Patents
Literature
33101results about "Packaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
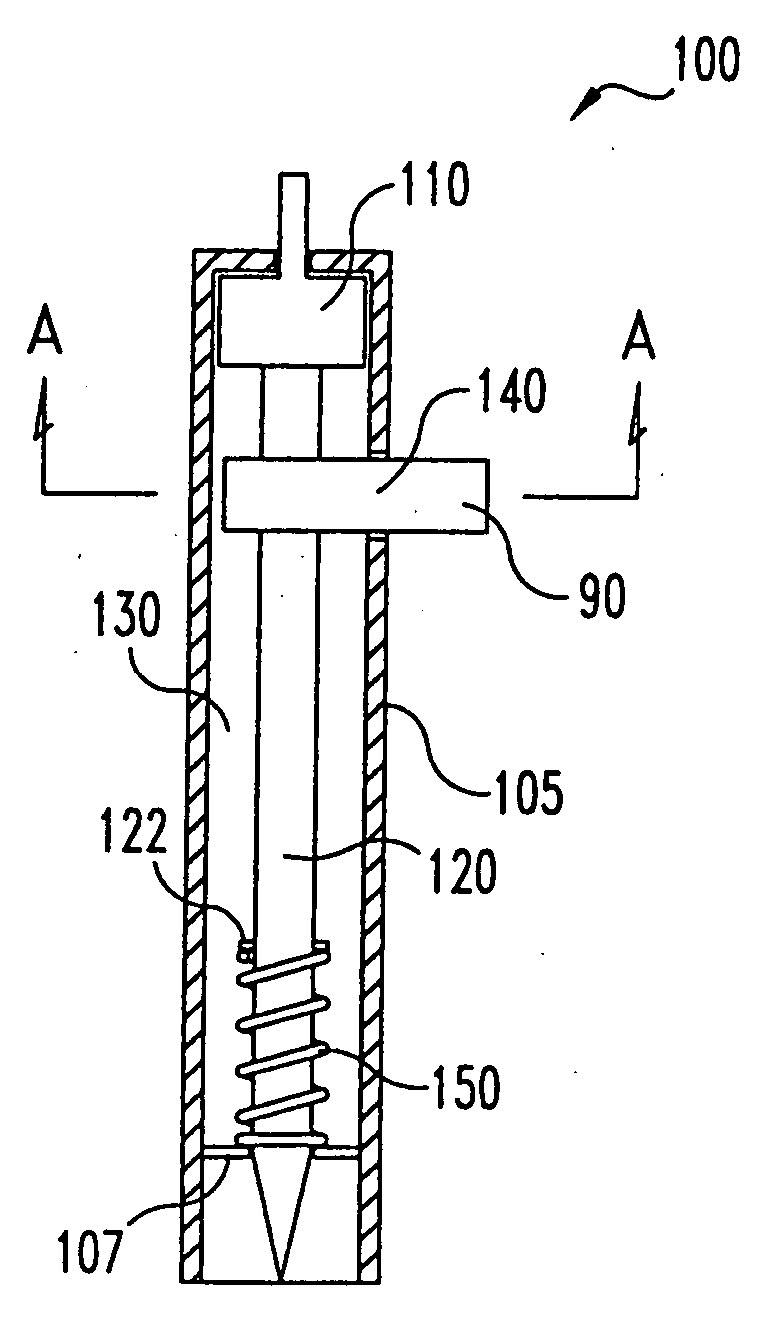
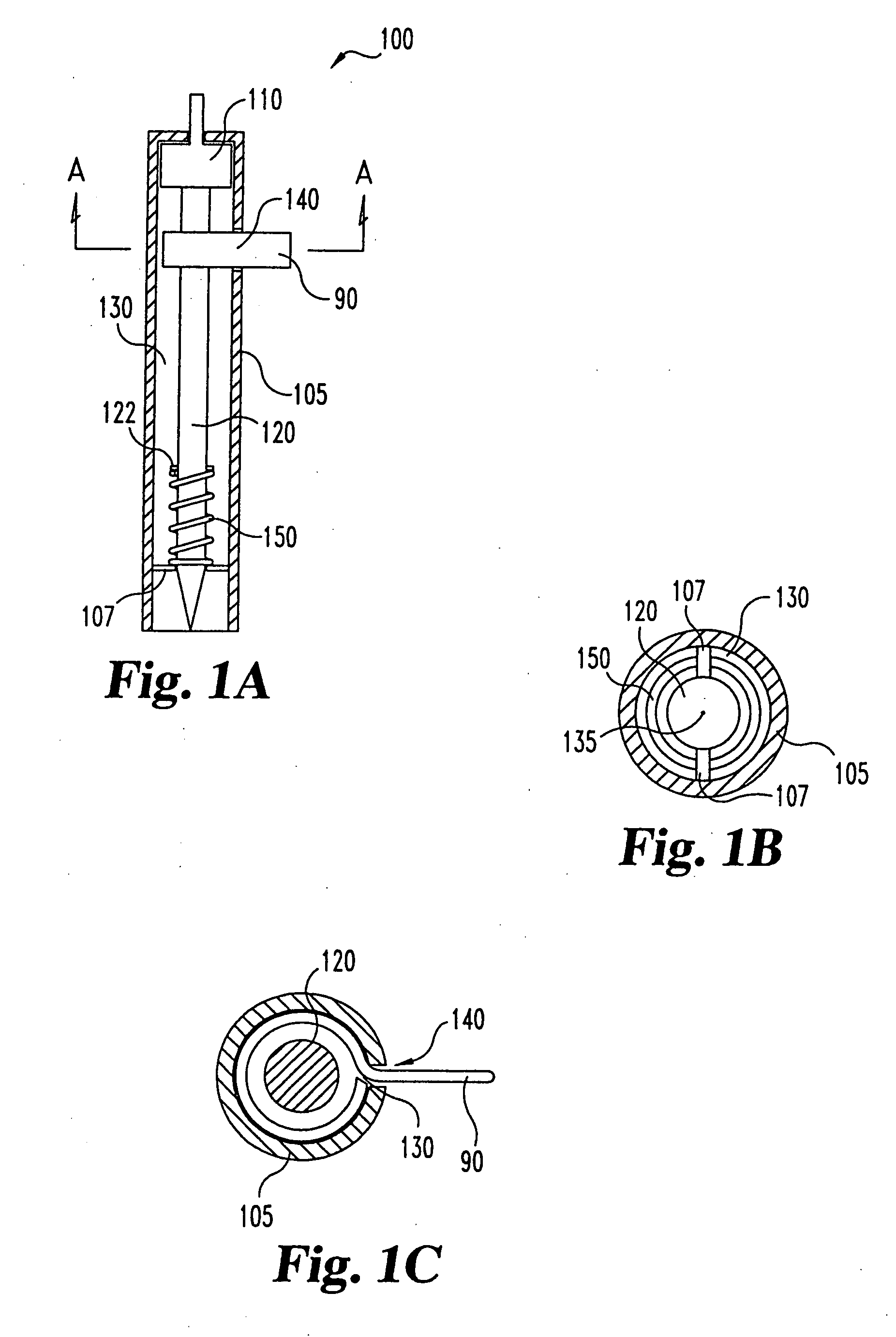
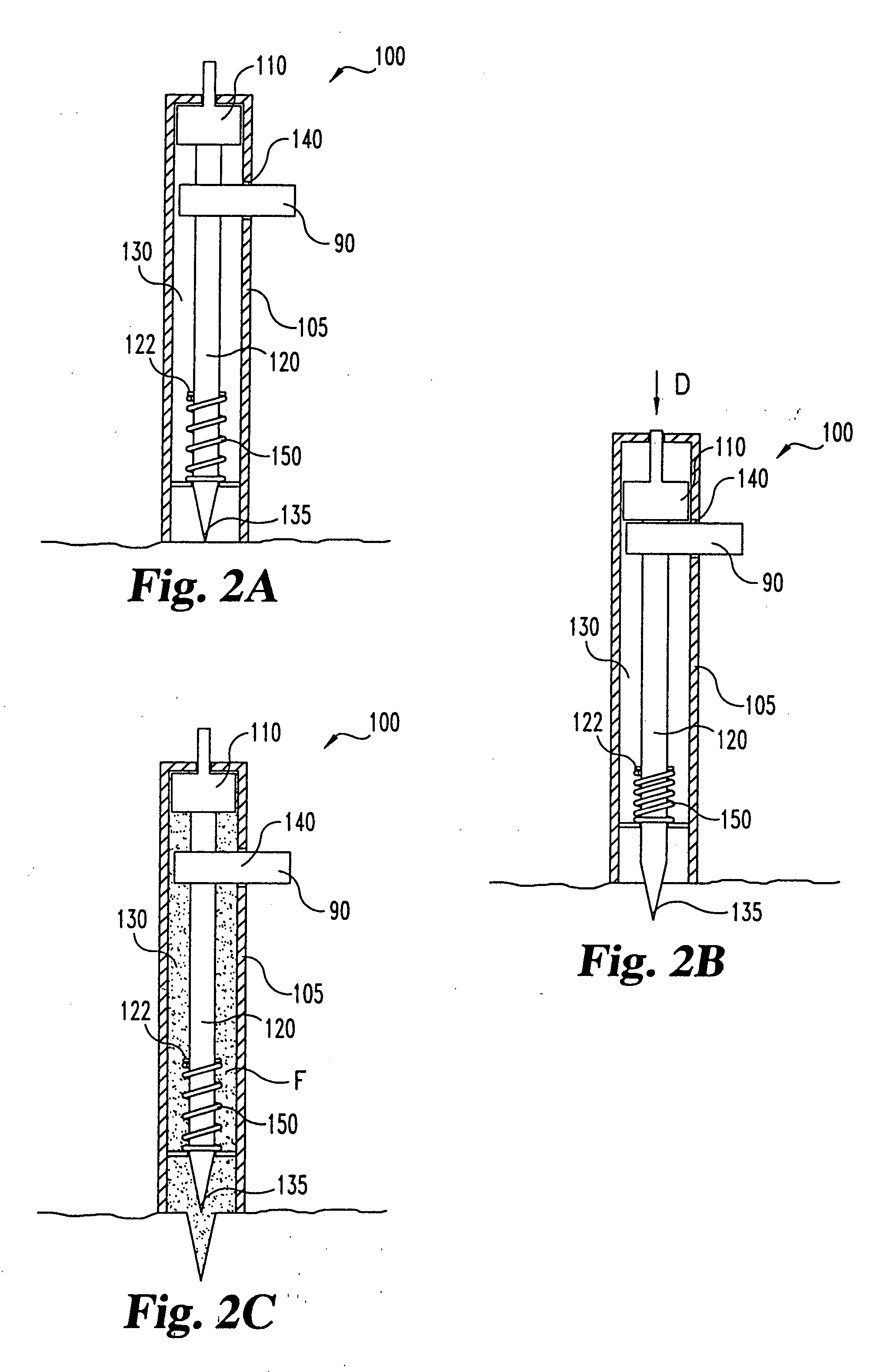
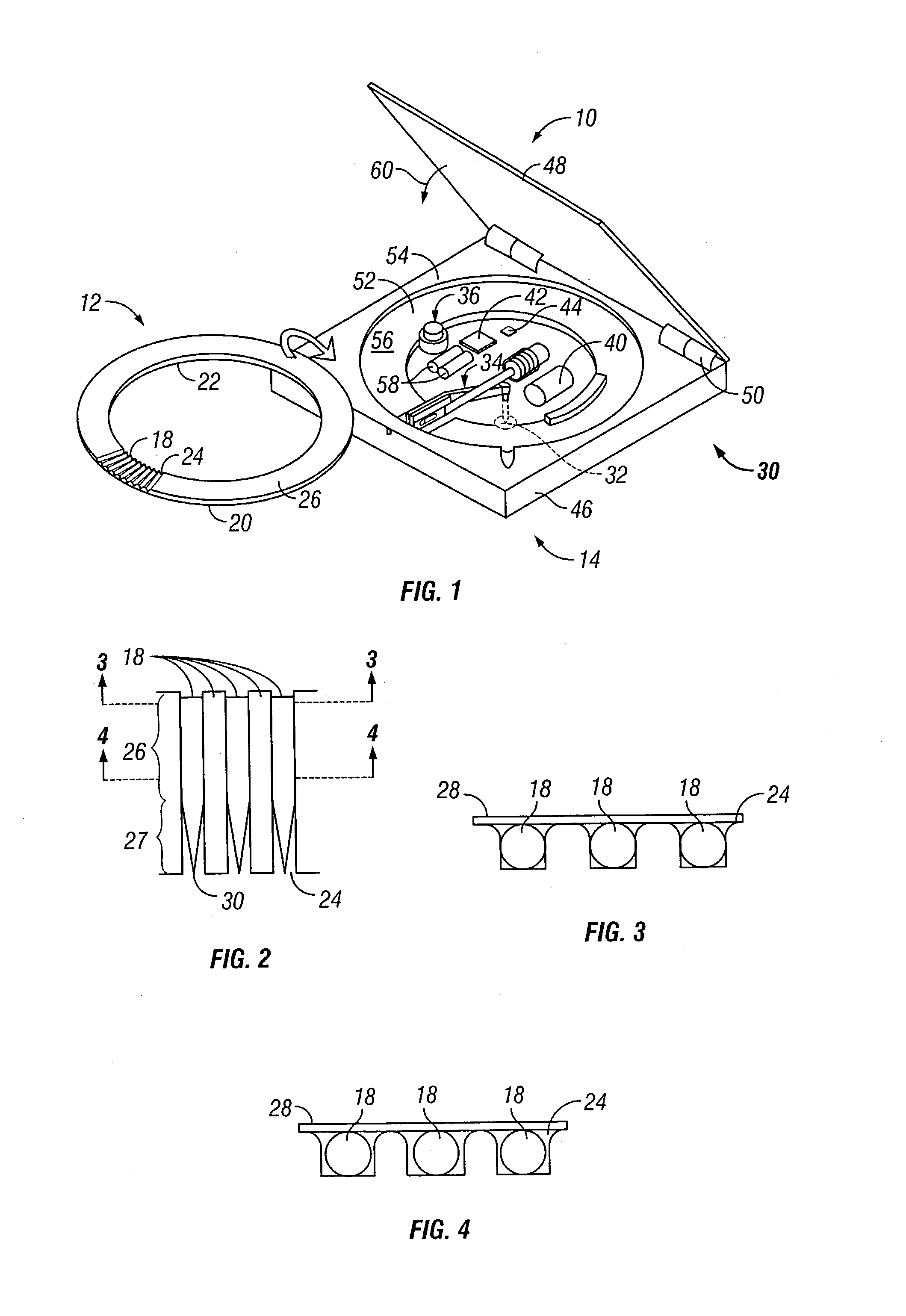
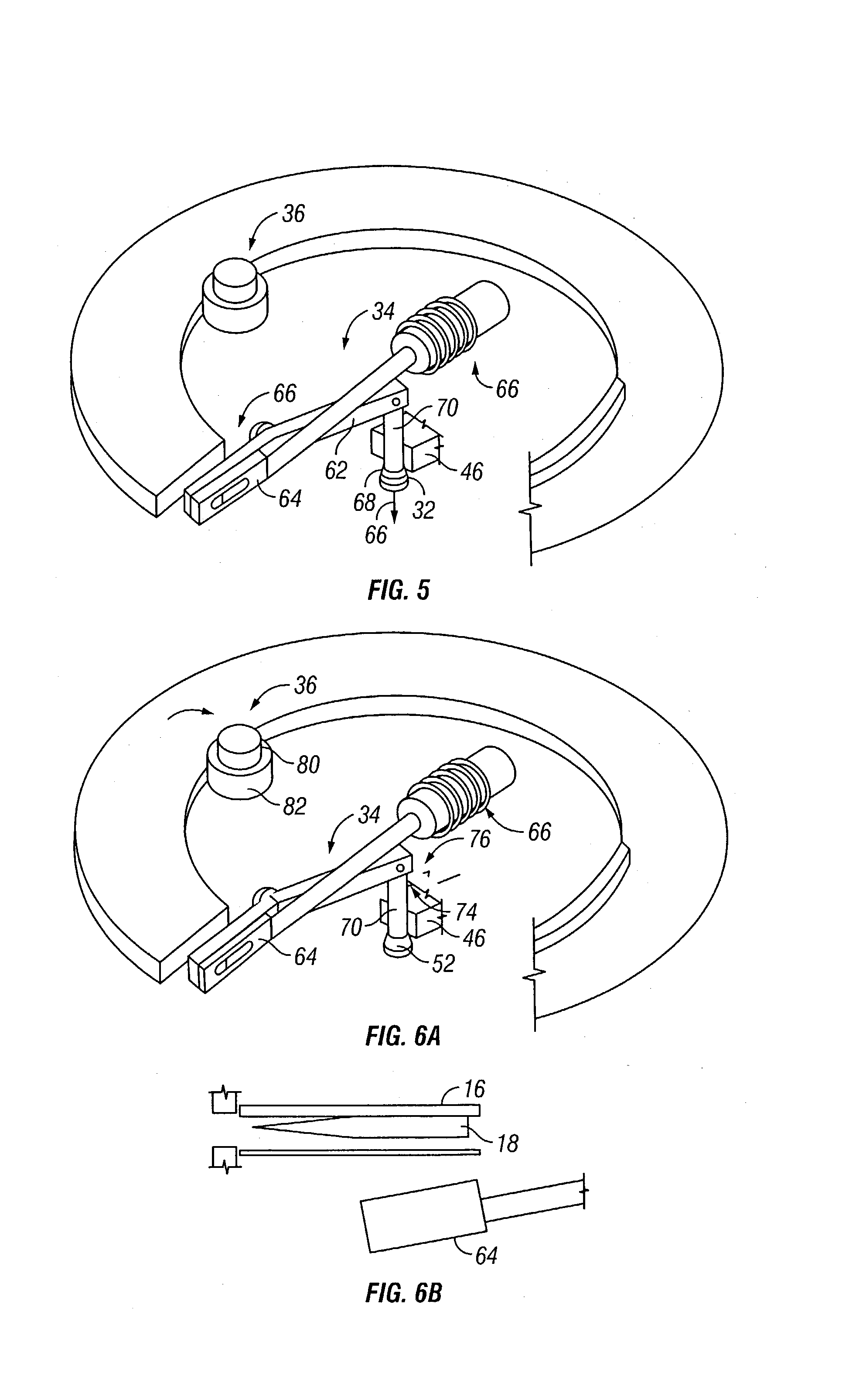
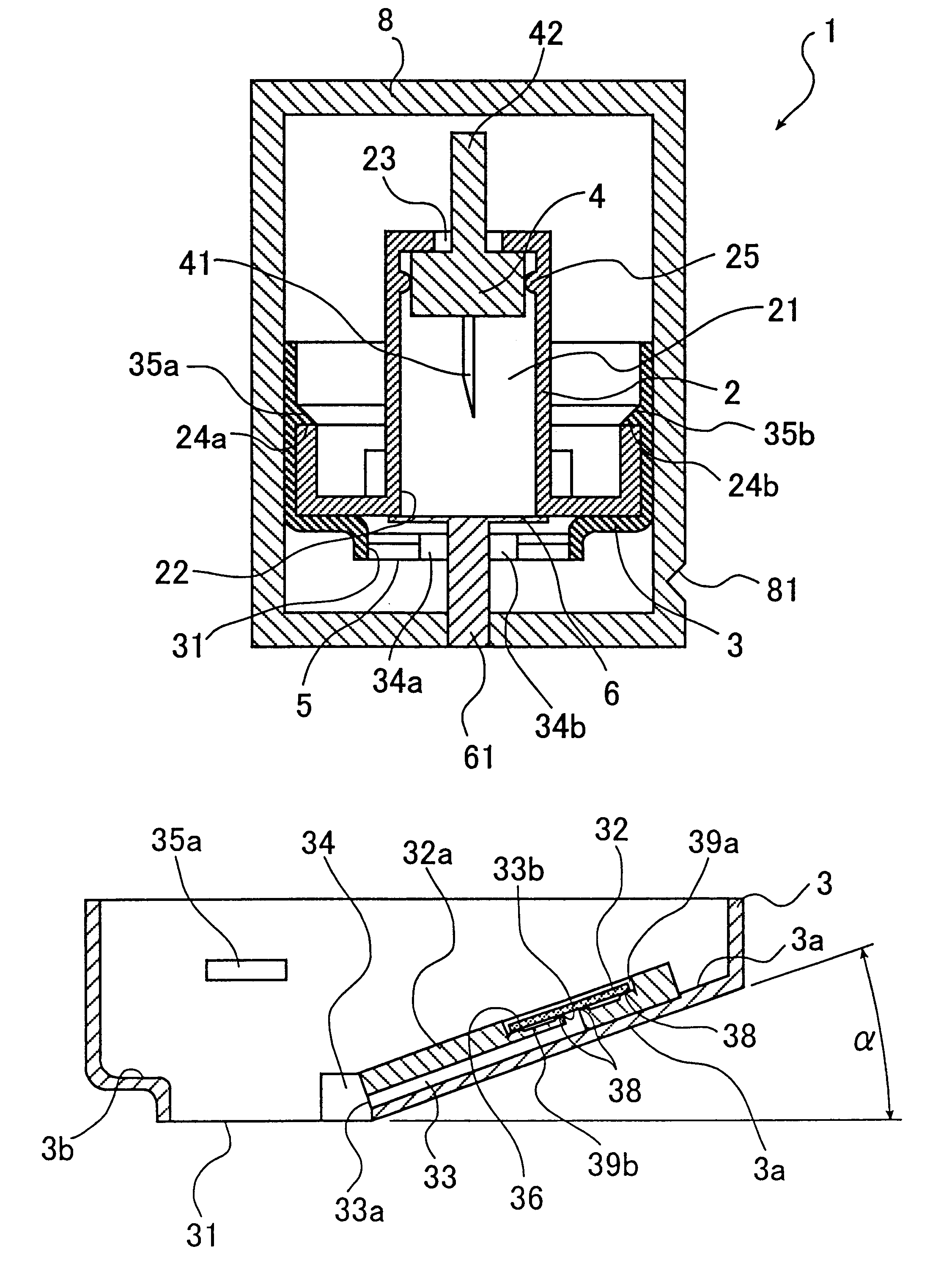
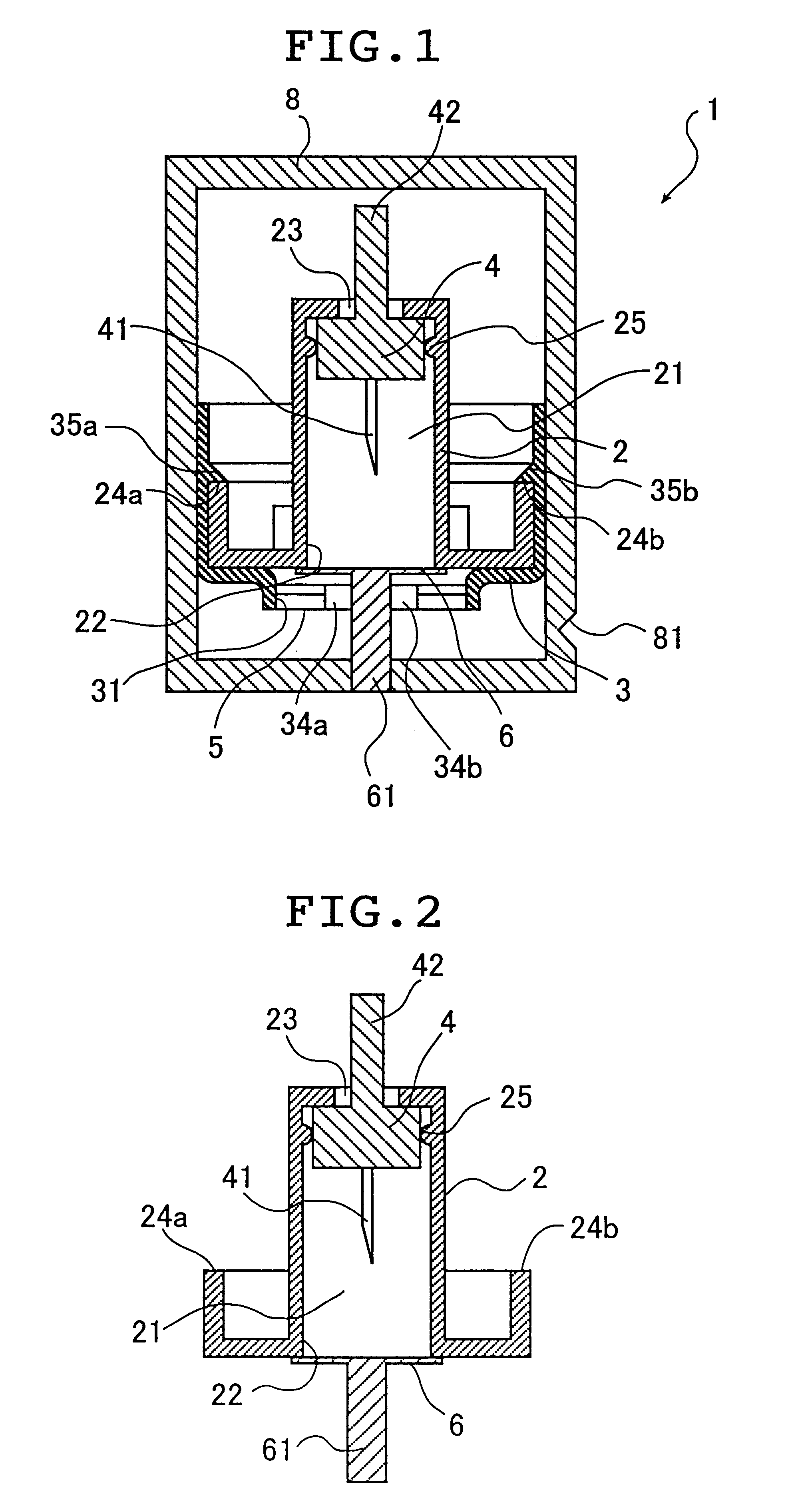
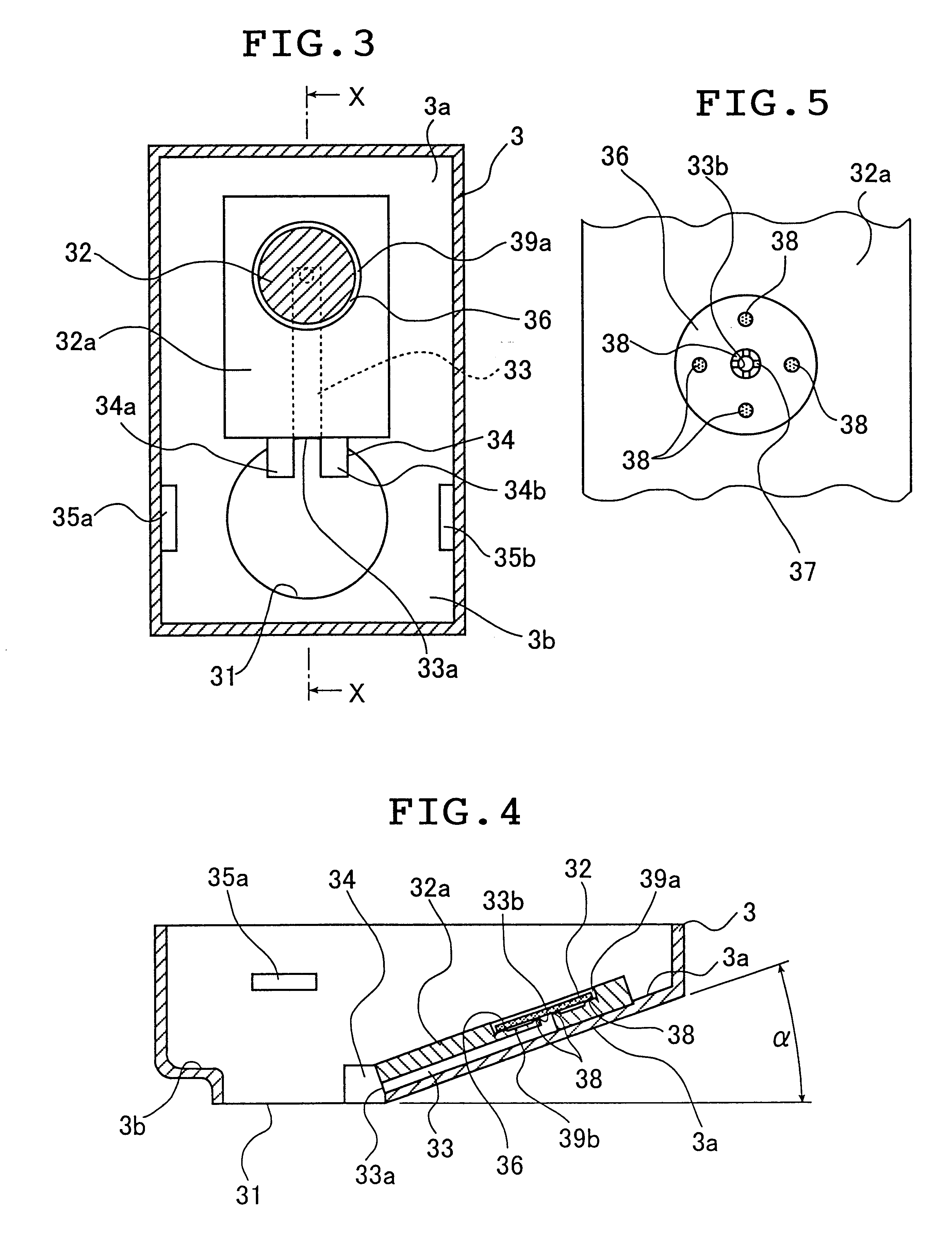
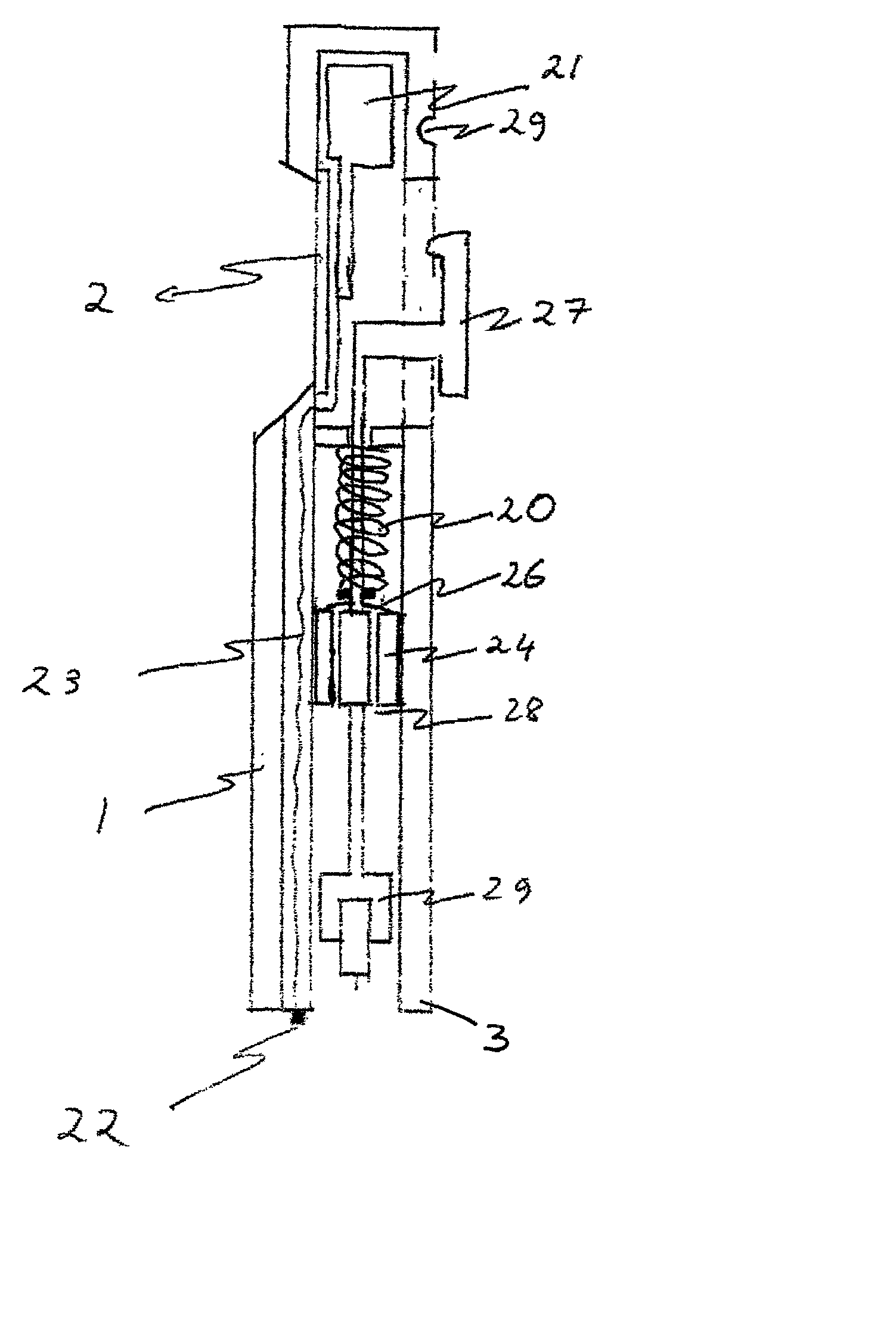
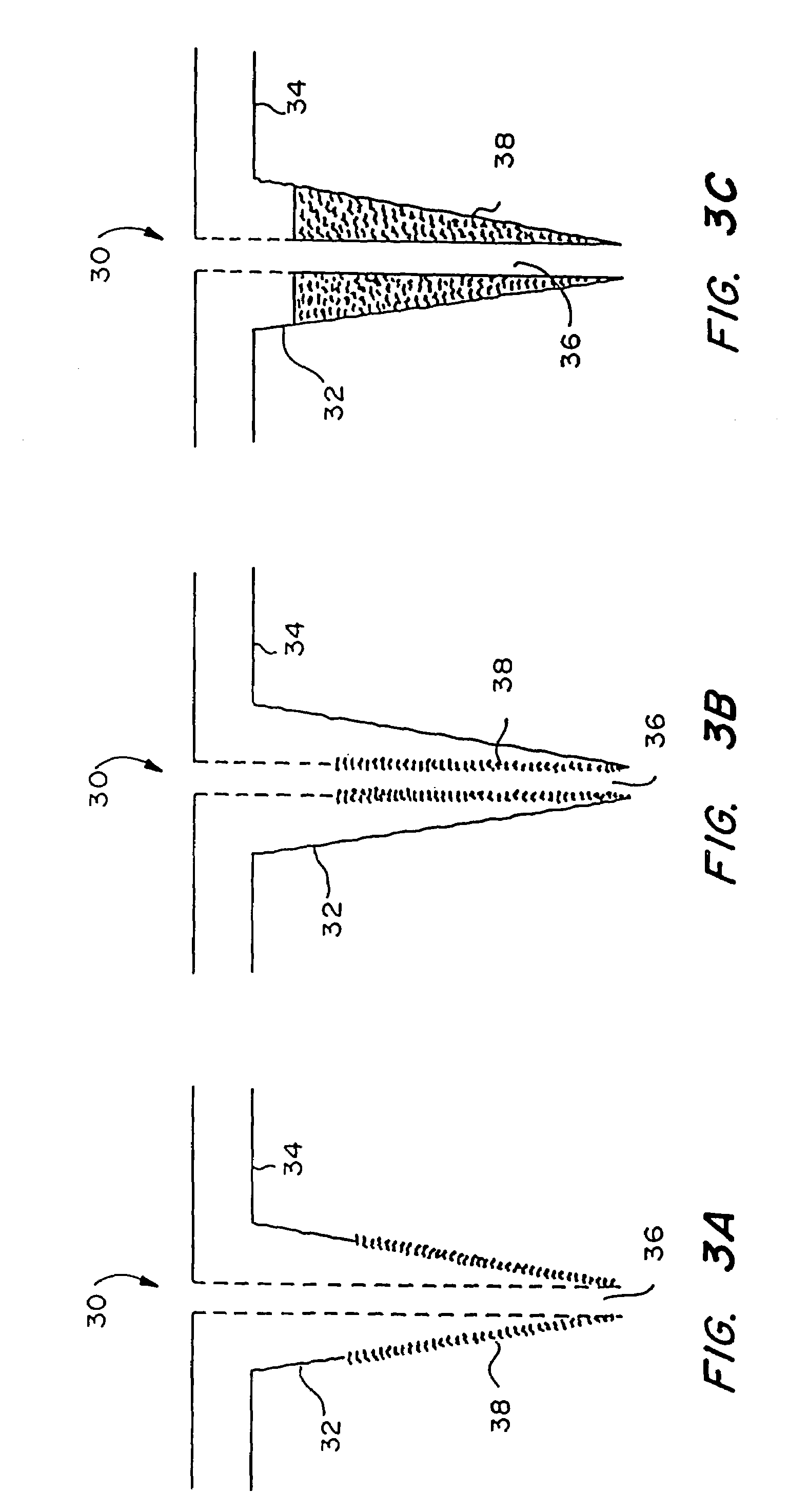
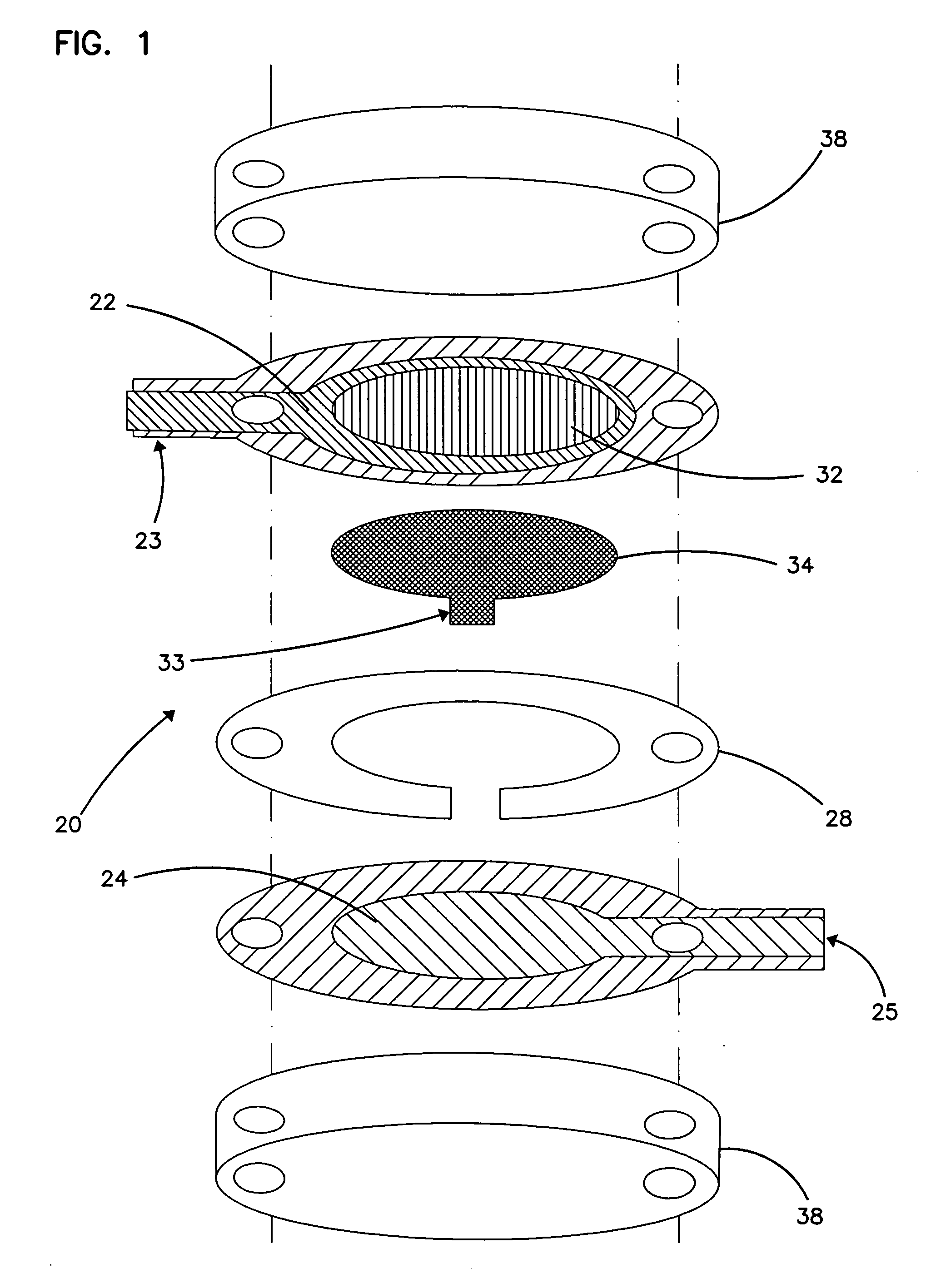
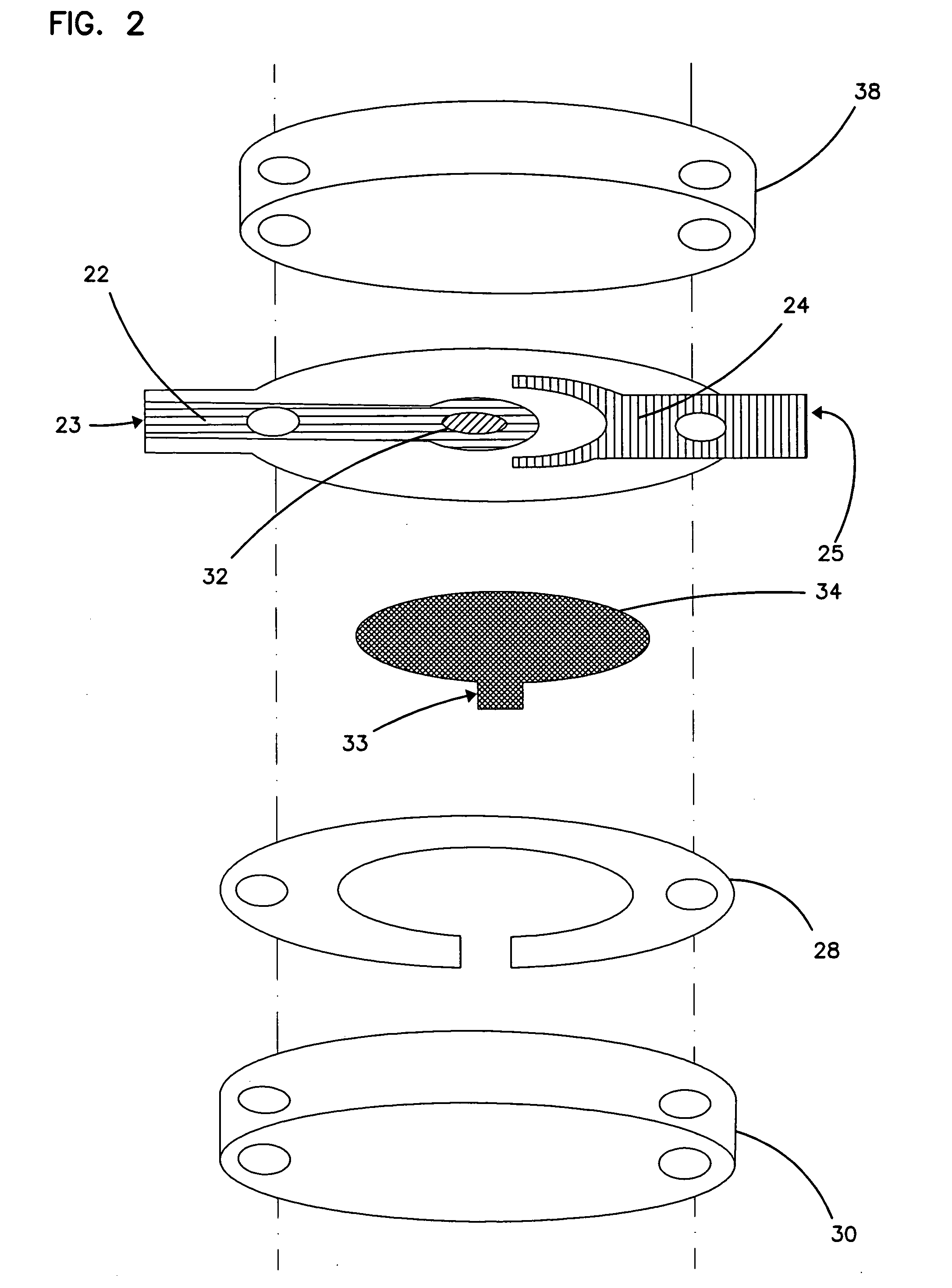
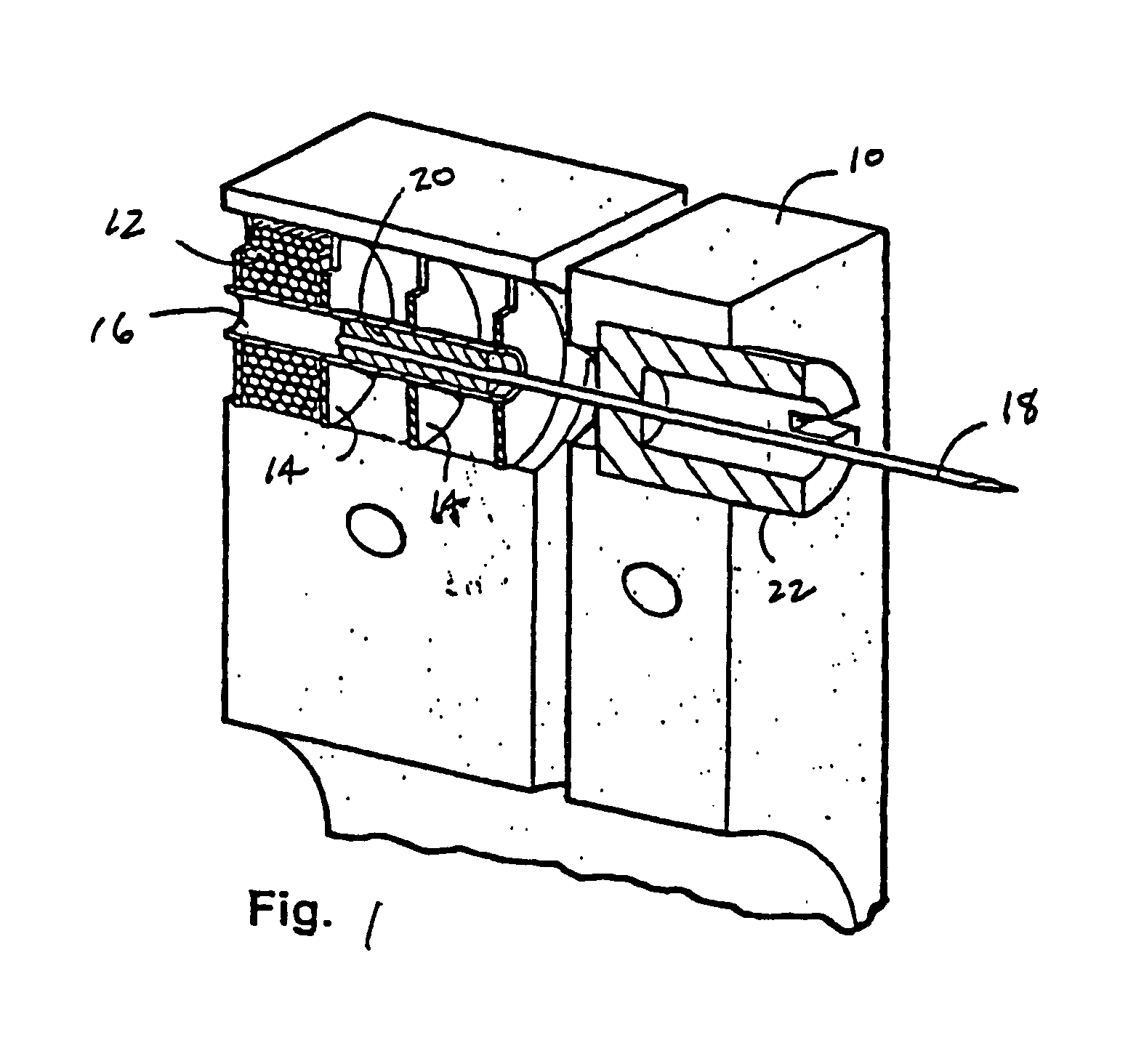
Lancet device having capillary action
InactiveUS20050004494A1Material minimizationReduced structureSamplingSurgeryVisual inspectionBody fluid
A device for sampling body fluid, the device comprising, a main body, a lancet disposed within the main body, a carrier disposed within the main body fixedly attached to the lancet, a biasing means in communication with the lancet and the carrier, an annular space disposed within the main body adjacent the lancet, and a means for measuring a body fluid. Wherein the means for measuring the body fluid may include micro-porous test strips, an electronic testing device, an optical / reflectance testing measuring device, or a visual inspection.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Method and apparatus for a multi-use body fluid sampling device with analyte sensing
A device for use with a penetrating member driver to penetrate tissue is provided. A plurality of penetrating members are coupled to a single cartridge and are operatively couplable to the penetrating member driver. The penetrating members are movable to extend radially outward from the cartridge to penetrate tissue. A plurality of analyte sensors are coupled to the single cartridge and are positioned on the cartridge to receive body fluid from a wound in the tissue created by the penetrating member.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Smokeless tobacco
InactiveUS20080173317A1Improve barrier propertiesObstruct passageTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentSodium bicarbonateEngineering
A smokeless tobacco product is provided. A water-permeable pouch containing a tobacco formulation and configured for insertion into the mouth of a user of that product is provided. The tobacco formulation includes granular tobacco and a buffer comprised of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate. An outer packaging material enveloping the pouch is provided and is sealed so as to allow a controlled environment to be maintained within.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Method and apparatus for obtaining blood for diagnostic tests
Method and apparatus for obtaining a sample of blood from a patient for subsequent diagnostic tests, e.g., glucose monitoring. In one aspect of the invention, the method comprises the steps of:(a) placing a blood collection device over a region on the surface of the skin from which said sample is to be obtained,(b) forming a seal between said blood collection device and said surface of the skin,(c) creating a vacuum sufficient to result in said surface of the skin becoming stretched and engorged with blood,(d) triggering a lancing assembly and causing a lancet to penetrate said skin,(e) retracting said lancet,(f) withdrawing blood toward and onto a fluid collector, and(g) releasing the vacuum.In another aspect of the invention, an apparatus for carrying out the method described previously is provided. The apparatus comprises:(a) a housing having a sealable chamber located therein and a sealable opening in fluid communication with said sealable chamber,(b) a power source,(c) a vacuum pump operably connected to said power source, said vacuum pump in communication with said sealable chamber,(d) a lancing assembly positioned within said housing, said lancing assembly capable of moving a lancet towards said sealable opening, and(e) a fluid collector positioned in said sealable chamber, said fluid collector in fluid communication with said sealable opening.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
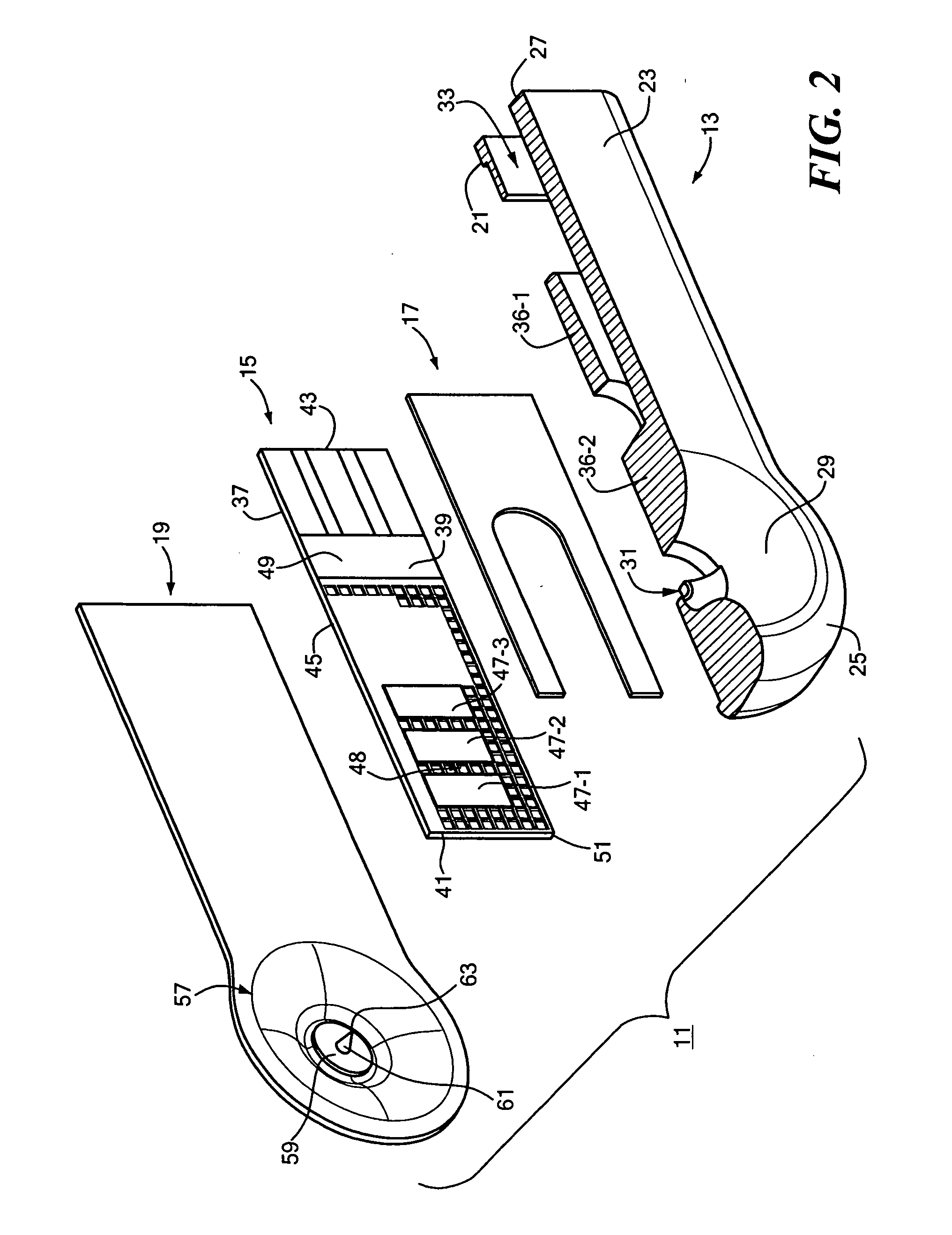
Assembly having lancet and means for collecting and detecting body fluid
An assembly to be detachably mounted on a body fluid monitoring system is provided. The assembly has a lancet and a device for collecting and detecting a body fluid. The lancet has a puncture needle. In this assembly, the puncture needle is maintained in sterilized conditions until its use, and the sterilization can be conducted with no adverse effects on the detection device. A readily sterilizable lancet unit and a body fluid-collecting and detecting unit adapted for use in such an assembly as well as a body fluid-monitoring system including such an assembly are also provided. The assembly comprises a first housing having a sleeve which movably accommodates the lancet in its interior, and a second housing having the body fluid detection device. The first housing and the second housing share an opening. The lancet is sterilized before the assembly. The body fluid-collecting and detecting section has a body fluid guide on the periphery of the inlet.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Combined lancet and electrochemical analyte-testing apparatus
InactiveUS20020130042A1Easy to takeReduces and eliminates disposal issueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteDisplay device
An apparatus for detection and quantitation of an electrochemically-detect- able analyte, such as glucose, in blood or interstitial fluid includes a meter unit, a lancet and an electrochemical sensor. Of these components, the meter is preferably reusable, while the lancet and the electrochemical sensor are preferably incorporated in assemblies intended for single-use. The meter unit has a housing, within which a lancet is engaged with a mechanism for moving then lancet; a connector disposed within the housing for engaging an electrochemical sensor specific for the analyte and transmitting a signal indicative of the amount of analyte, and a display operatively-associated with a connector for displaying the amount of the analyte to user. The electrochemical sensor is adapted for detection of a particular analyte. In addition, the electrochemical sensor has an absorptive member for uptake of a sample of blood or interstitial fluid. In one version, the lancet moves from a initial position to a piercing position in which skin of the user is pierced and optionally back to a retracted position. The electrochemical sensor is disposed such that the absorptive member takes up a sample from the pierced skin of the user when it is pierced by the lancet without movement of the apparatus. In an alternative version, the lancet is a hollow cannula through which blood or interstitial fluid is transported from the puncture site to an absorbent portion of the electrochemical sensor. In either version, the apparatus provides single-step operation in which sample acquisition and analysis occur as a result of the single action of pressing the apparatus against the users skin.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Microneedle device for extraction and sensing of bodily fluids
InactiveUS7344499B1Simple wayMinimal and no damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicroneedlesMetaboliteIrritation
Microneedle devices are provided for controlled sampling of biological fluids in a minimally-invasive, painless, and convenient manner. The microneedle devices permit in vivo sensing or withdrawal of biological fluids from the body, particularly from or through the skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The microneedle device includes one or more microneedles, preferably in a three-dimensional array, a substrate to which the microneedles are connected, and at least one collection chamber and / or sensor in communication with the microneedles. Preferred embodiments further include a means for inducing biological fluid to be drawn through the microneedles and into the collection chamber for analysis. In a preferred embodiment, this induction is accomplished by use of a pressure gradient, which can be created for example by selectively increasing the interior volume of the collection chamber, which includes an elastic or movable portion engaged to a rigid base. Preferred biological fluids for withdrawal and / or sensing include blood, lymph, interstitial fluid, and intracellular fluid. Examples of analytes in the biological fluid to be measured include glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, creatine, metabolic enzymes, hemoglobin, heparin, clotting factors, uric acid, carcinoembryonic antigen or other tumor antigens, reproductive hormones, oxygen, pH, alcohol, tobacco metabolites, and illegal drugs.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Consolidated body fluid testing device and method
A body fluid testing device includes a body member and a tissue penetrator carried by the body member. A test strip holder is carried by the body member, and a test strip is carried by the test strip holder. The test strip is capable of receiving a body fluid thereon and processing the body fluid into a form suitable for yielding test results relating to the content of the body fluid.
Owner:KLOEPFER DR HANS
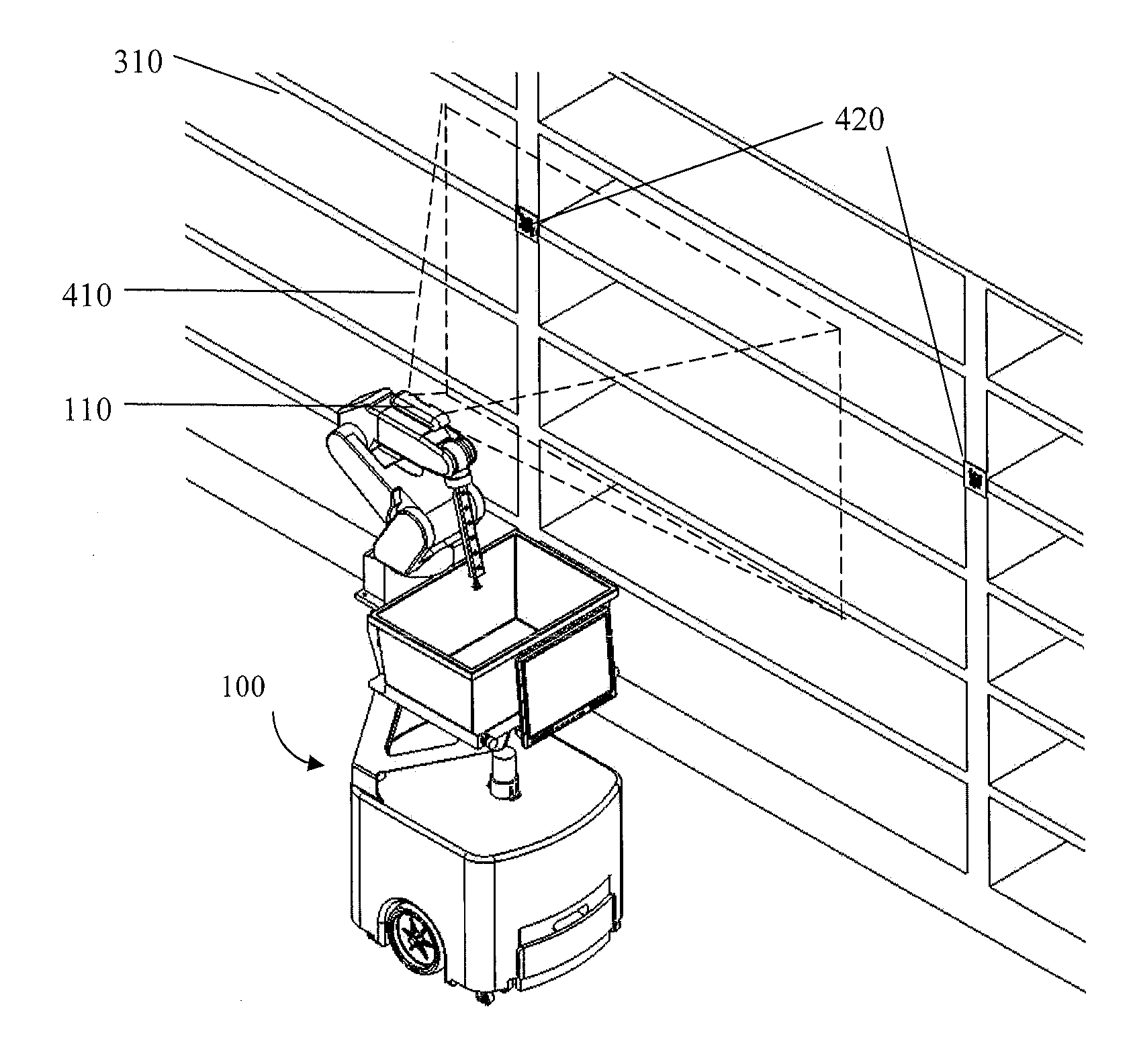
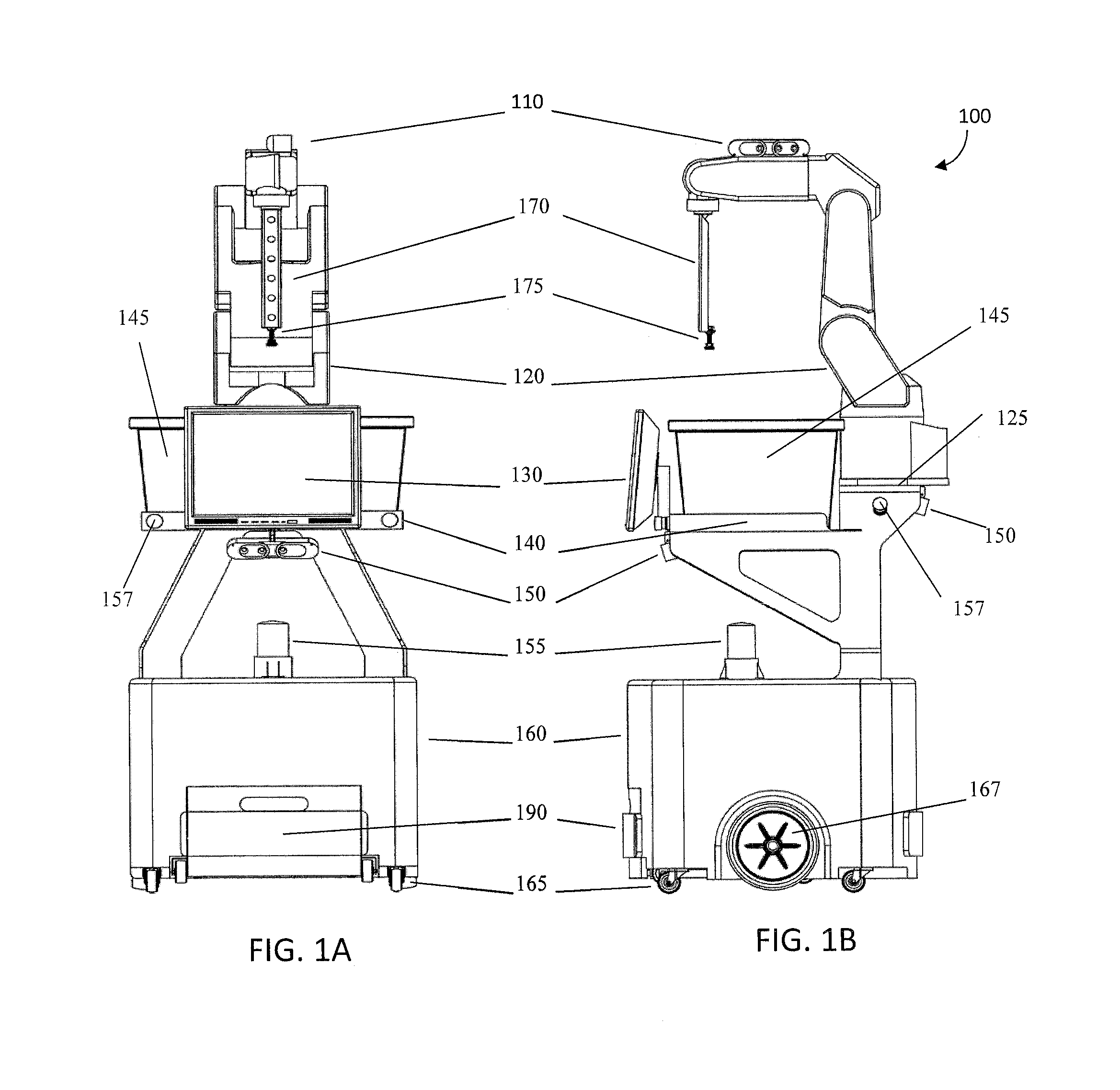
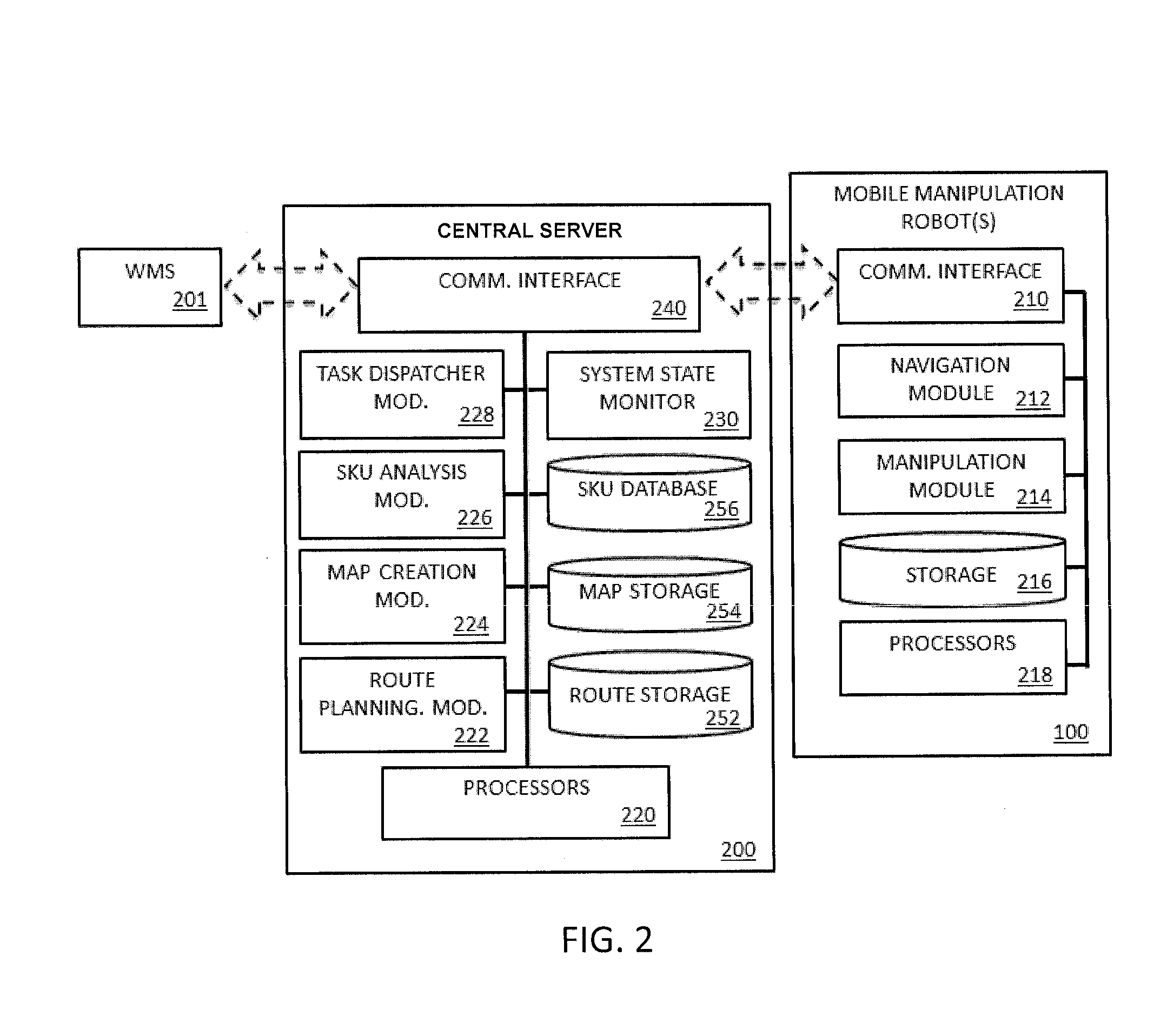
System and method for piece-picking or put-away with a mobile manipulation robot
ActiveUS20150032252A1Overcomes shortcomingReduce complexity and costProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processLogistics managementPosition dependent
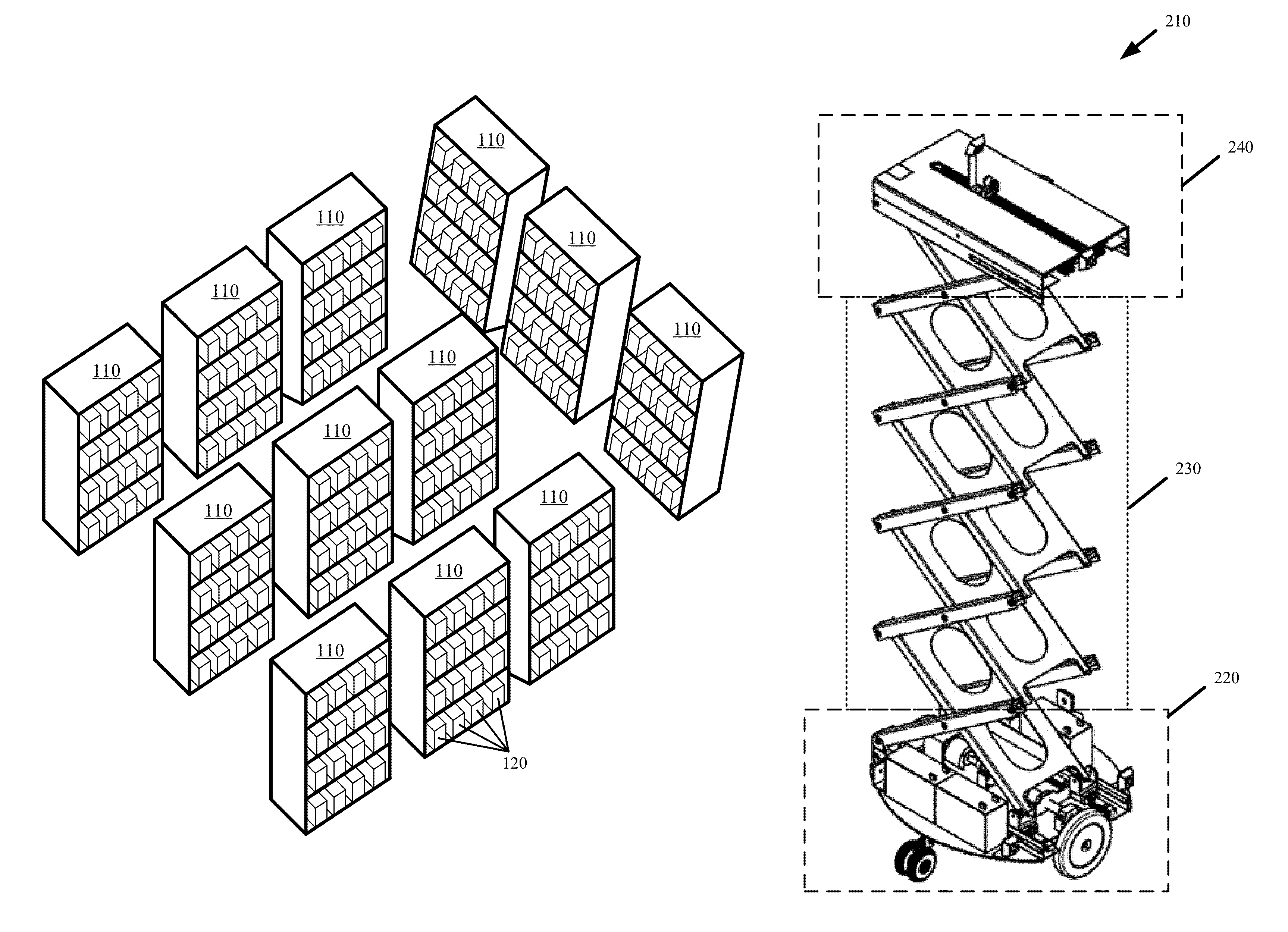
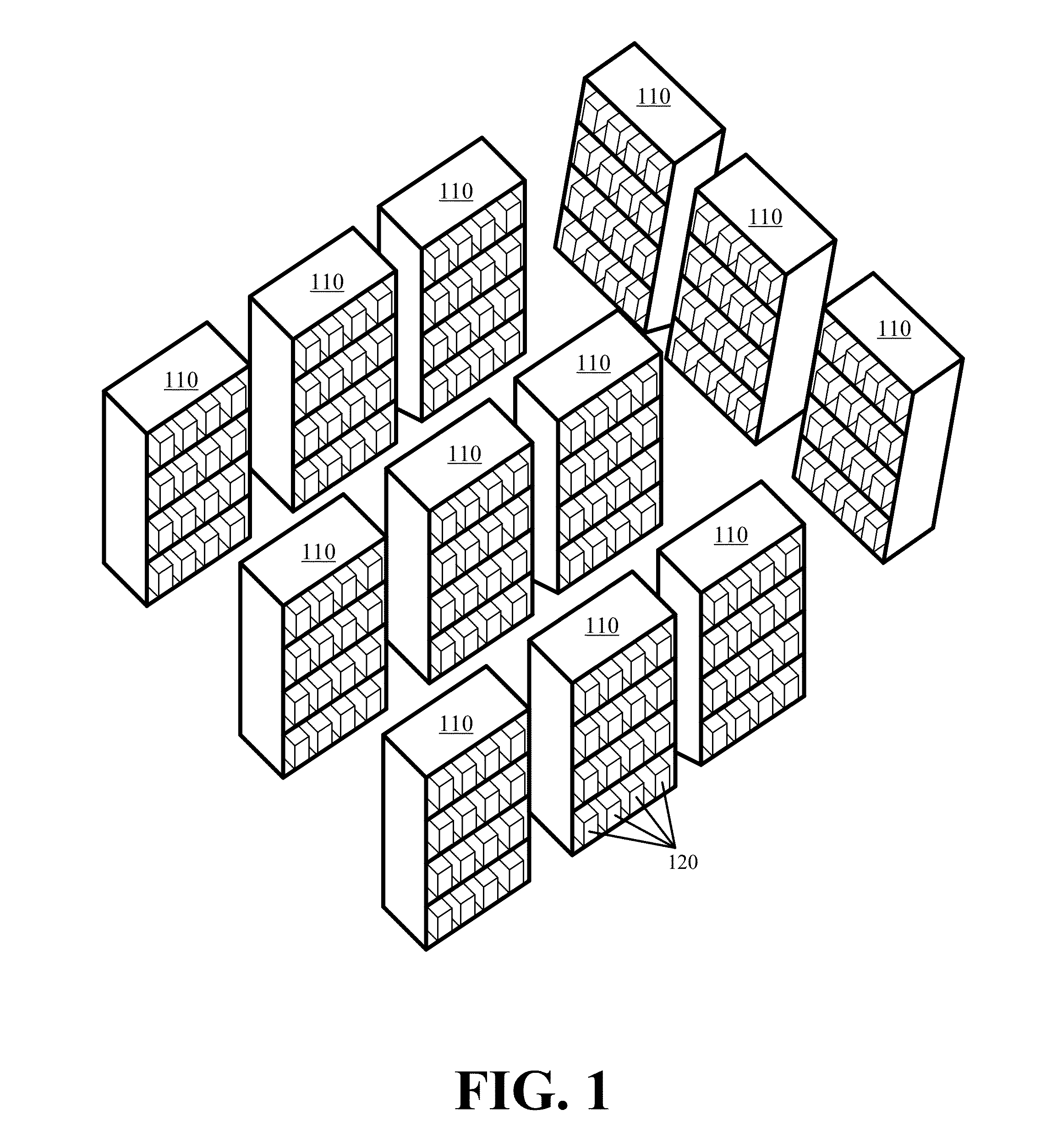
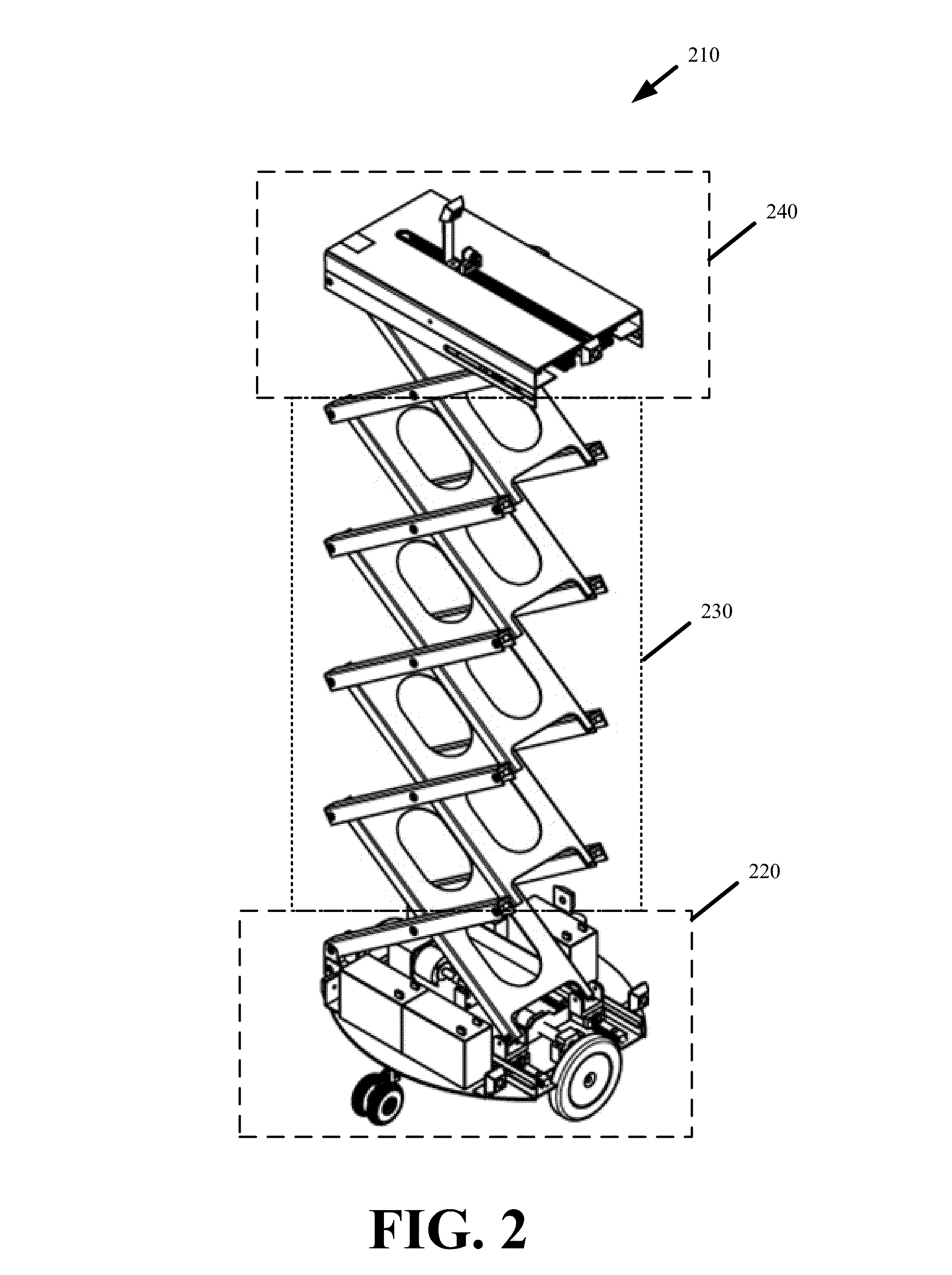
A method and system for piece-picking or piece put-away within a logistics facility. The system includes a central server and at least one mobile manipulation robot. The central server is configured to communicate with the robots to send and receive piece-picking data which includes a unique identification for each piece to be picked, a location within the logistics facility of the pieces to be picked, and a route for the robot to take within the logistics facility. The robots can then autonomously navigate and position themselves within the logistics facility by recognition of landmarks by at least one of a plurality of sensors. The sensors also provide signals related to detection, identification, and location of a piece to be picked or put-away, and processors on the robots analyze the sensor information to generate movements of a unique articulated arm and end effector on the robot to pick or put-away the piece.
Owner:IAM ROBOTICS
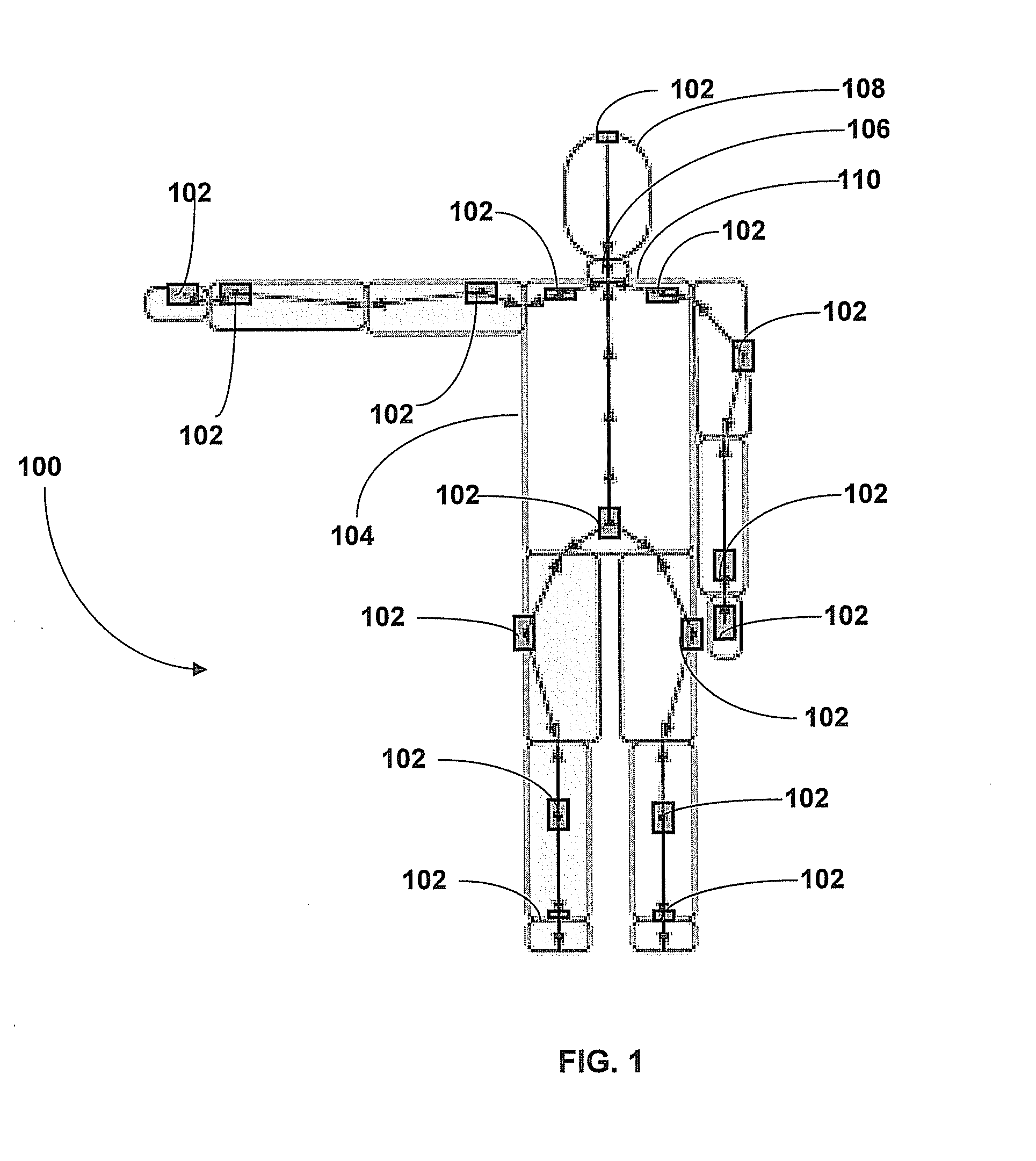
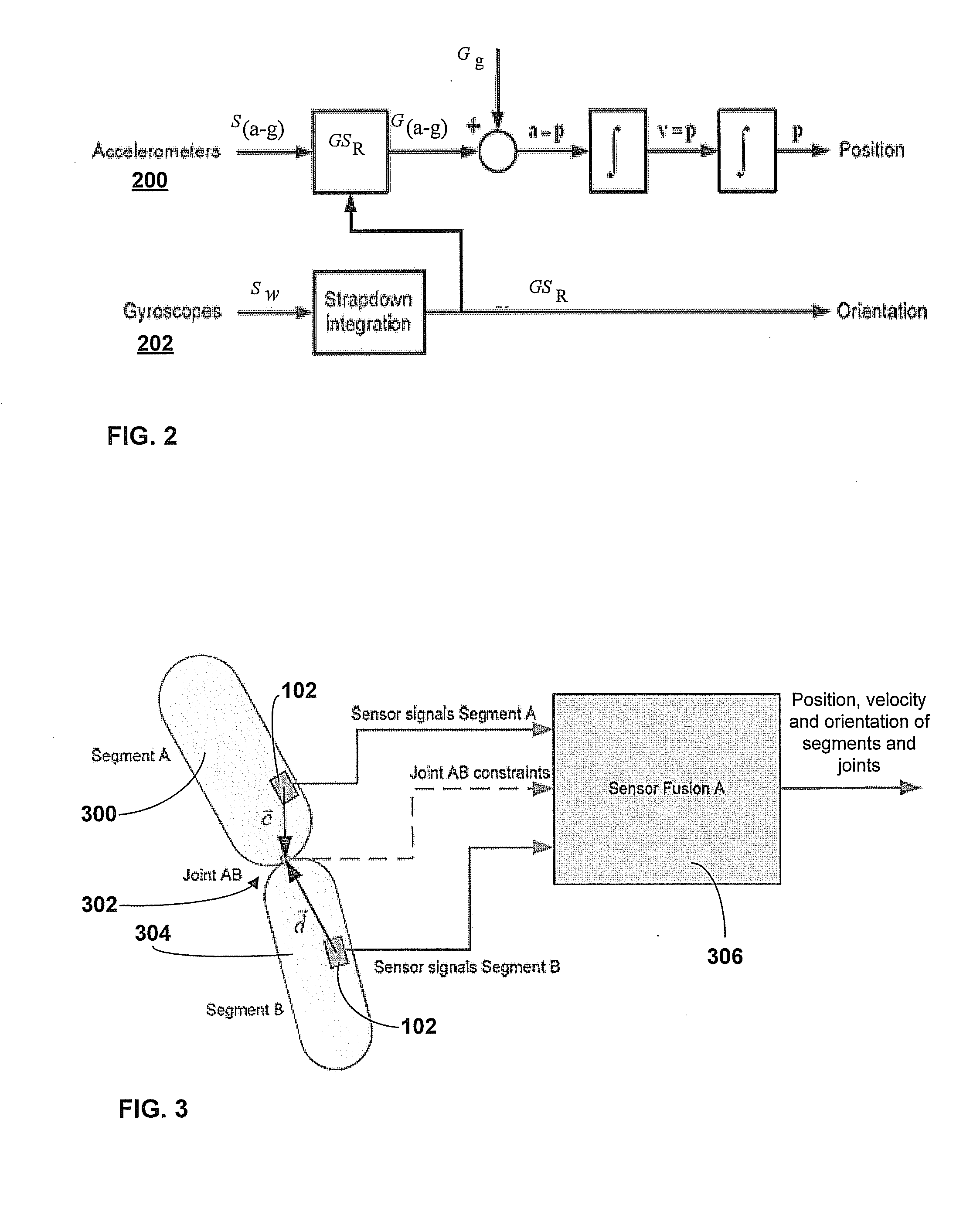
Motion Tracking System
ActiveUS20080285805A1High precisionAccurate recordProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationMovement trackingKalman filter
Owner:XSENS HLDG BV
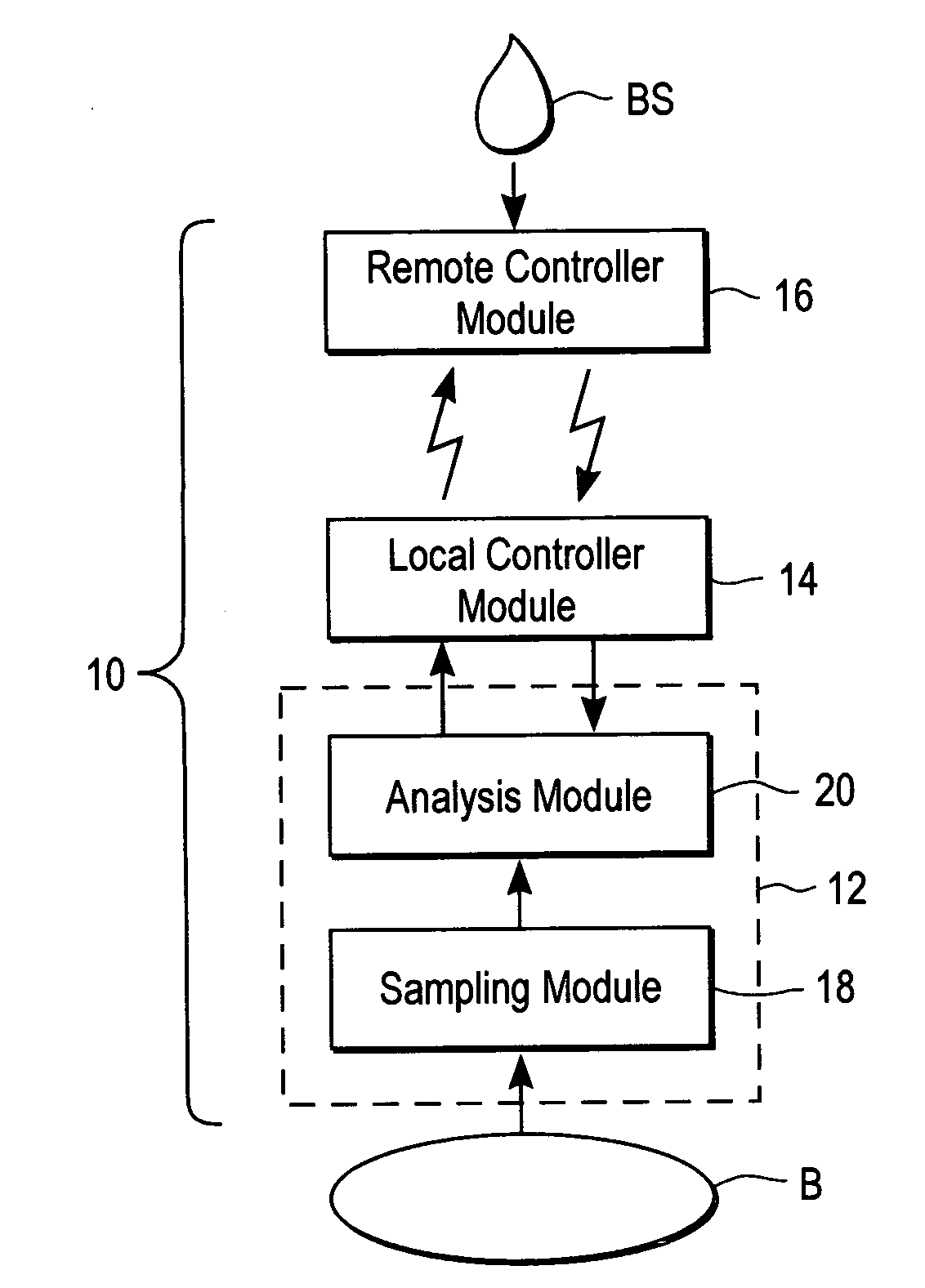
Devices, systems and methods for extracting bodily fluid and monitoring an analyte therein
ActiveUS20040249253A1Easy to useLittle painWithdrawing sample devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsAnalyteElectronic communication
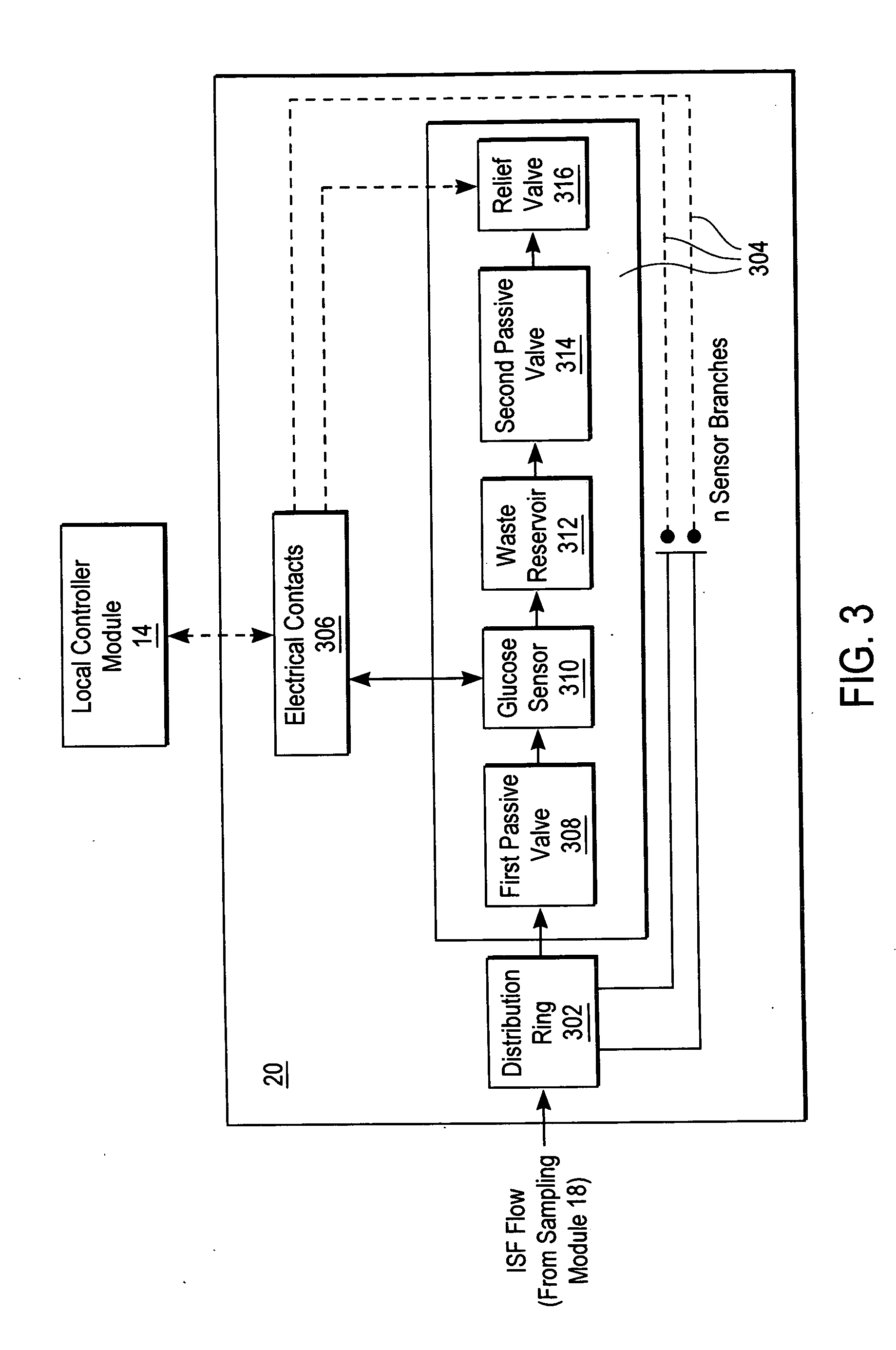
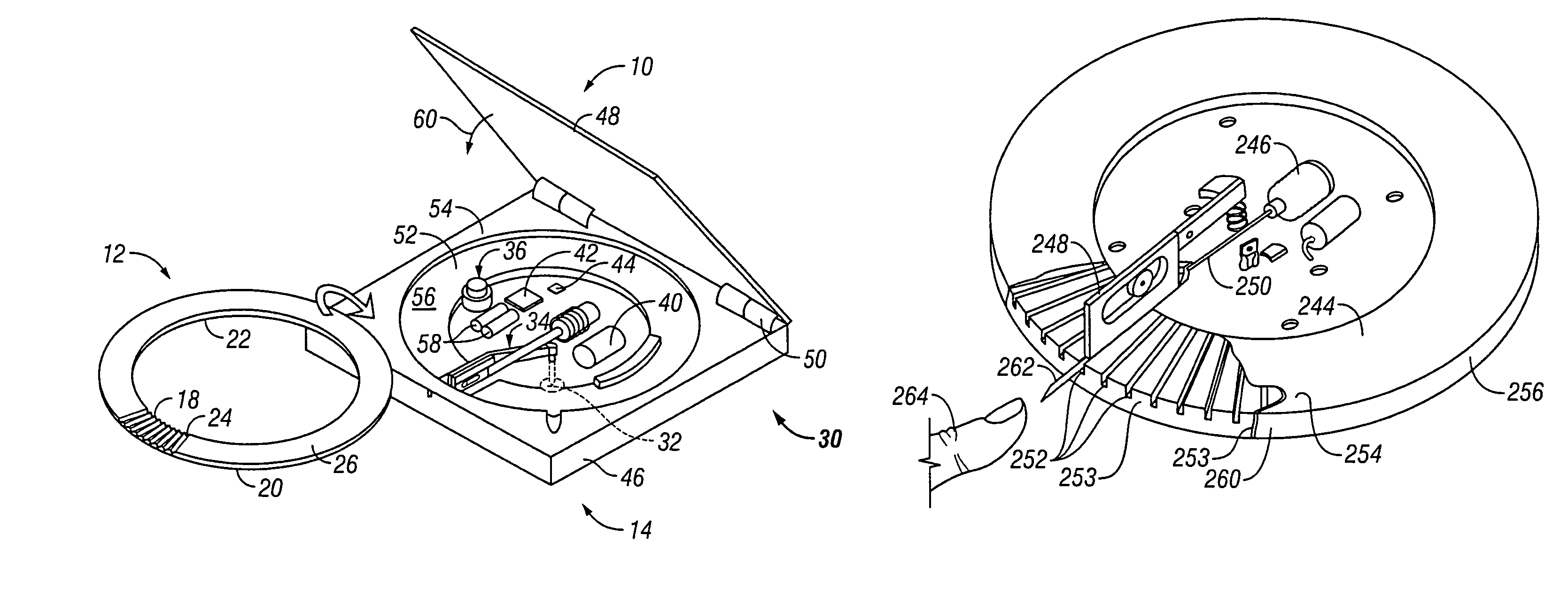
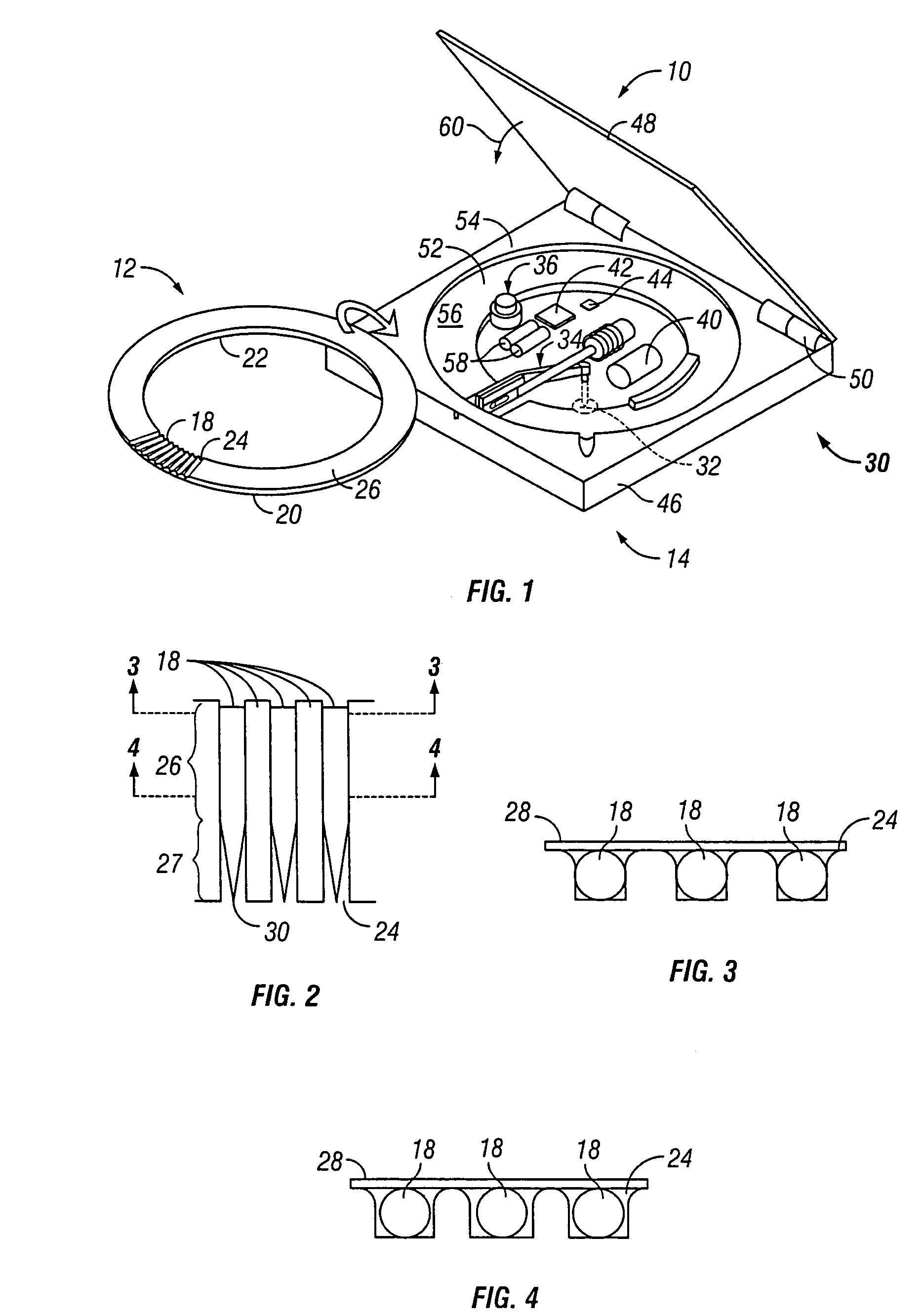
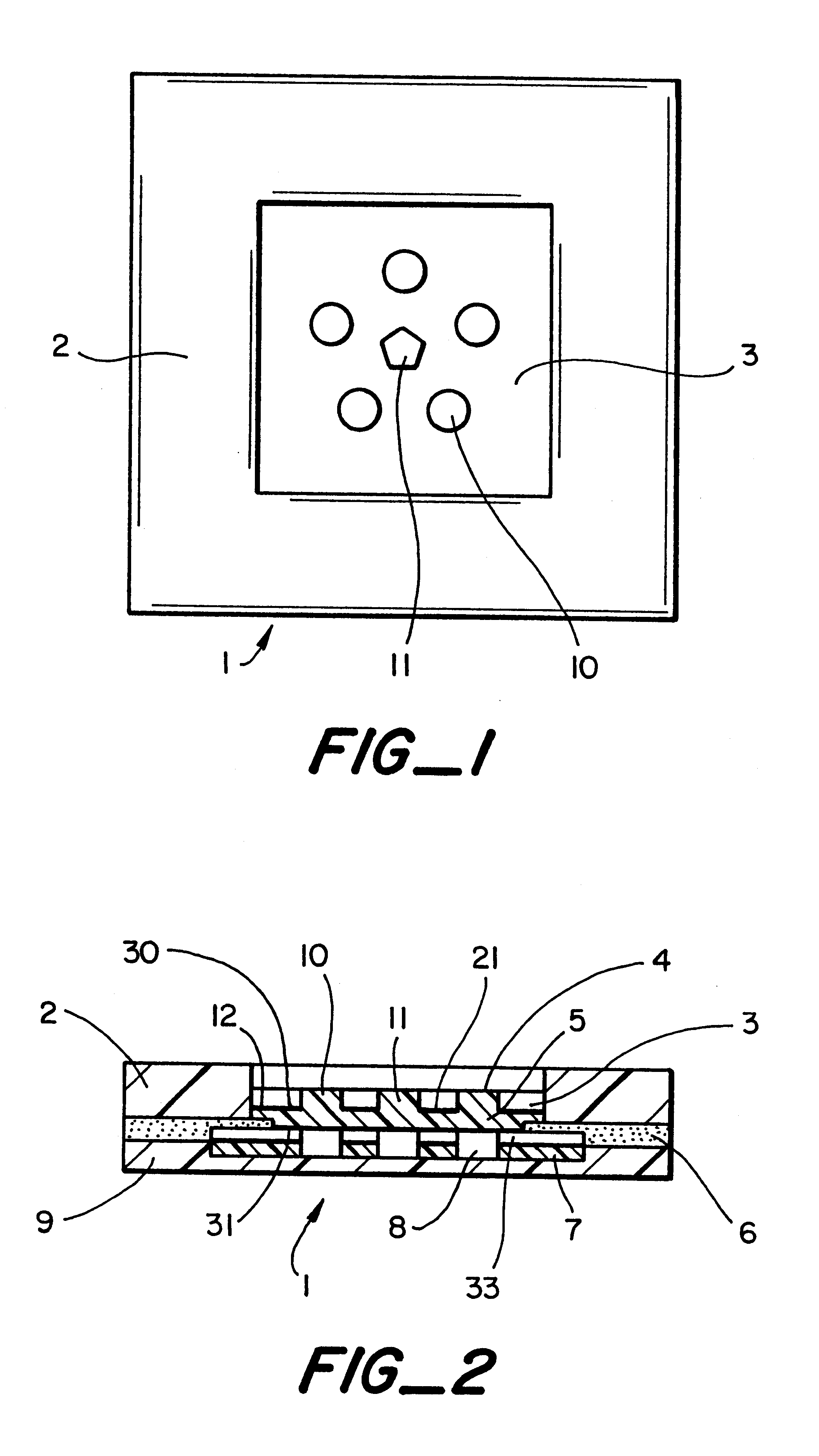
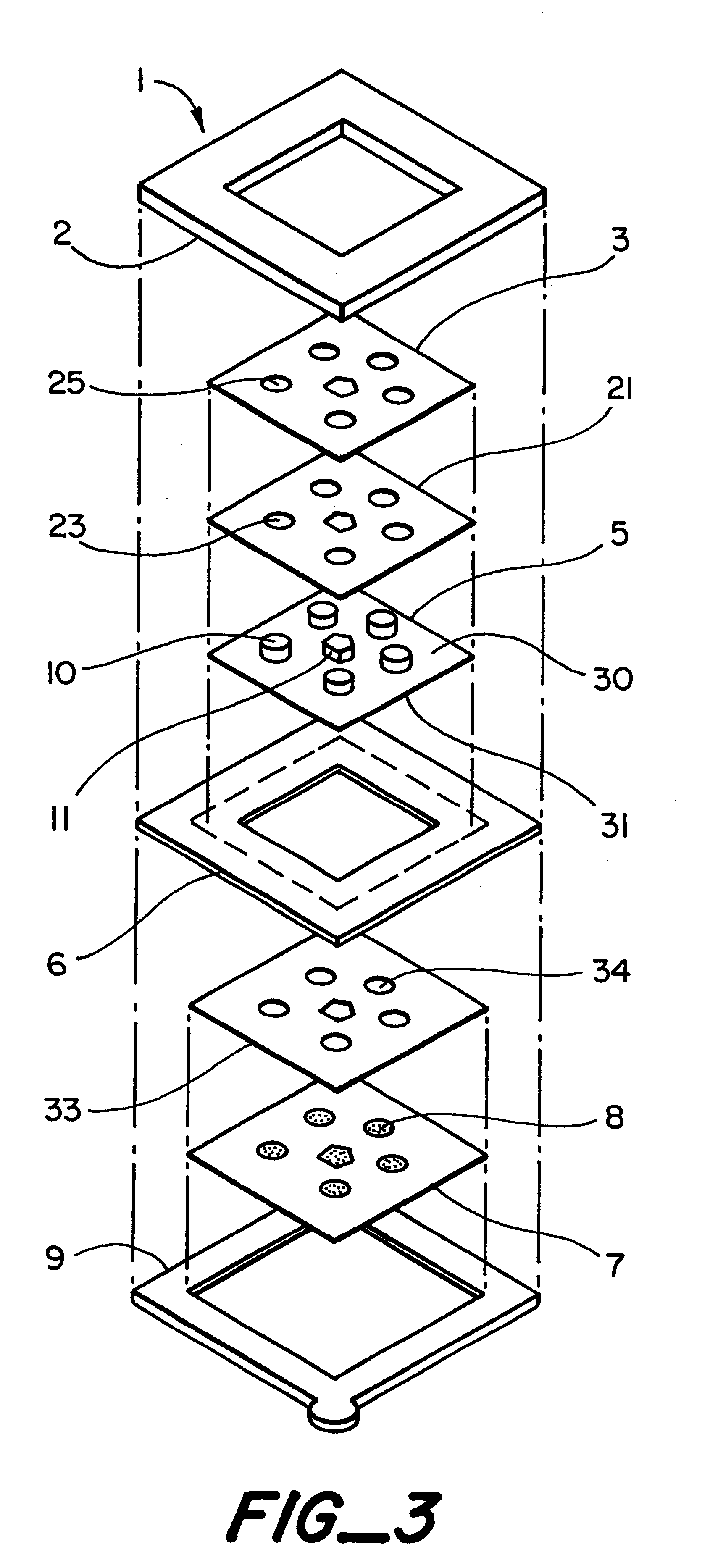
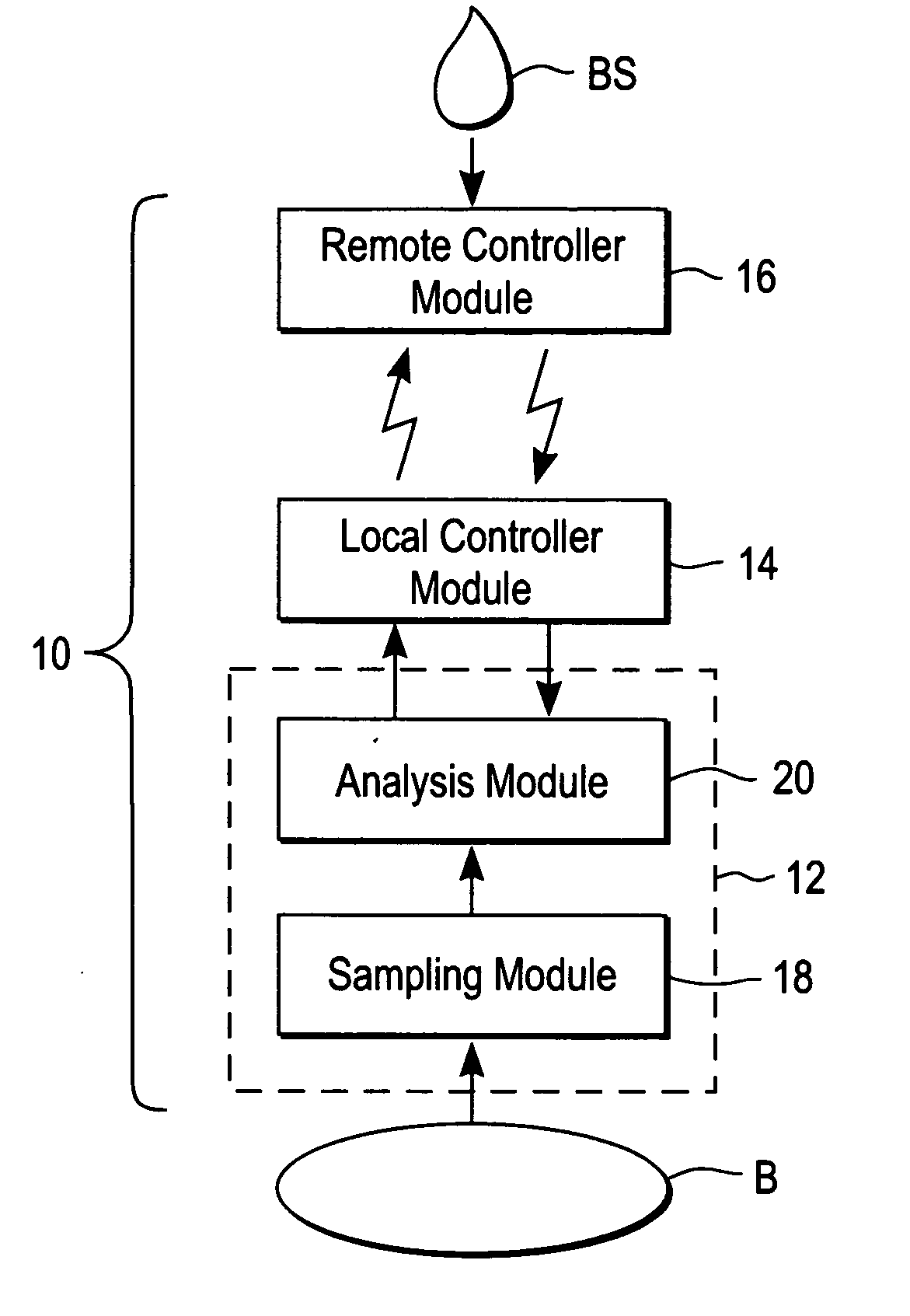
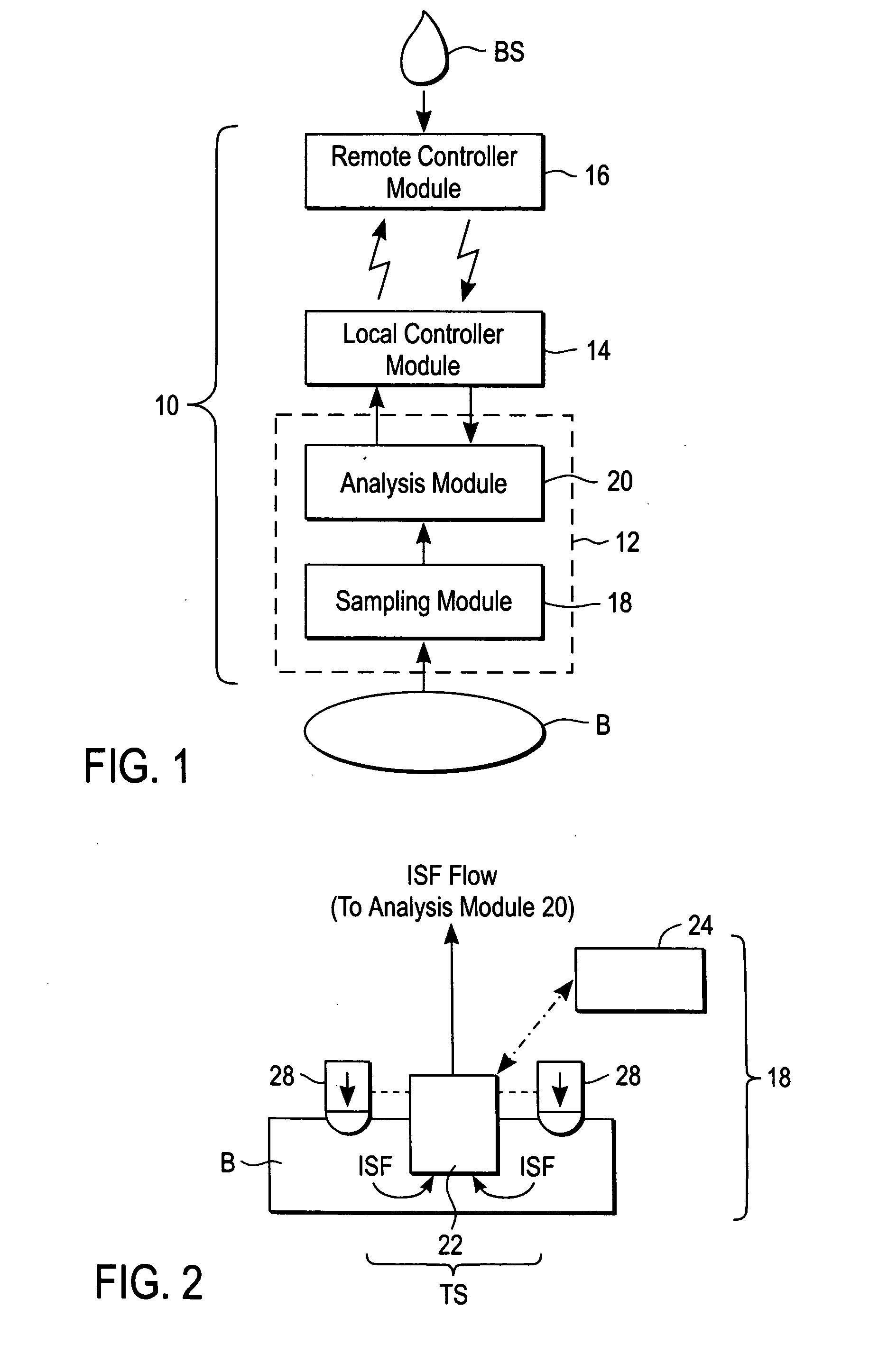
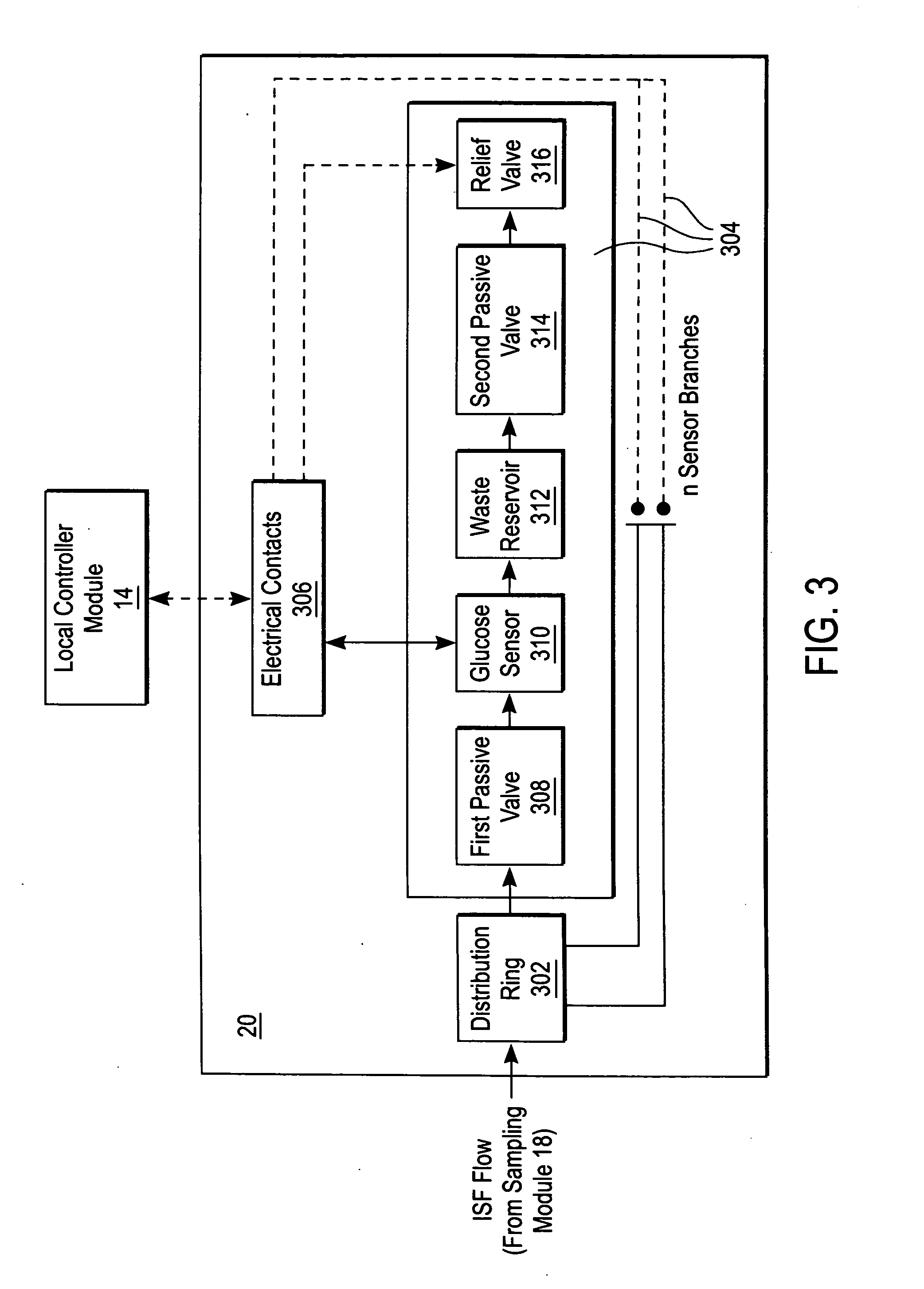
A system for extracting a bodily fluid sample (e.g., an interstitial fluid [ISF] sample) and monitoring an analyte therein includes a disposable cartridge and a local controller module. The disposable cartridge includes a sampling module adapted to extract a bodily fluid sample and an analysis module adapted to measure an analyte (e.g., glucose) in the bodily fluid sample. The local controller module is in electronic communication with the disposable cartridge and is adapted to receive and store measurement data from the analysis module. An ISF extraction device includes a penetration member configured for penetrating and residing in a target site of a user's skin layer and, subsequently, extracting an ISF sample therefrom. The device also includes a pressure ring(s) adapted for applying pressure to the user's skin layer in the vicinity of the target site. The device is configured such that the pressure ring(s) is capable of applying pressure in an oscillating manner whereby an ISF glucose lag of the ISF sample extracted by the penetration member is mitigated. A method for extracting ISF includes providing an ISF fluid extraction device with a penetration member and a pressure ring(s). Next, a user's skin layer is contacted by the pressure ring(s) and penetrated by the penetration member. An ISF sample is then extracted from the user's skin layer while pressure is being applied in an oscillating manner by the pressure ring(s). The oscillating pressure mitigates an ISF glucose lag of the extracted ISF sample extracted.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Autonomous mobile picking
ActiveUS20150073589A1Reduce labor costsFacilitates picking articleProgramme-controlled manipulatorData processing applicationsMobile vehicleOrder fulfillment
An order-picking method includes autonomously routing a plurality of mobile robotic units in an order fulfillment facility and picking articles to or putting articles from the robotic units in the order fulfillment facility. A material-handling robotic unit that is adapted for use in an order fulfillment facility includes an autonomous mobile vehicle base and a plurality of article receptacles positioned on the base. A visual indicator associated with the receptacle facilitates picking articles to or putting articles from the robotic unit.
Owner:DEMATIC
Method and device for sampling and analyzing interstitial fluid and whole blood samples
InactiveUS20070017805A1Less riskLess invasiveSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAnalyteWhole blood sample
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor with diffusible or non-leachable redox mediator
InactiveUS20060025662A1Lower the volumeAccurate and efficient measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteRedox mediator
A region of skin, other than the fingertips, is stimulated. After stimulation, an opening is created in the skin (e.g., by lancing the skin) to cause a flow of body fluid from the region. At least a portion of this body fluid is transported to a testing device where the concentration of analyte (e.g., glucose) in the body fluid is then determined. It is found that the stimulation of the skin provides results that are generally closer to the results of measurements from the fingertips, the traditional site for obtaining body fluid for analyte testing.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Analyte test device
ActiveUS20050245844A1Easy to useMinimal discomfortImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteWound site
An analyte test device is constructed as an integrated, single-use, disposable cartridge which can be releasably installed into a compatible analyte test monitor. In use, the device can be used in conjunction with the monitor to lance the skin of a patient to create a blood sample, express the blood sample from the wound site using vacuum forces and calculate the concentration of a particular analyte in the expressed blood sample. In one embodiment, the device includes a base which includes a top surface and a bottom surface. The base is also shaped to define an aperture which extends transversely through its top and bottom surfaces. An electrochemical test sensor is affixed to the base in such a manner so that a vacuum path is at least partially defined between the base and the test sensor, the vacuum path being in fluid communication with the aperture. A cover is affixed to the top surface of the base over the aperture, the cover comprising a flexible dome-shaped member and a lancet coupled to the member, the lancet being orientated such that its longitudinal axis extends at an approximate right angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the test sensor. The bottom surface of the base is shaped to include a skin receiving surface which at least partially defines the aperture in the base, the skin receiving surface having a steep inward contour to distend the skin of the patient when pressed thereagainst.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Article transport device
InactiveUS20070034477A1Small and simpleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl devices for conveyorsSolid of revolution
Owner:DAIFUKU CO LTD
Test media cassette for bodily fluid testing device
A bodily fluid sampling device includes a piercing device and a sensor enclosed in a housing. A cassette, which contains test media, is positioned proximal to the sensor so that the sensor is able to analyze a bodily fluid sample collected on the test media. The cassette includes a supply portion from which unused test media is supplied and a storage portion in which contaminated test media is stored after exposure to the bodily fluid. The cassette is adapted to collect a series of bodily fluid samples without requiring disposal of the test media.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
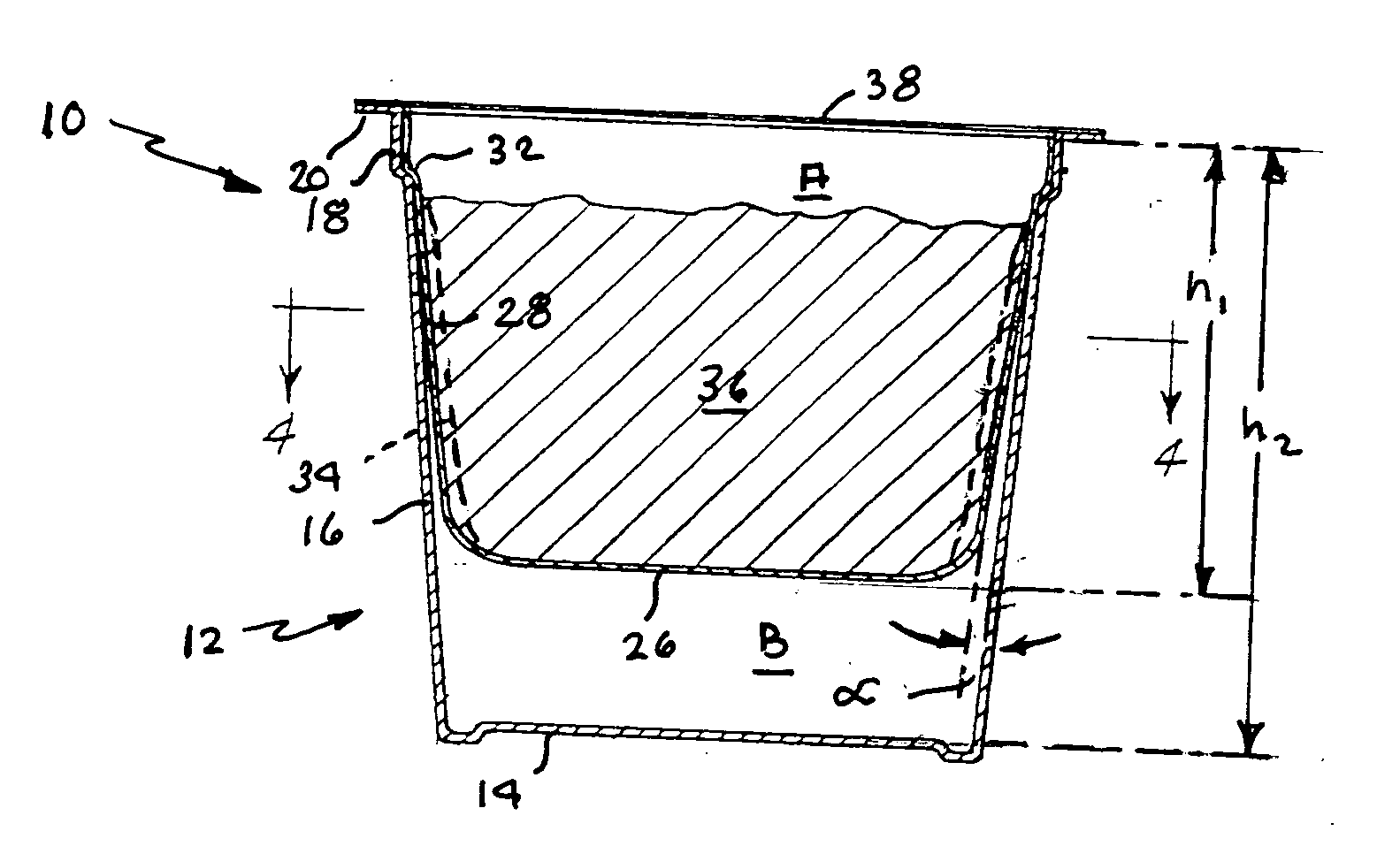
Beverage filter cartridge
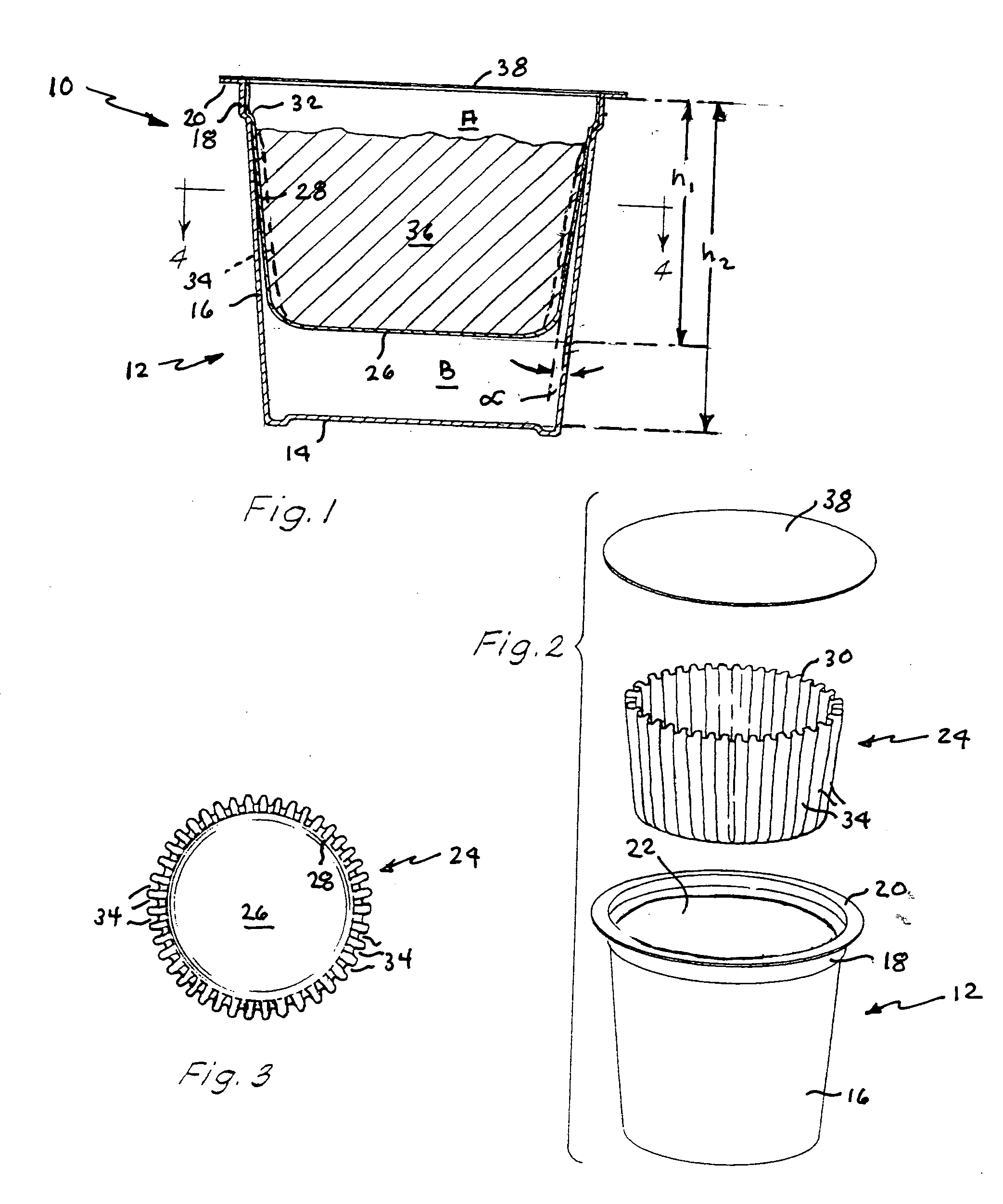
A beverage filter cartridge has an impermeable cup-shaped out container internally subdivided by a generally cup-shaped filter element into a first chamber inside the filter and a second chamber located between the filter bottom and the container bottom. The upper rim of the filter is joined at a peripheral juncture to the container side wall, and the filter side wall has exterior channels that face the container side wall and lead downwardly from the peripheral juncture to the second chamber.
Owner:KEURIG GREEN MOUNTAIN INC
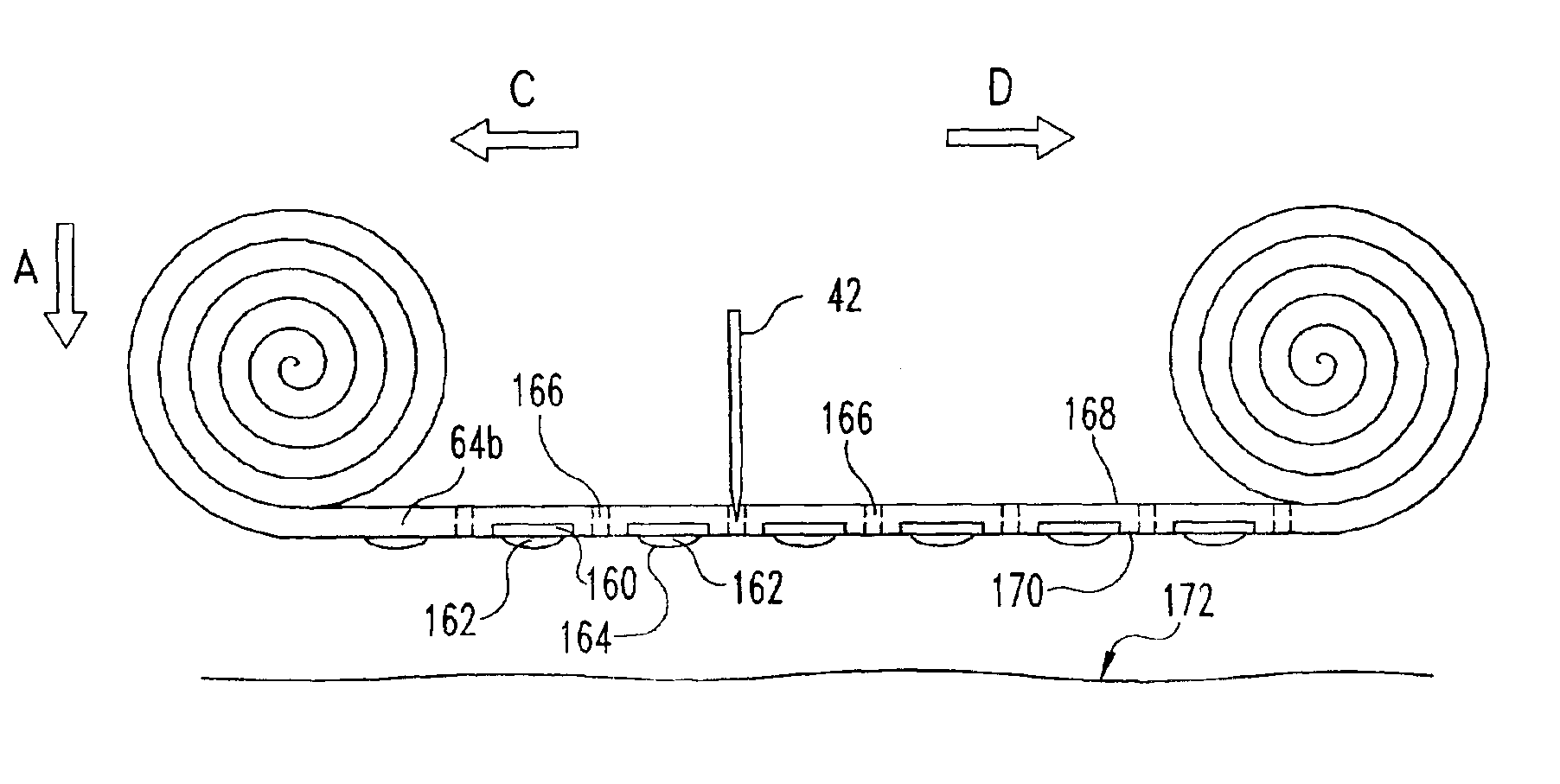
Method and apparatus for body fluid sampling with improved sensing
A device is provided for use with a body fluid sampling device for extracting bodily fluid from an anatomical feature. The device comprises a cartridge having a plurality of cavities. The device may include a plurality of penetrating members each at least partially contained in the cavities of the cartridge wherein the penetrating members are slidably movable to extend outward from openings on the cartridge to penetrate tissue. The device may also include a plurality of analyte detecting members and a plurality of chambers. Each chamber may be associated with one of the cavities, the chambers positioned along an outer periphery of the cartridge, wherein at least one of said analyte detecting members forms a portion of one wall of one of said plurality of chambers. In one embodiment, the device may also include a fluid spreader positioned over at least a portion of said analyte detecting member to urge fluid toward one of the detecting members.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Autonomous order fulfillment and inventory control robots
ActiveUS9120622B1Programme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsOrder fulfillmentInventory management
Some embodiments provide a system for fully autonomous order fulfillment and inventory management within a distribution site or warehouse. The system operates by autonomous robots directly pulling customer order items from distribution site shelves or pulling individual bins from distribution site shelves and dispensing appropriate quantities of items from the bins until all items of a customer order are retrieved without human involvement. The system further involves the robots autonomously monitoring item quantities within the distribution site, identifying and autonomously responding to shortages, and organizing the items within the distribution site for most efficient order fulfillment.
Owner:INVIA ROBOTICS INC
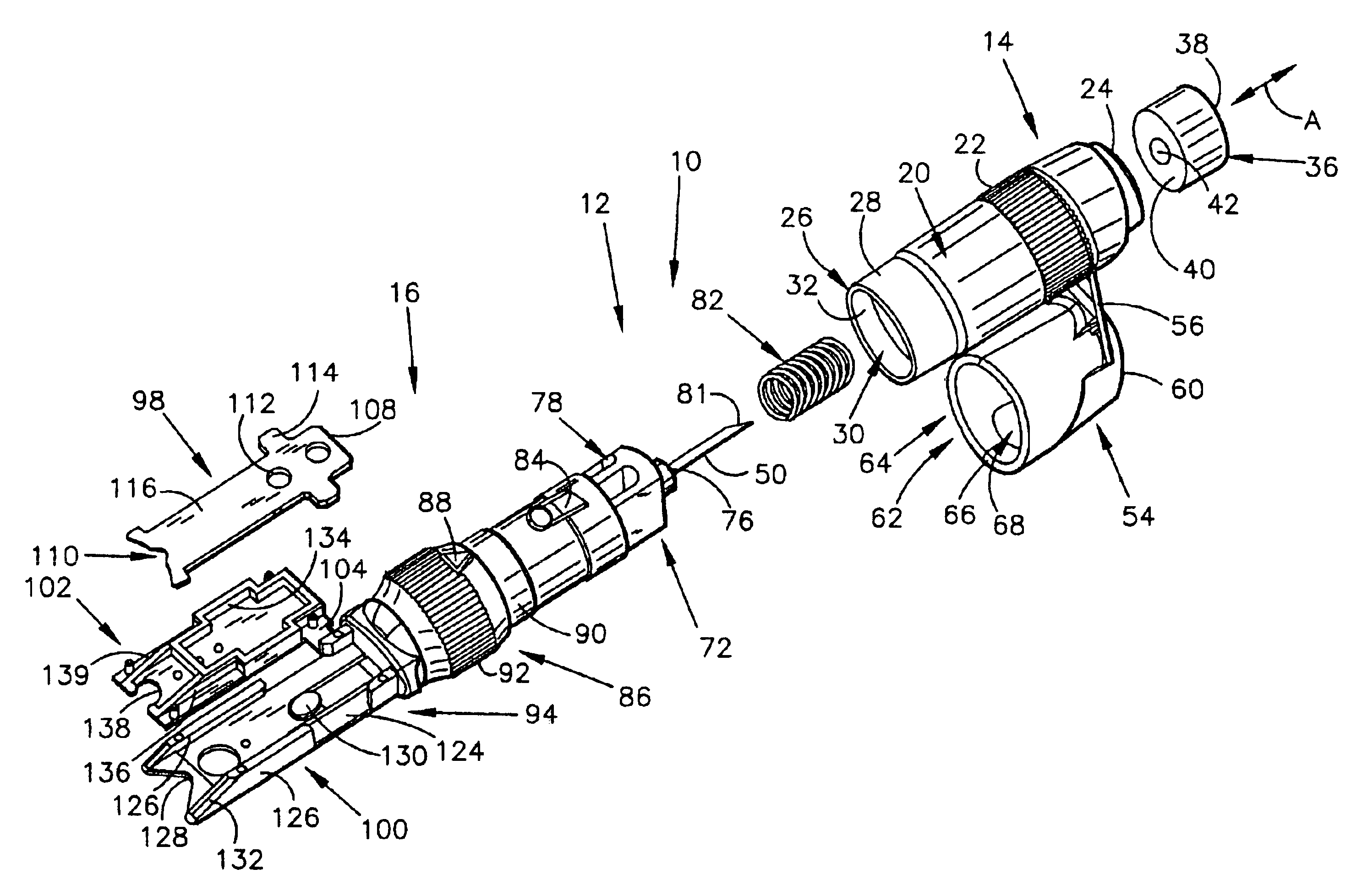
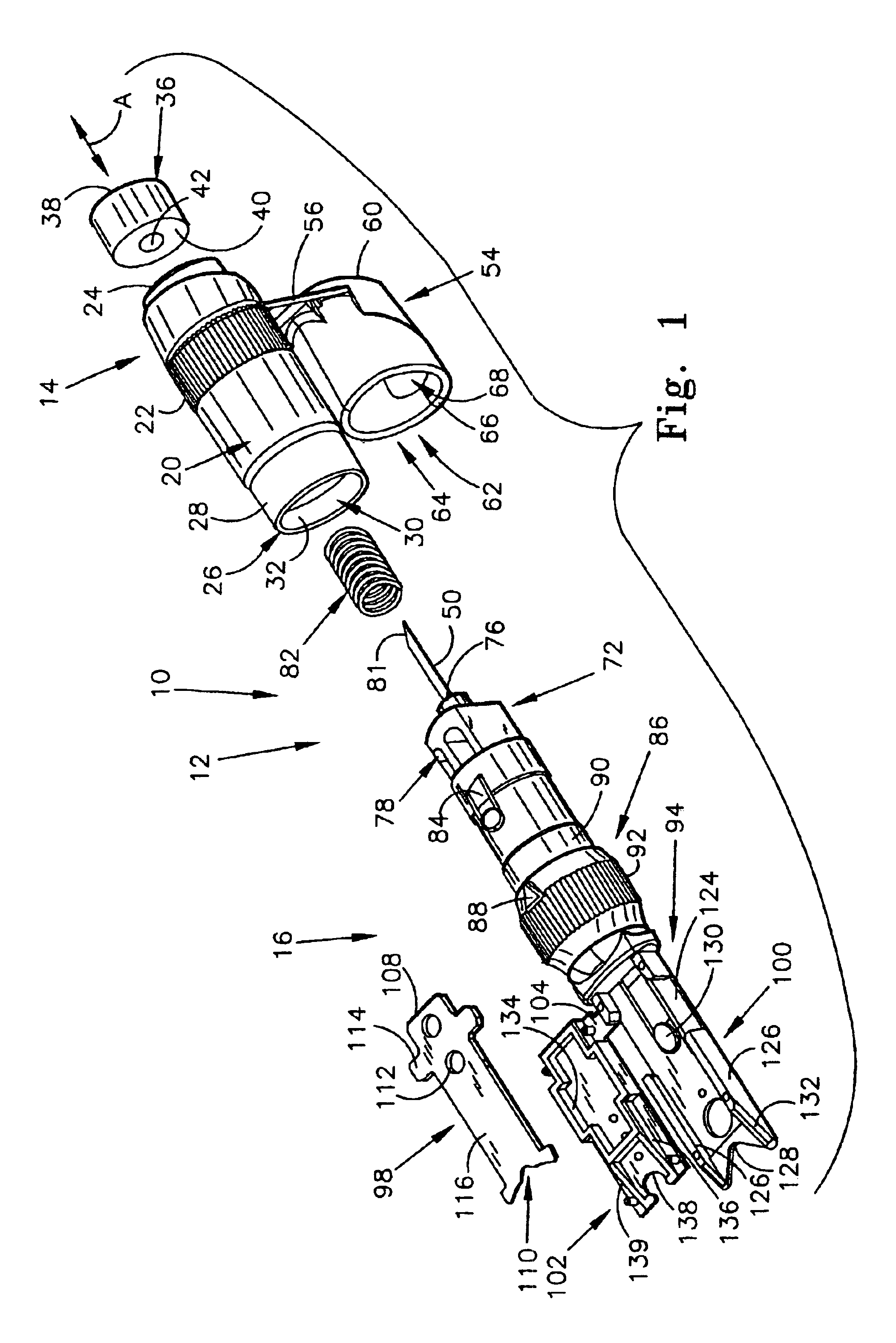
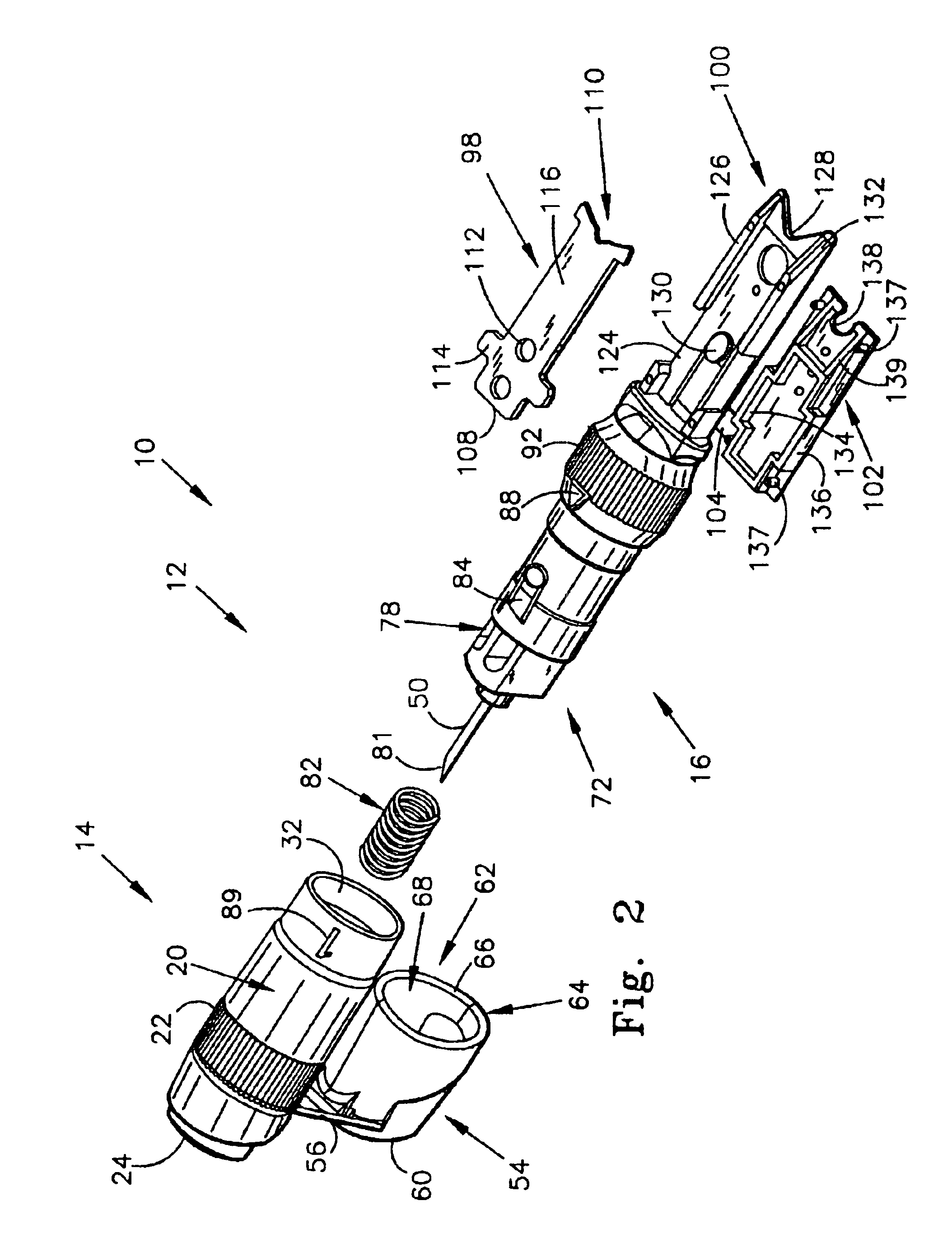
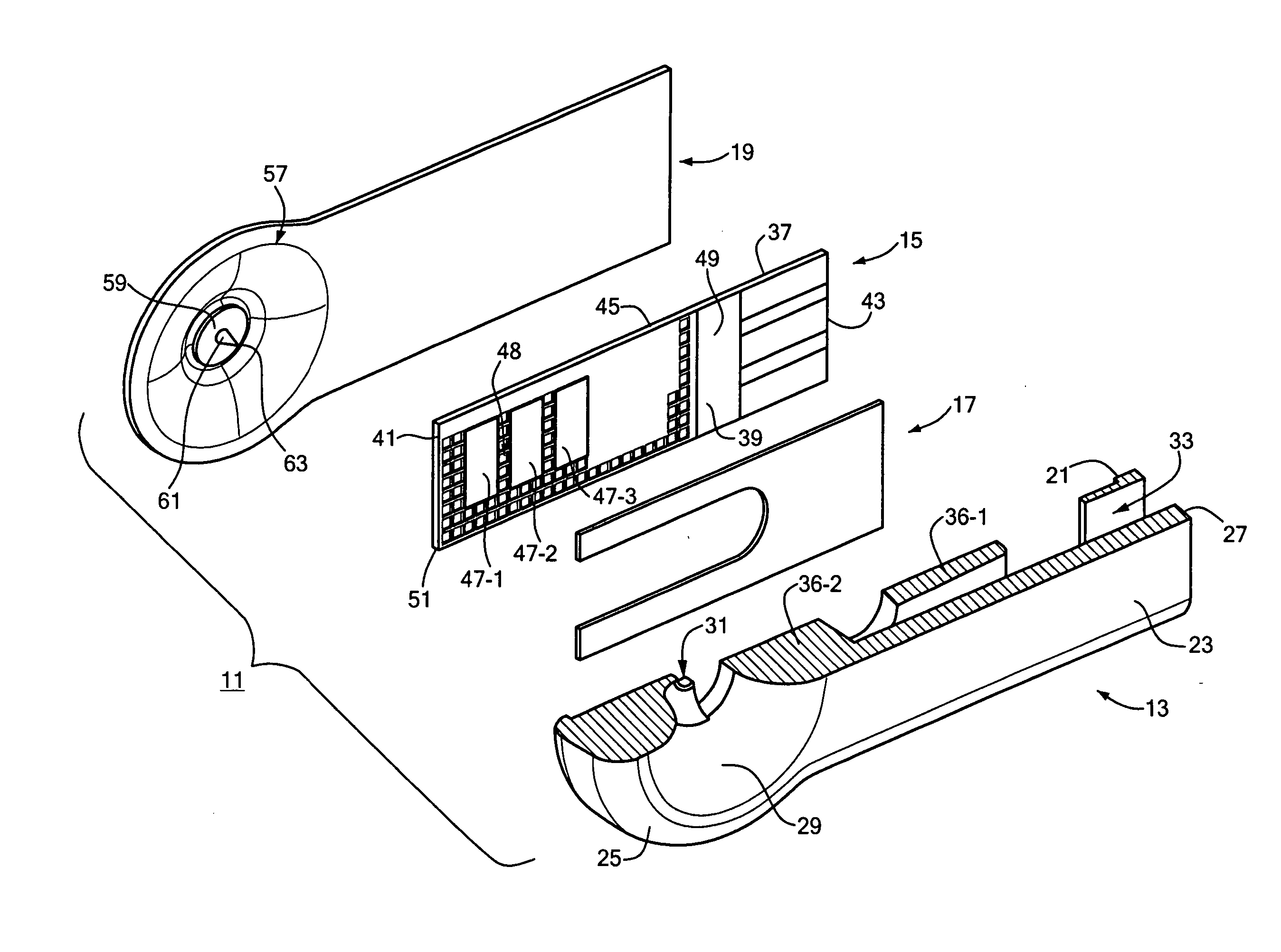
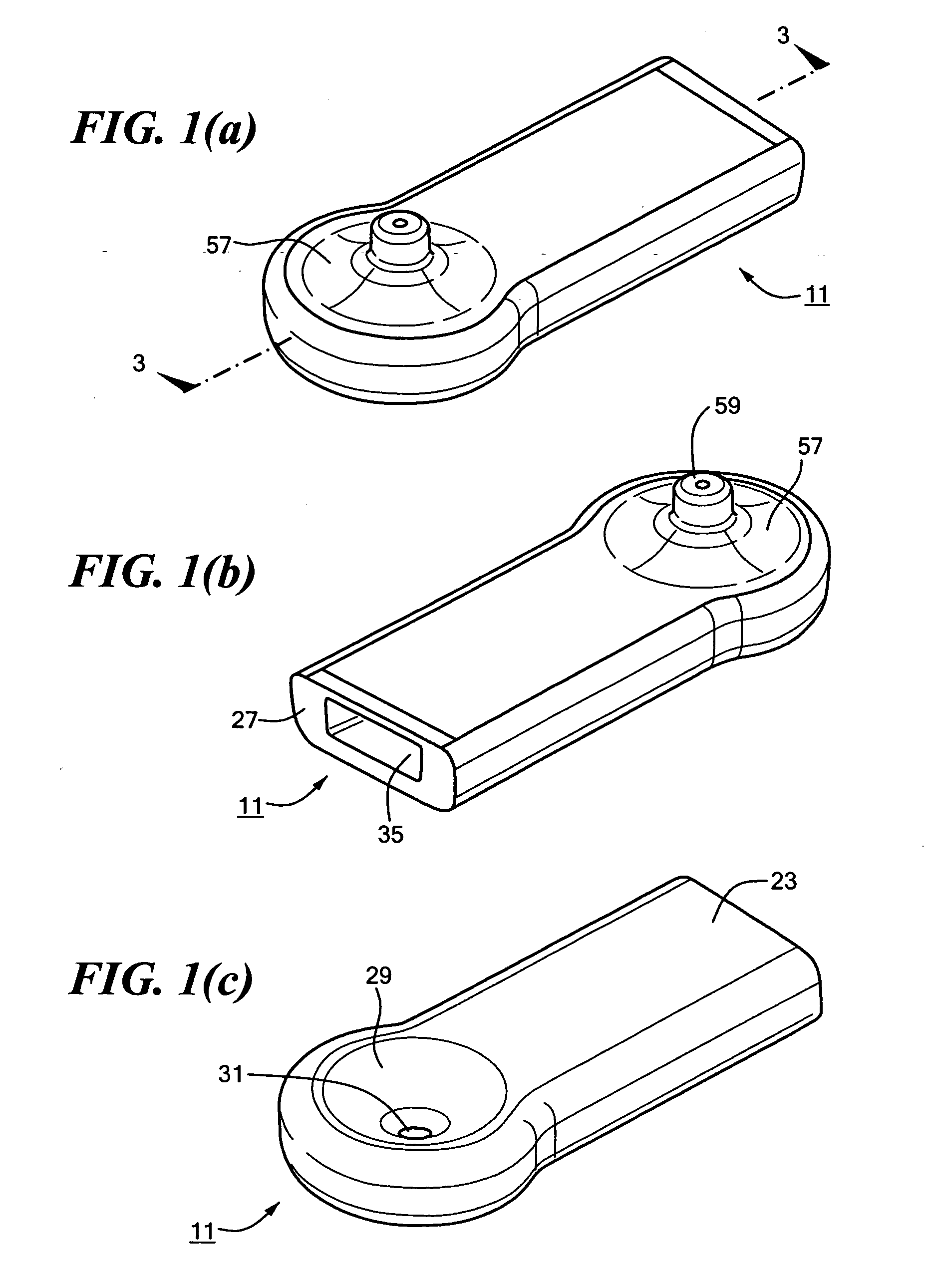
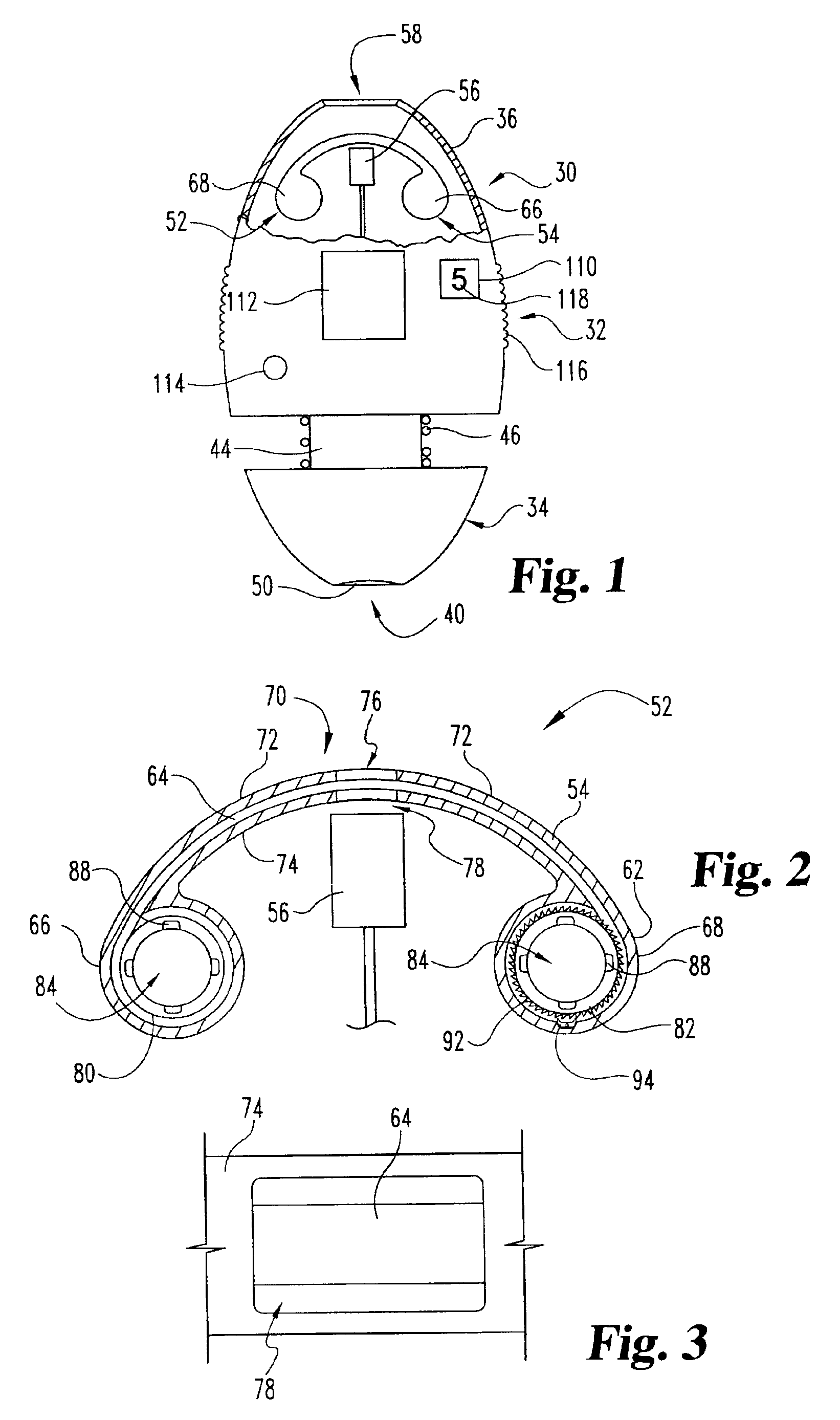
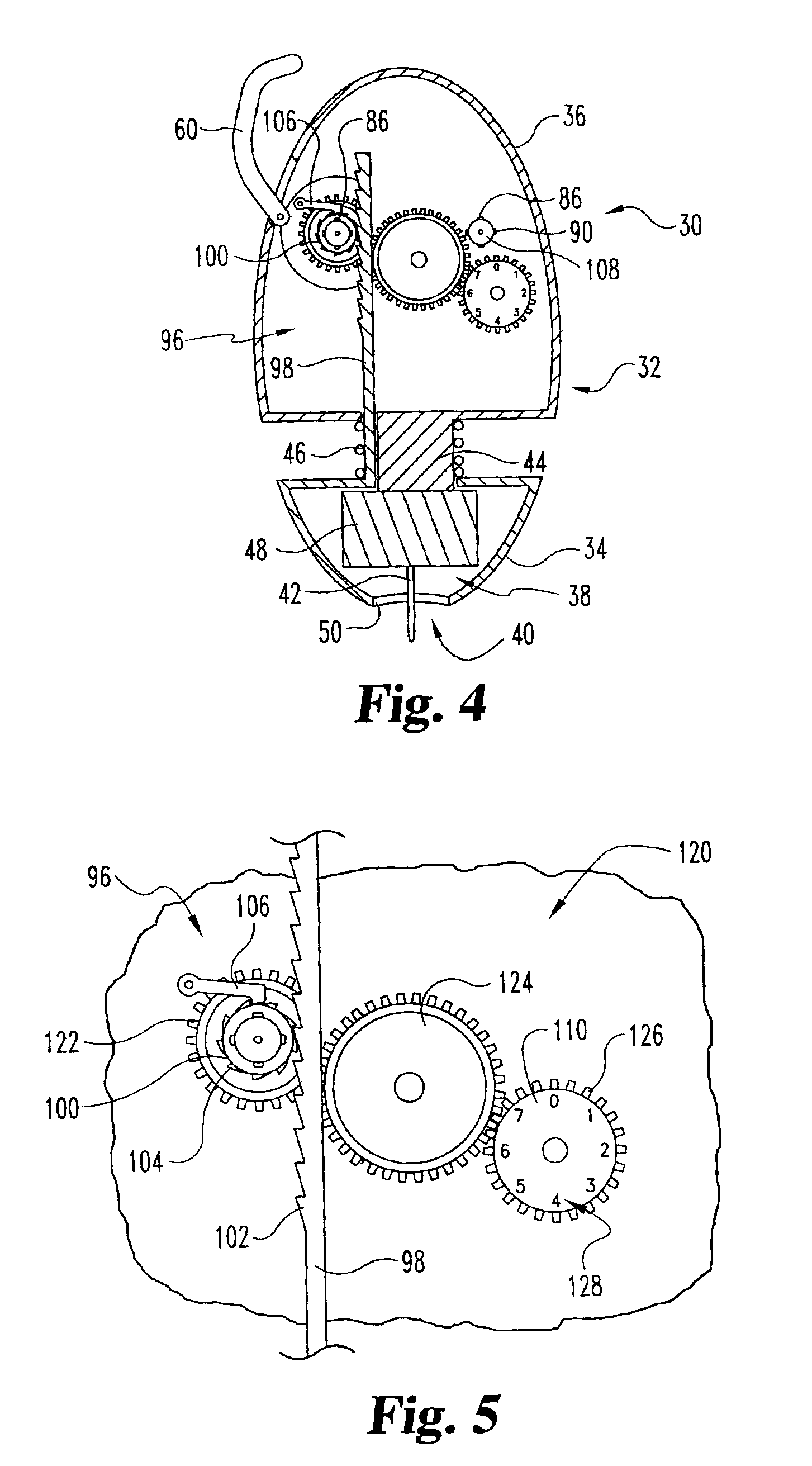
Body fluid sampling device and methods of use
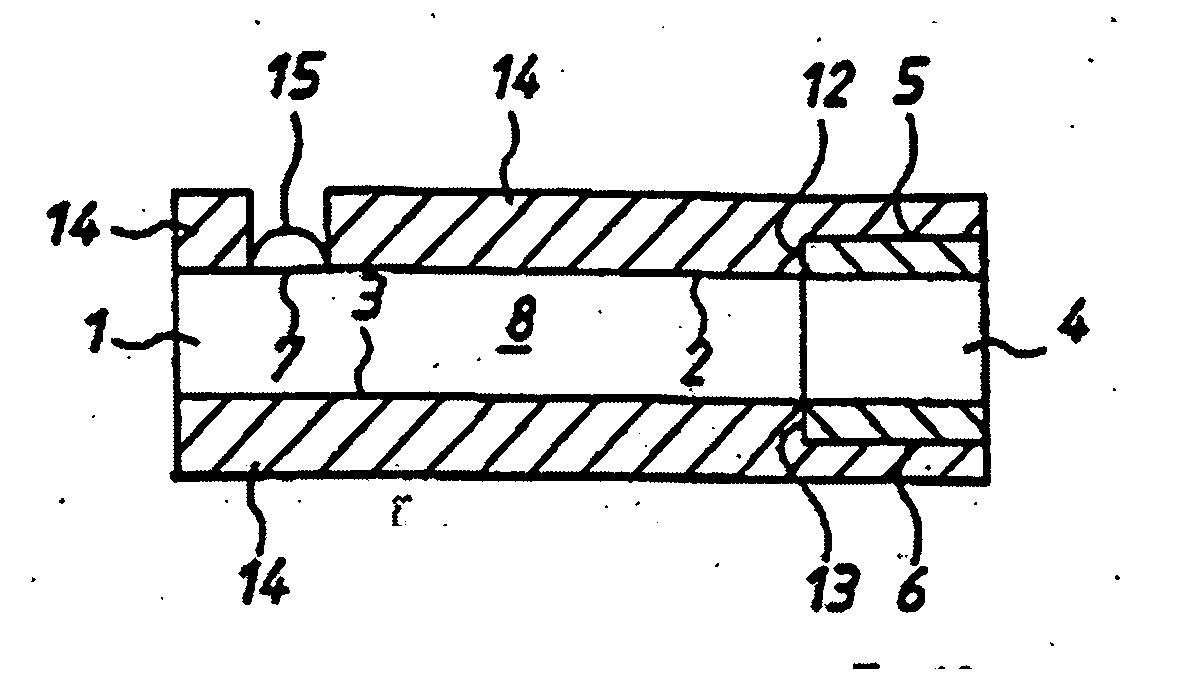
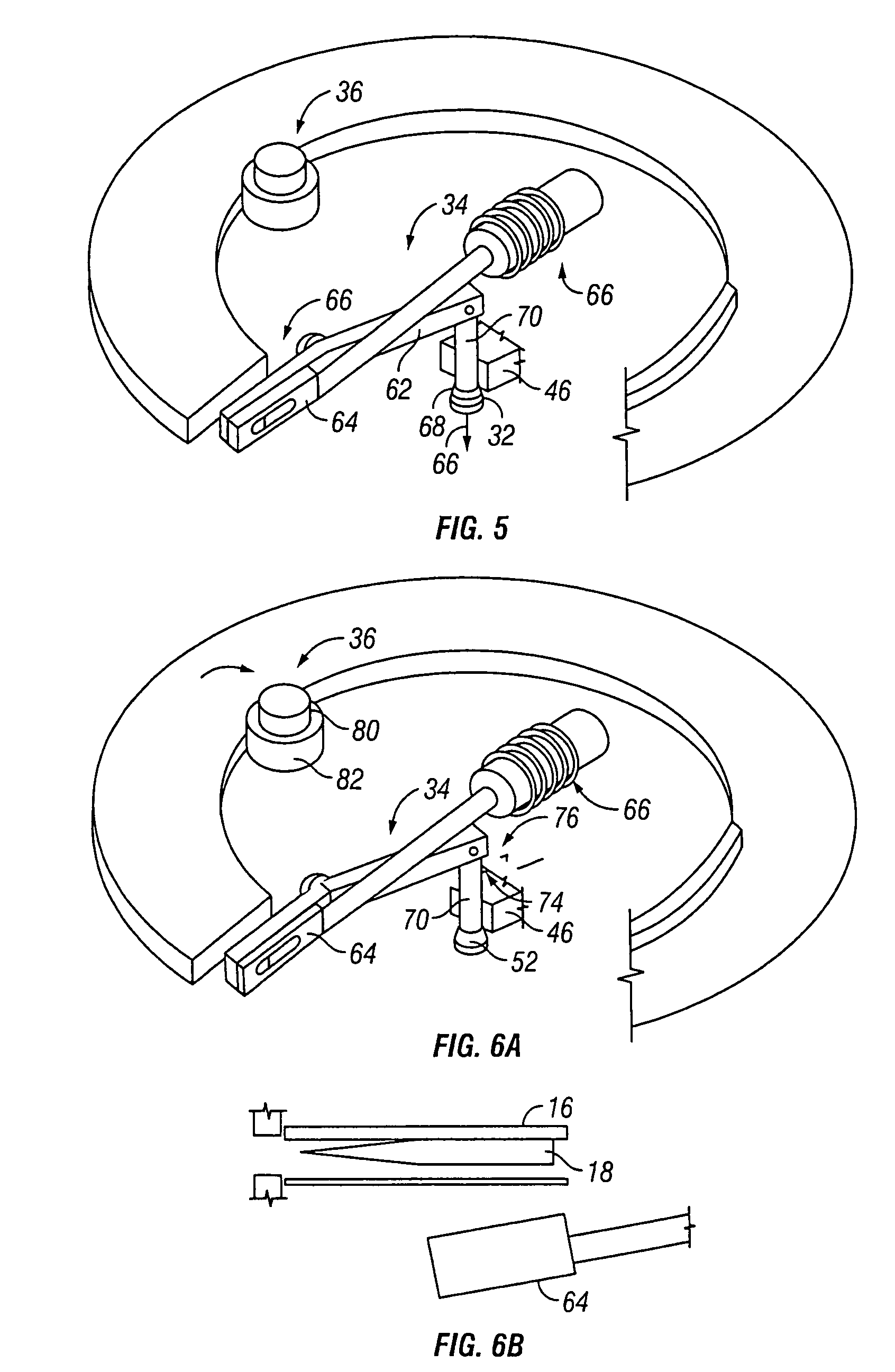
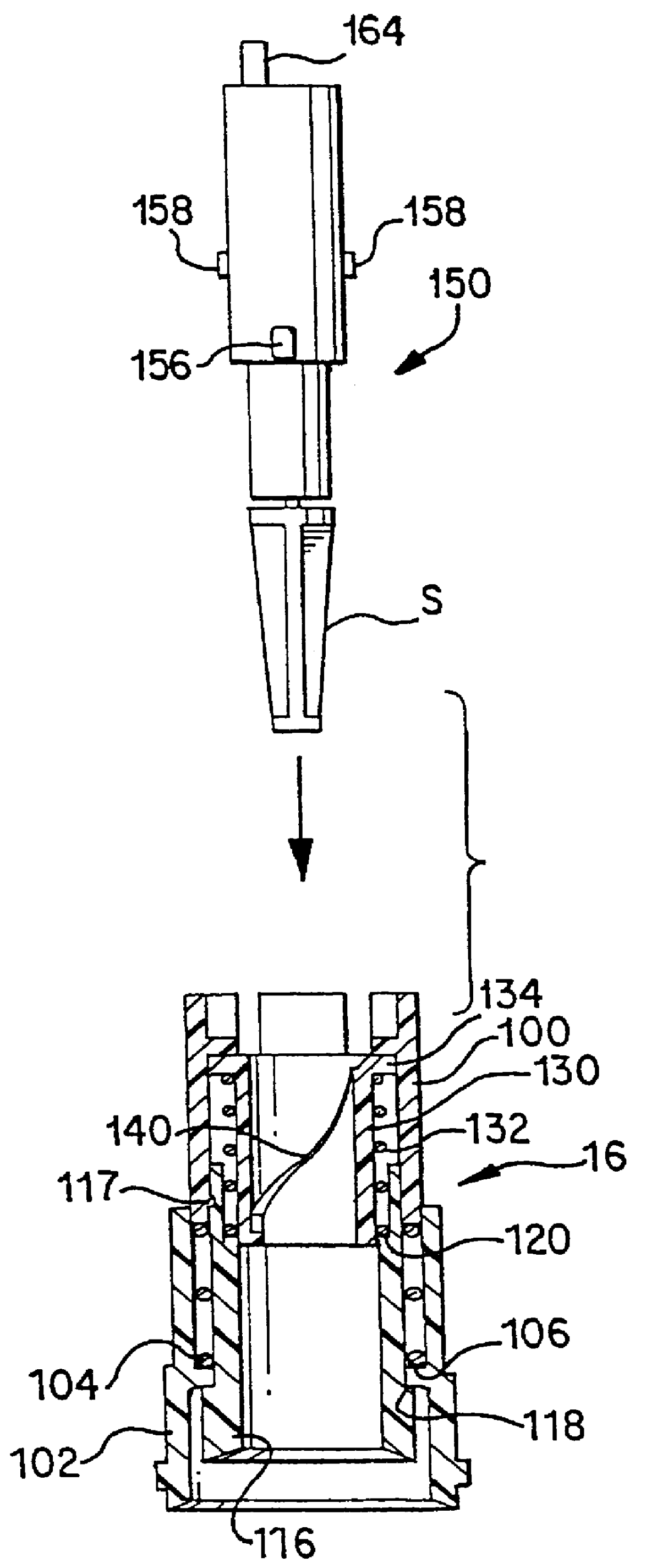
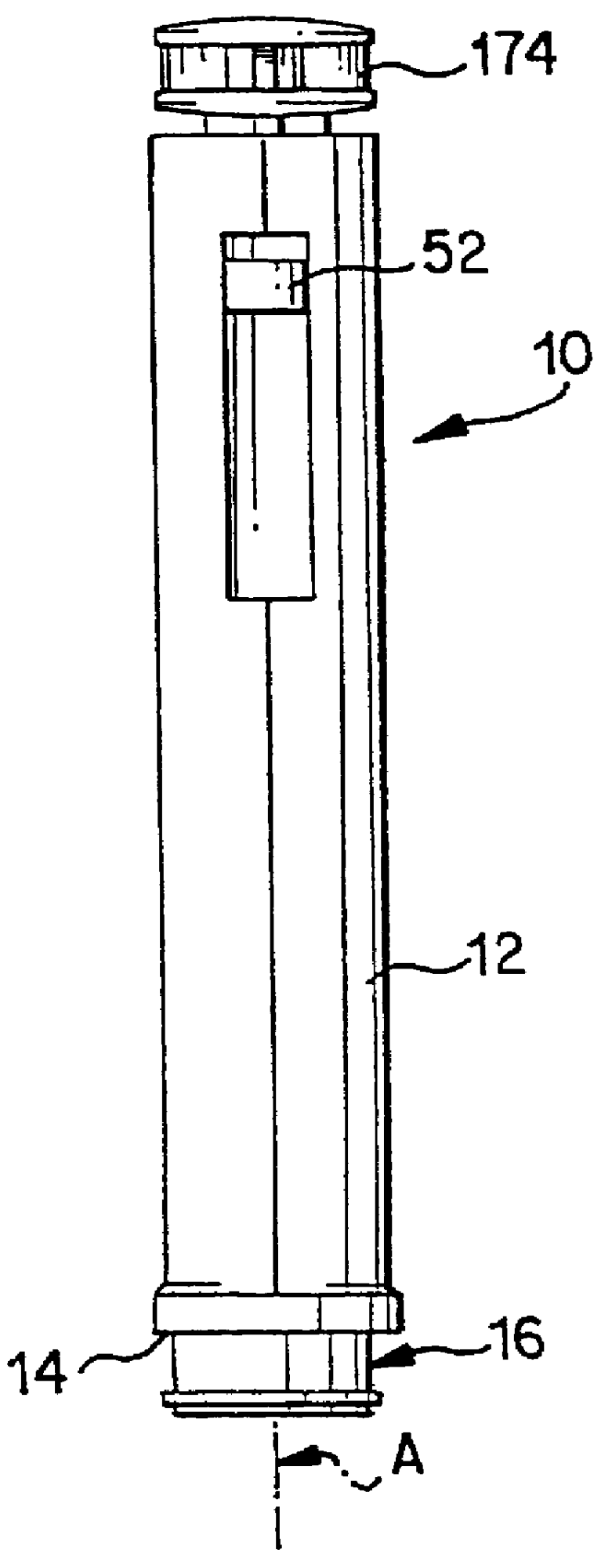
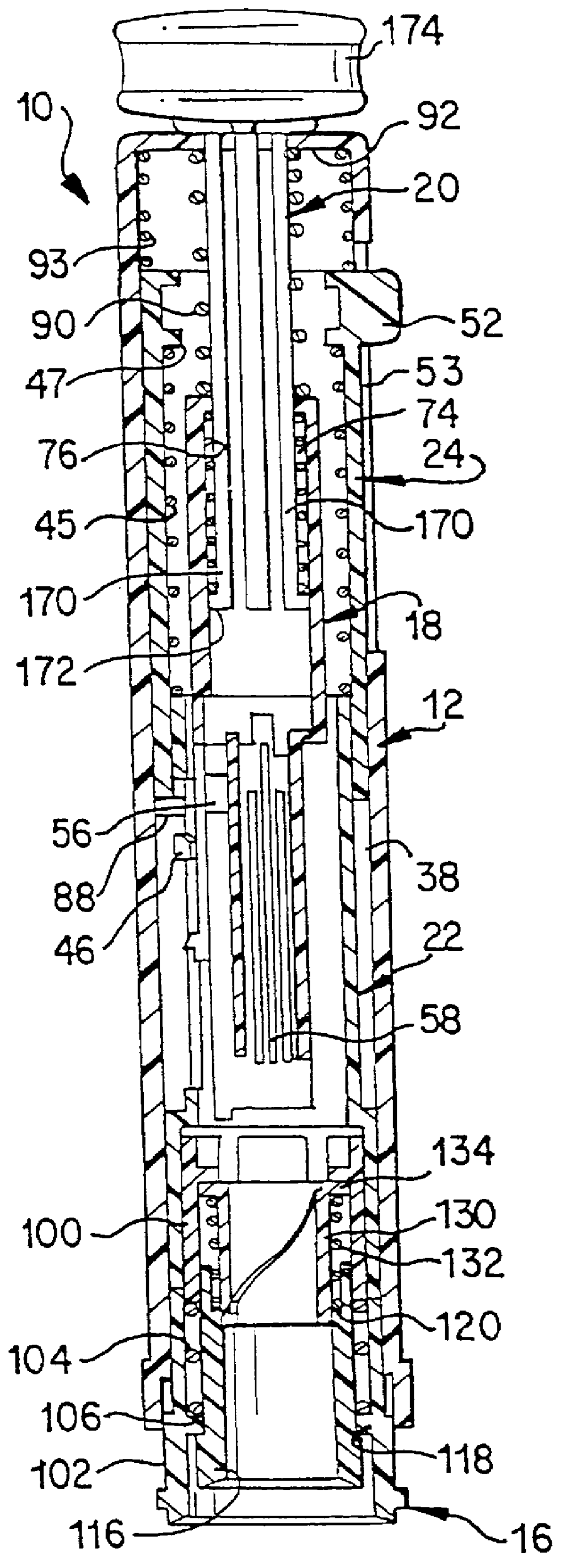
A device for sampling body fluid includes a housing having a sleeve at a forward end thereof which is displaceable in response to being pressed against a user's skin to trigger the firing of a lancet. After the lancet is removed from the incision, the sleeve is repeatedly pressed against the skin to depress a ring of body tissue in surrounding relationship to the incision to express body fluid outwardly through the incision. A pusher member is then actuated to push a capillary tube through a front end of the housing for drawing-in body fluid. The lancet is a disposable lancet which includes a body supporting a skin-lancing member and the capillary tube. The disposable lancet passes through an upper end of a lancet carrier when being installed or removed. The device cannot be armed until the disposable lancet is installed in the housing, because the capillary tube functions to push a safety device to a non-safety position.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Interstitial fluid methods and devices for determination of an analyte in the body
InactiveUS6251083B1Simpler to useFacilitate increased patient complianceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalytePorous membrane
Devices and methods for utilizing dry chemistry dye indicator systems for body fluid analysis, such as glucose level provided by incorporating a porous membrane in a disposable patch. The devices also provide for microtitration of fluid samples in fixed volumetric openings containing indicator reagent. The devices provided are low cost due to efficient manufacturing methods provided.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
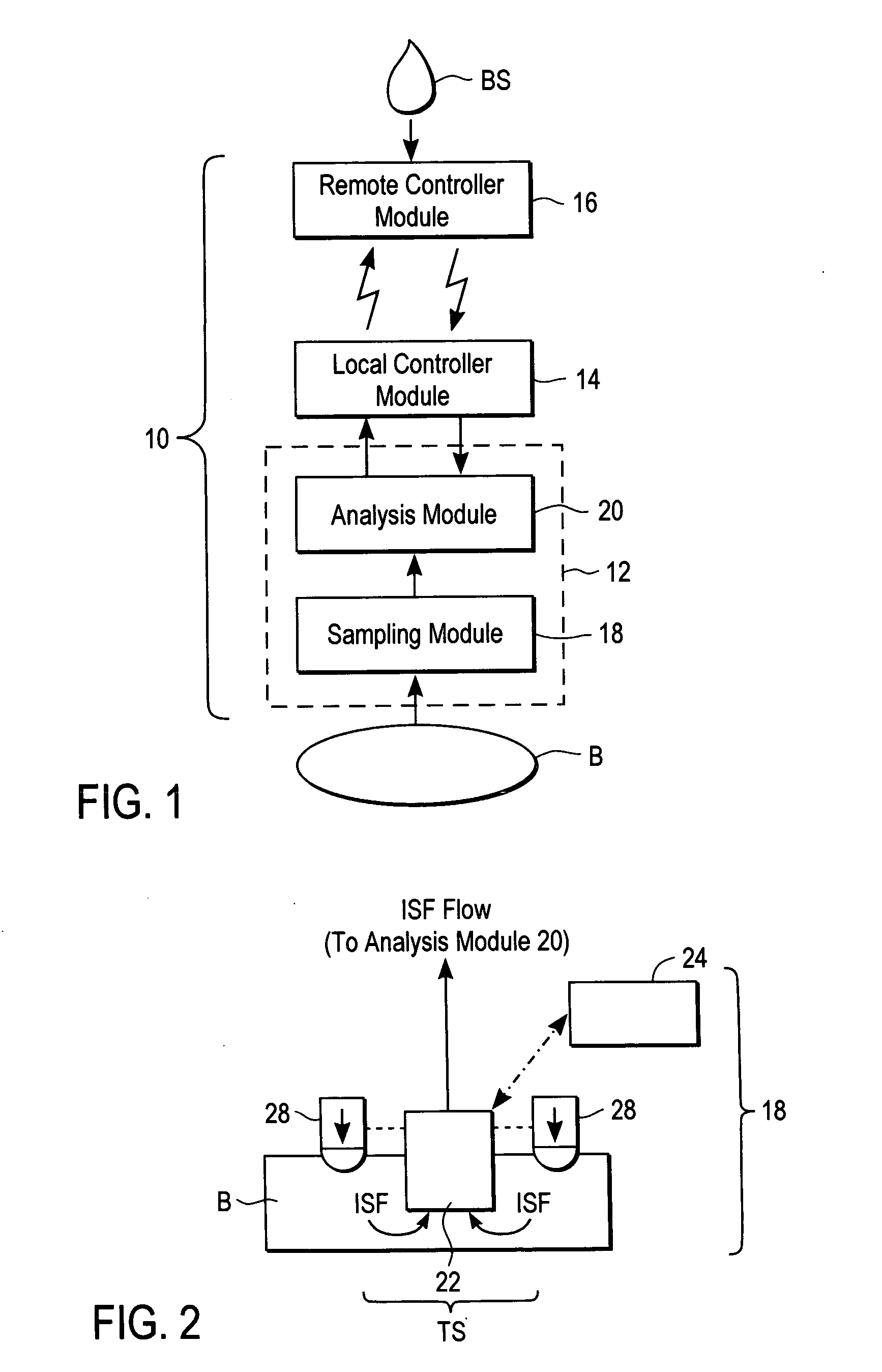
Devices, systems and methods for extracting bodily fluid and monitoring an analyte therein
InactiveUS20040249254A1Easy to useLittle painWithdrawing sample devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsAnalyteElectronic communication
A system for extracting a bodily fluid sample (e.g., an interstitial fluid [ISF] sample) and monitoring an analyte therein includes a disposable cartridge and a local controller module. The disposable cartridge includes a sampling module adapted to extract a bodily fluid sample and an analysis module adapted to measure an analyte (e.g., glucose) in the bodily fluid sample. The local controller module is in electronic communication with the disposable cartridge and is adapted to receive and store measurement data from the analysis module. An ISF extraction device includes a penetration member configured for penetrating and residing in a target site of a user's skin layer and, subsequently, extracting an ISF sample therefrom. The device also includes a pressure ring(s) adapted for applying pressure to the user's skin layer in the vicinity of the target site. The device is configured such that the pressure ring(s) is capable of applying pressure in an oscillating manner whereby an ISF glucose lag of the ISF sample extracted by the penetration member is mitigated. A method for extracting ISF includes providing an ISF fluid extraction device with a penetration member and a pressure ring(s). Next, a user's skin layer is contacted by the pressure ring(s) and penetrated by the penetration member. An ISF sample is then extracted from the user's skin layer while pressure is being applied in an oscillating manner by the pressure ring(s). The oscillating pressure mitigates an ISF glucose lag of the extracted ISF sample.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
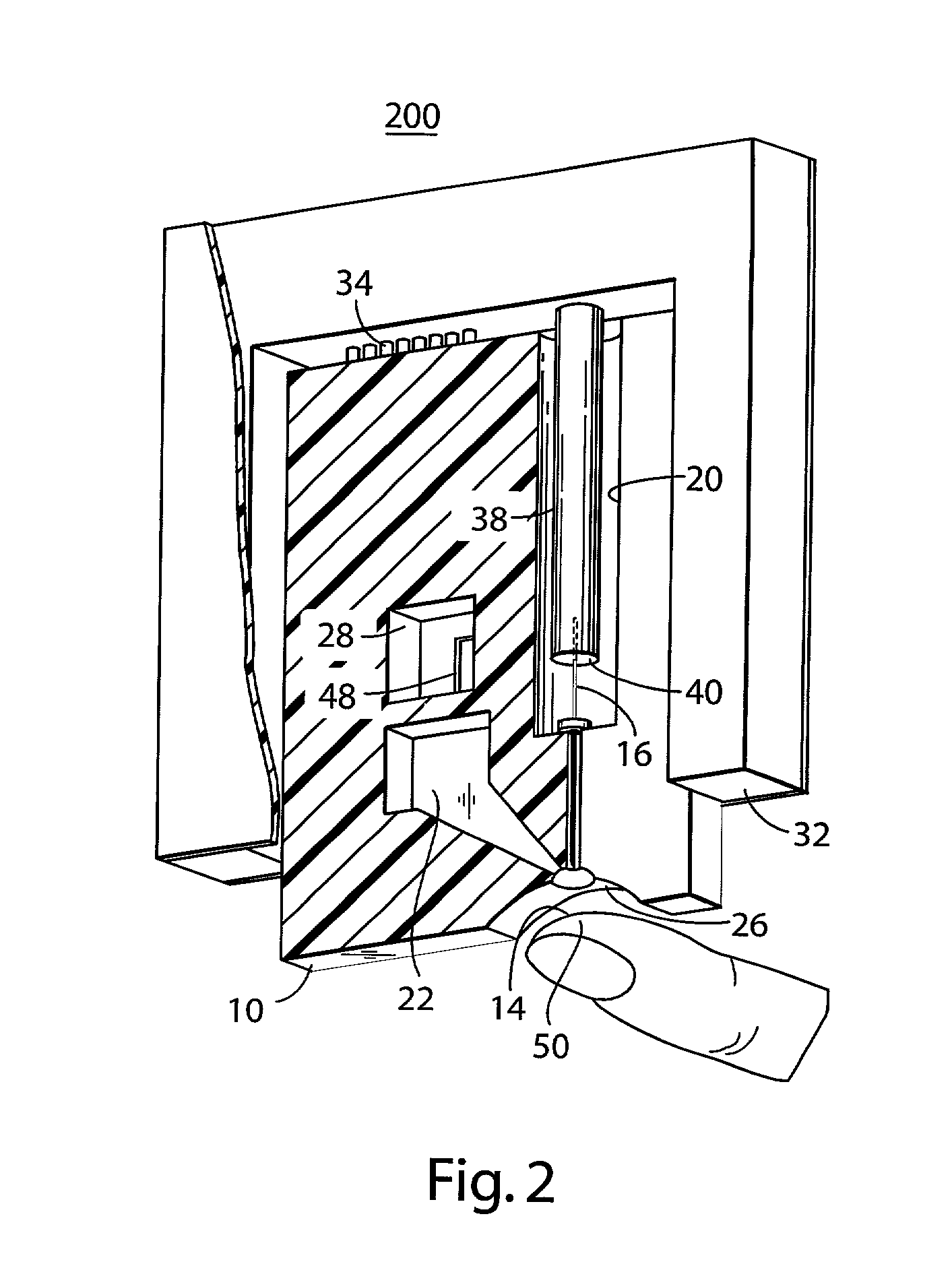
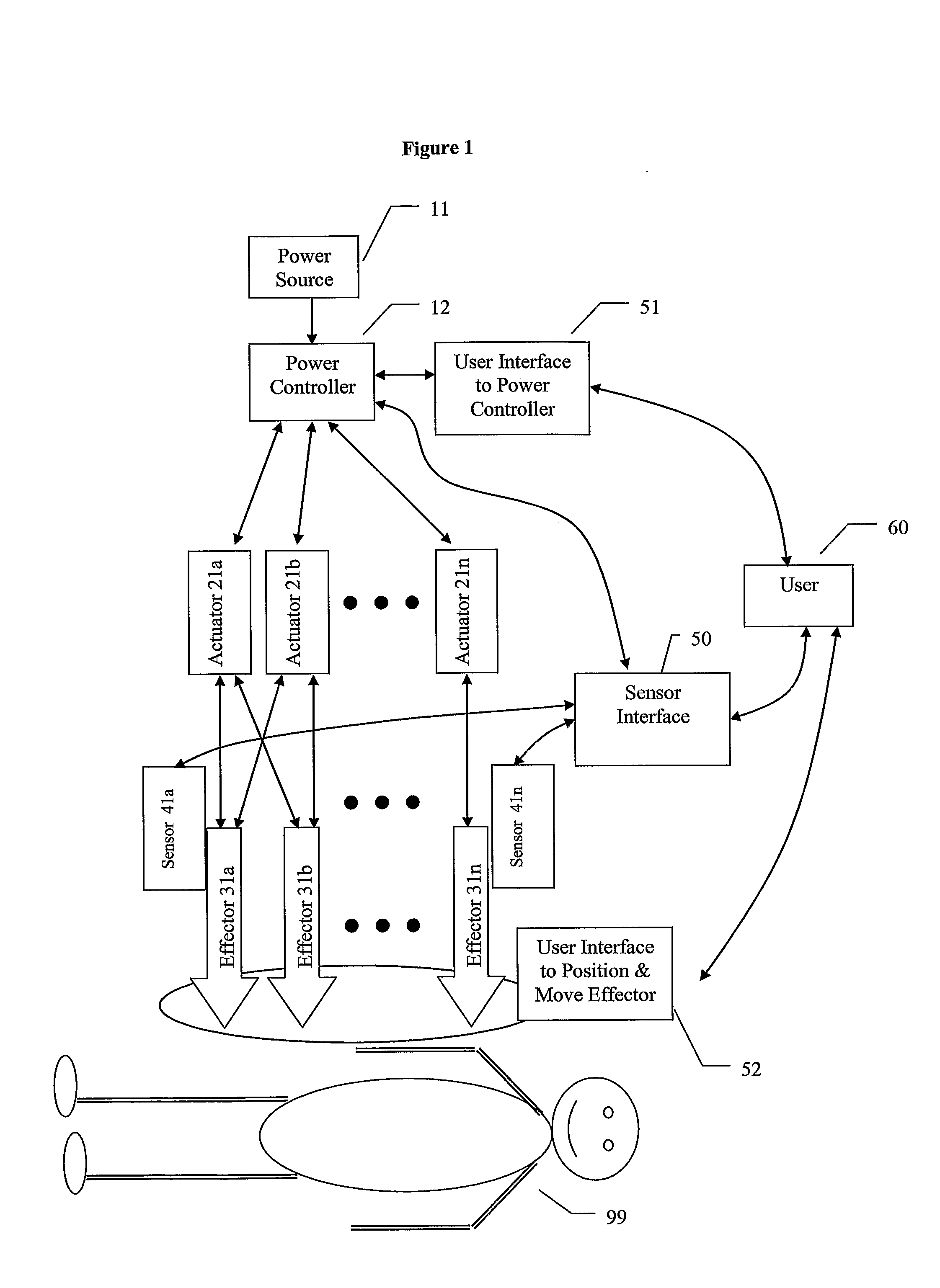
Attribute compensation for analyte detection and/or continuous monitoring
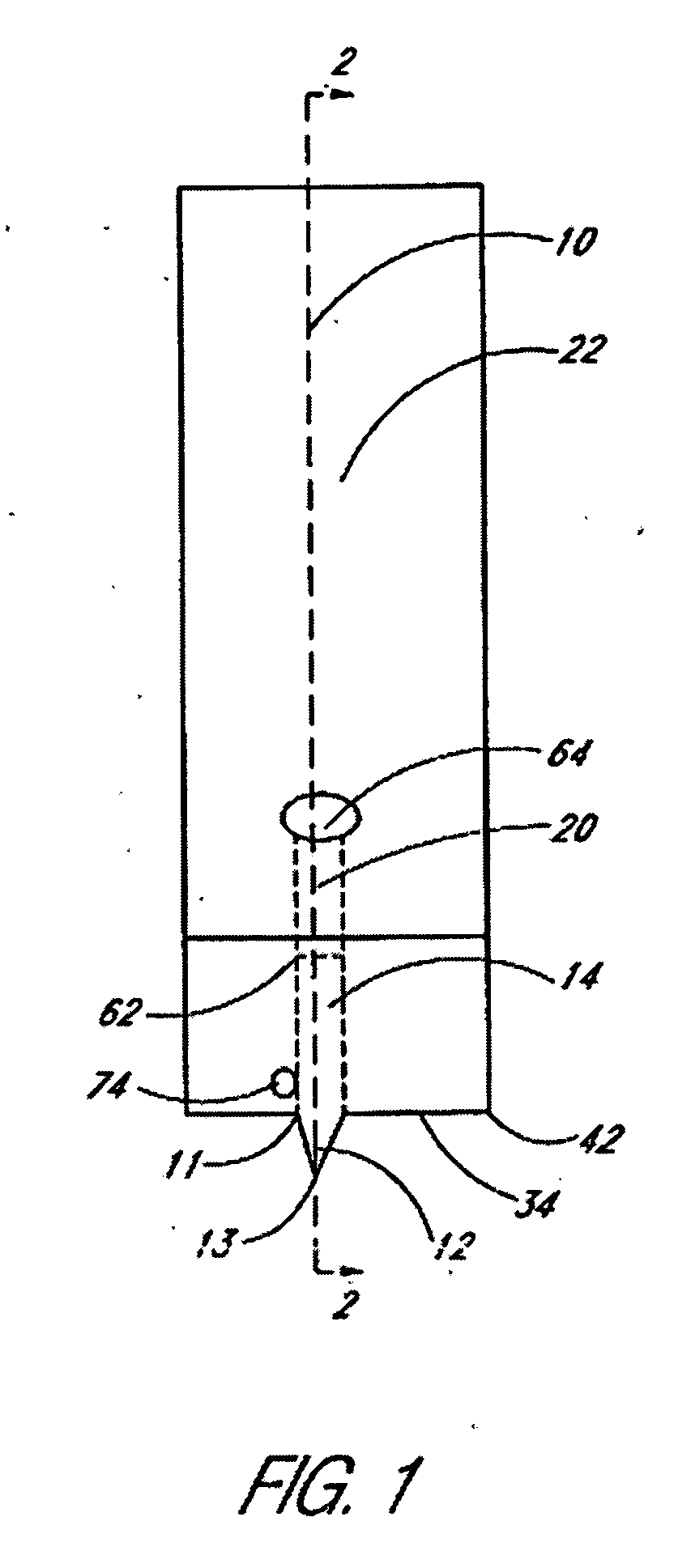
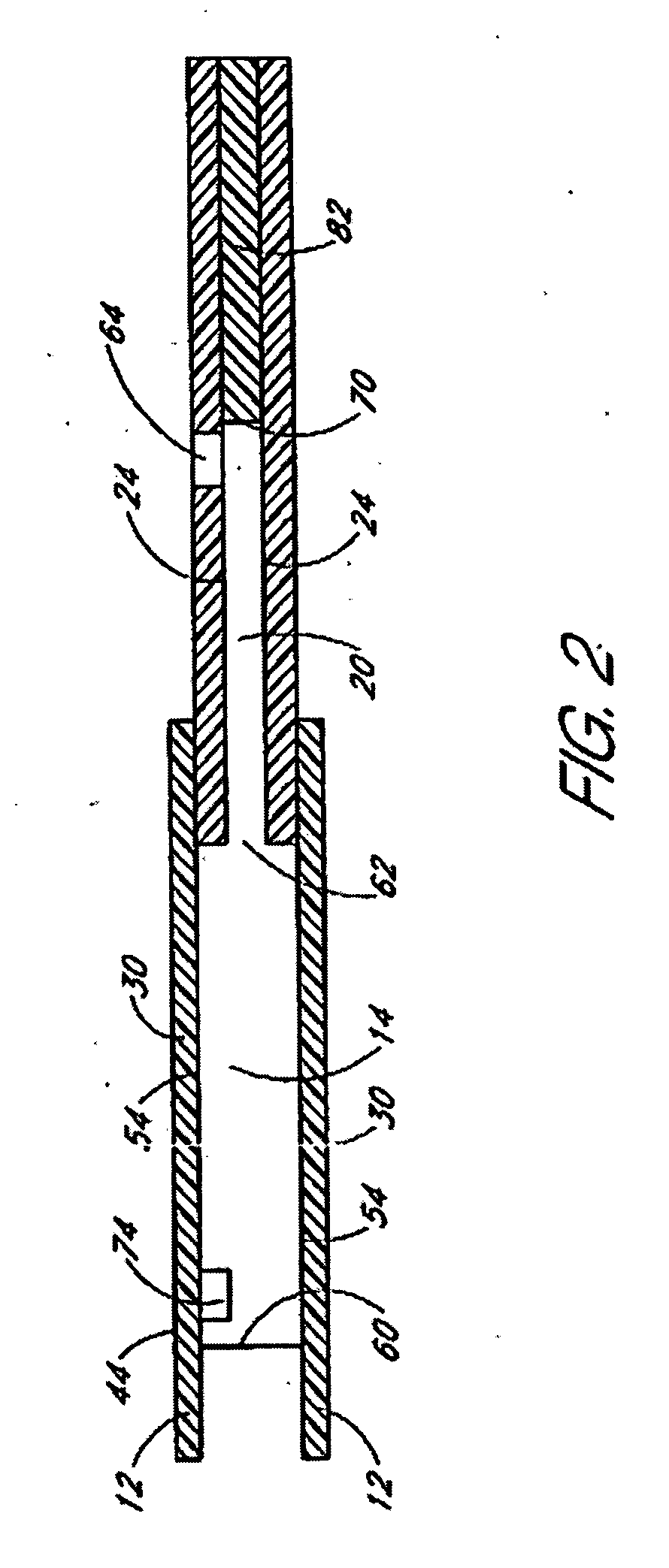
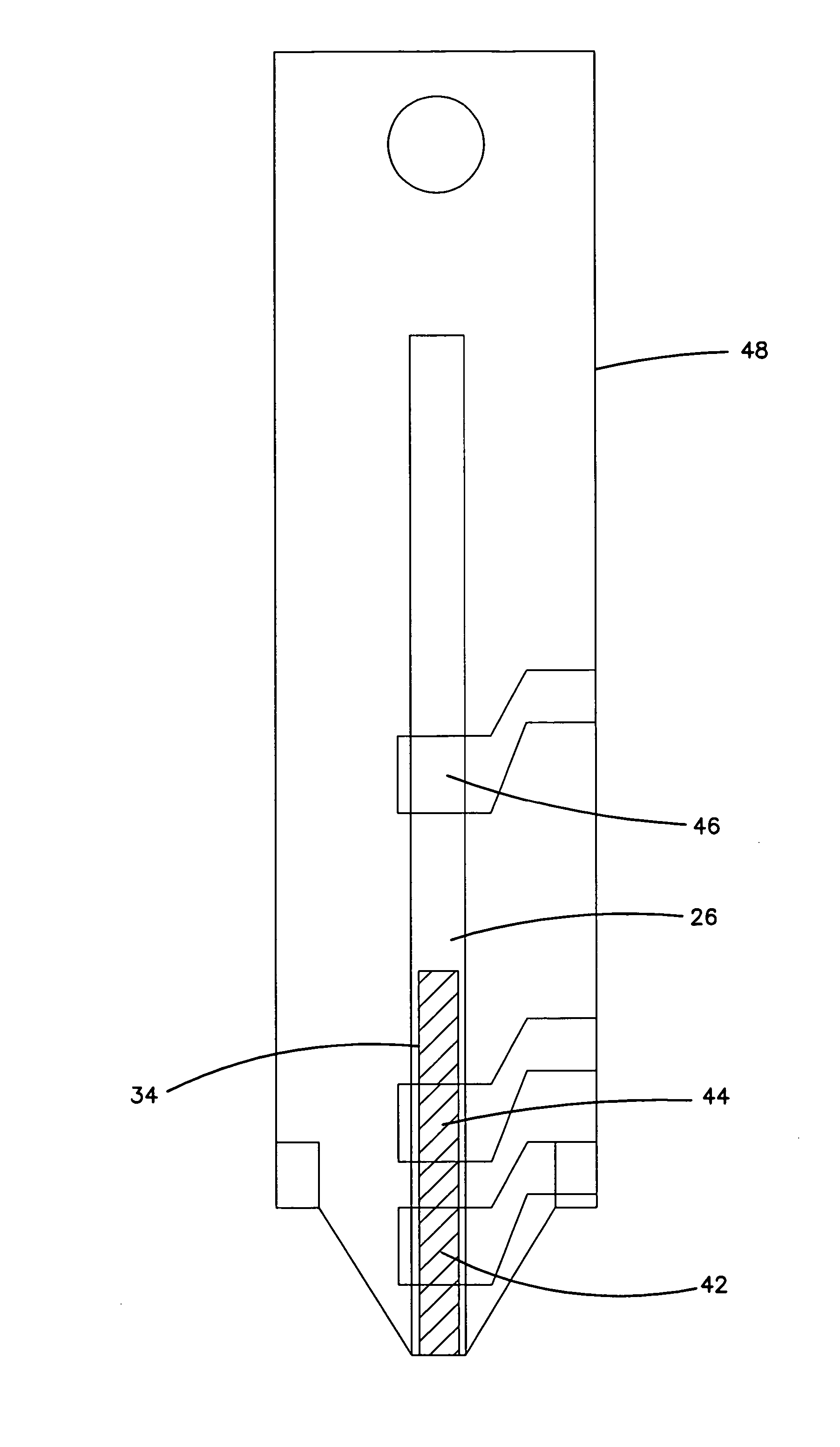
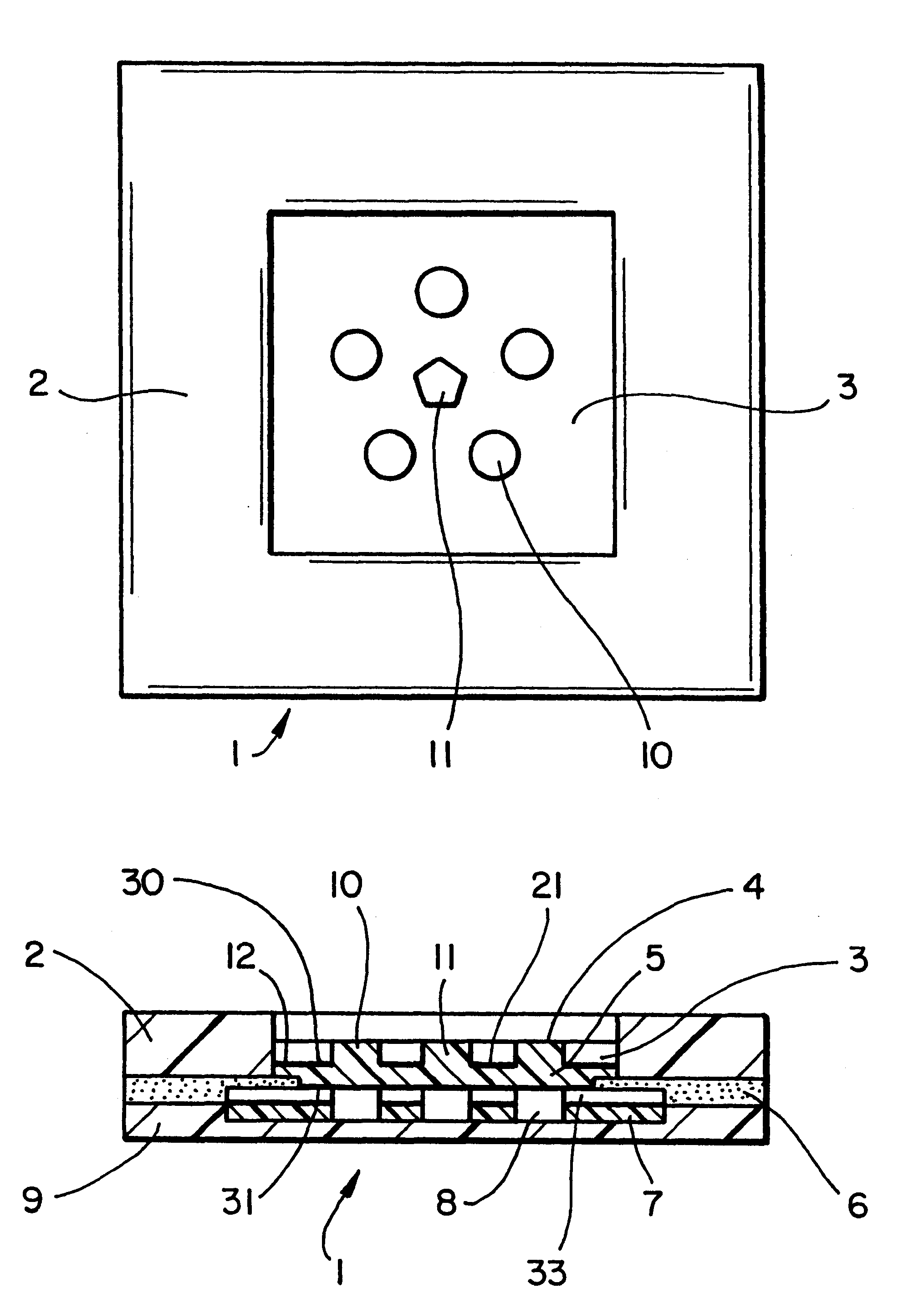
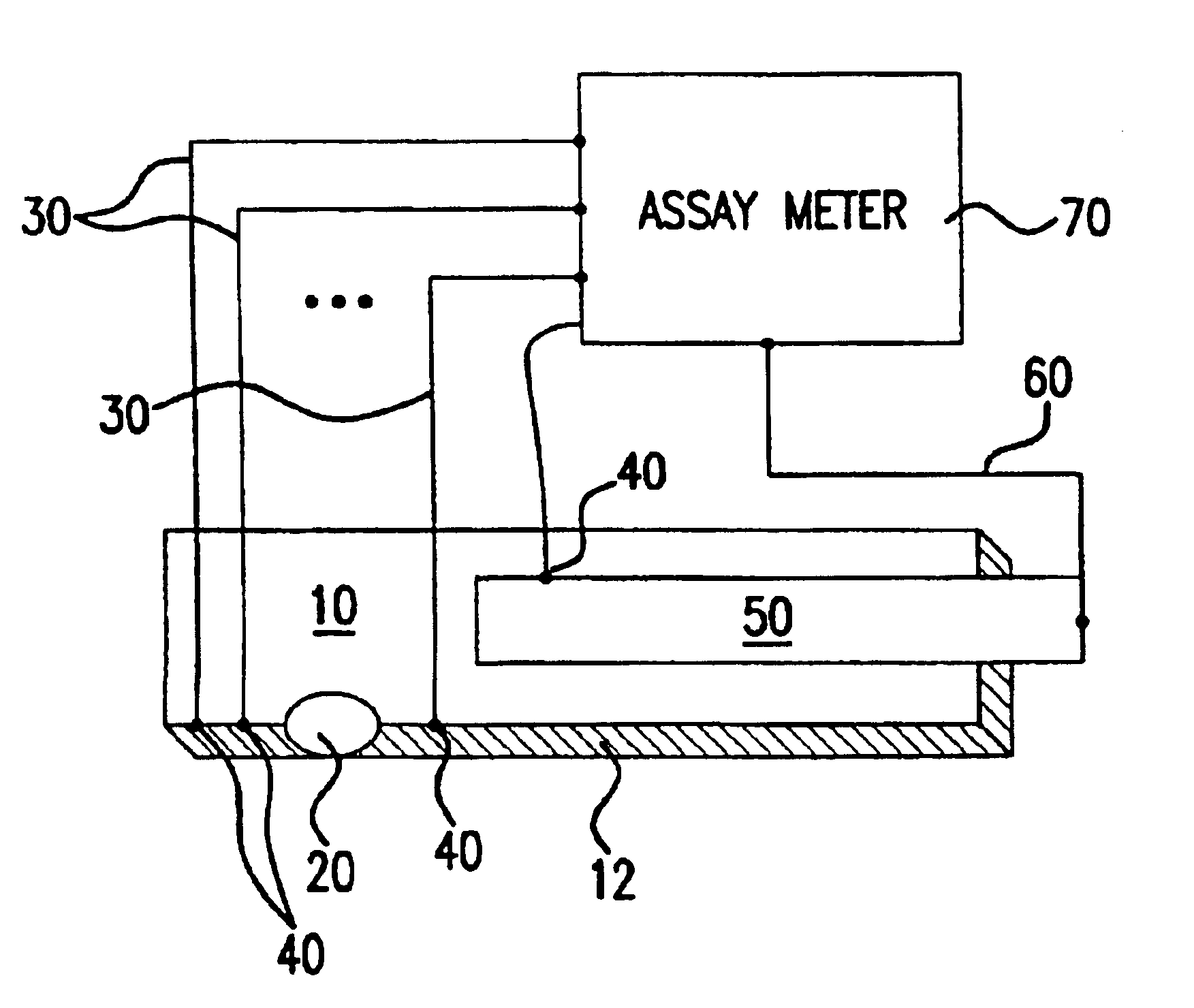
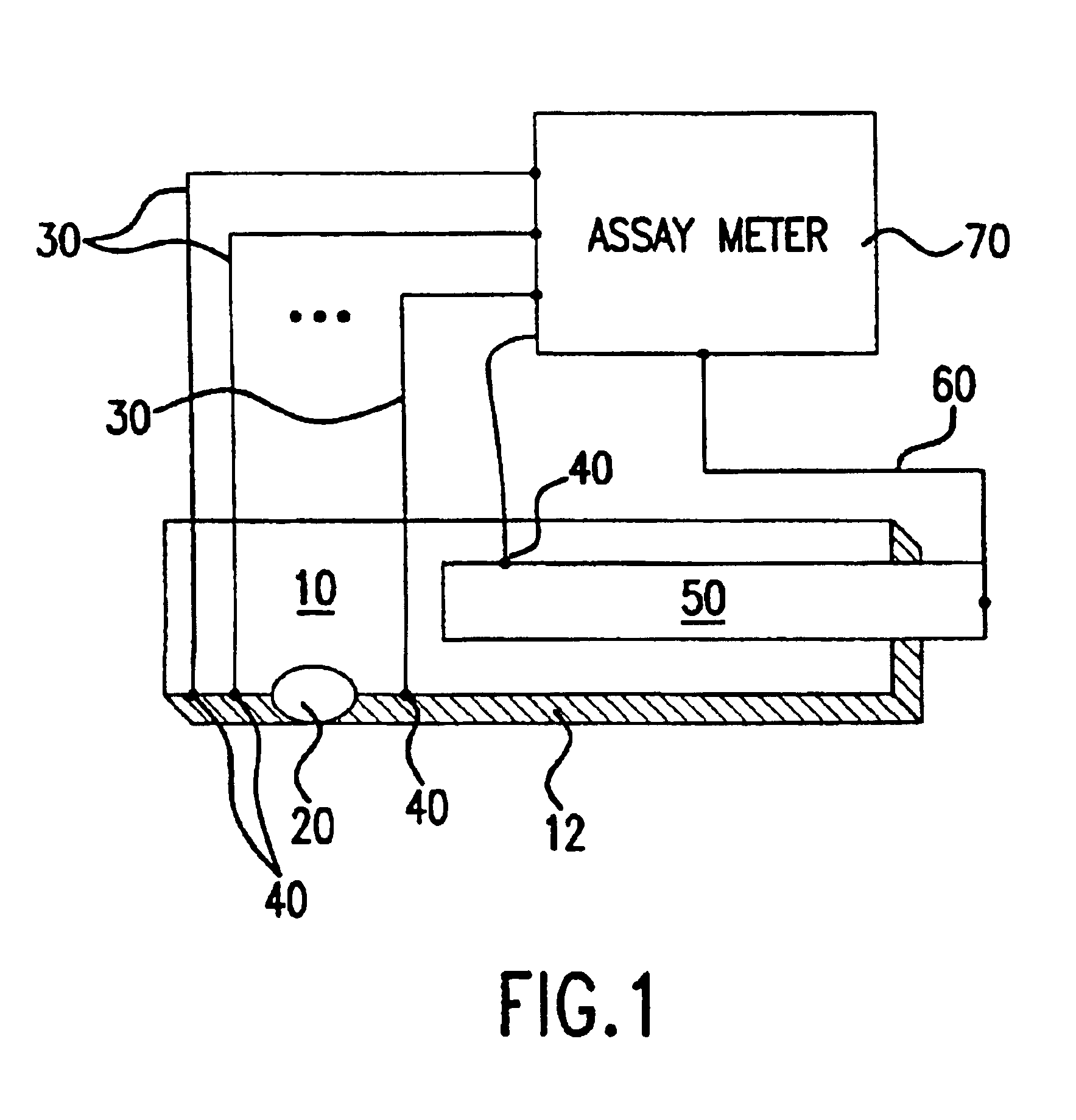
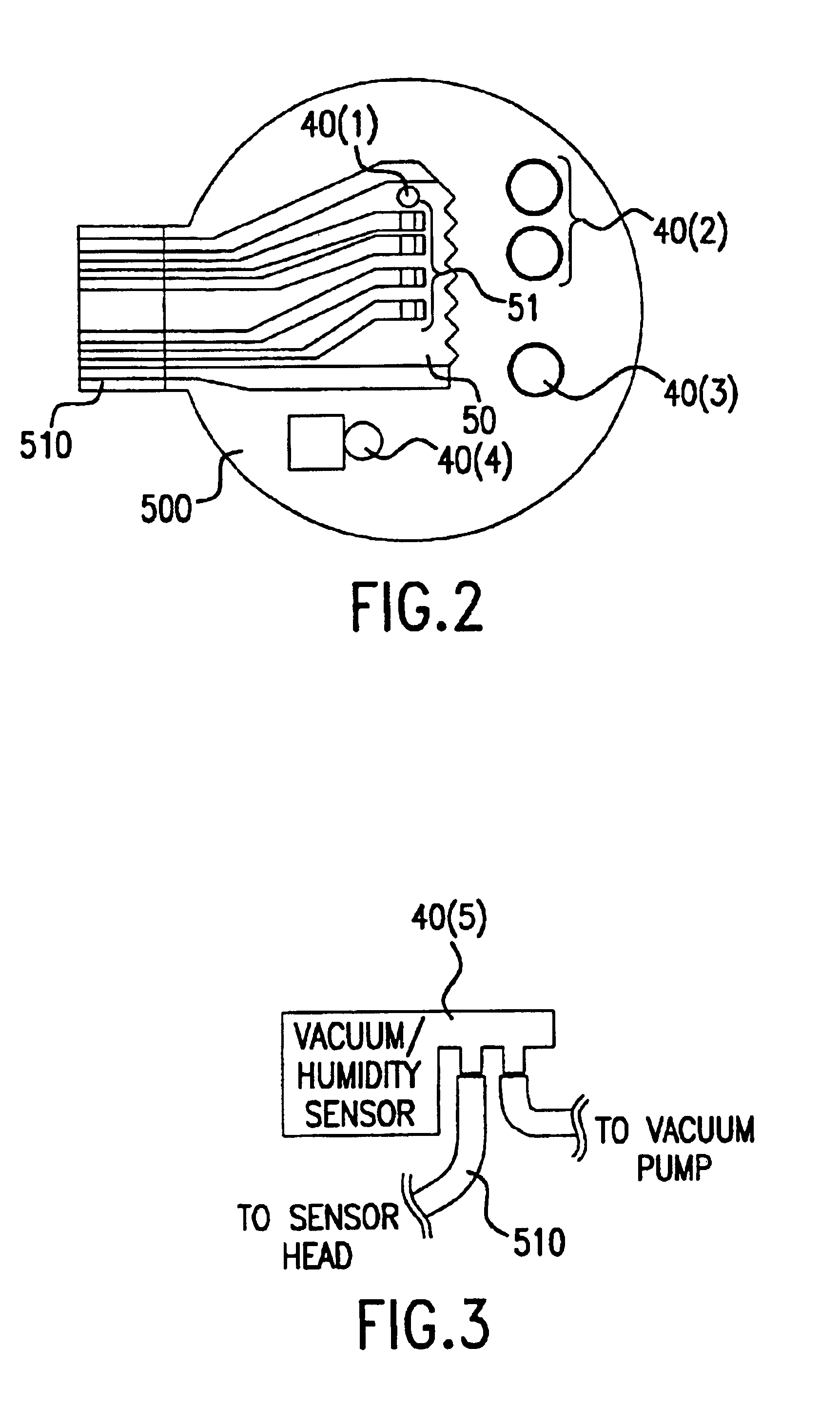
A system and method for detecting a measuring an analyte in a biological fluid of an animal. A harvesting device (10) is provided suitable for positioning on the surface of tissue of an animal to harvest biological fluid therefrom. The harvesting device (10) comprises an analyte sensor (50) positioned to be contacted by the harvested biological fluid and which generates a measurement signal representative of the analyte. At least one attribute sensor (40) is provided to measure an attribute associated with the biological fluid harvesting operation of the harvesting device (10) or the assay of the biological fluid, and which generates an attribute signal representative of the attribute. Adjustments are made to operational parameters of the harvesting device (10) based on the one or more attributes.
Owner:ALTEA THERAPEUTIC CORP +2
Valve for intravenous catheter
The present invention is directed to a valve assembly in an intravenous catheter that facilitates the administration of fluid to a patient through the intravenous catheter by a needleless device. The valve assembly of the present invention contains means for providing a positive displacement of fluid from the catheter at a time when a needleless device is removed from the valve assembly following its connection to the valve assembly.
Owner:SPAN-AMERICA MEDICAL SYSTEMS
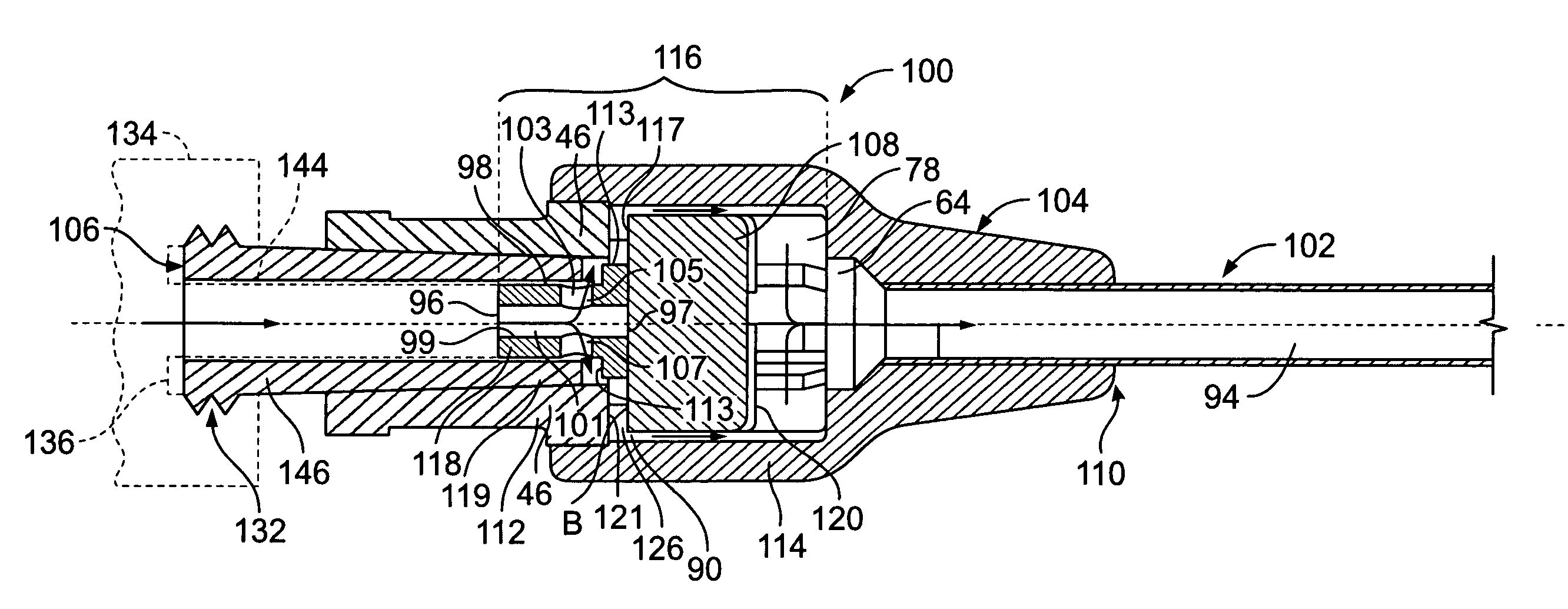
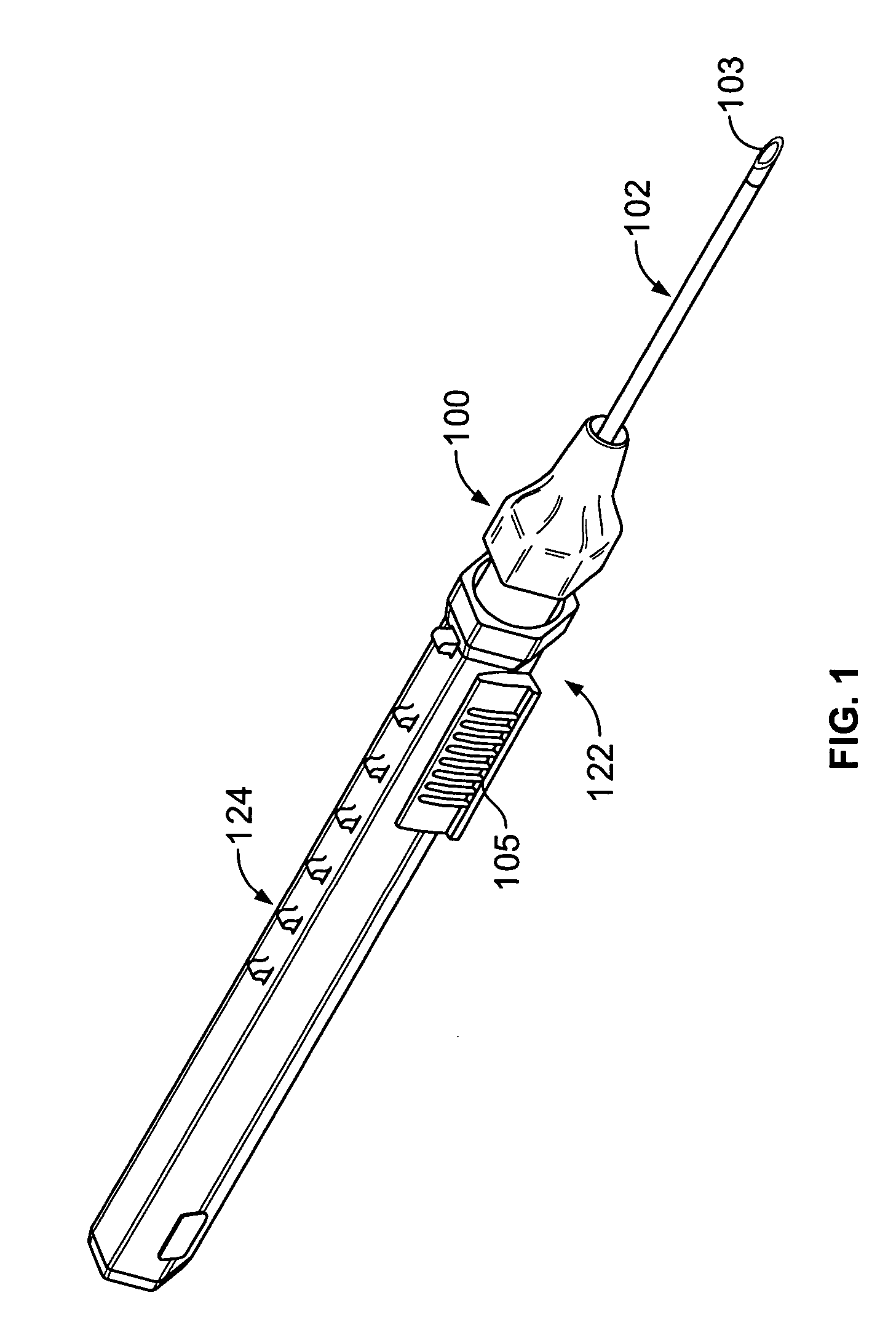
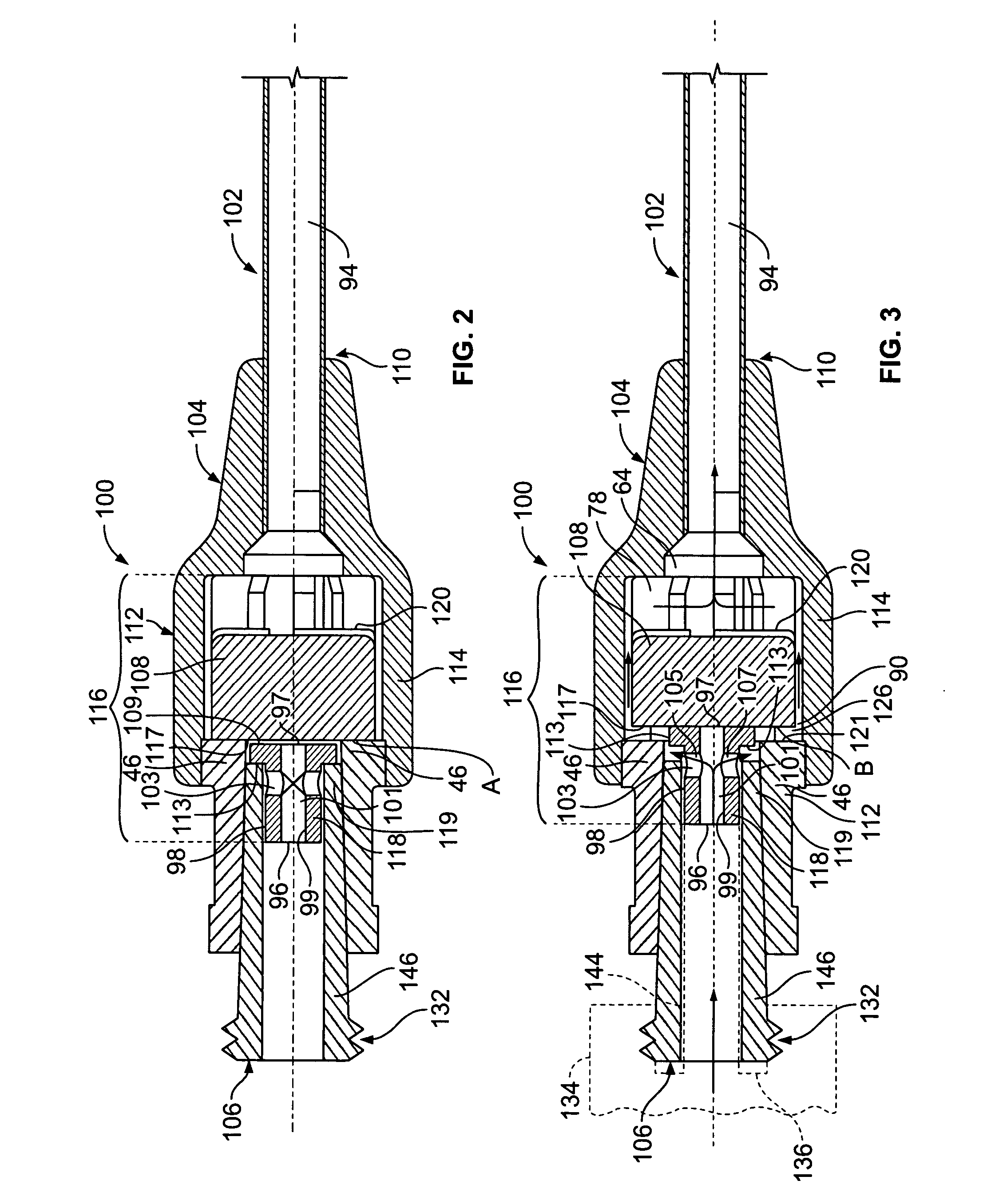
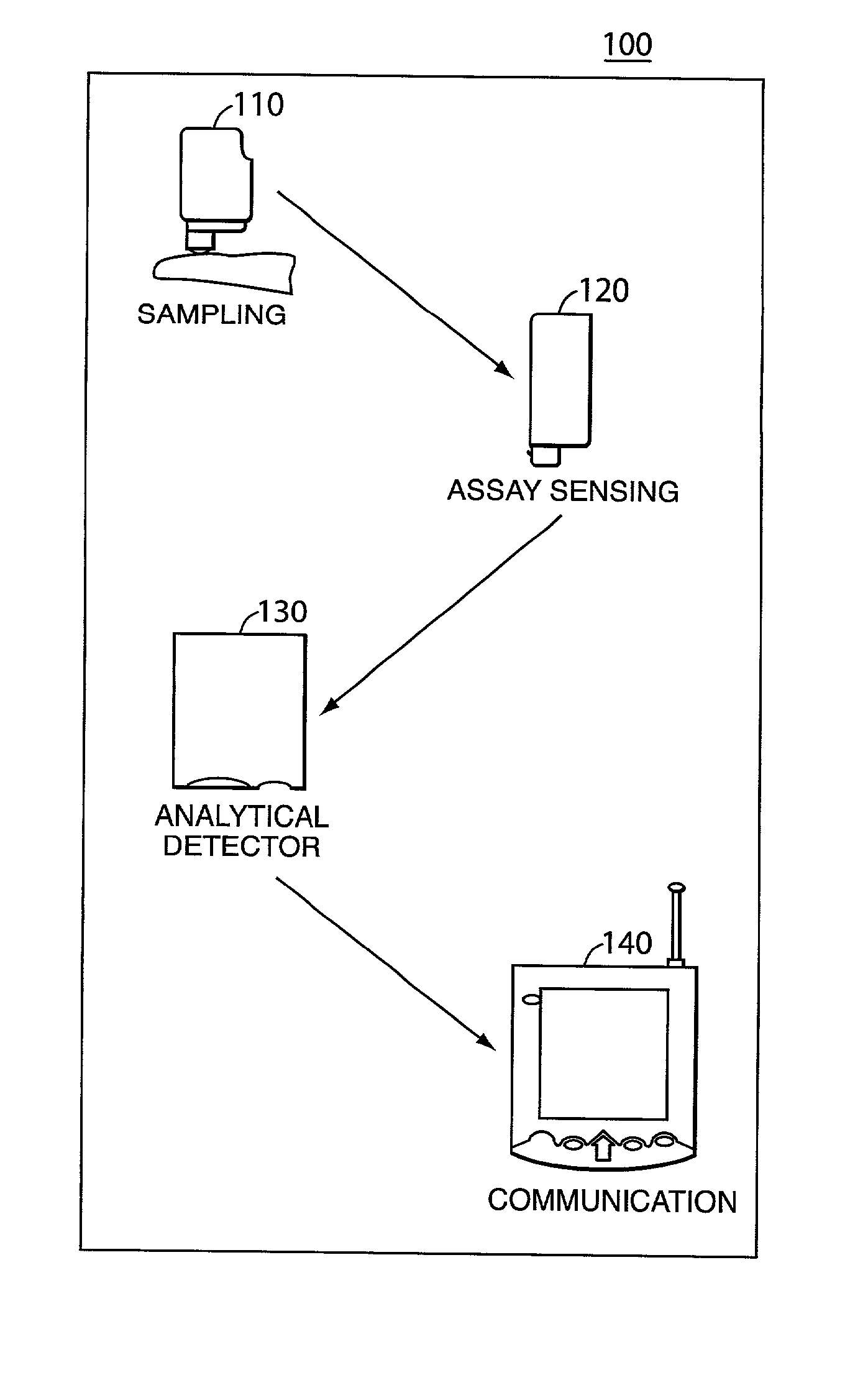
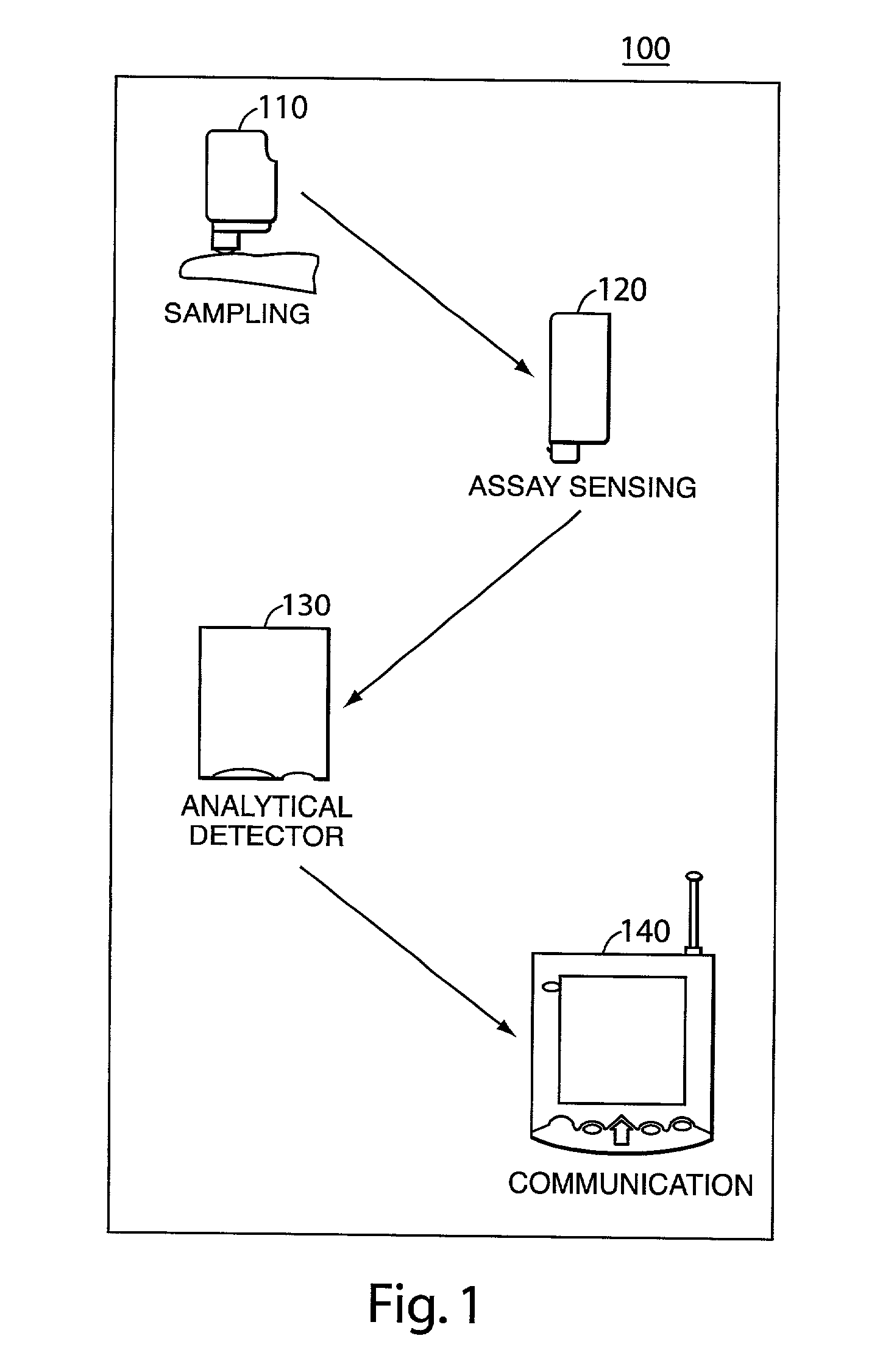
Universal diagnostic platform
A portable medical analyzer comprising a sampling module with a sample port for receiving body fluid, an assay sensor module for analysis of the body fluid, an analytical detector module with detection of information from the assay, and a communications module for transferring the information to a remote location via a wired or wireless network.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Analyte test device
InactiveUS7299081B2Easy to modifyMinimize the possibilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteAcute angle
An analyte test device is constructed as an integrated, single-use, disposable cartridge which can be releasably installed into a compatible analyte test monitor. In use, the device can be used in conjunction with the monitor to lance the skin of a patient to create a blood sample and, in turn, calculate the concentration of a particular analyte in the expressed blood sample. In one embodiment, the device includes a base and a cover which are affixed together to create a test cartridge which has a substantially flat and low profile design. A lancet carrier is disposed between the base and the cover and includes a anchor fixedly mounted on the base and a lancet support member which is slidably mounted on the base, the anchor and the lancet support member being connected by a spring. A lancet is removably mounted on the lancet support member is disposed directly beneath an analyte test strip which secured to the underside of the cover. In another embodiment, the device includes a cylindrical housing with an open top end and an open bottom end. A spring biased lancet is slidably mounted within the cylindrical housing. An analyte test strip is fixedly mounted within the cylindrical housing and is disposed at an acute angle relative to the lancet.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
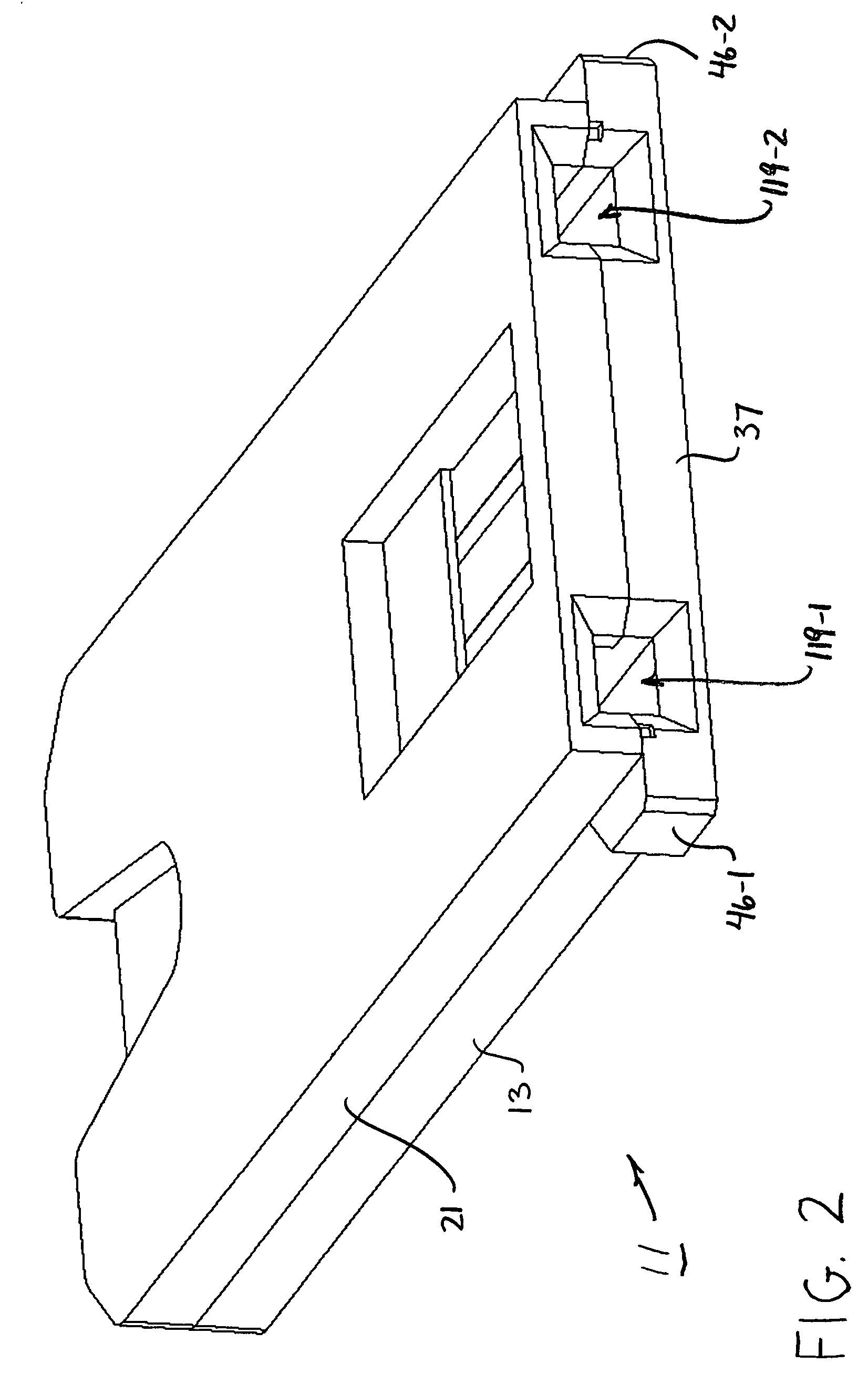
Energy Assisted Medical Devices, Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20080228104A1Readily penetrate tissueImprove abilitiesGuide needlesEar treatmentTissue sampleActuator
A device for penetrating tissue and removing a biological sample includes a biological sampling element to remove a biological sample. The biological sampling element includes a passage therethrough. The device further includes a penetrator positioned within the passage. The penetrator is energized in a repetitive manner to assist in penetrating tissue. The biological sample element can be adapted to remove a tissue sample or a biological fluid sample (for example, blood). A device for penetrating tissue and positioning a tissue resident conduit (for example, a catheter), includes a tissue resident conduit (for example, a catheter) including a passage therethrough; and a penetrator in operative connection with the catheter. A device for inserting a tissue resident conduit includes at least one component that is energized during penetration to assist in penetrating tissue. In one embodiment, the tissue resident conduit is flexible and the energized component is positioned or a forward end of the tissue resident conduit. The device can further include a mechanism for directing the penetration of the tissue resident conduit. A needle for penetrating tissue includes a first effector including a surface and at least one actuator in operative connection with the first effector. The actuator is adapted to cause motion of the first effector such that tearing of tissue takes place in regions where there is close proximity of tissue to the surface of the first effector.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
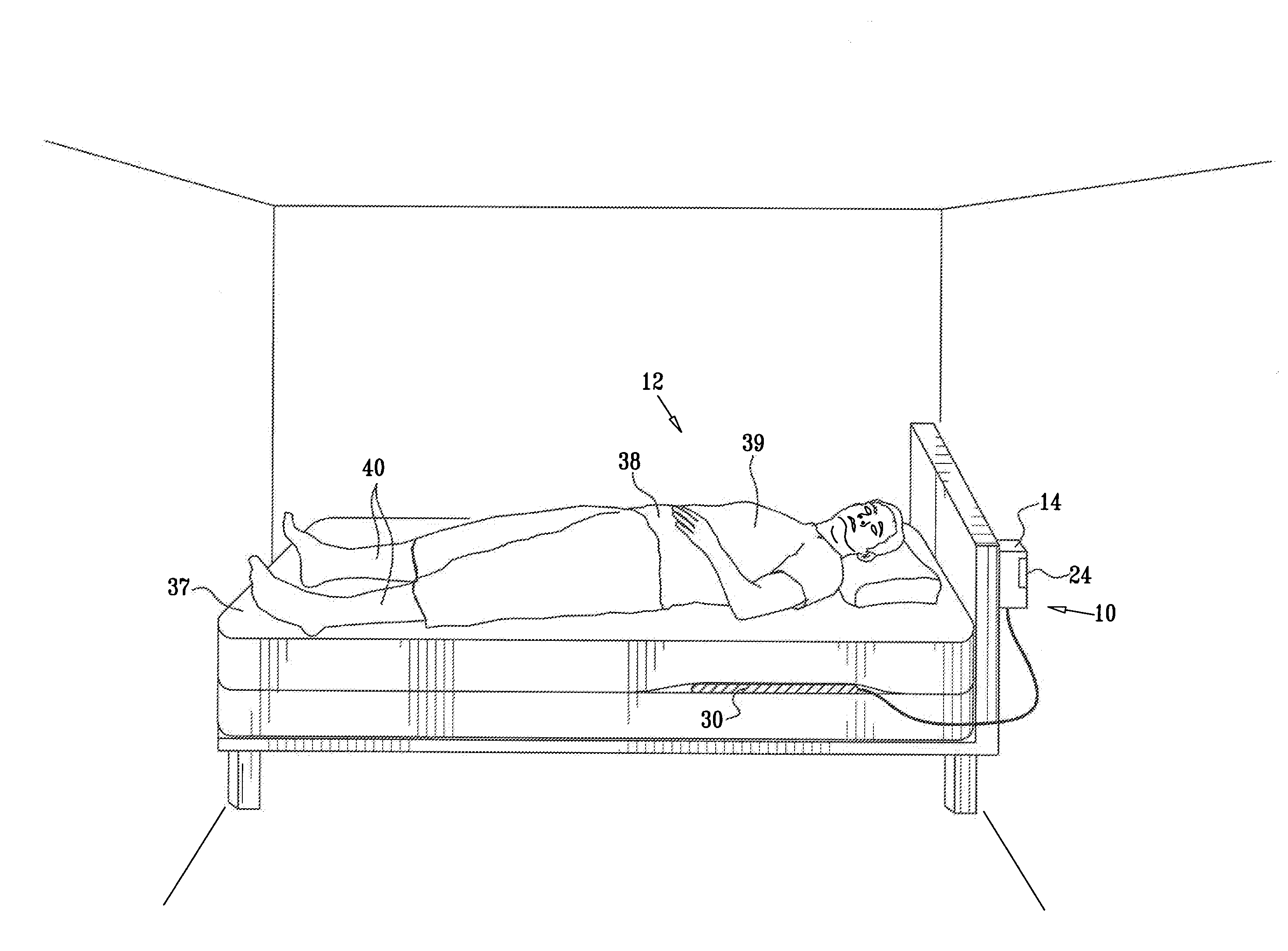
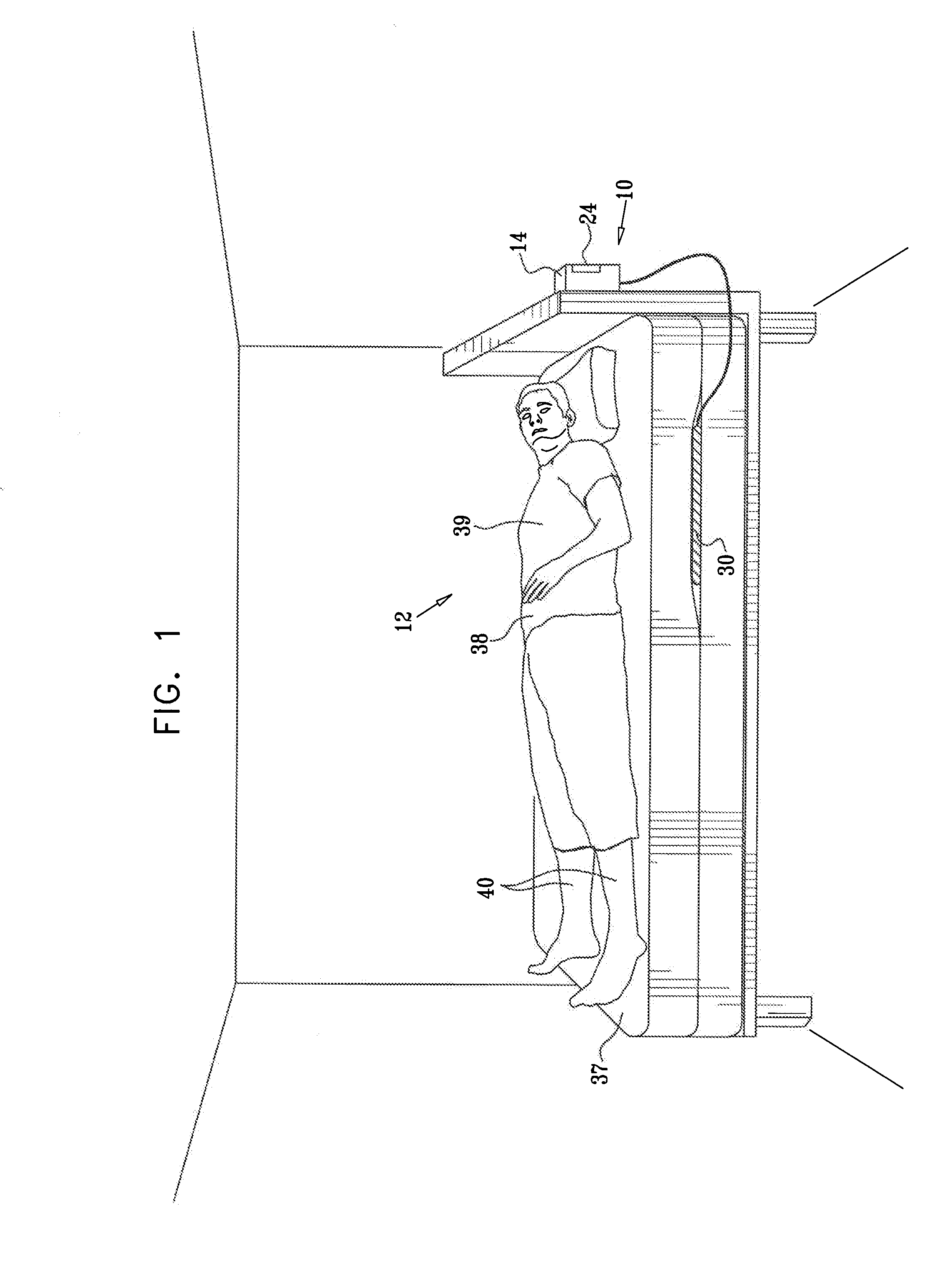
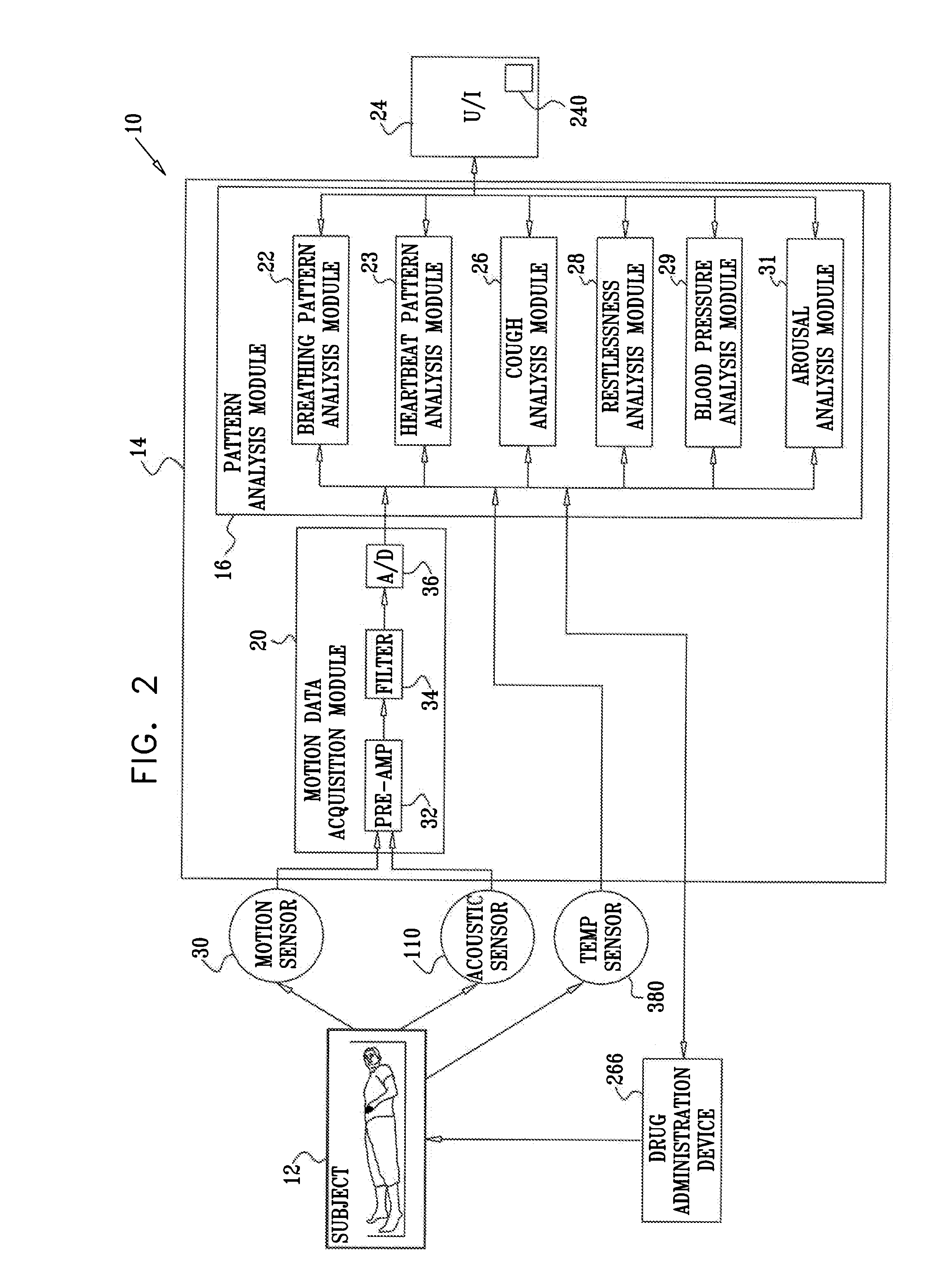
Prediction and monitoring of clinical episodes
ActiveUS20080269625A1Convenient treatmentReduces required dosageElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedicineAsthma attack
A method is provided for predicting an onset of an asthma attack. The method includes sensing at least one parameter of a subject without contacting or viewing the subject or clothes the subject is wearing, and predicting the onset of the asthma attack at least in part responsively to the sensed parameter. Also provided is a method for predicting an onset of an episode associated with congestive heart failure (CHF), including sensing at least one parameter of a subject without contacting or viewing the subject or clothes the subject is wearing, and predicting the onset of the episode at least in part responsively to the sensed parameter. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:HILL ROM SERVICES
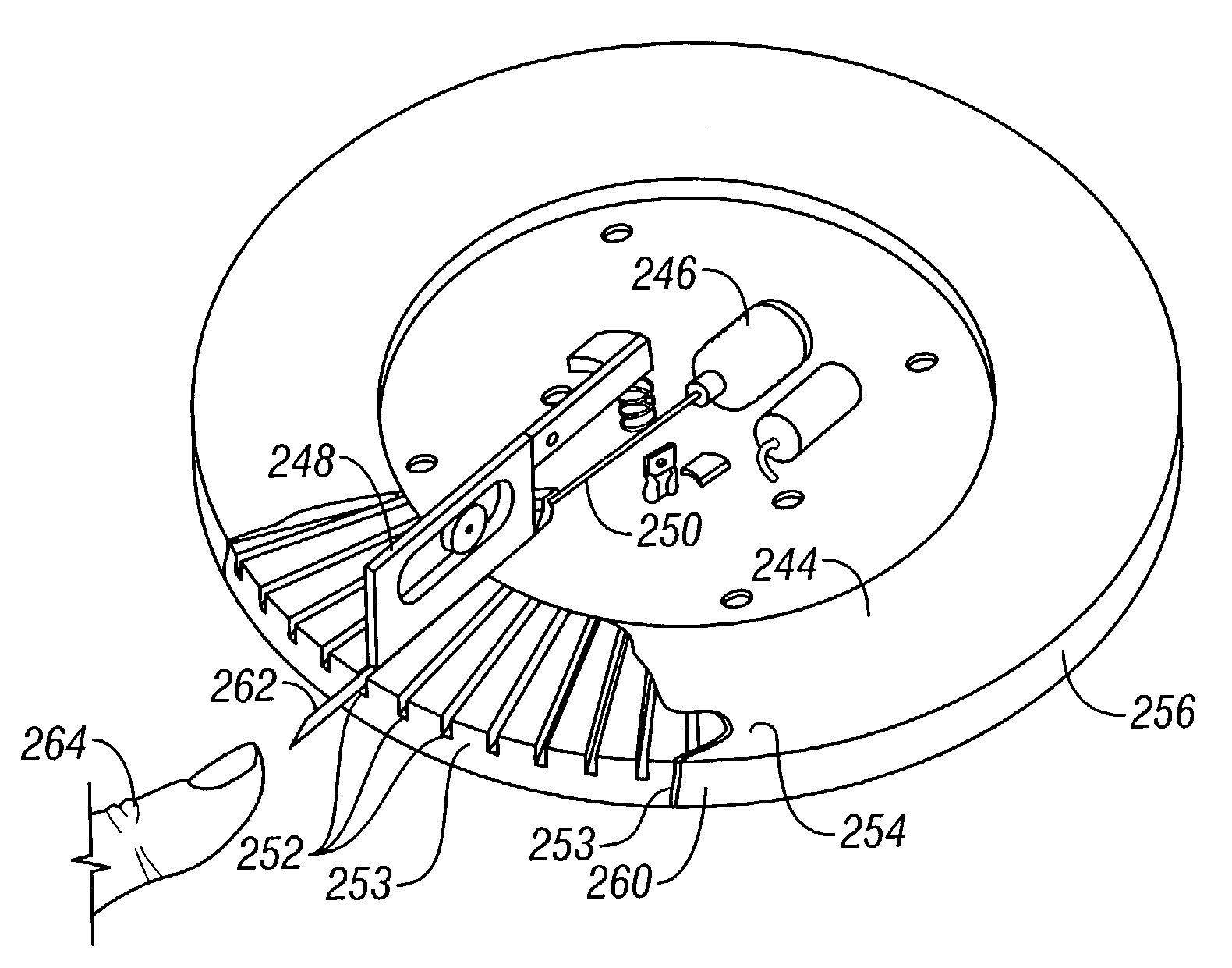
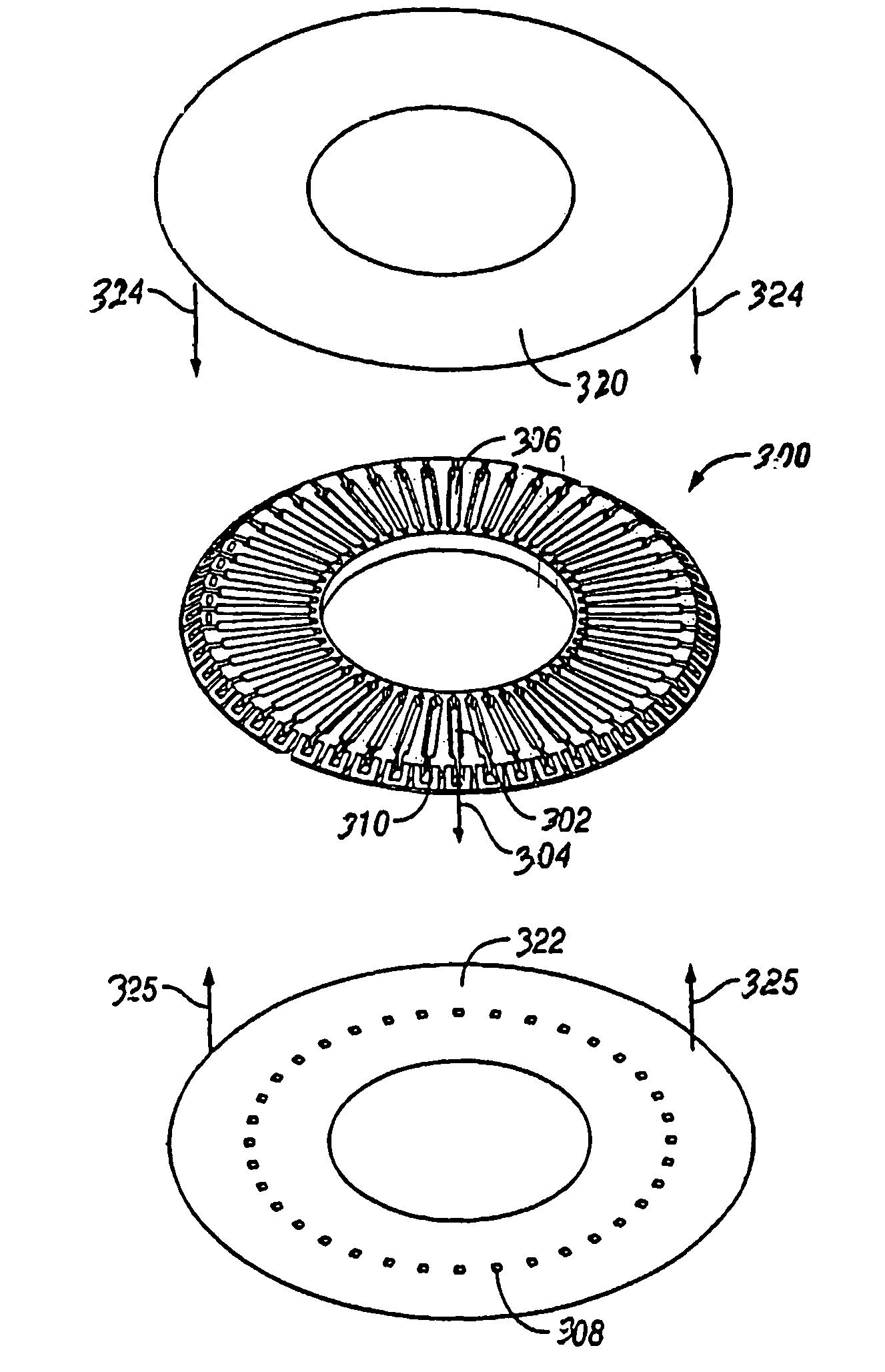
Method and apparatus for a point of care device
A plurality of Point-of-Care (POC) tests on a single cartridge (300) is provided such that sequential or nonsequential tests may be performed in an integrated fashion without changing the test cartridge. Each cartridge can contain a penetrating member sensor (302) combination in a radial disk format, interrogated and read by a single illumination / detection device. Alternatively a series of tests can be measured electrochemically and reported. Only those tests, which are required at the time, the sample is taken need to be reported, though all tests are carried out.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com