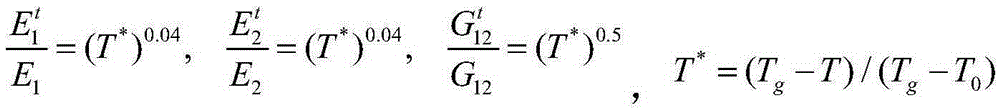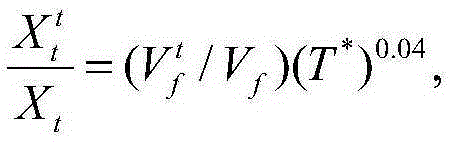Patents
Literature
378 results about "Constitutive equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
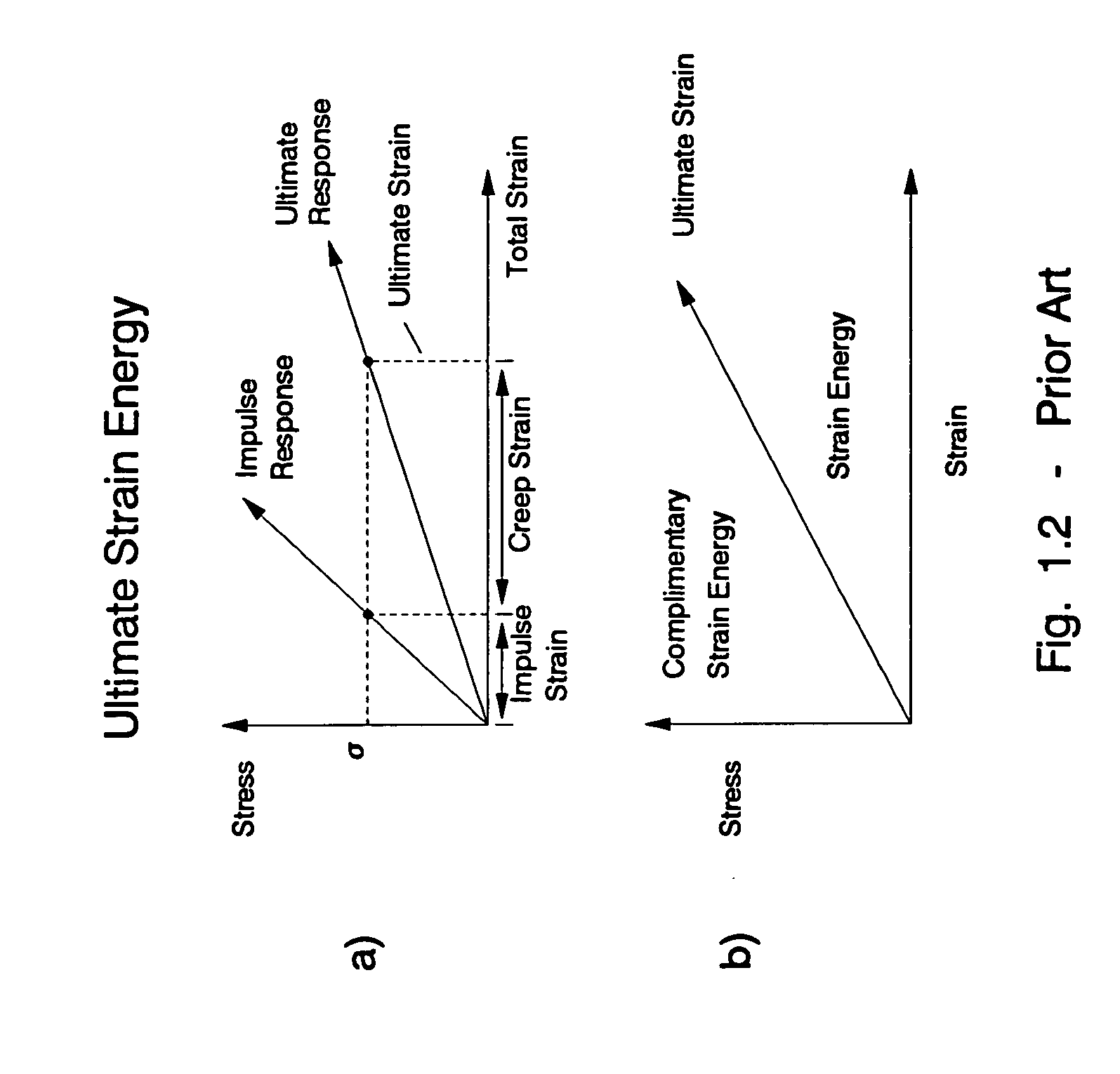
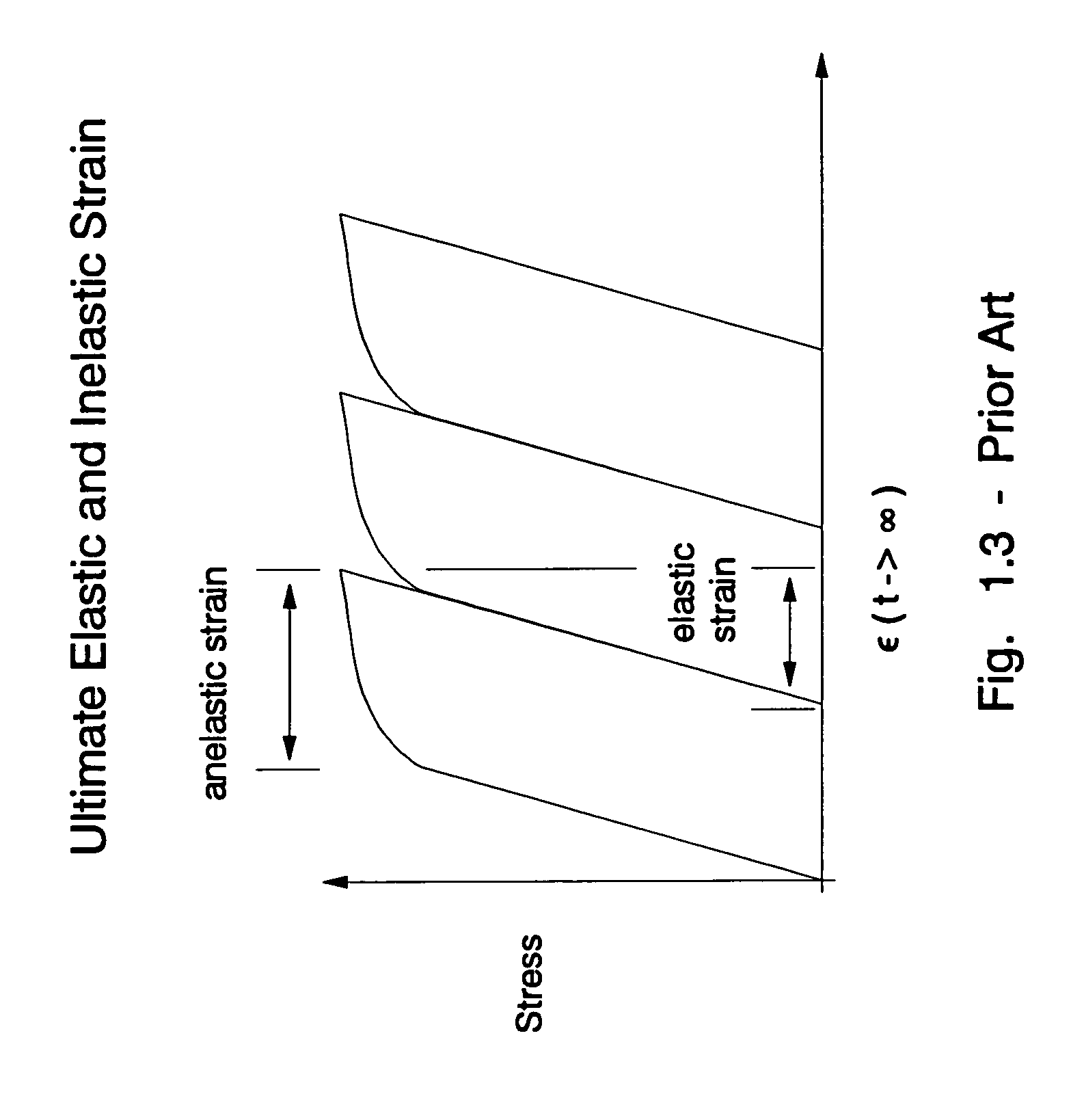
In physics and engineering, a constitutive equation or constitutive relation is a relation between two physical quantities (especially kinetic quantities as related to kinematic quantities) that is specific to a material or substance, and approximates the response of that material to external stimuli, usually as applied fields or forces. They are combined with other equations governing physical laws to solve physical problems; for example in fluid mechanics the flow of a fluid in a pipe, in solid state physics the response of a crystal to an electric field, or in structural analysis, the connection between applied stresses or forces to strains or deformations.
Method for producing alloy deposits and controlling the nanostructure thereof using negative current pulsing electro-deposition, and articles incorporating such deposits
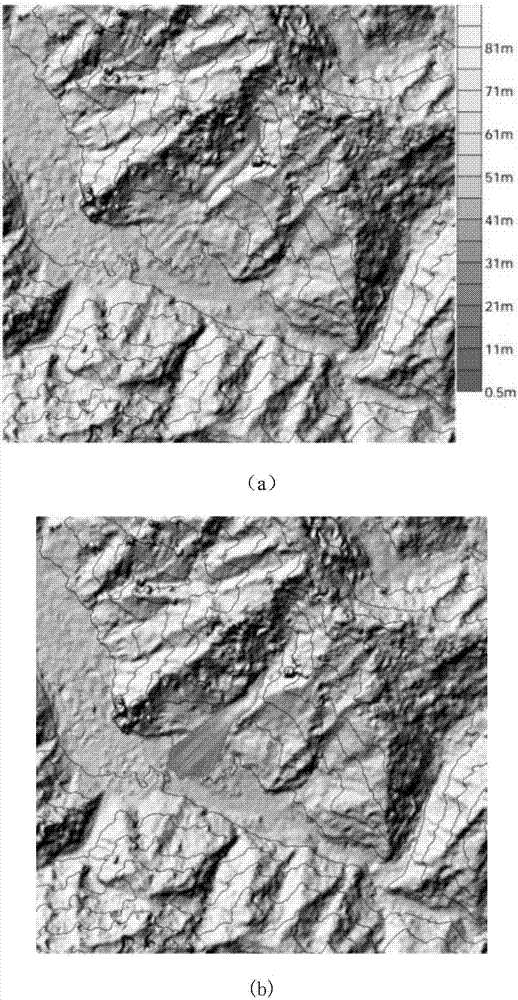
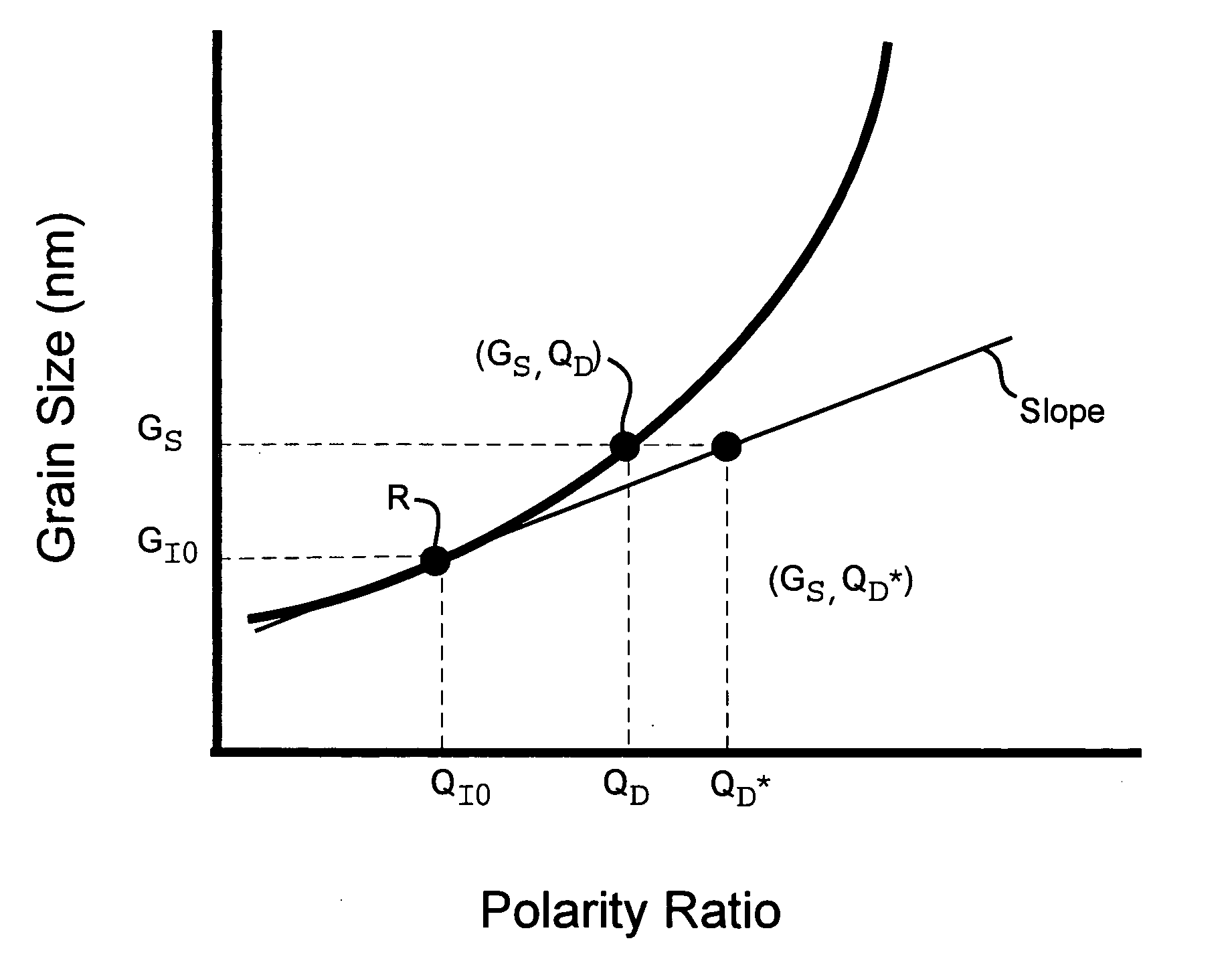
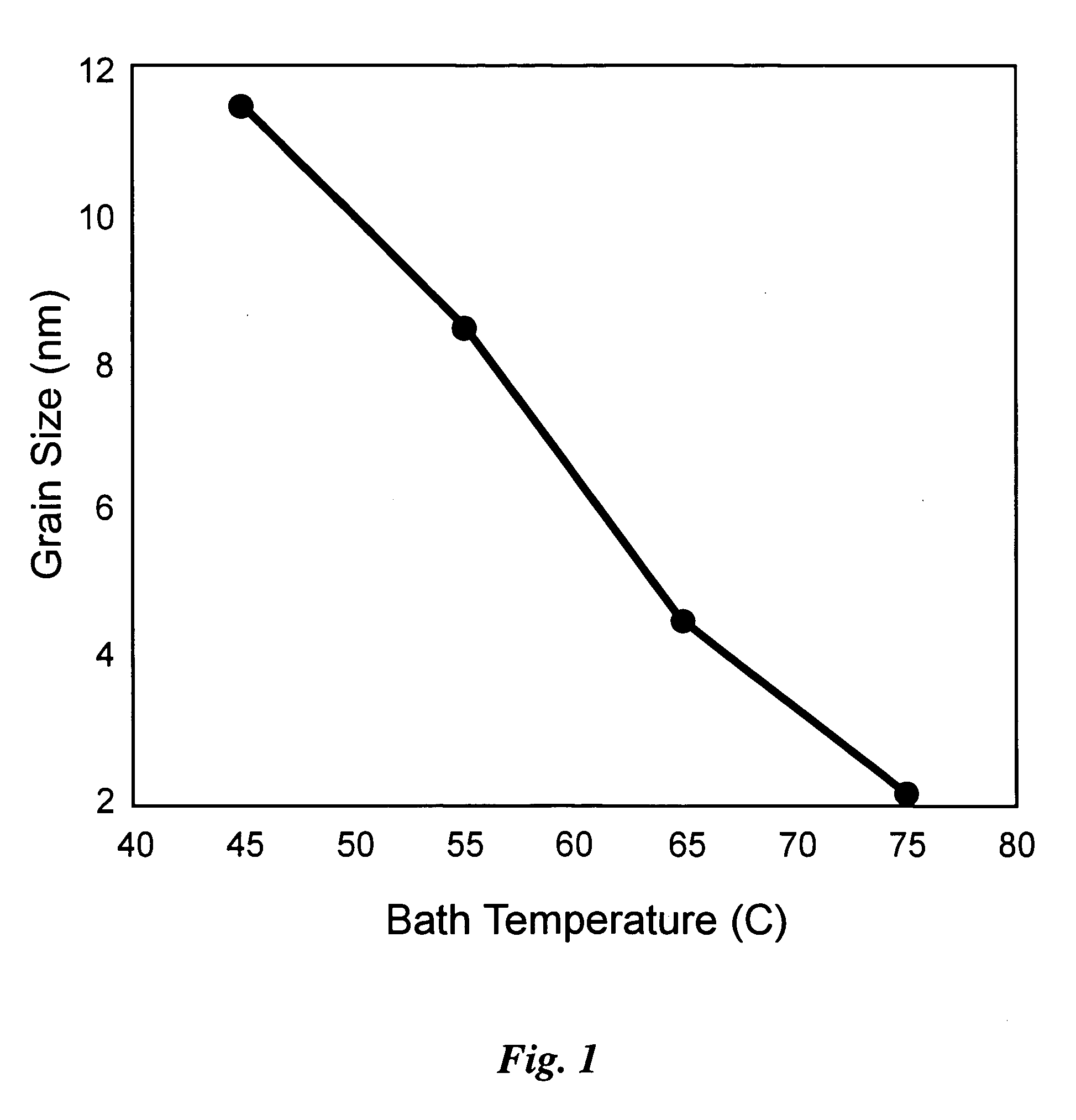
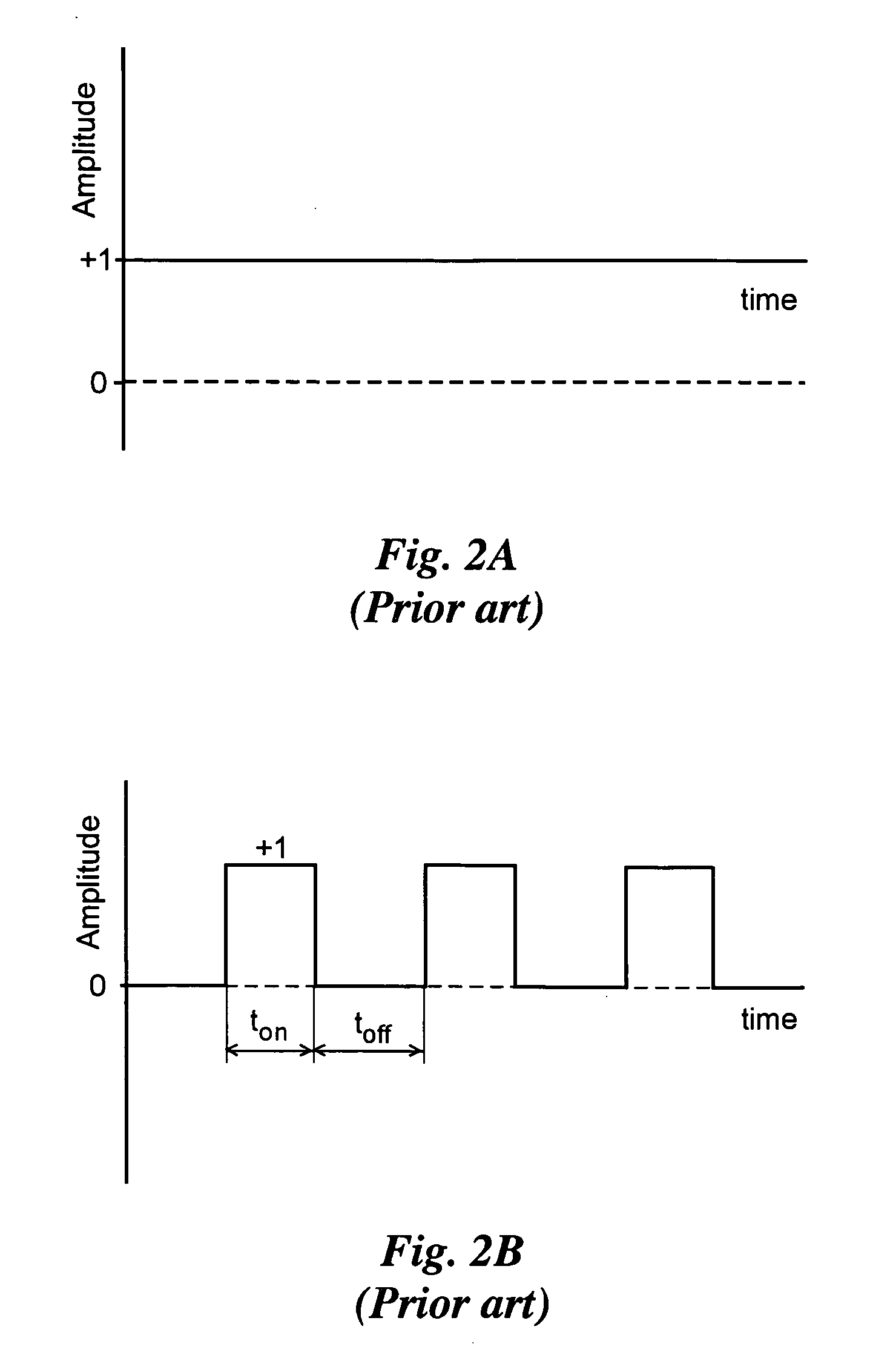
Bipolar wave current, with both positive and negative current portions, is used to electrodeposit a nanocrystalline grain size deposit. Polarity Ratio is the ratio of the absolute value of the time integrated amplitude of negative polarity current and positive polarity current. Grain size can be precisely controlled in alloys of two or more chemical components, at least one of which is a metal, and at least one of which is most electro-active. Typically, although not always, the amount of the more electro-active material is preferentially lessened in the deposit during times of negative current. The deposit also exhibits superior macroscopic quality, being relatively crack and void free. Parameters of current density, duration of pulse portions, and composition of the bath are determined with reference to constitutive relations showing grain size as a function of deposit composition, and deposit composition as a function of Polarity Ratio, or, perhaps, a single relation showing grain size as a function of Polarity ratio. A specified grain size can be achieved by selecting a corresponding Polarity Ratio, based on these relations. Coatings can be in layers, each having an average grain size, which can vary layer to layer and also in a region in a graded fashion. Coatings can be chosen for environmental protection (corrosion, abrasion), decorative properties, and for the same uses as a hard chrome coating. A finished article may be built upon a substrate of electro-conductive plastic, or metal, including steels, aluminum, brass. The substrate may remain, or be removed.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
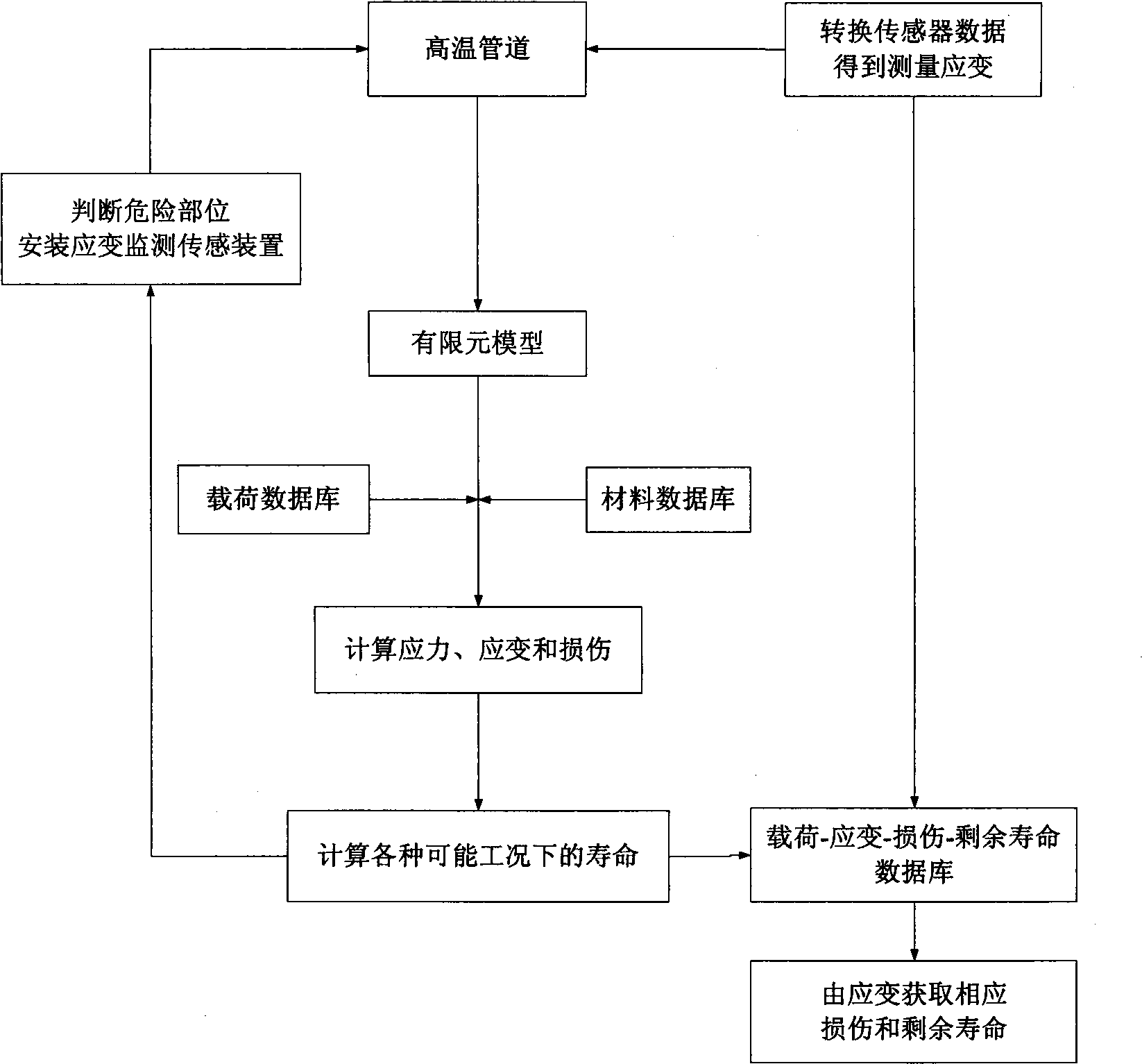
On-line prediction method for high-temperature pipe damage and longevity
InactiveCN101509855AGuaranteed real-time monitoringExtend your lifeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisPredictive methods
The invention relates to an online predicting method of damage and service life of a high temperature pipeline. The method comprises the following implementing steps of: (1) carrying out finite element simulation analysis of damage and coupling to the high temperature pipeline; (2) finding out important monitoring parts according to the analysis results, arranging a sensor and monitoring the strain of the sensor; (3) carrying out finite element analysis (including analytical subprogram of a constitutive equation) for different working conditions and establishing database with damage, strain and residual life and strain; and (4) carrying out online inquiry and comparison to strain values detected online and the value of the load working condition and the data in the database so as to obtain the assessment value of corresponding damage and residual life. The online predicting method has the advantages of being capable of carrying out real-time monitoring to the high temperature pipeline in operation while production is carried out normally, reflecting the deformation and damage of the important parts and key parts in time, making correct estimation to the use life and residual life of the pipeline, being beneficial to guaranteeing safe production, adjusting the production load, planning maintenance reasonably and effectively prolonging the service life of production equipment.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
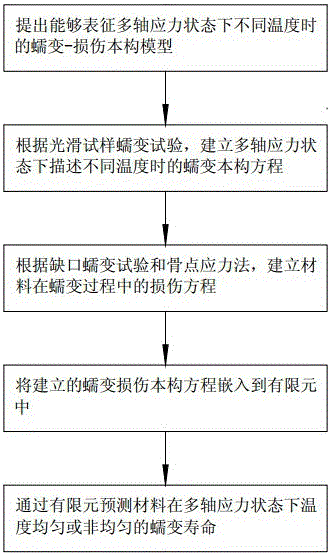
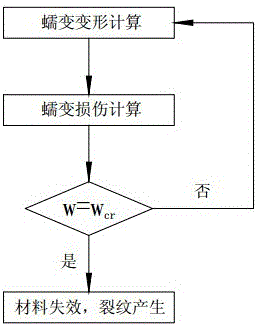
Creep-damage lifetime forecast method of material under multi-axial stress state
InactiveCN106557630APrediction is simpleThe result is accurateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsInfinite elementLife time
A creep-damage lifetime forecast method of a material under a multi-axial stress state belongs to the field of material lifetime forecast. The method of the material under the multi-axial stress state is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) building a creep-damage constitutive model which can represent different temperatures under the multi-axial stress state; (2) building a creep constitutive equation describing different temperatures under the multi-axial stress state; (3) building a damage equation of the material during the creep process; (4) embedding the creep-damage equations in the steps (2) and (3) into a finite element for lifetime analysis; and (5) forecasting creep lifetime of the material under the multi-axial stress state according to an analysis result of the infinite element. By the method of the material under the multi-axial stress state, the lifetime forecast of the material under a high-temperature condition can be achieved better, the forecast process is simple, and a result is accurate.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for correcting elasticity modulus and stress-strain curve in metal material compression test
ActiveCN104596846ASimplified operational requirementsImprove reliabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress–strain curveMetallic materials
The invention relates to a method for correcting an elasticity modulus and stress-strain curve in a metal material compression test and a related model. The model is a sandwiched model. According to the method for correcting a metal material compression elasticity modulus and stress-strain curve obtained by the model, most of national standard or non-national standard samples of metal materials with linear strengthening behaviors, particularly metal samples in which L is equal to (2.5-3.5) d or L is equal to (2.5-3.5) b or L is equal to 2d or L is equal to 2b can be corrected, so that the real compression elasticity modulus can be measured on samples which are unsuitable for measuring the compression elasticity modulus in the national standard stipulation; particularly, the method can be used for correcting the elasticity modulus and stress-strain curve of small-size non-national standard samples. According to the method, the construction of a mechanical constitutive equation is greatly convenient, and for research and development of novel materials, the requirements of the test technology on the sizes and shapes of the samples can be lowered, the measured mechanical parameters are reliable, and the research and development period is shortened.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A multi-axis creep fatigue prediction method based on ABAQUS
ActiveCN109885874AGain creep damageIntuitiveMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesDesign optimisation/simulationFatigue damageElement model
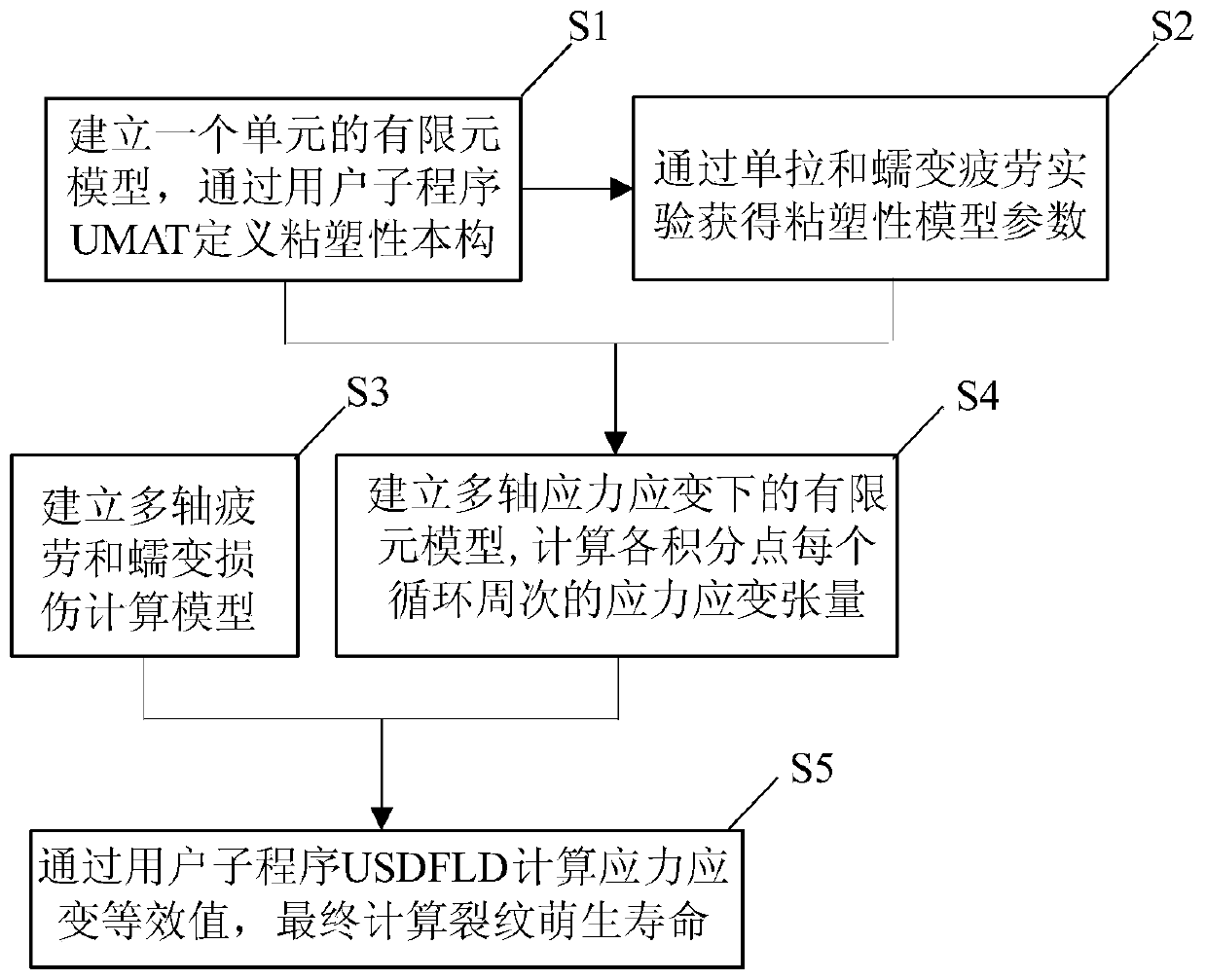
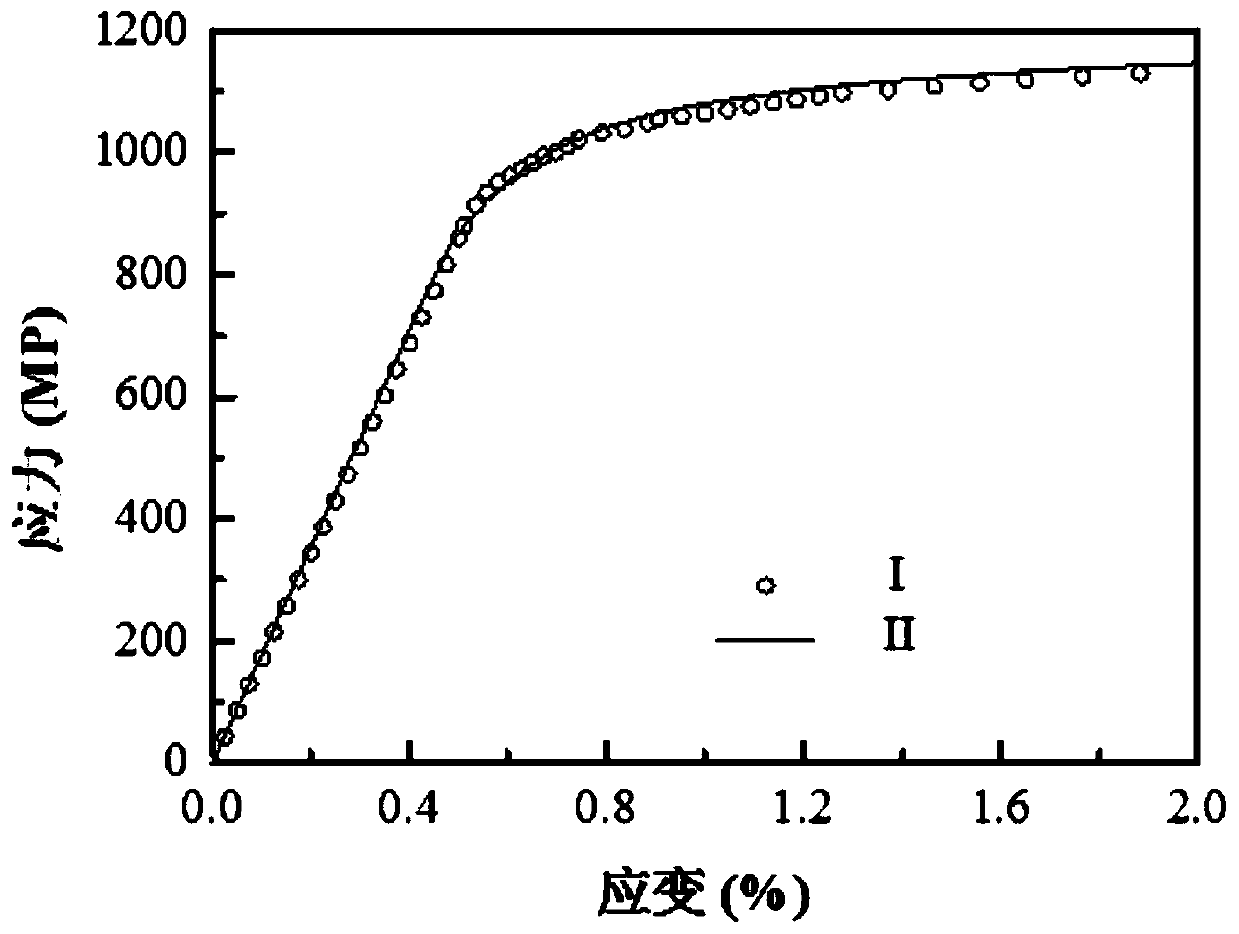
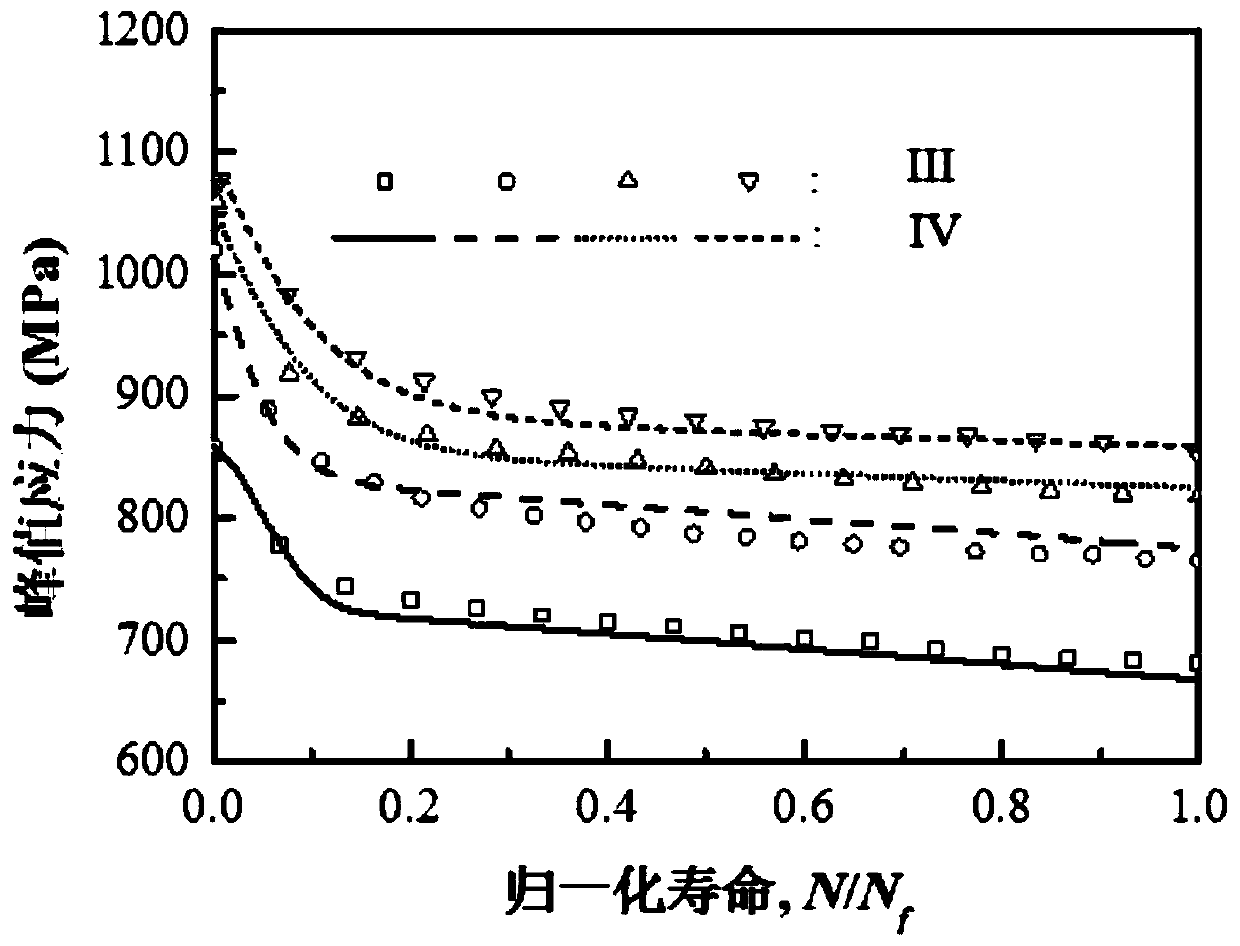
The invention discloses a multi-axis creep fatigue prediction method based on ABAQUS, and the method comprises the steps of S1, building an ABAQUS finite element model, and defining a viscoplastic constitutive equation of a to-be-tested material through a user subprogram UMAT; S2, determining model parameters required by the viscoplastic constitutive equation; S3, establishing a fatigue damage calculation model and a creep damage calculation model of the multi-axis stress-strain state of the to-be-tested material; S4, establishing an ABAQUS finite element model in a multi-axis stress-strain state, and calculating to obtain a stress-strain tensor of each cycle on the basis of the defined viscoplastic constitutive equation and model parameters; and S5, calculating equivalent stress and equivalent plastic strain through a user subprogram USDFLD, and superposing fatigue damage and creep damage of each cycle through a linear cumulative damage criterion on the basis of the fatigue damage calculation model and the creep damage calculation model in combination with the stress strain tensor to obtain the crack initiation life.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of multi-dimensional analysis of viscoelastic materials for stress, strain, and deformation
A method for solving any arbitrary multi-dimensional scientific or engineering design problem requiring solutions for stress, strain and deformation, and which therefore demands the incorporation of a material constitutive equation into the mathematical solution and wherein that constitutive equation, which quantitatively defines the relationship between stress and strain, incorporates independent tensor valued coefficients and a scalar valued constitutive function / s, and where the values of the tensor valued coefficients and the form of the constitutive function / s is specific to any particular material under consideration.
Owner:TRUNK FR J
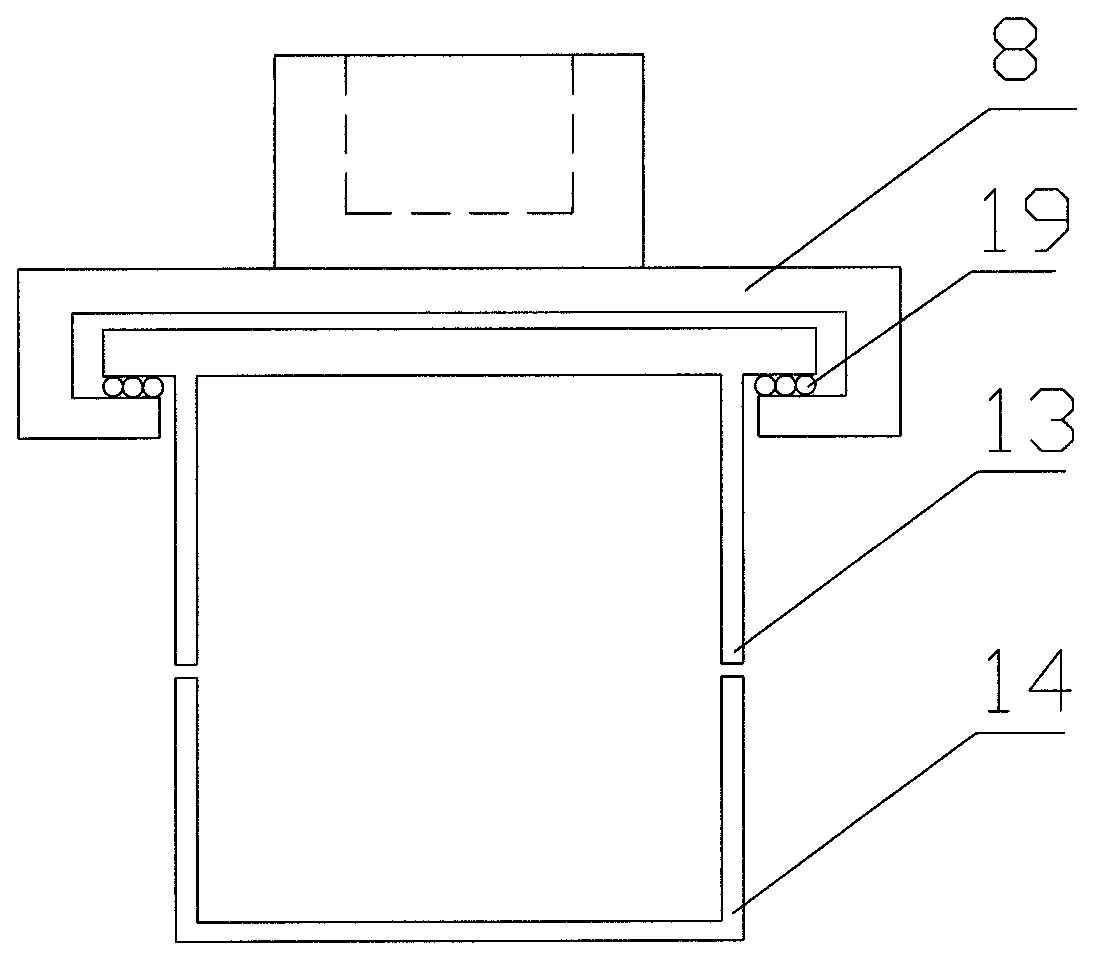
Rock tensile-shearing test system
ActiveCN103175738AGuaranteed free deformationImproving and Perfecting the Constitutive RelationsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesNormal tensionRock sample
The invention relates to a tensile-shearing test system for rock experiments in mechanics and belongs to the technical field of geotechnical engineering. The test system comprises a counter-force device, a vertical load system, a horizontal load system, upper and lower shearing boxes, a measurement system and a base, wherein the vertical load system and the upper shearing box are connected through a tensile plate of which the lower end is provided with two guide slots. The direct shear test for the rock under different tensions can be performed; due to the assembled design of the upper and lower shearing boxes, the rock sample can be conveniently adhered and detached; due to the design mode of the tensile plate and the upper shearing box, free deformation of the rock in the horizontal direction under the horizontal thrust can be guaranteed, and the stability of the horizontal load system under the tensile action can be guaranteed according to the roller row which is arranged in the horizontal load direction. The current situation that the strength criterion of the rock can only be researched by employing the compression shear experimental mode at present is changed, the intensity parameters of the rock under the action of different normal tensions can be provided, and the constitutive relation of the rock under the shear-resistant stress is improved and perfected.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
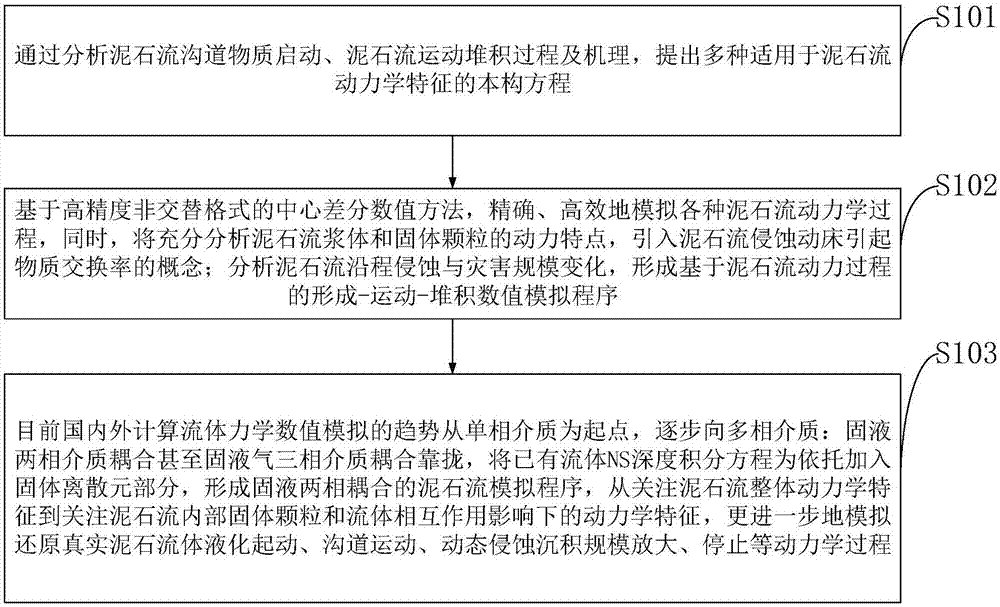
Novel dynamic numerical debris flow simulation analysis method and system
ActiveCN107506566AImprove targetingImprove the level of scienceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsScale variationSize change
The invention belongs to the technical field of debris flow disaster prevention and control and environmental governance, and discloses a novel dynamic numerical debris flow simulation analysis method and a novel dynamic numerical debris flow simulation analysis system. Through analysis on startup of a debris flow channel material and the process and the mechanism of debris flow movement accumulation, a number of constitutive equations suitable for the dynamic characteristics of a debris flow are obtained; meanwhile, based on a non-alternating format central difference numerical method, various dynamic processes of the debris flow are simulated; in addition, the dynamic characteristics of a slurry and solid particles of the debris flow are analyzed, a concept that a movable debris flow erosion bed causes the material exchange rate is introduced, and erosion along the distance as well as the disaster size change of the debris flow are analyzed so as to form a formation-movement-accumulation numerical simulation program based on the dynamic process of the debris flow. The numerical simulation program and a numerical calculation method, provided by the invention, have the characteristics of simpleness, high efficiency and the like, and are suitable to be used by workers in the related disaster field; the scientific levels of the debris flow prevention and control and environment protection are improved.
Owner:INST OF MOUNTAIN HAZARDS & ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
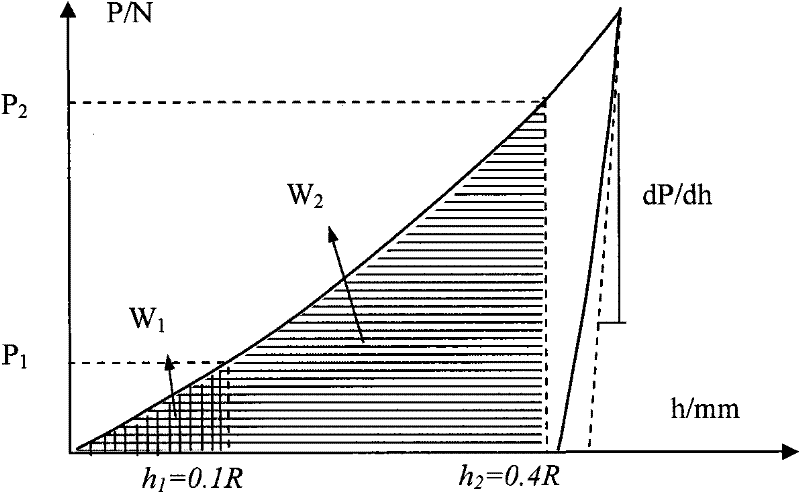
Method for obtaining mechanical property of metal material based on load-depth curve
ActiveCN102455263ARealize online detectionMeet the requirements of engineering useMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessTest materialTitanium alloy
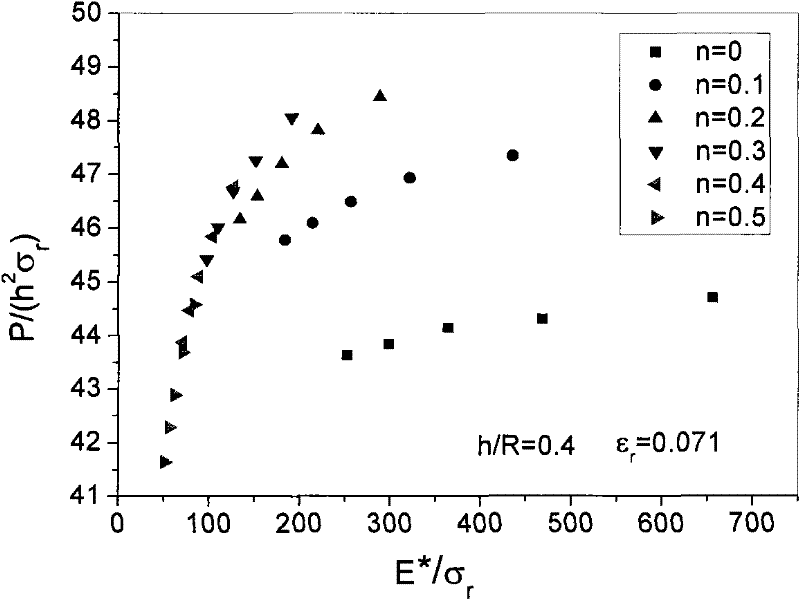
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the mechanical property of a metal material based on a load-depth curve and belongs to the technical field of material property test. On the basis of determining to adopt a large pressed depth ratio (the depth h / the radius R of a pressing head), three kinds of engineering materials, namely alloy steel, aluminum alloy and titanium alloy, of which the elasticity modulus has remarkable difference are treated respectively by adopting two depth combinations (h1=0.1R and h2=0.4R) so as to obtain the respective material property coefficients; a ball factor S which reflects a hardening index effect is introduced so as to obtain a relational expression among a dimensionless function, W / (h3sigmarS ) and E* / (sigmarS); and the mechanical property of a tested material can be finally determined through constitutive relations, obtained by simulation by adopting finite element values, between the coefficients and the materials. By the method, the obtained result is more accurate; and the method is easy and quick and applicable to engineering structural materials in accordance with the power law.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
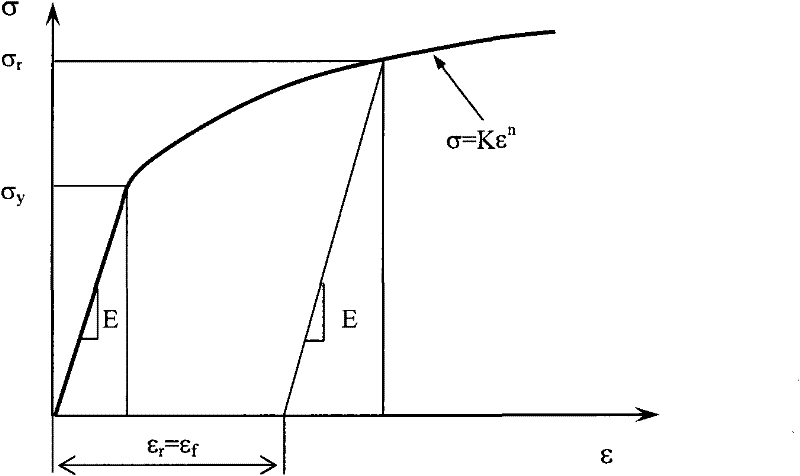
Method for forecasting uniaxial constitutive relation of material according to press hardness
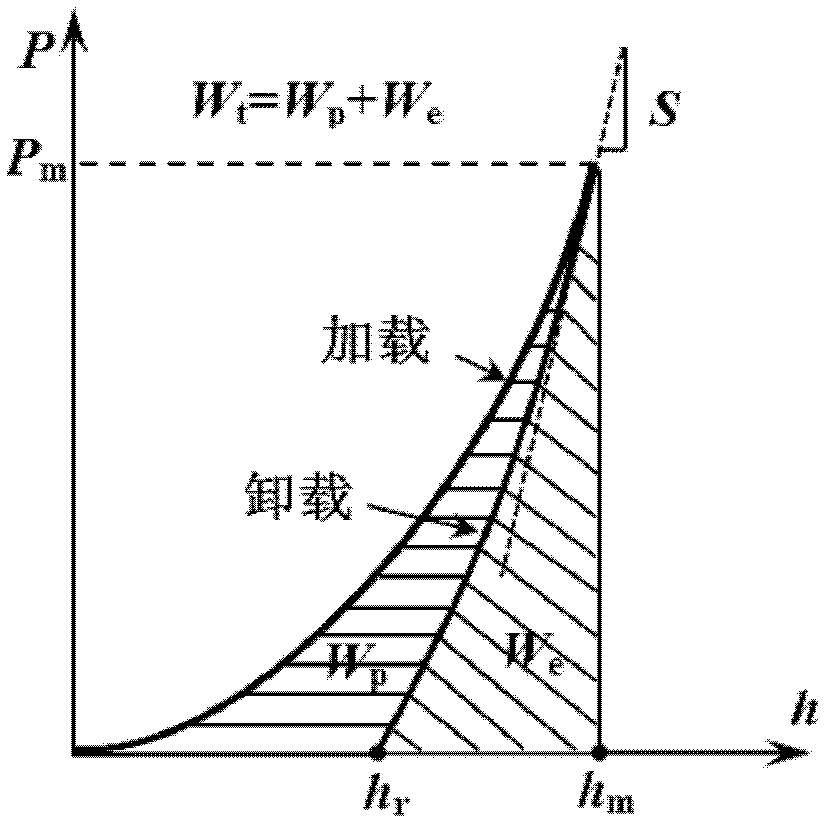
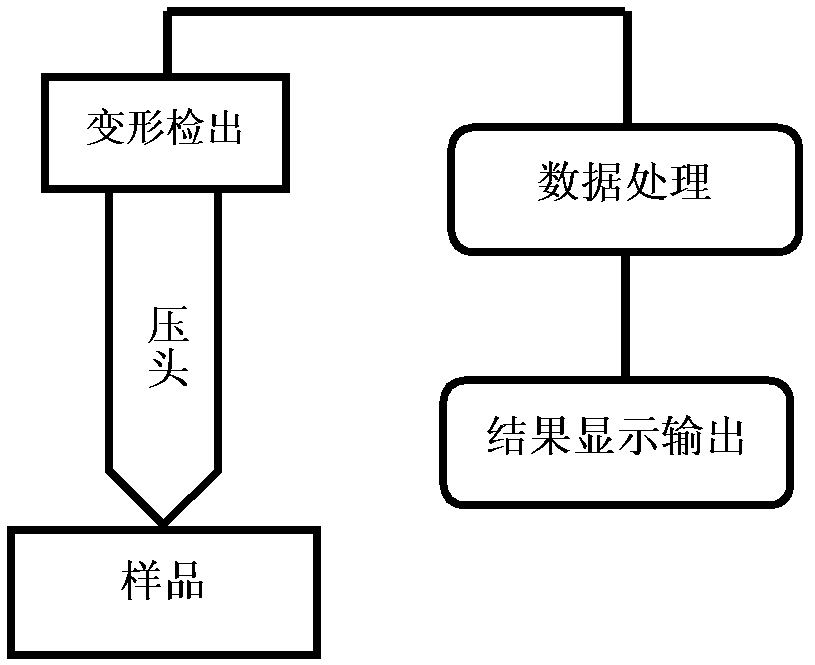
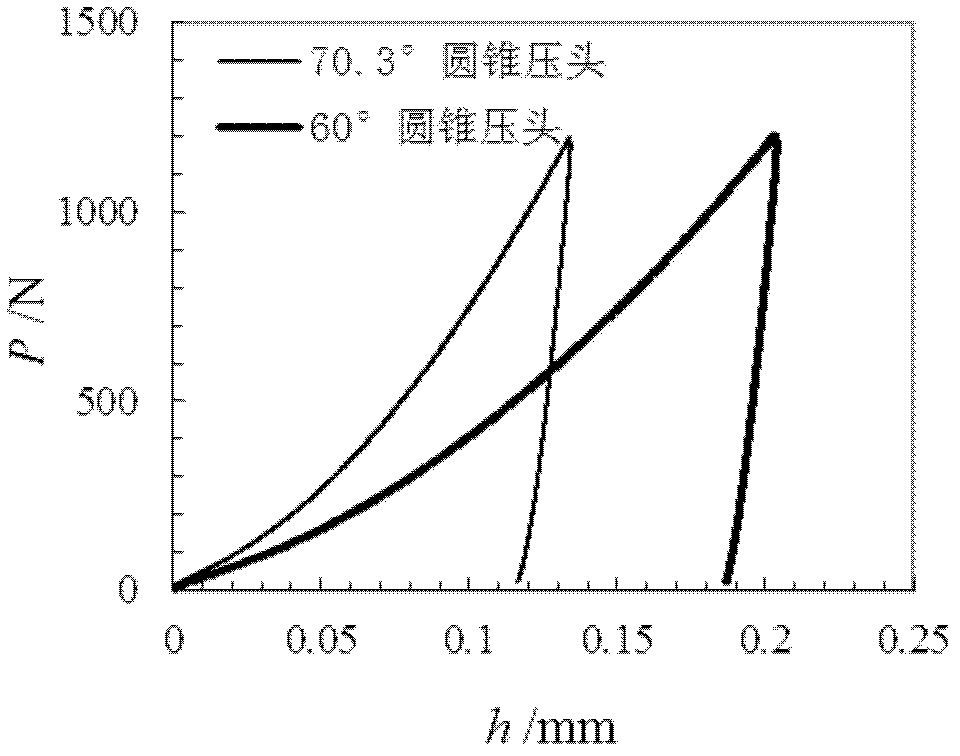
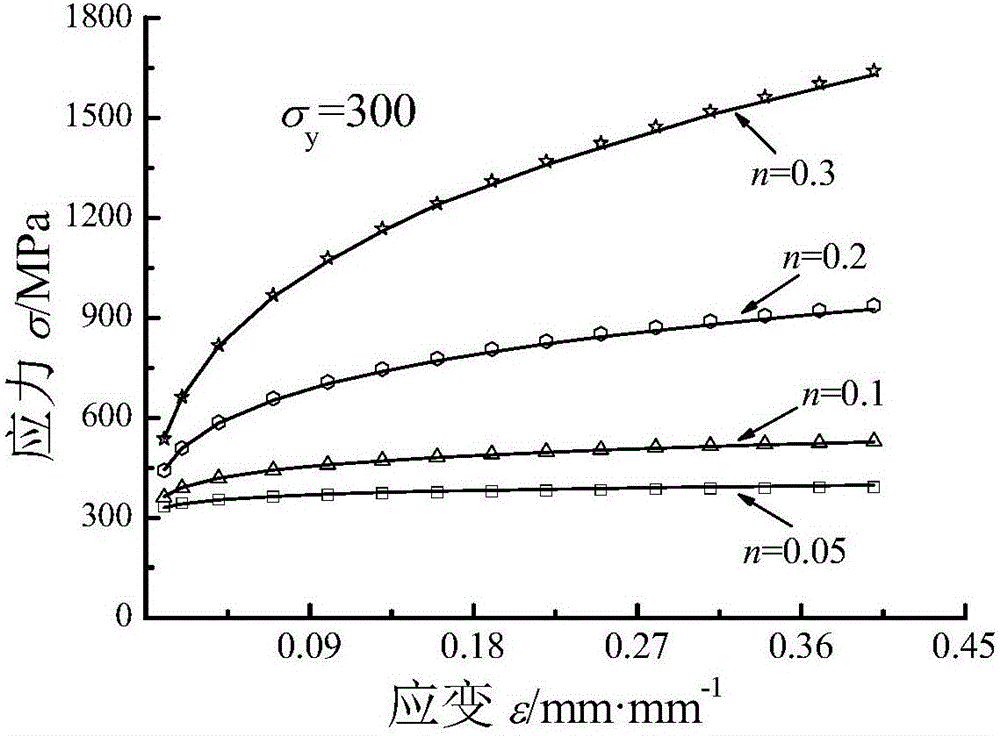
The invention discloses a method for forecasting the uniaxial constitutive relation of material according to press hardness, comprising the following steps: in a press hardness detecting system consisting of a press head loading unit, a deformation detecting unit and a data processing unit, the press head loading unit presses material to be detected by press heads with different appearances, and the deformation detecting unit detects the corresponding deformation of the material to be detected and inputs into the data processing unit to obtain the constitutive parameters E, sigma y and n of forecasting material, so that the portable measurement of the uniaxial constitutive relation of the material and the serviced structural part can be realized by the simple method for forecasting the uniaxial constitutive relation of the material according to the press hardness.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for establishing damaged rock constitutive relation by utilizing residual strength
InactiveCN102998180AEasy to implementDescribe the full stress-strain relationshipMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesResidual strengthStress–strain curve
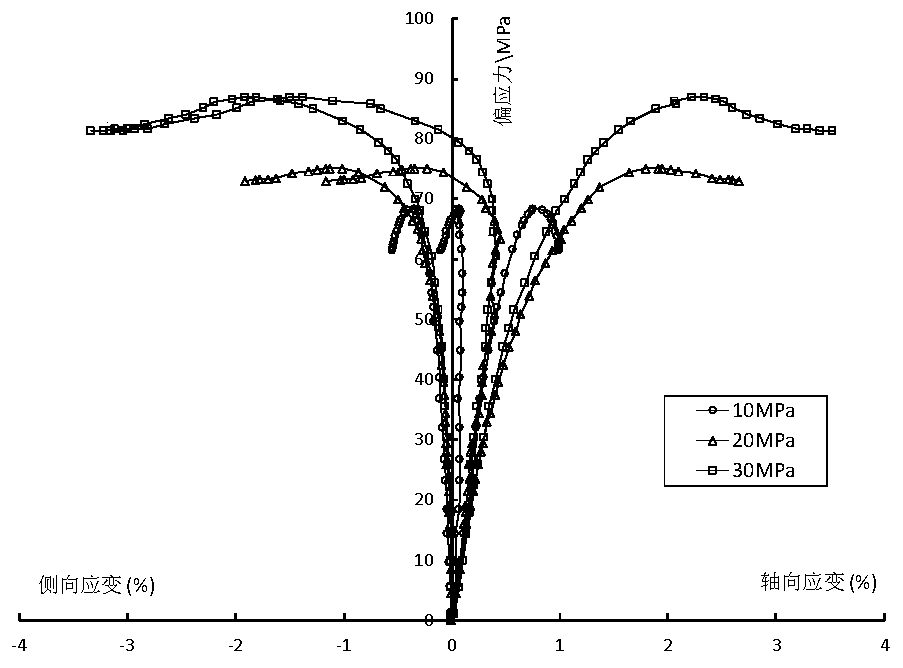
The invention relates to a method for establishing damaged rock constitutive relation by utilizing residual strength. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out a rock indoor triaxial compression experiment, measuring the axle load sigma1, the confining pressure sigma 3, the peak value intensity strain Epsilon 1c and the residual intensity sigma r of a rock sample, calculating the rock elastic modulus E and poisson ratio Mu, carrying out data regression according to triaxial compression test results, and calculating the uniaxial compressive strength sigma ci and an experience intensity parameter mi of a rock block; then establishing a three-dimensional damage statistic constitutive relation capable of reflecting a rock post-peak softening characteristic; and finally, solving constitutive relation parameters n and F0 according to four boundary conditions of a rock full-stress-strain curve geometric characteristic, and drawing a constitutive relation curve by utilizing Matlab software. The constitutive relation can fully reflect rock post-peak softening and residual intensity characteristics, and can describe the full-stress-strain relation of the rock damage process well, so that a theory formula well corresponds to the actual condition of a rock material; and the method can be realized simply, is widely applied to the theory analysis of the rock material, and has an actual value.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV +1
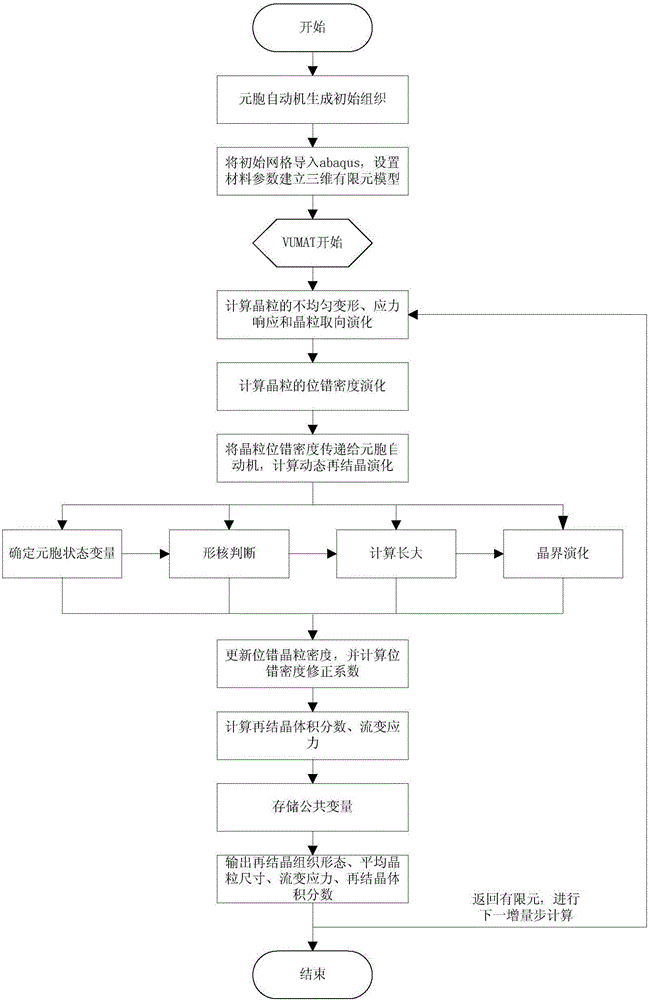
Method for predicting coupling responses of isothermal forming and dynamic recrystallization evolution of titanium alloys
ActiveCN106202675AAchieving Unified PredictionTightly deformedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCrystallization kineticsTitanium alloy
The invention provides a method for predicting coupling responses of isothermal forming and dynamic recrystallization evolution of titanium alloys. Grain stress responses, intercrystalline non-uniform deformation and non-uniform dislocation density caused by intercrystalline non-uniform deformation are obtained in an isothermal forming process of the titanium alloys and are adopted as variables and transmitted to a cellular automaton, dynamic recrystallization evolution of the grain size under the condition of non-uniform size deformation is obtained, and dynamic recrystallization nucleation and grown structure morphology as well as grain boundary evolution and updated dislocation density which are caused by the dynamic recrystallization nucleation and grown structure morphology are obtained. The obtained grain and grain boundary information including dynamic recrystallization nucleation and growth as well as the dislocation density is returned to a crystal plasticity finite element method, dislocation gliding resistance of each grain unit is updated, so that subsequent deformation of the titanium alloys is influenced, and the stress responses of the grain size are calculated according to the constitutive relation. The method realizes synchronous prediction of non-uniform deformation of the grain size in isothermal forming of the titanium alloys, dynamic recrystallization structure morphology evolution, recrystallized grain size evaluation, recrystallization kinetics, deformable bodies and grain flow stress.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
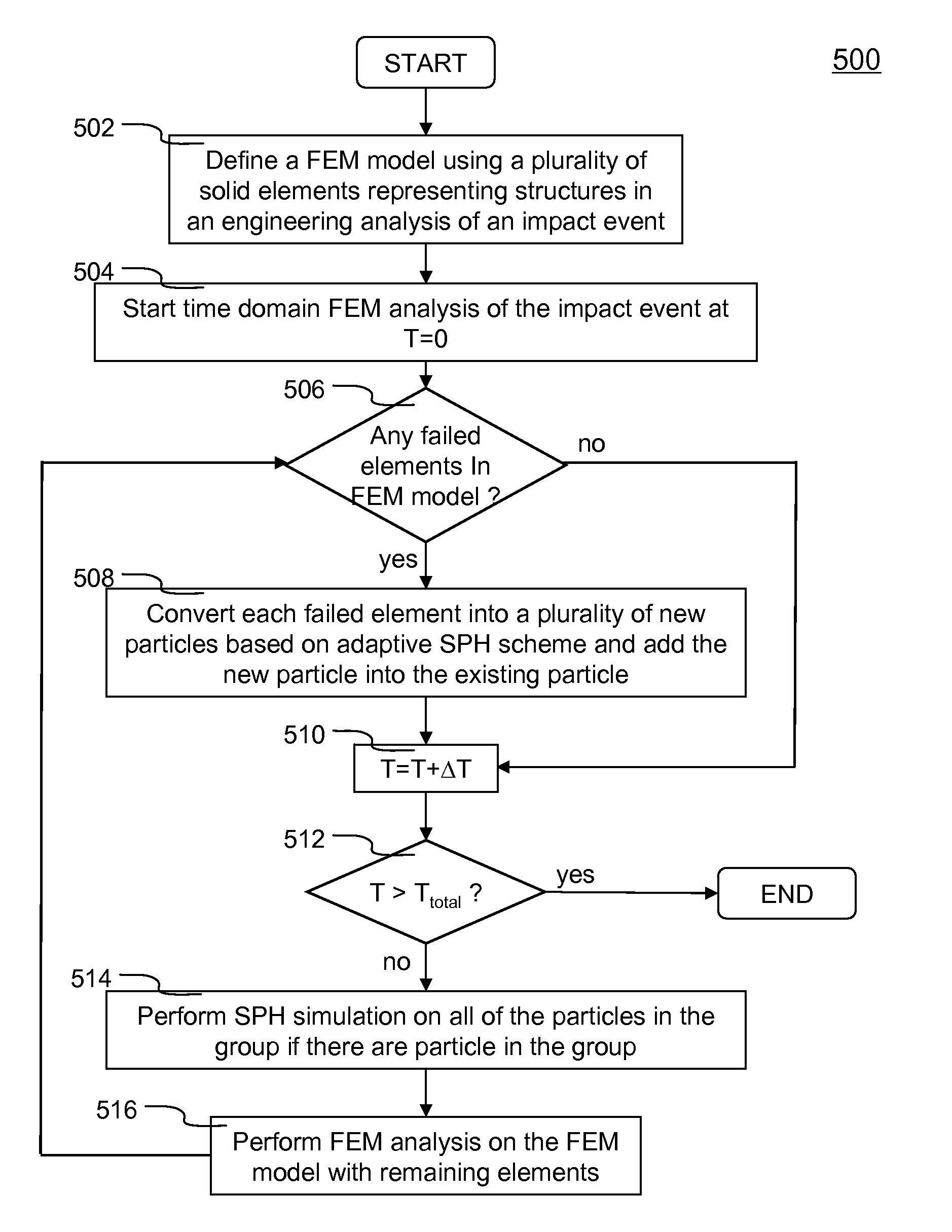
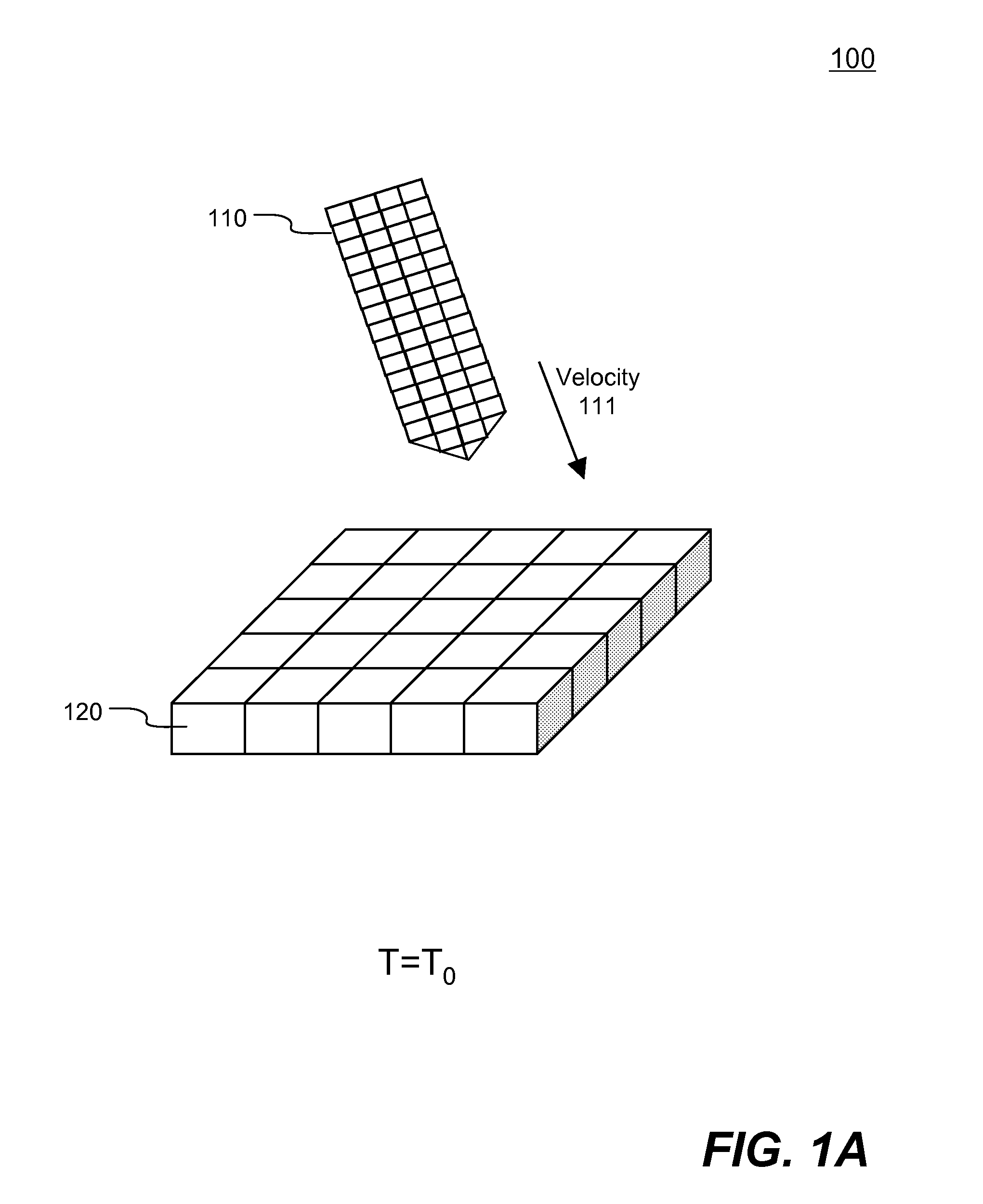
Methods and systems of engineering analysis using a hybrid approach with FEM and adaptive SPH
ActiveUS20090228246A1Real timeComputation using non-denominational number representationInvestigating material hardnessSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsMomentum
Systems and methods of computer aided engineering analysis using hybrid approach of finite element method (FEM) and adaptive smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) are described. According to one aspect, a computer-aided engineering analysis is performed to simulate an impact event between structures. A FEM grid model is created to represent the structures using a plurality of solid elements which represents geometry and material properties. Once a contact between two structures resulted into a material or structural failure according to predefined material constitutive equation, solid elements representing the failed portion of the structure are removed. Each failed solid element is then replaced by a plurality of particles to be analyzed using the SPH analysis. The particles replacing the failed element inherit all of the states and properties of the failed element, such as location, mass, velocity, acceleration, etc. The replacement is conducted according to the principles of mass, momentum and energy conservation.
Owner:ANSYS
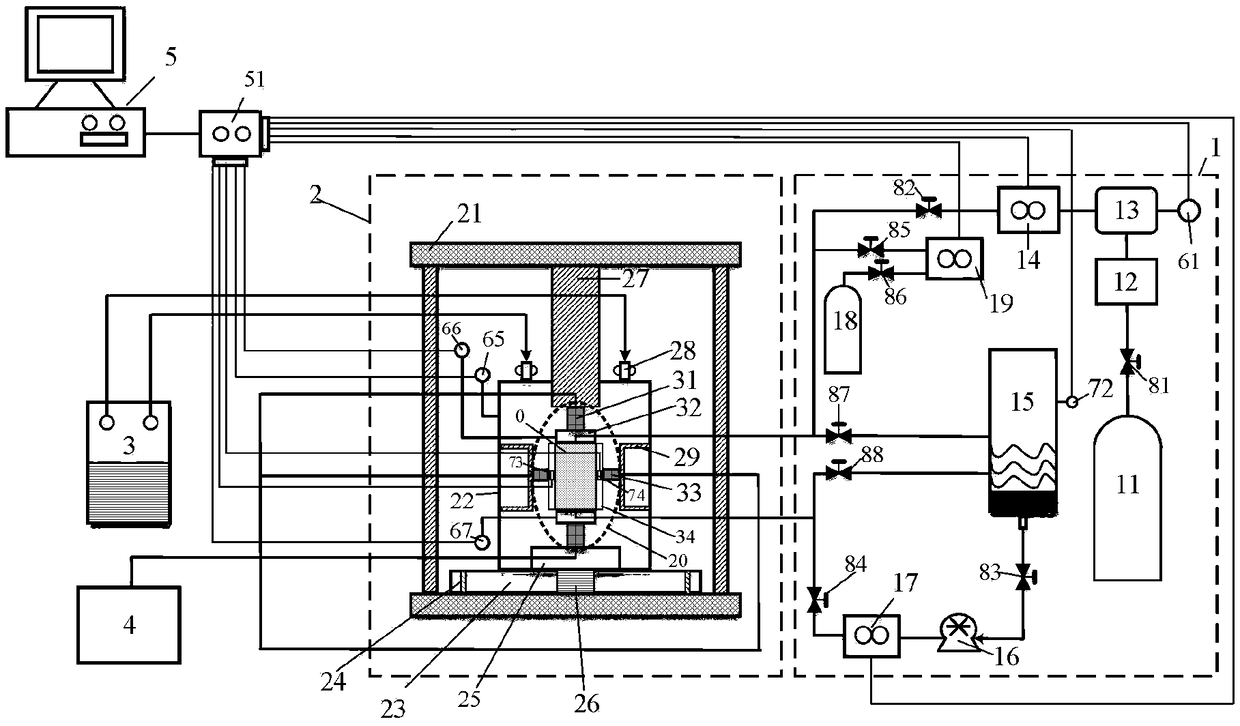
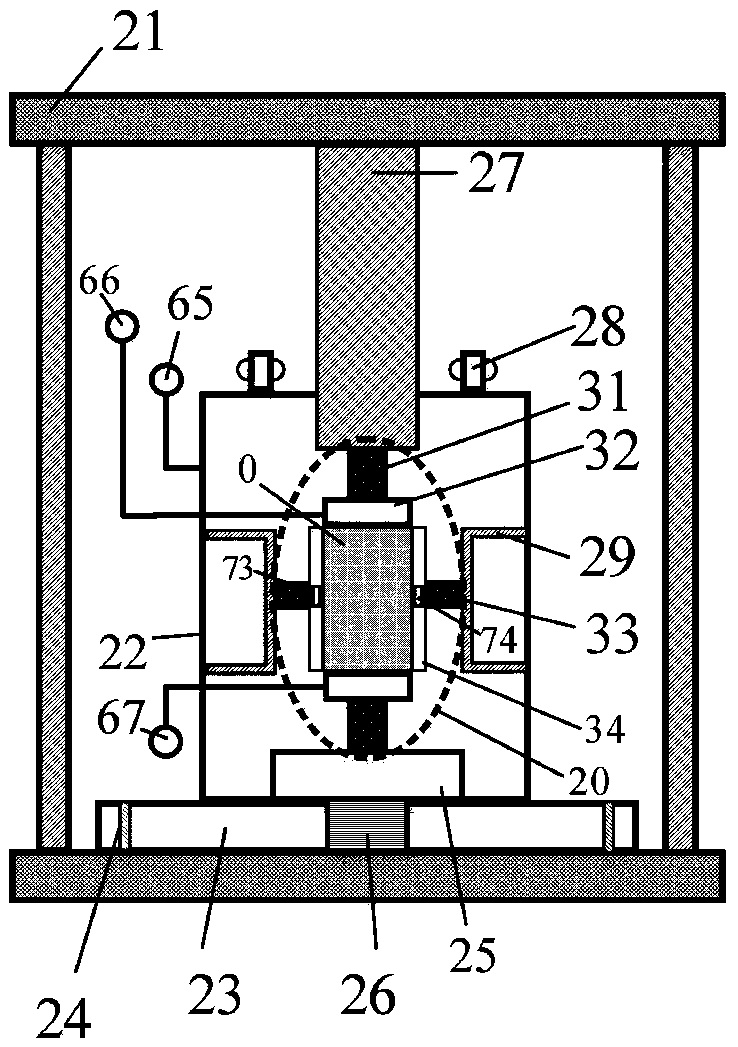
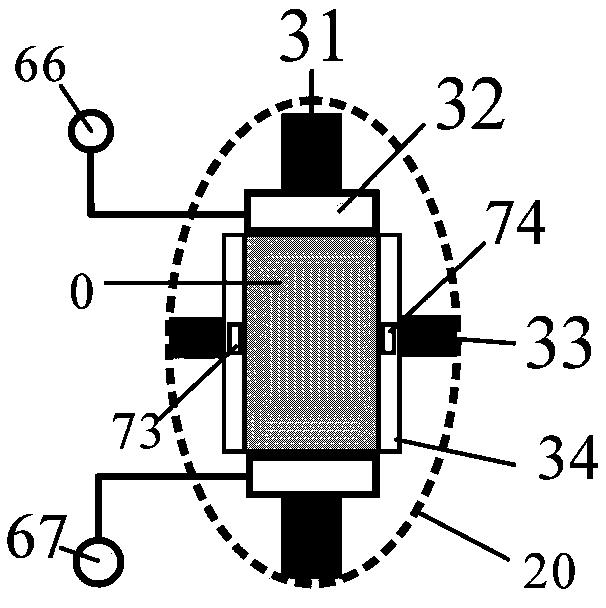
True triaxial test device for combustible ice sediments
ActiveCN108982228AEvenly loadedReflect the real force characteristicsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume measurement apparatus/methodsTriaxial shear testSoil mechanics
The invention belongs to the technical field of rock and soil mechanics, and relates to a true triaxial test device for combustible ice sediments. According to the true triaxial test device, the formation process of the combustible ice sediments in a deep sea reservoir stratum can be simulated in a laboratory, a true triaxial compression test is carried out on the combustible ice sediments, and therefore a technical guarantee and support are provided for accurately predicting the strength characteristics of the reservoir stratum and researching the constitutive relation of the reservoir stratum; and in the true triaxial compression test, main stress in three directions can be applied independently, the real stress characteristics of the combustible ice sediments in a bottom layer can be better reflected, but the boundary loading condition problem can be easily caused in the loading process, composite loading plates of rigid plates and deformation plates are adopted in the front-and-back pressurization direction, so that the pressure can be uniformly loaded on a sample through the composite loading plates in the front-back pressurization process, and therefore the problems that mutual interference of loading plates in three-directional loading is caused in the loading process, and loading is not uniform due to the fact that the sample is deformed in the loading expansion processcan be solved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
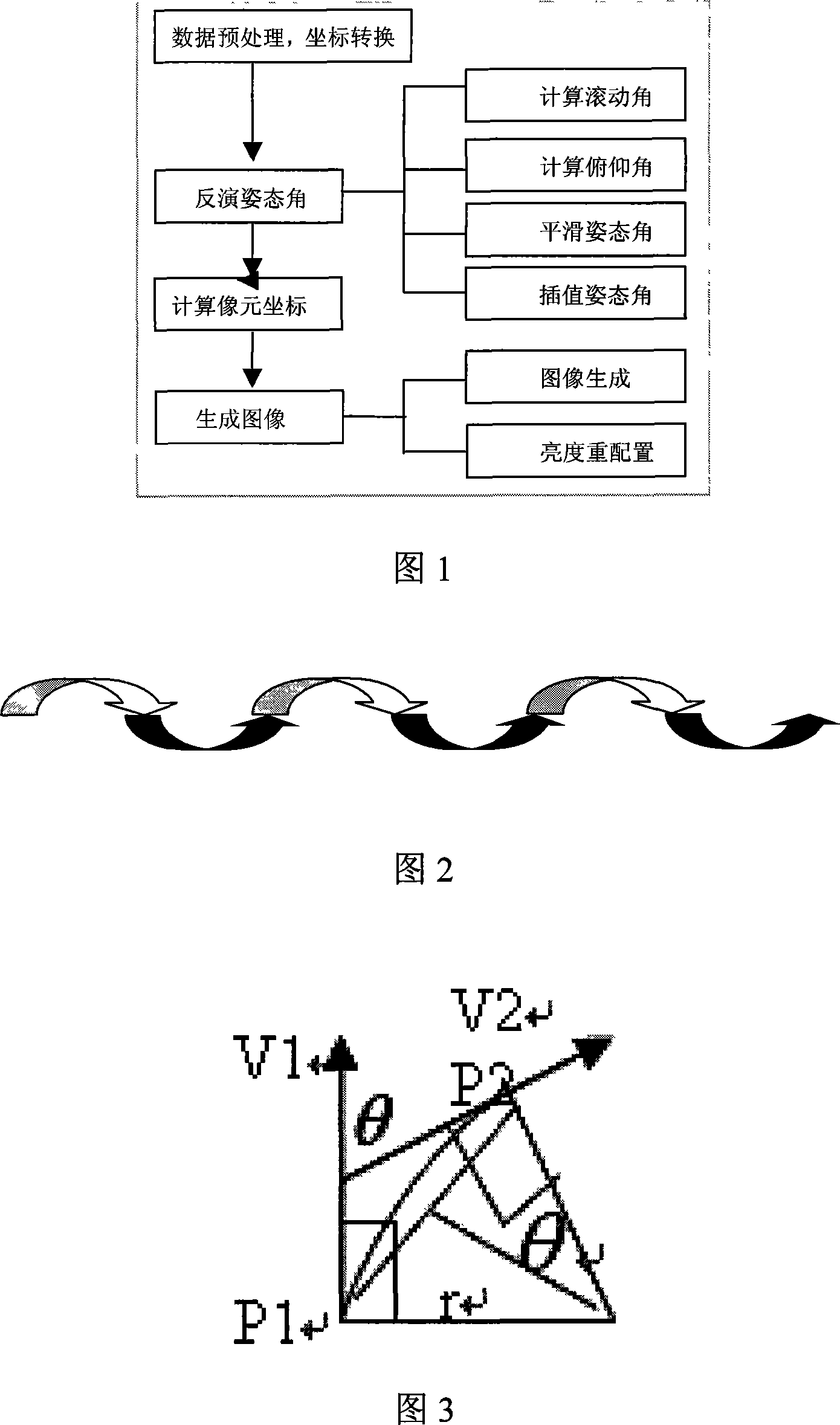
Navigation multiple spectrum scanner geometric approximate correction method under non gesture information condition
InactiveCN101114022AImprove geographic accuracyFlexible access toUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationAviationVertical plane
The invention discloses an avigation multi-spectral scanner geometric rough correction method under the conditions of no gesture information, which comprises the steps that: 1) the multi-spectral scanner data is carried out the coordinate conversion, the measured value in a WGS-84 ground coordinate system is converted to the value in a Gaussian plane Cartesian coordinate; 2) according to a ideal flight model, an one second mode is used for simulating a rolling angle; 3) a curve is fitted according to the height data in the vertical plane, then the flight pitching angle in each updated data point is calculated according to the cutting direction; 4) the central projection constitutive equation is used for obtaining the point coordinates; 5)according to the flight height, the scanning angel and the instantaneous scanning angel, the other points coordinates in the same scanning row are obtained by the scanning mode; 6) a direct method is used for producing a rough correction image. The invention improves the geographical accuracy of the avigation remote sensing, and is an innovation of the remote sensing technology under the conditions of no gesture information and improves the time effectiveness, so the avigation remote sensing technology can be better applied to the production and livelihood of the national economy.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
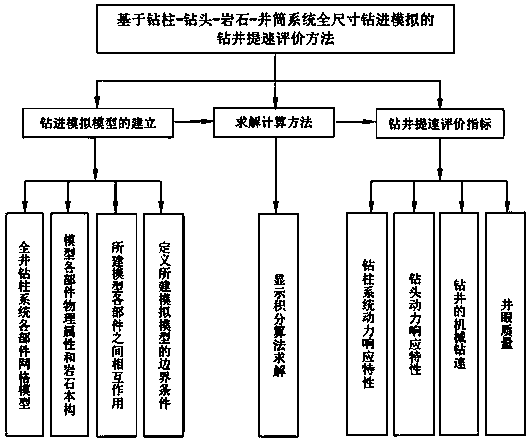
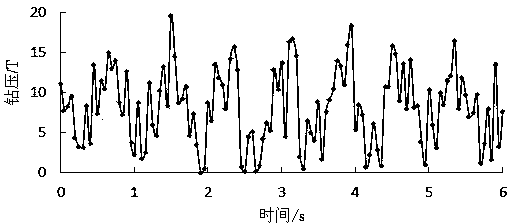
Drilling speed increase evaluation method based on drill stem-drill bit-rock-shaft system full-scale drilling simulation
The invention relates to a drilling speed increase evaluation method based on drill stem-drill bit-rock-shaft system full-scale drilling simulation. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a finite element model based on drill stem-drill bit-rock-shaft system full-scale drilling simulation, then, analyzing and solving the established model according to the explicit integration algorithm, and finally, evaluating the drilling speed increase according to established evaluation criteria. The process of establishing the finite element model comprises the following steps: establishing a grid model of all components, defining the physical properties of the components and the constitutive relation and breaking failure criteria of rock, establishing a drill tool and well wall random contact and impact model and a drill bit and rock interaction model, and defining boundary conditions. According to the method, the real-time drilling and rock breaking process is simulated with drill bit rock breaking as the boundary conditions of the lower end of the drill stem, and therefore simulation results are closer to the reality, and references are provided for on-site drilling design, drilling parameter optimization, drill bit model selection and drilling speed increase evaluation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
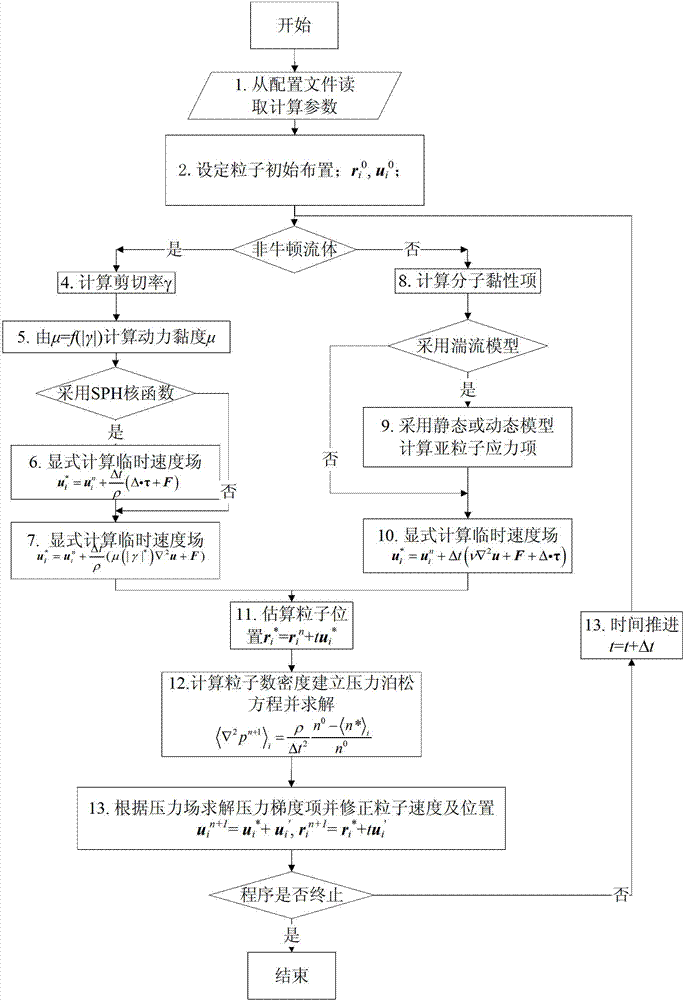
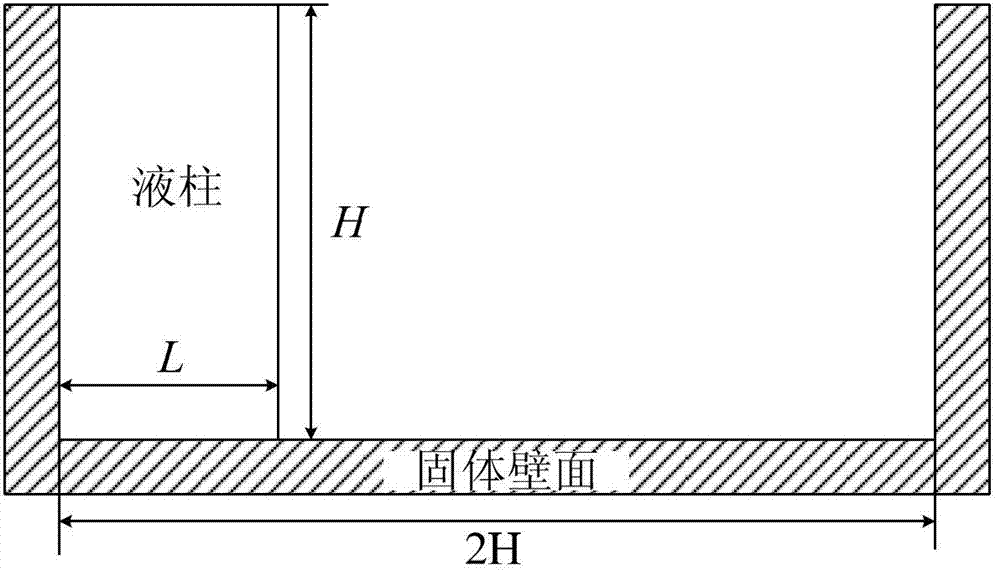
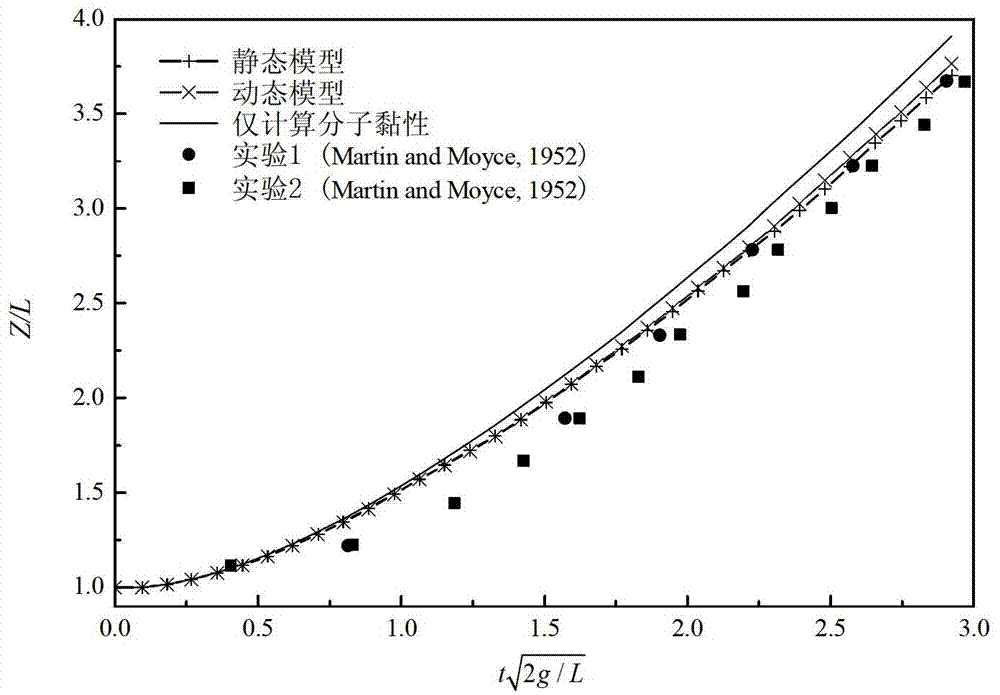
Establishment method for free surface flow model in moving particle semi-implicit algorithm
The invention provides an establishment method for a free surface flow model in a moving particle semi-implicit algorithm, comprising the following steps of: introducing a turbulence model which comprises a static Smagorinsky model and a dynamic Smagorinsky model in the form of Lagrange; treating a non-Newtonian fluid having a constitutive equation like mu = f(the absolute value ofgamma) by adopting a variable-viscosity Newtonian fluid model; and introducing a cubic spline kernel function, discretizing the shear stress of the non-Newtonian fluid by adopting the divergence discretization scheme of a smooth particle fluid dynamic method, and treating the free surface flow of the non-Newtonian fluid. According to the method provided by the invention, the sub-particle stress model of turbulence can be considered, and the method provided by the invention can be used for calculation for the non-Newtonian fluid.
Owner:江苏金洋造船有限公司
Composite structure failure prediction analytical method
InactiveCN105352816ABuild the stiffness matrixAccurate calculationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFinite element softwareMaterials science
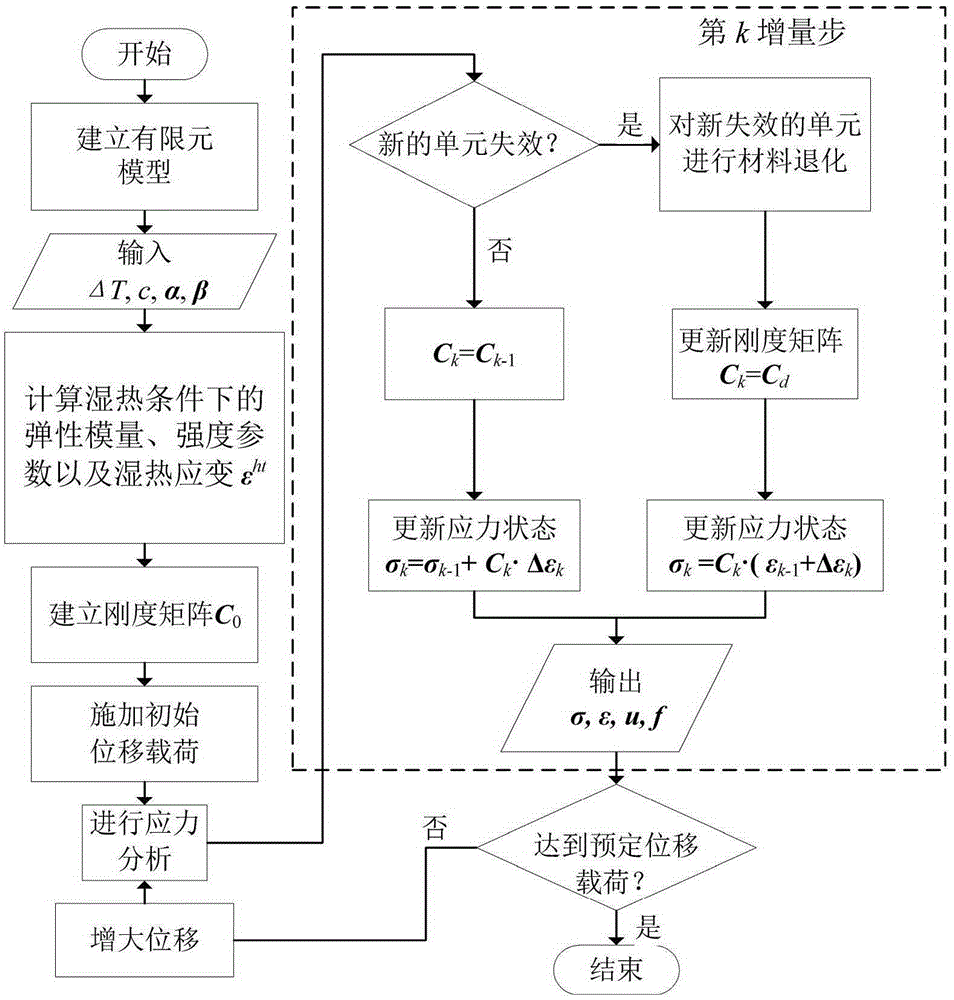
The invention provides a composite structure failure prediction analytical method. The constitutive equation expressing the stress-strain relation of an anisotropic composite under the influences of damp-heat environments is established through the combination of influences of damp-heat strain. Meanwhile, through the combination with an asymptotic damage analysis method, the influences of damp-heat effects on parameters such as rigidity and strength of materials are introduced to the three aspects of a stress analysis mode, a failure criterion and a material degradation model, a UMAT subprogram is complied, packaged and embedded in finite element software, and finally a more perfect asymptotic damage model capable of being used for composite failure analysis under the damp-heat environments is established. Compared with an existing failure asymptotic damage analysis method for various composite structures, the influences of damp-heat effects on failure behaviors of anisotropic composites are considered, the damage process of materials under damp-heat environments can be accurately expressed, and the composite structure failure prediction analytical method is suitable for prediction of simulation and strength of the composite structure damage process under the condition that temperature, humidity and other conditions are more complex.
Owner:SHENYANG AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
Method for constructing elastic-plastic-damage coupling mechanical constitutive model of rock material
PendingCN110705165AImprove accuracyWide applicabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesDesign optimisation/simulationMechanical modelsElastic plastic
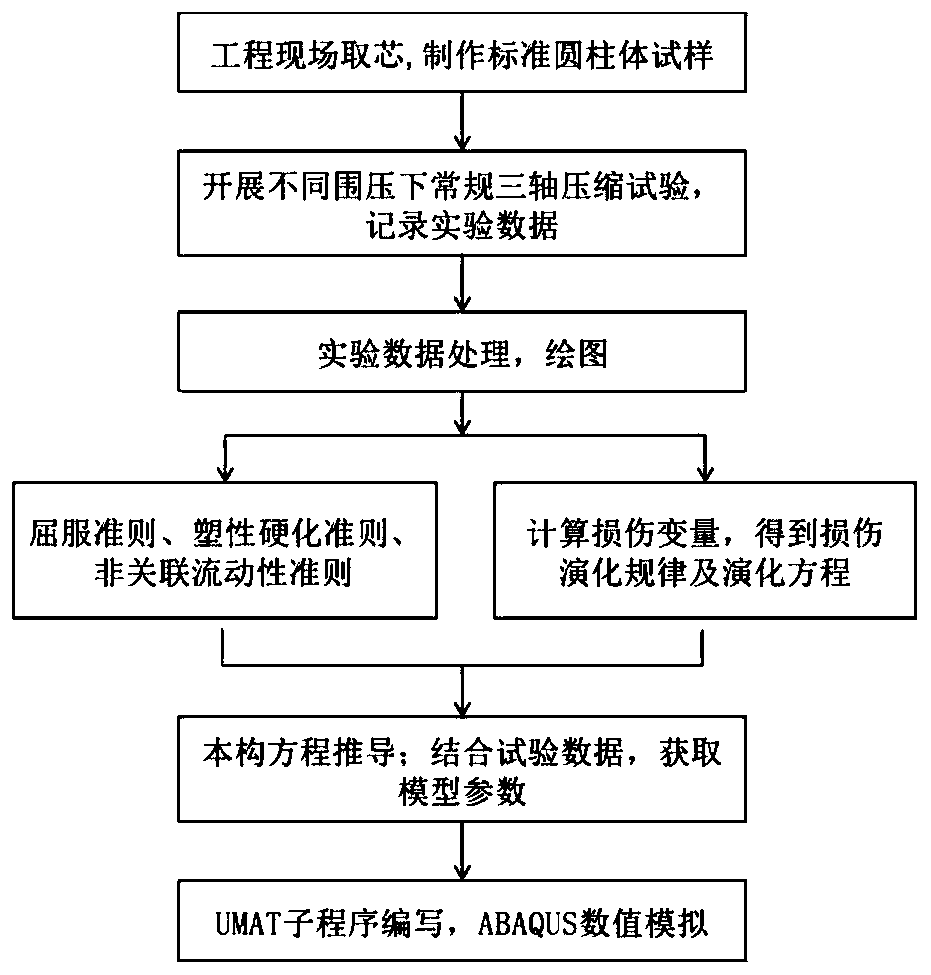
The invention discloses a method for constructing an elastoplasticity-damage coupling mechanical constitutive model of a rock material. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining the rock material on an engineering site, and manufacturing a standard cylinder sample; carrying out conventional triaxial compression mechanical tests under different confining pressures; obtaining a rock yield criterion, a plastic hardening criterion and a non-associated fluidity rule in combination with a test result; calculating a rock damage variable according to the stress-strain curve, and obtaininga rock damage evolution equation according to a damage variable-axial strain evolution rule; deriving a constitutive equation based on an elastic-plastic mechanics theory and an irreversible thermodynamic damage constitutive theory; combining the test data to obtain model parameters; writing the mechanical model into a UMAT subprogram, embedding the UMAT subprogram into ABAQUS finite element software, and carrying out triaxial test numerical simulation, so as to verify and improve the model. The method is clear in mechanical significance, simple in parameter acquisition, wide in application range and relatively high in accuracy.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for establishing earthquake response mode based on fracture equivalent medium model
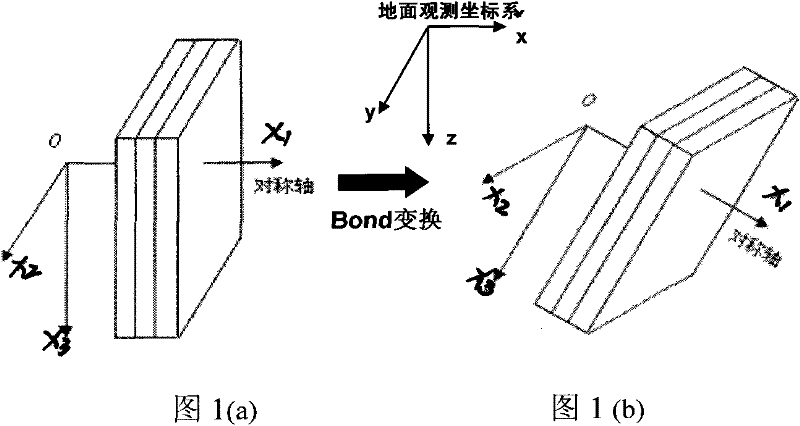
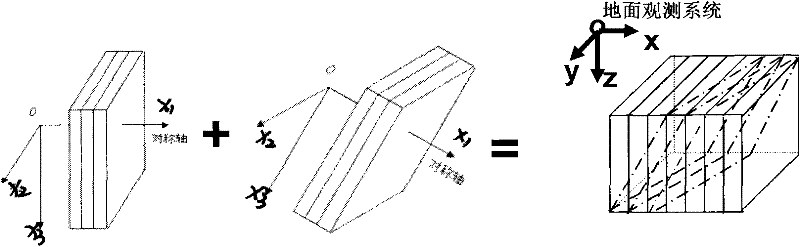
The invention discloses a method for establishing an earthquake response mode based on a fracture equivalent medium model, which belongs to the field of exploration geophysics. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: determining a relationship between fracture characteristic parameters and equivalent medium elastic parameters by quantificationally applying a fracture equivalent medium theory, establishing a constitution relation of a fracture network anisotropic equivalent medium model based on a Bond conversion and superposition principle, and placing the constructed fracture network equivalent medium model in an actual space position of strata, and establishing an actual stratigraphic fracture equivalent medium model; and establishing an earthquake response model of different tectonic positions and different lithologic fractured reservoirs by use of an earthquake wave field numerical simulation method. The method for establishing the fractured reservoir earthquake response mode based on the fracture equivalent medium model has strong practicability, and provides the basis for identifying the fractured reservoir from the prestack earthquake data.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method based on finite difference method
ActiveCN105044771AImplement iterative solutionEnables real-time propagation simulationSeismic signal processingDouble phaseFinite difference method
The invention discloses a 3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method based on a finite difference method. The 3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method comprises steps of obtaining a solid and fluid stress tensor and a solid and flow strain tensor and transforming the tensors to a constitutive equation, obtaining a geometry equation according to the corresponding relation of stress and the displacement, obtaining a motion differential equation according to the constitutive equation, the geometry equation and the fluid motion relative to the solid and the corresponding relation between the stress and the displacement, taking the divergence on two ends of the motion differential equation to obtain a first longitudinal wave equation and a second longitudinal wave equation of the seismic wave, as for the first longitudinal wave equation and the second longitudinal equation, enabling a partial derivative to y to be zero and performing difference discrete on the space partial derivative and the time partial derivative by employing an 2N order precision expansion formula and a 2-order precision center difference form to obtain a first difference equation and a second difference equation, and performing boundary absorbing condition processing on the first difference equation and the second difference equation to obtain the corresponding seismic wave field value. The invention realizes the real-time transmission simulation of the physics seismic wave field.
Owner:北京多分量地震技术研究院
Deep rock mass non-linear mechanics experimental equipment
The invention relates to a nonlinear mechanical test equipment for a deep rock body, belonging to the mechanical test equipment for the deep rock body in geotechnical engineering. At present, the conventional rock body mechanical test comprises a unidirectional compression test, a unidirectional tension test, a triaxial compression test and a shear test. The force and the mechanical behavior in the action process of the deep rock body have the very close relations with the loading process. The conventional rock body mechanical test modes and equipments can't reflect the special mechanical behavior related to the loading process of the deep rock body. Therefore, the invention adopts the scheme of that each direction of three dimensions of a hydraulic loading device is provided with an independent hydraulic power control device, and combines the corresponding test piece fixture to provide the nonlinear mechanical test equipment which implements the composite stress test for the engineering rock body, particularly for the deep engineering rock body in order to implement the intensive study for the stress state of the engineering rock body in the process of tension and compression, intensity character of tension and shear composite state, constitutive relation and construction.
Owner:何满潮
Method for obtaining uniaxial stress-strain relation of material through small punch test
ActiveCN106124293AQuantitative evaluation of degradation performanceTo overcome the shortcomings such as large size restrictionsStrength propertiesSmall sampleMaterials testing
The invention discloses a method for obtaining uniaxial stress-strain relation of a material through a small punch test. After a continuous load-displacement curve of a stamped wafer sample is obtained, power-law fitting is conducted on the stage III of the P-V curve, obtained load characteristics and displacement indexes are introduced to a Hollomon equation so as to obtain the uniaxial stress-strain relation of the material. The method is suitable for ductile and power-law isotropic hardening materials, the uniaxial stress-strain relation of the material can be obtained only by cutting out a small wafer sample from an existing member in special circumstances such as high temperature and irradiation, and accordingly the degradation properties of the material are assessed. The method has weaker destructiveness on the existing member, achieves the micro-damage detection, sample processing and testing principles are simpler, obtained results have higher accuracy, the shortcoming that a traditional uniaxial drawing test is largely limited by material size and the like is overcome, and the cost lower. The method has the greater advantages in testing of precious-metal servicing micro-force materials establishing constitutive relation of minimally invasive wafers and other small samples.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
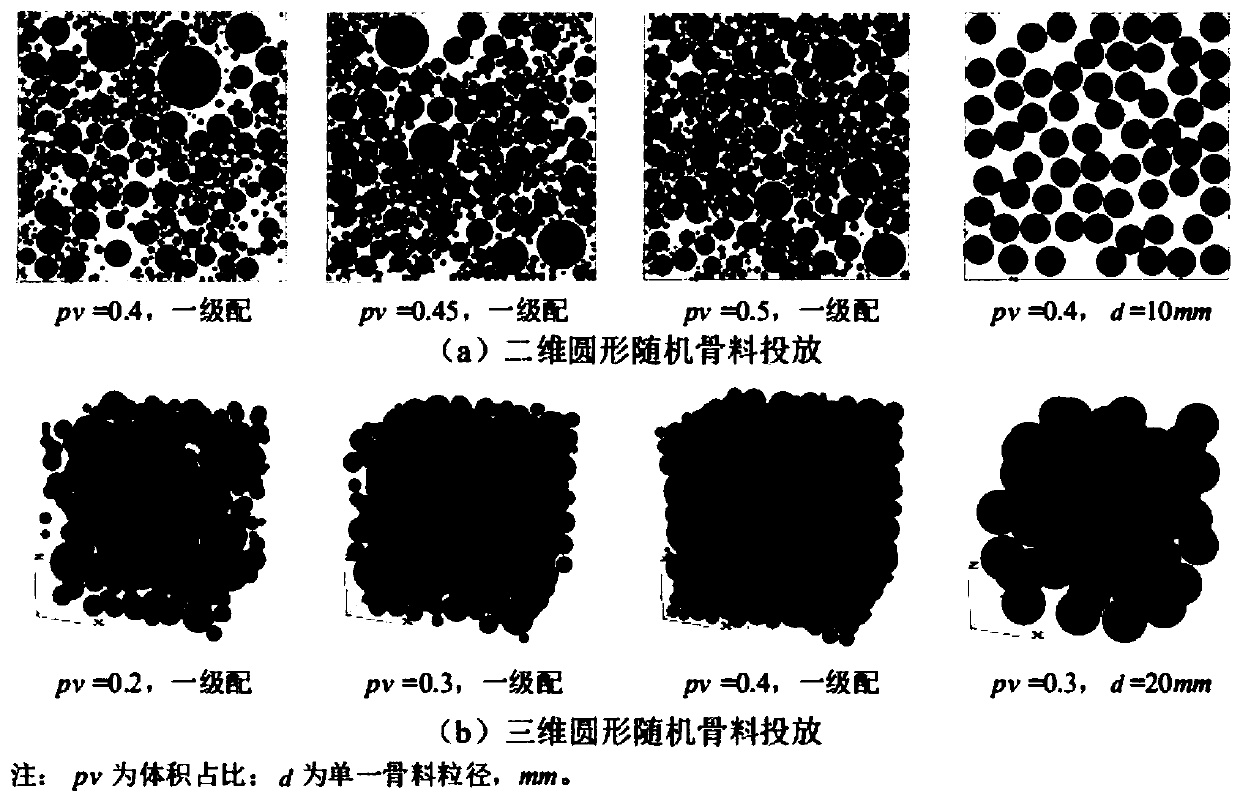
Method for establishing stainless steel bar concrete mesoscopic numerical model
ActiveCN110442922ASustainable transportationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesBond interfaceElement analysis
The invention discloses a method for establishing a stainless steel bar concrete mesoscopic numerical model. The method comprises the following steps: uncertain stainless steel bar concrete mesoscopicstructure composition, model establishment of each mesoscopic structure, constitutive relation of each mesoscopic component and determination of mesoscopic material parameters. Under the condition ofdetermining the mesoscopic material parameters of the coarse aggregate, the mortar, the mortar-coarse aggregate interface and the steel bar-mortar bonding interface, mesoscopic finite element analysis is carried out on the bonding performance of the stainless steel bar concrete. According to the method, based on a mesomechanics theory, detailed expression is carried out from the aspects of mesoscopic structure composition, constitutive relations of all mesoscopic components, determination of mesoscopic parameters, setting of boundary constraints and the like. A simplified method of a stainless steel bar solid structure in two-dimensional solid modeling is proposed, a parameter assignment method of a stainless steel bar-mortar matrix bonding layer microstructure material is studied, the influence of interface performance on bonding strength is analyzed, and the recommended value range of the tensile strength of a bonding layer is determined in combination with a calculation result.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
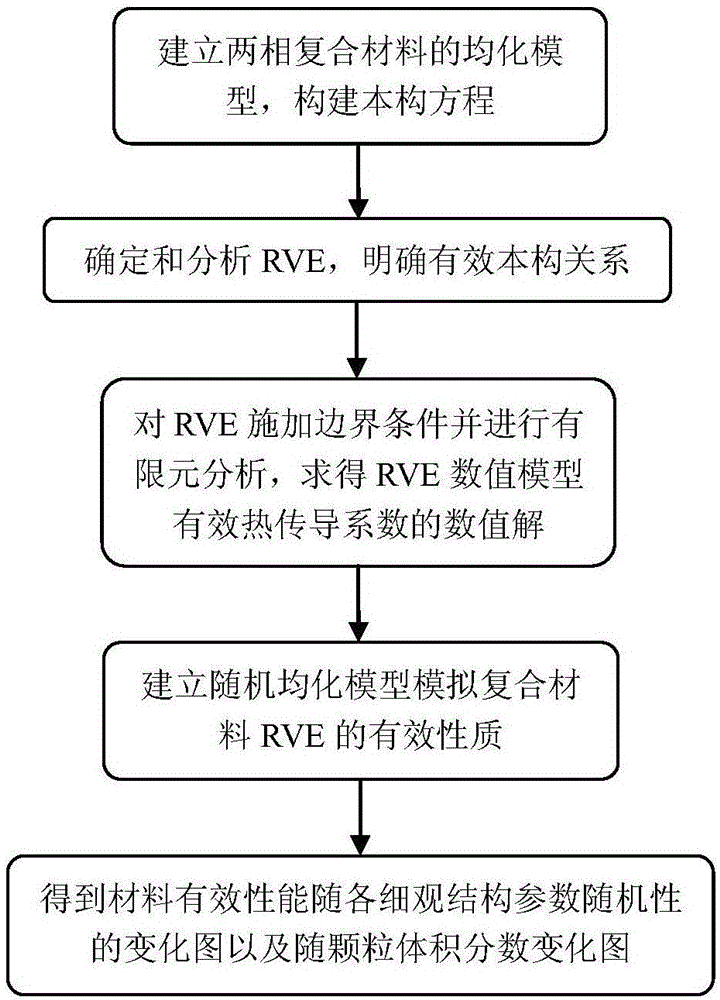
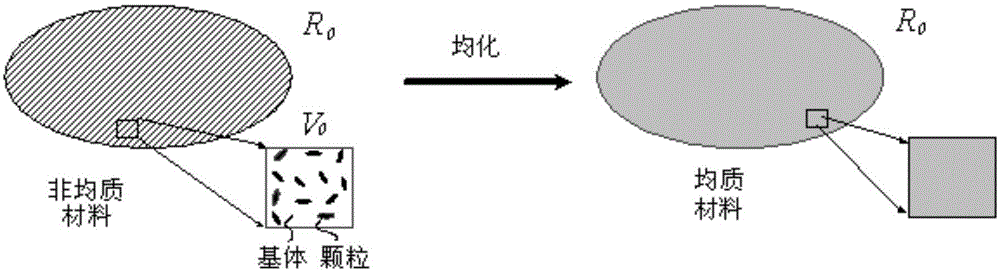
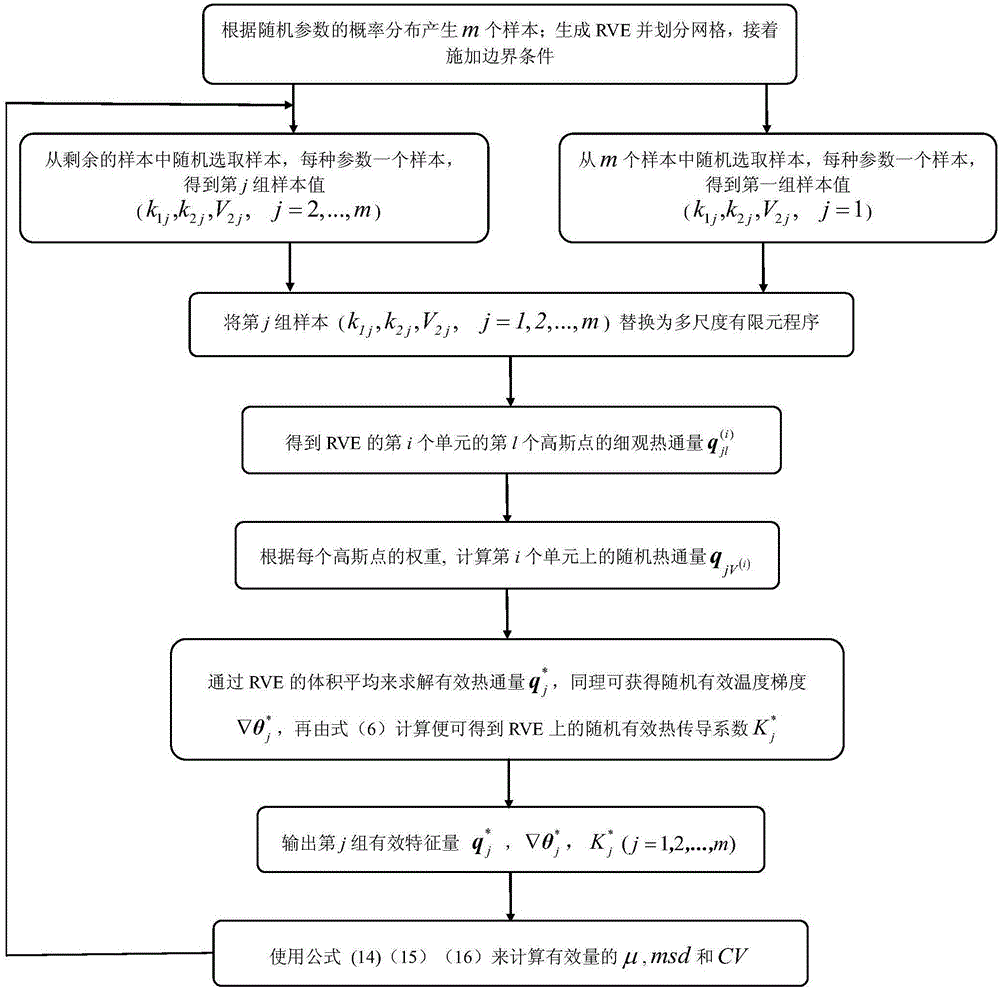
Random thermal homogenizing analysis method of two-phase composite material
ActiveCN105044146ASolving Numerical Modeling ProblemsMaterial heat developmentHeat fluxElement analysis
The invention discloses a random thermal homogenizing analysis method of a two-phase composite material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a corresponding microscopic homogenization model of a two-phase composite material composed of a matrix and particles, constructing constitutive equations, and calculating the thermal boundary values of the heterogeneous material; (2) determining and analyzing to obtain one RVE from the two-phase composite material, and determining the effective constitutive relationships among the effective heat conduction coefficient, the volumetric average temperature gradient and the volumetric average heat flux, wherein the volumetric average temperature gradient and the volumetric average heat flux are obtained from RVE; (3) applying boundary conditions on RVE, and at the same time carrying out finite element analysis and calculation to obtain the value of effective heat conduction coefficient of the RVE numerical model; (4) establishing a random homogenizing model to obtain the macroscopic effective quantity of the composite material. In the provided method, a finite element method and Matlab software are used to solve the problem of complicated RVE numerical modeling, the influences of parameter randomness of components of the composite material under three boundary conditions on the macroscopic thermal physical properties are taken into account comprehensively, and thus the provided method has an application value, a certain academic value, and theoretical significance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
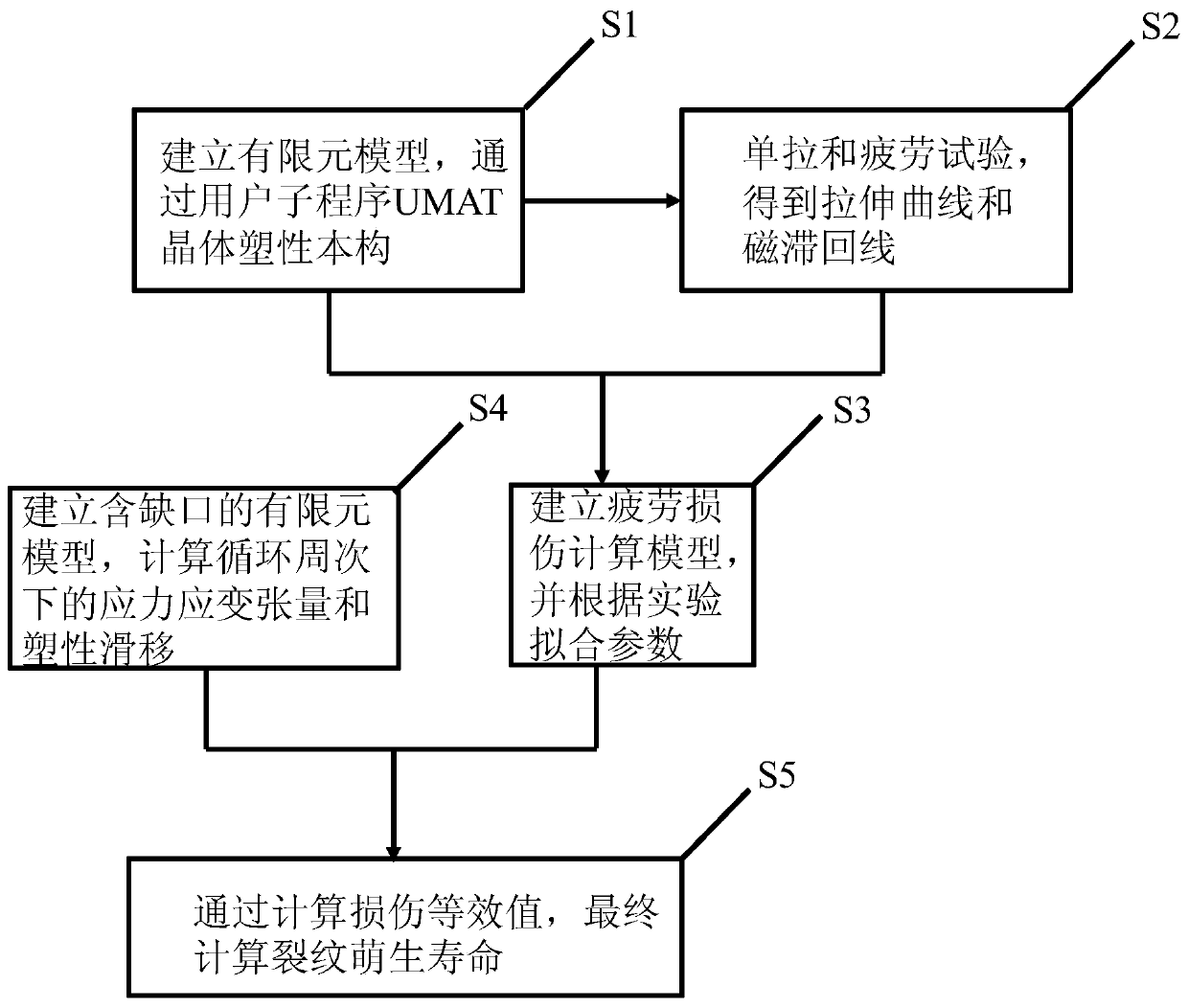
Fatigue life prediction method for geometric discontinuous structure
ActiveCN110826285AIntuitiveDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelCrazing
The invention provides a fatigue life prediction method for a geometric discontinuous structure. The method comprises the steps of building a geometric continuous first finite element model, defininga crystal plasticity constitutive equation, and obtaining a stress-strain relation of a material under a given cyclic load condition; carrying out a uniaxial tensile test and a uniaxial fatigue test to obtain a tensile curve and a hysteresis loop; fitting through a test parameter method to obtain a tensile curve and a hysteresis loop, and obtaining the material parameters and a fatigue plastic slip critical value required by a crystal plasticity constitutive equation; establishing a second finite element model of the geometric discontinuous structure, and obtaining a stress-strain relationshipand a single-cycle fatigue plastic slip value of each cycle; and calculating to obtain the crack initiation life of the notch sample. According to the fatigue life prediction method for the geometricdiscontinuous structure, the fatigue analysis of the geometric discontinuous structure at different temperatures can be better achieved, the crack initiation position can be accurately predicted, andthe fatigue life prediction method has the advantages of being visual, high in applicability and high in accuracy.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
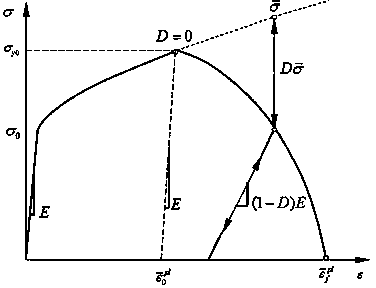
Creep damage calculation method and model under variable load history
ActiveCN109142083AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpecial data processing applicationsCreep strainComputational model
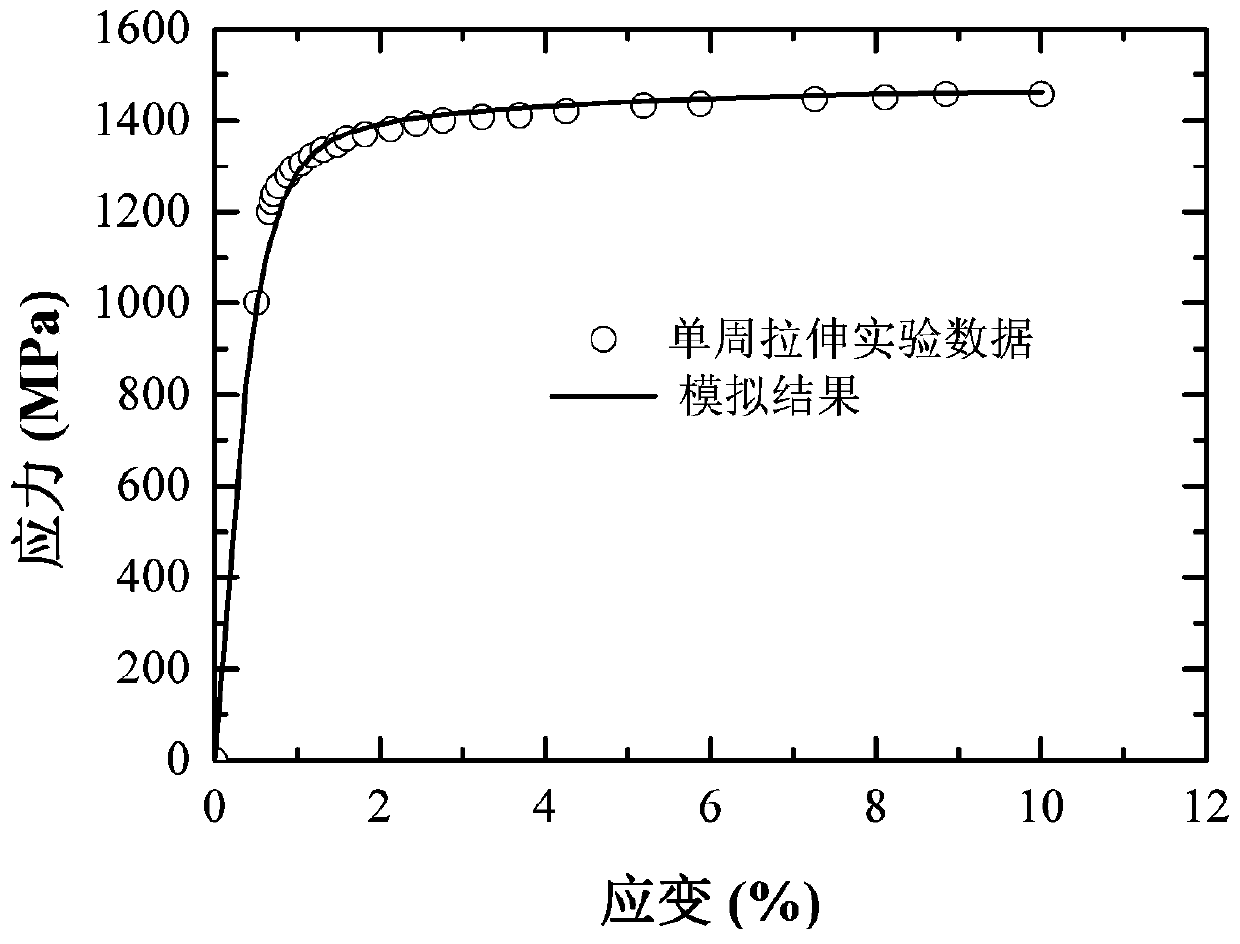
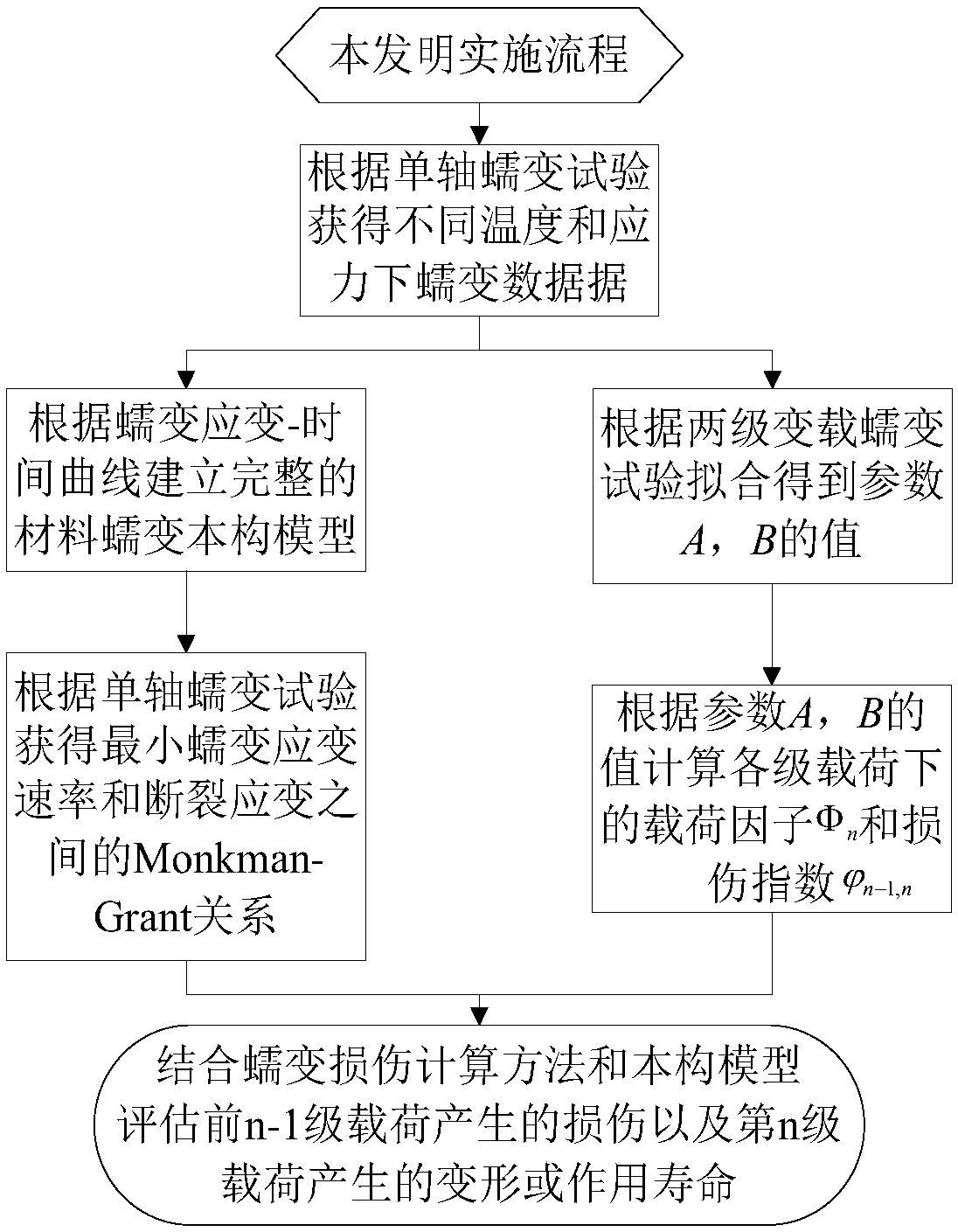
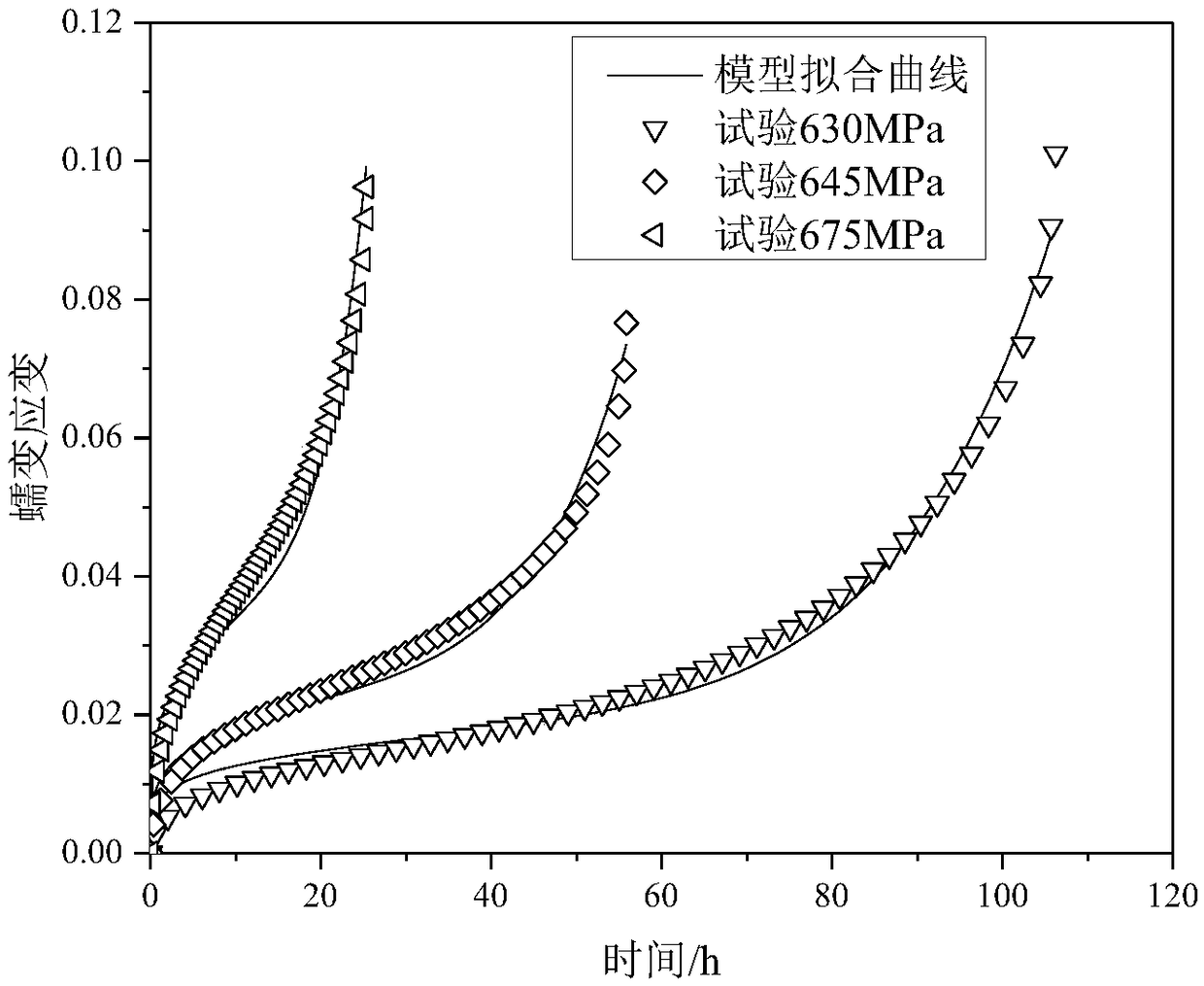
The invention discloses a creep damage calculation method and model under variable load history. The method includes: acquiring the creep strain-time curve, minimum creep rate epsilon<c>m, fracture creep strain epsilon<c>f and fracture life tf of a material under different temperature and stress according to a uniaxial creep test; selecting a creep constitutive equation, and using uniaxial creep test fitting to obtain the creep constitutive parameters of the material; acquiring parameters A and B according to two simple two-stage variable load creep test data fitting; recording deformation increment generated by each stage of load according to the multi-stage variable load creep test of the material; calculating creep damaged generated of the n-1 stage before the multi-stage variable loadcreep test of the material; according to the variable load creep damage calculation model, if the acting time of the nth-stage load is known, predicting the deformation of the material under the nth-stage load, and if the nth-stage load is loaded until fracture occurs, predicting the acting time of the nth-stage load. The method can precisely consider the loading history.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Slope progressive failure latent slide surface calculating method
ActiveCN105335607AStructural/machines measurementMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesFailure ratePrincipal stress
The invention provides a slope progressive failure latent slide surface calculating method-simplified as failure angle rotating method; aiming at the existing disadvantages, assuming geology material failure to satisfy a condition in which an angle between the maximum shear stress surface and the minimum principal stress axis is matched with a critical stress state; because the principal stress direction rotates in different positions when different external load and gravity load are applied on the slope, searching calculation of the slope latent slide surface is carried out, thus determining the latent slide surface, and defining failure rate and failure ratio concepts. The failure angle rotating method ensures that the fail point stress state is at the critical stress state in the slope failure process; in the failure process, the fail path changes along the stress changes; the failure rate and failure ratio concepts are employed, and a failure path constitutive relation considers softening characteristics under different normal stress effects, so the slope latent slide surface can be resolved on the value calculating base.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Porous material structure having three-dimensional negative Poisson's ratio
InactiveCN108394135AEliminate tension-shear coupling effectsWide range of changesLayered productsEngineeringSubstructure
The invention provides a porous material structure having a three-dimensional negative Poisson's ratio. The porous material structure comprises a plurality of net structures which are sequentially stacked in parallel along a Z-axis direction, and the upper net structure and the lower net structure which are adjacent are connected by a support ligament, wherein net structure extends along an XOY plane. The porous material structure having the three-dimensional negative Poisson's ratio eliminates the tensile-shear coupling effect of the two-dimensional substructure of the XOY plane during deformation, so the three-dimensional structure constitutive relationship usually is orthotropic, and can be easily designed and analyzed. Geometrical dimensions are adjusted to make the structure isotropicand greatly change the negative Poisson's ratio values in all three directions, so the choice of practical applications is increased.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method and system for representing numerical value of stress-strain constitutive relation of material
ActiveCN107305174AThe mechanical properties meetGuaranteed fitMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress–strain curveTensile testing
The invention relates to the field of materials and provides a method for representing a numerical value of a stress-strain constitutive relation of a material. The method comprises the following steps: setting a test parameter which includes sample temperature; performing tensile test on the material according to the test parameter, thereby acquiring tensile test data of the material, wherein the tensile test data include stress data and strain data; establishing a stress-strain curve according to the stress data and the strain data; and selecting a corresponding stress-strain numerical value model according to the properties of the material, fitting the stress-strain curve of the material and solving the parameters in the stress-strain numerical value model. An error between a result acquired according to the numerical value representing method and a practical value is smaller and the method is more practical. The invention also provides a system for performing the numerical value representing method and the method for acquiring the stress-strain constitutive relation of the material.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com