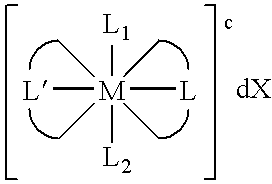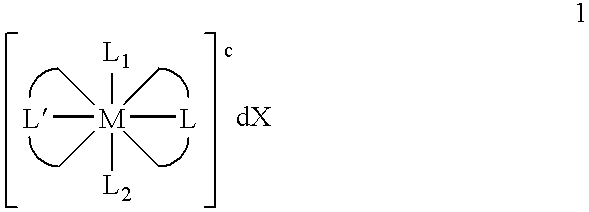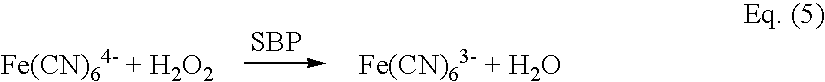Patents
Literature
161 results about "Redox mediator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
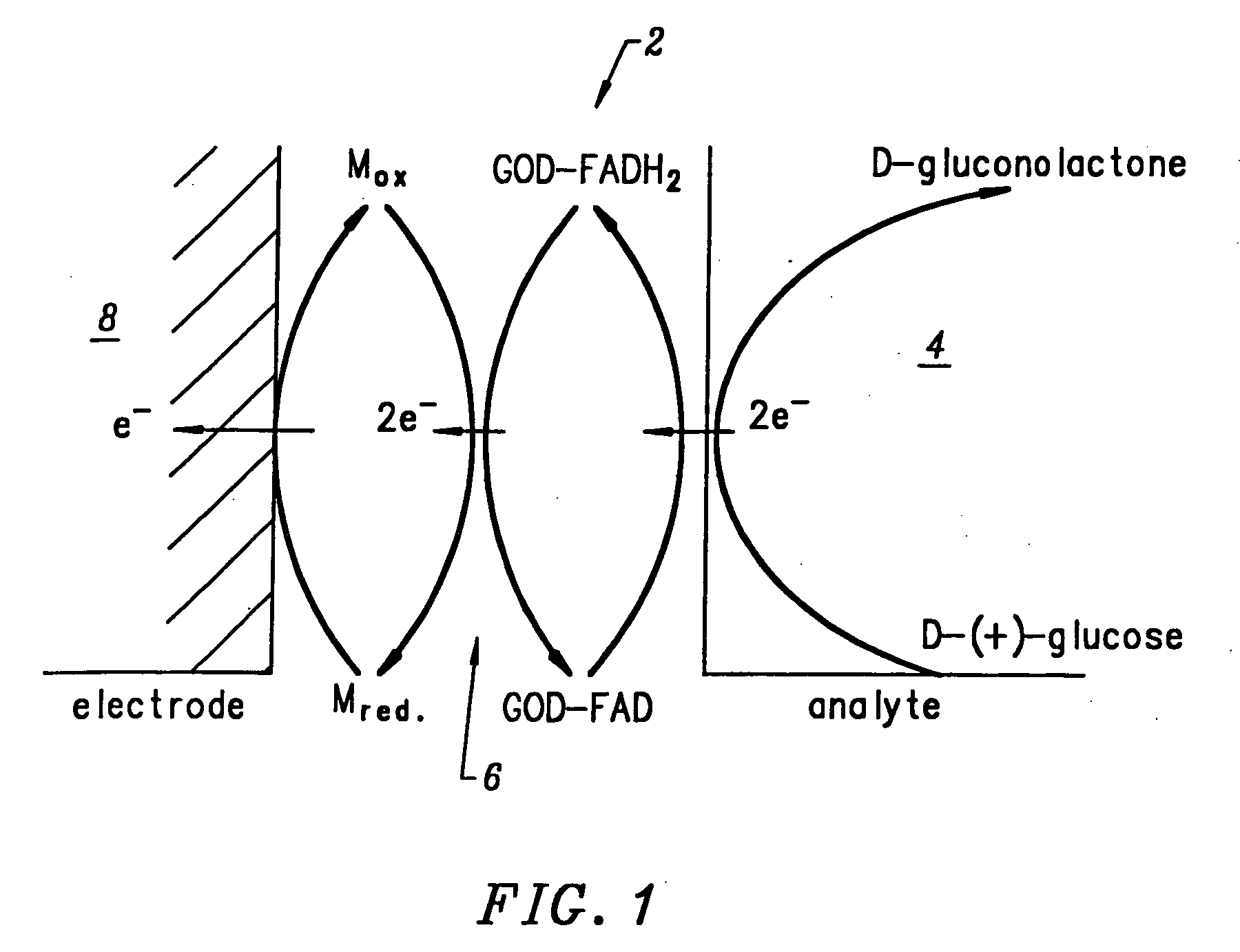
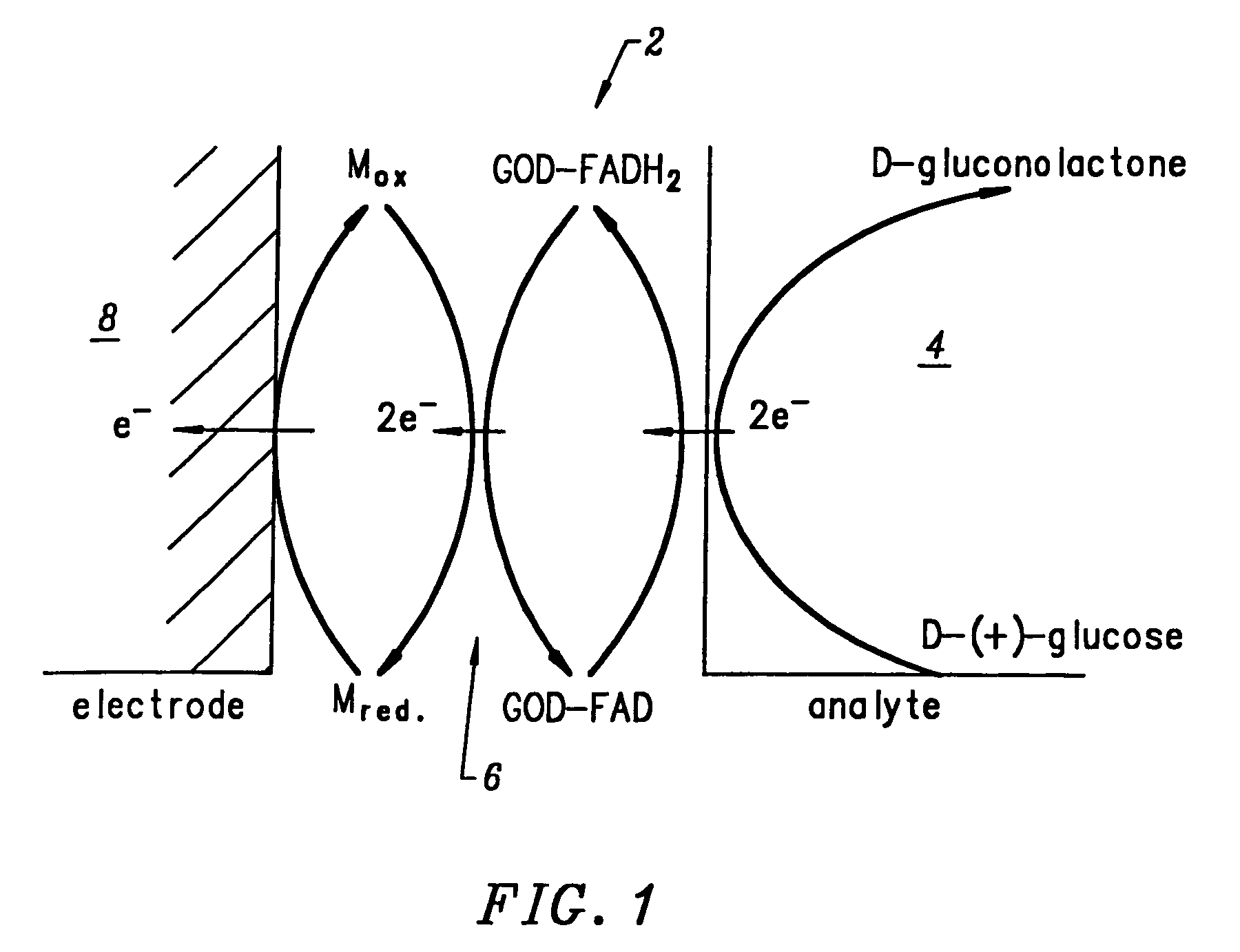
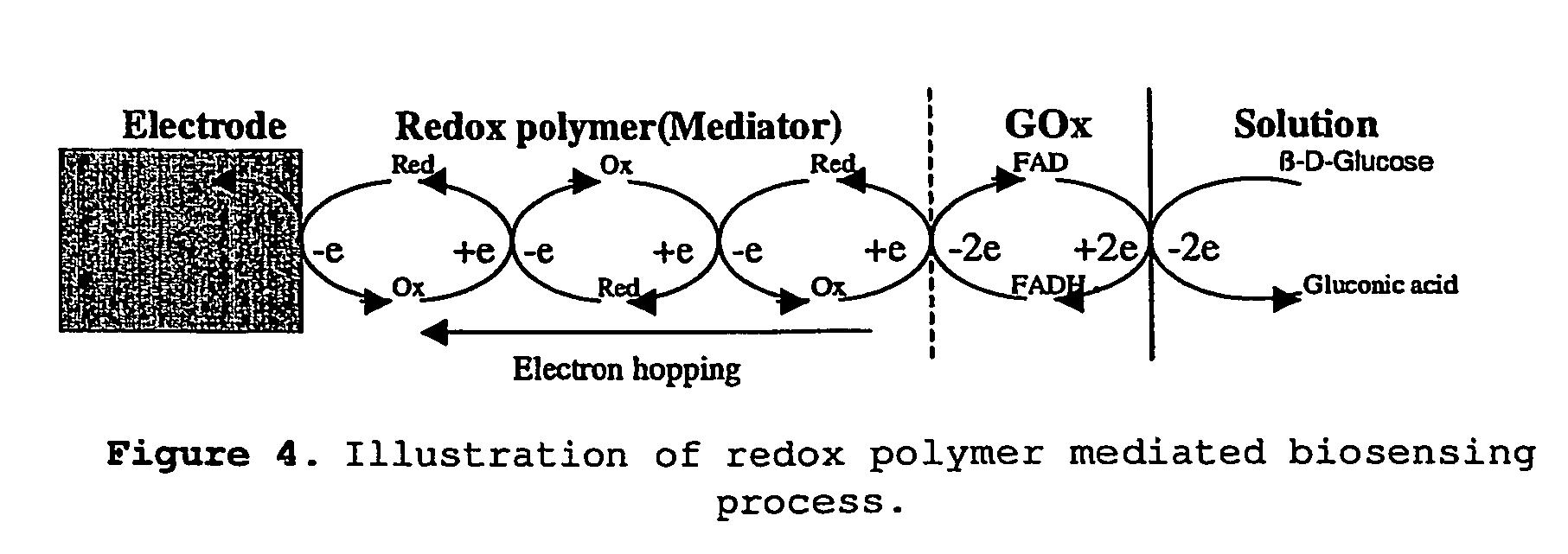
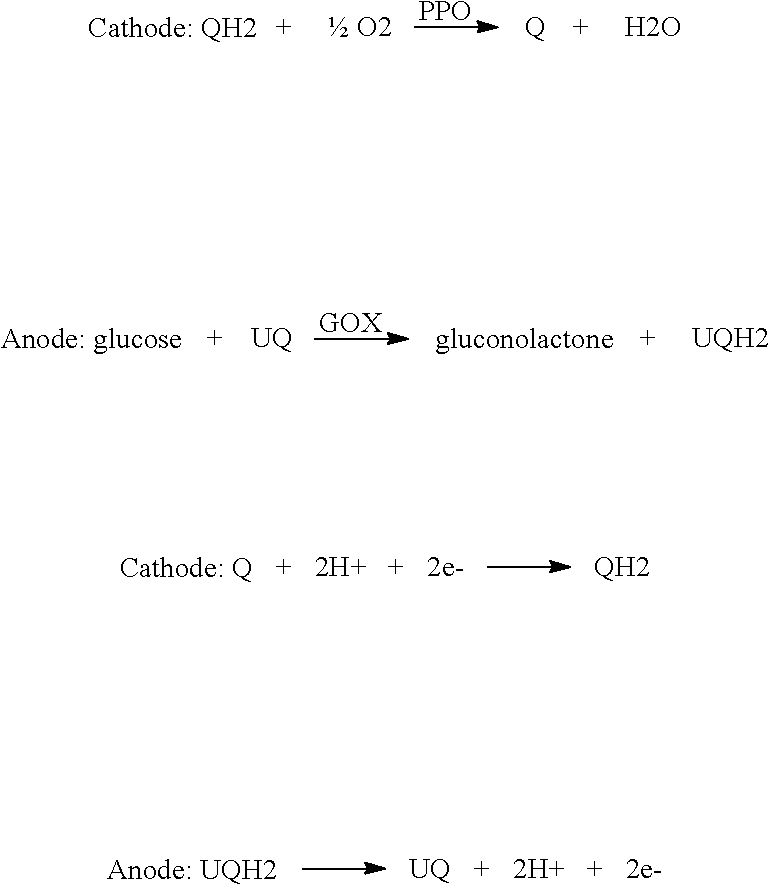
In DSC, the redox mediator, which can be a liquid or gel electrolyte or a solid hole conductor, plays the important role to regenerate the oxidized dye and transport the hole towards the cathode, where a catalyst (usually metallic platinum) regenerates the oxidized electrolyte or hole conductor, closing the circuit.
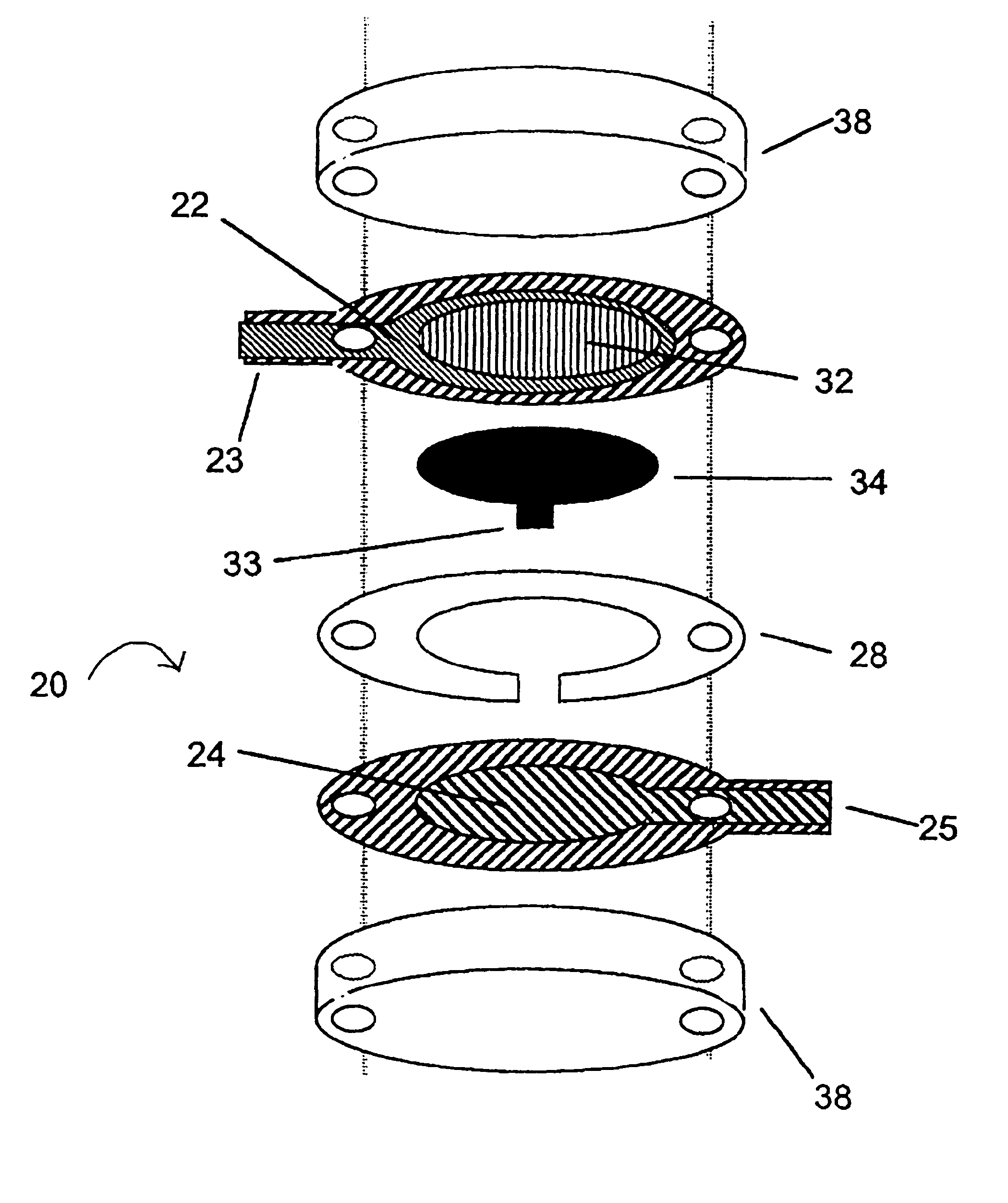
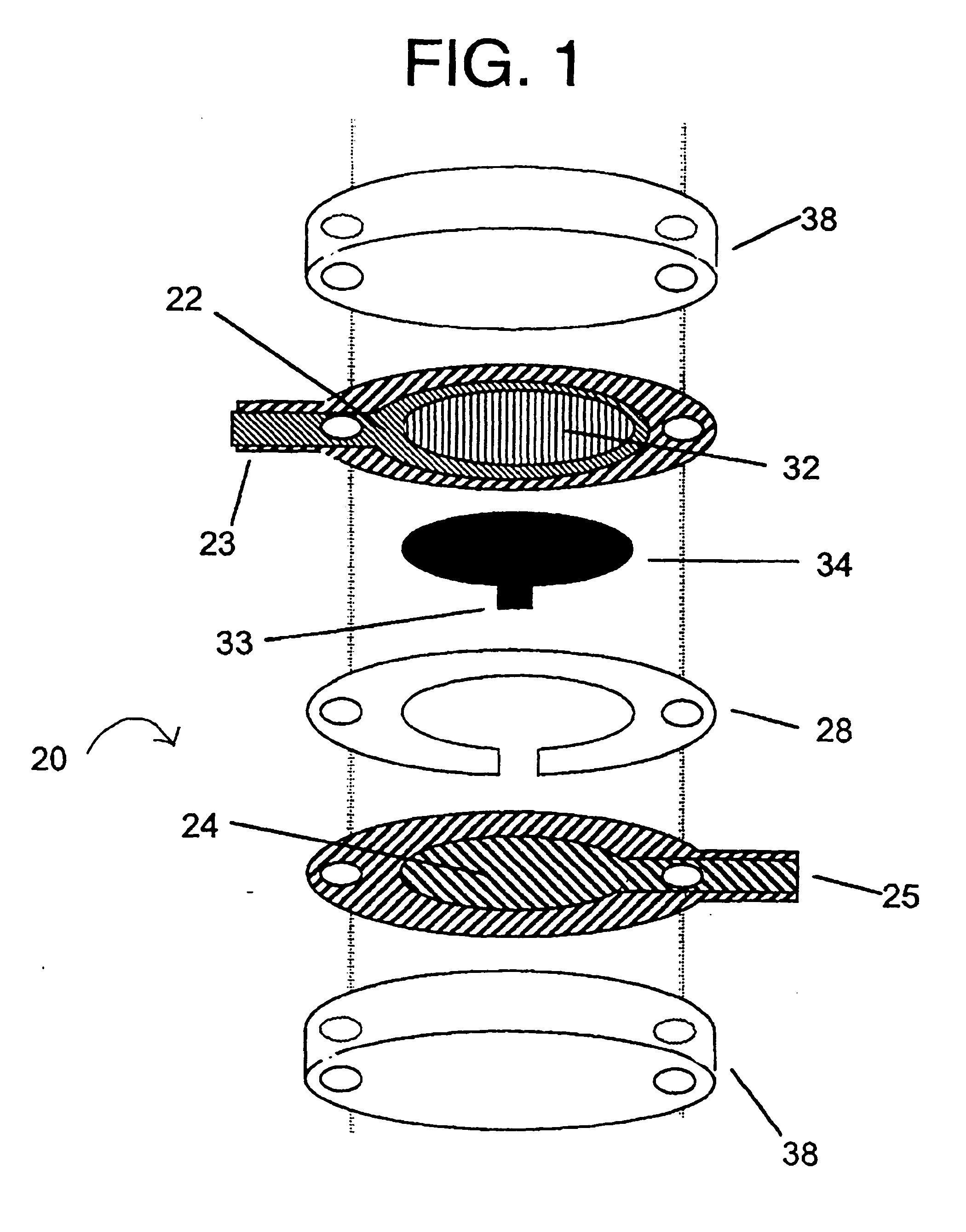
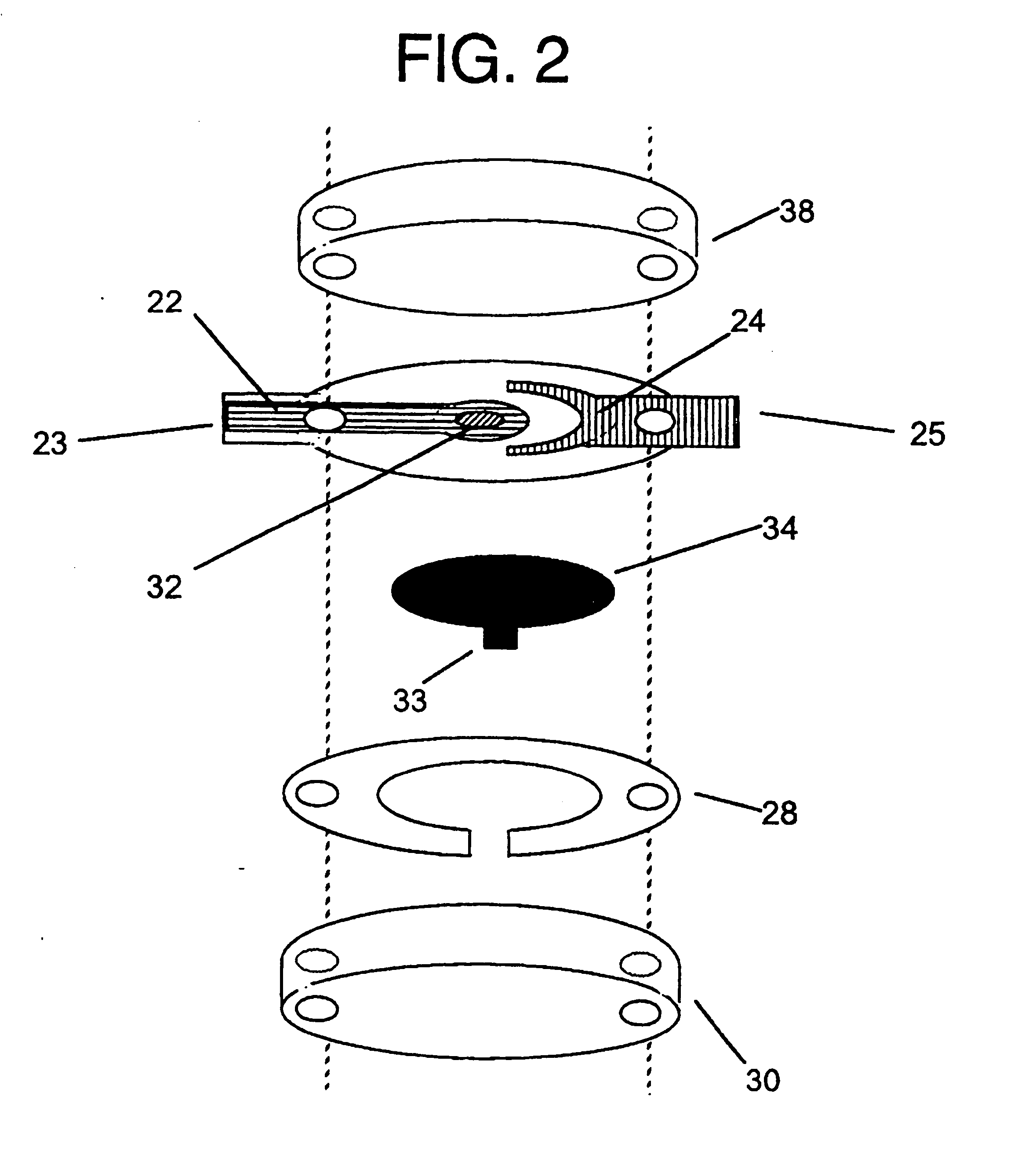
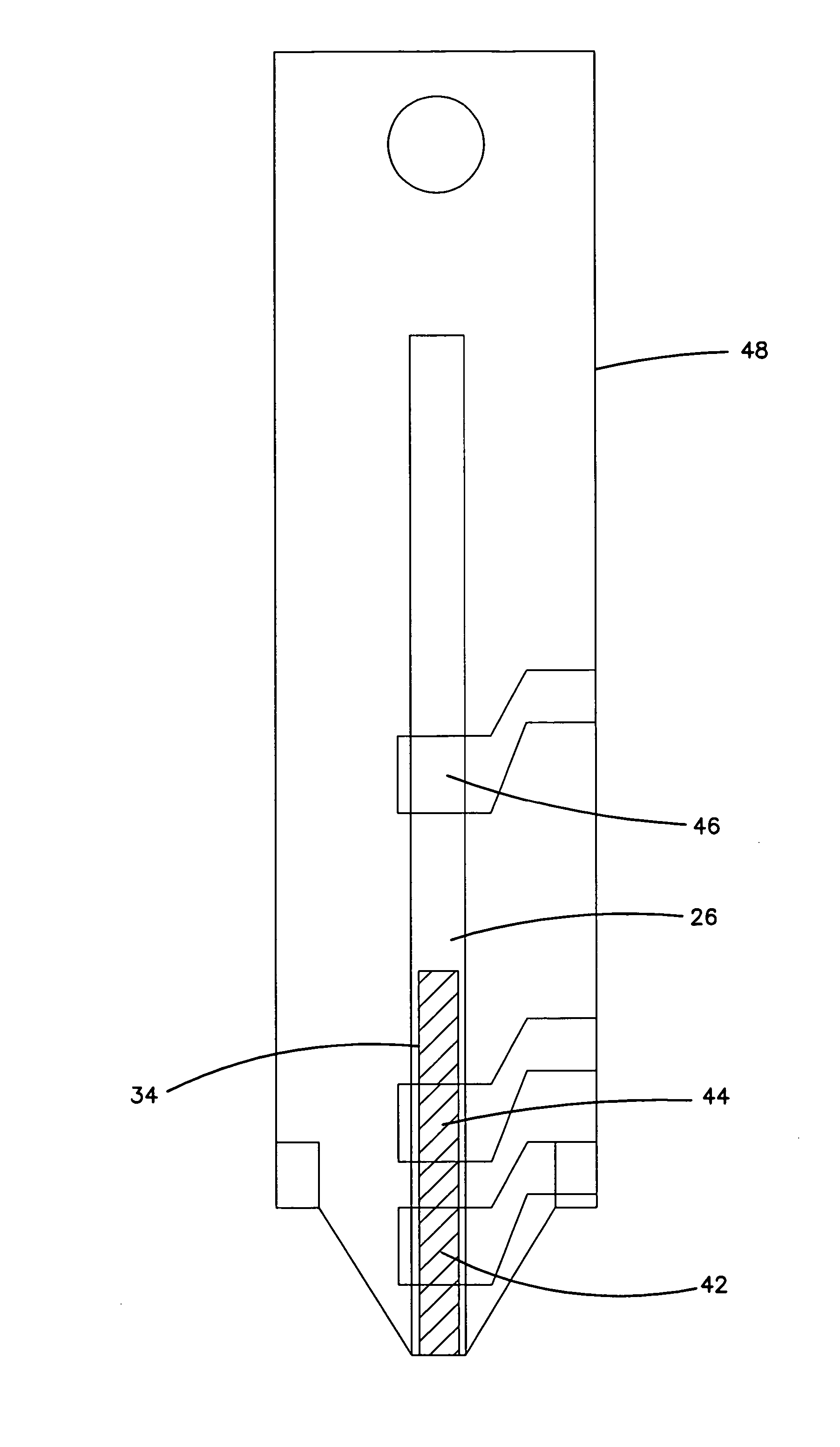
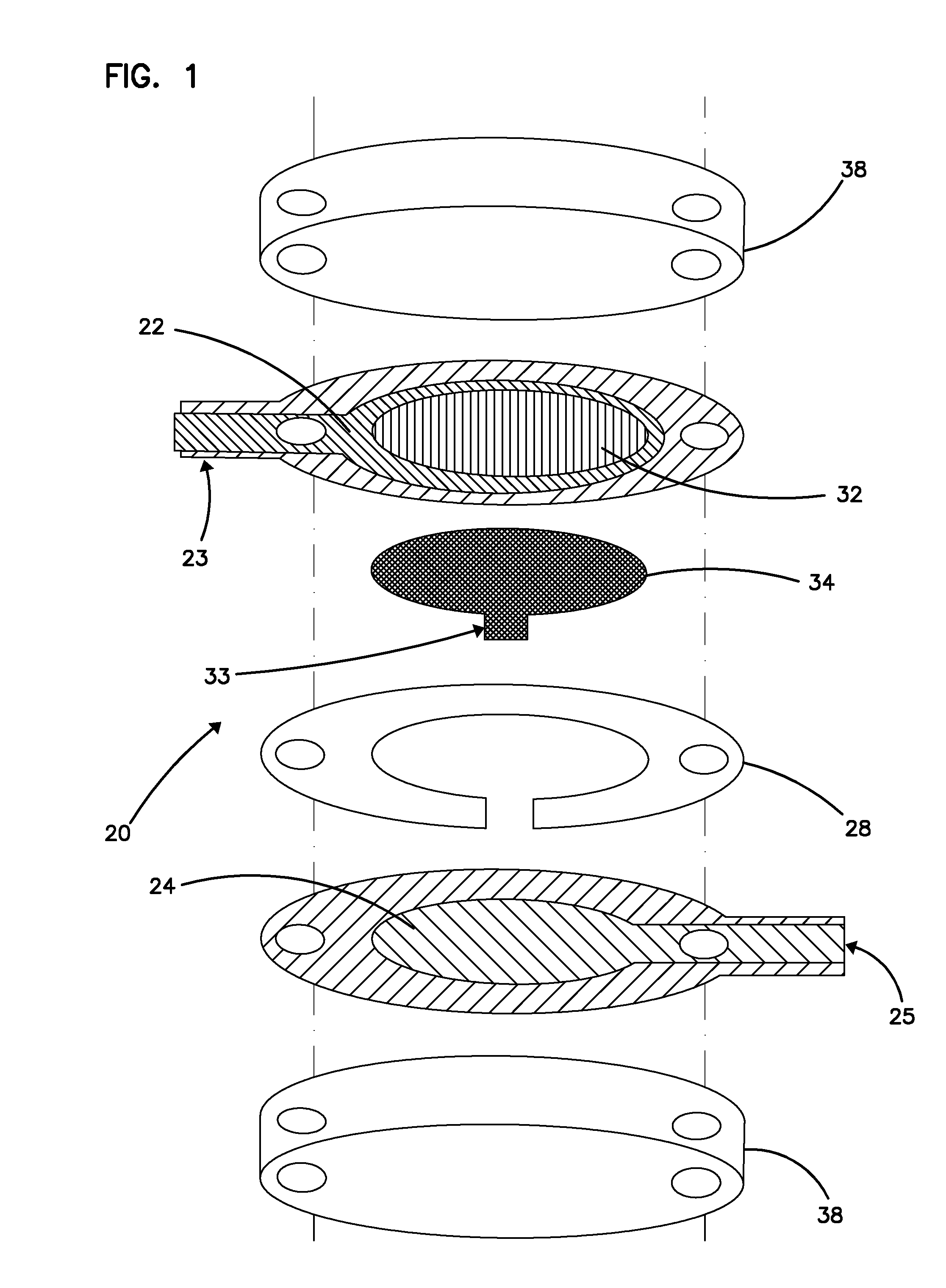
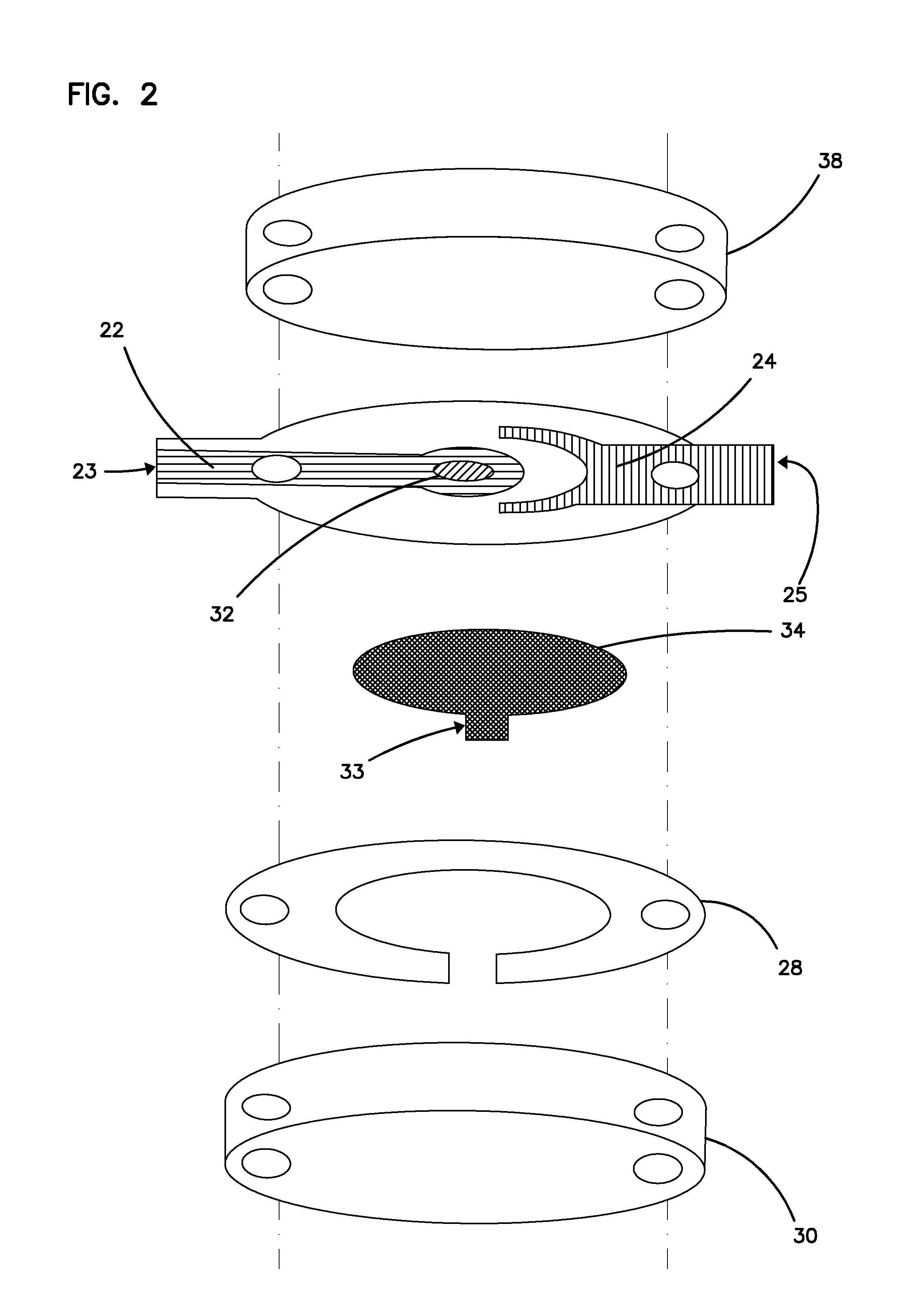
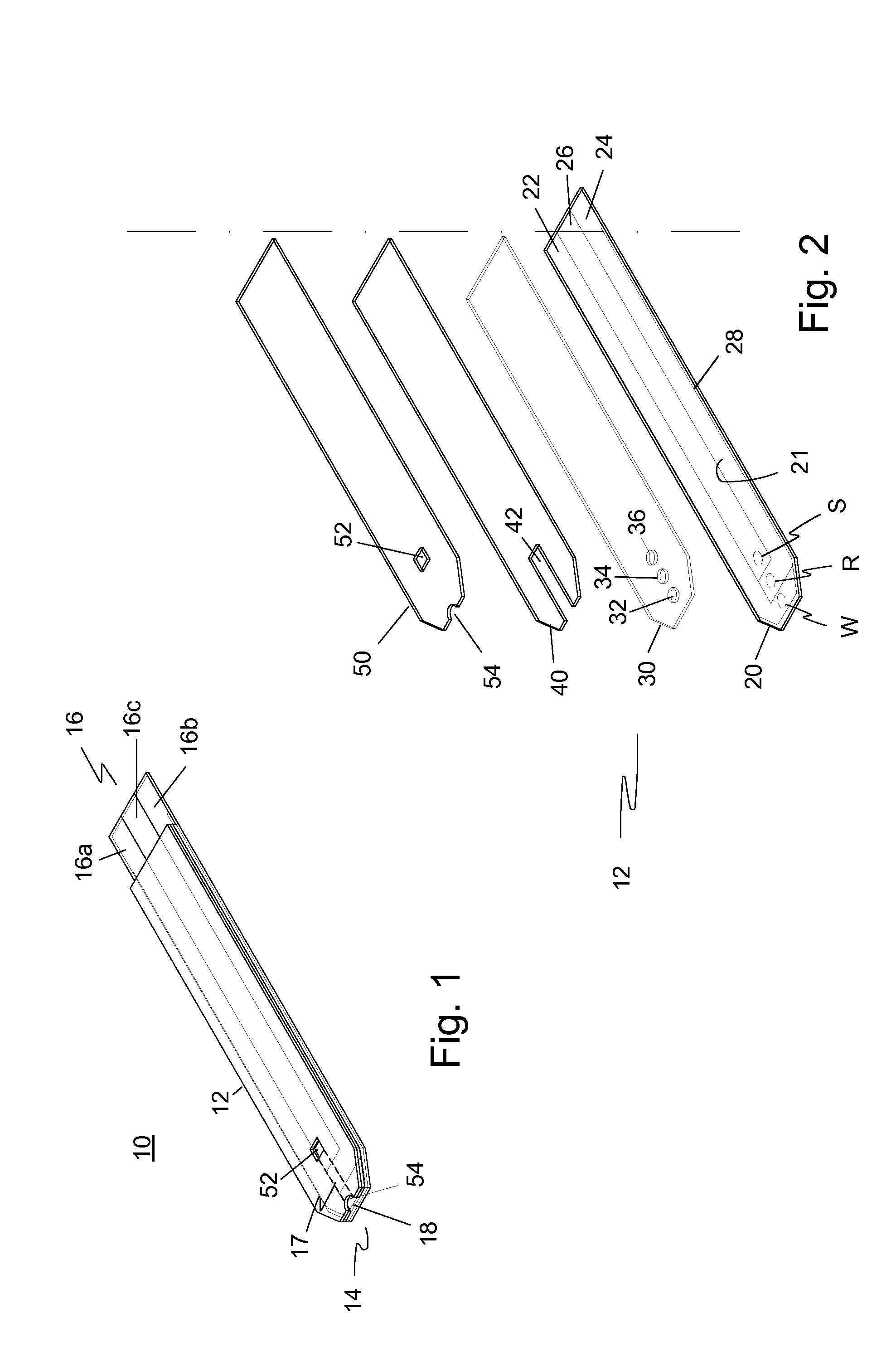
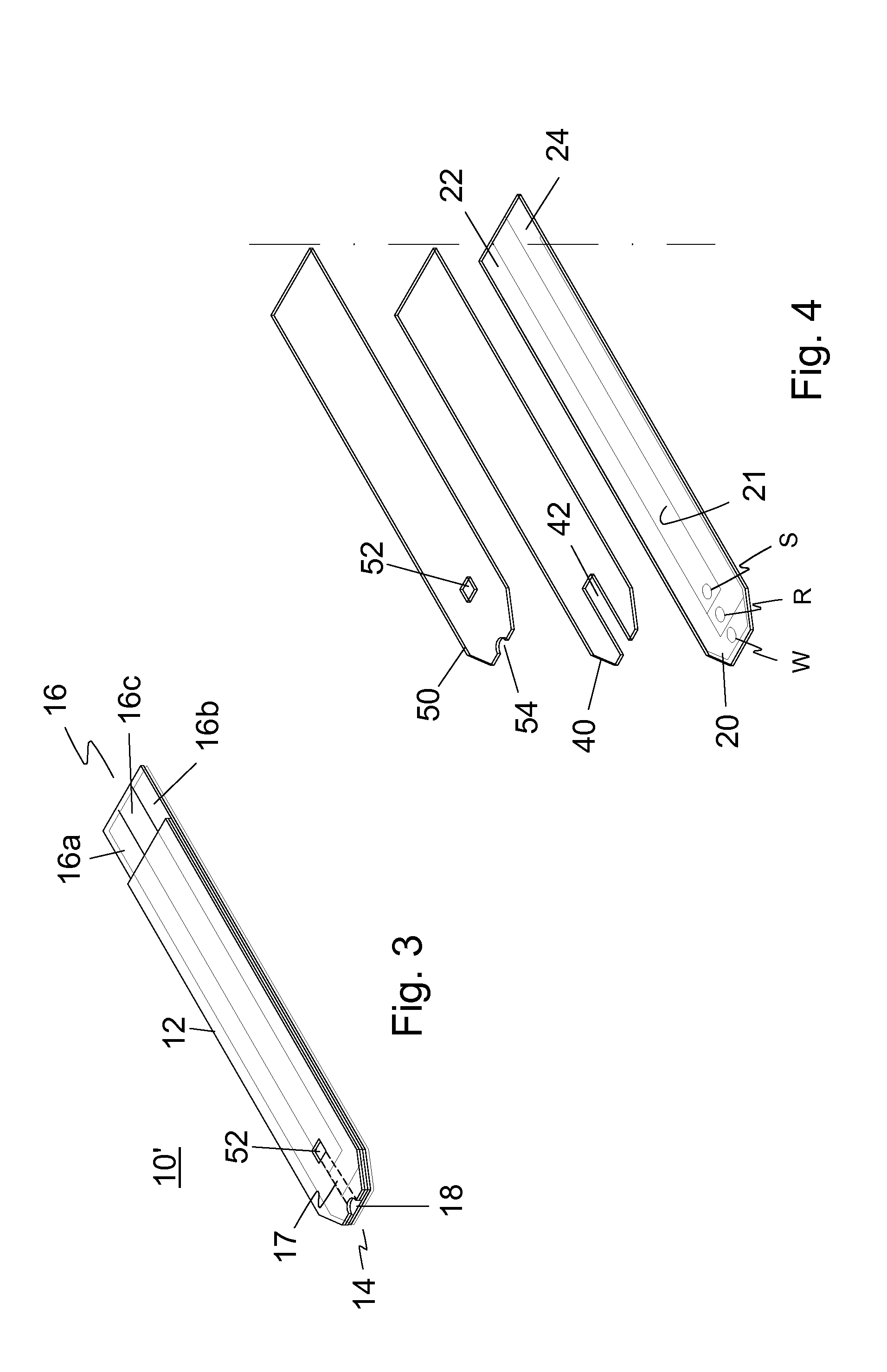
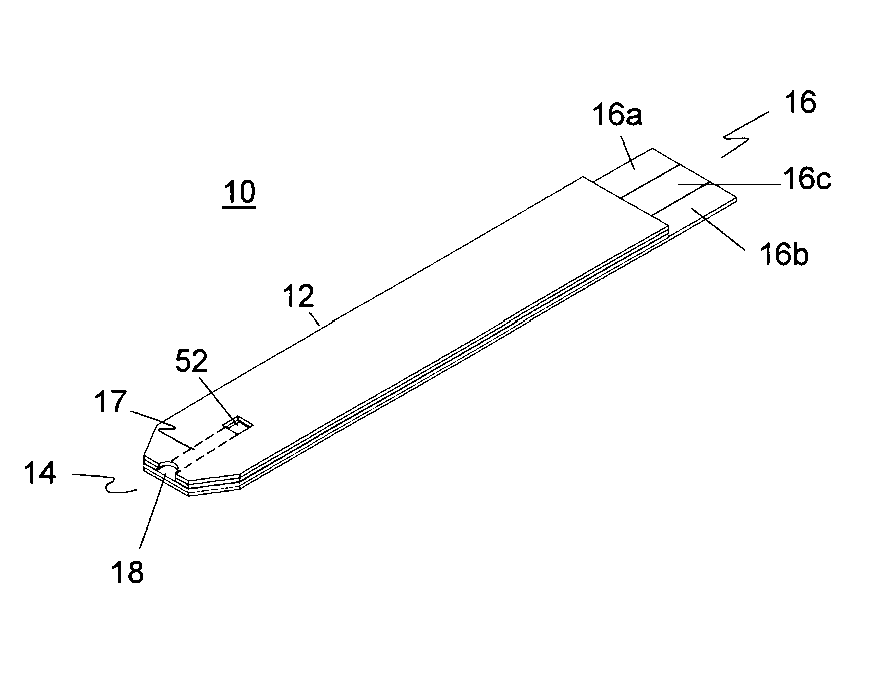
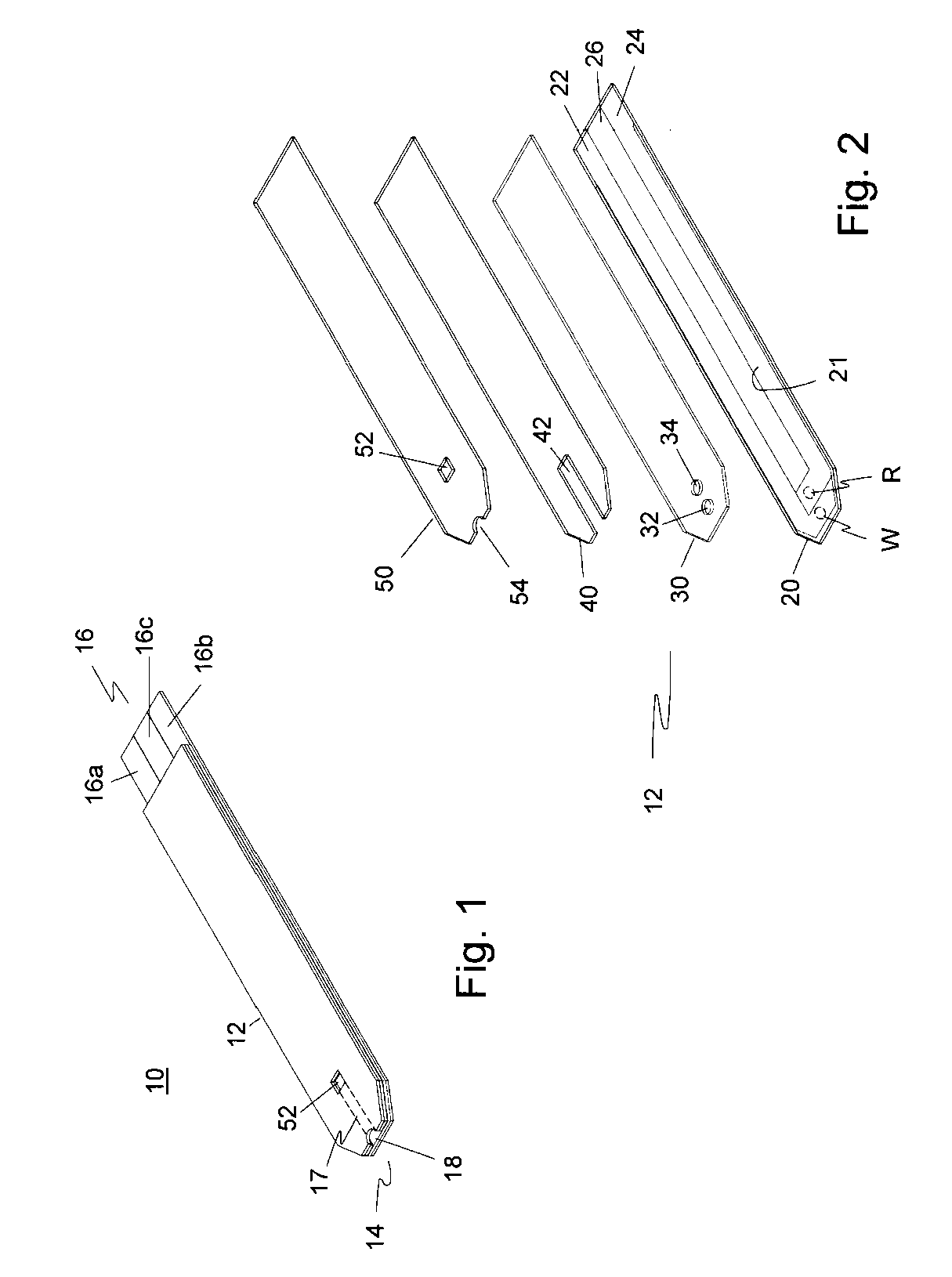
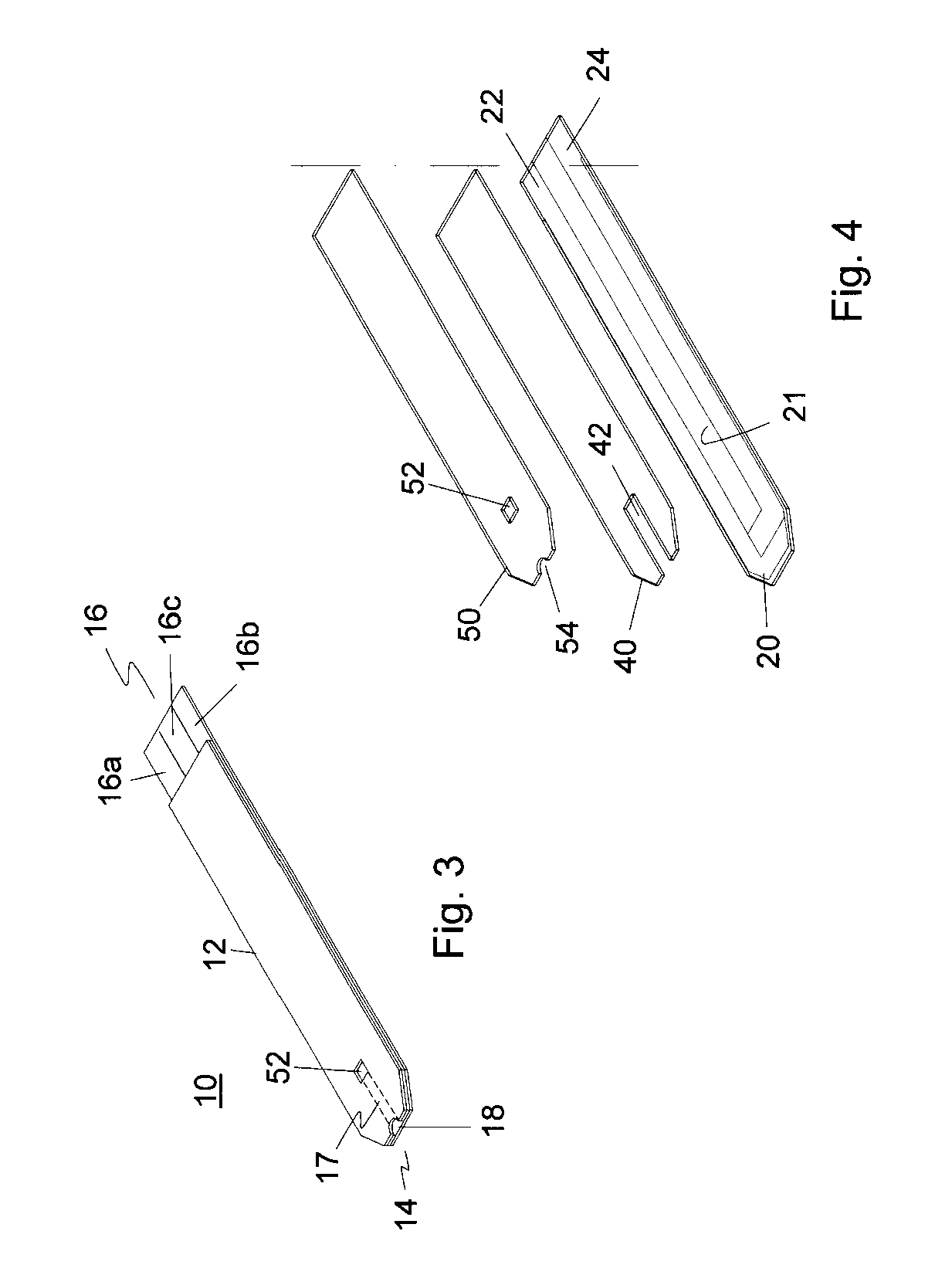
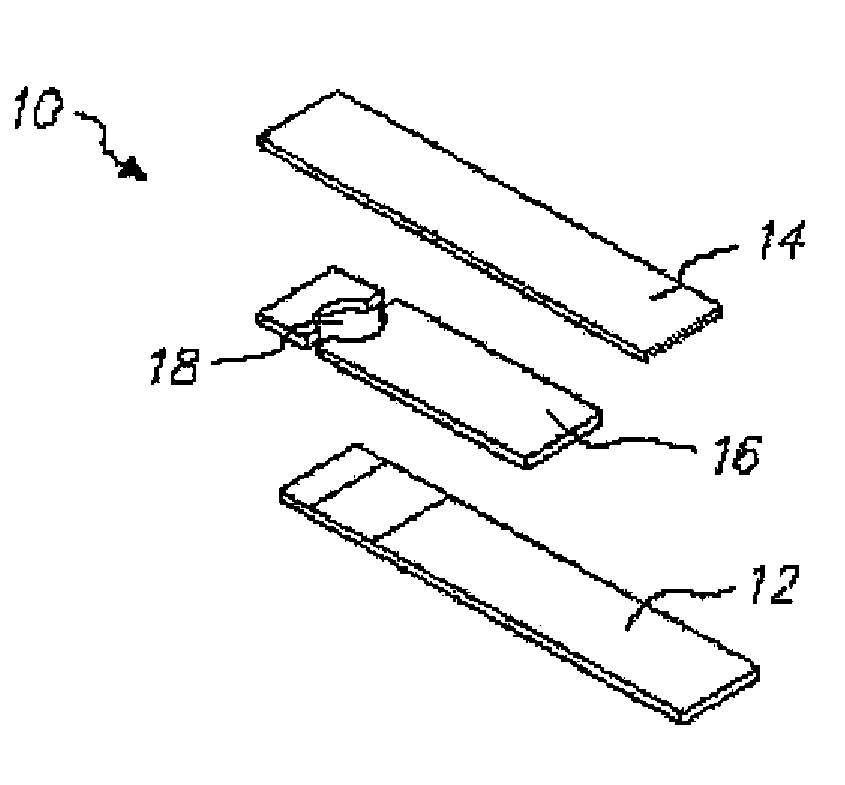
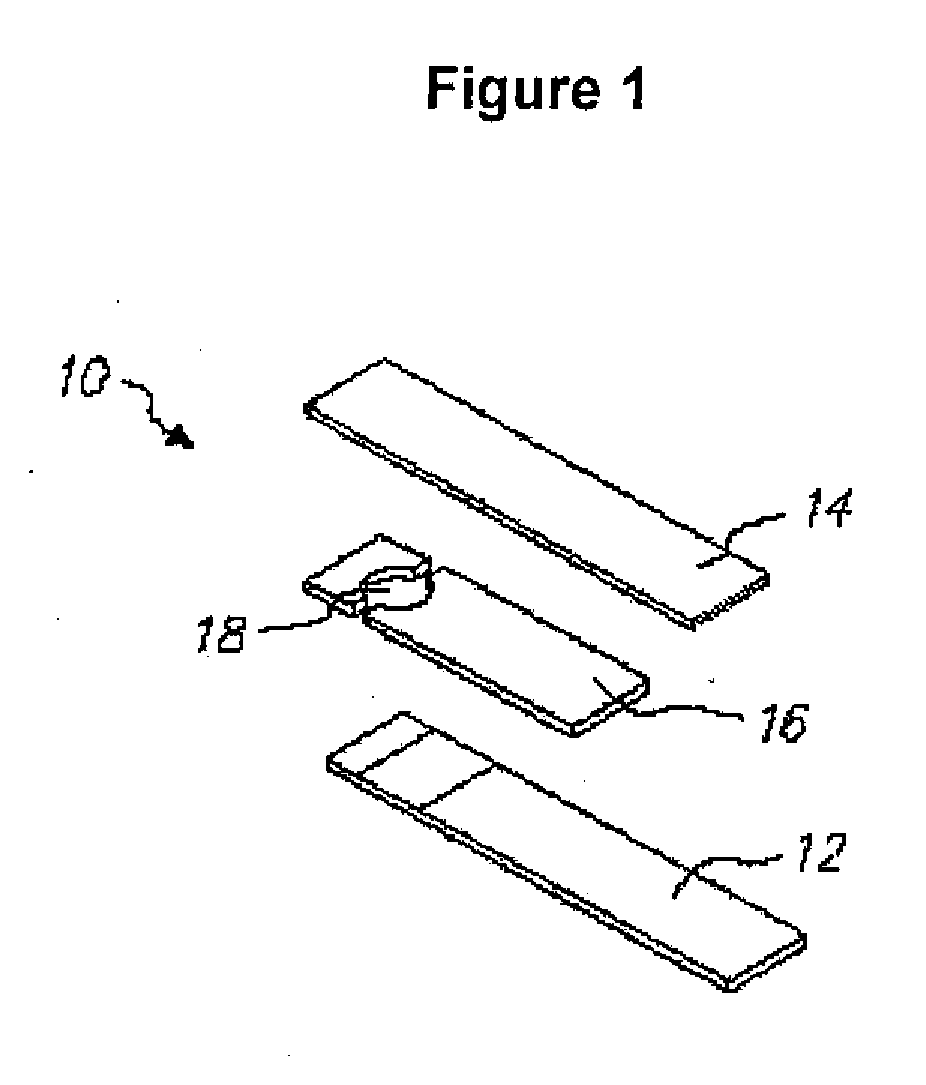
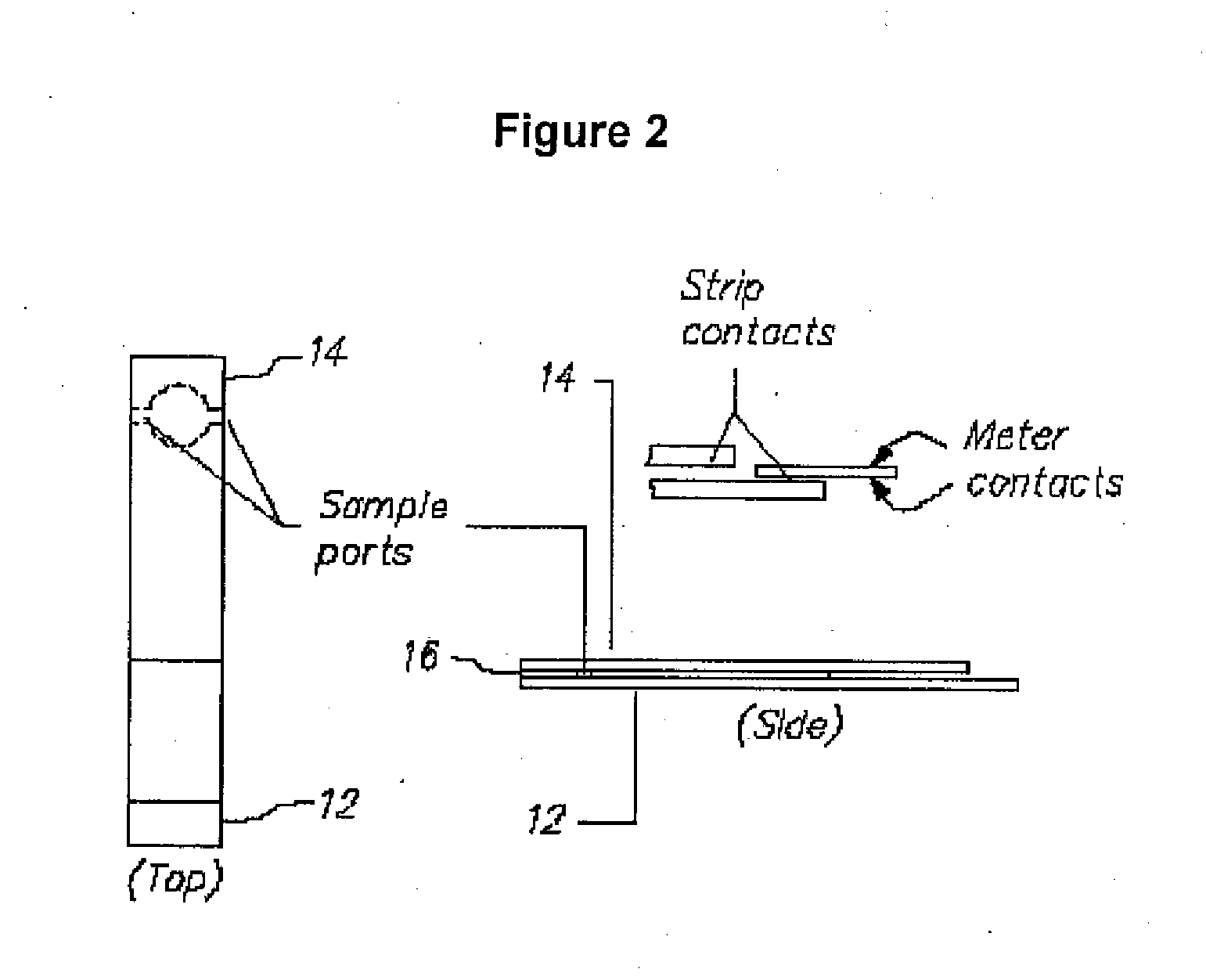
Integrated Lancing and Measurement Device
InactiveUS20080017522A1Accurate and efficient measurementLower the volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMeasurement device
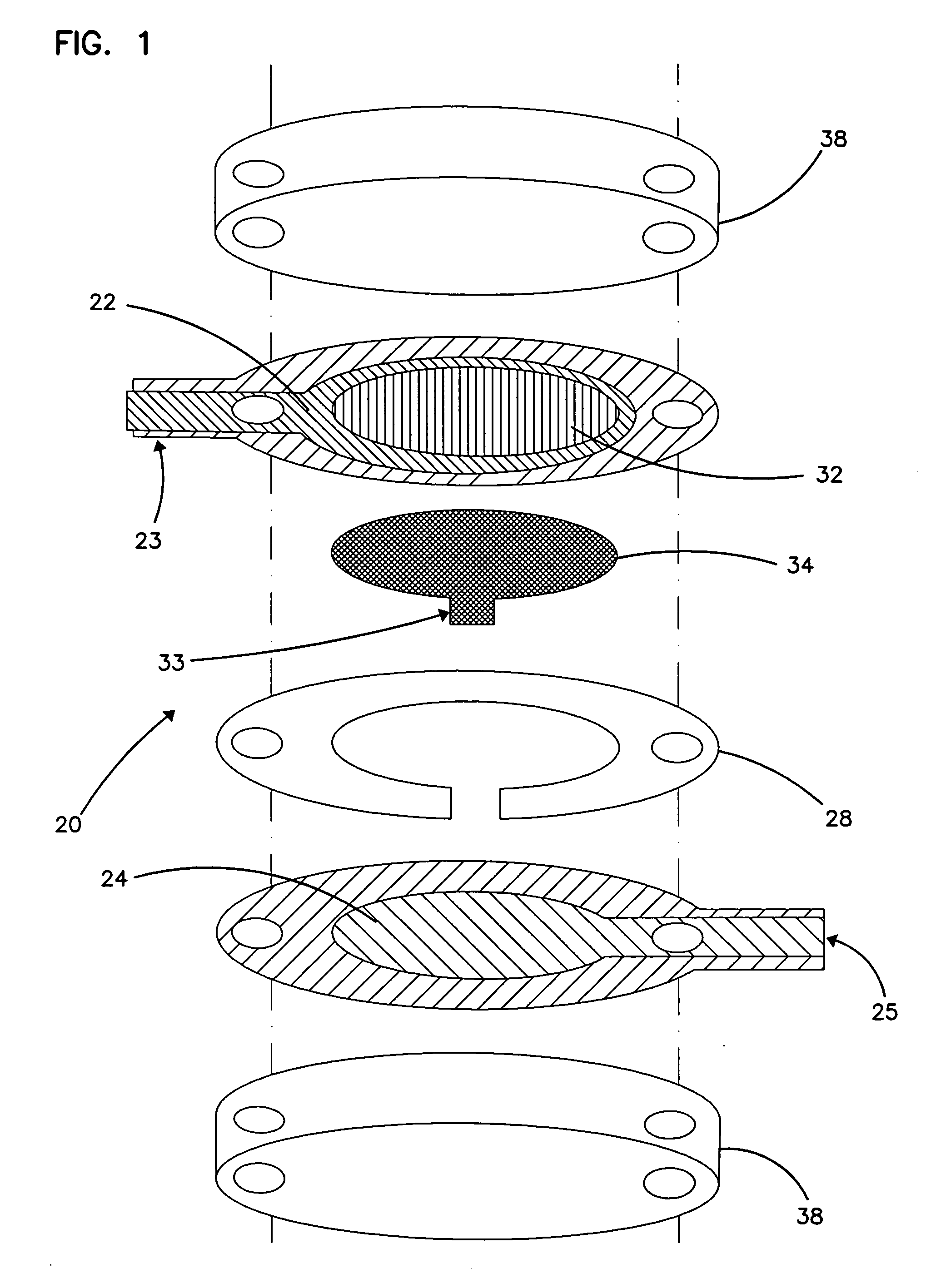
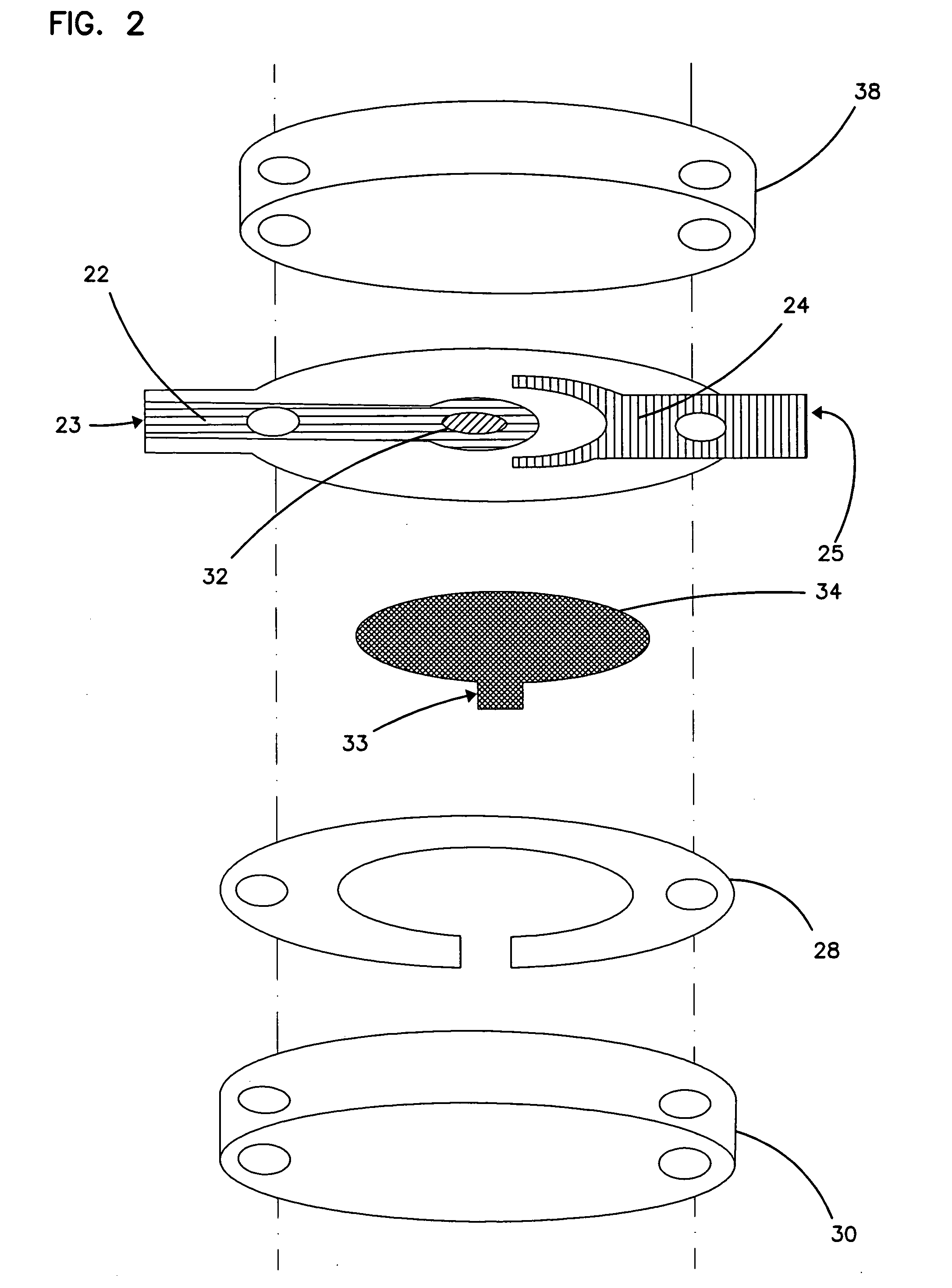
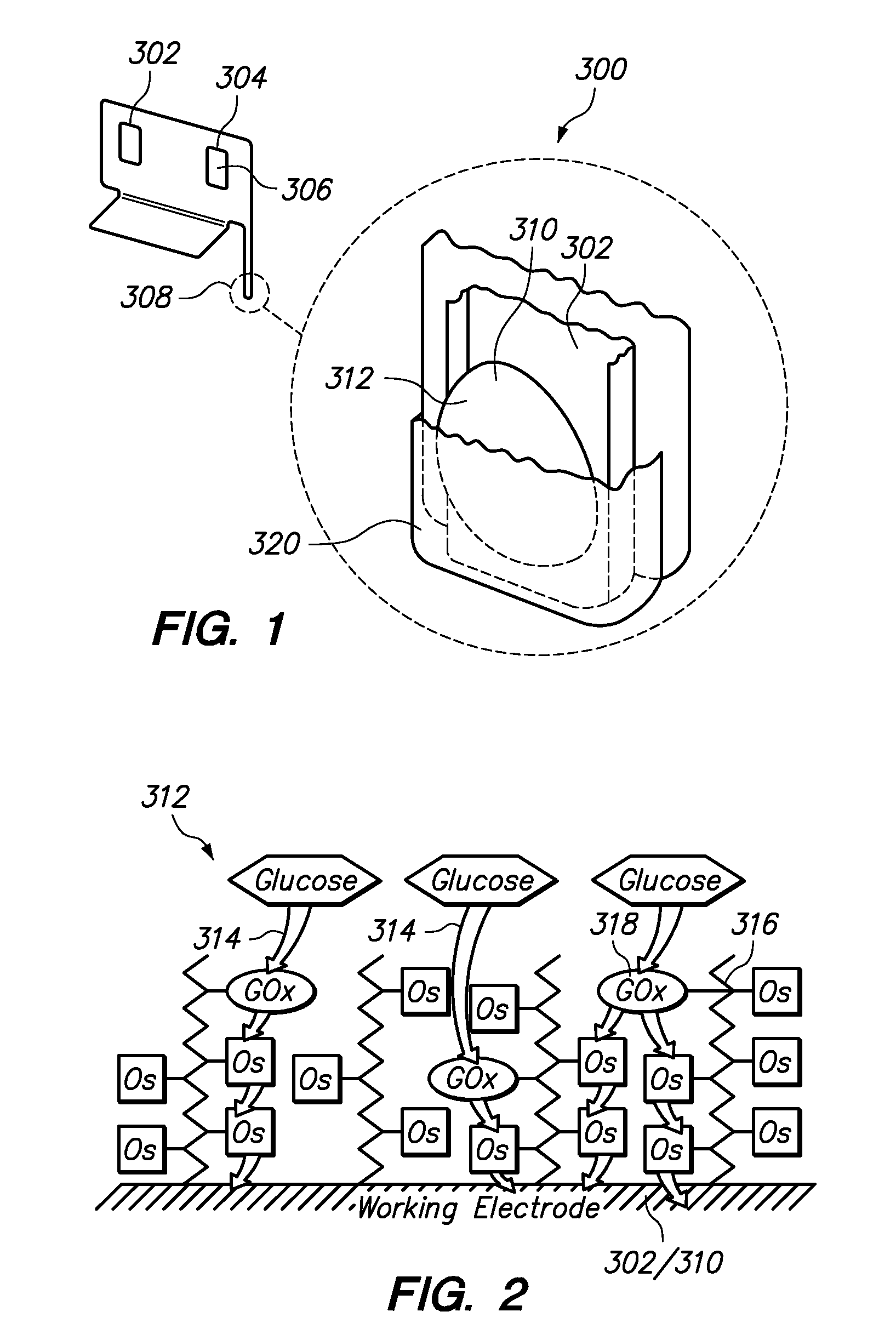
An integrated lancing and measurement device is provided comprising a sensor designed to determine the amount and / or concentration of analyte in a biological fluid having a volume of less than about 1 μL. A piercing member is adapted to pierce and retract from a site on the patient to cause the fluid to flow therefrom, and the sensor is positioned adjacent to the site on the patient so as to receive the fluid flowing from the site to generate an electrical signal indicative of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid. The sensor is comprised of a working electrode comprising an analyte-responsive enzyme and a redox mediator, and a counter electrode. An analyte monitor is operatively connected to the sensor and adapted to measure the signal generated by the sensor. Also provided are analyte measuring methods that optionally employ the integrated lancing and measurement device.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor with diffusible or non-leachable redox mediator
InactiveUS20060025662A1Lower the volumeAccurate and efficient measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteRedox mediator
A region of skin, other than the fingertips, is stimulated. After stimulation, an opening is created in the skin (e.g., by lancing the skin) to cause a flow of body fluid from the region. At least a portion of this body fluid is transported to a testing device where the concentration of analyte (e.g., glucose) in the body fluid is then determined. It is found that the stimulation of the skin provides results that are generally closer to the results of measurements from the fingertips, the traditional site for obtaining body fluid for analyte testing.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Molecular wire injection sensors
InactiveUS20060115857A1Rapid responseHigh sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConductive polymerMolecular wire
Disclosed is a sensor for sensing the presence of an analyte component without relying on redox mediators. This sensor includes (a) a plurality of conductive polymer strands each having at least a first end and a second end and each aligned in a substantially common orientation; (b) a plurality of molecular recognition headgroups having an affinity for the analyte component and being attached to the first ends of the conductive polymer strands; and (c) an electrode substrate attached to the conductive polymer strands at the second ends. The electrode substrate is capable of reporting to an electronic circuit reception of mobile charge carriers (electrons or holes) from the conductive polymer strands. The electrode substrate may be a photovoltaic diode.
Owner:KEENSENSE
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050164322A1Lower the volumeAccurate and efficient measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectron transferPolymer
A sensor designed to determine the amount and concentration of analyte in a sample having a volume of less than about 1 μL. The sensor has a working electrode coated with a non-leachable redox mediator. The redox mediator acts as an electron transfer agent between the analyte and the electrode. In addition, a second electron transfer agent, such as an enzyme, can be added to facilitate the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the analyte. The redox mediator is typically a redox compound bound to a polymer. The preferred redox mediators are air-oxidizable. The amount of analyte can be determined by coulometry. One particular coulometric technique includes the measurement of the current between the working electrode and a counter or reference electrode at two or more times. The charge passed by this current to or from the analyte is correlated with the amount of analyte in the sample. Other electrochemical detection methods, such as amperometric, voltammetric, and potentiometric techniques, can also be used. The invention can be used to determine the concentration of a biomolecule, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum. An enzyme capable of catalyzing the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the biomolecule is provided as a second electron transfer agent.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Transition metal complexes with (pyridyl)imidazole ligands
InactiveUS7074308B2Rapid electron exchangeFast dynamicsImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
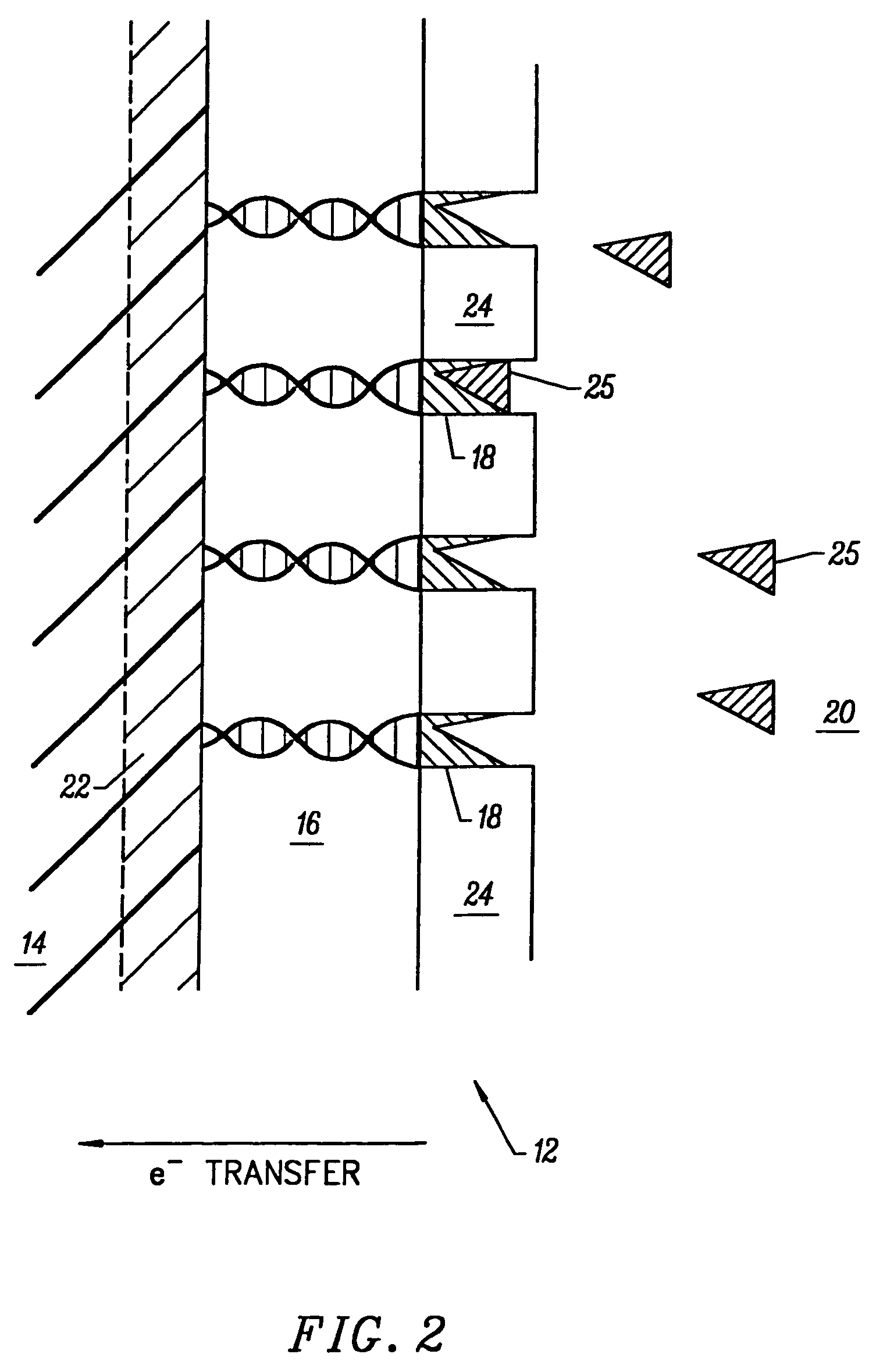
Novel transition metal complexes of iron, cobalt, ruthenium, osmium, and vanadium are described. The transition metal complexes can be used as redox mediators in enzyme-based electrochemical sensors. The transition metal complexes include substituted or unsubstituted (pyridyl)imidazole ligands. Transition metal complexes attached to polymeric backbones are also described.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor
InactiveUS20060169599A1Lower the volumePrecise processImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysisElectron transfer
A sensor utilizing a non-leachable or diffusible redox mediator is described. The sensor includes a sample chamber to hold a sample in electrolytic contact with a working electrode, and in at least some instances, the sensor also contains a non-leachable or a diffusible second electron transfer agent. The sensor and / or the methods used produce a sensor signal in response to the analyte that can be distinguished from a background signal caused by the mediator. The invention can be used to determine the concentration of a biomolecule, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. An enzyme capable of catalyzing the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the biomolecule is typically provided as a second electron transfer agent.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Biosensor and method
ActiveUS20040217019A1Keep for a long timeEasy to optimizeWeather/light/corrosion resistanceWave amplification devicesAnalytePeroxidase
An improved biosensor having at least a first working electrode and a first electrode material disposed on the first working electrode. The first electrode material is a mixture made by combining at least one enzyme where the at least one enzyme is a capable of reacting with the analyte to be measured, a redox mediator capable of reacting with a product of an enzymatic reaction or a series of enzymatic reactions involving the at least one enzyme, a peroxidase capable of catalyzing a reaction involving the redox mediator where the redox mediator is oxidized, a binder and a surfactant.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
Molecular wire injection sensors
InactiveUS6979544B2Accurate readingRapid responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConductive polymerMolecular wire
Disclosed is a sensor for sensing the presence of an analyte component without relying on redox mediators. This sensor includes (a) a plurality of conductive polymer strands each having at least a first end and a second end and each aligned in a substantially common orientation; (b) a plurality of molecular recognition headgroups having an affinity for the analyte component and being attached to the first ends of the conductive polymer strands; and (c) an electrode substrate attached to the conductive polymer strands at the second ends. The electrode substrate is capable of reporting to an electronic circuit reception of mobile charge carriers (electrons or holes) from the conductive polymer strands. The electrode substrate may be a photovoltaic diode.
Owner:KEENSENSE
Flow control of electrochemical-based assay devices
Various techniques for controlling the flow of a test sample through an electrochemical-based assay device are provided. The assay device contains a porous membrane provided with certain properties to selectively control the flow of a test sample to a detection working electrode. The detection working electrode communicates with affinity reagents, such as redox mediators and capture ligands. For instance, capture ligands that are specific binding members for the analyte of interest are applied to the detection electrode to serve as the primary location for detection of the analyte.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050278945A1Lower the volumeAccurate and efficient measurementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysisElectron transfer
A sensor utilizing a non-leachable or diffusible redox mediator is described. The sensor includes a sample chamber to hold a sample in electrolytic contact with a working electrode, and in at least some instances, the sensor also contains a non-leachable or a diffusible second electron transfer agent. The sensor and / or the methods used produce a sensor signal in response to the analyte that can be distinguished from a background signal caused by the mediator. The invention can be used to determine the concentration of a biomolecule, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. An enzyme capable of catalyzing the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the biomolecule is typically provided as a second electron transfer agent.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
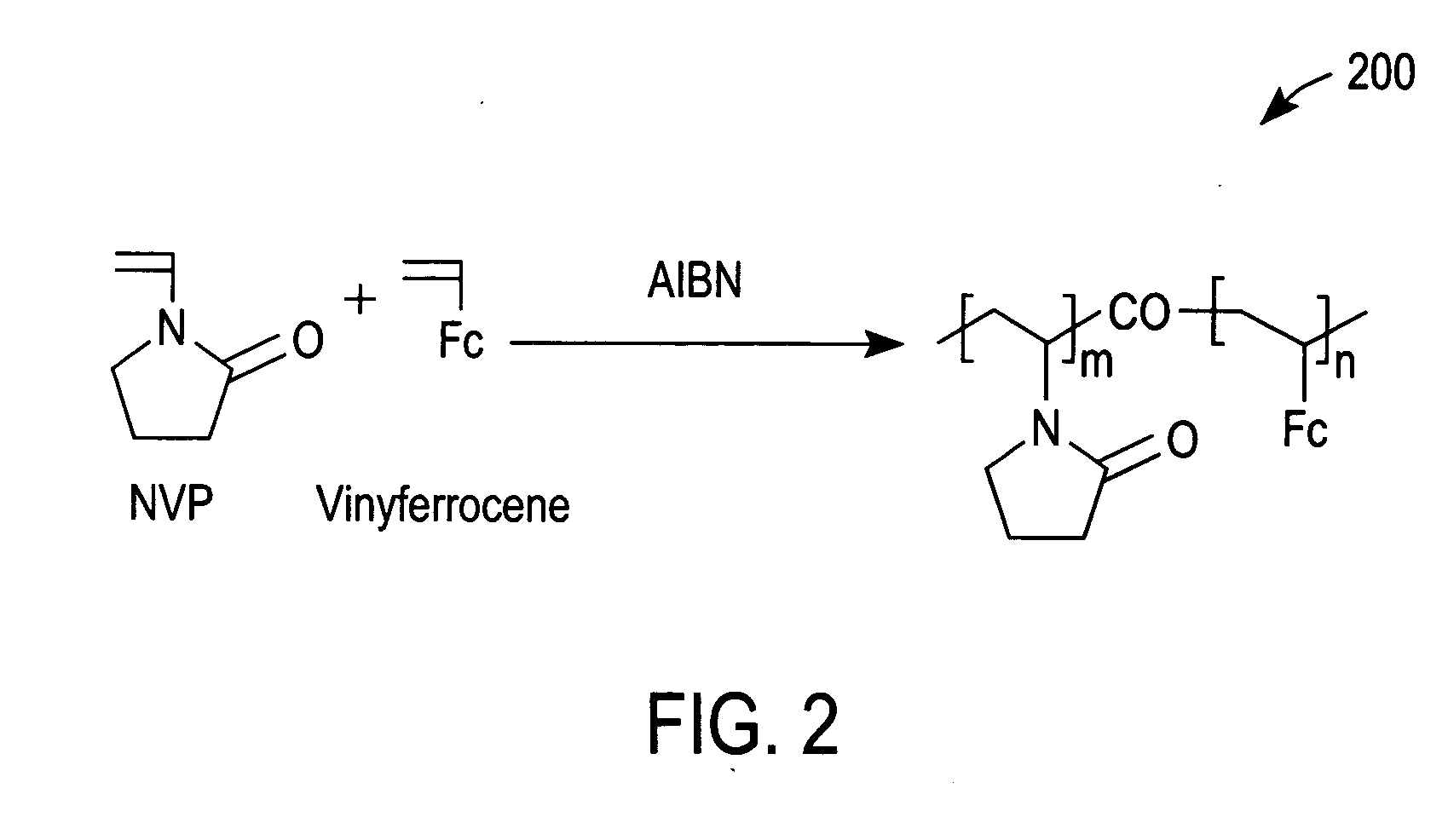
Ionic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymers for use in enzymatic electrochemical-based sensors
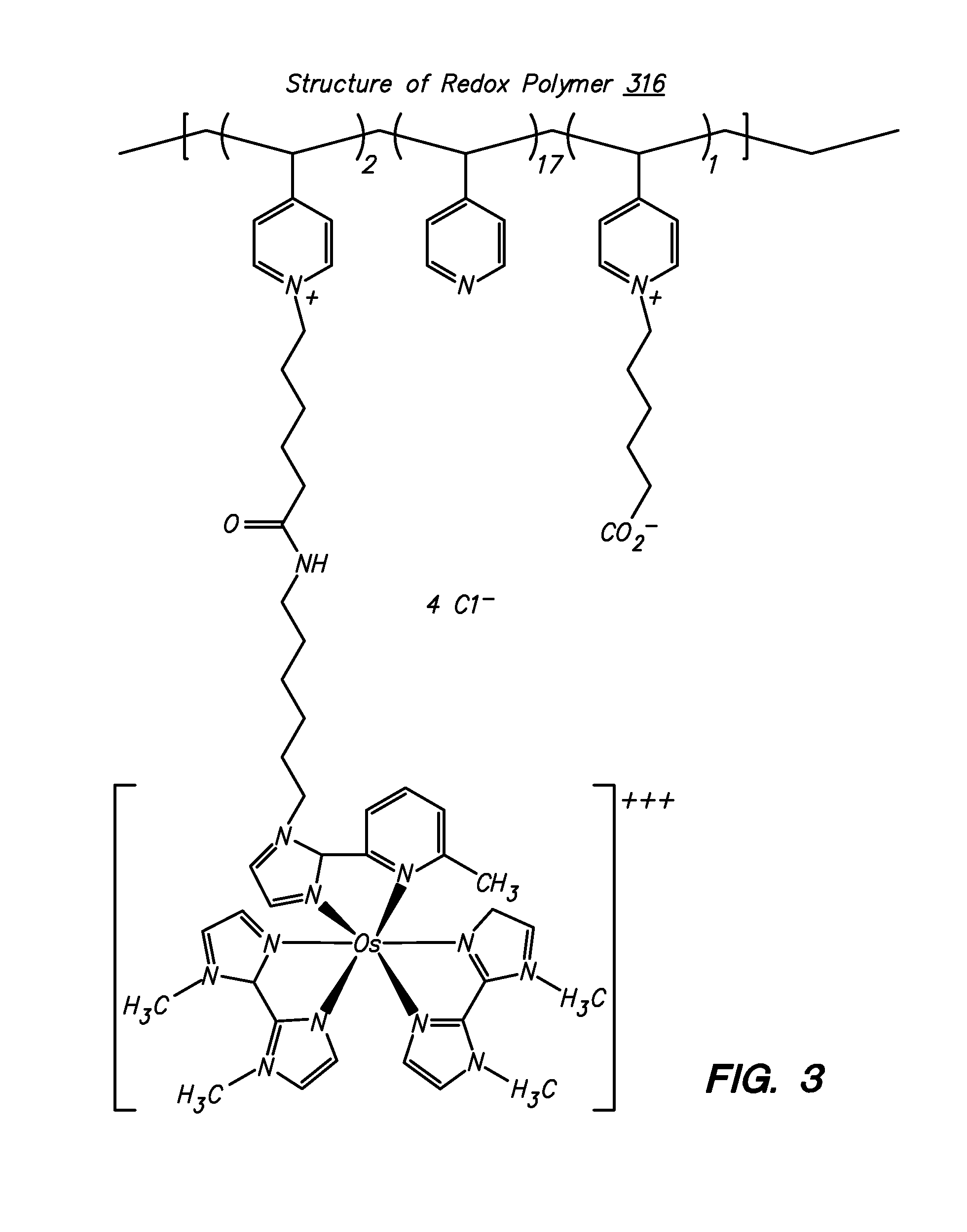
ActiveUS7351770B2Solve the lack of activityReduce leachingMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrophilic polymersFerrocene
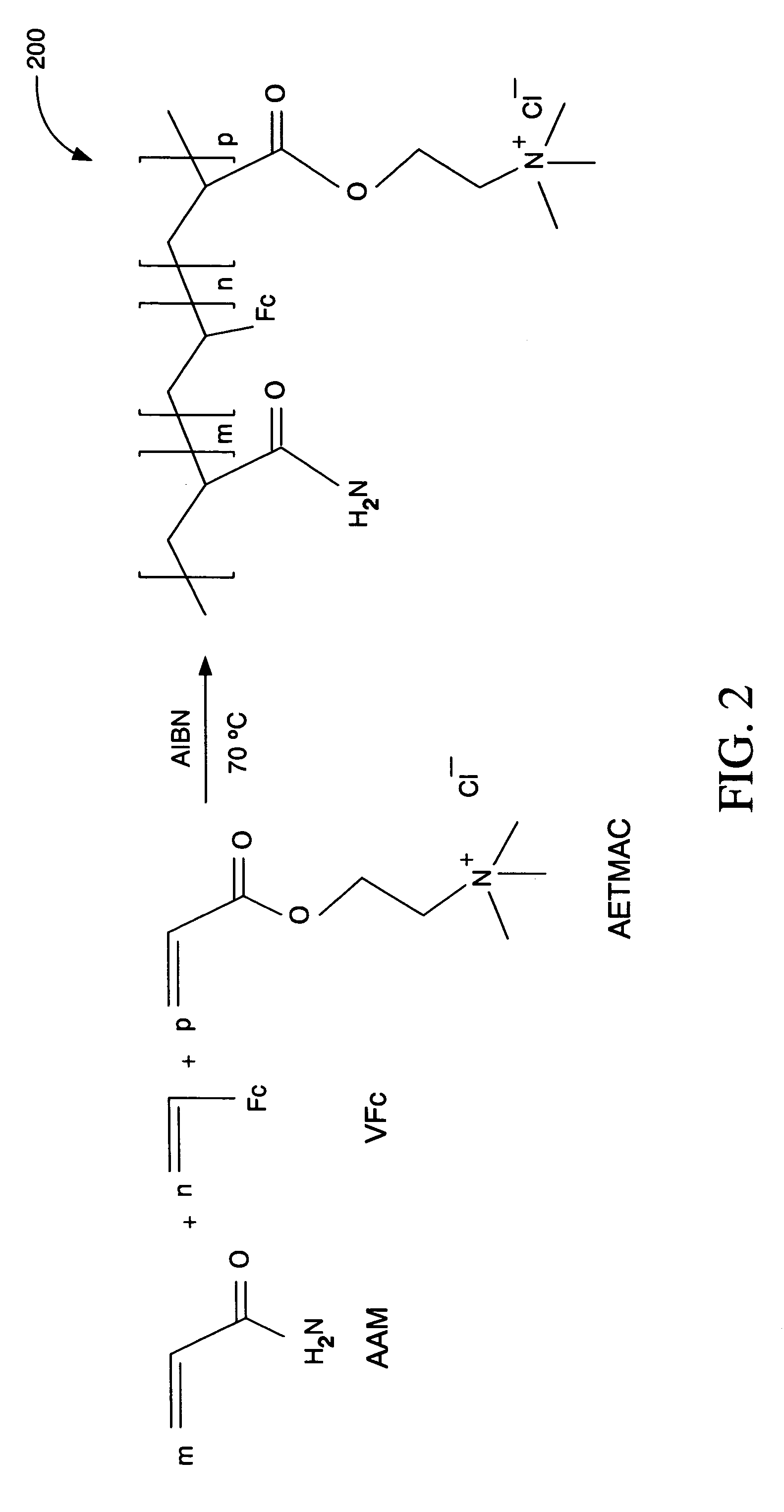
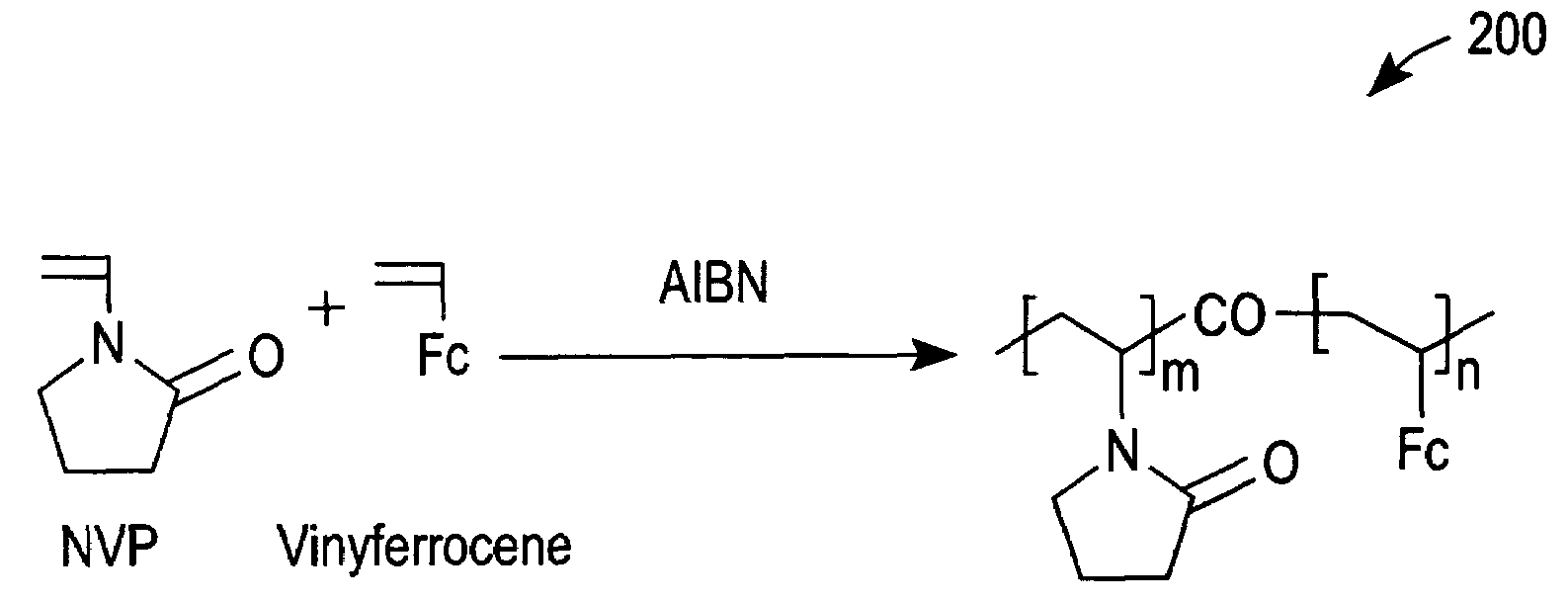
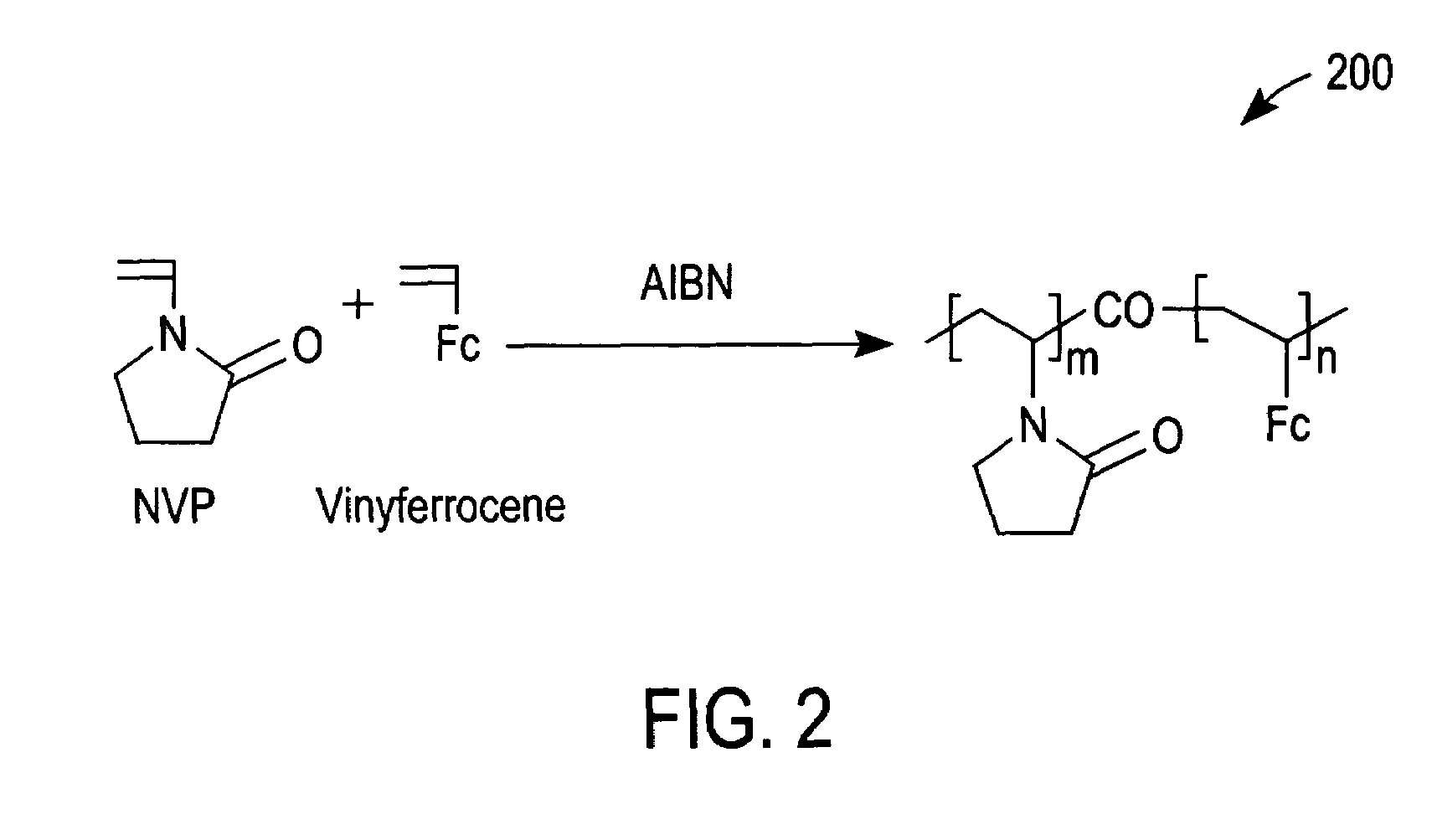
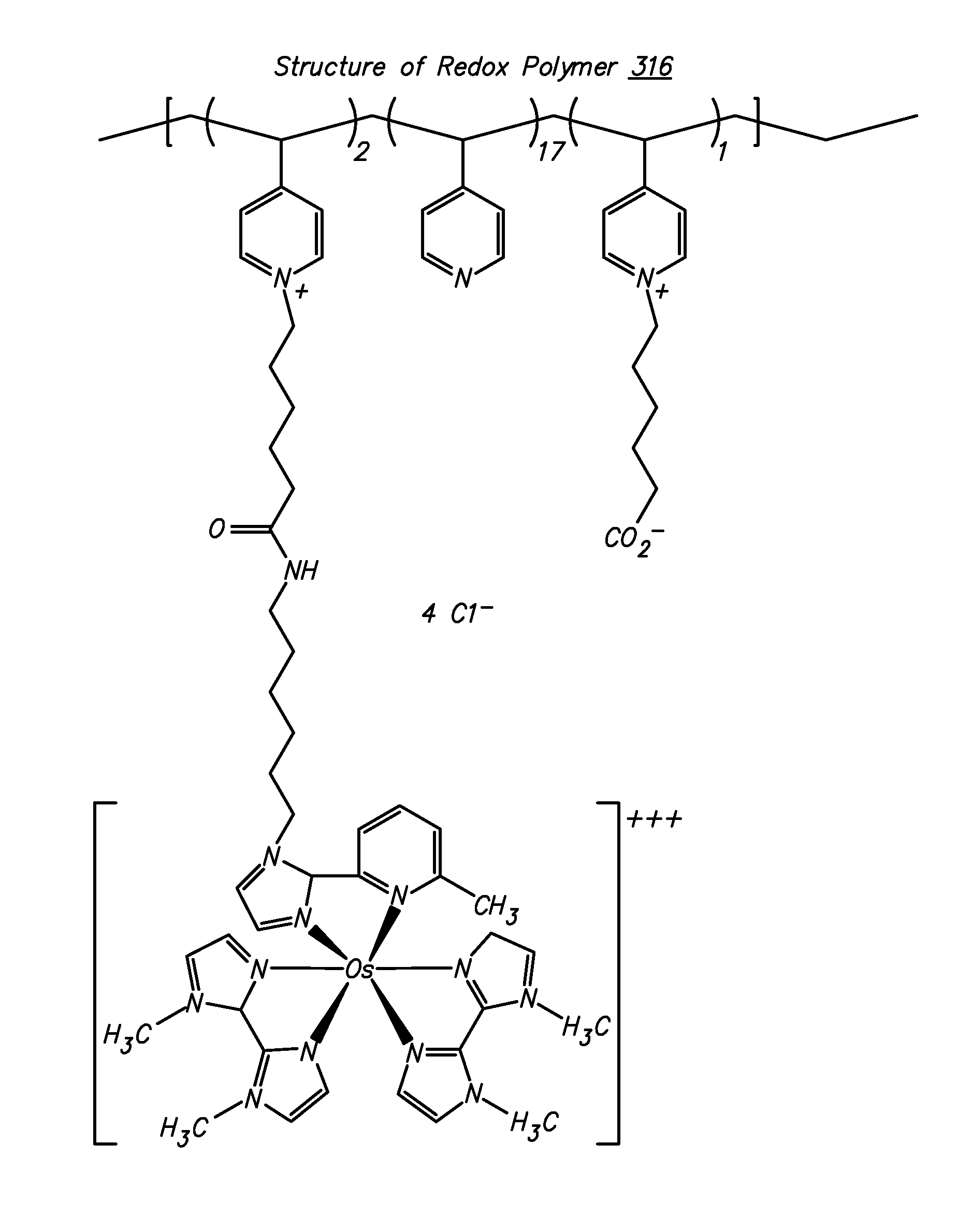
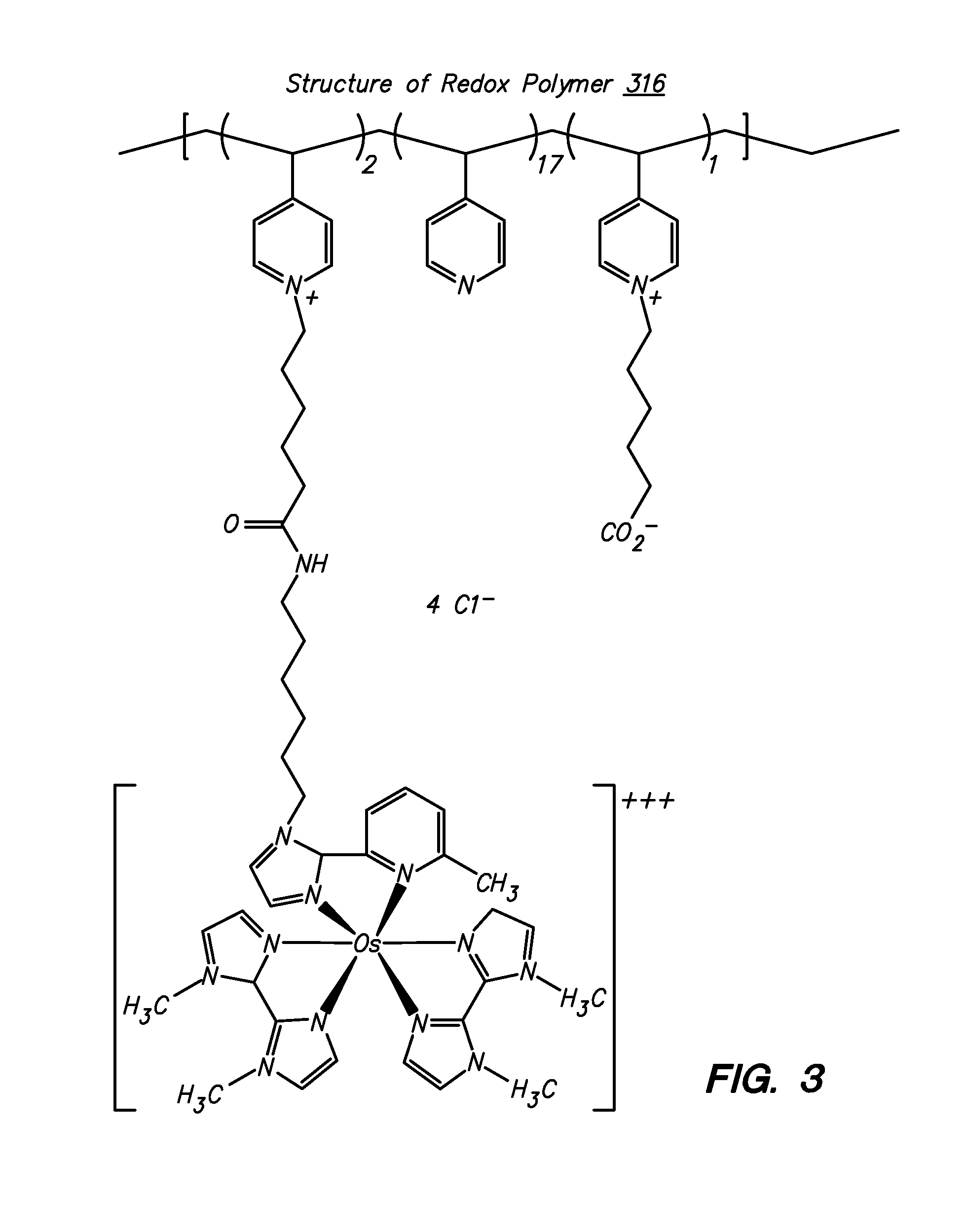
Ionic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymers for use in enzymatic electrochemical-based sensors include a hydrophilic polymer (such as a hydrophilic polymer backbone) with ionic portions (e.g., cationic monomers incorporated in the hydrophilic polymer backbone) and a plurality of attached redox mediators. The redox mediators can be, for example, covalently attached to the hydrophilic polymer in a pendant manner. An exemplary cationic hydrophilic high molecular weight redox polymer is synthesized by co-polymerization of a hydrophilic acrylamide monomer, [2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethyl ammonium chloride and vinyl ferrocene.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Electrochemical-based sensor with a redox polymer and redox enzyme entrapped by a dialysis membrane
ActiveUS7572356B2Rapid responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesDialysis membranes
An electrochemical-based sensor includes an electrode with at least one electrode surface, a film disposed on the electrode surface, and a dialysis membrane disposed on the film. The film includes a redox enzyme and a hydrophilic redox polymer (i.e., a polymer with an attached redox mediator(s)). In addition, the dialysis membrane serves to entrap the redox polymer and redox enzyme in the vicinity of the electrode. Such entrapment is accomplished by employing a redox enzyme and a hydrophilic redox polymer of a sufficiently high molecular weight that they do not pass through the dialysis membrane.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Flow-through assay devices
InactiveUS20050136500A1Easy to moveMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTarget analysisAnalyte
A flow-through assay device capable of detecting the presence or quantity of an analyte of interest is provided that is accurate, reliable, and easy-to-use. The device contains a substrate printed with a channel to facilitate the flow of a test sample to a detection working electrode. The detection working electrode communicates with affinity reagents, such as redox mediators and capture ligands. For instance, capture ligands that are specific binding members for the analyte of interest are applied to the detection electrode to serve as the primary location for detection of the analyte.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Photoelectrochemical Cell
InactiveUS20080286643A1Reduced current efficiencyCurrent efficiency downElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic capacitorsPhotoelectrochemical cellChemical species
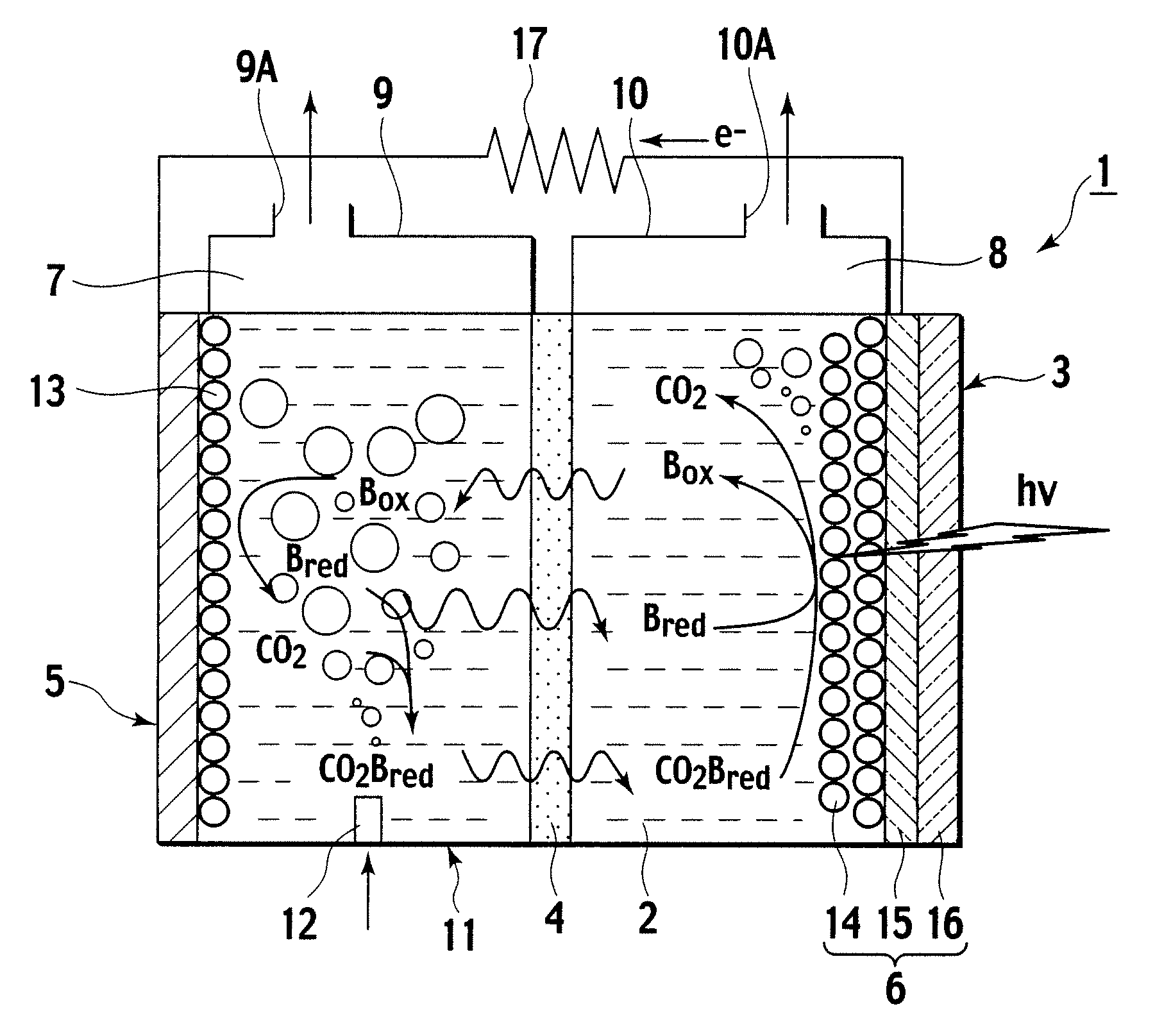
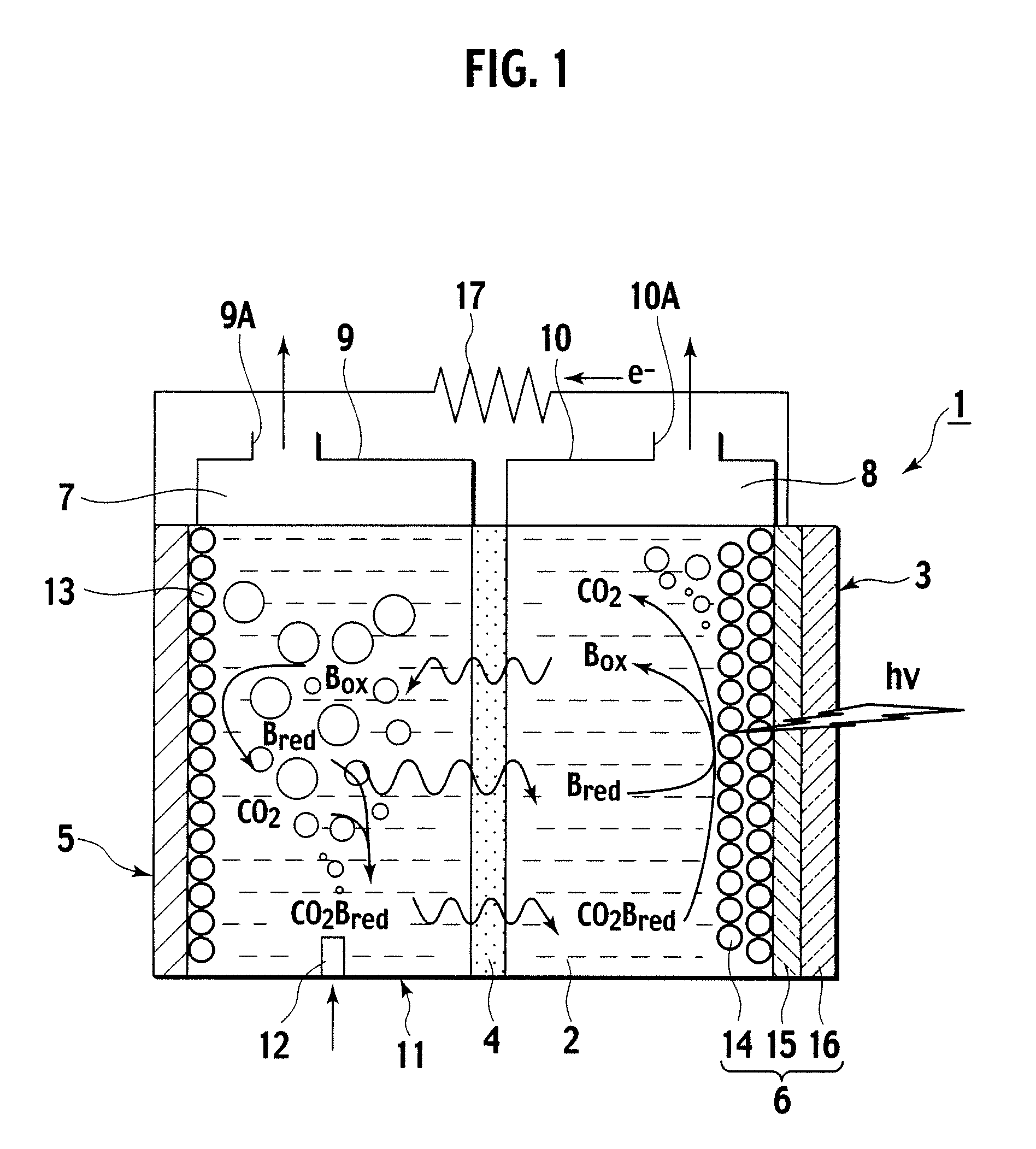
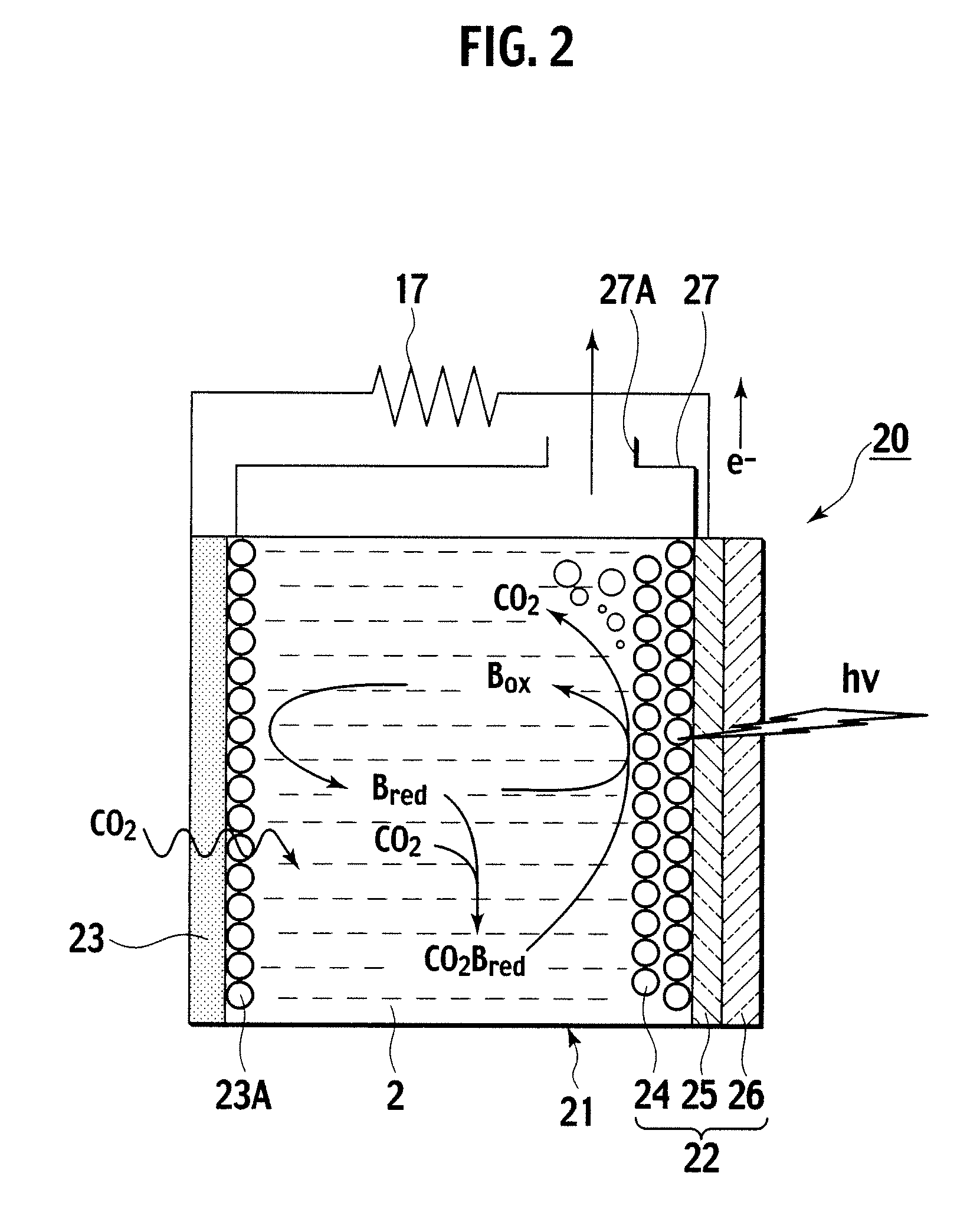
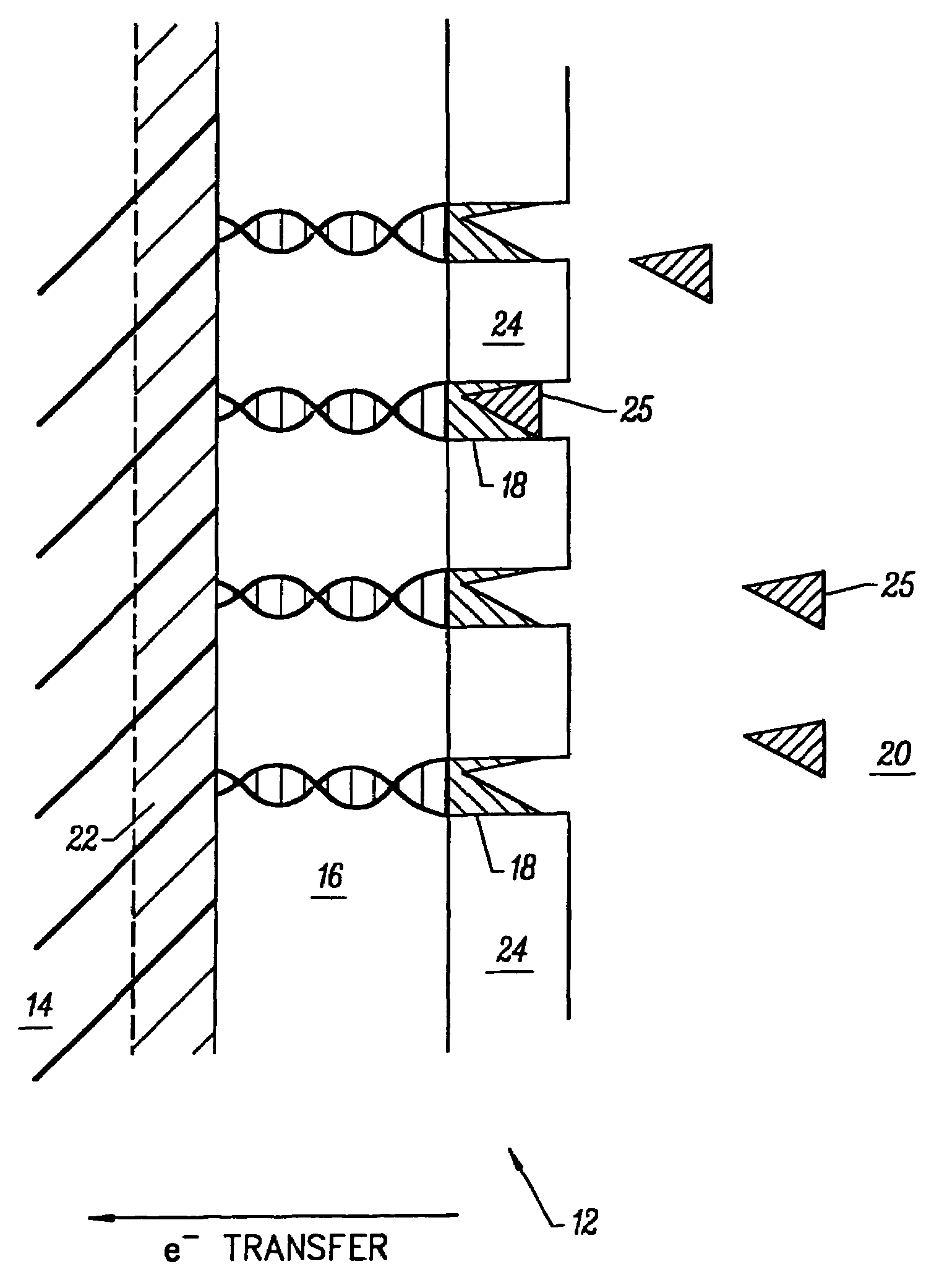
A photoelectrochemical cell (1) includes an electrolyte container (3) containing an ionic liquid (2), and a partitioning membrane (4) dividing an interior of the electrolyte container (3) into two being a CO2 capturing chamber (7) and a CO2 releasing chamber (8), having side walls opposing each other, with the partitioning membrane (4) in between, either as a carbon electrode (5) and the other as a photoelectrode (6). A redox mediator (B) has different bonding forces to carbon dioxide, as it appears as an oxidant Box and a reductant Bred, of which that one which has a greater bonding force serves as an intermediary chemical species carrying carbon dioxide to one of the paired electrodes (5, 6). Over the CO2 releasing chamber (10), an upper wall portion (10) is formed, which has a CO2 take-out port (10A) formed therein, for making use of oxidation and reduction of the redox mediator to achieve separation and concentration of carbon dioxide, converting photo energy of sunlight into electric power.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Molecular wire injection sensors
InactiveUS7220550B2Accurate readingRapid responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConductive polymerMolecular wire
Owner:KEENSENSE
Redox polymers for use in analyte monitoring
InactiveUS8444834B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHigh rateElectrochemical biosensor
Polymers for use as redox mediators in electrochemical biosensors are described. The transition metal complexes attached to polymeric backbones can be used as redox mediators in enzyme based electrochemical sensors. In such instances, transition metal complexes accept electrons from, or transfer electrons to, enzymes at a high rate and also exchange electrons rapidly with the sensor. The transition metal complexes include at least one substituted or unsubstituted biimidazole ligand and may further include a second substituted or unsubstituted biimidazole ligand or a substituted or unsubstituted bipyridine or pyridylimidazole ligand.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
High sensitivity amperometric biosensor with side-to-side hybrid configuration
InactiveUS20050089944A1High sensitivityFast response timeMicrobiological testing/measurementEngineeringAmperometric biosensor
An amperometric glucose biosensor comprises a sensing electrode and a reference electrode arranged in a side-by-side parallel configuration on an electrically insulating sheet. A passive cover electrode is placed over the side-by-side sensing electrode and reference electrode so that the active surface of the passive cover electrode opposes the active surfaces of the side-by-side electrodes. Physical contact between the passive covering electrode and the side-by-side electrodes is prevented by insulating spacers. The sensing electrode comprises a conductive graphite track coated with a formulation comprising a redox mediator and enzyme and the reference electrode is a parallel track comprising an Ag / AgCl formulation while the passive cover electrode comprising a conductive graphite track coated with a formulation comprising the same redox mediator as used in the sensing electrode but not including an enzyme. An opening either located in the middle or at one side of the passive cover electrode allows a liquid test sample to be introduced into the sensor. The biosensor of the present invention exhibits a sensitivity and response time equal to or surpassing that of the simple face-to-face configuration while can be efficiently manufactured and permit use with conventional electrical connectors.
Owner:KS BIOMEDIX LTD
Glucose biosensor with improved shelf life
InactiveUS20130098775A1Excellent long-term storage stabilityPrevent deterioration of sensor performanceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox mediatorPhotochemistry
A disposable biosensor having improved long term storage stability including a working electrode and a reference electrode formed on an insulating substrate and a dissolvable reagent layer composition disposed directly on the working electrode where the reagent layer composition contains a glucose-based enzyme, a reagent component selected from a phosphate buffer and a tris reagent, and a redox mediator.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
Disposable oxygen sensor and method for correcting oxygen effect on oxidase-based analytical devices
ActiveUS20060278537A1Easy to manufactureAccurate measurementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteOxygen sensor
A system and method for correcting the oxygen effect on oxidase-based analyte sensors includes an oxygen sensor with a working electrode, a reagent matrix disposed on at least the working electrode that contains a reduced form of a redox mediator, an oxidase and a peroxidase, an oxidase-based analyte sensor, a means for determining the oxygen concentration in a portion of a fluid sample using the oxygen sensor, means for determining an analyte concentration in another portion of the fluid sample using the oxidase-based analyte sensor, and means for using the oxygen concentration in the fluid sample to determine a corrected analyte concentration in the fluid sample.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
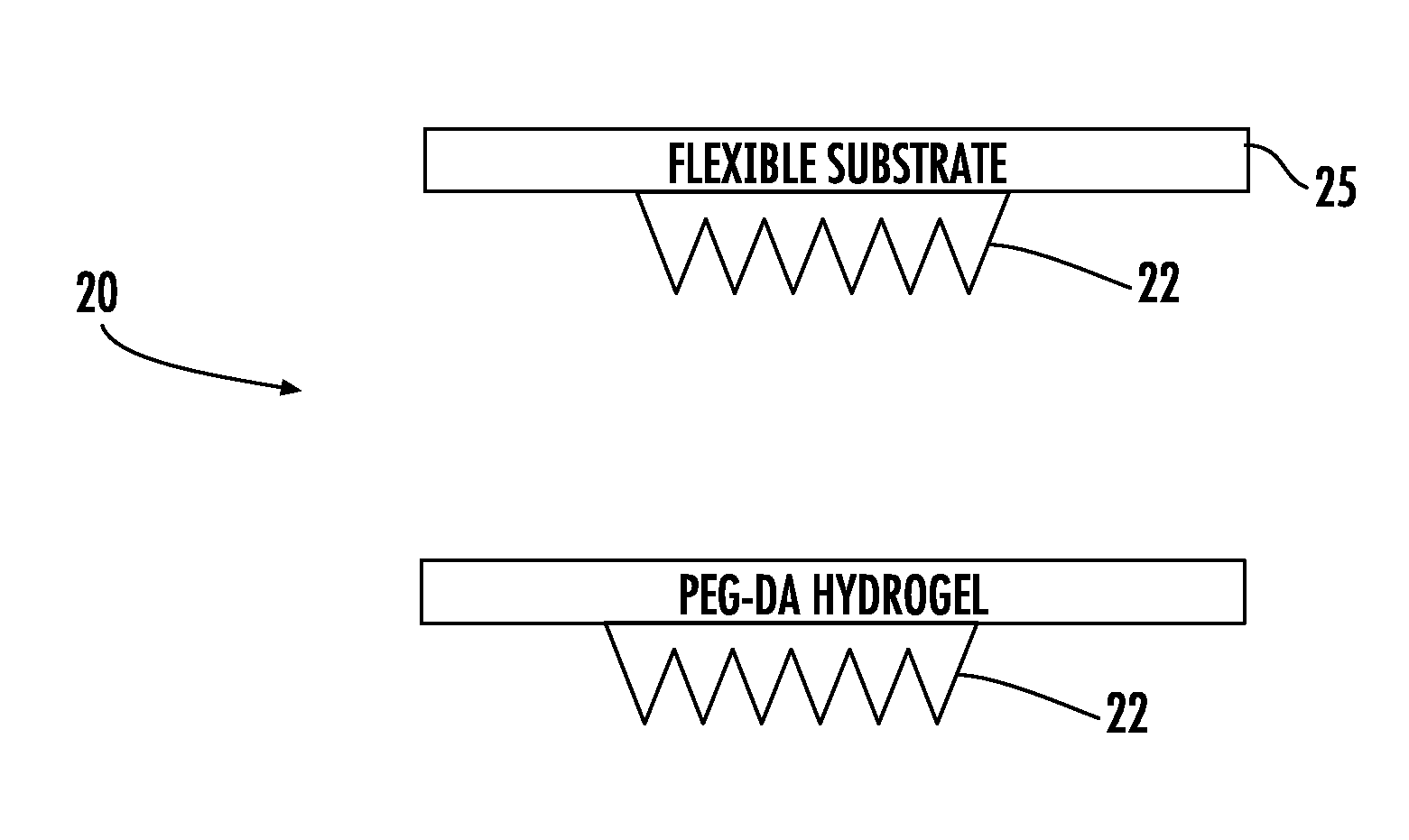
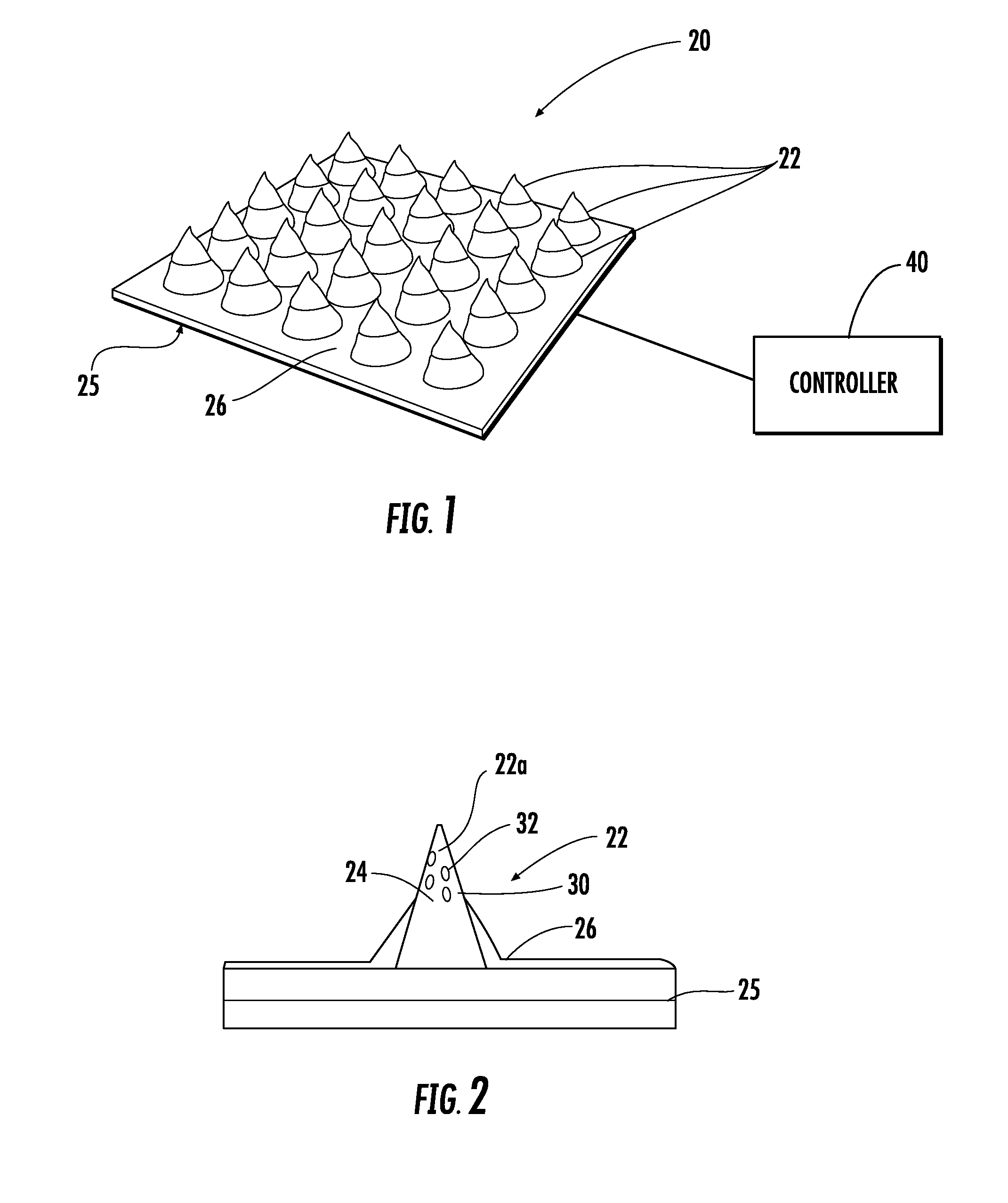
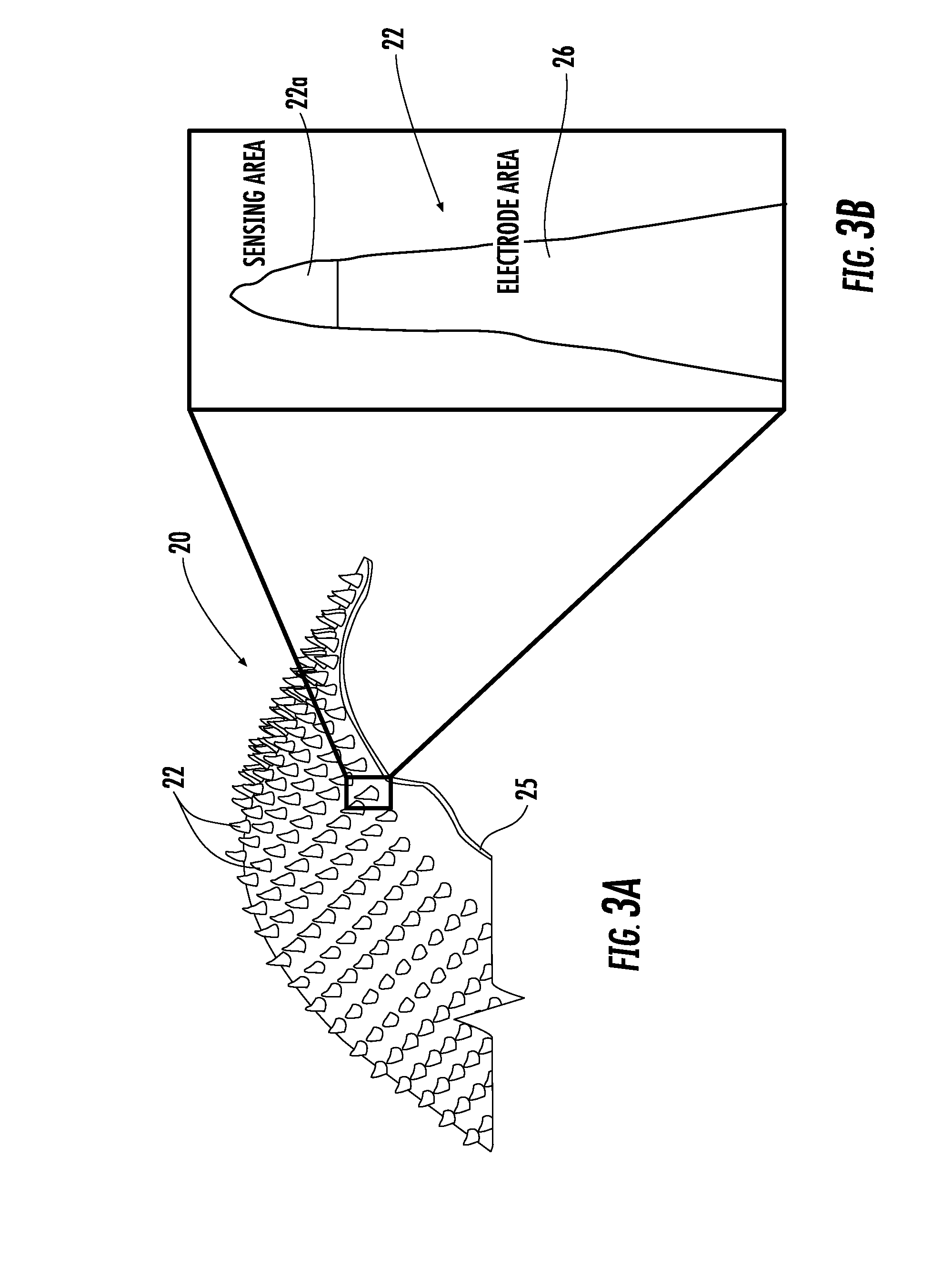
Microneedle array device and method of making
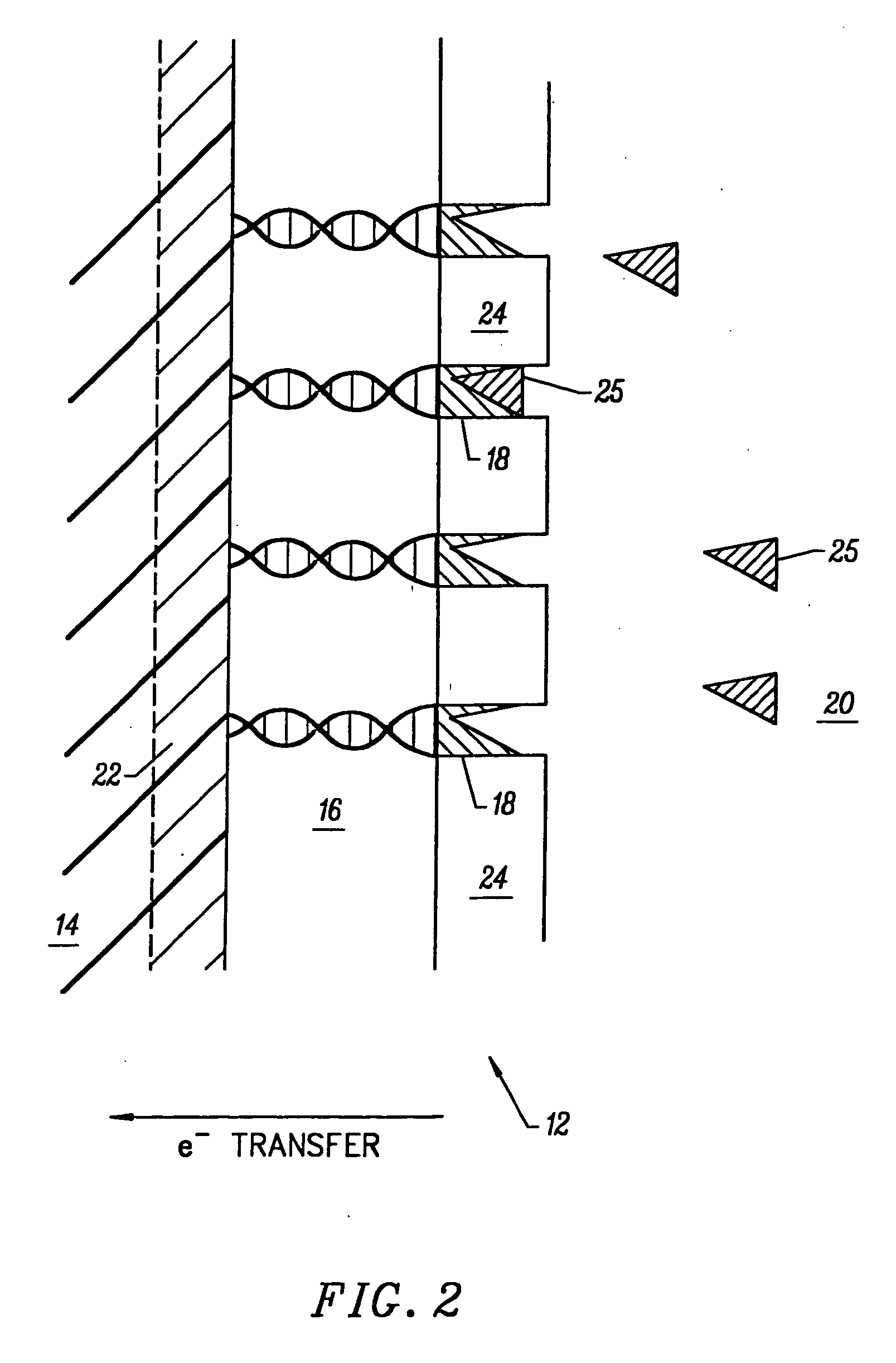
ActiveUS20160157764A1Facilitates electron transferMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroneedlesRedox enzymesOptoelectronics
A microneedle array device includes a substrate and an array of microneedles on the substrate. Each microneedle includes a redox enzyme and redox mediator and an electrically conductive layer on the substrate. The electrically conductive layer may extend partway up each microneedle exposing the tip thereof.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Electrically non-conductive, nanoparticulate membrane
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method and apparatus for the detection of microorganisms
InactiveUS20050208592A1Increase of first impedanceElectrotherapyBiological material analysisMicroorganismNanoparticle
The present application discloses a method for detecting a viable microorganism in a sample. The method may comprise (i) providing a detecting electrode and a counter electrode, (ii) contacting said sample with said detecting electrode and said counter electrode and (iii) measuring a difference in impedance between said detecting electrode and said counter electrode. The detecting electrode may comprise gold nanoparticles deposited thereon and / or a capture molecule. The capture molecule may be able to bind to the microorganism. A redox mediator can also be added to the sample prior to the impedance measurement. Also disclosed are related apparatuses and uses.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Redox polymers for use in analyte monitoring
InactiveUS20120132525A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorHigh rate
Polymers for use as redox mediators in electrochemical biosensors are described. The transition metal complexes attached to polymeric backbones can be used as redox mediators in enzyme based electrochemical sensors. In such instances, transition metal complexes accept electrons from, or transfer electrons to, enzymes at a high rate and also exchange electrons rapidly with the sensor. The transition metal complexes include at least one substituted or unsubstituted biimidazole ligand and may further include a second substituted or unsubstituted biimidazole ligand or a substituted or unsubstituted bipyridine or pyridylimidazole ligand.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Preparation method of porous inorganic filling materials-fixed quinone compound
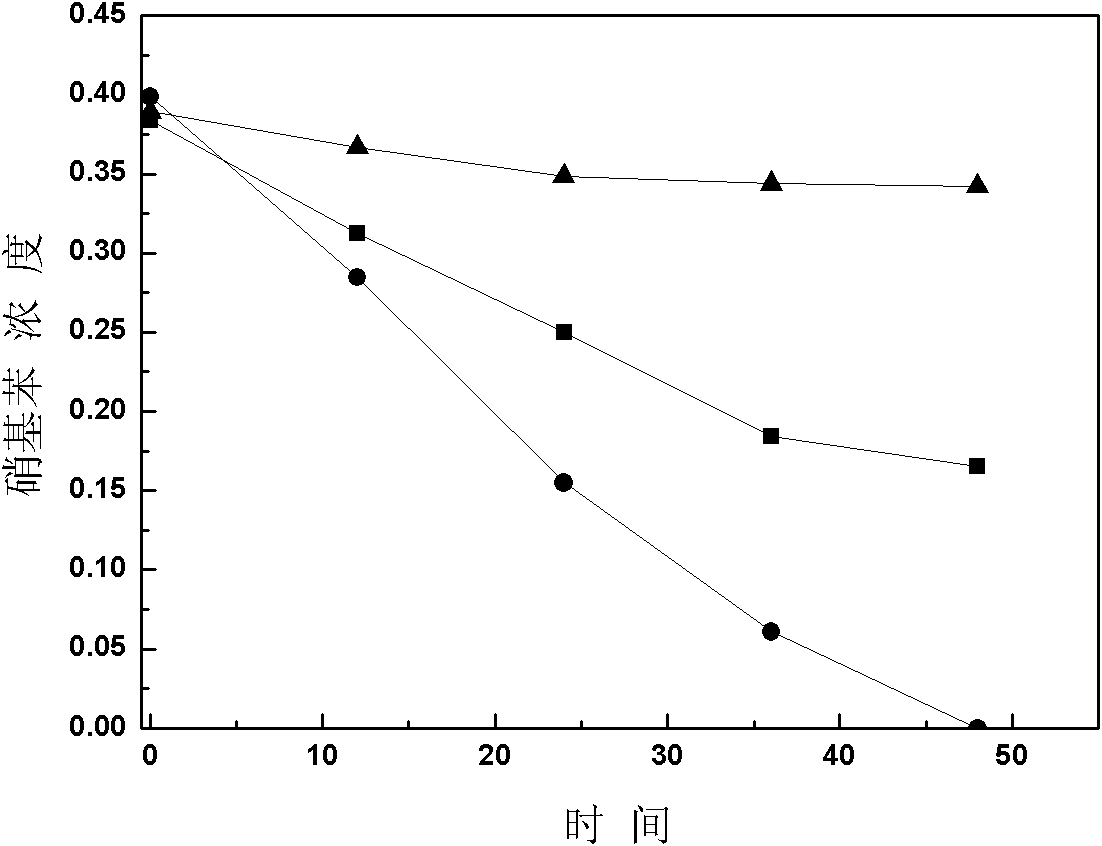
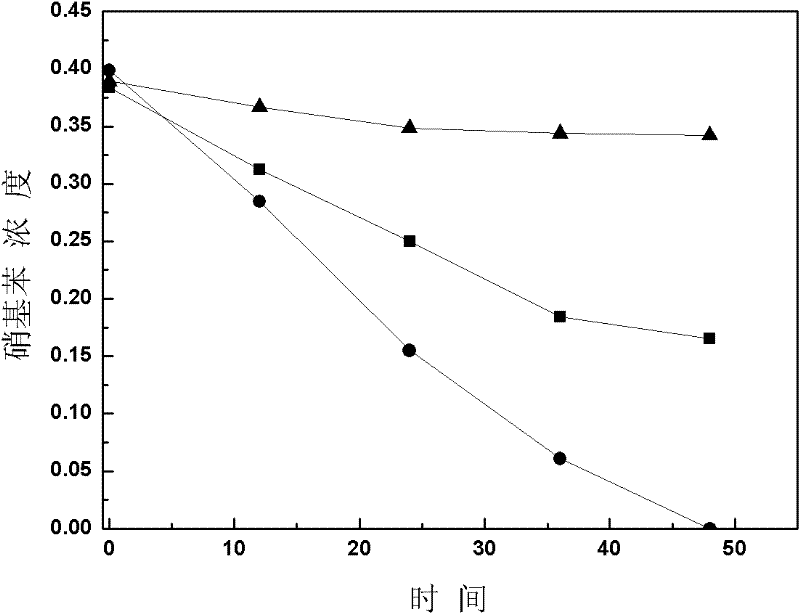
InactiveCN101862680AImprove catalytic performanceSolve the technical bottleneck of secondary pollutionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsWater contaminantsSulfonyl chlorideAnaerobic reactor
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous inorganic filling materials-fixed quinone compound, belonging to the technical field of water treatment in environmental engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting porous inorganic filling materials such as ceramsites, volcanics and the like; plating gamma-aluminum oxide on the surface of the materials; aminating, so that the surfaces of the porous inorganic filling materials contain a certain quantity of primary amidogen; putting the aminated materials into hydrochloric solution to have reaction for protecting the primary amidogen; and putting the reacted porous inorganic filling materials into sodium hydroxide solution, adding sulfonyl chloride group-containing anthraquinone compound which is dissolved in dichloromethane, and reacting for 6-10h under the room temperature to fix the water-soluble quinone compound. The quinone compound-containing macroporous polymer is applied to an anaerobic reactor to be capable of improving the biotransformation speed of an organic matter which is hardly degraded. The method covalently fixes the quinone compound on the macroporous polymer of a biologic carrier, so that the redox medium is easily contacted with the microbe, thereby overcoming the problem of the secondary pollution since the water-soluble quinone compound flows out with the water.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
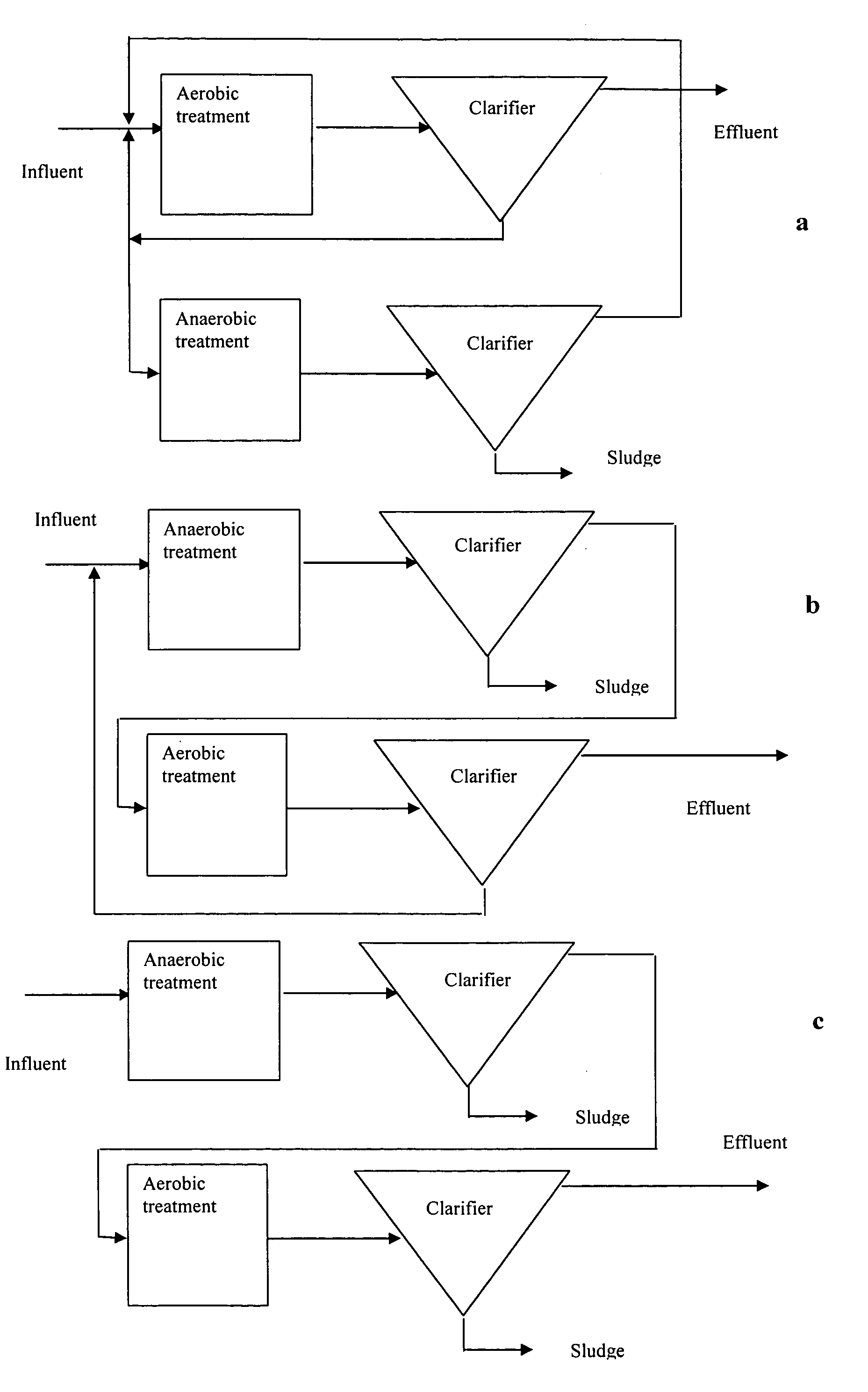
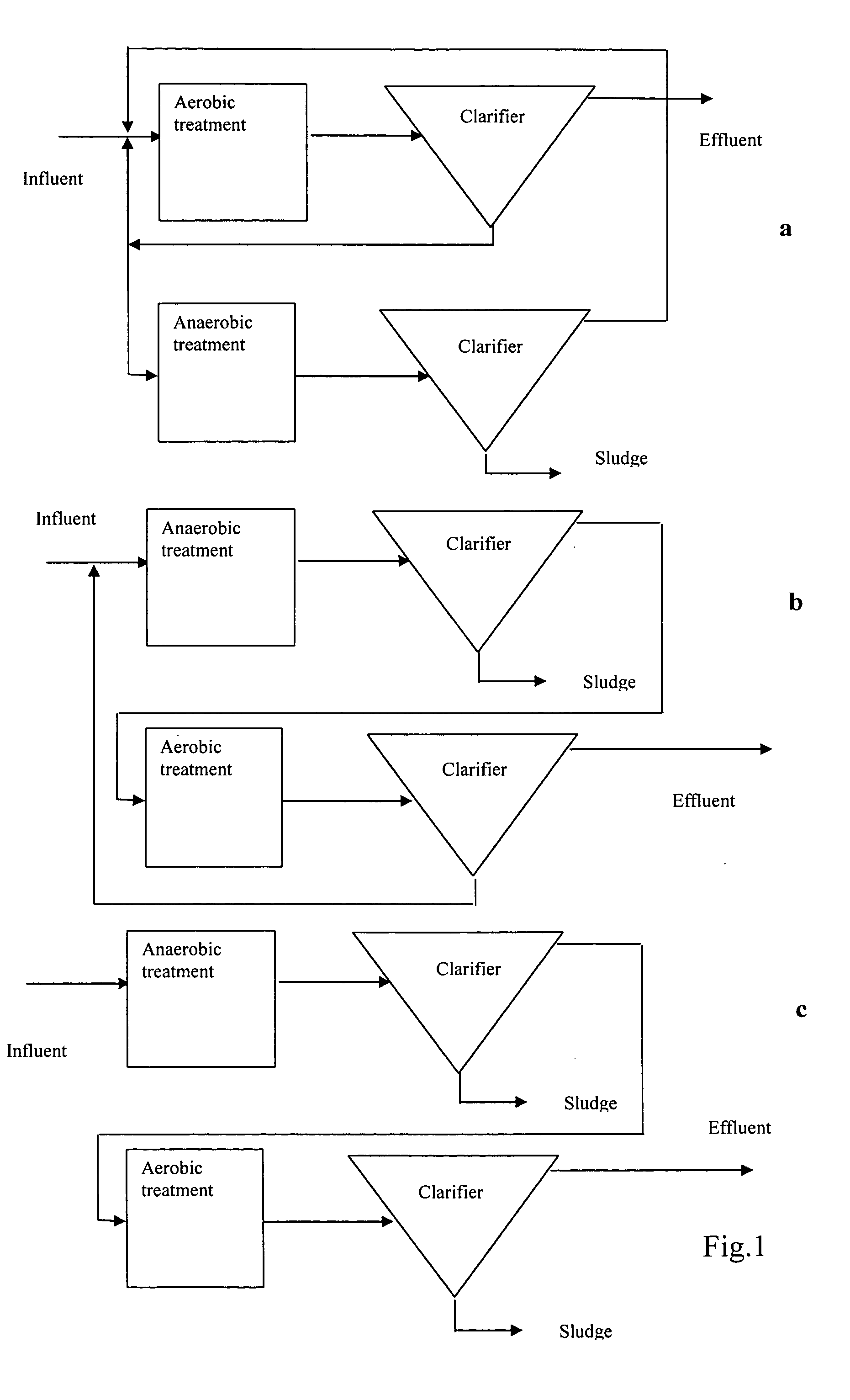
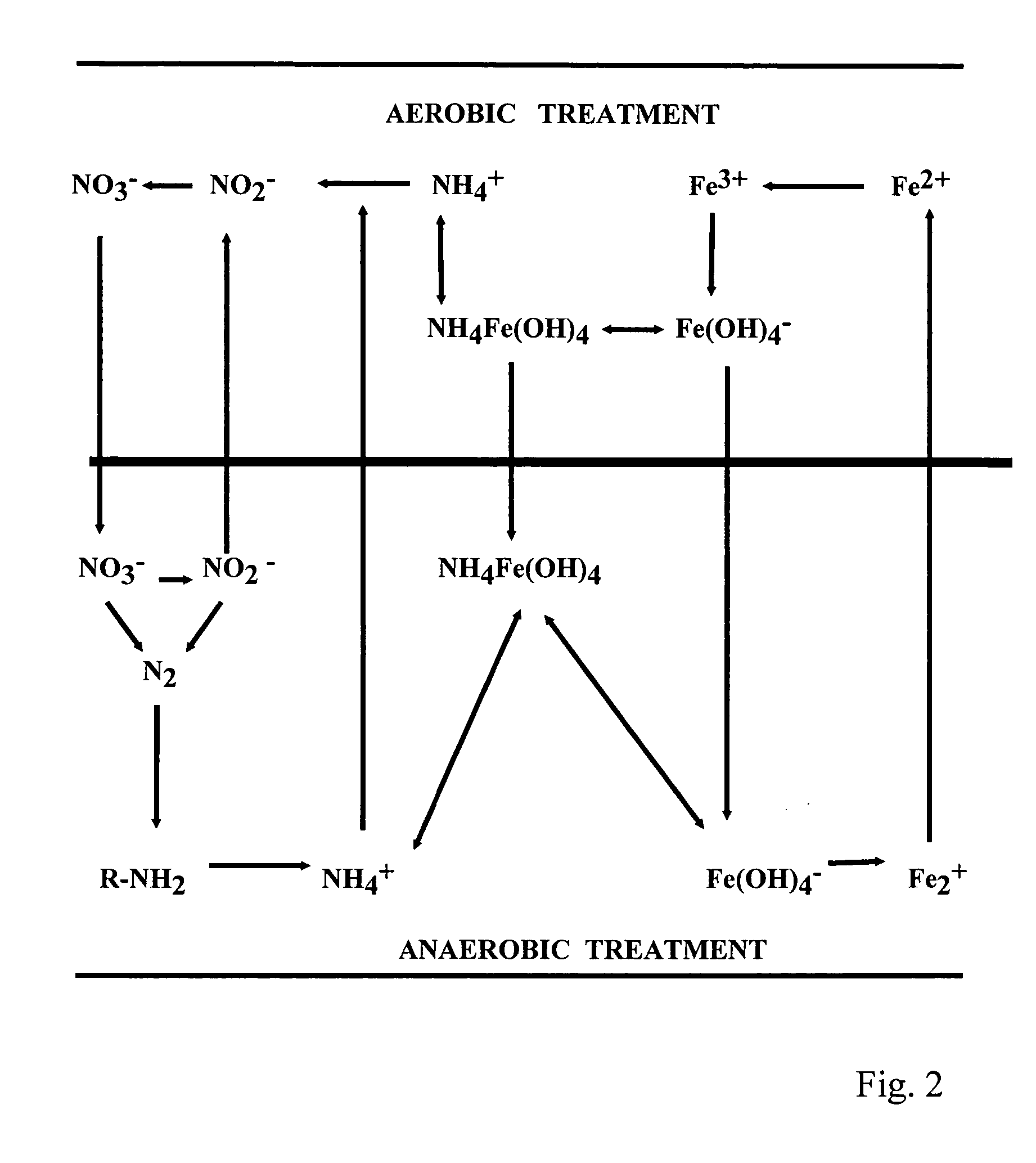
Compositions and methods for the treatment of wastewater and other waste
ActiveUS20060163154A1Diminish start-up periodEnhance anaerobic treatmentWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsChemical speciesOxidation-Reduction Agent
A method for processing environmental samples to remove or otherwise reduce the level of certain chemical species. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention contemplates a process for reducing the level of inorganic and / or organic chemical species in wastewater or other aqueous or semi-aqueous environments or other waste environments. The present invention further provides compositions of bacteria useful in modulating the redox potential of an environment to generate redox mediator species which facilitate the removal of particular inorganic or organic molecules from the environment samples. The redox potential is preferably modulated through microbial-mediated oxidation or reduction of metal cations under aerobic or anaerobic conditions, respectively. The present invention is further directed to a computer program which facilitates the controlled modulation of the redox potential of an aqueous or semi-aqueous environment or other environments.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Glucose biofuel cell
ActiveUS20110250510A1Easy to handleCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsLiquid mediumConductive materials
A biofuel cell intended to be immersed into a liquid medium containing a sugar and oxygen, wherein the anode includes an enzyme capable of catalyzing the oxidation of the sugar and a redox mediator of low redox potential capable of exchanging electrons with the anode enzyme and the cathode includes an enzyme capable of catalyzing the reduction of oxygen and a redox mediator of high redox potential capable of exchanging electrons with the cathode enzyme. Each of the anode and cathode electrodes is formed of a solid agglomerate of a conductive material mixed with the appropriate enzyme and redox mediator and is solid with an electrode wire.
Owner:UNIV GRENOBLE ALPES
Electrochemical-based sensor with a redox polymer and redox enzyme entrapped by a dialysis membrane
ActiveUS20060042944A1Rapid responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesDialysis membranes
An electrochemical-based sensor includes an electrode with at least one electrode surface, a film disposed on the electrode surface, and a dialysis membrane disposed on the film. The film includes a redox enzyme and a hydrophilic redox polymer (i.e., a polymer with an attached redox mediator(s)). In addition, the dialysis membrane serves to entrap the redox polymer and redox enzyme in the vicinity of the electrode. Such entrapment is accomplished by employing a redox enzyme and a hydrophilic redox polymer of a sufficiently high molecular weight that they do not pass through the dialysis membrane.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Mediator stabilized reagent compositions and methods for their use in electrochemical analyte detection assays
InactiveUS20080073207A1The result is accurateImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteConcentrations glucose
Mediator stabilized reagent compositions and methods for their use in electrochemical analyte determination assays are provided. The subject reagent compositions include an enzyme, a redox mediator and a mediator-stabilizing buffer. Optionally, the reagent compositions may further include one or more of a wetting agent, detergent, enzyme cofactor and combinations thereof. Also provided are electrochemical test strips that include the subject reagent compositions, systems and kits that include the same as well as methods for using the same in analyte detection assays. The subject invention finds use in a variety of different applications, including glucose concentration determination applications.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Preparation method of porous inorganic filling materials-fixed quinone compound
InactiveCN101862680BImprove catalytic performanceSolve the technical bottleneck of secondary pollutionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsWater contaminantsSulfonyl chlorideAnaerobic reactor
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous inorganic filling materials-fixed quinone compound, belonging to the technical field of water treatment in environmental engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting porous inorganic filling materials such as ceramsites, volcanics and the like; plating gamma-aluminum oxide on the surface of the materials; aminating, so that the surfaces of the porous inorganic filling materials contain a certain quantity of primary amidogen; putting the aminated materials into hydrochloric solution to have reaction for protecting the primary amidogen; and putting the reacted porous inorganic filling materials into sodium hydroxide solution, adding sulfonyl chloride group-containing anthraquinone compound which is dissolved in dichloromethane, and reacting for 6-10h under the room temperature to fix the water-soluble quinone compound. The quinone compound-containing macroporous polymer is applied to an anaerobic reactor to be capable of improving the biotransformation speed of an organic matter which is hardly degraded. The method covalently fixes the quinone compound on the macroporous polymer of a biologic carrier, sothat the redox medium is easily contacted with the microbe, thereby overcoming the problem of the secondary pollution since the water-soluble quinone compound flows out with the water.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Application of immobilized quinone compound in accelerating denitrification process of microorganism
InactiveCN102060379AReduced stabilityImprove stabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBiocompatibility TestingBio engineering
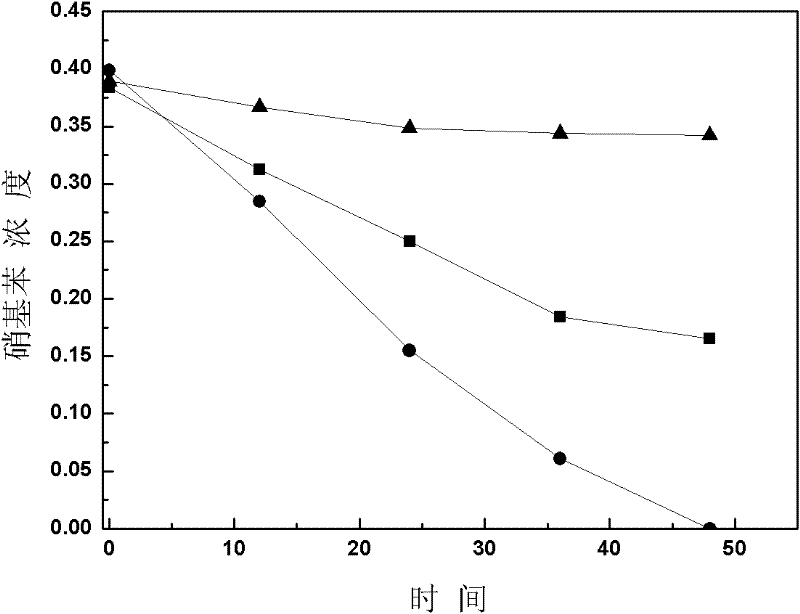
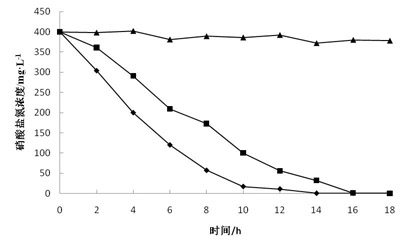
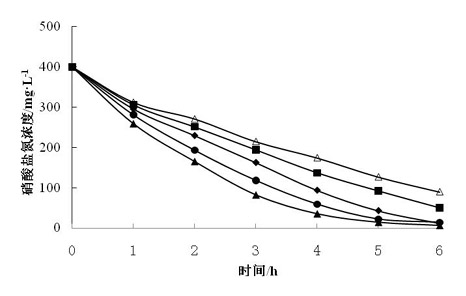
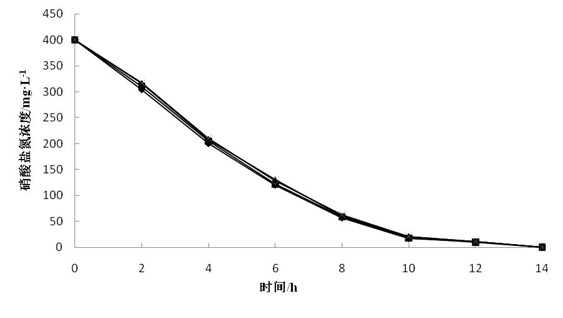
The invention relates to application of an immobilized quinone compound in accelerating the denitrification process of a microorganism, belonging to the technical field of chemical engineering, biological engineering and environmental engineering. The immobilized quinone compound is 1,8-dichloroanthraquinone and 1,5-dichloroanthraquinone or 1,4,5,8-tetrachloroanthraquinone. The immobilized quinone compound can intensify, regulate and control the denitrification process of an organism, accelerate the velocity and the capacity of the microorganism on the denitrification process of nitrogenous substances, effectively reduce the cost of water treatment and has the advantages of good stability, loss difficulty and reduced secondary pollution, low price of immobilized raw material sodium alginate, good biocompatibility, simple fixing process and low production cost and is easy to realize redox mediator recovery, regeneration and recycling.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com