Patents
Literature
775 results about "Boundary values" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
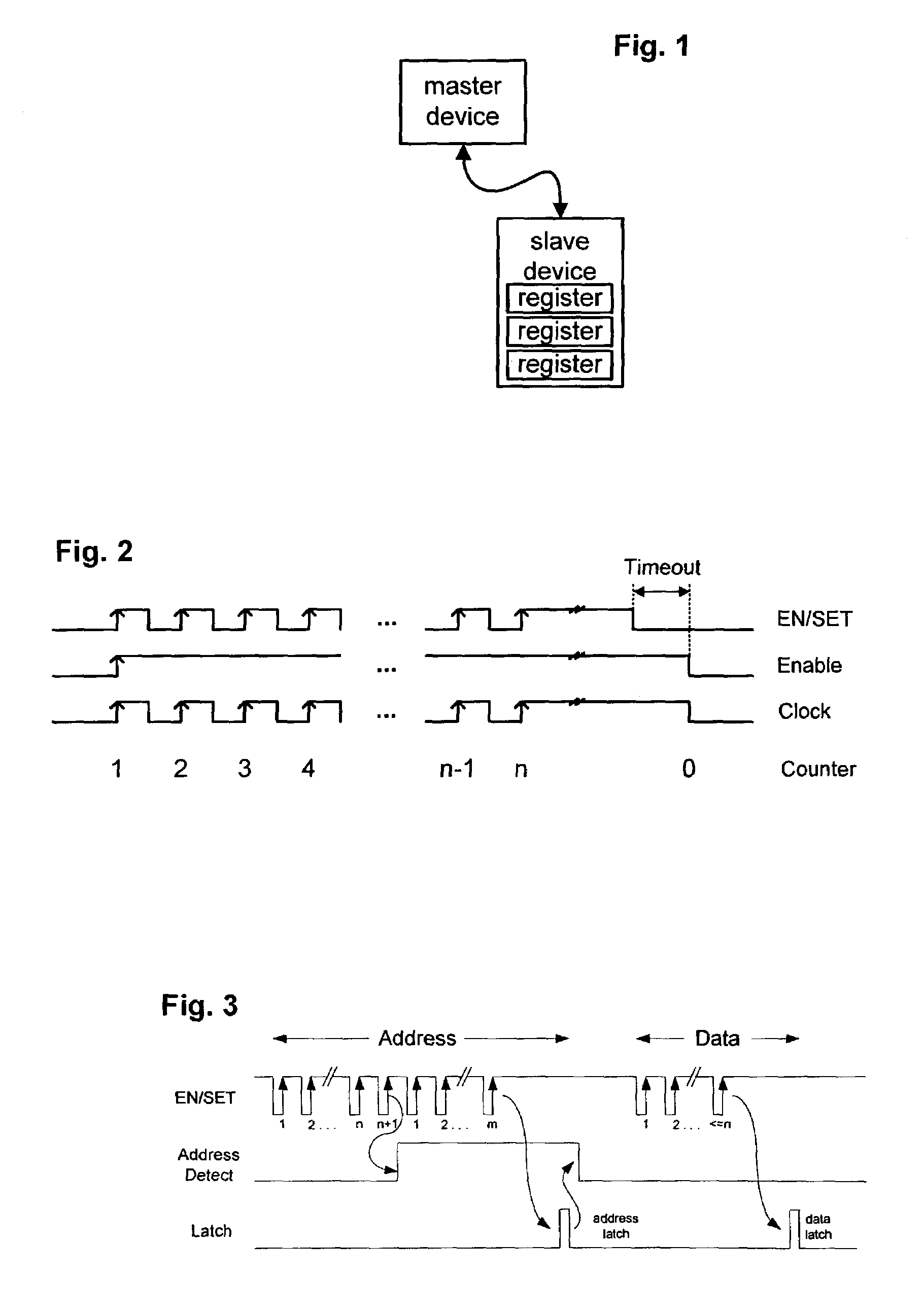
Boundary values are a set of conditions applied to a mathematical equation. The boundary values represent the extremes of a value set. In ergonomics, upper and lower boundary values are based on the 5th and 95th percentile of a selected population. Boundary values may also be called boundary conditions.
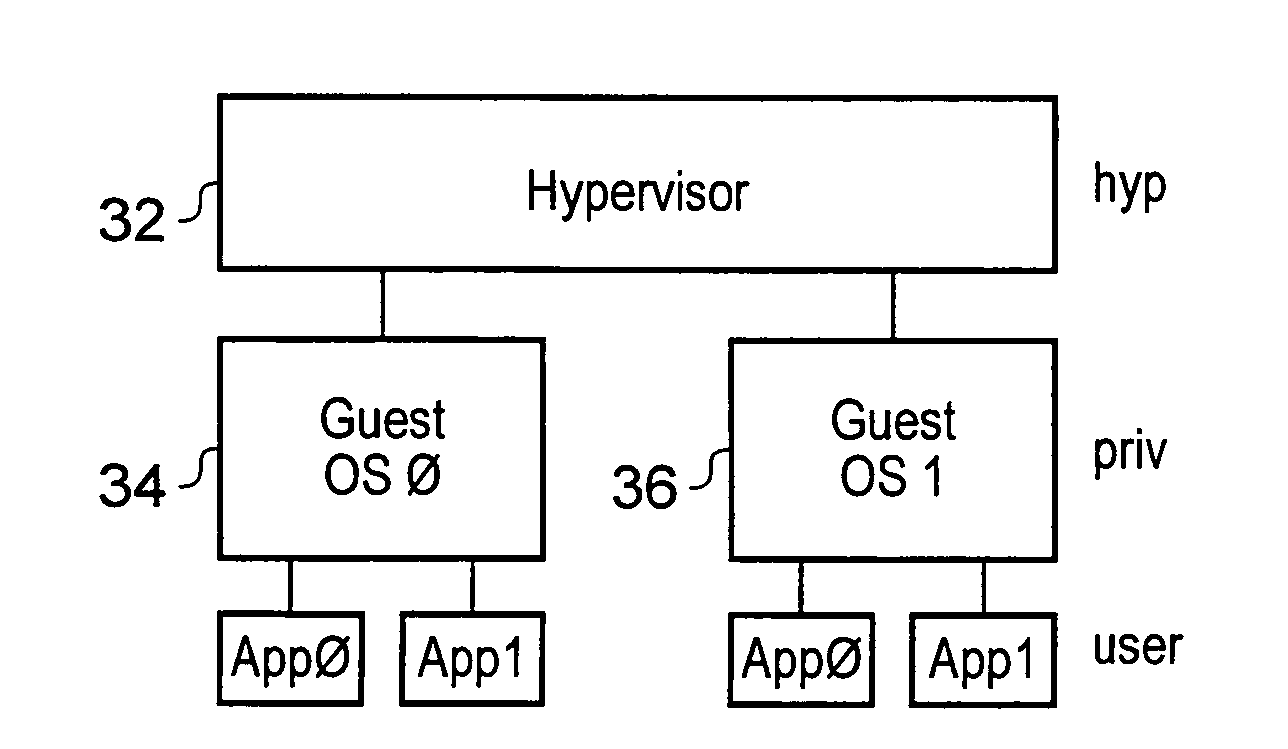
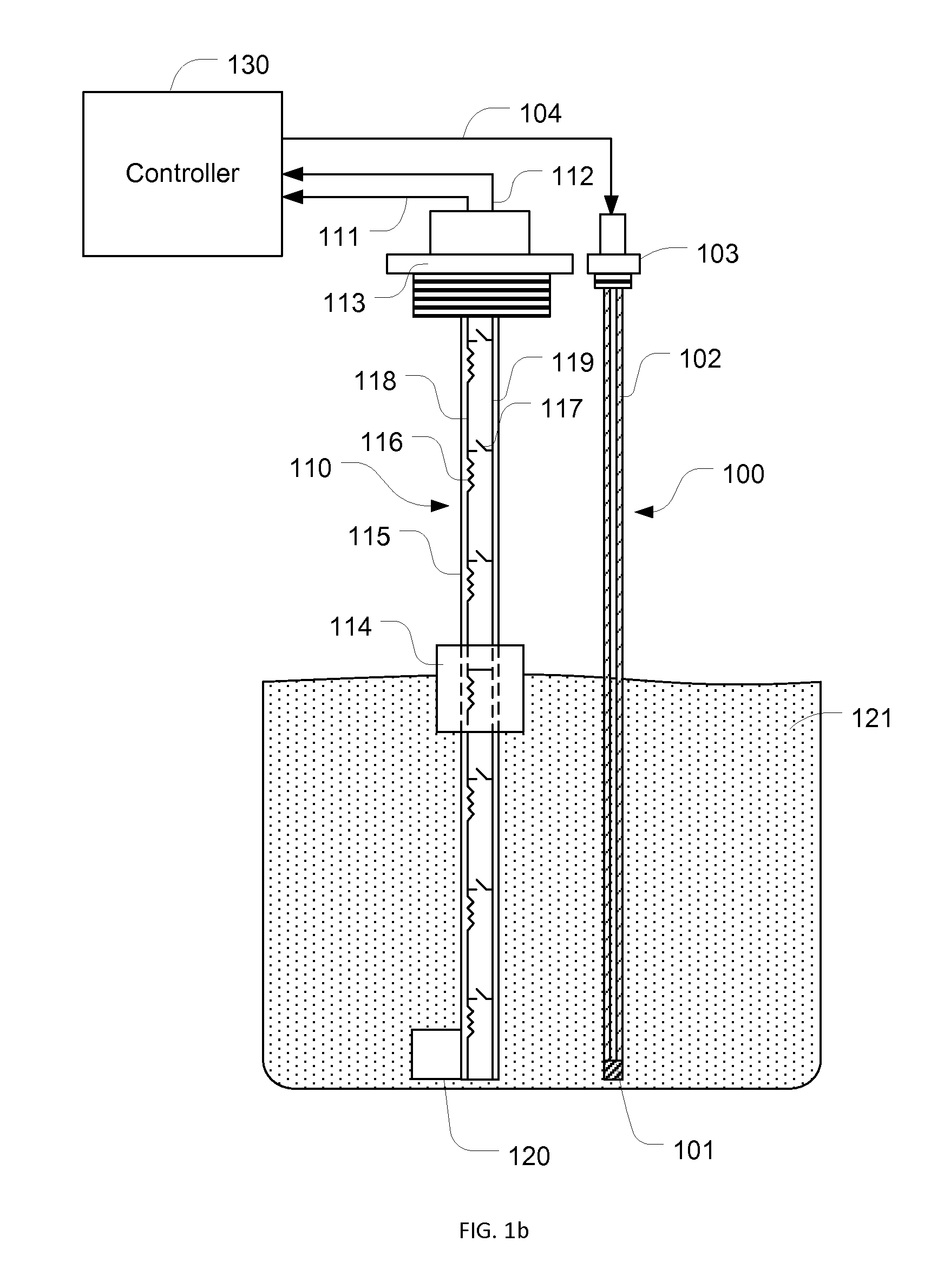
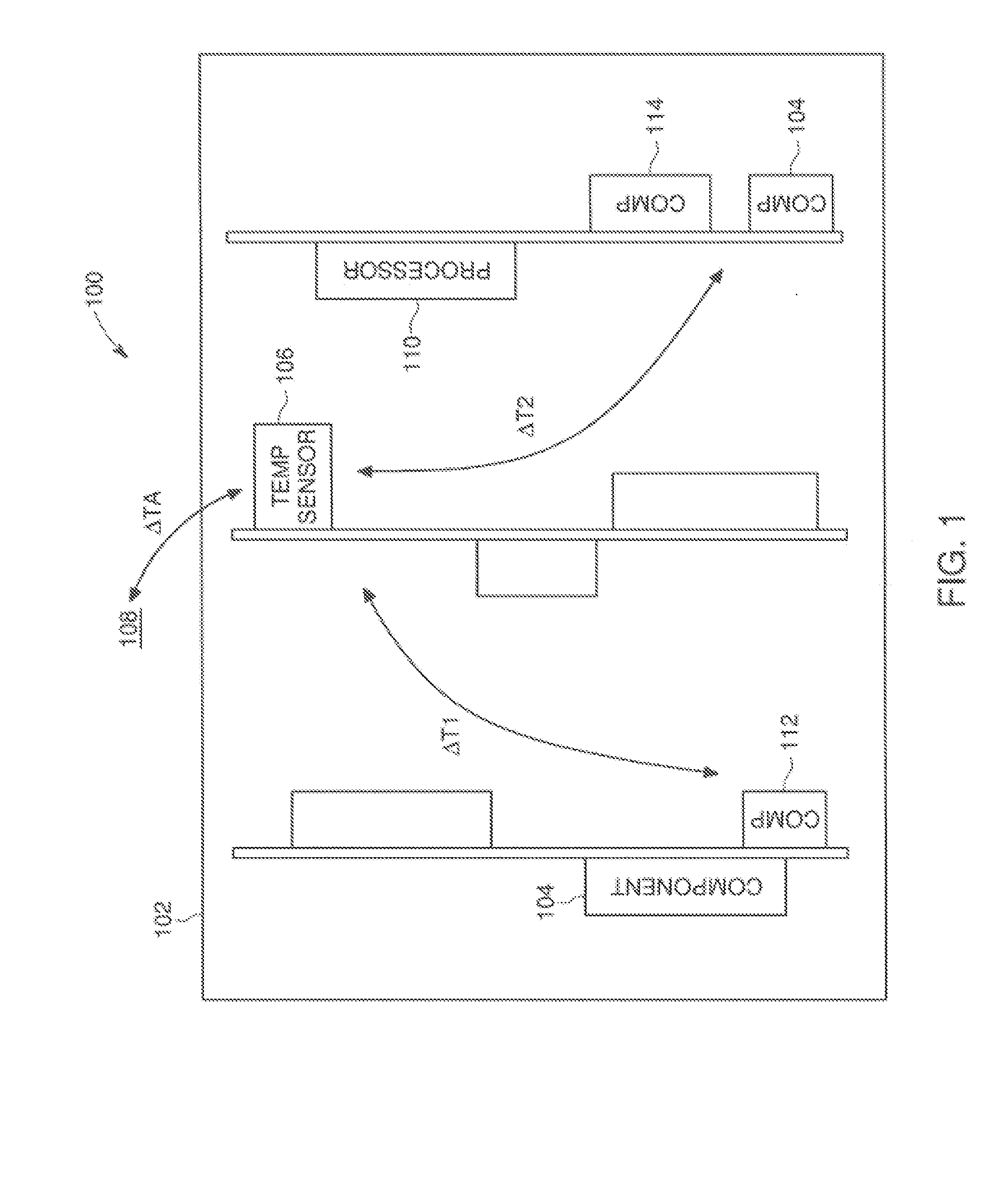
Endoscope system, processor device of endoscope system, and image processing method
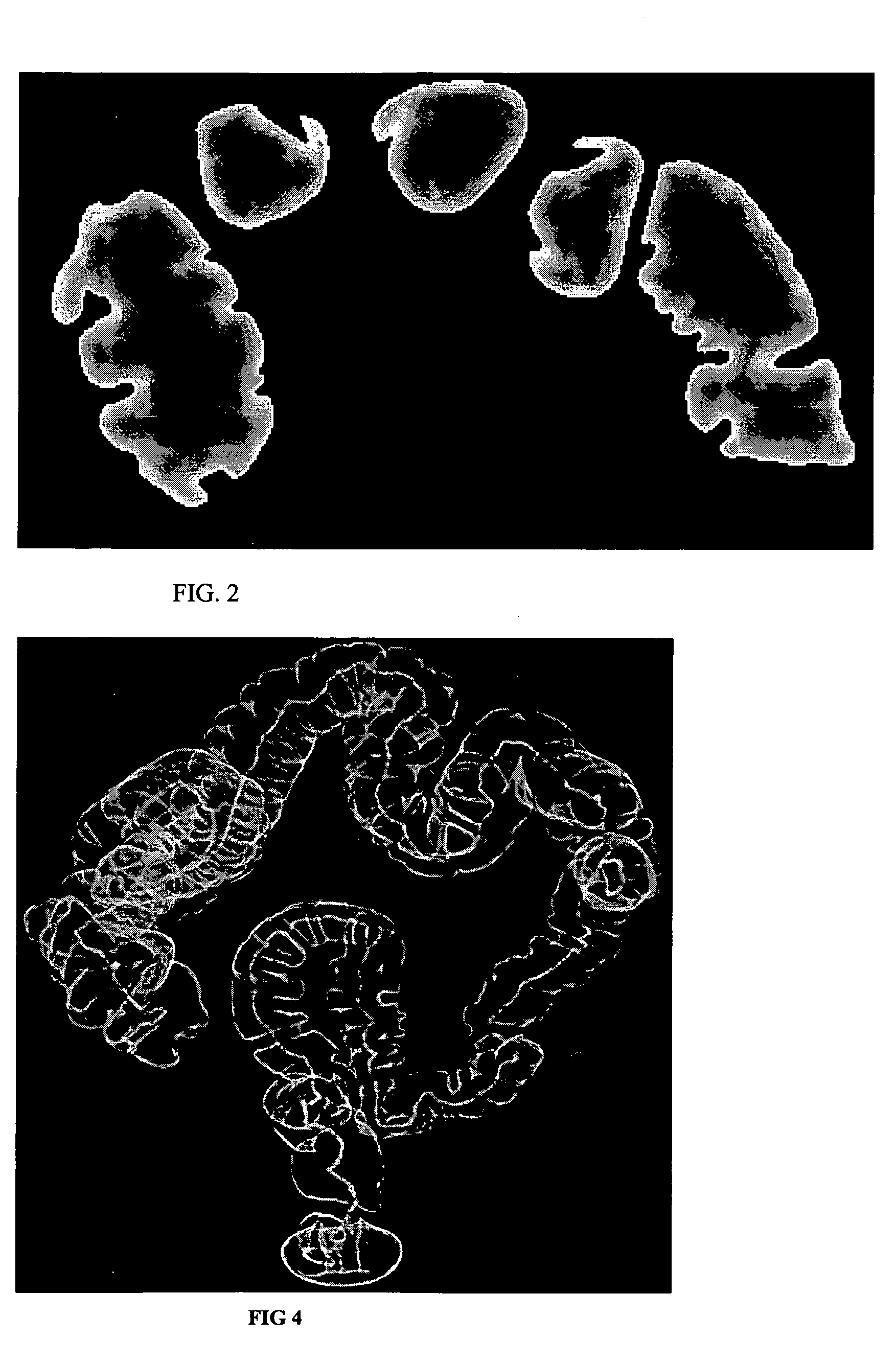
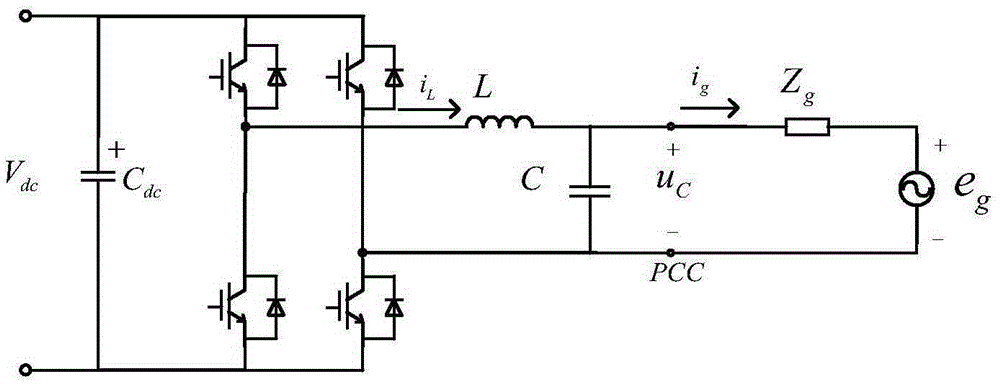
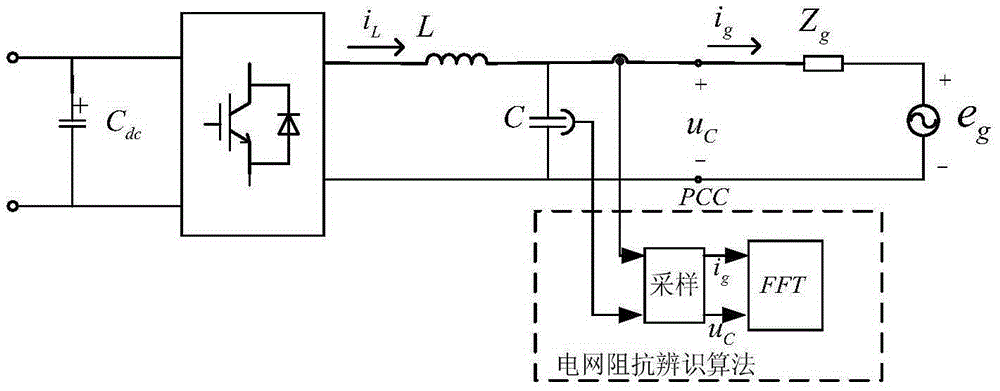
ActiveUS9943230B2Reliably extract a plurality of types of blood vesselsImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingBoundary values
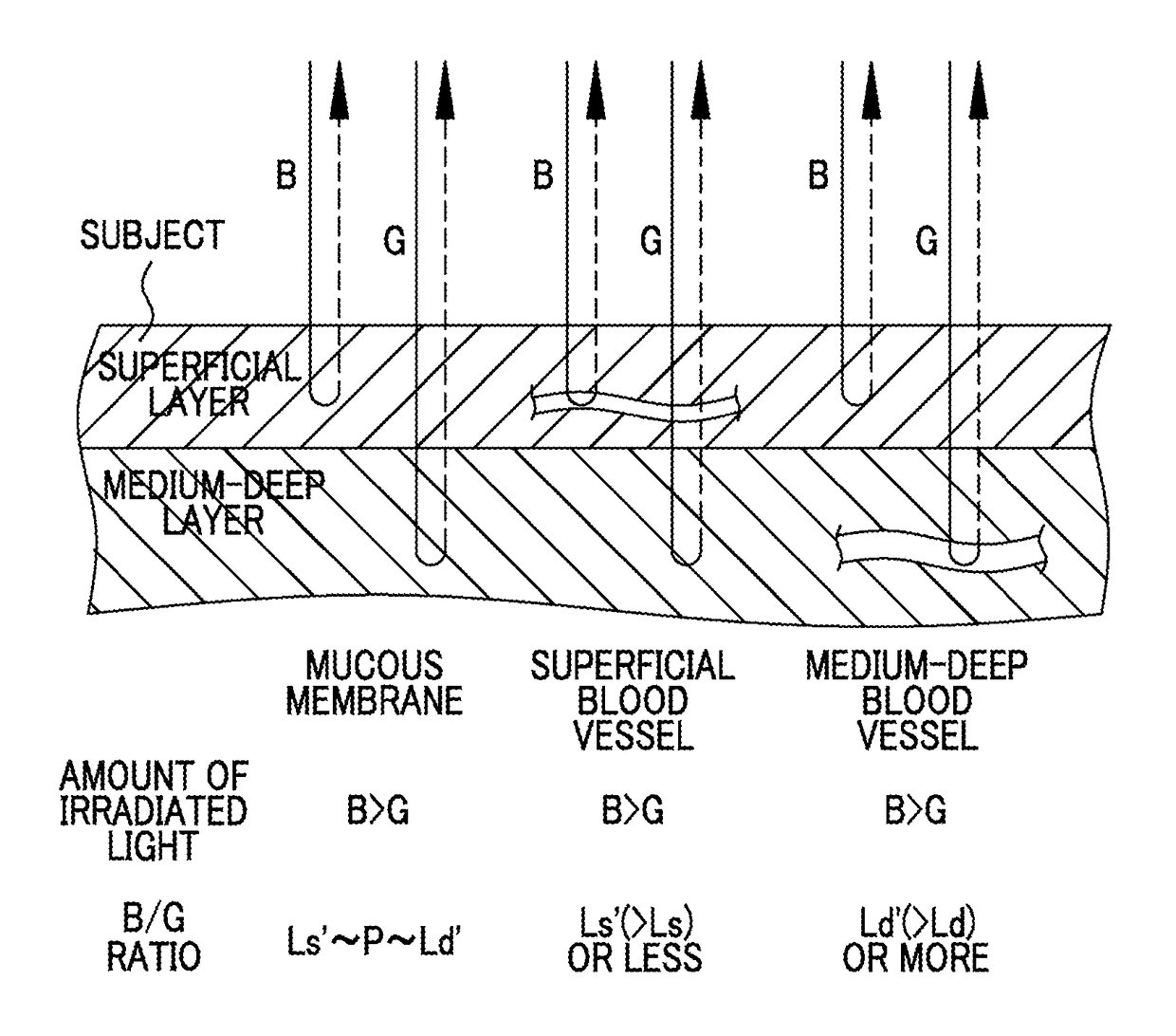
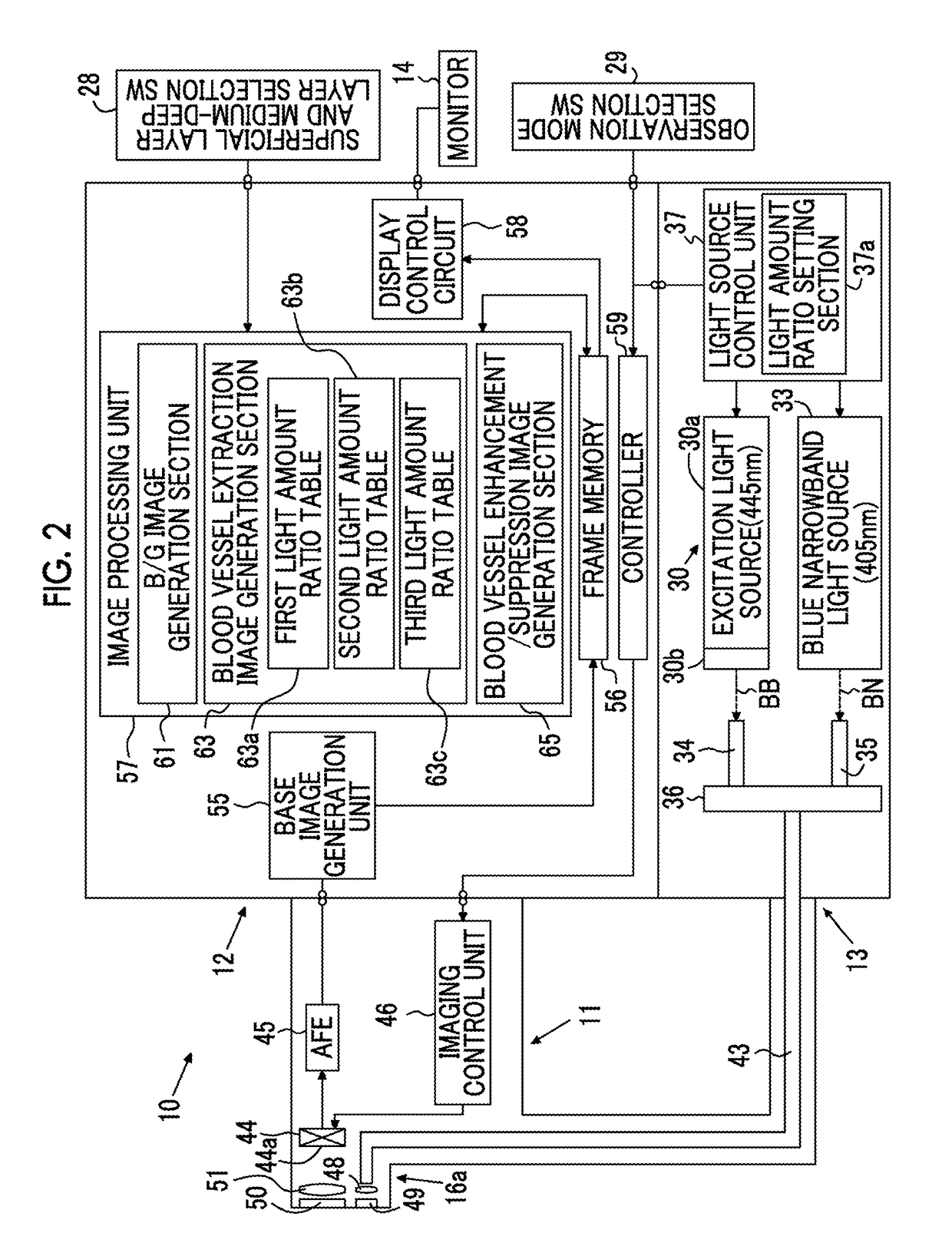
Even if the ratio between blue and green components of illumination light is changed, a plurality of types of blood vessels at different depths are reliably distinguished. A blue signal B, a green signal G, a red signal R is obtained by imaging the subject using a color CCD 44. A B / G image having a B / G ratio is generated. A superficial blood vessel extraction image is obtained by extracting a pixel, in which the B / G ratio is equal to or less than a boundary value Ls between the mucous membrane and the superficial blood vessel, from the B / G image. A medium-deep blood vessel extraction image is obtained by extracting a pixel, in which the B / G ratio is equal to or greater than a boundary value Ld between the mucous membrane and the medium-deep blood vessel. The boundary values Ls and Ld differ depending on the light amount ratio.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
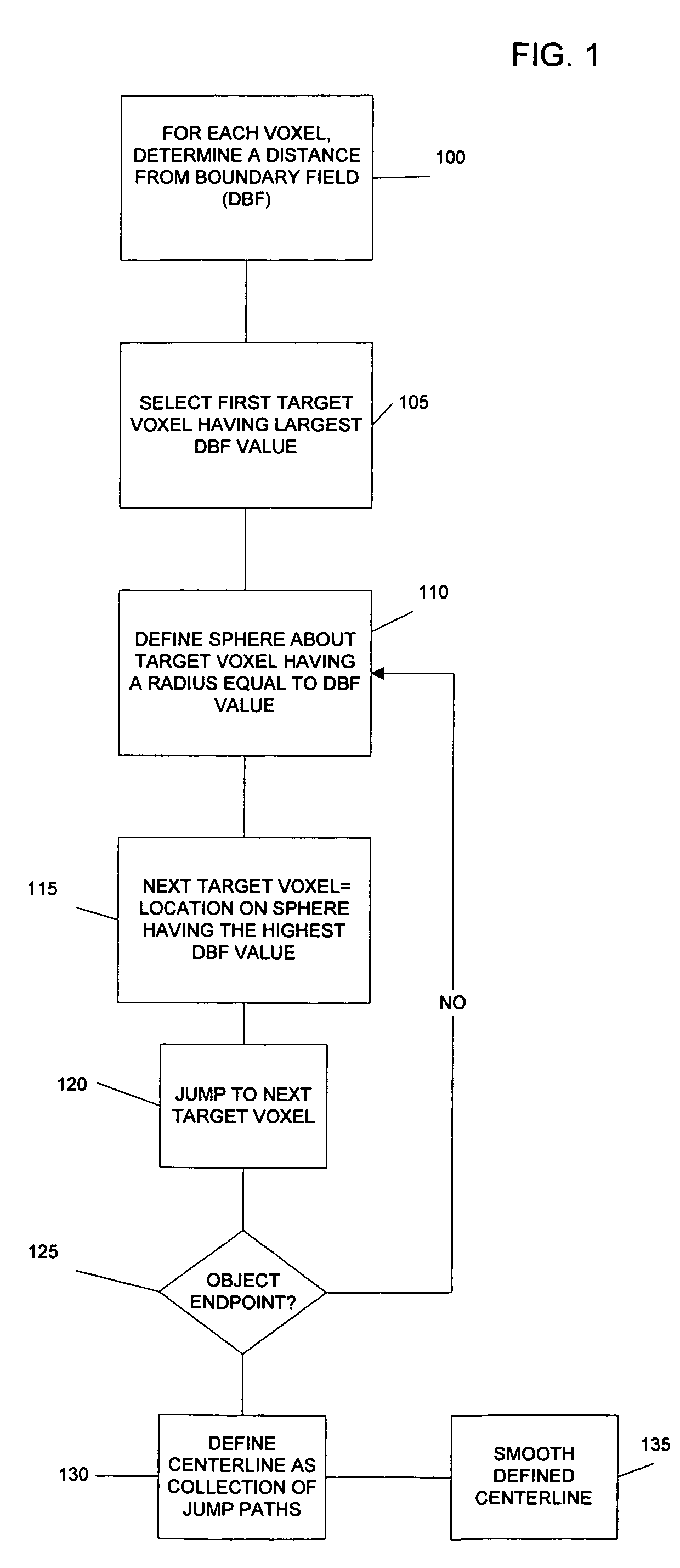
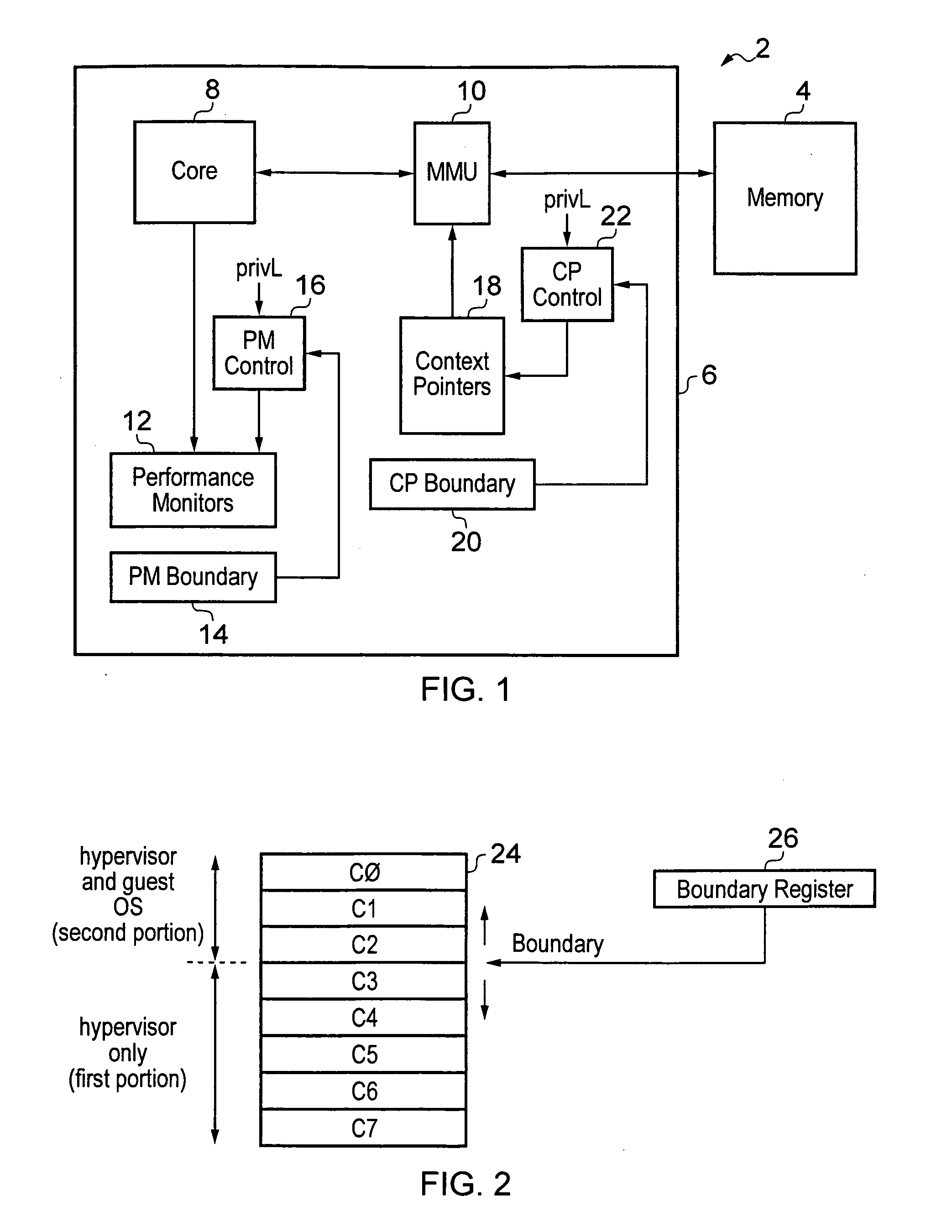
Method of centerline generation in virtual objects
InactiveUS7324104B1Increase speedImprove processing speedImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelBoundary values
Methods for generating a centerline or skeleton structure within a 3D virtual object are provided. A first method defines a centerline based on distance from boundary values along points of the defined centerline. A second method uses a distance from boundary field to assign costs to voxels in the virtual object and defines a minimum cost spanning tree based on assigned costs. The centerline is defined along the minimum cost spanning tree. Branches along the centerline are identified and added to the centerline to define a skeleton.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
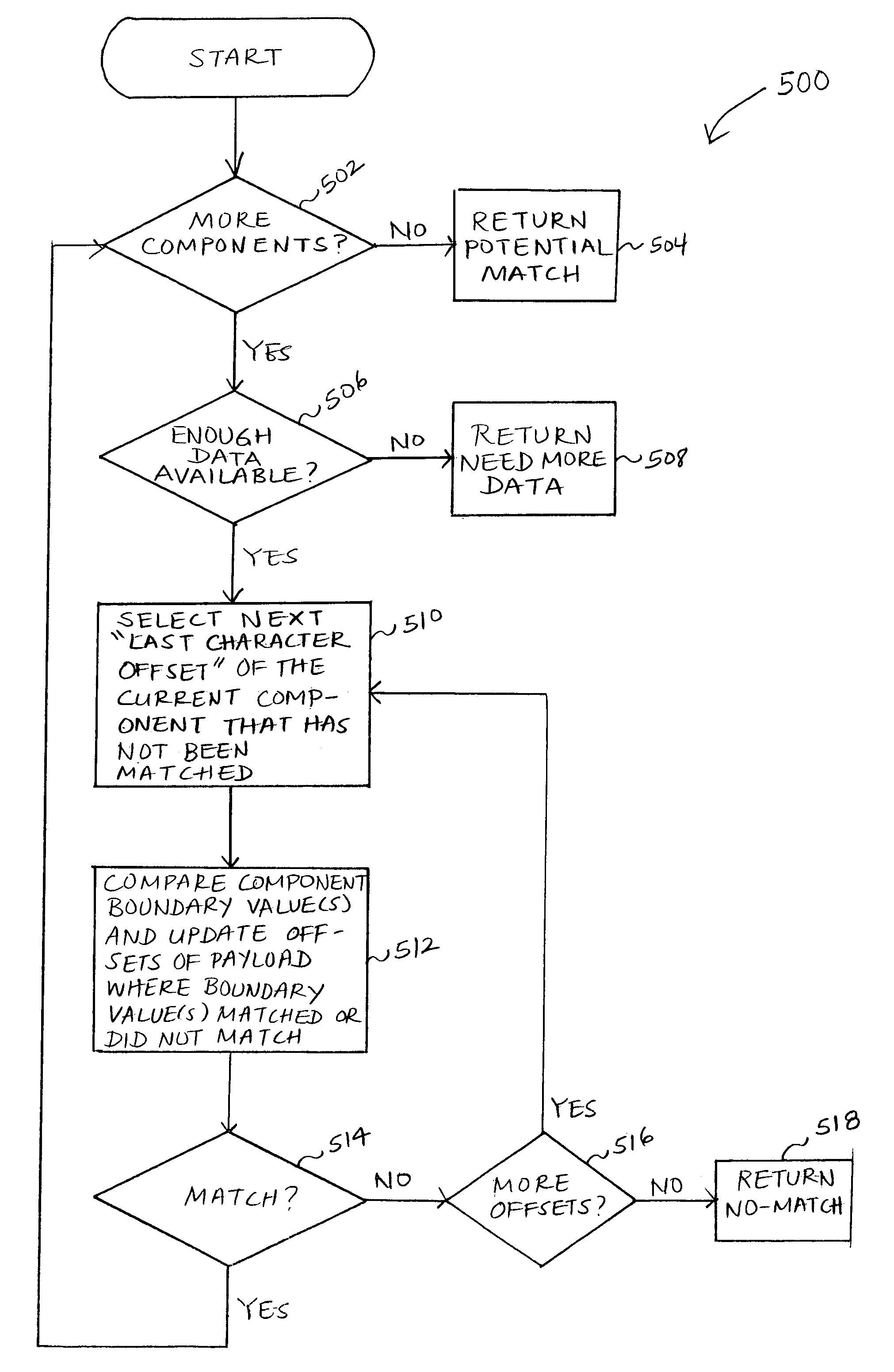
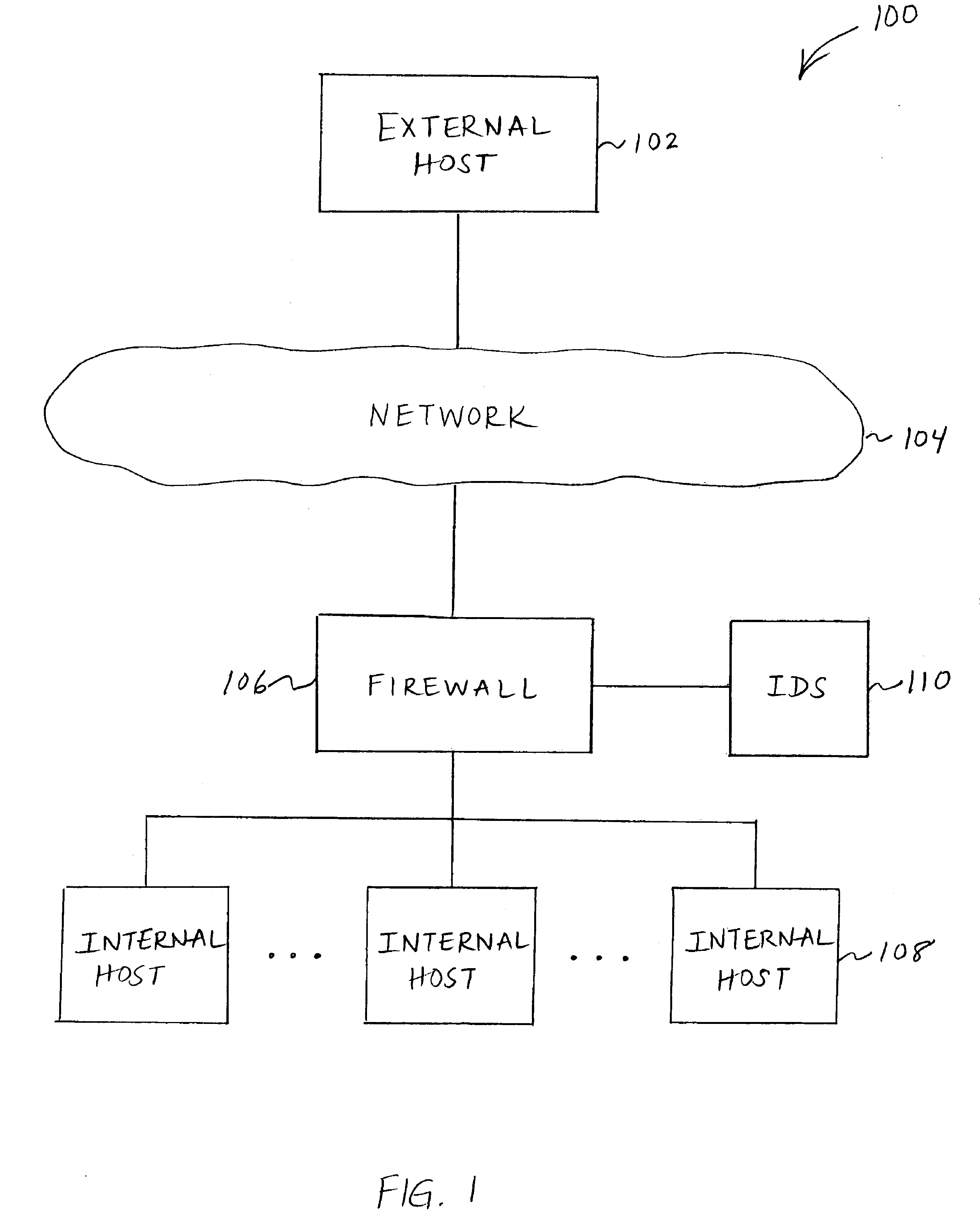
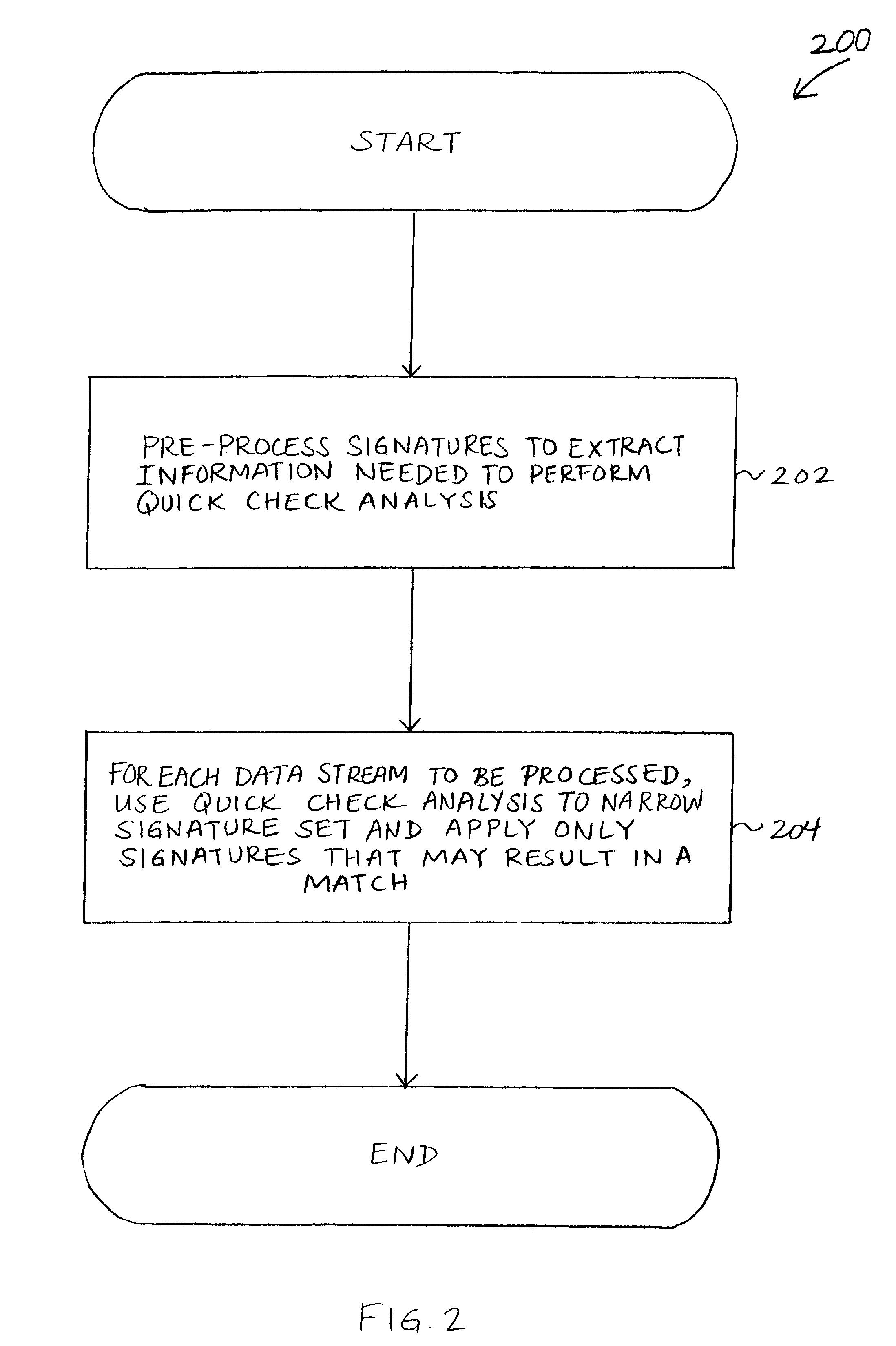
Performance enhancement for signature based pattern matching
InactiveUS7810155B1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionData streamPerformance enhancement
Performance enhancement for signature based pattern matching may include one or more signature preprocessing steps. The signatures in the signature set may be preprocessed prior to performing pattern matching, including by breaking each signature broken down into one or more components. For at least one of the one or more components, boundary values as well as possible offsets of the boundary values may be identified and matched against a data stream to determine whether the data stream does not match a particular signature, thereby allowing a quick narrowing of the set of signatures to be applied fully to the data stream.
Owner:CA TECH INC
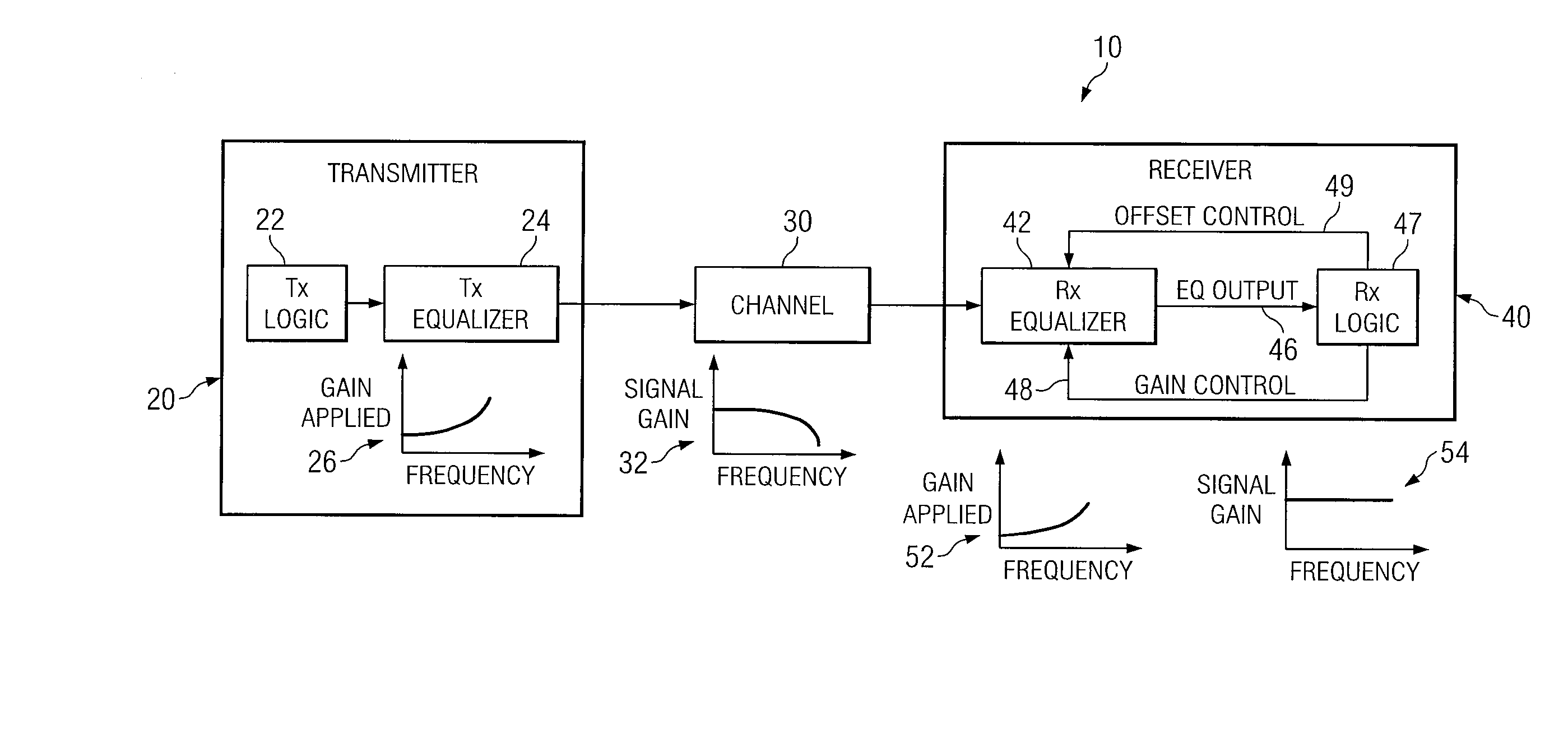
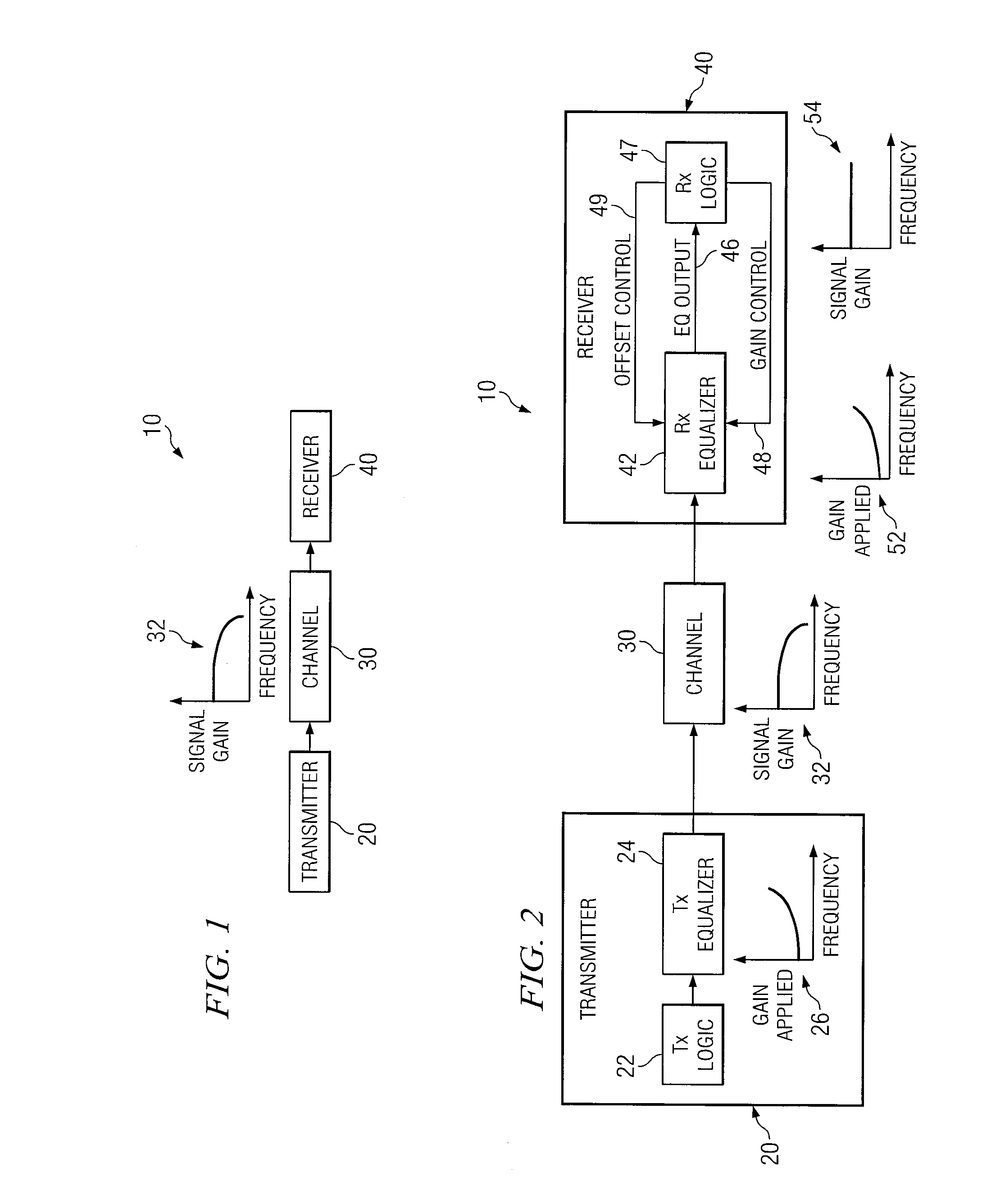
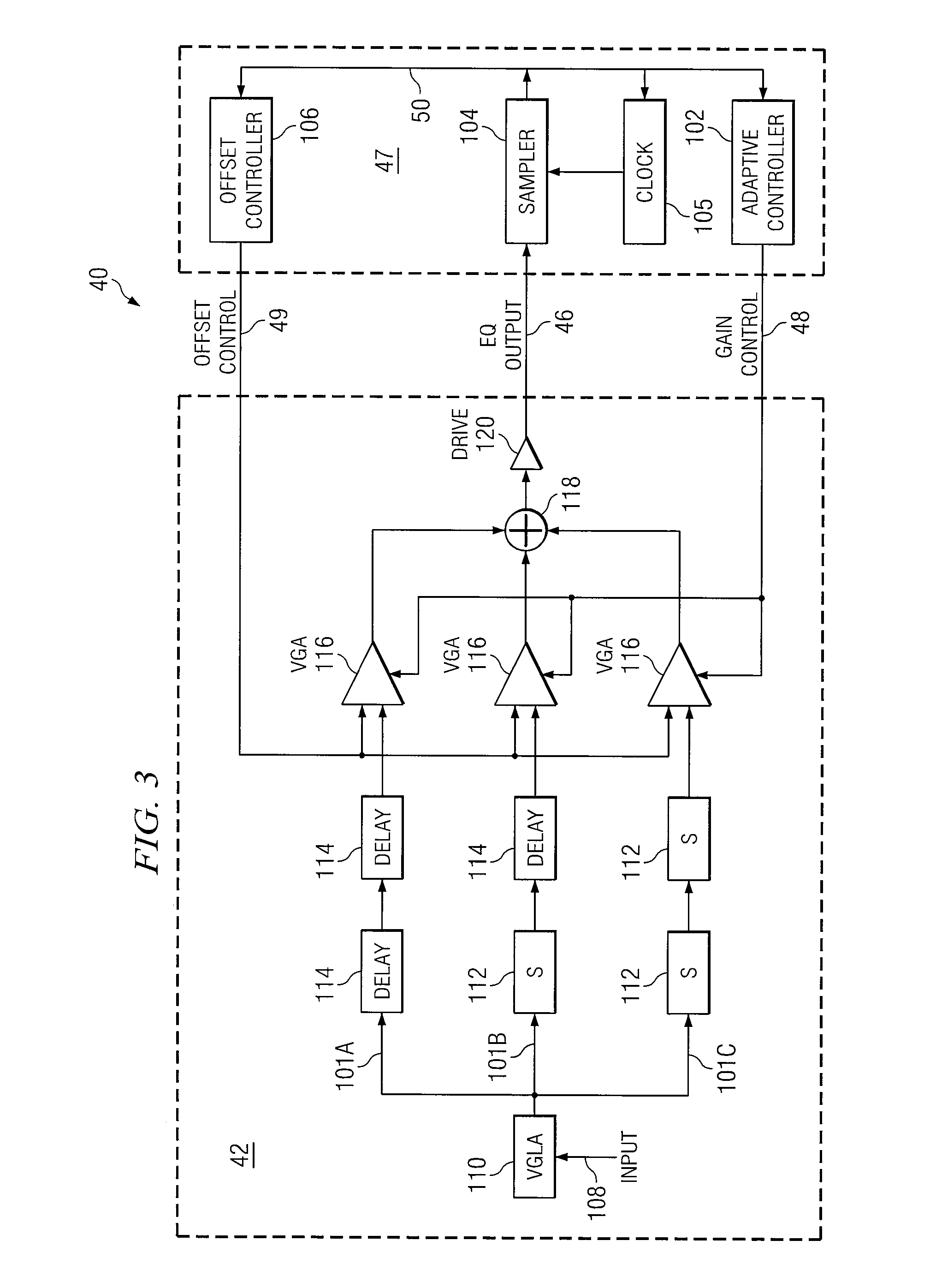
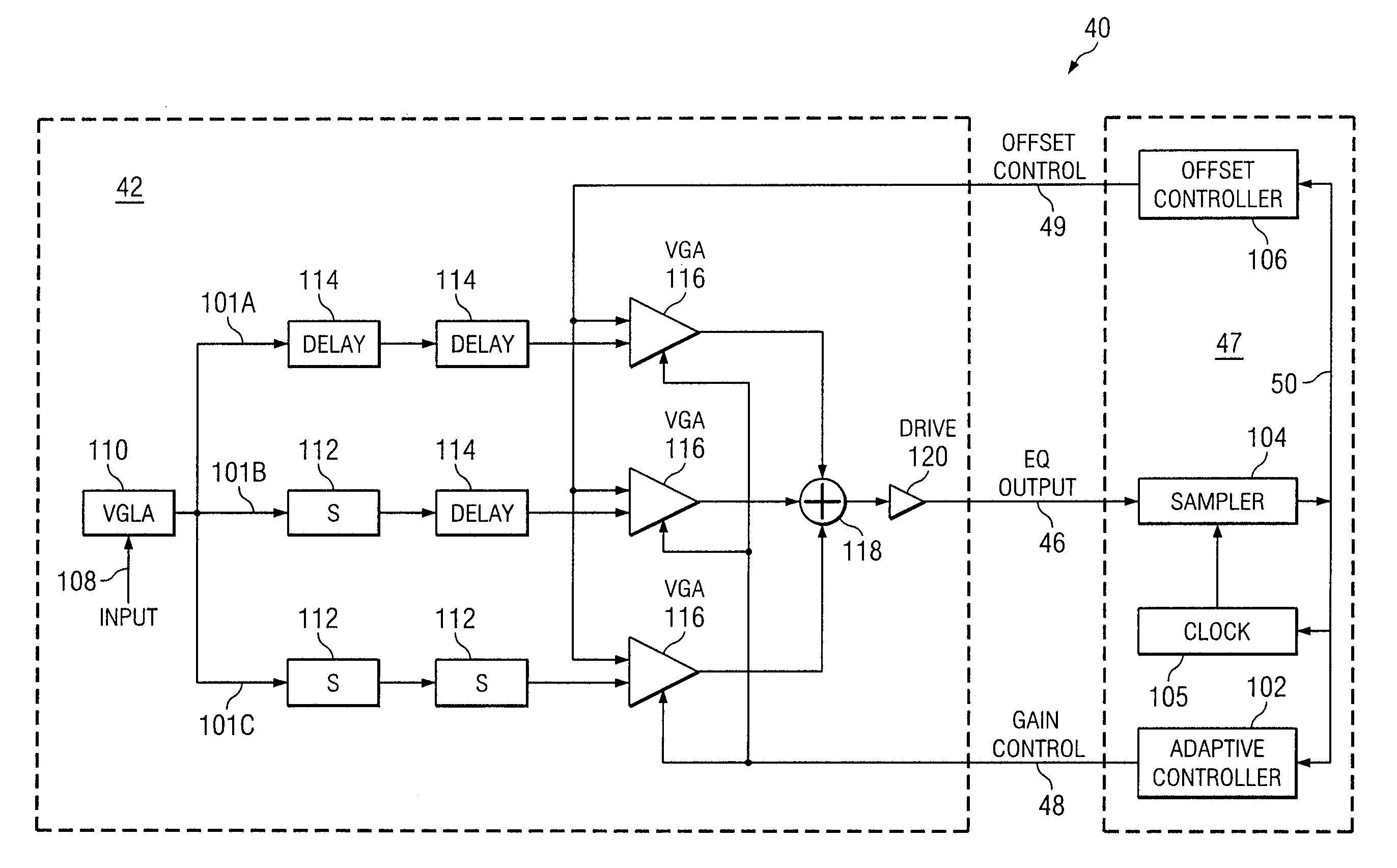
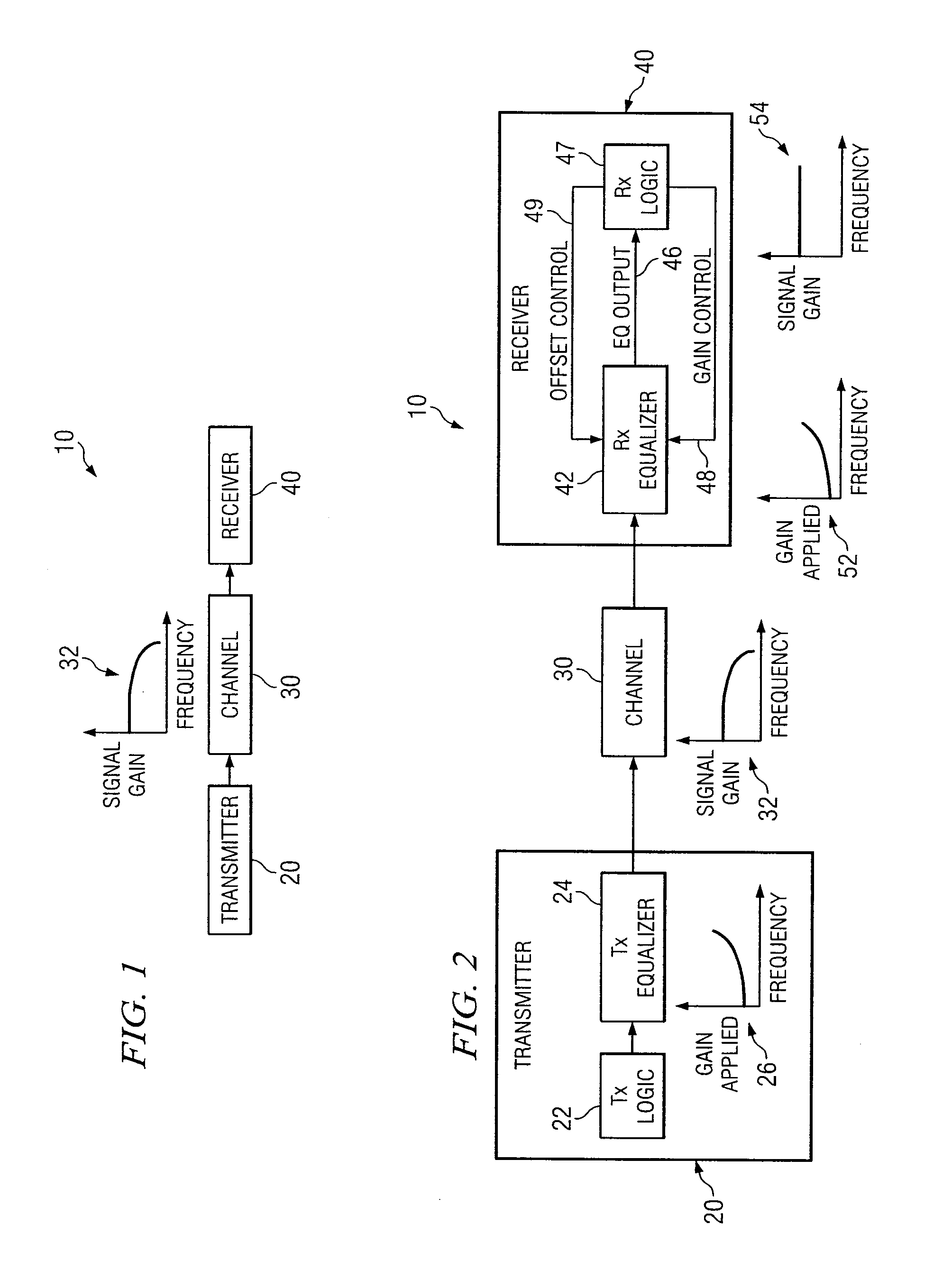
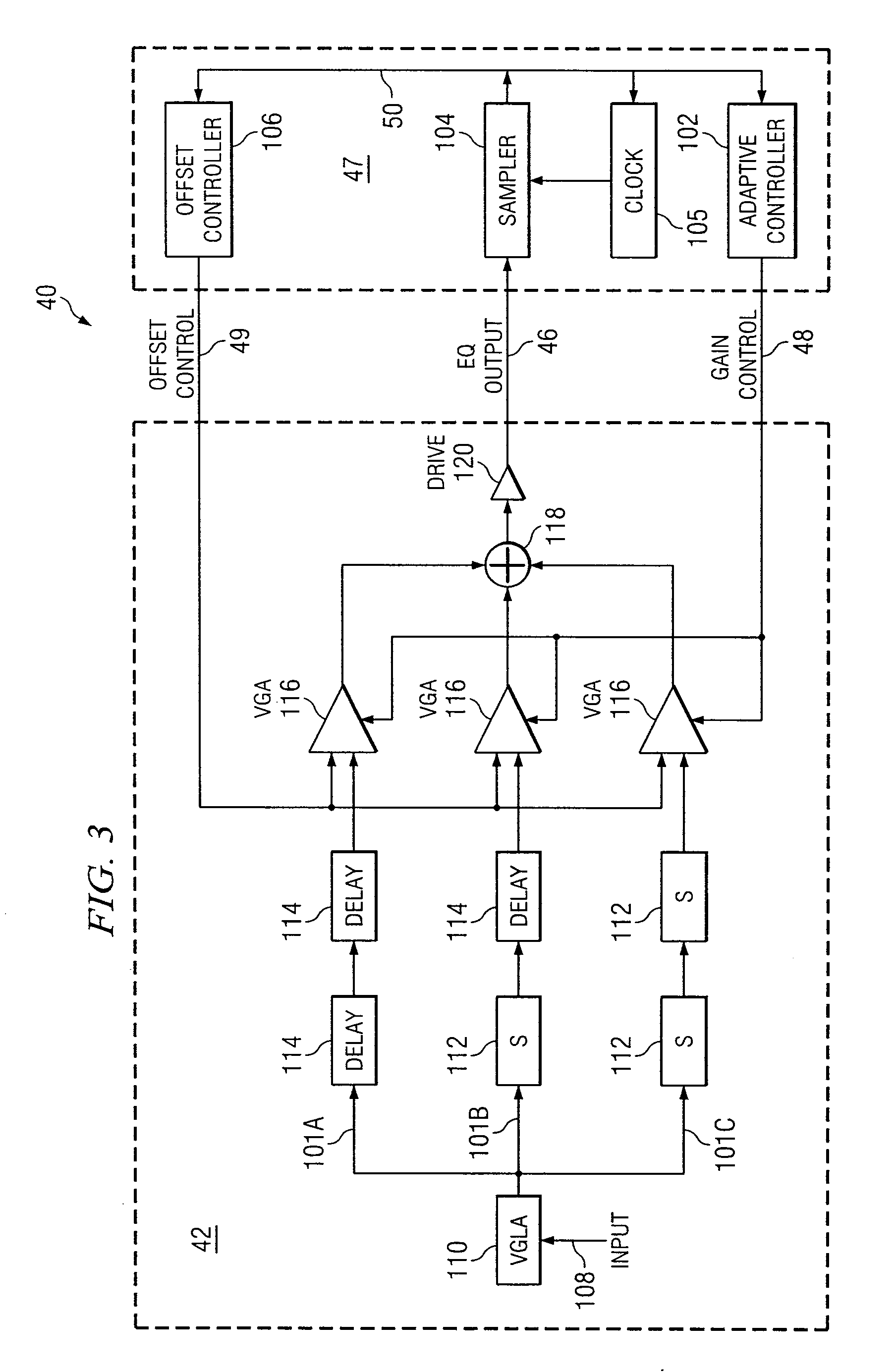
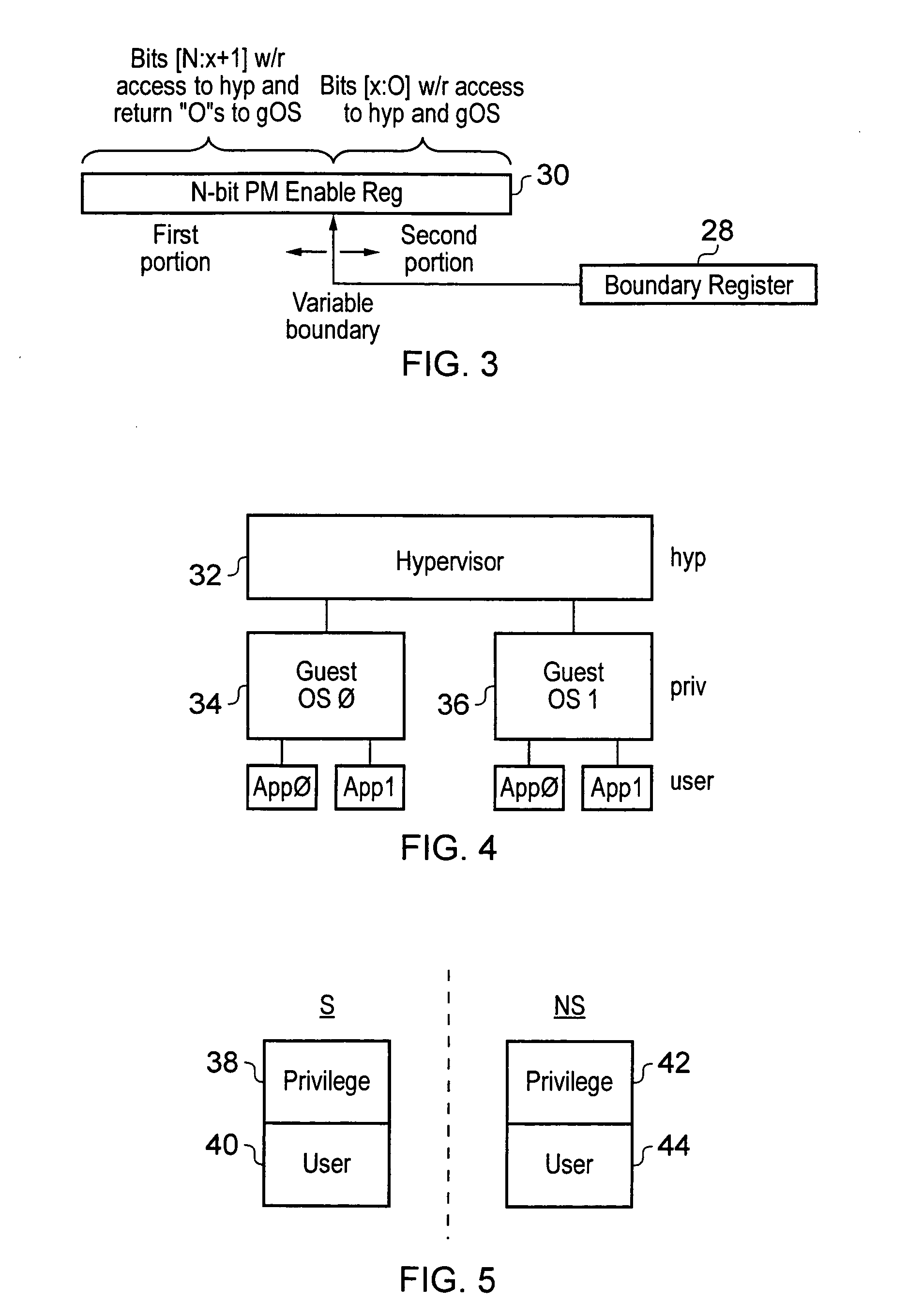
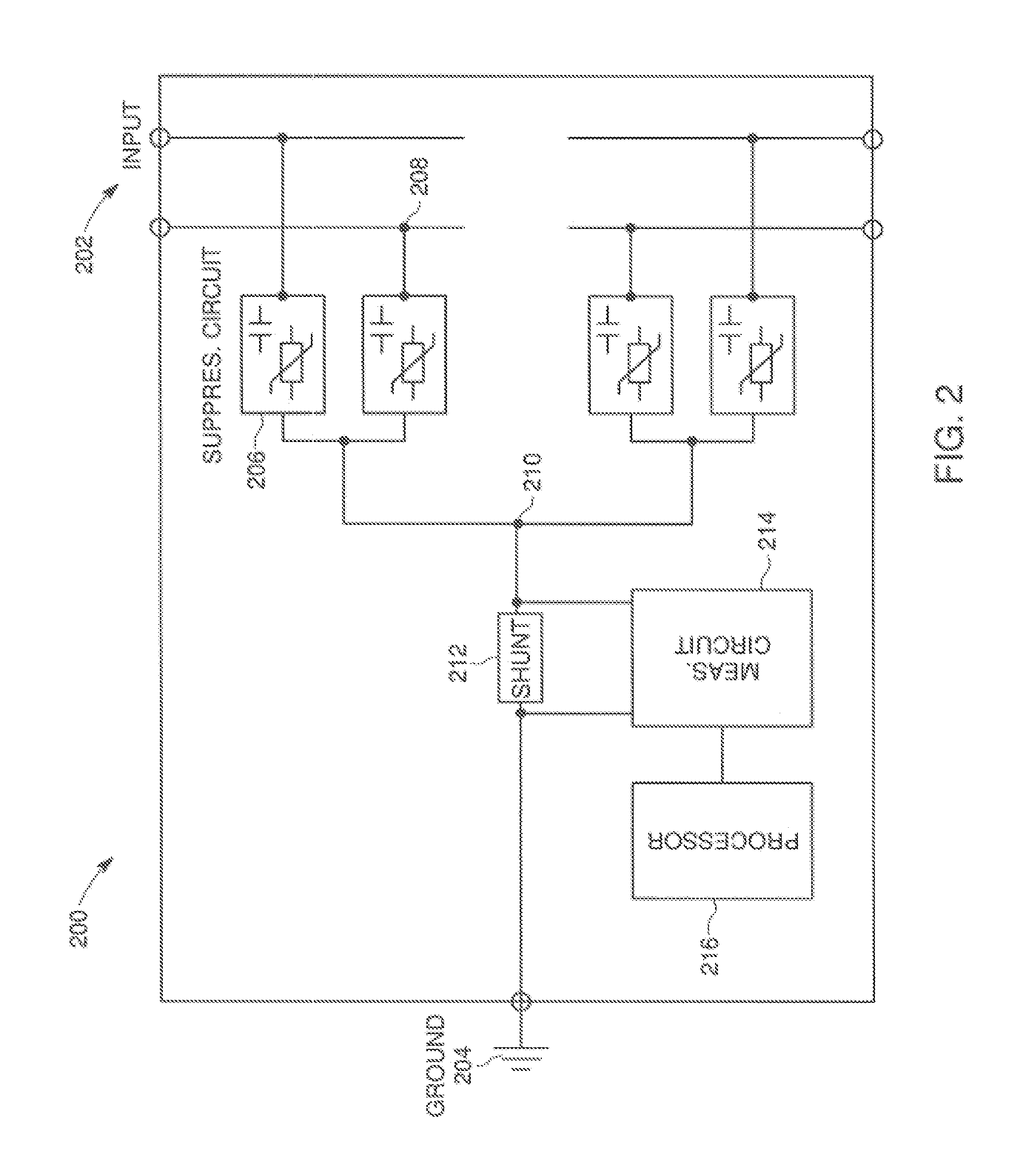
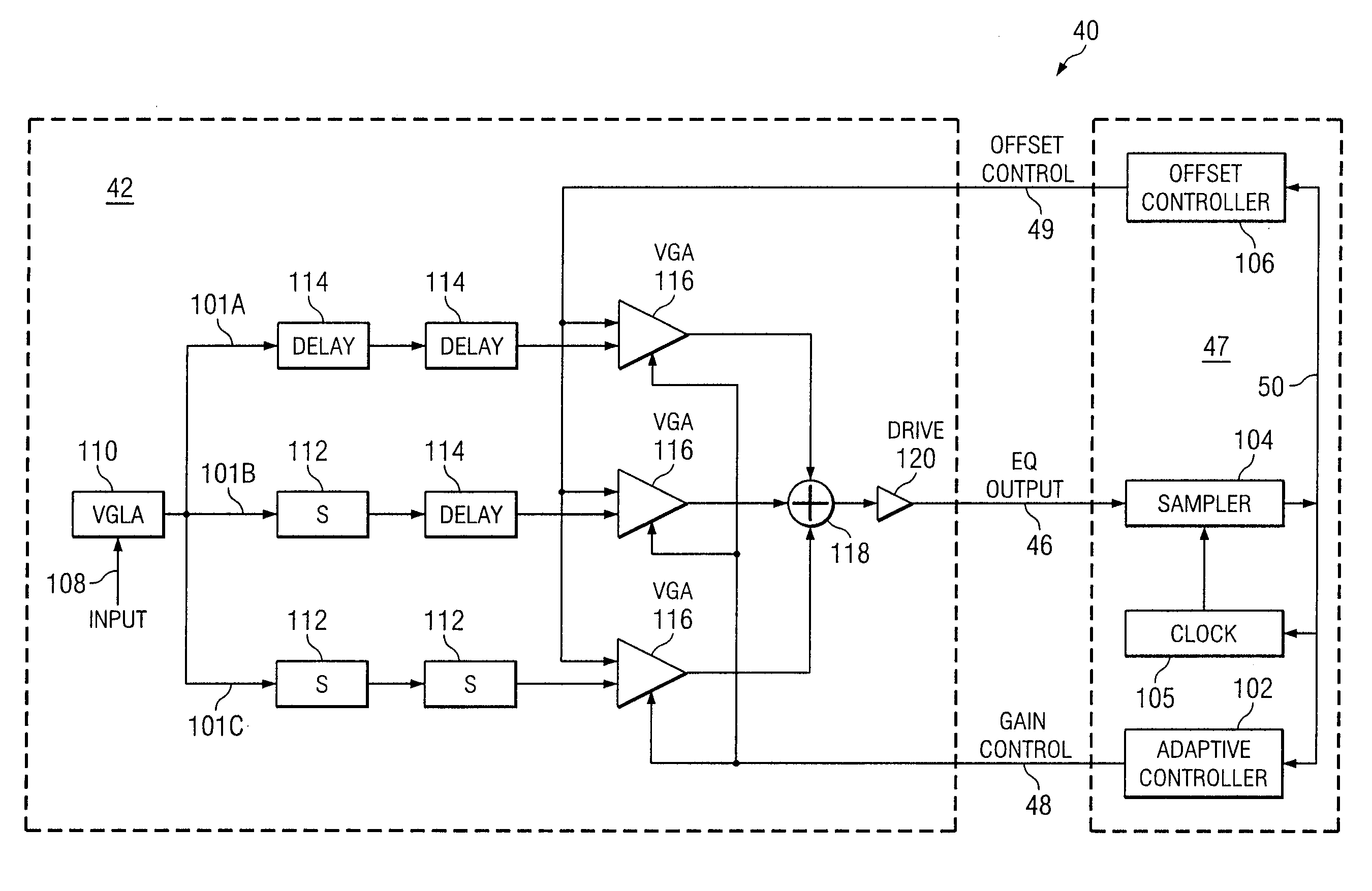
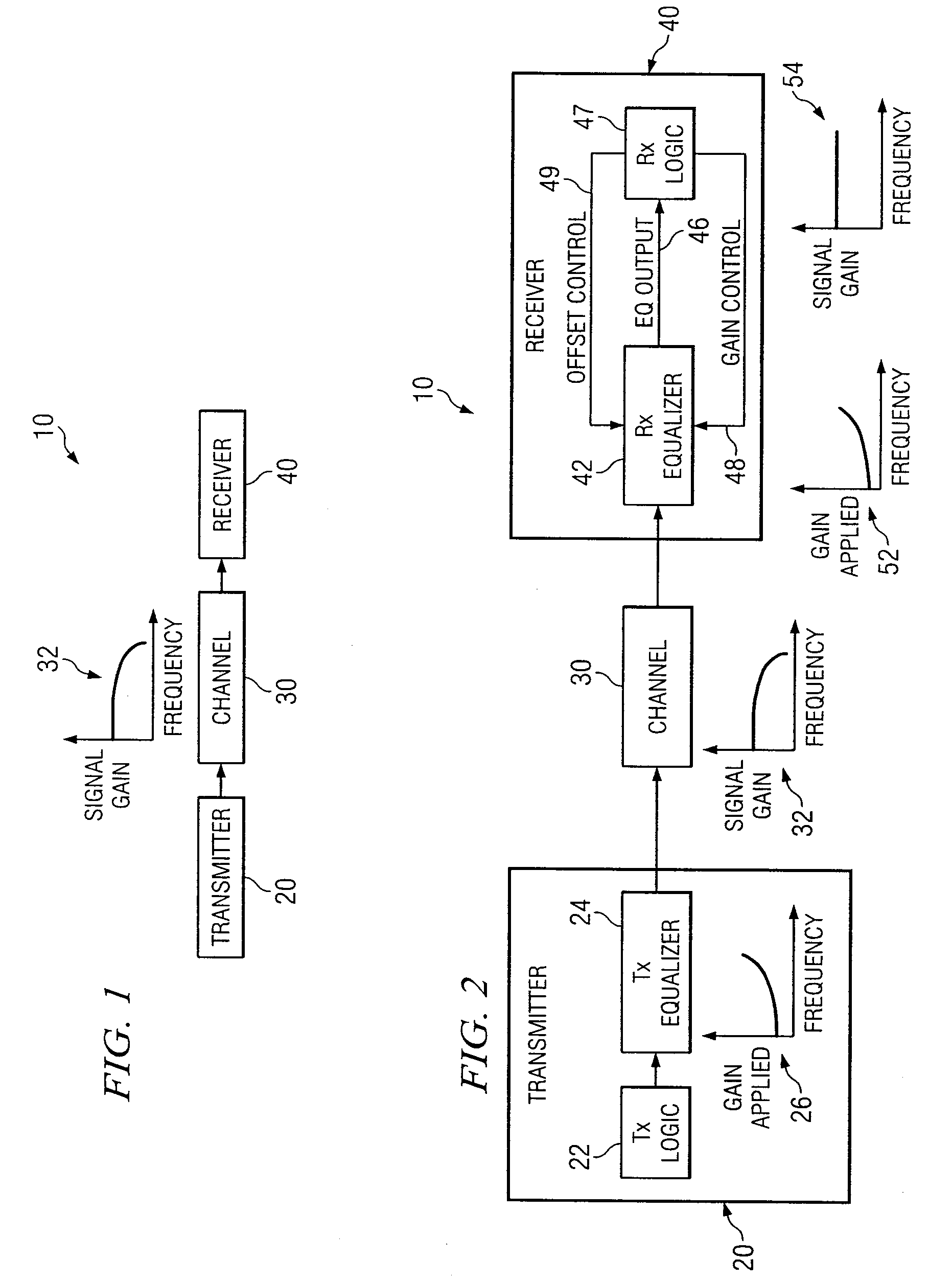
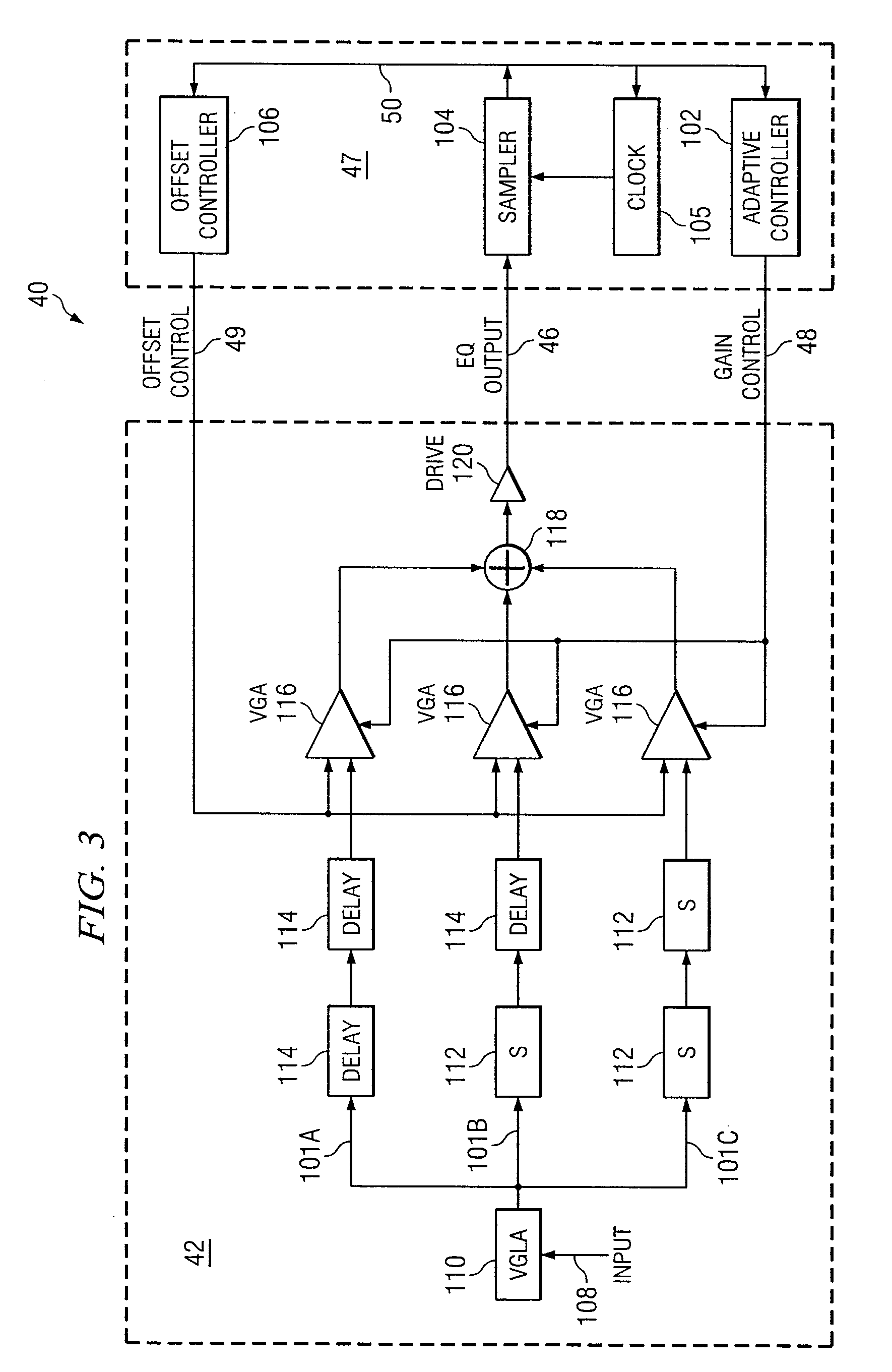
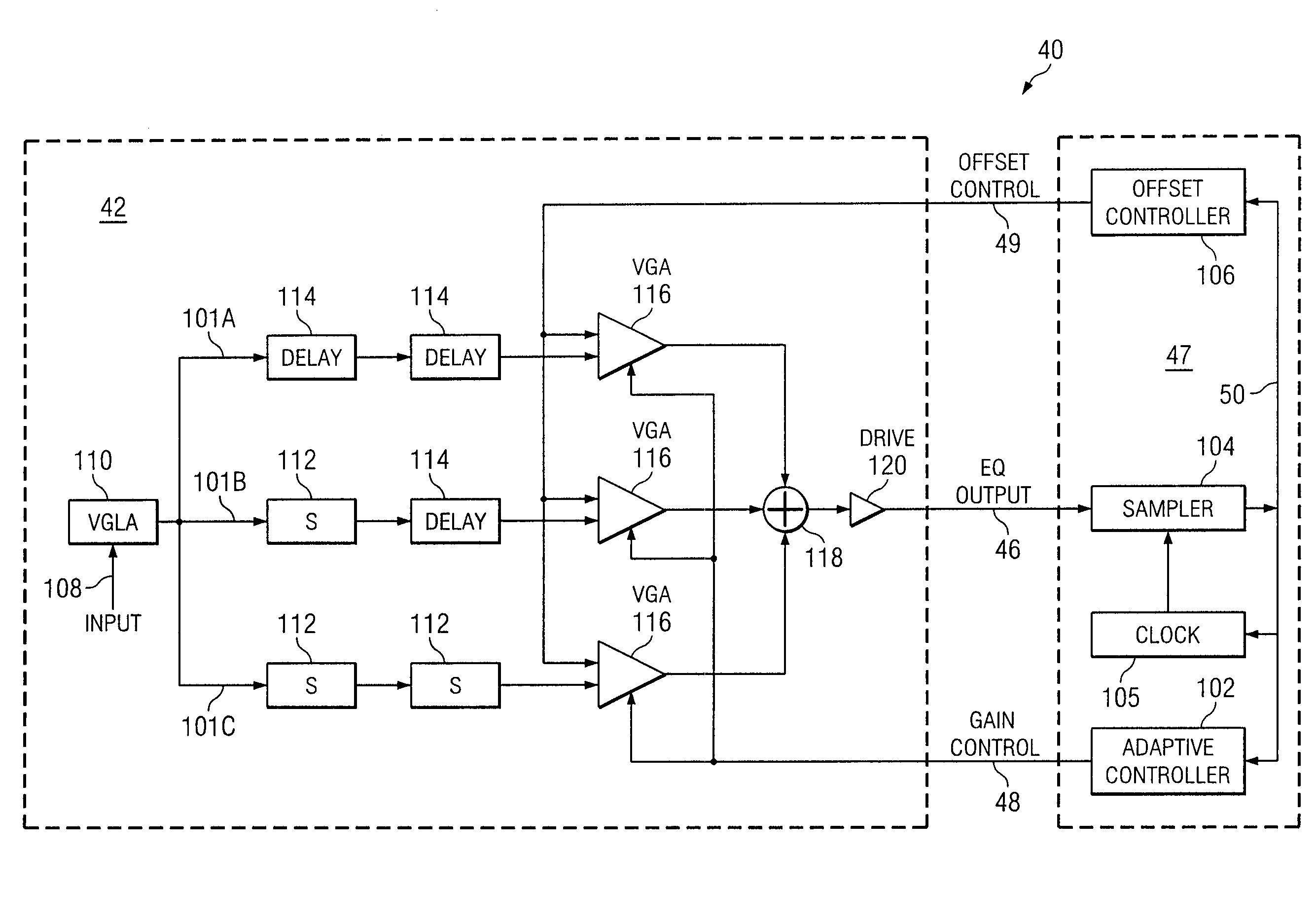
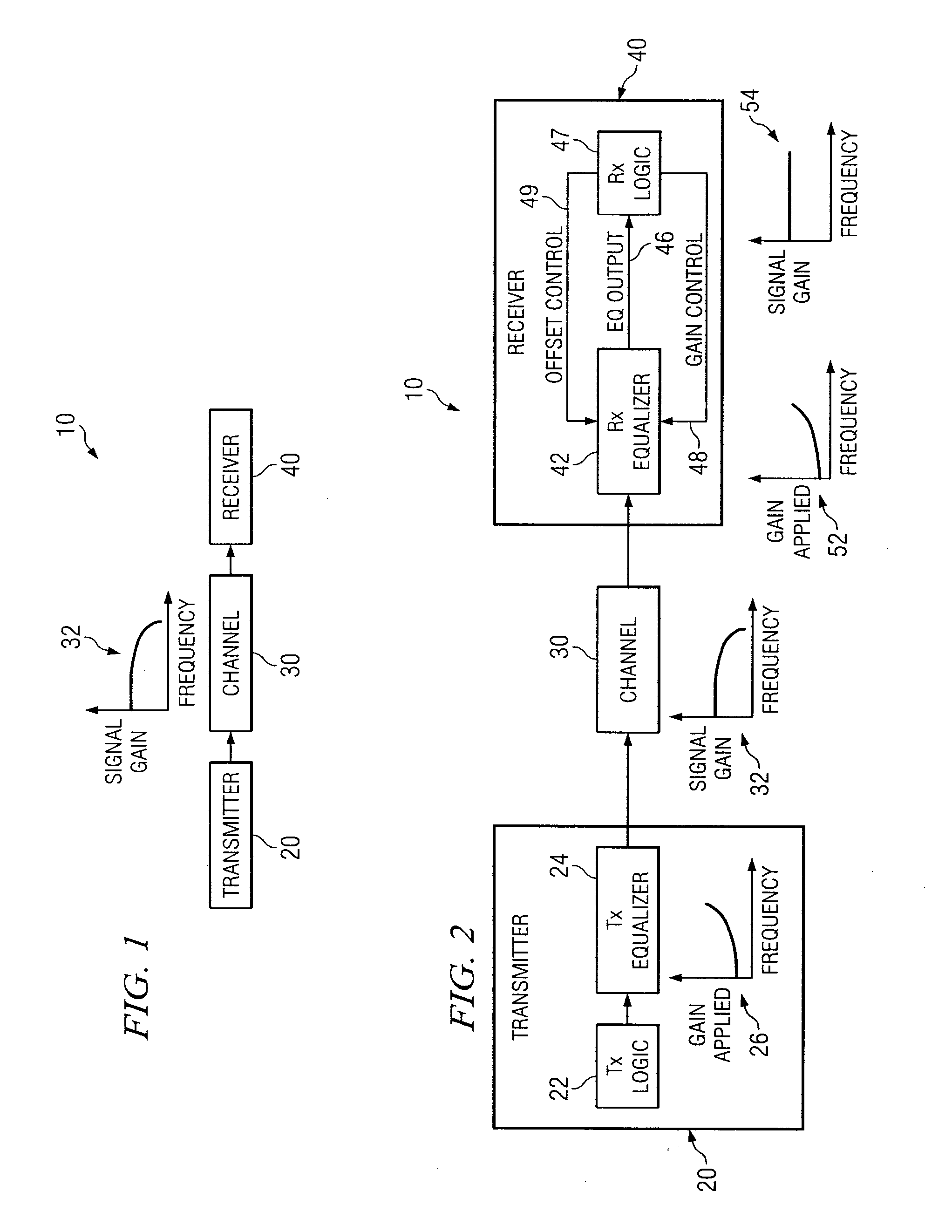
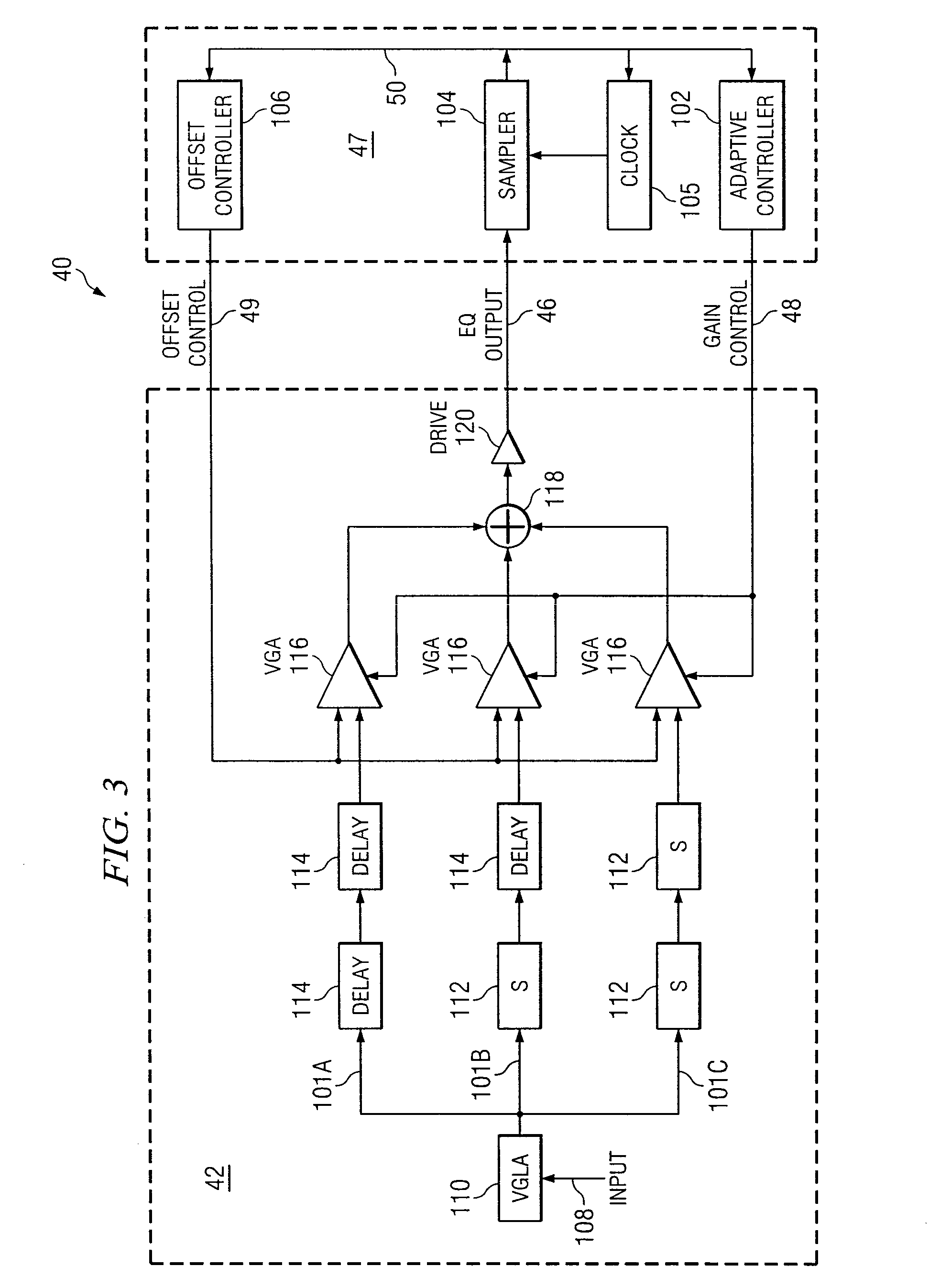
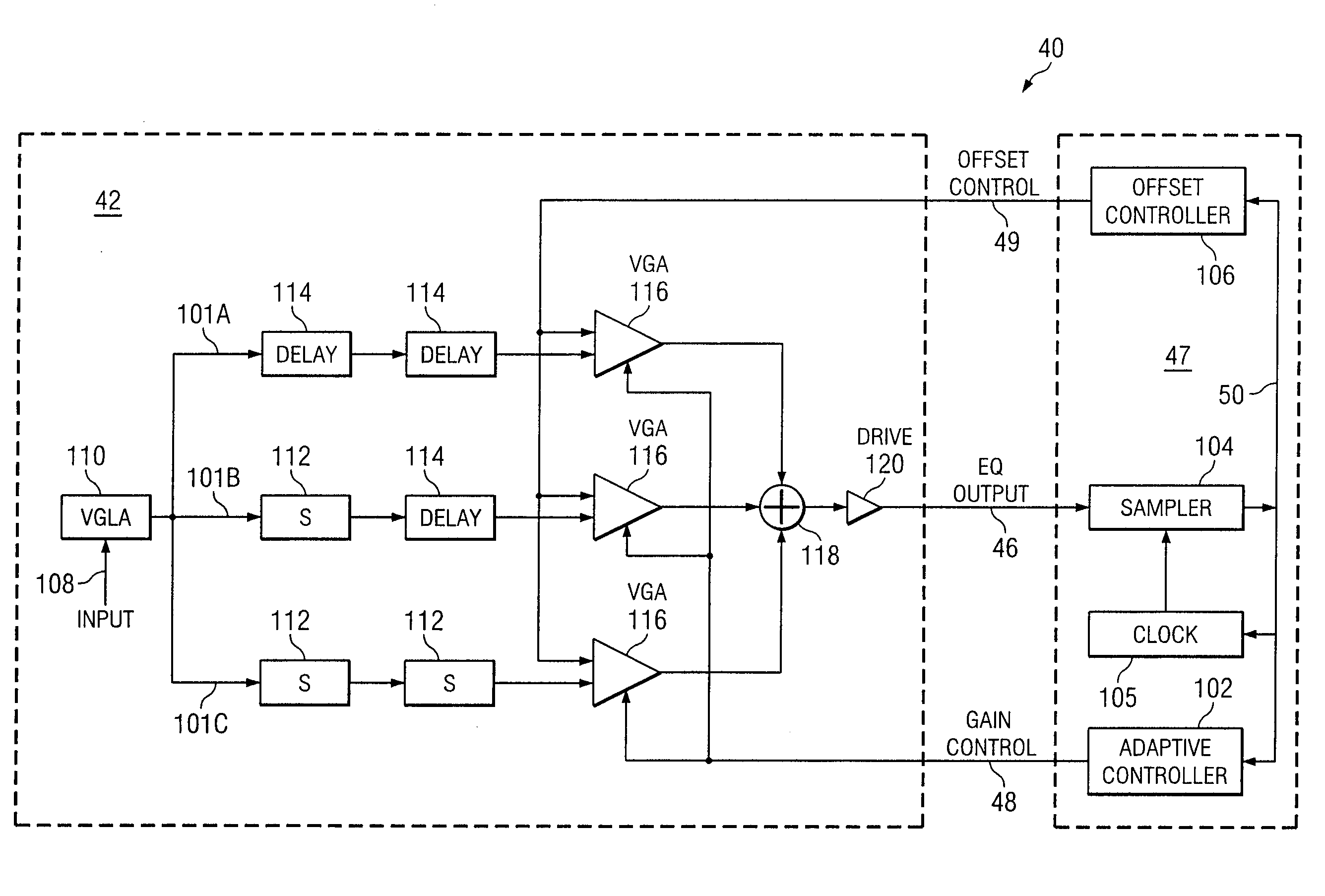
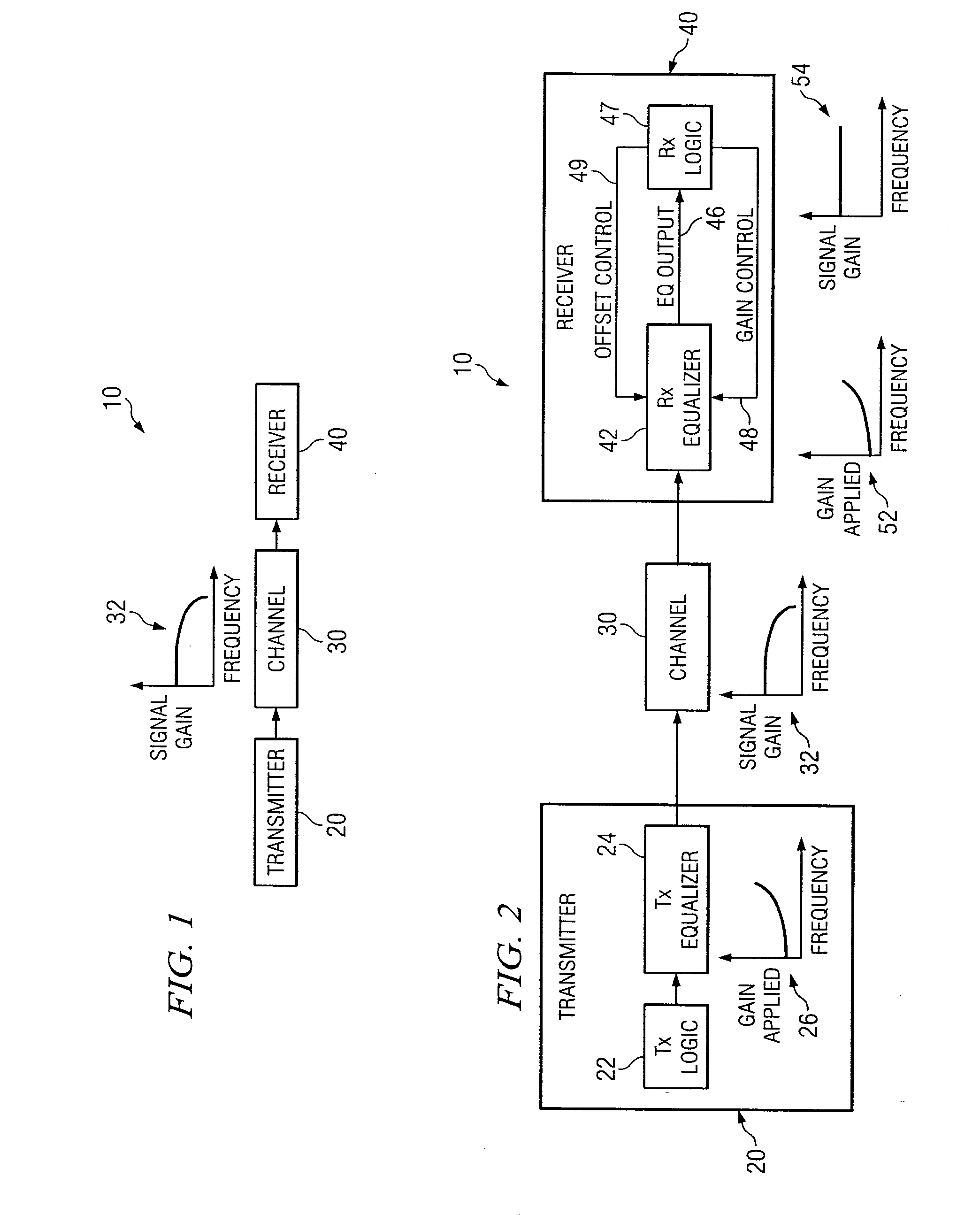
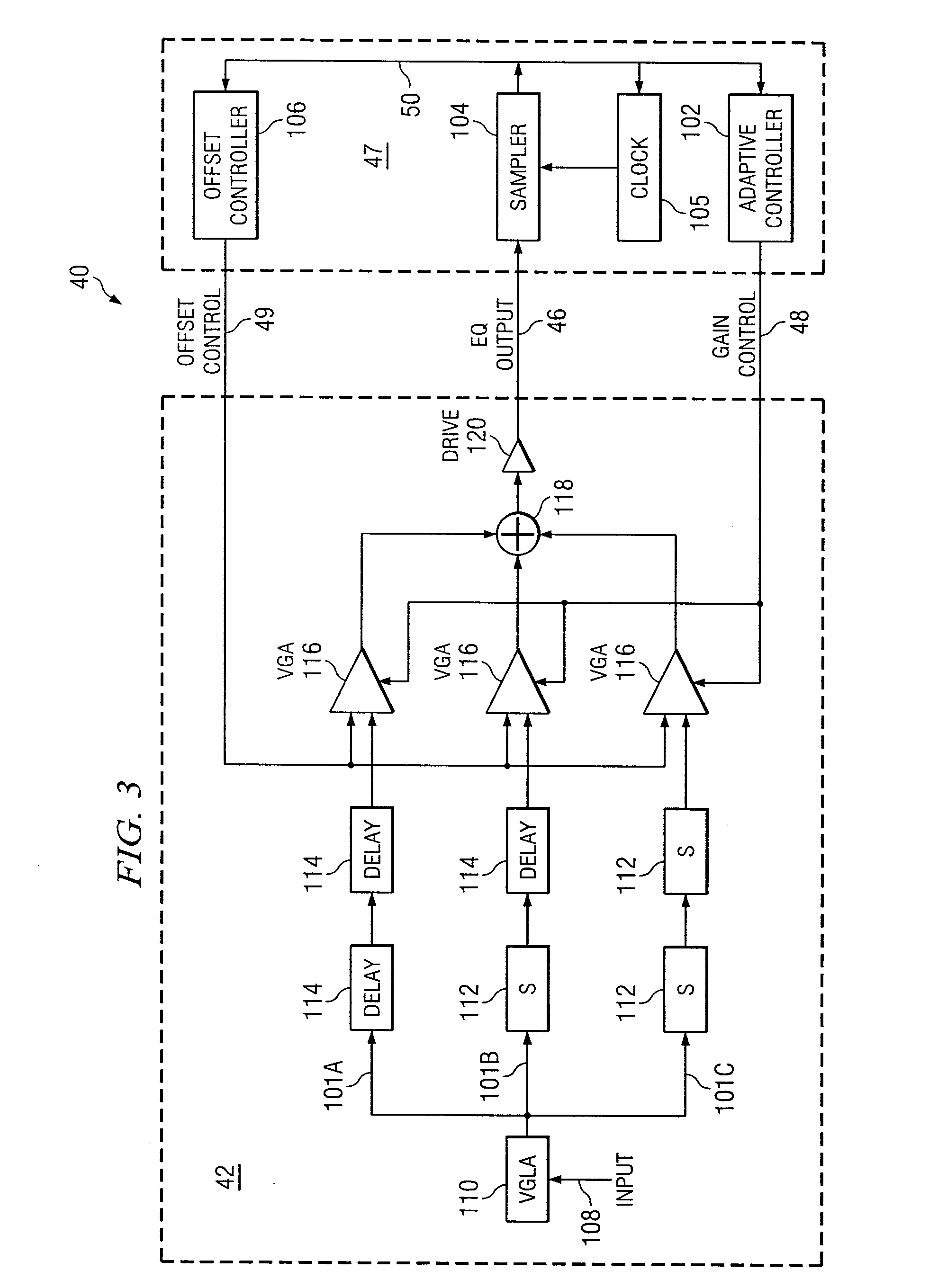
System and Method for Independently Adjusting Multiple Compensations Applied to a Signal
InactiveUS20080056344A1High sensitivityPrevent lockMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsBoundary valuesComputer science
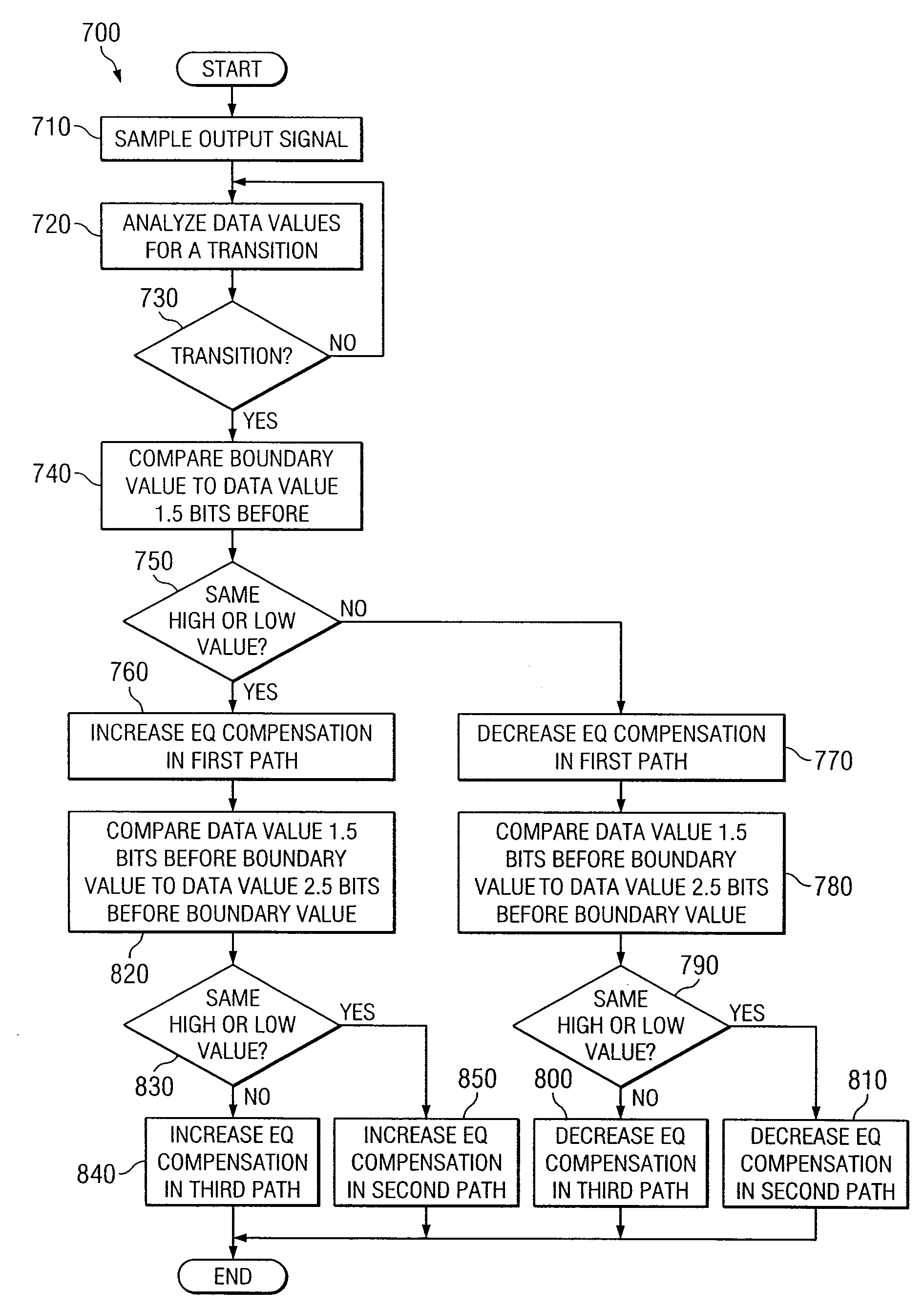
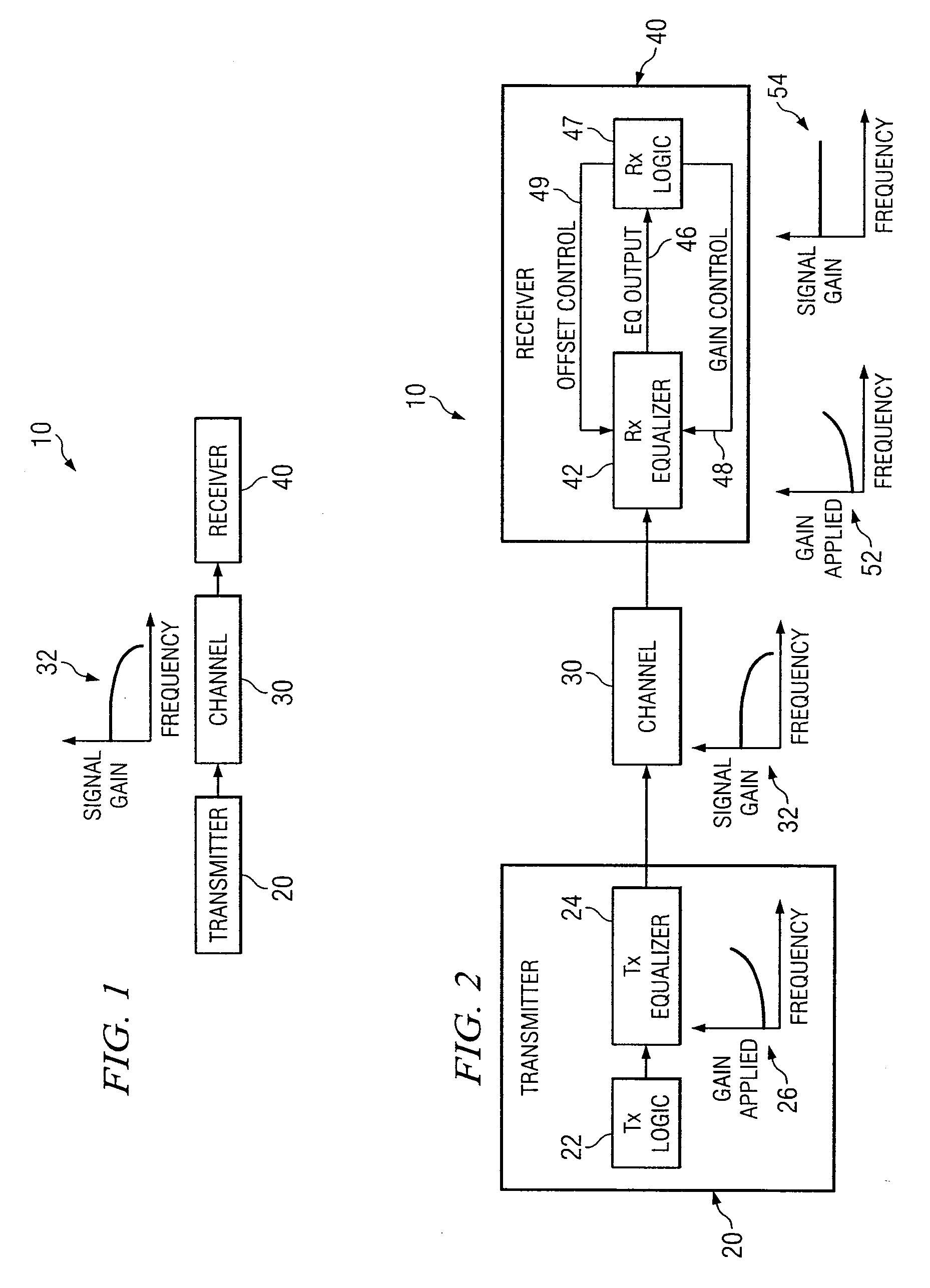
In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for adjusting a signal includes applying a plurality of compensation for distortion to a signal to generate an output signal. The method also includes, using a clock signal, sampling the output signal to generate a plurality of data values and boundary values, each value comprising either a high value or a low value based on the sampling of the output signal. The method also includes detecting a transition in value between two successive data values and determining a sampled boundary value between the two successive data values. The method further includes based at least on the high or low values of the boundary value and a plurality of data values before or after the boundary value, independently adjusting each compensation applied to the signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System and Method for Independently Adjusting Multiple Offset Compensations Applied to a Signal
InactiveUS20070280384A1High sensitivityPrevent lockError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionBoundary valuesSignal on
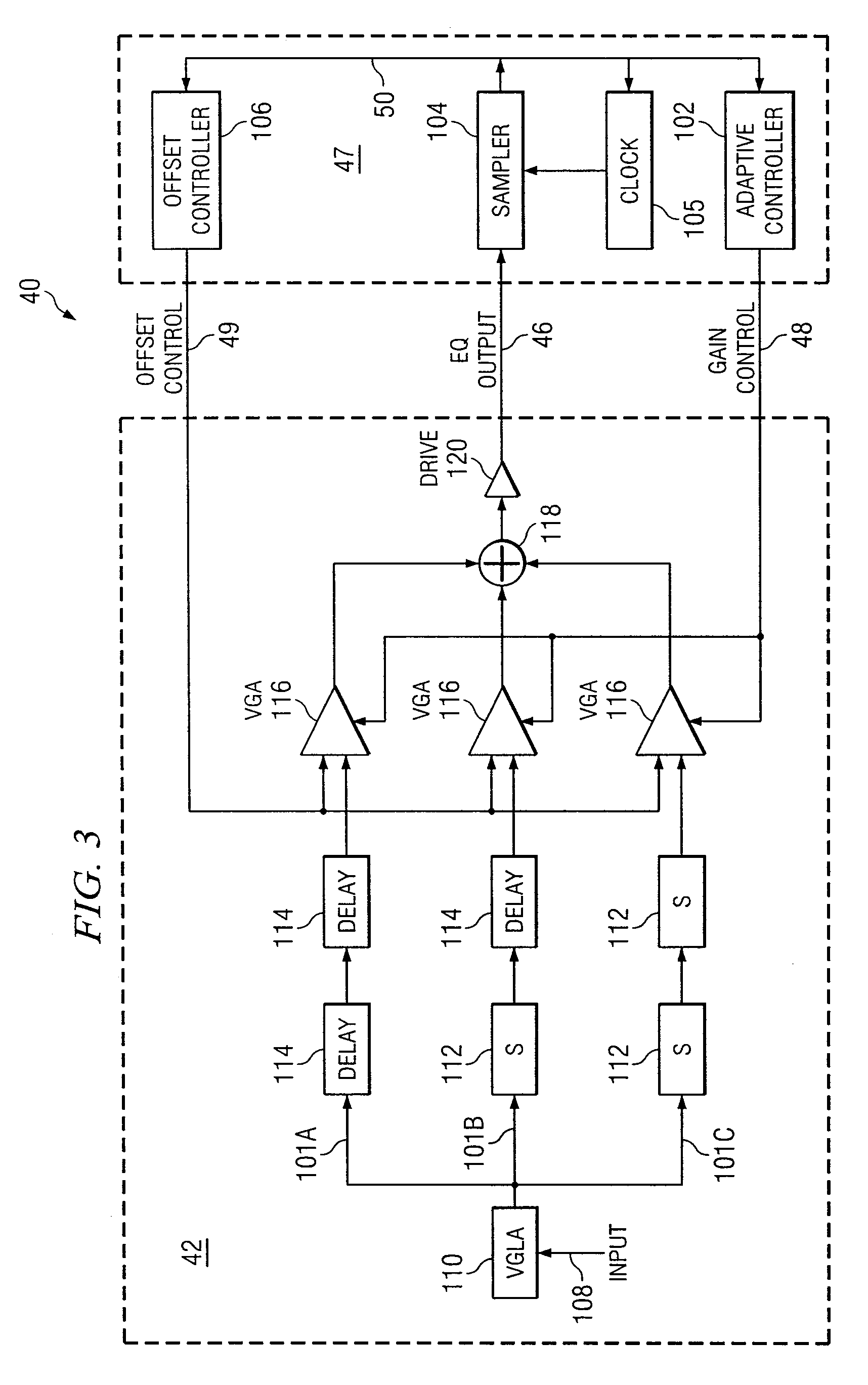
In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for adjusting a signal includes receiving an input data signal and communicating a first portion of the input data signal on a first path and a second portion of the input data signal on a second path. The method also includes applying a first offset compensation to the first path and a second offset compensation to the second path. The method further includes combining at least the first path and the second path to generate an output signal. The method also includes, using a clock signal, sampling the output signal to generate a plurality of data values and boundary values, each value comprising either a high value or a low value based on the sampling of the output signal. The method further includes detecting a transition in value between two successive data values and determining a sampled boundary value between the two successive data values. The method also includes, based at least on the high or low value of the boundary value and on the high or low value of at least two data values arriving immediately before the boundary value, independently adjusting the first offset compensation applied to the first path and the second offset compensation applied to the second path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for determining the hematocrit of a blood sample utilizing the intrinsic pigmentation of hemoglobin contained within the red blood cells
ActiveUS7951599B2Improve versatilitySuitable for useCharacter and pattern recognitionAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBoundary valuesPigmentations
A method for determining the hematocrit of a blood sample is provided that includes the steps of: 1) depositing the sample into an analysis chamber operable to quiescently hold the sample for analysis, the chamber defined by the interior surfaces of first and second panels and a height extending there between, wherein both panels are transparent, and the height is such that at least some of the red blood cells within the sample contact both interior surfaces of the panels and one or more lacunae within the quiescent sample extend between the interior surfaces; 2) imaging at least a portion of the quiescent sample, which sample portion contains the red blood cells and one or more lacunae to determine an optical density of the imaged portion of the sample on a per image unit basis; 3) selecting and averaging the optical density values of the image units aligned with the red blood cells contacting the interior surfaces, and assigning an upper boundary value of 100% to the average optical density value of those image units; 4) selecting the optical density values of the image units aligned with the one or more lacunae, and assigning a lower boundary value of 0% to the optical density values of those image units; and 5) determining the hematocrit of the sample by assigning relative values to the optical density value of each image of the imaged sample portion as a function of the upper and lower boundary values, and averaging the relative values.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Apparatus and method for controlling display backlight
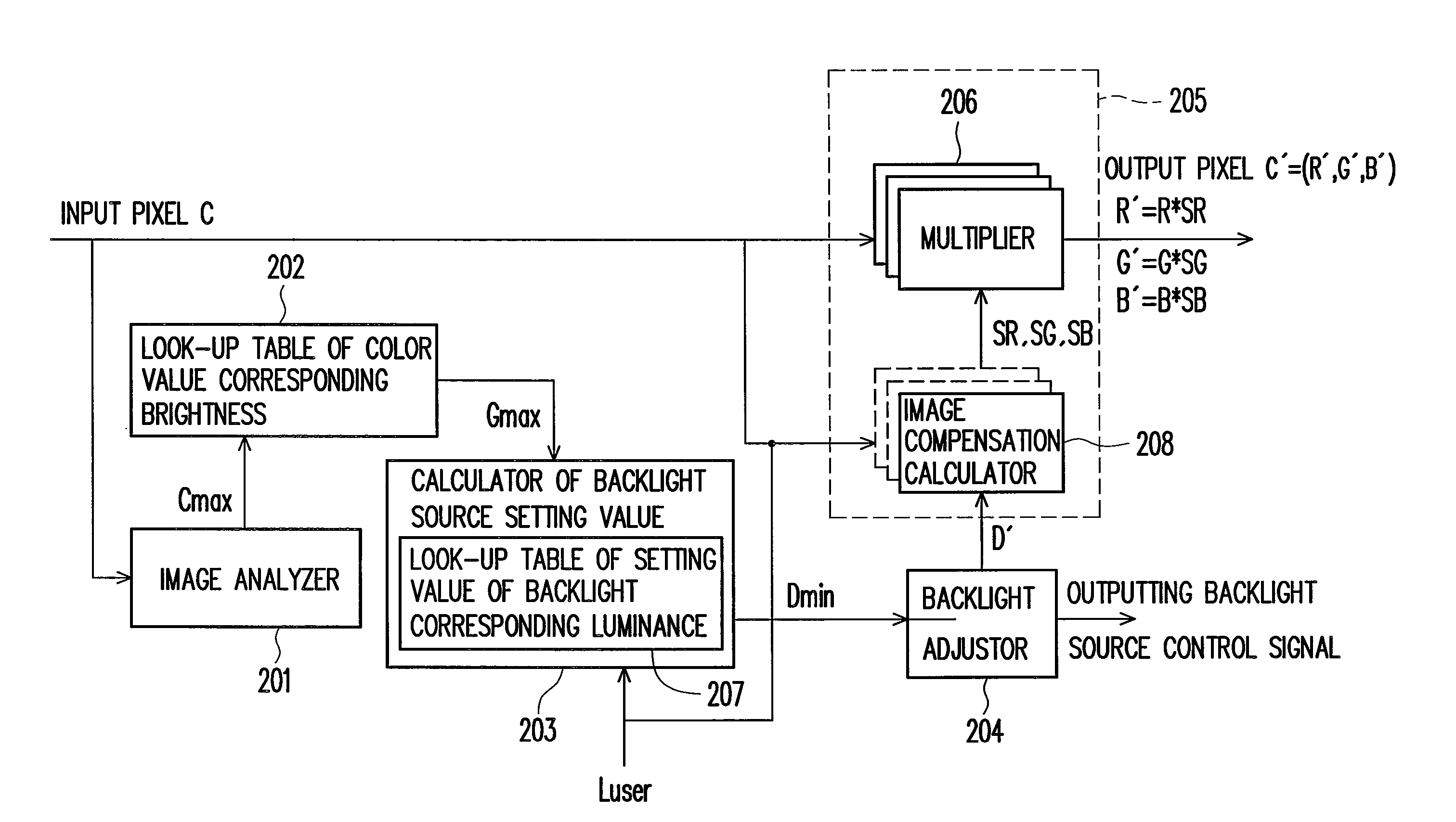
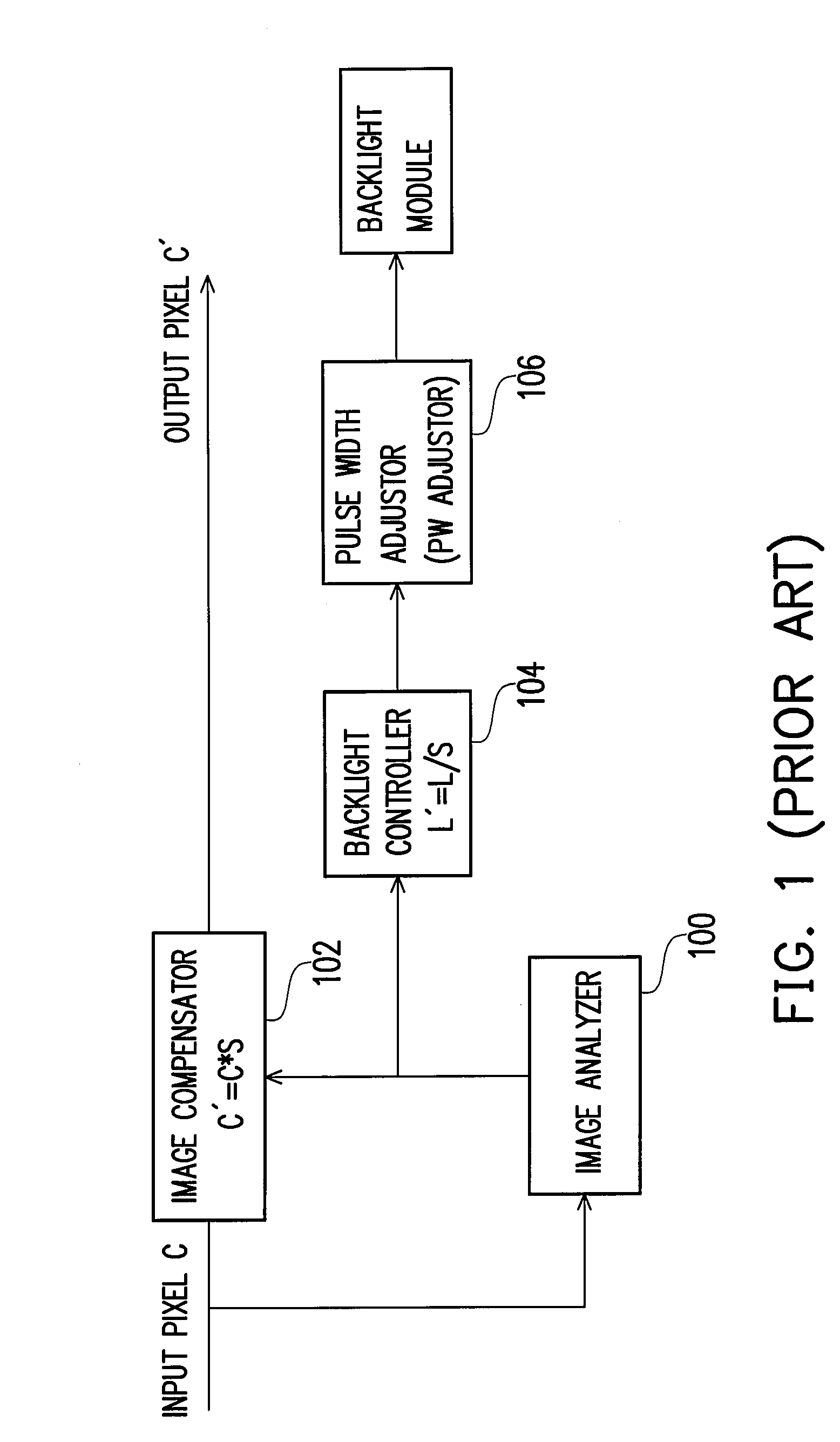
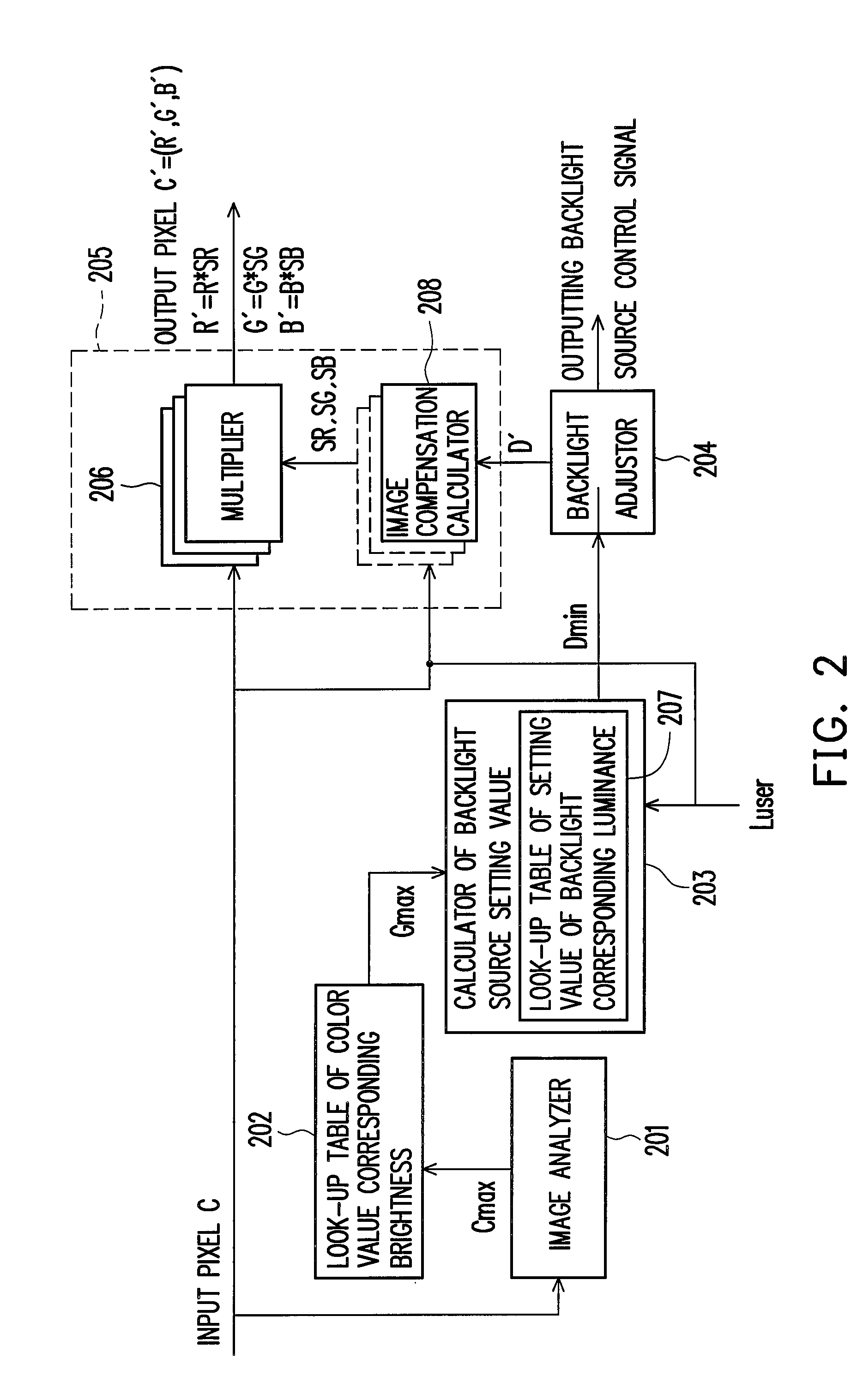
ActiveUS20070216636A1Prevents compliatcated nonlinear calculationMinimizing undesirable variationStatic indicating devicesBoundary valuesDisplay device
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
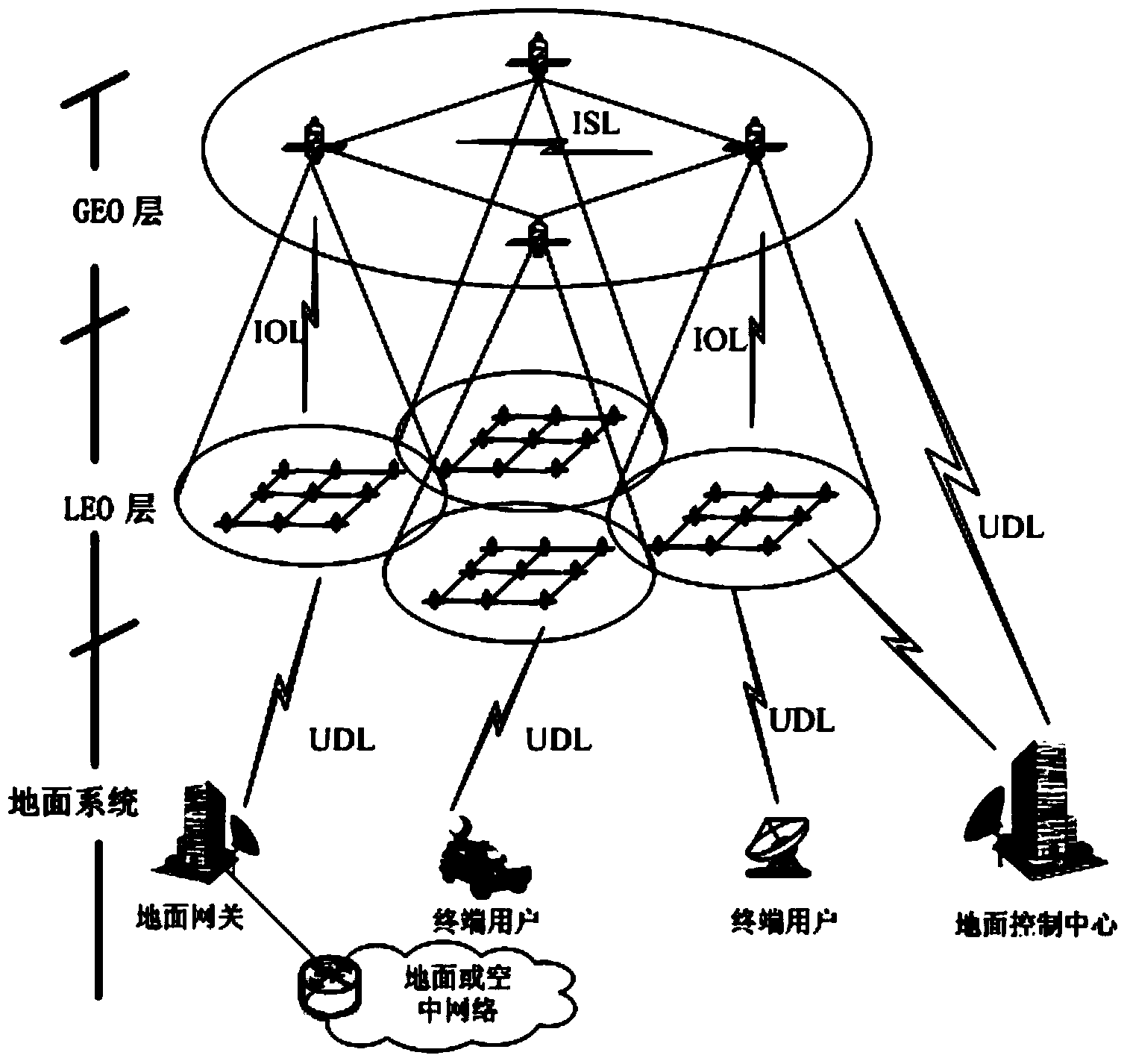
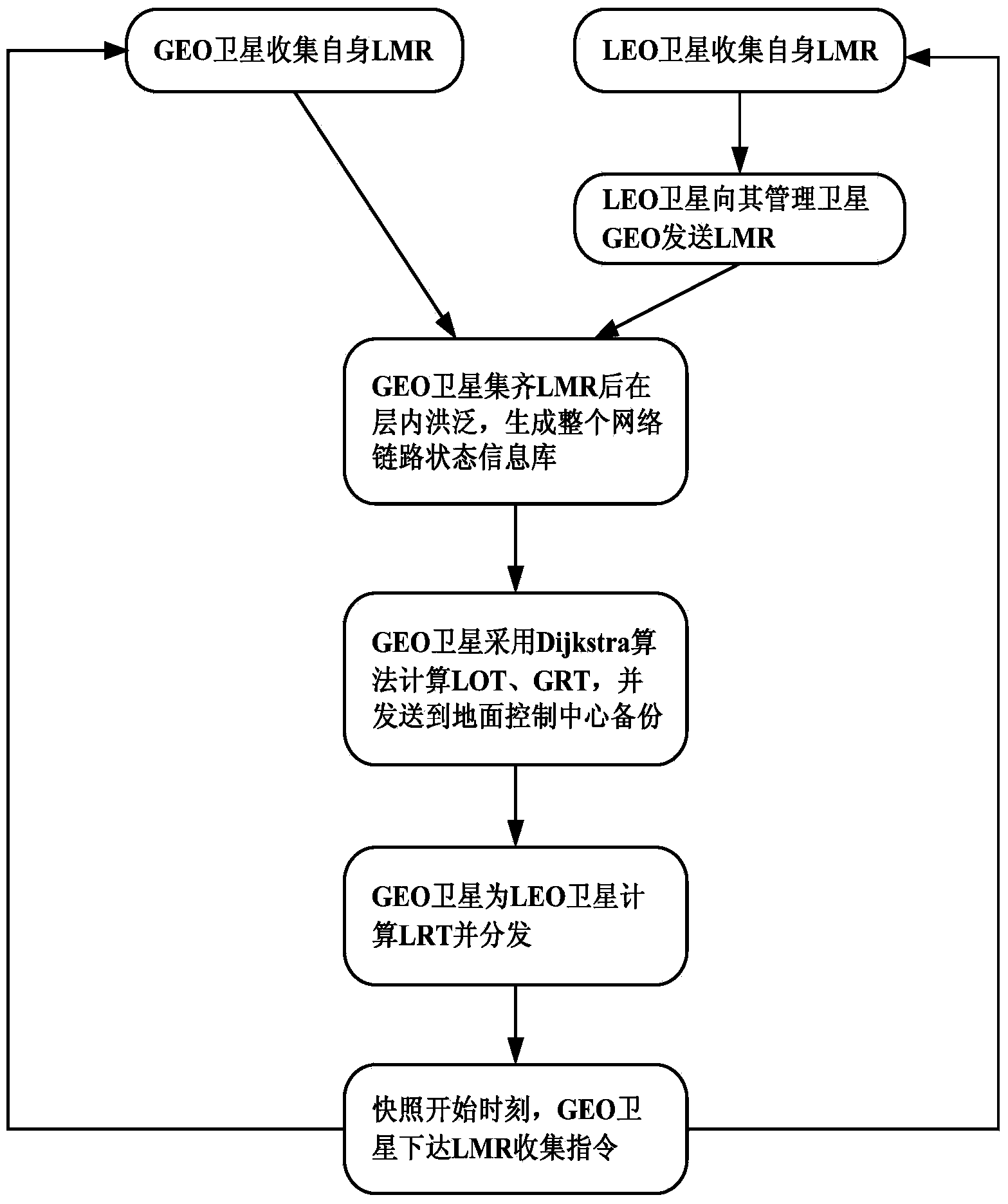
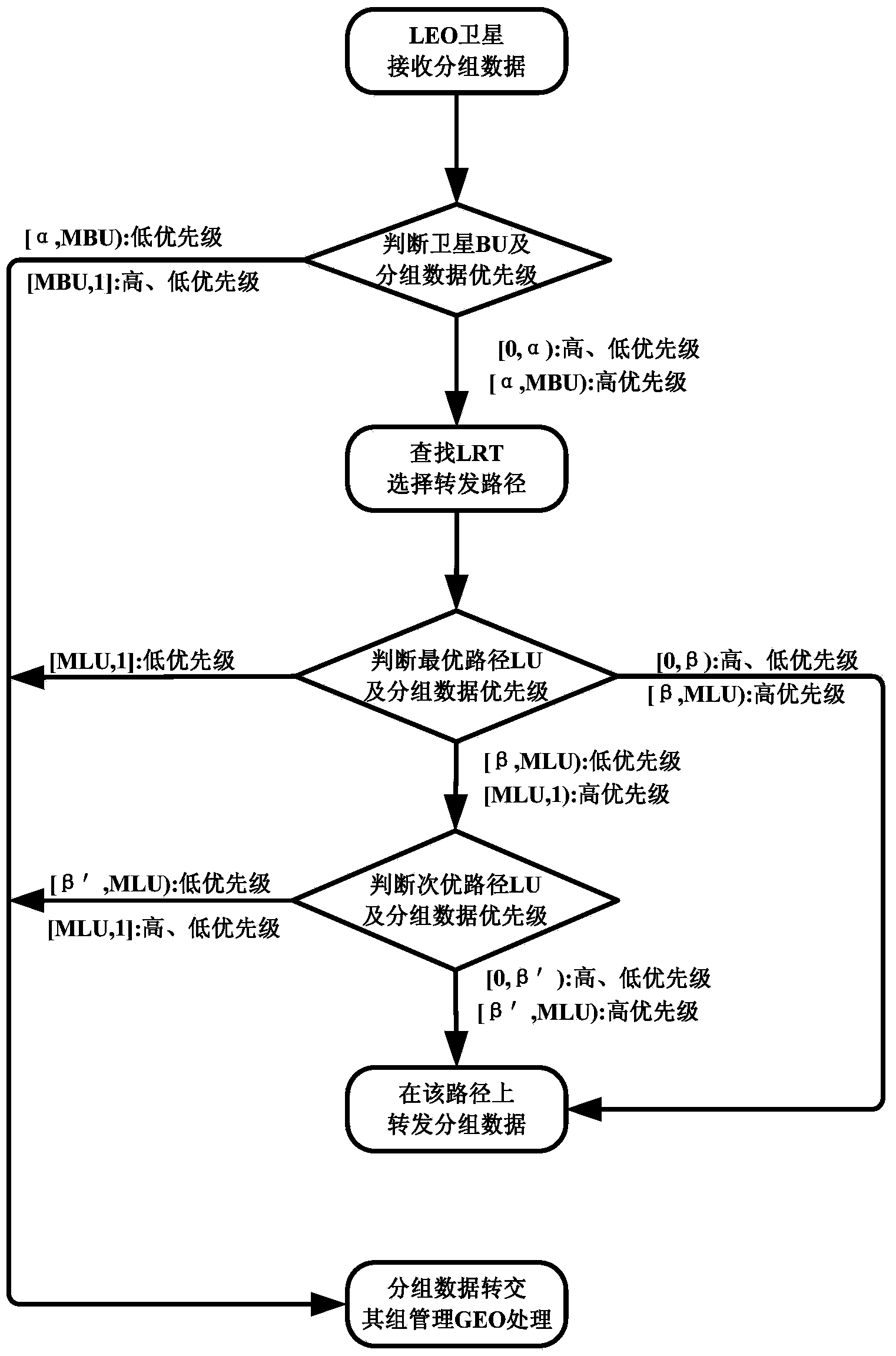
Route exchange method suitable for GEO/LEO double layered constellation network
InactiveCN103905306AReduce overheadShorten convergence timeData switching networksOn boardBoundary values
The invention discloses a route exchange method suitable for a GEO / LEO double layered constellation network. According to the method, a system period is divided into equal-duration time sections based on a dynamic boundary value; a GEO layer satellite high in on-board processing capacity is used for calculating the best route and the second best route for each LEO satellite; in the processes of information transmission and exchange, when loads of the LED satellites are large, the GEO satellite shares part of low priority services in time for the LED satellites, and it is guaranteed that important information is reliably transmitted in real time; when link congestion, node ineffectiveness and other emergency conditions happen in the satellite network, in order to avoid rerouting of the whole network, and the GEO satellite only calculates rerouting for affected routes; after link congestion is eliminated, the LED satellites recover route information in time before congestion in order to avoid link resource waste in the network. In the network that topology time varying happens, links are prone to congestion, on-board resources are limited, continuous high-load flows are prone to being generated, and nodes are prone to being ineffective at the special period, the method can reduce constellation system cost, shorten convergence time, save the on-board resources, increase the utilization rate of the link resources, guarantee that important information is reliably transmitted in real time and improve invulnerability and robustness of the satellite network.
Owner:中国人民解放军西安通信学院
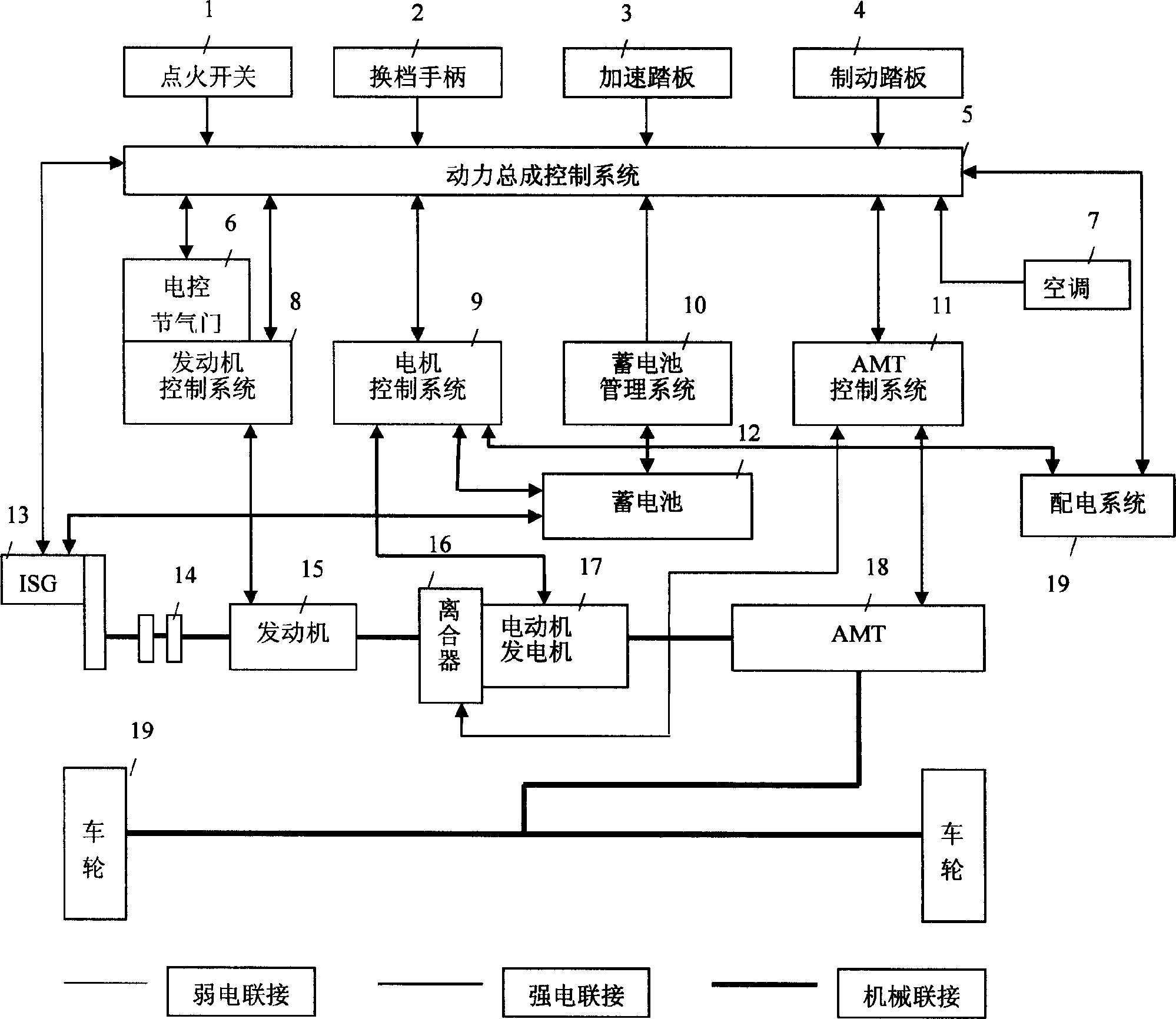
Power output changing-over method and control system for power assembly of mixed powder car
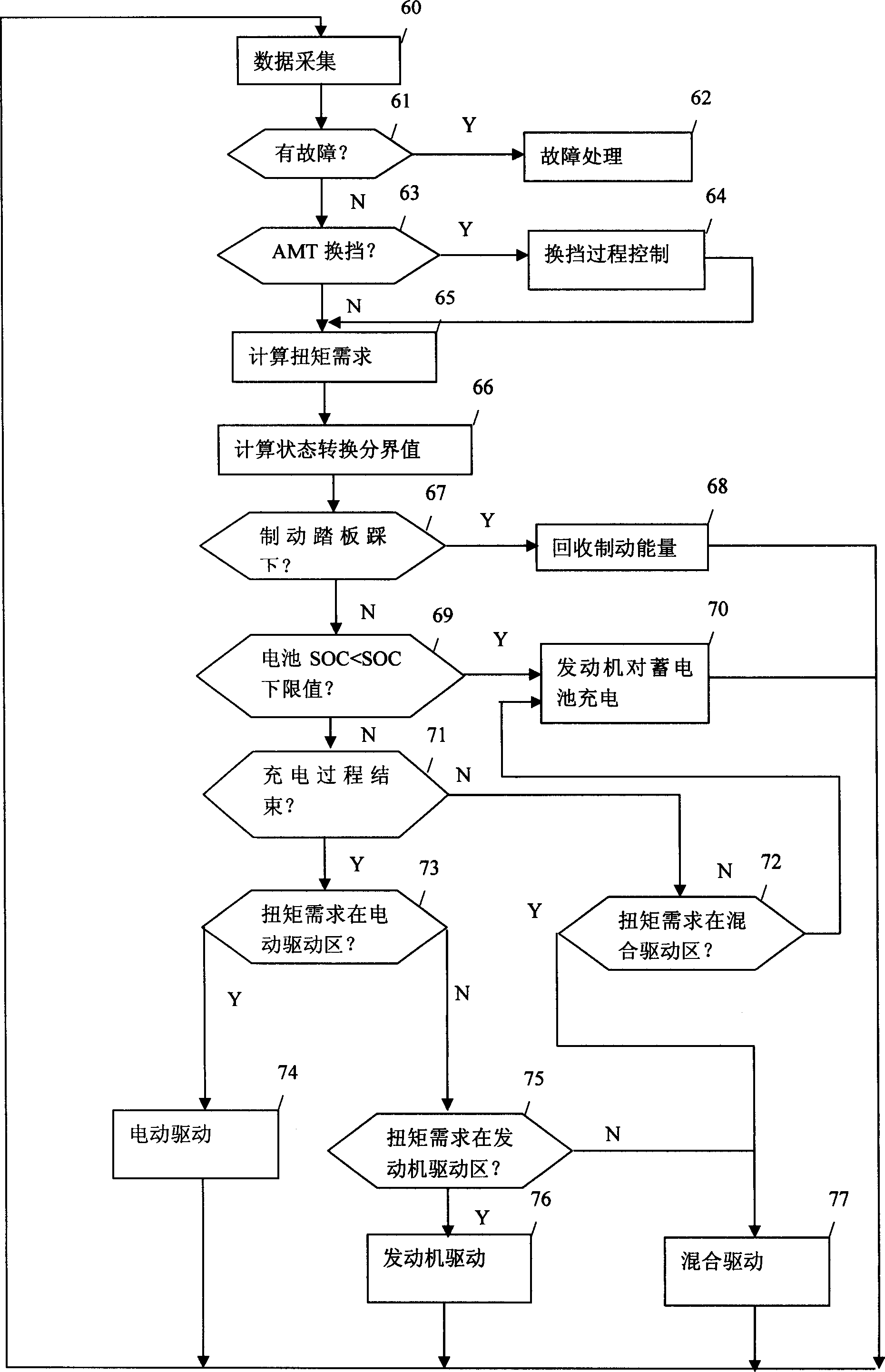
ActiveCN1528612AEmission reductionReduce fuel consumptionHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingBoundary valuesData acquisition
The invention is a power output switching method and control system of power assembly of mixed power saloon car. It can switch the power output and manage system energy, and according to state switching boundary value and result judgment of data collection, makes the power assembly switch to the states such as reclaiming plugging energy; charging accumulator by engine; electric driving; mixed driving; engine driving; etc to make coordination treatment. Its control system includes main chip, as well as switch quantity conditioning circuit, analogue quantity conditioning circuit, pulse signal conditioning circuit, CAN bus interface, D / A converting circuit, drive isolating circuit, etc, where they are all connected with the main chip. It can make the output torque realize fast smooth switch in a large range, and heightens the energy using efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
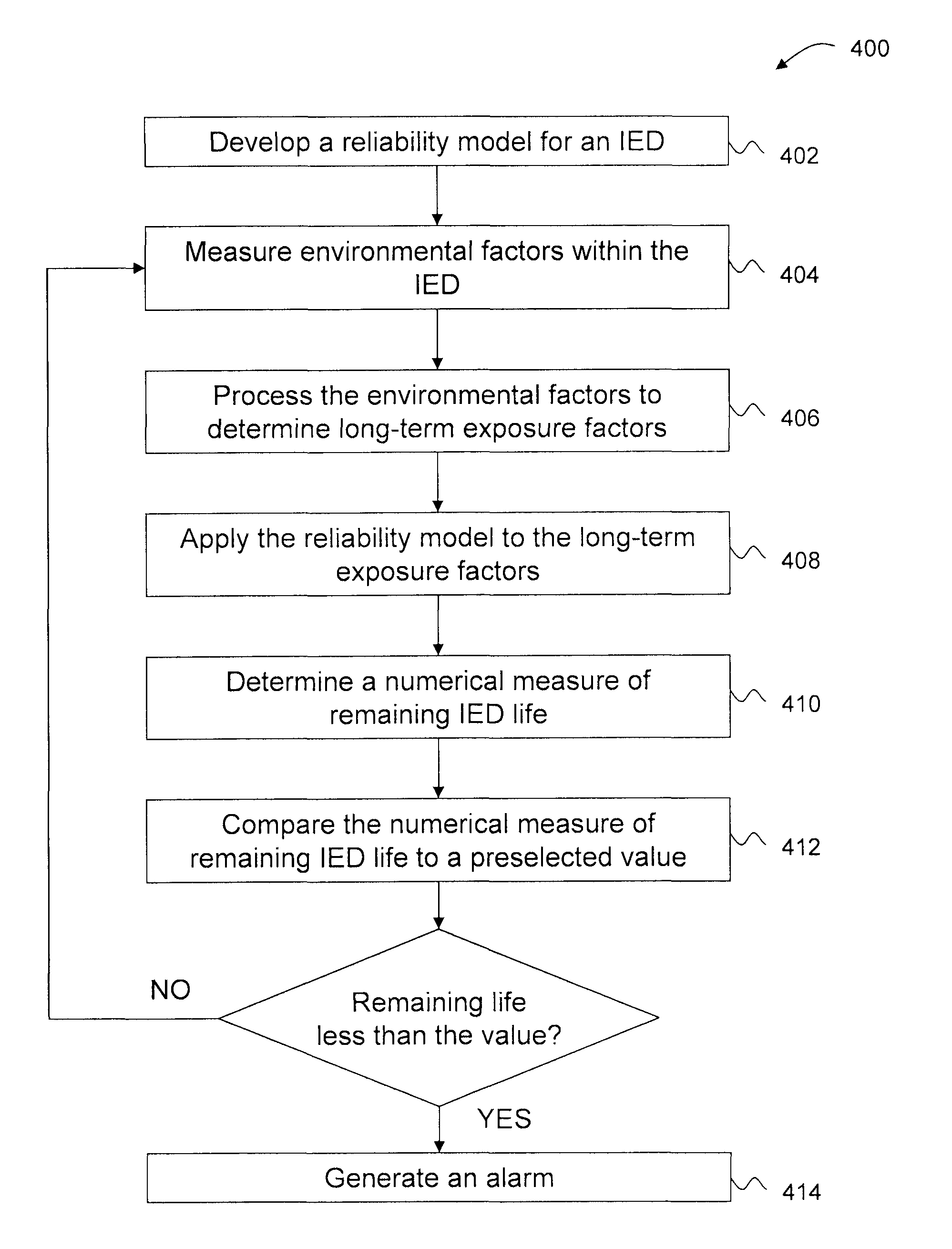
Systems and methods for predicting maintenance of intelligent electronic devices
ActiveUS7822578B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusElectric testing/monitoringBoundary valuesLife time
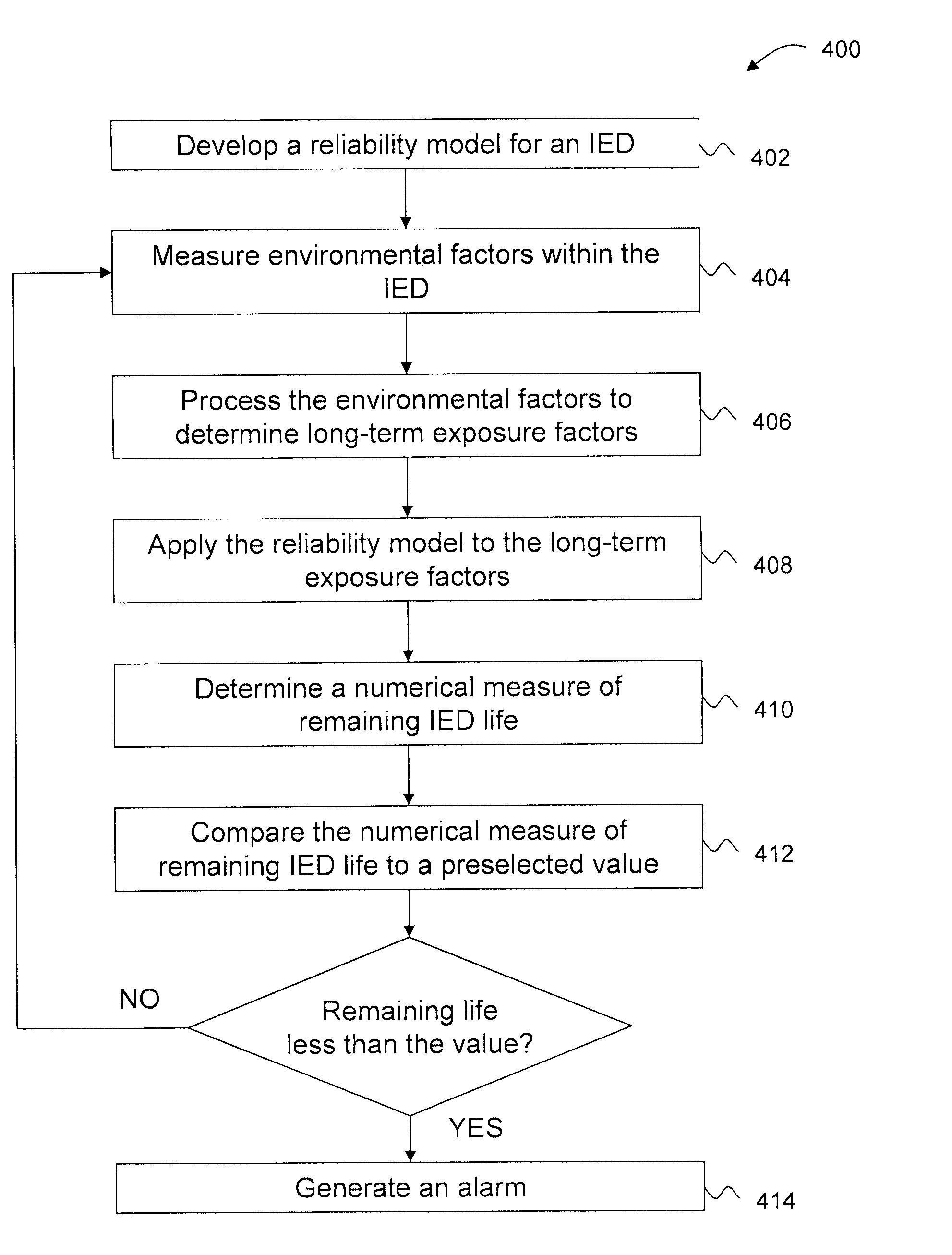
Predictive maintenance systems and methods are described. A method includes measuring environmental conditions using a plurality of sensors within the IED, processing the environmental measurements to determine long-term exposure factors representing historical operating conditions of the IED, applying a reliability model to the long-term exposure factors, determining a numerical measure of IED life based on the long-term exposure factors and the reliability model, comparing the numerical measure of IED life to preselected boundary values, and signaling if the numerical measure of IED life is outside of the preselected boundary values.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
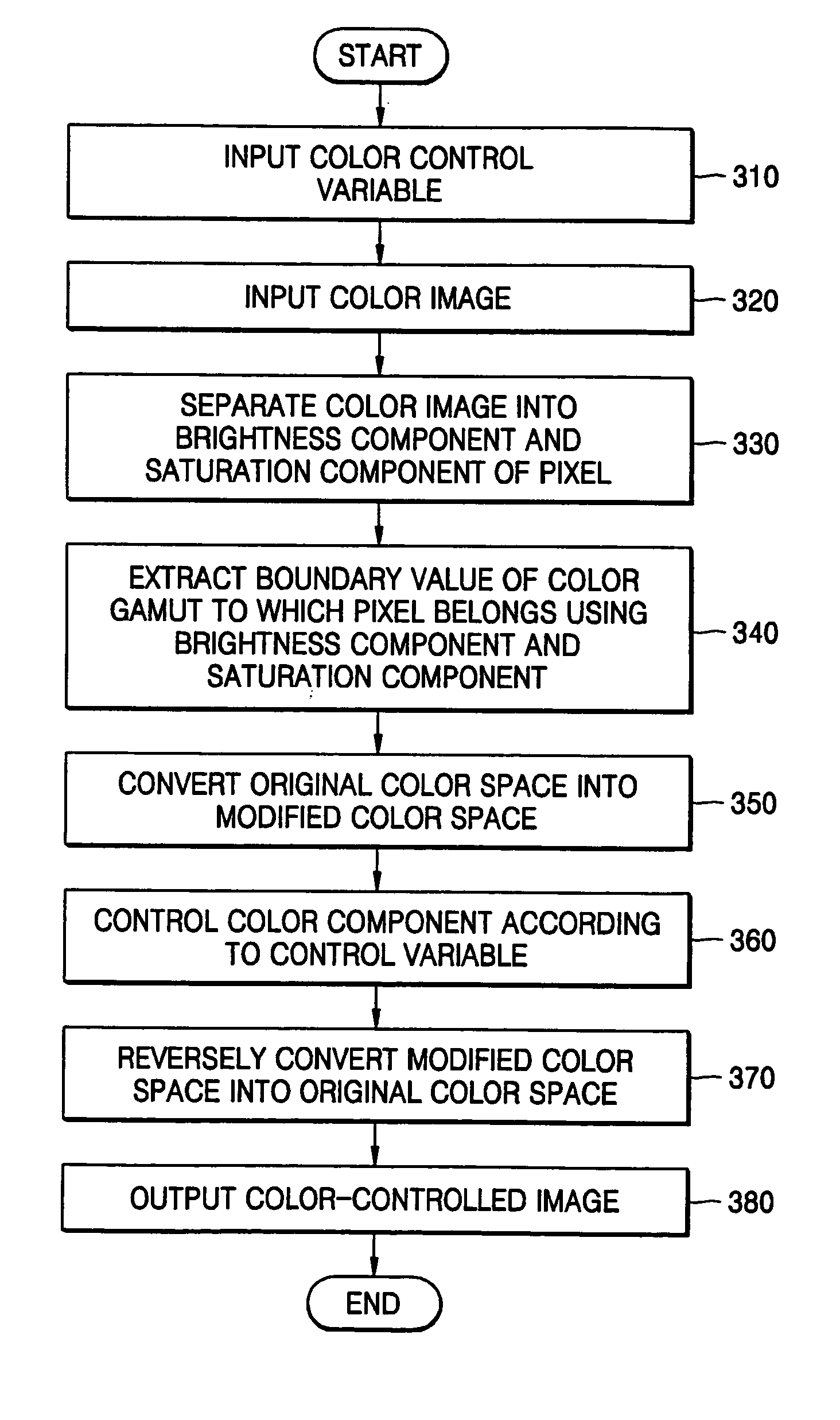
Apparatus and method for controlling colors of color image
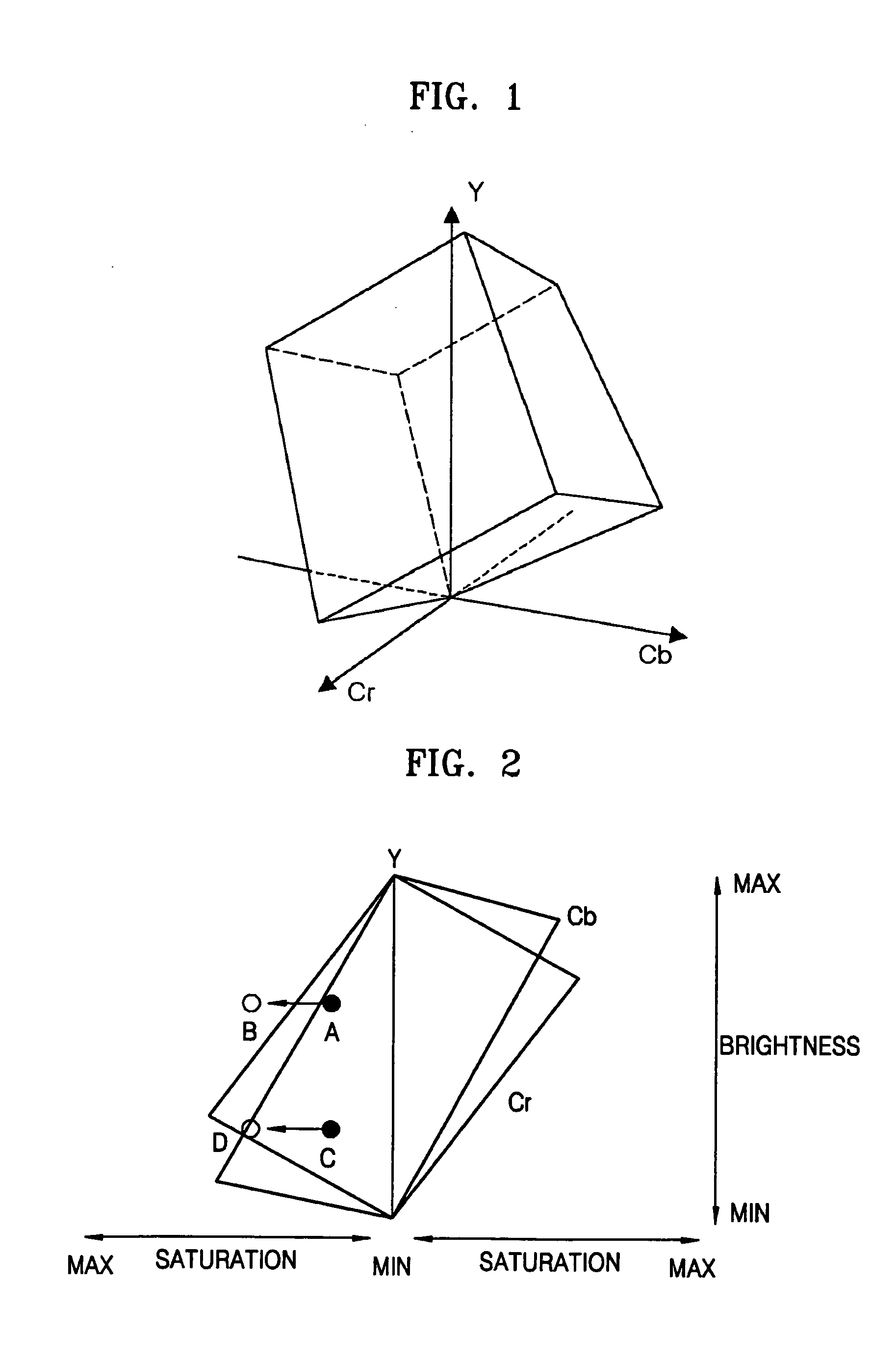
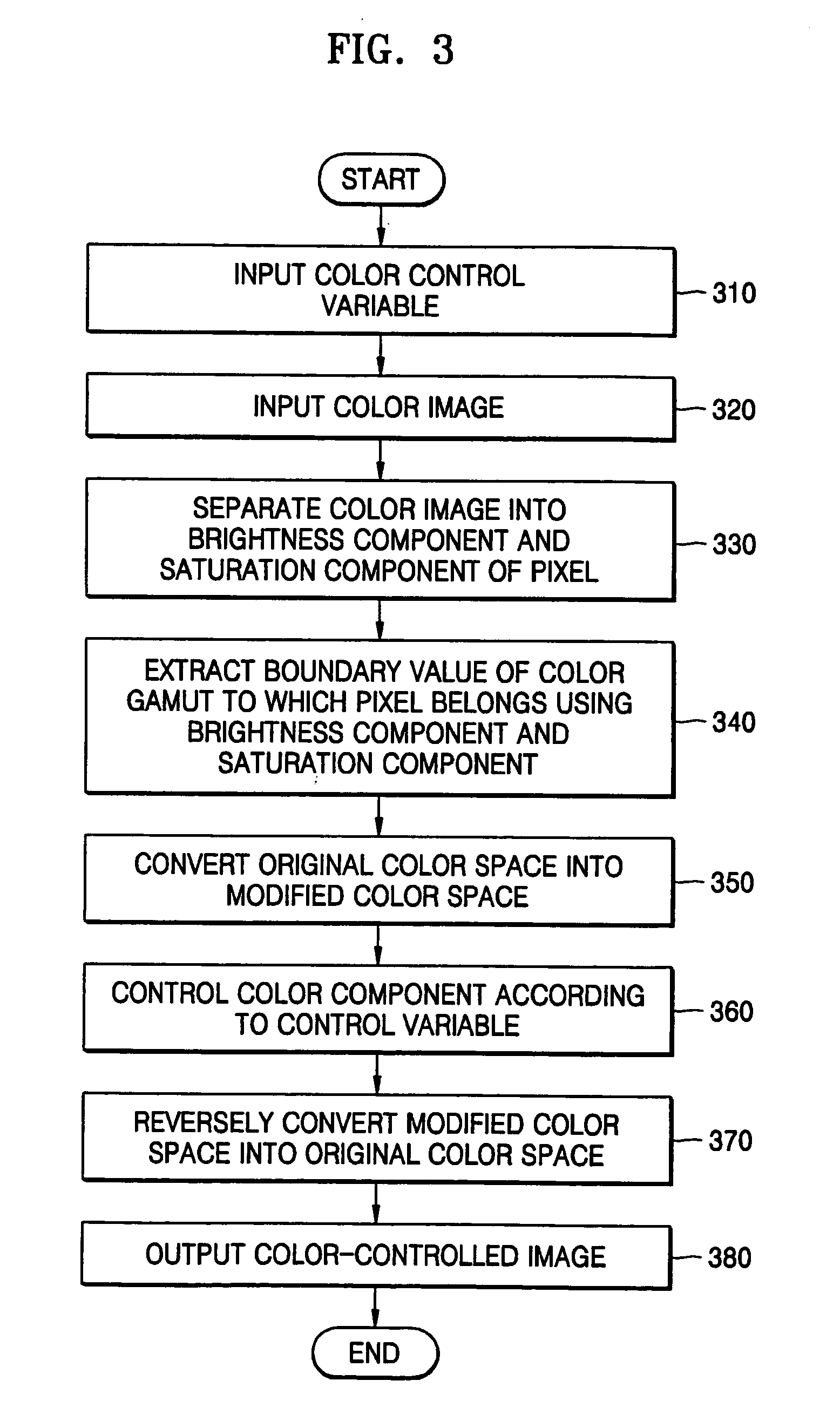
ActiveUS20050219574A1Digitally marking record carriersColor signal processing circuitsColor imageGamut
A method of and apparatus for converting a color space. The method includes: separating a color signal of a given pixel into a brightness component and a saturation component; obtaining a boundary value of the saturation component of a color gamut, to which the color signal belongs, in a first color space using the separated brightness component and saturation components; and converting the first color space into a second color space in which saturation components and hue components are independently controlled using the obtained boundary value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semantic crawler
InactiveUS20090024556A1Improve efficiencyQuality improvementWeb data indexingChaos modelsBoundary valuesAlgorithm
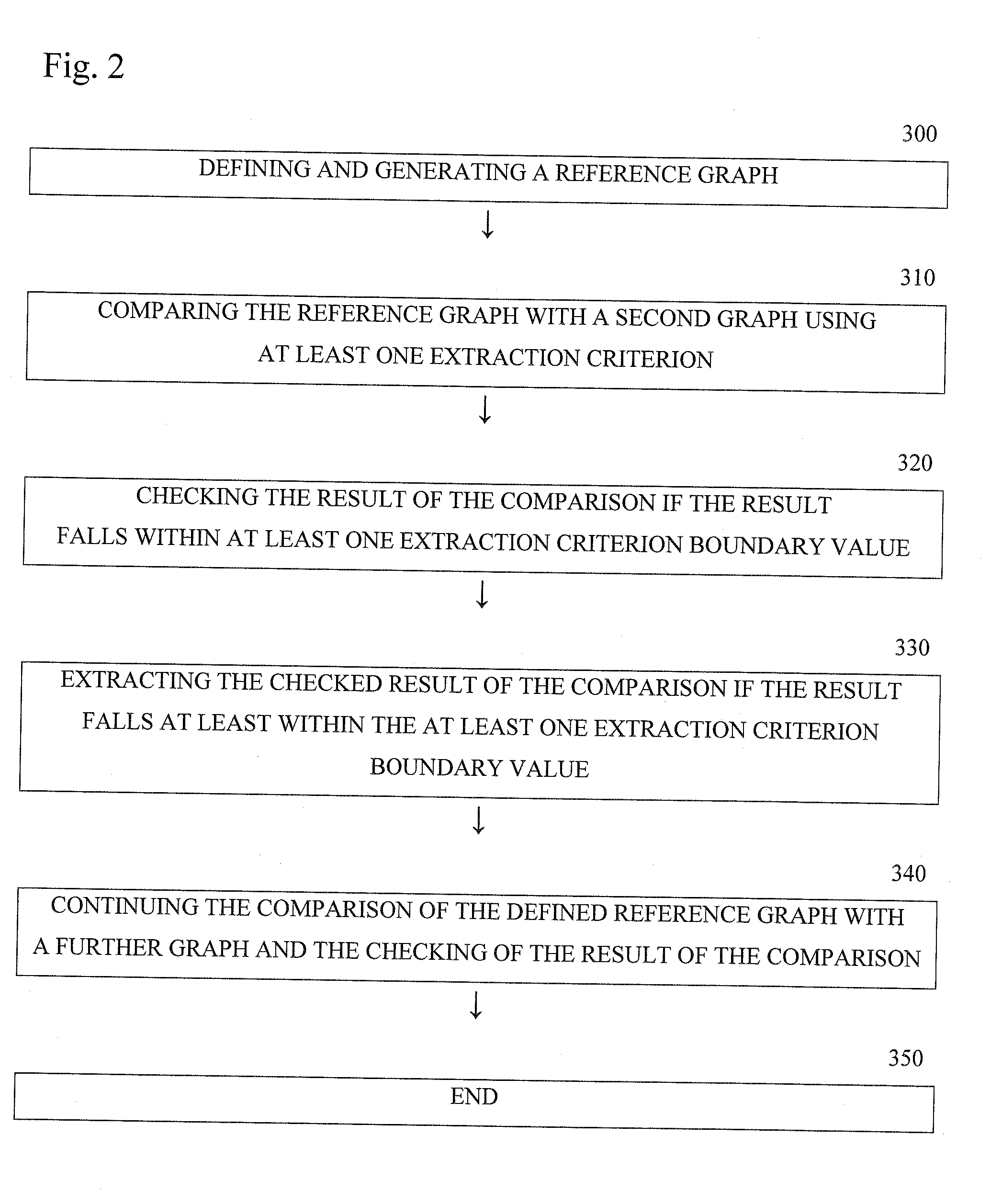
A method and an apparatus for extraction of information from a plurality of electronic text documents. The method comprises defining and generating a reference graph. The reference graph represents a specific theme of a reference text document. The method further comprises comparing the reference graph with a second graph using an extraction criterion. The second graph represents a specific theme of a second text document. Further, the result of the comparison is checked if the result falls within the extraction criterion boundary value. Then, the checked result of the comparison is extracted if the result falls at least within the extraction criterion boundary value. The method continues the comparison and the checking of the result of the comparison of the defined and generated reference graph with a further graph.
Owner:SEMGINE
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, information processing system and information processing program
InactiveUS20100090982A1Eliminate needAvoid difficult choicesInput/output processes for data processingInformation processingBoundary values
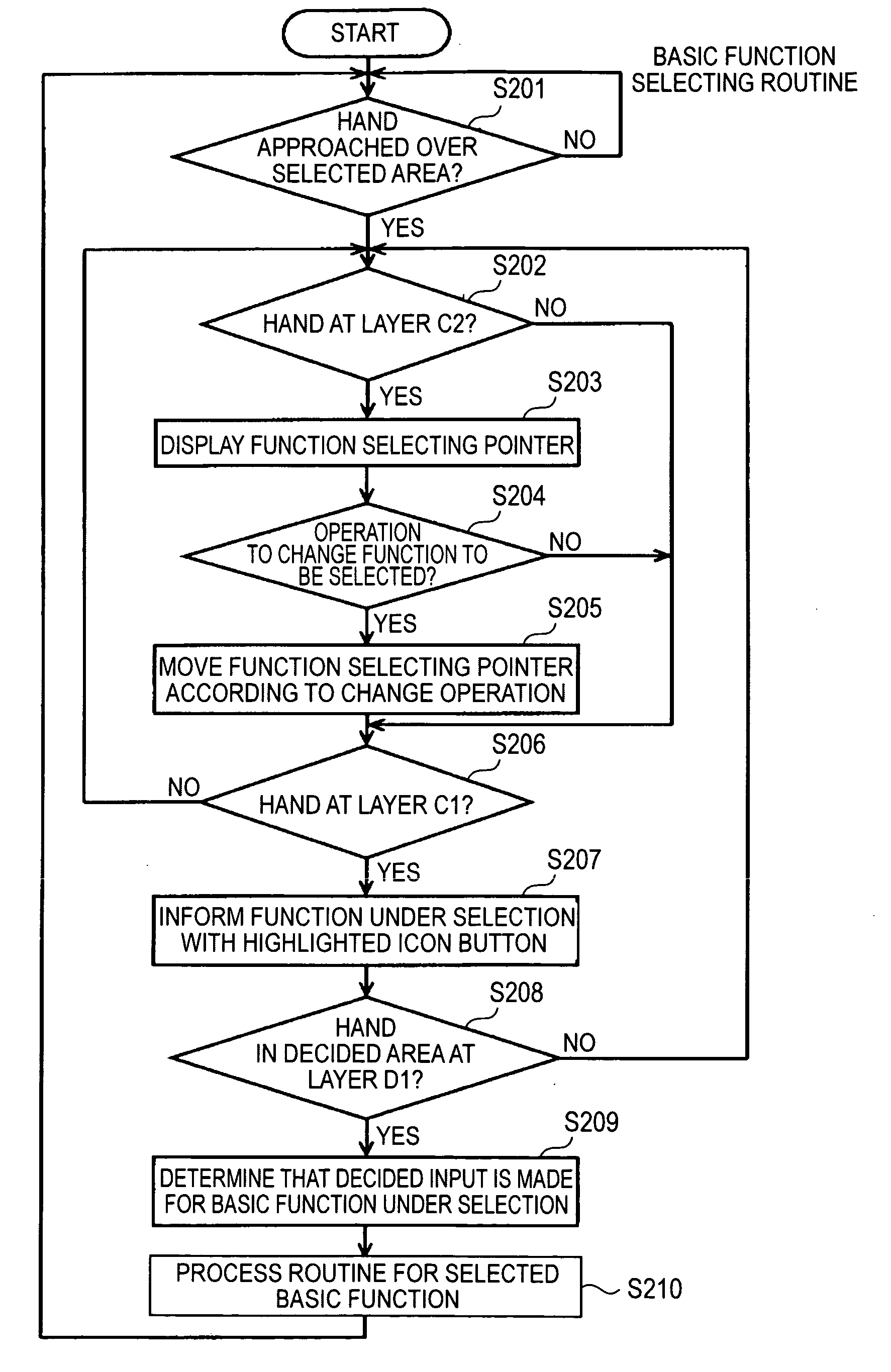
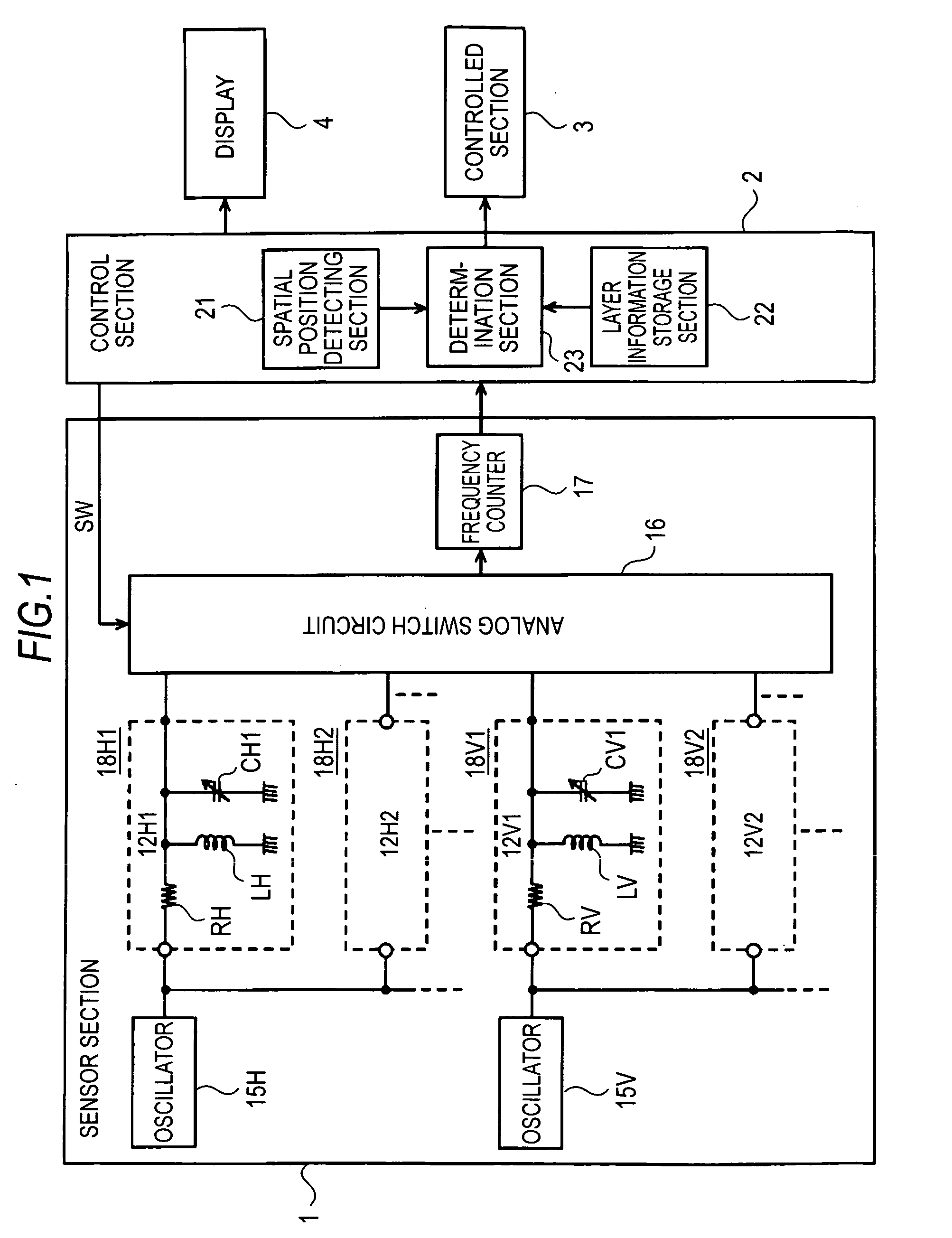
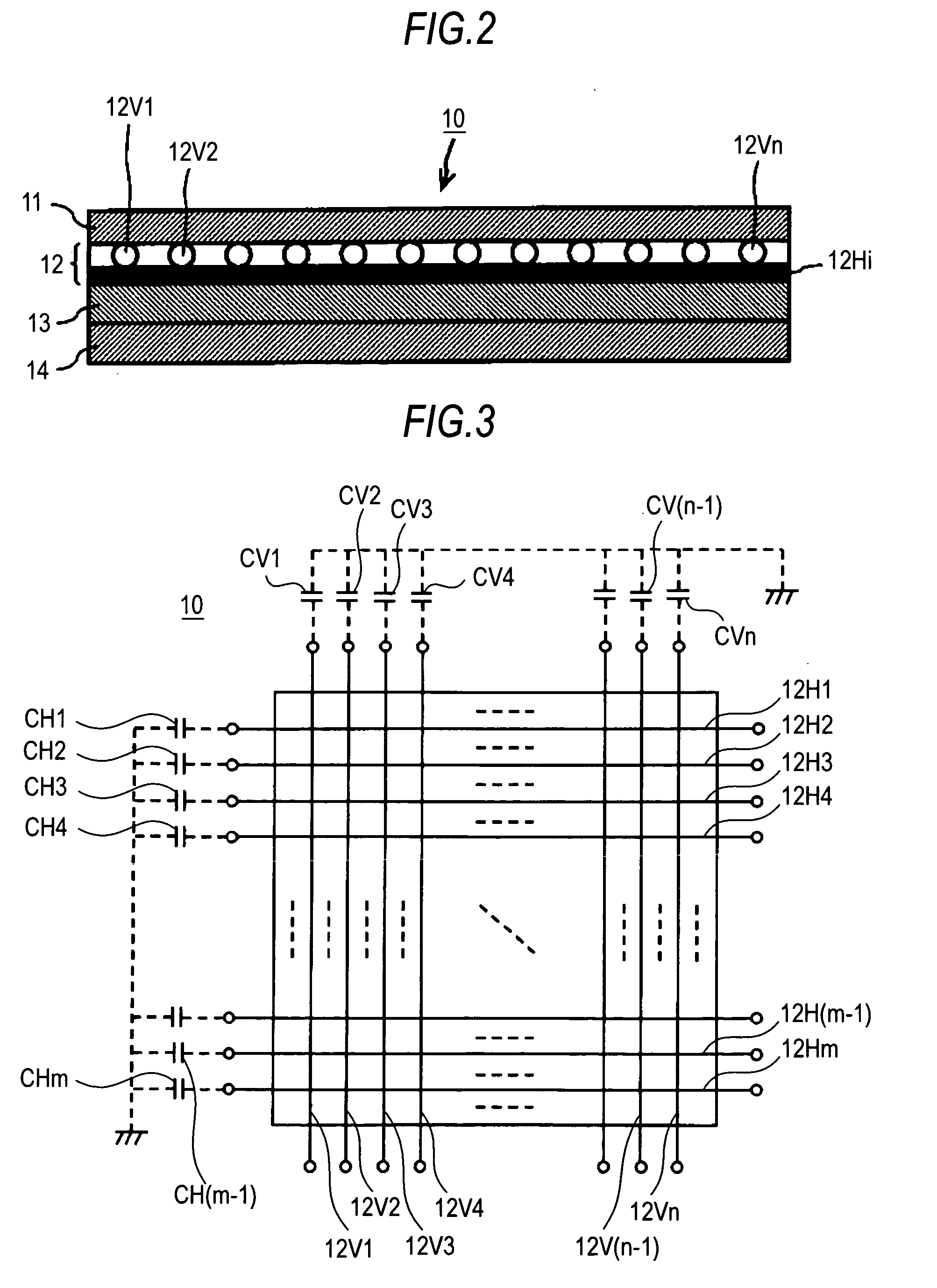
An information processing apparatus includes: sensor means for detecting a distance to a detection target spatially separated therefrom; storage means for storing information on boundary values of a plurality of layers to which different functions are respectively assigned, and which are set according to different distances; determination means for determining in which one of the plurality of layers the detection target is positioned, from the boundary values of the plurality of layers in the storage means and an output signal of the sensor means; and control means for executing a process about the function assigned to that layer where the detection target is positioned, based on a determination result from the determination means.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multiphase physical transport modeling method and modeling system
ActiveUS20050049838A1Reduce computing timeImprove availabilityComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputation complexityBoundary values
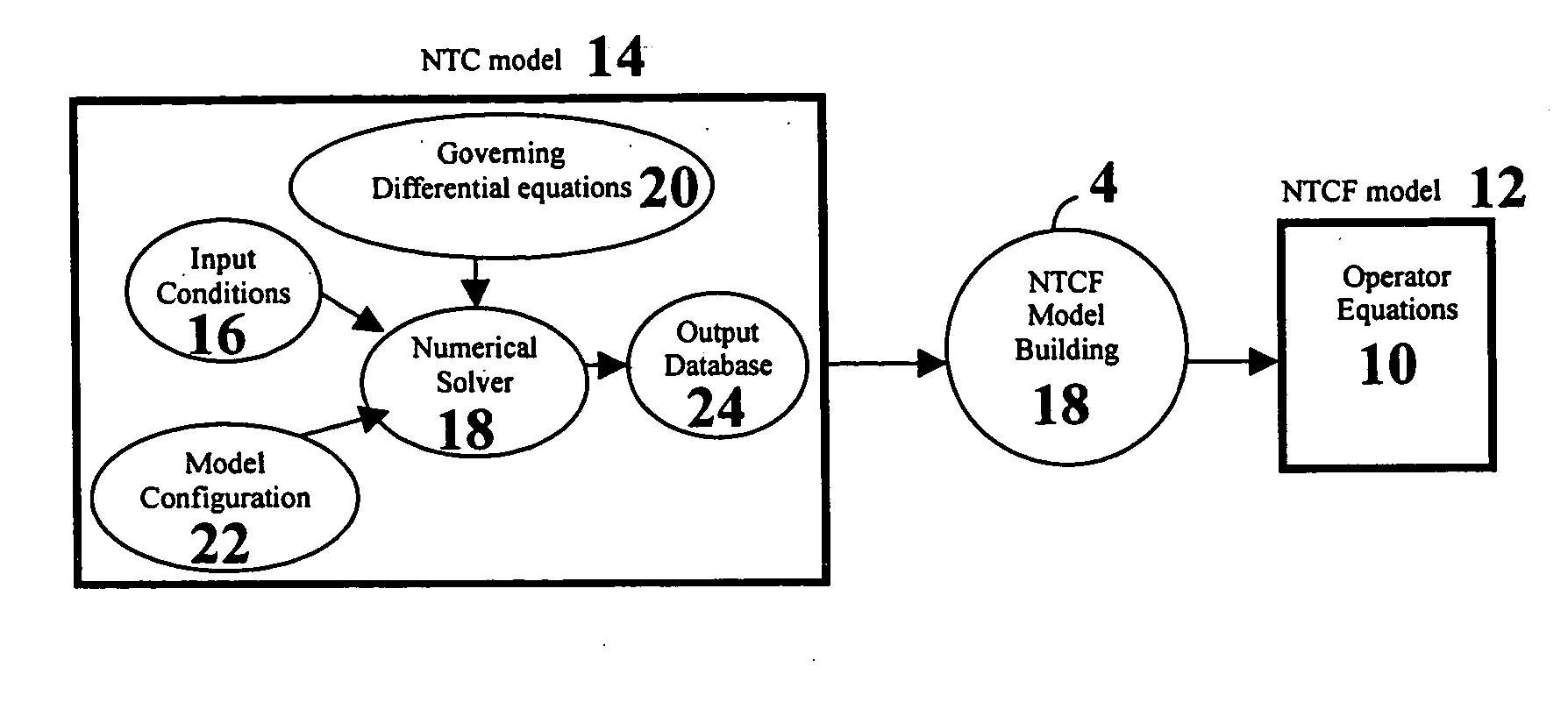
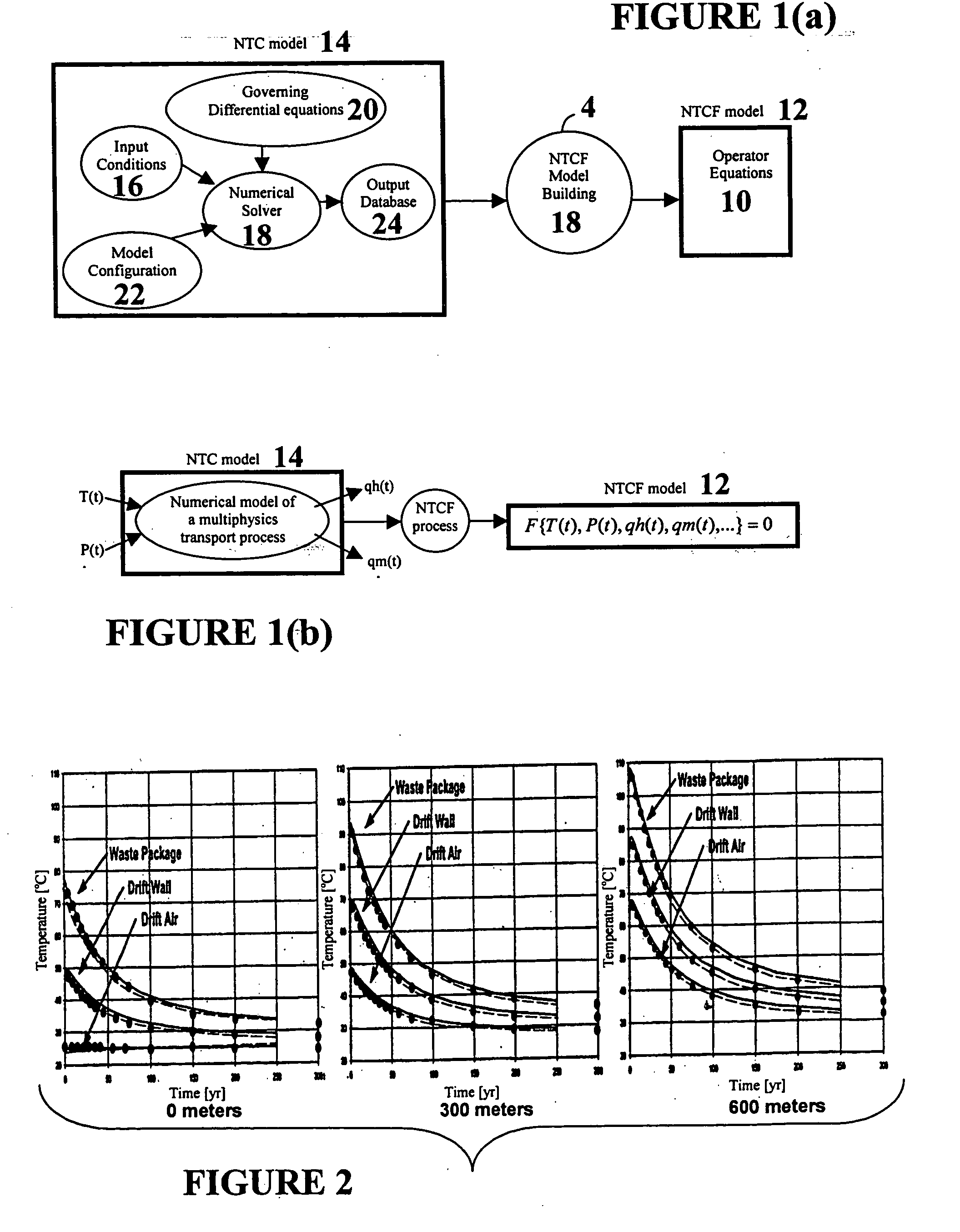
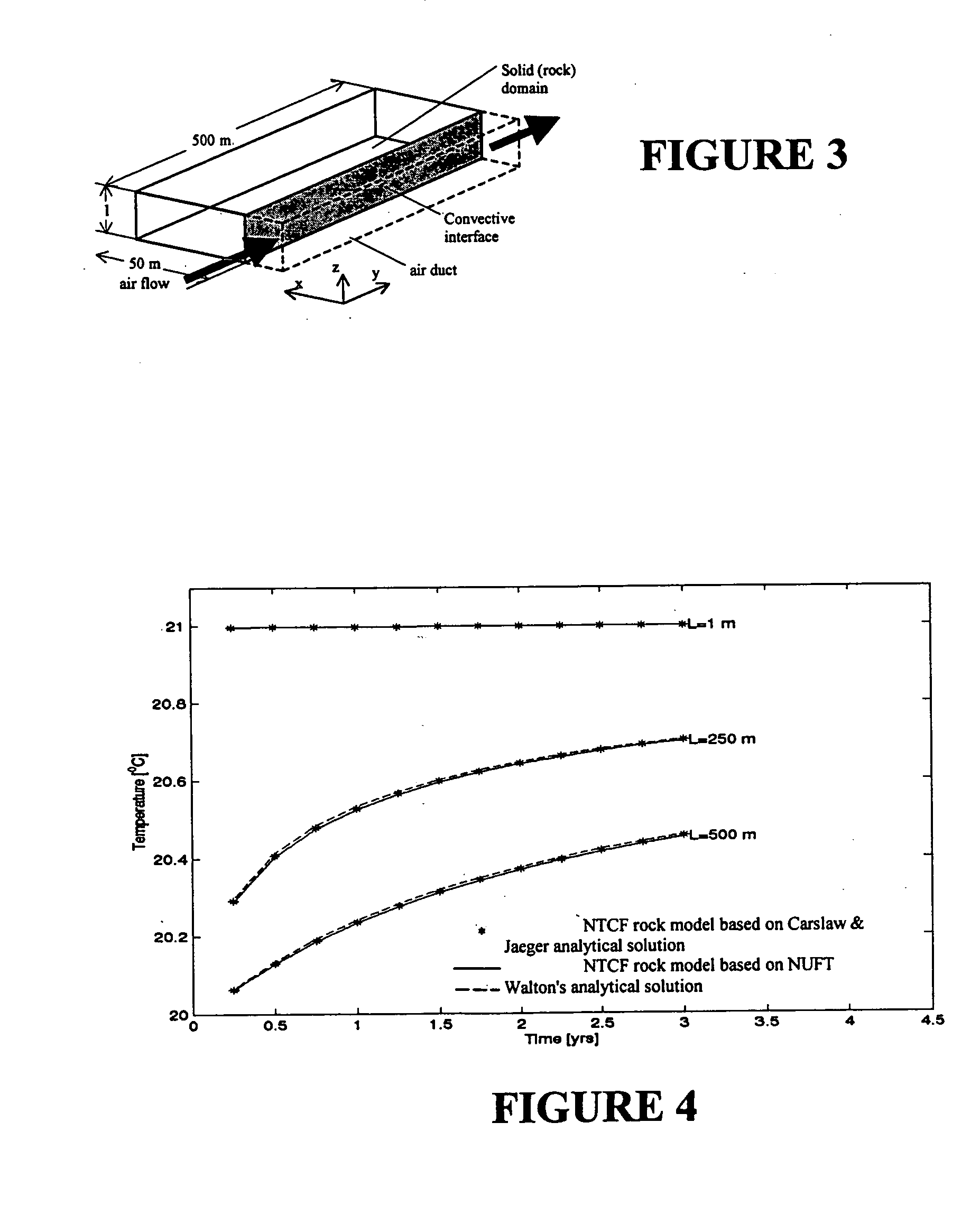
A general, computational-mathematical modeling method for the solution of large, boundary-coupled transport problems involving the flow of mass, momentum, energy or subatomic particles is disclosed. The method employs a modeling processor that extracts a matrix operator equation (or set of equations) from a numerical transport code (NTC). The outputs of software codes, available for modeling physical problems governed by conservation laws in the form of differential equations, can be processed into closed-form operator equations with the method. Included is a numerical transport code functionalization (NTCF) model which can be determined numerically, based on a system of solutions of an NTC, evaluating outputs for a given set of inputs. The NTCF model is a linear or nonlinear, multi-variable operator equation or set of such equations. The NTCF model defines relationships between general, time-variable inputs and outputs, some known and some unknown, considered as boundary values. The user of an NTCF model can directly work with the processed model output, instead of running the original numerical code in general applications of a boundary-value problem. The numerical transport code functionalization model can be employed as a surrogate for representing the numerical transport code to provide a solution to the transport problem. The invention enables modeling efficiency and availability to be increased, while computational complexity and cost decreased. Computational times for complex modeling problems can, in some cases, be dramatially reduced, for example by several orders of magnitude.
Owner:NEVADA RES & INNOVATION CORP
Computation of gamut boundary by sampling device-independent color space
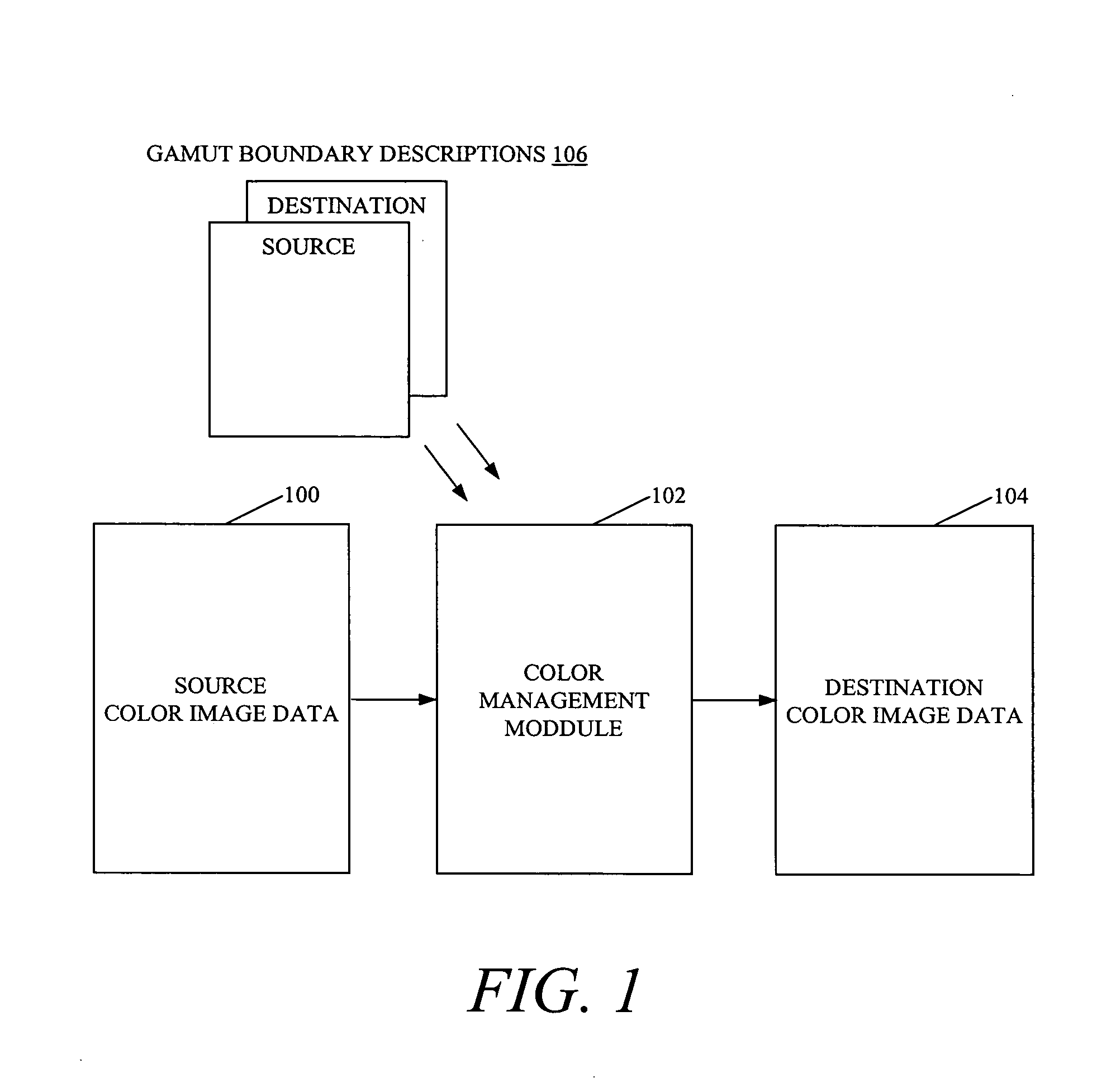
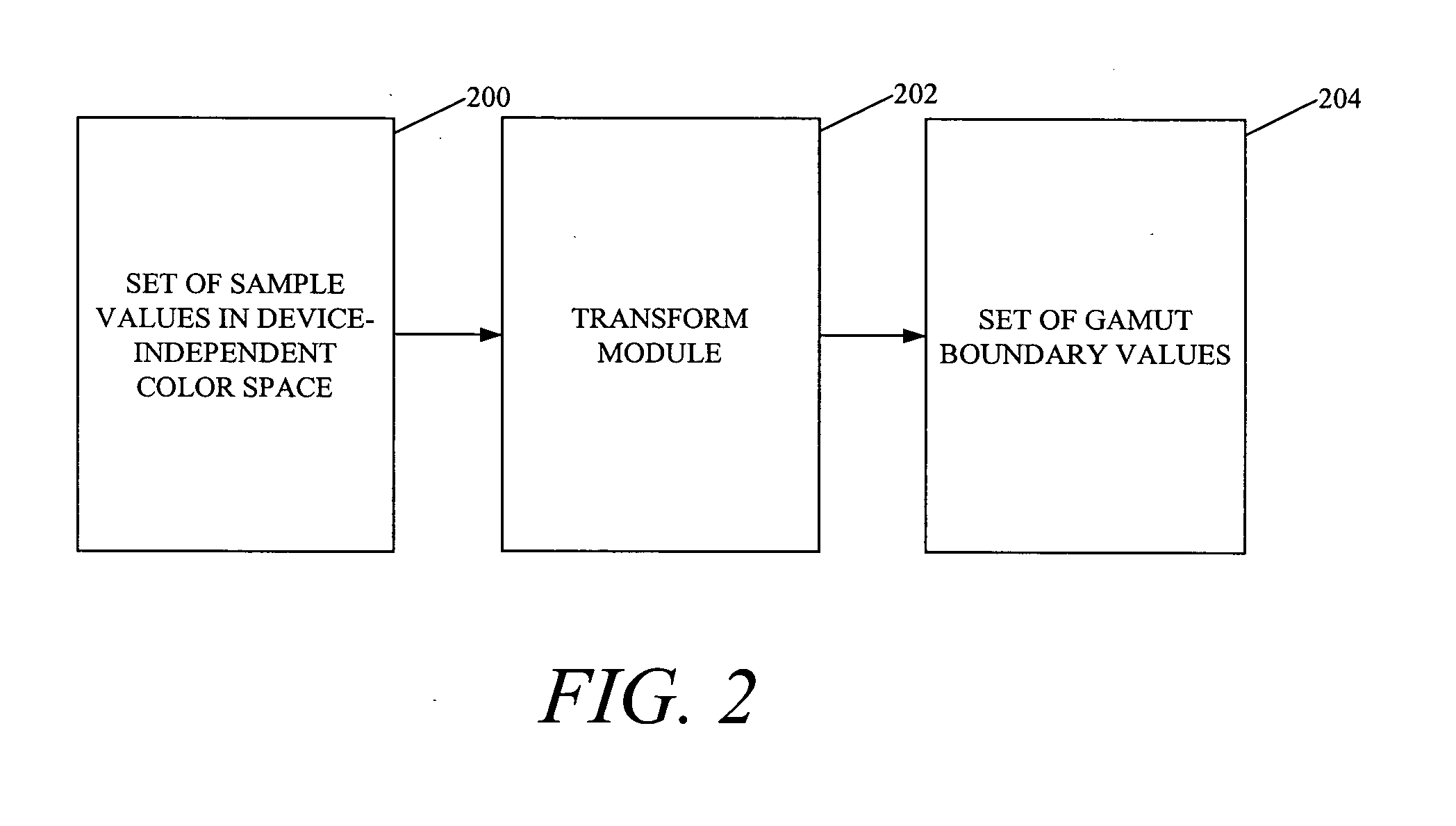
ActiveUS20070081176A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionGamut
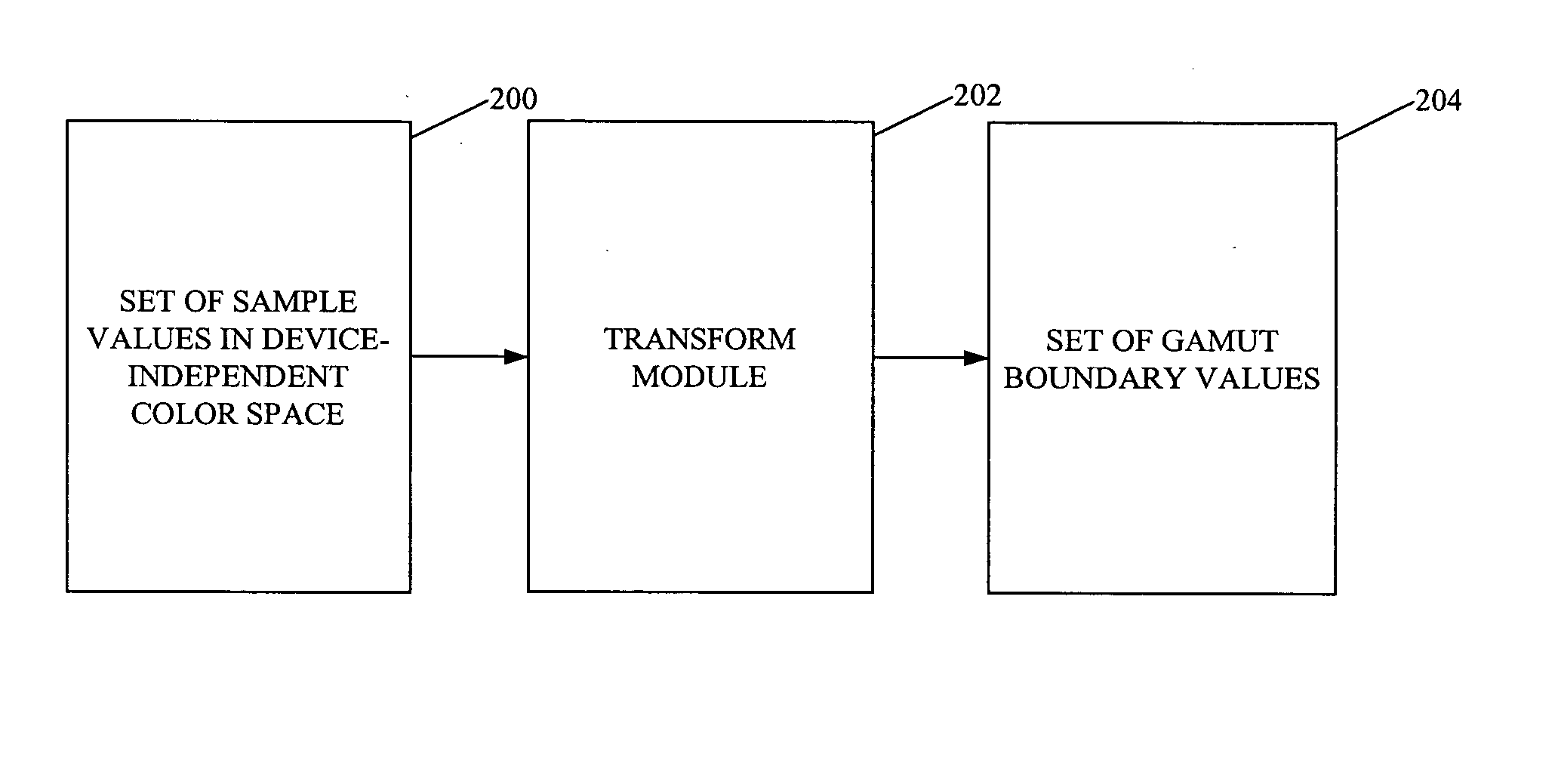
The present invention provides for determining a gamut boundary description for a color device, the color device being characterized at least by a destination transform which converts colors from a device-independent color space to a device-dependent color space and which reports out-of-gamut colors. A set of sample values is determined in the device-independent color space. For each of the sample values within the set of sample values, the destination transform is applied to the sample value, and in a case where the sample value is in gamut, the sample value is included within a set of gamut boundary values. The gamut boundary description is determined by forming a set of polygonal surfaces based on the set of gamut boundary values. Accordingly, a gamut boundary description is determined without necessarily having to sample additional color values as the number of colorant channels for the color device increases.
Owner:CANON KK +1
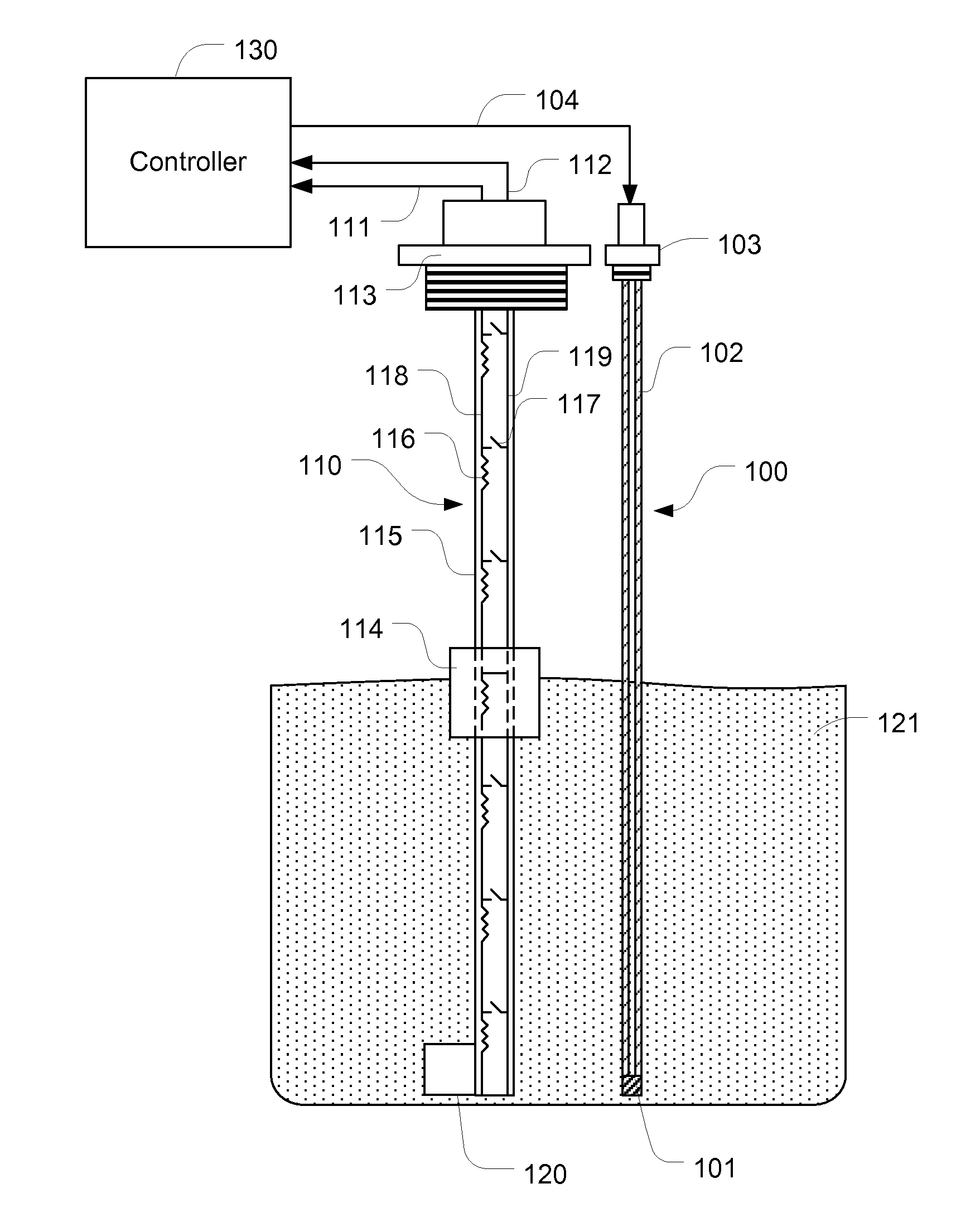
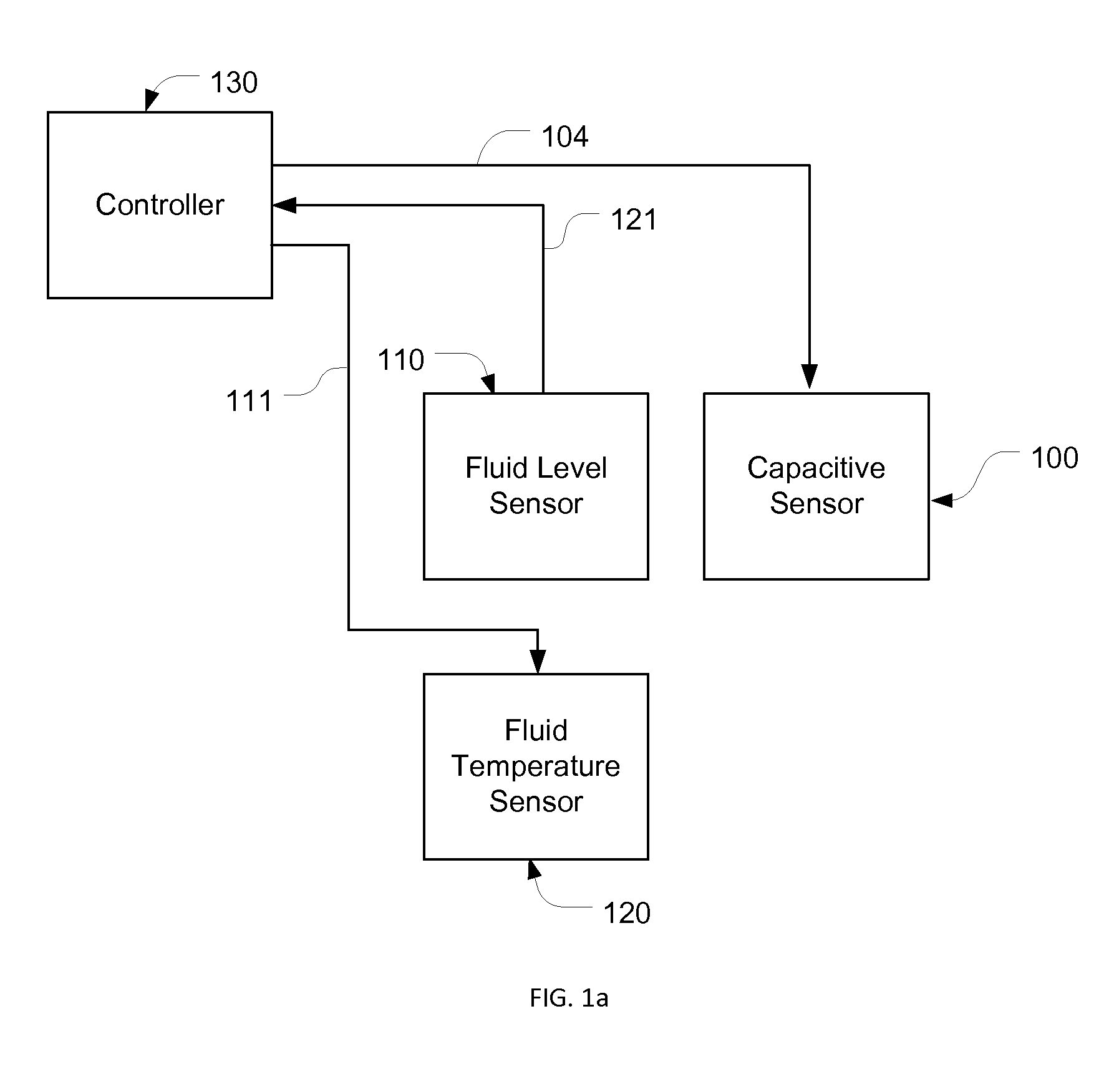
Multifunctional fluid level and quality sensing device
ActiveUS20150013646A1Improving fluid level sensing performanceQuality improvementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFuel injection apparatusBoundary valuesEngineering
A multifunctional fluid level and quality sensing device including a fluid level sensor and a capacitive sensor for detecting fluid level, fluid quality, errors in the sensing device, and issues in a fluid delivery system. In detecting fluid level, impedance of the capacitive sensor is used in improving sensing performance of the fluid level sensor, while in detecting fluid quality and errors in the sensing device, an expected impedance range with an upper boundary value and a lower boundary value is calculated, and a fault is generated when the measured impedance value is out of the expected impedance range. The fluid level and quality sensing device can also be used in a fluid delivery system for detecting system issues, and the results can be used for further isolating errors in the system. Operating status of higher level system provides more information for this purpose.
Owner:QI BAOHUA
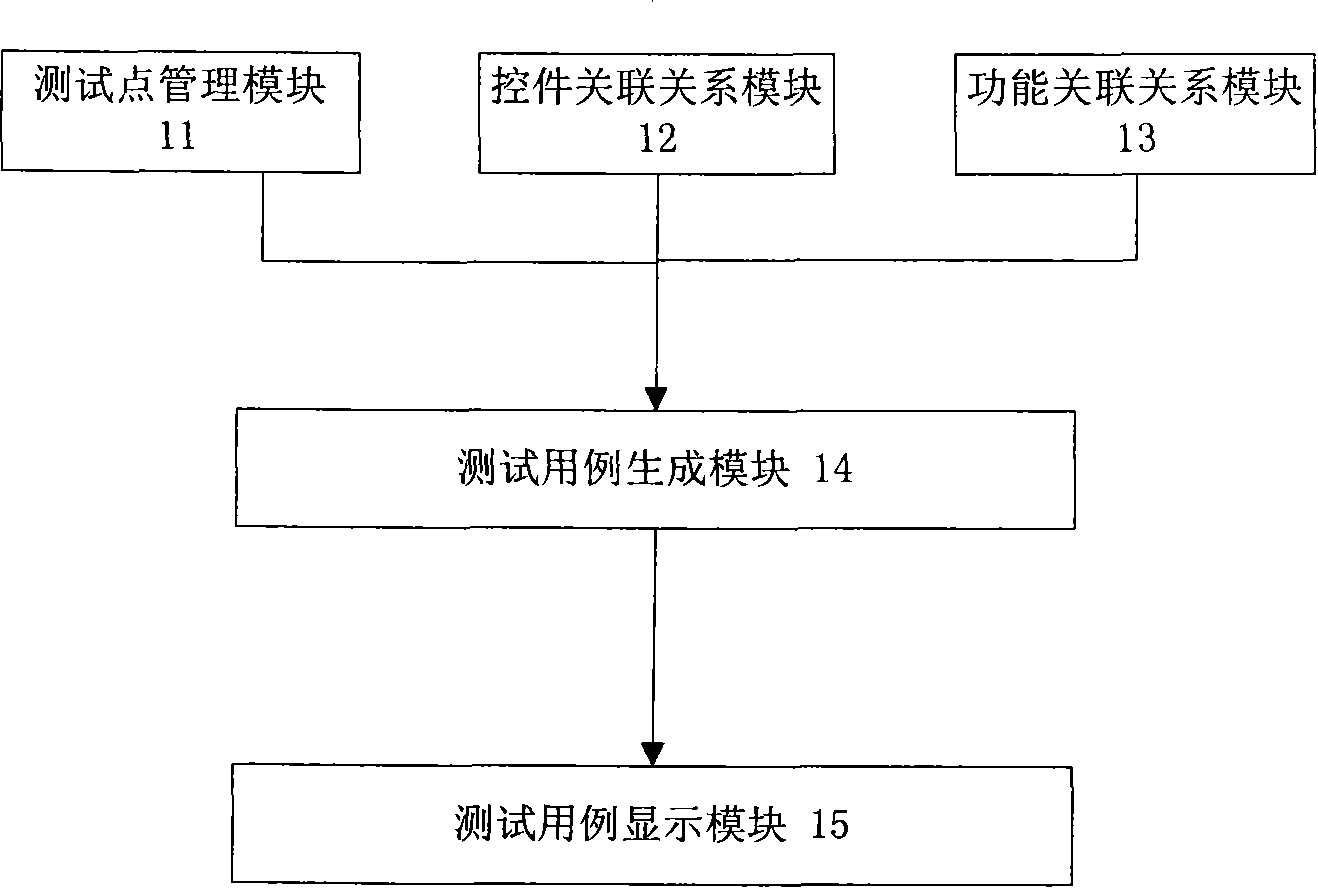
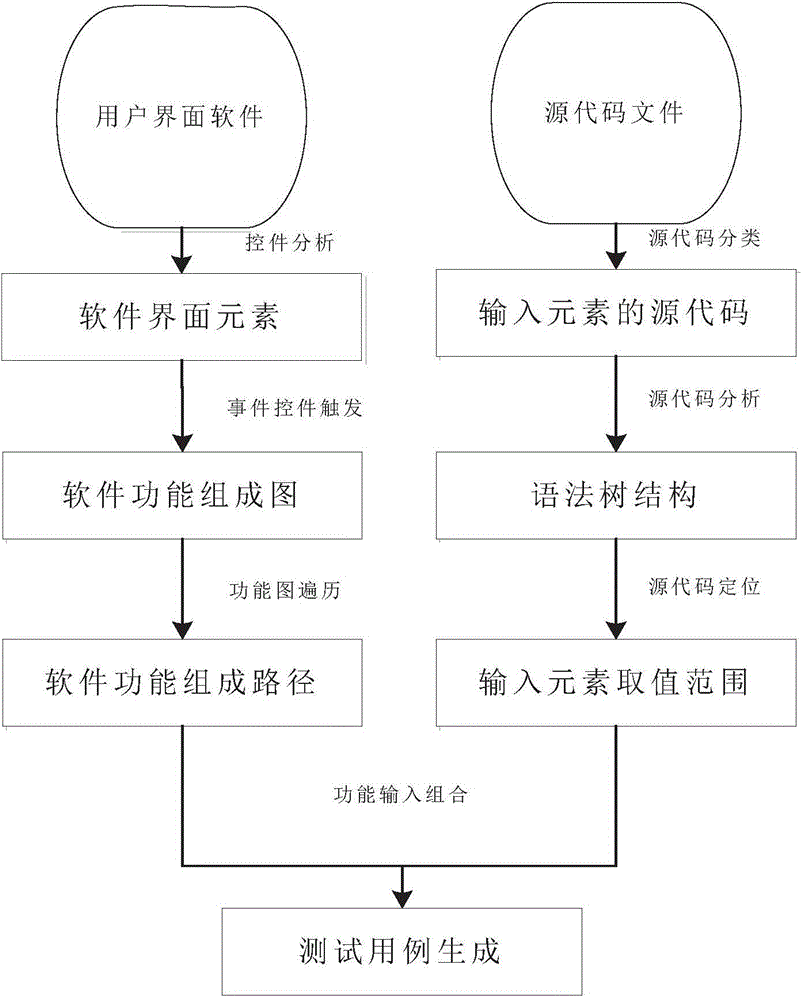
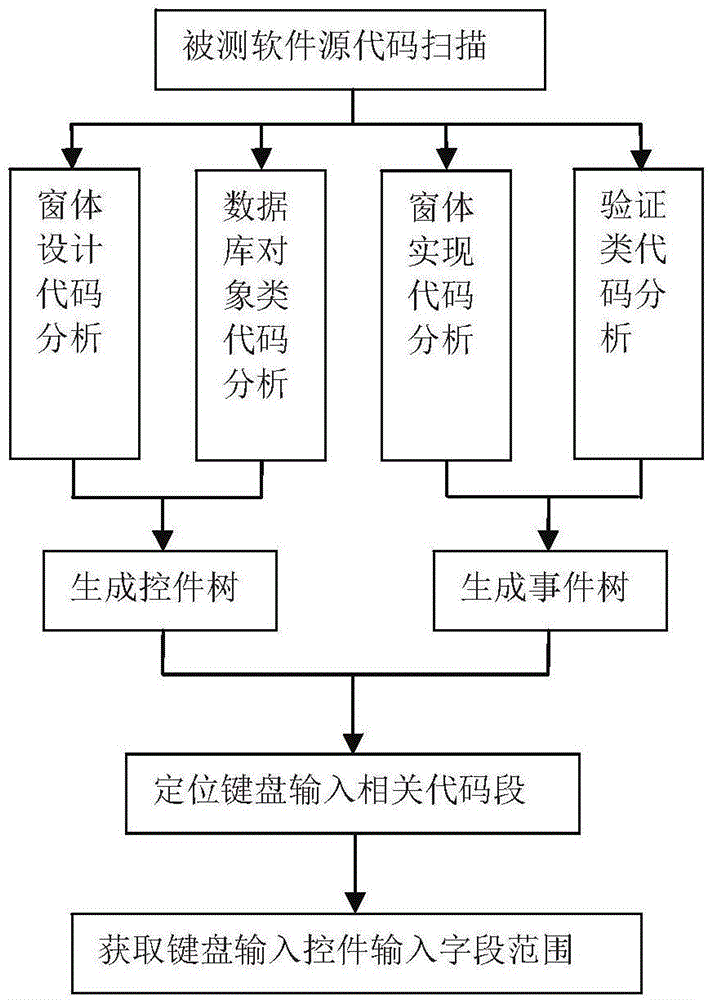
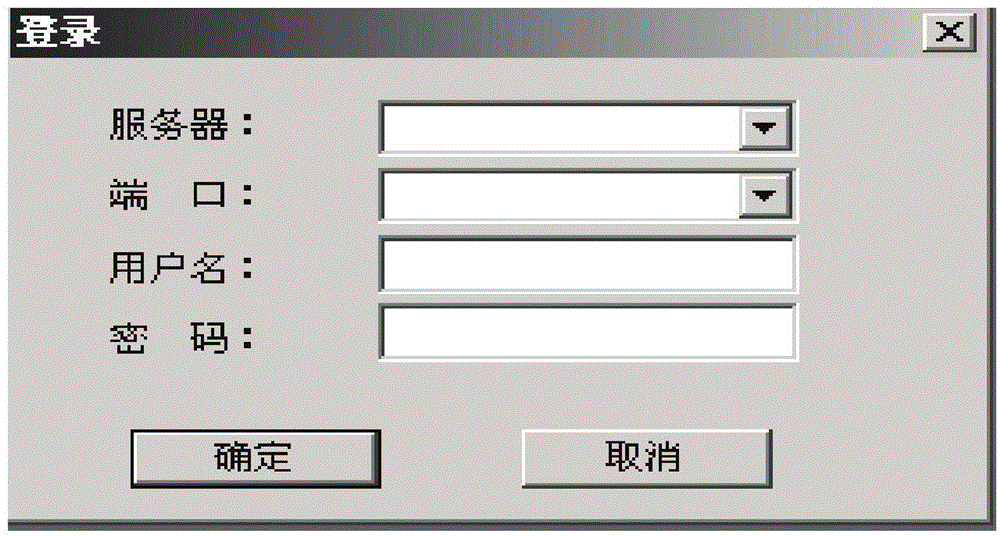
Test case generating method based on relationship
InactiveCN101251798AImprove efficiencyQuality improvementSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsTest design
The present invention relates a test example generating method based on relationship, comprising the following steps of: selecting the test point of each control of a graphical user interface to be tested, according to types; taking the value of each control according to a principle that all levels of each factor are taken and assembling the related controls completely, and then combining; generating a test example according to the reference relation of the function to be tested and the example template; combining the test examples to generate all test examples of the function to be tested. With boundary value testing and equivalence testing, the method carries out strict, normative and comprehensive test point design according to the common controls in an interface test. The test designing points of each type of controls are solidified into a group of test example generating criterion for citing and expanding. The example is designed with a control relation graph and a function relation graph according to the analysis of control relativity and function relativity, so that the selection of the input value of the test example has more pertinences, thereby being capable of greatly improving the efficiency and the quality of GUI test designing.
Owner:孙影 +4
System and Method for Adjusting Offset Compensation Applied to a Signal
InactiveUS20070297209A1High sensitivityPrevent lockMultiple-port networksMeasurement devicesBoundary valuesData signal
In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for adjusting a signal includes receiving an input data signal. The method also includes applying an offset compensation to the input data signal to generate an output signal. The method further includes, using a clock signal, sampling the output signal to generate a plurality of data values and boundary values, each value comprising either a high value or a low value based on the sampling of the output signal. The method also includes detecting a transition in value between two successive data values and determining a sampled boundary value between the two successive data values. The method further includes, based at least on the high or low value of the boundary value, adjusting the offset compensation applied to the input data signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Systems and methods for predicting maintenance of intelligent electronic devices
ActiveUS20090312999A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusElectric testing/monitoringBoundary valuesPredictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance systems and methods are described. A method includes measuring environmental conditions using a plurality of sensors within the IED, processing the environmental measurements to determine long-term exposure factors representing historical operating conditions of the IED, applying a reliability model to the long-term exposure factors, determining a numerical measure of IED life based on the long-term exposure factors and the reliability model, comparing the numerical measure of IED life to preselected boundary values, and signaling if the numerical measure of IED life is outside of the preselected boundary values.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
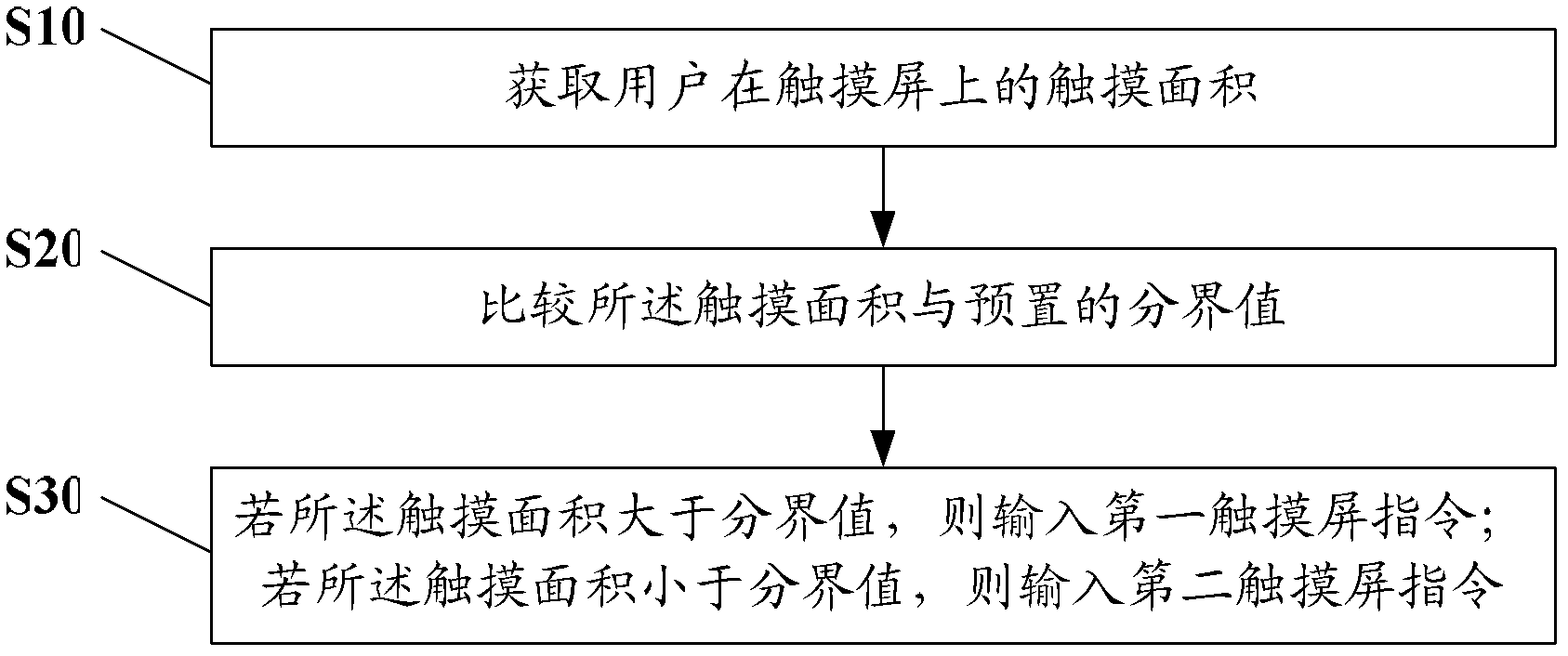
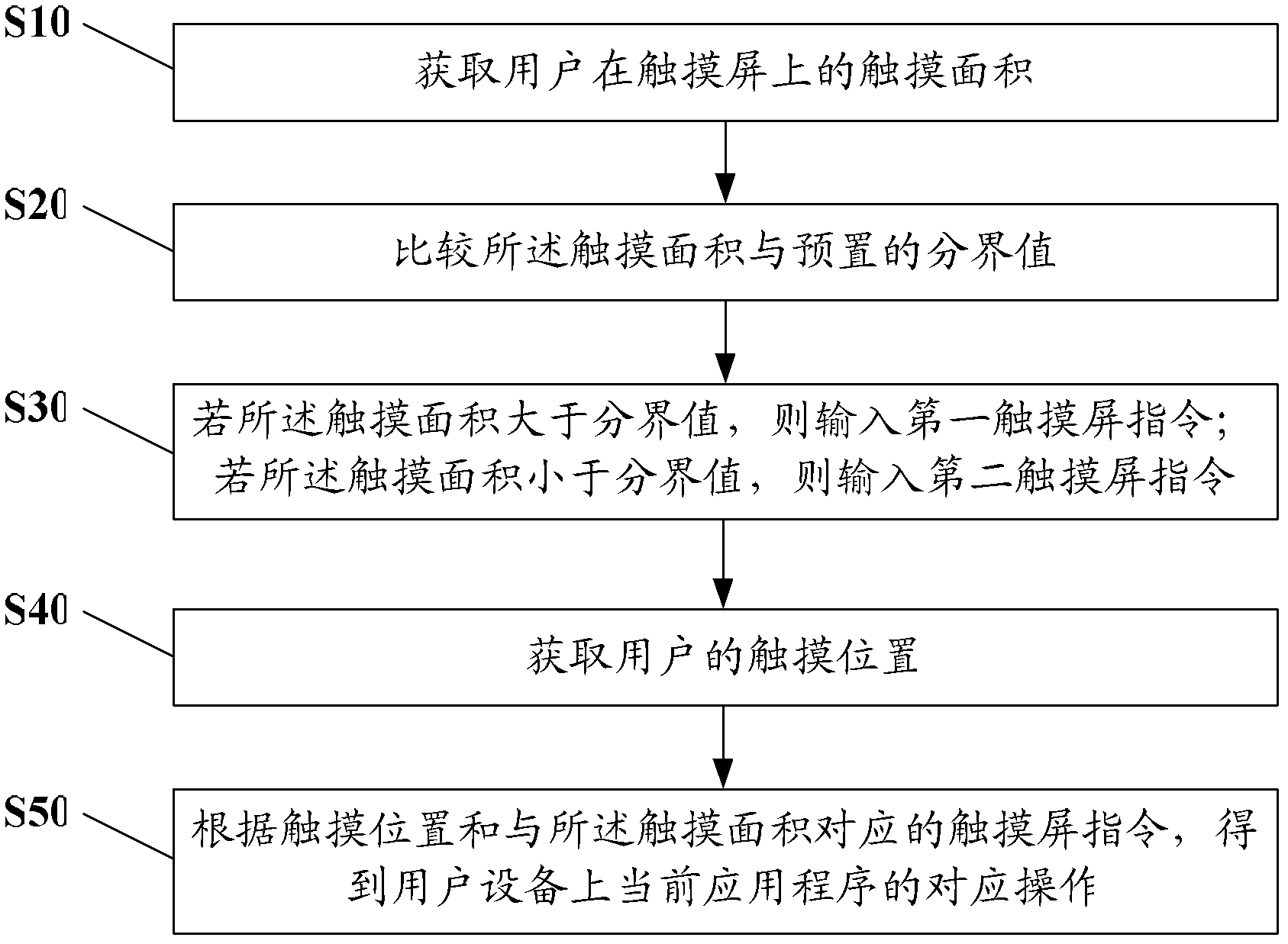
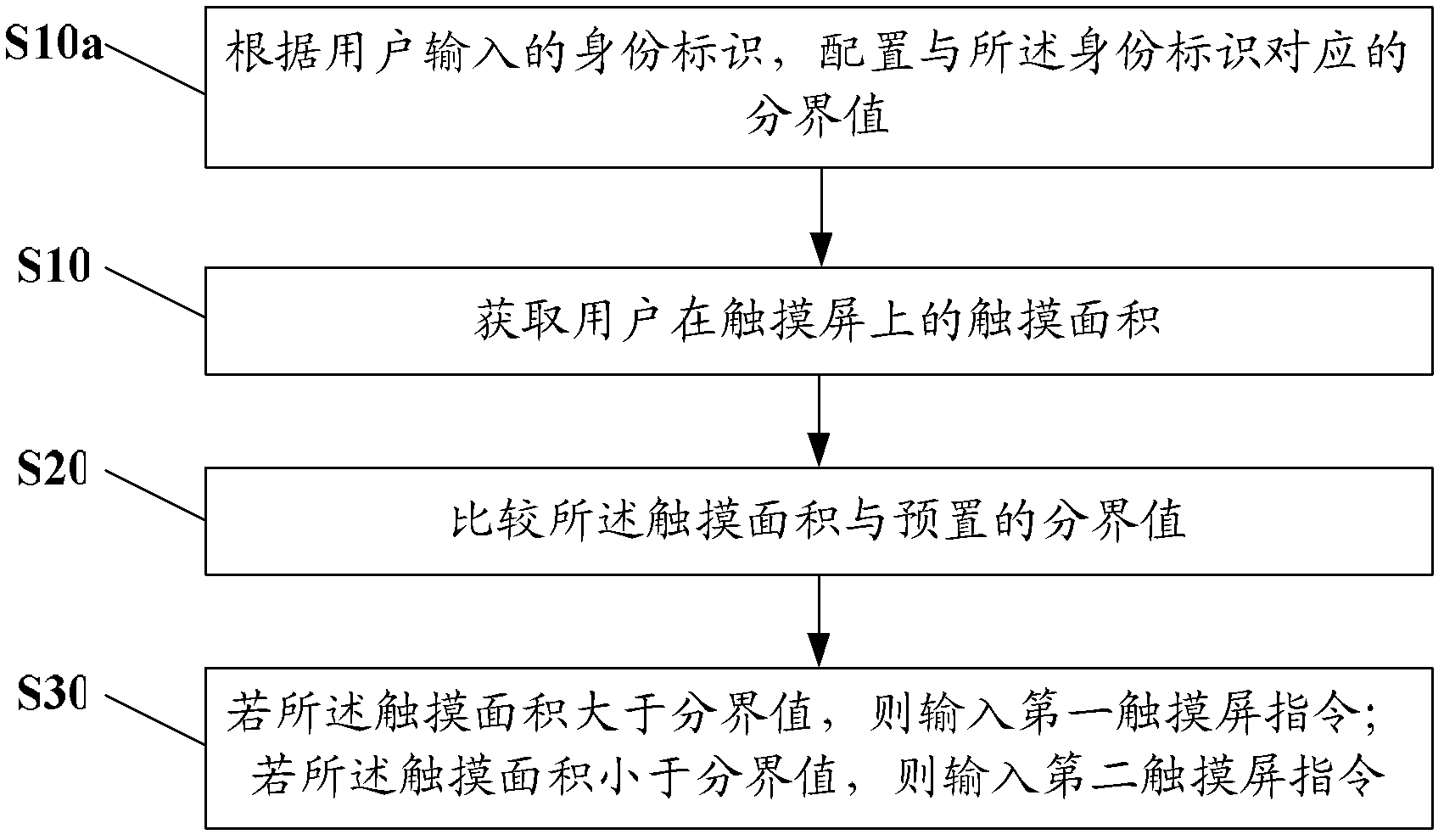
Touch screen command input method and user equipment
ActiveCN102221932AImprove operational efficiencyEnrich the way of inputting instructionsInput/output processes for data processingUser deviceBoundary values
The embodiment of the invention discloses a touch screen command input method and user equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the touch area of a user on a touch screen; comparing the touch area with a preset boundary value; if the touch area is greater than the boundary value, inputting a first touch screen command; and if the touch area is lower than the boundary value, inputting a second touch screen command. The touch area is divided into two intervals by using the boundary value, each interval corresponds to different touch screen commands, and the different input commands of the touch screen are correspondingly input by acquiring the touch area of the user, so the operating efficiency of the touch screen is improved, and touch screen command input modes are enriched.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
System and Method for the Non-Linear Adjustment of Compensation Applied to a Signal
InactiveUS20070280390A1High sensitivityPrevent lockMeasurement devicesModulated-carrier systemsBoundary valuesComputer science
In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for adjusting a signal includes applying loss compensation for frequency-dependent distortion to a signal before or after the distortion occurs to generate an output signal. The method also includes, using a clock signal, sampling the output signal to generate a plurality of data values and boundary values, each value comprising either a high value or a low value based on the sampling of the output signal. The method further includes, based only on the high or low values of one or more of the data values and boundary values, adjusting the loss compensation applied to the signal, where if the loss compensation applied to the signal is to be increased, the loss compensation is increased by a first amount, if the loss compensation applied to the signal is to be decreased, the loss compensation is decreased by a second amount, the magnitude of the first amount is not equal to the magnitude of the second amount, the first amount and the second amount are associated with a control target value, and the control target value is adjusted dynamically based on the value of the loss compensation applied to the signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Automatic test method and device for graphic user interface software
ActiveCN104699608AAccurate acquisitionEfficient acquisitionSoftware testing/debuggingGraphicsAutomatic test equipment
The invention discloses a method for testing graphic user interface software. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing the graphic user interface software, obtaining a function demand of the software through an interface element in a graphic user interface, and extracting a boundary value of the interface element; generating a test case according to the obtained function demand of the software and the boundary value of the interface element; automatically testing all functions of the graphic user interface software through the test case. According to the automatic test method and the device for the graphic user interface software, the graphic user interface software can be automatically tested quickly, accurately and efficiently through the automatically generated test case.
Owner:中国软件评测中心(工业和信息化部软件与集成电路促进中心)
System and Method for Decoupling Multiple Control Loops
InactiveUS20070280391A1High sensitivityPrevent lockError preventionMeasurement devicesBoundary valuesData mining
In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for adjusting a signal includes applying at least one of a loss compensation for frequency-dependent distortion and an offset compensation for DC-offset distortion to a signal before or after the distortion occurs to generate an output signal. The method also includes, using a clock signal, sampling the output signal to generate a plurality of data values and boundary values. The method further includes monitoring the sampled values for a first set of data patterns. The method also includes detecting in the sampled values a data pattern in the first set of data patterns. The method further includes adjusting at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation applied to the signal based on one or more of the sampled data values and boundary values associated with the detected data pattern in the first set of data patterns. The method further includes, after adjusting at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation, monitoring the sampled values for a second set of data patterns. The method also includes detecting in the sampled values a data pattern in the second set of data patterns. The method further includes adjusting at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation applied to the signal based on one or more of the sampled data values and boundary values associated with the detected data pattern in the second set of data patterns.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
System and Method for Asymmetrically Adjusting Compensation Applied to a Signal
InactiveUS20070280389A1High sensitivityPrevent lockMeasurement devicesBaseband systemsNon symmetricBoundary values
In one embodiment of the present invention, a method for adjusting a signal includes applying at least one of a loss compensation for frequency-dependent distortion and an offset compensation for DC-offset distortion to a signal before or after the distortion occurs to generate an output signal. The method also includes, using a clock signal, sampling the output signal to generate a plurality of data values and boundary values, each value comprising either a high value or a low value based on the sampling of the output signal. The method further includes, based only on the high or low value of one or more of the data values and boundary values, adjusting at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation applied to the signal, where if the at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation applied to the signal is to be increased, the at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation is increased by a first amount, if the at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation applied to the signal is to be decreased, the at least one of the loss compensation and the offset compensation is decreased by a second amount, and the magnitude of the first amount is not equal to the magnitude of the second amount.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
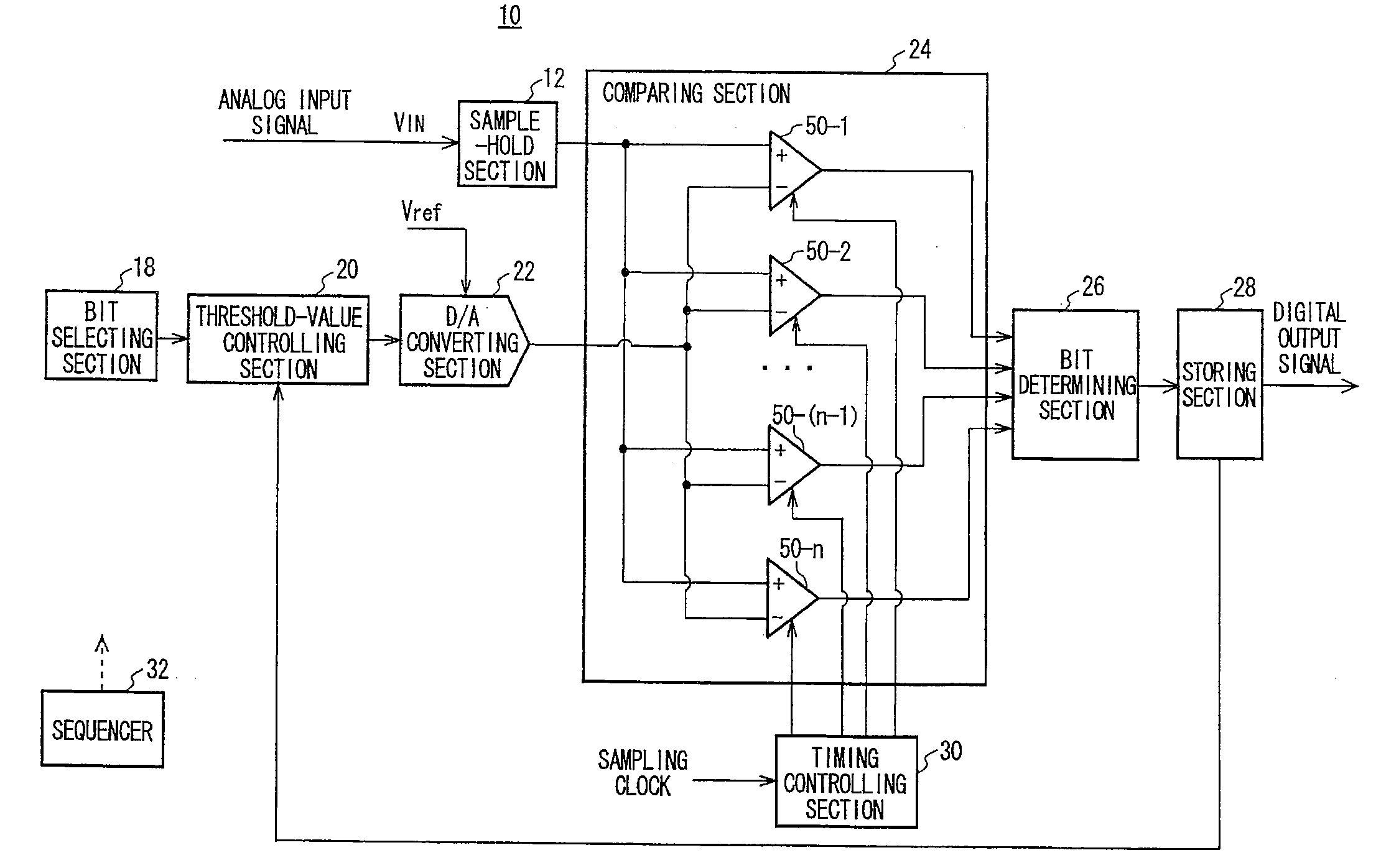
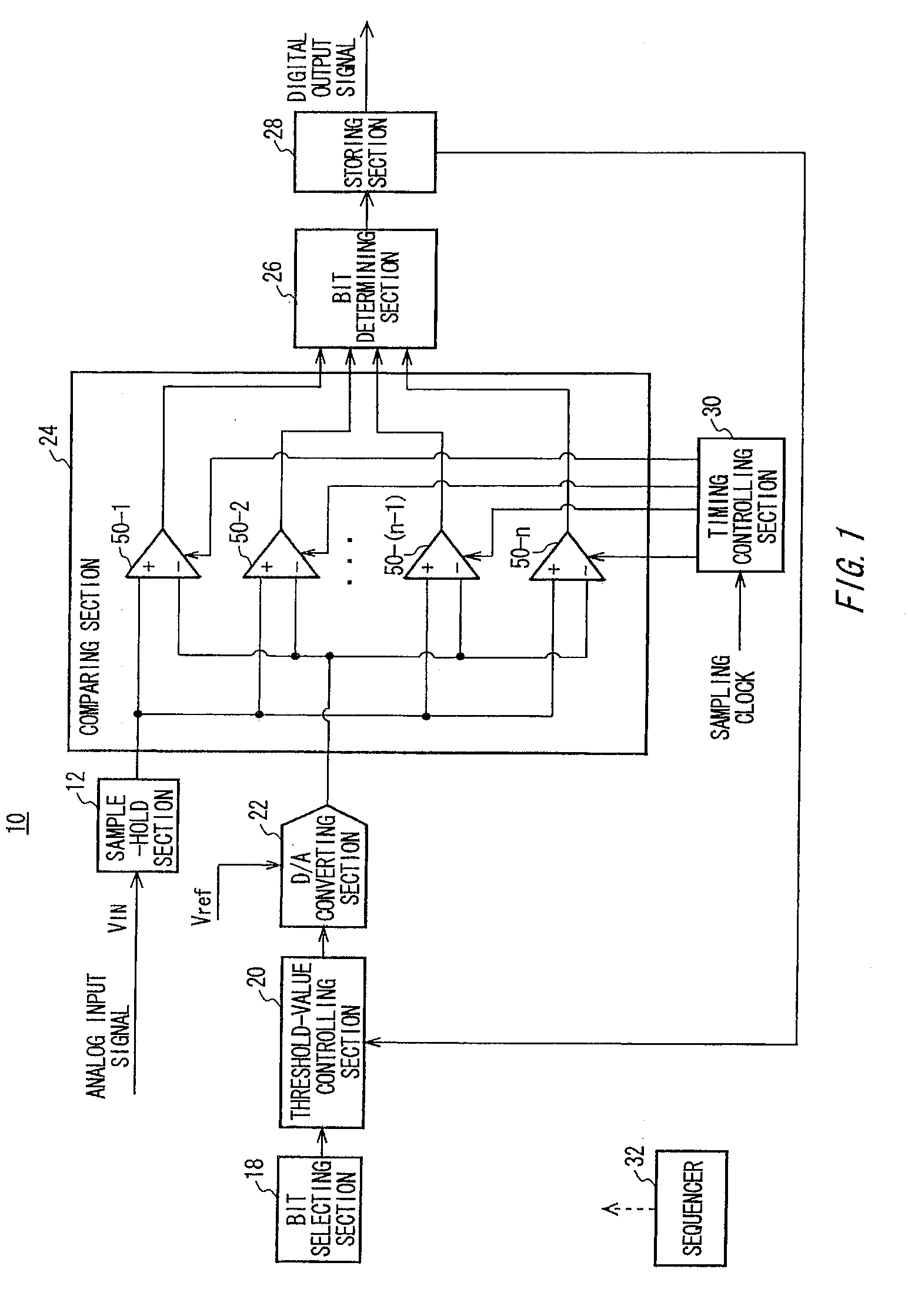
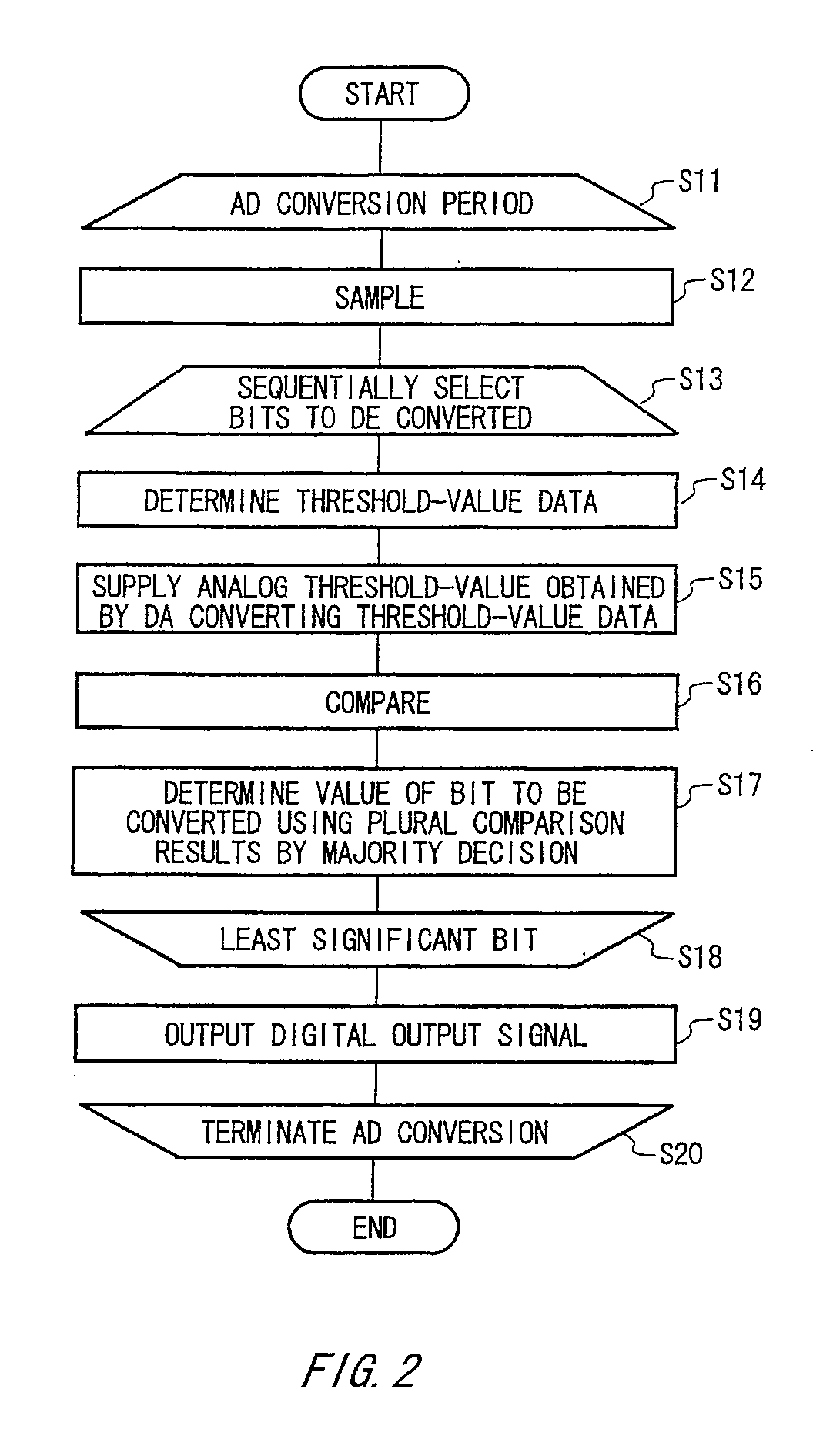
A-d converter and a-d convert method
ActiveUS20080218393A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionBoundary valuesA d converter
There is provided an A / D converter that outputs a digital output signal obtained by digitalizing an analog input signal. The A / D converter includes a bit selecting section that selects a conversion object bit from a high-order bit to a low-order bit of the digital output signal in order, a threshold-value controlling section that determines a threshold data expressing a boundary value between zero and one of the conversion object bit, a D / A converting section that digital-to-analog converts the threshold data and generates an analog threshold value, a comparing section that compares, at a plurality of different timings in a conversion time interval determining a value of the conversion object bit, the analog input signal and the analog threshold value and outputs a plurality of comparison results at the timings, and a bit determining section that determines the value of the conversion object bit.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP +1
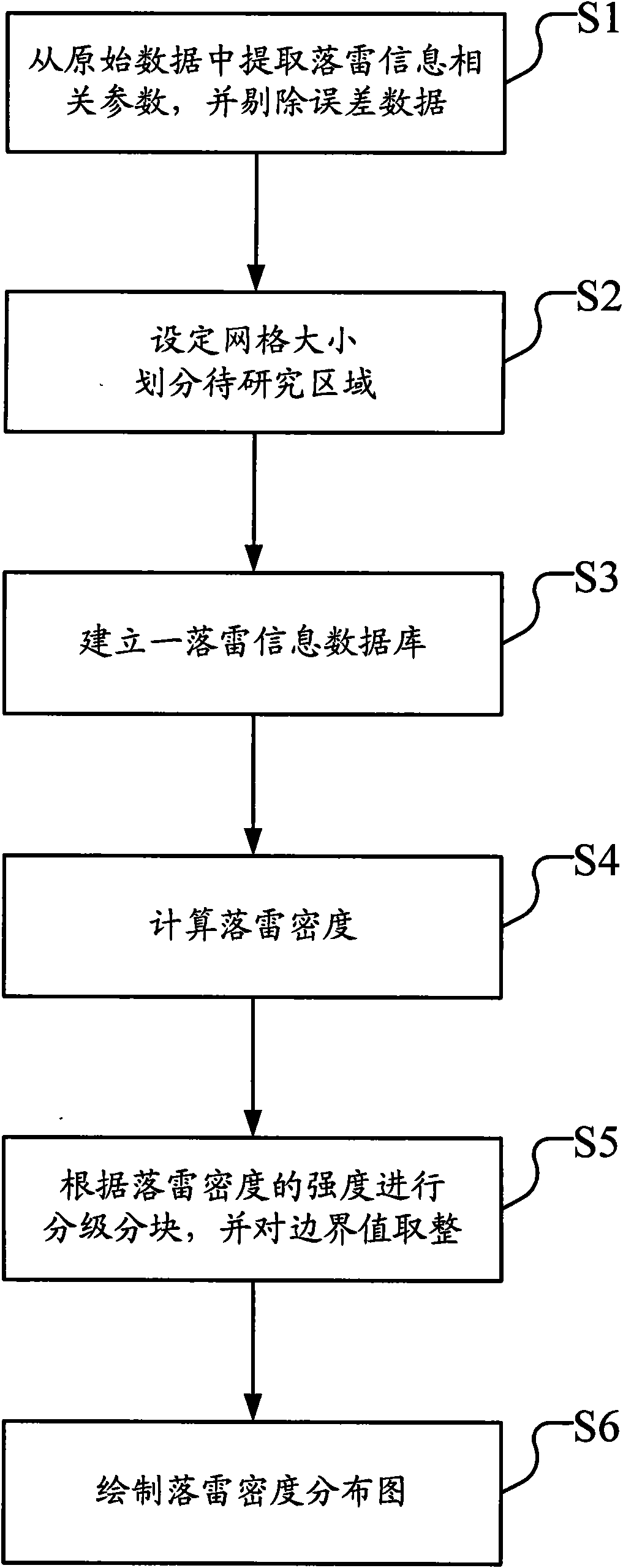
Method for calculating thunderbolt density
The invention provides a method for calculating thunderbolt density, which is used for calculating the thunderbolt density in a studying area and drawing a corresponding thunderbolt density distribution graph. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting parameters related to thunderbolt information from original data, and removing error data in the original data; secondly, setting size of grids of the thunderbolt density distribution graph, dividing the studying area according to the size of the grids, and relating the grids to the area corresponding to the grids; thirdly, calculating the thunderbolt frequency of the area corresponding to each grid in a certain period of time; fourthly, calculating the thunderbolt density of the area corresponding to each grid; fifthly, performing data processing, wherein classification and partition are carried out according to the strength of the thunderbolt density, and a boundary value is rounded; and finally, drawing the thunderbolt density distribution graph according to the result of the data processing. The method for calculating the thunderbolt density can obtain the thunderbolt density distribution of the studying area by processing the data of a thunderbolt positioning system so as to guide the thunderbolt prevention in the area.
Owner:EAST CHINA ELECTRIC POWER TEST & RES INST
Change data capture using nested buckets
ActiveUS20180218017A1Database updatingSpecial data processing applicationsBoundary valuesComputerized system
Systems and techniques are disclosed relating to management of a database. A method may include maintaining, by a computer system, a multi-tenant database operable to store a plurality of objects. Each object may be capable of including up to a maximum potential number of definable fields. Each field may have an associated index number that has been assigned sequentially. The method may include receiving user-defined data values for a subset of the maximum potential number of fields of a particular object, and storing, for the particular object, a boundary value indicating a range of index values that have been defined for the particular object. The method may further include, in response to determining that the particular object has been accessed, selectively processing a number of fields of the particular object. The number of fields may be determined based on the stored boundary value for the particular object.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
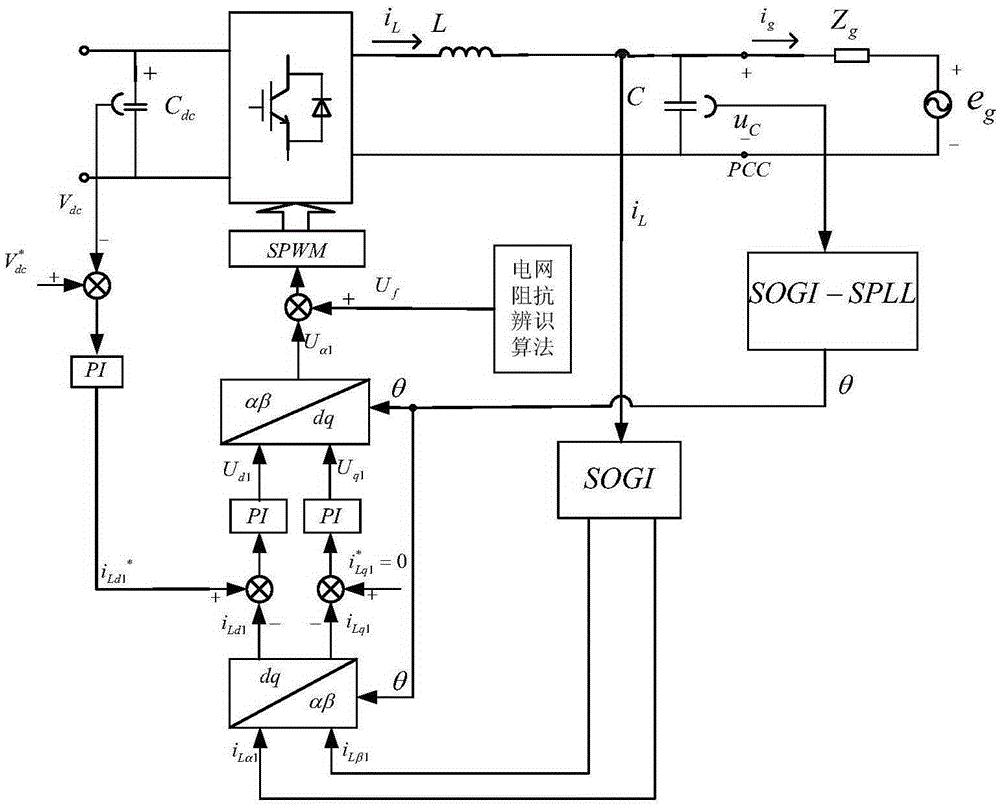
Power grid impedance self-adaption based LC type grid-connected inverter dual-mode control method
InactiveCN105356507AGuaranteed uptimeImprove stabilityAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHysteresisPower inverter
The invention discloses a power grid impedance self-adaption based LC type grid-connected inverter dual-mode control method. According to the invention, a power grid impedance boundary value of mutual switching between a current source grid-connected mode and a voltage source grid-connected mode of an inverter is determined at first, the inverter adopts a current source grid-connected mode control method when the power grid impedance boundary value is less than a switching boundary value, and the inverter adopts a voltage source grid-connected mode control method when the power grid impedance boundary value is greater than the switching boundary value; and an impedance hysteresis loop based switching mode is adopted in order to improve the stability in switching. The method disclosed by the invention solves a defect that the inverter can only operate stably within a small power grid impedance variation range when adopting a single current source or voltage source grid-connected mode under different power grid impedance conditions, and stable operations of the inverter within a large power grid impedance variation range are realized through mutual switching between the current source power-grid mode and the voltage source grid-connected mode.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
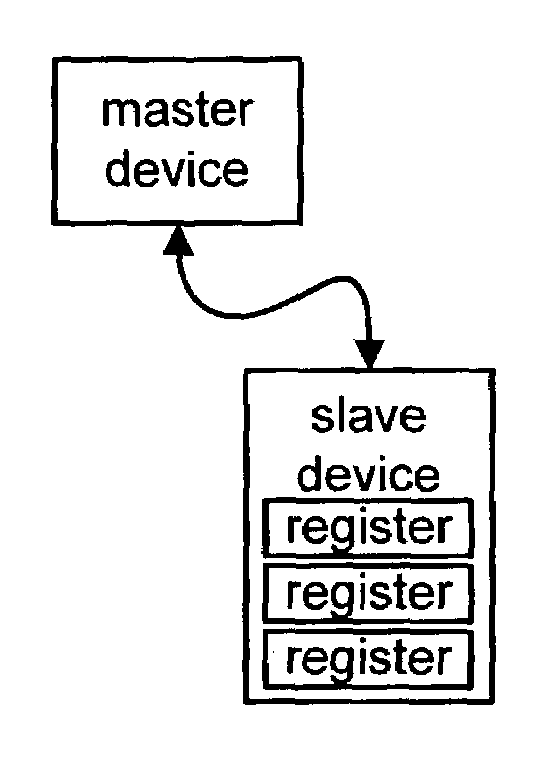
Single wire network for sending data in predetermined periods and next register address immediately thereafter and storing data in register identified in last cycle
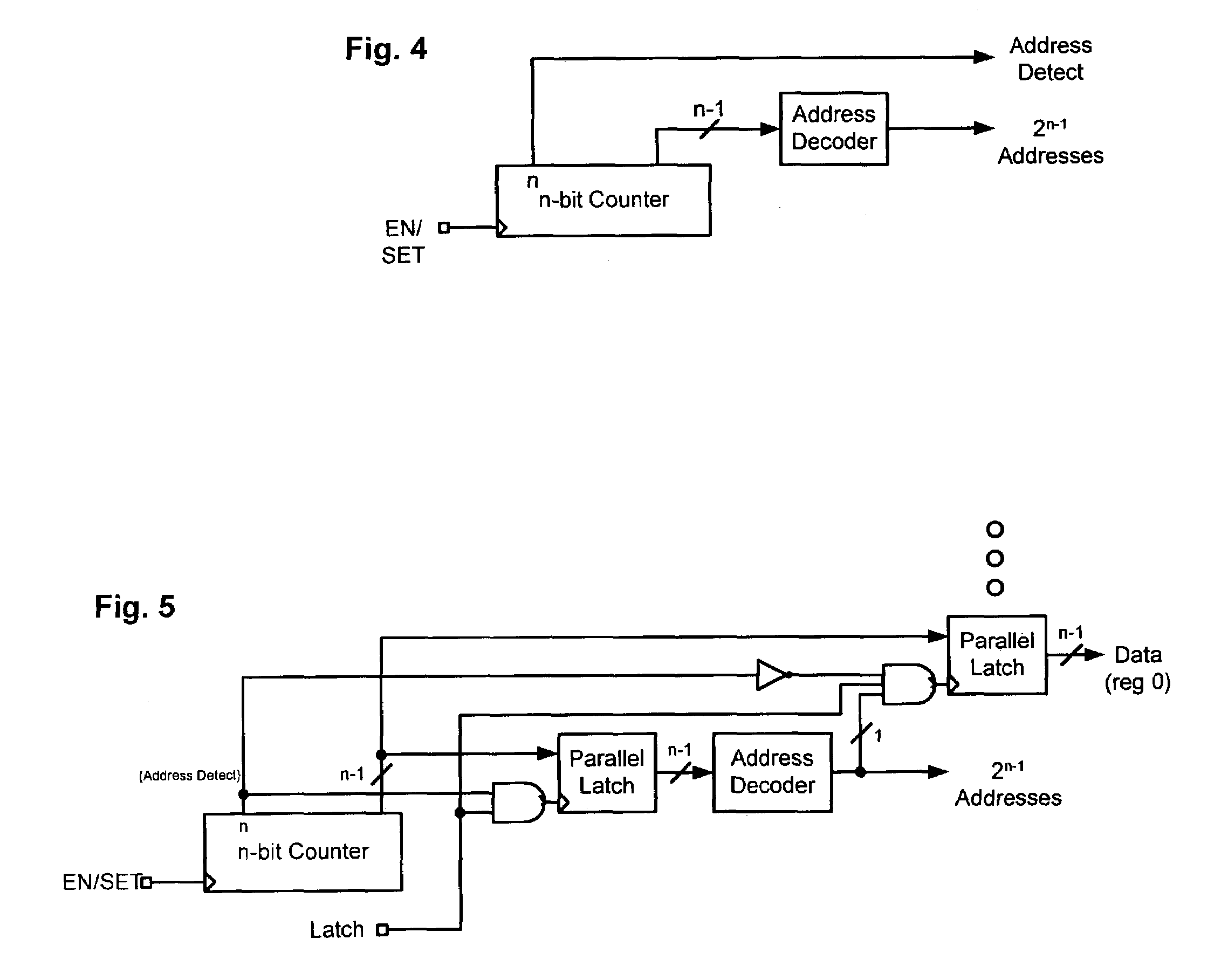
A device control protocol (and related implementation) is provided to control power ICs and other devices. For this protocol, a master device communicates with a slave device using a single wire. The device control protocol distinguishes between different types of information (such as register address information and register content information) by defining one or more boundary values. For one example, register content information is defined to be less than or equal to n. Register address information is defined to be more than n. To store data into a register of a slave device, a master device sends the register address using more than n rising edges of the EN / SET signal. The master device then sends the register contents using n or less rising edges of the EN / SET signal. The slave device decodes the address information, selects the corresponding register and stores the register contents.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com