Creep-damage lifetime forecast method of material under multi-axial stress state
A stress state and life prediction technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical and digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of uneven temperature distribution, inability to achieve life prediction, and difficulty in convergence, and achieve a simple and clear prediction process. Meaning, result accurate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
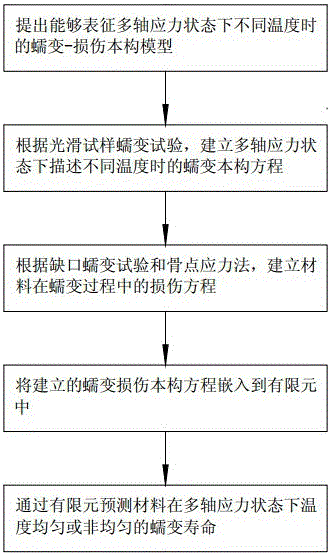
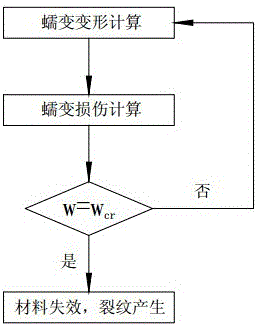
[0050] Such as figure 1 Shown: A creep-damage life prediction method for materials under multiaxial stress states based on the stress-damage criterion. When the cumulative value of creep damage reaches the critical value of damage, a crack is considered to appear in the material. The prediction of creep life is realized by defining different crack lengths as the judgment conditions of material failure. The creep-strain damage model is based on the fact that the material reaches the failure strain under the multiaxial stress state as the basis for the complete damage of the material. The multiaxial creep failure strain is usually converted from the uniaxial creep failure strain using a certain conversion relationship such as the Cocks and Ashby model, and the conversion results are relatively conservative. The creep-damage life prediction method of the material under the multiaxial stress state includes the following steps:
[0051] Step (1), establishing a creep-damage cons...
Embodiment 2
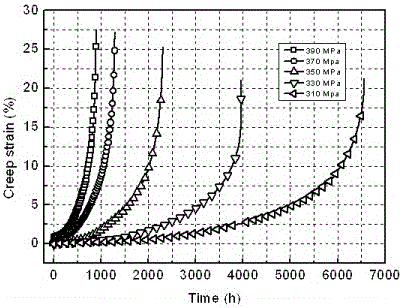
[0108] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that the creep crack growth of the brazed joint Inconel625 / BNi-2 at 650° C. is selected. The creep test curve of solder BNi-2 at 650 °C is as follows Figure 7 shown. Since the creep strain of the solder in the first stage of creep accounts for about 10% of the total failure strain, for the solder, the three stages of creep should be considered in the creep-damage analysis. Using the creep curves of solder under different stress states, the parameters obtained by fitting are =3.28e4, =333, n =2.92, p =2.70, =3.2307, , , m =0.29, Q =223kJ / mol. The material parameters of the Inconel 625 alloy are the same as those in Example 1. The comparison between the creep life of solder BNi-2 and the test value under the uniaxial stress state predicted by the present invention is as follows: Figure 8 It can be seen that the two are in good agreement. For the multiaxial creep performance parameters of nickel-ba...
Embodiment 3
[0111] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 2 is that the creep crack growth of the brazed joint Inconel625 / BNi-2 under the condition of non-uniform temperature is selected. Such as Figure 12 As shown: the highest temperature of the sample is 650°C, the lowest temperature is about 535°C, and the whole sample has a large gradient. Such as Figure 13 Shown: The creep crack growth of the brazed joint after creeping for 3200 hours under the temperature distribution state. The invention can successfully predict the creep crack expansion of the equipment components under the condition of uneven temperature, and realize the life prediction of the equipment according to the variation trend of the crack expansion.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com