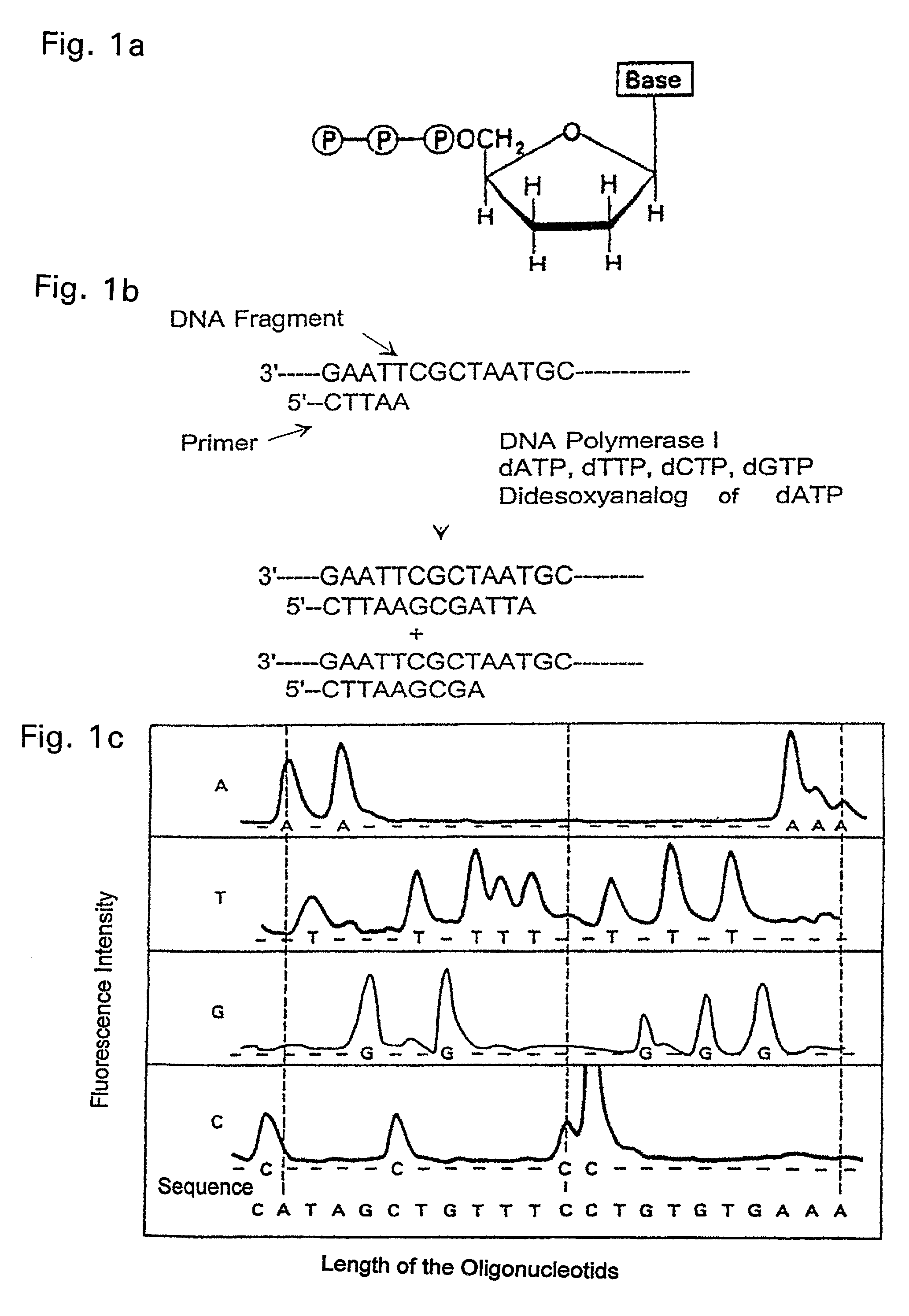
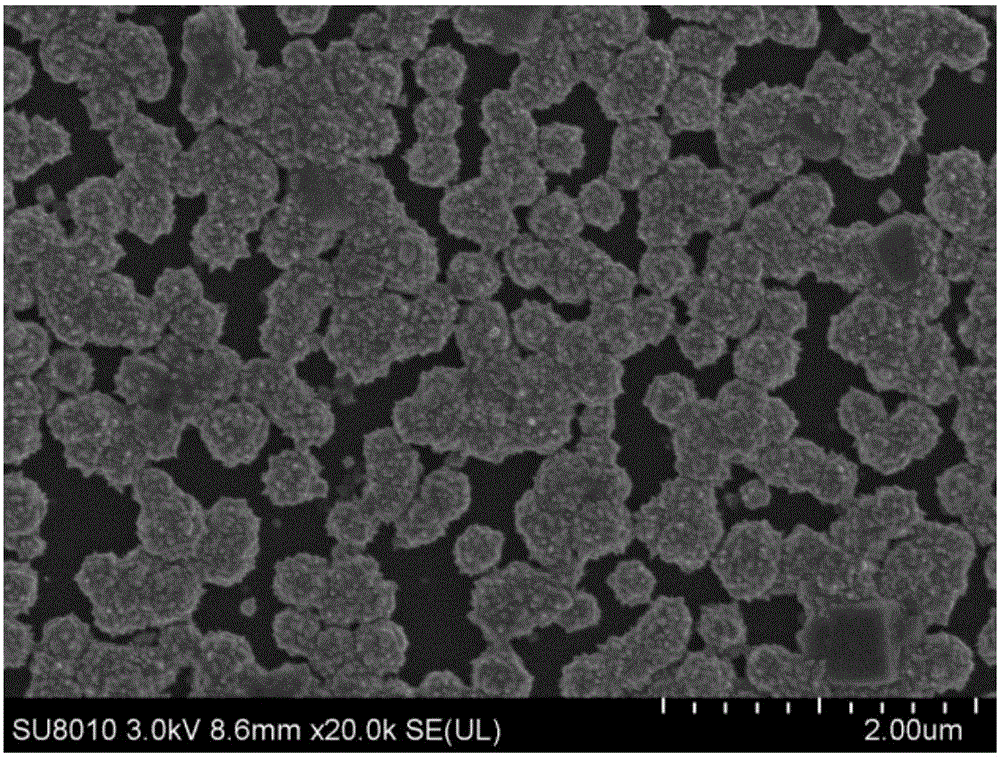
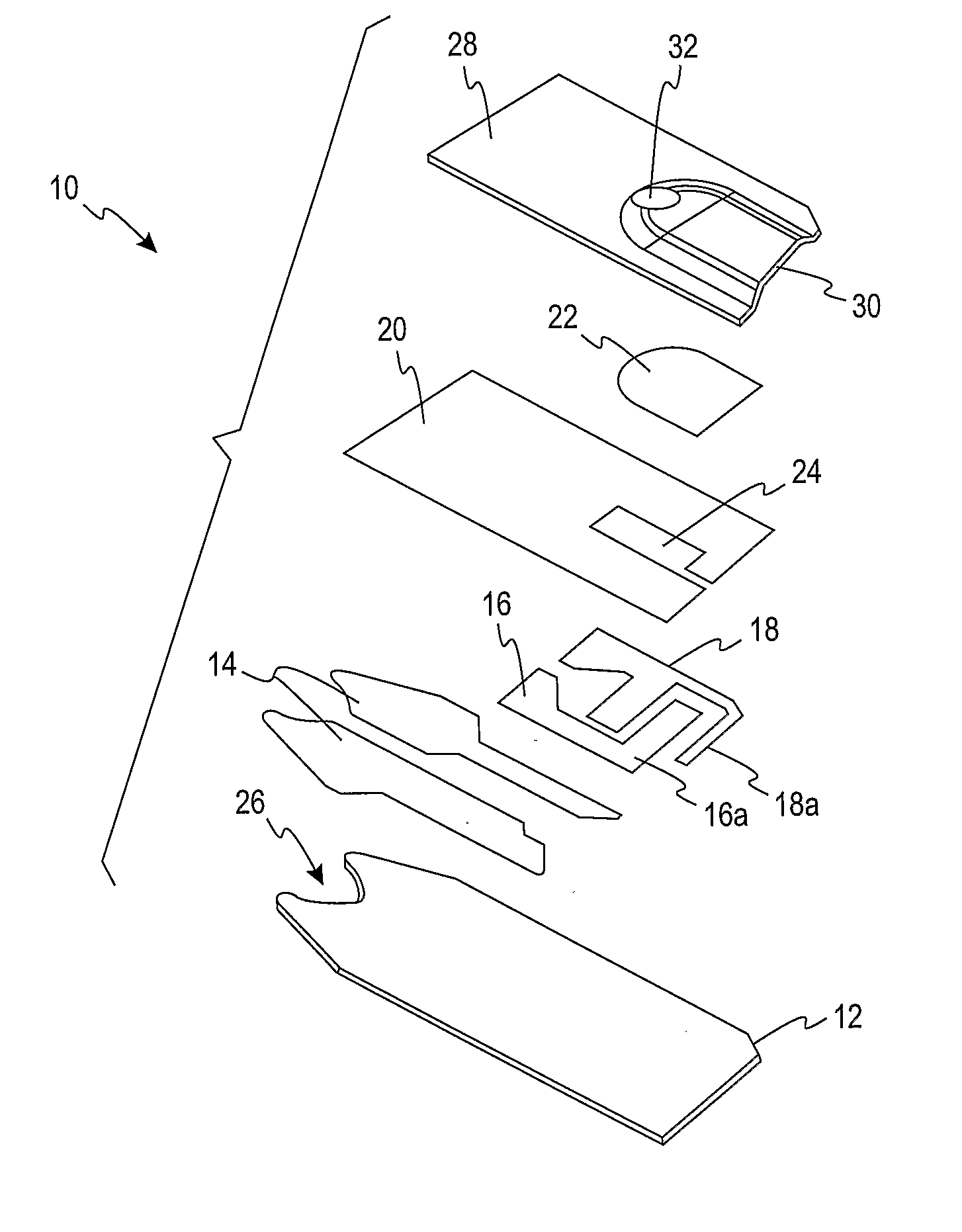
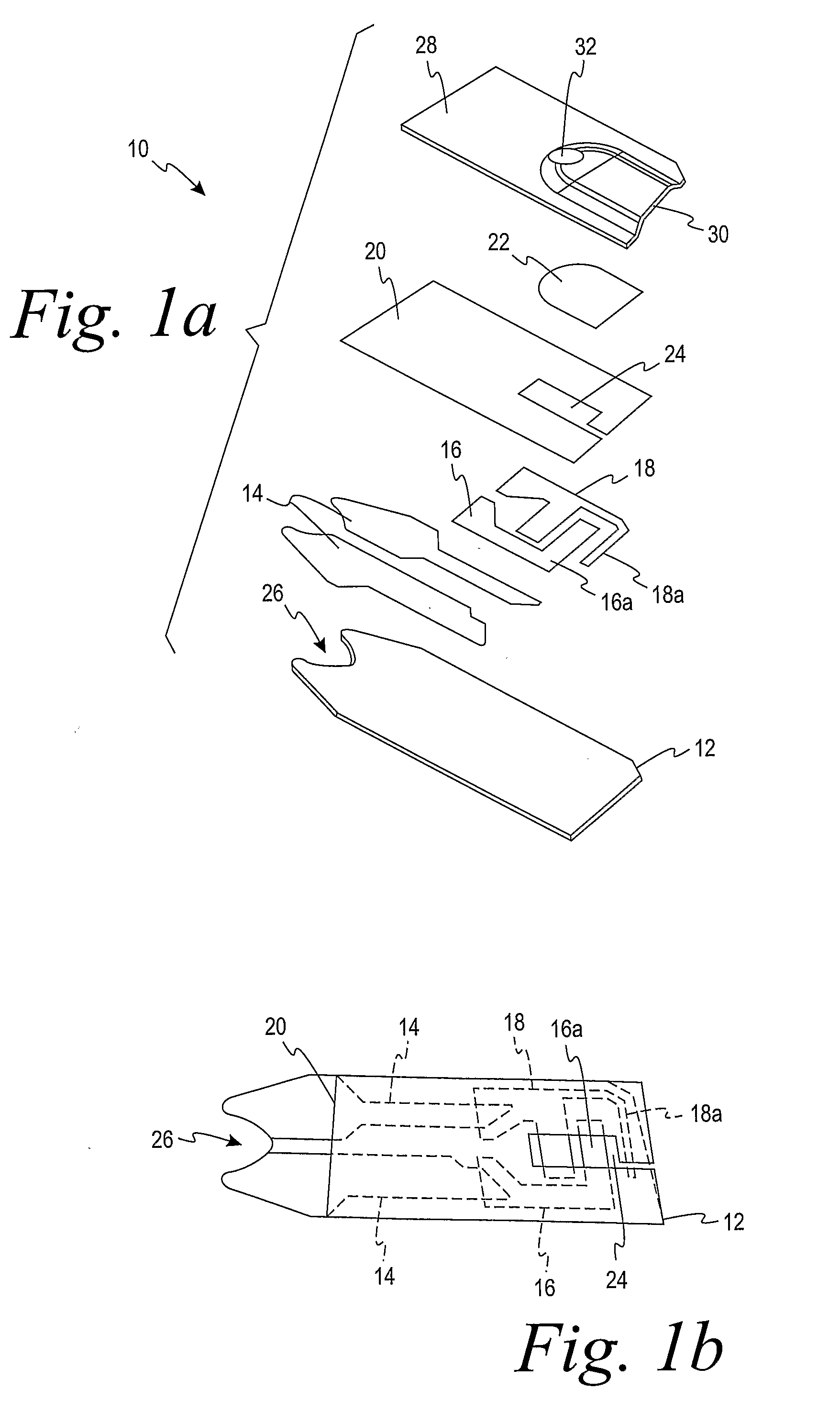
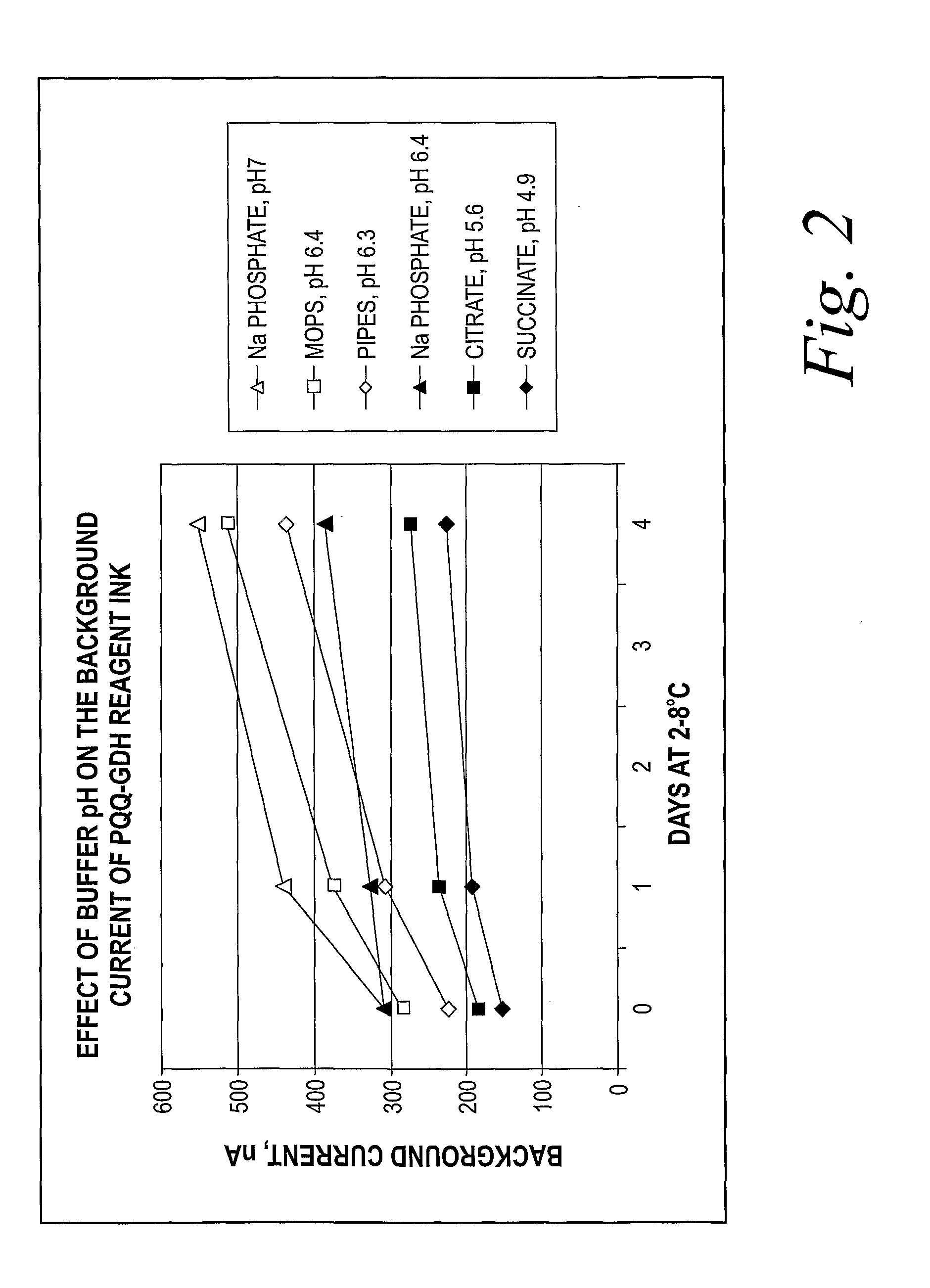
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Amperometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amperometry in chemistry is detection of ions in a solution based on electric current or changes in electric current. Amperometry is used in electrophysiology to study vesicle release events using a carbon fiber electrode. Unlike patch clamp techniques, the electrode used for amperometry is not inserted into or attached to the cell, but brought in close proximity of the cell. The measurements from the electrode originate from an oxidizing reaction of a vesicle cargo released into the medium. Another technique used to measure vesicle release is capacitive measurements.
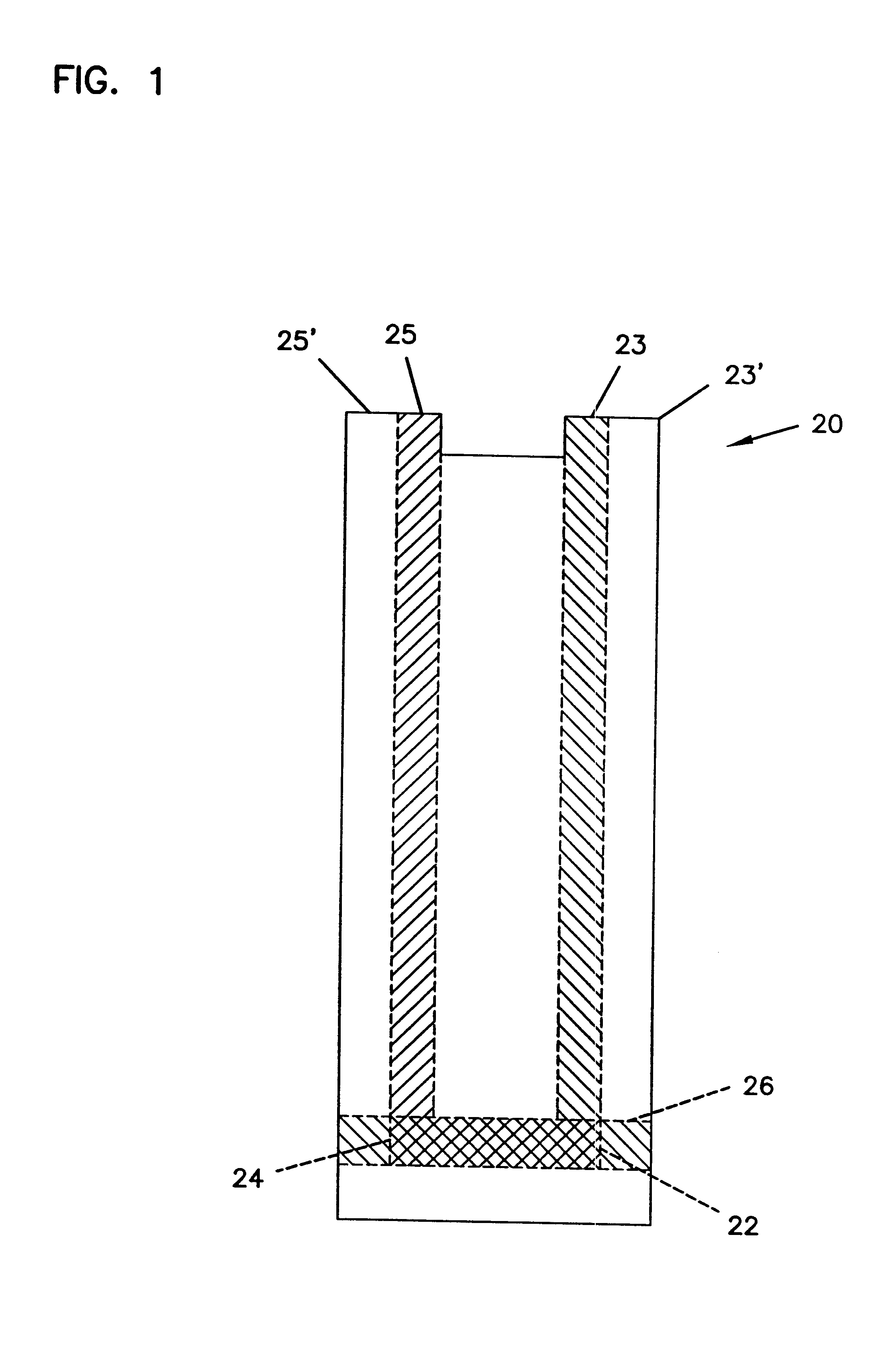
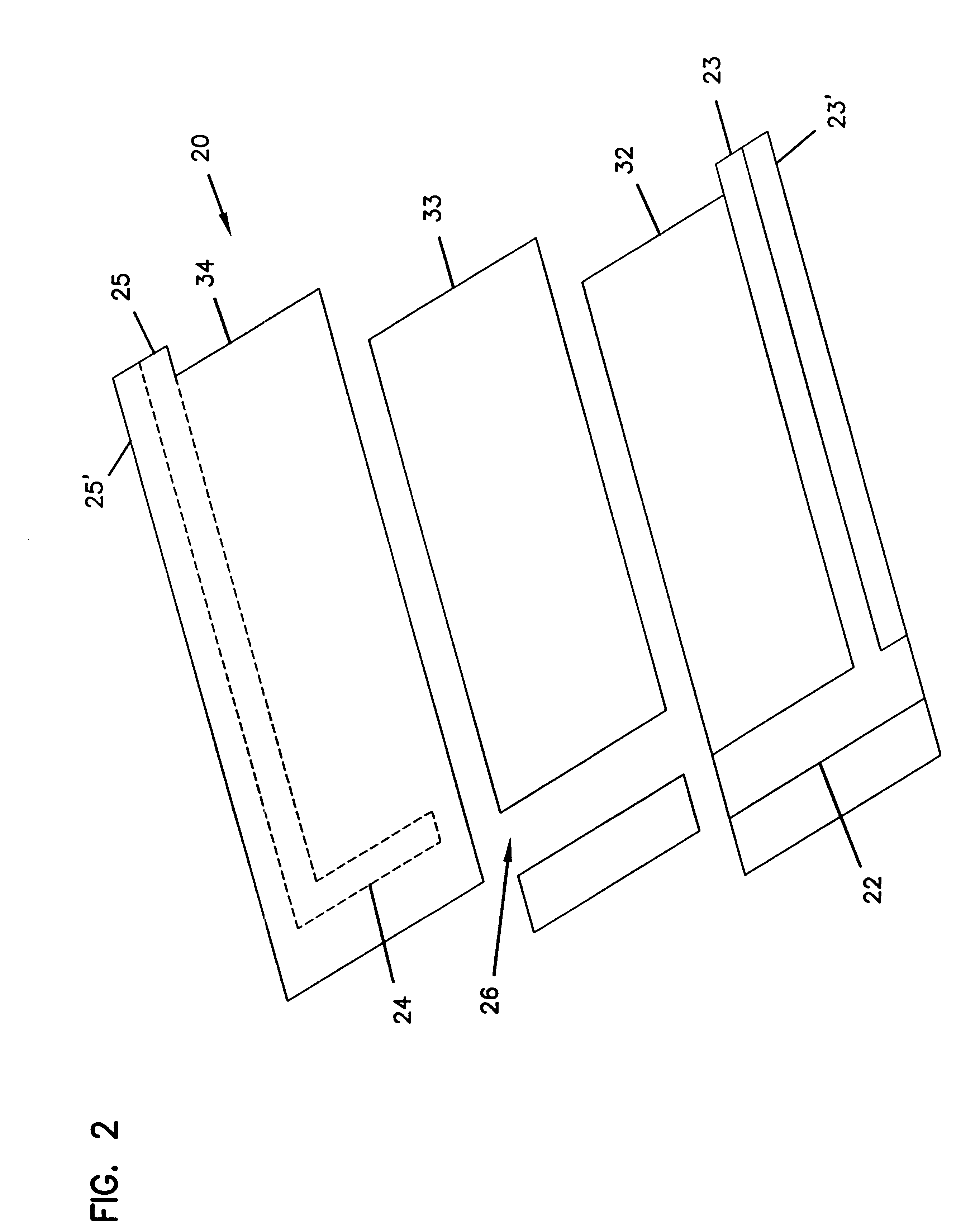
Analyte sensor with insertion monitor, and methods
InactiveUS20060091006A1Efficient and reliable methodEfficient methodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteGlucose polymers
A sensor, and methods of making, for determining the concentration of an analyte, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. The sensor includes a working electrode and a counter electrode, and can include an insertion monitoring trace to determine correct positioning of the sensor in a connector.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Analyte sensor with insertion monitor, and methods
InactiveUS20060191787A1Efficient methodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteD-Glucose
A sensor, and methods of making, for determining the concentration of an analyte, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. The sensor includes a working electrode and a counter electrode, and can include an insertion monitoring trace to determine correct positioning of the sensor in a connector.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor
InactiveUS20060169599A1Lower the volumePrecise processImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysisElectron transfer
A sensor utilizing a non-leachable or diffusible redox mediator is described. The sensor includes a sample chamber to hold a sample in electrolytic contact with a working electrode, and in at least some instances, the sensor also contains a non-leachable or a diffusible second electron transfer agent. The sensor and / or the methods used produce a sensor signal in response to the analyte that can be distinguished from a background signal caused by the mediator. The invention can be used to determine the concentration of a biomolecule, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. An enzyme capable of catalyzing the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the biomolecule is typically provided as a second electron transfer agent.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Small volume in vitro analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050278945A1Lower the volumeAccurate and efficient measurementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysisElectron transfer
A sensor utilizing a non-leachable or diffusible redox mediator is described. The sensor includes a sample chamber to hold a sample in electrolytic contact with a working electrode, and in at least some instances, the sensor also contains a non-leachable or a diffusible second electron transfer agent. The sensor and / or the methods used produce a sensor signal in response to the analyte that can be distinguished from a background signal caused by the mediator. The invention can be used to determine the concentration of a biomolecule, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. An enzyme capable of catalyzing the electrooxidation or electroreduction of the biomolecule is typically provided as a second electron transfer agent.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
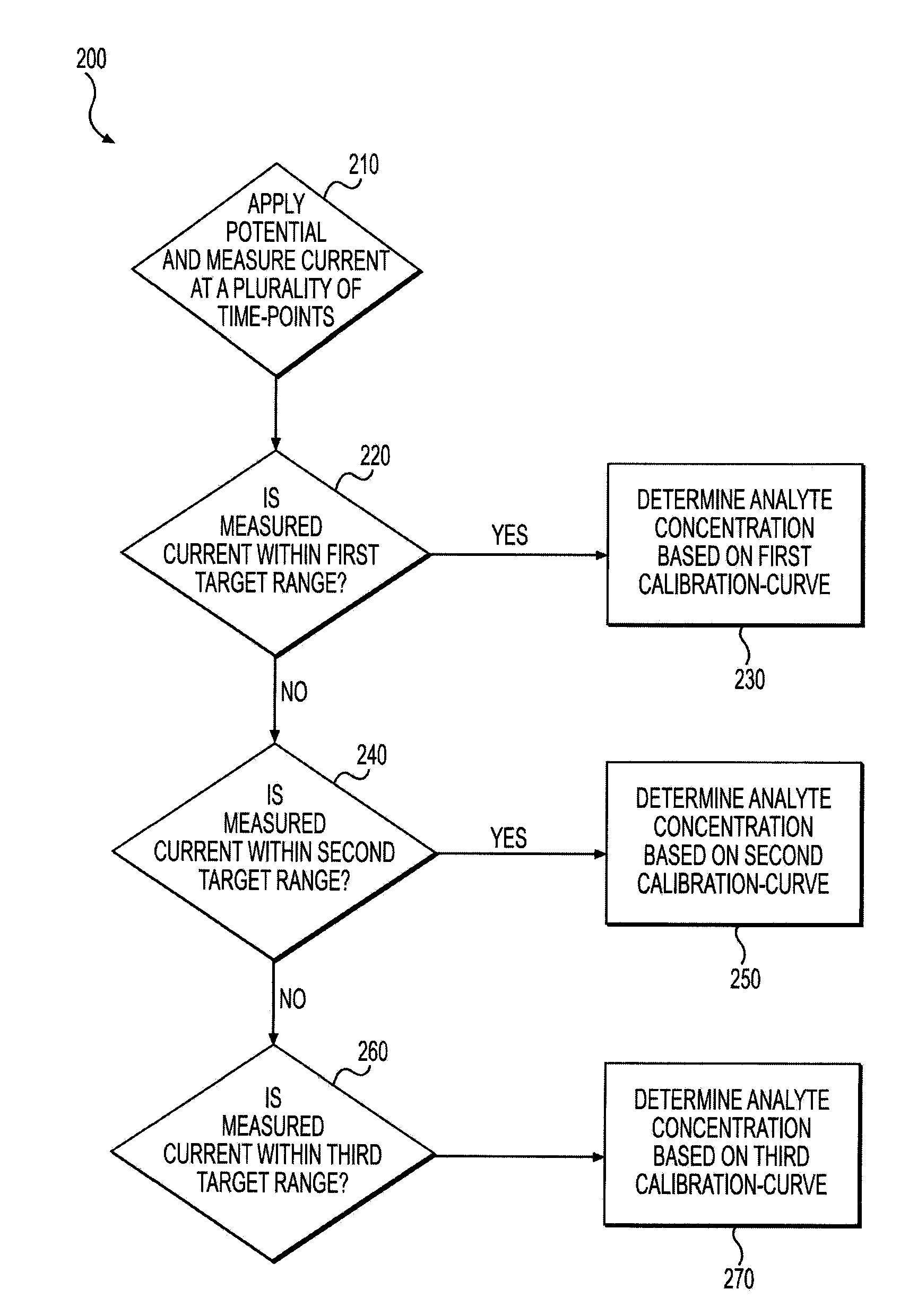
System and Methods for Determination of Analyte Concentration Using Time Resolved Amperometry
ActiveUS20090194432A1Improved determinationEasy to monitorImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteCurrent decay
A method for determining a concentration of an analyte is disclosed. The method includes applying a potential excitation to a fluid sample containing an analyte and determining if a current decay curve associated with the fluid sample has entered an analyte depletion stage. The method also includes measuring a plurality of current values associated with the fluid sample during the analyte depletion stage and calculating an analyte concentration based on at least one of the plurality of current values.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Small Volume in Vitro Analyte Sensor and Methods
InactiveUS20020157948A2Efficient methodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectric chargeEnvironmental geology
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A small volume sensor, and methods of making, for determining the concentration of an analyte, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. The sensor includes a working electrode and a counter electrode, and can include an insertion monitoring trace to determine correct positioning of the sensor in a connector. In one embodiment, the sensor determines the concentration of the analyte by discharging an amount of charge into the sample, determining the time needed to discharge the charge, and determining the current used to electrolyze a portion of the analyte using the amount of charge and the amount of time.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
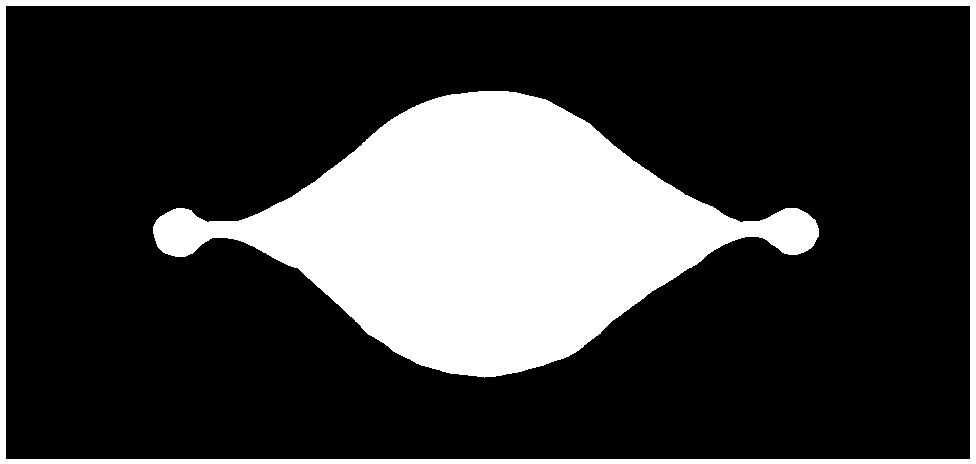
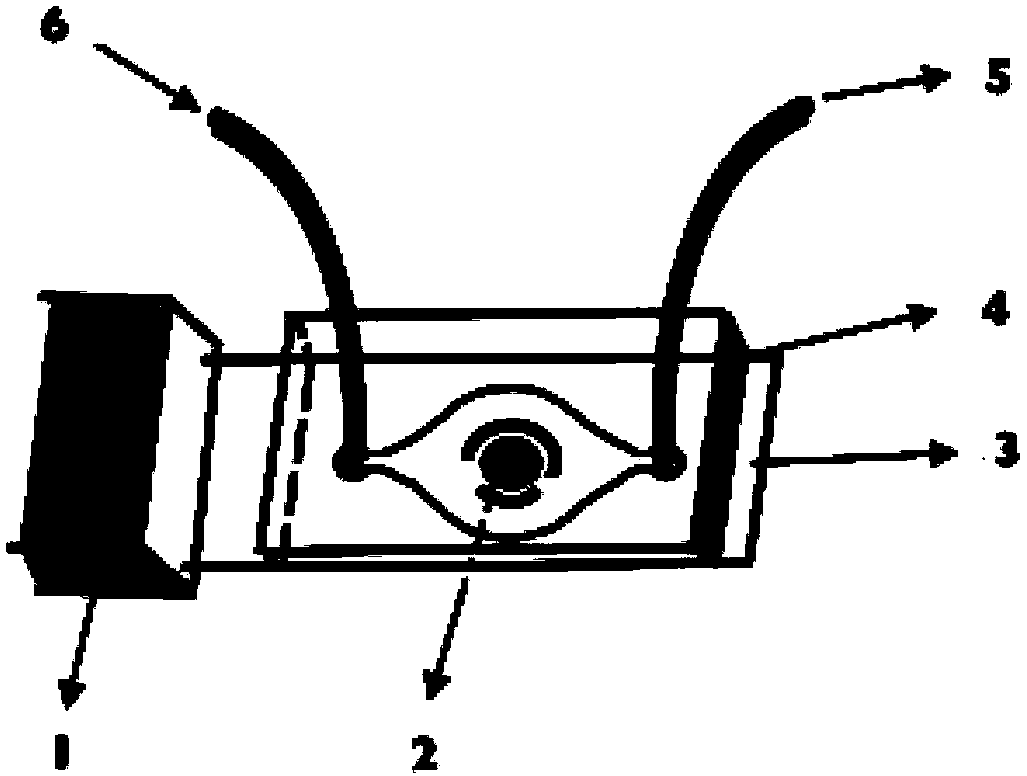
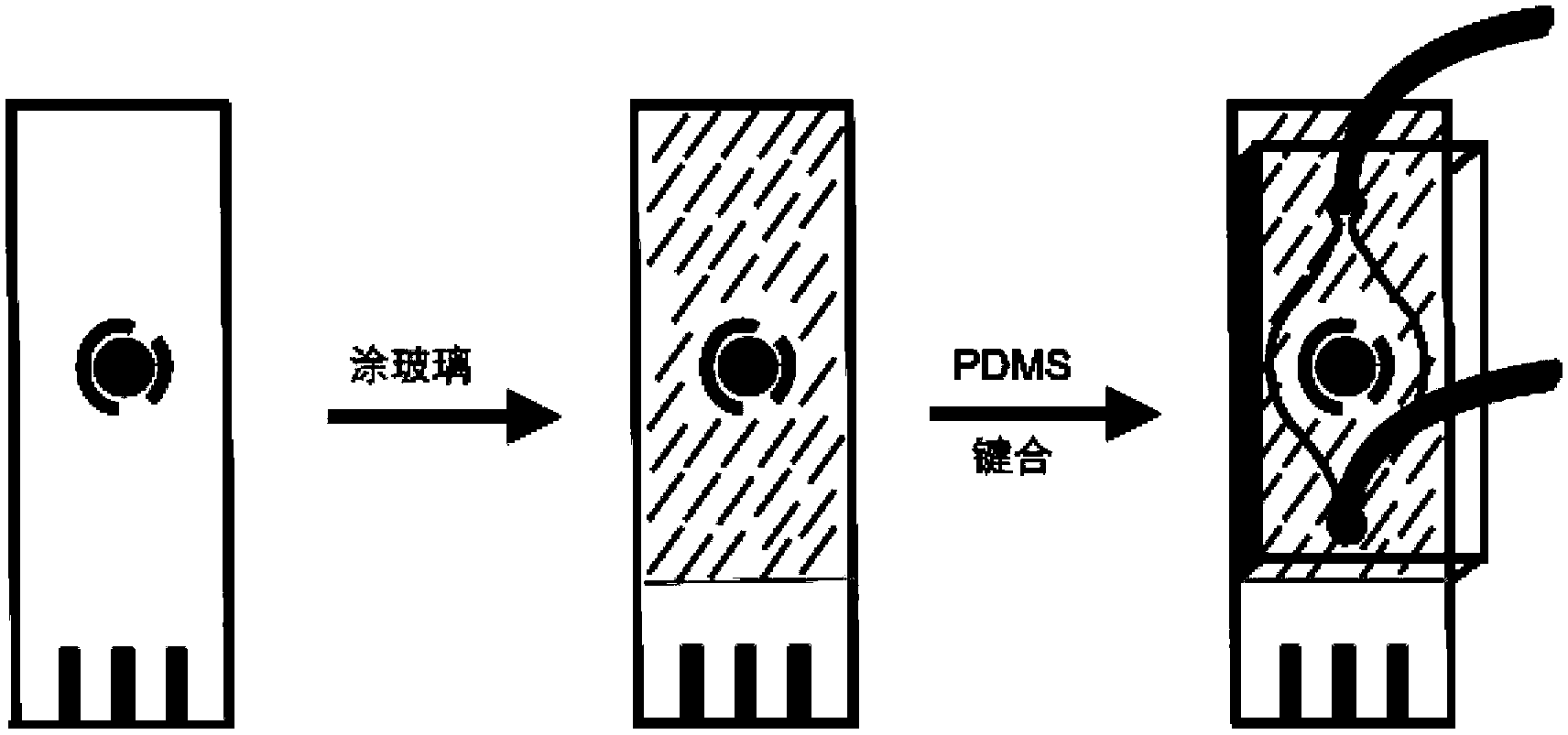
Preparation method and application of electrochemical micro-fluidic sensing chip
ActiveCN103182334AEasy to manufactureReduce weightMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresElectrochemical detectorStandardization
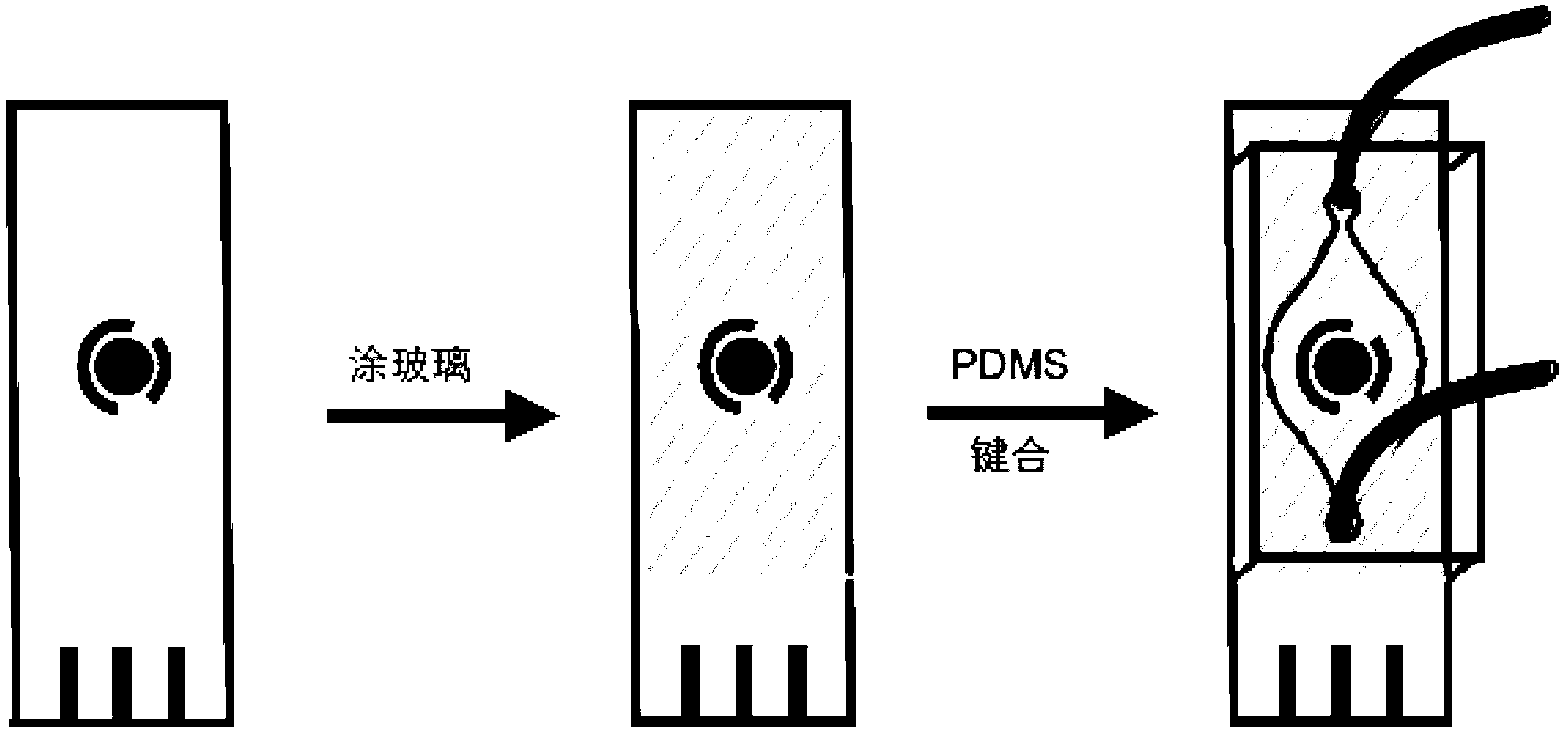
The invention provides a preparation method and the application of an electrochemical micro-fluidic sensing chip. The preparation method comprises the following steps: directly coating an improved glass solution on a commercial standard printed electrode; and performing vacuum plasma treatment on a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) chip with pre-designed pipelines and the printed electrode coated with the glass solution together, and directly bonding the PDMS chip on the commercial standard printed electrode to form a novel electrochemical microfluidic sensing platform. A sensor provided by the invention can perform ultrasensitive detection on various sample analytes in a biological fluid sample, taking the detection of a prostate cancer marker PSA (Prostate-specific Antigen) in human serum as an example, a coulomb amperometry is used for detection, and a result shows that the detection sensitivity can reach 0.84 pg / mL which is improved by two magnitudes than the standardized clinical testing requirement of 0.1 ng / mL, so that the sensor has superhigh detection sensitivity and accuracy, which are higher than those of other electrochemical detection devices, is convenient in operation, and can integrates sample processing, separation and the like on one micro electrochemical microfluidic sensing chip.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
System and methods for determination of analyte concentration using time resolved amperometry
A method for determining a concentration of an analyte is disclosed. The method includes applying a potential excitation to a fluid sample containing an analyte and determining if a current decay curve associated with the fluid sample has entered an analyte depletion stage. The method also includes measuring a plurality of current values associated with the fluid sample during the analyte depletion stage and calculating an analyte concentration based on at least one of the plurality of current values.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
System and Methods for Determination of Analyte Concentration Using Time Resolved Amperometry
ActiveUS20090101523A1Improved determinationEasy to monitorImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalytePower flow
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Microfluidic chip electrophoretic-electrochemical detecting device with adjustable pH after separation and use thereof
InactiveCN102788831AChange pHDoes not affect electrophoretic separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresElectrode placementAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a microfluidic chip electrophoretic-electrochemical detecting device with adjustable pH after separation and use of the device in aminoglycoside antibiotics analysis. The analysis device comprises a double-T shaped sampling channel, a separating channel, two auxiliary channels, a W-shaped channel and an electrode placement channel. Through adding the two auxiliary channels and the W-shaped channel at the tail end of the separating channel in a microfluidic chip, an alkaline solution is added through the auxiliary channels after being electrophoretically separated, and the solution from the separating channel and the auxiliary channels is mixed evenly through the W-shaped channel, a pH value of the solution in a working electrode determining region is improved, so that the solution meets a strong alkaline condition needed by the detection of carbohydrates, simultaneously, electrophoretic separation under an acidic separation buffer solution is not influenced. By the device disclosed by the invention, a transition metal nano material is decorated on the surface of the electrode by using an electrodeposition method and by means of the relatively large specific surface area and the special catalytic property of the metal nano material, so that the working electrode with high performance is obtained, and aminoglycoside antibiotics are determined through the amperometry.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS +1
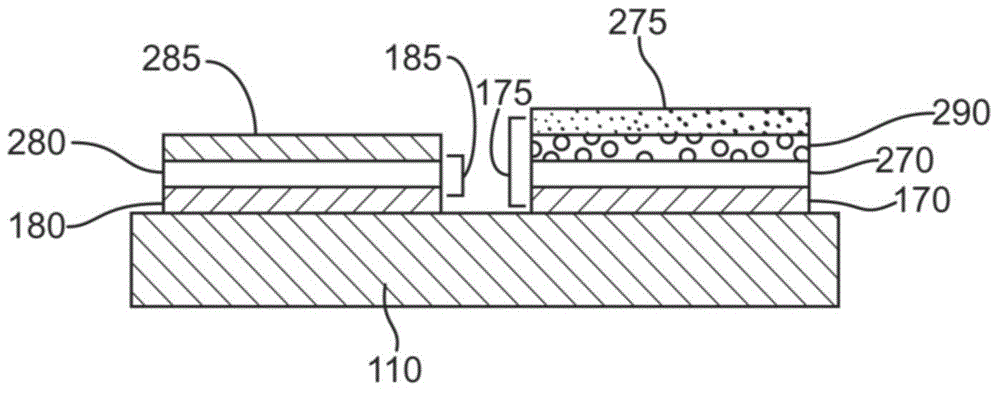
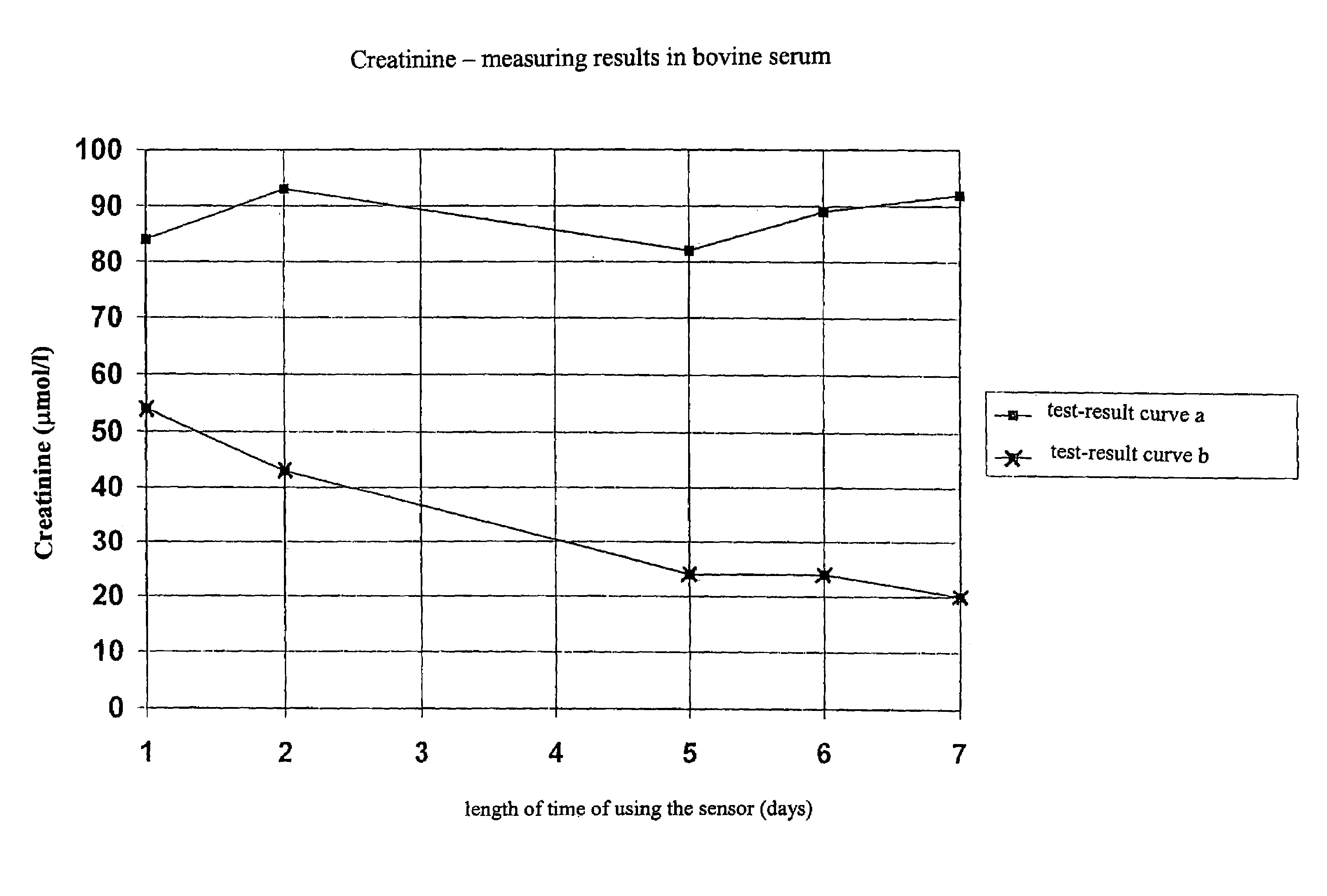
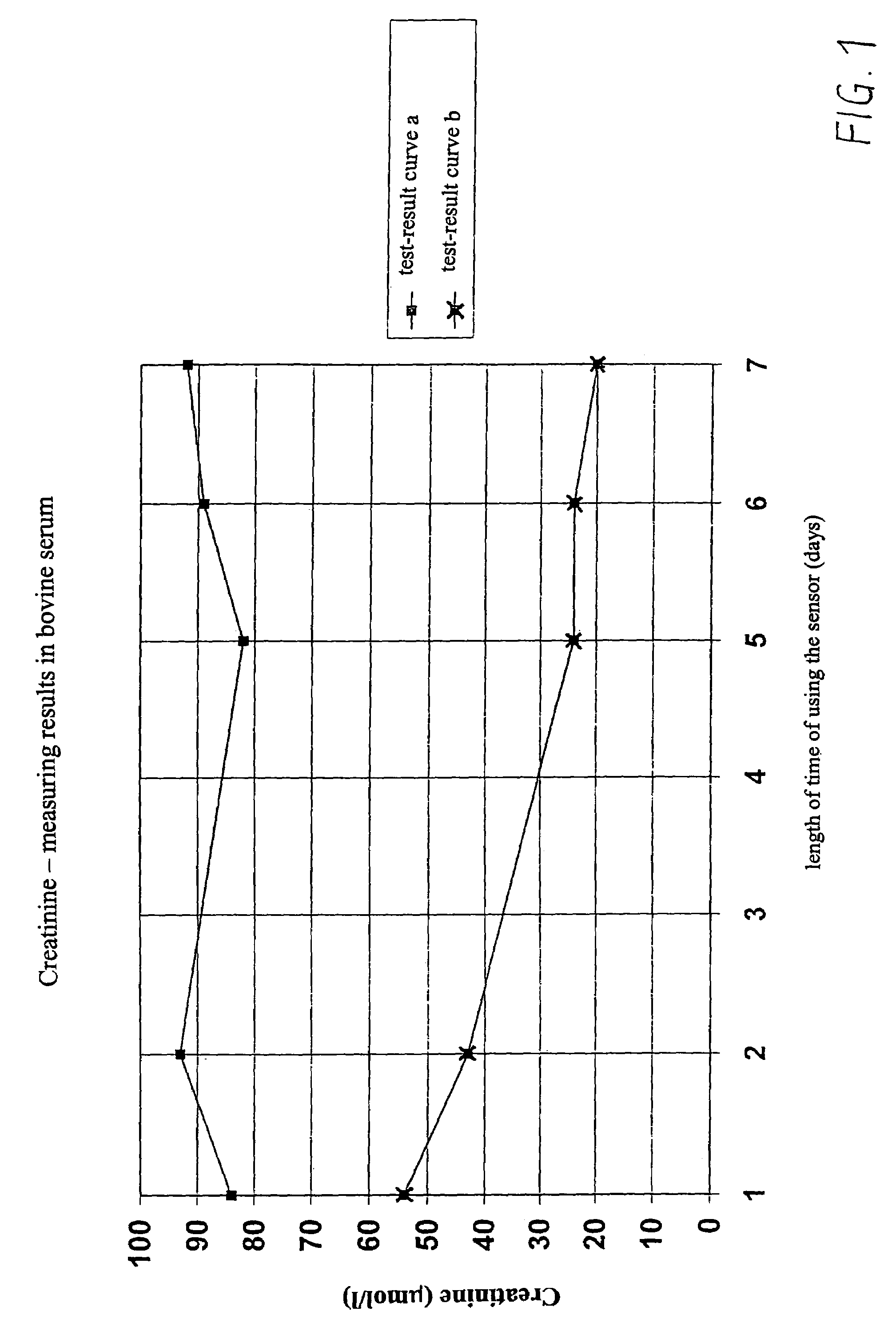
Creatinine Sensor Calibration
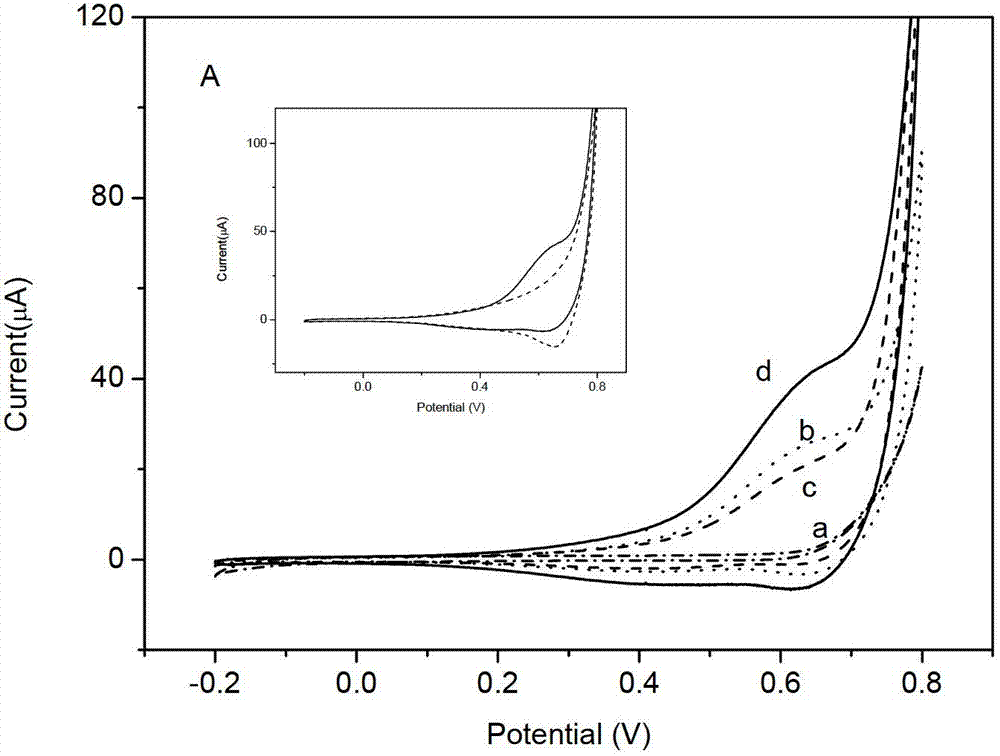
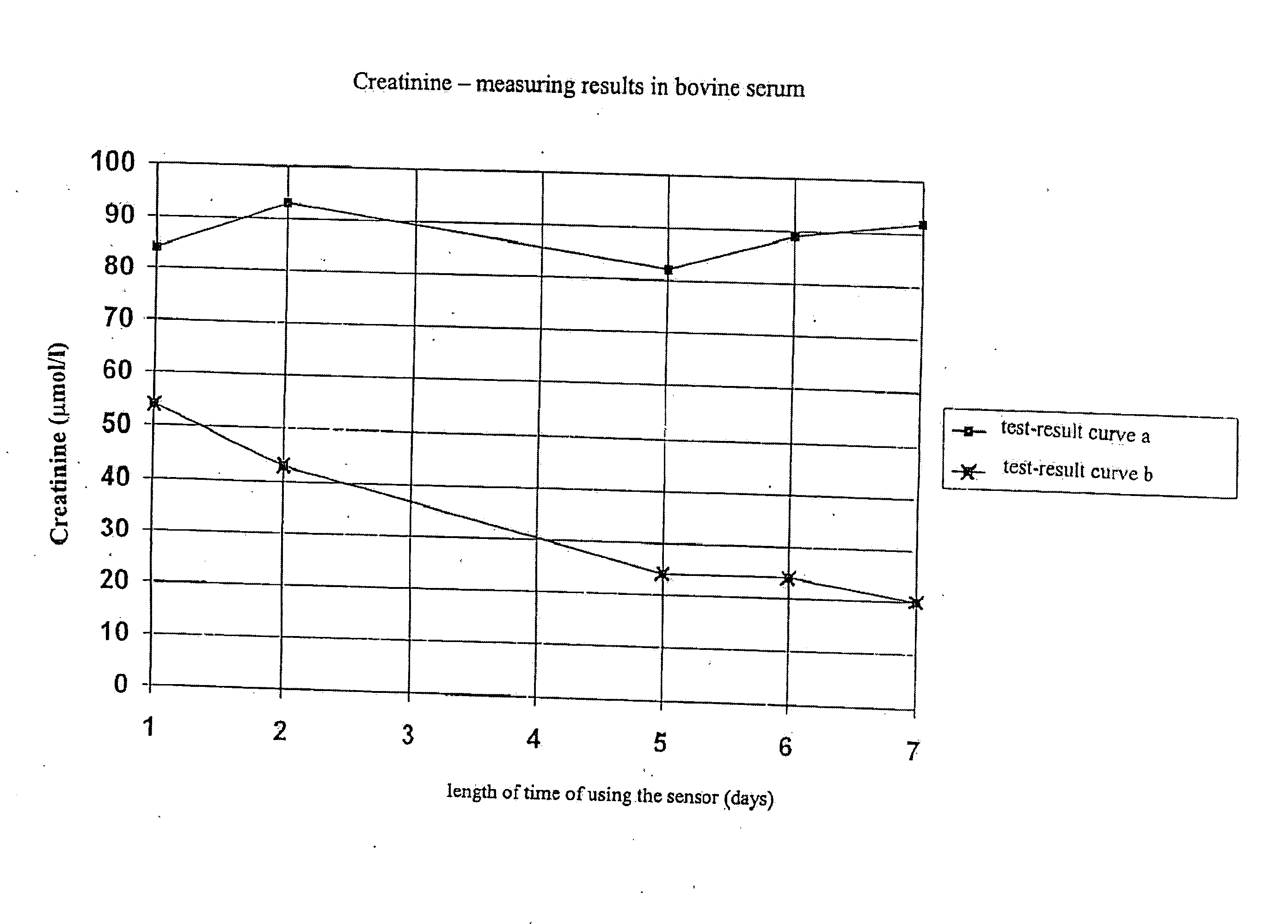
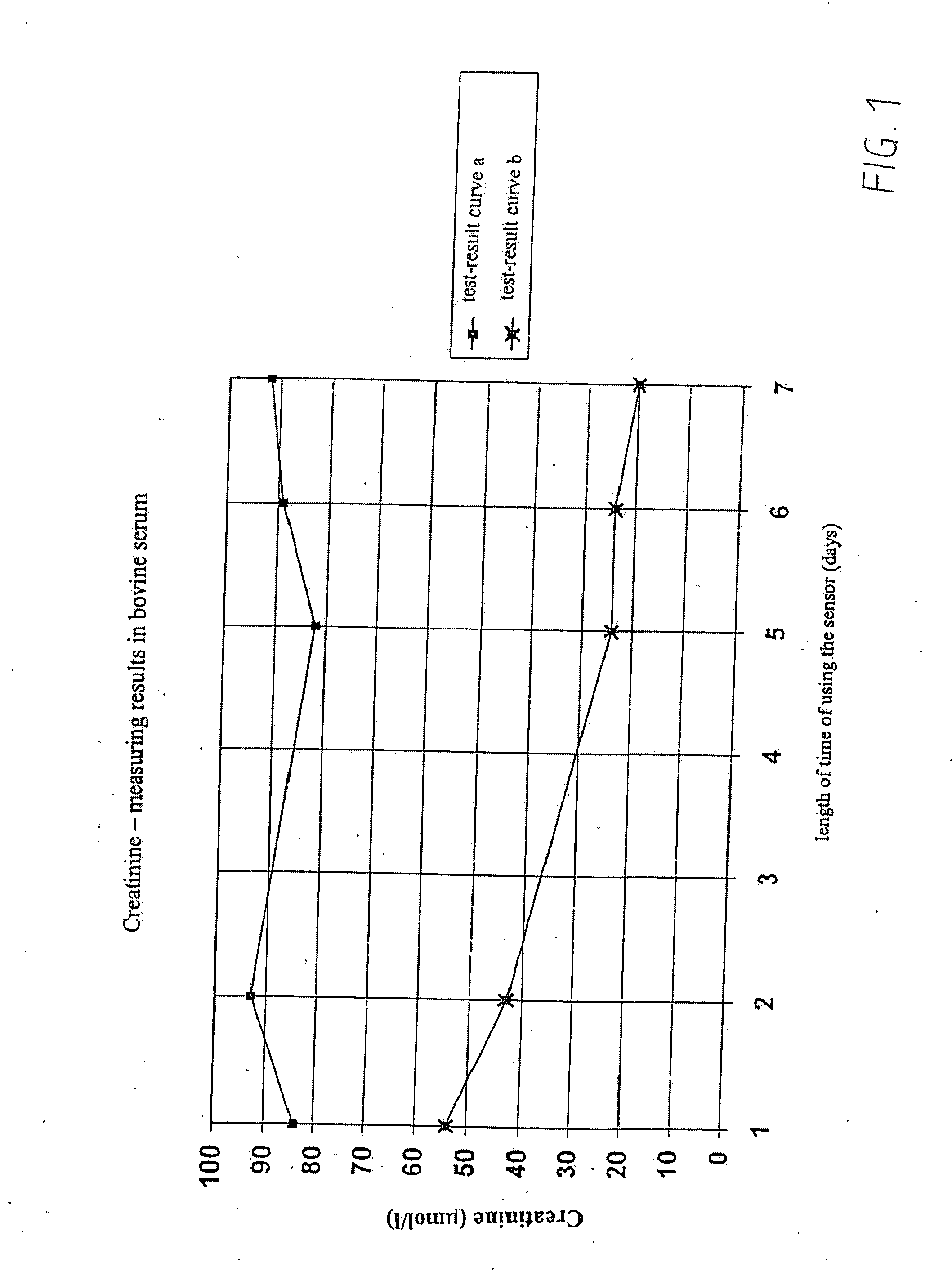
InactiveUS20080173064A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementCreatinine riseAmperometry
In a method for calibrating a biosensor for the amperometric determination of creatinine in biological liquids, consisting of one electrode system each for measuring the concentrations of creatinine and creatine, with at least two calibration solutions being used, the electrode system for measuring the creatinine concentration is calibrated with a creatinine solution which, prior to the calibration measurement, was mixed in the form of an acidic solution with an alkaline buffer solution, and the electrode system for measuring the creatine concentration is calibrated with a solution in which creatinine and creatine are at a thermodynamic equilibrium.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Apparatus and method for measuring concentration of whole blood samples
ActiveUS20160077037A1Reduce measurement errorEffectively and economically removing and minimizing hindranceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorMeasurement device
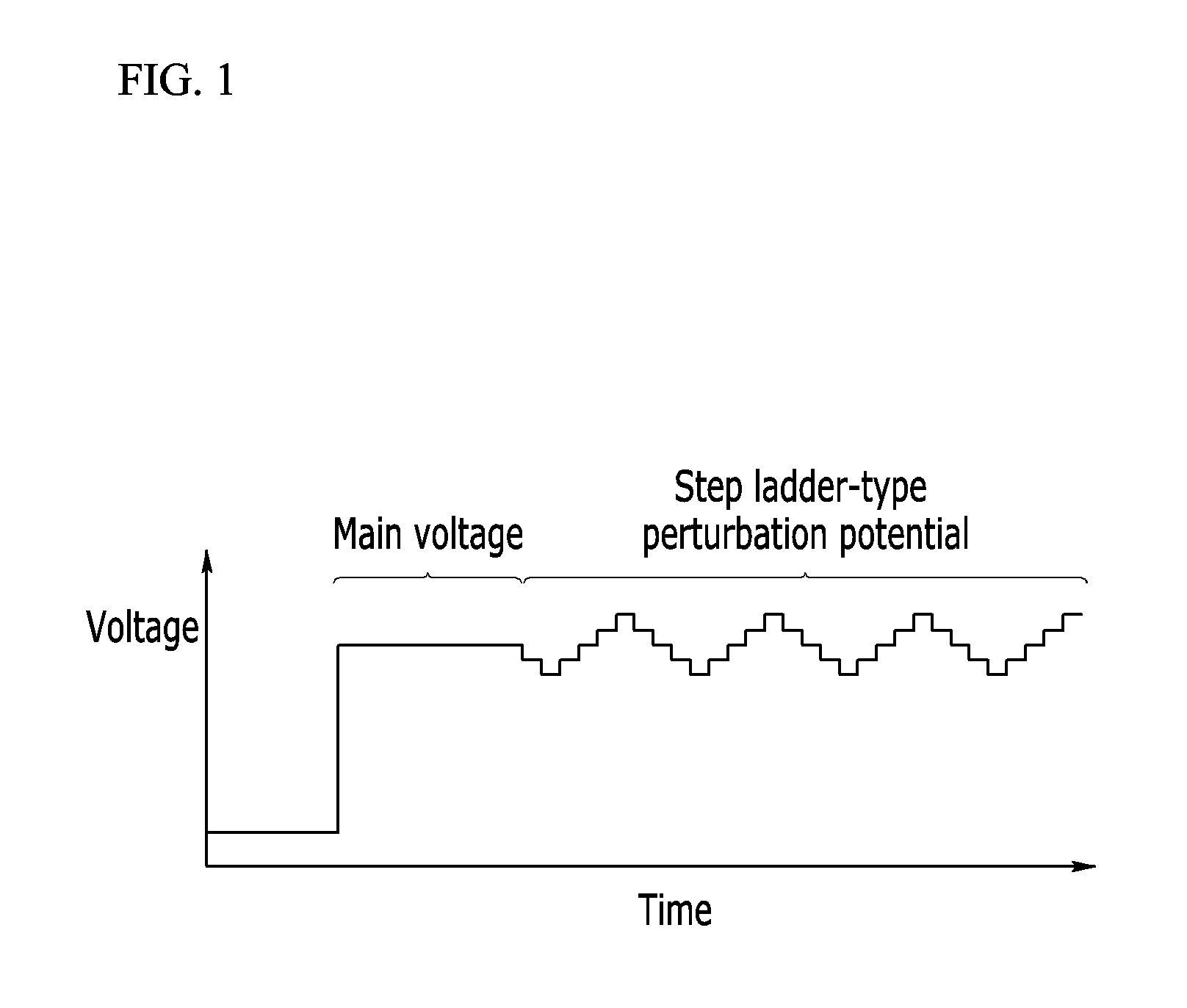
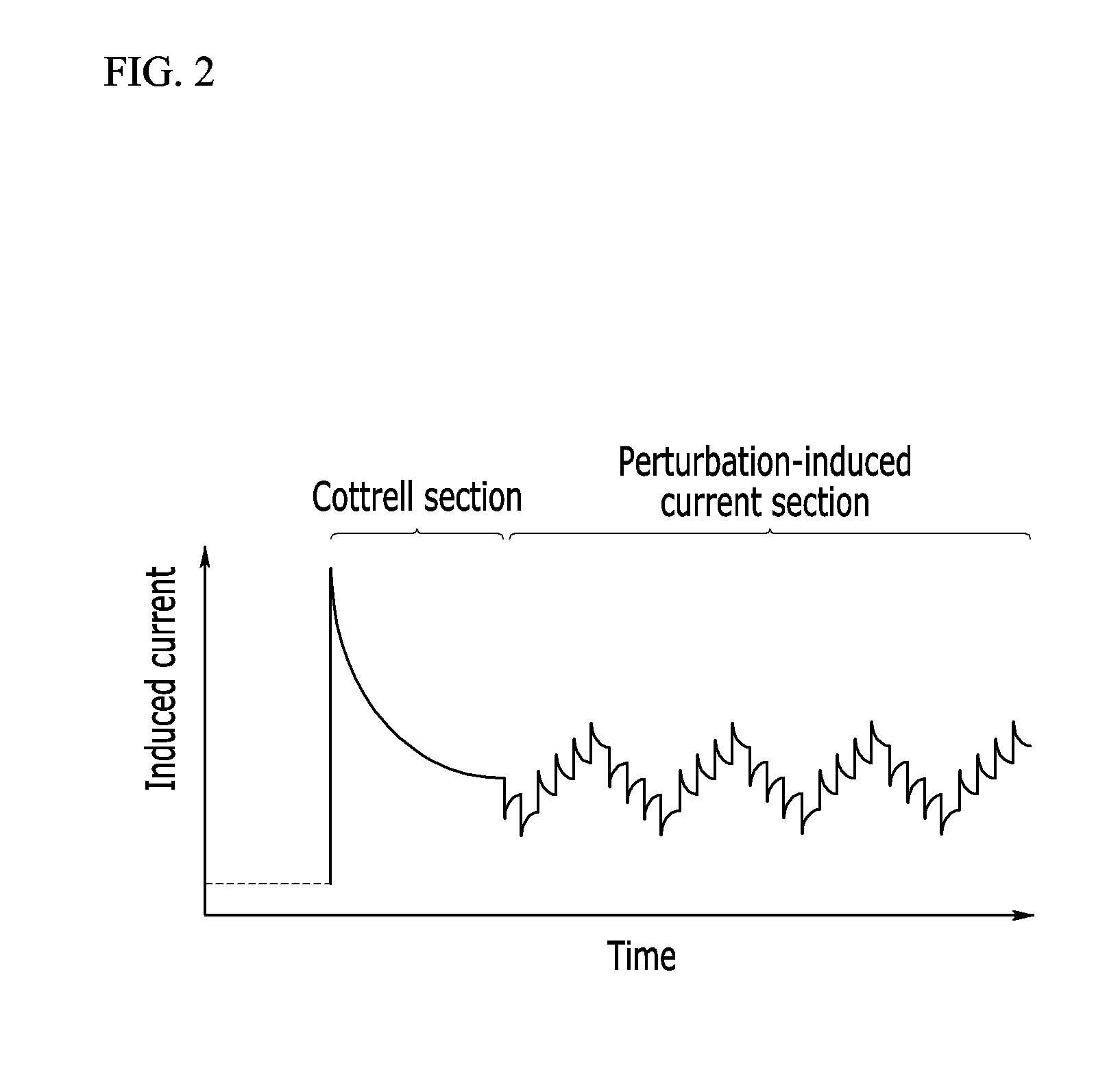
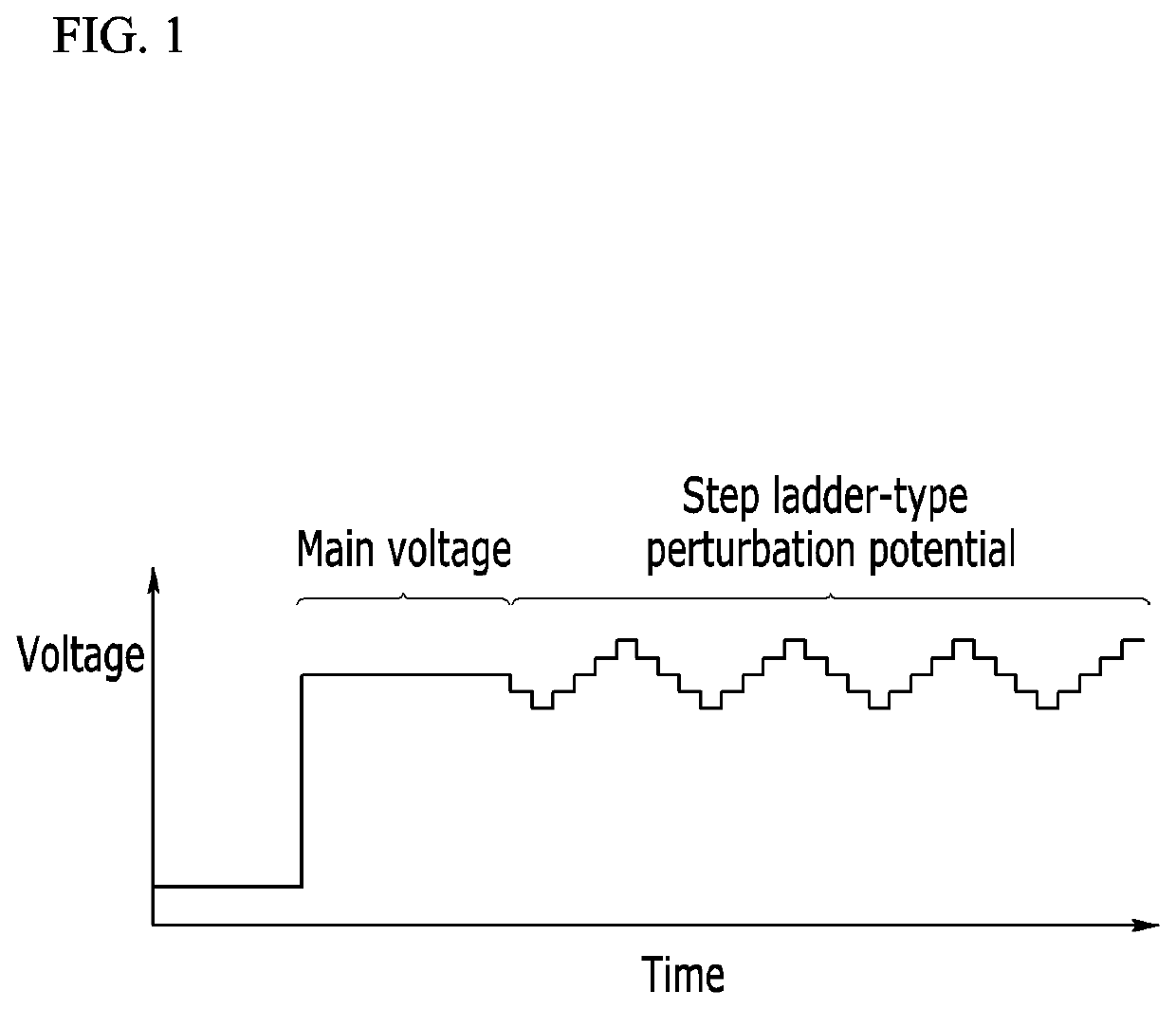
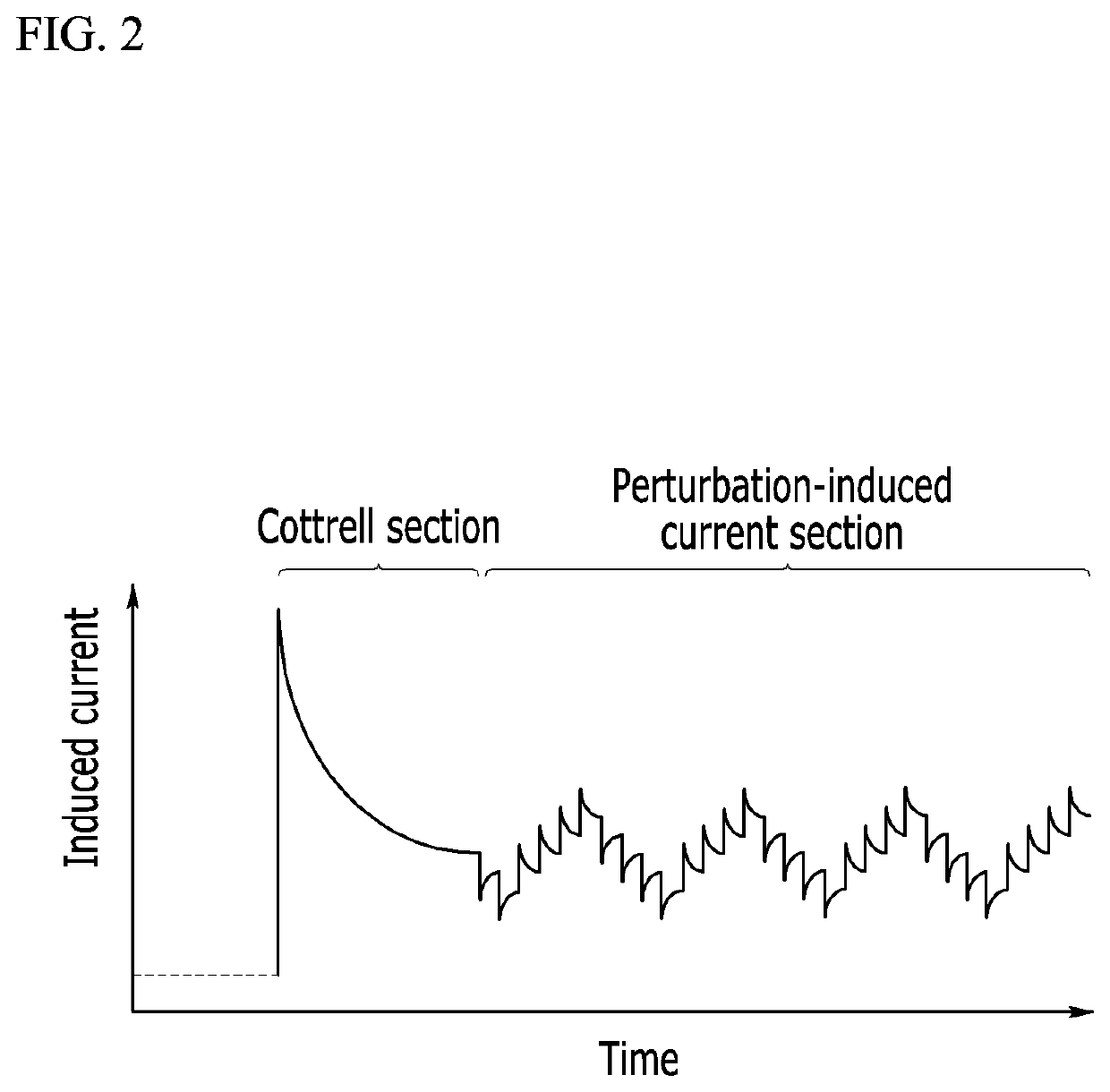
A method for measuring a concentration of an analyte in a bio-sample using an electrochemical bio-sensor according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is characterized by a step of obtaining predetermined features from induced currents obtained by applying a DC voltage according to chronoamperometry in which, after a whole blood sample is injected to the electrochemical bio-sensor, a concentration of an analyte is obtained from an induced current obtained by applying a DC voltage for a certain time and from all induced currents obtained by further applying several step-ladder perturbation potentials for a short time subsequent to the DC voltage for the certain time, and is also characterized by minimization of a measurement error caused by a hindering material by forming a calibration equation by combining the at least one feature in a function and optimizing various conditions of the bio-sample through Deleted Texts multivariable analysis.With this configuration, a perturbation potential application method added to a conventional measurement method can maintain a bio-sensor and a measuring apparatus already used, a line used in the measuring apparatus, and calibration of amperometry as they are, improve accuracy in measurement by effectively minimizing a matrix interference effect of a background material in a bio-sample, particularly an inaccuracy caused by a change in hematocrit, and also remarkably improve accuracy in measurement by simply upgrading a measurement program of a conventional measuring apparatus.
Owner:I SENS INC
Method of the electrochemical detection of nucleic acid oligomer hybrids
InactiveUS7056664B1Improve responseEconomical and simple methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCyclic voltametryDouble strand
The invention relates to a method for the electrochemical detection of sequence-specific nucleic acid oligomer hybridization events. To this end single DNA / RNA / PNA oligomer strands which at one end are covalently joined to a support surface and at the other, free end, covalently linked to a redox pair, are used as hybridization matrix (probe). As a result of treatment with the oligonucleotide solution (target) to be examined, the electric communication between the conductive support surface and the redox pair bridged by the single-strand oligonucleotide, which communication initially is either absent or very weak, is modified. In case of hybridization, the electric communication between the support surface and the redox pair, which is now bridged by a hybridized double-strand oligonucleotide, is increased. This permits the detection of a hybridization event by electrochemical methods such as cyclic voltametry, amperometry or conductivity measurement.
Owner:FRIZ BIOCHEM FUR BIOANALYTIK MBH
System and Methods for Determination of Analyte Concentration Using Time Resolved Amperometry
InactiveUS20090076738A1Accurately determineTesting/calibration apparatusMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteTime segment
This invention is a method for determining a concentration of an analyte. The steps include applying a potential excitation to a fluid sample containing an analyte, and measuring one or more currents associated with one or more time-segments. The method can also include calculating a final analyte concentration based on a first and second set of analyte concentrations, wherein each set of analyte concentration values is based on a first and second set of calibration data associated with first and second time-segments.
Owner:NIPRO DIAGNOSTICS INC
Gated amperometry
ActiveCN101297196AMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalytePulse sequence
A sensor system, device, and methods for determining the concentration of an analyte in a sample is described. Gated amperometric pulse sequences including multiple duty cycles of sequential excitations and relaxations may provide a shorter analysis time and / or improve the accuracy and / or precision of the analysis. The disclosed gated amperometric pulse sequences may reduce analysis errors arising from the hematocrit effect, variance in cap-gap volumes, non-steady-state conditions, mediator background, under-fill, temperature changes in the sample, and a single set of calibration constants.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Composite material modified electrode used for measuring glucose concentration and application thereof
ActiveCN106124593AMeasurement stabilityEasy to measureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responsePlatinum
The invention discloses a composite material modified electrode used for measuring glucose concentration and application thereof. According to the invention, firstly a polyamino acid modified electrode is prepared by virtue of a cyclic voltammetry, then the cyclic voltammetry is adopted for depositing metal nanoparticles on the surface of the polyamino acid film modified electrode, and a polyamino acid / metal nanocomposite material modified electrode is prepared. The obtained modified electrode is taken as a working electrode, a silver / silver chloride electrode is taken as a reference electrode, a platinum cylinder electrode is taken as an auxiliary electrode, and an amperometry is applied in a three-electrode system for realizing linear electrochemical response of glucose in a certain concentration range. The modified electrode has the characteristics of sensitive response and good stability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Reagent Composition and Methods of Using and Forming the Same
ActiveUS20080199937A1Avoids premature loss of activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrochemical biosensorHydrophilic polymers
A reagent composition containing GDH-PQQ as an enzyme-co-factor and screen-printed on working and counter electrodes of electrochemical biosensors, maintains activity of the enzyme reagents by proper selection of components. A preferred composition includes hydrophilic polymers, amorphous untreated silica, buffers, surfactants, and a mediator For example, the biosensor is useful in the amperometric determination of glucose.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY +1
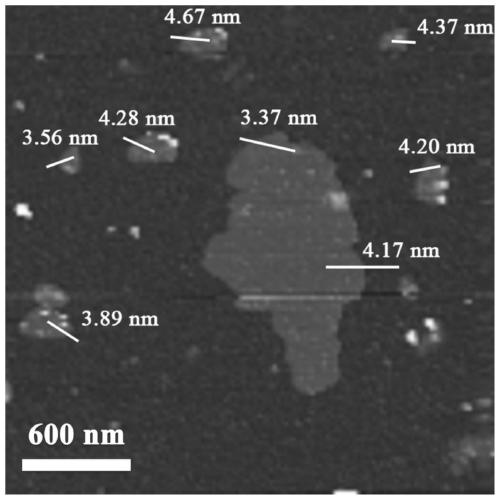
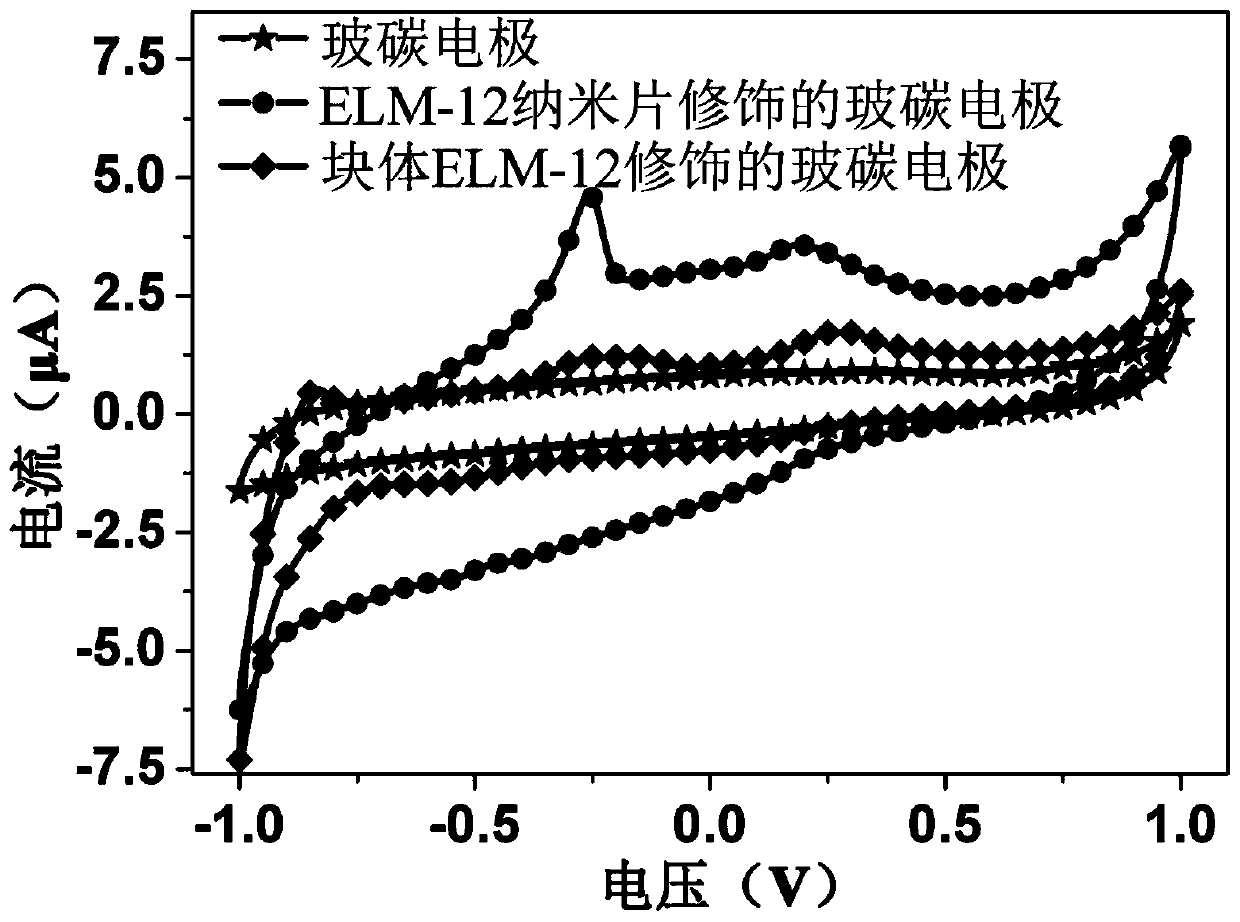
Preparation method and application for two-dimensional metal organic framework nanosheet
InactiveCN110387049AEase of industrial applicationCatalytic strongOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsNanotechnologyElectricityMetal-organic framework
The invention discloses a two-dimensional metal organic framework nanosheet and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a layered metal organic framework bulk material into a solvent, carrying out stripping under stirring, then carrying out standing to obtain a supernatant, and centrifuging the supernatant so as to obtain a precipitate, i.e., thetwo-dimensional metal organic framework nanosheet. The method provided by the invention can realize large-scale preparation of the two-dimensional metal organic framework nanosheet, and is convenientand practicable in operation. The two-dimensional metal organic framework nanosheet has a thickness of only 1 to 10 nm. The invention also discloses an application of the two-dimensional metal organicframework nanosheet in electrochemical detection of superoxide ions. Specifically, the two-dimensional metal organic framework nanosheet is made into a dispersion which is then subjected to drip-coating of an electrode, and then the superoxide ions are detected through a cyclic voltammetric method or / and an amperometric method. The two-dimensional metal organic framework provided by the inventionhas excellent electrocatalytic performance to the superoxide ions and is capable of converting the superoxide ions into water.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gated amperometry
ActiveCN103558284AMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringPower flowAnalyte
A sensor system, device, and methods for determining the concentration of an analyte in a sample is described. Gated amperometric pulse sequences including multiple duty cycles of sequential excitations and relaxations may provide a shorter analysis time and / or improve the accuracy and / or precision of the analysis. The disclosed gated amperometric pulse sequences may reduce analysis errors arising from the hematocrit effect, variance in cap-gap volumes, non-steady-state conditions, mediator background, under-fill, temperature changes in the sample, and a single set of calibration constants.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Creatinine sensor calibration
InactiveUS7371314B2Small amountWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementCreatinine riseAmperometry
In a method for calibrating a biosensor for the amperometric determination of creatinine in biological liquids, consisting of one electrode system each for measuring the concentrations of creatinine and creatine, with at least two calibration solutions being used, the electrode system for measuring the creatinine concentration is calibrated with a creatinine solution which, prior to the calibration measurement, was mixed in the form of an acidic solution with an alkaline buffer solution, and the electrode system for measuring the creatine concentration is calibrated with a solution in which creatinine and creatine are at a thermodynamic equilibrium.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Graphene/graphene oxide microarray electrode as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104655698ALow costSensitive assayMaterial electrochemical variablesCatalytic oxidationBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene / graphene oxide microarray and application of the graphene / graphene oxide microarray used as a chemical and cell-based sensor. A graphene / graphene oxide microarray electrode is prepared on an ITO glass substrate by combining a micro processing technology and an electrochemical method. By utilizing the electrochemical catalytic oxidation of the microelectrode prepared by the invention on hydrogen peroxide, the in vitro and intravital quantitative analysis and detection of hydrogen peroxide are realized by a timing amperometry. The preparation method is simple and feasible, the sensitivity is high, the response time is short, the biocompatibility is good, and the concentration of hydrogen peroxide can be quickly detected.
Owner:安徽中科大禹科技有限公司
Apparatus and method for measuring concentration of an analyte in whole blood samples
ActiveUS10690619B2Reduce measurement errorEffectively and economically removing and minimizing hindranceMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresChemical physicsAnalyte
A method for measuring a concentration of an analyte in a bio-sample using an electrochemical bio-sensor according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is characterized by a step of obtaining predetermined features from induced currents obtained by applying a DC voltage according to chronoamperometry in which, after a whole blood sample is injected to the electrochemical bio-sensor, a concentration of an analyte is obtained from an induced current obtained by applying a DC voltage for a certain time and from all induced currents obtained by further applying several step-ladder perturbation potentials for a short time subsequent to the DC voltage for the certain time, and is also characterized by minimization of a measurement error caused by a hindering material by forming a calibration equation by combining the at least one feature in a function and optimizing various conditions of the bio-sample through DeletedTextsmultivariable analysis. With this configuration, a perturbation potential application method added to a conventional measurement method can maintain a bio-sensor and a measuring apparatus already used, a line used in the measuring apparatus, and calibration of amperometry as they are, improve accuracy in measurement by effectively minimizing a matrix interference effect of a background material in a bio-sample, particularly an inaccuracy caused by a change in hematocrit, and also remarkably improve accuracy in measurement by simply upgrading a measurement program of a conventional measuring apparatus.
Owner:I SENS INC
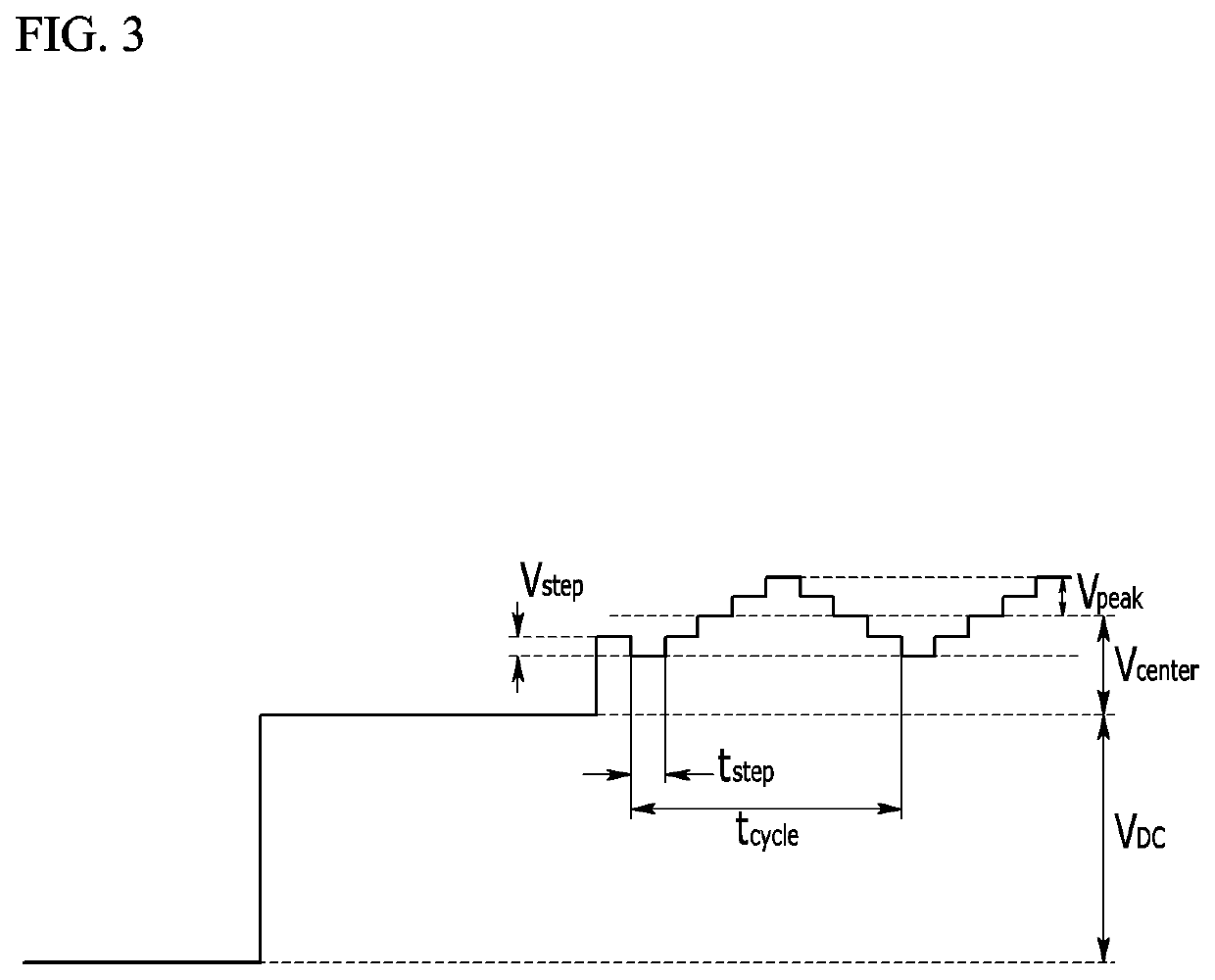
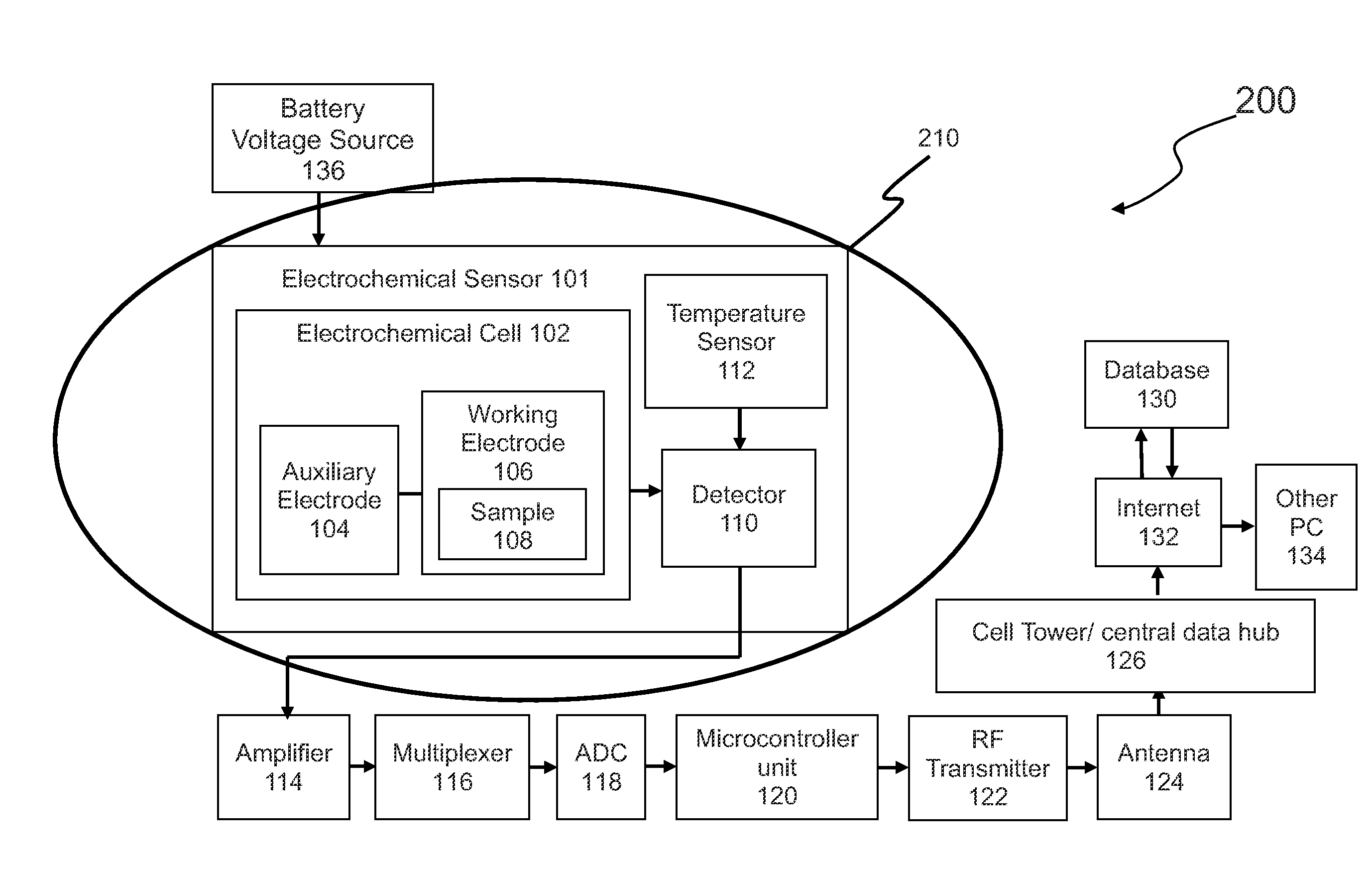
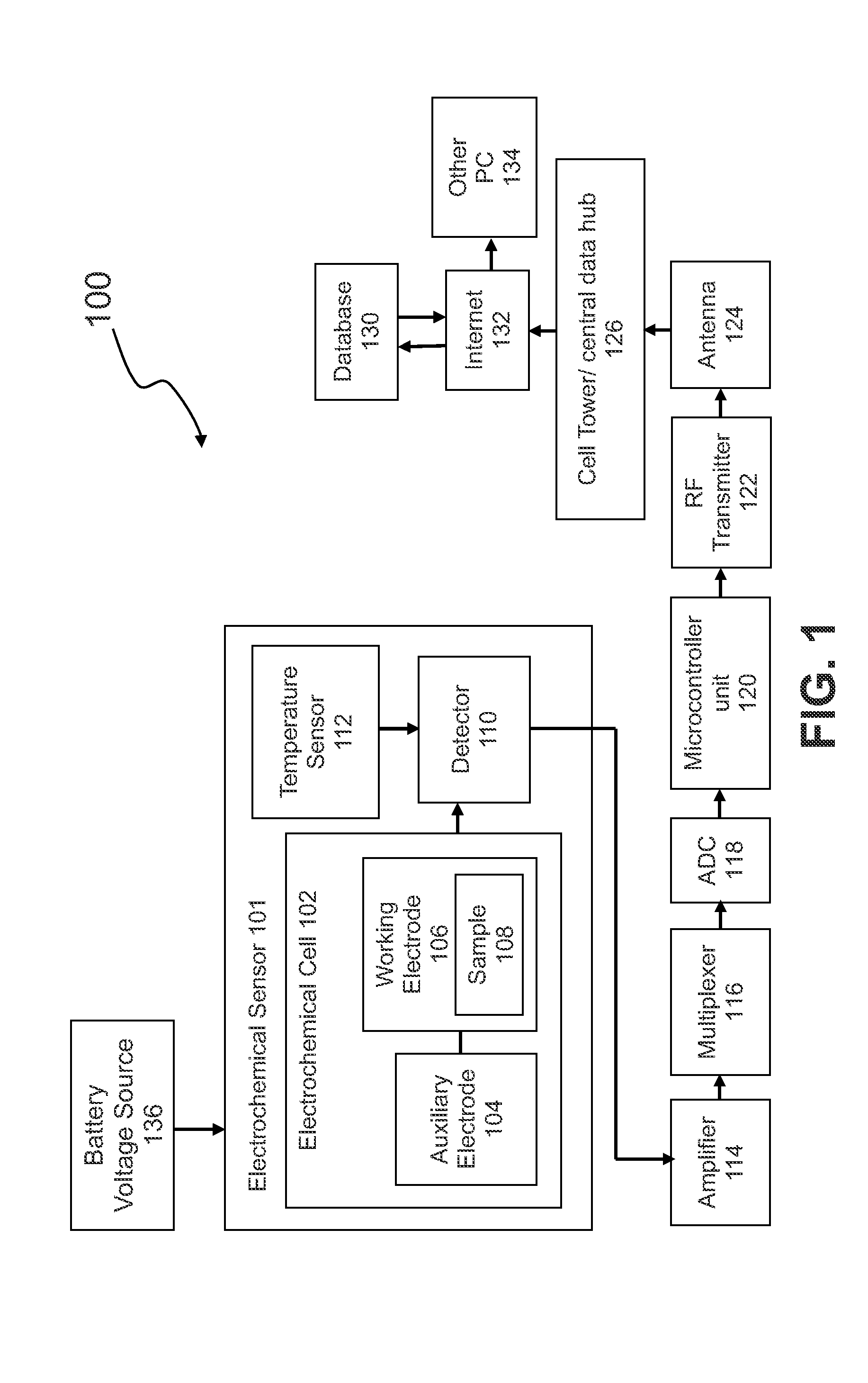
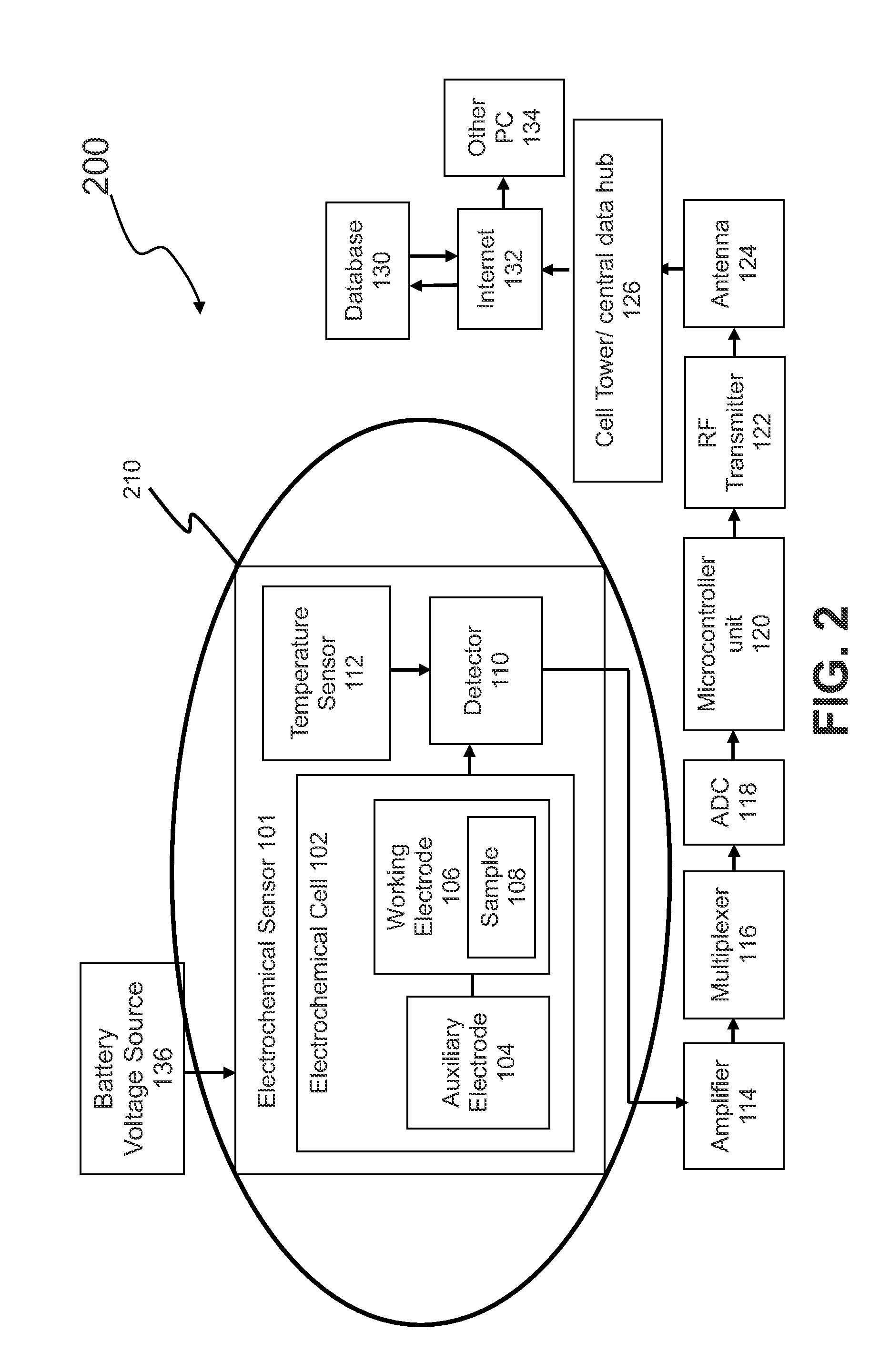
Electrochemical Amperometry-Based Sensor Combined With Long-Range Radio Communication For Measurement Of Analytes
InactiveUS20140158535A1Avoid generatingAvoid temperatureWaveguide type devicesElectrical componentsAnalyteComputer module
The methods and systems according to the present invention overcome the high-frequency radiation and thermal interferences on an electrochemical sensor combined with long range radio communication. A Faraday cage is used to shield the sensor from the radiation in one embodiment. In another embodiment, a controller is installed between the sensor and the antenna to deactivate the antenna emission when the electrochemical sensor is conducting measurement. To control thermal interference, the temperature rise is controlled. The battery temperature is monitored and charging cycle is controlled. The temperature rises can also be avoided via intermittent use of the radio, heat sink strategies to direct heat away from the radio circuitry, and radio module construction designed to minimize heat emission. The present invention discloses an electrochemical sensor combined with a long range radio communication that has an improved accuracy due to having a better control of high frequency radiation and thermal interferences.
Owner:JAVITT JONATHAN
Preparation method and application of electrochemical micro-fluidic sensing chip
ActiveCN103182334BEasy to manufactureReduce weightMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresElectrochemical detectorAntigen
The invention provides a preparation method and the application of an electrochemical micro-fluidic sensing chip. The preparation method comprises the following steps: directly coating an improved glass solution on a commercial standard printed electrode; and performing vacuum plasma treatment on a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) chip with pre-designed pipelines and the printed electrode coated with the glass solution together, and directly bonding the PDMS chip on the commercial standard printed electrode to form a novel electrochemical microfluidic sensing platform. A sensor provided by the invention can perform ultrasensitive detection on various sample analytes in a biological fluid sample, taking the detection of a prostate cancer marker PSA (Prostate-specific Antigen) in human serum as an example, a coulomb amperometry is used for detection, and a result shows that the detection sensitivity can reach 0.84 pg / mL which is improved by two magnitudes than the standardized clinical testing requirement of 0.1 ng / mL, so that the sensor has superhigh detection sensitivity and accuracy, which are higher than those of other electrochemical detection devices, is convenient in operation, and can integrates sample processing, separation and the like on one micro electrochemical microfluidic sensing chip.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Graphene/graphene oxide microarray electrode and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN104655698BLow costSensitive assayMaterial electrochemical variablesBiocompatibility TestingCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene / graphene oxide microarray and application of the graphene / graphene oxide microarray used as a chemical and cell-based sensor. A graphene / graphene oxide microarray electrode is prepared on an ITO glass substrate by combining a micro processing technology and an electrochemical method. By utilizing the electrochemical catalytic oxidation of the microelectrode prepared by the invention on hydrogen peroxide, the in vitro and intravital quantitative analysis and detection of hydrogen peroxide are realized by a timing amperometry. The preparation method is simple and feasible, the sensitivity is high, the response time is short, the biocompatibility is good, and the concentration of hydrogen peroxide can be quickly detected.
Owner:安徽中科大禹科技有限公司
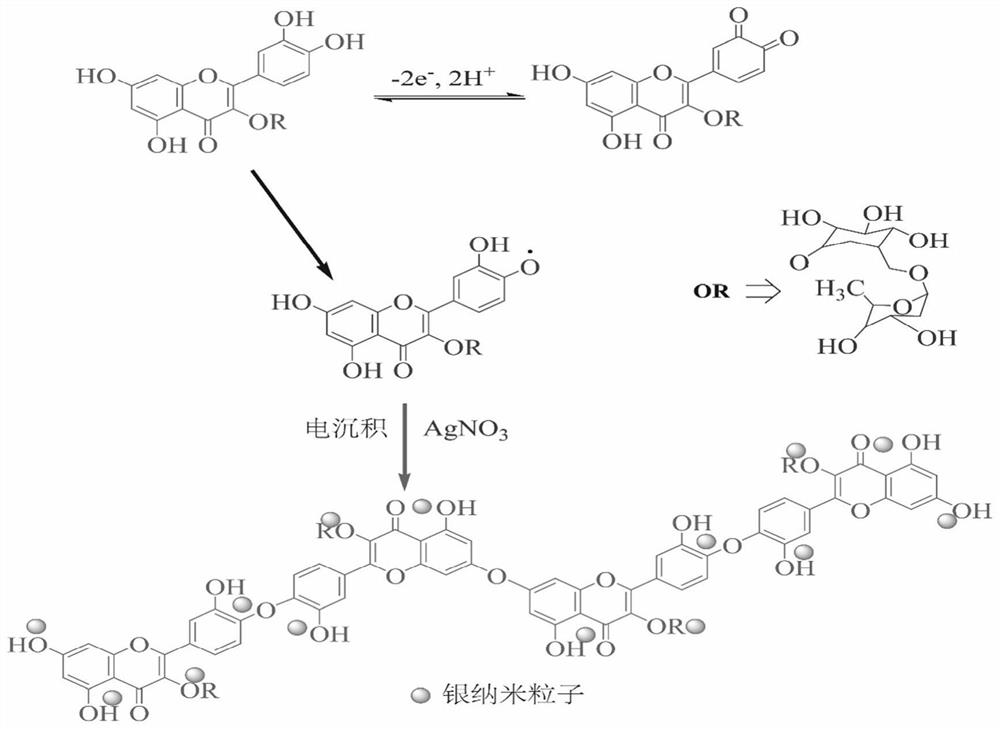
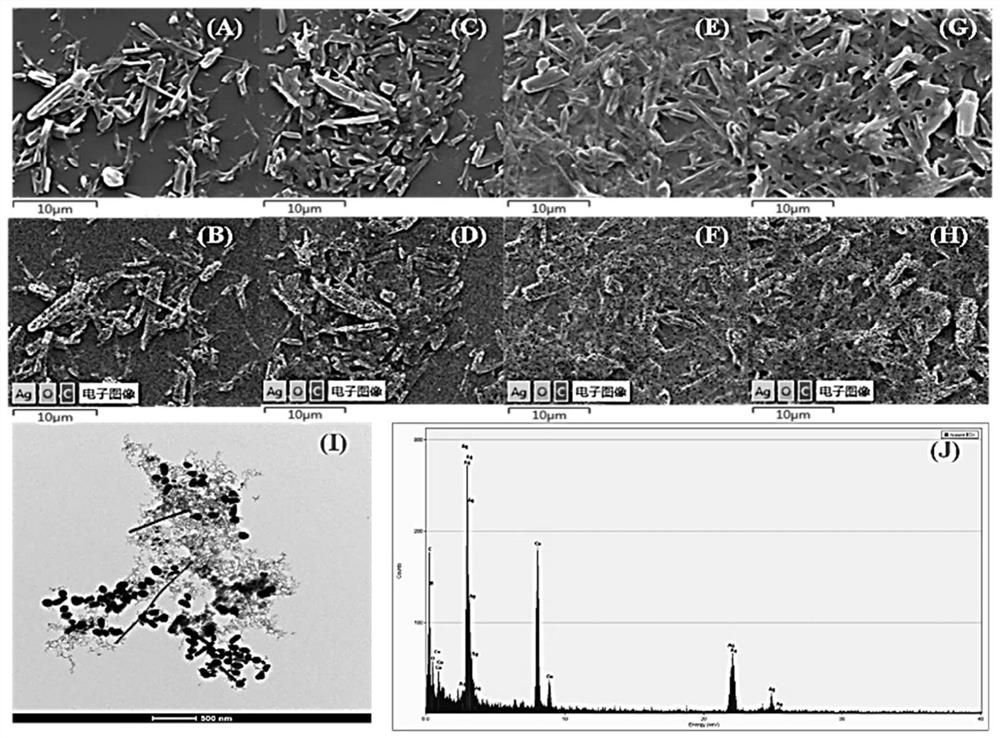
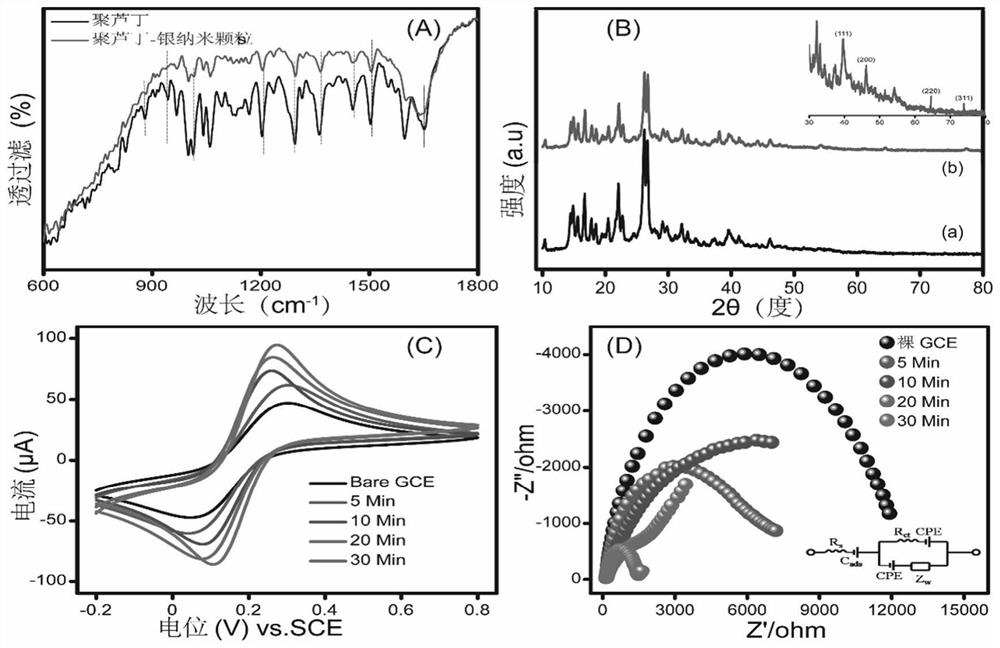
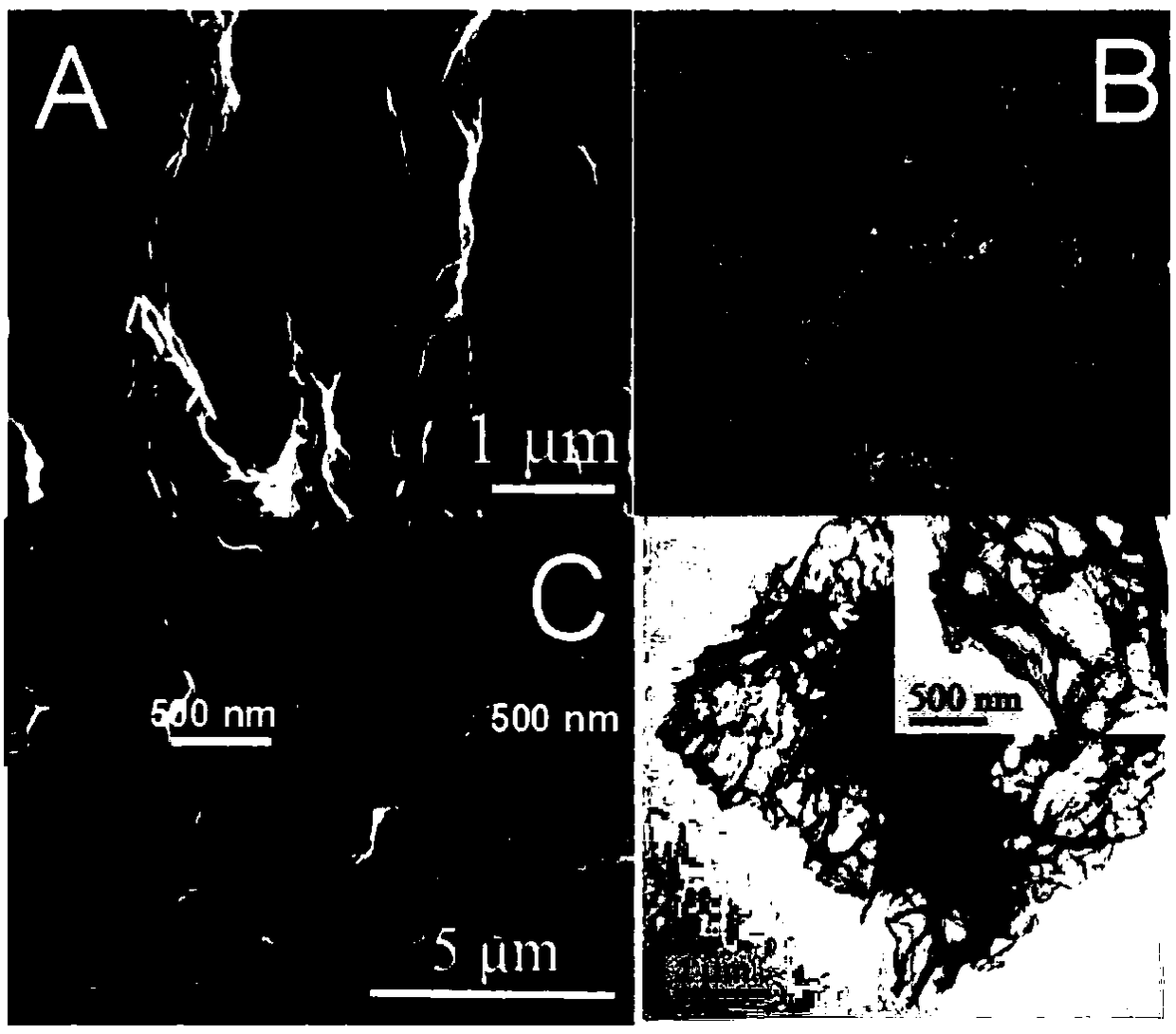
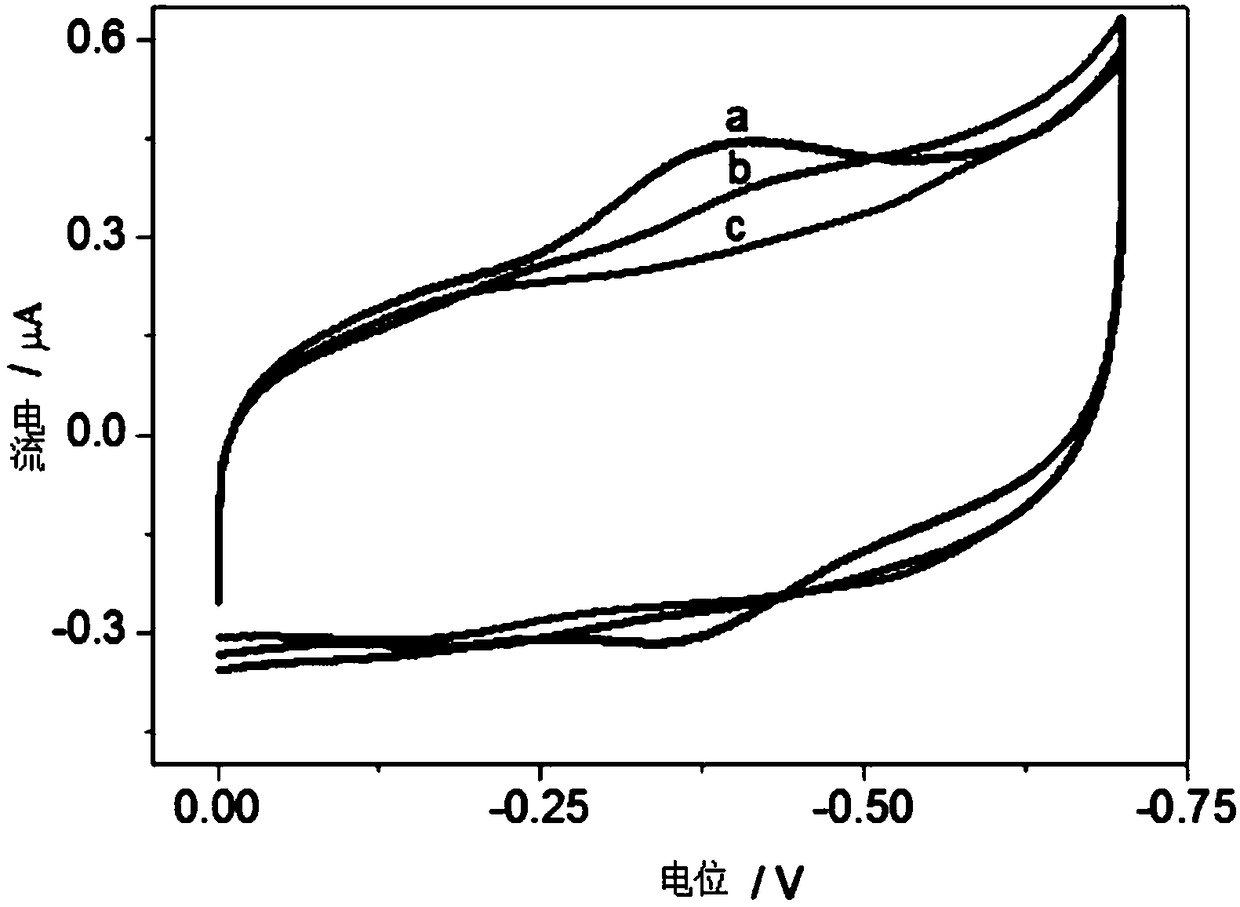
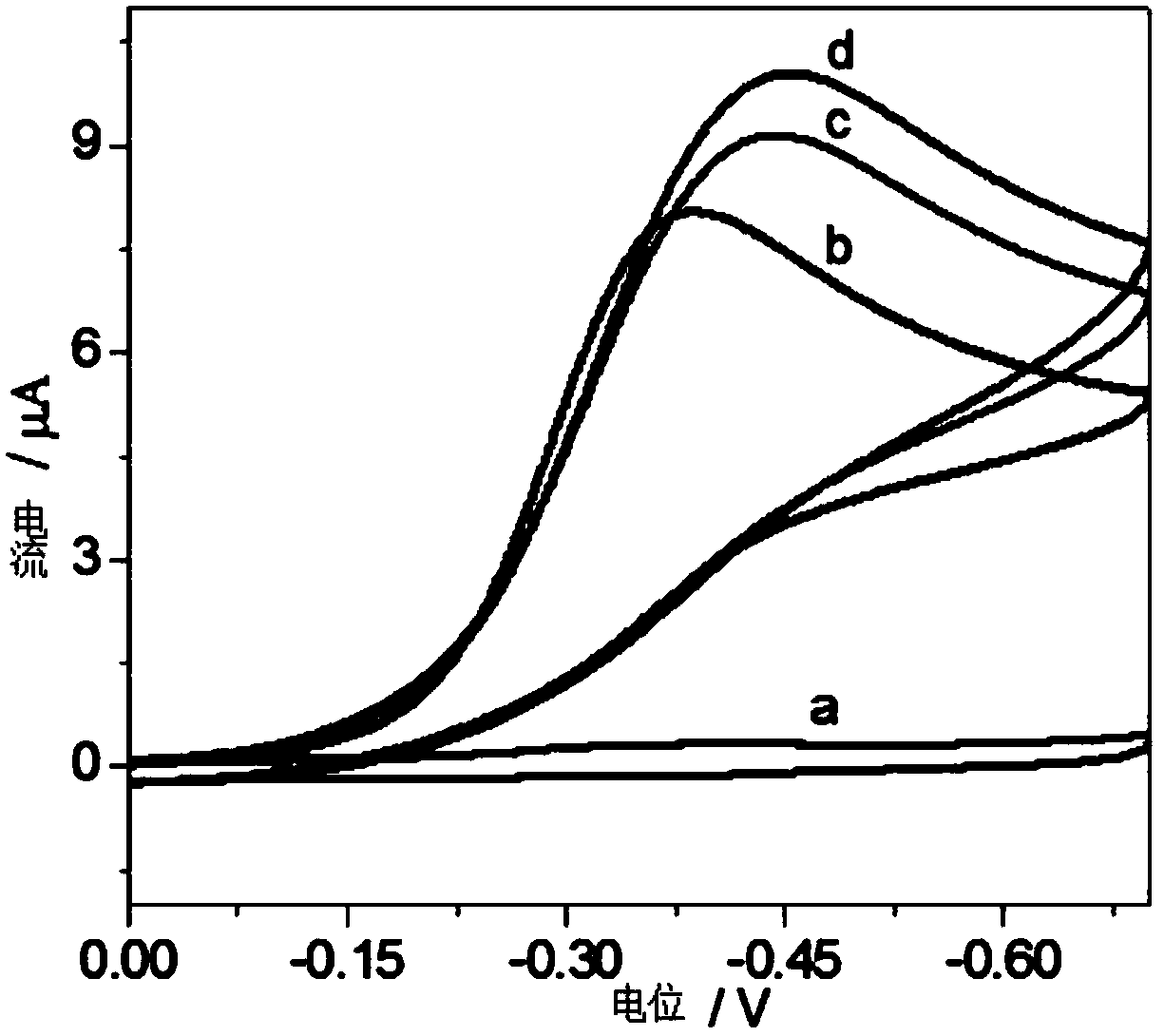
Polyrutin-silver nanoparticle-glassy carbon electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111693583ASimple stepsEasy to operateTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusSupporting electrolyteNanoparti cles
The invention relates to a polyrutin-silver nanoparticle-glassy carbon electrode and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: storing a glassy carbon electrode in an electrochemical electrolytic tank, wherein a supporting electrolyte of the electrochemical electrolytic tank is H2SO4 and contains rutin and AgNO3; and performing electrochemical deposition by adopting a timing ampere method to obtain the polyrutin-silver nanoparticle-glassy carbon electrode. The polyrutin-silver nanoparticle-glassy carbon electrode can be prepared by adopting an electrochemical deposition one-step preparation method, the steps are simple, and the operation is convenient; the electrode can rapidly detect various heavy metal ions in an environmental sample at the sametime, the heavy metals in different environmental samples (soil, water, hair and the like) can be rapidly detected, the sensitivity, the selectivity and the repeatability are good, the detection limitis low, the linear range is wide compared to the similar electrode in the prior art, and the significant difference does not exist in the detection of the heavy metals in the environmental samples compared to the widely-used inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry analysis technology.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Electrochemical detection method for endocrine disrupter on the basis of enzyme nano-reactor
InactiveCN108226250ASuperhydrophilicMaintain catalytic activityMaterial electrochemical variablesPerturbateurs endocriniensActive enzyme
The invention relates to an electrochemical detection method for an endocrine disrupter on the basis of an enzyme nano-reactor. Through functionalized SiO2 as a template, graphene oxide is mixed therewith via hydrophobic-hydrophobic effect, then the materials are frozen and calcined to prepare graphene foam; then by means of electrostatic adsorption and covalent bond process at the same time, active enzyme is immobilized in pores in the graphene foam in order to establish a CYP3A4 / PNGF enzyme reactor. The invention discloses the electrochemical analysis method which is low in cost, has simpleoperations and is convenient and quick. The enzyme nano-reactor allows pore diameter to be adjusted, so that through amperometry, metabolic behavior of the endocrine disrupter can be quickly and accurately detected. The method has high sensitivity and stability and is suitable for promotion and application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
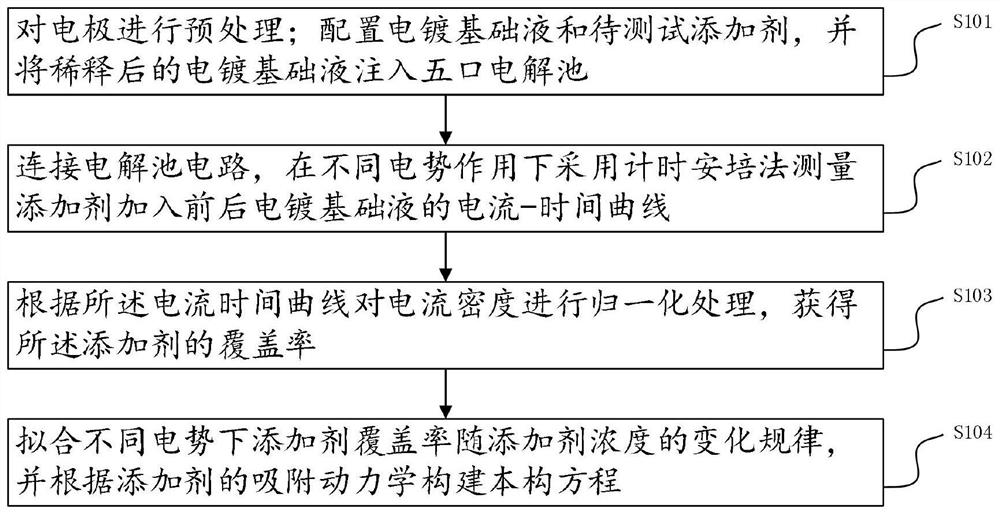
TSV electroplating filling additive constitutive model construction method and system
PendingCN113408227AScientific Data FittingSimplify the experimental stepsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHemt circuitsEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of integrated circuit three-dimensional packaging, and particularly relates to a TSV electroplating filling additive constitutive model construction method and system. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating an electrode; preparing an electroplating basic solution and a to-be-tested additive, and injecting the diluted electroplating basic solution into a five-opening electrolytic tank; connecting an electrolytic tank circuit, and measuring a current-time curve of the electroplating basic solution before and after the addition of the additive under the action of different potentials by adopting a chronoamperometry method; performing normalization processing on the current density according to the current-time curve to obtain the coverage rate of the additive; and fitting the change rules of the additive coverage rate along with the additive concentration under different potentials, and constructing the constitutive equation according to the adsorption kinetics of the additive. The experimental steps are simple, the cost is low, and the obtained constitutive model is high in reliability.
Owner:长沙安牧泉智能科技有限公司
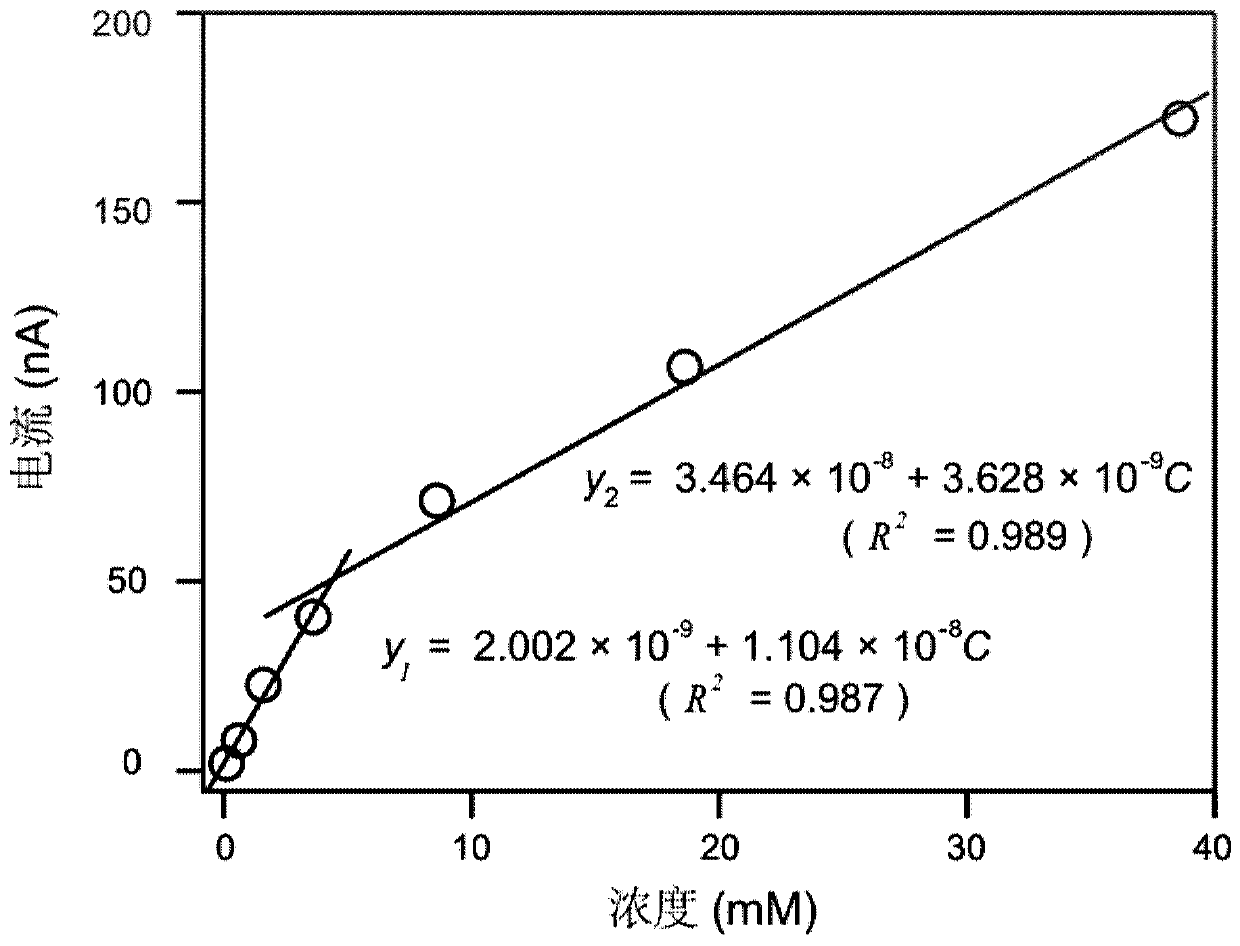
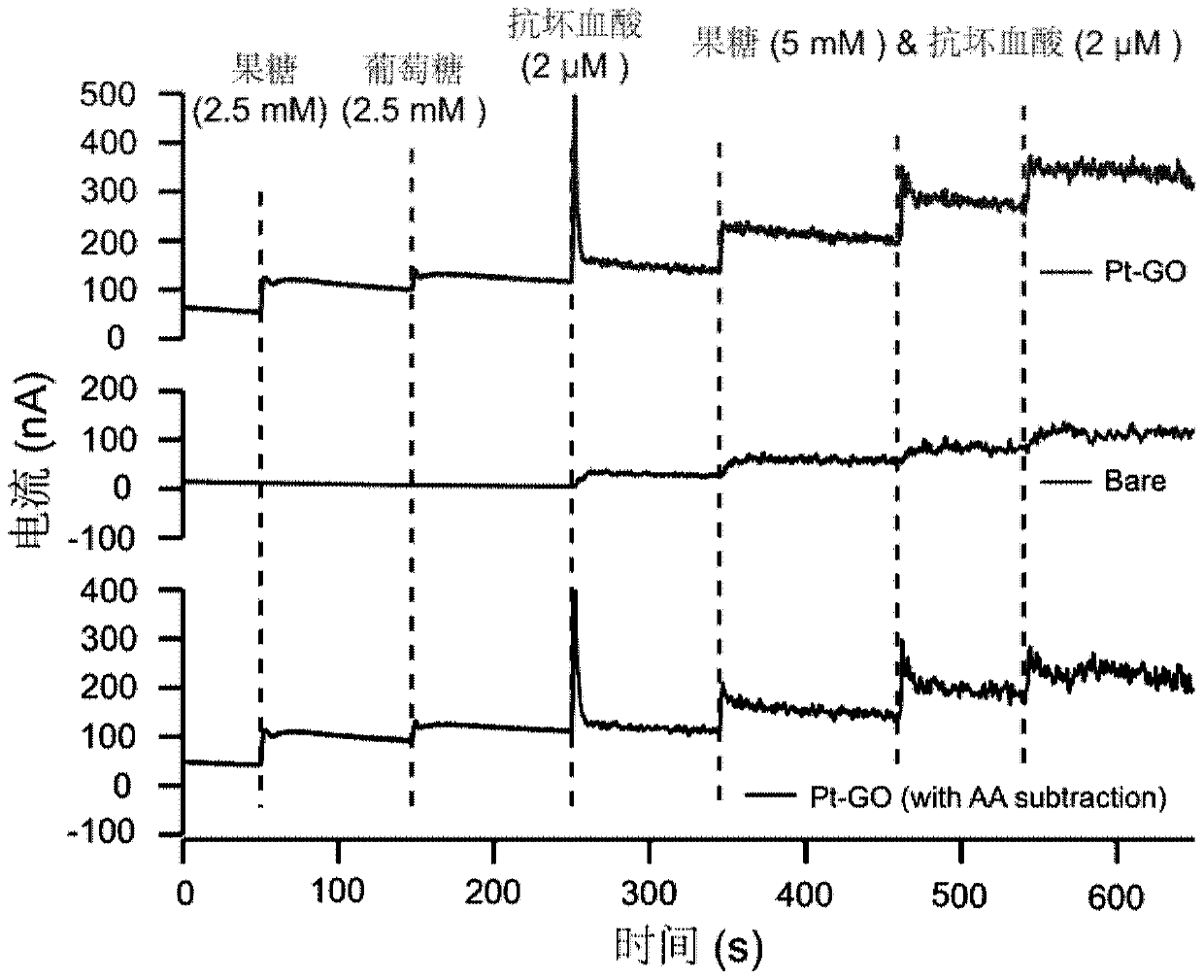
Fructose nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor and detection method thereof
InactiveCN110220956AAvoid preprocessing operationsRealize functionMaterial electrochemical variablesMedical treatmentChemical sensor
The invention relates to a fructose nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor and a detection method thereof. Platinum-graphene oxide nanoflower is assembled on a working electrode to prepare a fructose sensor based on the processing; under a neutral solution condition, the fructose and the glucose have characteristics of different oxidation potentials under the effect of the platinum-graphene oxide nanoflower, and the fructose oxidation signal can be specifically recognized by using an electrochemical amperometry, thereby reaching an aim of detecting the fructose. The influence on a fructose detection result by an interferent is reduced when a self-reference recording method in a dual-working electrode mode is used for detecting fructose, and a faster method is provided for the detection of thefructose in the medical treatment and food industry.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES +1
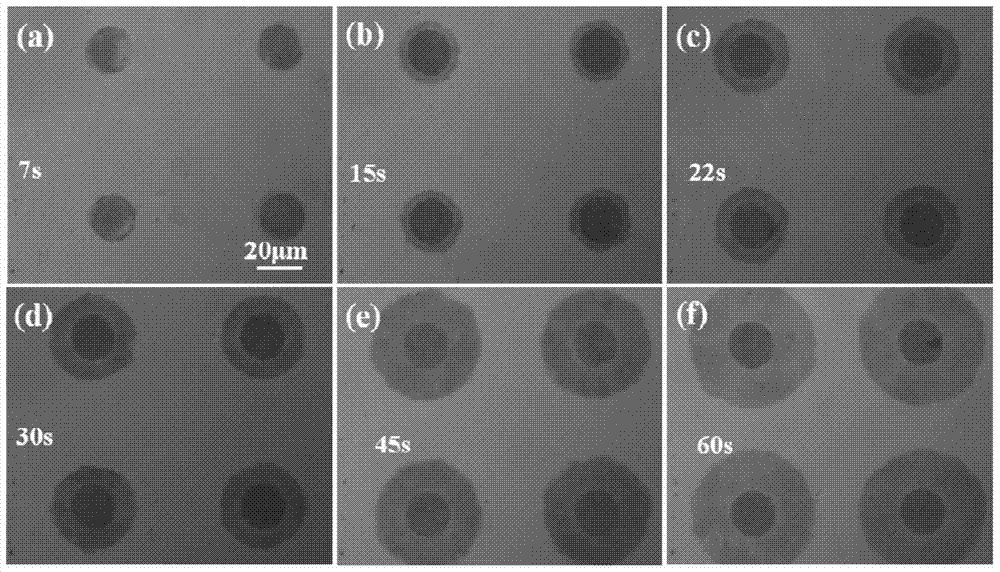
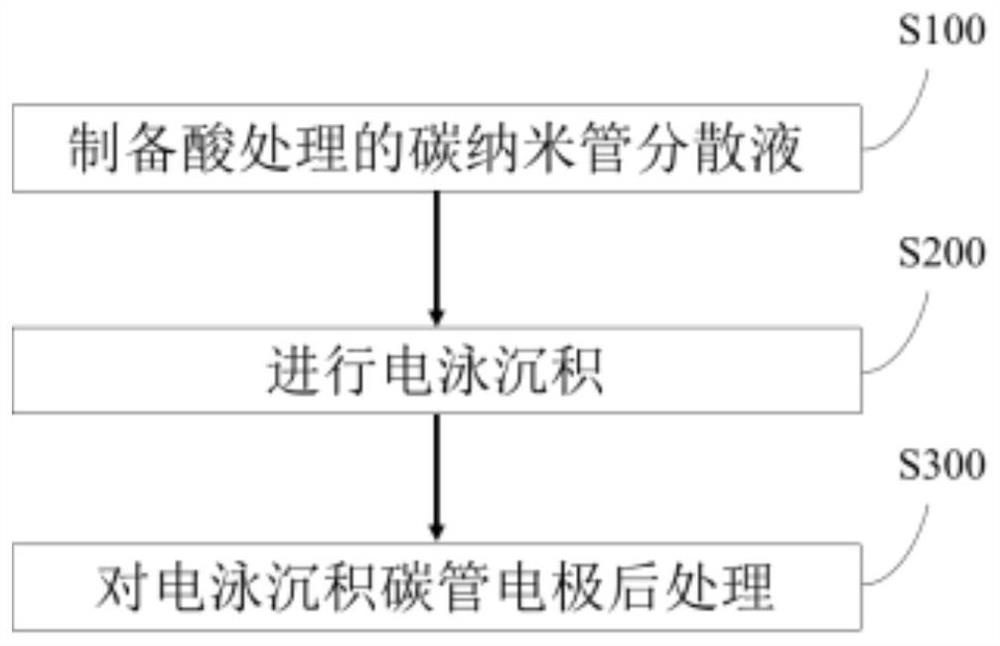
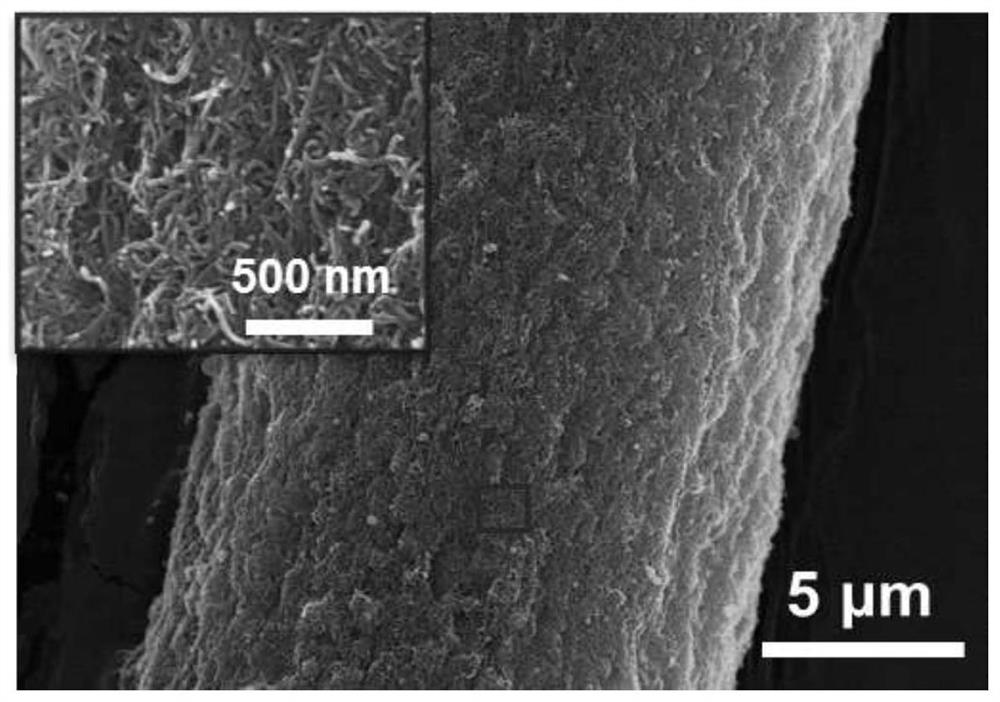
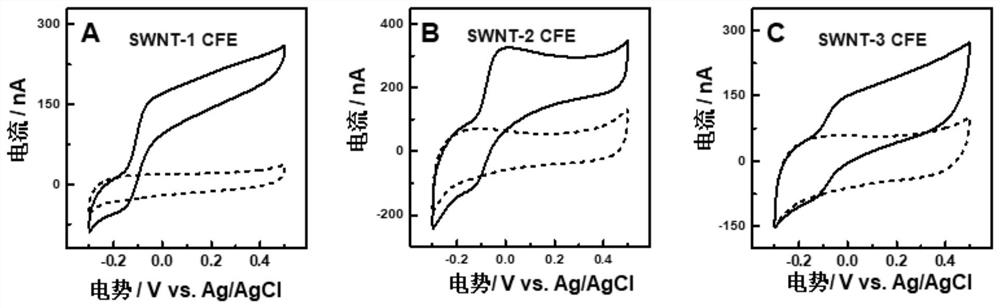
Electrophoretic deposition of carbon nanotubes modified carbon fiber electrode and its application in the detection of ascorbic acid in vivo
ActiveCN110057897BHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a new method used for modifying a carbon fiber electrode with carbon nano tubes. The method comprises the step of depositing single-walled carbon nano tubes on a carbon fiber electrode by adopting an electrophoretic deposition method, wherein electrophoretic deposition is realized by virtue of a two-electrode system, and the method comprises the following specific steps: inserting the carbon fiber electrode and a Pt wire into single-walled carbon nano tube dispersion, applying a voltage of 1.9-2.5V by virtue of amperometry and performing electrophoretic deposition for 10-100s, thus the carbon fiber electrode modified by the uniformly deposited carbon nano tubes can be obtained. Before in vivo analysis is performed, high temperature and electrochemical simple treatment is performed on the carbon nano tube modified carbon fiber electrode, so that the electrode can have high selectivity and sensitivity on ascorbic acid and can be used for in vivo intracerebral in situ determination on change of concentration of ascorbic acid.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com