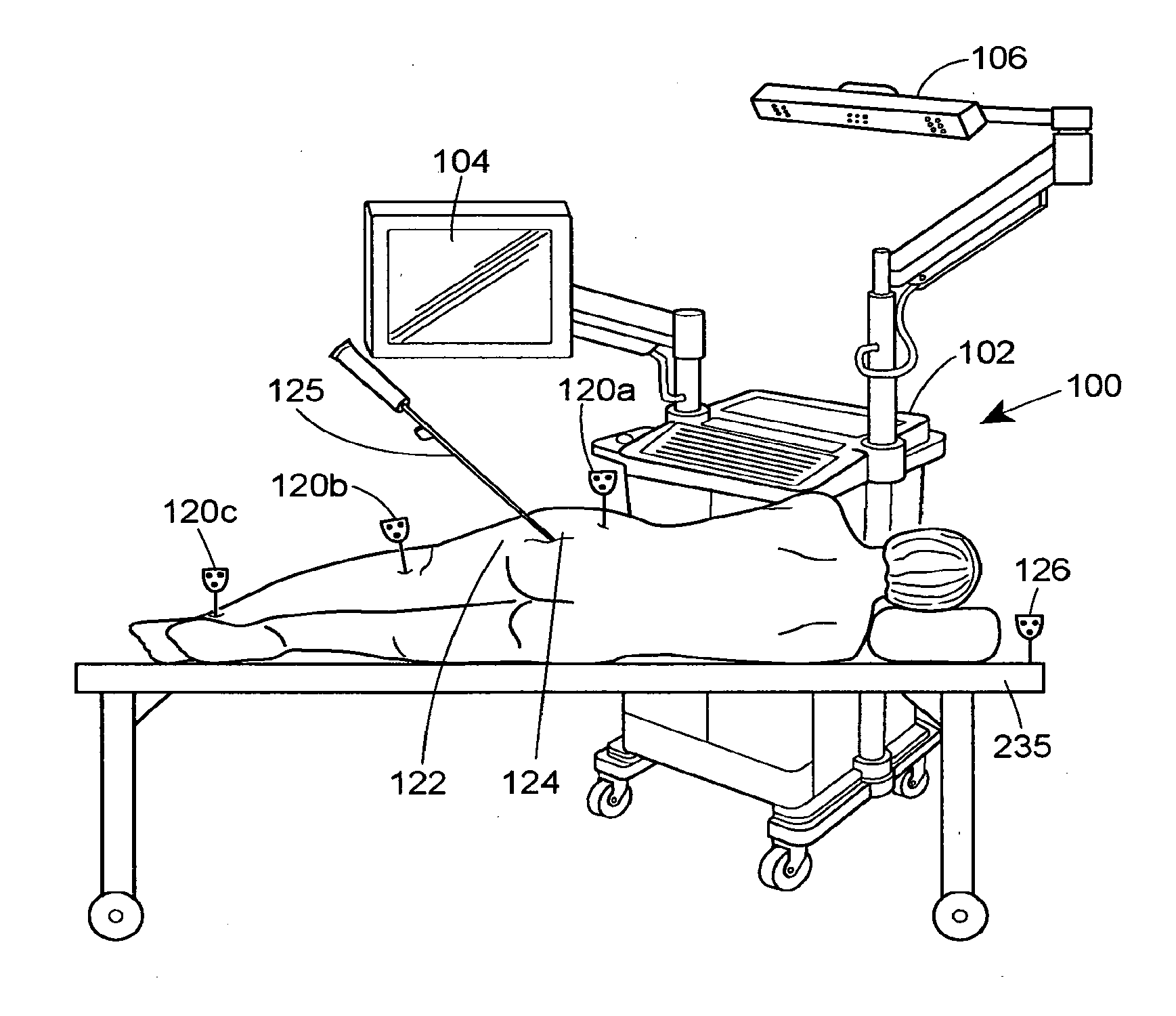
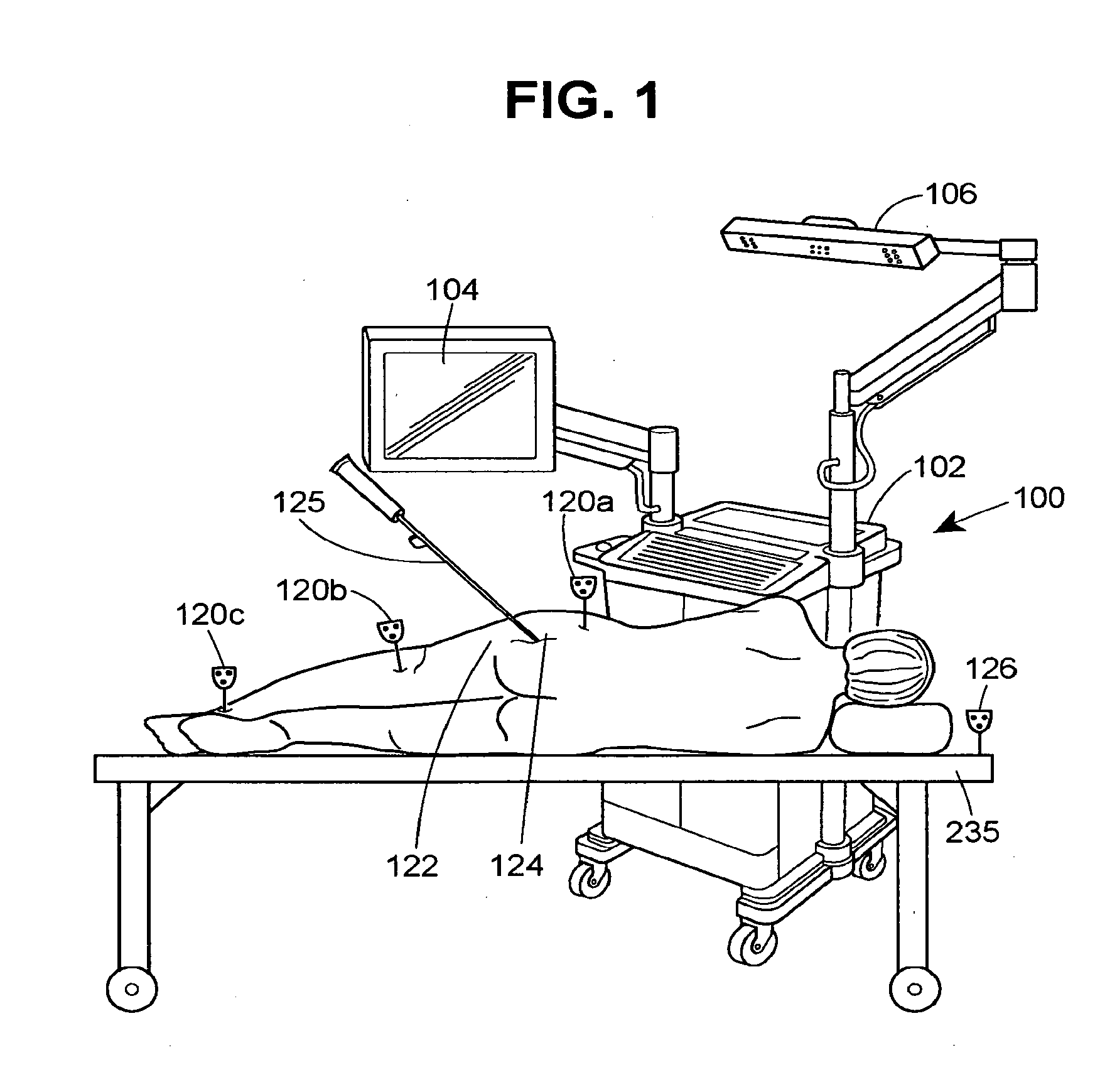
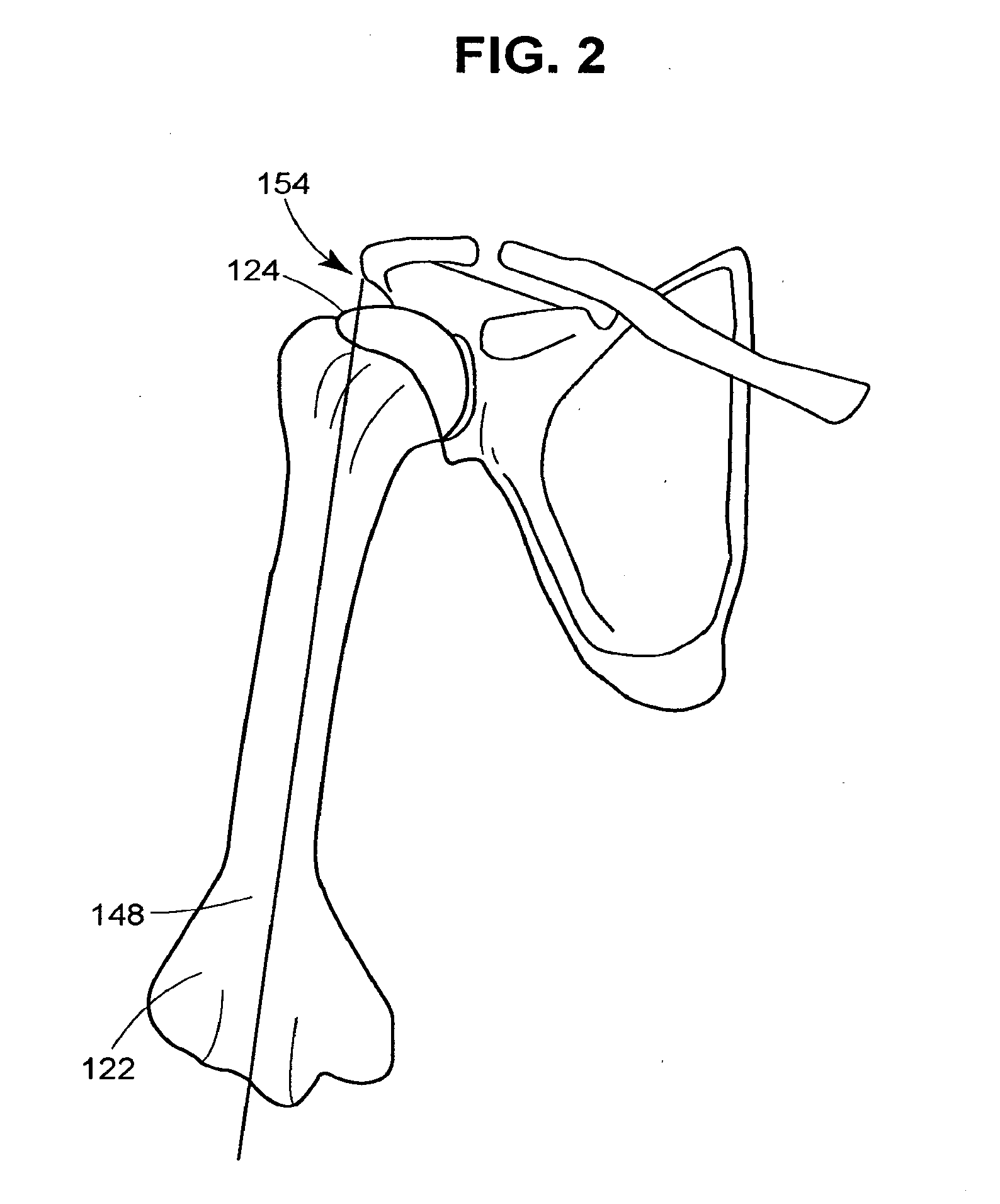
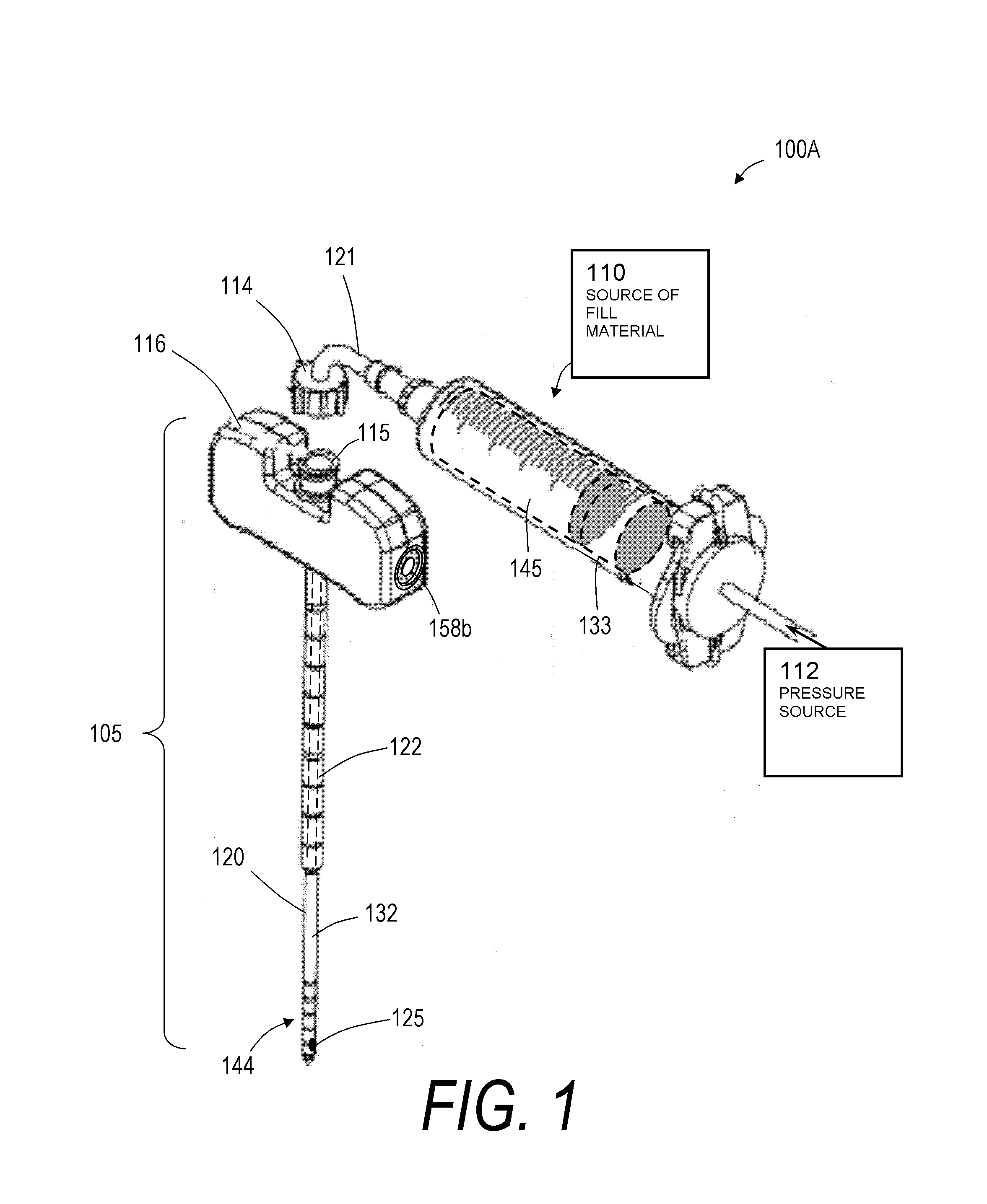
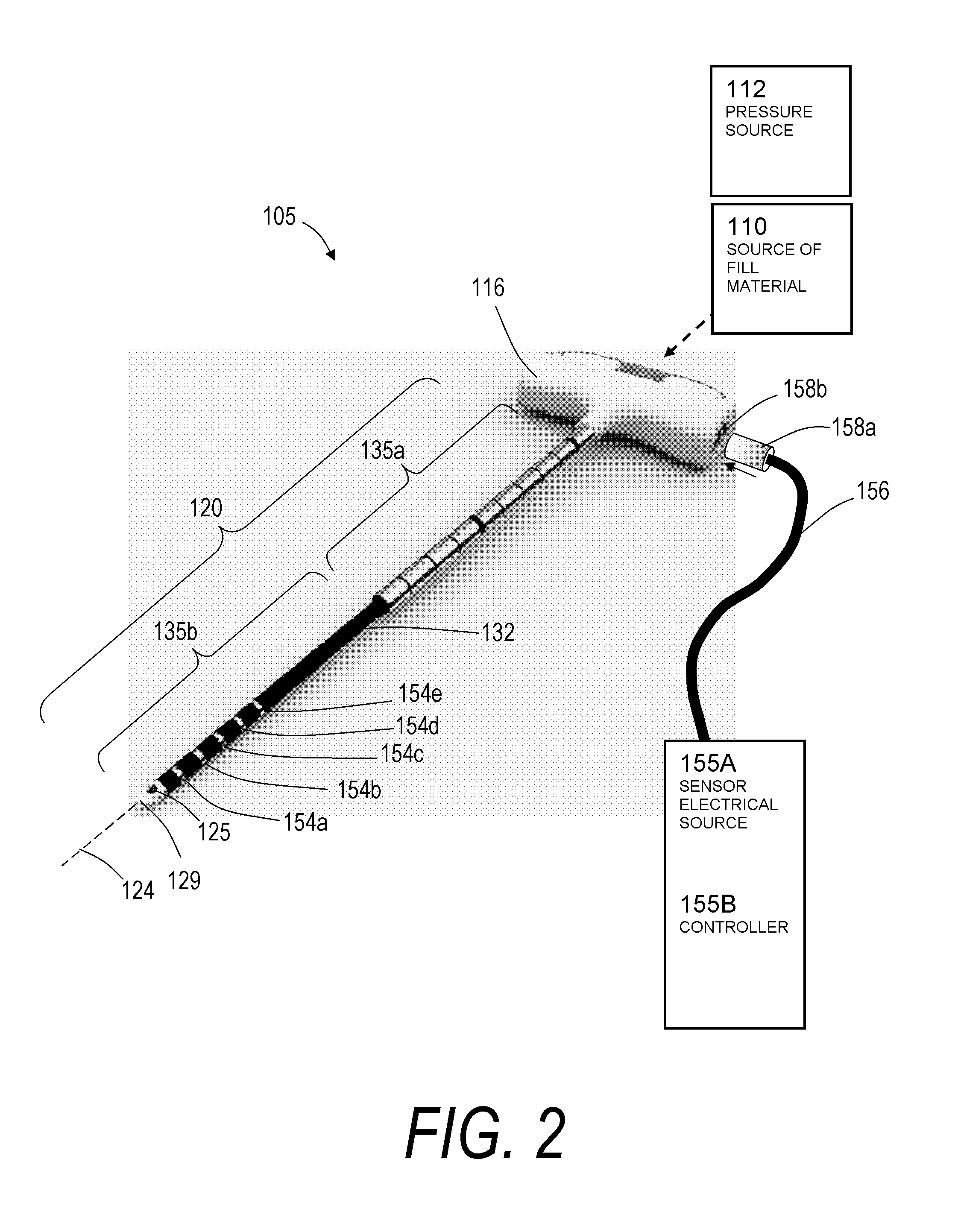
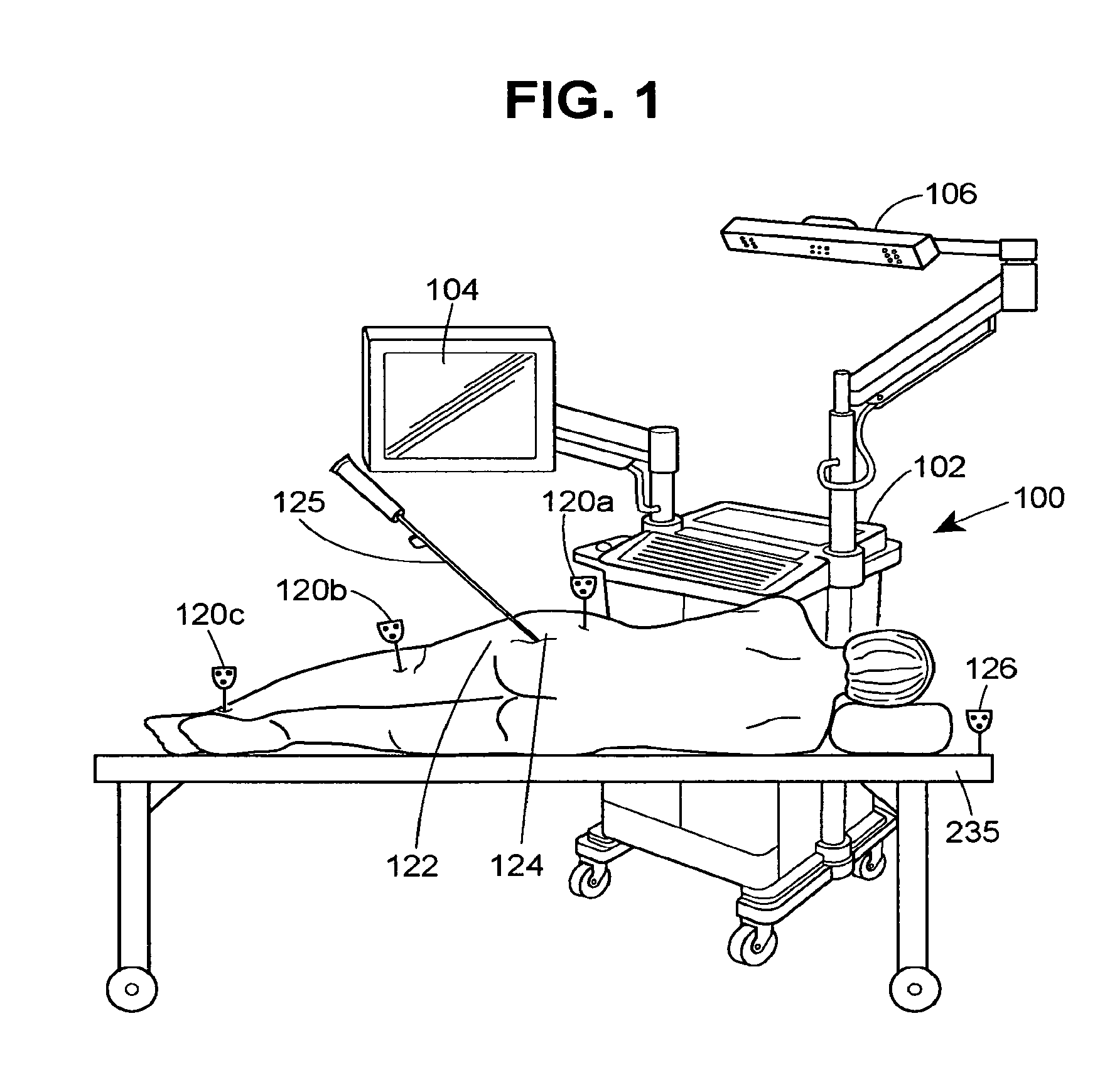
System and method for performing arthroplasty of a joint and tracking a plumb line plane
ActiveUS20060095047A1Improve stabilityMinimal potential for impingementSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationRange of motionNavigation system
A method of performing an arthroplasty of a ball and socket joint with a surgical navigation system includes the step of digitizing landmarks to provide geometrical parameters of the joint and a limb depending there from, including digitizing aspects of a socket region of the ball and socket joint. A range of motion parameter is determined. A soft tissue tension parameter is determined. A functional goal is computed based on landmark data, the range of motion parameter, the soft tissue tension parameter, and a database of potential implants. An optimal socket position is solved for to minimize impingement of potential implants. An implant is chosen based on the optimal socket position and the functional goal. The joint is prepared to receive the chosen implant. The chosen implant is installed into the joint.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
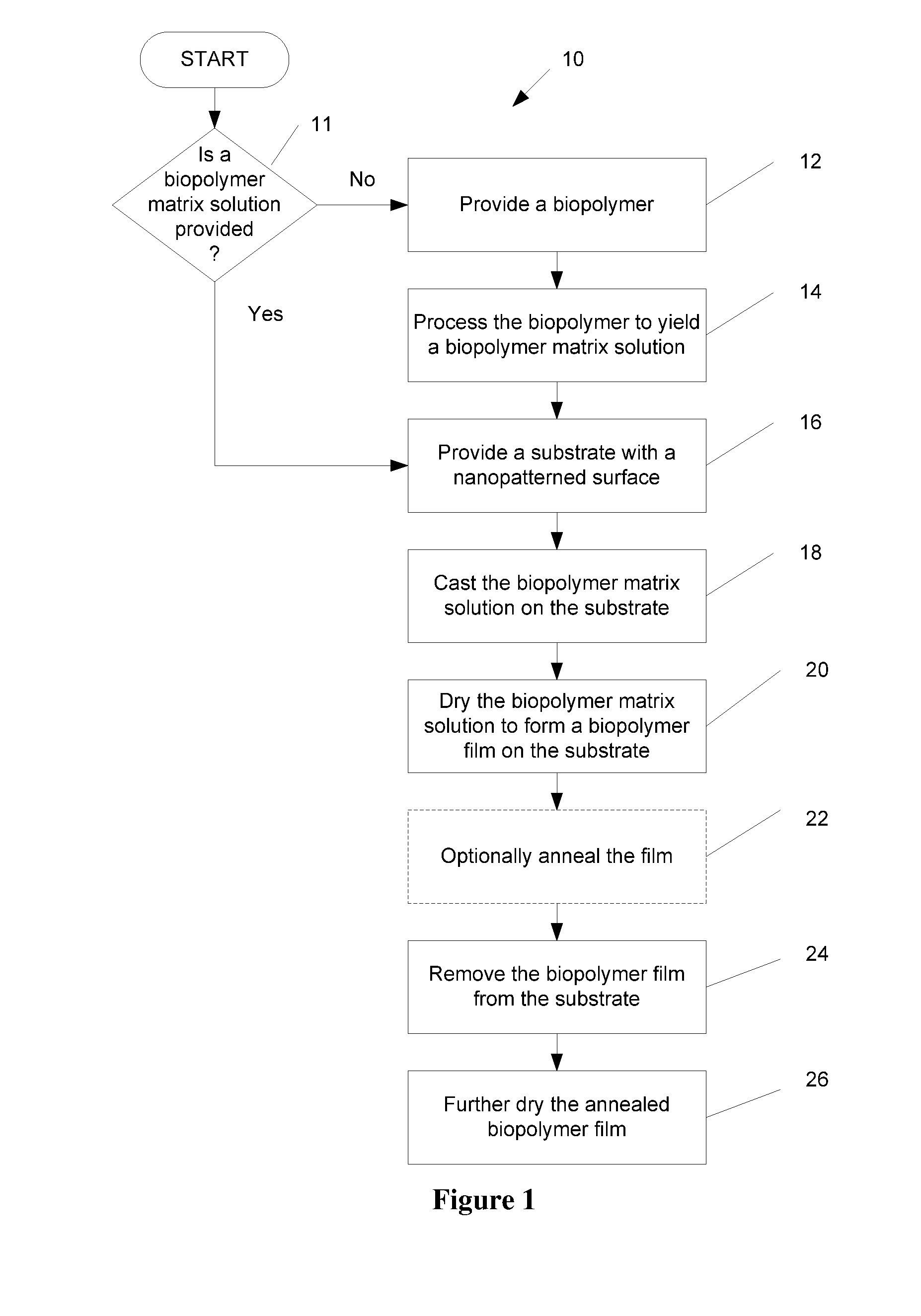
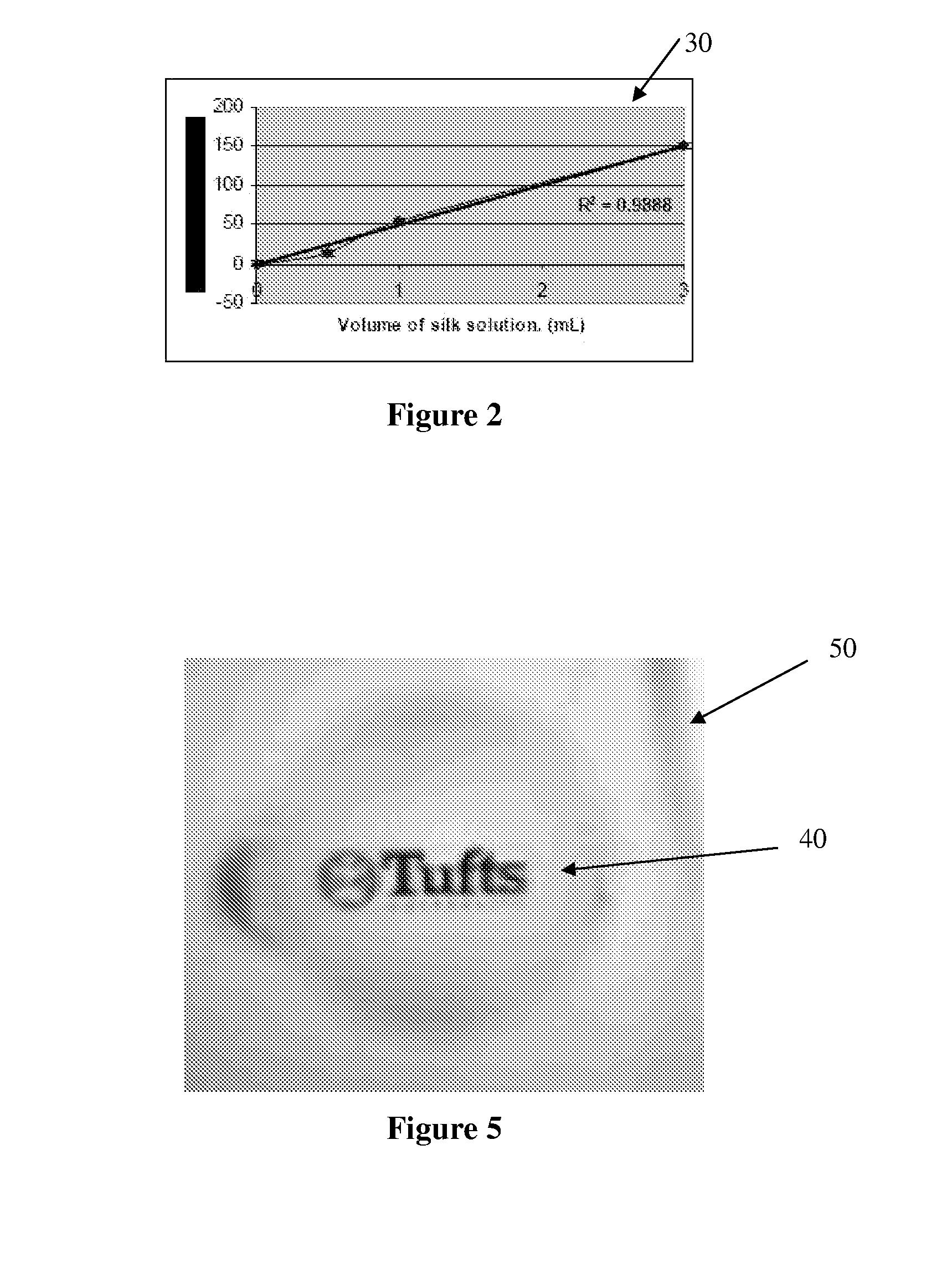
Nanopatterned biopolymer optical device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100120116A1Minimize negative impactImprove functional propertiesLayered productsOptical articlesMatrix solutionBiopolymer
A method of manufacturing a nanopatterned biopolymer optical device includes providing a biopolymer, processing the biopolymer to yield a biopolymer matrix solution, providing a substrate with a nanopatterned surface, casting the biopolymer matrix solution on the nanopatterned surface of the substrate, and drying the biopolymer matrix solution to form a solidified biopolymer film on the substrate, where the solidified biopolymer film is formed with a surface having a nanopattern thereon. In another embodiment, the method also includes annealing the solidified biopolymer film. A nanopatterned biopolymer optical device includes a solidified biopolymer film with a surface having a nanopattern is also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
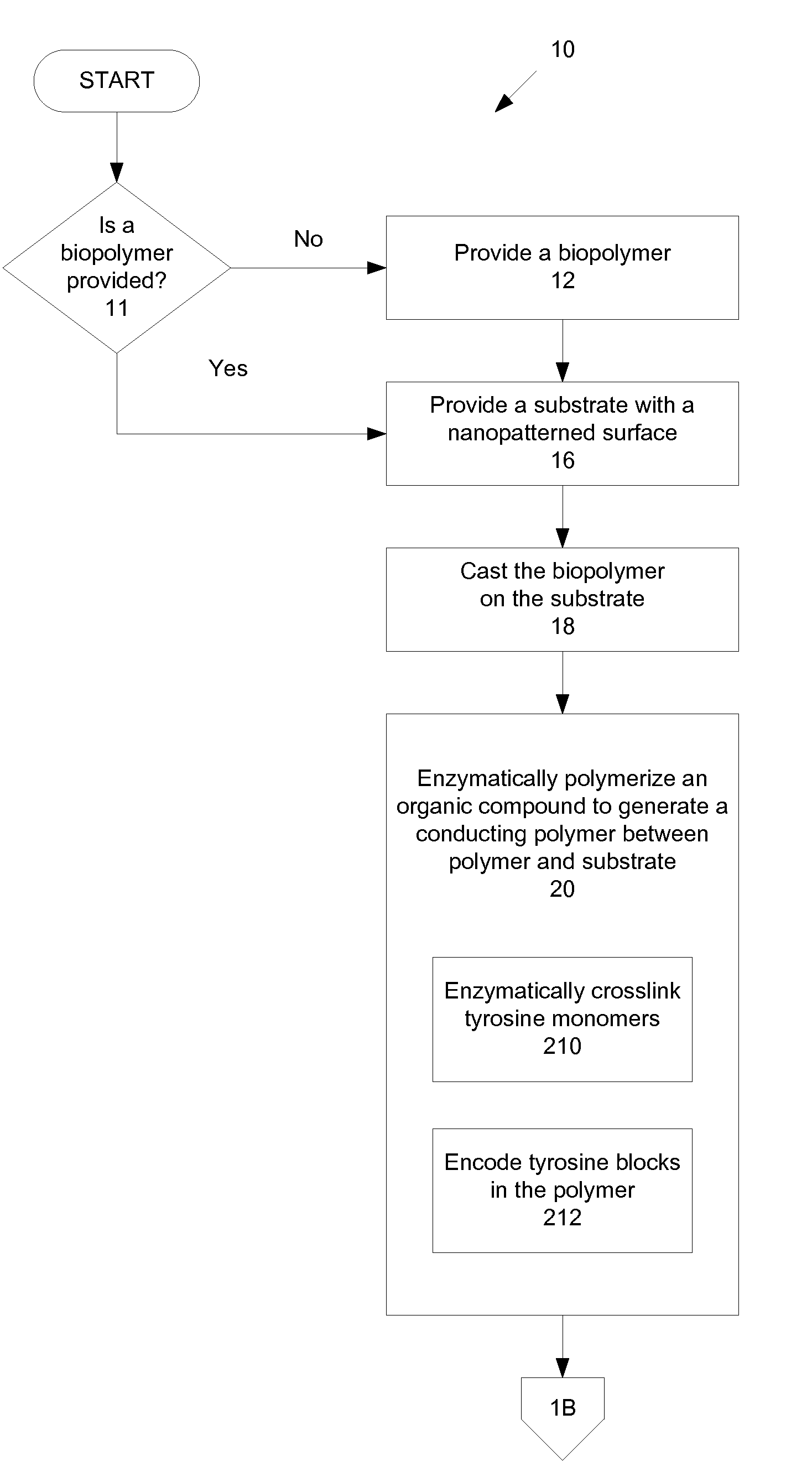
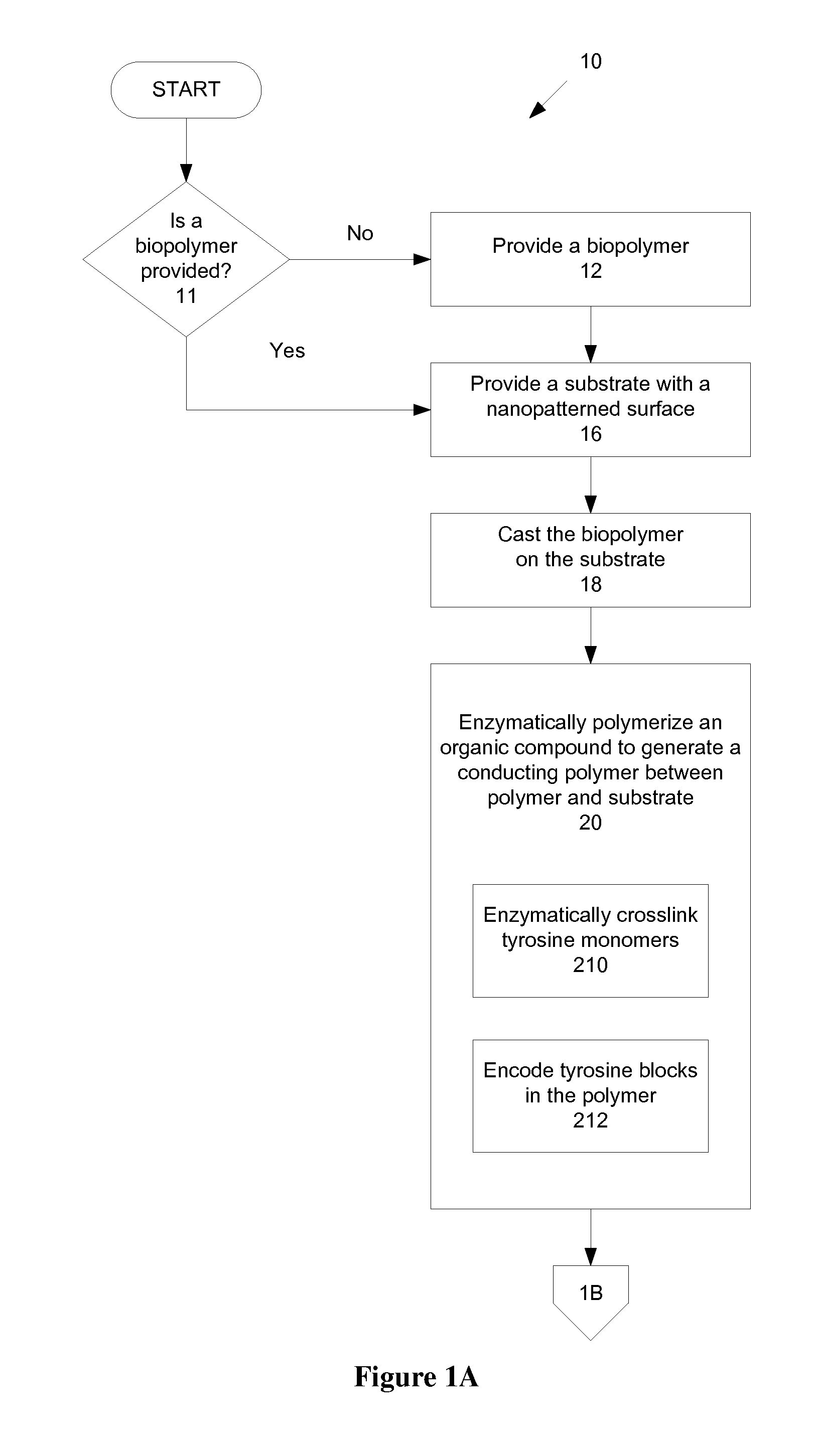
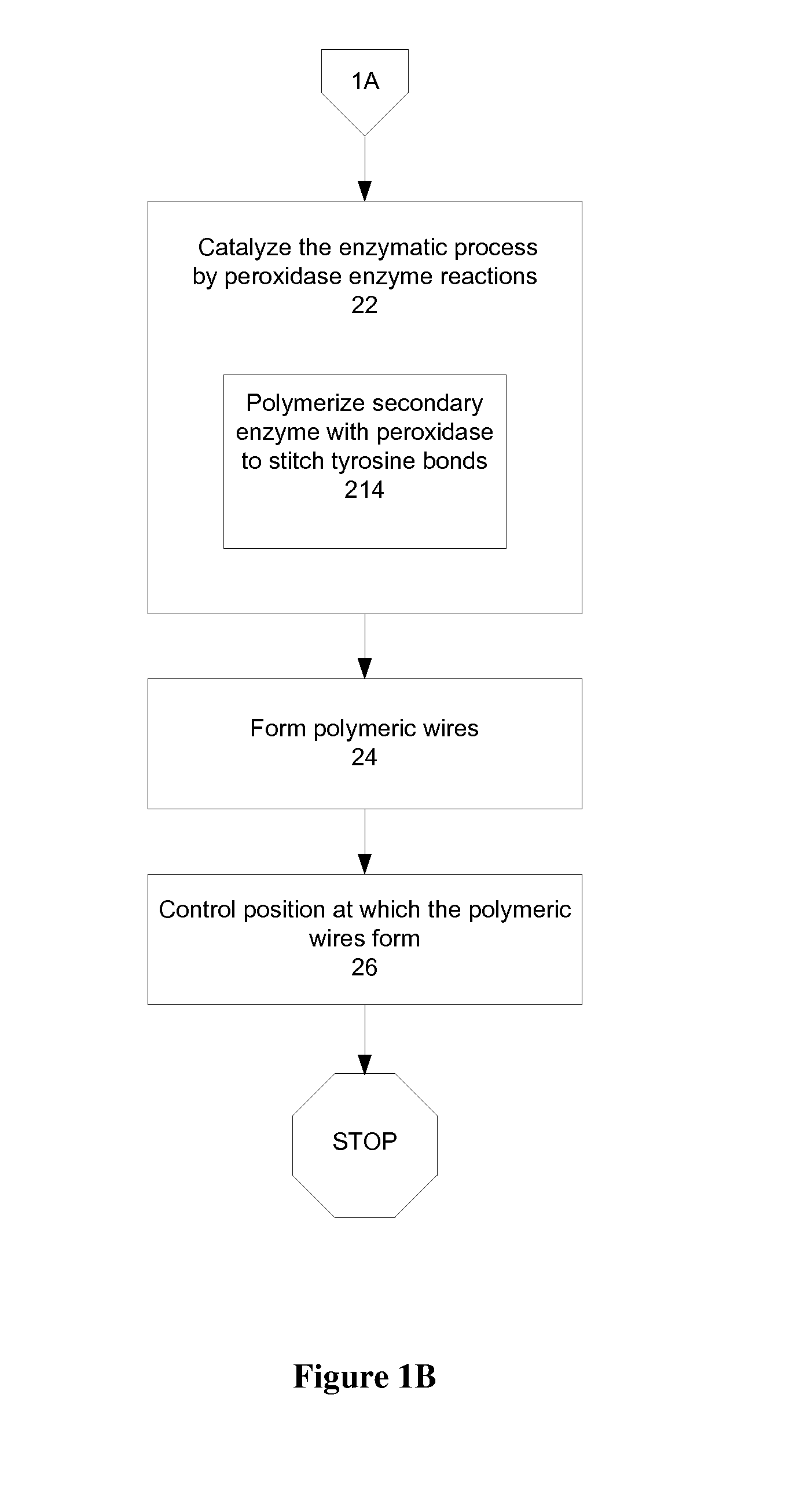
Electroactive biopolymer optical and electro-optical devices and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100065784A1Minimize negative impactImprove functional propertiesPowder deliveryConductive materialPolymer scienceBiopolymer
A method of manufacturing a biopolymer optical device includes providing a polymer, providing a substrate, casting the polymer on the substrate, and enzymatically polymerizing an organic compound to generate a conducting polymer between the provided polymer and the substrate. The polymer may be a biopolymer such as silk and may be modified using organic compounds such as tyrosines to provide a molecular-level interface between the provided bulk biopolymer of the biopolymer optical device and a substrate or other conducting layer via a tyrosine-enzyme polymerization. The enzymatically polymerizing may include catalyzing the organic compound with peroxidase enzyme reactions. The result is a carbon-carbon conjugated backbone that provides polymeric “wires” for use in polymer and biopolymer optical devices. An all organic biopolymer electroactive material is thereby provided that provides optical functions and features.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
Bone treatment systems and methods
InactiveUS20080065083A1Inhibit migrationHigh viscositySurgical needlesMedical devicesVertebra compression fractureBone cement
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to systems for treating vertebral compression fractures. In one embodiment, an elongated sleeve defines a passageway therethrough, and has a threaded portion configured to engage bone. The sleeve includes a seal configured to allow instrument exchange through the passageway and into the interior of the vertebra to perform at least one medical procedure, such as injection of bone cement into the vertebral body.
Owner:DFINE INC
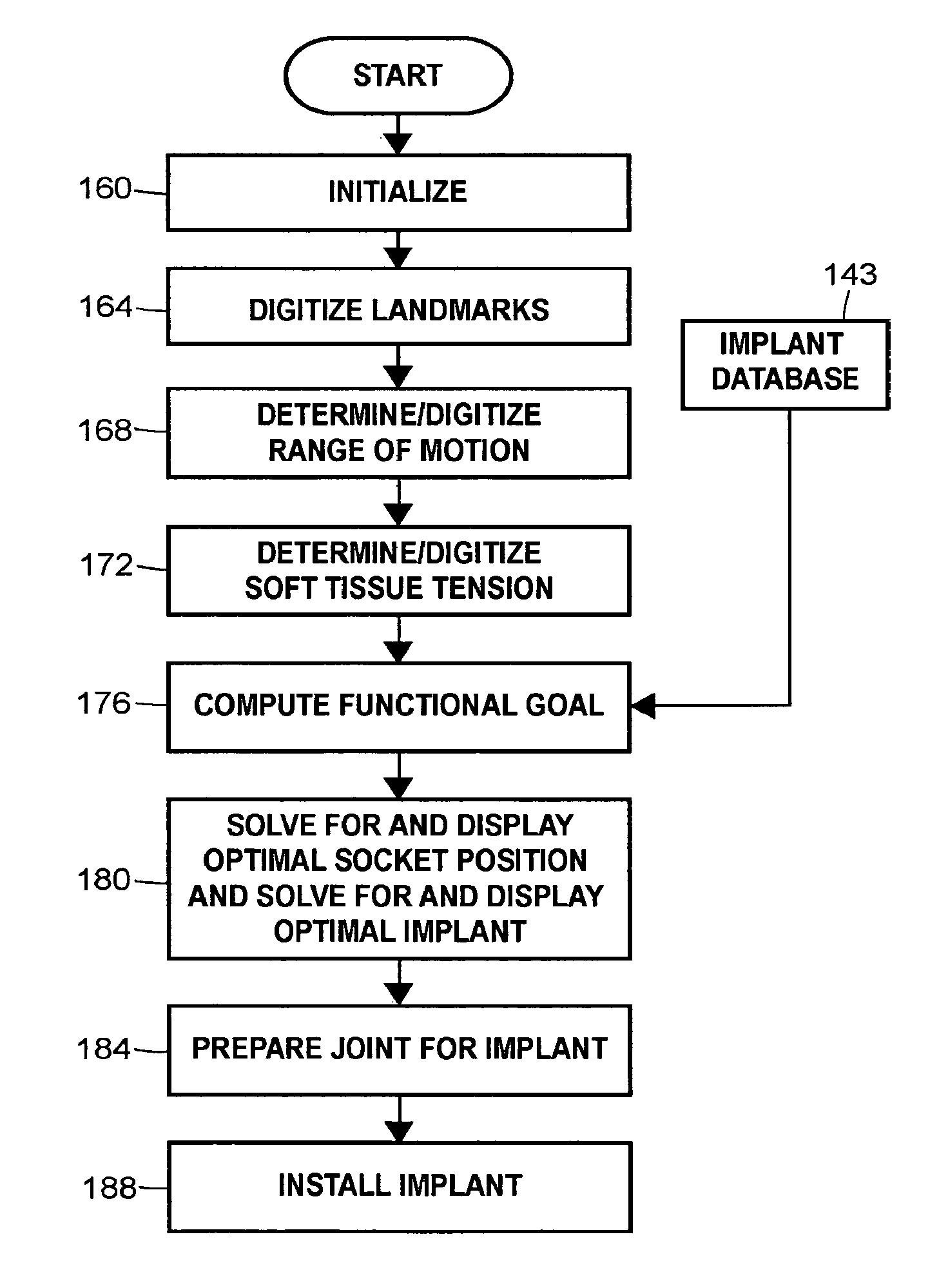
System and method for performing arthroplasty of a joint and tracking a plumb line plane
ActiveUS8007448B2Improve functional propertiesImprove stabilitySurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationRange of motionMotion parameter
A method of performing an arthroplasty of a ball and socket joint with a surgical navigation system includes the step of digitizing landmarks to provide geometrical parameters of the joint and a limb depending there from, including digitizing aspects of a socket region of the ball and socket joint. A range of motion parameter is determined. A soft tissue tension parameter is determined. A functional goal is computed based on landmark data, the range of motion parameter, the soft tissue tension parameter, and a database of potential implants. An optimal socket position is solved for to minimize impingement of potential implants. An implant is chosen based on the optimal socket position and the functional goal. The joint is prepared to receive the chosen implant. The chosen implant is installed into the joint.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
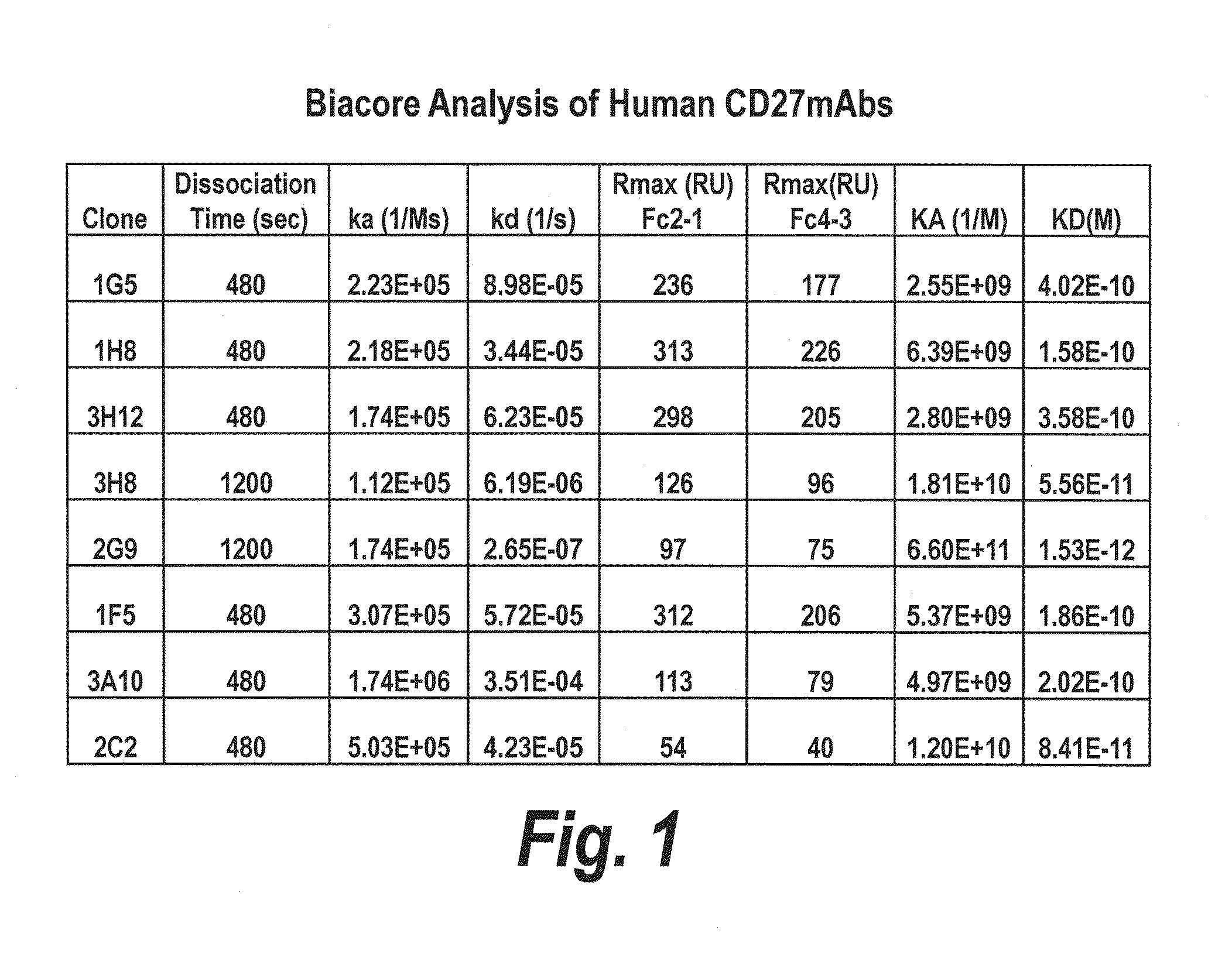
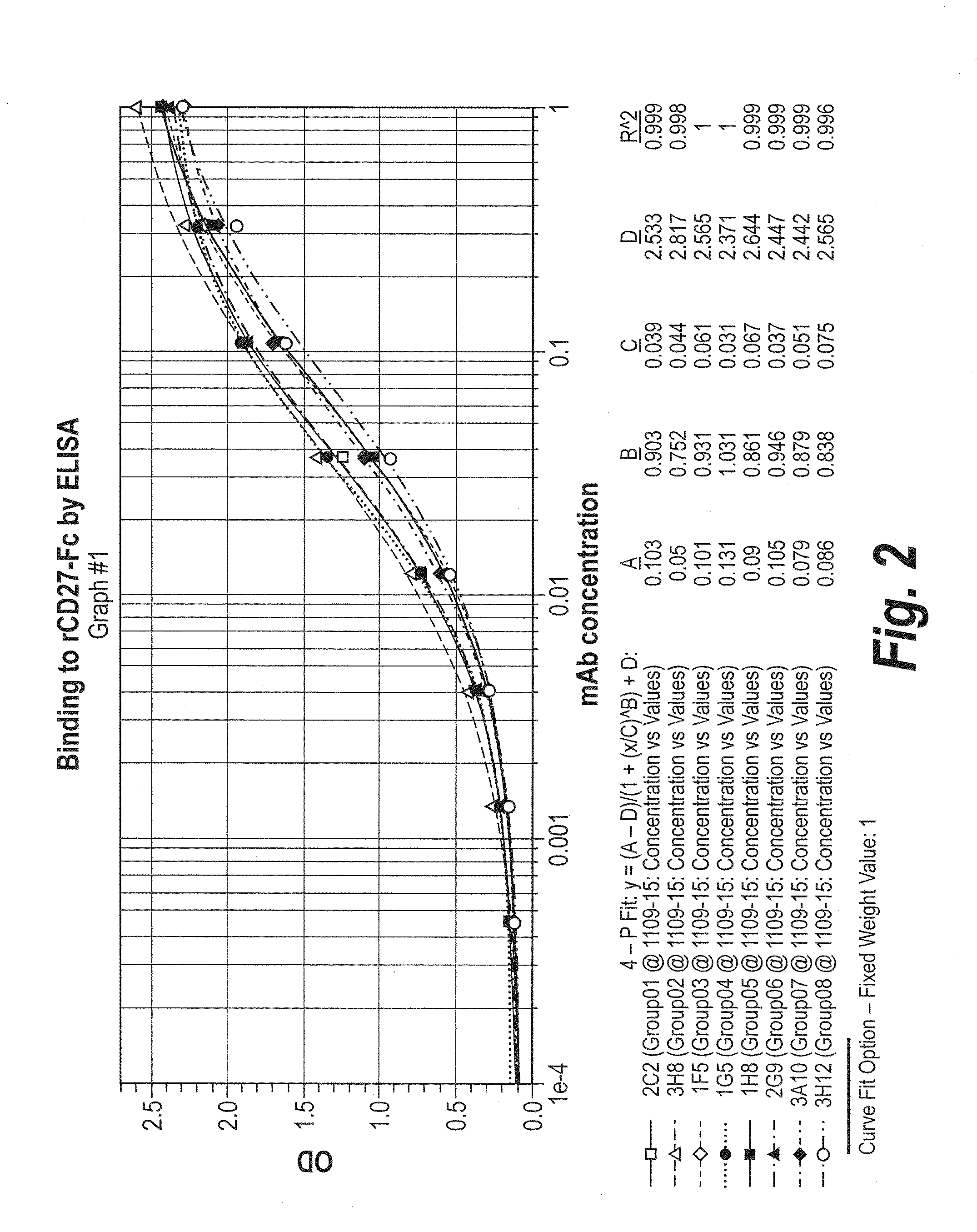
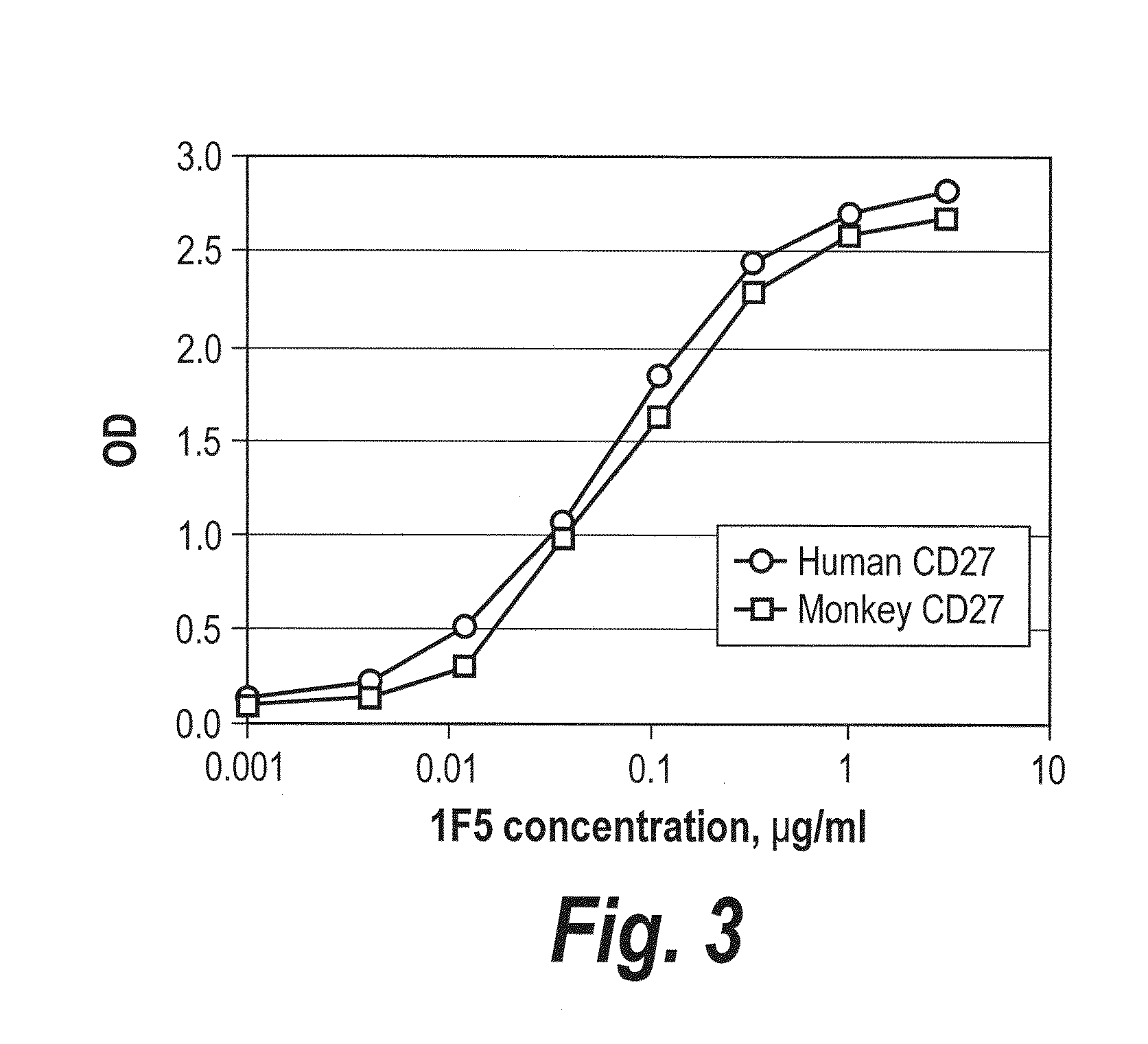
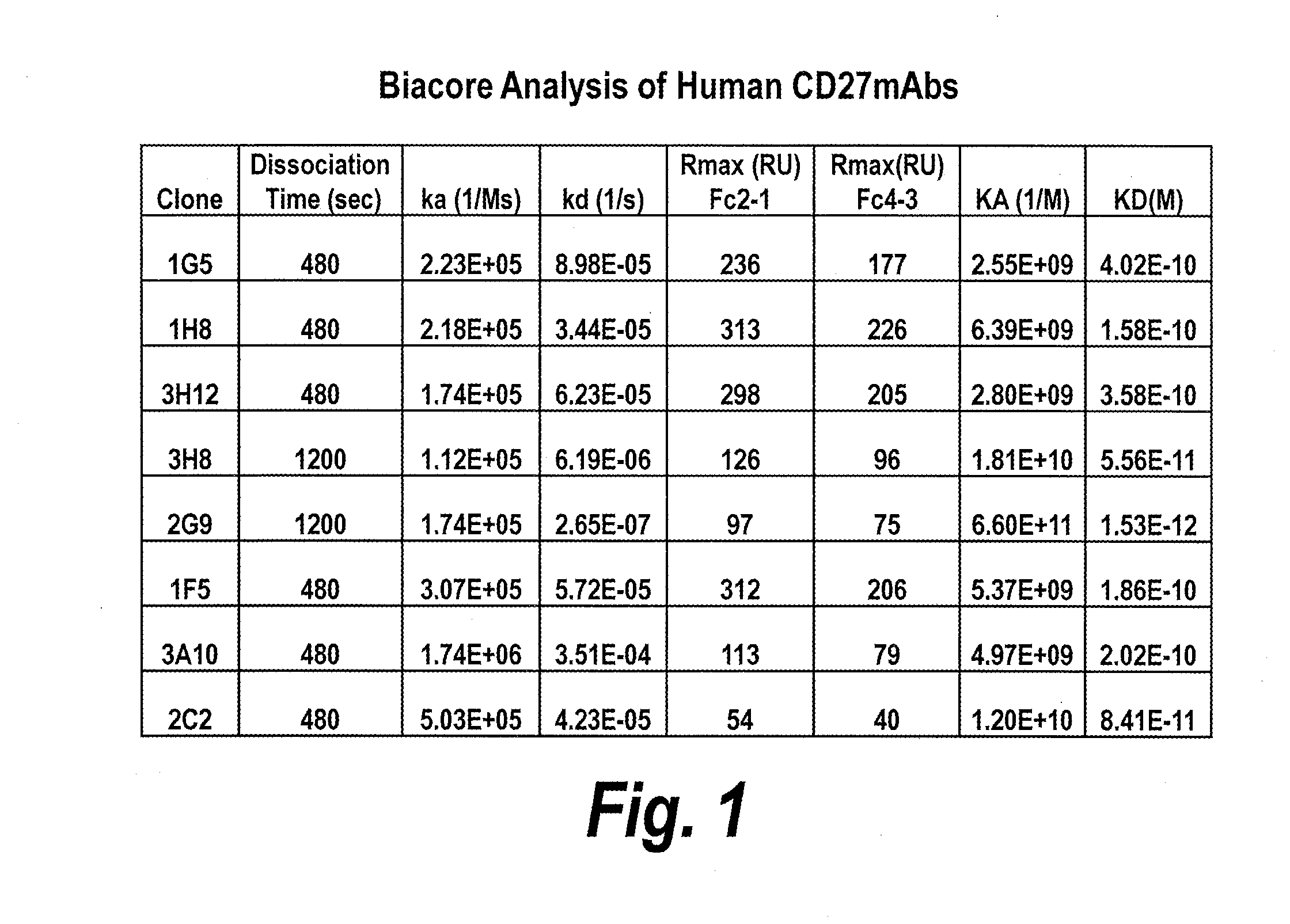
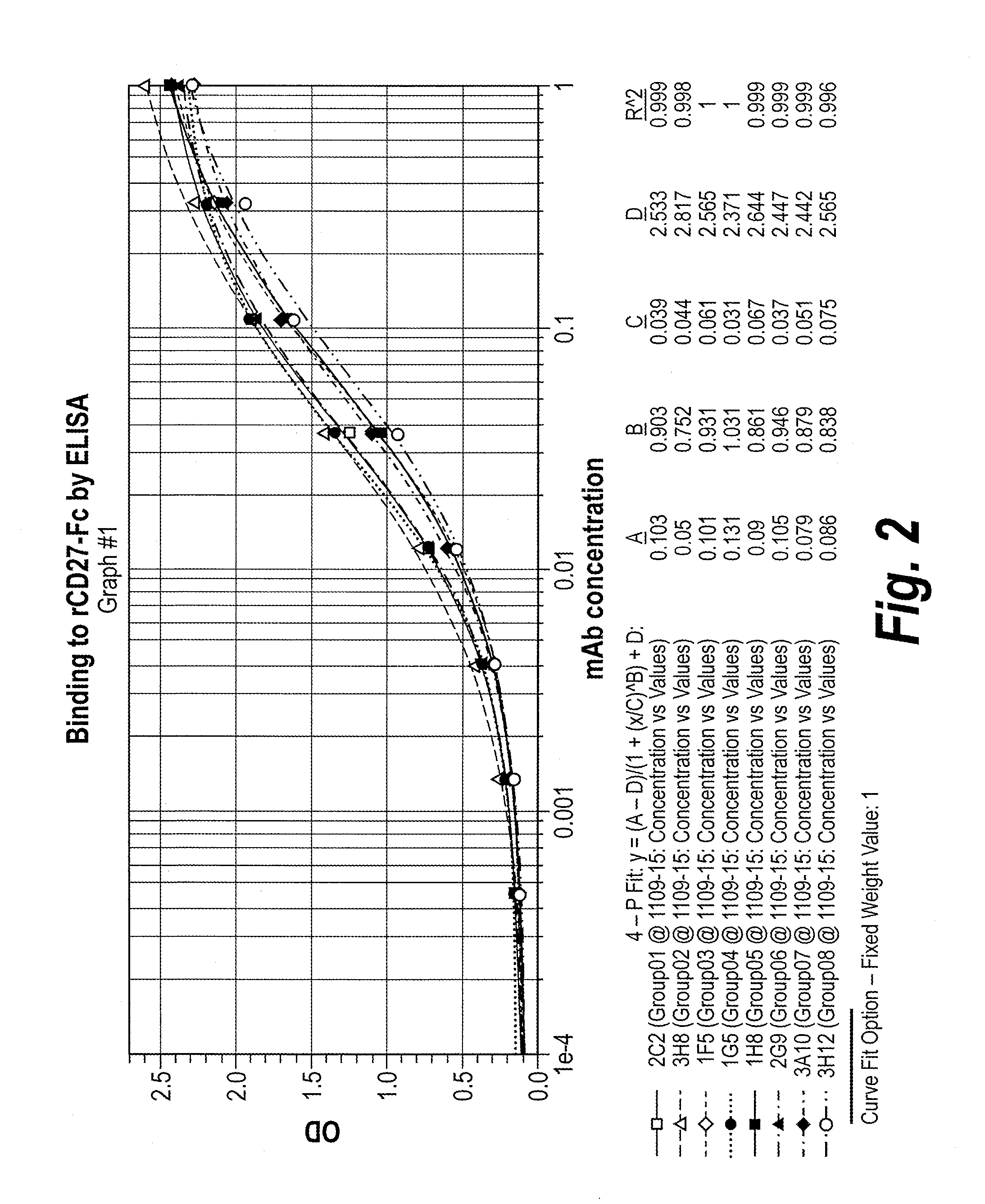
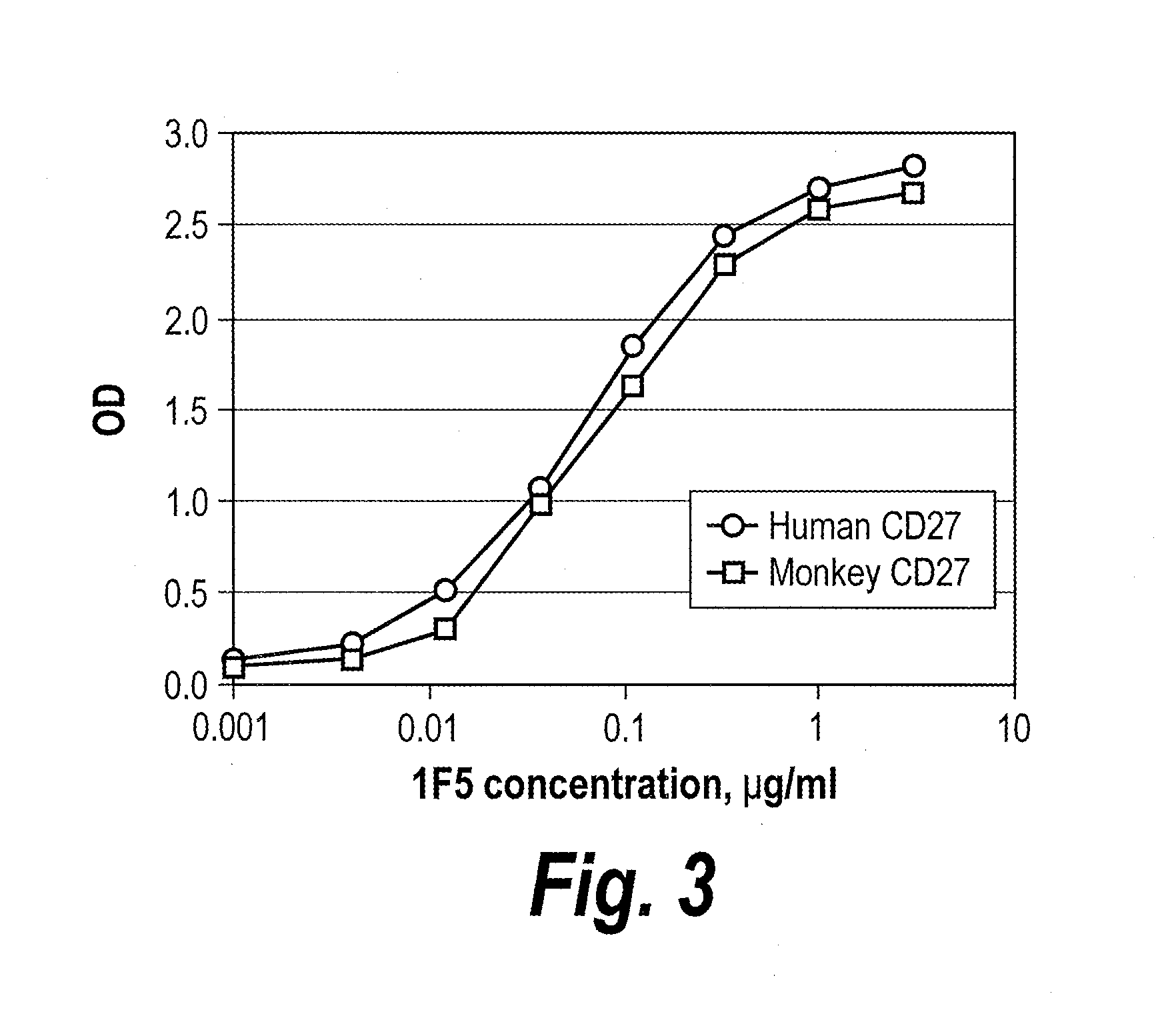
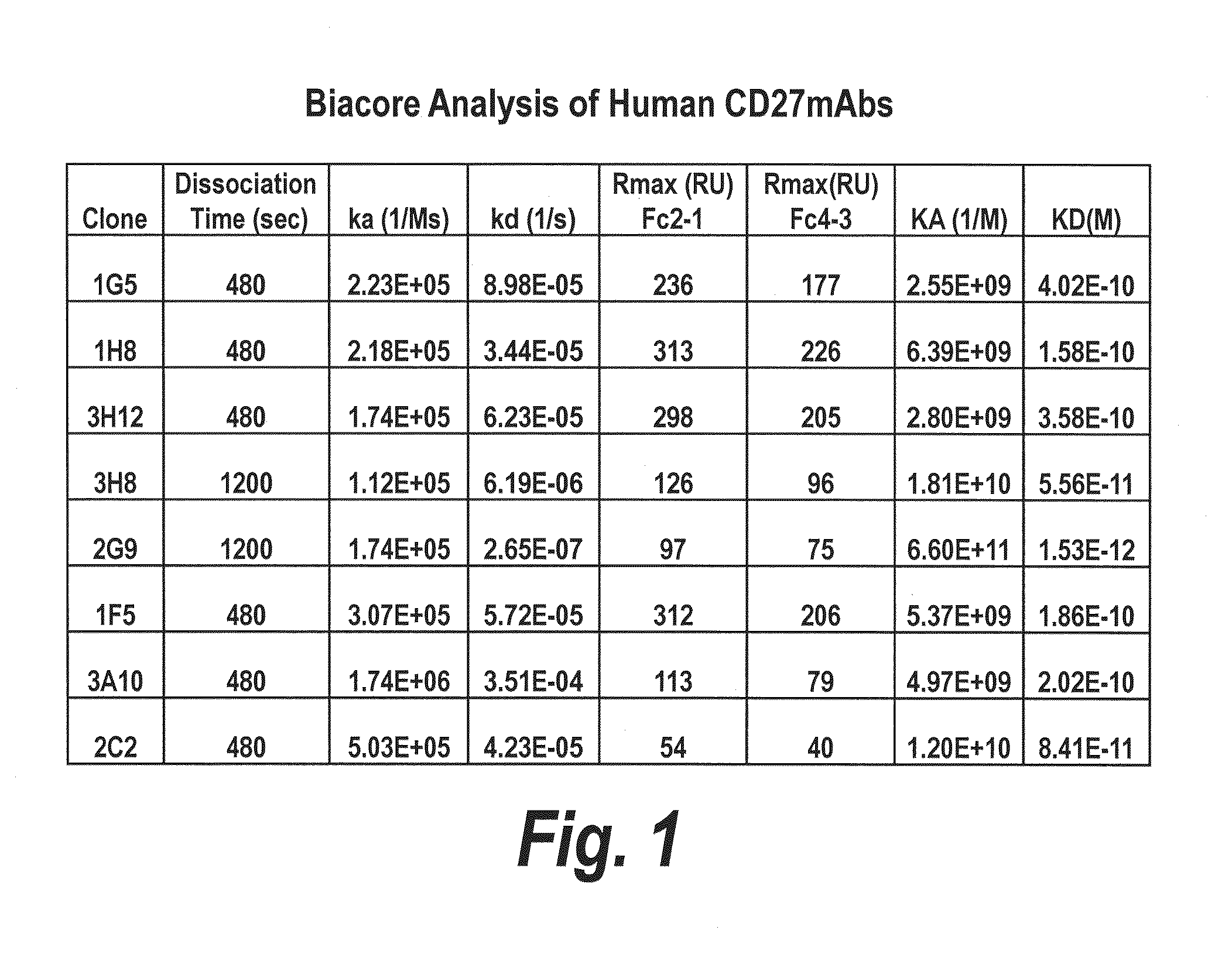
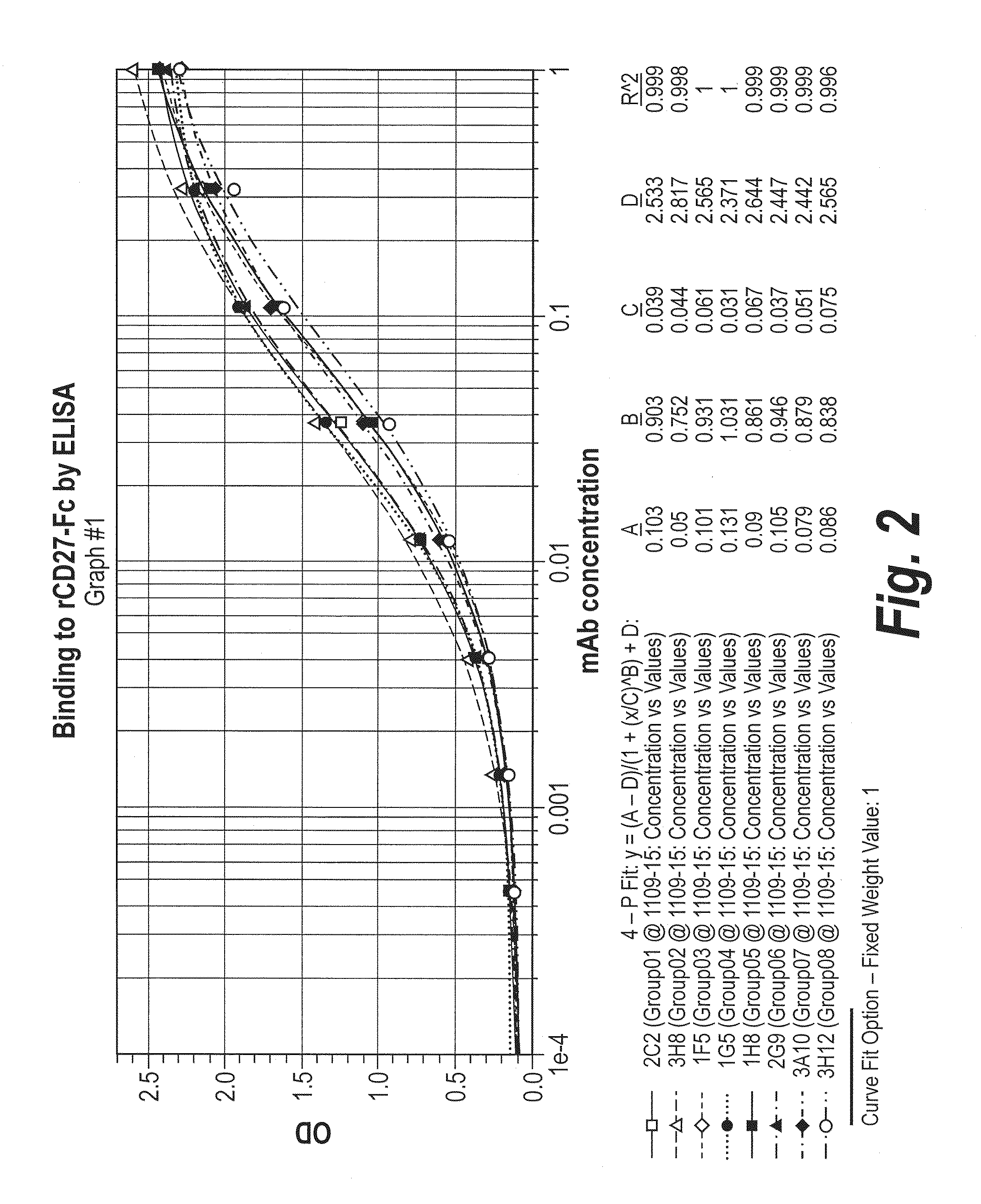
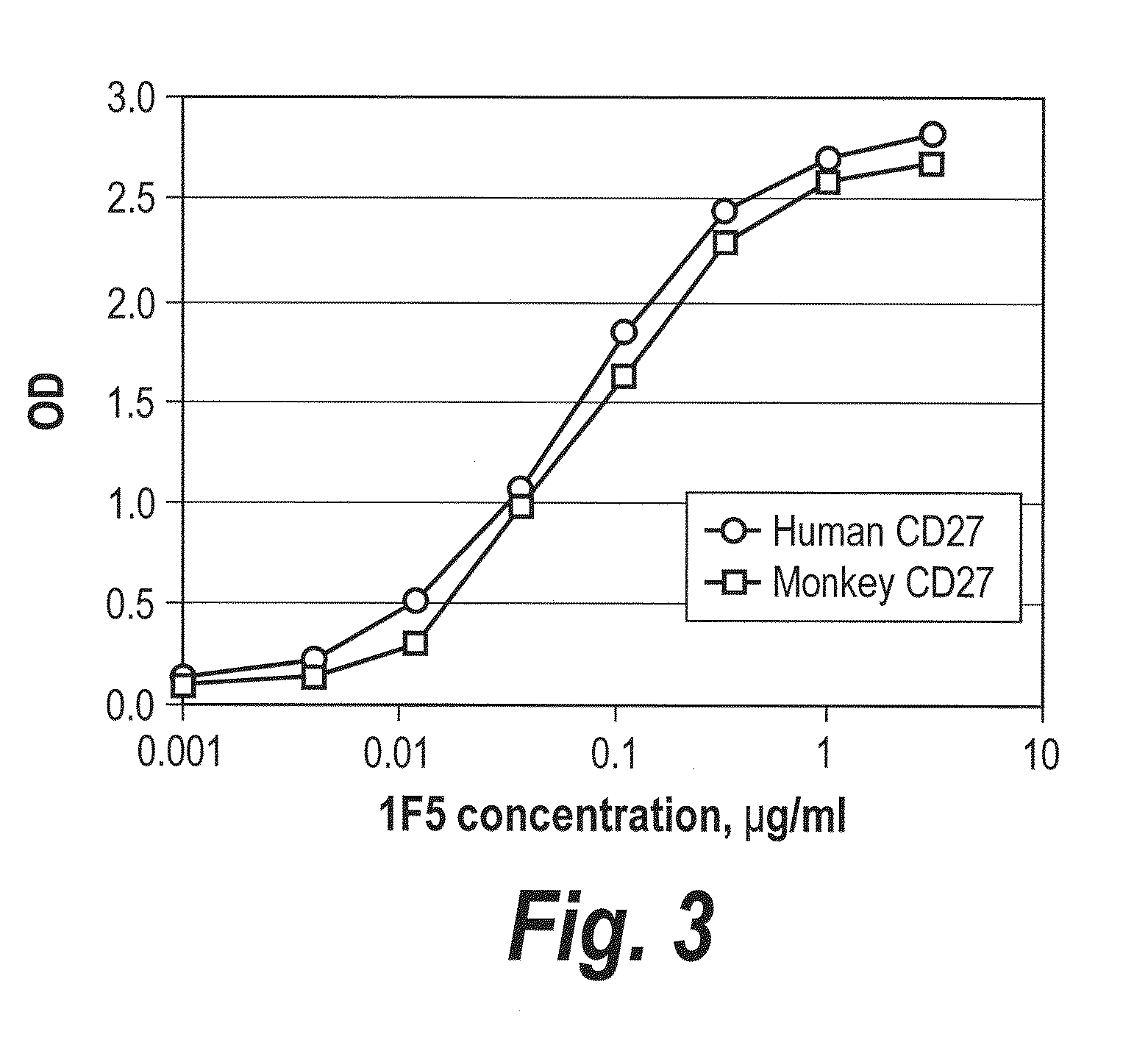
Antibodies that bind human cd27 and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110274685A1Enhance immune responseInduce expressionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderMonoclonal antibodyAntibody
Isolated monoclonal antibodies which bind to human CD27 and related antibody-based compositions and molecules are disclosed. Also disclosed are therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the antibodies.
Owner:CELLDEX THERAPEUTICS INC
Antibodies that bind human cd27 and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120213771A1Enhance immune responseInduce expressionAnimal cellsBacteriaMonoclonal antibodyDiagnostic methods
Isolated monoclonal antibodies which bind to human CD27 and related antibody-based compositions and molecules are disclosed. Also disclosed are therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the antibodies.
Owner:CELLDEX THERAPEUTICS INC
Finishing of textile fibers, tissues and fabrics
InactiveUS7056845B2Improve the level ofImprove functional propertiesOther chemical processesPhysical treatmentTextile fiberEngineering
A method is provided for the application of a finishing layer to a textile support material. A water repellent or oil repellent layer, a so-called finishing layer, is applied to a textile support material selected from the group of fibers, tissues, and fabrics. The water repellent or oil repellent finishing layer comprises at least two water repellent or oil repellent components wherein a first component comprises one or more dispersants and a second component comprises one or more dispersed phases or colloids, and wherein the dispersant and the dispersed phase are present in the gel state.
Owner:SCHOELLER TEXTIL
Antibodies that bind human CD27 and uses thereof
ActiveUS9169325B2Enhance immune responseInduce expressionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderMonoclonal antibodyDiagnostic methods
Isolated monoclonal antibodies which bind to human CD27 and related antibody-based compositions and molecules are disclosed. Also disclosed are therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the antibodies.
Owner:CELLDEX THERAPEUTICS INC
Humanization of rabbit antibodies using a universal antibody framework
ActiveUS8293235B2Reliably retain the spatial orientation of the rabbit antibodiesImprove bindingSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody receptorRabbit Antibody
The present invention relates to an universal antibody acceptor framework and to methods for grafting non-human antibodies, e.g., rabbit antibodies, using a universal antibody acceptor framework. Antibodies generated by the methods of the invention are useful in a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
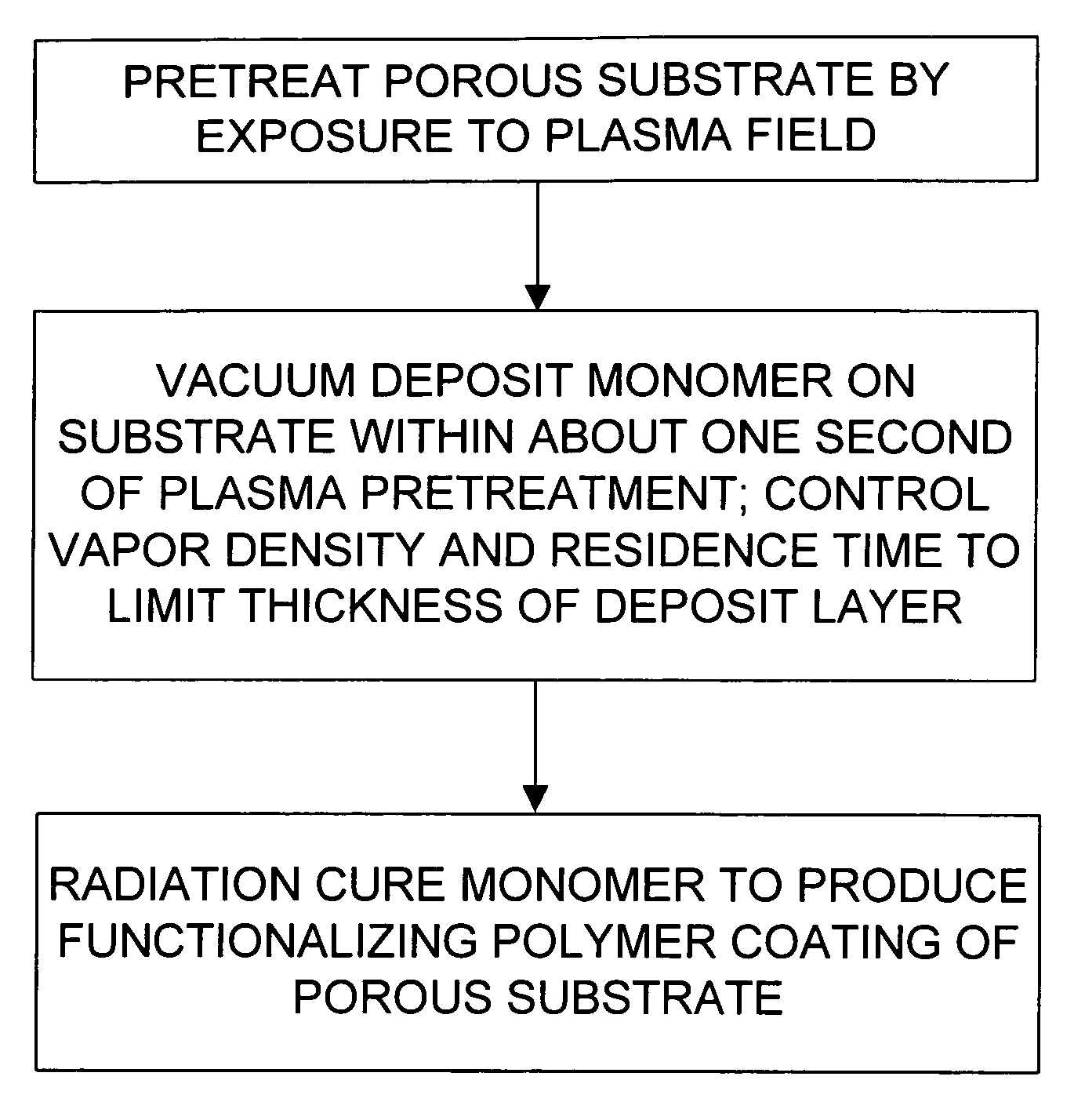
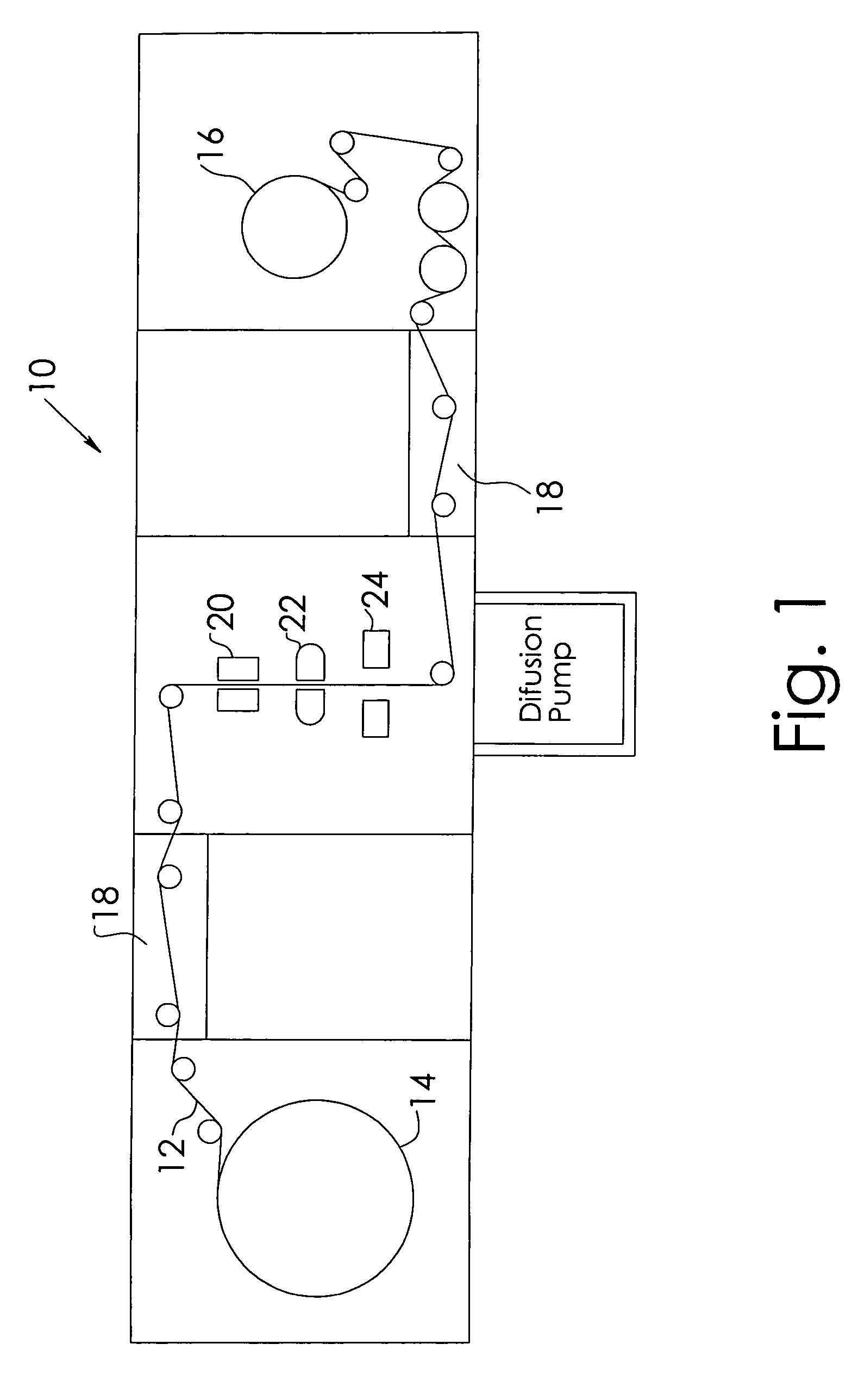
Functionalization of porous materials by vacuum deposition of polymers
InactiveUS7157117B2Improve reflectivityReduced durabilitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesPorous substrateFiber
A porous substrate is pretreated in a plasma field and a functionalizing monomer is immediately flash-evaporated, deposited and cured over the porous substrate in a vacuum vapor-deposition chamber. By judiciously controlling the process so that the resulting polymer coating adheres to the surface of individual fibers in ultra-thin layers (approximately 0.02–3.0 μm) that do not extend across the pores in the material, the porosity of the porous substrate is essentially unaffected while the fibers and the final product acquire the desired functionality. The resulting polymer layer is also used to improve the adherence and durability of metallic and ceramic coatings.
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
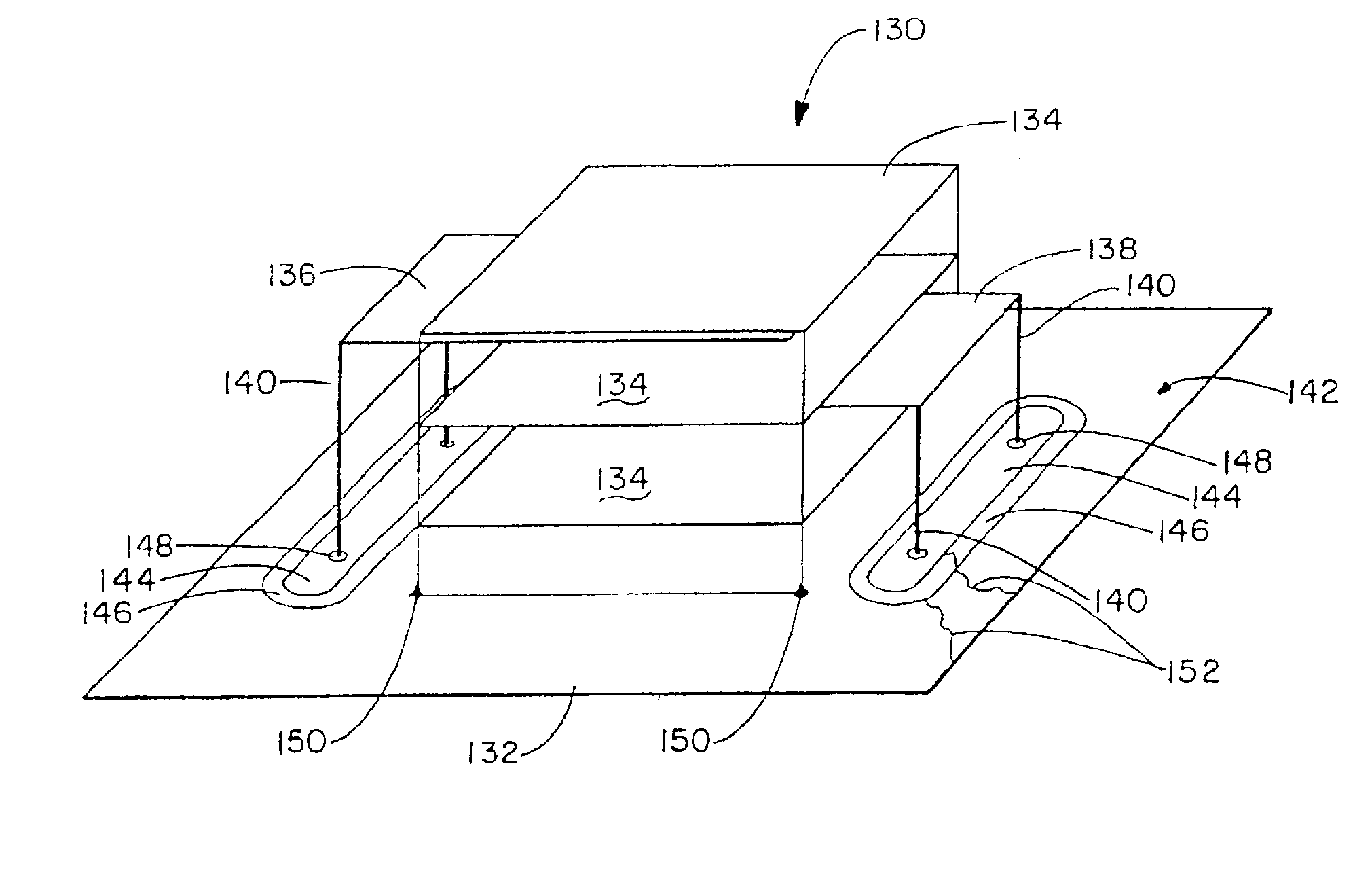
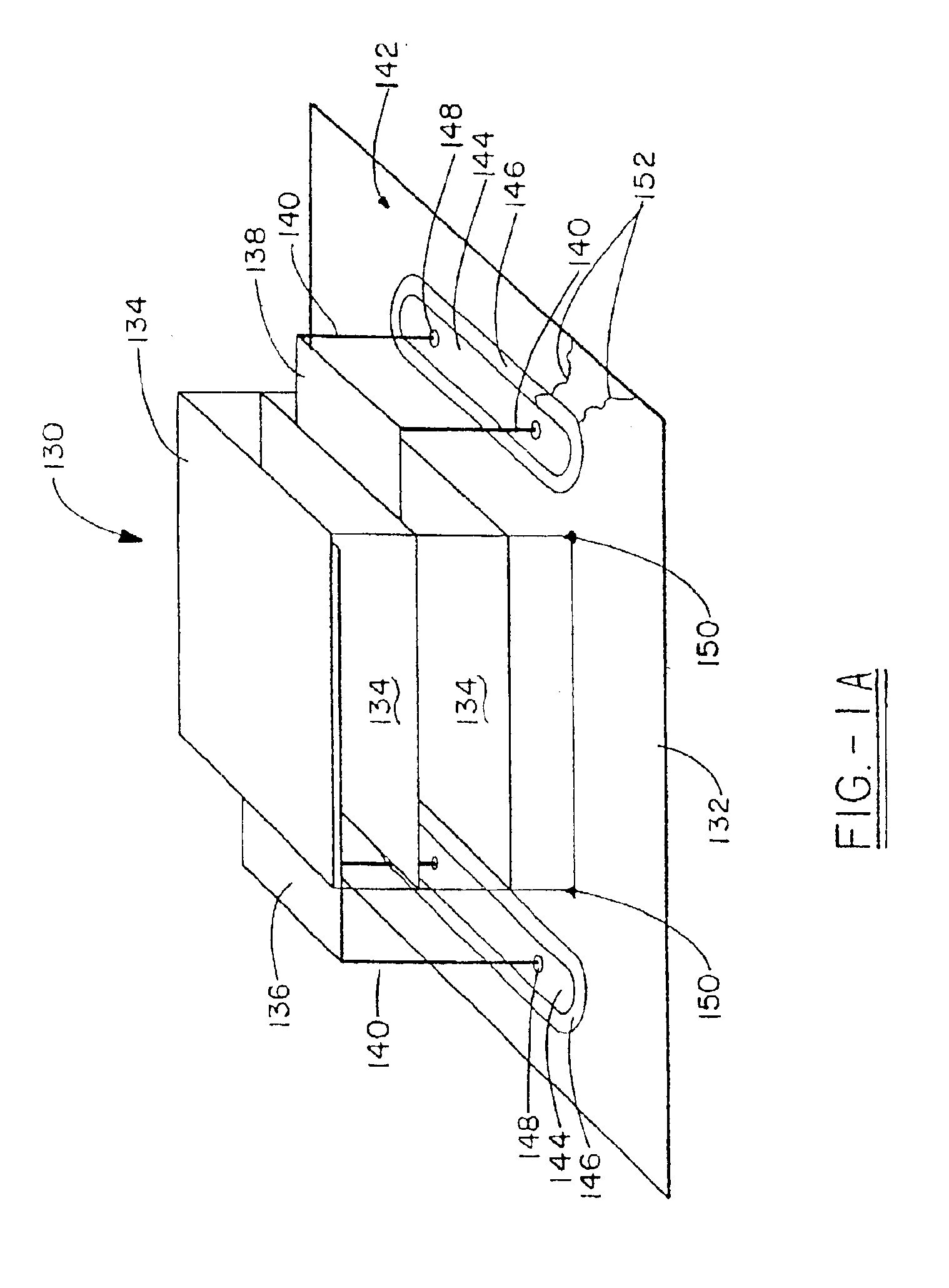
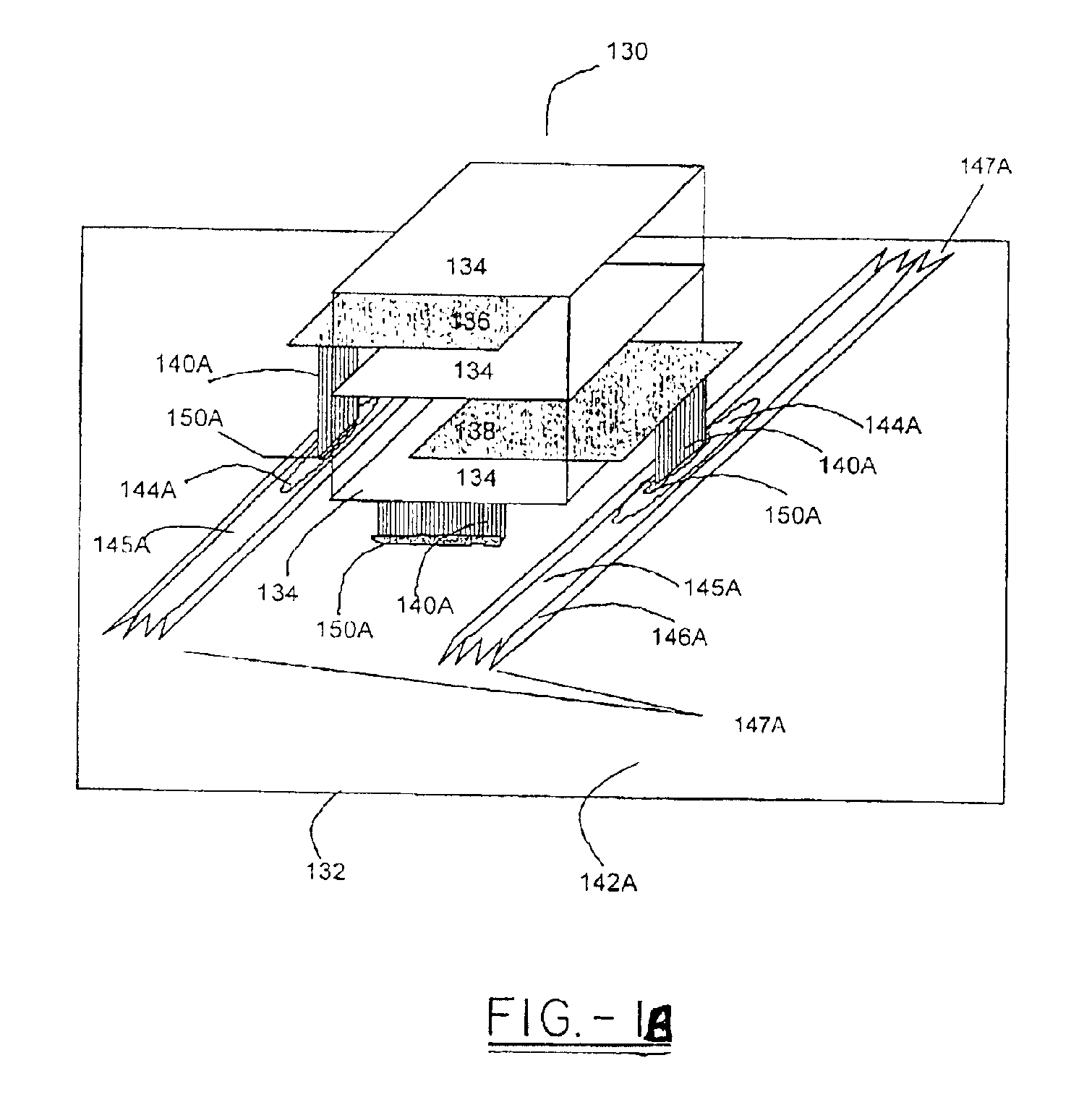
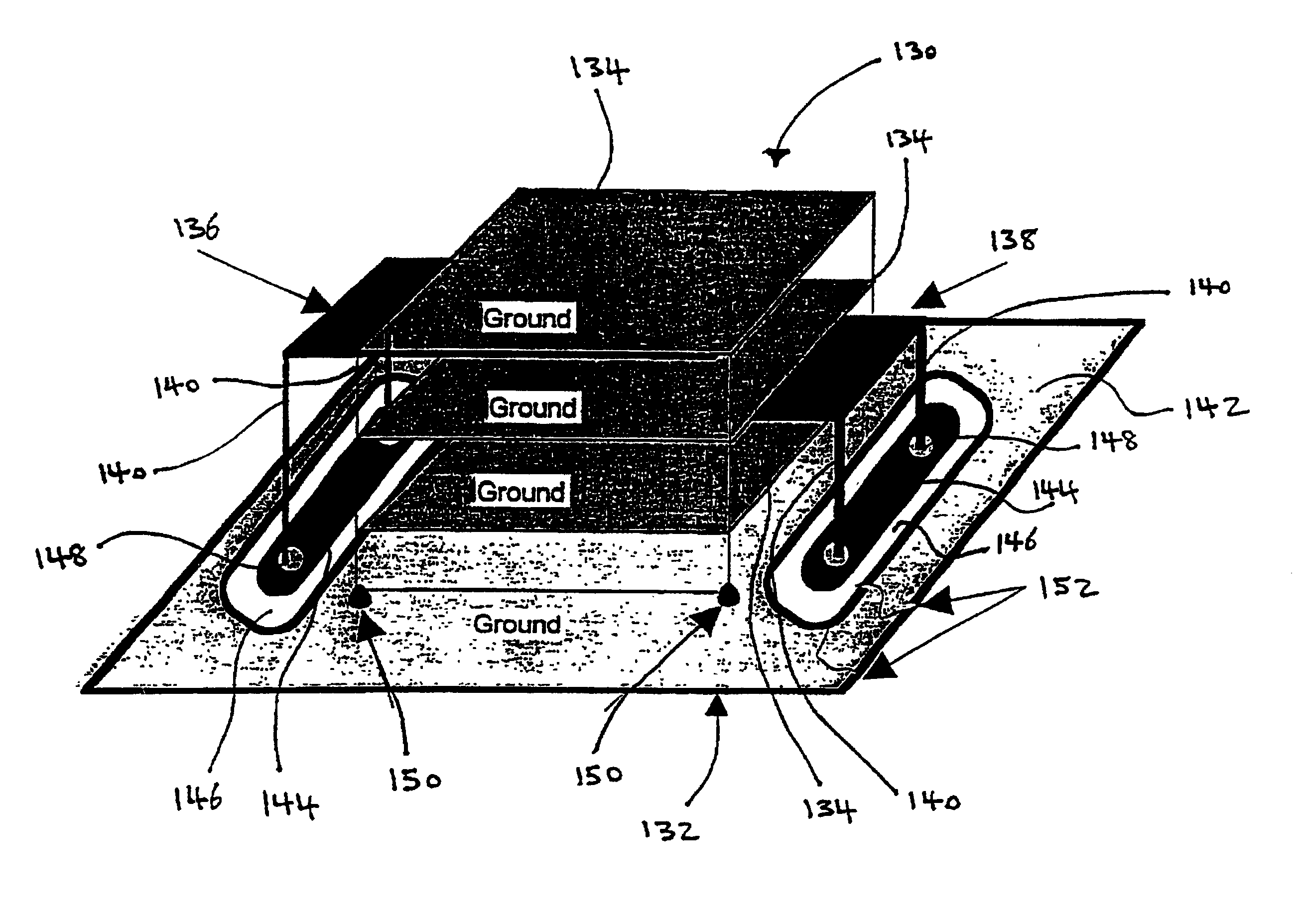
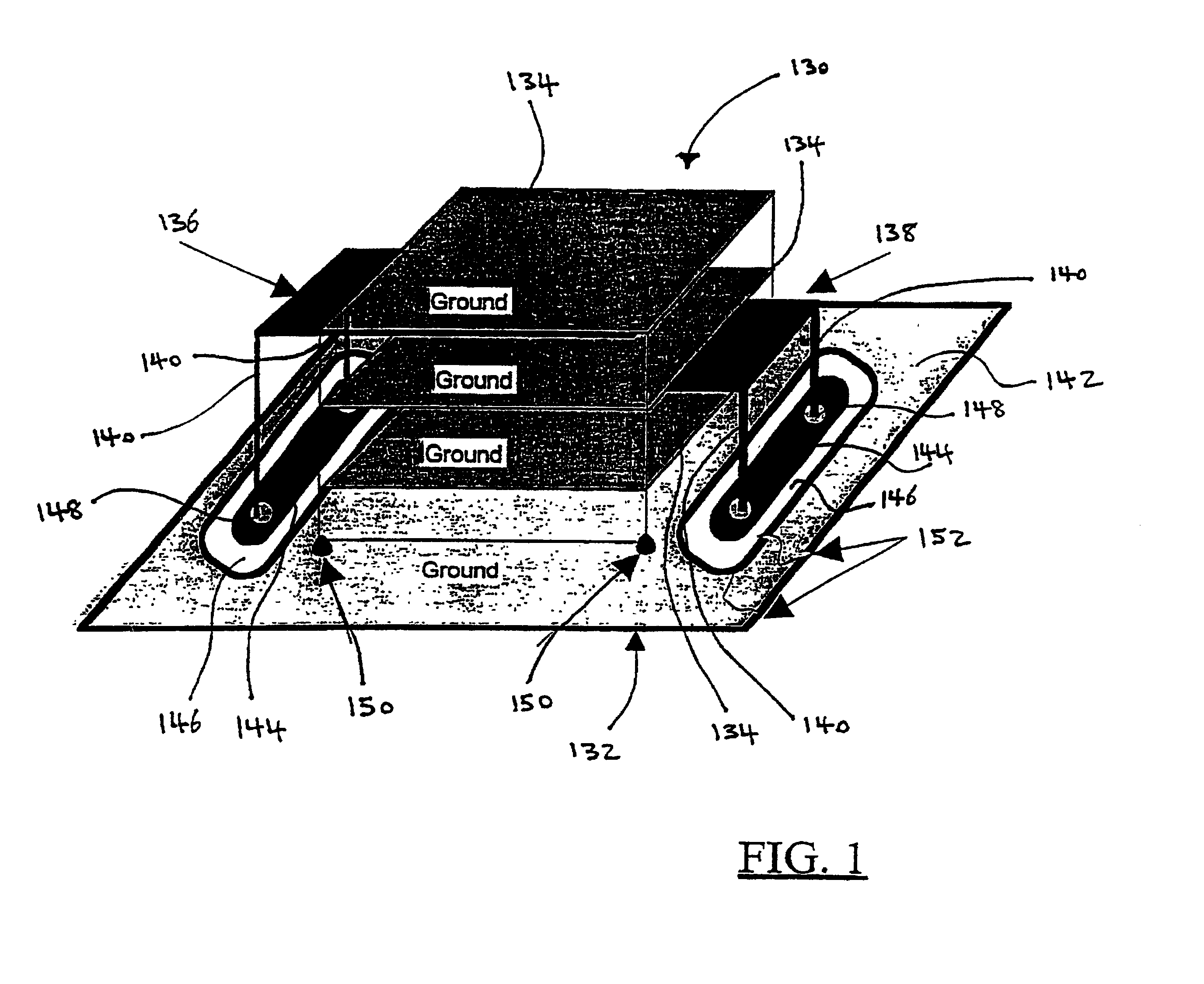
Energy conditioning circuit assembly
InactiveUS7042303B2Improve shielding effectFine surfaceMultiple-port networksCoupling for high frequencyElectricityEnergy regulation
The present invention is a component carrier (132) consisting of a plate of insulating material having a plurality of apertures (140) for accepting the leads of a thru-hole differential and common mode filter (130). Another embodiment consists of a surface mount component carrier (10) comprising a disk (16) of insulating material having a plurality of apertures (24). The same concept for the above described carrier is also incorporated into several alternate embodiments, either independently, embedded within electronic connectors. The overall configuration and electrical characteristics of the concepts underlying the present inventions are also described as an energy conditioning circuit assembly which encompasses the combination of differential and common mode filters and component carriers optimized for such filters. The various embodiments of component carriers provide increased physical support and protection to differential and common mode filters and substantially improve the electrical characteristics of the filters due to the increased shielding provided by the carriers. Embodiments of the carrier energy conditioning assembly include integrated circuit construction for a differential and common mode filter coupled to the power bus of an integrated circuit.
Owner:X2Y ATTENUATORS L L C
Component carrier
InactiveUS6995983B1Less susceptibleEasily assemblePrinted circuit aspectsEmergency protective arrangement detailsCarrier signalElectricity
The present invention is a component carrier comprising a plate of insulating material having a plurality of apertures for accepting the leads of a thru-hole differential and common mode filter. Another embodiment comprises a surface mount component carrier comprised of a disk of insulating material having a plurality of apertures. The same concept for the above described carrier is also incorporated into several alternate embodiments, either independently or embedded within electronic connectors, or configured for use with electric motors. The overall configuration and electrical characteristics of the concepts underlying the present inventions are also described as an electrical circuit conditioning assembly which encompasses the combination of differential and common mode filters and component carriers optimized for such filters. The various embodiments of component carriers provide increased physical support and protection to differential and common mode filters and substantially improve the electrical characteristics of the filters due to the increased shielding provided by the carriers.
Owner:X2Y ATTENUATORS L L C
Modified silk films containing glycerol
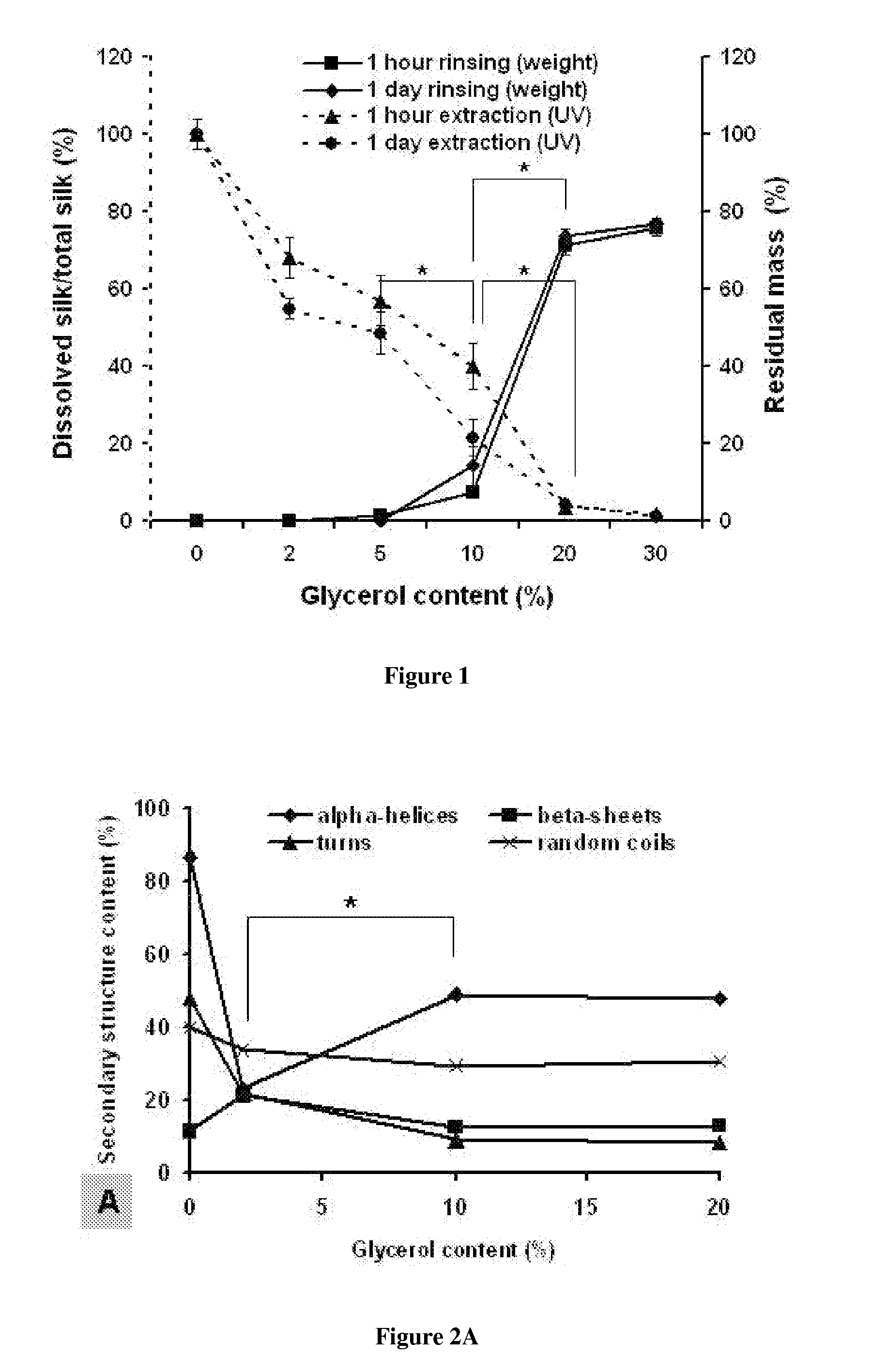
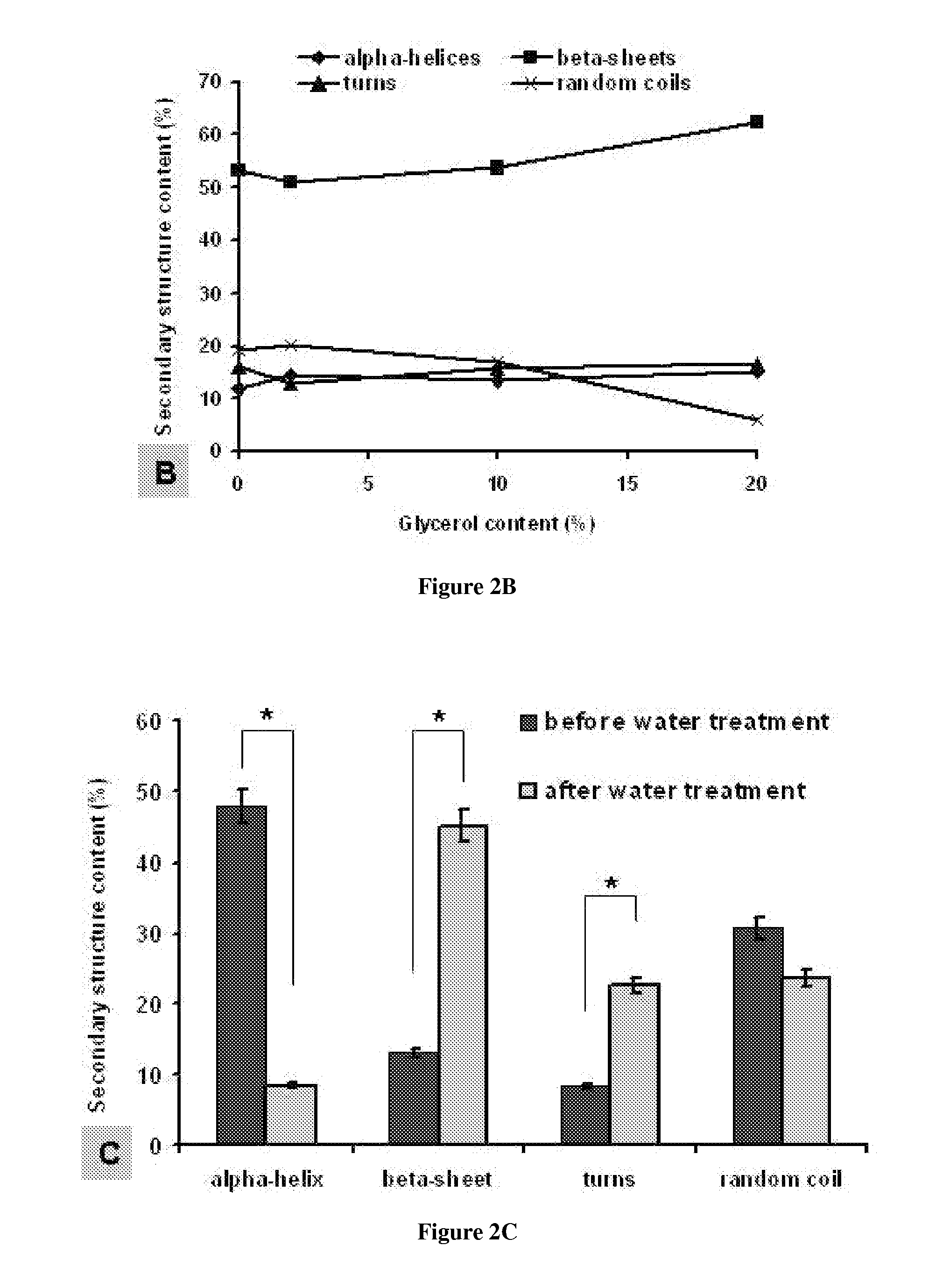
InactiveUS20110223153A1Distinct propertyAdds “ green chemistry ” valueAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsActive agentGlycerol
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for preparing aqueous insoluble, ductile, flexible silk fibroin films. The silk films comprise silk fibroin and about 10% to about 50% (w / w) glycerol, and are prepared by entirely aqueous processes. The ductile silk film may be further treated by extracting the glycerol from and re-drying the silk film. Active agents may be embedded in or deposited on the glycerol modified silk film for a variety of medical applications. The films may be into 3-dimentional structures, or placed on support surfaces as labels or coatings. The glycerol modified silk films of the present invention are useful in variety of applications such as tissue engineering, medical devices or implants, drug delivery, and edible pharmaceutical or food labels.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Acidic, protein-containing drinks with improved sensory and functional characteristics
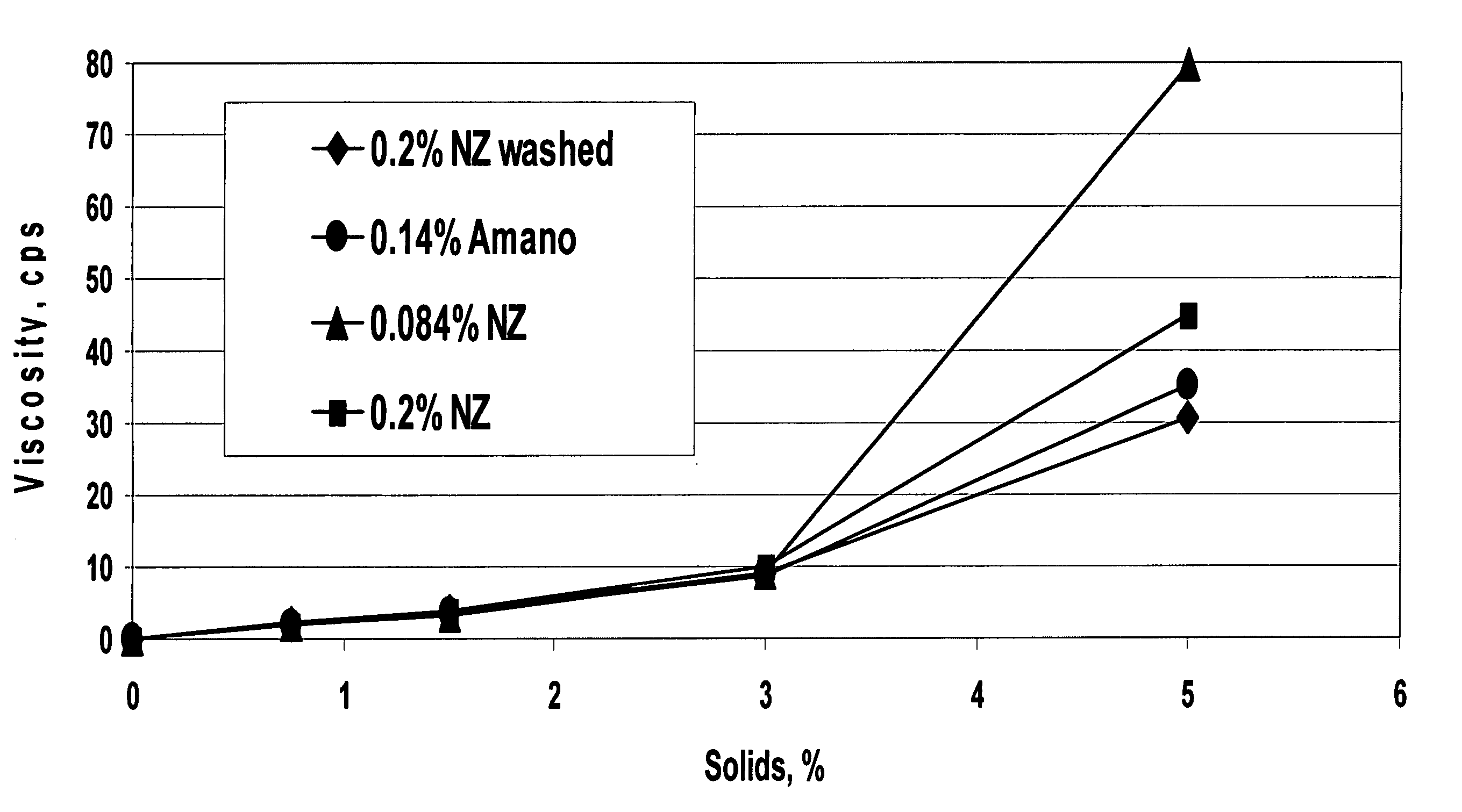
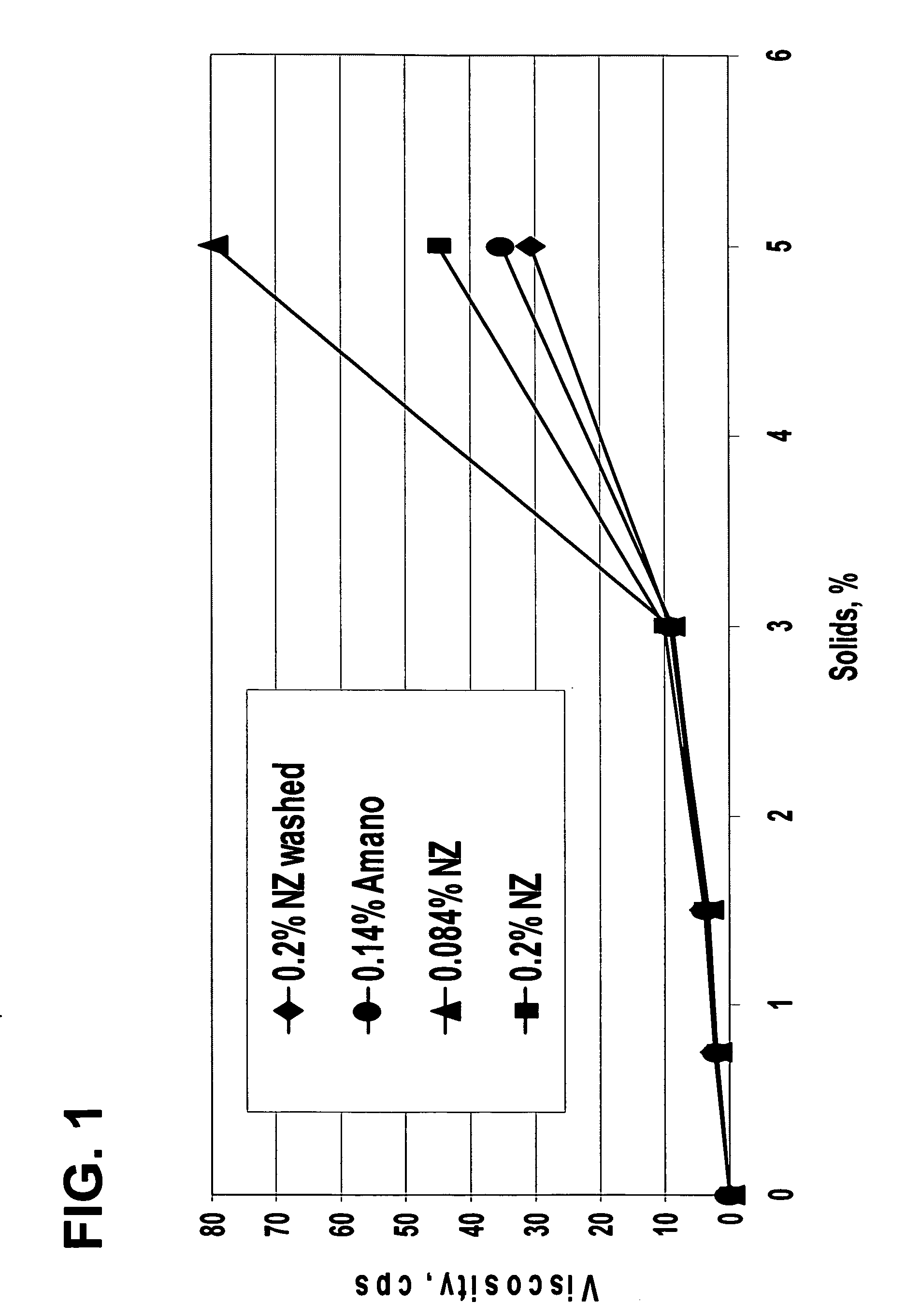
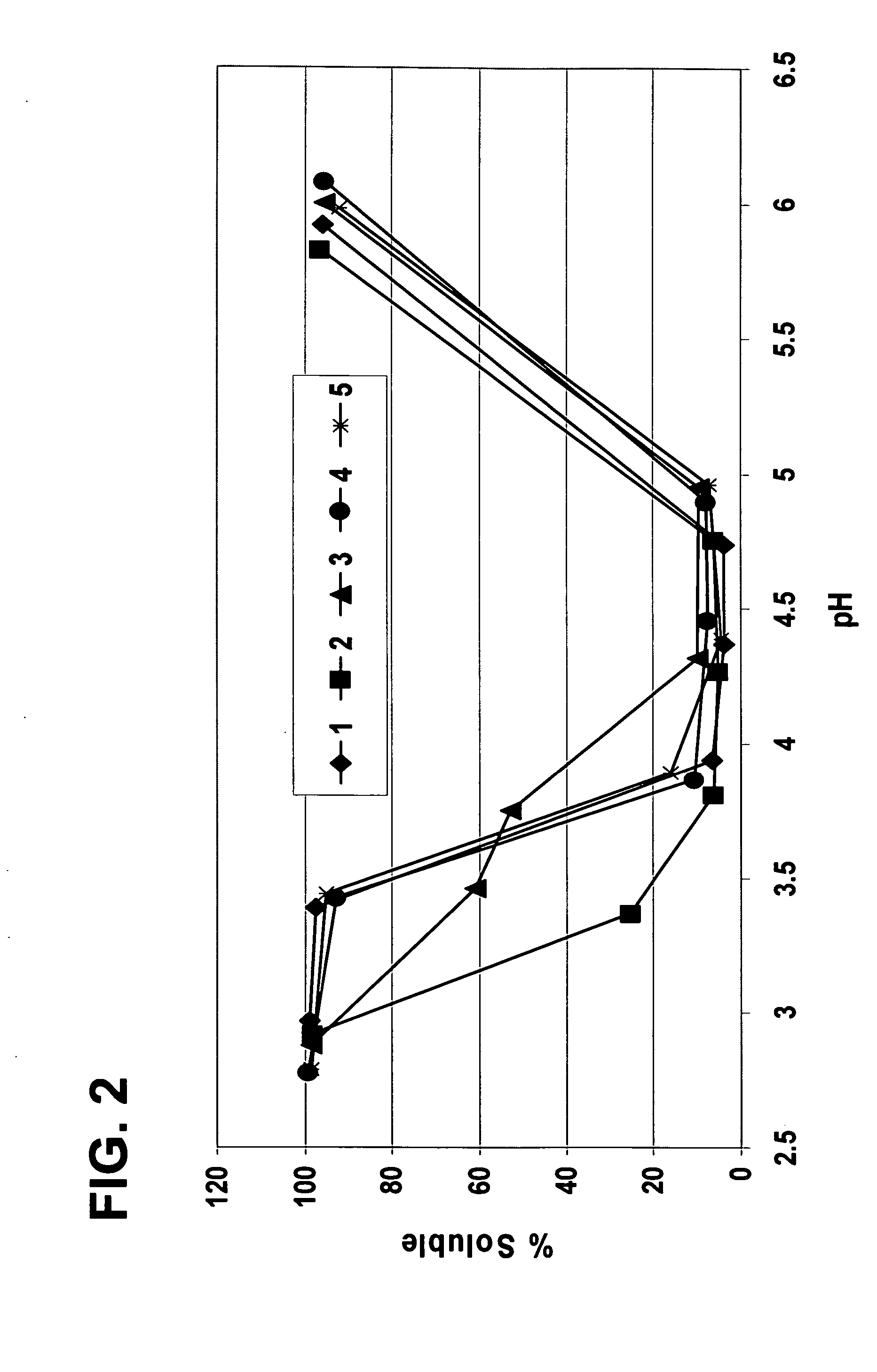
InactiveUS20070014910A1Improve suspendabilityWell flavorHydrolasesVegetable proteins working-upPlant proteinReduced viscosity
Processes for producing acidic, protein-containing drinks are disclosed. Specifically, the processes comprise producing acidic, protein-containing drinks comprising plant protein material. The acidic, protein-containing drinks have improved sensory and functional characteristics such as reduced viscosity, improved sedimentation rate, and improved mouthfeel.
Owner:ALTEMUELLER ANDREAS G +1
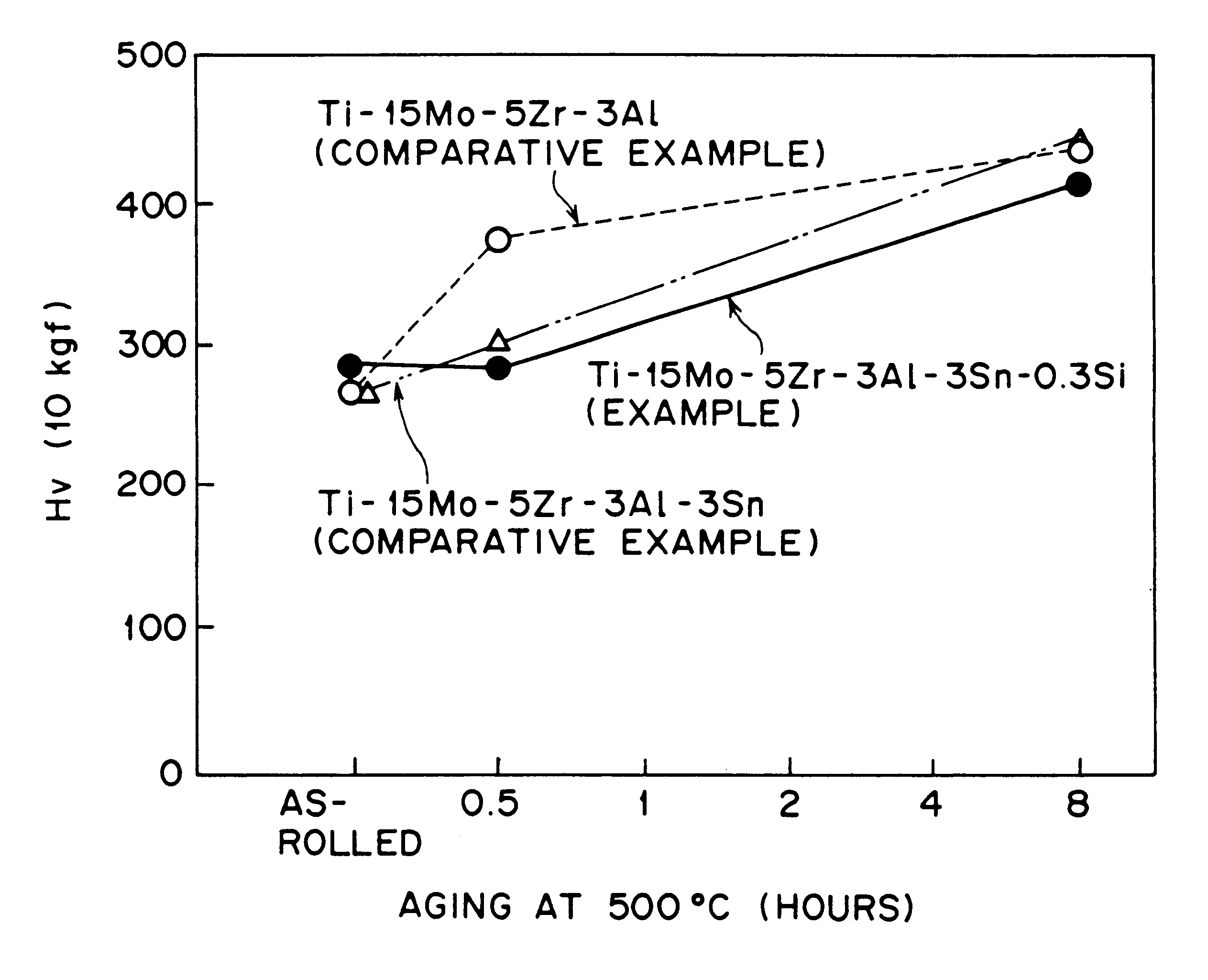
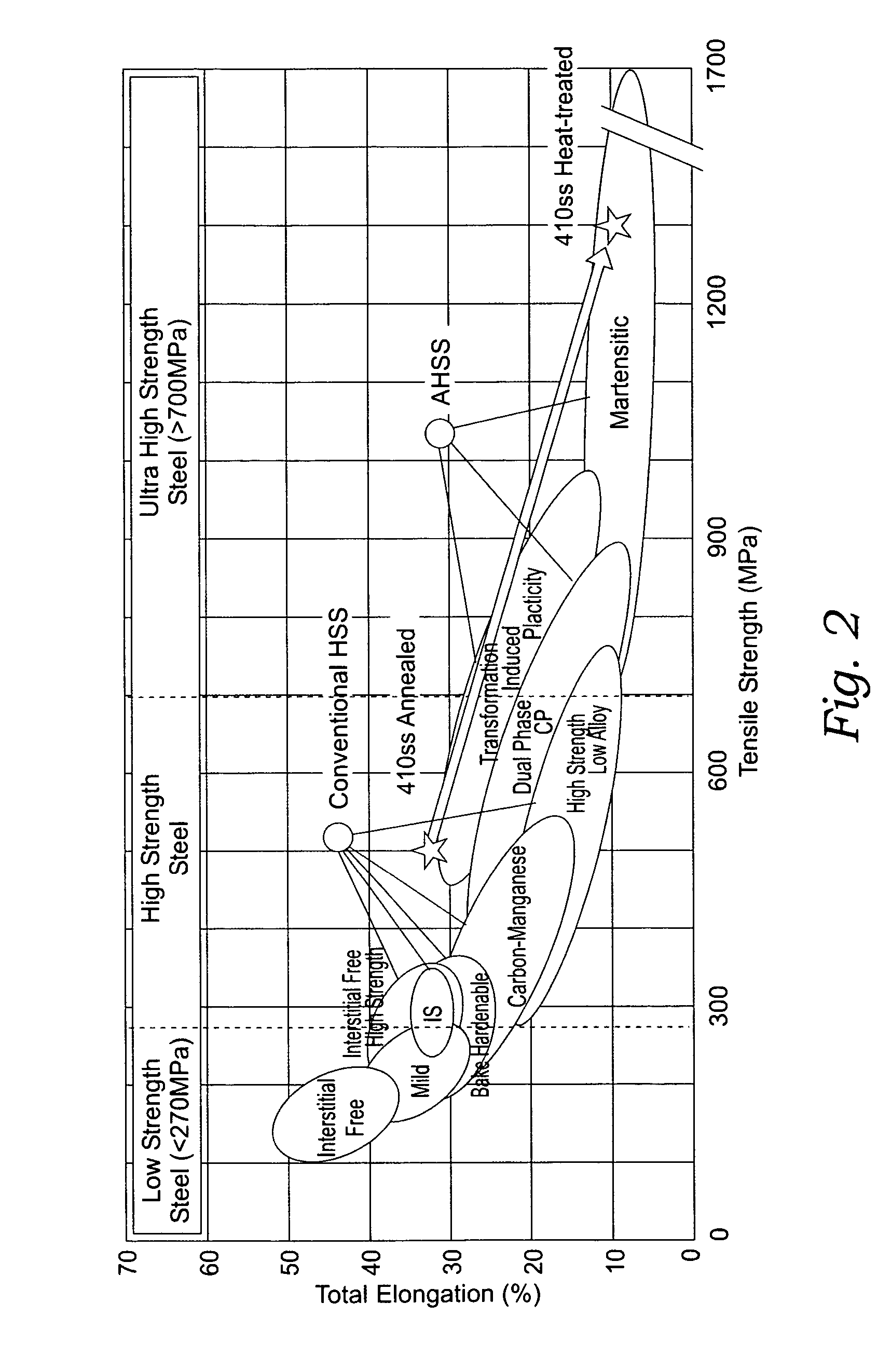
Titanium alloy and production thereof
A near-beta or beta titanium alloy having high strength, high ductility, and high toughness which is capable of coil rolling at a high temperature and recoiling for high productivity, and a process for producing said titanium alloy. The titanium alloy contains not more than 1.0% (excluding 0%) of Si alone or in combination with not more than 10% of Sn. The process comprises heating a beta alloy or near-beta alloy containing not more than 1.0% (excluding 0%) of Si alone or in combination with not more than 10% of Sn and subjecting said alloy to plastic deformation while keeping silicides solved in it at a temperature above the beta-transus, so that silicides precipitate in the form of fine particles, with recrystallization suppressed. The resulting titanium alloy is good in workability and has high strength after aging treatment.< / PTEXT>
Owner:LG PHILIPS LCD CO LTD +1
Pegylated Factor VII Glycoforms
InactiveUS20080039373A1Improve functional propertiesFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIIOligosaccharide
The invention concerns a preparation comprising a plurality of Factor VII polypeptides or Factor VII-related polypeptides, wherein the polypeptides comprise asparagine-linked and / or serine-linked oligosaccharide chains, and wherein at least one oligosaccharide group is covalently attached to at least one polymeric group.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Resistant starch-hydrocolloid blends and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080233260A1Improve functional propertiesHighly suitableMilk preparationAnimal feeding stuffResistant starchAlpha-amylase
Interacted starch products made up of resistant starch and hydrocolloid are provided which exhibit at least about 20% resistance to α-amylase digestion. The products are prepared by mixing together quantities of resistant starch and hydrocolloid in water with mixing and optional heating, followed by drying. Foods containing the interacted starch products are also disclosed.
Owner:MGPI PROCESSING
Multifocal Iol
InactiveUS20080312738A1Easy to switchImprove functional propertiesIntraocular lensIntraocular lensPhysics
Intraocular lens consisting of a centrally located lens part with supporting parts (haptics) on either side. According to the invention one supporting part is non-deformable and another supporting part, located approximately opposite said supporting part, is deformable. In this way it is achieved that when the ciliary cell contracts the reduction in the space therein is used for moving the centre of the lens part. By arranging the transition between distance and near part in a multifocal lens on said centre, switching from the distance part to the near part can be obtained for the user in an almost natural way.
Owner:OCULENTIS HLDG
Means for replacing common sugars if foods for enhanced nutrition
InactiveUS20080260925A1Great tasteSuperior digestive toleranceFood ingredient functionsFood preparationLow glucoseSide effect
A means for replacing common sugars (particularly sucrose) in a range of foods that maximizes sugar-like taste, texture and other key properties of sugar while minimizing the undesirable traits such as blood sugar response, digestive side effects, high caloric content and aftertastes. Various differing ratios and combinations of high intensity sweetening agents, high molecular weight bulking agent(s), substantially non-digestible sugar(s), and low molecular weight sugar alcohol(s) are used for various applications such as tabletop sugar substitute, frozen deserts, condiments, baked goods, chocolate and confectionaries have different formulations. These sugar replacement approaches are highly relevant to the production of diabetic-friendly foods, diet and / or reduced calorie foods, non-cariogenic (tooth-friendly) foods and other sweet, low-glycemic foods.
Owner:ZINK GALEN PAUL
Silane additives for lubricants and fuels
InactiveUS6887835B1Improve functional propertiesSilicon organic compoundsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsSilanesZinc
Lubricants, especially lubricating oils, and fuels, especially hydrocarbon fuels, contain a class of anti-wear, anti-fatigue, and extreme pressure additives that are derived from silanes. The additives can be used as either partial or complete replacements for zinc dialkyldithiophosphates currently used in lubricants and fuels.
Owner:CHEMTURA CORP
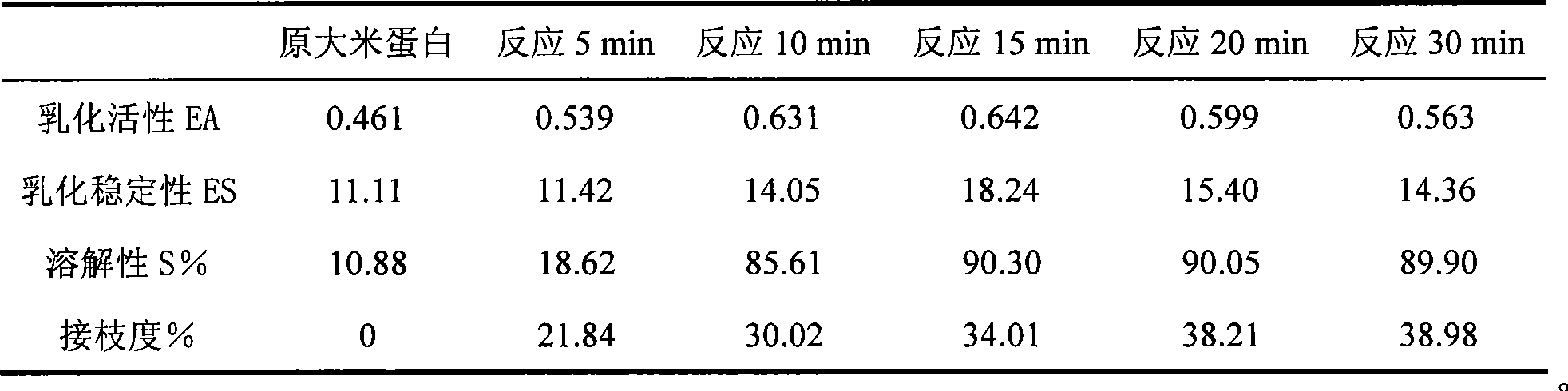
Method for improving rice protein functional property with protein-polysaccharide graft coupling technology
InactiveCN101429226AImprove functional propertiesImprove the level of comprehensive utilizationPeptide preparation methodsPhosphorylationRice protein
The invention provides a method for improving functional property of rice protein by protein-polyoses graft coupling technology, which belongs to the technical field of hydrophobicity vegetable protein modification. The method is to carry out glycosylation modification on a side product of producing rice starch and rice syrup, namely the rice protein as a raw material by different glycosyl donors through a wet method. Dissolvability, emulsibility, foamability and other functional properties of the rice protein are effectively improved and sufficiently utilized through the graft reaction of the rice protein and sugar. Compared with methods chemically modifying the vegetable protein, such as alkylation, phosphorylation, deamidization and the like, the method is safe and environment friendly, a rice protein-polyoses graft coupling product can be used as a natural macromolecular emulsifying agent or a protein nutritional reinforcing agent to sufficiently reflect and exert low sensitivity and high nutritive characteristic of the rice protein, thereby effectively expanding the application field of the rice protein. Meanwhile, the method provides theoretical reference for deep research and development of the hydrophobicity vegetable protein.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Roof vent having labyrinth features
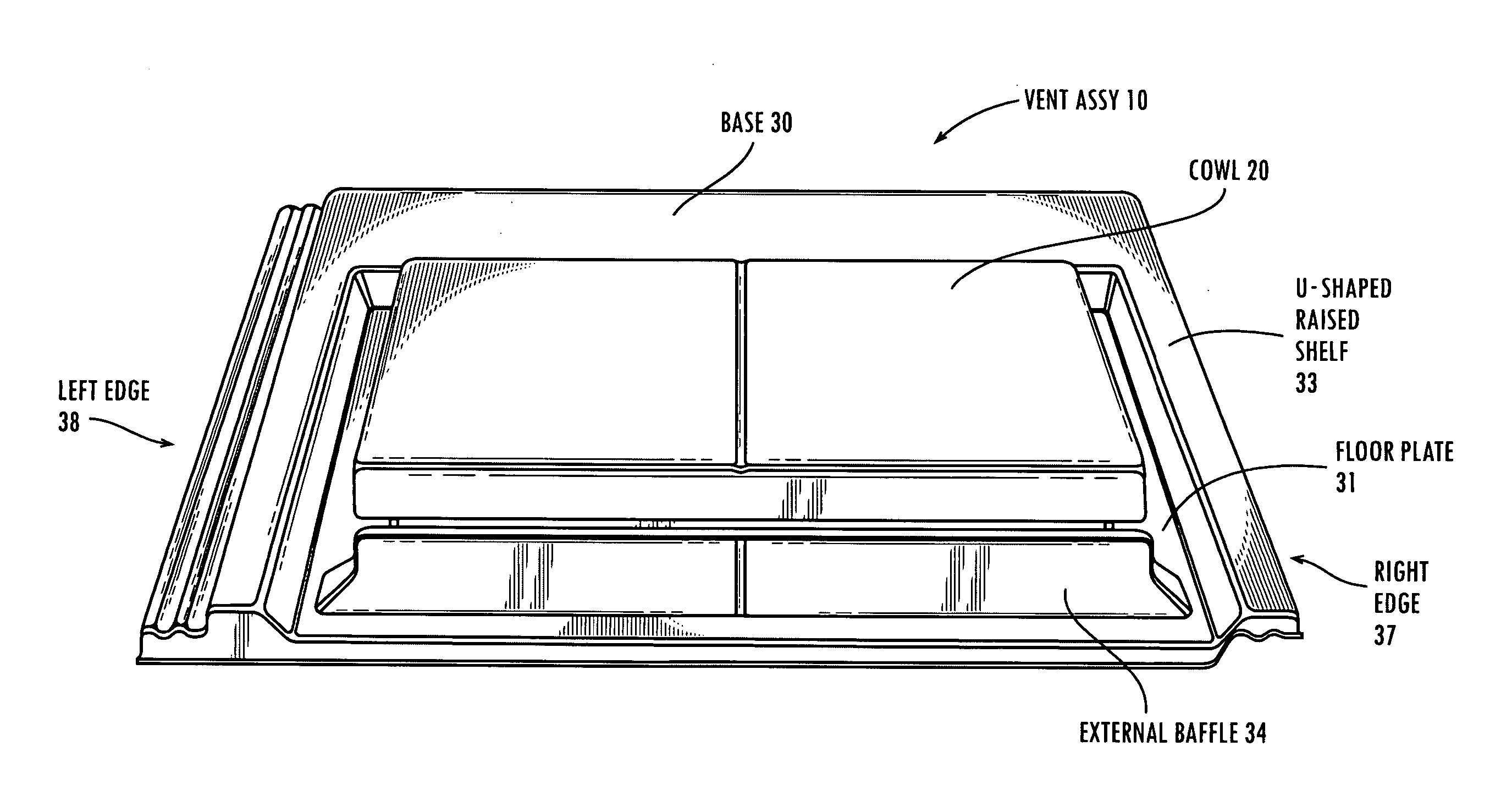
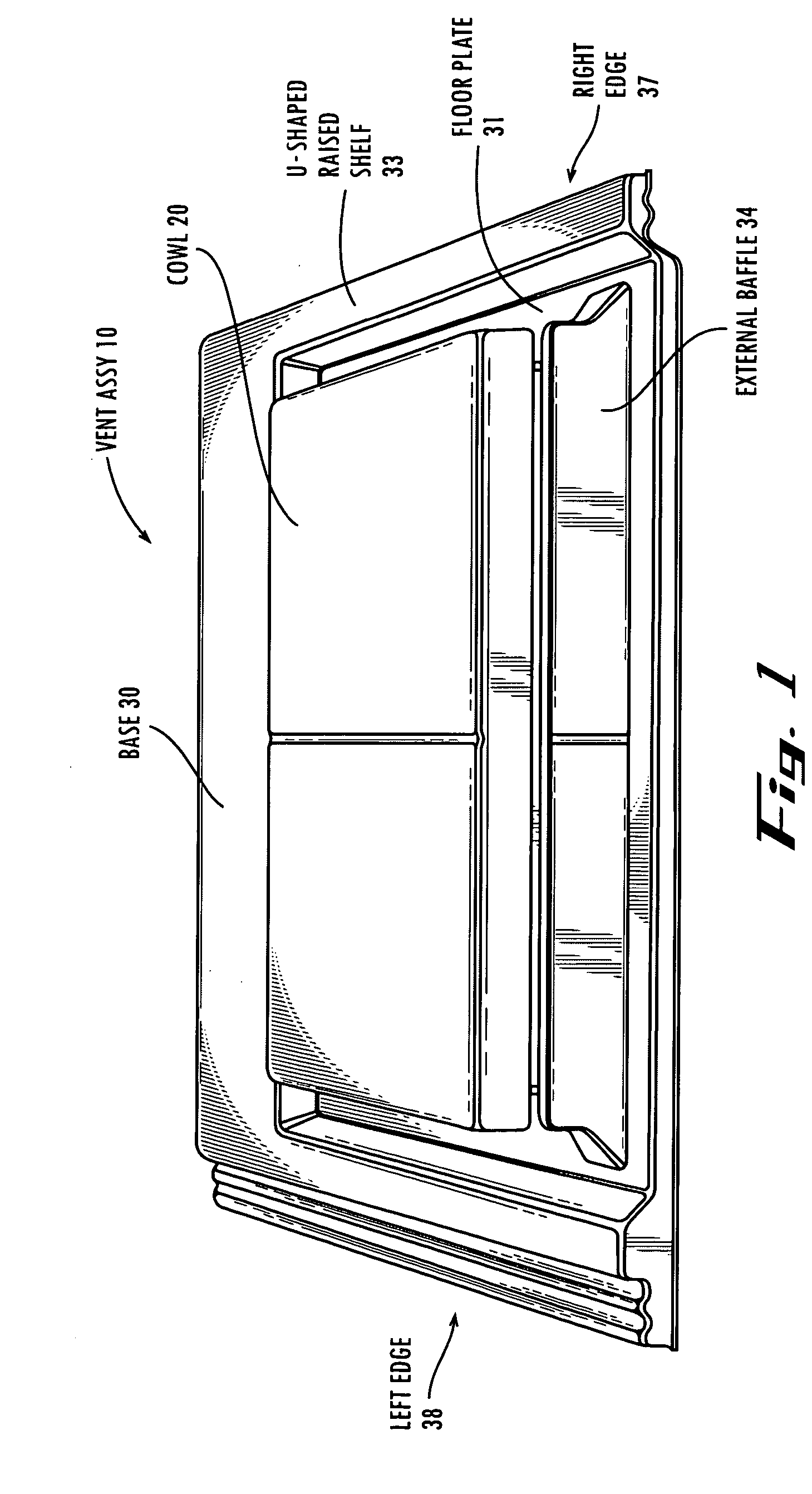
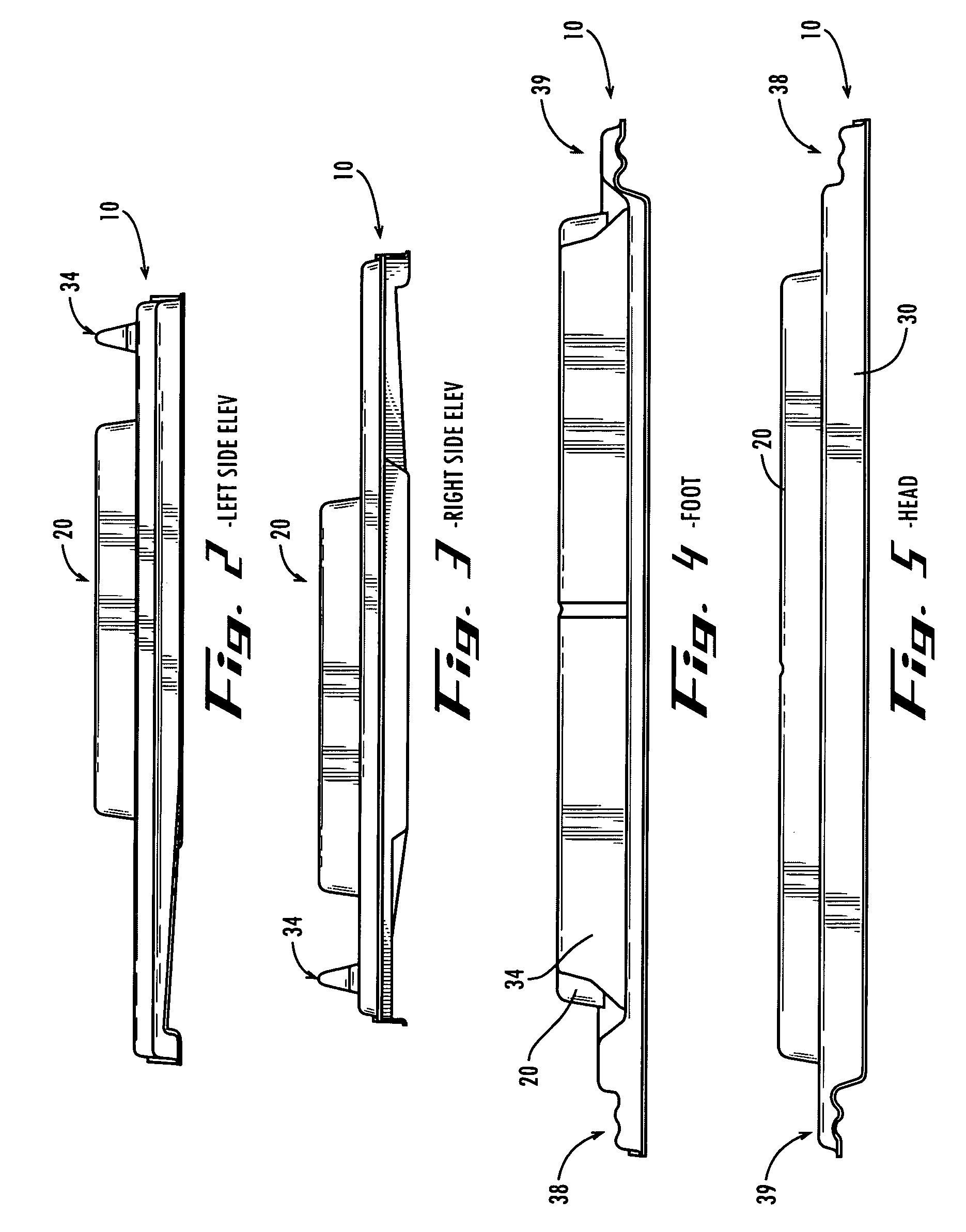
InactiveUS20050130581A1Feature is removedAdd aesthetic featuresRoof covering using tiles/slatesLighting and heating apparatusLeading edgeBrick
A roof vent construction which is comprised of an assembly including a cowl, a base, and a cowl retaining member. These elements provide a structure which provides cover for rain and discourages rain from entering the vent underneath the cowl, but nevertheless allows for suitable ventilation as needed. In one embodiment a configuration is used in which an external baffle is used which air passes before passing underneath a cowl. Once the air is passed underneath the cowl, the air then passes over one and one configuration two internal baffles before the air passes out of a pair of vent cavities defined by the base. In a second configuration, a cowl extends substantially to the leading edge of the construction. Air flows underneath the leading edge of the cowl and then passes over a large internal baffle, over a first small internal baffle, and finally over a second small internal baffle before passing through the vent cavities and out of the structure. Another invention relates to the use of two surface portions on the vent assembly, one surface portion configured to match a first course of tiles and the other surface portion configured to match a second course of tiles adjacent to said first course of tiles.
Owner:BORAL LIFETILE +1
Cardboard tampon applicator with optical enhancing material coated on inner layers
Owner:EDGEWELL PERSONAL CARE BRANDS LLC +1
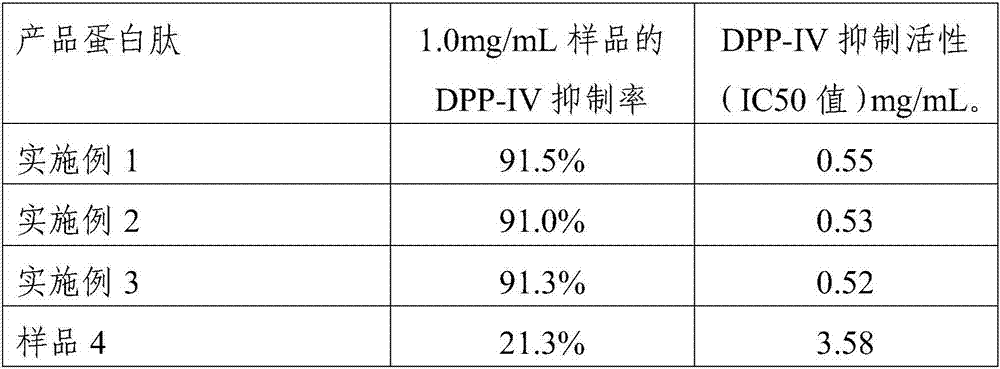
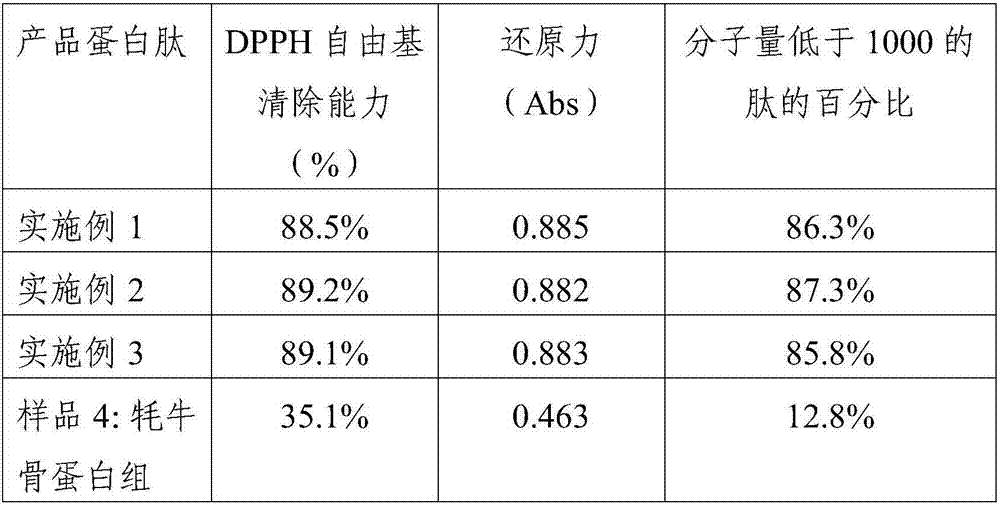
Yak bone protein peptide with DPP-IV inhibitory activity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107141336AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove antioxidant functionMilk preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptideAnti oxidative
The invention provides yak bone protein peptide with DPP-IV inhibitory activity and a preparation method thereof. The yak bone protein peptide provided by the invention is optimally prepared from the enzymolysis products by conducting multiple-step enzymolysis by multilevel compound protease on the yak bone protein prepared from yak bone, and the compound protease contains alkali protease, neutral proteinase, trypsin and flavourzyme. The yak bone protein peptide provided by the invention has excellent DPP-IV inhibition and antioxidation functions, and can be used as a DPP-IV inhibitor and antioxidation raw material to be applied to special foods and nutritional foods.
Owner:人民国肽集团有限公司
Method for manufacturing automotive structural members
InactiveUS20070006461A1Reduce hardnessKeep the heatMetal-working apparatusFurnace typesMartensitic stainless steelHardness
A method for making structural automotive components and the like includes providing a blank of air hardenable martensitic stainless steel in the annealed condition. The steel blank has a thickness in the range of 0.5-5.0 mm., and is formed utilizing stamping, forging, pressing, or roller forming techniques or the like into the form of an automotive structural member. The automotive structural member is then hardened by application of heat, preferably to between 950° C. and 1100° C. for standard martensitic stainless steels. Thereafter, the automotive structural member is preferably cooled at a rate greater than 25° C. per minute to achieve a Rockwell C hardness of at least 39. The automotive structural member may undergo additional heat treating processes including high temperature or low temperature tempering processes which may incorporate electro-coating.
Owner:CODD DANIEL SHAWN
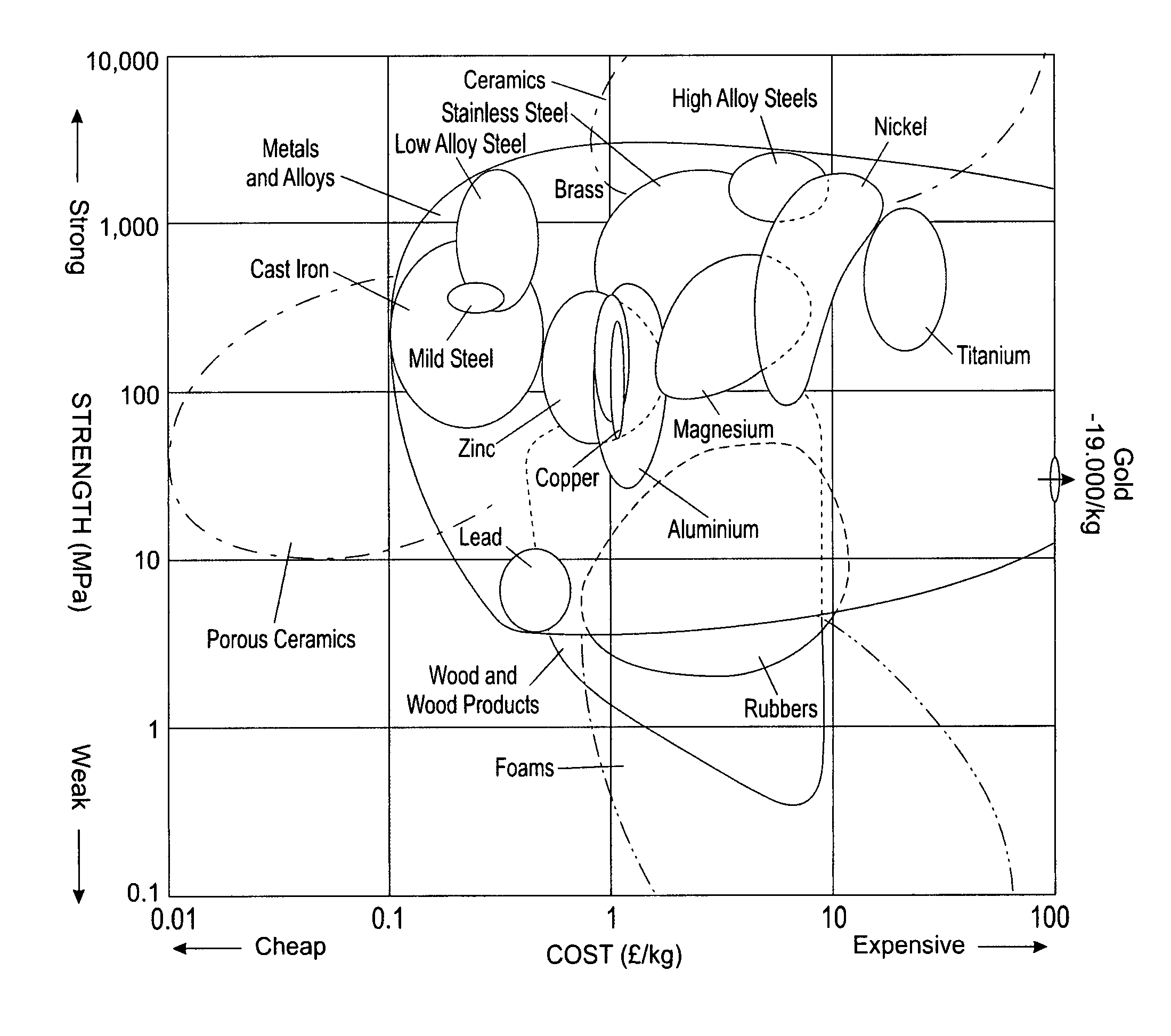
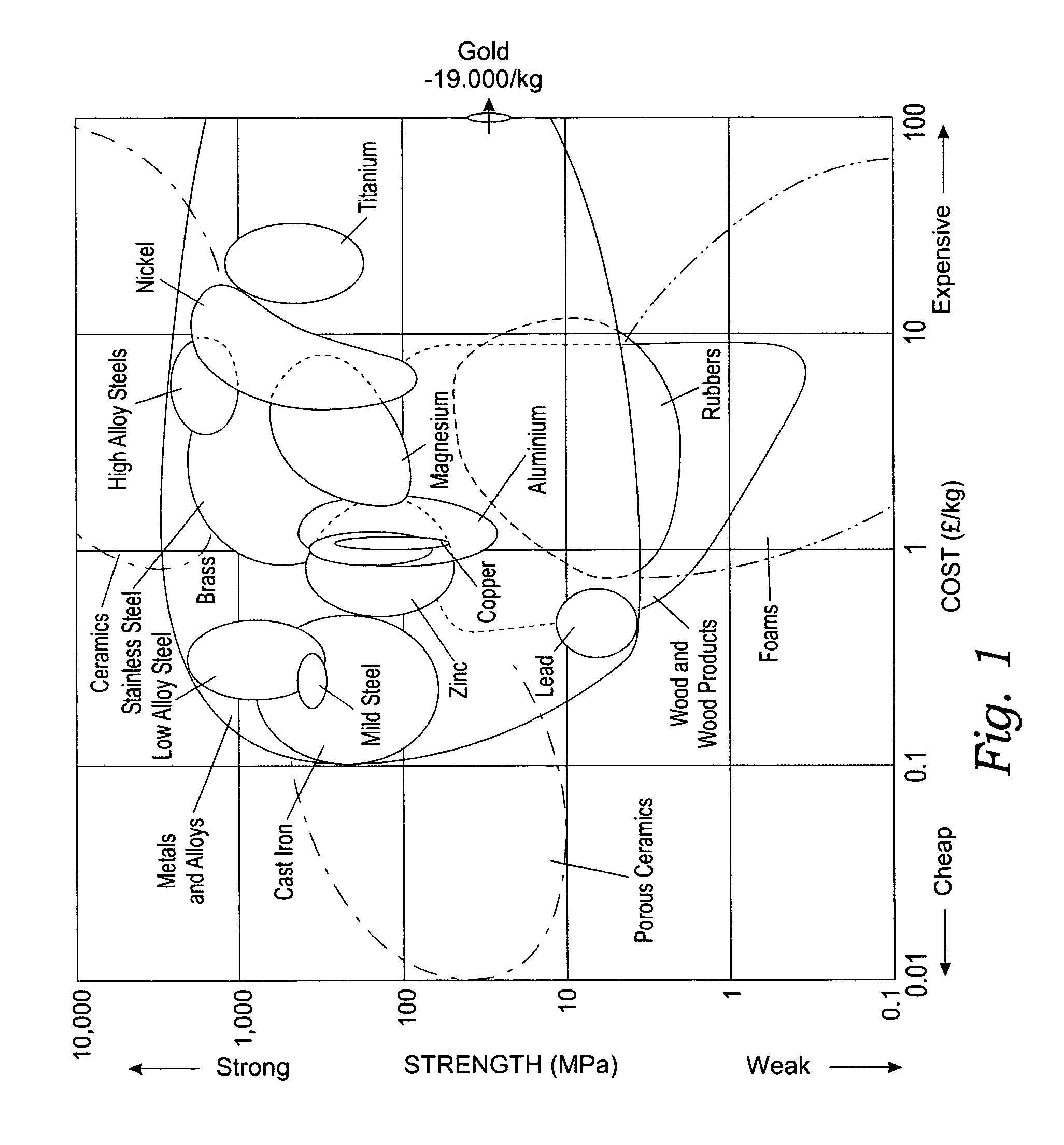
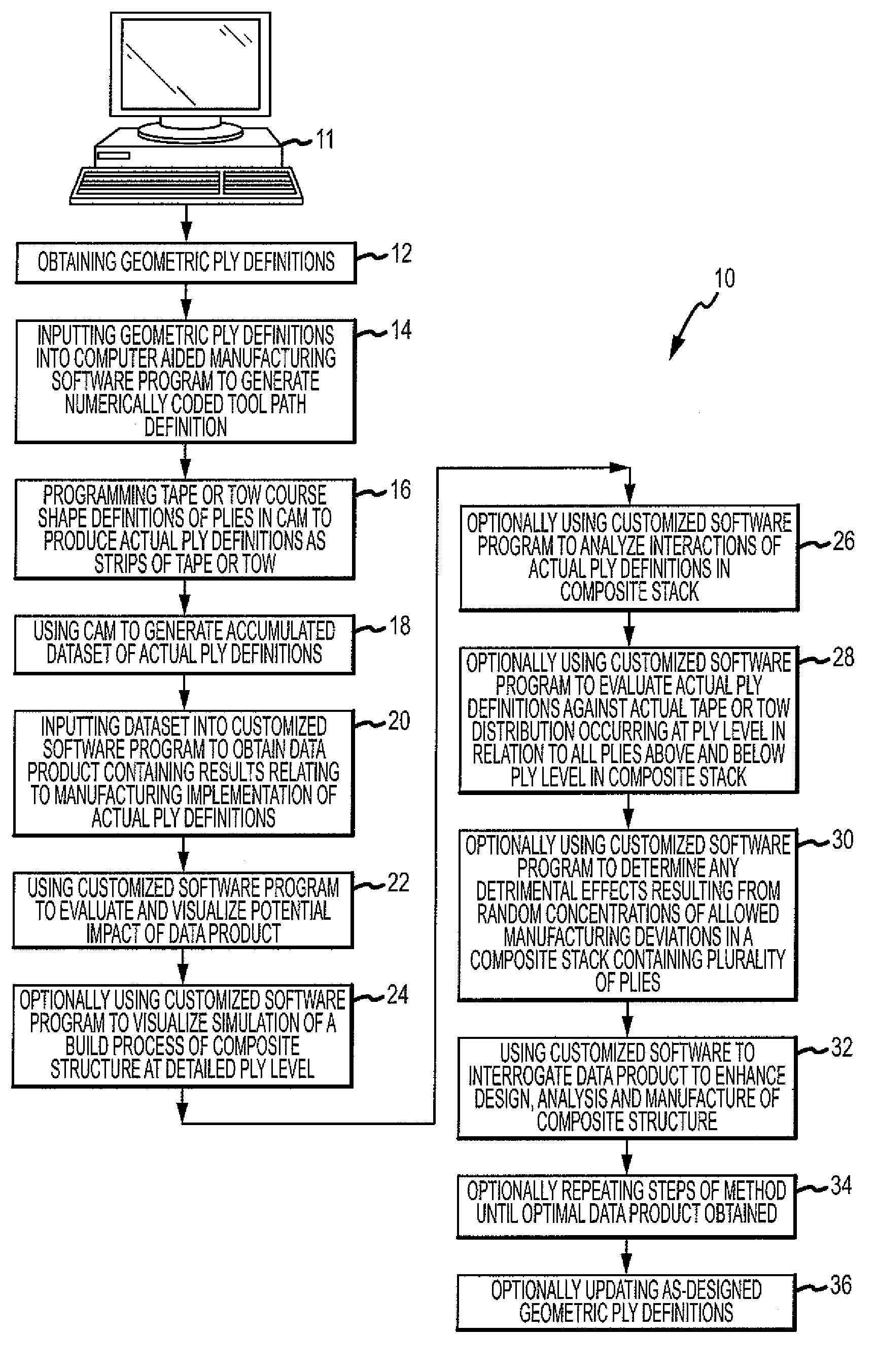
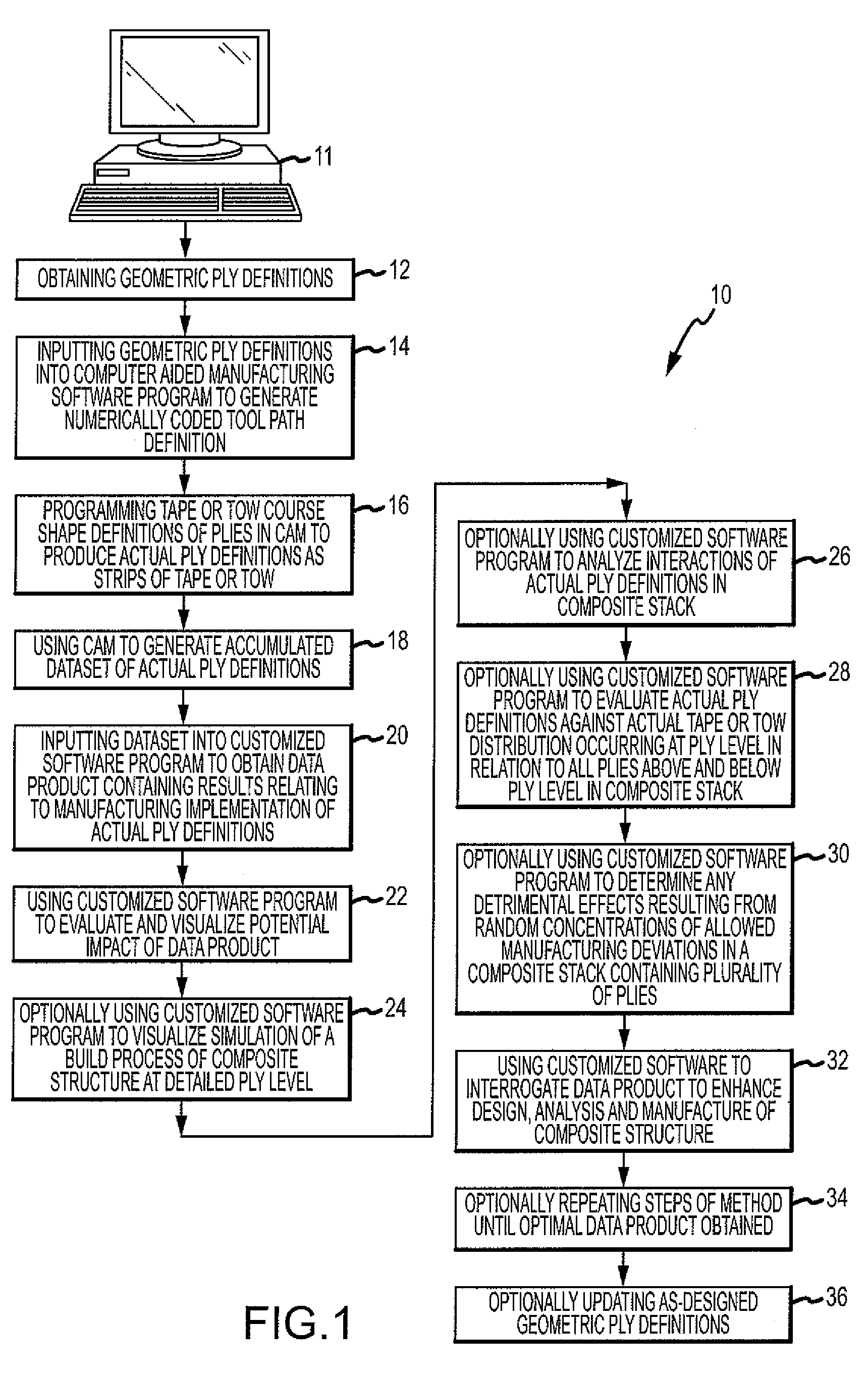
Method of analyzing composite structures
ActiveUS8108058B2Simple designImprove manufactureProgramme controlTotal factory controlData setPotential impact
A method is provided for generating a data product that allows for enhanced design, analysis and manufacture of a composite structure comprising a plurality of plies. The method comprises the steps of obtaining geometric ply definitions, inputting the geometric ply definitions into a computer aided manufacturing (CAM) software program to generate a numerically coded tool path definition containing centerline data for each tape or tow comprising a ply, programming tape or tow course shape definitions of a plurality of plies in CAM to produce actual ply definitions, using CAM to generate an accumulated dataset of actual ply definitions, using a customized software program to analyze the dataset to obtain a data product containing results relating to manufacturing implementation of the actual ply definitions, and using the customized software program to evaluate and visualize potential impact of the data product and to interrogate the data product.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for Producing a Glass Pane
InactiveUS20090241317A1Reduced risk of damageWide applicationPackagingGlass severing apparatusThermal energyEngineering
A method is described for producing a glass pane having at least one edge section delimiting the glass pane, for whose production the glass pane has been severed along the edge section with the aid of a severing procedure comprising a thermal energy introduction.The invention of the glass pane is enclosed at least sectionally and preferably along the entire edge section by a sheath immediately after production of the at least one edge section using a severing procedure comprising a thermal energy introduction.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
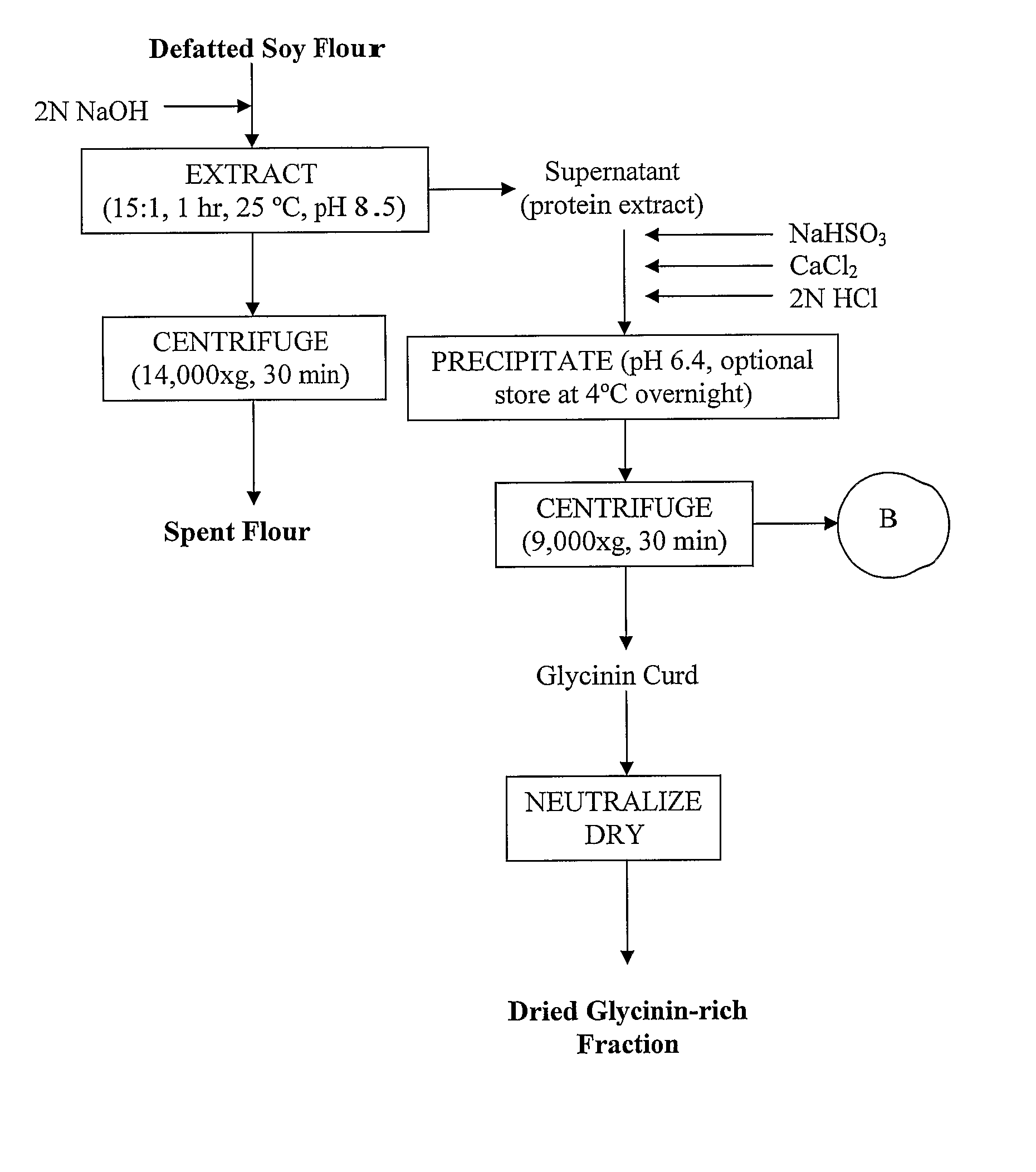
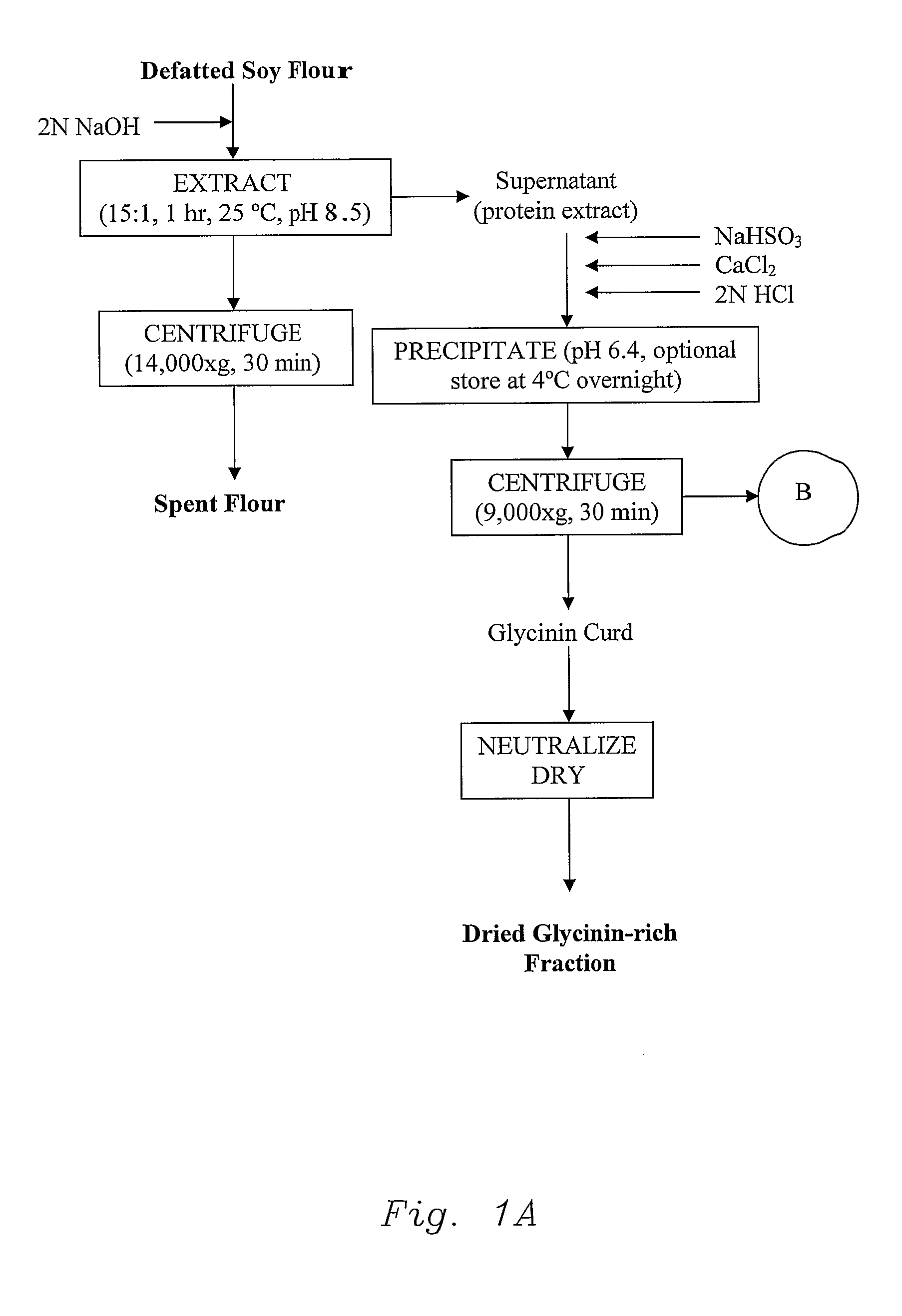
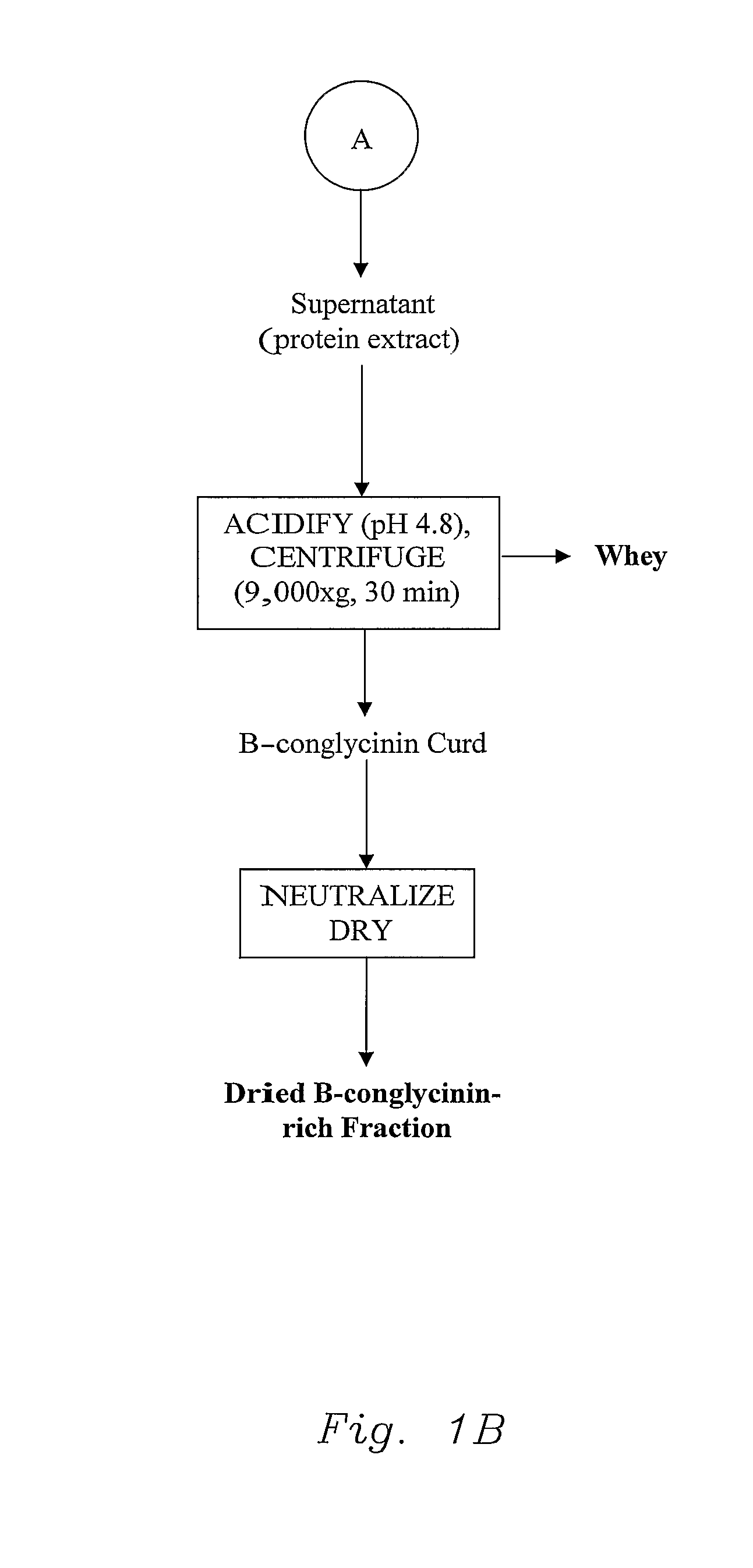
Novel Vegetable Protein Fractionization Process And Compositions
InactiveUS20080095914A1High in isoflavone contentUnique functional and nutritional applicabilityProtein composition from vegetable seedsDepsipeptidesFood industryFractionation
According to the invention a novel vegetable protein fractionation procedure is disclosed which includes a straightforward process to obtain 7S-rich (β-conglycinin-rich) and 11S-rich (glycinin-rich) isolated protein fractions with unique functional and nutritional properties desired by the food industry. The process is much simplified compared to the art and avoids multiple steps in the usual fractionation of soy protein and uses very small amounts of salts avoiding the necessity of excessive washing and desalting steps. The process yields high amounts of protein fractions with high isoflavone contents and improved functional properties.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com